Building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose
A technology of Pediococcus lactis and glucose, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
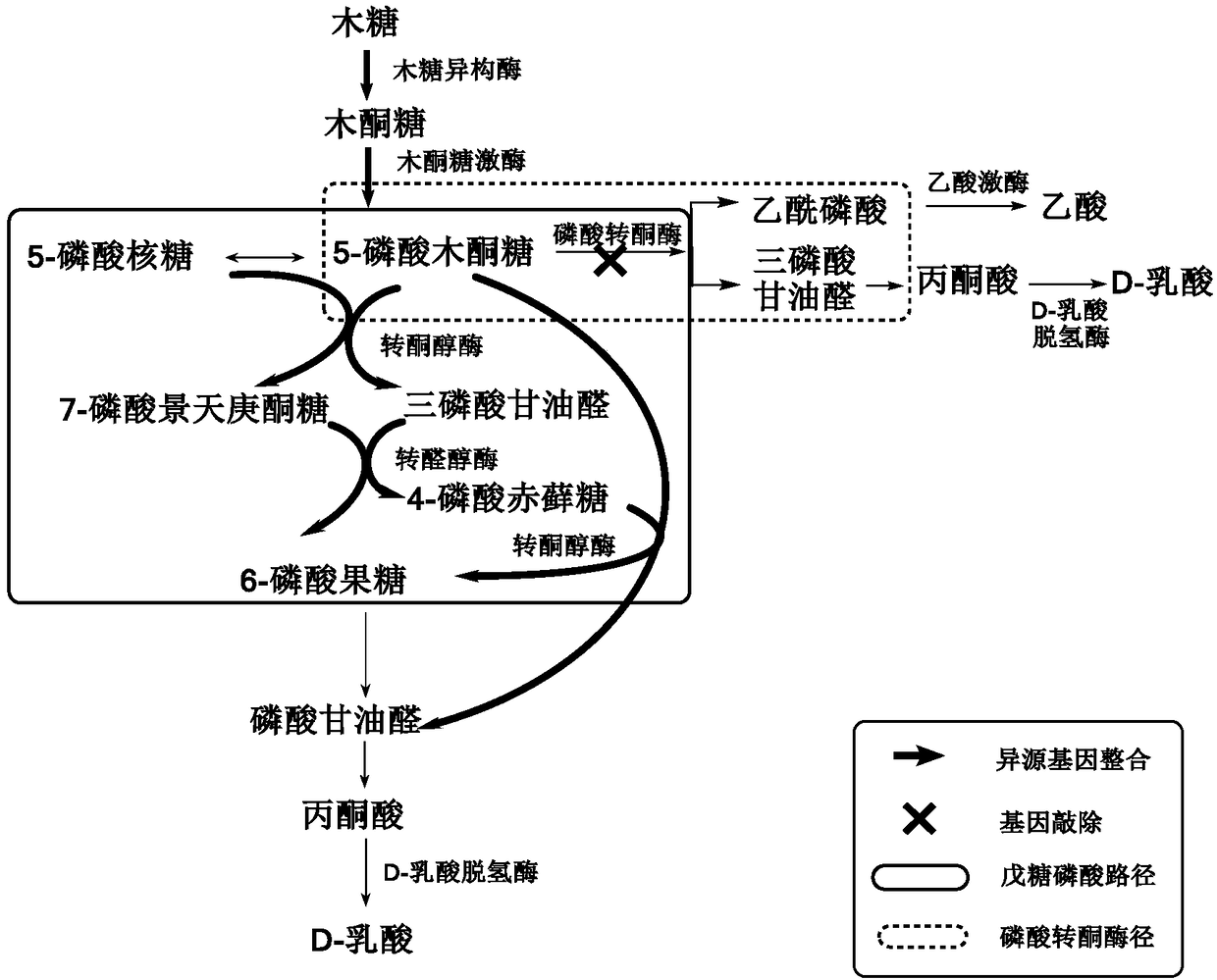
[0038] Implementation case 1: Comparison of xylose fermentation performance of P. acidilactici ZP26 carrying different xylAB expression cassettes.
[0039] (1) PCR amplification of different promoters and different xylAB operons
[0040] The genomes of P. acidilactici ZP26, P. acidilactici DSM20284 and P. pentosaceus ATCC25745 were extracted according to the method described in the Tiangen Genome Extraction Kit. Using the P.acidilacticiZP26 genome as a template, design primers Pldh-F (SEQ ID NO: 1) and Pldh-R (SEQ ID NO: 2) to amplify the ldh promoter Pldh (SEQ ID NO: 3), and design primer PldhD -F (SEQ ID NO: 4) and PldhD-R (SEQ ID NO: 5) were amplified to obtain the ldhD promoter PldhD (SEQ ID NO: 6); using the P. acidilactici DSM20284 genome as a template, the primer xylAB_2911-F was designed (SEQ ID NO: 7) and xylAB_2911-R (SEQ ID NO: 8) were amplified to obtain xylAB_2911 (SEQ ID NO: 9); using the P.acidilactici DSM20284 genome as a template, amplified to obtain xylAB_30...
