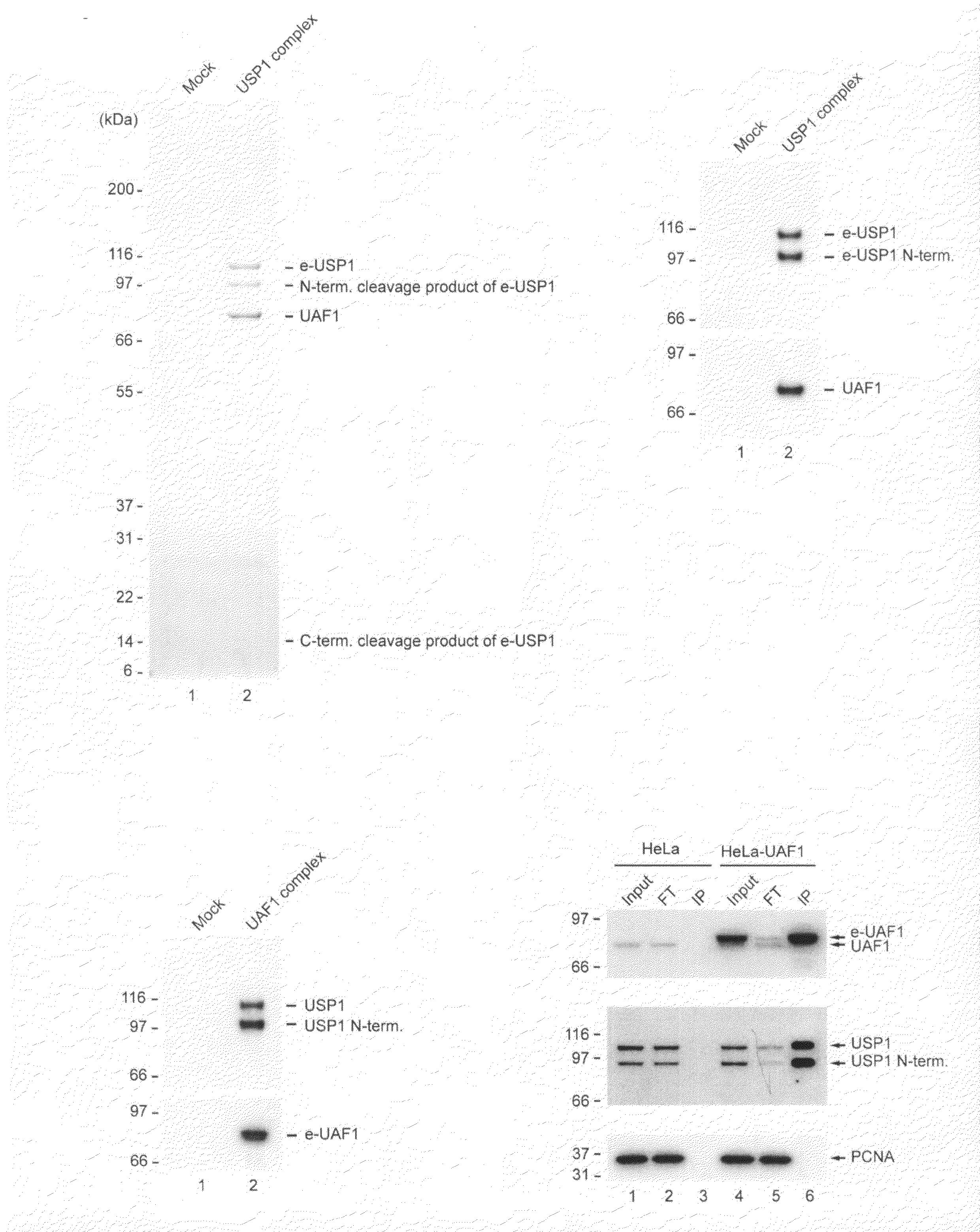Patents
Literature
335 results about "DNA Damage Repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome.
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
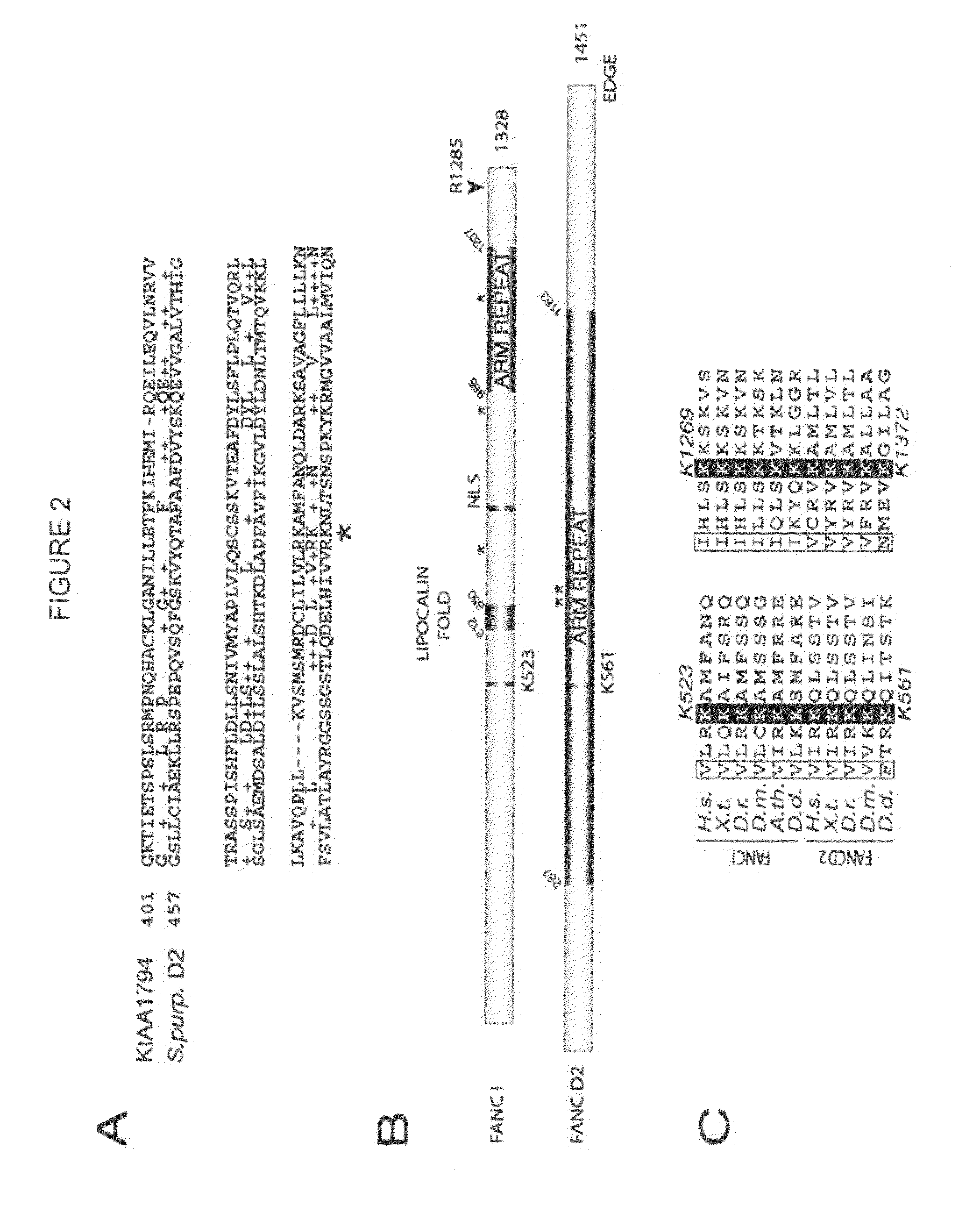
Prognostic, diagnostic, and cancer therapeutic uses of FANCI and FANCI modulating agents
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer. In particular, the present invention identifies and characterizes the FANCI polypeptide as a vital component of the Fanconi anemia pathway and discloses inhibitors of FANCI and methods of using same. Such inhibitors are useful in inhibiting DNA damage repair and can be useful, for example, in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +2
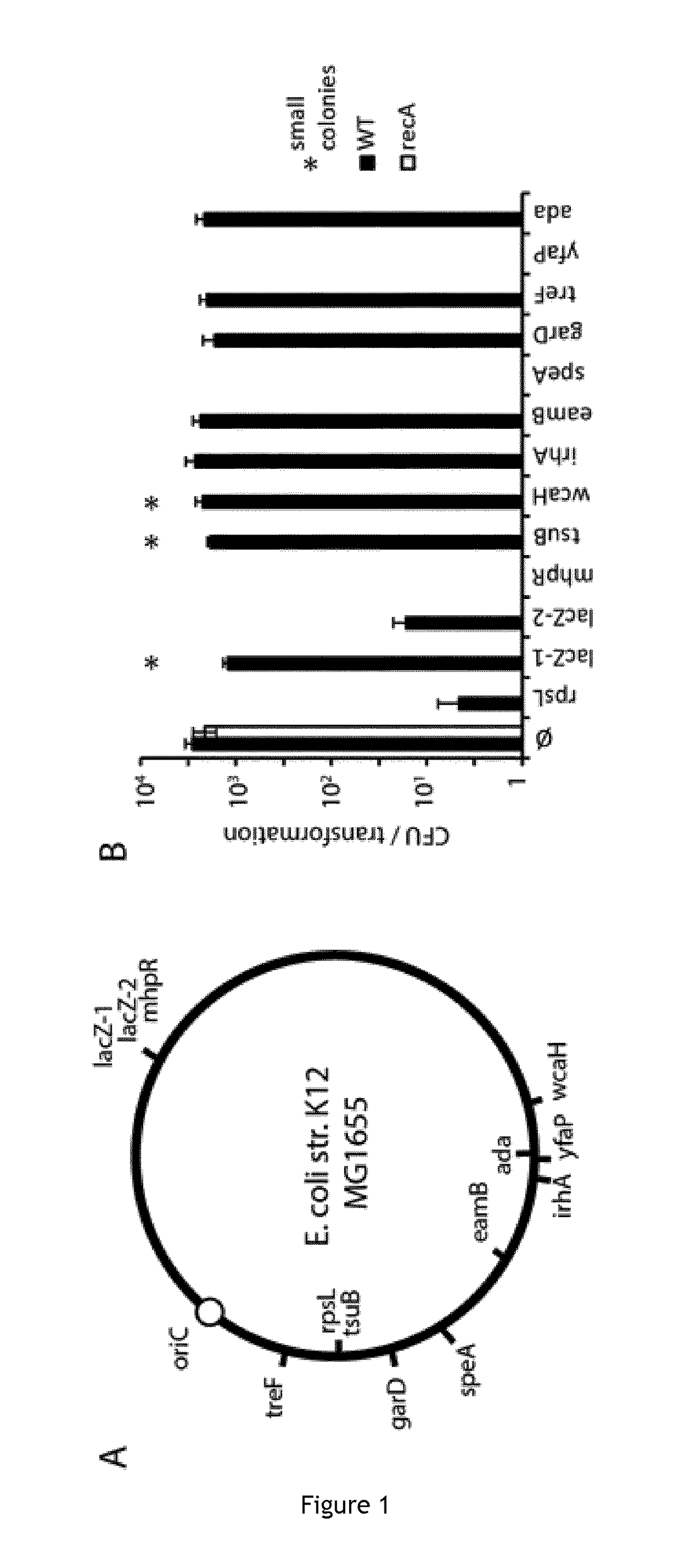
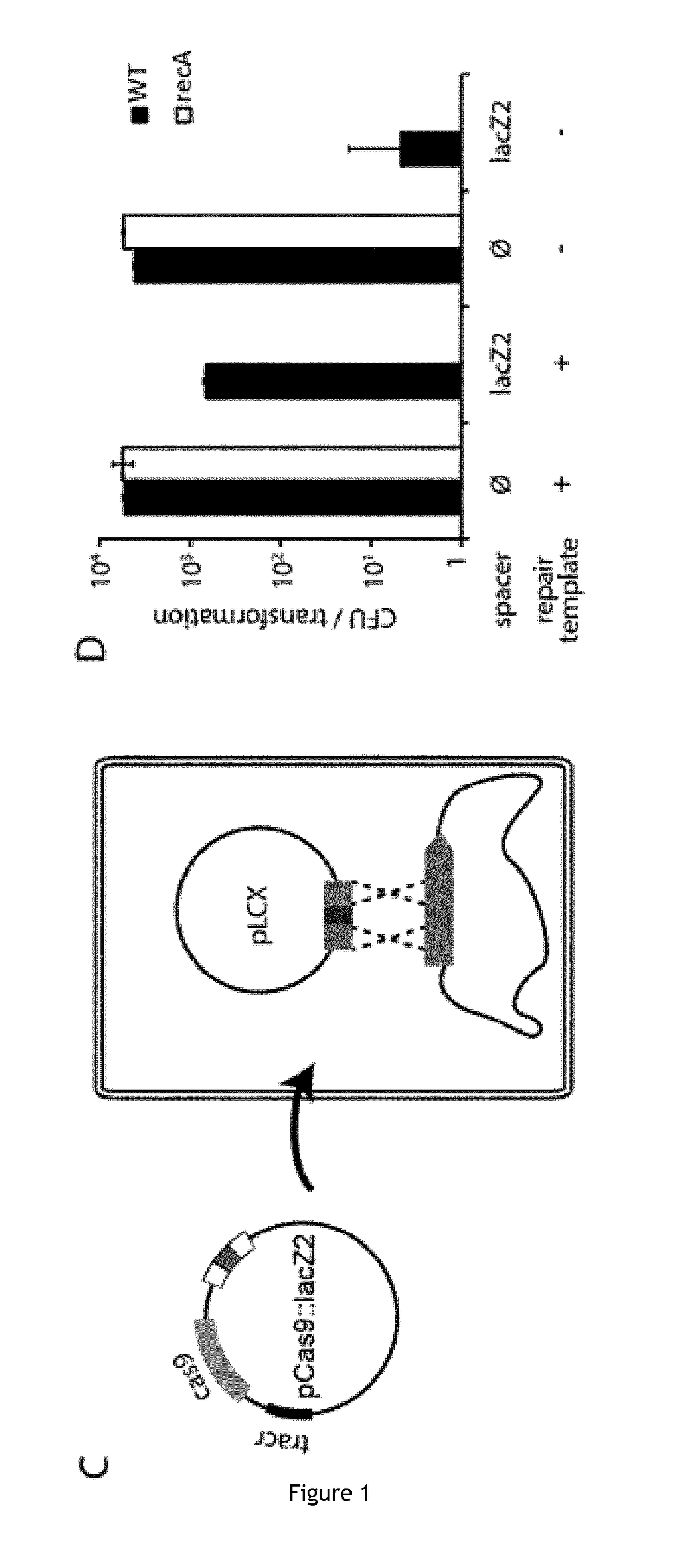
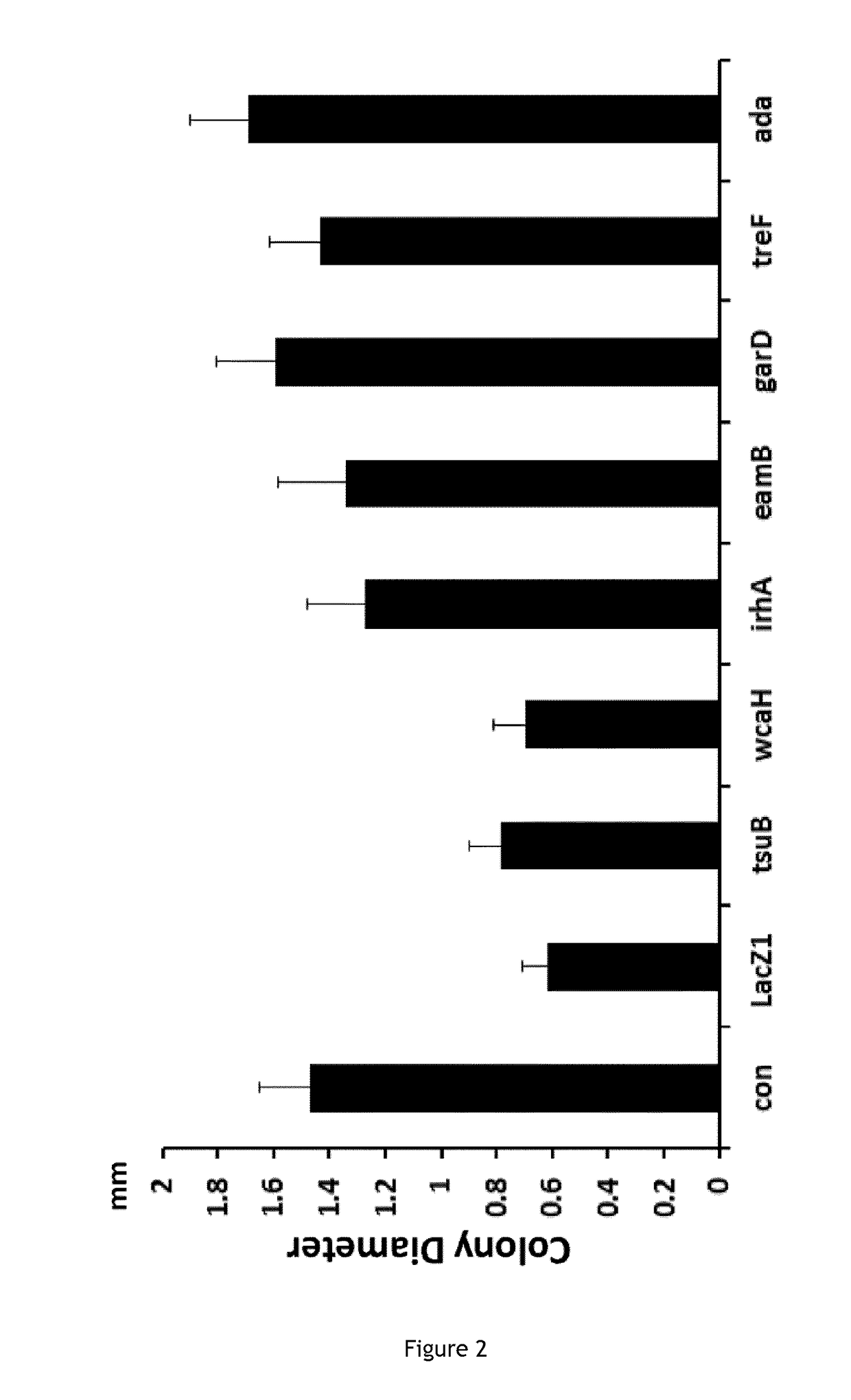
Improving sequence-specific antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair
The invention relates to the improvement of endonuclease-based antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair of double-strand break(s) (DSB(s)) in prokaryotic cells. In this respect, the invention especially concerns a method involving blocking DNA repair after a nucleic acid has been submitted to DSB, in particular by a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) associated programmable double-strand endonuclease. The invention particularly relates to the use of an exogenous molecule that inhibits DNA repair, preferably a protein that binds to the ends of the double-stranded break to block DSB repair. The invention also relates to vectors, particularly phagemids and plasmids, comprising nucleic acids encoding nucleases and Gam proteins, and a pharmaceutical composition and a product containing these vectors and their application.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Method of preparation and composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species uncaria
The present invention is directed to a method of preparation and the composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria. The present invention is also directed to the pharmaceutical use of the composition for the enhancement of the immune, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and DNA repair processes of warm blooded animals. The present preparation of the water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria results in the depletion of many of the ingredients which lead to various toxic side effects associated with other extracts or compositions derived from Uncaria. Also, the present preparation leads to the depletion of many of the active ingredients commonly associated with other extracts and compositions of the plant species Uncaria. Therefore, the present invention teaches that the hot water extraction of the crude plant parts of Uncaria and the subsequent dialysis of the solubilized products yields a low molecular weight composition which maintains a high degree of the anti-tumor, inflammatory and immune stimulatory activities associated with the crude plant parts.
