Building method of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strains capable of synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and glycyrrhetinic acid, which is applied in the field of construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, can solve problems such as difficulties in production and chemical synthesis methods, and achieve the effects of saving fermentation costs, low raw material costs, and stable expression genetics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for constructing an engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid, firstly using the β-aromatic alcohol synthase GgbAS gene derived from Glycyrrhiza glabra (Genbank registration number is AB037203) and the cytochrome P450 derived from Glycyrrhiza uralensis The oxidase CYP88D6 gene (Genbank registration number is AB433179) and the cytochrome P450 oxidase CYP72A154 gene (Genbank registration number is AB558146), and the cytochrome reductase CPR1 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana (Genbank registration number is AB433179) GgbAS gene fragment, CYP88D6 gene fragment, CYP72A154 gene fragment, CPR1 gene fragment and CPR2 gene fragment were prepared with cytochrome reductase CPR2 gene (Genbank registration number AB558146). The above gene fragments, yeast promoter and yeast terminator were passed through Two-step overlap extension PCR ligation to obtain gene expression cassettes FBA1p-GgbAS-FBA1t, PGK1p-CYP88D6-GMP1t, ALA1p-CPR1-ALA1t, ENO2p...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Verification of fermentation production of glycyrrhetinic acid by engineering strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
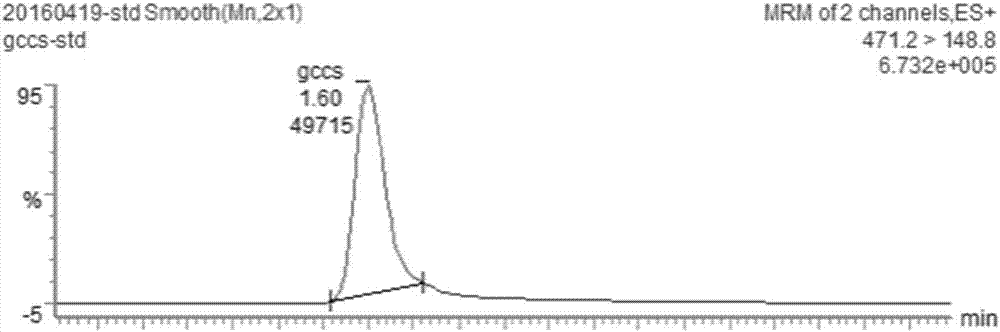
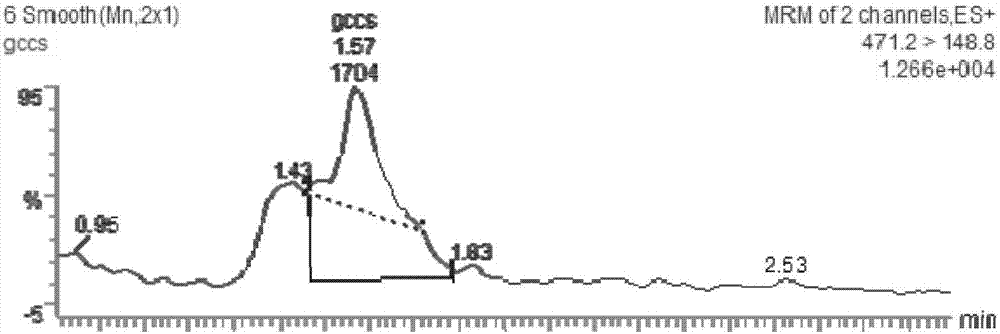
[0064] Select the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strains selected in Example 1, and culture them in a 30°C shake flask in a medium containing 2% glucose, 2% peptone and 1% yeast powder. After 7 days, take 50ml of the cultured Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid and centrifuge at 8000rpm After 10 min, remove the culture medium, wash with 30 ml sterile water, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells with 2 ml saturated sodium chloride solution. Use a cell column breaker to break the cells 5 times for 5 minutes, add an equal volume of ethyl acetate to the centrifuge tube, vortex for 3 minutes, and fully extract the yeast extract. Centrifuge at 8000rpm for 10min, draw the organic phase into a chicken heart bottle, evaporate ethyl acetate in a rotary evaporator, add 1ml methanol to fully dissolve it, pass through a 0.22μ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce glycyrrhetinic acid
[0067] The single colony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria selected in Example 1 was inoculated into a 30 mL medium containing 2% glucose, 2% peptone and 1% yeast powder, and cultured with shaking at 30°C and 150 rpm. The culture solution after 36 hours was used as the seed solution . Inoculate the seed liquid according to 10% of the inoculum into a 500 mL shake flask containing 150 mL of culture medium, culture with shaking at 30°C and 170 rpm, add glucose to a concentration of 0.5 to 1.0% every 12 hours after 24 hours, and measure after 5 days of fermentation The content of glycyrrhetinic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells was found to synthesize 35.5μg / L of glycyrrhetinic acid by Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria.
[0068] After 24 hours of fermentation, ethanol was used as a carbon source to feed every 12 hours. It was found that when the supplement concentration was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com