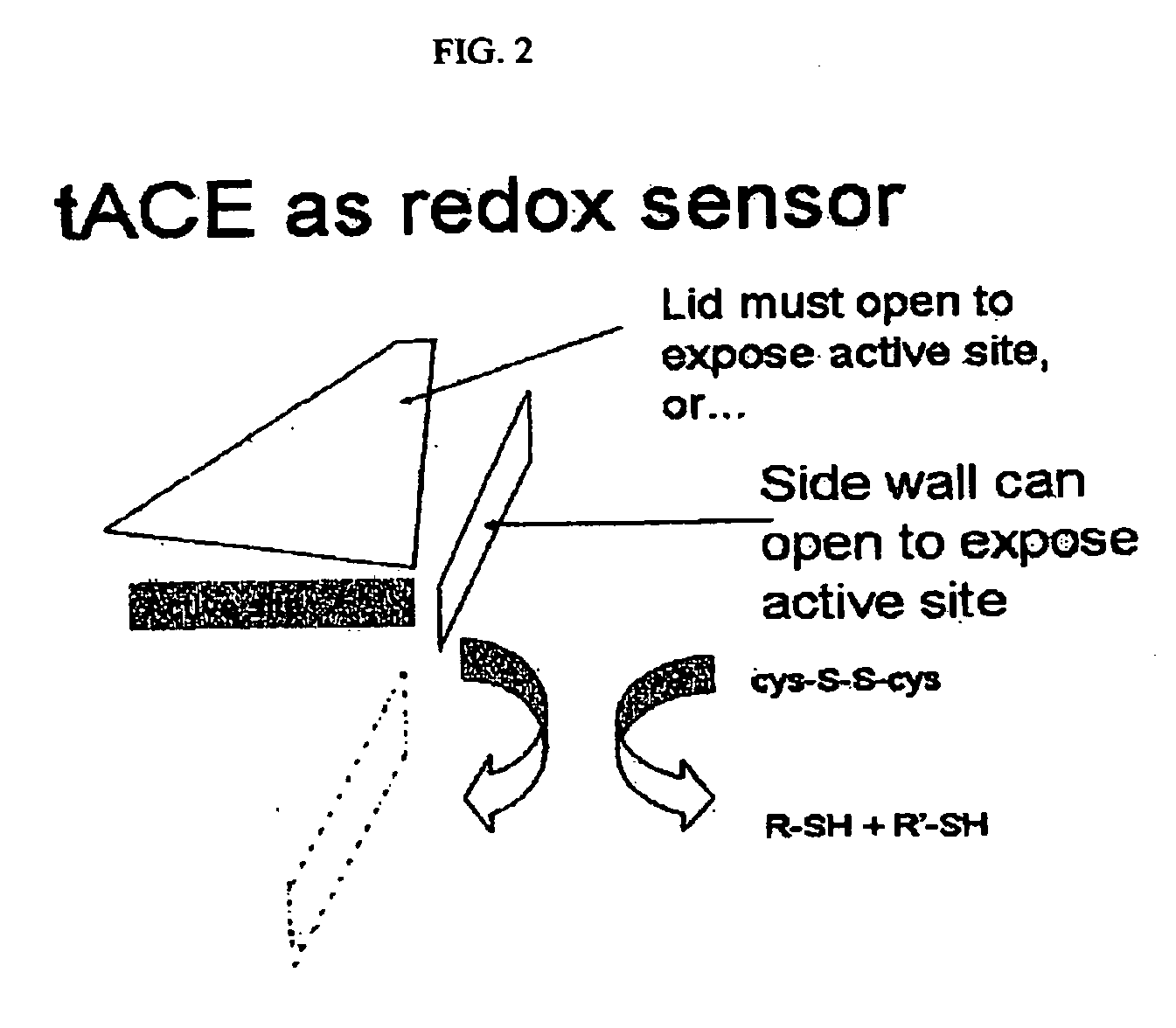
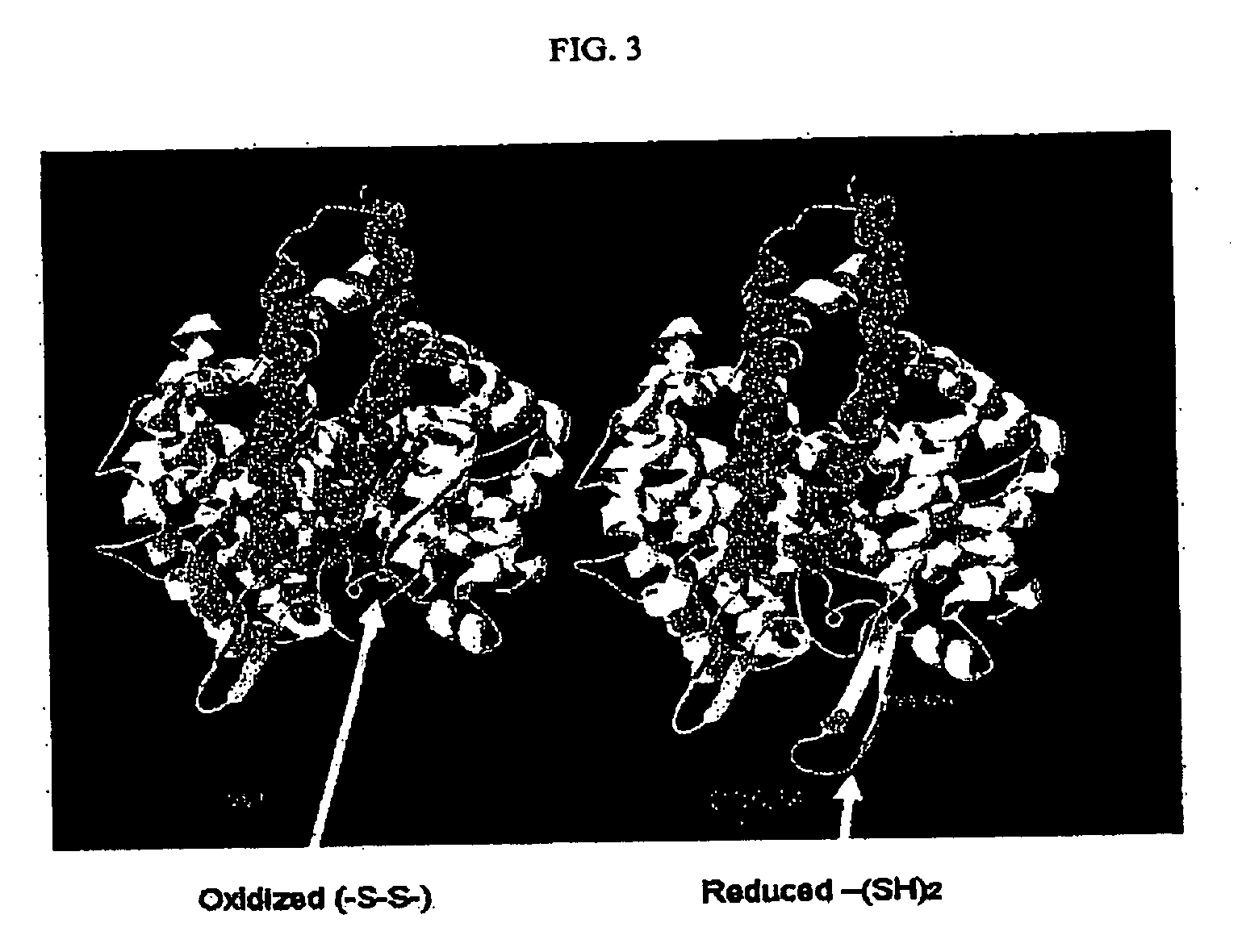
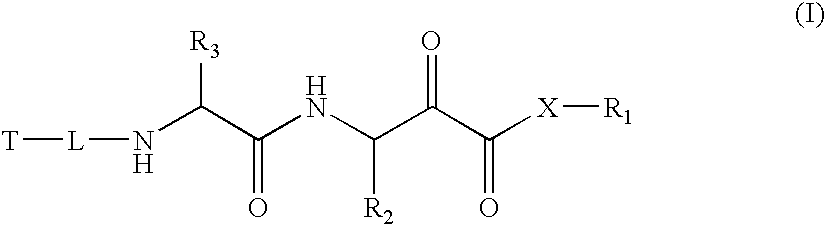
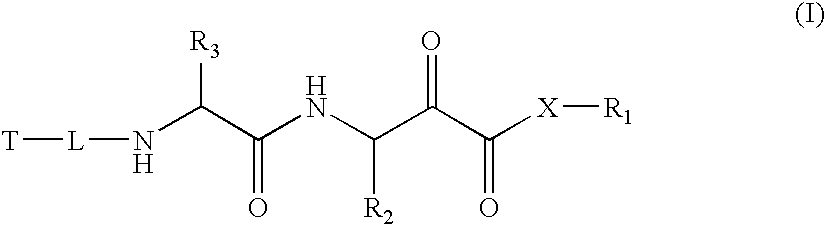
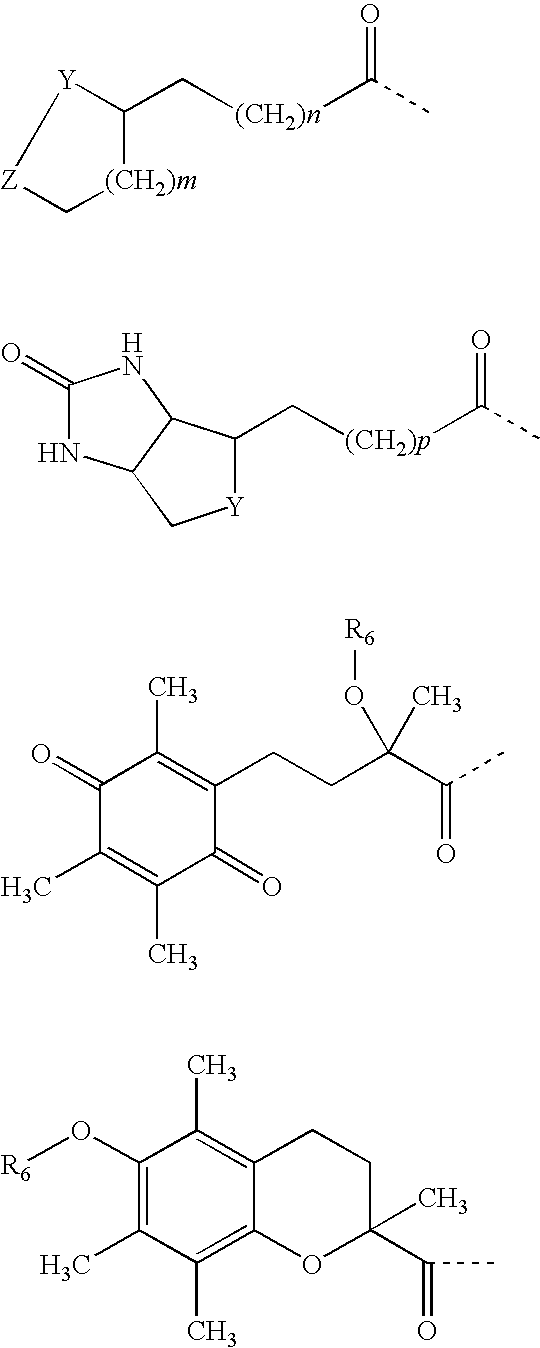
Patents
Literature
115 results about "Neuromuscular disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A disorder that causes lack of strength, fatigue and inability to do day to day activities.
Method for treating neuromuscular disorders and conditions with botulinum toxin types A and B
A method of treating a patient suffering from a disease, disorder or condition includes the administration to the patient of a therapeutically effective amount of botulinum toxin of a selected serotype until the patient experiences loss of clinical response to the administered botulinum toxin and thereafter administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of another botulinum toxin of a different serotype.
Owner:SOLSTICE NEUROSCI
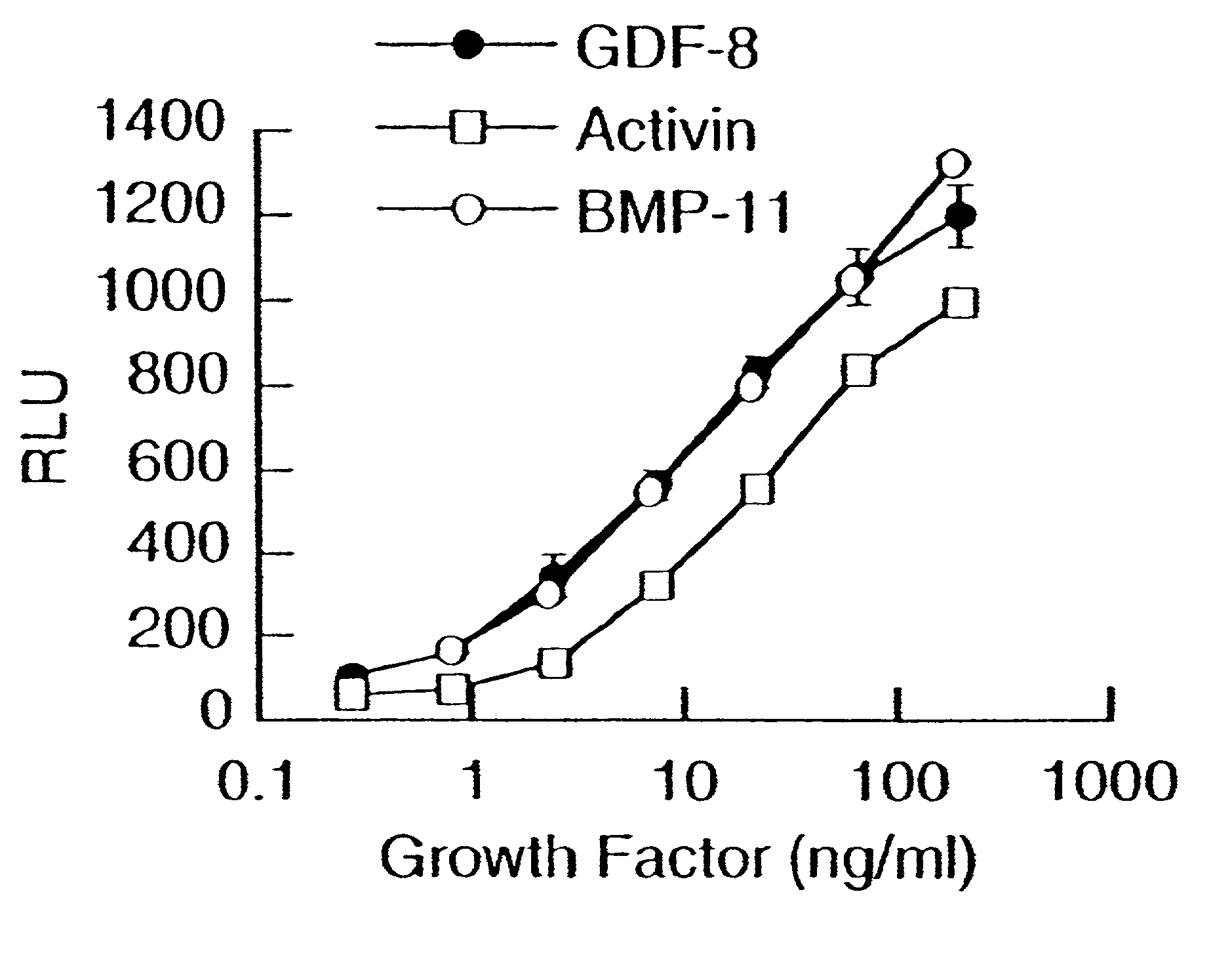
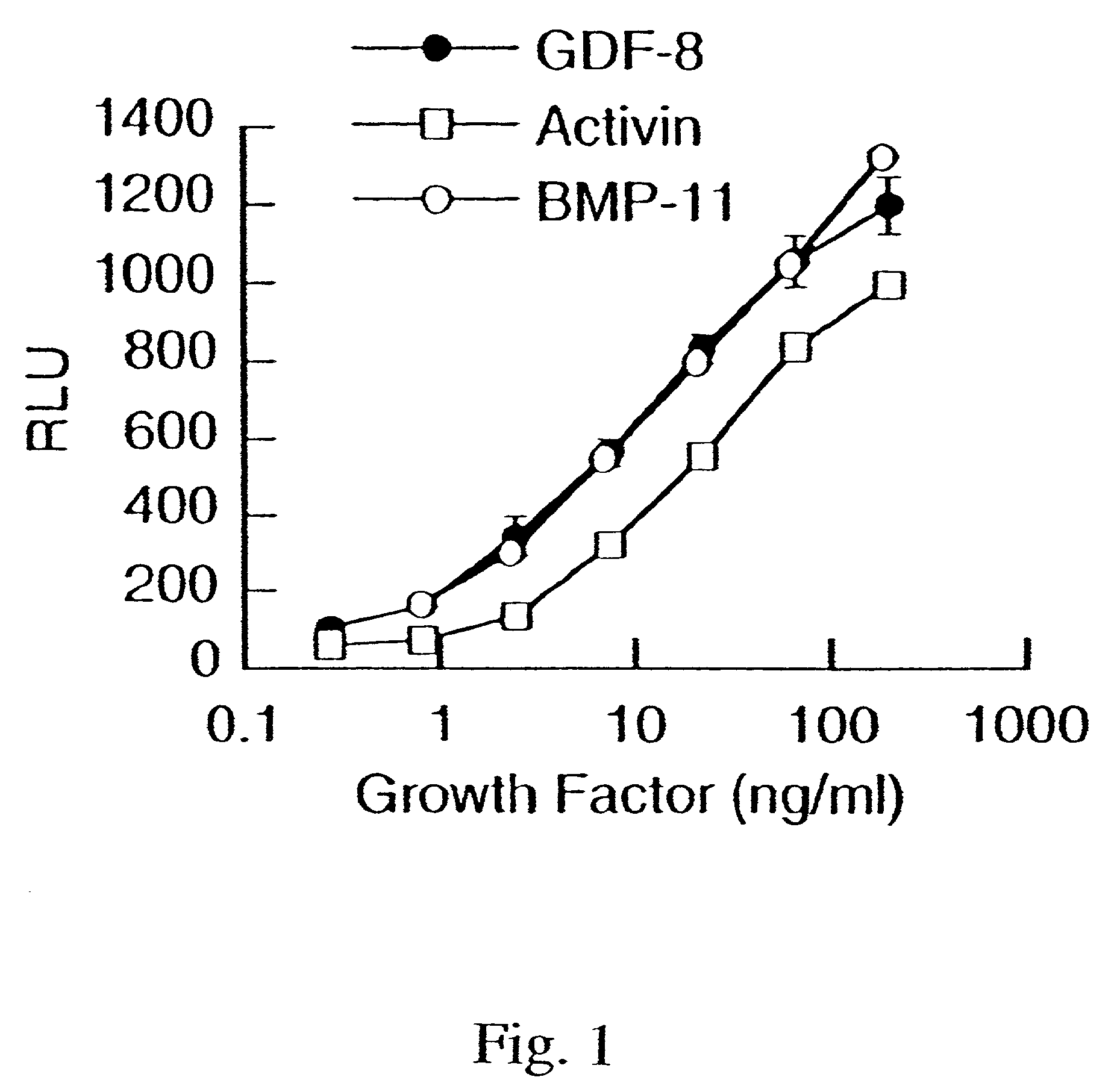
Modified and stabilized GDF propeptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7202210B2Prevent practical therapeuticPrevent prophylactic utilityFungiBacteriaAcute hyperglycaemiaMuscle tissue
Modified and stabilized propeptides of Growth Differentiation Factor proteins, such as GDF-8 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-11, are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for making and using the modified propeptides to prevent or treat human or animal disorders in which an increase in muscle tissue would be therapeutically beneficial. Such disorders include muscle or neuromuscular disorders (such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy, congestive obstructive pulmonary disease, muscle wasting syndrome, sarcopenia, or cachexia), metabolic diseases or disorders (such as such as type 2 diabetes, noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, or obesity), adipose tissue disorders (such as obesity), and bone degenerative diseases (such as osteoporosis).
