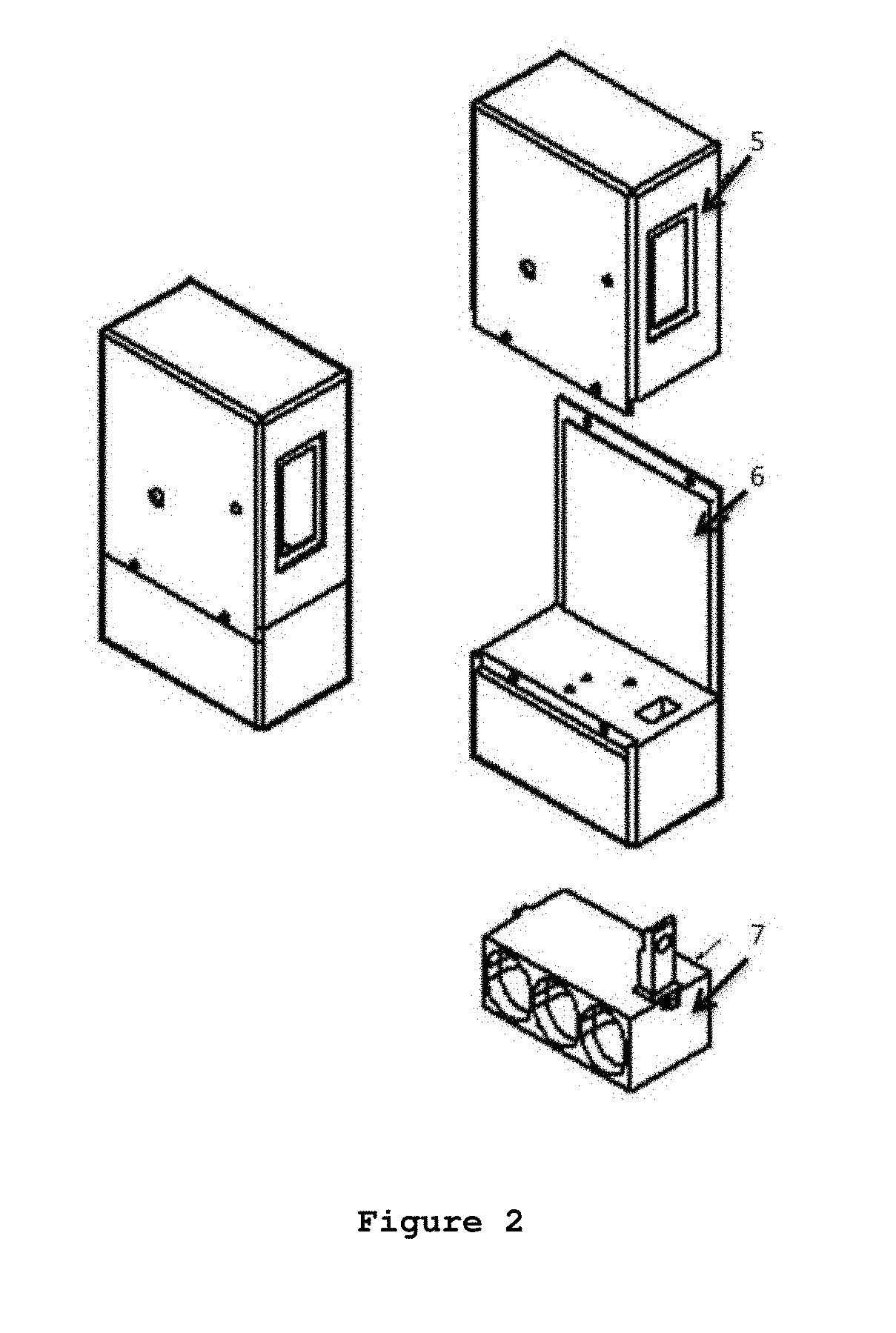
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Magnetocardiography device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Psychographic device fingerprinting
ActiveUS20120072546A1Broadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionComputer security arrangementsMagnetocardiography deviceComputer science
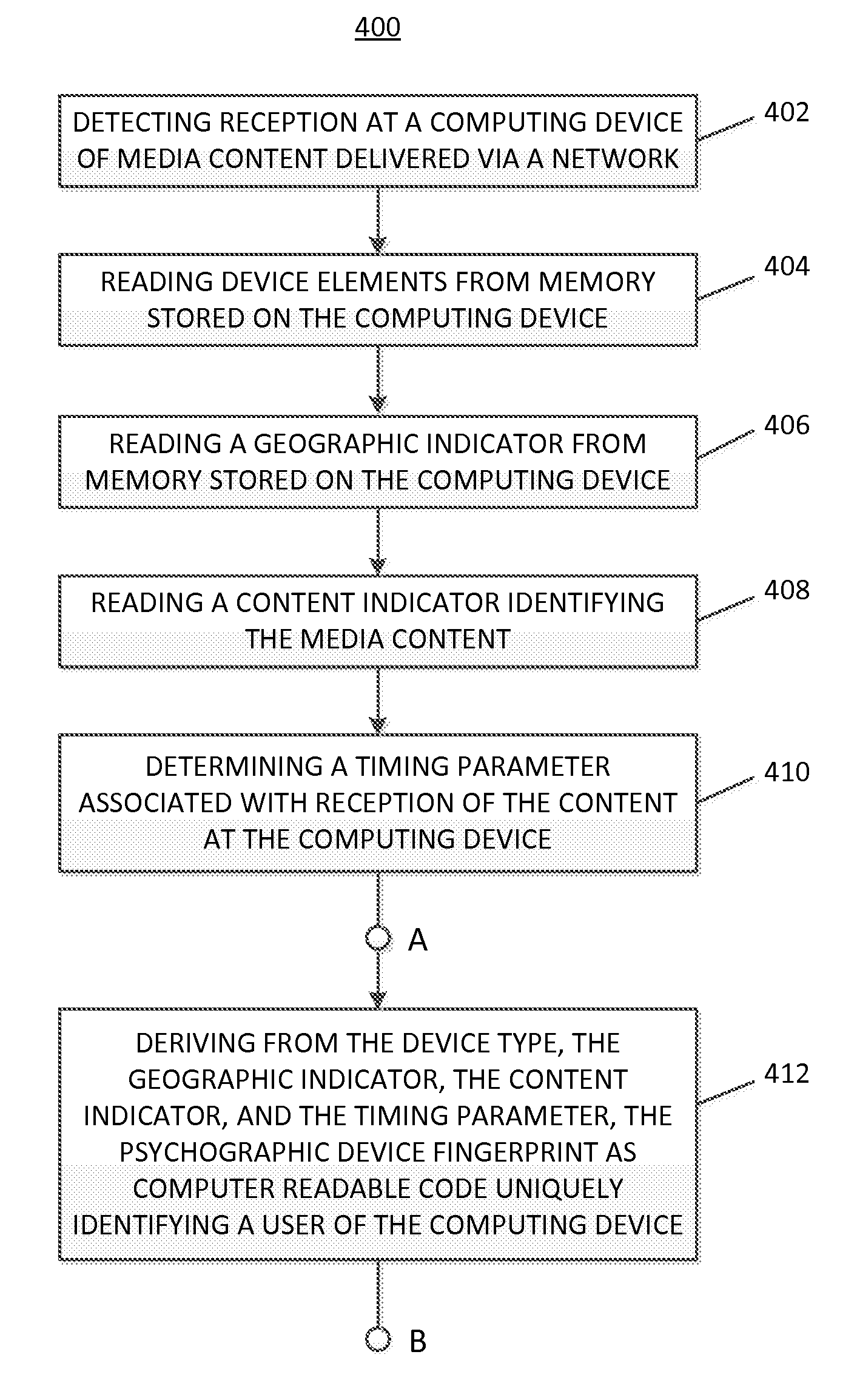
A system for generating a psychographic device fingerprint includes a server in communication with a network and memory storing a program which, when executed by the server, performs steps for (a) detecting reception at a computing device of media content delivered via the network, (b) reading device elements stored on the computing device, (c) reading a geographic indicator from the computing device, (d) reading a content indicator identifying the media content, (e) determining a timing parameter associated with reception of the content at the computing device, and (f) deriving from the device type, the geographic indicator, the content indicator, and the timing parameter, the psychographic device fingerprint as computer readable code uniquely identifying a user of the computing device. The steps may further include recording media content received by multiple computing devices, and generating a viewership report relating computing devices and psychographic device fingerprints to the media content received.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Electrocardiogram device
InactiveUS8731632B1Facilitates accurateFacilitates consistent electrode positioningElectrocardiographySensorsMagnetocardiography devicePhysical therapy
Owner:SEREBOFF JOEL L +1
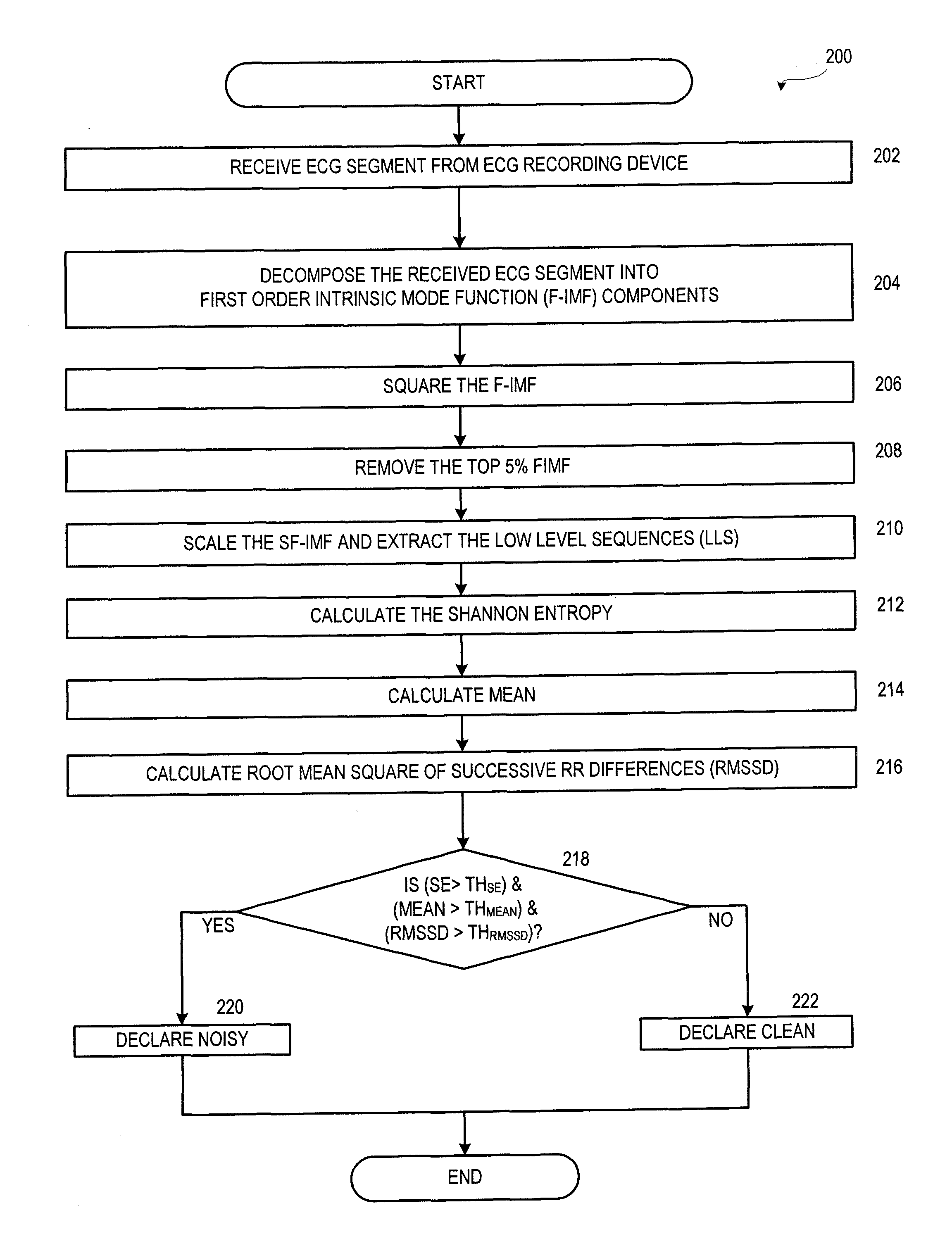
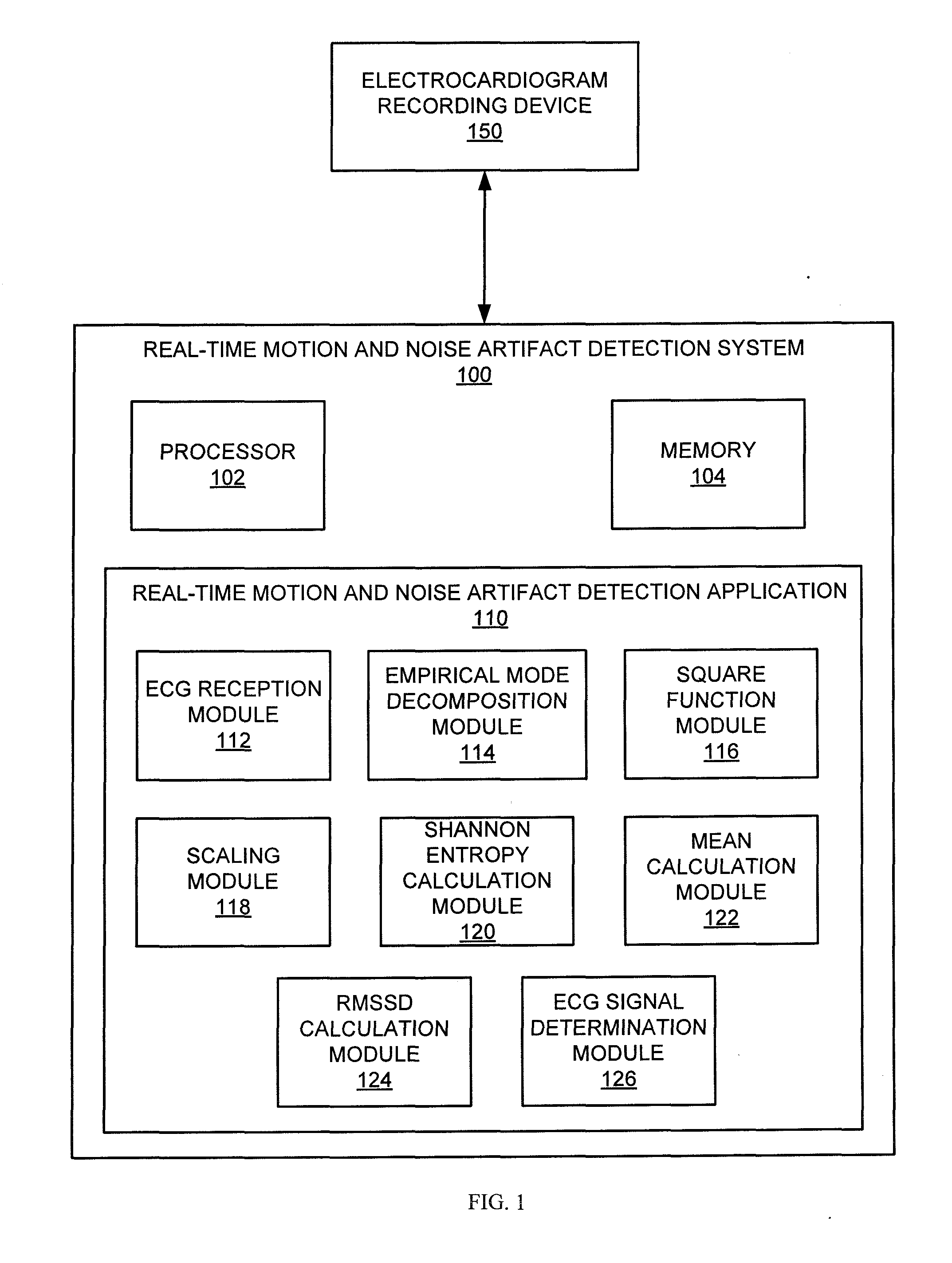
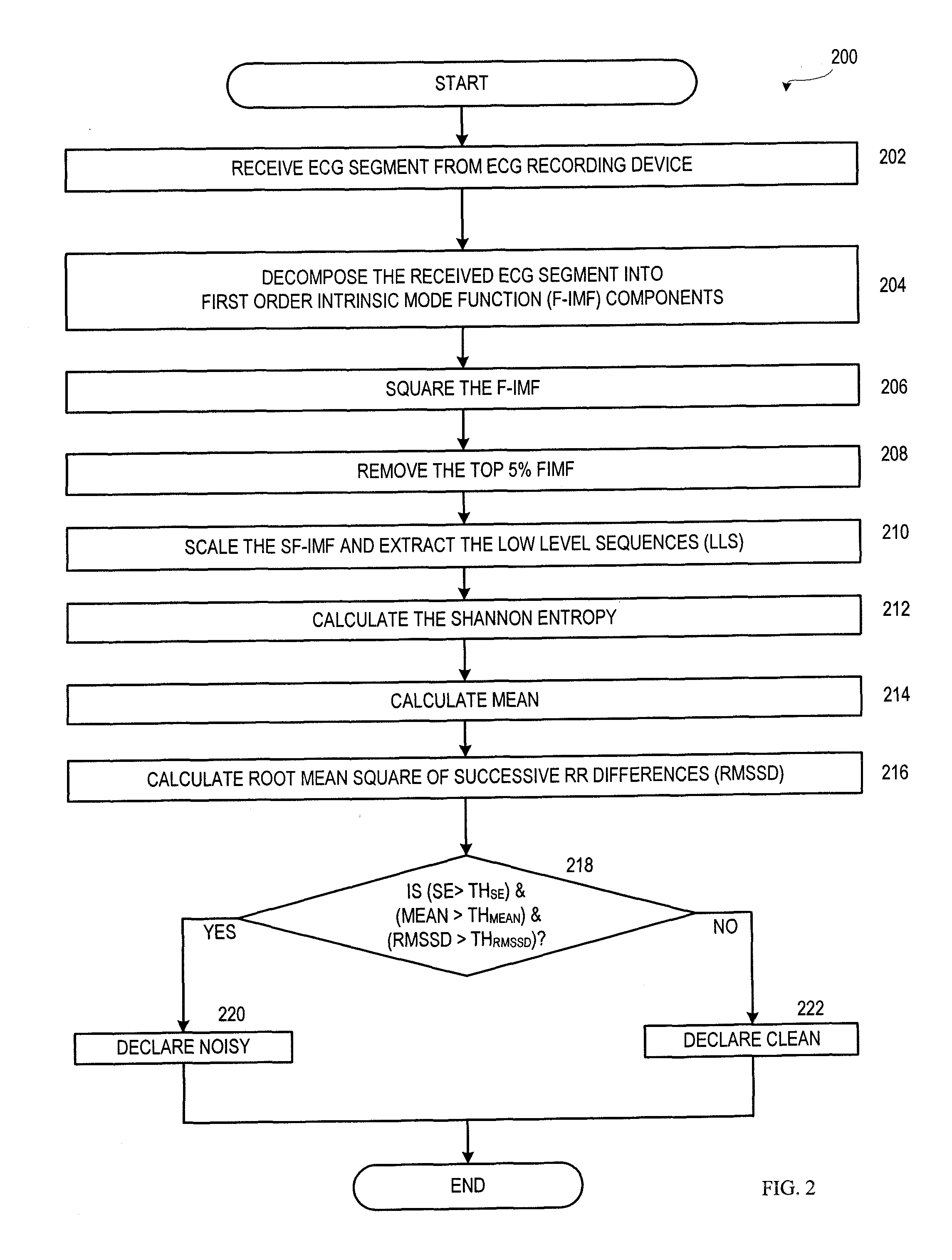
Motion and noise artifact detection for ECG data
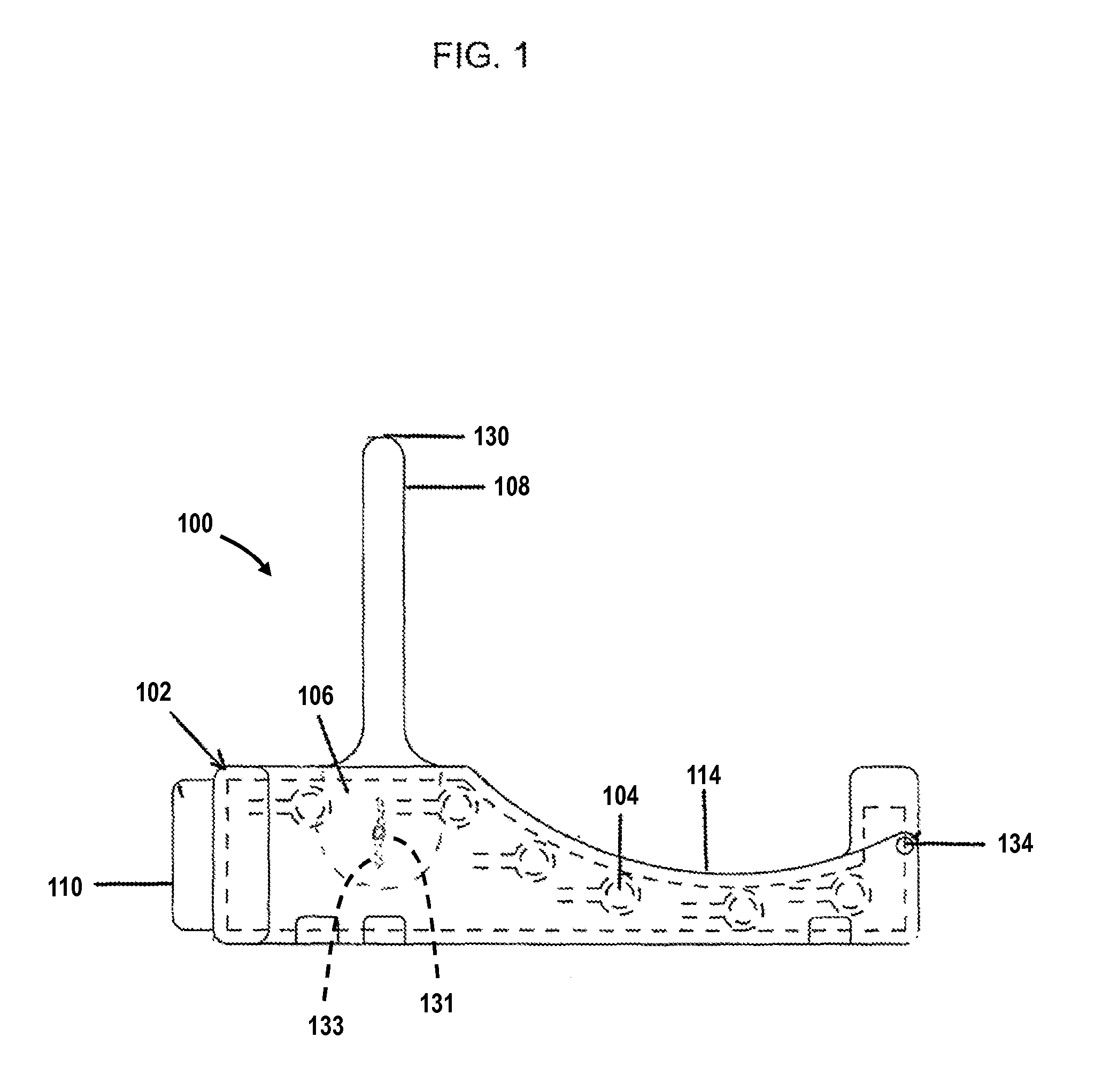
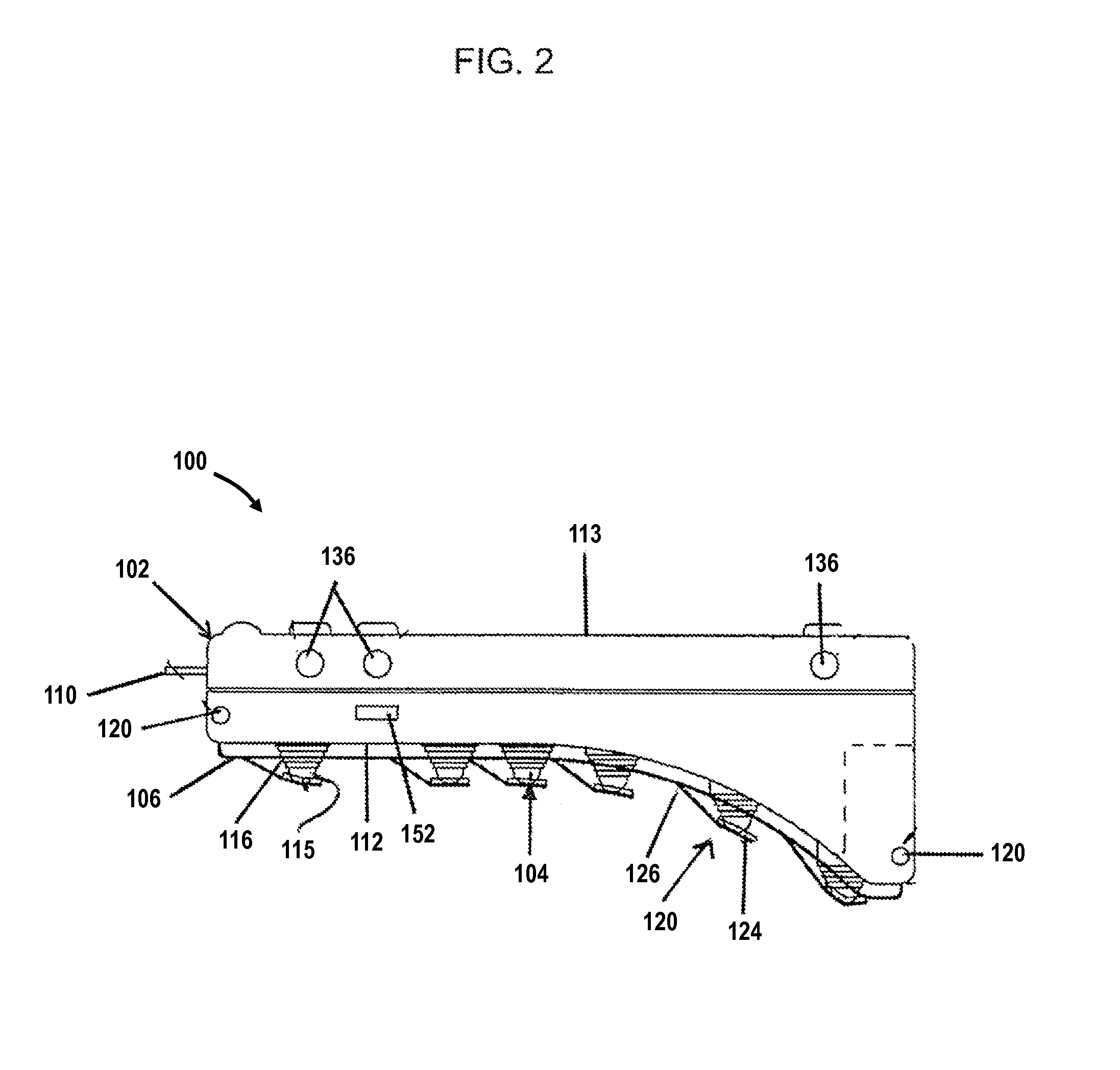
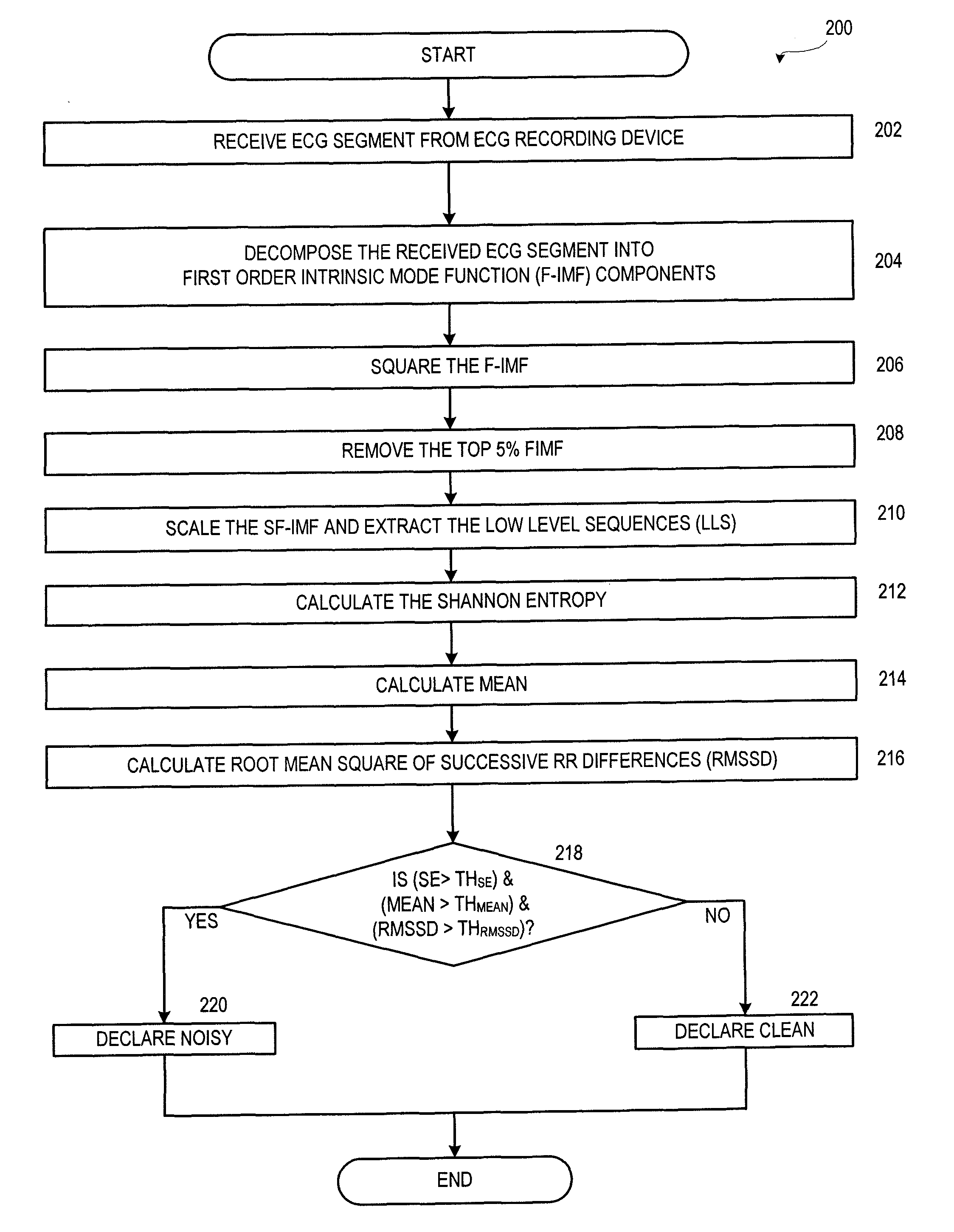
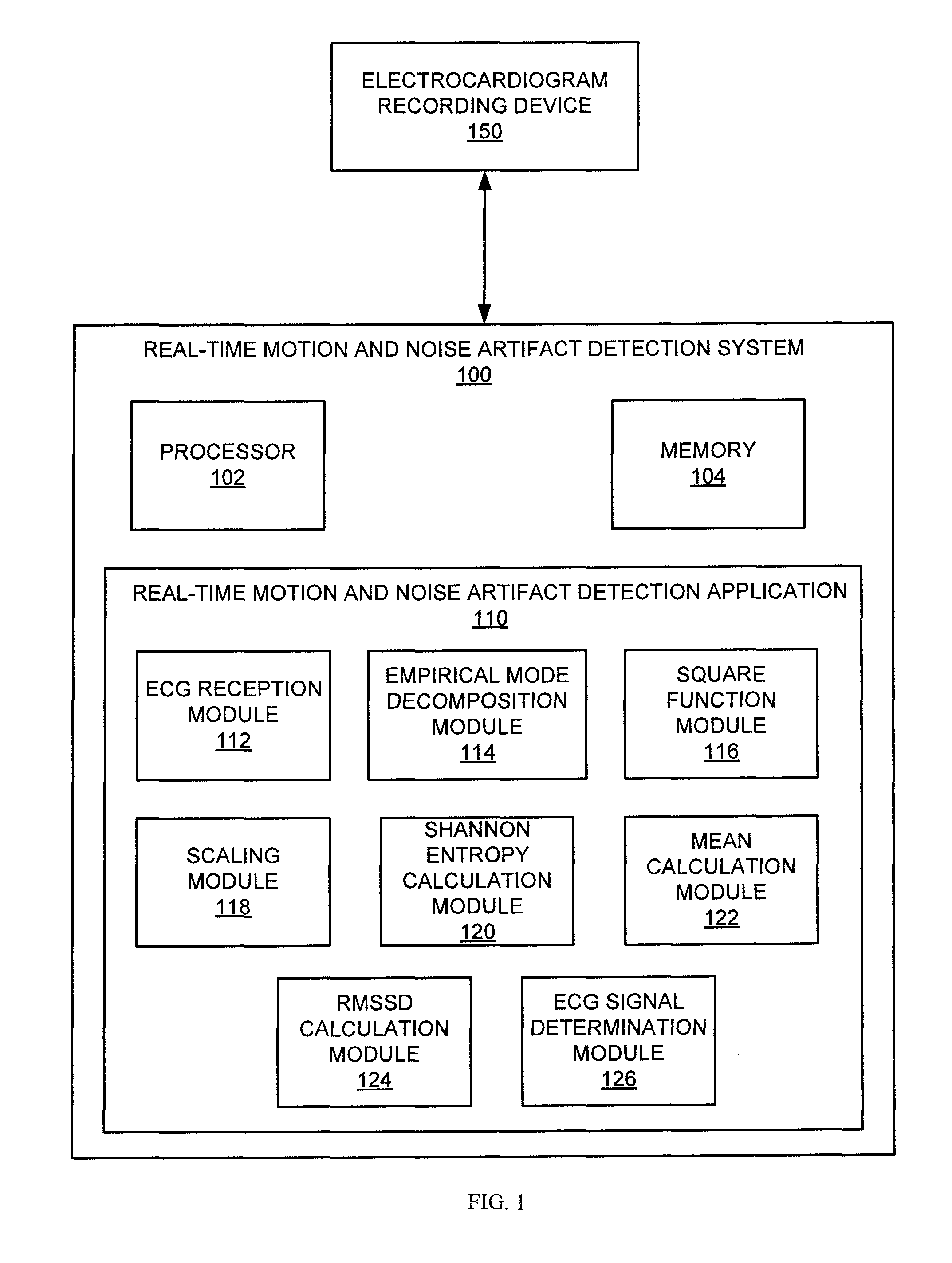
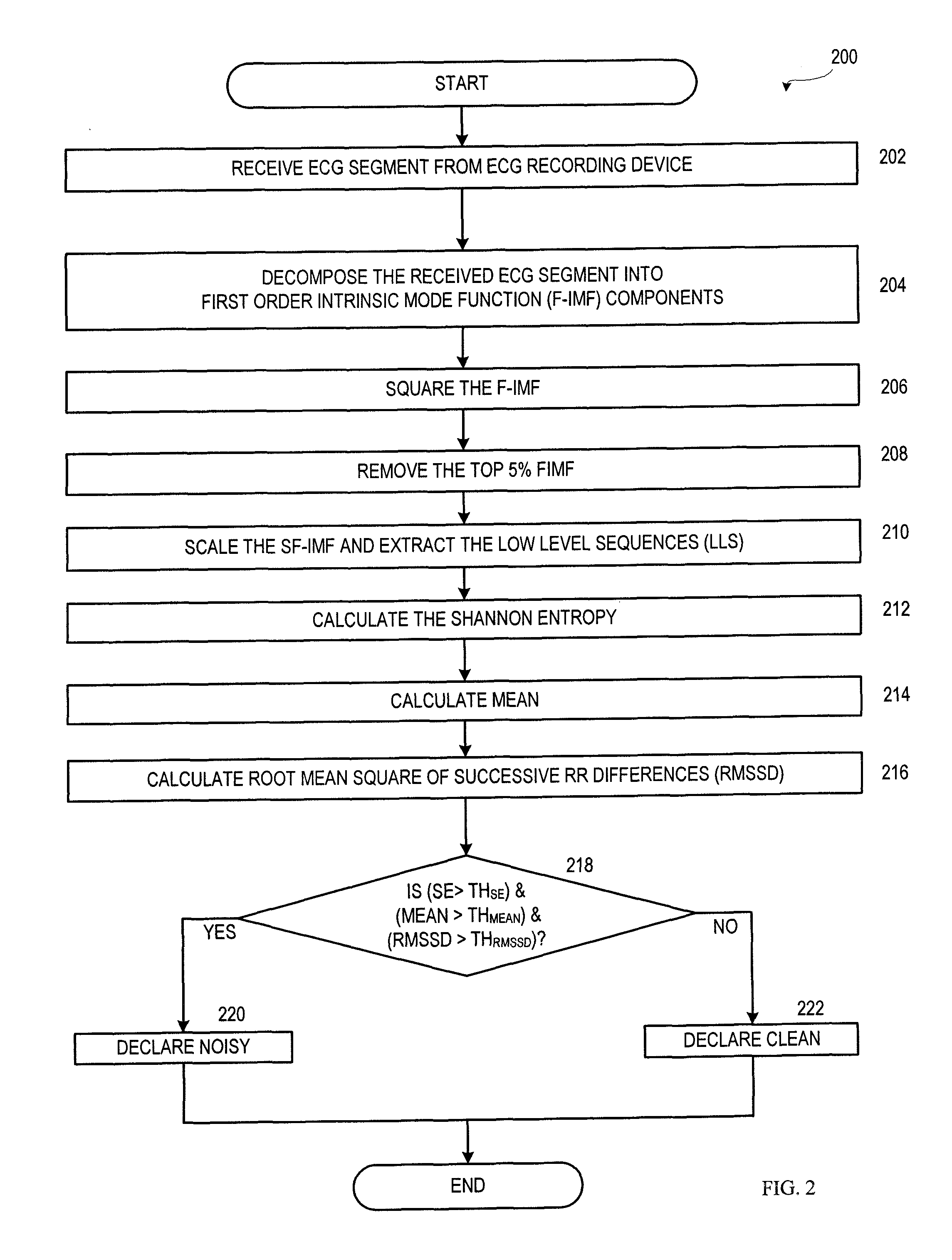
Technologies are provided herein for real-time detection of motion and noise (MN) artifacts in electrocardiogram signals recorded by electrocardiography devices. Specifically, the present disclosure provides techniques for increasing the accuracy of identifying paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) rhythms, which are often measured via such devices. According to aspects of the present disclosure, a method for detecting MN artifacts in an electrocardiogram (ECG) recording includes receiving an ECG segment and decomposing the received ECG segment into a sum of intrinsic mode functions. The intrinsic mode functions associated with MN artifacts present within the ECG segment are then isolated. The