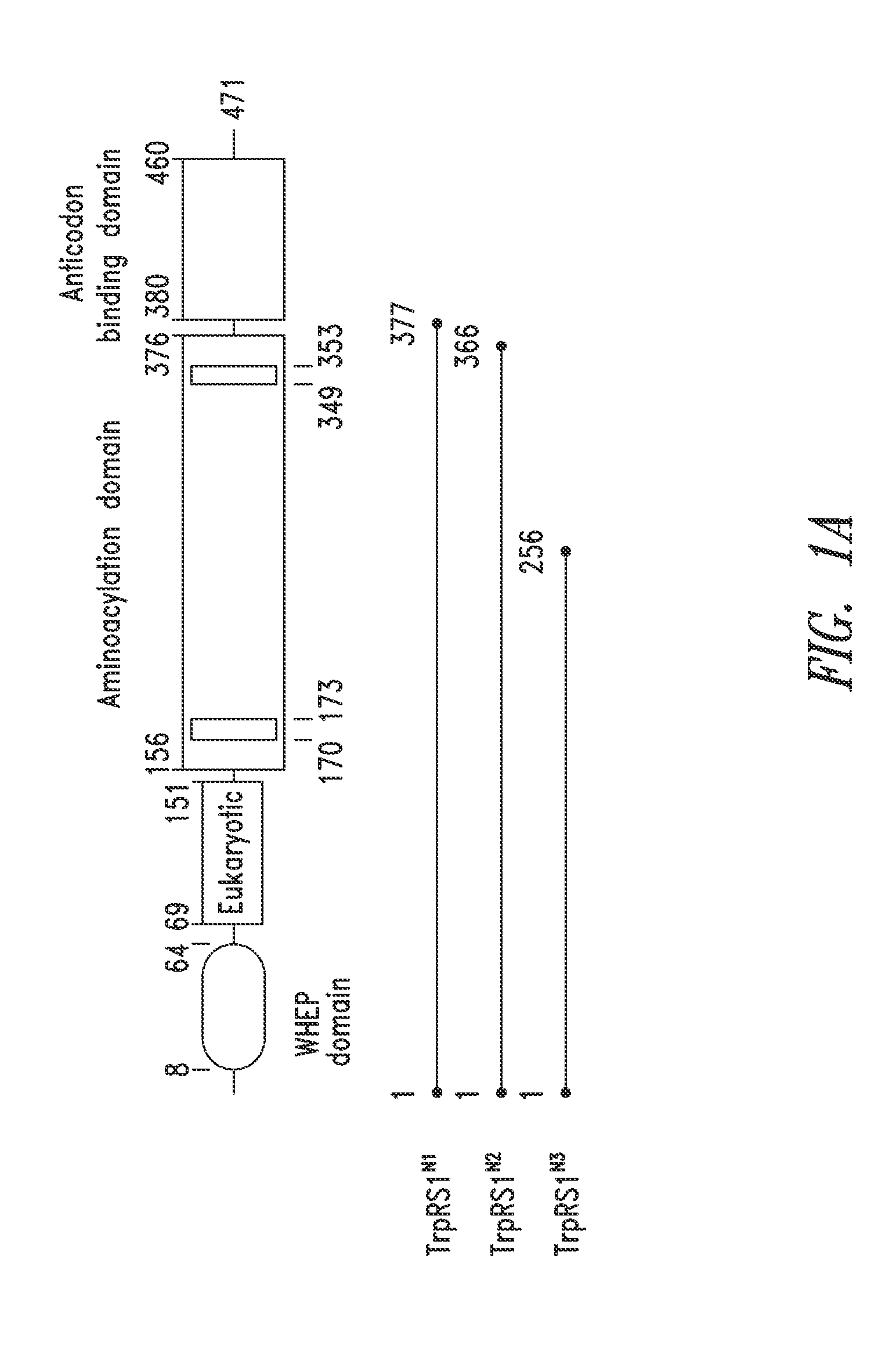
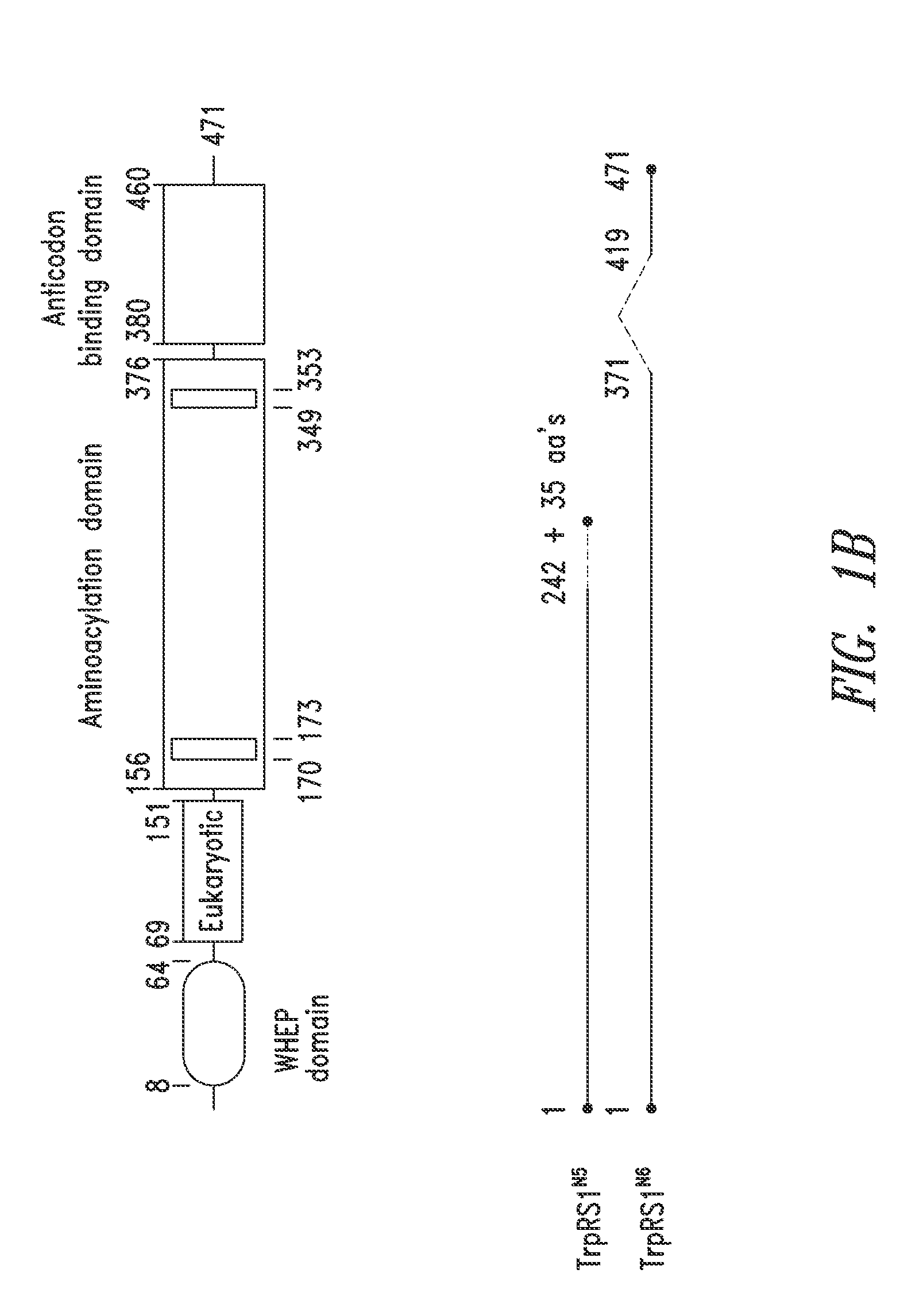
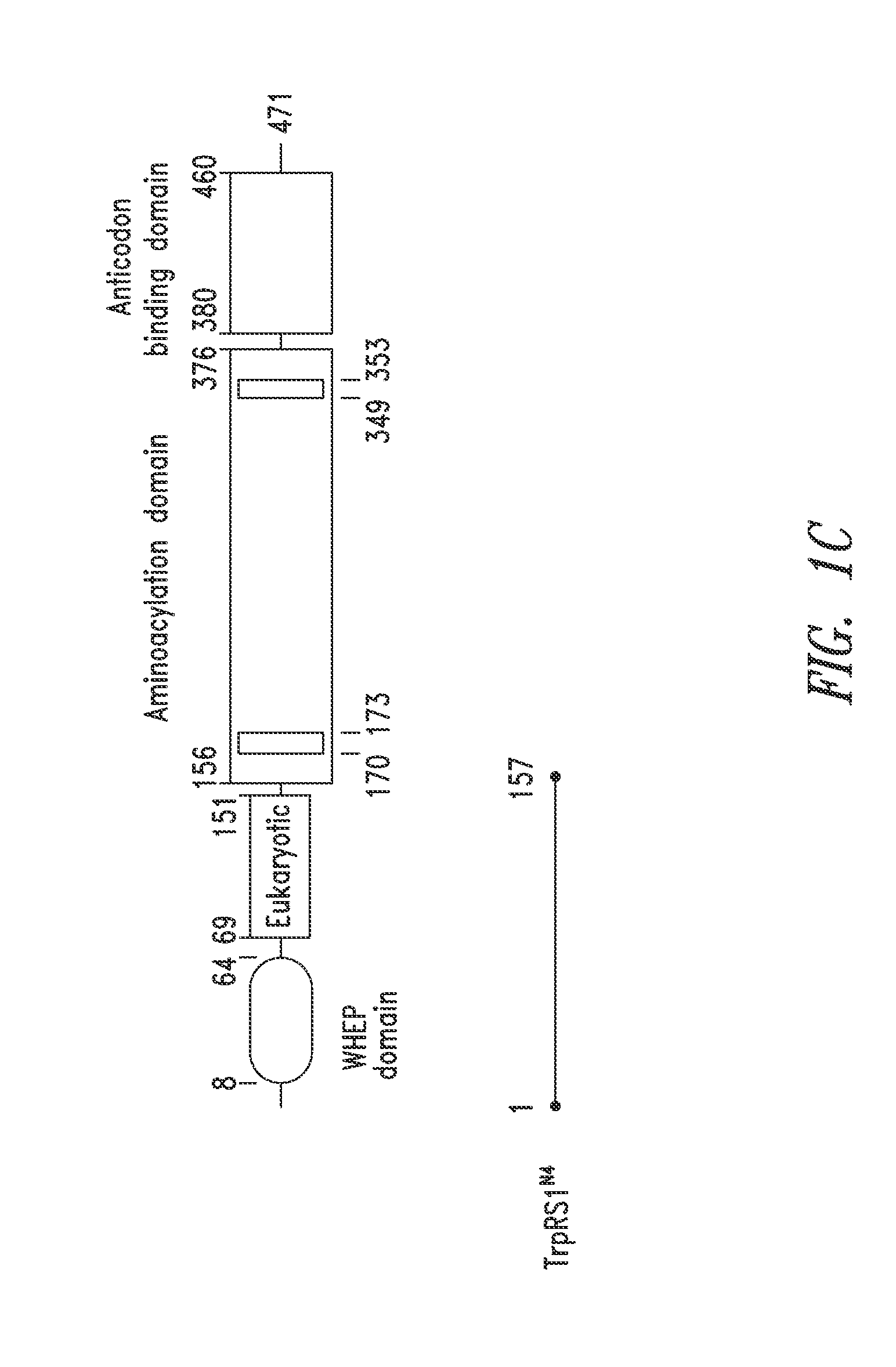
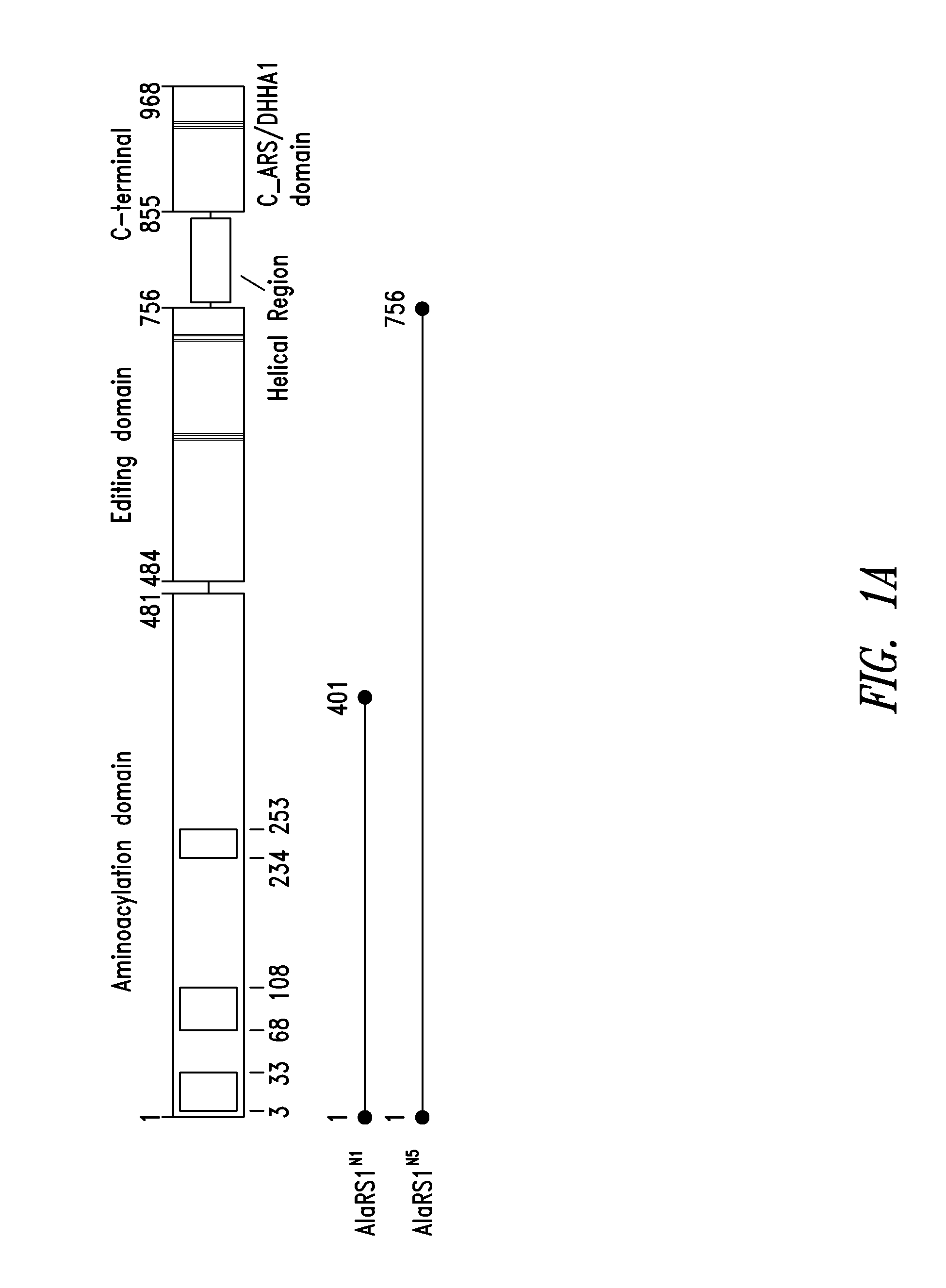
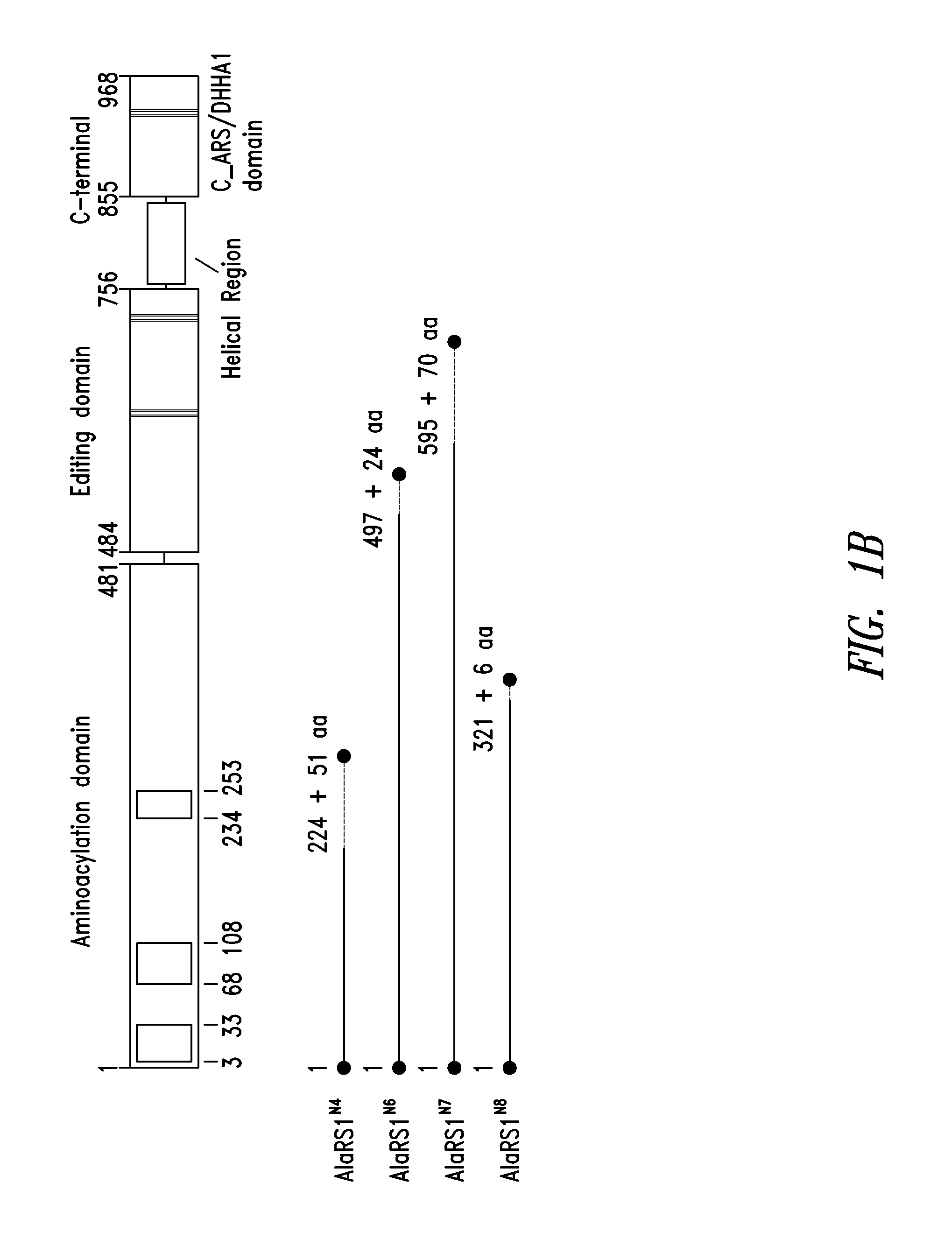
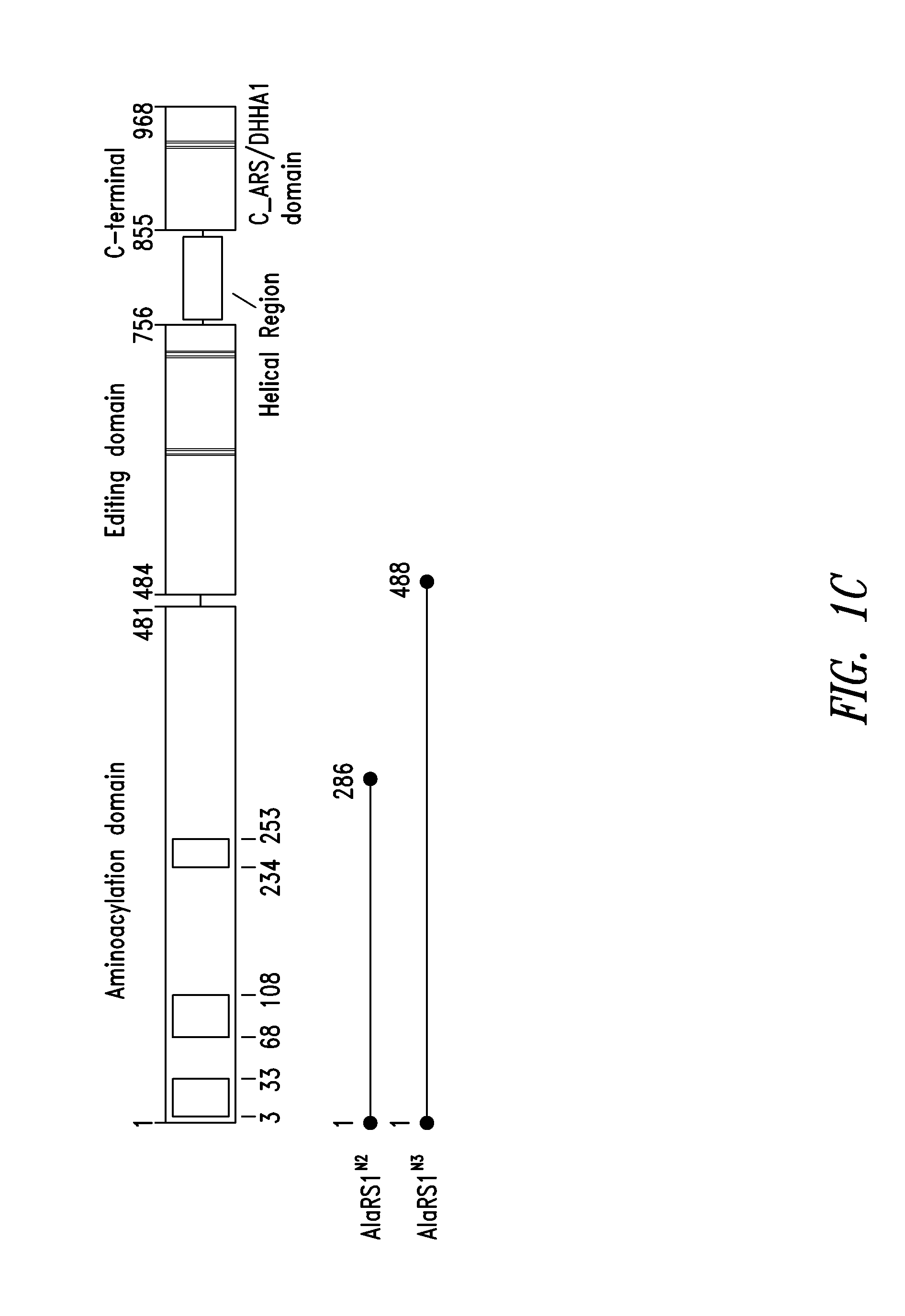
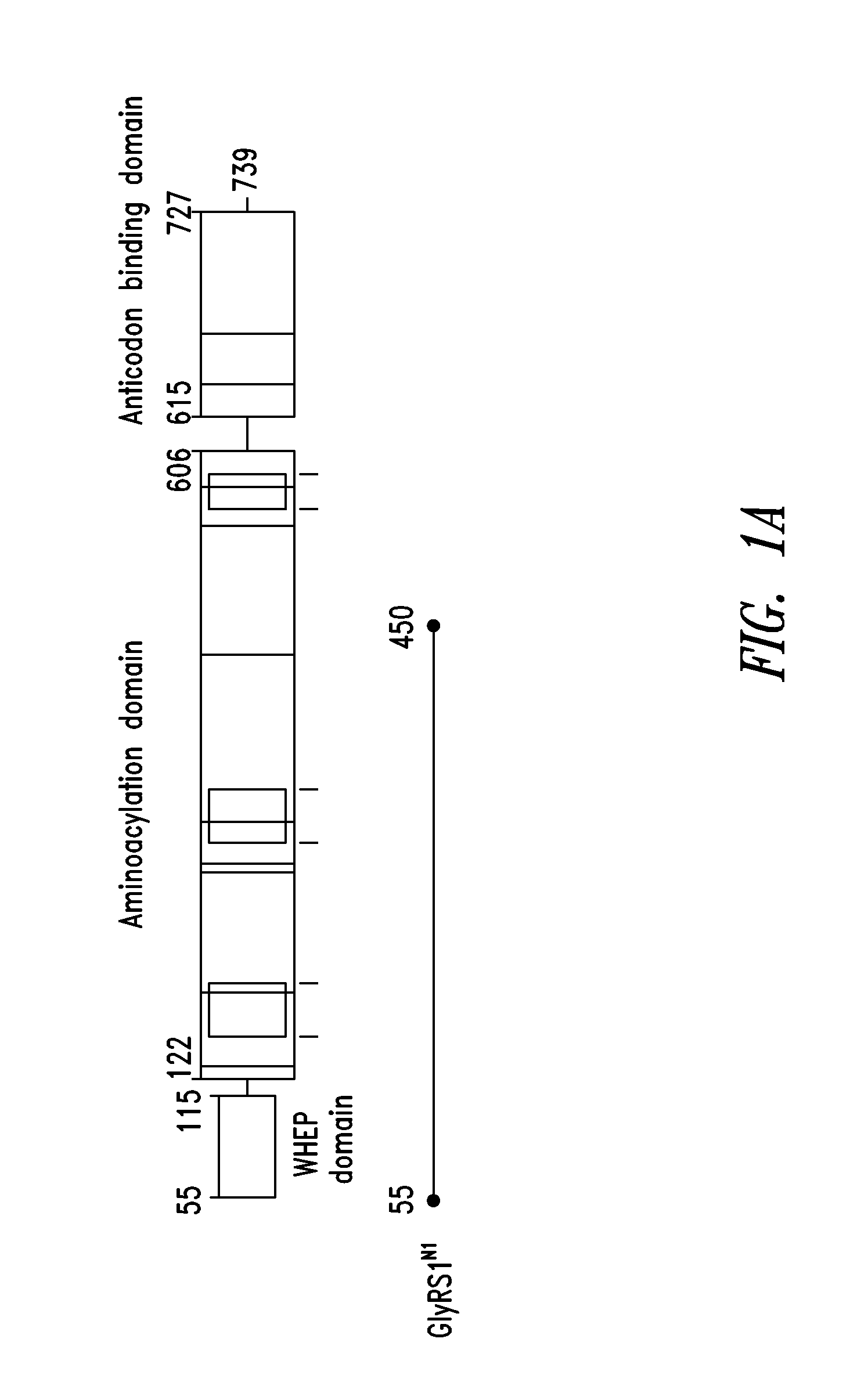
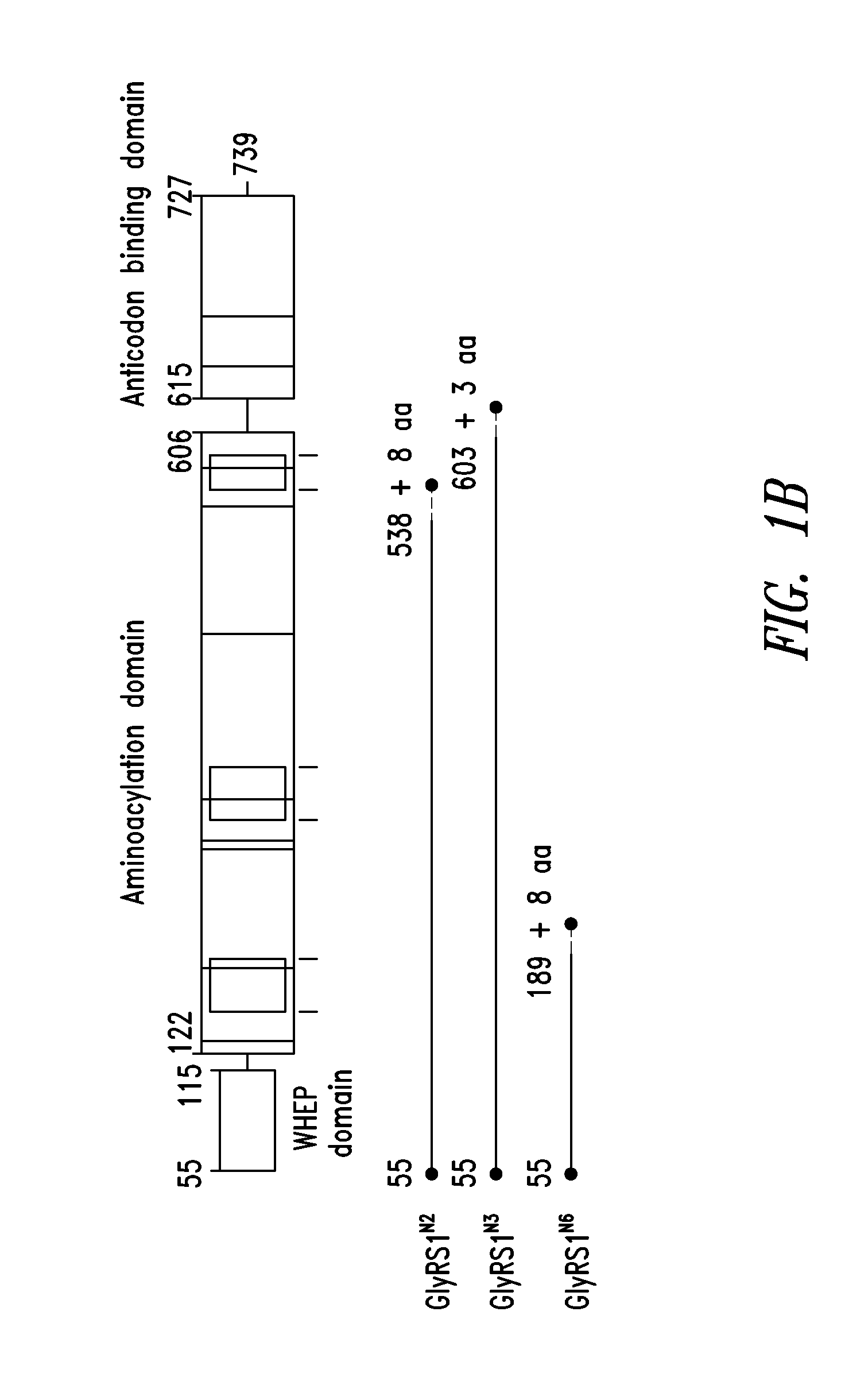
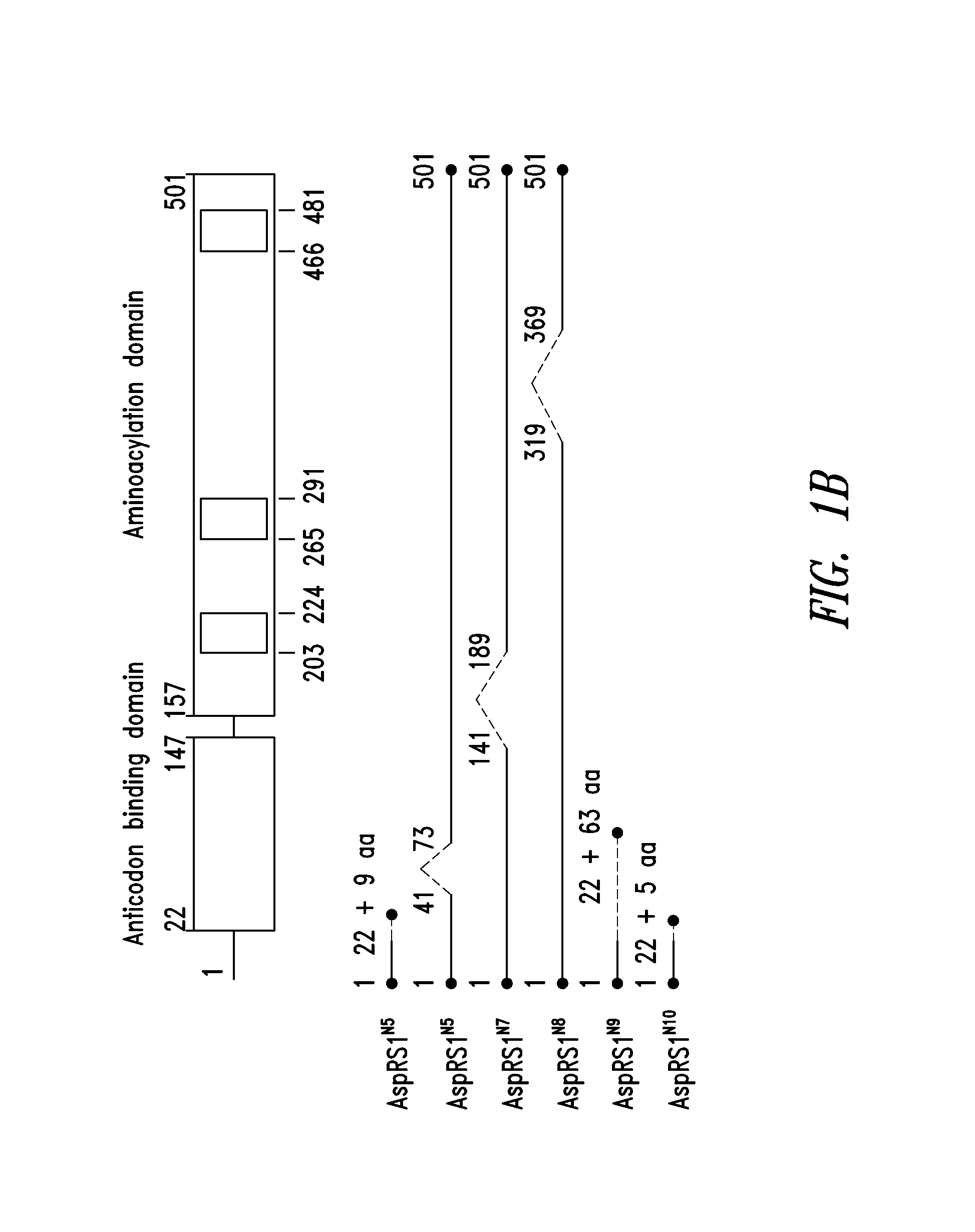
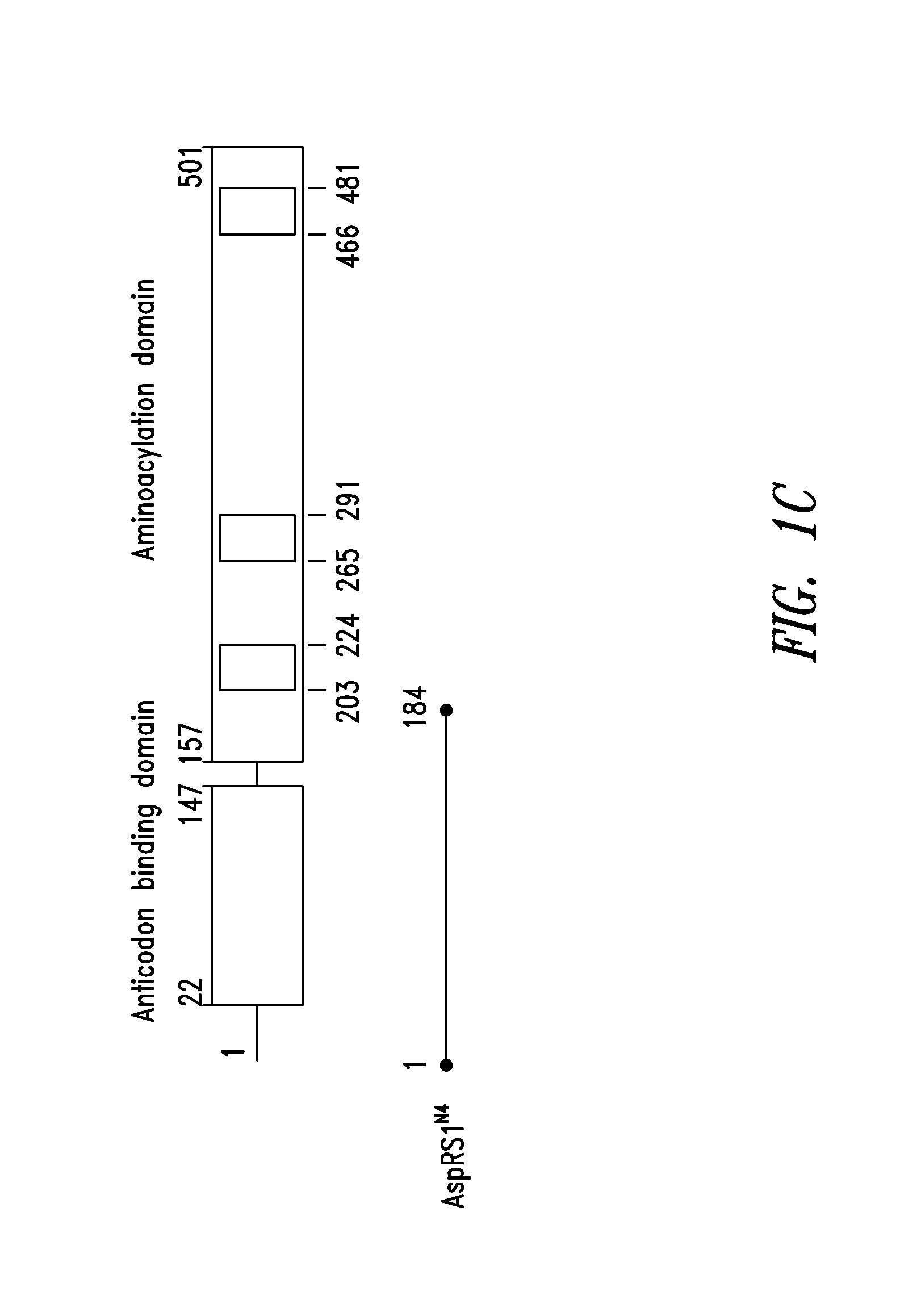
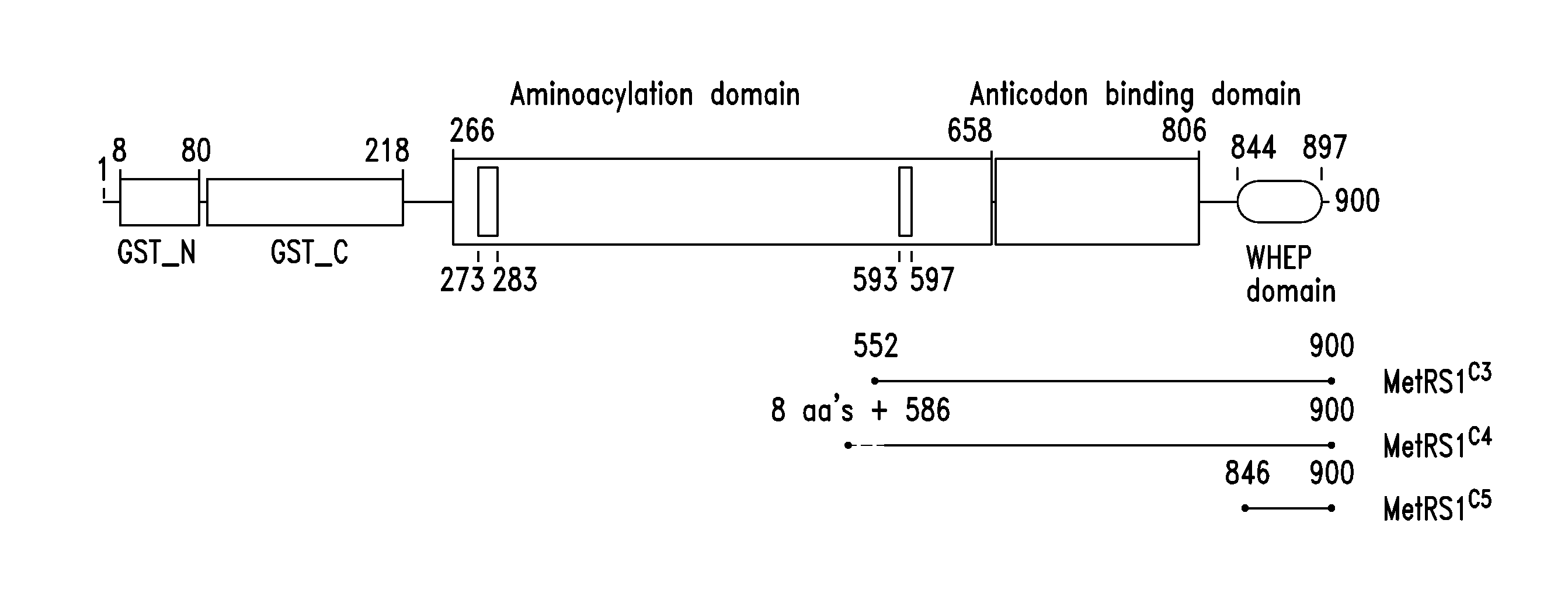
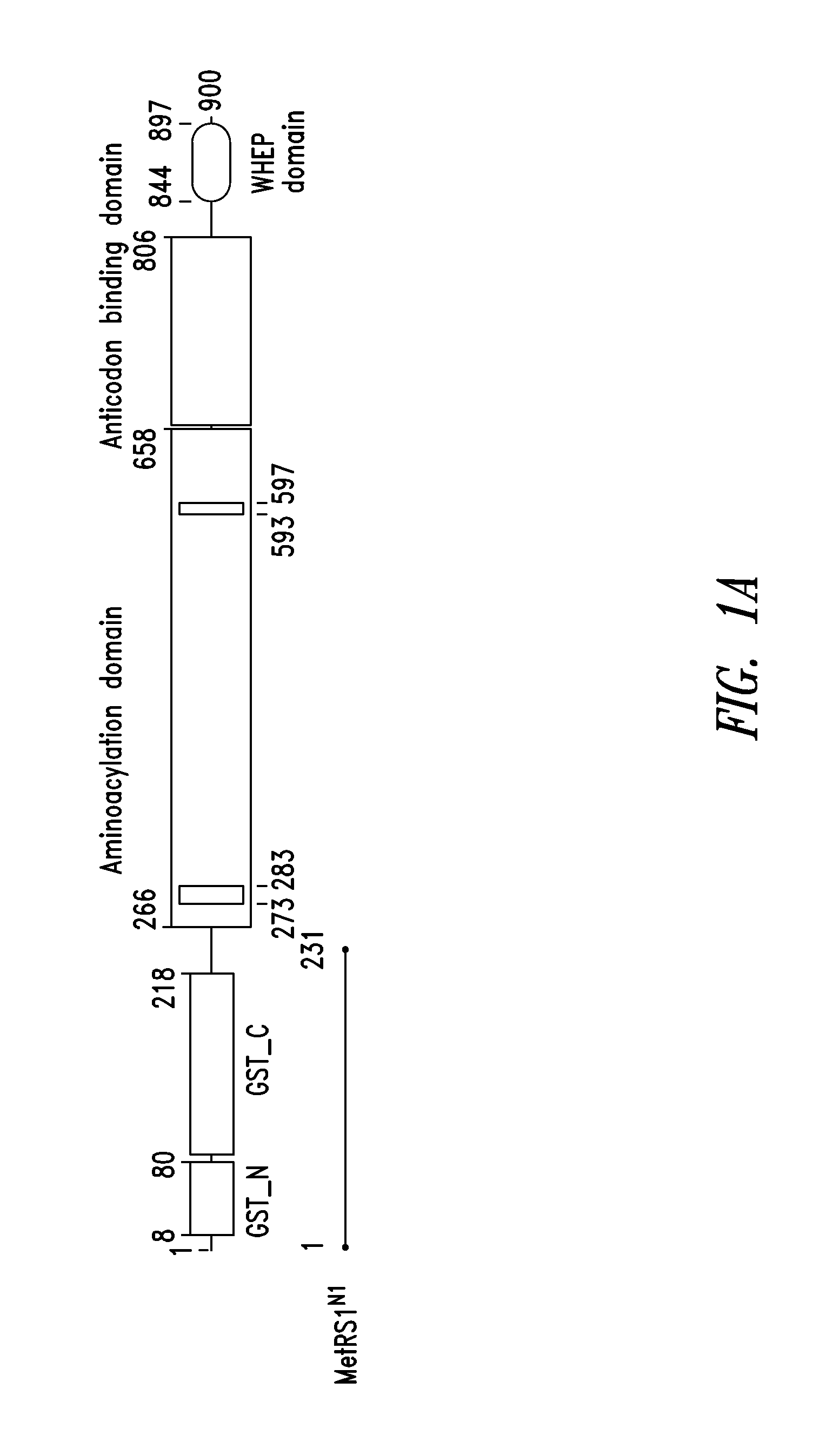
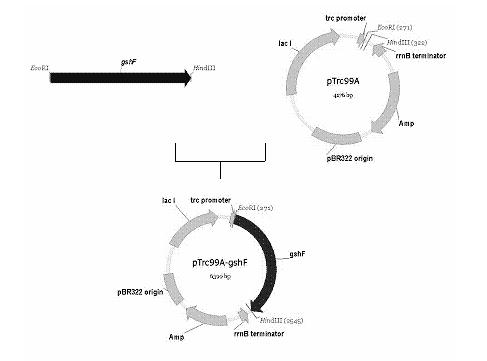
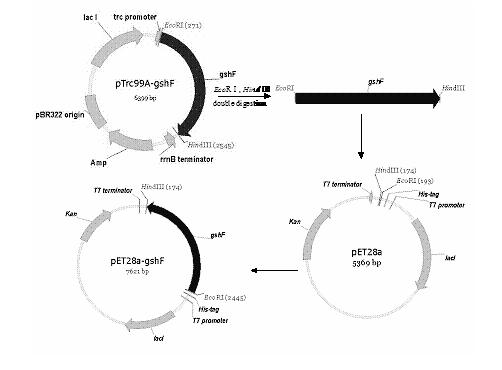
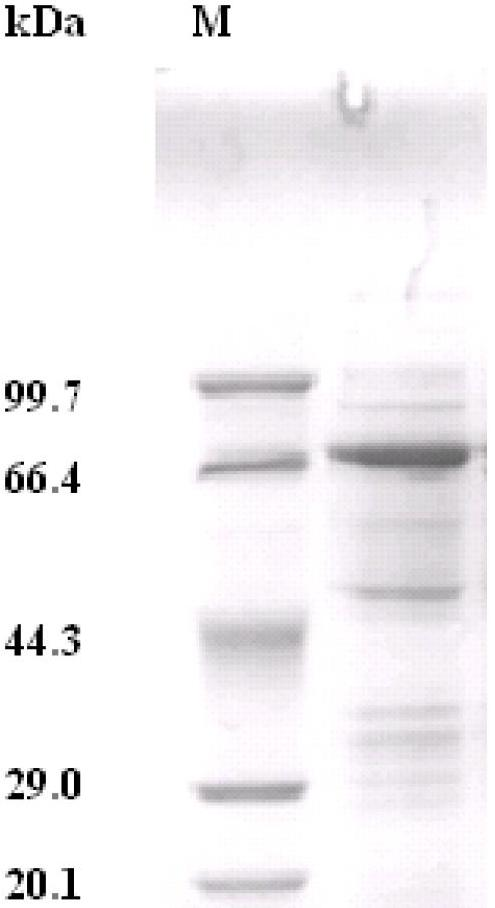
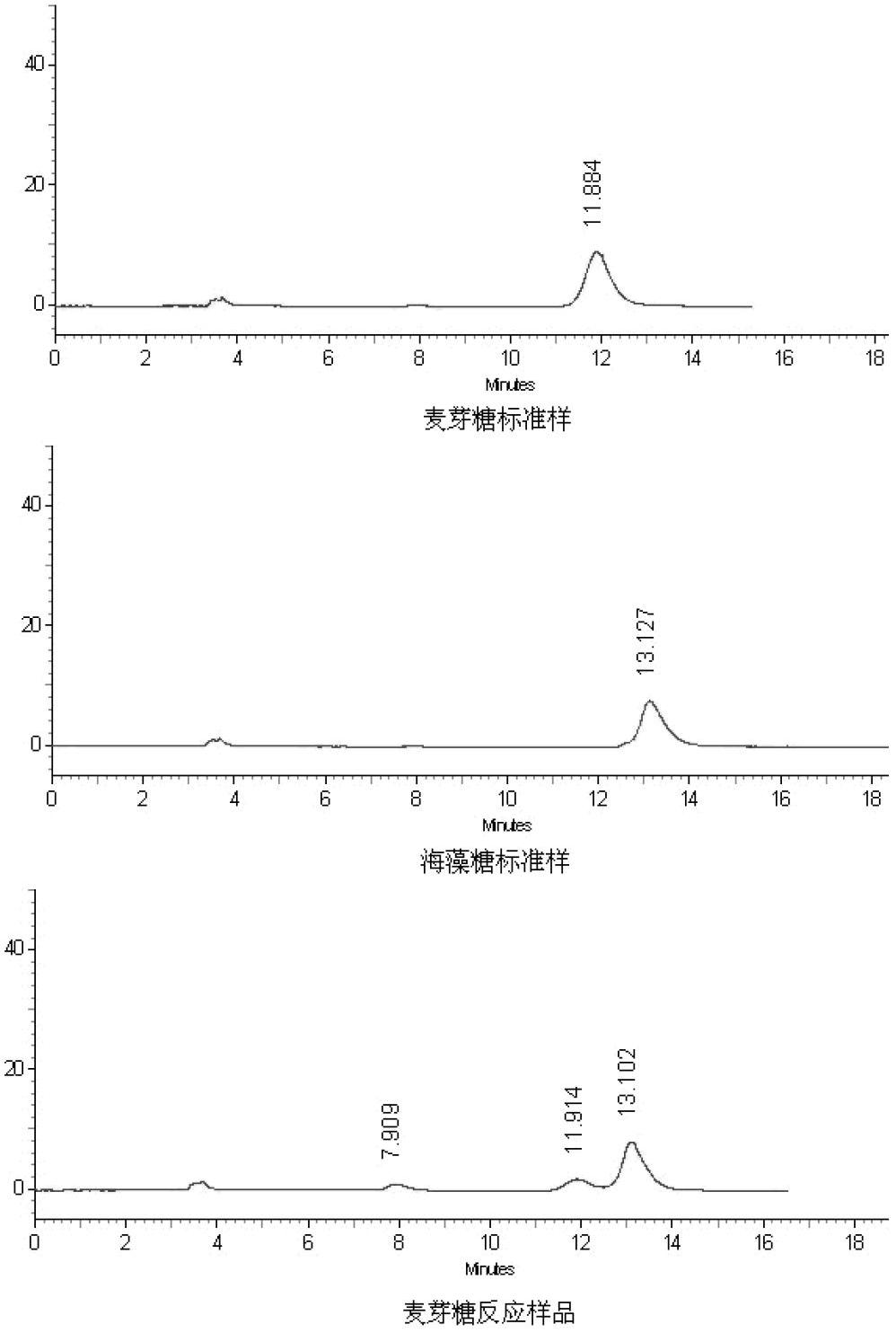
Patents
Literature
156 results about "OSB-CoA synthetase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MenE, the o-succinylbenzoate (OSB)-CoA synthetase from bacterial menaquinone biosynthesis, is a promising new antibacterial target. Sulfonyladenosine analogues of the cognate reaction intermediate, OSB-AMP, have been developed as inhibitors of the MenE enzymes from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (mtMenE), Staphylococcus aureus (saMenE) and Escherichia coli (ecMenE).
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of tryptophanyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130330312A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAminoacyl-tRNA synthetasesNucleotide
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of alanyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130287755A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of glycyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130224174A1Relieve symptomsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideProtein Fragment
Owner:PANGU BIOPHARMA +1
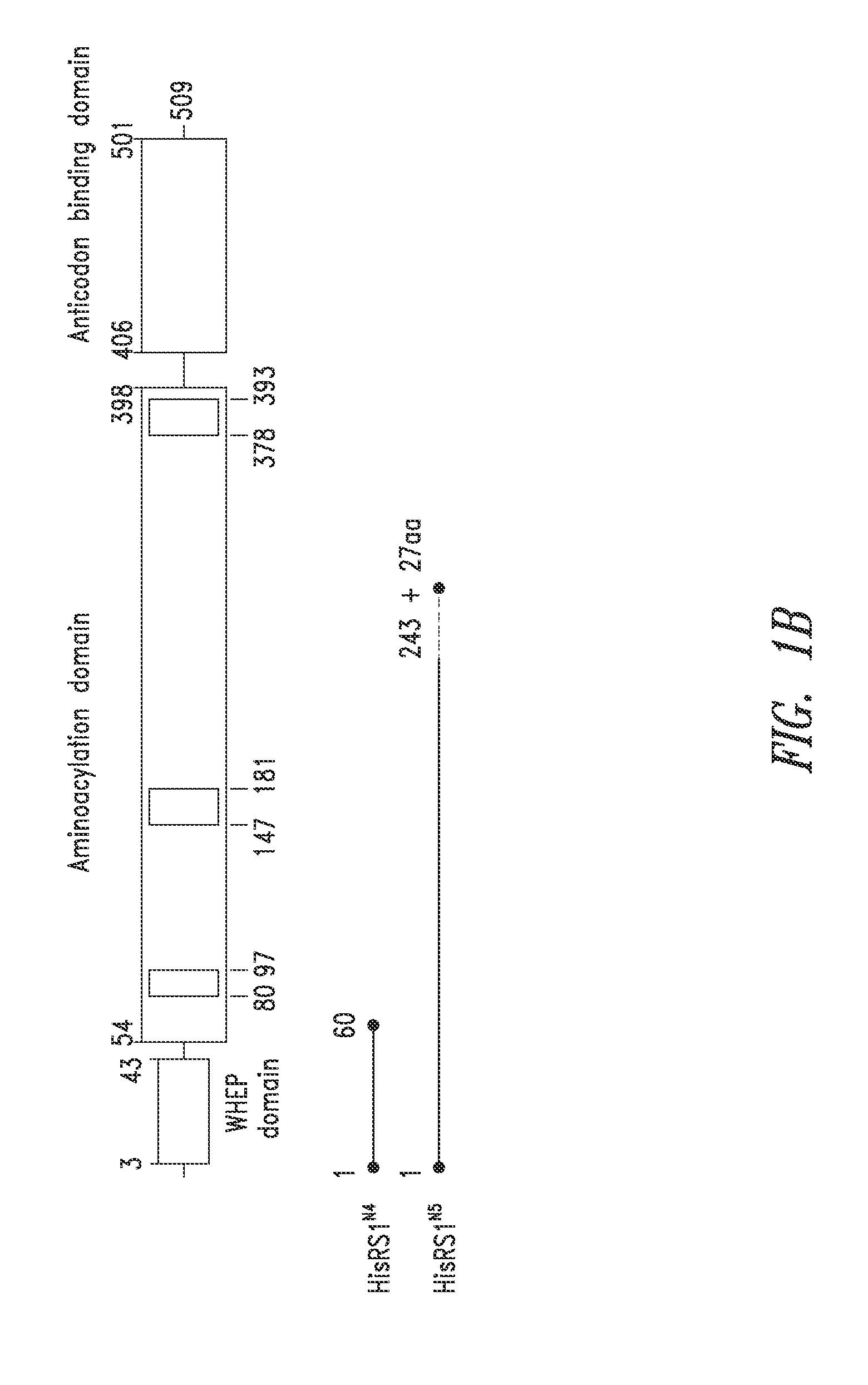
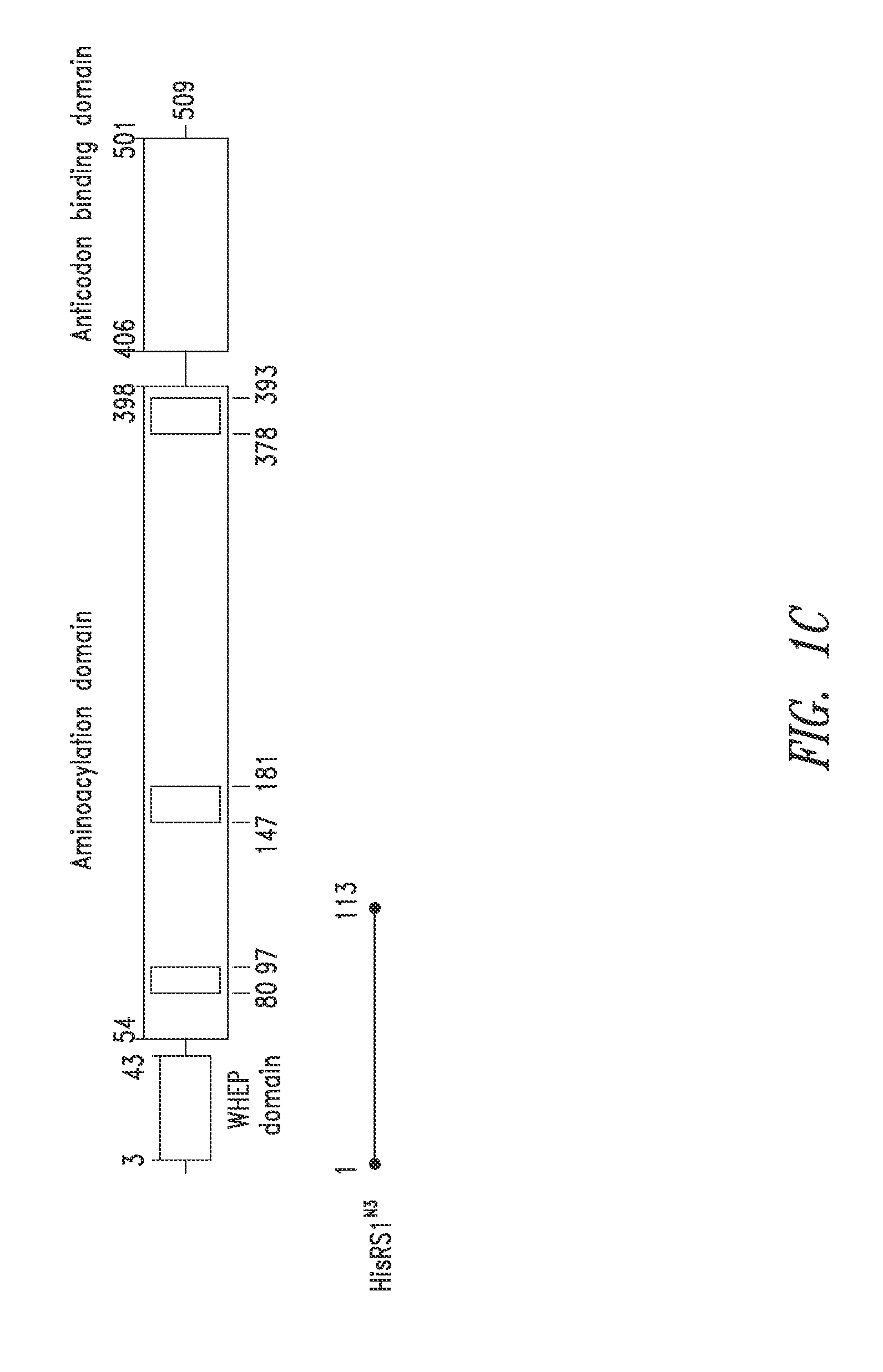
Structures of human histidyl-trna synthetase and methods of use
InactiveUS20140066321A1Improve homogeneityLibrary screeningAnalogue computers for chemical processesMedicineX-ray
Provided are histidyl-tRNA synthetase variant polypeptides, X-ray crystallographic and NMR spectroscopy structures of HRS polypeptides, and related compositions and methods for therapy and drug discovery.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of aspartyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130280230A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideProtein Fragment
Owner:PANGU BIOPHARMA
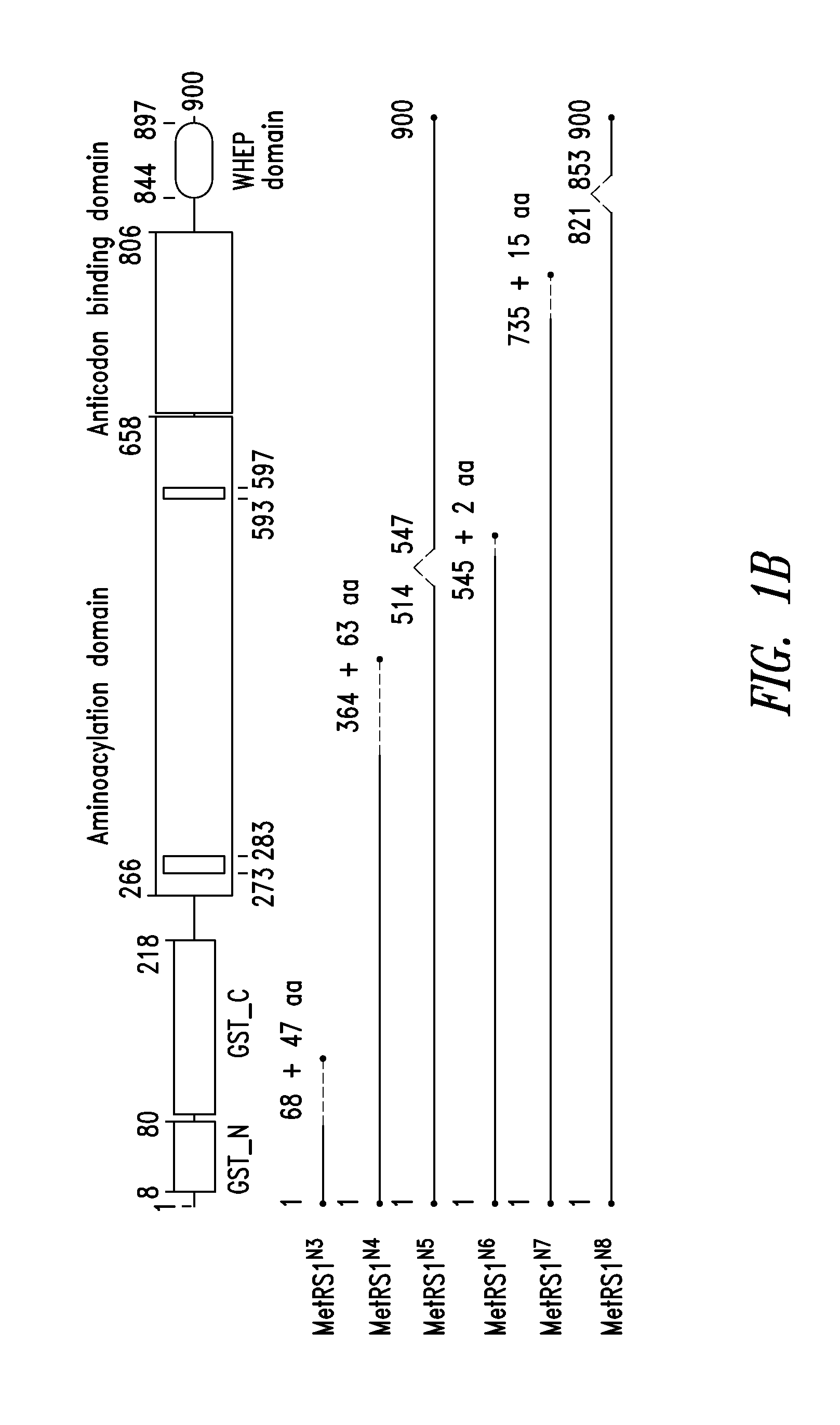
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of methionyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130236440A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideMethionyl-tRNA synthetase
