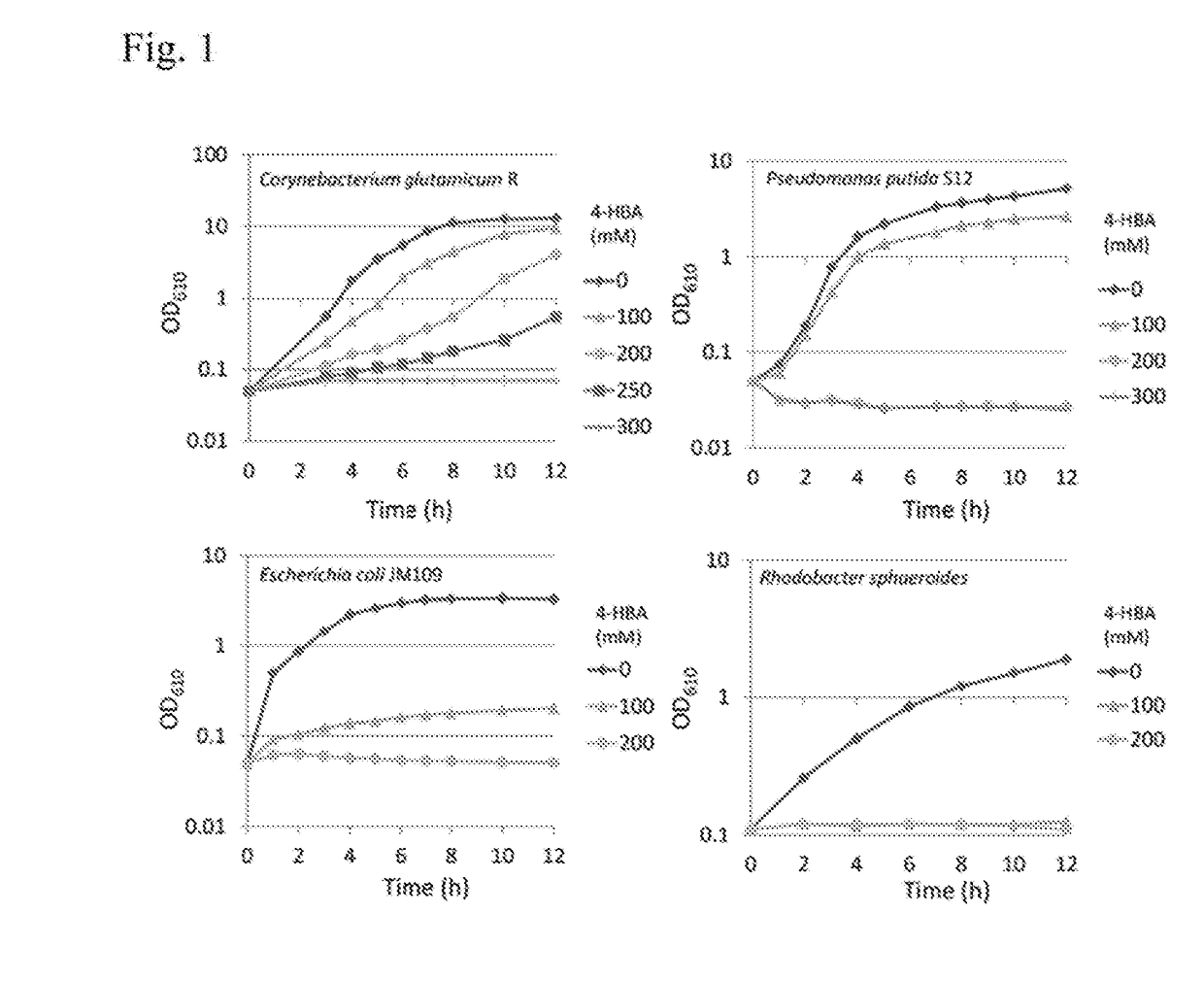
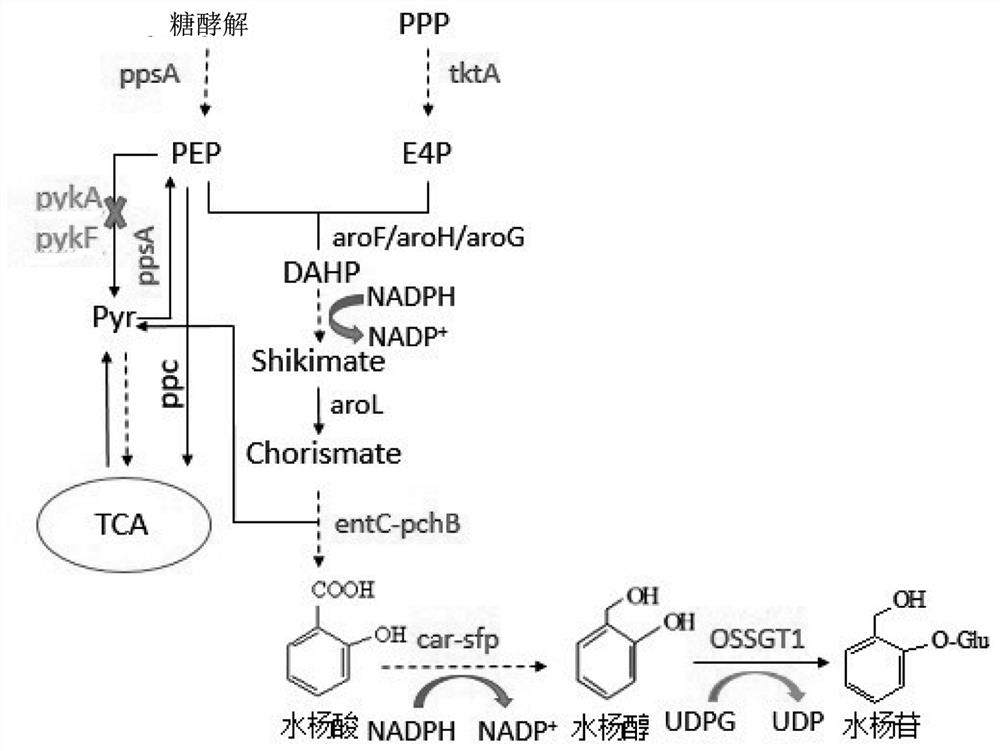
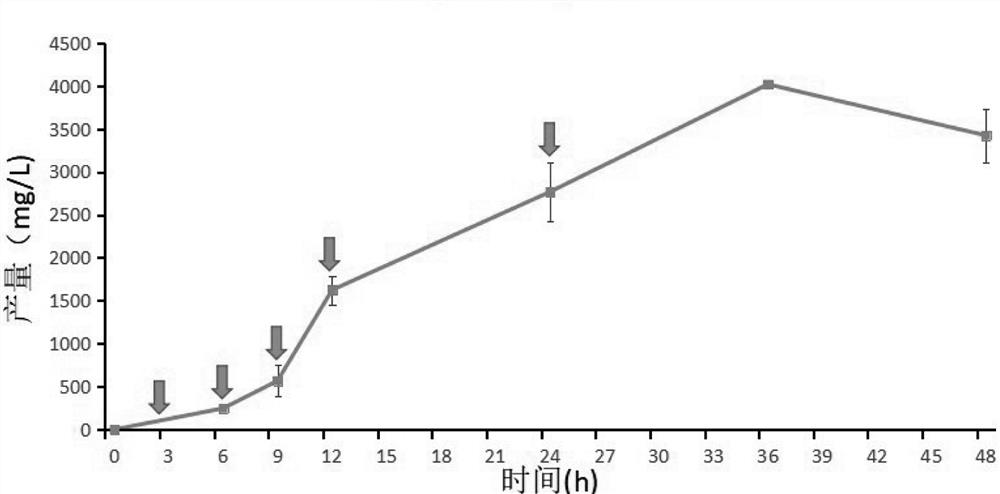
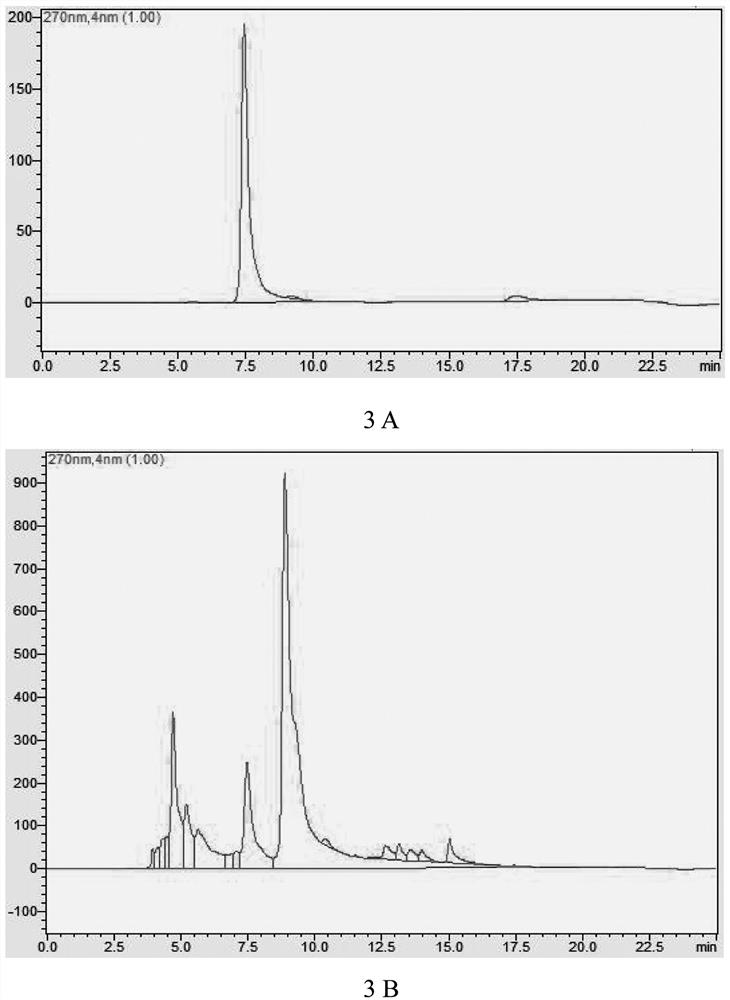
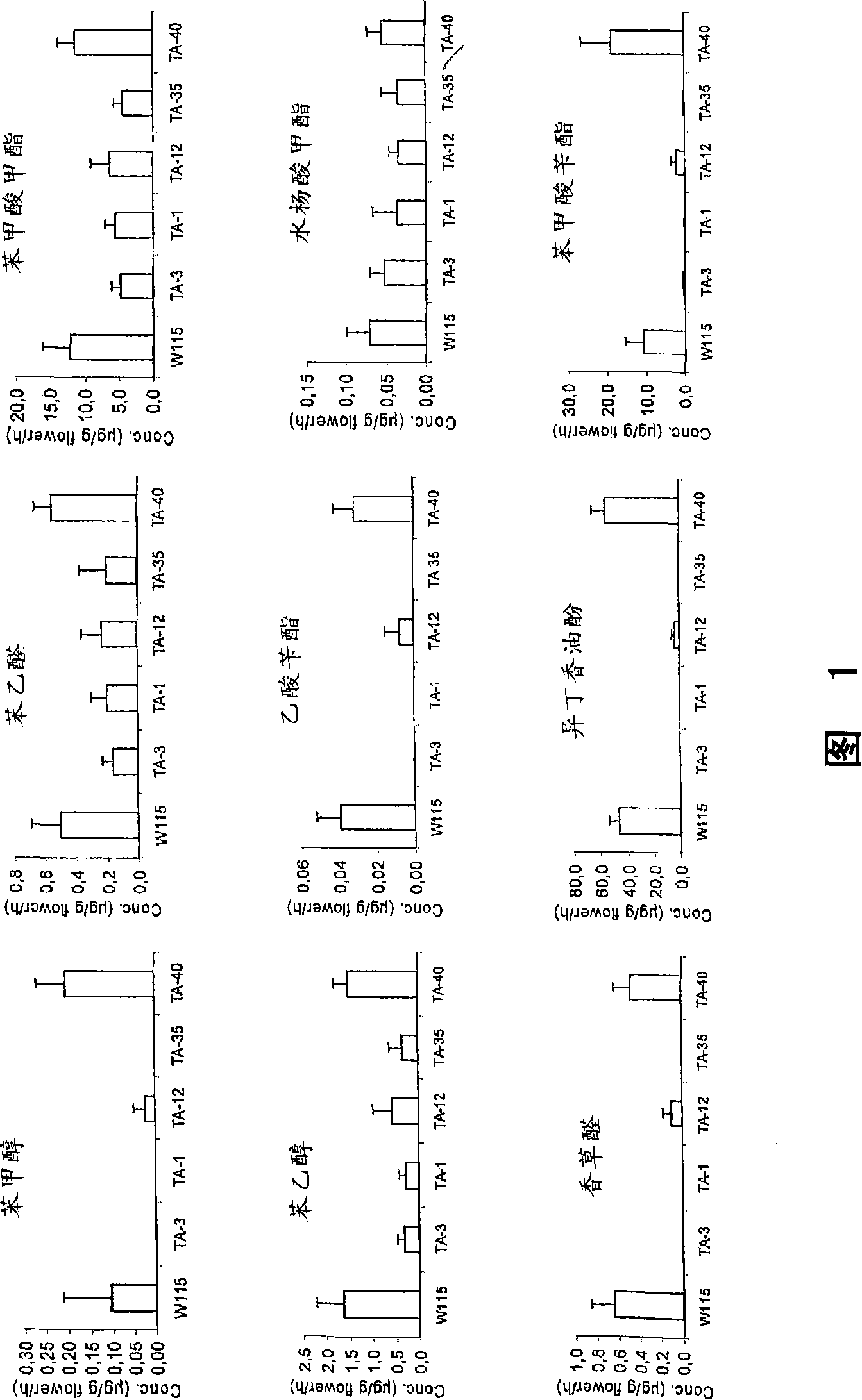
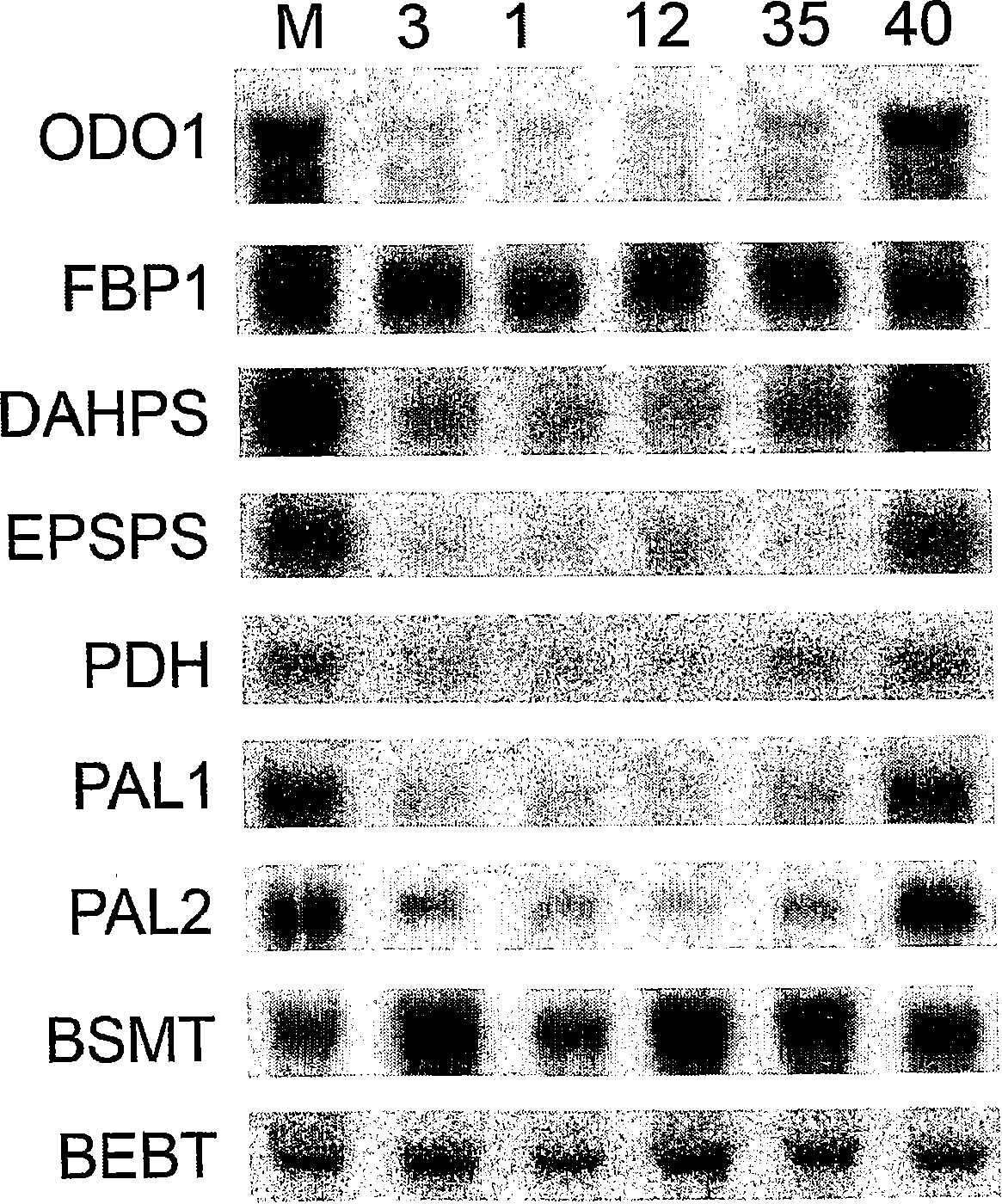
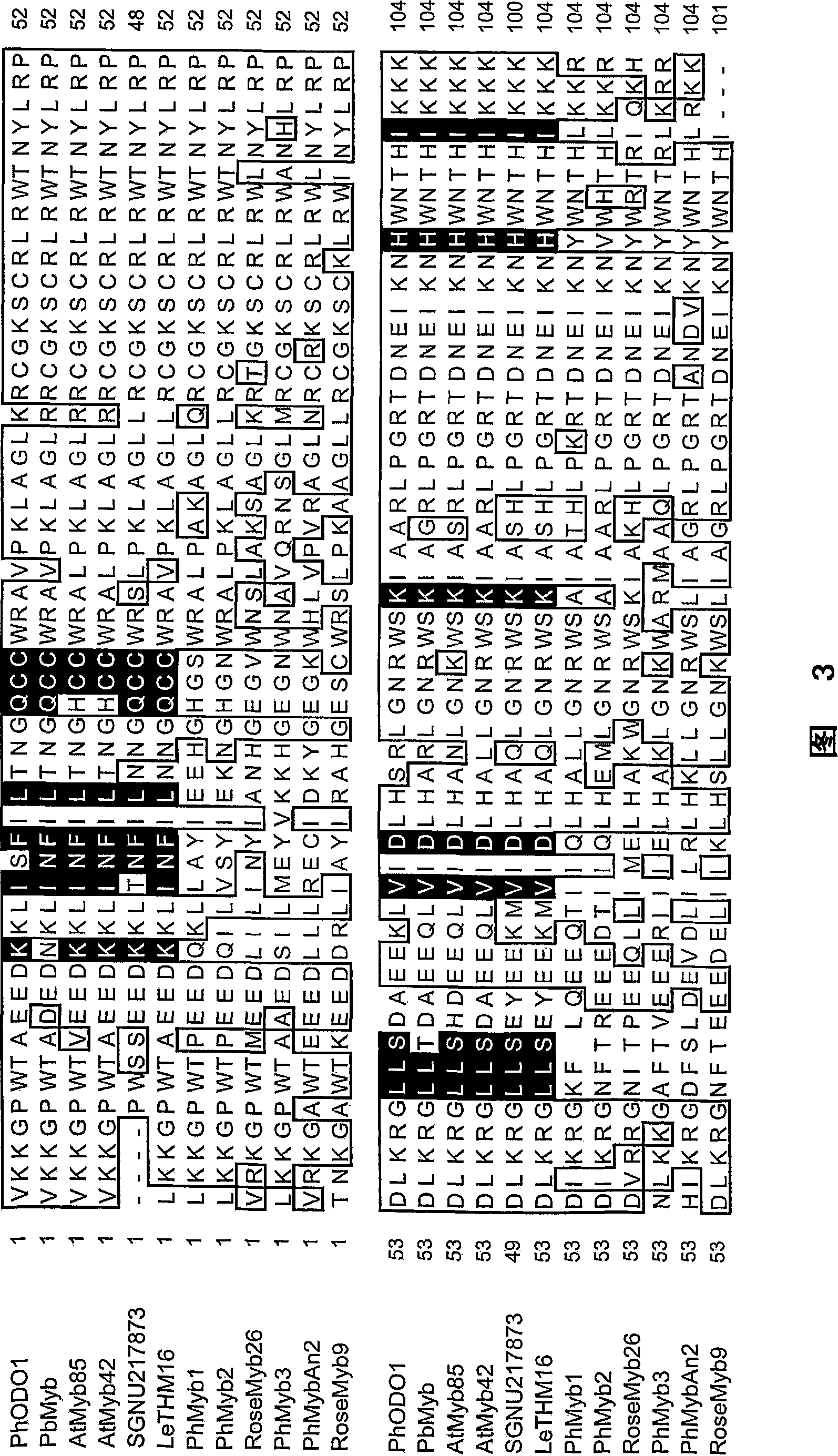
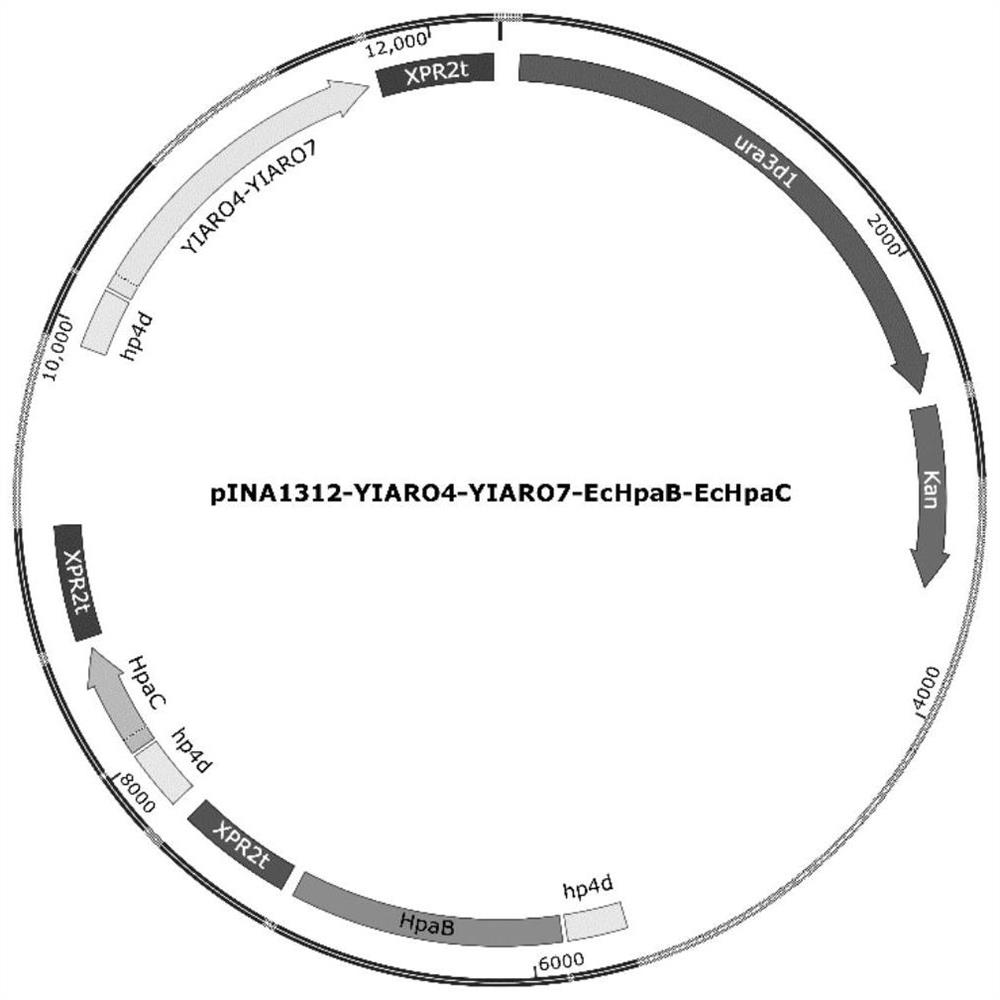
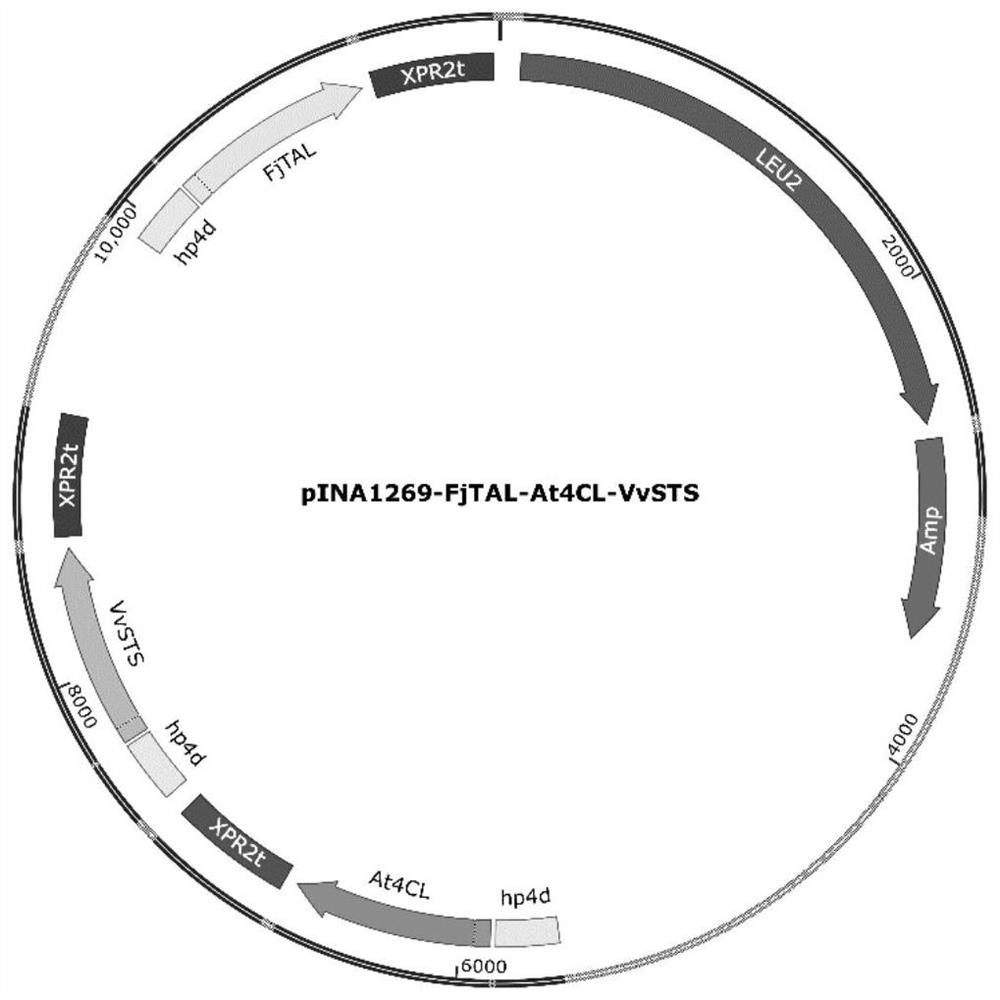
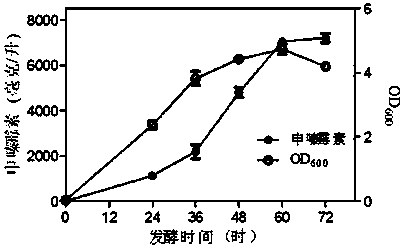
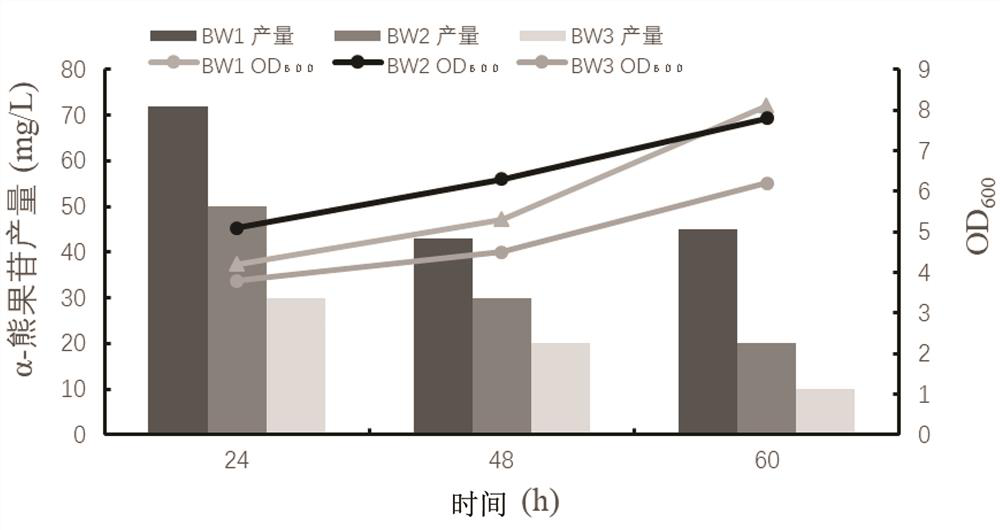
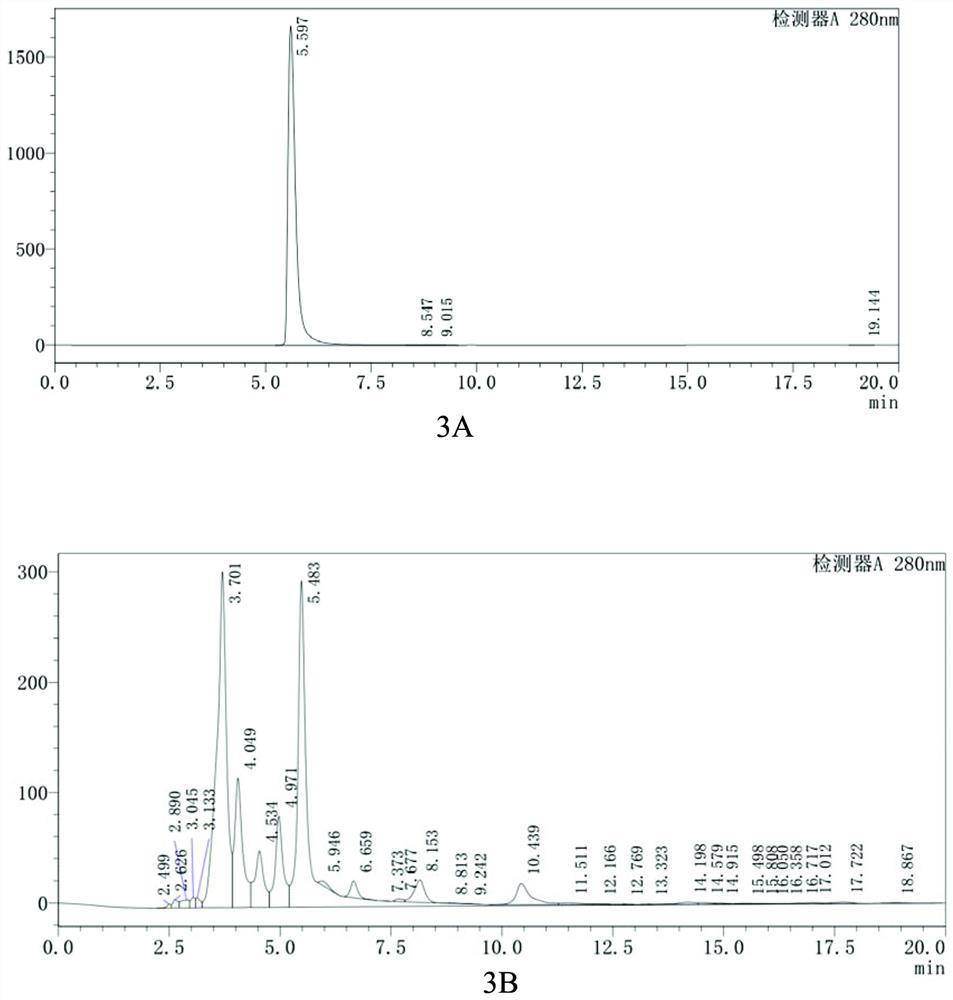