method further includes determining randomness and variability characteristic values associated with the isolated intrinsic mode functions and comparing the randomness and variability characteristic values to threshold randomness and variability characteristic values. If the randomness and variability characteristic values exceed the threshold characteristic values, the ECG signal is determined to include MN artifacts.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNICINSTITUTE
System and method for crossing a native heart valve with a guidewire
A system for crossing a heart valve with a guidewire includes an advancement motor and a controller. The controller controls when the advancement motor advances and retracts the guidewire. The controller is coupled to an electrocardiogram device and determines the systolic and diastolic phase of the heart from information / data from the electrocardiogram device. The guidewire advances or retracts based on the controller's determination of the systolic or diastolic phase corresponding with the heart valve being in an open configuration. The system may include a catheter including a lumen through which the guidewire is disposed. The system may further include a sensor. The sensor is in communication with the controller, and the controller will stop advancement of the guidewire if the controller determines the guidewire has not advanced between open leaflets of the heart valve based upon information / data from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
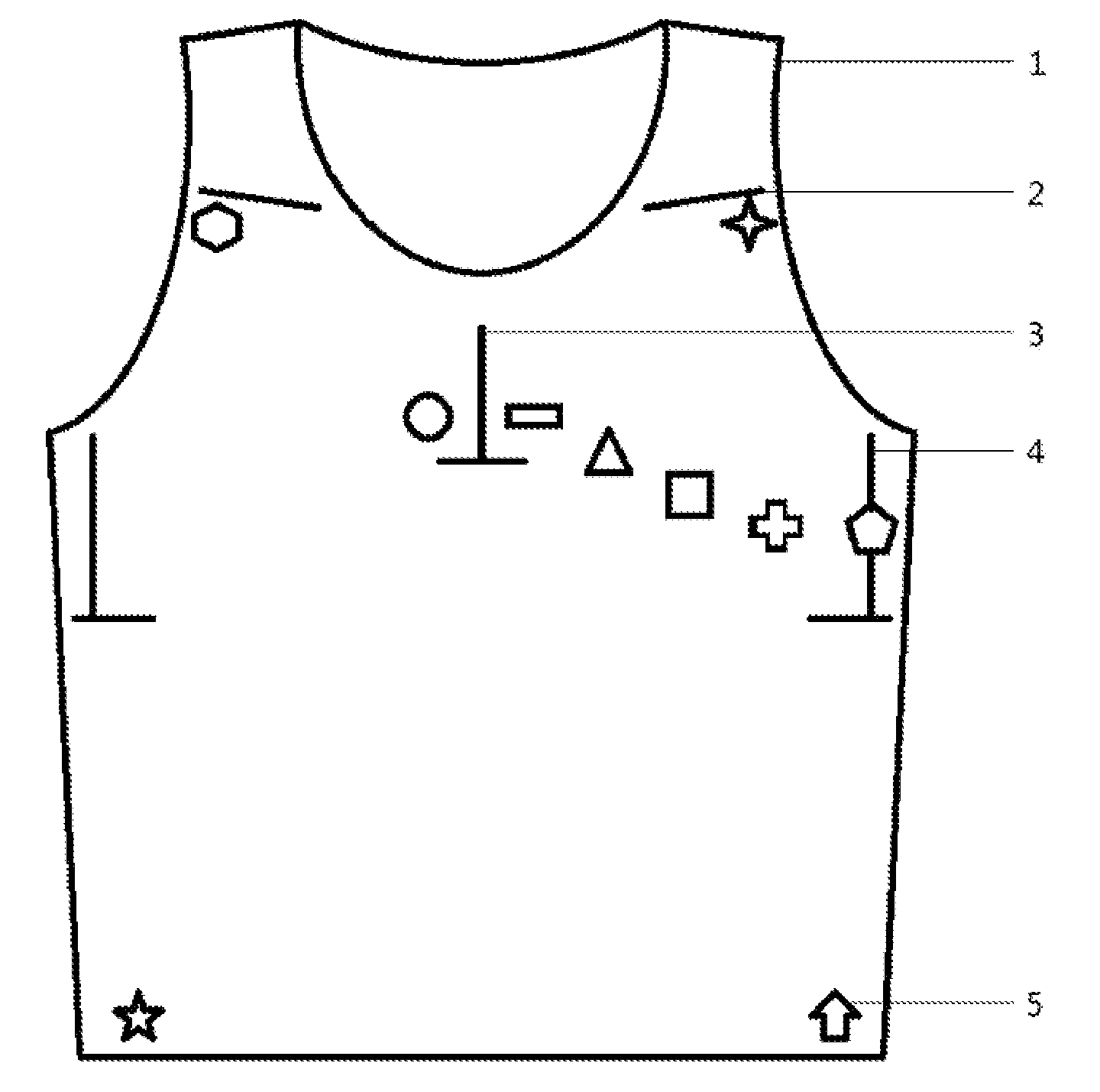
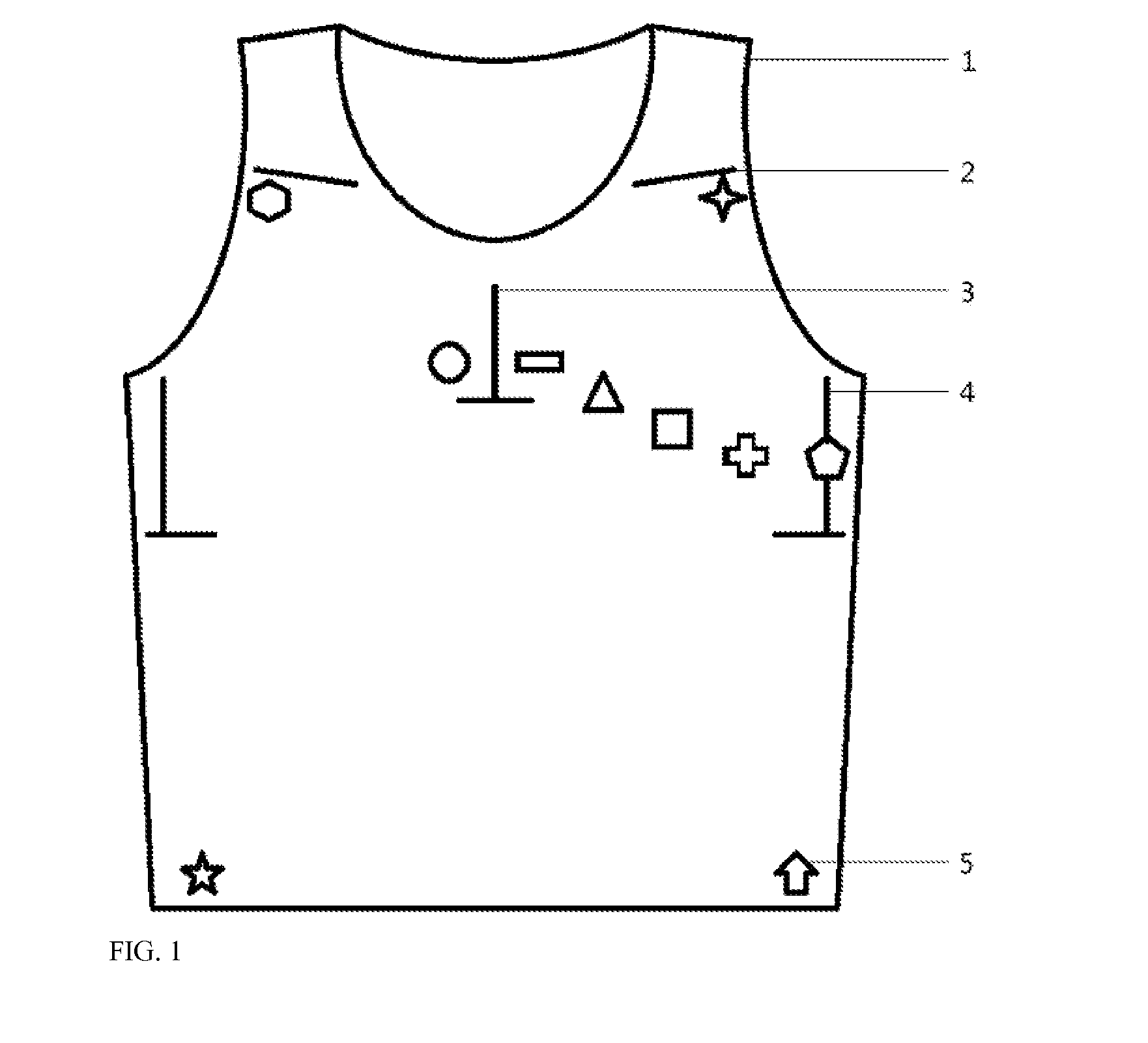
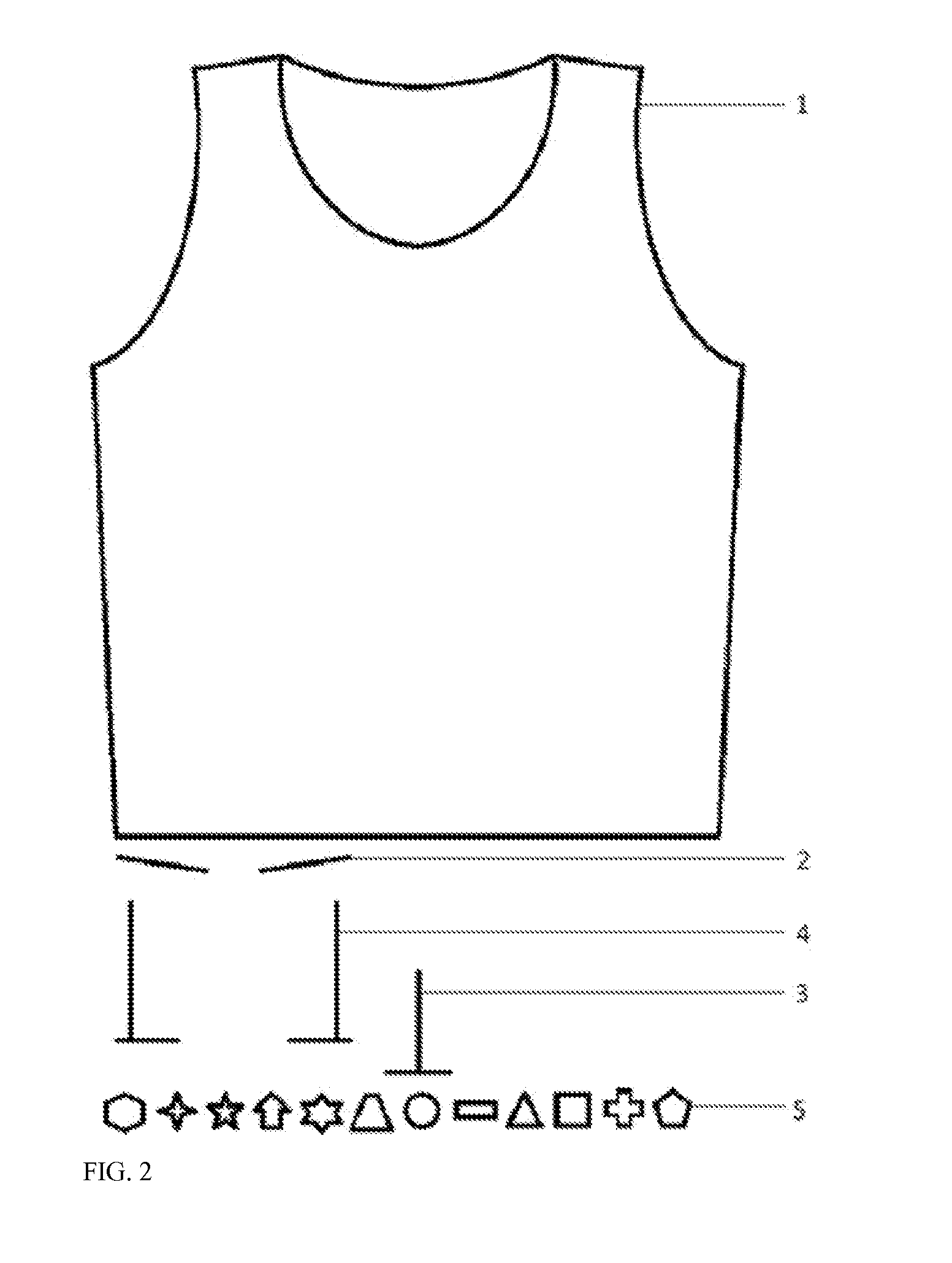
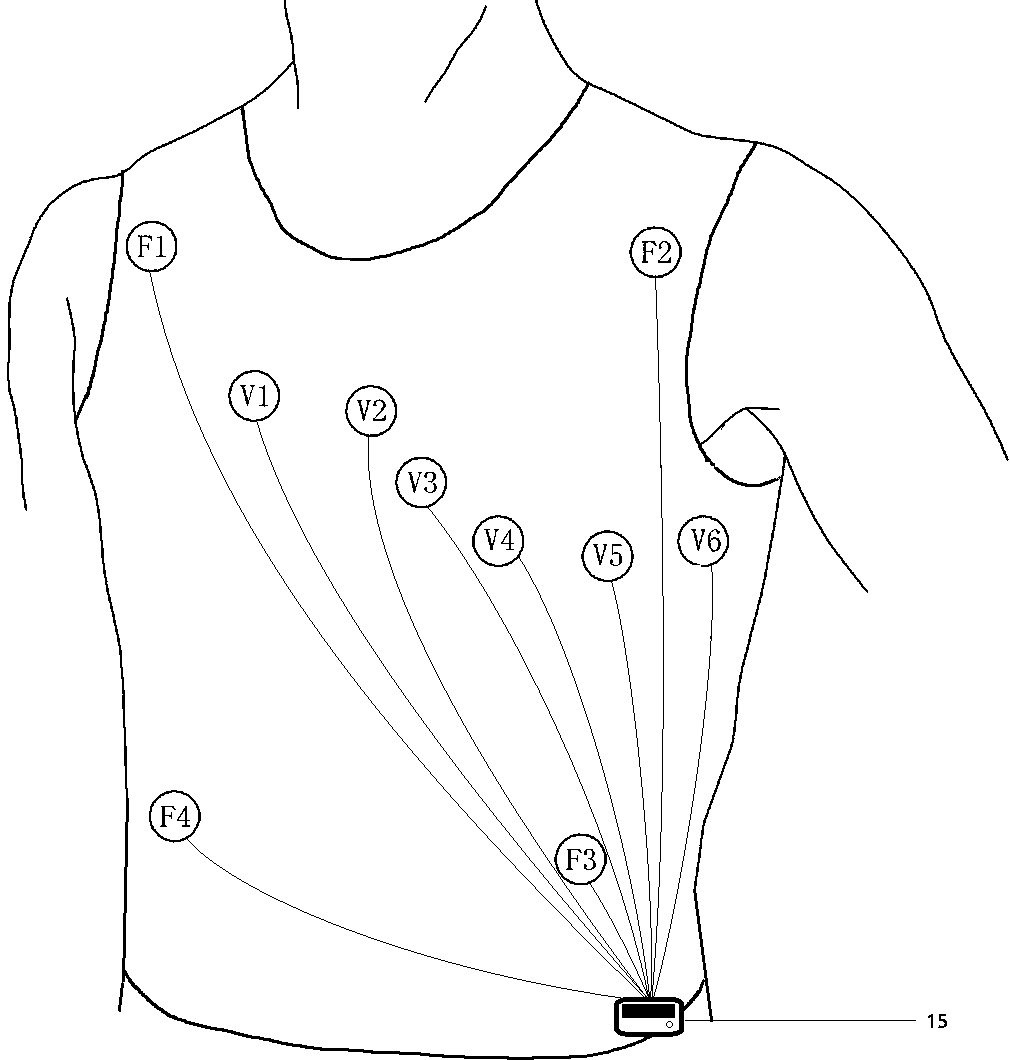
Elastic garment for positioning and fixing ECG electrodes
InactiveUS20160066809A1Precise positioningProperly fixedElectrocardiographySensorsBody shapeEngineering
An elastic garment provides an easy, quick, user-friendly way of positioning and fixing ECG electrodes. The elastic textile can offset the impact of body shape on the position of ECG electrodes. The elasticity ensures good electrode abutment and prevent electrode dislocation. The garment has labels indicating the significant bony landmarks, which help user wear the garment correctly thus ensuring the position of the electrodes. Optional features include: labels to indicate the position of electrodes; embedded wires, electrodes and connectors to external ECG device. The garment makes it possible for non-professionals to perform ECG examination including the standard 12-lead ECG. It also minimizes electrode dislocation and uncomfortable feelings of wearing ECG device, especially for those under long-term ECG monitoring. It can also help avoid the inconvenient procedure of undressing a patient during ECG examination.
