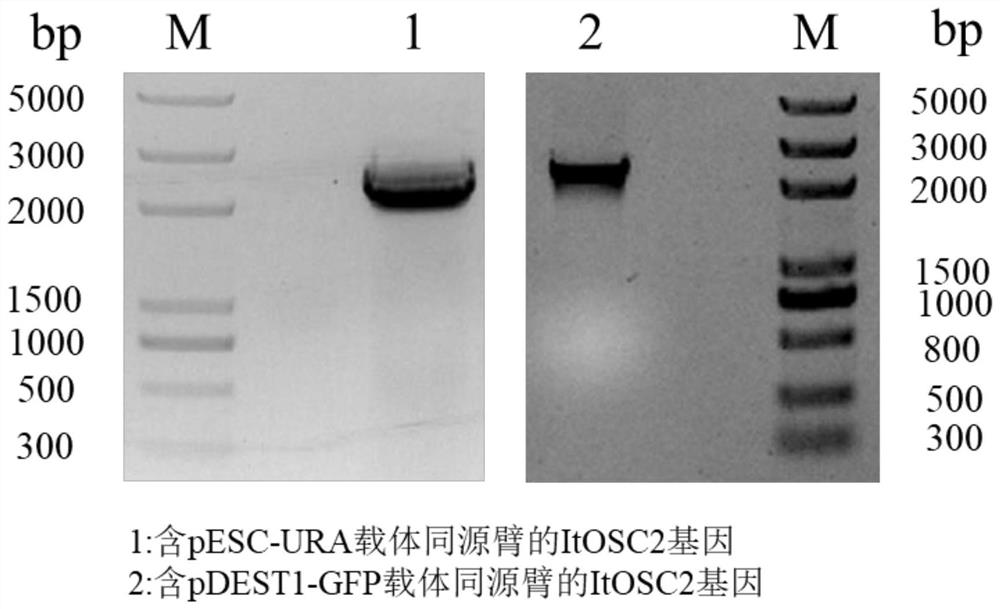
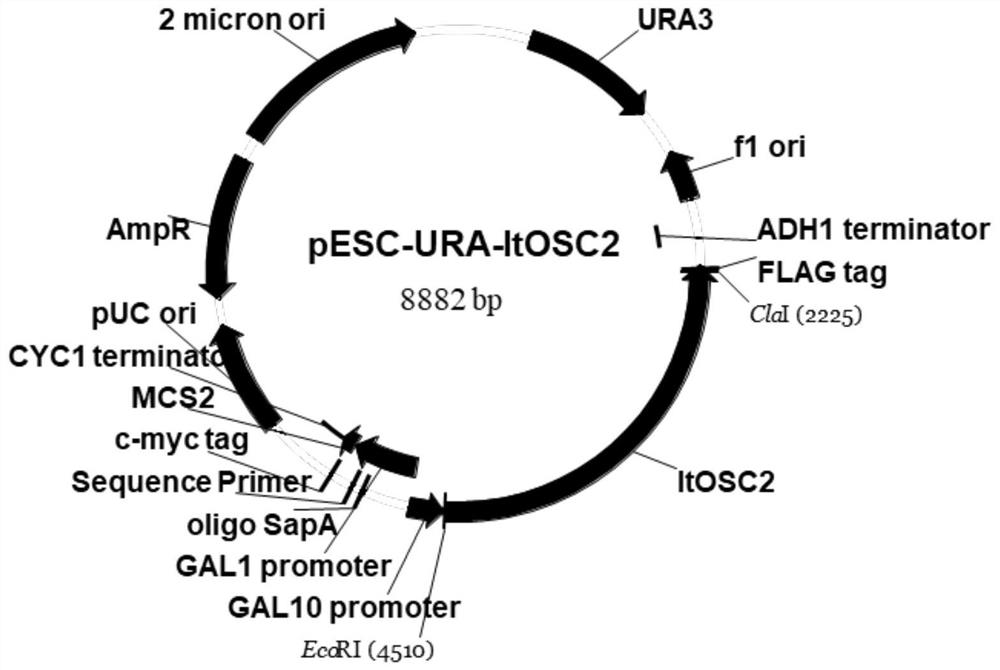
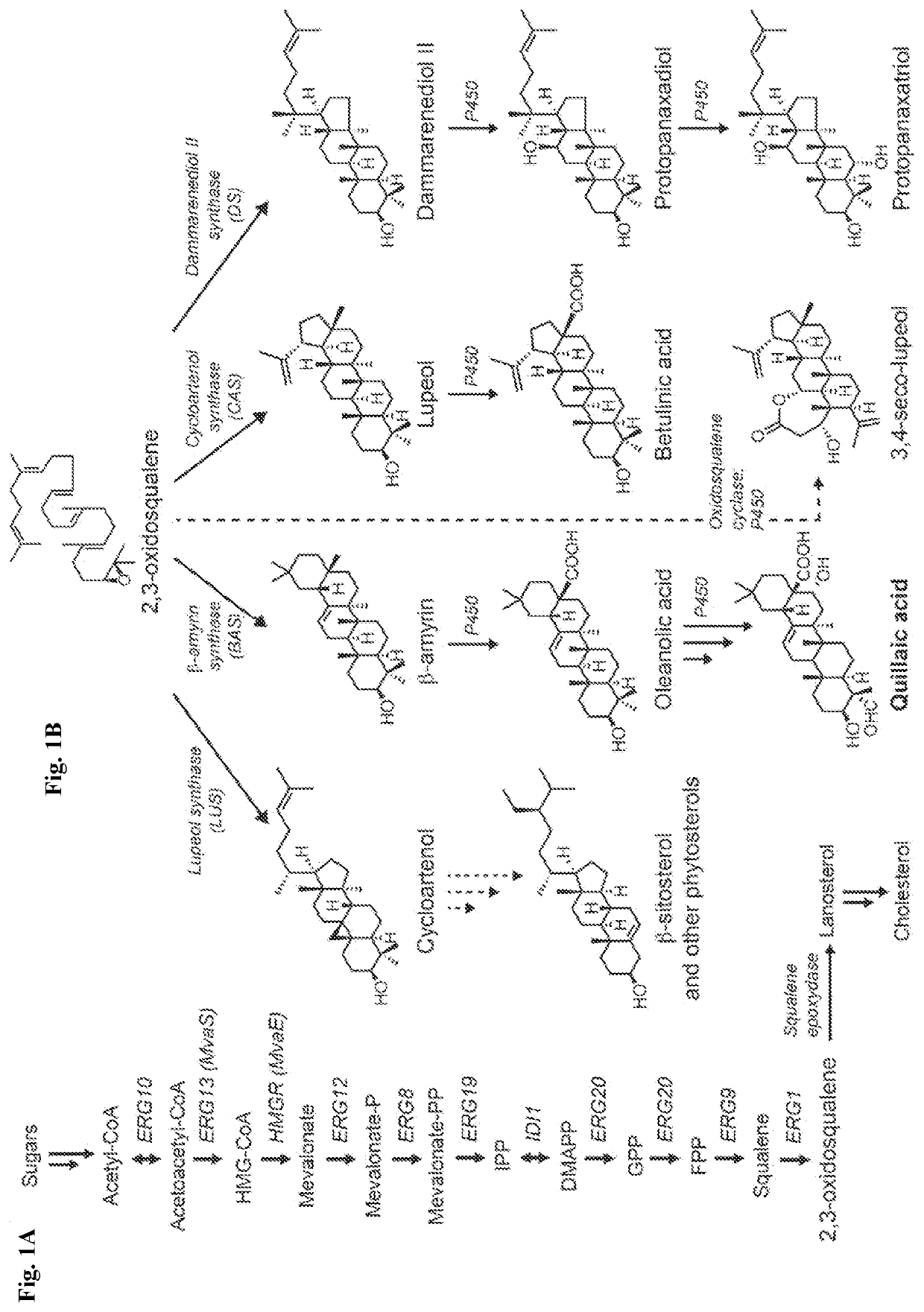
Patents
Literature
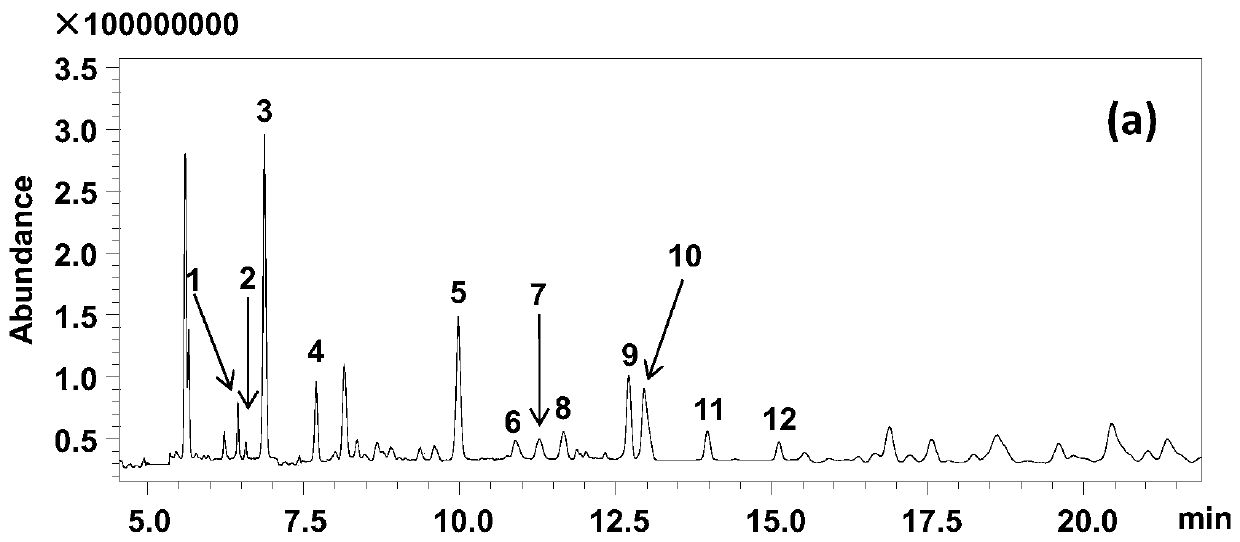
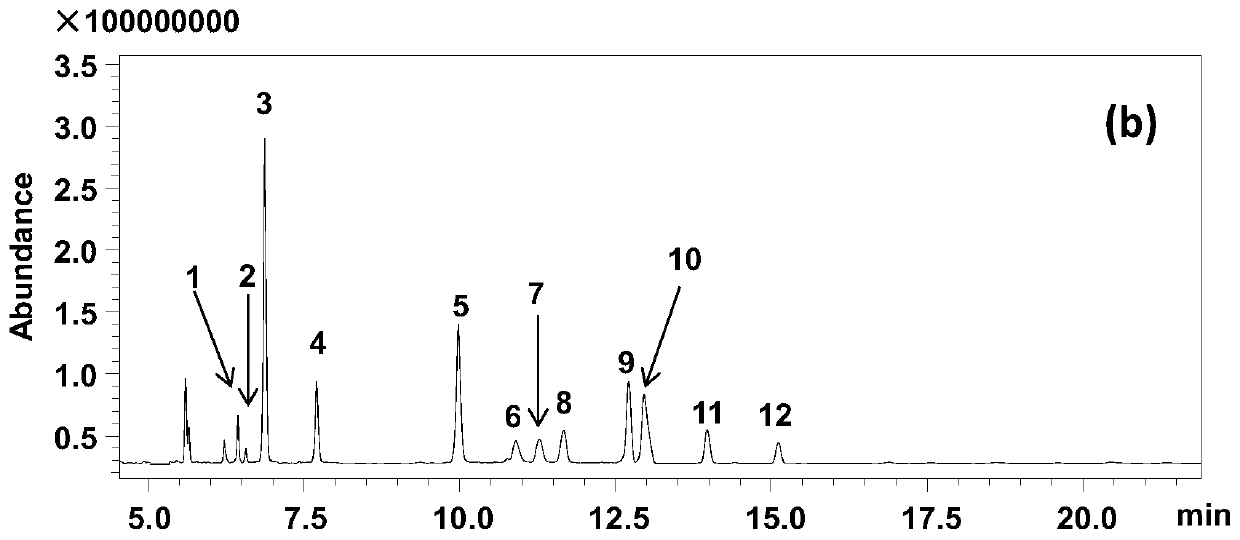
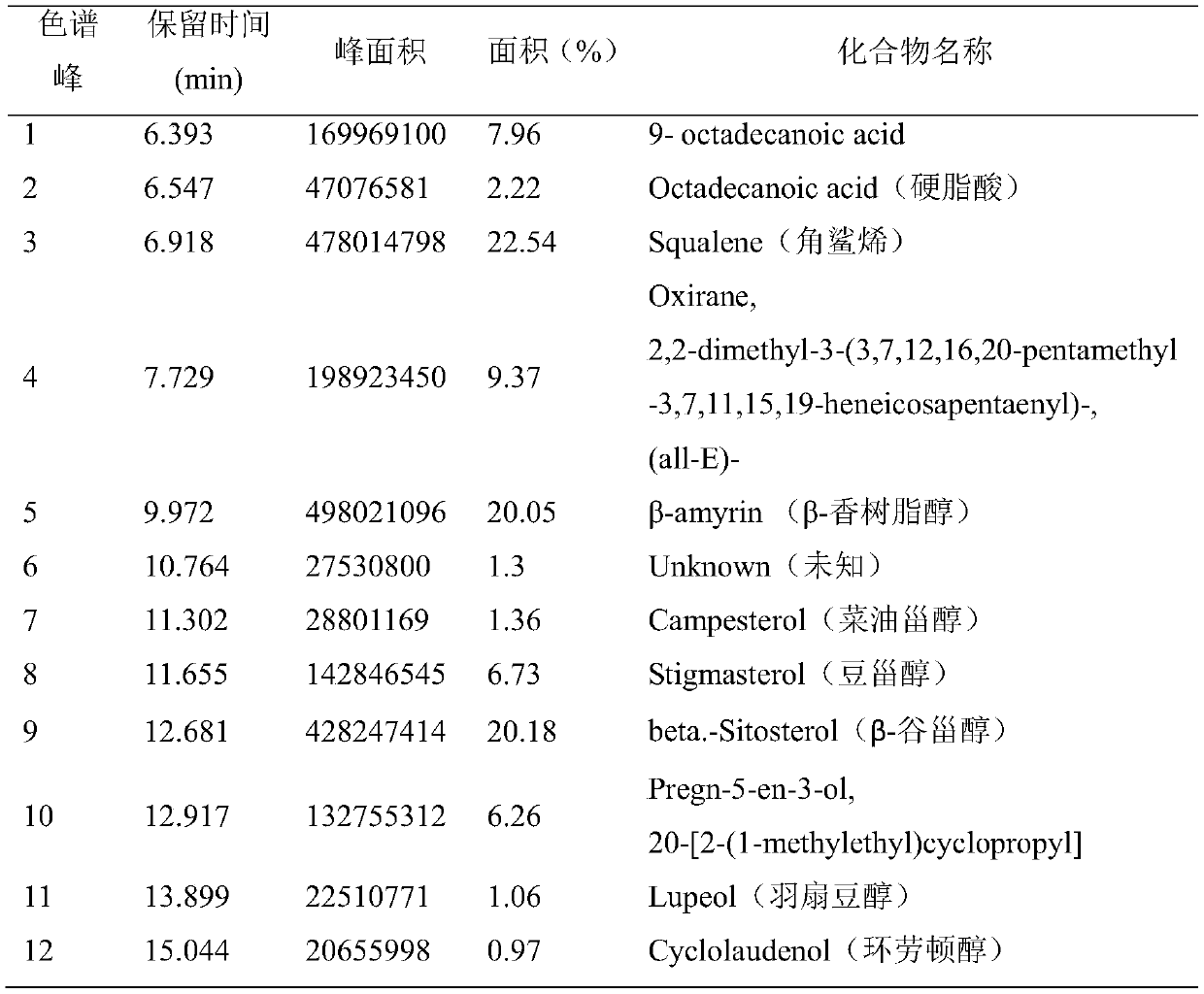
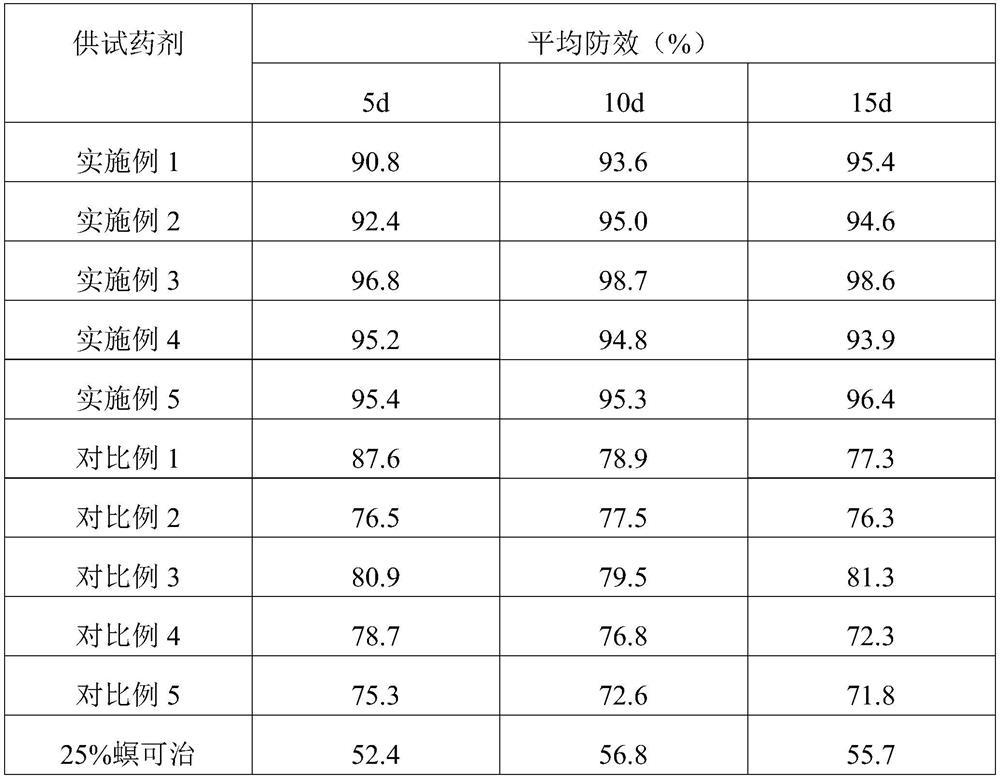
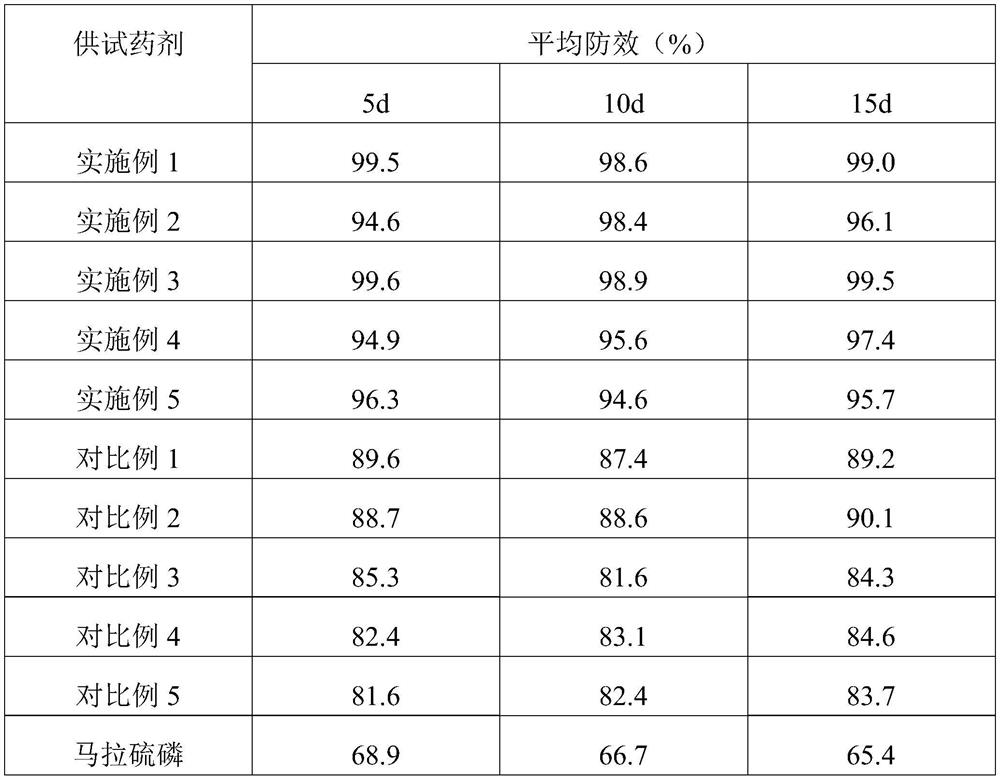
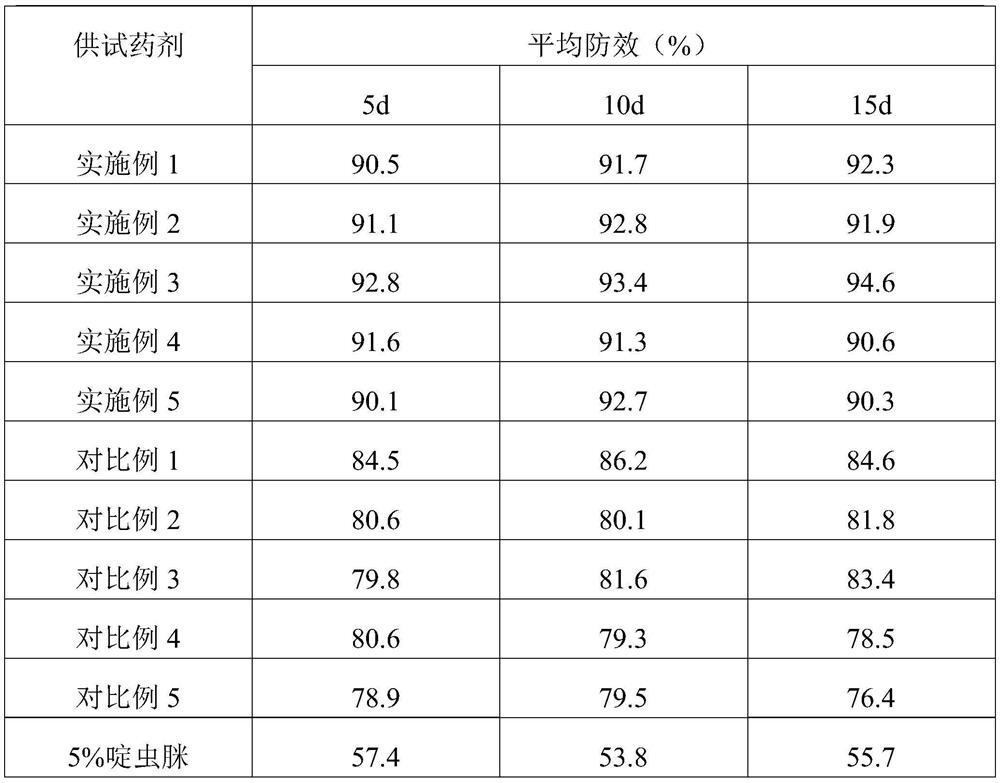
44 results about "Amyrin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
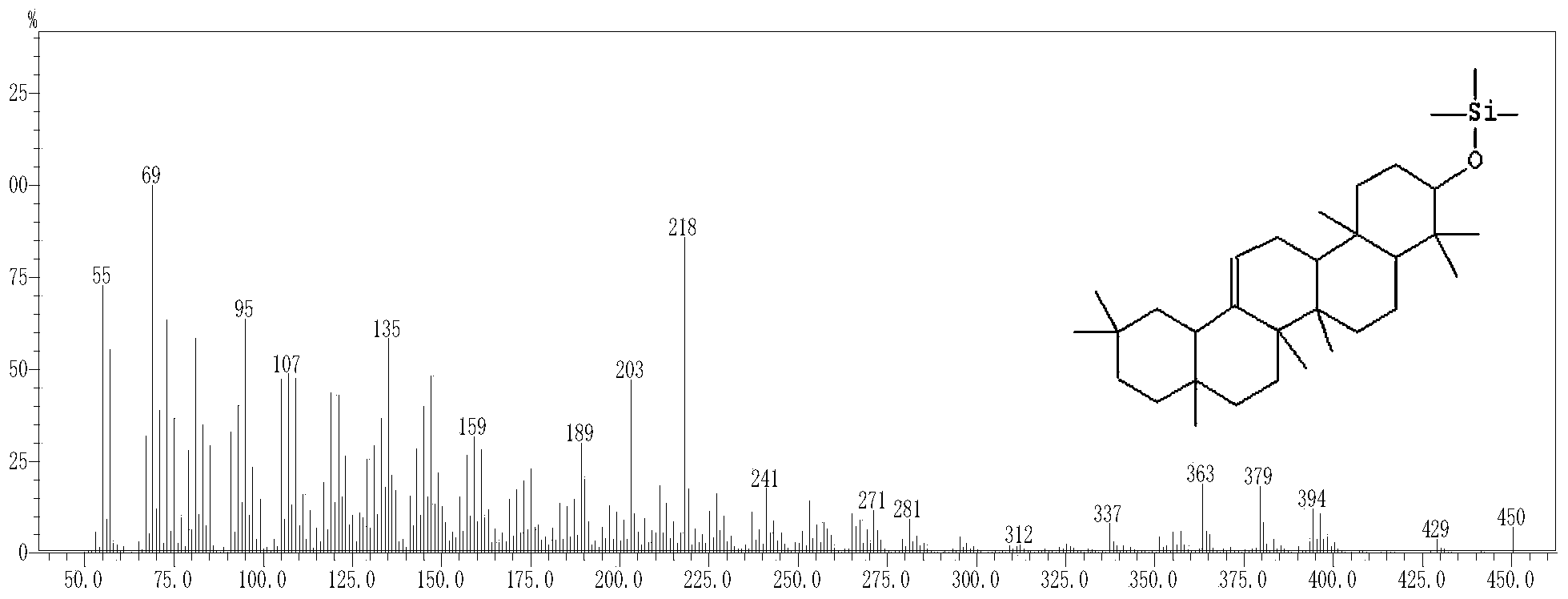
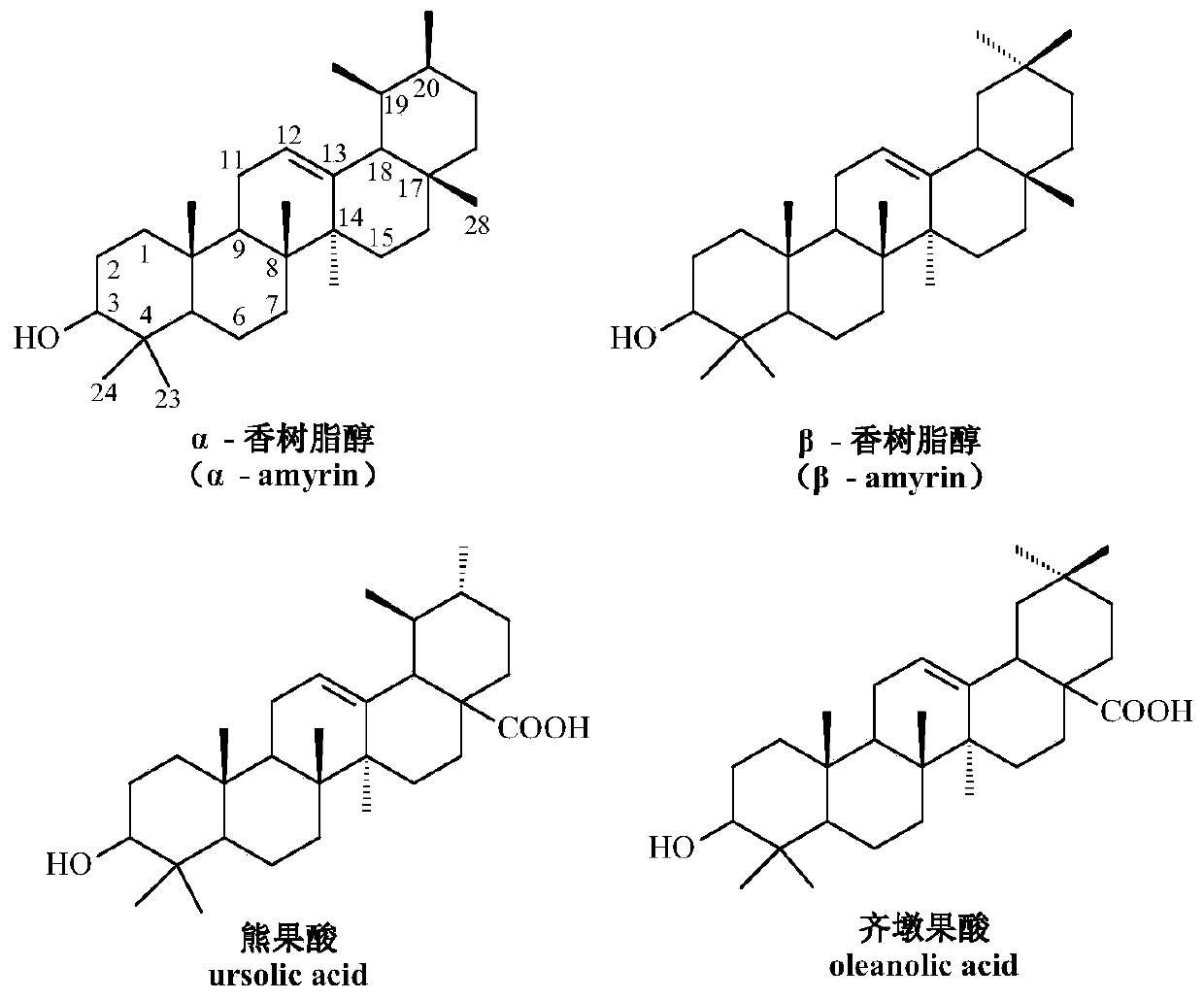
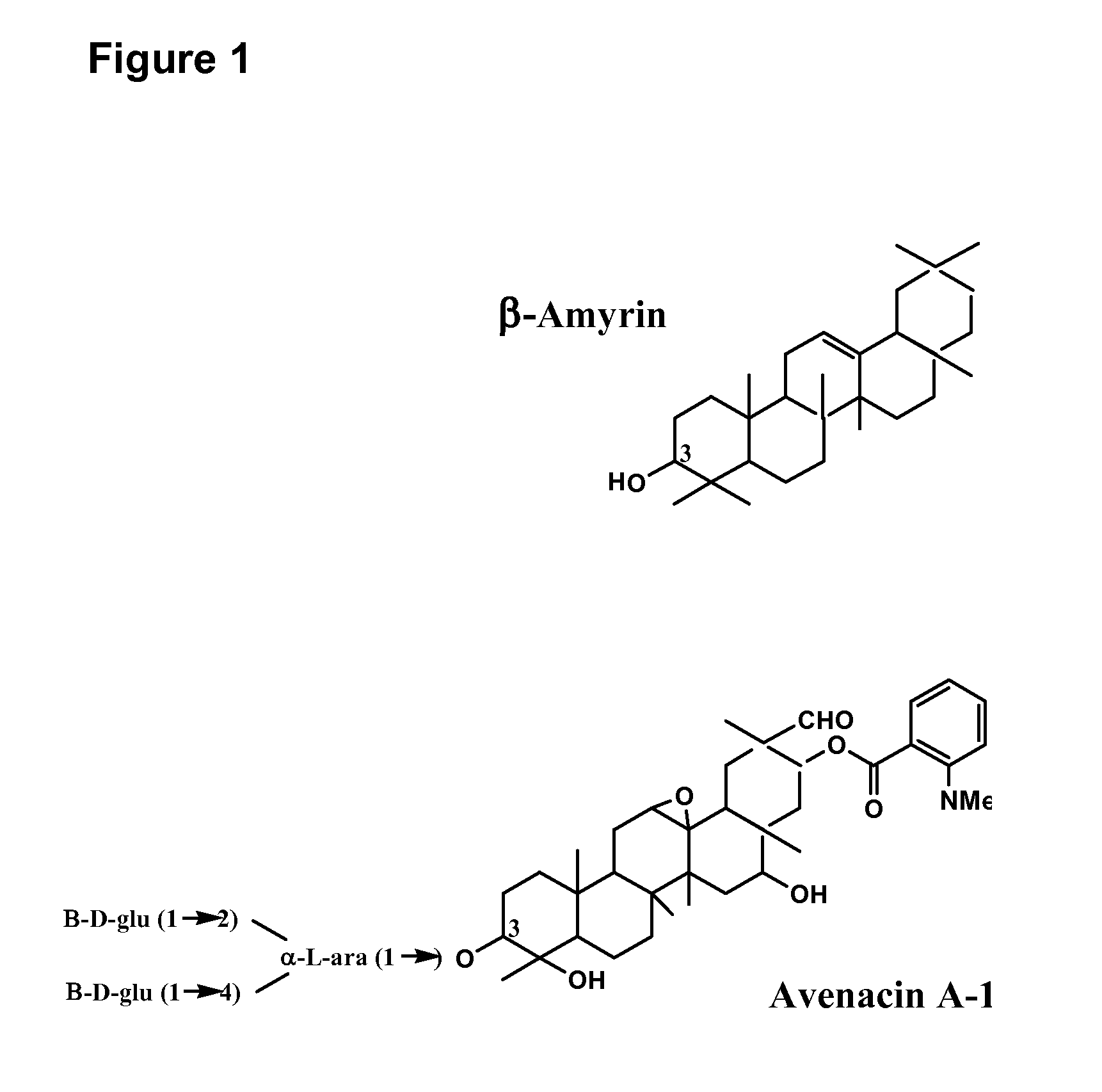
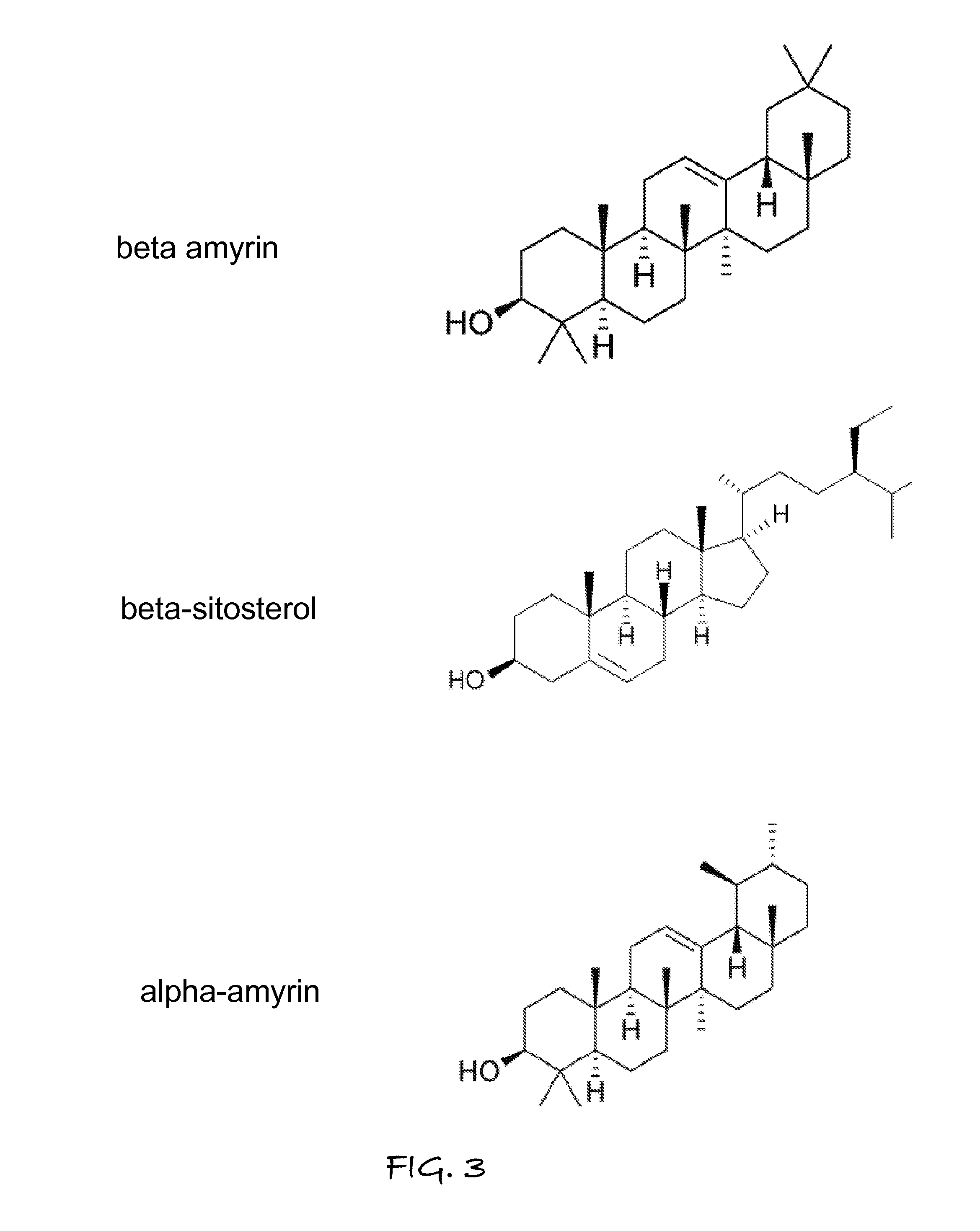
