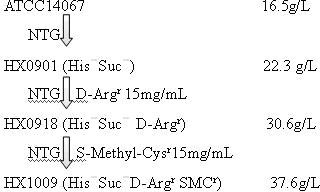Patents
Literature
142 results about "Auxotrophic strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of auxotrophic. : requiring a specific growth substance beyond the minimum required for normal metabolism and reproduction by the parental or wild-type strain auxotrophic mutants of bacteria.
Immunogenic compositions comprising DAL/DAT double mutant, auxotrophic attenuated strains of listeria and their mehods of use
InactiveUS20050048081A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiologyGenus Listeria
The invention includes auxotrophic attenuated mutants of Listeria and methods of their use as vaccines.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Protein expression systems
ActiveUS20090325230A1High protein yieldEfficient productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyRecombinant protein production
The present invention provides an improved expression system for the production of recombinant polypeptides utilizing auxotrophic selectable markers. In addition, the present invention provides improved recombinant protein production in host cells through the improved regulation of expression.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
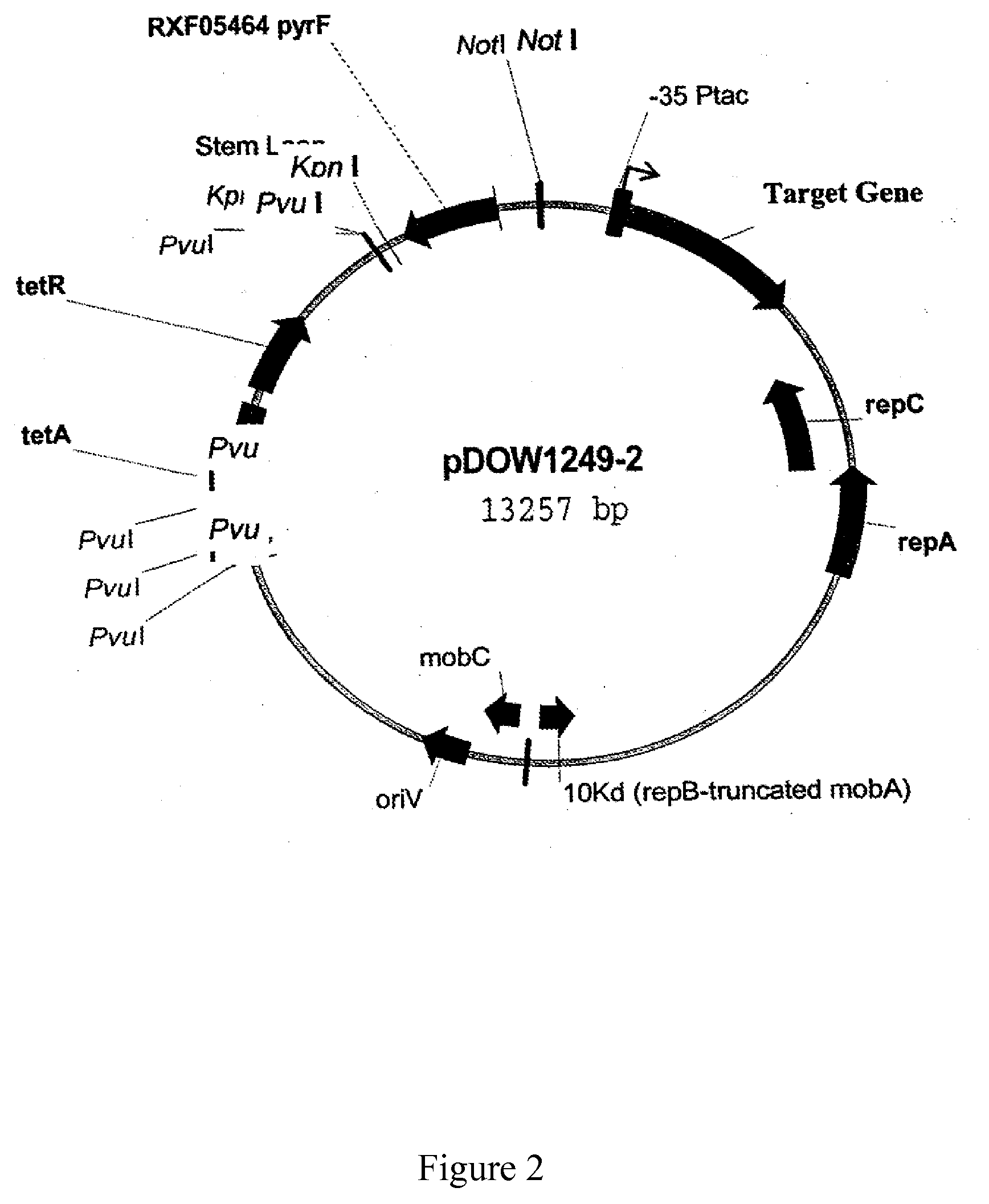
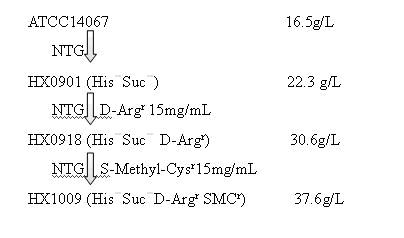
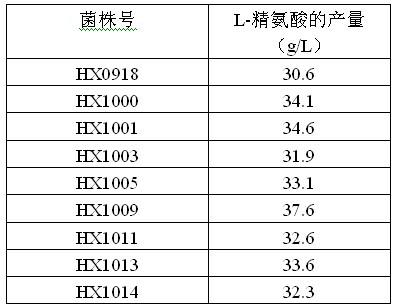
Strain capable of producing L-arginine and method for producing L-arginine by same
The invention relates to a strain capable of producing L-arginine and a method for producing the L-arginine by the strain and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. For the strain, Brevibacterium flavum ATCC 14067 is used as a starting strain; nitrosoguanidine is adopted to carry out mutagenesis step by step; mutant strains with histidine and succinic acid auxotrophic strains are screened out so as to cut off a competitive metabolic pathway; and mutant strains (His-, Suc-, D-Argr, SMCr) with resistances of arginine structural analogs and cysteine structural analogs are screened out. The strain is named as Brevibacterium flavum HX1009, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4464 and has the genetic characters of histidine auxotroph His-, succinic acid auxotroph Suc-, D-arginine resistance D-Argr and S-methyl cysteine resistance SMCr for improving the yield of the L-arginine. Under the optimized condition, the L-arginine is produced by fermentation on a fermentation tank with the volume of 5L to 5M3 and the arginine production level achieves 50 to 70g / L.
Owner:FUJIAN GUTIAN PHARMA
Preparation of soluble human selenium-containing single-chain abzyme
InactiveCN101280015AEasy to prepareIncrease vitalityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method to prepare soluble human selenium-containing catalytic single-chain antibodies, belonging to biotechnology field. The method includes the following steps: with glutathione derivatives as target antigen, filtrating the recombinant phage display human single-chain antibody library through immune affinity selection method to obtain single-chain antibodies B3 and D8; assembling the single-chain antibodies to secretory procaryon or eucaryon expression vector; translating colon bacillus or yeast cell; expressing and purifying the single-chain antibody proteins in procaryon or eucaryon; introducing GPX catalytic group SeCys at the substrate combining sites of the antibodies through chemical mutation method or directly expressing the soluble single-chain antibody proteins which contain GPX catalytic groups at the substrate combining sites with auxotrophic colon bacillus through genetic mutation techniques to endue the antibodies with GPX catalytic activity. The method of the invention is simple and the human selenium-containing catalytic single-chain antibodies prepared with the method are of high catalytic activity; the proteins expressed by the antibodies are soluble; therefore the method is good for large-scale production and is of broad application prospect in biological pharmacy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods of screening for introduction of DNA into a target cell
InactiveUS20020192755A1Facilitate to conferReduce necessityCompound screeningFungiTransformation cellPolynucleotide
The present invention provides methods of introducing a polynucleotide into a target cell, wherein the method employs a light generating protein coding sequence acting as a reporter. An important advantage of the methods described herein is that drug resistant target cells or target cells having no useful auxotrophic markers can be effectively transformed. The present invention also includes transformed cells produced by the methods described herein. Also described are light generating protein coding sequence modifications, a variety of vectors, and methods of using the transformed cells of the present invention.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
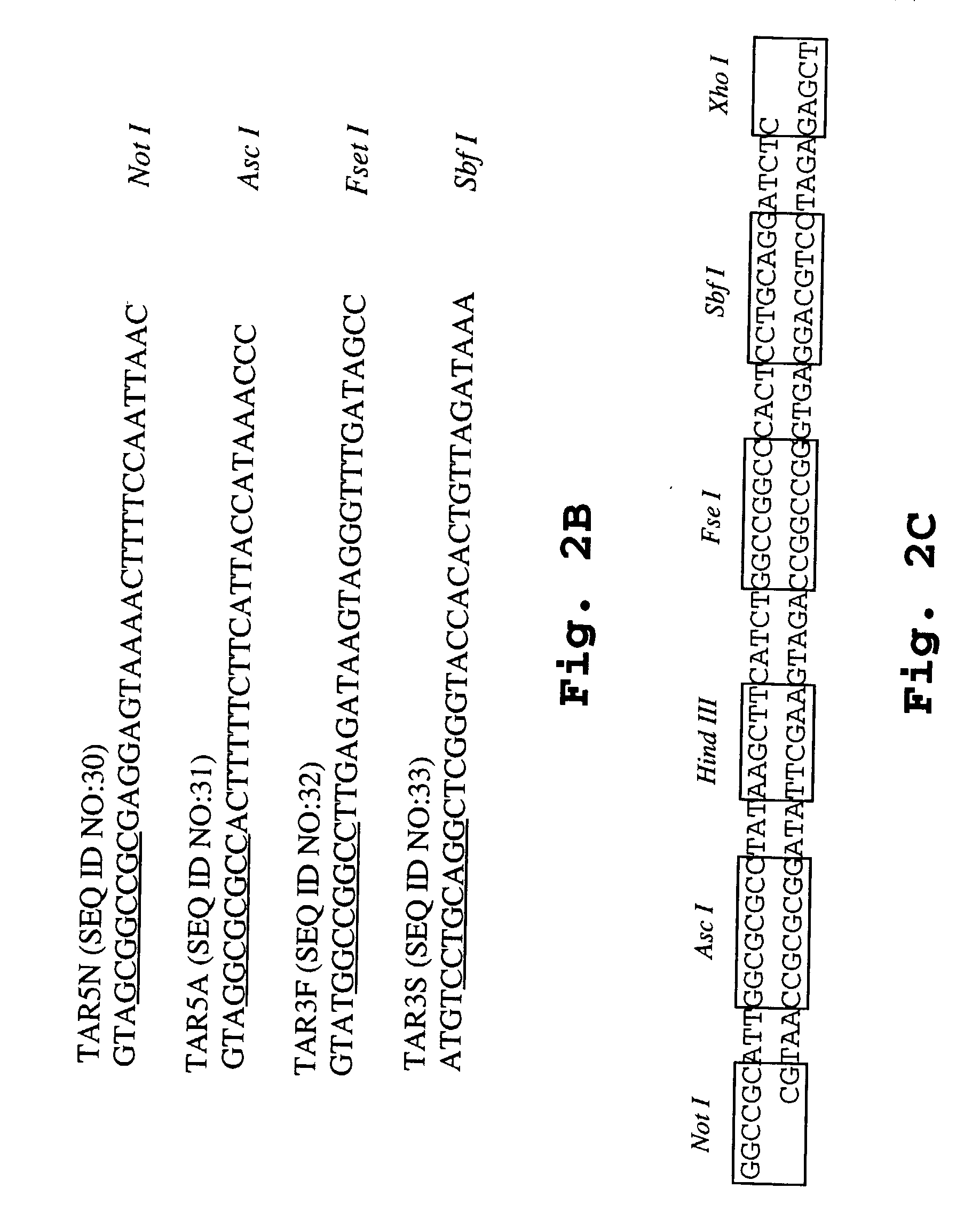
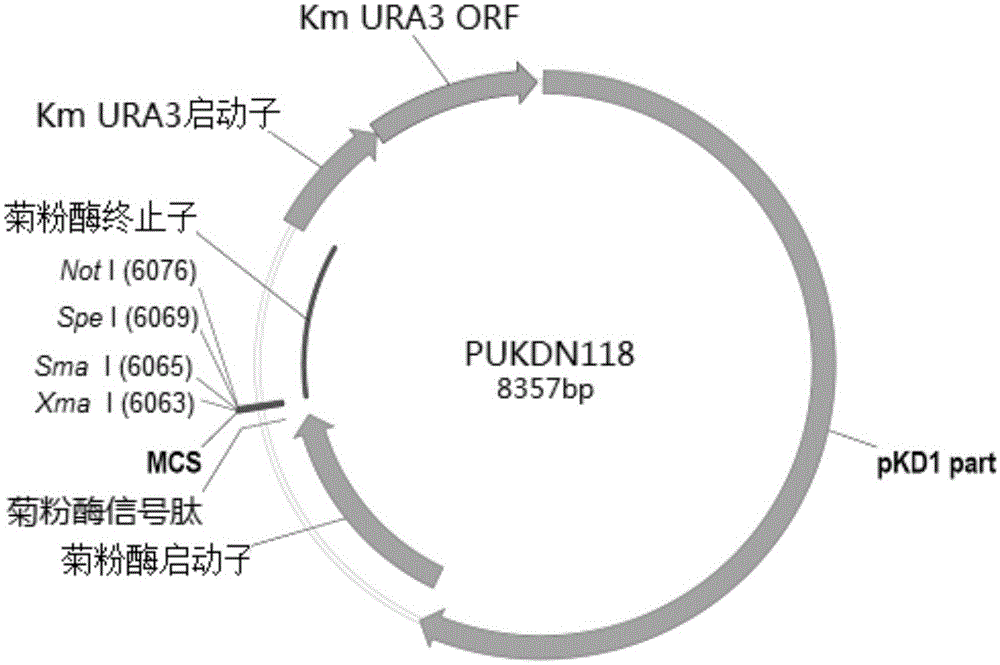
Recombinant vector used in Kluyveromyces marxianus auxotrophic strain
InactiveCN105063081AFungiVector-based foreign material introductionOpen reading frameKluyveromyces sp.