Owner:CAMPAMED +2
Compositions and methods for modulating DNA repair
InactiveUS20050220796A1Reduce and prevent formationConvenient introductionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionA-DNAIn vivo
Compositions and methods for modulating a DNA repair process in vivo or in vitro are provided. One aspect of the disclosure provides a pharmaceutical composition including a DNA repair modulator. The DNA repair modulator includes, but is not limited to, compositions such as polypeptides, for example antibodies; modified polypeptides; and branched or unbranched aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, substituted aliphatic, aromatic hydrocarbons, or heterocyclic carbon-based compounds that associate with a DNA repair polypeptide, for example, DNA-PKcs.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Method and compositions for treating skin
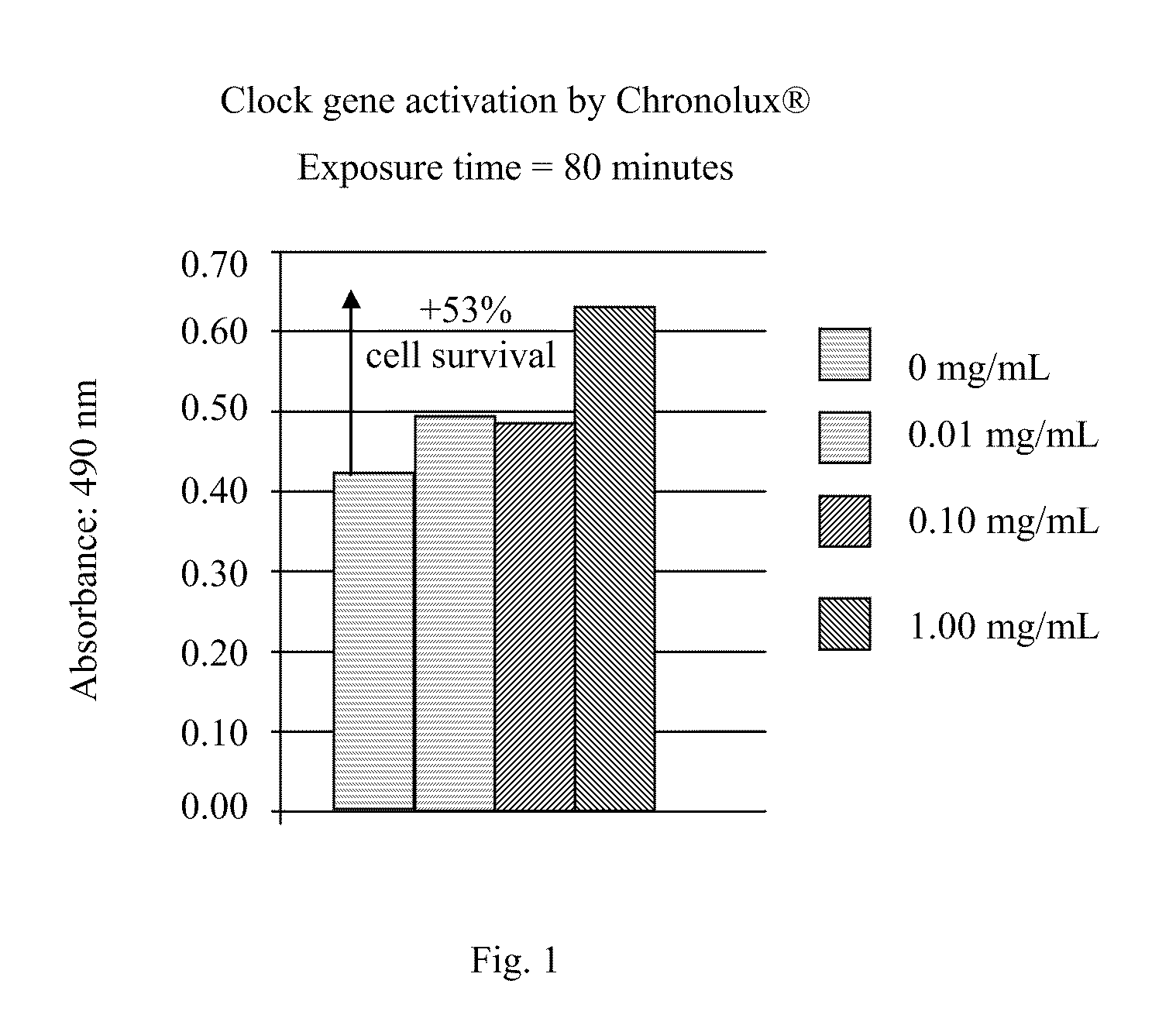
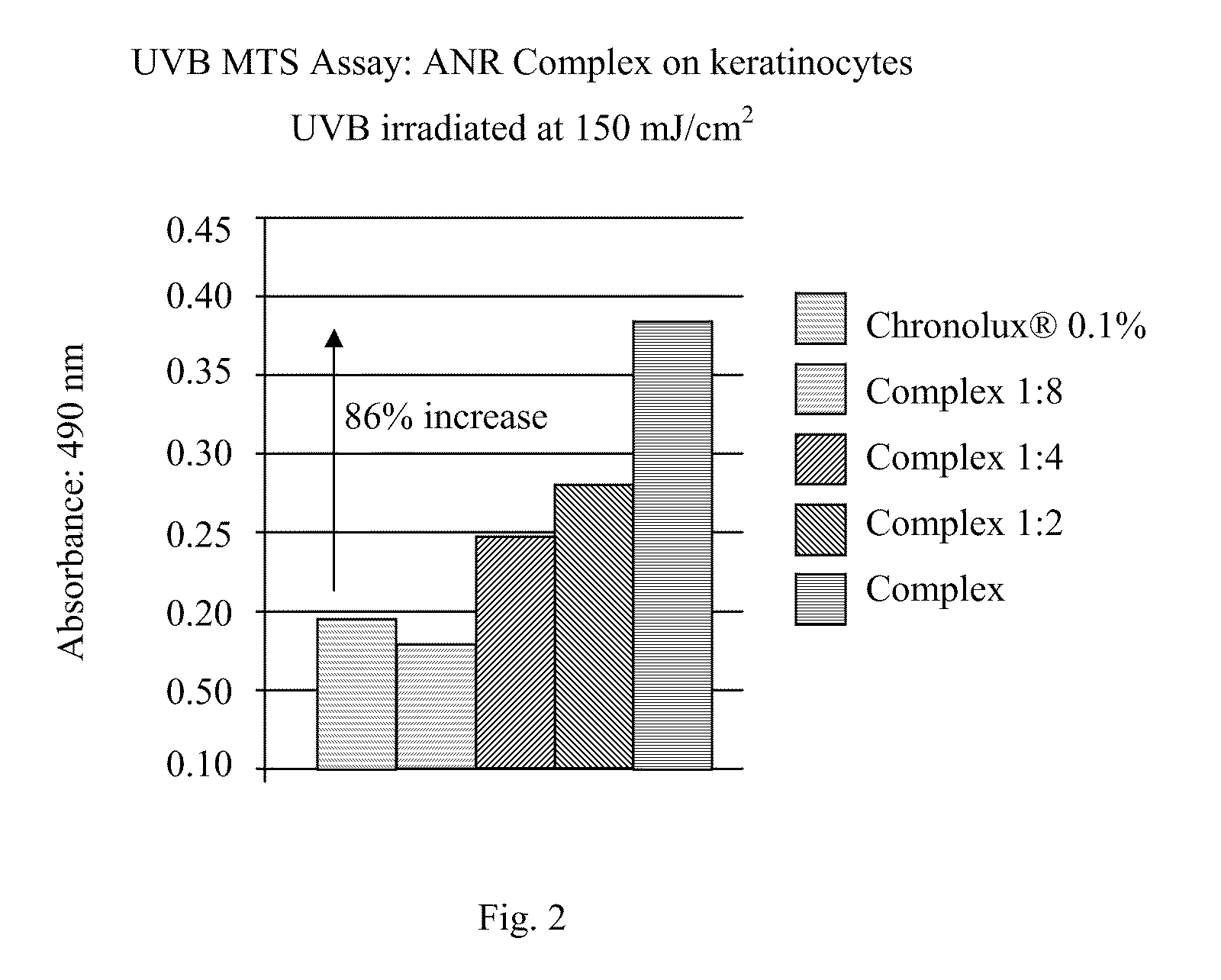
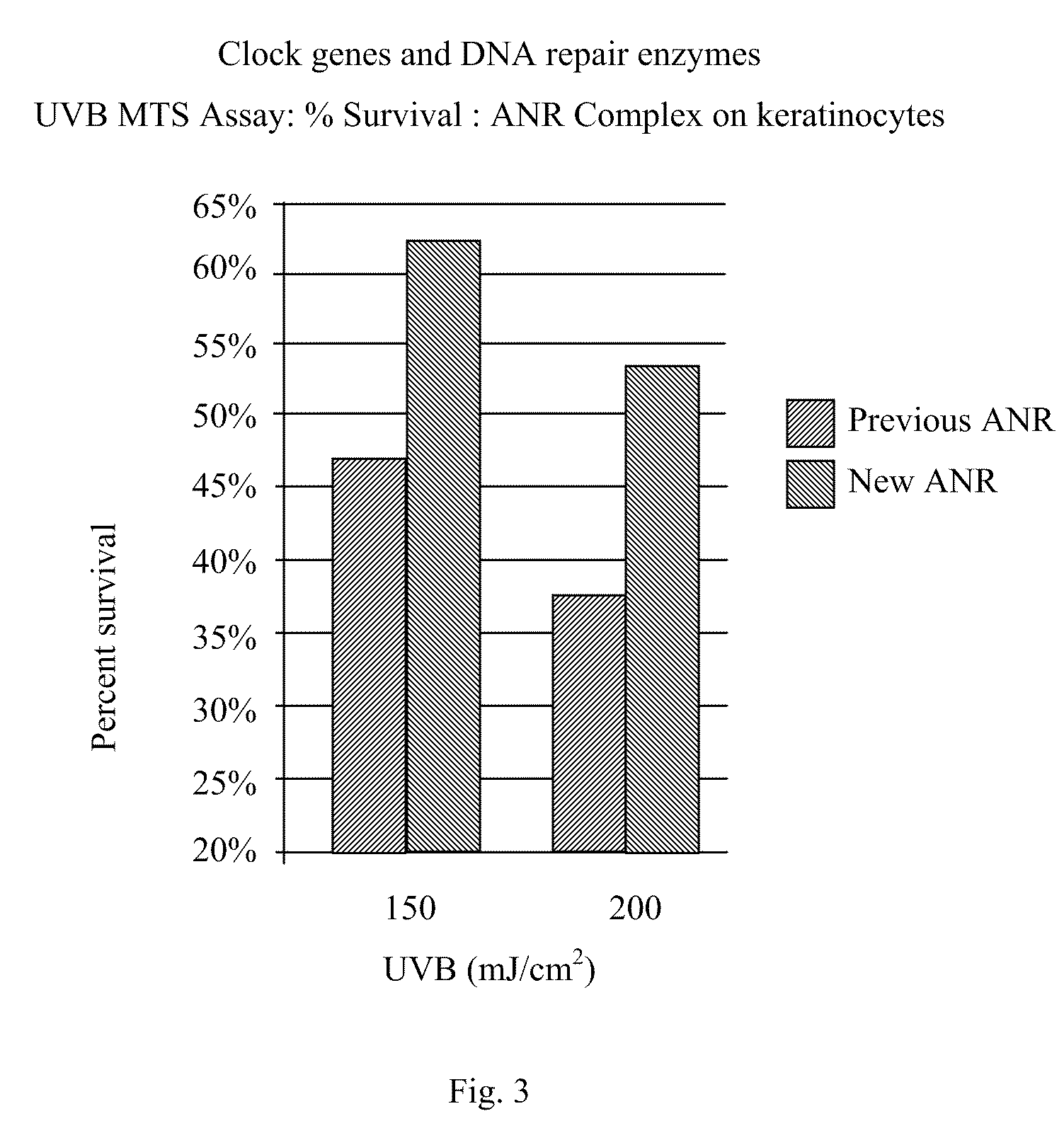
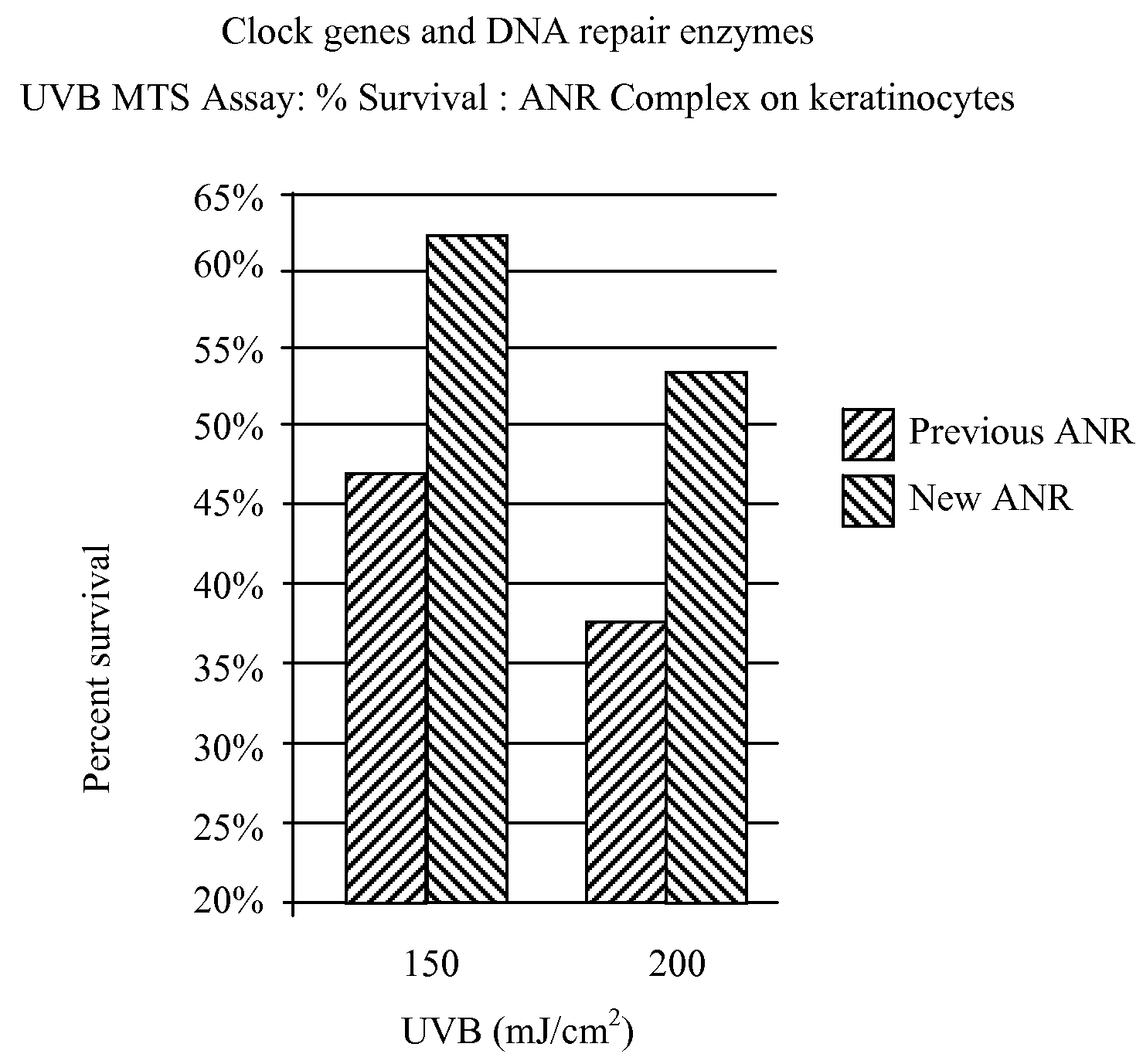
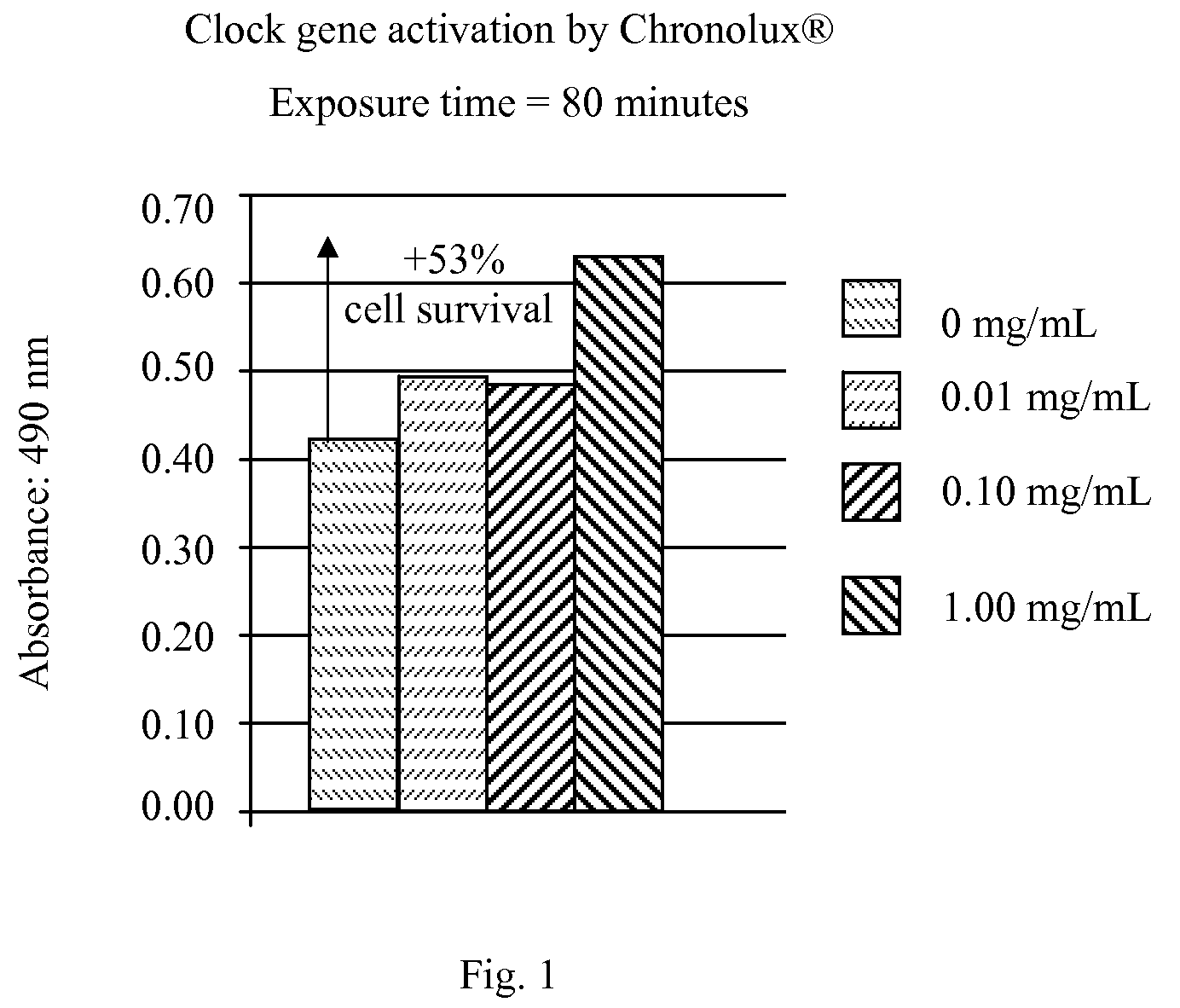
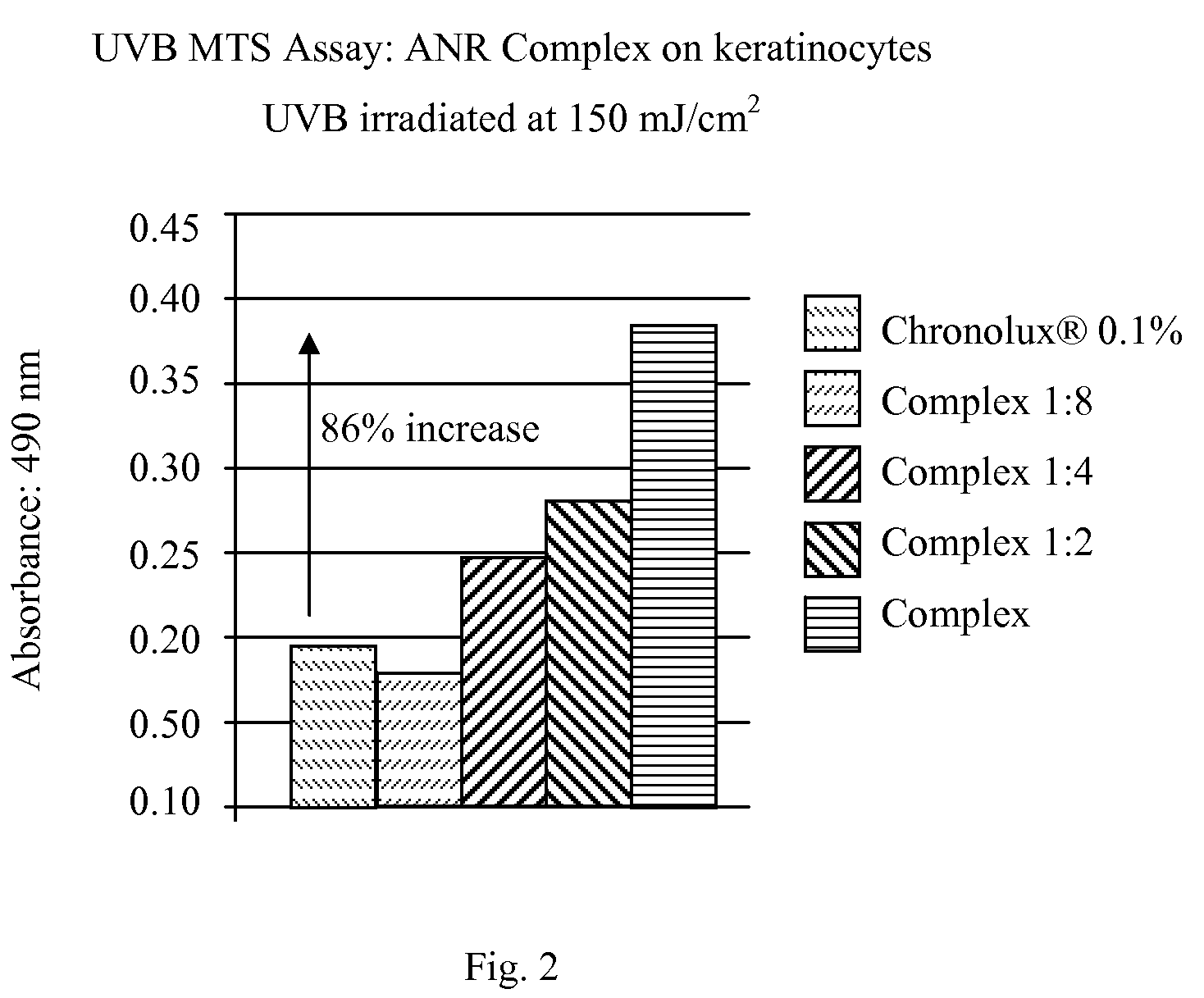
A skin care composition comprising at least one keratinocyte CLOCK or PER1 gene activator and at least one DNA repair enzyme; a method for inhibiting damage to human keratinocytes due to environmental aggressors by applying a composition comprising at least one keratinocyte CLOCK or PER1 gene activator and at least one DNA repair enzyme; and a method for repairing DNA damage in human keratinocytes.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Methods for repairing degraded DNA
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
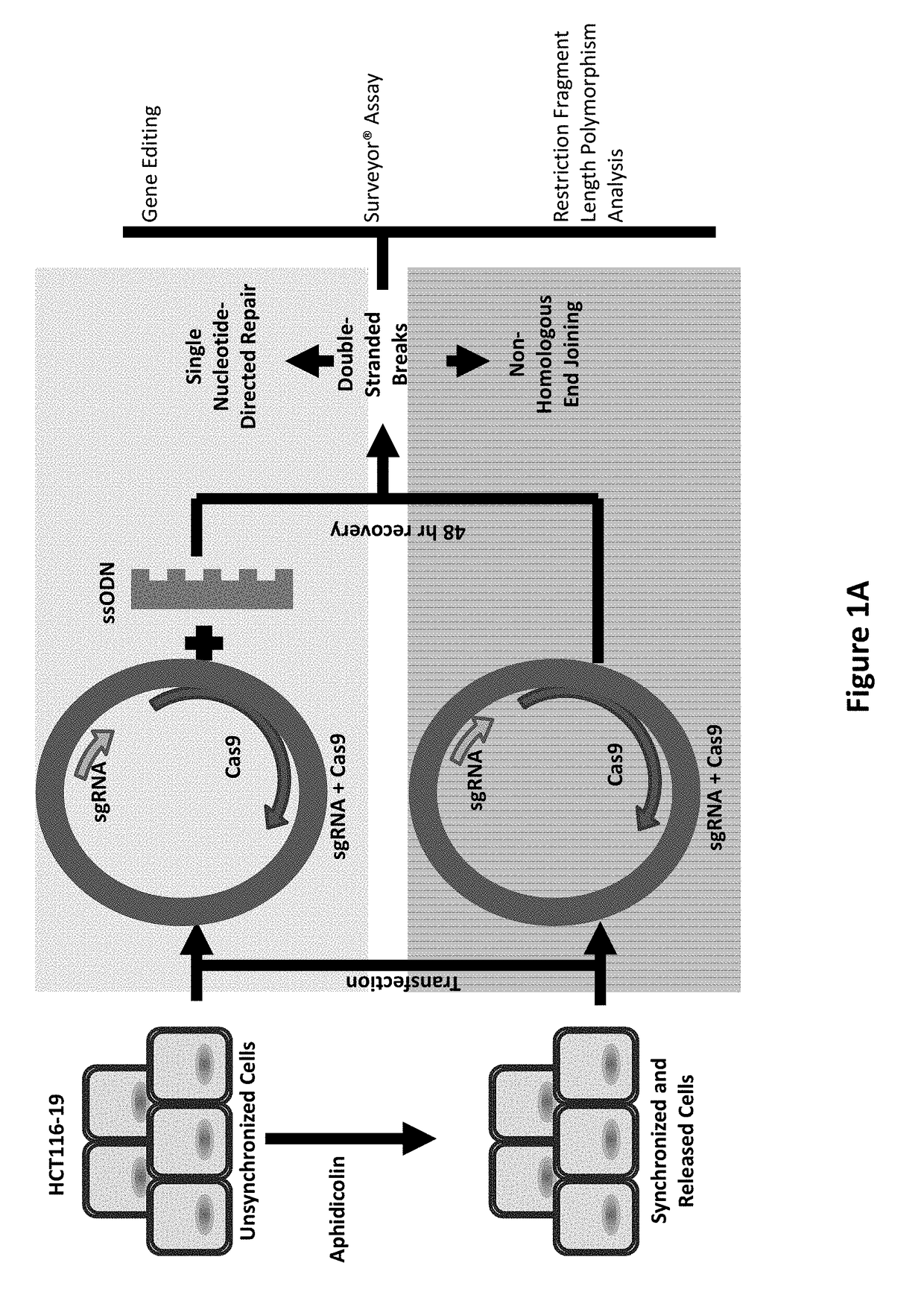
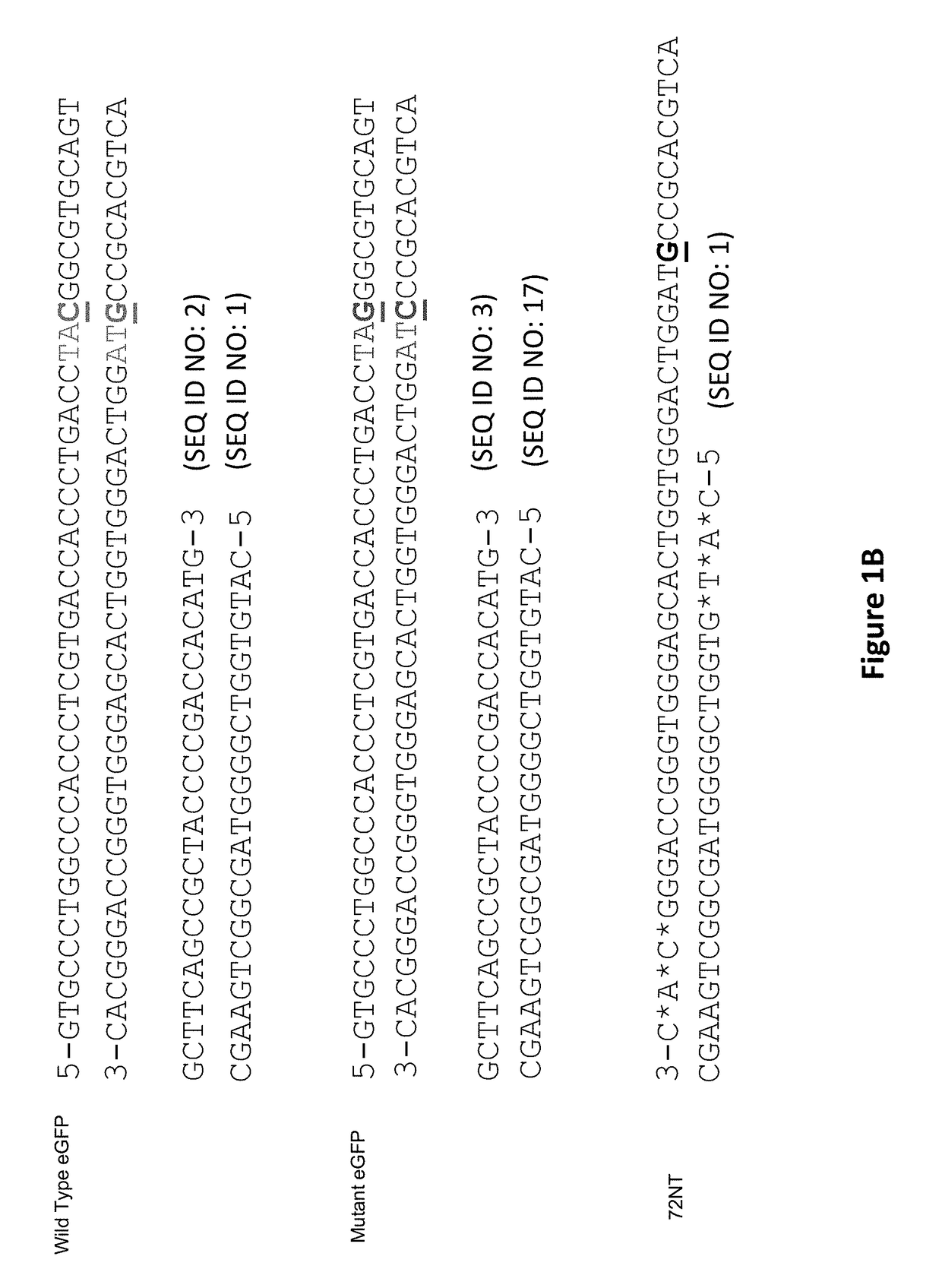
Compositions and Methods for Improving Homogeneity of DNA Generated Using a CRISPR/Cas9 Cleavage System
The invention relates to the unexpected discovery of a system and methods for precise homology directed repair after CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage. The invention includes a DNA cleavage and repair system comprising a CRISPR / Cas9 system and an oligonucleotide 100% complementary to cleaved DNA to promote homology directed DNA repair. The invention further includes methods for inducing homology directed repair of cleaved DNA and repairing a CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage.
Owner:CHRISTIANA CARE HEALTH SERVICES INC
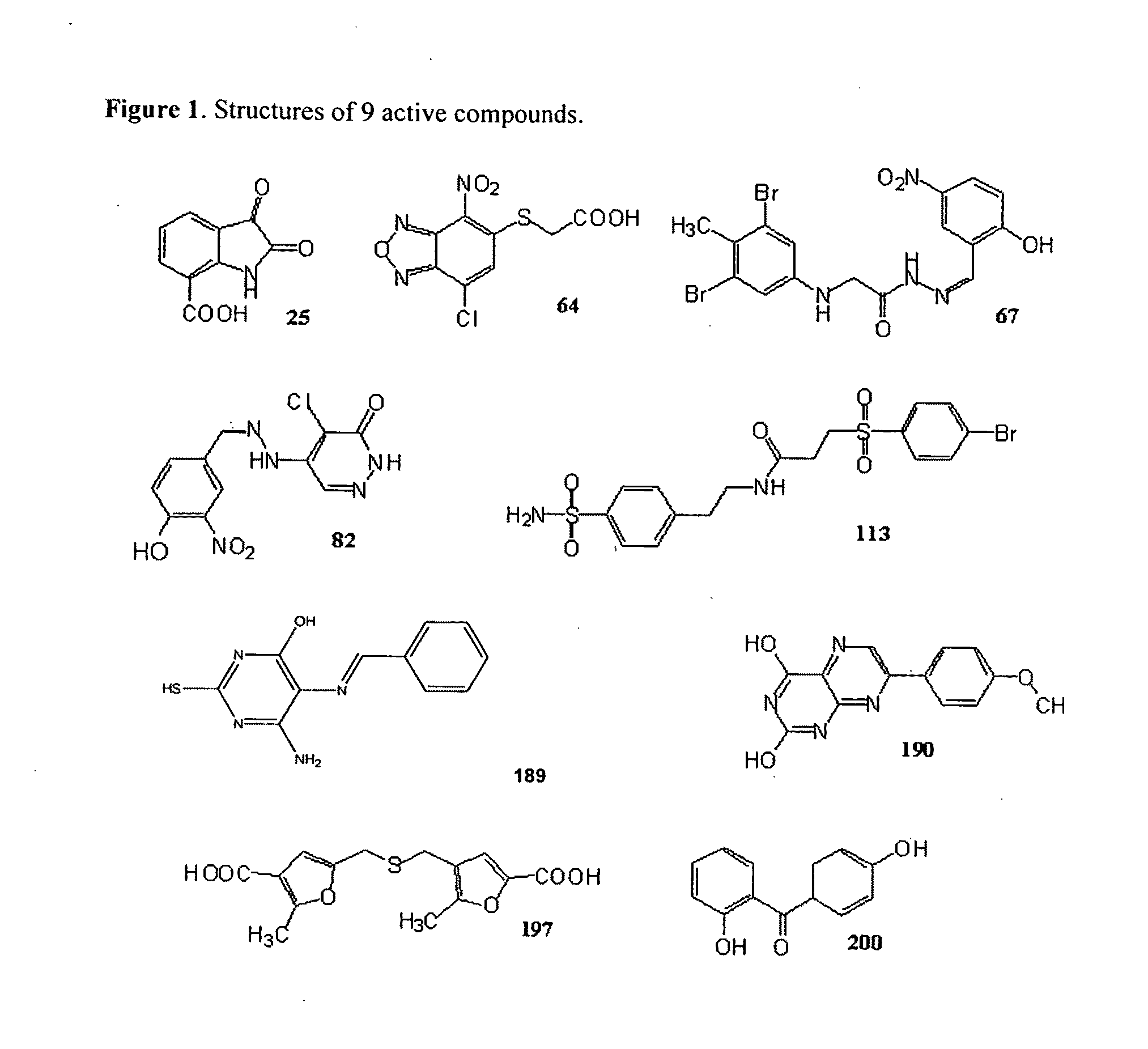
