Patents
Literature
58 results about "Giant cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A giant cell (multinucleated giant cell, multinucleate giant cell) is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells (usually histiocytes), often forming a granuloma. It can arise in response to an infection, such as from tuberculosis, herpes, or HIV, or foreign body. These multinucleate giant cells (MGCs) are cells of monocyte or macrophage lineage fused together.
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20060140936A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory diseases, using multispecific antagonists that target at least two different markers are disclosed. The different targets include (i) proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system, (ii) coagulation factors, and (iii) targets specifically associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, wherein the targets included in group (iii) are neither a proinflammatory effector of the immune system nor a coagulation factor. When the multispecific antagonist reacts specifically with a target associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, it also binds specifically with at least one proinflammatory effector of the immune system or at least one coagulation factor. Thus, the multispecific antagonist contains at least one binding specificity related to the diseased cell or condition being treated and at least one specificity to a component of the immune system, such as a receptor or antigen of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, and dendritic cells, a modulator of coagulation, or a proinflammatory cytokine. The multispecific antagonists are used in the treatment of various diseases that are generated or exacerbated by, or otherwise involve, proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system or coagulation factors. Such diseases more particularly include acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, giant cell arteritis, septicemia and septic shock, coagulopathies (including diffuse intravascular coagulation), neuropathies, graft versus host disease, infectious diseases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, granulomatous diseases, transplant rejection, asthma, cachexia, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Other diseases also responsive to these therapies include cancers and conditions with pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20080108794A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20080241141A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory diseases, using multispecific antagonists that target at least two different markers are disclosed. The different targets include (i) proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system, (ii) coagulation factors, and (iii) targets specifically associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, wherein the targets included in group (iii) are neither a proinflammatory effector of the immune system nor a coagulation factor. When the multispecific antagonist reacts specifically with a target associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, it also binds specifically with at least one proinflammatory effector of the immune system or at least one coagulation factor. Thus, the multispecific antagonist contains at least one binding specificity related to the diseased cell or condition being treated and at least one specificity to a component of the immune system, such as a receptor or antigen of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, and dendritic cells, a modulator of coagulation, or a proinflammatory cytokine. The multispecific antagonists are used in the treatment of various diseases that are generated or exacerbated by, or otherwise involve, proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system or coagulation factors. Such diseases more particularly include acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, giant cell arteritis, septicemia and septic shock, coagulopathies (including diffuse intravascular coagulation), neuropathies, graft versus host disease, infectious diseases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, granulomatous diseases, transplant rejection, asthma, cachexia, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Other diseases also responsive to these therapies include cancers and conditions with pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Kit for genotyping VZV, production method of kit and application of kit
