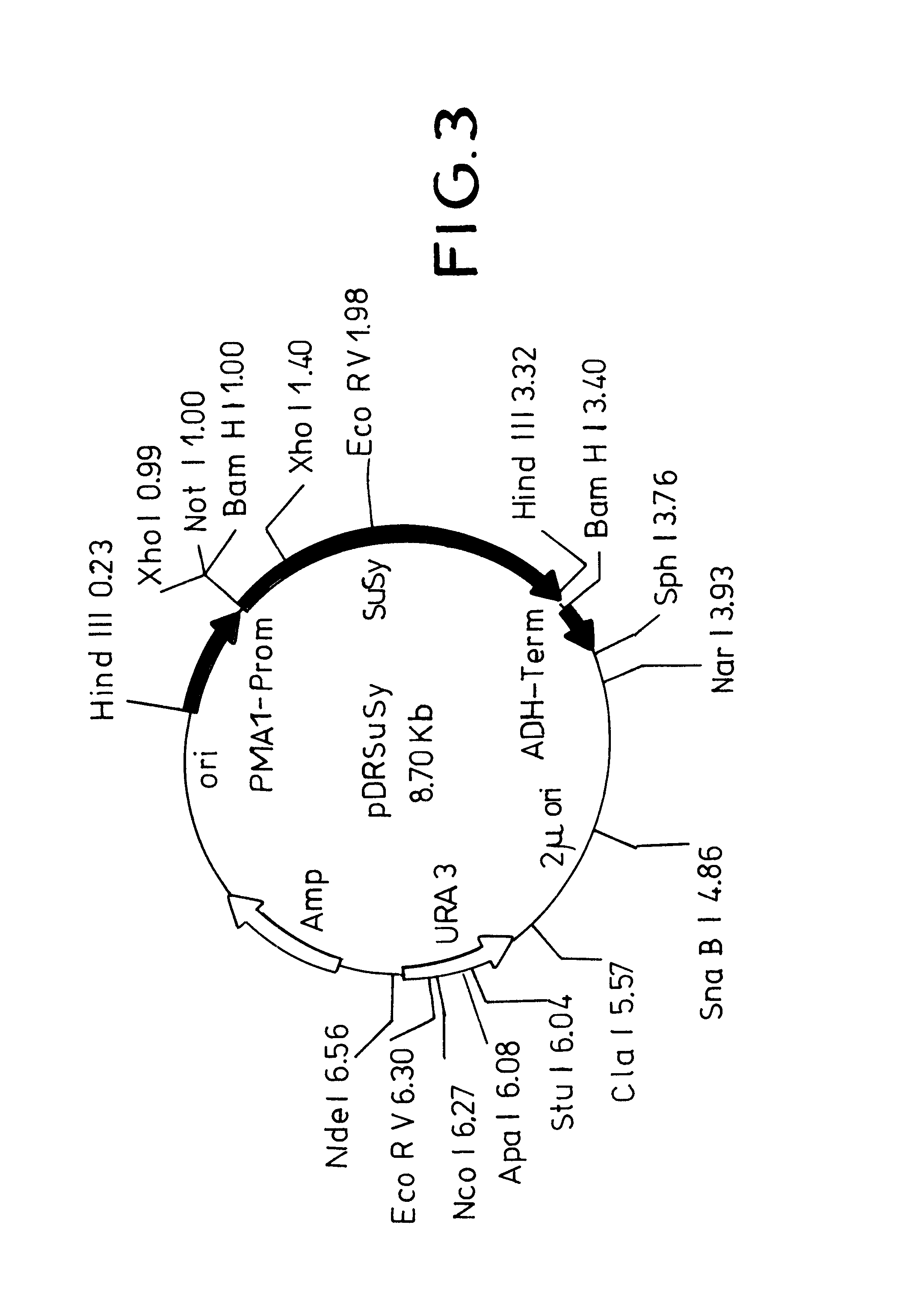
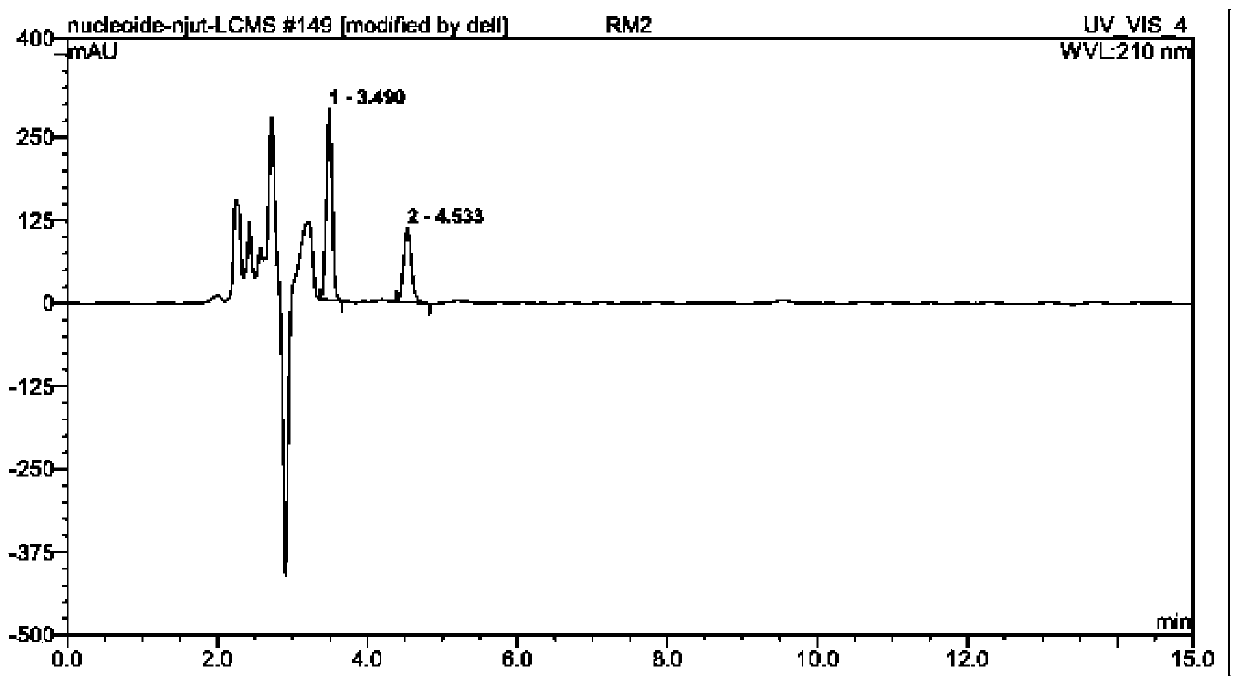
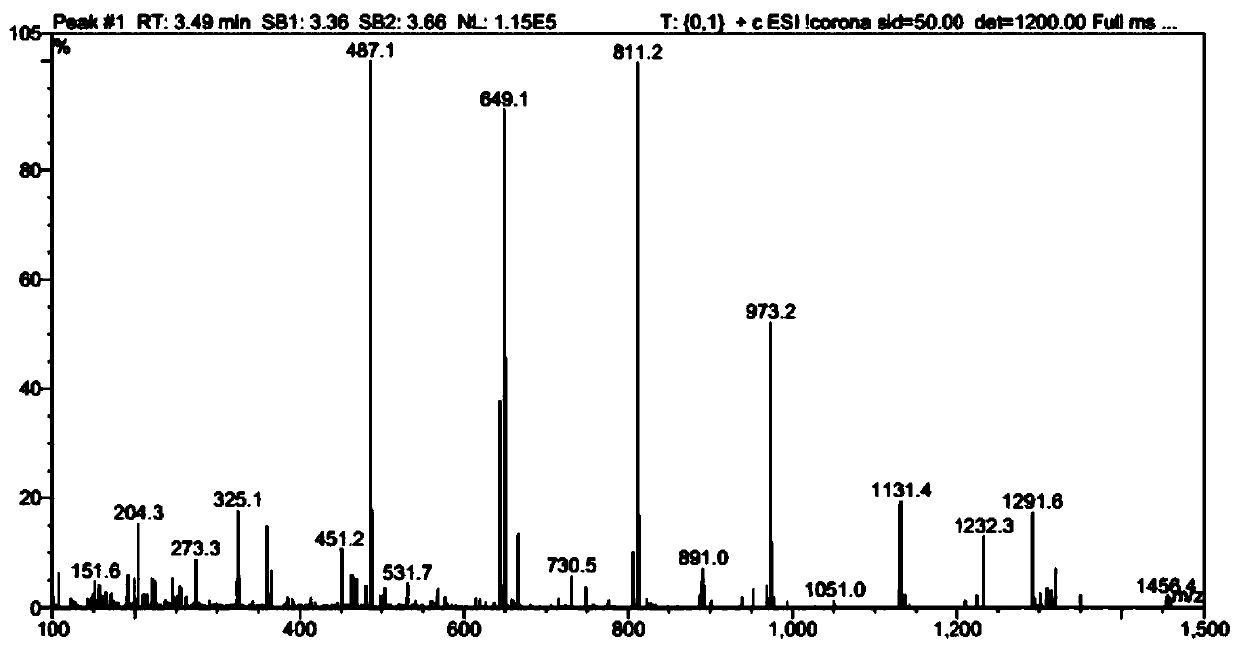
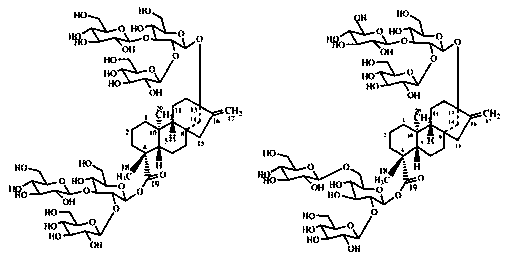
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Sucrose synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a sucrose synthase (EC 2.4.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction...
Method for preparing rebaudioside-M by enzymic method
ActiveCN104726523AHigh reaction conversion rateReduce manufacturing costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionUdp glycosyltransferaseSucrose synthetase
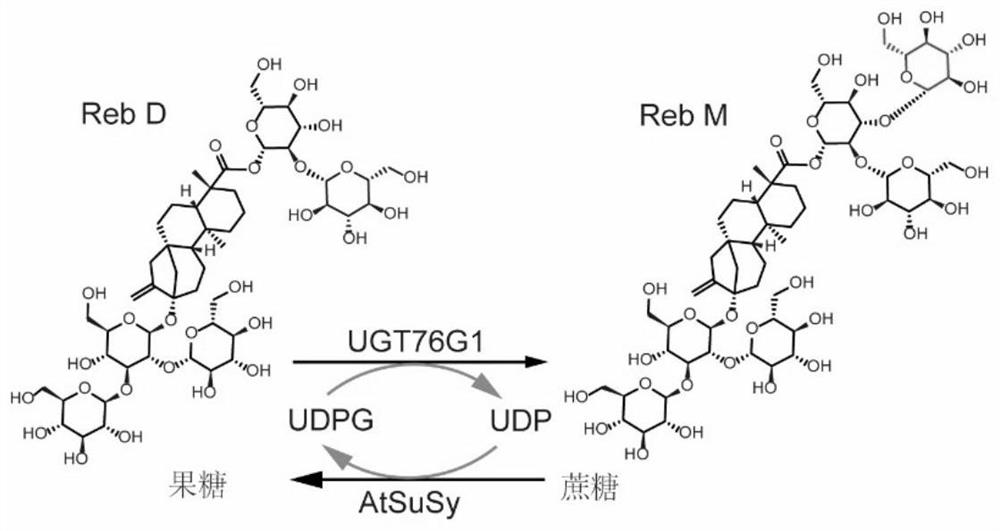
The invention discloses a method for preparing rebaudioside-M by an enzymic method. The method comprises the steps of utilizing tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase and potato sucrose synthetase, and using rebaudioside-A and sucrose as raw materials for producing rebaudioside-M. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the high-yield recombinant strain of UDP-glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthase is obtained by virtue of a genetic engineering technology at first, then a bio-enzyme crude product is collected, a catalytic reaction is directly carried out, UDP or UDP-glucose is not added in the reaction system, the rebaudioside-A and the sucrose are used as the raw materials, and the rebaudioside-A is catalyzed to generate the rebaudioside-M through the efficient circulation of catalyzing the UDP-glucose by the sucrose synthase, and through the action of the tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase. Compared with the existing preparation method for rebaudioside-M, the process is short in steps, low in cost, important in application value, and good in economical efficiency.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Novel catalytic system for preparing rare ginsenosides and application thereof
ActiveCN105087739AHigh catalytic efficiencyReduce use costFungiBacteriaSucrose synthetaseProtopanaxadiol
The invention discloses a co-catalytic reaction system for preparing rare ginsenosides. The co-catalytic reaction system comprises glycosyltransferase GT (a); sucrose synthase SUS (b); uridine diphosphate UDP (c); and saccharose (d). Experiments show that in the presence of the saccharose and little UDP, an enzyme combination composed of the glycosyltransferase and the saccharose is capable of replacing an in-vitro reaction system to synthesize UDP sugar, one of expensive materials for the rare ginsenosides, and efficiently and economically converting substrates such as protopanoxadiol or protopanaxatriol into the rare ginsenosides, wherein the UDP is about 1 / 4 of the UDP sugar in price and is 1% of its original dosage; thus, preparation cost of the rare ginsenosides is greatly saved, and large-scale commercial preparation of the ginsenosides is better facilitated.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
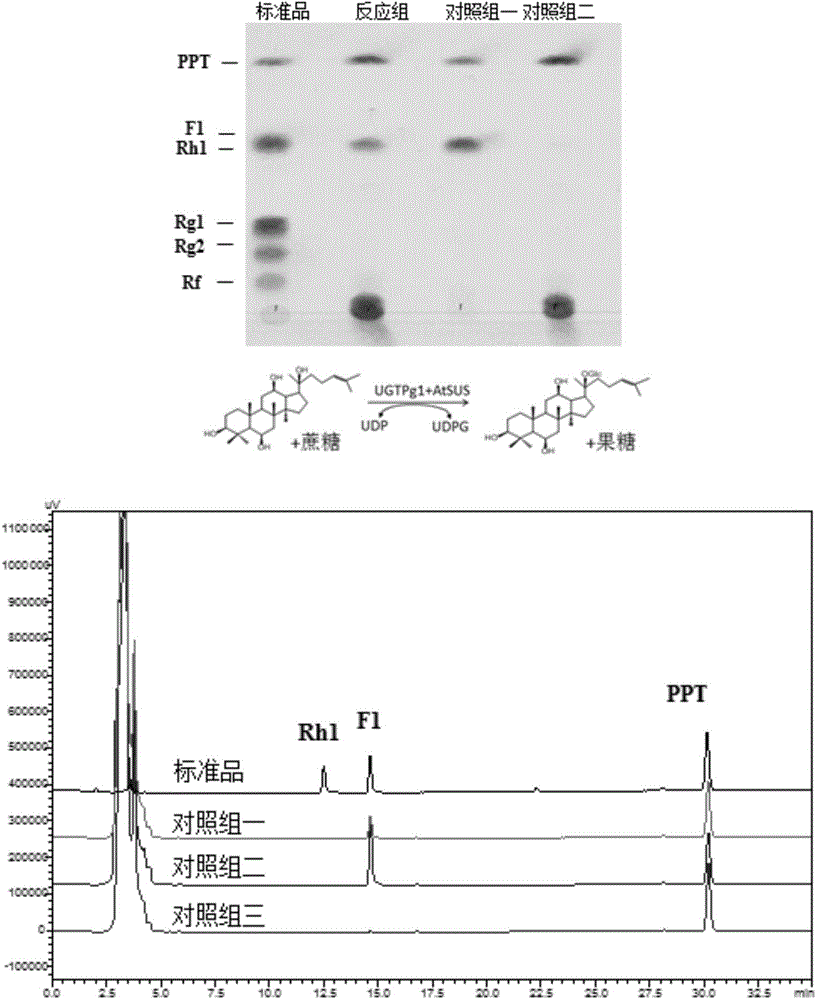
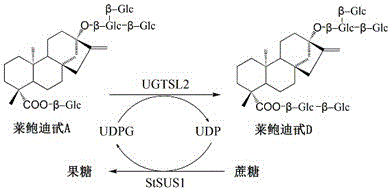
Recombinant bacterium and application of recombinant bacterium to generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A
ActiveCN106754595AAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
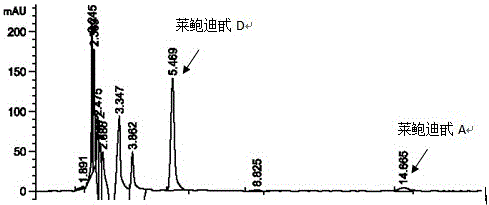
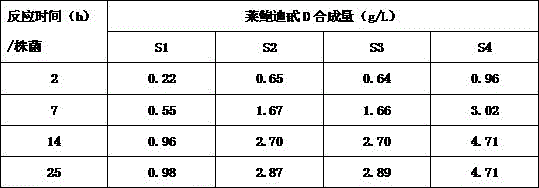
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to the generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene; the tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induction expression, the recombinant bacterium is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside D; in reaction, crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder does not need to be produced; UDP (Uridine Diphosphate) or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added into a reaction solution, so that the recombinant bacterium has a better environment-friendly property. The yield of the rebaudioside D can reach 10.8g / L.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Glycosyl transferase mutant and method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside M by using glycosyl transferase mutant