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
DNA encoding apoptosis-induced eucaryotic initiation factor-5A and deoxyhypusine synthase and a method for controlling apoptosis in animals and humans
InactiveUS6867237B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce translationBiocideLaser detailsAntisense OrientationInitiation factor
Genes encoding an apoptosis-induced eukaryotic initiation Factor-5A (eIF-5A) and an apoptosis-induced deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS), whose expressions are induced by the onset of apoptosis, are identified. The DHS gene and the eIF-5A gene, alone or in combination, as well as inhibitors of the DHS reaction, are used to modulate apoptosis in animals and humans. For example, modulation of apoptosis in cells of animals and humans is achieved by introduction of a gene or gene fragment encoding apoptosis-induced eIF-5A, apoptosis-induced DHS, or both into the animal or human cell in antisense orientation.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
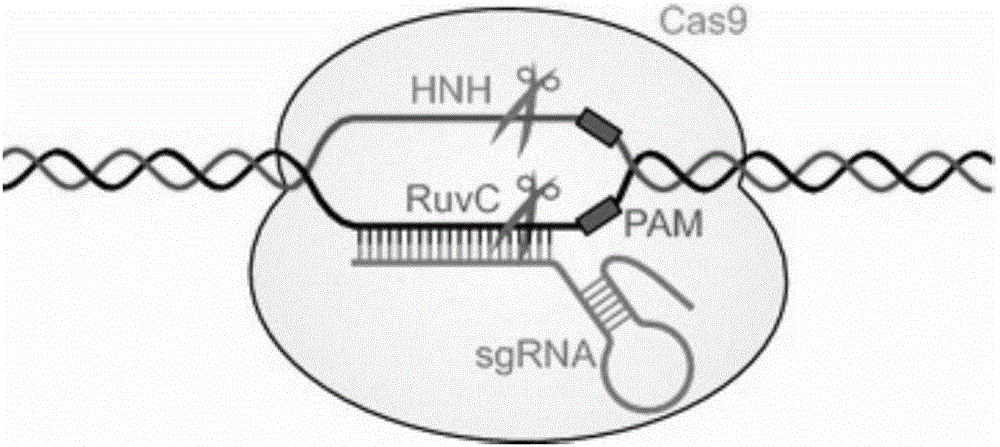
Establishment method of caffeine synthetase CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing vector
InactiveCN105821075ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionGolden Gate Cloning
The invention relates to an establishment method of a caffeine synthetase CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing vector. The method comprises the following steps: designing two target sequences T1 and T2 on the basis of tea tree caffeine synthetase genes; respectively establishing sgRNA expression cassettes of the target sequences T1 and T2; and carrying out enzyme digestion-coupling reaction on a double-element expression vector pYLCRISPR / Cas9P35S-H, the T1sgRNA expression cassette and the T2sgRNA expression cassette so that the T1sgRNA expression cassette and the T2sgRNA expression cassette are connected and inserted into the double-element expression vector, thereby obtaining the CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing vector. By taking the tea tree caffeine synthetase as the example, conventional PCR (polymerase chain reaction), Overlapping PCR and Golden Gate Cloning techniques are combined to establish the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vector comprising the tea tree caffeine synthetase double targets, thereby laying a solid foundation for application of the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technique in tea trees, and providing technical supports for the establishment of CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vectors of other plants.