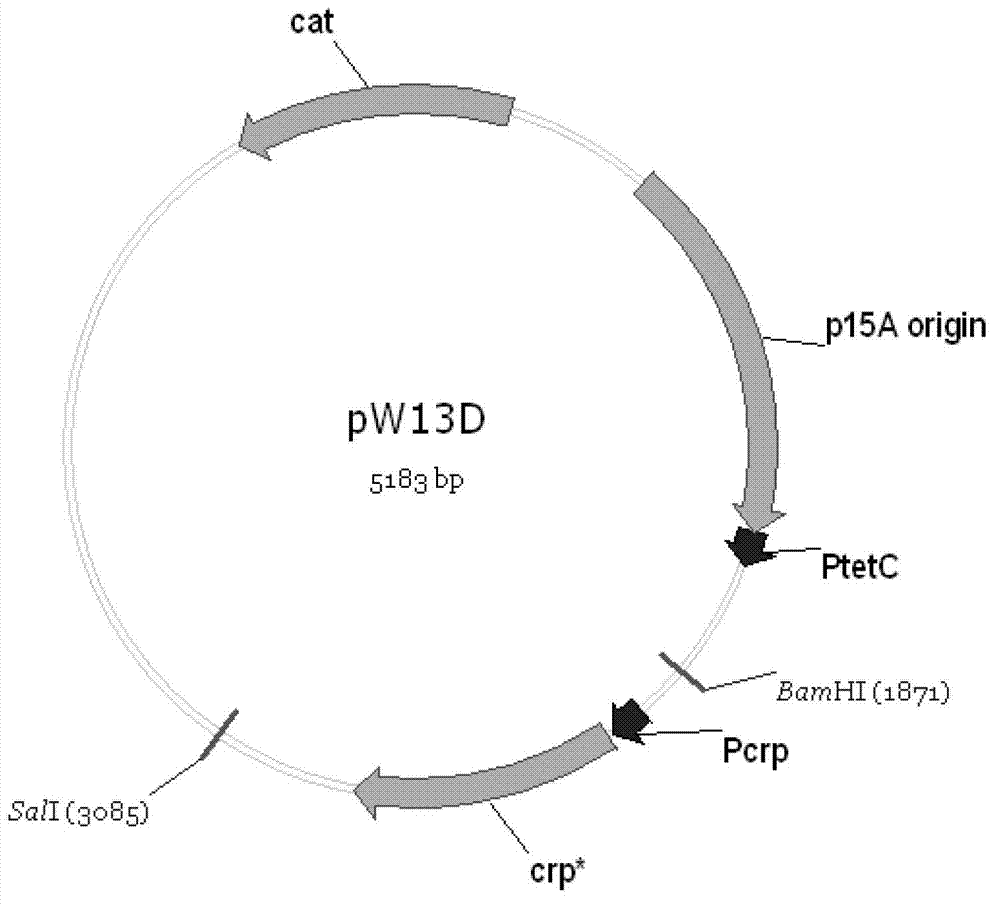
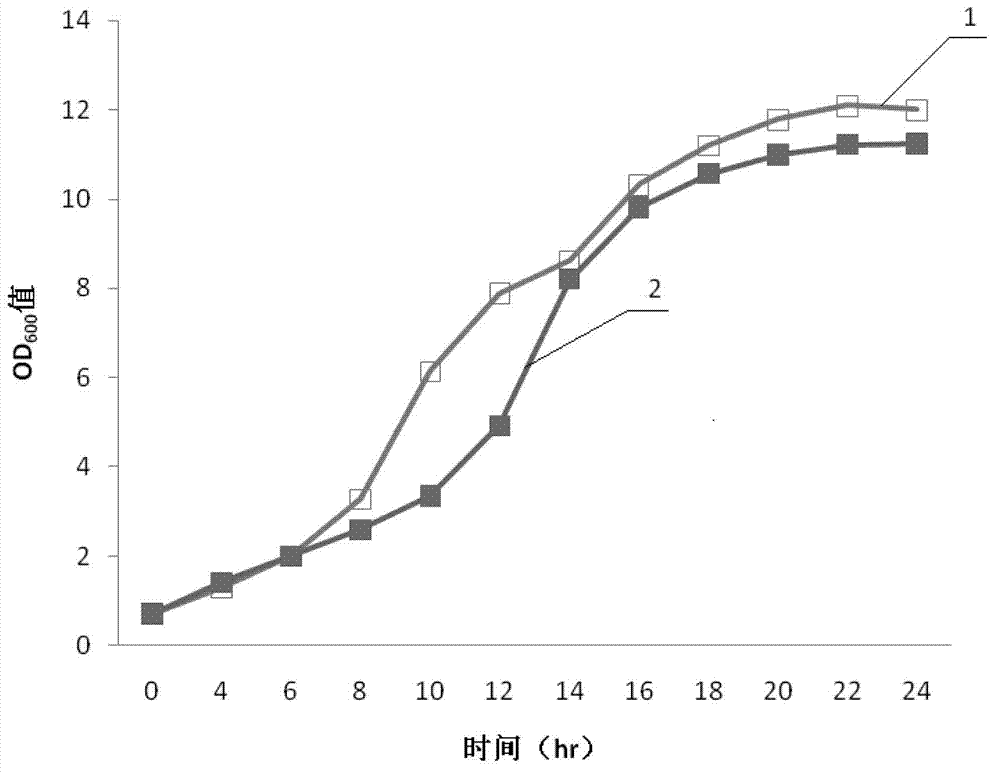
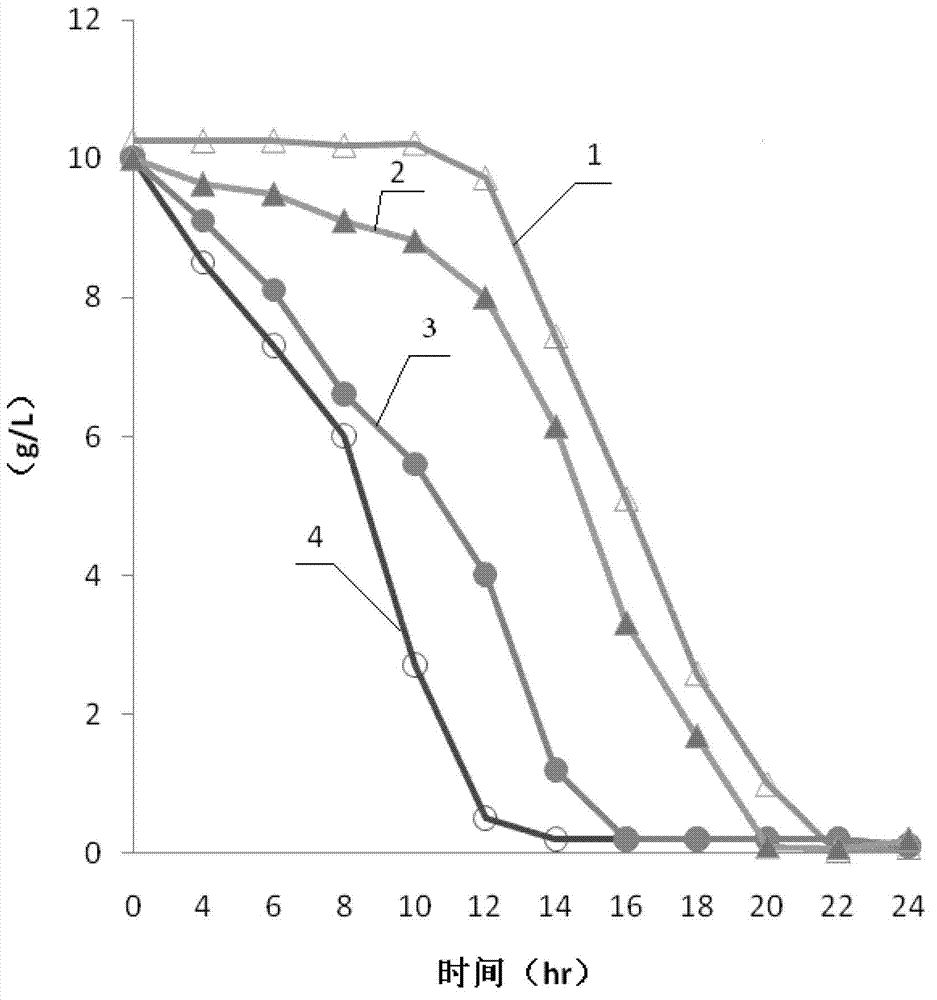
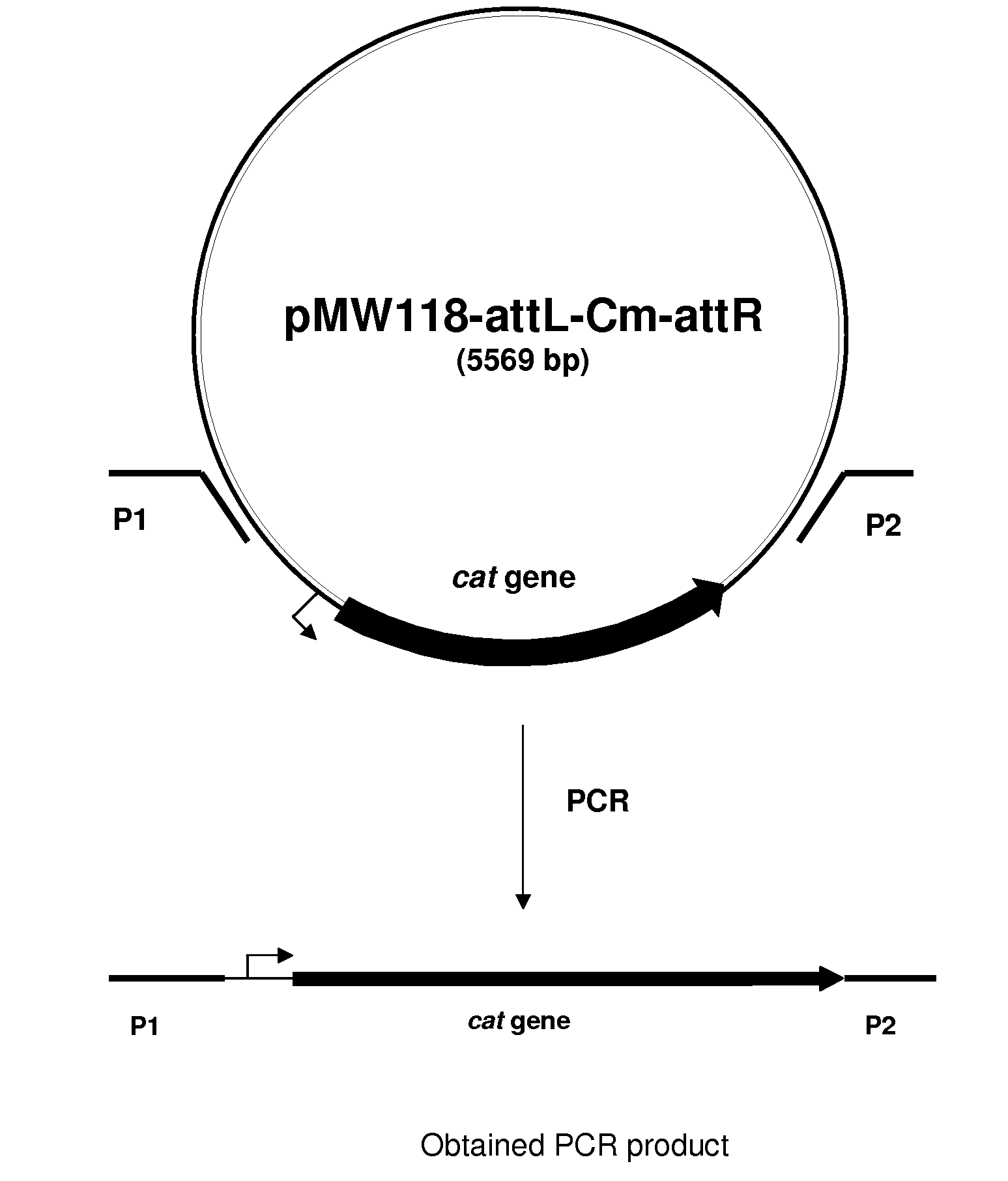
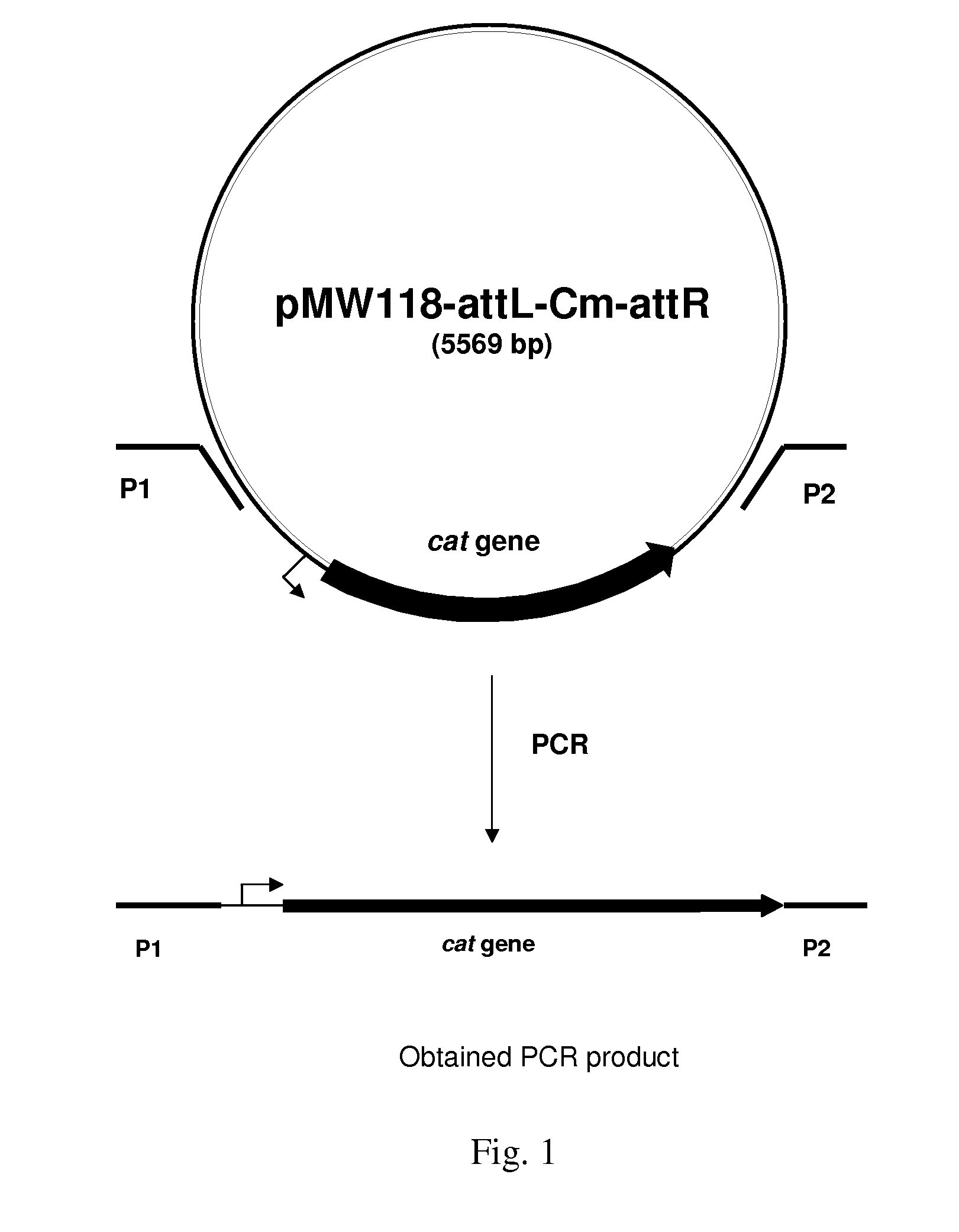
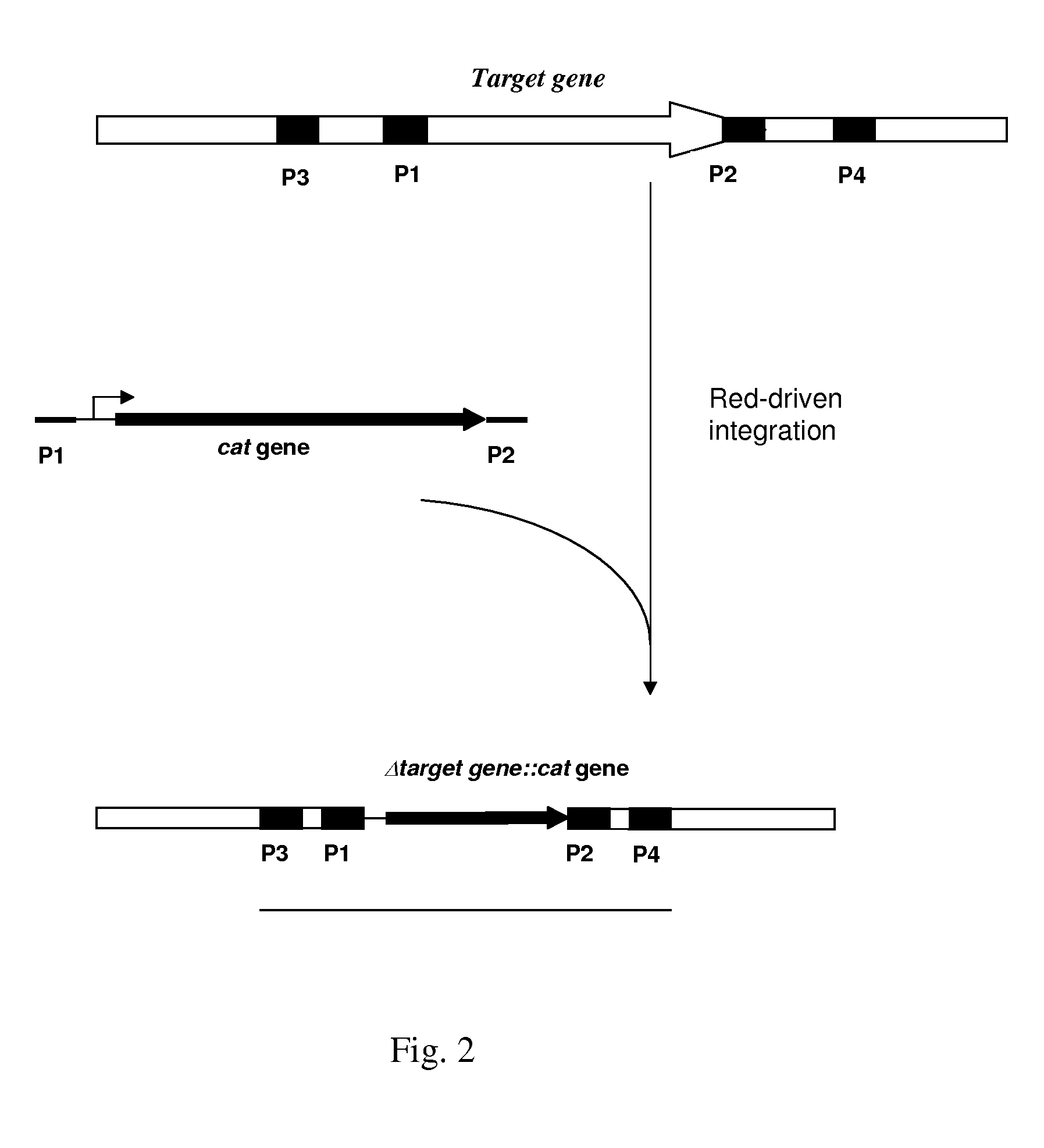
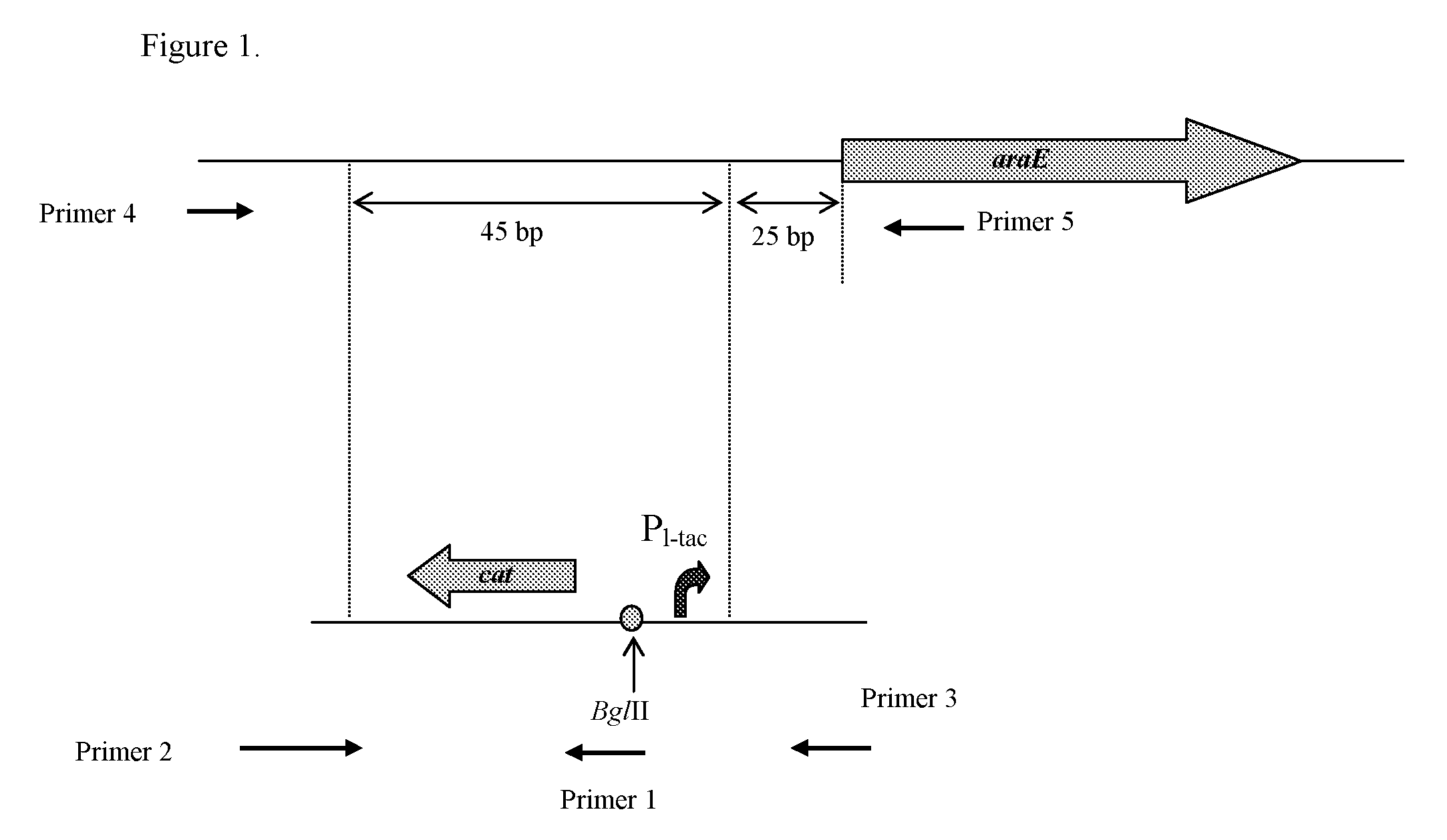
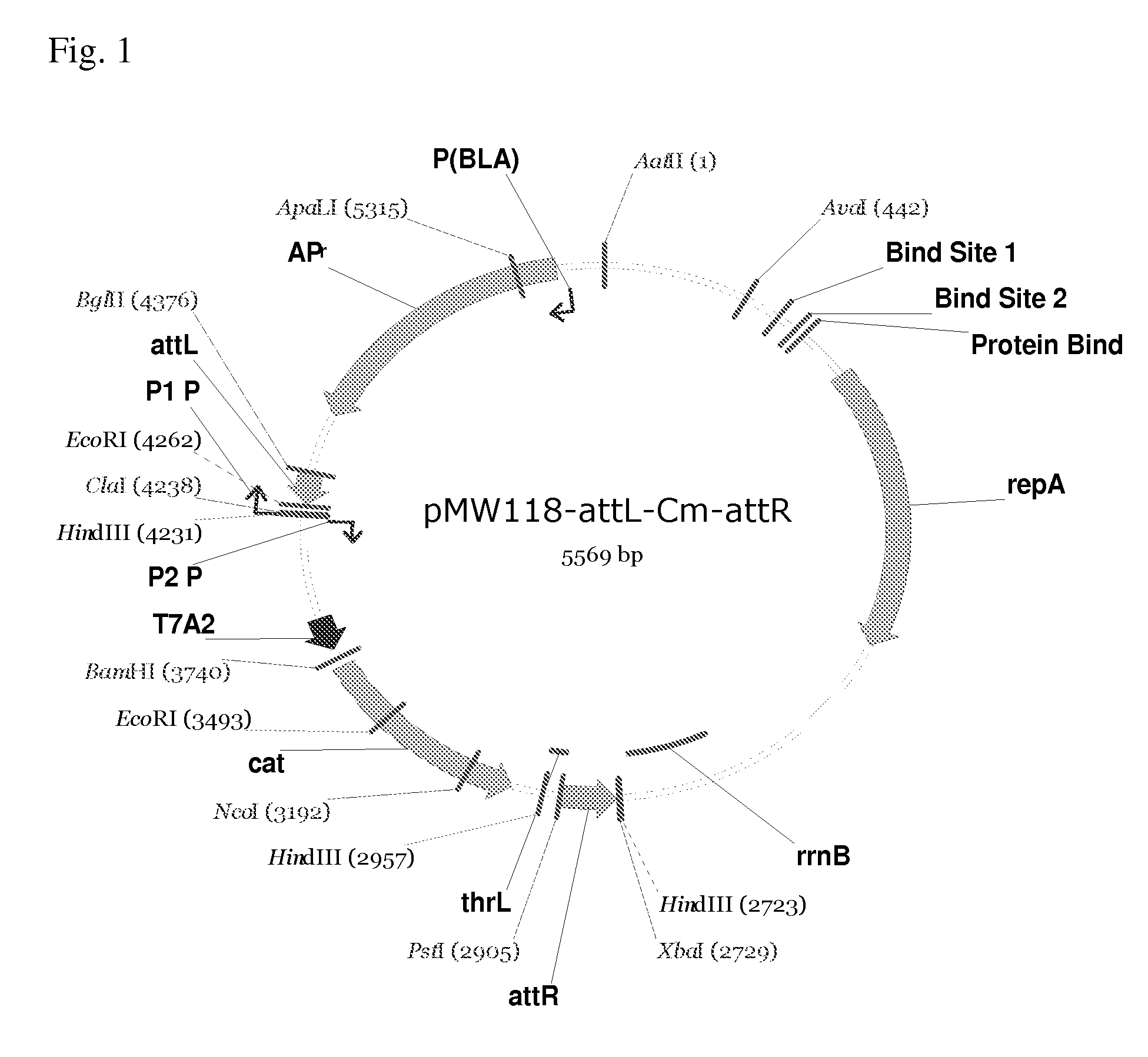
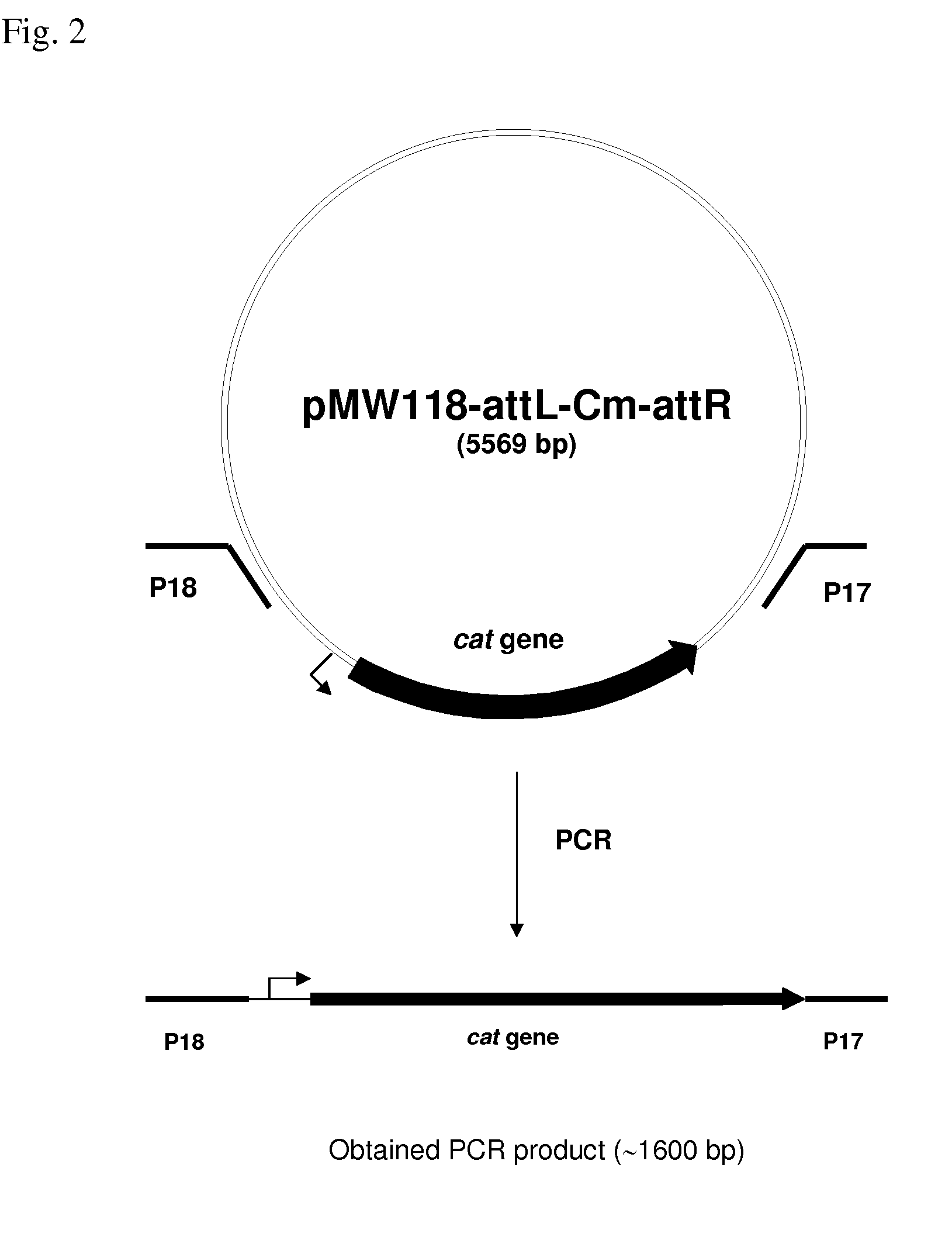
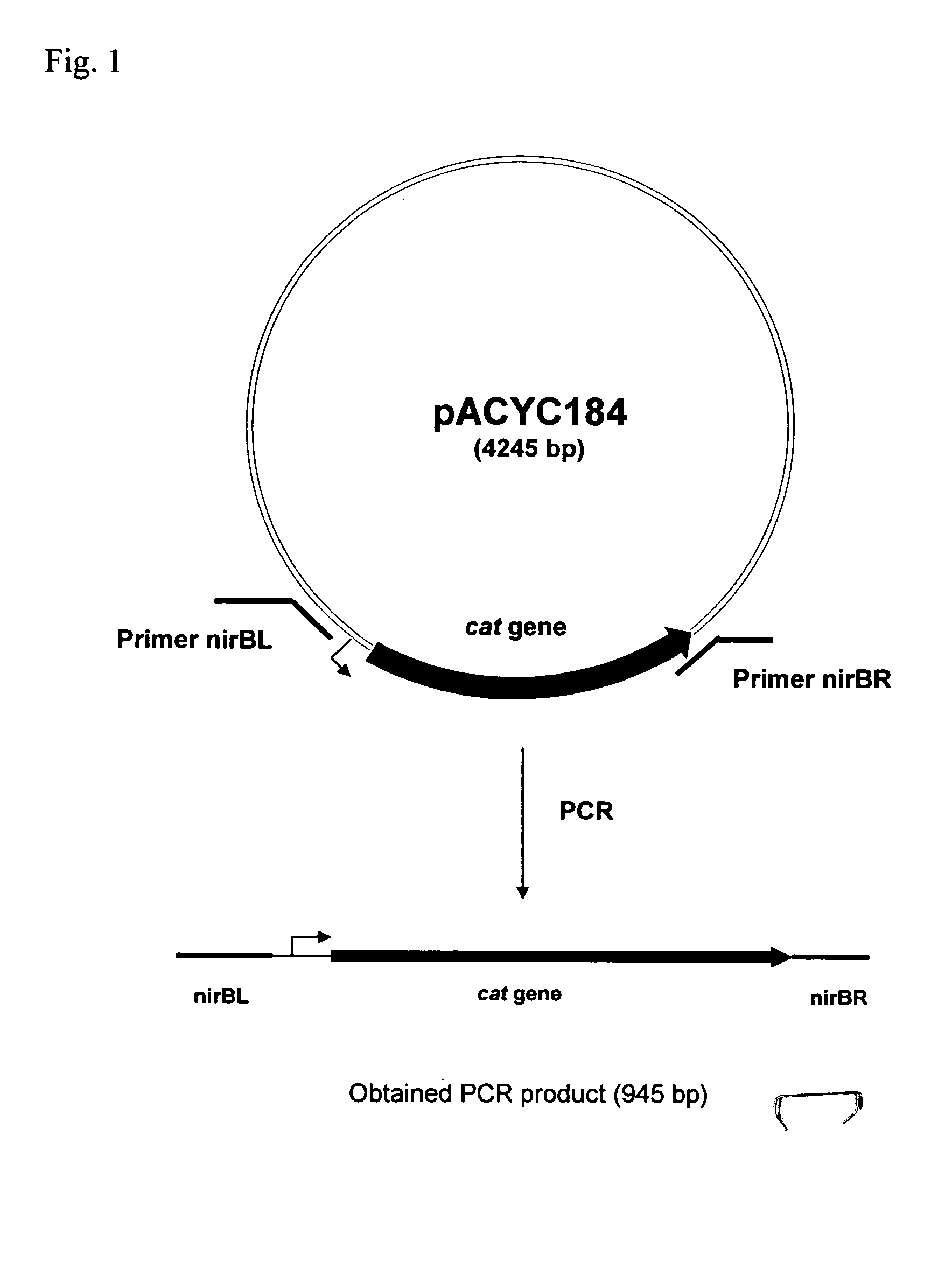
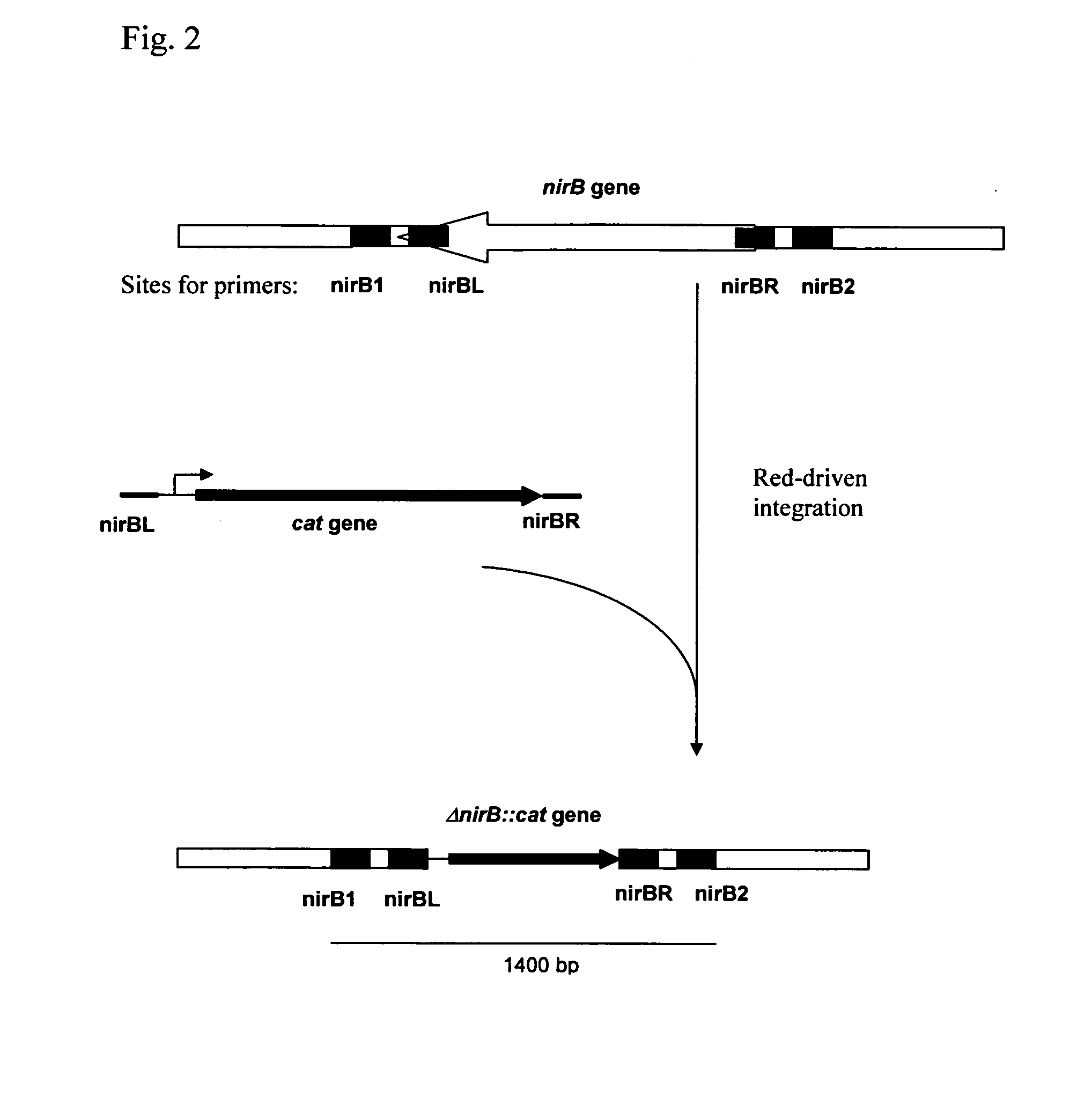
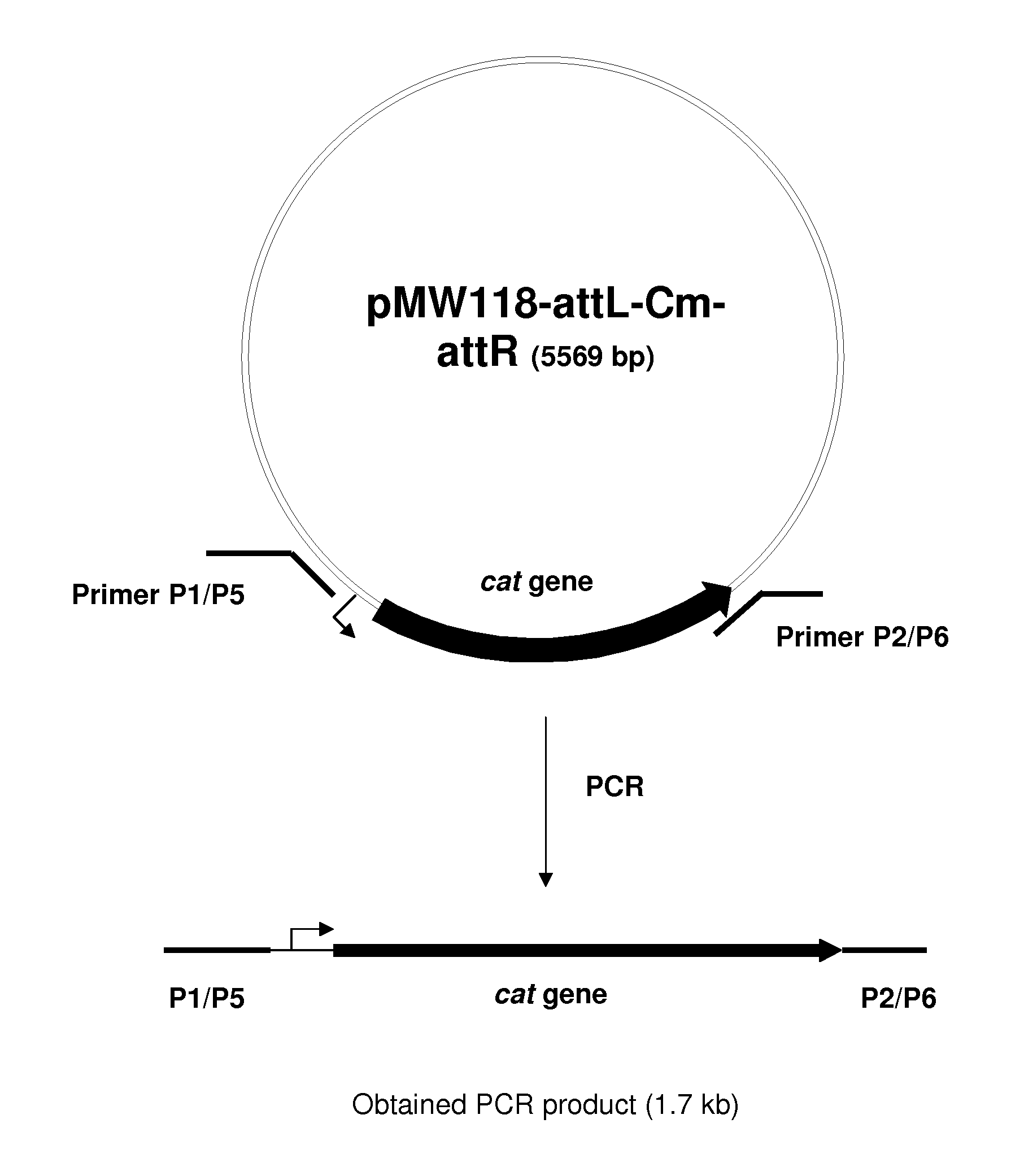
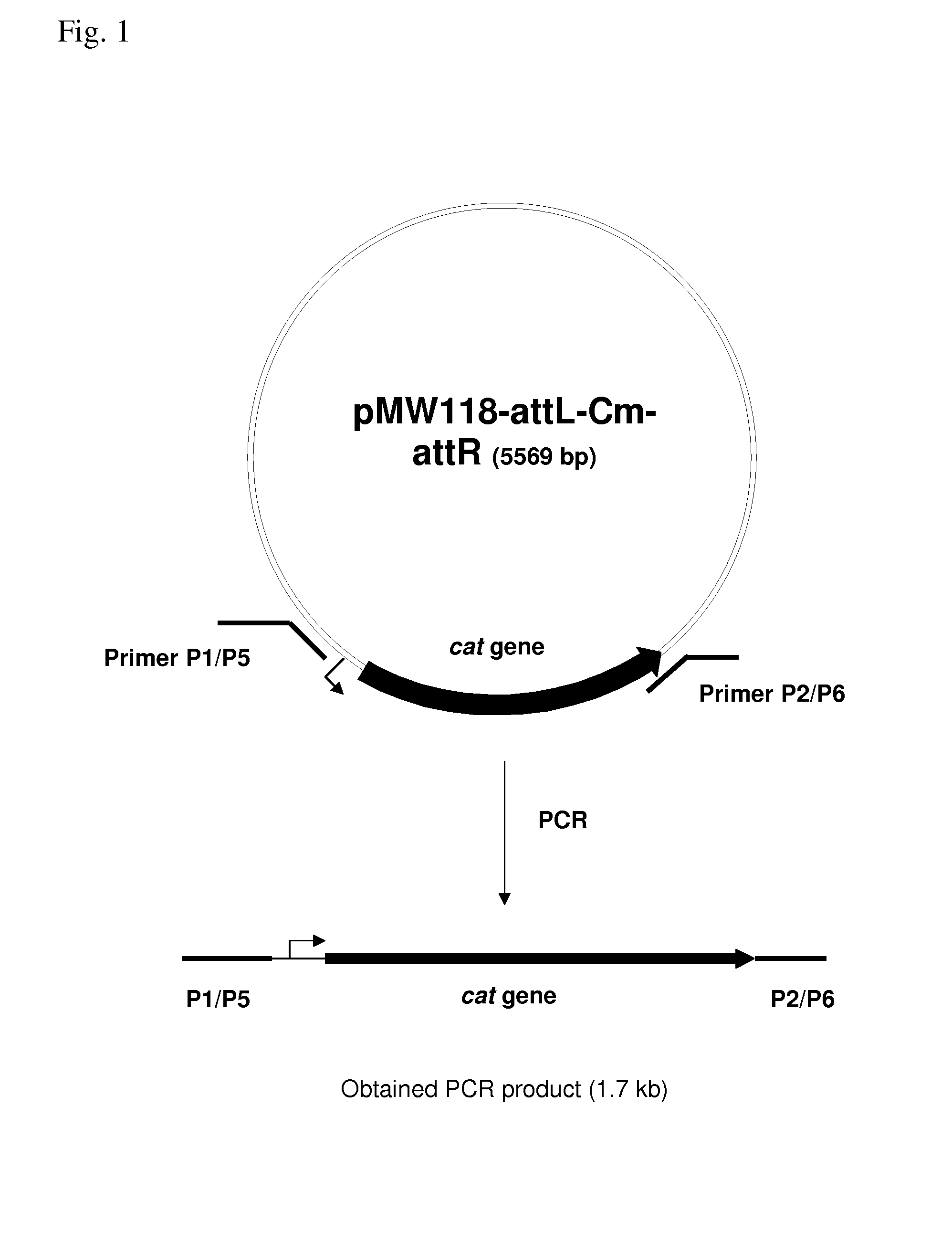
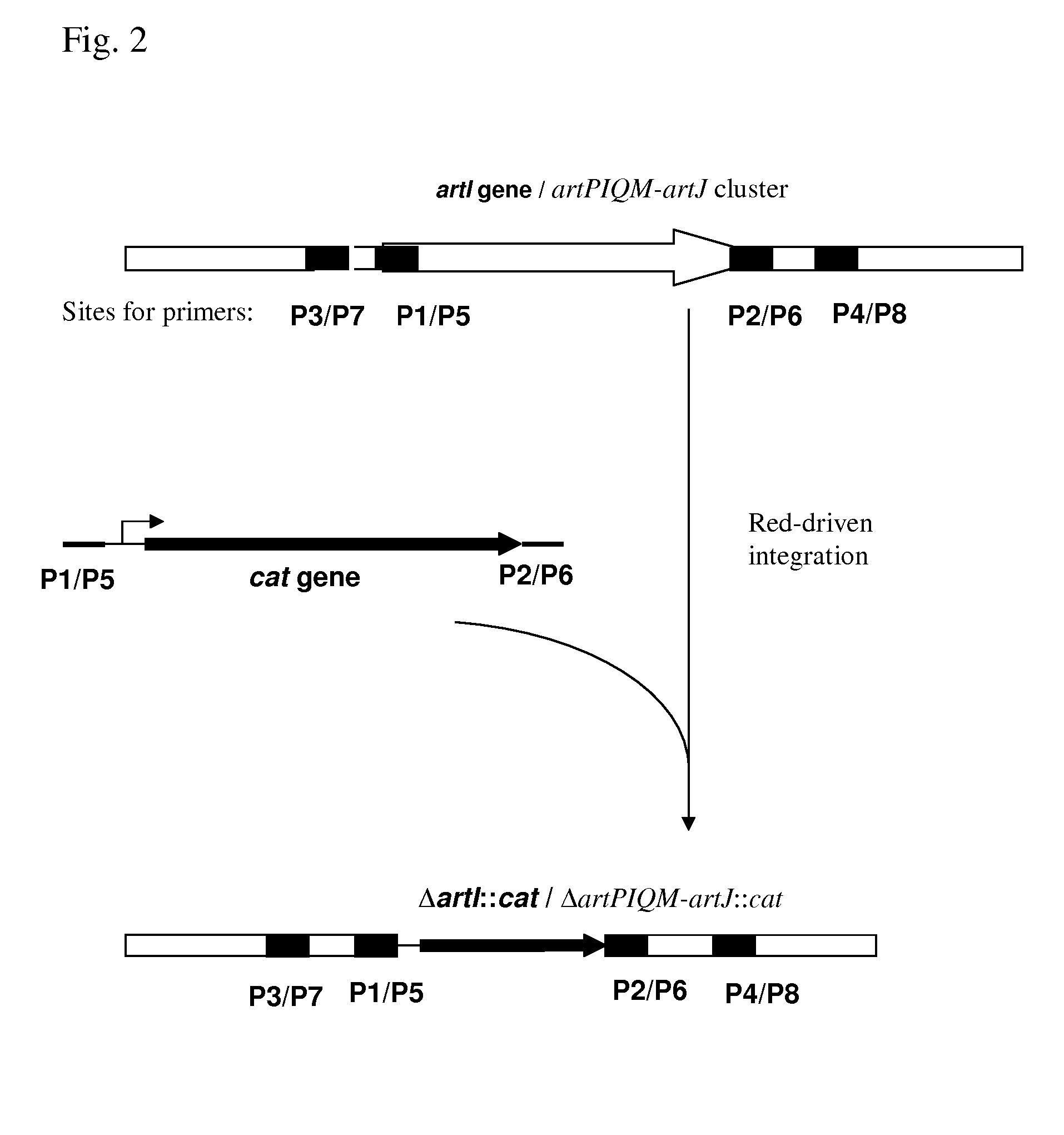
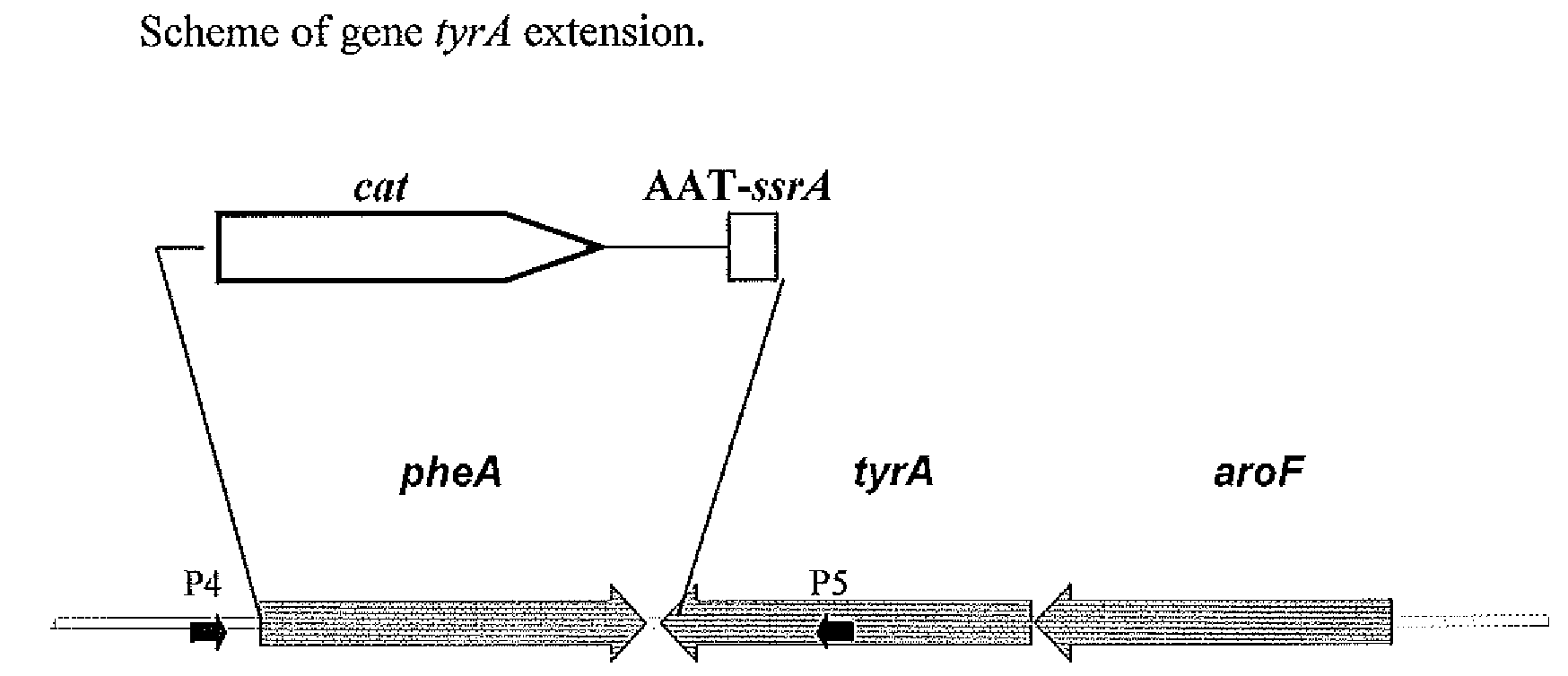
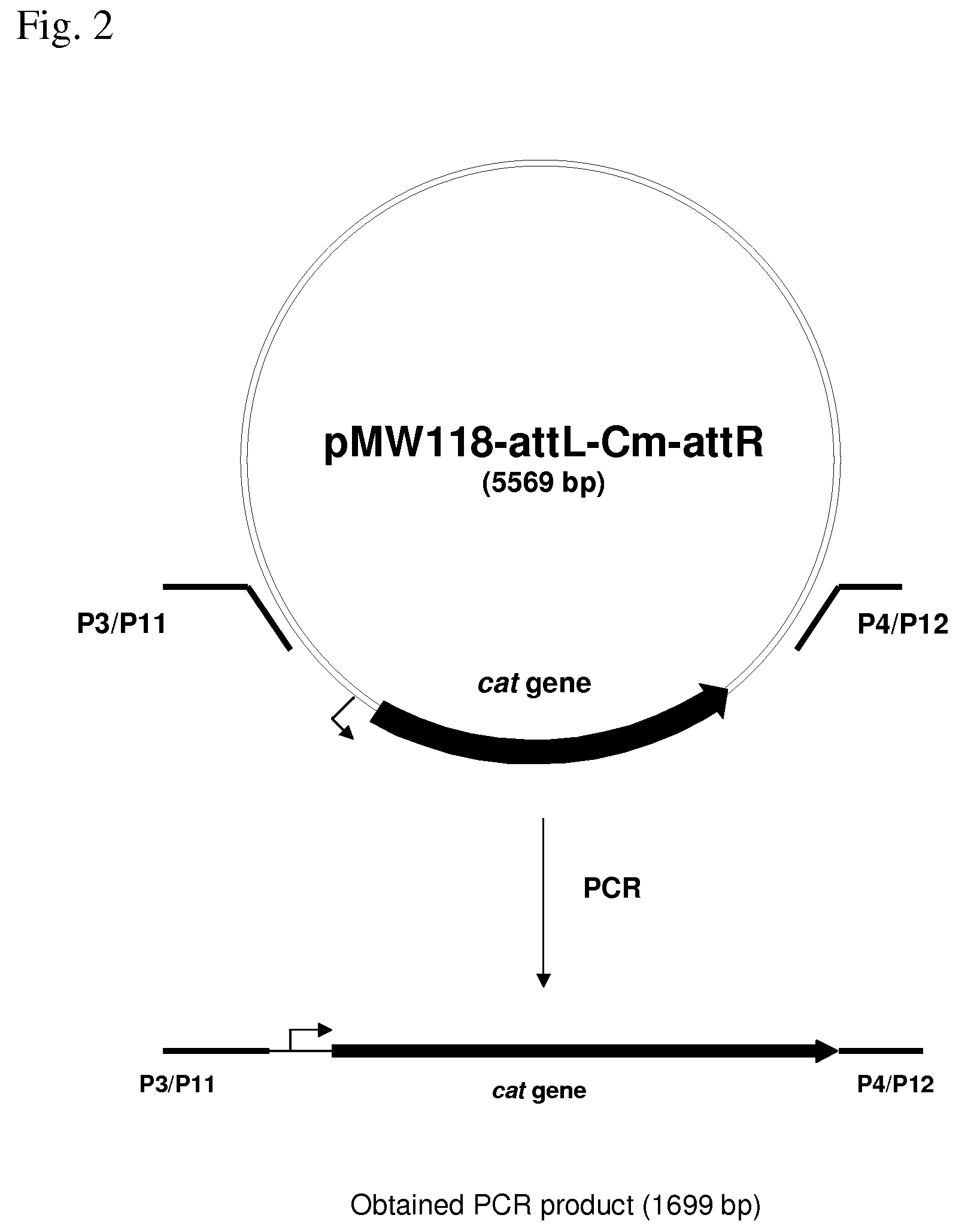
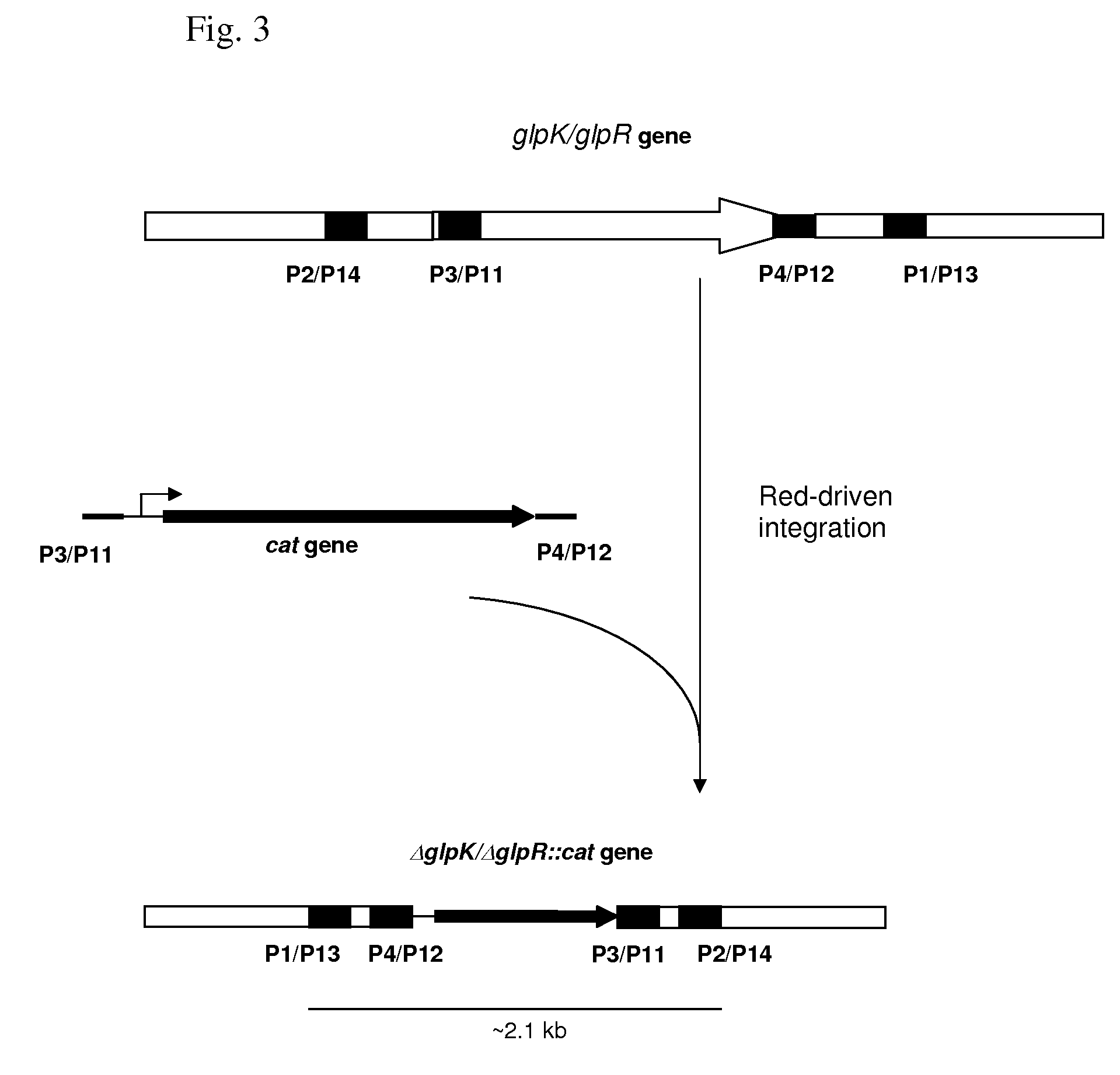
Patents
Literature
101 results about "Enterobacteriaceae bacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
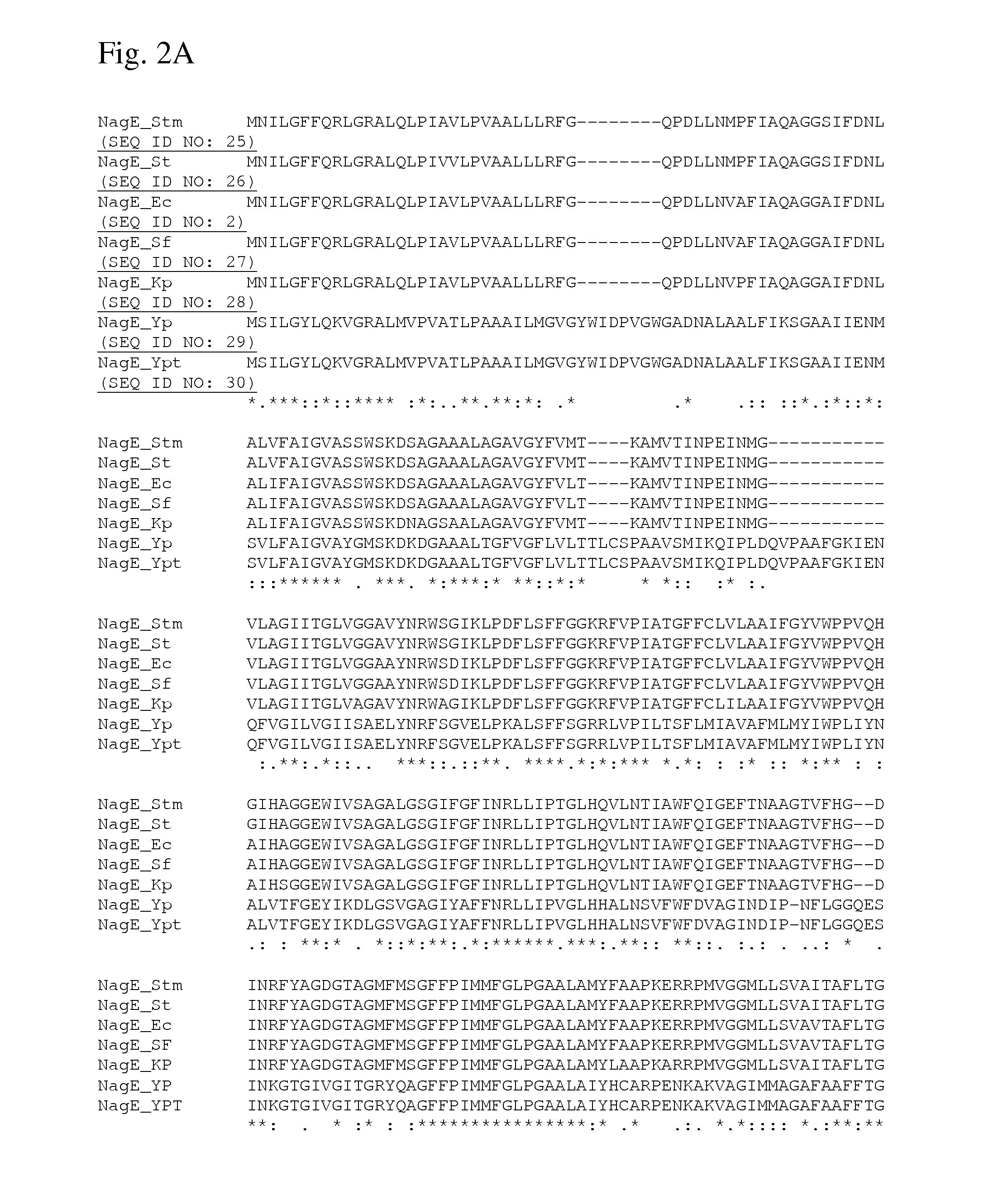
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
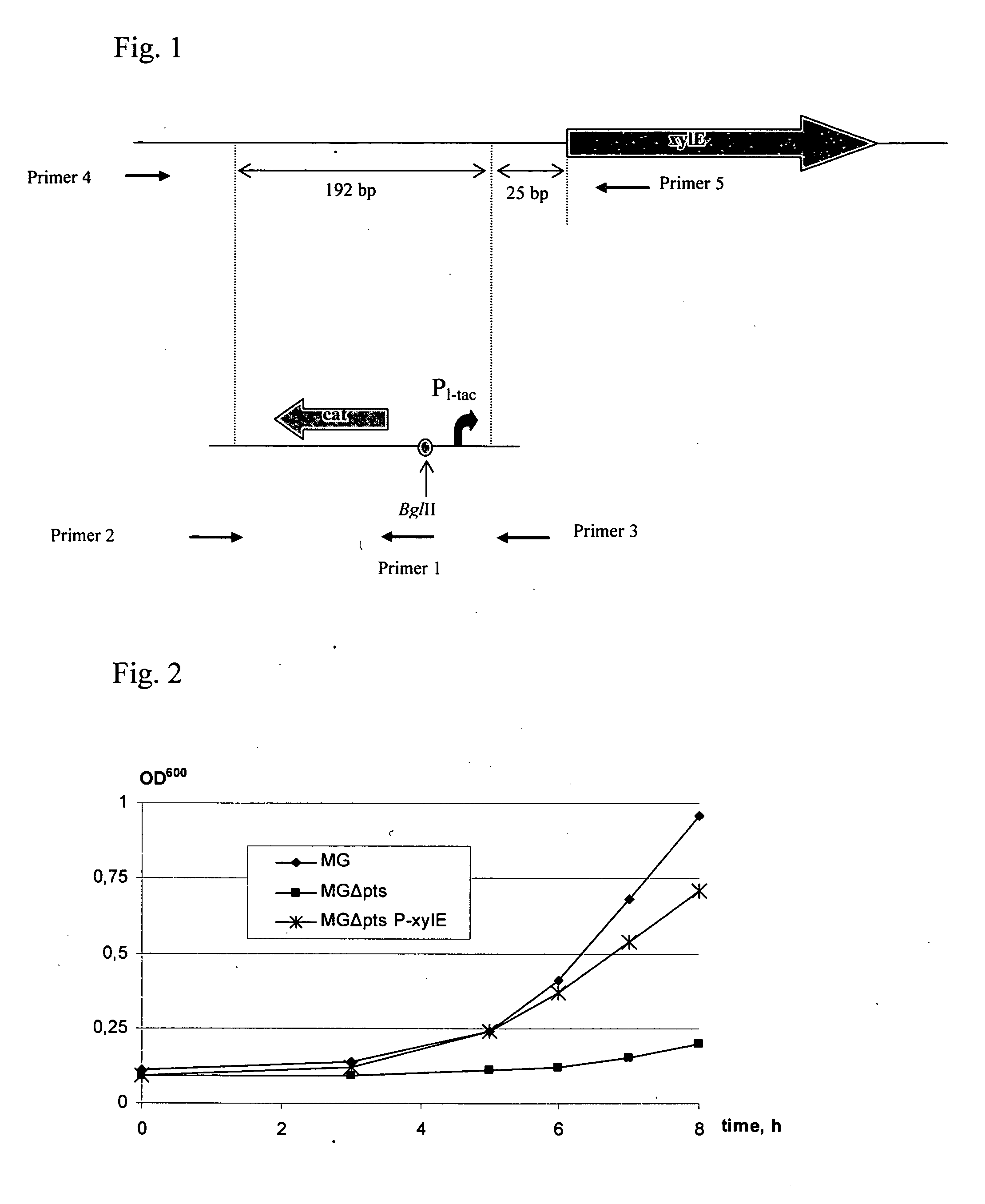
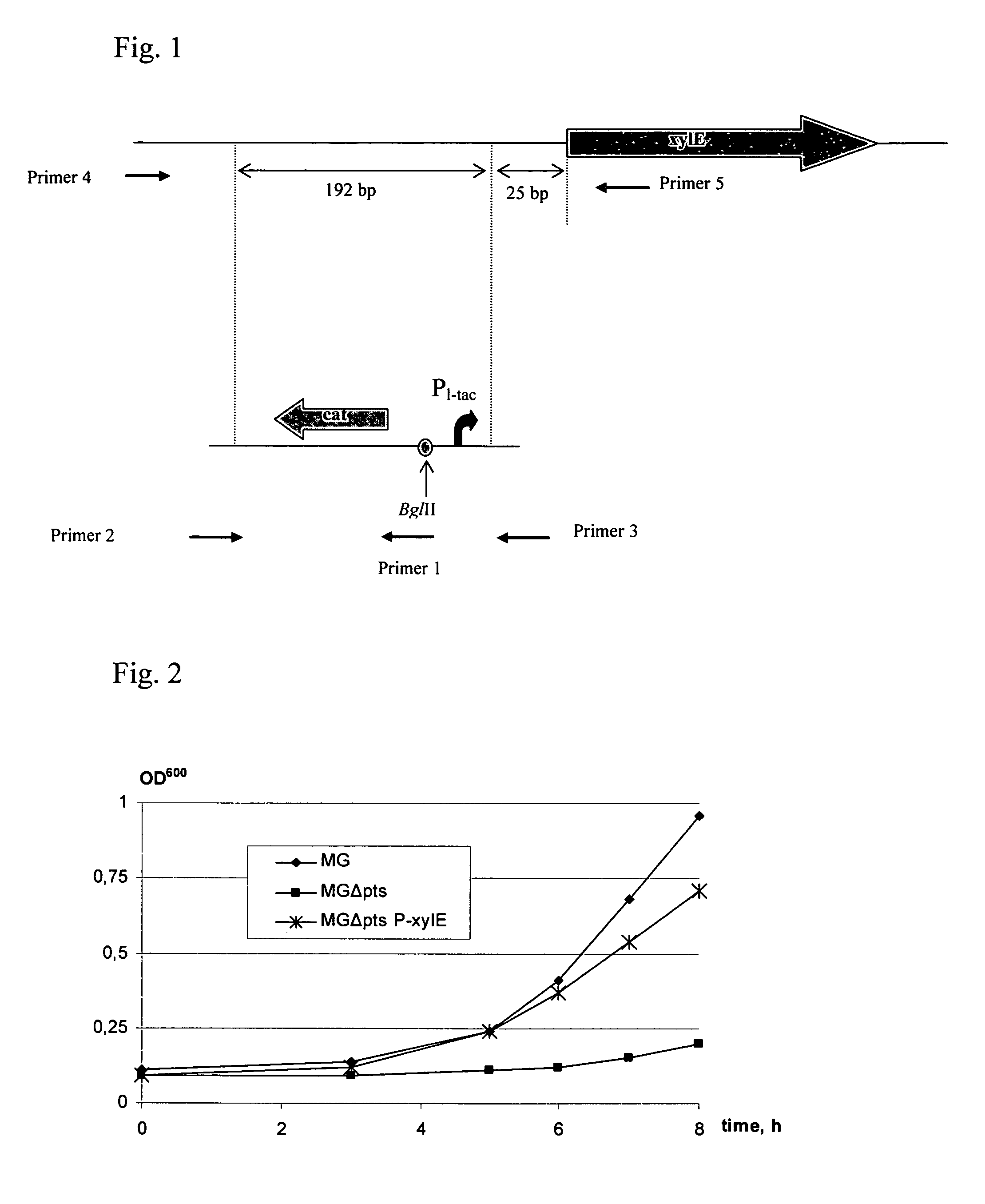
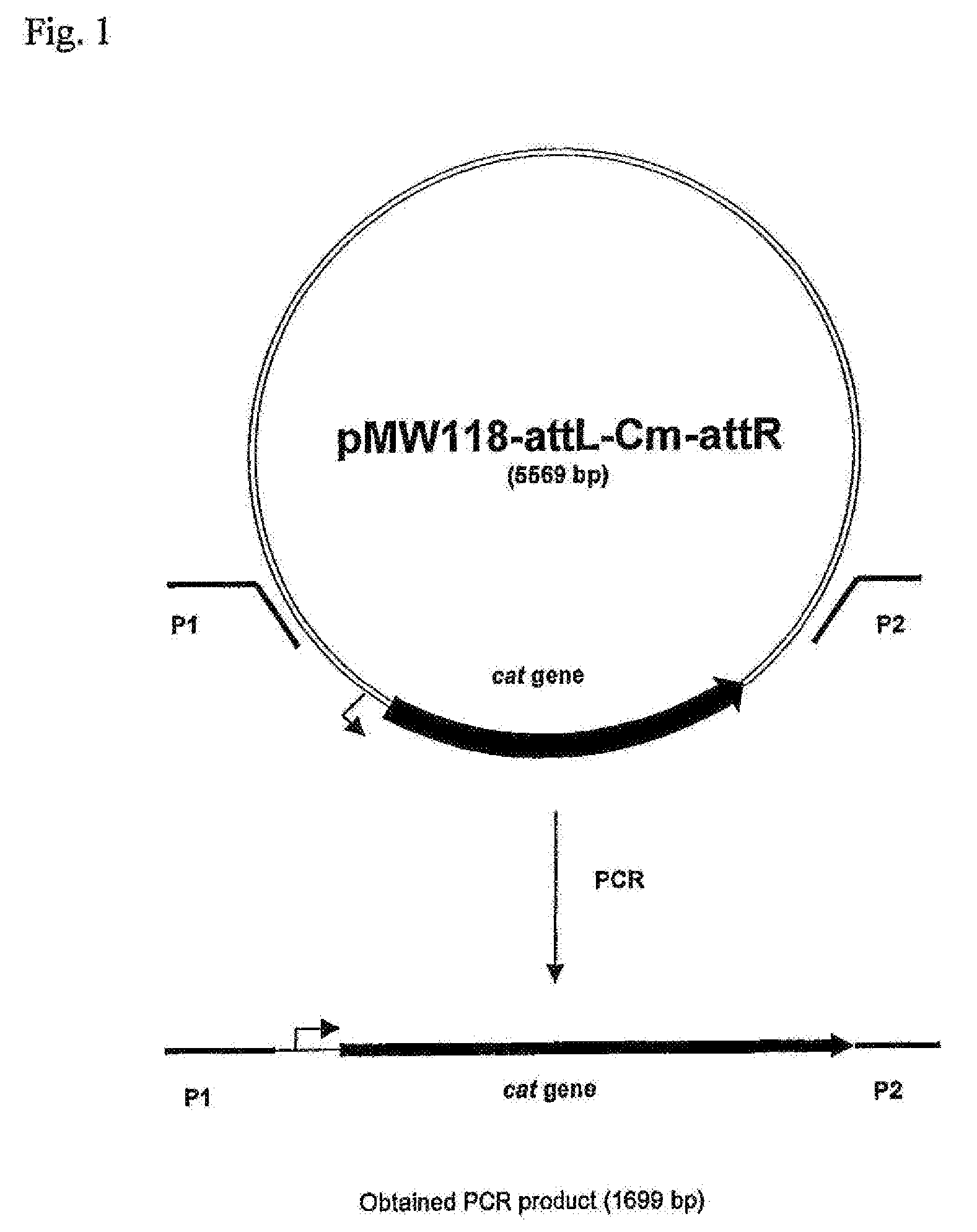
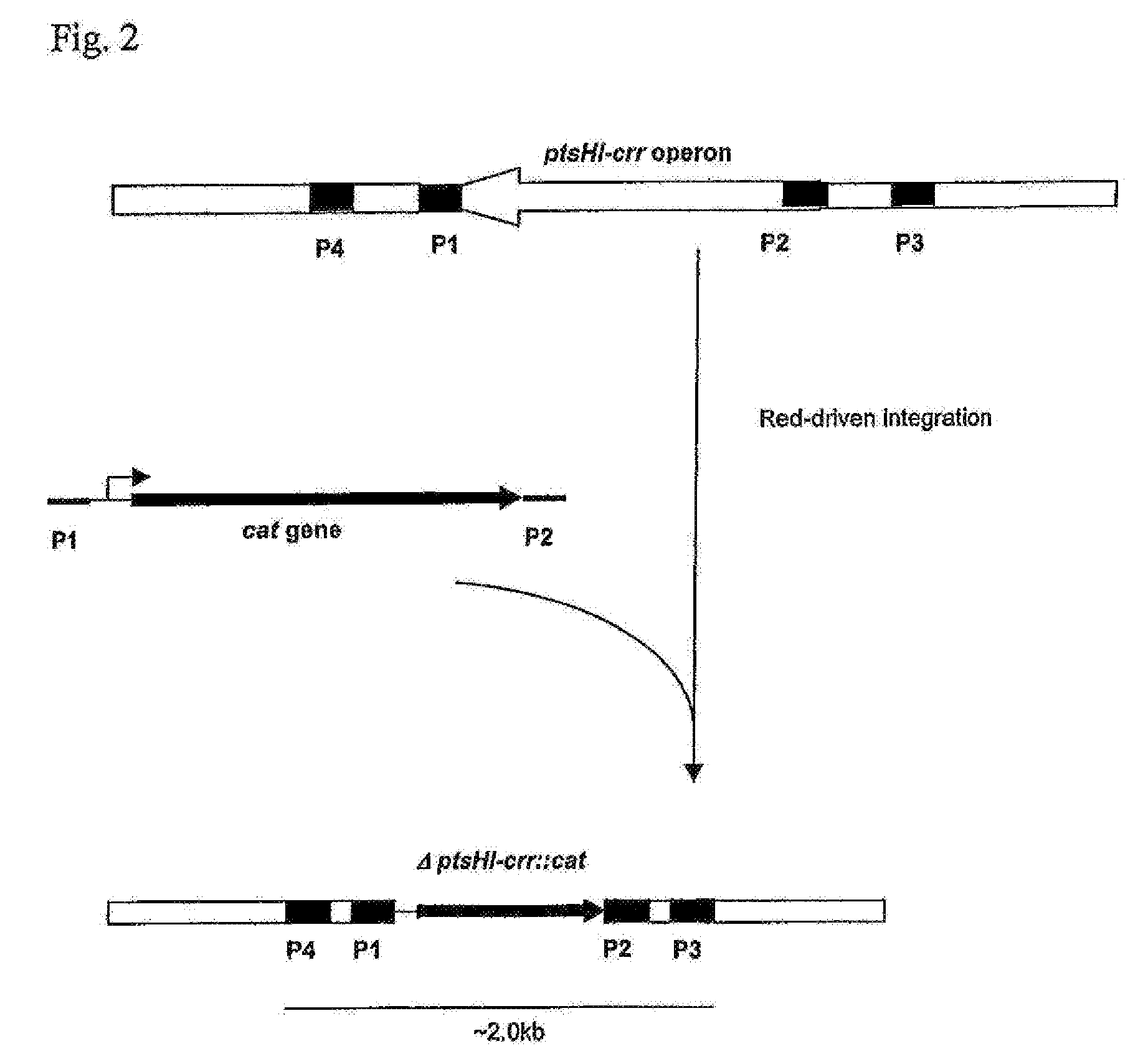
ActiveUS20060088919A1Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesL-threonineArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
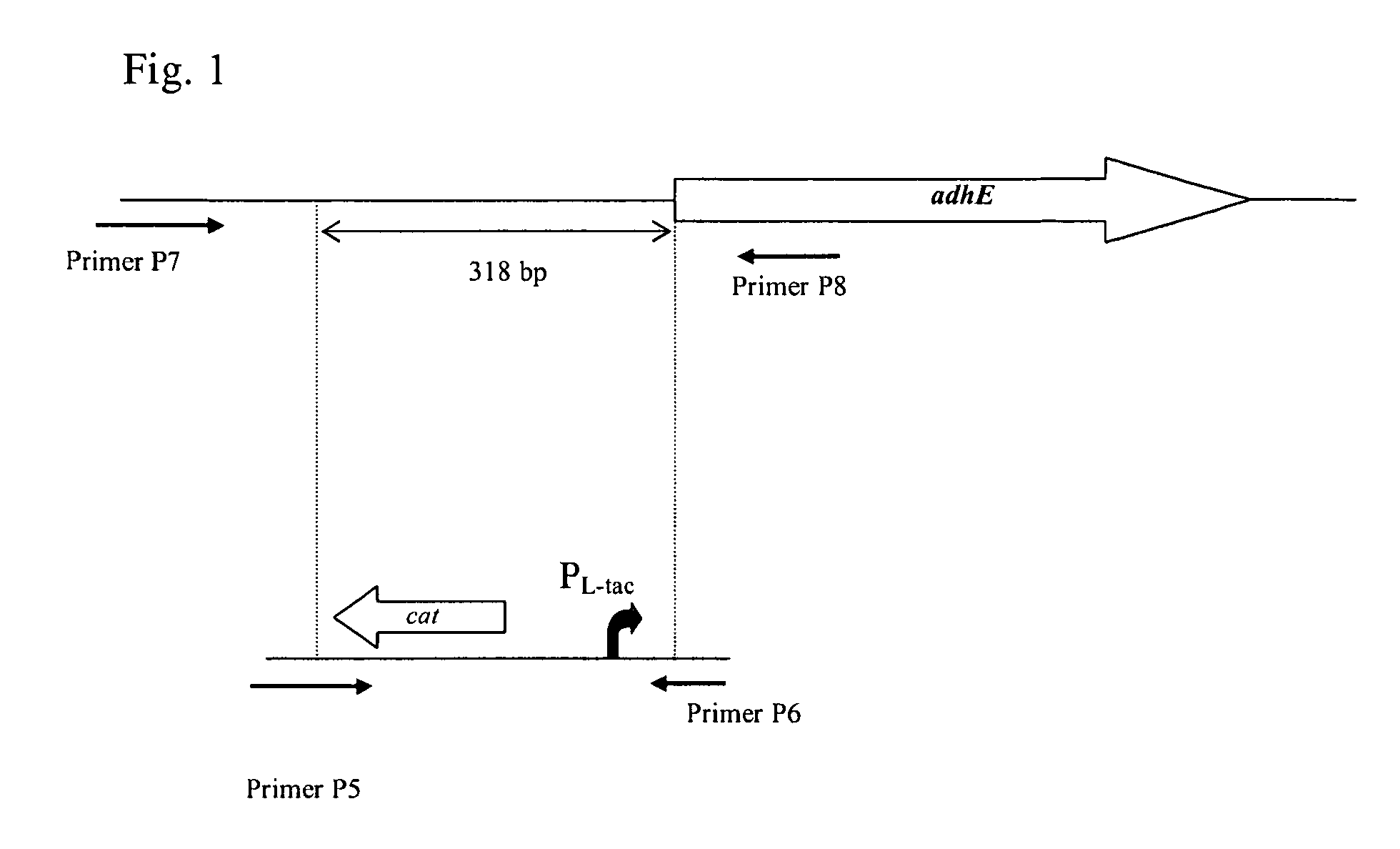
InactiveUS20090203090A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesArginine
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of a wild-type alcohol dehydrogenase encoded by the adhE gene or a mutant alcohol dehydrogenase which is resistant to aerobic inactivation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase and method for producing L-histidine