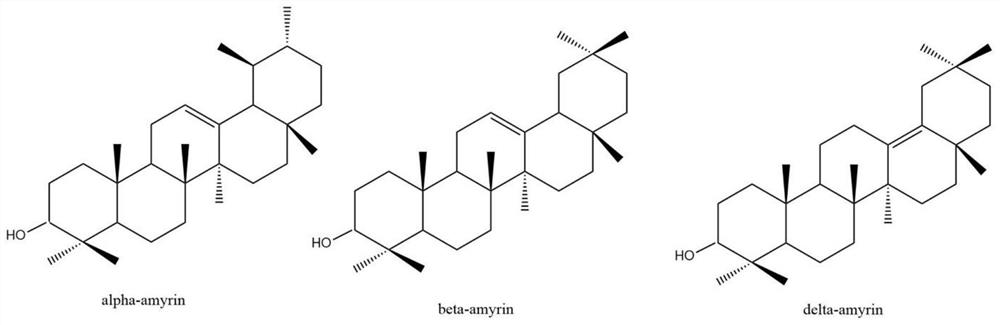
The amyrins are three closely related natural chemical compounds of the triterpene class. They are designated α-amyrin (ursane skeleton), β-amyrin (oleanane skeleton) and δ-amyrin. Each is a pentacyclic triterpenol with the chemical formula C₃₀H₅₀O. They are widely distributed in nature and have been isolated from a variety of plant sources such as epicuticular wax. In plant biosynthesis, α-amyrin is the precursor of ursolic acid and β-amyrin is the precursor of oleanolic acid. All three amyrins occur in the surface wax of tomato fruit. α-Amyrin is found in dandelion coffee.