Owner:WYETH LLC
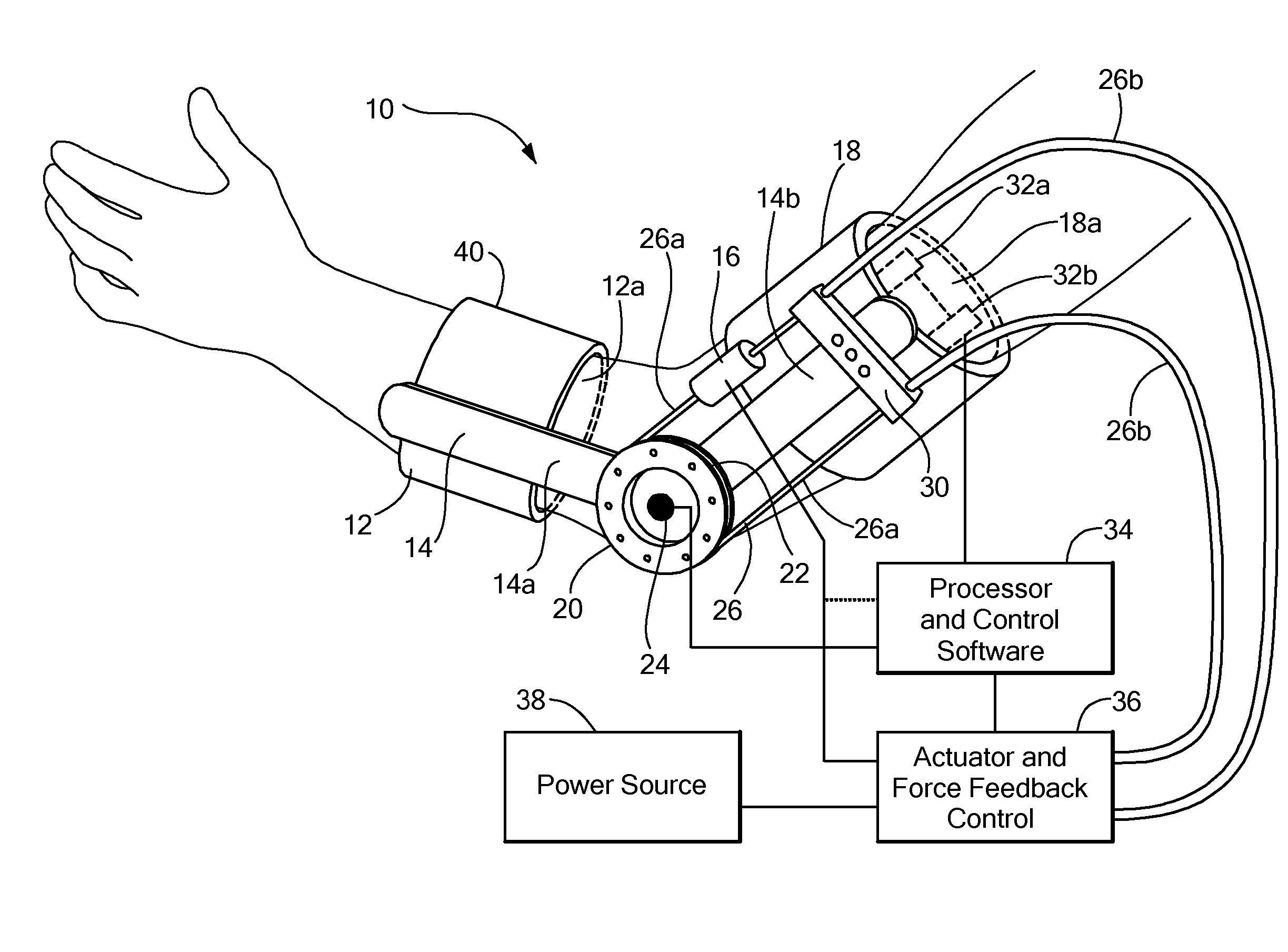
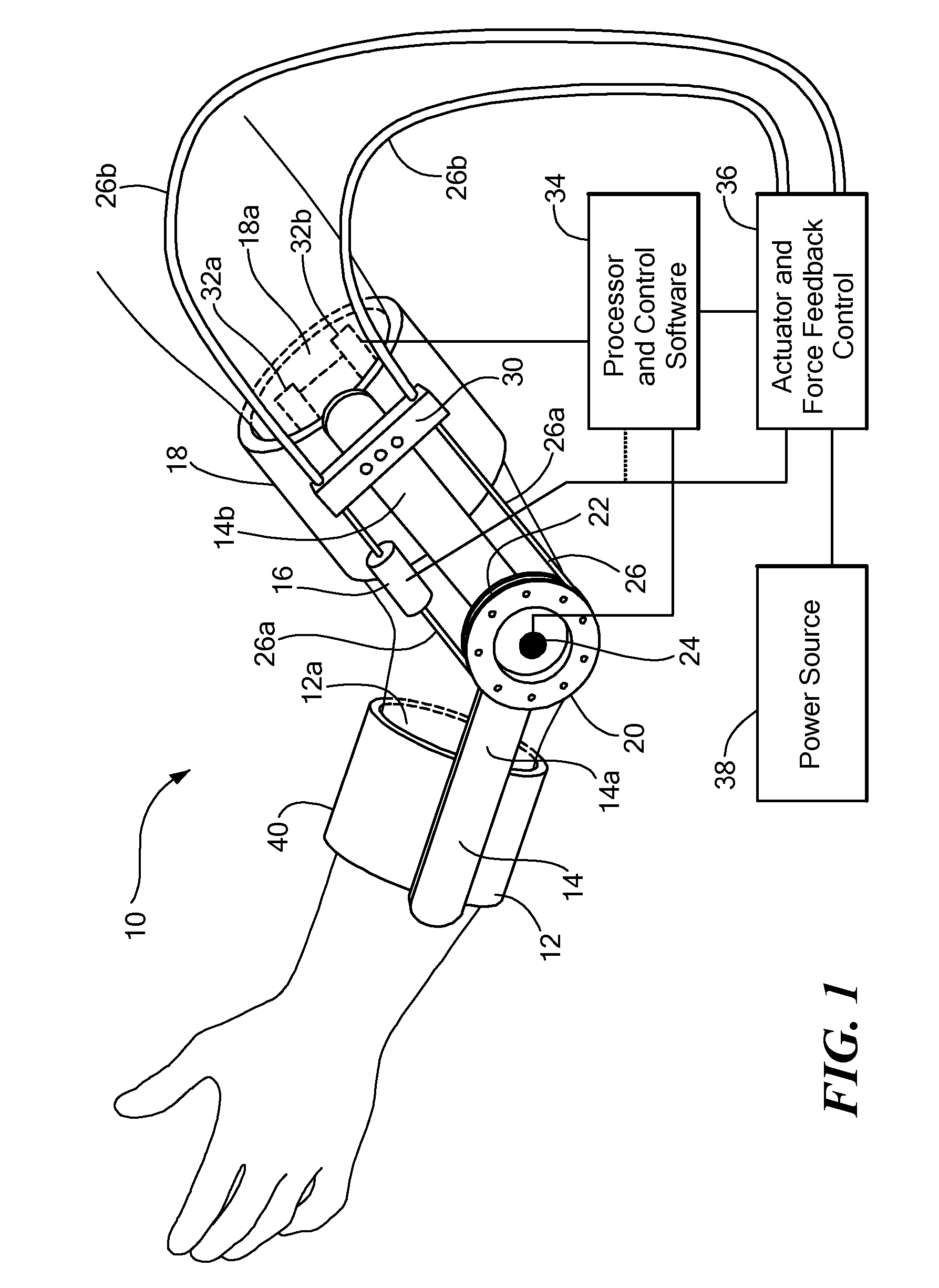
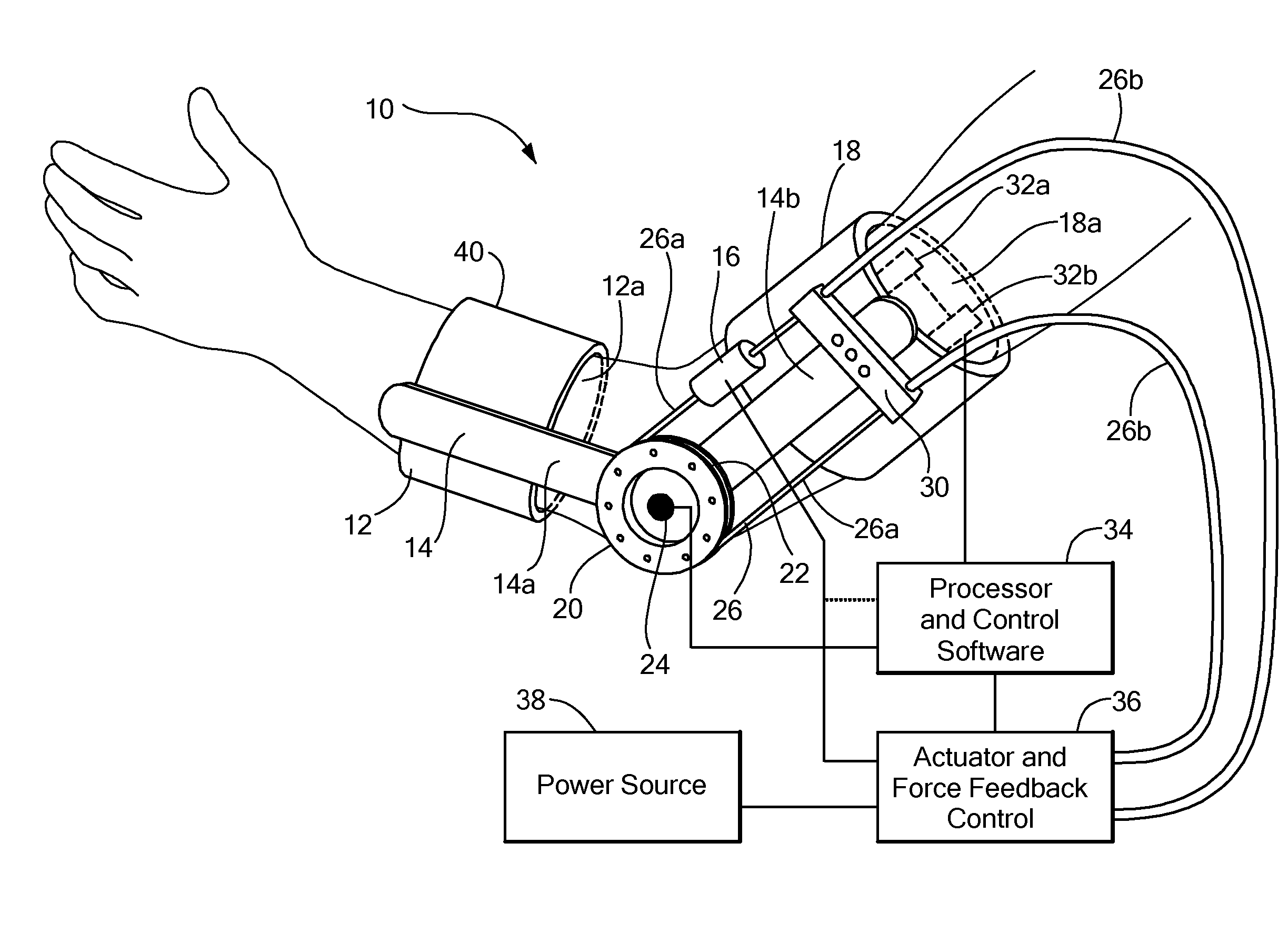
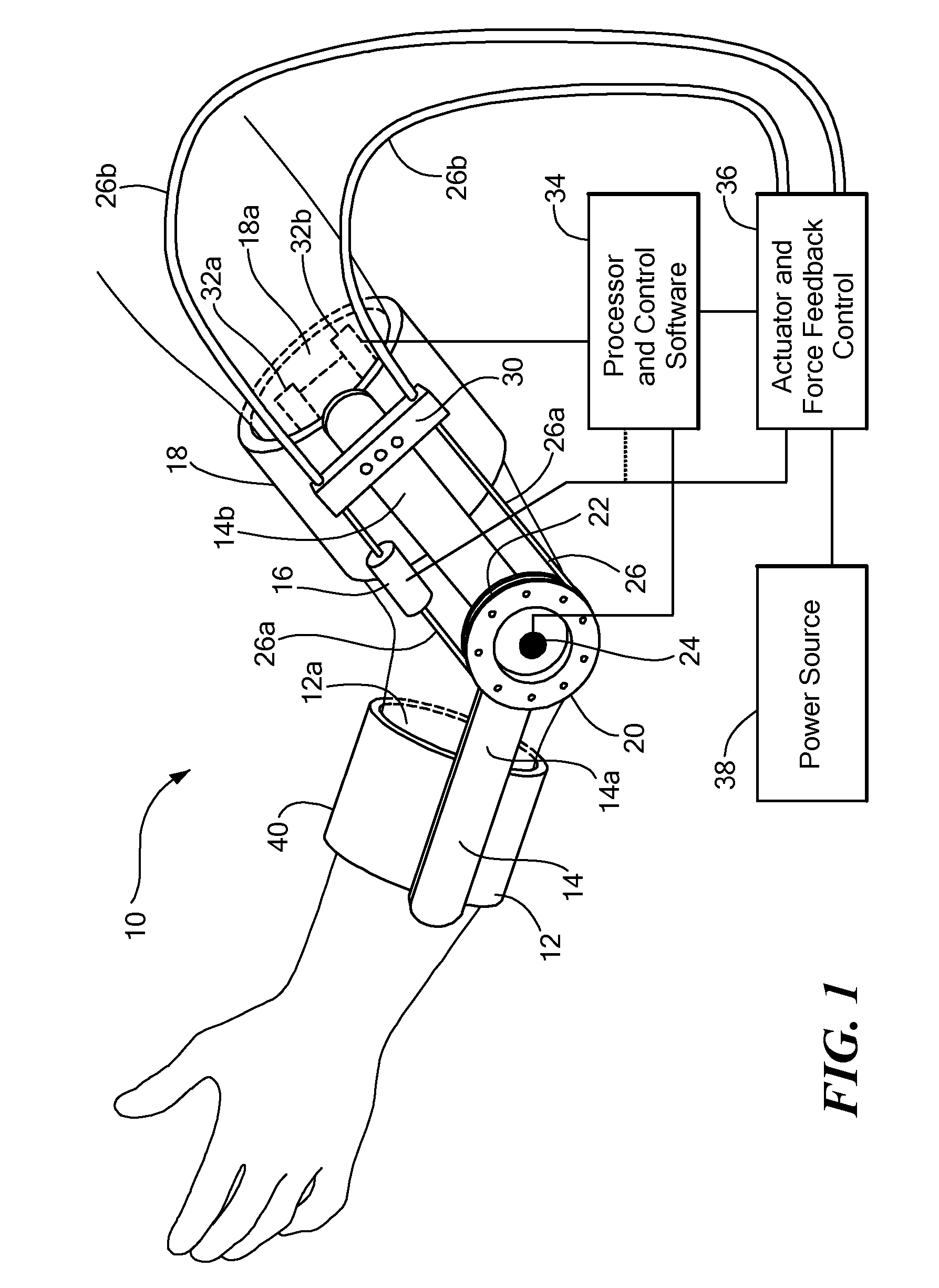
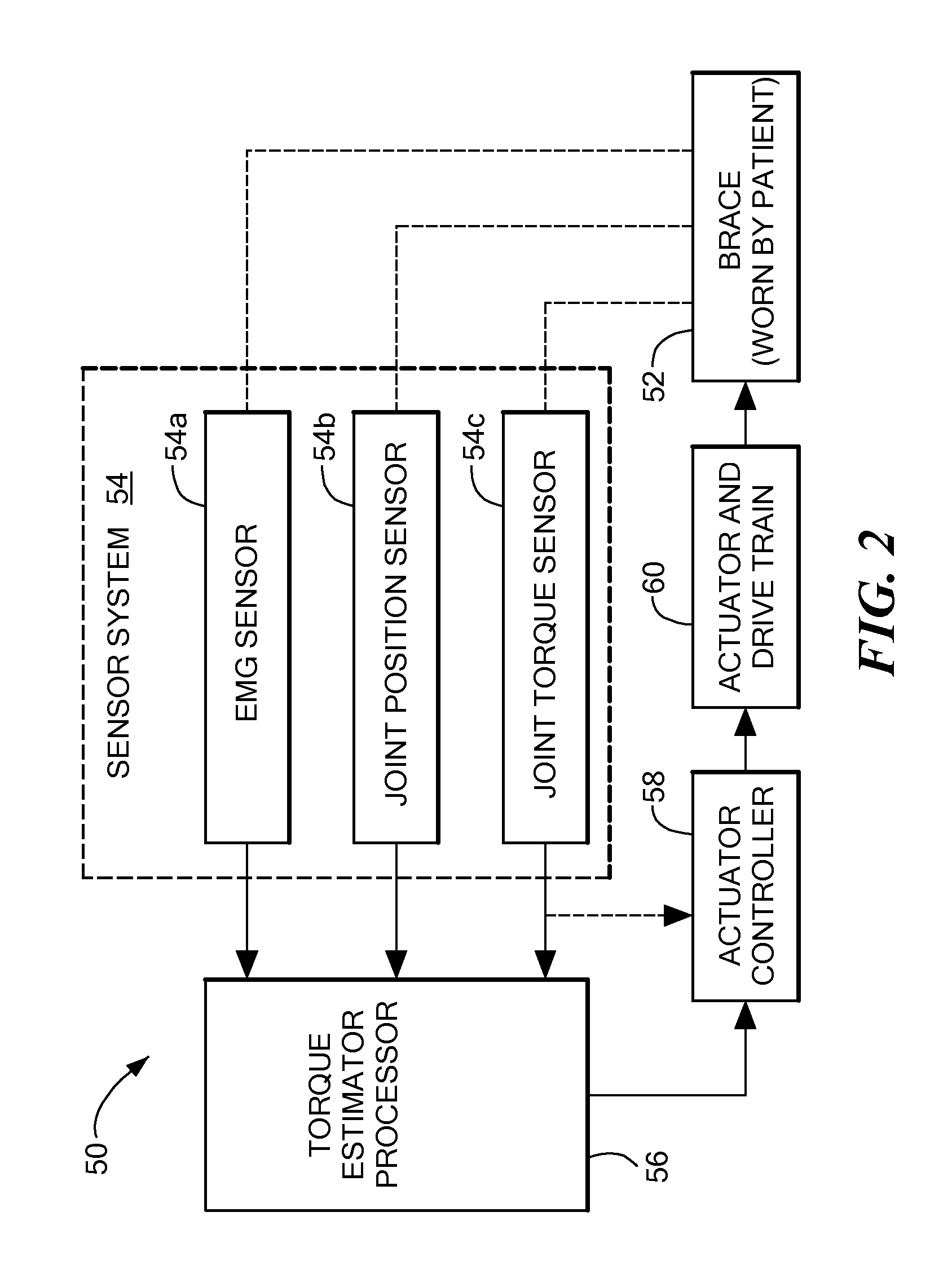
Method of using powered orthotic device
InactiveUS7367958B2Smooth movementHigh strengthElectromyographyChiropractic devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Therapeutic and prophylactic methods for neuromuscular disorders
InactiveUS20050014733A1Improve muscle massHigh strengthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The disclosure provides methods for treating neuromuscular disorders in mammals. The disclosed methods include administering therapeutically effective amounts of a GDF-8 inhibitor and a corticosteroid to a subject susceptible to, or having, a neuromuscular disorder, so as to maintain desirable levels of muscle function.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Systems and methods for estimating surface electromyography
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of Using Powered Orthotic Device
ActiveUS20070191743A1Smooth movementAugments human physical capabilityElectromyographyChiropractic devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
A method of providing rehabilitation movement training for a person suffering from nerve damage, stroke, spinal cord injury, neurological trauma or neuromuscular disorder in attempting to move a body part about a joint using a powered orthotic device includes sensing at least one electromyographic signal of a muscle associated with motion about the joint, applying in a first direction with respect to the joint a force having a magnitude that is a first function of the at least one sensed electromyographic signal, and applying in a second direction with respect to the joint a return force that is a second function of the at least one sensed electromyographic signal, wherein the second function differs from the first function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Improved carriers for delivery of nucleic acid agents to cells and tissues
InactiveUS20090011004A1Reduce deliveryRescue protein expression defectNervous disorderTetracycline active ingredientsDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