The invention provides a recombinant vector used in a Kluyveromyces marxianus auxotrophic strain, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant vector sequentially comprises a PKD1 vector, an inulase promoter, an inulase signal peptide, a polyclone site, an inulase terminator, a nutrient gene promoter and a nutrient gene open reading frame. The constructed recombinant vector and preparation method thereof can be used for constructing a transformant, thereby implementing expression of the exogenous gene.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
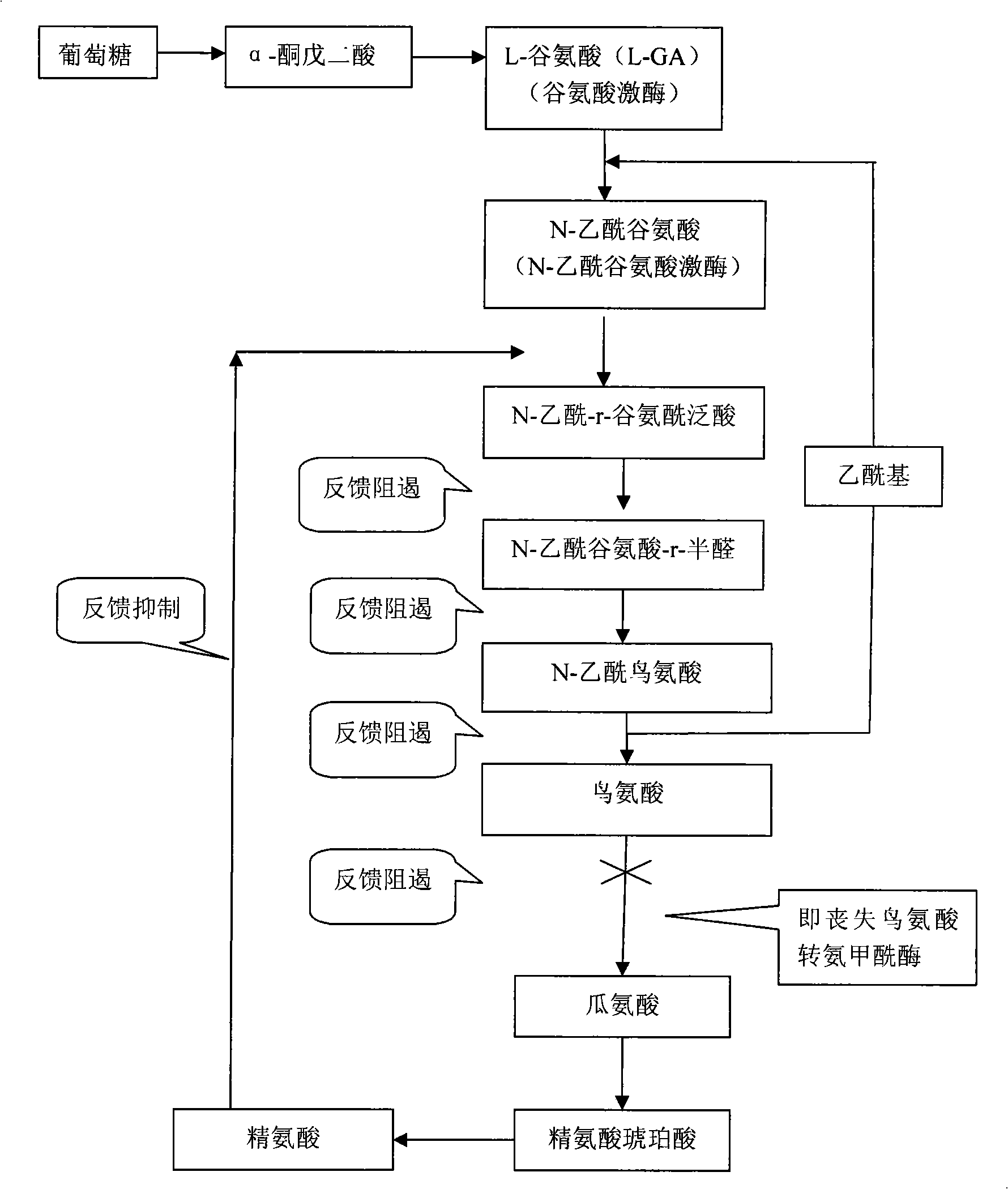
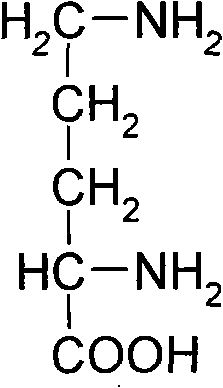
Method for producing L-ornithine by microorganism fermentation
InactiveCN101323866AFast acid productionImprove sugar conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSolubilityChemical treatment
The invention provides a method for producing L-ornithine by microbial fermentation, namely, using Corynebacterium glutamate to obtain the strains of CS-189(cit<(-)>+SG<r>) by chemical treatment, and obtain the L-ornithine hydrochloride by fermentation, culture solution micro-filtration by a ceramic membrane, ion exchange resin and extraction by a hydrothermal crystallization method with decompression concentration. The strains used in the method are auxotrophy resistant to sulfaguanidine, which significantly enhances acid yield by fermentation. Meanwhile, aiming at the problem that the solubility of the L-ornithine hydrochloride in water is extremely difficult, the hydrothermal crystallization method is adopted to obtain better extraction rate under the condition that flammable and explosive alcohol is not used. The method simplifies processes and reduces extraction cost.
Owner:上海聚瑞生物技术有限公司
Methods of inducing immune responses through the administration of auxtrophic attenuated dal/dat double mutant Listeria strains
The present invention includes a method of eliciting a T-cell immune response to an antigen in mammal. The method of eliciting a T-cell immune response includes administering mammal an auxotrophic attenuated strain of listeria which expresses the antigen. The auxotrophic attenuated strain of listeria includes a mutation in at least one gene whose protein product is essential for growth of bacteria.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for increasing yield of biomass of and/or components of biomass from marine microorganisms
The present invention provides an optimized method of continuously culturing an auxotrophic marine microorganism in a fermentor under aerobic conditions at Y g / l of cell dry matter, CDM, wherein Y is in the range from 100-300 g / l, comprising culturing said auxotrophic marine microorganism in a culture medium comprising a carbon source, gradually added, in an amount of (Y×h) gram per litre of culture broth, wherein h is in the range from 1.1-3.0, and with a residence time of 20-100 h. The method maintains a high productivity of cellular lipids, especially polyenoic acids.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Attenuated microorganisms for the treatment of infection
The present invention pertains to a Salmonella microorganism having an attenuating mutation which disrupts the expression of a gene located within the Spi2 pathogenicity island, and an auxotrophic mutation. The microorganism therefore has a double mutation which helps prevent reactivity of the microorganism while maintaining the effectiveness of the microorganism to elicit an immune response. The present invention also pertains to vaccine compositions and methods for treating and preventing a Salmonella infection in a patient.
Owner:PROKARIUM
Recombinant intracellular pathogen immunogenic compositions and methods for use
Immunogenic compositions comprising recombinant attenuated intracellular pathogens that have been transformed to express recombinant immunogenic antigens of the same or other intracellular pathogens are provided. Exemplary immunogenic compositions include, but are not limited to attenuated recombinant Mycobacteria expressing the major extracellular non-fusion proteins of Mycobacteria and / or other intracellular pathogens. Other embodiments are provided wherein the recombinant attenuated intracellular pathogen is auxotrophic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method For Increasing Yield of Biomass of and/or Components of Biomass From Marine Microorganisms
