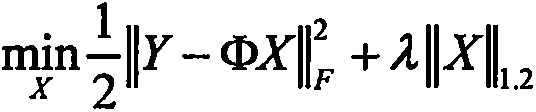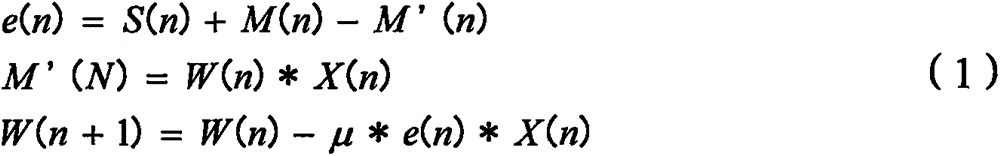Patents
Literature
126 results about "Photoplethysmogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
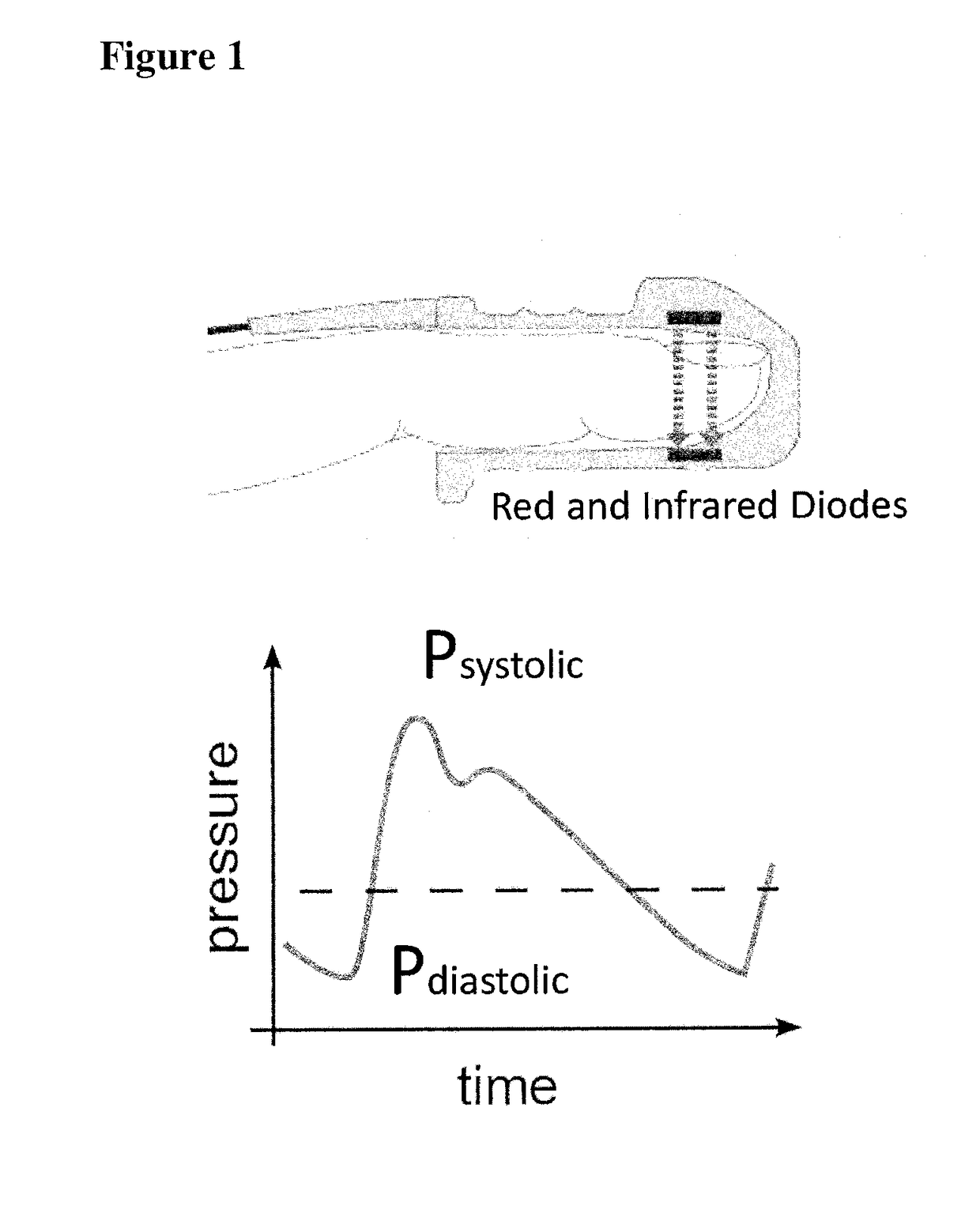
A photoplethysmogram (PPG) is an optically obtained plethysmogram that can be used to detect blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. A PPG is often obtained by using a pulse oximeter which illuminates the skin and measures changes in light absorption. A conventional pulse oximeter monitors the perfusion of blood to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin.
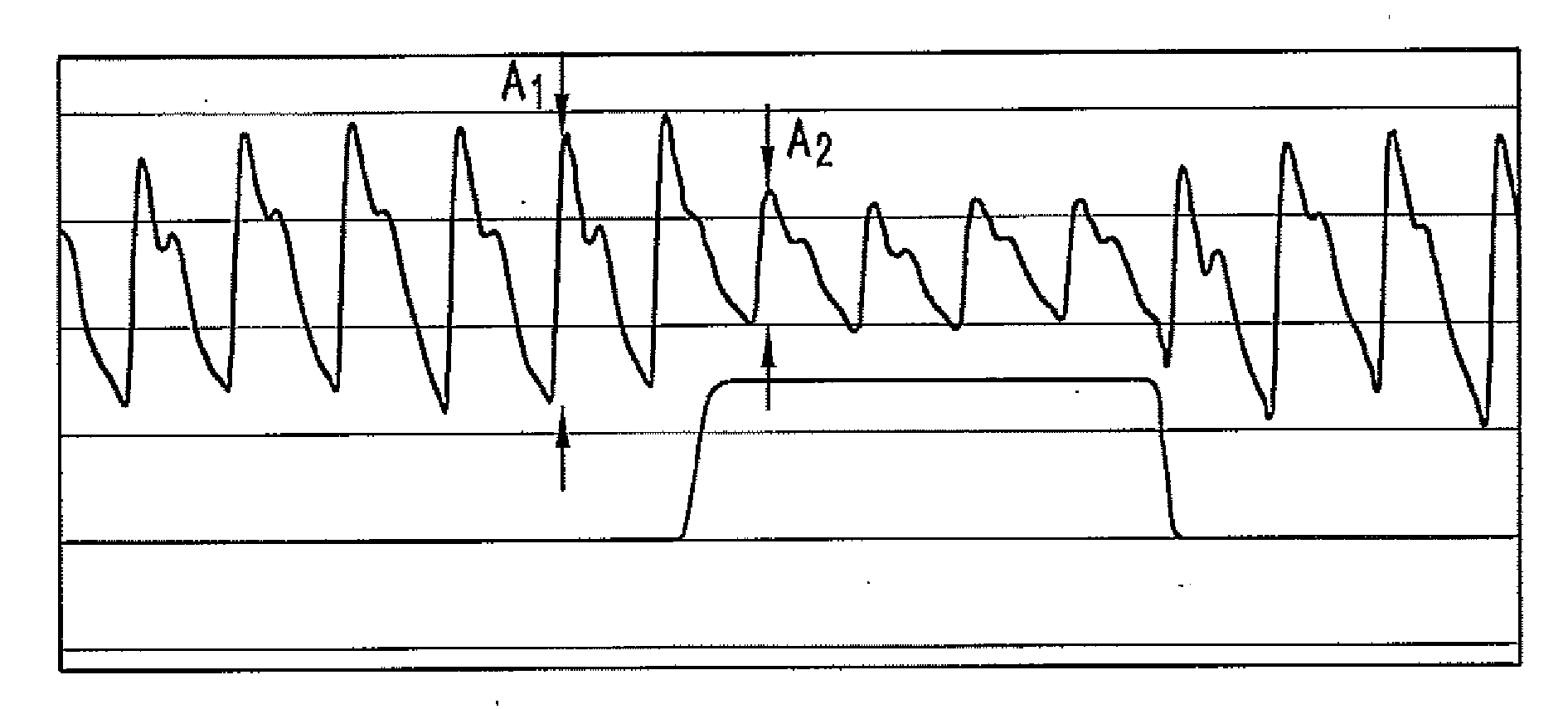
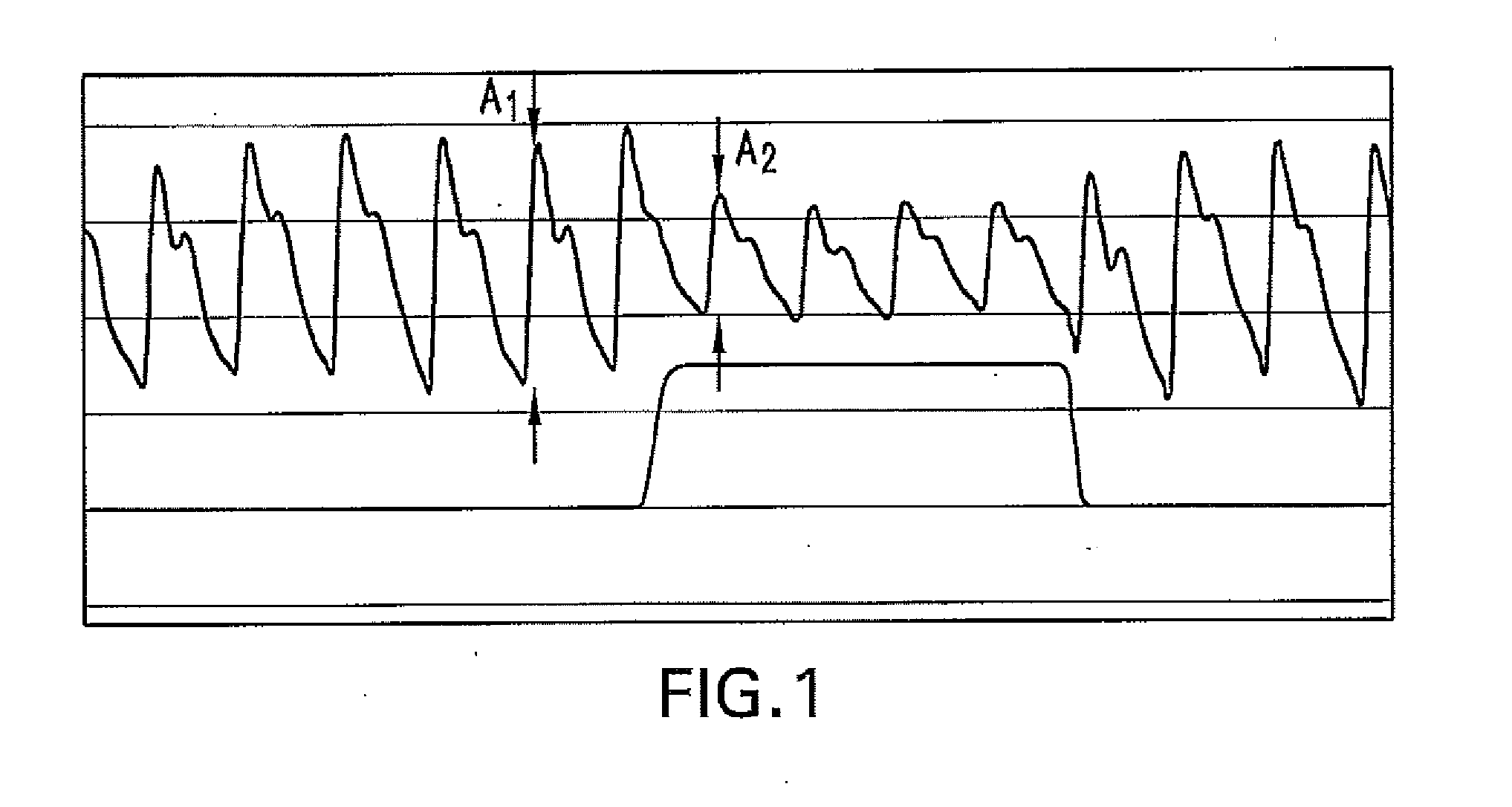
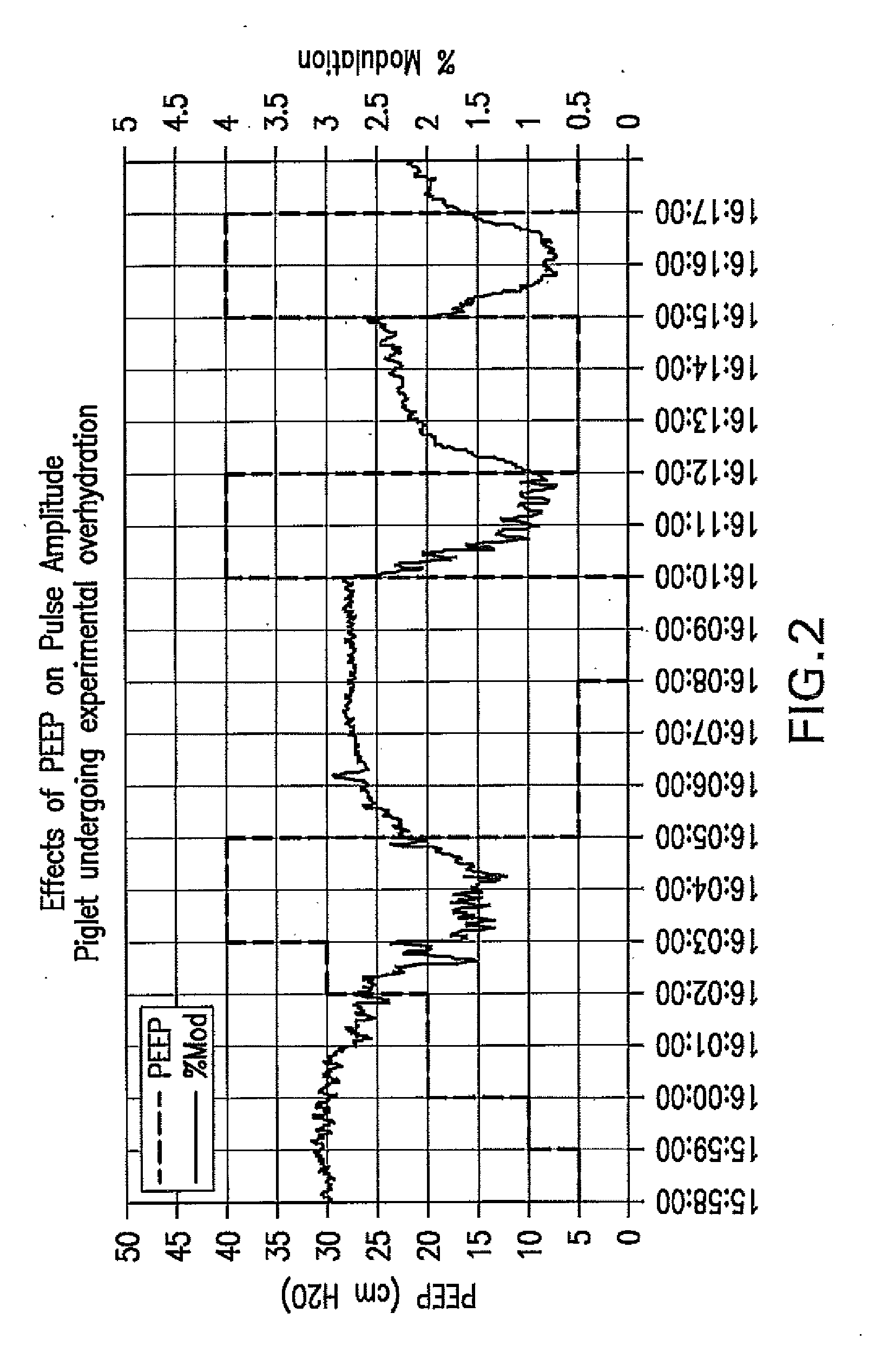
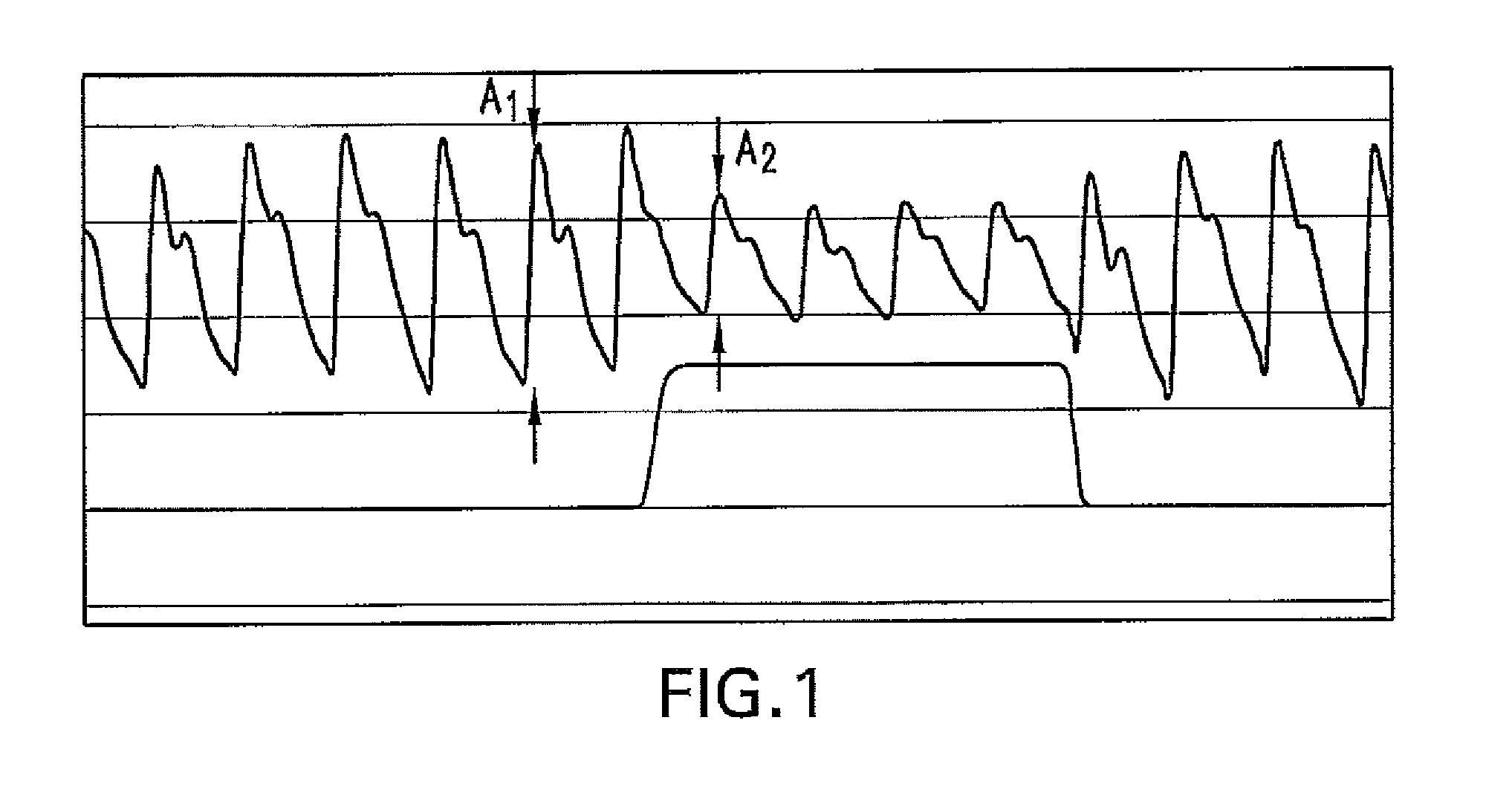
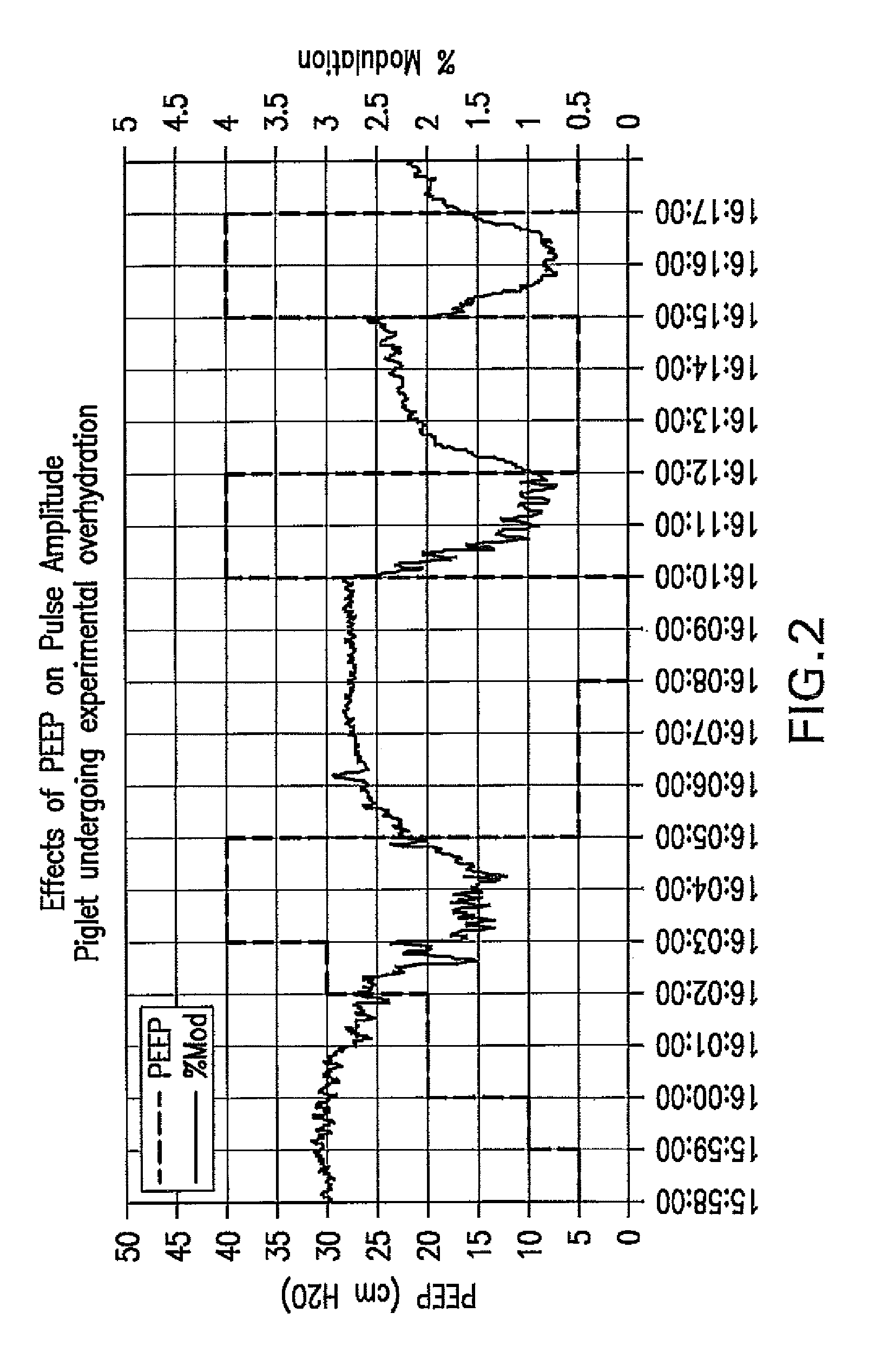
Method For Determining Hemodynamic Effects Of Positive Pressure Ventilation
The present disclosure relates, in some embodiments, to devices, systems, and / or methods for collecting, processing, and / or displaying stroke volume and / or cardiac output data. For example, a device for assessing changes in cardiac output and / or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support may comprise a processor; an airway sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the airway sensor is configured and arranged to sense pressure in the subject's airway, lungs, and / or intrapleural space over time; a blood volume sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the blood volume sensor is configured and arranged to sense pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject over time; and a display