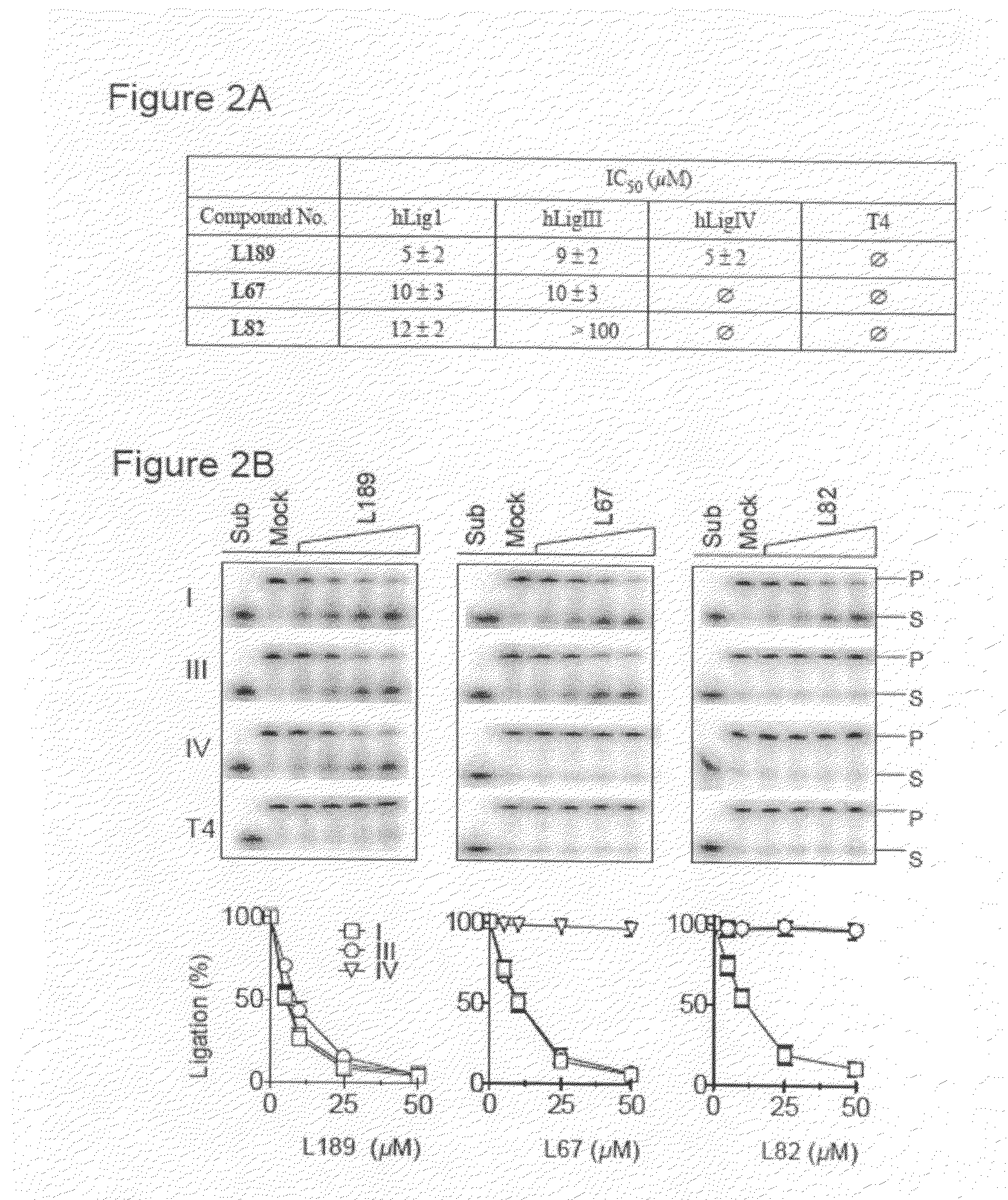
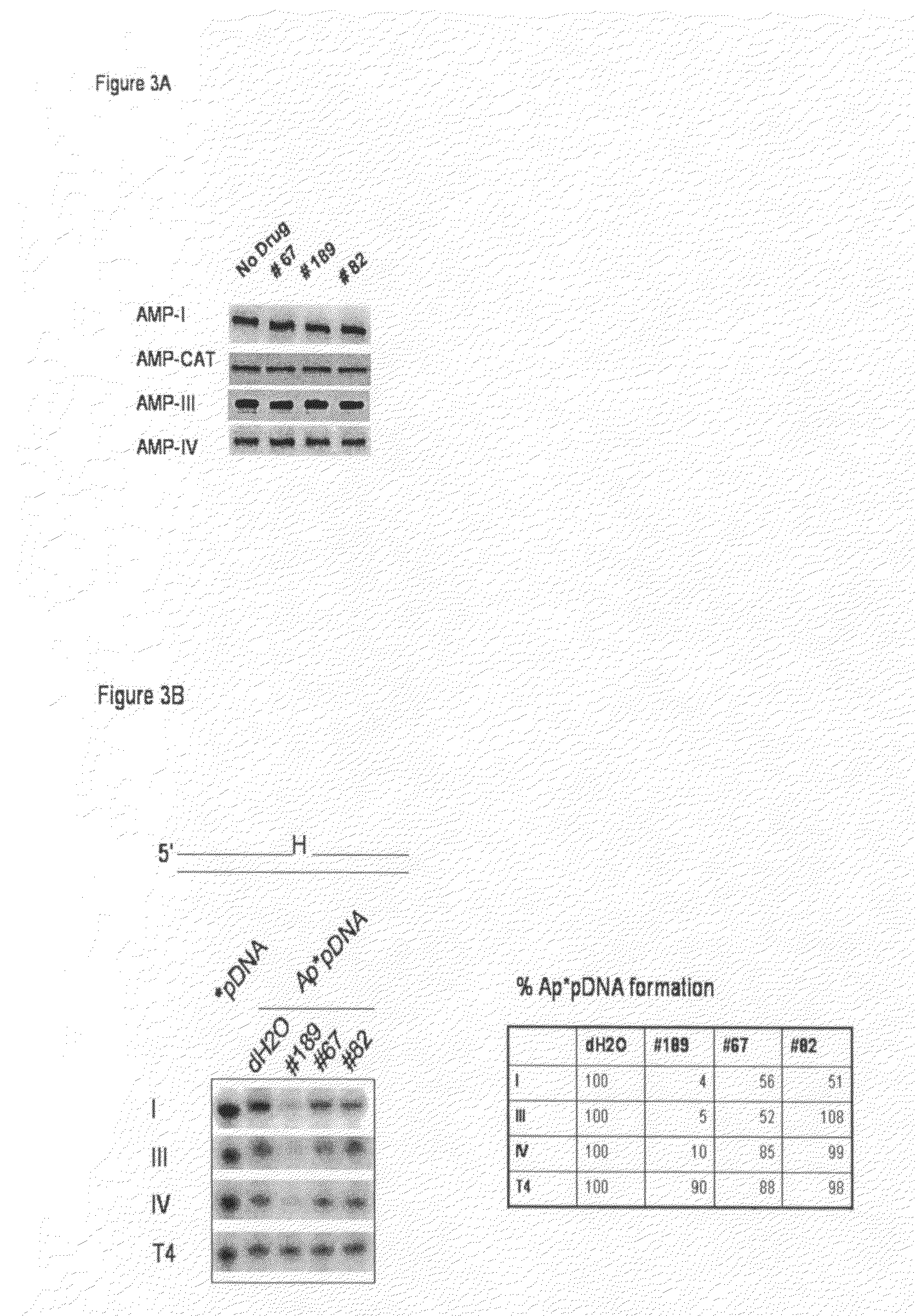
Compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases and methods of treating cancer
ActiveUS20100099683A1Strong cytotoxicityInhibit cell growthBiocideOrganic chemistryScreening methodBiochemistry
Methods for treating cancer using compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases. Methods for using compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases to provide insights into the reaction mechanisms of human DNA ligases, for example to identify the human DNA ligase involved in different DNA repair pathways. Screening methods for compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Methods for repairing degraded DNA
The present invention provides methods and kits for repair of degraded DNA which may then be used as a template for efficient amplification by a number of different amplification reactions. The method relies upon a series of enzymatic activities provided by DNA repair enzymes.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
The present invention relates to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of an amide substituted indazole which are inhibitors of the enzyme poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP), previously known as poly(ADP-ribose)synthase and poly(ADP-ribosyl) transferase. The compounds of the present invention are useful as mono-therapies in tumors with specific defects in DNA-repair pathways and as enhancers of certain DNA-damaging agents such as anticancer agents and radiotherapy. Further, the compounds of the present invention are useful for reducing cell necrosis (in stroke and myocardial infarction), down regulating inflammation and tissue injury, treating retroviral infections and protecting against the toxicity of chemotherapy.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
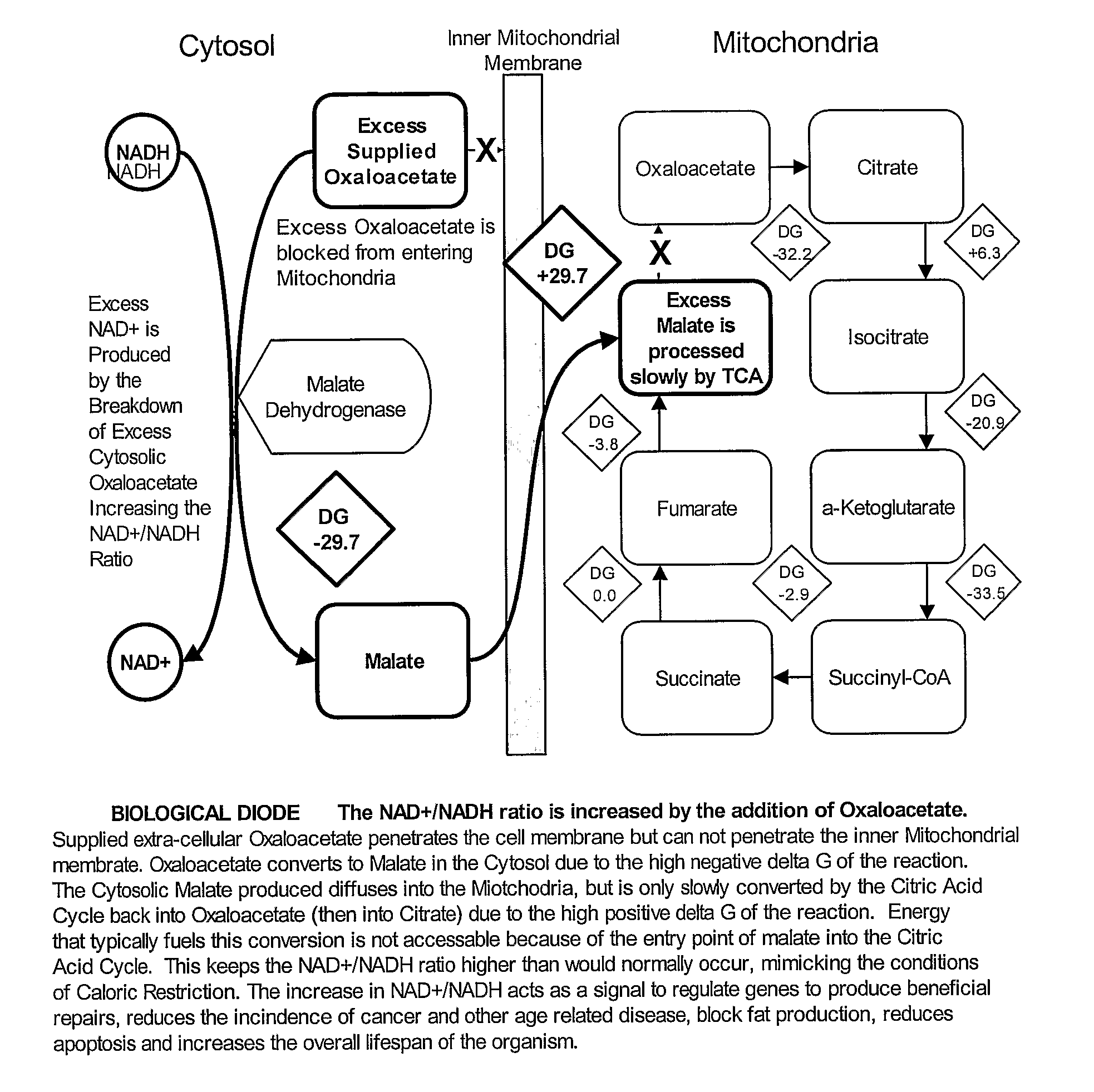
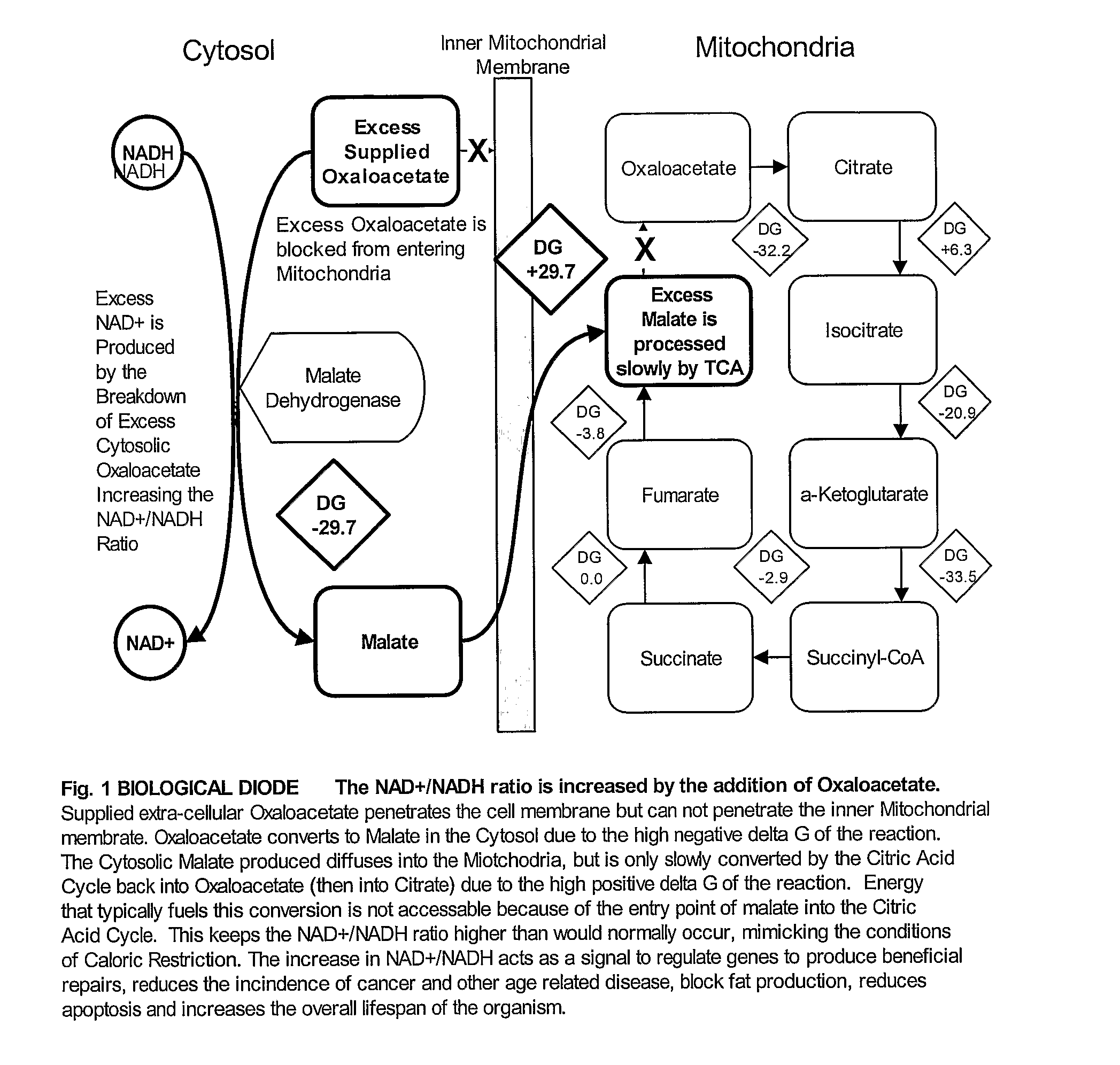
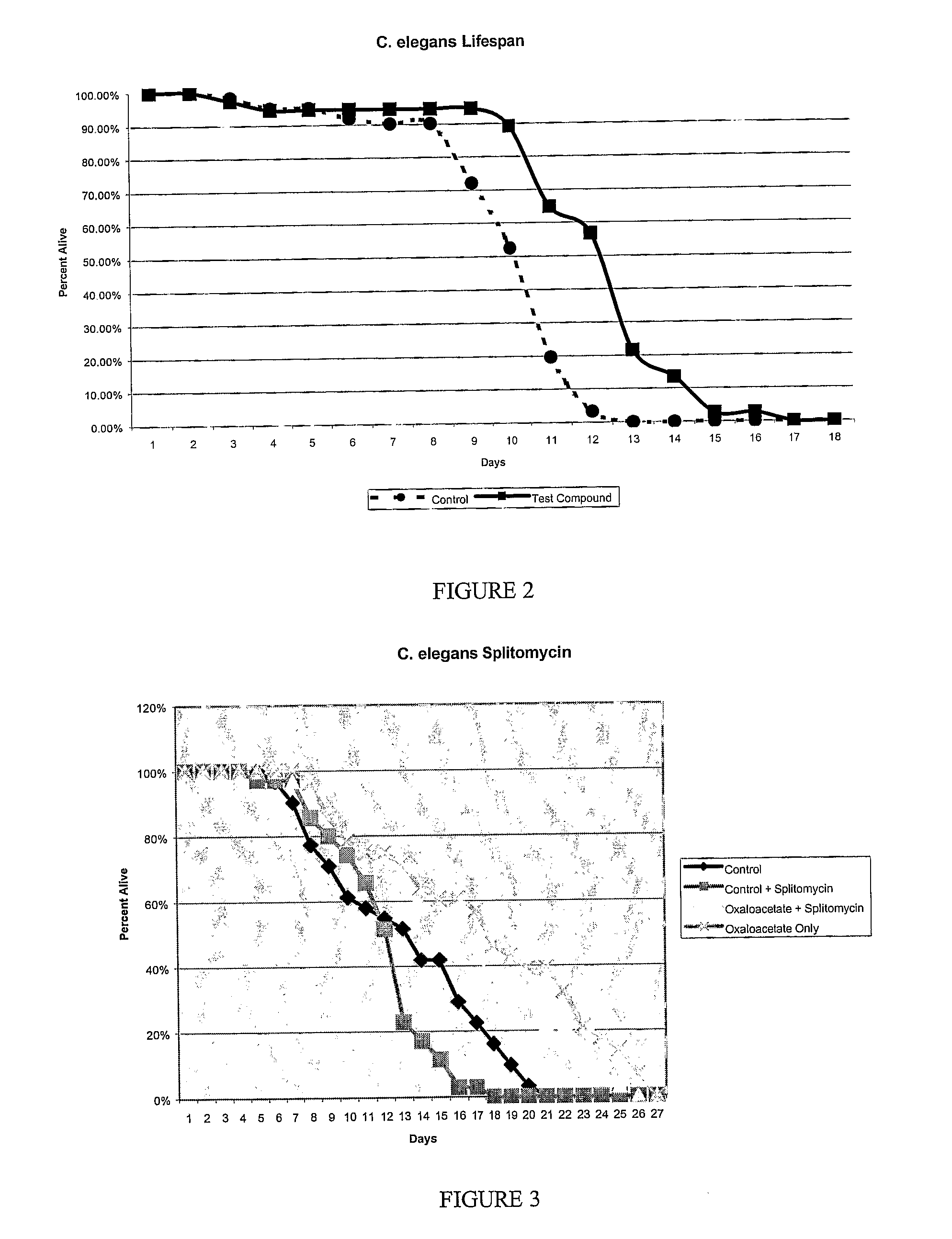
Method for Extending Lifespan Delaying the Onset of Age-Related Disease
ActiveUS20080279786A1Relieve symptomsAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCaloric restrictionsAcetic acid