This invention relates to drug delivery and specifically to the preparation and use of functionalized carriers such as nanopolymers and nanovesicles for improved delivery of nucleic acid agents (NAA) to tissues and cells. These compounds have broad applicability for treating numerous diseases and disorders, including neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders. The concept encompasses preferably polymeric carriers for delivery of a class of oligonucleotides that modulate RNA splicing.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP +1
Use of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) to treat diseases associated with excess ACE
Disclosed are methods of treating neuropsychiatric diseases, neuromuscular diseases, viral infections, neurodegenerative diseases and ricin poisoning using angiotensin II receptor blockers.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ DAVID W
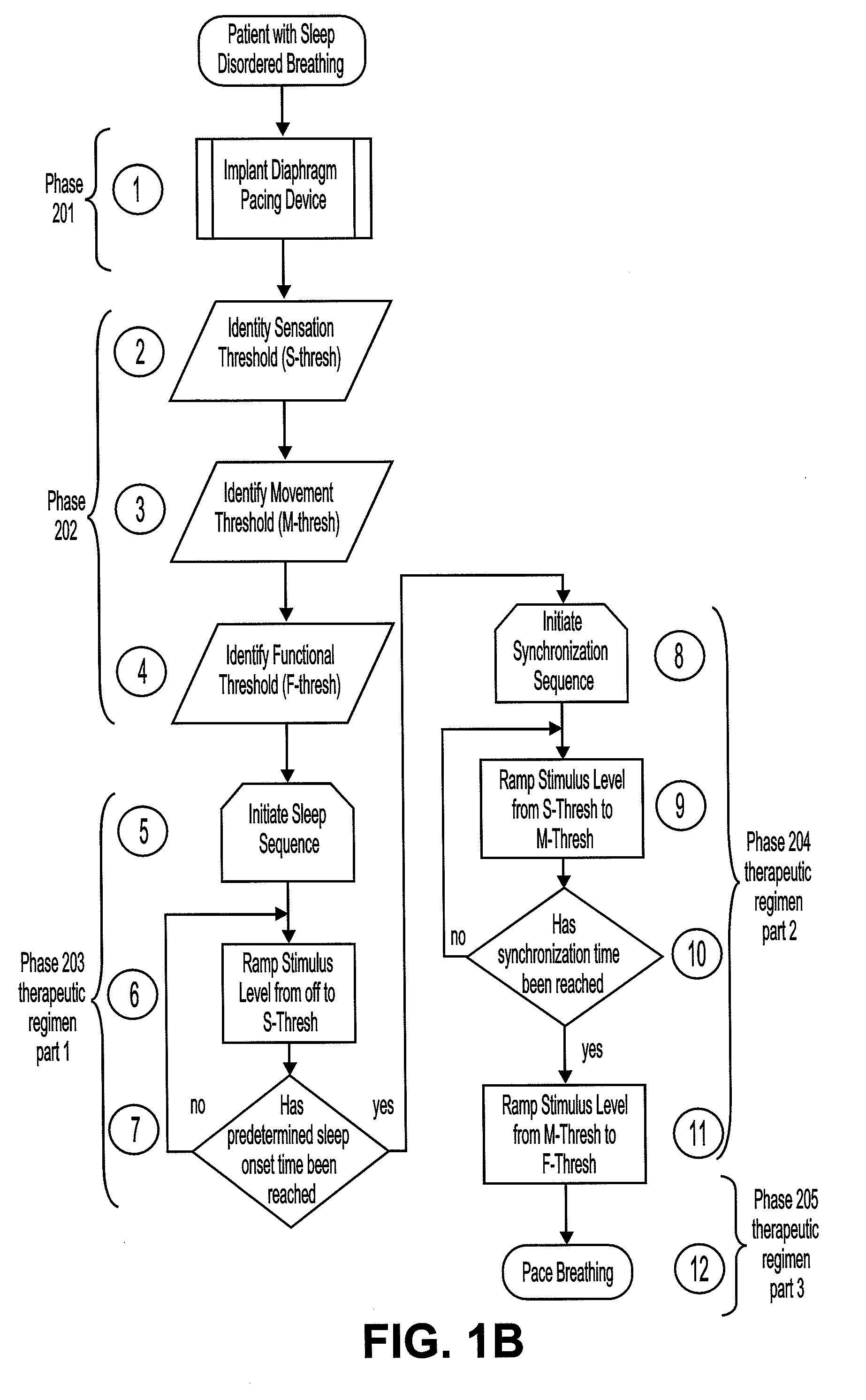
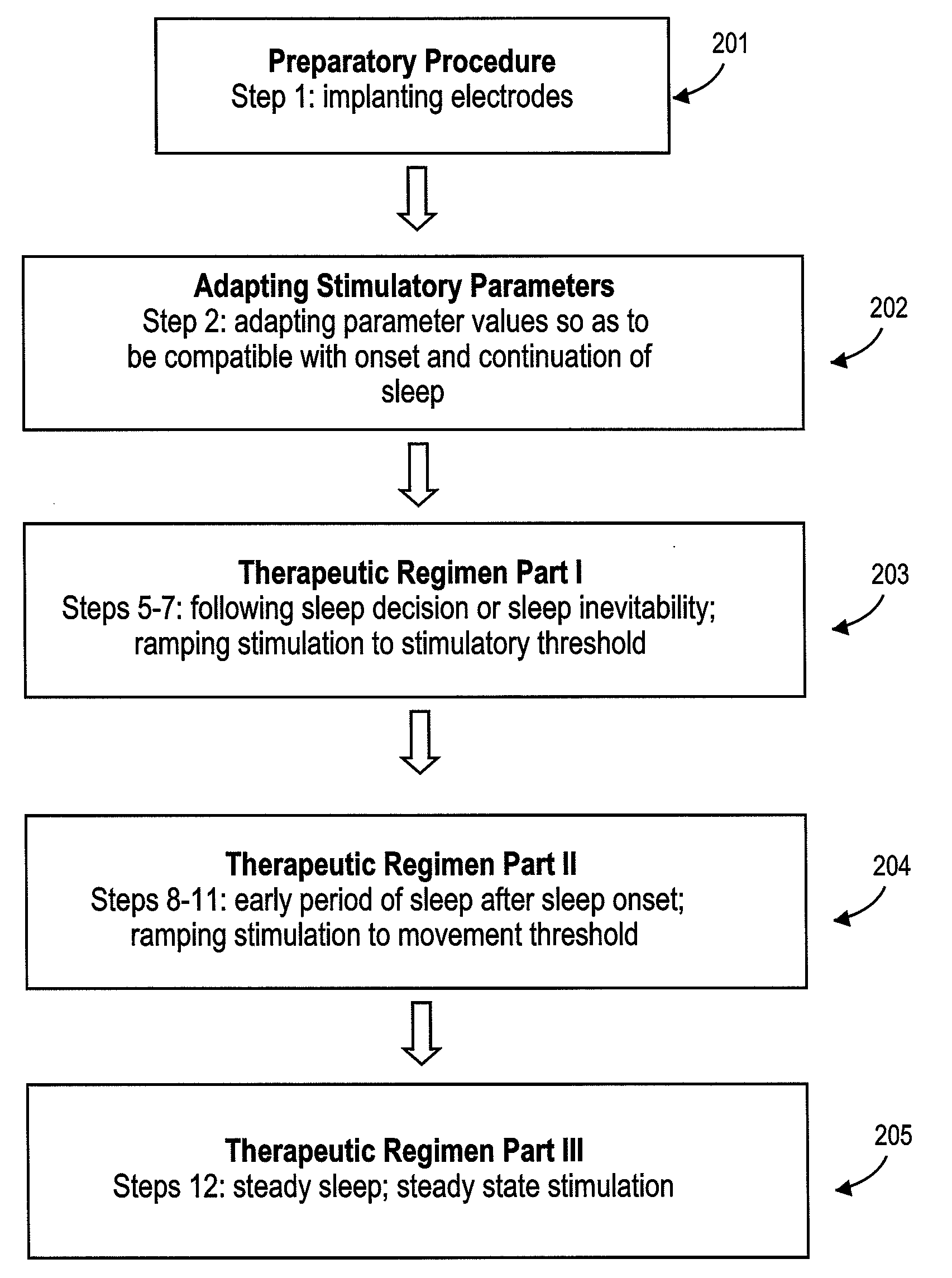
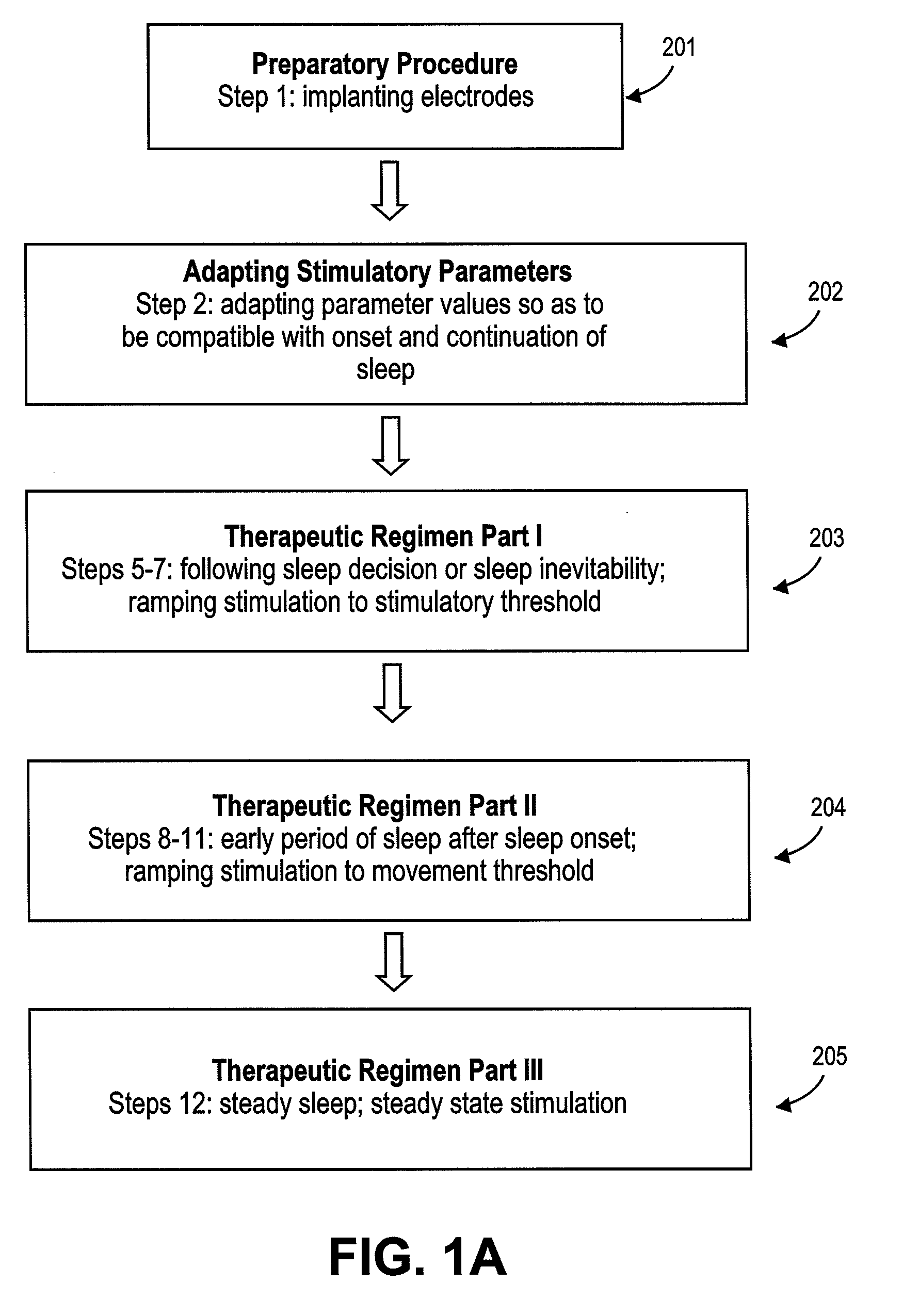
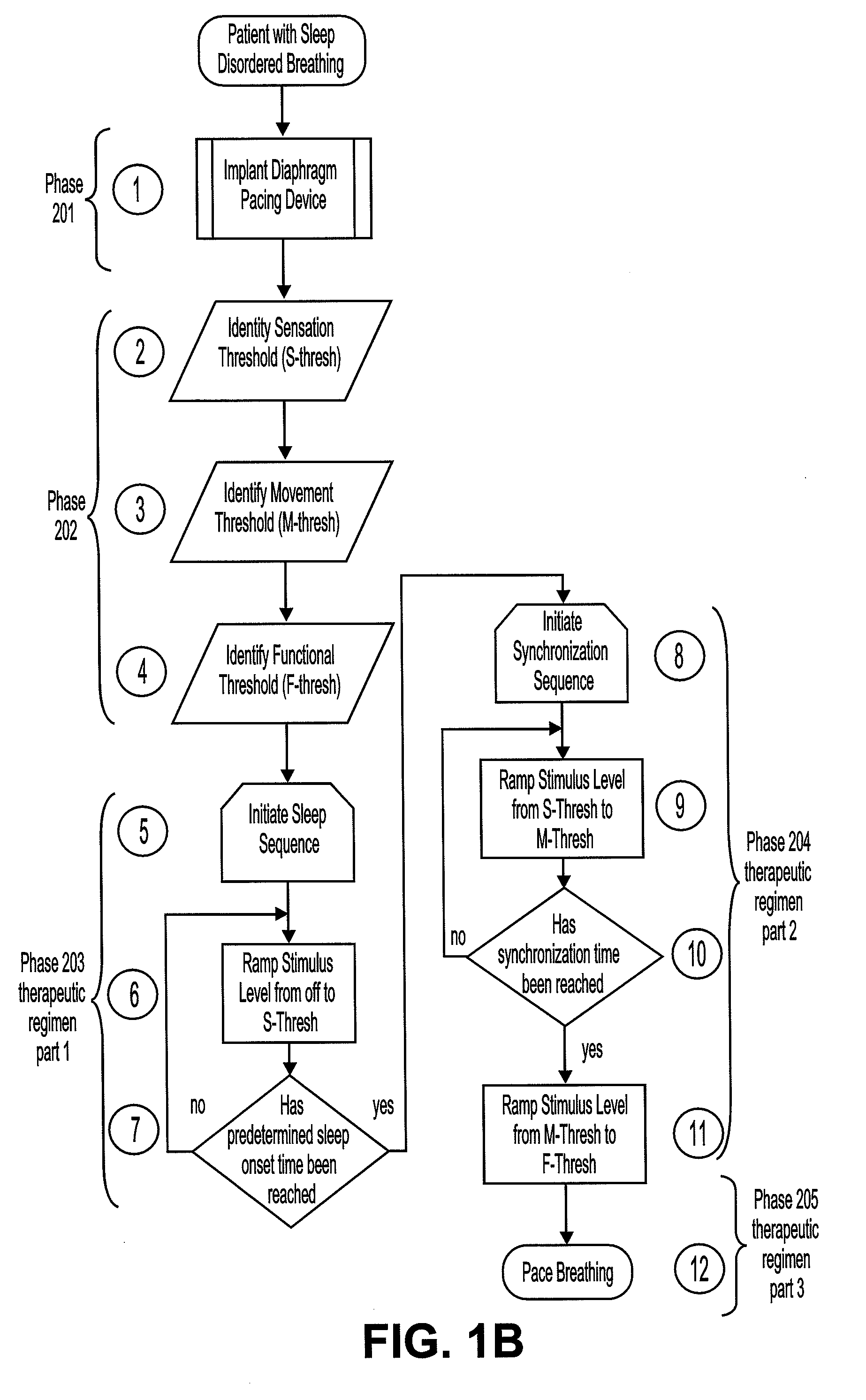
Method of improving sleep disordered breathing
ActiveUS8478412B2ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringSleep disordered breathingSommeil paradoxal
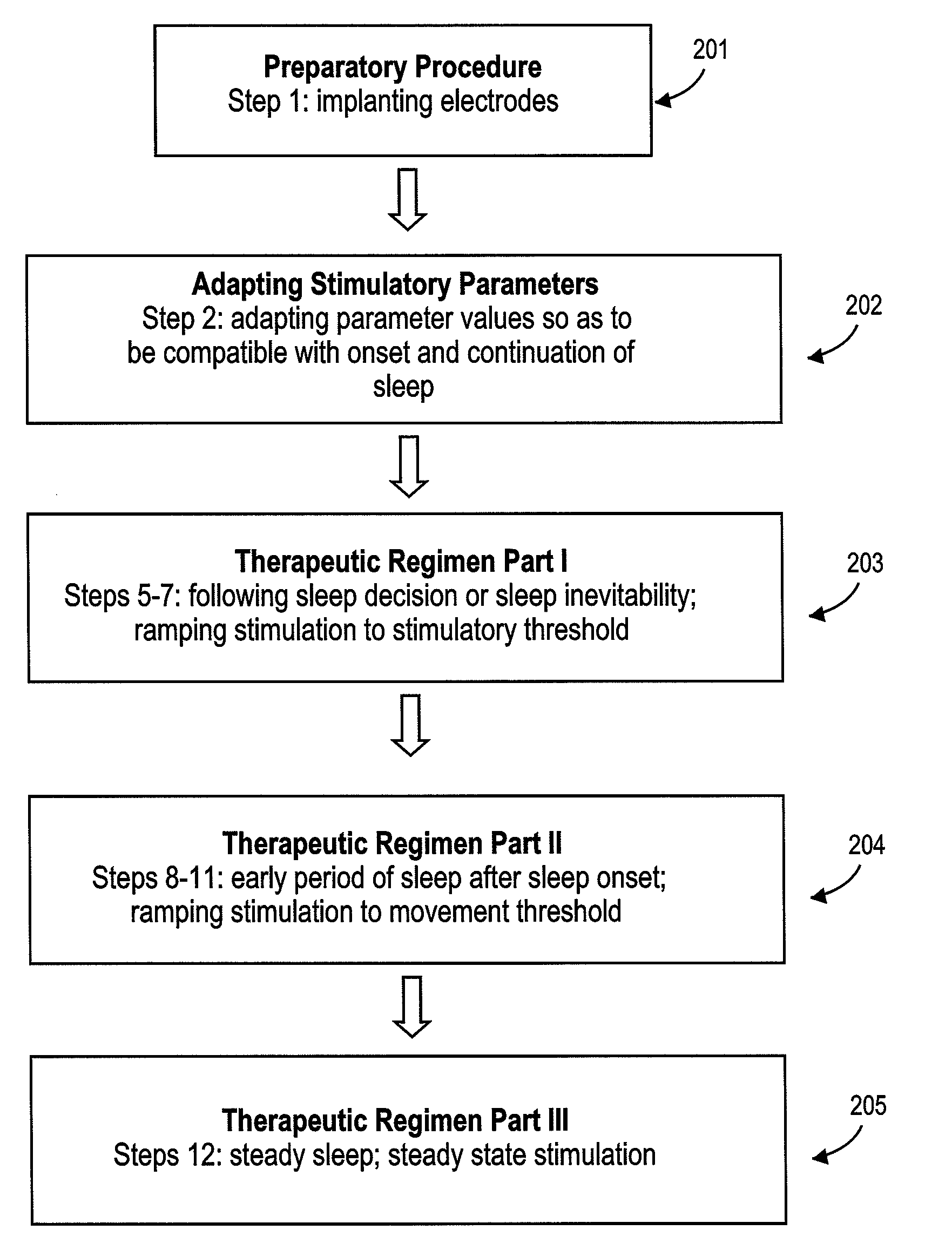
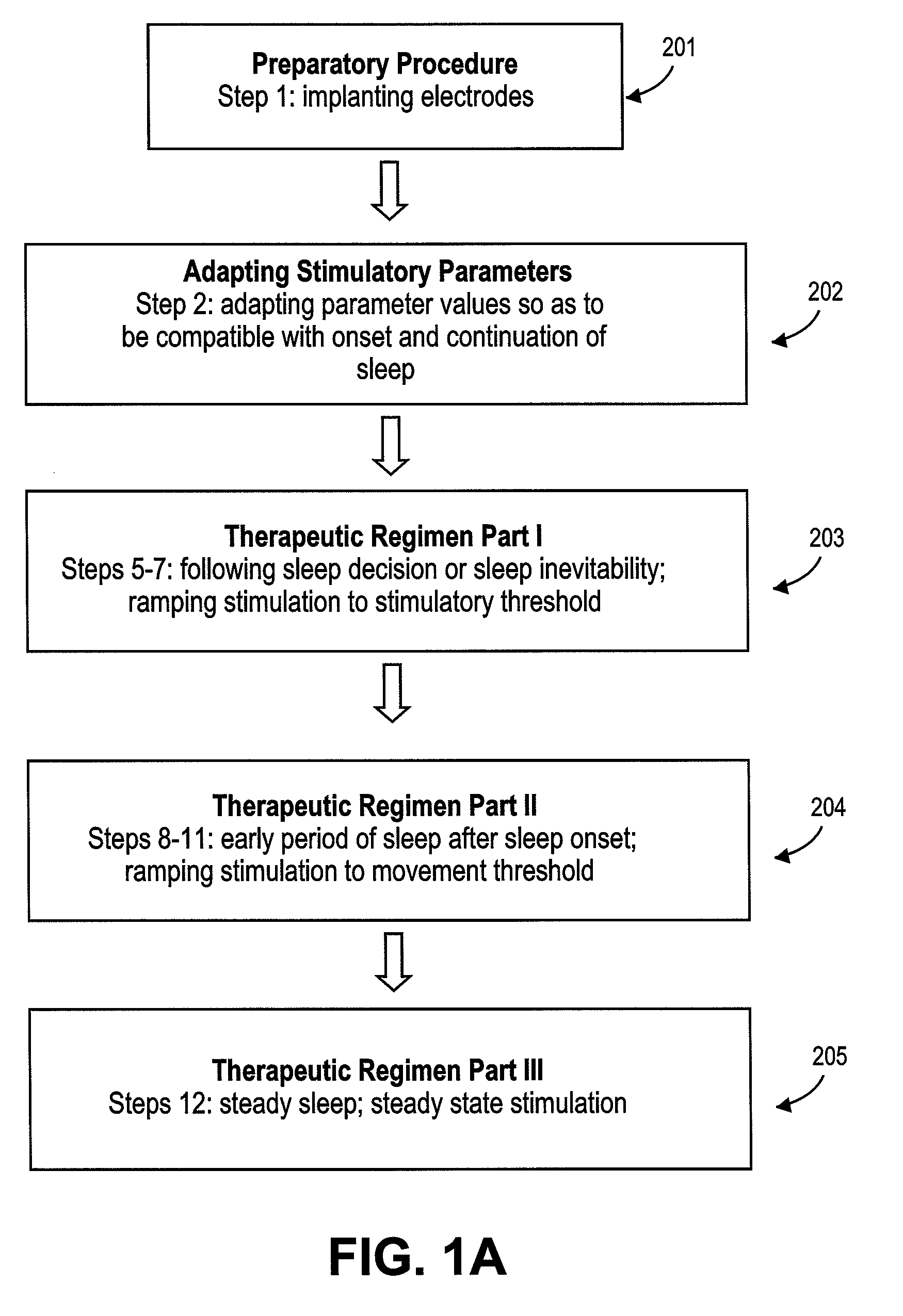
A diaphragm pacing stimulatory method and a system to implement the method are provided to improve respiratory function and the quality of sleep in patients whose sleep is compromised by poor respiration. The diaphragm pacing method includes adaptations that make it particularly compatible with the onset of sleep and sustaining sleep. Embodiments of the method are operated independently of breathing effort the patient may make during sleep. Patients for whom the invention is appropriate include those with a neuromuscular disease, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). System elements include an external electrical stimulator coupled to one or more implanted electrodes that stimulate diaphragm contraction. The system and method provide for a pacing of the diaphragm, improved breathing, and improved sleep. Features of improved sleep include longer sleep time, an increased amount of REM sleep, and fewer episodes of wakefulness and restlessness.