configured and arranged to display a representative of an airway pressure, a pulsatile blood volume, a photoplethysmogram, a photoplethysmogram ratio, the determined cardiac output and / or stroke volume, or combinations thereof. A method of assessing changes in cardiac output or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support from a breathing assistance system may comprise sensing pressure in the subject's airway as a function of time, sensing pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject as a function of time, producing a photoplethysmogram from the sensed pulsatile volume, determining the ratio of the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during inhalation to the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during exhalation, and determining the change in cardiac output or stroke volume of the subject using the determined ratio.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
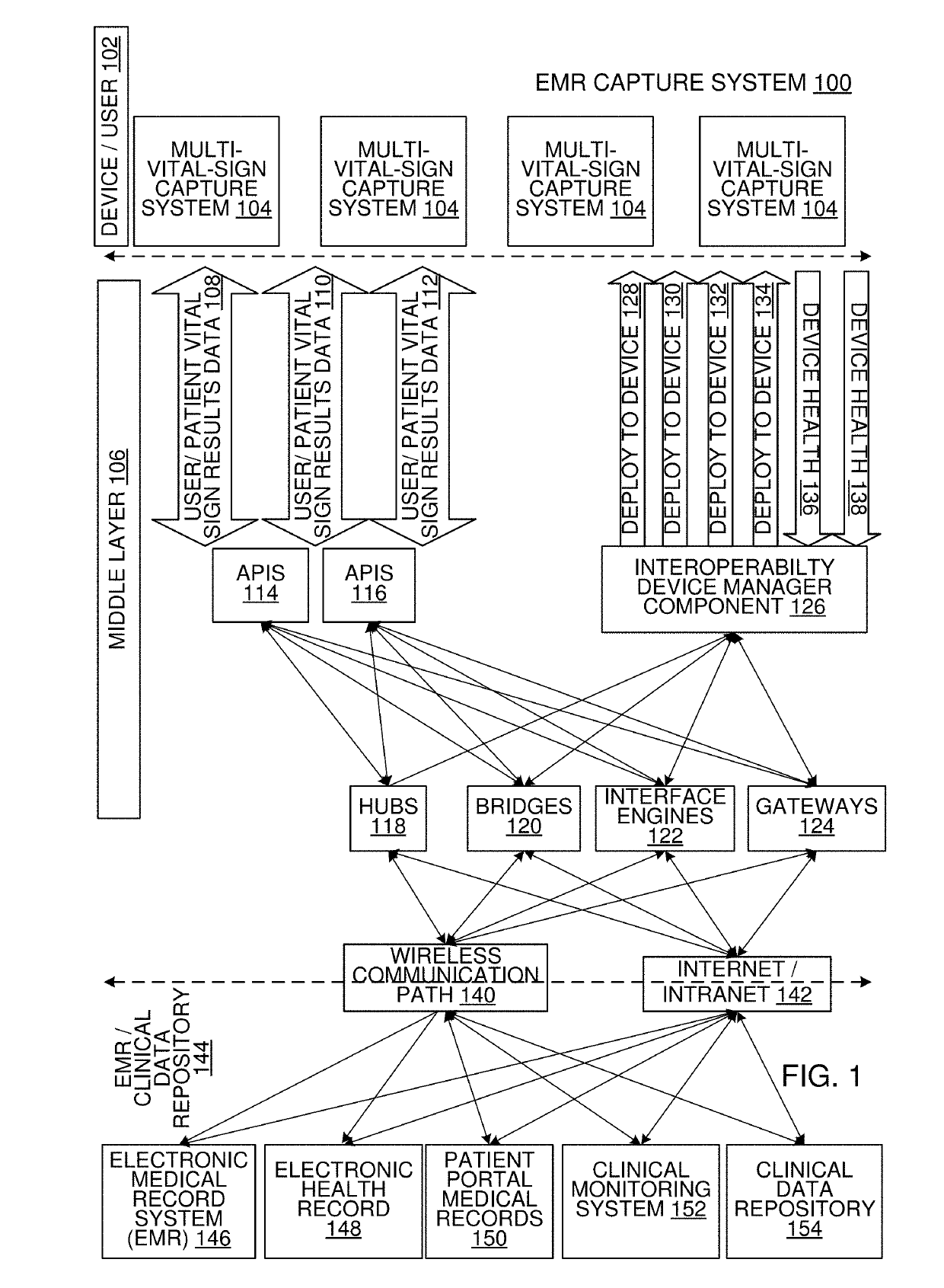
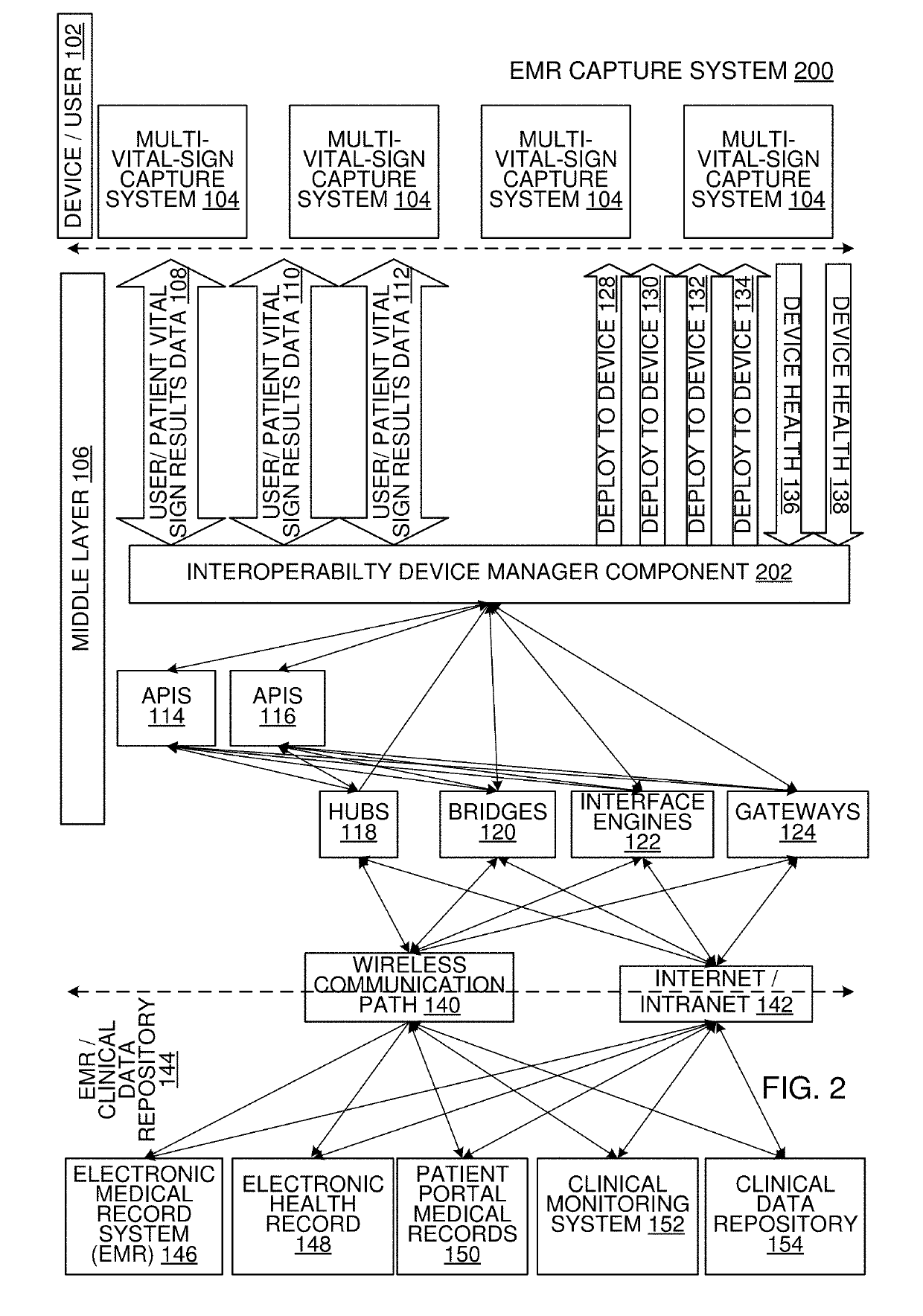
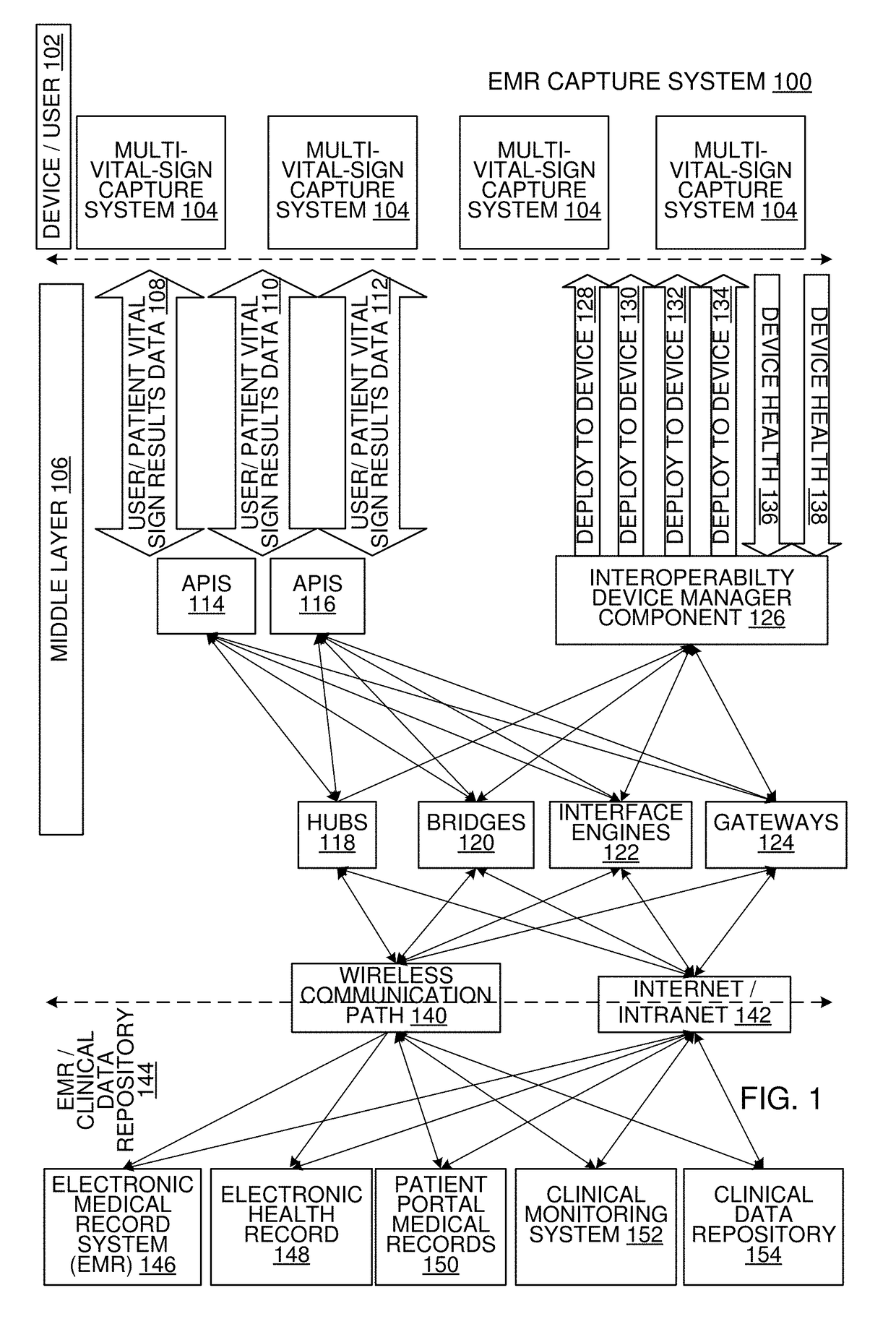
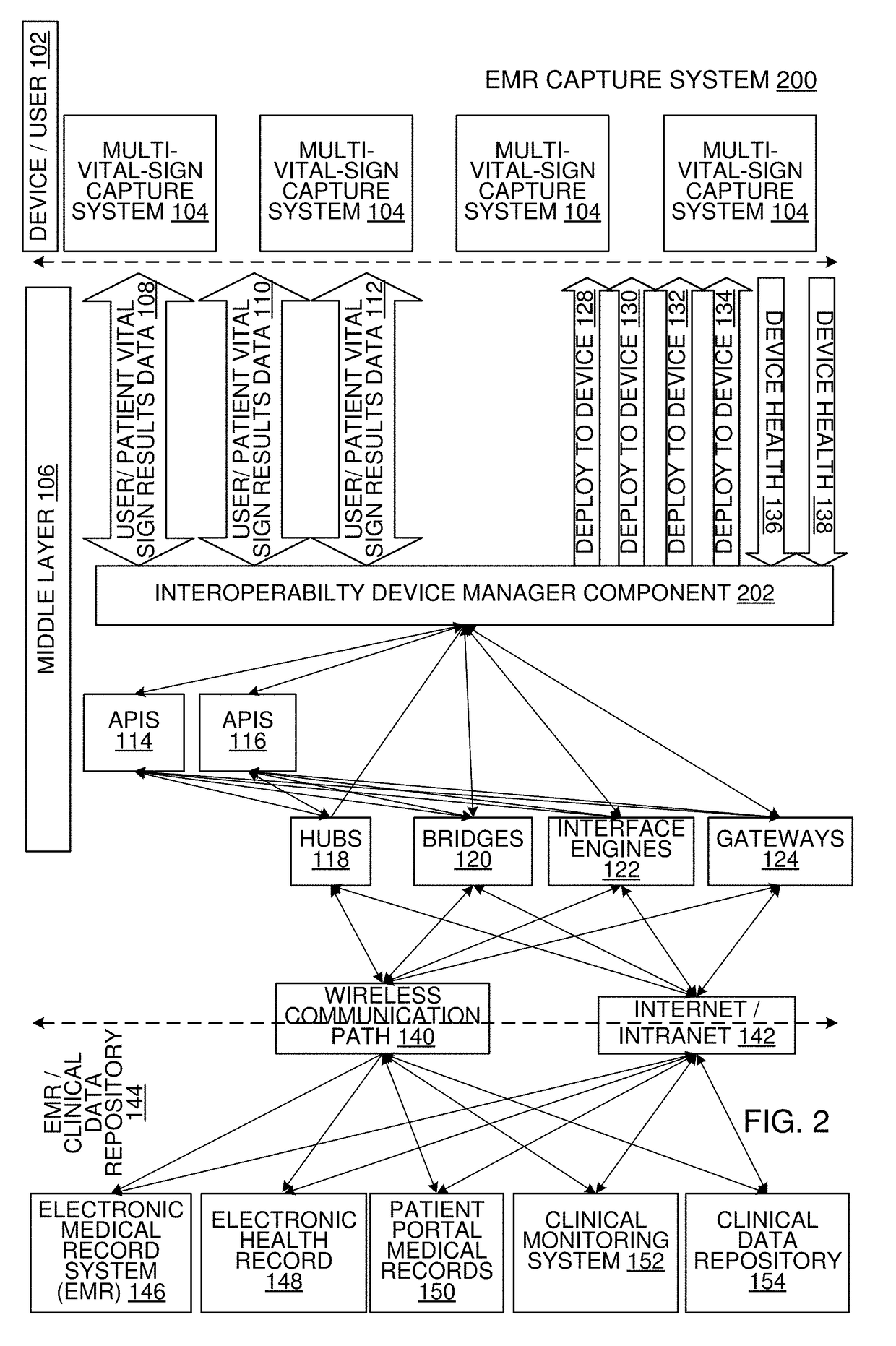
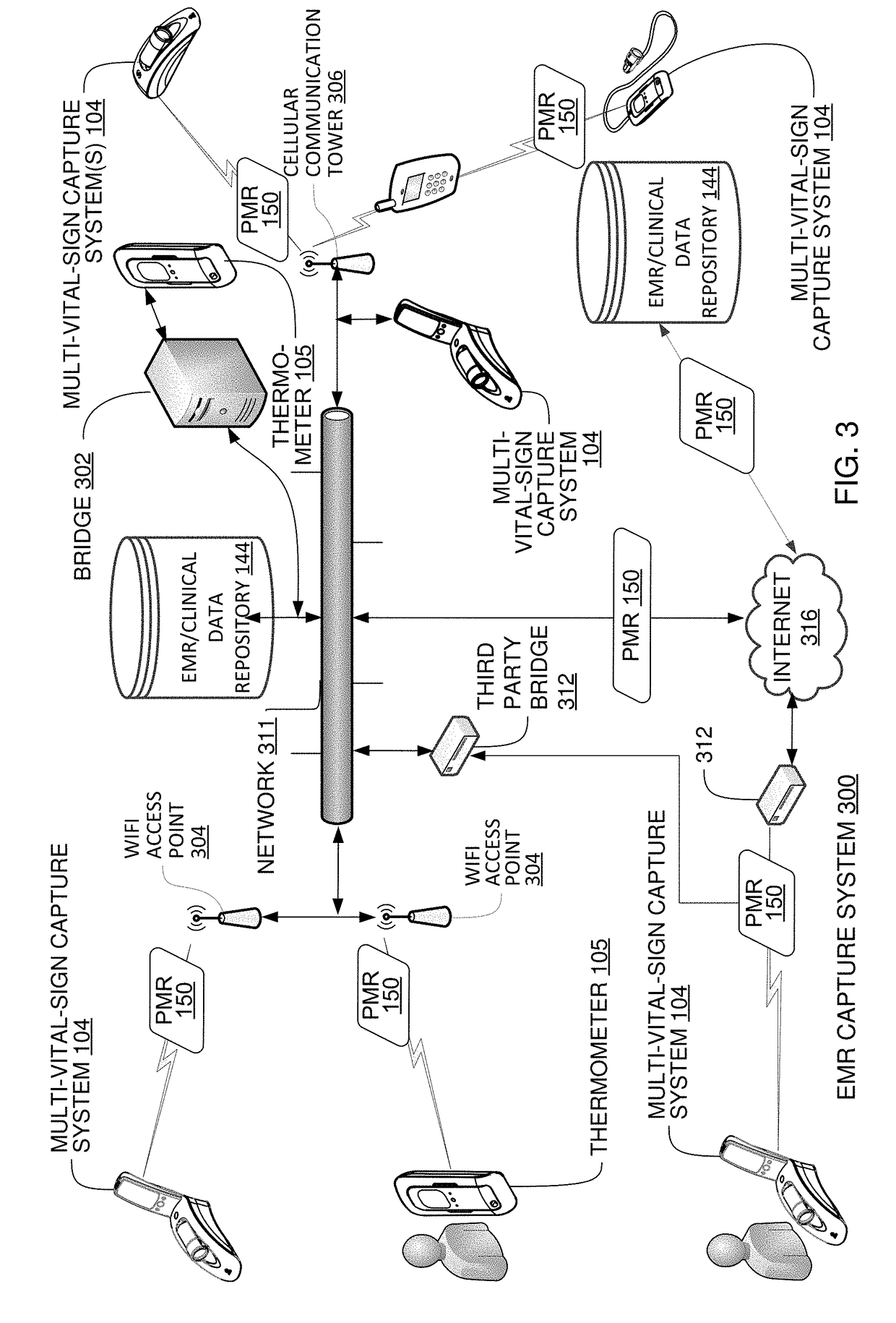
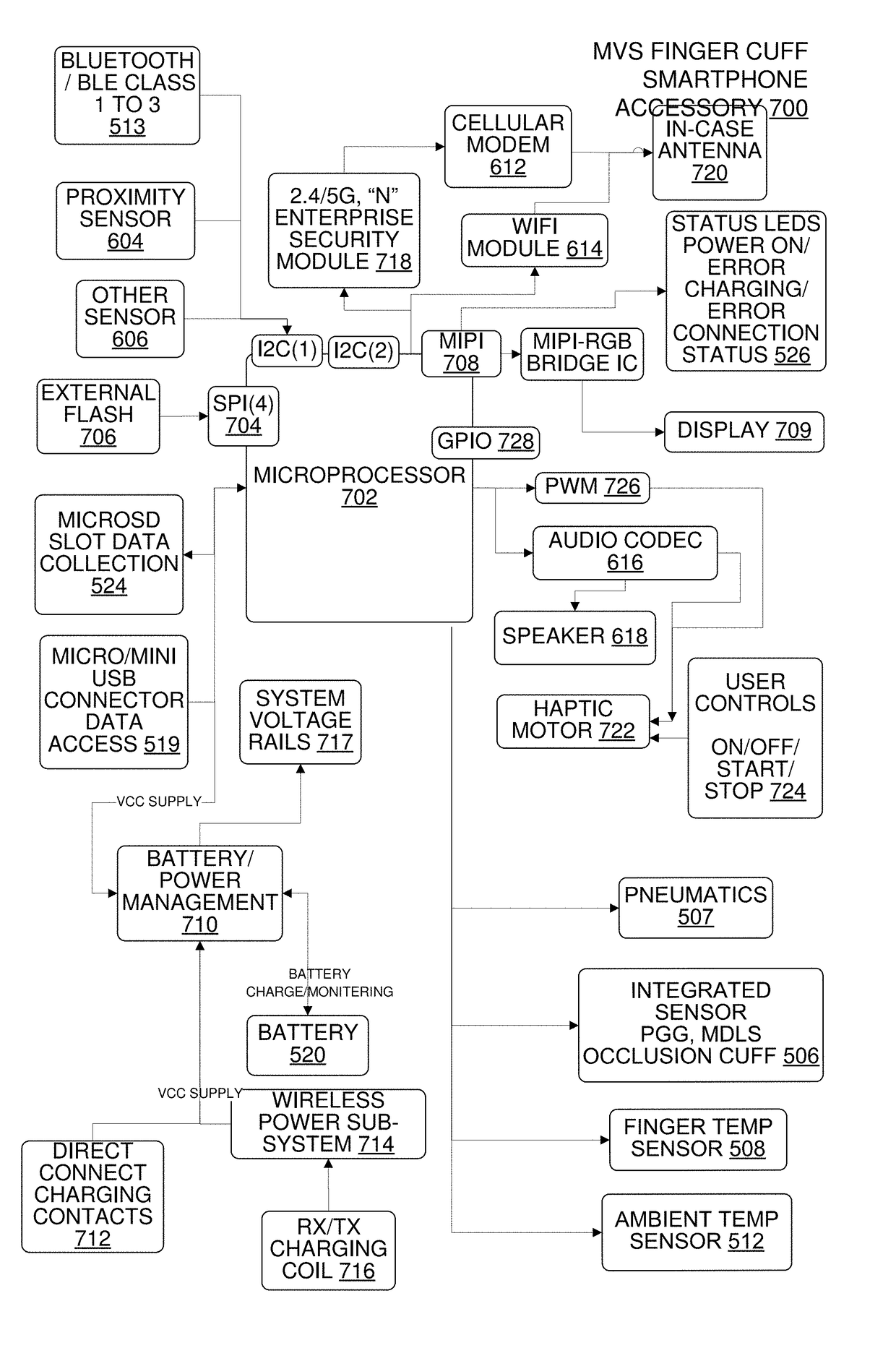
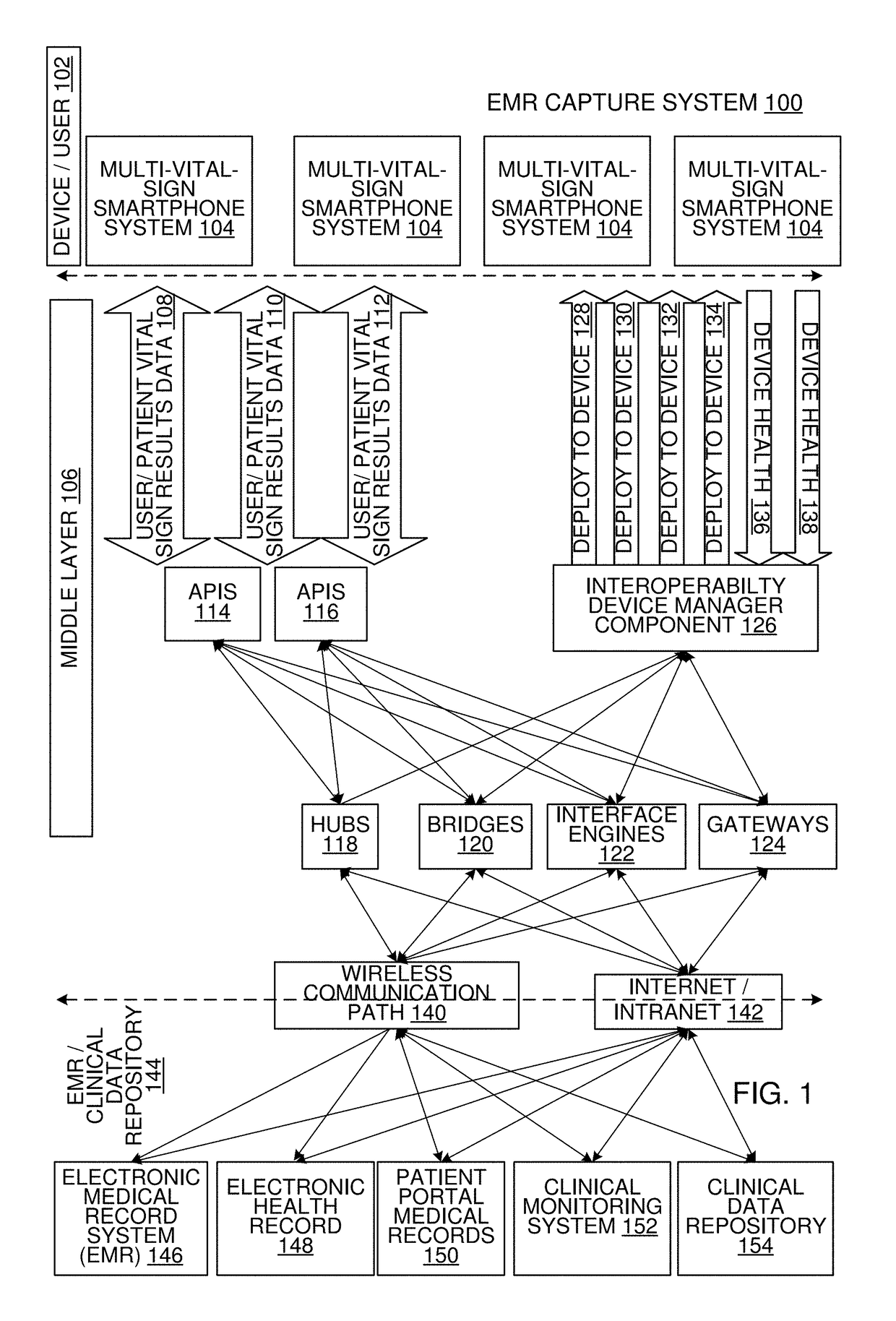
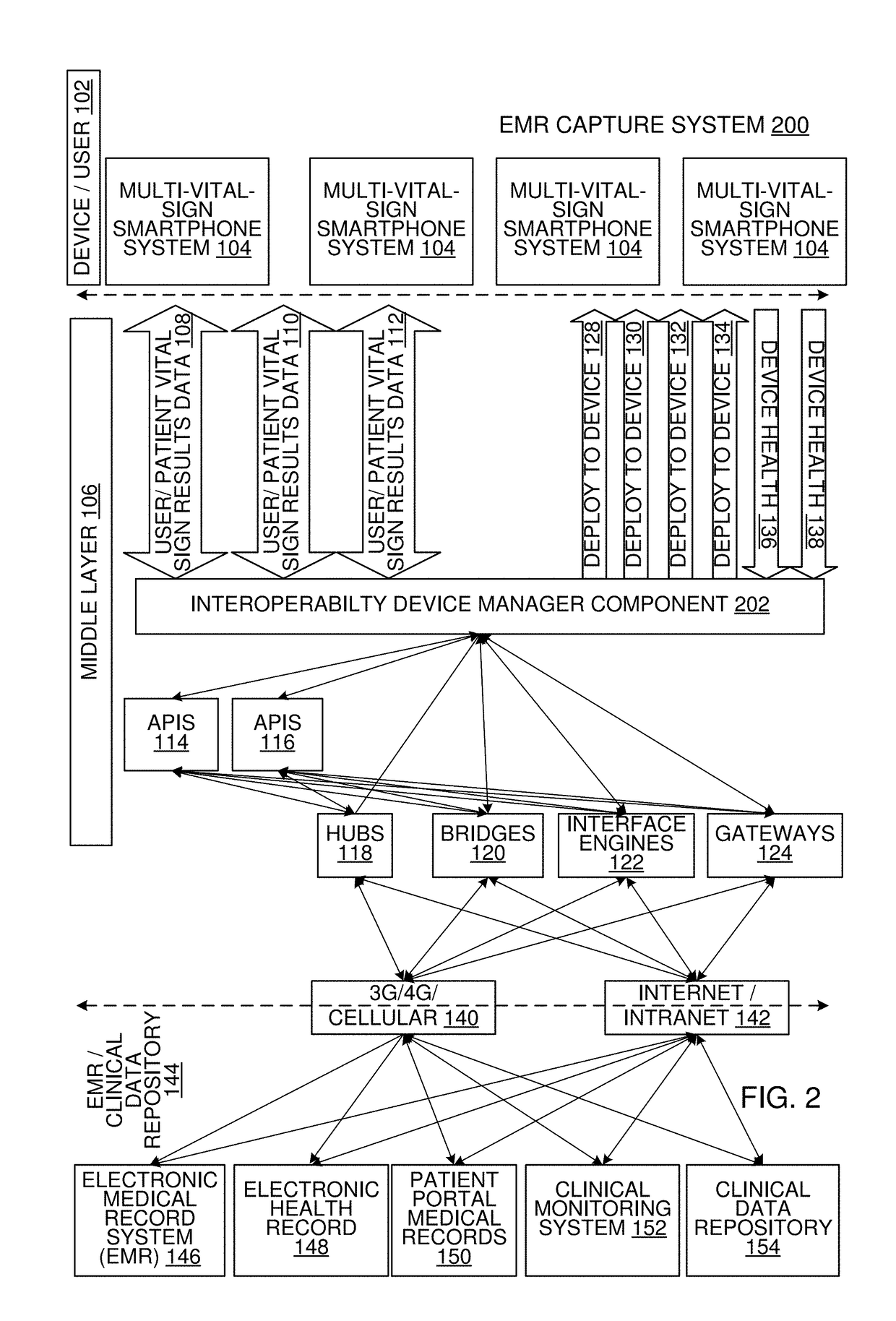
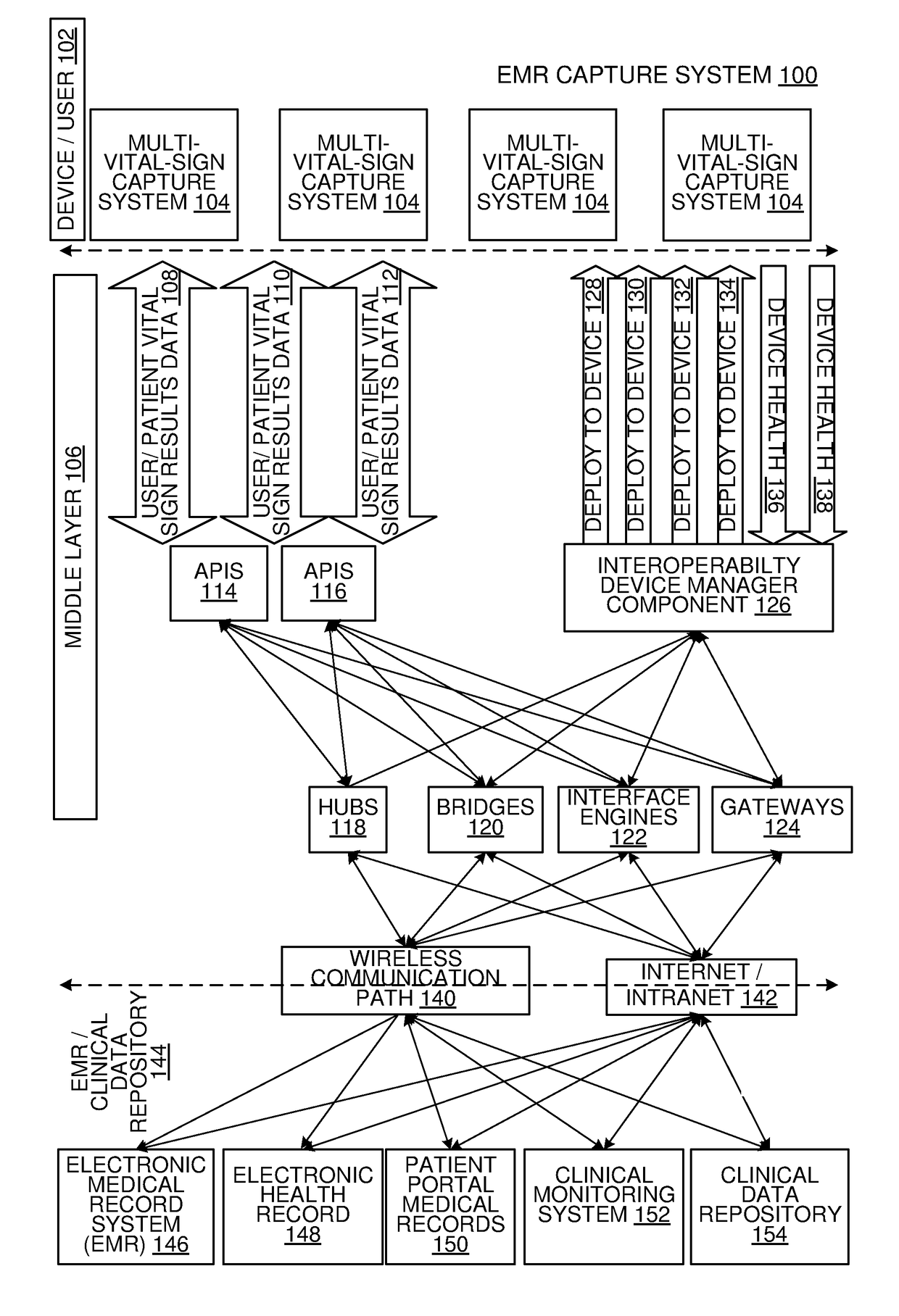
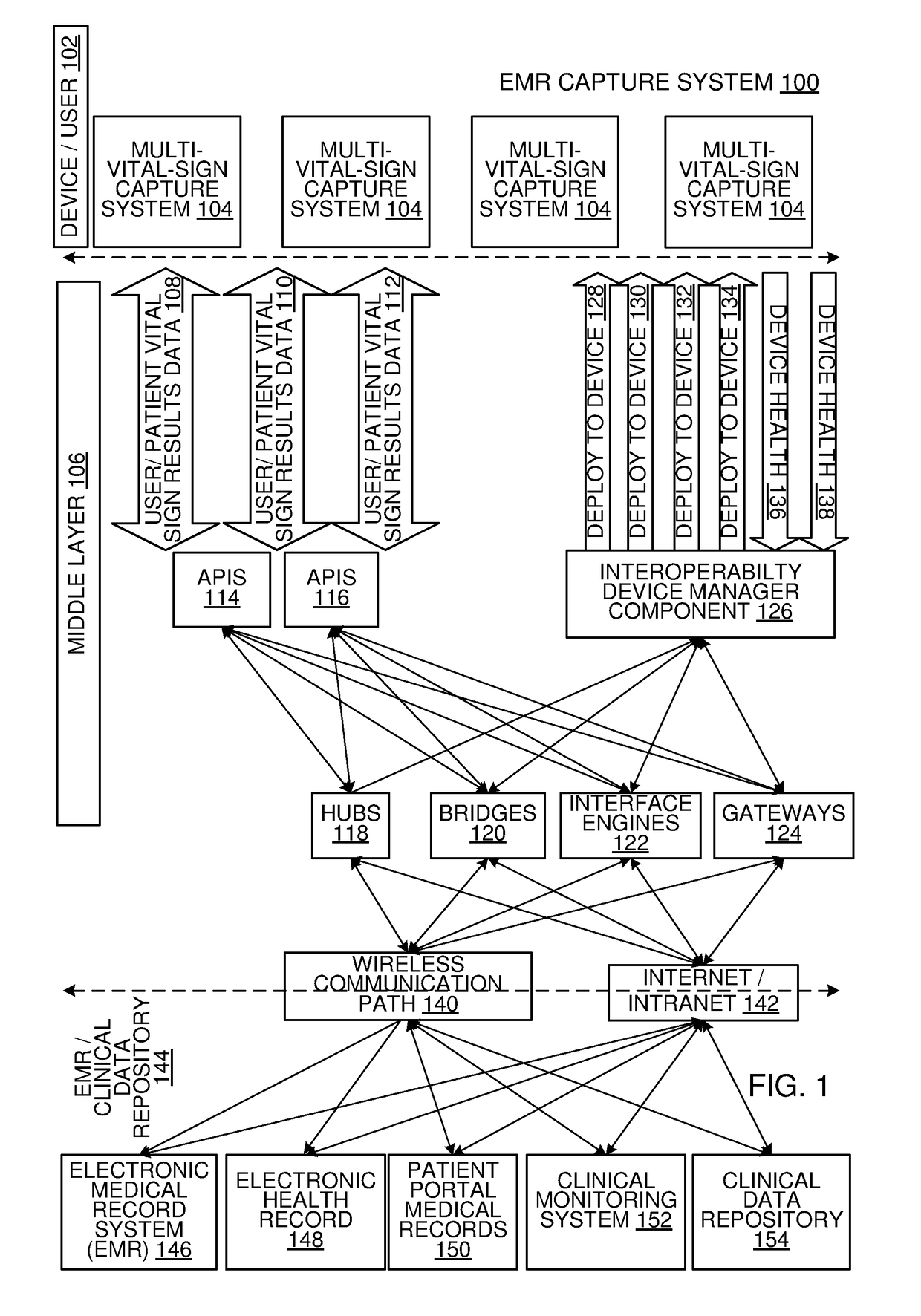
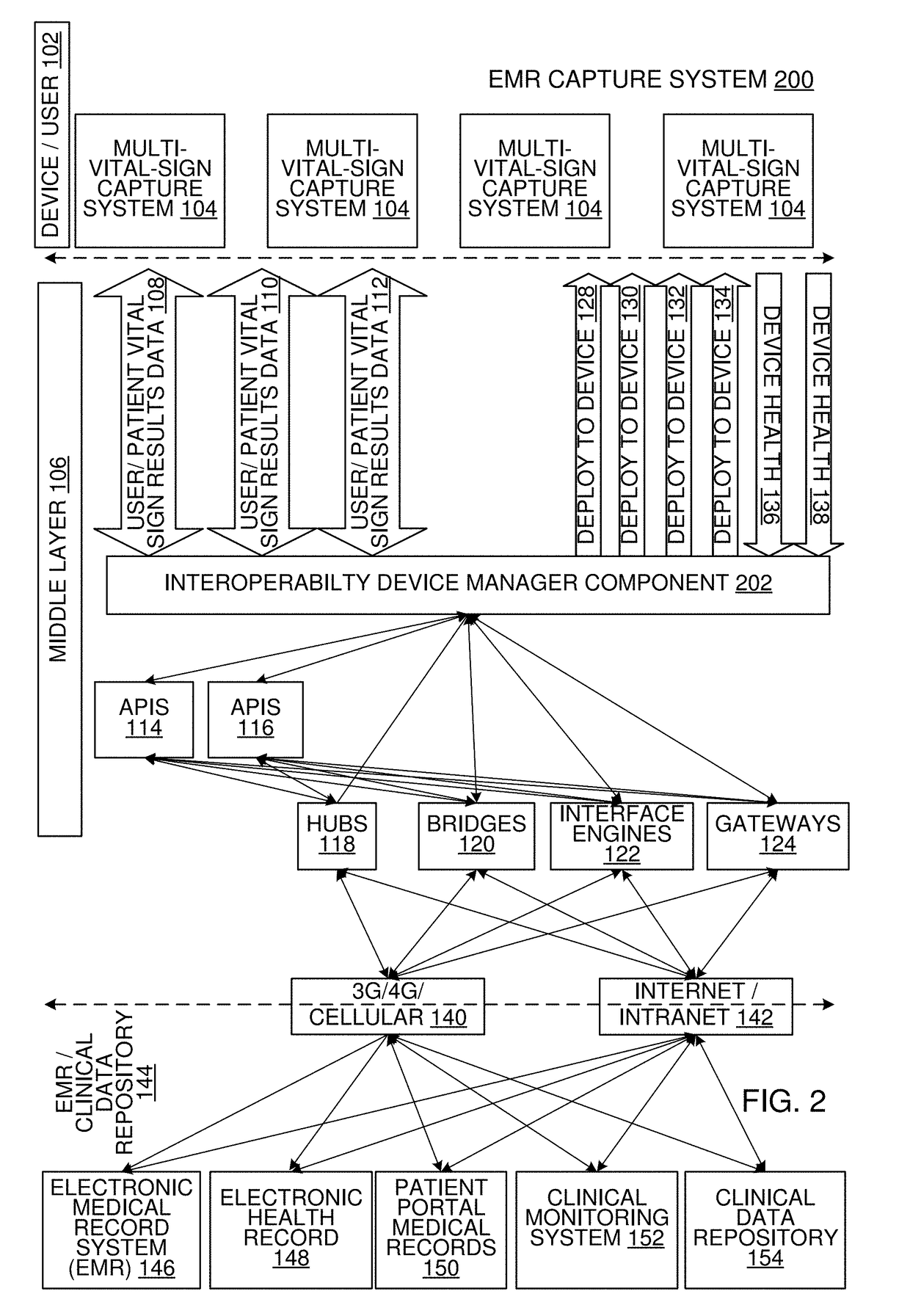
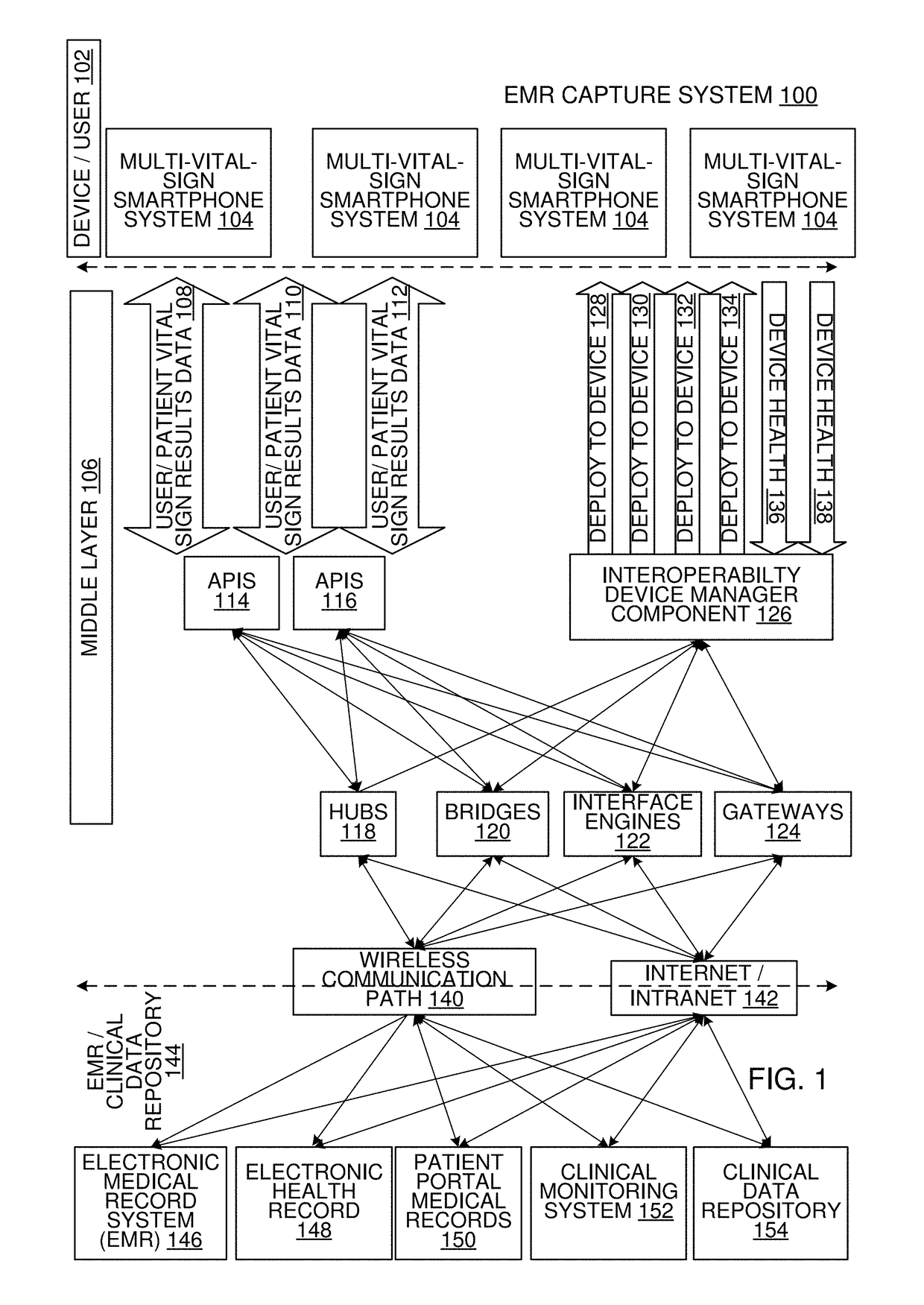
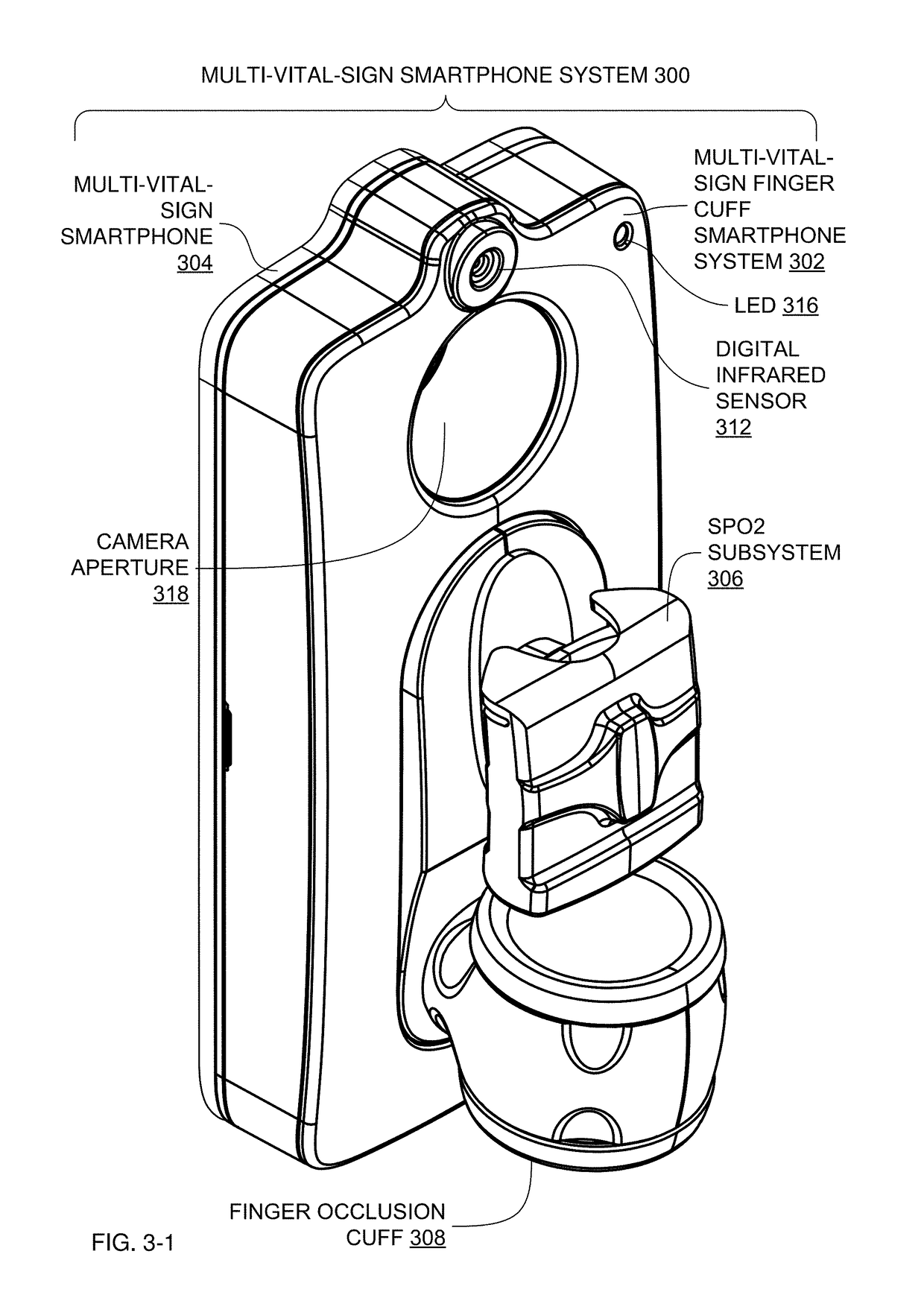
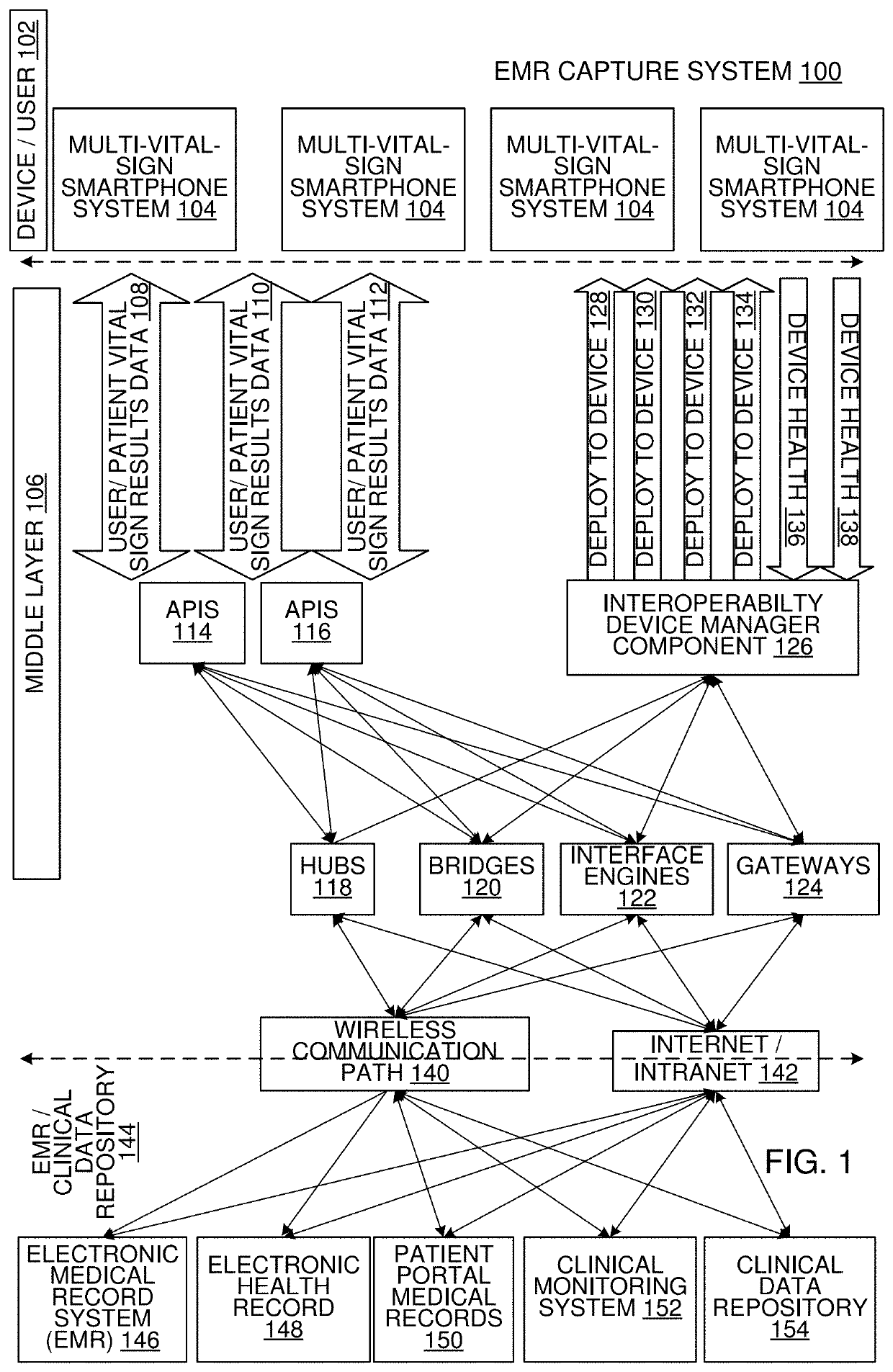
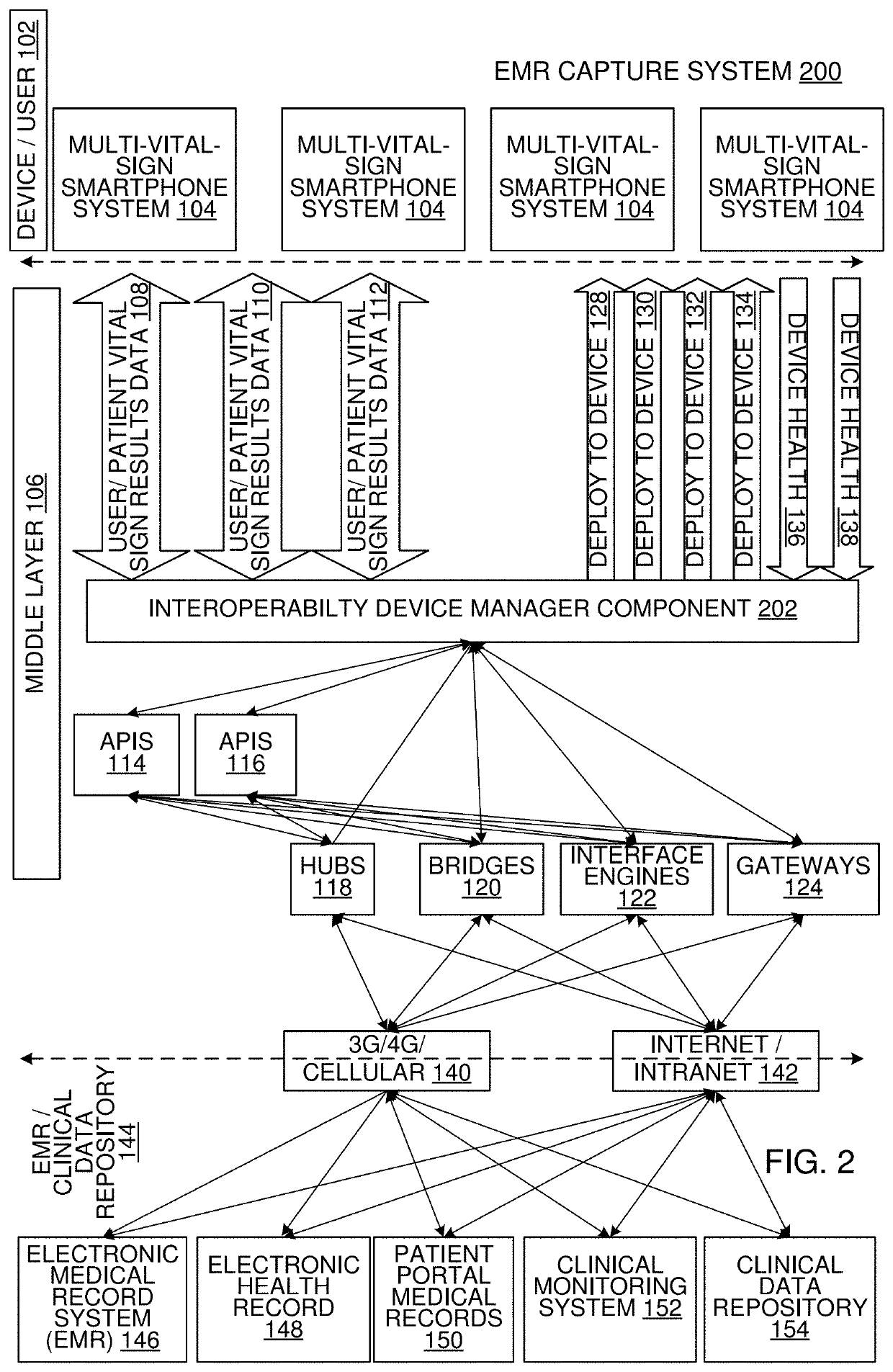
Multi-Vital Sign Detector in an Electronic Medical Records System