The present invention provides an optimized method of continuously culturing an auxotrophic marine microorganism in a fermentor under aerobic conditions at Y g / l of cell dry matter, CDM, wherein Y is in the range from 100-300 g / l, comprising culturing said auxotrophic marine microorganism in a culture medium comprising a carbon source, gradually added, in an amount of (Y×h) gram per litre of culture broth, wherein h is in the range from 1.1-3.0, and with a residence time of 20-100 h. The method maintains a high productivity of cellular lipids, especially polyenoic acids.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacterium for producing beta-carotene and application of yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacterium
InactiveCN111321087AEasy to buildIncrease productionFungiStable introduction of DNAUracilMicrobiology
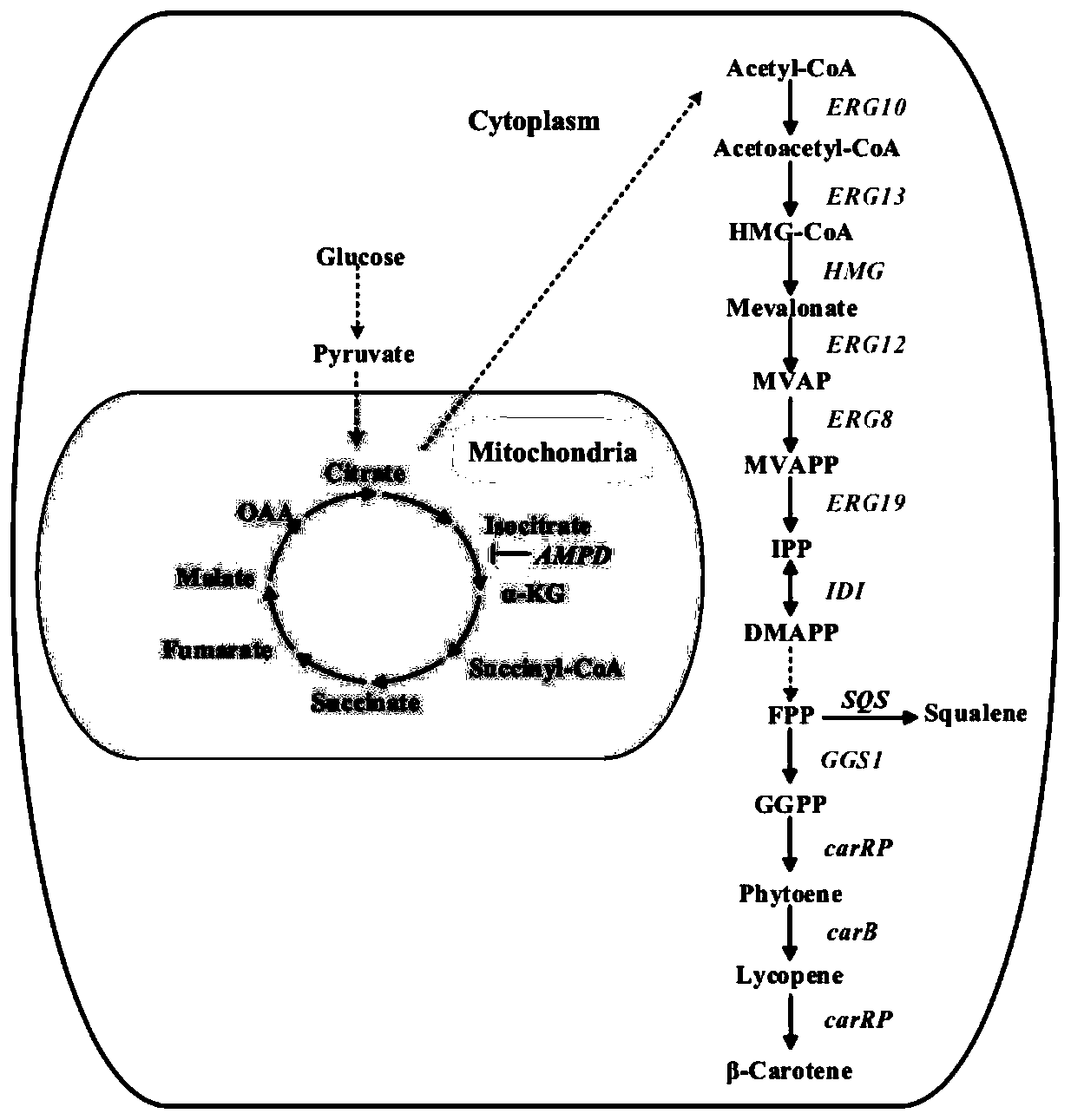
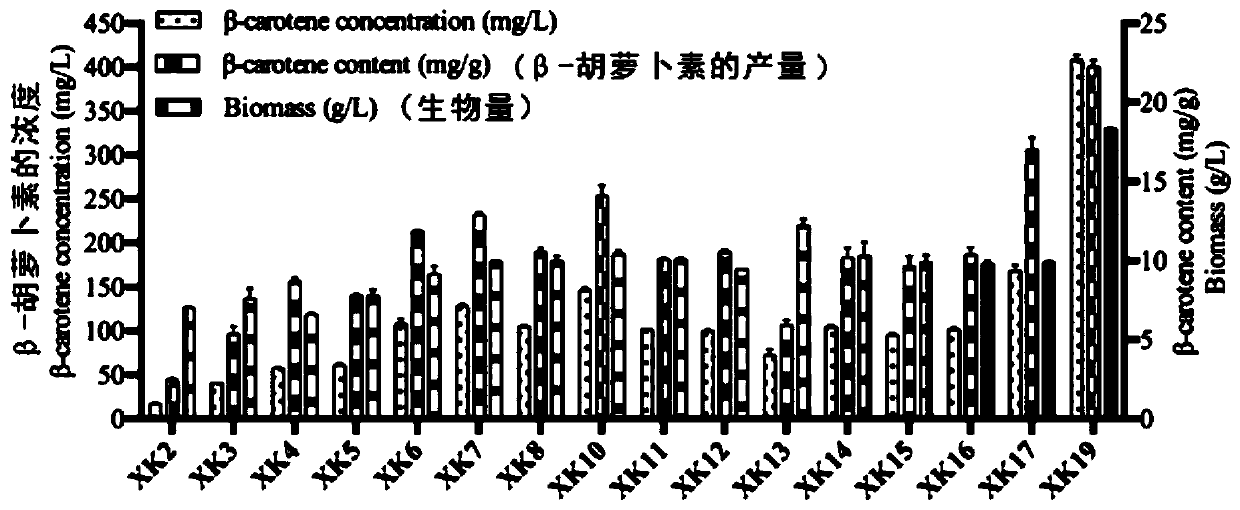
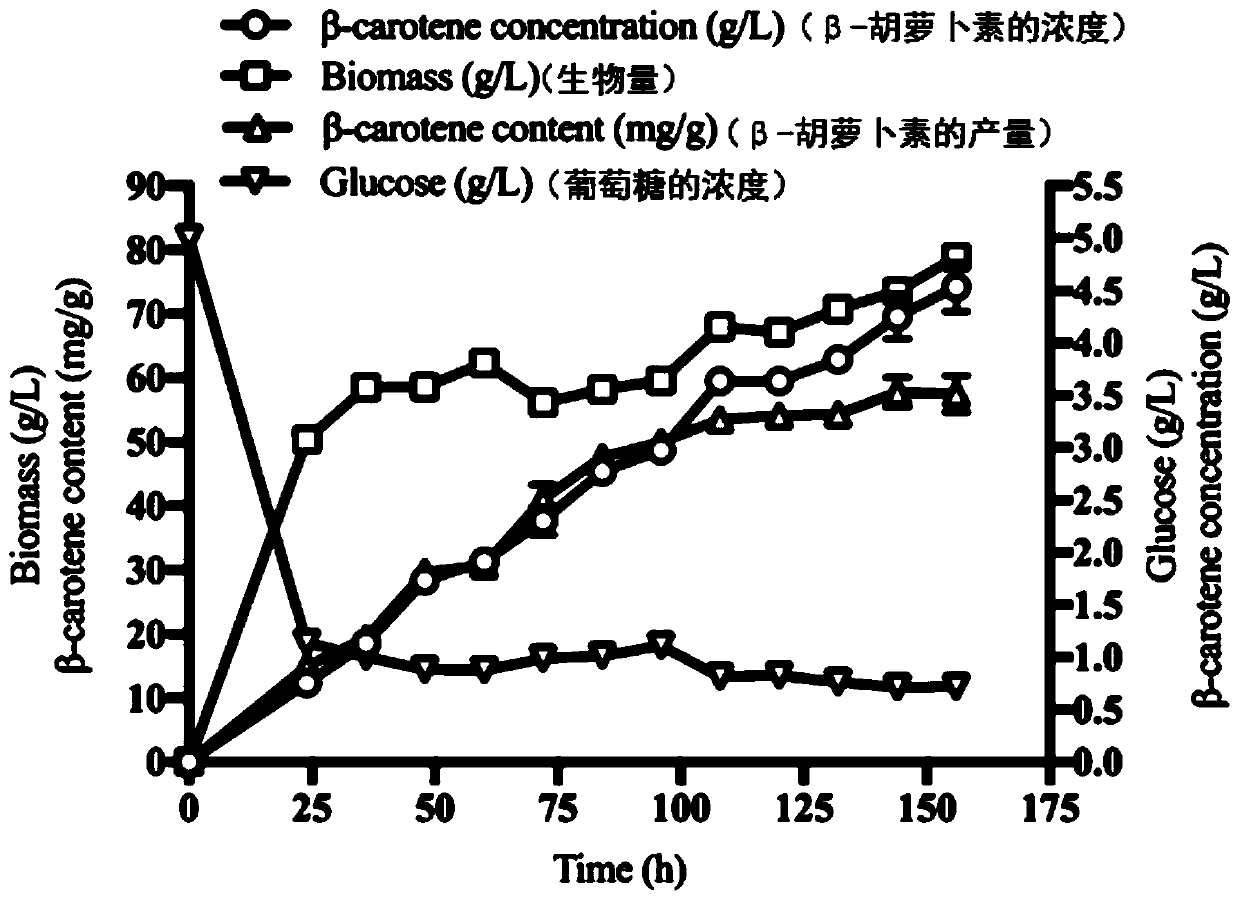
The invention provides a yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacterium for producing beta-carotene is prepared bythe following steps: knocking a carRP gene and a carB gene into chromosomes of uracil and leucine auxotrophic yarrowia lipolytica, then knocking a GGGS1 gene, a HMG gene, two copied carRP gene, one copied of carB gene, and an ERG13 gene into the chromosomes, and finally performing backfilling by two auxotrophic screening markers of uracil and leucine. Continuous feeding fermentation is performed,and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 4.5g / L. The yarrowia lipolytica genetic engineering bacteria constructed according to the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation andstable and reliable performance, and can be applied to large-scale commercial production, and the obtained beta-carotene can be safely used, so that a good prospect is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetically engineered recombinant escherichia coli producing l-tryptophan having originally l-phenylalanine productivity, and method for producing l-tryptophan using the microorganism
ActiveUS20100028956A1High yieldConfirming production of L-tryptophanBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to a microorganism having L-tryptophan productivity and a method for producing L-tryptophan using the same. More precisely, the present invention relates to the recombinant E. coli strain CJ600 (KCCM 10812P) having tryptophan productivity produced from the mutant form (KFCC 10066) of E. coli having L-phenylalanine productivity, wherein tryptophan auxotrophy is released, L-phenylalanine biosynthesis is blocked but tryptophan productivity is enhanced by reinforcing the gene involved in tryptophan biosynthesis, and a method of producing L-tryptophan using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Expression system for producing proteins
InactiveUS6551797B1Improve expression rateImprove productivityFungiSugar derivativesAntibiotic YTrametes
An expression system for producing a protein in a filamentous fungus, consisting of a) a host organism selected from the species Trametes and Polyporus and b) a DNS vector containing a selection marker gene. This selection marker gene code is a protein which allows the selection of positive transformants after the transformation of the host organism and which is selected from the group of: antibiotics-resistant genes coding for proteins which eliminate the growth-inhibitory effect of antibiotics against which the host organism is not resistant. Genes coding proteins which are capable of a color-causing reaction; and genes complementing a genetic defect of the host organism (auxotrophy), the expression of the selection marker gene is controlled by at least one active genetic regulation element in the host organism, and c) a DNS vector containing a gene which codes the protein to be produced. The expression of this gene and optionally, the secretion of the protein so produced are controlled by an active genetic regulation element in the host organism. The DNS vector containing a section marker gene and the DNS vector containing the gene which codes the protein to be produced can also be in the form of one DNS vector.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Method for breeding lipid-producing fungus
