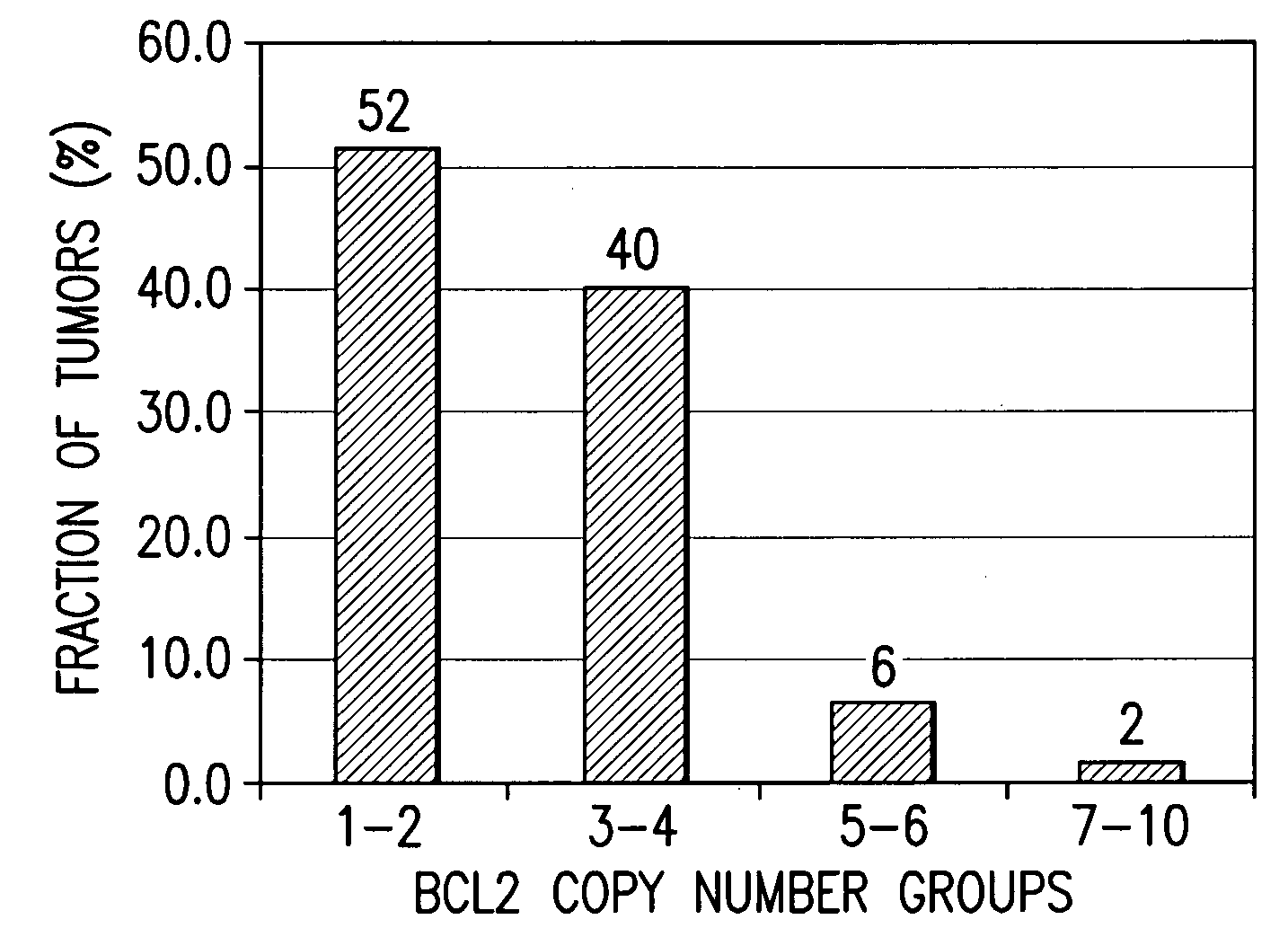Patents
Literature
220 results about "Chromatosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
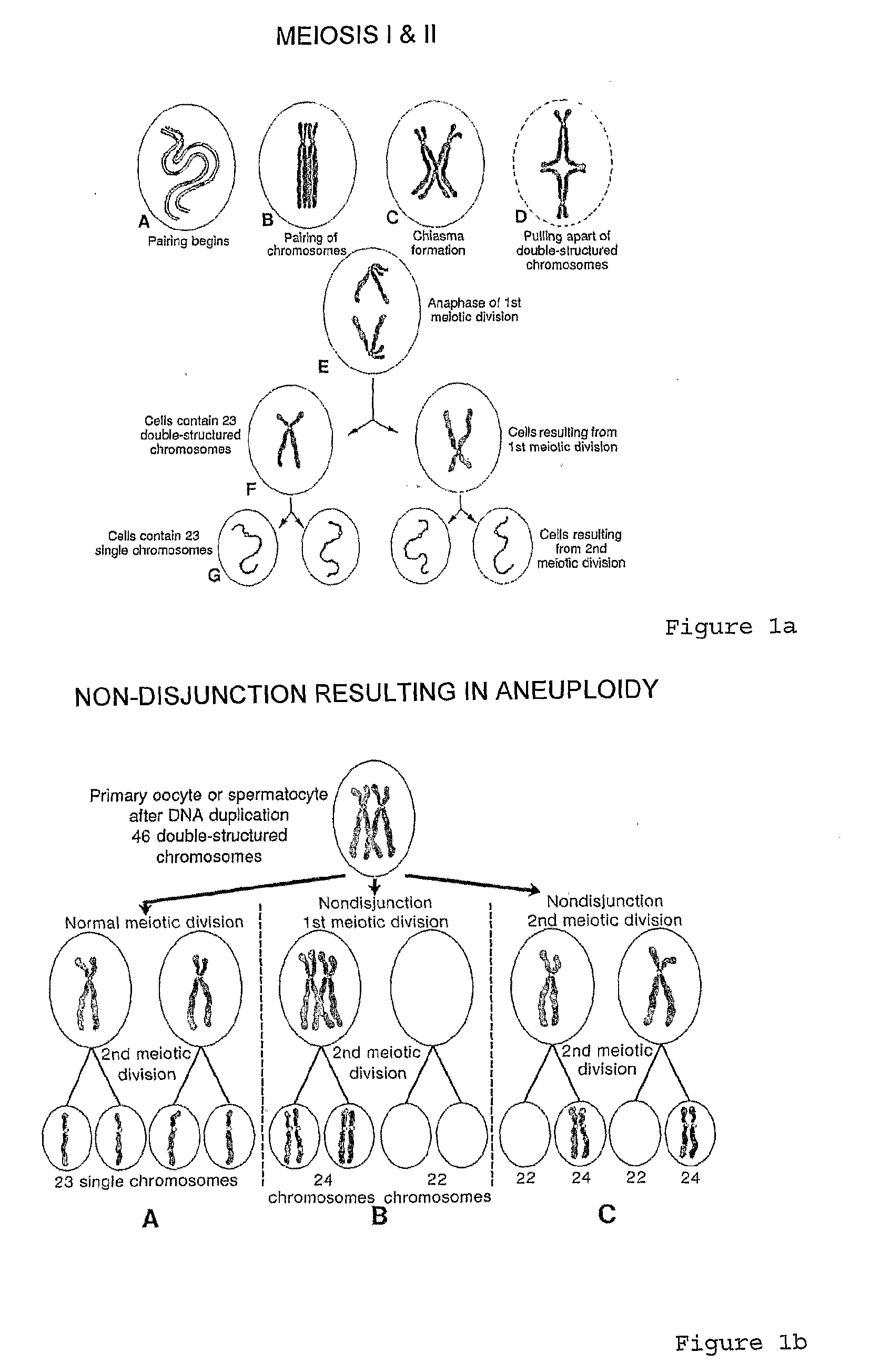
A chromatosome is a result of histone H1 binding to a nucleosome, which contains a histone octamer and DNA. The chromatosome contains 166 base pairs of DNA. 146 base pairs are from the DNA wrapped around the histone core of the nucleosome. The remaining 20 base pairs are from the DNA of histone H1 binding to the nucleosome. Histone H1, and its other variants, are referred to as linker histones. Protruding from the linker histone, are linker DNA. Chromatosomes are connected to each other when the linker DNA, of one chromatosome, binds to the linker histone of another chromatosome. Human genes are made up of thousands to millions of base pairs.
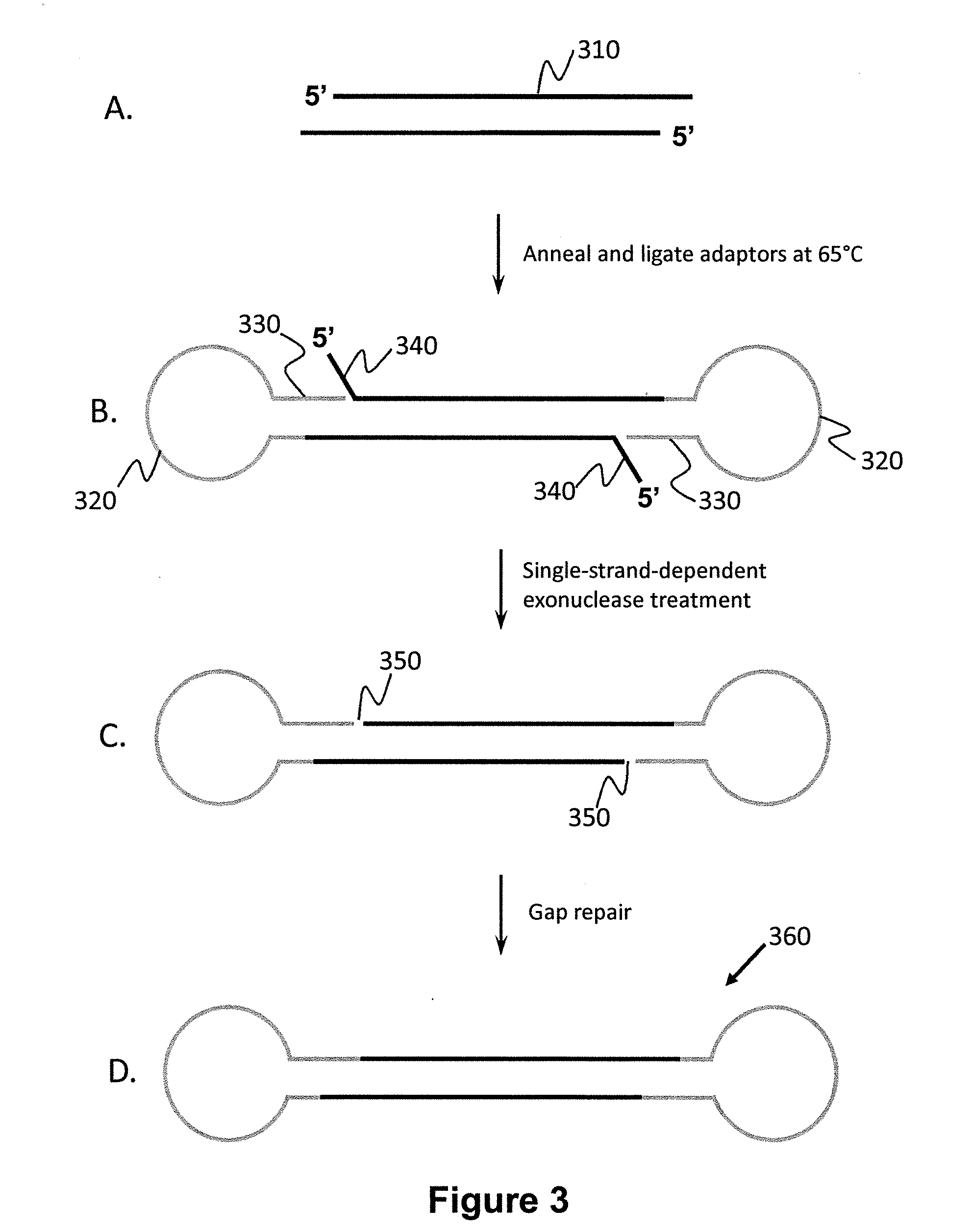
Modulation of gene expression by oligomers targeted to chromosomal DNA
Synthesis of a target transcript of a gene is selectively increased in a mammalian cell by contacting the cell with a polynucleotide oligomer of 12-28 bases complementary to a region within a target promoter of the gene under conditions whereby the oligomer selectively increases synthesis of the target transcript.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
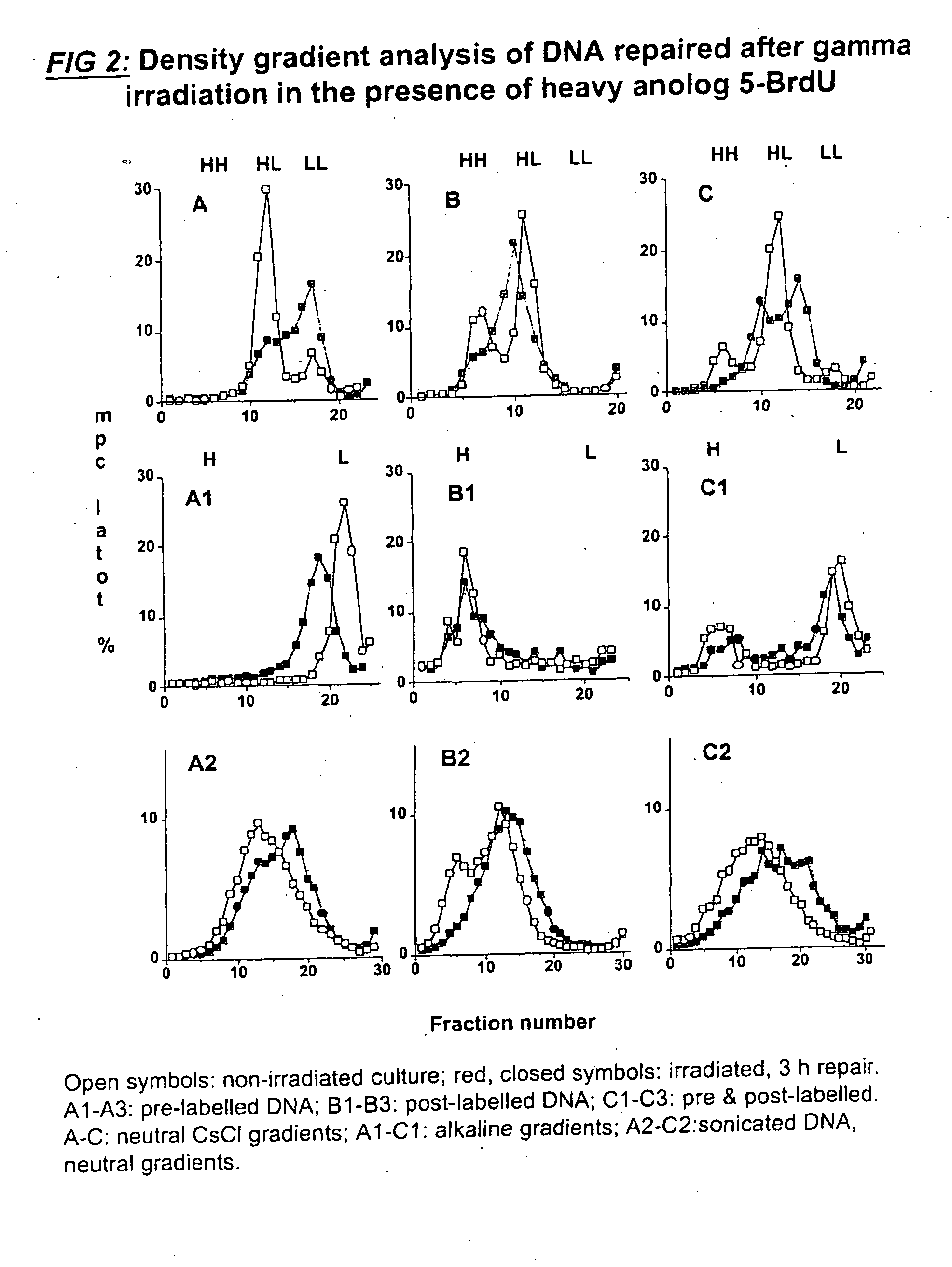
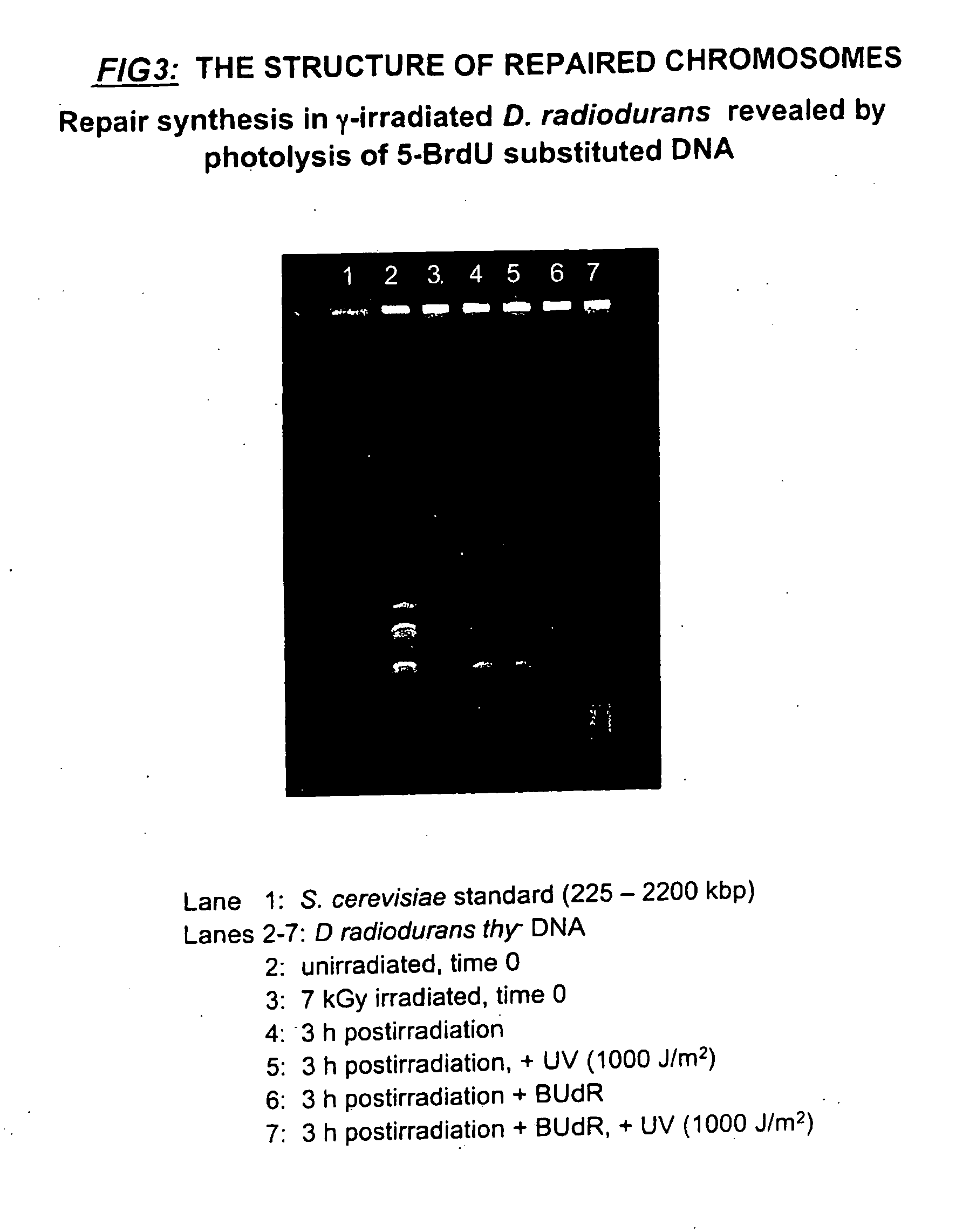
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
Compositions and methods for selection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20140134610A1Reduce complexityIncreased complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisGenomic DNA
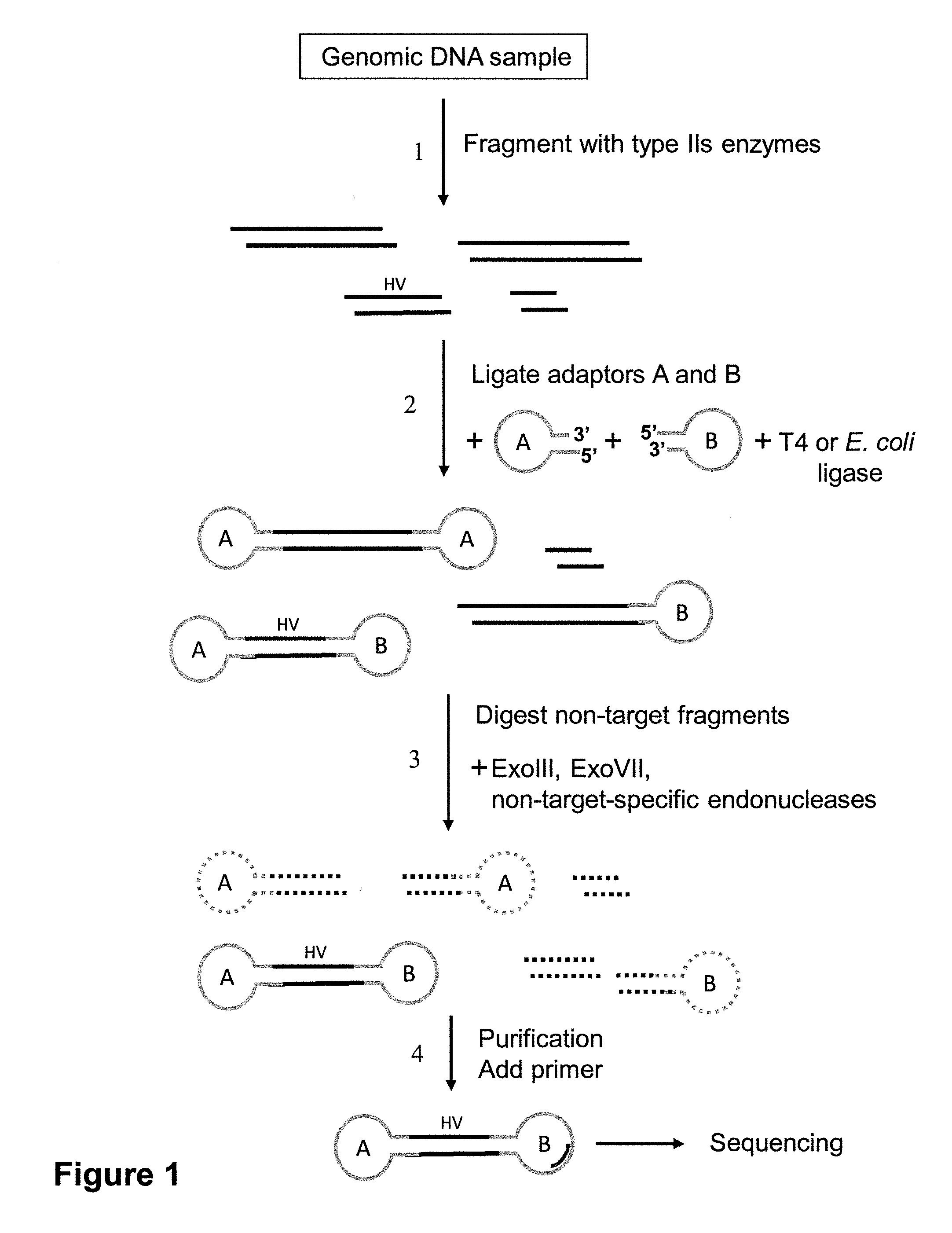
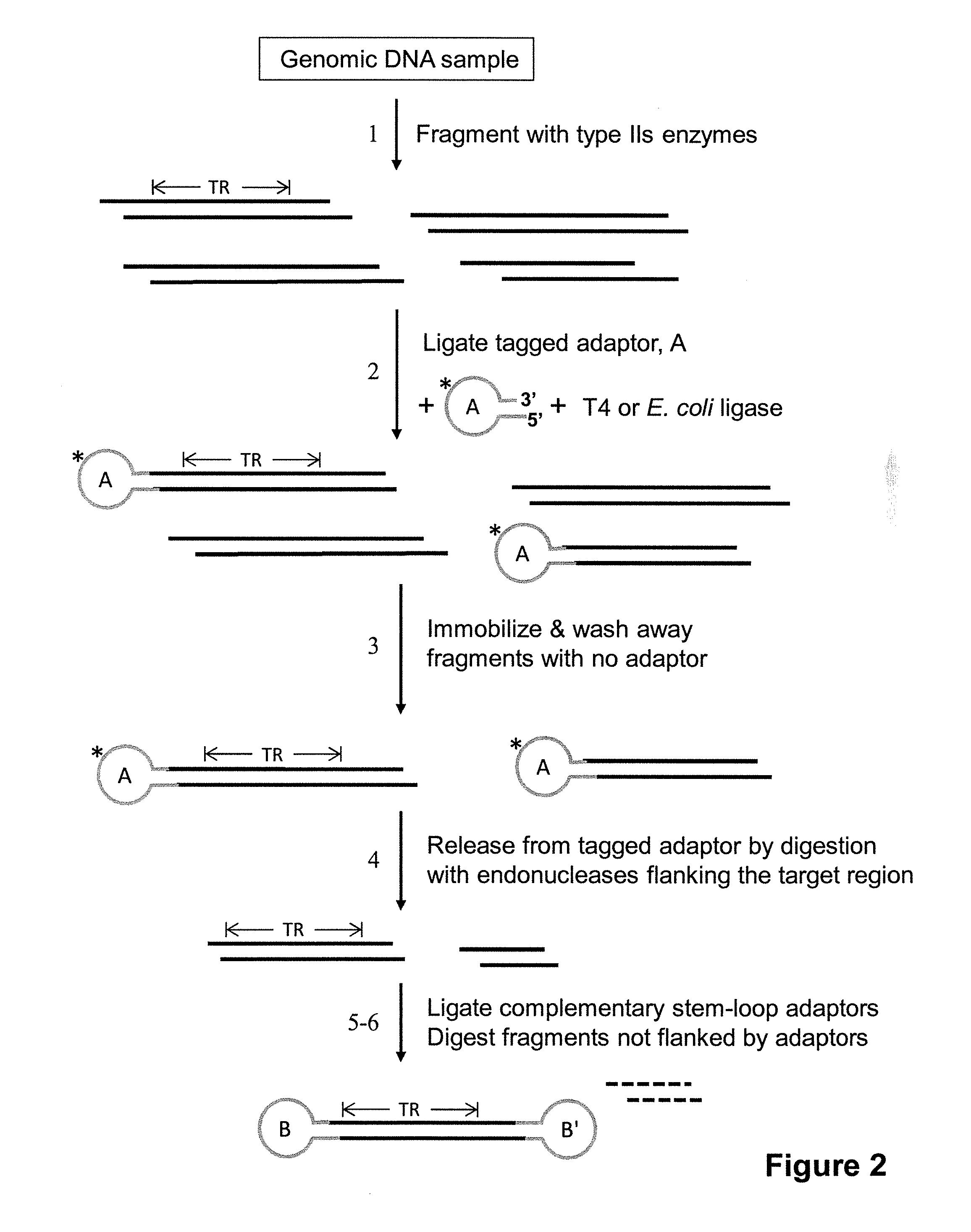
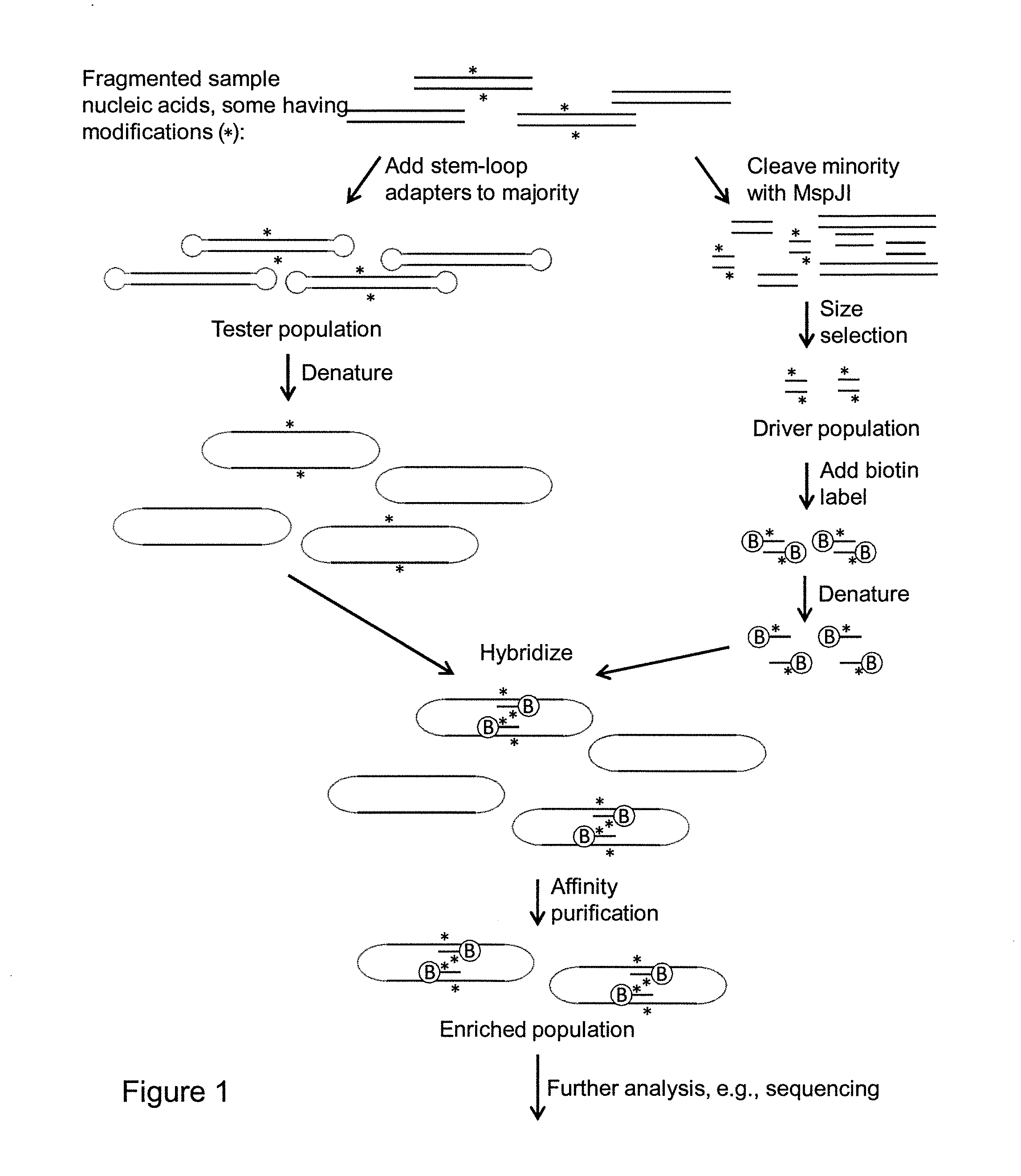
Methods are provided for reducing the complexity of a population of nucleic acids prior to performing an analysis of the nucleic acids, e.g., sequence analysis. The methods result in a subset of the initial population enriched for a target region, which is typically located within one or more target fragments. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing populations having a high degree of complexity, e.g., chromosomal-derived DNA, whole genomic DNA, or mRNA populations.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