ActiveUS20190313907A1Evaluation of blood vesselsMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordDynamic light scattering
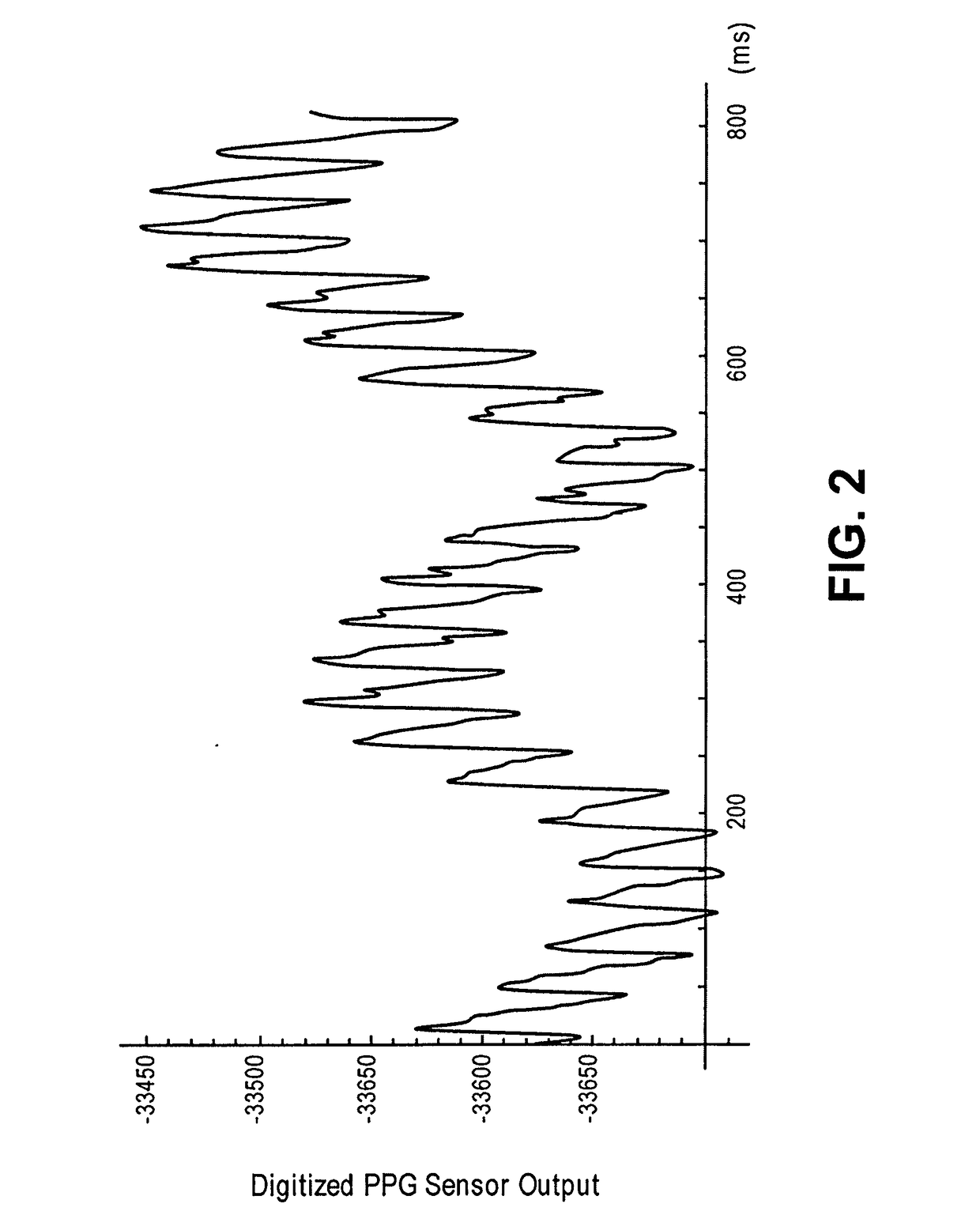
In one implementation, a device detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES +1
Multi-Vital Sign Detector in an Electronic Medical Records System
In one implementation, a device detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:VVV HLDG LTD +1
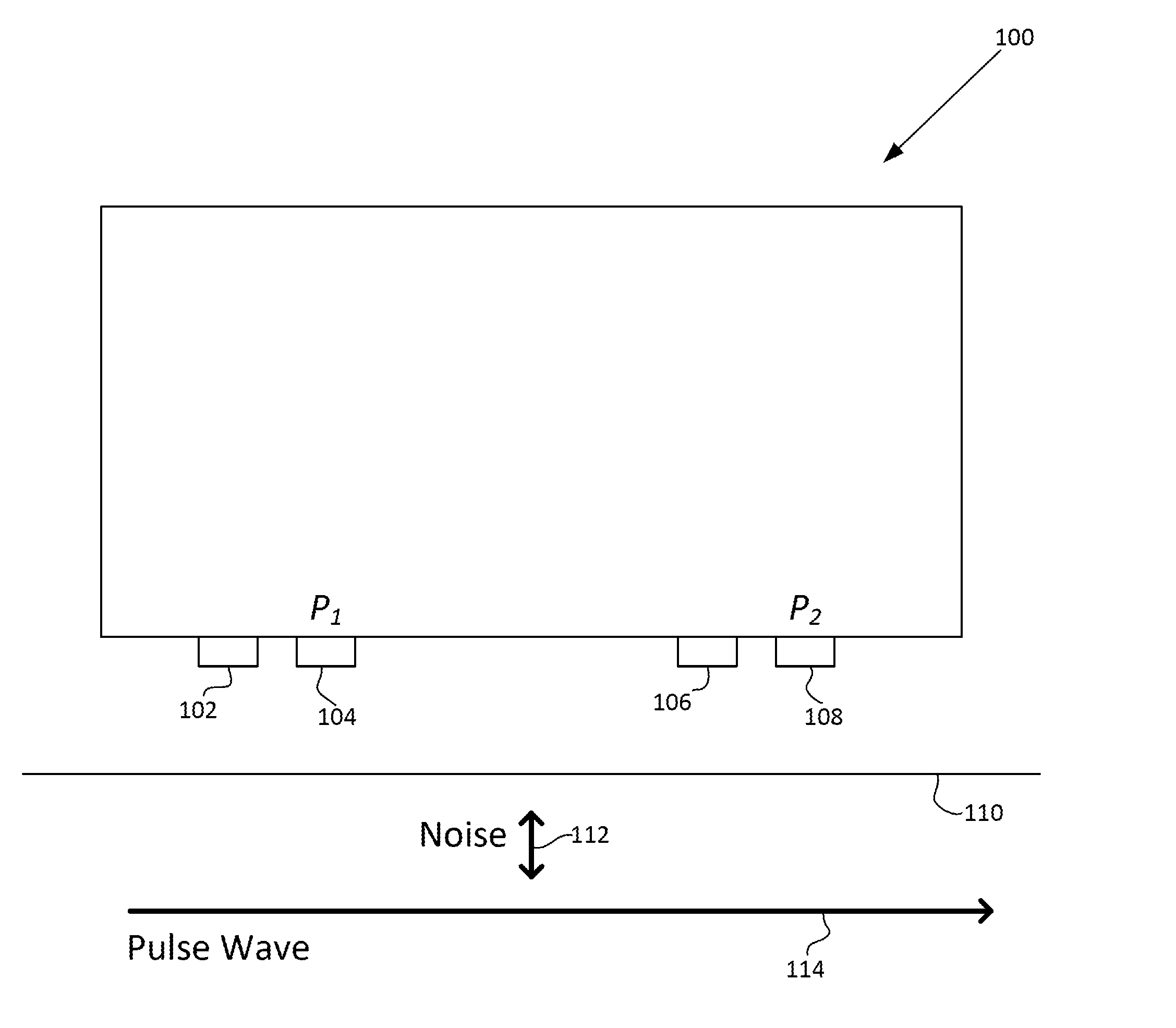
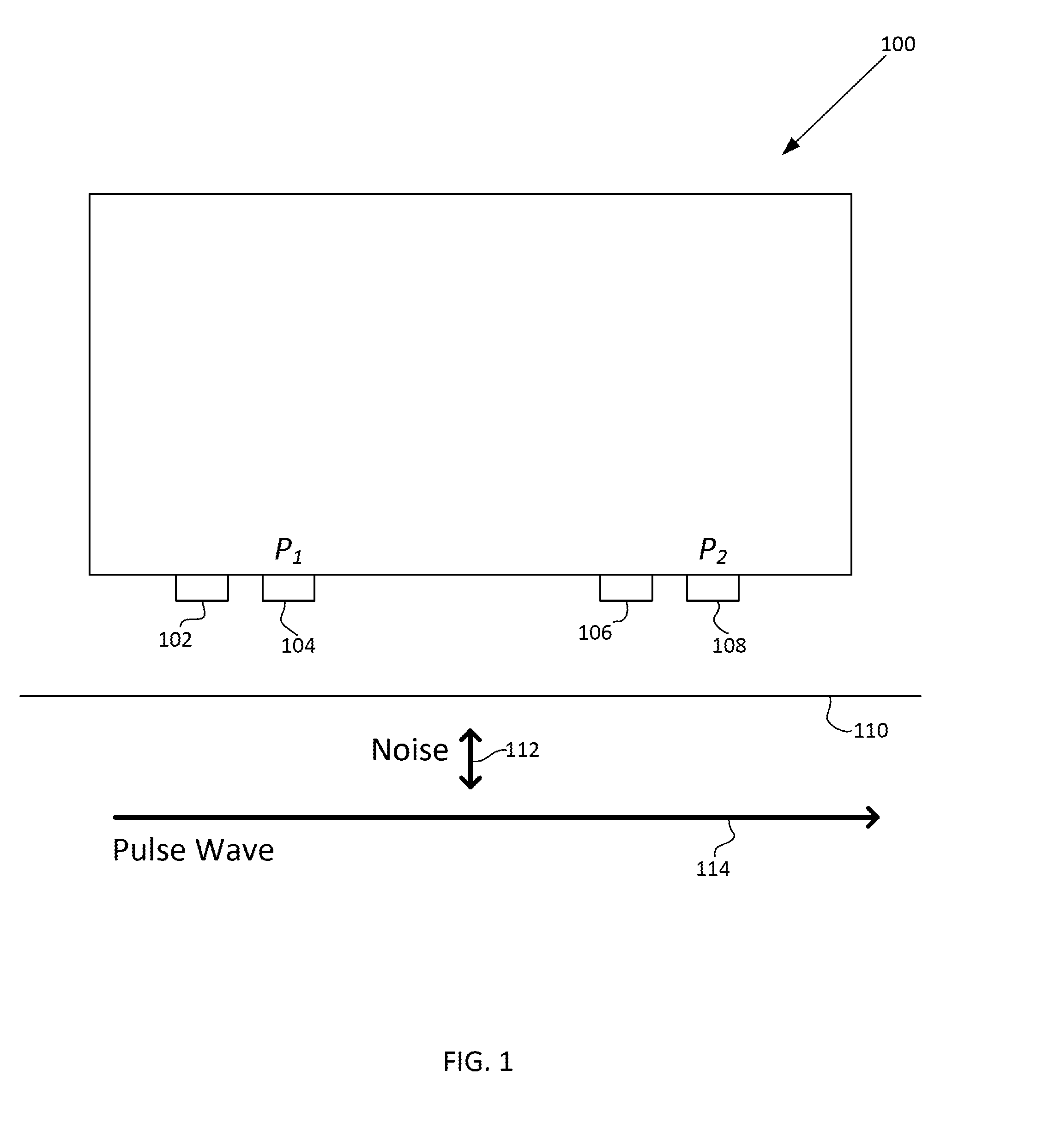
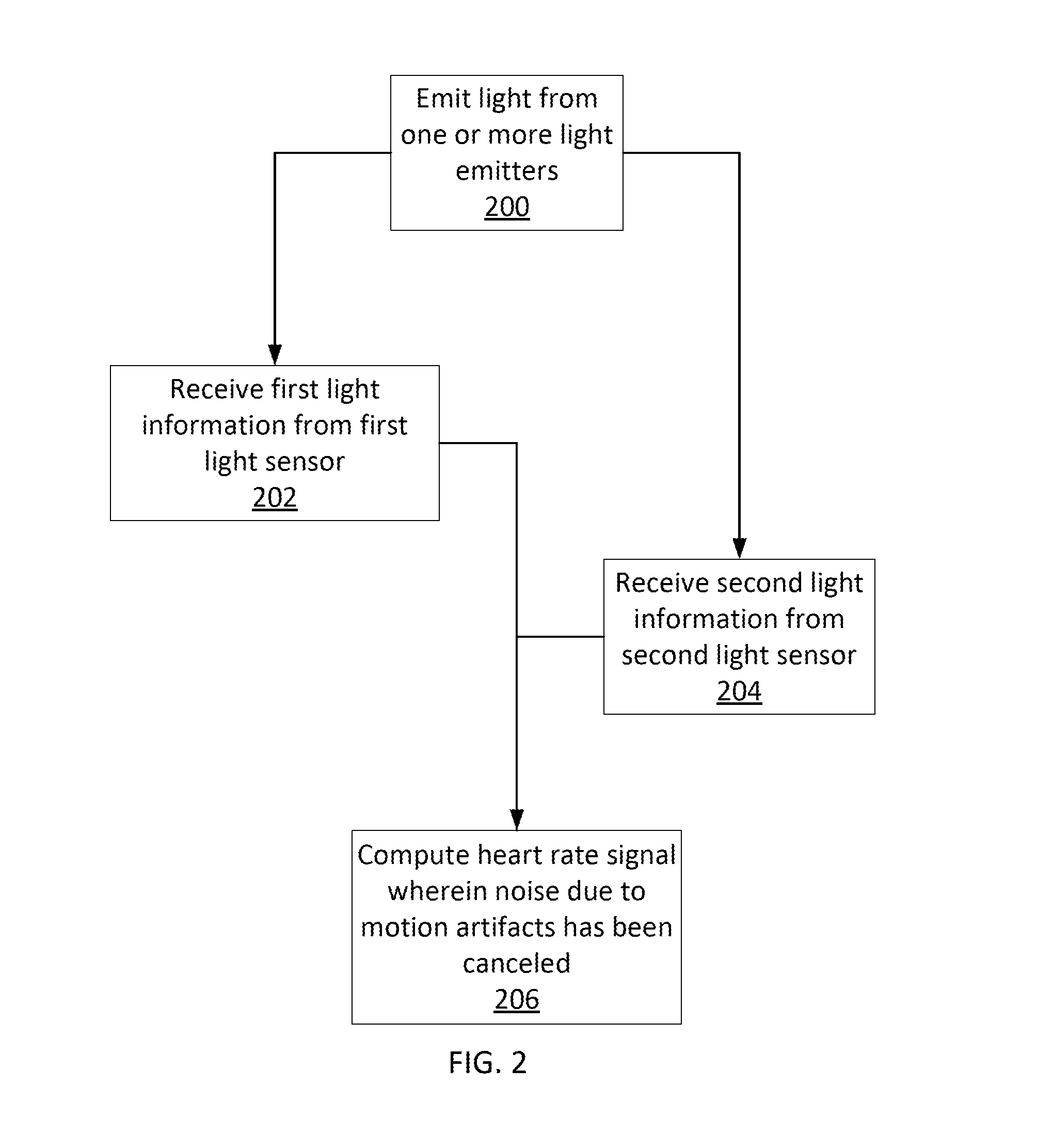
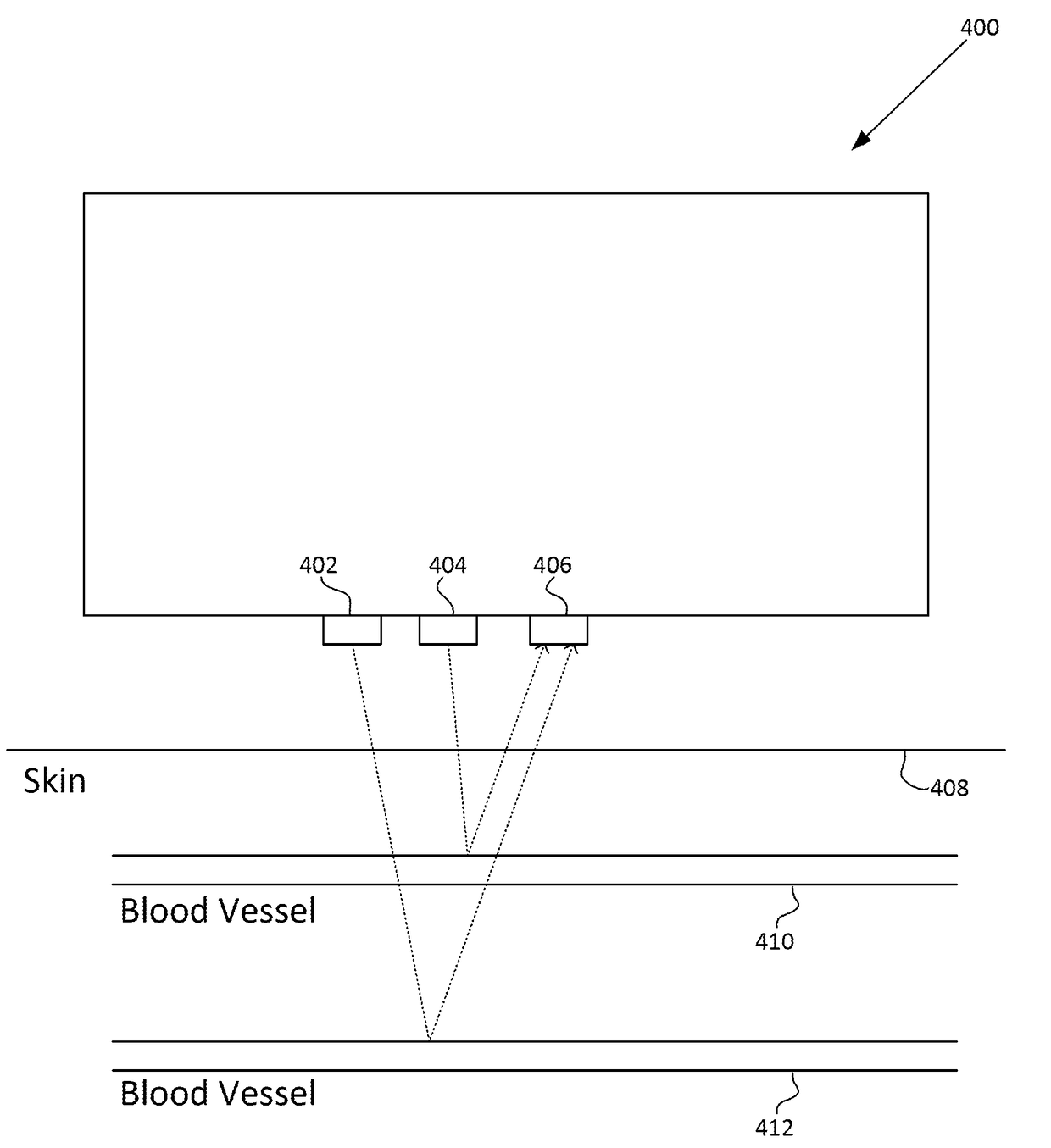
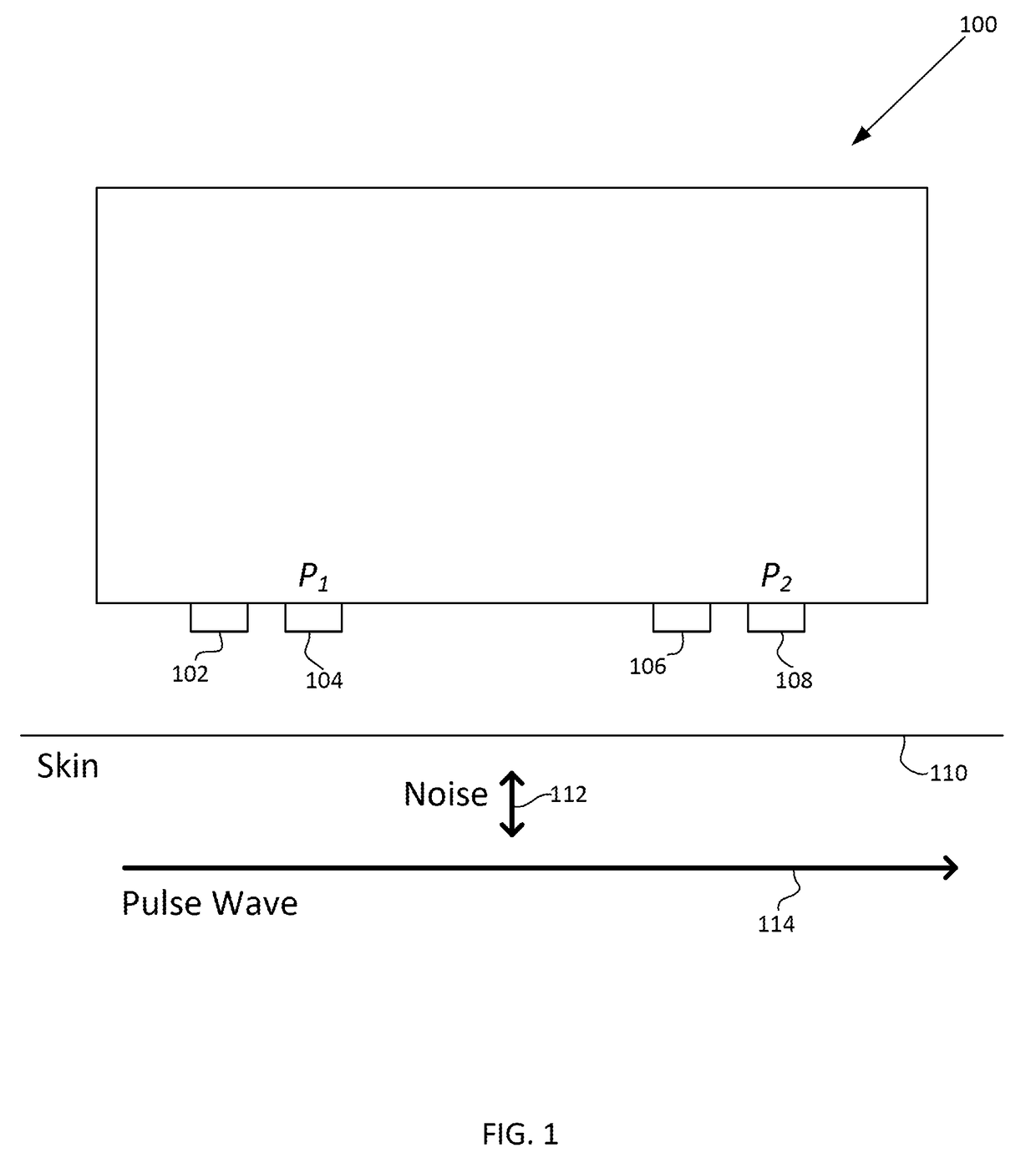
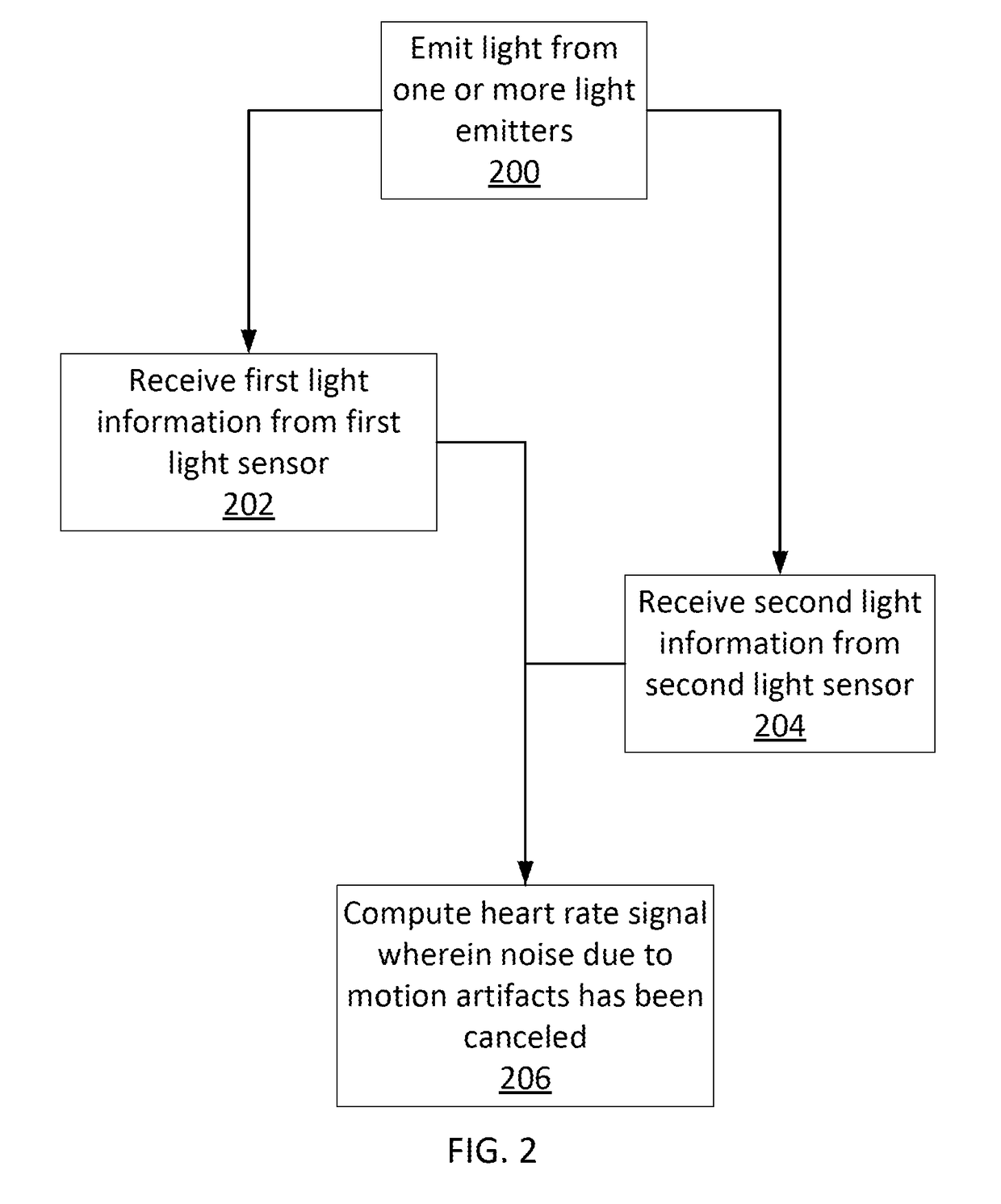
Motion artifact cancelation
A photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal may be obtained from a pulse oximeter, which employs a light emitter and a light sensor to measure the perfusion of blood to the skin of a user. However, the signal may be compromised by noise due to motion artifacts. That is, movement of the body of a user may cause the skin and vasculature to expand and contract, introducing noise to the signal. To address the presence of motion artifacts, examples of the present disclosure can receive light information from two light sensors situated in a line parallel to the direction of the blood pulse wave. The light information from each sensor may include the same noise signal, and thus subtracting one from the other can result in a heart rate signal where the noise has been canceled out. In some examples, a signal from one of the light sensors may be multiplied by a scaling factor before cancellation to account for response differences in each light sensor.