Methods of identifying genes for the manipulation of triterpene saponins
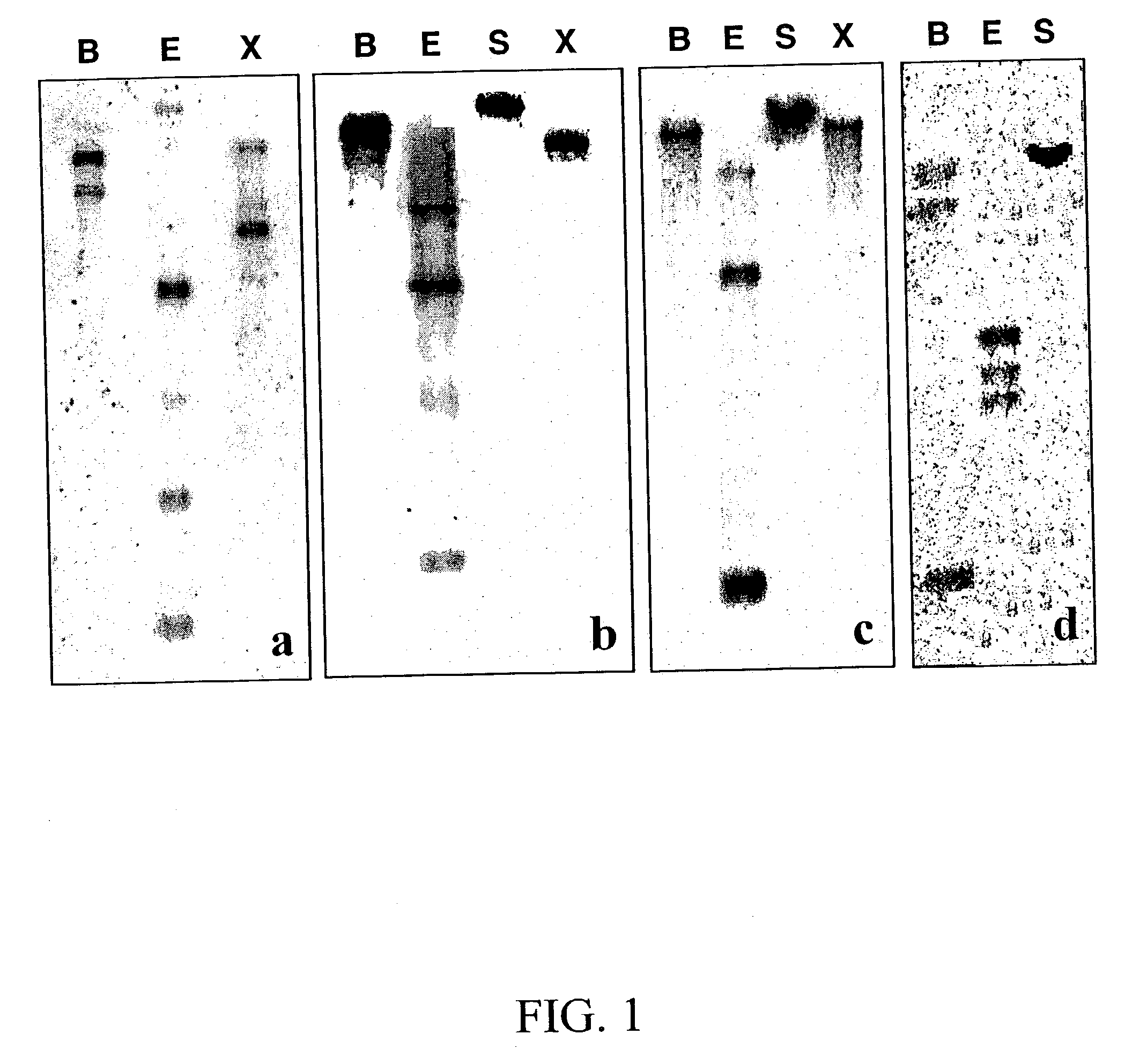
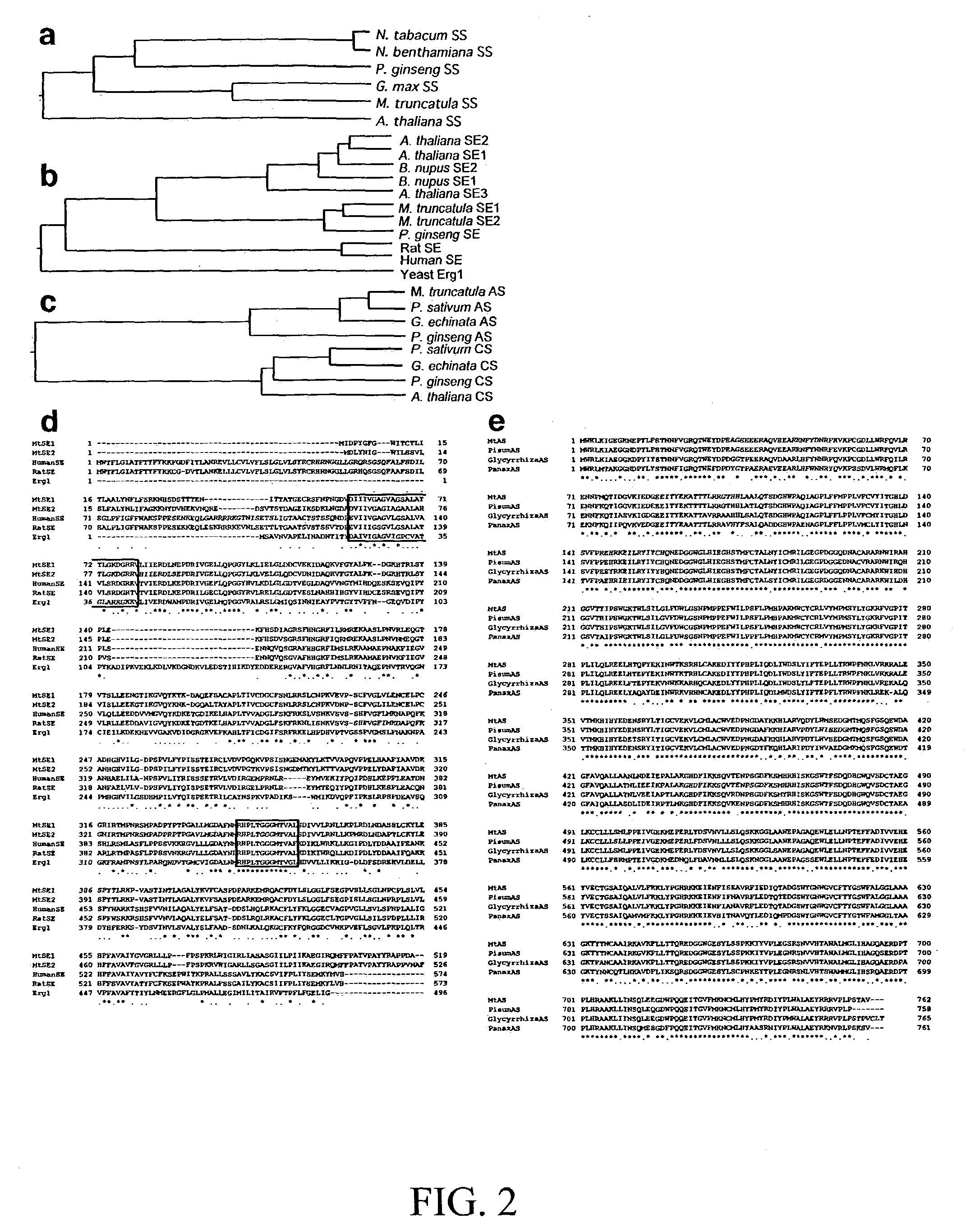
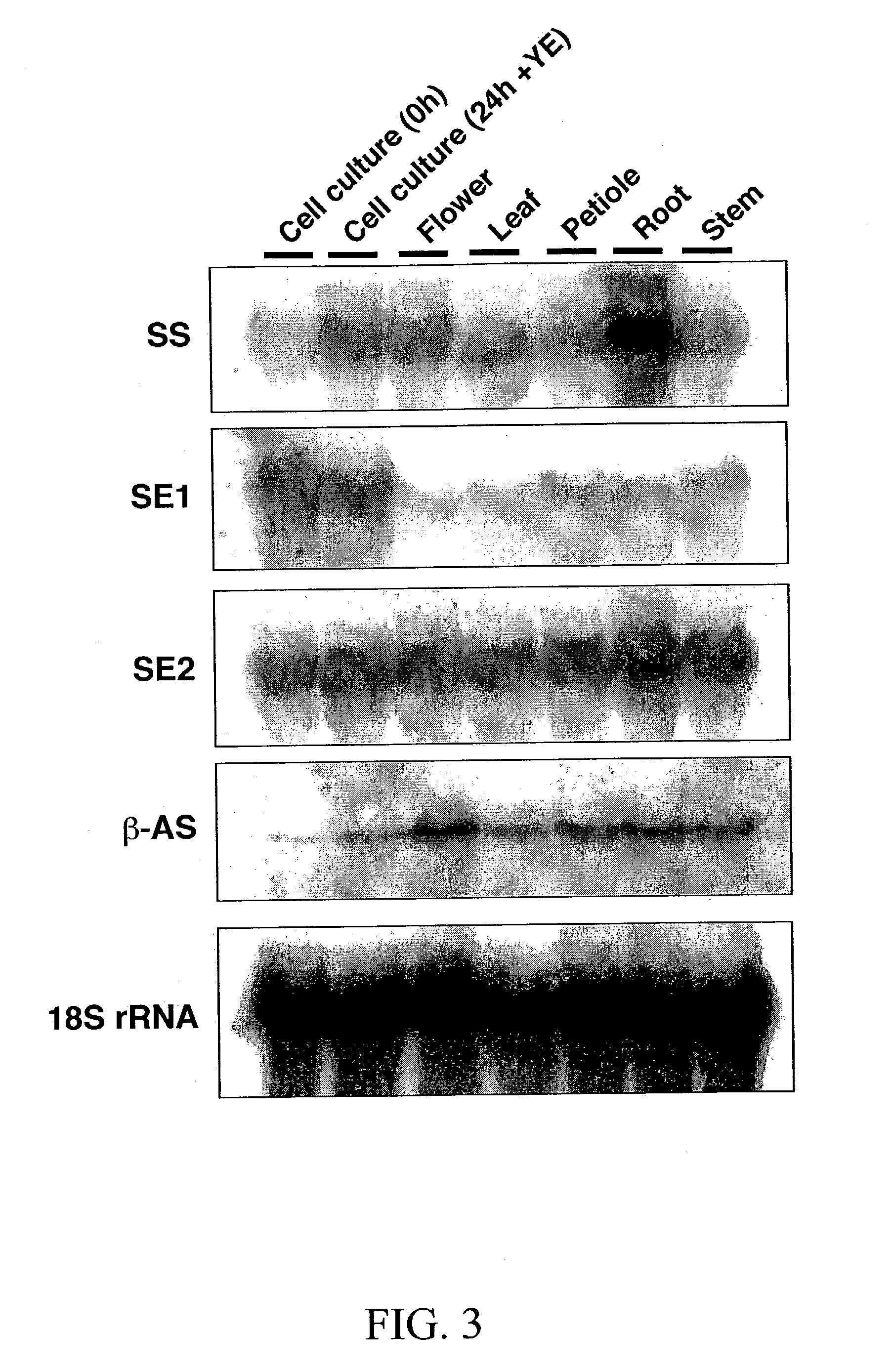
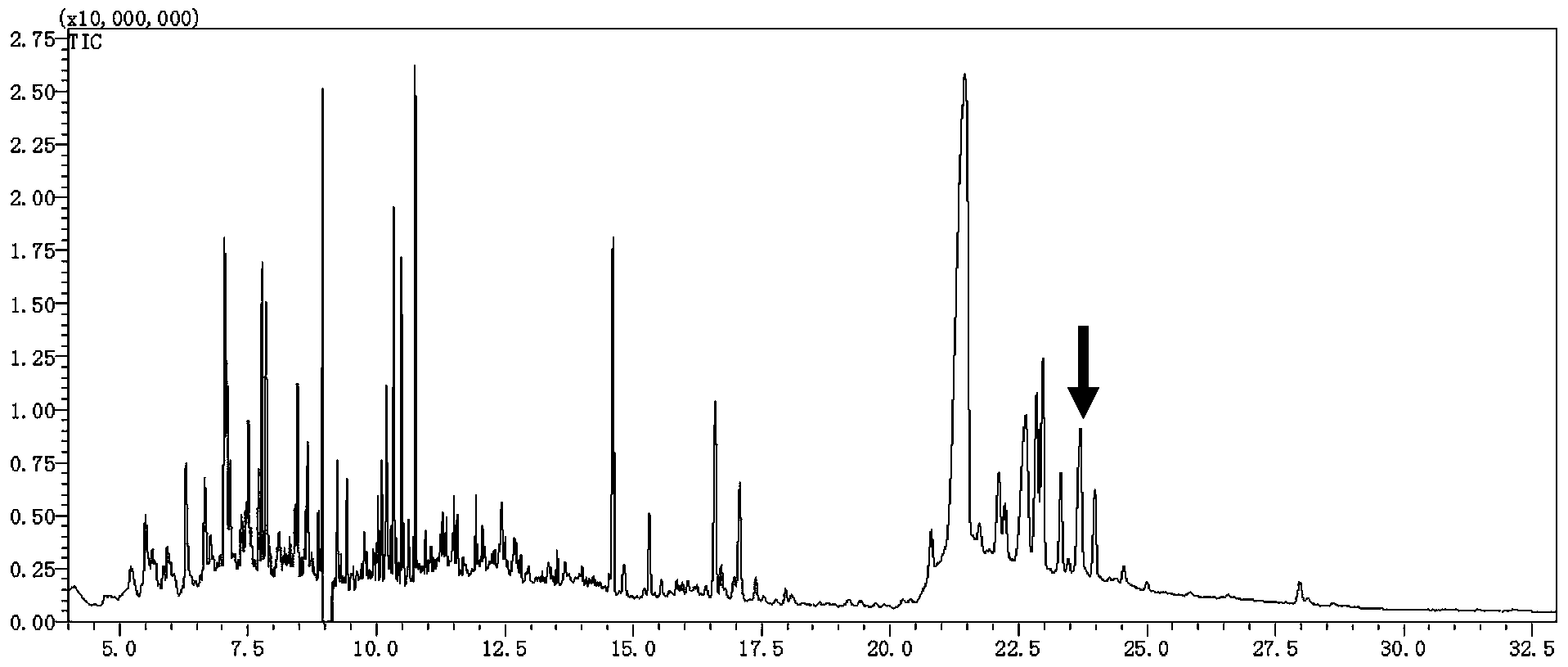
The invention provides methods for the isolation of plant genes and their regulatory sequences involved in the biosynthesis of triterpene saponins. Also provided by the invention are genes involved in the biosynthesis of triterpenes, including squalene synthase, squalene epoxidase and beta-amyrin synthase from Medicago truncatula. The identification of triterpene biosynthesis genes allows genetic modification of the content and composition of triterpene saponins in plants for crop improvement and the development of drugs, nutriceuticals and functional foods.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
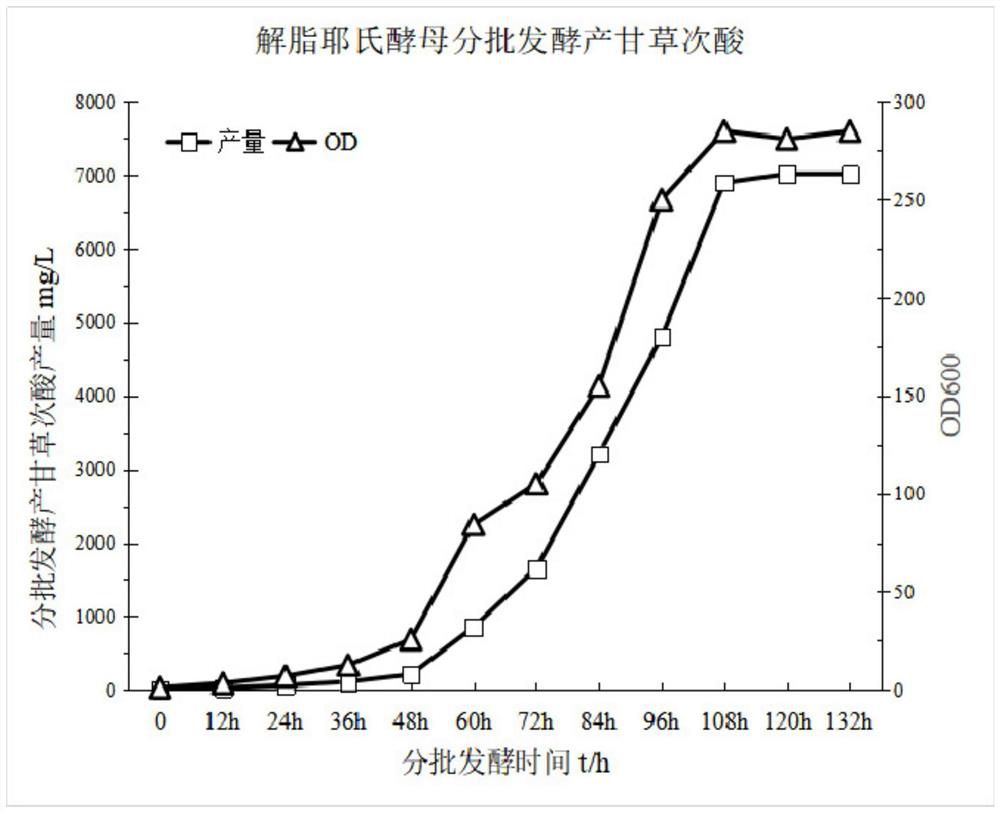
Method for producing beta-amyrin with saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium
ActiveCN103509726AEfficient assemblyGene manipulation is easyFungiMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisEnzyme Gene
The invention provides a method for producing beta-amyrin with a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium, and belongs to the field of biochemical engineering. According to the method, a 2,3-oxidized squalene monooxygenase gene is cloned from candida albicans, a glycyrrhiza glabra beta-amyrin synthase gene subjected to codon optimization is chemically synthesized, a gene expression cassette is constructed by utilizing a saccharomyces cerevisiae constitutive promoter, the gene expression cassette and a plasmid after double digestion jointly invert saccharomyces cerevisiae, and assembly of the gene expression cassette and the plasmid is achieved by a homologous recombination function of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that 2,3-oxidized squalene monooxygenase is reinforced, and beta-amyrin synthase is led in. Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium metabolizable glucose directly synthesizes beta-amyrin, and synthesis of beta-amyrin is coupled with growth of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that artificial synthesis of the saccharomyces cerevisiae of a plant secondary metabolism product, namely beta-amyrin is achieved. The method requires no effect agent induction, is simple in technology, and can be used for fermenting and producing beta-amyrin.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
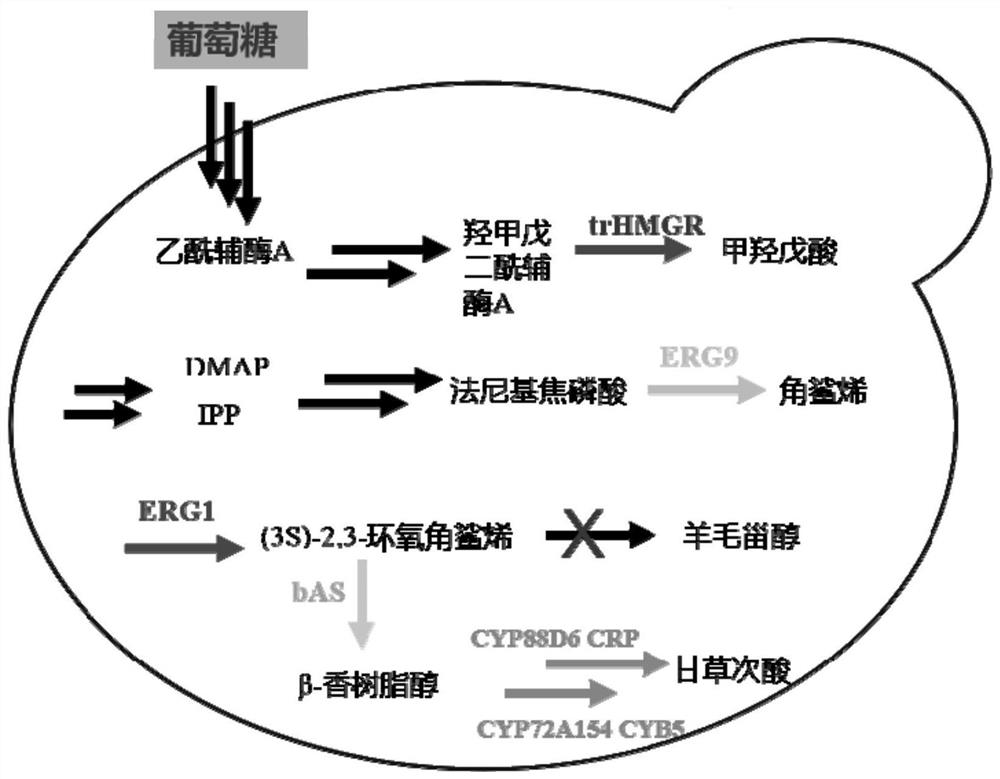
Building method of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strains capable of synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid
InactiveCN106987533ARealize artificial synthesisReduced stabilityFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering and particularly relates to a building method of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strains capable of synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid. The building method includes: beta-amyrin synthase gene GgbAS from Glycyrrhiza glabra, cytochrome P450 oxidases CYP88D6 and CYP72A154, cytochrome P450 oxidoreductases CPR1 and CPR2 from Arabidopsis thaliana are used to build gene expression cassettes, the gene expression cassettes are co-transformed in saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strains with complete glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthetic pathways are assembled and formed by the homologous recombination ability of the saccharomyces cerevisiae. By the method, the complete glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthetic pathways are introduced in the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strains, the glycyrrhetinic acid can be produced through fermentation, and artificial synthesizing of the glycyrrhetinic acid in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is achieved.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
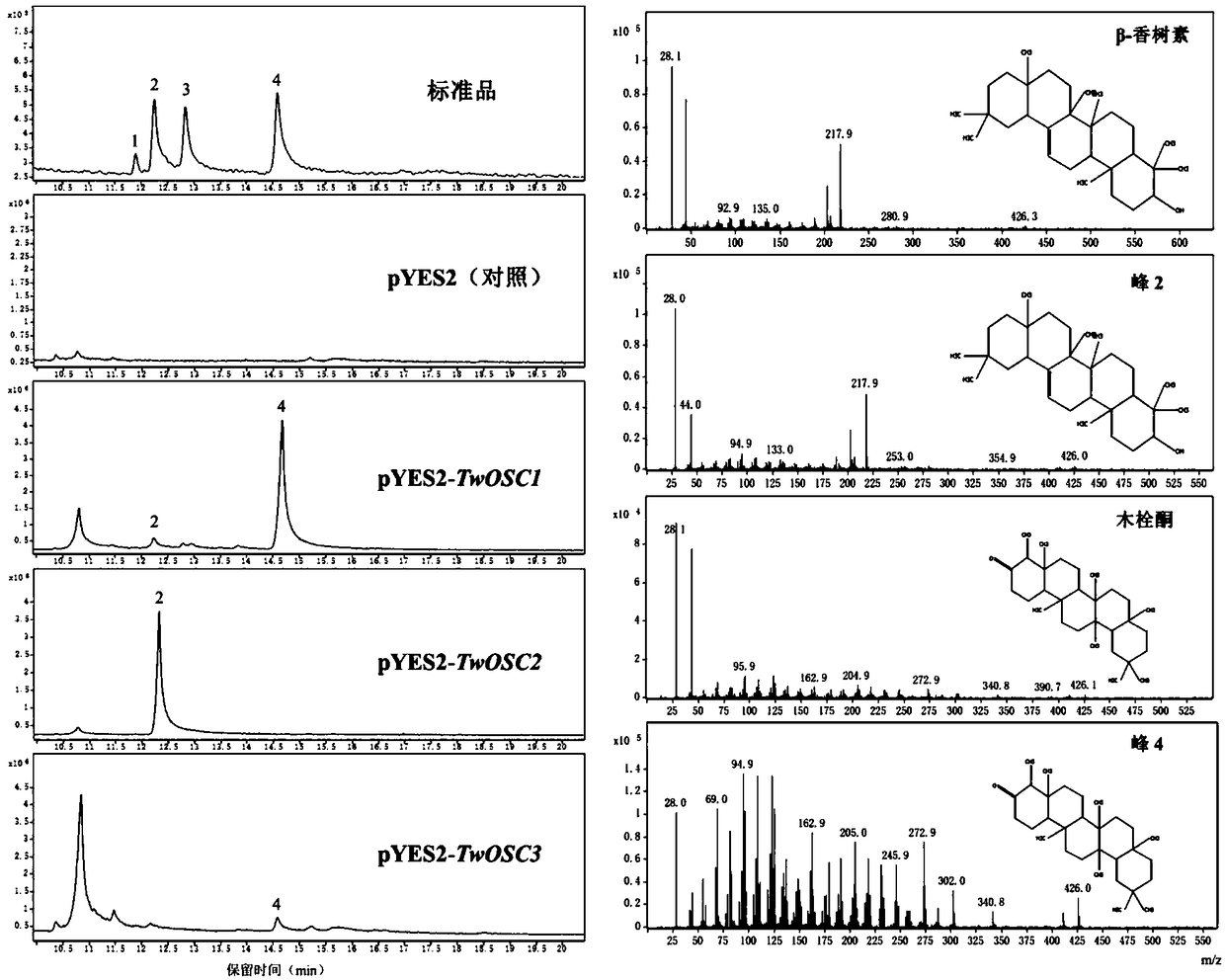
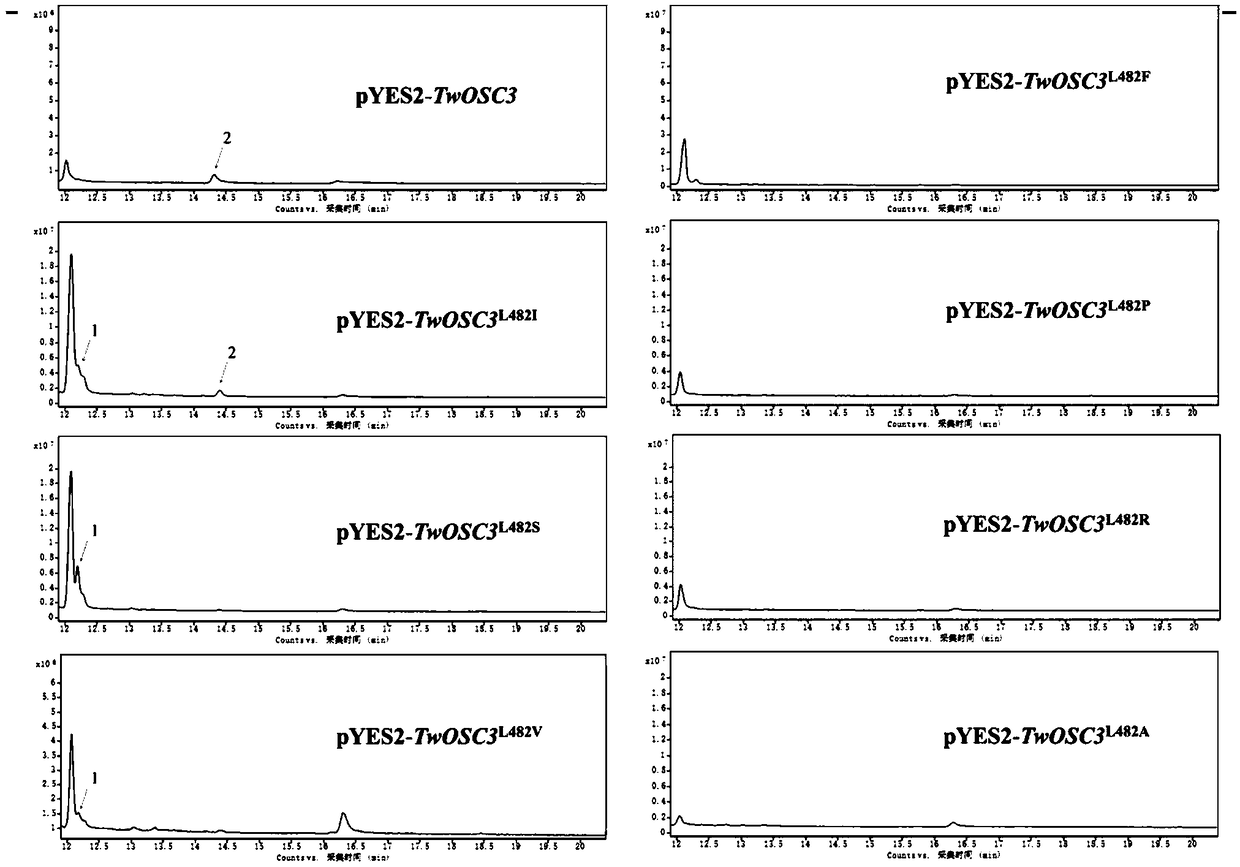
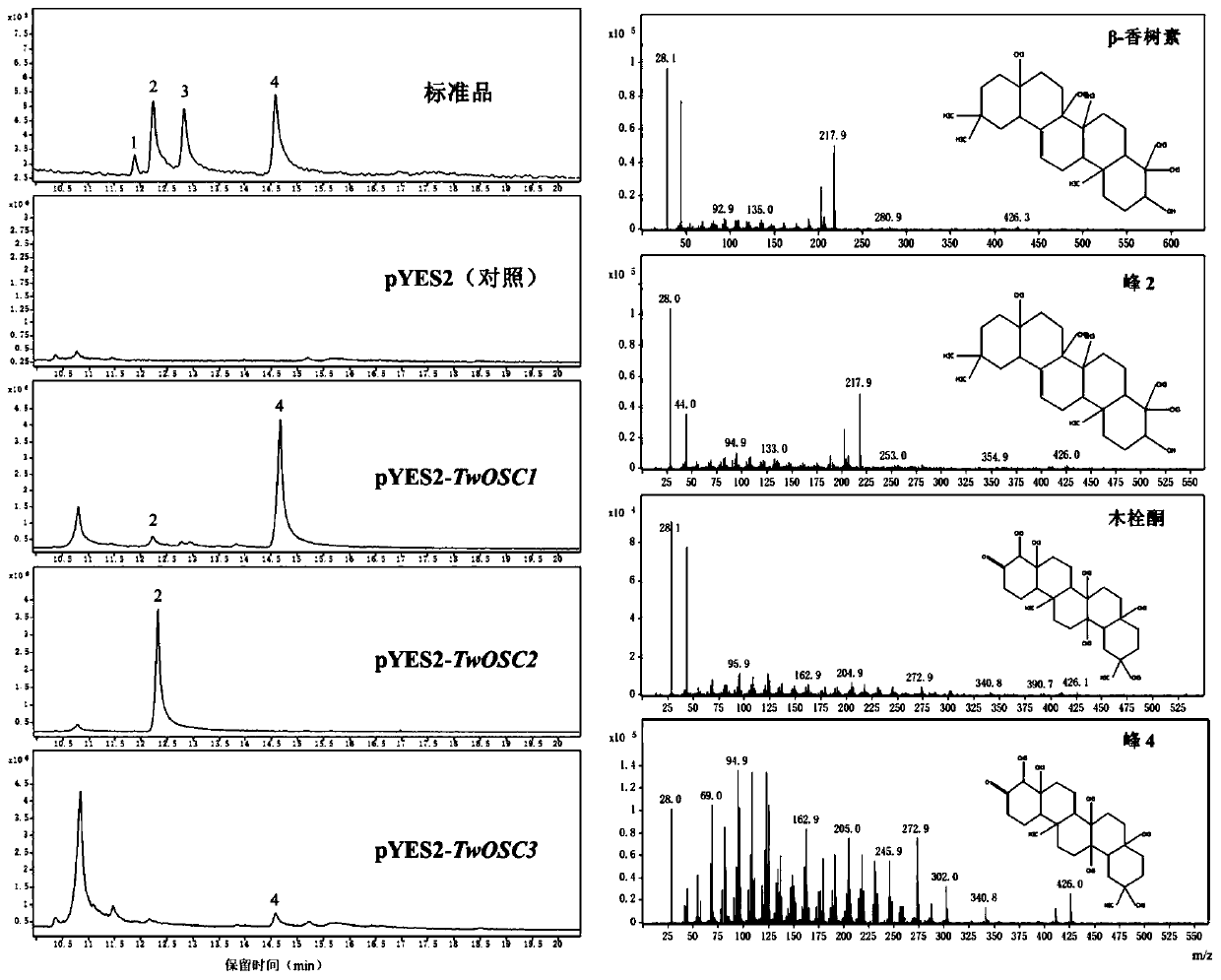
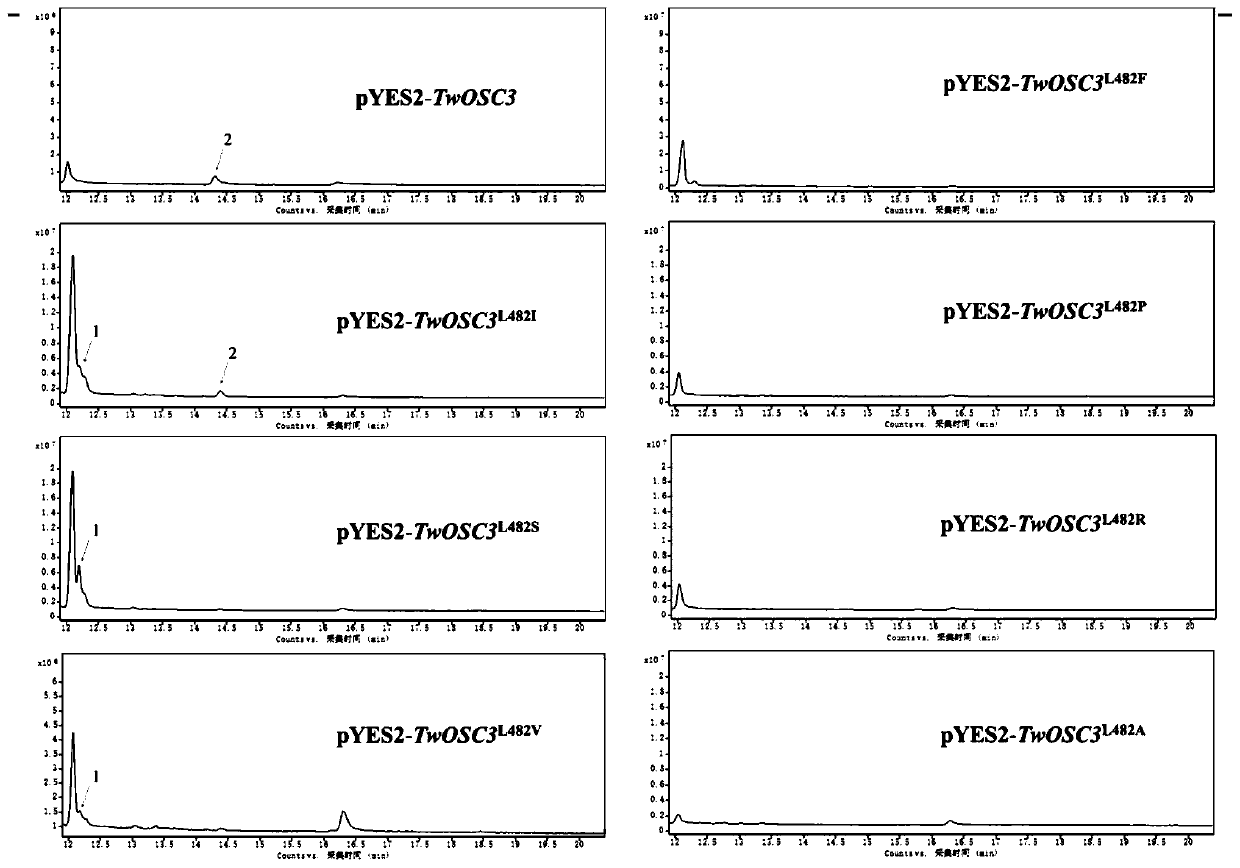
Triterpene synthase of tripterygium wilfordii TwOSC3, encoding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a triterpene synthase of tripterygium wilfordii TwOSC3 protein and an encoding gene thereof. A recombinant expression vector with a Twosc3 gene is constructed by cloning cDNAof the Twosc3 gene onto a eukaryotic expression vector pYES2, and then the recombinant expression vector is shifted to yeast expression host bacteria, so as to acquire friedelin. A mutation research result shows that amino acid 482 encoded by the Twosc3 gene is a key site, and the yield of friedelin or amyrin can be increased or reduced; a gene gun mediated interference experiment shows that the interference of the Twosc3 gene has an obvious inhibiting effect on the synthesis of celastrol in tripterygium wilfordii; the TwOSC3 protein and the encoding gene thereof provided by the invention canbe used for biosynthesizing plant triterpenoids and cultivating high-quality tripterygium wilfordii.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Process for simultaneously abstracting essential oil, chromocor and triterpenes components from agastache