InactiveCN105132584ANo cross reactionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHuman DNA sequencingChemical structure
The invention provides a kit for genotyping VZV (Varicella-Zoster Viruses). The kit is characterized by comprising a nucleotide sequence shown as the Table 3 in the specification, and specific primers and specific probes corresponding to clade1-5 type VZV of chemical structures. The kit has the function of detecting various kinds of VZV DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid); the detection sensitivity is 10<2> copies / reaction; no cross reaction with human genome, herpes simplex viruses type I / type II, cytomegaloviruses and EB viruses exists; and the kit is applicable to the virus gene diagnosis of clinical VZV infected persons, and can also be used for the epidemiology survey of different Clade types of VZV.
Owner:CHENGDU MILITARY GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Microfluidic device for detection of five indicators of sound child rearing
ActiveCN107102139AImplement automatic detectionEasy to operateLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisCell specificAntigen
The present invention discloses a microfluidic device for detection of five indicators of sound child rearing, the microfluidic device includes a microfluidic chip, a temperature control module, a micro motor moving module and a CCD detection module, through the mutual matching of the micro motor moving module, the temperature control module and the microfluidic chip, the processes of capture of target cell specific antigens and cleaning of cell antigens non-specifically adsorbed on microsphere surface by use of antibodies coating the microsphere surface, capture of enzyme labelled antibodies by use of the target cell antigens non-specifically adsorbed on the microsphere surface and catalytic chemiluminiscence of an excitation liquid by use of enzymes non-specifically adsorbed on the microsphere surface and the like can be respectively completed, the CCD detection module is cooperated for acquisition and detection of chemicalluminescence signals on the microsphere surface so as to achieve integration operation of the capture and detection process of five indicator antigens of sound child rearing in serum samples; the five indicators of sound child rearing comprise TOX (Toxoplasma gondii), RUB (Rubella), CMV (cytomegalovirus), HSV-1 (herpe-1), and HSV-2 (herpe-2).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
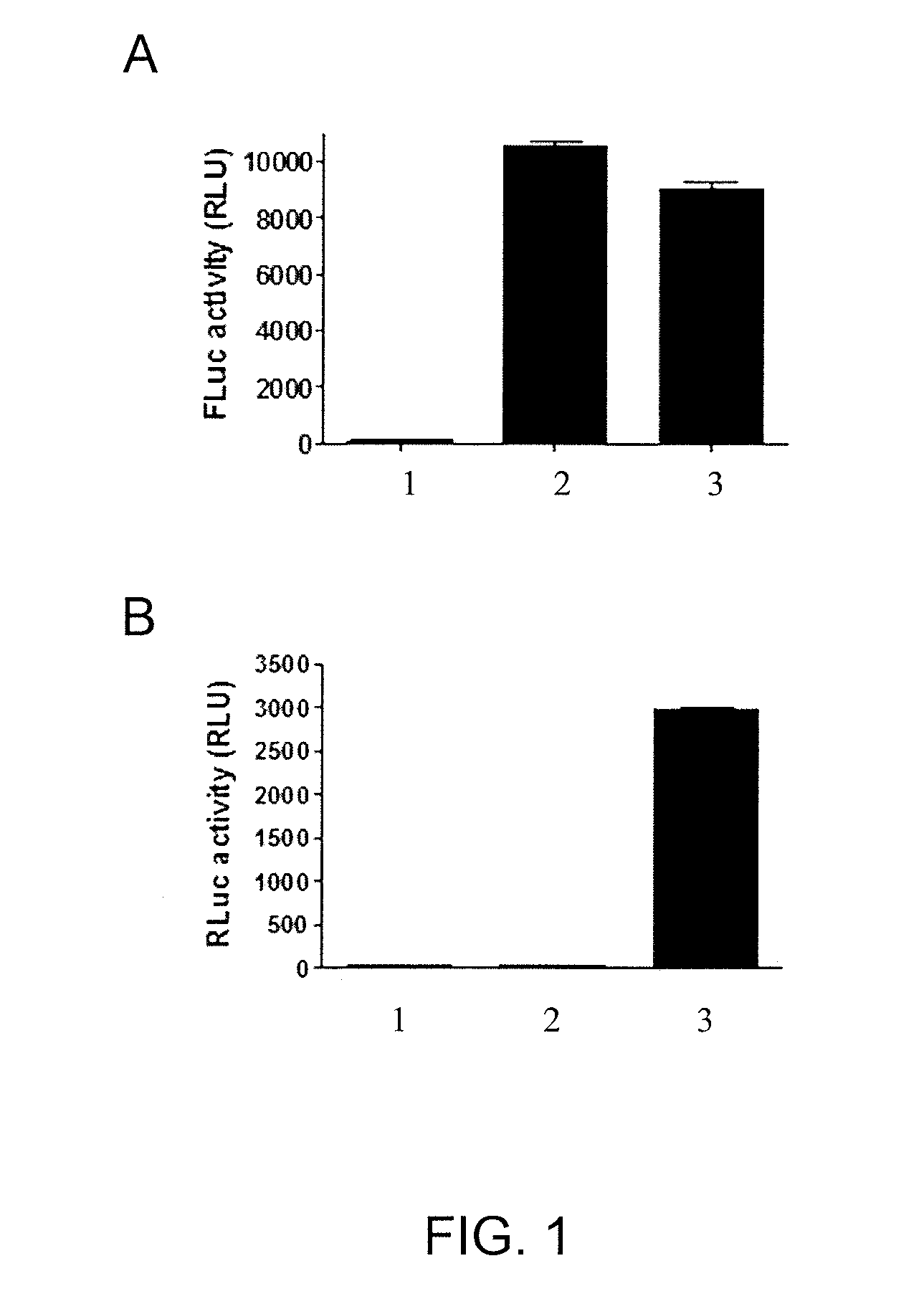
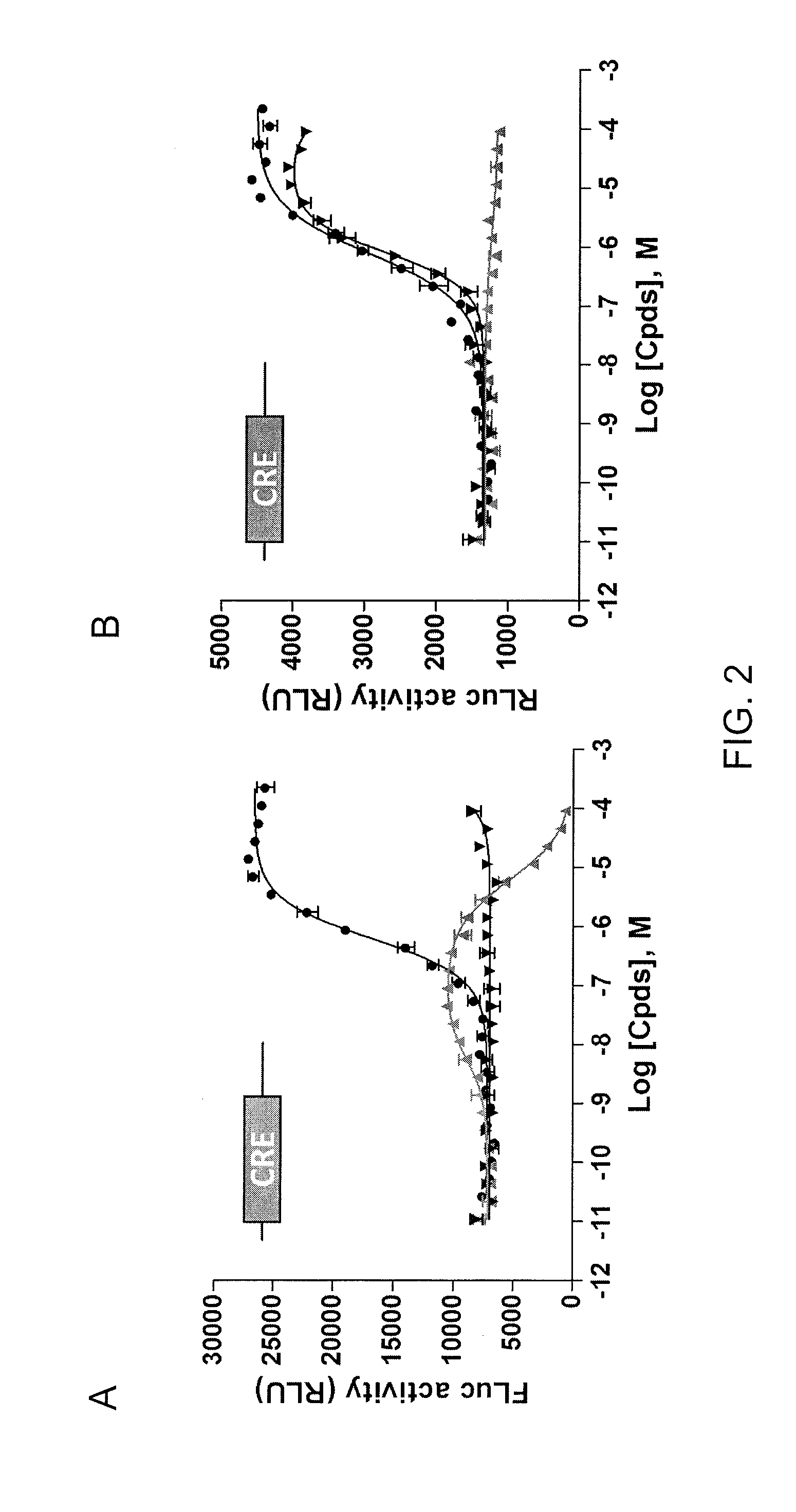
Coincidence reporter gene system
Disclosed is a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding (i) two or more reporters comprising a first reporter and a second reporter that is different from the first reporter; and (ii) one or more ribosomal skip sequences, wherein a ribosomal skip sequence is positioned between the first and second reporters, wherein the first and second reporters are stoichiometrically co-expressed from the nucleotide sequence and the nucleic acid does not comprise a cytomegalovirus-immediate early (CMV-IE) promoter. Also disclosed are methods of screening test compounds for ability to modulate a biological activity of interest using the nucleic acid, as well as related recombinant expression vectors, host cells, and populations of cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
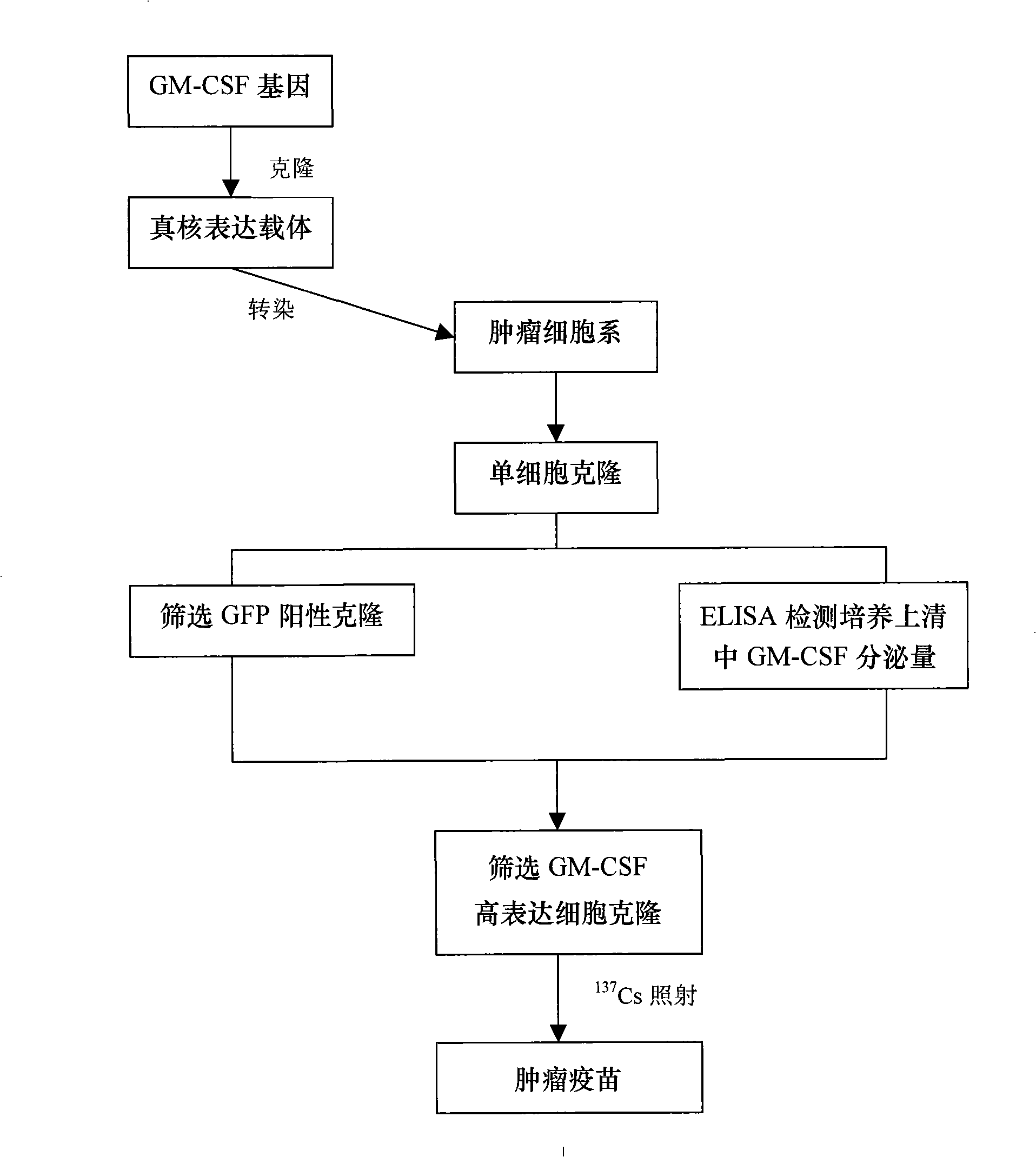
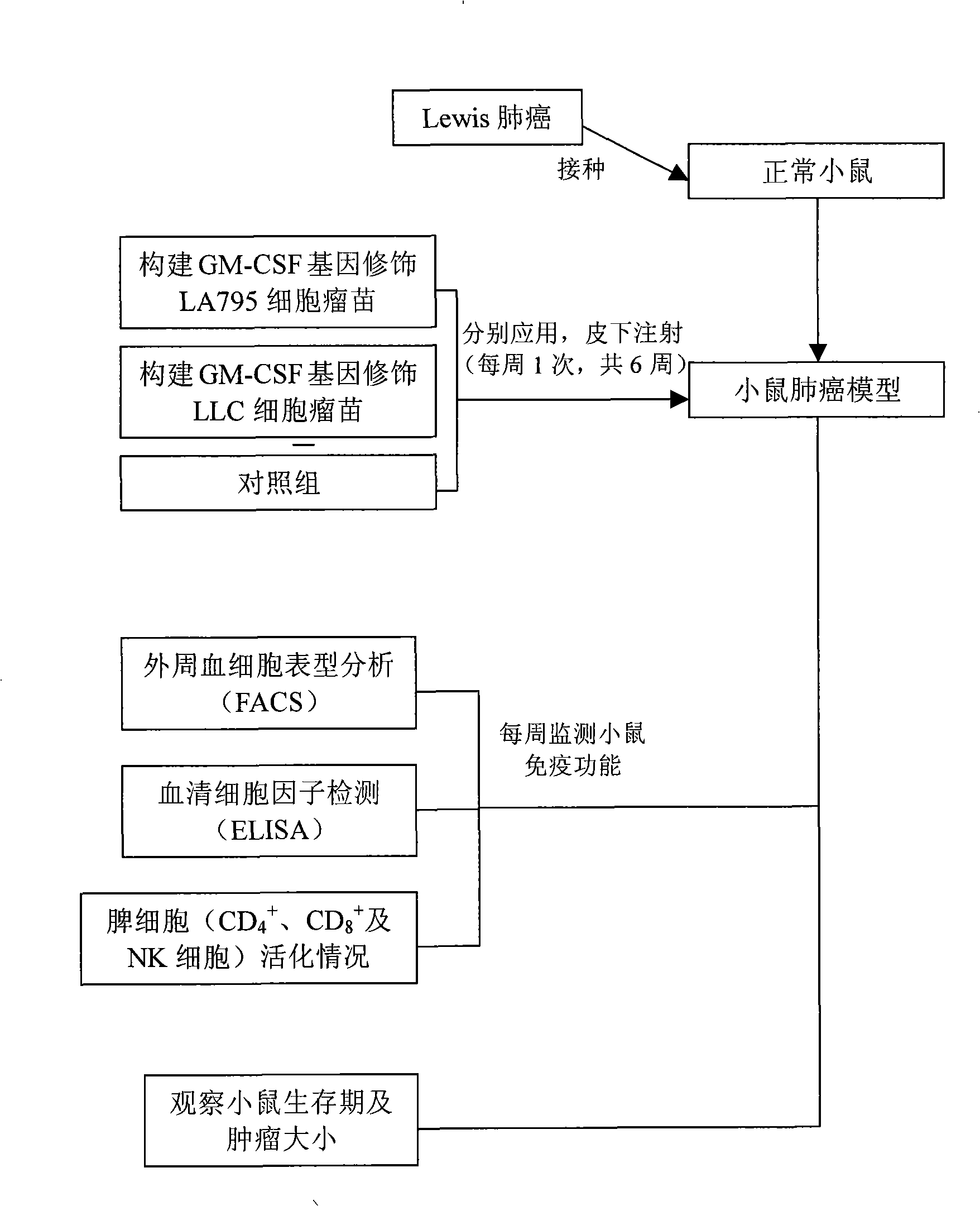
Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor gene modified allogene tumour cell vaccine