Owner:LUO ZHIYUAN +1
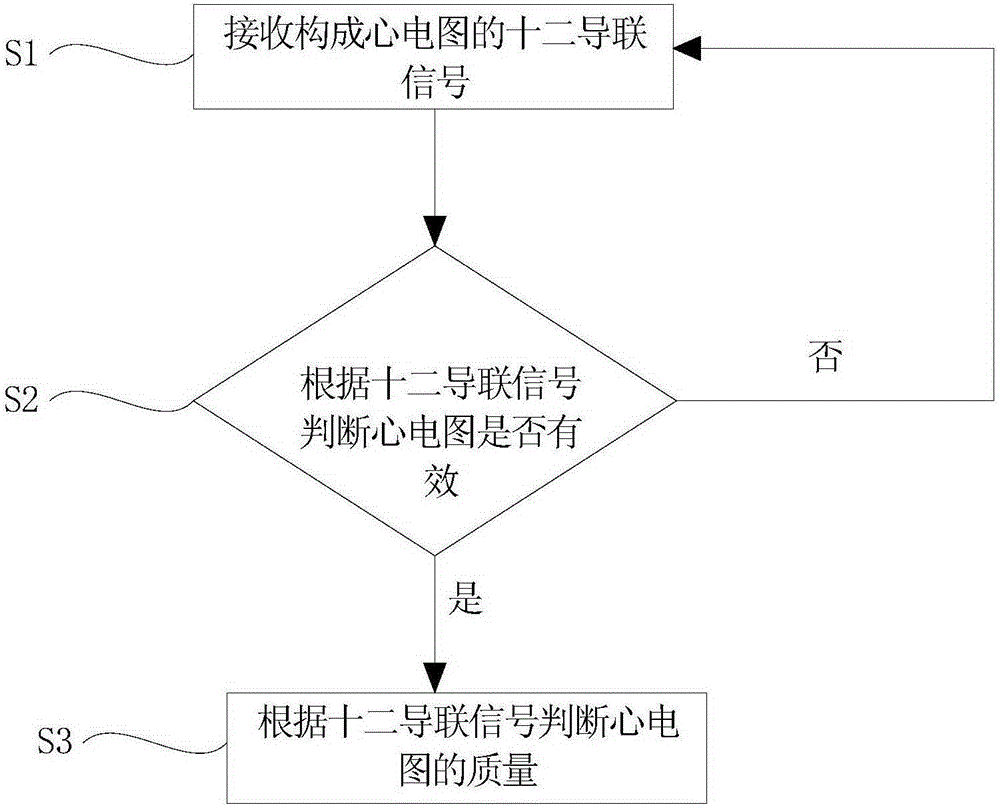
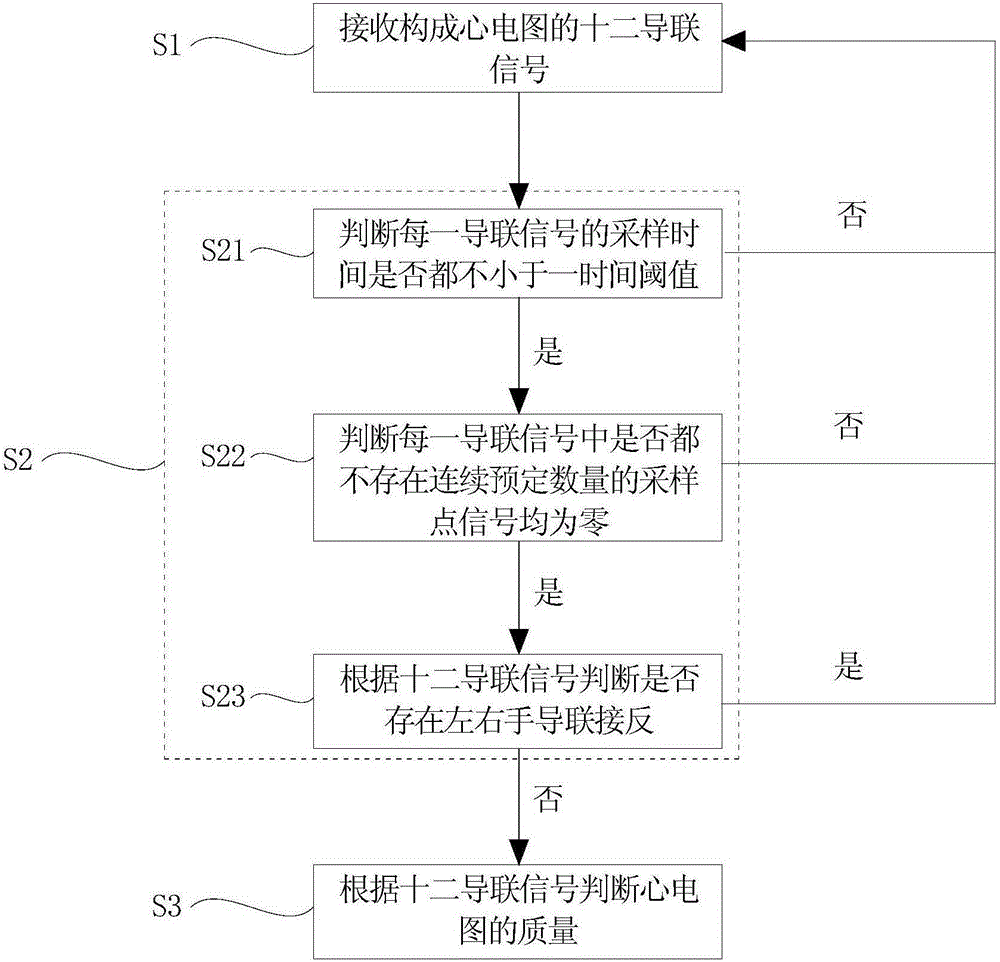
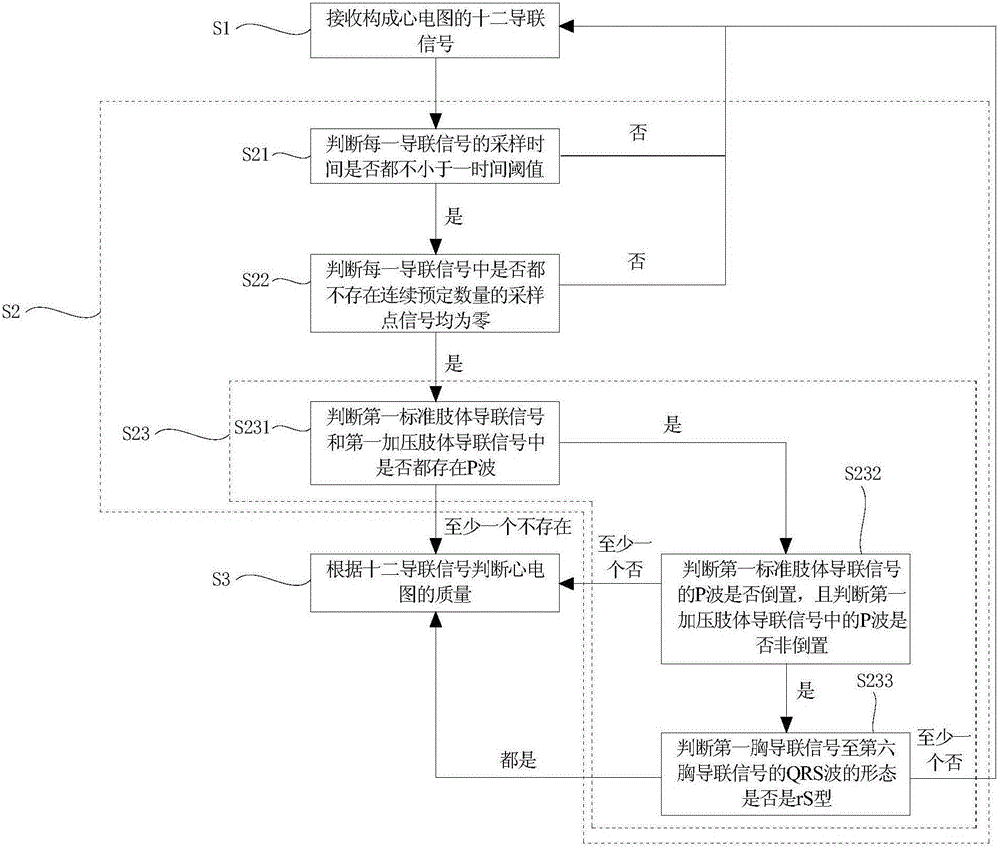
Quality judgement method and quality judgement system for electrocardiogram
InactiveCN106580307AEasy to keepWith lead signal acquisition functionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal qualityMagnetocardiography device
The invention provides a quality judgment method for electrocardiogram. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a 12-lead signal forming electrocardiogram; judging whether the electrocardiogram is valid or not according to the 12-lead signal; and judging the quality of the electrocardiogram according to the 12-lead signal if the electrocardiogram is valid. The invention further provides a quality judgment system for electrocardiogram. When the quality judgement system and quality judgement method for electrocardiogram are applied to electrocardiogram equipment, the electrocardiogram equipment has a lead signal collection function and a lead signal quality judgment function. Furthermore, according to the quality judgement system and quality judgement method, the electrocardiogram of which the quality does not achieve a preset standard is graded, so that important information of the electrocardiogram of which the quality does not achieve the preset standard can be better maintained.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Motion and noise artifact detection for ECG data
Technologies are provided herein for real-time detection of motion and noise (MN) artifacts in electrocardiogram signals recorded by electrocardiography devices. Specifically, the present disclosure provides techniques for increasing the accuracy of identifying paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) rhythms, which are often measured via such devices. According to aspects of the present disclosure, a method for detecting MN artifacts in an electrocardiogram (ECG) recording includes receiving an ECG segment and decomposing the received ECG segment into a sum of intrinsic mode functions. The intrinsic mode functions associated with MN artifacts present within the ECG segment are then isolated. The method further includes determining randomness and variability characteristic values associated with the isolated intrinsic mode functions and comparing the randomness and variability characteristic values to threshold randomness and variability characteristic values. If the randomness and variability characteristic values exceed the threshold characteristic values, the ECG signal is determined to include MN artifacts.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNICINSTITUTE
Cardiac electricity detecting system using embedded right leg drive
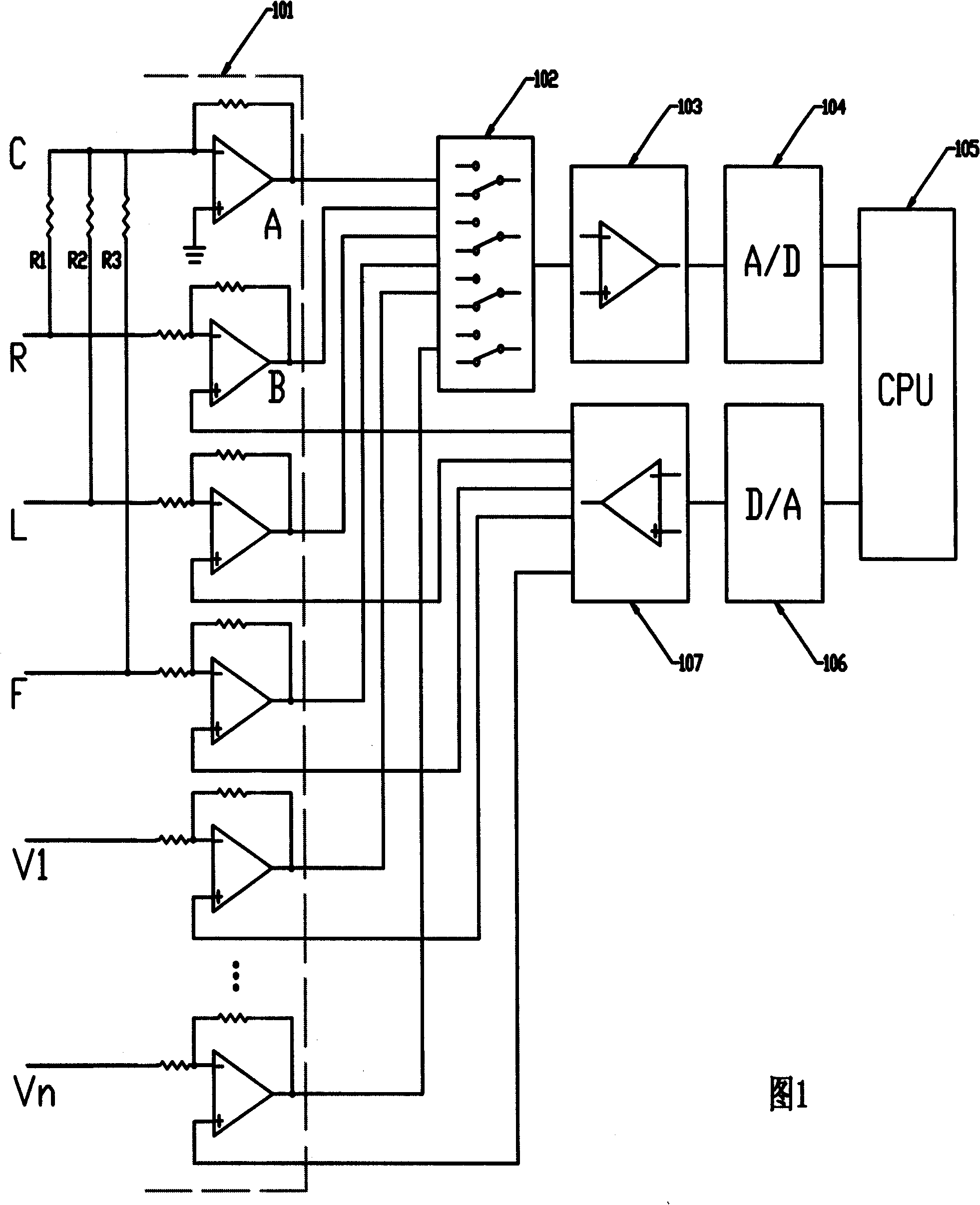
The invention relates to an electrocardio detection system which is provided with a right leg drive that is internally arranged, which comprises a preamplifier, a multi-channel analogue switch, a main amplifier, an A / D converter, a D / A converter, an output amplifier, a microprocessor, etc. The electrocardio detection system is provided with the right leg drive, which can respectively compensate signals to each lead and eliminate signal aberration of the right leg drive caused by excursion of a 'central electrode', thereby anti-interference capacity is further enhanced and detection quality of electrocardio signals is greatly improved. In the electrocardio detection system composed by the technique, a right leg drive electrode does not need to be connected externally and therefore, the operation process of the electrocardio detection is simplified. The detection system can be applied to the electrocardio detection system such as electrocardiogram devices, electrocardiogram monitoring devices and dynamic electrocardiogram devices, etc.
Owner:廉姜芳 +1
Spontaneous exercise electrocardiogram system
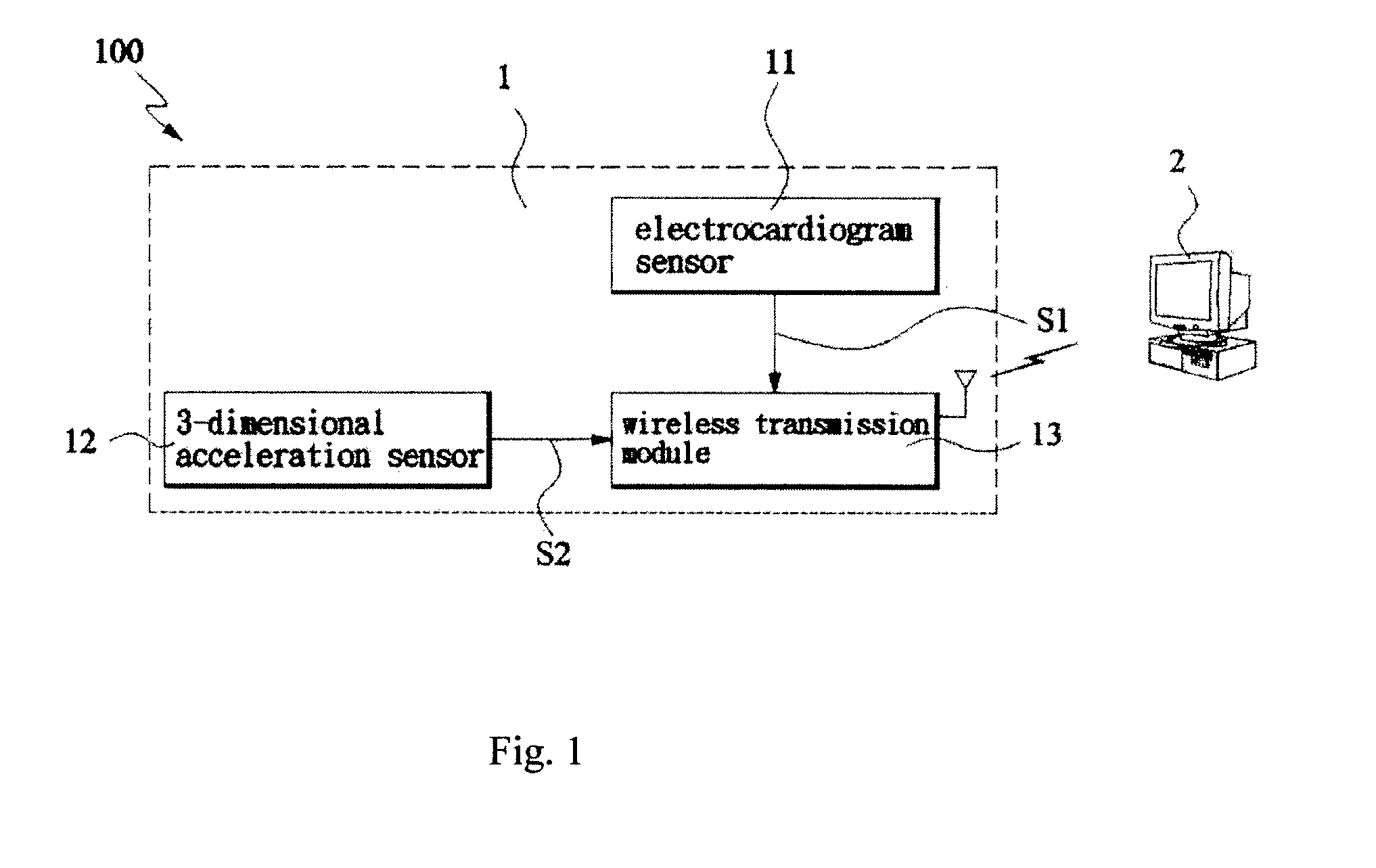
InactiveUS20120029318A1Short examination timeData augmentationElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsRR intervalMagnetocardiography device
Disclosed is a spontaneous exercise electrocardiogram system, adapted to synchronously record and analyze a user to obtain a spontaneous exercise electrocardiogram. The system comprises a electrocardiogram device and a analyzing computer. The electrocardiogram device comprises: an electrocardiogram sensor and a 3-dimensional acceleration sensor for detecting the user's electrocardiogram signals and acceleration signals, respectively. Upon the analyzing computer receives the information from the electrocardiogram device, an indicator of physical activity (PA) or new physical activity (NPA) can be determined. After the heart rate of electrocardiogram and heart rate variability being matched and analyzed, the user's spontaneous exercise electrocardiogram can be established.
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
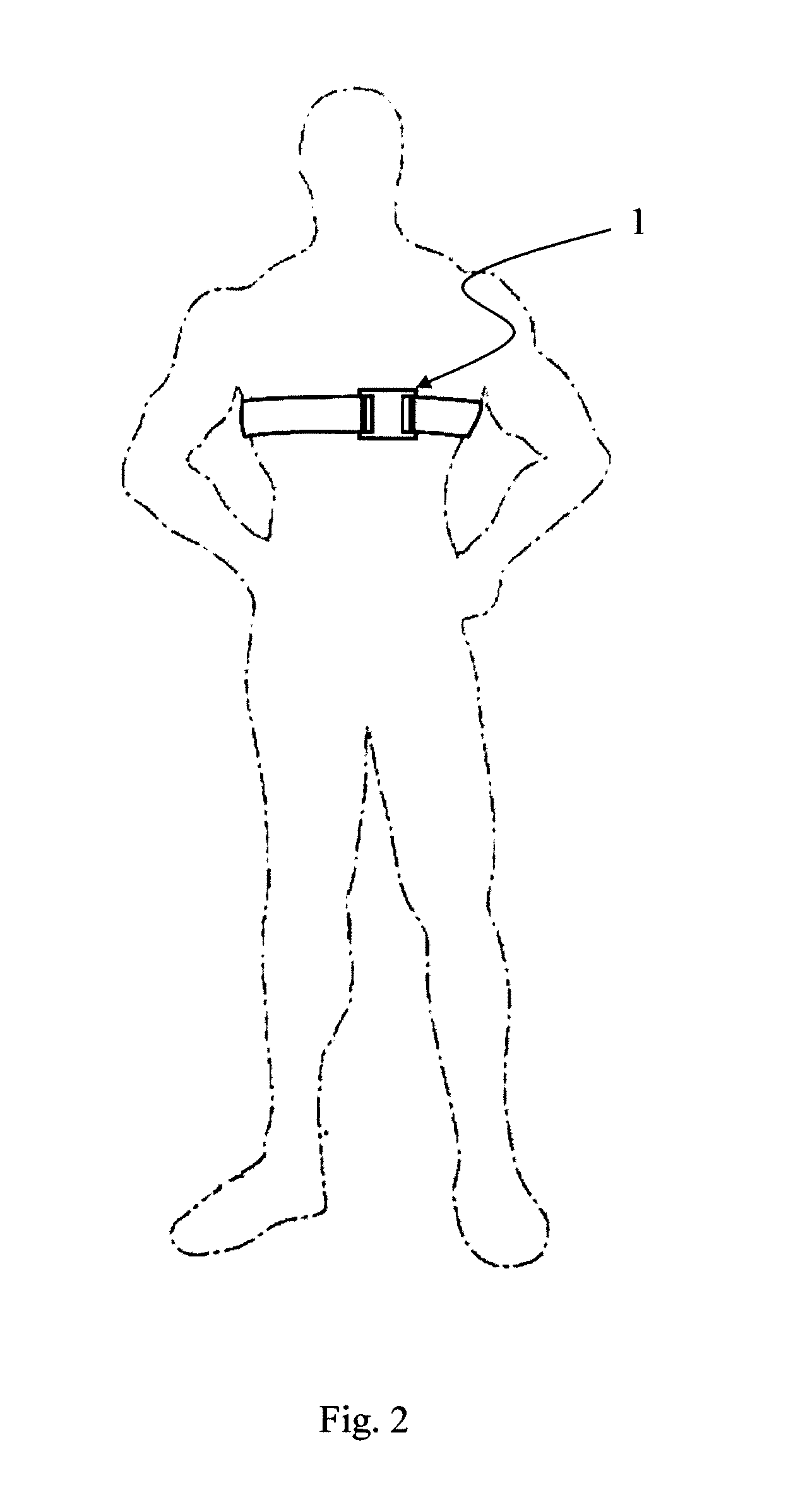
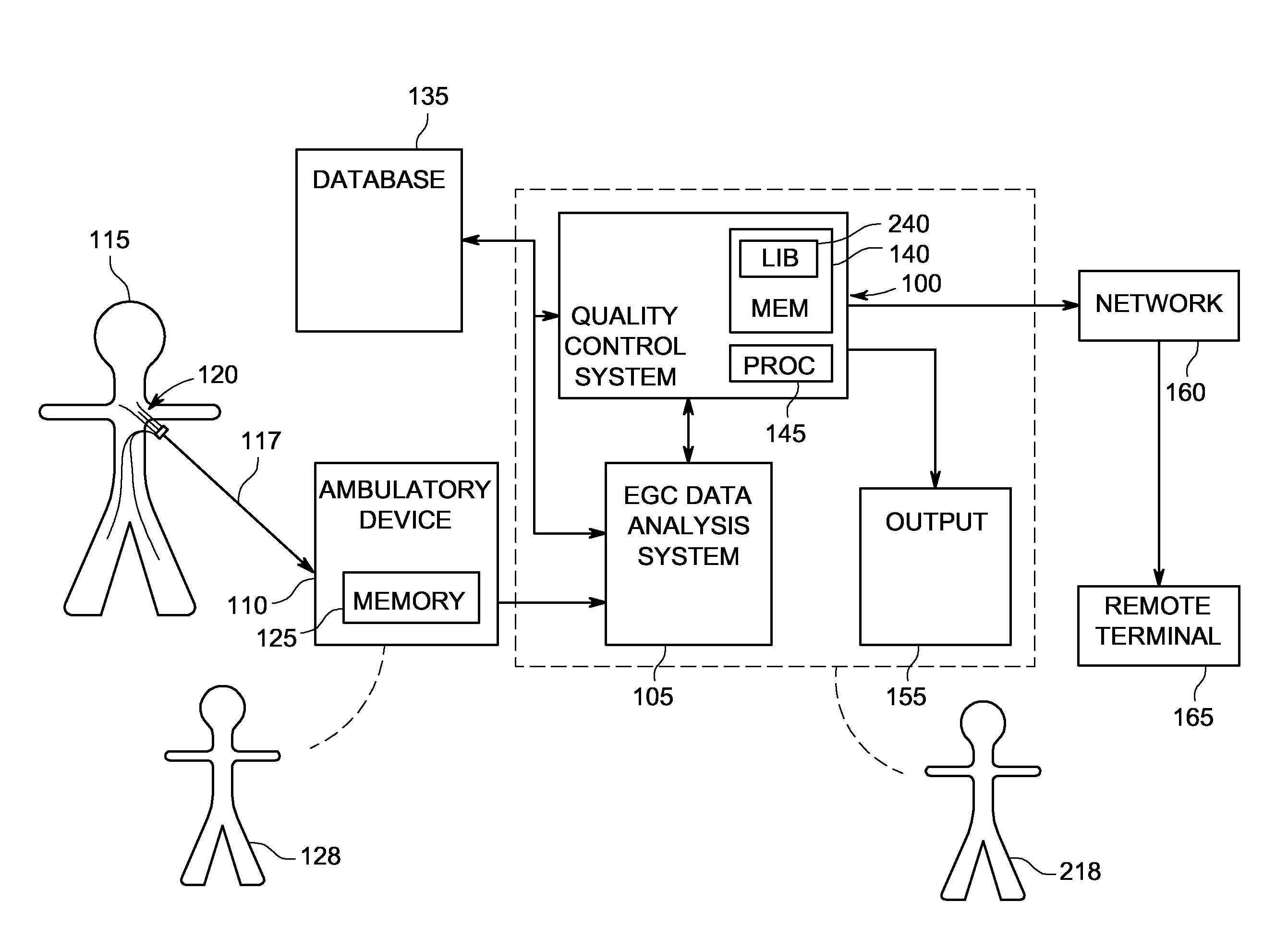
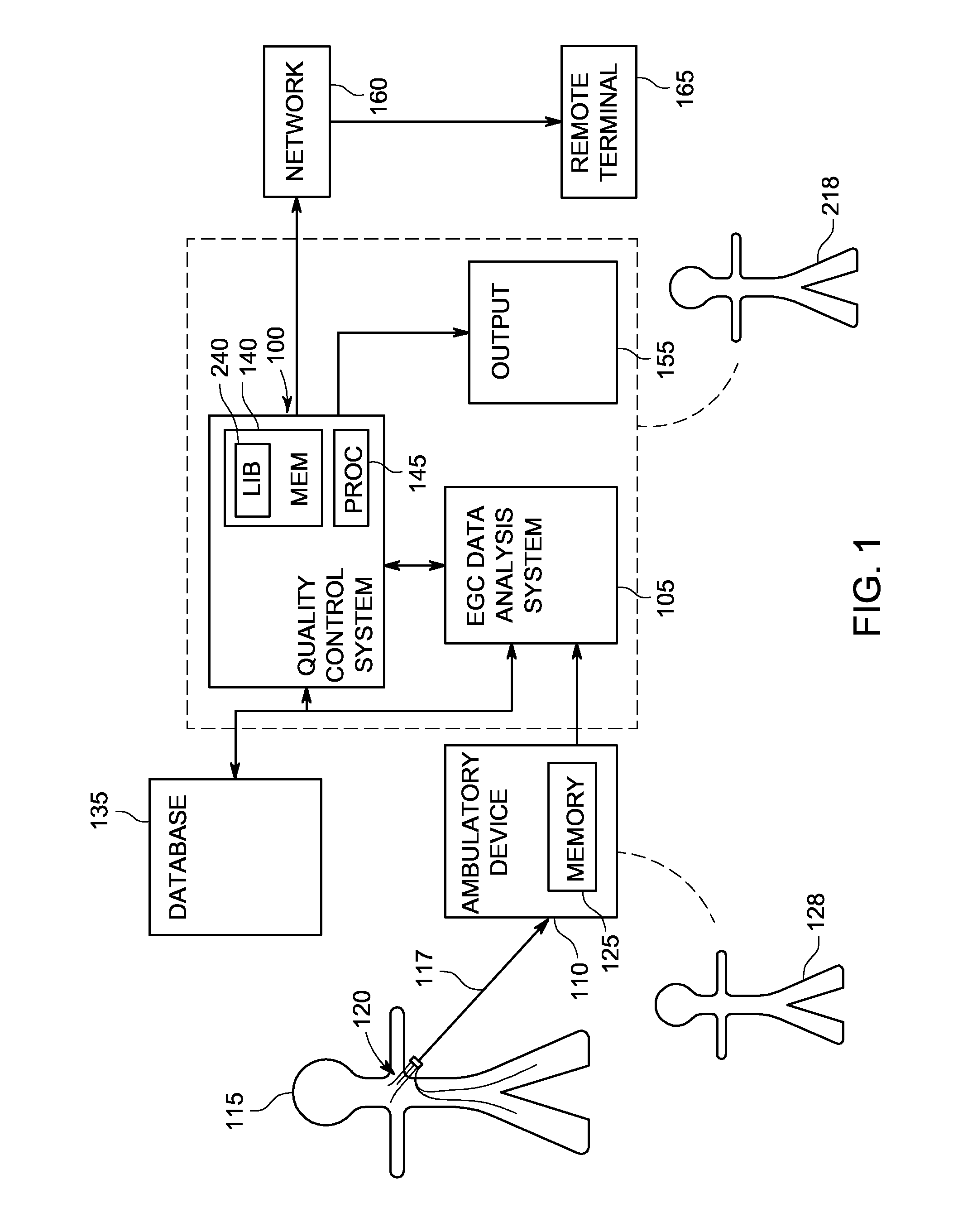
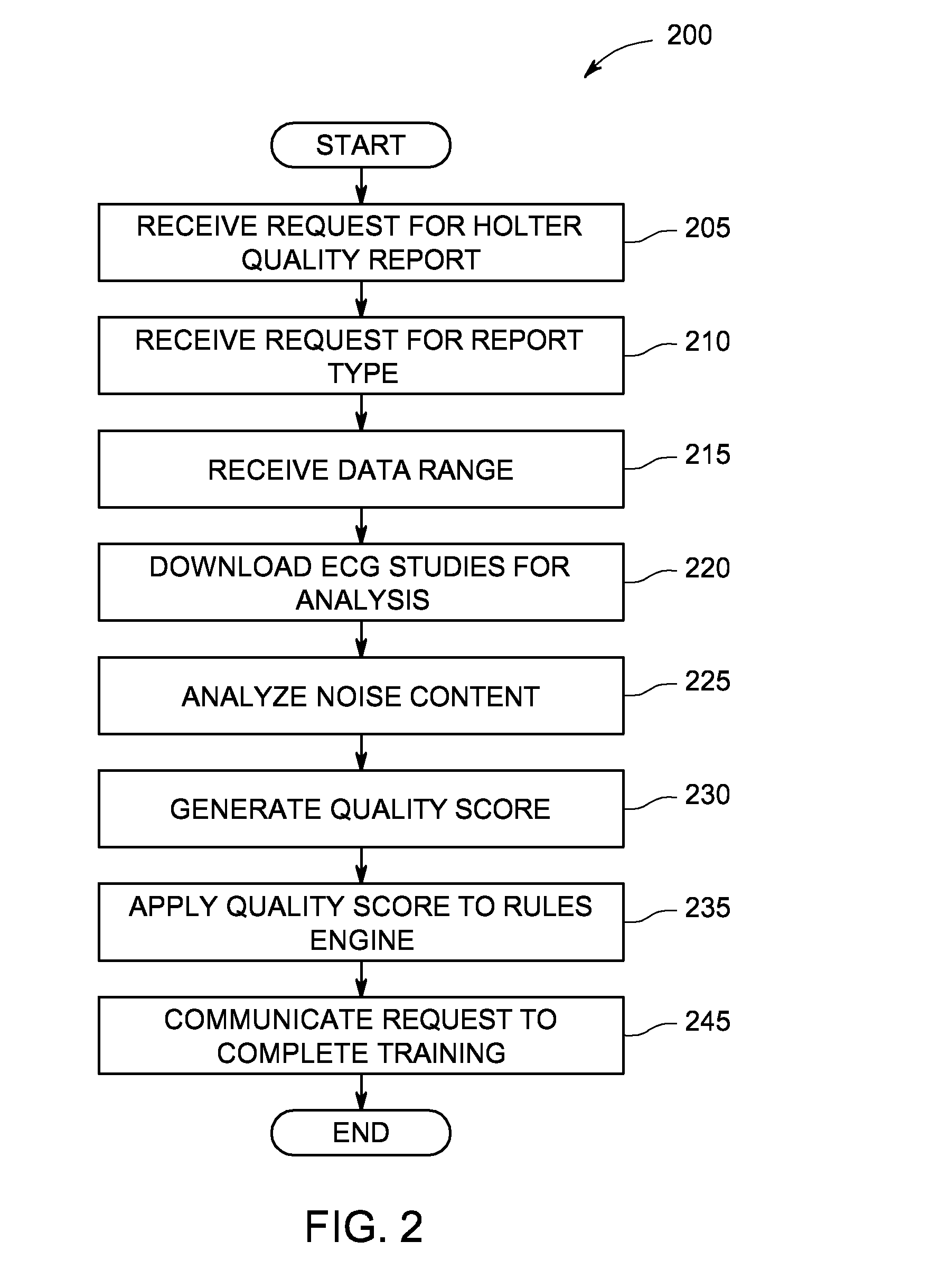
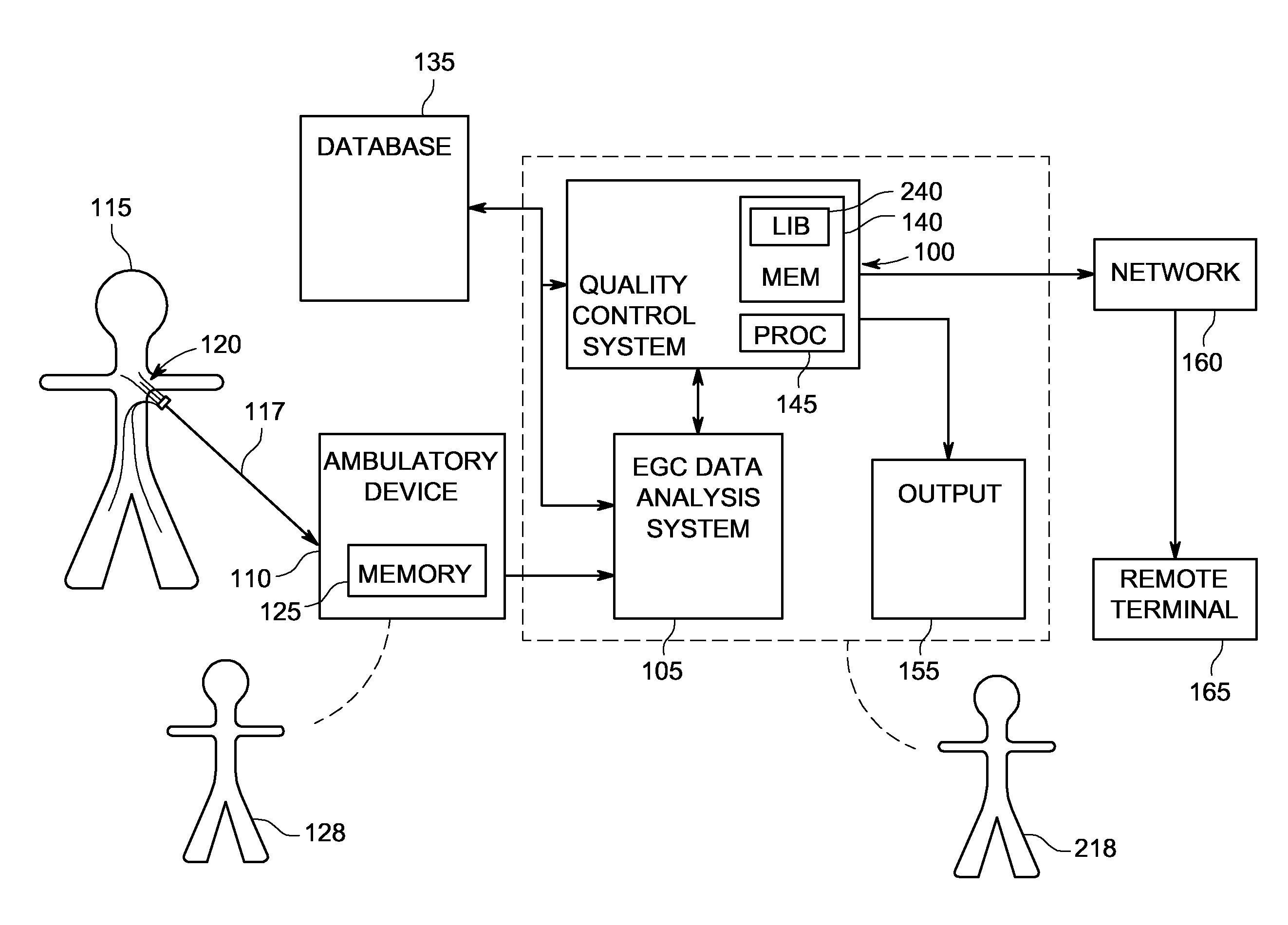
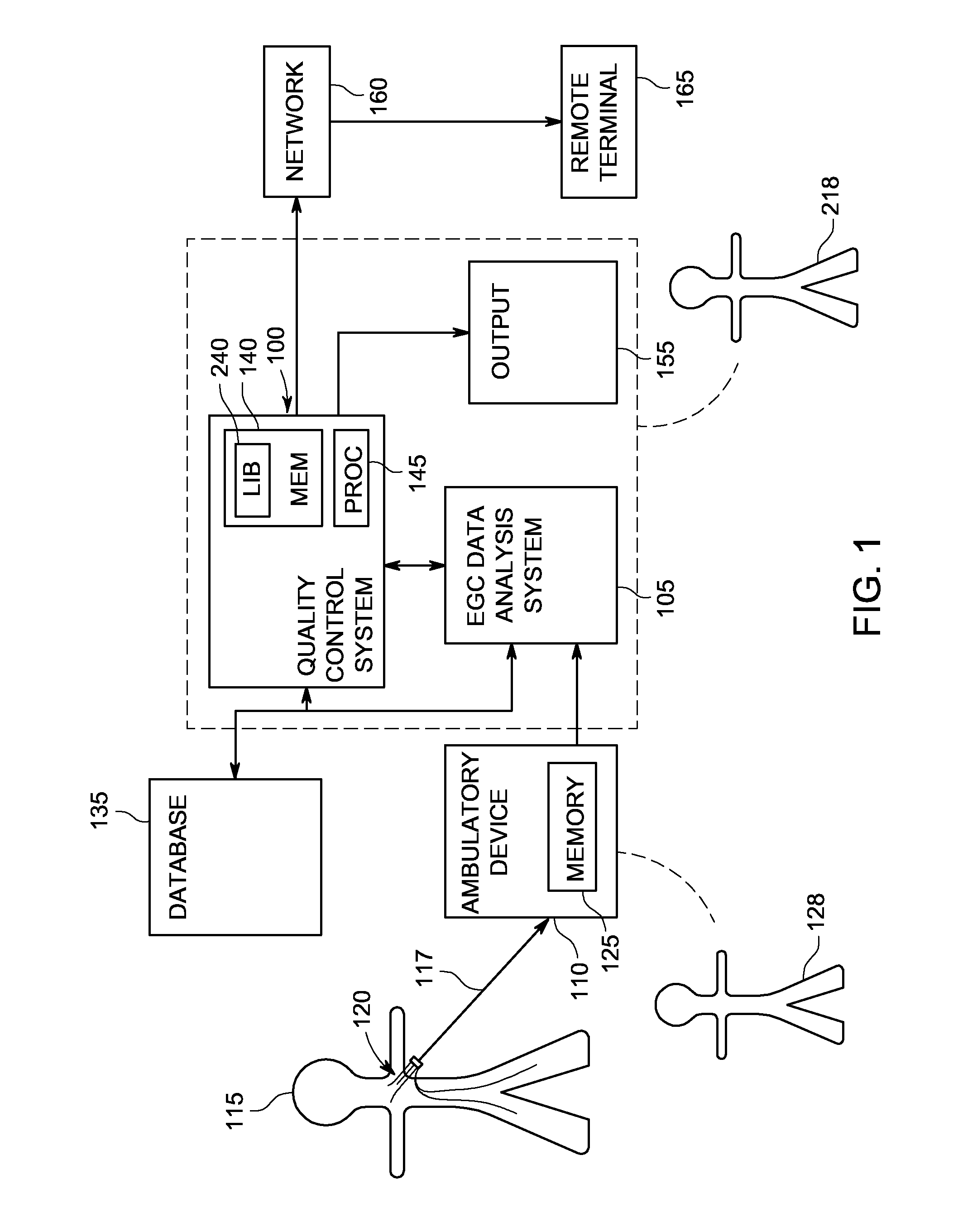
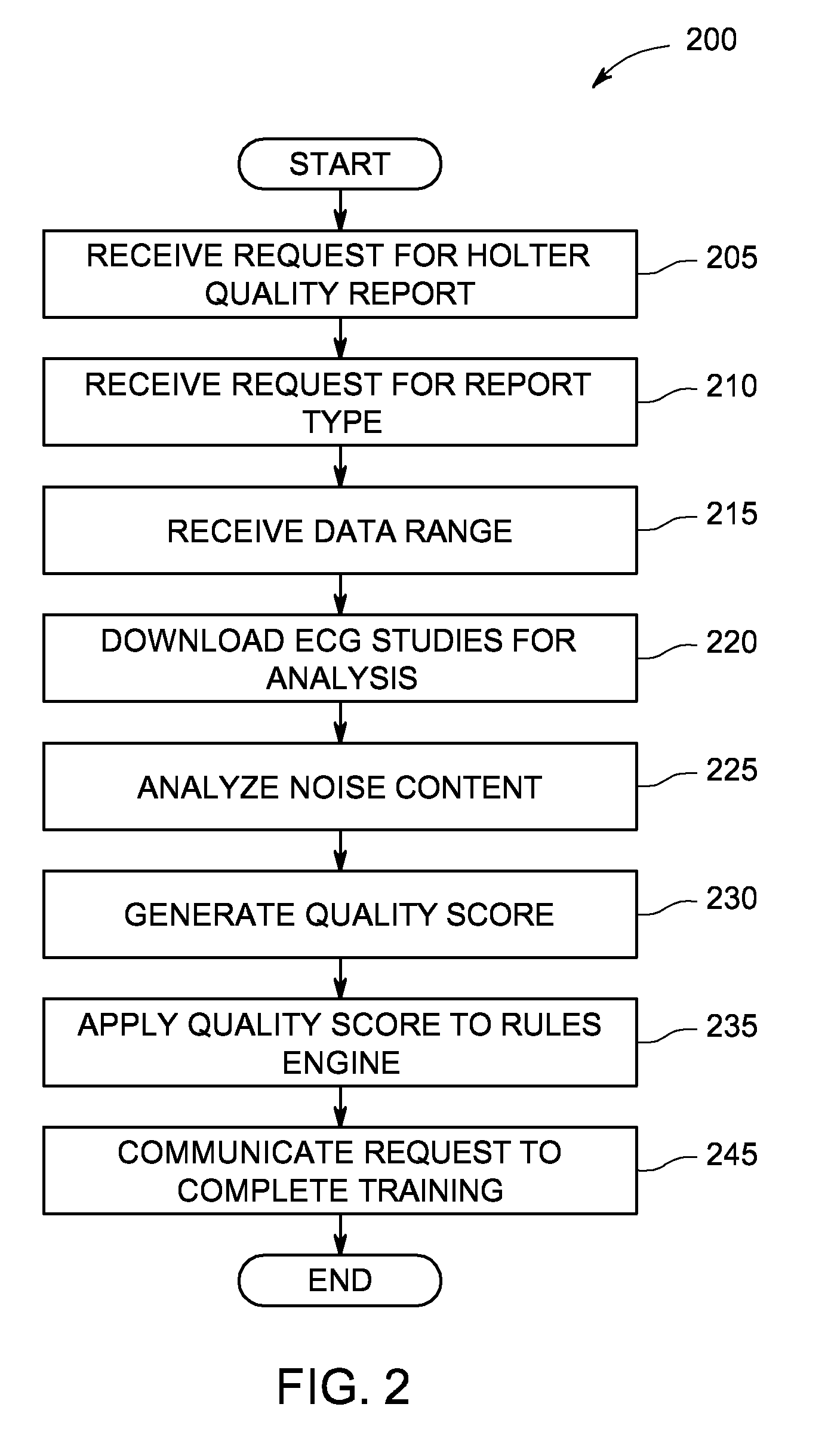
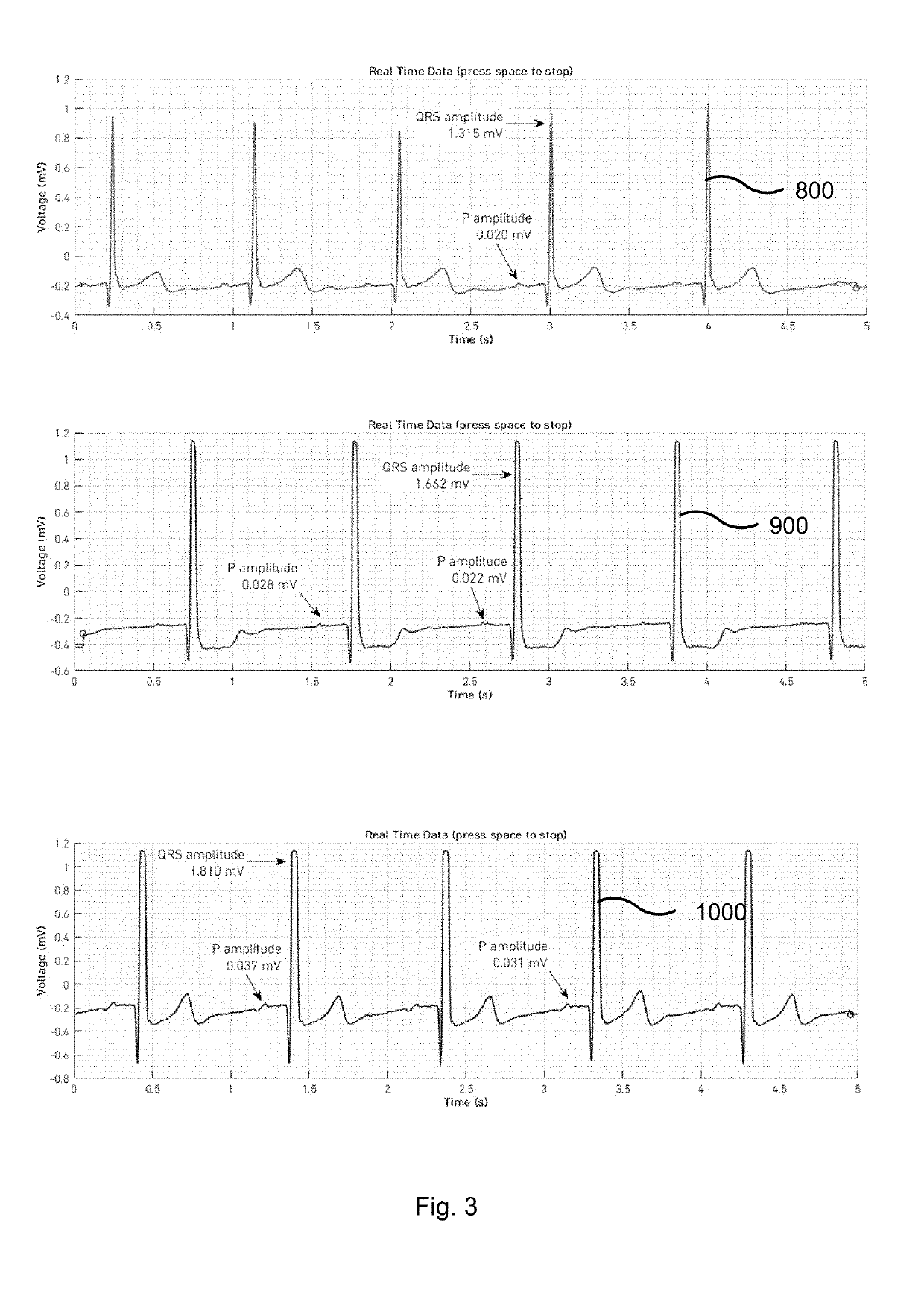
