Patents
Literature
84 results about "Resuscitator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
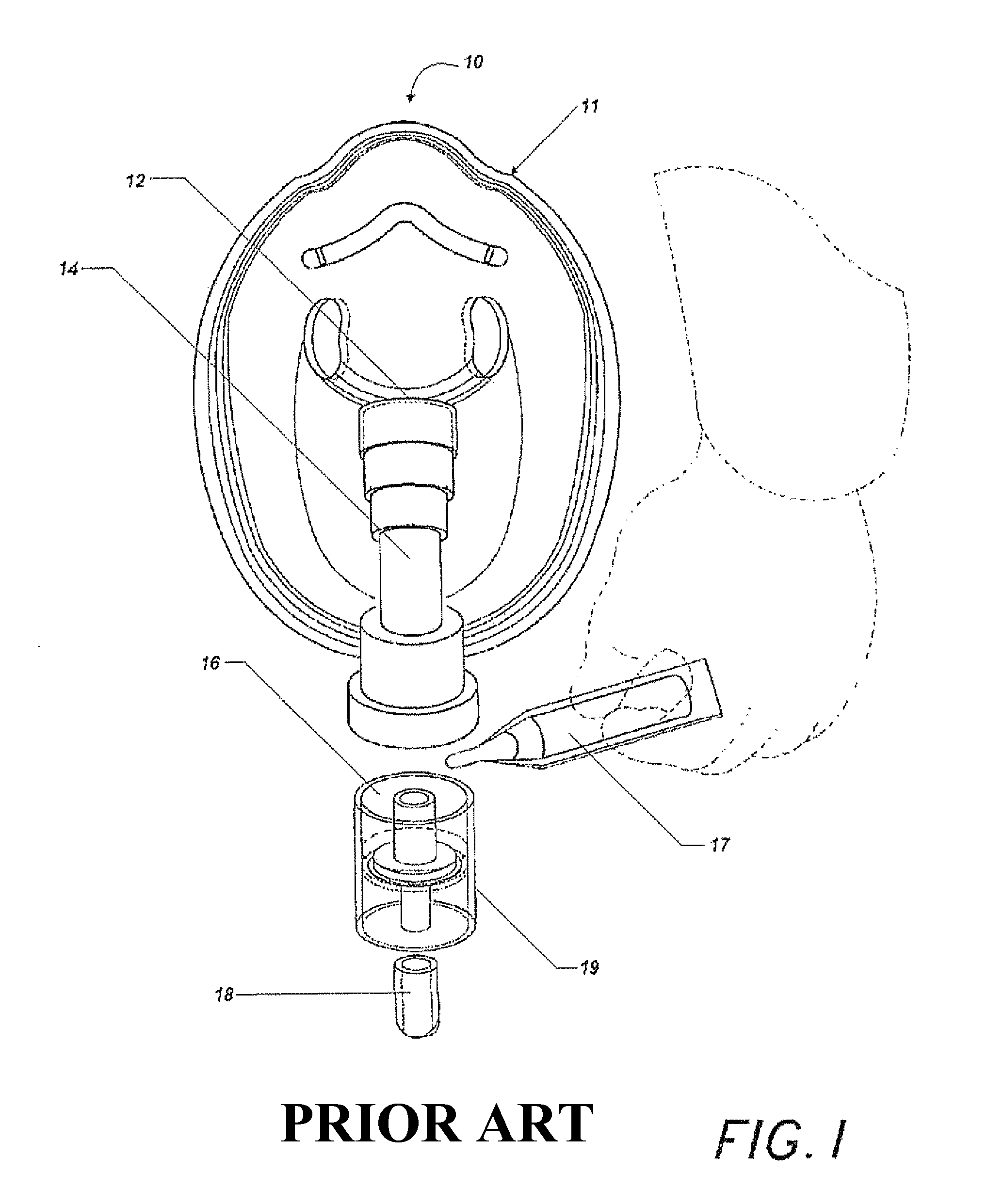
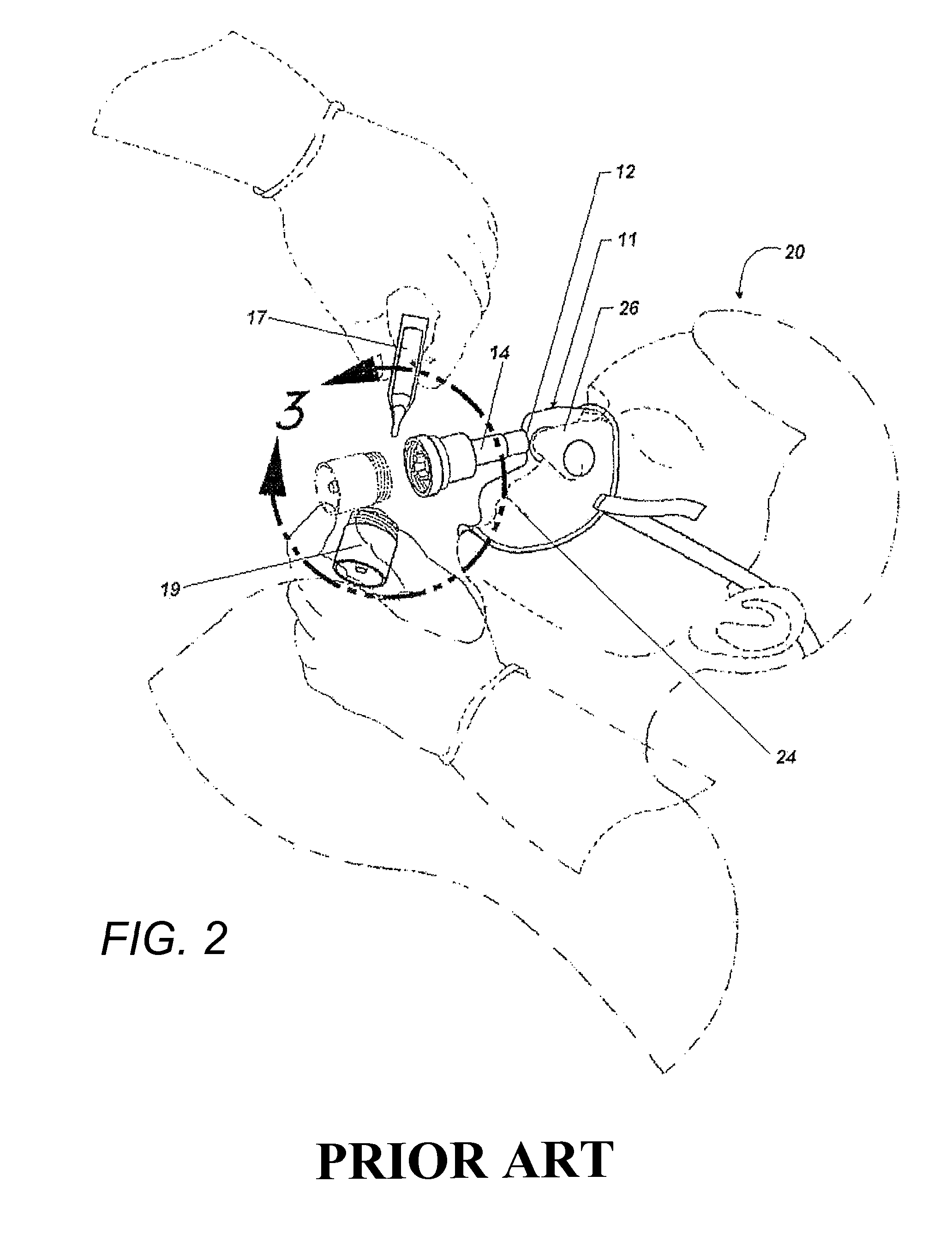
A resuscitator is a device using positive pressure to inflate the lungs of an unconscious person who is not breathing, in order to keep them oxygenated and alive. There are three basic types: a manual version (also known as a bag valve mask) consisting of a mask and a large hand-squeezed plastic bulb using ambient air, or with supplemental oxygen from a high-pressure tank. The second type is the Expired Air or breath powered resuscitator. The first appearance of the second type was the Brooke Airway introduced in 1957. The third type is an oxygen powered resuscitator. These are driven by pressurized gas delivered by a regulator, and can either be automatic or manually controlled. The most popular type of gas powered resuscitator are Time Cycled, Volume Constant Ventilators. In the early days of pre-hospital emergency services, pressure cycled devices like the Pulmotor were popular but yielded less than satisfactory results. One of the first modern resuscitation ventilators was the HARV, later called the PneuPac 2R or Yellow Box. Most modern resuscitators are designed to allow the patient to breathe on his own should he recover the ability to do so. All resuscitation devices should be able to deliver >85% oxygen when a gas source is available.
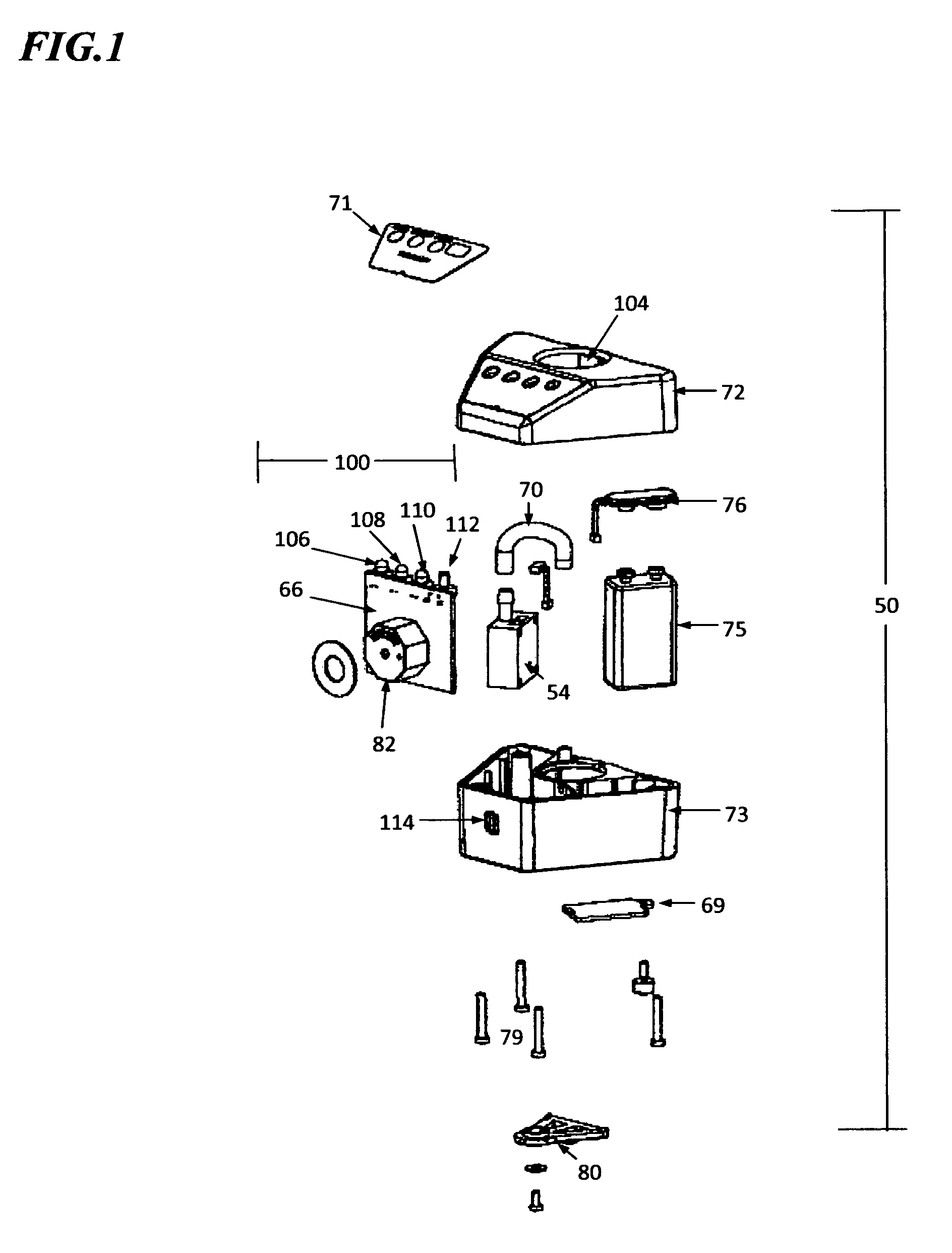
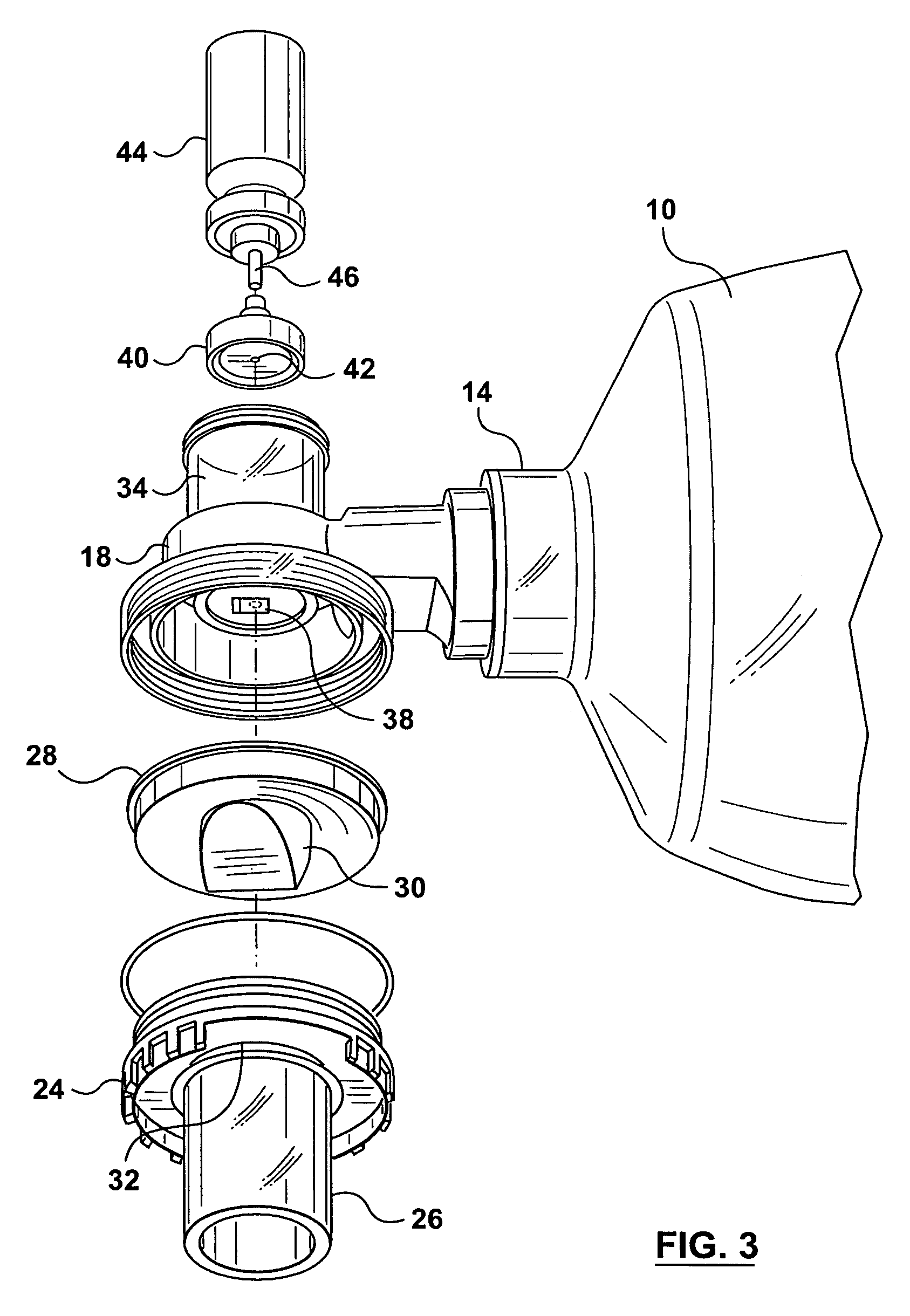
Improvements to Electrically Operable Resuscitators
InactiveUS20100170512A1Avoid flowShorten speedTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLinear motorPiston
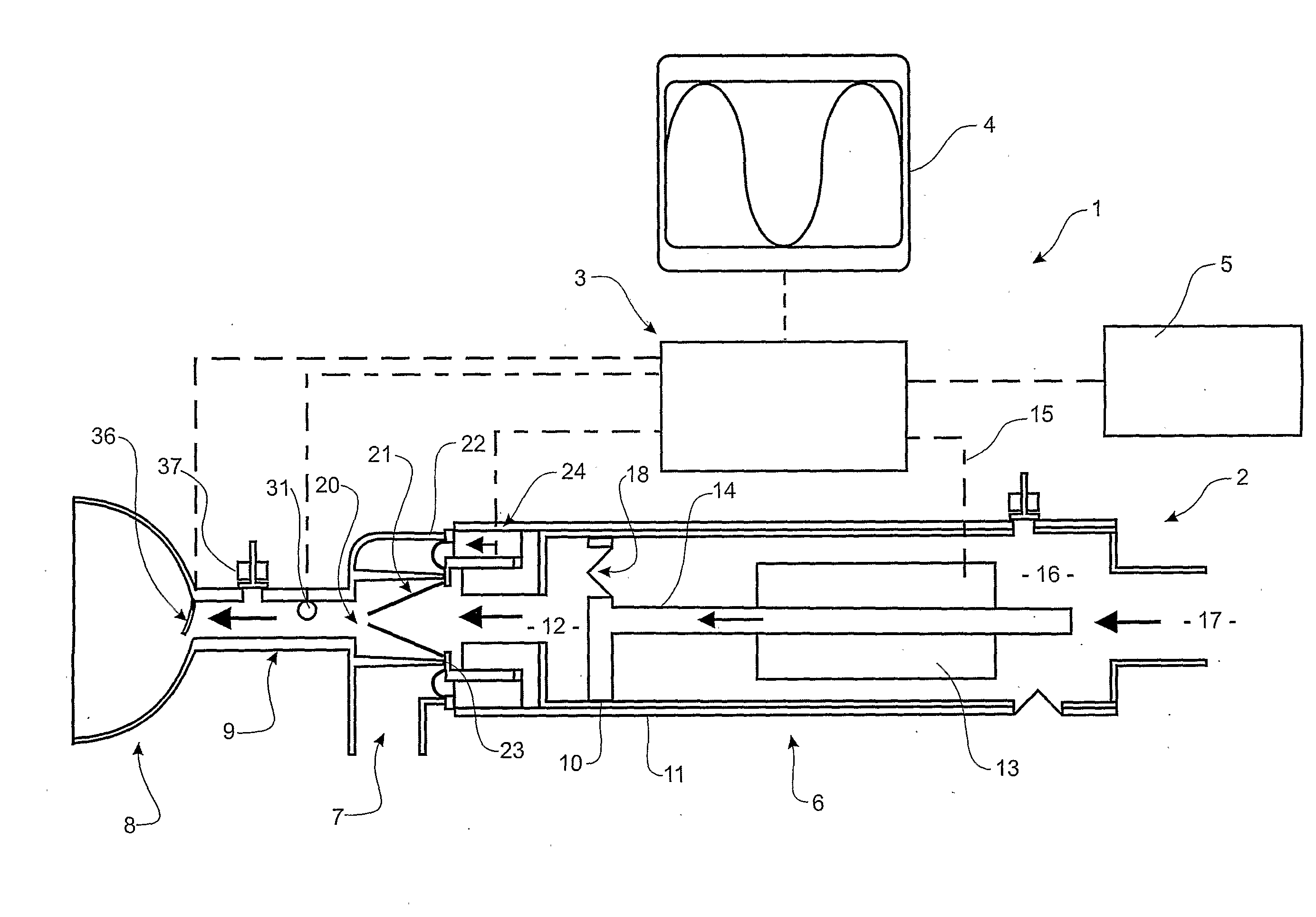
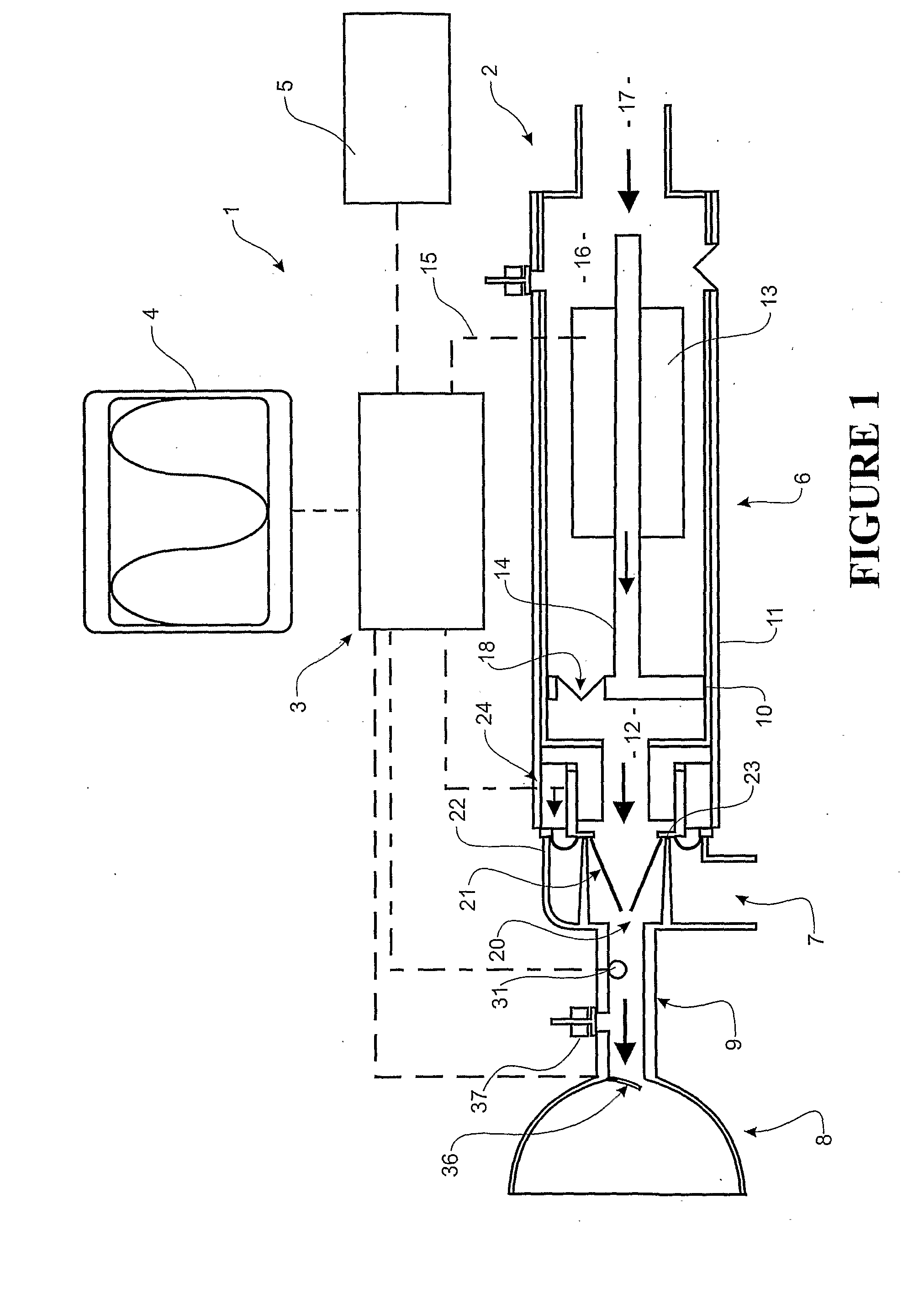
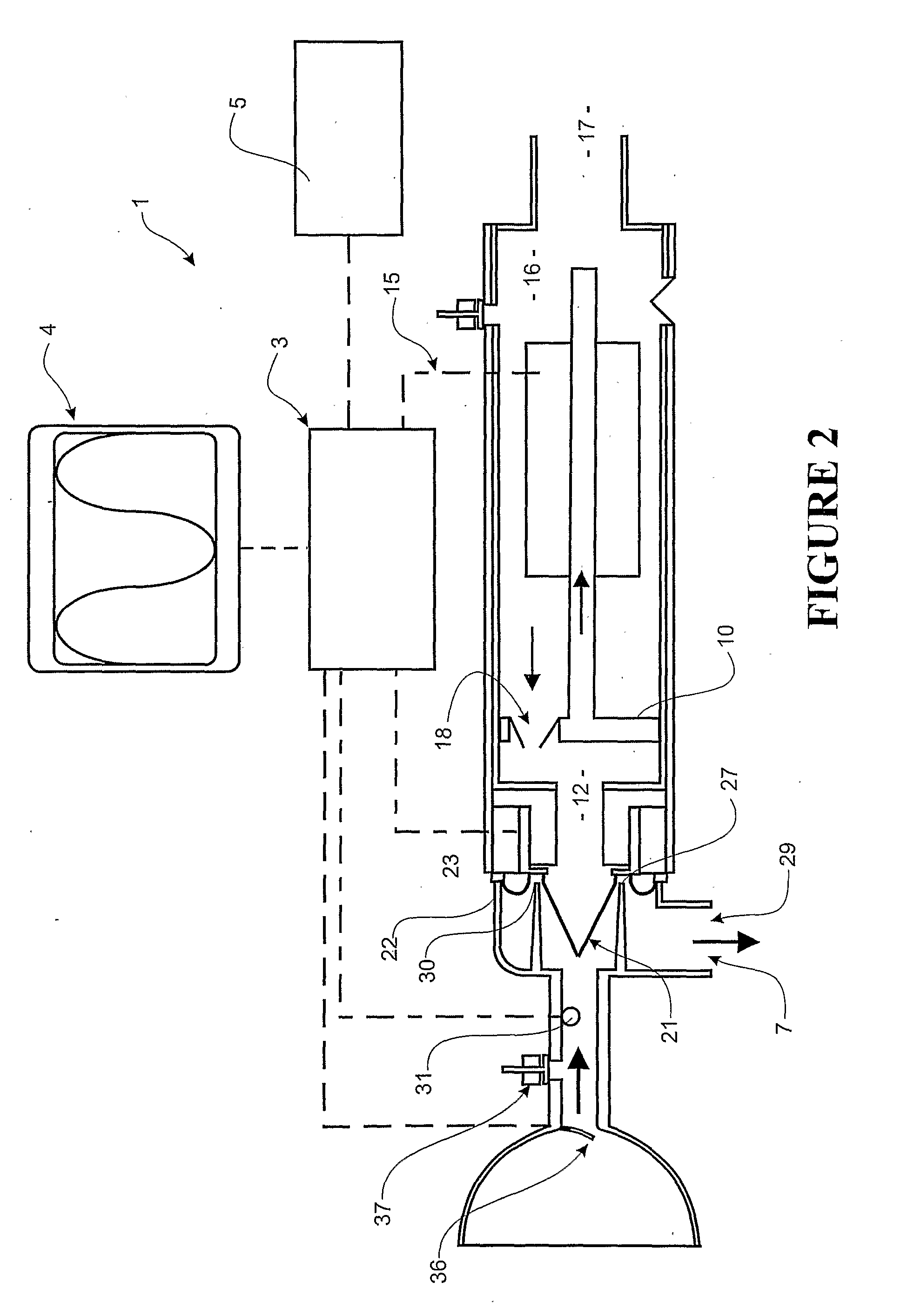