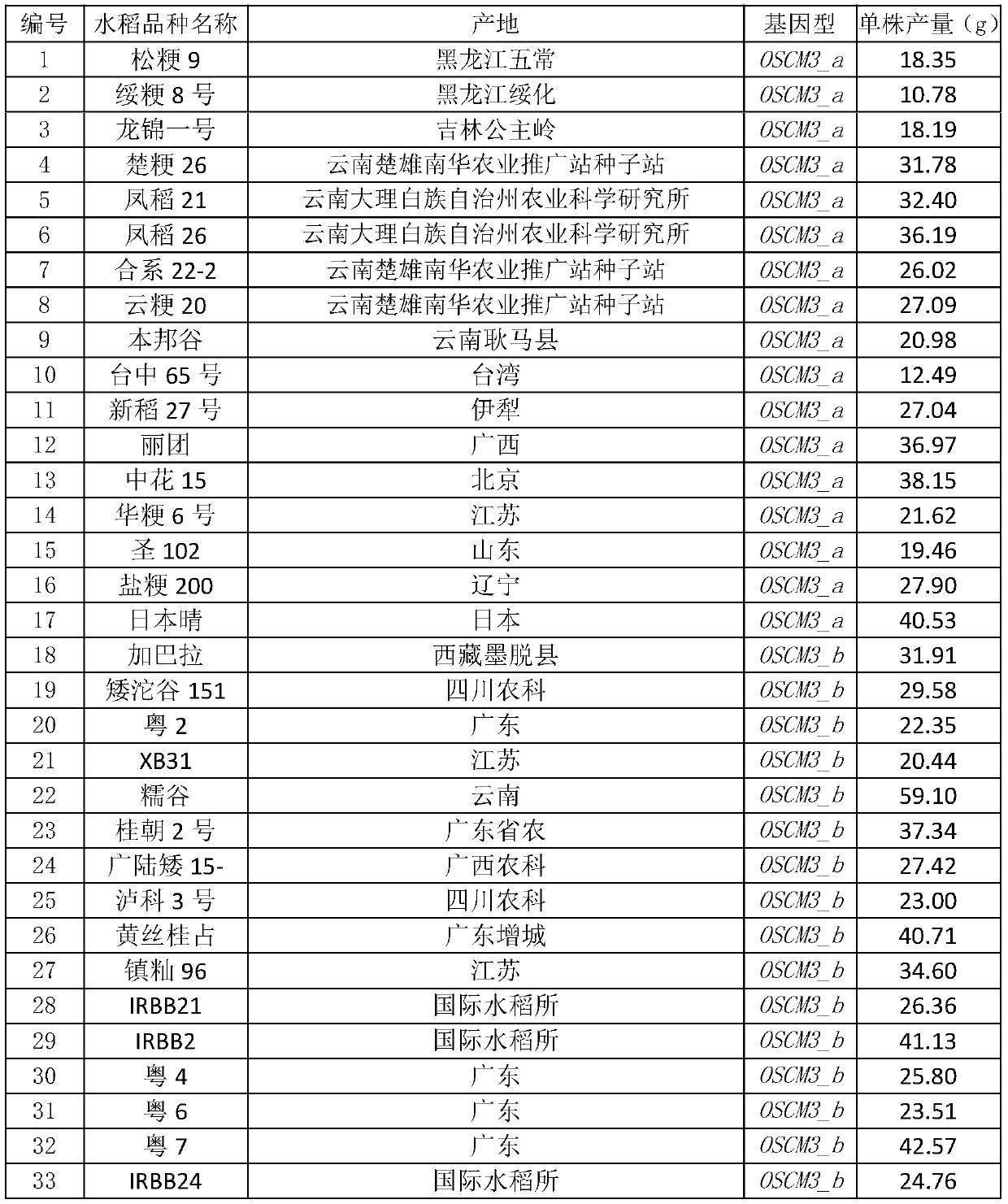
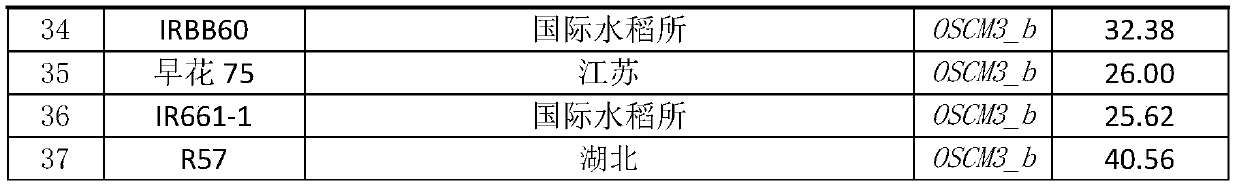
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Chorismic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
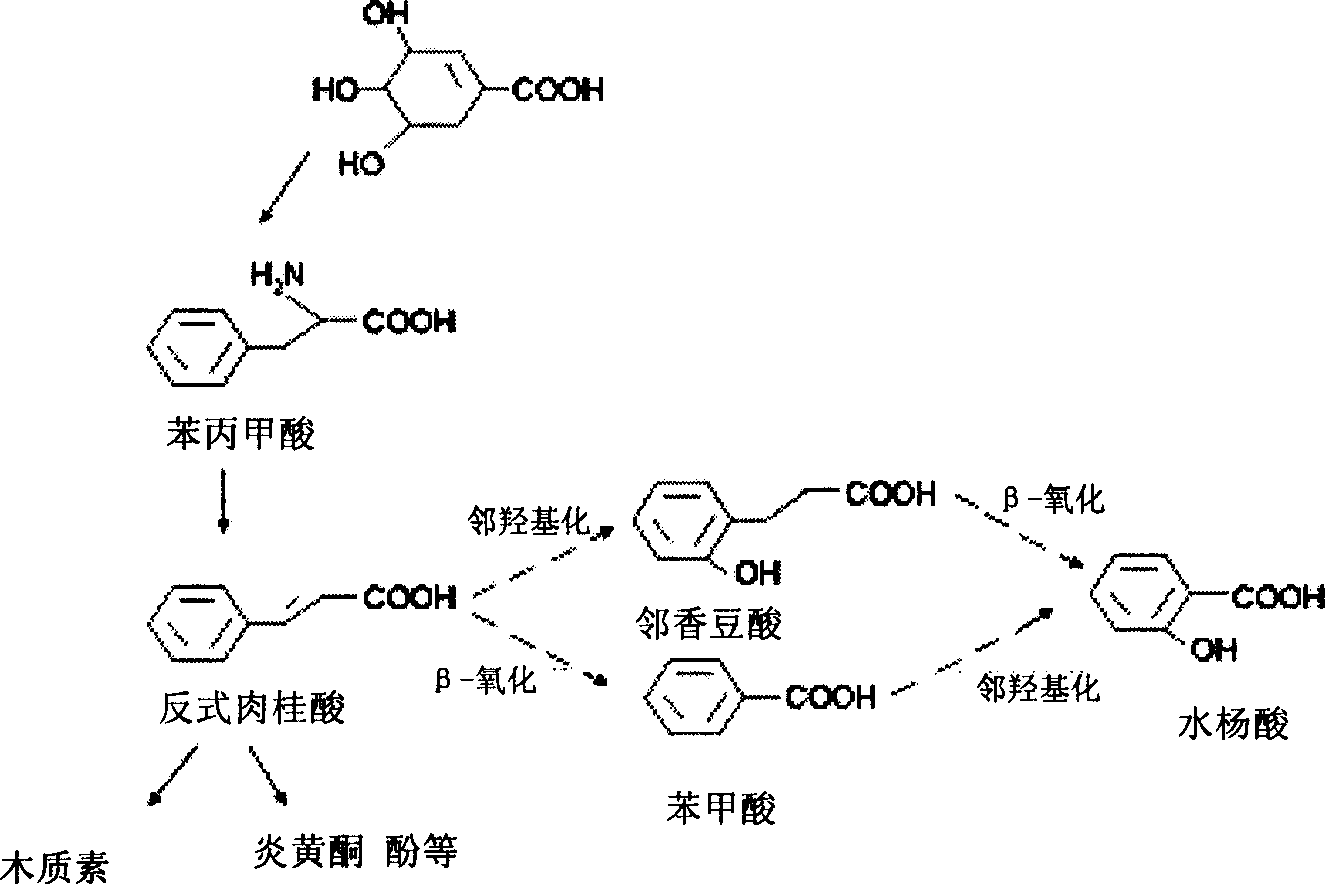
Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. The name chorismic acid derives from a classical Greek word χωρίζω meaning "to separate", because the compound plays a role as a branch-point in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis.