InactiveUS20050176033A1High expressionImprove production yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesPurineEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The present invention relates to a mutant bacterial PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, and a method for producing L-histidine using the bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family wherein the L-amino acid productivity of said bacterium is enhanced by use of the PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, coded by the mutant prsA gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
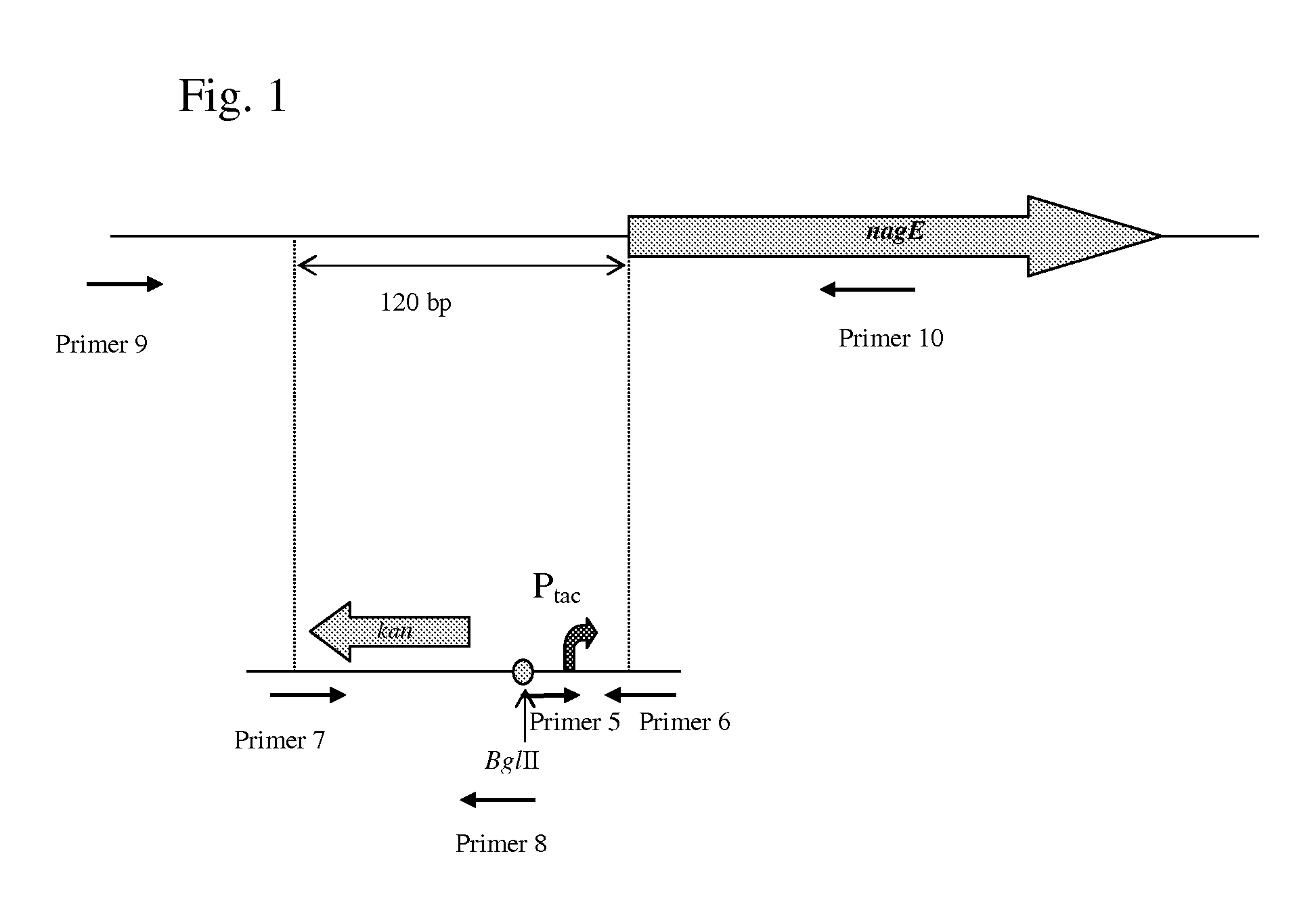
Method for producing l-amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20070212764A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationL-threonineArginine
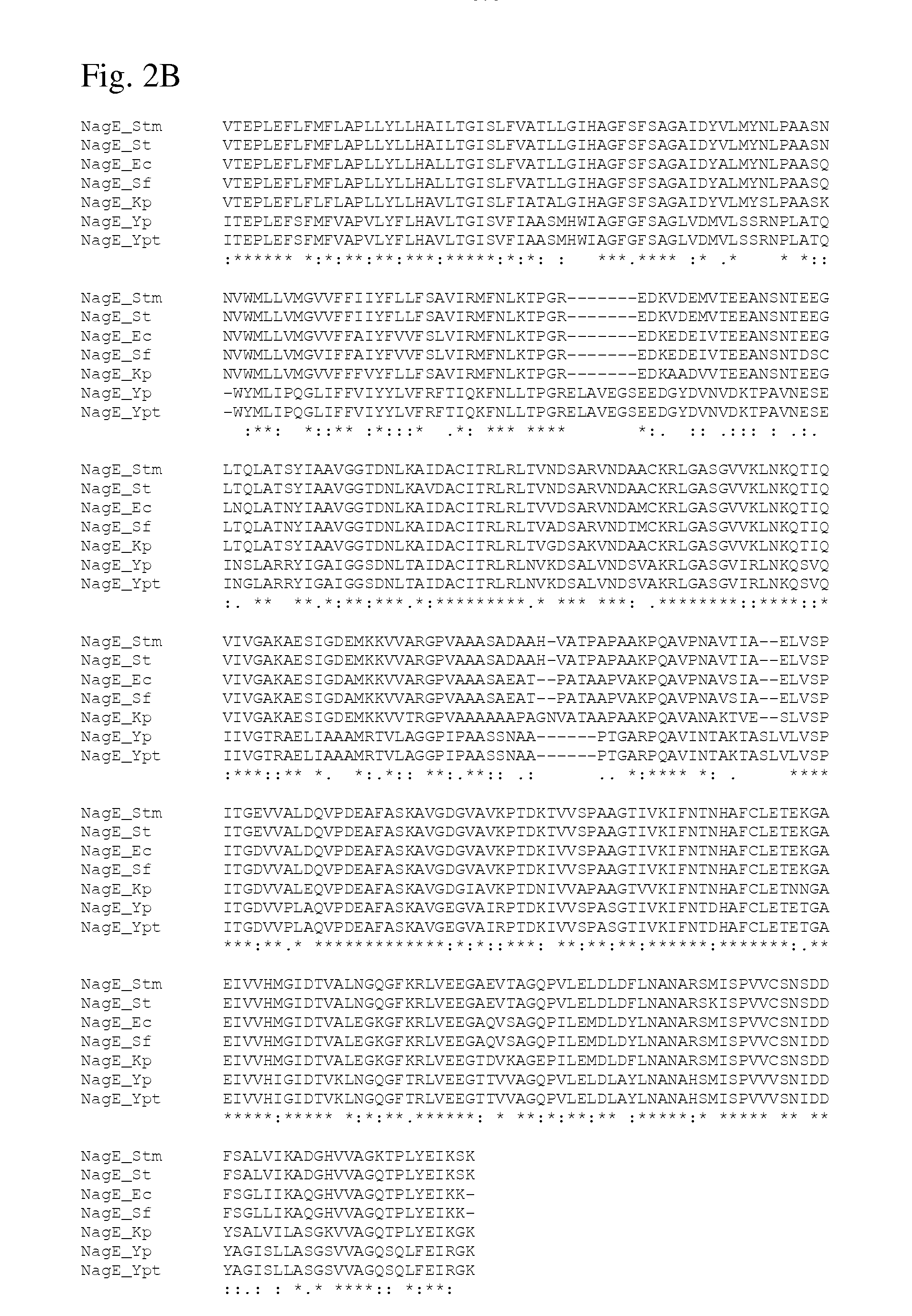
There is disclosed a method for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of N-acetylglucosamine permease encoded by the nagE gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, kit and detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli
ActiveCN103614465APrecise screeningSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The invention discloses loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, a kit and a detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli. In the LAMP primers disclosed by the invention, klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and new delhi metallo-b-lactamase (NDM) primer groups can detect all subtypes except for NDM-10; hypoxanthine nucleotide (IMP) and vimentin (VIM) primer groups can detect common subtypes at home and abroad. The LAMP kit built by the invention is applied to joint detection of KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes, can cover the common carbapenemase genes of non-fermentative bacteria and enterobacteriaceae, can accurately and quickly screen the common