InactiveUS20070072275A1Efficiently and effectively performBreeding effectiveFungiHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyLipid formation
It is intended to provide a breeding method whereby a lipid-producing fungus belonging to the genus Mortierella can be effectively and efficiently bred without resort to antibiotics. Transformation is carried out with the use of an auxotroph (for example, uracil auxotroph) of a fungus belonging to the Mortierella as a host. More specically speaking, a gene compensating for the auxotrophy, which is employed as a marker, is transferred into the host (the gene transfer step). Next, a transformant is selected by using the recovery from the auxotrophy as the marker (the selection step). The lipid-producing fungus may be M. aplina, for example.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
High-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method
ActiveCN103320406AIncrease vitalityImprove protectionOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenes mutationNatural source
A high-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method belong to the field of biotechnology. A mutant gene is obtained by a gene mutation or synthesis method, and then a catalytic group SeCys of GPX is introduced into a substrate binding part of the mutant through an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP low-temperature combined expression system so as to endow the mutant with high GPX activity; or a target gene, along with a SeCys insertion sequence, is firstly assembled onto a secreting type mammalia cellular expression vector, and then a binding protein 2 of the SeCys insertion sequence is assembled onto an intracellular mammalia cellular expression vector, contransfection of the same lactation cell strain is carried out by the two vectors, and GPX is synthesized by the lactation cell in the presence of sodium selenite. The method provided by the invention is simple. The mutant provided by the invention has advantages of high activity, high yield and good stability. Yield decreasing and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body are avoided. Thus, natural GPX source limitation and unstable properties are solved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A genetic transformation method mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens with Aspergillus flavus mycelium as receptor
ActiveCN109182368ASimple processLow costMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNutritional deficiency
The invention discloses a genetic transformation method mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens with Aspergillus flavus mycelium as a receptor, belonging to the field of microbiology. The method comprises the following steps: the divalent vector pAg1-H3 is digested to remove the hygromycin resistance gene fragment, and ligated with the target fragment containing the pyrithione resistance gene ptrA derived from Aspergillus oryzae to construct a pAg1-Pt binary vector; the binary vector pAg1-Pt plasmid is transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens to obtain Agrobacterium tumefaciens positive transformant and prepare bacterial liquid; Aspergillus flavus mycelium homogenate is prepared; Aspergillus flavus is transformed by co-culturing the prepared mycelium and mycelium homogenate; selective culture is performed, Aspergillus flavus transformants are screened and positive clones are identified. As the mycelium of Aspergillus flavus is used as the transformation acceptor, the transformation efficiency is high and stable without the restriction of the sporulation ability of the Aspergillus flavus strain, and the method is applicable to Aspergillus flavus strains with different genetic background and nutritional deficiencies.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Yeast transformation vector containing auxotrophic dominant gene yeast transfomant containing it and their preparation
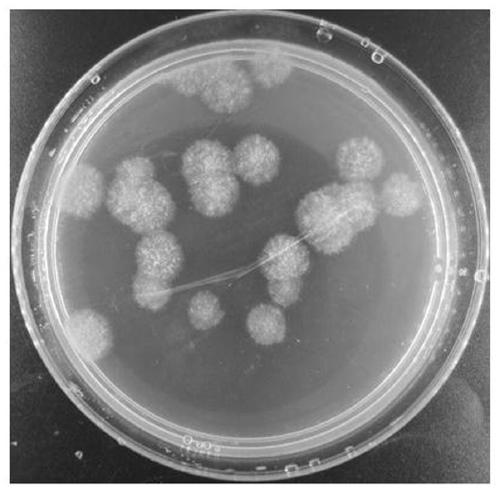
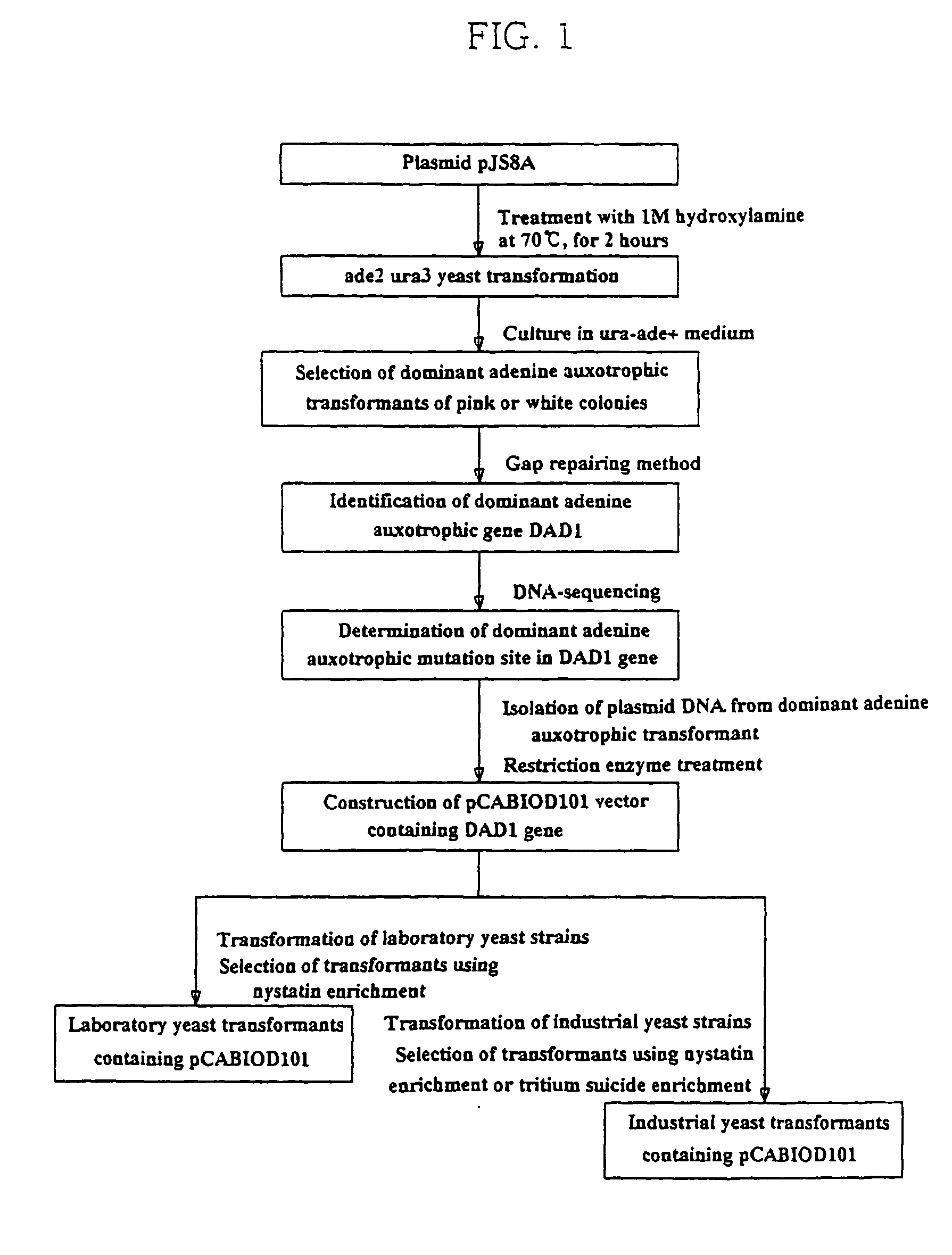
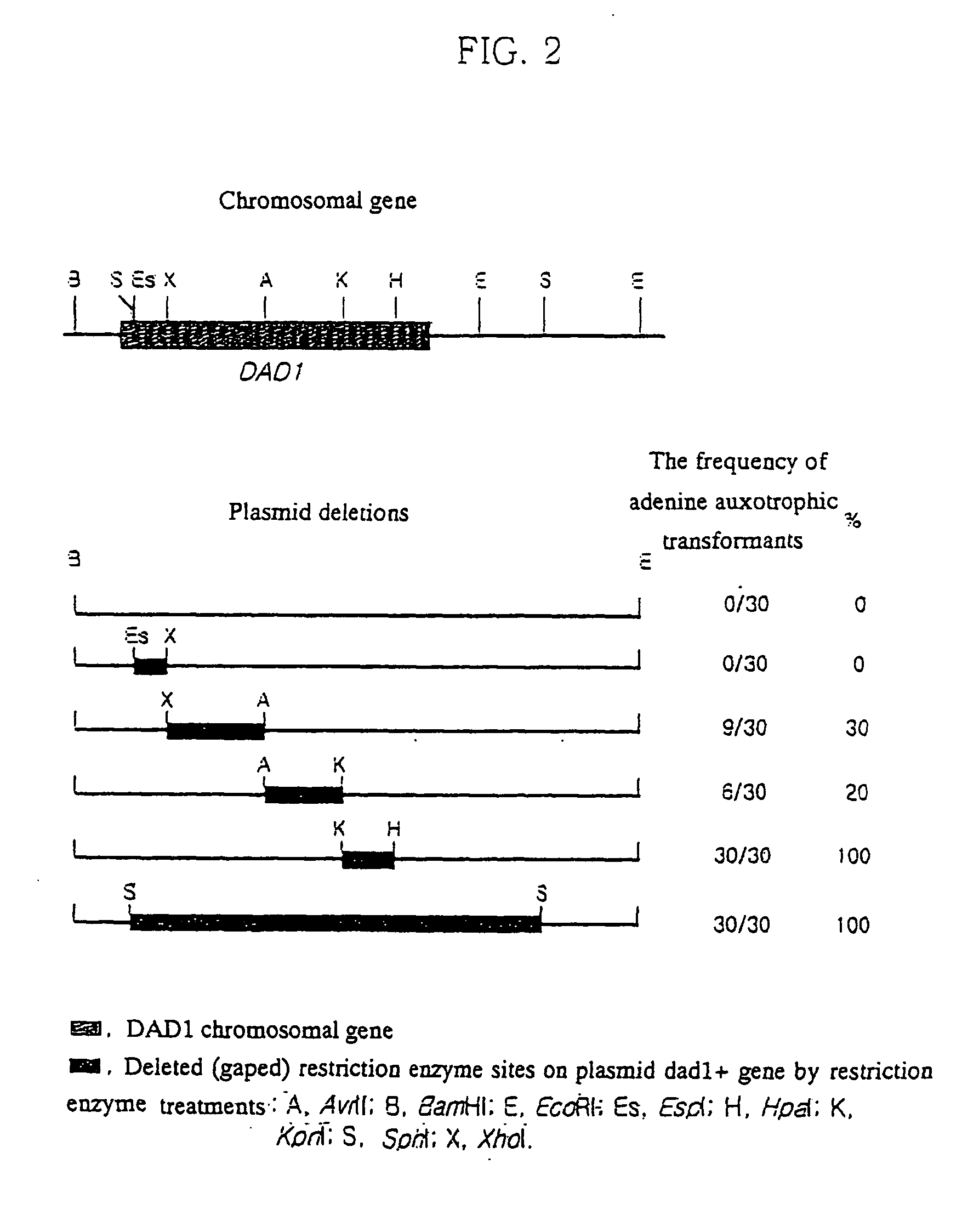
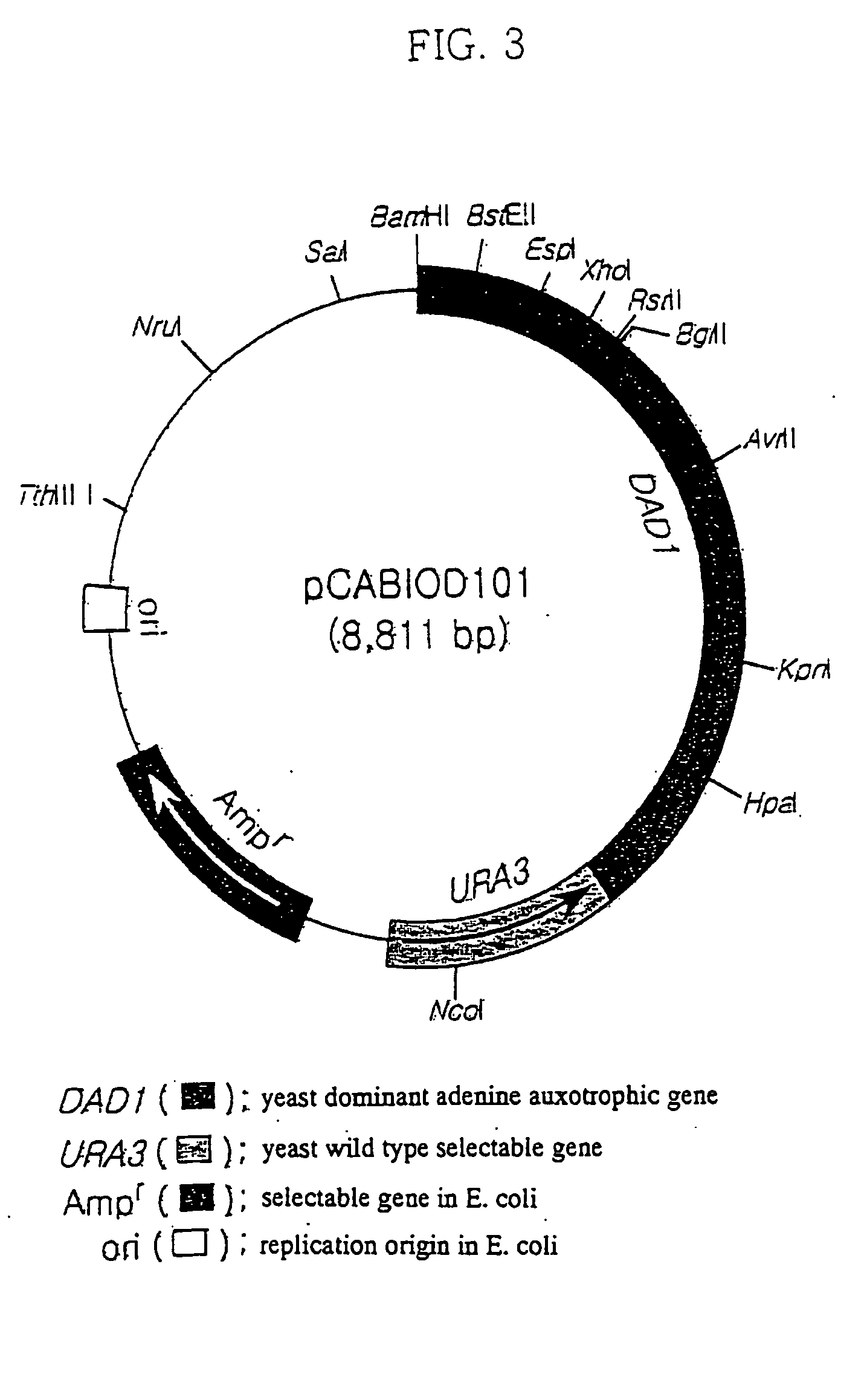