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN102586369AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationGamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following stages of: (1) carrying out batch culture or fed-batch culture to obtain a great deal of recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase, wherein the bifunctional glutathione synthetase is protein which simultaneously has activities of gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase; (2) carrying out over-expression on the bifunctional glutathione synthetase obtained in the stage (1); and (3) adding L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine and glycine precursor amino acids to realize high-efficiency production of glutathione by fermentation. According to the invention, the recombinant Escherichia coli strain expressing the exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase is used for producing glutathione by fermentation, so that the method not only has high GSH (Glutathione) synthesizing capability, but also is free from GSH feedback inhibition, and has the advantages of rapid reaction, high glutathione yield and short production period.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
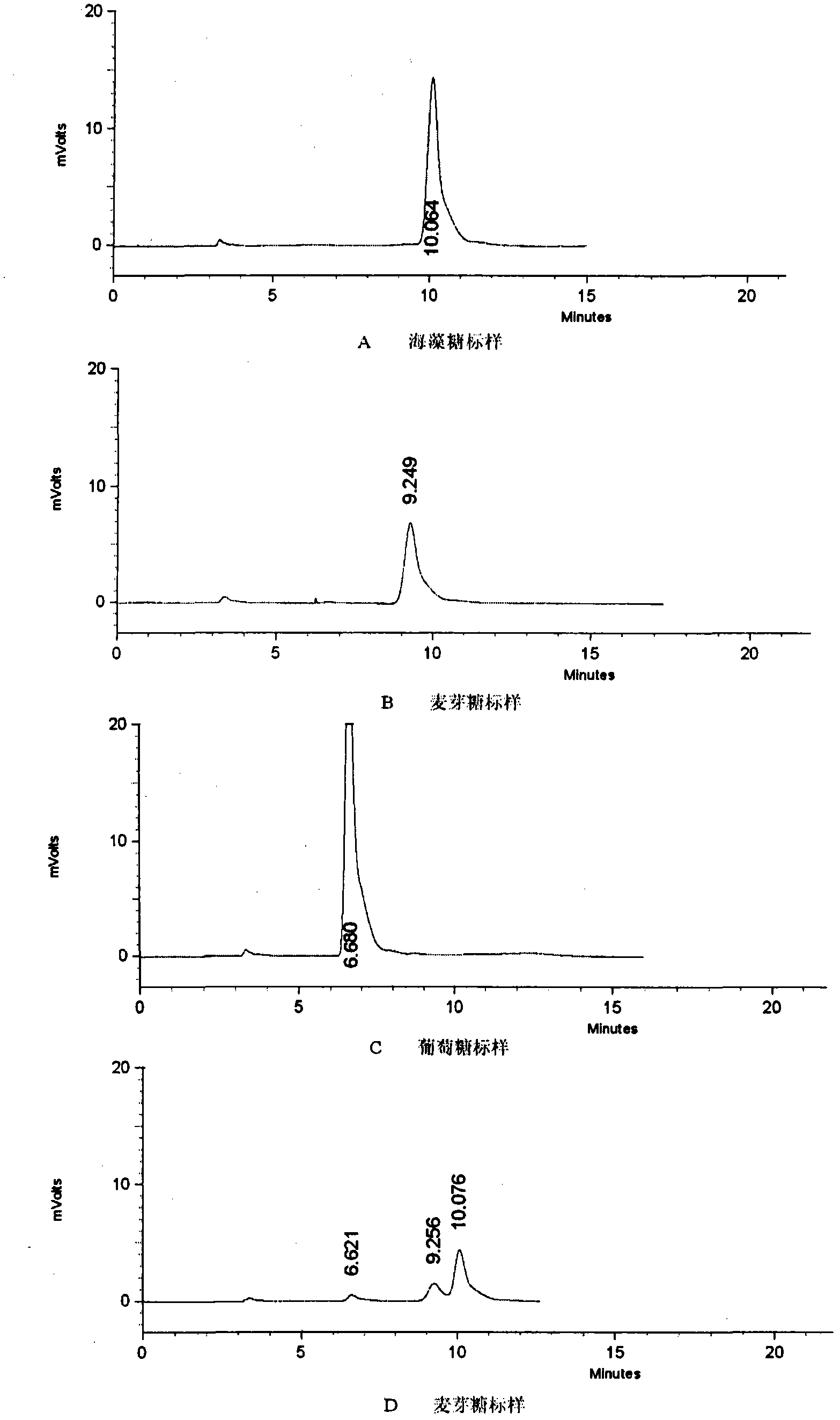
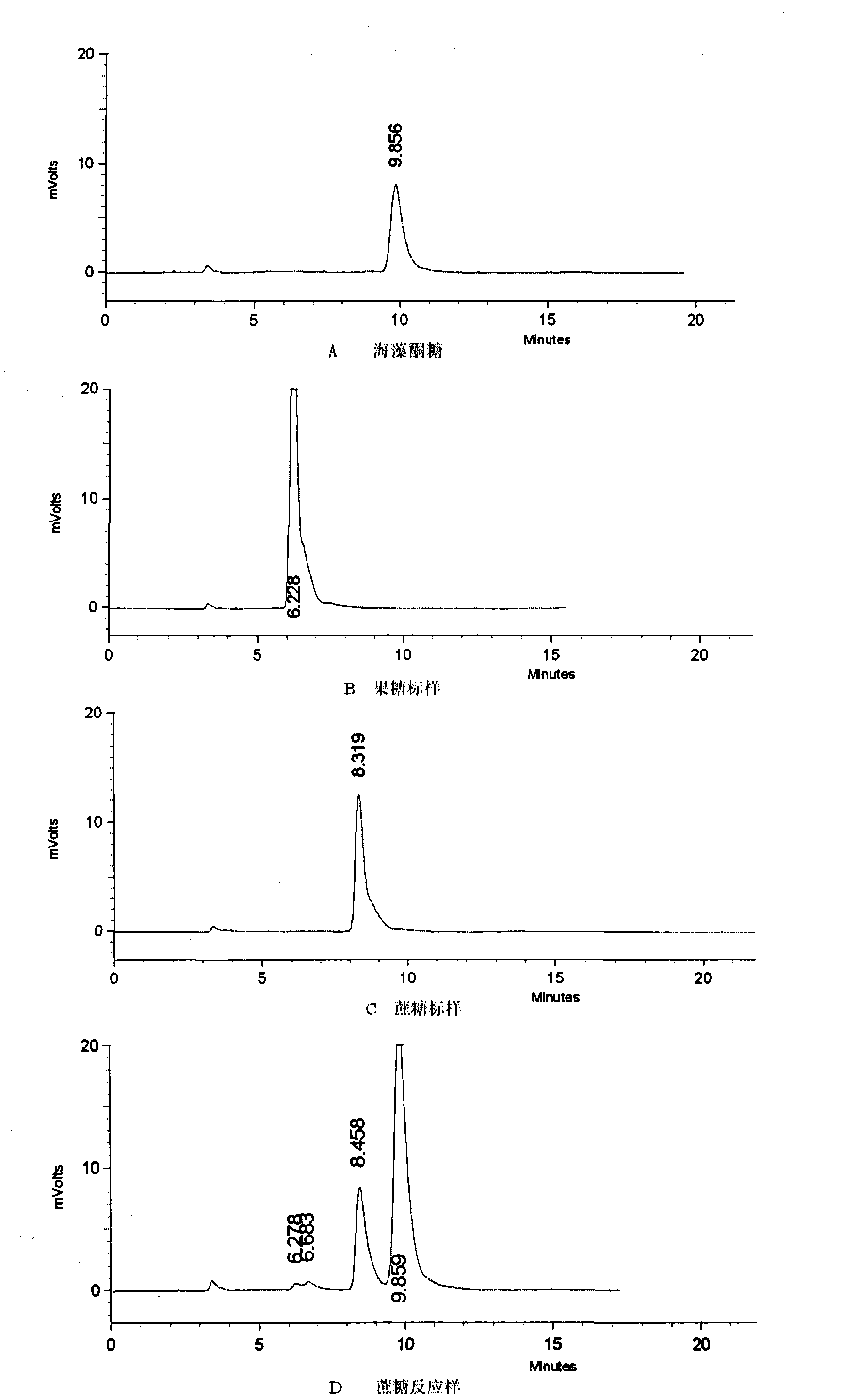
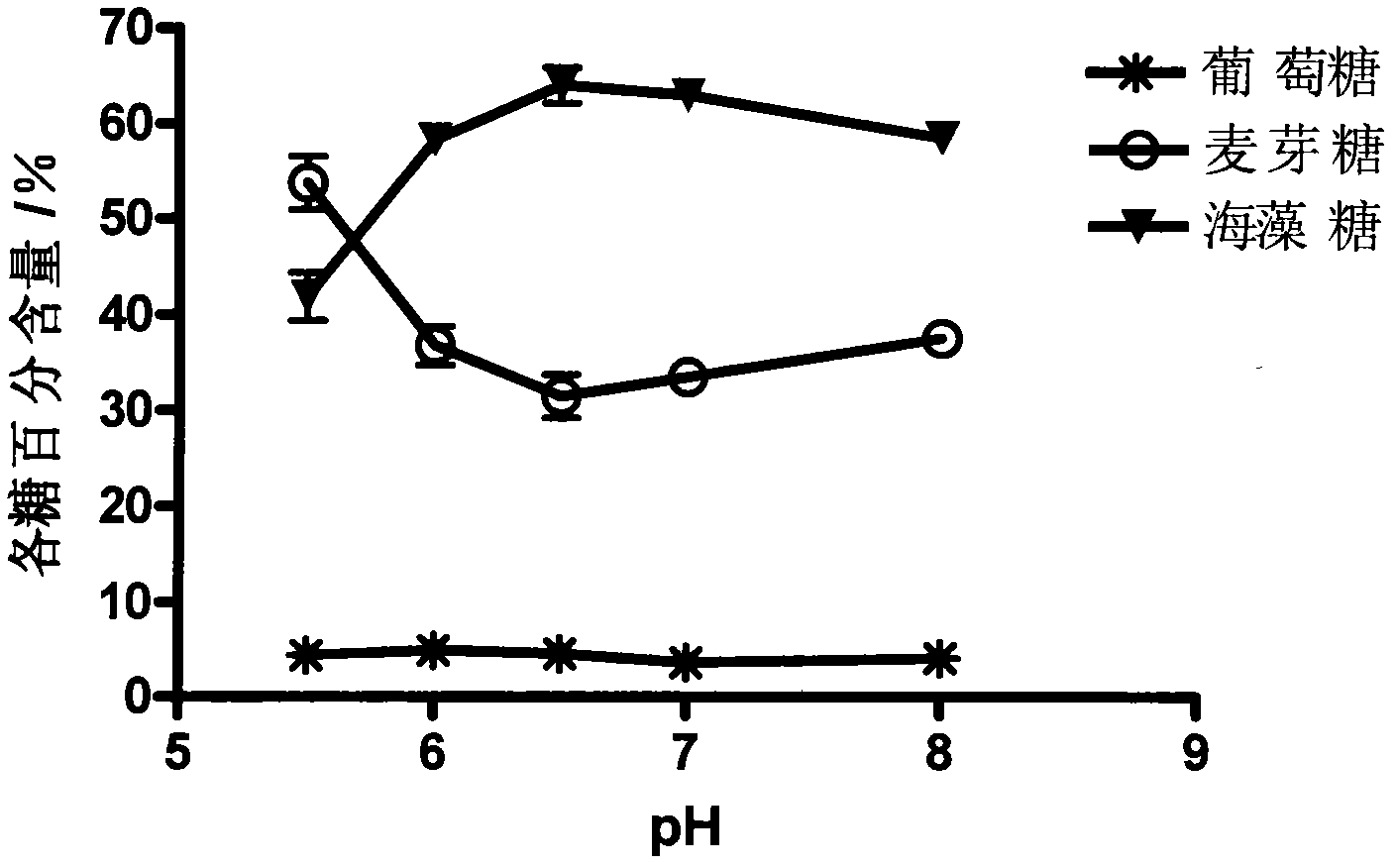
Trehalose synthase of streptomyces griseochromogenes and coding gene and application of trehalose synthase
ActiveCN102690795AReduce occupancyReduce energy consumptionBacteriaTransferasesHydrogenStreptomyces griseochromogenes
The invention discloses trehalose synthase of streptomyces griseochromogenes and a coding gene and application of the trehalose synthase. The trehalose synthase gene is cloned from the streptomyces griseochromogenes. The trehalose synthase can convert maltose to generate trehalose, the proper reaction temperature of the trehalose synthase is 15-35 DEG C and is 20-25 DEG C preferably, and the proper pH (potential of hydrogen) of the trehalose synthase ranges from 6.0 to 8.0 and ranges from 7.0 to 7.5 preferably. The conversion efficiency of the trehalose synthase is high, the maltose is used as a substrate, conversion rate of the maltose is about 80% at the reaction temperature of 25 DEG C, and less than 5% of glucose is generated to be beneficial to increase of the conversion rate of the substrate. The trehalose synthase can be used for converting commercial ultrahigh malt syrup to prepare the trehalose, and a novel method using an enzymic method to produce the trehalose industrially can be provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing trehalose through utilizing immobilized trehalose synthase