carbapenemase genes, and has great clinical significance for timely detecting and further controlling fulminant epidemic caused by propagation of the carbapenemase genes in enterobacteriaceae. The kit disclosed by the invention is high in detection sensitivity and the minimum detection limits of the KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes can reach 100 CFU / reaction.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Bacterium for fermenting L-tryptophan from mixed saccharum and fermentation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and in particular relates to a bacterium for fermenting L-tryptophan from mixed saccharum and a fermentation method thereof. The Enterobacteriaceae bacterium for producing L-tryptophan can have the capability of simultaneously utilizing hexose and pentose to produce the L-tryptophan because of containing the coding gene of a cAMP receptor protein mutant. The cAMP receptor protein mutant is obtained through mutating one or a plurality of amino acid loci of the cAMP receptor protein. The bacterium provided by the invention consumes glucose and xylose in a culture medium containing the glucose and the xylose at the same time, and the yield and conversion rate of the L-tryptophan are increased.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20090098621A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesGemella
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
There is disclosed a method for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of L-arabinose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Synthetase and Method for Producing L-Histidine
The present invention relates to a mutant bacterial PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, and a method for producing L-histidine using the bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family wherein the L-amino acid productivity of said bacterium is enhanced by use of the PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, coded by the mutant prsA gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
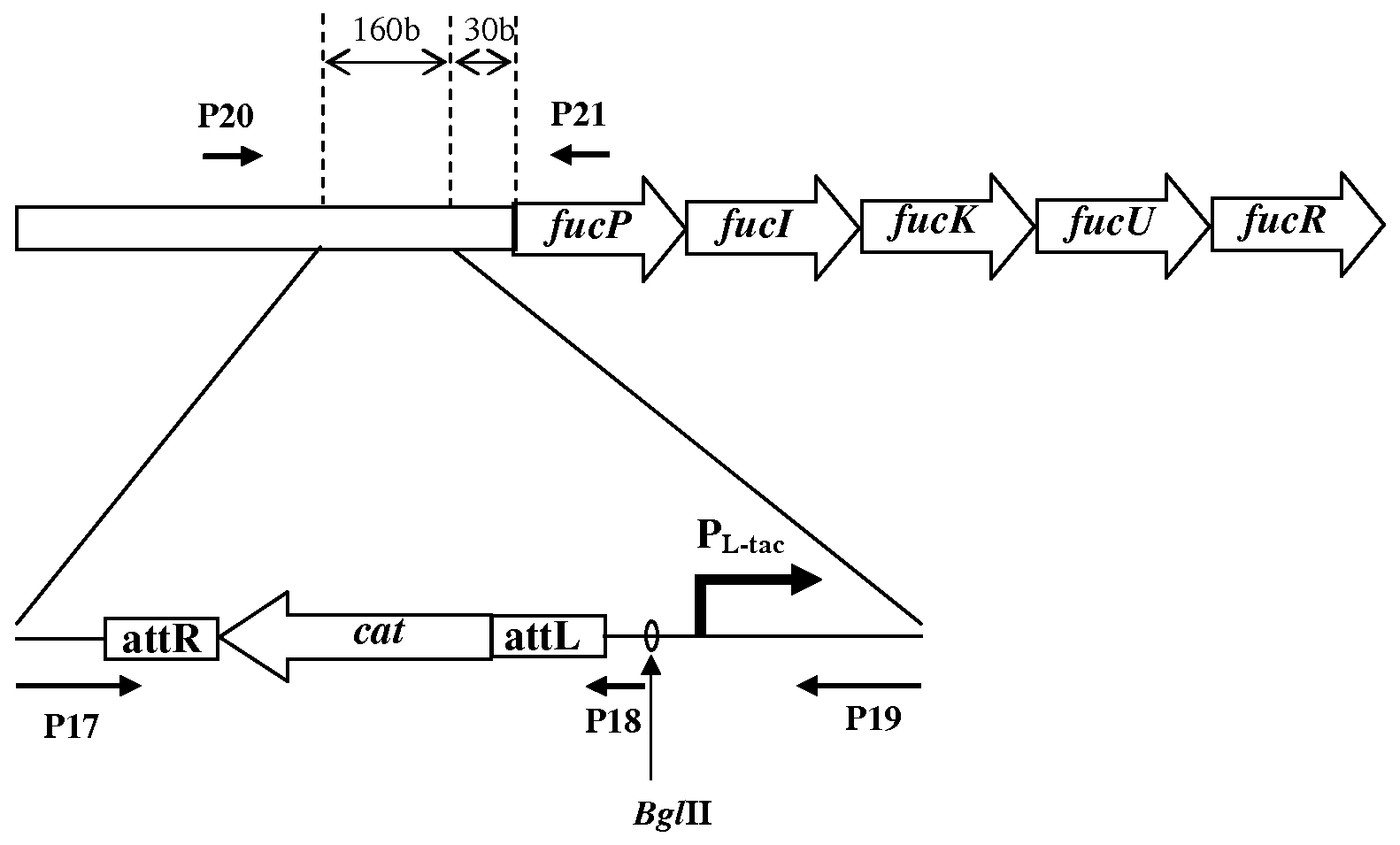
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae Family With Enhanced Expression of the fucPIKUR Operon
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to enhance expression of at least one gene of the fucPIKUR operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-amino acid using bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family, having nir operon inactivated
A method is provided for producing L-amino acid, such as L-arginine using a bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging the genus Escherichia, with an inactivated nir operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS7915018B2Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesBacteroidesArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
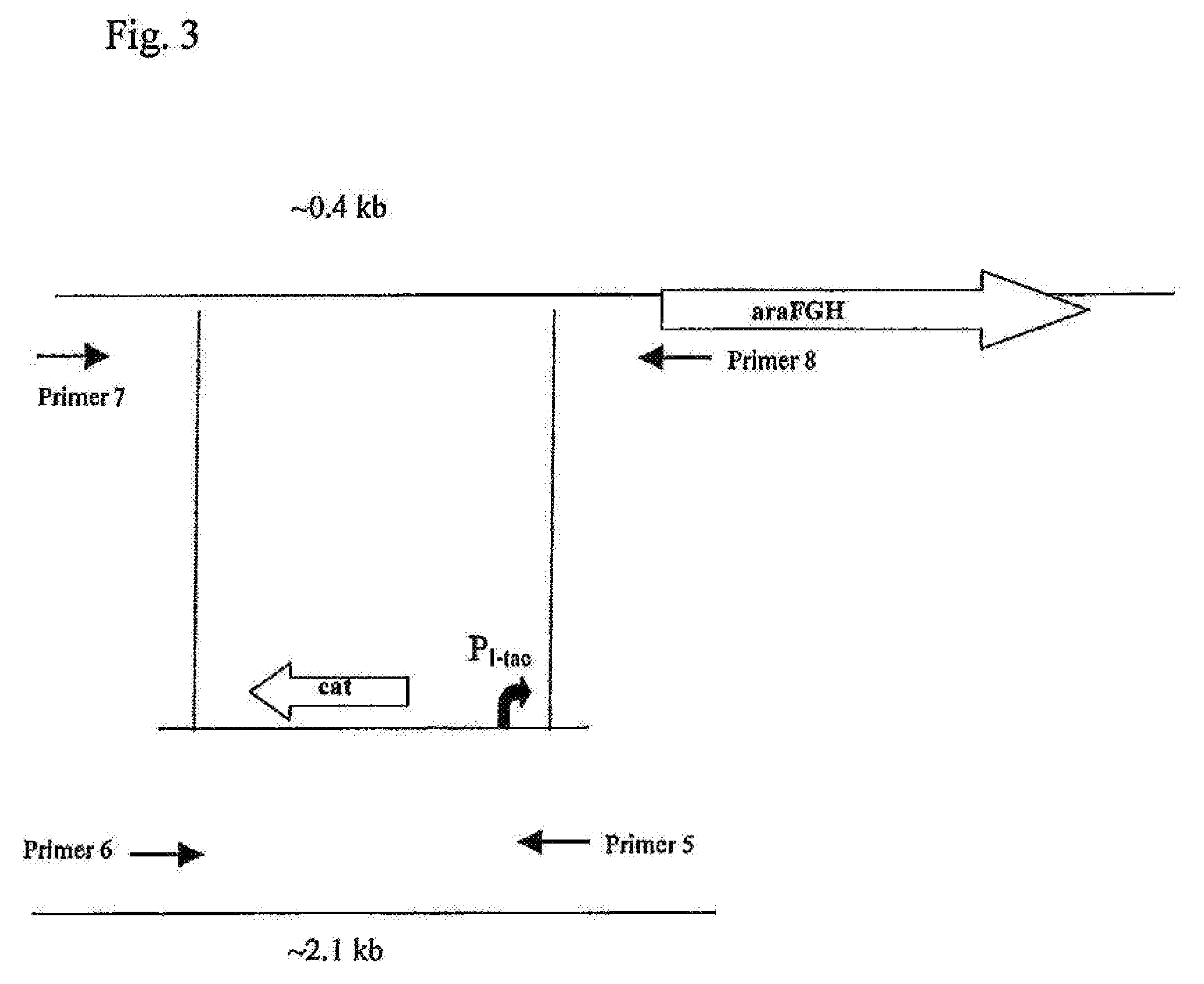
A method is described for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-leucine, L-histidine, L-cysteine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, L-glutamic acid, L-valine, and L-isoleucine, by fermentation of glucose using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance the activity of the high-affinity arabinose transporter coded by the araFGH operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-arginine using a bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family, having attenuated expression of a gene encoding an l-arginine transporter