Owner:SYNAPSE BIOMEDICAL INC
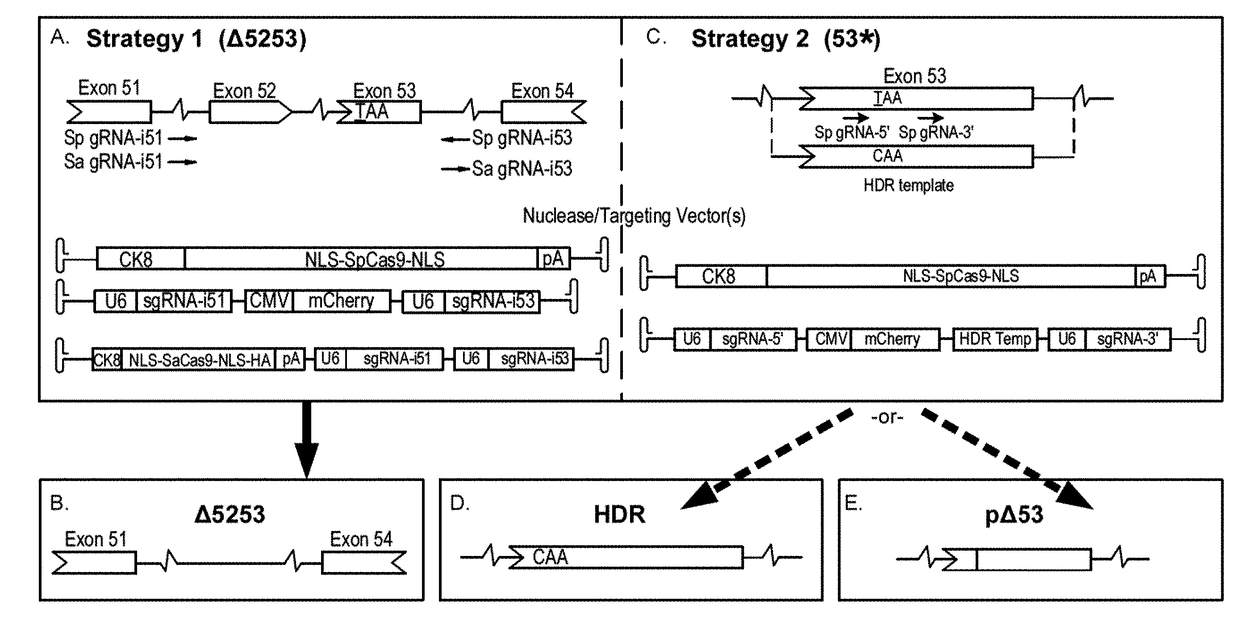
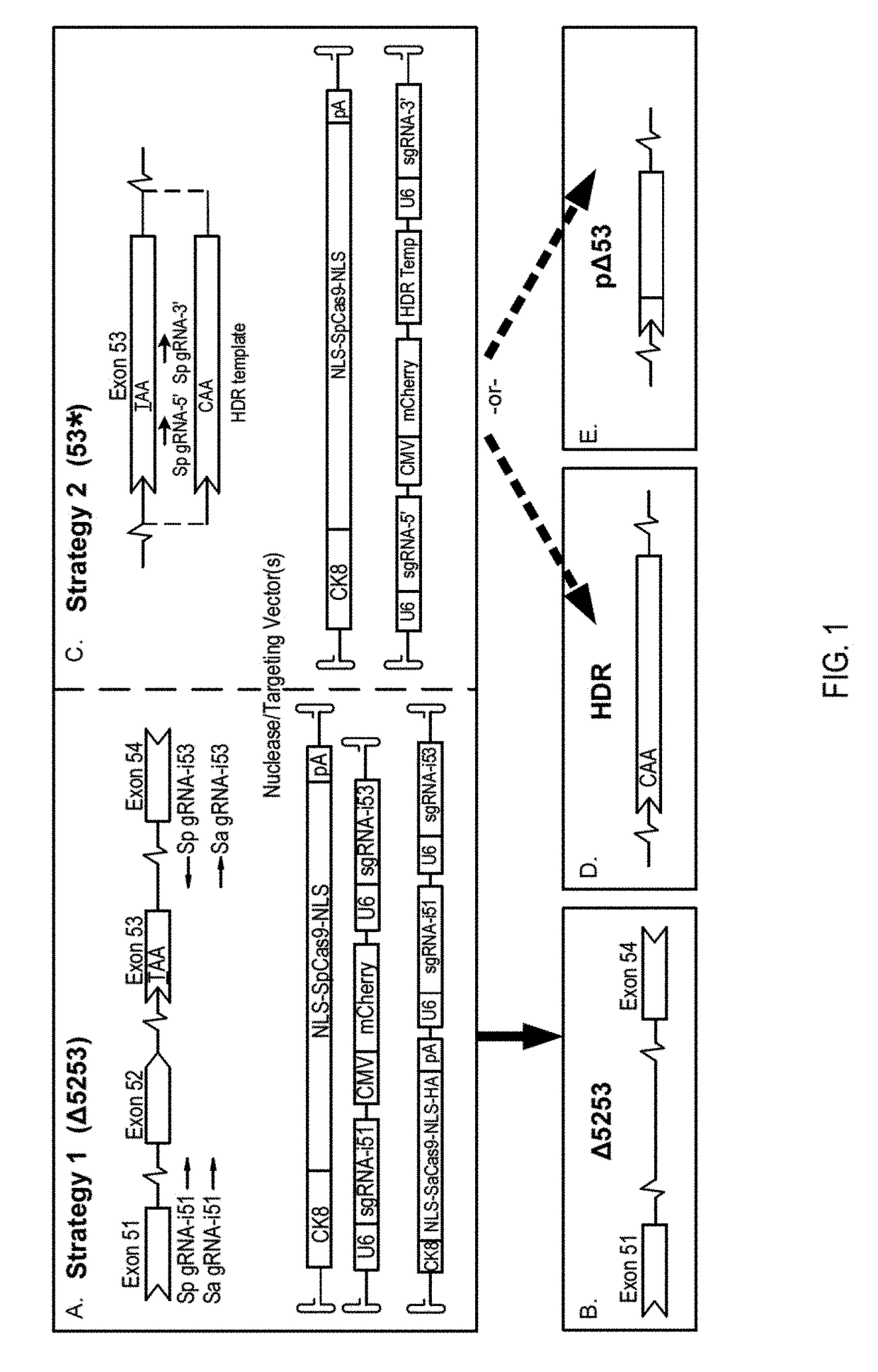
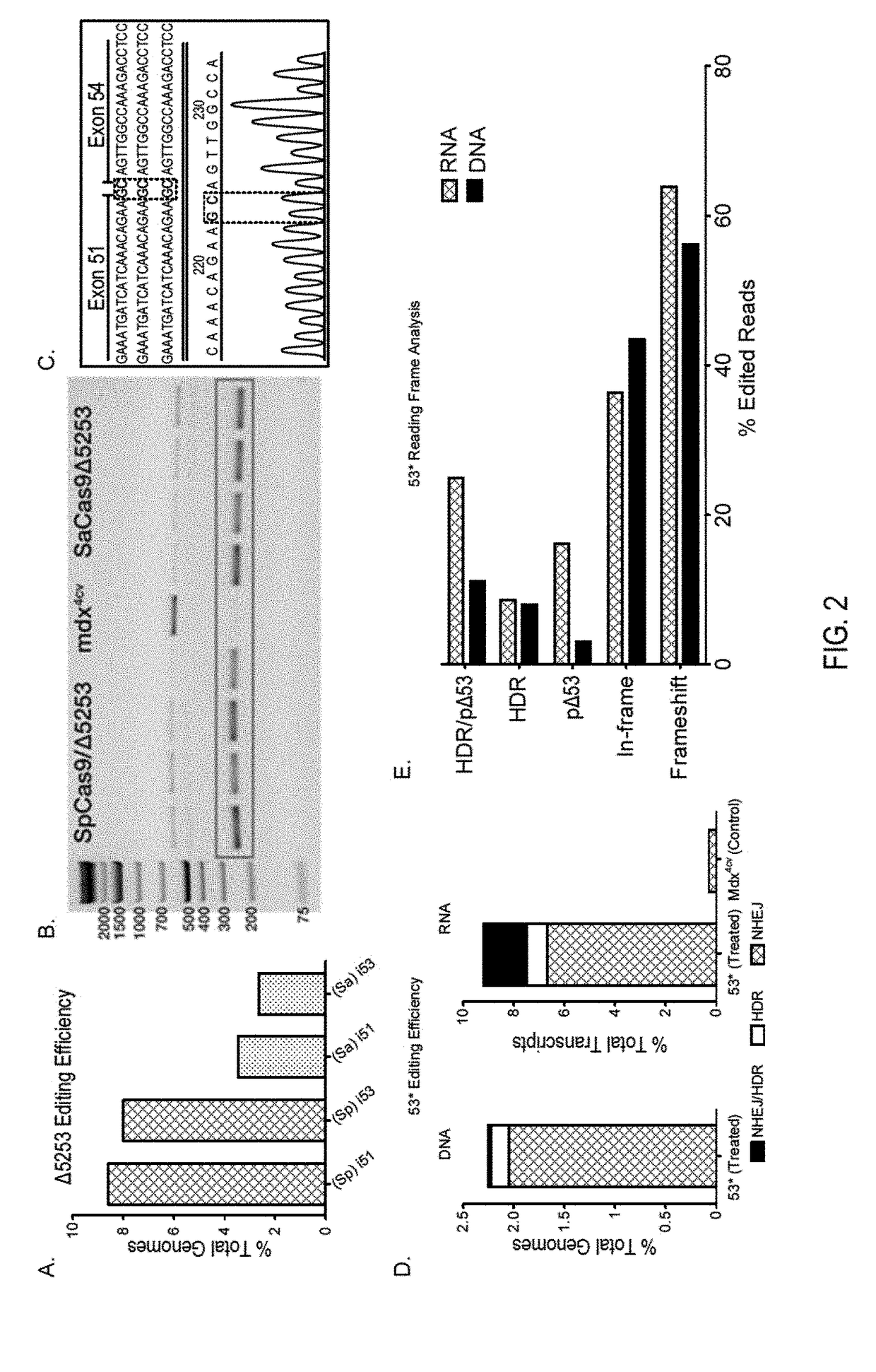
Muscle-specific crispr/cas9 editing of genes
Pharmaceutical compositions including a muscle-specific nuclease cassette, one or more guide RNA cassettes, and a delivery system for delivery of the muscle-specific nuclease cassette and the one or more gRNA cassettes are provided. The pharmaceutical composition may also include a mutation-corrected DNA template including a modification to be made in a target nucleic acid sequence. Methods for treating a subject having a muscular or neuromuscular disorder are also provided. The methods may include administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition. Methods of modifying or editing the sequence of a target nucleic acid sequence in a muscle cell are also provided. The methods may include contacting or transducing the muscle cell with a muscle-specific nuclease cassette and one or more gRNA cassettes.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Pharmaceutical botulinum toxin compositions
Owner:REVANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
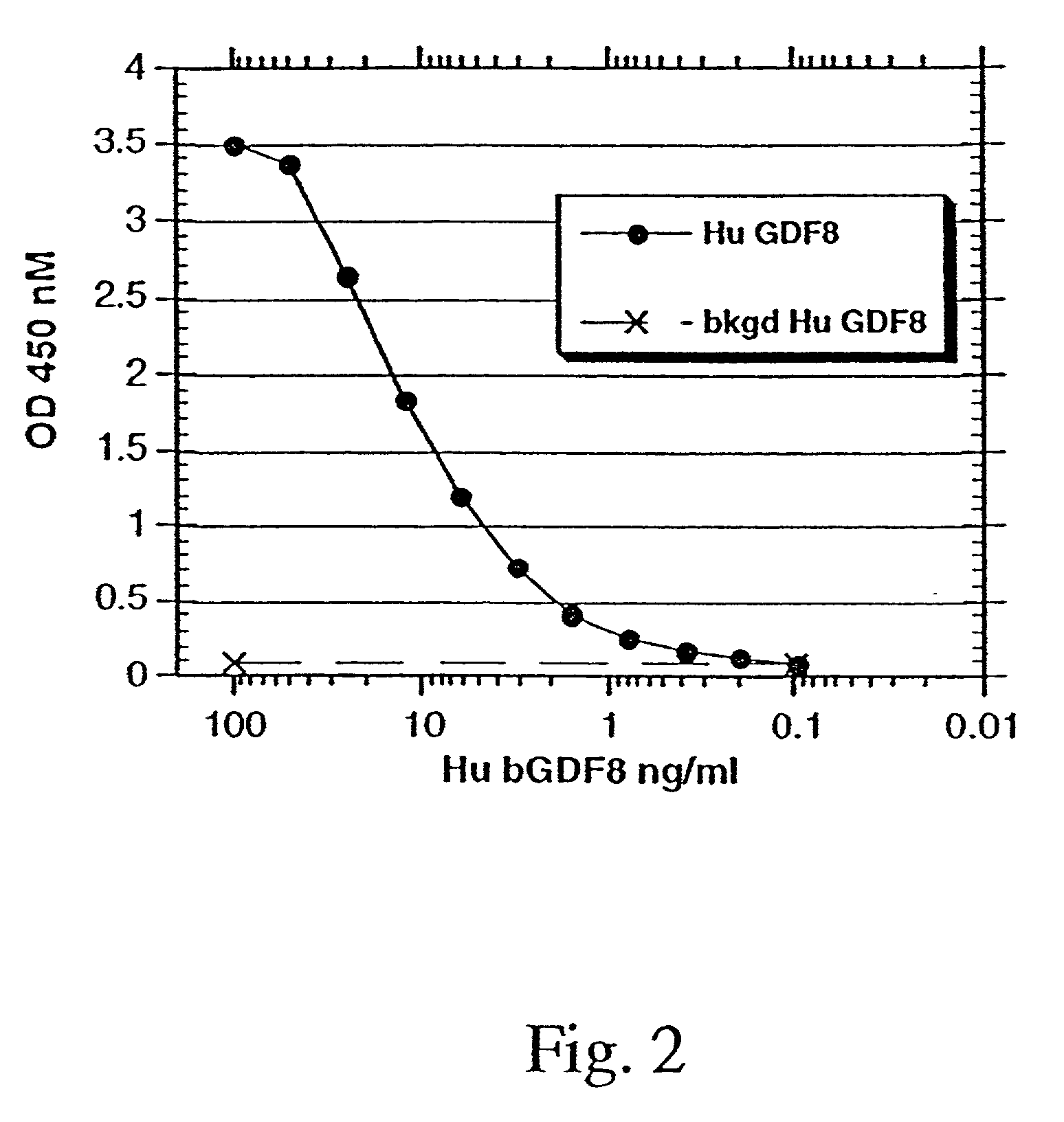
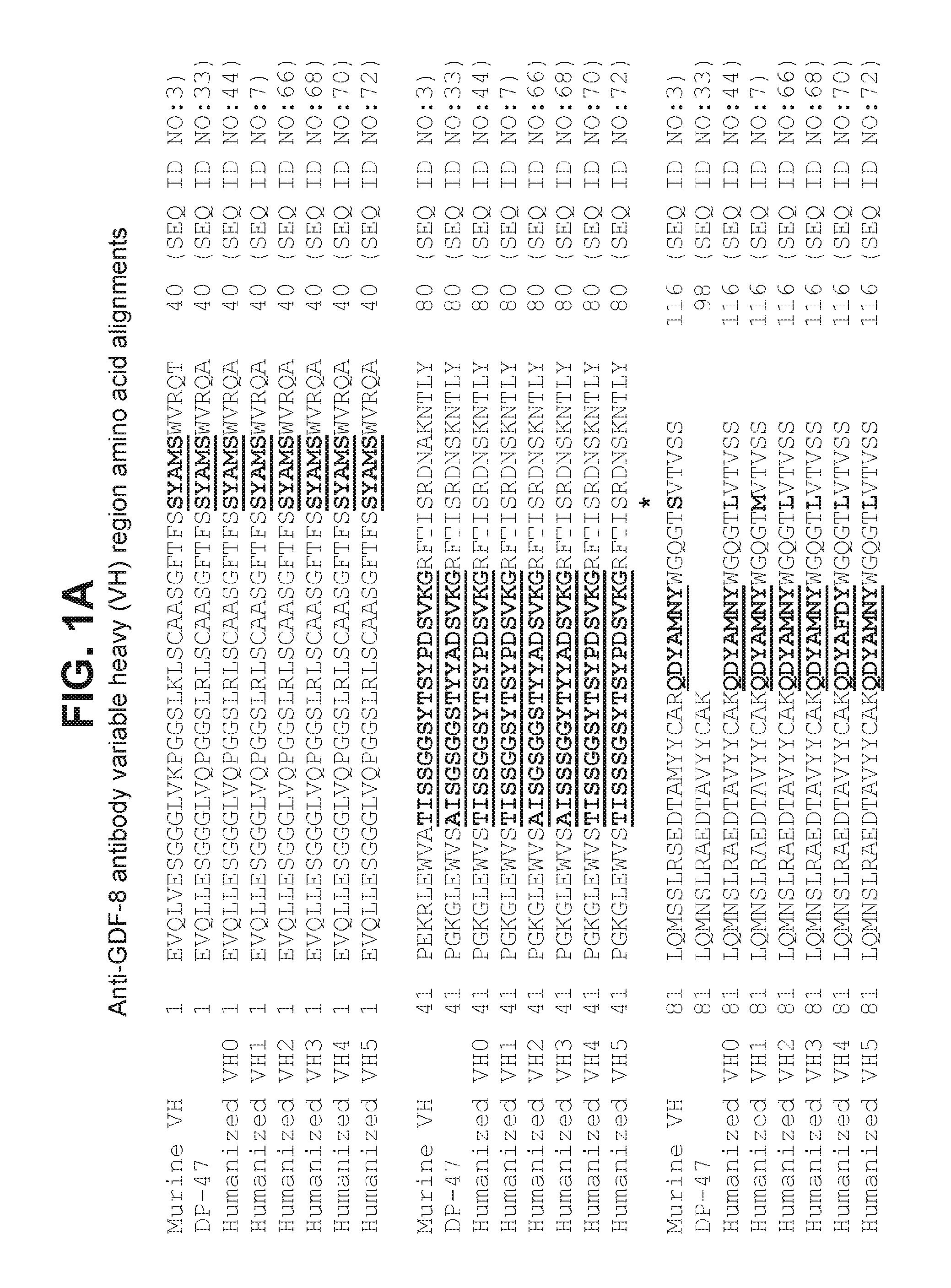
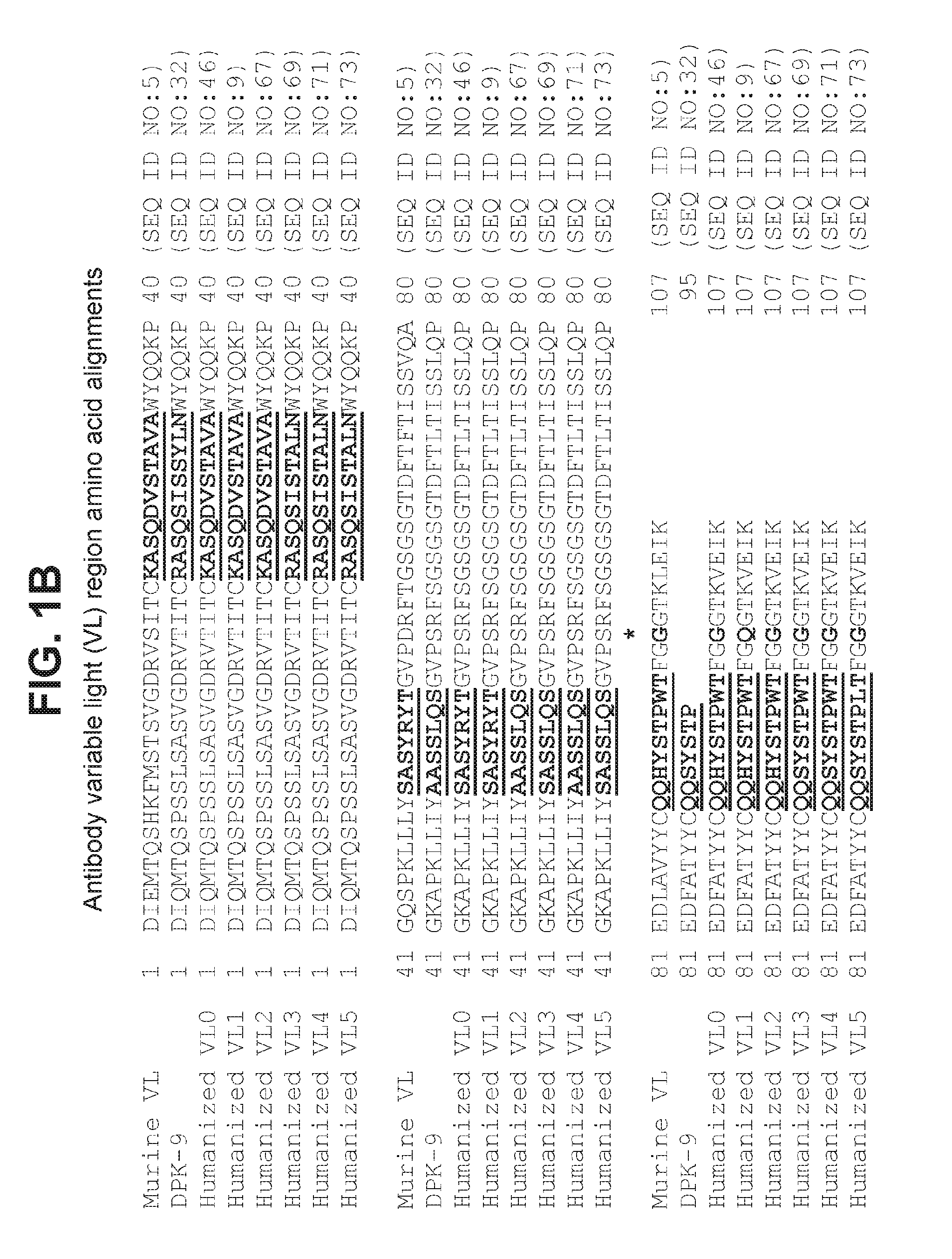
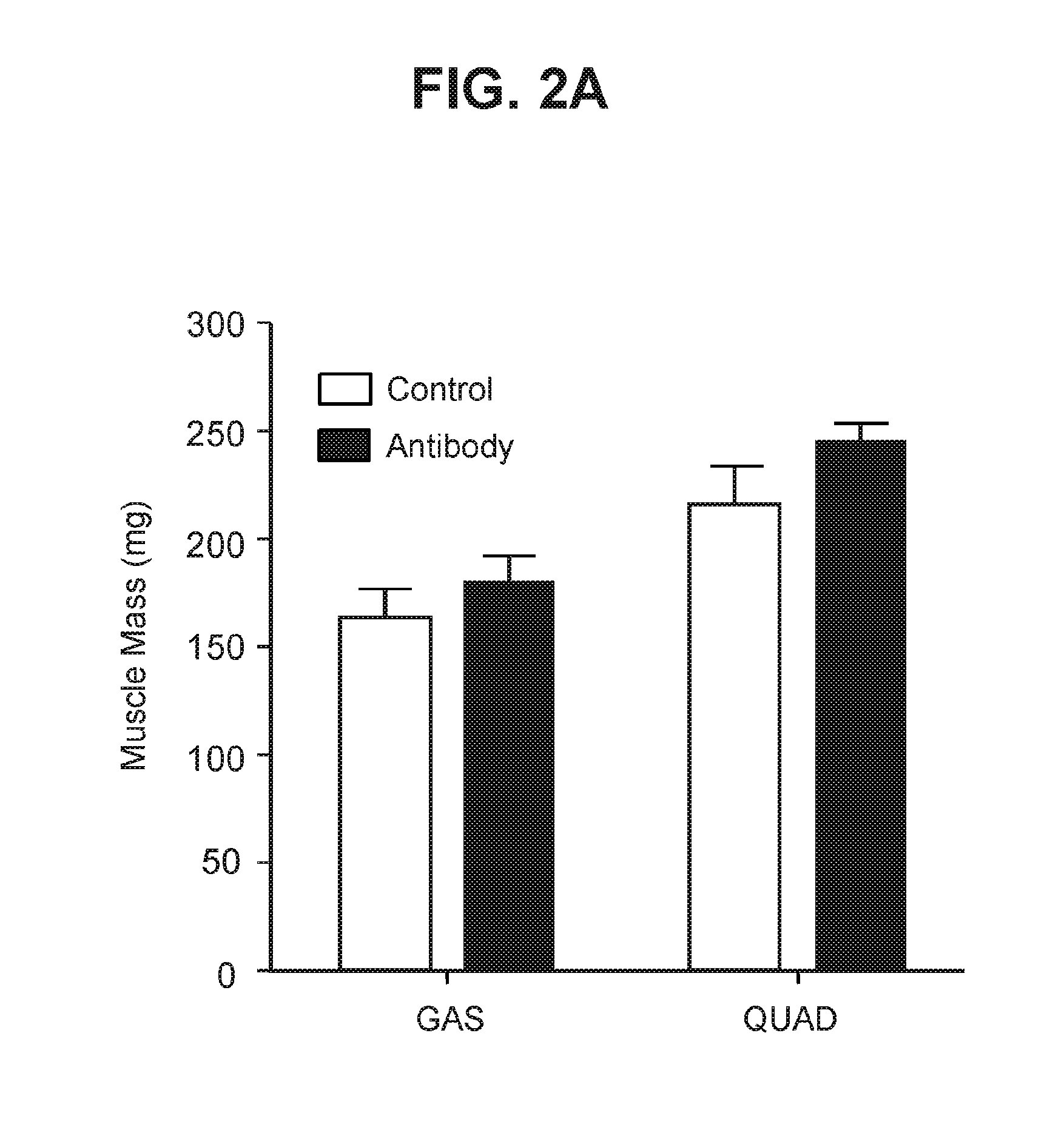
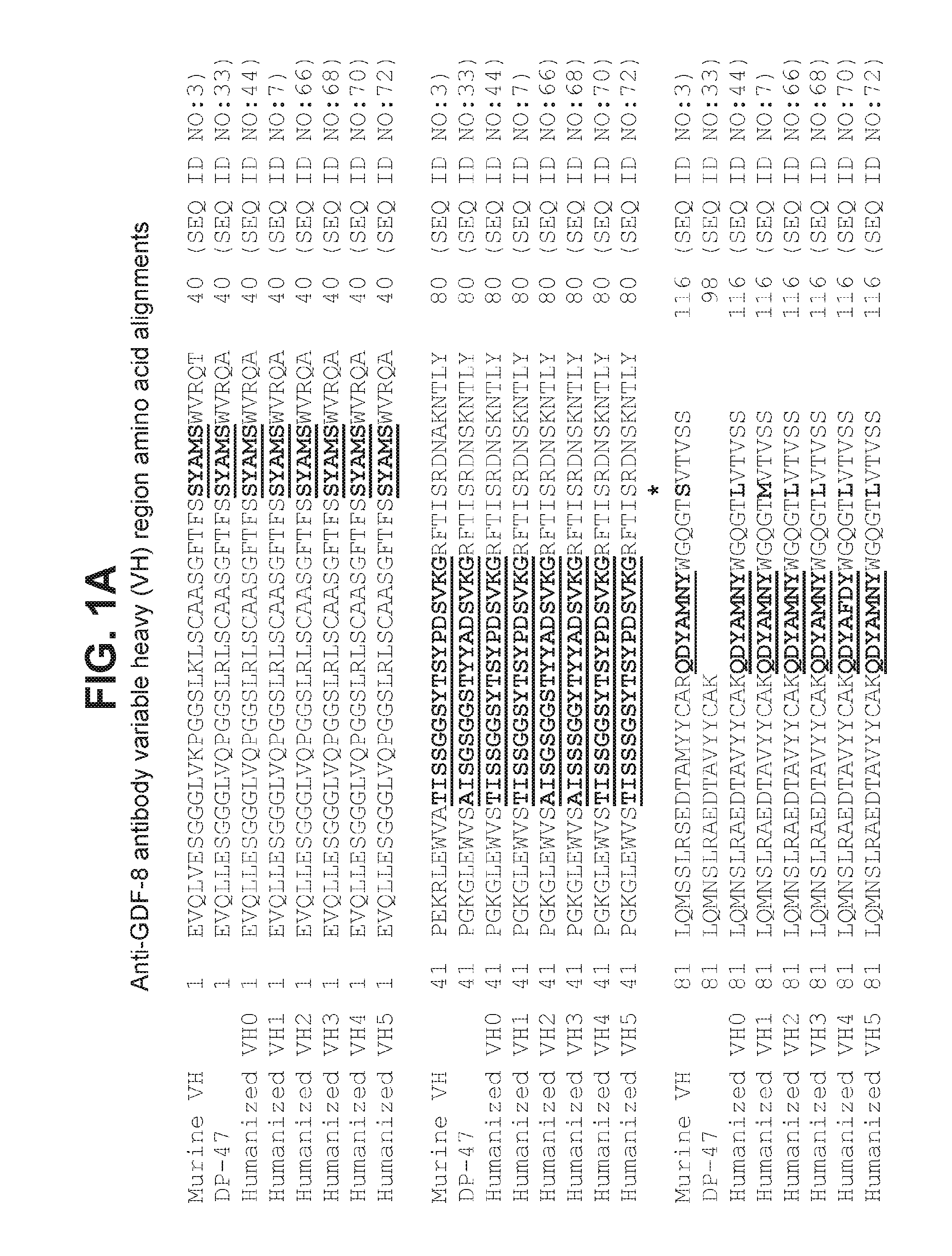
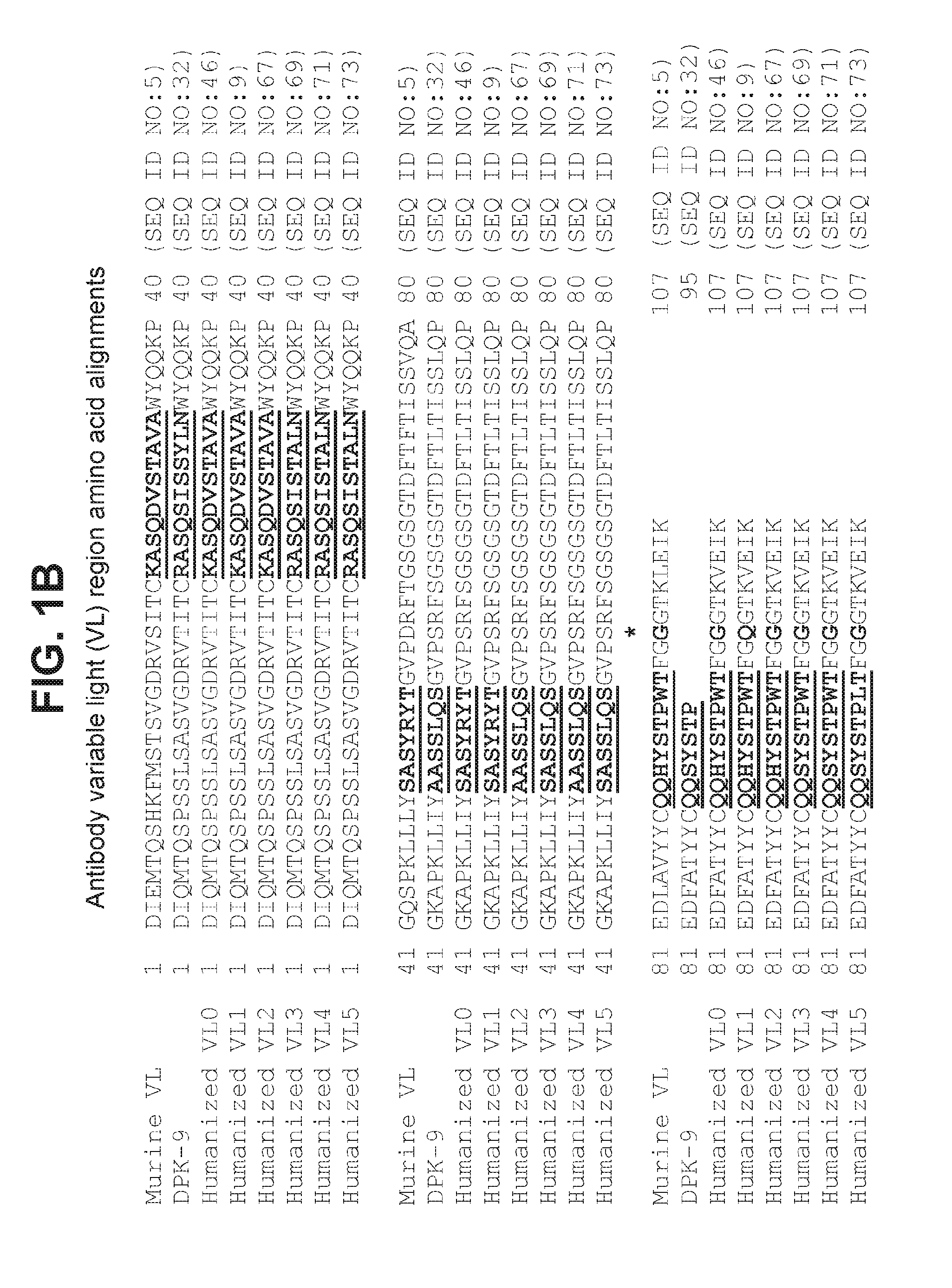
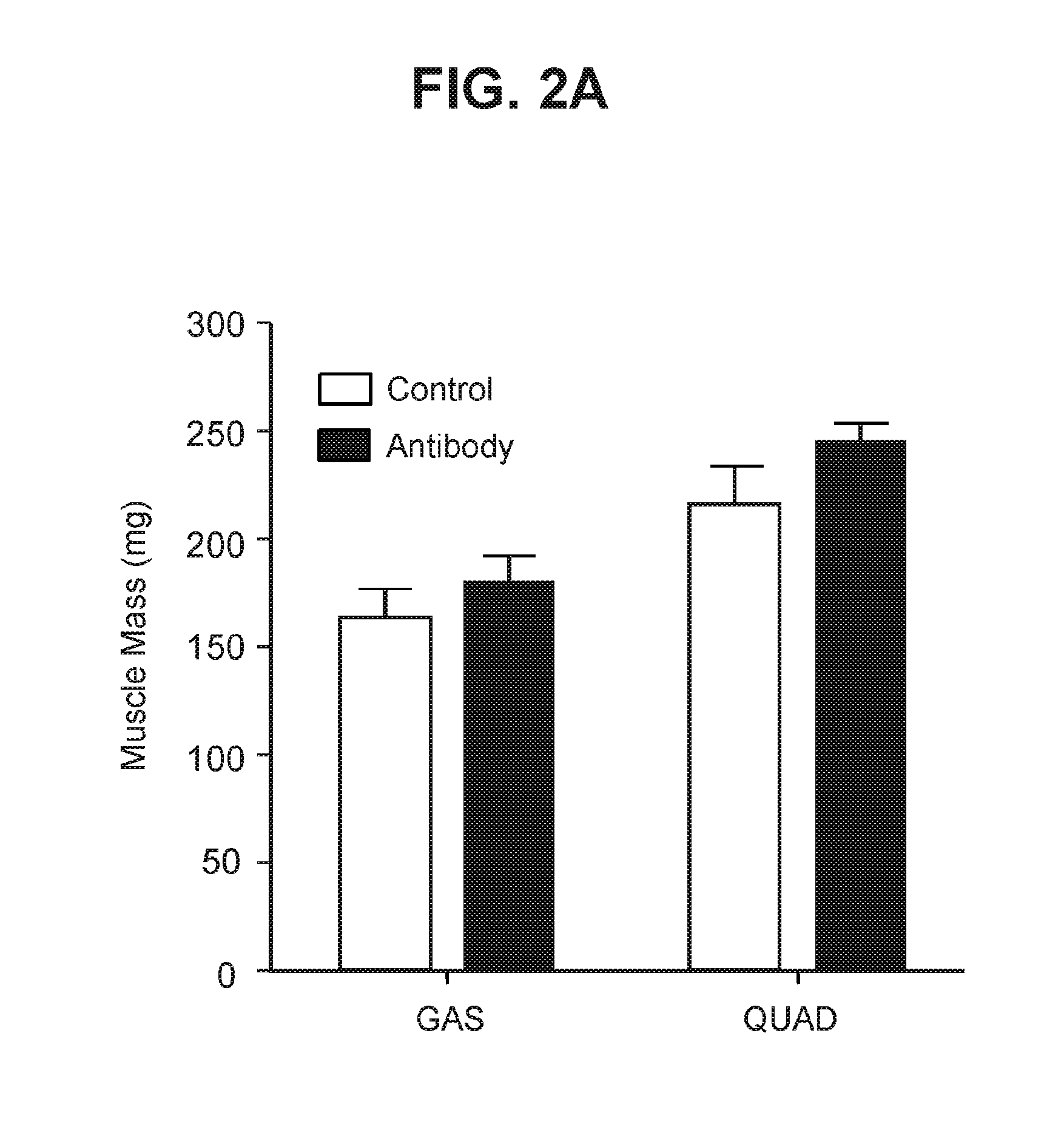
Antagonist antibodies against GDF-8 and uses therefor
The disclosure provides improved neutralizing anti-GDF-8 antibodies capable of substantially higher levels of expression in host cells compared to previous anti-GDF-8 antibodies. Also provided are methods of using compositions comprising such antibodies to increase muscle mass or strength, and to treat or prevent muscular disorders, neuromuscular disorders, metabolic disorders, adipose tissue disorders or bone disorders.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Antagonist antibodies against gdf-8 and uses therefor
InactiveUS20130336982A1Improve performanceLoss of massSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The disclosure provides improved neutralizing anti-GDF-8 antibodies capable of substantially higher levels of expression in host cells compared to previous anti-GDF-8 antibodies. Also provided are methods of using compositions comprising such antibodies to increase muscle mass or strength, and to treat or prevent muscular disorders, neuromuscular disorders, metabolic disorders, adipose tissue disorders or bone disorders.
Owner:PFIZER INC
High-potency botulinum toxin formulations
InactiveUS7691394B2Reduce secretionPromote growthNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The present invention provides improved formulations of botulinum toxin that increase delivery of the botulinum toxin to neural and associated tissues and exhibit a higher specific neurotoxicity and higher potency (in LD50 Units) than available formulations of botulinum toxins. These improved formulations enable physicians to treat a wide variety of pathological conditions with a lower toxin load that reduces the risk of inducing an immune response against the toxin and its associated proteins that may ultimately lead to the development of toxin resistance. These benefits are particularly important in the treatment of conditions that require high-dose or chronic administration of botulinum toxin. Additionally, the decreased in LD50 Unit doses of inventive formulations allows for controlled administration limits diffusion. The present invention also provides methods of treating neuromuscular diseases and pain, using low-dose botulinum toxin.