InactiveCN101353645AMammal material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsGene ModificationTumor cells
Owner:TIANJIN TUMOR HOSPITAL
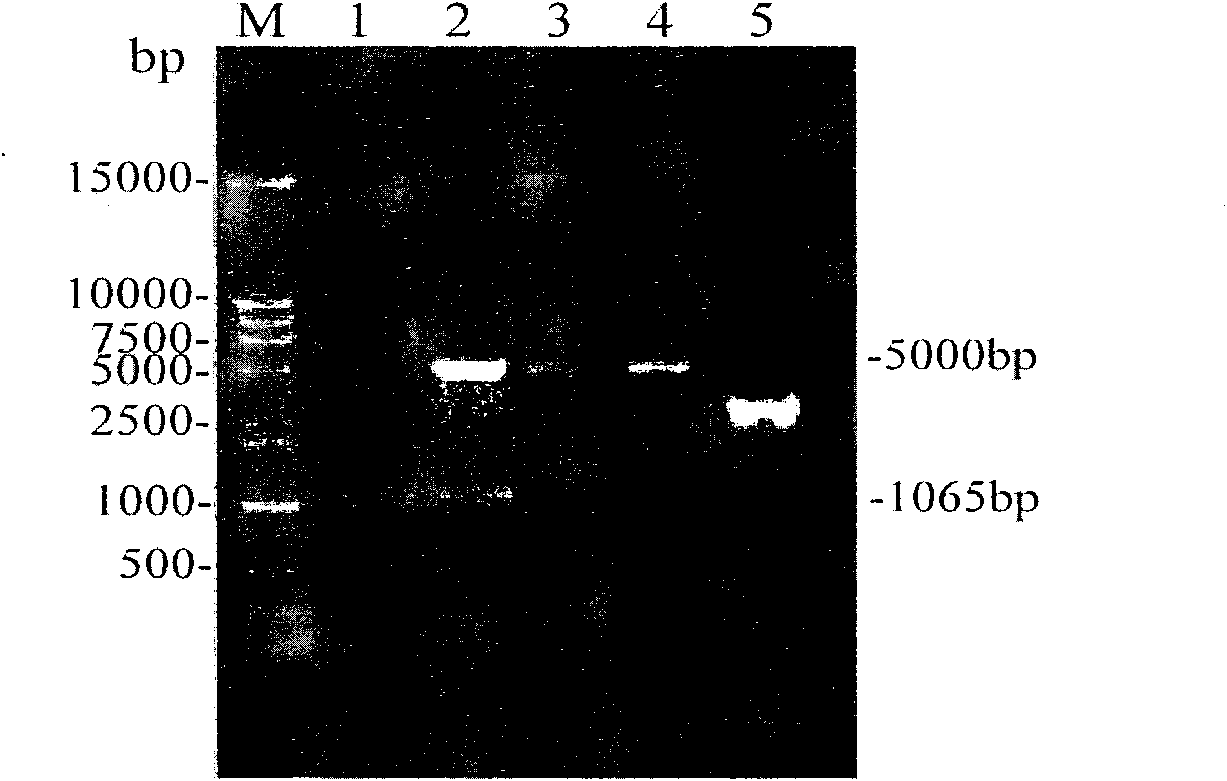
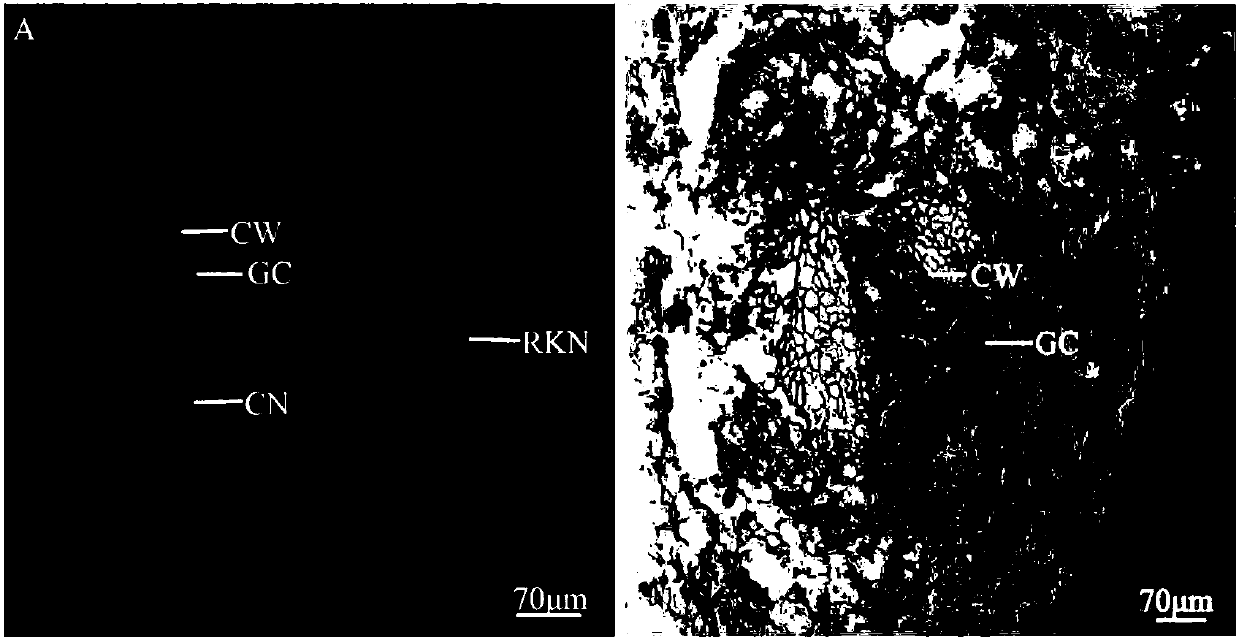
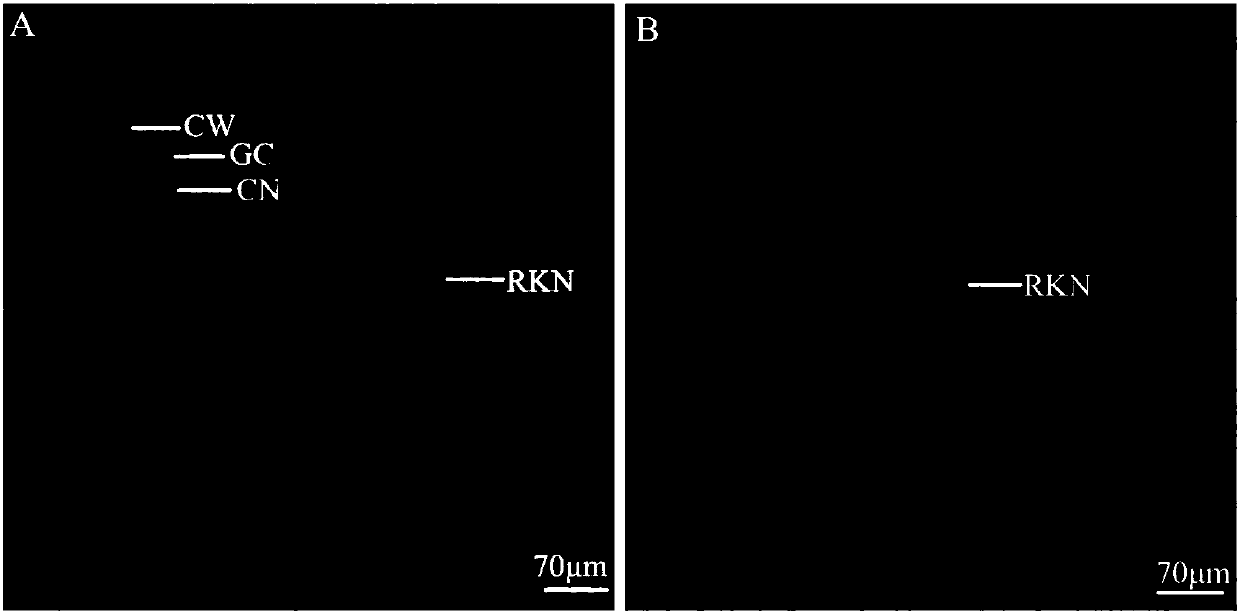
Method for manufacturing water convolvulus root-knot nematode giant cell paraffin sections
InactiveCN107702966AImprove slicing efficiencyGuaranteed slice qualityPreparing sample for investigationPlant tissueStaining
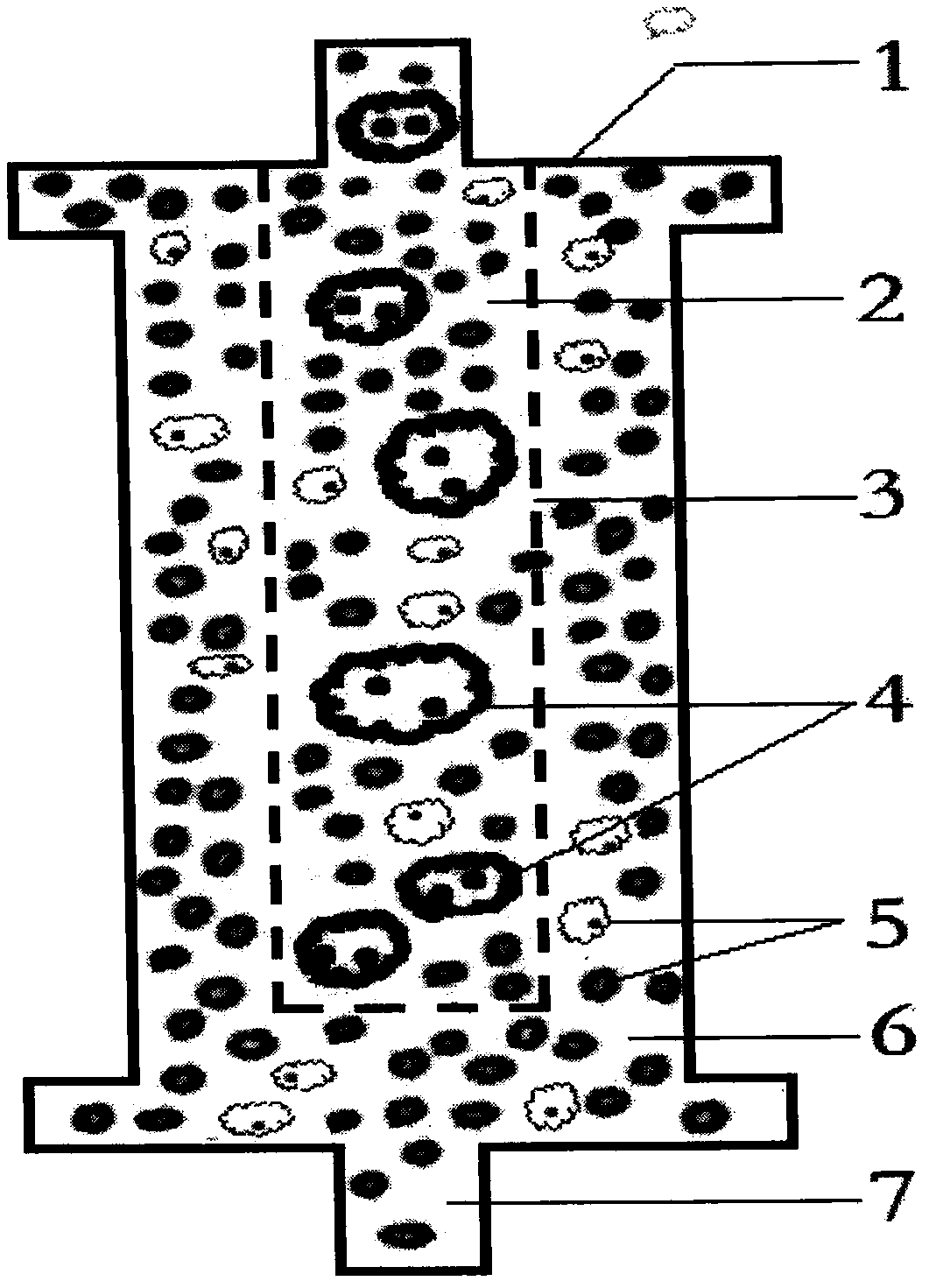
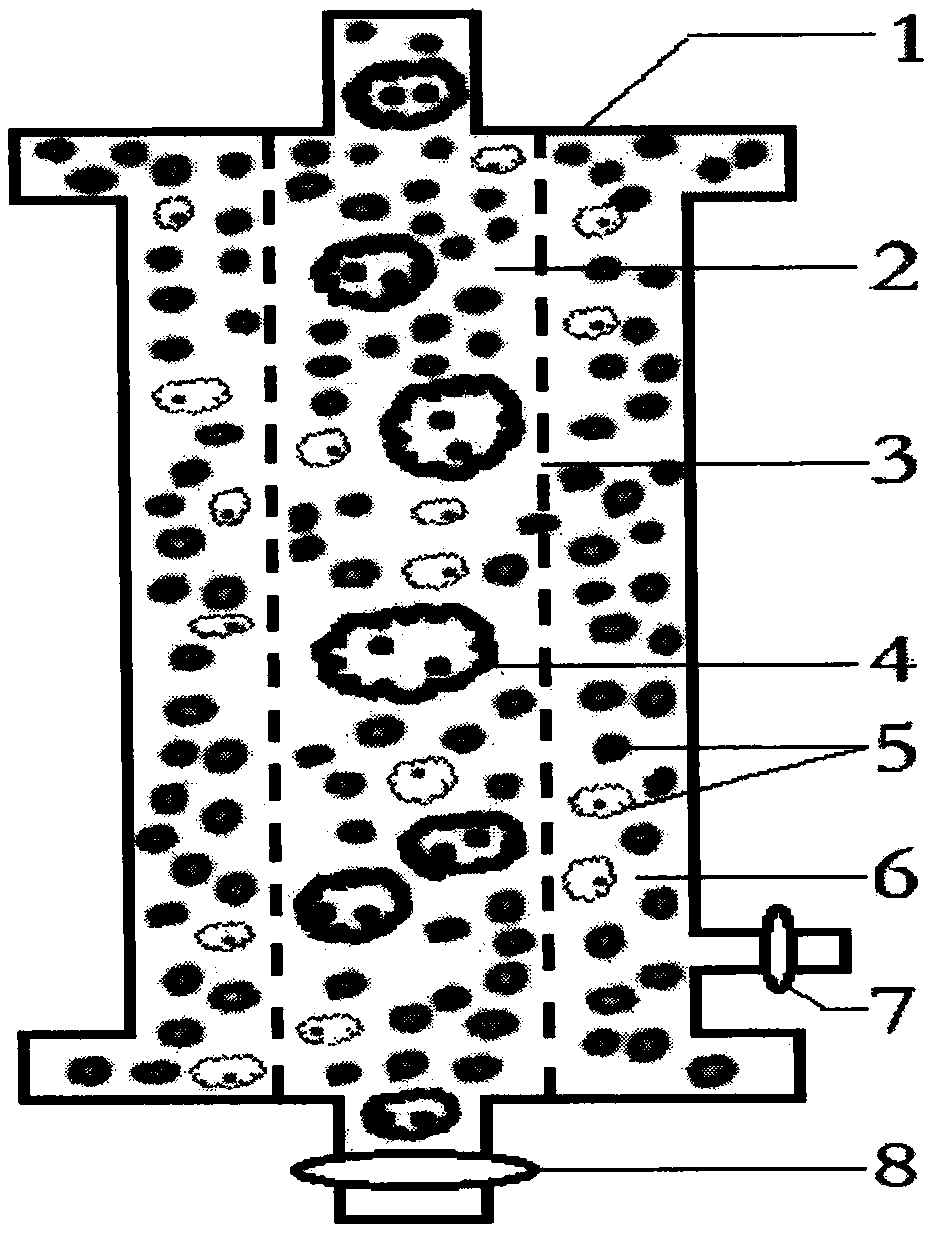
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing water convolvulus root-knot nematode giant cell paraffin sections. According to the method, steps of staining, cross-sectioning angle, de-waxing andthe like are improved on the basis of conventional paraffin section technologies. The Ehrlich's hematoxylin staining solution is used for staining of plant tissues, and traditional dewaxing before staining is changed into mass staining before dewaxing. Section angle adopts cross-sectioning, and section thickness is 5-10 microns. According to the invention, dewaxing mode is also improved, and a TO-type biological slice-making transparent reagent is used to replace xylene for dewaxing. By the manufacturing method of water convolvulus root-knot nematode giant cell paraffin sections, staining effect of water convolvulus root-knot nematode giant cell paraffin sections is obviously enhanced, work efficiency is raised, and the effect of water convolvulus root-knot nematode giant cell paraffin sections is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
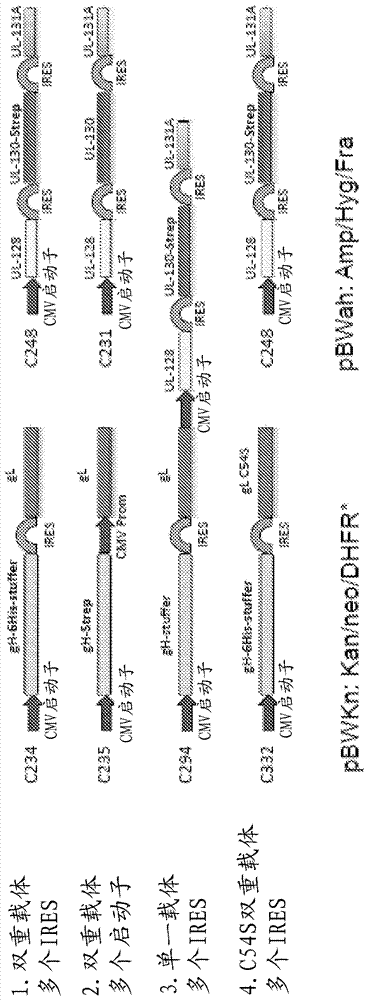
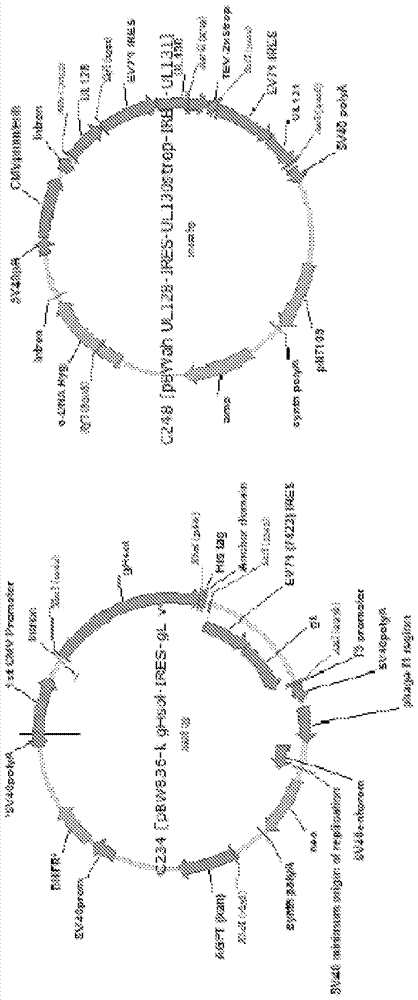
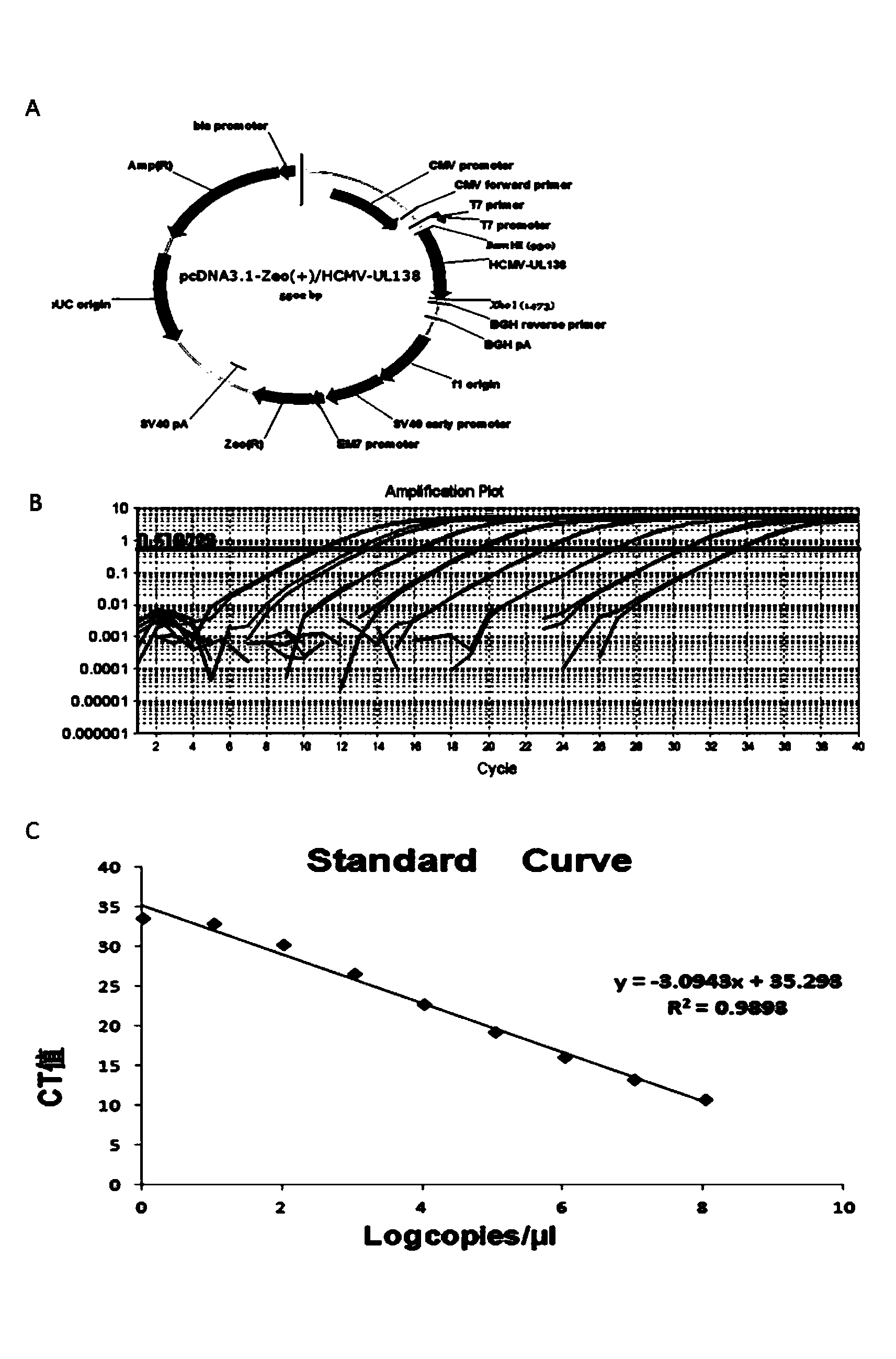
Mammalian cells expressing cytomegalovirus antigens
This invention relates to cytomegalovirus (CMV) proteins suitable for vaccine uses. Provided herein are mammalian host cells, in particular CHO cells, in which the sequence(s) encoding CMV proteins gH, gL, pUL128, pUL130, pUL131 (or a complex-forming fragment thereof) are stably integrated into the genome.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Optimized lentiviral transfer vectors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20200399655A1Increase productionIncreased nuclear export of RNAPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyHeterologousOrigin of replication
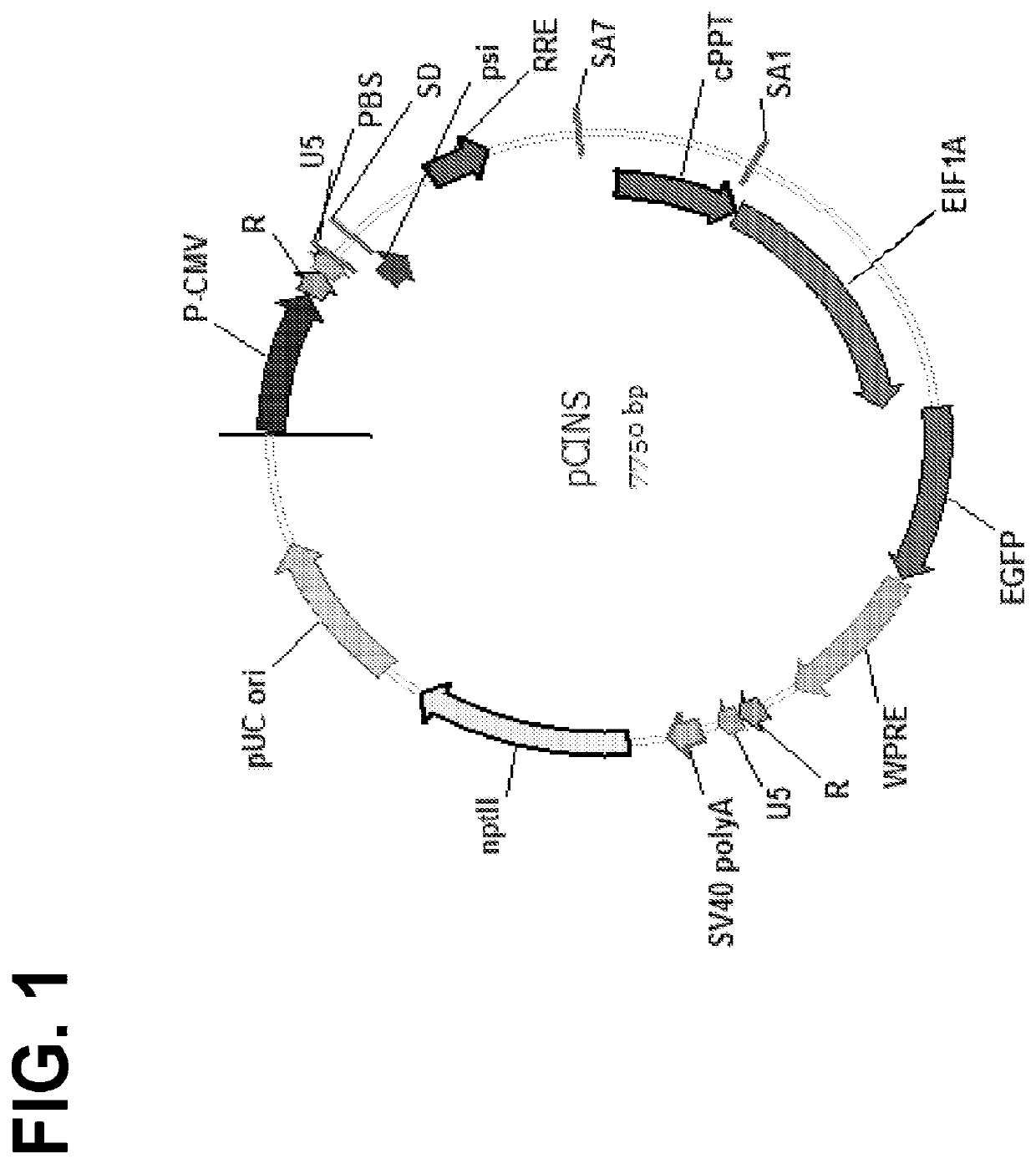
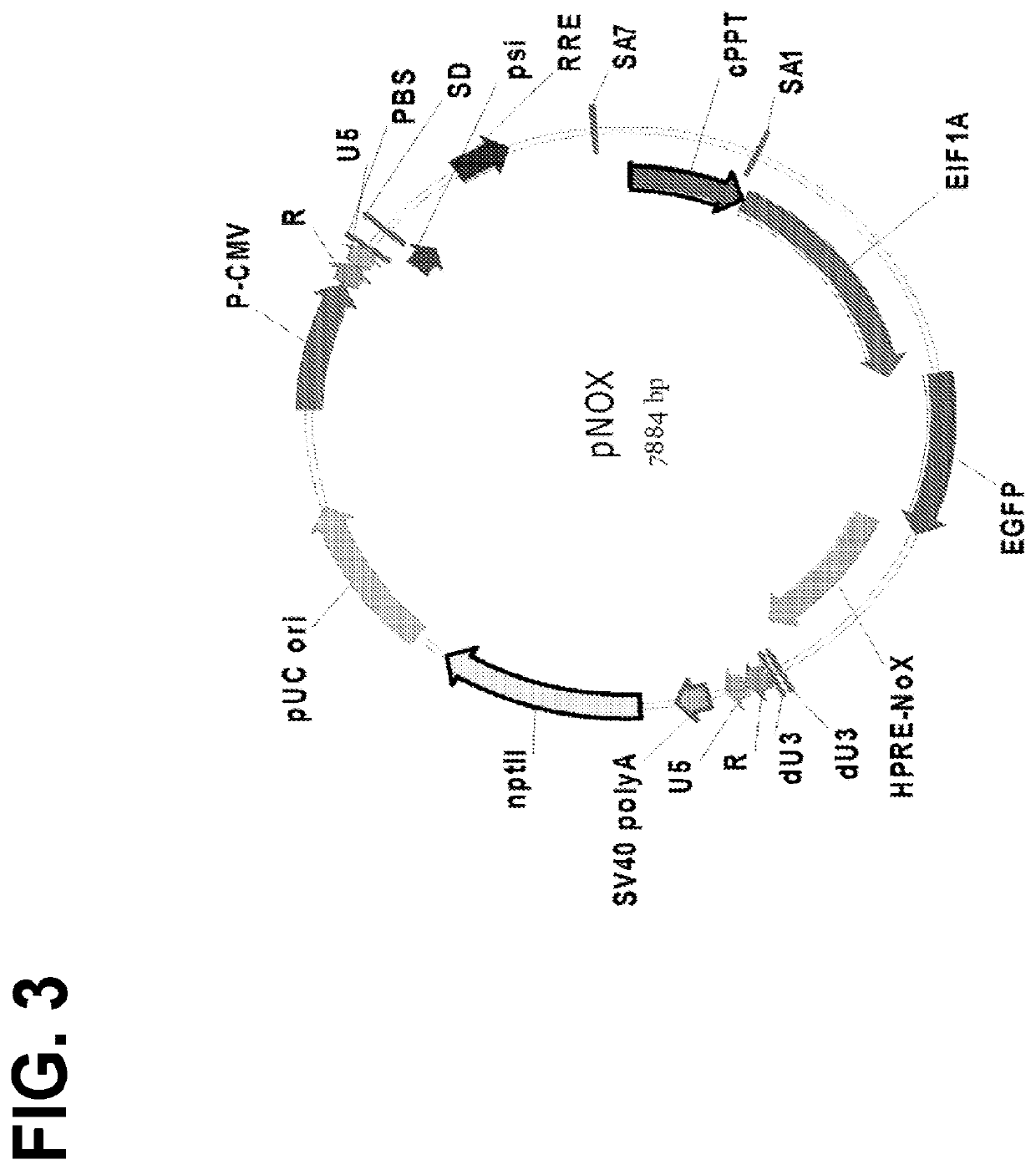
The invention features lentiviral transfer vectors that include heterologous nucleic acids to be introduced into a cell. The lentiviral transfer vector may be characterized by the following features: (a) including a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter; (b) including a polynucleotide encoding a partial gag protein that includes a mutated INS1 inhibitory sequence that reduces restriction of nuclear export of RNA; (c) not including a polynucleotide encoding the INS2, INS3, and INS4 inhibitory sequences of gag; (d) not including an SV40 origin of replication and / or an f1 origin of replication; (e) including a cPPT sequence that contains splice site; (f) including an EF1alpha promoter with intact splice donor and acceptor sites; and (g) including hepatitis B PRE with mutation in start codon of X protein ORF.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Immunity colloidal gold reagent for detecting IgM antibody of giant cells virus and its preparing method
The sample pad and the binding pad, which is the conjugate coated with the anti U chain monoclonal antibody and colloidal gold, are adhered to the one end with PVC back covered in sequence. The cellulose nitrate film coated with the specificity surface film antigen of giant cells virus and the anti rat IgG of sheep (or rabbit) is adhered to the middle of the reagent. The water uptake pad is adhered to another end of the reagent. The reagent features high specificity and sensivitiy, simple and fast. The reagent is applicable to the detection in site within 30 minutes for the full testing procedure. Operation personnel can complete the operation by reading the menu and without need of professional training.
