Methods and system for processing changes to existing purchase orders in an object-oriented order processing system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
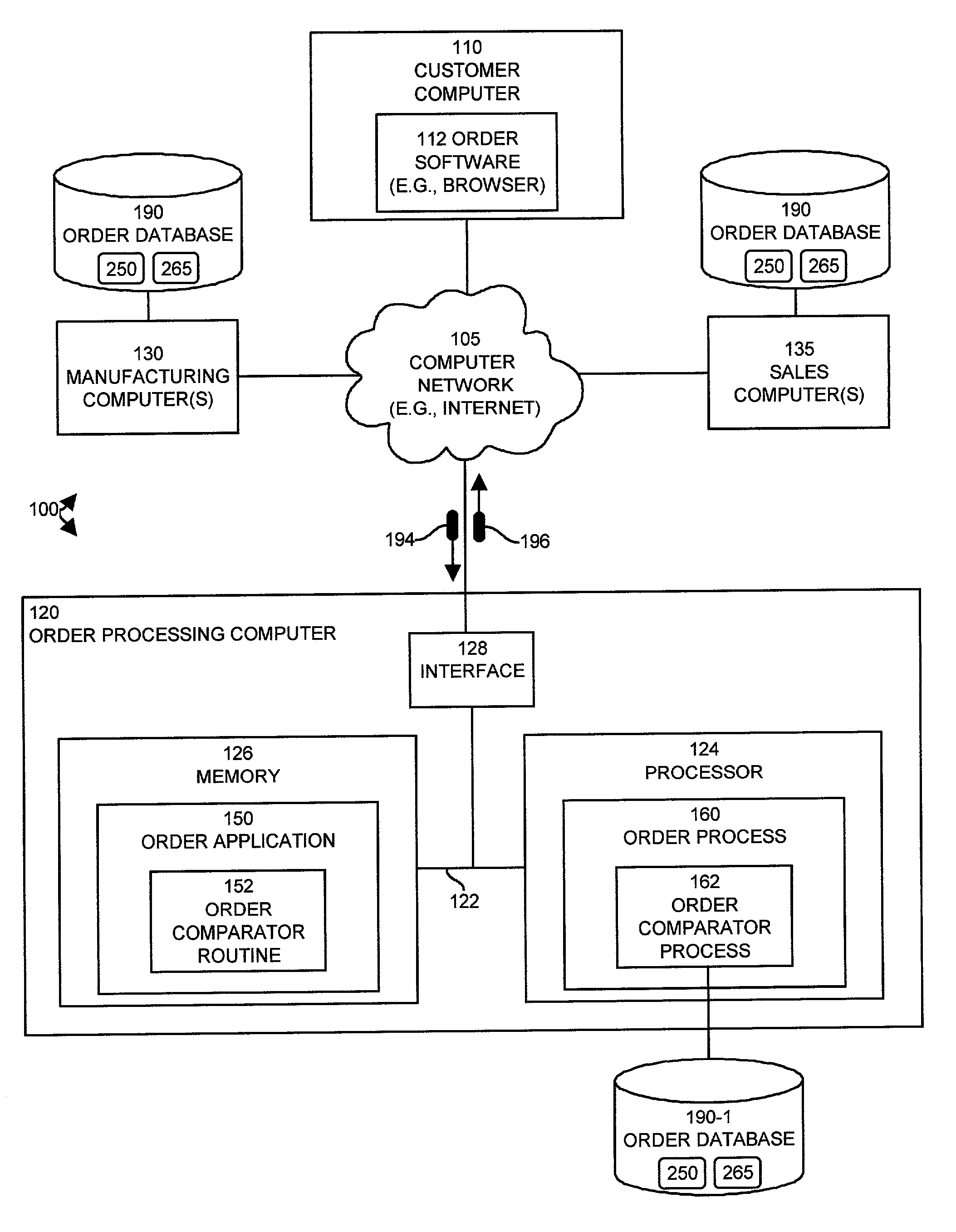
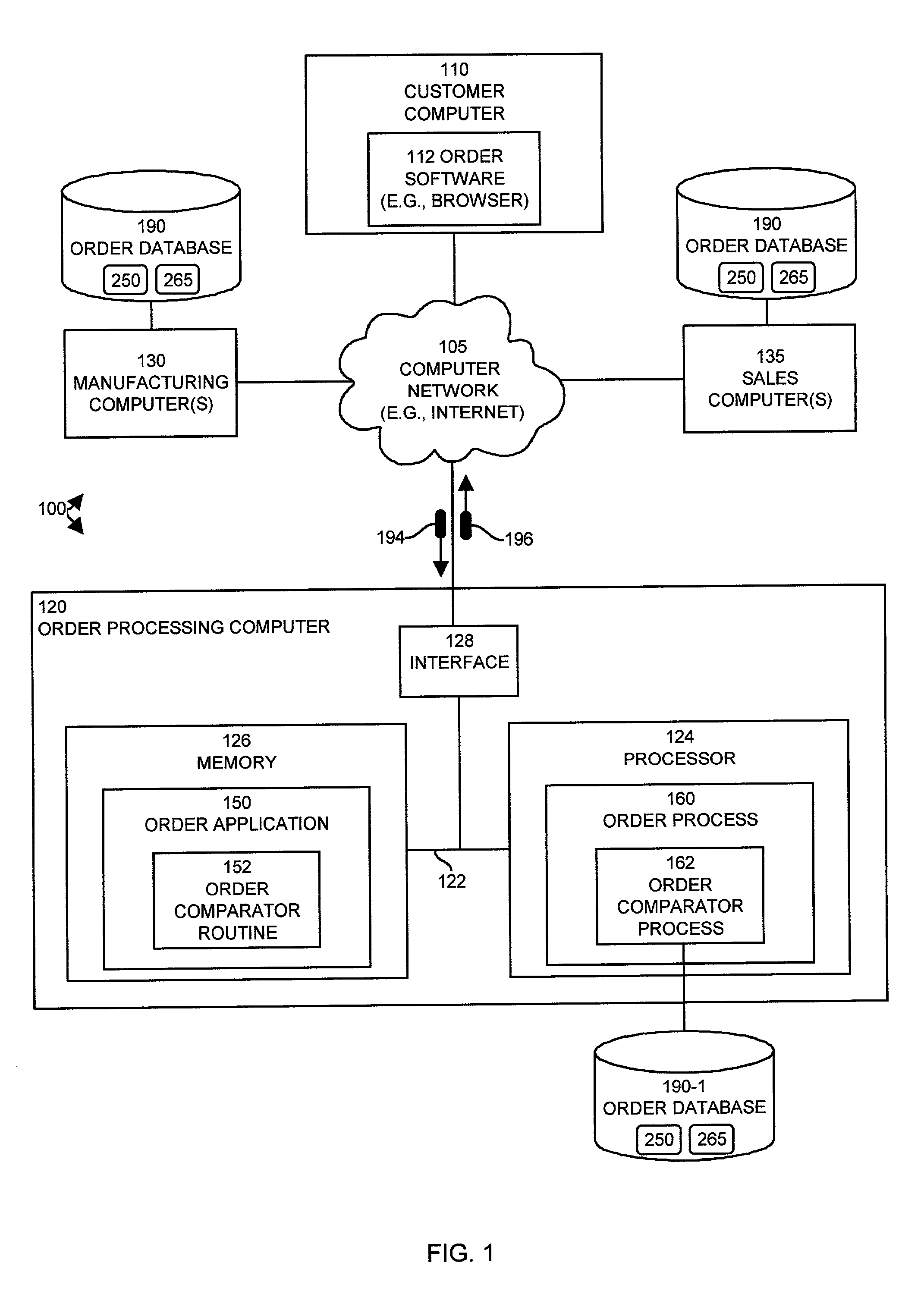
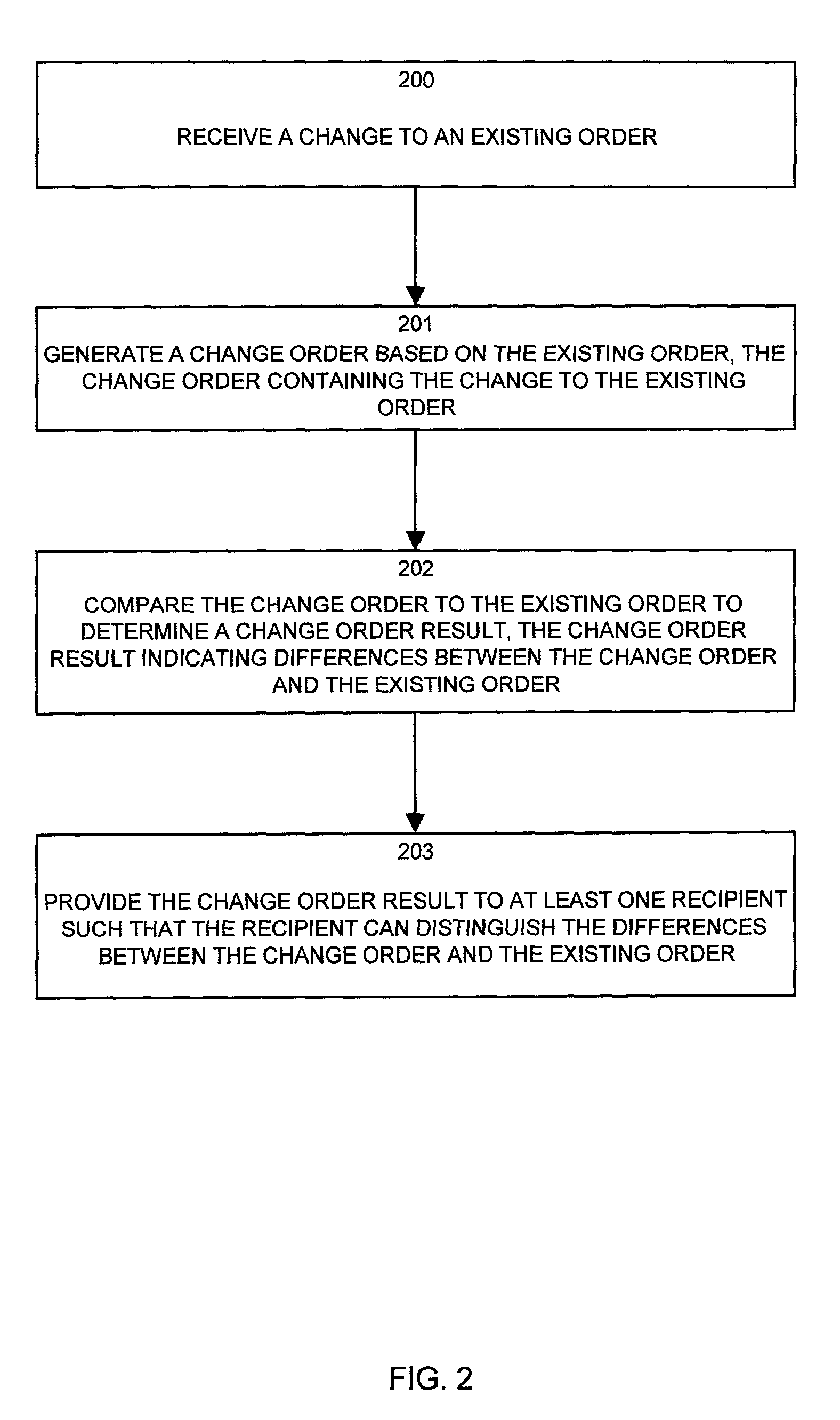
[0039]Generally, embodiments of the invention enable a customer or other qualified person (e.g., salesperson) to make changes to an existing order within an order processing system. Based on such changes, embodiments of the invention create a change order containing the changes and then the embodiments compare and contrast those changes in the change order with existing information (i.e., unchanged information) in the existing order to produce a change order result. The embodiments then present the change order result to a customer (or other recipient) in real-time to allow the customer to better understand the changes that the order undergoes (e.g., during fulfillment of the order or any time after placement of the original existing order). The embodiments of the invention can customize the change order result for presentation to a recipient in specific formats depending upon the identity of the recipient of the change order result. For example, if the recipient of the change order...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com