ActiveCN113462670AIncrease productionHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetasePtru catalyst
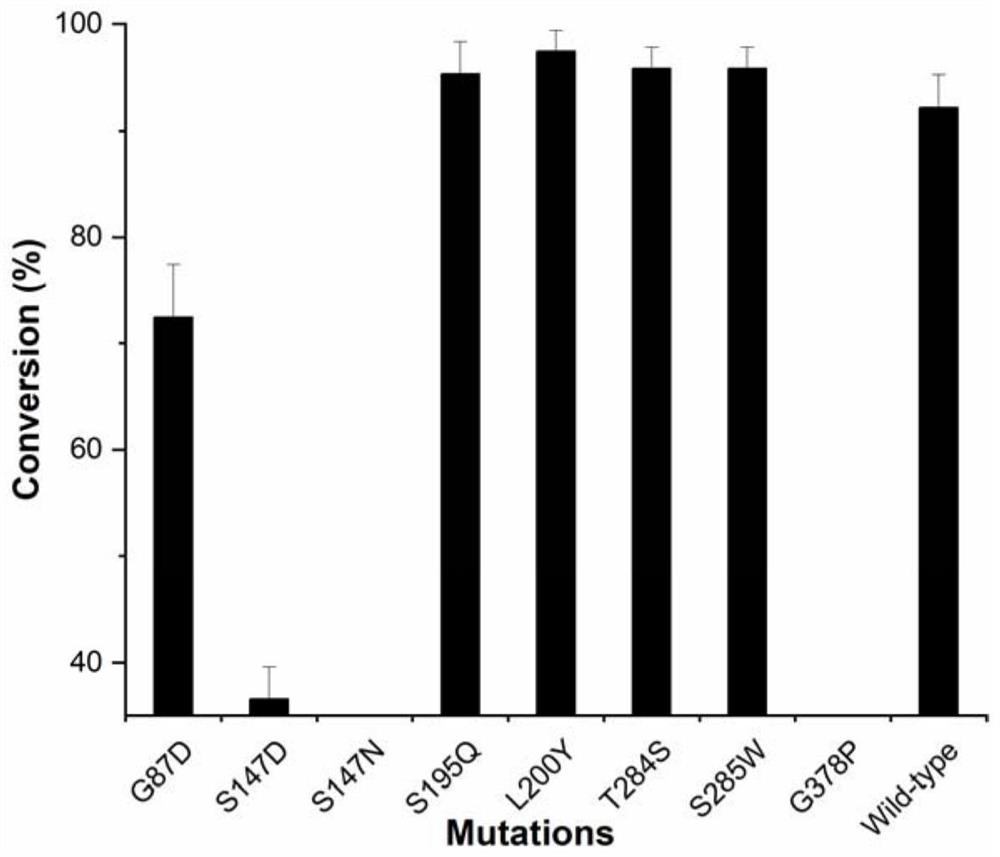
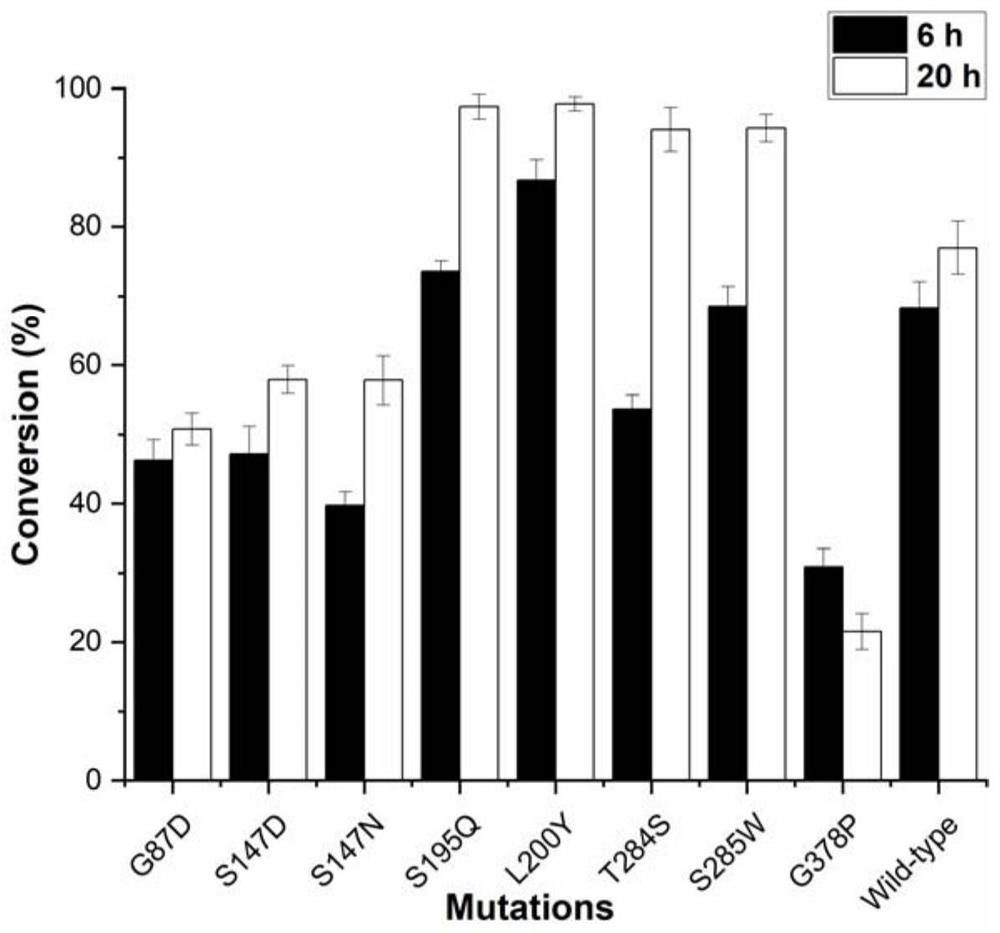
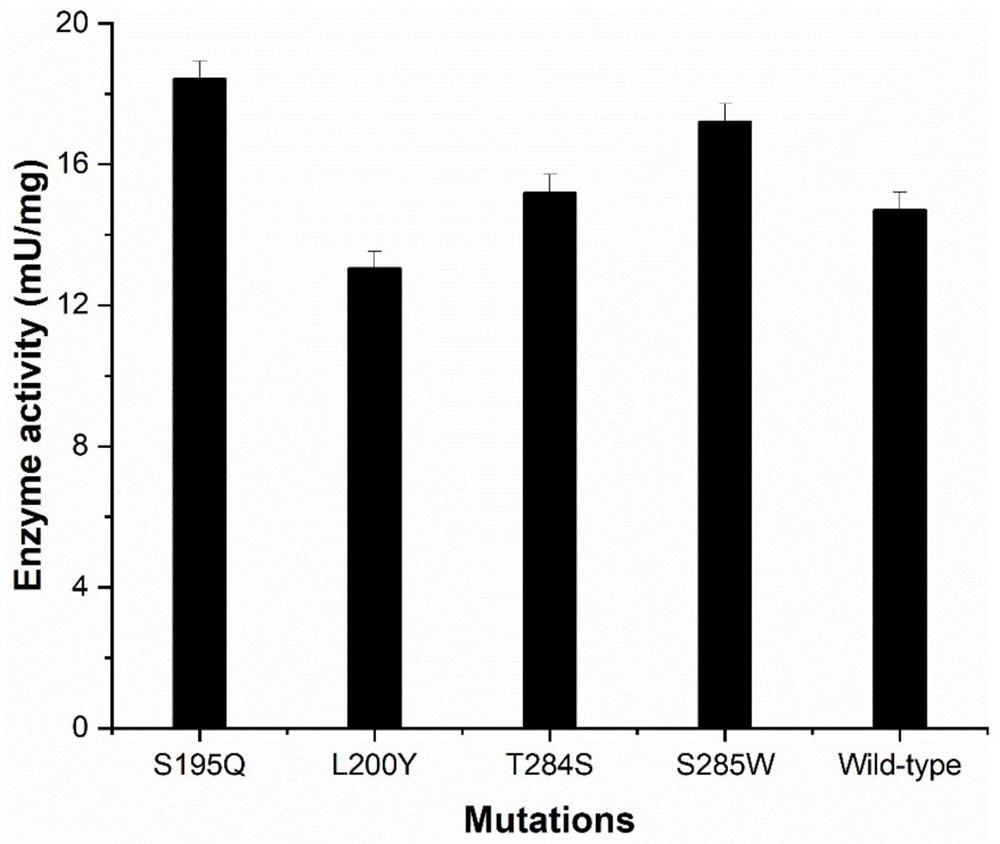
The invention discloses a glycosyl transferase mutant and a method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside M by using the glycosyl transferase mutant. The mutant is obtained by performing mutation on the basis of a glycosyl transferase amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, performing induced expression on a mutant strain to obtain a mutant enzyme, and catalyzing 20g / L RebE to synthesize 12.8 g / L RebM by using the mutant enzyme as a catalyst and the enzymic method. The kinetic parameters of the mutant S195Q on rebaudioside E and rebaudioside D and the Michaelis constant of the mutant are 56.34 + / -2.02 mu M and 214.48 + / -14.54 mu M respectively, and are 1 / 3 and 2 / 5 of those of a wild type. The glycosyl transferase mutant is coupled with sucrose synthase to realize efficient catalytic synthesis of rebaudioside M. According to the present invention, the recombinant strain of the glycosyl transferase UGT76G1 or the mutant thereof and the sucrose synthase is constructed so as to achieve the efficient catalytic synthesis of the rebaudioside M; the method has the optimal yield in the current enzymatic catalytic synthesis experiment of rebaudioside M, and is green, environment-friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Method for preparing rebaudioside a from stevioside
ActiveUS20160010133A1High purityNo side-productsSugar derivativesFermentationSucrose synthetaseSaccharophagus degradans
The present invention relates to an in-situ method for preparing rebaudioside A from sucrose and stevioside by sucrose synthase and glycosyltransferase.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
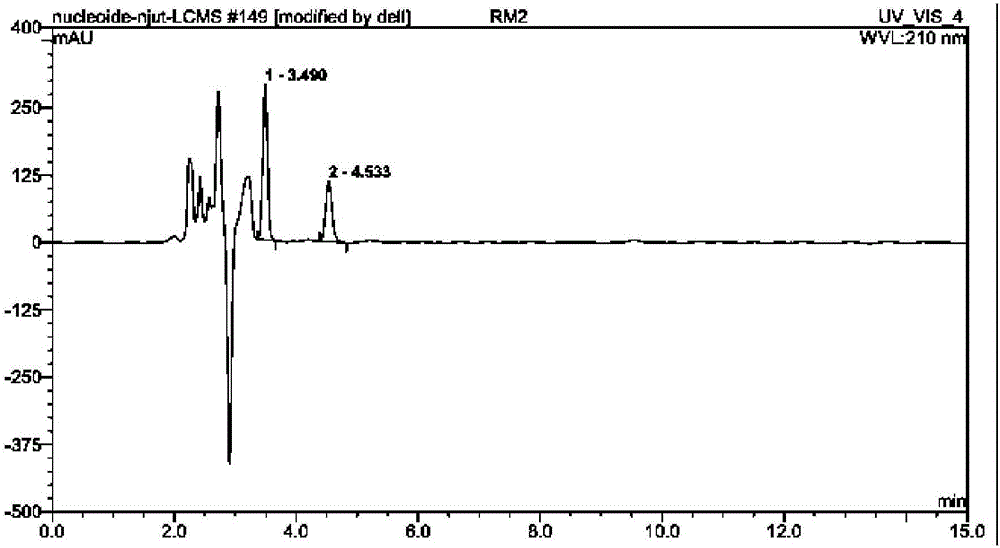
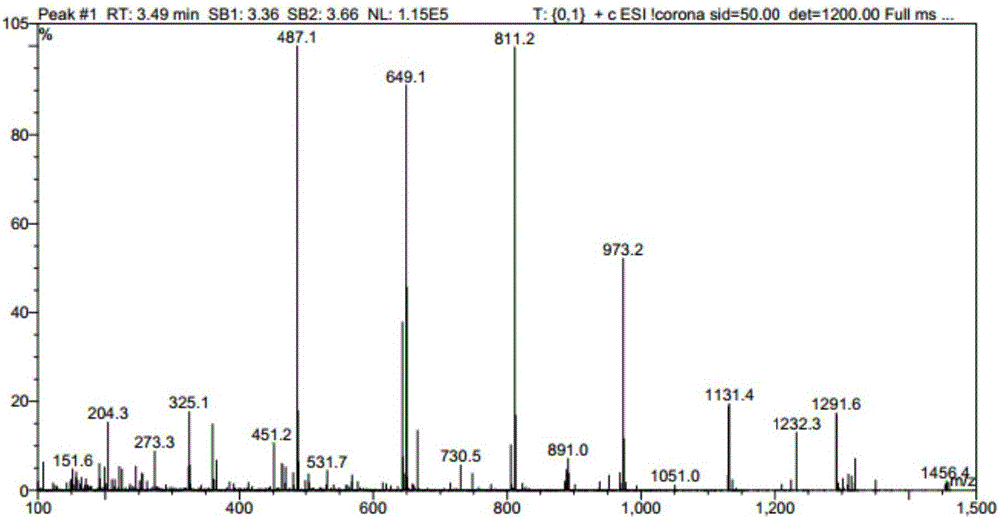
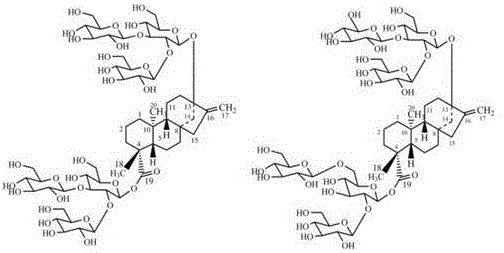
Method for preparing rebaudioside M2 by catalyzing rebaudioside A through recombinant bacterium
ActiveCN106834389AAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to preparation of rebaudioside M2 by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene at the same time; the tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induced expression, crude enzyme liquid is taken and is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside M2; in a reaction process, the crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder is also not needed and substrates including rebaudioside D and UDP or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added, so that the environmental friendliness is better. The yield of the rebaudioside M2 reaches 11.09g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Use of a seed specific promoter to drive odp1 expression in cruciferous oilseed plants to increase oil content while maintaining normal germination
ActiveUS20100257635A1High oil contentOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologySucrose synthetase
A recombinant DNA construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an ODP1 polypeptide operably linked to a sucrose synthase 2 promoter where this construct can be used to increase oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination is disclosed. A method for increasing oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination using this construct is also disclosed.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Glycosyltransferase mutant and method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside A by using same
ActiveCN112375750AIncreased expression of solubleImprove efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesSucrose synthetaseEnzyme system