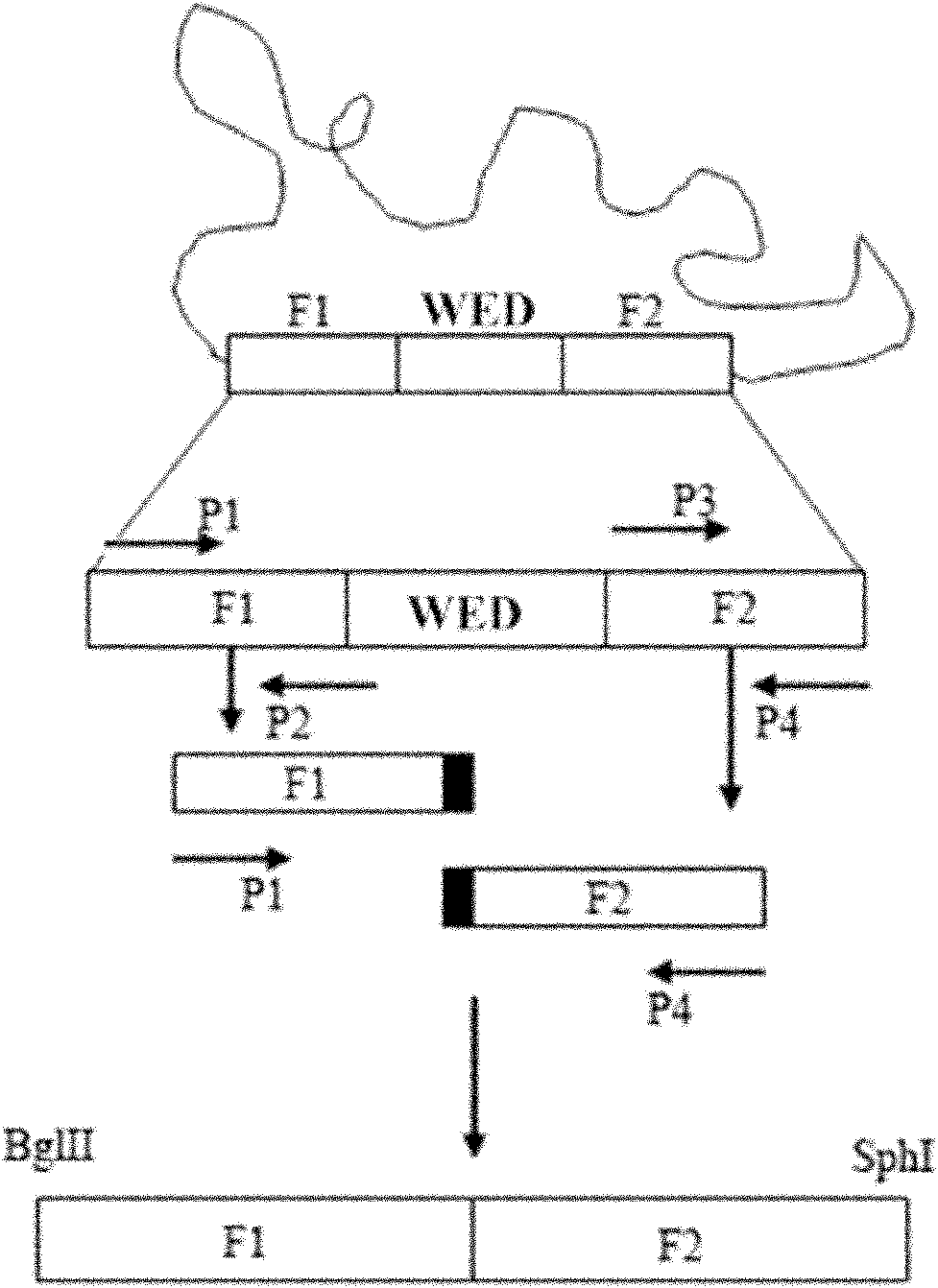
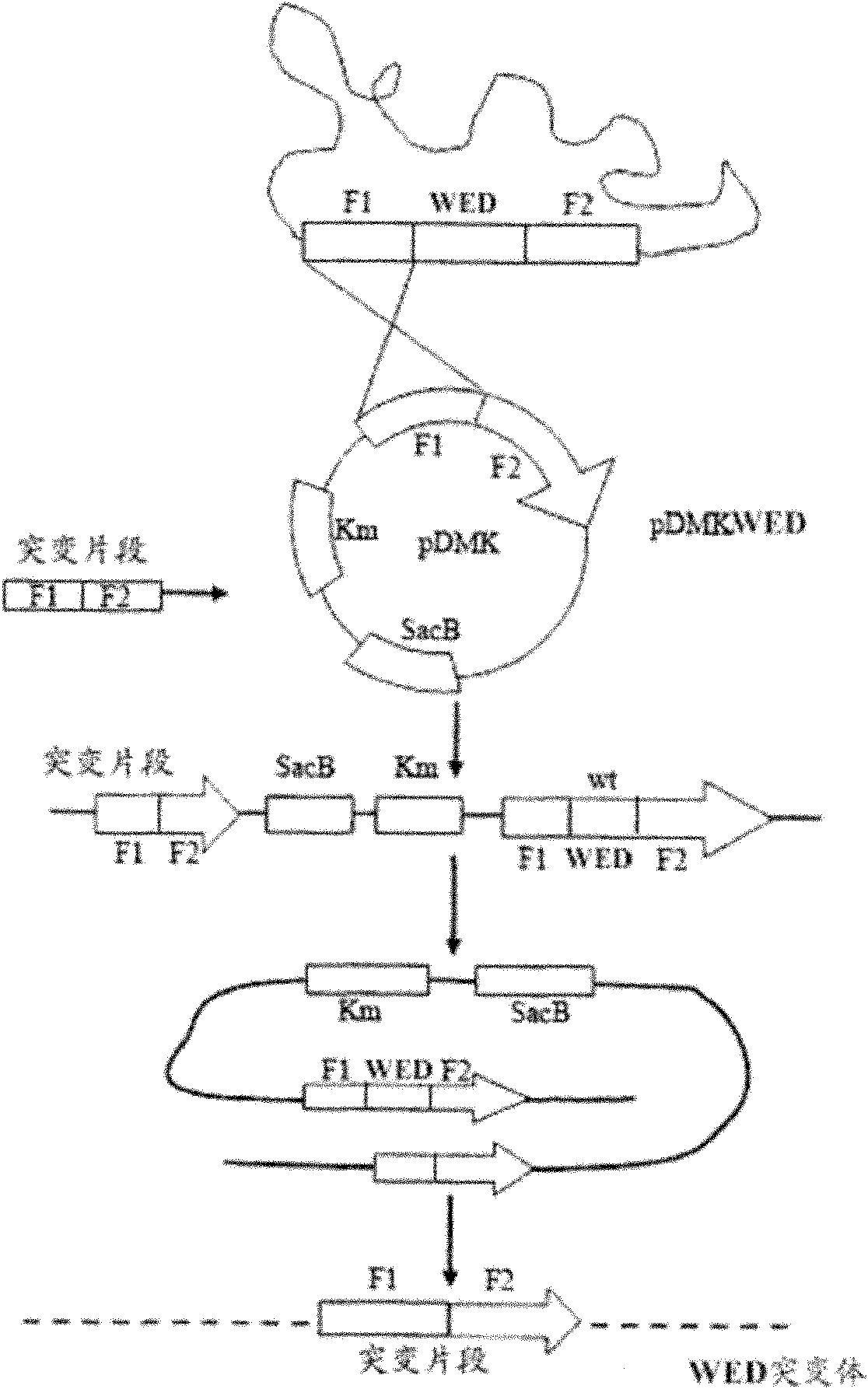
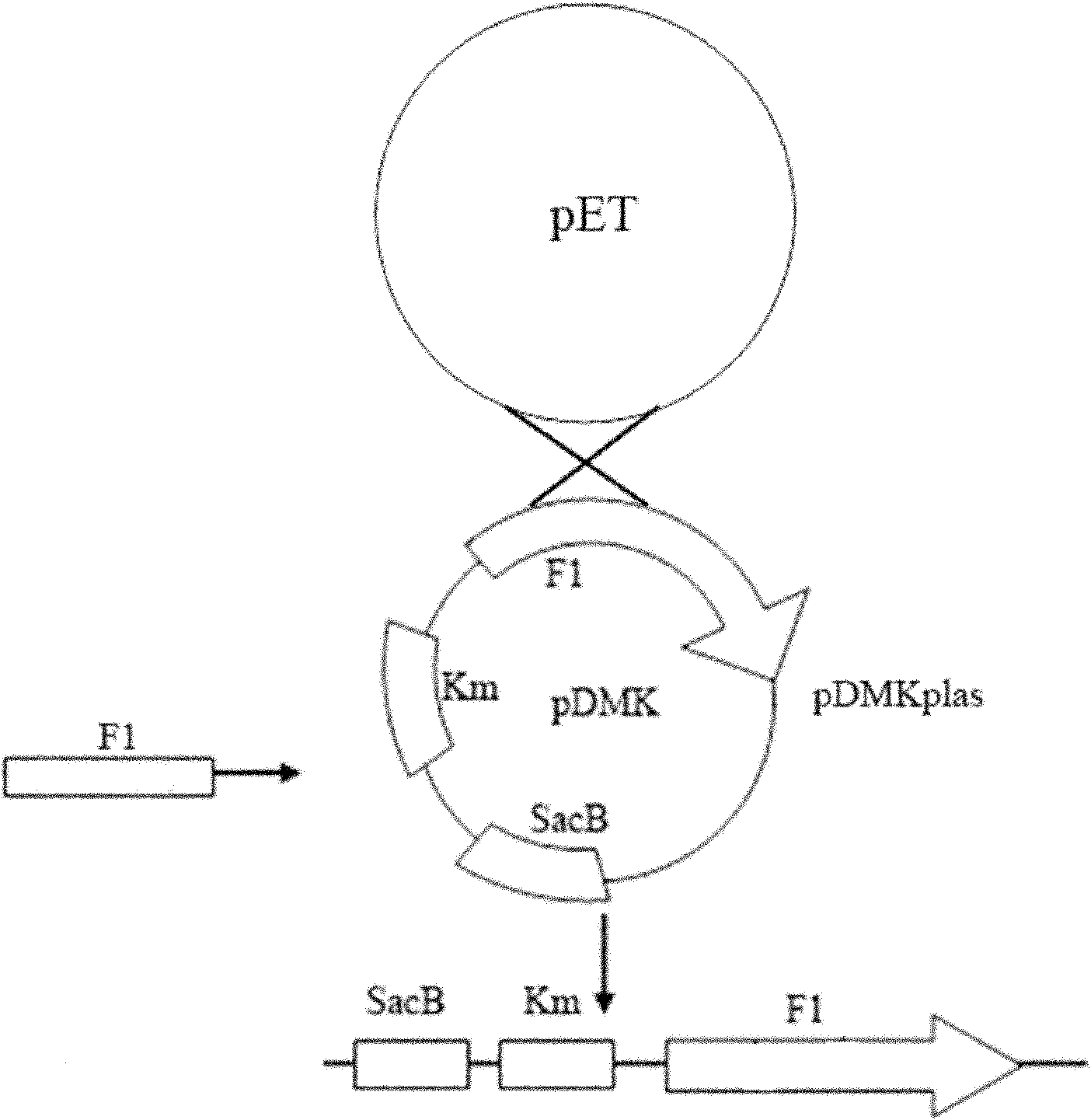
Marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of Edwardsiella tarda wild strain as well as relevant preparations and application thereof
ActiveCN101974472AGood control effectImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsChorismic acidAttenuated Live Vaccine
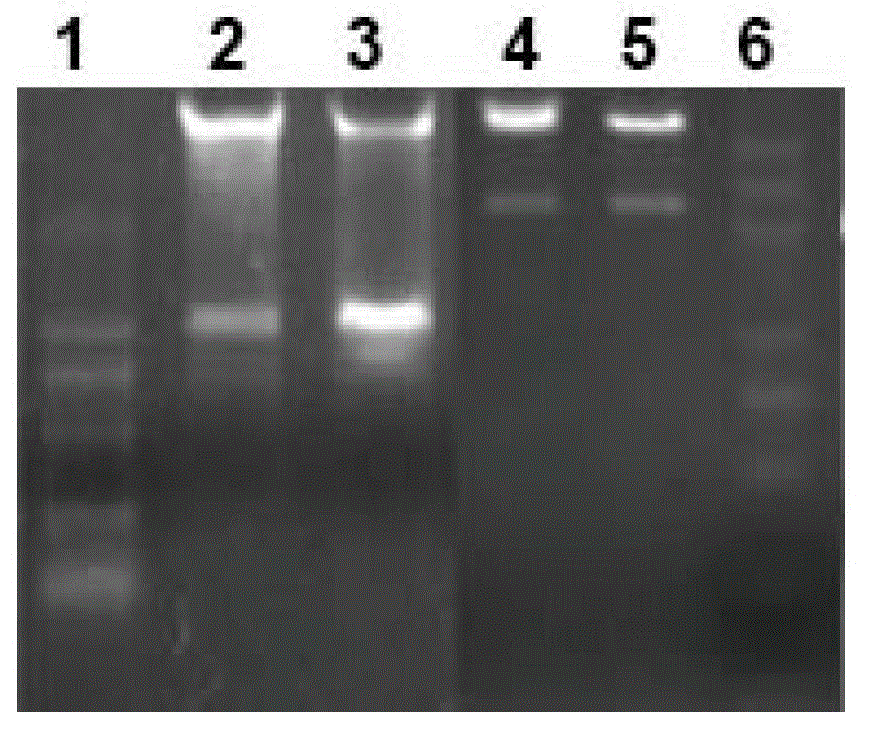
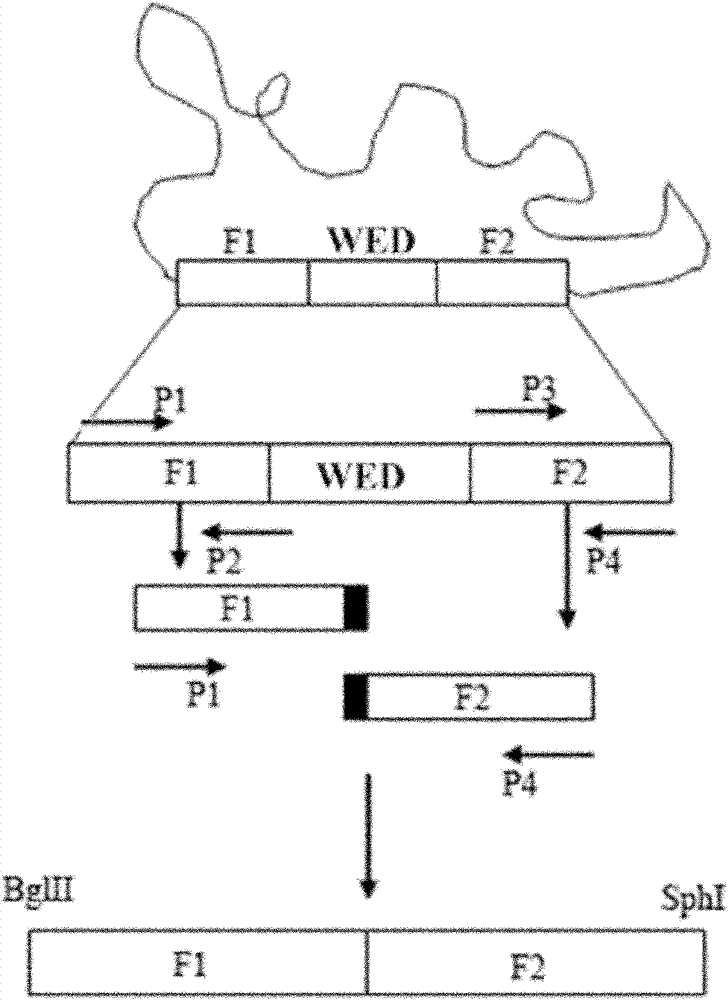
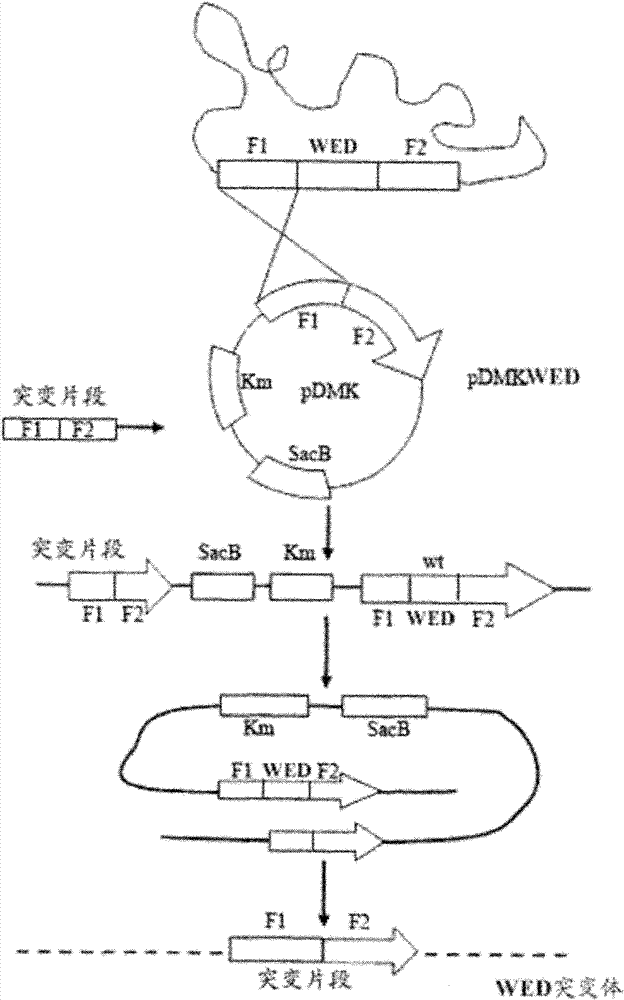
The invention relates to a marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of an Edwardsiella tarda wild strain. The marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain is an attenuated live vaccine of an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, which deletes the chorismic acid synthase gene aroC of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, three types of secretion system response element genes of eseB, escA, eseC and eseD and an endogenous plasmid, preferably, the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain EIB202 with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M208068; the endogenous plasmid is a plasmid of pEIB202; and the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an attenuated strain WED with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M2010278. The invention also provides relevant preparations and application of the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain. The attenuated mutant strain or relevant preparations eliminate the potential environment and safety risk of products existing in the traditional attenuated live vaccines generally and is a safe, effective and economic vaccine aiming at Edwardsiella tarda diseases of cultured fishes.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
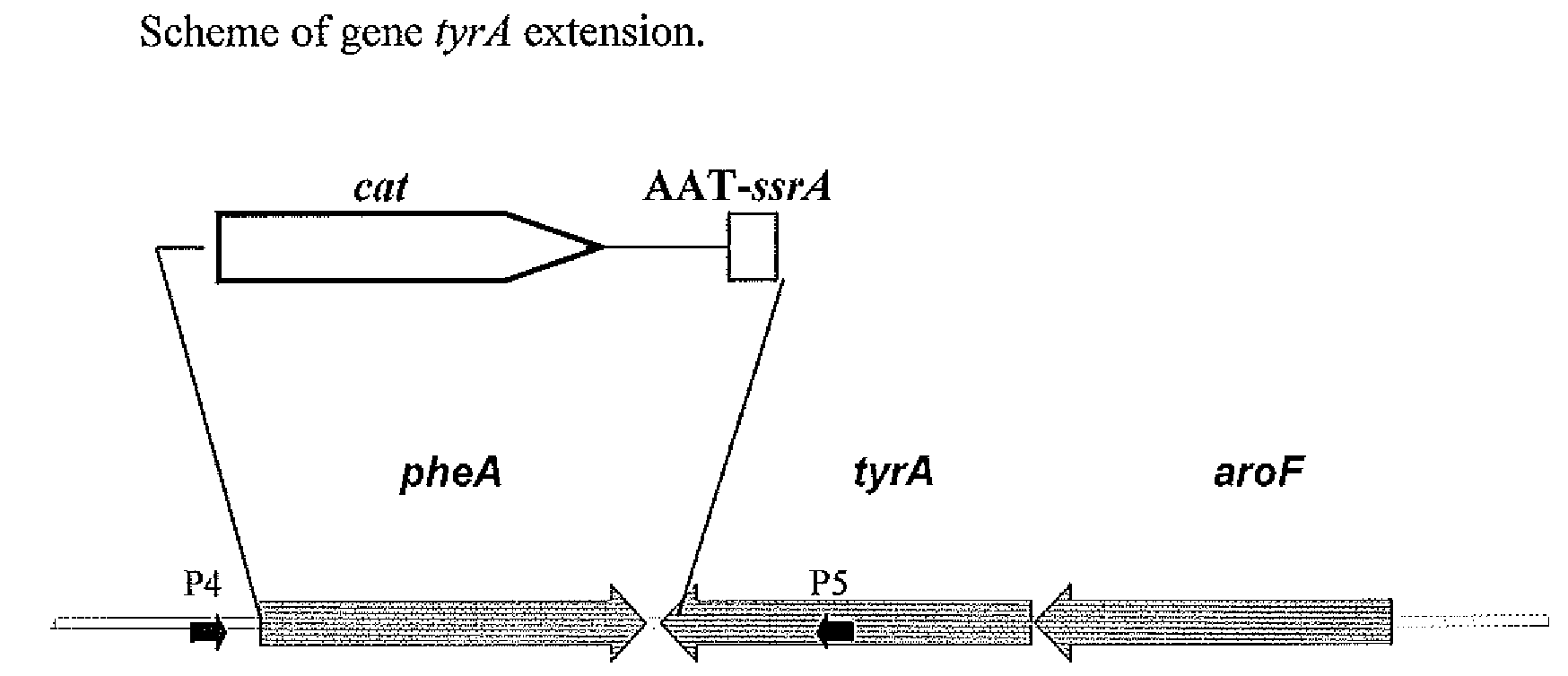
Method for producing amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20090137010A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesDNA fragmentationA-DNA
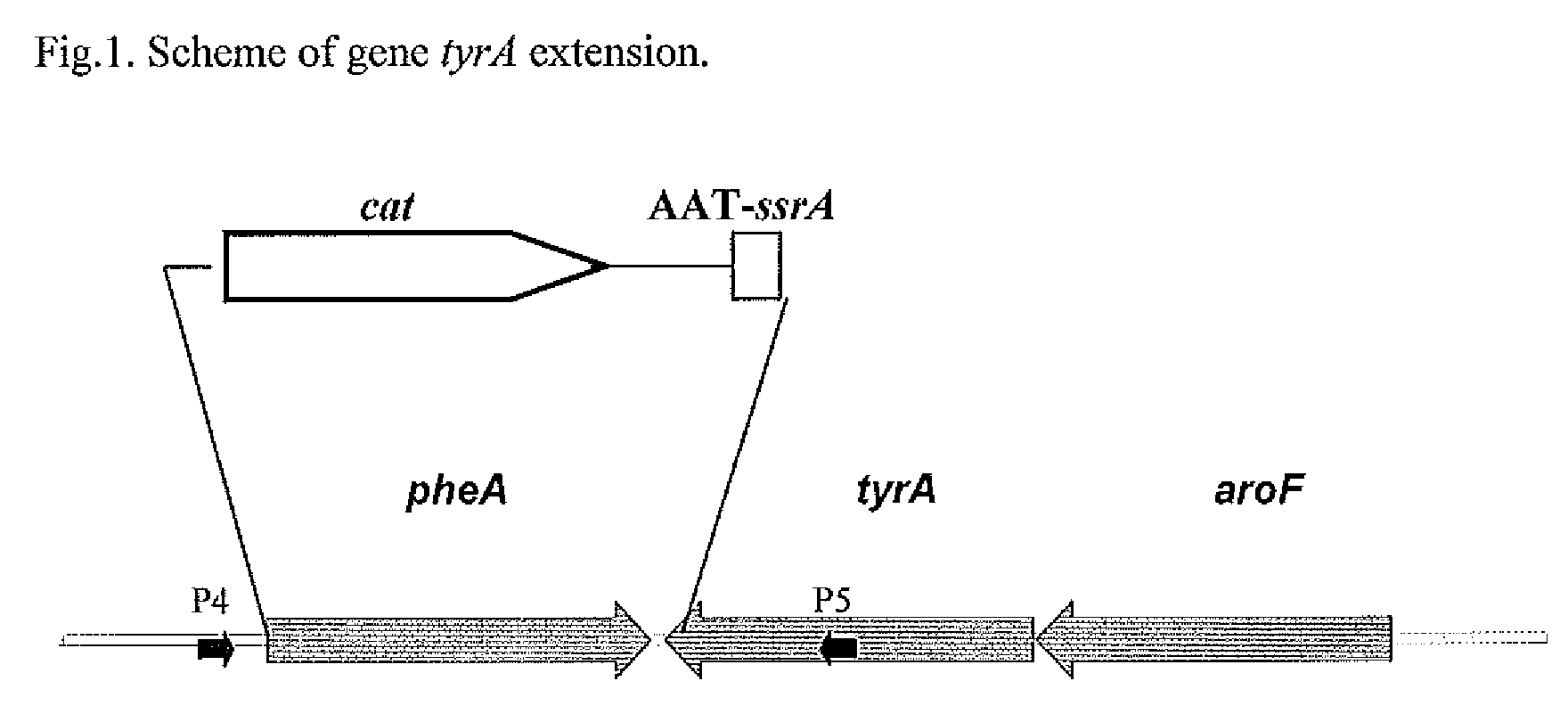
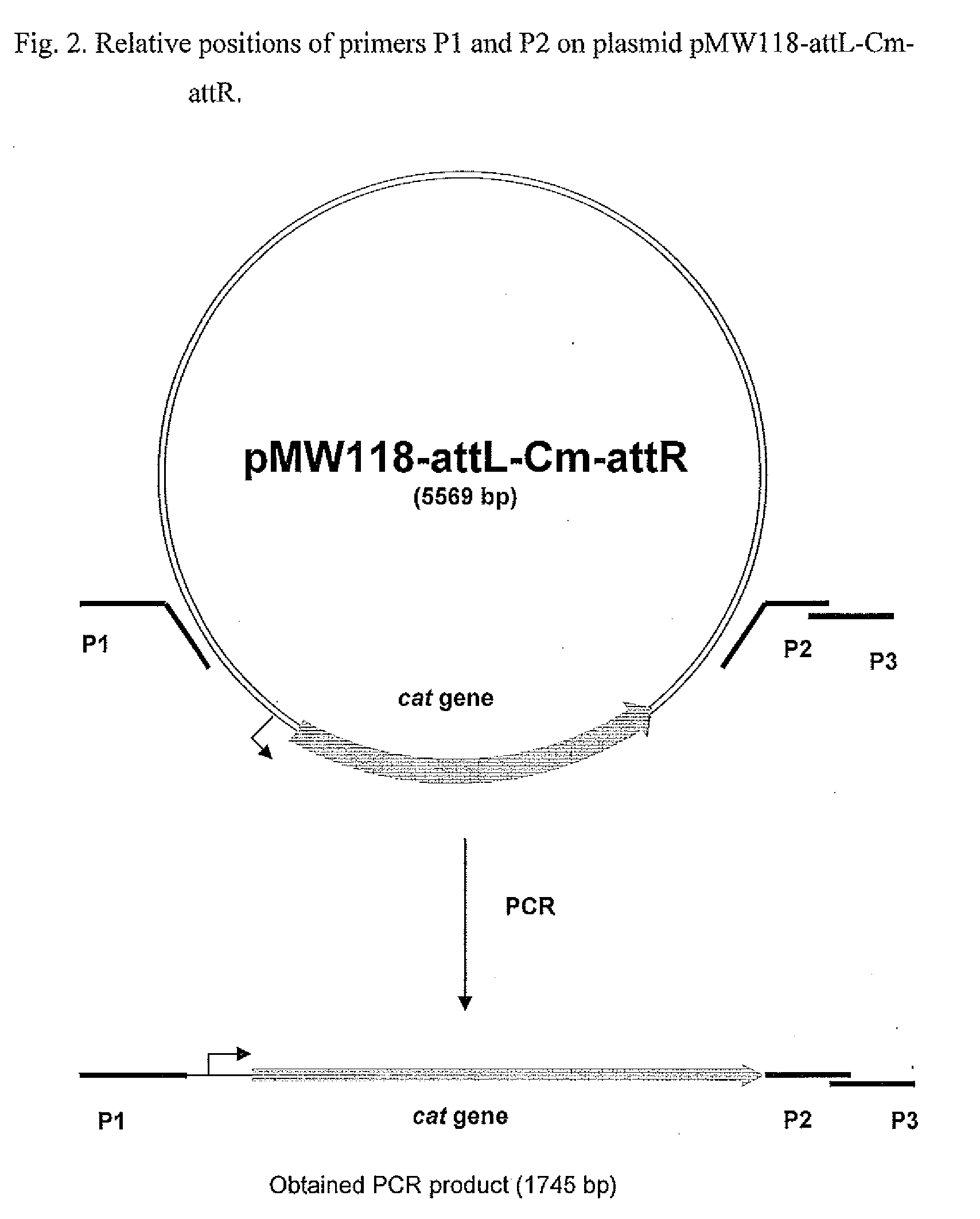
