A genetic transformation method mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens with Aspergillus flavus mycelium as receptor
A genetic transformation method, Agrobacterium-mediated technology, applied in the field of genetic transformation using Aspergillus flavus mycelium as a receptor, can solve the problems of cumbersome steps, genetic transformation of Aspergillus flavus strains, high cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1, Construction of the pAg1-pt-mC binary vector carrying the fragment of interest
[0053] Use the binary vector pAg1-H3 with Hin d III and Sma The hygromycin resistance gene fragment was removed by I double enzyme digestion, and the pAg1 vector fragment was recovered; the pPTR I-mCherry plasmid (Nie X, Yu S, Qiu M et al., J. Agric. Food Chem ., 2016, 64(35):6772-6782) as a template, using the forward primer 5'-TCGGTACCAAGGCCCGGGCATCCGG
[0054] ATGTCGAAGGCTTG-3' (SEQ ID NO. 1); and reverse primer 5'-GGGAGTCACGAAGCTTGGGC
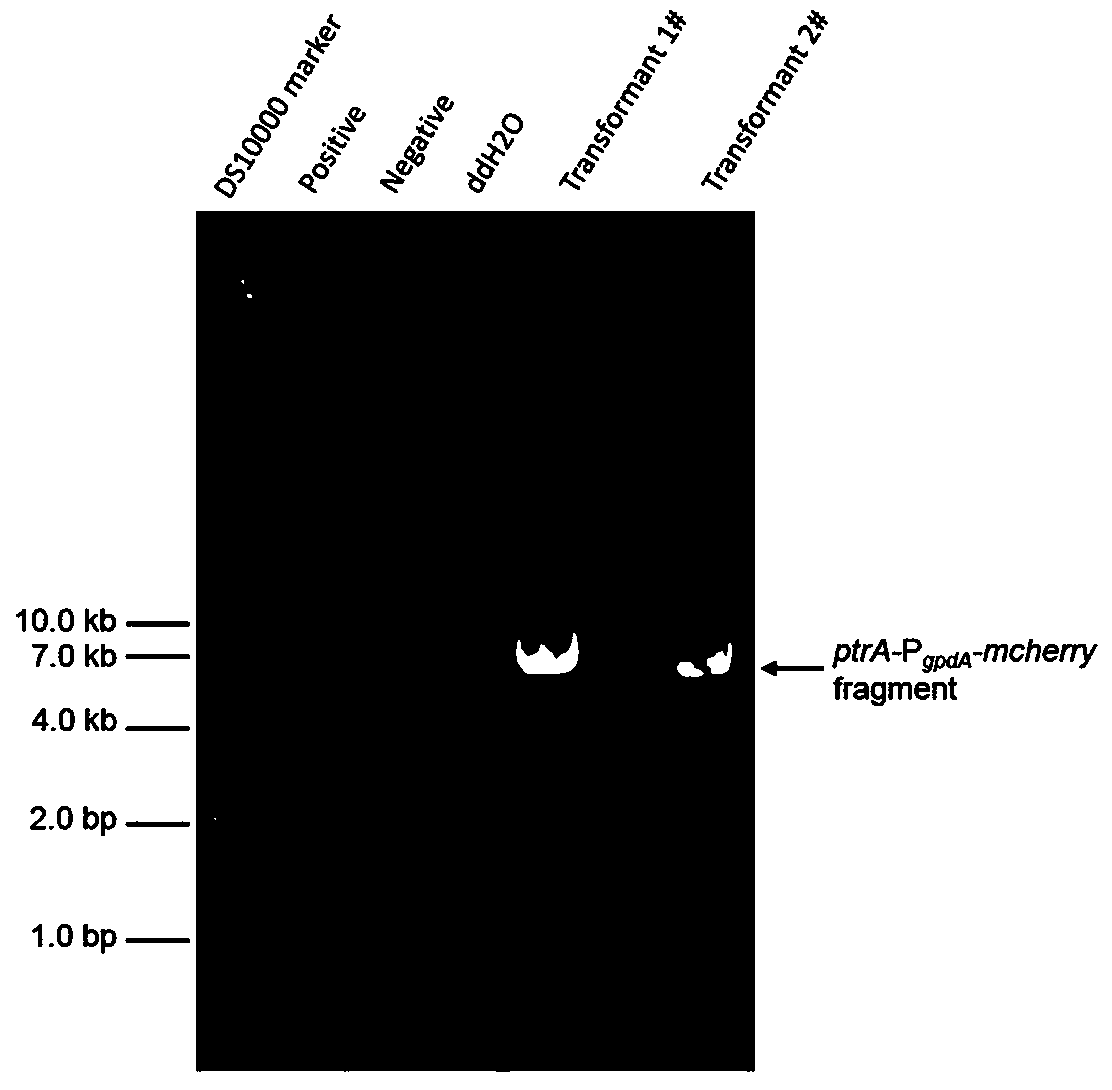
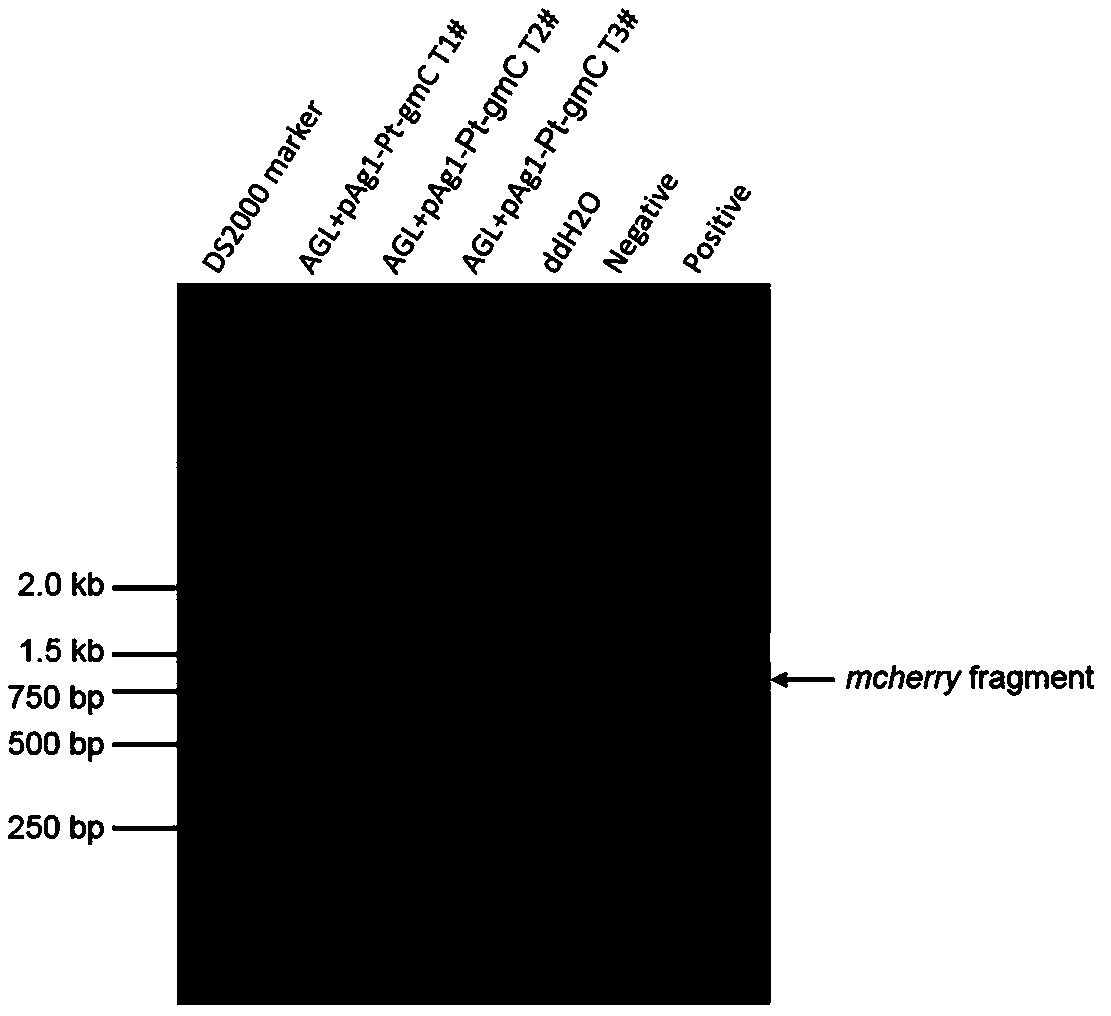
[0055] AATTGATTACGGGA-3' (SEQ ID NO.2) amplified 5227 bp target fragment ptrA- P gpdA -mcherry , the target fragment contains ptrA Gene and its promoter and terminator sequence (SEQ ID NO.3), derived from Aspergillus nidulans wxya promoter P gpdA Sequence (SEQ ID NO.4) and red fluorescent protein gene sequence derived from coralline animals mcherry (SEQ ID NO. 5).