InactiveUS20100143983A1Improve productivityIncreased ability to produce L-arginineBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing L-arginine using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of one or several genes encoding an L-arginine transporter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20090137010A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesDNA fragmentationA-DNA
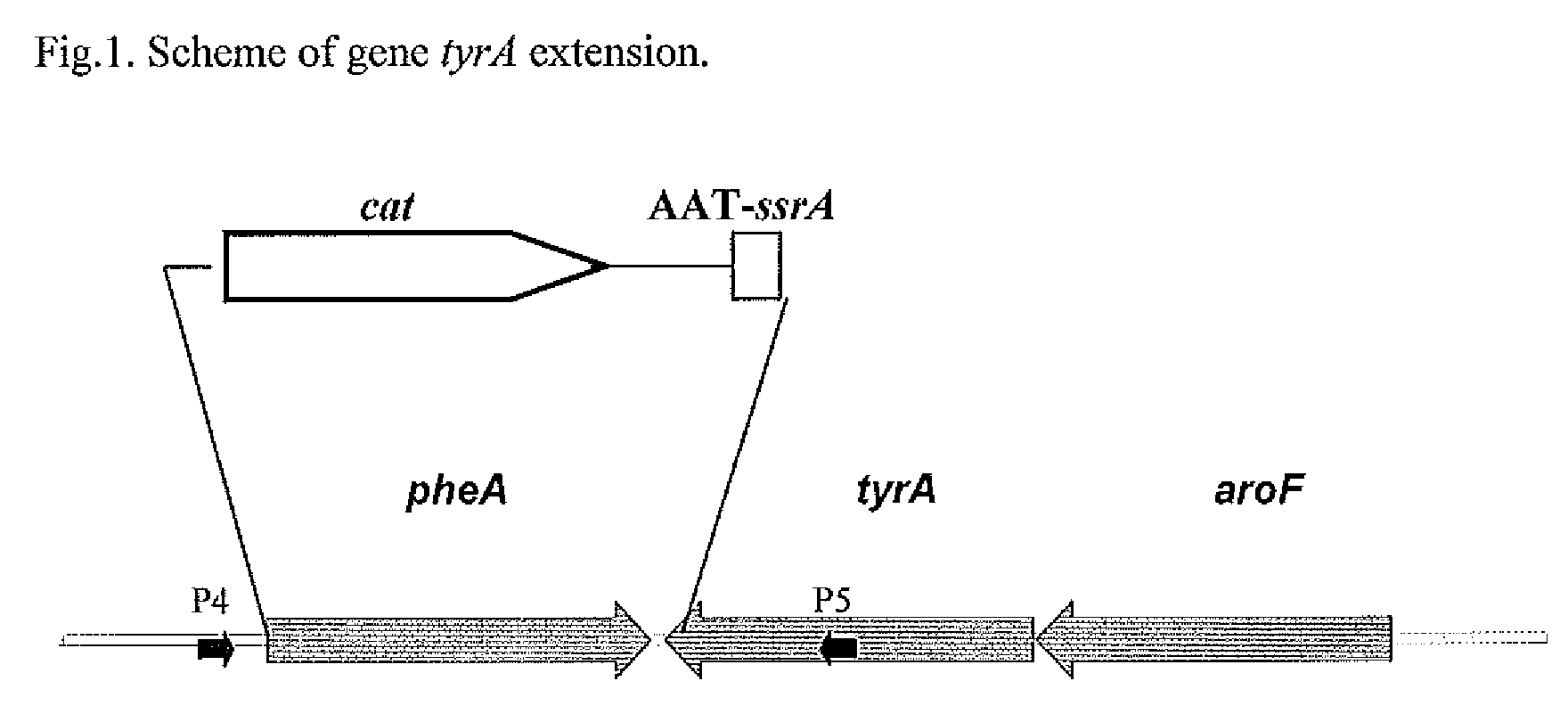
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example, L-phenylalanine and L-histidine, by fermentation using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified by attaching a DNA fragment able to be transcribed encoding the peptide represented in SEQ ID NO: 2, or a variant thereof, particularly a portion of the ssrA gene, to the 3′-end of gene encoding for the bacterial enzyme, which influences on the L-amino acid biosynthesis, such as chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydrogenase or phosphoglucose isomerase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium having an enhanced ability to utilize glycerol
InactiveUS20090317876A1Improve abilitiesProducing L-aminoBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to have glycerol kinase in which feedback inhibition by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is desensitized, thereby having enhanced ability to utilize glycerol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20110177566A1Improve productivityIncrease productionPeptidesFermentationBacteroidesMicrobiology
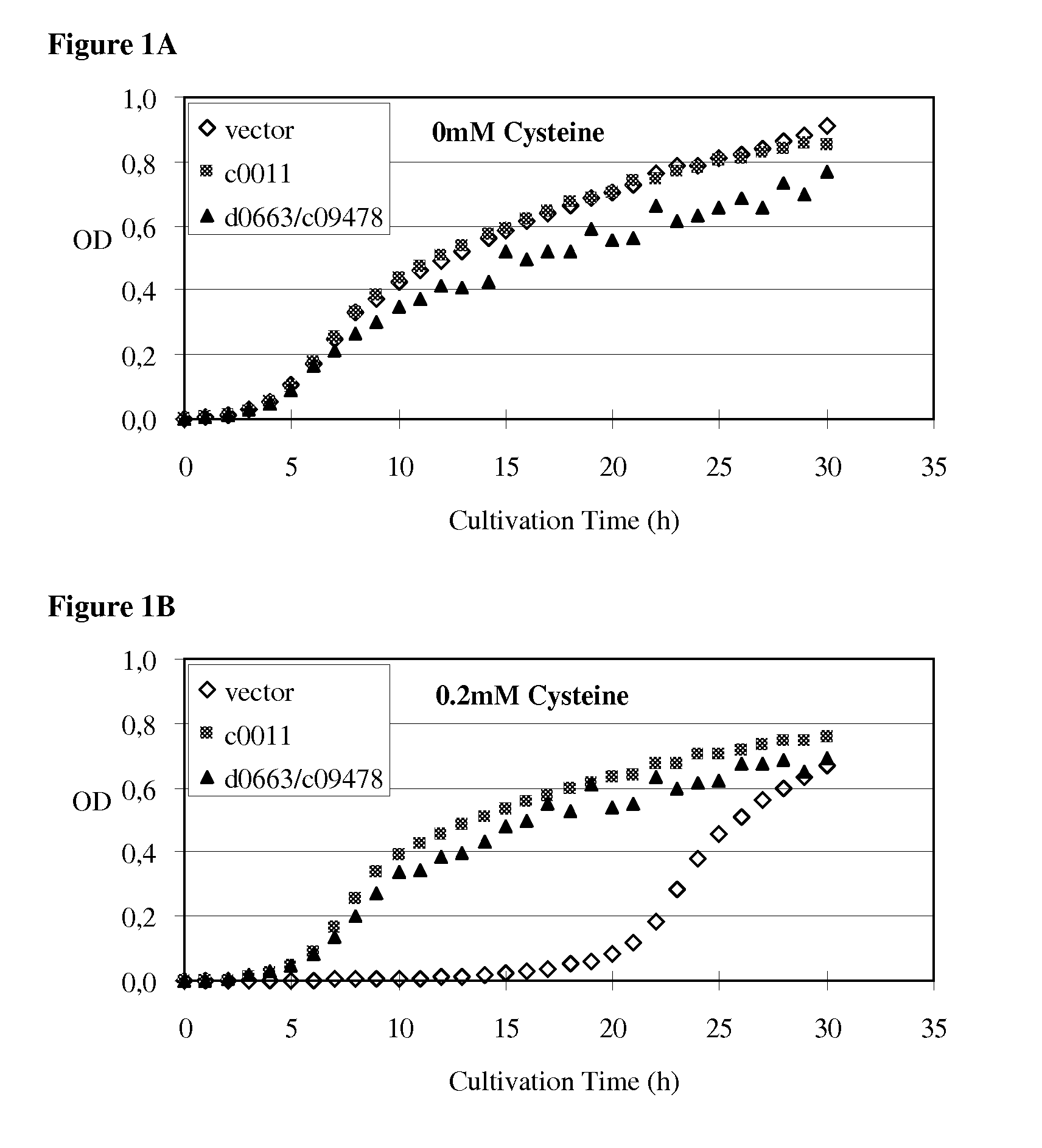
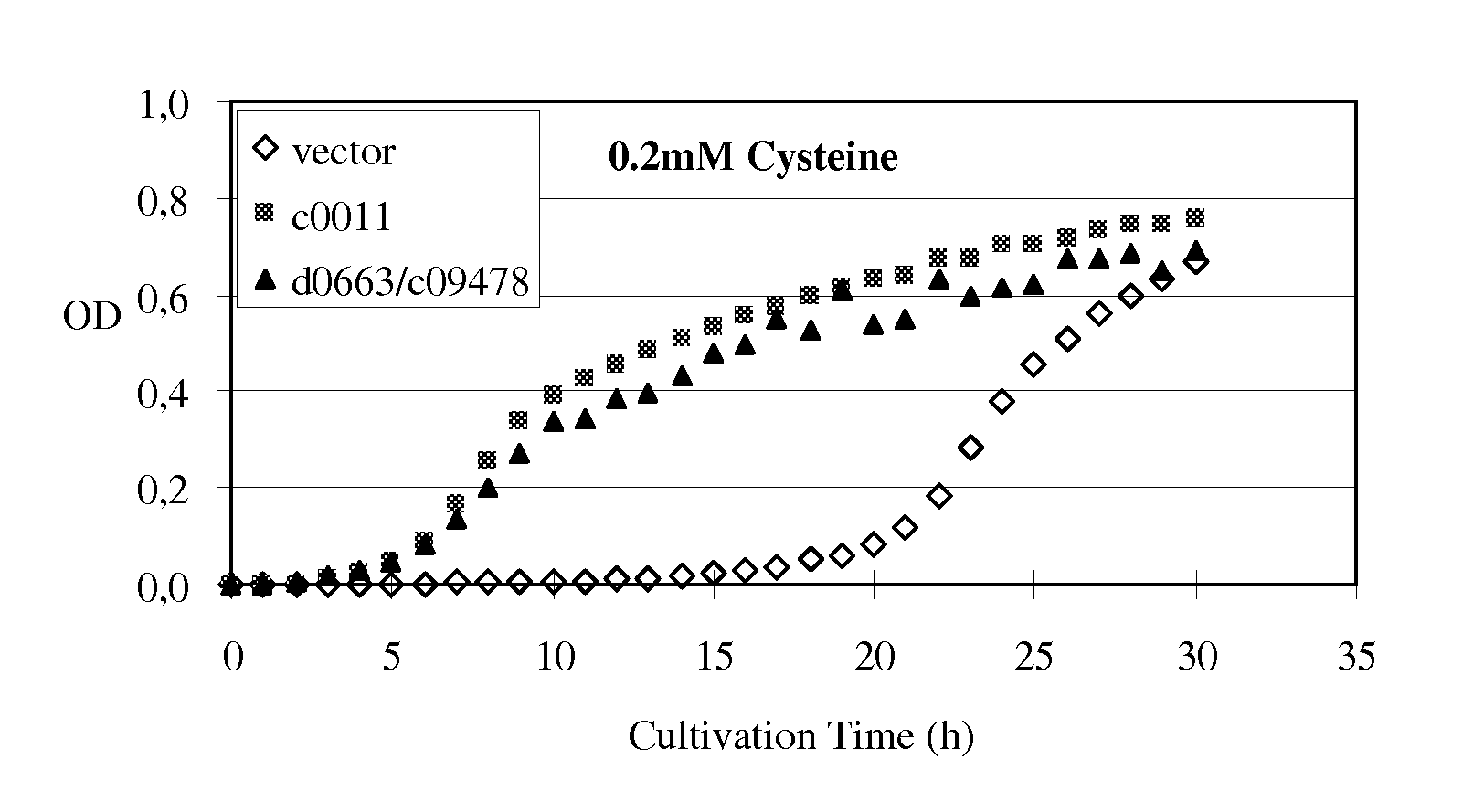
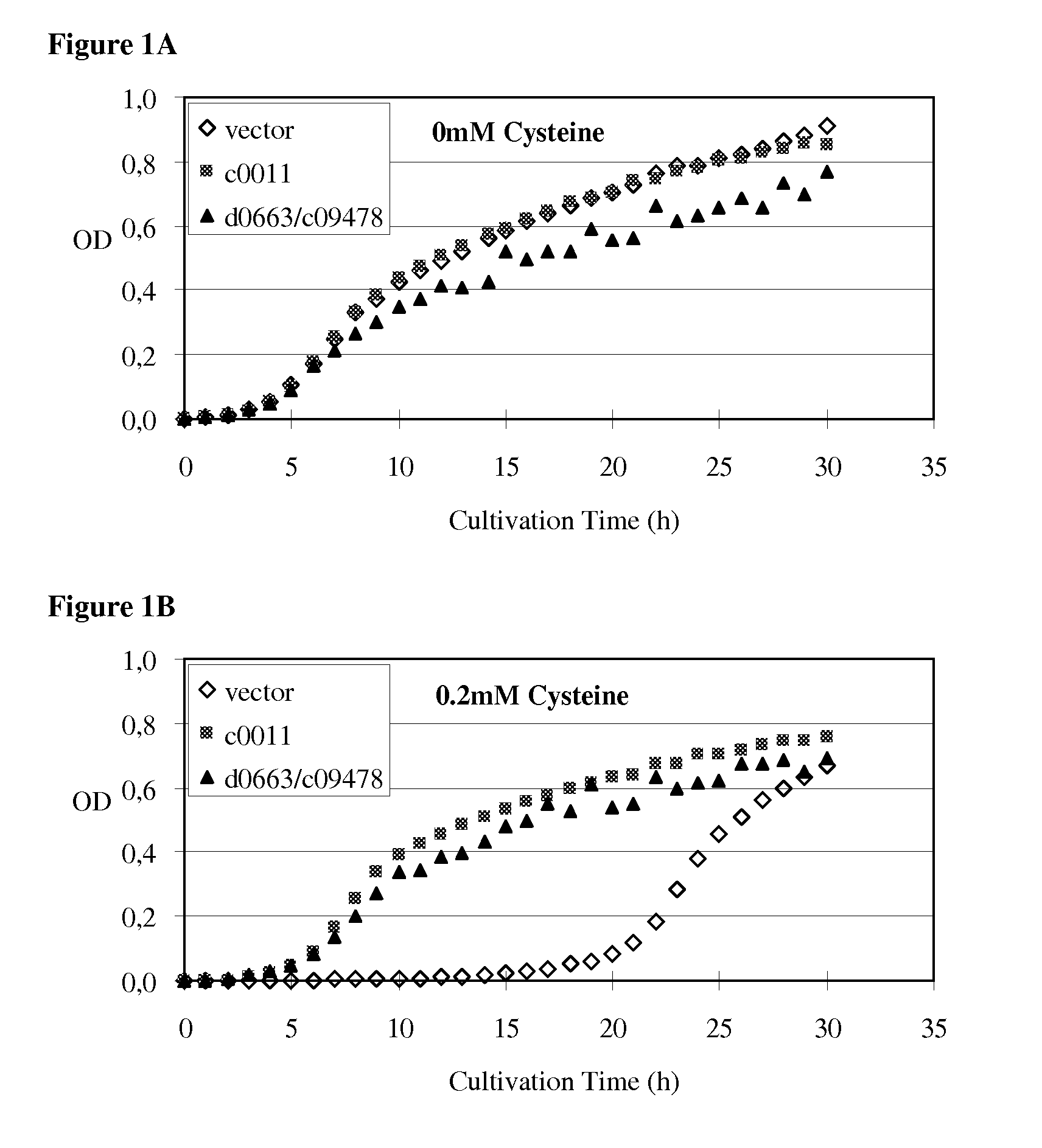