A method and composition for extending the lifespan of an individual and delaying the onset of age-related disease is provided. The method includes the administration of an effective dose of oxaloacetate, wherein the oxaloacetate acts to mimic the cellular conditions obtained under caloric restriction to provide similar benefits. The invention further includes methods and compositions for reducing the incidence or treatment of cancer. Compositions and methods for reducing body fat by administering an effective amount of oxaloacetate are likewise provided. Compositions for DNA repair in UV damaged cells is provided are also provided. Similarly, a method for treating a hang-over comprising administering an effective amount of oxaloacetate is disclosed.
Owner:B CASH ALAN
Composition and method for promoting internal health and external appearance
The present invention relates to a new composition comprising substances that promote DNA repair, reduce body fat levels and increase lean body mass and that decrease wrinkle appearance and / or improvement in skin surface. In some aspects, the composition of the present invention include resveratrol, forskohlin and astaxanthin. In another aspect the composition of the present invention further comprises carboxy alkyl ester. The present invention also relates to a method of promoting internal health and external appearance in a subject in need, said method comprising administering to the subject a composition that promotes DNA repair, reduces body fat levels and increases lean body mass and that decreases wrinkle appearance and / or improvement in skin surface.
Owner:NUVOCARE HEALTH SCI
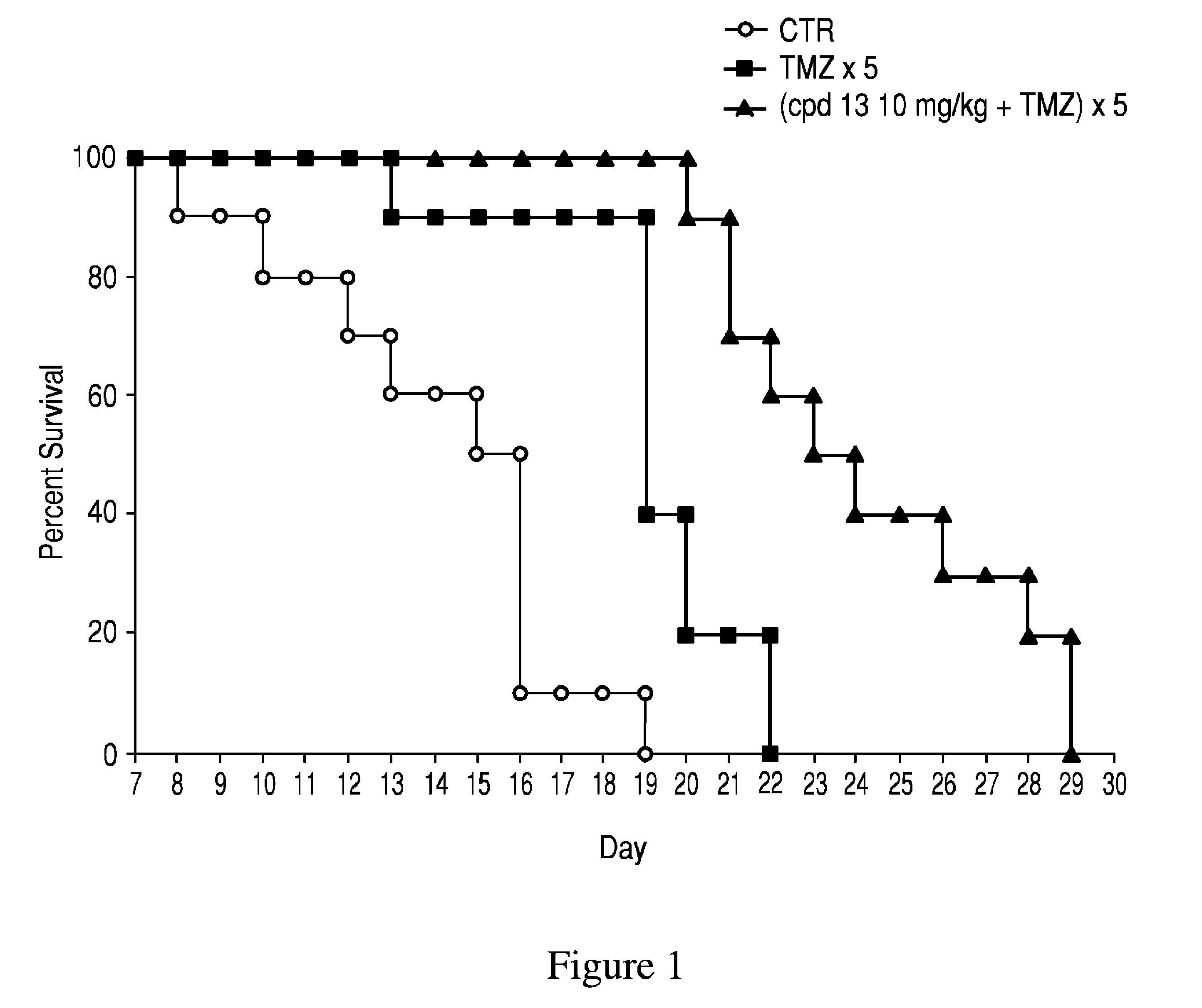
PARP inhibitor compounds, compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS8236802B2Improve survivalGrowth inhibitionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSide effectPolymerase L
The present invention relates to tetraaza phenalen-3-one compounds which inhibit poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and are useful in the chemosensitization of cancer therapeutics. The induction of peripheral neuropathy is a common side-effect of many of the conventional and newer chemotherapies. The present invention further provides means to reliably prevent or cure chemotherapy-induced neuropathy. The invention also relates to the use of the disclosed PARP inhibitor compounds in enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents such as temozolomide. The invention also relates to the use of the disclosed PARP inhibitor compounds to radiosensitize tumor cells to ionizing radiation. The invention also relates to the use of the disclosed PARP inhibitor compounds for treatment of cancers with DNA repair defects.