Owner:REVANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
Method of improving sleep disordered breathing
ActiveUS20090118785A1Improve sleepingElectrotherapySurgerySleep disordered breathingSommeil paradoxal
A diaphragm pacing stimulatory method and a system to implement the method are provided to improve respiratory function and the quality of sleep in patients whose sleep is compromised by poor respiration. The diaphragm pacing method includes adaptations that make it particularly compatible with the onset of sleep and sustaining sleep. Embodiments of the method are operated independently of breathing effort the patient may make during sleep. Patients for whom the invention is appropriate include those with a neuromuscular disease, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). System elements include an external electrical stimulator coupled to one or more implanted electrodes that stimulate diaphragm contraction. The system and method provide for a pacing of the diaphragm, improved breathing, and improved sleep. Features of improved sleep include longer sleep time, an increased amount of REM sleep, and fewer episodes of wakefulness and restlessness.
Owner:SYNAPSE BIOMEDICAL INC
Therapeutic methods for muscular or neuromuscular disorders
InactiveUS7785587B2Add additional massHigh strengthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The disclosure provides methods for treating neuromuscular disorders in mammals. The disclosed methods include administering therapeutically effective amounts of a GDF-8 inhibitor and a corticosteroid to a subject susceptible to, or having, a neuromuscular disorder, so as to maintain desirable levels of muscle function.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Antisense oligonucleotide against human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and uses thereof
InactiveUS7074915B2Increase physical strengthReduce muscle fatigueOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNervous systemNeuromuscular disease
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Molecules for targeting compounds to various selected organs, tissues or tumor cells
The invention provides conjugates, comprising an organ, tissue or tumor cell homing molecule linked to a moiety. Such a moiety can be, for example, an oligonucleotide, small interfering RNA, gene, virus, protein, pharmaceutical or detectable agent. In addition the invention provides methods to diagnose or treat neuronal or neuromuscular disease, or a pathology of the brain, or a tumor of neuronal or neuroectodermal origin, by administrating to a subject having or suspected of having a pathology a molecule or conjugate that homes to, binds to and is taken up by the brain cells or neuronal cells, or by the tumor cells of neuronal or neuroectodermal origin. The invention also provides a method of identifying and measuring neurite growth in neuronal cells.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
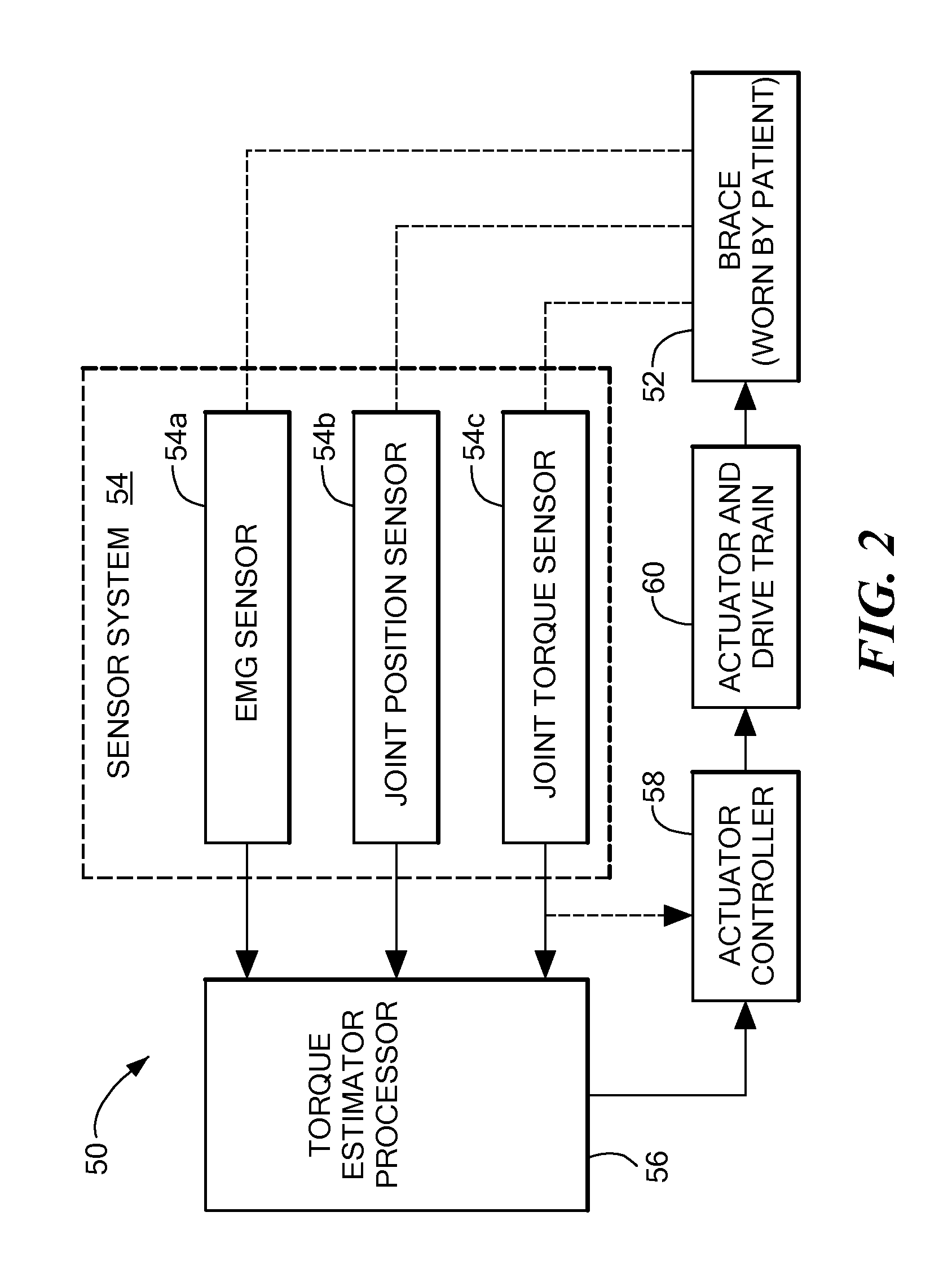
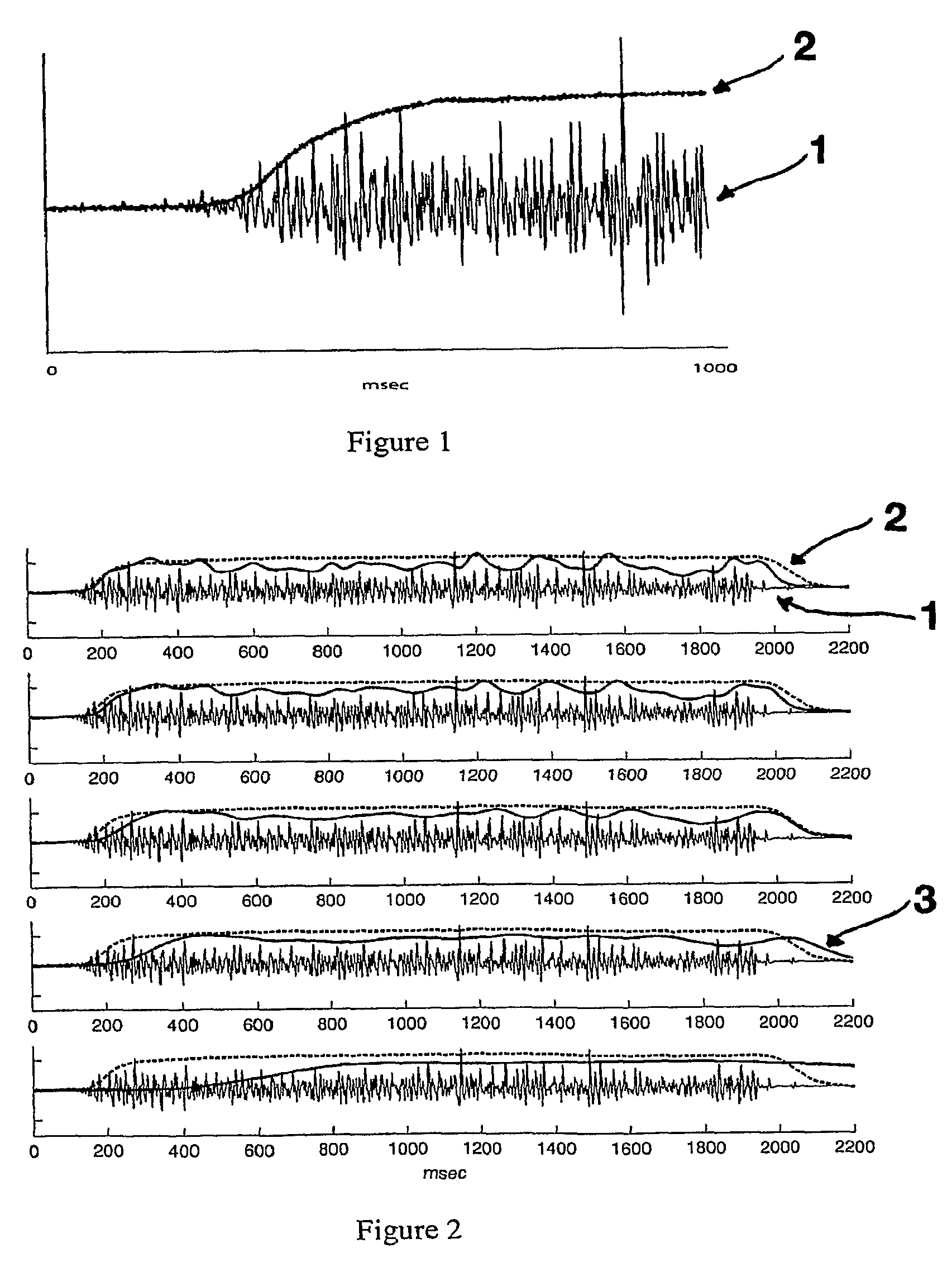
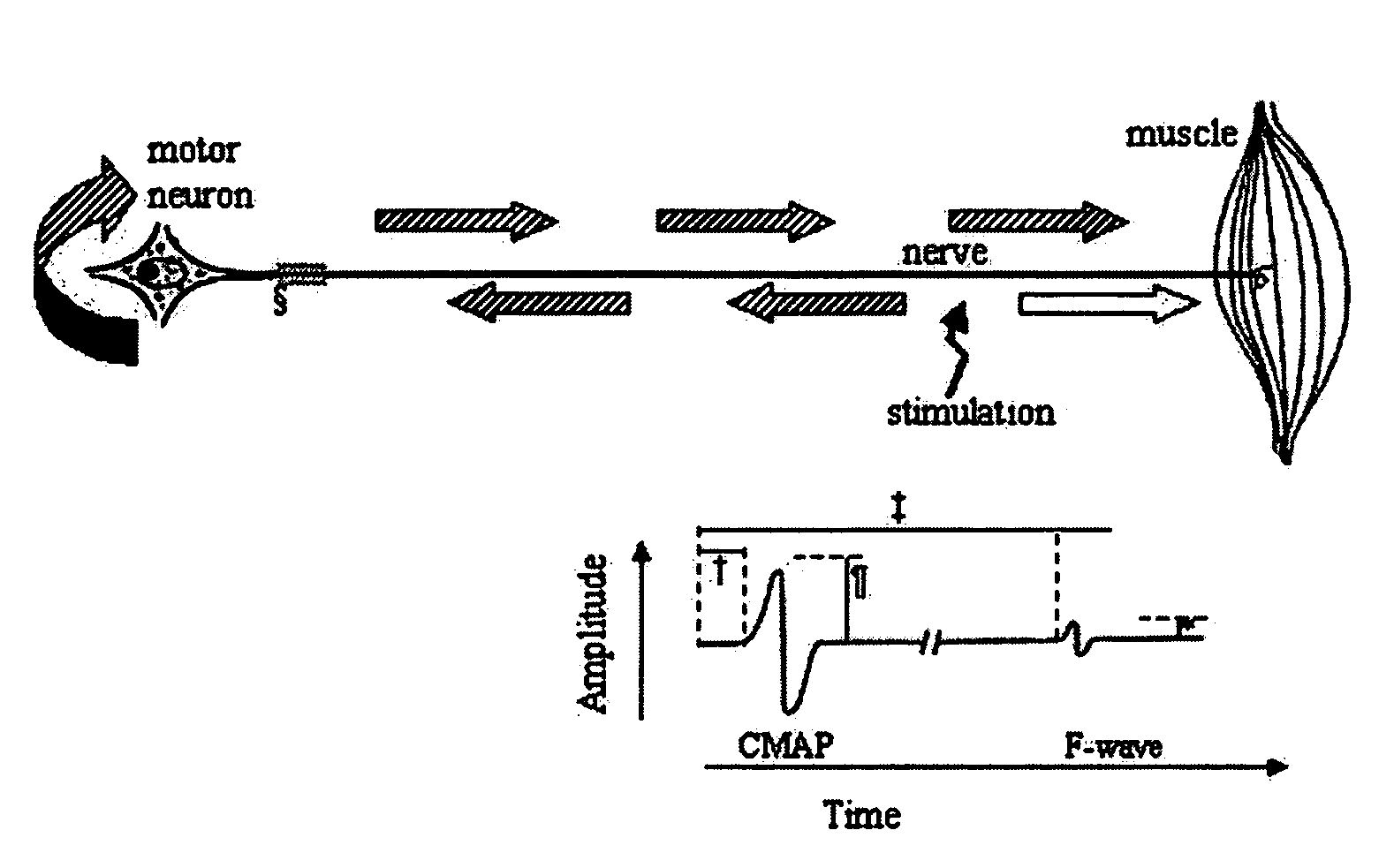
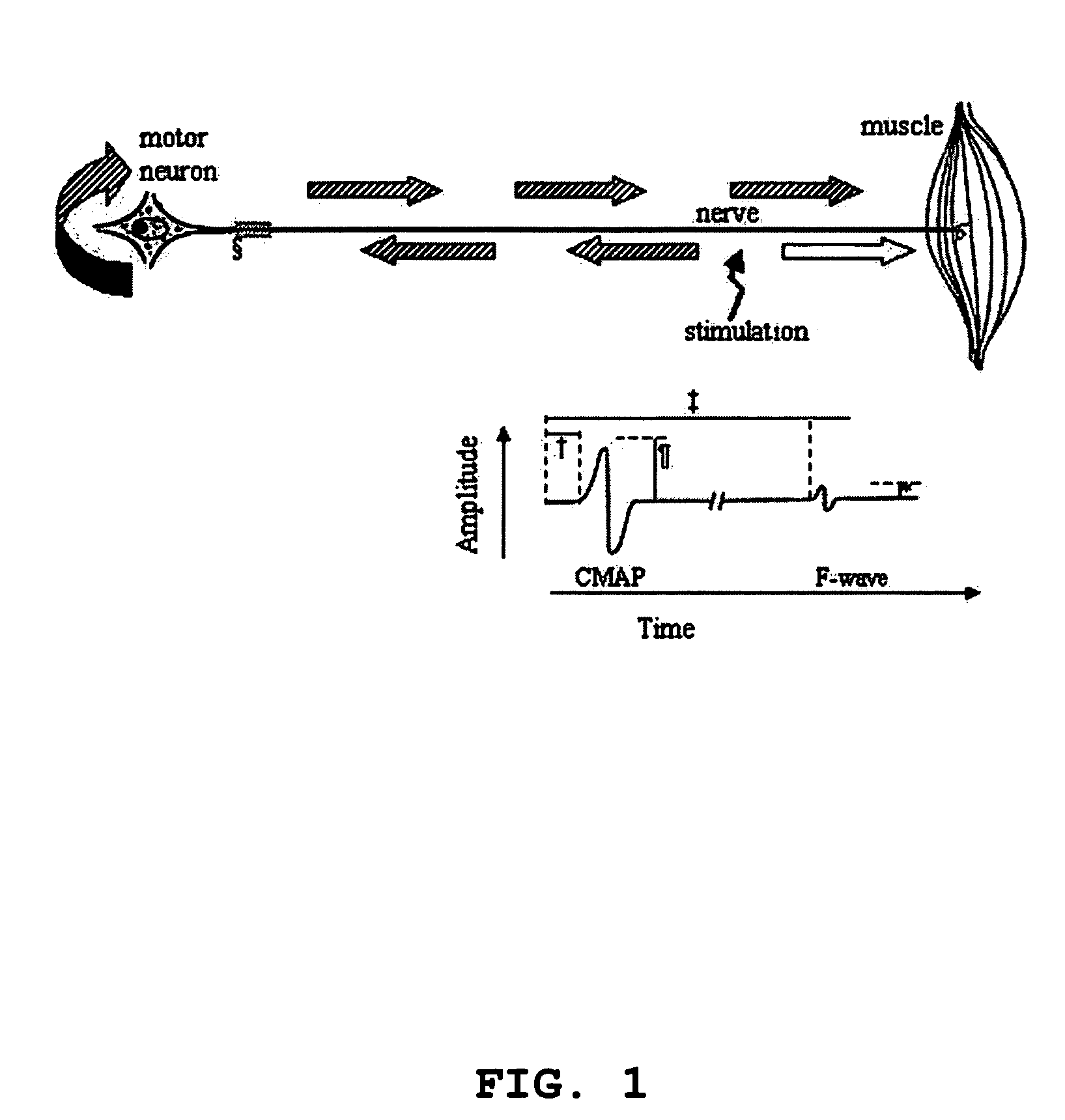
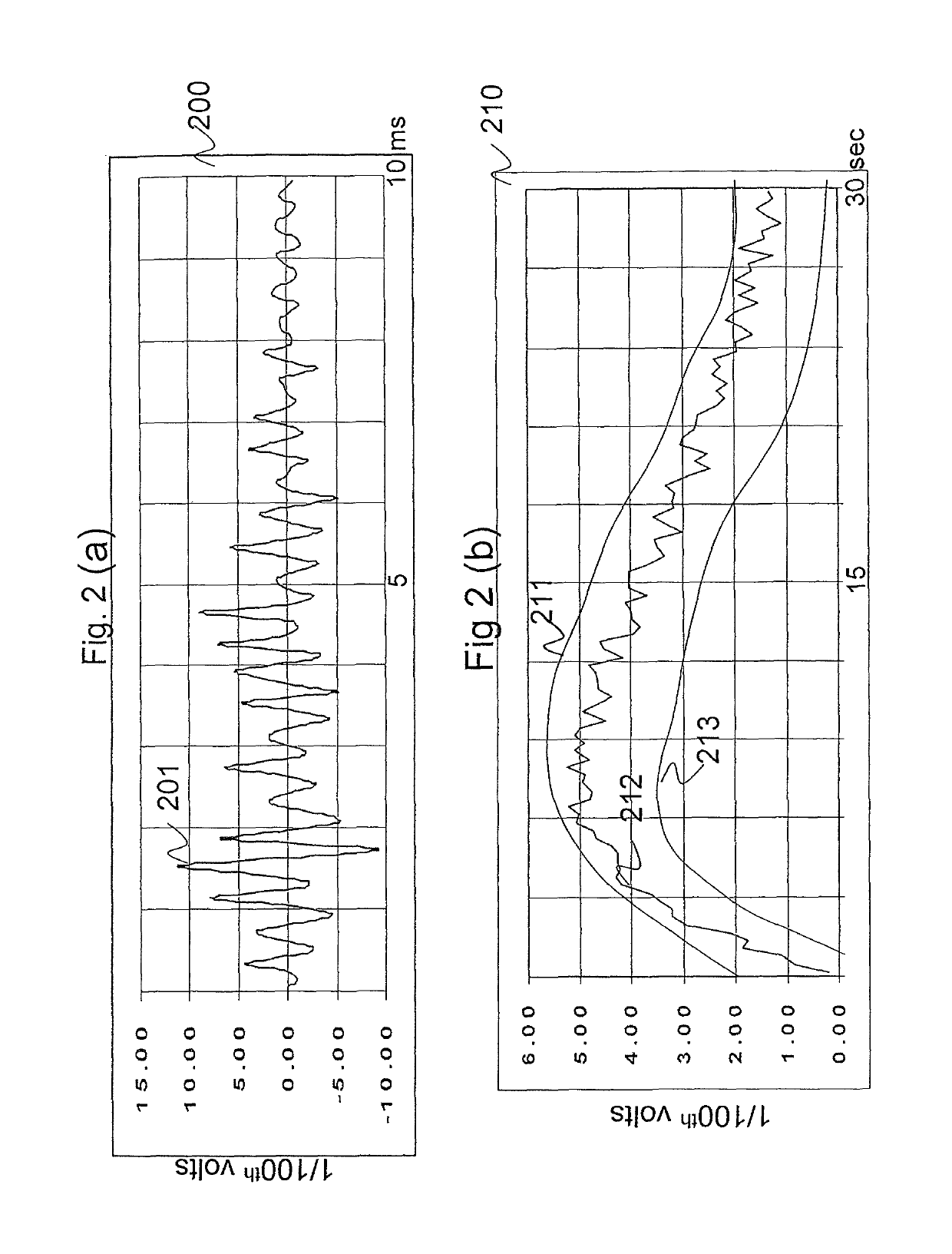
