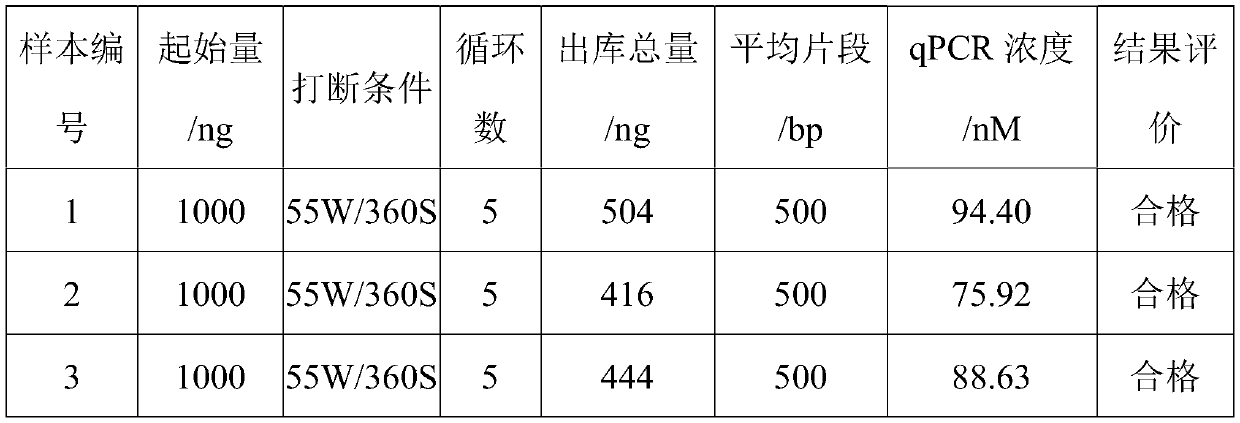
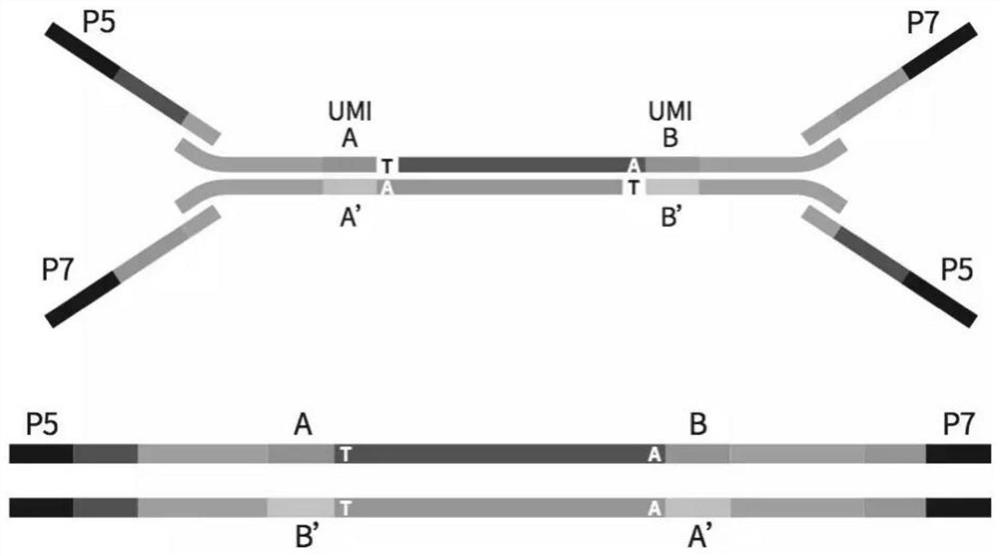
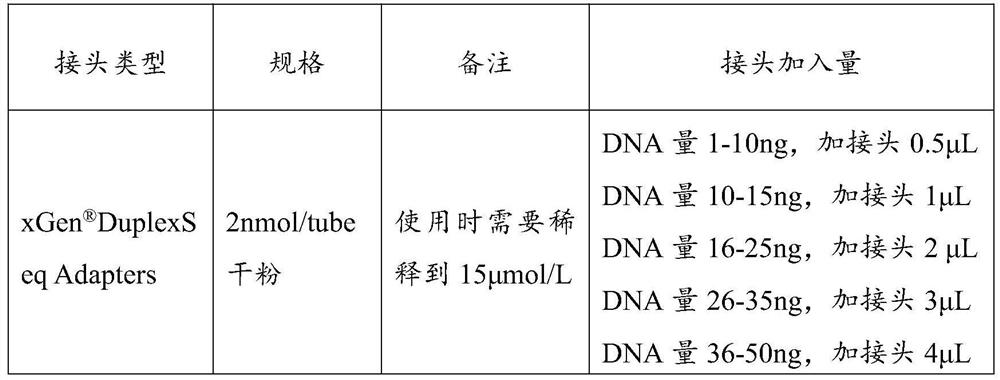
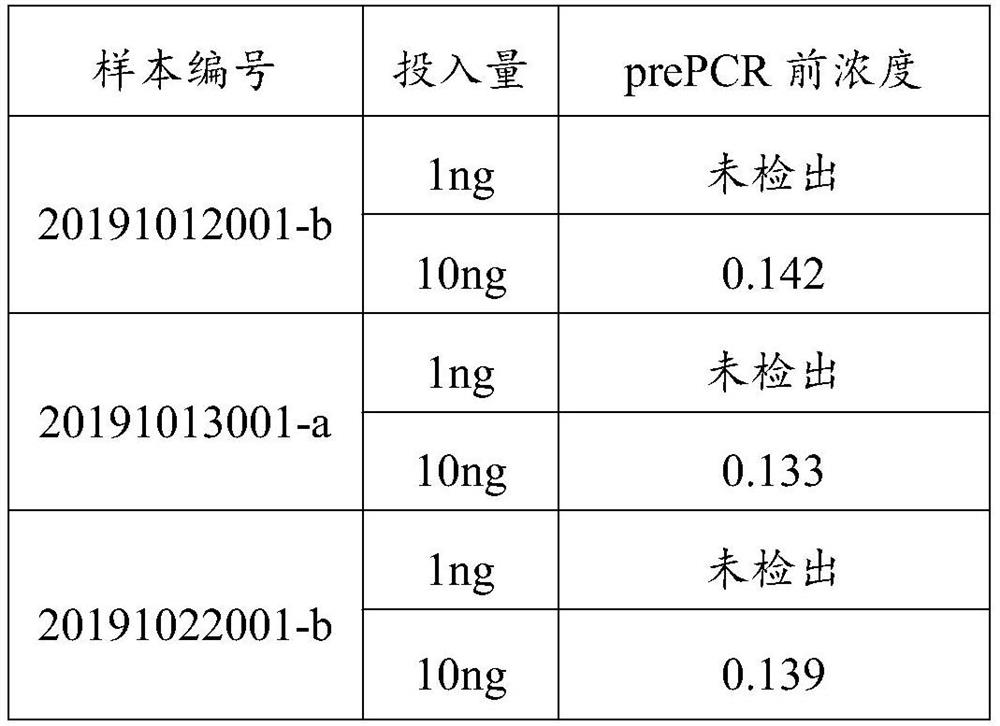
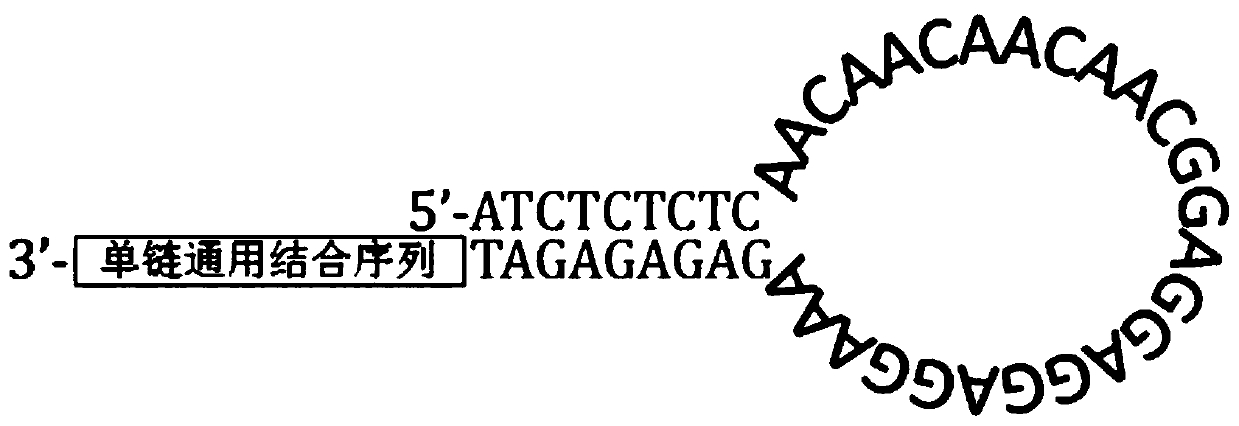Patents
Literature
35 results about "Repair enzymes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA Damage Repair Enzymes. DNA Damage Repair Enzymes are necessary for the repair of errors introduced during DNA replication or recombination or as a result of treatment with exogenous genotoxic agents. These enzymes can be used in vitro to detect specific forms of DNA damage or for repair assays.
Method for assembling PCR fragments of DNA
InactiveUS7629120B2Simple stepsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrigin of replicationSite-specific recombination
A process for assembling a series of DNA fragments generated by PCR into an ordered circular arrangement for replication and genetic work in cells. The PCR fragments are made with a modified nucleotide in the primers that can be removed with a DNA excision repair enzyme to generate a 3′ overhang. The 3′ overhangs are designed to allow directional annealing and thus sequential PCR fragments can be assembled by annealing the overhangs and subsequent ligation. Sequential addition of PCR fragments is facilitated by growing the chain on a solid support, and the assembled chain can be removed with a site specific recombinase if the first and last primers contain the recombinase site. The circularized assembled fragment can be directly used for cell transformation if the appropriate sequences are included, such as an origin of replication and a selectable marker.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Methods and kits for determining a risk to develop cancer, for evaluating an effectiveness and dosage of cancer therapy and for correlating between an activity of a DNA repair enzyme and a cancer
Methods and kits for (i) determining a risk of a subject to develop cancer; (ii) evaluating an effectiveness and dosage of cancer therapy administered to a cancer patient; and (iii) determining a presence of correlation or non-correlation between an activity of at least one DNA repair enzyme and at least one cancer, are disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
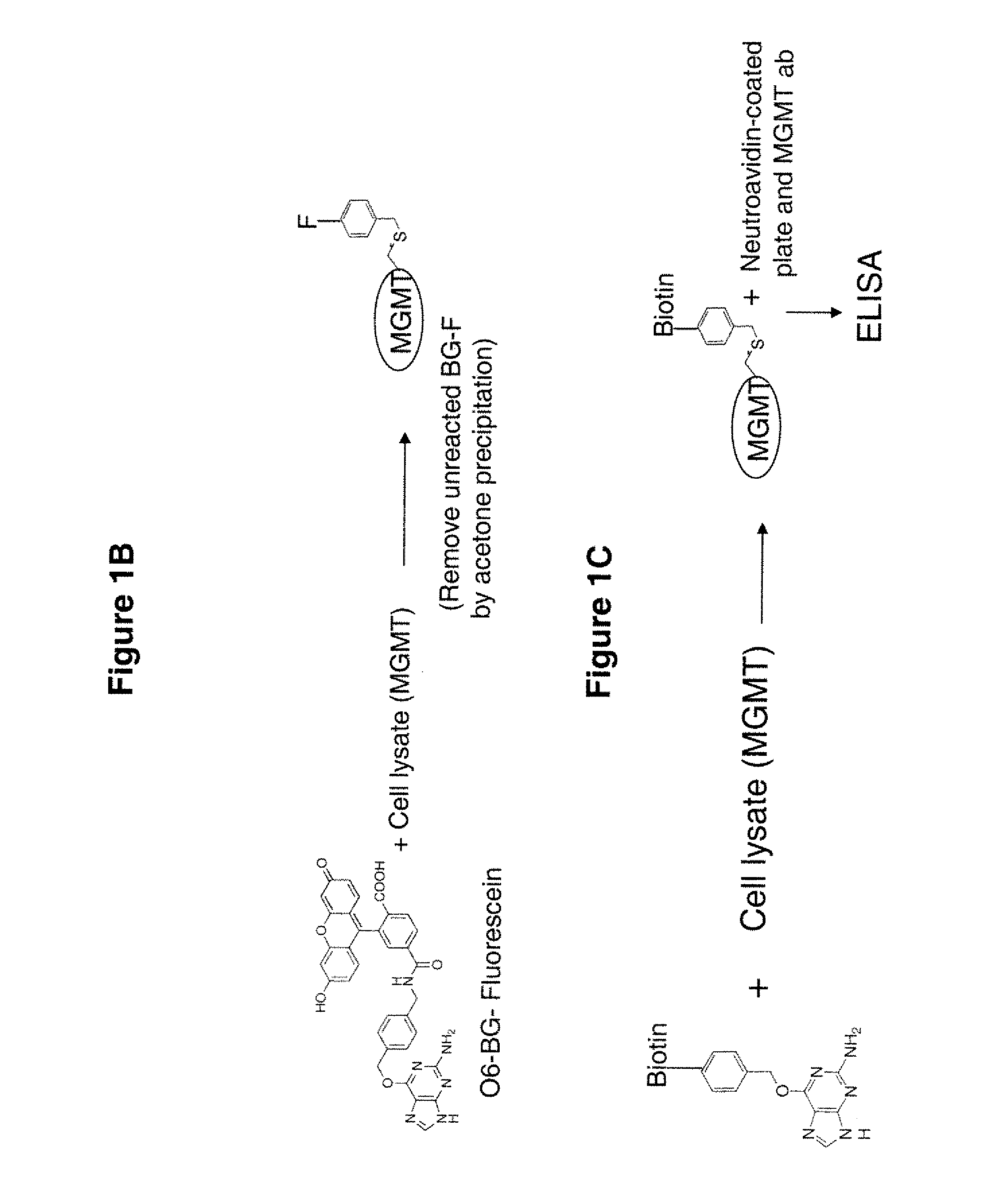
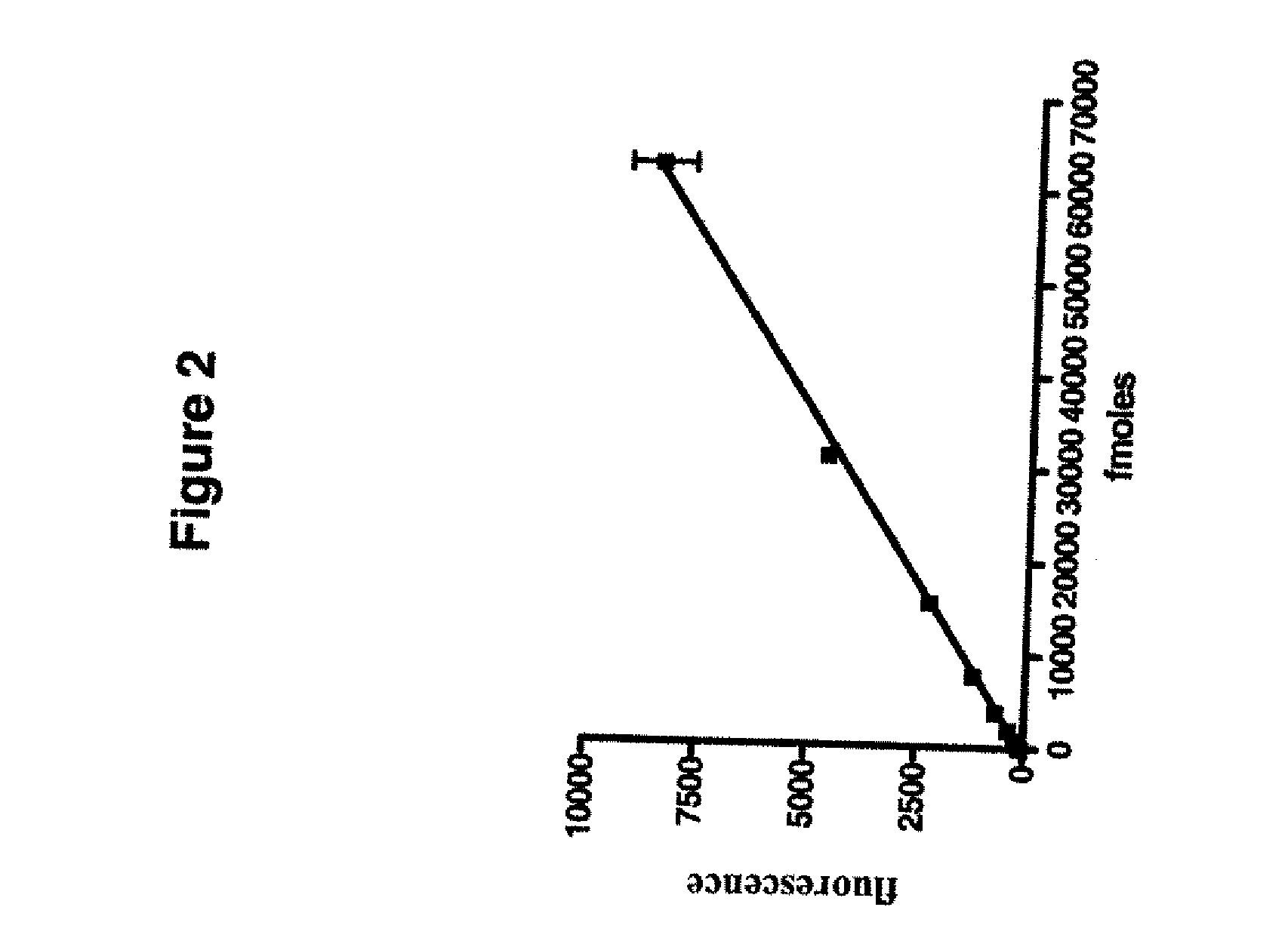
Development of a novel assay for mgmt (methyl guanine methyl transferase)
InactiveUS20070264672A1Shorten the timeLower potentialBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceRepair enzyme
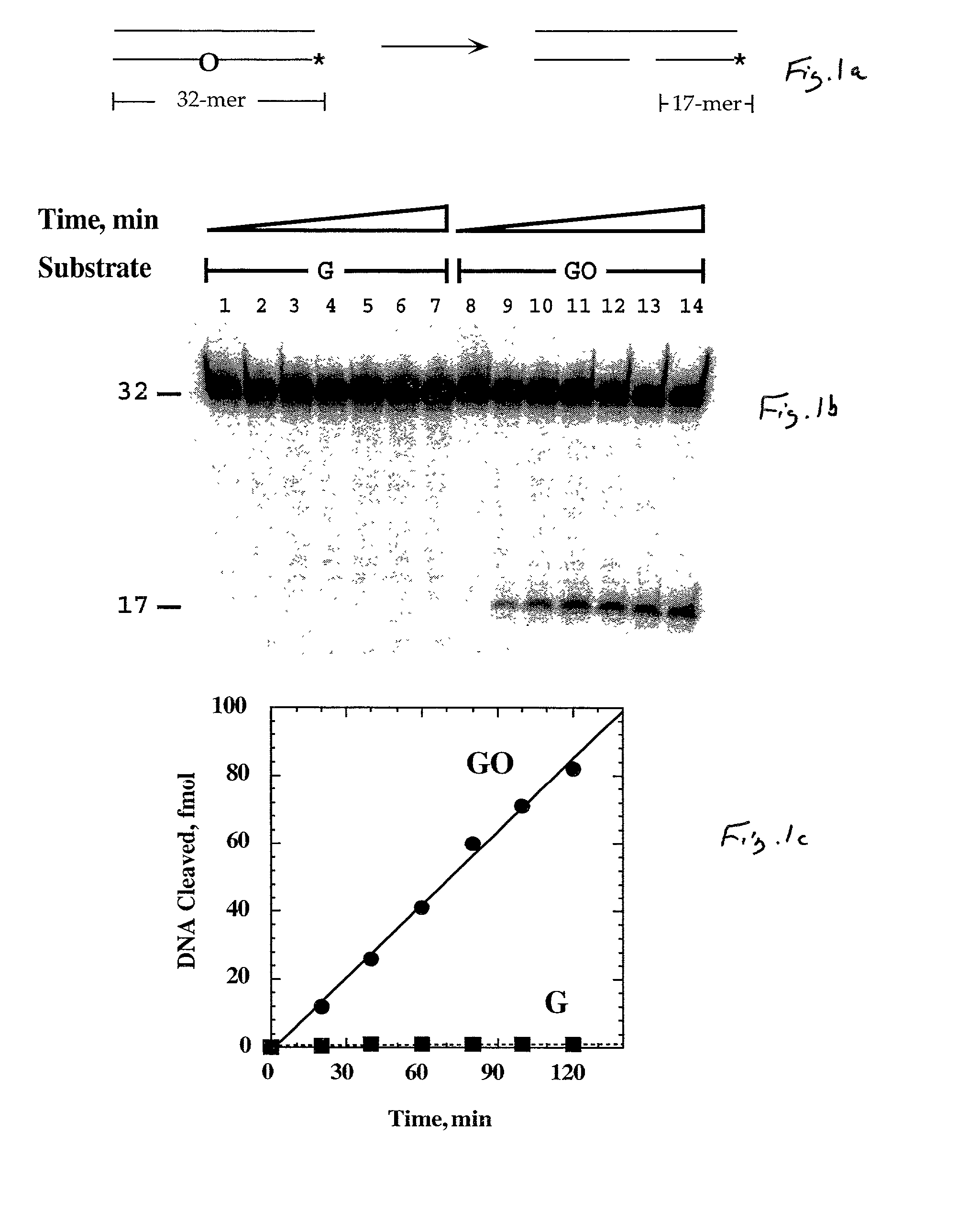
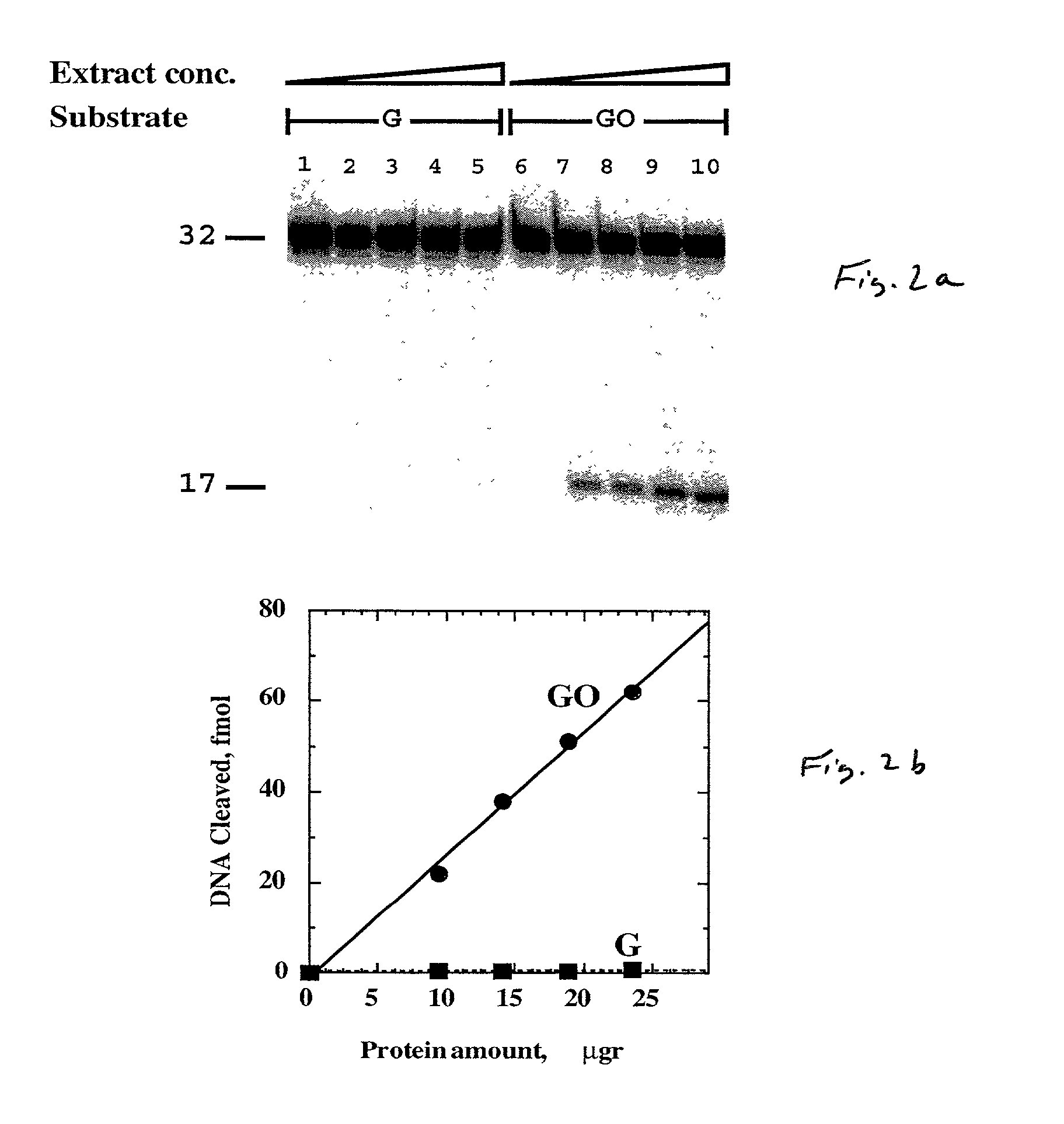
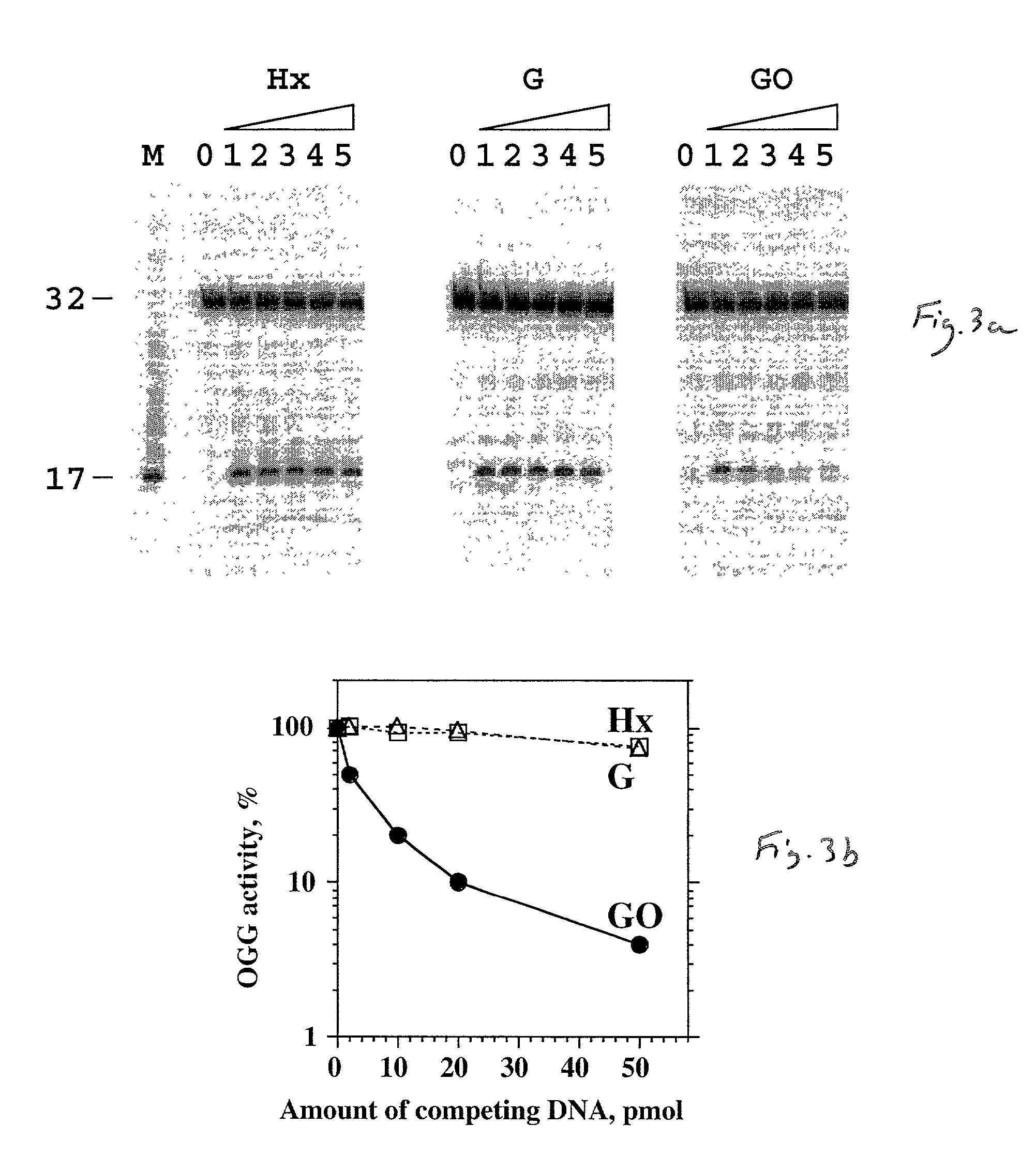
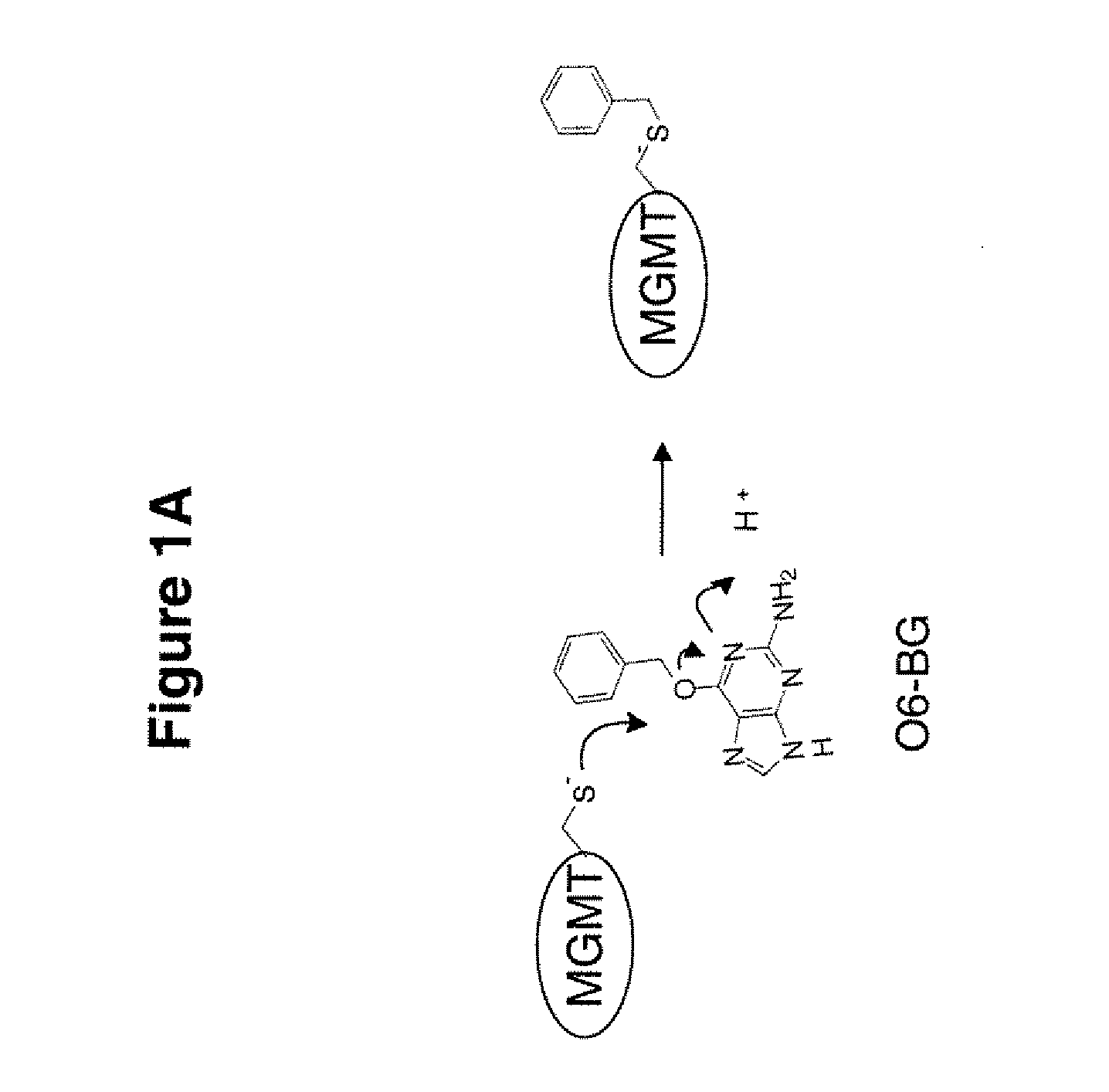
The present invention provides improved methods for assessing the level of MGMT activity in a variety of biological preparations. MGMT, a DNA repair enzyme, can reduce the chemotherapeutic efficacy of alkylating agents by repairing the damage that alkylating agents do to tumor cell DNA. The methods of the present invention can be used, inter alia, to measure MGMT levels and to thereby predict the clinical response to alkylating agents. The present invention includes three preferred assays for assessment of MGMT activity: (1) the immunoassay technique, (2) the labeled O6—BG technique, and (3) the fluorescence polarization technique. Kits useful for the performance of such assays are also provided.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Kit for genetic detection of colorectal cancer