Owner:EISAI INC
Method of preparation and composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria for enhancing immune, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor processes of warm blooded animals
The present invention is directed to a method of preparation and the composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria. The present invention is also directed to the pharmaceutical use of the composition for the enhancement of the immune, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and DNA repair processes of warm blooded animals. The present preparation of the water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria results in the depletion of many of the ingredients which lead to various toxic side effects associated with other extracts or compositions derived from Uncaria. Also, the present preparation leads to the depletion of many of the active ingredients commonly associated with other extracts and compositions of the plant species Uncaria. Therefore, the present invention teaches that the hot water extraction of the crude plant parts of Uncaria and the subsequent dialysis of the solubilized products yields a low molecular weight composition which maintains a high degree of the anti-tumor, inflammatory and immune stimulatory activities associated with the crude plant parts.
Owner:OPTIGENEX INC
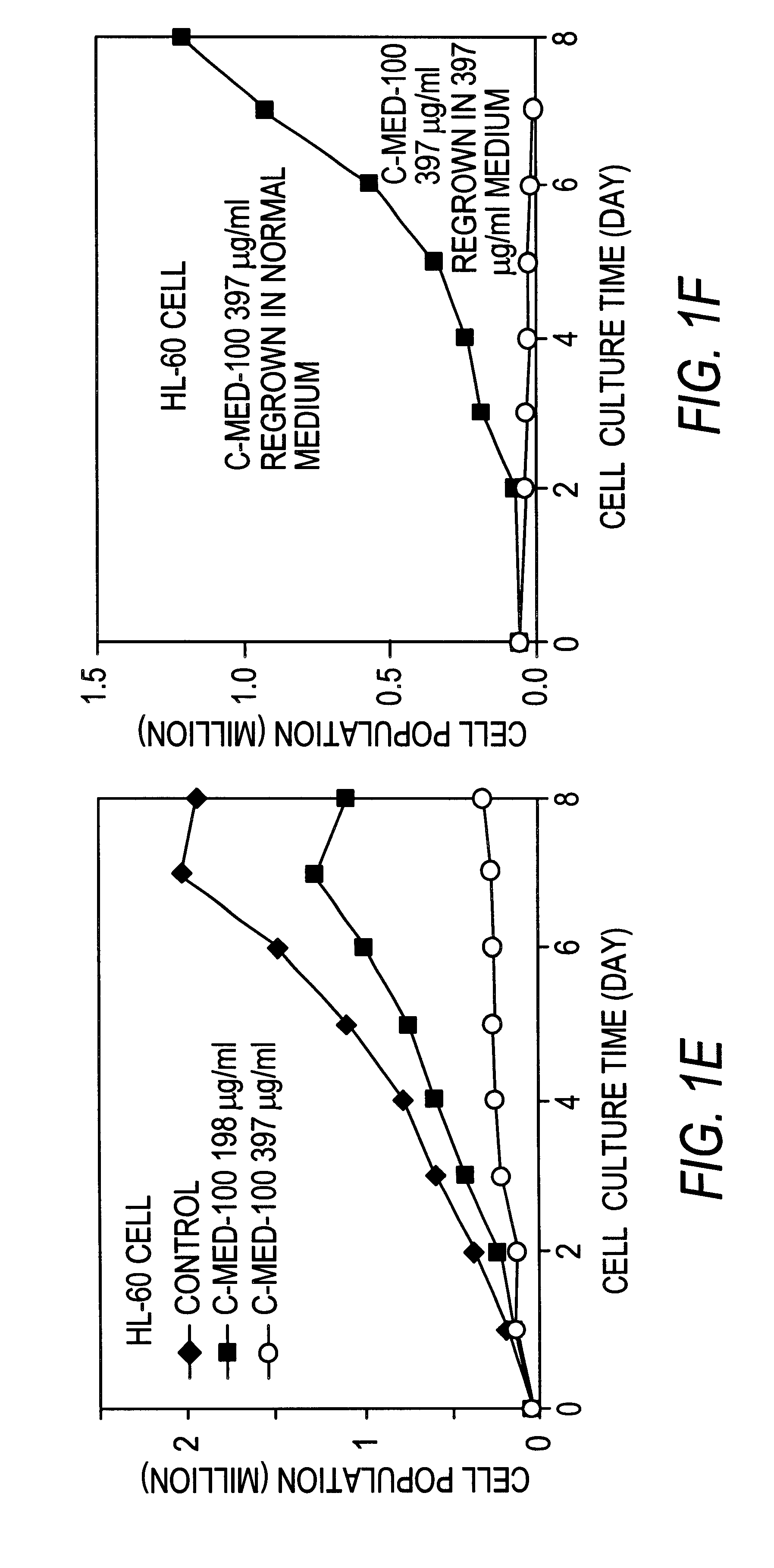
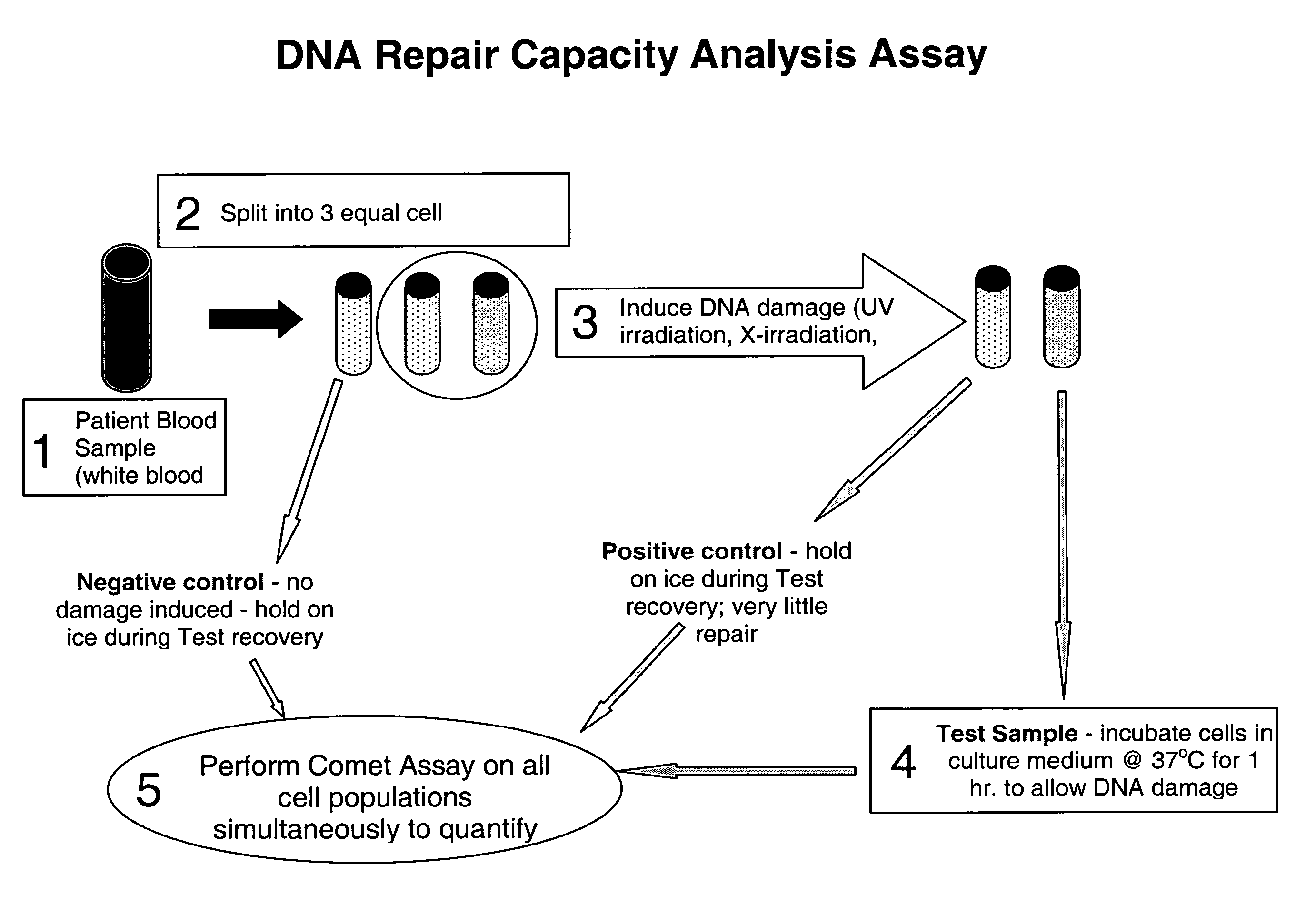
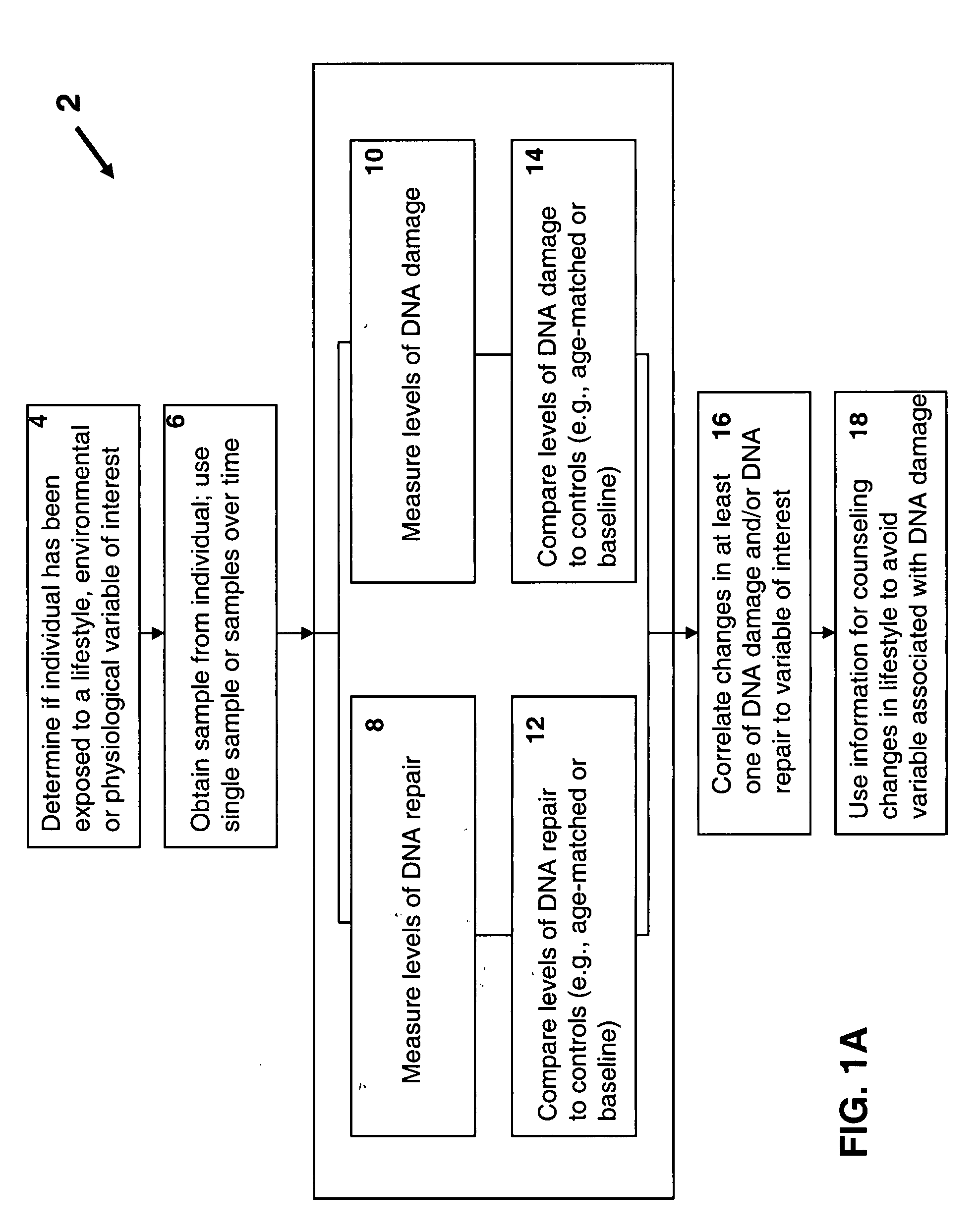
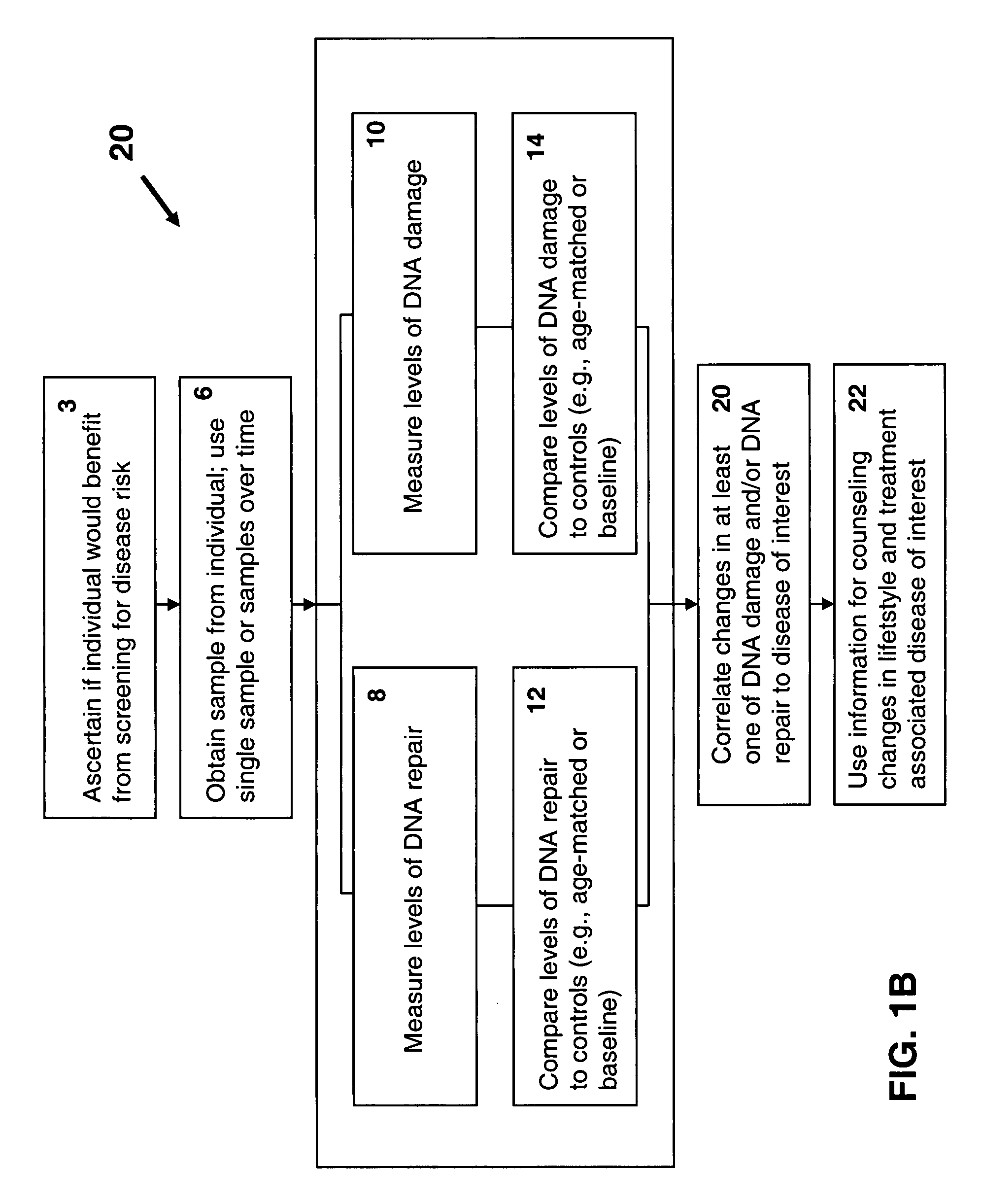
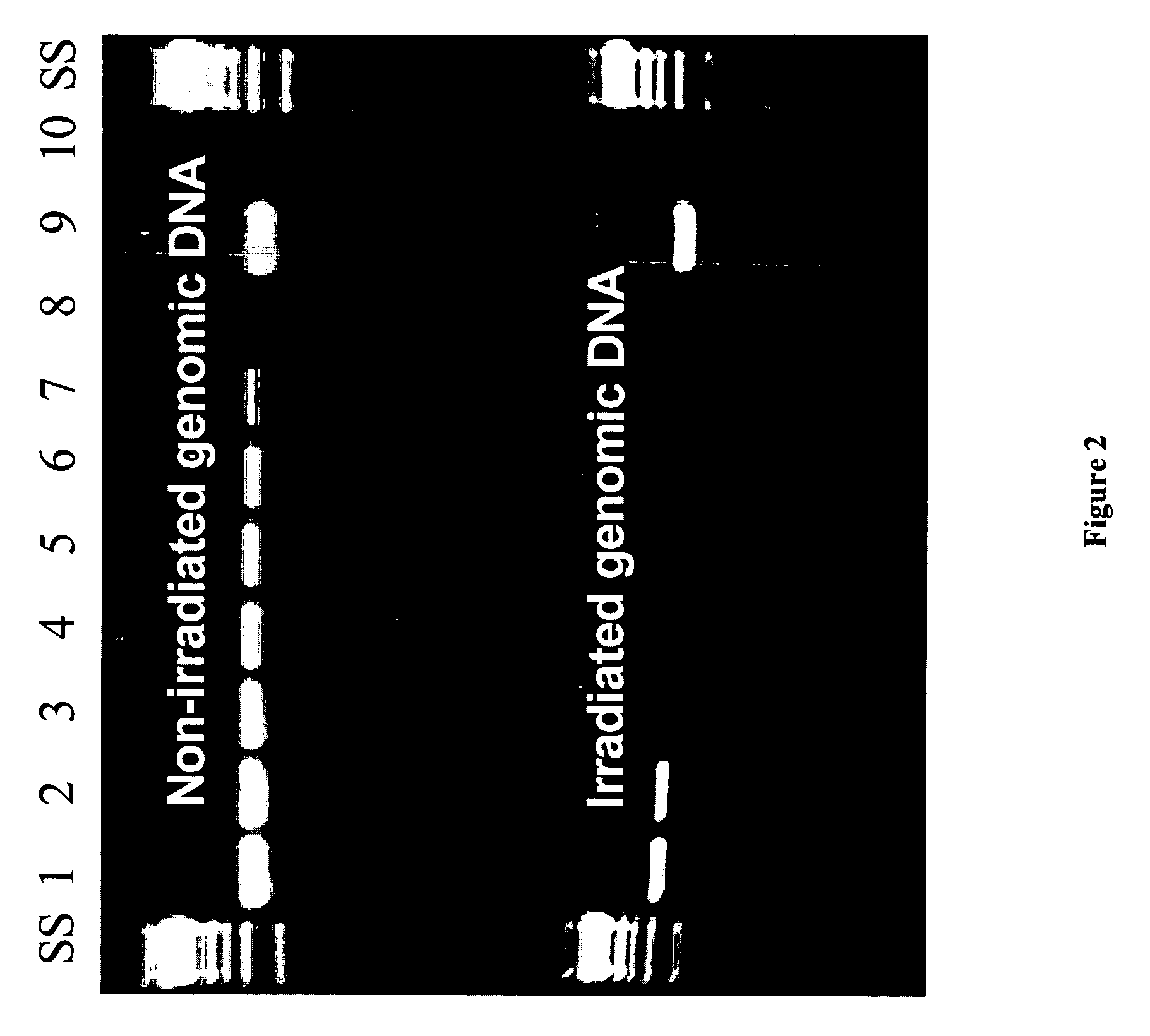
Methods and systems for evaluating health risk factors by measurement of DNA damage and DNA repair
InactiveUS20070269824A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHealth riskIncreased risk
Disclosed are methods for measuring the effects of environmental, physiological, or lifestyle variables on DNA damage and DNA repair activity as well as the use of measurements of DNA damage and DNA repair activity to predict increased risk for disease. Embodiments of the methods involve the use of a combination of assays to measure DNA damage and DNA repair activity in an individual and comparing these measurements to suitable controls using the selected assays for normal healthy individuals of varying ages. In other embodiments, the methods may comprise a comparison of DNA damage levels to DNA repair levels to obtain an apparent net measurement of DNA damage accumulation.