Method and apparatus for the detection of neuromuscular disease using disease specific evoked neuromuscular response analysis
A method and apparatus for assessing neuromuscular pathology in an individual, by (a) applying a plurality of stimuli to a peripheral nerve; (b) recording from the peripheral nerve, or from a muscle innervated by the peripheral nerve, at least one response to each stimulus; (c) processing each response into at least one response characteristic; (d) compiling the response characteristics from all of the responses into a plurality of descriptive parameters of the response characteristics; and (e) analyzing the plurality of descriptive parameters according to a function specific to the neuromuscular pathology so as to yield an indicator of the pathology.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX
Multiple botulinum toxins for treating neuromuscular disorders and conditions
InactiveUS20010021695A1Alleviation of muscle spasmsHelp with painNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
A method and composition for treating a patient suffering from a disease, disorder or condition include the administration to the patient of a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of at least two neurotoxins selected from a group consisting of botulinum toxin types A, B, C, D, E, F and G. The amount of each selected neurotoxin administered is further selected to control a duration of therapeutic activity of the administered combination.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
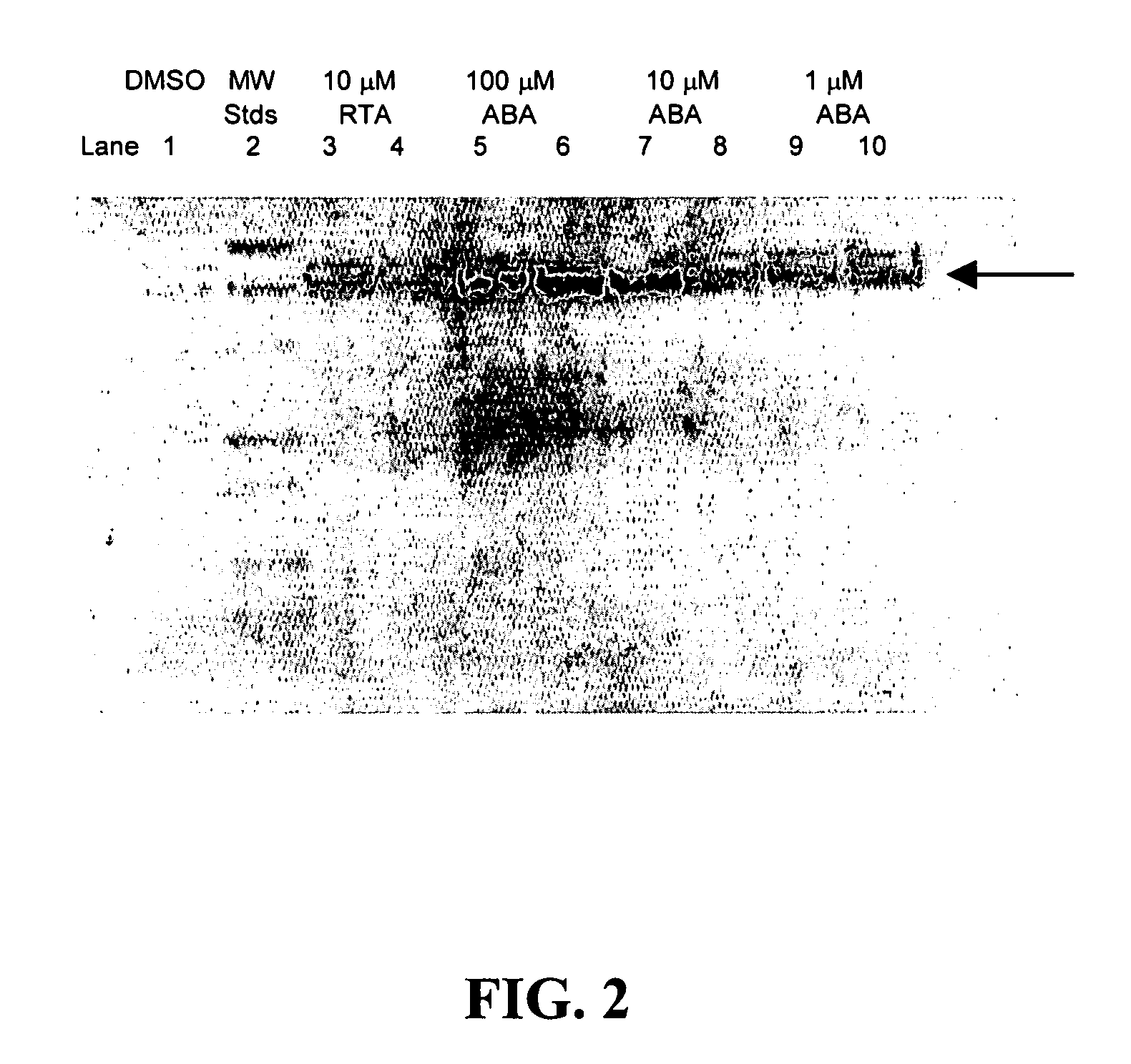
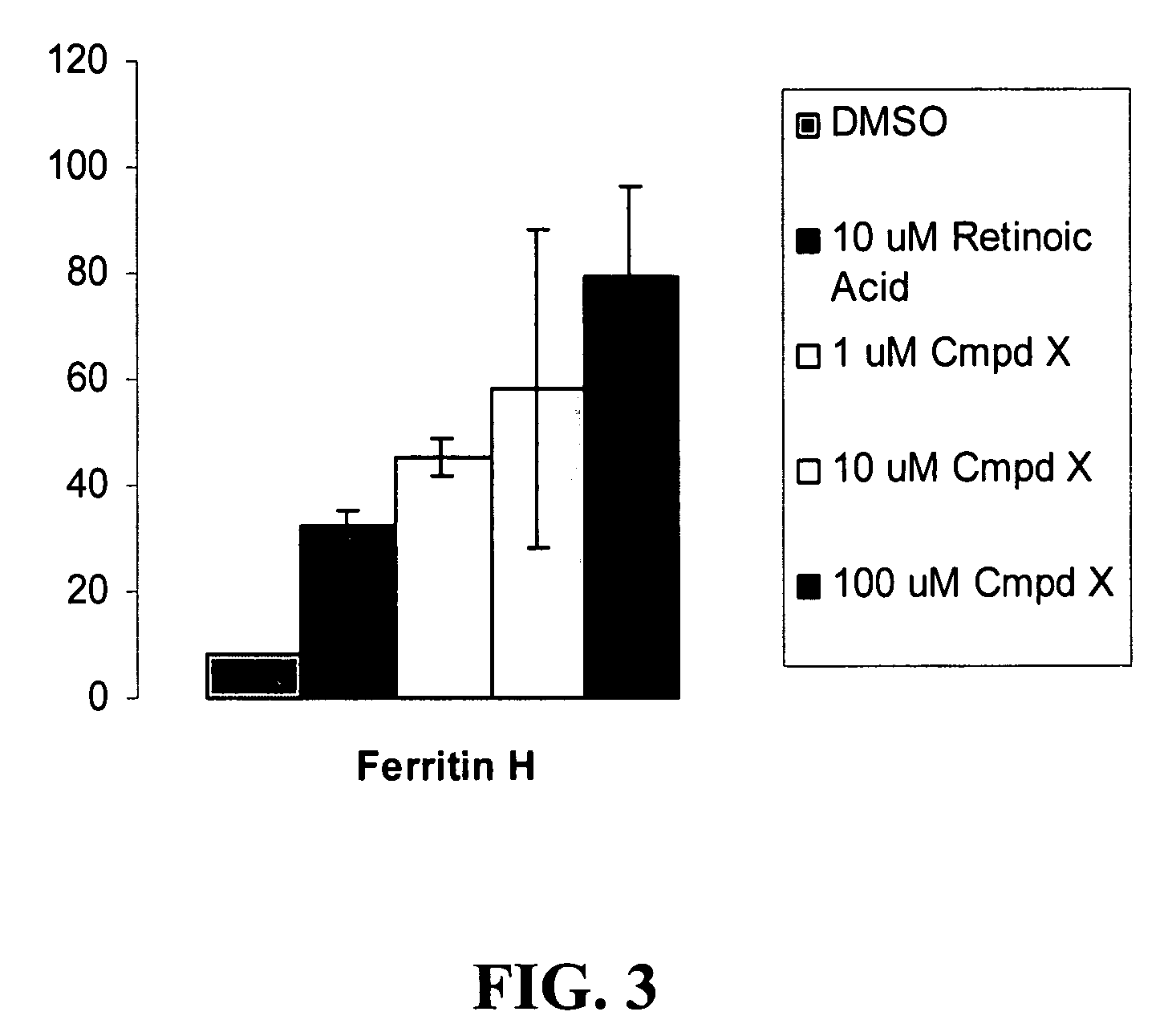
Abscissic acid and derivatives thereof for the treatment of diseases
InactiveUS7718699B1Reduce concentrationIncrease in iron in the subjectBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The present invention relates generally to the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology. More particularly, it concerns the use of abscissic acid to treat various diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and neuromuscular diseases.
Owner:BROYLES ROBERT H +3
Method for determining rehab protocol and behavior shaping target for rehabilitation of neuromuscular disorders
ActiveUS10271768B1Improves access and delivery and efficacyQuality improvementElectrotherapyElectromyographyDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
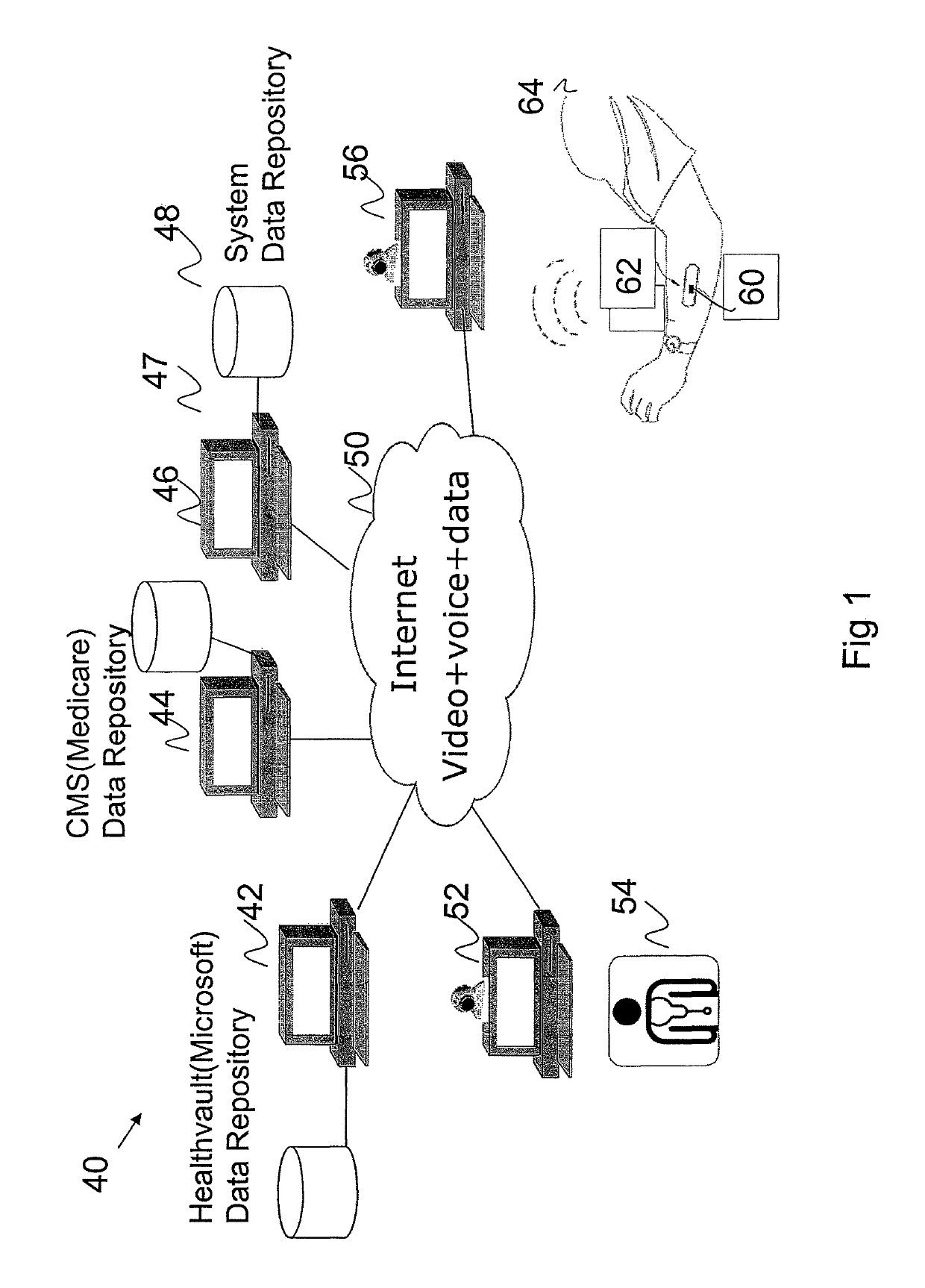
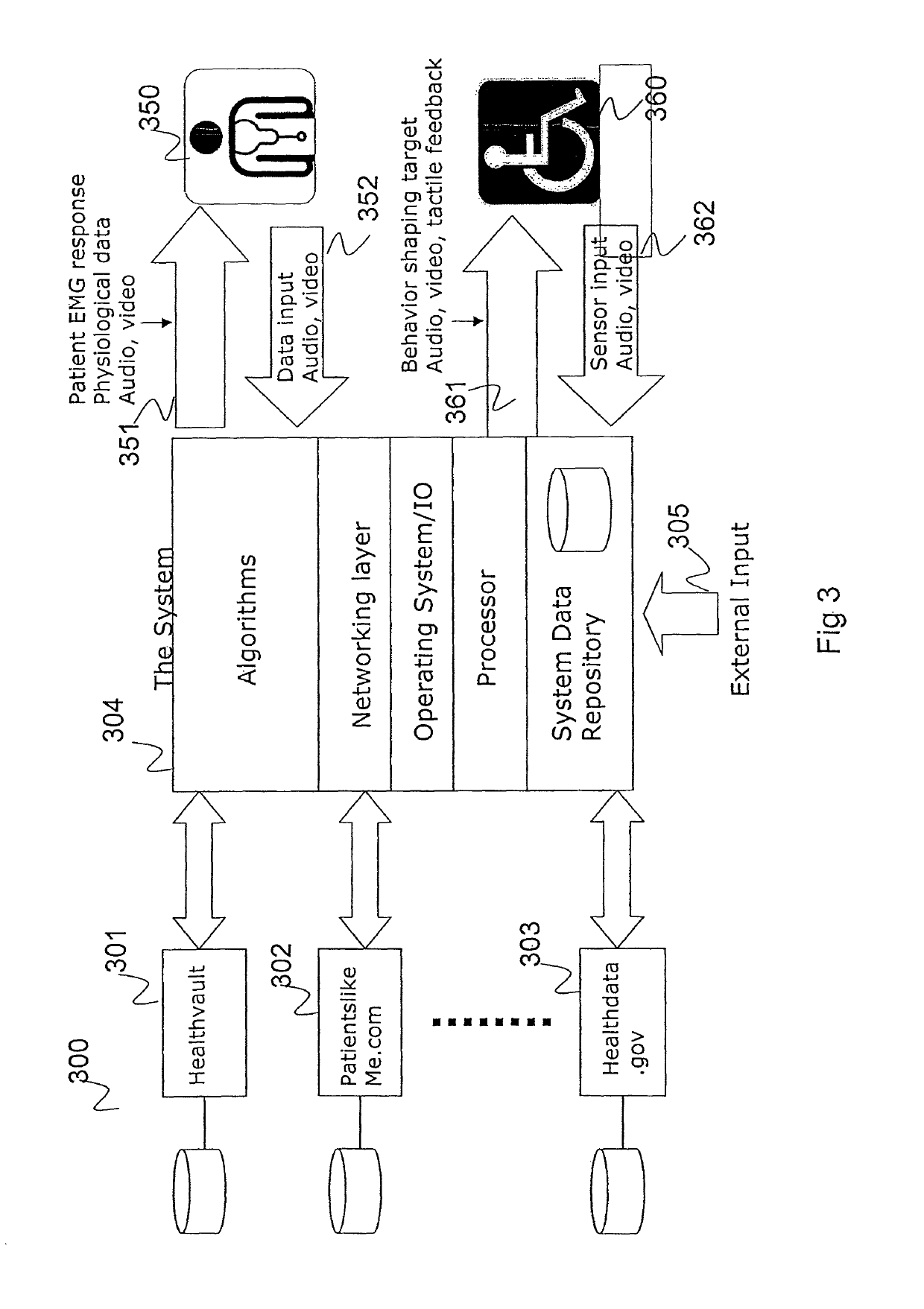
A system for treating a patient with neurological disorders of movement includes a patient computing device for use in rehabilitative training and a sensor worn about a body part being rehabilitated. A healthcare computing device is used by a healthcare professional to assist remote patient rehabilitation by accepting input signals and determining for the patient a rehab protocol depending on selected parameters, and determining for the patient a behavior shaping target depending on selected parameters and the rehab protocol and behavior shaping target is communicated to the patient while the patient is undergoing rehabilitation. A plurality of remote health data sites and other public repositories of health data of patients undergoing rehabilitation following neurological events can be included. The remote computing device can include a data repository of publicly available patient data and patient data gathered by system of present invention.