Owner:博顿生物检验技术(杭州)有限公司
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell technology for reproductive health
InactiveCN103243069ARich sourcesNo infectionMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTissue typingSide effect
The invention provides a technology of isolating and culturing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cords of volunteers for reproductive health, relates to the fields of basic medicine and reproductive health medical science. Stem cells are isolated and purified from umbilical cord tissues of a volunteer, and cultured for multiplication in a particular culture system. When the total stem cells reach a certain number, the stem cells are used for maintenance of the reproductive system through intravenous infusion. The mesenchymal stem cells can be used for maintenance of reproductive system and treatment of dysfunction, and have the advantages that the source is rich, the cells are stored in kind and can be recovered or cultured and amplified when necessary, the in vitro amplification ability is high, tissue typing is not needed for transplantation, and the graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection do not occur. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell technology for health care or treatment has no toxic side effects and adverse reactions.
Owner:孙勇
Use of endogenous viral vaccine in chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy
ActiveUS11116834B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyViral VaccineTGE VACCINE
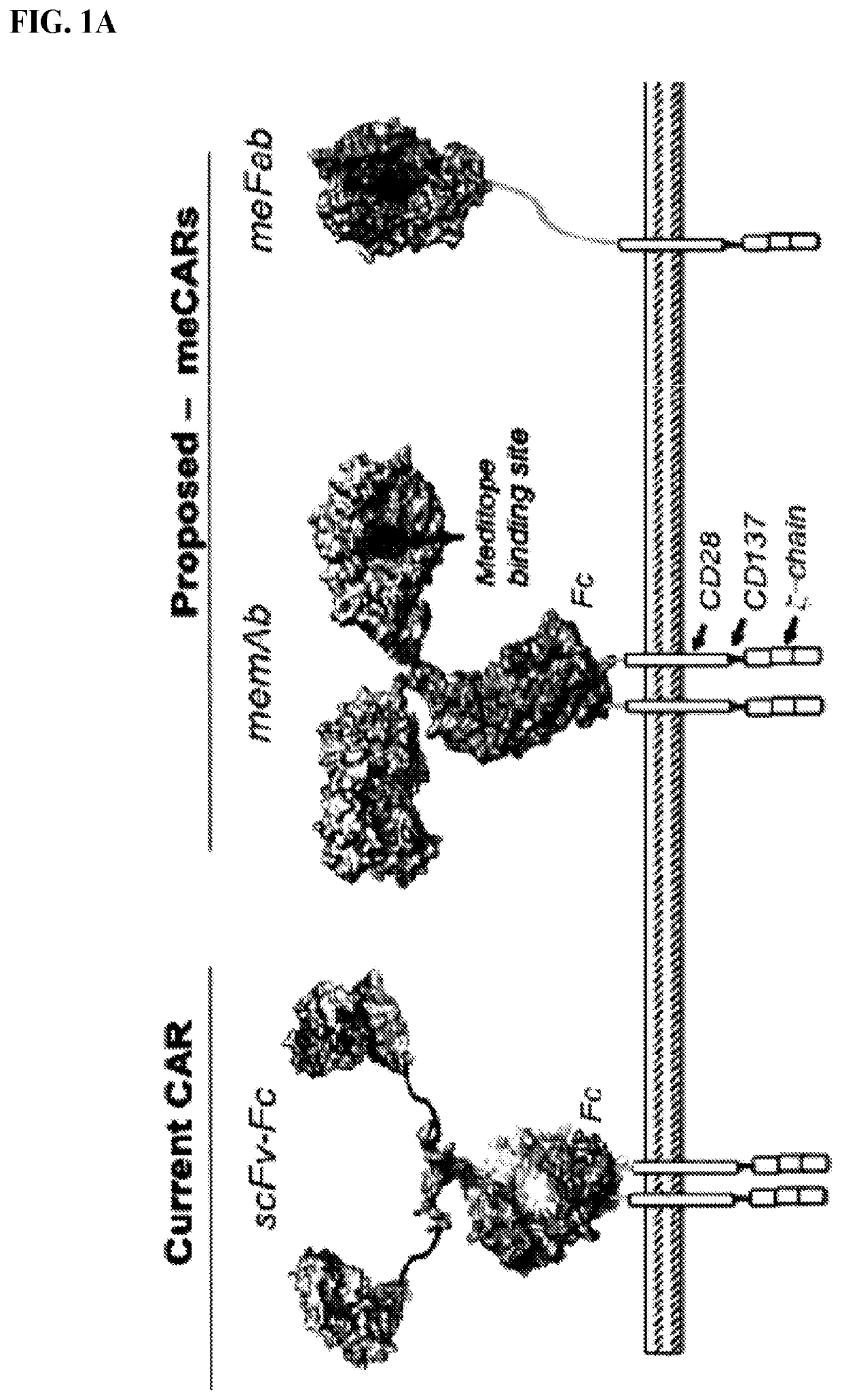
Provided herein are, inter alia, methods and compositions including T cells expressing (i) a recombinant CAR protein which includes a peptide binding site and is capable of specifically binding cancer-specific antigens and (ii) a T cell receptor specific for a viral antigen (e.g., a CMV pp65 protein). The engineered T cells provided herein may be used in combination with a viral vaccine (e.g. cytomegalovirus (CMV) Triplex Vaccine) to treat a variety of cancers. The methods described herein also permit in viva expansion of CMV-specific CAR T cells, instead of or in addition to ex vivo expansion, avoiding excessive T cell exhaustion that results in some cases from ex vivo manufacturing.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Method of detecting and quantifying cytomegalovirus
InactiveCN1888074AHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFluorescenceOligonucleotide Primer
Provided are detection and assay of CMV that can rapidly amplify and detect the beta 2.7 gene originating from CMV at a certain temperature through a one-step operation. The mRNA of beta 2.7 gene originating from CMV is amplified by utilizing the combination of specifically amplifiable oligonucleotide primers and the RNA amplification step comprising these combinations of oligonucleotide primers is measured and detected by using an oligonucleotide probe that is marked with an intercalated fluorescent dye, to settle above topic.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Novel and highly-sensitive detection method for latent human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in cell
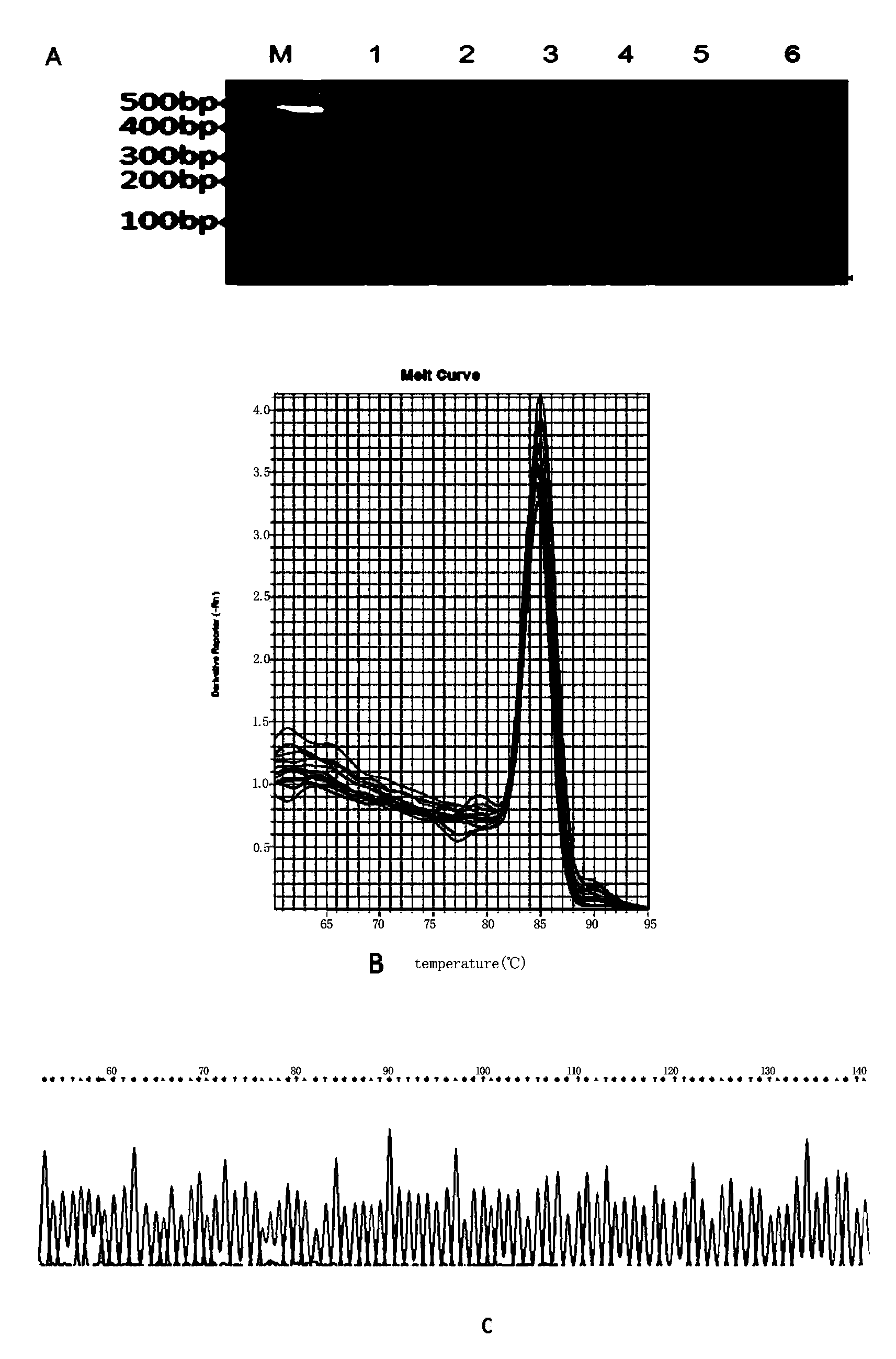
InactiveCN103627822AHigh homologyMicrobiological testing/measurementPeripheral blood mononuclear cellHCMV Infection