Owner:ALBRECHT JEFFREY +3
Business methods for commercializing antimicrobial and cytotoxic compounds
Business methods for the commercialization of antimicrobial and cytotoxic compounds, including antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents, are disclosed. According to one embodiment of the invention, drugs that are found to be effective but unsafe at therapeutic dosages are rescued by way of the use of an inhibitor of DNA repair, recombination, or replication, which sensitized microorganisms and cells, thereby permitting their use at a lower and safe dosage. In another embodiment, drugs that are found to be effective but cost prohibitive are rescued by way of the use of an inhibitor of DNA repair, recombination, or replication, thereby permitting their use at lower dosages and costs. A biopharmaceutical company may then, commercialize or charge royalties on such drugs.
Owner:ACHAOGEN
Cell penetrating nucleolytic antibody based cancer therapy
ActiveUS20150376279A1Enhance and augment efficacyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellAutoantibody production
Cancer cells with defects in DNA repair are highly susceptible to DNA-damaging agents, but delivery of therapeutic agents into cell nuclei can be challenging. A sub-set of autoantibodies having nucleolytic activity are capable of nuclear penetration. These antibodies can be used as therapeutic agents targeted towards DNA repair-deficient malignancies.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Compositions and methods for the treatment of cancer
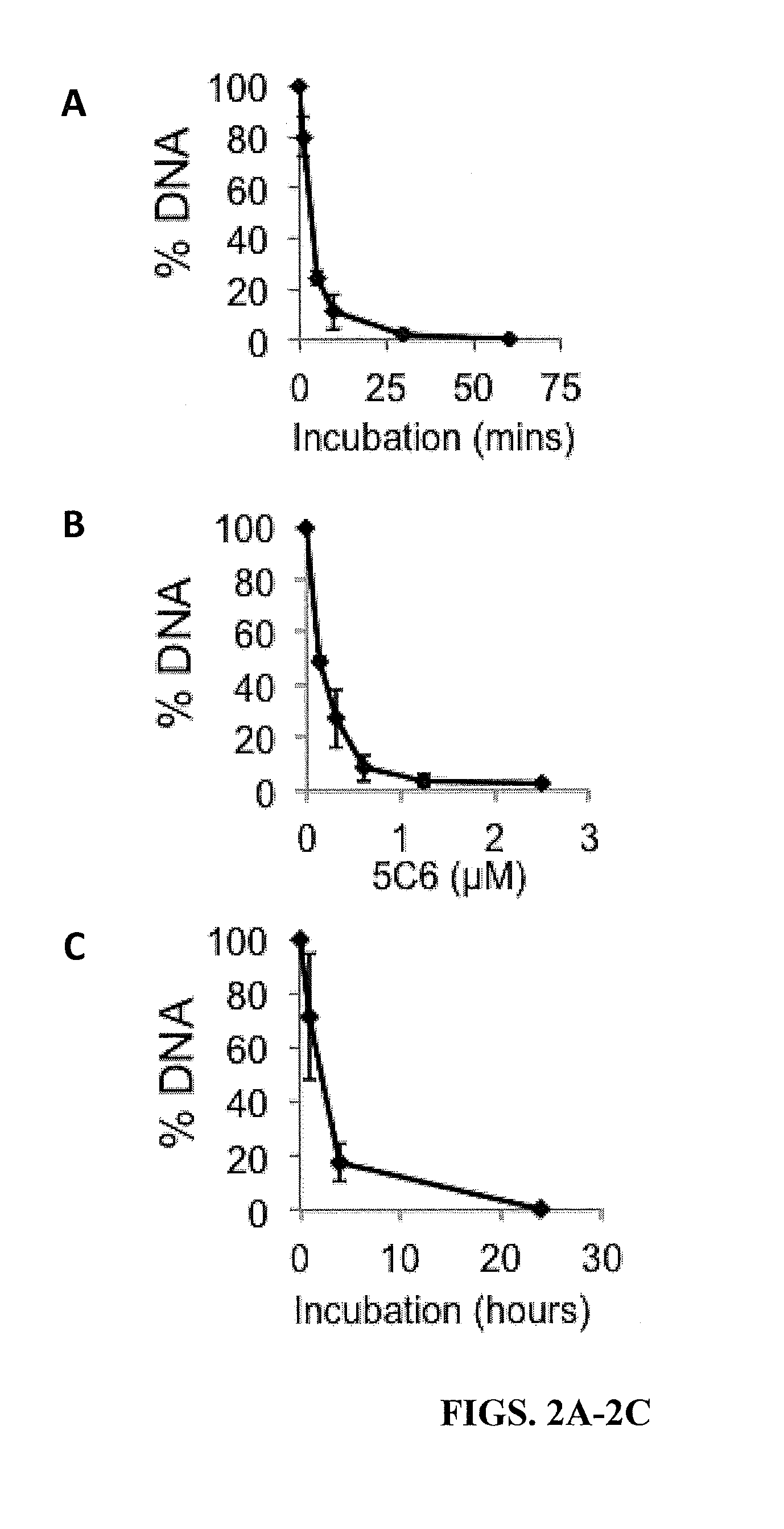
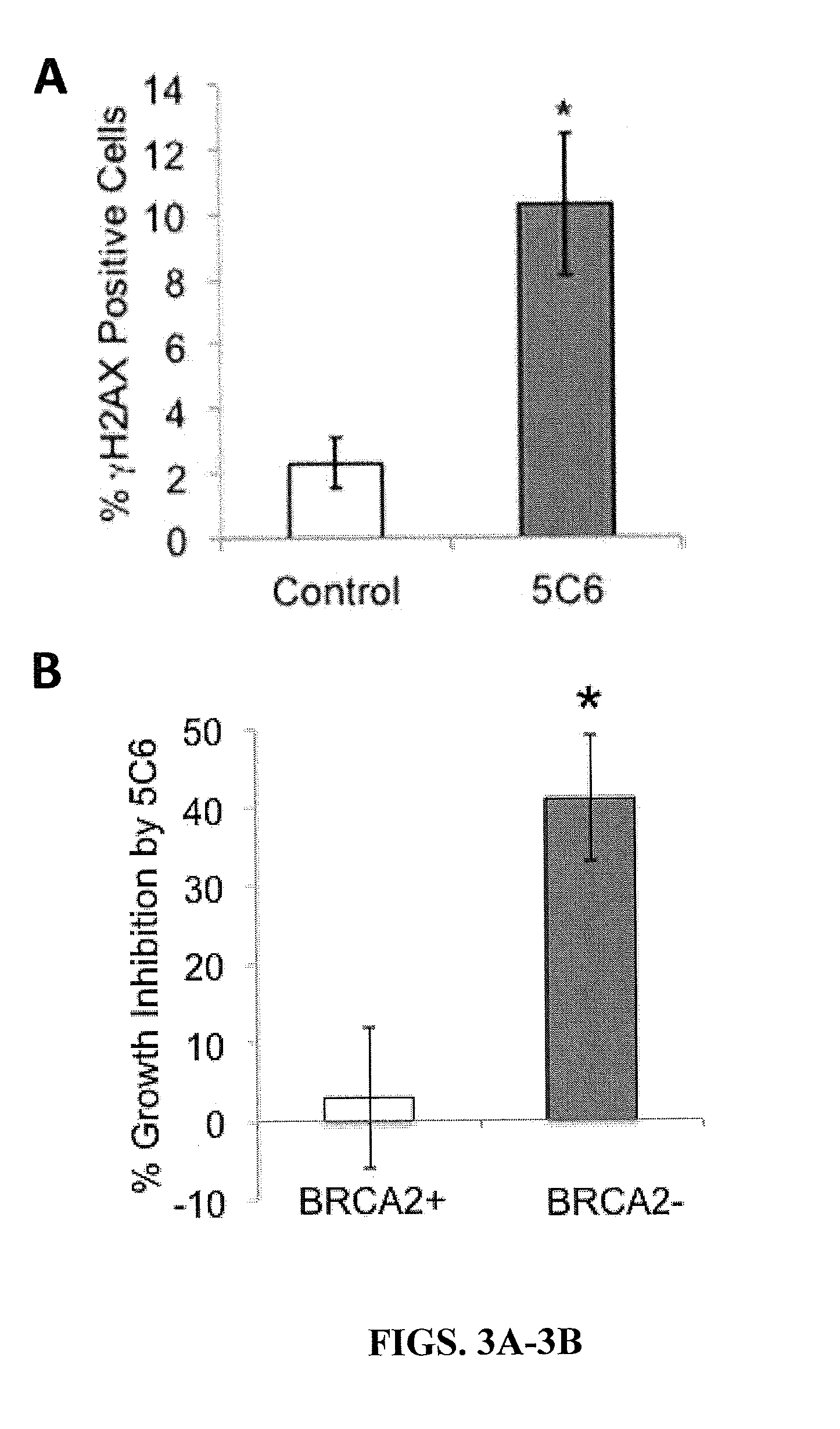
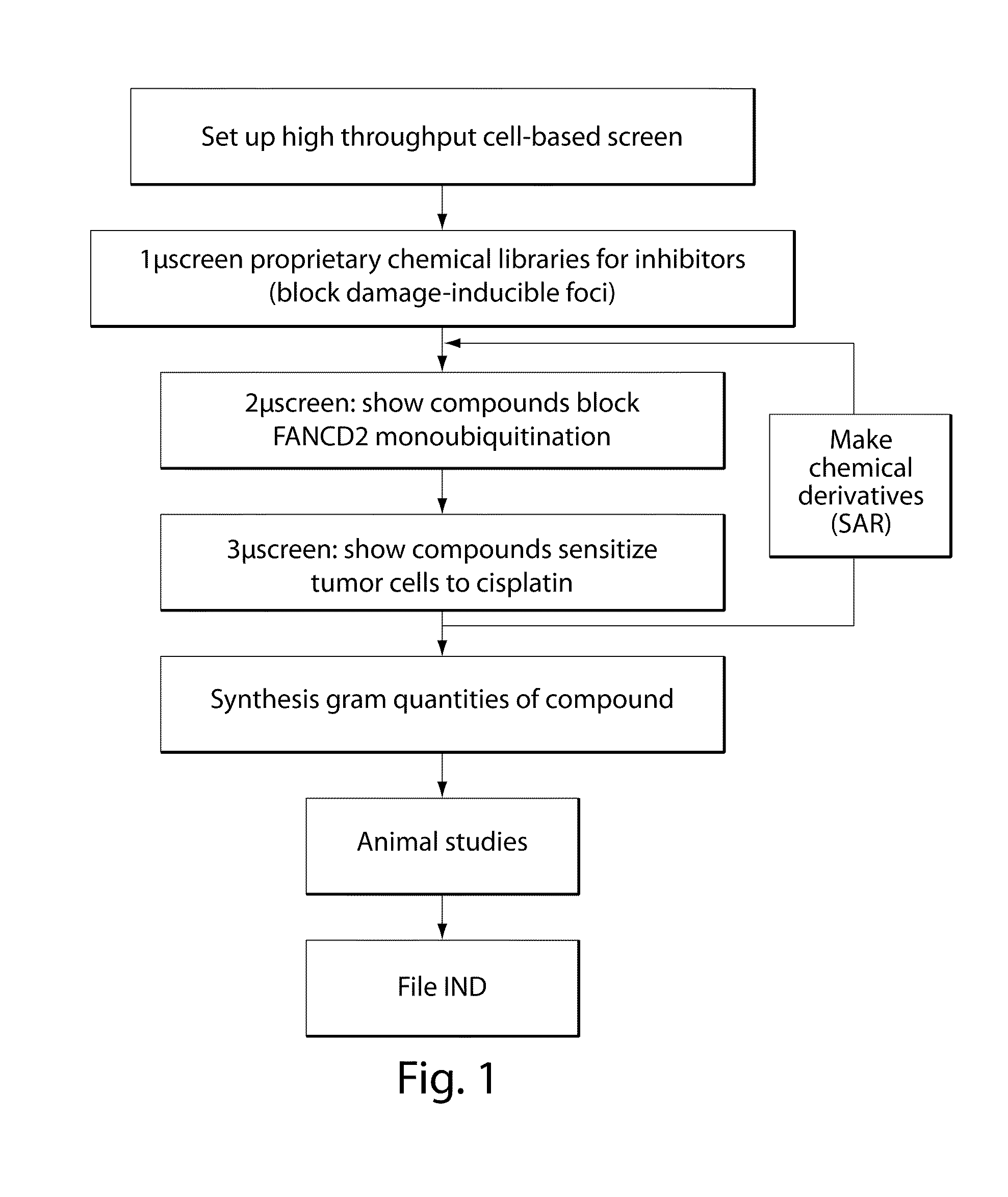
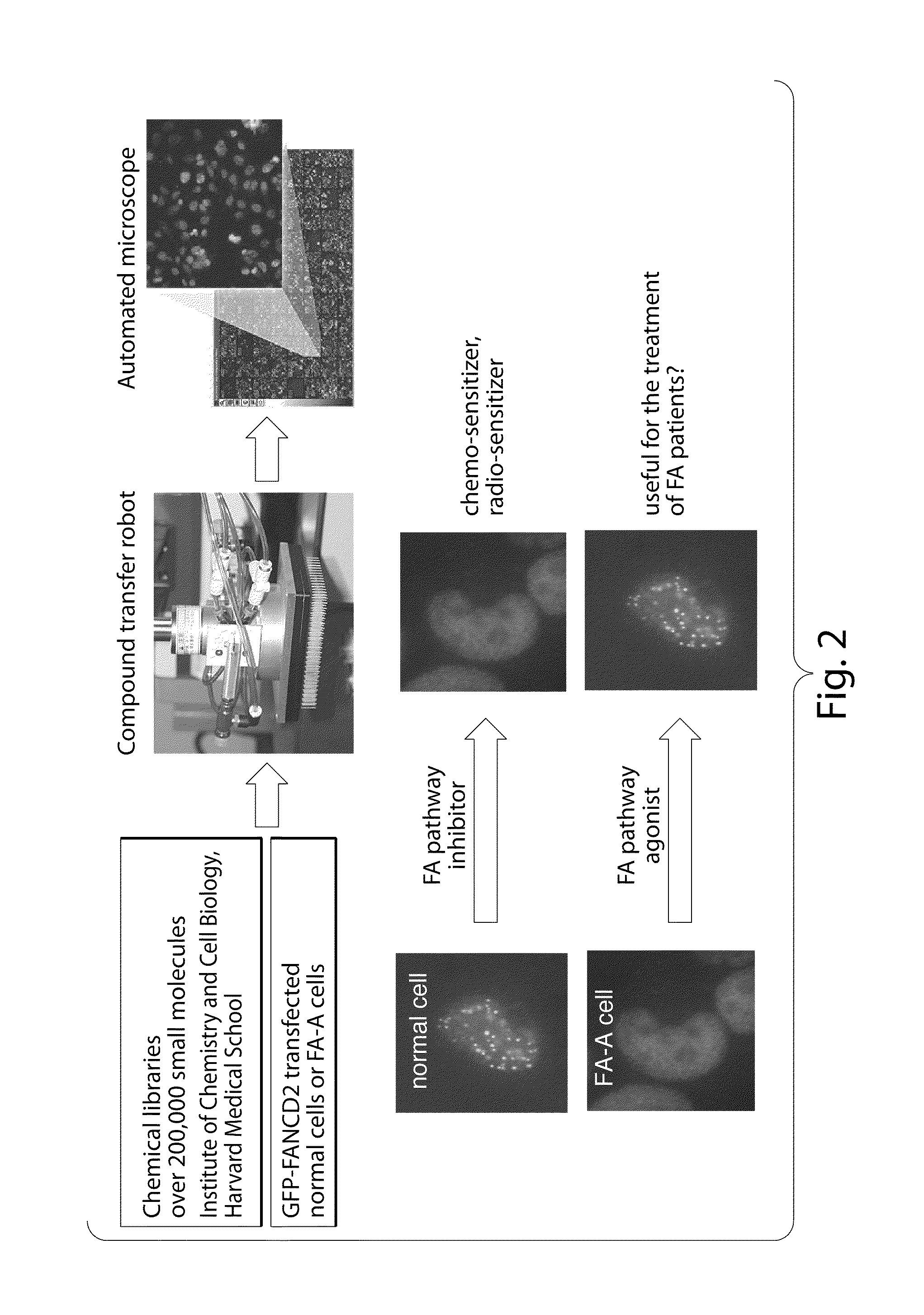
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer. In particular, the present invention discloses inhibitors of the Fanconi anemia pathway and methods using same. Such inhibitors are useful in inhibiting DNA damage repair and can be useful, for example, in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Method and apparatus for the treatment of respiratory and other infections using ultraviolet germicidal irradiation
InactiveUS20050256553A1Inherent accessibilityReduce riskOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesUltravioletMold infection
Method and apparatus for using computer controlled, fiber-coupled laser delivery of treatment specific wavelength, intensity and duration of UV irradiation to control bacterial, fungal, viral and mold infections in bodily cavities, fluids and external applications. The method of treatment is focused on DNA breakdown beyond repair by natural DNA repair mechanisms of the pathogen, with less than damaging doses to tissues being treated, thus avoiding mutagenicity and carcinogenicity. The minimal intensity and duration and exposure area of any given surface of tissue to be treated is to be pre-determined by tissue and pathogen testing to optimize the therapeutic ratio. External applications include specifically Trichophyton Rubrum (toenail fungus) through the nail and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa infections in burns and elsewhere.
Owner:PINPOINTE US
Cosmetic Methods And Compositions For Repairing Human Skin
InactiveUS20100080845A1Good curative effectRepairing or amelioratingCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman skinSun exposure
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for repairing adverse effects of the environment, daily stress, sun exposure, or pre-mature aging on human skin, comprising applying to the skin, prior to a period of bodily rest, a topical composition that contains resveratrol or a derivative thereof and at least one DNA repair enzyme.
Owner:MAES DANIEL H +2
DNA Repair Proteins Associated With Triple Negative Breast Cancers and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090239229A1High riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention provides methods of detecting triple negative breast cancer recurrence using biomarkers.