The present invention relates to an electrically operable resuscitation device comprising a pump including a rigid cylinder including at least one gas inlet and at least one gas outlet, a piston to travel in said cylinder, and at least one valve, the or each valve configured to allow gas to be displaced into said cylinder through said at least one gas inlet during at least one of a first stroke direction and second stroke direction of said piston in said cylinder, and for allowing gas to displaced through said at least one gas outlet during an opposite of said at least one of the first stroke direction and second stroke direction of said piston in said cylinder; a motor, selected from one of a stepper motor and feedback motor and stepper motor with feedback and linear motor, operatively connected to said piston to move said piston in said cylinder; a patient interface in ducted fluid connection with said pump to receive gas via said at least one gas outlet and to deliver said gas to said patient.
Owner:KUYPERS GILBERT JACOBUS +1
Gas concentrator
InactiveUS6253767B1Simpler tooling devicesReduce manufacturing costRespiratorsEngineeringProduct gas
A gas concentrator adaptable for use within a breathing apparatus, particularly for use within a resuscitator, Trach T, patient tee, or a high oxygen concentration mask. The gas concentrator distributes gas into the resuscitating device through a substantially elongated member that has a number of perforations at one end and a stopper at an opposite end. In addition, the gas concentrator has one or more air check valves that are in fluid communication with the reservoir of the resuscitating device and the atmosphere. A front manifold is used to couple the reservoir to a patient breather apparatus which regulates the flow of oxygen or gas to the patient.
Owner:MANTZ ROBERT F