A yeast transformation vector containing a dominant auxotrophic gene, a yeast transformant containing the same and a method of preparation thereof. An adenine auxotrophic transformant able to grow in the presence of adenine can be obtained by inducing a dominant adenine auxotrophic (DAD) mnutation, isolating the dominant adenine auxotrophic gene DAD1, DNA sequencing the DAD1 gene to determine its mutation site, constructing pCABIOD101 vector containing the DAD1 gene (accession number: KCTC 1013BP), and transforming haploid laboratory yeast strains and diploid industrial yeast strains respectively with the pCABIOD101 vector. Therefore, the transformation vector system of the present invention can be used in improving existing industrial yeasts and various microorganisms.
Owner:SONG JAE MAHN
Colibacillus engineering bacterium taking glucose as substrate for synthesizing muconic acid
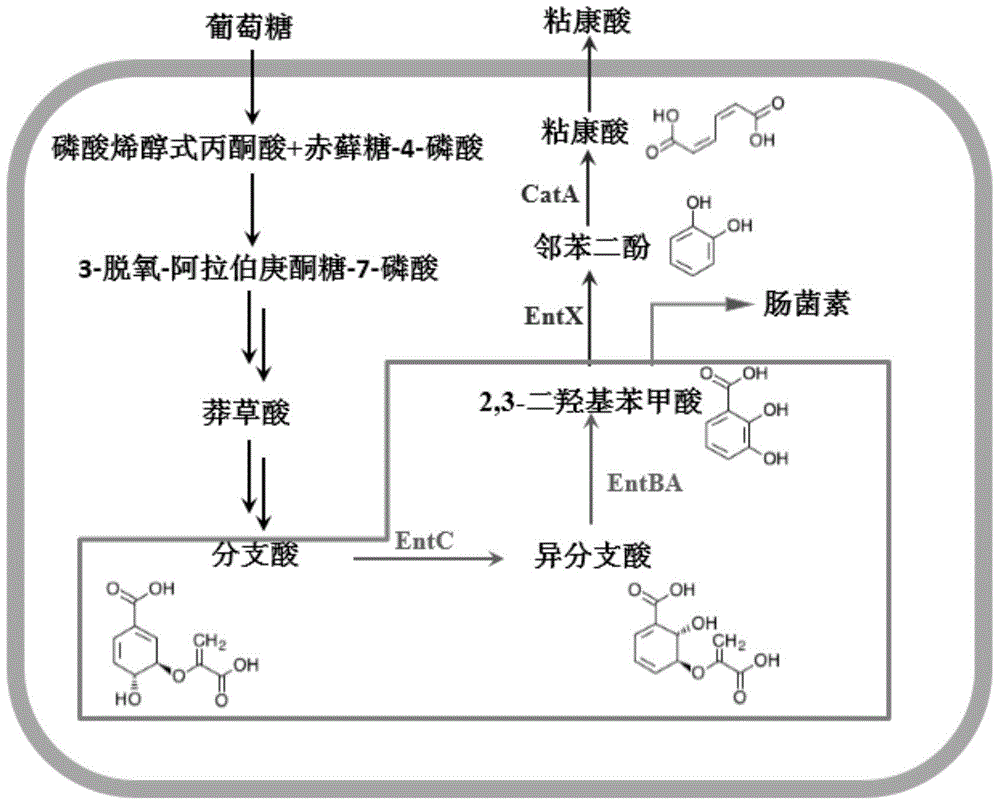
InactiveCN104099284AReduce the burden onReduce incompatibilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBenzoic acid
The invention discloses a colibacillus engineering bacterium taking glucose as a substrate for synthesizing muconic acid, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. 2,3-dihydroxy benzoic acid (2,3-DHB) is led to colibacillus during the metabolic pathway of muconic acid (MA); the metabolic pathway of colibacillus from glucose to 2,3-DHB is reinforced. The colibacillus engineering bacterium has the advantages that less foreign genes are required; the foreign gene expression load of a host bacterium is reduced; the incompatibility problem of the foreign genes is solved. Moreover, the host bacteria are not auxotroph; the foreign addition of expensive shikimic acid or other aromatic amino acid is avoided; the flask shaking fermentation yield of muconic acid is 1.15 g / L.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGQIANG CHEM IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
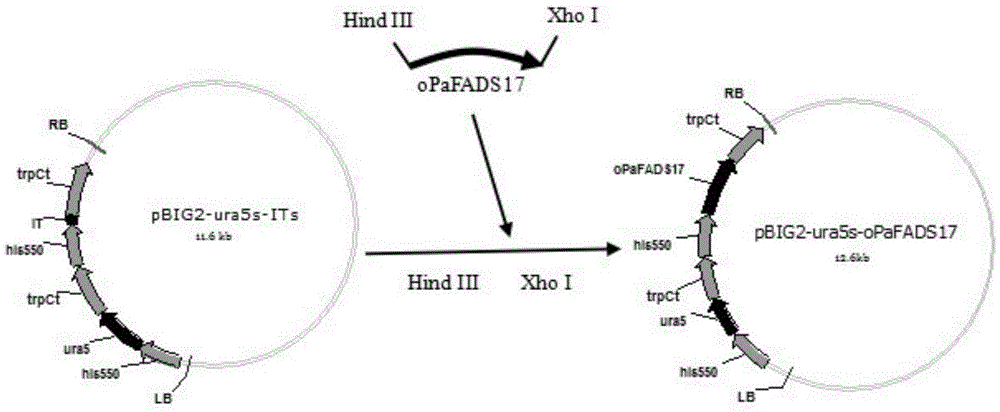
Recombinant strain for expressing heterogenous Omega-3 desaturase in mortierella alpina and construction method thereof
The invention provides a recombinant mortierella alpina strain Ma-oPaFADS17 with heterologous expression coming from pythium aphanidermatum Omega-3 desaturase genes and a method for constructing the mortierella alpina strain with heterologous expression coming from pythium aphanidermatum Omega-3 desaturase genes. The method adopts mortierella alpine uracil auxotrophic strain CCFM 501 as materials and uses an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated genetic manipulation technology to obtain a recombinant strain with a high yield of EPA in the environment of normal temperature, wherein the yield of EPA reaches 617.1 mg / L, and the content of the EPA accounts for 18.7 percent of the total amount of fatty acid, which has an important meaning for the basic research and product development of oil-producing fungus mortierella alpine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase
ActiveCN103224915AHigh activity of recombinant GPXAvoid yieldEnzymesFermentationInclusion bodiesPeroxidase
The invention provides a gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase, which belongs to the field of biological technology. The method comprises the following steps: assembling a target gene to a secretion type prokaryotic expression vector, introducing a catalytic group SeCys of GPX into a substrate combination position of GPX by a gene mutant method in an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP combined expression system, thereby the activity of the GPS is very high; or assembling the target gene with the SeCys insertion sequence into a secretion type mammalia cell expression vector, assembling a SeCys insertion sequence binding protein 2 into an intracellular type mammalia cell expression vector, and cotransfecting the two vectors into the same lactation cell strain, and synthesizing the GPX under the existence of sodium selenite. The invention the advantages of simple method, recombined GPX vitality, high output and good stability, thereby avoiding decreased yield and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body, and solving the problem that the natural GPX source is limited and the property is not stable.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Vibrio cholerae strains VCUSM1 and VCUSM4, method of producing same, and vaccine derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20060099229A1Limited in vitroLimited in in vivo growthAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAmino-Levulinic AcidKanamycin