The invention provides a novel and highly-sensitive detection method for human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). The method represents a nested quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique which can detect both free HCMV and HCMV that infects a cell, and is characterized in that nucleic acid is extracted from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and a first round of PCR amplification is carried out through specific outer upstream and downstream primers; with the products of the first round of PCR amplification serving as a template, a second round of quantitative PCR amplification is carried out through specific inner upstream and downstream primers. By adopting the detection method provided by the invention, the HCMV detection sensitivity can reach 8 copies per microliter. Compared with the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay) method, compared with the ELISA method, the method adopting the PCR method for the detection of the latent HCMV infection has the advantages of rapidness, simplicity, high sensitivity, strong specificity, good stability and the like, and is a clinical method for early detection and diagnosis.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
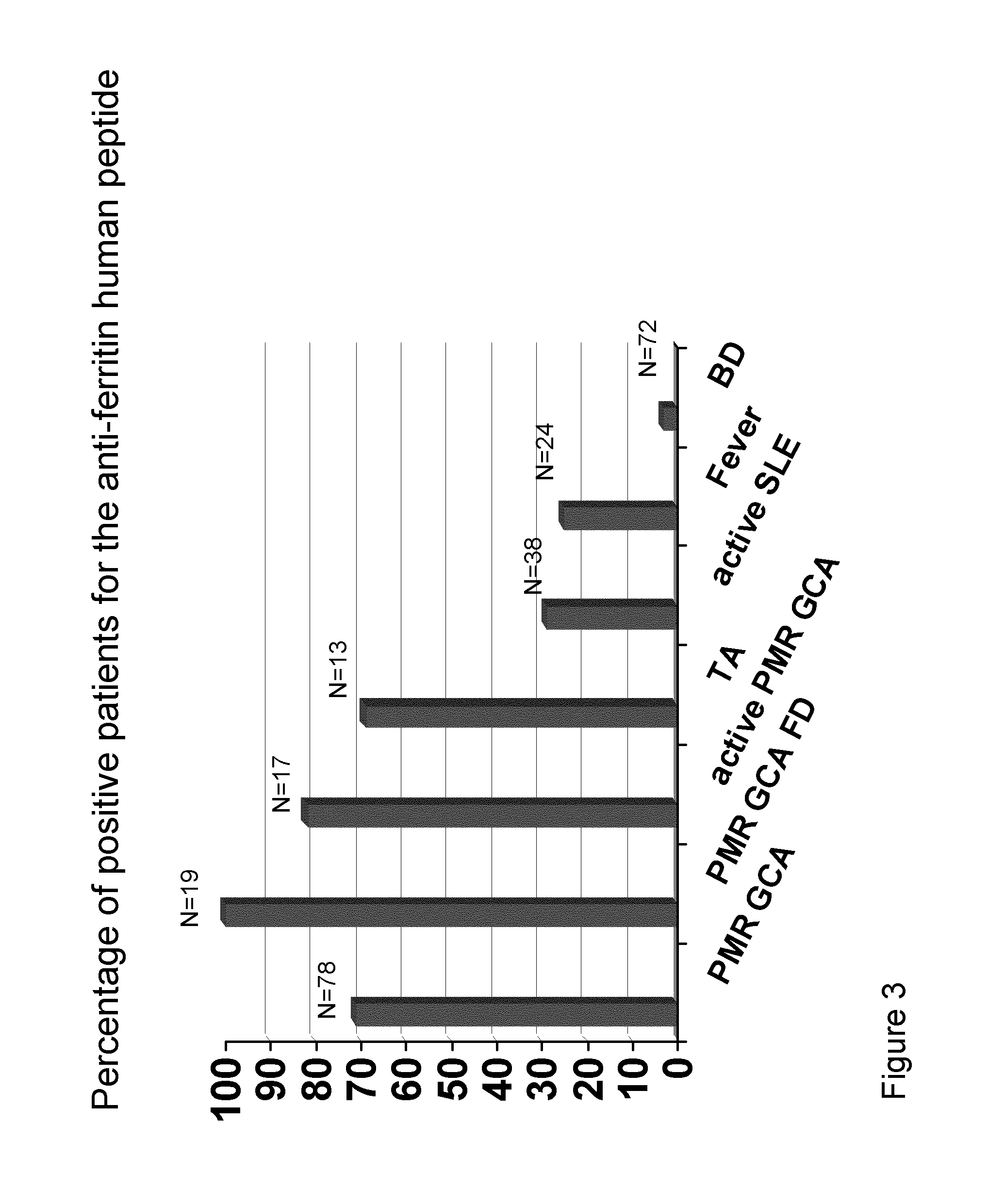
Methods and Means for Diagnosing Vasculitis
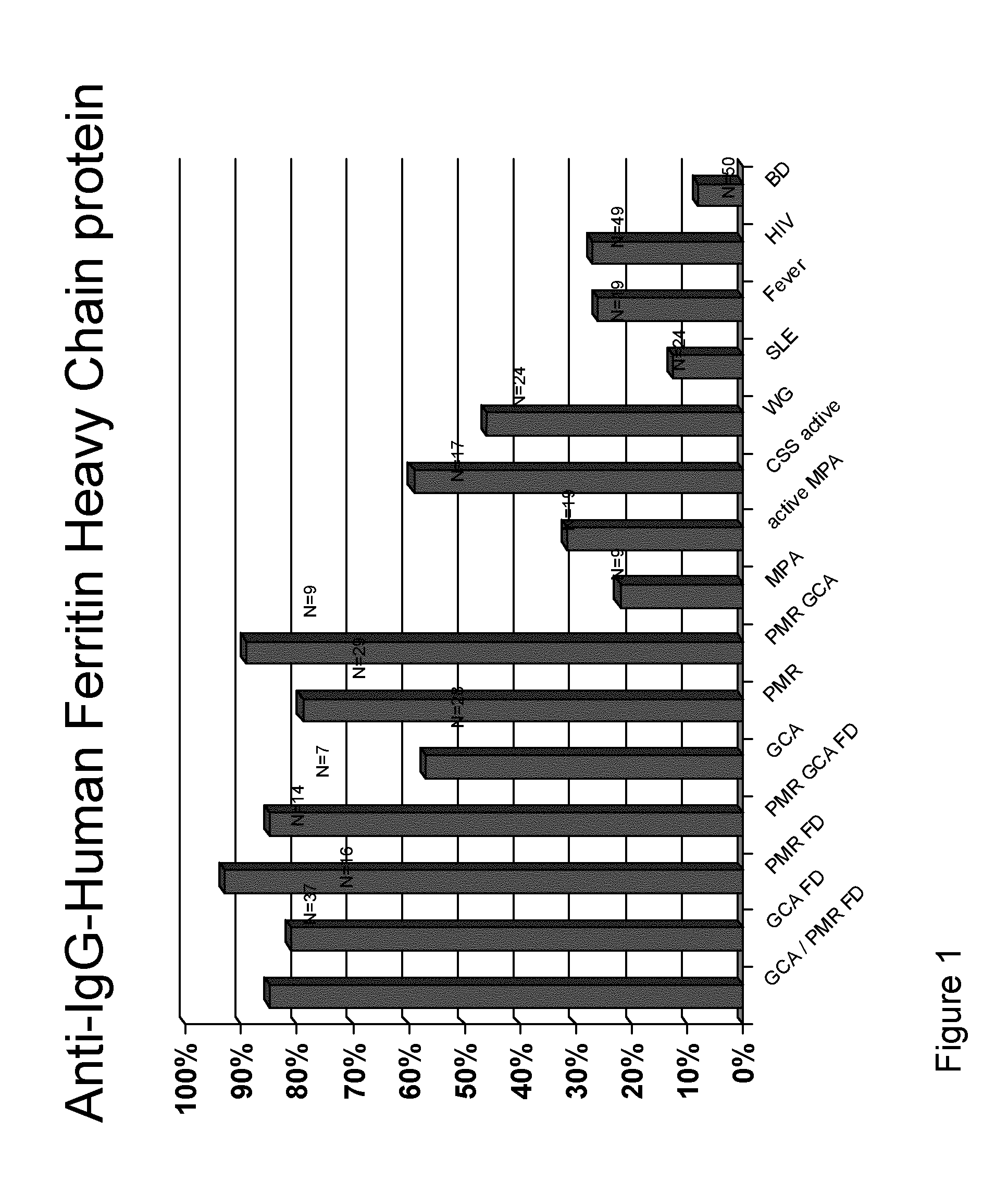
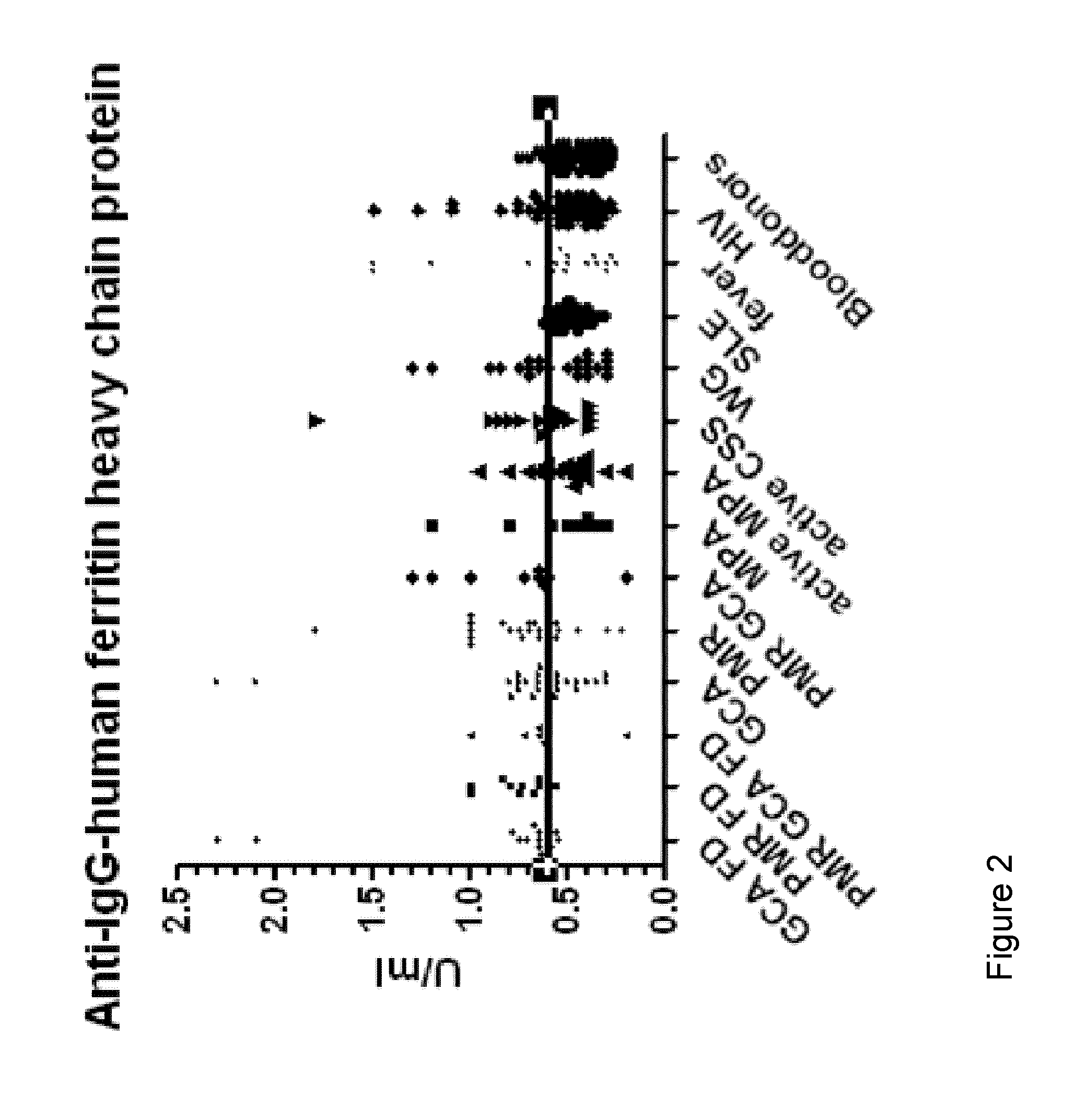
InactiveUS20130310273A1Cost-intensiveEarly diagnosisLibrary screeningPeptide preparation methodsBacterioferritinMammal
The present inventions relates generally to methods for diagnosing the presence or the risk of development or the therapy control of vasculitis, in particular, of large vessel vasculitis, like giant-cell arteritis (GCA), polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and Takayasu's arteritis in a subject, in particular, in mammals. In addition, the present invention relates to test kits for use in the diagnosis of the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of vasculitis, in particular of large vessel vasculitis, like GCA, PMR and Takayasu's arteritis, in a subject. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for diagnosing the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of vasculitis, in particular of large vessel vasculitis, like GCA, PMR and Takayasu's arteritis, in a subject analyzing for the presence of antibodies against ferritin, in particular heavy chain ferritin or immunoreactive peptides thereof or ferritin analog protein, preferably bacterial ferritin analog protein, or immunoreactive peptides thereof, in a subject. The presence of antibodies against ferritin or immunoreactive peptides thereof is indicative for the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of vasculitis, in particular of large vessel vasculitis, like GCA, PMR and Takayasu's arteritis. In particular, detection of the presence of antibodies against ferritin or immunoreactive peptides thereof, allows early diagnosis of vasculitis, in particular of large vessel vasculitis, like GCA, PMR and Takayasu's arteritis.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
Preparation method and application of K562 cell strain for stably expressing human cytomegalovirus pp65 protein in nucleus
InactiveCN104630273ASuitable for large-scale productionSuitable for mass productionGenetic engineeringFermentationAntigenWhite blood cell
The invention discloses a new establishment method and application of a cell strain for stably human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) pp65 protein in nucleus. A nucleus localization signal (pp65-NLS) is added to the 3' end of the HCMV pp65 gene, so that the endonuclear expressed pp65 gene transfected by the gene has the same cellular localization as the host-cell-infected HCMV; and the pp65-NLS is integrated into the K562 cell under the mediation of slow virus, thereby establishing the K562 cell strain for stably expressing 9965-NLS. The cell strain can be used as a positive reference substance of an HCMV 9965 antigenemia detection kit, thereby implementing the reliable application of the kit in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:BIOHIT BIOTECH HEFEI
Broad-spectrum chemokine receptor antagonistic polypeptide and application thereof
InactiveCN101914135AInhibition formationInhibition of replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticFactor iiCell membrane