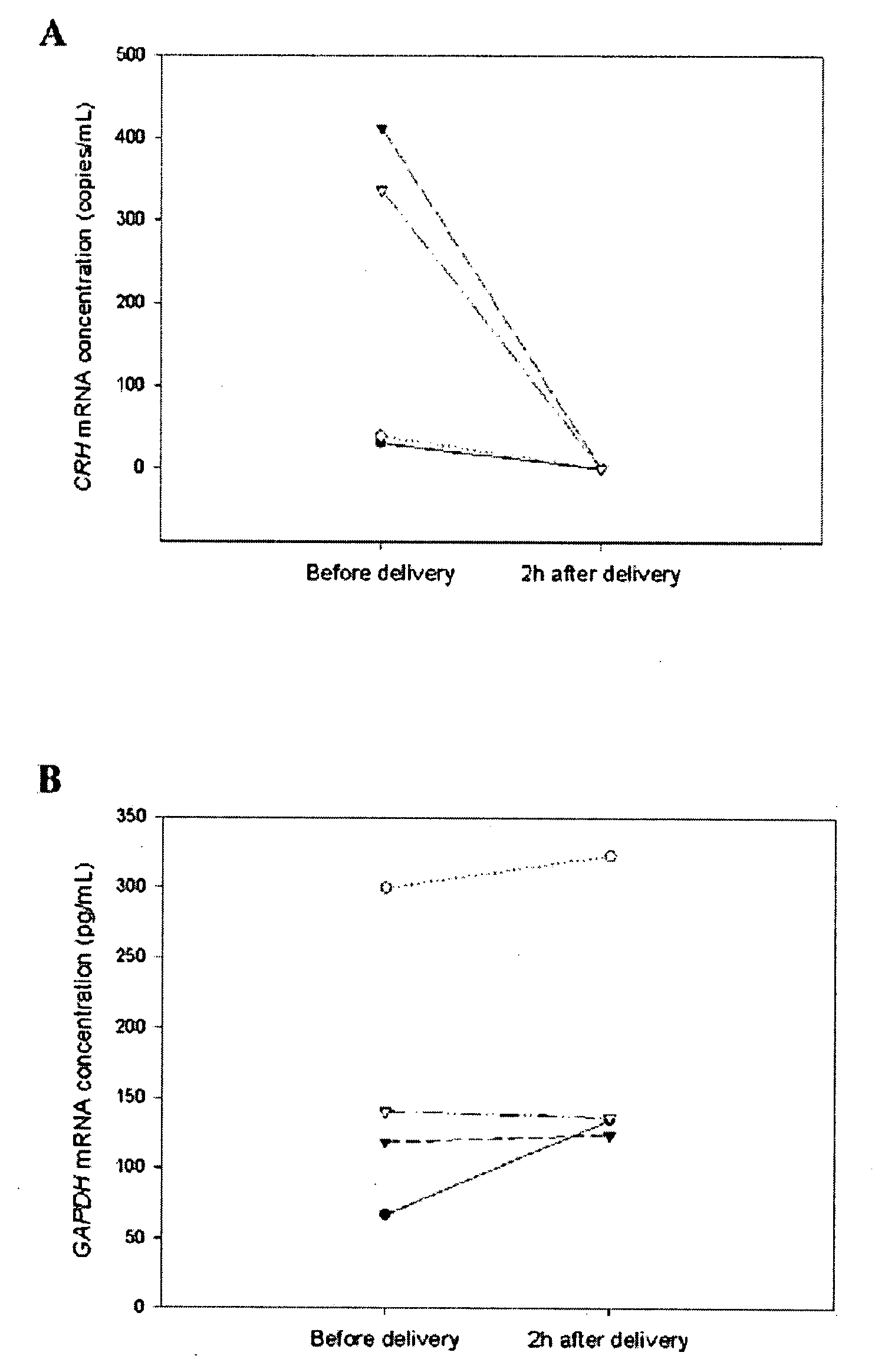
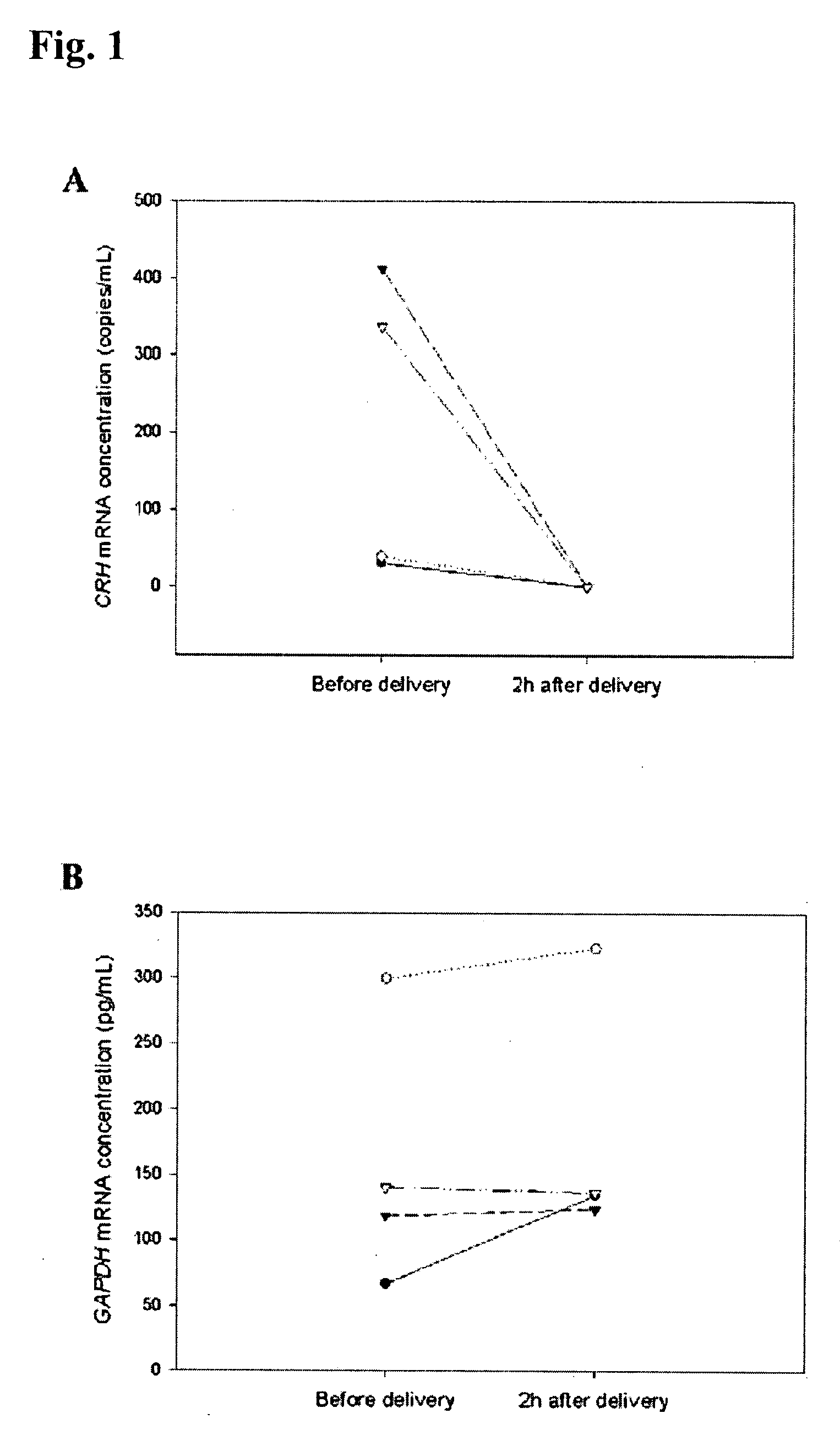
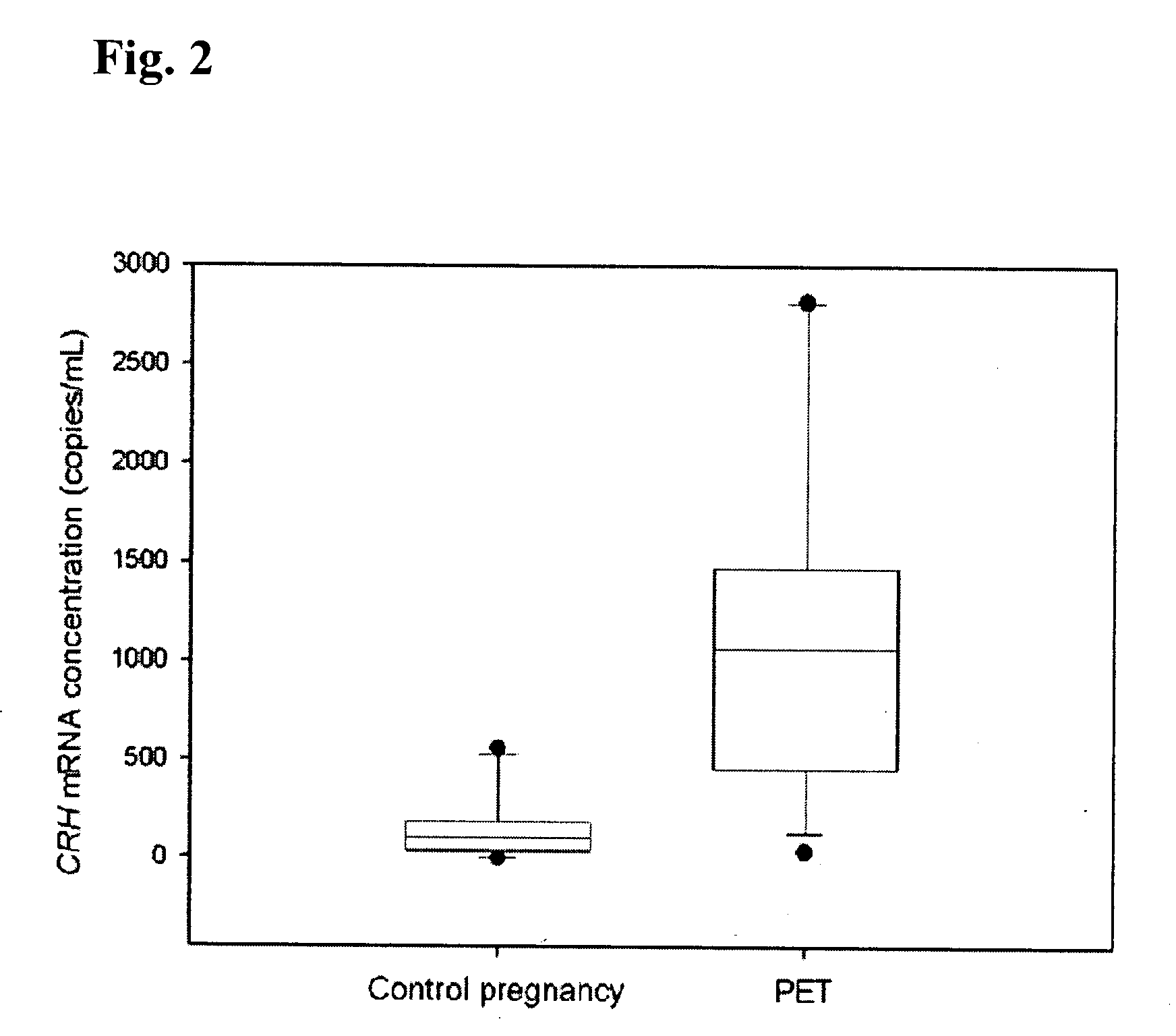
Circulating mRNA as diagnostic markers
Methods and kits are provided for diagnosing, monitoring, or predicting the conditions of pre-eclaimpsia, fetal chromosomal aneuploidy, and pre-term labor in a pregnant woman, as well as for detecting pregnancy in a woman, by quantitatively measuring in the maternal blood the amount of one or more mRNA species encoding human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (hCG-β), human placental lactogen (hPL), human corticotropin releasing hormone (hCRH), KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor (KISS1), tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TPFI2), placenta-specific 1 (PLAC1), or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and comparing the amount of the mRNA species with a standard control.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
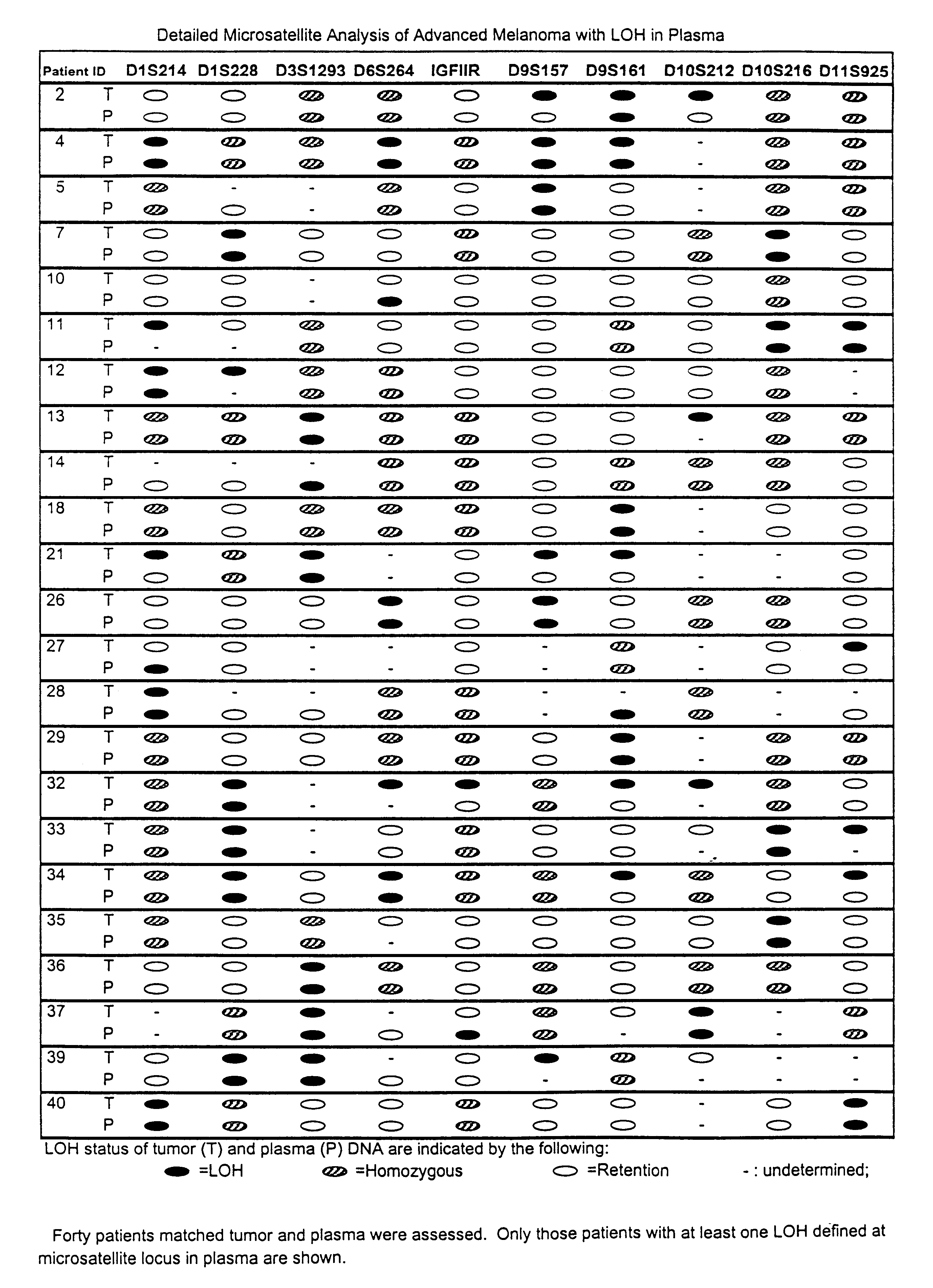
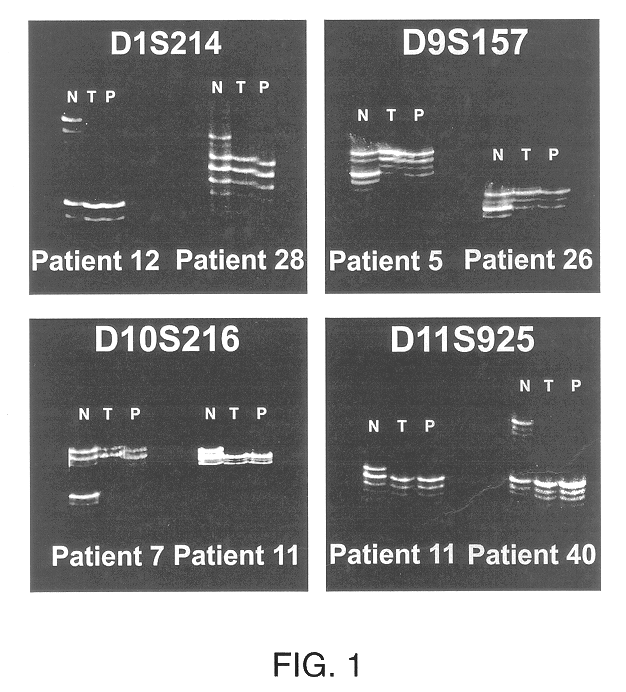
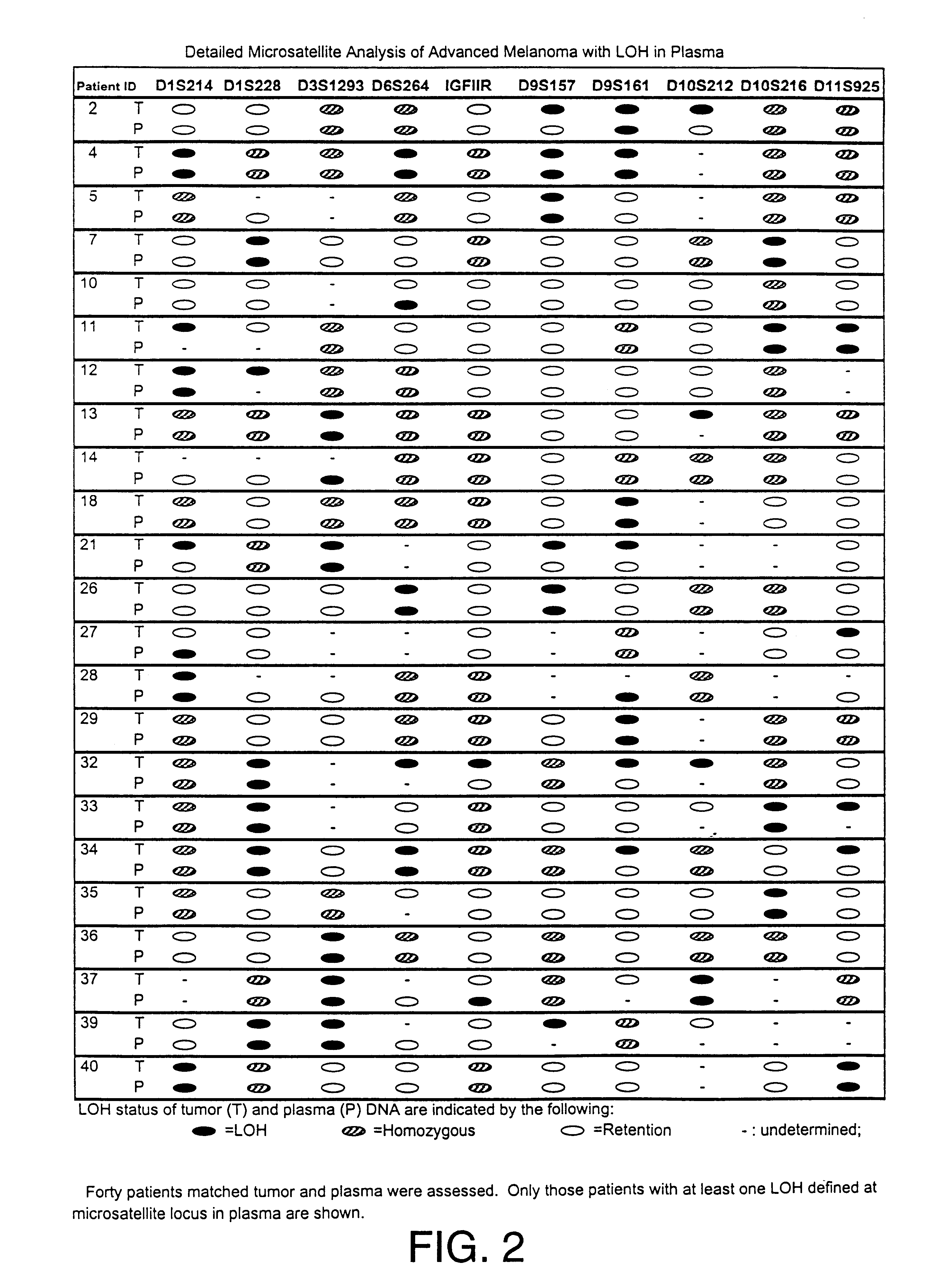
Detection of loss of heterozygosity in tumor and serum of melanoma patients
A method is provided for assessing allelic losses on specific chromosomal regions in melanoma patents. The method relies on the evidence that free DNA may be released in the plasma / serum of cancer patients allowing the detection of DNA with LOH in the plasma / serum of cancer patients by analysis for microsatellite markers. The amount of and specific allelic loss allows a prognosis to be made regarding tumor diagnosis and progression, tumor metastasis, tumor recurrence, and mortality.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
Compositions, Kits, and Methods for the Identification, Assessment, Prevention, and Therapy of Cancer
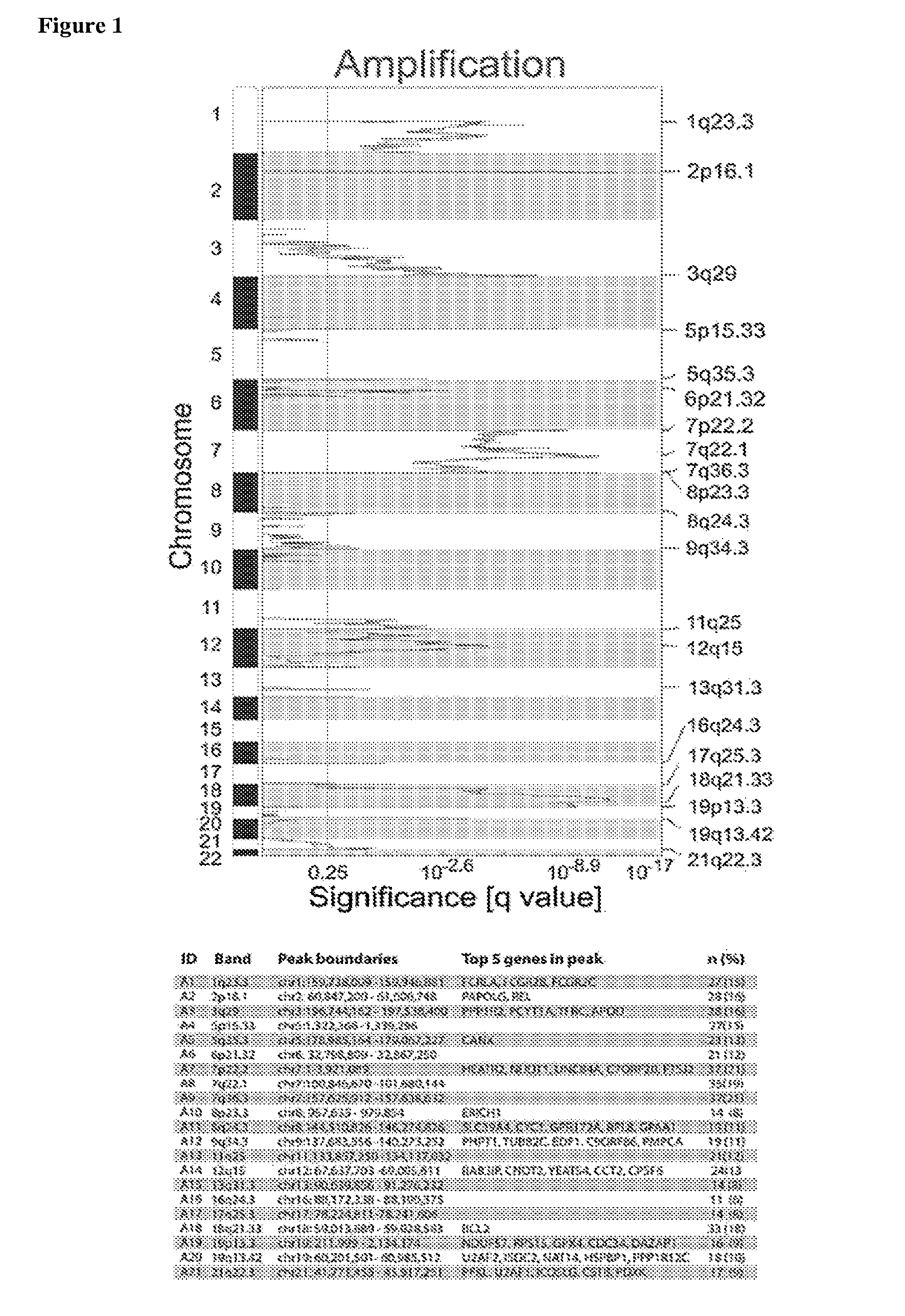