InactiveCN101285021AAchieve separationHigh extraction rateEssential-oils/perfumesSteroidsHerpes zoster virusEssence oil
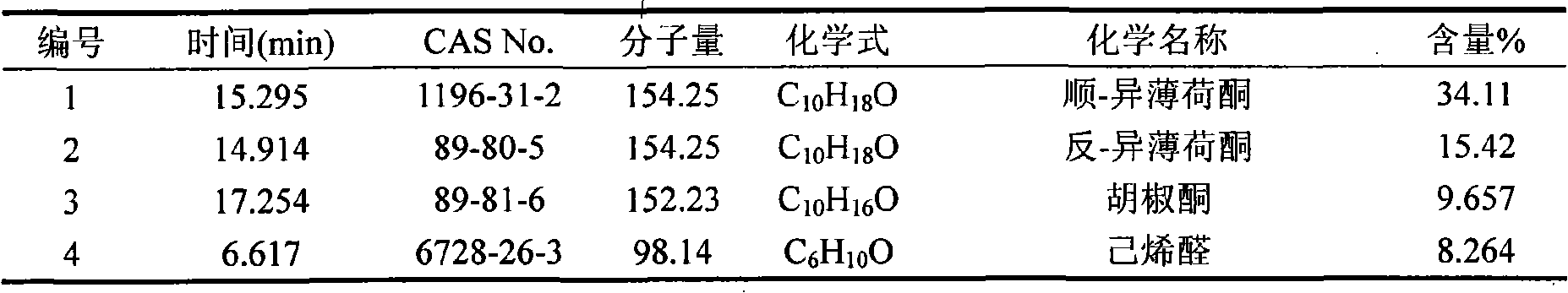
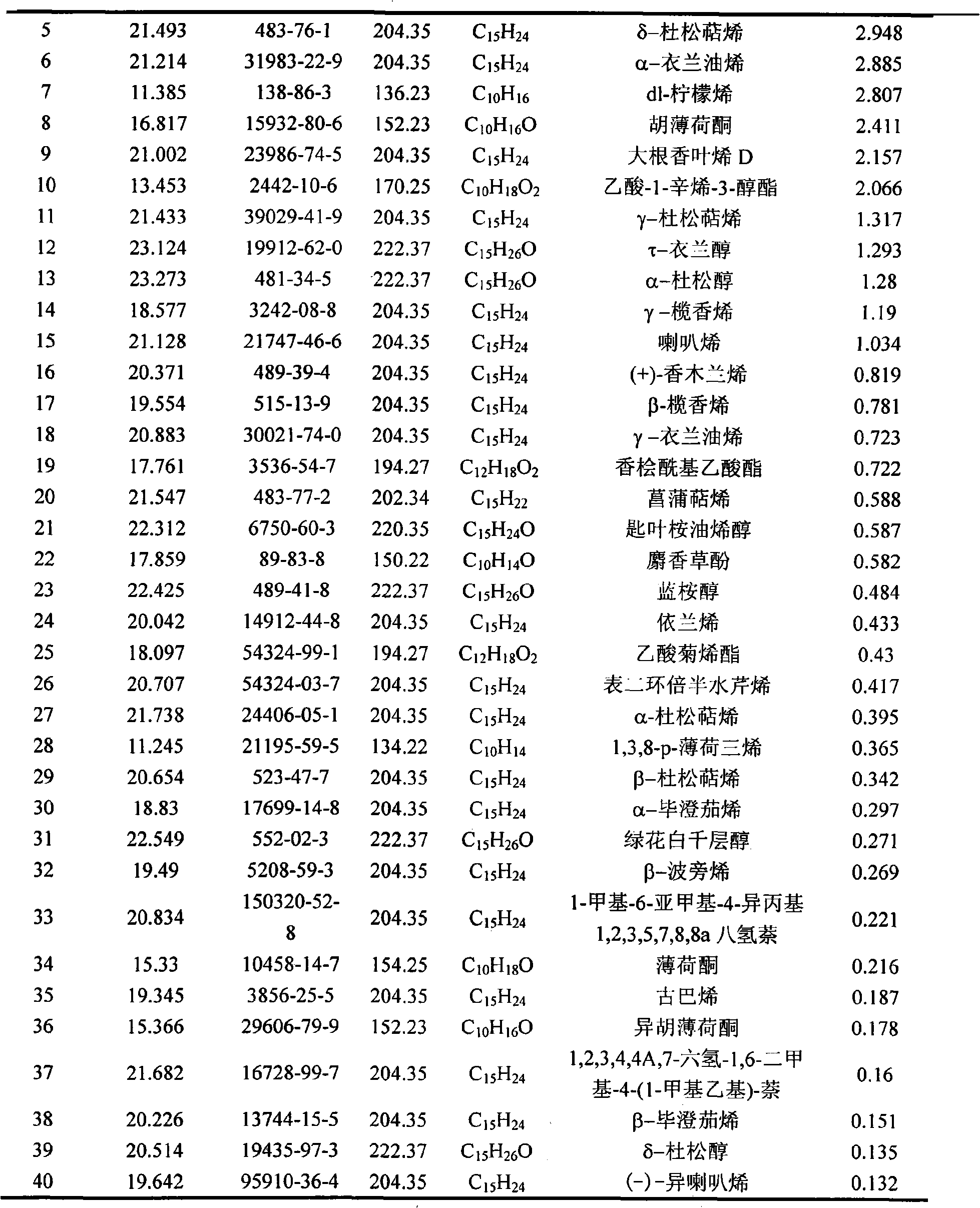
The invention belongs to natural products separating and extracting technical field, particularly relating to a process for simultaneously extracting essential oil, flavone and triterpene out of wrinkled giant hyssop. The invention provides a novel separating and extracting process, which can simultaneously separate and extract essential oil, flavone and triterpene by taking wrinkled giant hyssop as raw materials; the used raw materials can be wrinkled giant hyssop as well as cablin pacholi, fresh or dried herbs as well as fresh or dried leaves, stems or other parts. When fresh wrinkled giant hyssop leaves are used as the raw materials, the essential oil thereof comprises more than 40 volatile components such as cis form - isomenthone, anti form - isomenthone piperitone, hexenoic aldehyde, delta-cadinene, cadinol, alpha-muurolene, limonene and pulegone, wherein main volatile components are the cis form - isomenthone and the anti form- isomenthone, contents of which are 34.11 percent and 15.42 percent respectively; the total flavone comprises flavonoids such as acacia substance, tilianin, linarin, agastachoside, isoagastachoside, agastachin, apigenin, apigenin-7- glucoside, 6-methoxyl group apigenin, luteolin and luteolin-7- glucoside, etc., wherein main flavone components are the agastachoside and the isoagastachoside , contents of which are 25.8 percent and 8.21 percent respectively; the triterpene materials comprises triterpene compounds such as cralaegolic acid, oleanolic acid, 3-acetyl oleanolic aldehvde, 3- acetyl oleanolic acid, alpha-amyrin, beta- amyrin, campesterol, campestanol, ursolic acid, erythrodiol, erythrodiol-3-acetic ester, wherein the main triterpene component is the cralaegolic acid , the content of which is 34.6 percent. The components have wide biological activities and a plurality of effects such as liver protection, anti-tumor, anti-HIV-1, anti-proteinase activity of HIV-1, anti-herpes zoster virus and immunity improvement, etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of beta-amyrin and oleanolic acid and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of beta-amyrin and oleanolic acid and a construction method. The construction method comprises the step of introducing an optimized beta-amyrin synthase coding gene, an optimized oleanolic acid synthase coding gene and an optimized cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 coding gene into Yarrowia lipolytica, thereby obtaininga recombinant strain 2. Proven by experiments, the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica capable of yielding the beta-amyrin and the oleanolic acid is obtained through a homologous recombination method, and thus, the yield of the beta-amyrin and the oleanolic acid is increased; and the method disclosed by the invention provides a foundation for artificial synthesis of the beta-amyrin and the oleanolicacid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for the preparation of lariciresinol cyclolariciresinol and secoisolariciresinol
A method for the preparation of lariciresinol, cyclolariciresinol or secoisolariciresinol, which method includes the steps of a) reducing hydroxymatairesinol to give 7-hydroxy-secoisolariciresinol, and b) subjecting the 7-hydroxy-secoisolariciresinol obtained in step a) to i) cyclization to give lariciresinol, or ii) cyclization to give cyclolariciresinol, or iii) catalytic hydrogenolysis to give secoisolariciresinol
Owner:HORMOS MEDICAL OY LTD
Triterpene synthase of tripterygium wilfordii TwOSC1, encoding gene and application thereof
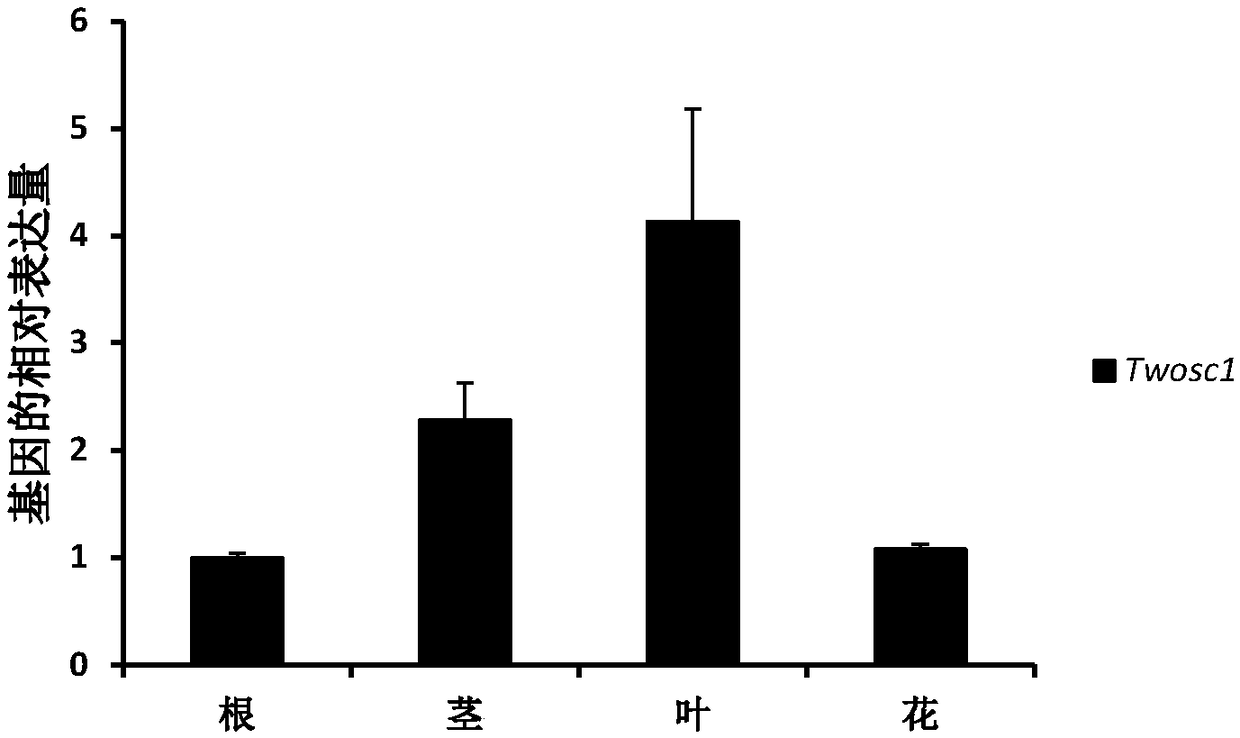
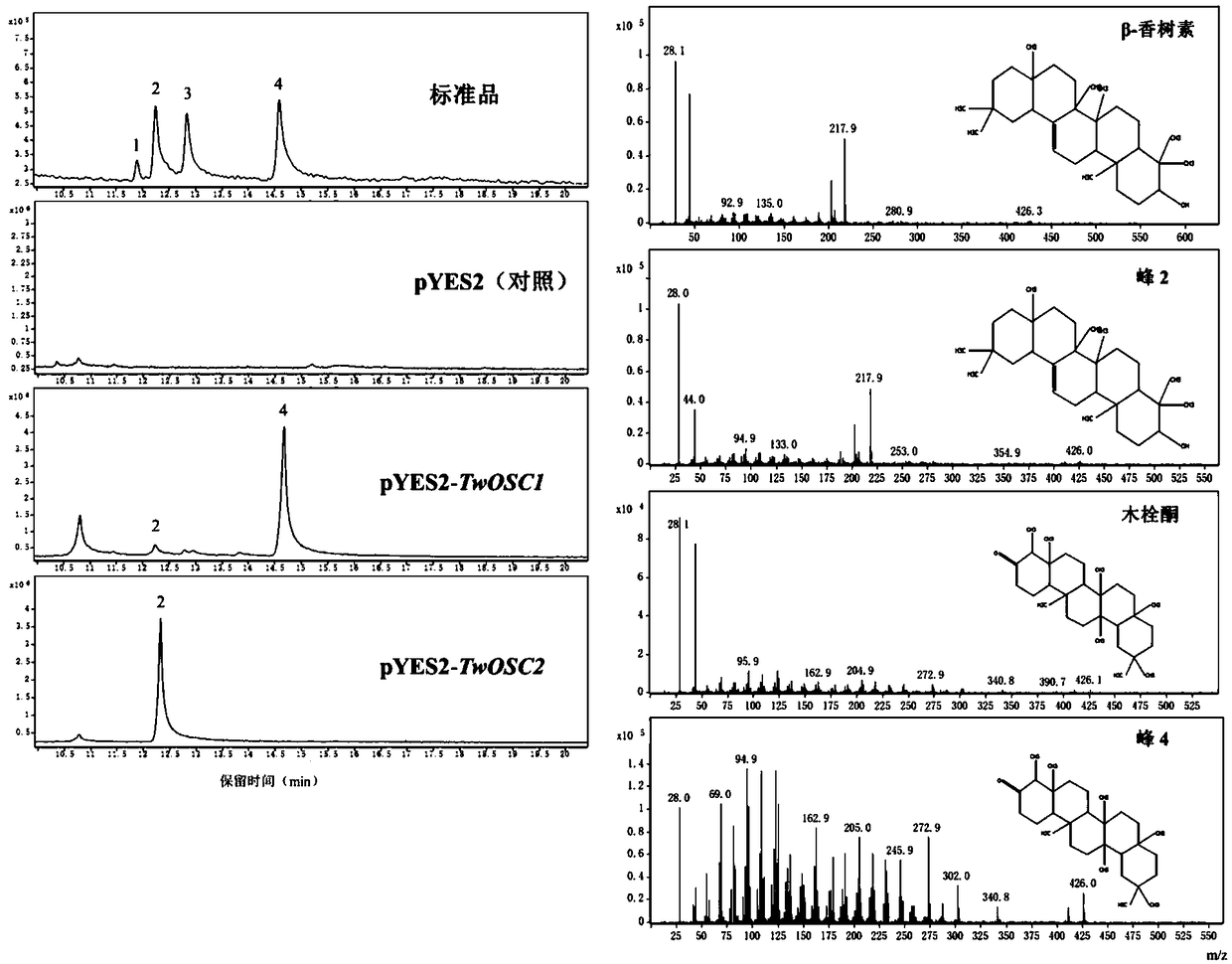
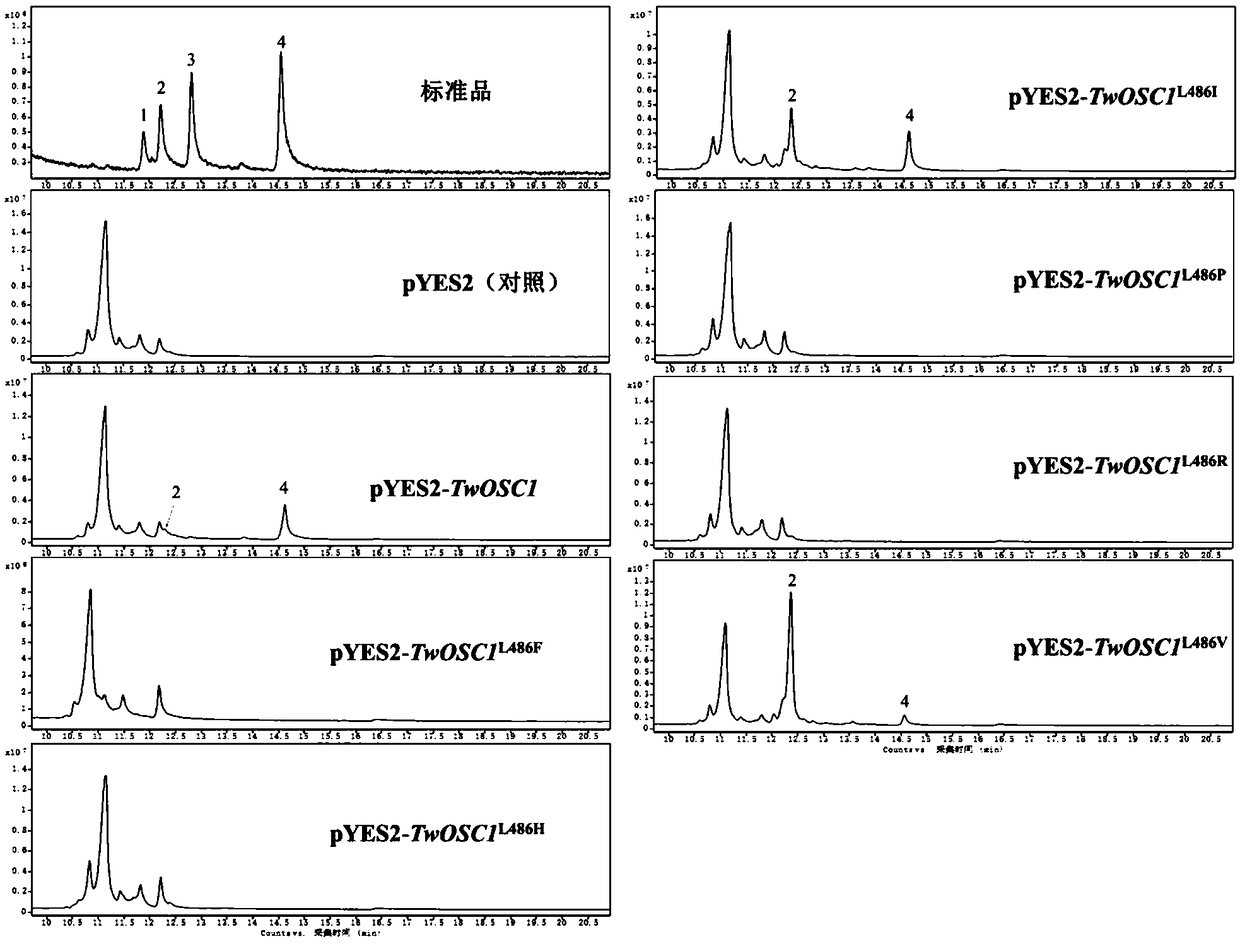
The invention relates to a triterpene synthase of tripterygium wilfordii TwOSC1 protein and an encoding gene thereof. A recombinant expression vector with a Twosc1 gene is constructed by cloning cDNAof the Twosc1 gene onto a eukaryotic expression vector pYES2, and then the recombinant expression vector is shifted to yeast expression host bacteria, so as to acquire some triterpenoids, such as friedelin and amyrin. A mutation research result shows that amino acids 486 and 502 encoded by the Twosc1 gene are key sites, and the yield of friedelin or amyrin can be increased or reduced; a gene gun mediated interference experiment shows that the interference of the Twosc1 gene has an obvious inhibiting effect on the synthesis of celastrol in the tripterygium wilfordii; through further experiments, a gene gun mediated overexpression experiment shows that the overexpression of the Twosc1 gene can increase the yield of the celastrol in tripterygium wilfordii suspension cells; the TwOSC1 proteinand the encoding gene thereof provided by the invention can be used for biosynthesizing plant triterpenoids and cultivating high-quality tripterygium wilfordii.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae