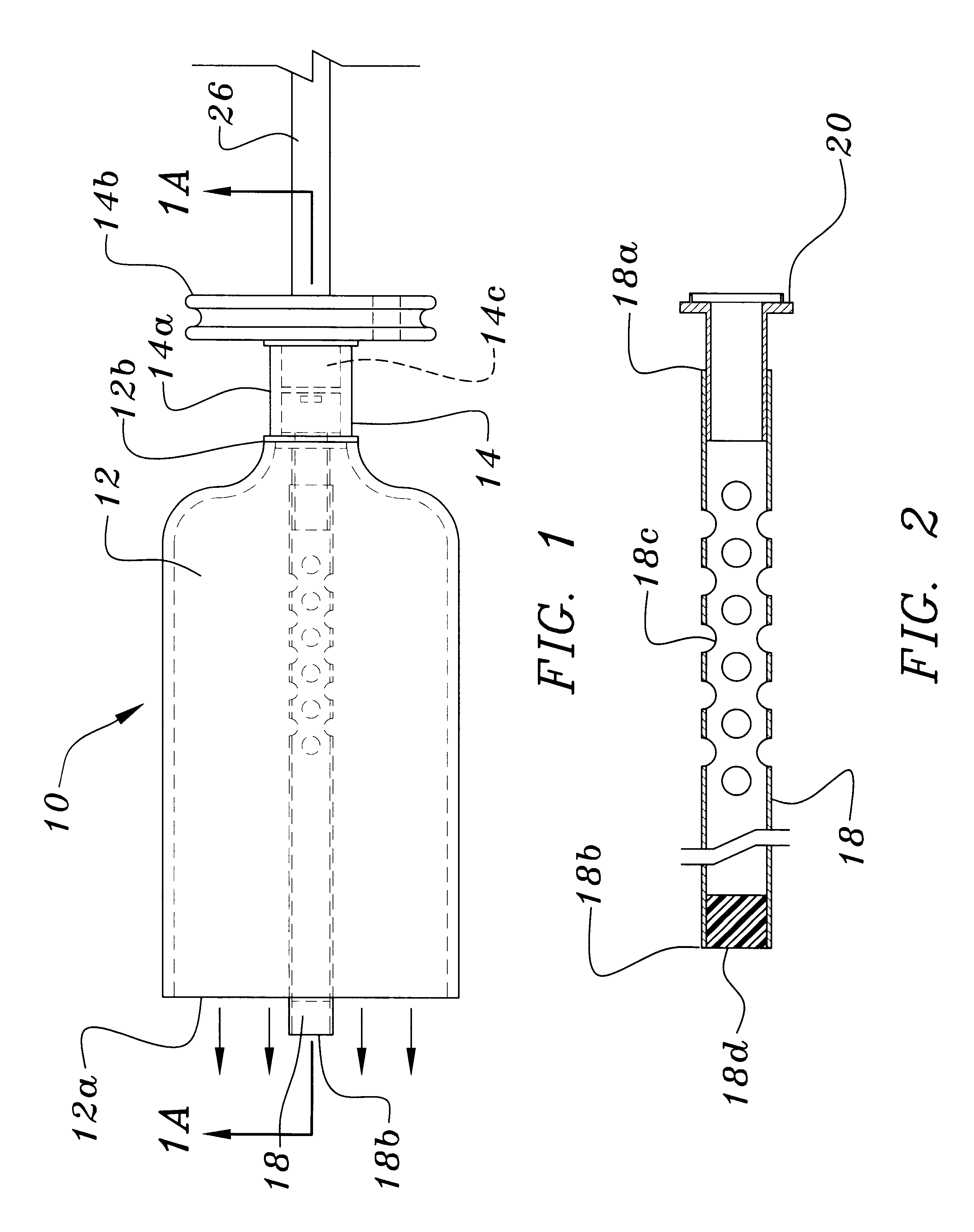
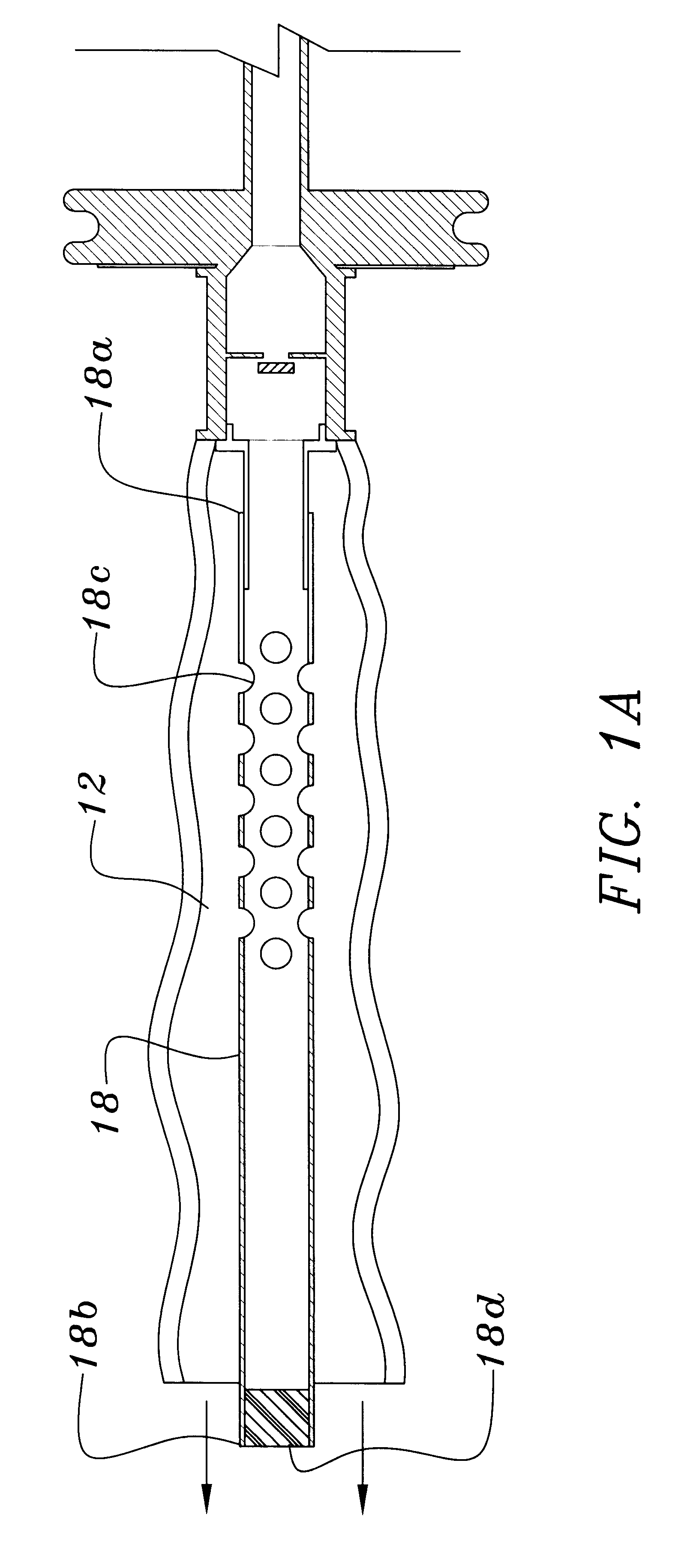
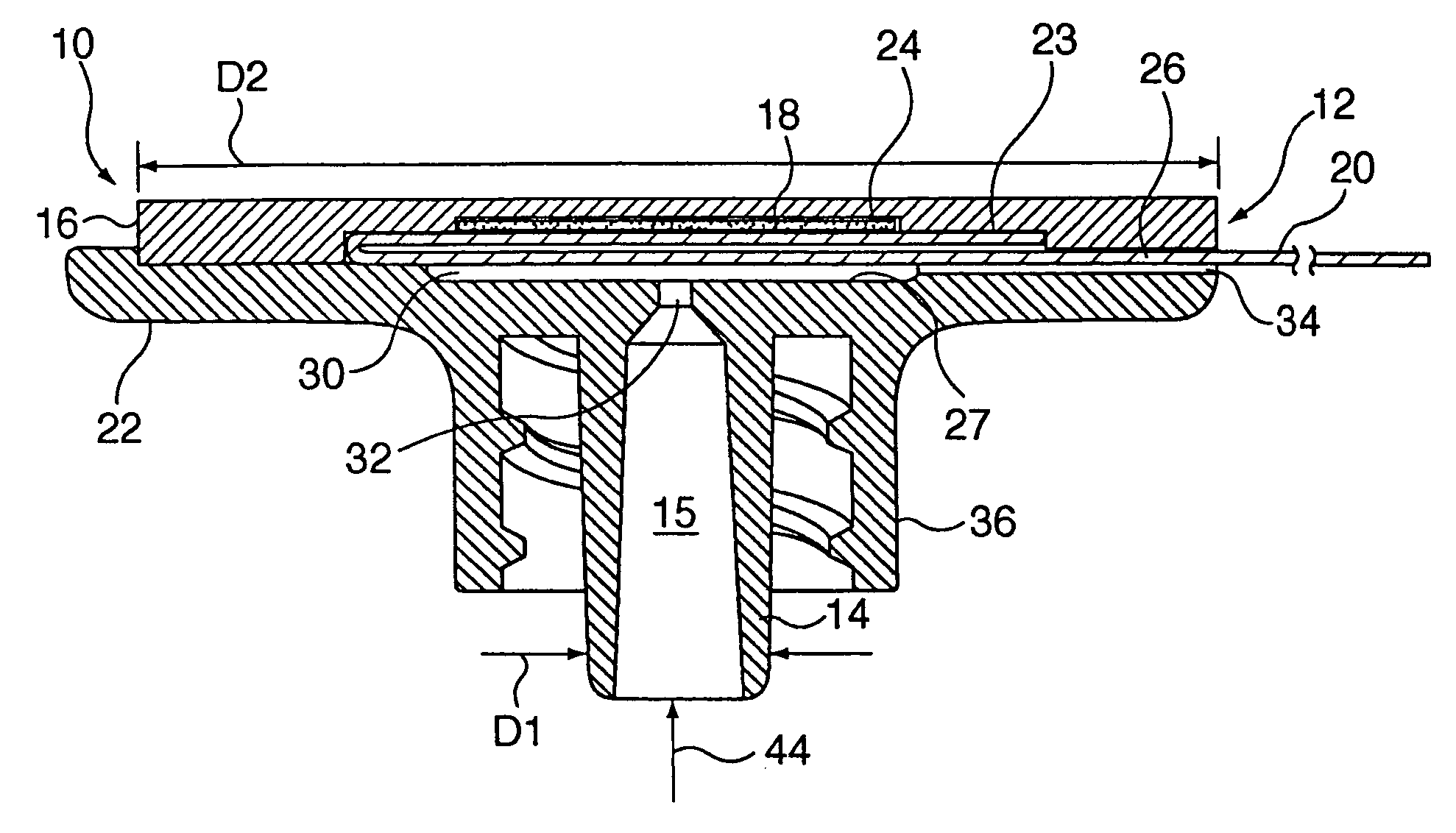
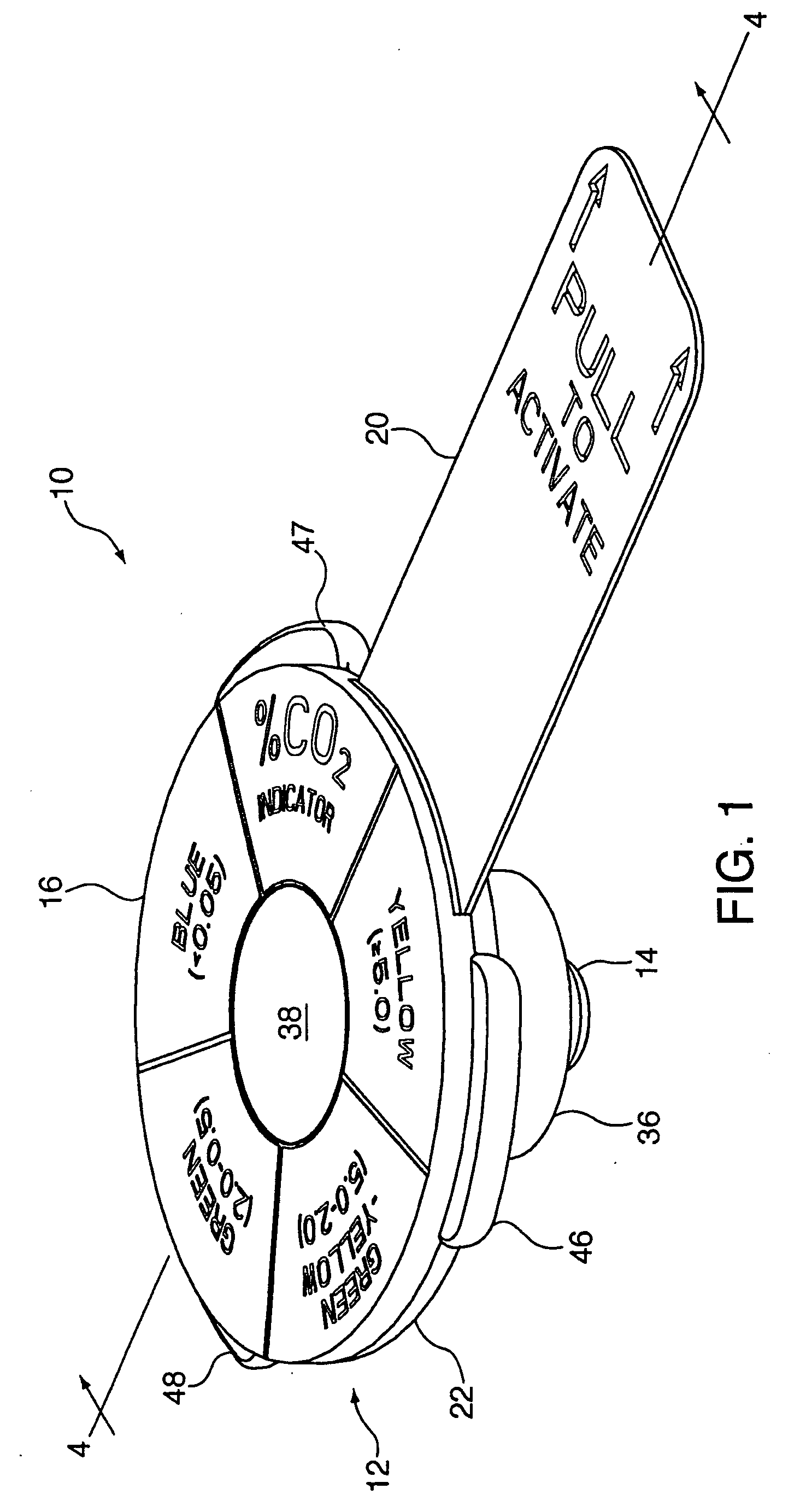
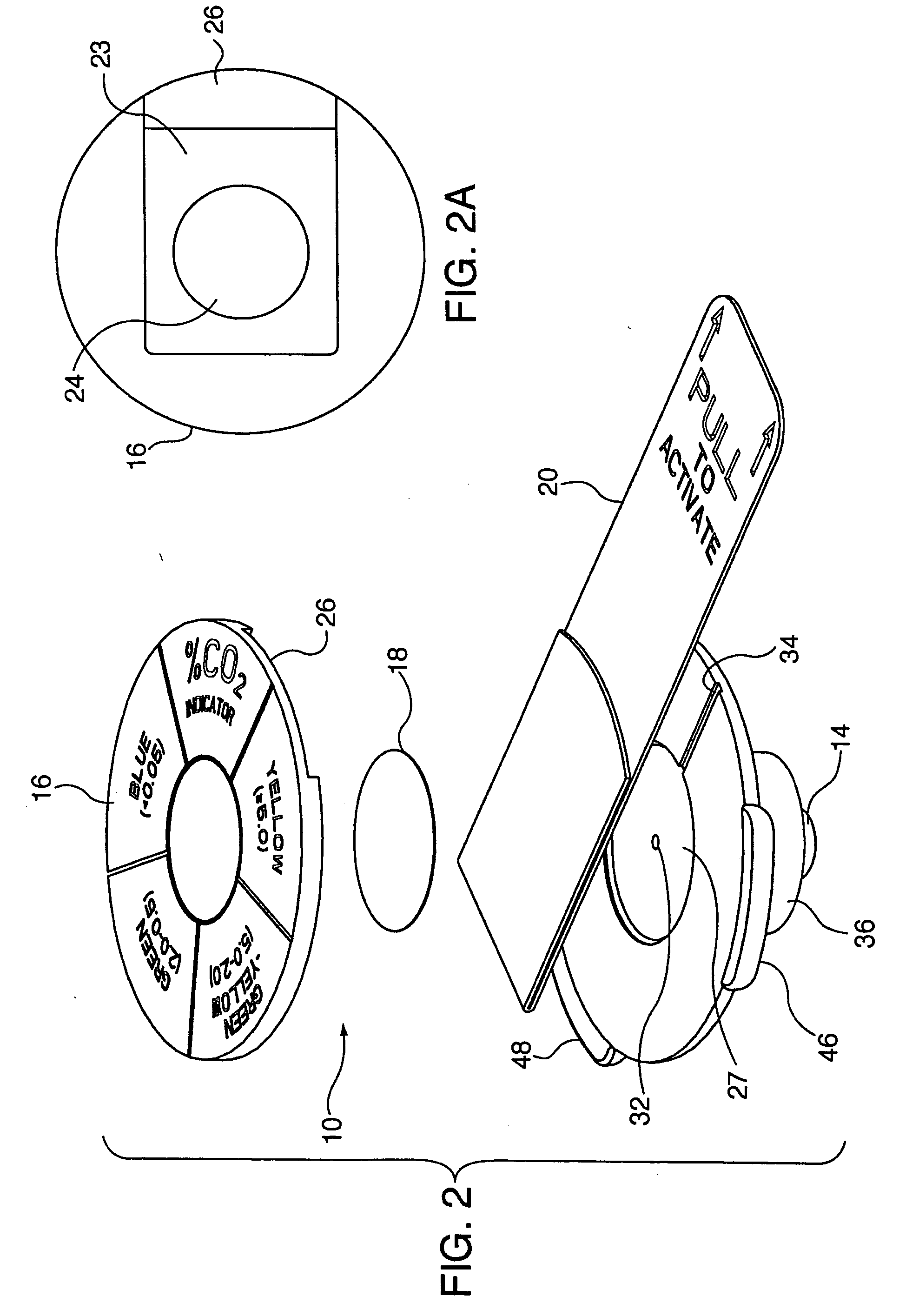
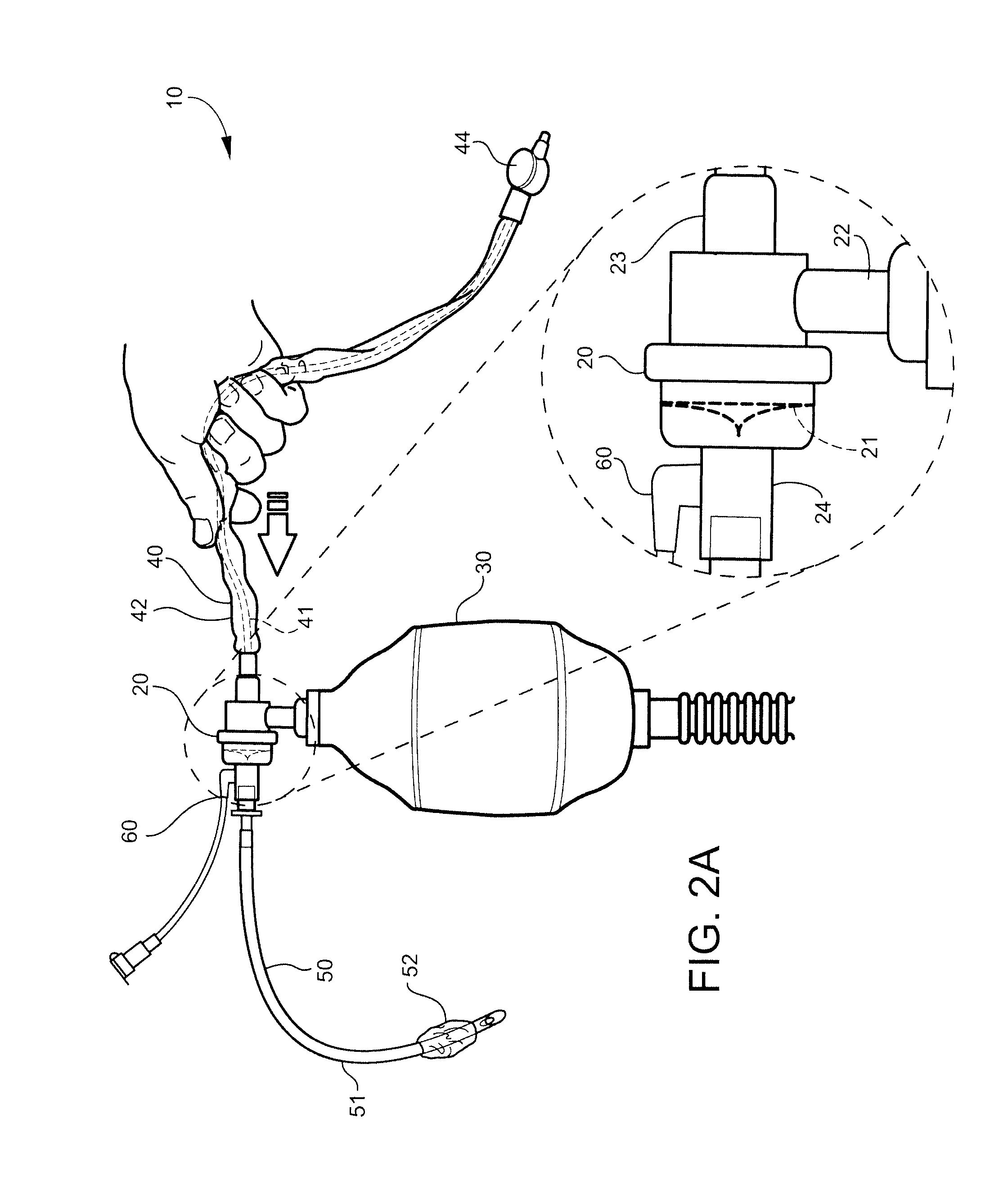
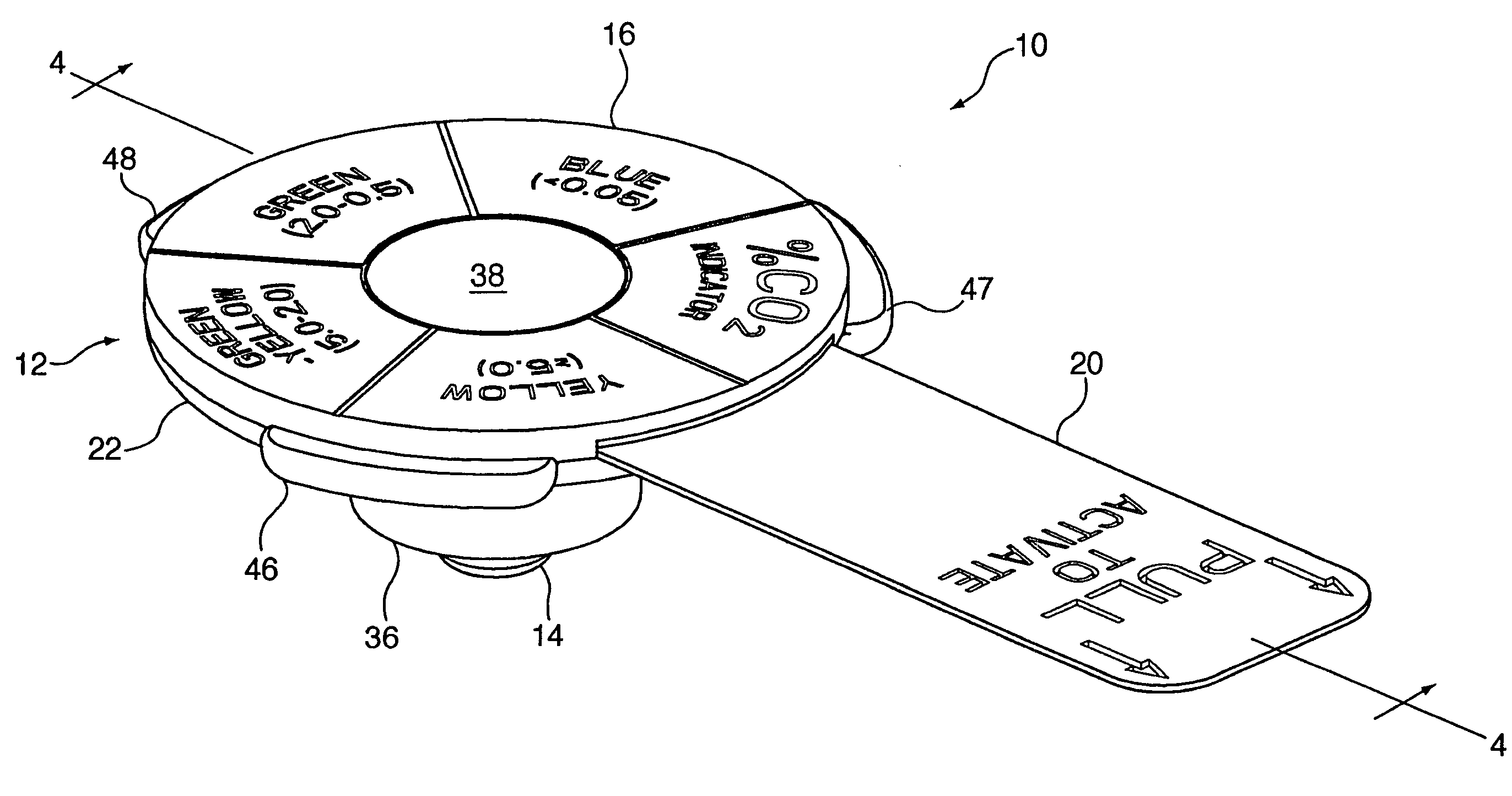
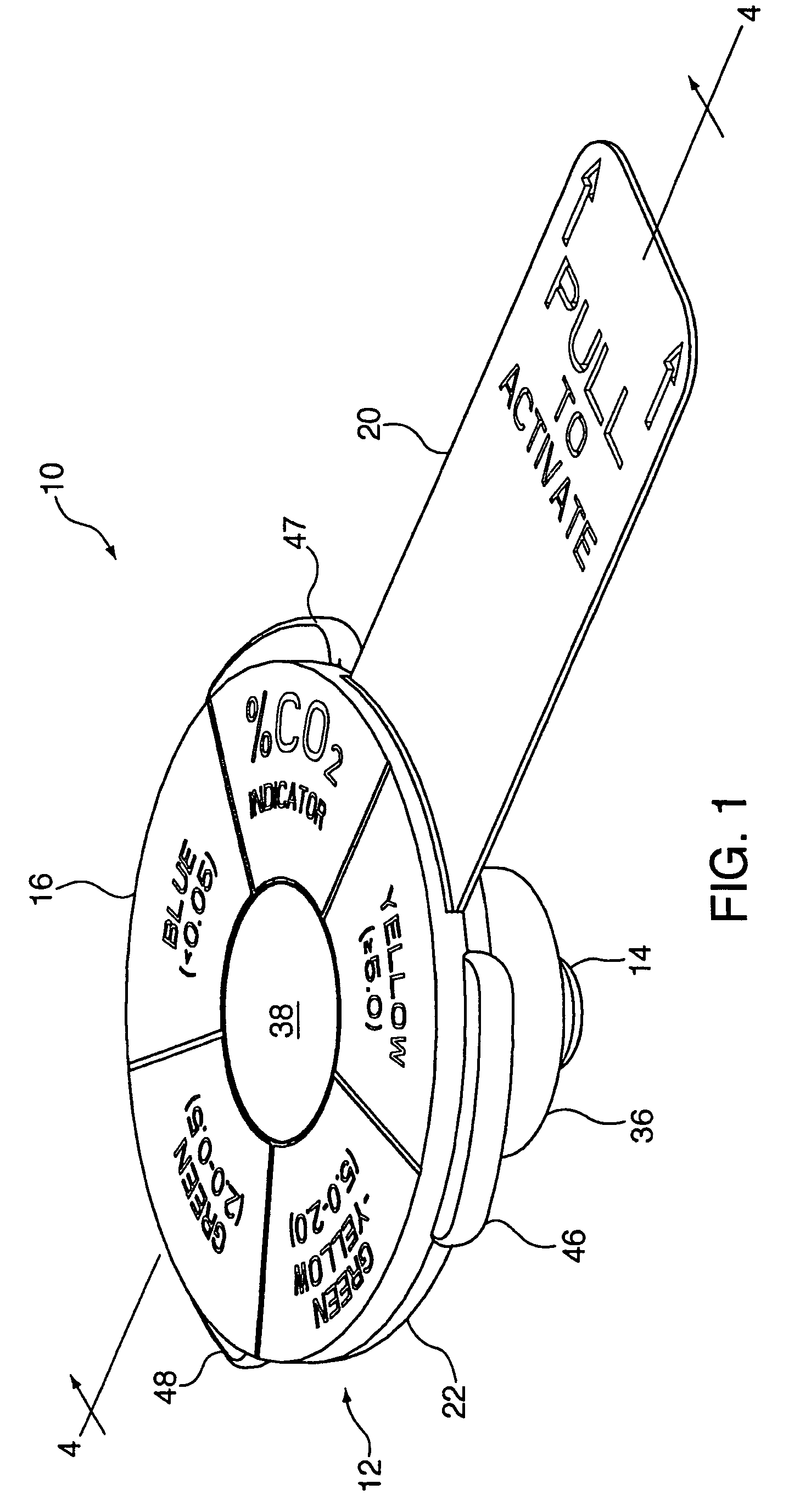
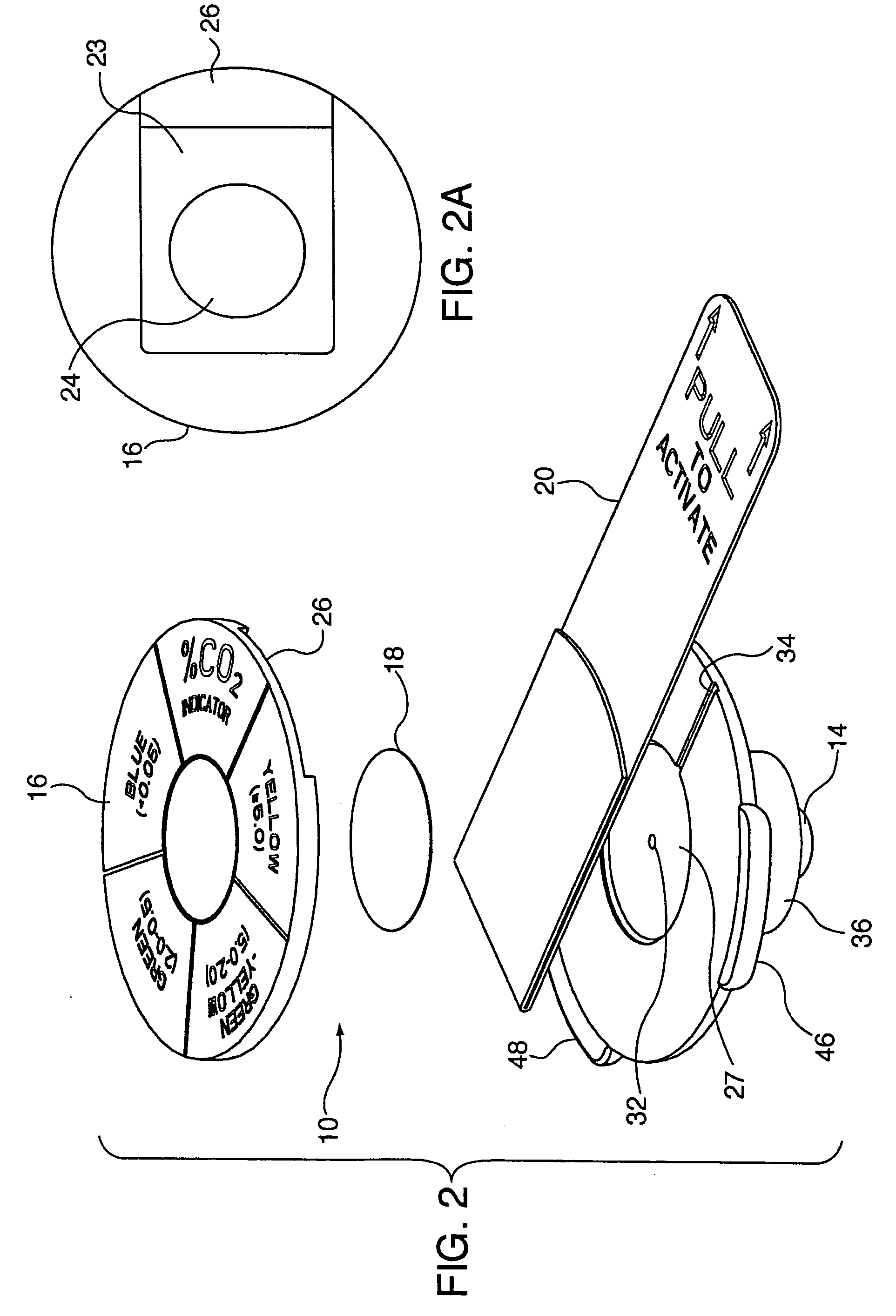
Carbon dioxide indicating apparatus, particularly, disk-like carbon dioxide indicating apparatus
Carbon dioxide indicator for receiving gas containing carbon dioxide and for providing a visible indication of the presence of carbon dioxide in the gas, the indicator includes a connector for removably connecting the indicator to a source of gas containing carbon dioxide and which connector is for communicating at least a portion of such gas to the indicator. The carbon dioxide indicator may be a disk indicator and the connector may be a male luer or a locking male luer. The carbon dioxide indicator may include removable ultraviolet radiation shielding permitting the carbon dioxide indicator to be preassembled to a patient's respiratory or breathing circuits or to a resuscitator.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL CONSUMABLES LLC
Auto-pumping unit for bag-valve-mask resuscitator
An auto-pumping unit for a bag-valve-mask resuscitator includes a housing, a pressure device, and driving mechanism. The housing has a receiving space for accommodating a bag of the bag-valve-mask, and a baffle mounted at a side of the receiving space. The pressure device is movably mounted at the other side of the receiving space opposite to the baffle. The driving mechanism is mounted in the housing and controlled to drive the pressure device to move close to or away from the baffle to compress or release the bag at a predetermined speed.