The invention discloses a glycosyltransferase mutant and a method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside A by using the same. The amino acid sequence of original glycosyltransferase is SEQ ID NO:1. According to the experiment, Asn196, Asn78, Asn400, Asn69, Gln72, Gln198, Gln178, Gln160 and Thr319 are screened on the basis of prediction obtained by starting from surface residues Q, N and T ofUGT76G1 and combining data analysis results of solvent accessible surface area, B-factor and the like, and finally, a UGT-SuSy system of the better mutant strain 76G1_Q72E-N196D-T319E is screened outby virtue of single-point or multi-point iterative mutation in Thr81, so as to realize efficient catalytic synthesis of the rebaudioside A. The glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 or a mutant gene thereof isconnected with a sucrose synthase gene to obtain a recombinant plasmid, and a double-enzyme co-expressed recombinant strain is constructed. By constructing a double-enzyme system, regeneration of in-vivo UDPG is realized, the problem of sources of expensive glycosyl donors is effectively solved, the cost is reduced, and application of biotechnology industry is promoted. The mutant is simple to prepare, the rebaudioside A is synthesized through efficient catalysis in a short time, and the biological enzyme catalysis method is green, environmentally friendly and pollution-free and is more suitable for current green industrial processing and production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for cultivating starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation
InactiveCN103173485AImprove conversion rateHigh total starch contentTransferasesFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation. According to the transgenic plant cultivation method provided by the invention, a selection marker gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit gene, a sucrose synthase gene, and a granule-bound starch synthase gene are introduced into a target plant, such that a transgenic plant is obtained. The total starch content of the transgenic plant is higher than that of the target plant. As a result of experiment of the invention, a plurality of genes can be simultaneously transferred in one-time through one time of gene gun bombardment, such that transgenic material cultivation period and work load can be greatly shortened. Specifically, the 4 genes related to starch metabolism are simultaneously transferred in, such that the total starch content of a transgenic regenerated plant is higher than that of wild-type plant.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
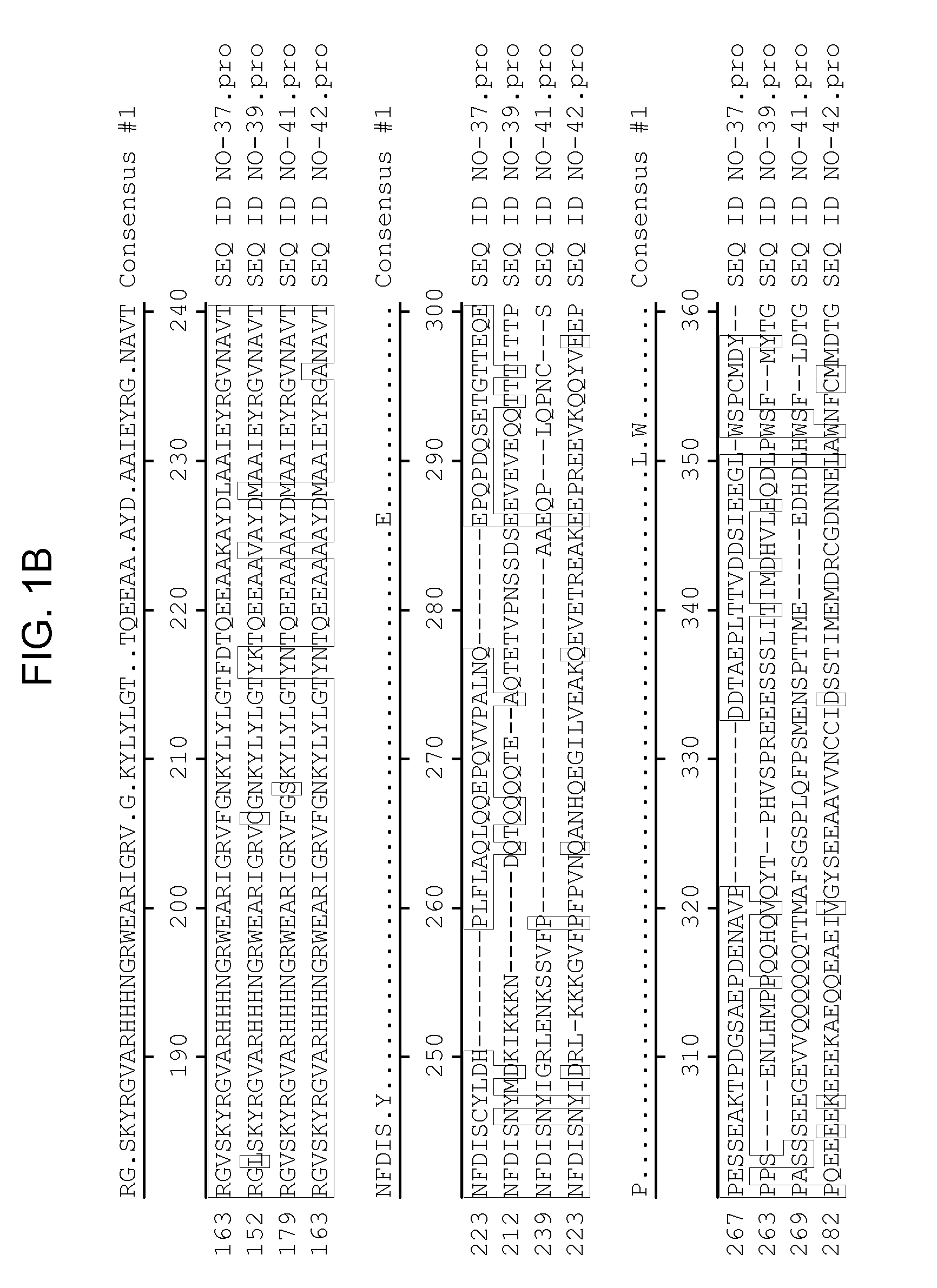
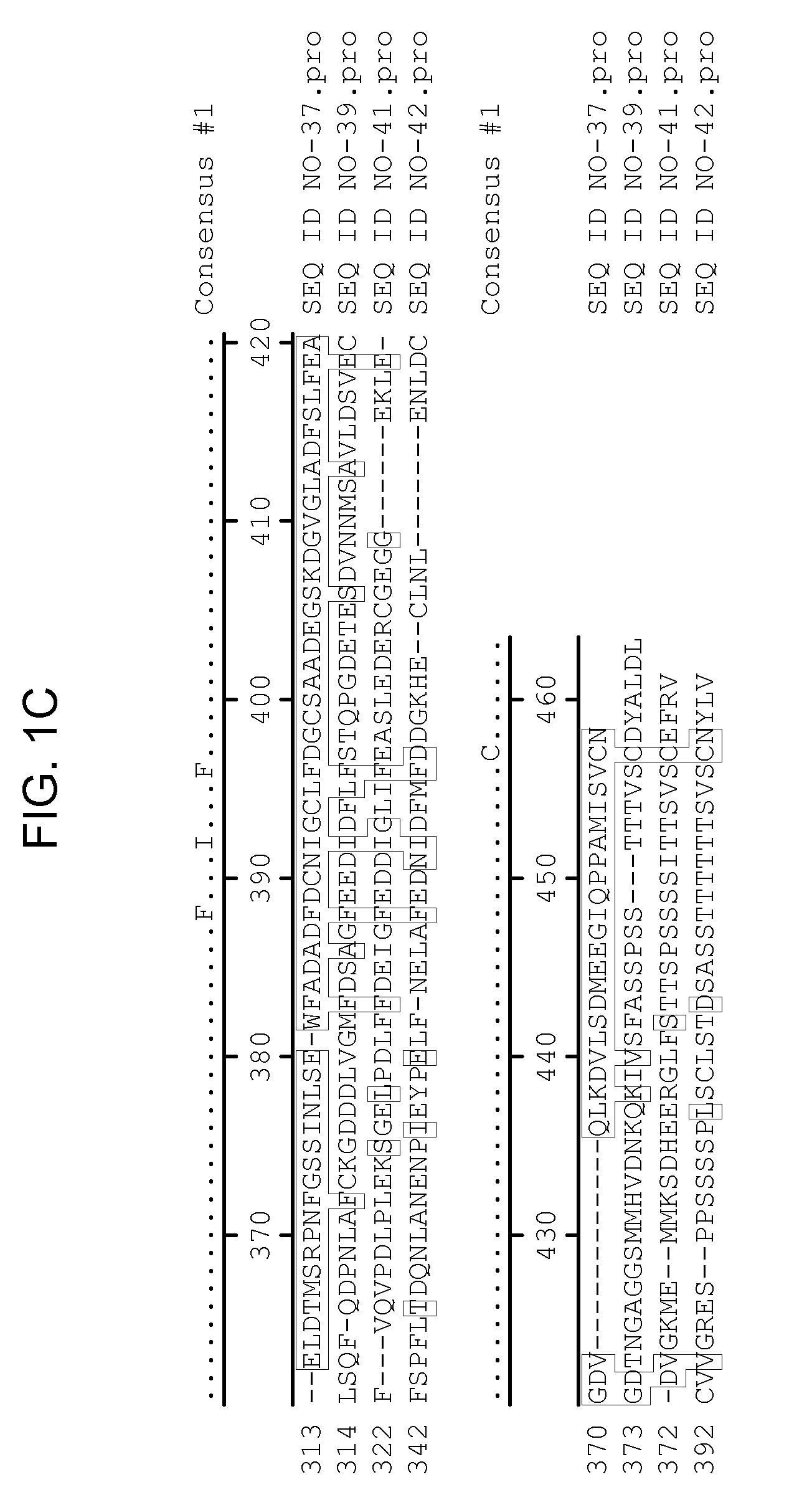
Isolated sucrose sythase polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7091398B2Alter grain quality qualityAlter quality plant stalk qualityHydrolasesTransferasesSucrose synthetaseNucleotide
The invention provides a novel isolated sucrose synthase nucleic acid and its encoded protein. The present invention also provides methods and compositions relating to altering sucrose synthase levels in plants, and in particular, in plant stalks and / or plant seeds. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, transgenic plants, and transgenic seeds.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Composite growth regulator for increasing yield and saccharinity during sugar accumulating period of beetroot and usage
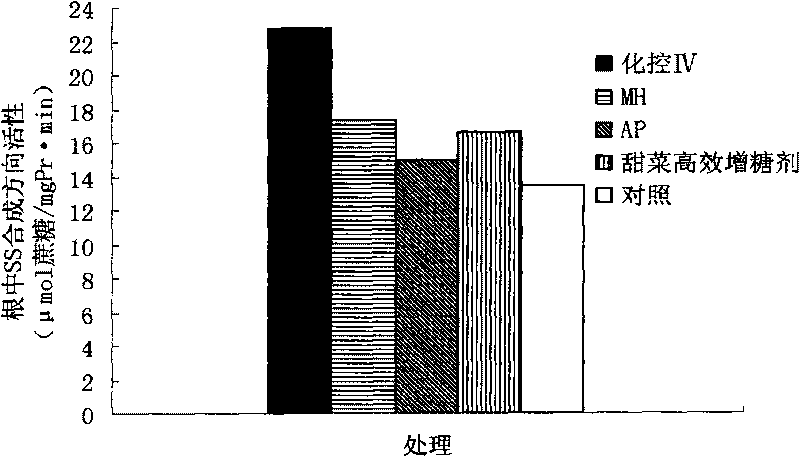
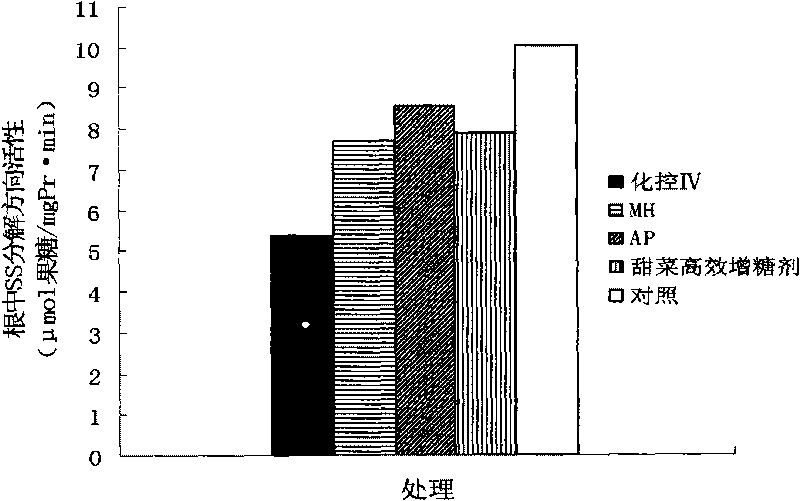
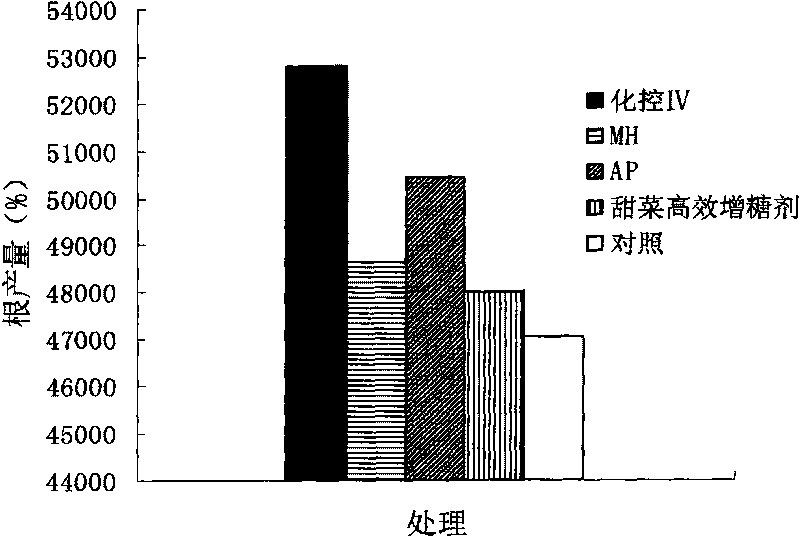
The invention relates to a composite growth regulator for increasing yield and saccharinity during the sugar accumulating period of beetroot and a usage, which are particularly suitable for the application under the arid environment, and have obvious effect on increasing yield and saccharinity through the foliage spray in late August. The regulator can not only control the injury caused by the stress of the environment, and keep the duration of the function foliage at the maximum, but also increase the activity of sucrose synthase, reduce the consumption of glycogen, promote coordination and uniform of the beetroot and the environment, individual and group, root and overground part, the external shape of the plant and internal physiological function during the sugar accumulating period, and finally reach the goal of improving the yield and saccharinity. Under the environment of the west of Jilin province, with less than 300 mm of the amount of precipitation, 0.47 percent of salt content and PH value of 8.6, the yield of beetroot reaches to 52,766.25kg / hm2, the yield is increased by 12.18 percent, and the sugar content is 17.0 percent, which is increased by 1.4 percent.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method and application of non-natural ginsenoside