The present invention relates to compositions, kits, and methods for detecting, characterizing, preventing, and treating cancer (e.g., hematological malignancies in humans). A variety of biomarker chromosomal number alterations (CNAs) and biomarkers corresponding thereto, are provided, wherein alterations in the copy number of one or more of the biomarker CNAs and / or alterations in the amount, structure, and / or activity of one or more of the biomarkers comprised within the CNAs is associated with cancer status.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Methods of inserting molecular barcodes
InactiveUS20180087050A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatosomeMolecular biology
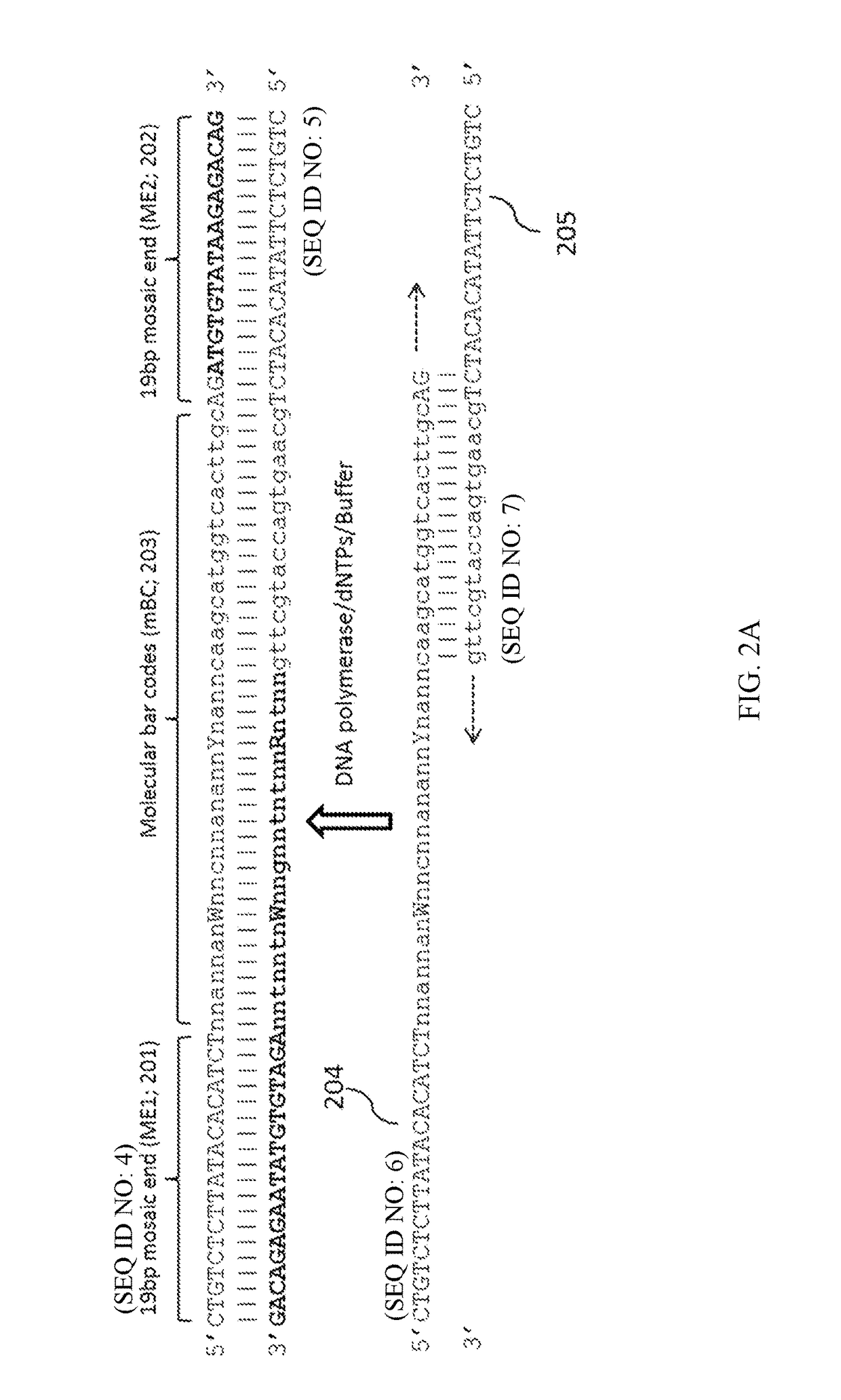
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for inserting a plurality of synthetic transposons each comprising a different nucleic acid sequence (i.e., molecular barcode) in a target nucleic acid of interest to allow extraction of contiguity information in the target nucleic acid. The molecular barcodes are also useful for reducing amplification or sequencing bias and errors, and for guiding accurate sequence assembly of the target nucleic acid from sequencing reads. The compositions, methods, and kits described herein have many applications, including haplotyping, genome assembly, sequencing of repetitive regions, detection of structural variations and copy number variations, chromosomal conformation analysis, and methylation analysis.
Owner:ZHENG JIANBIAO +1
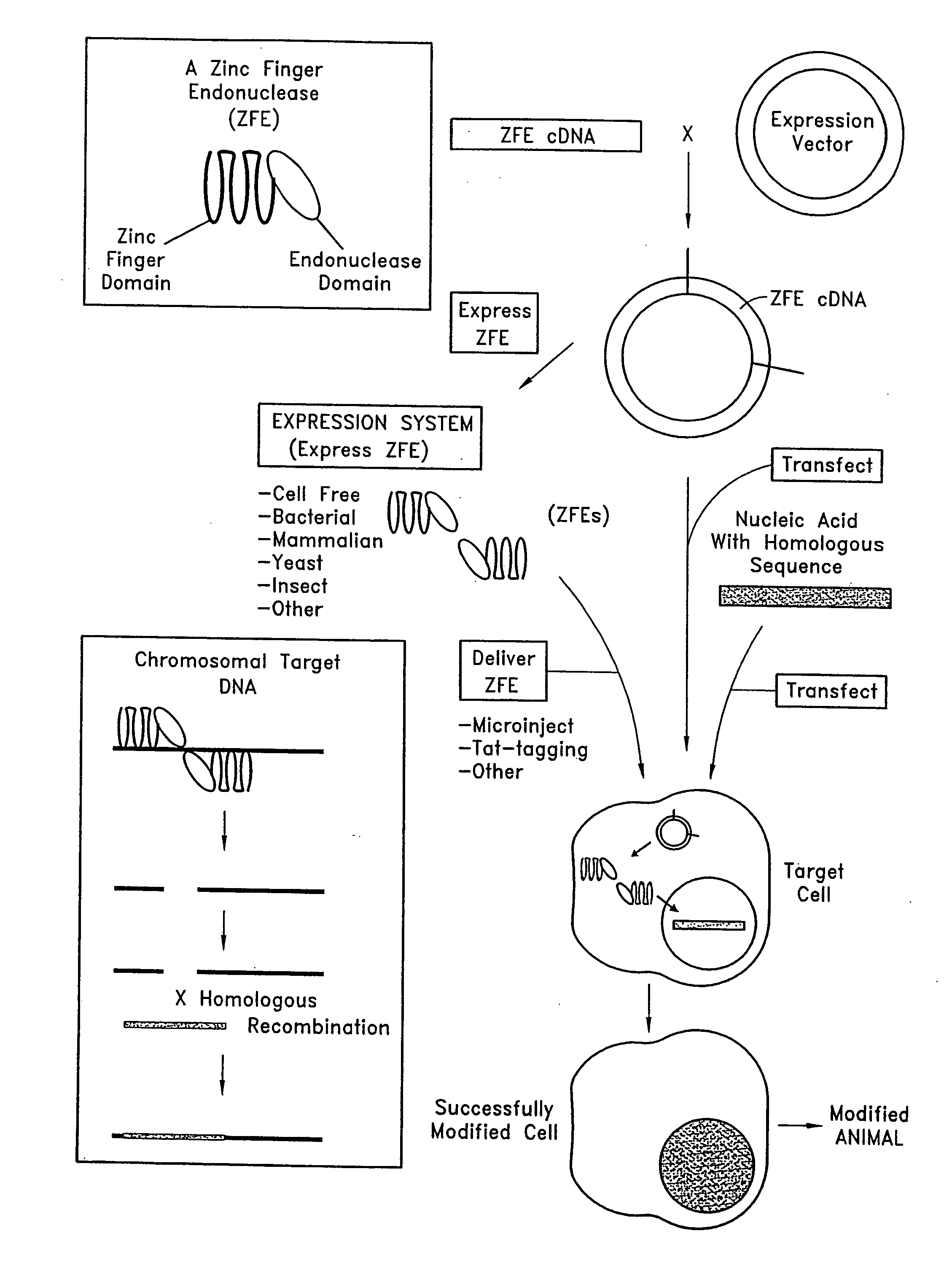
Methods and compositions for using zinc finger endonucleases to enhance homologous recombination
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Non-invasive prenatal genetic diagnosis using transcervical cells
InactiveUS20050003351A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenetic analysisNon invasive
A non-invasive, risk-free method of prenatal diagnosis is provided. According to the method of the present invention transcervical specimens are subjected to trophoblast-specific immuno-staining followed by FISH, PRINS, Q-FISH and / or MCB analyses and / or other DNA-based genetic analysis in order to determine fetal gender and / or identify chromosomal and / or DNA abnormalities in a fetus.