Owner:LIN JIMMY
Nebulizer apparatus
A nebulizer apparatus for delivering medication in the form of an aerosol to a patient. The apparatus includes a medication reservoir for receiving liquid medication, a face mask for delivering aerosol to a patient, an attachment to a nebulizer machine or Bag resuscitator to generate carrier gas flow, a face mask or tubing to deliver the aerosol to the patient, and hosing to inter-connect the nebulizer components. The medication reservoir of the nebulizer apparatus includes rapid injection ports for the addition of medication to the medication reservoir, and is connected to the face mask via a dual sided ball and socket connection.
Owner:CARE 2 INNOVATIONS
Resuscitation device with onboard processor
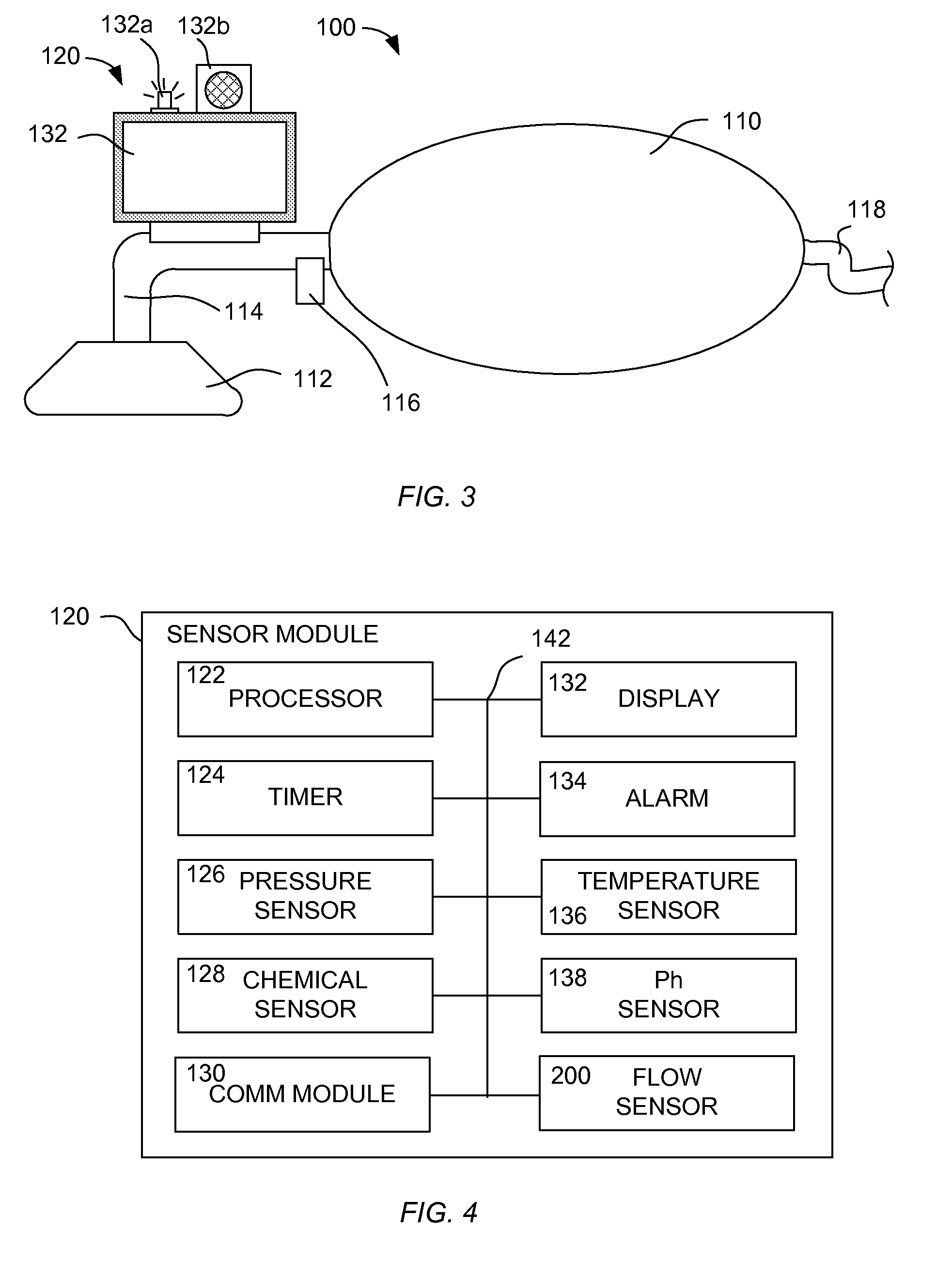
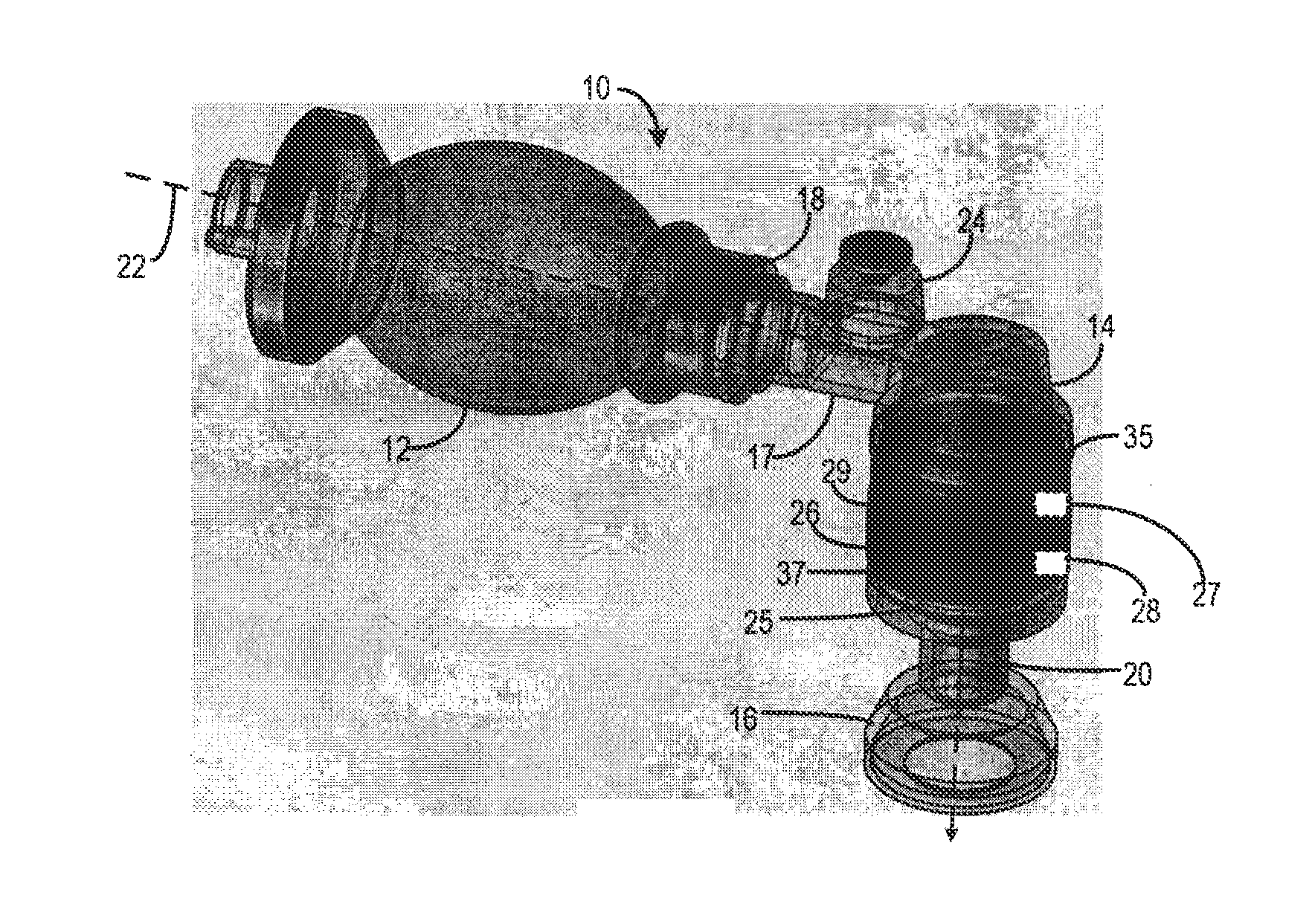
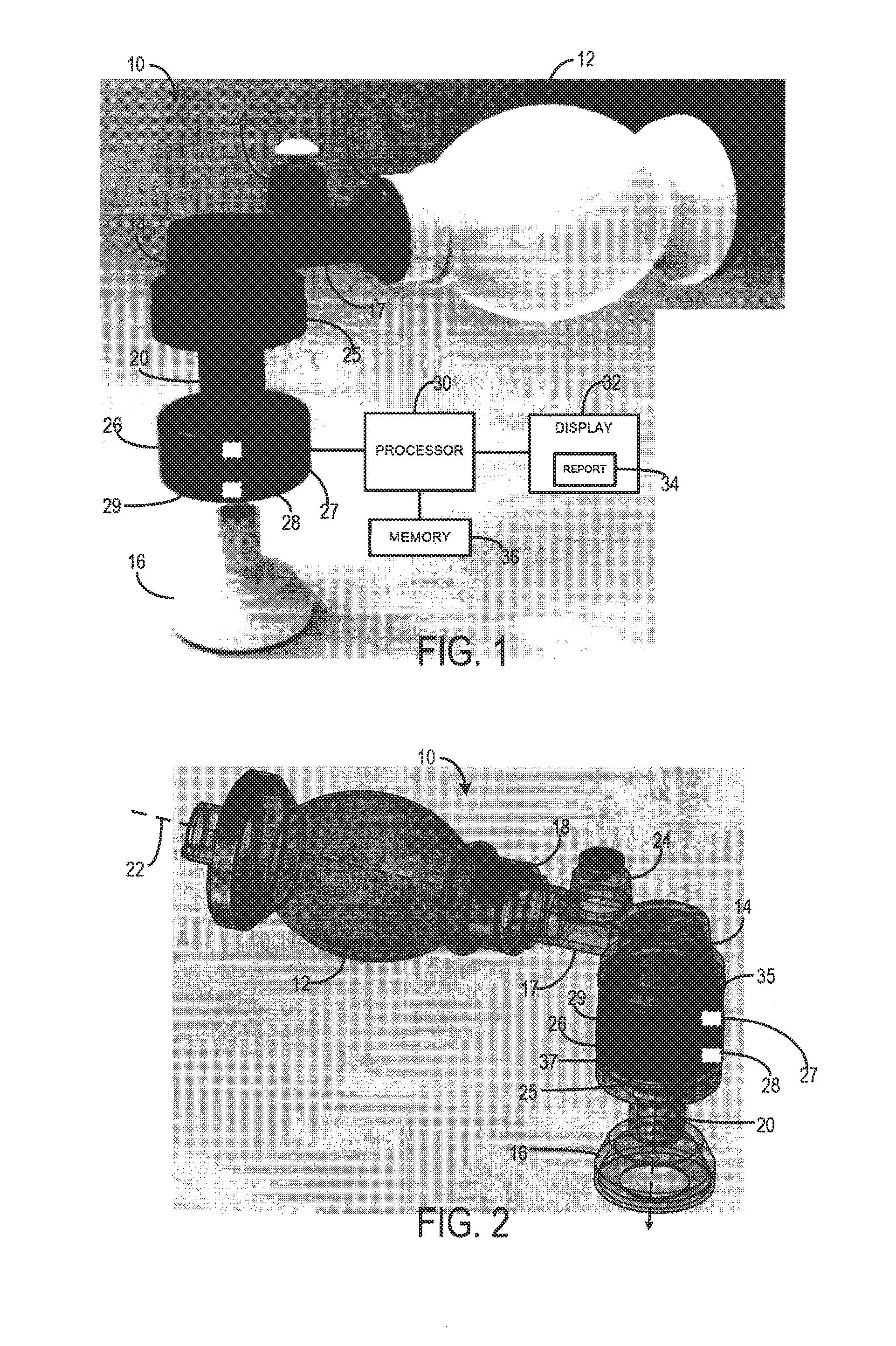
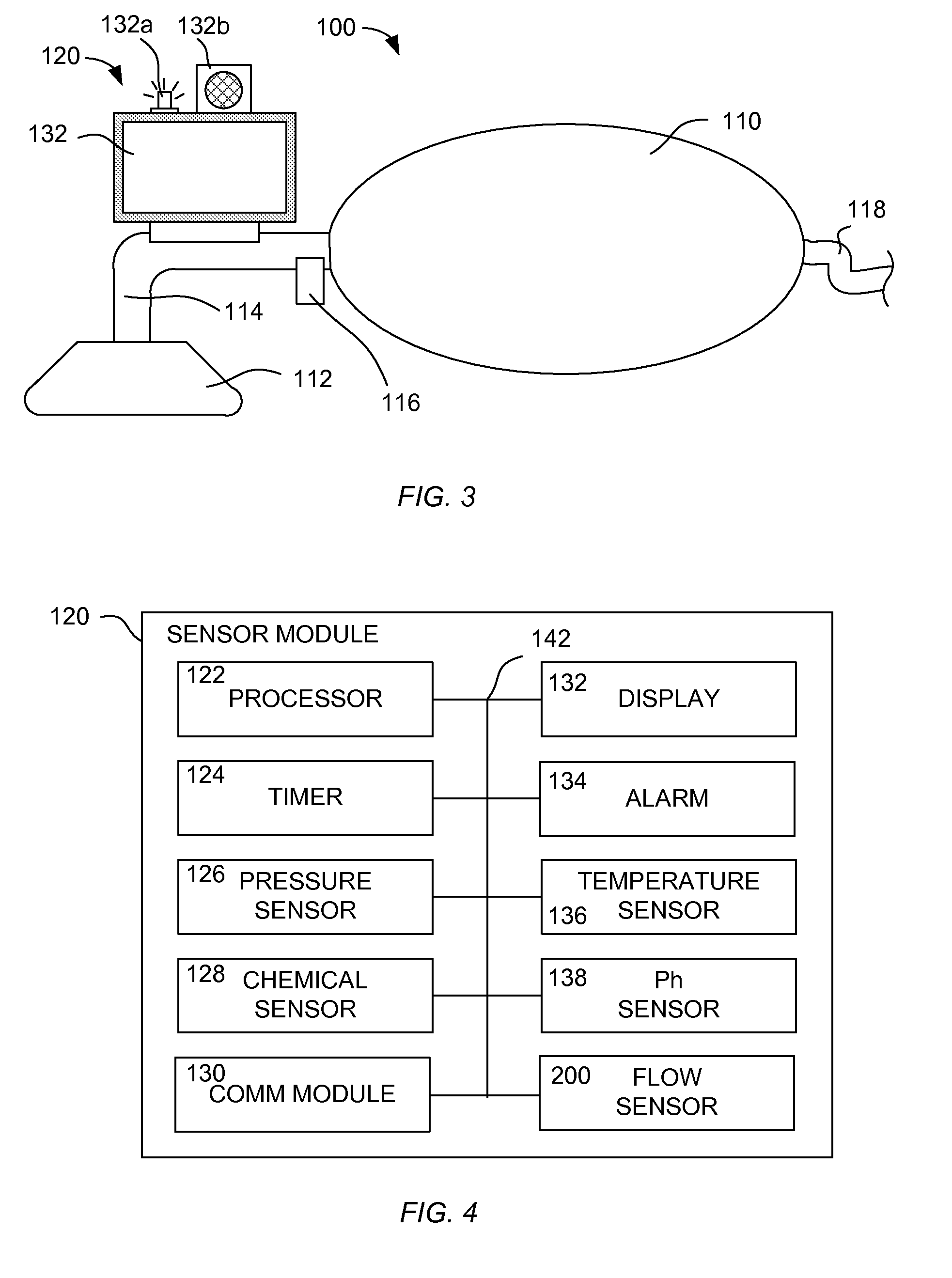
A resuscitator has a patient airway interface device, a bag, a flow passage coupled between the bag and patient airway interface device, and a sensor assembly. The patient airway interface device may be a mask or an endotracheal tube. The sensor assembly has a display, at least one sensor coupled to the flow passage and configured to provide a measurement of at least one parameter, and a processor coupled to the display and the at least one sensor. The processor is configured to receive the measurement from the sensor and provide information on the display based on the received measurement. The information may include a current breath rate, a pressure-vs-time curve, and guidance to the user to assist in achieving a target breath rate.