Embodiment example 2
[0048] Example 2: The xylAB expression cassette was integrated into the ldh gene locus of P.acidillactici ZP26
[0049] (1) Construction of integrated plasmid pSET4E-Δldh::xylAB
[0050] First, using the P. acidilactici ZP26 genome as a template, the gene sequence up-ldh about 1,000 bp upstream of ldh was amplified, and the gene sequence down-ldh about 1,000 bp downstream of ldh was amplified. Using the expression plasmid pMG36e-PldhD_xylAB_2911 obtained in Example 1 as a template, PldhD_xylAB_2911 was amplified. Then by restriction endonuclease ligation, the up-ldh fragment was inserted between the Pst I and BamH I sites of pSET4E, and the down-ldh fragment was inserted between the BamH I and EcoR I sites, to obtain the ldh gene knockout Plasmid pSET4E-Δldh, and then the expression cassette PldhD_xylAB_2911 was inserted between Xho I and BamH I of pSET4E-Δldh to obtain the integrated plasmid pSET4E-Δldh::xylAB.
[0051] (2) Genomic integration of xylAB
[0052]The integrat...
Embodiment example 3
[0055] Example 3: Knockout of the phosphoketolase gene pkt
[0056] (1) Construction of knockout plasmid pSET4E-Δpkt
[0057] Using the P. acidilactici ZP26 genome as a template, the upstream about 1,000 bp fragment (up-pkt) and the downstream about 1,000 bp fragment sequence (down-pkt) of the pkt gene were amplified. The down-pkt fragment was inserted between the BamH I and Sac I sites of pSET4E, and then the up-pkt fragment was inserted between the Pst I and Sal I sites to obtain the plasmid pSET4E for pkt gene knockout-for get.
[0058] (2) Knockout of pkt
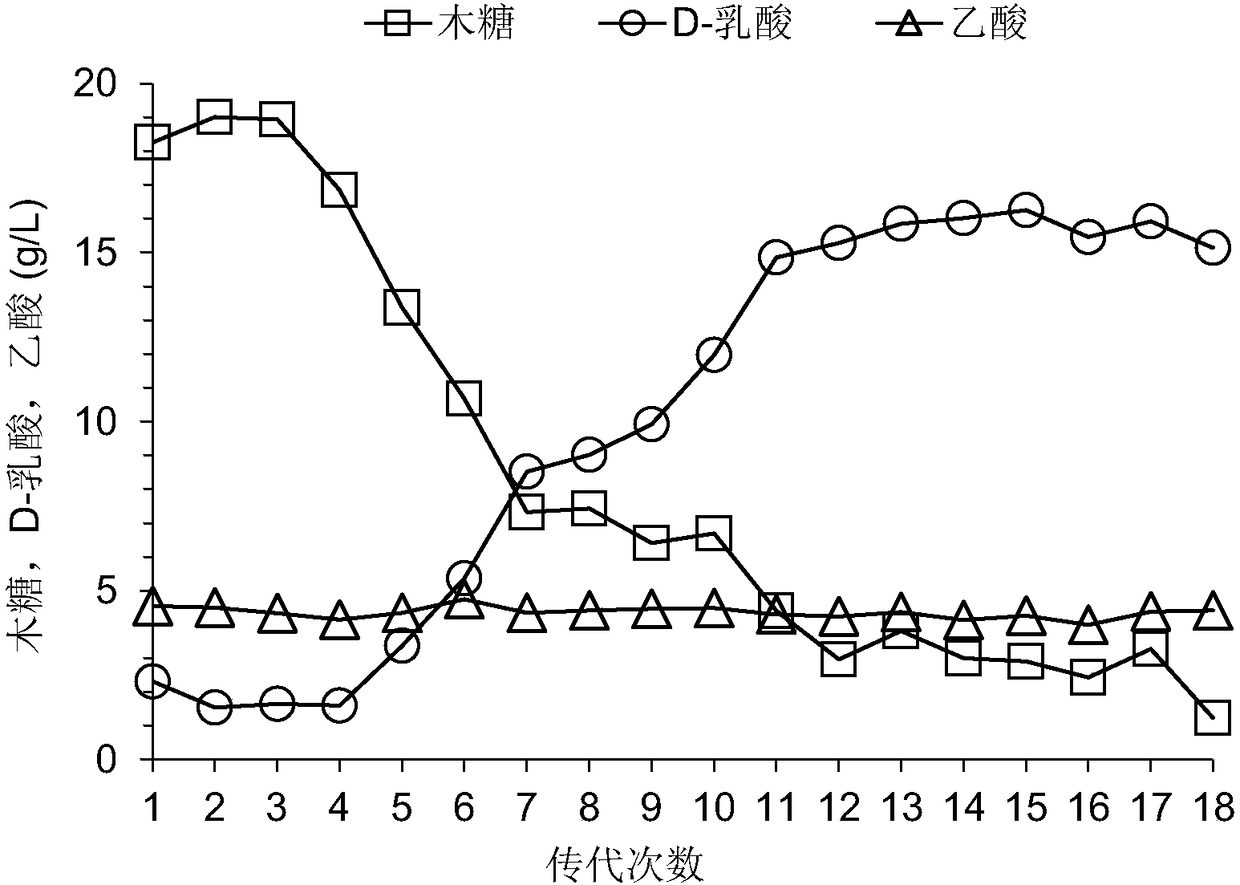
[0059] The knockout plasmid pSET4E- was used to obtain electrotransformation into the bacterial strain P.acidilactici ZP26::xylAB obtained in Case 2 to obtain the recombinant strain P.acidilactici ZP26::xylAB (pSET4E-Δpkt), and then the recombinant strain was placed at 42°C, After 12 hours of culture in the MRS medium added with erythromycin, the bacterial solution was diluted 10 6 Spread it on the MRS plate contain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com