Owner:MONALIZA MEDICAL
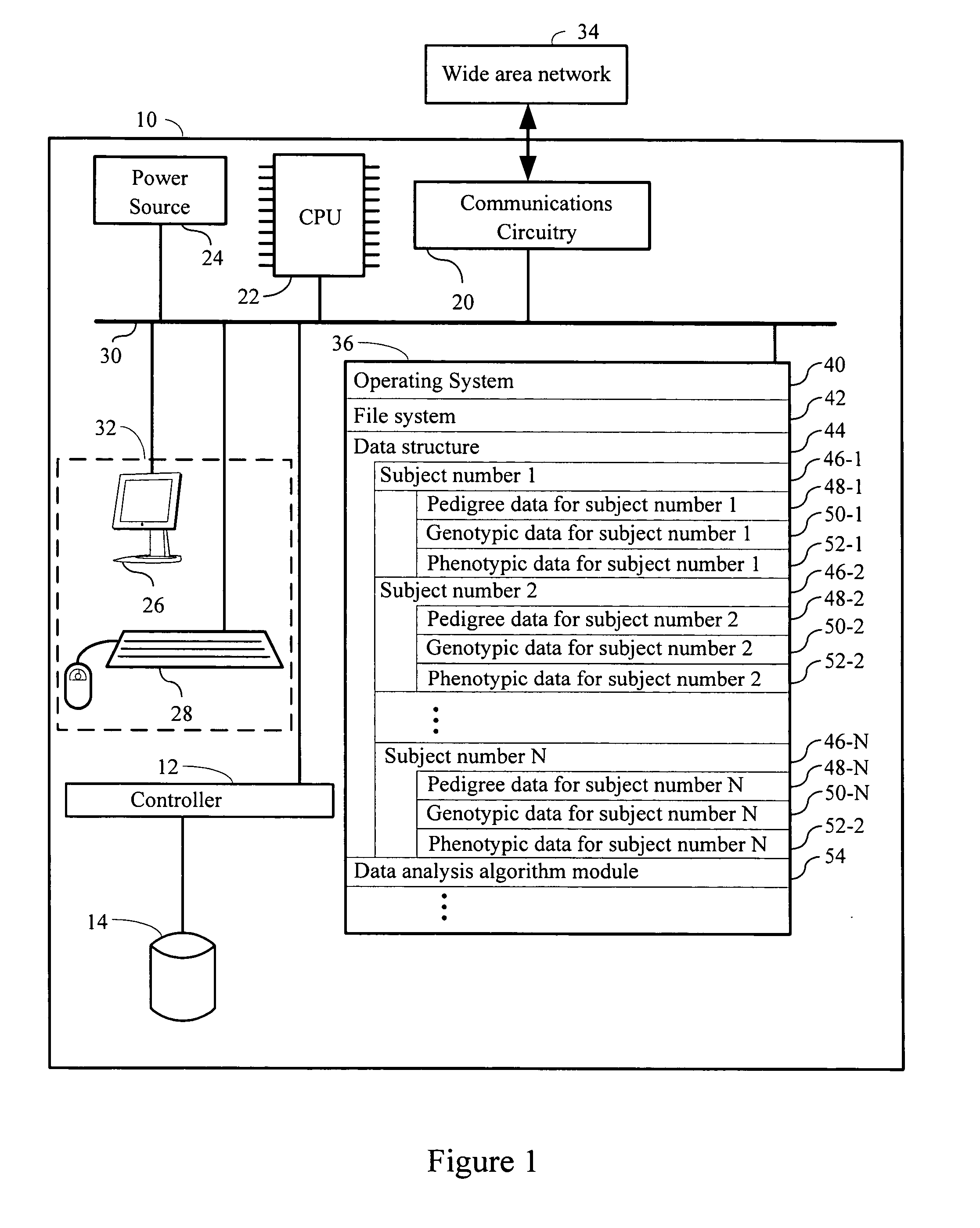
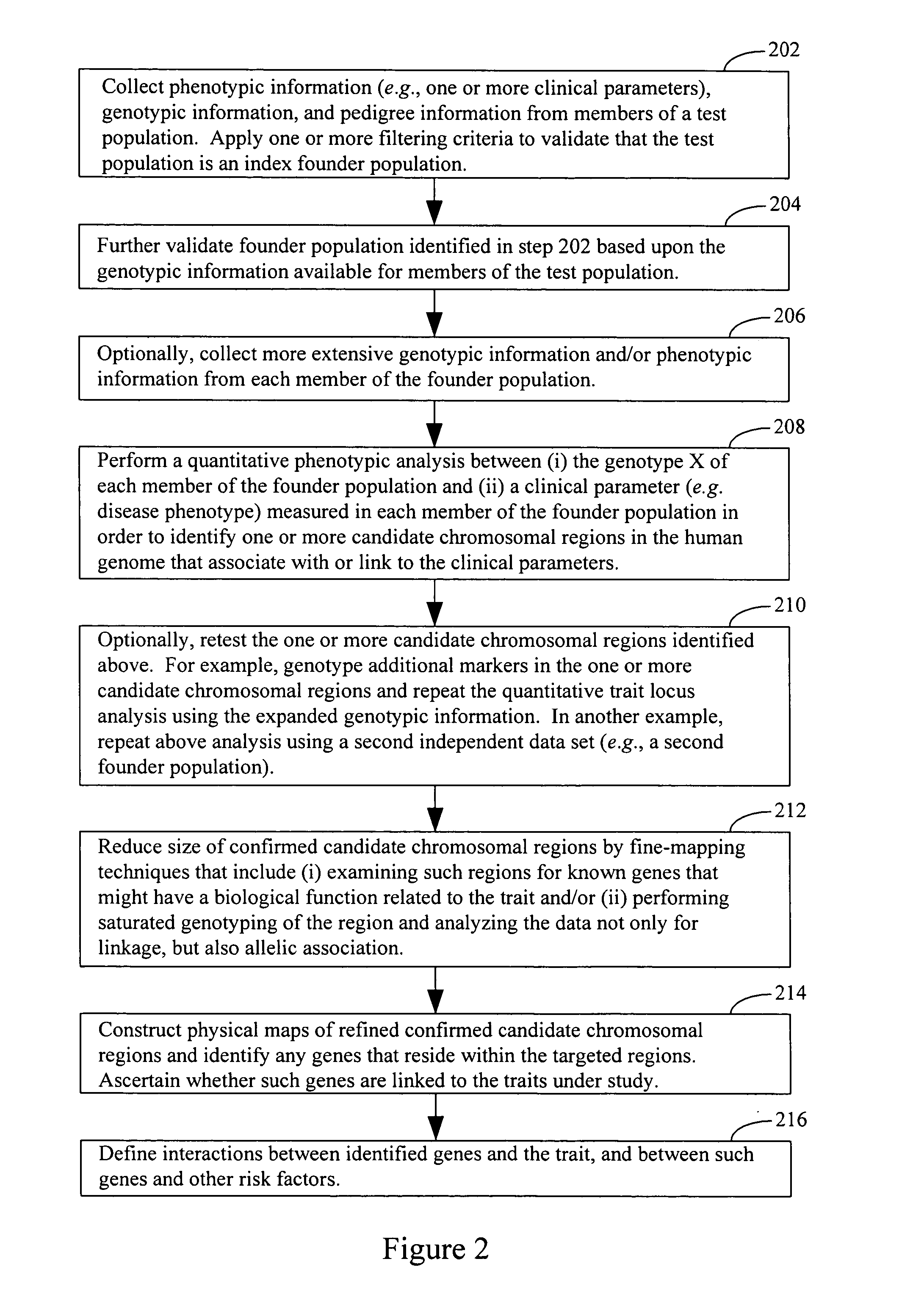
Systems and methods for the biometric analysis of index founder populations
InactiveUS20070111247A1Medical data miningMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulation basedHuman DNA sequencing
Systems, methods and apparatus for associating a clinical parameter with one or more candidate chromosomal regions in the human genome are provided. An index founder population is identified in a test population based upon the genotype X of each member of the test population such that the posterior probability Pr(K|X) for the index founder population is greater for K=1 than any other integer K, where K is the number of subpopulations in the index founder population. The clinical parameter is measured for each respective member of the index founder population. Then a quantitative phenotypic analysis is performed between (i) the genotype X of each respective member of the index founder population and (ii) the clinical parameter thereby identifying one or more candidate chromosomal regions in the human genome that associate with the clinical parameter.
Owner:MOTIF BIOSCI
Non-invasive prenatal genetic diagnosis using transcervical cells
InactiveUS20050181429A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPrenatal diagnosisStaining
A non-invasive, risk-free method of prenatal diagnosis is provided. According to the method of the present invention transcervical specimens are subjected to trophoblast-specific immuno-staining followed by FISH, PRINS, Q-FISH and / or MCB analyses and / or other DNA-based genetic analysis in order to determine fetal gender and / or identify chromosomal and / or DNA abnormalities in a fetus. Also provided is a method of in situ chromosomal, DNA and / or RNA analysis of a prestained specimen by incubating the prestained specimen in ammonium hydroxide. Also provided is a method of identifying embryonic cells according to a nucleus / cytoplasm ratio of at least 1:1 and the presence of at least variably condensed chromatin.
Owner:MONALIZA MEDICAL
Companion diagnostic assays for cancer therapy
InactiveUS20080193943A1Promote stratificationParticular utilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhenacylOncology
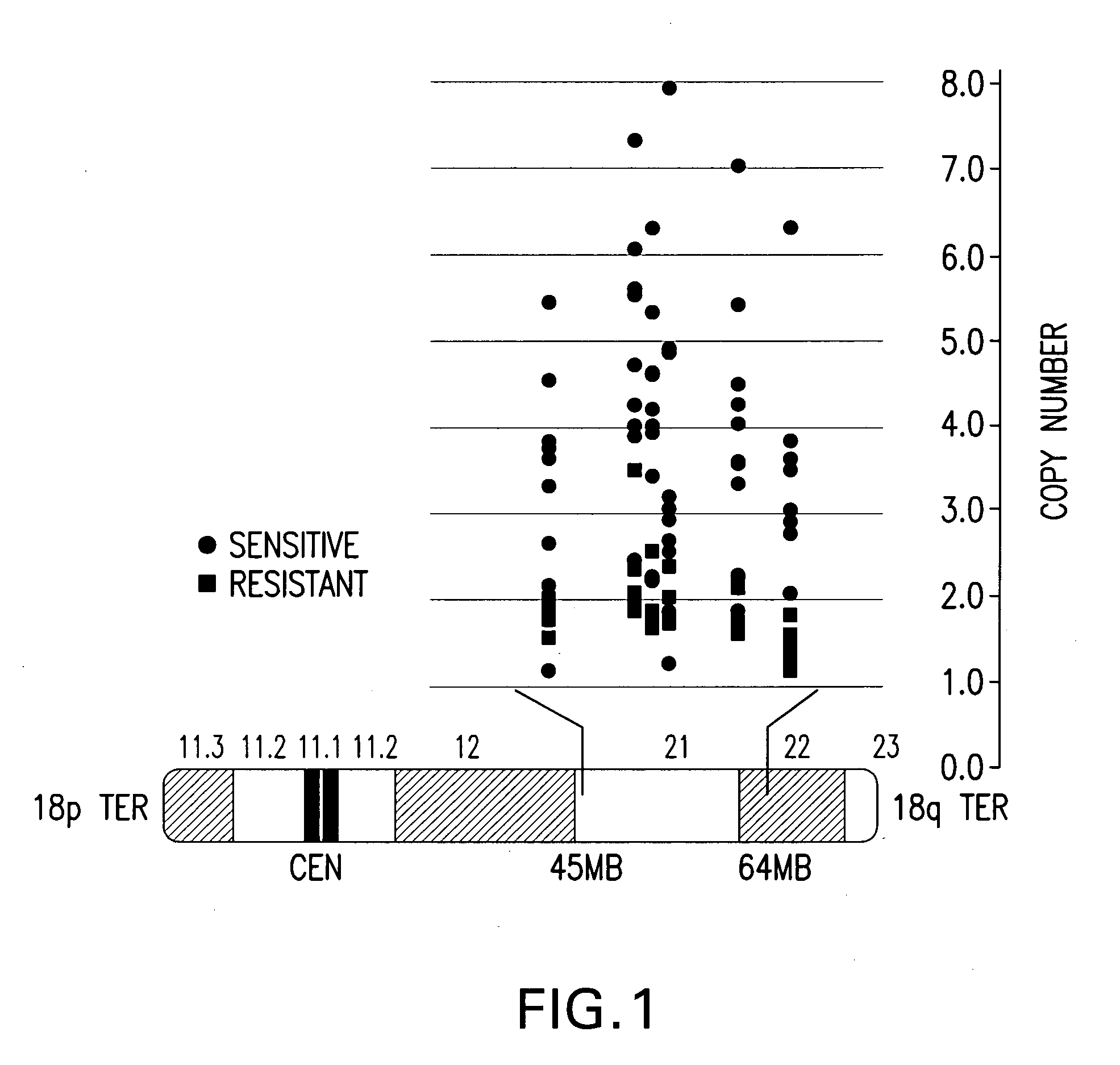
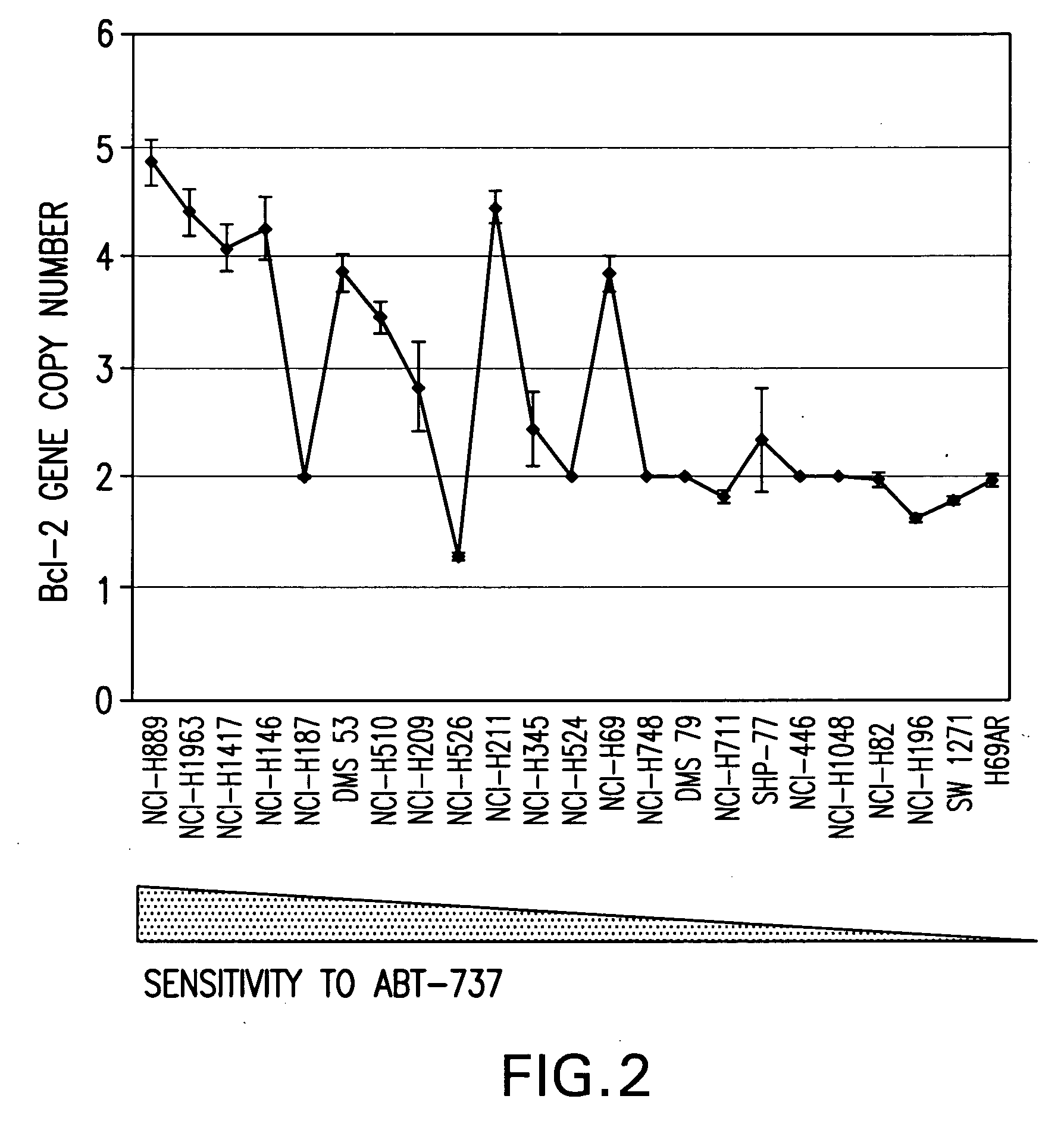
A method for classifying cancer patients as eligible to receive cancer therapy with a small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 comprising determination of the presence or absence in a patient tissue sample of chromosomal copy number status at the chromosomal locus 13q14 comprising the microRNA's miR-15a and miR-16-1 or at the chromosomal locus 11q23.1 comprising the microRNA miR-34c. The classification of cancer patients based upon the presence or absence of 13q14 loss or gain allows better selection of patients to receive chemotherapy with a small molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor such as N-(4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-1-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl) methyl)piperazin-1-yl)benzoyl)-4-(((1R)-3-(morpholin-4-yl)-1-((phenylsulfanyl) methyl)propyl)amino)-3-((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)benzenesulfonamide, and for monitoring patient response to this therapy.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
High efficiency gene targeting in plants
The present invention provides a method for the targeted insertion of a nucleotide of interest into a specific chromosomal site within a plant cell. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing a plant cell, the plant cell optionally but preferably having a heterologous target site on a chromosome thereof, wherein said target site is flanked by at least one recombination site; and then (b) transforming said plant cell with a transformation vector (e.g., with an Agrobacterium transformation vector) carrying a nucleotide sequence of interest, wherein said nucleotide sequence of interest is flanked by at least one recombination site that corresponds to the recombination sites of said target site, so that said nucleotide of interest is inserted into said chromosome at said target site (when a target site is employed).