Owner:SUNMED GRP HLDG LLC
Respiratory valve
ActiveUS20120048274A1Reduce the possibilityWithout any supportRespiratorsMultiple way valvesLung CollapseEndotracheal tube
A respiratory valve apparatus with a housing having an inner chamber, an endotracheal tube connection port, a respirator connection port and a resuscitation bag connection port. A valve positioned within the inner chamber can switch the flow between a manual resuscitation bag port and a ventilator port enabling the patient to be treated without having to disconnect the respirator support system to thereby connect the resuscitation bag. This prevents the loss of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) in the lungs and guards against lung collapse and hemodynamic compromise. The valve includes preloaded seals that will create minimal dragging during valve actuation and work under both positive and negative pressure. The apparatus includes a tethered cover for closure of the resuscitation bag port for sealably covering the port when a bag is not attached or the ventilator connector during patient transport. A sealing arrangement within the resuscitator bag port insures that PEEP in maintained when the resuscitator bag adapter is inserted into the housing.
Owner:BAYWIN
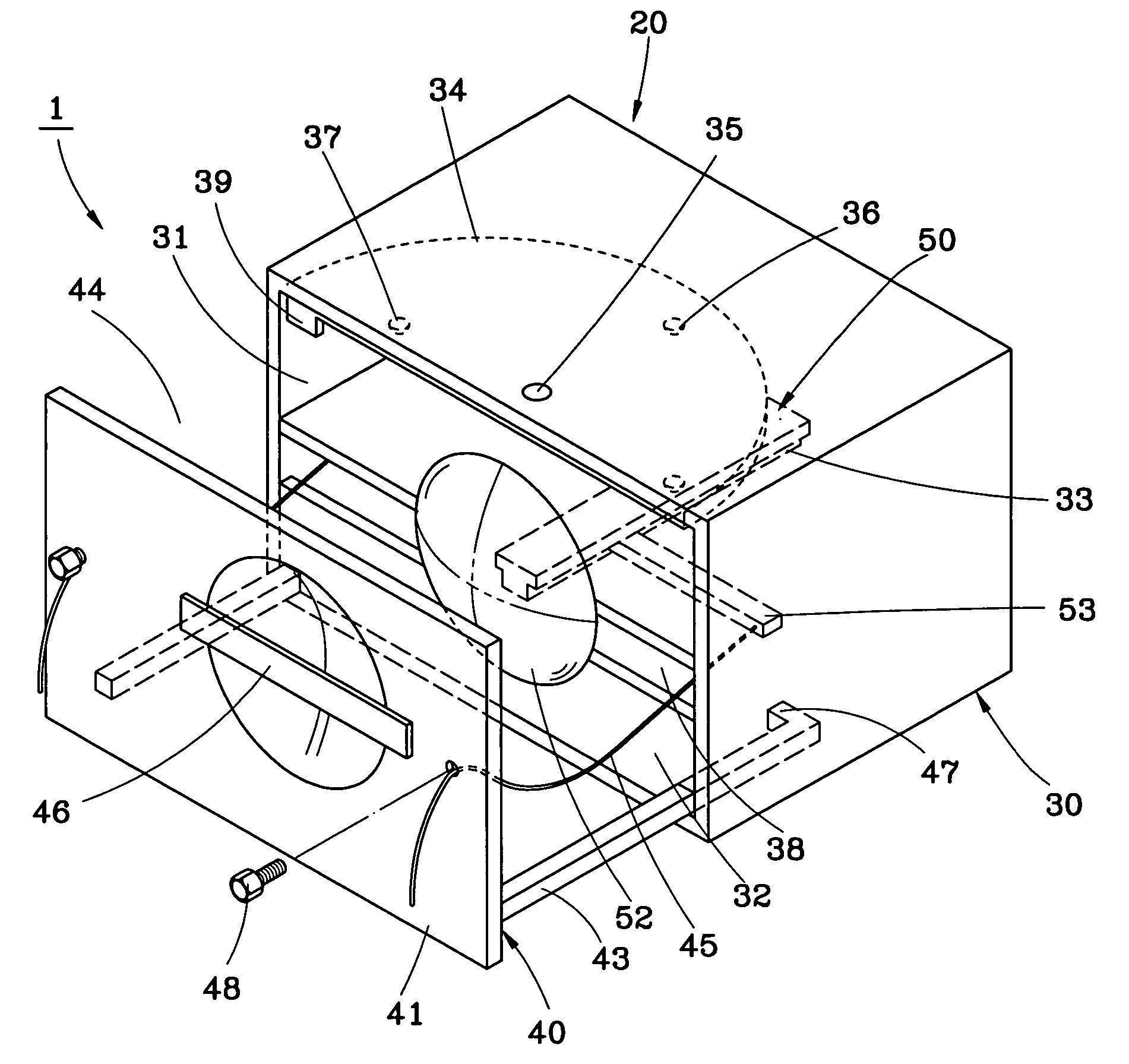
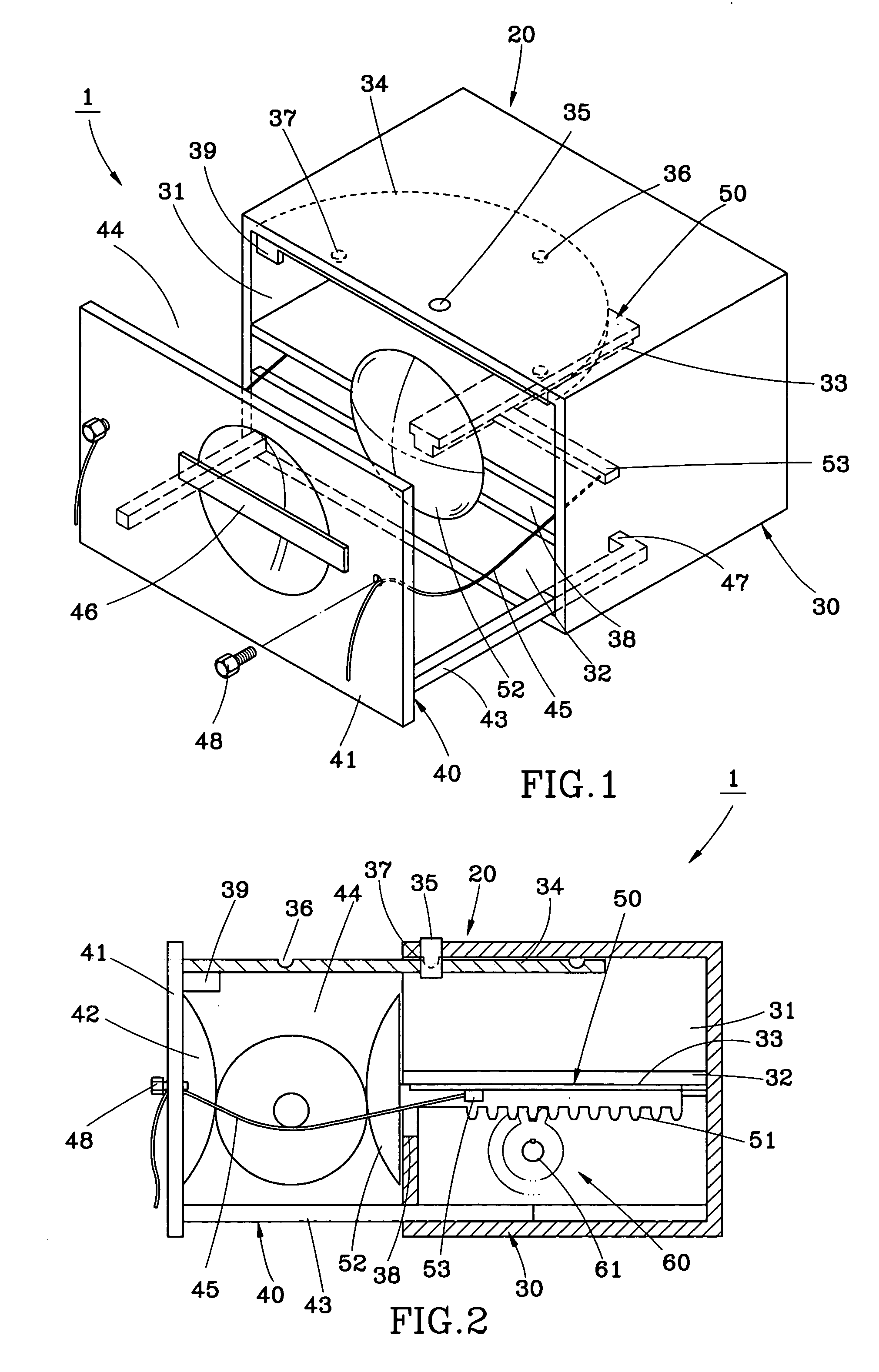
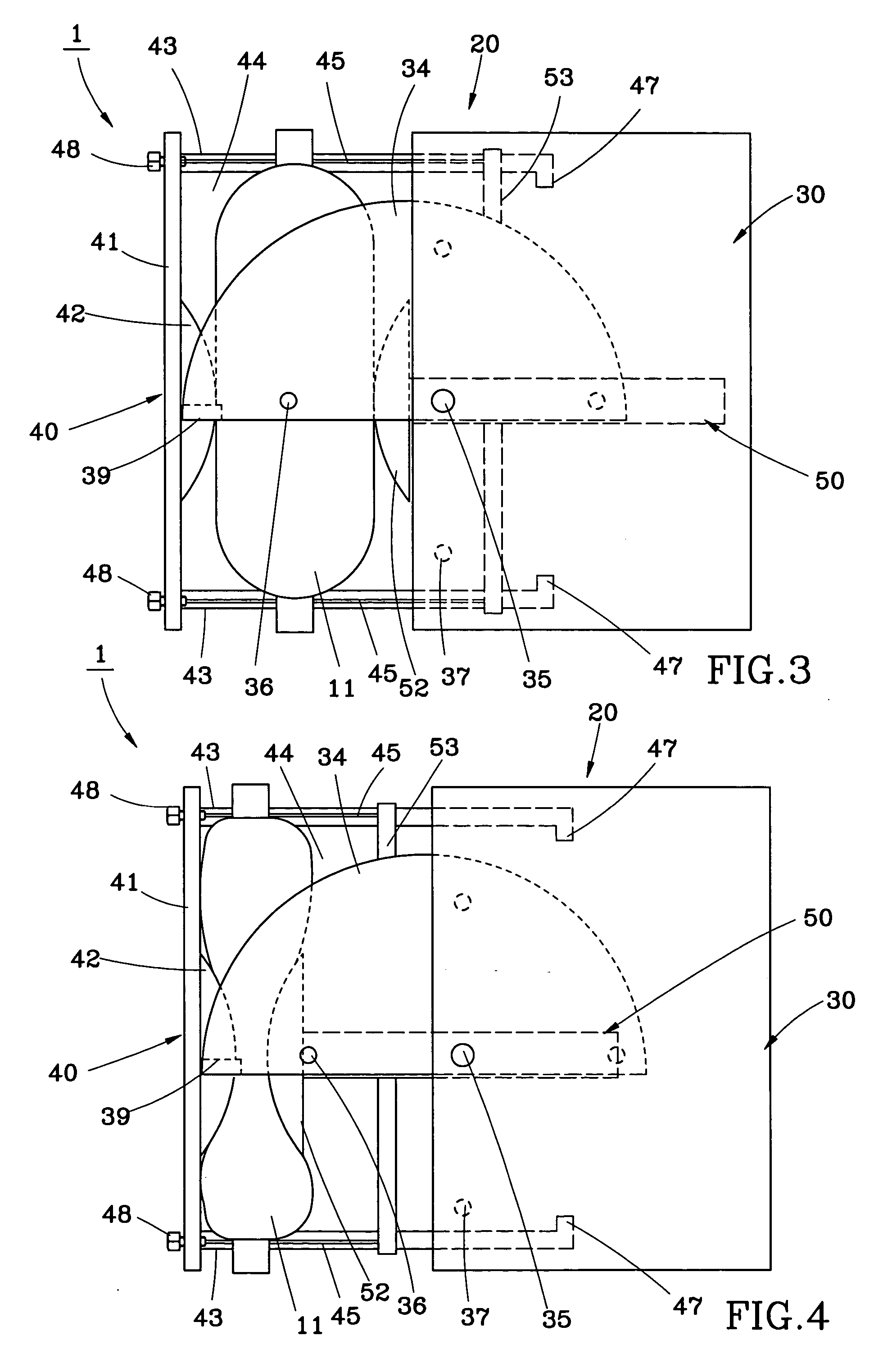
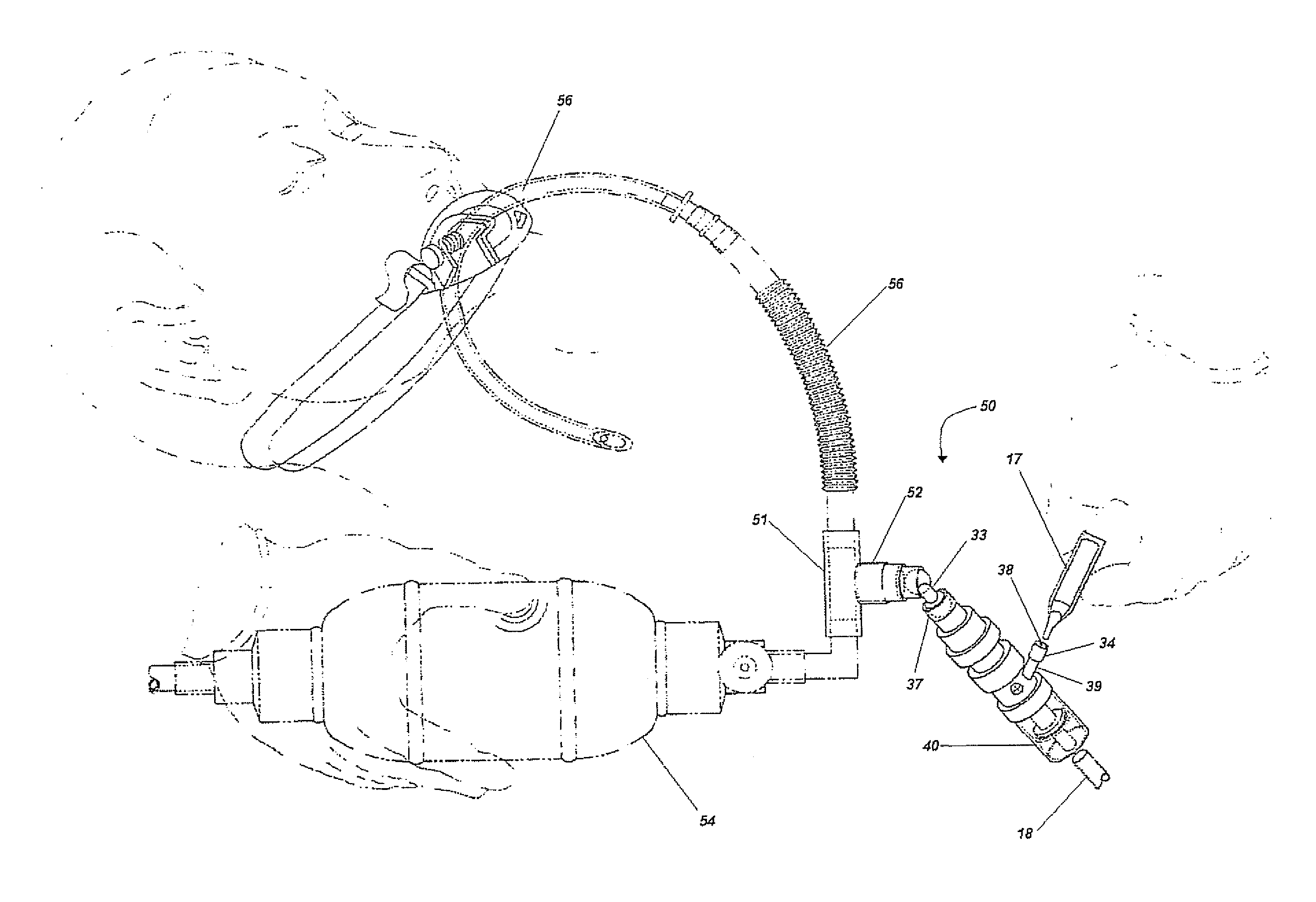
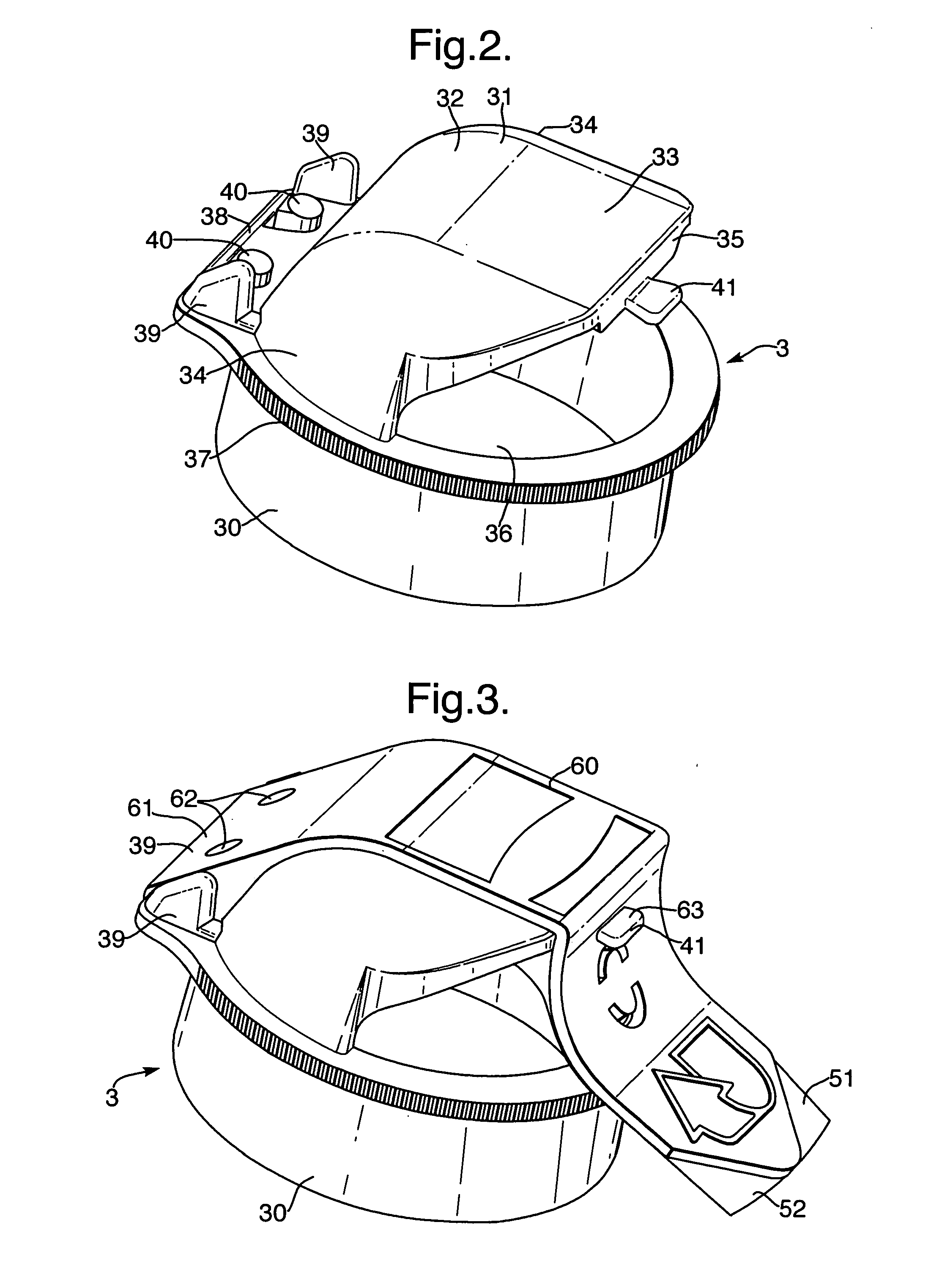
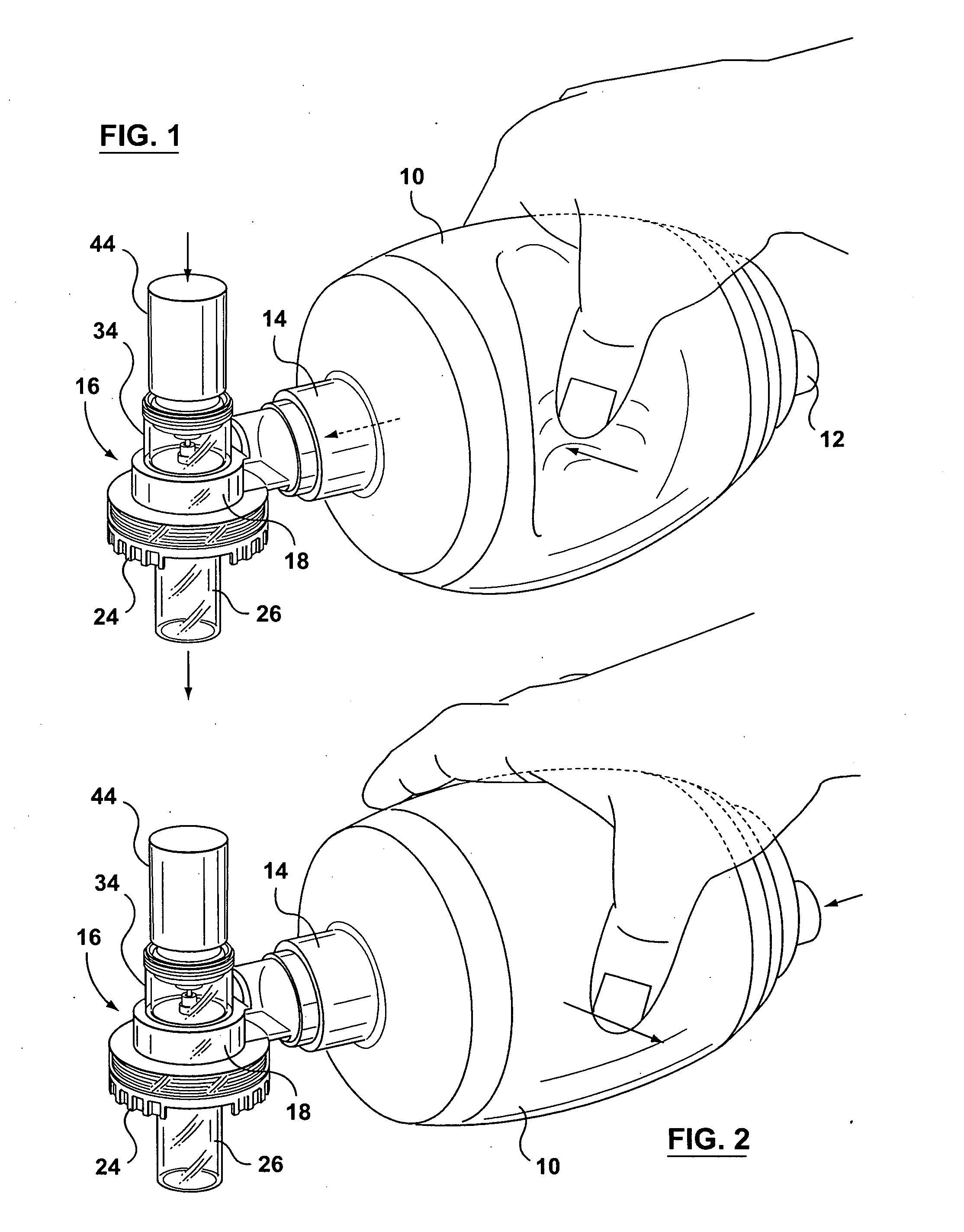
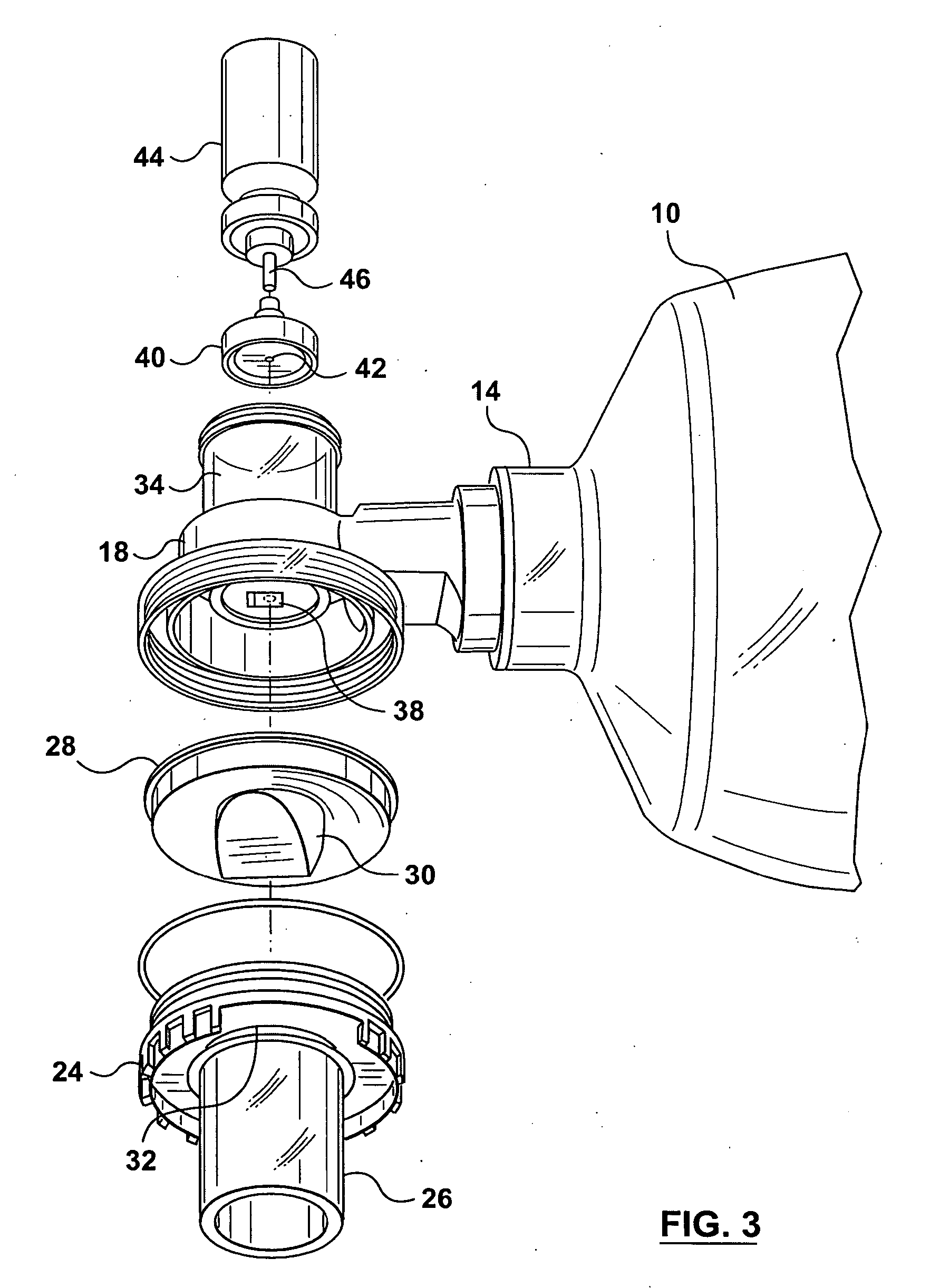
Resuscitators, parts and assemblies
A squeeze bag resuscitator has a flow diverter push fitted onto its exhaust outlet in any desired orientation. The diverter has a colour change carbon dioxide indicator strip fixed to the inside surface of a transparent deflector plate. The indicator is protected from light externally by an opaque elastomeric strip attached by engaging surface formations to the outside of the plate. The indicator is also protected on the interior of the plate by an opaque strip, which projects from the diverter so that it can be removed by pulling on the free end.
Owner:SMITHS GRP PLC
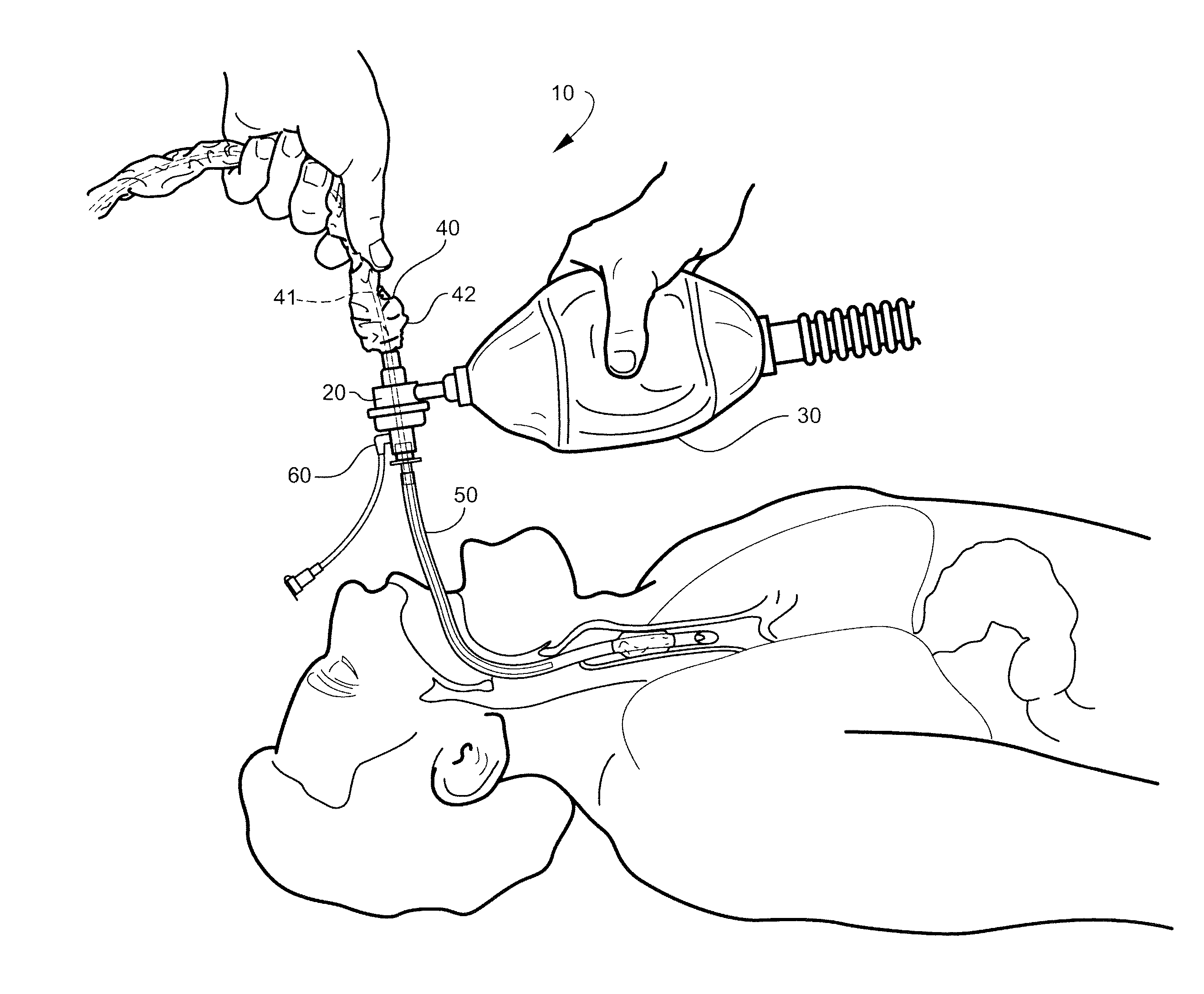
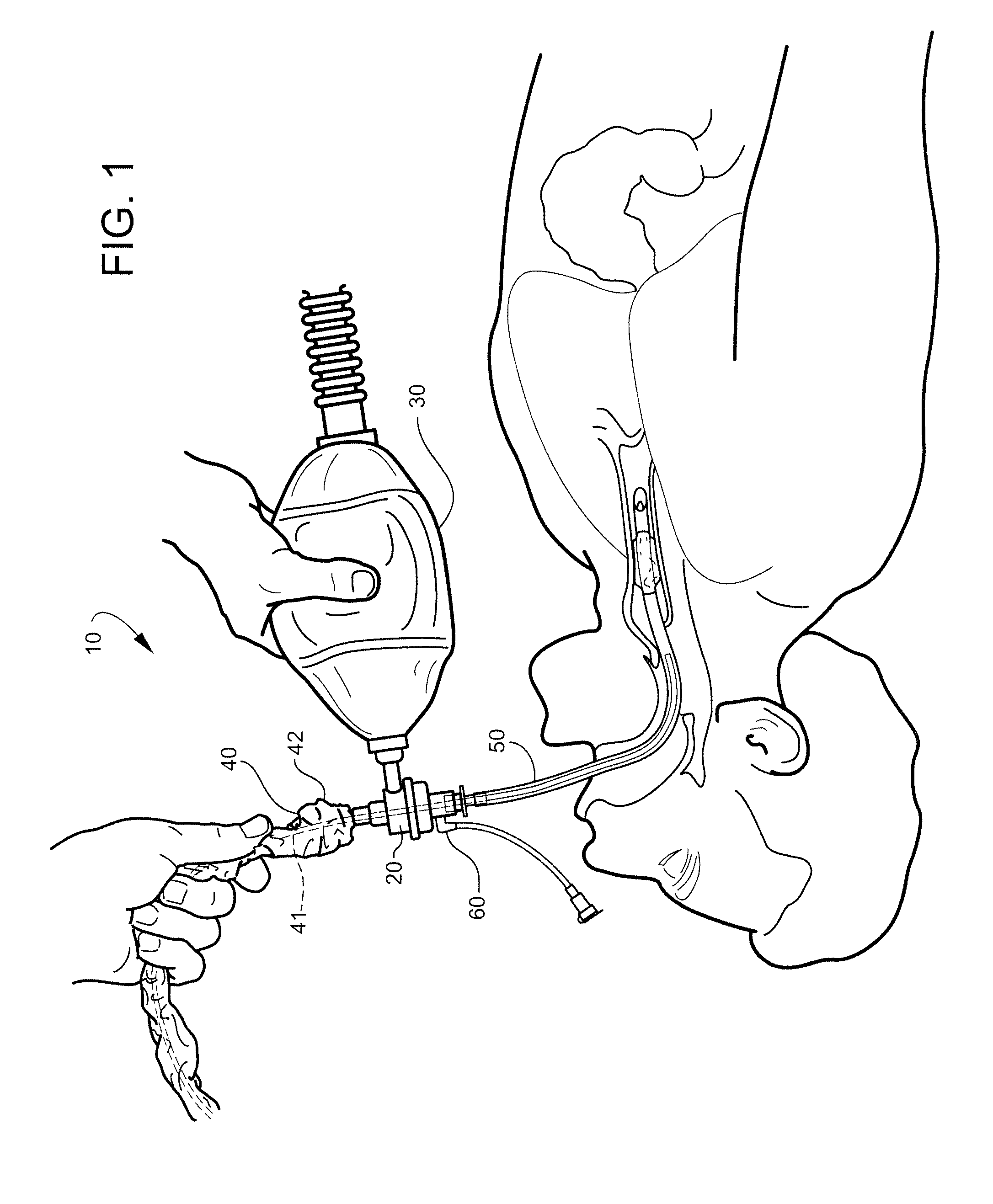
System and method for monitoring resuscitation or respiratory mechanics of a patient
ActiveUS20150283342A1Overcomes drawbackTracheal tubesRespiratory device testingAir volumeLung pressure
A system and method for monitoring resuscitation and respiratory mechanics of a patient is provided. A pressure sensor detects air pressure within an air-flow path of a resuscitator and generates a first detection signal in response thereto. A flow-rate sensor detects the flow-rate within the air-flow path and generates a second detection signal In response thereto. A processor receives and processes the first and second detection signals using an algorithm to identify a ventilation rate, a lung pressure, and an air volume corresponding to the respiratory air. A report is generated of real-time feedback about respiration of the patient that includes the ventilation rate, lung pressure, and air volume.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
