Methods for determining the risk of prenatal complications
A risky, individual technique for use in biochemical devices and methods, patient-specific data, microbiological assays/tests, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
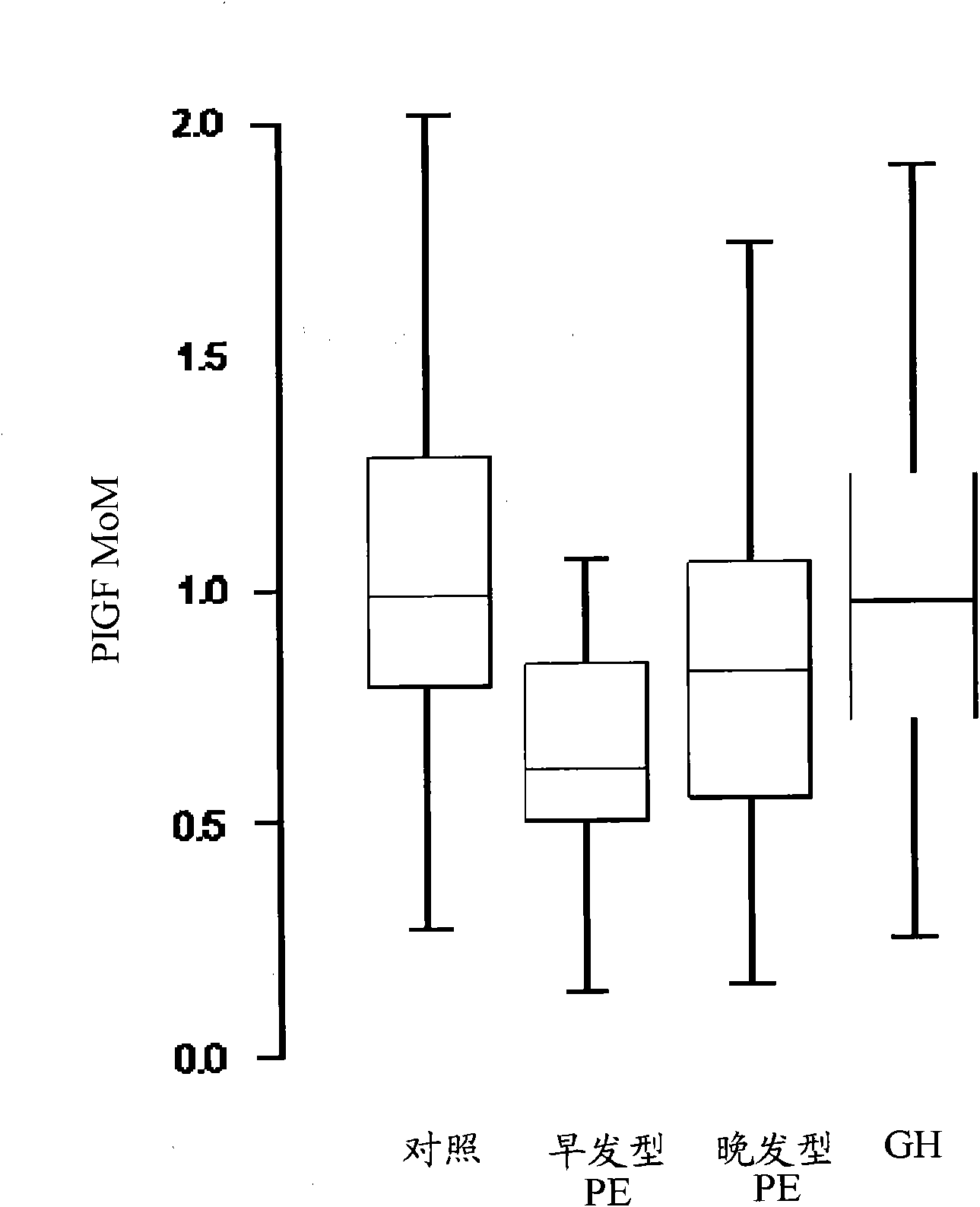
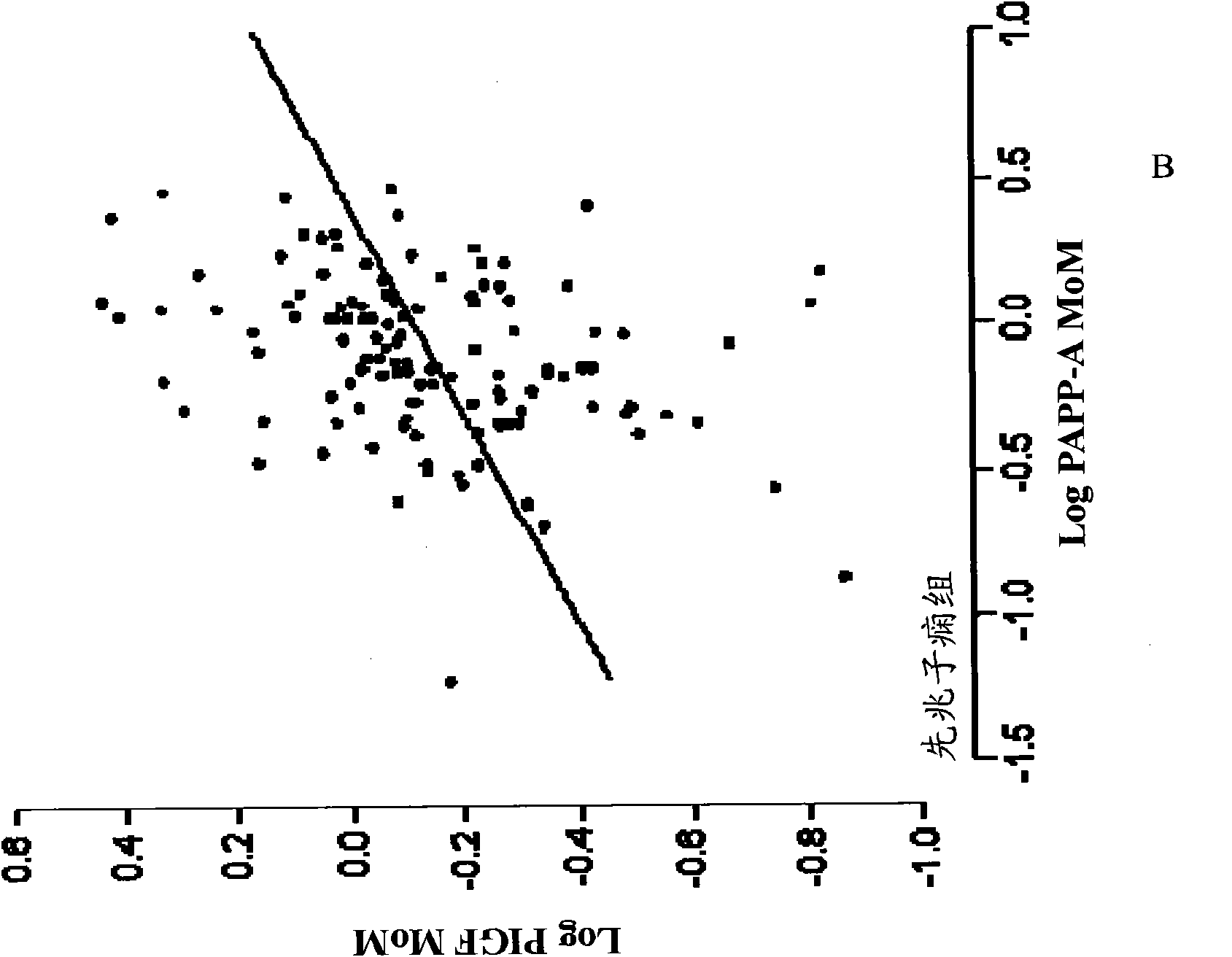
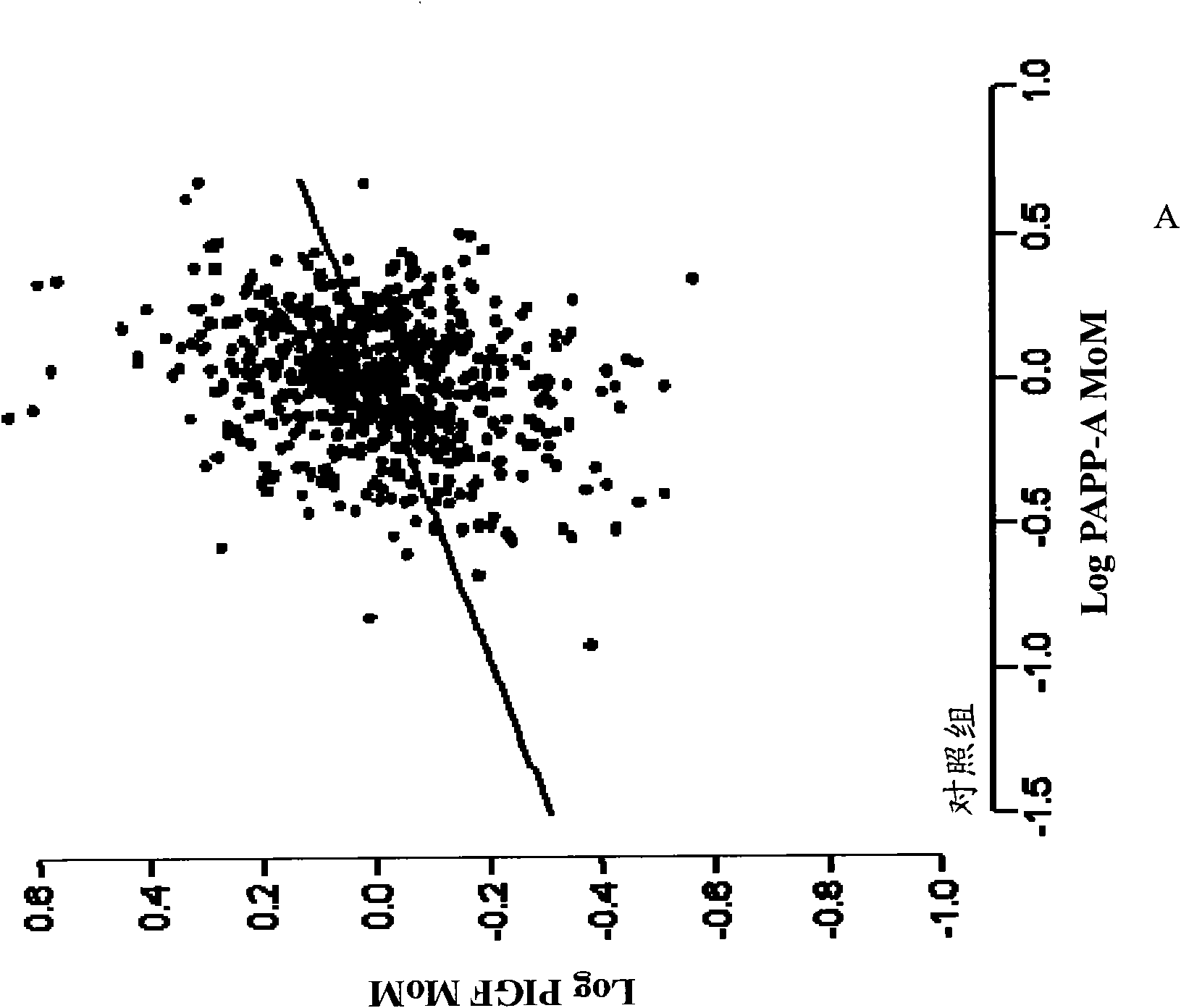
[0078] Example 1. Clinical study of the role of PlGF, PAPP-A and biophysical markers in the detection of preeclampsia bed study
[0079] This example illustrates the effectiveness of various combinations of biochemical and biophysical markers, including maternal blood pressure, uterine Doppler pulsatility index, PlGF, PAPP- A and PP13.
[0080] Studies were conducted to screen for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women participating in routine assessment for risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Maternal characteristics and medical history were recorded and blood was collected. Serum was stored at -80°C for subsequent biochemical analysis. Written informed consent was obtained from female patients who agreed to participate in this study, which was approved by the King's College Hospital Ethics Committee. Additional information regarding clinical populations and sample collection is described in Example 3.