Owner:DNAR
Prevention of nuclear, solar, and other radiation-induced tissue damage
InactiveUS20070293458A1Reduced cell attachmentHigh strengthBiocideAntinoxious agentsPhosphorylationPyrophosphate
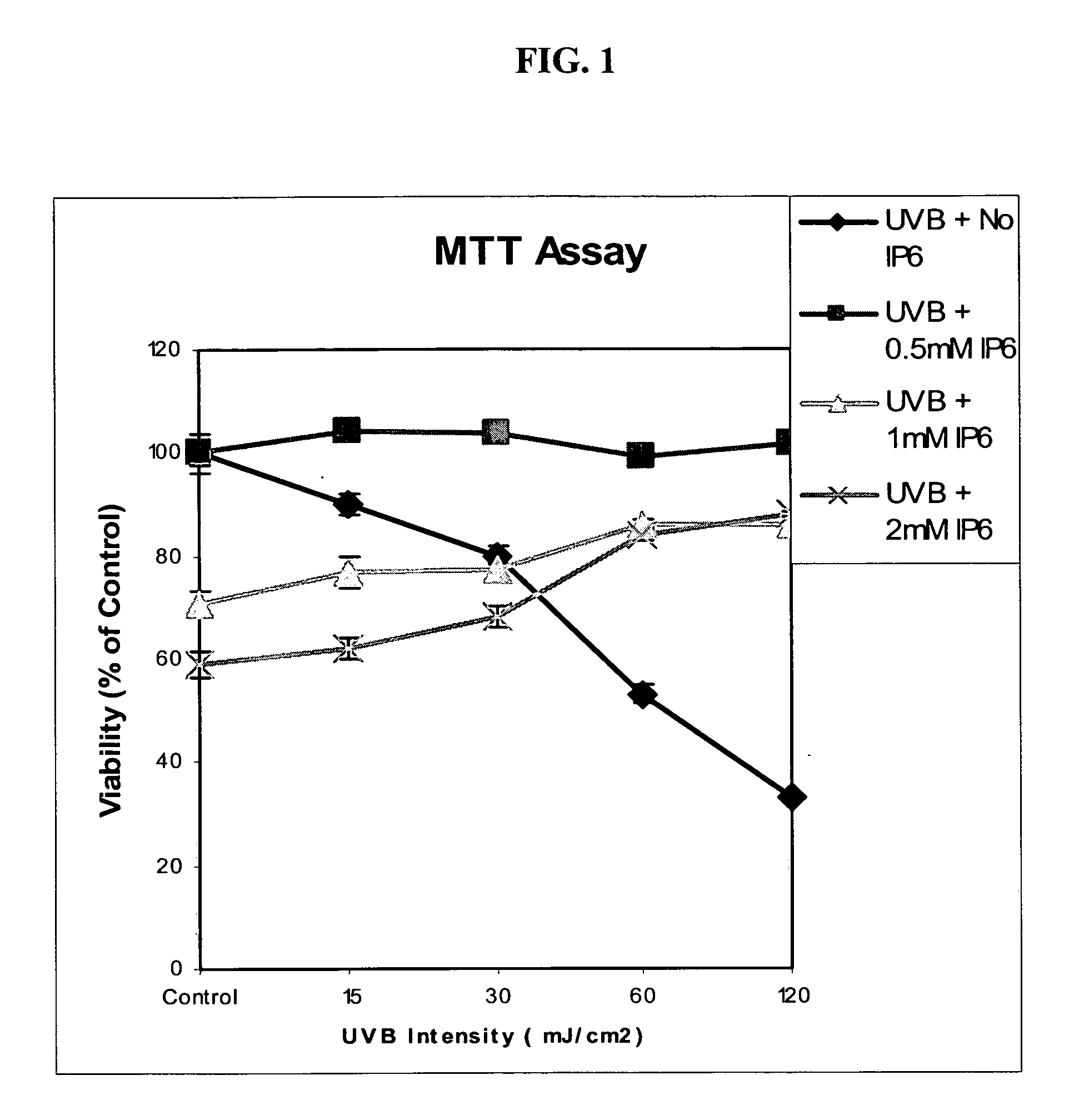
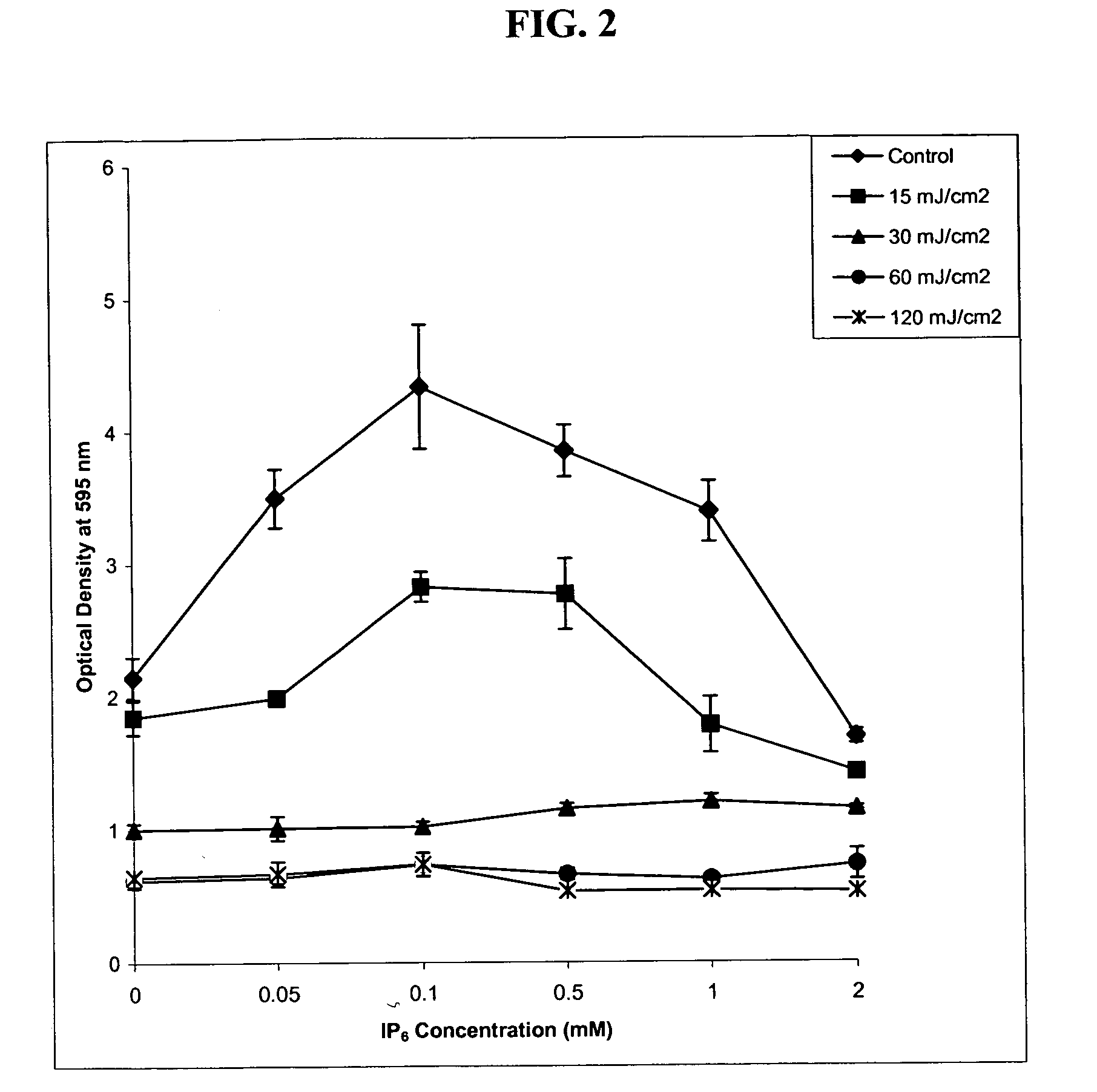
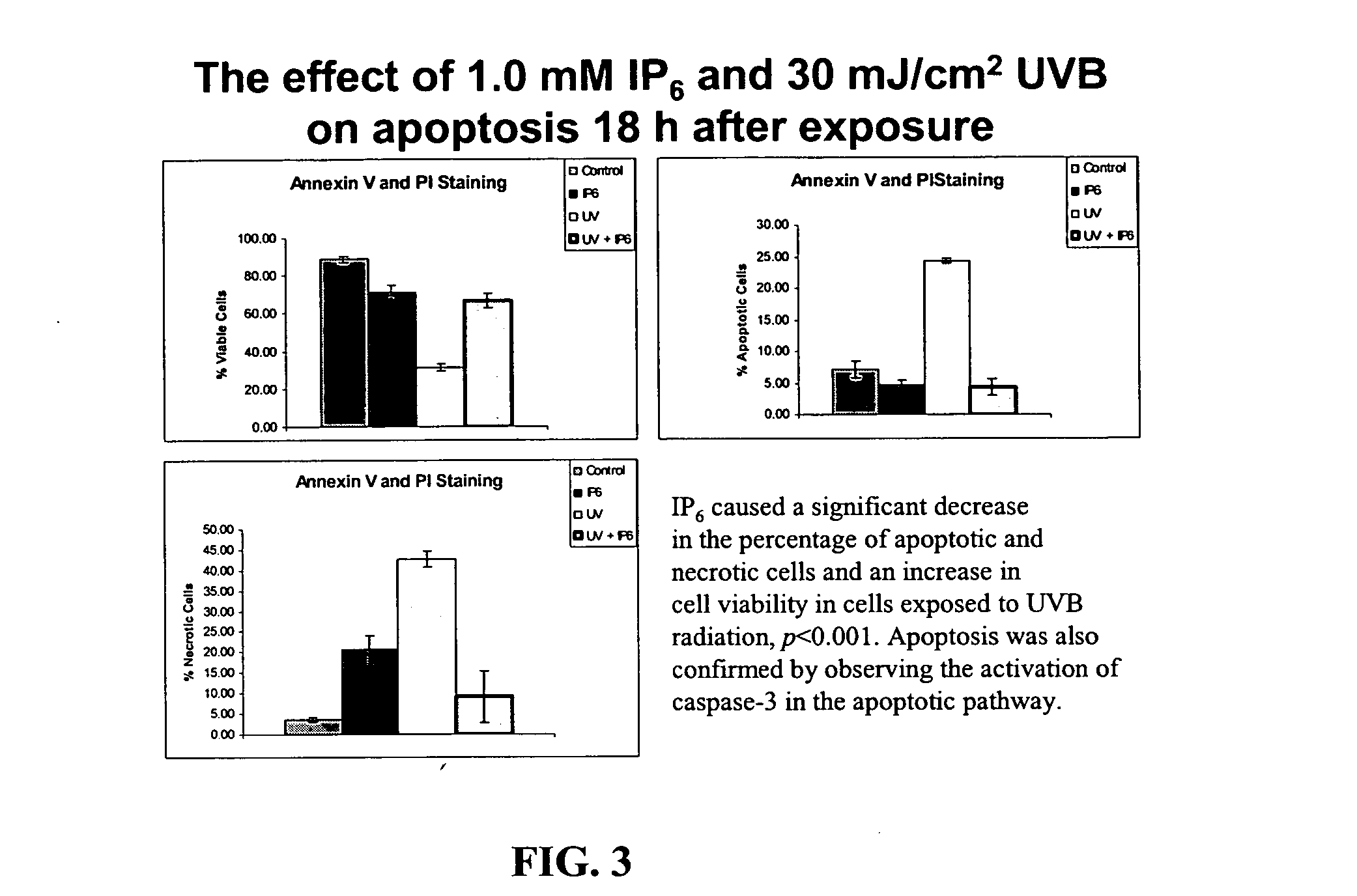
Inositol hexaphosphate (IP-6) is a polyphosphorylated carbohydrate with potent antioxidant activity to prevent active oxygen species-mediated mutagenesis, cell injury and carcinogenesis. IP-6 also activates DNA repair mechanisms. Sublethal radiation causes DNA damage through the formation of free radicals, reactive oxygen species, and pyrimidine crosslinks leading to cellular proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In the skin it results in the induction of skin cancer, premature skin aging, immuno-suppression, inflammation, and cell death. Likewise sublethal exposure to ionizing radiation as in nuclear blasts (war-time, accidental, terrorist-induced etc), cosmic radiation, etc. also causes the same spectrum of damage to the cells and the organisms with acute symptoms and eventual high risk of many cancers. IP-6 and / or inositol and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives, including pyrophosphates and citrate derivatives, significantly counteract the harmful effects of radiation, affecting cell cycle progression in a protective manner (more cells in the protective GI phase) as well as decreasing apoptosis and caspase-3 activation. Various salts of IP-6 are used with comparable efficacy and the combination of IP-6+inositol affords the best protection against radiation-induced cell injury. Thus IP-6 and inositol are effective agents for protection against nuclear, solar and other radiation injuries.
Owner:IP 6 RES
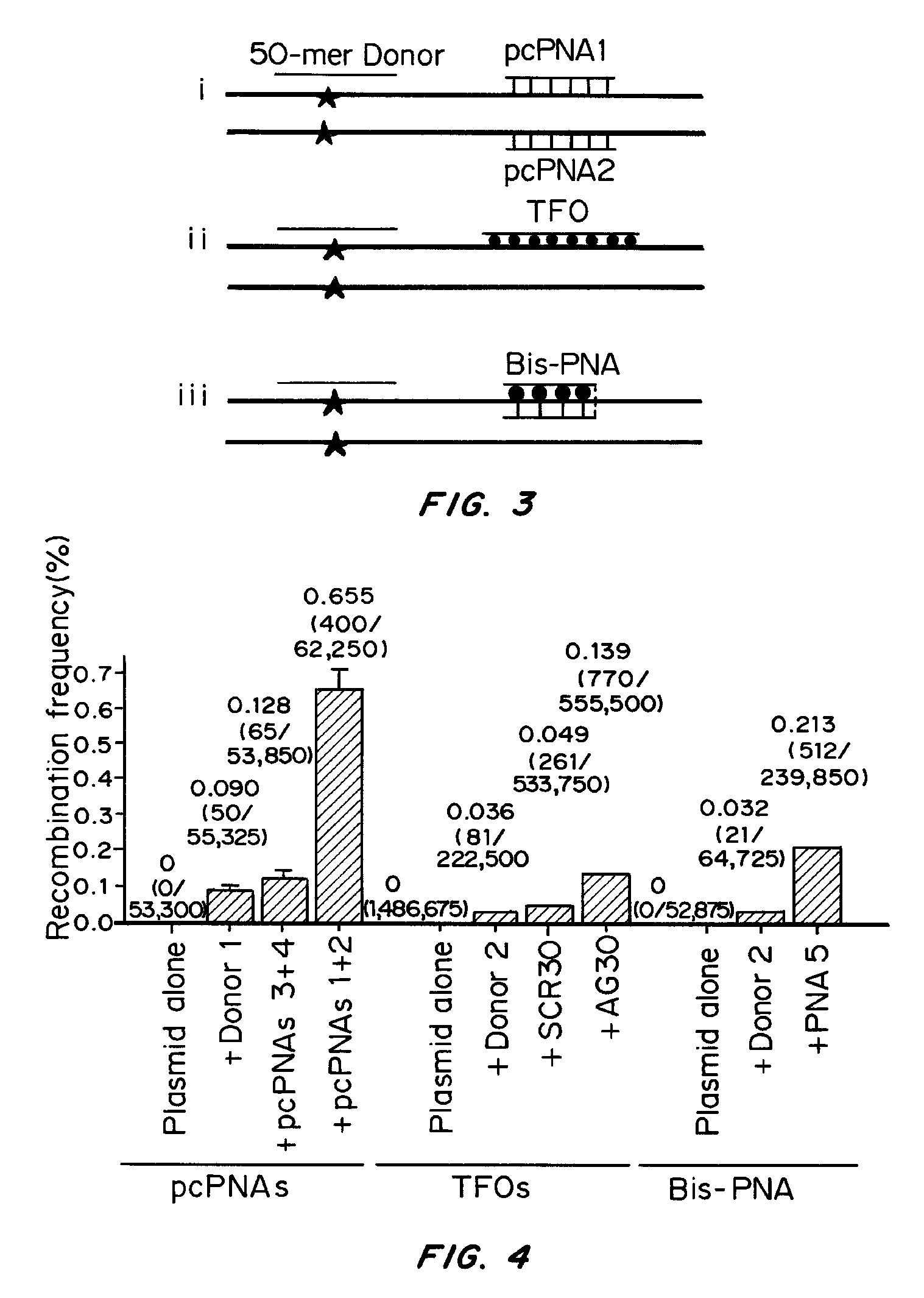
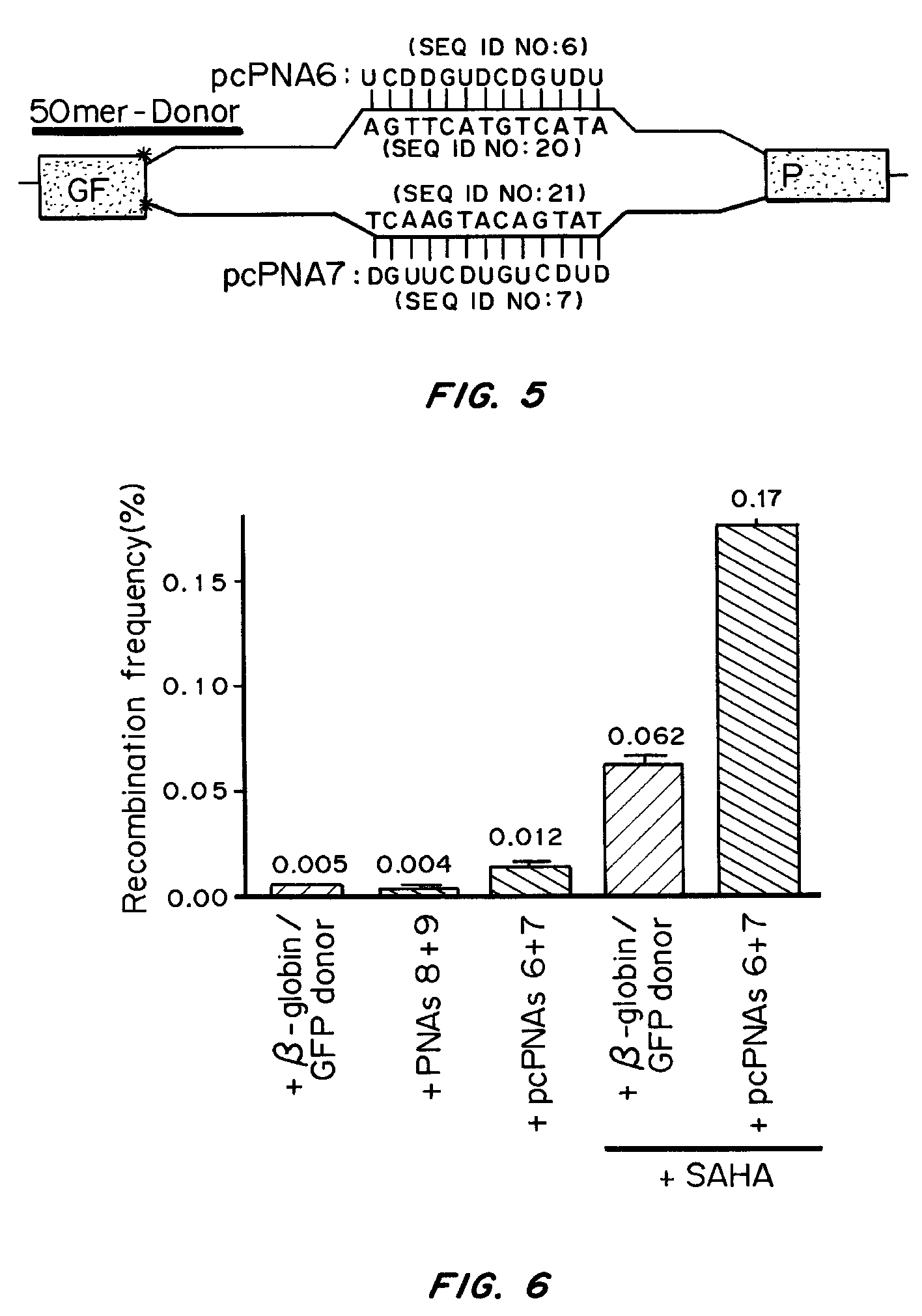
Pseudocomplementary oligonucleotides for targeted gene therapy
ActiveUS8309356B2Increase flexibilityImprove efficiencySugar derivativesCarbohydrate active ingredientsCellular mechanismDouble stranded
Owner:YALE UNIV
Topical composition for anti-aging skin treatment using dual DNA repair mechanism and method of use
InactiveUS8911774B2Reduction of degreeReduce pigmentationBiocideCosmetic preparationsSkin colorMethylsulfonylmethane
A topical composition for anti-aging treatment of the skin includes water soluble extract of Uncaria species, Arabidopsis thaliana extract, lipoic acid, dimethylethanolamine, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate, dimethyl sulfoxide, Glycyrrhiza Glabra(Licorice) root extract, methylsulfonylmethane, phytosterols, D-ribose, tocotrienol, tocopherol, glucosamine hydrochloride, Pisum sativum extract; Bambusa vulgaris extract, and a dermatologically acceptable liposomal delivery medium. Further disclosed is a method using the topical composition for anti-aging skin treatment utilizing DNA repair in both the nucleus and the mitochondria. The topical composition can be applied on the skin of a person daily, and can also be applied in a dermal infusion treatment, with or without micro-dermal abrasion or skin suction. Topical application of the composition achieves effective reduction of pigmentation spots and degree of winkles, and improvement of skin color tone.