System and method of quality analysis in acquisition of ambulatory electrocardiography device data
A quality control system in combination with an ECG data analysis system to analyze ECG data acquired by an ambulatory electrocardiography device via a cable having a plurality of leads connected to a subject is provided. The quality control system includes a memory having programmable instructions for execution by a processor to perform the steps of calculating a trend of a quality score in the ECG data dependent on a noise content in the ECG data; and calculating a probability that one of a hardware and the Hookup personal, each associated with collecting the ECG data from the subject, is a substantial cause of the quality score for the ECG data. The probability can be calculated based on a comparison the trend of the quality score associated with the Hookup personnel versus the trend of the quality score of the hardware employed in acquiring the ECG data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heartbeat anomaly recognition algorithm based on deep learning technology
PendingCN109887595AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSignal quality
Owner:成都蓝景信息技术有限公司
Method and system for associating an EKG waveform with a CT image
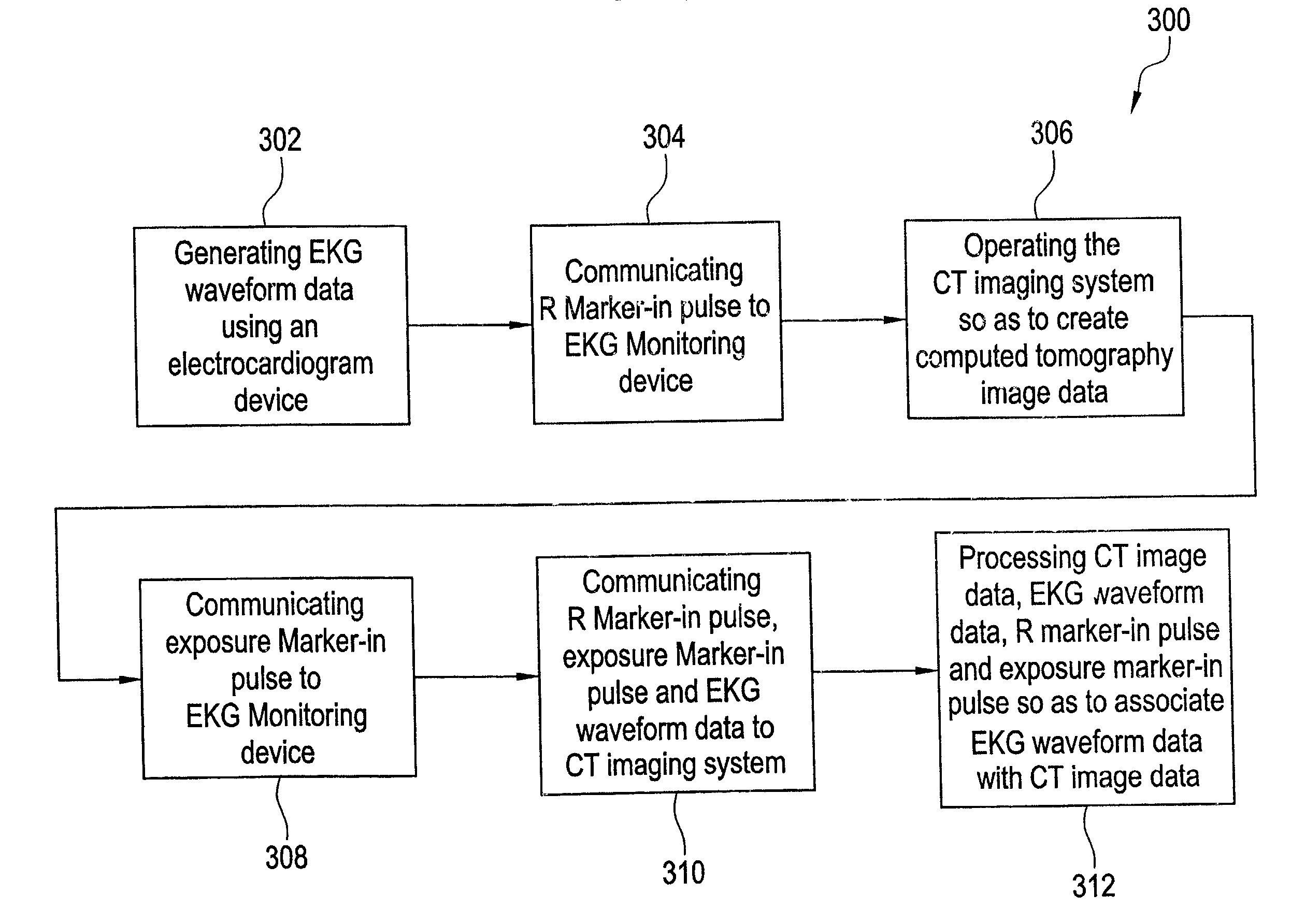
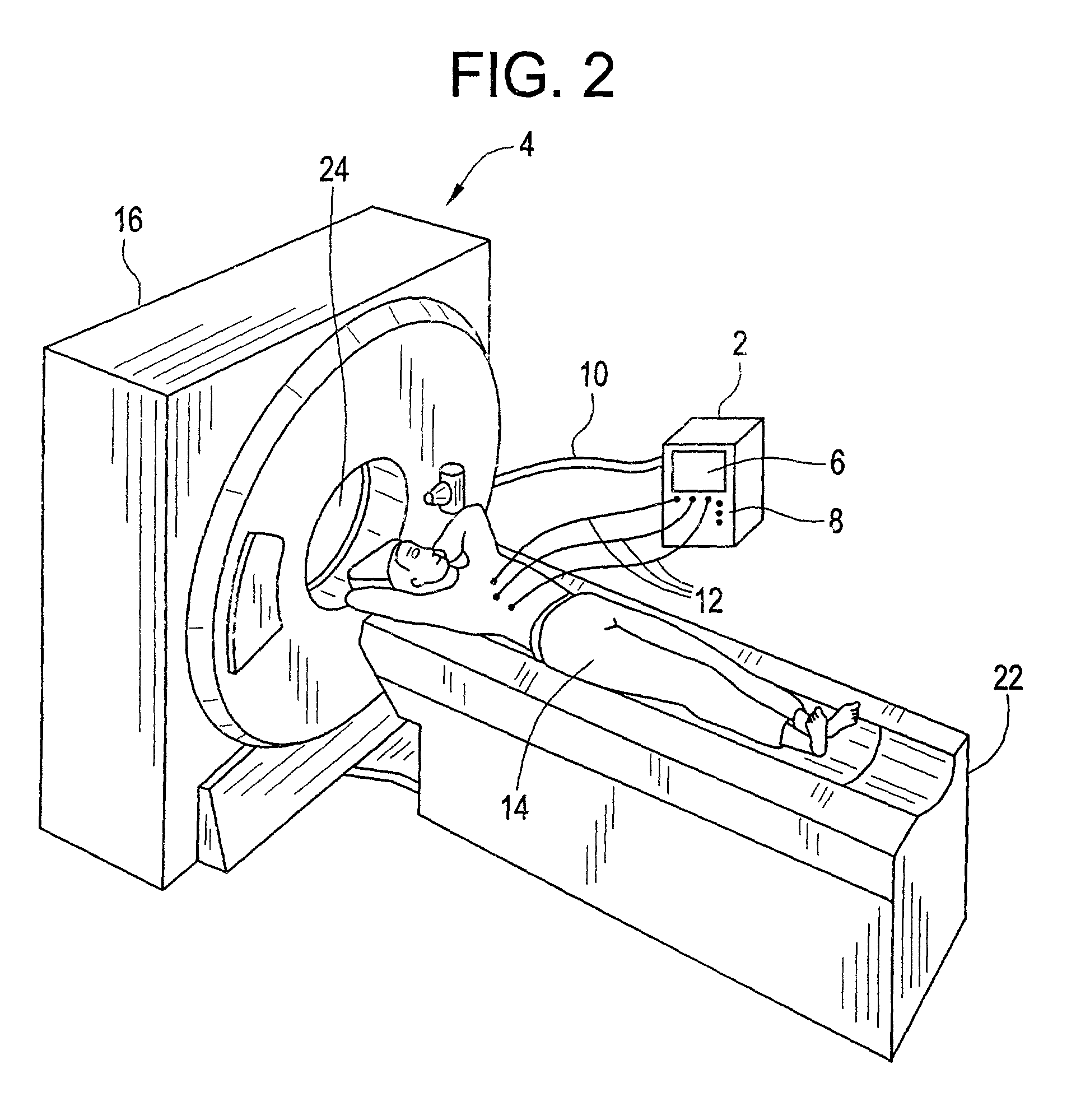
ActiveUS7477928B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData synchronizationMagnetocardiography device
A method for associating EKG waveform data with computed tomography image data using a data synchronization scheme including generating the EKG waveform data using an electrocardiogram device, operating a computed tomography imaging system so as to create the computed tomography image data, communicating an exposure marker-in signal to the electrocardiogram device such that the exposure marker-in signal is associated with the EKG waveform data and processing the computed tomography image data, the EKG waveform data and the exposure marker-in signal, so as to correlate the EKG waveform data with the computed tomography image data. Also claimed is a medium encoded with a machine-readable computer program code for associating EKG waveform data with image data generated by an imaging system using a data synchronization scheme, the medium including instructions for causing controller to implement the aforementioned method.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Electrocardiogram device and methods
ActiveUS10441184B2Improve accuracyStrong specificityMedical automated diagnosisSensorsFourier transform on finite groupsMagnetocardiography device
Devices and methods are described that provide improved diagnosis from the processing of physiological data. The methods include use of transforms prior to submitting the data to a multiple level neural network. In one embodiment for ECG analysis, a template is used to subtract data that is not pertinent to the diagnosis and then a Fourier transform is applied to the time series data. Examples are shown with applications to electrocardiogram data, but the methods taught are applicable to many types of physiological data.
Owner:VENTRILINK CORP
Accessory device for twelve-lead electrocardiography apparatus
An accessory device for a twelve-lead electrocardiography (ECG) apparatus includes a blanket. The ECG apparatus includes an ECG machine that has ten first electrical couplers, and ten electrodes each having a second electrical coupler. The blanket includes a sheet body configured to cover the body of a patient and formed with ten holes that are arranged according to a standard electrode placement for twelve-lead ECG measurement and that are configured to permit the second electrical couplers of the ten electrodes to extend therethrough, respectively.
Owner:HUANG WEI CHUN
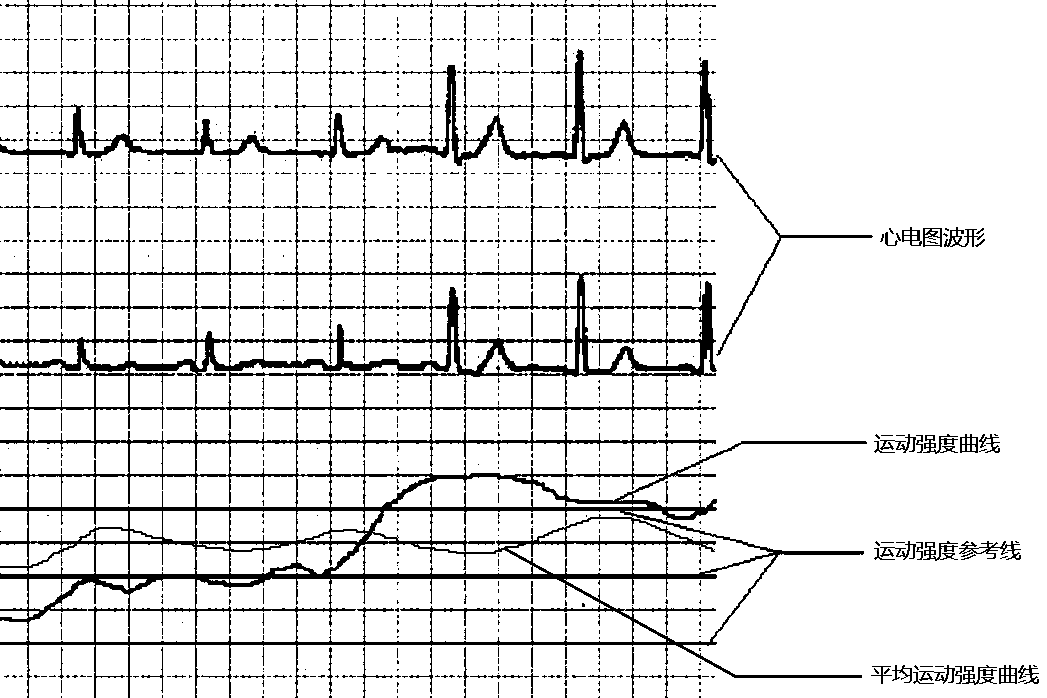
Portable electrocardiogram (ECG) machine with motion monitoring function
InactiveCN105496396ADiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous ECG monitoringMagnetocardiography device
The invention provides a portable electrocardiogram (ECG) machine with a motion monitoring function and an ECG output scheme for synchronous display of an ECG and exercise intensity, and belongs to the technical field of ECG detection. The ECG device at present does not have a motion monitoring module, and cannot synchronously monitor and record the motion state of a user during long-term and continuous ECG monitoring, so that while an ECG is output, the motion state of the user cannot be provided synchronously for reference for medical personnel or an analysis program, thereby limiting the practicability of long-term and continuous ECG monitoring. The portable ECG machine provided by the invention is provided with a motion monitoring module, and can synchronously record motion data of the user during ECG measurement, a system in local or cloud calculates the exercise intensity according to original motion data, the system can synchronously output the exercise intensity and the average exercise intensity data of the user in a chart, color or grayscale mode while outputting the ECG, and medical personnel or the analysis program can judge the heart health condition of the user by combining exercise loads.