InactiveCN101608224AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceFhit gene
The invention discloses a kit for genetic detection of colorectal cancer. The kit comprises a specific primer pair and a specific probe pair which are used for detecting the mononucleotide polymorphism loci genotype of a 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene (MTHFR), a glutathione-s-transferase T1 gene (GSTT1), a glutathione-s-transferase M1 gene (GSTM1), a cytochrome P450 2E1 gene (CYP2E1), and a mismatching repair enzyme gene (hMLH1), a fluorescent quantitative PCR general component, a PCR reaction component and the like. The kit can evaluate the genetic risk of individuals suffered from the colorectal cancer by detecting the polymorphism loci genotype of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of the colorectal cancer at the same time.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
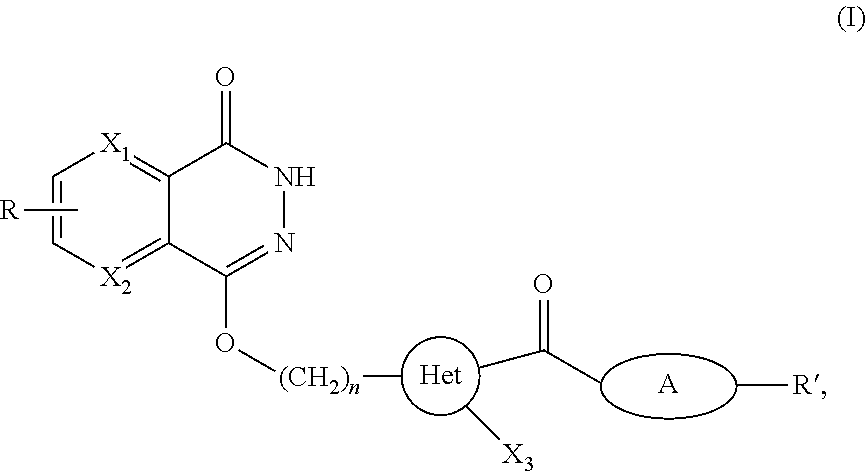
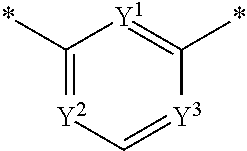
5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof
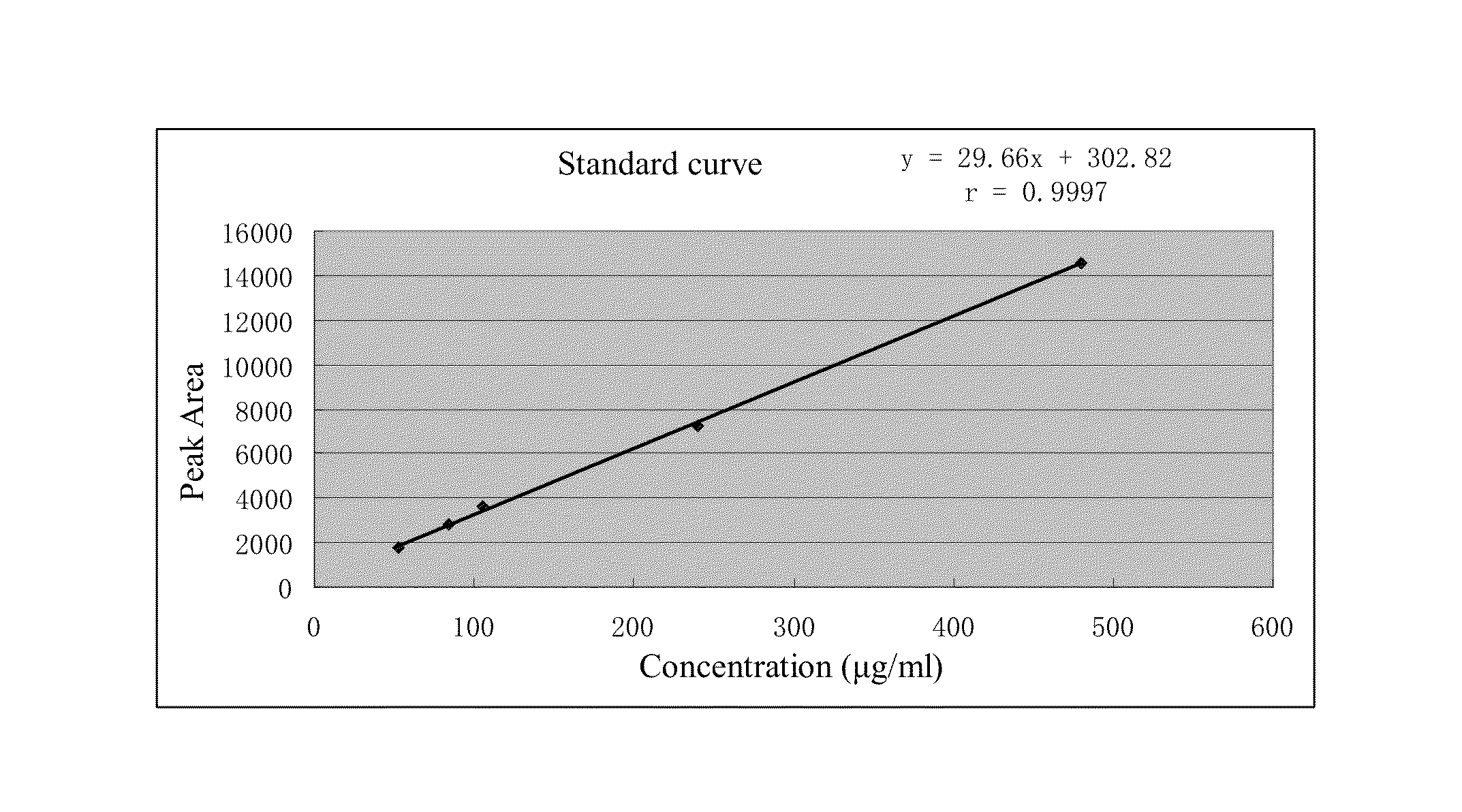
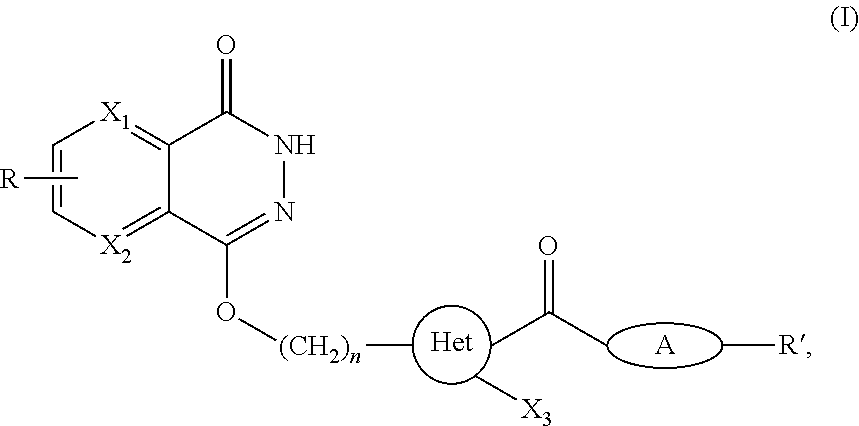
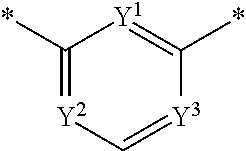
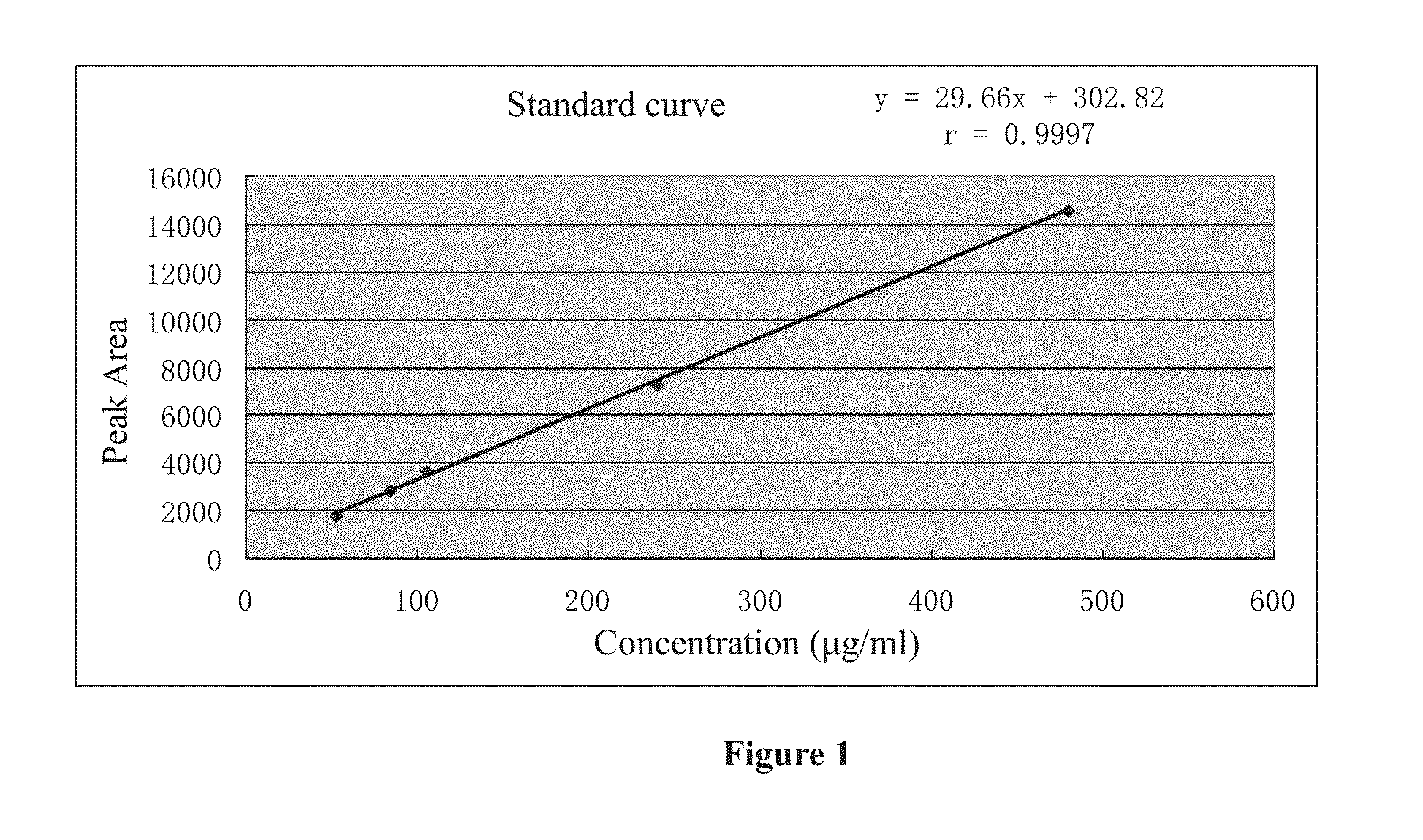
The present invention pertains generally to the field of therapeutic compounds. More specifically the present invention pertains to 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile compounds (referred to herein as “TFM compounds”) which, inter alia, inhibit Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) kinase function. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo, to inhibit CHK1 kinase function, and in the treatment of diseases and conditions that are mediated by CHK1, that are ameliorated by the inhibition of CHK1 kinase function, etc., including proliferative conditions such as cancer, etc., optionally in combination with another agent, for example, (a) a DNA topoisomerase I or II inhibitor; (b) a DNA damaging agent; (c) an antimetabolite or a thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor; (d) a microtubule targeted agent; (e) ionizing radiation; (f) an inhibitor of a mitosis regulator or a mitotic checkpoint regulator; (g) an inhibitor of a DNA damage signal transducer; or (h) an inhibitor of a DNA damage repair enzyme.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
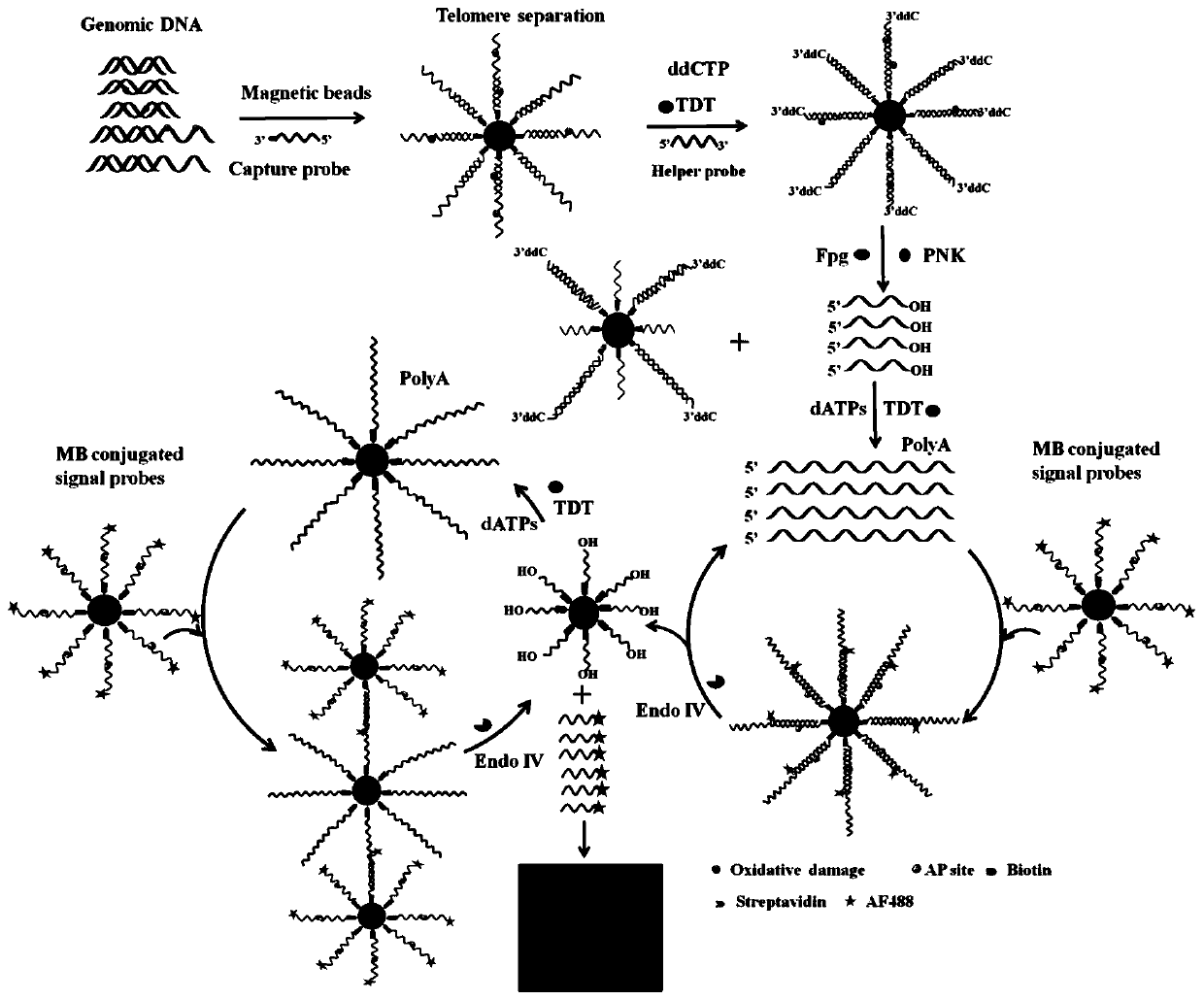
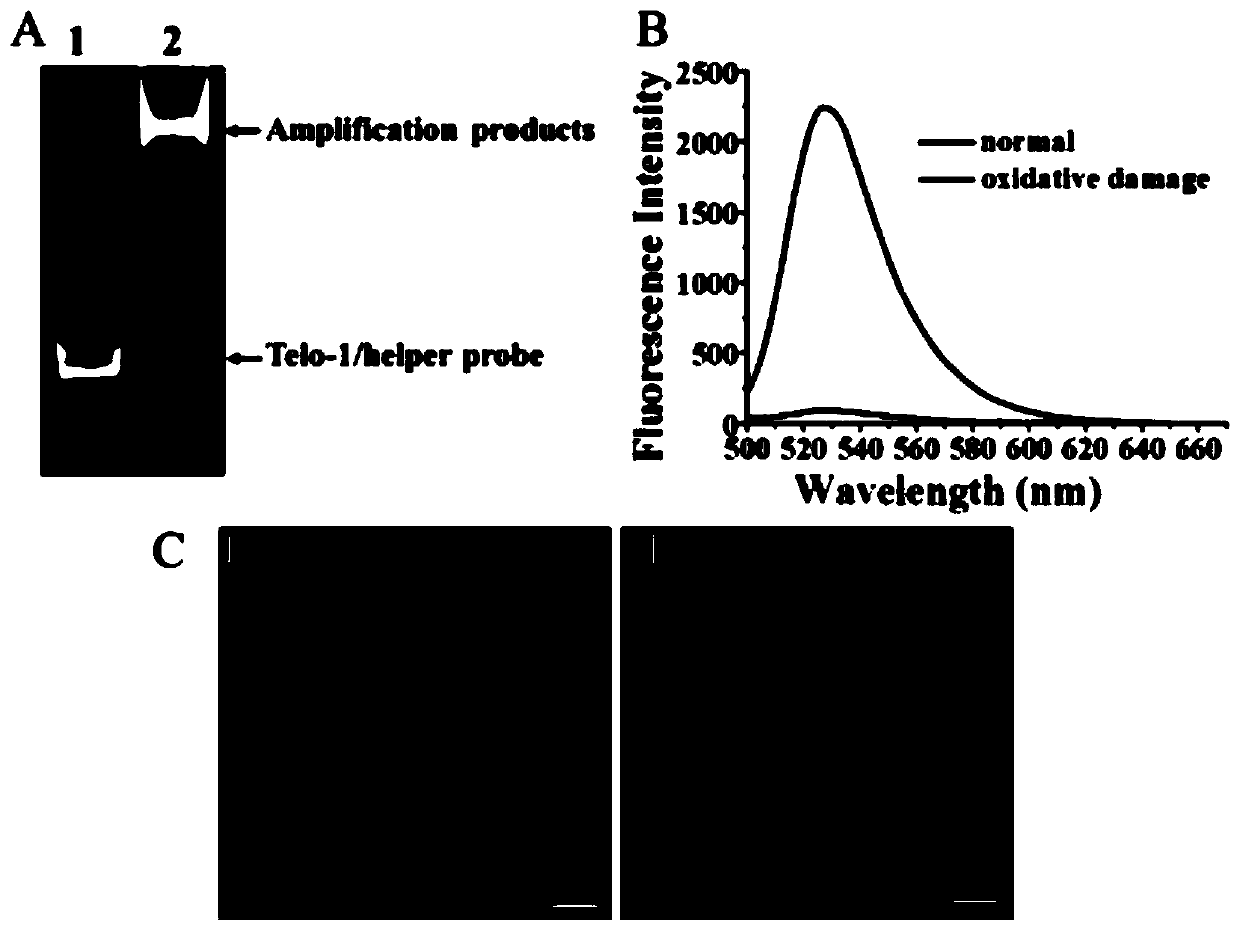
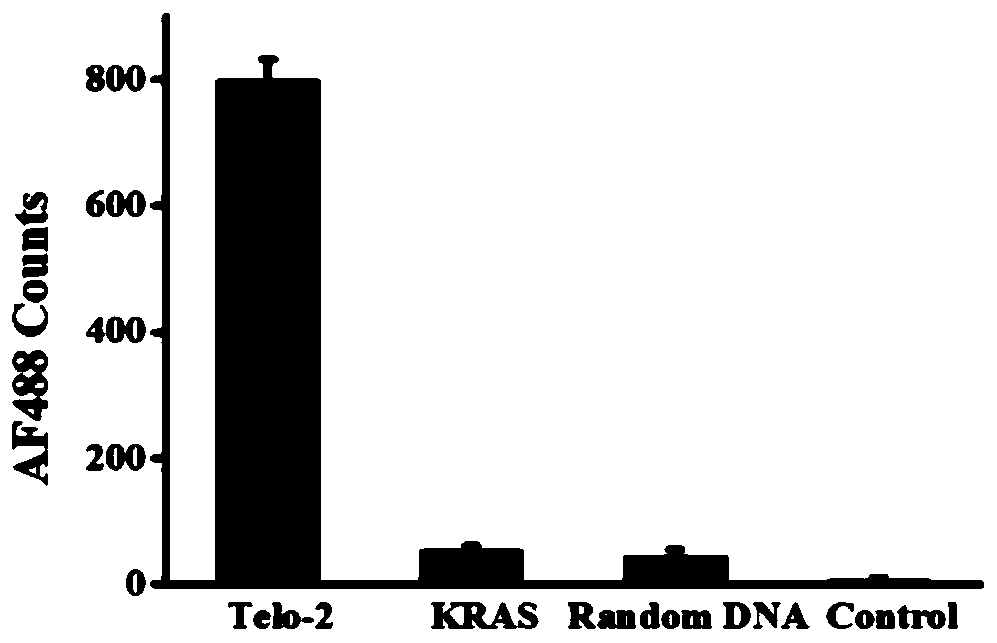
Fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and application of fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method
ActiveCN110144384AReduce consumptionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreRepair enzymes