Owner:APPLE INC
Measuring respiration rate with multi-band plethysmography
A photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal may be obtained from a pulse oximeter, which employs a light emitter and a light sensor to measure the perfusion of blood to the skin of a user, and multiple wavelengths of light may be employed. For various wavelengths, relatively long wavelengths may interrogate relatively deep blood vessels in comparison to relatively short wavelengths, which may interrogate relatively shallow blood vessels. Accordingly, for co-located emitters of different wavelengths, there may be a time delay in the pulse signal measured by each wavelength. The time delay as a function of time may vary according to the constriction and dilation of the blood vessels, which itself may vary according to the respiratory rate of a user.
Owner:APPLE INC
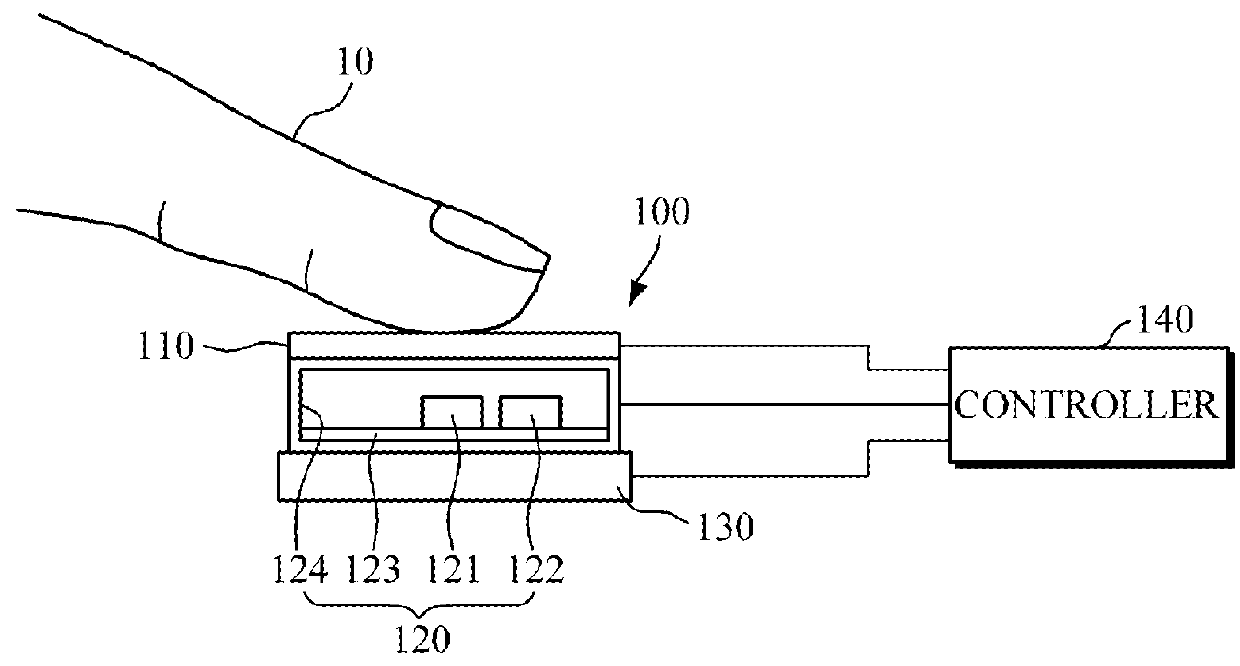
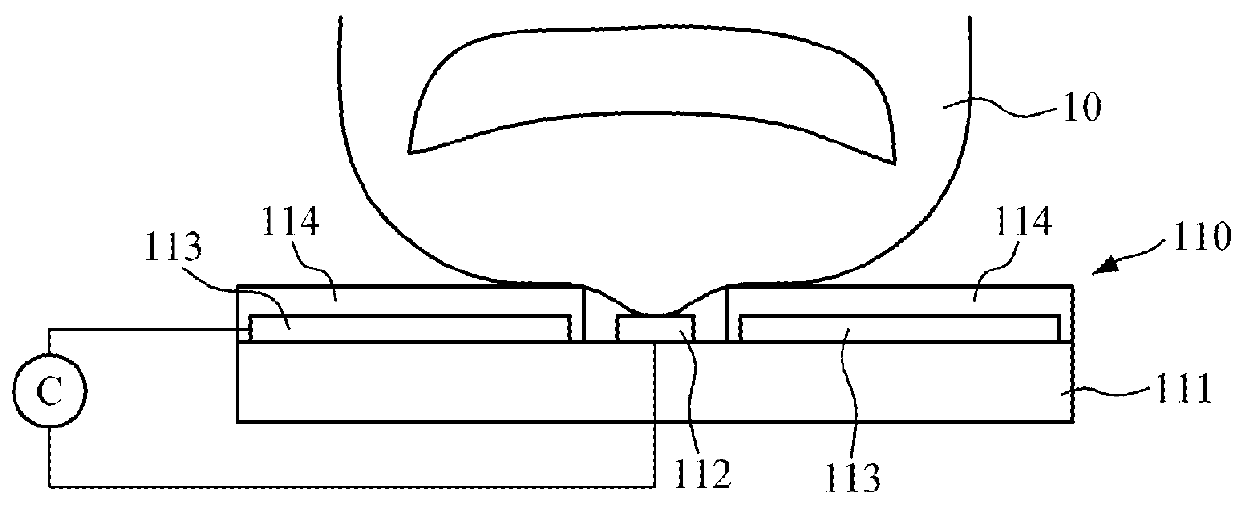
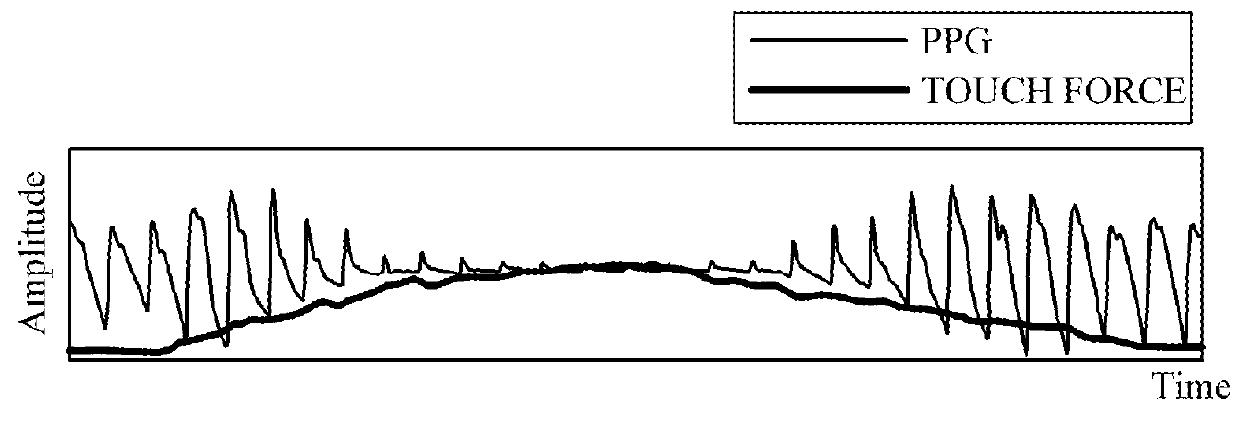
Touch-type blood pressure measurement apparatus and method
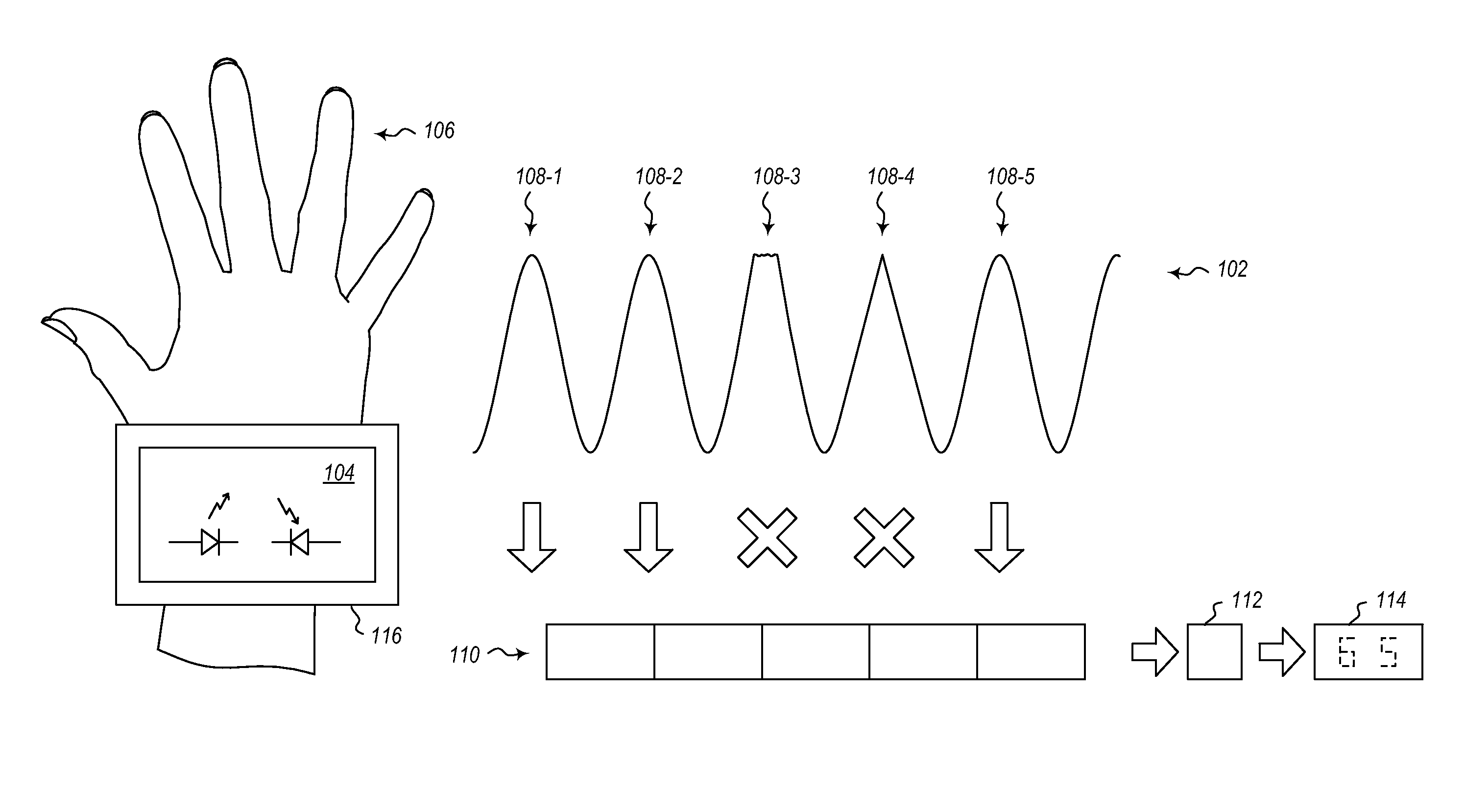
A touch-type blood pressure measurement apparatus is provided. The touch-type blood pressure measurement apparatus include: a touch sensor configured to generate a contact area signal when a finger of a user is in contact with the touch sensor; at least one photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor configured to generate a PPG signal of the user while the finger is in contact with the touch sensor; a force sensor configured to generate a touch force signal of the finger in contact with the touch sensor; and a controller configured to obtain a blood pressure of the user based on the contact area signal, the PPG signal, and the touch force signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
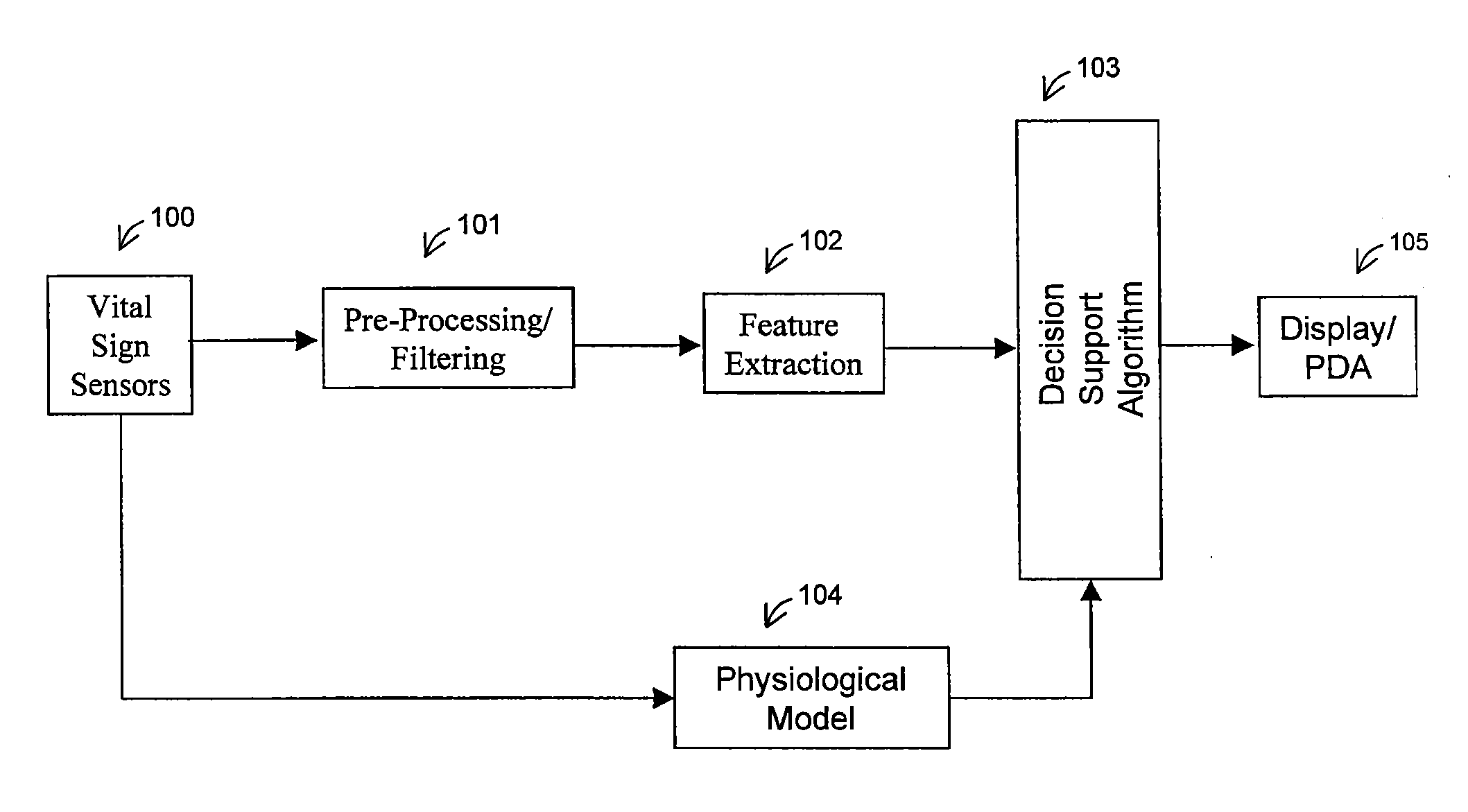
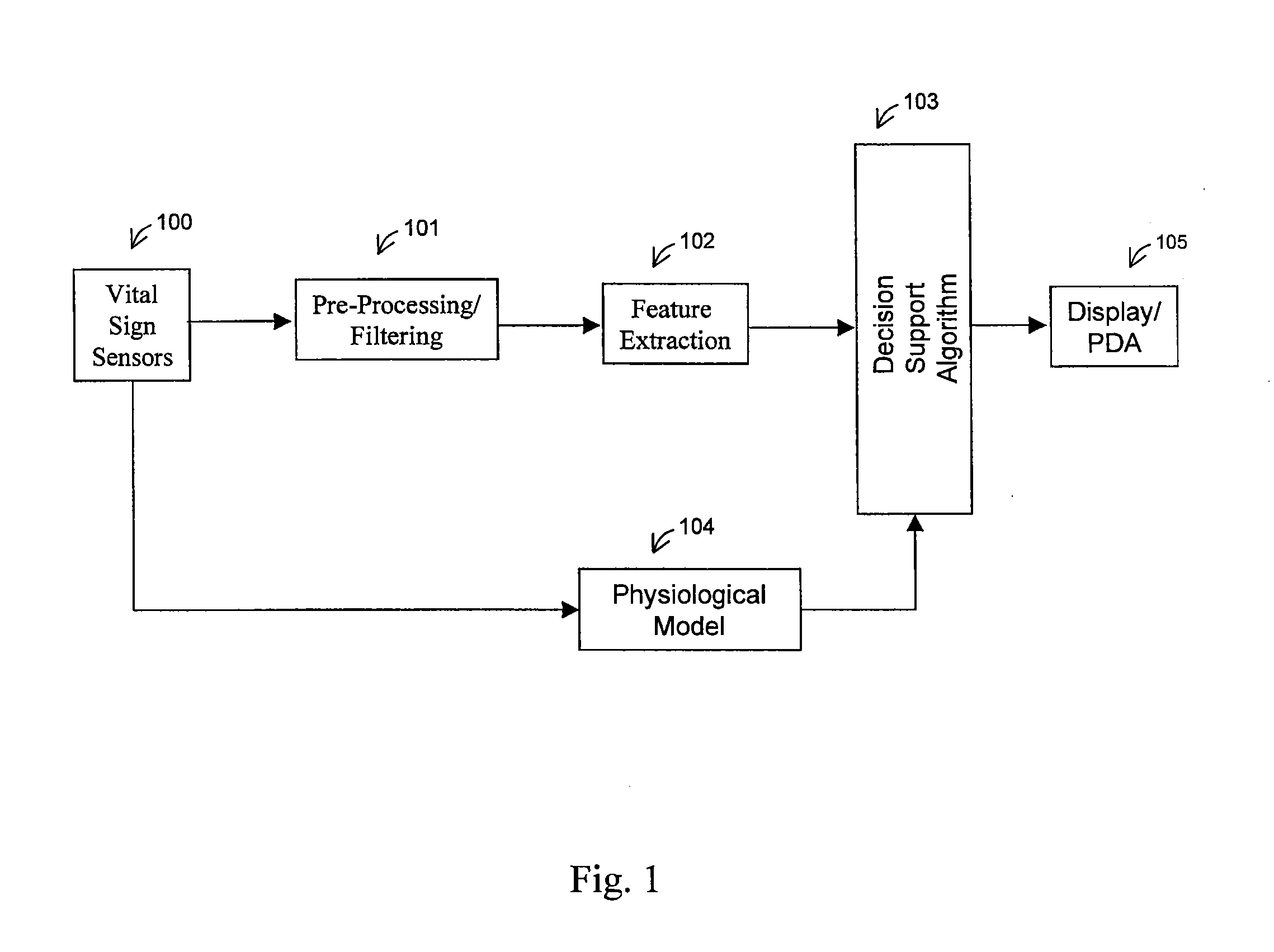
Methods and systems for non-invasive, internal hemorrhage detection
InactiveUS20110319724A1Increase chances of survivalElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisInternal hemorrhagePhotoplethysmogram
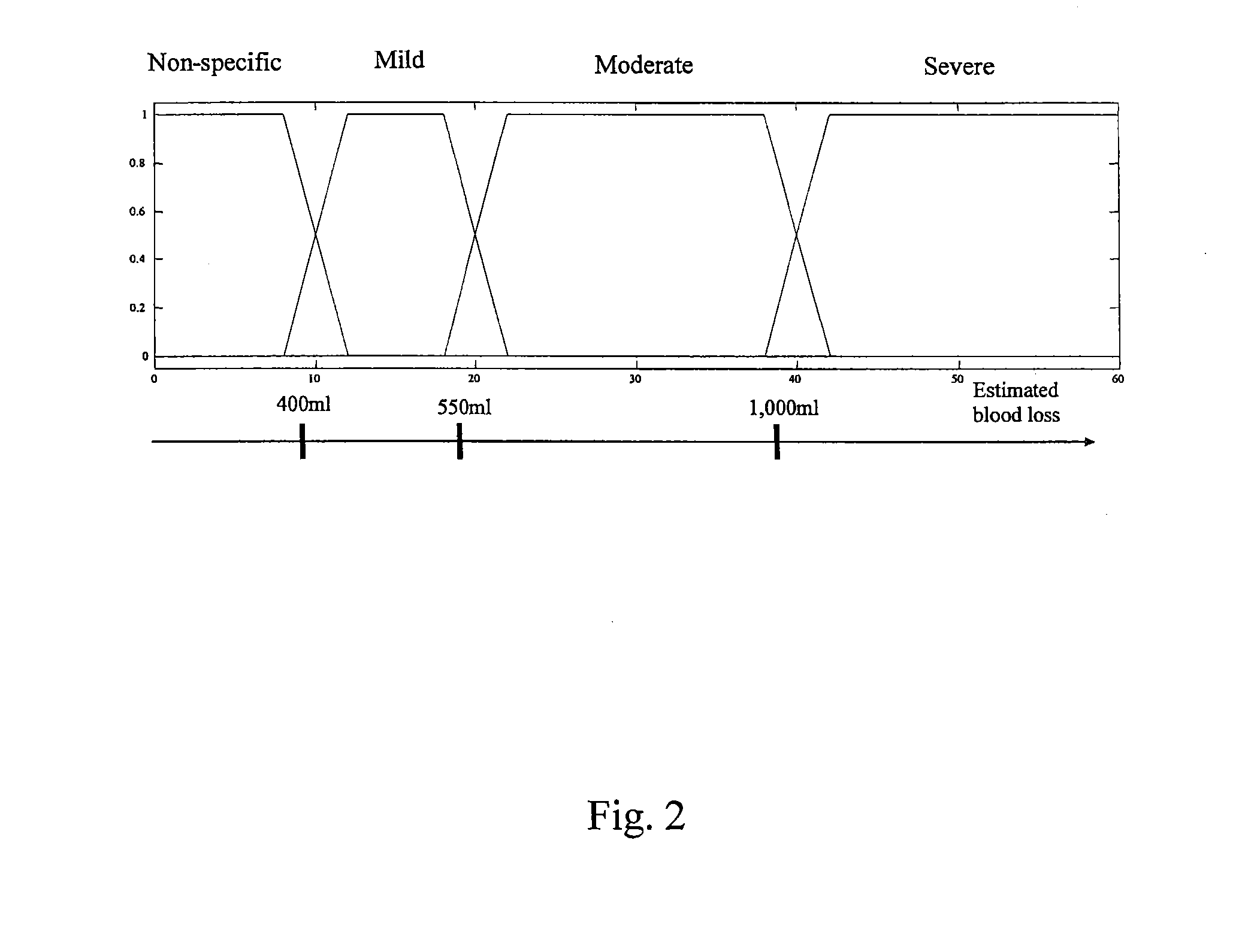
Methods and systems for detecting internal hemorrhaging in a person are provided. In an exemplary embodiment, one method includes the steps of measuring physiological conditions associated with the person and processing the measured physiological conditions using a probabilistic network to determine if the person has internal hemorrhaging. The method also includes the steps of determining the severity of any internal hemorrhaging by determining the amount of blood lost by the person and classifying this loss as non-specific, mild, moderate, and severe. The physiological measurements include an electrocardiogram, a photoplethysmogram, and oxygen saturation, respiratory, skin temperature, and blood pressure measurements. The probabilistic network included with one system determines whether there is internal hemorrhaging based on a number of factors including a physiological model, medical personnel inputs, transfer function, statistical, and spectral information, short and long term trends, and previous hemorrhage decisions.
