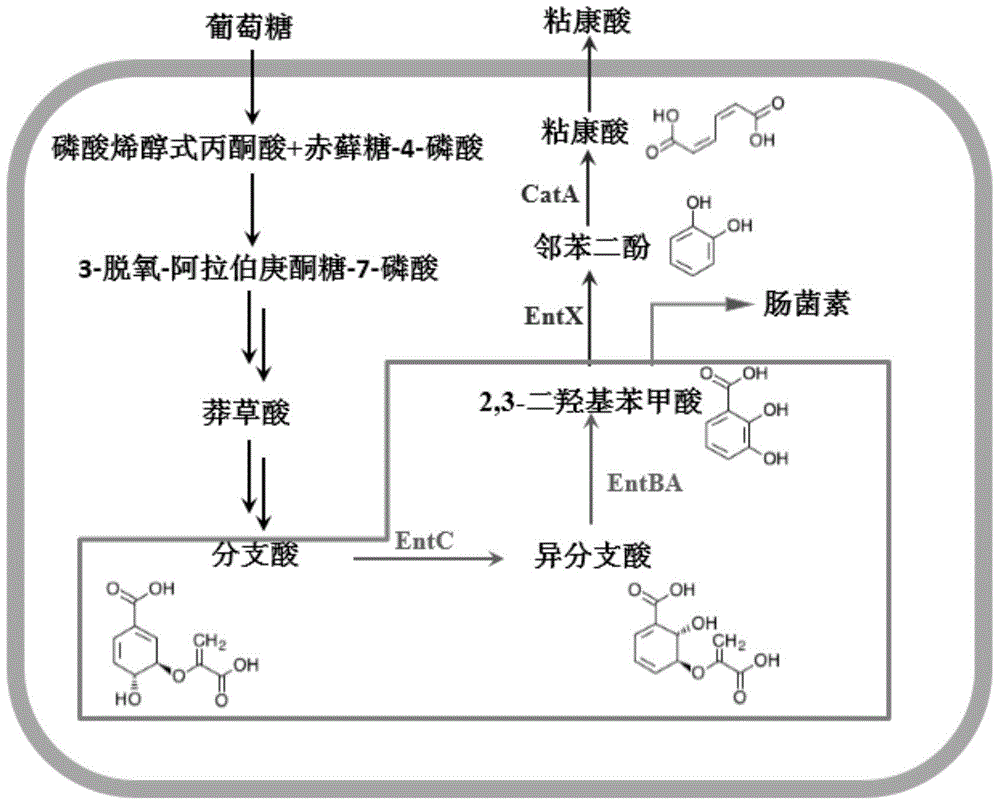
Colibacillus engineering bacterium taking glucose as substrate for synthesizing muconic acid
A technology of Escherichia coli and glucose, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as increasing difficulty, limiting yield improvement, expensive shikimic acid, and achieving the effect of reducing burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1 Construction of plasmids pACYC-XA and pET-XA.
[0061] Respectively, pACYCDuet-1 and pETDuet-1 were used as co-expression vectors for the synthesis of exogenous muconic acid genes.
[0062] Use primers A1 and A2 by PCR to obtain entX (SEQ ID NO.1 encoding 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid decarboxylase) from Klebsiella pneumoniae CICIM B7001 genome clone; The clone obtained catA (SEQ ID NO.2 encoding catechol 1,2-dioxygenase). After the PCR products and expression vectors of the two genes were digested with corresponding restriction enzymes, the DNA fragments were simultaneously inserted into the corresponding restriction sites of pACYCDuet-1 and pETDuet-1 to obtain recombinant plasmids pACYC-XA and pET- XA.
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2 Construction of plasmid pRSF-CBA.
[0064] Select pRSFDuet-1 as the expression vector of entC and entBA genes. entC (encoding chorismate isomerase) was cloned from the Escherichia coli JM109 genome by PCR using primers C1 and C2; entBA (encoding isochorisate lyase and 2,3 - dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase). After the PCR product and the expression vector were digested with corresponding restriction endonucleases, the DNA fragment was inserted into the corresponding restriction site of pRSFDuet-1 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pRSF-CBA.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Construction of plasmid pCDF-GL.
[0066] Select pCDFDuet-1 as aroG fbr and the expression vector of aroL gene. This vector has double T7 promoters, and the expression of foreign genes can be realized with or without addition of IPTG. 3-deoxy-arabinoheptulose-7-phosphate synthase is referred to as DAHP synthetase for short, consists of AroG, AroF, AroH, aroG encodes AroG, wherein AroG is subject to feedback inhibition by phenylalanine, using the site-directed mutagenesis method (primers E1, E2, E3 and E4), the aspartic acid (GAT) at position 46 of AroG is mutated into asparagine (AAT), and the gene aroG after mutation is obtained fbr , which relieves the feedback inhibition of phenylalanine. aroL, cloned from the genome of E. coli JM109 by PCR using primers F1 and F2. After the PCR product and the expression vector were digested with corresponding restriction endonucleases, the DNA fragment was inserted into the corresponding restriction site of pCDFDuet-1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com