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium contains a protein which is able to confer resistance to growth inhibition by L-cysteine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an L-amino acid using bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS7803584B2Improve productivityIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesPantoea
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS8460903B2Improve productivityIncrease productionPeptidesFermentationCysteine thiolateMicrobiology
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing microorganism which has been modified to inactive the fimH gene, and a method for producing I-amino acid
InactiveUS7547531B2Improve productivityProducing an L-amino acidSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismBiotechnology
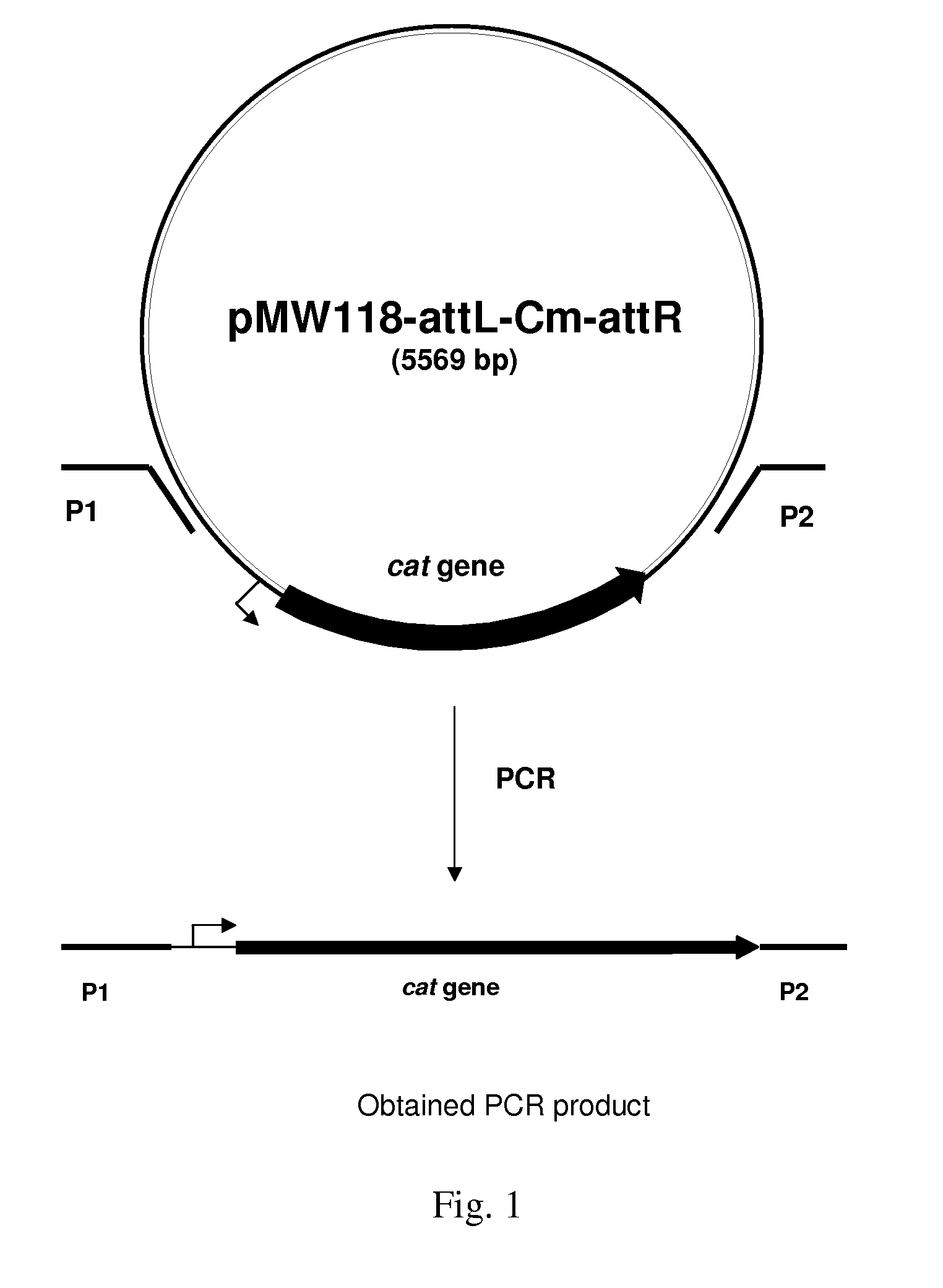
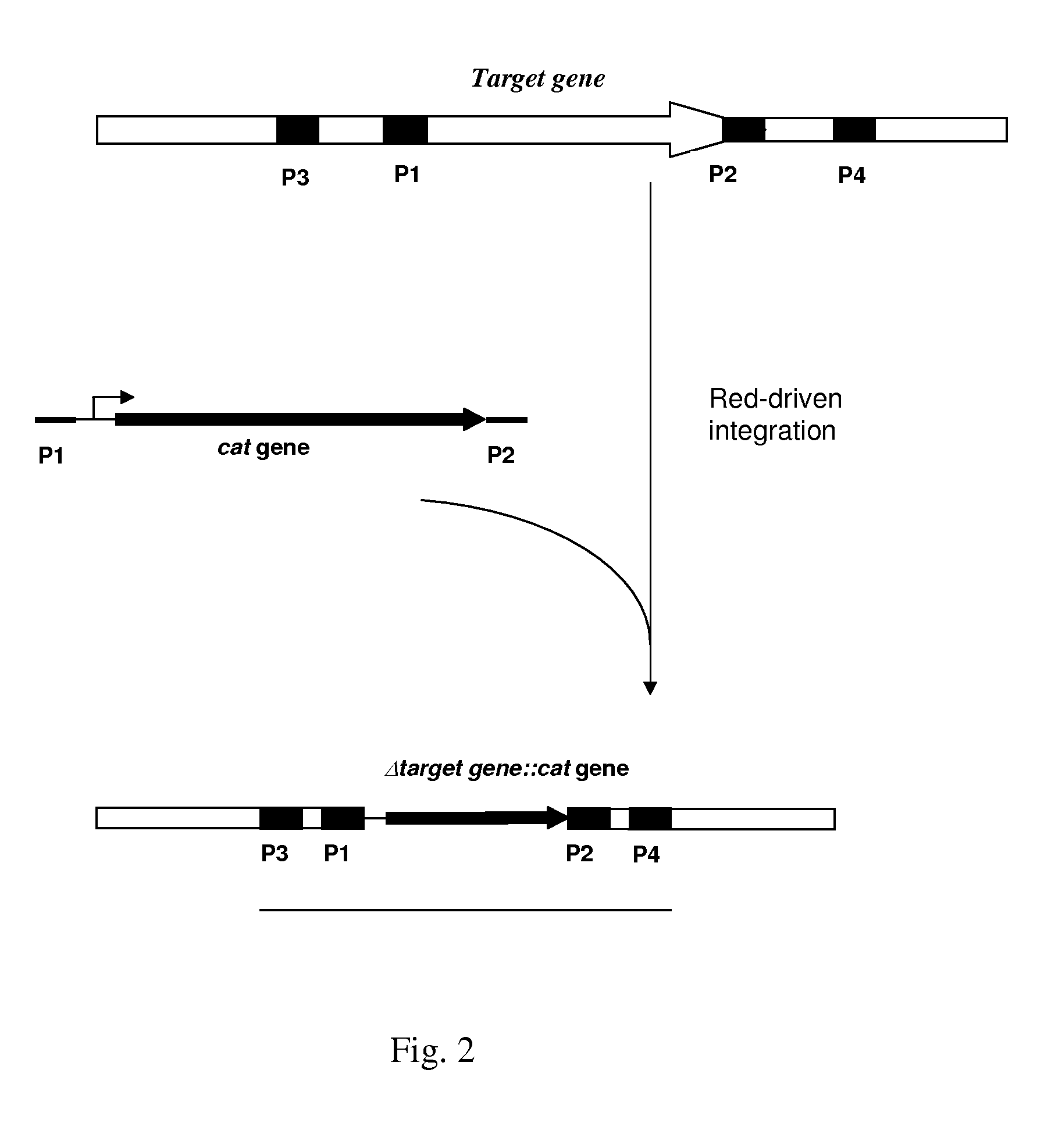
An L-amino acid producing bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family is described, wherein the bacterium has been modified so as to not produce type I fimbrial adhesin protein is cultured in a medium to produce and excrete said L-amino acid in the medium, and collecting said L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20100311129A1Improve productivityIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesPantoea
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-cysteine, l-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof or a mixture thereof using a bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20120237986A1Increase gene expressionImprove productivityBacteriaHydrolasesSulfurEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The present invention provides a method for producing L-cysteine, L-cystine, a derivative or precursor thereof or a mixture thereof using a bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family which has been modified to have enhanced expression of the genes involved in the process of sulphur assimilation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-isoleucine using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae having overexpressed the cycA gene
