Engineering strain high in lactoflavin yield and application of engineering strain high in lactoflavin yield
A technology of riboflavin and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, treatment of microorganisms with electricity/wave energy, and introduction of foreign genetic material using carriers, etc. It can solve the problem of difficult to obtain riboflavin production strains, Bacillus subtilis to improve riboflavin Problems such as the limitation of the production capacity of hormones and the difficulty of strain transformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Construction of Riboflavin Production Chassis Cells for High Throughput Screening
[0037] (1) Construction of riboflavin auxotrophic strains
[0038] Using Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome as template, use primers UPrib-F, UPrib-R to amplify UPrib fragment, use primers DNrib-F, DNrib-R to amplify DNrib fragment; use pC194 plasmid as template, use primers cat-F, cat- R amplifies the cat fragment with adapter. UPrib fragment, cat fragment and DNrib fragment were assembled into rib-UCD fragment by fusion PCR. The rib-UCD fragment Spizizen was transformed into Bacillus subtilis 168 to obtain riboflavin auxotrophic strain BS168△rib.
[0039] (2) Construction of riboflavin operon revertant strain
[0040] Using Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome as template, use primers UPrib-F, UPrib-R to amplify UPrib fragment, use primers DNrib-F, DNrib-R to amplify DNrib fragment; use Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strainSRCM101267 chromosome as template, use primers rib-F, rib-...
Embodiment 2
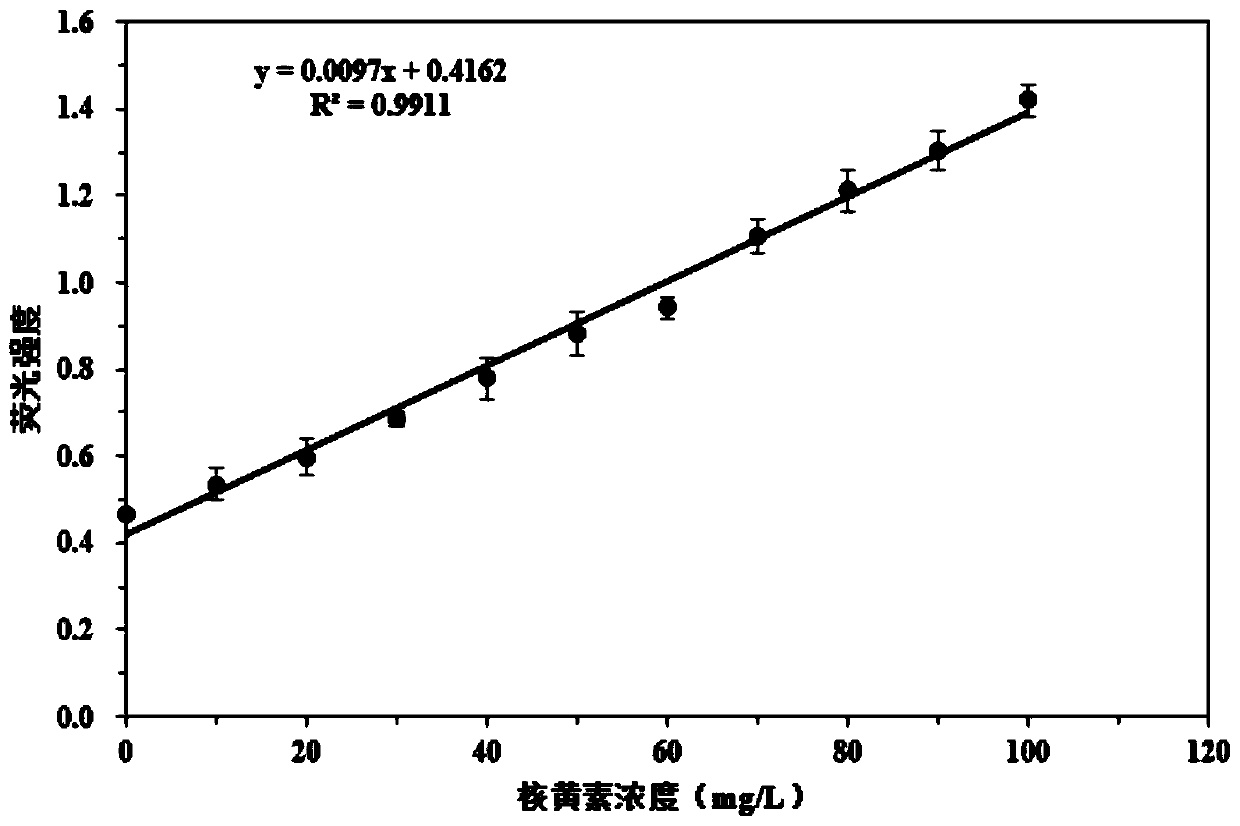
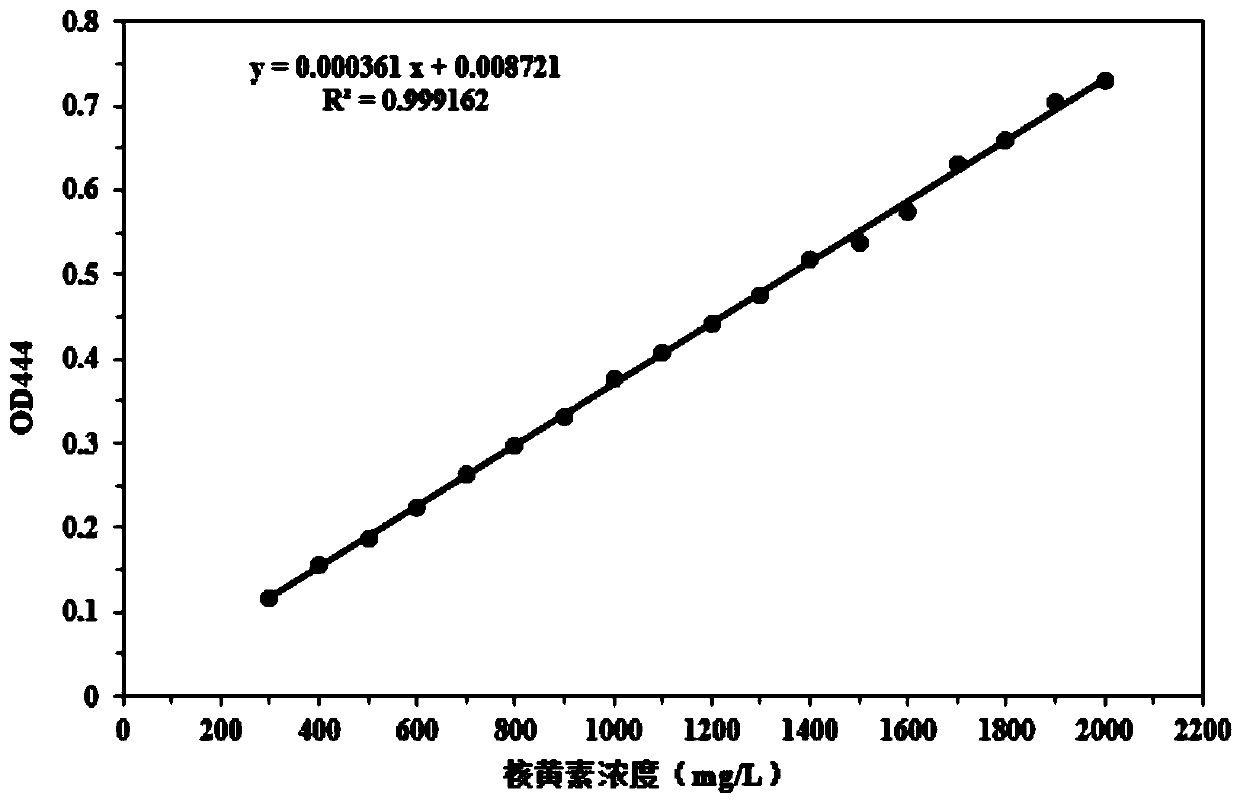
[0054] Example 2: The relationship between droplet microfluidic detection of riboflavin concentration and fluorescence intensity
[0055] Riboflavin is a natural fluorescent substance. In order to verify that different concentrations of riboflavin standard products can display fluorescent signals of different intensities through droplet microfluidics, we use fermentation medium (the composition of the fermentation medium is: corn steep liquor dry powder 10g / L , sucrose 30g / L, magnesium sulfate 2g / L, ammonium sulfate 7g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 3g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L) with different concentrations of riboflavin standard products, different concentrations of riboflavin standard products are used After the droplet was embedded, the fluorescent signal was detected by droplet microfluidics, and the results were as follows: figure 1 As shown, the riboflavin concentration in the droplet has a certain linear relationship with the fluorescence signal intensi...