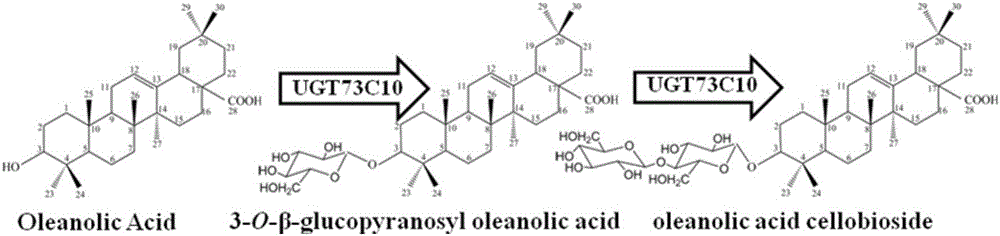
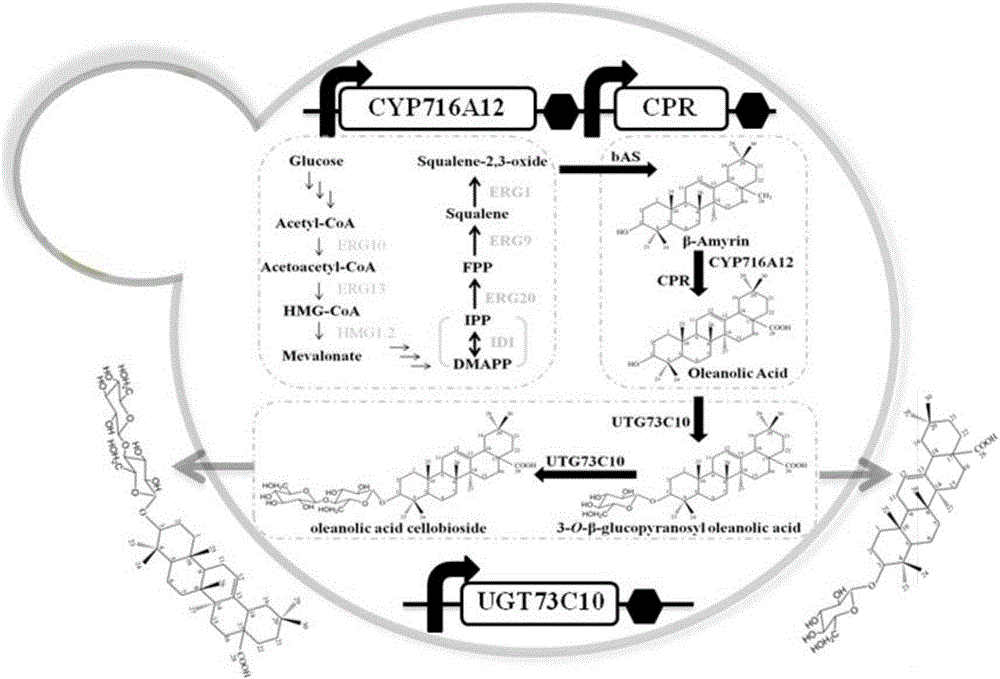
ActiveCN106318966AIncrease productionThe fermentation process is simpleFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention provides a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a codon optimized P450 cytochrome monooxygenase gene, a cytochrome reductase gene and a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene by a chemical method; constructing corresponding gene expression boxes by combining a saccharomyces cerevisiae promoter with a terminator; constructing gene expression vectors by a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) klenow fragment assembling method, and importing the gene expression vectors into the saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of producing beta-amyrin. Direct synthesis of the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid serving as plant secondary metabolites in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized for the first time; in addition, two synthesized compounds can span cytomembrane of the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and a downstream separation and extraction process is simplified, so that a new idea is provided for producing pentacyclic triterpene compounds with low water solubility and difficulty in spanning membranes by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method is simple in process and can be used for producing the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid by fermenting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
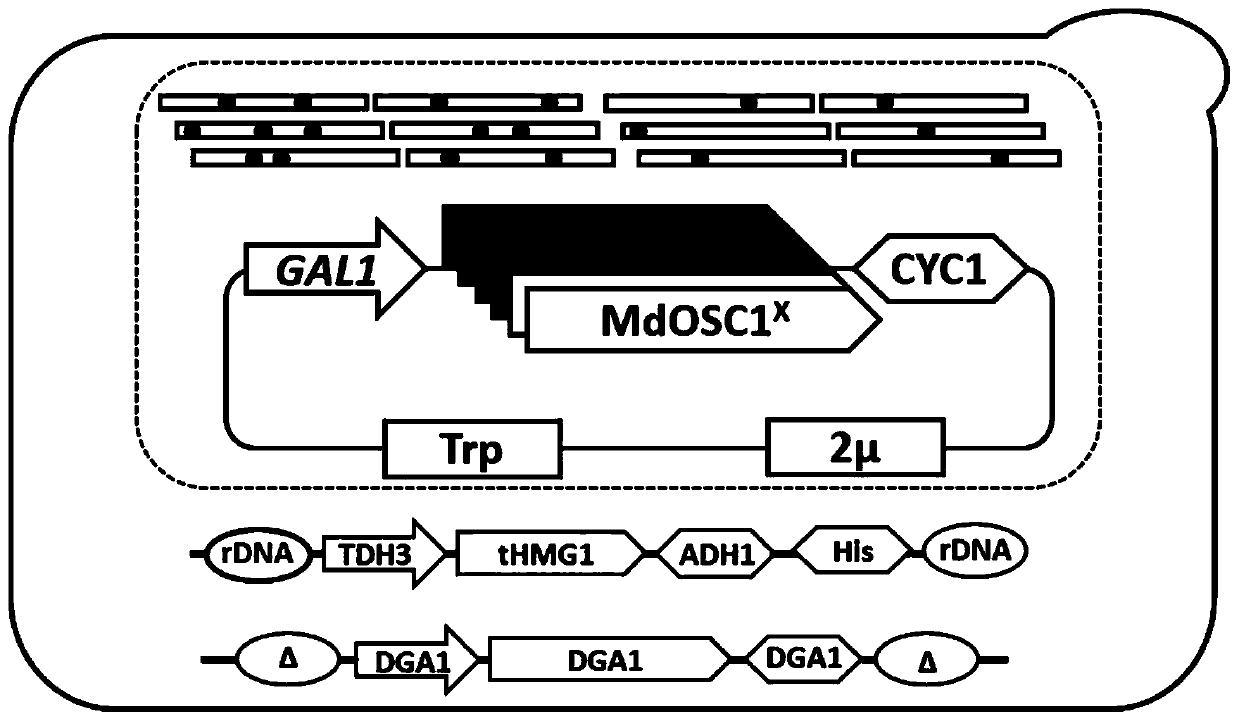
Saccharomyces cerevisiae construction method for efficiently synthesizing alpha-amyrin
The invention provides a method for constructing Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficiently synthesizing alpha-amyrin, which belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out semi-rational design on alpha-amyrin synthase derived from Malus domestica, and carrying out saturated mutation and iterative mutation on key amino acid residue sites to obtain a series of mutants including an MdOSC1 mutant with the highest catalytic activity; then performing overexpression on key genes in an alpha-amyrin synthesis route, and meanwhile, performing overexpressionon diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGA1) so that the storage capacity of alpha-amyrin in saccharomyces cerevisiae cells is improved. The yield of the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain capable of producing alpha-amyrin at high yield constructed by the method reaches 213.79 mg / L, efficient production of alpha-amyrin in saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized, and the engineering strain has important significance in production.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid and a construction method. The construction method comprises steps as follows: an optimized mixed amyrin synthase encoded gene, an optimized ursolic acid synthase encoded gene and an optimized cytochrome-NADPH-reductase encoded gene are imported into yarrowia lipolytica, and recombinant bacteria 2 are obtained; and experiments prove that the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for producing alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid is obtained with a homologous recombination method, so that theyield of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid is improved. the method provides a basis for artificial synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
CYP450 gene catalyzing oxidation of C-28 site of amyrin and coding product and application of CYP450 gene
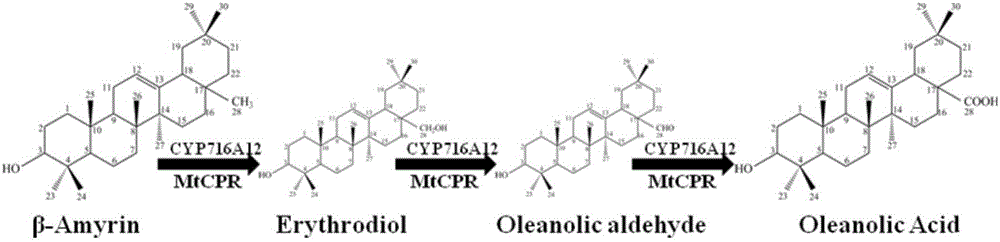
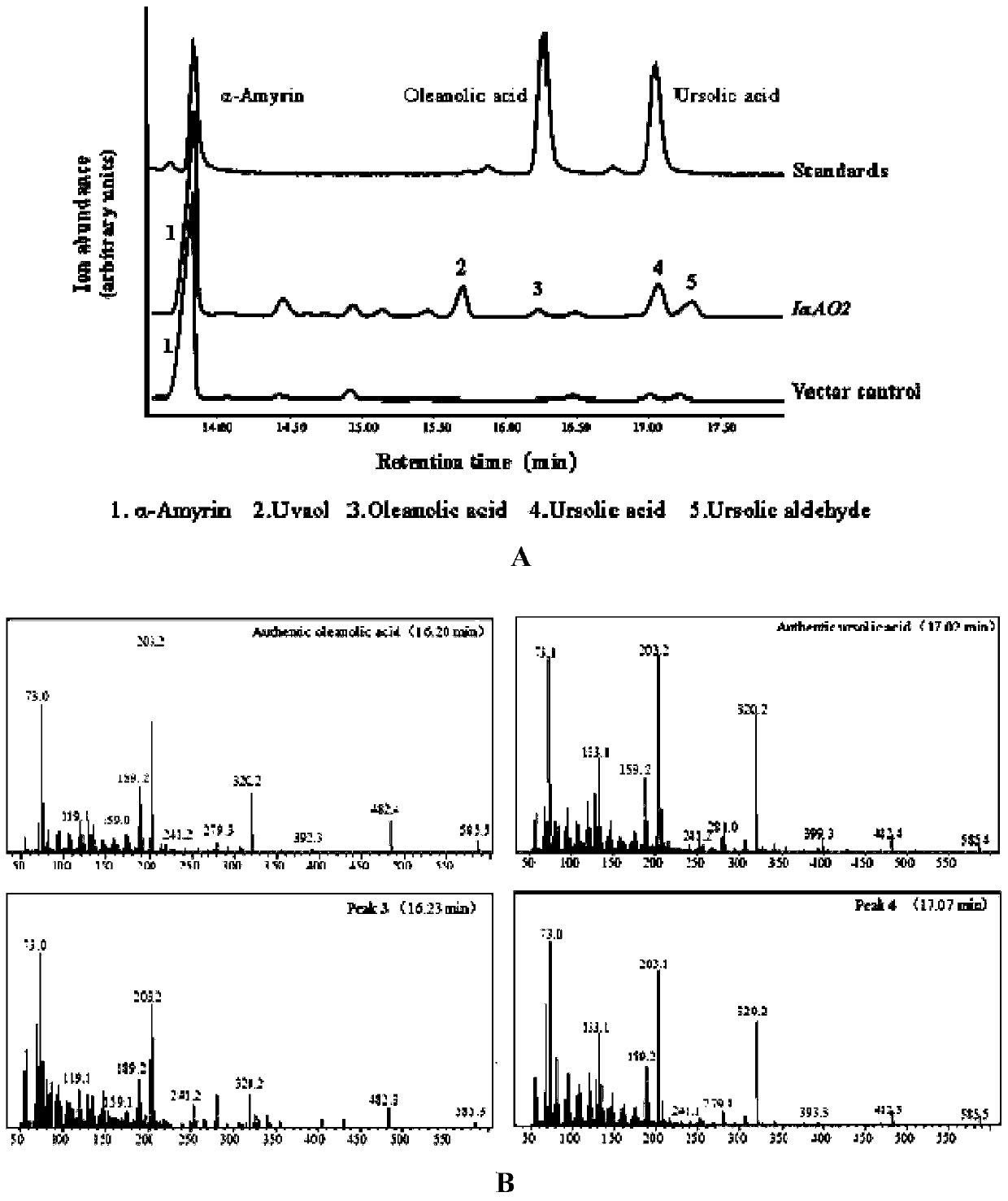
The invention discloses a CYP450 gene IaAO2 catalyzing the oxidation of the C-28 site of amyrin. A protein which catalyzes the oxidation of the C-28 site of amyrin is encoded, and the CYP450 gene IaAO2 can be induced and expressed in engineered strains to catalyze alpha-amyrin and beta-amyrin to be oxidized into ursolic acid and oleanolic acid separately. The nucleotide sequence of the CYP450 geneIaAO2 is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the amino acid sequence of the CYP450 gene IaAO2 is as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The invention further discloses an expression vector and host bacterium of the CYP450 gene IaAO2 and application of the CYP450 gene IaAO2 to preparation of triterpenoid compounds, compounds catalyzing the oxidation of the C-28 site of pentacyclic triterpenes and compounds catalyzingthe oxidation of alpha-amyrin and beta-amyrin of pentacyclic triterpenes. The invention further discloses a method for performing homologous gene modification based on the sequence characteristics ofthe gene IaAO2 and a novel gene tIaAO1 obtained by the method. The IaAO2 gene has a shorter nucleotide sequence than a homologous gene, a genetically modified organism can be constructed by using theIaAO2 gene to synthesize a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound with important economic value, and good application prospects are achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Optimized triterpenoid synthase coding gene and application thereof