The invention discloses a broad-spectrum chemokine receptor antagonistic polypeptide and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the broad-spectrum chemokine receptor antagonistic polypeptide is VLNAHCALH. The broad-spectrum chemokine receptor antagonistic polypeptide in the invention can be well combined with US28 receptors on cell membranes, lowers the increased calcium ion concentration caused by combination of physiological chemokines and receptors, has an effect of blocking receptor signal transduction, inhibits human cytomegalovirus AD169 and HIV-1 induced negativecolony fromformation in vitro, restrains virus from reproducing in cells, reduces death of cells infected by virus, and can be used as an antagonist for broad spectrum inflammation and virus chemokine and applied in relative work for researching virus prevention and treatment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Extractive of compound formula of ophiopogon decoction and caper euphorbia seed and reed stem soup and application thereof in preparing medicament for inhibiting H460 cell proliferation
InactiveCN101647970AGrowth inhibitionCytotoxicAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsAdemetionineEthyl acetate
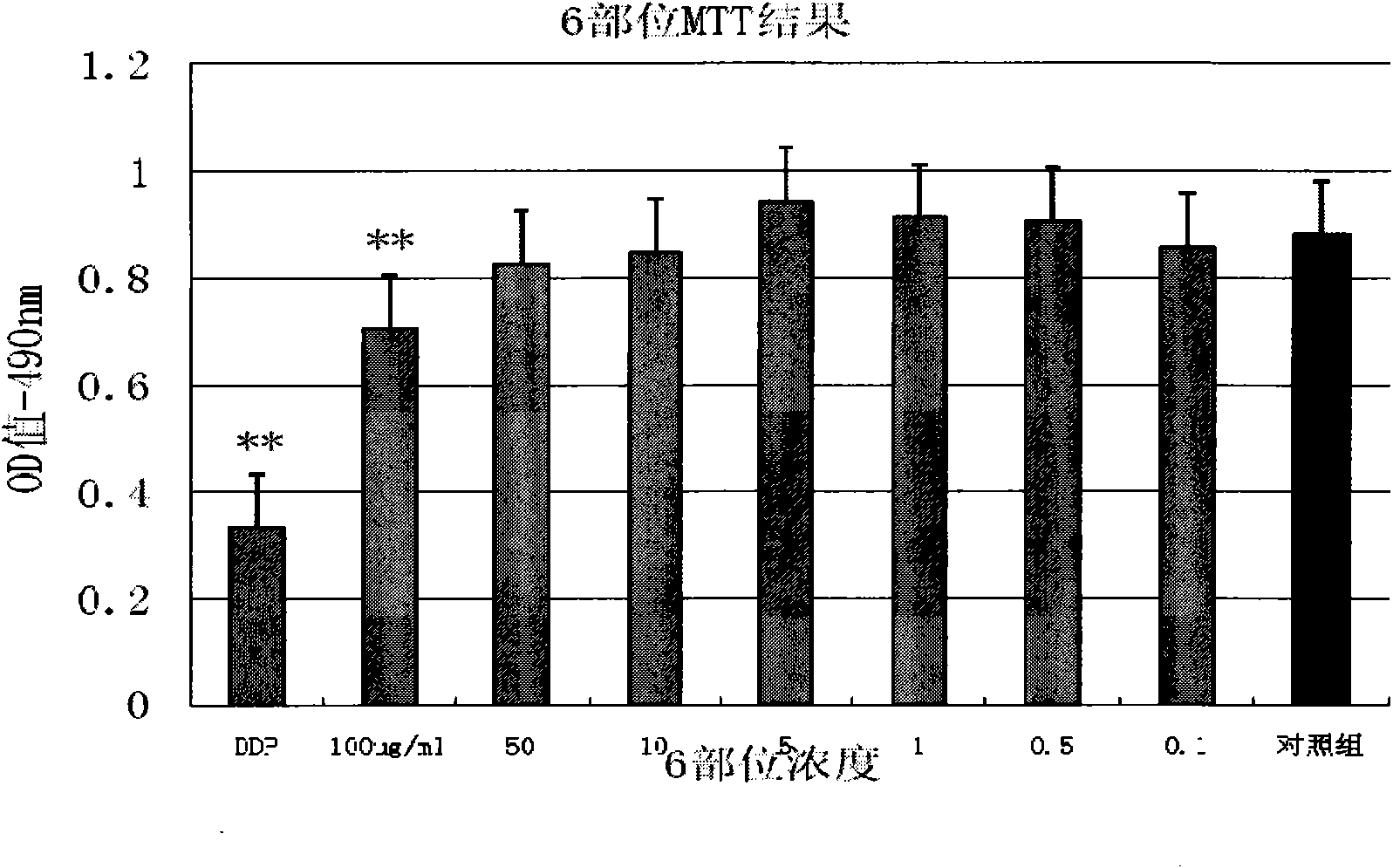
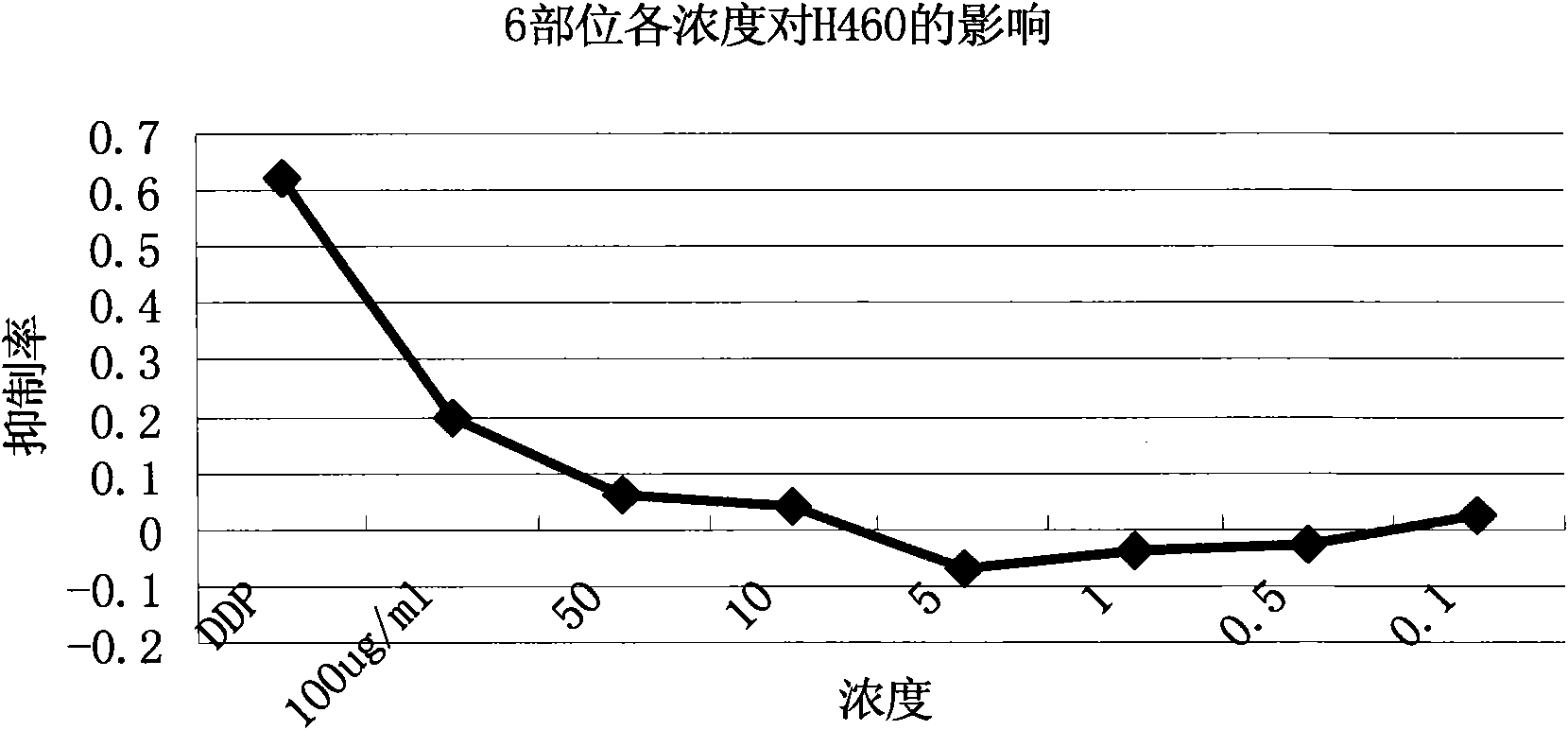
The invention discloses an extractive of a compound formula of ophiopogon decoction and caper euphorbia seed and reed stem soup. The extractive is thick paste which is obtained by treating a compoundformula of ophiopogon decoction and caper euphorbia seed and reed stem soup by a series of steps of water extraction, alcohol precipitation and extraction of cyclohexane and ethylacetate. The invention discloses a preparation method of the extractive and also discloses the application of the extractive in preparing a medicament for inhibiting H460 cell proliferation. The extractive of a compound formula of ophiopogon decoction and caper euphorbia seed and reed stem soup is characterized in that the extraction of the ethylacetate can obviously inhibit the growth of human lung giant cell carcinoma H460 and has no obvious influences on human normal cells, and the extraction has the effect of cell mediated cytotoxicity and can further separate and screen components and monomeric compounds forinhibiting the proliferation of the human lung giant cell carcinoma H460.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Quinoline compound or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for treating giant-cell tumor of bone
PendingCN111840289AIncrease lethalityLower doseOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsCell tumorQuinoline
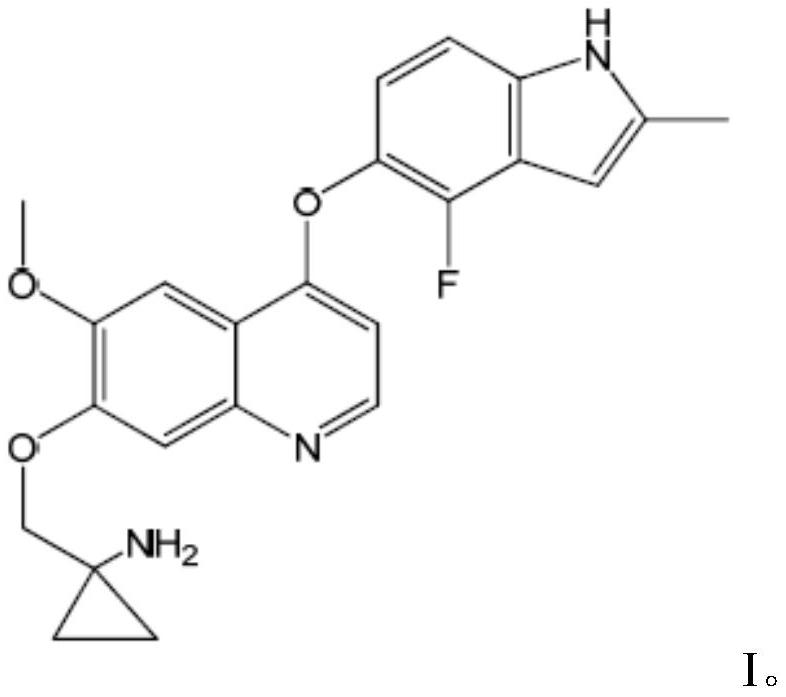
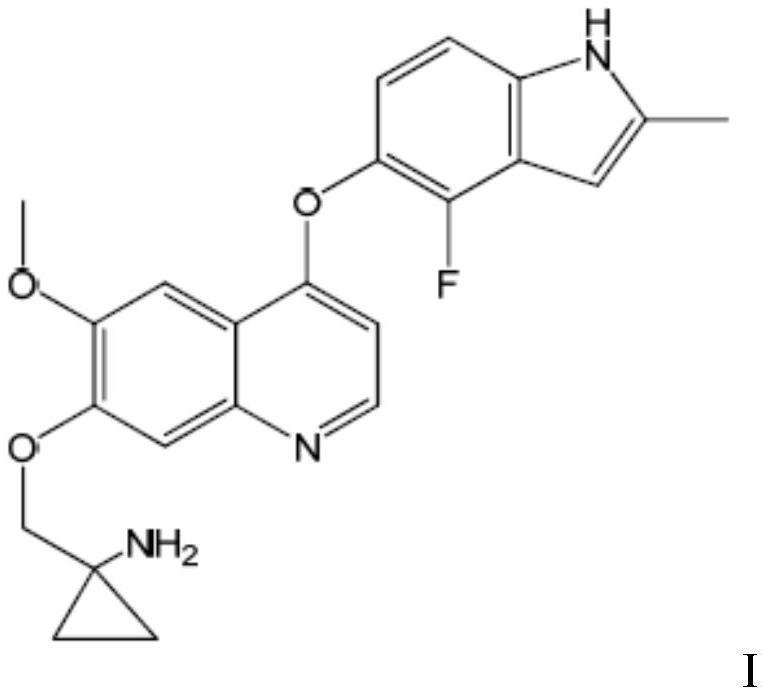
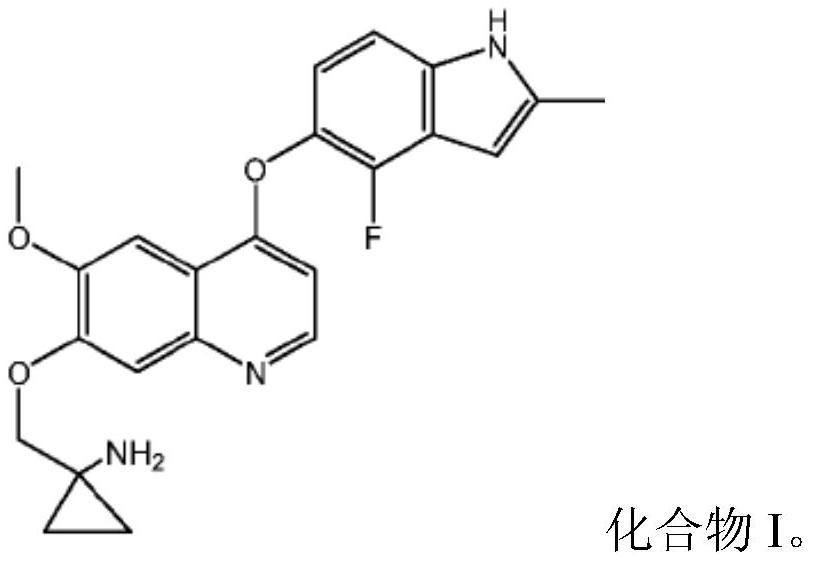
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, and provides a quinoline compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for treating the giant-cell tumor of bone. Specifically, the inventionrelates to the application of a therapeutically effective amount of a quinoline compound I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparation of a medicine for treating the giant-cell tumorof bone, the application of a combination of a therapeutically effective amount of the quinoline compound I or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a second therapeutic agent in preparation of a combined medicine for treating the giant-cell tumor of bone. The chemical name of the quinoline compound I is 1-[[[4-(4-fluoro-2-methyl-1H-indol-5-yl)oxy-6-methoxyquinolin-7-yl]oxy]methyl]cyclopropylamine.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Csf1r inhibitors for use in treating cancer
PendingCN113453684AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTumor-associated macrophageOncology
Described herein are CSF1R inhibitors for use in methods of treating cancers and other tumors related to the decreased proliferation, the depletion, or the repolarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and treatment of associated disorders, including tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) and diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumor (DTGCT).