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Chromosomal Analysis By Molecular Karyotyping
ActiveUS20080318235A1Highly accurate linkage analysisAccurate detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsY haplotypeChromosomal analysis
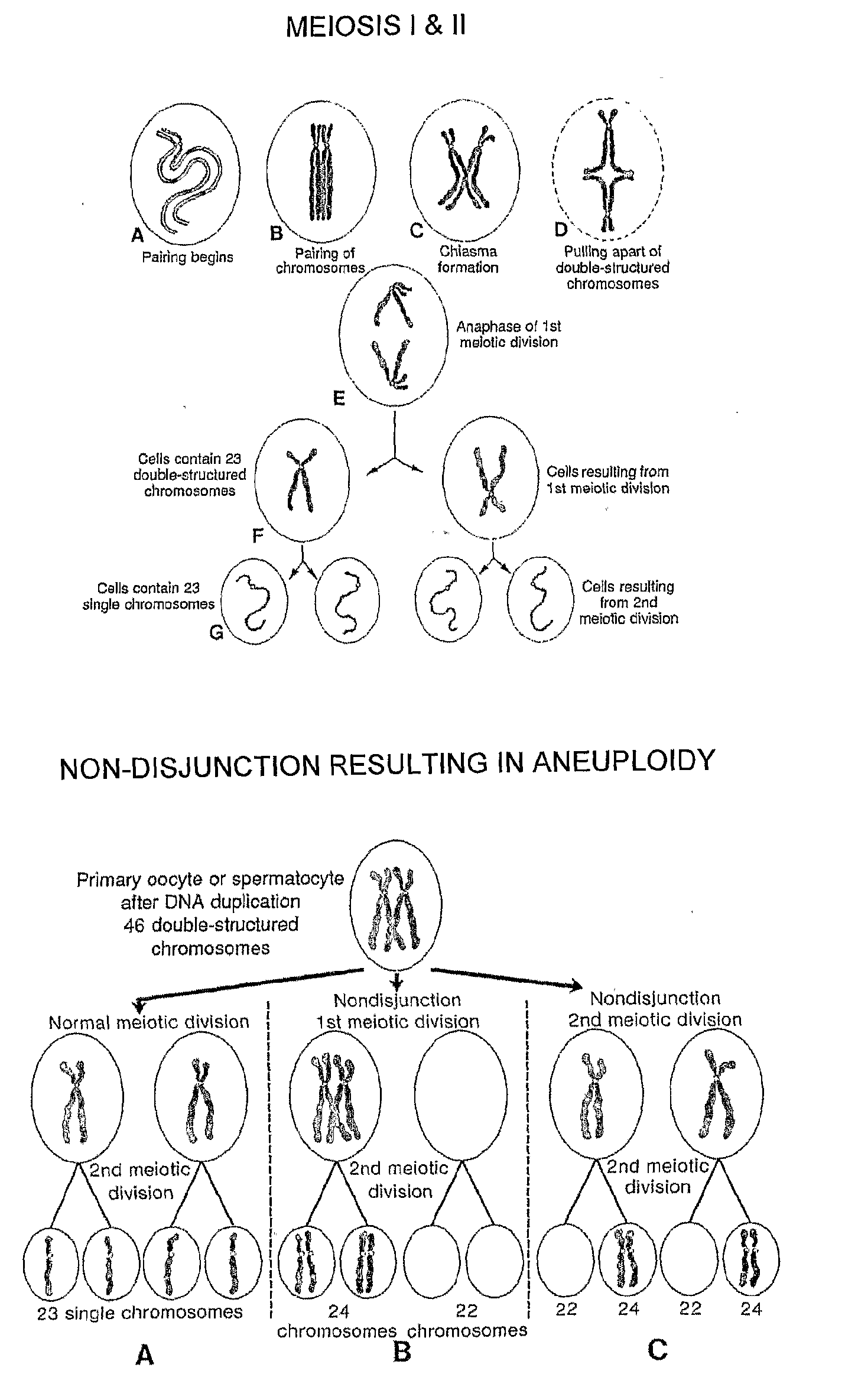
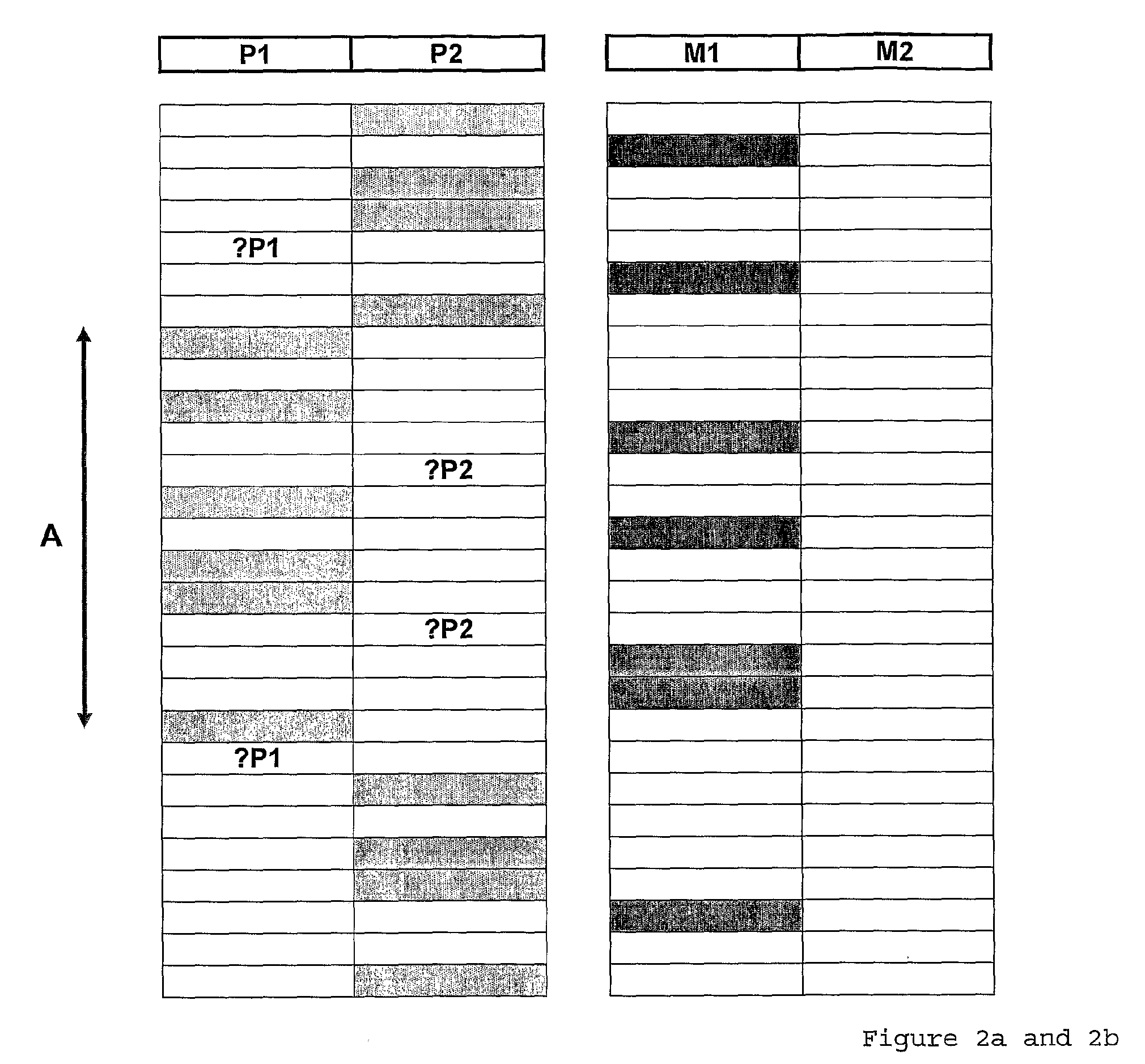
The invention provides a method of karyotyping (for example for the detection of trisomy) a target cell to detect chromosomal imbalance therein, the method comprising: (a) interrogating closely adjacent biallelic SNPs across the chromosome of the target cell (b) comparing the result at (a) with the SNP haplotype of paternal and maternal chromosomes to assemble a notional haplotype of target cell chromosomes of paternal origin and of maternal origin (c) assessing the notional SNP haplotype of target cell chromosomes of paternal origin and of maternal origin to detect aneuploidy of the chromosome in the target cell. Also provided are related computer-implemented embodiments and systems.
Owner:BLUEGNOME
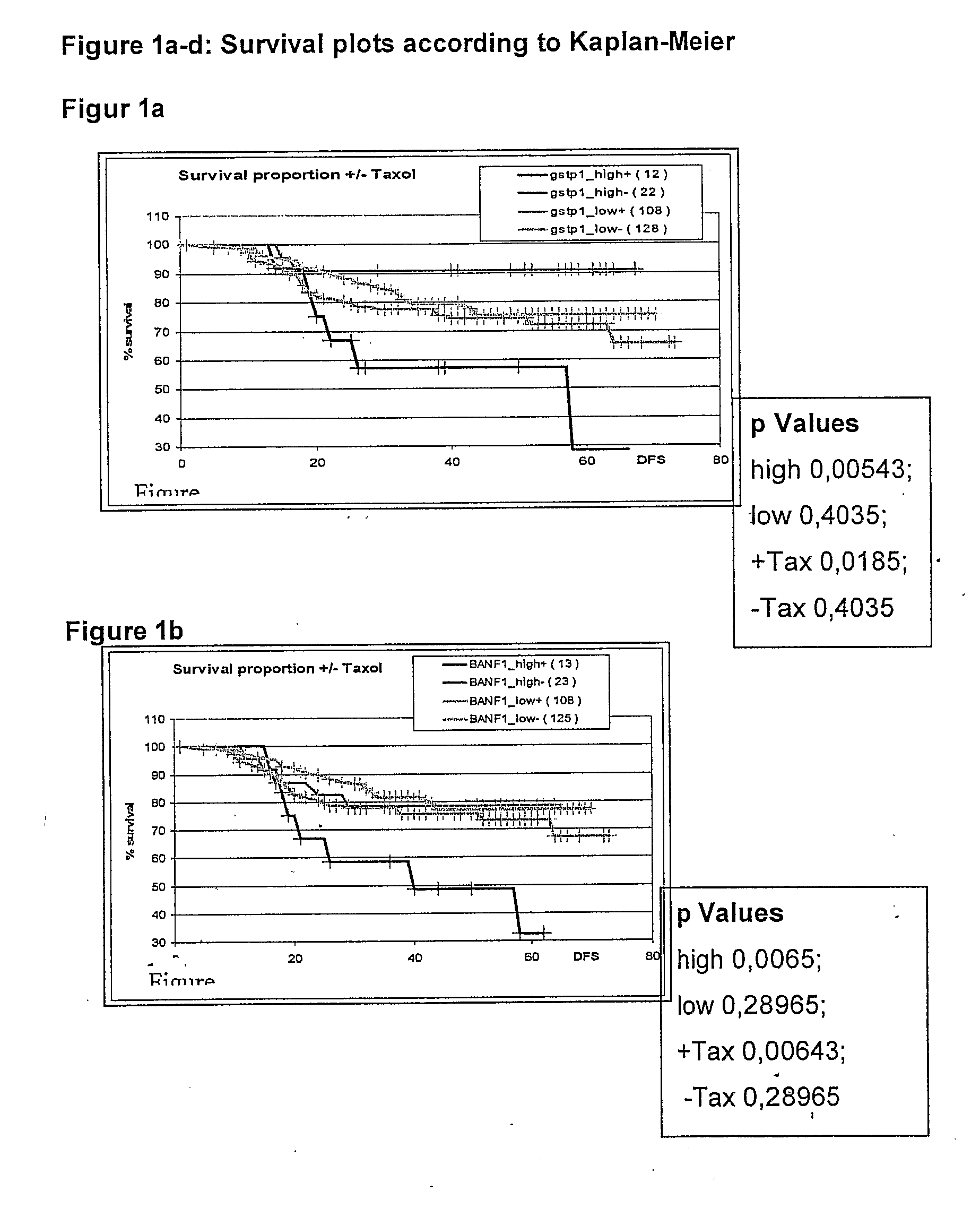
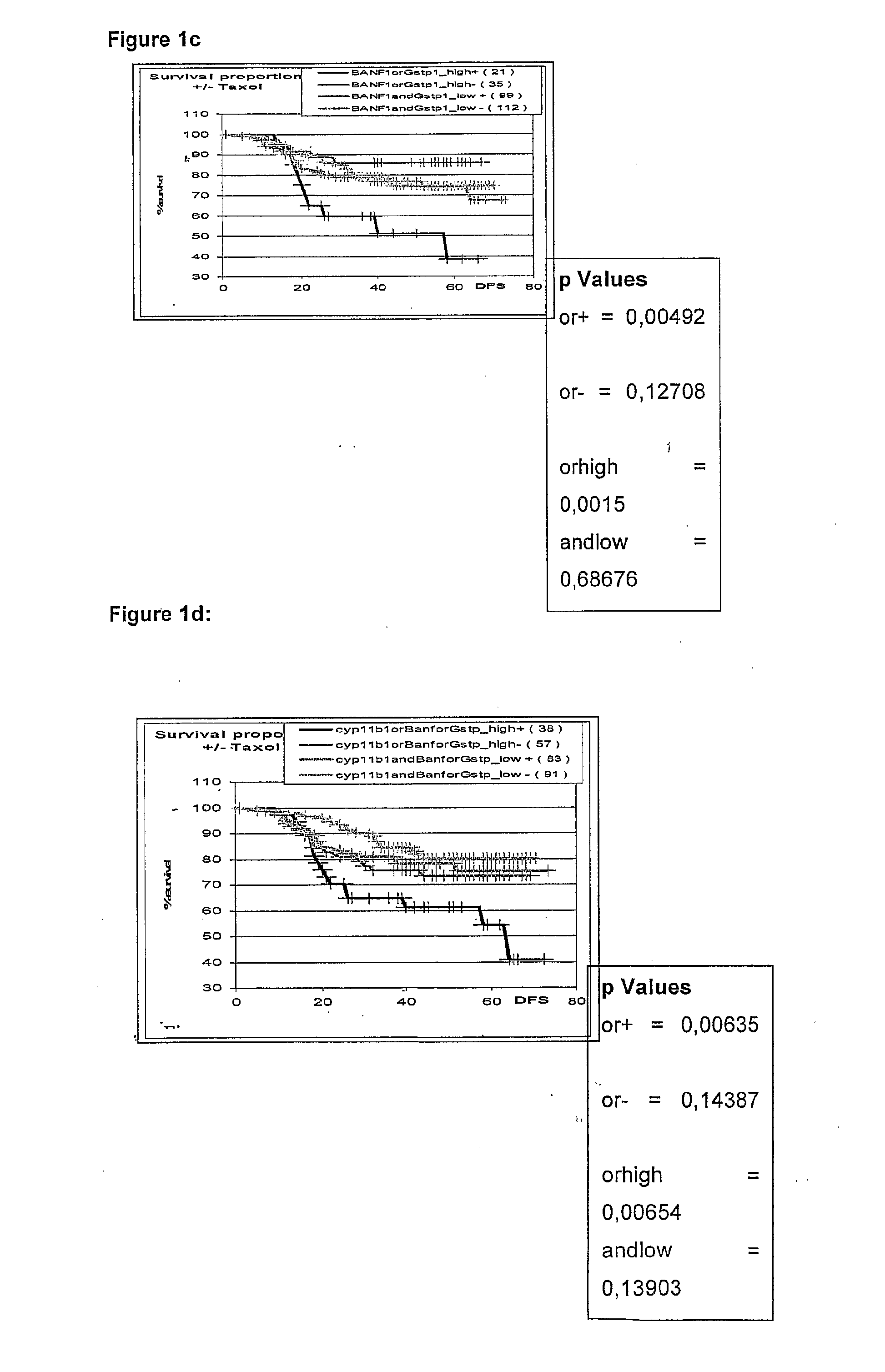
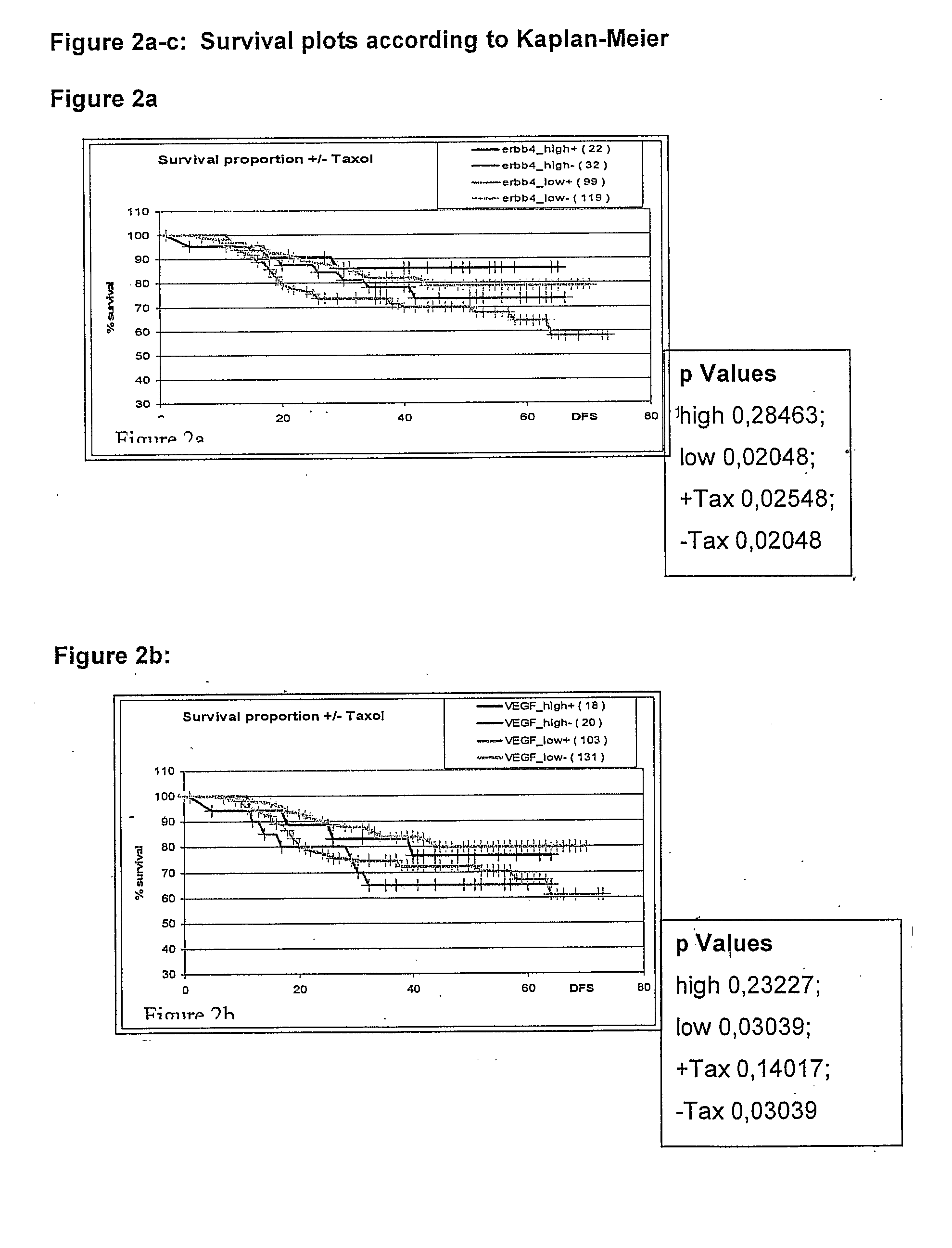
Genetic Alterations Useful For The Response Prediction of Malignant Neoplasia to Taxane-Based Medical Treatments
The invention provides novel compositions, methods and uses, for the diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, prevention and aid in treatment of malignant neoplasia such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, mesenchymal cancer, bladder cancer or non-small cell lung cancer. Genes that are chromosomally amplified in breast tissue of breast cancer patients are disclosed. Further disclosed are chromosomally amplified genes and non-amplified genes that correlate to Taxane resistance, Taxane benefit or adverse Taxane reaction, which can be used as an aid to make therapy dicisions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Method of and composite for in situ fluorescent hybridization
InactiveUS6043039AMaximize denaturationReduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHybridization probeSingle strand
A fluorescent in situ hybridization method including the steps of (a) obtaining a chromosome spread of a species; (b) preparing a hybridization composite containing a plurality of chromosomal paints each of the plurality of chromosomal paints being labeled with a different fluorophore-or-combination-of-fluorophores, such that an averaged specific activity of highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite substantially equals an averaged specific activity of unique sequences in the hybridization composite; (c) denaturing the hybridization composite and subjecting the hybridization composite to conditions for allowing at least a part of the highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite to reanneal while at least a part of the unique sequences in the hybridization composite remaining single stranded; (d) contacting under hybridization conditions the hybridization composite with the chromosome spread; (e) washing away excess of the hybridization composite; and (d) analyzing and presenting images of the now hybridized chromosome spread.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