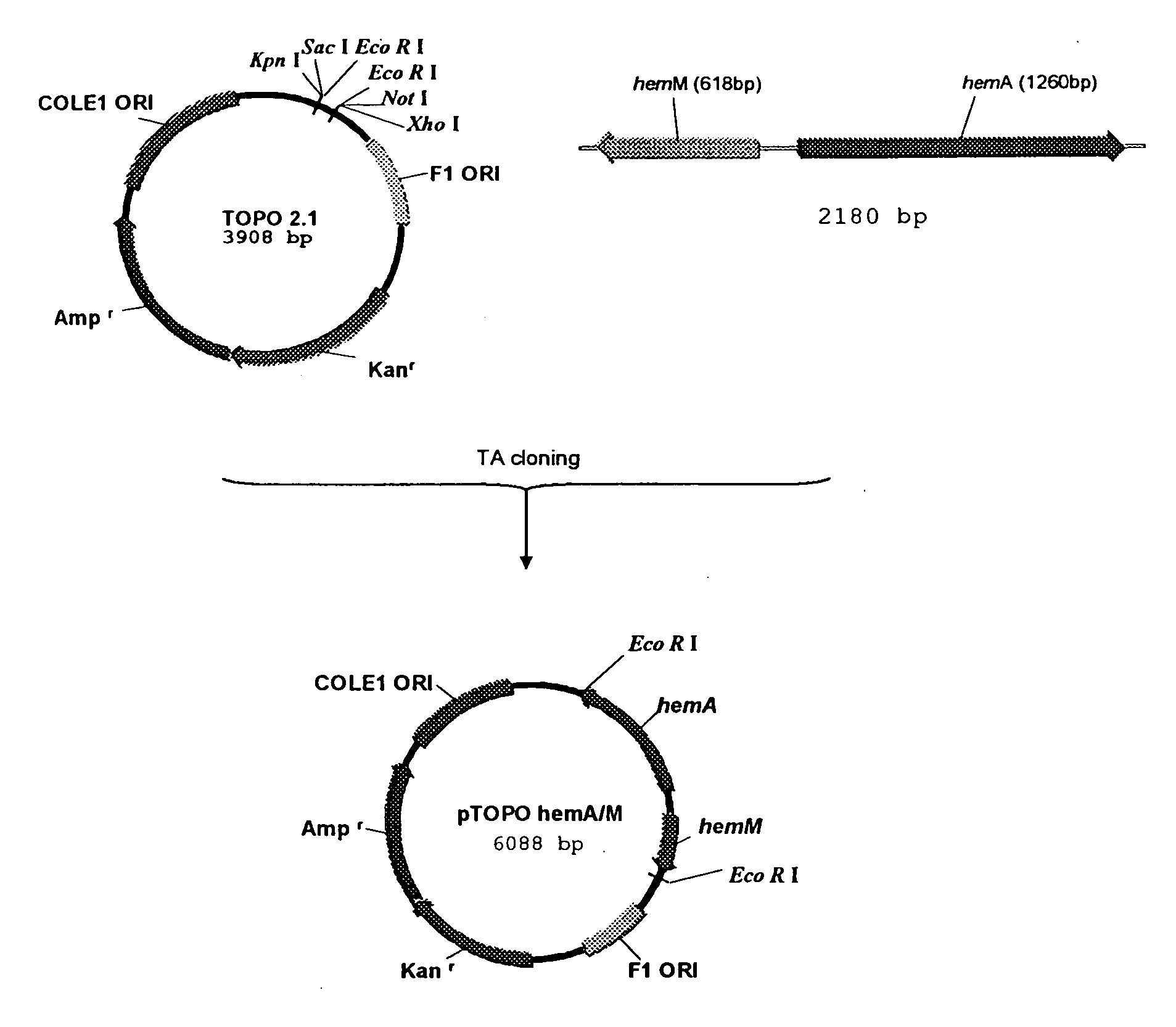
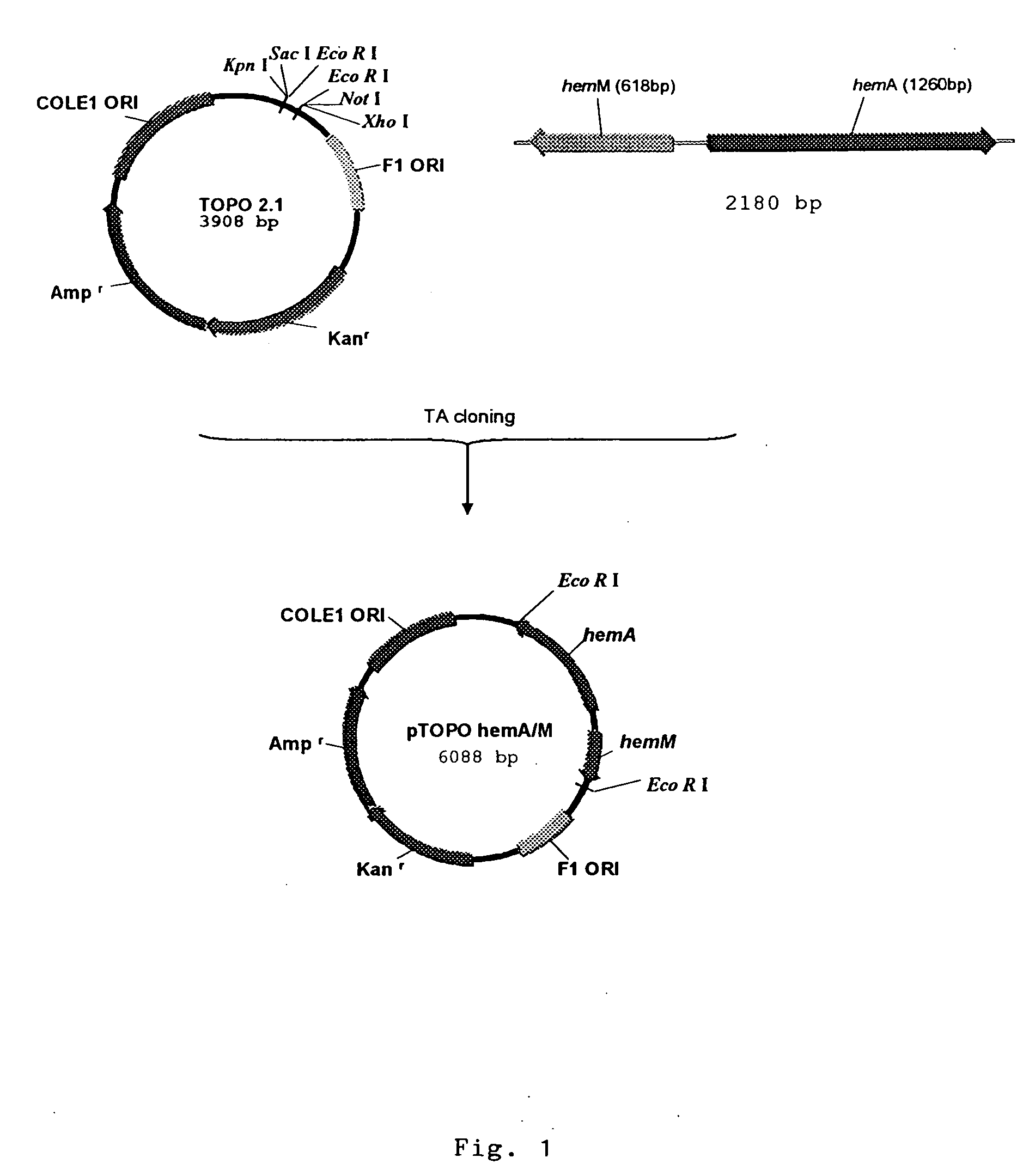
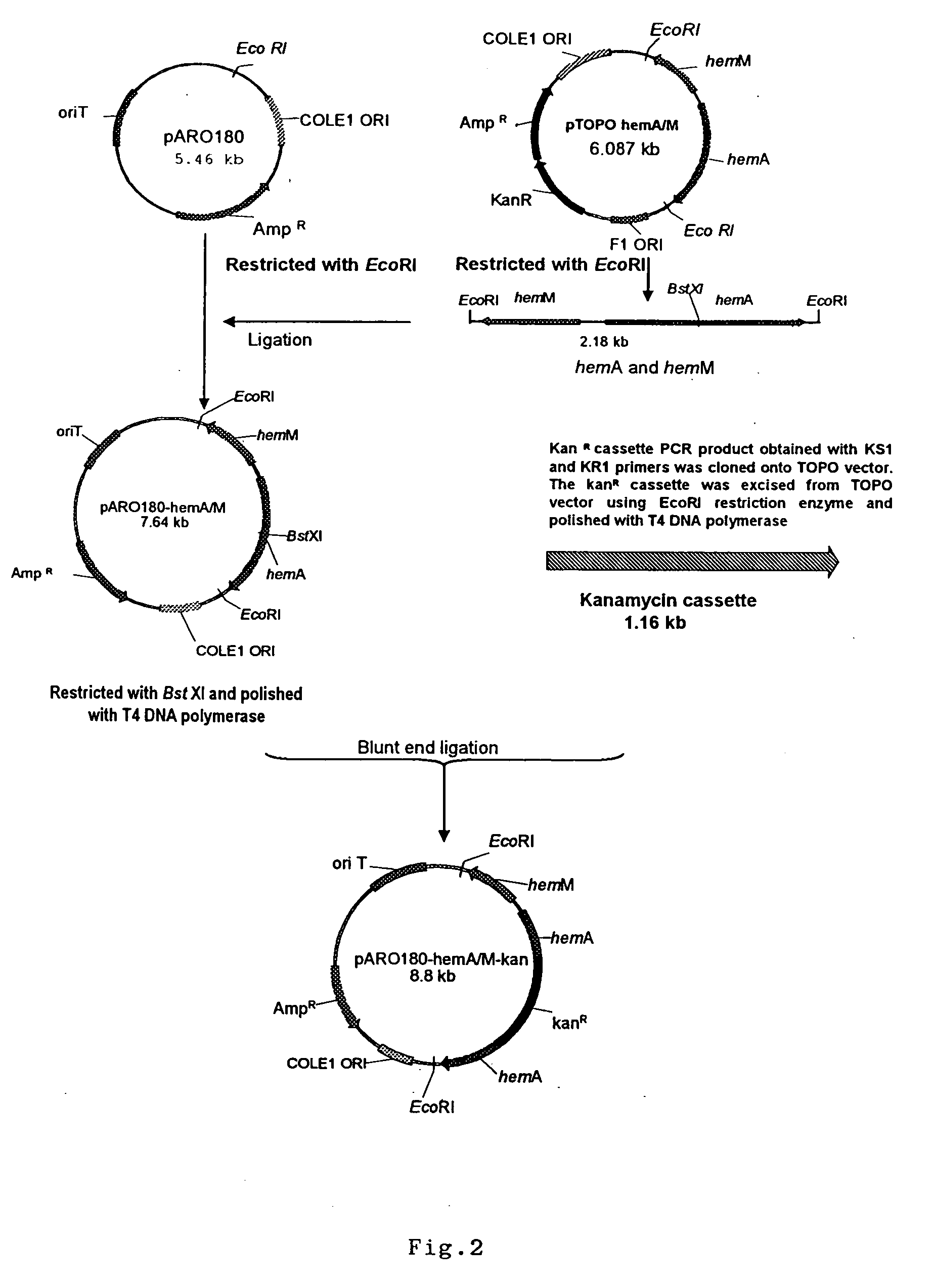
Metabolic auxotroph of Vibrio cholerae 0139 synonym Bengal which has a mutation in its hem A gene and which is not capable of synthesizing aminolevulinic acid (ALA) de novo and which is obtained from a parent strain originally isolated from a patient's coproculture having all the identifying characteristics of Vibrio cholerae 0139 synonym Bengal is described. In this strain the hem A gene is mutated by inserting a kanamycin resistant gene cassette. Another metabolic auxotroph of Vibrio cholerae 01 El Tor where the hem A gene is mutated by a frame shift mutation is disclosed. Methods of producing the strains are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA
Method of breeding lipid-producing fungus
It is intended to provide a breeding method whereby a lipid-producing fungus belonging to the genus Mortierella can be effectively and efficiently bred without resort to antibiotics. Transformation is carried out with the use of an auxotroph (for example, uracil auxotroph) of a fungus belonging to the Mortierella as a host. More specically speaking, a gene compensating for the auxotrophy, which is employed as a marker, is transferred into the host (the gene transfer step). Next, a transformant is selected by using the recovery from the auxotrophy as the marker (the selection step). The lipid-producing fungus may be M. aplina, for example.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
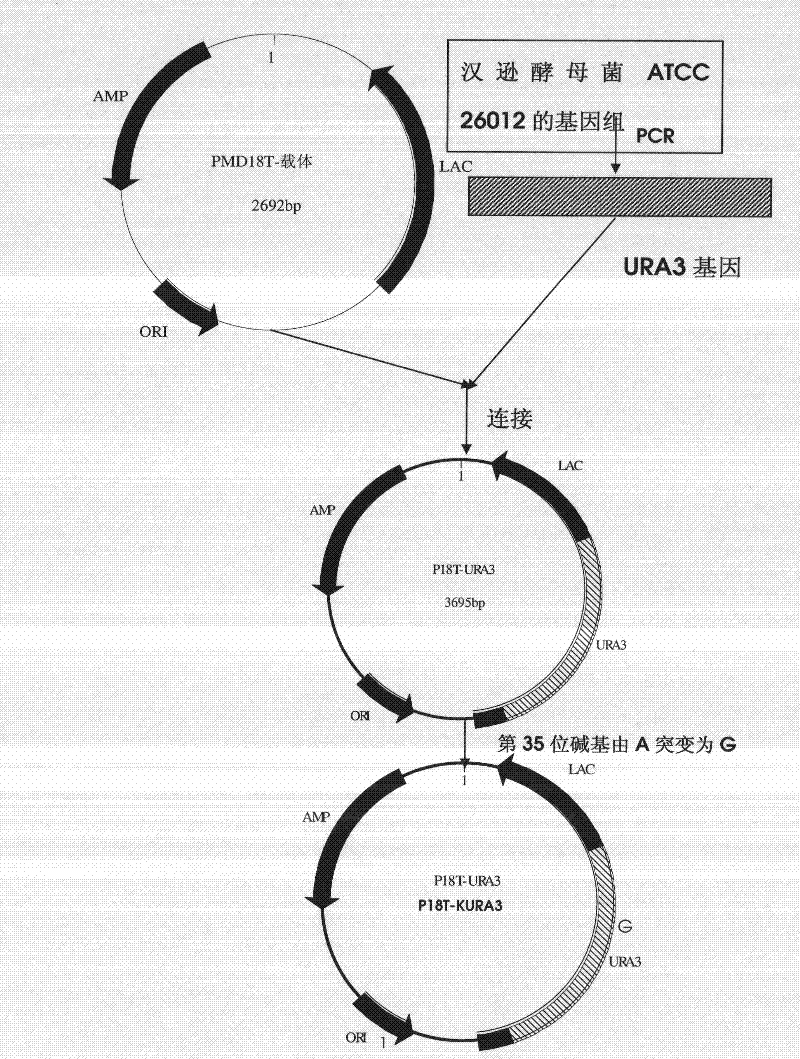
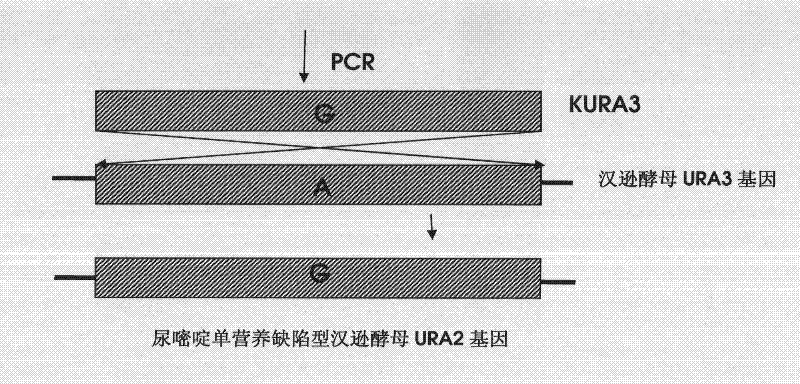
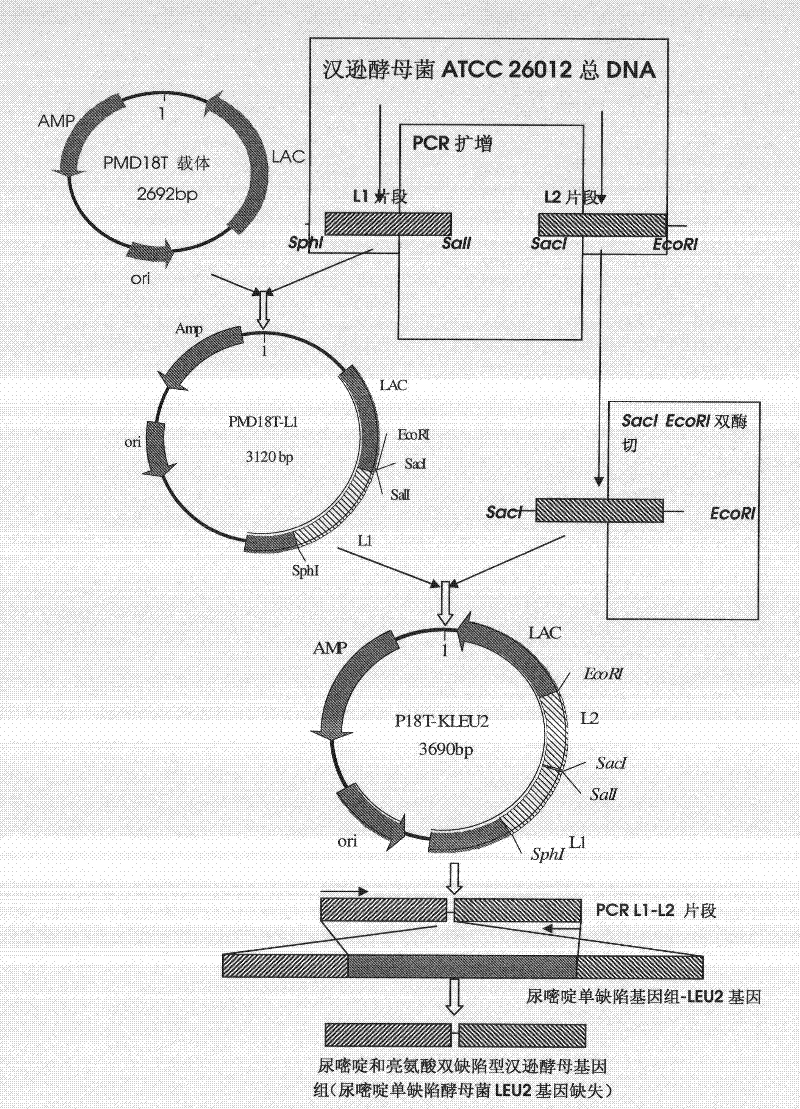
DNA sequence, recombinant vector, single and double auxotrophic Hansenula polymorpha, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102234620AConvenient sourceSuitable for researchFungiMicroorganism based processesVaccine ProductionPhosphate
The invention relates to a double auxotrophic yeast, wherein the yeast is Hansenula polymorpha, and the orotic glycoside-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene and the beta-isopropyl malate dehydrogenase gene of the Hansenula polymorpha are blocked. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the double auxotrophic yeast. In addition, the invention also provides a DNA sequence and a recombinant vector used to prepared the double auxotrophic yeast. The double auxotrophic yeast of the invention has the advantages of low reverse mutation, high genetic stability, high biomass, and the like, and plays an important role in genetic engineering vaccine production; for example, HPV16-type L1 and 58L2 protein have double expression with high efficiency in the yeast.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD
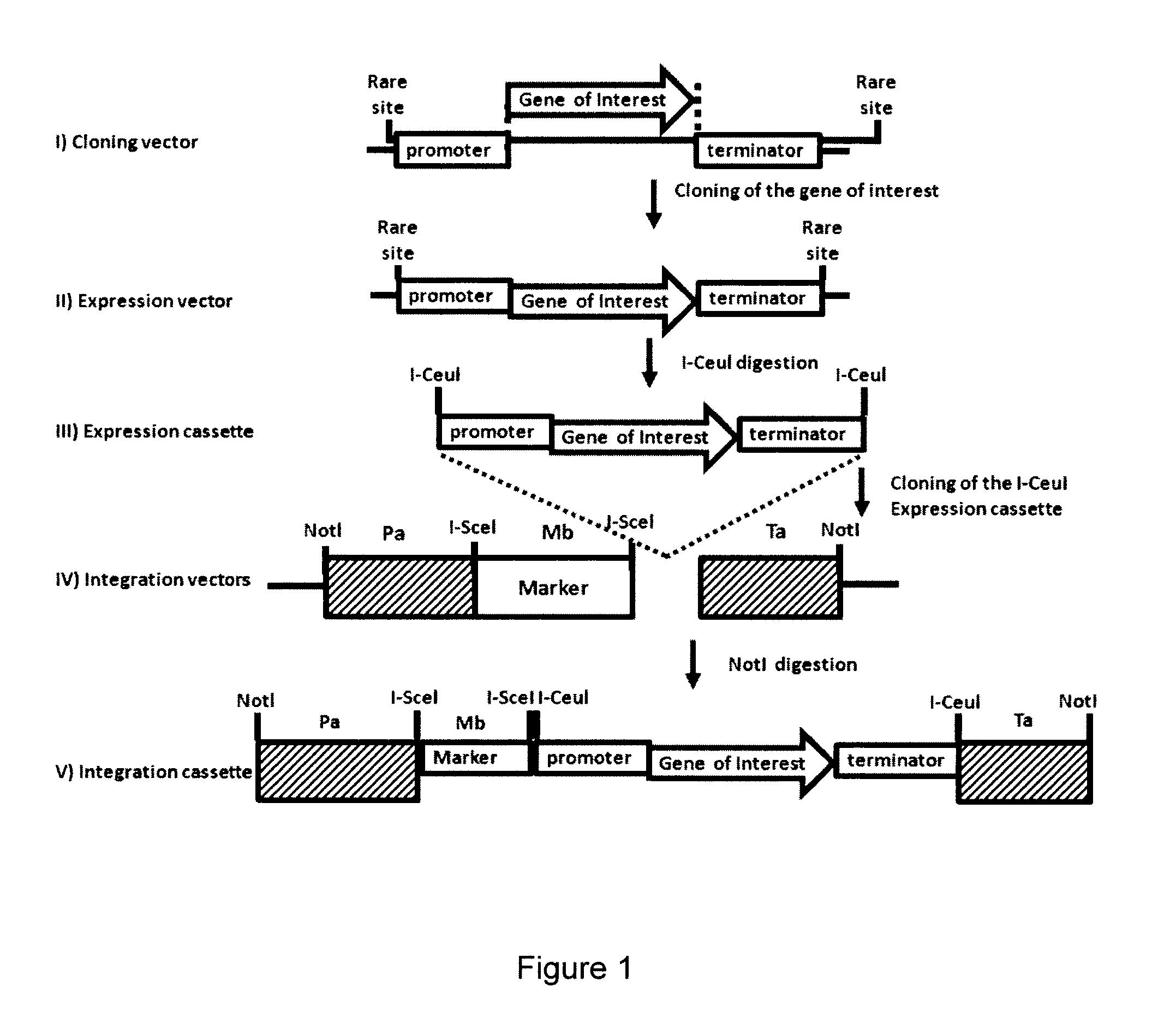
Method for the Targeted Integration of Multiple Copies of a Gene of Interest in a Yarrowia Strain
This invention concerns a method for the targeted integration of at least three copies of a gene of interest in the genome of a Yarrowia strain including the steps of: (a) cultivating a Yarrowia strain, said strain including a deletion among at least three genes, the phenotype associated with each of these deletions corresponding to an auxotrophy or to a dominant character for this strain; (b) transforming said Yarrowia strain thus obtained with at least three recombinant vectors that include selection markers allowing, for this strain, the complementation of auxotrophy and, potentially, of the dominant character resulting from each of these deletions; and (c) selecting, on a minimum medium, the yeasts having integrated said at least three recombinant vectors. This invention also includes a method for producing a polypeptide of interest using this method as well as a method for obtaining a modified Yarrowia strain including a deletion among at least three genes, the phenotype associated with each of these deletions corresponding to an auxotrophy or to a dominant character for this strain.