The invention provides a fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and an application of the fluorescent chemical sensor and the detection method. Specificity of a repair enzyme and polymerization mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase are combined so as to start a cycle cutting signal probe induced by endonuclease IV, induce an AP sitein an Endo IV splitting signal probe, cause release of AF488 fluorophore on the signal probe, and besides, generate a signal probe having free 3'-OH end. Each signal probe having free 3'-OH can be effectively extended through TdT to generate a long poly-A sequence. The released poly-A sequence and a newly-generated poly-A sequence can induce the repeated cycle cutting of the signal probe so as torelease more AF488 fluorophore. Under magnetic separation, the fluorophore in supernatant can be imaged and quantified by unimolecule. The fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method have favorable actual application value.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method of predicting the clinical response to chemotherapeutic treatment with alkylating agents
The present invention provides methods relating to chemotherapeutic treatment of a cell proliferative disorder. In particular, a method is provided for predicting the clinical response to certain types of chemotherapeutic agents. Alkylating agents, used for the treatment of certain types of tumors including tumors of the nervous system and lymph system, are efficacious agents when the damage they do to tumor cell DNA is not repaired by cellular DNA repair mechanisms. The present invention provides a method for determining the activity of a gene encoding a DNA repair enzyme, thus providing a prediction of the clinical response to alkylating agents.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for assembling PCR fragments of DNA
InactiveUS20050048514A1Simple stepsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrigin of replicationSite-specific recombination
A process for assembling a series of DNA fragments generated by PCR into an ordered circular arrangement for replication and genetic work in cells. The PCR fragments are made with a modified nucleotide in the primers that can be removed with a DNA excision repair enzyme to generate a 3′ overhang. The 3′ overhangs are designed to allow directional annealing and thus sequential PCR fragments can be assembled by annealing the overhangs and subsequent ligation. Sequential addition of PCR fragments is facilitated by growing the chain on a solid support, and the assembled chain can be removed with a site specific recombinase if the first and last primers contain the recombinase site. The circularized assembled fragment can be directly used for cell transformation if the appropriate sequences are included, such as an origin of replication and a selectable marker.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Construction method of sequencing library for pathogenic microorganism detection
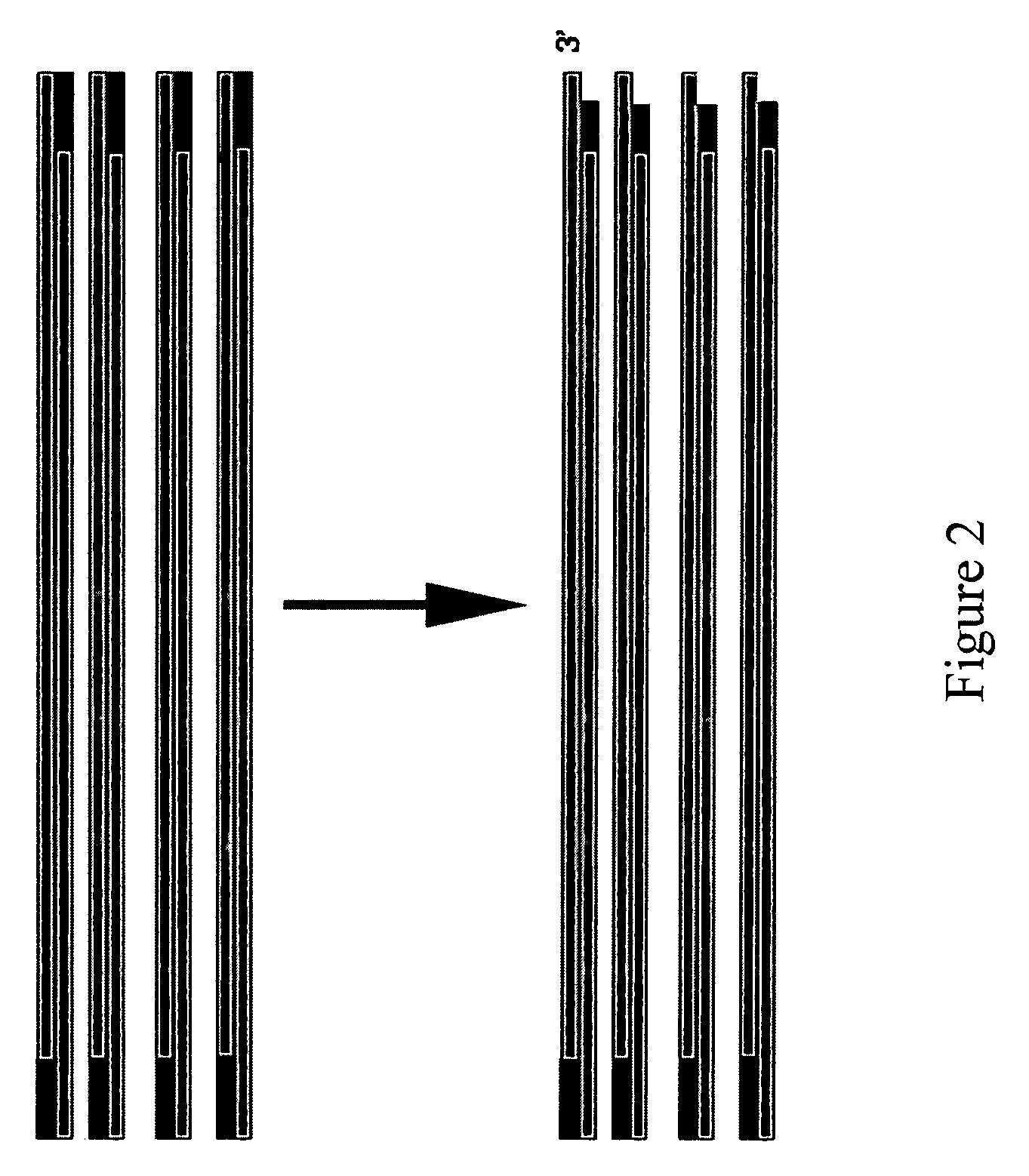
PendingCN112011835ARealize simultaneous database buildingSave operating timeLibrary creationPathogenic microorganismA-DNA