ActiveCN103266152AImprove conversion rateImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierTrehalose synthaseReaction speed
Owner:BAOLINGBAO BIOLOGY
Marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of Edwardsiella tarda wild strain as well as relevant preparations and application thereof
ActiveCN101974472AGood control effectImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsChorismic acidAttenuated Live Vaccine
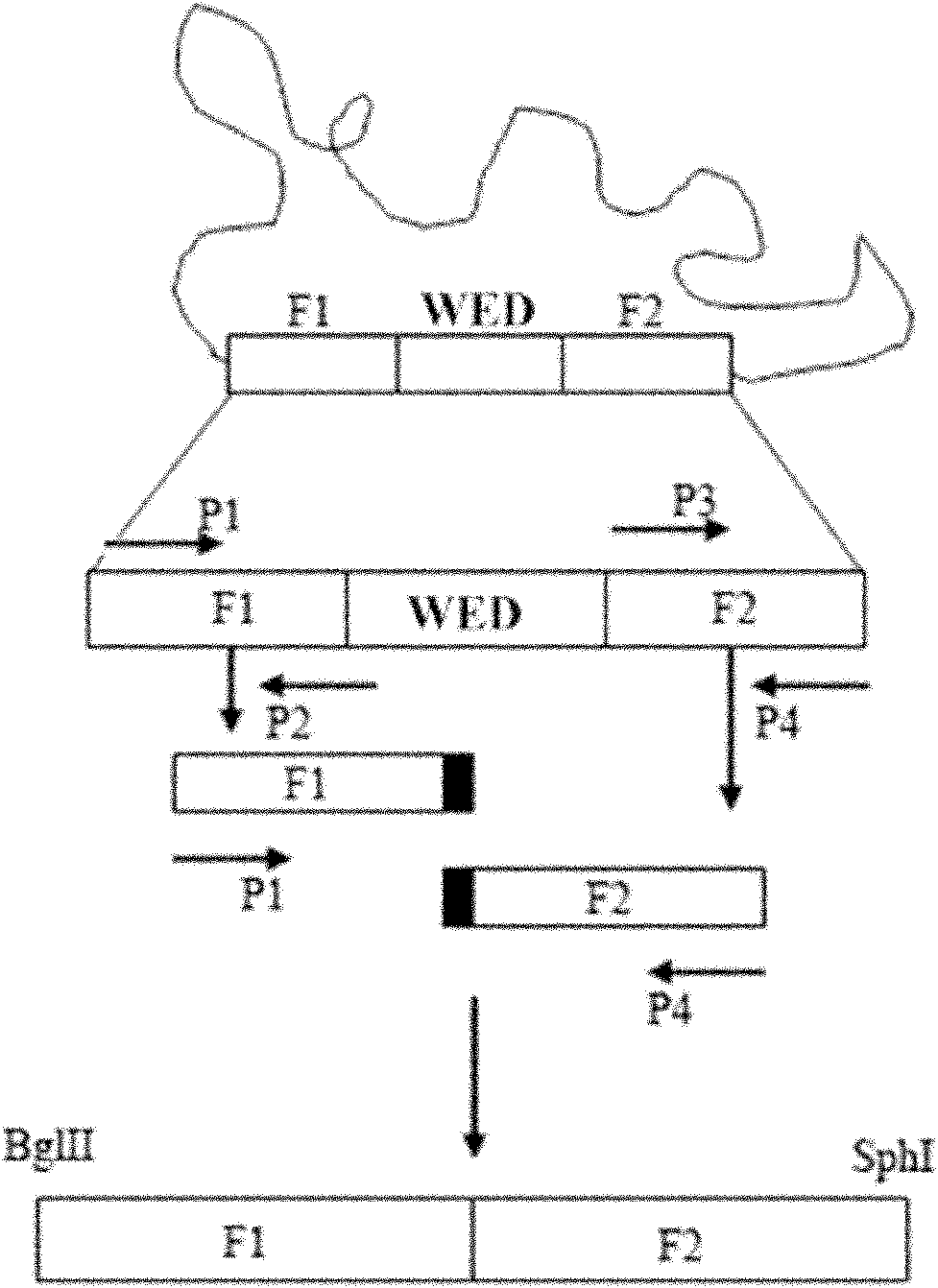
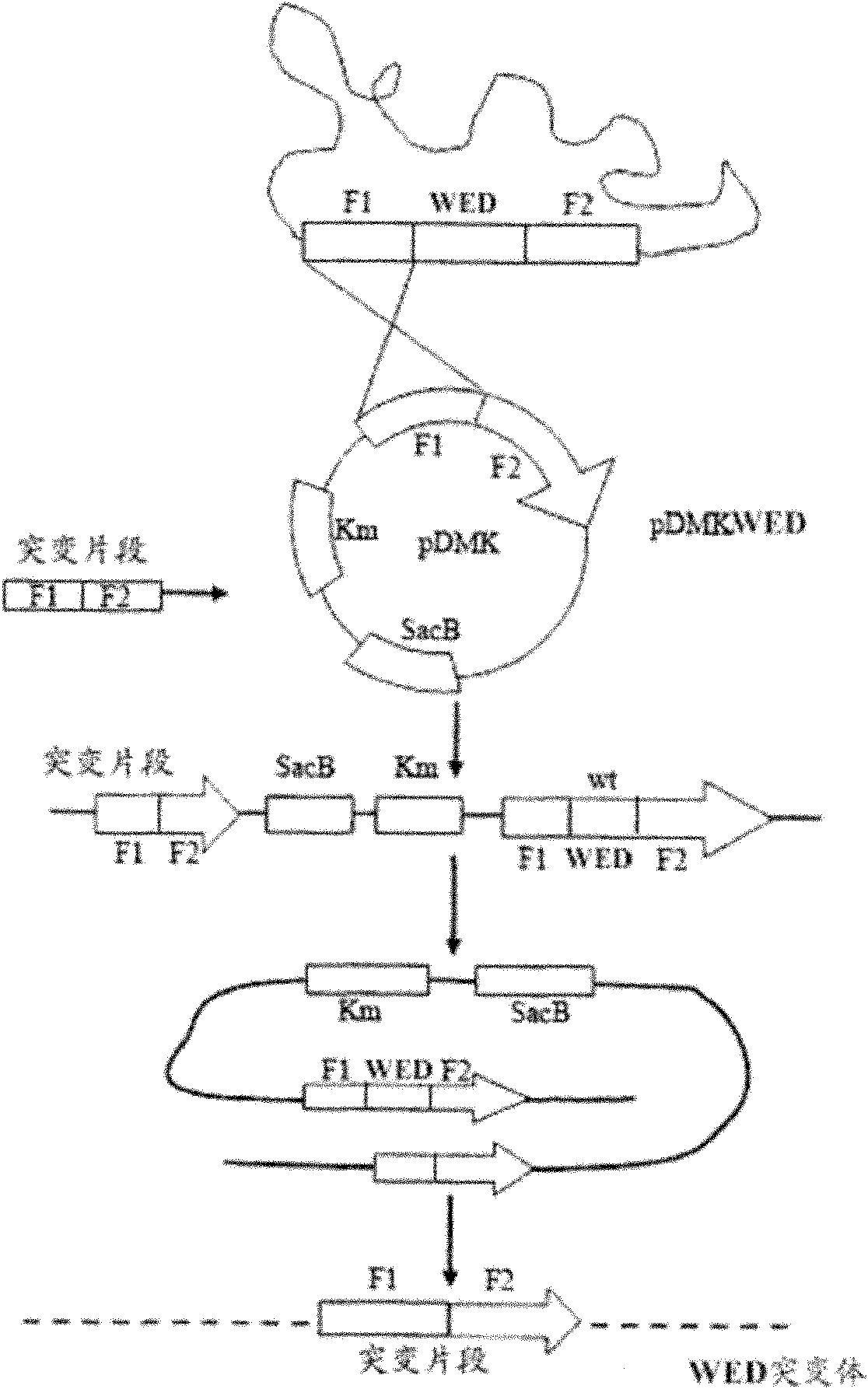
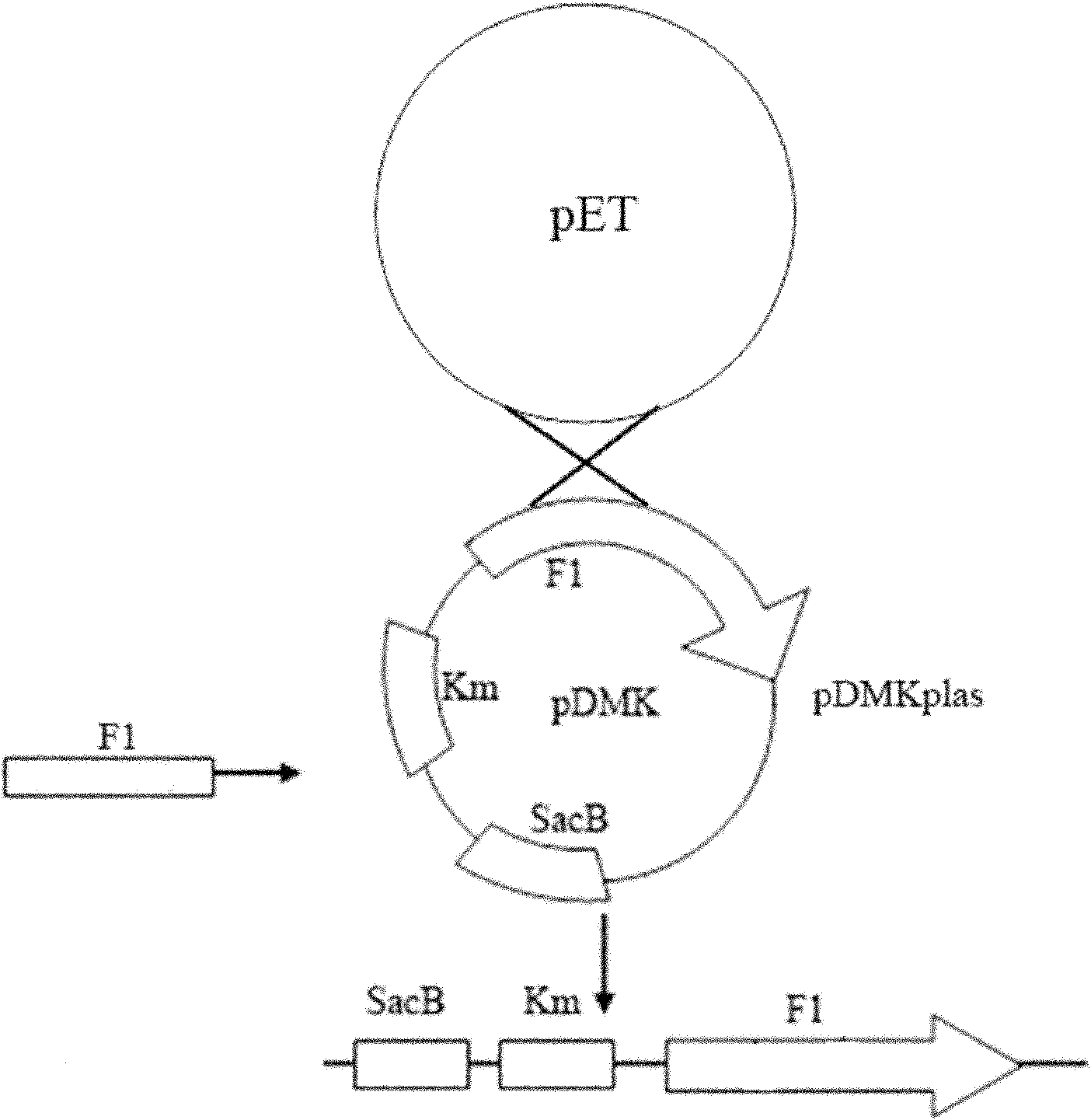
The invention relates to a marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of an Edwardsiella tarda wild strain. The marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain is an attenuated live vaccine of an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, which deletes the chorismic acid synthase gene aroC of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, three types of secretion system response element genes of eseB, escA, eseC and eseD and an endogenous plasmid, preferably, the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain EIB202 with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M208068; the endogenous plasmid is a plasmid of pEIB202; and the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an attenuated strain WED with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M2010278. The invention also provides relevant preparations and application of the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain. The attenuated mutant strain or relevant preparations eliminate the potential environment and safety risk of products existing in the traditional attenuated live vaccines generally and is a safe, effective and economic vaccine aiming at Edwardsiella tarda diseases of cultured fishes.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
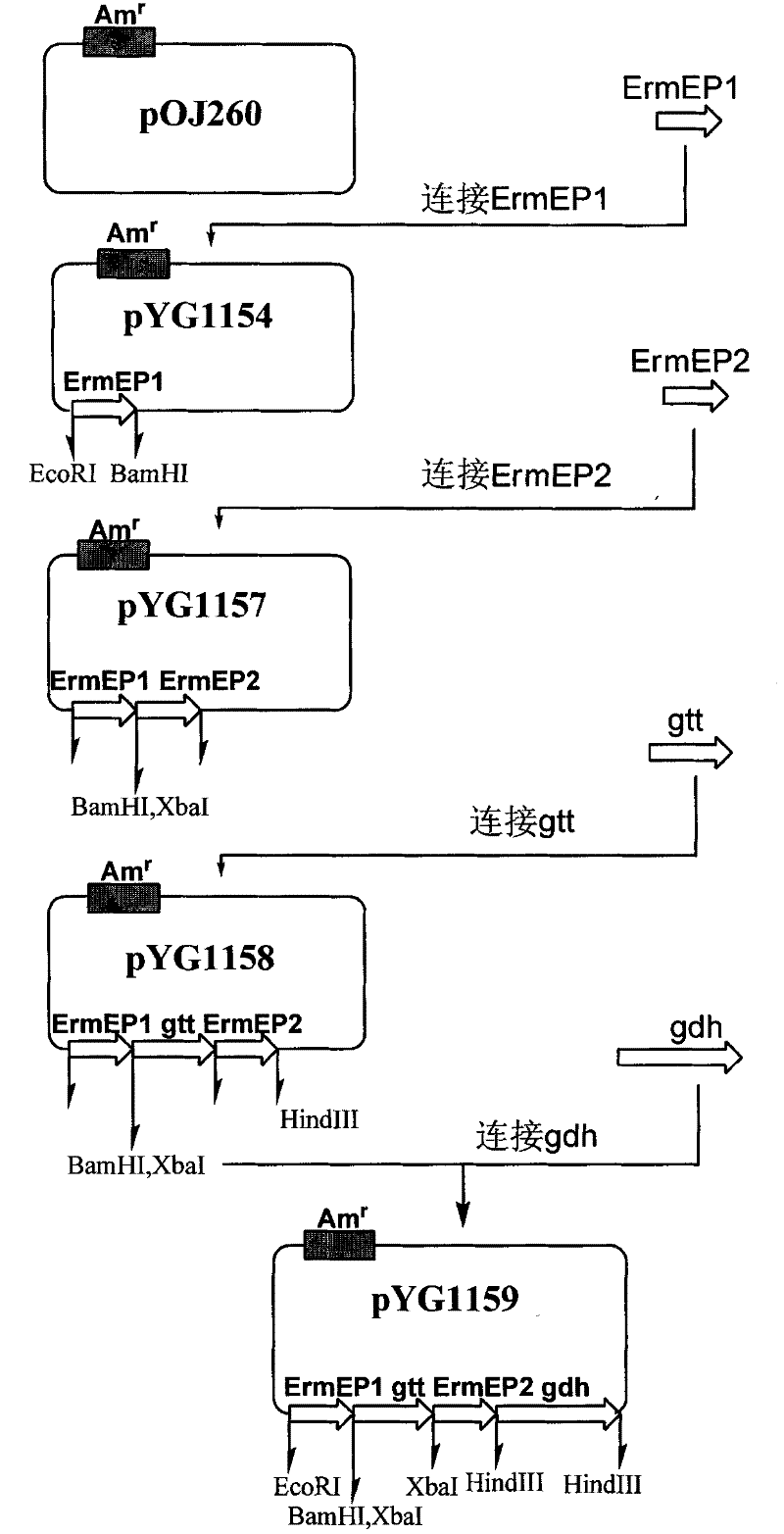
Gene engineering bacteria capable of highly producing pleocidin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102191208AIncrease productionRaise the fermentation unitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneSaccharopolyspora
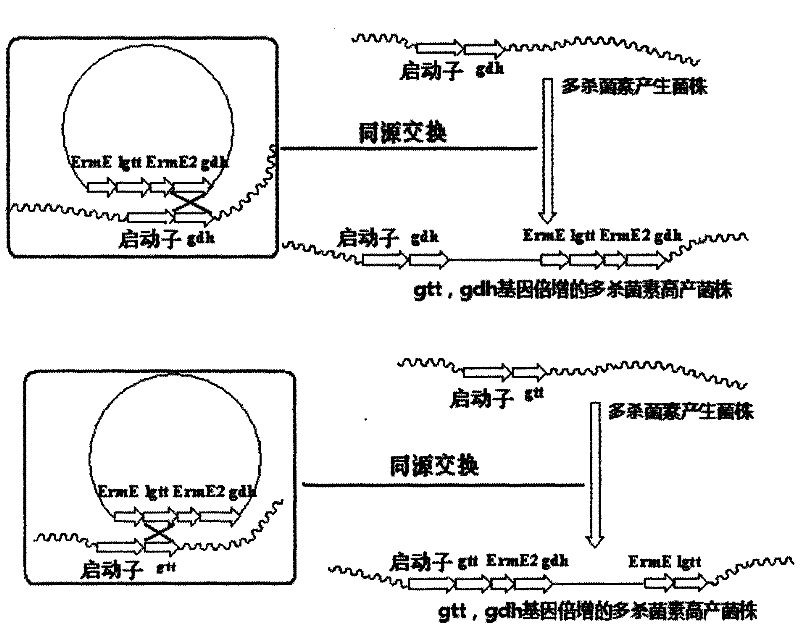
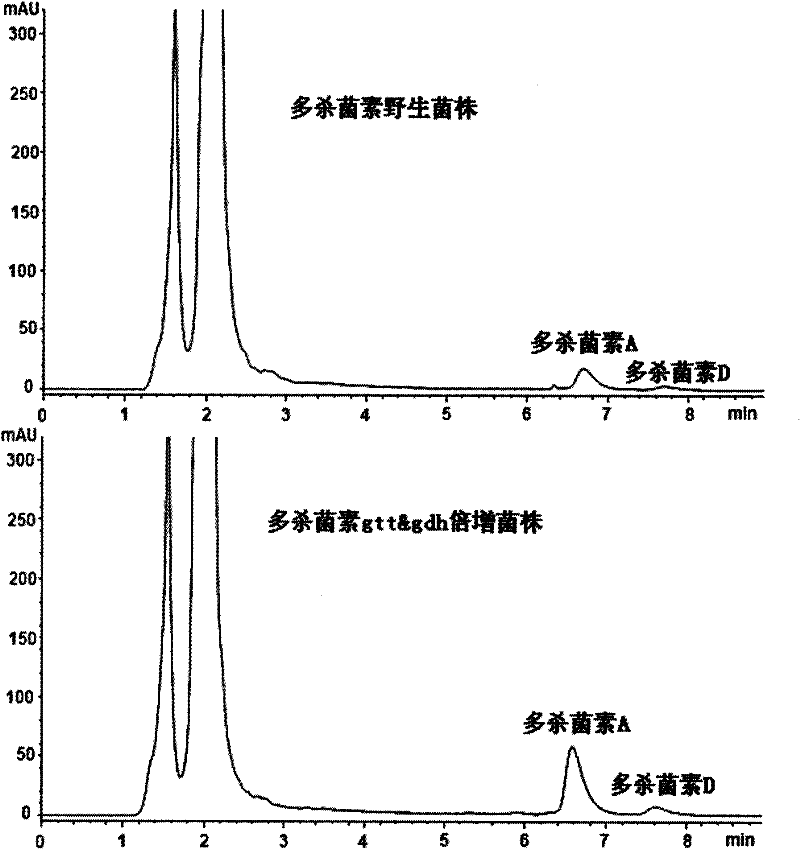
The invention discloses gene engineering bacteria capable of highly producing pleocidin and a preparation method thereof. In the gene engineering bacteria, an expression box of NDP-glucose synthesized enzyme gene gtt of NDP-4-ketone-6-deoxidation-Dglucose and an expression box of genes of NDP-glucose reductase gene gdh are integrated in genomes of Saccharopolyspora spinosa wild bacterial strains. According to fermentation validation, the fermenting units of the pleocidin of the gene engineering bacteria is increased by more than three times compared with that of the wild bacterial strains.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