Owner:INST NAT DE RECH POUR LAGRICULTURE LALIMENTATION & LENVIRONNEMENT
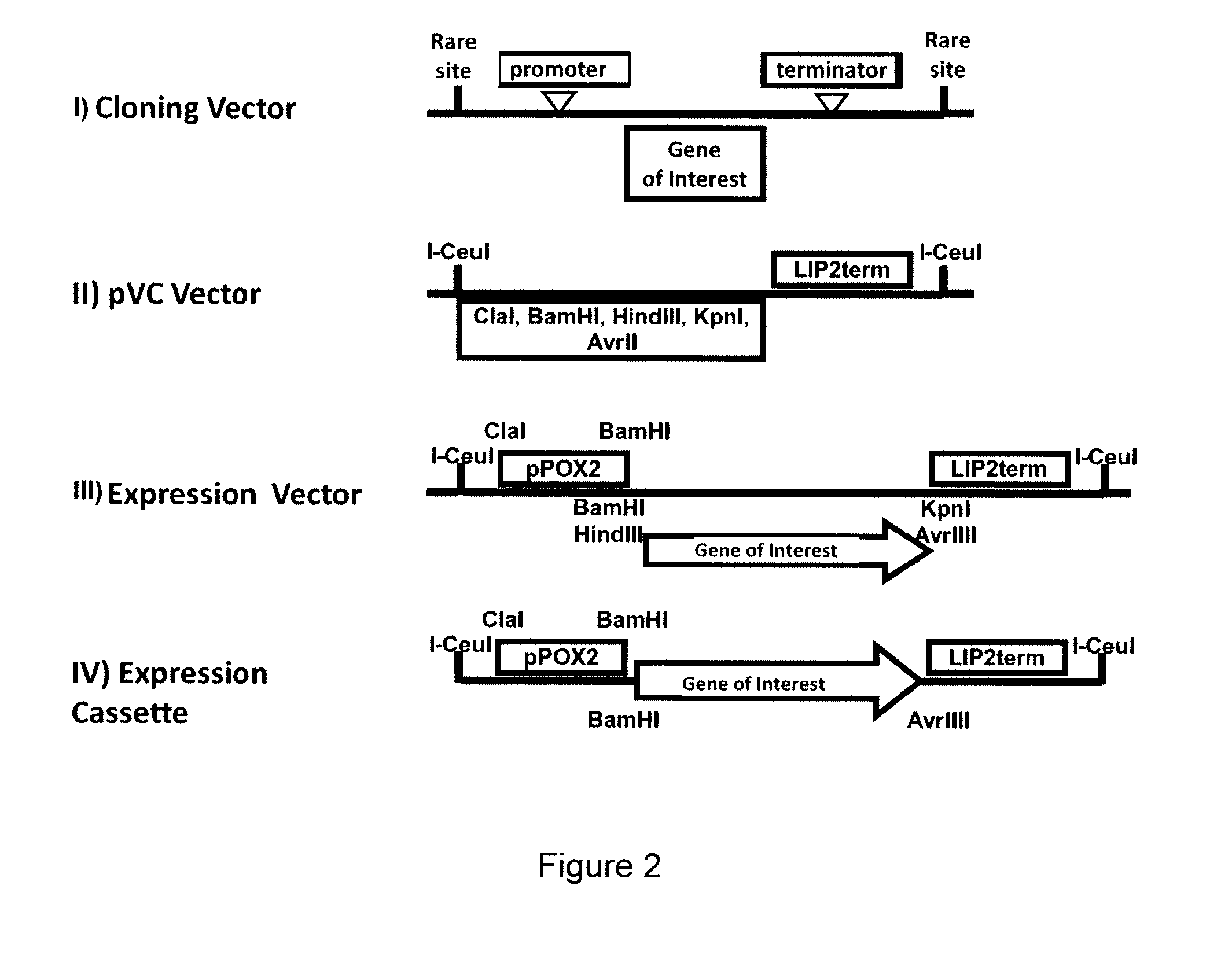
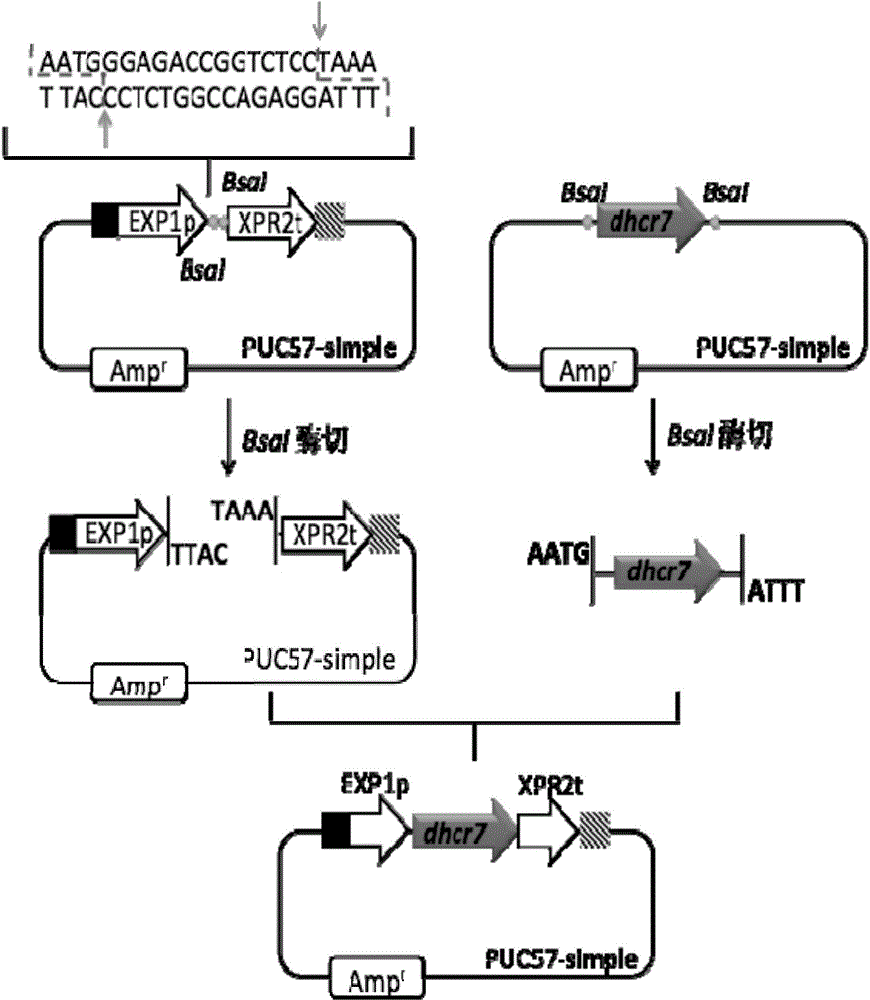
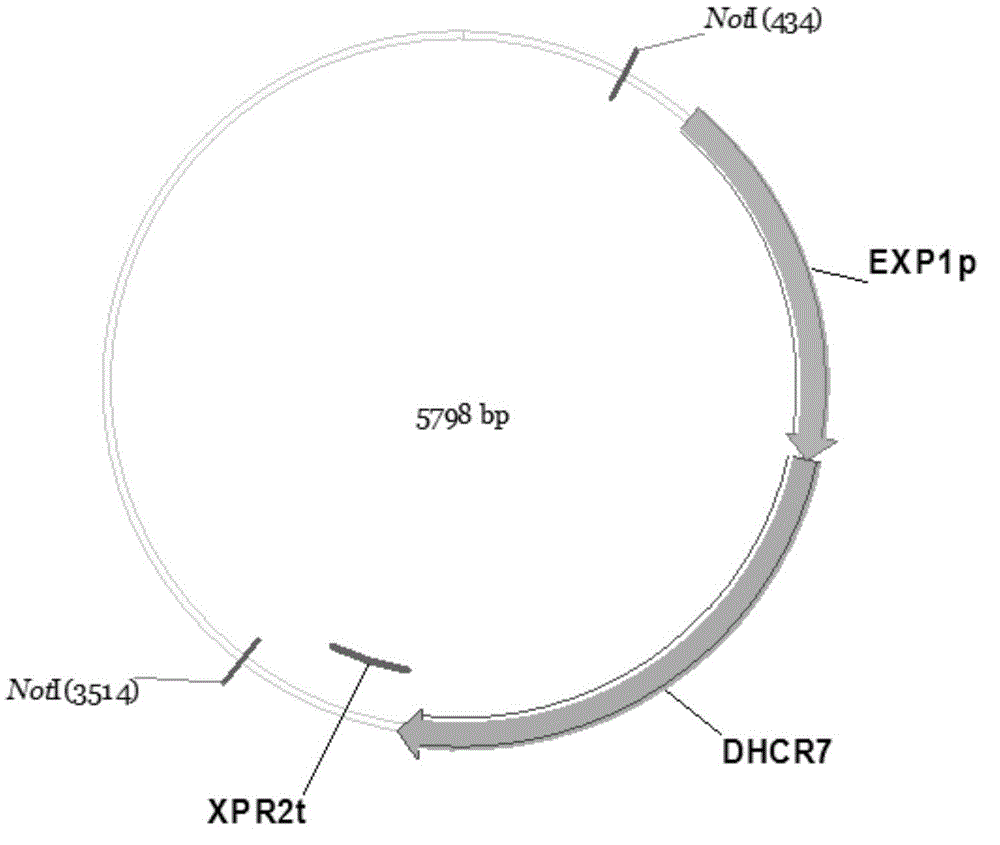
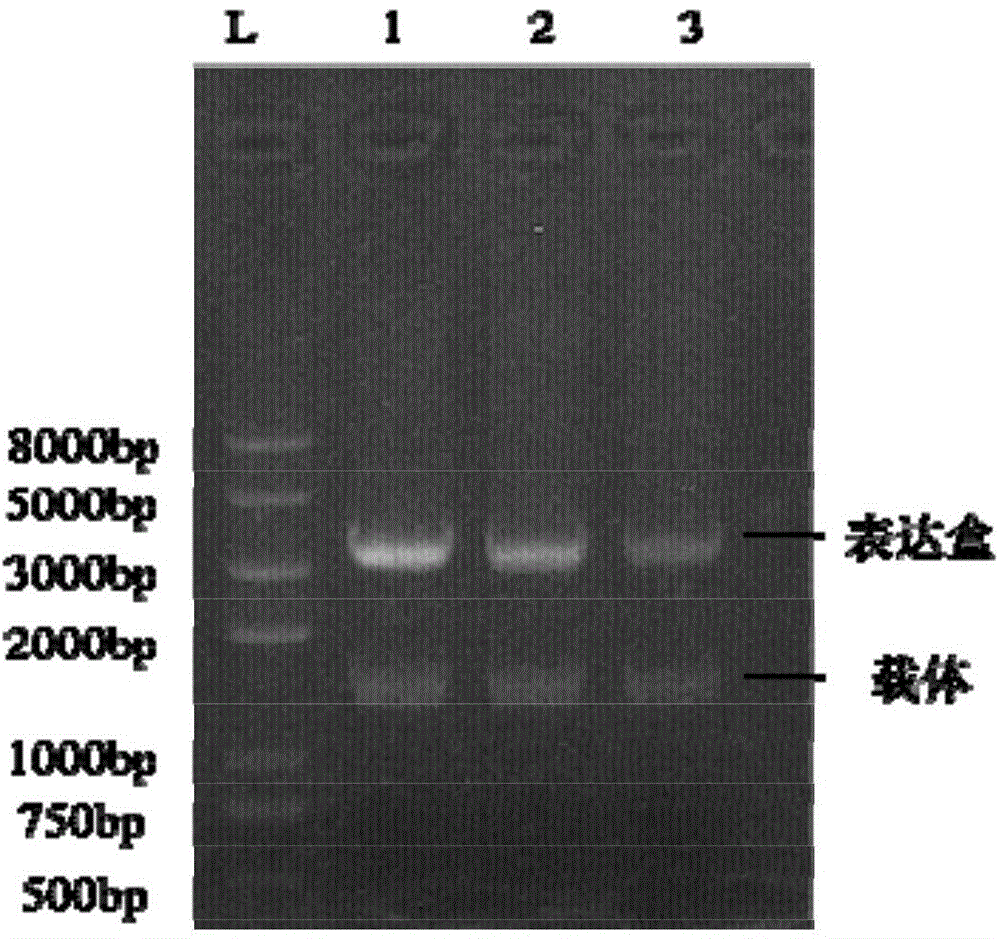
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly discloses a recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain as well as a construction method and an application thereof. A genome of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NO: 1-3. The construction method comprises the following steps of constructing a key gene dhcr7 in a biosynthesis way of campesterol expressed by a single-gene expression cassette through an OE-PCR (overlap extension-polymerase chain reaction) method; cutting down the single-gene expression cassette through restriction enzyme, transferring the single-gene expression cassette into yeast at one time to perform homologous recombination among fragments and integration of a special erg5 lotus of the genome, screening a completely-assembled converter through an auxotrophic culture medium and genome PCR to obtain a novel recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain. The novel recombinant yarrowia lipolytica bacterial strain can be applied to biosynthesis of campesterol, and a relatively high yield can be kept.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Construction method and applications of genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine
InactiveCN103966151AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColiform bacilli
The invention relates to a construction method and applications of a genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine. The invention discloses a novel genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing L-arginine. Recombinant plasmid pXMJ19-argH can be orderly converted and introduced into colibacillus and auxotroph brevibacterium flavum AN78 by the genetic engineering bacterium strain, and