The invention discloses a construction method of a sequencing library for pathogenic microorganism detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting DNA and RNA from a sample, and carrying out reverse transcription on tbe RNA; S2, adding a double-strand synthesis reaction solution and a double-strand synthetase into step S1 to make RNA / cDNA composite double strands form double-strand cDNA; S3, purifying; S4, adding a DNA interruption repair reaction solution and a DNA interruption repair enzyme mixture into the purified product obtained in step S3, and performing fragmentation, terminal repair and A tail addition on the product at the same time; S5, directly adding a linker, a linker reaction liquid and ligase into the fragmented solution without purifying, and performinglinker connection to obtain a linker connection product; S6, purifying; S7, carrying out library amplification; and S8, purifying the amplification product in step S7 to obtain the original DNA / RNA sequencable library. The method is short in time; and when the RNA is subjected to one-strand synthesis and two-strand synthesis, only RNA is acted, DNA existing in a system is not interfered, and after RNA is converted into double-strand cDNA, RNA and double-strand DNA are fragmented together, so that the effect of co-building the library in one process is truly achieved.
Owner:南京实践医学检验有限公司
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor
ActiveUS9187430B2Avoid damageMinimize damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicinePolymerase L
Disclosed are a phthalic hydrazide (phthalazine ketone) compound, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. As a DNA repair enzyme poly (ADP-ribozyme) polymerase inhibitor, the compound and the pharmaceutical composition can effectively treat diseases involving PARP enzymatic activity, including cancer, neural degenerative diseases, inflammation and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU DIAO PHARMA GROUP
Poly (adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitor
Disclosed are a phthalic hydrazide (phthalazine ketone) compound, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. As a DNA repair enzyme poly (ADP-ribozyme) polymerase inhibitor, the compound and the pharmaceutical composition can effectively treat diseases involving PARP enzymatic activity, including cancer, neural degenerative diseases, inflammation and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU DIAO PHARMA GROUP
Methods and kits for determining a risk to develop cancer, for evaluating an effectiveness and dosage of cancer therapy and for correlating between an activity of a dna repair enzyme and a cancer
Methods and kits for (i) determining a risk of a subject to develop cancer; (ii) evaluating an effectiveness and dosage of cancer therapy administered to a cancer patient; and (iii) determining a presence of correlation or non-correlation between an activity of at least one DNA repair enzyme and at least one cancer, are disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Rapid full-length amplicon library construction method, primers and sequencing method applicable to PacBio platform
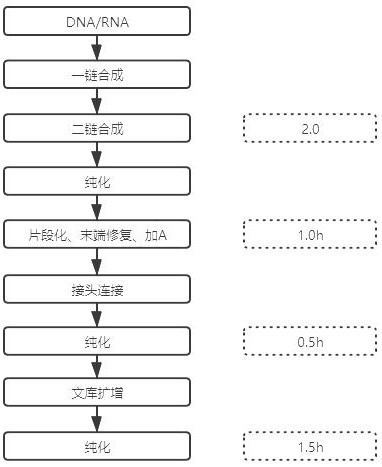
InactiveCN111455023ASimplify the build processImprove work efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsEngineering
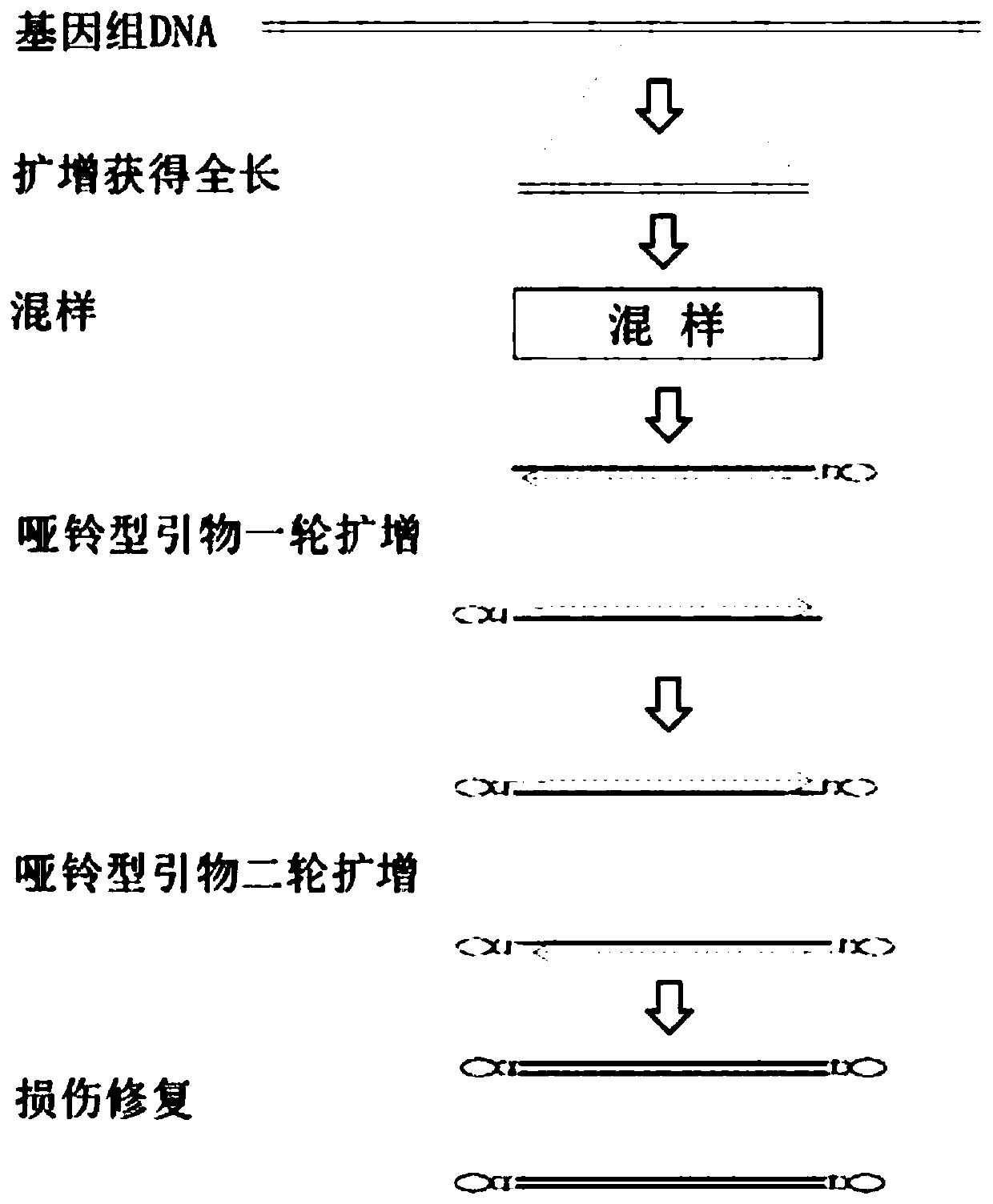