ActiveCN107929296AEnhanced inhibitory effectWide variety of sourcesOrganic active ingredientsGlycoside steroidsSucrose synthetaseProtopanaxadiol
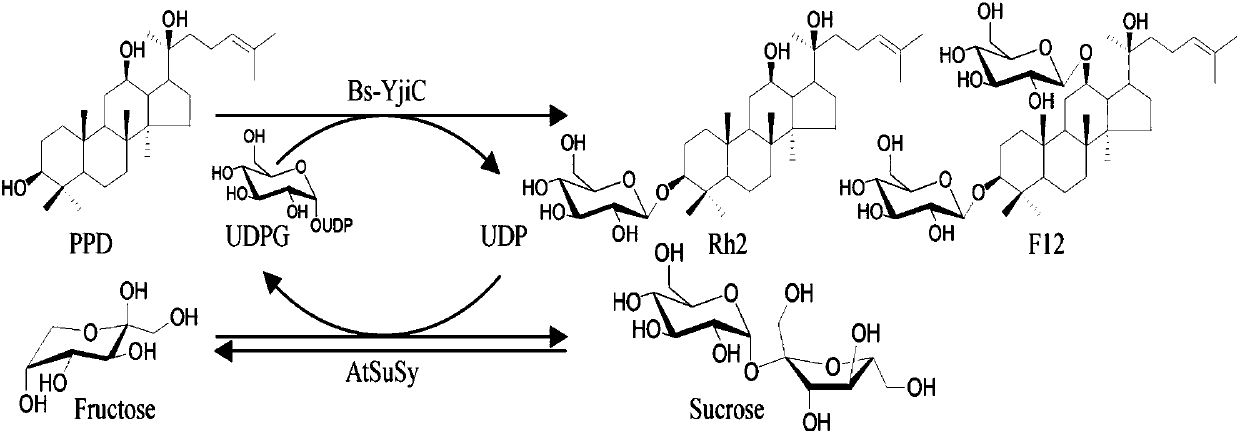
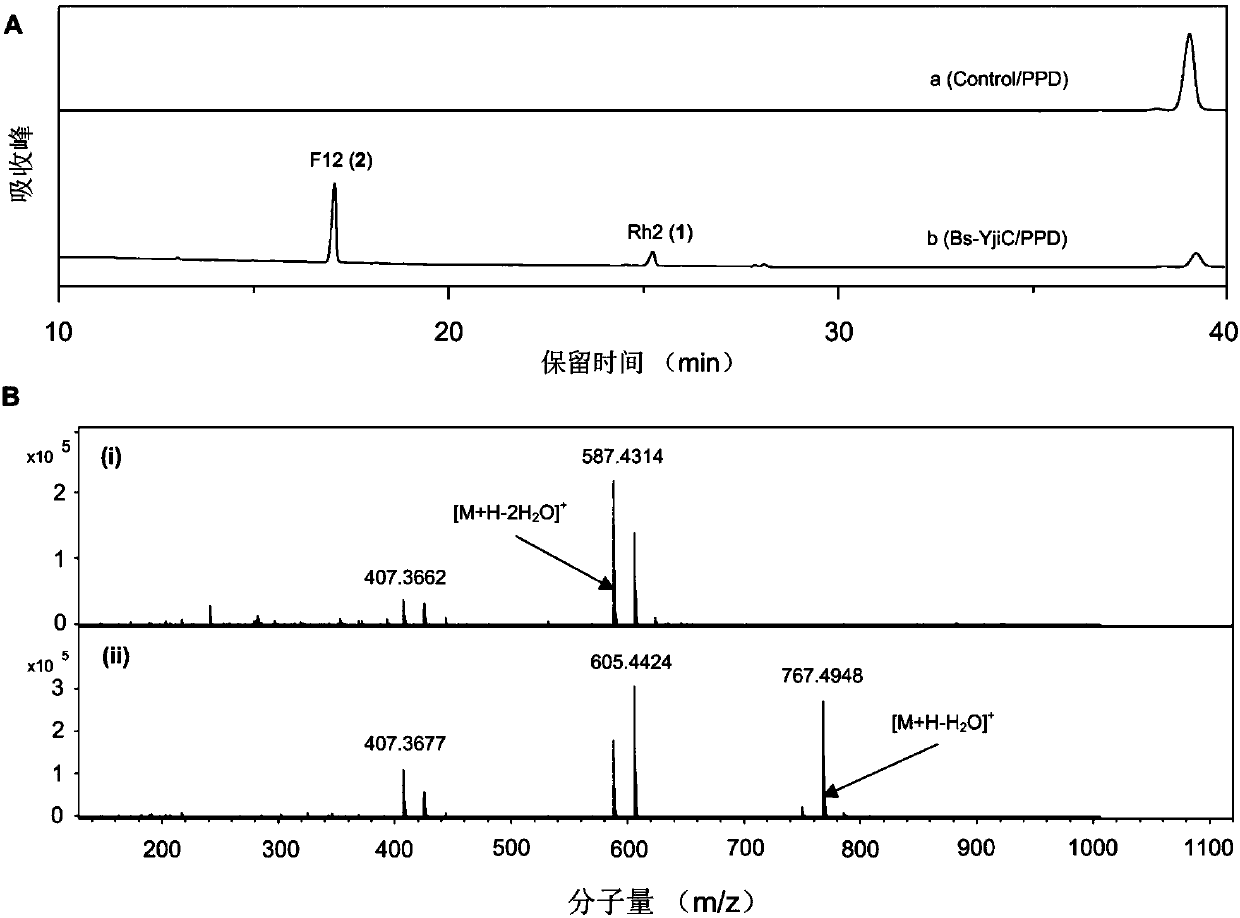
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of non-natural ginsenoside, specifically to an antitumor drug containing the non-natural ginsenoside F12 (3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-12-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol). The antitumor drug of the invention has significant inhibitory effect on colon cancer cells, liver cancer cells, lung cancer cells and gastric cancer cells. According to the invention, cheap sucrose is used as a glucose glycosyl donor, glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthase are used as coupled catalysts, and protopanaxadiol (PPD) is used as a glycosylacceptor so as to realize high-efficiency catalysis of glycosylation of hydroxyl groups at the position C3 and the position C12 of protopanaxadiol for production of the non-natural ginsenoside F12; and the method has the characteristics of wide sources of a substrate, good specificity of reactions, high catalysis efficiency, simple purification of the non-natural ginsenoside, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for biosynthesis of quercetin glycoside
The invention discloses a method for biosynthesis of quercetin glycoside, which connects the gene of glycosyltransferase UGT73G1 or mutant thereof with sucrose synthase gene to obtain a recombinant plasmid, and constructs a recombinant bacterium containing a double enzyme system; The recombinant strain was inoculated in LB liquid medium, cultured at 25-40 DEG C until OD600 reached 2-3, adding inducer lactose to induce for 12 to 20 hour, centrifuging that fermentation broth to collect bacterial cells, crushing the bacterial cell, and centrifuging to collect supernatant to obtain crude enzyme solution; dissolving quercetin or isoquercetin in DMSO, add crude enzyme solution, sucrose, reaction 8-30 h, adding methanol to stop that reaction, and centrifuging to obtain the supernatant quercetin-3, 4'-Diglucoside; diglucoside. The amino acid sequence of the glycosyltransferase mutant is an amino acid sequence in which the amino acid sequence shown in SEQID NO: 1 is mutated, and the mutated amino acid site is selected from one or more of S151, T168, K274, T293, G361, S365, V371 and F381. The mutant is simple in preparation and high in yield, and realizes the function of quercetin The yieldof 3, 4 '-diglucoside was increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Identification of a novel type of sucrose synthase and use thereof in fiber modification
Owner:BAYER BIOSCIENCE N V +1
Method for improving resistance of rice blast by using sucrose synthase
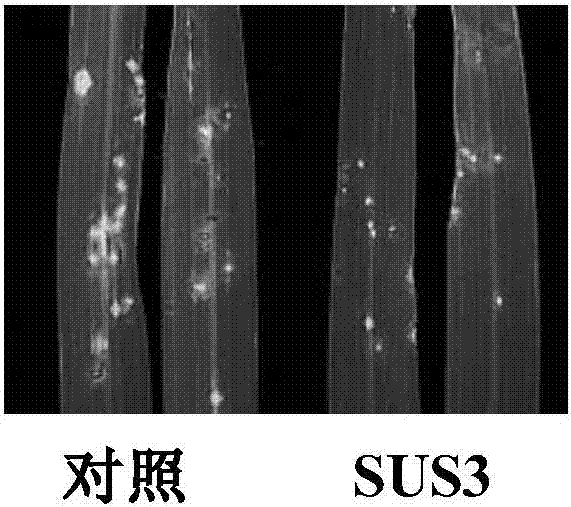
InactiveCN106854658AHigh expressionLesion length reductionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGenetically modified riceSucrose synthetase
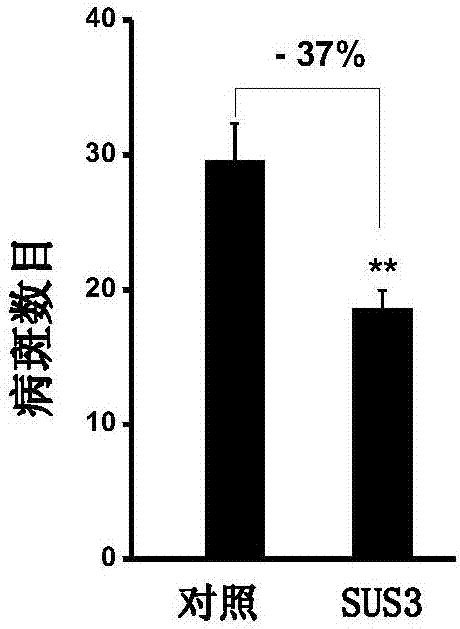
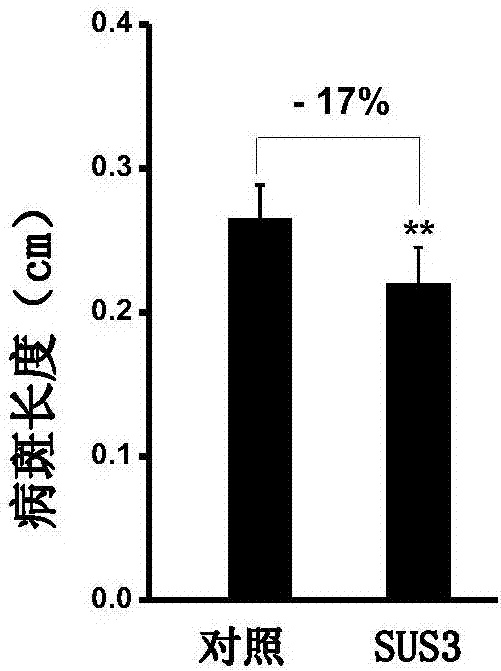
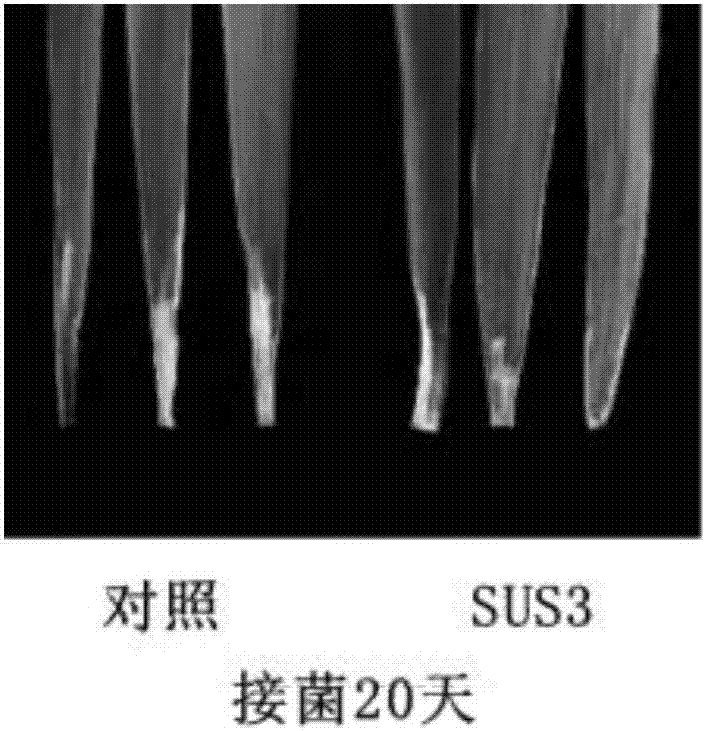
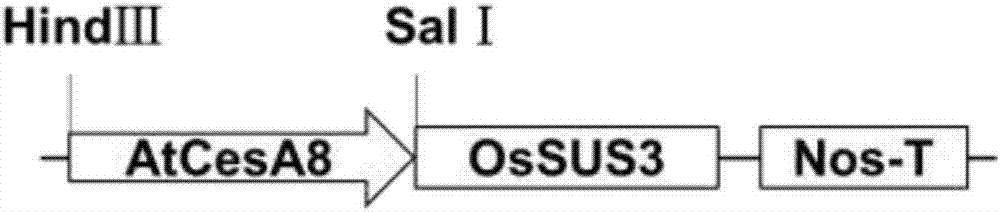