Owner:LIFE SCI INT
Method and compositions for treating skin
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
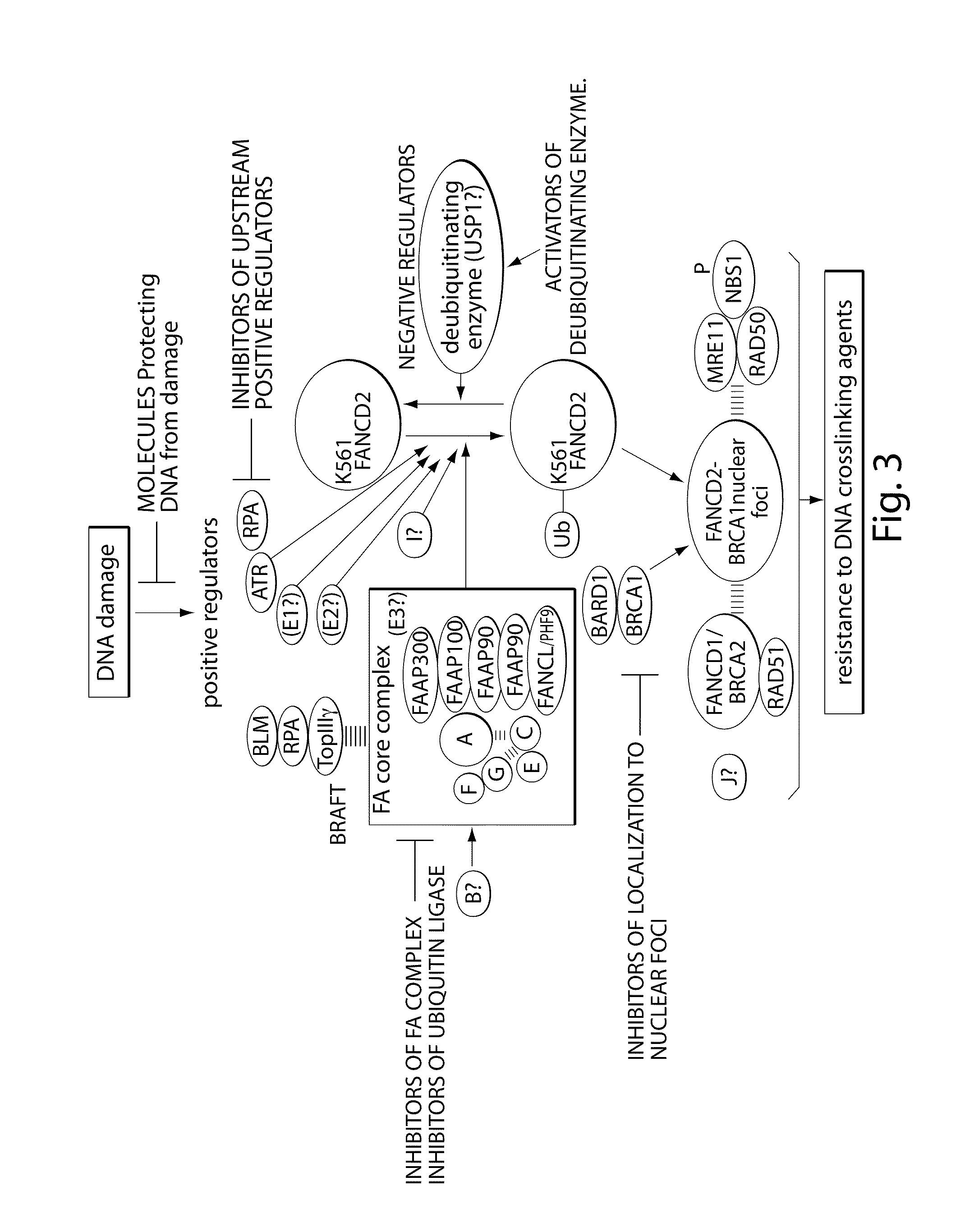
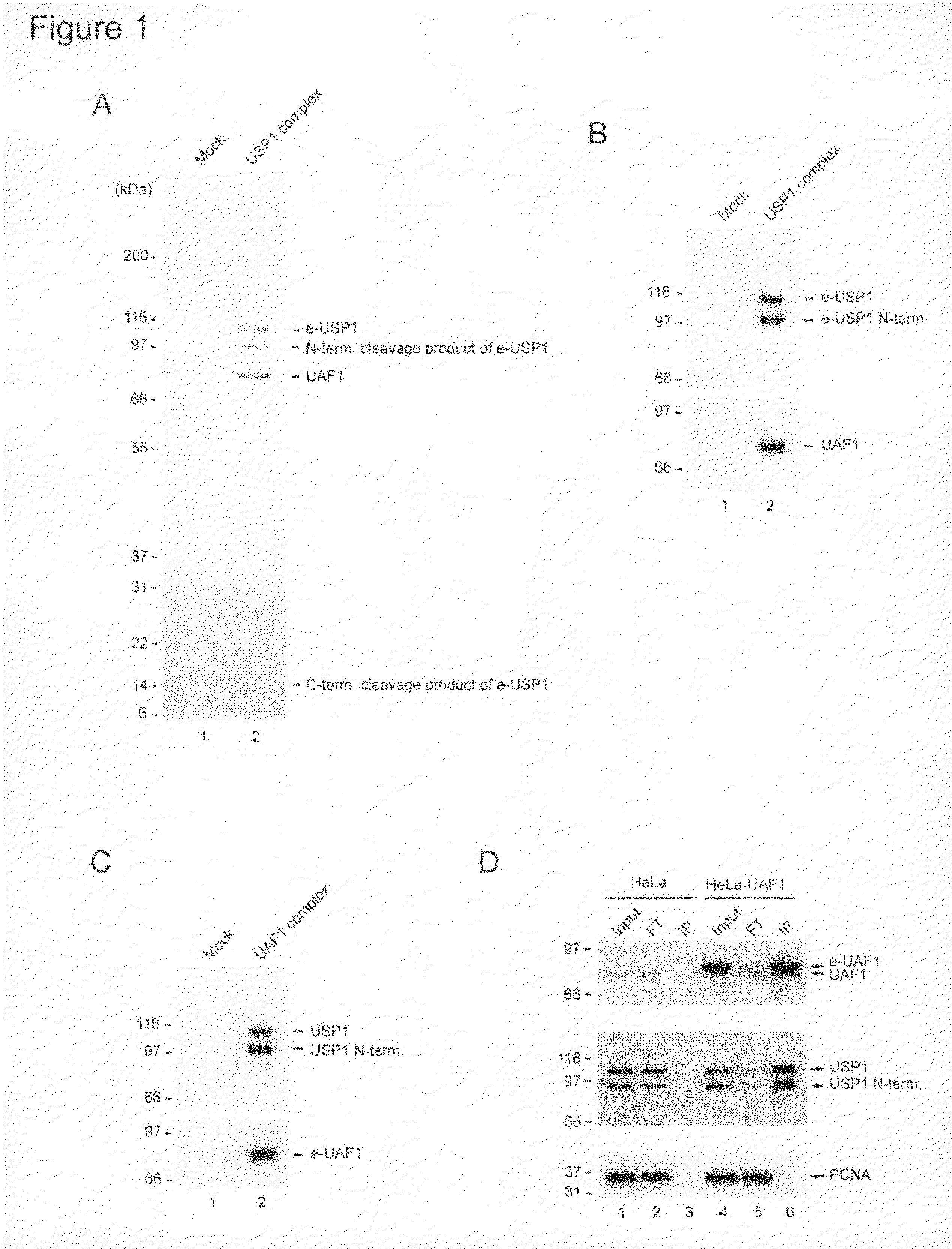
Inhibitors of USP1 deubiquitinating enzyme complex
ActiveUS20080167229A1Improve the level ofEnhance cell viabilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer preventionBone marrow failure
The invention provides compositions and methods used to inhibit USP1 deubiquitinase activity and to identify new inhibitors of USP1 deubiquitinase. The inhibitors can be used to treat or prevent cancer, bone marrow failure, and damage to cells or DNA resulting from genotoxic agents such as antineoplasic agents, including chemotherapeutic agents and radiation. The inhibitors include siRNA directed at inhibiting the expression of USP1 or UAF1, a protein which forms a heterodimeric complex with USP1. The inhibitors can be used to enhance cell survival if administered either before or after radiation exposure. Methods are also provided to enhance chemotherapy or radiotherapy of cancer and to enhance DNA repair. Transgenic knockout animals and knockdown cells are provided, whose USP1 expression is impaired.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Anti-cancer medicine composition
InactiveCN1616099AAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical active ingredientsWhole bodyTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to an anticancer medicine composition and belongs to the field of medicine technology. The anticancer medicine composition contains topomerase inhibitor and medicinal supplementary material. The topomerase inhibitorcan inhibit intracellular DNA repair function and reduce the tolerance one tumor cell on anticancer nitrosourea medicine; and the medicine supplementary material is mainly degradable biocompatible polymer. During the degrading and absorption process of the supplementary material, the anticancer medicine is released slowly to the tumor part, and this can lower the systemic toxic reaction while maintaining local effective medicine concentration. The anticancer medicine composition contains also anticancer nitrosourea medicine, and is set to the tumor part locally to enhance the treatment effect.
Owner:孔庆忠
Engineering strain high in lactoflavin yield and application of engineering strain high in lactoflavin yield
The invention discloses a lactoflavin engineering bacterium and a constructing method thereof, and the preservation number of the lactoflavin engineering bacterium is CGMCC NO.16132. Through a geneticengineering means, a lactoflavin auxotroph strain is constructed, then a chromosome integrates and expresses a lactoflavin operon demodulated by bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and the lactoflavin production capacity of the strain is restored; then an expression vector overexpresses the lactoflavin operon demodulated by the bacillus subtilis, so that the lactoflavin production capacity of the straincan be improved; in addition, through point mutation of a ribC gene, the catabolism of lactoflavin is diminished; and finally, a recA gene which is responsible for homologous recombination and DNA repair on the chromosome is inserted for inactivation, and a lactoflavin production chassis cell is constructed. Based on the lactoflavin production chassis cell, through combination of the characteristic that the lactoflavin is a natural flroresence substance, and a strain high in lactoflavin yield is screened out through liquid drop micro-fluidic control. The invention also discloses a method for producing the lactoflavin through fermentation with the bacillus subtilis, and an application of the strain high in lactoflavin yield to lactoflavin production and an application of the strain high inlactoflavin yield to medicines, foods and feeds.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Molecular diagnostic test for cancer
ActiveUS20140051591A1Inorganic active ingredientsHealth-index calculationCancer typeChemotherapeutic drugs
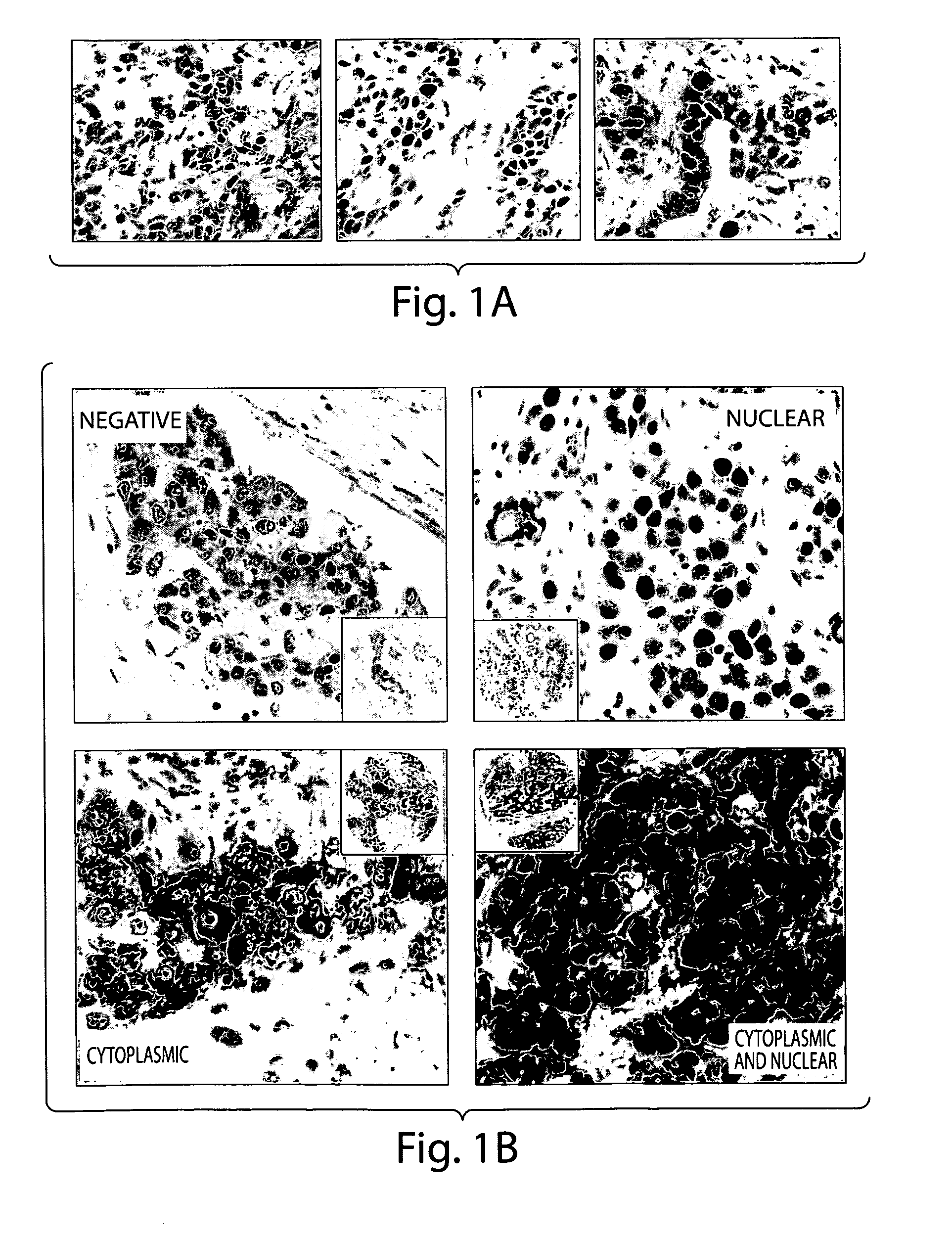
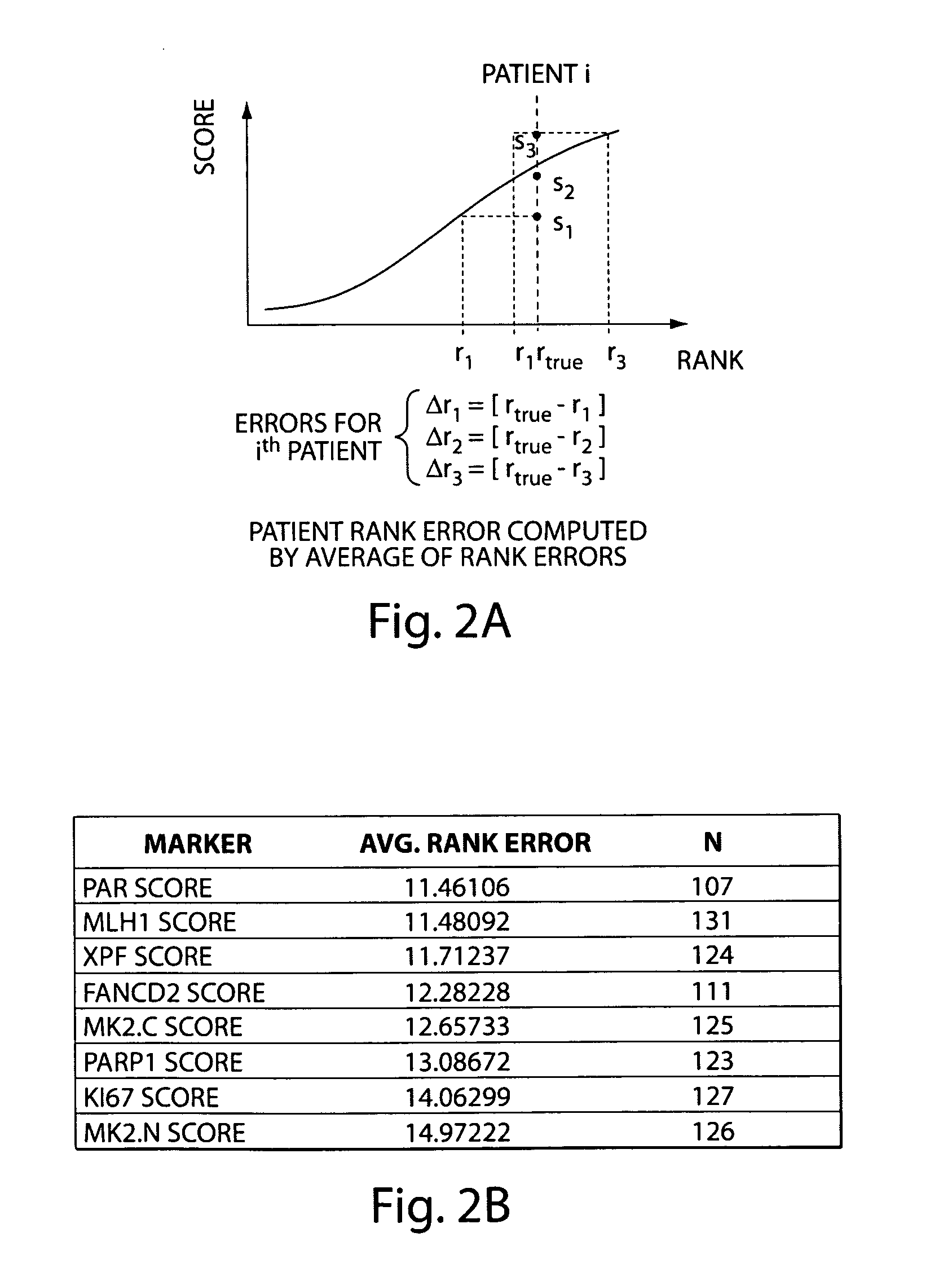
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for cancer. The test defines a novel DNA damage repair deficient molecular subtype and enables classification of a patient within this subtype. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any chemotherapy. This test may be used in different cancer types and with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect DNA damage or repair, such as many of the standard cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs currently in use. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS SERVICES LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1f812d7e-7417-41a4-a843-6a7bbf0c1bd5/US08436185-20130507-C00001.png)