Embodiment 3
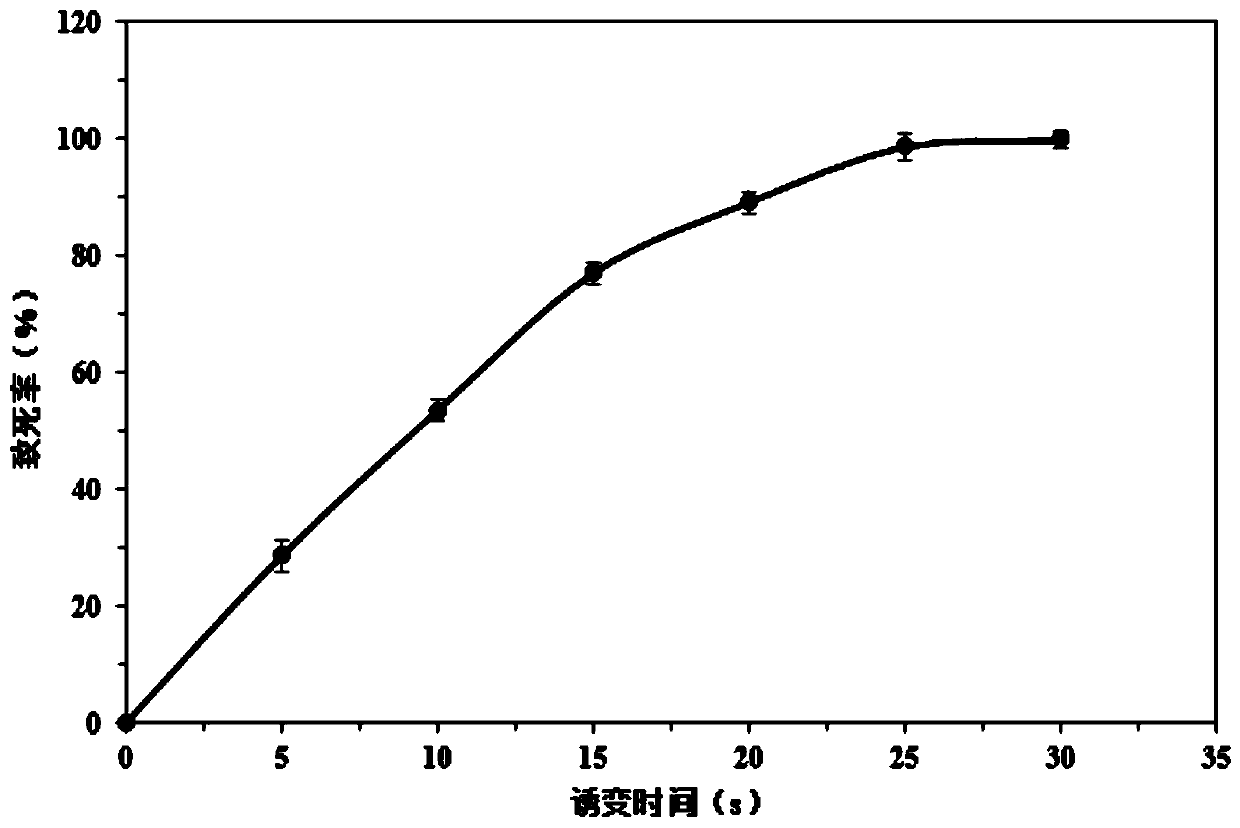
[0056] Example 3: Determination of Atmospheric Room Temperature Plasma (ARTP) Mutagenesis Time, Construction of Mutant Library and Droplet Microfluidic Sorting
[0057] (1) Determination of lethality
[0058] To obtain a relatively broad mutant library, we performed atmospheric room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis on the chassis cell SF0. First, the lethality of SF0 under plasma mutagenesis conditions was determined. SF0 cells seeded to mid-log phase were diluted with 0.8% NaCl solution to 10 8 1 cell / mL suspension, take 10uL of the suspension and spread it evenly on the iron plate, and carry out ARTP mutagenesis, the mutagenesis time is 0s, 5s, 10s, 15s, 20s, 25s, 30s 2 replicates, 3 replicates of plated at each time point. After mutagenesis, the iron sheet with cells was placed in 1 mL of sterile water and vortexed to wash the cells, and the cell suspension was diluted 10 times to 10 -2 , take 100 μL of the diluted cell suspension to spread on the plate, and count ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com