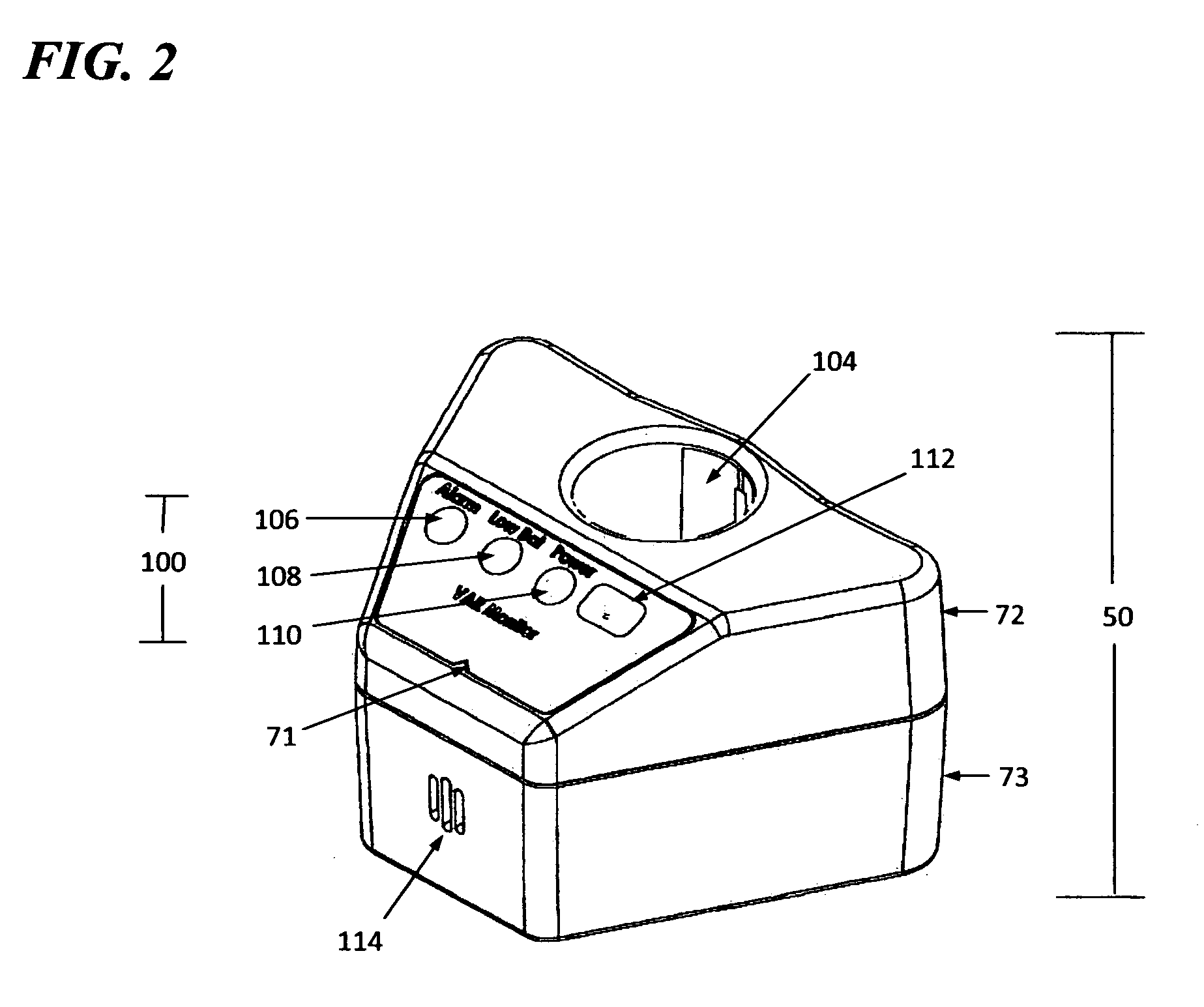
Monitor for automatic resuscitator with primary and secondary gas flow control
The present invention pertains generally to a monitoring system for a resuscitator which detects operation of the resuscitator and a controller unit for a supply of therapeutic gas to a resuscitator, and more specifically, a flow controller for a supply a therapeutic gas to an automatic resuscitator which is triggered by a single point pressure signal provided by the cycling of the automatic resuscitator from a controlled inhalation phase to a controlled exhalation phase. The monitoring aspect of the system detects single point low pressure signals which are sequentially compared against a time clock. Failure of the resuscitator system itself to generate a low pressure signal against the integrated time clock causes an alarm condition. Further, gas management is effected by a flow controller integrated into the monitor, a gas management system which responds to the single point low pressure signal and operate a primary gas control valve attached between a gas supply and an automatic resuscitator such that gas is allowed to flow to the resuscitator when the resuscitator is in an inhalation mode and gas flow is interrupted when the resuscitator is in an exhalation mode. A secondary gas control valve is integrated into the gas management system in parallel to the primary gas control valve. The flow controller includes a low threshold pressure sensor which is actuated by means of a recurrent low pressure pulse generated by the automatic resuscitator itself through the cycling of the resuscitator and remains essentially unaffected by the respiratory cycling of the patient, thus preventing false triggers and greatly simplifying the flow controller operation and format. The low threshold pressure sensor is coupled to a processor wherein the processor reads the occurrence of a pressure event at the pressure sensor and which then closes the primary gas control valve and starts a clock. As the pressure is decreased in the gas management system resulting from the primary gas control being moved to a closed position, the secondary gas control valve moves to open state, thus allowing the gas management system to vent to atmosphere during exhalation, reducing the pressure of the system to an operator defined positive level. Once the clock reaches a pre-defined duration, the primary gas control valve is reopened, the pressure in the gas management system increases thus closing the secondary gas control valve, the automatic resuscitator continues into an inhalation mode, and the process repeats.