Owner:罗致远
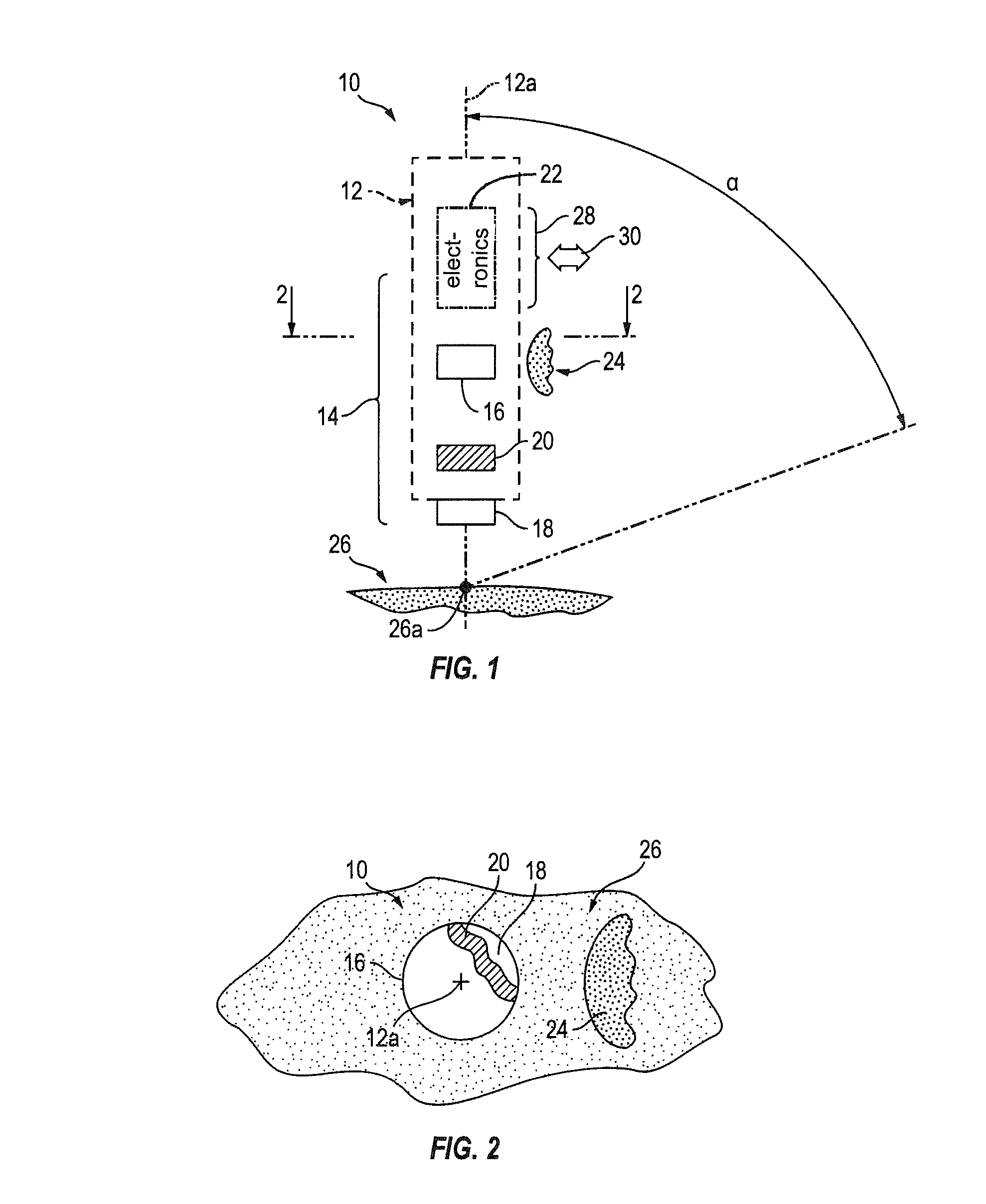
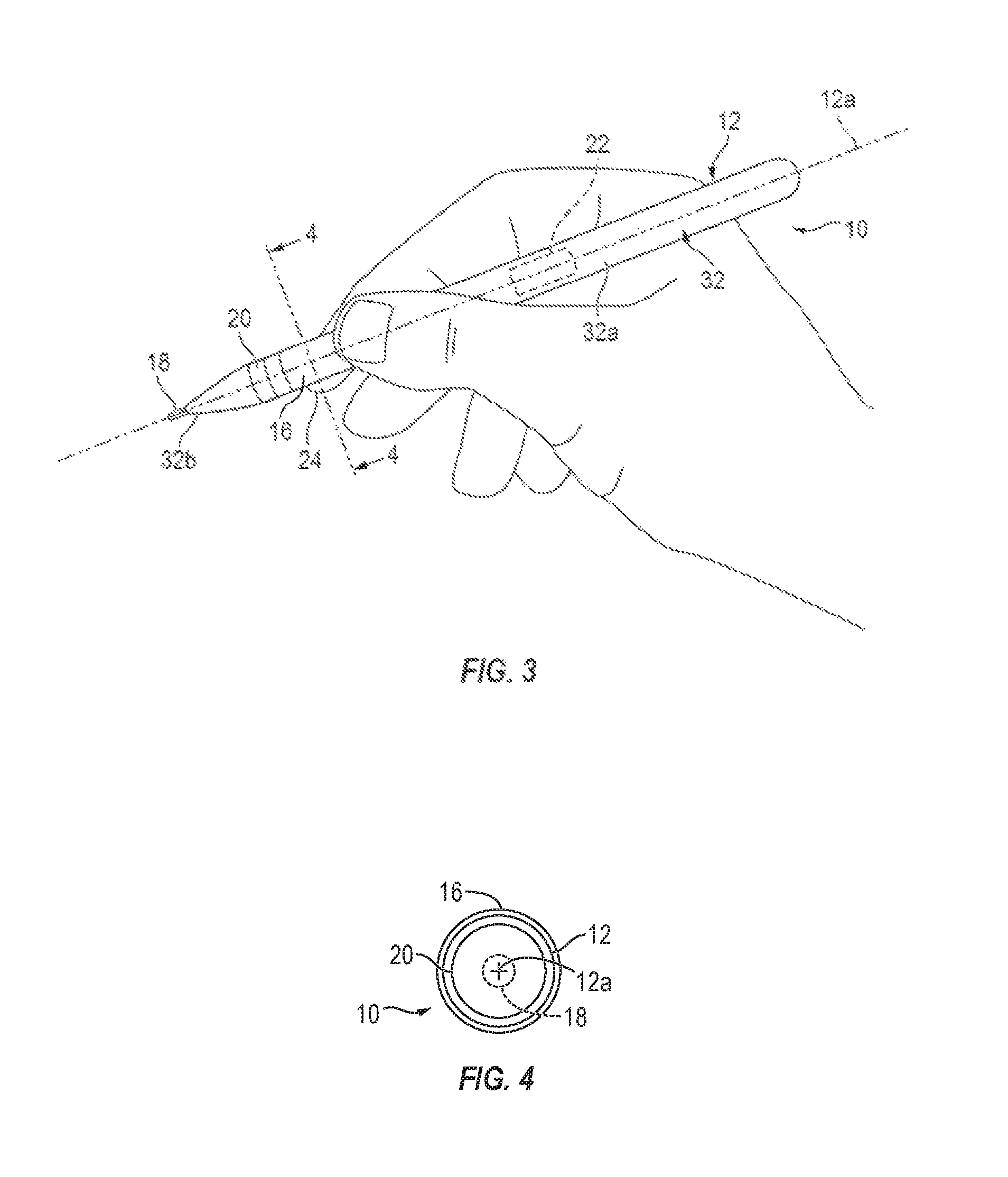
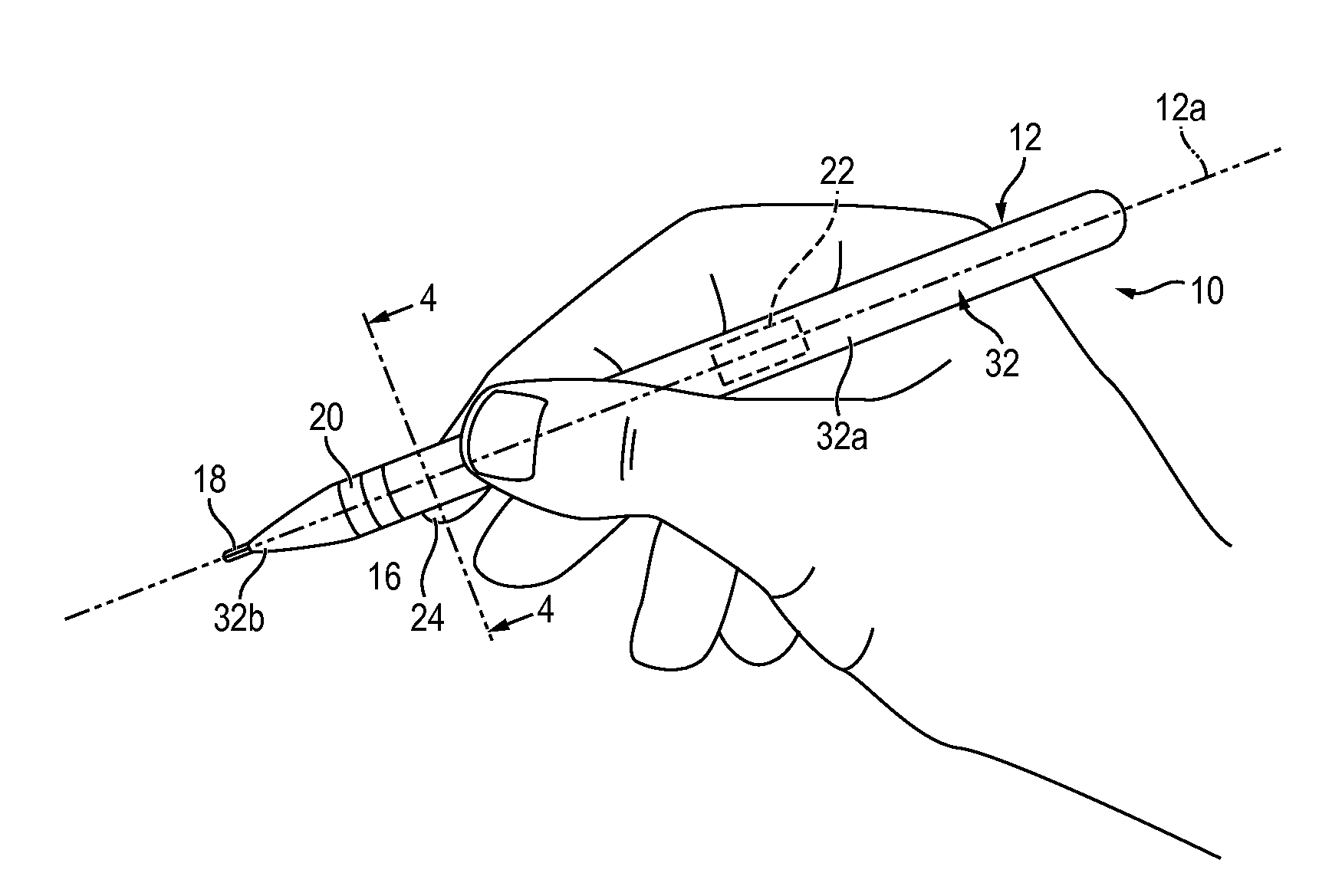
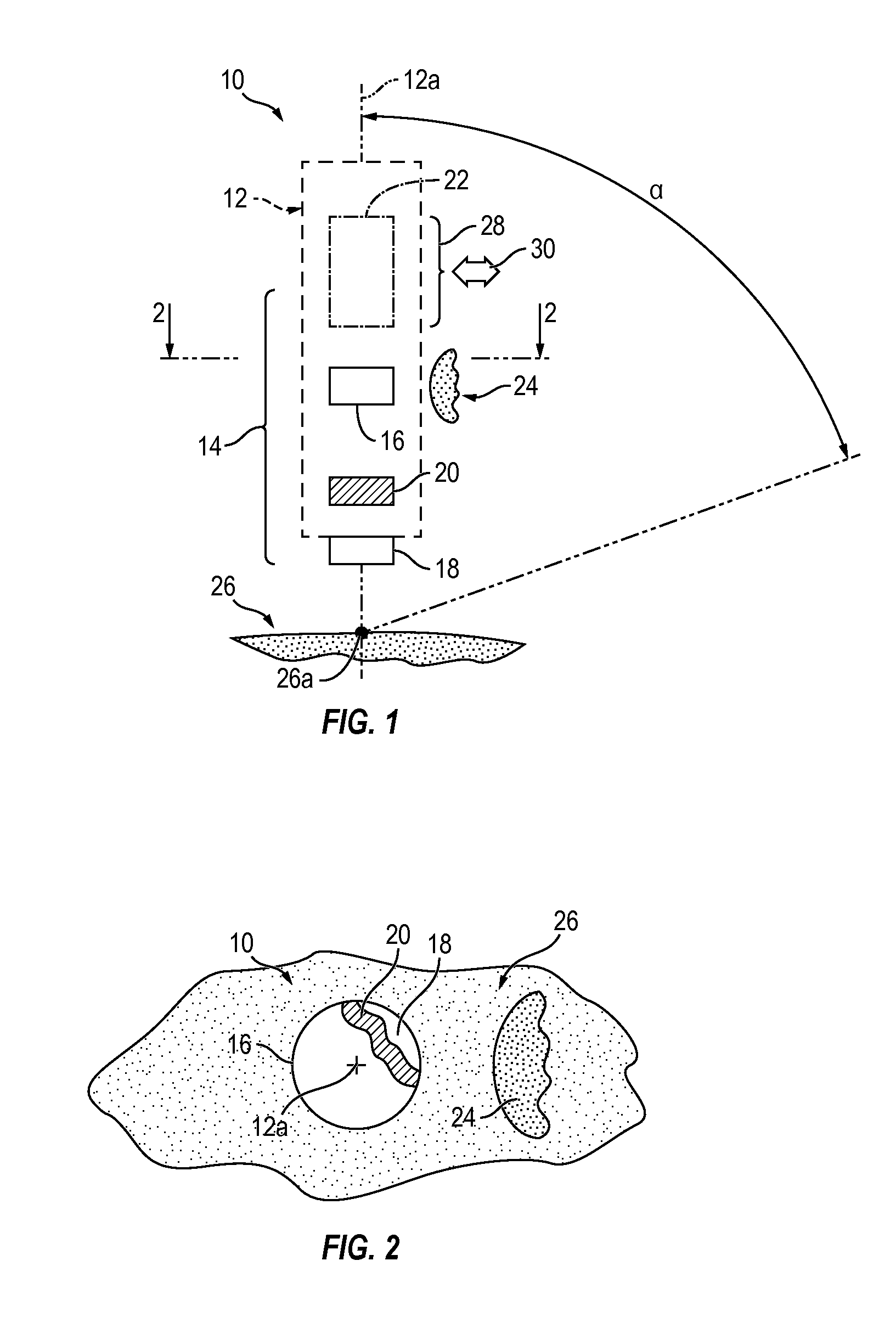
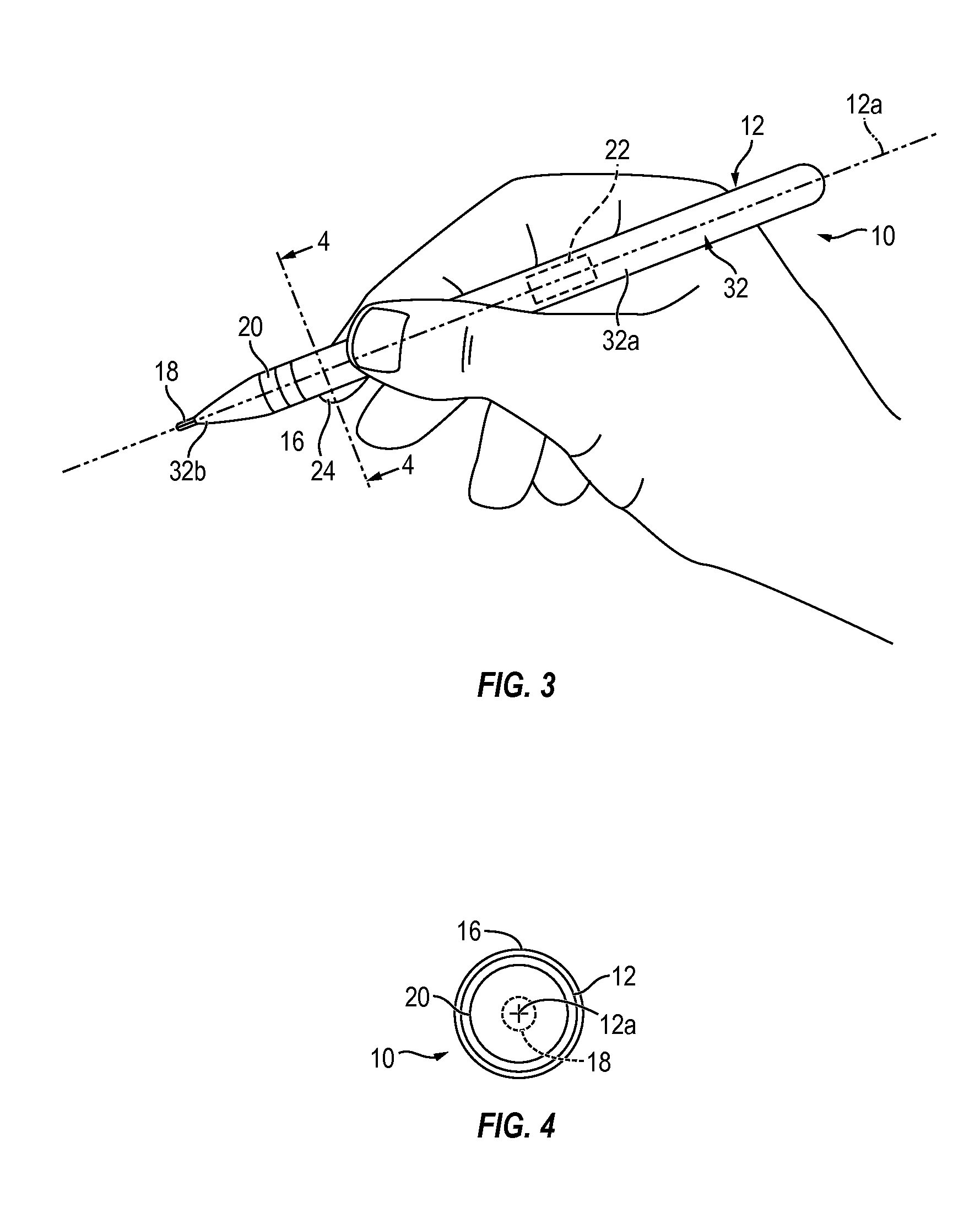
Hand-manipulable, ECG and acoustic, cardiography device
ActiveUS9451896B2Easy to operateEnhanced-user-friendliness equipmentElectrocardiographyStethoscopeInformation processingCardiovascular diagnosis
Compact, single-handedly manipulable, cardiography devices, structured for personal use in two, selectively different, functional-cardiography styles, enabling, respectively, one or both of (a) non-acoustic, and (b) acoustic, cardiography, such use involving, as appropriate to the particular functional-cardiography style to be implemented, the collecting and recording of personal cardiography-relevant data—ECG only in a non-acoustic case, and both ECG and heart-sound together in an acoustic case—suitable for subsequent data-analysis processing, and associated cardiovascular diagnosis. Two, representative device overall configurations are illustrated, including (1) a stylus pen-like shape, and (2) a finger-mountable ring-like shape. Collected-data analysis processing, and associated cardiovascular diagnosis, may be performed by device-included electronic information-handling structure, or may, via operation of such electronic structure, be communicated appropriately “outwardly” from the relevant device for external processing and analysis.
Owner:INOVISE MEDICAL
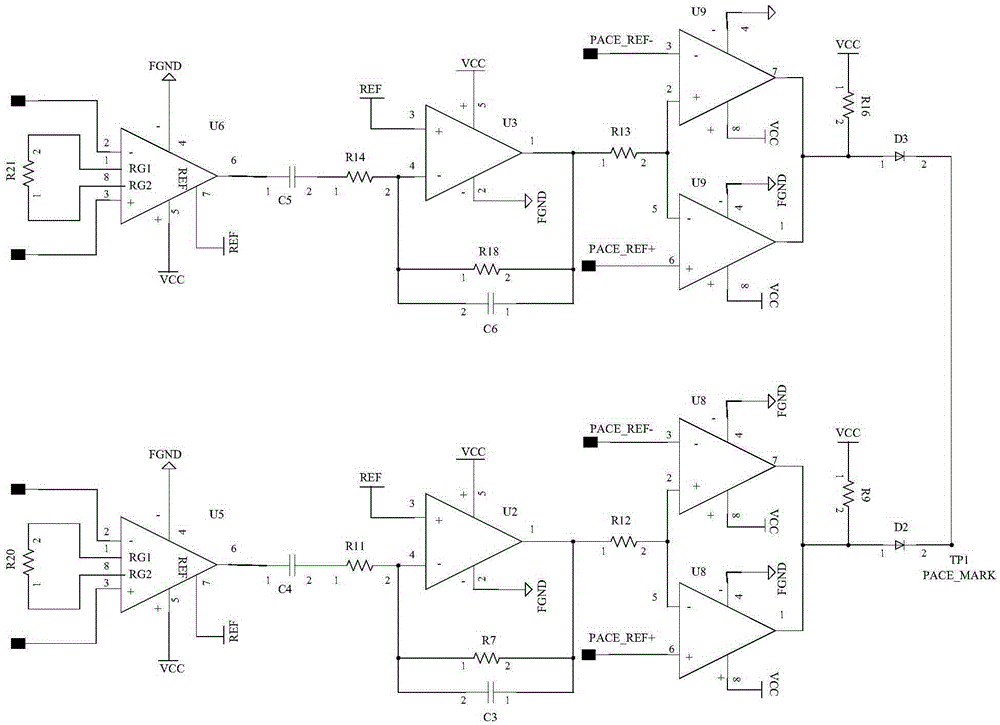
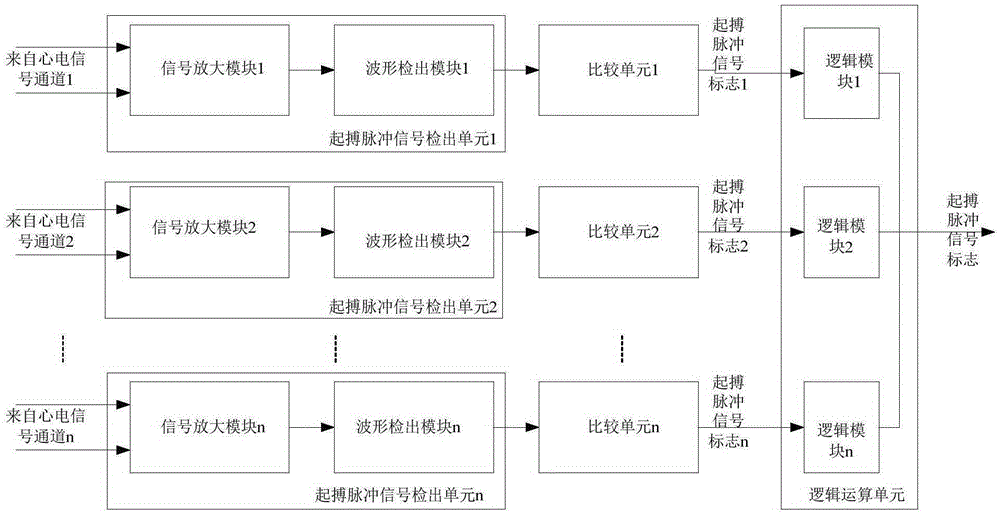
Cardiac electric pacing pulse signal detecting device and electrocardiogram equipment
ActiveCN105344007AAccurate judgmentImprove anti-interference abilityHeart stimulatorsEcg signalSignal on
The invention relates to a cardiac electric pacing pulse signal detecting device. The cardiac electric pacing pulse signal detecting device comprises a pacing pulse signal detection unit and a comparing unit, wherein the pacing pulse signal detection unit is used for screening pacing pulse signals from an electrocardiosignal channel, converting the pacing pulse signals into positive and negative pulse pairs with a zero crossing point and transmitting the obtained pulse pairs to the comparing unit; the comparing unit is used for respectively comparing positive and negative vertex levels of the inputted pulse pairs to set positive and negative threshold values; and comparison results are in parallel connection to obtain marker bits judging whether the cardiac electric pacing pulse signals on the electrocardiosignal channel exist or not. The invention also relates to electrocardiogram equipment using the cardiac electric pacing pulse signal detecting device. The cardiac electric pacing pulse signal detecting device and the electrocardiogram equipment thereof have the advantages of high judgment and antijamming capability and accuracy.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
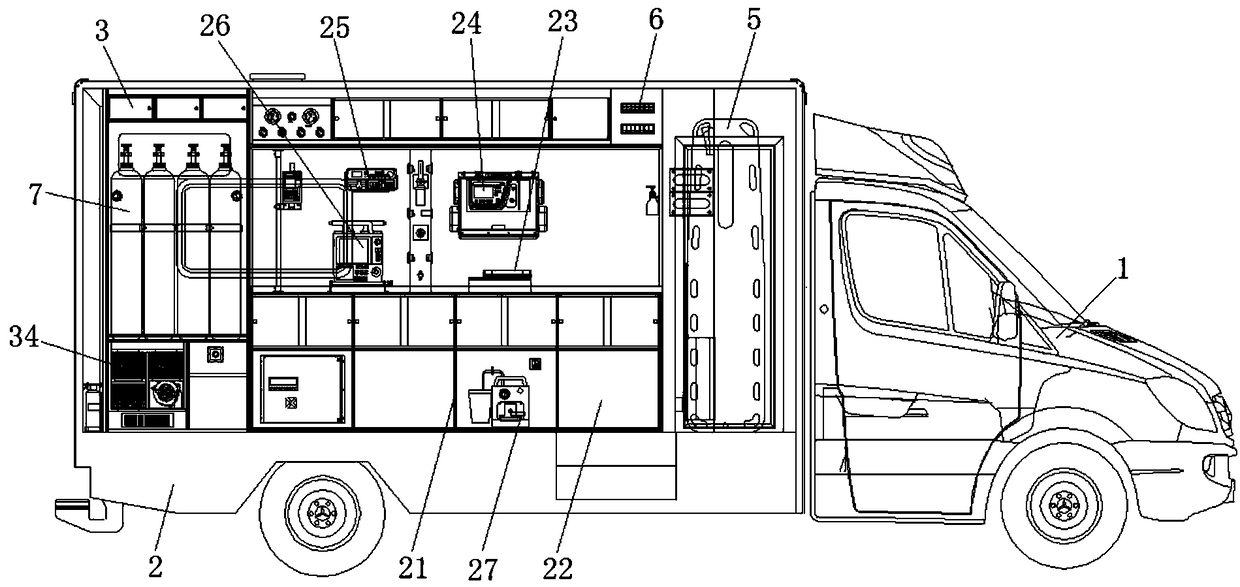
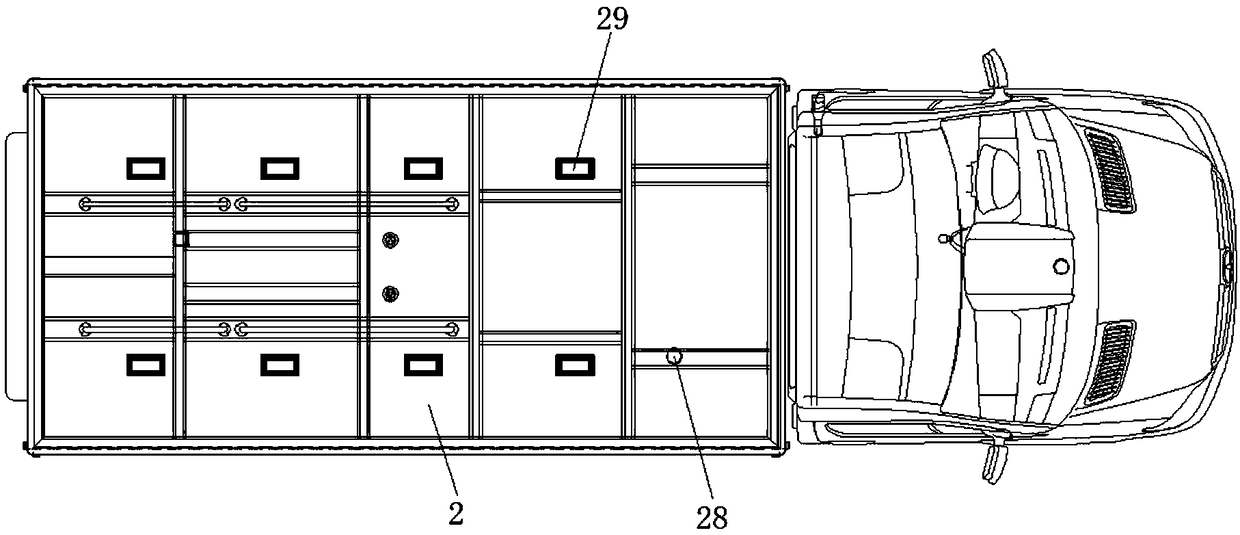
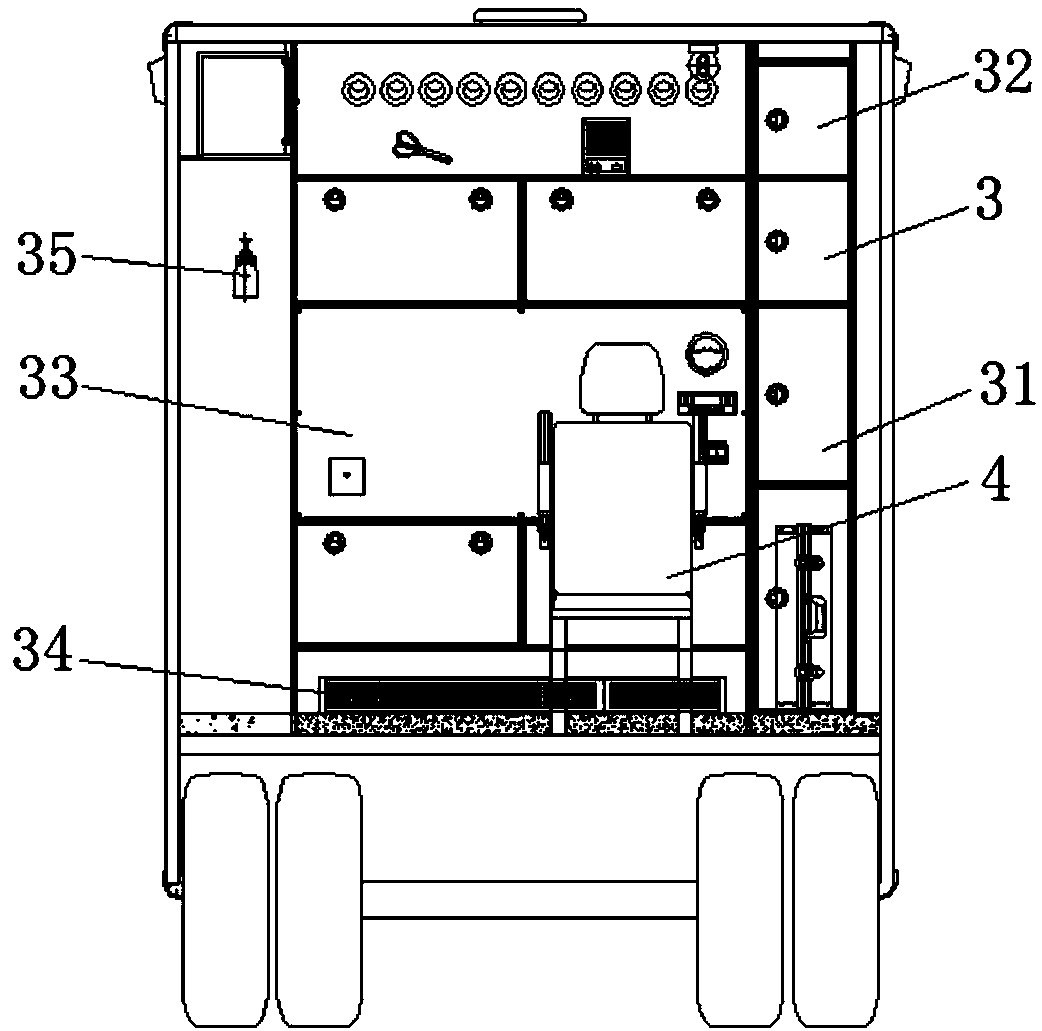
Intelligent ward-type ambulance for ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) emergency treatment
PendingCN109498291AEliminate arrhythmiasRestore sinus rhythmAmbulance serviceForeign matterEngineering
The invention discloses an intelligent ward-type ambulance for ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) emergency treatment. The intelligent ward-type ambulance comprises an ambulance body and a compartment, wherein the ambulance body is fixed to the bottom of the compartment and used for providing power and electric power for the compartment. The intelligent ward-type ambulance is characterizedin that emergency treatment equipment for on-site emergency treatment of critical patients is mounted inside the compartment and combined with a vehicular ECMO technology to finish the emergency treatment process of the critical patients. The emergency treatment equipment is arranged inside the ambulance body and comprises a cardio-pulmonary resuscitator, an electrocardiogram device, a respirator, an infusion and injection pump and a defibrillator, pulse current acts on a heart to implement electric-shock treatment and eliminate heart disorder, so that a heart restores sinus rhythm, the emergency treatment equipment is used in the emergency treatment process of the patients, an aspirator is used for adsorbing foreign matters in the surgical process, smoothness of the emergency treatment process is facilitated, so that the emergency treatment equipment can be combined with the vehicular ECMO technology in the emergency treatment process, the life of the critical patients is timely supported and rescued, and the use range of the ambulance is widened.