Owner:COX PAUL G
Deep learning approach for long term, cuffless, and continuous arterial blood pressure estimation
ActiveUS20200015755A1Strong generalizationMathematical modelsElectrocardiographyBlood arterialPhotoplethysmogram
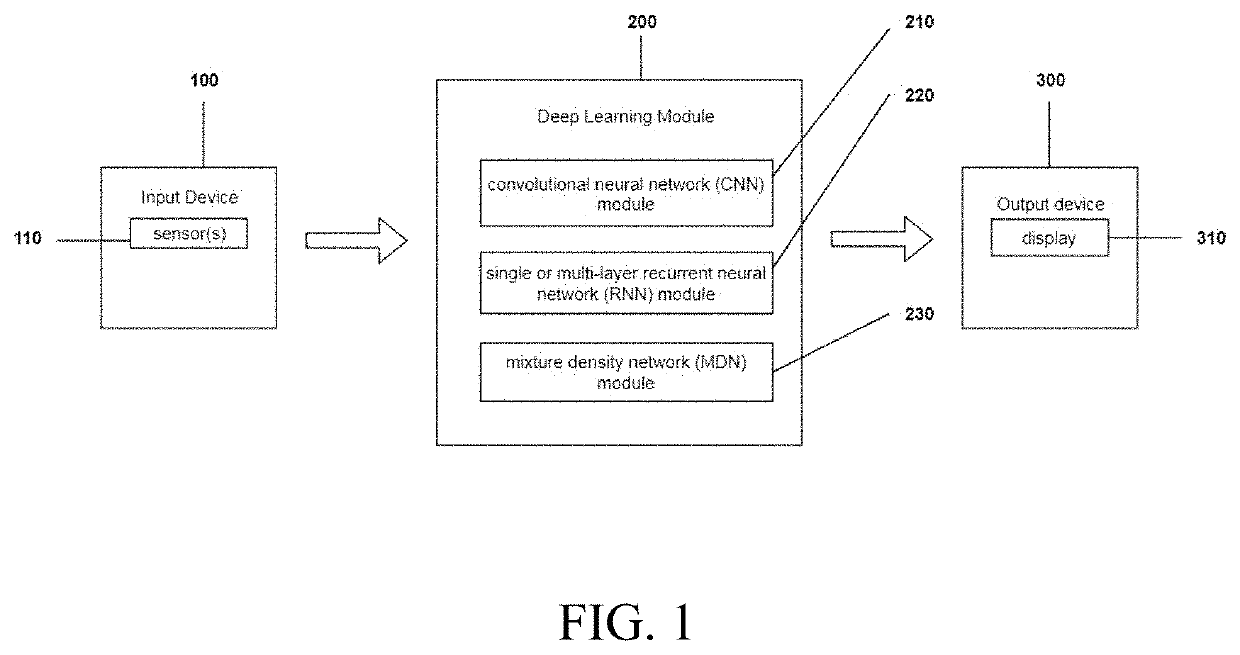
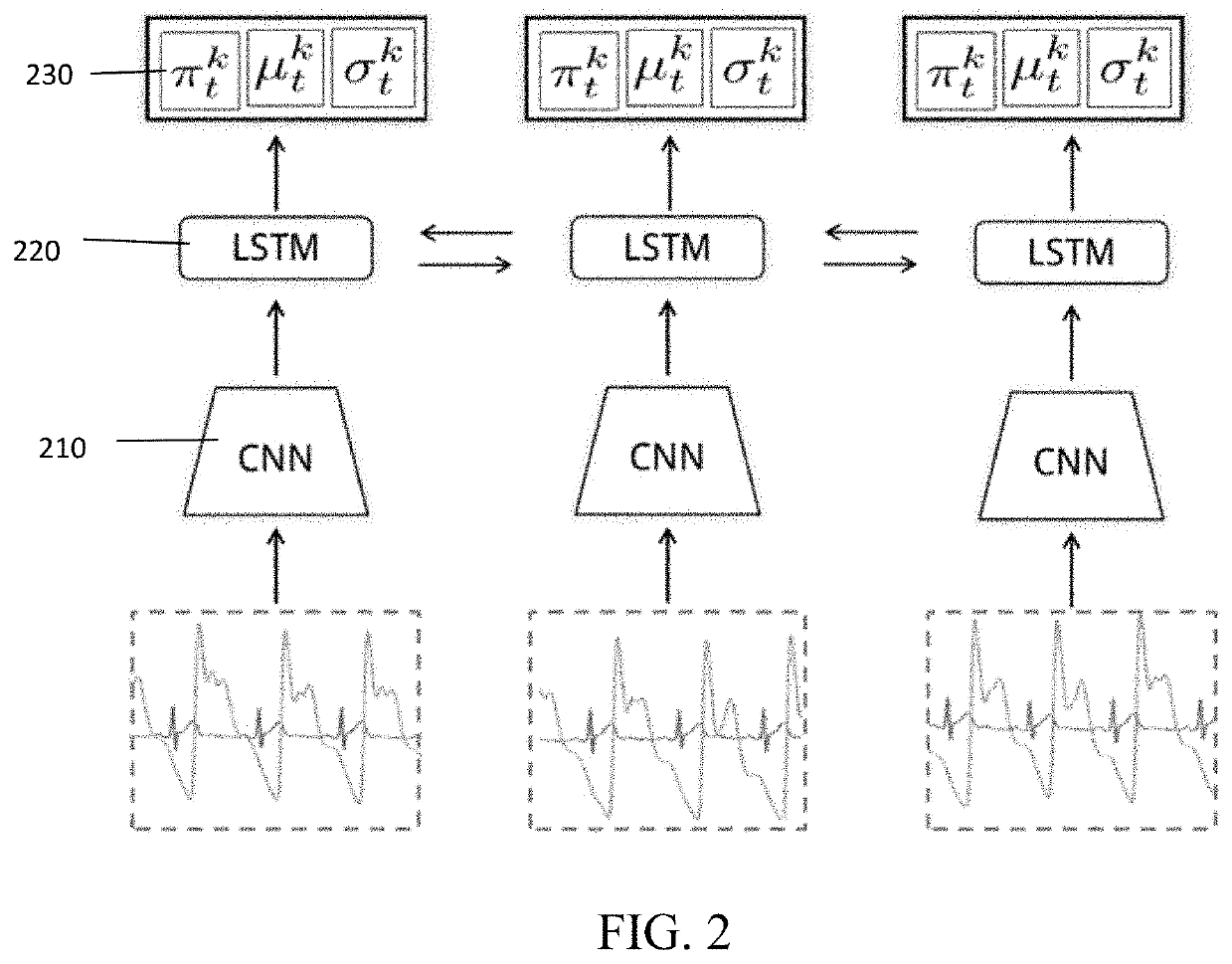
Methods and devices for long term, cuffless, and continuous arterial blood pressure estimation using an end-to-end deep learning approach are provided. A deep learning system comprises three modules: a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) module for learning powerful features; a one- or multi-layer recurrent neural network (RNN) module for modeling the temporal dependencies in blood pressure dynamics; and a mixture density network (MDN) module for predicting final blood pressure value. This system takes raw physiological signals, such as photoplethysmogram and / or electrocardiography signals, as inputs and yields arterial blood pressure readings in real time.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
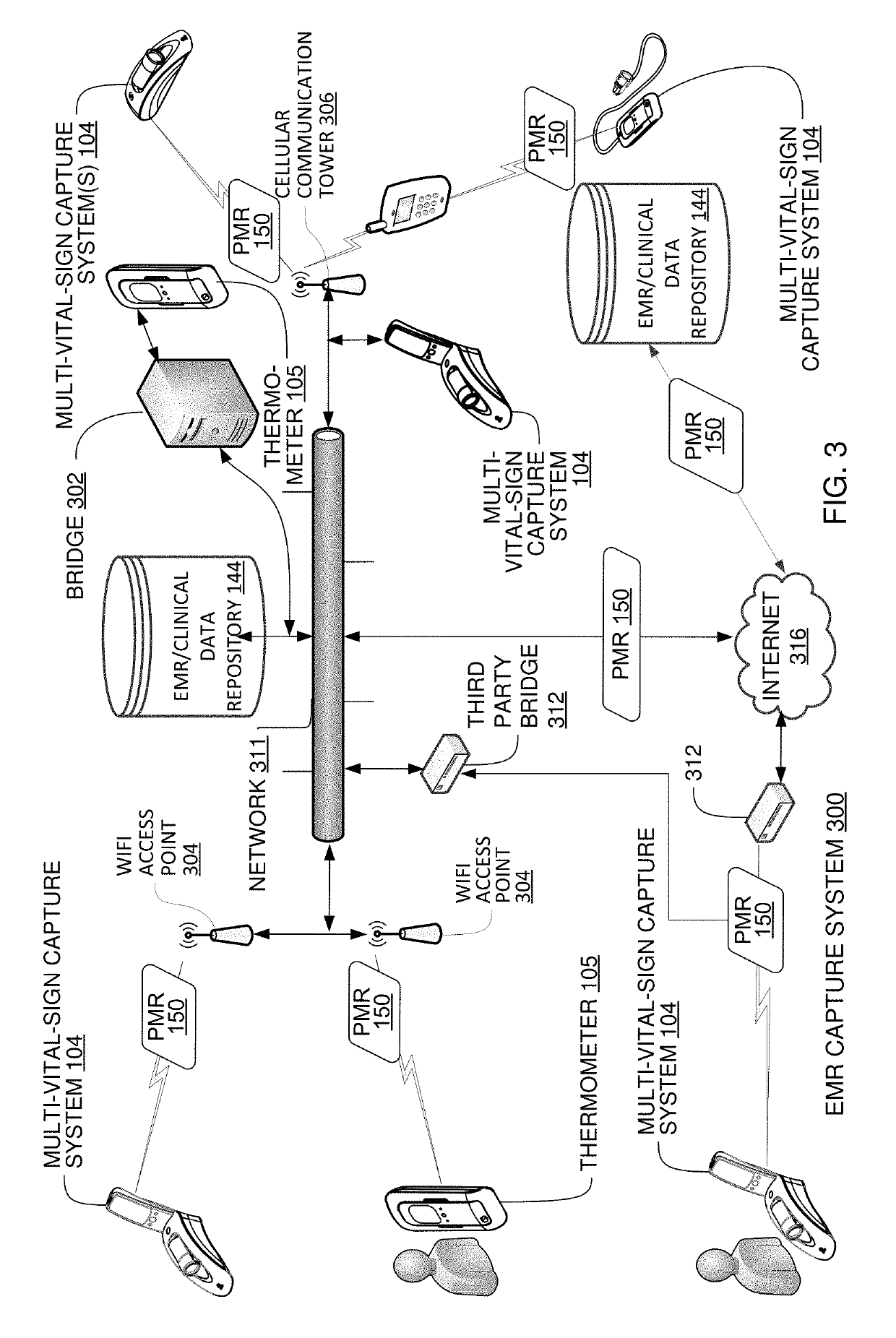
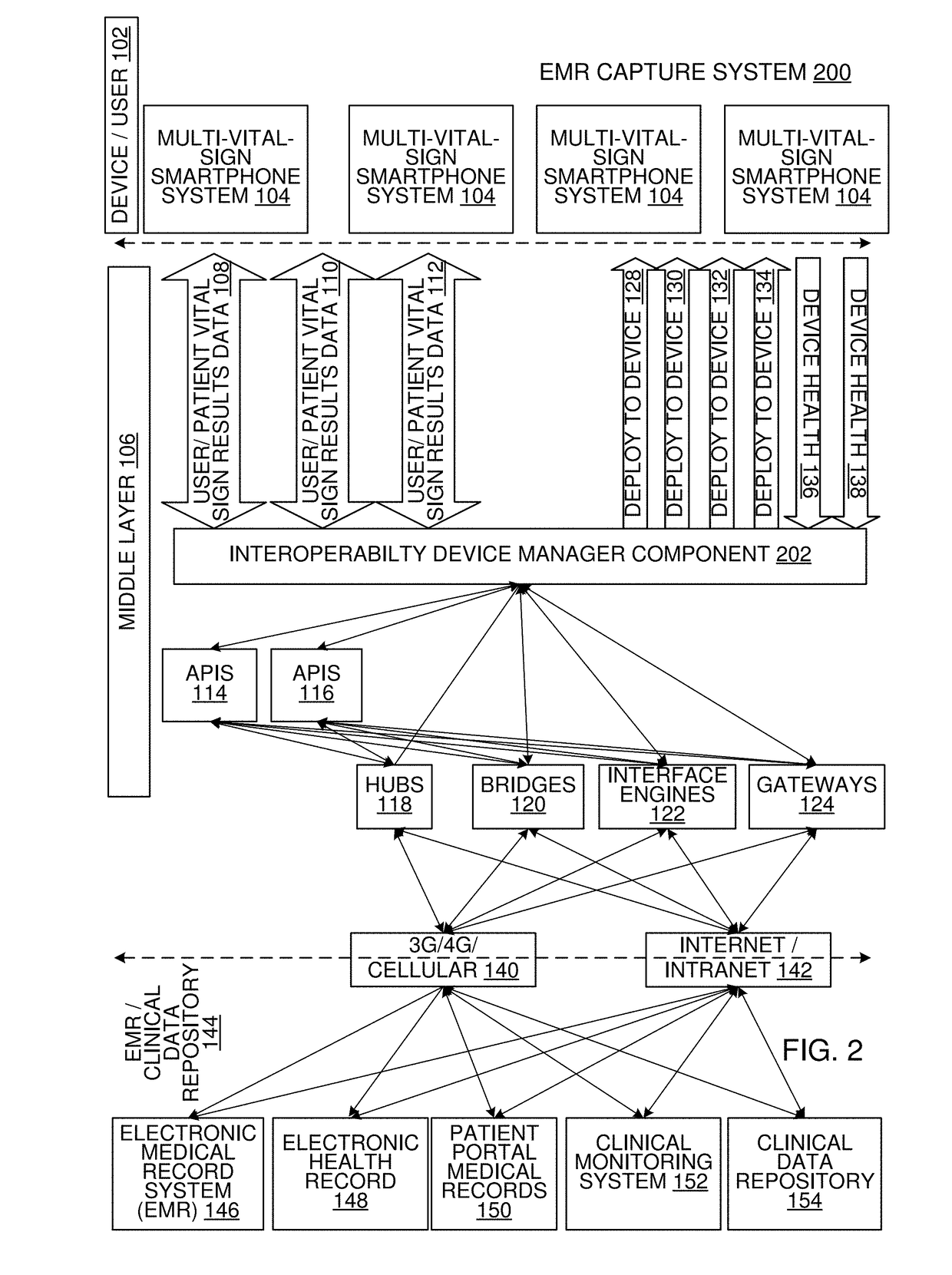
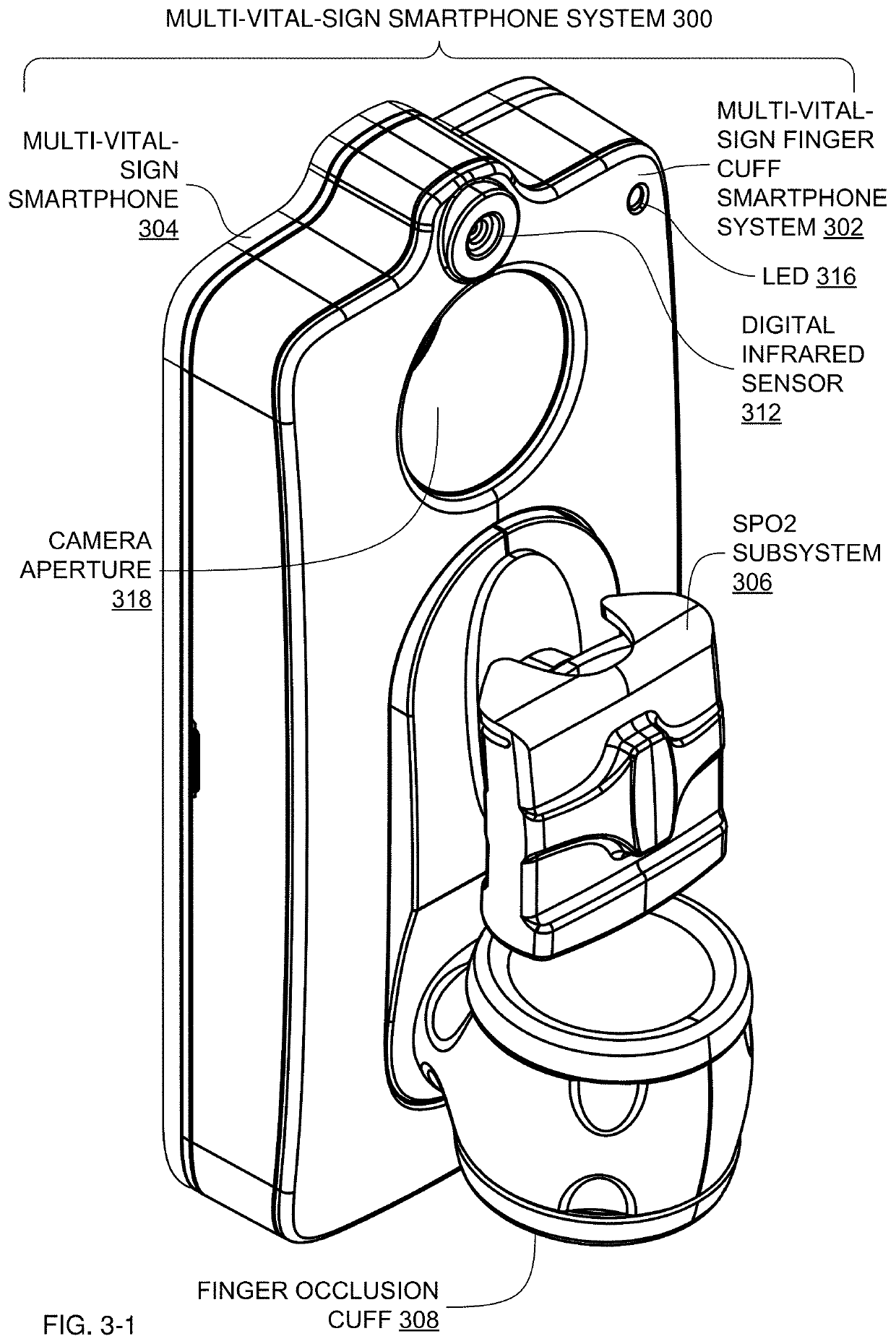
Multi-Vital-Sign Smartphone System in an Electronic Medical Records System
ActiveUS20180235468A1Digital data processing detailsDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedical recordDynamic light scattering
In one implementation, a multi-vital-sign smartphone system detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
Systems and Methods for Determining Blood Pressure
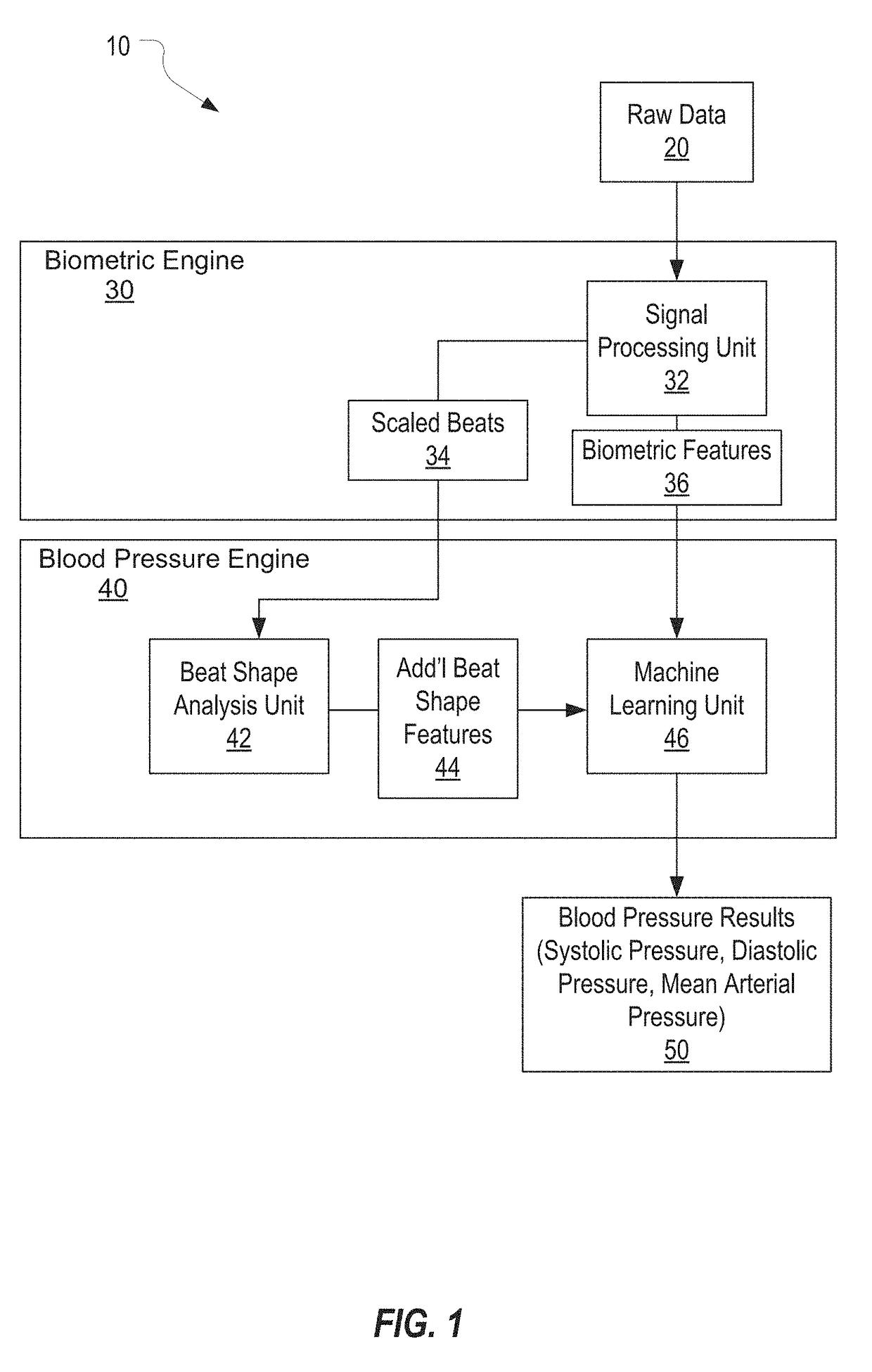
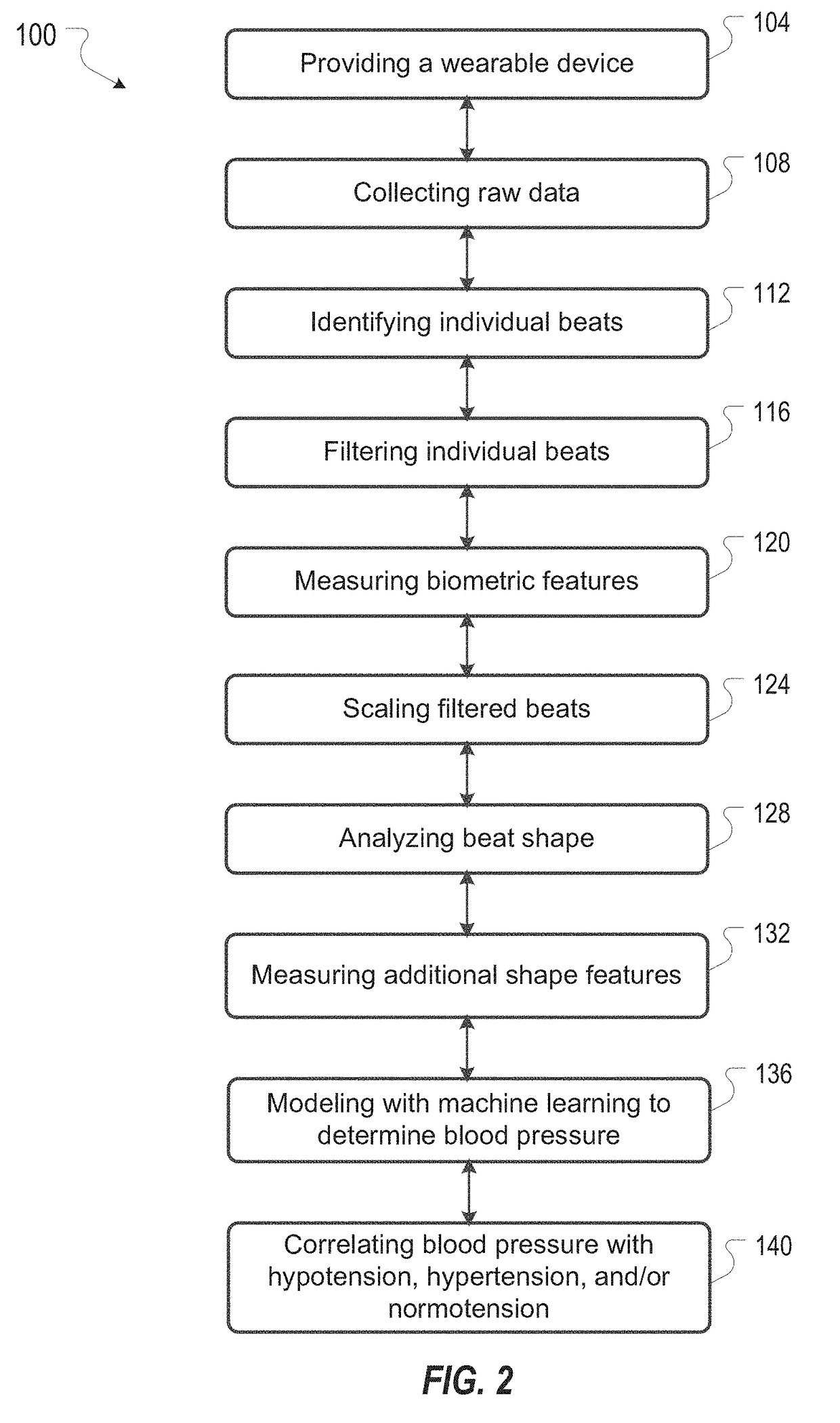
Systems and methods for determining a blood pressure of a subject from a photoplethysmogram are disclosed. The systems and methods include acquiring raw photoplethysmogram (PPG) data from a subject by measuring light reflected from or transmitted through a portion of the subject's body, determining a mean beat shape from the raw PPG data, and analyzing the mean beat shape to determine a blood pressure of the subject. The method can include analyzing a distinct shape of the mean beat shape to determine the blood pressure. The method can include identifying individual beats within the raw PPG data, collecting motion data and filtering the individual beats against the motion data, measuring biometric features of filtered beats, scaling individual beats in time and amplitude, and measuring additional shape features of scaled beats.
Owner:AMIIGO
System and method to detect significant arrhythmic events through photoplethysmogram (PPG) and accelerometer
ActiveCN104837401AReliable detectionAppropriate responseInternal electrodesInertial sensorsFeature vectorAccelerometer
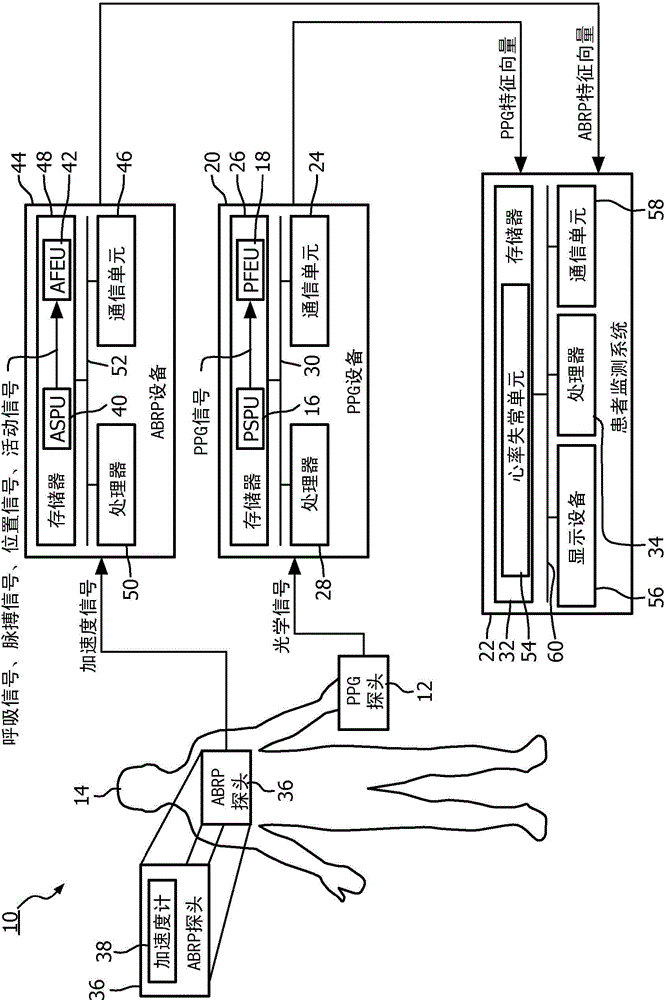
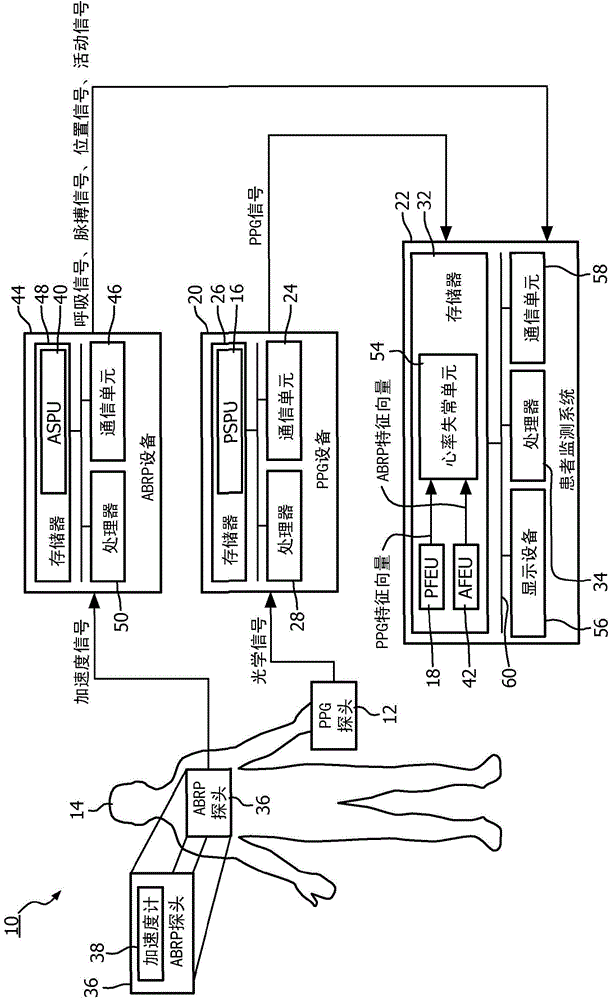
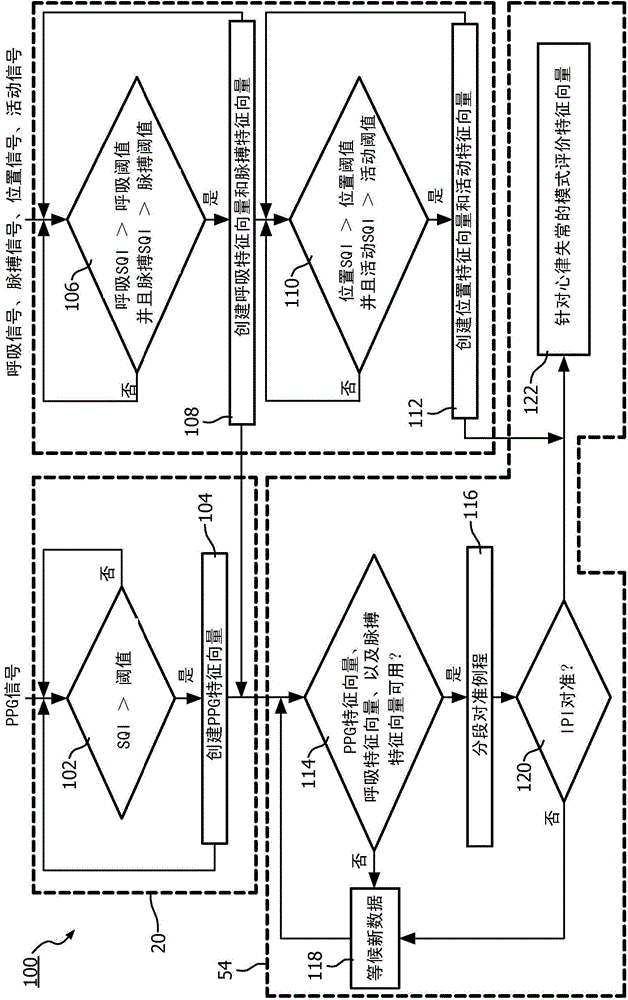
A medical system (10) and method detect arrhythmi cevents. The medical system (10)includes at least one processor (28, 34, 50) programmed to perform the method. A photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal generated using a PPG probe (12)positioned on or within a patient (14) anda pulse signal generated using an accelerometer (38)positioned on or within the patient (14) received. Features from the PPG signal are extracted to PPG feature vectors, and features are extracted from the pulse signal to pulse feature vectors. The PPG feature vectors are correlated with the pulse feature vectors, and correlated PPG feature vectors and correlated pulse feature vectors are evaluated to detect arrhythmic events.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
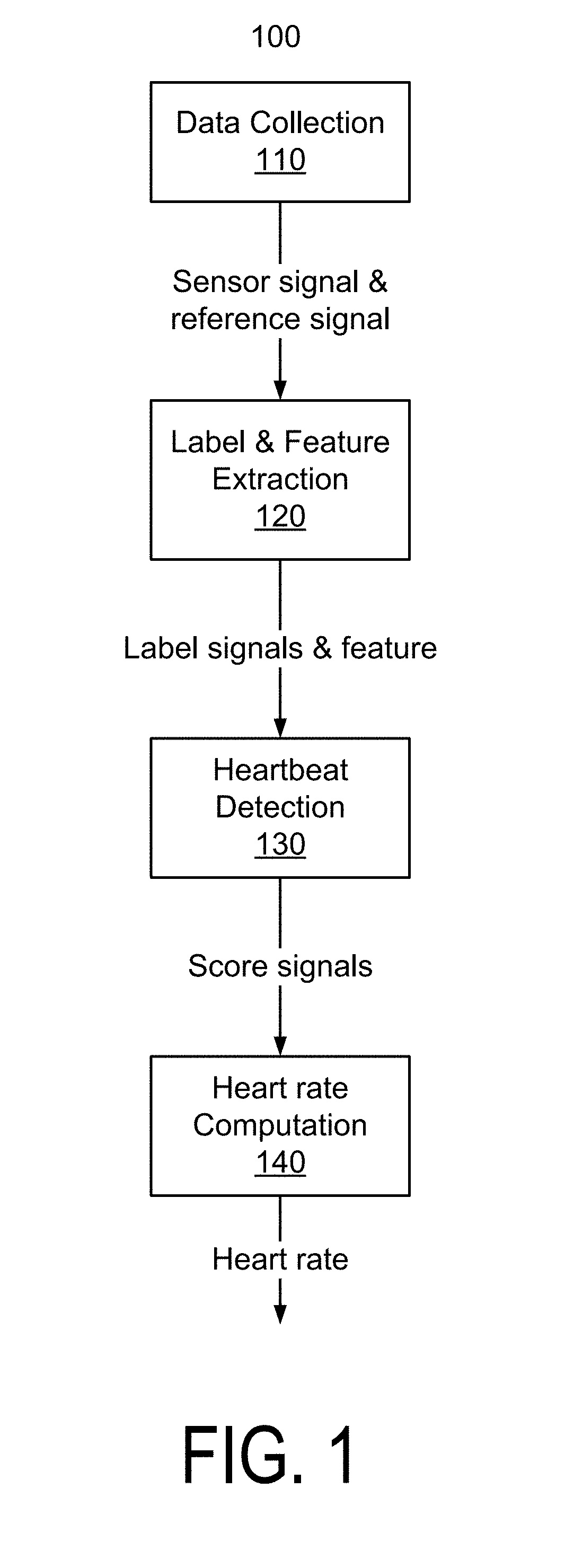
Deep learning algorithms for heartbeats detection
A system that detects heartbeats includes a sensor or a transducer and algorithms based on deep learning. The algorithms employ techniques of artificial intelligence that enable the system to extract heartbeat features under low signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) conditions when a user is exercising. The algorithms can be applied to various technologies for heart rate monitoring such as ultrasound Doppler, photoplethysmogram (PPG), electrocardiogram (EKG), acoustic, pressure / force sensing and laser / RF Doppler, among other types of sensing methods.