[0056] Combine the pAg1 vector fragment recovered above w...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2, the preparation of the Agrobacterium bacterium liquid carrying target gene
[0058] Agrobacterium AGL-1 strain was taken out from -80 ℃, inoculated on LB solid medium containing rifampicin with a final concentration of 25 μg / mL, and activated at 28 ℃ until a single clone appeared; pick a single clone and inoculate it into 3 mL In LB liquid medium (containing rifampicin at a final concentration of 25 μg / mL), shake culture at 28 °C and 220 rpm for 24 h; take the above bacterial liquid and inoculate it into 100 mL of LB liquid medium (containing a final concentration of 25 μg / mL rifampicin), 28 ℃, 220 rpm shaking culture to OD 600 =0.5; ice-bathed bacterial solution for 30 min, centrifuged at 4200 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, collected the bacterial cells, removed the supernatant, and washed with pre-cooled 20 mMCaCl 2 Resuspend the washed cells, place on ice for 20 min; centrifuge at 4200 rpm, 4 °C for 10 min, collect the cells, remove the supernatant, and wash w...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3, the preparation of aspergillus flavus mycelia homogeneous liquid
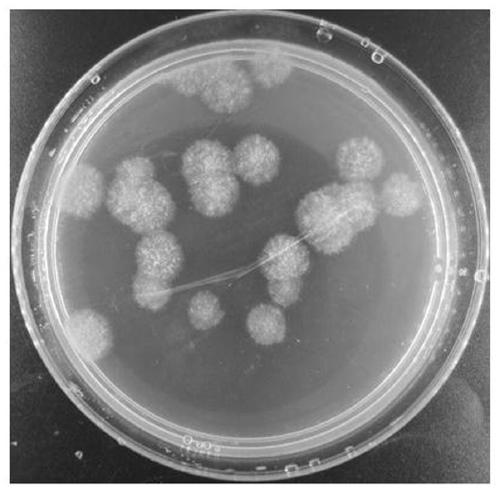
[0062] Inoculate the spores or hyphae of Aspergillus flavus NRRL3357 strain on PDA solid medium, and culture in the dark at 37 °C for 2 days; the aerial hyphae on the surface of the eluted medium were inoculated in GMM liquid medium, and cultured at 37 °C for 12 hours with shaking at 180 rpm until the diameter of mycelial balls is 2 mm; remove the medium by filtering with sterile filter paper, collect 80 mg of mycelial balls in a 1.5 mL sterile centrifuge tube, add sterile small steel balls with a diameter of 2 mm, and homogenize with a homogenizer at the 12th gear Plastify mycelia for 20 min and resuspend in 5 mL of IM medium (containing a final concentration of 25 μg / mL rifampicin, a final concentration of 100 μg / mL kanamycin and a final concentration of 200 μM acetosyringone) Mix to obtain a homogeneous liquid of Aspergillus flavus mycelium.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com