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example, L-phenylalanine and L-histidine, by fermentation using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified by attaching a DNA fragment able to be transcribed encoding the peptide represented in SEQ ID NO: 2, or a variant thereof, particularly a portion of the ssrA gene, to the 3′-end of gene encoding for the bacterial enzyme, which influences on the L-amino acid biosynthesis, such as chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydrogenase or phosphoglucose isomerase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene modification application and bacterial strain obtained through gene modification
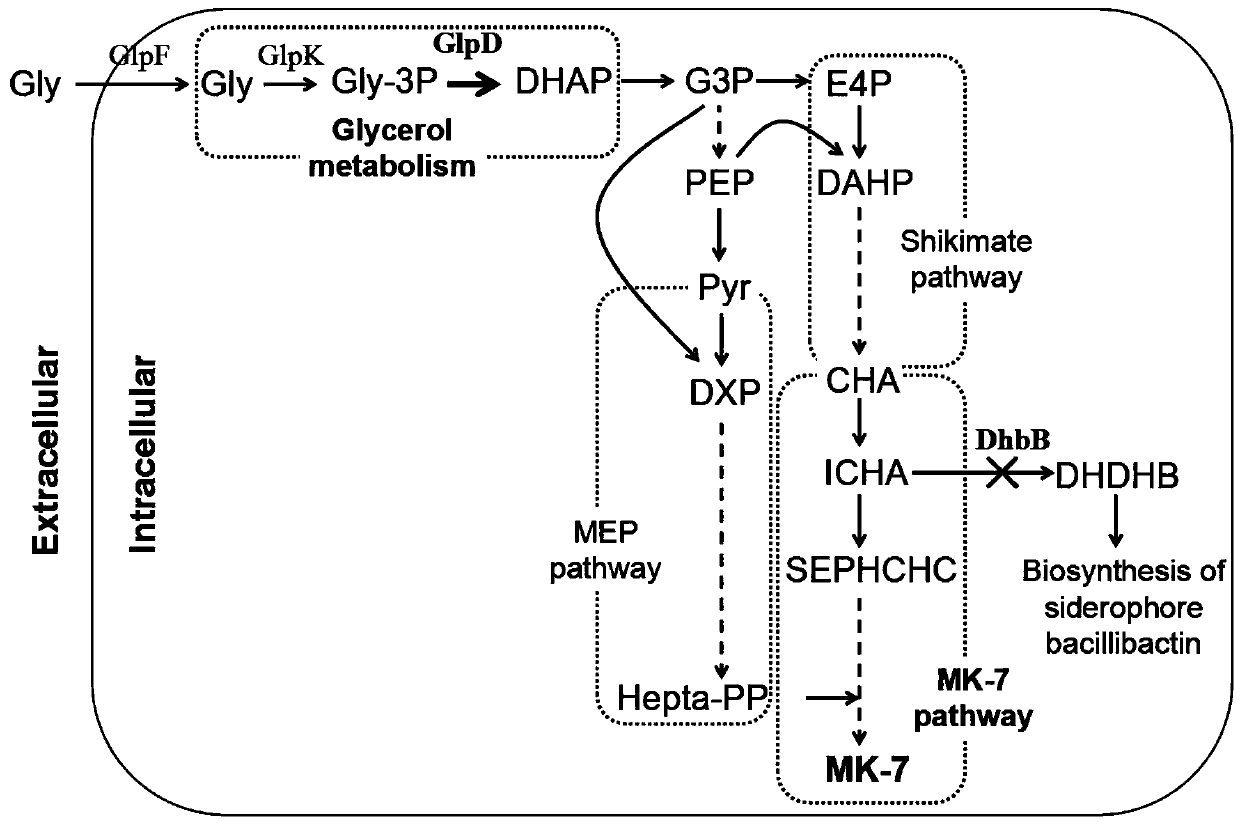
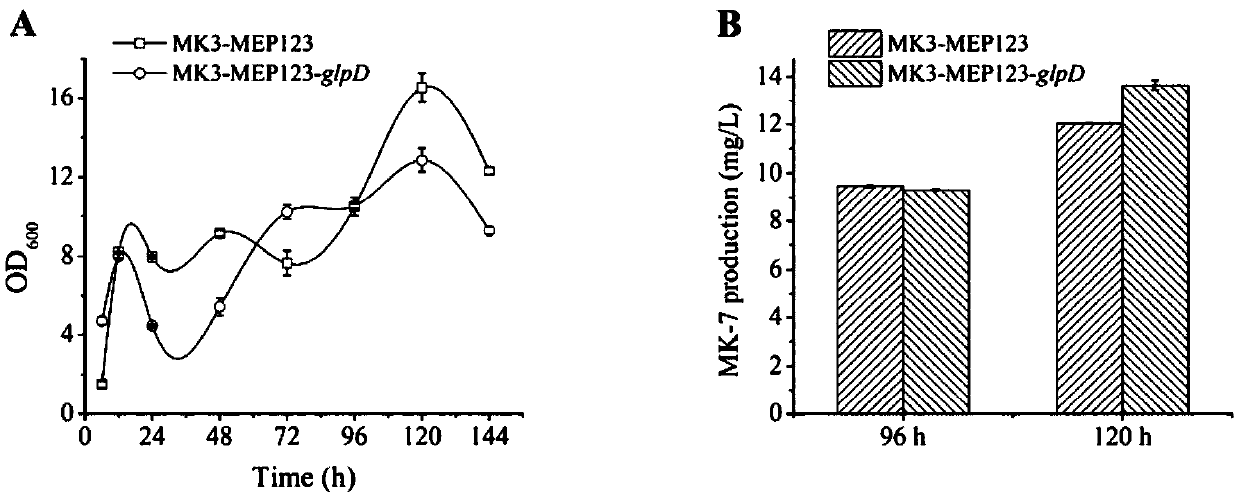
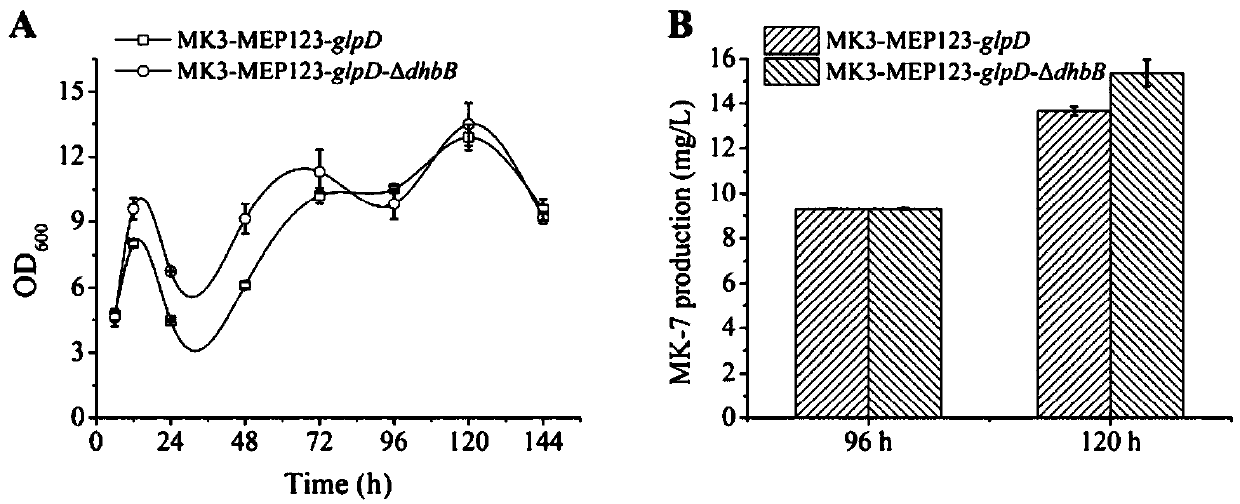
The invention relates to the technical scheme of organisms, in particular to gene modification application and a bacterial strain obtained through gene modification. MK3-MEP123, sourced from B.subtilis168 and established in a laboratory, is used as an original strain, at first, glycerinum-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GlpD) is subjected to overexpression, the transformation from glycerinum-3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate is improved, and the influence on MK-7 synthesis is inspected; then, dhbB genes are knocked out, consumption of isochorismate is reduced, and the influence on MK-7 synthesis is inspected; and finally the influence of the supply of an oxygen and carbon and nitrogen source on MK-7 synthesis is inspected through 2L shake flask fermentation. A fundamental research and theoretical basis is provided for establishing a high-yield MK-7 bacterial strain of bacillus natto by a metabolic engineering method industrially.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Gene engineering strain capable of safely and efficiently producing Phenazino-1-carboxylic acid and application thereof
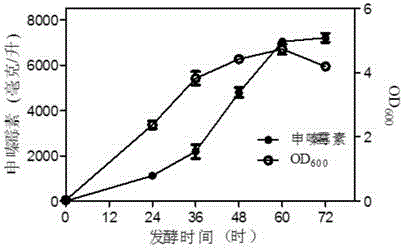
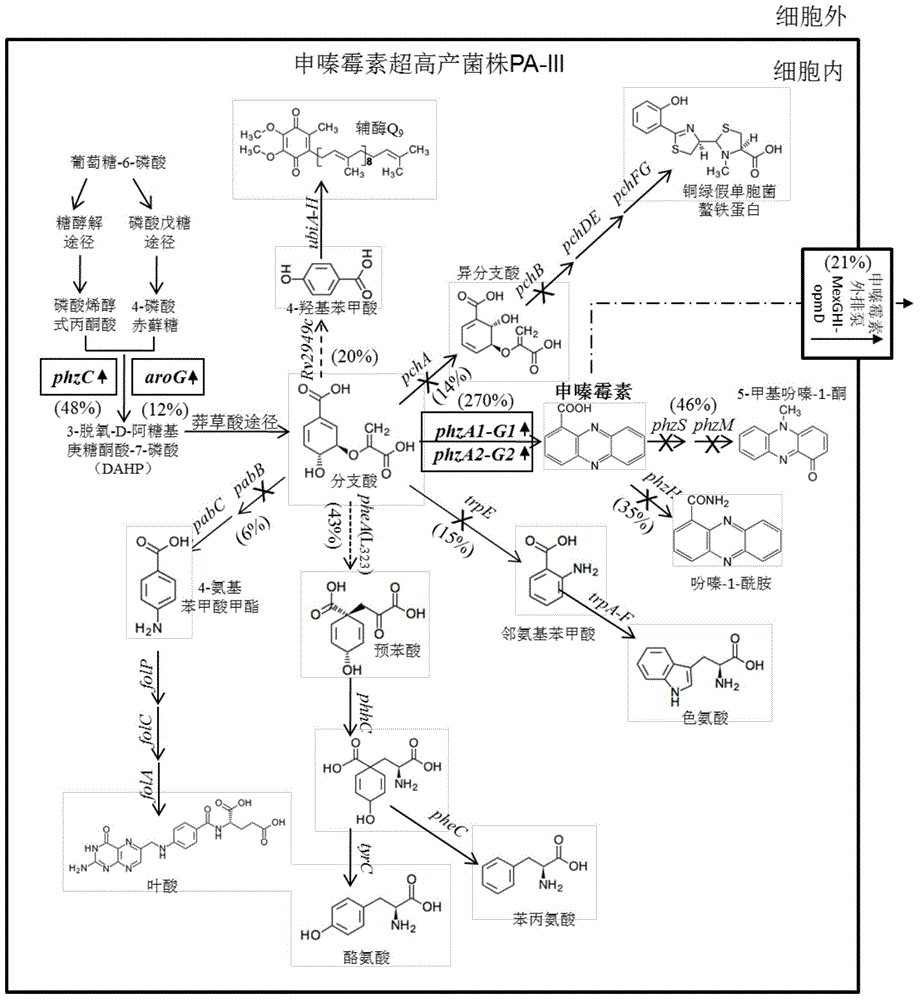
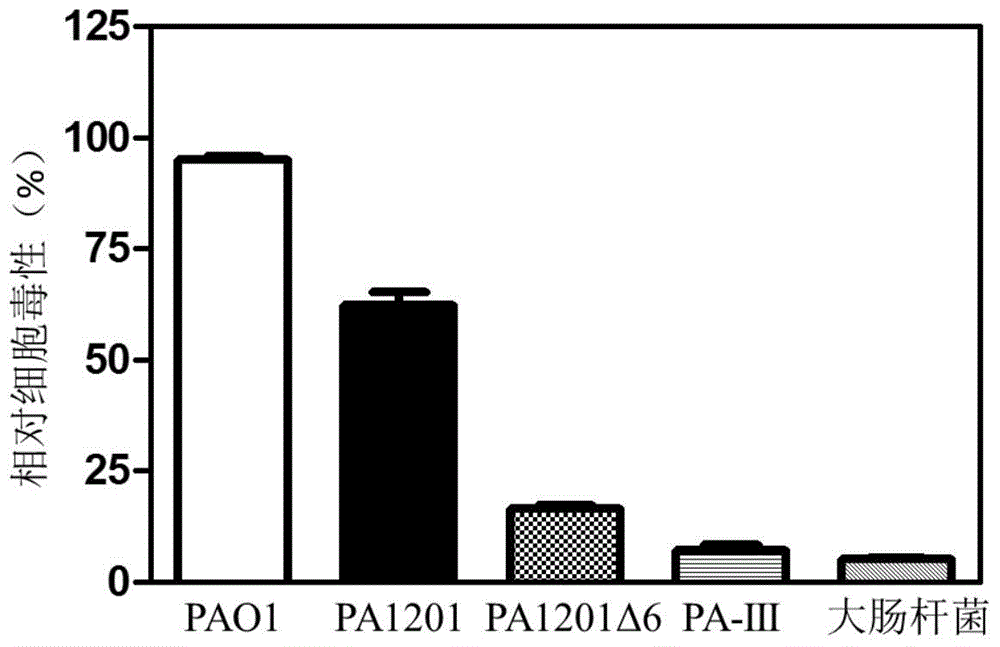