The invention relates to a rapid full-length amplicon library construction method and primers applicable to PacBio platform and a full-length amplicon sequencing method based on the library construction method. According to the characteristic that PCR is required for full-length amplicon sequencing, an amplicon primer with a general binding sequence and a dumbbell-shaped primer matched with the general binding sequence are designed in combination with a dumbbell-shaped library joint structure of the PacBio sequencing platform, the rapid full-length amplicon library construction method applicable to the PacBio platform is provided based on the two primers with special structures, through library construction by the method, addition of sequencing joints can be realized by increasing two cycles of annular primer amplification only after conventional amplification, and meanwhile, a PCR product becomes a standard library applicable to the PacBio sequencing platform under the action of damage repair enzyme. The method optimizes an original PacBio standard library construction process into only one-step amplification and repair, the library construction process of a full-length amplicon is greatly simplified, and the sequencing cost is significantly reduced.
Owner:WUHAN FRASERGEN CO LTD
Nucleic acid nano structure probe and preparation method and application thereof
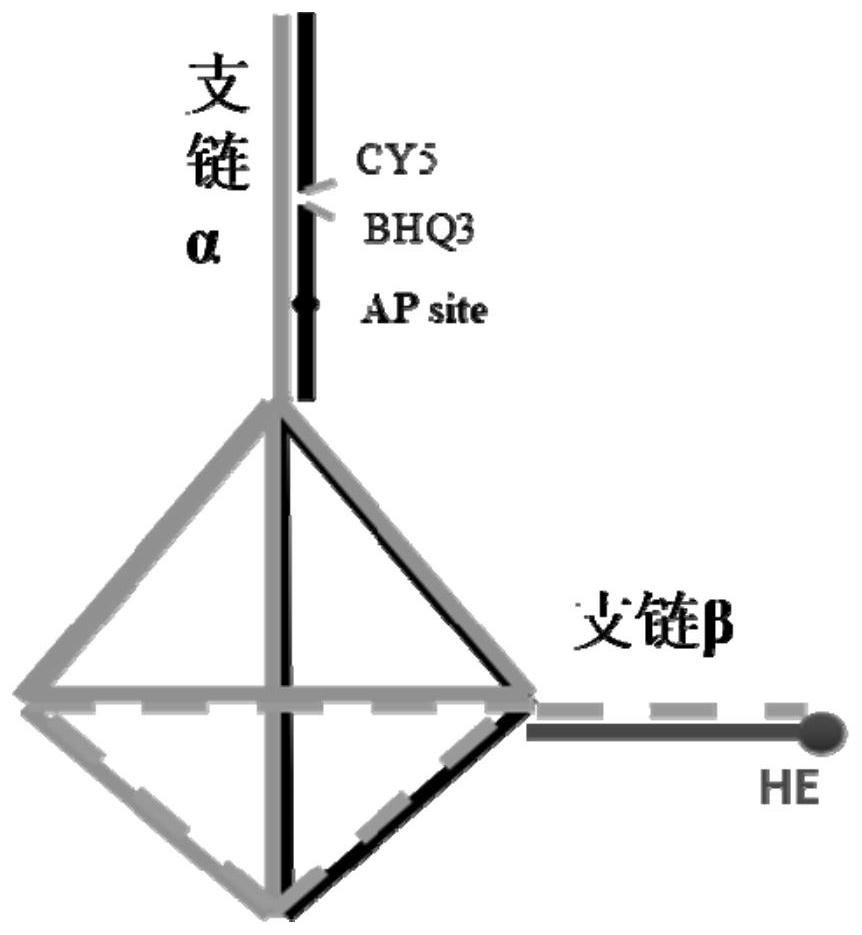
ActiveCN111676269AImprove stabilityImprove cell entry efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAP siteNucleic Acid Probes
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure probe and a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of molecular detection. The nano nucleic acid probe comprises: a, a nano-molecular cage with a tetrahedral structure composed of four main chain DNA single strands, wherein two of the main chain DNA single strands respectively have a branched chain alphaand a branched chain beta that extend out of the tetrahedral structure; b, two non-main chain DNA single strands bound to the branched chain alpha through base complementary pairing, wherein one of the two non-main chain DNA single strands is modified with a fluorescent group, and the other is modified with an AP site and a quenching group; and c, the other non-main chain DNA single strand containing dihydroethidium bound to the branched chain beta through base complementary pairing. The invention also discloses the preparation method and application of the nucleic acid nano structure probe. The nucleic acid nano probe of the invention can simultaneously detect APE1 and O<2>.<-> in cells, and can be used to simultaneously determine nucleic acid repair enzymes and small reactive oxygen molecules. Through a confocal imager, the space distribution of the target detection objects APE1 and O<2>.<-> in cells can be detected.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS
Antibodies immunologically specific for a DNA repair endonuclease and methods of use thereof
An isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding a human DNA repair enzyme, MED1, is disclosed. Like other mismatch repair genes which are mutated in certain cancers, MED1, encoding nucleic acids, proteins and antibodies thereto may be used to advantage in genetic or cancer screening assays. MED1, which recognizes and cleaves DNA, may also be used for the diagnostic detection of mutations and genetic variants.