Owner:VORTRAN MEDICAL TECH 1
Resuscitators, parts and assemblies
A squeeze bag resuscitator has a flow diverter push fitted onto its exhaust outlet in any desired orientation. The diverter has a color change carbon dioxide indicator strip fixed to the inside surface of a transparent deflector plate. The indicator is protected from light externally by an opaque elastomeric strip attached by engaging surface formations to the outside of the plate. The indicator is also protected on the interior of the plate by an opaque strip, which projects from the diverter so that it can be removed by pulling on the free end.
Owner:SMITHS GRP PLC
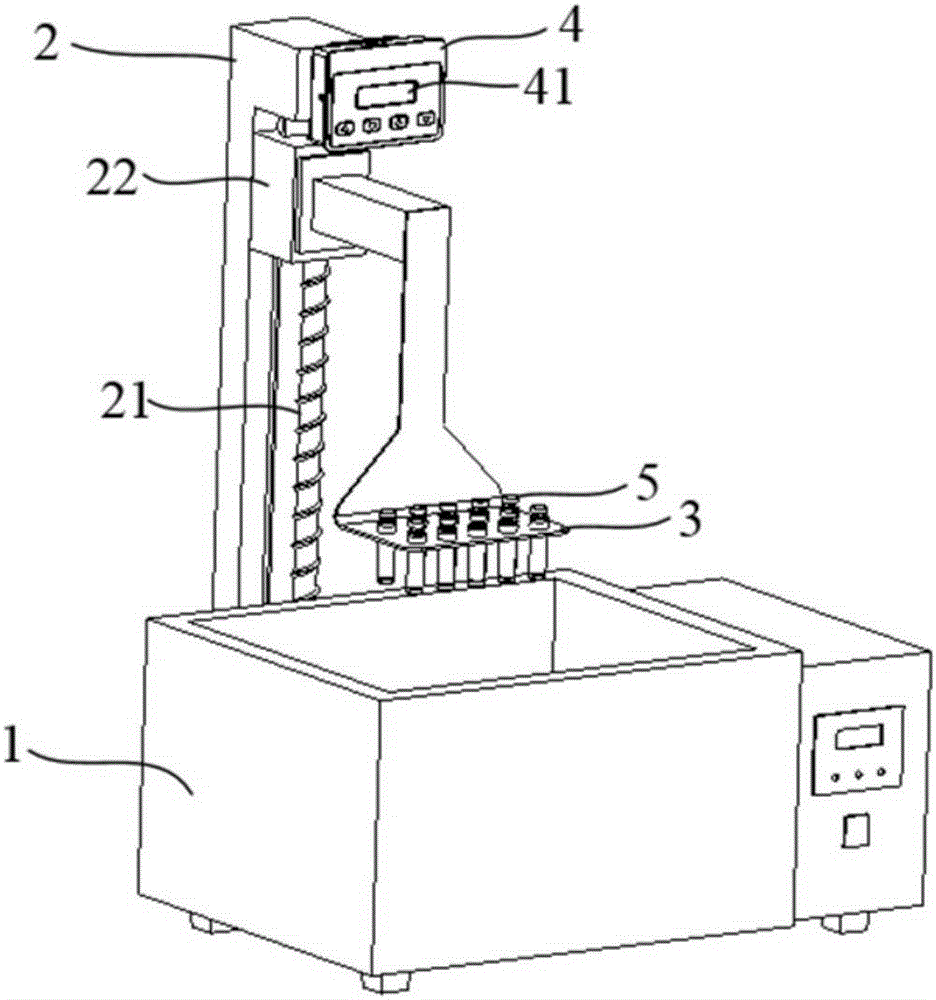
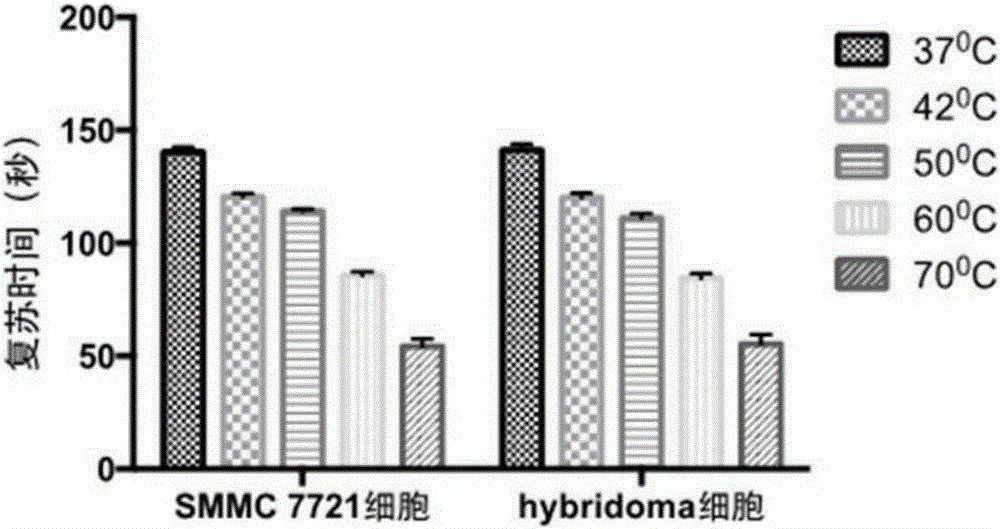
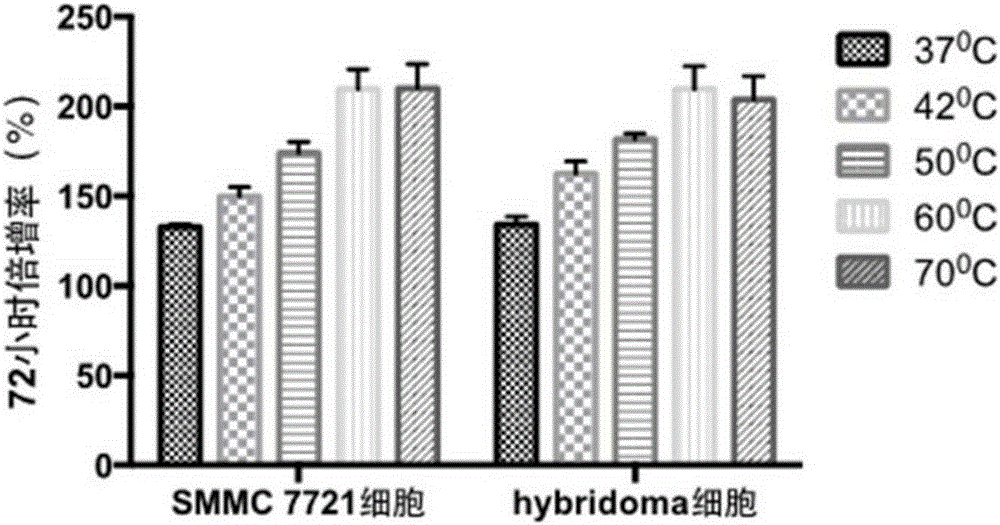
Cell resuscitator
ActiveCN105199950AImprove consistencyAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater bathsElectricity
The invention discloses a cell resuscitator. The cell resuscitator comprises a water bath kettle, a lifting mechanism, a carrying device and a controller, wherein the carrying device is arranged on the lifting mechanism; the controller is electrically connected with the lifting mechanism and is used for controlling the movement of the lifting mechanism and putting the carrying device into the water bath kettle. According to the cell resuscitator disclosed by the invention, by the combination of the lifting mechanism and the controller, a process of automatically resuscitating cells in large batches is achieved, the time and temperature of resuscitation can be accurately controlled, and the process parameters of resuscitation are recorded; moreover, the possible pollution on frozen cells caused by water in the water bath kettle is avoided, the resuscitation quality of the cells is greatly improved, the burden on an operator is alleviated, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGINCELL BIOLOGICAL CRYO EQUIP CO LTD