Owner:珠海鹏宇汽车有限公司
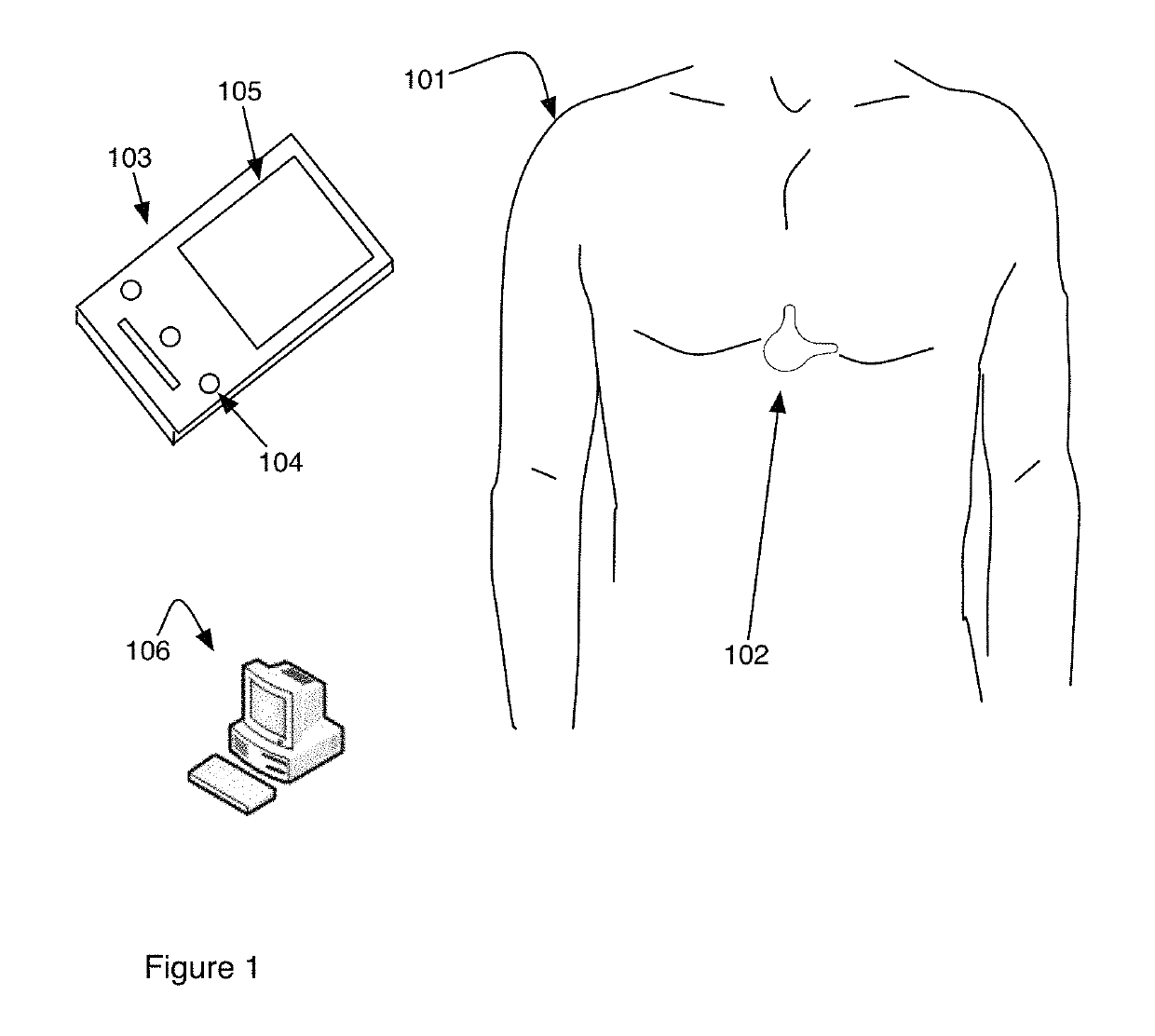
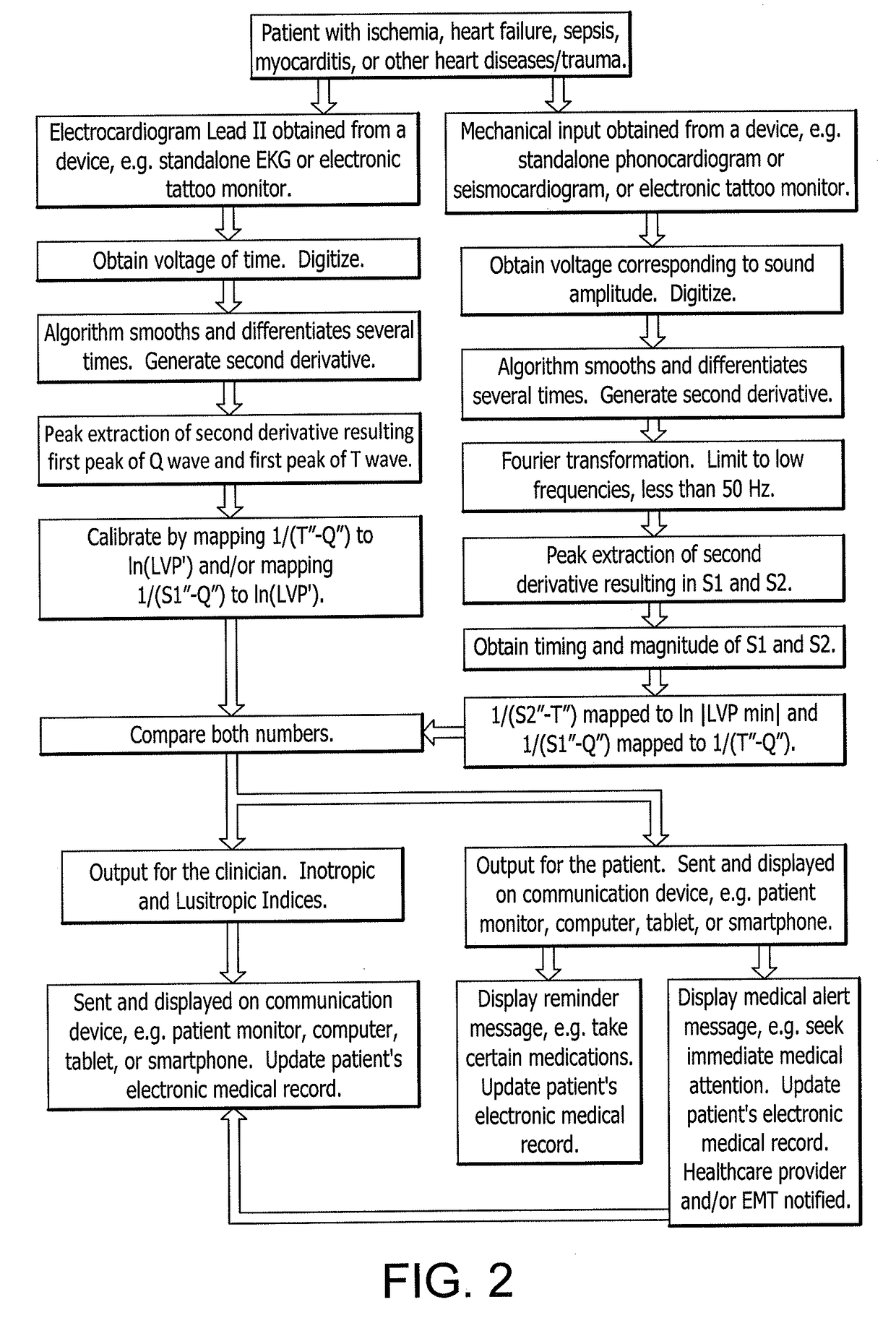
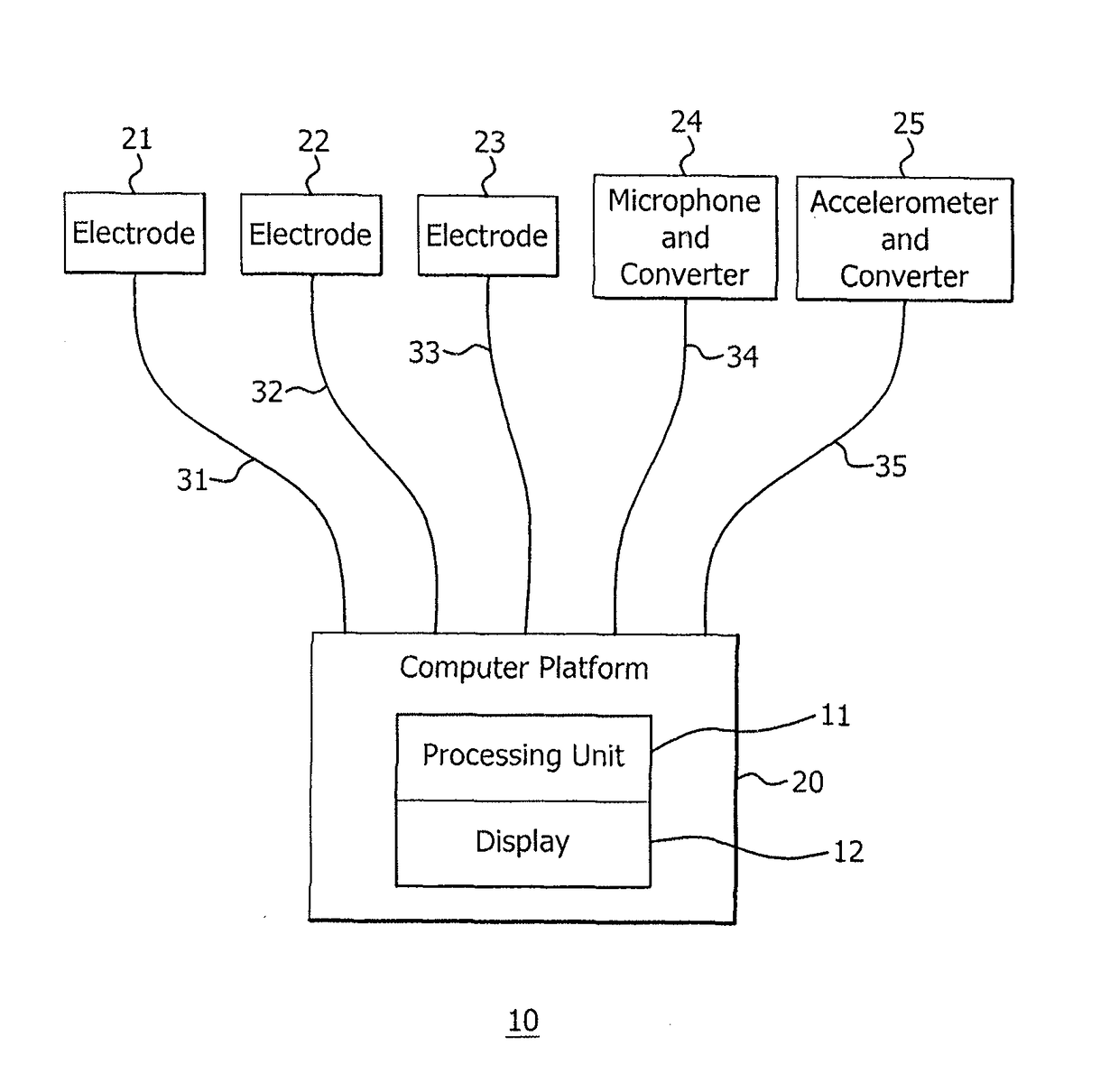
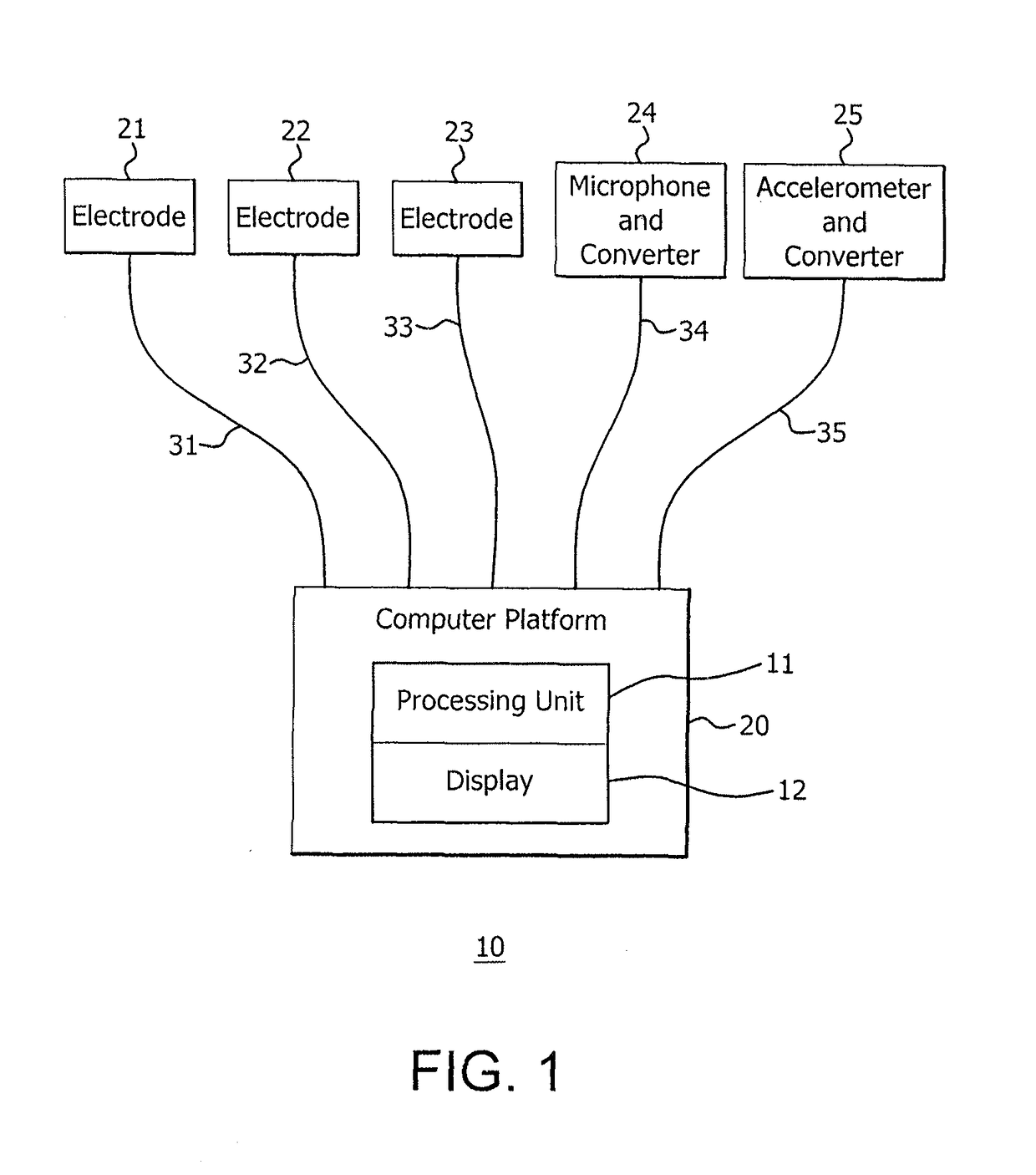
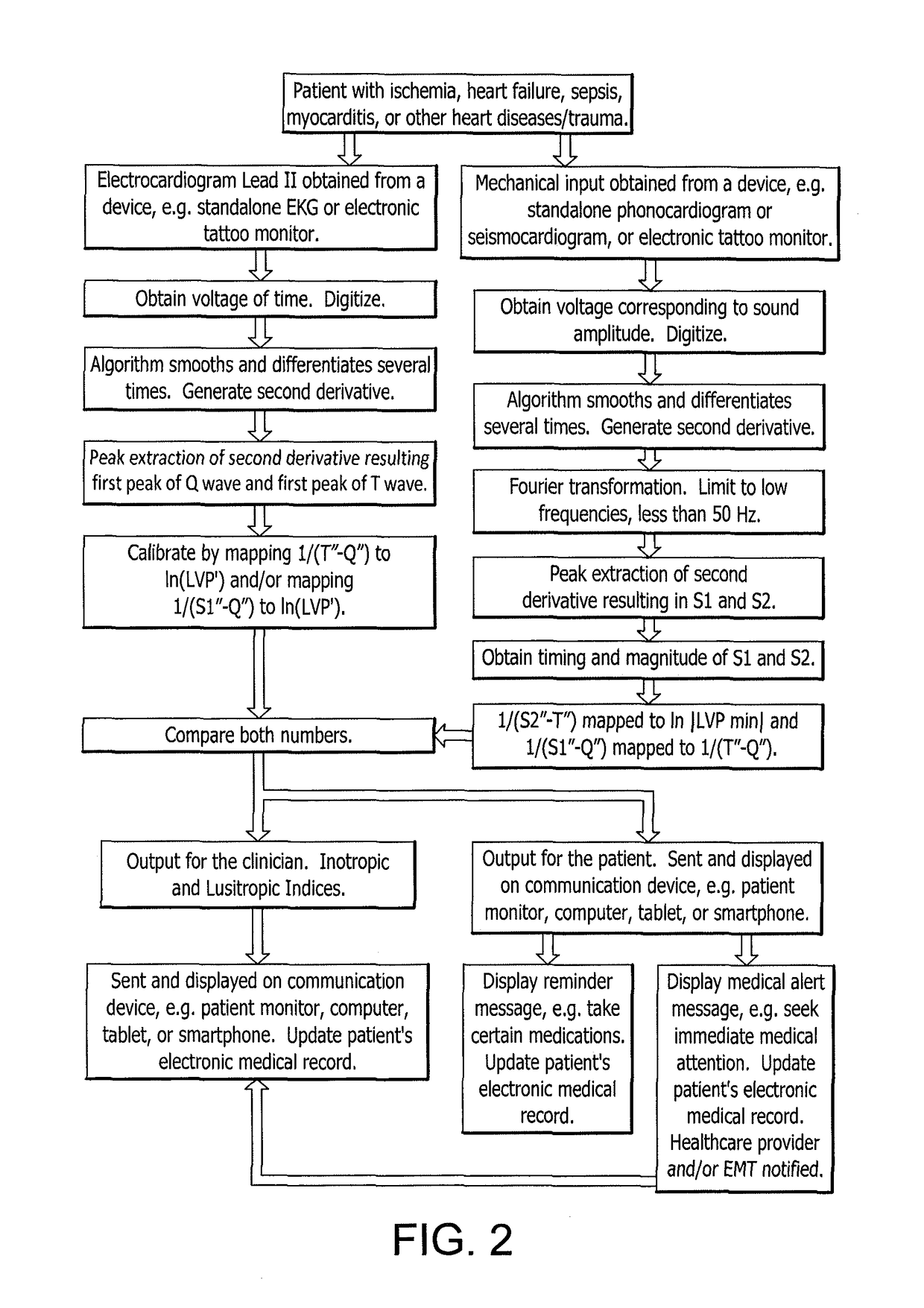
Non-invasive system and method for monitoring lusitropic myocardial function in relation to inotropic myocardial function
ActiveUS20180098709A1Faster and cheap and safe careExpand accessElectrocardiographyStethoscopeThe InternetCardiac activity
A system and method for non-invasively monitoring the hemodynamic state of a patient by determining on a beat-by-beat basis the ratio of lusitropic function to inotropic function as an index of myocardial well-being or pathology for use by clinicians in the hospital or by the patient at home. In one embodiment of the system a smartphone running an application program that is connected through the internet to the cloud processes electronic signals, first, from an electrocardiogram device monitoring electrical cardiac activity, and second, from a seismocardiogram device monitoring mechanical cardiac activity in order to determine such ratio as an instantaneous measurement of the hemodynamic state of the patient, including such states as sepsis, myocardial ischemia, and heart failure.