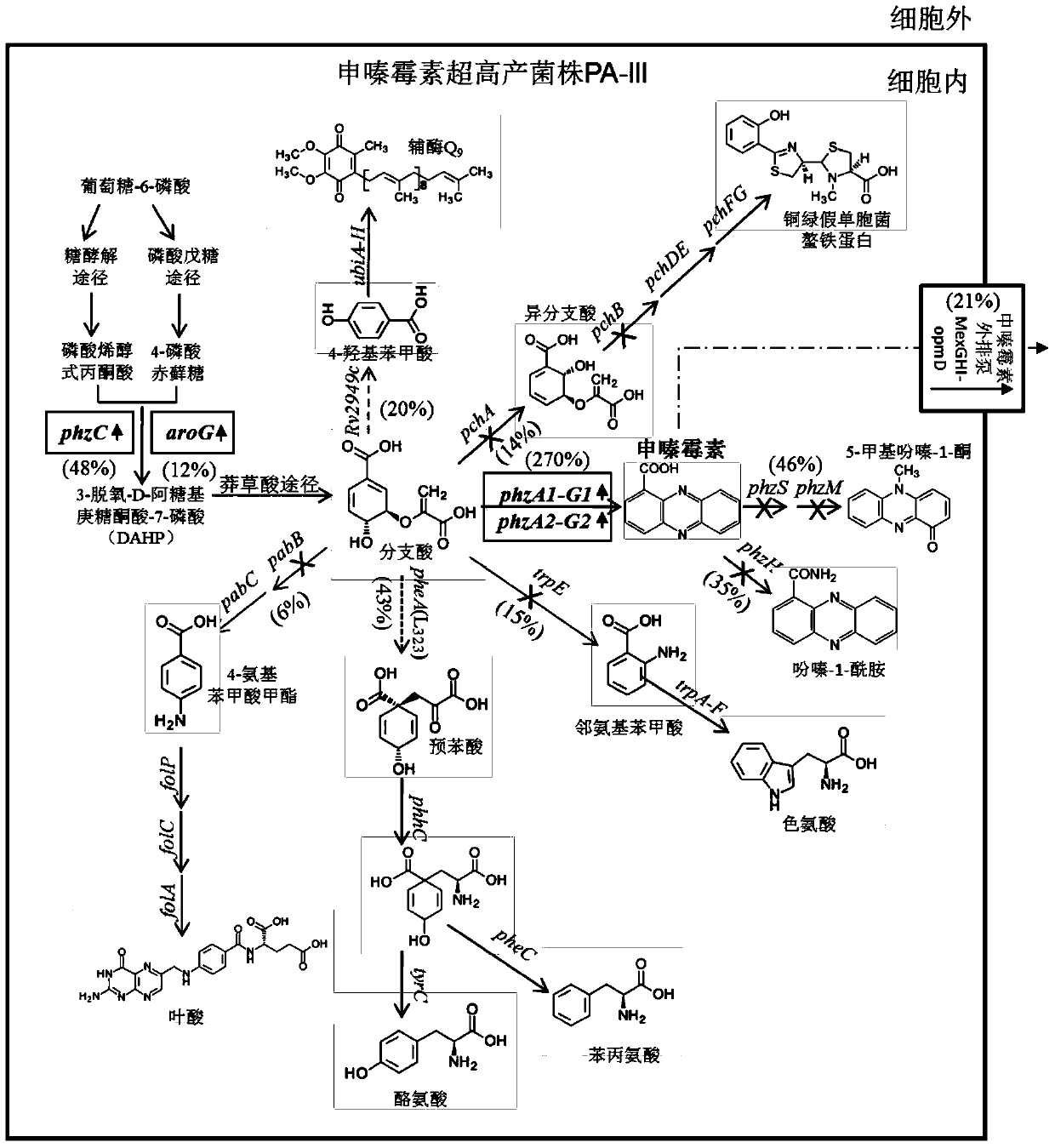
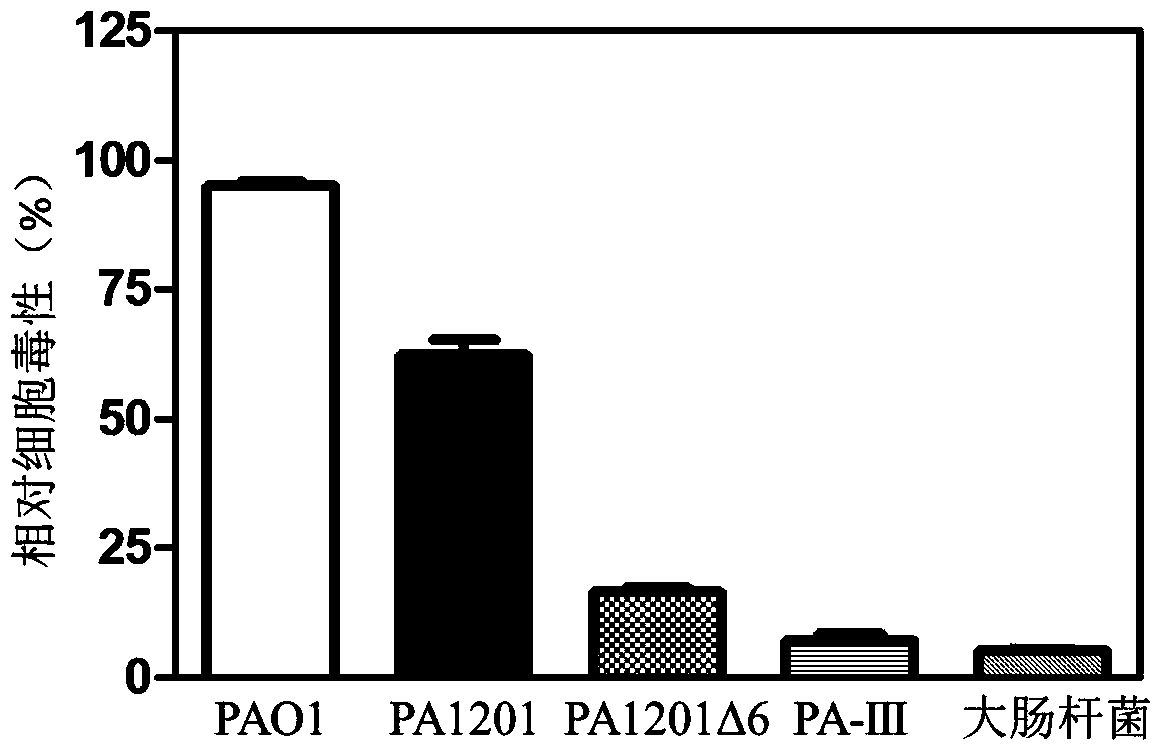
ActiveCN104946552AImprove securityDisease controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The invention discloses a gene engineering strain capable of safely and efficiently producing Phenazino-1-carboxylic acid. The gene engineering strain is Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a collection number of CCTCC No. M2015040. The gene engineering strain is prepared according to the following steps: performing pathogenic gene knockout on a strain PA1201; then, performing Shenqinmycin metabolizing gene knockout and metabolize metabolizing gene knockout; then, performing point mutation to reduce the bioactivity of PheA; performing isozyme substitution method to reduce the bioactivity of chorismic acid / pyruvic acid lyase; increasing a phzC gene copy number in a genome; replacing an aroG promoter with a strong promoter Ptac so as to enhance the gene expression level of DAHP synthase; and enhancing the Phenazino-1-carboxylic acid biosynthetic gene cluster expression level and Phenazino-1-carboxylic acid efflux pump MexGHI-OpmD expression level by a promoter replacement method. The obtained strain is capable of safely and economically producing Phenazino-1-carboxylic acid with superhigh yield.
Owner:周莲
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing phenol using the same
ActiveUS20130273624A1Efficient productionSufficient efficiencyBacteriaFermentationChorismate pyruvate lyaseCorynebacterium amycolatum
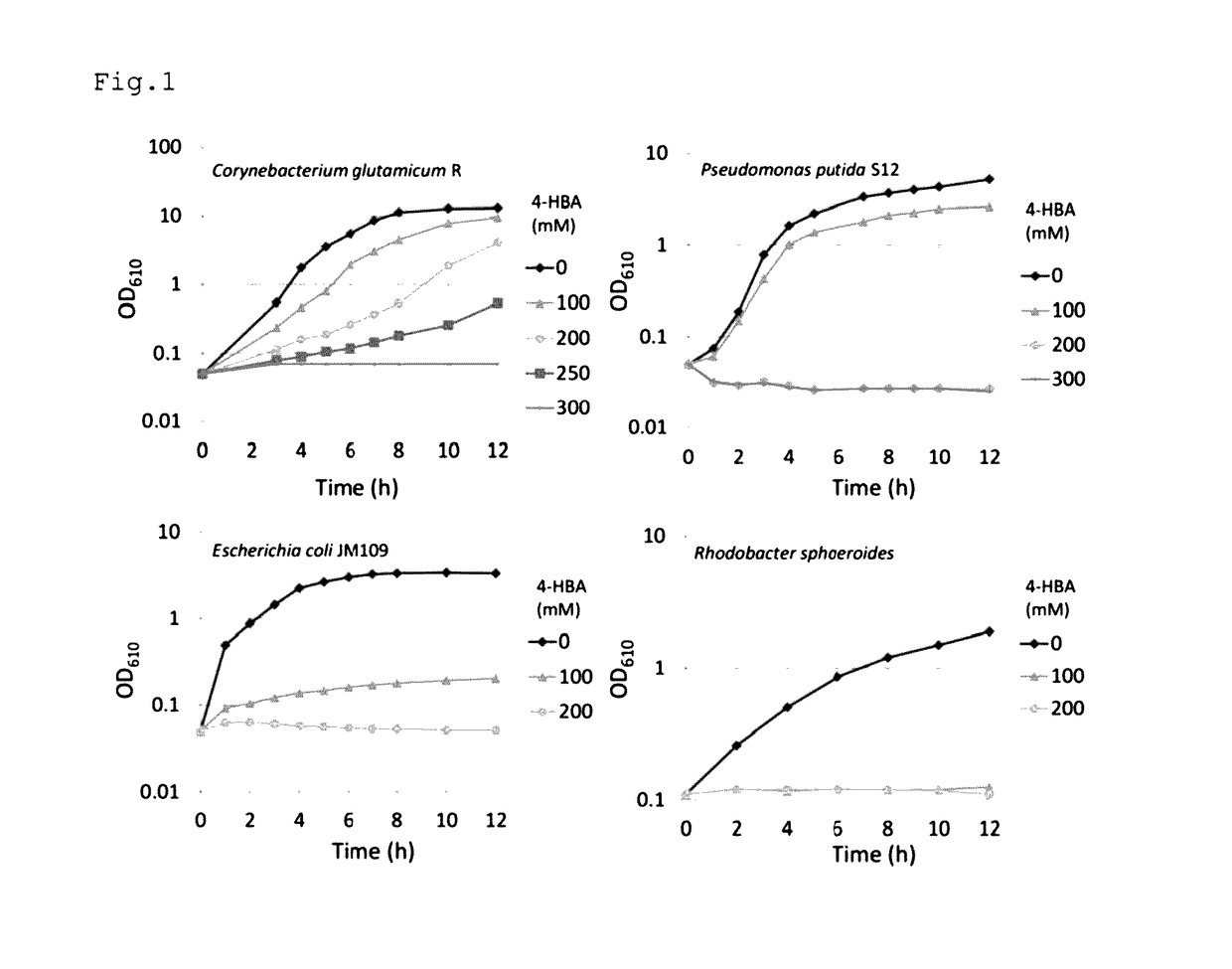
Provided is a phenol-producing transformant constructed by transferring a gene which encodes an enzyme having chorismate-pyruvate lyase activity and a gene which encodes an enzyme having 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase activity into a coryneform bacterium as a host. Also provided is a process for producing phenol, which comprises a step of allowing the transformant to react in a reaction mixture containing a saccharide under reducing conditions, and a step of collecting phenol from the reaction mixture.