The invention discloses a method for improving the resistance of rice blast by using sucrose synthase (OsSUS3), and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology of sucrose synthase rice. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, cloning OsSUS3 gene cDNA from rice; secondly, constructing an OsSUS3 gene over-expression vector, converting rice middle flowers 11 to obtain transgenetic seedlings, wherein the OsSUS3 gene converted rice seeds Sus3(Oryza sativa Sus3) are preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Jan. 3rd, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:P201702; and thirdly, carrying out rice blast resistance measurement on the rice material of the obtained over-expression OsSUS3 gene. According to the method, the expression quantity of the OsSUS3 gene is increased, so that the rice blast scab length of transgenic rice is decreased by 17%, and the number of scabs is decreased by 37%.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
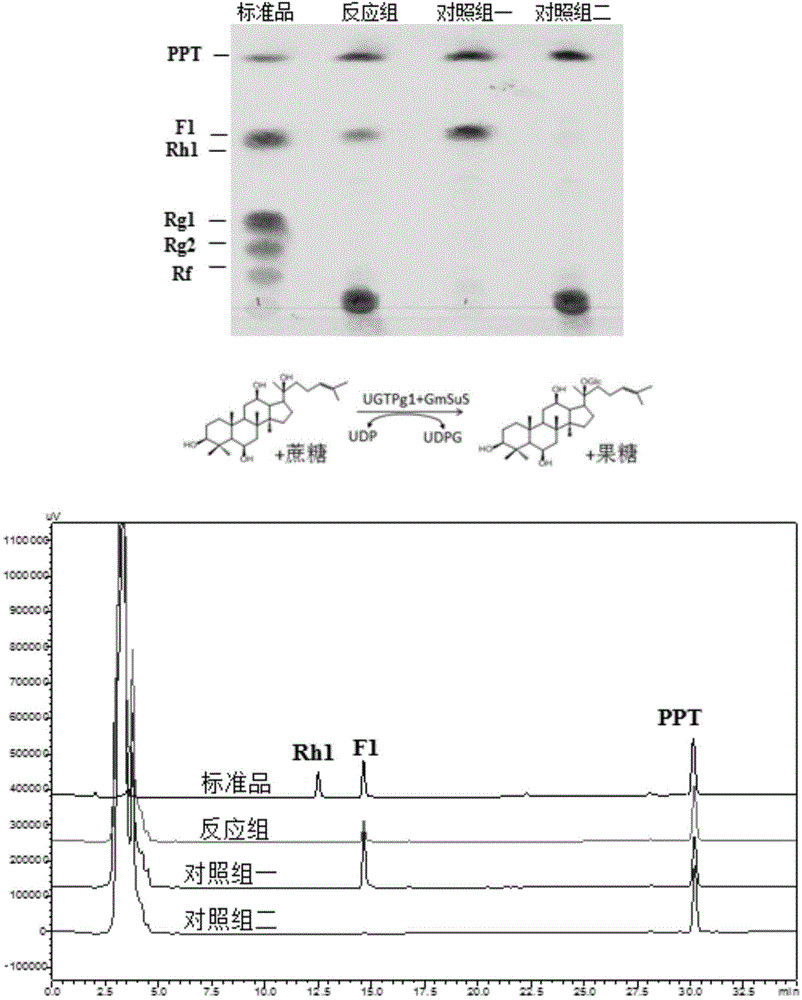
Application of glycosyl transferase mutant in directional synthesis of non-natural ginsenoside
ActiveCN114836398AEasy to purifyHigh selectivityTransferasesFermentationSucrose synthetaseCancer cell proliferation
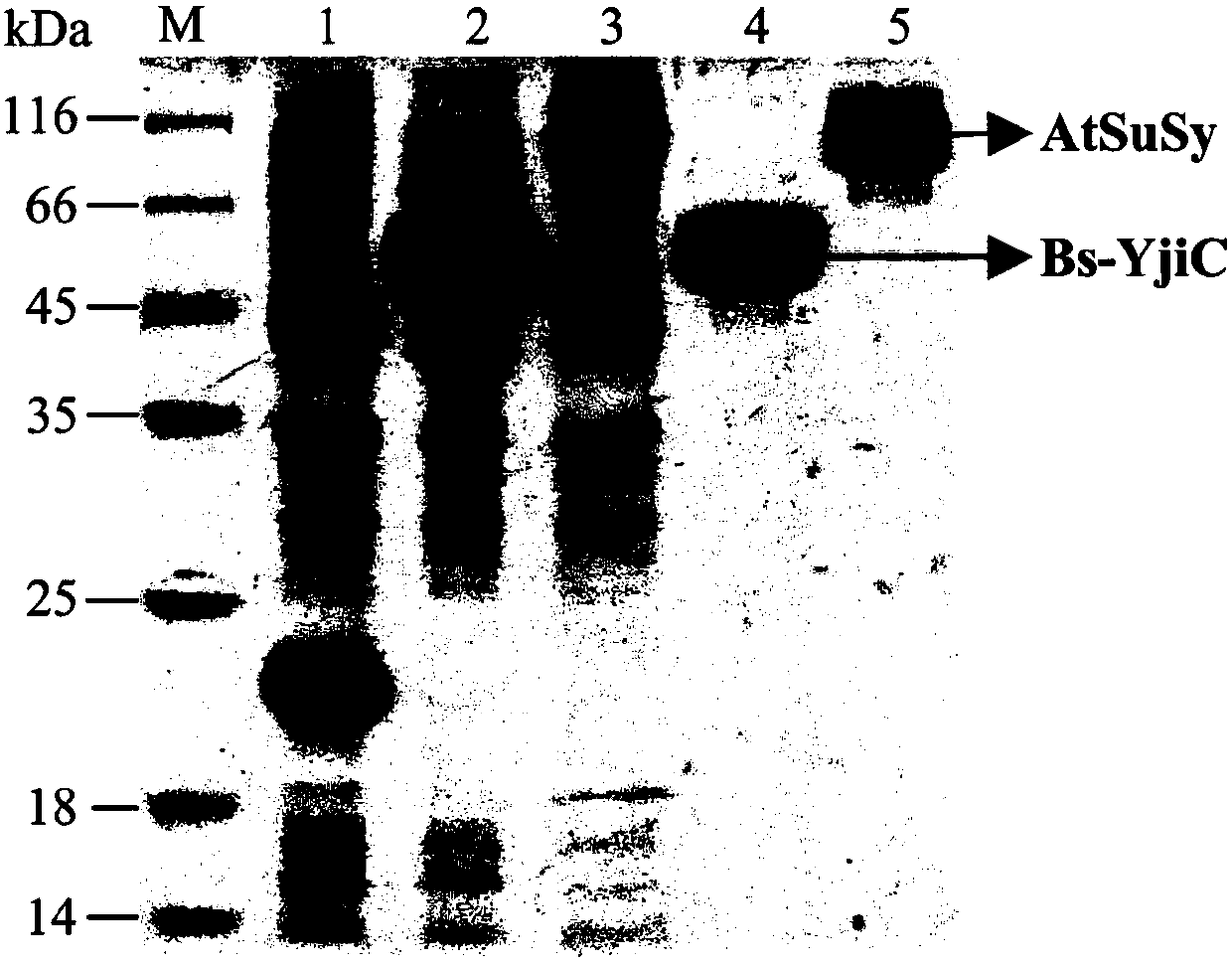
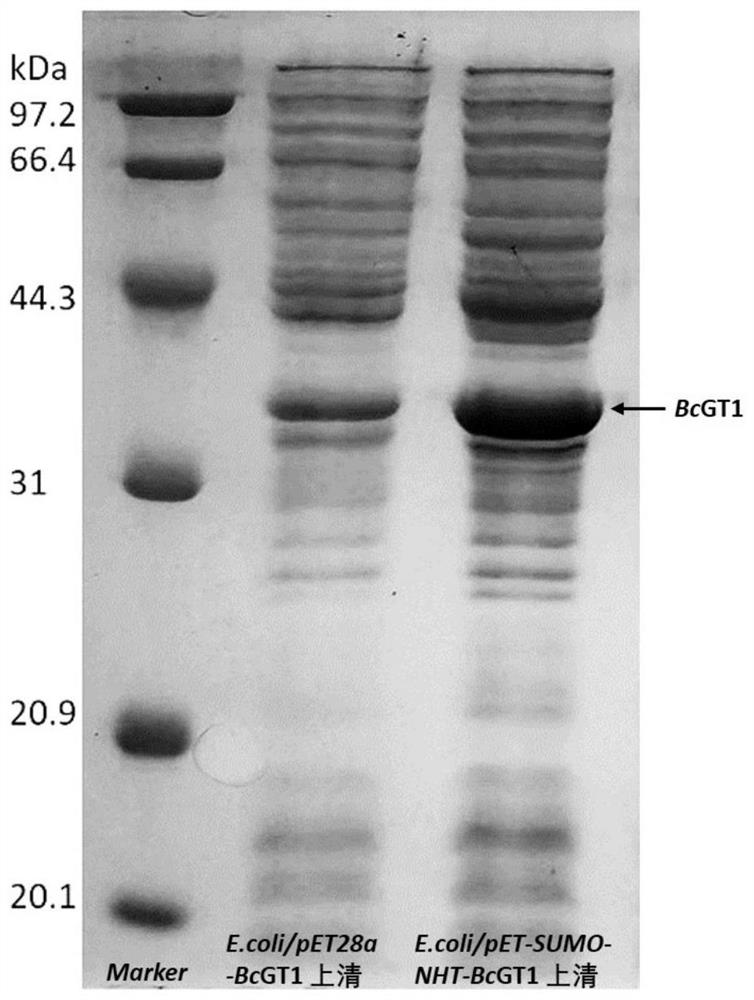
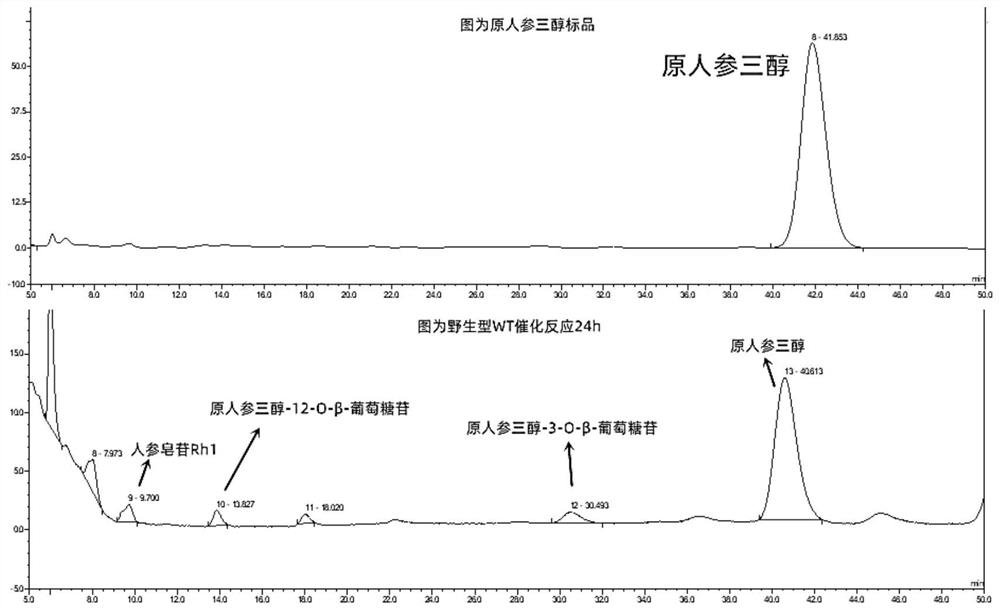
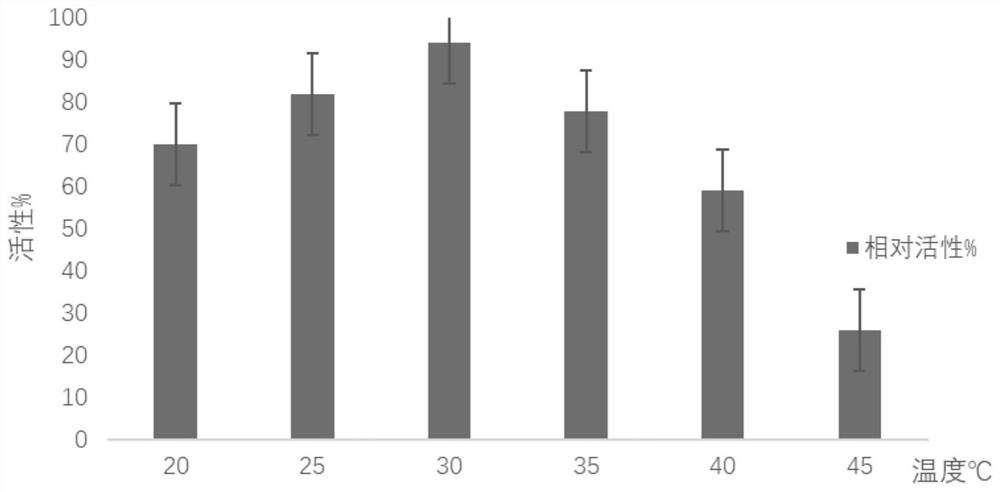
The invention relates to an application of a glycosyl transferase mutant in directional synthesis of non-natural ginsenoside. The mutant is obtained by mutating one or more of 18th and 133rd amino acid residues in an amino acid sequence of glycosyl transferase BcGT1 into another amino acid residue; the amino acid sequence of the glycosyl transferase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the glycosyl transferase mutant and sucrose synthase AtSuSy double-enzyme coupled catalytic system constructed by the invention, non-natural ginsenoside 12-O-beta-Glc-PPT or 12-O-beta-Glc-PPD can be directly and directionally synthesized by a one-step method, and the preparation process of the non-natural ginsenoside is simplified; and the product is relatively single, so that the subsequent separation step is reduced, and the purification process of the product is simplified. The non-natural ginsenoside has a stronger lung cancer cell proliferation inhibition effect than natural ginsenoside Rg3, Rh2 and the like, so that the non-natural ginsenoside has a great prospect in the development of new drugs.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Method for producing rebaudioside A through double-enzyme fermentation catalysis
PendingCN111662942AReduce stepsHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSucrose synthetase
The invention relates to a method for producing rebaudioside A through double-bacterium fermentation catalysis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) connecting a glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 gene and a sucrose synthase AtSUSY gene to a pUC18 plasmid vector, transferring the pUC18 plasmid vector to DH5alpha escherichia coli competent cells, inoculating an LB culture medium, and culturing at 25-37 DEG C and 200-250 rpm for 10-18 h; (2) inoculating to a seed tank according to the inoculum size of 0.5%-15%, and culturing for 5-16 h at the speed of 150-400rpm and the ventilation ratio of 0.1-1.5 V / V.min at the temperature of 25-37 DEG C; (3) inoculating into a fermentation tank according to the inoculum size of 1%-10%, and culturing for 20-40 h at the speed of 100-1,000 rpm, the ventilation ratio of 0.2-2 V / V.min and the pH of 6.6-8.5 at the temperature of 25-37 DEG C; (4) adding an inducer when the OD600 value reaches 20-100, wherein the concentration of the inducer is 0.1-1.5 mmol / L; (5) carrying out filter pressing, resuspending, crushing and filter pressing on the fermentation liquid to obtain a crude enzyme liquid; and (6) mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate, a phosphate buffer solution and the crude enzyme solution according to a mass ratio of (40-100):(1-4):(400-600):(50-100), and performing reaction at 25-40 DEG C for 24-48 h. The method has the advantages that two crude enzyme solutions are obtained through one-time fermentation, and operation steps are few; the enzyme activity is high and the production cost is low.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