Owner:LOGOS CARE INC
Method and system for cuffless blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmogram features and pulse transit time
ActiveUS20180235487A1Maximize accuracyEvaluation of blood vesselsMedical automated diagnosisEcg signalEstimation methods
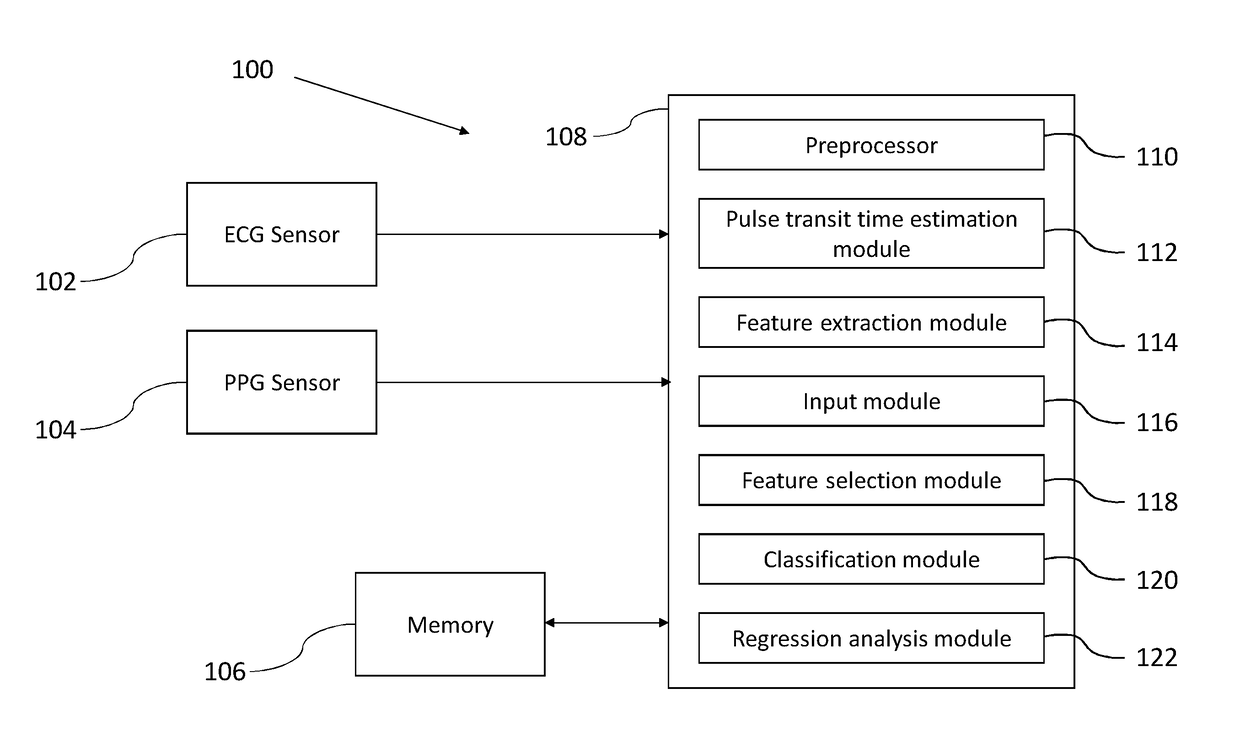
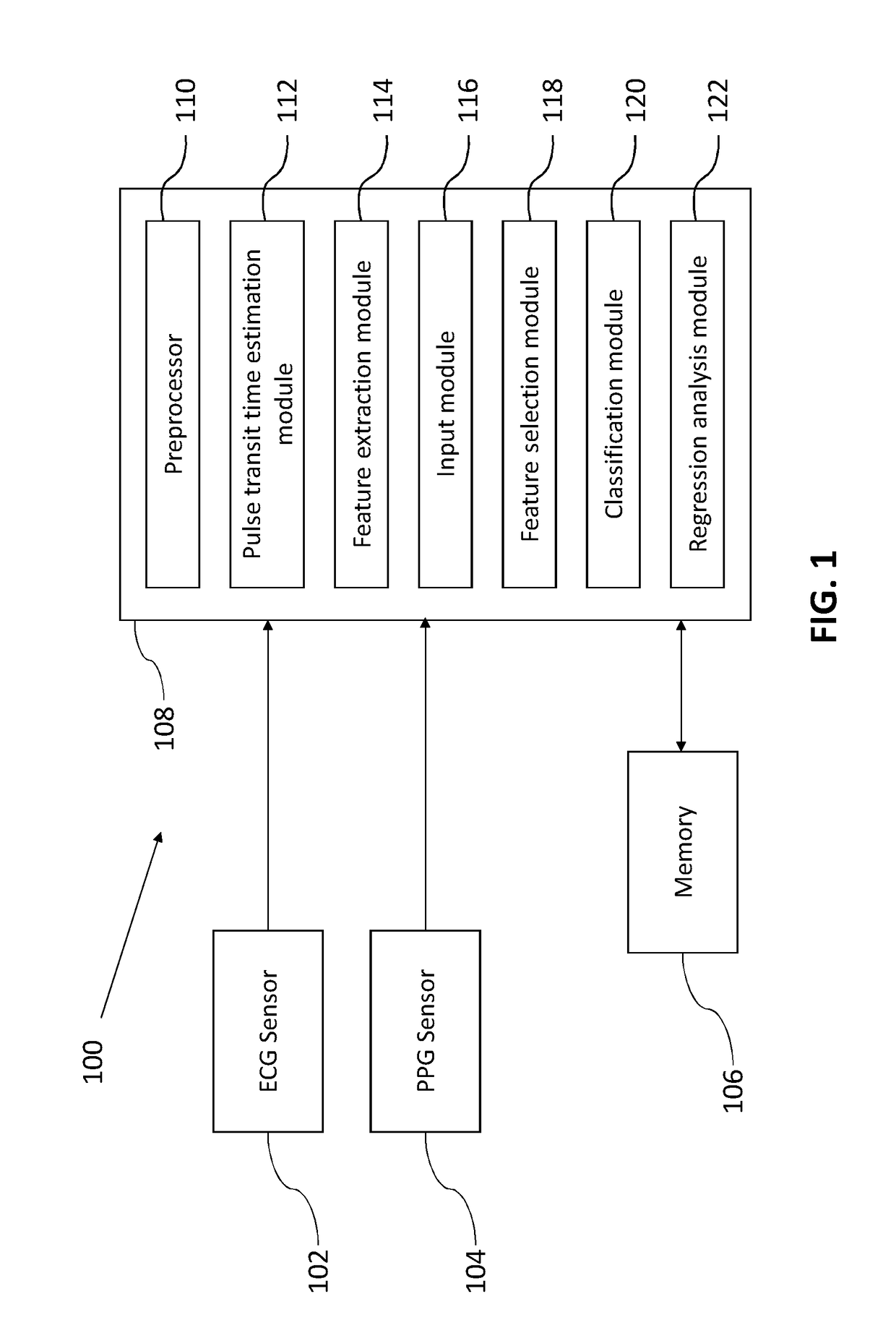
A method and system for blood pressure (BP) estimation of a person is provided. The system is estimating pulse transit time (PTT) using the ECG signal and PPG signal of the person. A plurality of features are extracted from the PPG. The plurality of PPG features and the PTT are provided as inputs to an automated feature selection algorithm. This algorithm selects a set of features suitable for BP estimation. The selected features are fed to a classifier to classify the database into low / normal BP range and a high BP range. The correctly classified normal BP data are then used to create a regression model to predict BP from the selected features. The current methodology uses automated feature selection mechanism and also employs a block to reject extreme BP data. Thus the available accuracy in predicting BP is expected to be more than the existing BP estimation methods.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
Optical Photoplethysmogram Signal Shape Feature Biological Monitor
InactiveUS20160360984A1Optical sensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateTime domainPhotoplethysmogram
A system is described for providing the value of a biological characteristic. The system includes a sensor. The sensor is configured to generate a time domain photoplethysmogram (PPG) input signal. The system further includes a first computation module coupled to the sensor. The first computation module is configured to evaluate portions of the generated time domain PPG signal against predetermined quality criteria. The system further includes a second computation module coupled to the first computation module. The second computation module is configured to use portions of the generated time domain PPG signal that meet the predetermined quality criteria to generate an output value. The output value characterizes a biological characteristic at a point in time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
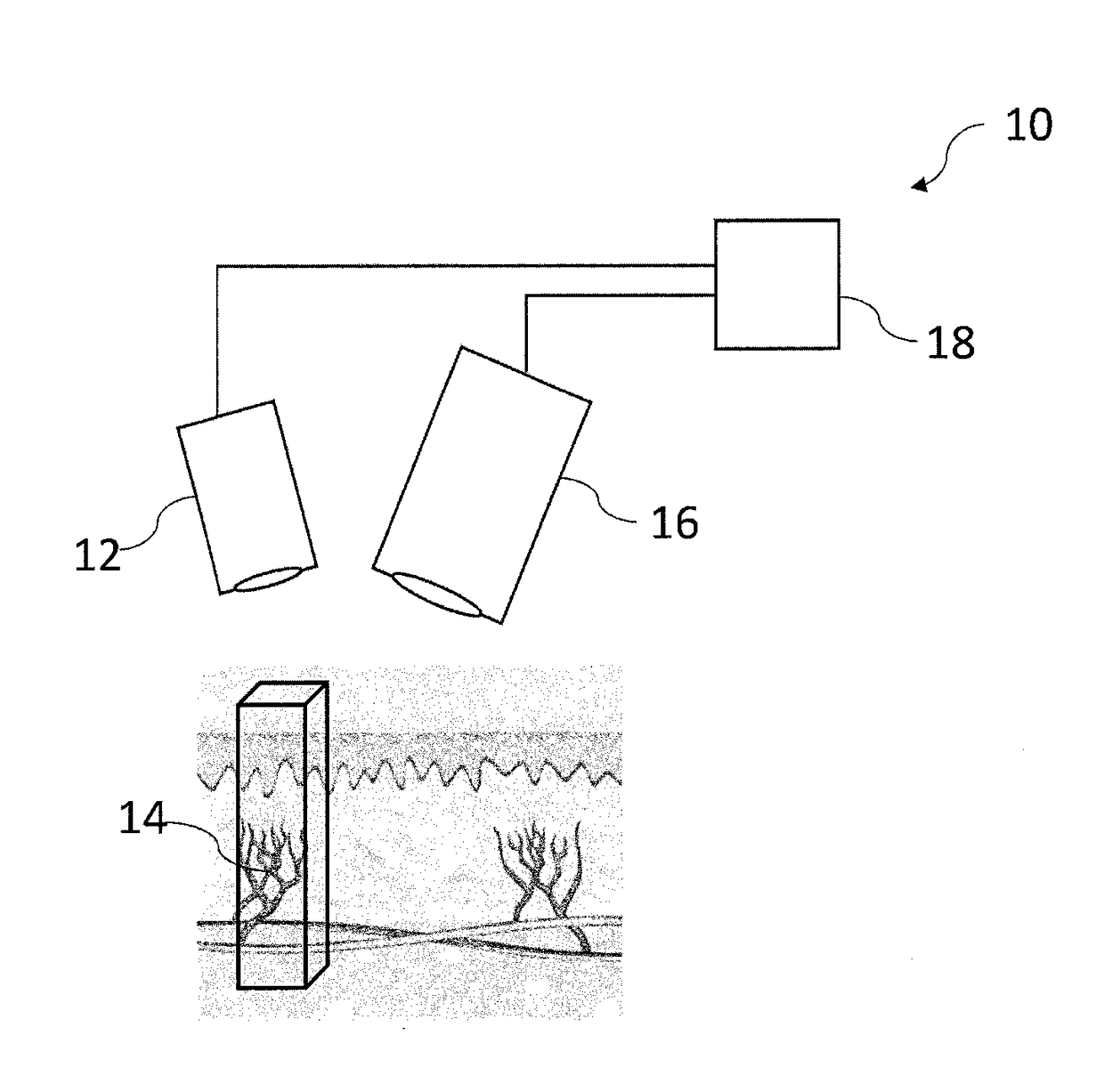
Quantification of absolute blood flow in tissue using fluorescence-mediated photoplethysmography
A method, an apparatus, and a kit including the apparatus and a fluorescence agent are provided for measuring a time-varying change in an amount of blood in a tissue volume, and include exciting a fluorescence agent in the blood, acquiring a time-varying light intensity signal during a pulsatile flow of the blood through the tissue volume, the pulsatile flow having a systolic and a diastolic phase resembling a conventional photoplethysmogram, and processing the acquired signal by applying a modified Beer-Lambert law to obtain a measurement of the time-varying change in the amount of blood in the tissue volume. The instantaneous molar concentration of the fluorescence agent is determined by utilizing a concentration-mediated change in a fluorescence emission spectrum of the fluorescence agent. There is further provided a fluorescence agent for use in the method.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Real-time blood pressure monitoring system and method based on ballistocardiogram and photoelectrical signals
PendingCN108186000AAccurately obtain real-time ambulatory blood pressureReal-timeEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationNursing care
The invention relates to a real-time blood pressure monitoring system and method based on ballistocardiogram and photoelectrical signals. The system comprises a PC (personal computer), a bed, a photoplethysmogram acquisition device, a ballistocardiogram acquisition device and a synchronous signal acquirer; the photoplethysmogram acquisition device is a PPG (photoplethysmogram) sensor used for acquiring PPG from a testee and mounted at the testee's fingertip; the ballistocardiogram acquisition device is an acceleration sensor that is mounted on a cross beam of the bed; a signal acquiring direction of the acceleration sensor is parallel to the spine; accelerated vibration signals of a nursing bed due to ballistic shock can be acquired with no binding; both the PPG sensor and the accelerationsensor are connected to the PC through the synchronous signal acquirer; monitoring results are output from a display screen of the PC; the synchronous signal acquirer processes the two signals by means of external triggering. The system has the advantages of good timeliness, goo continuity, zero invasion and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
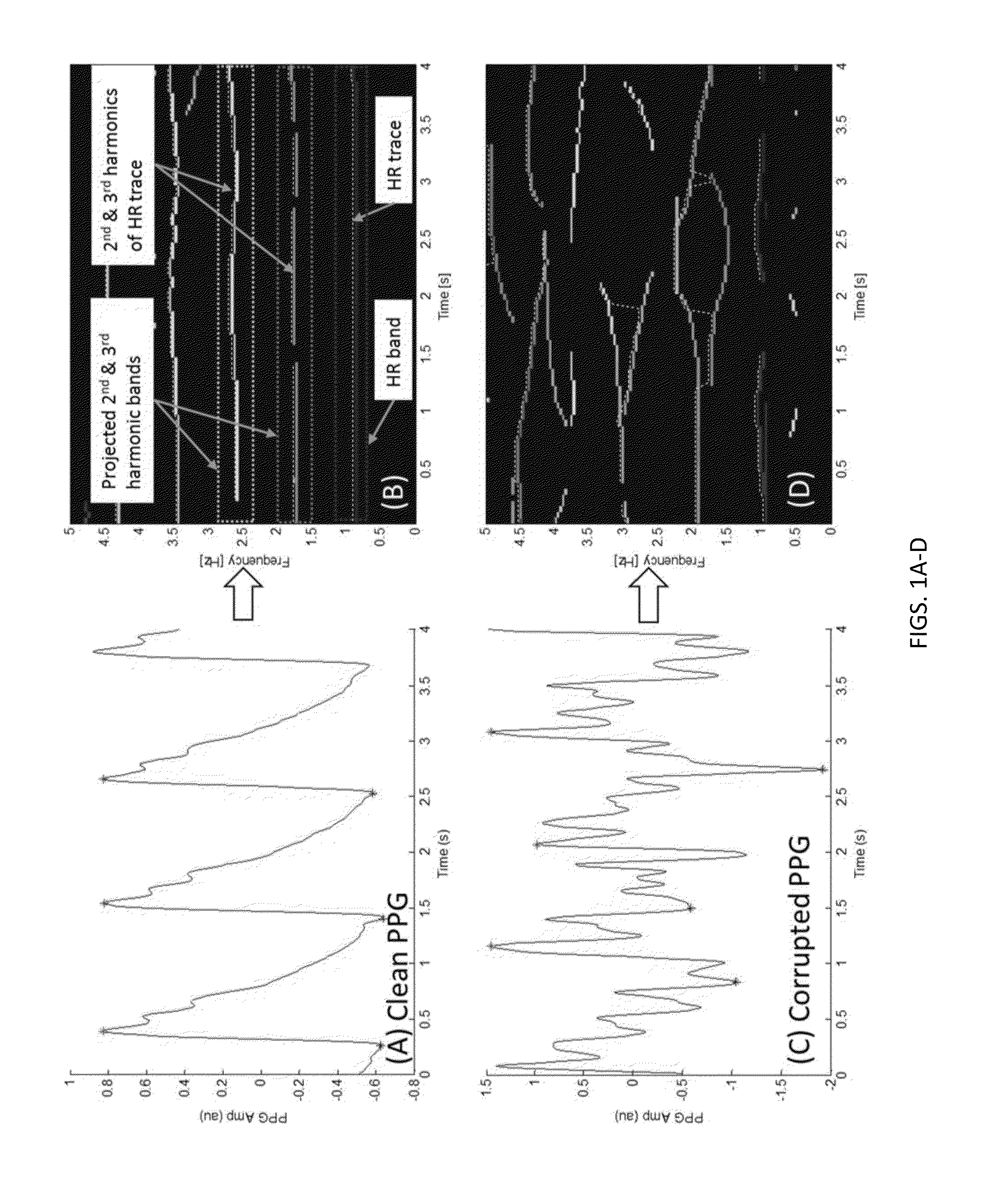
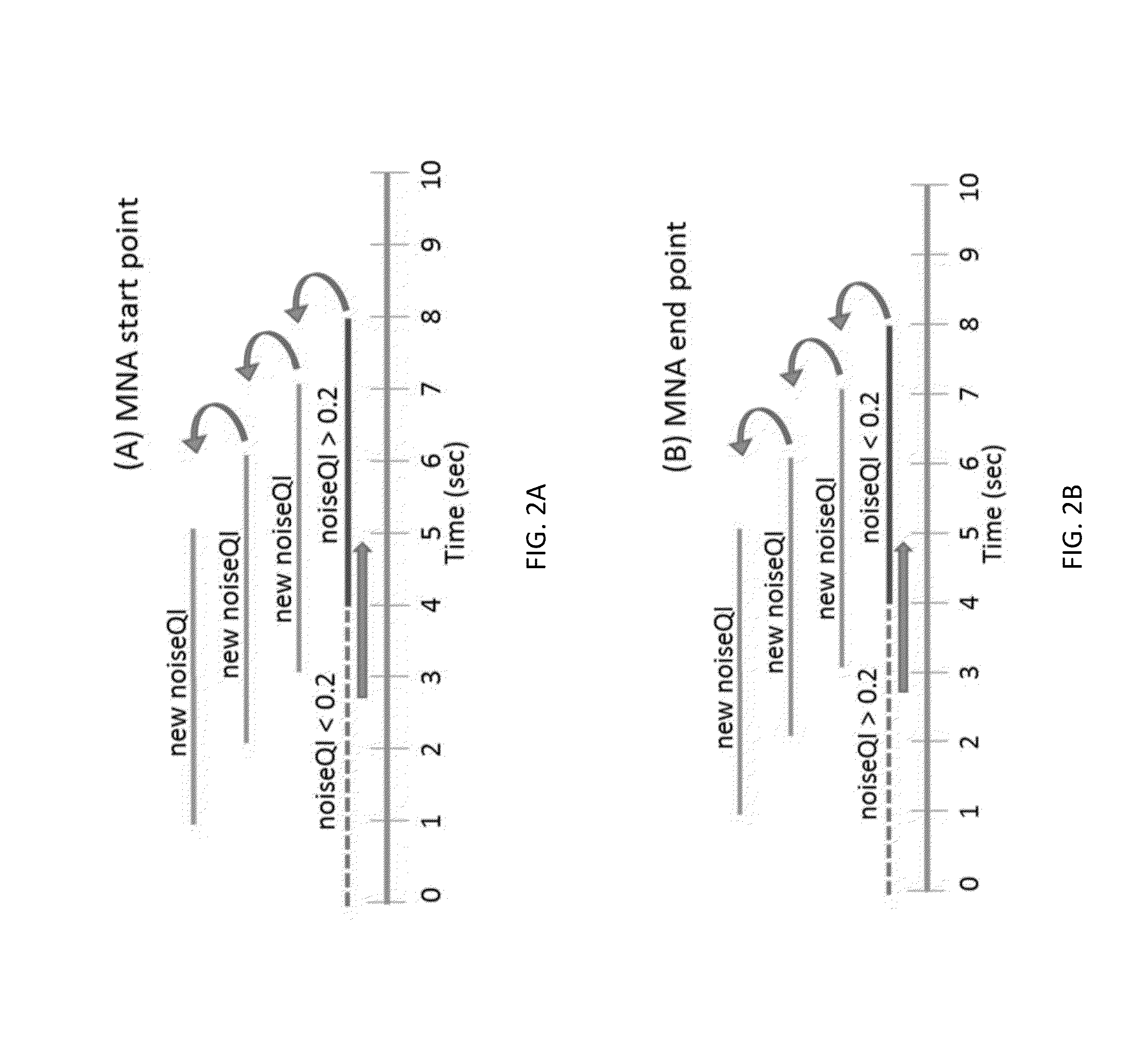
Motion and noise artifact detection and reconstruction algorithms for photoplethysmogram and equivalent signals
ActiveUS20160220188A1Reduce misreadingSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePattern recognitionPulse oximeters
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Device and method to measure ventricular arterial coupling and vascular performance
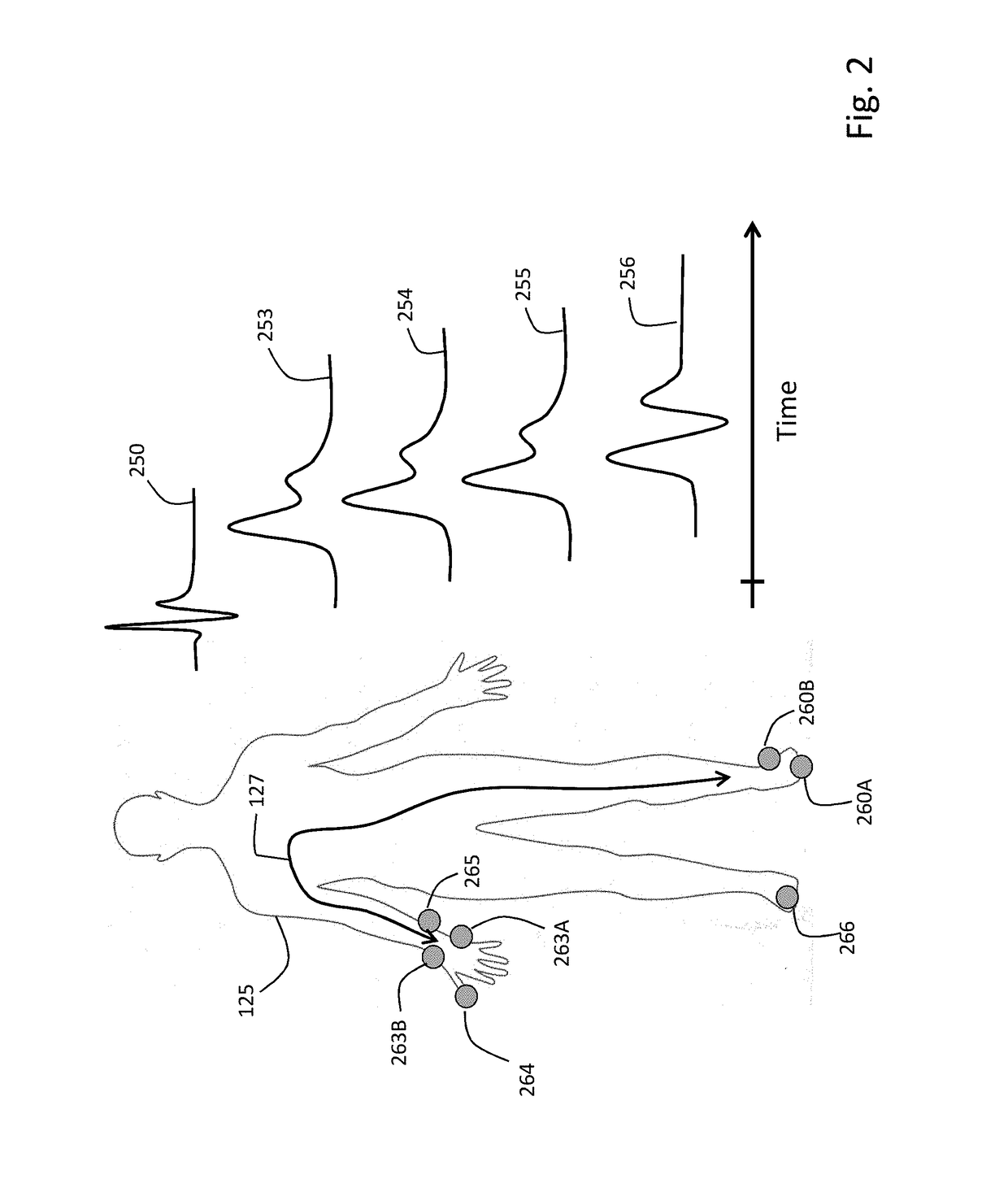
A device for measuring a ventricular-arterial coupling of a subject includes first and second inputs. The first input receives signals from a plurality of electrocardiogram sensors that are coupled to the subject at a plurality of first locations. The second input receives signals from a plurality of photoplethysmogram sensors that are coupled to the subject at a plurality of second locations. The second locations are selected from the group consisting of a head of the subject, an arm of the subject, and a leg of the subject. The signals received from the electrocardiogram sensors and the signals received from the photoplethysmogram sensors are received simultaneously. The device also includes a monitor configured to display the signals from the electrocardiogram sensors and the signals from the photoplethysmogram sensors.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
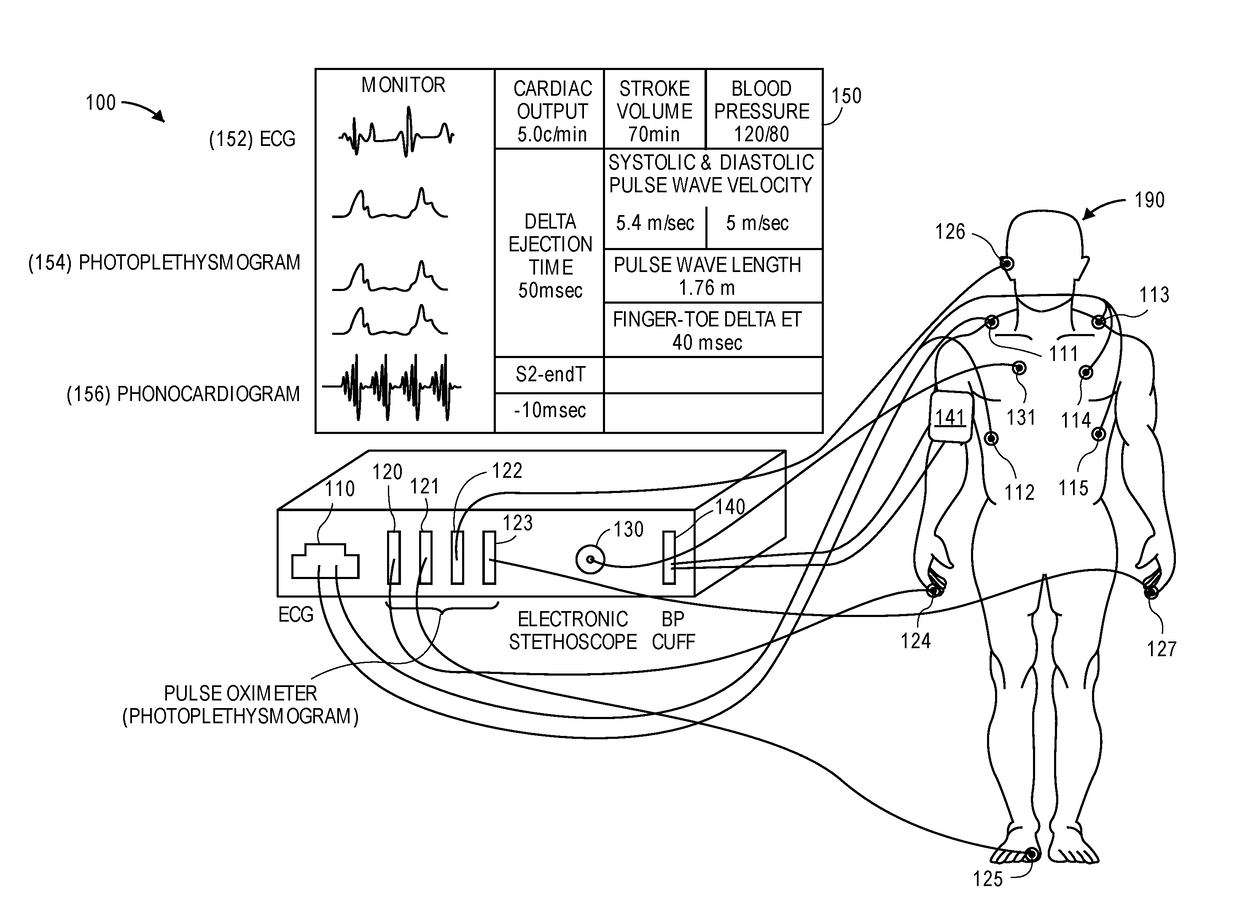
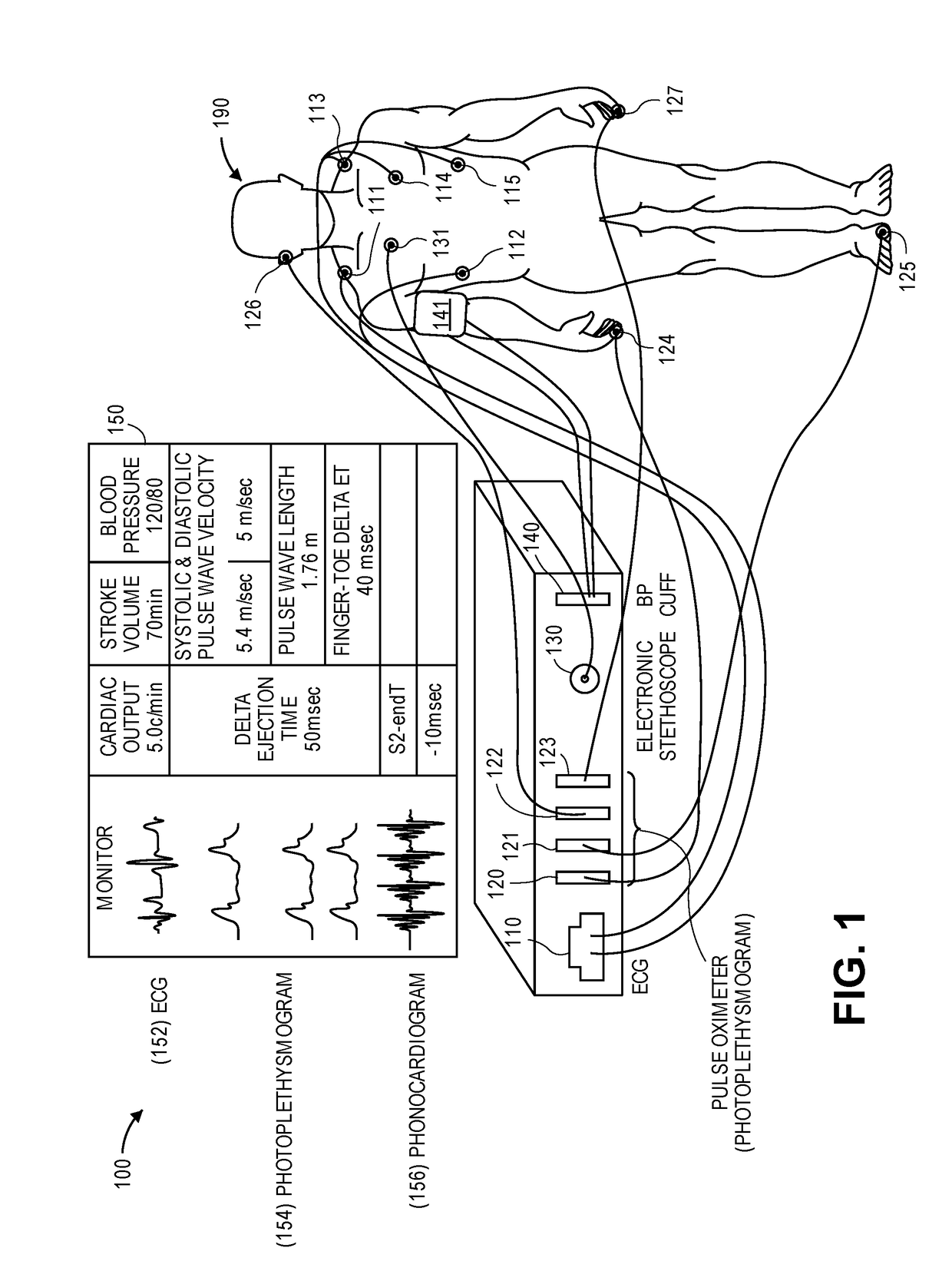
Physiological monitor for monitoring patients undergoing hemodialysis
PendingUS20190133516A1Easy to monitorGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyStethoscopeHemodialysisWireless transceiver
The invention provides a system for characterizing a patient undergoing hemodialysis, featuring: 1) a body-worn biometric sensor, worn on a single location of the patient, and featuring: i) sensing elements for measuring electrocardiogram (ECG), thoracic bio-impedance (TBI), photoplethysmogram (PPG), and phonocardiogram (PCG) waveforms; ii) a processor for collectively analyzing the ECG, TBI, PPG, and PCG waveforms to determine a set of physiological parameters; and iii) a first wireless transceiver configured to transmit the set of physiological parameters; 2) a gateway system comprising a second wireless transceiver configured to receive the set of physiological parameters; and 3) a data-analytics system configured to analyze the set of physiological parameters to determine the patient's status.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method and device for detecting blood pressure calibration time point
An electronic device includes housing, a user interface disposed in a first part of the housing, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor disposed to be exposed through a second part of the housing, the PPG sensor configured to calculate a blood pressure value while contacting a portion of a body, at least one sensor, a wireless communication circuit disposed in the interior of the housing, a processor disposed in the interior of the housing, and operatively connected to the user interface, the PPG sensor, the at least one sensor, and the wireless communication circuit, and a memory operatively connected to the processor, wherein the memory stores instructions that, when executed by the processor, control the electronic device to: receive first data from the at least one sensor, receive second data from the PPG sensor based at least in part on the received first data, determine a pulse arrival time (PAT) value, a heart rate (HR) value, and a pulse transit time (PTT) value from the second data, calculate a first blood pressure value (BP1) and a second blood pressure value (BP2) by applying the determined values to pulse wave velocity (PWV) algorithms of Equations 1 and 2, wherein BP1≅a1PAT+b1HR+c1 . . . Equation 1, BP2≅a2 ln(PTT)+b2 . . . Equation 2 in Equations 1 and 2, a1, a2, b1, b2, and c1 are constant values for matching blood pressure values measured during calibration with blood pressure values measured by a cuff hemodynamometer, determine a calibration time point based at least in part on a difference between the first blood pressure value and the second blood pressure value, and provide guide information related to the calibration time point through the user interface based at least in part on the determination.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
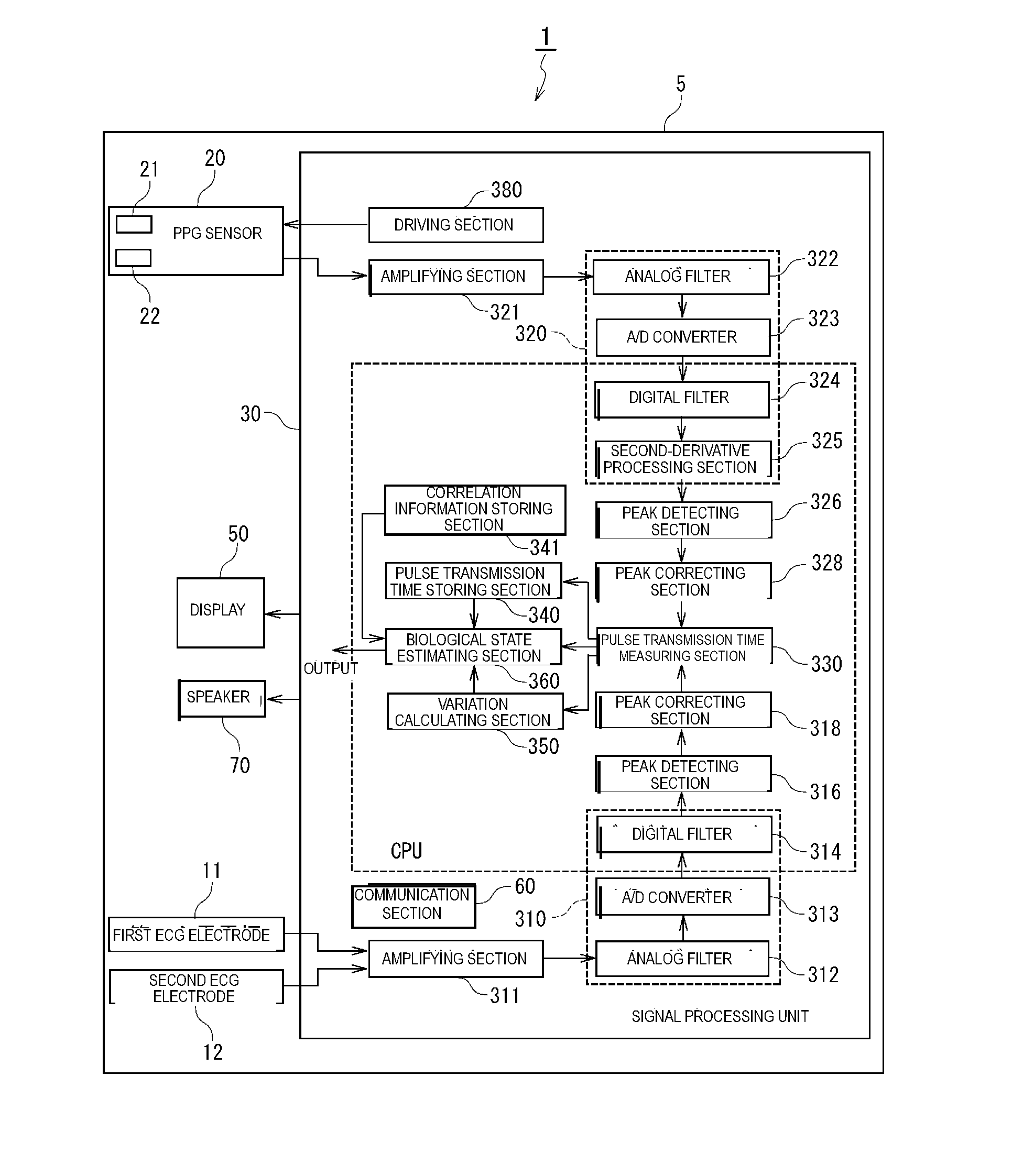
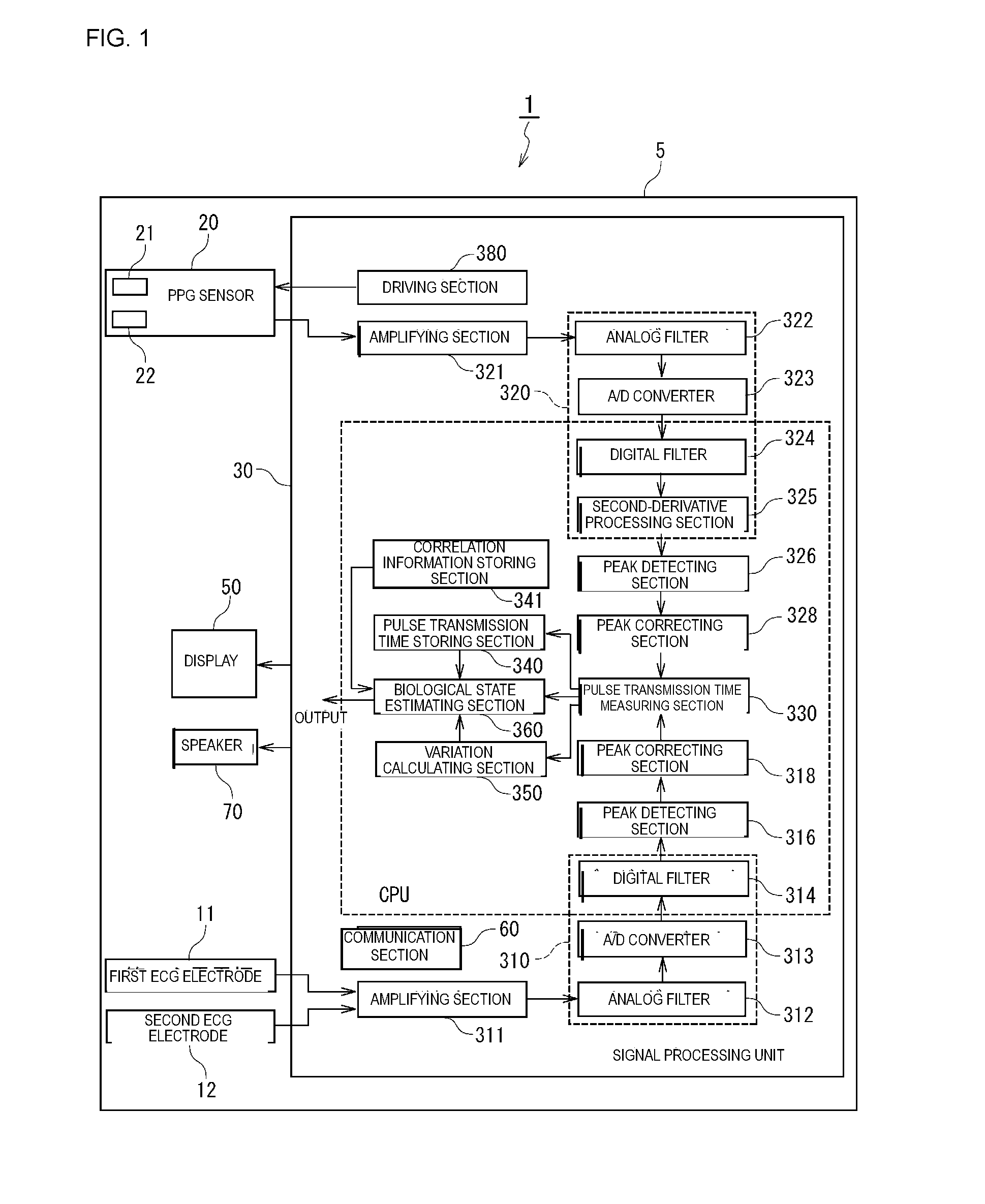
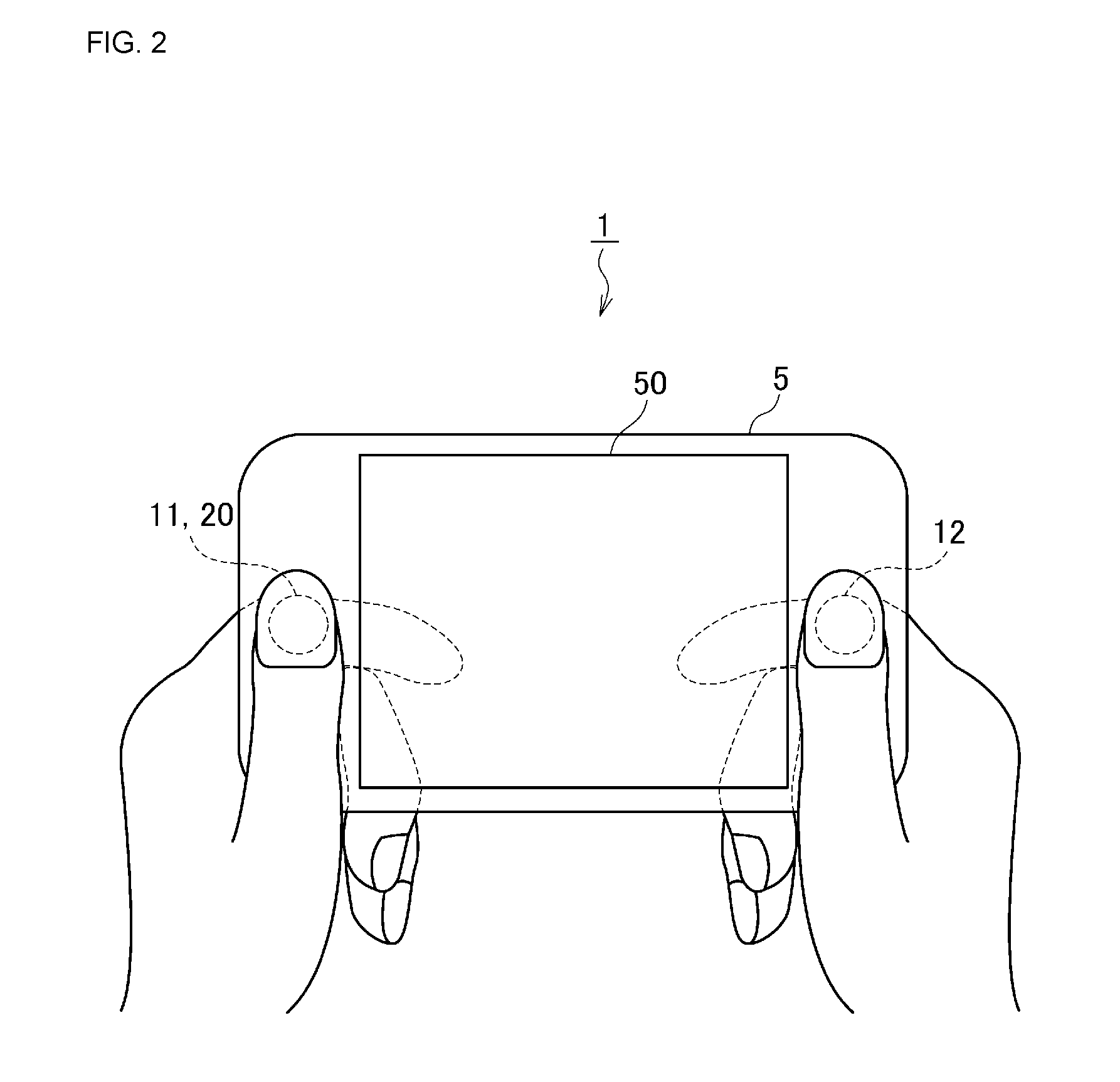
Biological state eliminating apparatus and method
A biological state estimating apparatus includes a pair of electrocardiographic electrodes, a photoplethysmographic sensor, and a controller that includes a peak detecting section, a pulse transmission time measuring section, a correlation information storing section, and a biological state estimating section. The electrocardiographic electrodes detect an electrocardiogram signal and the photoplethysmographic sensor, which has light-emitting and light-receiving elements, detects a photoplethysmogram signal. The controller detects peaks of the electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram signals and determines a pulse transmission time from the time difference between the respective peaks of the photoplethysmogram and the electrocardiogram signal. Memory stores information determined in advance based on the relationship between pulse transmission time and biological state. The controller further estimates the biological state of the user on the basis of the pulse transmission time, and the correlation information stored in the correlation information storing section.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
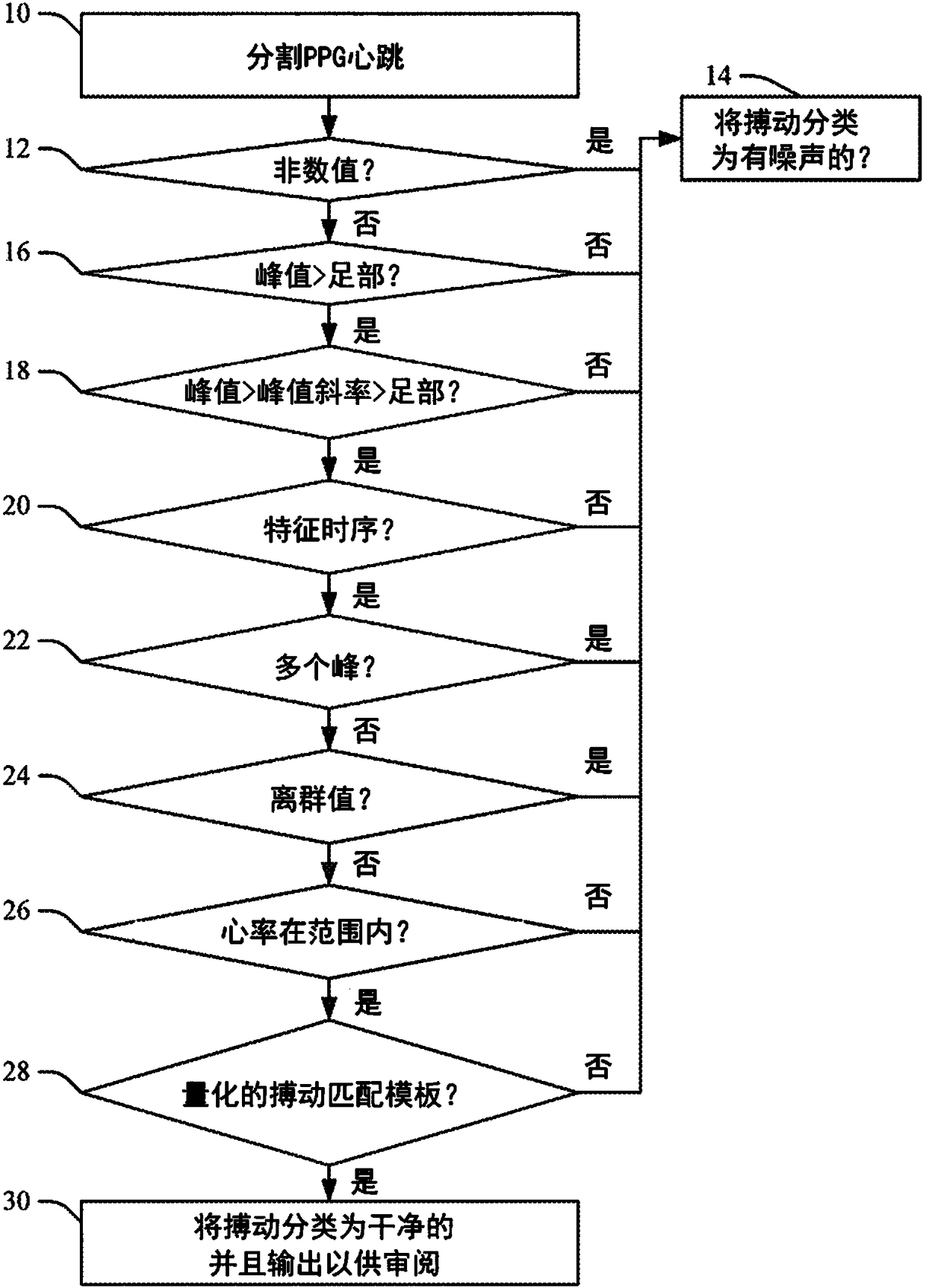
Method to quantify photoplethysmogram (PPG) signal quality
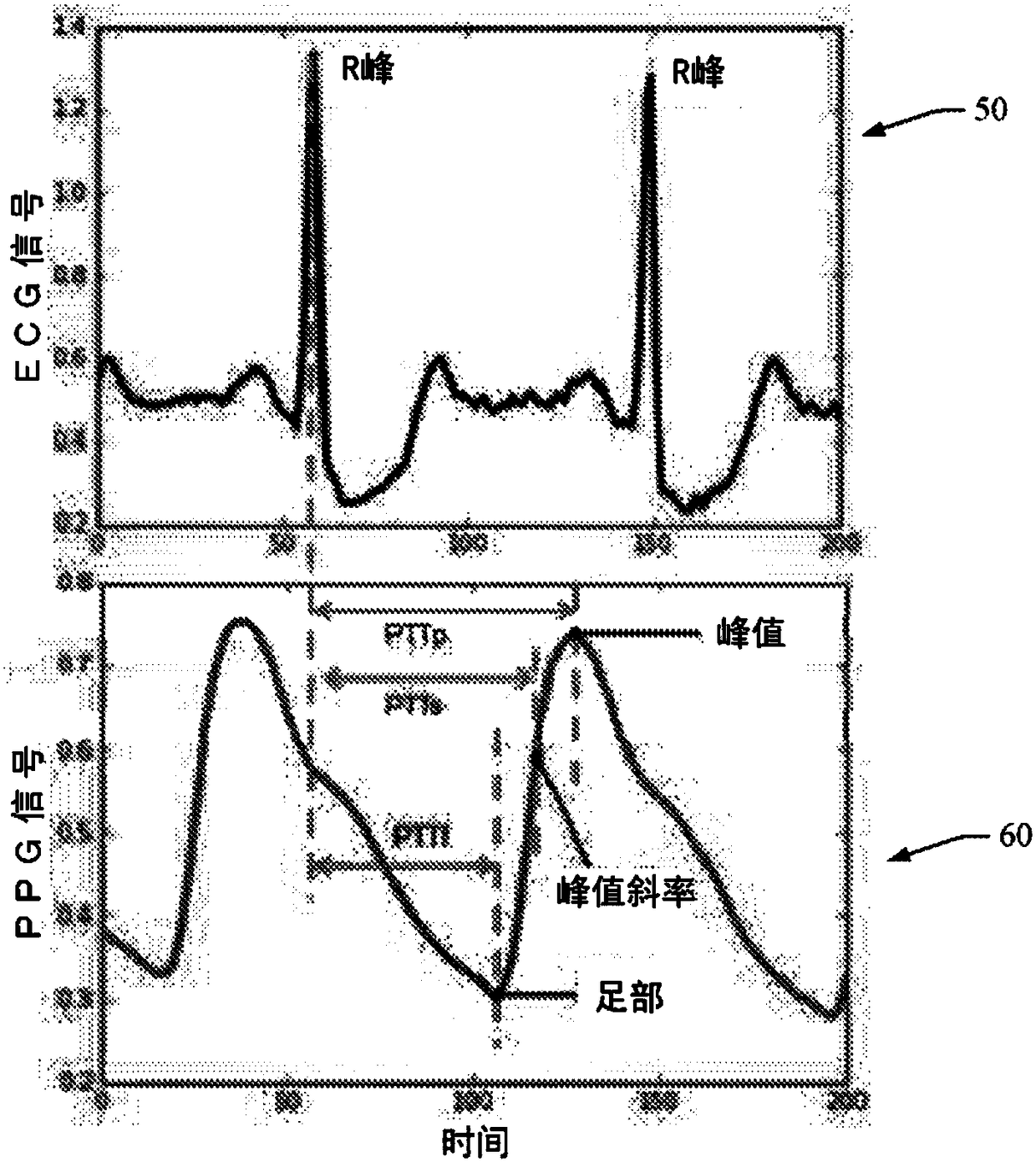
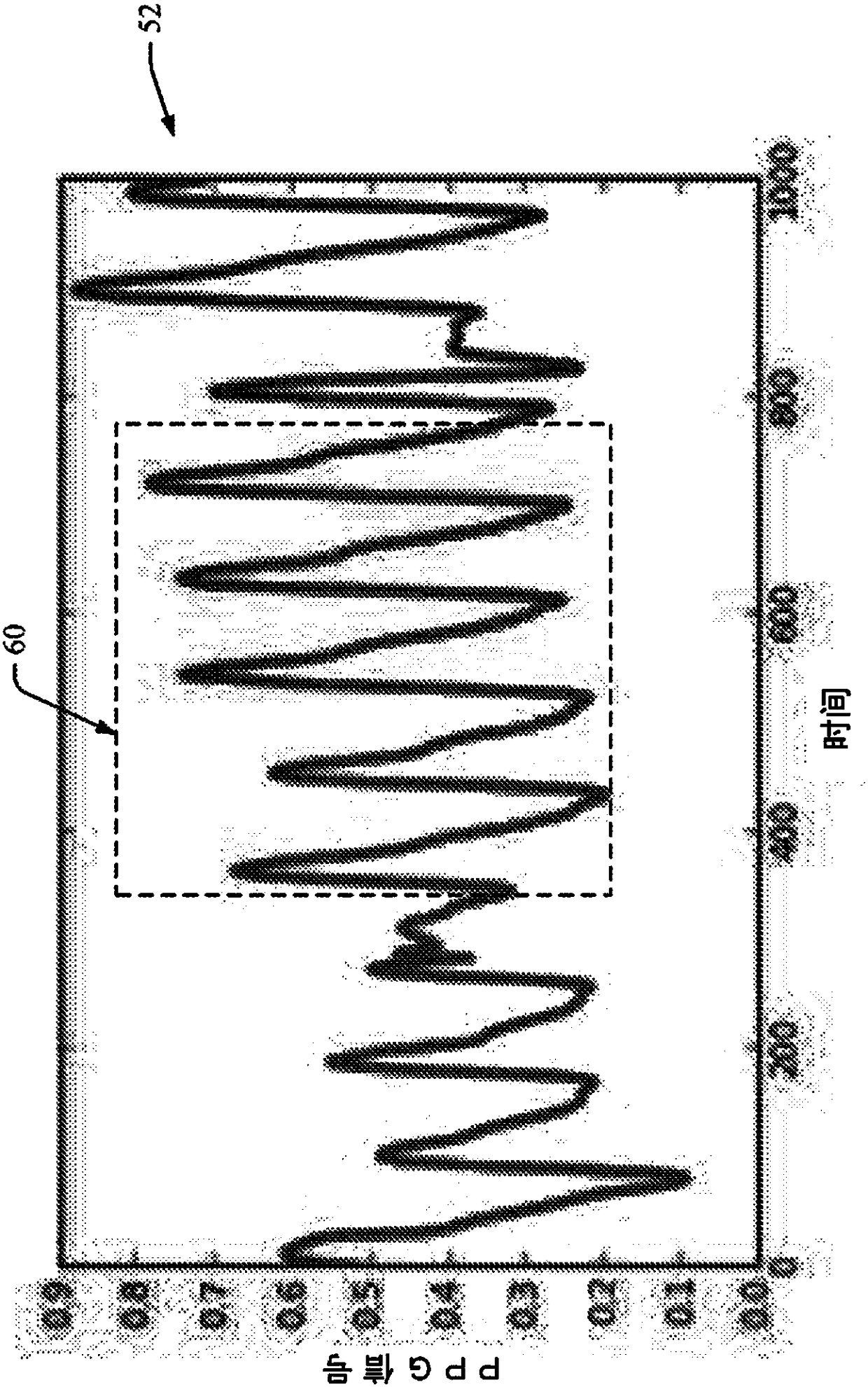
ActiveCN108289615AEvaluation of blood vesselsMedical automated diagnosisTemplate matchingSignal quality
When evaluating the quality of photoplethysmography (PPG) signal (52) measured from a patient monitor (e.g., a finger sensor or the like), multiple features of the PPG signal are extracted and analyzed to facilitate assigning a score to the PPG signal or portions (e.g., heartbeats) thereof. Heartbeats in the PPG signal are segmented out using concurrently captured electrocardiograph (ECG) signal (50), and for each heartbeat, a plurality of extracted features are analyzed. If all extracted features satisfy one or more predetermined criteria for each feature, then the heartbeat waveform is compared to a predefined heartbeat template. If the waveform matches the template (e.g., within a predetermined match percentage or the like), then the heartbeat is classified as 'clean'. If the heartbeatdoes not patch the template, or if one or more of the extracted features fails to satisfy its one or more predetermined criteria, the heartbeat is classified as 'noisy'.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for real-time non-invasive optical monitoring of decompression sickness state
Described herein is a device and system and method for the detection of naturally occurring gas bubbles in the bloodstream; in one embodiment, a wireless optical device may be placed on various parts of the body including a finger or earlobe or is coupled with the SCUBA mouthpiece and detects certain vital signs such as heart rate, blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) and respiration rate by analyzing the photoplethysmogram (PPG) from a miniature sensor. There is also a method and apparatus for real-time non-invasive optical monitoring of actual state of decompression sickness are presented. The method is based on simultaneous measurements of PPG signals in different locations of human body and analysis of such a factor as phase shifts between various locations, change the shape of PPG signal between different locations, existence and modification of slow trends and low frequency modulations and angular distributions of the out-coming light.
