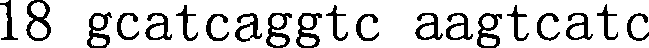High-flux microorganism identification method
An identification method and microorganism technology, applied in the field of microorganism identification, to achieve the effect of high sensitivity and resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Embodiment 1: Extract is the high-throughput microbial identification method of DNA or RNA
[0069] (1) Sampling
[0070] DNA was extracted from the cultured bacteria, and when the OD value of the culture reached about 0.2, about 50 microliters of the culture were transferred to 300 microliters of ATL buffer (Qiagen Company) for pretreatment.
[0071] (2) Extraction of genetic material
[0072] Use Qiagen's DNeasy Tissue kit for gene extraction, and follow the instructions.
[0073] (3) Amplification
[0074] The PCR conditions during the bacteria detection process are: 50 microliters of reaction volume, carried out in a 96-well PCR reaction plate. The PCR reaction composition was: 4ul, 1×buffer II (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), 1.5mM magnesium chloride, 0.4M betaine, 800μM dNTP mixture and 250nM of each primer. The mixture was kept at 95° C. for 10 minutes. The cycle reaction conditions were: 95° C. for 30 minutes, 48° C. for 30 minutes, and 72° C. for 30 min...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2: High-throughput microbial identification method for extracts as proteins
[0096] (1) Sampling
[0097] Samples can come from various media such as throat swabs, blood, urine, pus, soil, and food. After melting or diluting the protective solution, the size of the sample is determined according to the volume of the adsorption column and the viscosity of the solution. .
[0098] (2) Extraction and purification of genetic material
[0099] The collection of the samples is performed due to the application of the principle of affinity chromatography. The adsorption column contains specific antibodies capable of adsorbing pathogenic proteins, and the type of antibodies can be changed according to the amount of the target. The chromatographic column after absorbing the sample is washed with washing solution to remove residual impurities.
[0100] (3) Enrichment
[0101] Then, the specific protein is eluted from the adsorption column by the eluent. After collect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com