Method for catalytically synthesizing curcumin glycoside compounds by biological method
ActiveCN113322219AGood water solubilityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSucrose synthetase
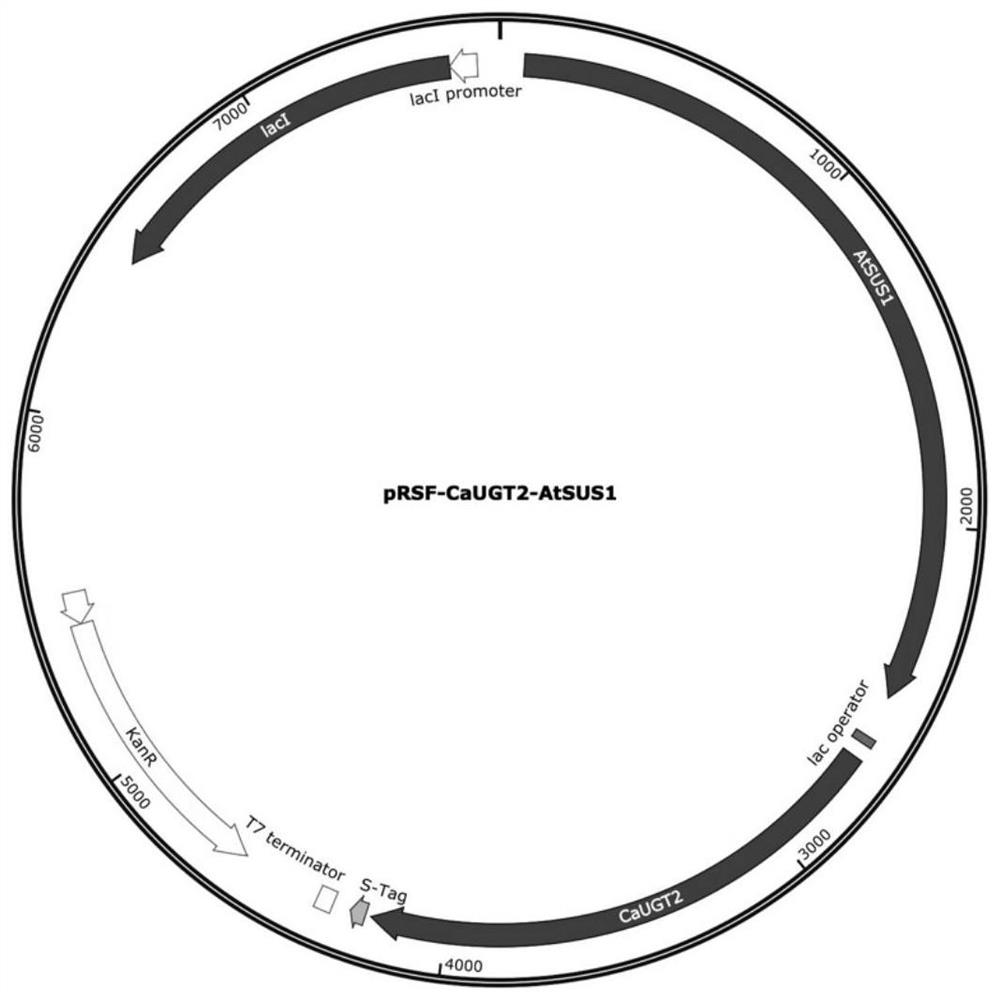
The invention discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing curcumin glycoside compounds by a biological method. A glycosyl transferase gene CaUGT2 and a sucrose synthase gene AtSUS1 are constructed on an expression vector and are introduced into escherichia coli to obtain a recombinant strain, the soluble expression quantity of the recombinant strain after induced expression is improved compared with that of glycosyl transferase from other plants, and a substrate curcumin can be efficiently catalyzed. A recombinant plasmid is pRSF-CaUGT2-AtSUS1, a sucrose synthase AtSUS1 gene is inserted into Nco I and EcoR I, glycosyl transferase CaUGT2 is inserted into Xho I and NdeI, a co-expression recombinant plasmid pRSF-CaUGT2-AtSUS1 is formed, the recombinant plasmid is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells, and a recombinant strain CaUGT2-AtSUS1 is obtained. After the recombinant strain is subjected to induced expression, the soluble expression quantity of the glycosyl transferase CaUGT2 is increased compared with that of glycosyl transferase from other plants, the conversion rate of catalytic synthesis of curcumin glycoside compounds reaches 98%, curcumin is catalyzed to generate curcumin monoglucoside and curcumin diglucoside, the water solubility of the curcumin monoglucoside and curcumin diglucoside is superior to that of curcumin, and the problem that curcumin is poor in water solubility is solved. The concentration of the substrate curcumin is 75 mM, the concentration of a catalytic substrate is relatively high, and the method is more suitable for food and medicine industries in industrialization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
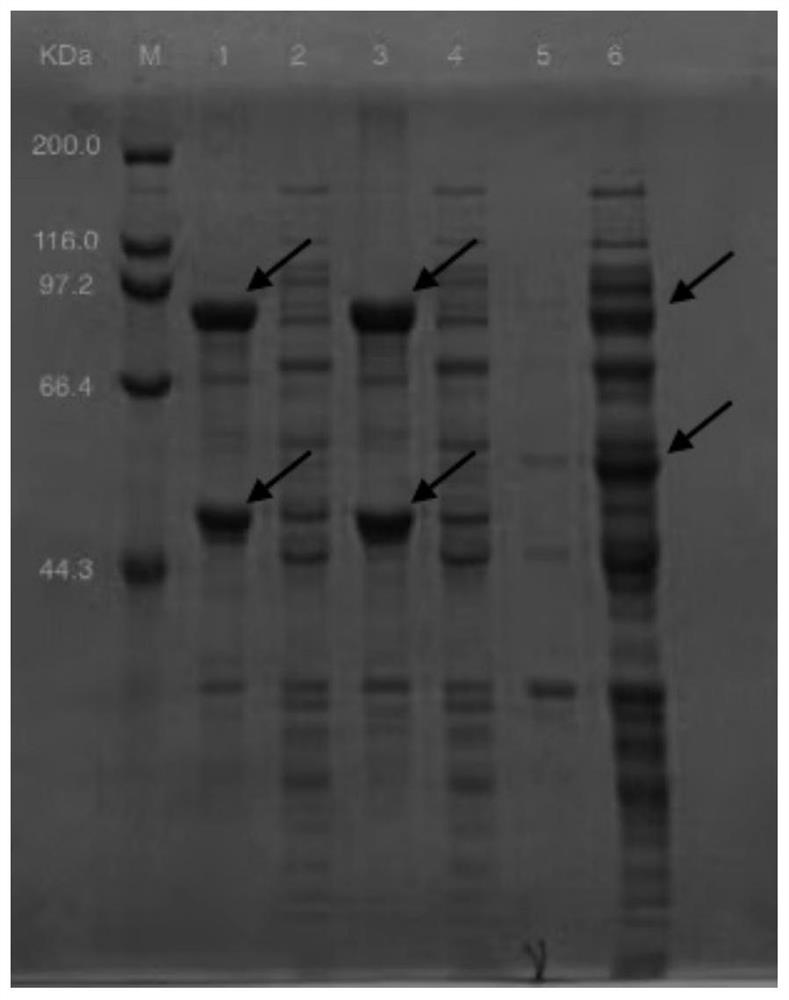
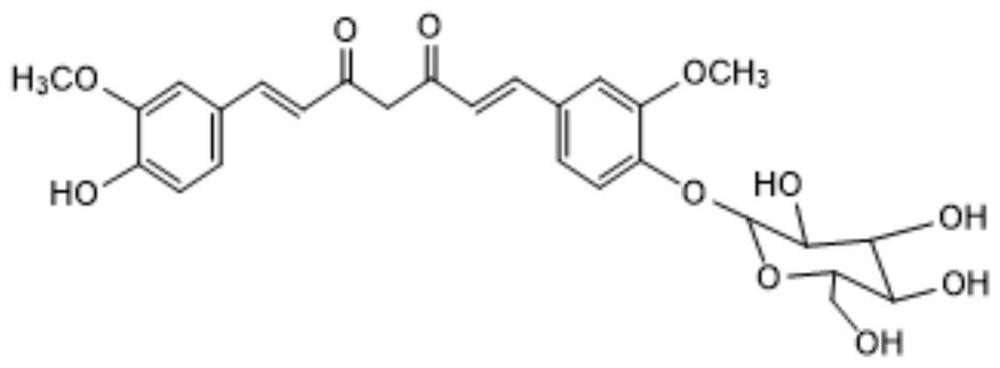
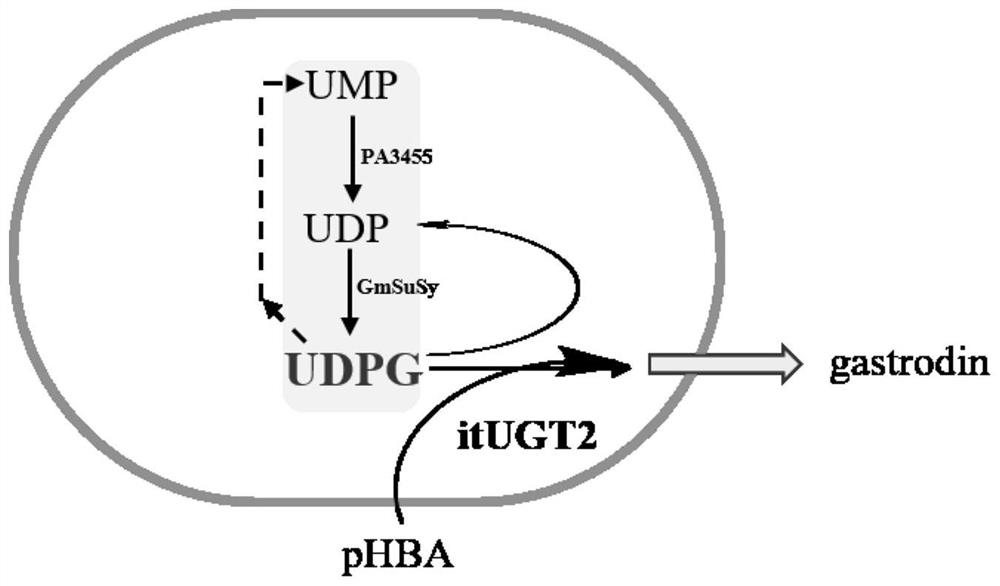
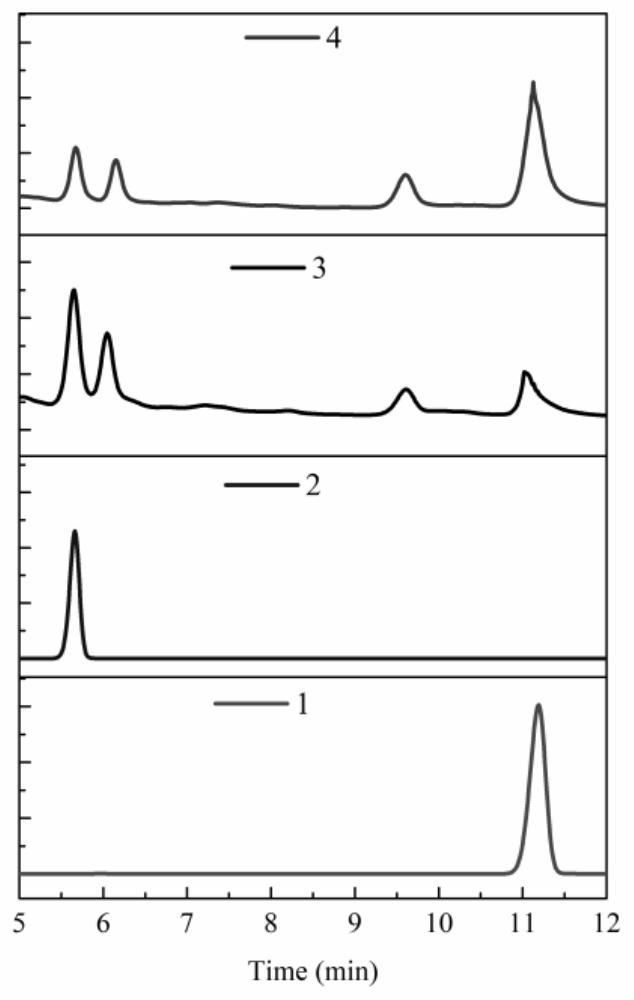
Recombinant genetically engineered bacterium for producing gastrodin, construction method and application
PendingCN113604414AImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationSucrose synthetaseEngineered genetic
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a recombinant genetically engineered bacterium for producing gastrodin, a construction method and application. According to the recombinant genetically engineered bacterium, glycosyl transferase is introduced into a host, glycosyl transferase is expressed through a host strain to catalyze a substrate to synthesize gastrodin, sucrose synthase and polyphosphate kinase are introduced into the host, synthesis and cyclic regeneration of UDPG are achieved, the amount of glycosyl donor of a glycosylation reaction is increased, a whole-cell catalytic conversion method is constructed, on the basis that no extra UPDG is added, the conversion rate of gastrodin reaches up to 95% or above, the gastrodin yield is increased, and the gastrodin production cost is reduced.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Method for improving production and transformation efficiency of erythrite and application of method
ActiveCN110628834AImprove conversion rateEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesFermentationSucrose synthetaseCyclodextrin
The invention relates to a method for improving production and transformation efficiency of erythrite and an application of the method. The method comprises the steps that glucose is used as a raw material, yeast is used as a fermentation and transformation bacterial strain, and in the fermentation and conversion process, sucrose synthase and malt cyclodextrin-glucan transferase are added, so thatthe conversion rate of glucose into erythrite can be increased. The method is simple to operate and low in cost, and the conversion rate is notably increased.