Owner:GREEN CHEM
Transformant producing secondary metabolite modified with functional group and novel biosynthesis genes
An objective of the present invention is to provide a transformant altered so as to produce a secondary metabolite in which a benzene ring of the secondary product is modified at the para-position with a functional group containing a nitrogen atom. A transformant according to the present invention is a transformant of an organism producing a secondary metabolite having a benzene ring skeleton without substitution at the para-position with a functional group containing a nitrogen atom, said transformant being transformed by introducing genes involved in a biosynthetic pathway from chorismic acid to p-aminophenylpyruvic acid, including a gene encoding an amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2) having 4-amino-4-deoxychorismic acid synthase activity, a gene encoding an amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 4) having 4-amino-4-deoxychorismic acid mutase activity and a gene encoding an amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 6) having 4-amino-4-deoxyprephenic acid dehydrogenase activity, so as to produce a secondary metabolite having a benzene ring skeleton substituted at the para-position with a functional group containing a nitrogen atom. Another objective of the present invention is to provide a novel gene involved in the biosynthetic pathway from chorismic acid to p-aminophenylpyruvic acid. A novel gene according to the present invention comprises genes encoding the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 2, 4 and 6 or modified sequences thereof.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Method for increasing salicylic acid content in plant, and its special carrier
ActiveCN1850978AIncreased salicylic acid contentPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
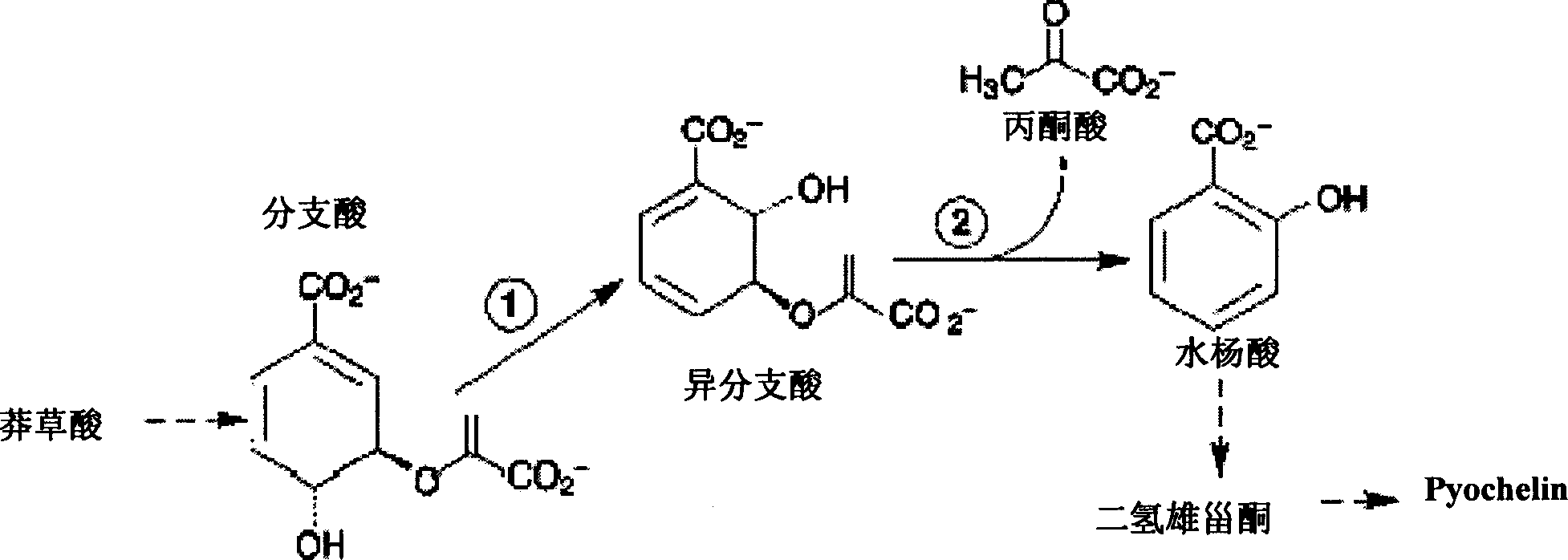
The invention discloses the method of improving the content of the salicin in the plant and the appropriative carrier. The carrier is the plant expressing carrier containing the separating offset acid composing enzyme gene and the separating offset acid-the pyruvic splitting dividing enzyme gene. The method uses the salicin composing approach and guides the different ICS gene and the IPL gene into the plant. The invention guides the said carrier into the plant group or the cell to gain the turning gene plant of the content of the salicin improved. The transferring gene test indicates that the dissociating state SA content in the transferring gene rice is mostly nine times than the wildness type. The method of the invention and the appropriative carrier can improve the content of the salicin in the plant greatly and provides the new method of amending the plant breed and improving the crop.
Owner:SINOBIOWAY BIO AGRI GRP CO LTD
Method for producing aniline derivative by fermentation from carbon source
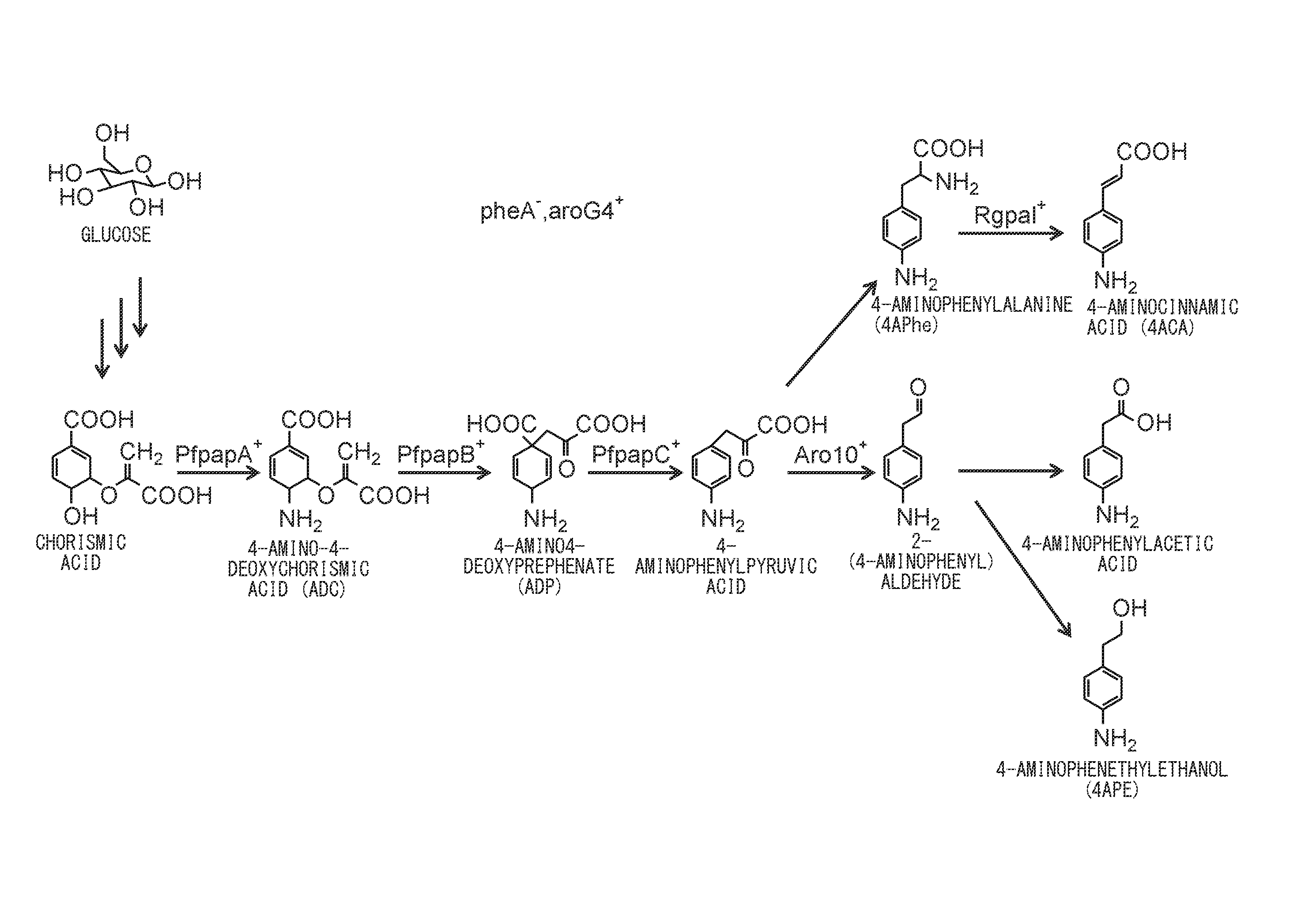
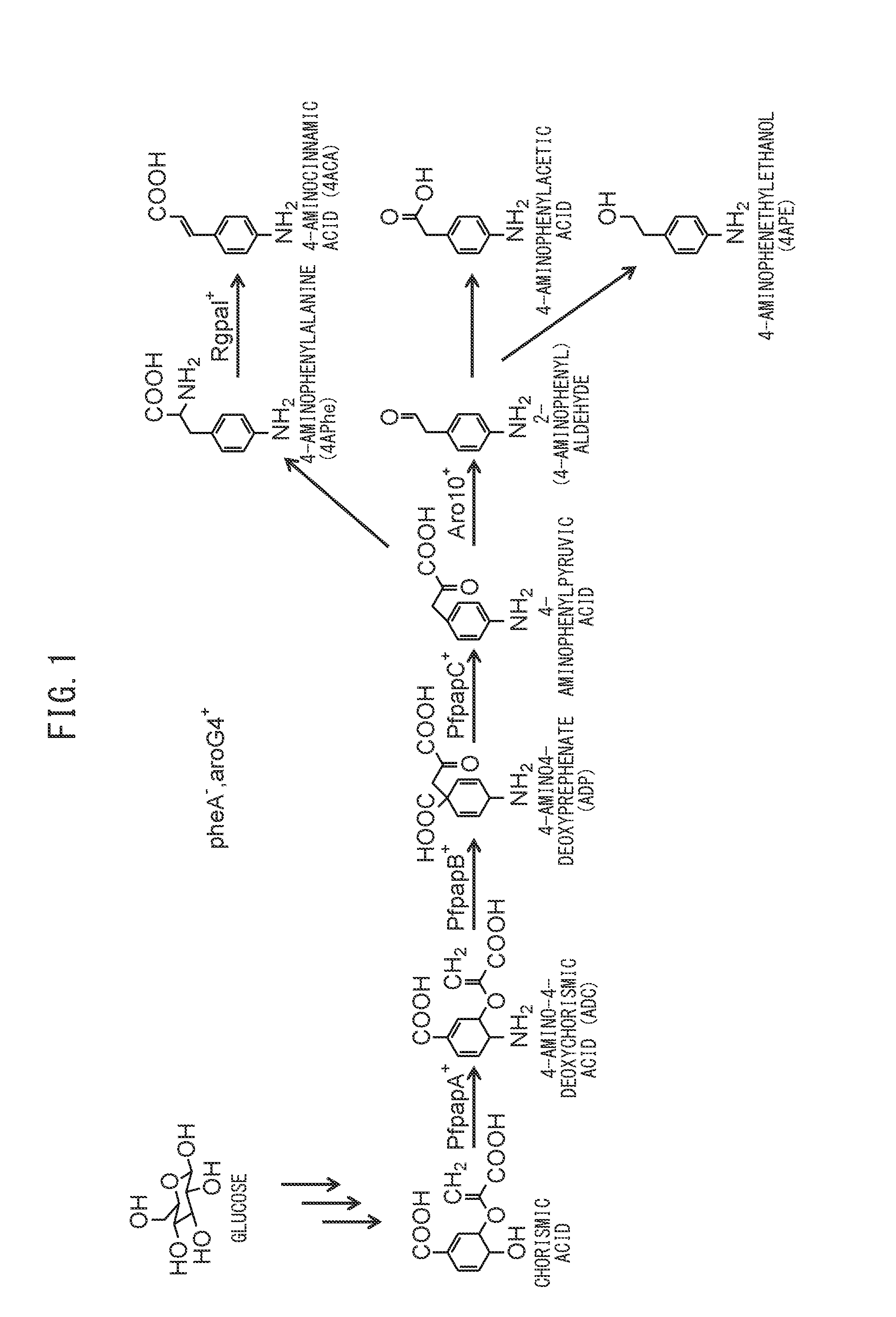
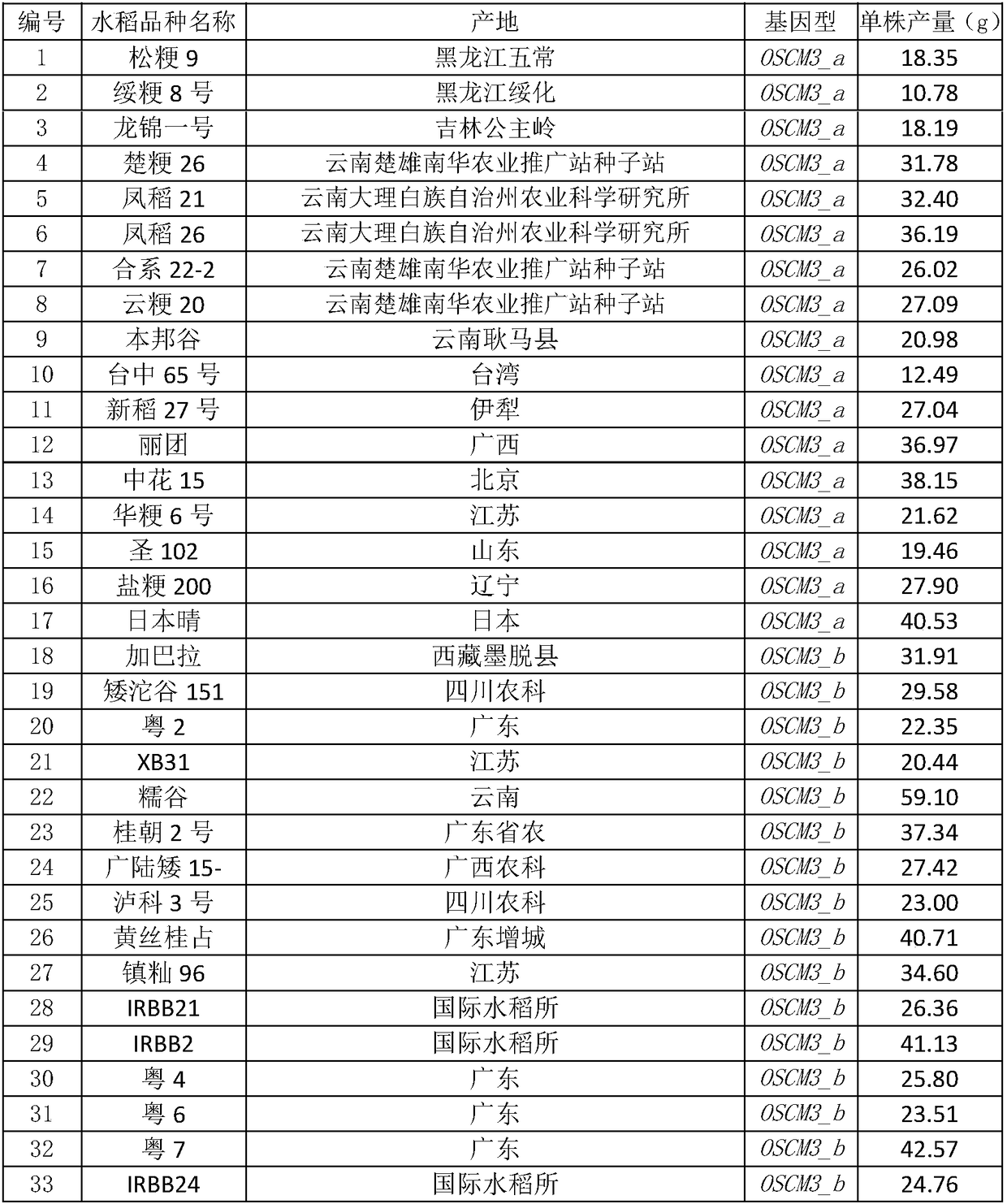
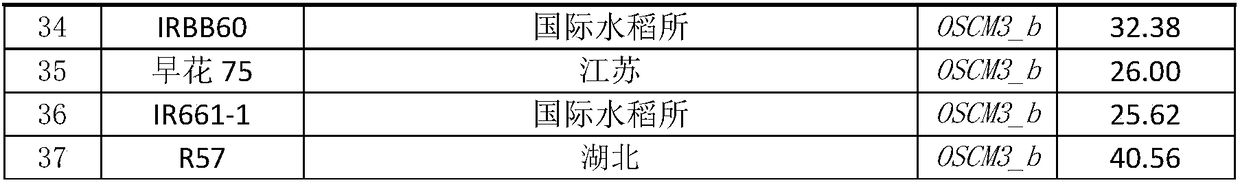
Provided is a method for producing an aniline derivative by fermentation from a carbon source such as glucose. The method comprises the following steps: production of microorganisms capable of producing 1.8 g / L or more of 4-aminophenylalanine (4APhe) under prescribed culture conditions by introducing at least three exogenous genes into microorganisms having the ability to biosynthesize 4-aminophenylpyruvic acid from chorismic acid; and production of at least one aniline derivative selected from the group consisting of 4-aminophenylalanine (4APhe), 4-aminocinnamic acid (4ACA), 2-(4-aminophenyl)aldehyde, 4-aminophenylacetic acid, and 4-aminophenethylethanol (4APE) by bringing these microorganisms into contact with a carbon source under conditions suited to the growth and / or maintenance of these microorganisms.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
A rapid sputum dissolution preservation solution
ActiveCN106967778BDissolve fastSimple preparation processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEthylene diamineSulfonate
The invention discloses rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid. The rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid comprises the following components in parts by weight: ethanol 10-20 parts, glycerine 10-20 parts, vegetable oil 1-2 parts, chorismic acid 0.1-1 part, disodium EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) 0.01-0.2 part, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate) 0.001-0.1 part, thiosugar 2-10 parts, and distilled water 50-80 parts. The rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid can rapidly dissolve sputum and prevent mycobacterium tuberculosis from cracking; and meanwhile, the storage time of the dissolving and storing liquid is long, the rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid can still be used after being continuously stored for 3-5 years, and the activity is not weakened obviously.