Owner:JOGOHEALTH INC
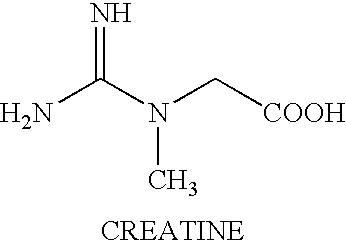
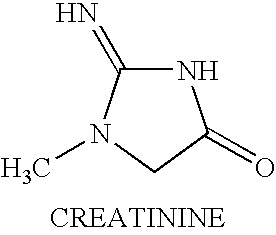
Treating neuromuscular disorders with an oral formulation of creatine derivatives
InactiveUS20060062853A1Extended shelf lifeEliminate water absorptionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseShellac
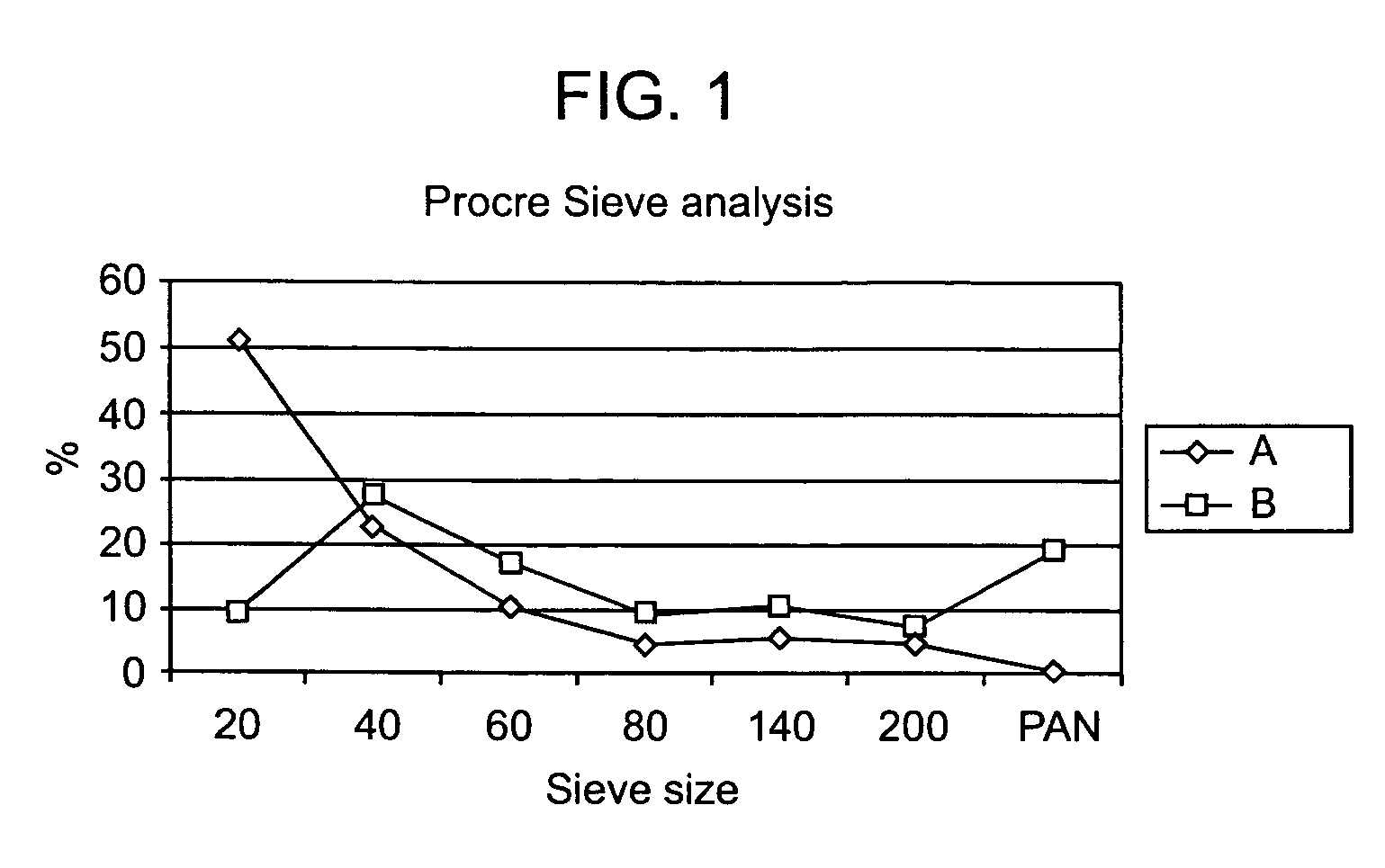
Treating human muscle tissue by the oral administration of a formulation of creatine derivative and in particular creatine esters and more particularly ethyl esters of creatine are described. The formulations comprise a phosphate such as dicalcium phosphate, a biodegradable polymer such as a polyvinyl pyrrolidine and a starch. The formulation may further comprise other excipients such as metal salt of a stearate, e.g. magnesium stearates. The formulation is produced as flowable particles with a sieve size of about 20 to 60 which particles are coated with a shellac to mask taste, avoid moisture uptake, and extend shelf life.
Owner:MEDICAL RES INT
Assay for neuromuscular diseases
InactiveUS20060278532A1CellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The present invention is an assay for determining if a patient has a neuromuscular disease. The method comprises collecting a biological sample from a patient, separating the proteins present in the biological sample, quantitating a panel of proteins by proteomic techniques, analyzing the quantity of the protein panel using biostatistics, and determining whether or not the patient has a neuromuscular disease based on the statistical analysis of the results.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
Molecules for targeting compounds to various selected organs, tissues or tumor cells
InactiveUS20100184947A1Improving in vivo uptakeNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiseaseGerm layer
The invention provides conjugates, comprising an organ, tissue or tumor cell homing molecule linked to a moiety. Such a moiety can be, for example, an oligonucleotide, small interfering RNA, gene, virus, protein, pharmaceutical or detectable agent. In addition the invention provides methods to diagnose or treat neuronal or neuromuscular disease, or a pathology of the brain, or a tumor of neuronal or neuroectodermal origin, by administrating to a subject having or suspected of having a pathology a molecule or conjugate that homes to, binds to and is taken up by the brain cells or neuronal cells, or by the tumor cells of neuronal or neuroectodermal origin. The invention also provides a method of identifying and measuring neurite growth in neuronal cells.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
Therapeutic and prophylactic methods for neuromuscular disorders
InactiveUS20100322942A1Add additional massHigh strengthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The disclosure provides methods for treating neuromuscular disorders in mammals. The disclosed methods include administering therapeutically effective amounts of a GDF-8 inhibitor and a corticosteroid to a subject susceptible to, or having, a neuromuscular disorder, so as to maintain desirable levels of muscle function.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Alpha-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors
InactiveUS20060258598A1Maintain good propertiesSenses disorderNervous disorderCathepsin HPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to novel α-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and neuromuscular diseases including Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Muscular Dystrophy and other muscular dystrophies. Disuse atrophy and general muscle wasting can also be treated. Diseases of the eye, in particular cataract, can be treated as well. Generally all conditions where elevated levels of calpains are involved can be treated. The compounds of the invention may also inhibit other thiol proteases such as cathepsin B, cathepsin H, cathepsin L, papain or the like. Multicatalytic Protease (MCP) also known as proteasome may also be inhibited and the compounds can therefore be used to treat cell proliferative diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, and restenosis. The compounds of the present invention are also inhibitors of cell damage by oxidative stress through free radicals and can be used to treat mitochondrial disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, where elevated levels of oxidative stress are involved.
Owner:SANTHERA PHARMA SCHWEIZ
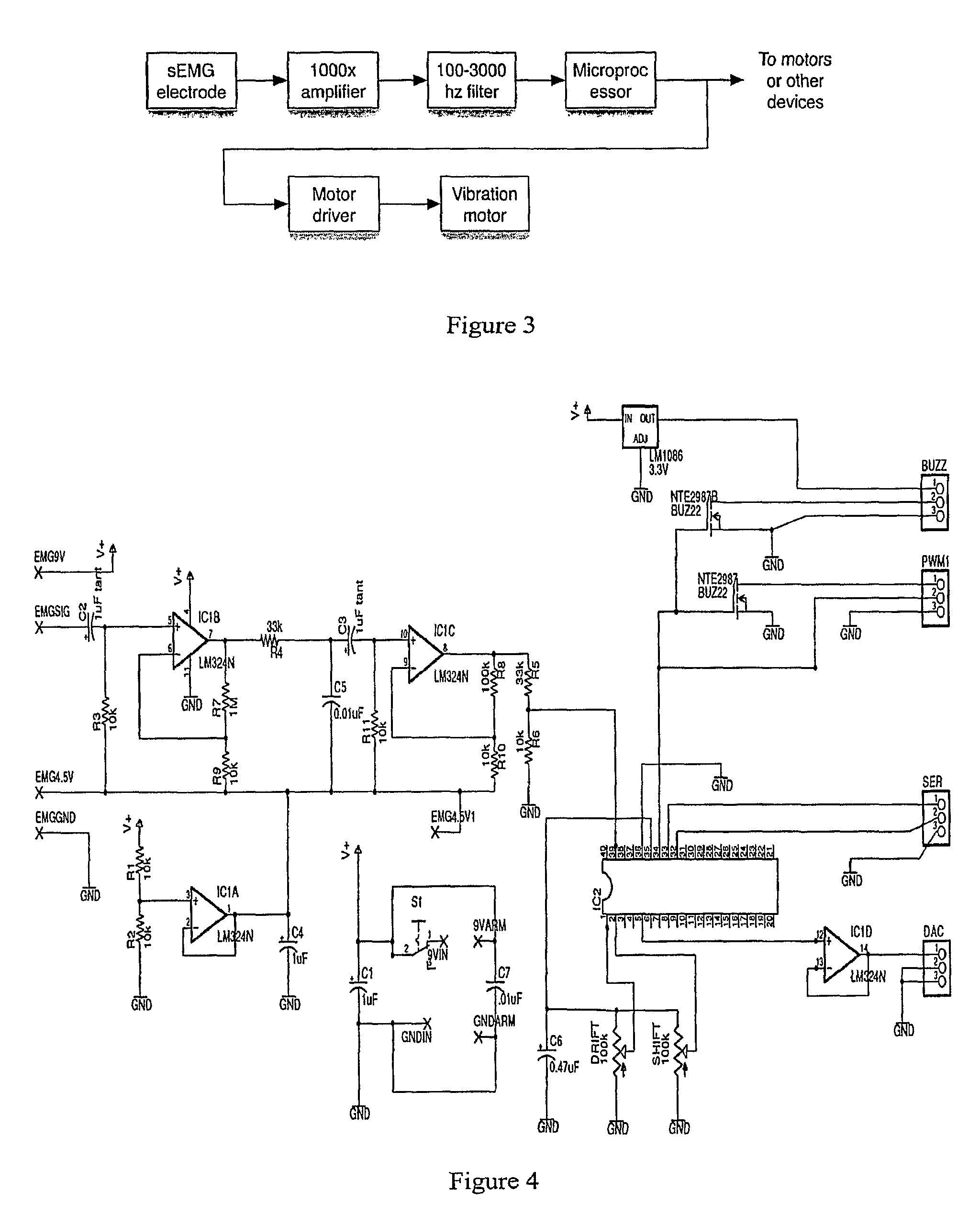
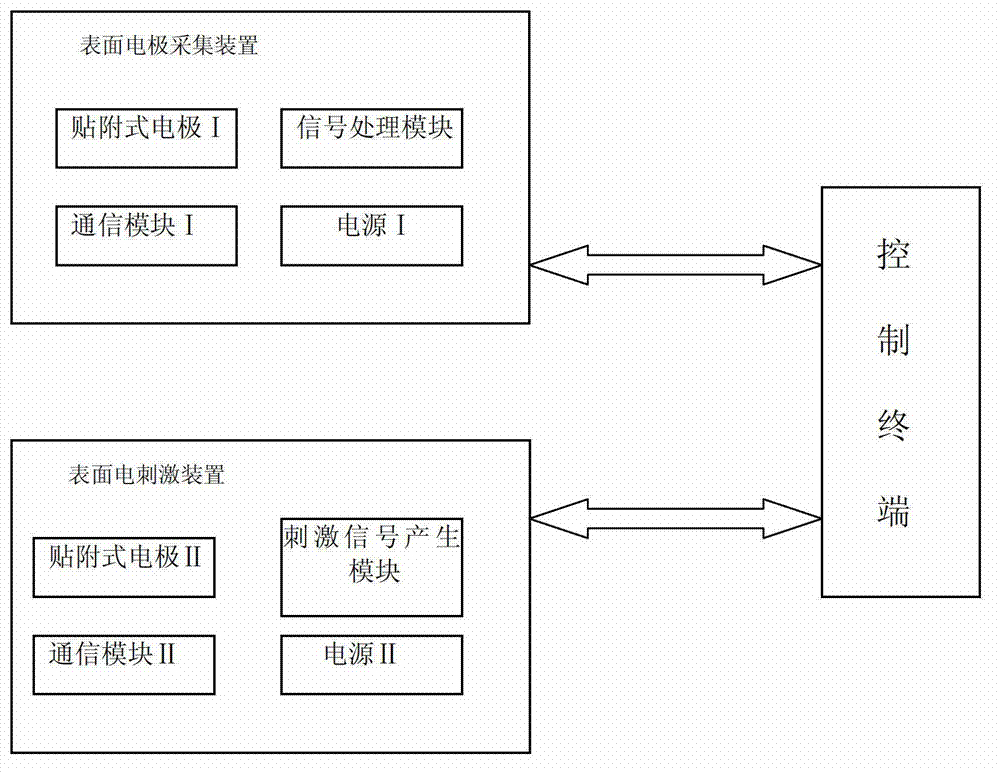
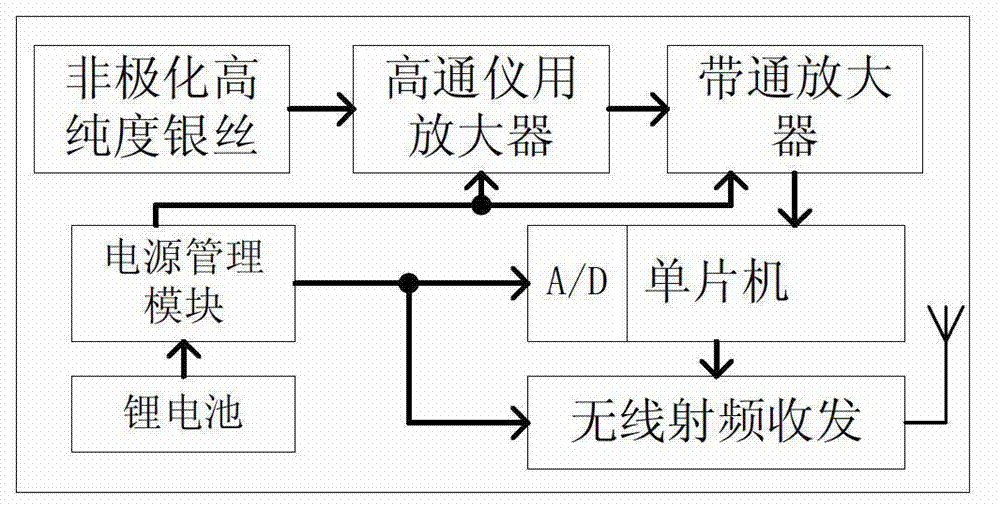
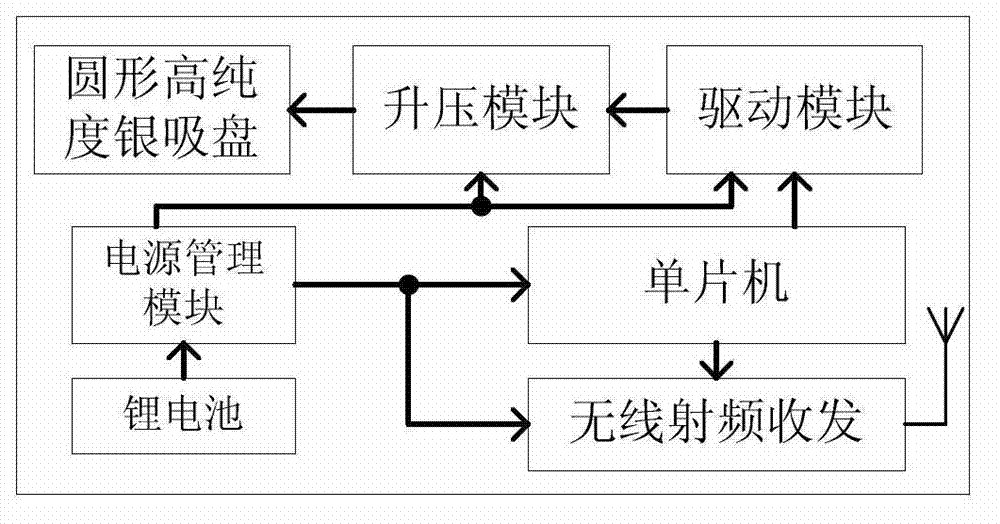
Non-invasive neuromuscular disease inspection system based on attached electrode
The invention discloses a non-invasive neuromuscular disease inspection system based on an attached electrode, and belongs to the field of a medical apparatus. The system comprises a surface electrode collecting device, a surface electrical stimulation device and a control terminal, wherein the surface electrode collecting device comprises an attached electrode I, a signal processing module, a communication module I and a power supply I; the attached electrode I collects a human physiological signal and transmits the signal to the signal processing module; the signal processing module processes the signal and then transmits the signal to the control terminal through the communication module I; the surface electric simulation device comprises an attached electrode II, a stimulating signal generation module, a communication module II and a power supply II; and the stimulating signal generation module receives a control signal transmitted by the control terminal through the communication module II, then generates an electric stimulating signal, and carries out electric stimulation on the human surface through the attached electrode II. Great pain on a sufferer caused by a needle electrode is overcome by the system; and a portable non-invasive detection method is provided for neuromuscular diseases such as amyotrophy and motor neuron disease.