then the argininosuccinase in the AN78 containing recombinant plasmids is over-expressed and fermented to produce L-arginine. The invention further discloses a construction method and applications of the genetic engineering bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can increase the L-arginine production output and reduce the production cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH
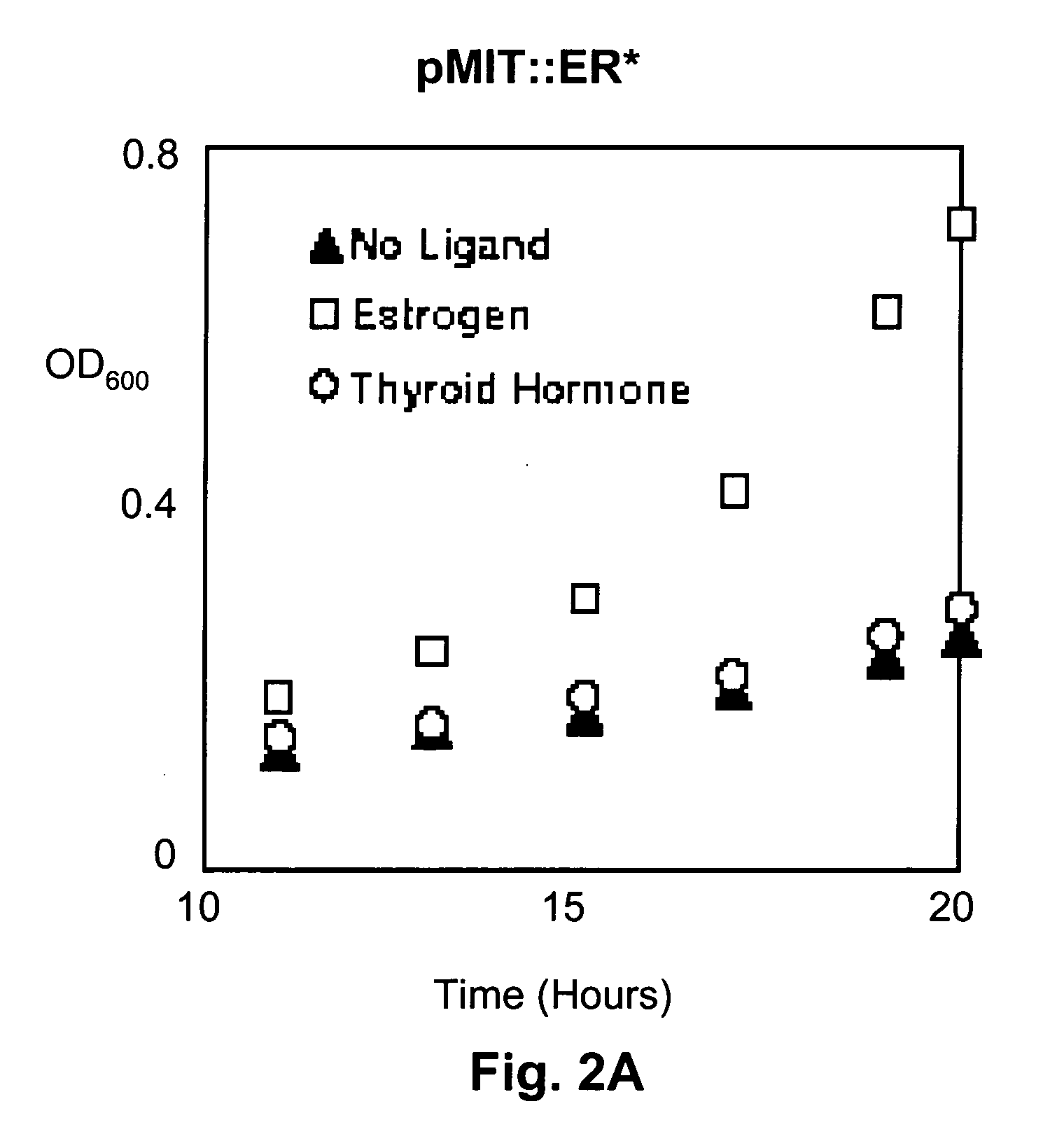
Bacterial ligand-binding sensor
InactiveUS20060211046A1BacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifInteinEstrogen receptor
The invention relates to fusion proteins and bacteria encoding them. The fusion proteins include a ligand-binding domain interposed between the splicing domains of an intein. An auxotroph-relieving protein domain is fused to one of the splicing domains so that the auxotroph-relieving function of the domain is activated upon ligand binding. The fusion proteins can be expressed in bacterial cells and used as sensors of binding of compounds with the ligand-binding domain of proteins such as the human estrogen receptors or the human thyroid hormone receptor. The bacterially expressed fusion proteins can detect and report agonist and antagonist activity characteristic of the naturally-occurring hormone with the ability to modulate the function of the protein from which the ligand-binding domain of the fusion protein is derived.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
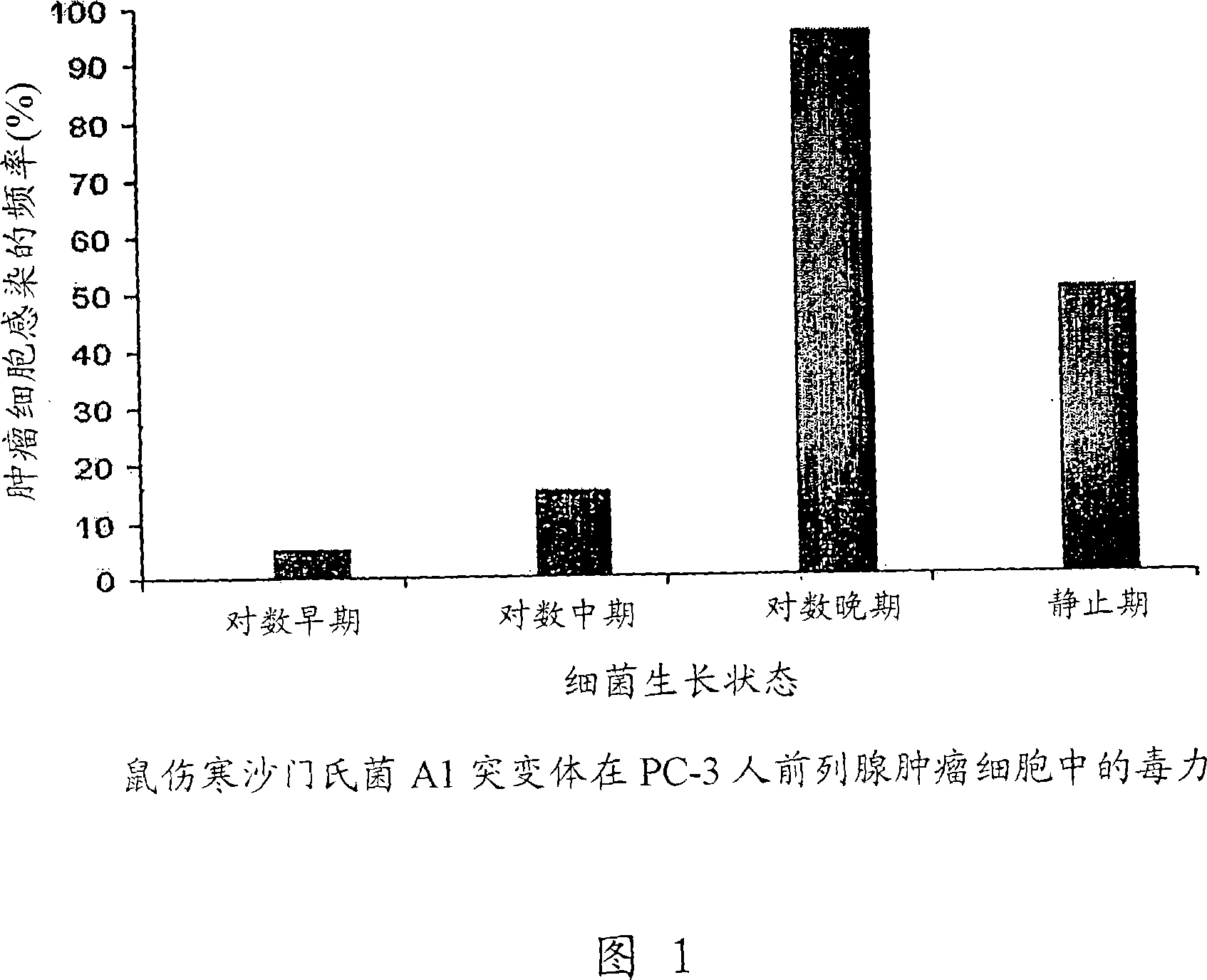
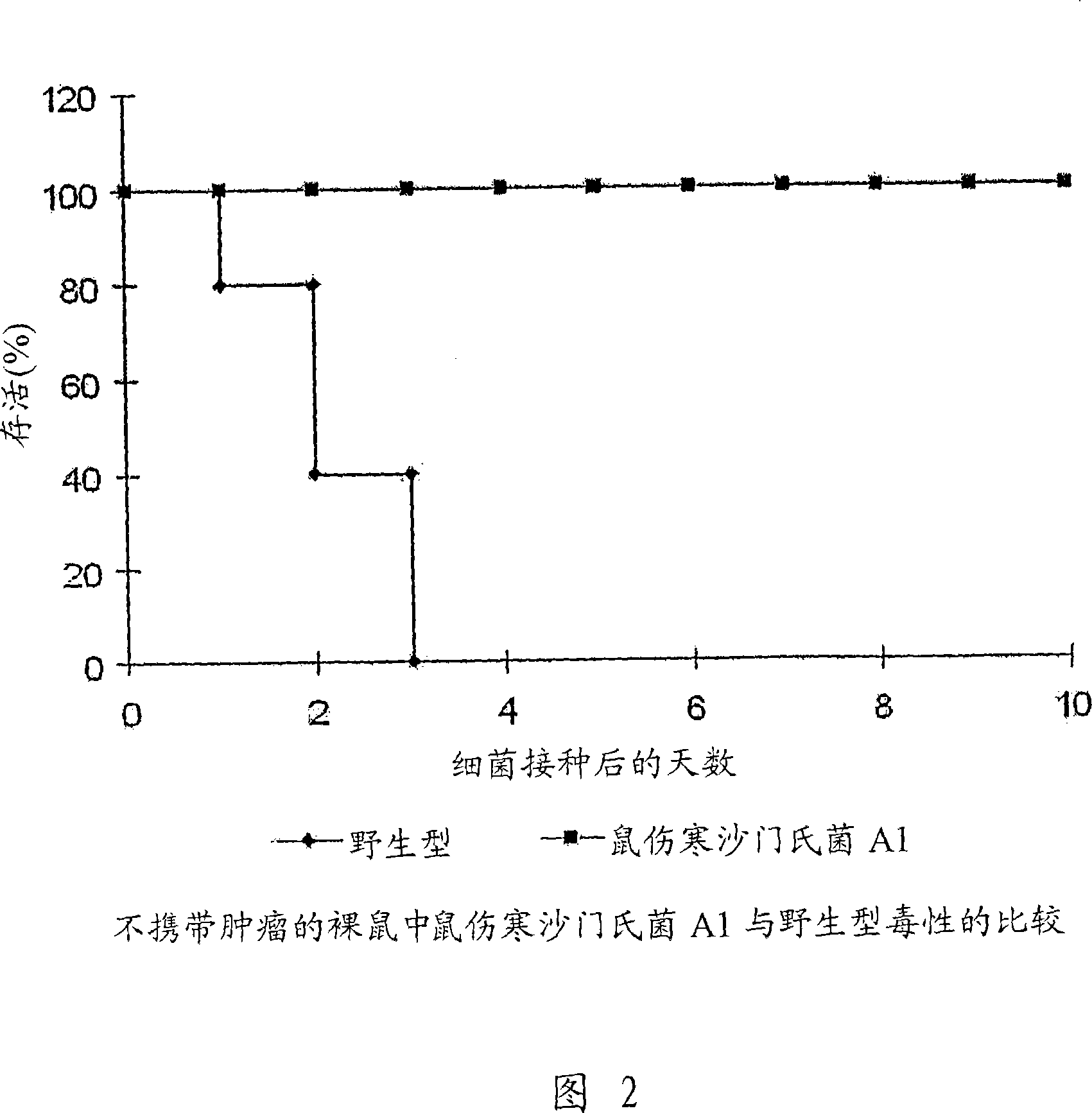
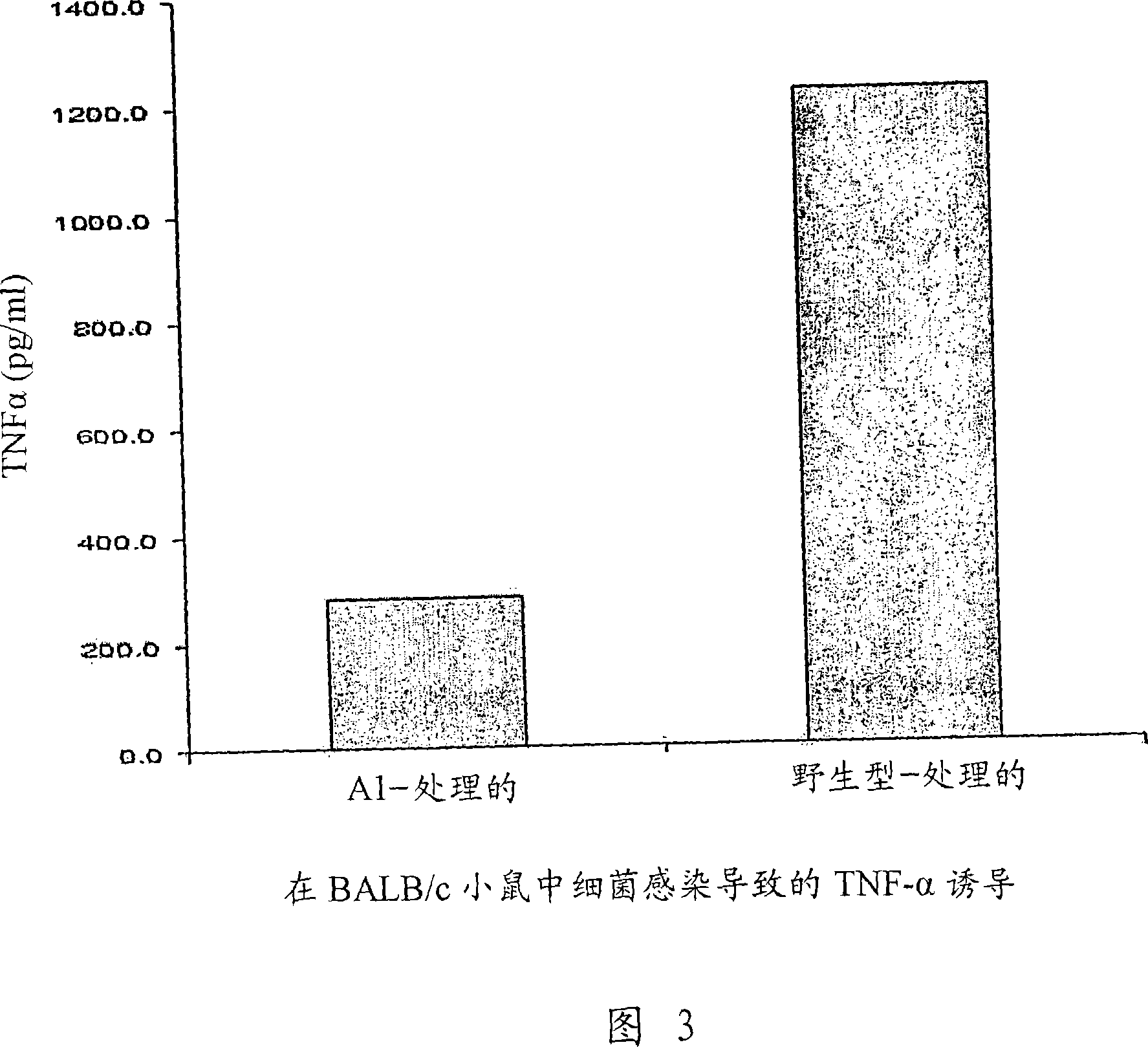
Cancer selective auxotrophs
Bacteria that are auxotrophic for at least two amino acids found in at least one tumor are effective antitumor treatments, labeling agents, and vaccines against infection. Improved antitumor effects can also be provided such strains by passage through an appropriate tumor model.
Owner:ANTICANCER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com