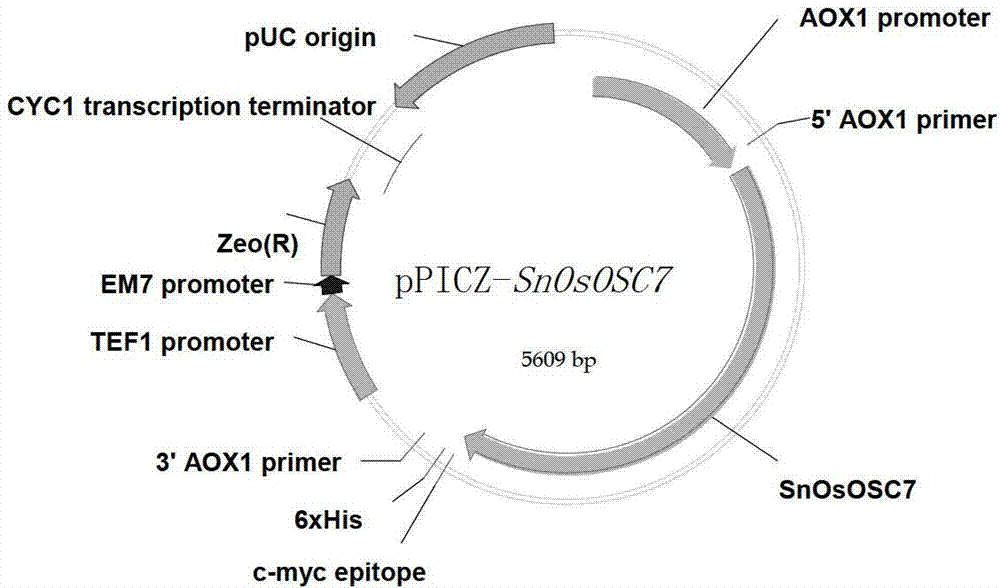
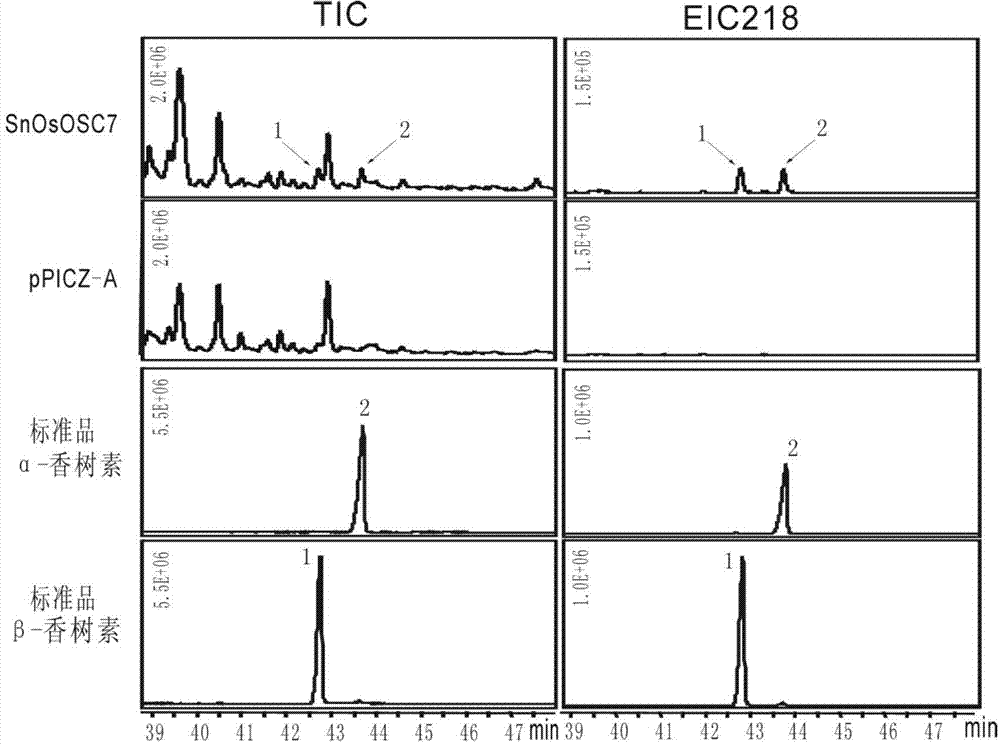
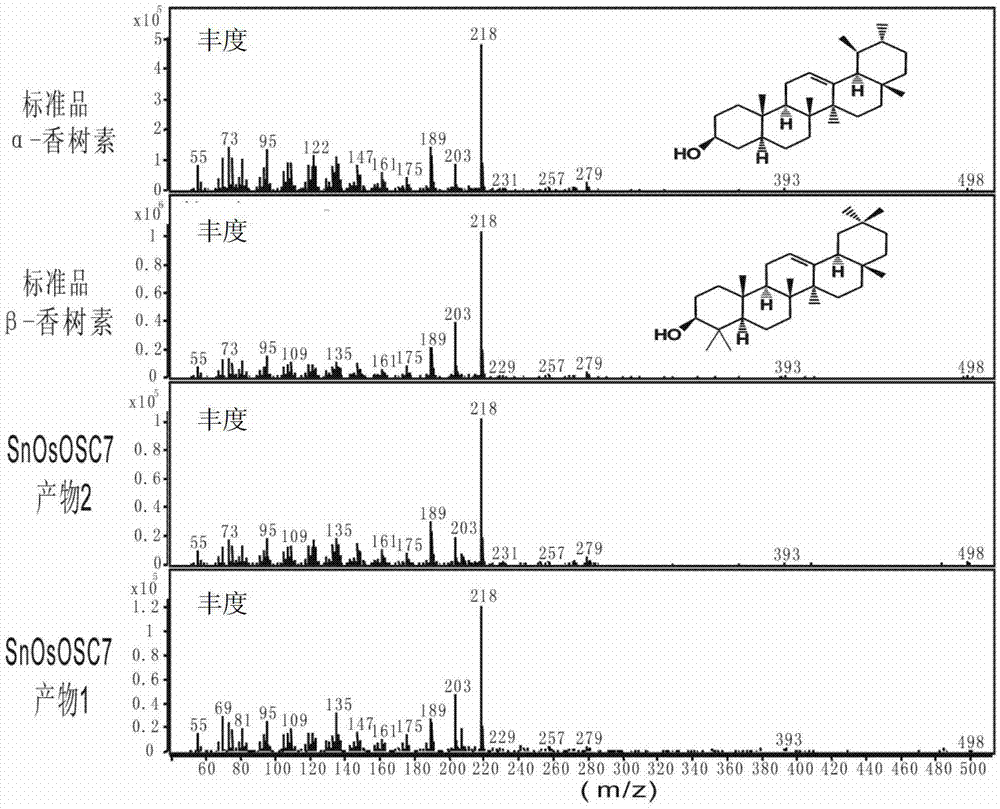
The invention discloses an optimized triterpenoid synthase coding gene and application thereof. A DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) molecule provided by the invention is any one of DNA molecules as follows: (1) the DNA molecule shown in a sequence I of a sequence table; (2) the DNA molecule which is hybridized with the DNA sequence defined in (1) and is coded and synthesized into a gap-associated protein of a triterpene compound under strict conditions; and (3) the DNA molecule which has at least 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98% or 99% homology with the DNA sequence defined in (1) and is used for synthesizing the gap-associated protein of the triterpene compound. Experiments prove that the sequence of rice SnOsOSC7 gene subjected to codon optimization, which is provided by the invention, can be used for preparing the triterpene compound alpha-amyrin and / or beta-amyrin.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of unsaponifiable matters in ginseng seed oil
InactiveCN111012810AImprove production efficiencyReduce consumptionMetabolism disorderDigestive systemOil and greaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention, which belongs to the field of preparation methods of ginseng extracts, provides a preparation method of unsaponifiable matters in ginseng seed oil. The method comprises the following steps: processing dried ginseng seeds into powder, adding petroleum ether, performing extracting by using a reflux method, and pouring out a petroleum ether solution after extraction finishing; adding sodium hydroxide and an ethanol solution into the petroleum ether solution, and performing stirring and heating; performing standing after heating finishing, taking a petroleum ether layer, and performing washing with sodium hydroxide and an ethanol solution; taking a petroleum ether layer, and performing washing with an ethanol solution; taking the petroleum ether layer, and performing concentrating under a reduced pressure or normal pressure to obtain an unsaponifiable matter in ginseng seed oil. The preparation efficiency of unsaponifiable matters in grease is improved by 20-50%, and the consumption of petroleum ether is reduced by about 50%. Gas chromatography and mass spectrometry technologies are used for detection; and the unsaponifiable matters mainly contain squalene, beta-sitosterol and beta-amyrin, and a normalization method is used for calculating that the three matters account for over 60% of the total unsaponifiable matter.
Owner:CHANGCHUN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
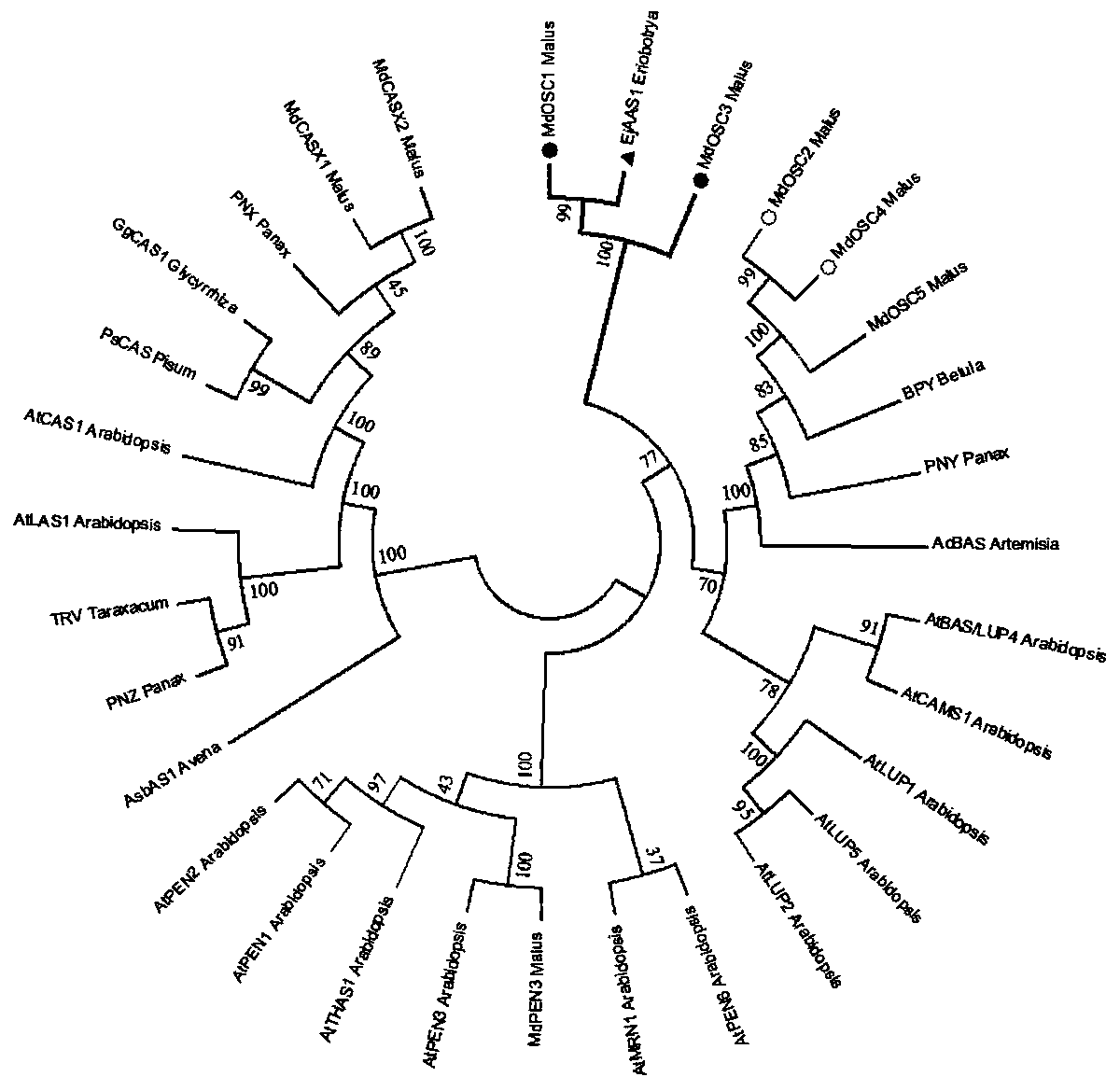
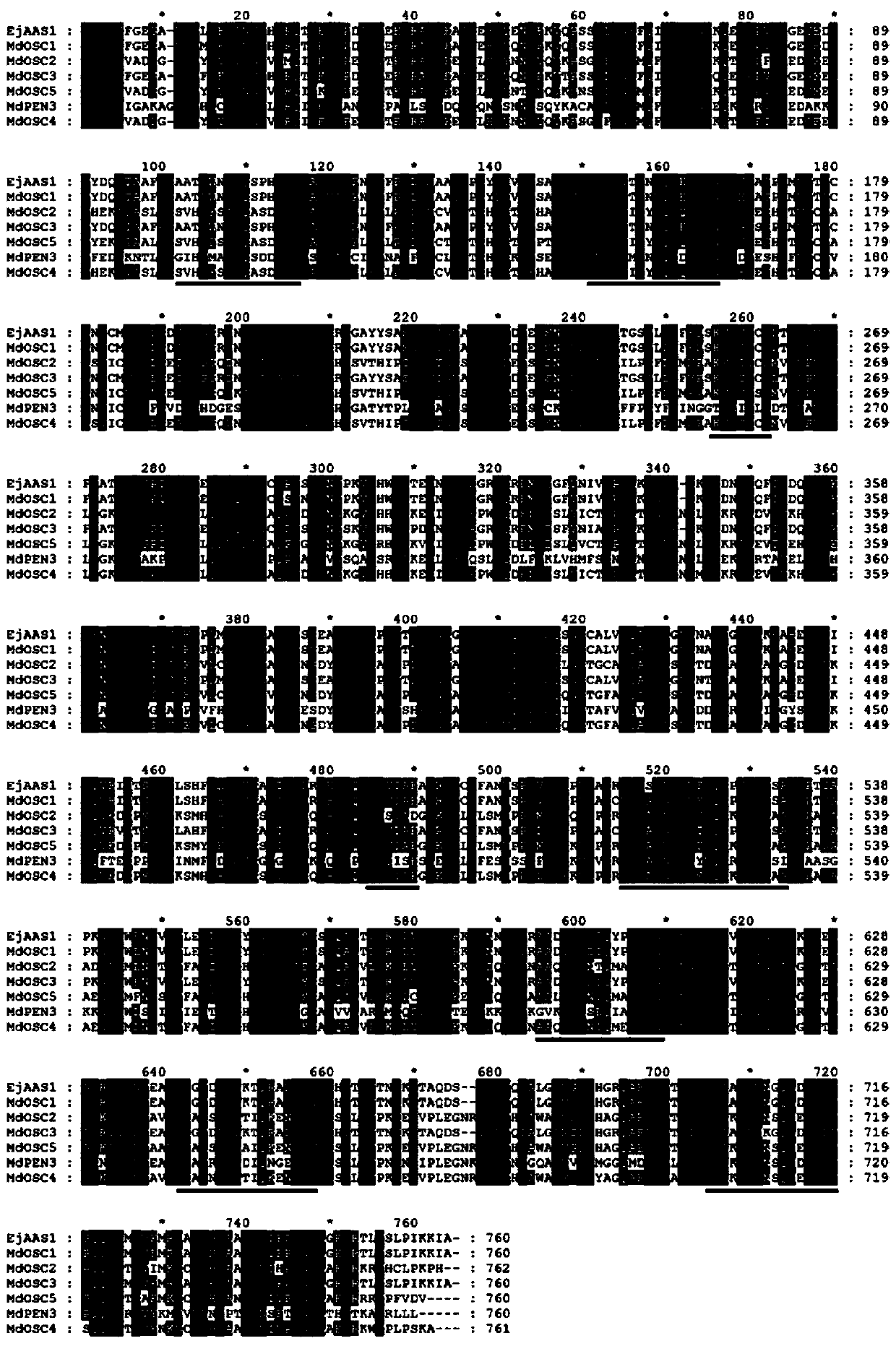
Alpha-amyrin synthetase gene EjAAS1 and application thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-amyrin synthetase gene EjAAS1 and application thereof and specially discloses application of an encoding gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 as a loquat alpha-amyrin synthetase gene and an application of protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 as loquat alpha-amyrin synthetase. According to the invention, a fact that the alpha-amyrin synthetase gene EjAAS1 of which the expression changes in different tissues are significantly positively correlated with the content of triterpene acid is demonstrated for the first time; thegene is transiently expressed in tobacco leaves and the alpha-myrcidin can be heterologously synthesized in the tobacco leaves; and thus synthesis of loquat alpha-amyrin and in-vitro biosynthesis ofalpha-amyrin and a derivative ursoside glycoside triterpene acid can be promoted. A foundation is laid for application of synthetic biological methods such as gene tandem expression and biological generators in loquat metabolism research and a theoretical support is provided for modification and utilization of functional components.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Amyrin cinnamate extract and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106518950AEasy to operateEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticAdditive ingredientGradient elution