Owner:BINZHOU SANYUAN BIOLOGICAL TECH
Application of sucrose synthase in regulating of development of plant fruits
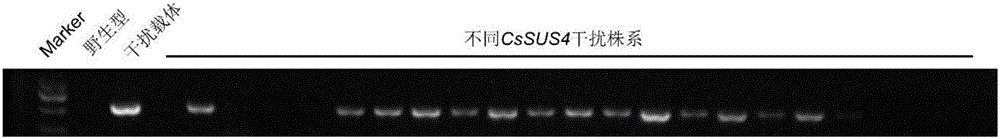
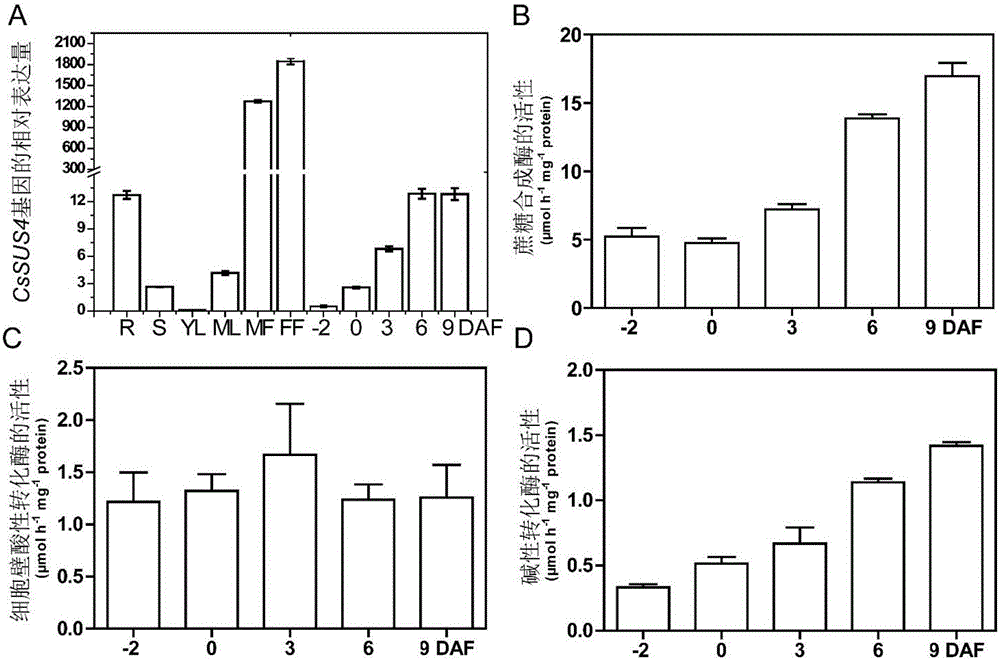
The present invention discloses application of sucrose synthetase in regulating of development of plant fruits. The present invention provides a method for cultivation of a transgenic plant, a sucrose synthase encoding gene is introduced into the plant to obtain a transgenic plant, and fruit yield of the transgenic plant is higher than that of a target plant. The sucrose synthase encoding gene may be sucrose synthase gene CsSus4. A key role in the development of cucumber fruits of the sucrose synthase gene CsSus4 is discovered, sink strength can be regulated, and the development of the fruits can be promoted. The good function has guiding significance for effectively improving cucumber yield.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for method
ActiveCN112239771ARaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseUridine Diphosphoglucose
The invention discloses a method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for the method. The method for producing the uridine diphosphate glucose comprises the following steps of by using uridine monophosphate and sucrose as raw materials, producing the uridine diphosphate glucose under the action of the engineering bacteria, wherein the engineering bacteria arerecombinant bacteria for expressing functional protein and are obtained by introducing a gene for encoding the functional protein into starting bacteria, and the functional protein comprises polyphosphokinase, uridine monophosphate kinase and sucrose synthase. The method is of great significance to industrial production of the uridine diphosphate glucose.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Special growth regulator for peanut pod setting
InactiveCN103960297BHigh in chlorophyllIncrease net photosynthetic ratePlant growth regulatorsBiocideSucrose synthetaseSeaweed extract
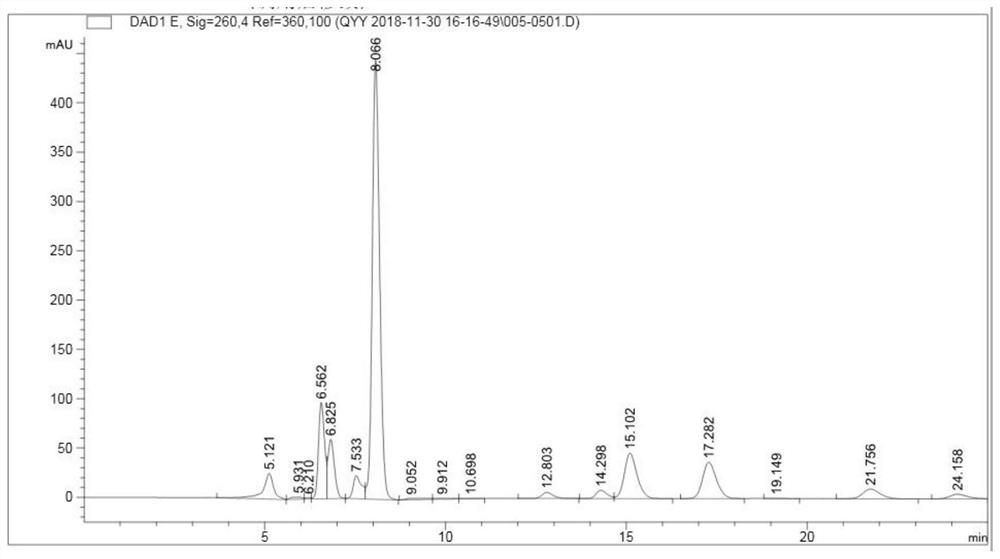
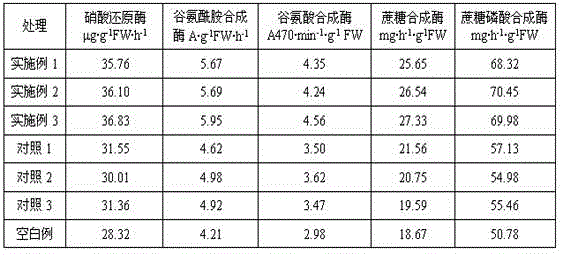
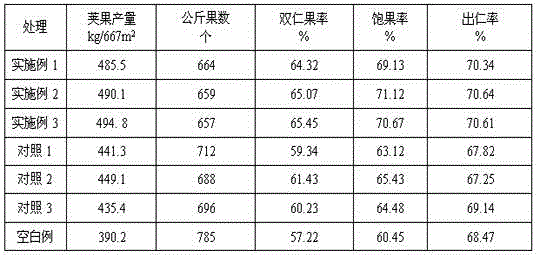
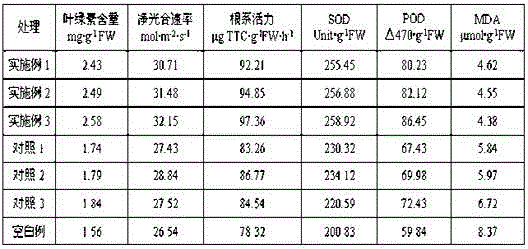
The invention relates to the technical field of peanut cultivation, in particular to a special growth regulator for peanut pod setting stage: paclobutrazol wettable powder 20-30 g, chitosan oligosaccharide 2.5-3.0 g, seaweed extract 50-100 g, sucrose 115-180 g g. The chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate, and root activity of peanut leaves treated with this regulator at the pod stage were significantly higher than those of the controls, and the SOD activity and POD activity of the leaves were significantly higher than that of the controls, while the malondialdehyde content was significantly lower than that of the controls, indicating that Using this regulator can remove oxygen free radicals very well and delay aging; this regulator can significantly improve the activity of leaf nitrate reductase, glutamine synthetase and glutamic acid synthase, and increase the activity of leaf sucrose synthase and sucrose synthase. Phosphate synthase activity is beneficial to the accumulation of dry matter in pods and the synthesis of protein and fat in seeds. Significantly increased the yield of peanut pods. The reason for the increased yield is that the weight of a single fruit was significantly increased, the rate of full fruit was increased, and the rate of double-seed fruit and the rate of kernels were greatly increased.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving resistance to bacterial blight of rice by using sucrose synthase
InactiveCN107058349AHigh expressionReduced blight spot lengthFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGenetically modified riceSaccharum
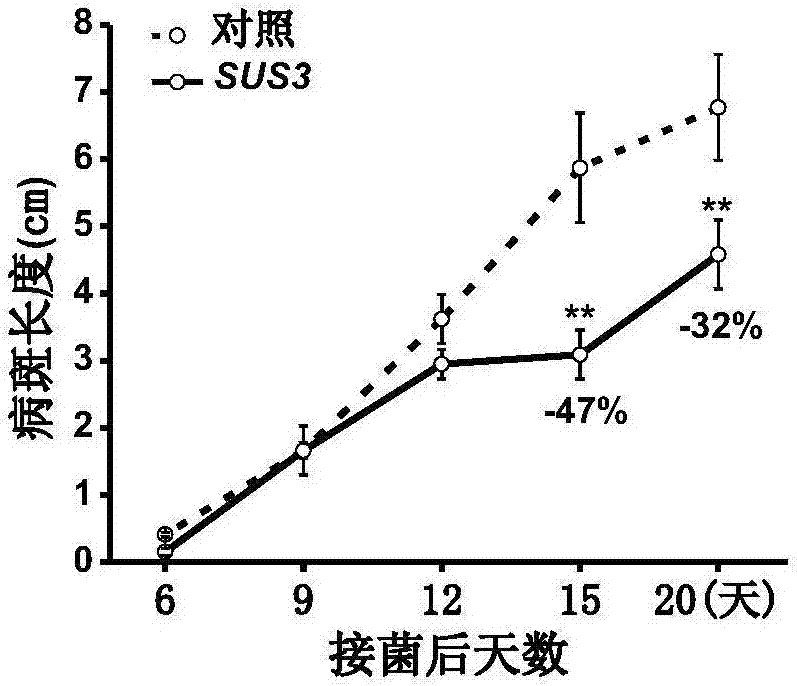
The invention discloses a method for improving the resistance to bacterial blight of rice by using sucrose synthase, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology of transforming sucrose synthase rice. The method comprises the steps of (1) cloning an OsSUS3 gene cDNA from rice; (2) building an over-expression vector of the OsSUS3 gene, transforming rice Zhonghua (Chinese character) II and obtaining a transgenic plant, wherein rice seeds Sus3 (oryza sativa Sus3) of transforming OsSUS3 gene are preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 3, 2017; and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:P201702; and (3) measuring the resistance to bacterial blight of the rice material of the obtained over-expressed OsSUS3 gene. The expression quantity of the OsSUS3 gene in the rice is increased, and the lengths of transgenic rice bacterial blight spots are reduced by 47% on the 15th day and reduced by 32% on the 20th day after inoculation in comparison with those in a control group.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