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family producing L-aspartic acid or L-aspartic acid-derived metabolites and a method for producing L-aspartic acid or L-aspartic acid-derived metabolites
InactiveUS9051591B2Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesMetabolite
The presently disclosed subject matter provides a bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family producing L-aspartic acid or an L-aspartic acid-derived metabolite modified to have aspartate dehydrogenase and a method for producing L-aspartic acid or an L-aspartic acid-derived metabolite, such as L-threonine, L-lysine, L-arginine, L-methionine and L-homoserine, using such bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family producing l-aspartic acid or l-aspartic acid-derived metabolites and a method for producing l-aspartic acid or l-aspartic acid-derived metabolites
InactiveUS20120329105A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesMetabolite
The presently disclosed subject matter provides a bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family producing L-aspartic acid or an L-aspartic acid-derived metabolite modified to have aspartate dehydrogenase and a method for producing L-aspartic acid or an L-aspartic acid-derived metabolite, such as L-threonine, L-lysine, L-arginine, L-methionine and L-homoserine, using such bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-amino acids using bacteria of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20110143403A1Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedFermentationBacteroidesArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
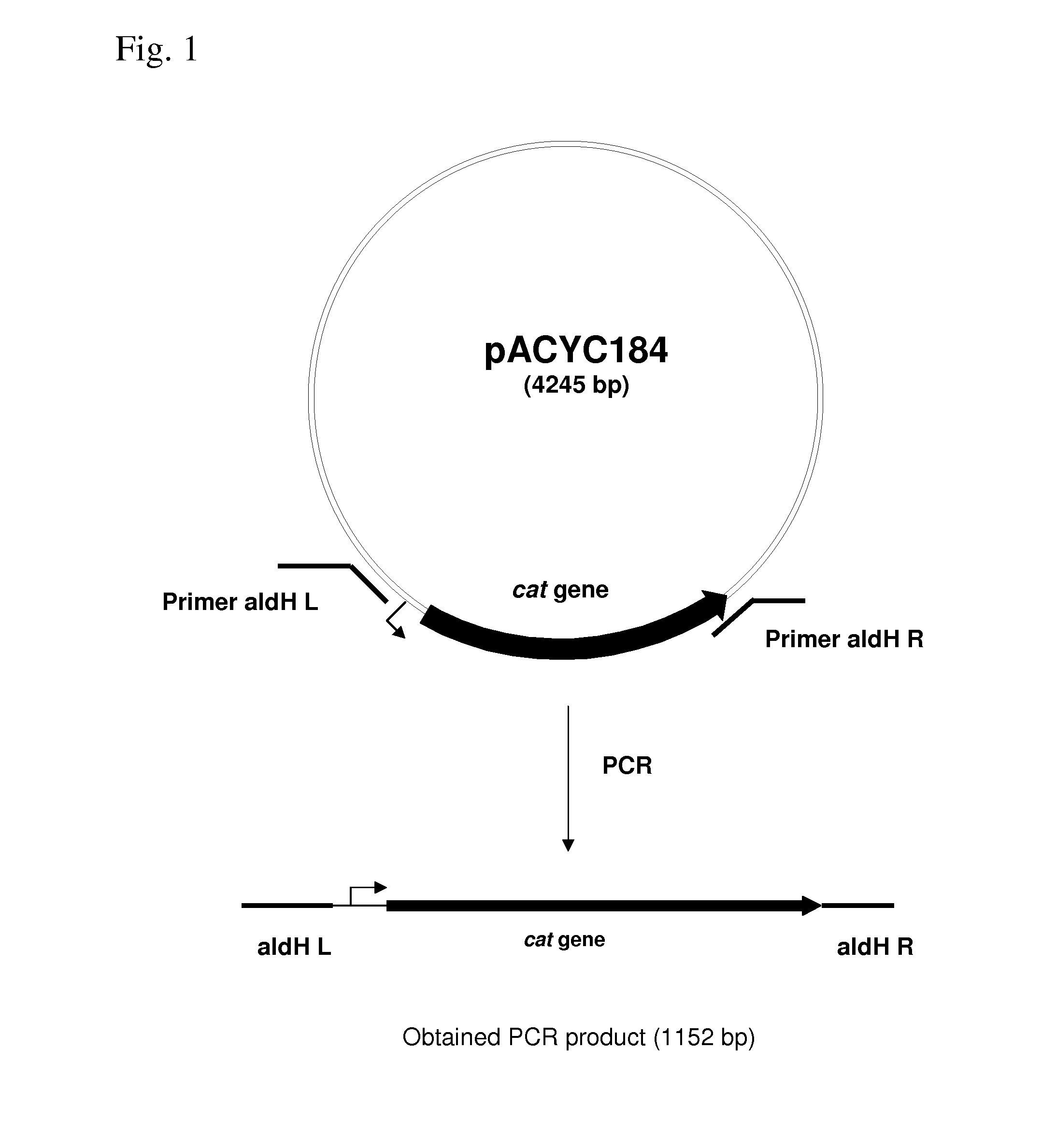
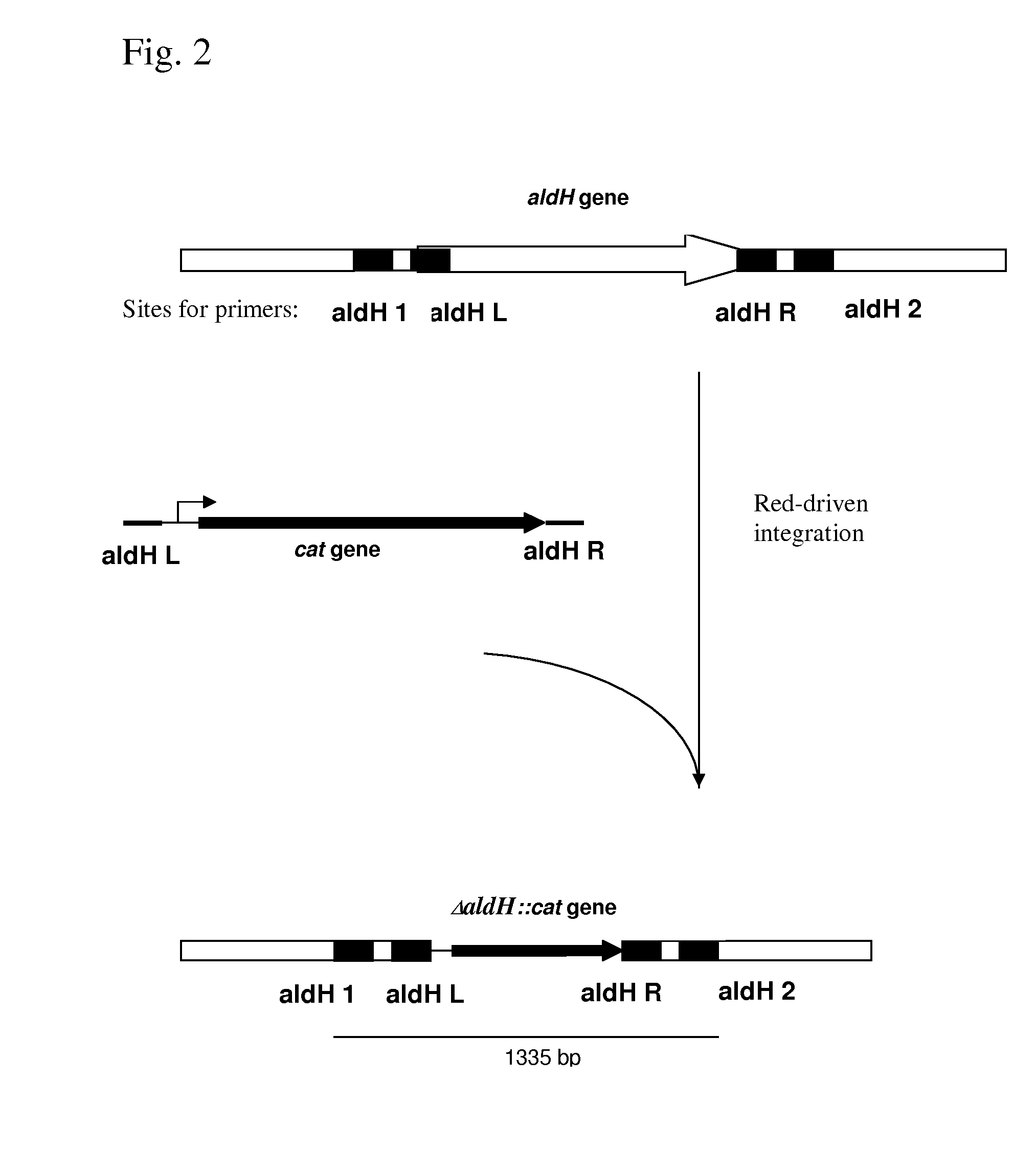
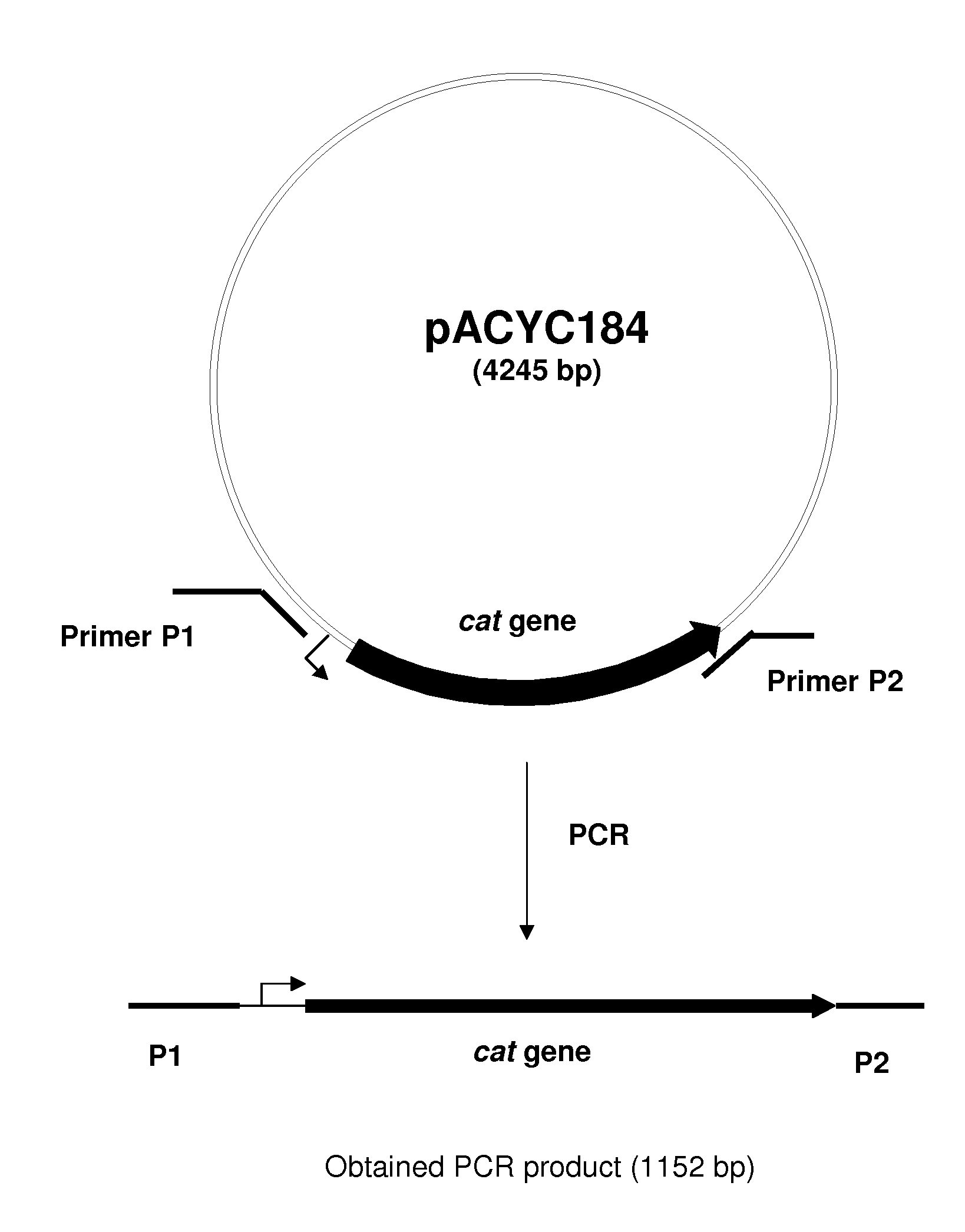
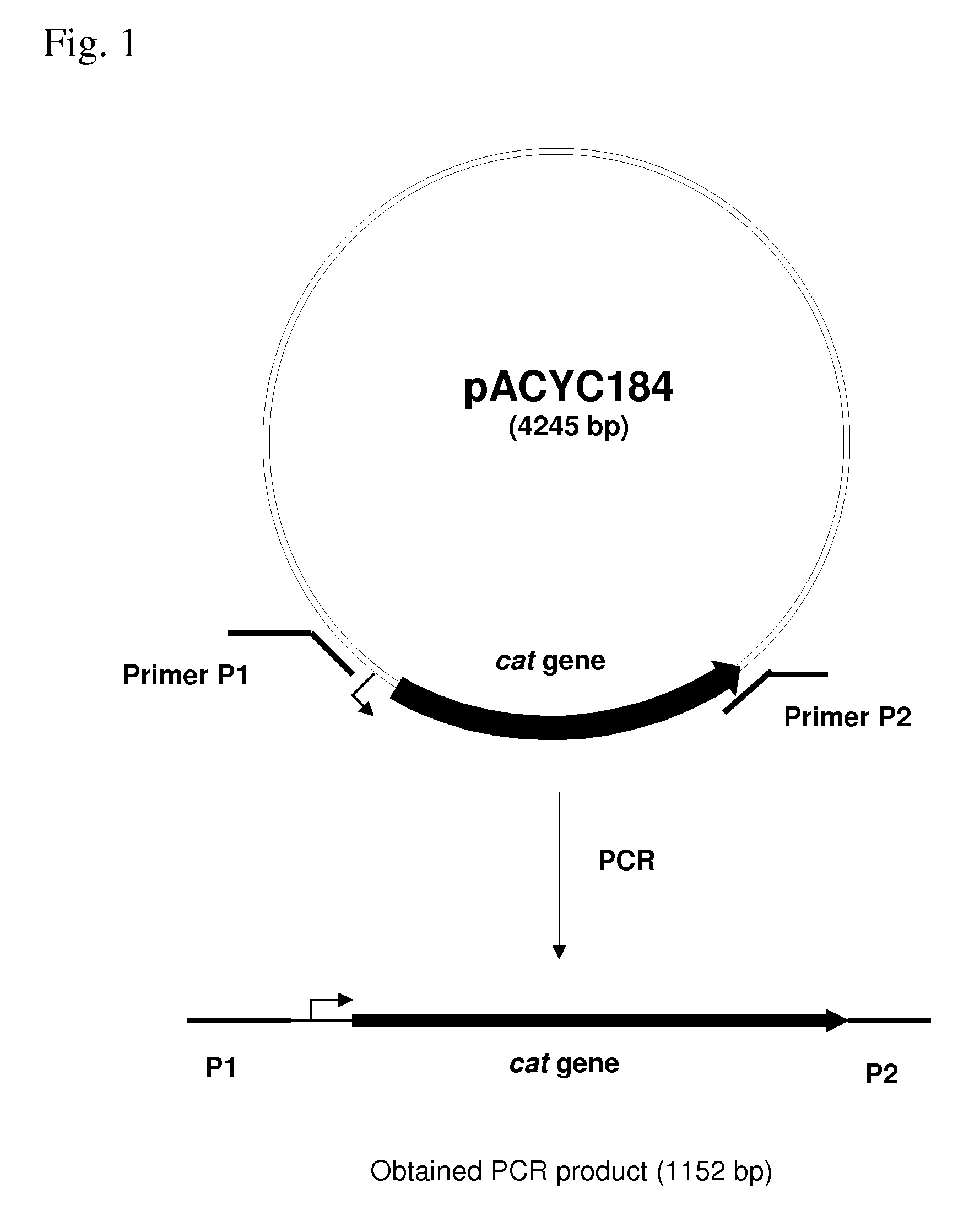
METHOD FOR PRODUCING AN L-AMINO ACID USING A BACTERIUM OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE FAMILY WITH ATTENUATED EXPRESSION OF THE aldH GENE
InactiveUS20100143982A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesEnterobacter
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the aldH gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
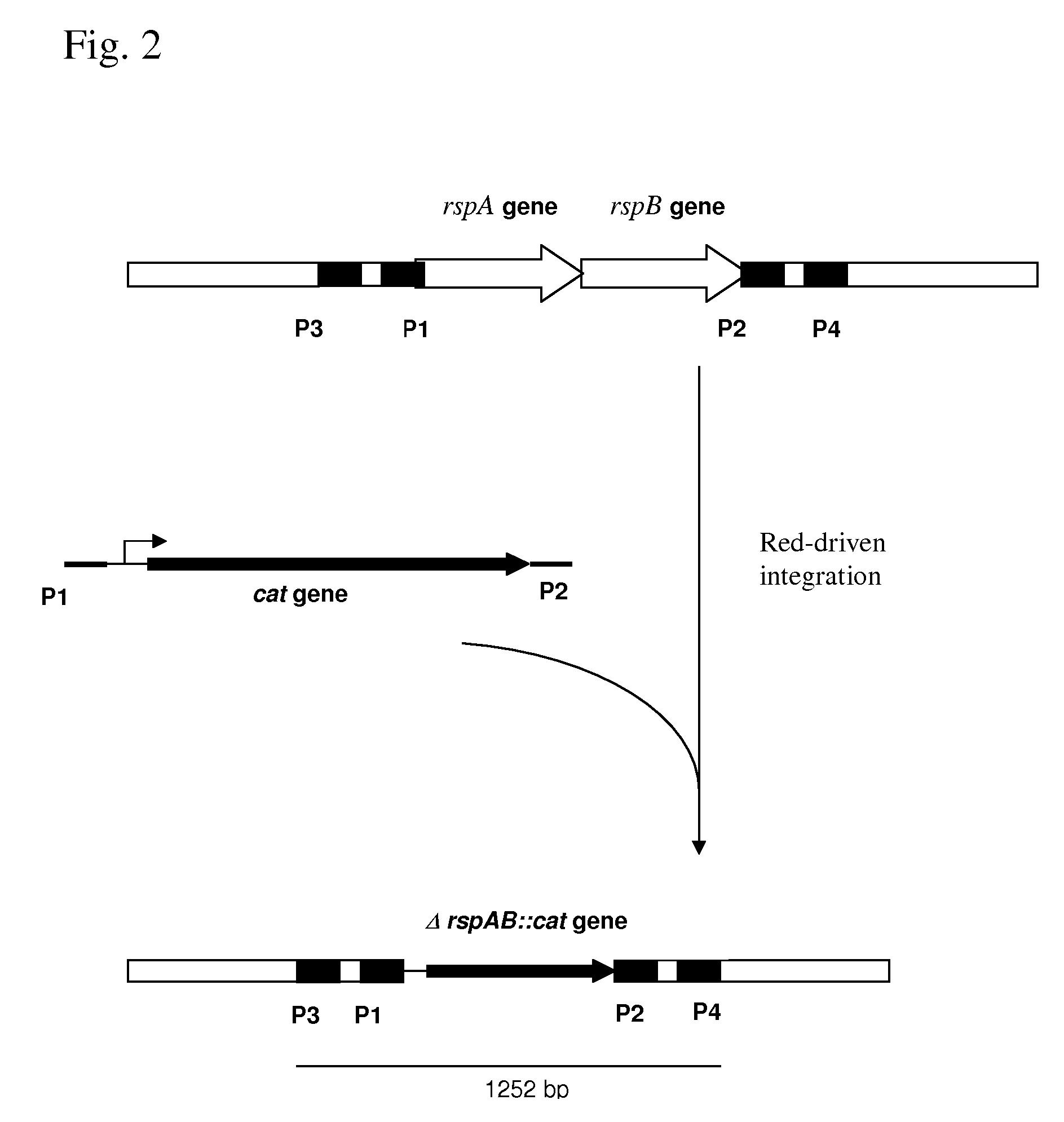
METHOD FOR PRODUCING AN L-AMINO ACID USING A BACTERIUM OF THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE FAMILY WITH ATTENUATED EXPRESSION OF THE rspAB OPERON
InactiveUS20090170169A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesArs operon
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of the rspAB operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
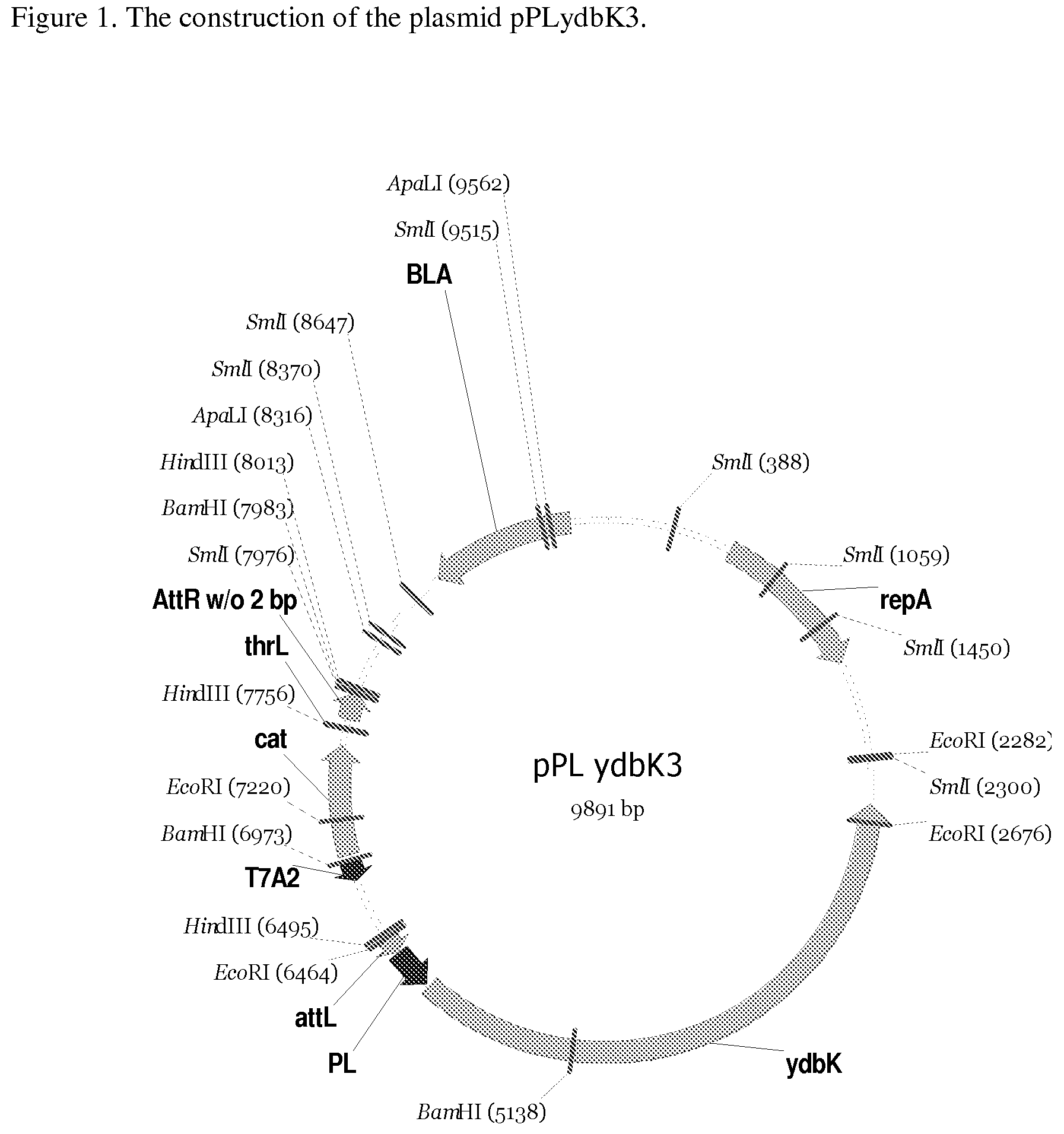
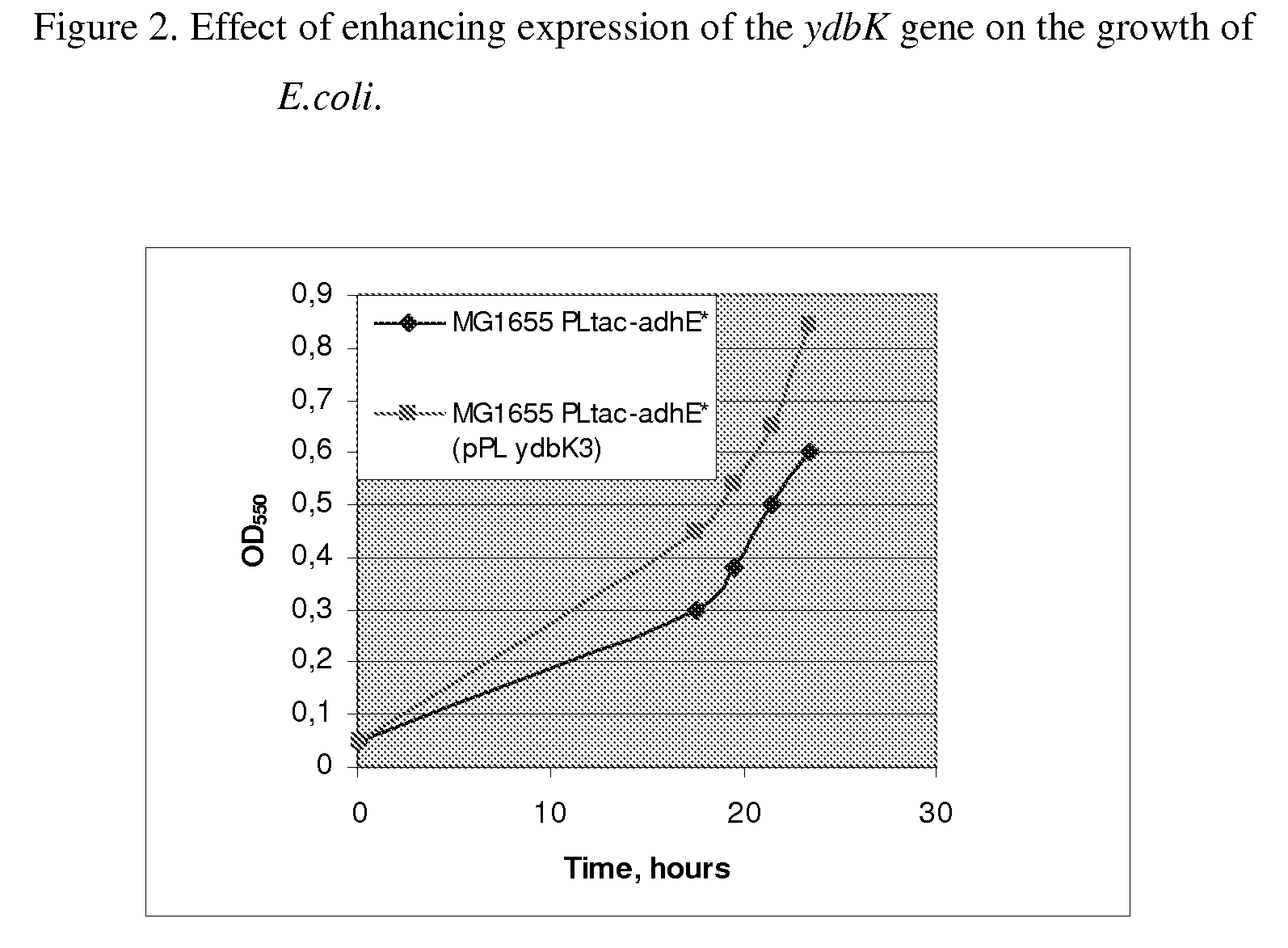
Method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS8679798B2Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid from ethanol using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance the expression of the ydbK gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium having an enhanced ability to utilize glycerol
InactiveUS7811798B2Improve abilitiesProducing L-aminoBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to have glycerol kinase in which feedback inhibition by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is desensitized, thereby having enhanced ability to utilize glycerol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com