Owner:THE COOPER HEALTH SYST
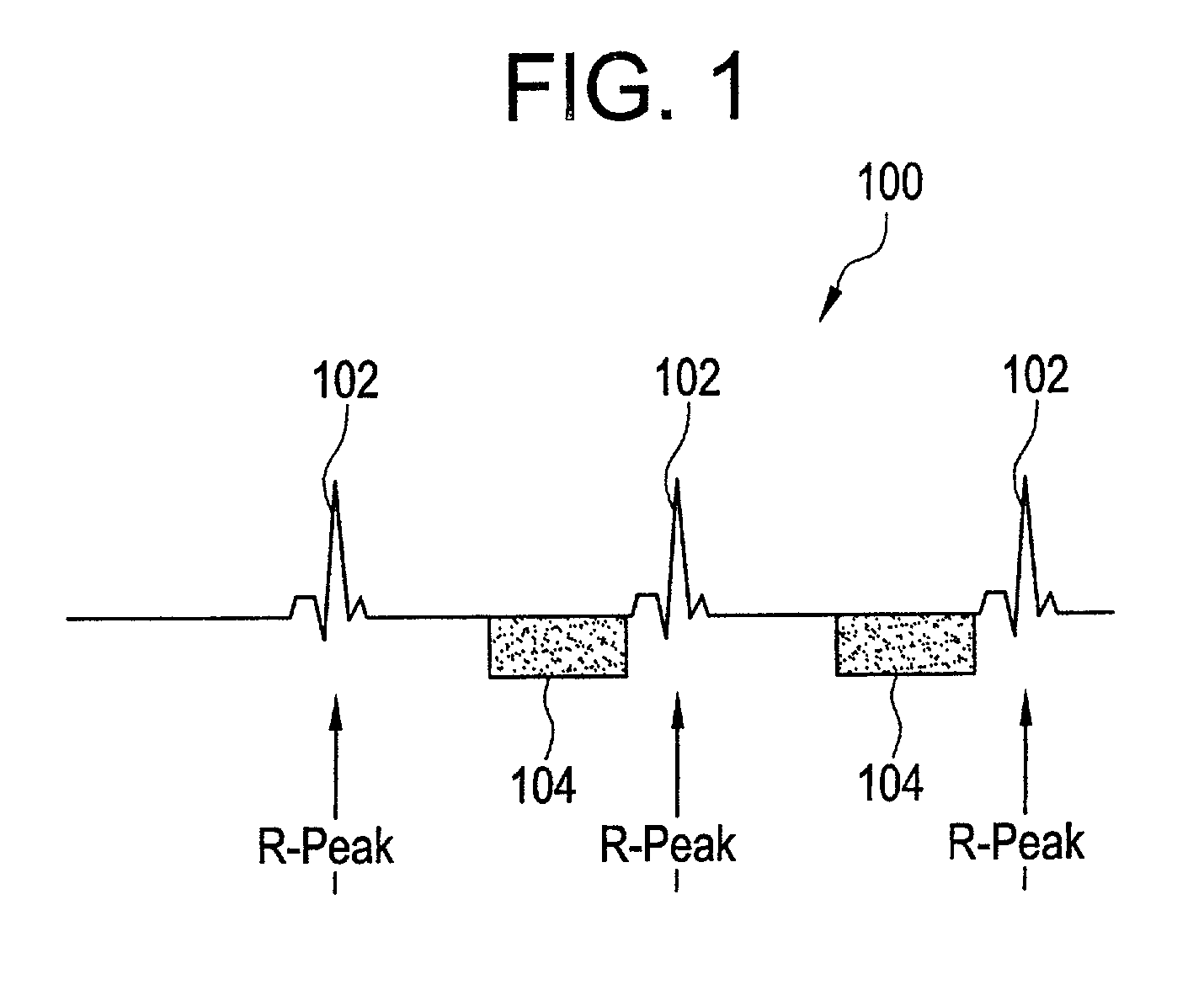
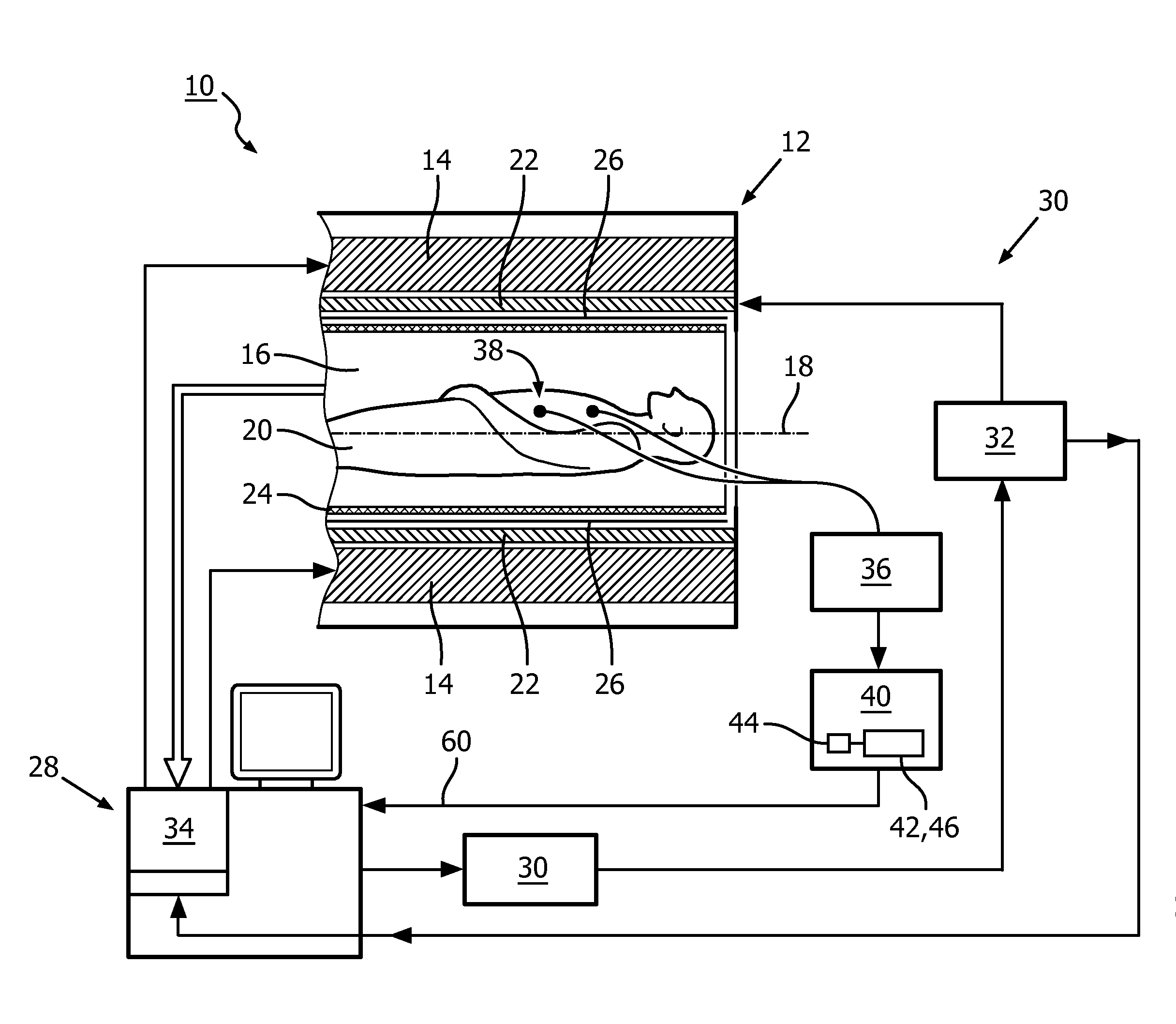
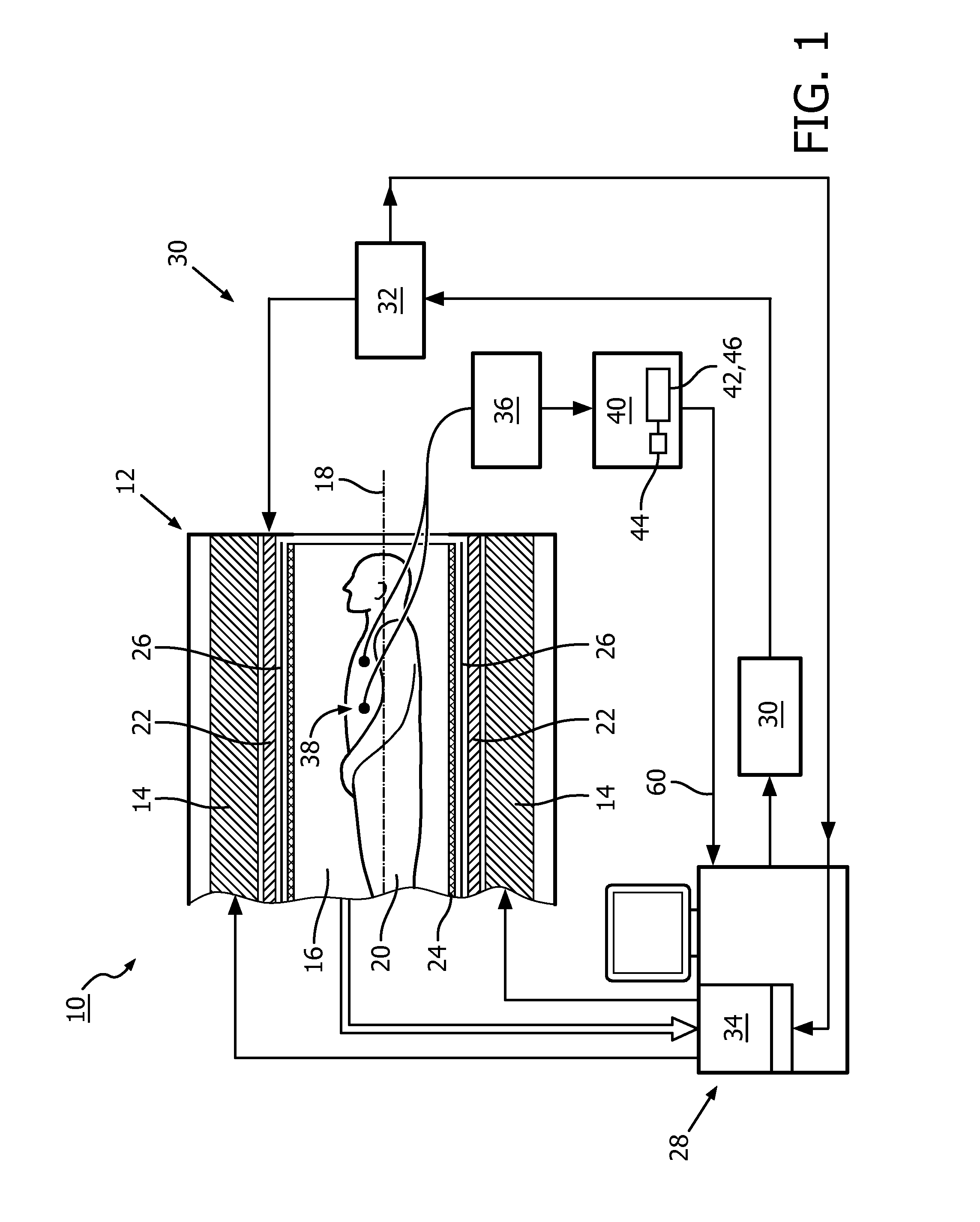
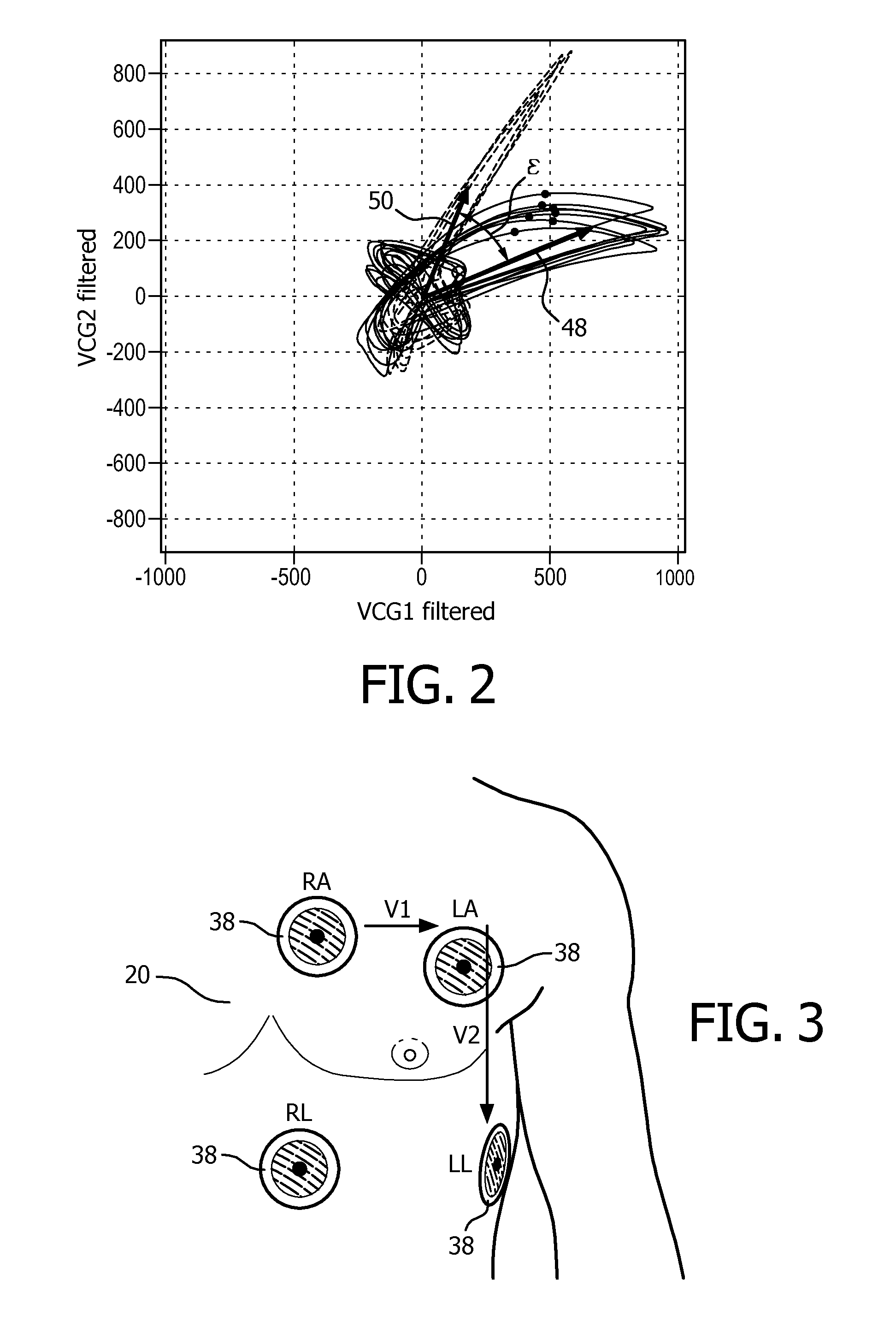
Improved ecg-based triggering for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160202337A1Reduce in quantityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging processingMedicine
A method of imaging, by means of magnetic resonance, at least a portion of a human or animal subject of interest (20) positioned in a static magnetic field, the method comprising: —taking measurements of electrocardiogram data; —generate vector cardiogram data from the electrocardiogram data; —determining at least one parameter of an acquisition period of acquiring magnetic resonance signals from the vector cardiogram data in order to synchronize measurement of magnetic resonance signals to a cyclic movement of the heart of the subject of interest (20); wherein the at least one parameter of the acquisition period is determined from an actual value of a discriminating function and a predetermined reference function, wherein for determining the at least one parameter of the acquisition period, a step of adapting at least one of the discriminating function and the predetermined reference function is executed, dependent on a breathing status of the human or animal subject of interest (20); and—a magnetic resonance imaging system (10) for acquisition of images of at least a portion of a human or animal subject of interest (20), synchronized to a cyclic movement of the heart of the subject of interest (20), comprising: —a control unit (28) for controlling functions of the magnetic resonance imaging system (10); —an image processing unit (34) provided for processing acquired magnetic resonance signals; —an electrocardiogram device (36) for taking measurements of electrocardiogram data of the heart of the subject of interest (20); —a synchronization unit (40) coupled to the electrocardiogram device (36) and configured for determining at least one parameter of an acquisition period from the vector cardiogram data, wherein the synchronization unit (40) is configured to provide trigger signals (60) indicative of the determined at least one parameter of the acquisition period to the control unit (28); and wherein the synchronization unit (40) is configured to adapt at least one of the discriminating function and the predetermined reference function, dependent on a breathing status of the human or animal subject of interest (20).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
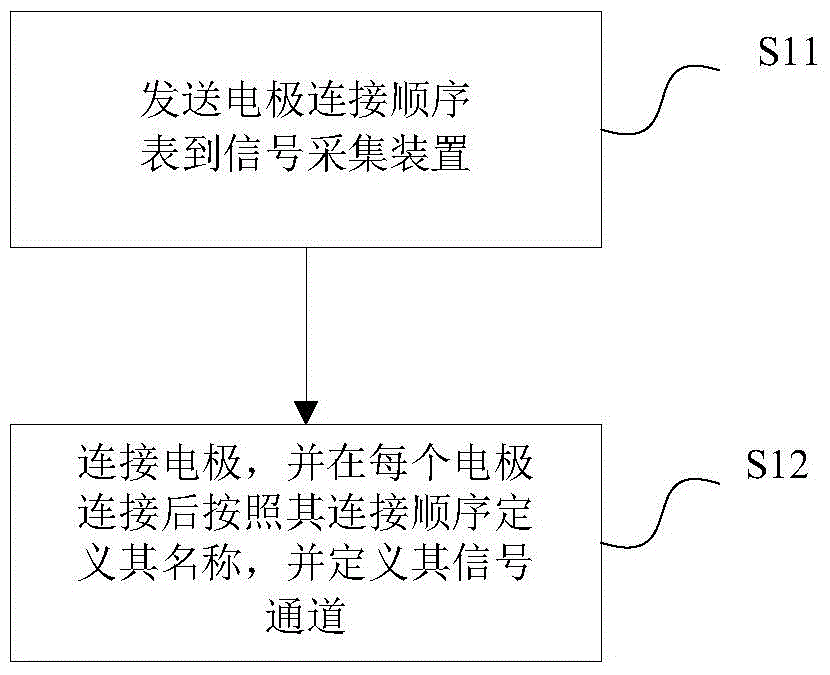
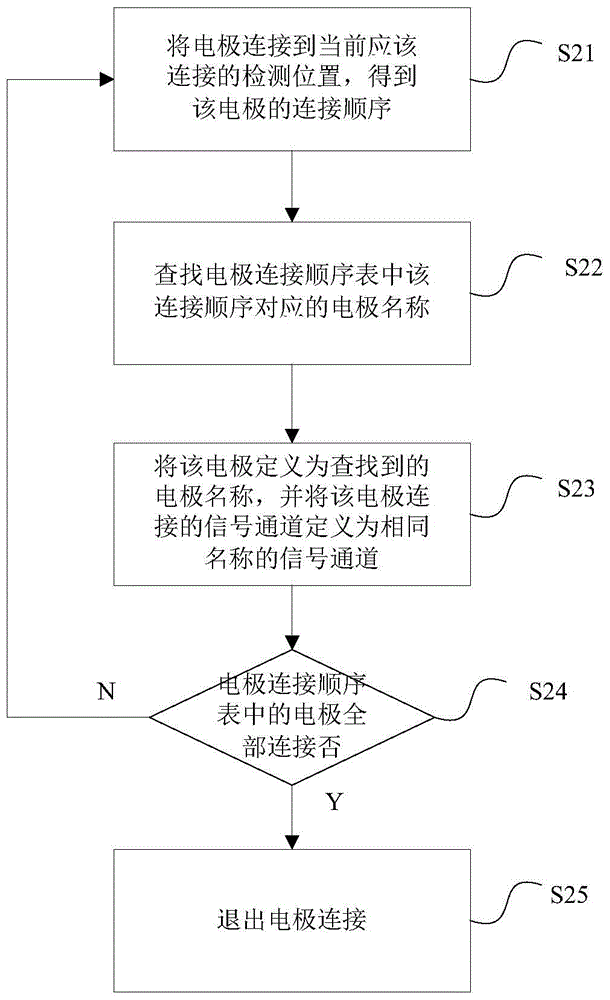
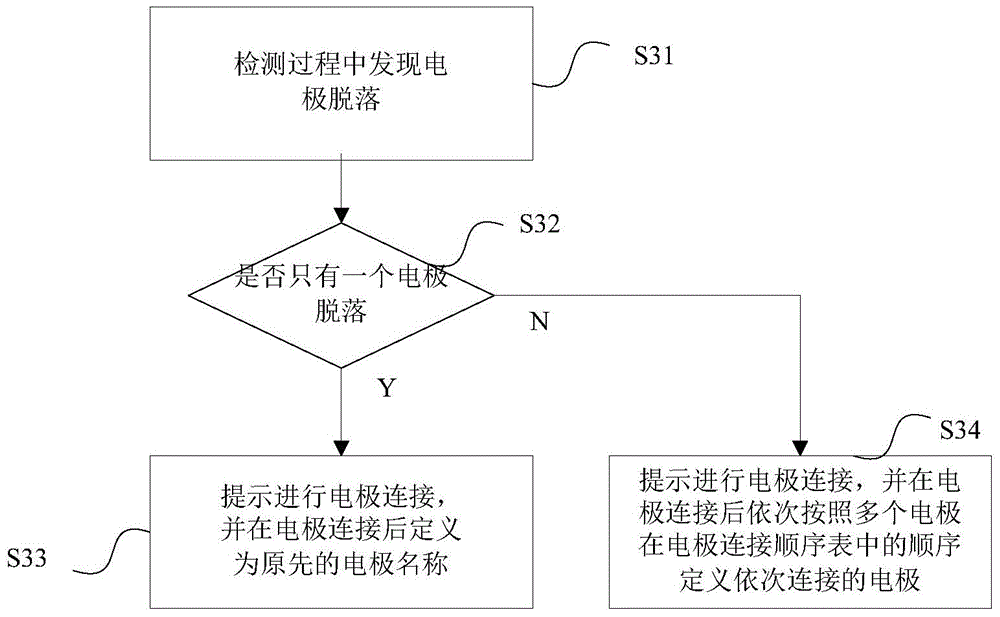
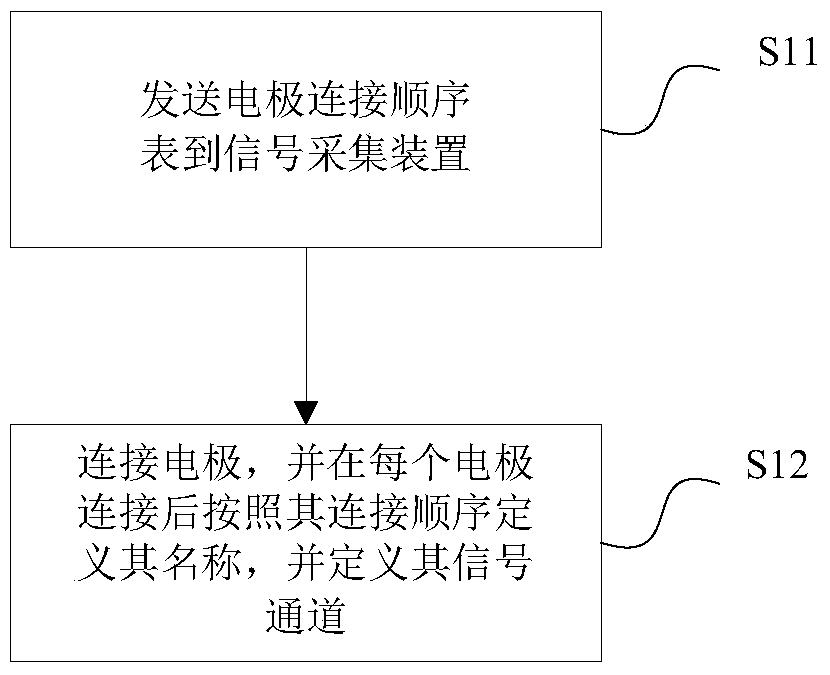
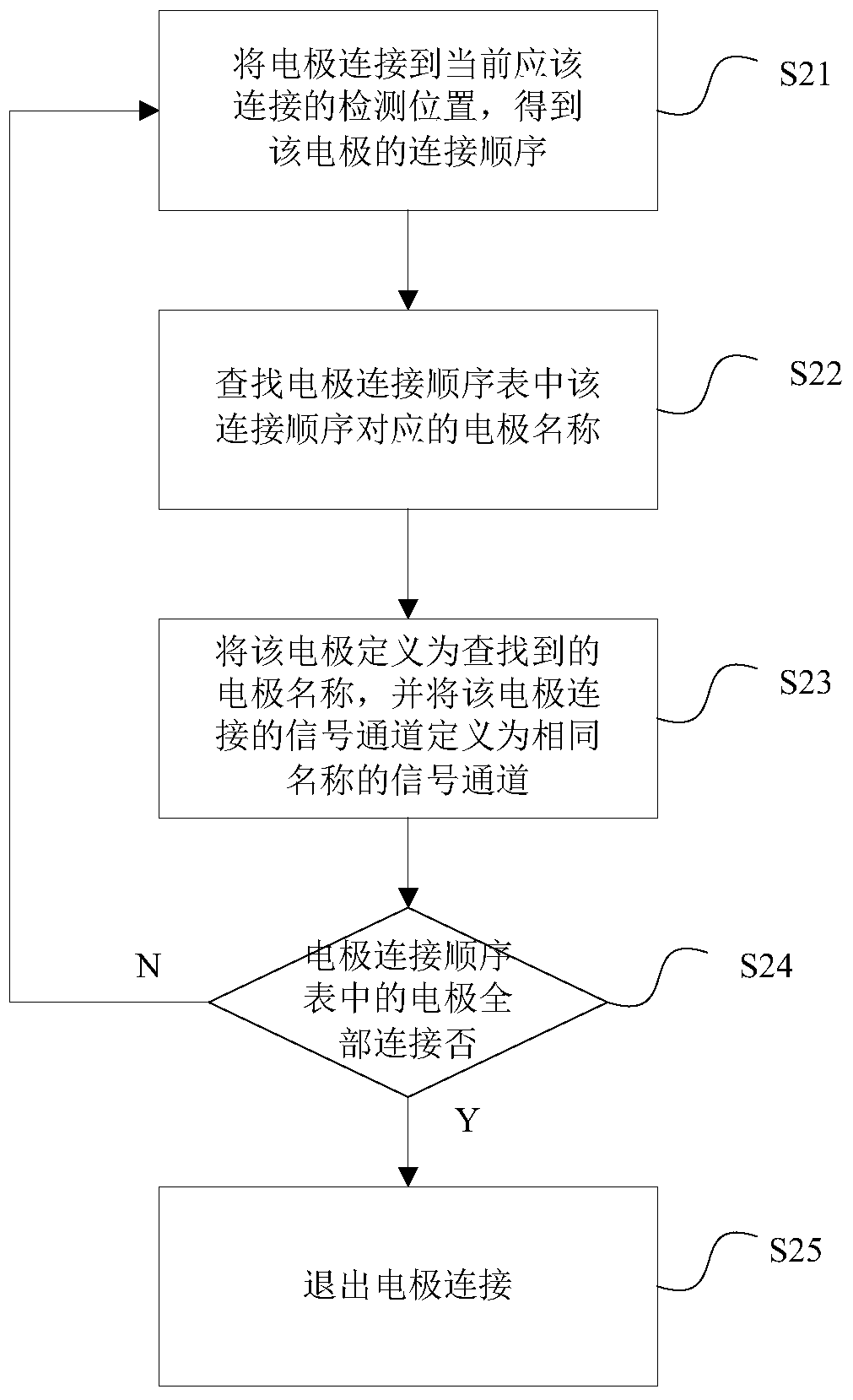
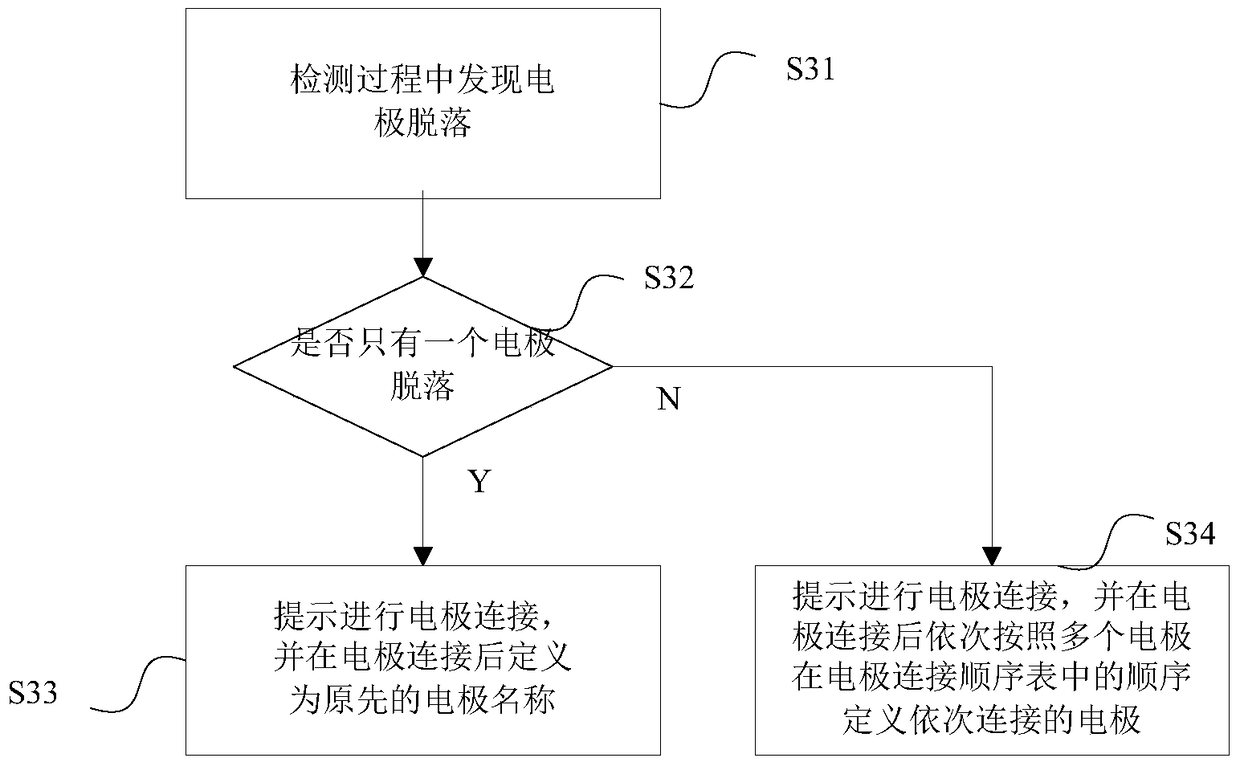
Electrode connection method and device for electrocardiogram equipment
ActiveCN105726020AEasy to useReduce workloadDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetocardiography deviceWorkload
The invention relates to an electrode connection method for electrocardiogram equipment. The method comprises the following steps that a preset electrode connection sequence list is sent to a signal collecting device of the electrocardiogram equipment; multiple electrodes are connected to corresponding positions of a measured person according to a set sequence, and after all the electrodes are connected, the electrodes are defined to be electrodes with the same positions in the electrode connection sequence list according to the positions of the connection sequence during the detection; signal channels connected with the electrodes are defined to be corresponding signal ports, signals collected by the electrodes can pass the signal channels, and names for the defined electrodes serve as signal names of the signals and are input into the electrocardiogram equipment. The invention further relates to a device achieving the method. The electrode connection method and device for the electrocardiogram equipment have the advantages that use is more convenient, and the workload is small.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
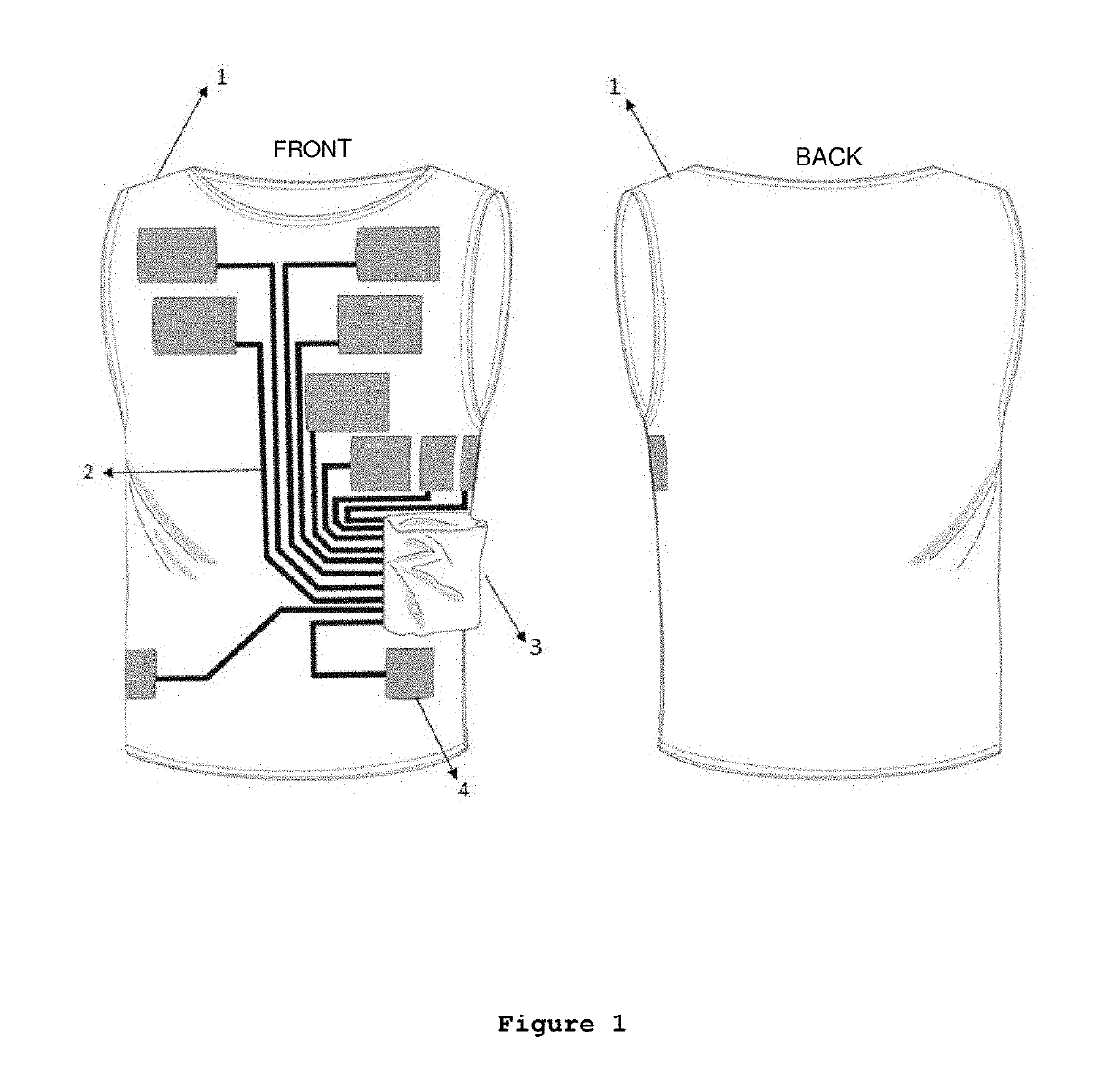
Wearable electrocardiographic monitoring technology (ECG) with an airtight container for medicines, and integrated medical monitoring system
ActiveUS20190313968A1Shortening time to definite treatmentSmall article dispensingGarment special featuresCardiac lesionModem device
The present invention refers to a wearable, individual, customized and different sized technology for men and women, composed of electrodes, conductive track and airtight container for medicines, coupled to one another, and a mini electrocardiogram (ECG) apparatus containing a GSM (Global System Mobile) modem and a GPS (Global Positioning System) or a Bluetooth system which, through a wireless network specification within a personal scope (Wireless Personal Area Networks—PANs) deemed as PAN-type or even WPAN, the electrical signal acquisition begins when the user press the button down. It is in the field of medical, recreational and / or sport applications, aiming at monitoring patients at high cardiovascular risk, being possible to diagnose it as soon as possible, aiming at shortening time to definite treatment of those who present acute coronary syndrome (ACS), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), acute atrial fibrillation-type (AAF) cardiac arrhythmias, and other cardiac arrhythmias or other cardiac pathologies capable to be detected by the electrocardiographic trace. Moreover the invention has tools to analyze a bunch of data—big data analytics and deeplearning—by utilizing artificial intelligence. Finally, the invention also has a module to proper administer the drug contained into the airtight container.