Owner:NANJING BANGBO BIOTECH CO LTD
Novel chorismate mutase gene from the potato cyst nematode globodera rostochiensis
The nucleotide sequence of a 992 bp region of cDNA and the nucleotide sequence of a 1973 bp (or a 1913 bp) of genomic DNA of the Gr-cm-1 gene were determined for G. rostochiensis. PCR primers and probes specific for G. rostochiensis and G. pallida were generated. PCR assays, including a real-time TaqMan PCR were used to identify G. rostochiensis and G. pallida and to differentiate G. rostochiensis from G. pallida. Transgenic hairy roots expressing Gr-cm-1 dsRNA were generated. There was a 52% reduction in the average number of females per root in the Gr-cm-1 dsRNA transgenic lines when compared with the infected control lines.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Chorismate mutase nucleotide sequence related to high yield of rice and application thereof
ActiveCN108179222AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAgricultural scienceGenotype
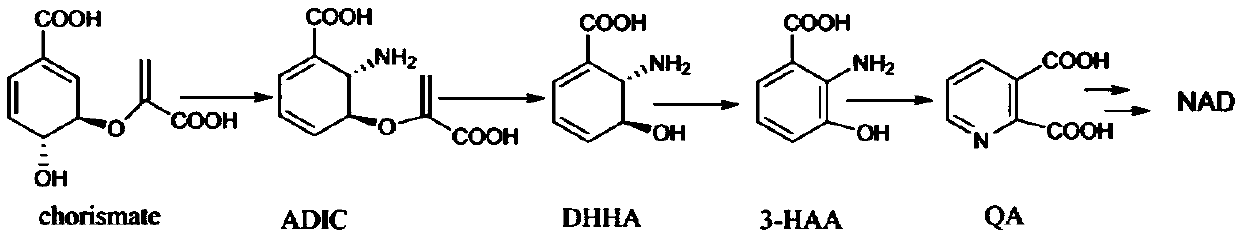
The invention discloses a chorismate mutase nucleotide sequence related to high yield of rice and application thereof. A method for screening rice with different yield traits provided by the inventioncomprises the following steps: (1) detecting the genotype based on a specific gene fragment, of the to-be-detected rice, wherein the specific gene fragment, OSCM3, is located in the rice genome, andhas two allelic forms: OSCM3_a and OSCM3_b; the OSCM3_a is shown by the sequence 1 of a sequence table; and the OSCM3_b is shown by the sequence 2 of the sequence table; and (2) judging in the following way: comparing tow genotypes in an adjoining growth condition, to determine that the average yield of the OSCM3_b homozygotic type rice population is higher than average yield of the OSCM3_a homozygotic type rice population. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention can effectively screen the rice with different traits in yield per plant, and has the advantages of easiness inoperation and high accuracy, thereby having an important application value in rice breeding.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthesis method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide compound
ActiveCN110607335ADecouplingIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBenzoic acidNucleotide
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide compound. A synthesis path provided by the invention takes chorismic acid as a starting point, under the action ofPhzD protein, a transamination rearrangement reaction is carried out to generate amino deoxy isobranched acid, pyruvic acid is removed from amino deoxy isobranched acid under the catalysis of the PhzEprotein to generate 2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxyanthranilicacid, 2,3-dihydro-3- hydroxyanthranilicacid is catalyzed to generate 3-hydroxyanthranilicacid by adopting a specific enzyme, quinolinic acid is generated from 3-hydroxyanthranilicacid through an oxidation ring-opening rearrangement reaction under the action of nabC protein, and then enters an NAD remediation way to finish NAD synthesis. According to the present invention, the coupling between the NAD synthesis and the tryptophan or aspartic acid synthesis is removed, and the chorismic acid widely exists in various life forms, and has less influence on other life essential metabolic pathways.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
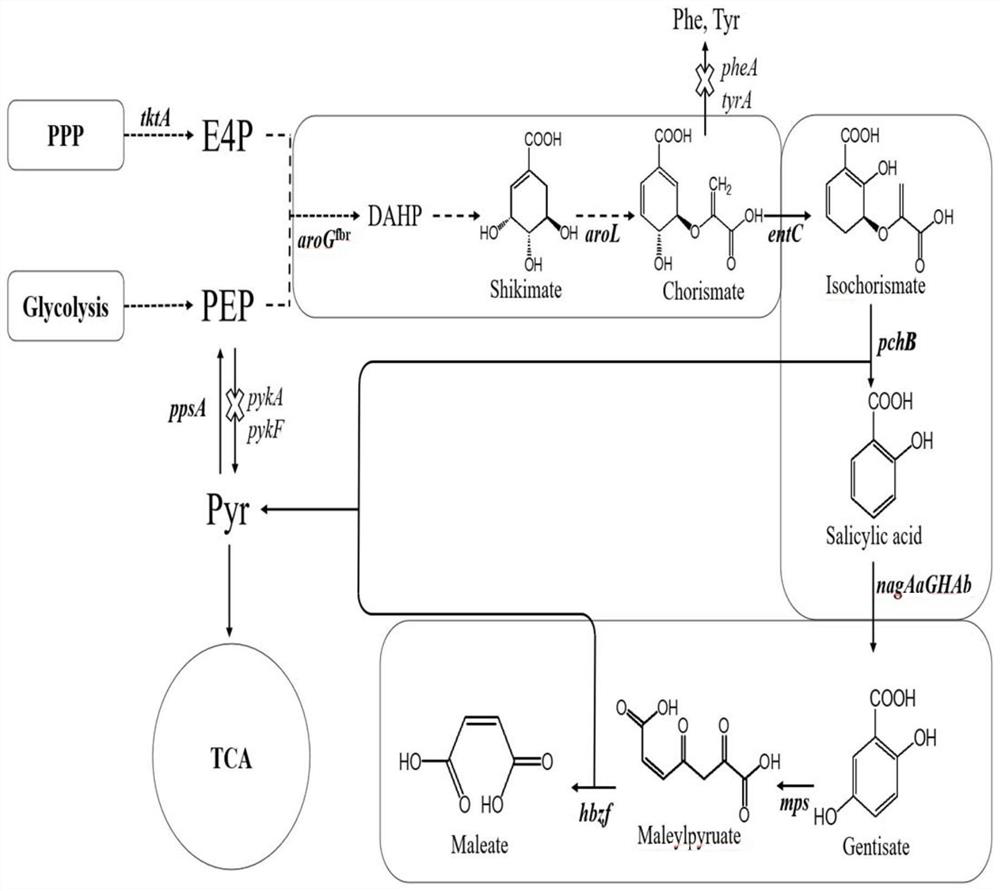
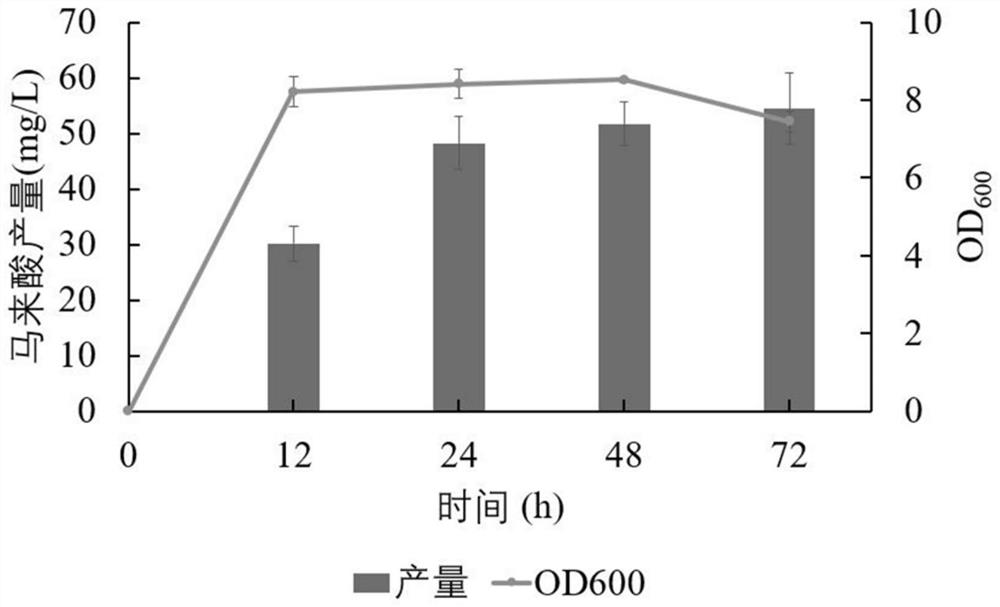
Engineering bacteria for producing maleic acid, and construction method and applications thereof
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing maleic acid, and a construction method and applications thereof, and relates to the technical field of bioengineering. The provided engineering bacteria include genes that can be co-expressed and code isochorismate synthase, isochorismate pyruvate lyase, salicylic acid-5-hydroxylase, maleylpyruvate isomerase and maleylpyruvate lyase in a host. The above engineering bacteria also include the genes that are over-expressed and code shikimate kinase, DAHP synthetase, PEP synthetase and transketolase A in the host so as to realize the increased production of maleic acid. A construction method and applications of the engineering bacteria for producing the maleic acid are also provided. Through the utilization of the engineering bacteriato produce the maleic acid by taking glucose and / or glycerol as carbon source, the de novo synthesis of the maleic acid can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Novel Regulatory Protein
The present invention relates to a polypeptide which belongs to the R3R3-type MYB family and which regulates the shikimate pathway towards the production of benzenoids. The shikimate pathway is a biosynthesis pathway through which the three essential aromatic amino acids tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan are synthesized in plants, bacteria and fungi. The present invention provides for the first time a regulatory protein in the shikimate pathway and a means to regulate the biosynthesis of these three essential amino acids which cannot be produced by mammals. At the same time, it opens up the way for the regulation of the biosynthesis of aromatic and non-aromatic compounds which are derived from these essential amino acids. A polypeptide or polynucleotide of the invention may be used in a method for manipulating the transcript levels of the genes of the shikimate pathway towards benzenoids for instance the genes of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (DAHPS), 5-enol-pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and chorismate mutase (CM).
Owner:KEYGENE NV
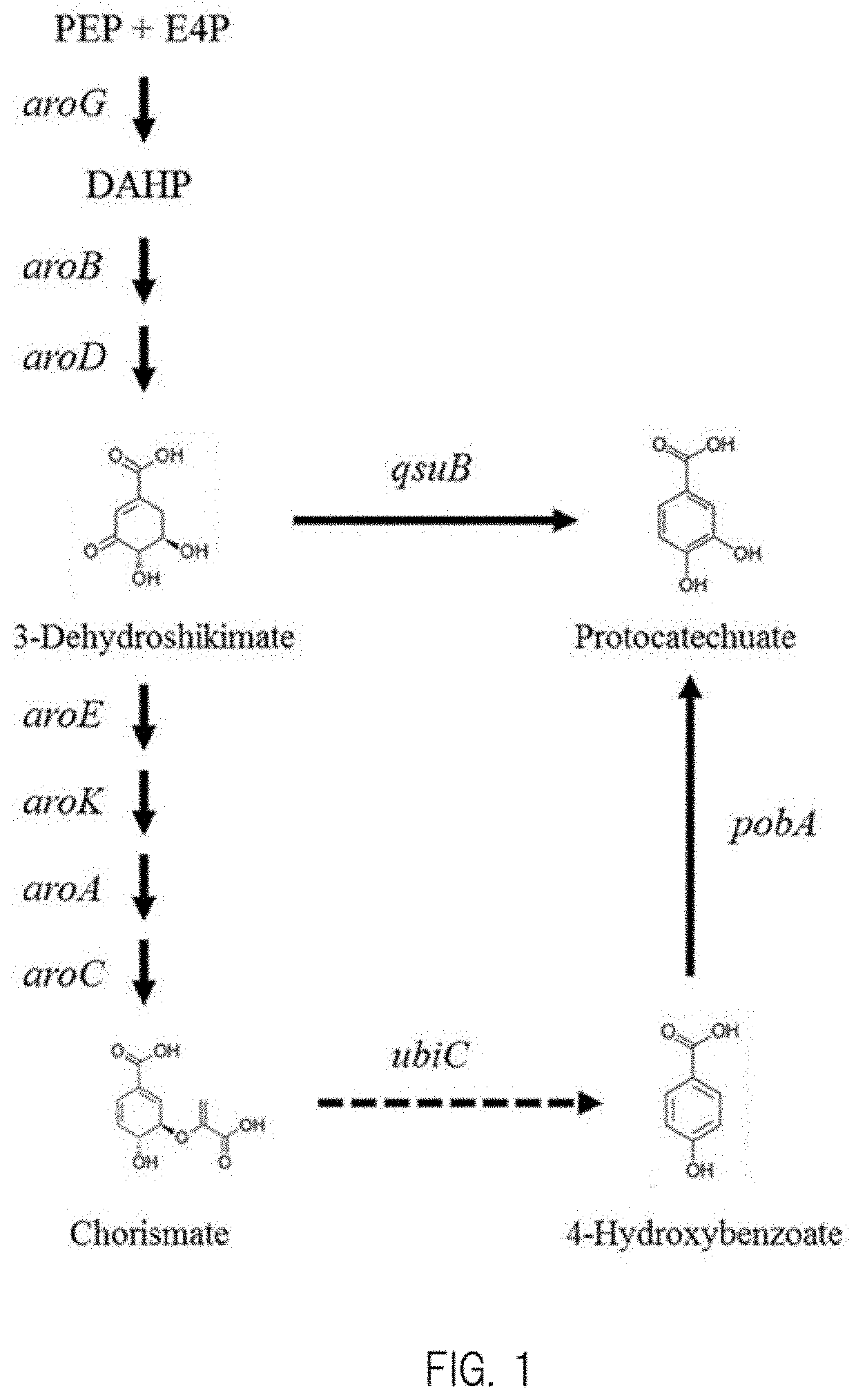
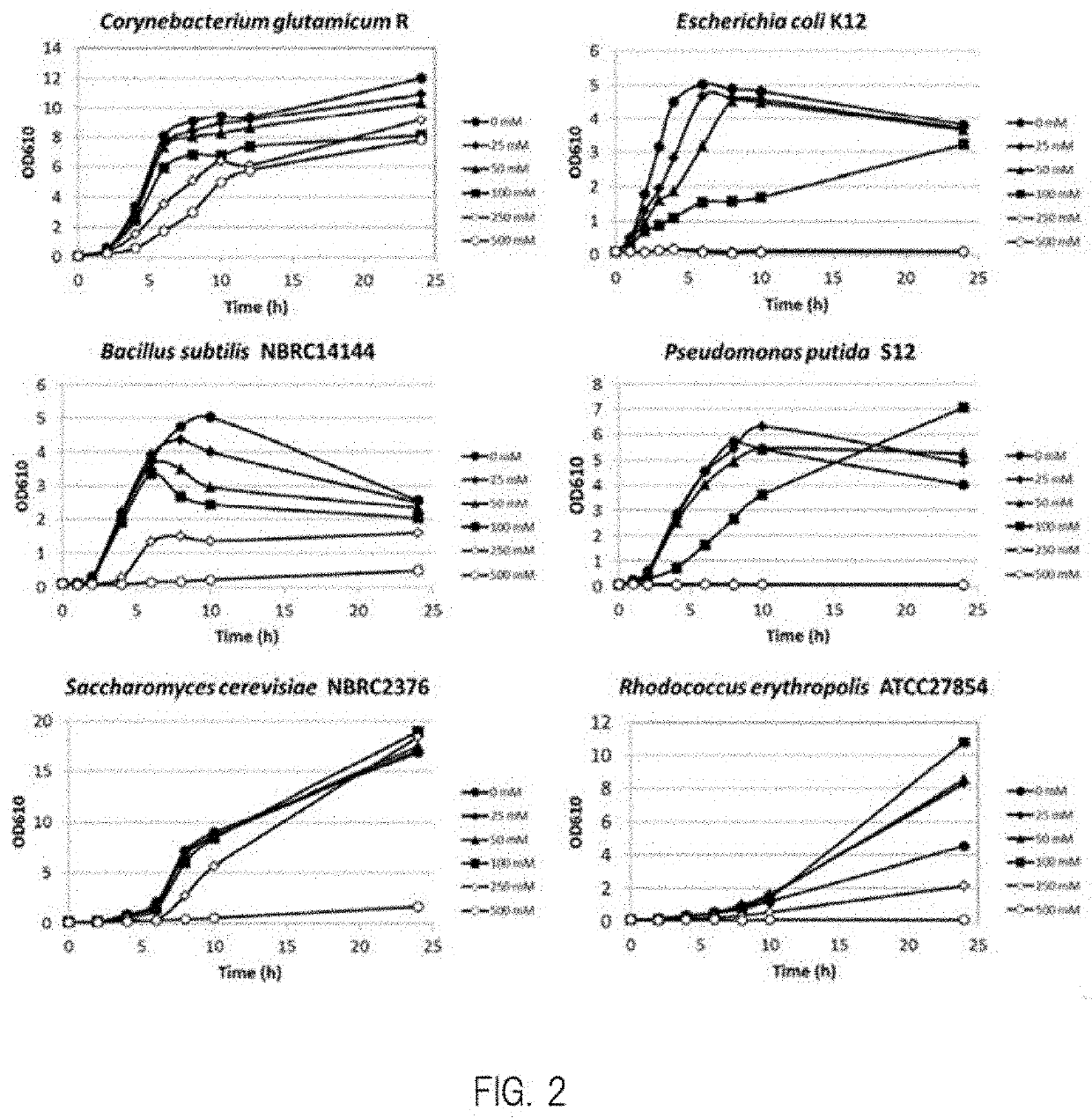
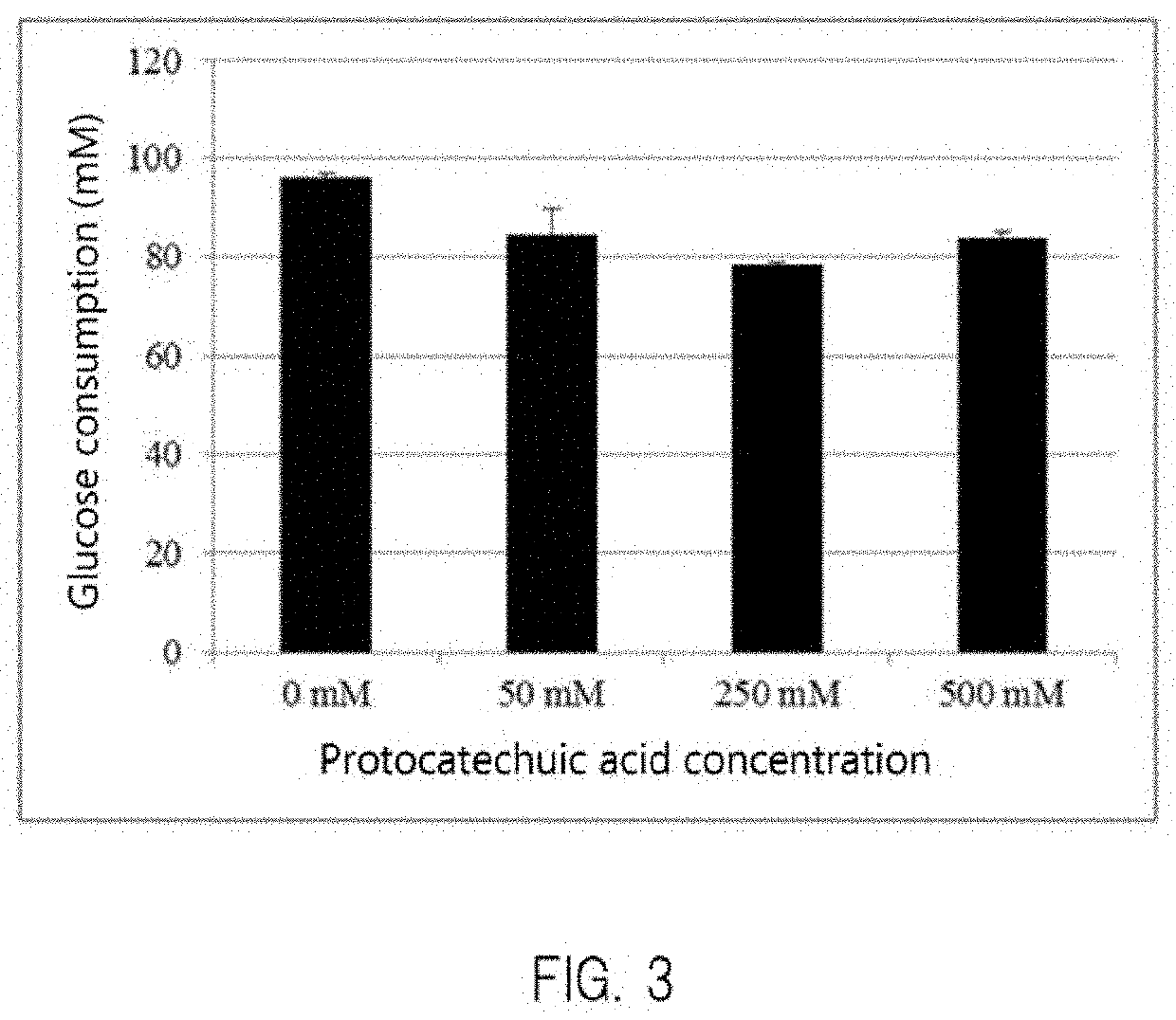
Transformant, and method for producing protocatechuic acid or salt thereof using same
Provided is a microorganism that is able to efficiently produce protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof by using a saccharide as a raw material, and a method of efficiently producing protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof by using the microorganism. Provided is a transformant having protocatechuic acid producing ability, subjected to modifications of enhancement of 3-dehydroshikimate dehydratase activity; enhancement of chorismate pyruvate lyase activity; and enhancement of 4-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase activity. Also provided is a method of producing protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof, including the step of culturing the transformant in a reaction solution containing a saccharide so as to cause the transformant to produce protocatechuic acid or a salt thereof.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
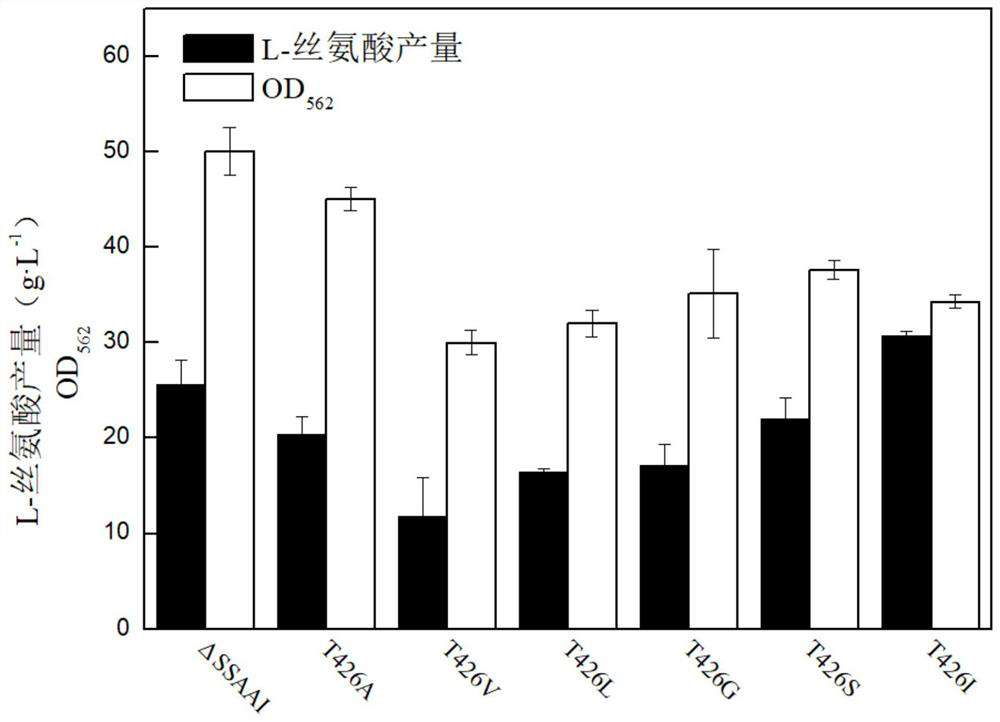
Enzymatic activity-changed amino deoxychorismate synthetase mutant T426I and application thereof
ActiveCN112094829AAltered synthetase activityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesGeneticsEngineered genetic
The invention discloses an enzymatic activity-changed amino deoxychorismate synthetase mutant T426I and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. According to the enzymatic activity-changed amino deoxychorismate synthetase mutant T426I, a T426 locus of amino deoxychorismate synthetase in parent Corynebacterium glutamicum delta SSAAI (the preservation name of a strain is delta SSAAI, and the preservation number is CGMCC No 15170) is mutated into isoleucine, and the enzymatic activity of the obtained mutant is reduced by 15.2%. A genetically engineered bacterium constructed by the mutant is fermented, and the yield of L-serine is increased by 18.75%. The enzymatic activity-changed amino deoxychorismate synthetase mutant T426I effectively changes the activity of the amino deoxychorismate synthetase through point mutation, creates conditions for constructing the genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently producing the serine, and has good industrial application value and prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Coryneform bacterium transformant having highly active mutant enzyme highly expressed therein, and process for producing 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or salt thereof using the same
ActiveUS20170073658A1Sufficient practical efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionChorismate pyruvate lyaseAmino acid replacement
The mutant chorismate-pyruvate lyase (A) or (B) as described below is capable of producing 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or a salt thereof with sufficient practical efficiency.(A) A mutant chorismate-pyruvate lyase obtained by replacing the valine at position 80 in a chorismate-pyruvate lyase (ubiC) from Pantoea ananatis consisting of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 with one or more other amino acids.(B) A mutant chorismate-pyruvate lyase obtained by replacing an amino acid in another chorismate-pyruvate lyase, the amino acid being at a position enzymologically homologous with that of the above valine, with one or more other amino acids.
Owner:GREEN CHEM
Engineering bacterium for synthesizing salicin as well as construction method and application of engineering bacterium
The invention provides an engineering bacterium suitable for salicin, which comprises a host and a recombinant plasmid vector, and the recombinant plasmid vector is connected with a gene for expressing and coding glucosyltransferase. The recombinant plasmid vector is also connected with a gene for coding carboxylic acid reductase and phosphoryl transferase, which is co-expressed with the gene for coding glucosyltransferase. The recombinant plasmid vector is also connected with genes for over-expressing and coding shikimic acid kinase, pyruvate kinase, transketolase, 3-deoxy-7-phosphoenanthate synthase, iso-chorismate pyruvate lyase and isochorismate synthase; and the host is also knocked out of genes for coding pykA and pykF, so that the yield of salicin is increased. The invention also provides a construction method and an application of the engineering bacterium for synthesizing salicin. By utilizing the engineering bacteria for synthesizing the salicin, the salicin is produced by using glucose and / or glycerol and other carbon sources, so that efficient biosynthesis of the salicin is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or salt thereof using the same
ActiveUS20170114374A1Efficient productionSufficient efficiencyBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesChorismate pyruvate lyase
A transformant constructed by introducing a gene which encodes an enzyme having chorismate-pyruvate lyase activity into a coryneform bacterium as a host is capable of efficiently producing 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or a salt thereof from a sugar. When the transformant is cultured under aerobic conditions where the transformant does not grow, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or a salt thereof can be produced in a particularly efficient manner.
Owner:GREEN CHEM
Rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid
ActiveCN106967778ADissolve fastSimple preparation processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSulfonateEthylene diamine