Owner:CHONGQING DELING TECH
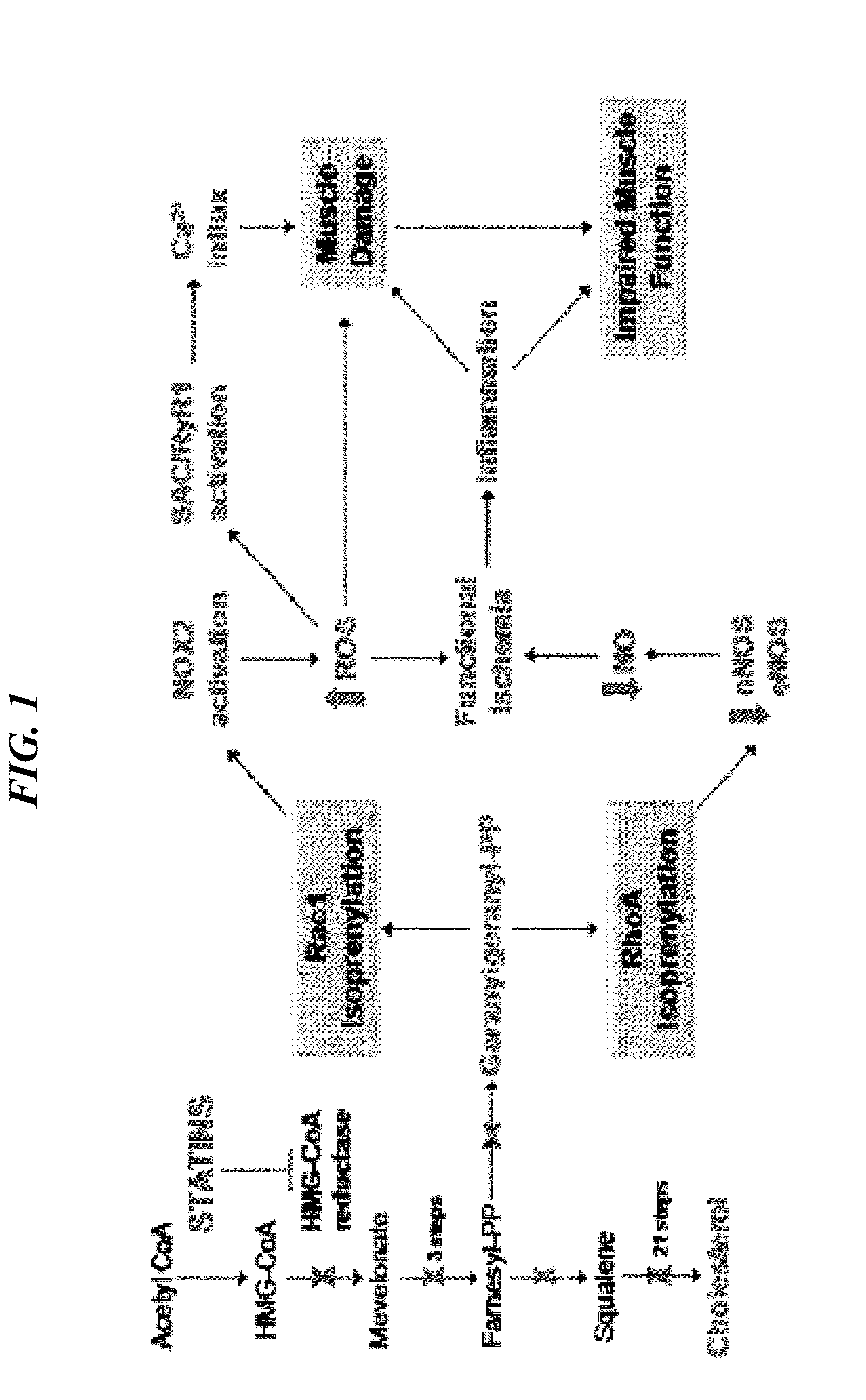
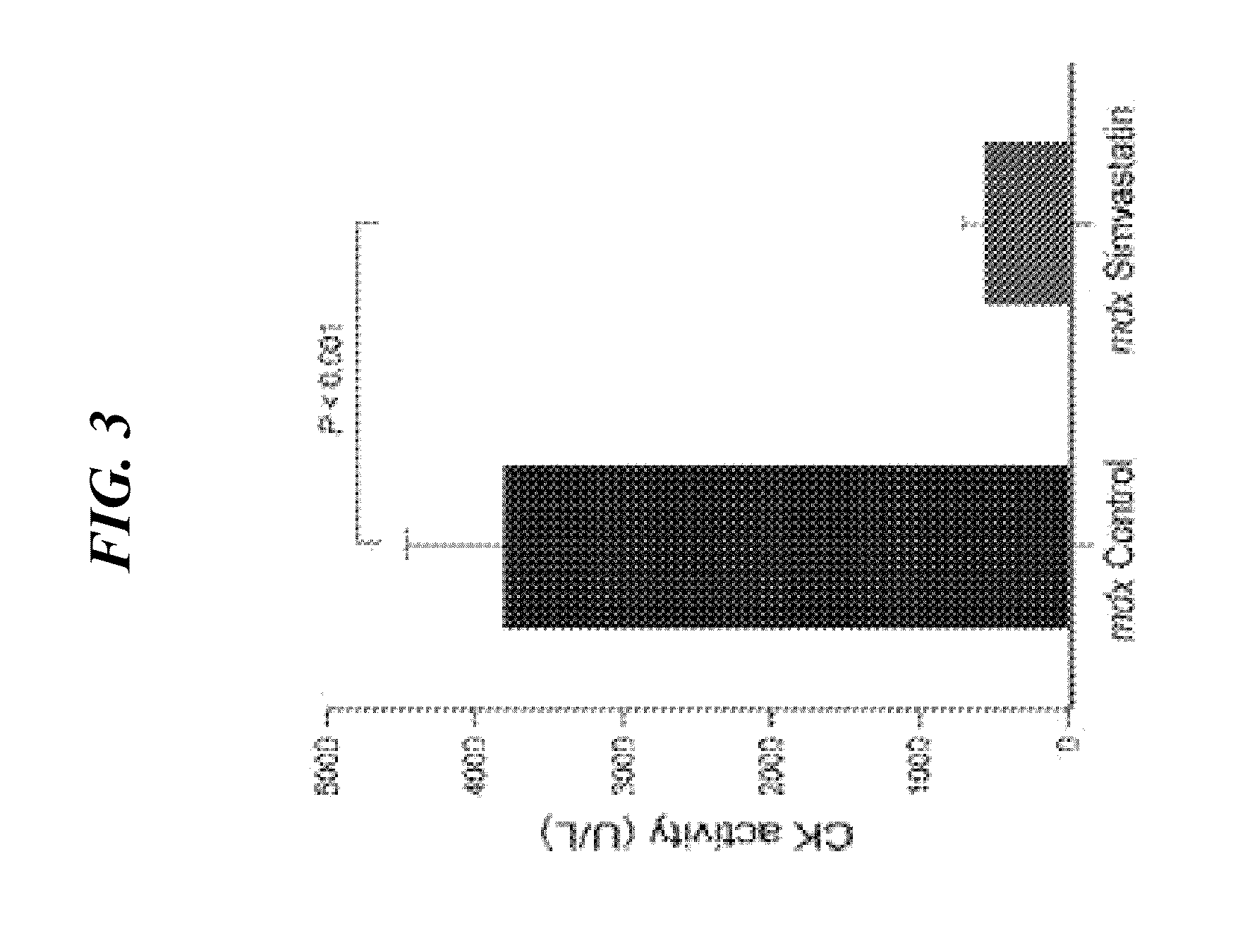
Statins in the treatment of muscular dystrophies and myopathies
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating neuromuscular diseases including, but not limited to muscular dystrophies. It is demonstrated herein that statin drugs are therapeutic for neuromuscular disease, including, but not limited to muscular dystrophies.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
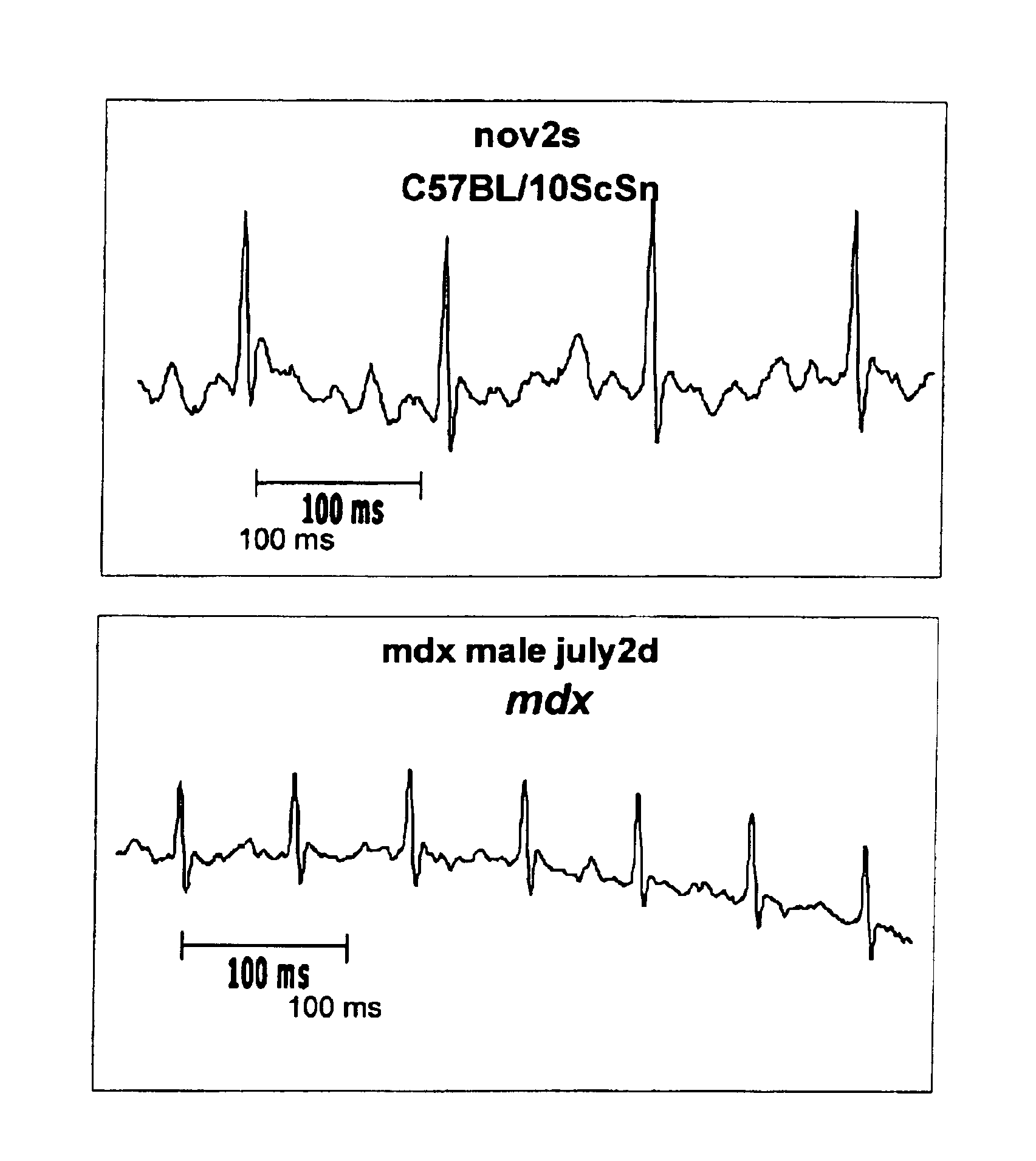
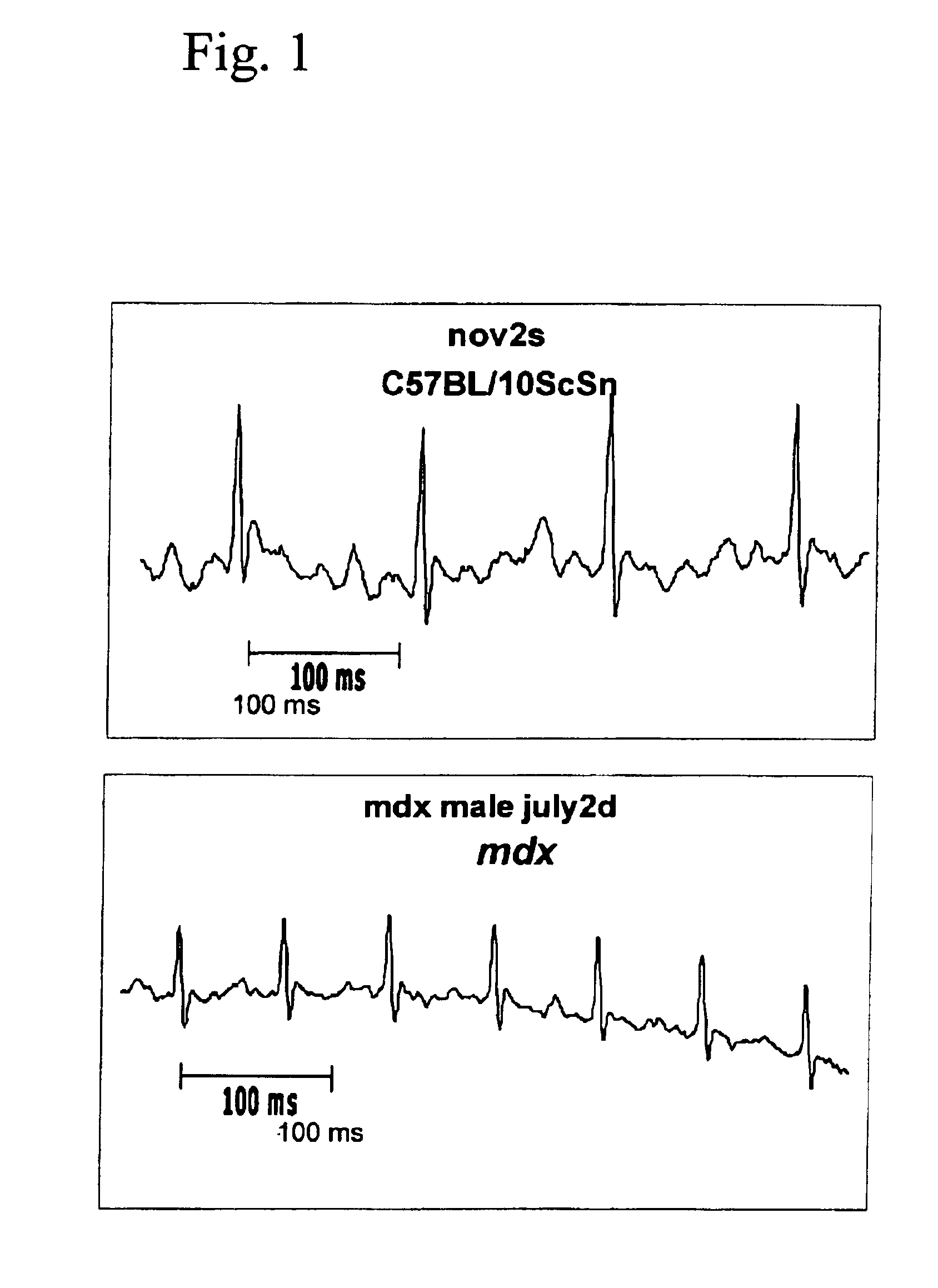
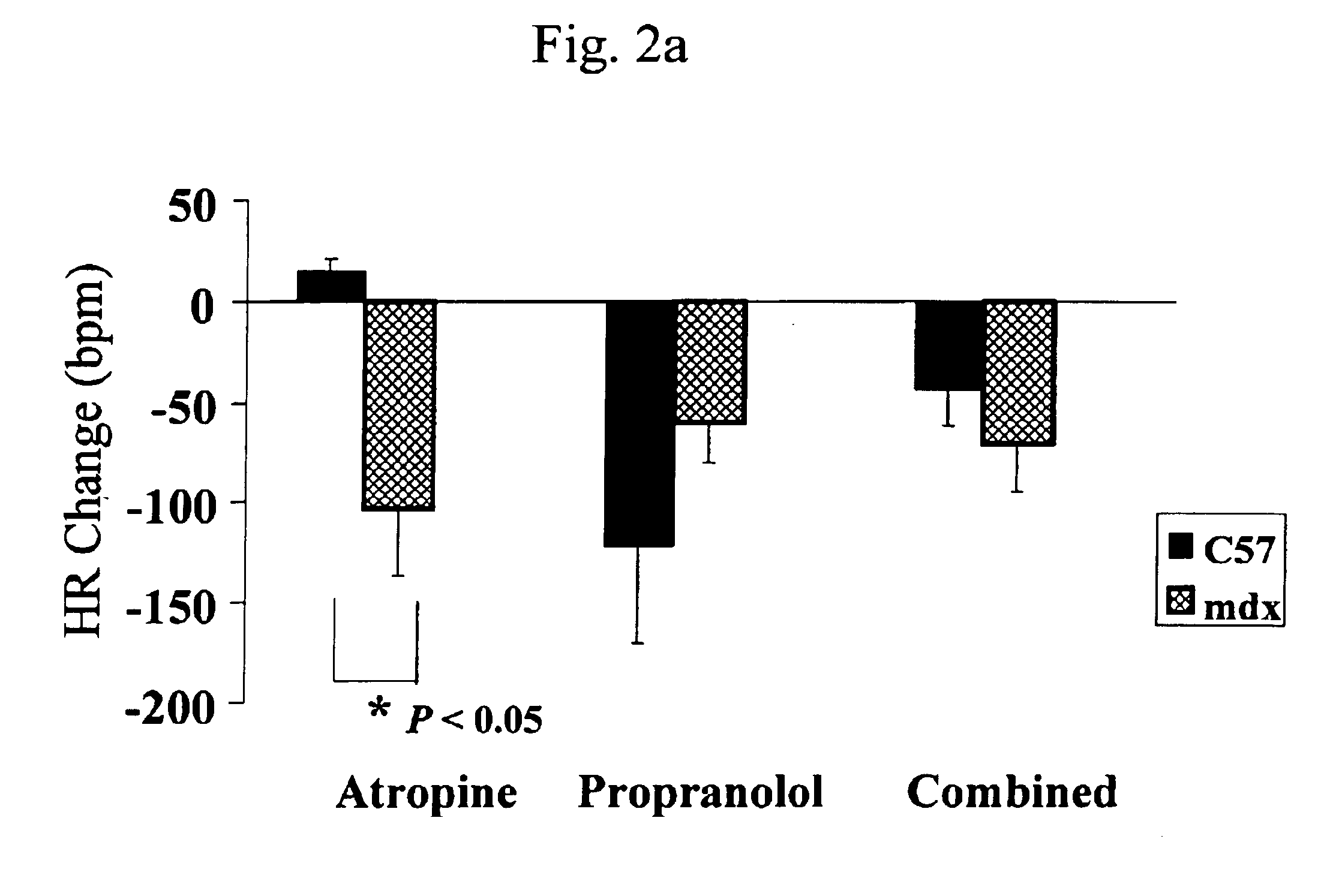
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
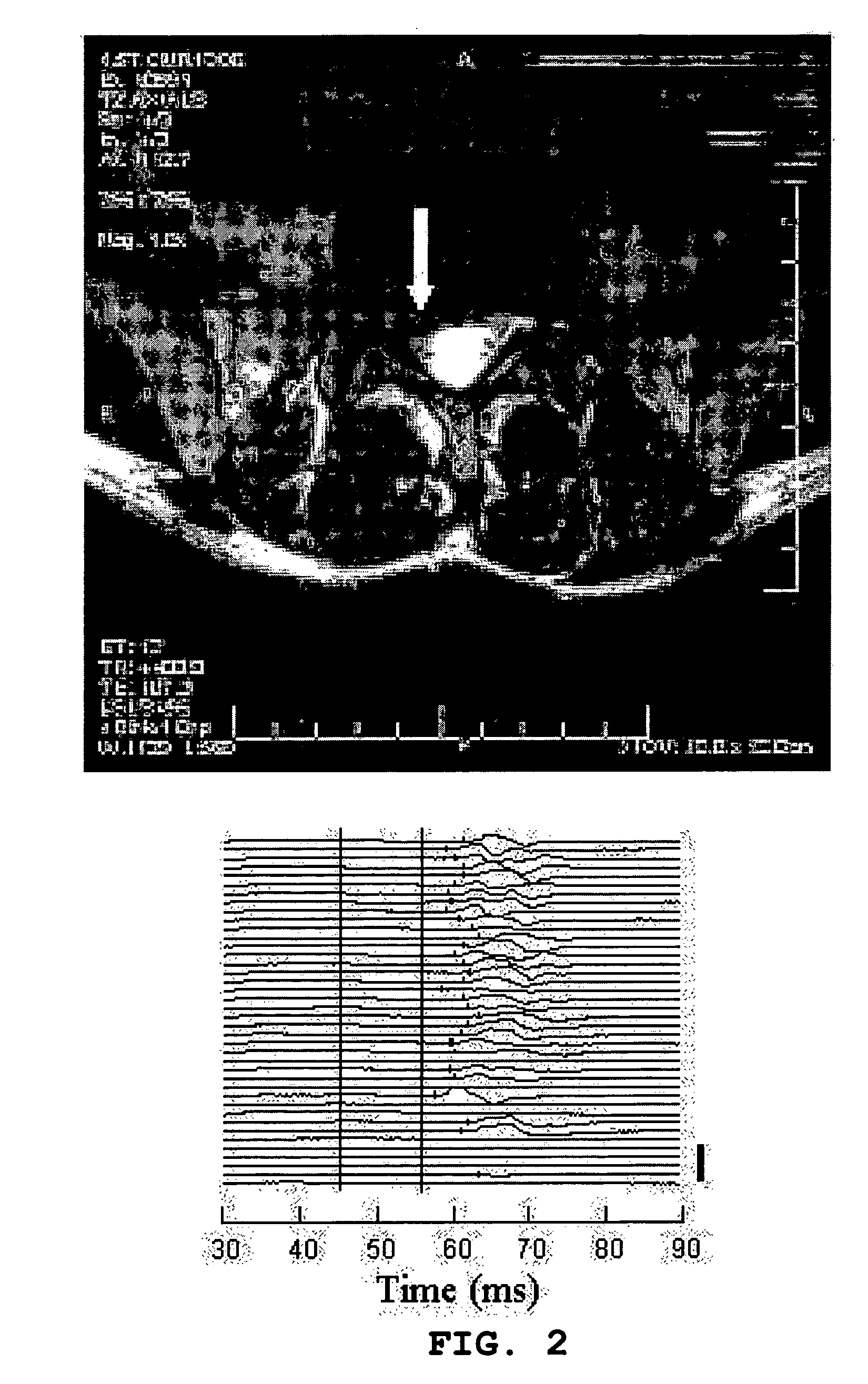
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
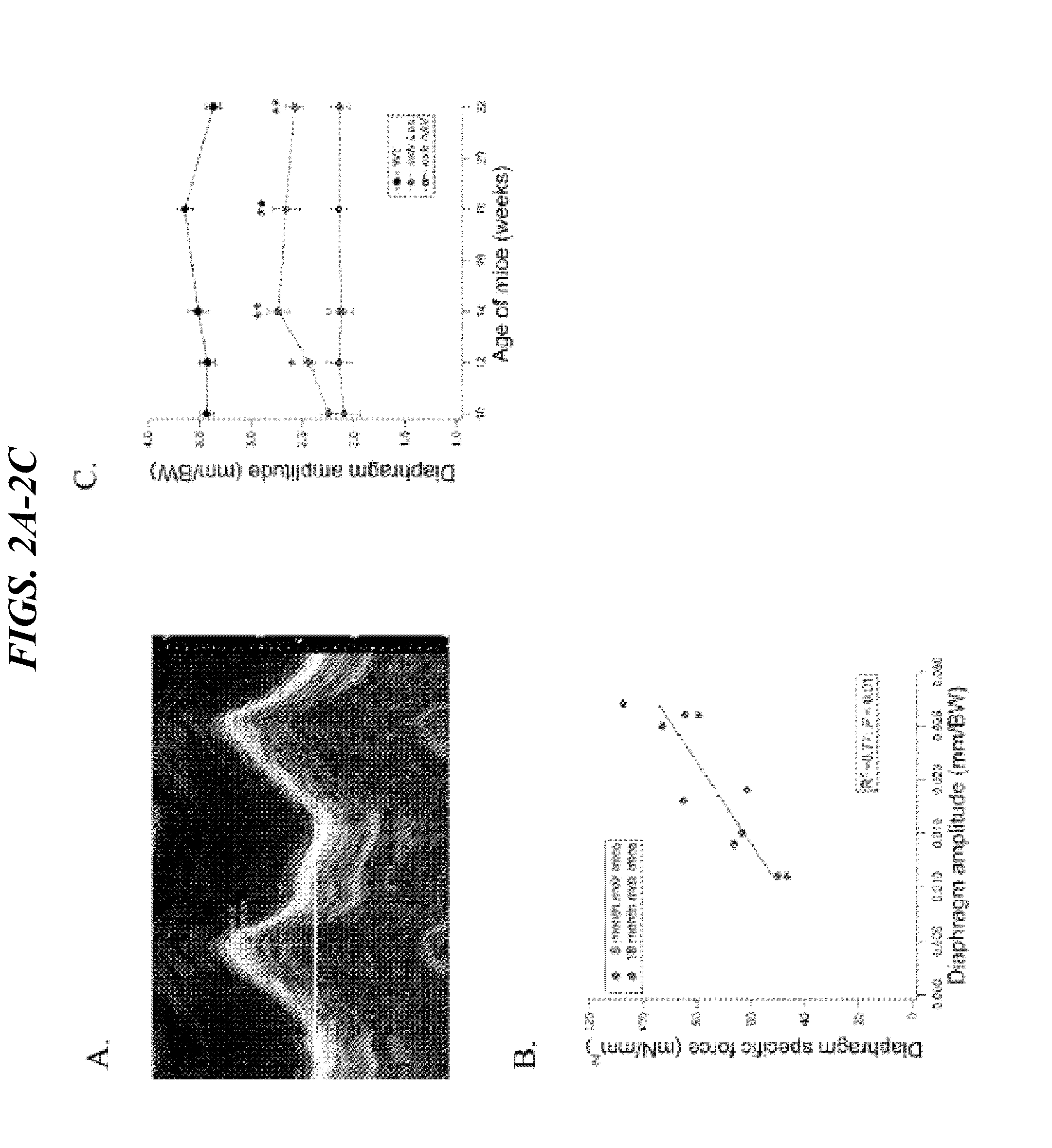
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com