The invention discloses an amyrin cinnamate extract and a preparation method thereof. The amyrin cinnamate extract is prepared from gymnema sylvestre fruit. The preparation method of the amyrin cinnamate extract comprises the following specific steps of (1) preparation of extract; (2) preparation of extract in all positions; (3) obtaining of the amyrin cinnamate extract: taking the extract in the position of petroleum ether, separating by using silica gel column chromatography, carrying out gradient elution by using petroleum ether-ethyl acetate as an eluting agent, obtaining a yellow oily matter in a 40 to 1 eluting part, and at least repeatedly carrying out four times of recrystallization by using acetone after washing off the yellow oily matter from a solution by using the petroleum ether, thus obtaining white feather-like crystals, i.e., a compound-the amyrin cinnamate extract. According to the amyrin cinnamate extract and the preparation method of the amyrin cinnamate extract, disclosed by the invention, the ingredient of amyrin cinnamate is extracted from the gymnema sylvestre fruit for the first time, the preparation method is simple and easy to operate, and the obtained total extract yield is up to 12.18 percent to 12.93 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Recombinant saccharomycetes for producing ursolic acid and oleanolic acid and construction method and application of recombinant saccharomycetes
ActiveCN111205993AImprove synthesis abilityIncrease productionFungiTransferasesUrsolic acidOxidative enzyme
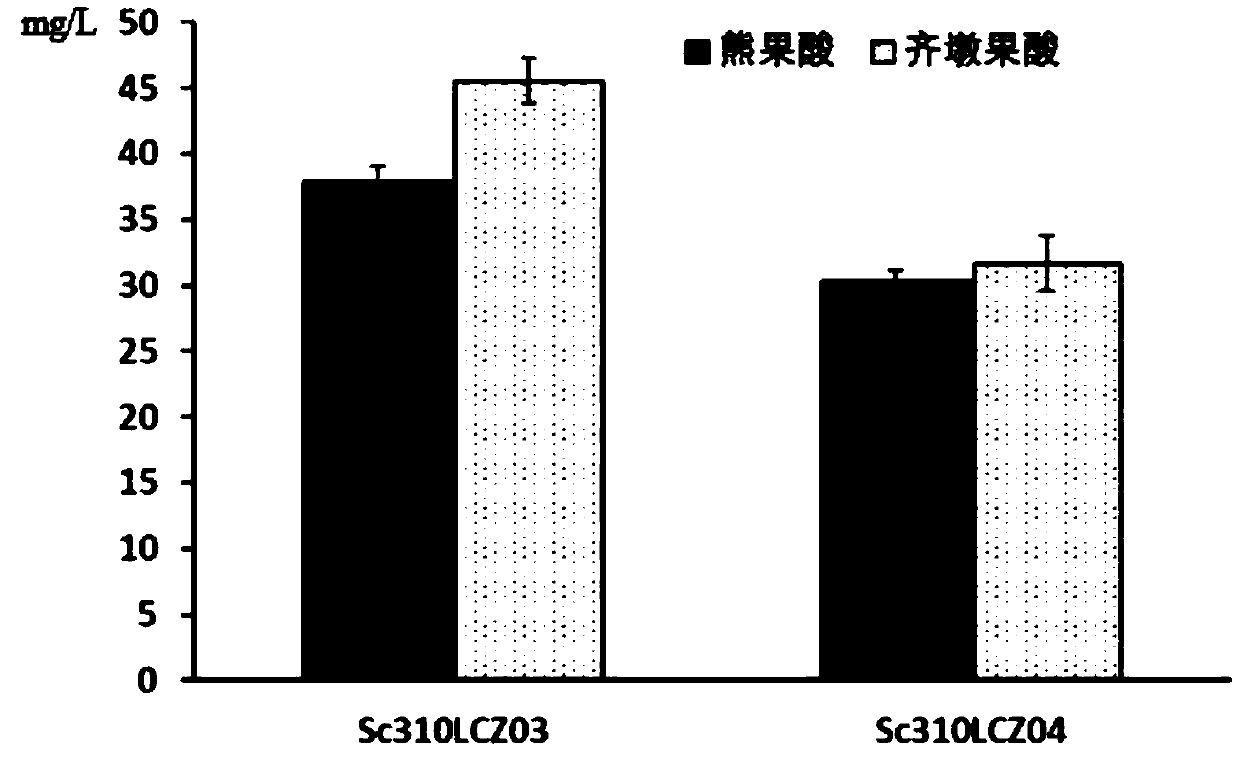
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomycetes for producing ursolic acid and oleanolic acid and a construction method and application of the recombinant saccharomycetes. The construction methodcomprises the following steps: by using a homologous recombination method, introducing an oxidase encoding gene CYP716A12 at a C-28 locus of a-amyrin and an encoding gene AtCPR1 of arabidopsis cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 into a recombinant bacterium Sc310LCZ02 so as to obtain a recombinant strain Sc310LCZ03; or introducing an oxidase encoding gene CYP716A1 at the C-28 locus of a-amyrin and the encoding gene AtCPR1 of arabidopsis cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 into the recombinant bacterium Sc310LCZ02 so as to obtain a recombinant strain Sc310LCZ04; and producing a mixture of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid of different ratios by using the recombinant strains. The invention makes bases for artificial synthesis of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Enzymes involved in triterpene synthesis
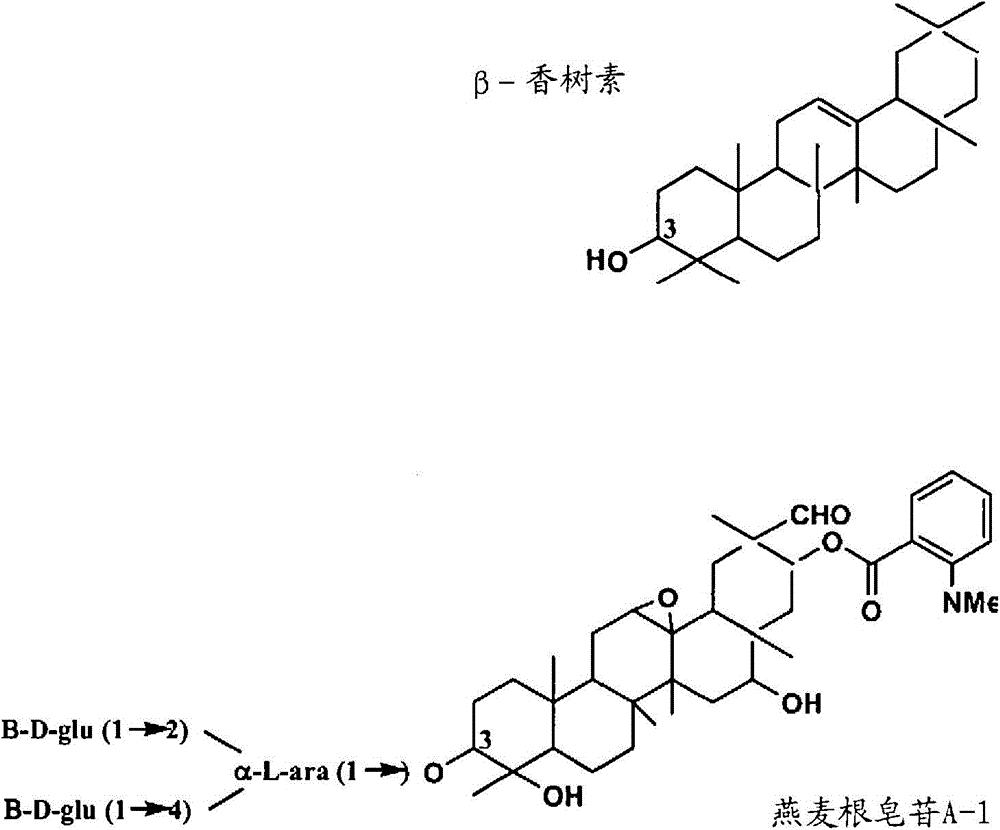
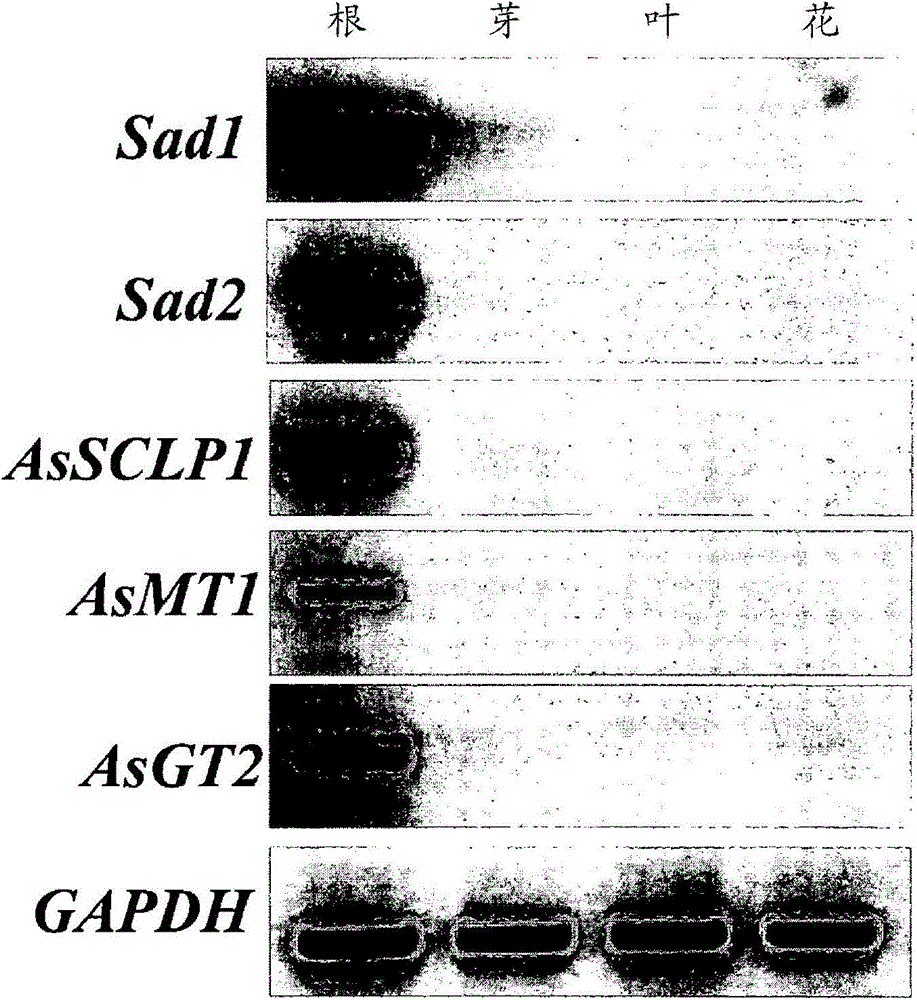
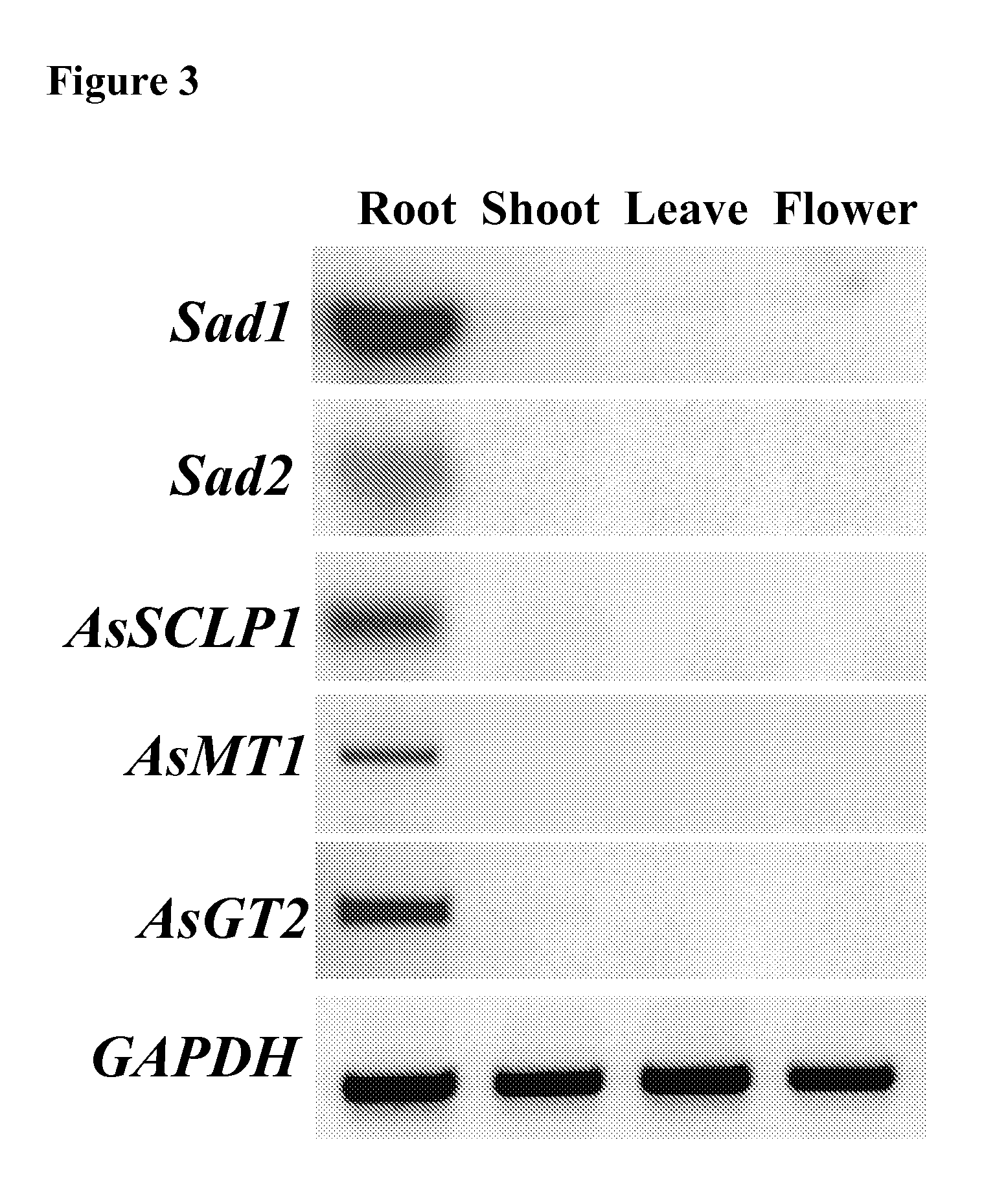
The invention discloses enzymes involved in triterpene synthesis, and particularly relates to isolated polynucleotides. The polynucleotides encode enzymes comprising a carboxypeptidase-like protein, a methyltransferase and a glucosyltransferase. The enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of beta-amyrin-derived triterpenes in plants and seeds. The invention also relates to construction of recombinant DNA constructs comprising all or a portion of the isolated polynucleotides. The polynucleotides are, in sense or antisense orientation, operably linked to at least one regulatory sequence.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
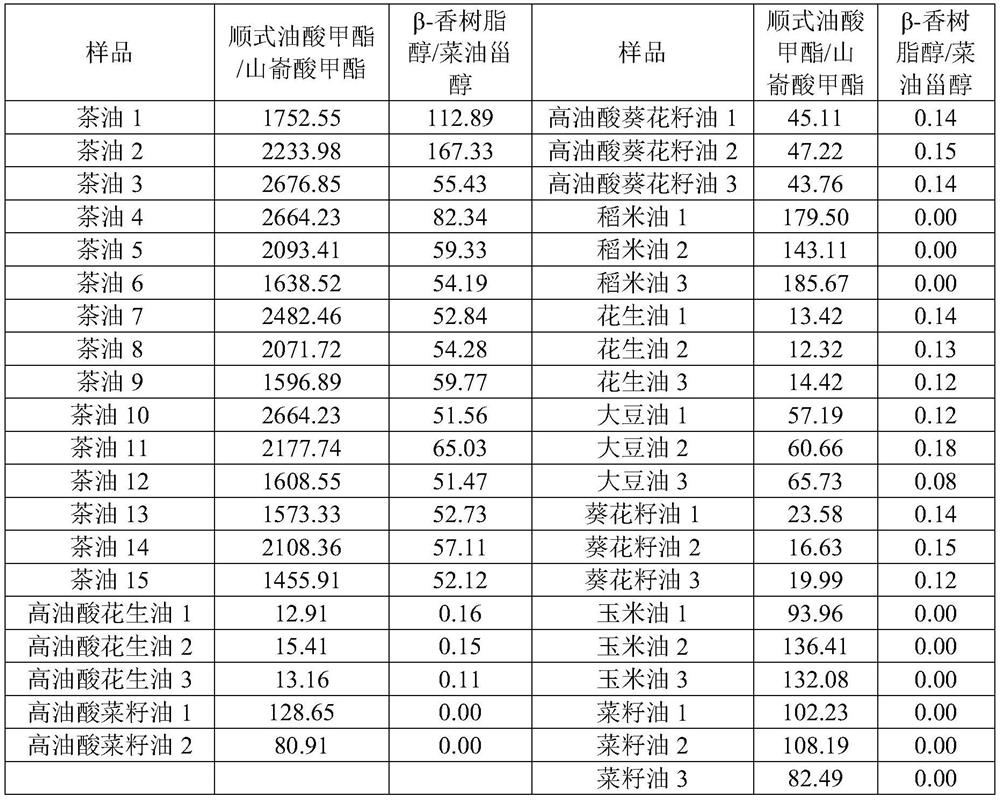
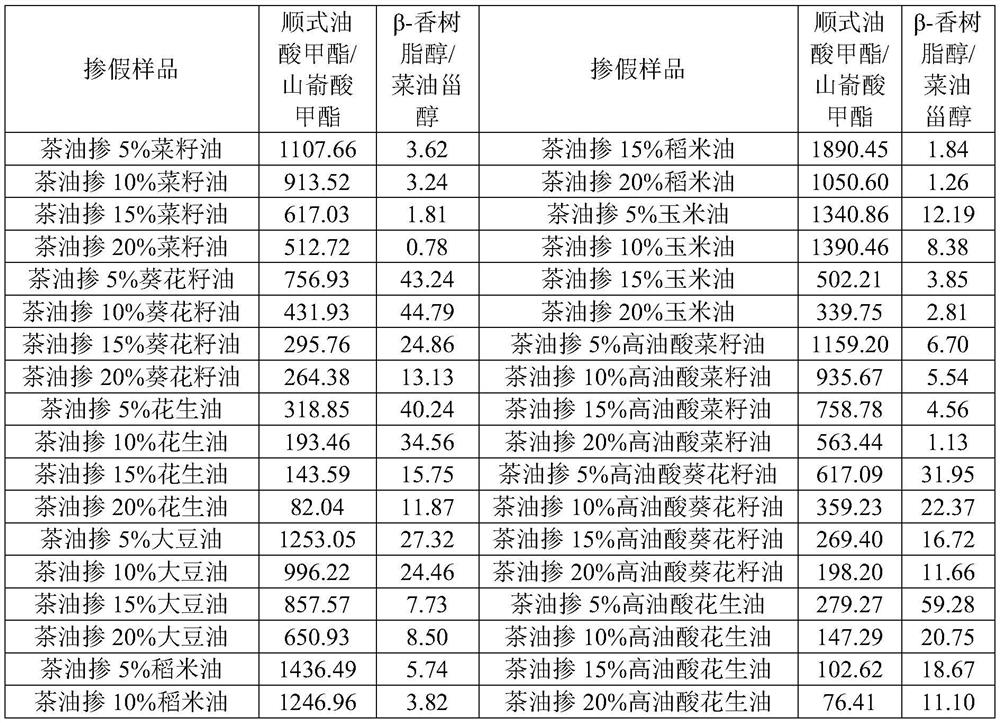
Camellia oleosa seed oil adulteration detection method based on oleic acid/behenic acid and beta-amyrin/campesterol ratios
PendingCN112305108ARapid adulterated false differential analysisLow in behenic acidComponent separationBiotechnologyVegetable oil
The invention belongs to the field of food inspection and detection, and discloses a camellia oleosa seed oil adulteration detection method based on oleic acid / behenic acid and beta-amyrin / campesterolratios. Camellia oleosa seed oil and different vegetable oils are saponified, saponified substances are subjected to fatty acid content detection, non-saponified substances are subjected to triterpenoid compound detection, and through two ratios of oleic acid / behenic acid to beta-amyrin / campesterol, the content of fatty acid in the saponified substances is detected. Adulteration qualitative identification analysis can be rapidly carried out on rice oil, sunflower seed oil, corn oil, rapeseed oil, soybean oil, peanut oil and novel high-oleic-acid vegetable oil (high-oleic-acid peanut oil, high-oleic-acid sunflower seed oil and high-oleic-acid rapeseed oil) which are common in the market at present. According to the method, the adulteration in the pure tea oil can be judged through comprehensive judgment of two indexes, namely the ratio of methyl cis-oleate to methyl behenate is smaller than 1200 or the ratio of beta-amyrin to campesterol is smaller than 40, the adulteration characteristic of the pure tea seed oil can be visually presented, and the adulteration of the pure tea seed oil can be qualitatively identified.