[0081] For the analyzes described herein, all biochemical and biophy...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Example 2: When multiple biochemical and biophysical markers are used to detect preeclampsia and related placental disorders Clinical research on the role of
[0131] This example illustrates the effectiveness of a combination of multiple biochemical markers for determining the risk of preeclampsia and related disorders in pregnant individuals. Specifically, the biochemical markers MMP3, PlGF, TNFR1 and PP13 (PerkinElmer DELFIA assay format) have been found to be statistically significant for predicting pre-eclampsia and related disorders. One or more markers shown to be predictive for the detection of pre-eclampsia can be used in combination with the marker panels described herein (eg, PlGF and / or PAPP-A and MAP).
[0132] Studies were conducted to screen for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women participating in routine assessment for risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Maternal characteristics and medical history were recorded and blood was collected. Serum was st...
Embodiment 3
[0171] Example 3.: Clinical study of the role of biochemical markers and Doppler biophysical markers in the detection of maternal hypertensive disorders
[0172] This example illustrates the effectiveness of a combination of various biochemical and biophysical markers, including PlGF, PAPP-A, uterine artery PI.
[0173] A study was conducted to screen for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women who participated in routine assessment for risk of chromosomal abnormalities by assessing pregnancy11 +0 -13 +6 The thickness of the fetal cervical translucence membrane (thickness) and the measurement of maternal serum PAPP-A and free β-hCG were carried out. Maternal characteristics and medical history were recorded, and uterine artery PI was measured by transabdominal color Doppler, and serum was stored at -80°C for subsequent biochemical analysis. Written informed consent was obtained from female patients who agreed to participate in this study, which was approved by the King's Colleg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com