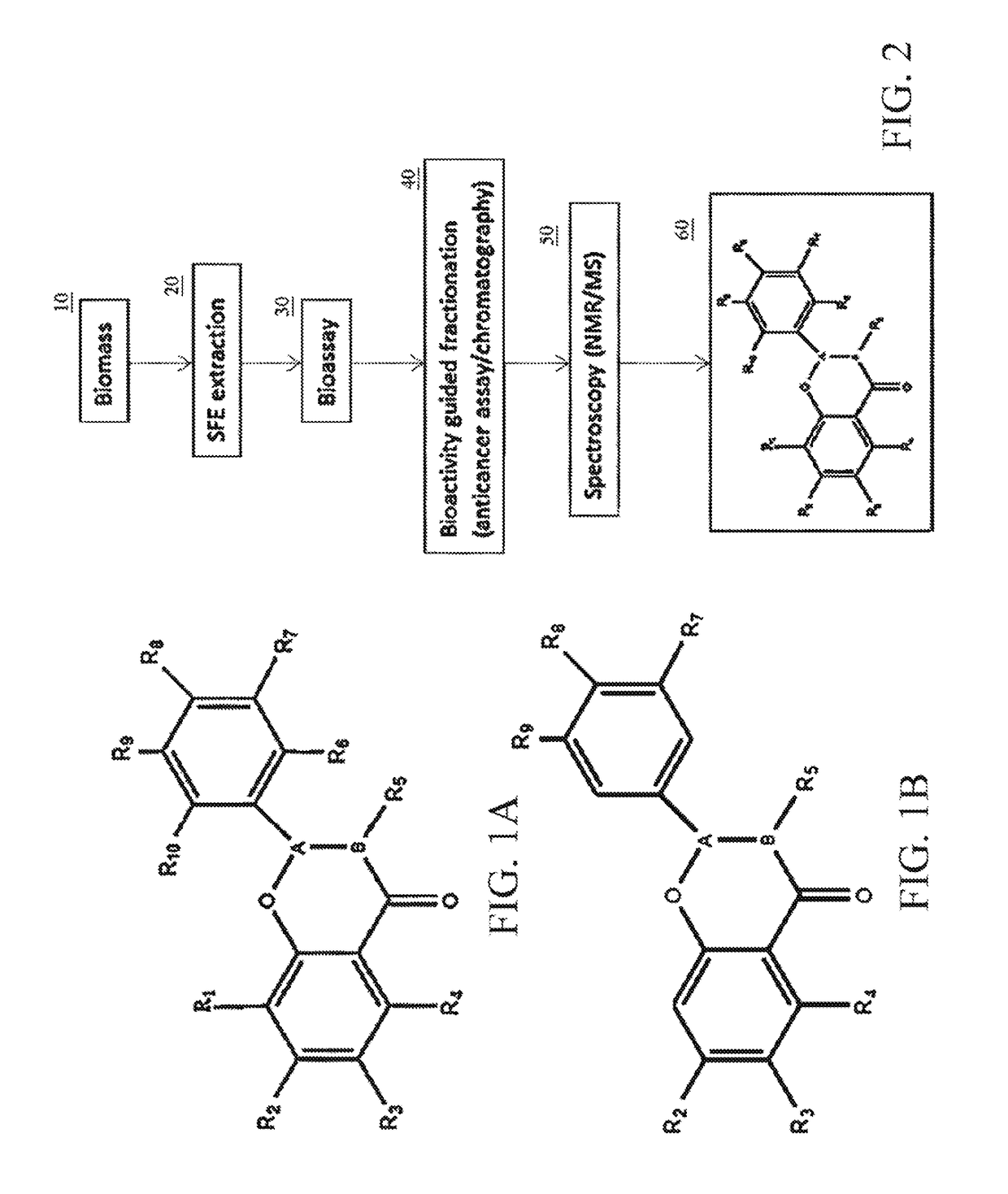
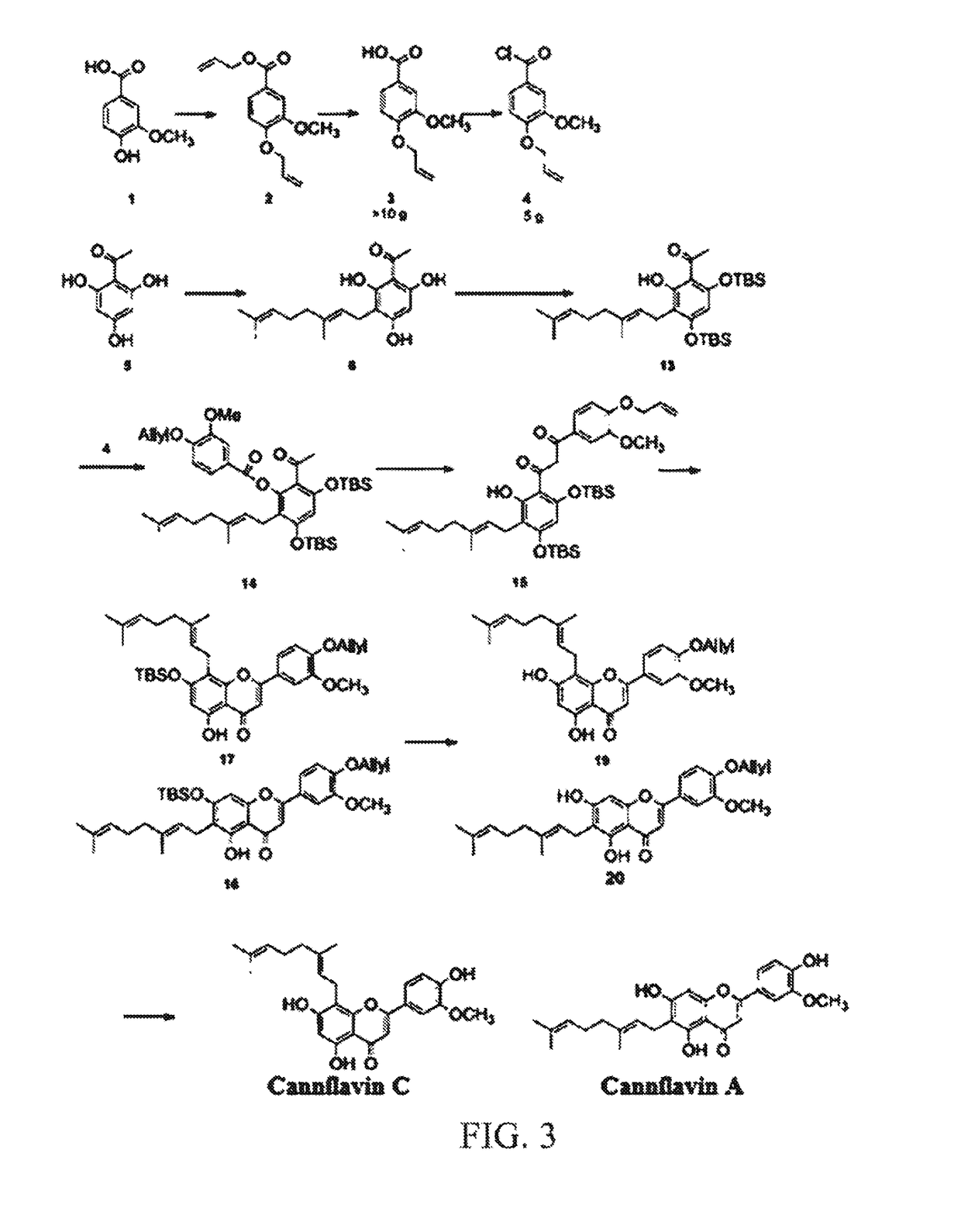
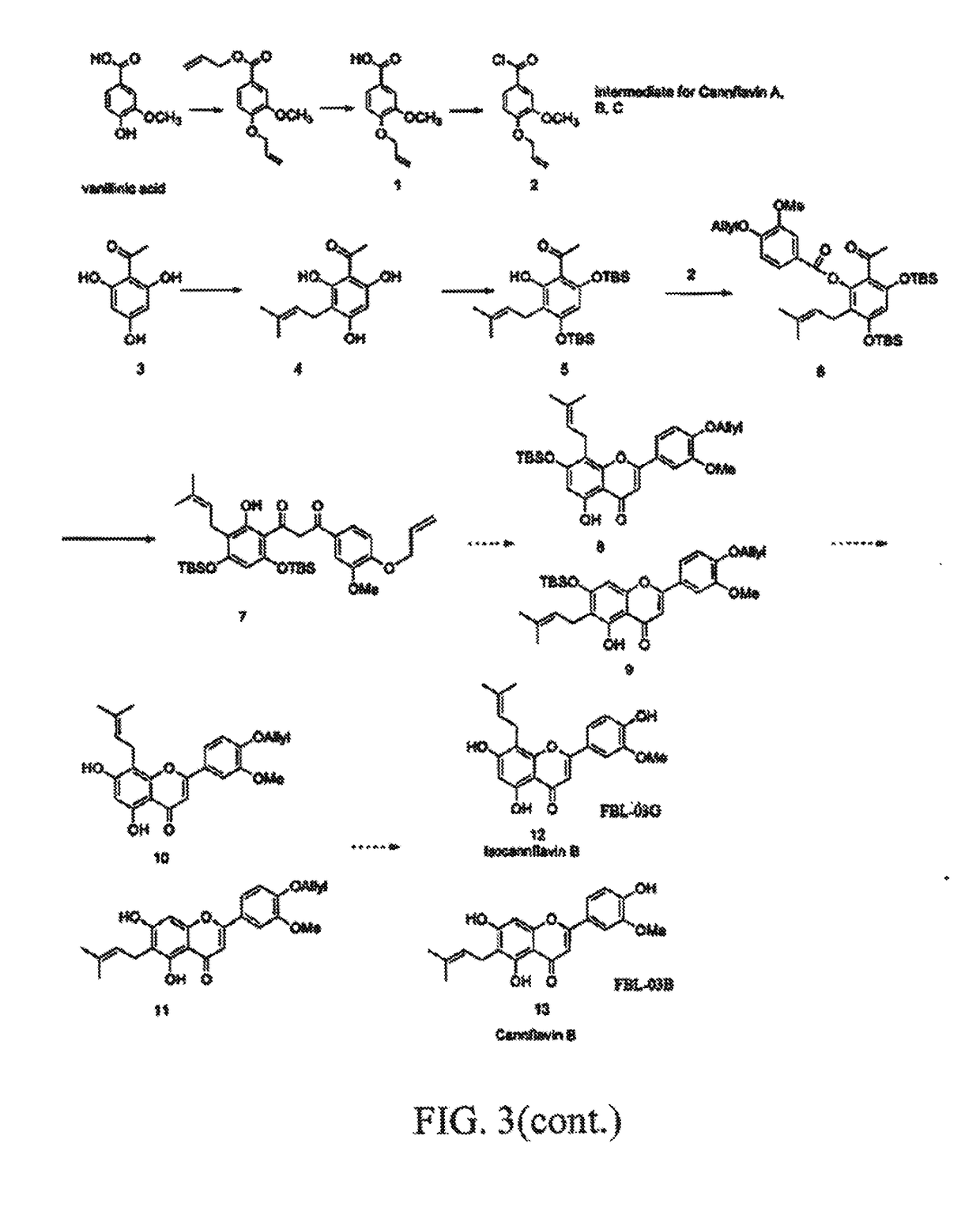
Therapeutic agents containing cannabis flavonoid derivatives targeting kinases, sirtuins and oncogenic agents for the treatment of cancers
A cannabis-based flavonoid pharmaceutical composition including any one or more selected from among the group of Cannflavin A, Cannflavin B. Cannflavin C, Chrysoeriol, Cosmosiin, Flavocannabiside and their derivatives selected from among the group of Geraldol, Rhamnetin, Isorhamnetin, Rhamnazin, or their synthases, for the prevention and treatment of certain cancers that can be treated by therapeutically targeting oncogenic factors including kinases, sirtuins, bromodomains, matrix metalloproteinases and histone acetylases. Some of the cancers that can be treated by use of cannabis flavonoids based on the inhibition of these therapeutic targets include but are not limited to brain, breast, colon, renal liver, lung, pancreatic, pigmented villonodular synovitis, prostate, leukemia, melanomam, tenosynovial giant cell tumor, as well as any other cancers that overexpress the oncogenic factors inhibited, by the cannabis flavonoids or their derivatives herein identified.
Owner:FLAVOCURE BIOTECH INC
Thermomonospora curvata mycose synthetase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102154327AEase of industrial productionEasy to produceEnzymesFermentationSaccharumSaccharophagus degradans
The invention discloses a thermomonospora curvata mycose synthetase gene and application thereof. The gene is cloned from thermomonospora curvata. Mycose synthetase expressed by the gene has two different transformation functions. The mycose synthetase can be used for transforming maltose into mycose and transforming cane sugar into kelp ketose under normal biochemical reaction conditions. The gene can be applied to the production of mycose by transforming maltose, and can be used for transforming cane sugar into kelp ketose. The mycose and the kelp ketose can be applied to the fields of food industry, beverages, functional foods, beautifying cosmetics, medical biological products and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
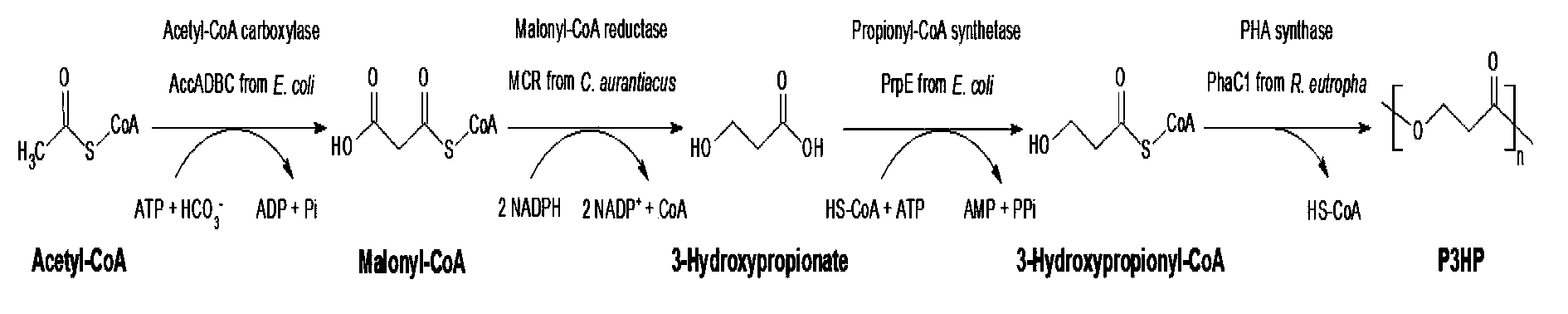
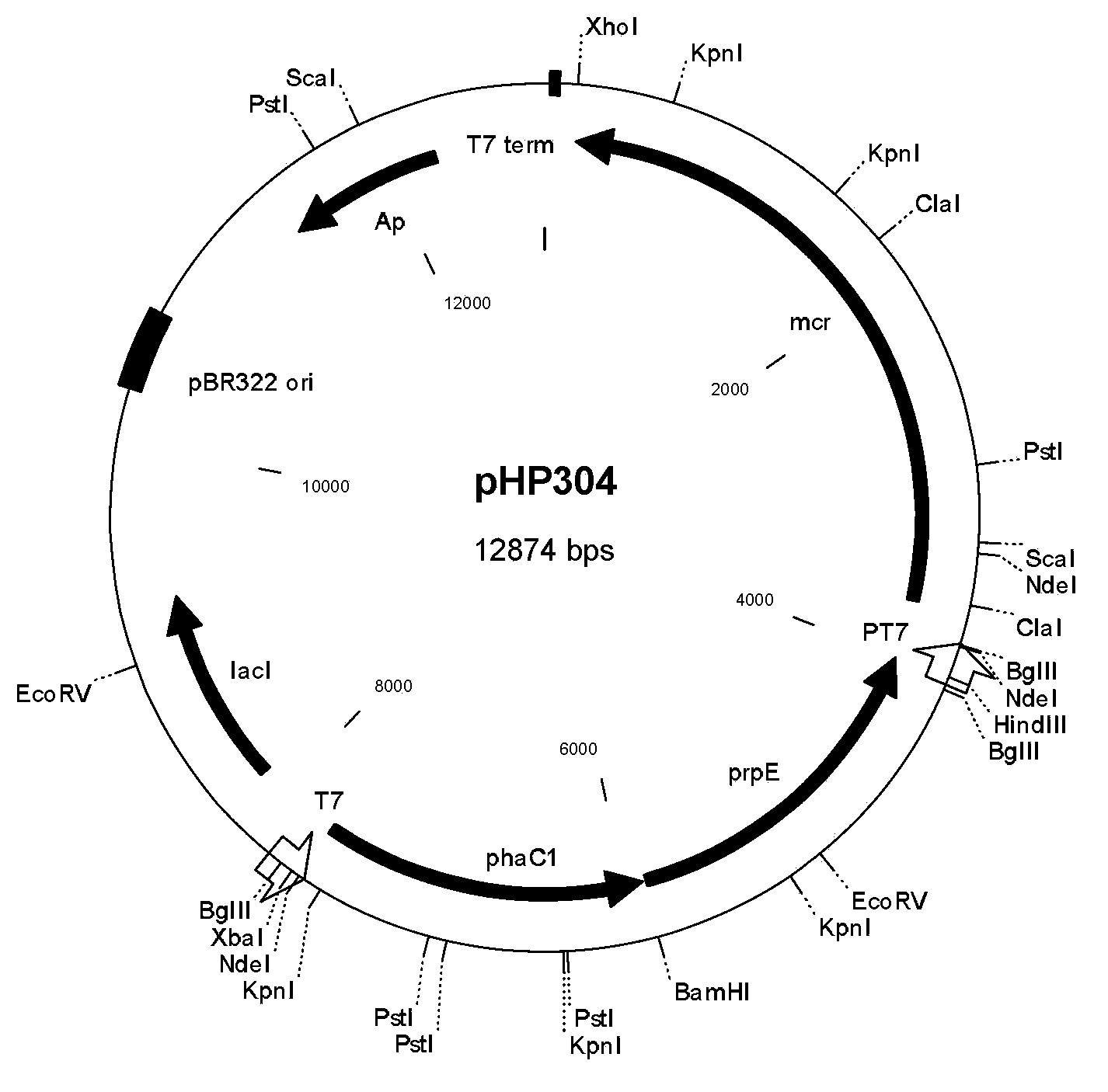