Owner:MASSOVA IRINA
Multi-Vital Sign Detector in an Electronic Medical Records System
InactiveUS20180235478A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyEvaluation of blood vesselsMedical recordDynamic light scattering
In one implementation, a device detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
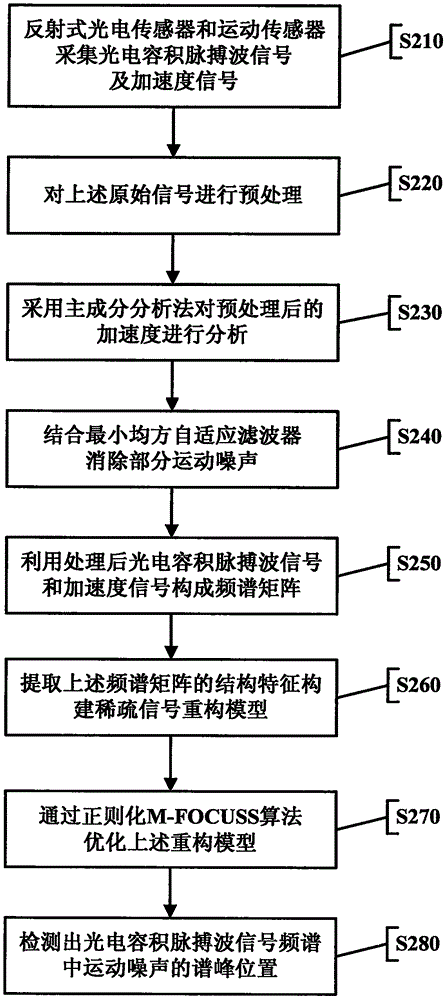
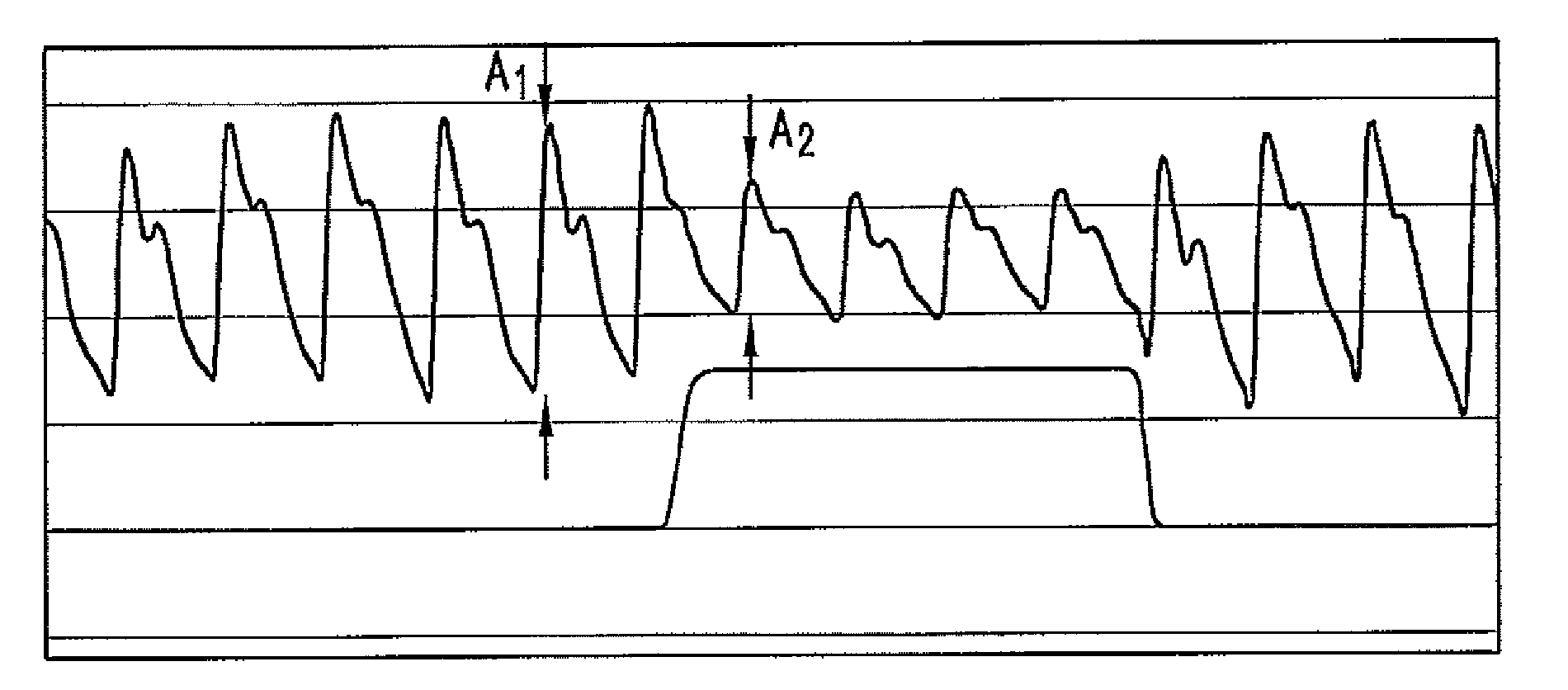
Motion noise detecting method based on photoplethysmography signals
InactiveCN106137167AImprove detection accuracyReduce computational complexityCatheterSensorsFrequency spectrumHeart rate measurement
The invention discloses a motion noise detecting method based on photoplethysmography signals. The method lays a foundation for follow-up work of heart rate measurement. In the method, multiple photoplethysmography signals and acceleration signals within the same period are acquired by a reflecting type photoelectric sensor and a motion sensor; the acceleration signals are processed with a principal component analysis method, a reference signal related with motion noise is produced, and part of motion noise is eliminated in combination with a least mean square adaptive filter; the multiple processed photoplethysmography signals and acceleration signals form a frequency spectrum matrix, sparse structure features of rows of the frequency spectrum matrix are extracted, and a sparse signal reconstruction model is constructed; finally, the sparse signal reconstruction model is optimized with a regularization algorithm, and the spectrum peak position of the motion noise in the frequency spectra of multiple photoplethysmography signals is acquired. The motion noise in the photoplethysmography signals can be detected accurately, and high-accuracy measurement of the heart rate is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for determining hemodynamic effects
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for measuring blood pressure
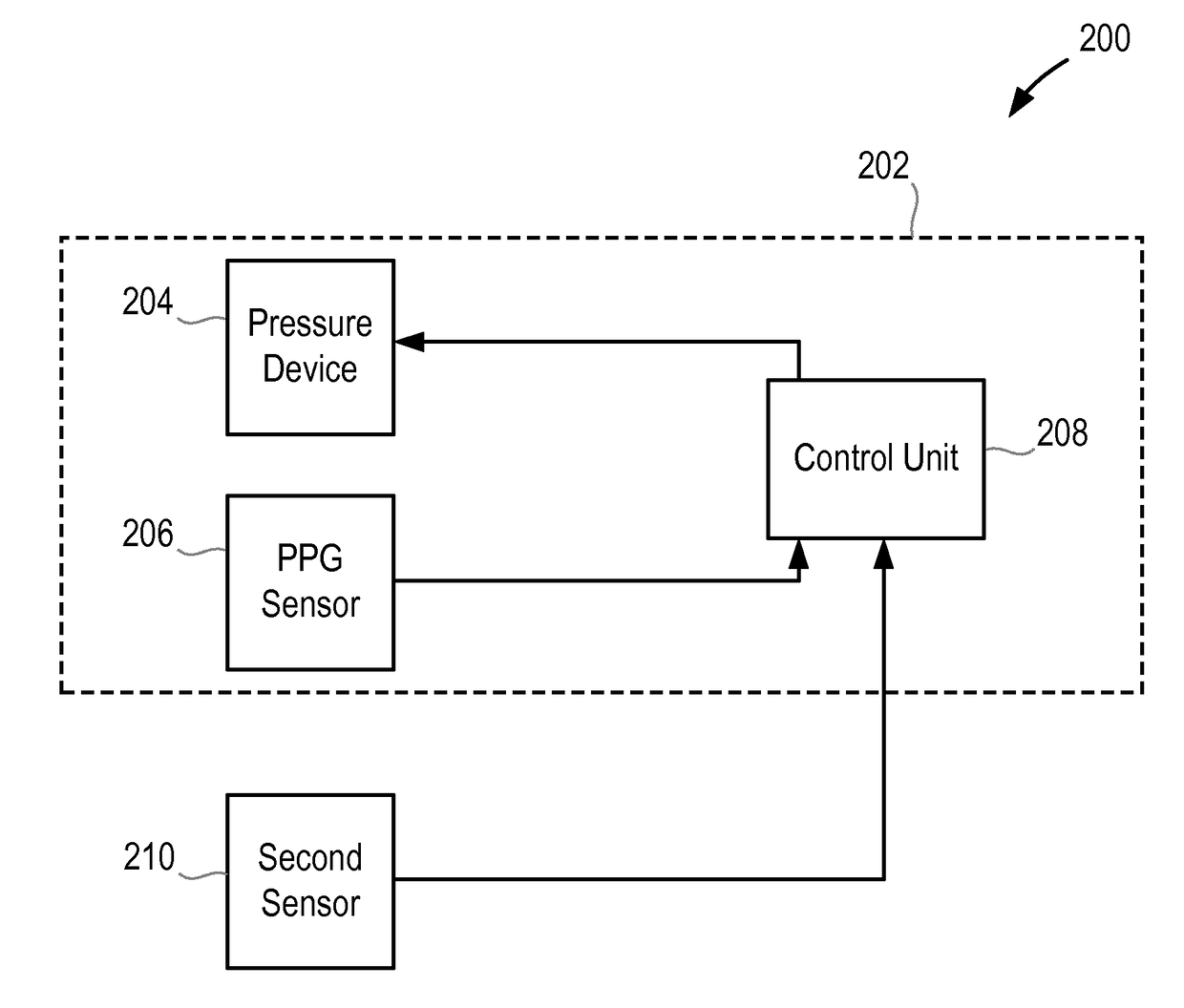
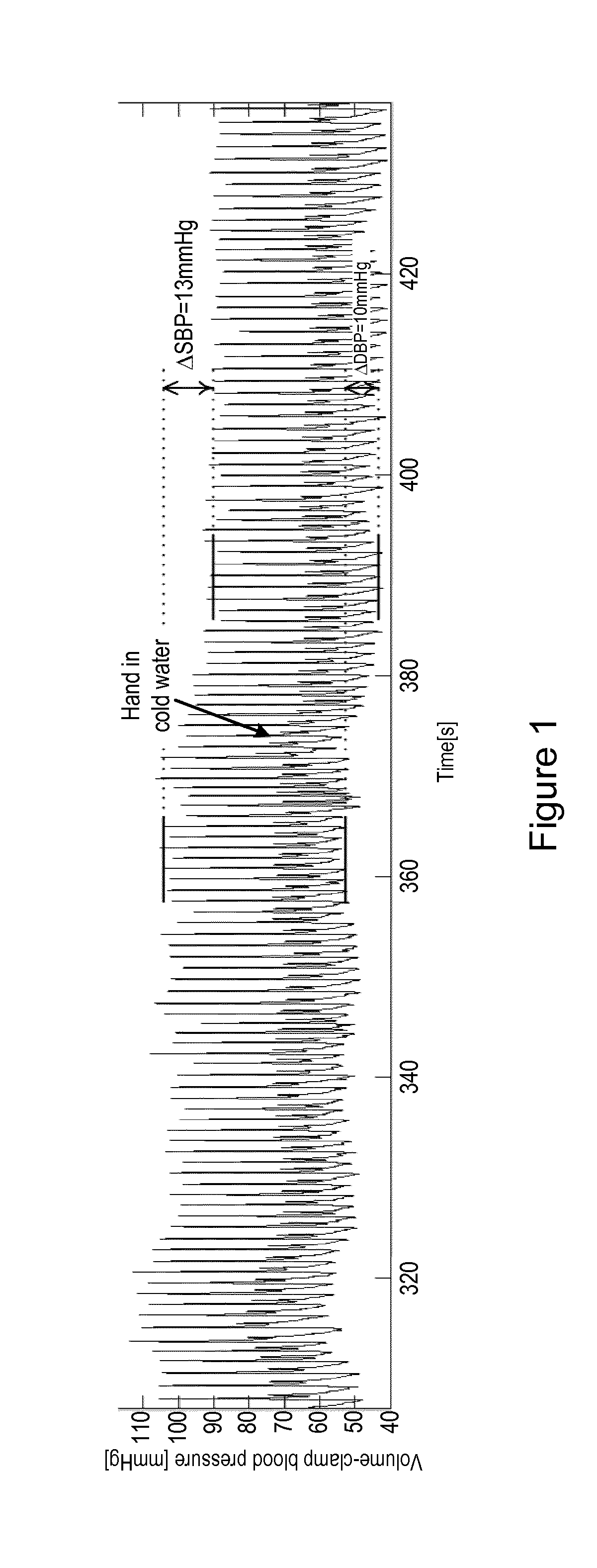
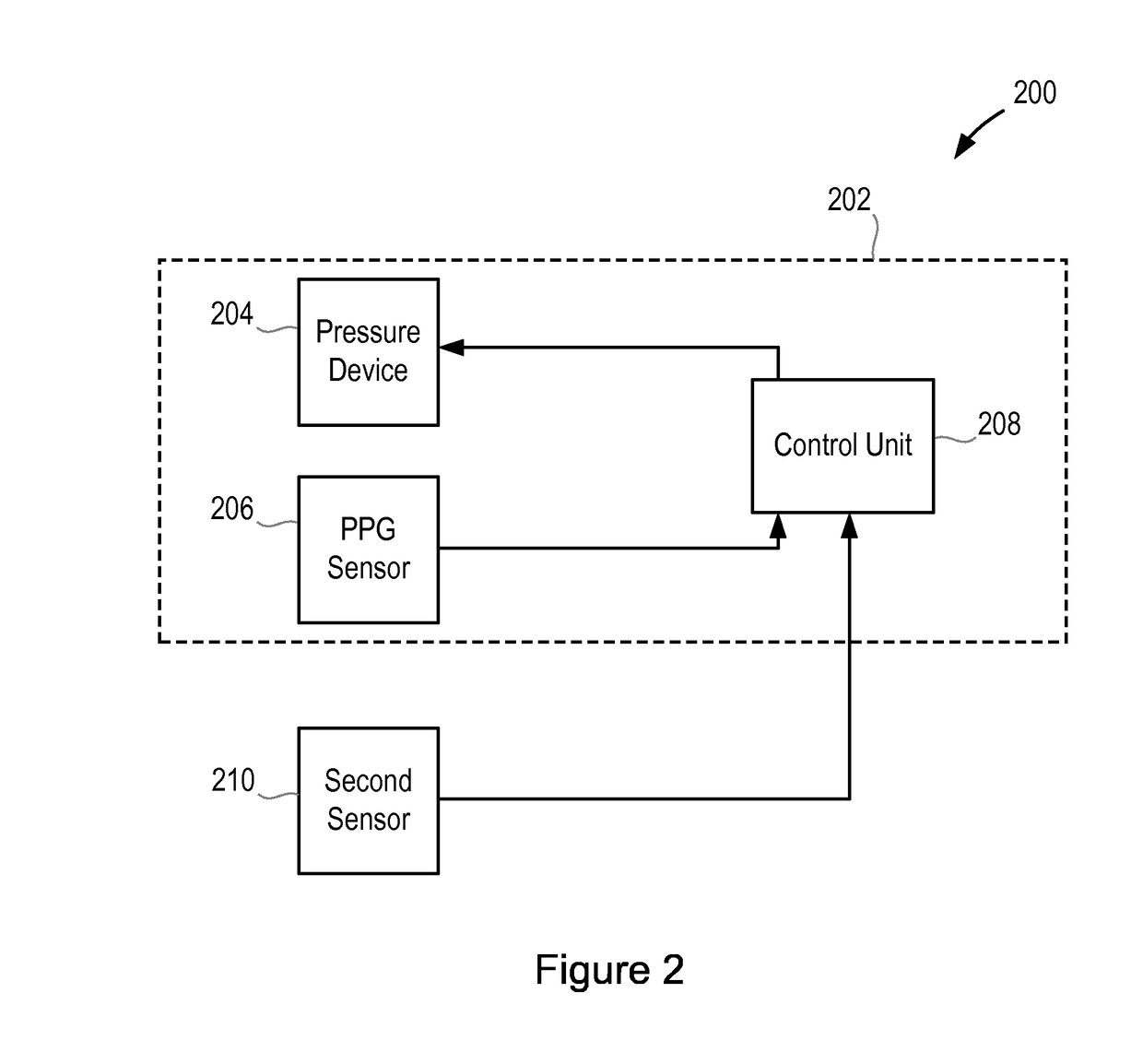
According to an aspect, there is provided an apparatus for measuring the blood pressure, BP, of a user, the apparatus comprising a volume-clamp BP monitoring device that comprises a first pressure device for applying pressure to a first part of the body of the user, a first photoplethysmogram, PPG, sensor for obtaining a first PPG signal from the first part of the body of the user, and a control unit that is configured to analyse the first PPG signal and to control the pressure of the first pressure device; wherein the control unit is configured to adjust the pressure of the first pressure device to maintain the first PPG signal at a constant level and to determine the BP of the user from the pressure of the first pressure device; and a second sensor, separate from the first PPG sensor, for measuring a physiological characteristic of the user in a second part of the body of the user, wherein the second part of the body is separate from the first part of the body; wherein the apparatus is configured to analyse the measured physiological characteristic to determine a measure of the blood perfusion in the second part of the body of the user, and to determine whether to perform a recalibration of the volume-clamp BP monitoring device on the basis of changes in the blood perfusion.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Physiological monitoring system featuring floormat and wired handheld sensor
InactiveUS20170188858A1Easy to measureEasy to useElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsEngineeringPhotoplethysmogram
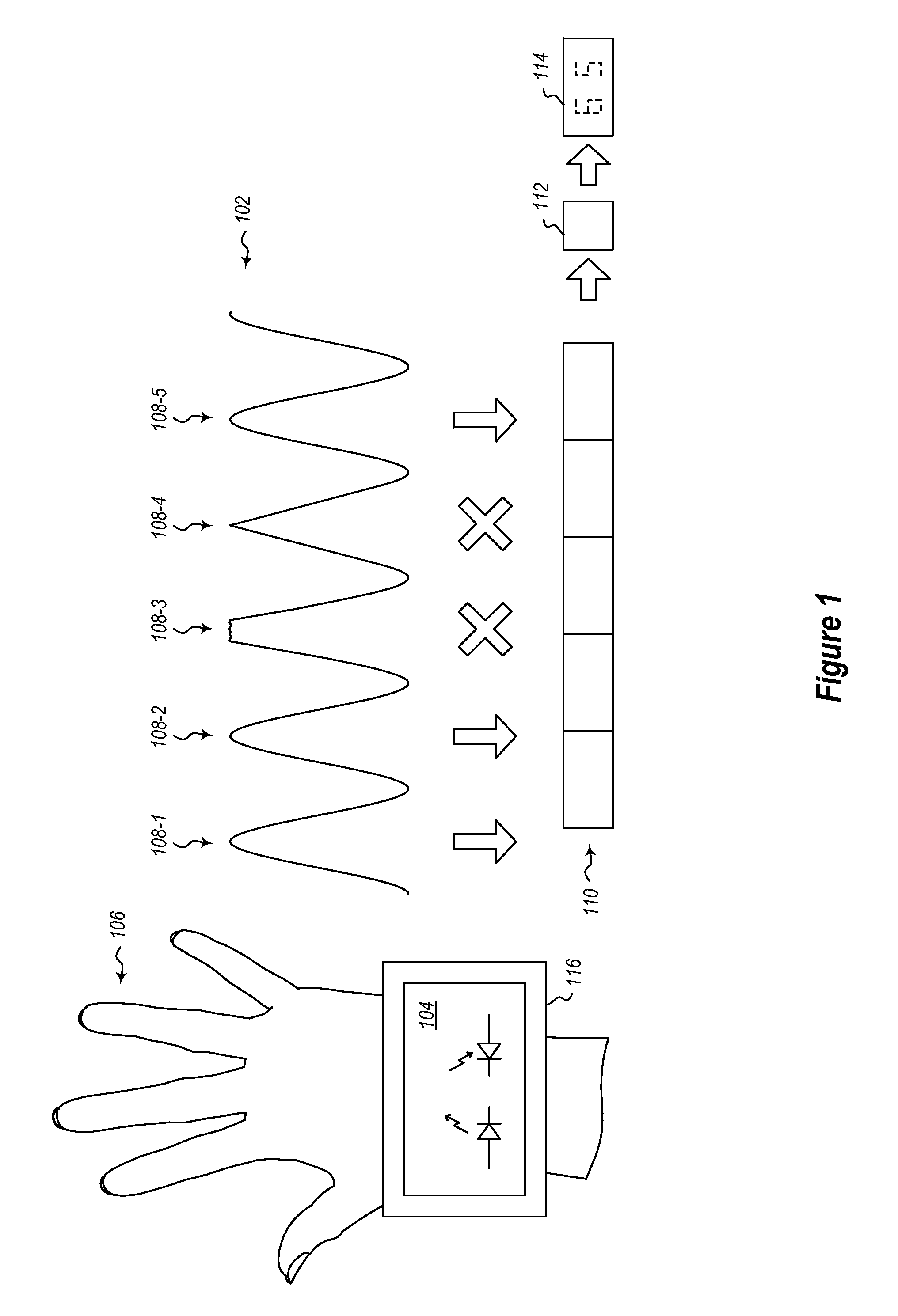
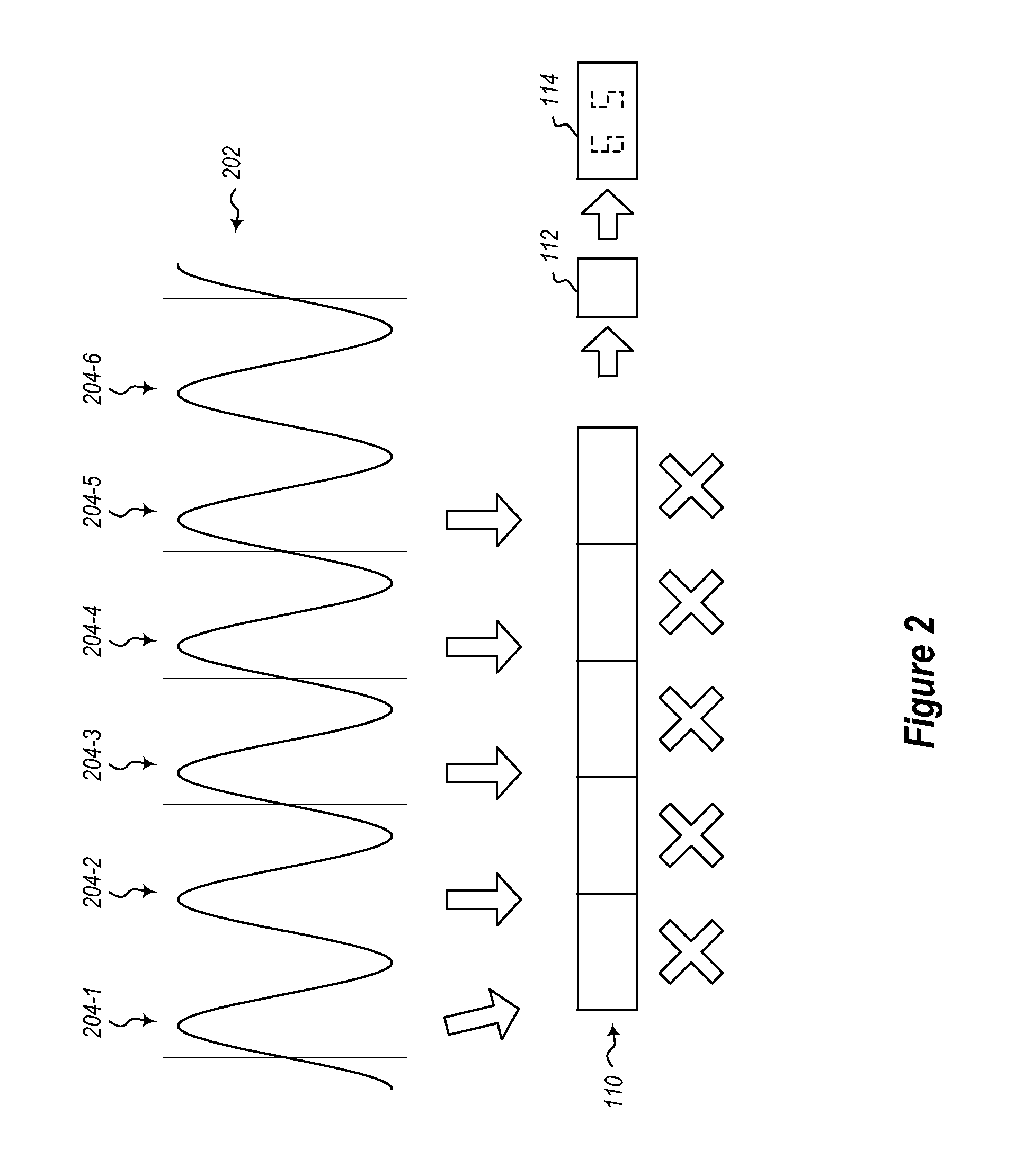
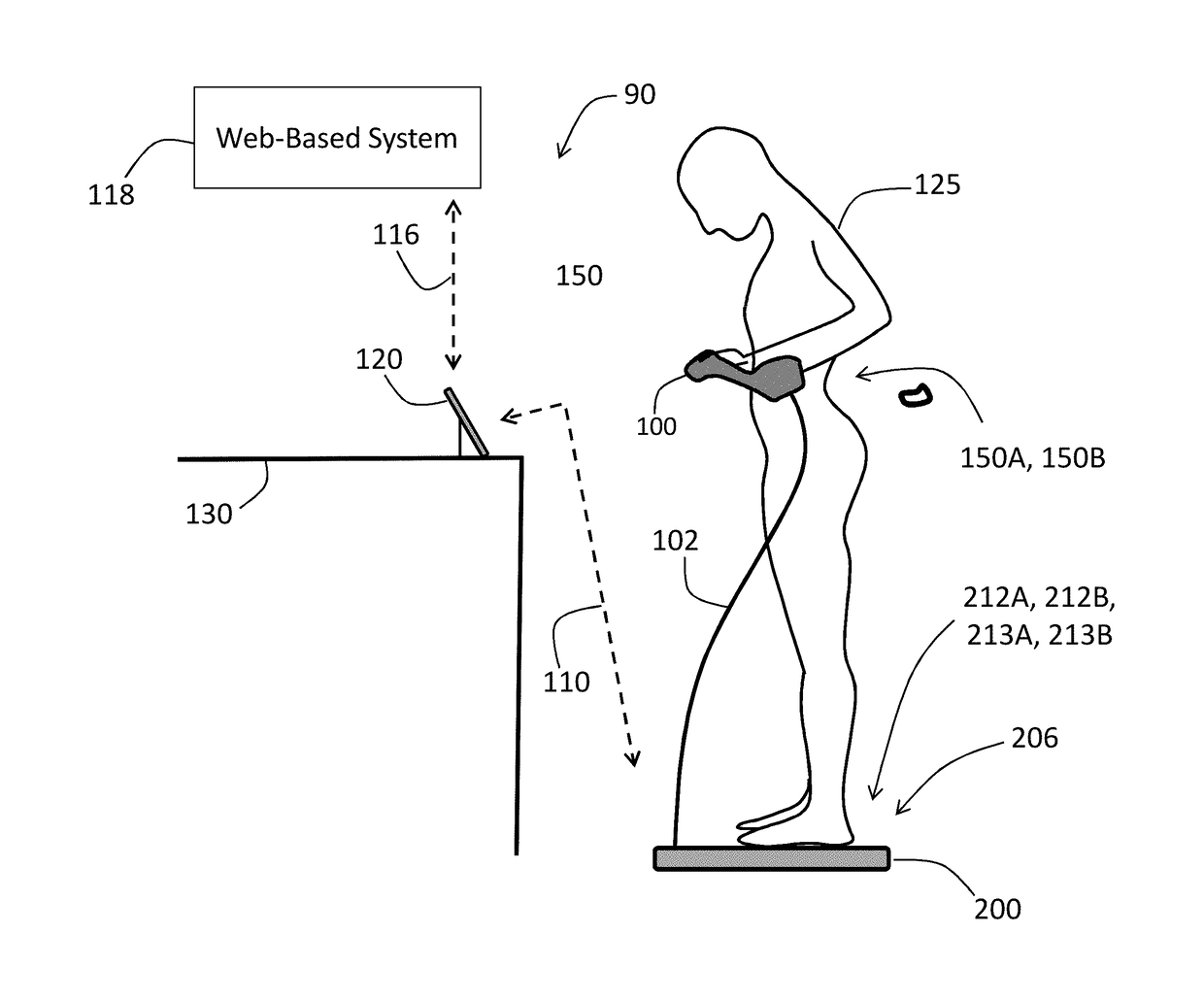
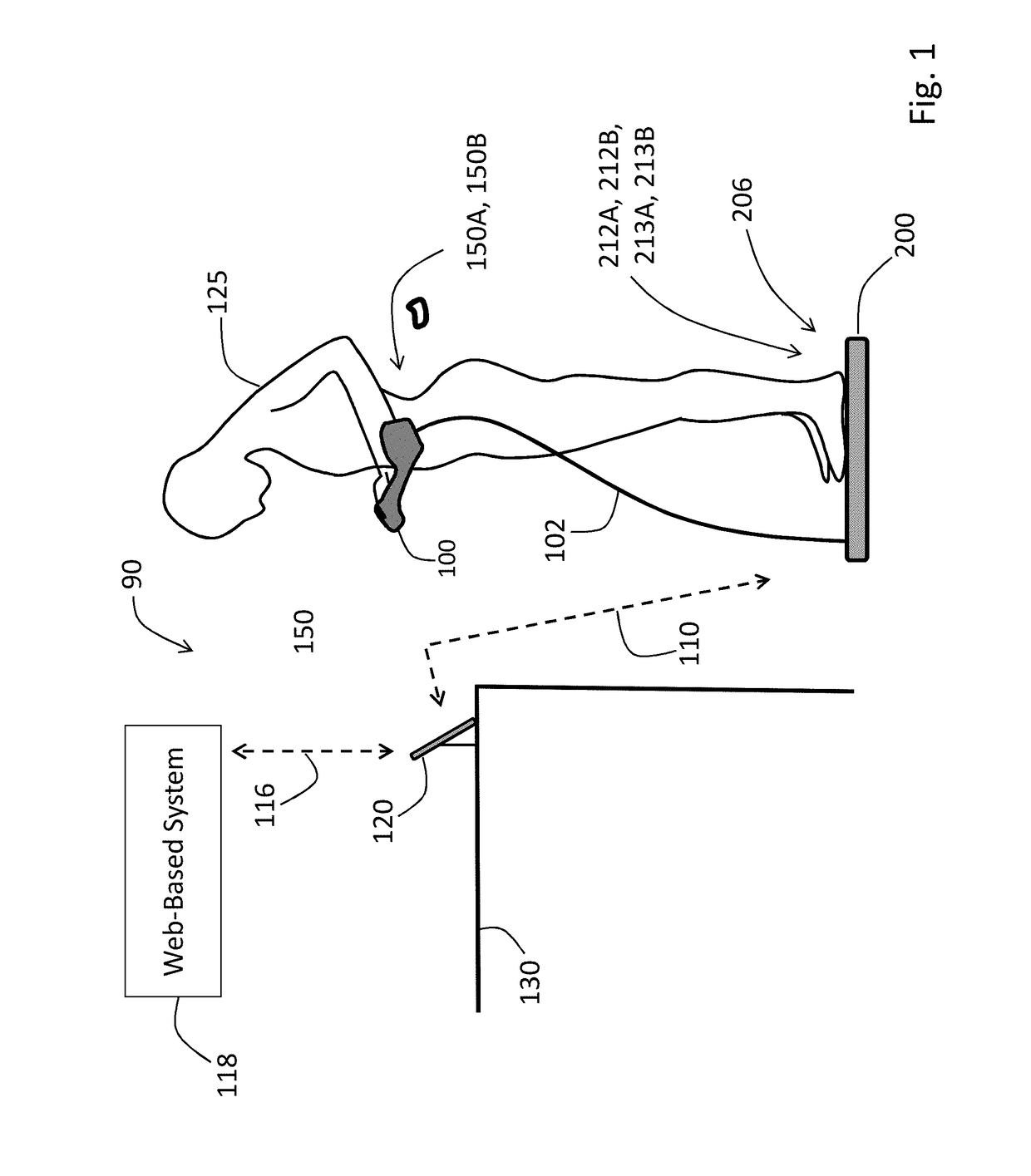
A physiological monitoring system features a Floormat and Handheld Sensor connected by a cable. A user stands on the Floormat and grips the Handheld Sensor. These components measure time-dependent physiological waveforms from a user over a conduction pathway extending from the user's hand or wrist to their feet. The Handheld Sensor and Floormat use a combination of electrodes that inject current into the user's body and collect bioelectric signals that, with processing, yield ECG, impedance, and bioreactance waveforms. Simultaneously, the Handheld Sensor measures photoplethysmogram waveforms with red and infrared radiation and pressure waveforms from the user's fingers and wrist, while the Floormat measures signals from load cells to determine ‘force’ waveforms to determine the user's weight, and ballistocardiogram waveforms to determine parameters related to cardiac contractility. Processing these waveforms with algorithms running on a microprocessor yield the vital sign, hemodynamic, and biometric parameters.
Owner:TOSENSE
Multi-Vital-Sign Smartphone System in an Electronic Medical Records System
ActiveUS20190046121A1Medical imagingRespiratory organ evaluationMedical recordDynamic light scattering
In one implementation, a multi-vital-sign smartphone system detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
Multi-vital-sign smartphone system in an electronic medical records system
In one implementation, a multi-vital-sign smartphone system detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com