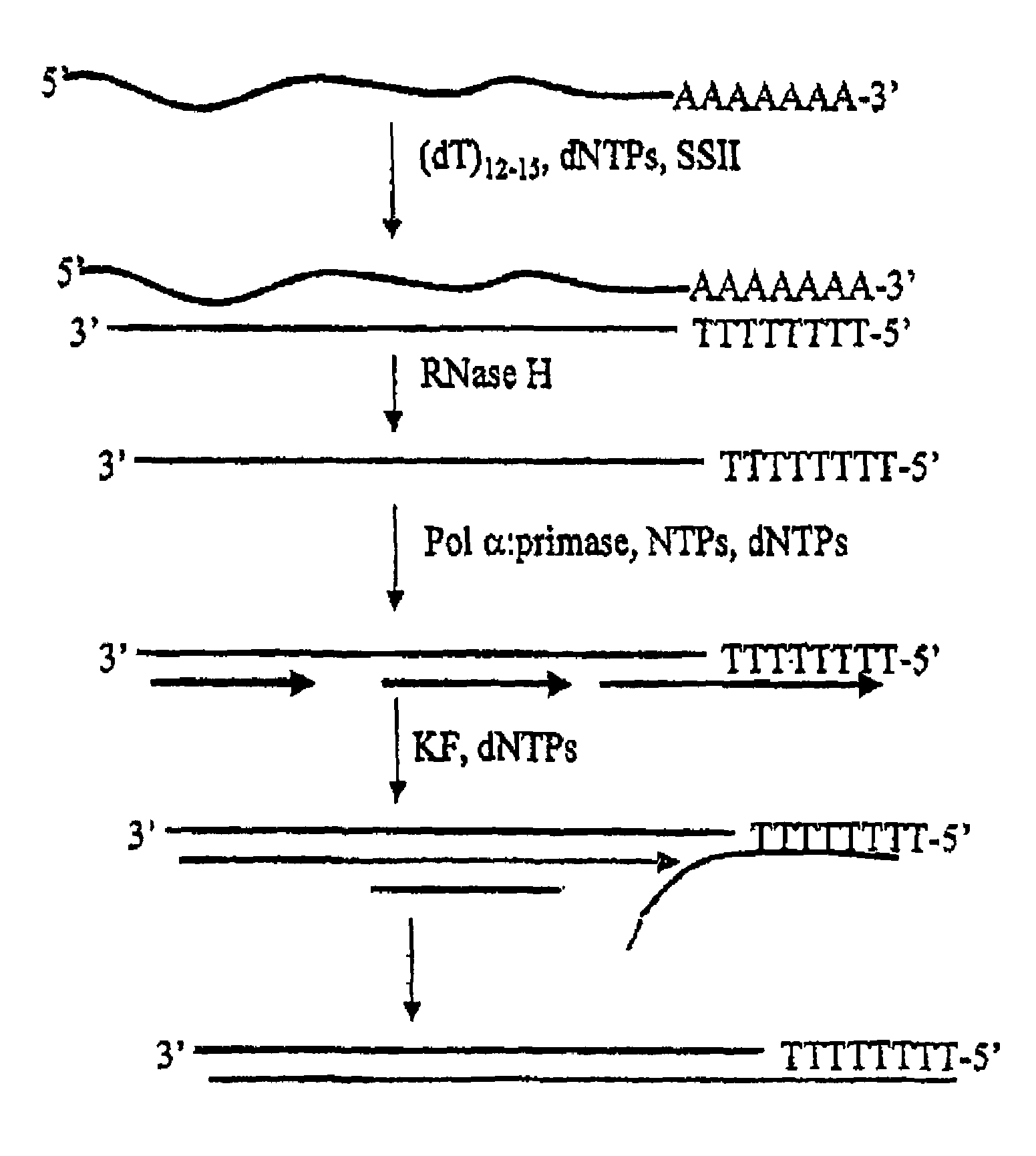
Method for synthesis of the second strand of cDNA
a synthesis method and cdna technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid synthesis, can solve the problems of few or no primers for synthesis, loss or rearrangement of sequences corresponding to the 5′ terminus of the mrna, and inefficient ligation reaction, etc., and achieve the effect of high processivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0040]A first cDNA strand of an in vitro T7 transcript (ca. 1000 nucleotides long) containing a 3′ polyA tail is generated using 200 U SUPERSCRIPT II (RT), 500 uM dNTPs, 100 pmol oligo(dT)12-18, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, 75 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2, and 10 mM DTT. The reaction is performed at 40° C. for 60 min., followed by heat inactivation of the RT at 70° C. for 10 min. One unit of RNAse H is added to degrade the RNA portion of the RNA:DNA hybrid. After heat inactivation of the RNase H activity at 70° C. for 10 minutes, the first strand is purified by ethanol precipitation. The second strand is generated by the addition of 2 mM NTPs, 25 uM a-32P[dATP], dGTP, dCTP, dTTP, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mg / mL BSA, and 2 U pol α:primase. The reaction is incubated at 37° C. for 60 minutes. The reaction is split into two part, and 1 U Klenow fragment is added to one of the fractions to extend all of the products to full length products. The reaction is incubated at 37° C. for 30 minut...
example 2
[0041]A double-stranded cDNA is generated, followed by T7 amplification. The first strand is generated as described in Example 1, with the only difference being an oligo(dT) primer containing a T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The second strand is synthesized using pol ∝-primase and Klenow fragment, as in Example 1, but only cold dNTPs are used. The generated ds cDNA is then used as a substrate in a T7 amplification reaction, using standard procedures as those described in Van Gelder et al. (1990) PNAS USA 87:1663; Phillips amd Eberwine (1996) Methods: a companion to Methods in Enzymol, 10:283; Eberwine et al. (1992) PNAS USA 89:3010; Eberwine (1996) Biotechniques 20:584; and U.S. Pat. No. 6,132,997. The transcripts are then analyzed by denaturing electrophoresis. The product is primarily 1000 nucleotides in length.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com