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Glutathione synthetase mutant, encoding gene and application
ActiveCN104328092AHigh catalytic activityReduce manufacturing costPeptidesLigasesGlycineSodium Glutamate
The invention discloses a glutathione synthetase mutant, an encoding gene and an application. The glutathione synthetase mutant is obtained through point mutation of the sequence 2 in a sequence table, wherein the point mutation is at least one mutation at the 128th position, the 256th position and the 320th position. By means of mutation of the glutathione synthetase gene sequence, the glutathione synthetase mutant having high catalytic activity is finally obtained and is higher than a parent by at least 50% in glutathione synthetase catalytic activity with disodium adenosine triphosphate, L-sodium glutamate, L-cysteine and glycine being a substrate. When immobilized glutathione synthetase is employed for preparing glutathione, the concentration of the prepared glutathione is higher than 50 mM, so that the glutathione synthetase mutant is available in industrialized production of the glutathione with production cost being reduced and market competitiveness of related products being enhanced.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
Method for producing trehalose synthase from integrated recombinant bacillus subtilis and manufacturing trehalose
ActiveCN103215300AEasy to manufactureStable passageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibacterial activityMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for producing trehalose synthase by taking integrated recombinant bacillus subtilis as a strain and producing trehalose from the trehalose synthase. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: integrating a trehalose synthase expression element in a bacillus subtilis chromosome to construct integrated recombinant bacillus subtilis, and fermenting in a nutrient culture medium to produce the trehalose synthase by taking the recombinant bacillus subtilis as a strain, wherein via simple separation, the trehalose synthase in the fermentation liquor can be directly used for manufacturing trehalose. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the trehalose synthase is produced by virtue of a food safety expression system, the exogenous gene contained in the strain with integrated expression can be used for stable passage and expression, and the expressed trehalose synthase is secreted to the outside of cells, has no antimicrobial activity, and achieves the requirements of food applications for enzymic preparation, thus being beneficial to further manufacturing for trehalose.