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
DNA library construction kit based on illumina sequencing platform, library construction method and application
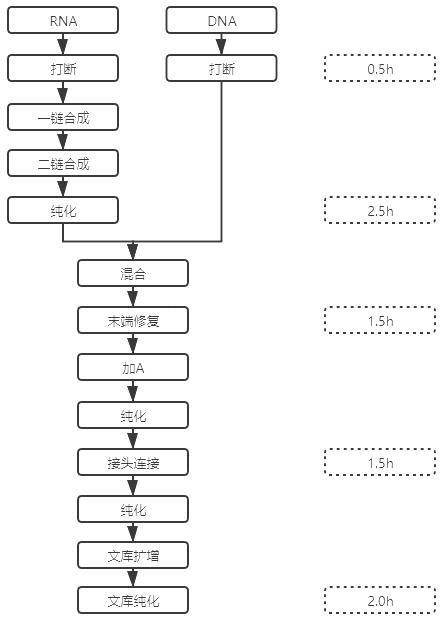
PendingCN111005074AImprove connection efficiencyReduce the cost of building a libraryMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention provides a DNA library construction kit based on an illumina sequencing platform, a library construction method and application. The kit comprises a P7 linker, a P5 linker, an enzyme composition or a buffer solution, wherein the enzyme composition comprises any one or a combination of at least two of a terminal repair enzyme, a PCR amplification enzyme or a T4DNA ligase; and the buffer solution comprises a tail end repairing buffer solution and / or a connecting buffer solution. According to the kit disclosed by the invention, a reaction solution is prepared by adopting commercially available reagents, so that the library construction cost is reduced, the reaction procedure is simplified, a terminal repair reaction system and an A-adding reaction system are combined in one system, the reaction time is shortened, and the enzyme connection efficiency is improved.
Owner:江西海普洛斯医学检验实验室有限公司
Method for investigating cytosine methylation in dna by means of dna repair enzymes
InactiveUS20070160995A1Easy to detectIncrease probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDisease causeUracil formation
The following invention concerns a method for investigating cytosine methylation by means of DNA repair enzymes. Here, the DNA is first converted so that unmethylated cytosines are converted to uracil, while 5-methylcytosine remains unchanged. Then the DNA is hybridized to oligonucleotides, whereby hybrids will be formed with or without erroneous base pairings, in each case depending on the methylation status of the DNA. Following this, the erroneously paired hybrids will be cleaved by repair enzymes. Then the methylation status of the DNA can be determined in different ways. The method according to the invention is particularly suitable for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer disorders and other diseases associated with a change of the methylation status as well as for predicting undesired drug effects.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Ultramicro nucleic acid sample library building method applied to NGS platform
PendingCN112680794AQuality improvementRepair damageMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationRepair enzymesDNA extraction
The invention discloses an ultramicro nucleic acid sample library building method applied to an NGS platform. The ultramicro nucleic acid sample library building method comprises the following steps: adding nucleic acid repair enzyme into an ultramicro nucleic acid sample for nucleic acid repair before DNA extraction of the ultramicro nucleic acid sample; then carrying out DNA extraction on the ultramicro nucleic acid sample containing the nucleic acid repair enzyme; and carrying out library construction on the extracted DNA to obtain a sequencing library of the ultramicro nucleic acid sample. According to the ultramicro nucleic acid sample library building method, nuclease repair is carried out on sample DNA before DNA extraction; in addition, nucleic acid repair enzyme is added in the DNA extraction process; DNA damage can be effectively repaired, reaction false positive is reduced, DNA extraction quality is improved, and the constructed library can be better suitable for NGS sequencing. According to the library building method, the problems that the DNA extracted from the FFPE sample is poor in quality and low in total quantity, and the library cannot be effectively built are solved.
Owner:深圳海普洛斯医学检验实验室 +1
An anticancer sustained release injection carrying clorfarabine and its synergist
InactiveCN1875934AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryAdjuvantMicrosphere
Disclosed is an anticancer slow release injection carrying both clofarabine and its synergistic agent, which comprises slow release micro-balloons and dissolvent, wherein the slow release microballoons comprise anti-cancer active constituents and slow release auxiliary materials, the dissolvent being specific dissolvent containing suspension adjuvant. The anticancer effective ingredients include clofarabine and its synergistic agents selected from phosphoinositide-3-enzyme inhibitor, pyrimidine analog and / or DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor, the slow release auxiliary materials are selected from polylactic acid and copolymer, polyethylene glycol, PLA-COOH copolymer, di-aliphatic acid and sebacylic acid copolymer, poly(erucic aciddipolymer-sebacylic acid), poly(fumaric acid-sebacylic acid), Polifeprosan, poly(lactic acid) and EVAc, the viscosity of the suspension adjuvant is 100-3000cp (at 20-30 deg C), and is selected from sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
Owner:JINAN KANGQUAN PHARMA TECH
Method for remediating halogenated hydrocarbon-contaminated sites by using reductive dechlorinase