Owner:江西省食品检验检测研究院
Gentiana straminea beta-amyrin synthetase gene GsAS1 and use thereof
InactiveCN101475945AIncreased oleanolic acid contentSteroidsVector-based foreign material introductionGentianaBiotechnology
The invention discloses a twisted Gentiana beta-amyrin synthetase gene GsAS1 and yeast and plant expression vector containing the gene GsAS1, also discloses a twisted Gentiana beta-amyrin synthetase gene GsAS1 and the applications of the plant expression vector containing the gene GsAS1 in the preparation of the oleanolic acid. The invention provides a theoretical basis and practical basis for improving the oleanolic acid content in the target products.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Enzymes involved in triterpene synthesis
InactiveUS20130247245A1Improve plant resistanceReduce cholesterolSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPolynucleotideMethyltransferase
This invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding enzymes consisting of a carboxypeptidase-like protein, a methyltransferase and a glucosyltransferase, involved in the biosynthesis of β-amyrin-derived triterpenes in plants and seeds. The invention also relates to the construction of recombinant DNA constructs comprising all or a portion of the isolated polynucleotides of the invention, in sense or antisense orientation, operably linked to at least one regulatory sequence.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Disease-preventing and insect-preventing composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113396936AEnhanced bactericidal propertiesImprove the effect of disease preventionBiocideFungicidesCitrus x limoniaBacillus thuringiensis
The invention provides a disease-preventing and insect-preventing composition as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1 to 3 parts of trichoderma harzianum bacterial liquid, 2 to 4 parts of beauveria bassiana bacterial liquid, 2 to 4 parts of metarhizium anisopliae bacterial liquid, 3 to 7 parts of bacillus thuringiensis bacterial liquid, 1 to 3 parts of morchella esculenta bacterial liquid, 0.3 to 2 parts of agilawood spiral alcohol, 0.1 to 0.5 part of amino-oligosaccharin, 0.2 to 0.9 part of salicylic acid, 0.1 to 0.9 part of dextran, 1 to 3 parts of apiane, 1 to 5 parts of limonene amine and 2 to 6 parts of beta-amyrin. The composition is based on scientific proportioning of all the raw materials, so that the activity and the insecticidal effect of the composition have a remarkable synergistic effect. The composition has a remarkable killing effect in the aspect of preventing and treating insect pests of crops, and especially has the best effect on stem borers, aphids and thrips. The composition can also be used for preventing and treating various crop pathogenic bacteria, especially powdery mildew, downy mildew, gray mold, rice blast, late blight and anthracnose.
Owner:HAINAN JINYUFENG BIOLOGICAL ENG
Yarrowia lipolytica engineering strain for biologically synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid by taking glucose as substrate as well as construction and application thereof
PendingCN113930348AIncrease productionConducive to large-scale industrial productionFungiTransferasesCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome P450
The invention discloses a yarrowia lipolytica engineering strain for biologically synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid by taking glucose as a substrate as well as construction and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the engineering strain, a beta-amyrin synthase expression module, a 11 / 30 site-oxidized beta-amyrin synthase expression module, a cell P450 oxidase expression module and a cytochrome P450 reductase expression module are integrated on a genome; the construction method comprises the following steps: constructing to obtain glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module plasmids: beta-amyrin synthase bAS, cytochrome P450 oxidase 88D6CYP88D6, 11 / 30-site-oxidized beta-amyrin synthase CYP725A4 and cytochrome P450 reductase CPR, integrating the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module onto a yarrowia lipolytica tool plasmid, and linearizing the plasmids integrated with the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module, and introducing the linearized plasmids into yarrowia lipolytica to obtain the yarrowia lipolytica engineering bacteria of which the genome is integrated with the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module. The yield of glycyrrhetinic acid produced by the engineering strain is remarkably improved and reaches 7g / L to the maximum.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
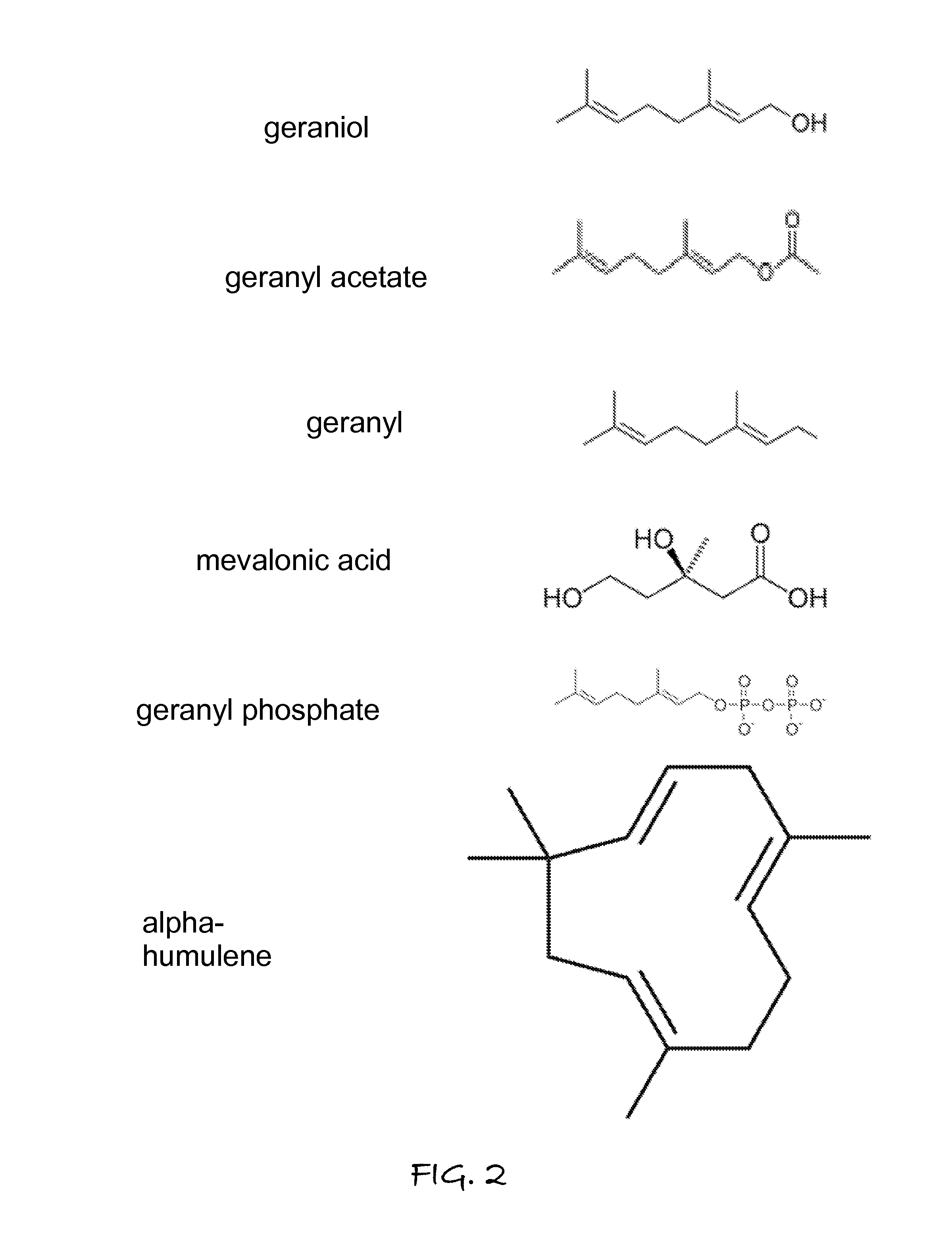
Plant Activator Composition
A plant activator composition increases the concentration of terpenes a terpenoids in aromatic plant oils, and hence resulting in an increased concentration terpene and terpenoids in the harvested dried plant or fruit. The composition contains one of more bio-active compounds that are optionally extracted from plants selected from one or more of the group consisting of mango, citrus (including grapefruit), Catharanthus roseus and Pelargonium odoratissimum, but alternatively may include one or more synthetic compounds selected from the group consisting of geranyl acetate, geraniol, beta-sitosterol, alpha-amyrin, beta amyrin, carotenoid, geranyl acetate, alpha-humulene, mevalonate kinase and geranyl. Depending on the type of plant being treated, the formulation is added during watering and feeding in optimum doses during the vegetative growth, flowering, and fruit set and / or swell stages.
Owner:RHIZOFLORA
A kind of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered bacteria producing glycyrrhetinic acid or its precursor and its construction method
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Protein for catalytic synthesis of amyrin, and preparation method and application for protein
The invention discloses a protein for catalytic synthesis of amyrin, and a preparation method and an application for the protein, and relates to the technical field of biomolecules. The protein has anamino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, or has a sequence which has 90% or above of sequence homology with the sequence as shown in the SEQ ID No. 2 and has the same protein function as the sequence as shown in the SEQ ID No. 2. According to the protein, 2,3-squalene oxide is used as a substrate; alpha-amyrin, beta-amyrin and delta-amyrin can be catalytically synthesized simultaneously; thealpha-amyrin is mainly synthesized; and a new direction is provided for research of multifunctional OSC enzymes.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
External quick-acting medicament for treating tumor and breast cancer and production process thereof
InactiveCN101732448AAchieve the fast effect of excluding lesionsPrevent diseaseOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLinaloolAlkaloid
The invention relates to an external quick-acting medicament for treating a tumor and a breast cancer and production process thereof. The medicament comprises the following raw material components in percentage by weight: 25 to 30 percent of peach twig extract dry powder, 40 to 50 percent of perilla leaf extract dry powder and 25 to 30 percent of oxalicacid crystal product extract dry powder. In addition, each 150g of medicament is mixed with 20 to 30g of clerodendrum bungei extract paste for diminishing inflammation of wounds and curing the wounds. The peach twig extract dry powder contains 1 to 1.6 percent of natural plant antibiotics with properties of alkaloid, and also contains amyrin, naringenin, persicoside, persicogenin and salipurposide; a perilla leaf extract comprises alpha-bergamotene, beta-caryophyllene, cumic acid, dihydro perillyl alcohol, isoegomaketone, l-limonene, linalool, menthol-b, 1.2methylenedioxy-4-methoxy-5-allyl-benzene-3-alkynyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside, perilla olefine aldehyde, and beta-sitosterol; and the oxalicacid crystal dry powder is water-soluble powder. The external quick-acting medicament has the effects of killing viral cells one time, calcifying lesion tissues and discharging focus out of body, and achieves obvious and quick effect of treating both tip and root.
Owner:祝根华
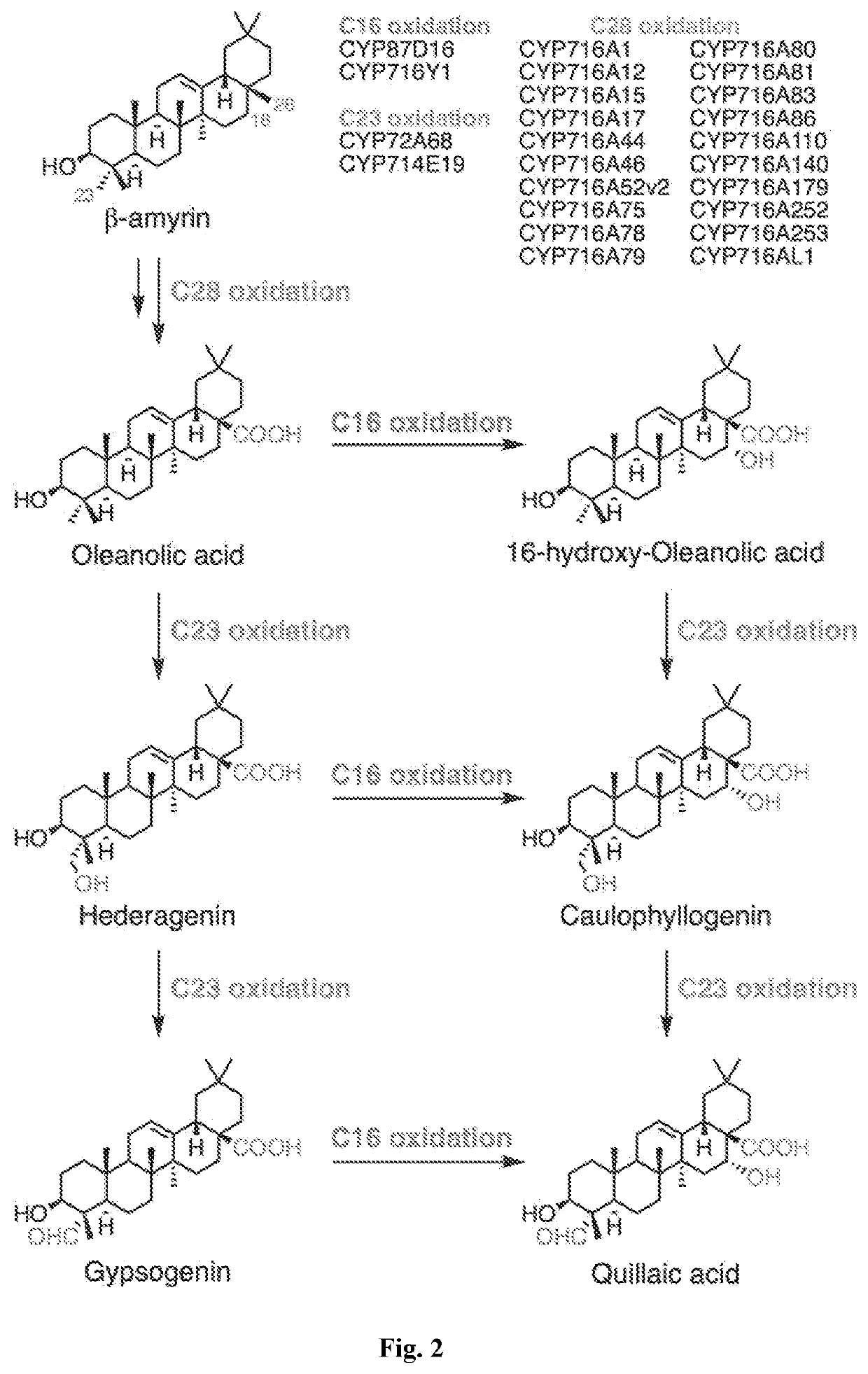
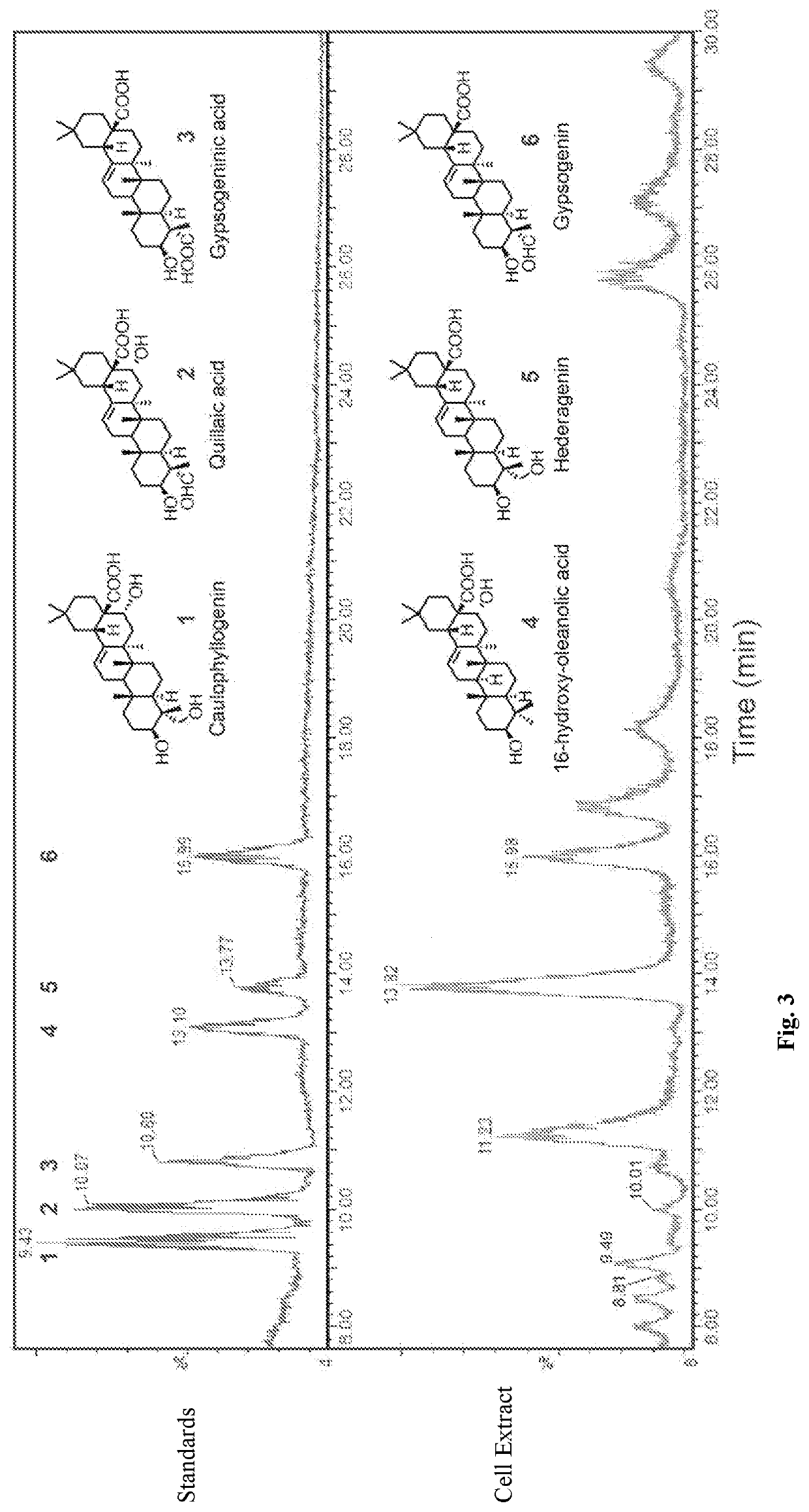
Triterpene Production
An engineered microbial cell expressing a β-amyrin synthase, a cytochrome P450 reductase, a cytochrome P450 C28 oxidase, a cytochrome P450 C16 oxidase and a cytochrome C23 oxidase is used to make quillaic acid from β-amyrin.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tripterygium wilfordii triterpene synthase twosc3 and its coding gene and application
The invention relates to a triterpene synthase of tripterygium wilfordii TwOSC3 protein and an encoding gene thereof. A recombinant expression vector with a Twosc3 gene is constructed by cloning cDNAof the Twosc3 gene onto a eukaryotic expression vector pYES2, and then the recombinant expression vector is shifted to yeast expression host bacteria, so as to acquire friedelin. A mutation research result shows that amino acid 482 encoded by the Twosc3 gene is a key site, and the yield of friedelin or amyrin can be increased or reduced; a gene gun mediated interference experiment shows that the interference of the Twosc3 gene has an obvious inhibiting effect on the synthesis of celastrol in tripterygium wilfordii; the TwOSC3 protein and the encoding gene thereof provided by the invention canbe used for biosynthesizing plant triterpenoids and cultivating high-quality tripterygium wilfordii.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Compositions for targeting receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) in a chronic inflammatory condition
PendingUS20220193005A1Inhibit expressionSkeletal disorderAntinoxious agentsBisdemethoxycurcuminInflammation
The invention discloses compositions and methods comprising enriched Bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC) present not less than 20% w / w for use in inhibiting Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products (RAGE) expression in a subject with chronic-inflammatory condition. The composition further comprises β-amyrin palmitate (BAP). The invention also includes disclose the use of the above composition in the management of chronic inflammatory condition in a subject
Owner:SAMI SABINSA GRP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com