Owner:南宁中诺生物工程有限责任公司
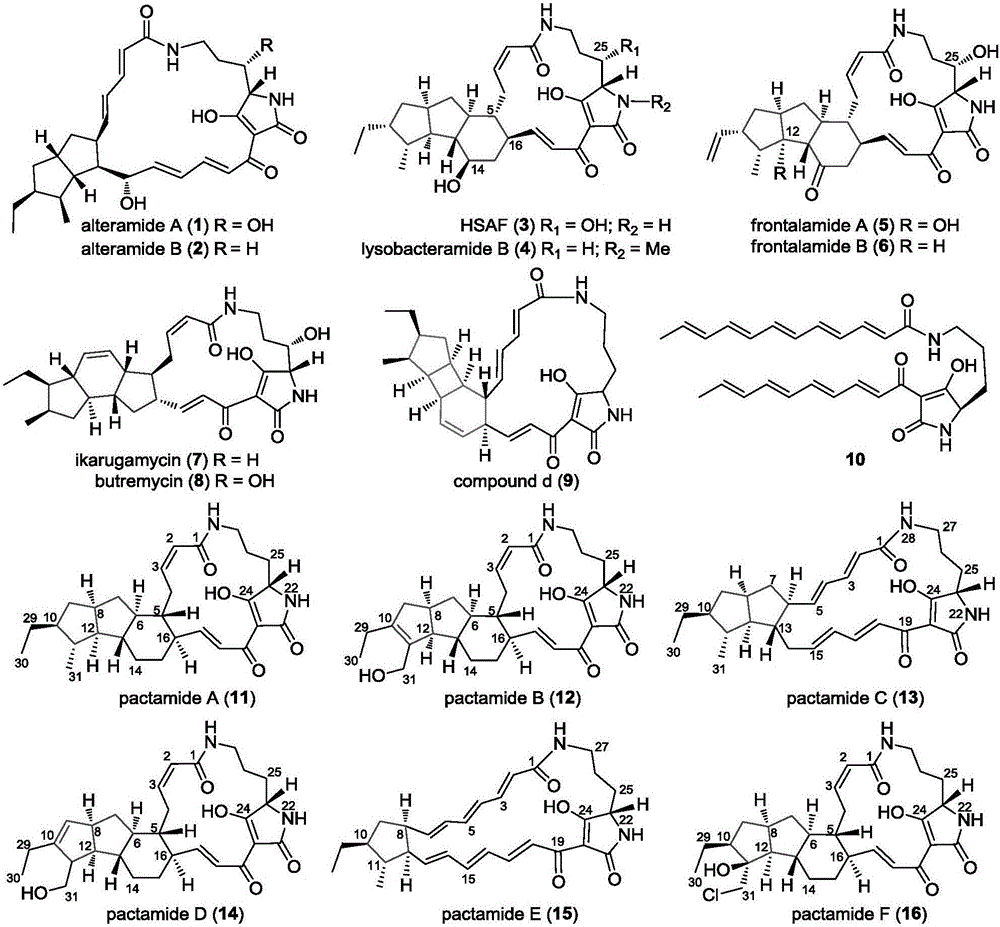
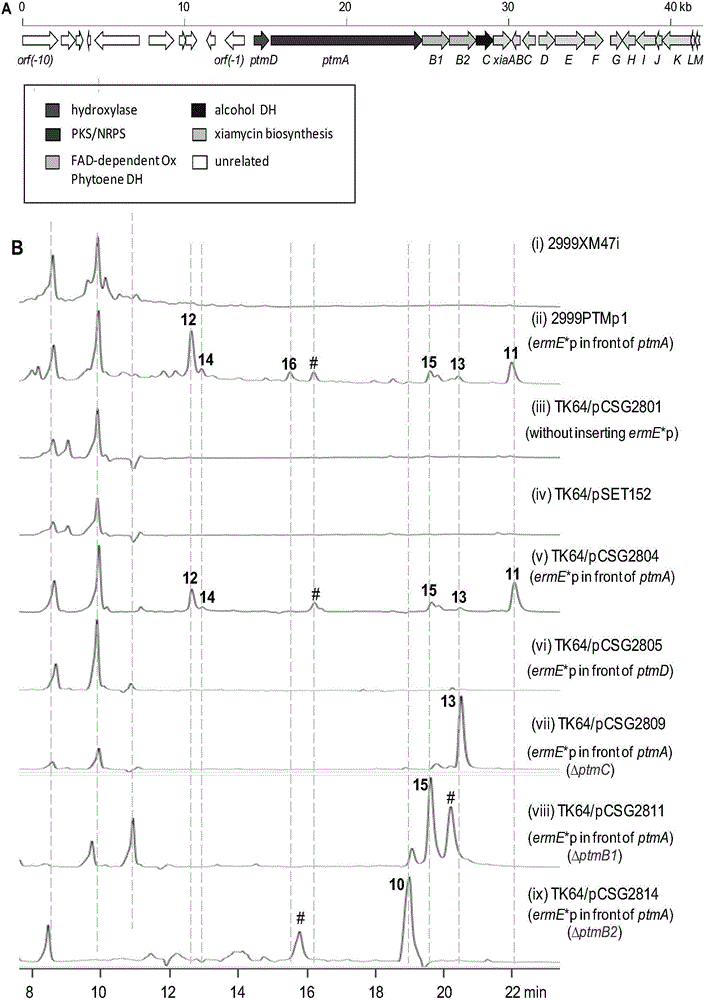
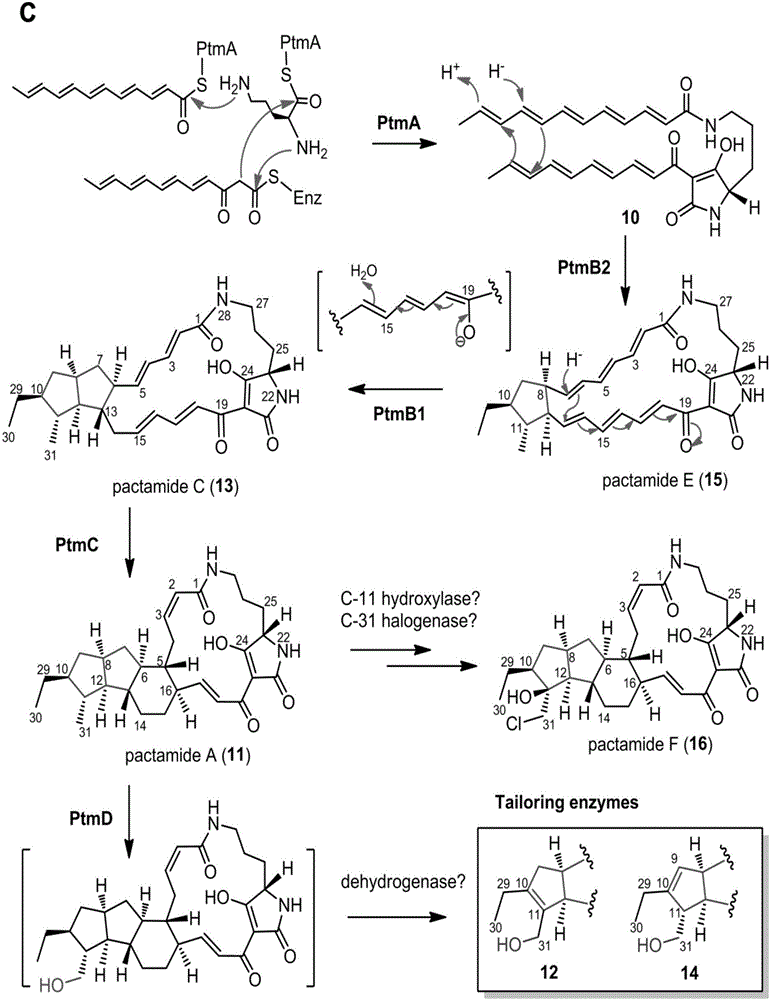
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN109777763AIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Trehalose synthase-trehalose hydrolase fusion enzyme, expression gene thereof and application
The invention relates to a trehalose synthase-trehalose hydrolase fusion enzyme, an expression gene thereof and application. Amino acid sequences of the maltooligosyl trehalose synthase-maltooligosyl trehalose tetrahydrolase fusion enzyme are shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and nucleotide sequences of the expression gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The trehalose synthase-trehalose hydrolase fusion enzyme, the expression gene and the application have the advantages that the novel maltooligosyl trehalose synthase-maltooligosyl trehalose tetrahydrolase fusion enzyme is constructed by the aid of genetic engineering technologies and has the activity of maltooligosyl trehalose synthase and the activity of maltooligosyl trehalose tetrahydrolase, and accordingly production processes can be effectively simplified as compared with the traditional two-enzyme methods.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
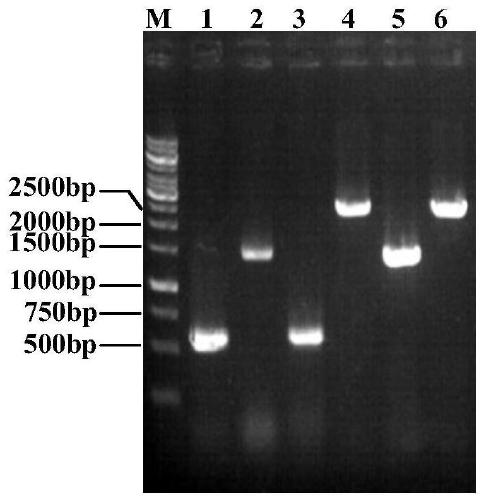
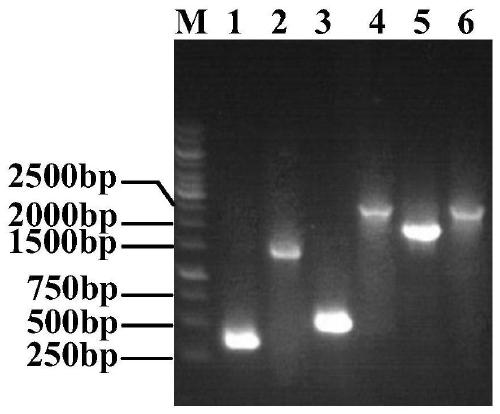
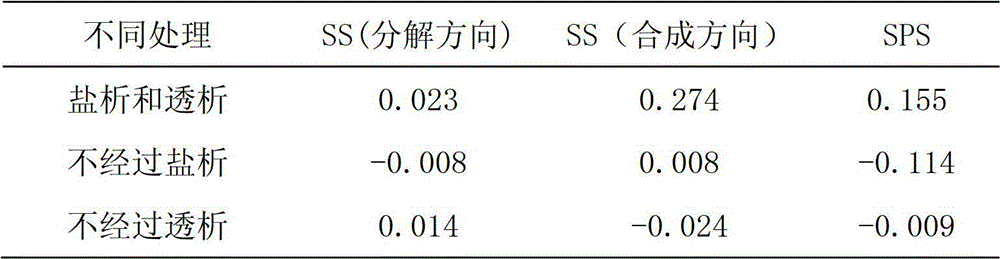
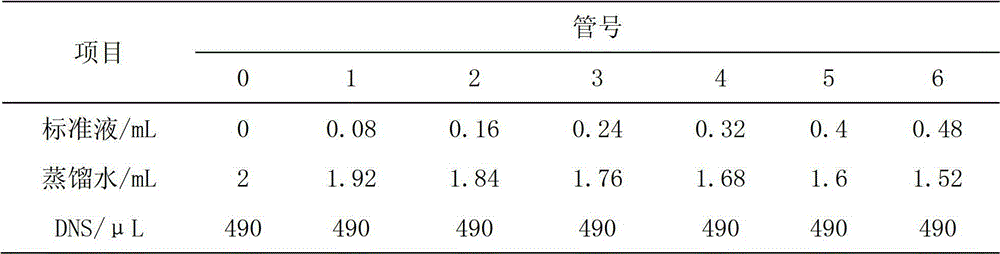
Method for extracting sucrose synthase and sucrose phosphate synthase of pear fruit and activity determination method thereof
InactiveCN102747055AImprove qualityFull salting outMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesSaccharumSucrose synthetase
The invention belongs to the field of plant physiology, and discloses a method for extracting sucrose synthase and sucrose phosphate synthase of pear fruits and an activity determination method thereof. Small molecules such as sugar, ions and the like can be usually removed from a primary extraction enzyme solution through adding a salting-out step and a dialysis step in the extracting process of the sucrose synthase and the sucrose phosphate synthase, so that activities of the sucrose synthase and the sucrose phosphate synthase in the fruits can be accurately detected. The method provides physiological basis for disclosing accumulation differences of the sugar in the fruits, and further provides theoretical basis for improving the quality of fruit sweetness and flavor.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Producing biofuels using polyketide synthases
The present invention provides for a non-naturally occurring polyketide synthase (PKS) capable of synthesizing a carboxylic acid or a lactone, and a composition such that a carboxylic acid or lactone is included. The carboxylic acid or lactone, or derivative thereof, is useful as a biofuel. The present invention also provides for a recombinant nucleic acid or vector that encodes such a PKS, and host cells which also have such a recombinant nucleic acid or vector. The present invention also provides for a method of producing such carboxylic acids or lactones using such a PKS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
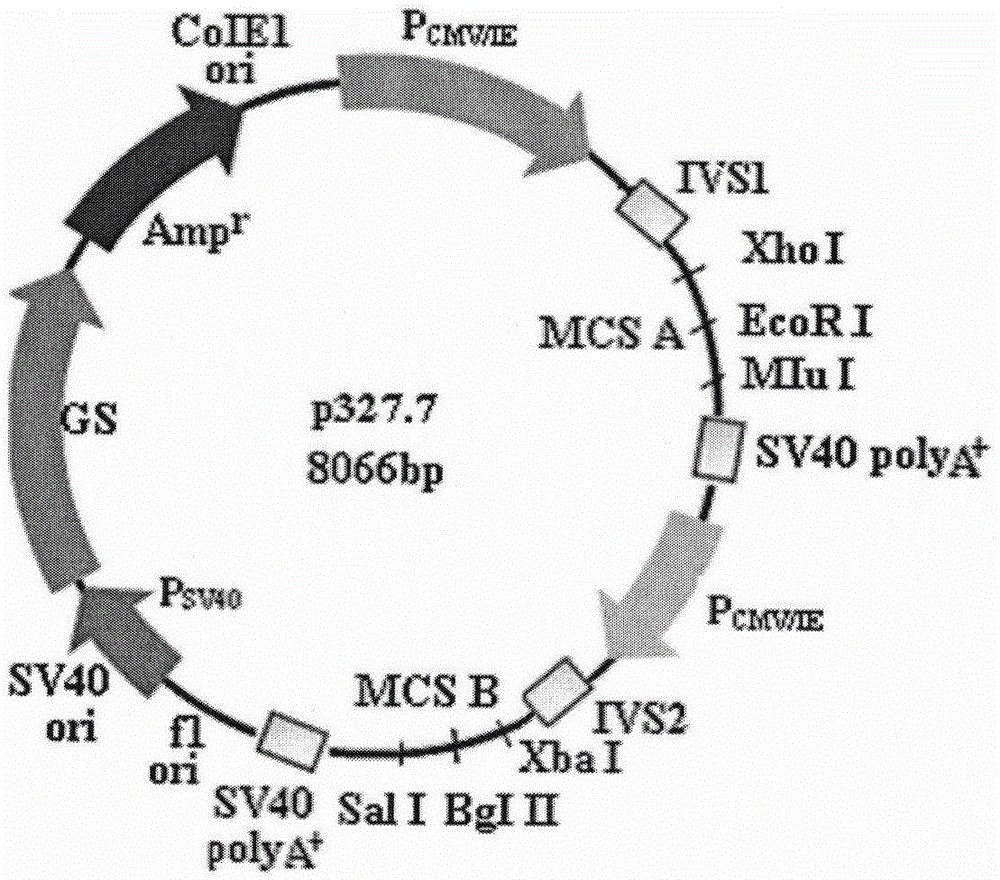
Glutamine synthetase high-efficiency expression vector with dual expression cassettes
ActiveCN104195173BHigh expressionEasy to filterVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationCloning SiteHydrolysis
The invention relates to a glutamine synthetase expression vector which can be amplified and have two expression cassettes. The main components of the glutamine synthetase expression vector include the following six parts: a first expression cassette component, a second expression cassette component, an f1 replicon, a glutamine synthetase expression cassette component, an ampicillin beta lactamase hydrolysis expression cassette component and a ColE1 replicon, wherein a strong enhancer / promotor CMV (Cytomegalovirus) and an immediate early enhancer / promotor are adopted to the first expression cassette component and the second expression cassette component; a weak promotor / enhancer SV40 is adopted to the glutamine synthetase expression cassette component, so that the expression of glutamine synthetase is reduced, and the screening of high-expression cloning is facilitated; and expression protein coding genes are respectively cloned to the expression vector through a multiple cloning site A and a multiple cloning site B. The glutamine synthetase expression vector disclosed by the invention is suitable for simultaneously expressing 1-2 proteins efficiently in mammalian cells and especially suitable for expressing antibody proteins.