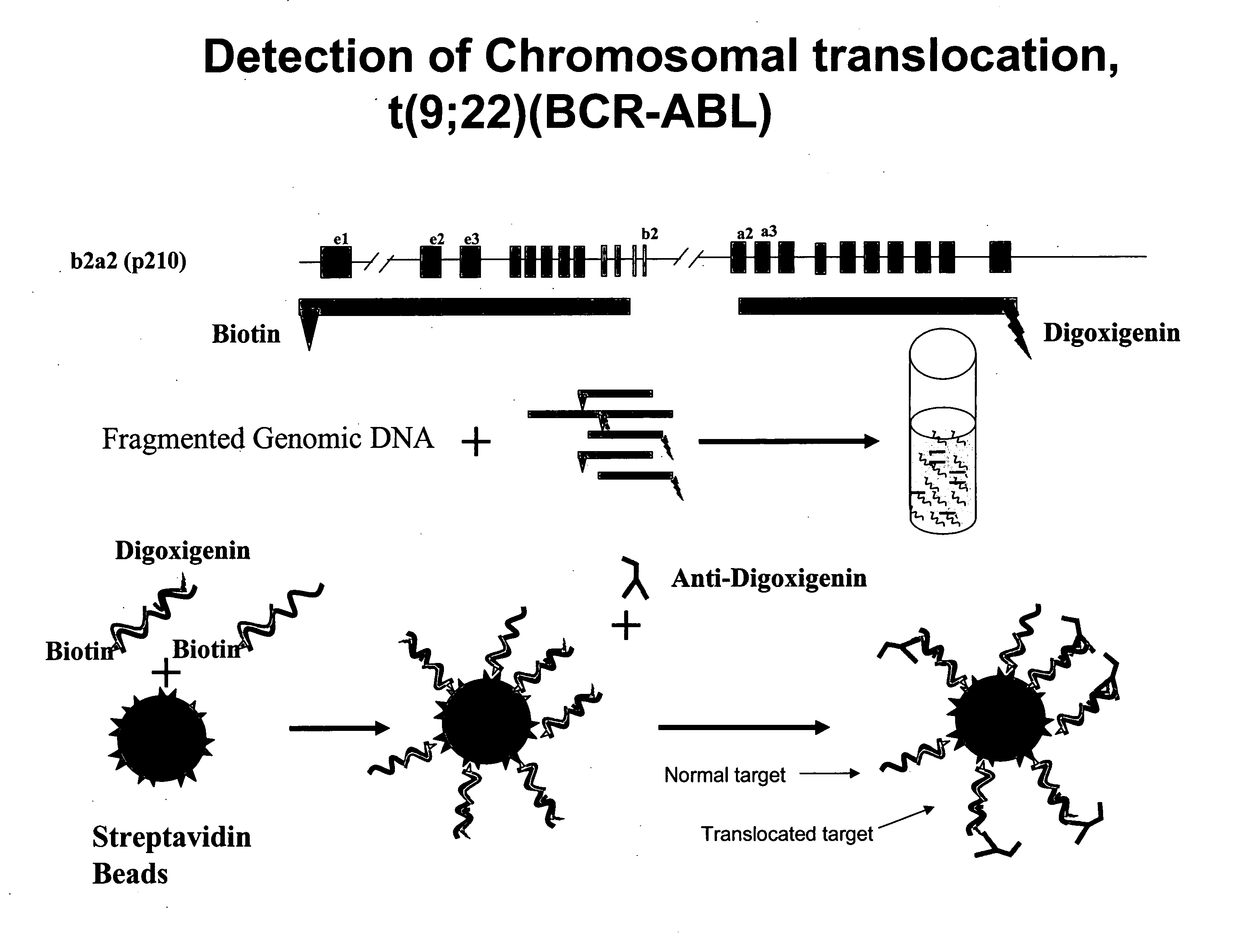
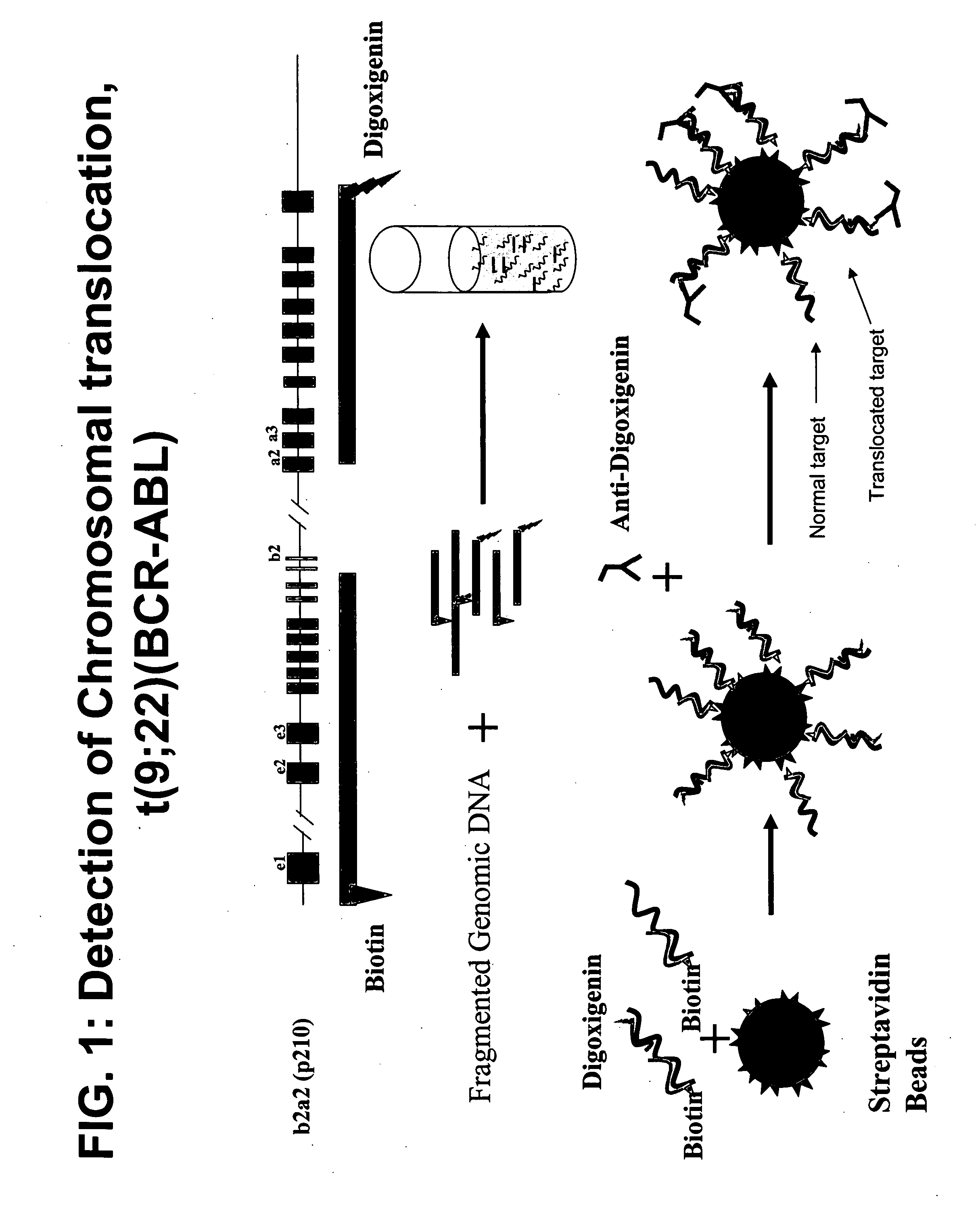
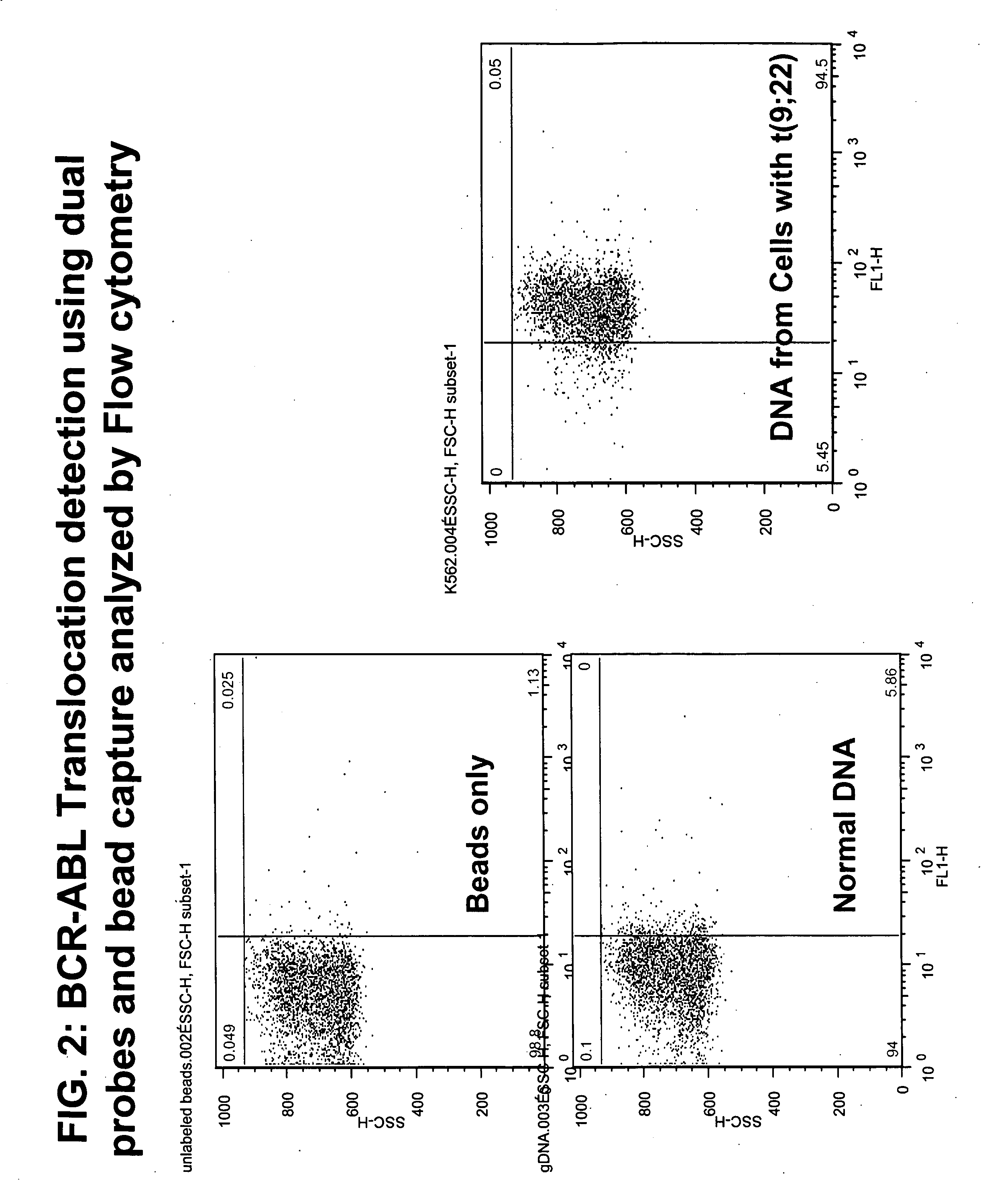
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Genomic editing of genes involved in tumor suppression in animals
InactiveUS20110023149A1Improve effectivenessUntoward effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesZinc finger nucleaseMedicine
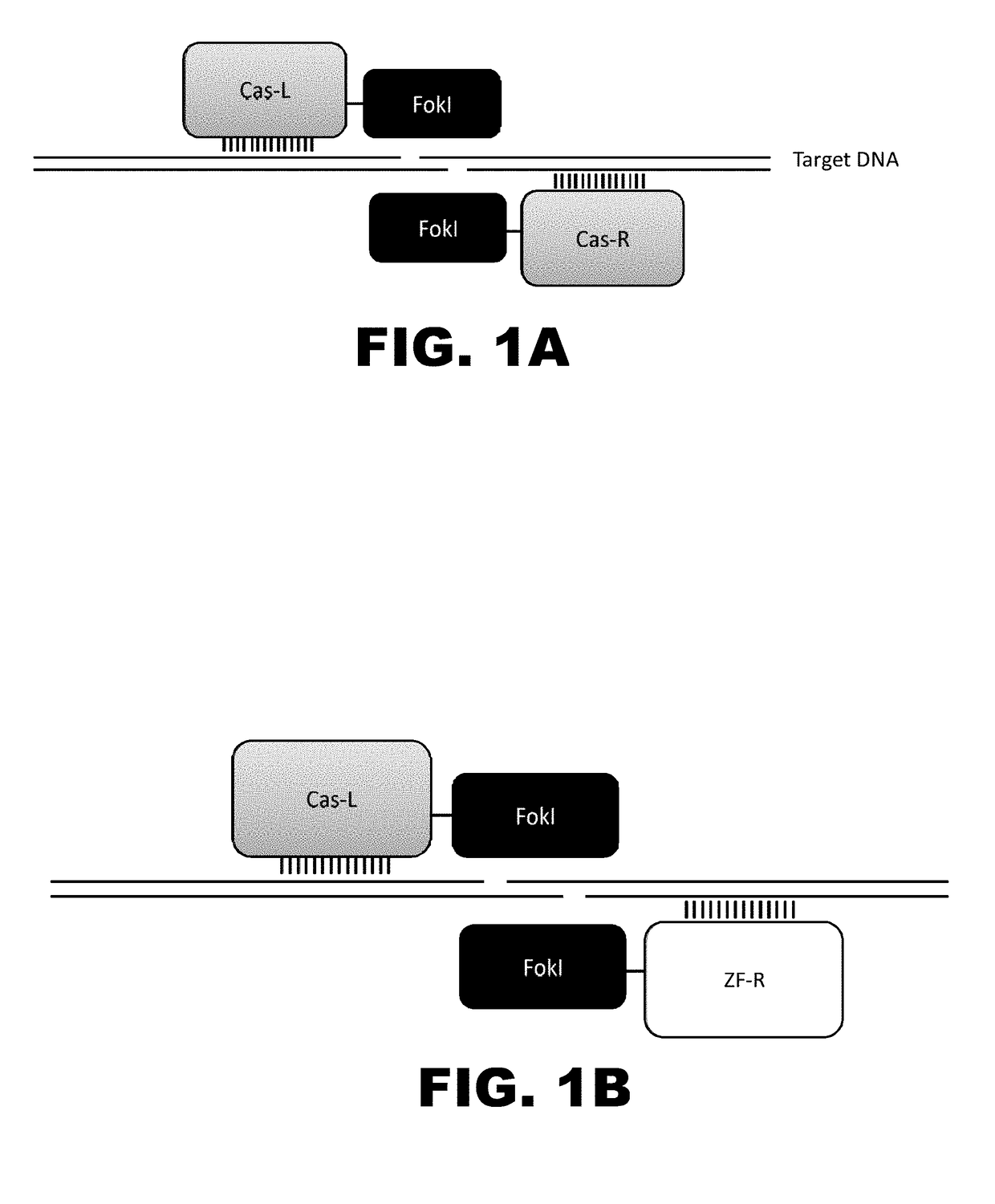
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences involved in tumor suppression. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. The invention also provides zinc finger nucleases that target chromosomal sequence involved in tumor suppression and the nucleic acids encoding the zinc finger nucleases. Also provided are methods of assessing the effects of agents in genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences involved in tumor suppression.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Compositions and methods for selection of nucleic acids containing modified bases
InactiveUS20140179564A1Reduce complexityIncreased complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence analysisGenomic DNA
Methods are provided for reducing the complexity of a population of nucleic acids prior to performing an analysis of the nucleic acids, e.g., sequence analysis. The methods result in a subset of the initial population enriched for a desired property, or lacking nucleic acids having an undesired property. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing populations having a high degree of complexity, e.g., chromosomal-derived DNA, whole genomic DNA, or mRNA populations. In addition, such methods allow for analysis of pooled samples.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Canine genome editing with zinc finger nucleases
The present invention provides a genetically modified canine or cell comprising at least one edited chromosomal sequence. In particular, the chromosomal sequence is edited using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. The disclosure also provides zinc finger nucleases that target specific chromosomal sequences in the canine genome.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Methods for reducing complexity of nucleic acid samples
InactiveUS20020055112A1Reduce complexityReduce time and costMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic Acid ProbesGenomic DNA
The invention provides several methods for reducing the complexity of a population of nucleic acids prior to performing an analysis of the nucleic acids on a nucleic acid probe array. The methods result in a subset of the initial population enriched for a desired property, or lacking nucleic acids having an undesired property. The resulting nucleic acids in the subset are then applied to the array for various types of analysis. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing populations having a high degree of complexity, for example, chromosomal-derived DNA, or whole genomic DNA, or mRNA population. In addition, such methods allow for analysis of pooled samples.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Treatments Related to Mitochondrial Disorders