Owner:LOTUS MEDICINA AVANCADA
System and method of quality analysis in acquisition of ambulatory electrocardiography device data
A quality control system in combination with an ECG data analysis system to analyze ECG data acquired by an ambulatory electrocardiography device via a cable having a plurality of leads connected to a subject is provided. The quality control system includes a memory having programmable instructions for execution by a processor to perform the steps of calculating a trend of a quality score in the ECG data dependent on a noise content in the ECG data; and calculating a probability that one of a hardware and the Hookup personal, each associated with collecting the ECG data from the subject, is a substantial cause of the quality score for the ECG data. The probability can be calculated based on a comparison the trend of the quality score associated with the Hookup personnel versus the trend of the quality score of the hardware employed in acquiring the ECG data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
ECG device
ActiveUS20190183369A1Maximize potential outputOutput maximizationElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsPotential differenceMagnetocardiography device
We disclose a portable wearable device for measuring electrocardiographic signals, the device comprising a first portion comprising at least two electrodes; a second portion comprising at least three electrodes; the first portion and the second portion being vertically spaced from one another; a controller configured to take: a first potential difference measurement using one of the electrodes of the first portion and one of the electrodes of the second portion; a second potential difference measurement using one other of the electrodes of the first portion and one other of the electrodes of the second portion; and a third potential difference measurement using one other of the electrodes of the first portion and one other of the electrodes of the second portion. The controller is configured to simultaneously take the first, second and third potential difference measurements at three independent positions of a user's body.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE HEARTWEAR LTD
Method and system for performing real-time cardiac monitoring by using wearable electrocardiogram device
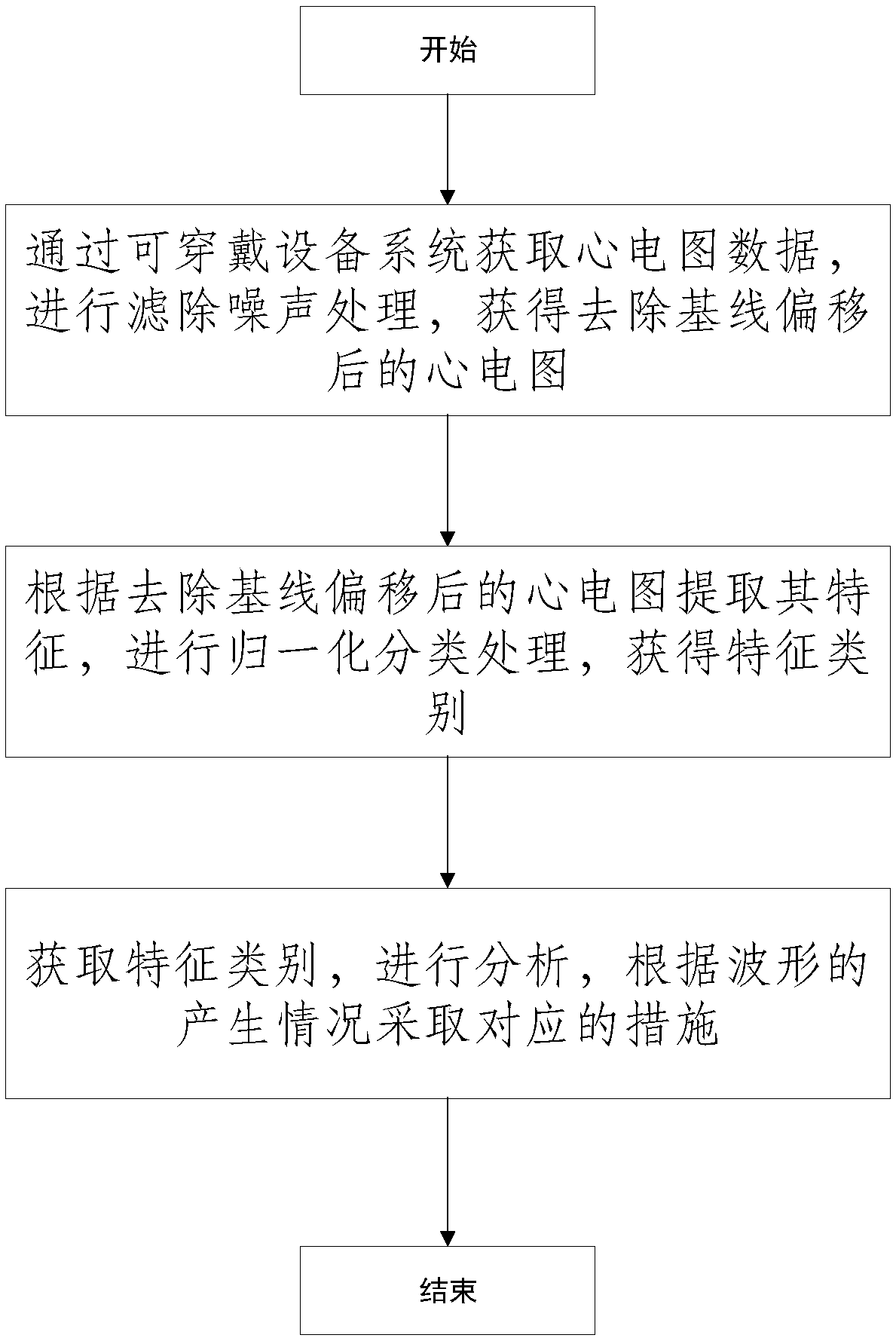
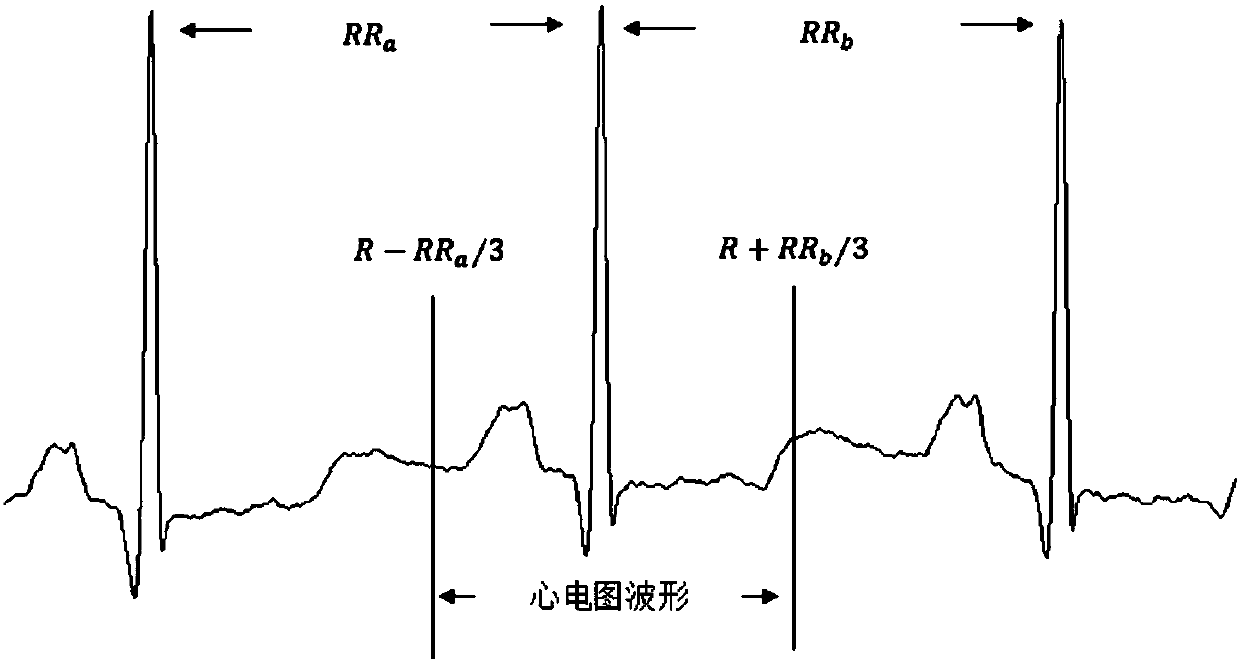
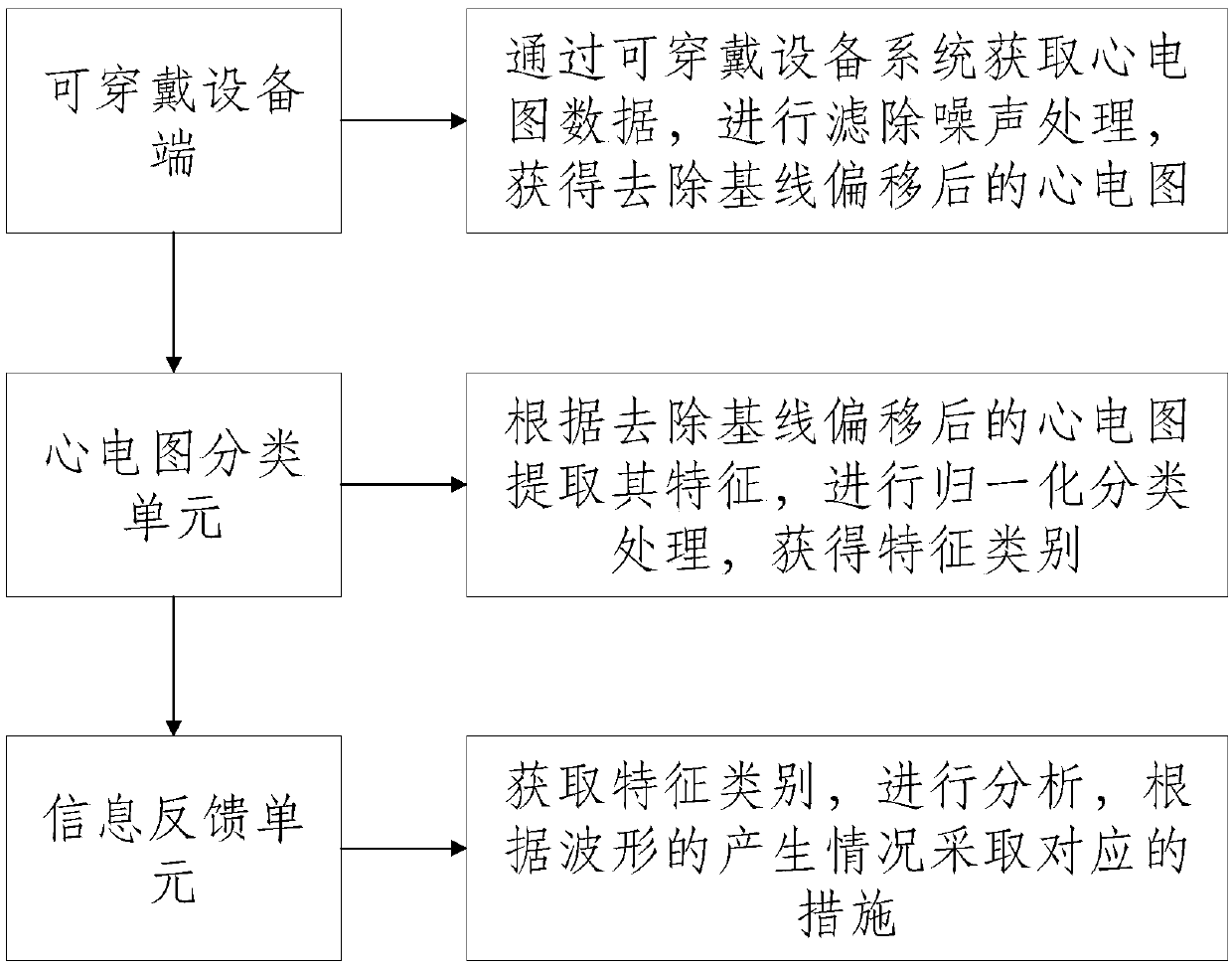
InactiveCN107736888AEasy to operateHealth status is easily monitoredUser/patient communication for diagnosticsSensorsMobile appsCardiac monitoring
The invention discloses a method and a system for performing real-time cardiac monitoring by using a wearable electrocardiogram device. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining electrocardiogram data through a wearable device system, performing noise filtering, and obtaining a baseline shift-removed electrocardiogram; extracting the characteristics according to the baseline shift-removed electrocardiogram, and performing normalized classification to obtain a characteristic category; analyzing the obtained characteristic category, and taking corresponding measures according to the waveform generation situation. By implementing the embodiment of the invention, the cardiac health situation of patients whose cardiac health conditions are difficult to know and who are difficult to rescue in emergency situations can be easily monitored by a simple operation method; by using a mobile APP, two levels of danger warnings are established, the first level of danger warning helps the patients learn of cardiac discomfort and the second level of danger warning alerts emergency contacts that the patients are in an unexpectedly dangerous condition.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Cardiac ejection fraction calculation method and device
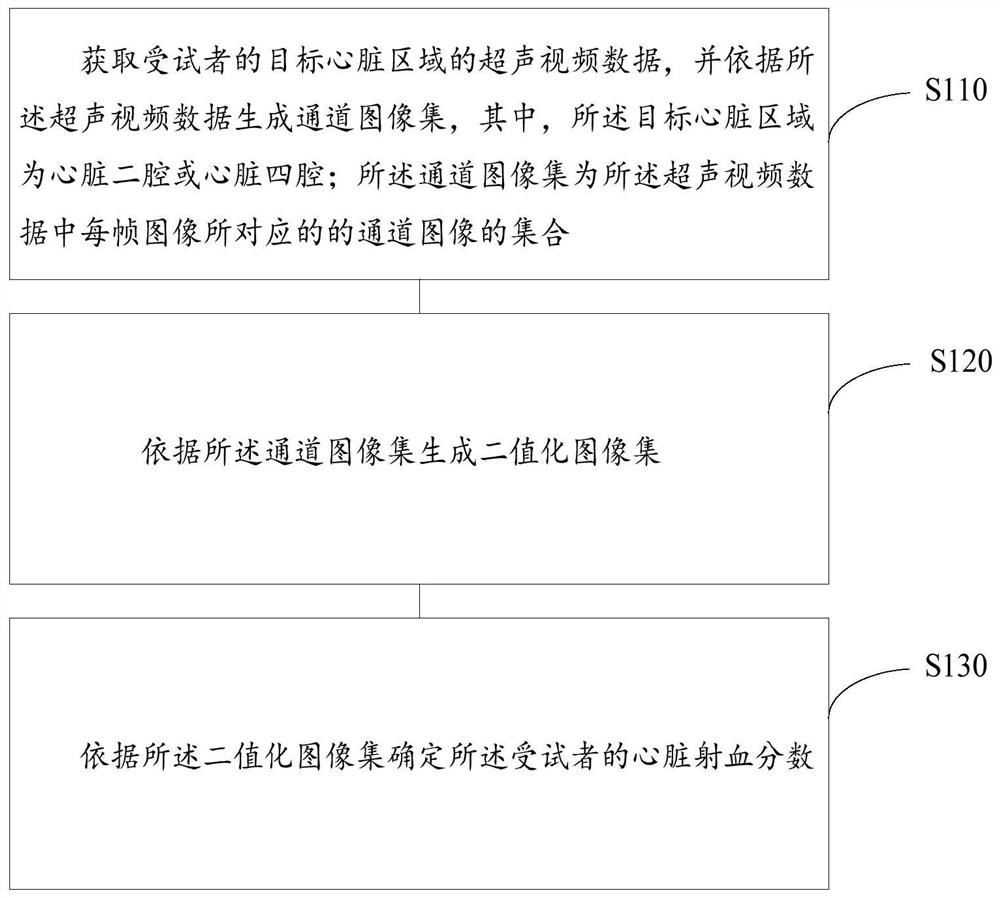
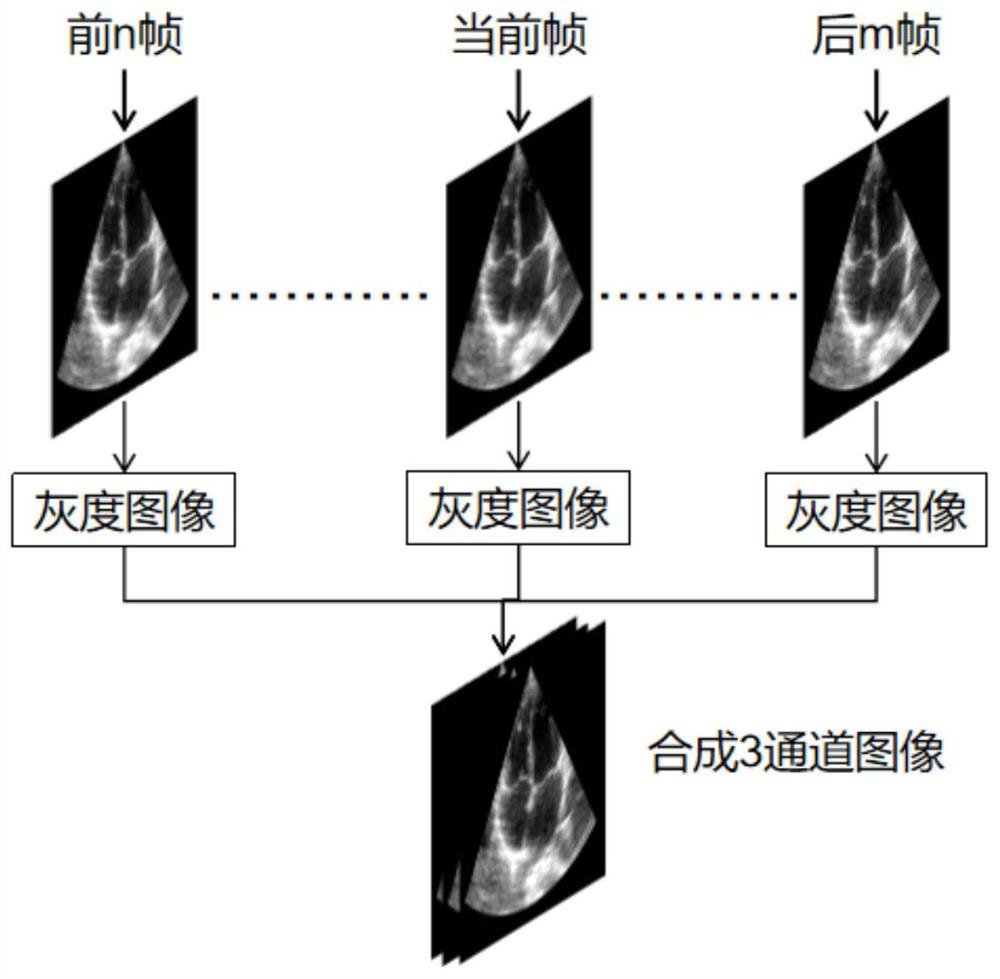
PendingCN112381895ARealize automatic calculationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleMagnetocardiography device
The embodiment of the invention provides a cardiac ejection fraction calculation method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining ultrasonic video data of a target cardiac region of asubject, and generating a channel image set according to the ultrasonic video data, wherein the target heart region is a cardiac two-cavity or heart four-cavity; wherein the channel image set is a setof channel images corresponding to each frame of image in the ultrasonic video data; generating a binary image set according to the channel image set; and determining the cardiac ejection fraction ofthe subject according to the binarized image set. By utilizing the self-learning function of the neural network, the cardiac ejection fractions of multiple cardiac cycles are automatically calculated, the defects of a traditional calculation method are overcome, the method does not depend on other devices such as electrocardiogram devices and cross-cardiac cycle analysis devices, and the invention has the advantages of being high in accuracy, high in usability, repeatable and the like. Sufficient and accurate reference data is provided for classification, diagnosis and treatment of heart failure.
Owner:深圳蓝影医学科技股份有限公司
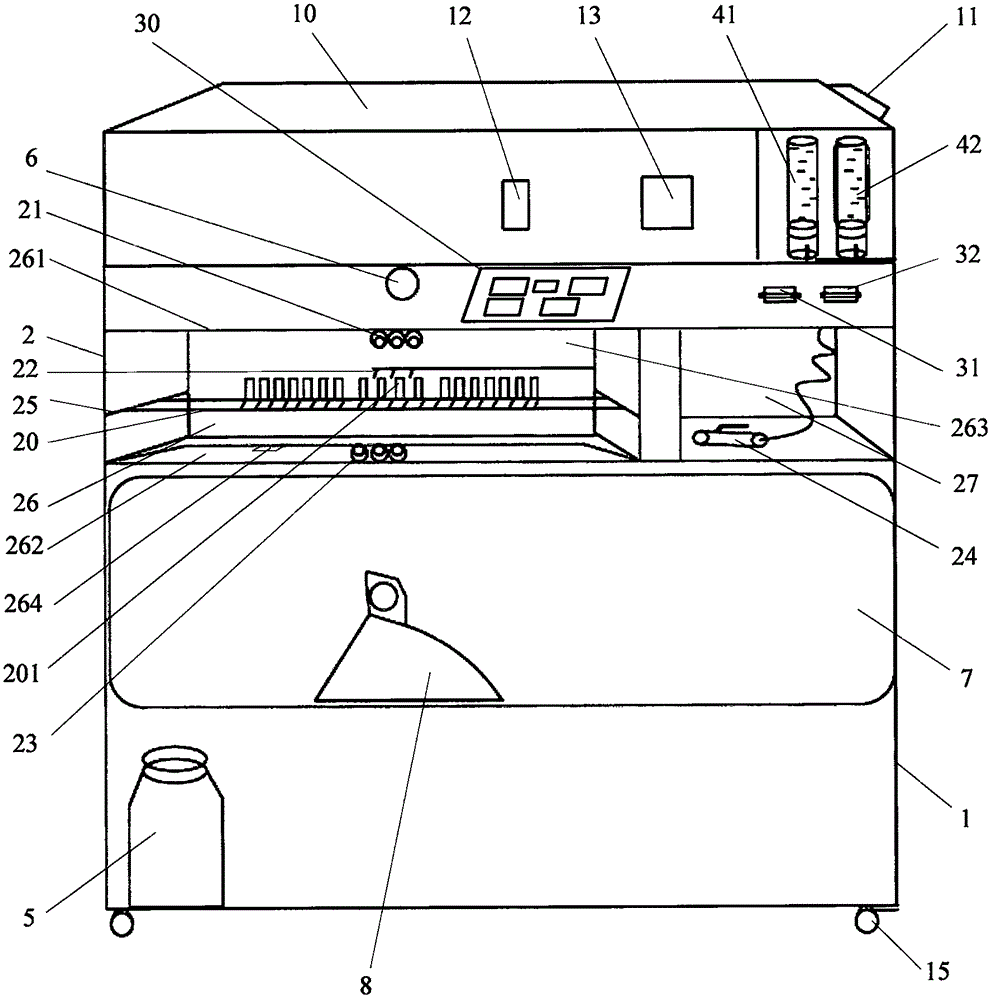
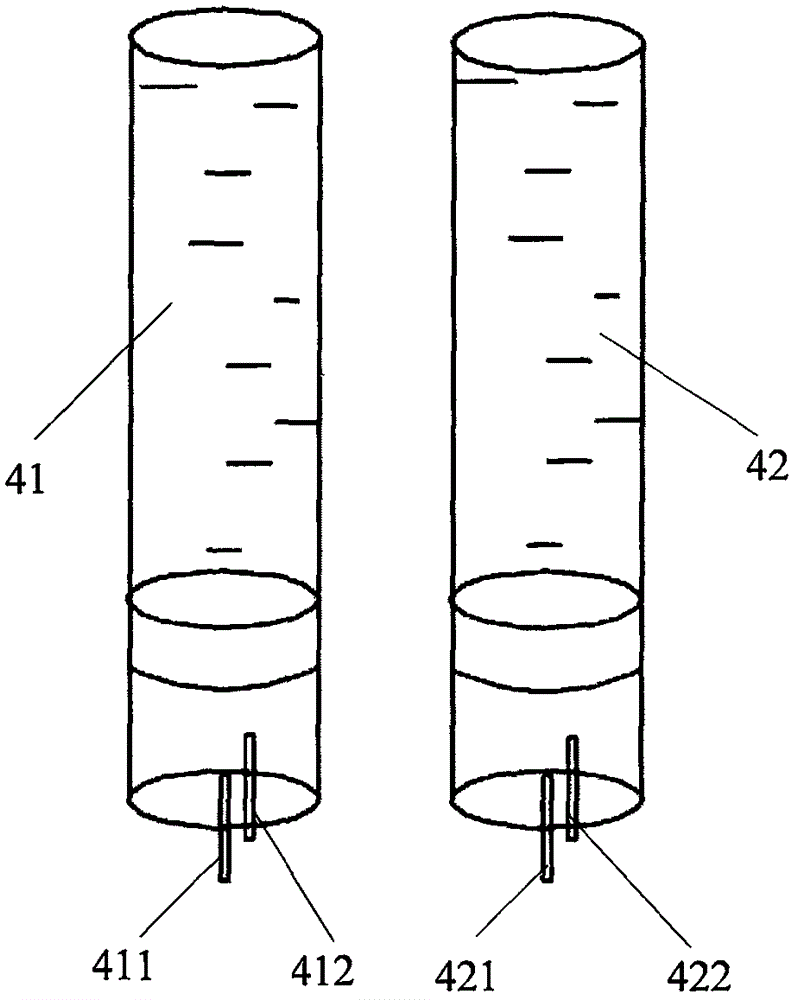
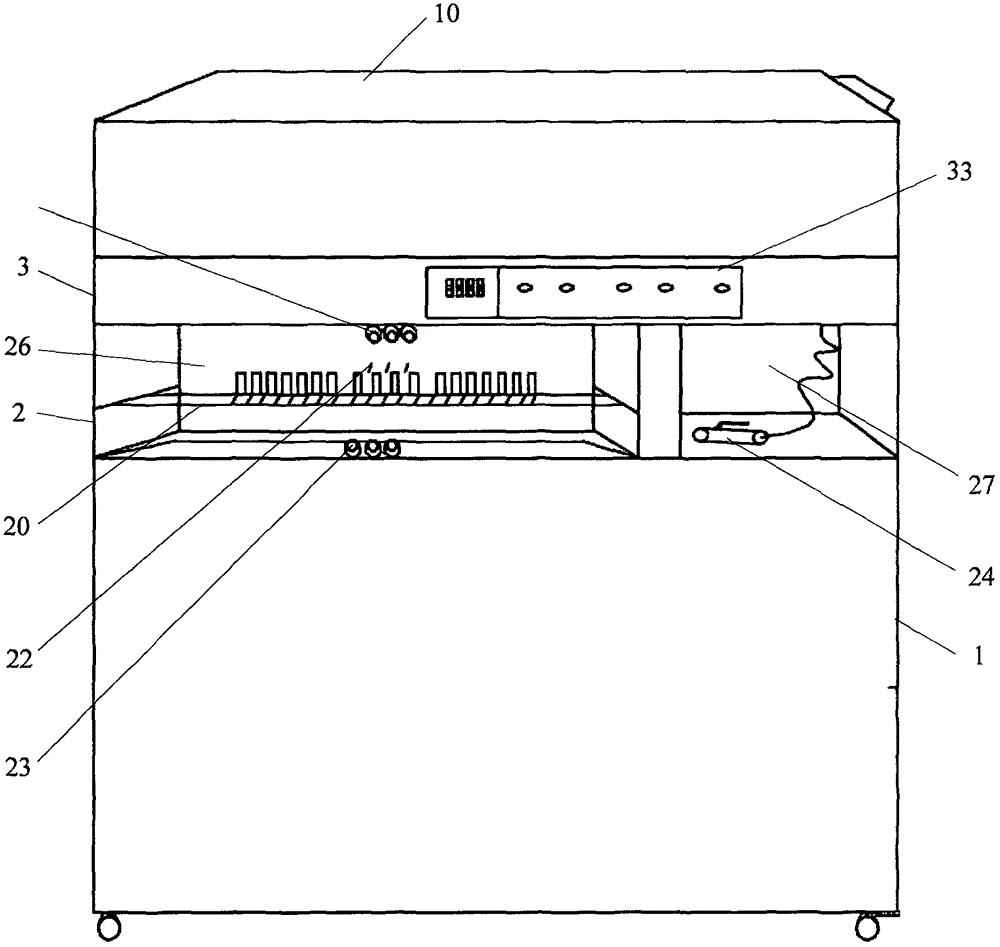
Electrocardiogram device lead disinfecting machine
An embodiment of the invention provides an electrocardiogram device lead disinfecting machine. The electrocardiogram device lead disinfecting machine comprises a machine body, a storage platform for holding an electrocardiogram device is arranged at the top of the machine body, a disinfecting cabinet, a control circuit board and a first pressurizer are installed in the machine body, the first pressurizer is electrically connected with the control circuit board and is positioned above the disinfecting cabinet, a first disinfectant bottle is installed above the first pressurizer, a grating disinfecting frame for holding electrocardiogram device leads is installed in the middle of the disinfecting cabinet, first disinfecting nozzles, second disinfecting nozzles and third disinfecting nozzles which are used for disinfecting the leads are installed in the disinfecting cabinet sequentially from top to bottom, the first disinfectant bottle is communicated with the first disinfecting nozzles, the second disinfecting nozzles and the third disinfecting nozzles through the first presurizer, the first disinfecting nozzles and the second disinfecting nozzles are positioned above the grating disinfecting frame, and the third disinfecting nozzles are positioned below the grating disinfecting frame.
Owner:徐进
Non-invasive system and method for monitoring lusitropic myocardial function in relation to inotropic myocardial function
ActiveUS10085665B2Many timesLong window of opportunityElectrocardiographyStethoscopeThe InternetCardiac activity
Owner:THE COOPER HEALTH SYST
Electrode connection method and device for ECG equipment
ActiveCN105726020BEasy to useReduce workloadDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetocardiography deviceWorkload
Owner:EDAN INSTR
Hand-manipulable, ECG and acoustic, cardiography device
ActiveUS20160081571A1Easy to useGood conditionElectrocardiographyStethoscopeMagnetocardiography deviceElectronic information
Compact, single-handedly manipulable, cardiography devices, structured for personal use in two, selectively different, functional-cardiography styles, enabling, respectively, one or both of (a) non-acoustic, and (b) acoustic, cardiography, such use involving, as appropriate to the particular functional-cardiography style to be implemented, the collecting and recording of personal cardiography-relevant data—ECG only in a non-acoustic case, and both ECG and heart-sound together in an acoustic case—suitable for subsequent data-analysis processing, and associated cardiovascular diagnosis. Two, representative device overall configurations are illustrated, including (1) a stylus pen-like shape, and (2) a finger-mountable ring-like shape. Collected-data analysis processing, and associated cardiovascular diagnosis, may be performed by device-included electronic information-handling structure, or may, via operation of such electronic structure, be communicated appropriately “outwardly” from the relevant device for external processing and analysis.
Owner:INOVISE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com