The invention relates to a contaminated site remediation method which is mainly used for remedying a contaminated site mainly containing halohydrocarbon pollutants, in particular to remediation adopting the reductive dechlorination enzyme. According to the specific efficiency of the reductive dechlorination enzyme on the halohydrocarbon pollutants, one method for improving the activity of the reductive dechlorination enzyme is proposed, so that the halohydrocarbon DNAPL (dense non-aqueous phase liquid) pollutants in the deep position of the contaminated site are rapidly and thoroughly removed. The method for remedying the halohydrocarbon contaminated site through the reductive dechlorination enzyme comprises the step that biological enzyme is injected to the underground part of the halohydrocarbon contaminated site and transferred to a pollution source area for pollutant degradation, and is characterized in that the biological enzyme is the reductive dechlorination enzyme, and the reductive dechlorination enzyme is prepared to form a liquid enzyme preparation containing the reductive dechlorination enzyme, diethyl aminoethyl synthetic plasma and polymeric alcohol. The activity of the enzyme in the reductive dechlorination enzyme preparation prepared with the method can keep longer than one week, and the practicability of the preparation for site remediation is guaranteed.
Owner:山东碧泉环境工程技术有限公司
A kind of method for measuring the content of pyrimidine dimer on DNA chain
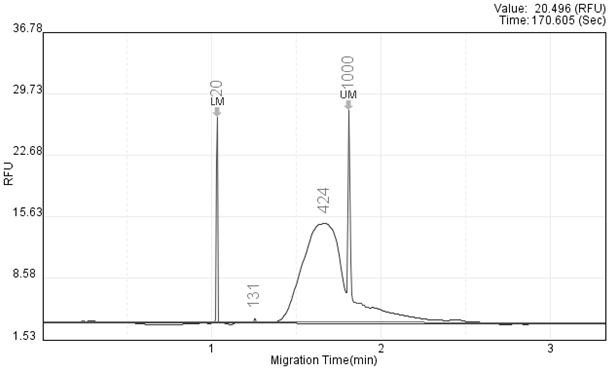
InactiveCN1945332BQuick checkQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsDimerHuman health
The method for measuring the content of pyrimidine dimer on the DNA chain of the present invention is characterized in that the probe DNA with a pyrimidine dimer modified at the end is fixed on the surface of the chip; the standard product of pyrimidine dimer is prepared; Mix the 80nm pyrimidine dimer standard with 0.2-5 μg / ml pyrimidine dimer antibody, and plot the response value of the surface plasmon resonance sensor to detect the mixture flowing over the chip surface against the concentration of pyrimidine dimer to obtain a standard curve; The sample is mixed with the antibody at the same concentration as the standard curve is established, and the response value of the mixture flowing through the chip surface is detected, and the concentration of pyrimidine dimer in the sample can be obtained according to the standard curve. The invention has the advantages of rapid detection, accurate quantification and good reproducibility; the chip can be reused, and the detection cost is low; the range of detectable samples is wide; Evaluate the effects of ozone layer depletion on human health.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
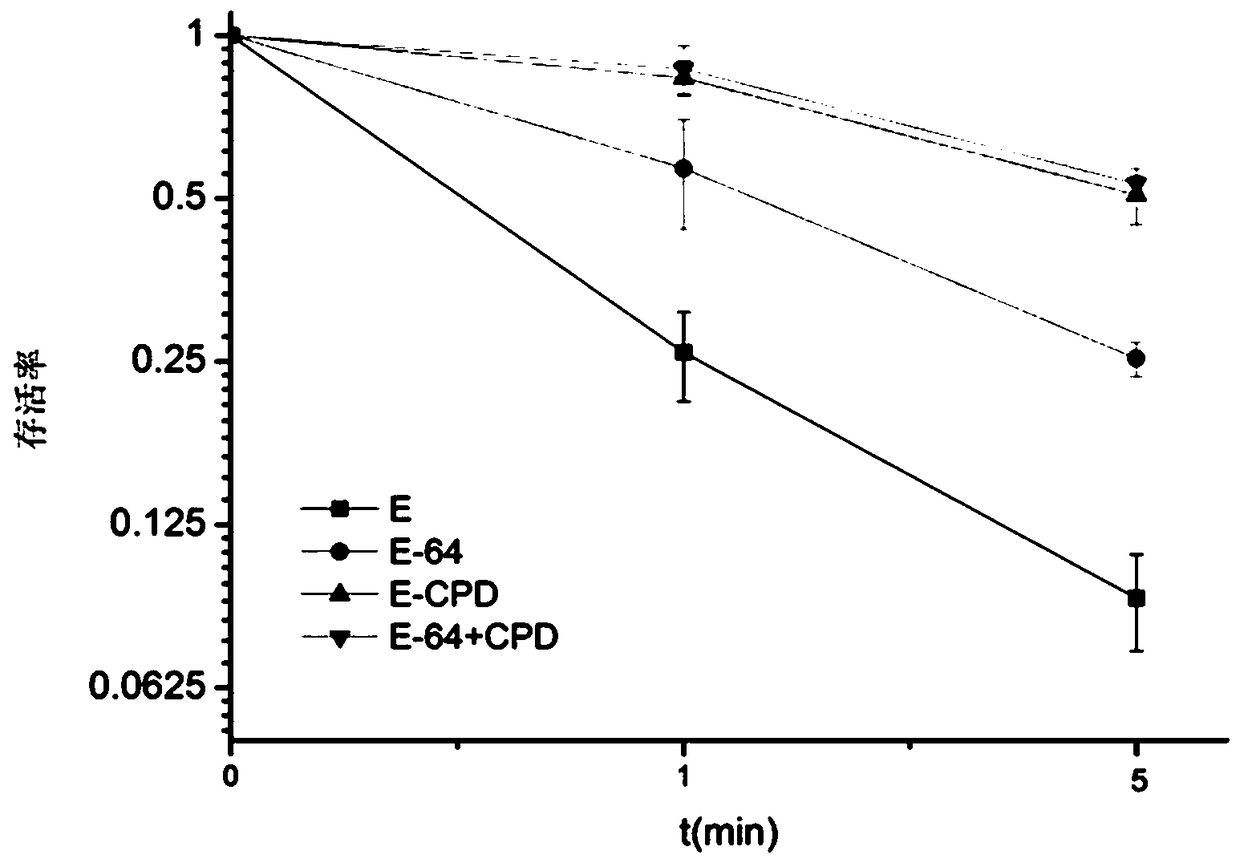
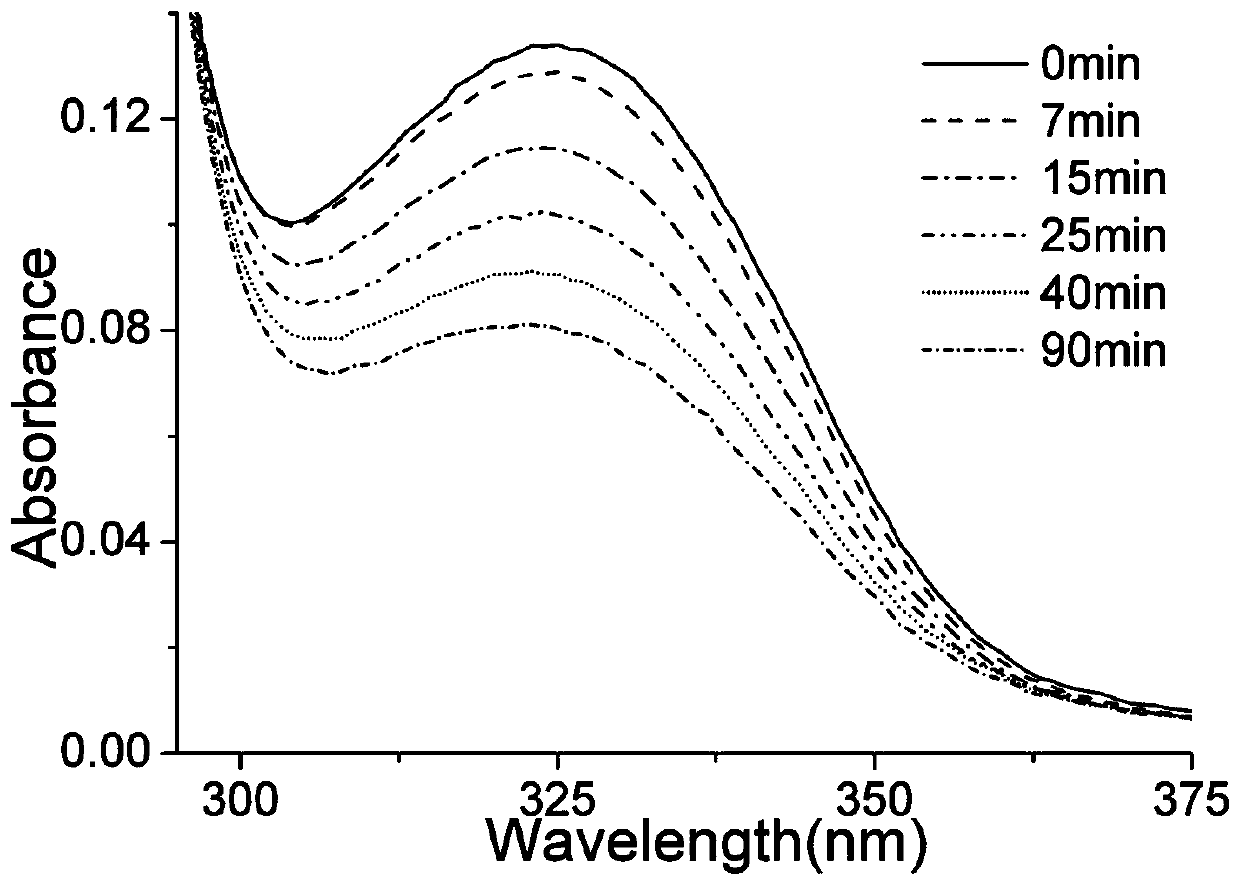
Mutant CPD photo-repair enzyme and 6-4 photo-repair enzyme double-plasmid co-expression bacterial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109370968AAbility to repair damageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUltravioletBacterial strain
The invention provides a mutant CPD photo-repair enzyme, a 6-4 photo-repair enzyme double-plasmid co-expression bacterial strain and application thereof. The co-expression strain is obtained by transforming plasmids of the CPD photo-repair enzyme into the 6-4 photo-repair enzyme expression strain and then mutating a glutamic acid on the site 323 of the CPD photo-repair enzyme into alanine. The mutant CPD photo-repair enzyme and the 6-4 photo-repair enzyme double-plasmid co-expression strain are constructed; and the bacterial strain has the ability of the CPD photo-repair enzyme and a 6-4 photo-repair enzyme to effectively repair the DNA damage caused by ultraviolet radiation. The bacterial strain obtained by the site-directed mutagenesis of the CPD photo-repair enzyme significantly improves the ability of resistance to ultraviolet radiation, and is of great significance for studying the effect of UV-B on living organisms and the life mechanism of the living organisms to adapt to UV-B enhancement.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
A site-directed mutation Aspergillus niger 6-4 photorepair enzyme and its construction method
ActiveCN109971728BIncrease vitalityVitality lasting and stableNucleic acid vectorEnzymesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses Aspergillus niger 6-4 photolyase with site-specific metagenesis and a construction method thereof. The Aspergillus niger 6-4 photolyase with site-specific metagenesis has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. A 6-4 photolyase gene sequence acquired from existing WT Aspergillus is subjected to artificial codon optimization; a metagenesis primer is designed to acquirea metagenetic gene fragment; the gene fragment is linked with pET22b plasmid to construct a recombinant expression plasmid; the recombinant expression plasmid is converted to Escherichia coli competent cells to construct a genetically engineered bacterium for photolyase expression, which is well expressed under 20 DEG C and 1 mM IPTG. Compared with WT photolyase, the mutant enzyme S60N expressed herein has higher activity which is stably maintained longer, can better restore DNA damage caused by ultraviolet, and can be more easily used as cosmetics, and pharmaceutical additives in people's daily lives.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
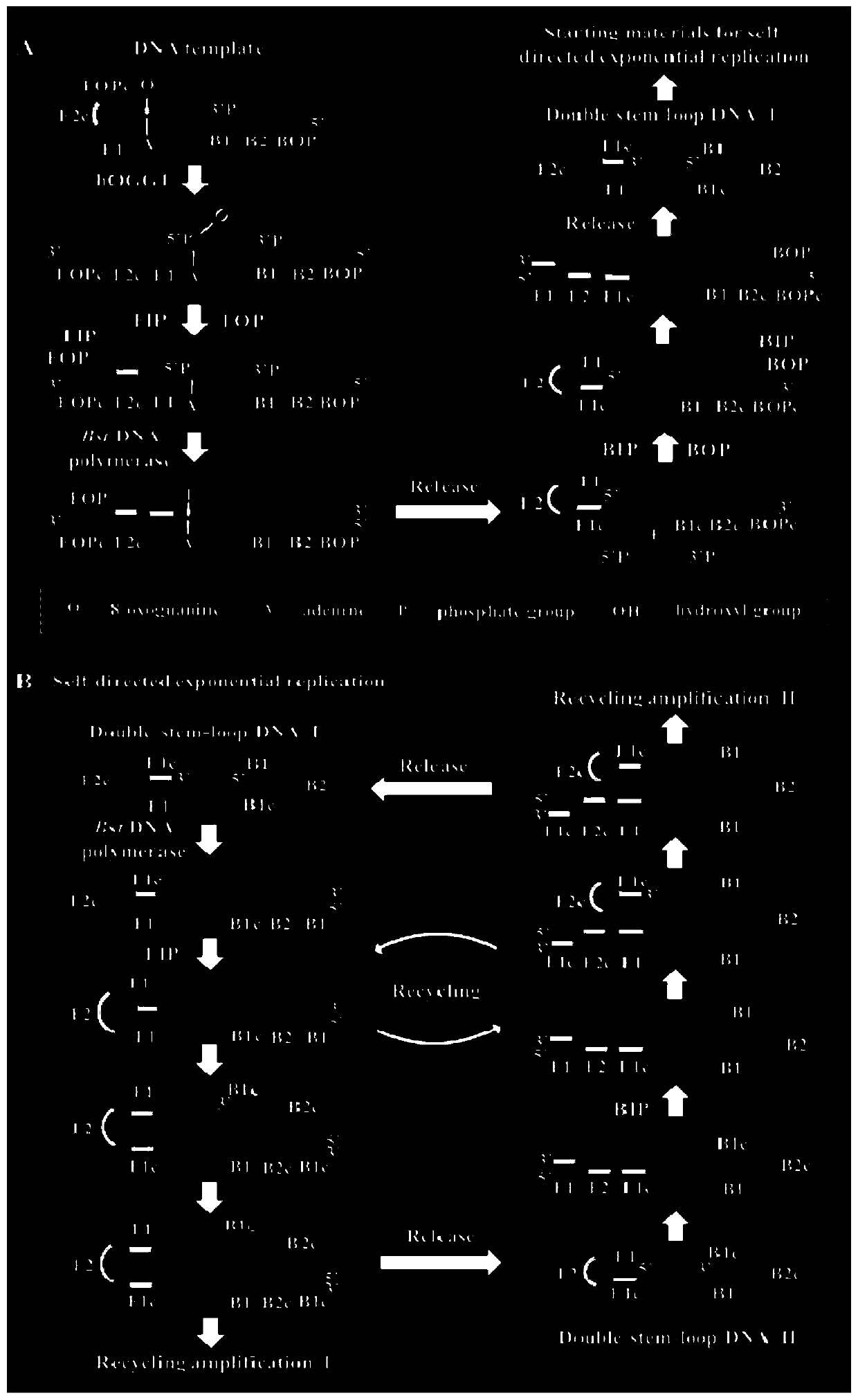
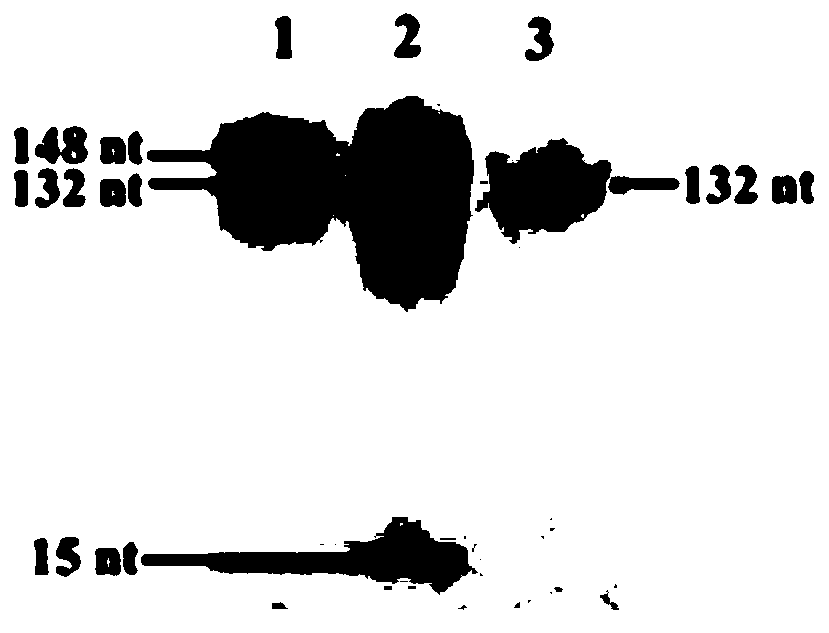
Biosensor for detecting repair glycosylase and detection method and application of biosensor
PendingCN110846385AHigh selectivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JRepair enzymes