Abstract: The invention is based in part on the discovery that chromosomal disorders such as Down Syndrome can be diagnosed by assessing maternal mitochondrial status. Thus the invention relates to diagnostic and therapeutic methods and related products for chromosomal disorders such as Downs Syndrome, for example, for identifying a risk of fetal Downs syndrome and methods of mitigating that risk. The methods also re useful for other therapies where it is desirable to manipulate mitochondria such as tissue generation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Identification and treatment of estrogen responsive prostate tumors
InactiveUS20090036415A1Great chance of notDecrease in tumor massBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAgonistEstrogen Receptor Antagonists
The present invention is directed to specific chromosomal rearrangements that are associated with prostate tumors that respond to compounds acting at estrogen receptors. Patients having the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, may be treated with agonists of the estrogen beta receptor or antagonists of the estrogen alpha receptor.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Recombinant cells that highly express chromosomally-integrated heterologous gene
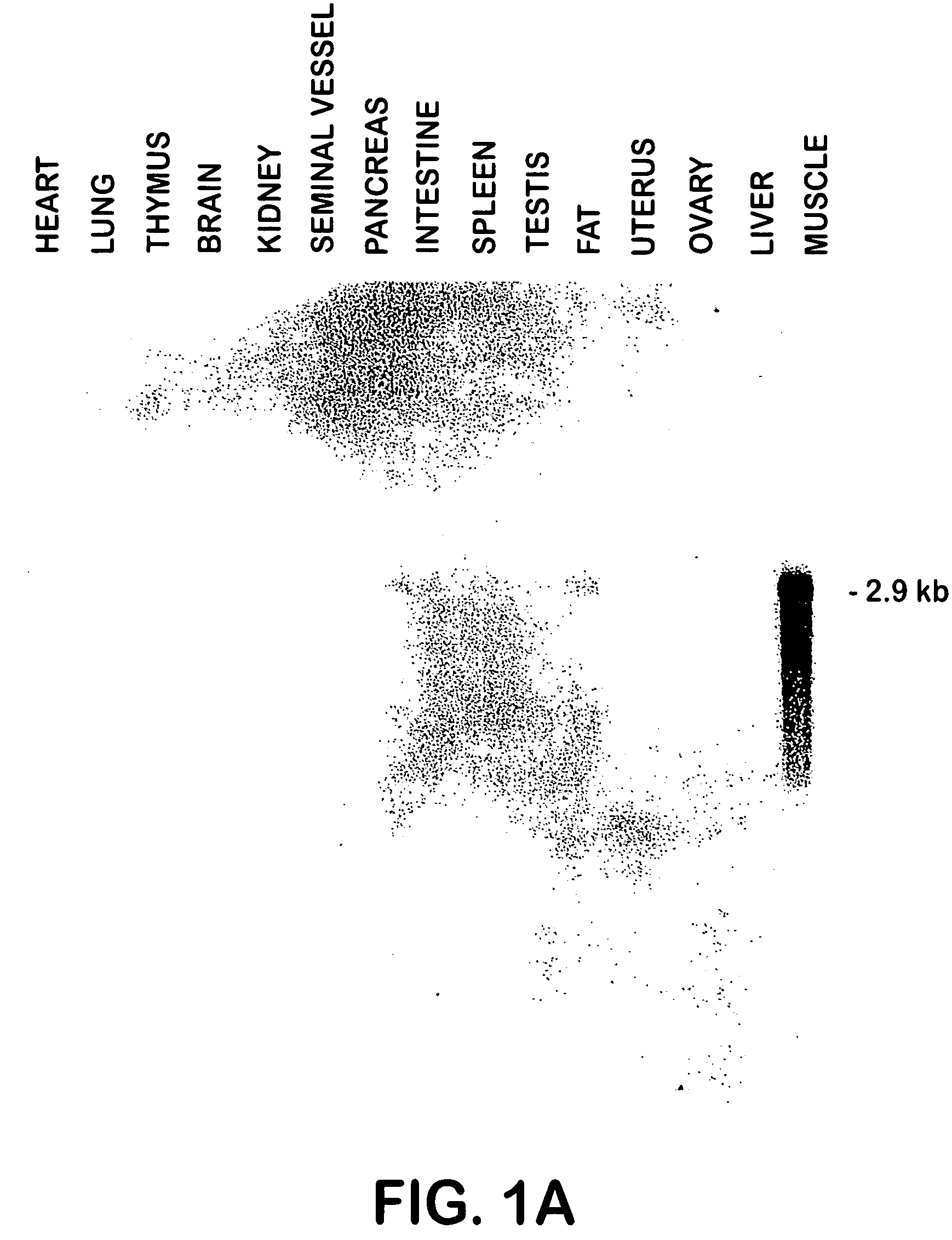
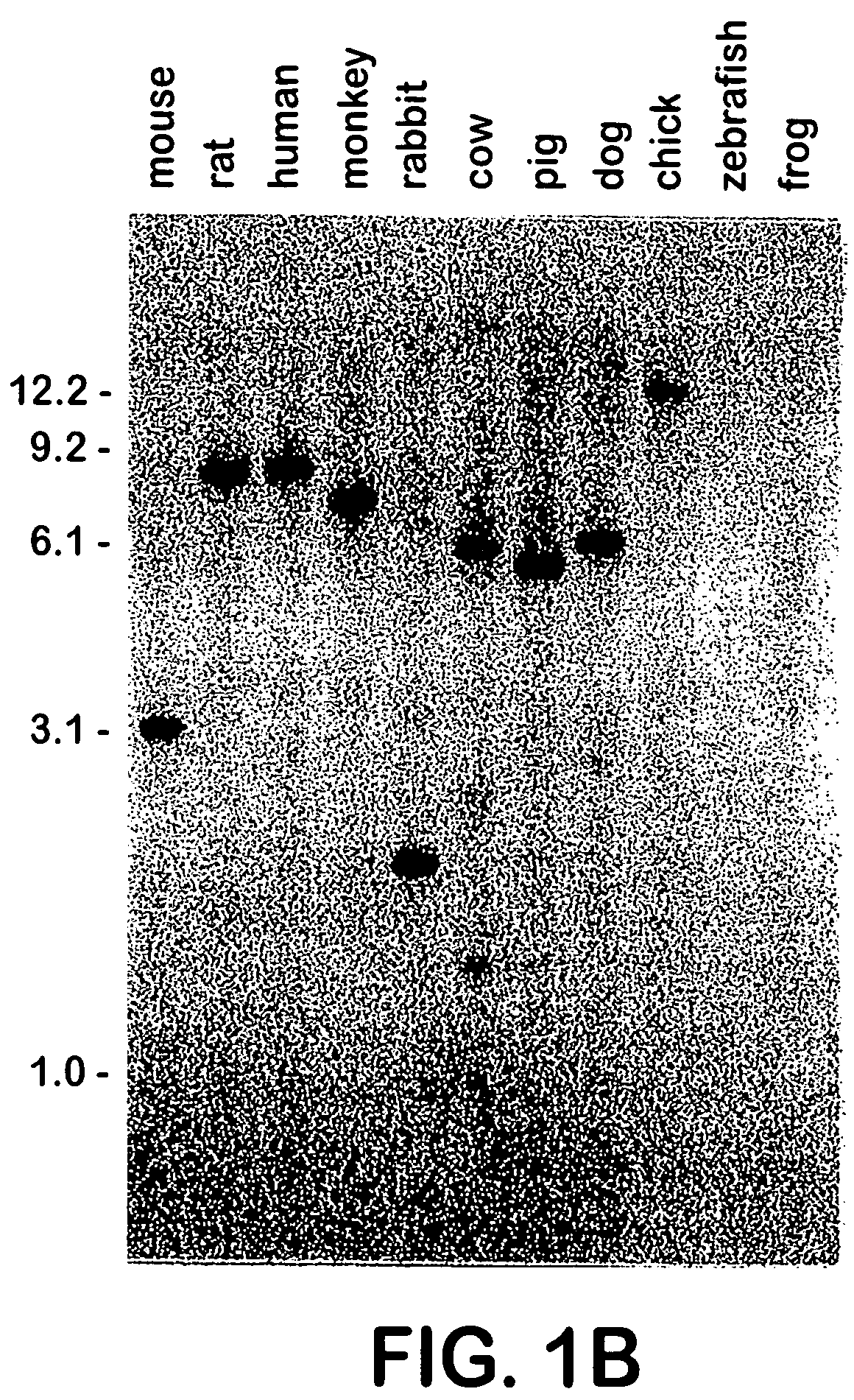
InactiveUS7192772B1Impairs succinate productionReduce productionSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliHeterologous
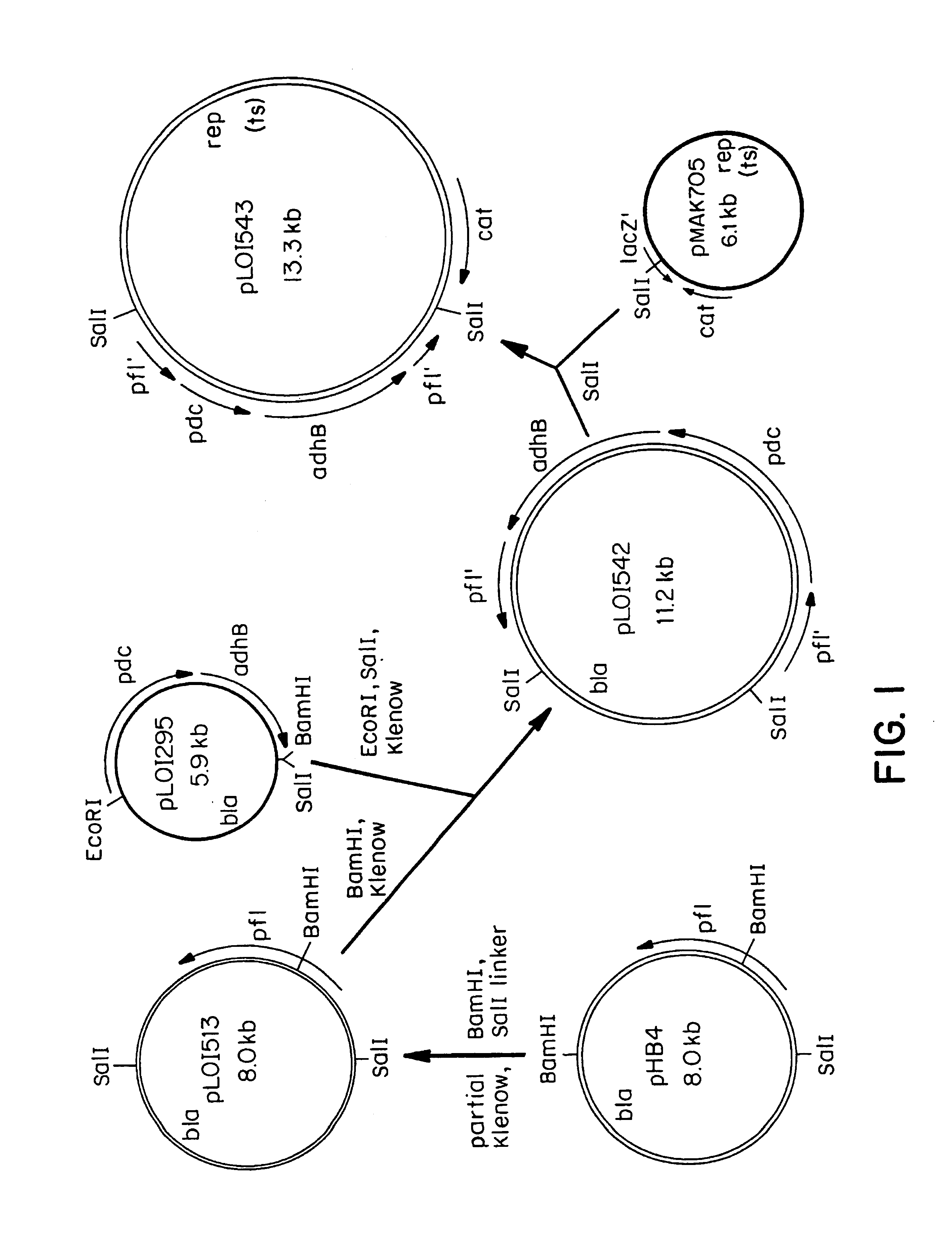
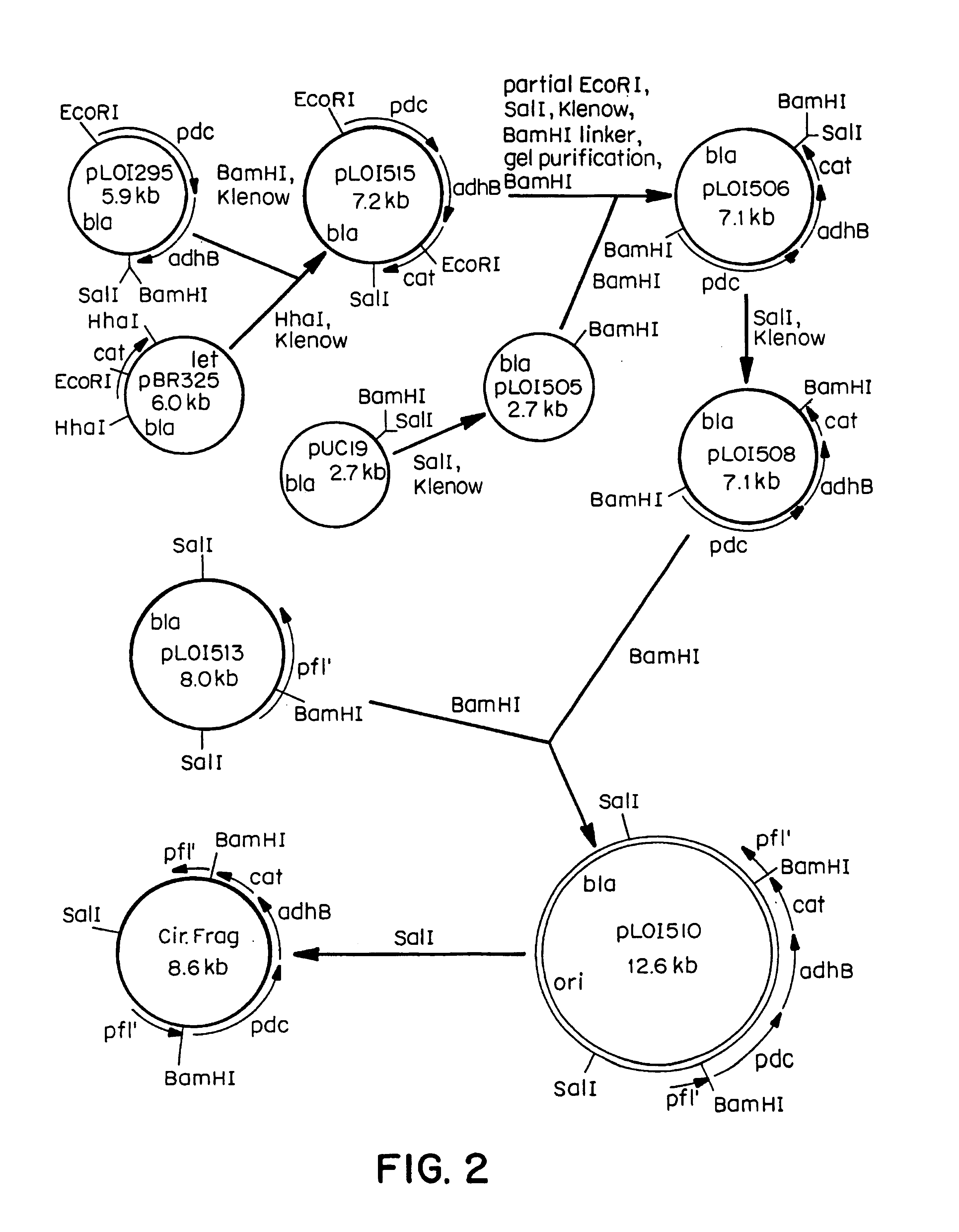
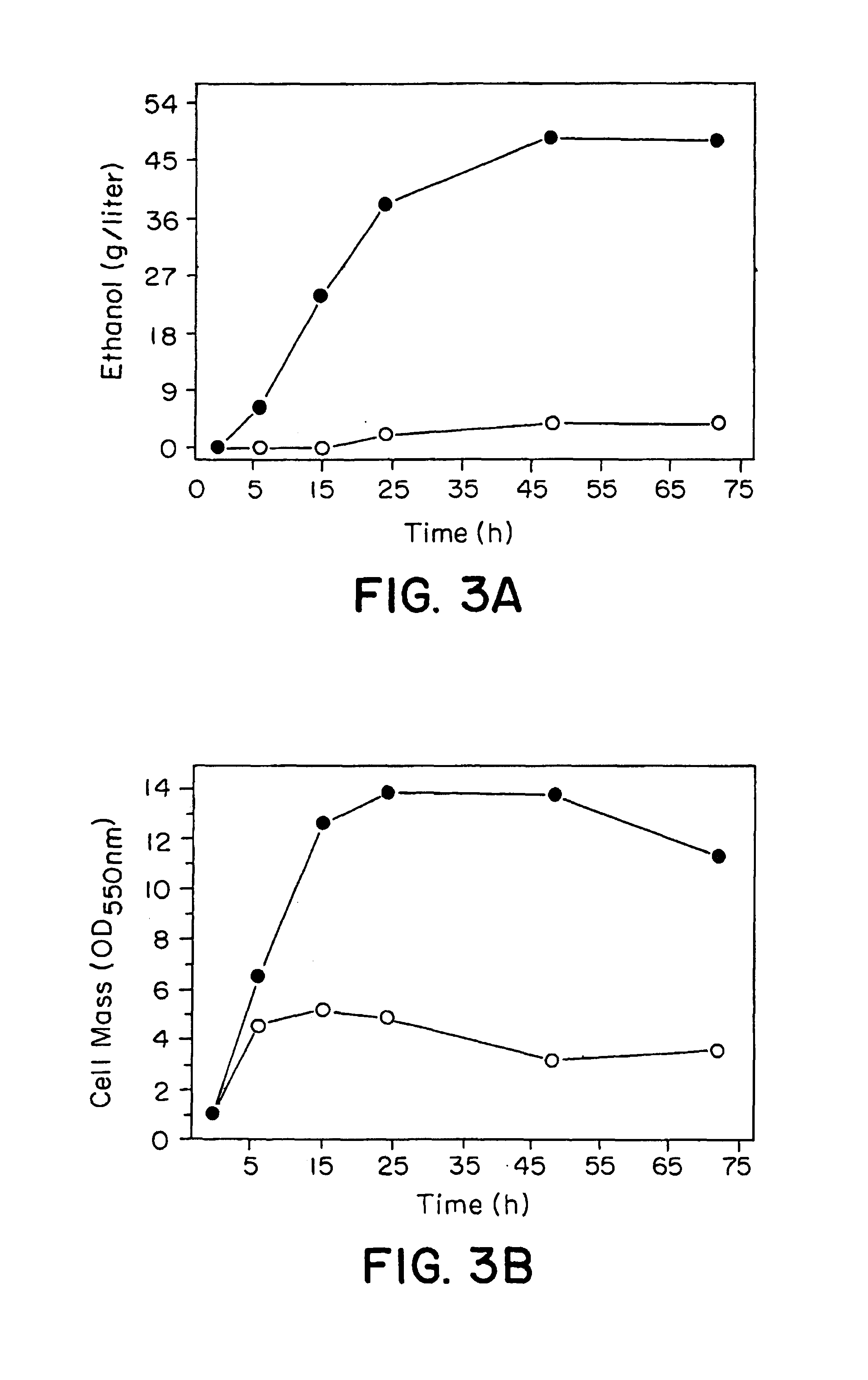
Recombinant host cells are obtained that comprise (A) a heterologous, polypeptide-encoding polynucleotide segment, stably integrated into a chromosome, which is under transcriptional control of an endogenous promoter and (B) a mutation that effects increased expression of the heterologous segment, resulting in enhanced production by the host cells of each polypeptide encoded by that segment, relative to production of each polypeptide by the host cells in the absence of the mutation. The increased expression thus achieved is retained in the absence of conditions that select for cells displaying such increased expression. When the integrated segment comprises, for example, ethanol-production genes from an efficient ethanol producer like Zymomonas mobilis, recombinant Escherichia coli and other enteric bacterial cells within the present invention are capable of converting a wide range of biomass-derived sugars efficiently to ethanol.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
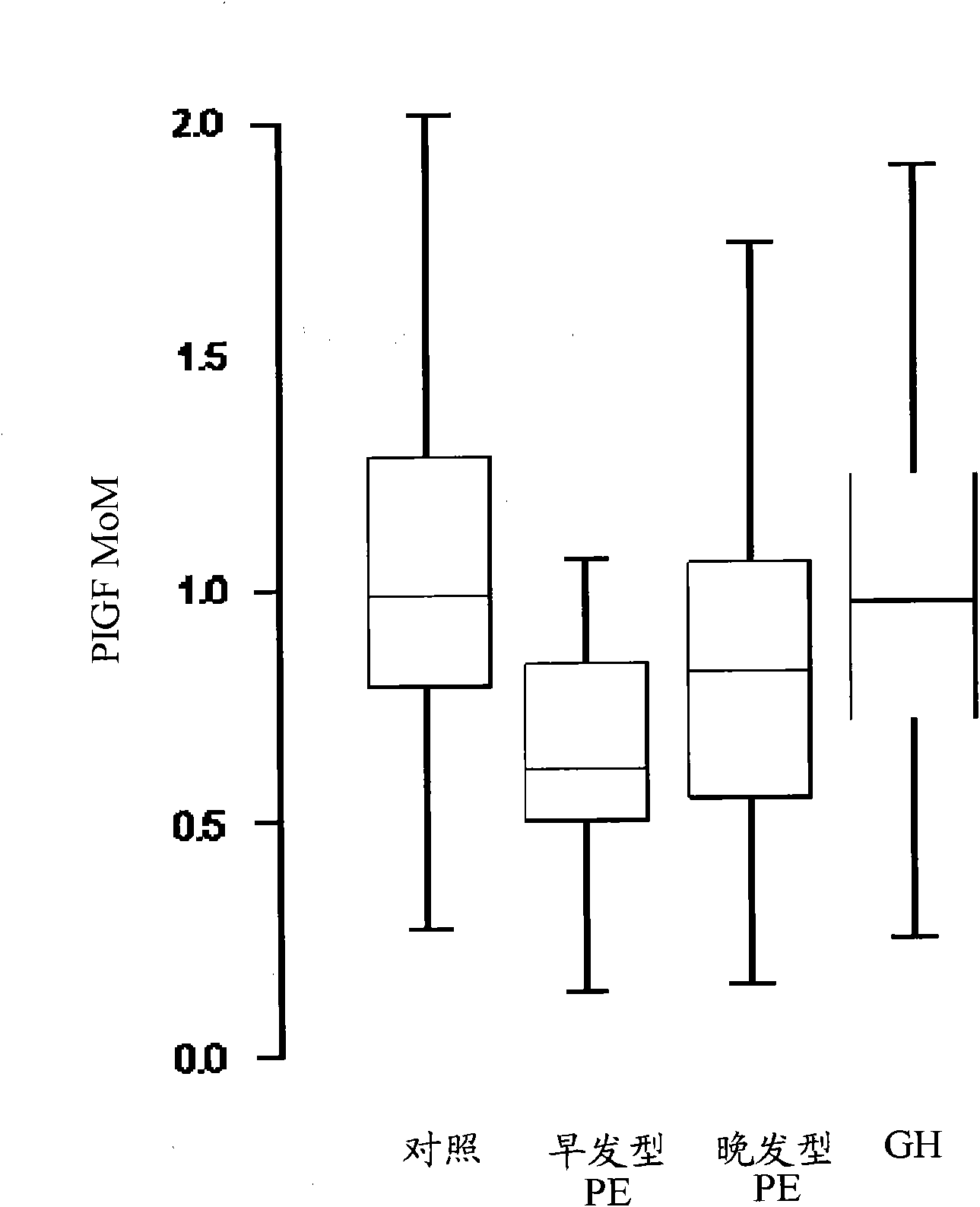
Methods for determining the risk of prenatal complications
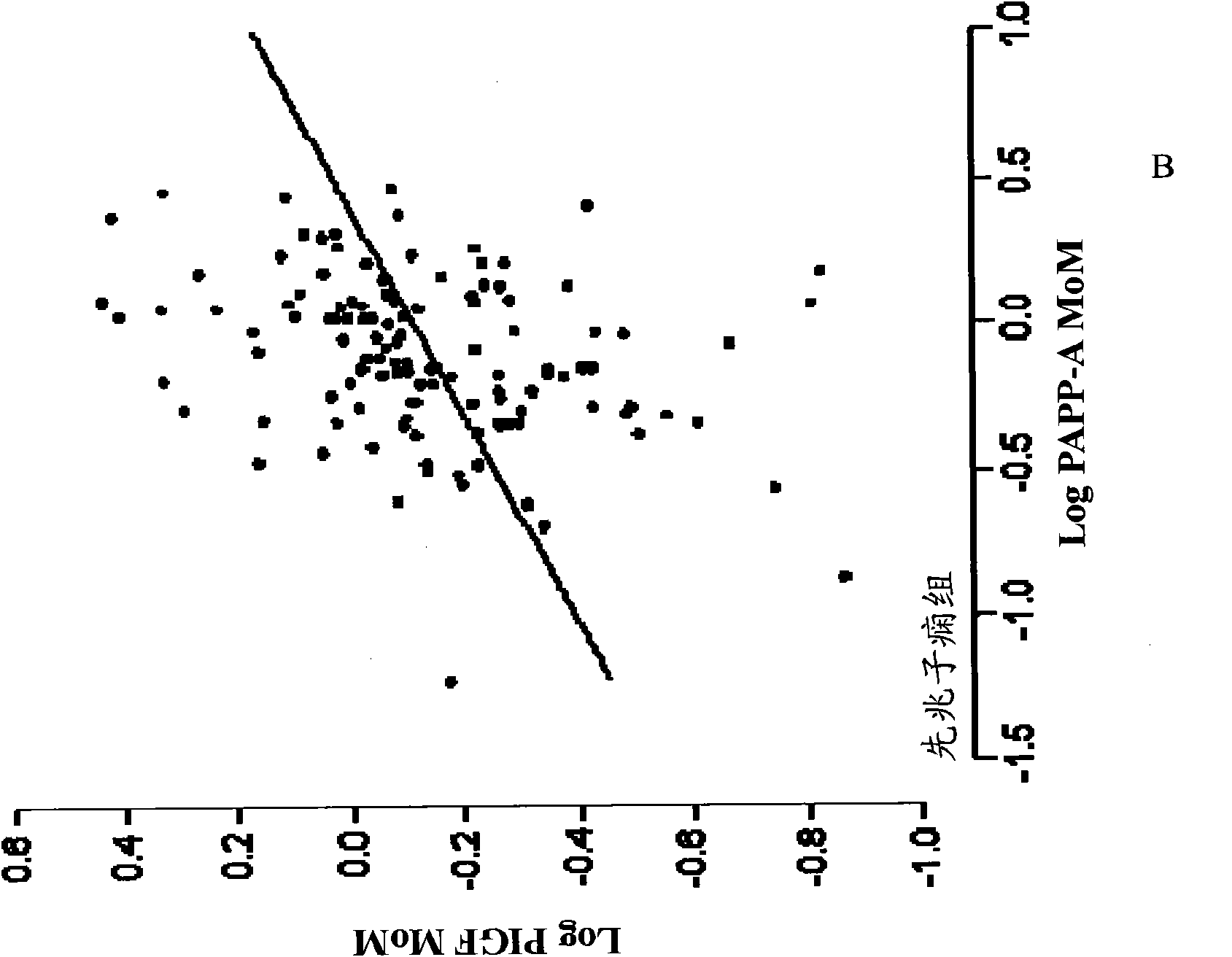
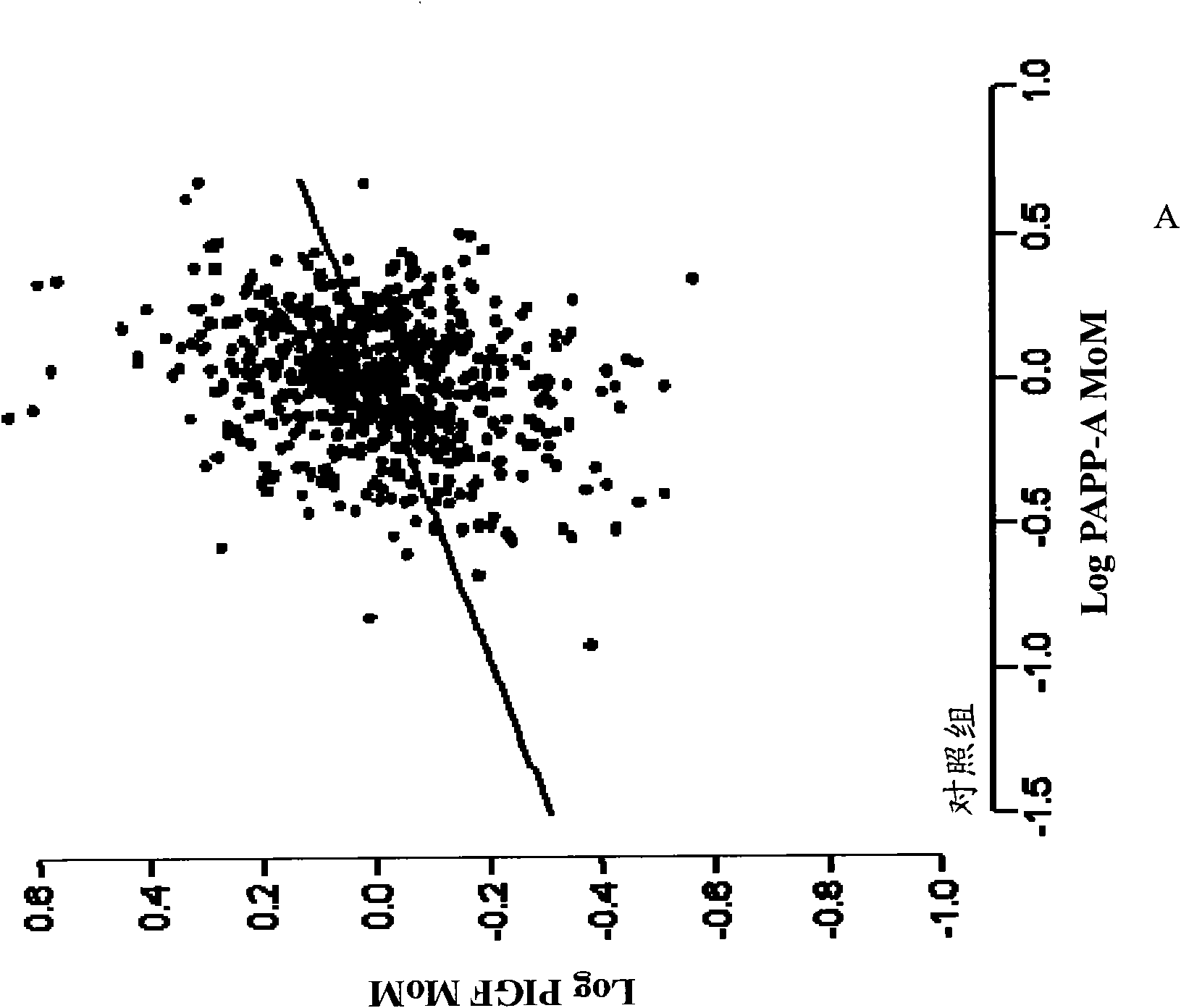
The disclosure relates to methods, medical profiles, kits and apparatus for use in determining the risk that a pregnant individual has for developing pre-eclampsia based on amounts of certain biochemical markers in a biological sample from the individual and biophysical markers. The disclosure also relates to methods, medical profiles, kits and apparatus for use in determining the risk that a pregnant individual is carrying a fetus having a chromosomal abnormality based on amounts of certain biochemical markers in a biological sample from the individual and biophysical markers.