Owner:DECIPHERA PHARMA LLC
Recombinant replication-defective adenovirus for expressing hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a recombinant replication-defective adenovirus for expressing an hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase) gene. A target gene hTERT is obtained by virtue of enzyme digestion from a plasmid pIRES2-EGFP(enhanced green fluorescent protein)-hTERT, the target gene hTERT is inserted to downstream of a cytomegalovirus promoter in a pSG218 shuttle vector to obtain a recombinant shuttle vector with the hTERT gene; and the recombinant shuttle vector and a virus framework vector pPE3-F11B are co-transferred to a human embryo kidney 293 cell to obtain replication-defective adenovirus with hTERT. The recombinant adenovirus infects a human multiple myeloma cell, so that the cell excessively expresses the hTERT gene, and therefore, drug resistance of the cell on pharmorubicin is strengthened. The recombinant replication-defective adenovirus disclosed by the invention is mainly used for establishing a multiple myeloma cell strain model for excessively expressing hTERT gene, and further researching a mechanism that the hTERT gene participates in drug resistance of the multiple myeloma cell based on the model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
New application of piceatannol in preventing and treating human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveCN109394738ASignificant anti-HCMV effectHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntiviralsFibroblastEmbryo
The invention provides a new application of piceatannol in preparing a medicament for preventing and treating human cytomegalovirus infection. Experiments show that the single treatment of the piceatannol has no obvious toxicity to HCMV in vitro host cells, namely human embryo lung diploid fibroblast WI-38 in the range of 0-20micrometre, the expression of the immediate early protein IE1 / 2 and theearly protein UL44 of HCMV in WI-38 was inhibited in the range of 10-20micrometre by piceatannol, and the amplification of HCMV was inhibited in the range of 10-20micrometre by piceatannol. Piceatannol exerts anti-HCMV activity by inhibiting the HCMV-induced host cell senescence, and the specific mechanism is to inhibit the HCMV-induced high expression of p16INK4a and the increase of active oxygenfree radical level, thereby exerting the anti-HCMV effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HOSPITAL
Method for identifying resistance of plant to meloidogyne
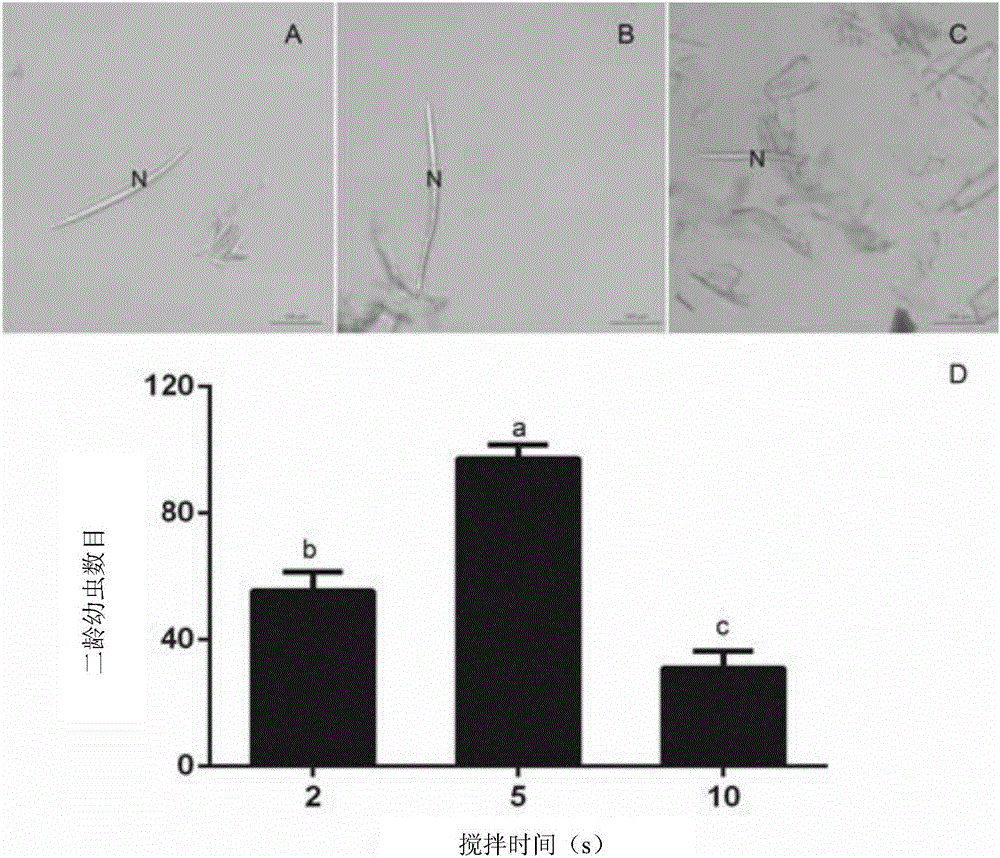
The invention discloses a method for identifying resistance of a plant to meloidogyne. The method comprises the steps of 1, grafting meloidogyne on a plant, and conducting cultivation; 2, after the step 1 finishes, taking plant root tissue, and observing the growth state of meloidogyne in the plant root tissue; 3, after the step 1 finishes, taking the plant root tissue, and calculating the number of meloidogyne in the plant root tissue; judging the resistance of the plant to meloidogyne according to the result. According to the method for identifying the resistance of the plant to meloidogyne, toluidine blue is applied to dyeing of a root-knot paraffin slice, an optimal dyeing time is found, and the growth state of the nematodes and giant cells can be clearly observed; moreover, the dyeing time is fast, and the effect is good. Aiming at the statistics on the number of the nematodes, a grinding method and a screening method are combined, an optimal grinding time is found, and convenience is brought to the statistics on the number of the nematodes. The two methods can combined into application, and the resistance of the plant to the statistics on the number of the nematodes can be expressed from two aspects of the growth state and the nematodes and the number of the nematodes.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Tumor vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104117060AOvercome many repetitionsOvercome the disadvantages of obvious side effectsRespiratory disorderAntibody medical ingredientsSequence signalPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention provides a tumor vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: extracting mRNA from human peripheral blood monouclear cells, synthesizing cDNA in vitro, employing polymerase chain reaction technology to clone granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) cDNA containing a signal peptide, recombining with sendai virus vector, so as to construct a recombinant sendai virus vector GM-CSF-SV containing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor cDNA; and employing a packaging cell 293T with relatively high safety to package the recombinant sendai virus vector GM-CSF-SV containing GM-CSF gene, so as to generate he recombinant sendai virus vector which is high in titer and does not have duplication capability; and infecting human lung cancer cell strain A549, so as to establish a gene engineering human lung cancer cell with GM-CSF expression activity, and employing <60>Co to irradiate and inactivate a tumor vaccine and performing heat shock processing, and preparing the GM-CSF gene modified human lung cancer cell tumor vaccine after different irradiation amounts are explored.
Owner:TIANJIN MEIDE BAITAI MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Low-macrophage-adhesion/activation culture devices and methods thereof for continuous hematopoiesis and expansion of hematopoietic stem cells
PendingUS20200131462A1Reduce adhesionGood shape retentionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBone marrow cellHydrocortisone
Hematopoietic stem cells are extremely difficult to maintain or expand in vitro. Two observations in traditional long-term bone marrow cultures strongly suggest that macrophages may be at the root of the problem: First, micromolar concentrations of hydrocortisone improve the longevity of long-term bone marrow cultures and hydrocortisone is known as a potent inhibitor of macrophage production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, enzymes, nitrogen oxide and reactive oxygen species and redirects macrophages to the anti-inflammatory differentiation pathway; Second, the decline of hematopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures coincides with the development of large numbers of adherent and non-adherent macrophages including foreign body giant cells. These adherent macrophages and foreign body giant cells exhibit well-spread morphology, contain numerous lysosomes and phagolysosomes in the cytoplasm and are metabolically active. We hypothesize that hydrocortisone fails to suppress all aspects of macrophage pro-inflammatory activation / differentiation, resulting in the production of inhibitors or toxins of hematopoiesis. Macrophage adhesion in cell culture depends on serum proteins pre-adsorbed to the tissue-culture-treated polystyrene (TC-PS), which adsorbs proteins via mostly hydrophilic interactions. TC-PS is used in almost all tissue culture devices currently available. Cellular adhesion provides a strong stimulus for metabolic, mitotic and certain gene activities. Therefore, we seek to reduce macrophage adhesion and activation by culturing bone marrow cells in tissue culture devices composed of or covered with polymers with very different protein-binding characteristics than TC-PS such as polyethylene (PE) and other polyolefins, the latter bind proteins via exclusively hydrophobic interactions. As a result, polyolefins bind different proteins and in lower quantities than TC-PS. Furthermore, PE does not contain additional chemical features like the phenolic rings of polystyrene that might contribute to protein binding and macrophage adhesion / activation. Using these new culture devices, we developed a drastically different long-term bone marrow culture, the “Low Macrophage-Adhesion / Activation” (LoMAC) bone marrow culture. In LoMAC bone marrow culture, hematopoiesis continues for months to over a year and hematopoietic stem cells are amplified gradually. In stark contrast to traditional long-term bone marrow cultures, de novo erythropoiesis and megakaryocytopoiesis proceed robustly in the LoMAC bone marrow culture and B-lymphocyte and natural killer cell progenitors can be continuously derived. Thus, these new culture devices and the associated LoMAC culture method offer a new way to study hematopoiesis in vitro and provide a more robust platform for the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors ex vivo.