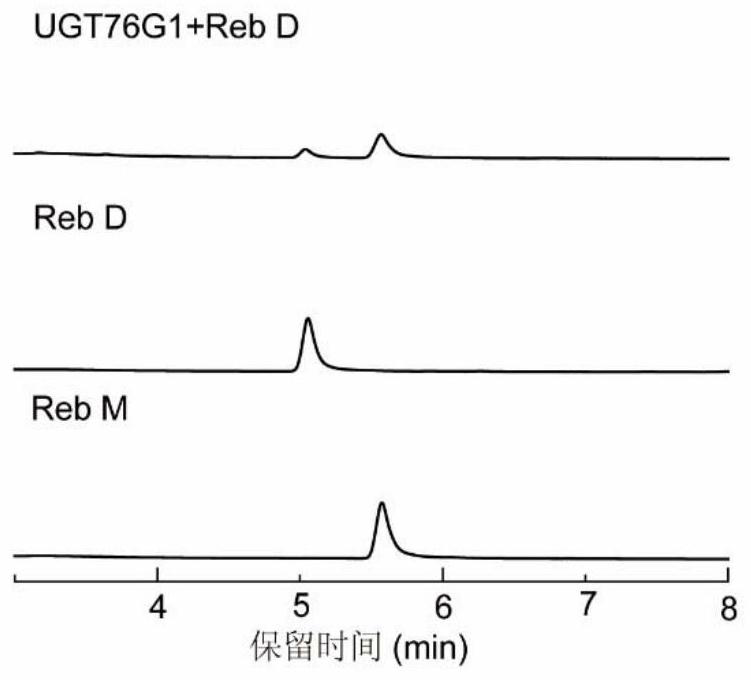
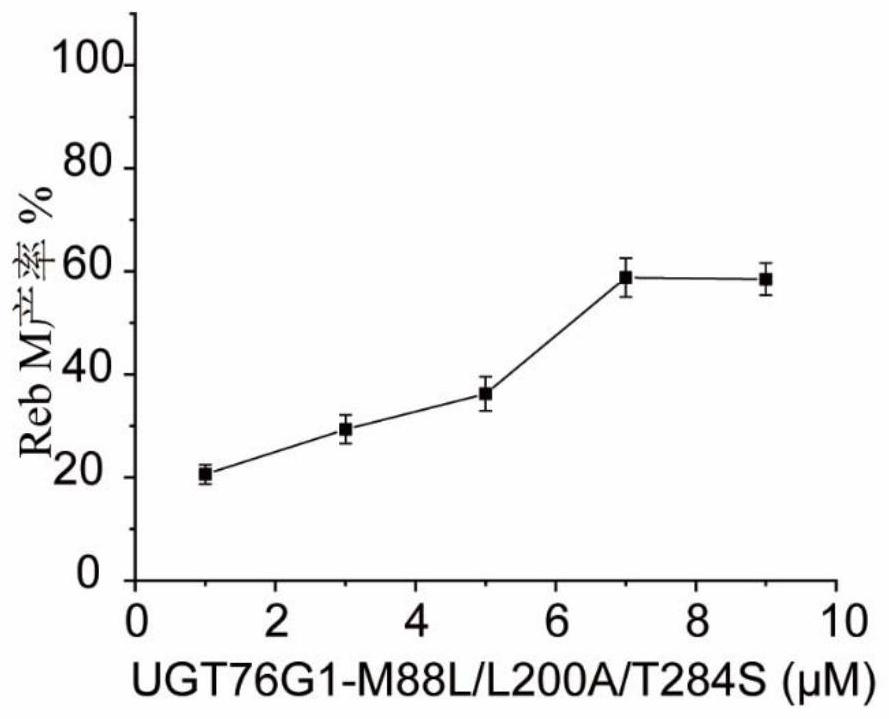
Method for efficiently biosynthesizing rebaudioside M by using glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 mutant
PendingCN114574460AImprove the efficiency of synthetic RebMHigh catalytic activityBacteriaTransferasesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
The invention discloses a method for efficiently biosynthesizing rebaudioside M by using a glycosyl transferase UGT76G1 mutant, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, the mutant UGT76G1-T284S / M88L / L200A with high catalytic activity is obtained through directed evolution. A glycosyl transferase mutant UGT76G1-T284S / M88L / L200A and Arabidopsis thaliana-derived sucrose synthase AtSuSy are used for constructing a coupled reaction, the rebaudioside M is efficiently catalyzed and synthesized by taking rebaudioside D as a substrate, 23.37 g / L Reb M is efficiently synthesized by supplementing and adding a substrate Reb D and taking 22.58 g / L (20mM) Reb D as the substrate to react for 7h, the yield of the Reb M reaches 90.5%, and an efficient and green new way is provided for the production of the Reb M.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
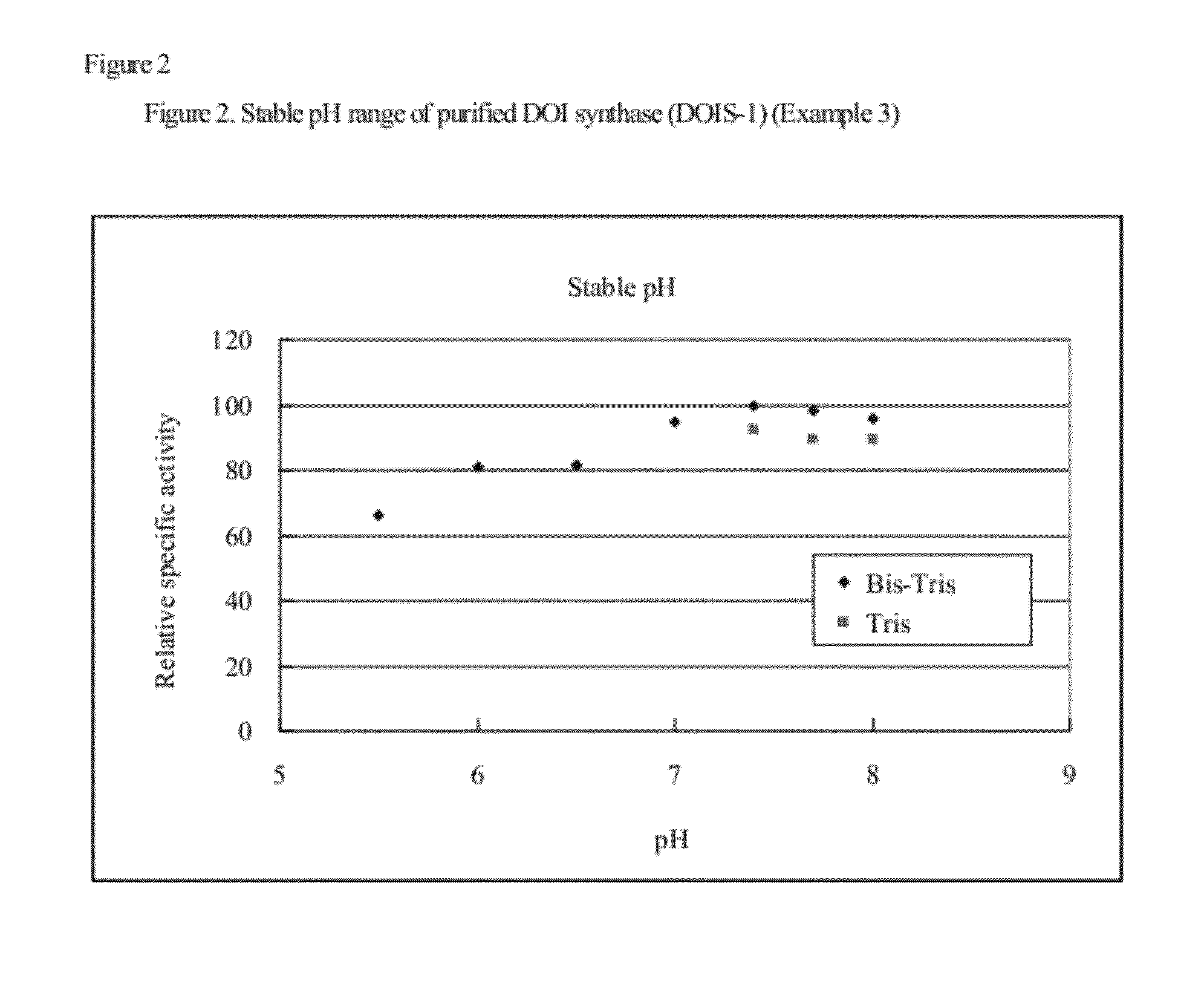
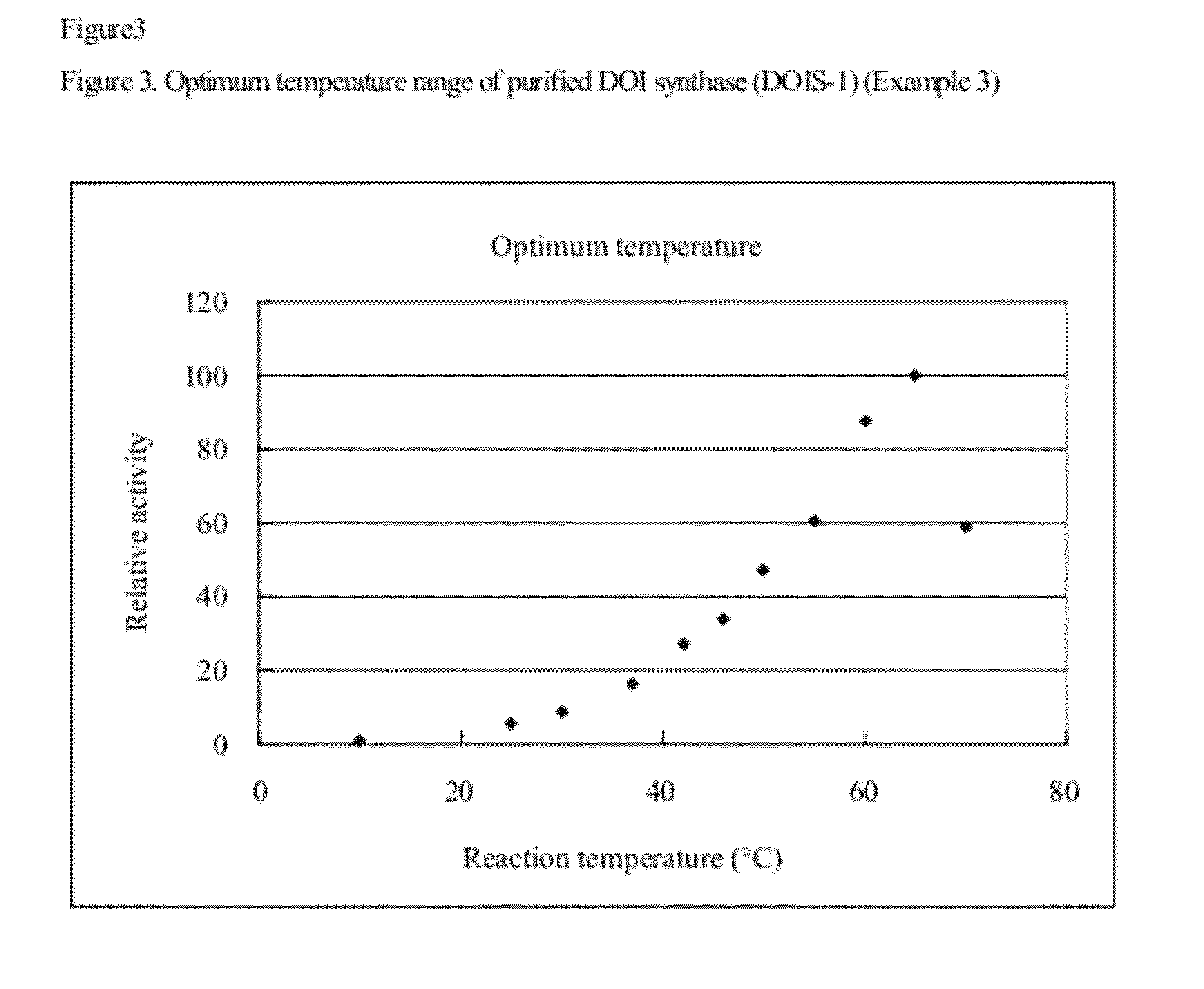
2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase
An object of the present invention is to provide a DOI synthase having properties such as stability to heat and pH, which are superior to those of conventional enzymes, and a method for producing DOI using the above-mentioned enzyme. The present invention provides a 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase having the properties described in the following (1), (2), (4), (6) and (7), and also having the properties described in the following (3) and / or (5):(1) action: the enzyme has a function to convert glucose-6-phosphate to 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose;(2) optimum pH range: pH 7.0 to 7.7;(3) stable pH range: pH 6.0 to 8.0;(4) optimum temperature range: 55° C. to 70° C.;(5) stable temperature range: 20° C. to 46° C.;(6) coenzyme used: NAD+; and(7) molecular weight: 39,000 to 42,000.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Method for preparing rebaudioside A from stevioside
ActiveUS10472660B2High purityNo side-productsSugar derivativesFermentationSaccharumSucrose synthetase
The present invention relates to an in-situ method for preparing rebaudioside A from sucrose and stevioside by sucrose synthase and glycosyltransferase.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Use of fructokinases and sucrose synthases for increasing cell wall polymers
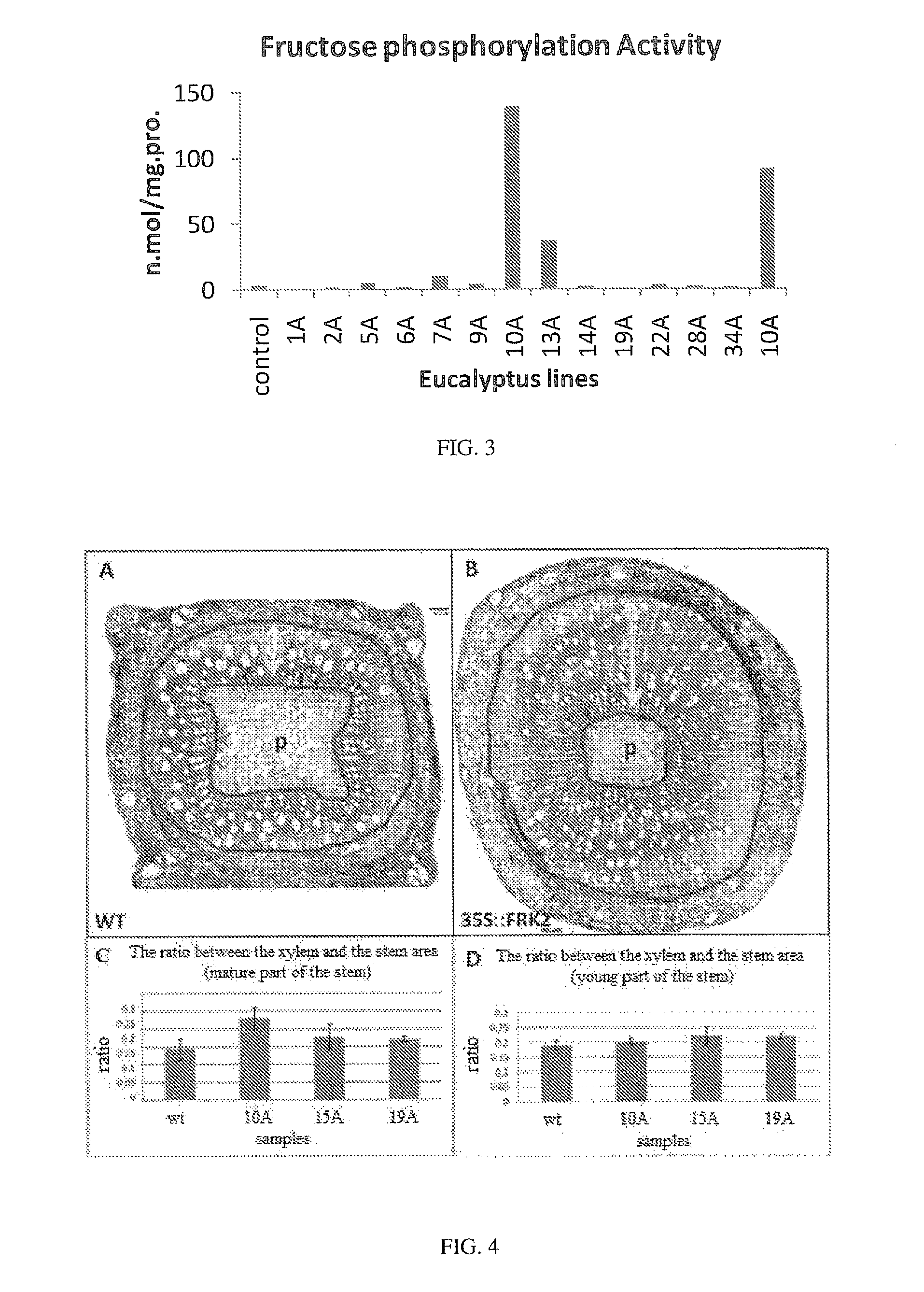
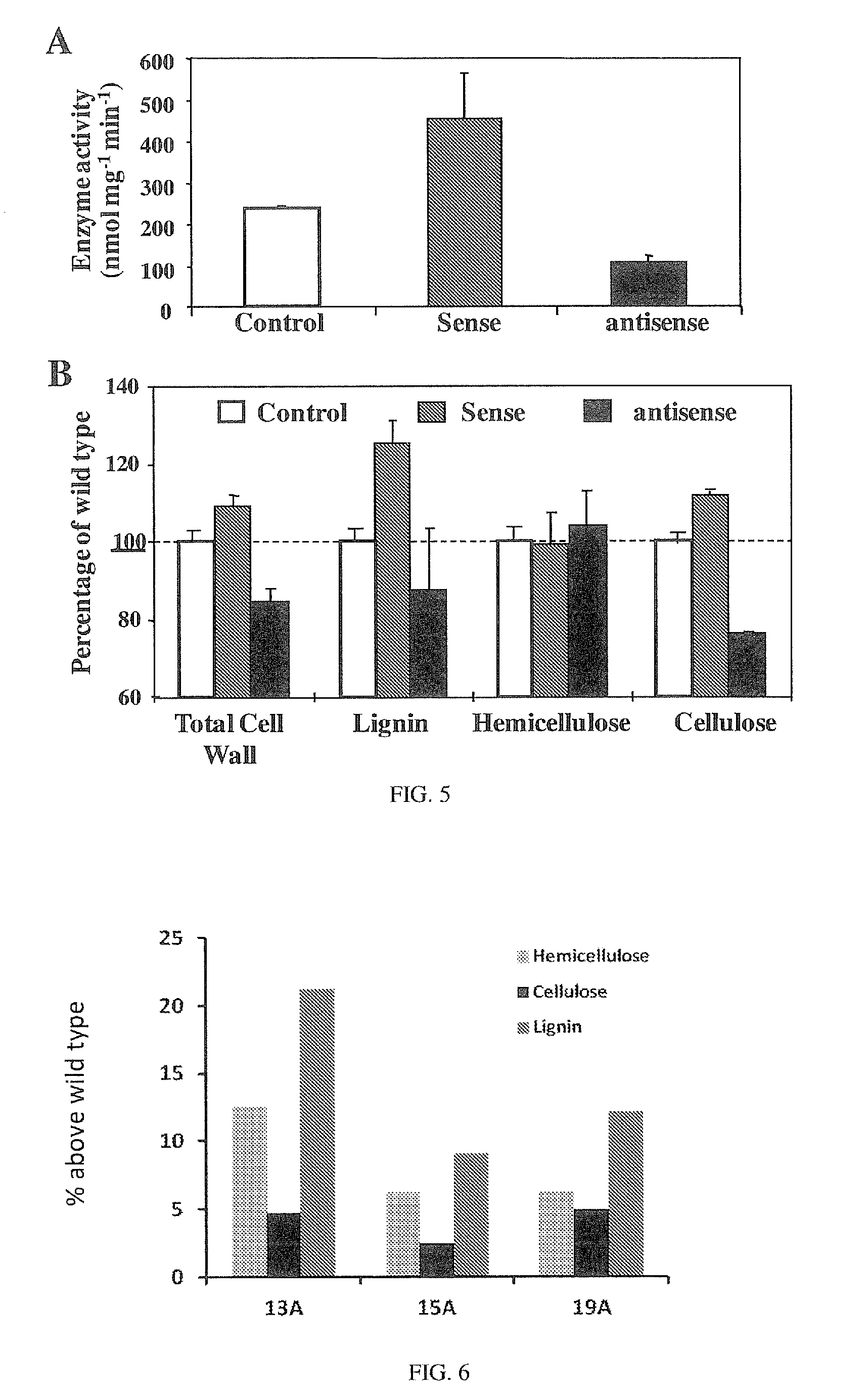
InactiveUS9556421B2Promote plant growthHigh expressionTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionSucrose synthetaseCell wall
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Method for increasing the gene expression of saccharose synthase
The invention relates to a method for increasing the gene expression of saccharose synthase. To this end the invention provides for the expression of the saccharose synthase gene to be placed under the control of a proton-ATPase promoter. According to a preferred version of the invention gene expression of the saccharose synthase is also increased by increasing the number of copies of the saccharose synthase gene and of the proton-ATPase promoter.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
A kind of method that recombinant bacterium catalyzes rebaudioside a to prepare rebaudioside m2
ActiveCN106834389BAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to preparation of rebaudioside M2 by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene at the same time; the tomato-based glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-based sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 and is constructed to obtain a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induced expression, crude enzyme liquid is taken and is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside M2; in a reaction process, the crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder is also not needed and substrates including rebaudioside D and UDP or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added, so that the environmental friendliness is better. The yield of the rebaudioside M2 reaches 11.09g / L.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com