Owner:WALLAC
Growth differentiation factor-8
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
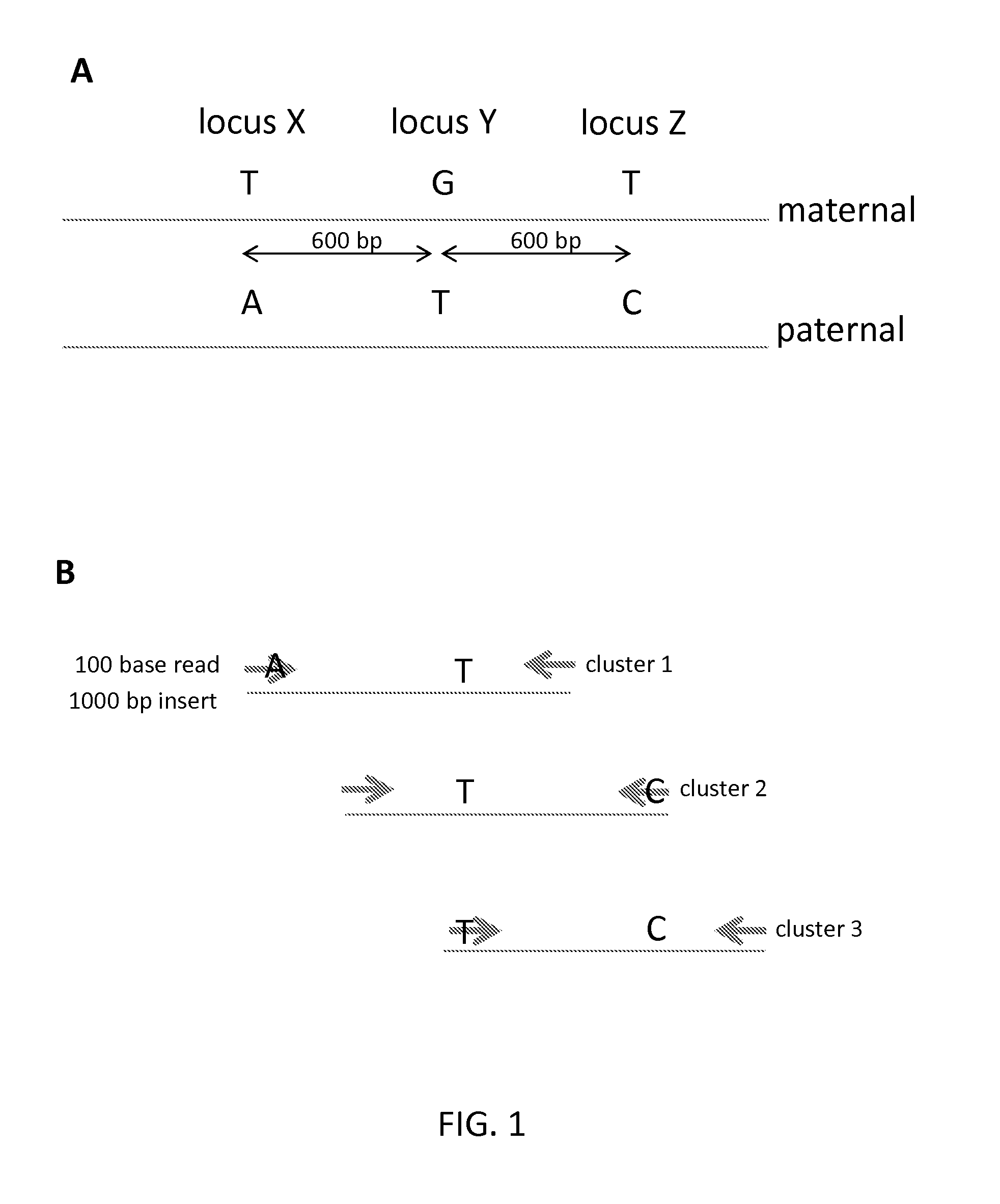
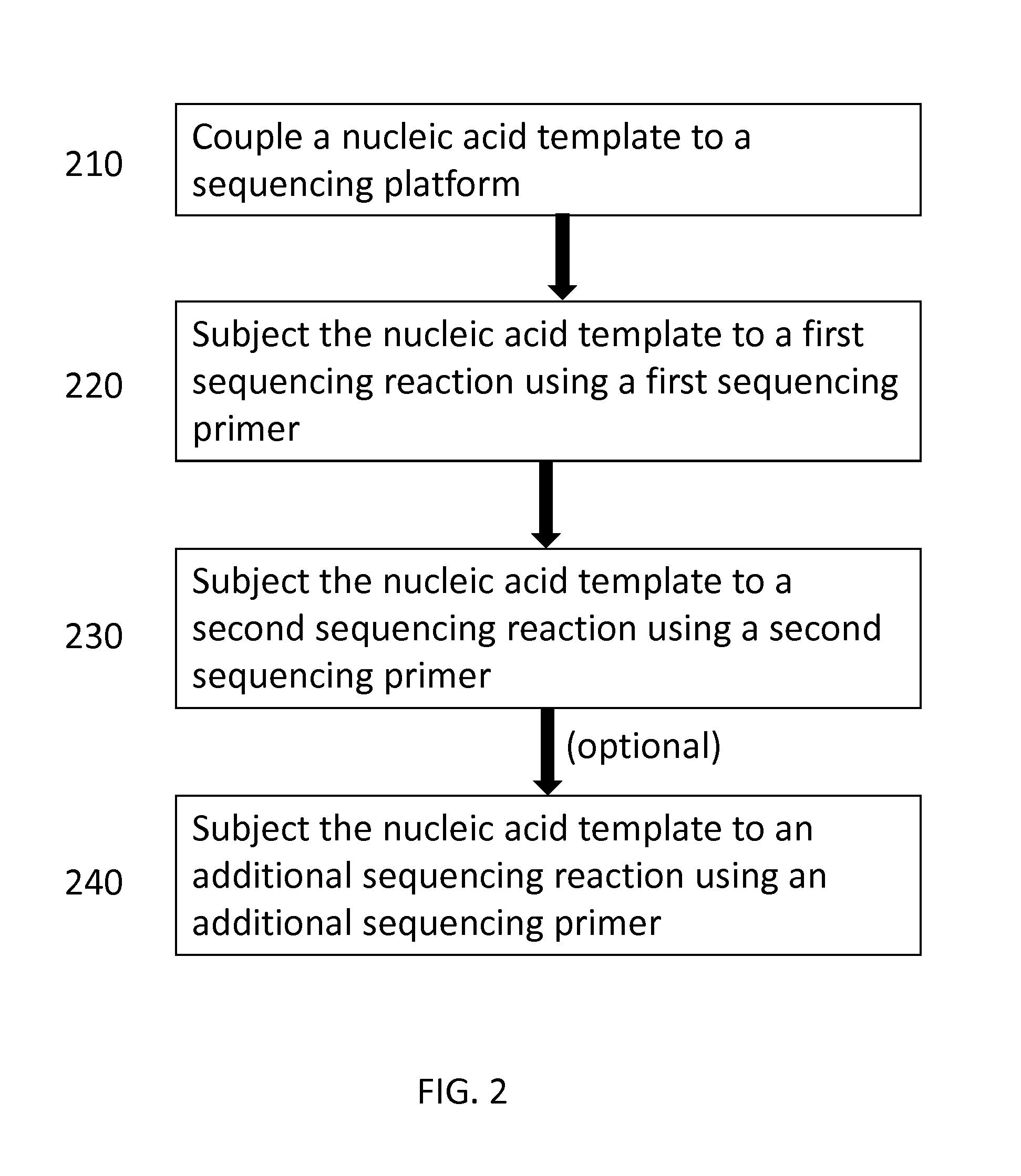
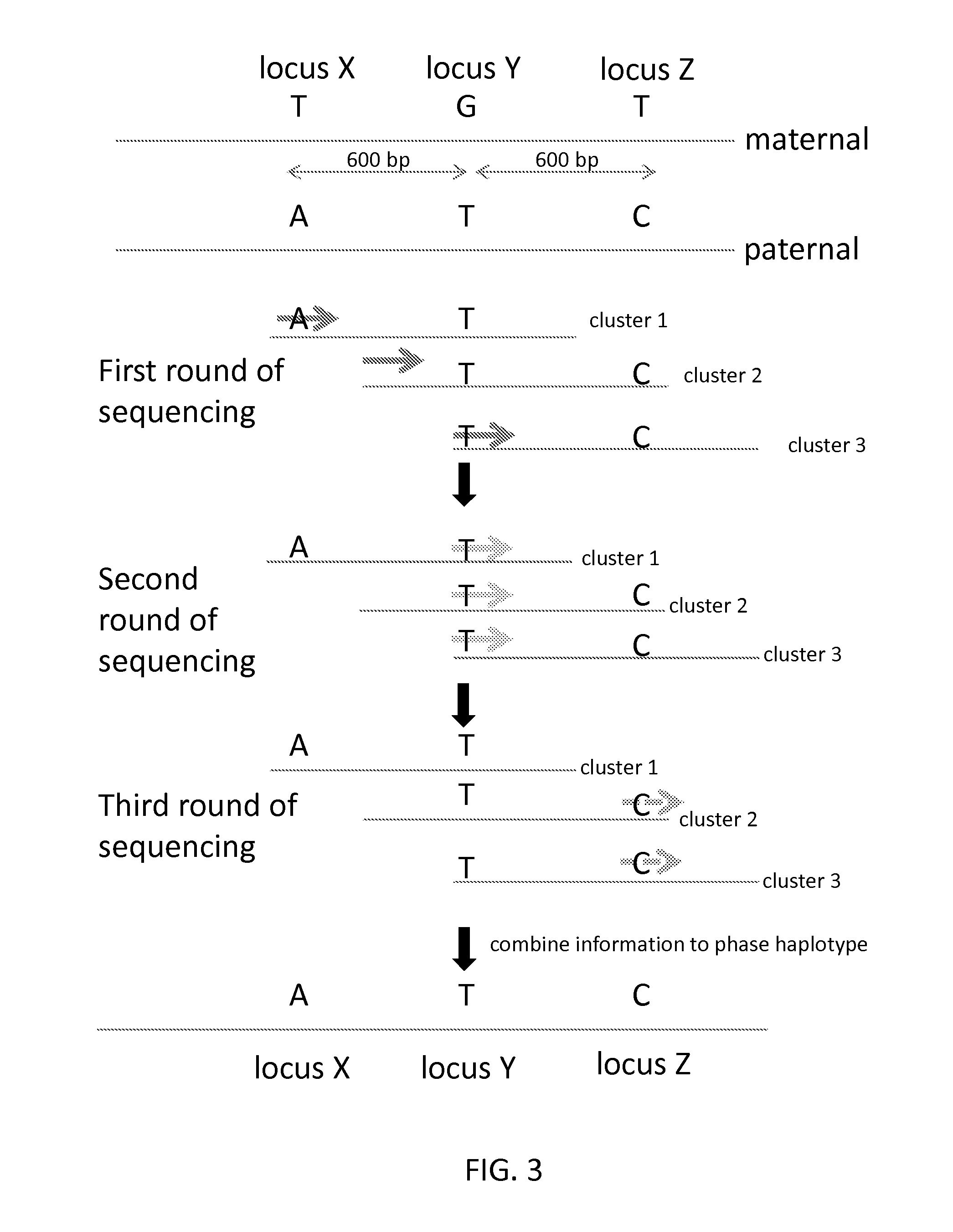
Sequential sequencing
ActiveUS20160251711A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Described herein are improved methods, compositions and kits for next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits described herein enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (which can comprise regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information can be obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein can be useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
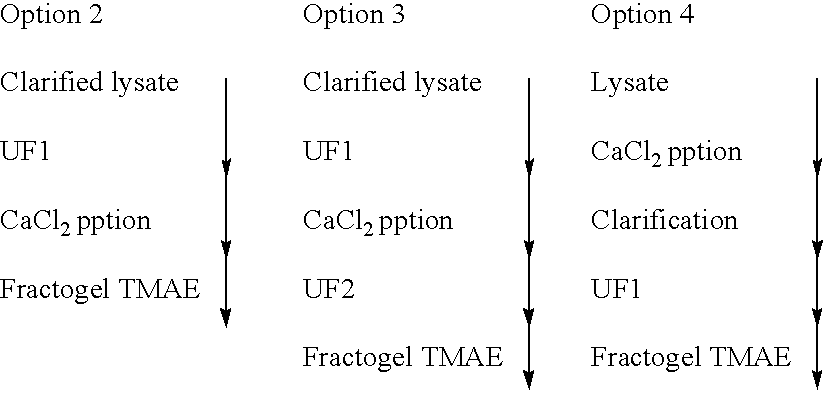
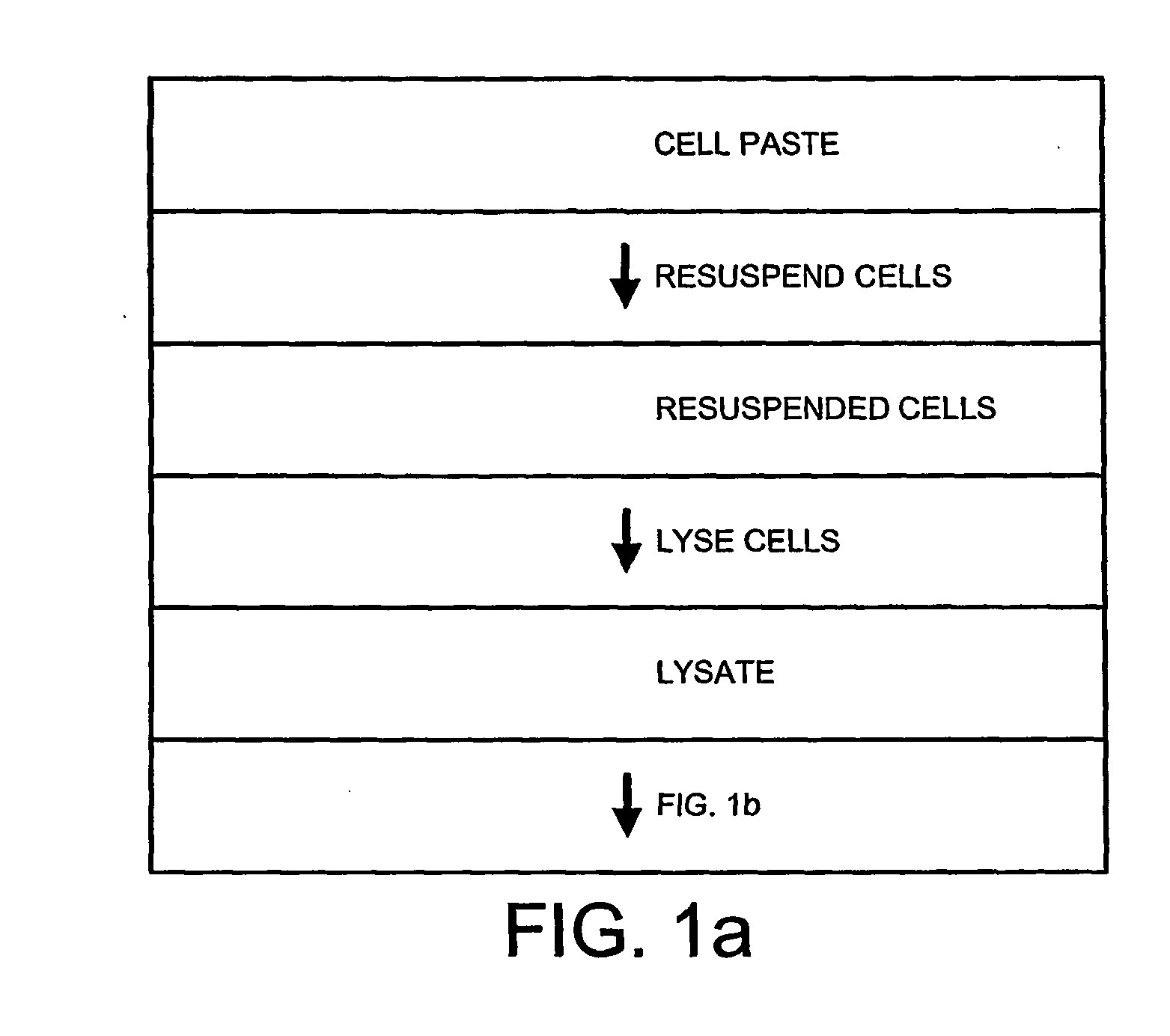
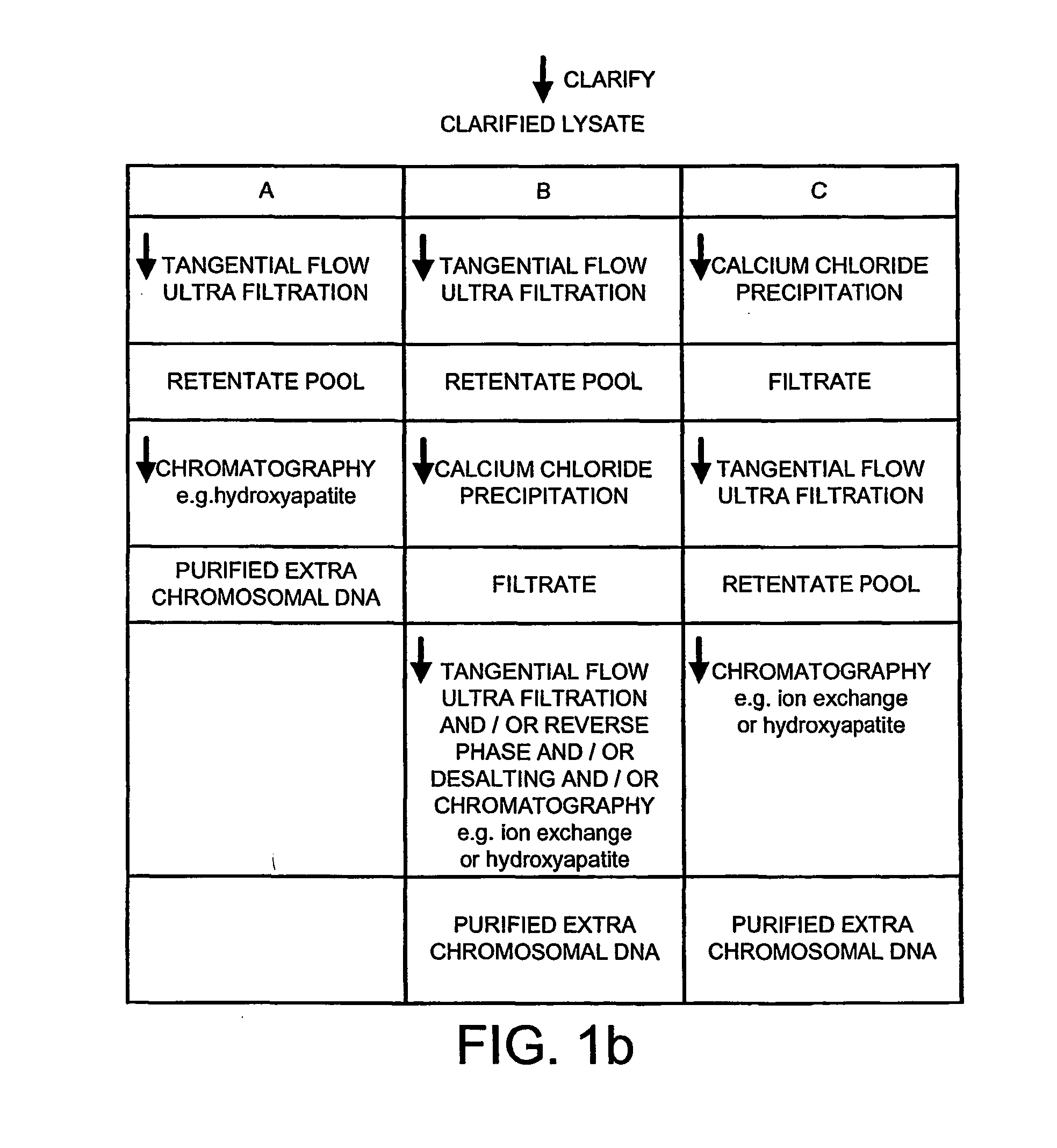
Method of separating extra-chromosonal dna from other cellular components
The invention relates to a method of separating extra-chromosomal DNA from RNA. It also relates to DNA produced by the method and pharmaceuticals derived from such DNA, for example, DNA vaccines. The method comprises separating extra-chromosomal DNA from RNA without first digesting the RNA, and comprises: i) lysing cells comprising extra-chromosomal DNA to form a lysate; ii) clarifying the lysate; and iii) subjecting the clarified lysate to tangential flow ultra filtration under conditions, which allow a substantial amount of the RNA to pass through a membrane whilst the extra-chromosomal DNA is retained. The preferred conditions include the use of a diafiltration buffer of low conductivity and diafiltration volumes of over 10 volume equivalents.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LIMITED OF GLAXO WELLCOME HOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com