The invention provides a biosensor for detecting repair glycosylase and a detection method and application of the biosensor. The biosensor comprises a stem ring DNA template and linear primer probes;the linear primer probes are LAMP primer probes, at least four primer probes are arranged, and comprises two front positive outer and inner primers, namely FIP and FOP, and two rear positive outer andinner primers BIP and BOP. A target base to be detected to repair glycosylase is designed in a stem region of the stem ring DNA template; and the stem ring DNA template is further provided with a region complementary to or identical to a primer probe sequence. The biosensor prepared by the invention actually constructs a self-directed replication system, and can be used for zero background, highsensitivity and high specificity detection of repair glycosylase activity. A simple, robust and universal platform is provided for repairing enzyme related biomedical research and early clinical diagnosis.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
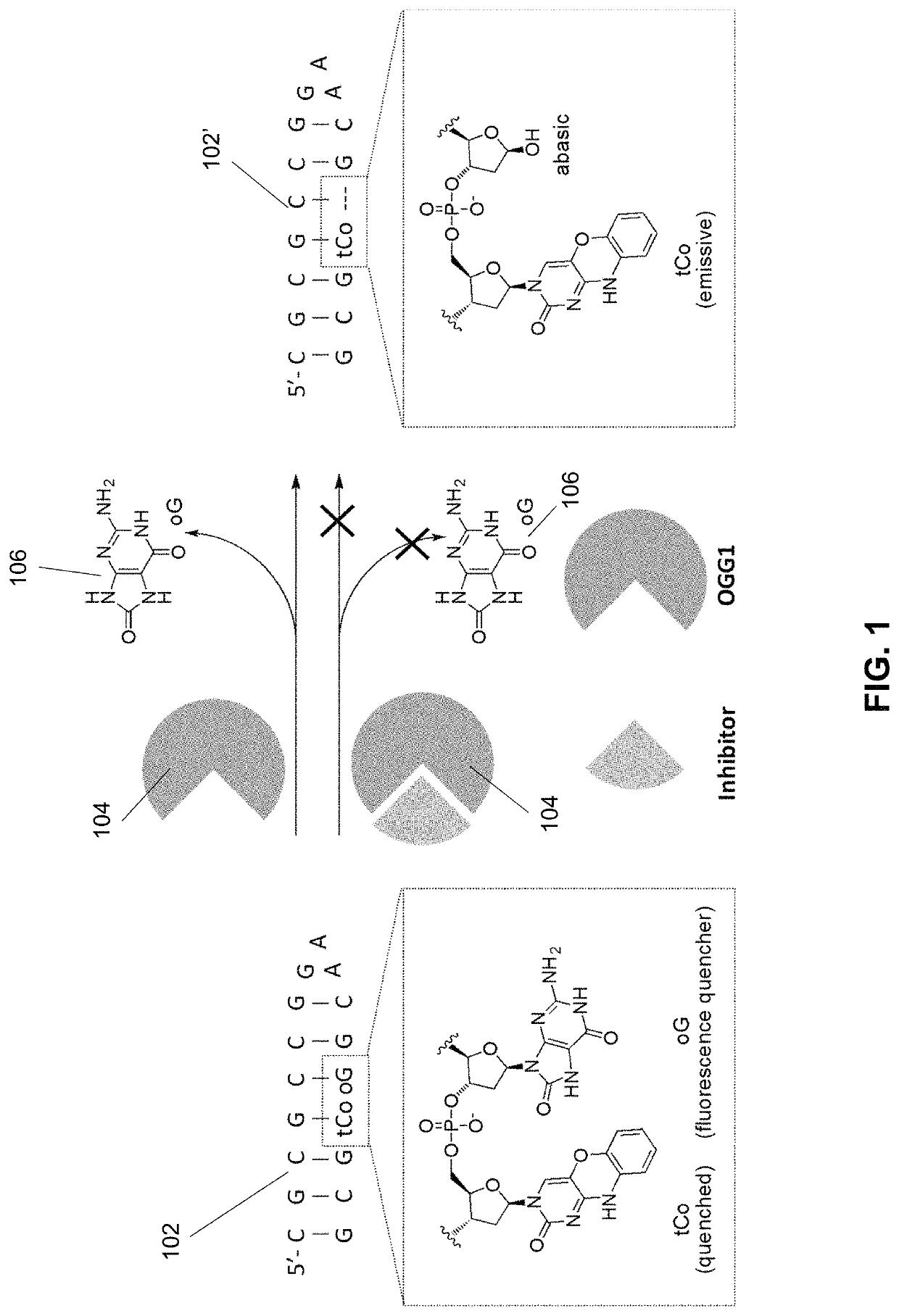
Inhibitors of Base Excision Repair Activity and Therapeutic Methods Based Thereon
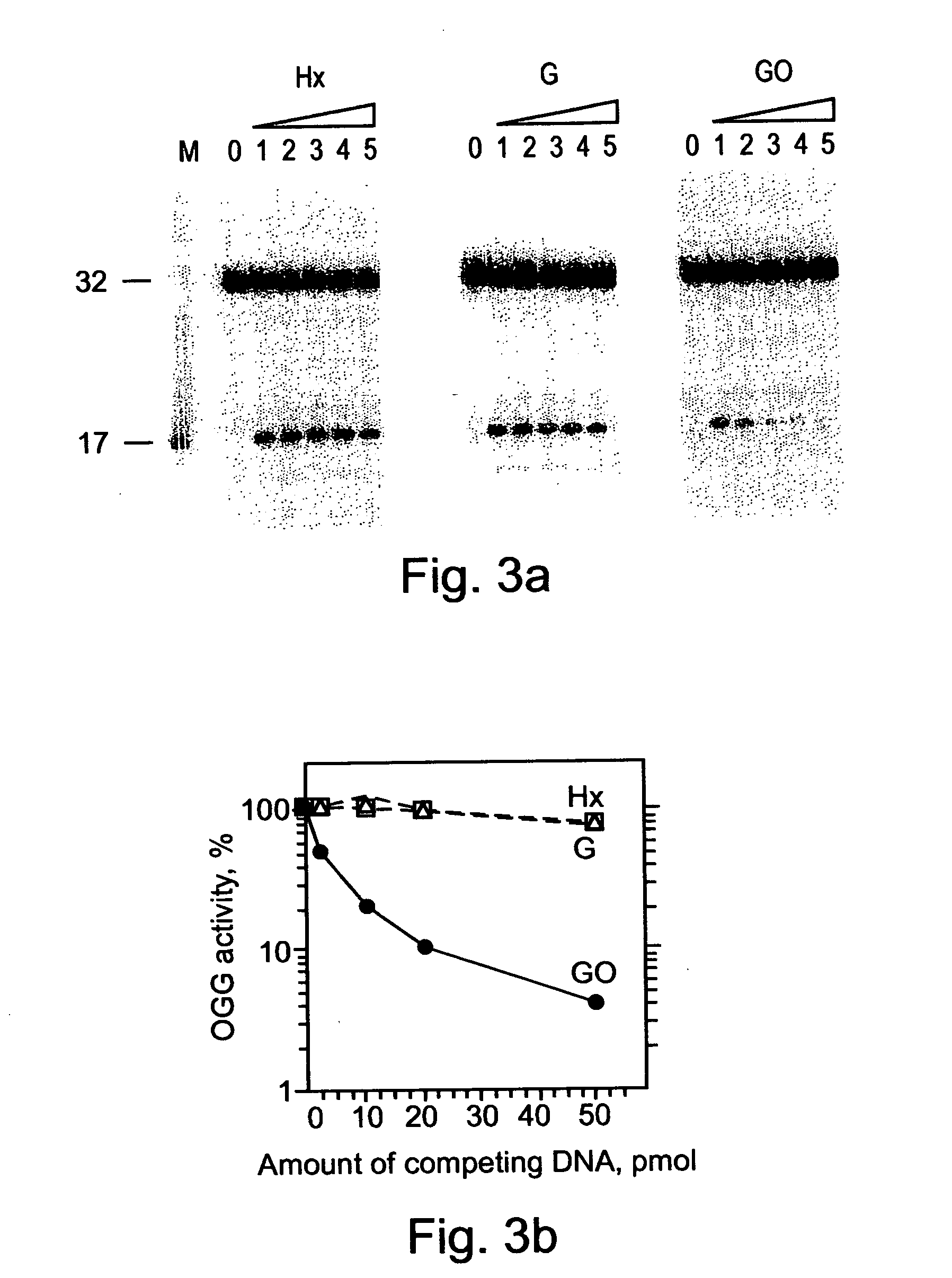
Noncovalent small-molecule inhibitors of the enzyme OGG1, methods of their manufacture, and applications for their administration are provided. Small molecule inhibitors were shown to be selective for inhibiting OGG1 over multiple repair enzymes, including other base excision repair enzymes, and it displayed no toxicity in two human cell lines. The inhibitors provide a tool for the study of the role of OGG1 in multiple disease-related pathways, and a therapeutic target for the treatment thereof.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Compound platinum medicine sustained-release agent
InactiveCN101380306APharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntineoplastic agentsSuspending AgentsTherapeutic effect
A slow release compound platinum drug is a slow release injection which is composed of slow release microspheres and a dissolvant. The slow release microspheres comprise anticancer active components and a slow release adjuvant, and the dissolvant is a common dissolvant or a special dissolvant containing a suspending agent. The anticancer active components are platinum drugs such as ormaplatin, hetaplatin, lobaplatin, nedaplatin or oxaliplatin, and the like, and / or platinum drug synergists selected from a phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and / or a DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow release adjuvant is selected from the copolymer of polylactic acid, EVAc, polifeprosan, sebacic acid copolymer, and the like; the viscosity of the suspending agent is 100cp-3,000cp (at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C), and the suspending agent is selected from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and the like. The slow release microspheres can be also made into a slow release implant. By injecting the slow release injection or placing in tumors or around the tumors, the general toxic reaction of the drug can be reduced, the local drug concentration of the tumors can be selectively improved, and the curative effects of non-operative therapies such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and the like, can be improved.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
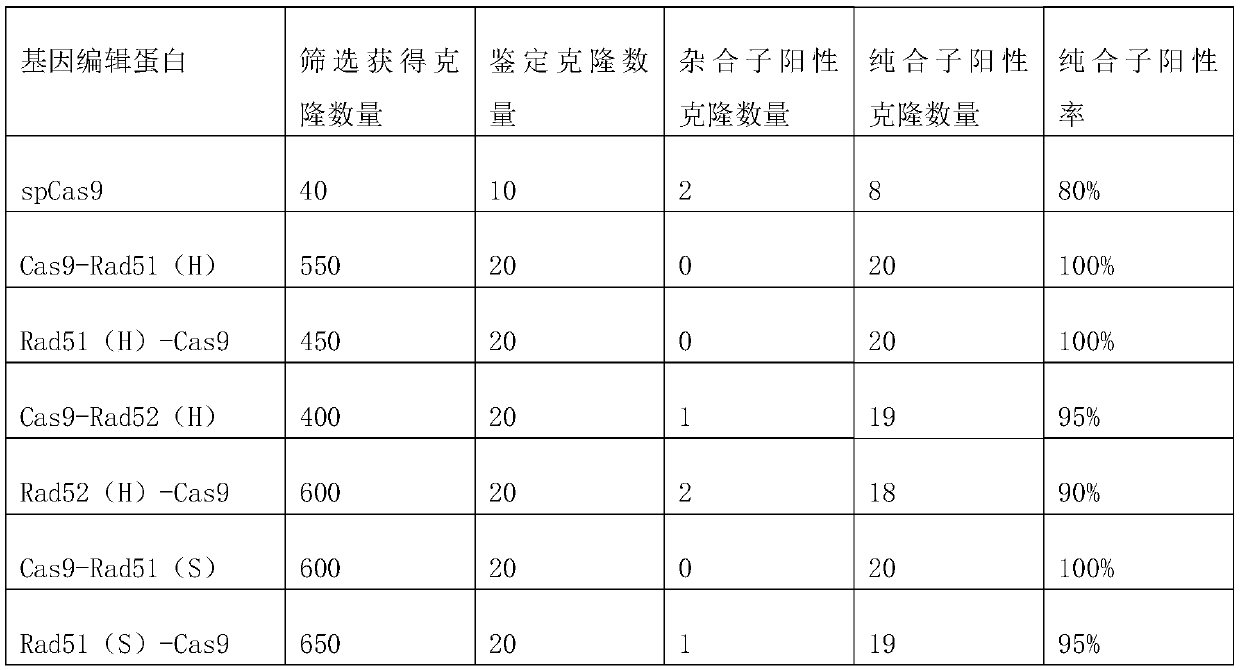
Genetically modified bacteria producing three DNA repair enzymes and method for the evaluation of DNA repair activity
PendingUS20220042024A1Improve performanceHigh purityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBifunctionalTransgene
Three recombinant E. coli strains produce the enzymes CPD-photolyase, 6,4-bifunctional photolyase and 6,4-photolyase, from bacterial Antarctic isolates of the genus Hymenobacter the first one and Sphingomonas the others. It is also disclosed a process of production and purification of the recombinant enzymes with high performance, high degree of purity and high catalytic repair activity, having applications in, but it is not limited to, cosmetics and pharmaceutical industry. A fast, cheap and qualitative method is provided for the determination of the CPD photolyase activity.
Owner:UNIV DE LA REPUBLICA +1
Fusion protein and design method thereof
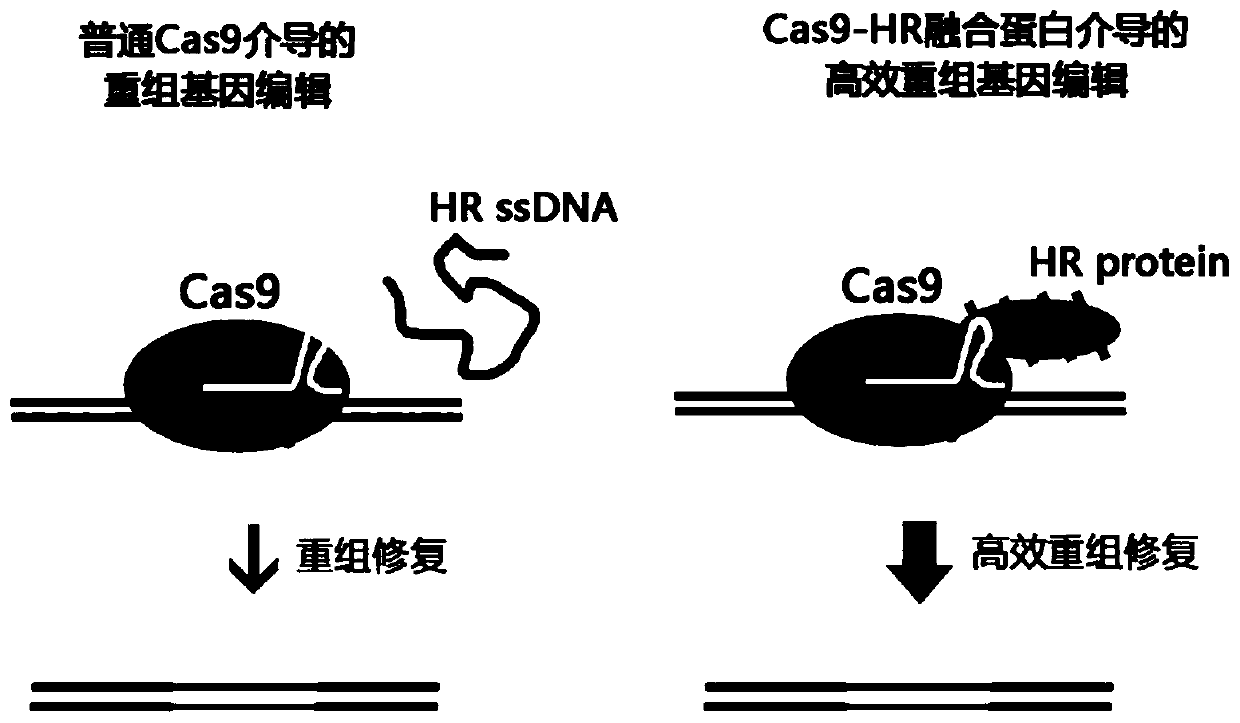
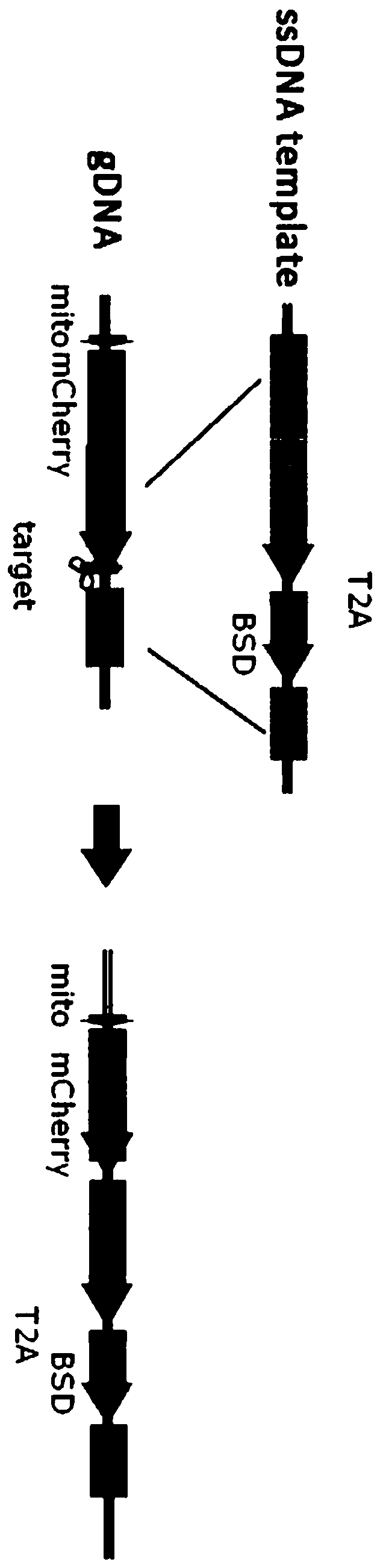
InactiveCN111518220AImprove the efficiency of recombination repairFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesRepair enzymesA-DNA
The invention discloses a fusion protein and a design method thereof. The design method comprises the following steps: fusing a recombinant helper protein with the DNA binding function and a protein with the DNA cleavage function. When the fusion protein with the DNA cleavage function performs cleavage, the recombinant helper protein provides a DNA recombinant repair template near a cleavage site,and recruits recombinant repair enzyme, so that the recombinant repair efficiency is greatly improved. The fusion protein has the advantage that the recombination repair efficiency is improved.
Owner:重庆英茂盛业生物科技有限公司
Method for investigating cytosine methylation in DNA by means of DNA repair enzymes
InactiveUS7723026B2Easy to detectIncrease probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHistone methylationDisease cause
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines as inhibitors of repair enzyme 8-oxoguanine deoxyribonucleic acid glycosylase activity
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00001.png)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00002.png)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00003.png)