The invention discloses rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid. The rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid comprises the following components in parts by weight: ethanol 10-20 parts, glycerine 10-20 parts, vegetable oil 1-2 parts, chorismic acid 0.1-1 part, disodium EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) 0.01-0.2 part, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate) 0.001-0.1 part, thiosugar 2-10 parts, and distilled water 50-80 parts. The rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid can rapidly dissolve sputum and prevent mycobacterium tuberculosis from cracking; and meanwhile, the storage time of the dissolving and storing liquid is long, the rapid sputum dissolving and storing liquid can still be used after being continuously stored for 3-5 years, and the activity is not weakened obviously.
Owner:NANJING BANGBO BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for increasing yield of vitamin K2 by utilizing recombinant bacillus natto
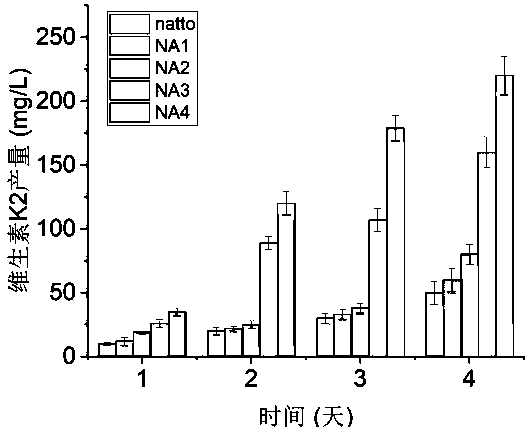
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of vitamin K2 by utilizing recombinant bacillus natto. The method comprises the following steps: overexpressing a flutalosin synthetase gene mqnA on a bacillus natto chromosome through a constitutive promoter P43; on the basis of the obtained strain NA1, the strain NA1 is obtained; the method comprises the following steps: overexpressing agene of deoxyxanthine flutalosin synthetase on a bacillus natto chromosome by using a P43 promoter; on the basis of the obtained bacterial strain NA2; a Phbs promoter is used for replacing a natural promoter of an O-succinylbenzoic acid-CoA ligase gene in bacillus natto; on the basis of the obtained strain NA3, isobranching acid genes on bacillus natto chromosomes are replaced with 1, 4-dihydroxy-6-naphthoic acid synthase genes which contain Phbs promoters and are derived from streptomyces coelicolor, and a seed solution of the recombinant bacteria is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium according to the inoculation amount of 3%-6%. According to the invention, four recombinant bacteria NA1-NA4 are constructed, wherein the NA3-NA4 significantly improves the yield of vitamin K2.
Owner:西宝生物科技(上海)股份有限公司
Novel regulation protein
The present invention relates to a polypeptide which belongs to the R2R3-type MYB family and which regulates the shikimate pathway towards the production of benzenoids. The shikimate pathway is a biosynthesis pathway through which the three essential aromatic amino acids tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophane are synthesized in plants, bacteria and fungi. The present inventiont provides for the first time a regulatory protein in the shikimate pathway and a means to regulate the biosynthesis of these three essential amino acids which cannot be produced by mammals. At the same time, it opens up the way for the regulation of the biosynthesis of aromatic and-non- aromatic compounds which are derived from these essential amino acids. A polypeptide or polynucleotide of the invention may be used in a method for manipulating the transcript levels of the genes of the shikimate pathway towards benzenoids for instance the genes of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (DAHPS), 5-enol-pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), L- phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and chorismate mutase (CM). Through these enzymes, biosynthetic processes at lower levels may be influenced. For instance, compounds of the invention may be used in a method to regulate scent in flowers or to regulate resistance to pest insects or pathogenic organisms.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Engineering bacterium for microbial synthesis of piceatannol by taking glucose as substrate as well as construction and application of engineering bacterium
PendingCN114395497AIncrease contentIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiBiotechnologyTyrosine
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for microbial synthesis of piceatannol by taking glucose as a substrate as well as construction and application of the engineering bacterium. According to the invention, L-tyrosine ammonolysis enzyme, p-coumaroyl-coenzyme A ligase, resveratrol synthetase, DAHP synthetase, chorismate mutase and hydroxylase complex genes are over-expressed in the engineering strain, so that the de novo synthesis strategy of piceatannol is realized, and the content of the product piceatannol is remarkably increased; and a simple and effective implementation method is provided for safe biotransformation. The yield of the engineering bacterium for synthesizing piceatannol by using the glucose as the substrate microorganism disclosed by the invention can reach 7-8g / L.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
Genetically engineered strains for safe and efficient production of shenzamycin and its application
ActiveCN104946552BImprove securityLow toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChorismate pyruvate lyaseBiosynthetic genes
The invention discloses a genetically engineered strain for safe and efficient production of shenzamycin and its application; Shenzimycin metabolism gene knockout, chorismate metabolism gene knockout, point mutation method to reduce the biological activity of PheA, isozyme replacement method to reduce the biological activity of chorismate pyruvate lyase, increase the copy number of phzC gene in the genome, aroG promoter Replaced with a strong promoter Ptac to enhance the expression level of the DAHP synthase gene, the promoter replacement method to enhance the expression level of the sphenazimycin biosynthetic gene cluster and the expression level of the shenazinamycin efflux pump MexGHI-OpmD, to obtain; the bacterial strain can be safely , economical, super-high yield of Shenzimycin.
Owner:周莲
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292BIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of Edwardsiella tarda wild strain as well as relevant preparations and application thereof
ActiveCN101974472BGood control effectImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEnzyme GeneTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to a marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of a Edwardsiella tarda wild strain. The marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain is an attenuated live vaccine of an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, which deletes the chorismic acid synthase gene aroC of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, three types of secretion system response element genes of eseB, escA, eseC and eseD and an endogenous plasmid, preferably, the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is a Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain EIB202 with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M208068; the endogenous plasmid is a plasmid of pEIB202; and the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an attenuated strain WED with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M2010278. The invention also provides relevant preparations and application of the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain. The attenuated mutant strain or relevant preparations eliminate the potential environment and safety risk of products existing in the traditional attenuated live vaccines generally and is a safe, effective and economic vaccine aiming at Edwardsiella tarda diseases of cultured fishes.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of carboxamide phenazine biological fungicide
ActiveCN109251947BPromote growthPromote generationBiocideMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNutrient solution
The invention provides a preparation method of a formamide phenazine bio-fungicide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, implementing shake-flask culture on activated pseudomonas chlororaphis and pseudomonas aeruginosa, so as to obtain a seed solution A and a seed solution B; inoculating a fermentation medium with the seed solution A, conducting fermentation culture for 20h, inoculating the fermentation medium with the seed solution B, simultaneously refilling a nutrient solution, and continuing to implement fermentation culture for 40-50h, so that fermentation brothis obtained; centrifuging the fermentation broth at high speed, regulating pH value, and conducting extracting and concentrating, so as to a crude product; and implementing column chromatography and separating, so that the formamide phenazine bio-fungicide is obtained. The culture medium and culture conditions provided by the invention are quite suitable for growth of strains; the refilled nutrient solution contains chorismic acid; two strains undergo mixed fermentation; the content of formamide phenazine in the fermentation broth is obviously improved; based upon a series of post-treatment, afinished product that purity is higher than 99% is separated and obtained; and the finished product takes a strong inhibitory effect on pathogenic fungi of plants.
Owner:JIANGXI POROR CROPS ENG
Engineering bacterium for producing alpha-arbutin, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112646762AEase of industrial productionEasy to solveBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides an engineering bacterium for producing alpha-arbutin. The engineering bacterium comprises genes for co-expressing and encoding alpha-arbutin synthetase, PchB, SalABCD, and GD in a host, wherein the alpha-arbutin synthetase is one of or any combination of HGE, XgtA, and DGAS. The engineering bacterium further comprises genes for co-expressing AroL, ppsA, tktA, aroG<fbr>, and EntC from escherichia coli, so that the yield of the alpha-arbutin is increased. The invention also provides a construction method and application of the engineering bacterium for producing the alpha-arbutin. By utilizing the engineering bacterium for producing the alpha-arbutin, the alpha-arbutin is produced by using carbon sources such as maltose and / or glycerol, so that the denovo synthesis of the alpha-arbutin is realized.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Nucleotide sequence of chorismate mutase related to rice high yield and its application
ActiveCN108179222BEasy to operateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a chorismate mutase nucleotide sequence related to high yield of rice and application thereof. A method for screening rice with different yield traits provided by the inventioncomprises the following steps: (1) detecting the genotype based on a specific gene fragment, of the to-be-detected rice, wherein the specific gene fragment, OSCM3, is located in the rice genome, andhas two allelic forms: OSCM3_a and OSCM3_b; the OSCM3_a is shown by the sequence 1 of a sequence table; and the OSCM3_b is shown by the sequence 2 of the sequence table; and (2) judging in the following way: comparing tow genotypes in an adjoining growth condition, to determine that the average yield of the OSCM3_b homozygotic type rice population is higher than average yield of the OSCM3_a homozygotic type rice population. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention can effectively screen the rice with different traits in yield per plant, and has the advantages of easiness inoperation and high accuracy, thereby having an important application value in rice breeding.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com