Owner:BEIJING BIYANG BIOTECH
Streptomyces griseus subsp.griseus trehalose synthetase gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN102533801AReduce the numberEase of industrial productionEnzymesFermentationFood industryReaction speed
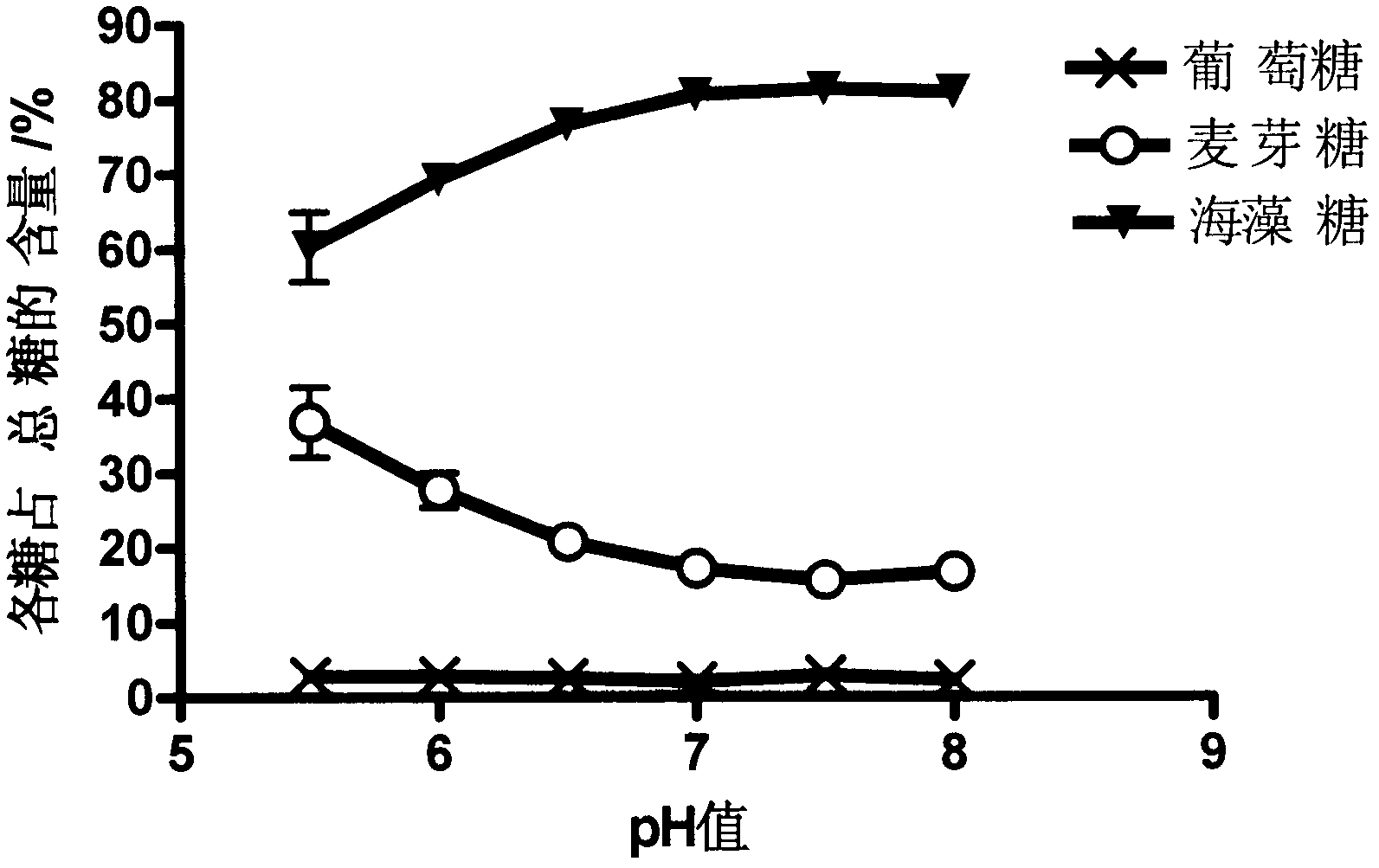
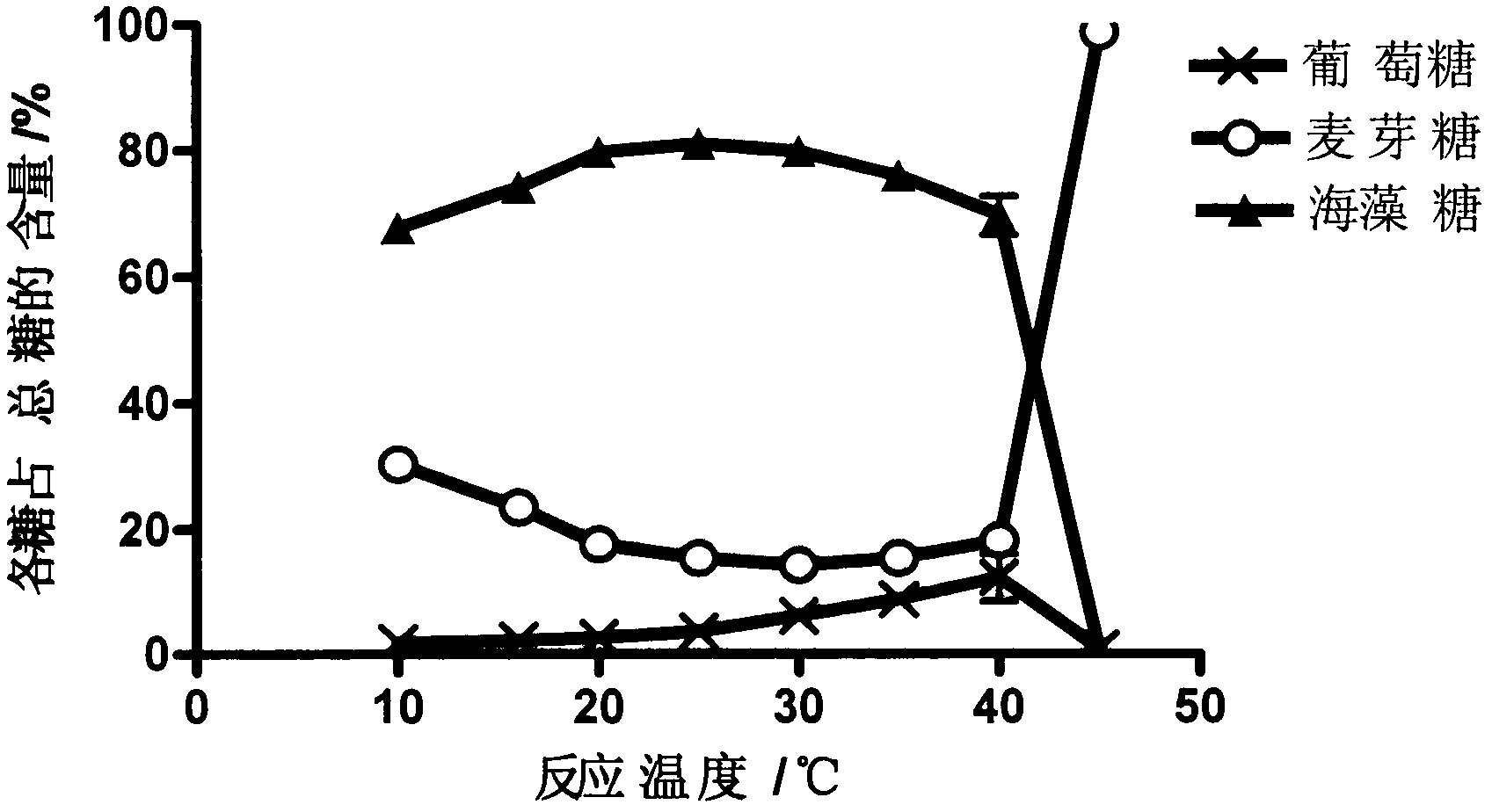
The invention relates to a Streptomyces griseus subsp.griseus trehalose synthetase gene and applications thereof. The gene is cloned from Streptomyces griseus subsp.griseus, and the synthetase gene expressed by the gene is capable of converting maltose into trehalose. The gene has the biggest characteristics of high conversion efficiency and high reaction speed. Under the reaction condition provided by the invention, the content of the trehalose in the reaction product of the trehalose generated by converting the maltose can reach 87 percent, and moreover, only 3.8 percent of glucose is produced, thereby being beneficial to increasing the conversion rate of a substrate and reducing the production cost. Recombinant trehalose synthetase produced by applying the gene can be used for preparing trehalose by using maltose syrup sold in the market or maltose syrup prepared from starch. The trehalose can be applied to the field of food industry, facial cosmetics, pharmaceutical and biological products and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for constructing highly expressed trehalose synthase engineering bacteria by using Pcry3Aa promoter
ActiveCN105779489AGood synthesis effectImprove stabilityBacteriaTransferasesSequence signalProtein target
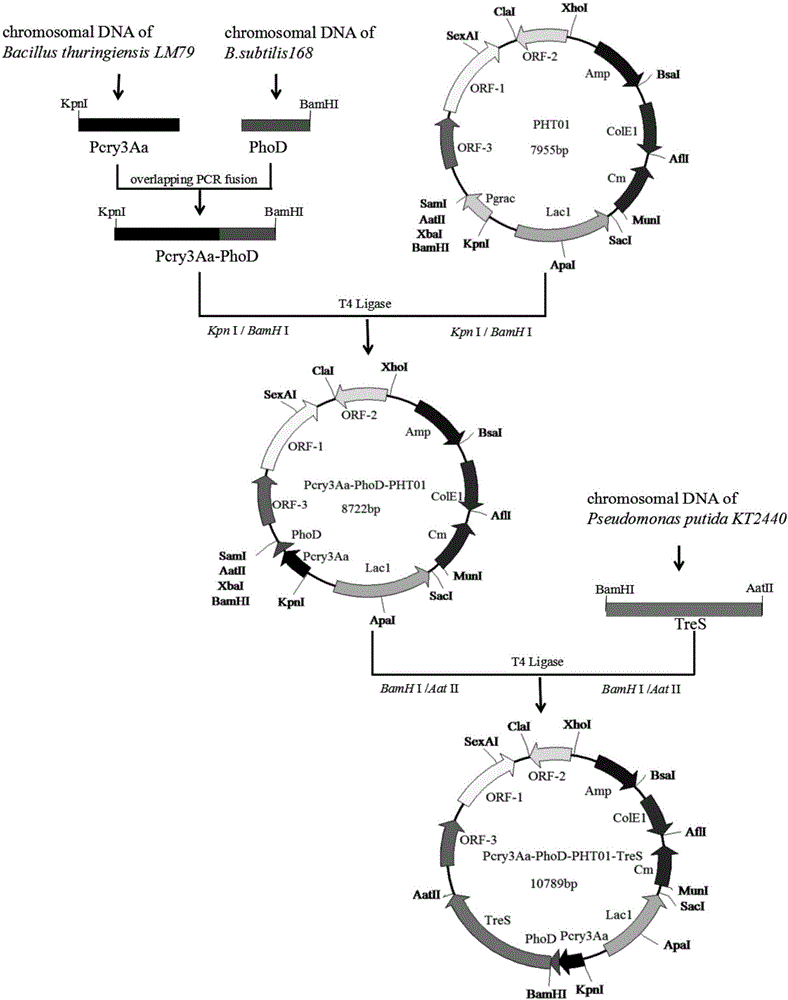
The invention relates to a method for constructing highly expressed trehalose synthase engineering bacteria by using a Pcry3Aa promoter. For a recombinant carrier, a Pcry3Aa-PhoD fragment by which a Pcry3Aa promoter fragment and a PhoD signal peptide fragment are connected by an overlap PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is inserted at the upstream of a restriction enzyme cutting site BamHI of a shuttle plasmid PHT01, and a target protein trehalose synthase TreS fragment is inserted between two restriction enzyme cutting site, i.e., BamHI and AatII. The invention further relates to a method for constructing the highly expressed trehalose synthase engineering bacteria by using the recombinant carrier. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Pcry3Aa promoter is adopted to naturally induce the synthesis of trehalose synthase; because the Pcry3Aa promoter contains a special STAB-SD structure, the stability of the Pcry3Aa promoter to transcribe mRNA is improved, the half-life period of mRNA is prolonged, the mRNA translation level of a downstream target gene is improved, and therefore the trehalose synthase is highly expressed.
Owner:山东开盾生物科技有限公司
Heterocyclic modulators of lipid synthesis
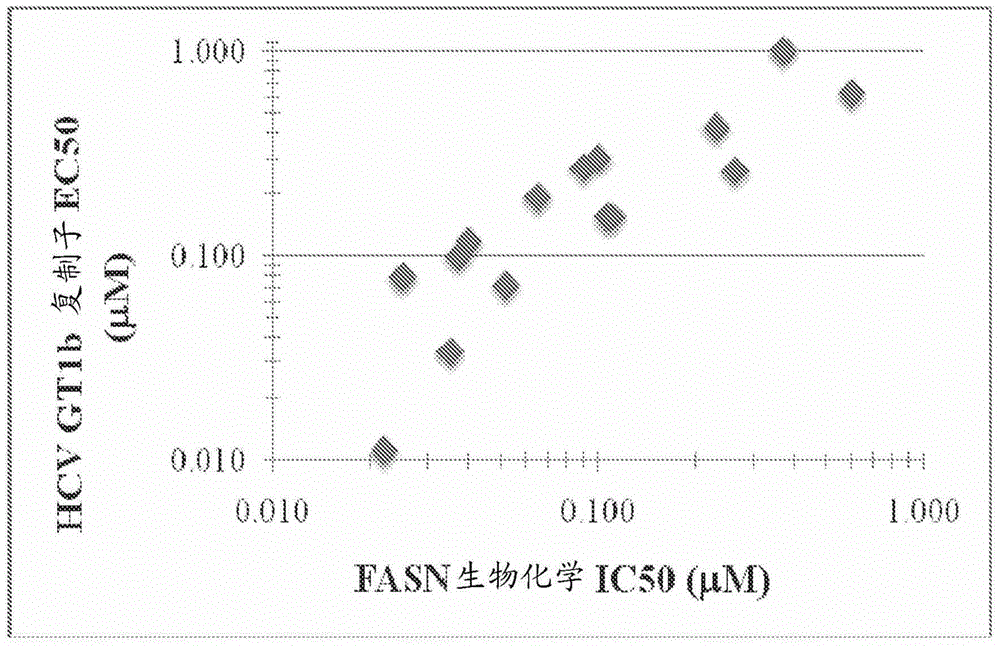
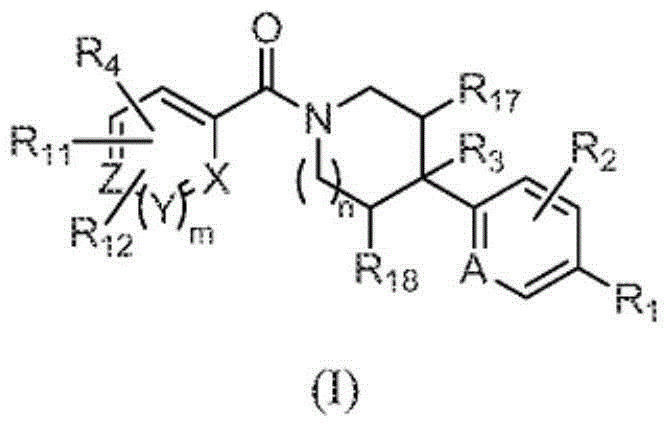
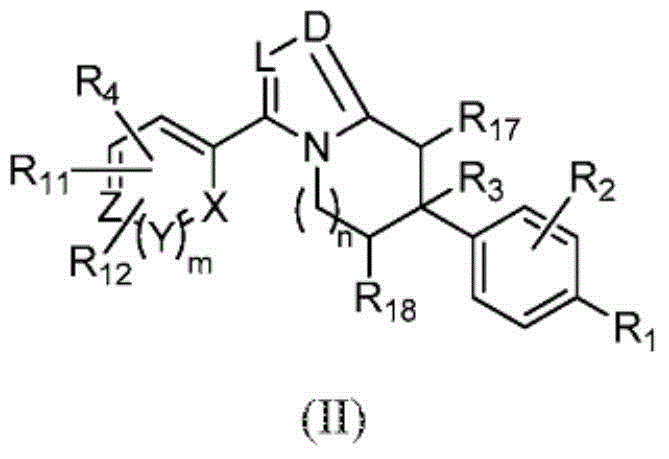
ActiveCN103561576AImproved antiviral activityHigh anticancer activityBiocideSenses disorderFatty acid biosynthesisMembrane lipid metabolism
Compounds that are fatty acid synthesis modulators are provided. The compounds may be used to treat disorders characterized by disregulation of the fatty acid synthase function by modulating the function and / or the fatty acid synthase pathway. Methods are provided for treating such disorders including viral infections, such as hepatits C infection, cancer and metabolic disorders.
Owner:GANNEX PHARM CO LTD
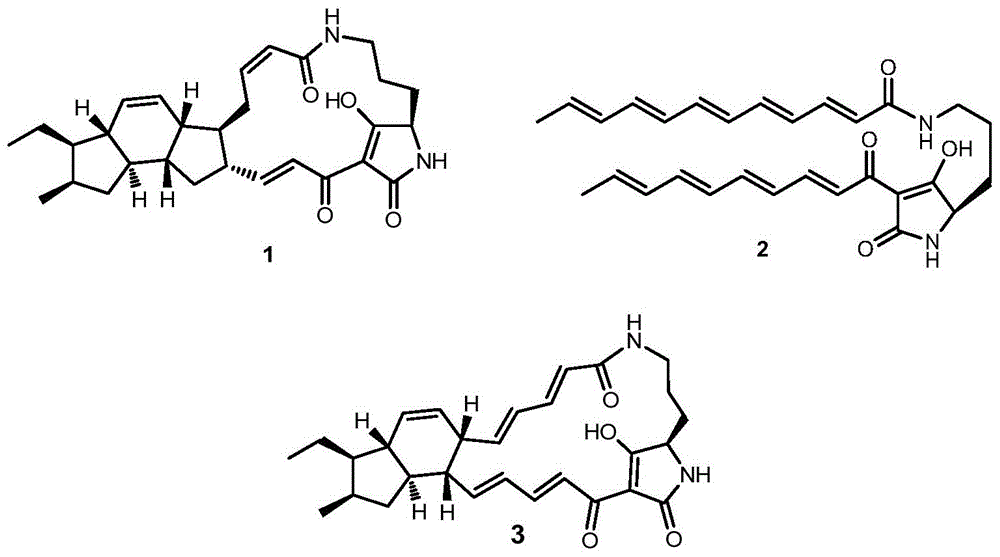
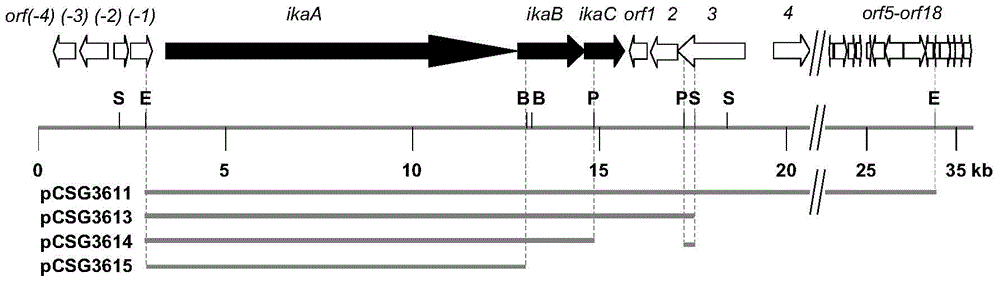
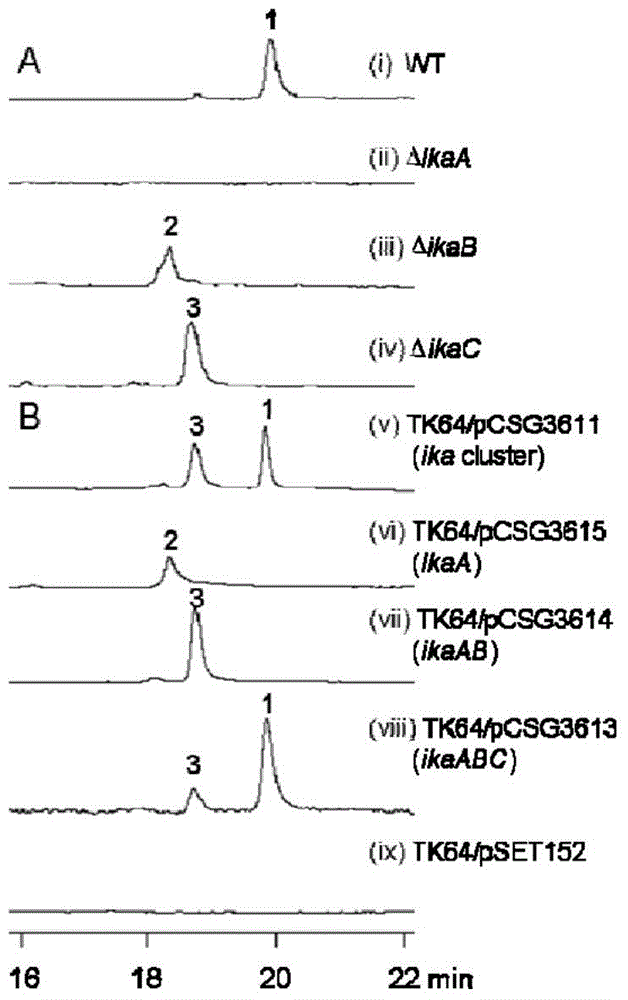
Biosynthetic gene cluster of ikarugamycin and application of biosynthetic gene cluster
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of ikarugamycin and an application of the biosynthetic gene cluster. The nucleotide sequence of the biosynthetic gene cluster of the ikarugamycin is as shown in the 3411th to 15678th sites of SEQ ID NO. 1 and contains three genes, namely a heterozygous polyketone / non-ribosomal polypeptide synthetase gene ikaA, FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) dependent oxidoreductase gene ikaB and similar Michael cyclization reaction enzyme gene ikaC. All the genes and protein information relevant to the biosynthesis of the ikarugamycin are helpful to interpret the biosynthesis mechanism of natural products of a polycyclic tetramate large-ring lactam family so as to provide a theoretical basis and materials for further genetic modification. The genes and proteins can be used for digging or creating compounds or genes and proteins applicable to the medicine and health industry and industry and agriculture in nature.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com