Owner:TSAI SCHICKWANN
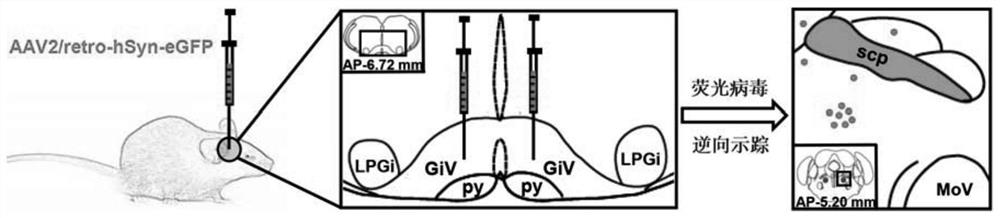
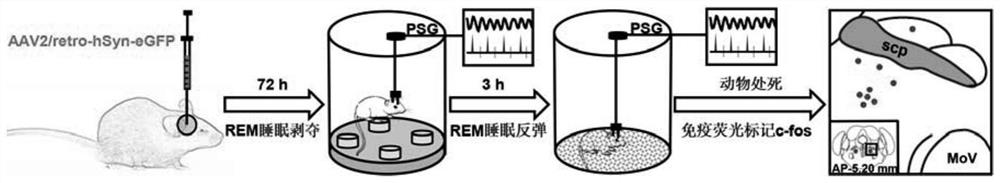
Experimental method for determining anatomo-functional delimitation of sublaterodorsal tegmental nucleus (SLD)
The invention relates to a method for positioning an animal SLD nucleus. The invention provides a method for determining the anatomo-functional delimitation of a sublaterodorsal tegmental nucleus (SLD) of a tested object. The method comprises the following steps that 1) a reverse transport virus vector is stereodirectionally injected into an SLD downstream nucleus abdominal side gigantocellular reticular nucleus (GiV), and under the action of a neuron alternative promoter, the reverse transport virus vector can specifically express a first marker in an upstream efferent neuron; 2) REM sleep deprivation and rebound experiments are conducted on a subject, and a functional active neuron is determined through a second marker, wherein the second marker is different from the first marker; and 3) the anatomo-functional delimitation of the SLD nucleus is determined according to the co-marker fusion range of the first marker and the second marker. According to the method, through ingenious combined application of nerve fiber projection and sleep physiology research methods, the anatomo-functional delimitation of the SLD nucleus can be determined visually and accurately.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
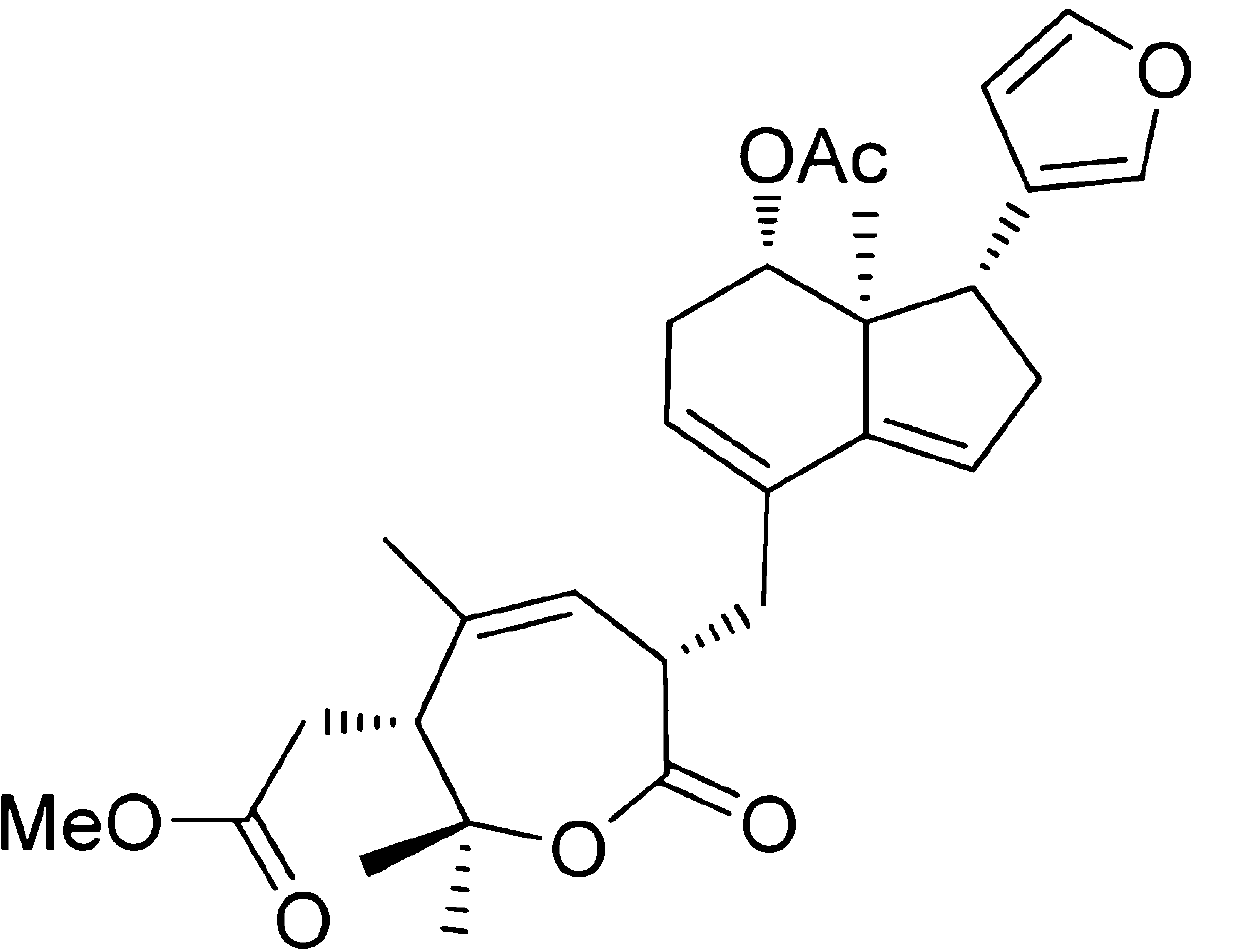
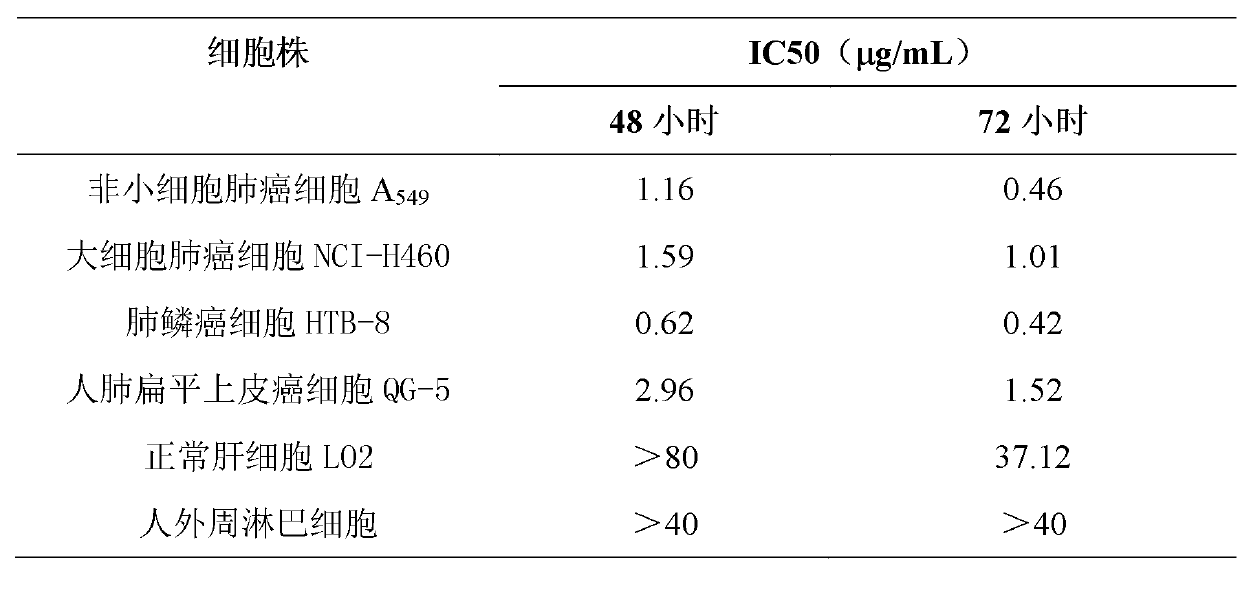
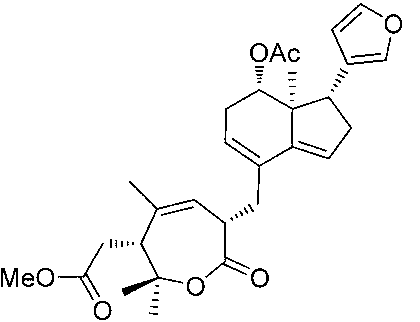
Application of Aphanamixoid A to lung cancer treatment medicine
The invention discloses application of Aphanamixoid A to lung cancer treatment medicine and belongs to the technical field of novel application of medicine. The compound has good lung cancer resistance activity and can be used for preparing the lung cancer resistance medicine. The Aphanamixoid A can significantly inhibit non-small cell lung cancer cells A 549, giant-cell lung cancer cells NCI-H460, lung squamous carcinoma cells HTB-8 and human lung pavement epithelium cancer cells QG-5, wherein the non-small cell lung cancer cells A 549, the giant-cell lung cancer cells NCI-H460, the lung squamous carcinoma cells HTB-8 and the human lung pavement epithelium cancer cells QG-5 are cultured in vitro; the inhibiting effect of the Aphanamixoid A on normal human hepatic cells LO2 and peripheral blood lymphocyte is small, and therefore obvious selectivity is achieved. The application of the Aphanamixoid A to preparation of the lung cancer treatment medicine is made public for the first time. The skeleton type is fully novel, and inhibitory activity to the lung cancer cells is surprisingly strong.
Owner:吴俊华
AIDS immune cell therapy instrument
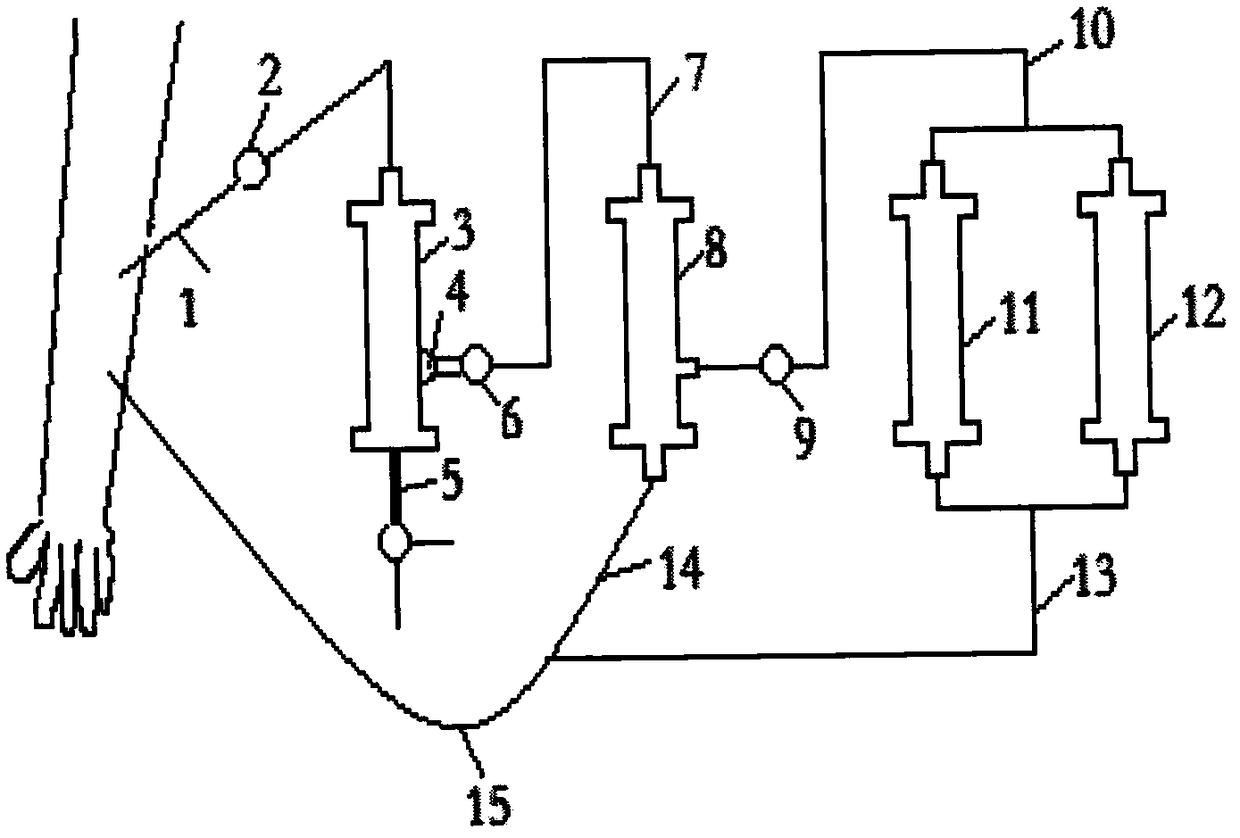
ActiveCN106267424BFacilitate the binding reactionPore reductionOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationExtracorporeal circulationMultinucleate
The invention discloses an AIDS immune cell therapy apparatus, which is applicable to the medicine field. The AIDS immune cell therapy apparatus is characterized in that blood and plasma separators, by which plasma, individual blood cells and multinuclear giant cells which are formed due to HIV boarding, are prepared; by virtue of an exogenous gene transfection technique, a CD4+T cell line, which can bond HIV, is prepared, the CD4+T cell line undergoes amplification and the CD4+T cell line is covered by virtue of a high-biocompatibility material, so that a purifier is prepared; and then, agarose, which is subjected to a gradient concentration, is added, and the CD4+T cell line in the purifier is immobilized so as to take an effect on adsorbing the HIV; the purifier, together with the separators, functions as key parts of an extracorporeal circulation device; when blood passes through the blood separator, the multinuclear giant cells which contain the HIV are filtered out, subsequently, when the plasma, which is separated by virtue of the plasma separator, passes through the purifier, HIV in the plasma is adsorbed and scavenged by virtue of a purifying agent, the purified plasma joins with the individual blood cells which are separated by virtue of the plasma separator, and then the plasma is returned back, so that the purpose of scavenging the HIVs inside and outside the blood cells by virtue of a detoxifying and purifying therapy is achieved.
Owner:运城同创医疗管理有限公司
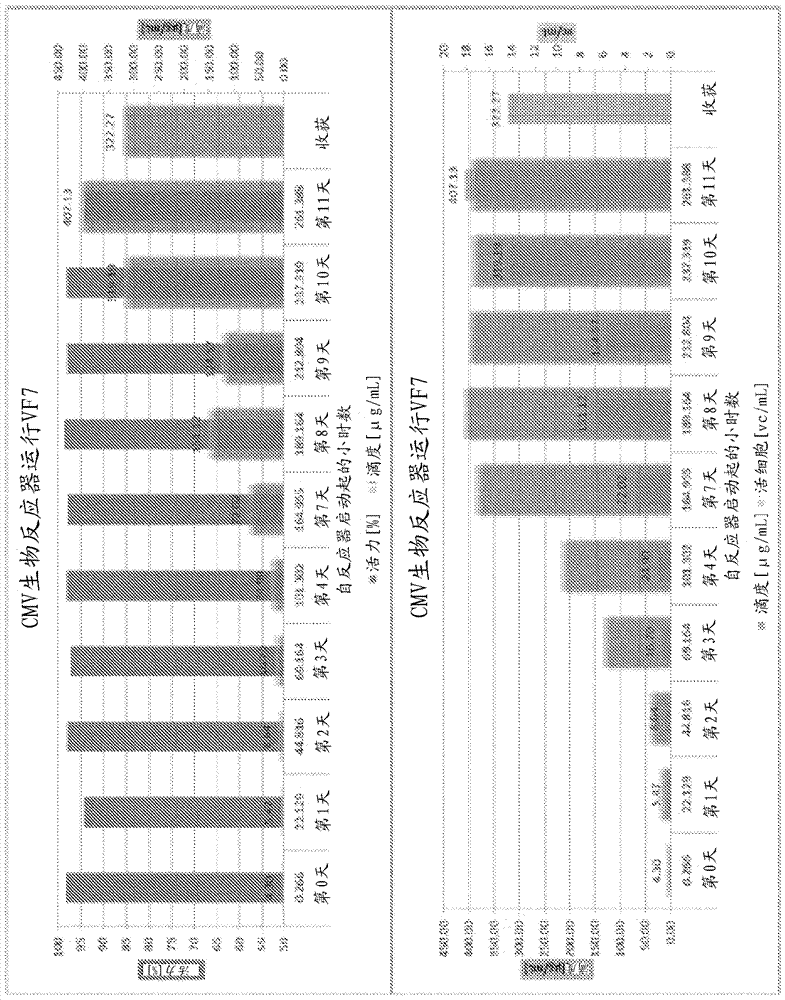
Scalable chromatography process for purification of human cytomegalovirus
PendingUS20210047626A1Cation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersCell culture mediaAnion-exchange chromatography
The present invention relates to a scalable process for the purification of human cytomegalovirus particles from cell culture medium. In particular, the process involves a two step chromatography process starting with an anion exchange chromatography step followed by a polishing chromatography step selected from mixed mode chromatography or cation exchange chromatography.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com