Resuscitator device
ActiveUS20140318544A1Reduce riskInflation difficultRespiratory masksMedical devicesTidal volumePositive pressure
A manually actuated, self-inflating bag valve mask provides users with a positive pressure ventilation device that reliably provides a proper tidal volume to the patient and controls the rate of ventilation of the patient. The bag valve mask is lightweight, compact, durable, and quickly deployable in the field. The device is preferably operable with one hand and can be configured for use in low-light environments.
Owner:SAFEGUARD MEDICAL HOLDCO LLC
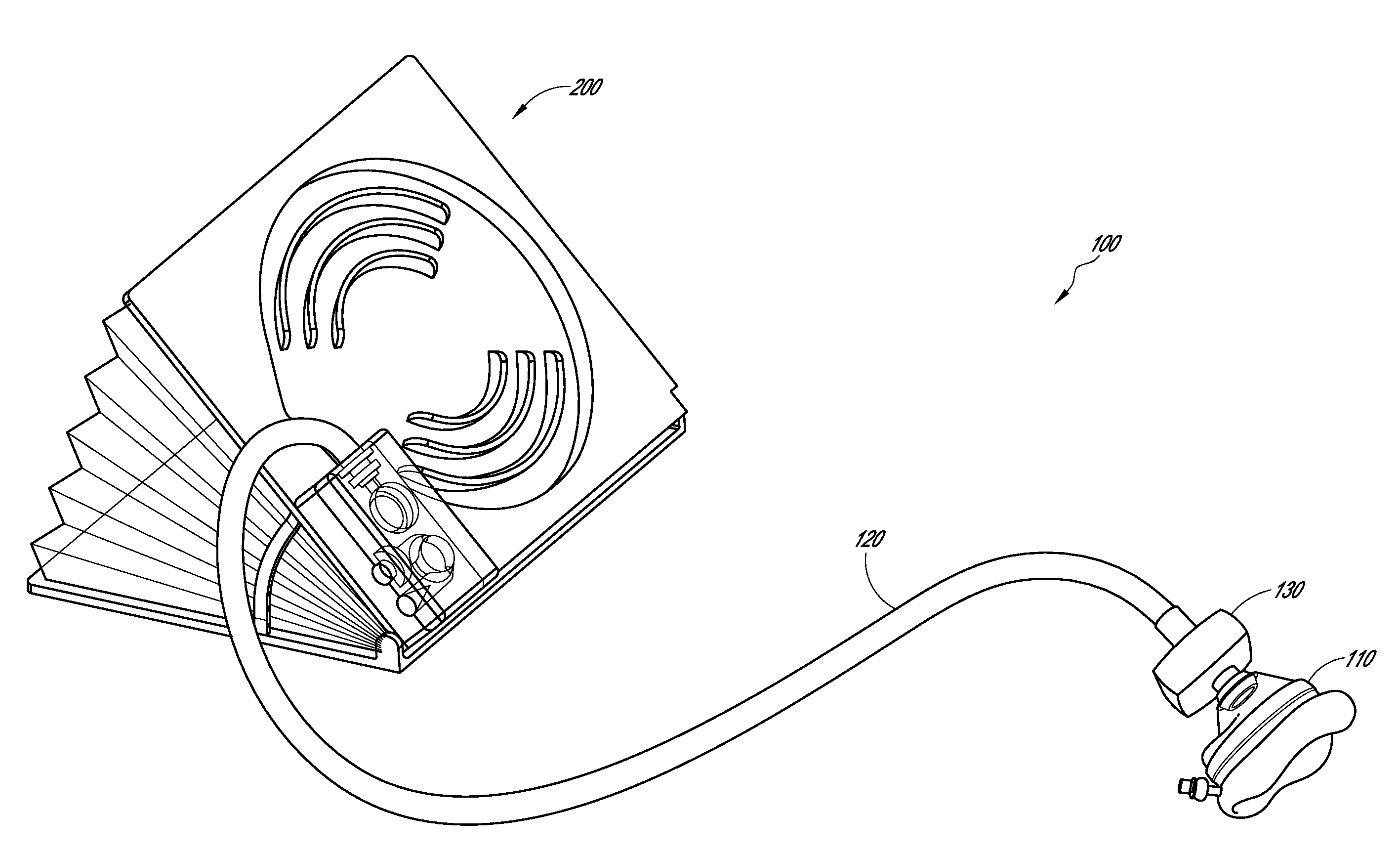
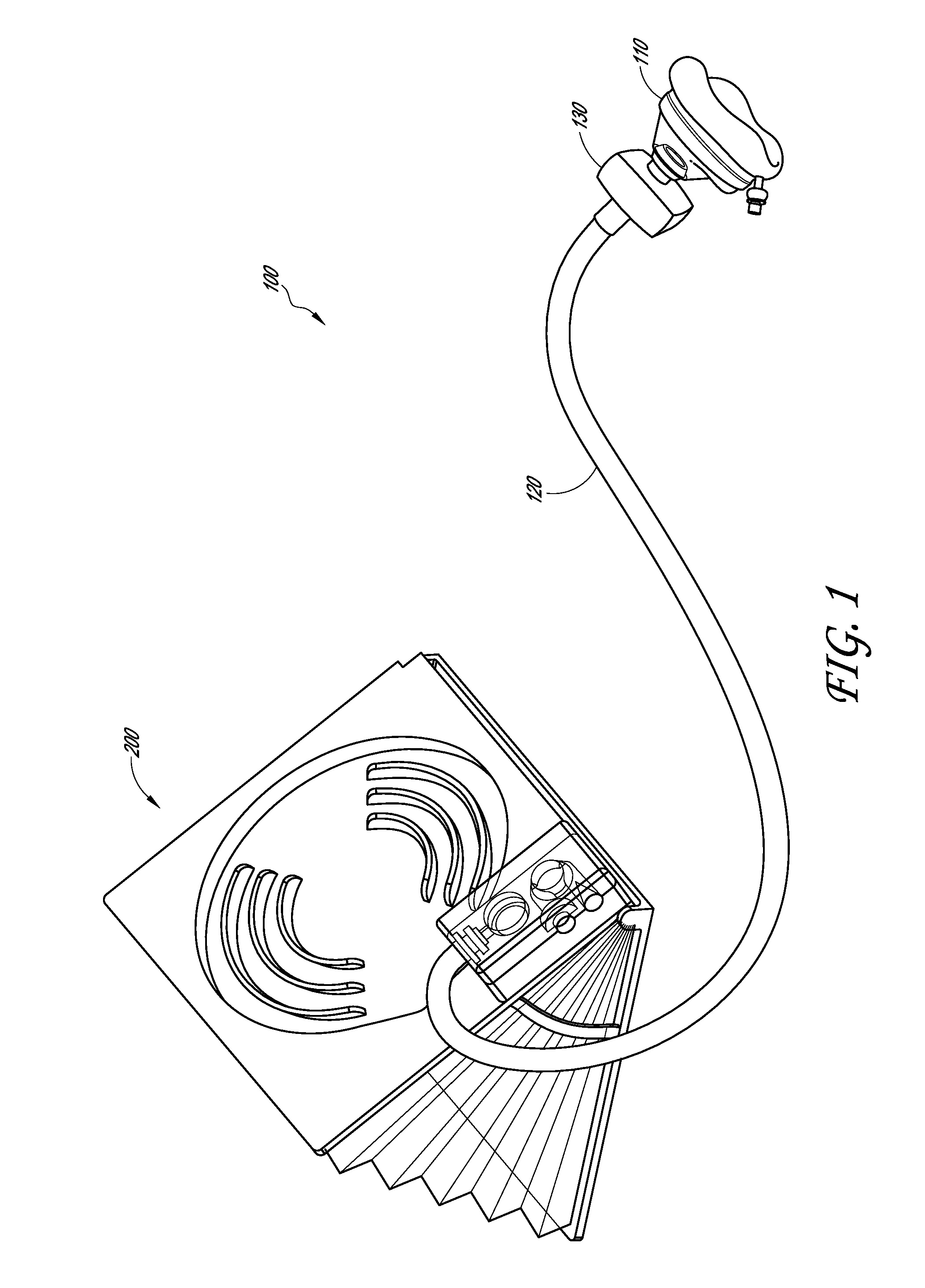
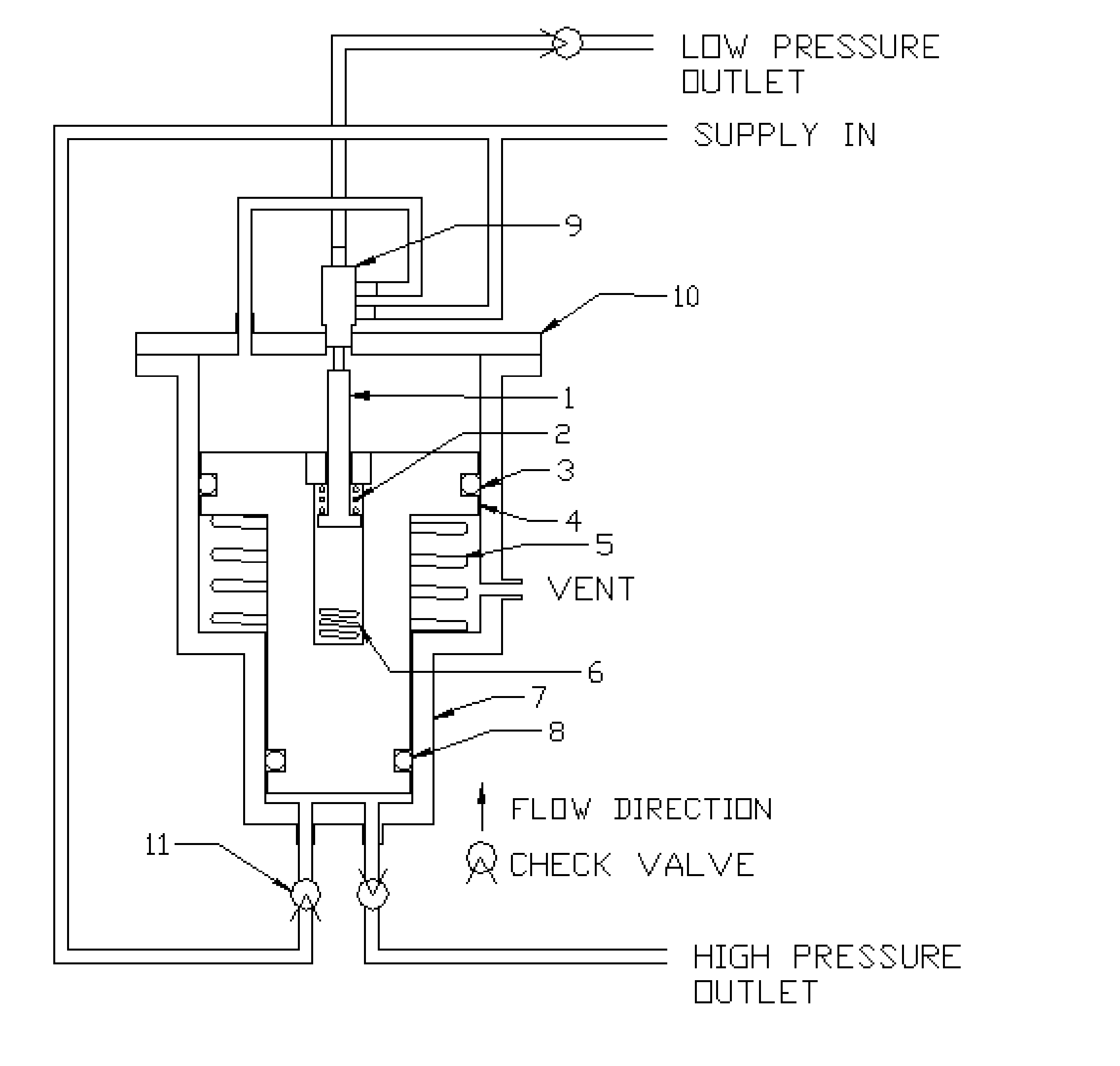
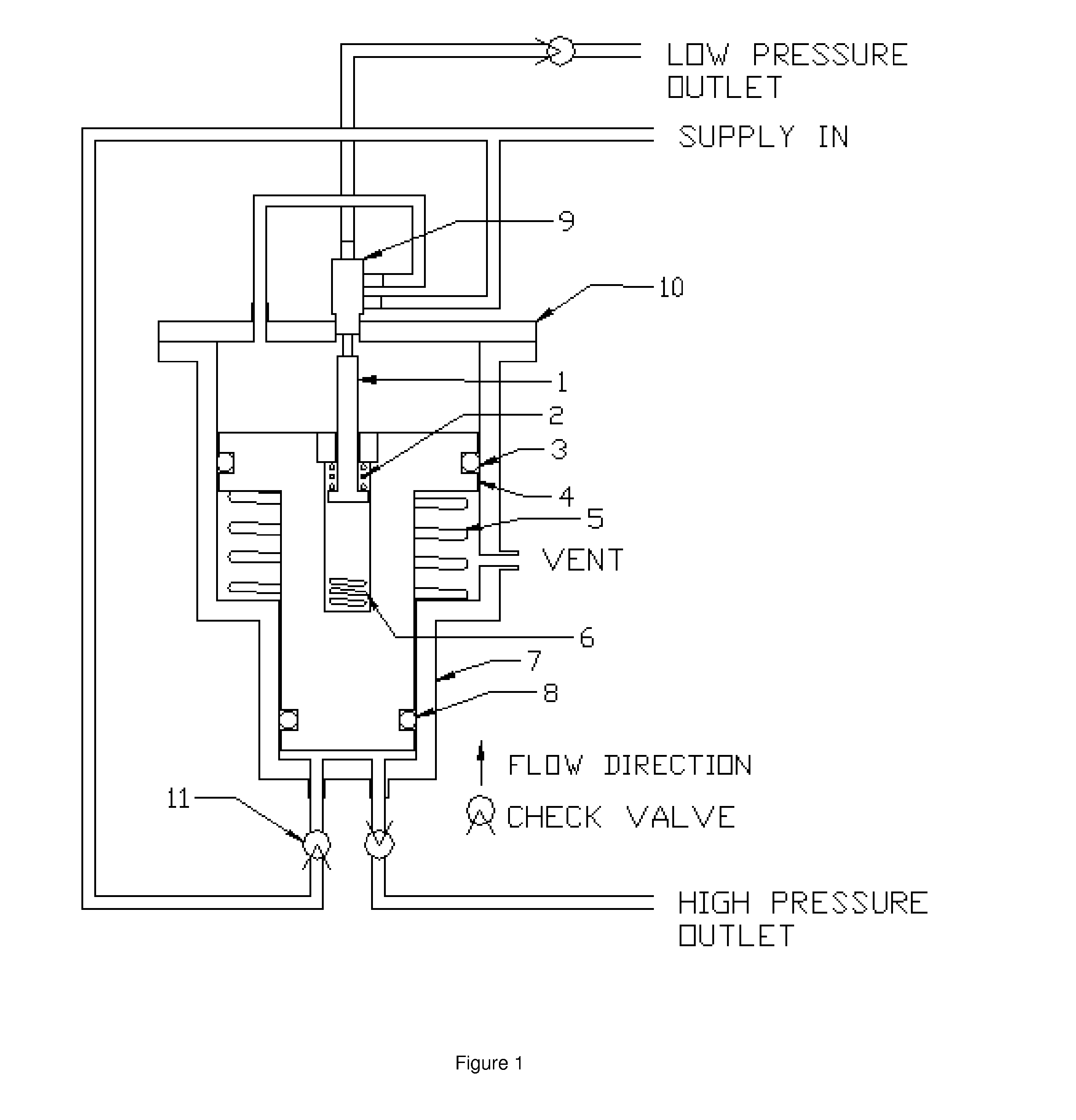
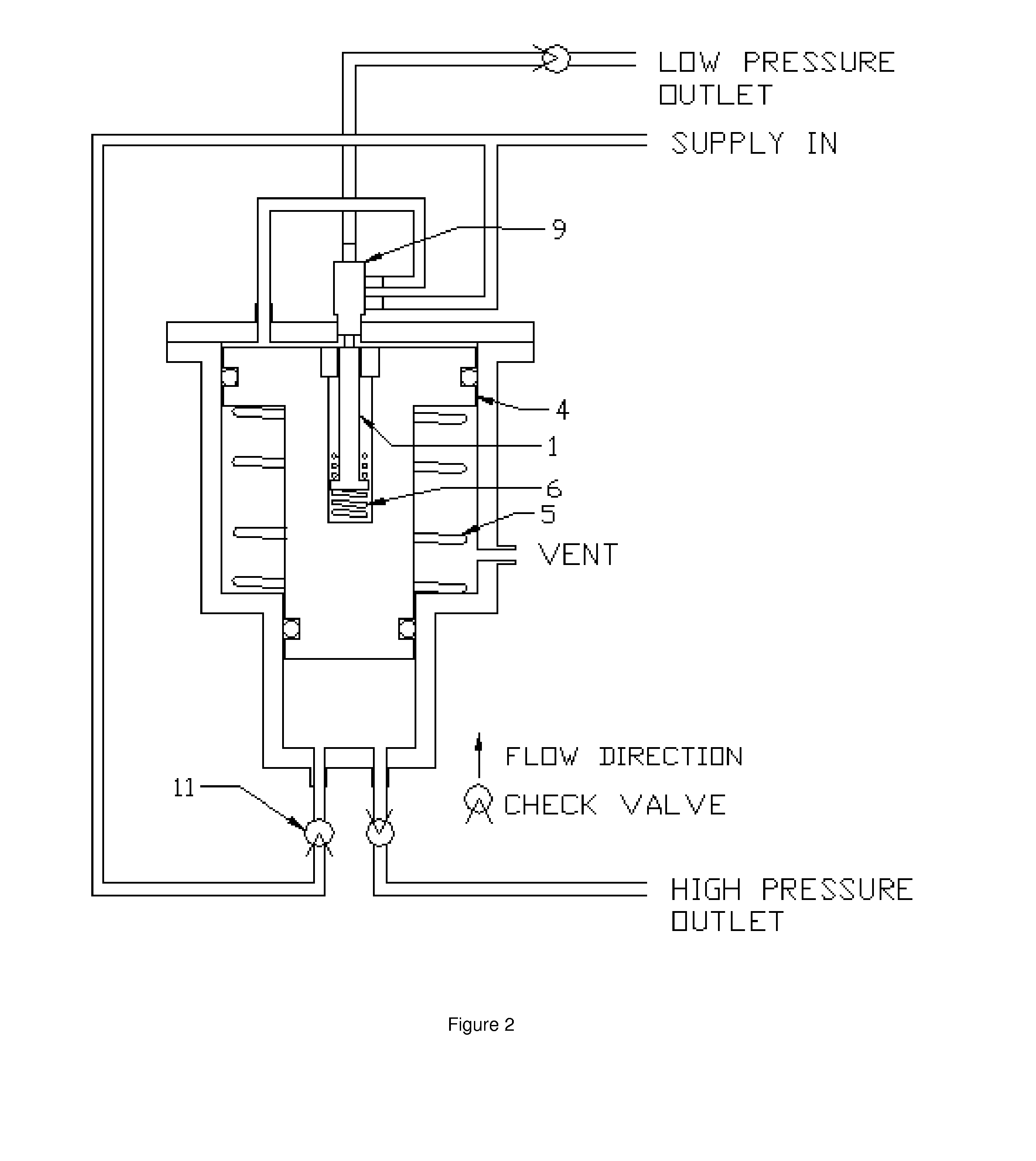
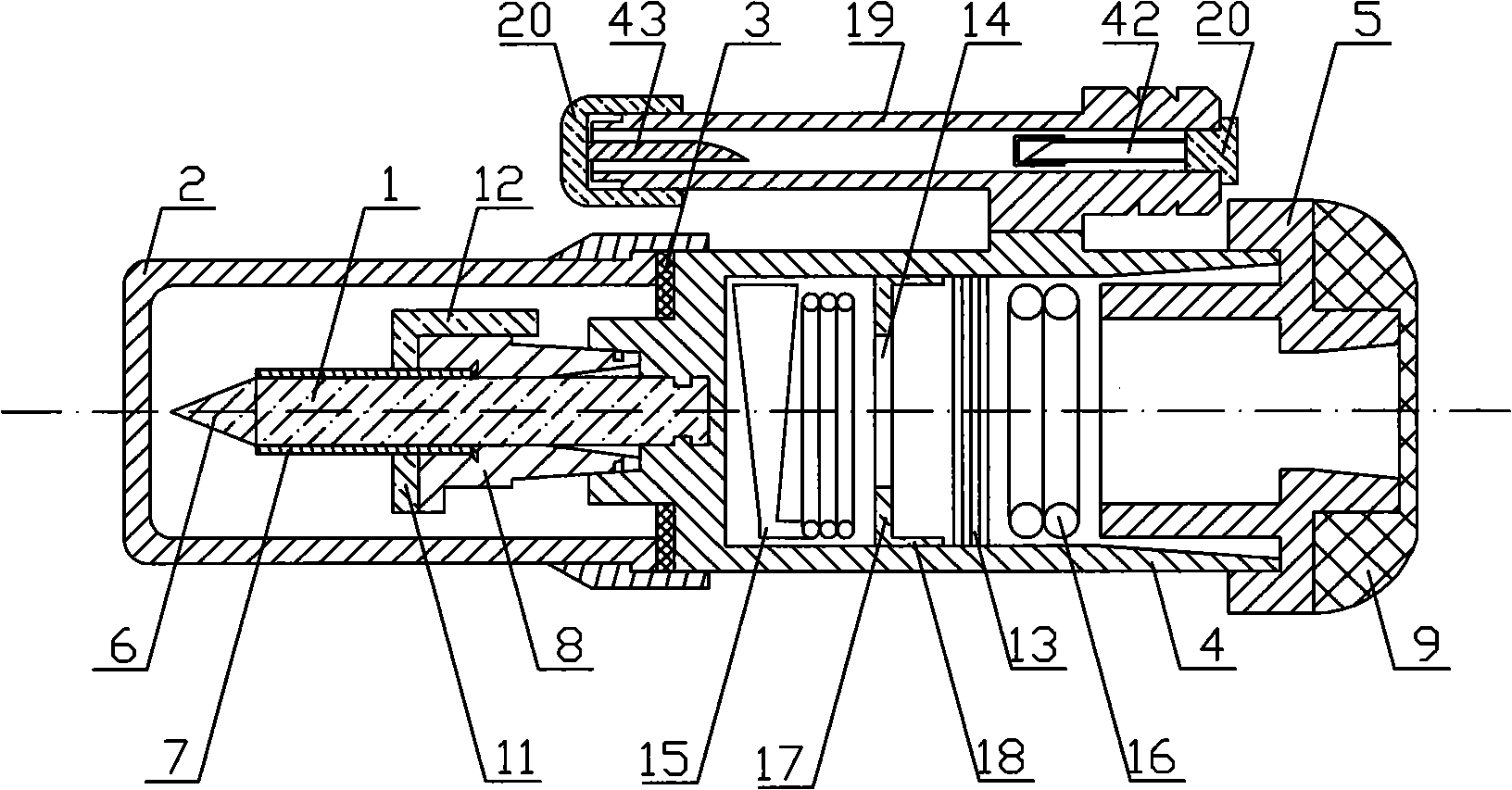
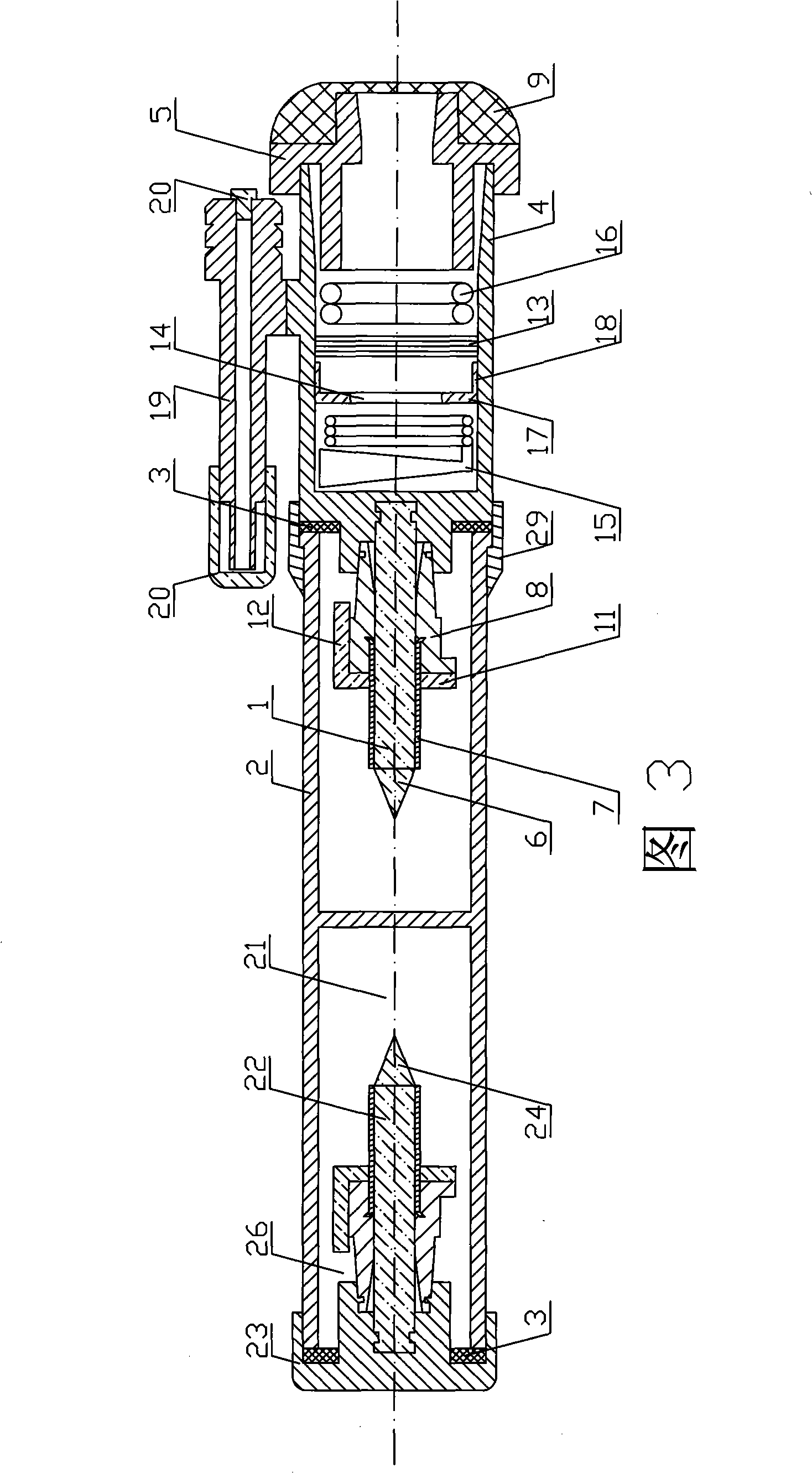
Resuscitator
A resuscitator with a rigid top plate, a rigid bottom plate and a rigid bottom plenum assembly. The top plate is hingeldy joined at its forward end to the bottom plate. A flexible accordion member is located between the top plate and the bottom assembly forming a standard air pump. When a person pushes down on the top plate, air is forced out of and outflow tube located on the top plate. An internal spring returns the top plate to its original position and in doing so causes air to be drawn into the plenum assembly. A top plate travel limiting member, such as a cord, includes a plurality of spaced protuberances that act as restraining members that can be retained under a slot in the side of the plenum assembly thereby adjusting the travel distance of the accordion member and controlling the resulting volume of air output to a patient being resuscitated.
Owner:PEARCE RICHARD
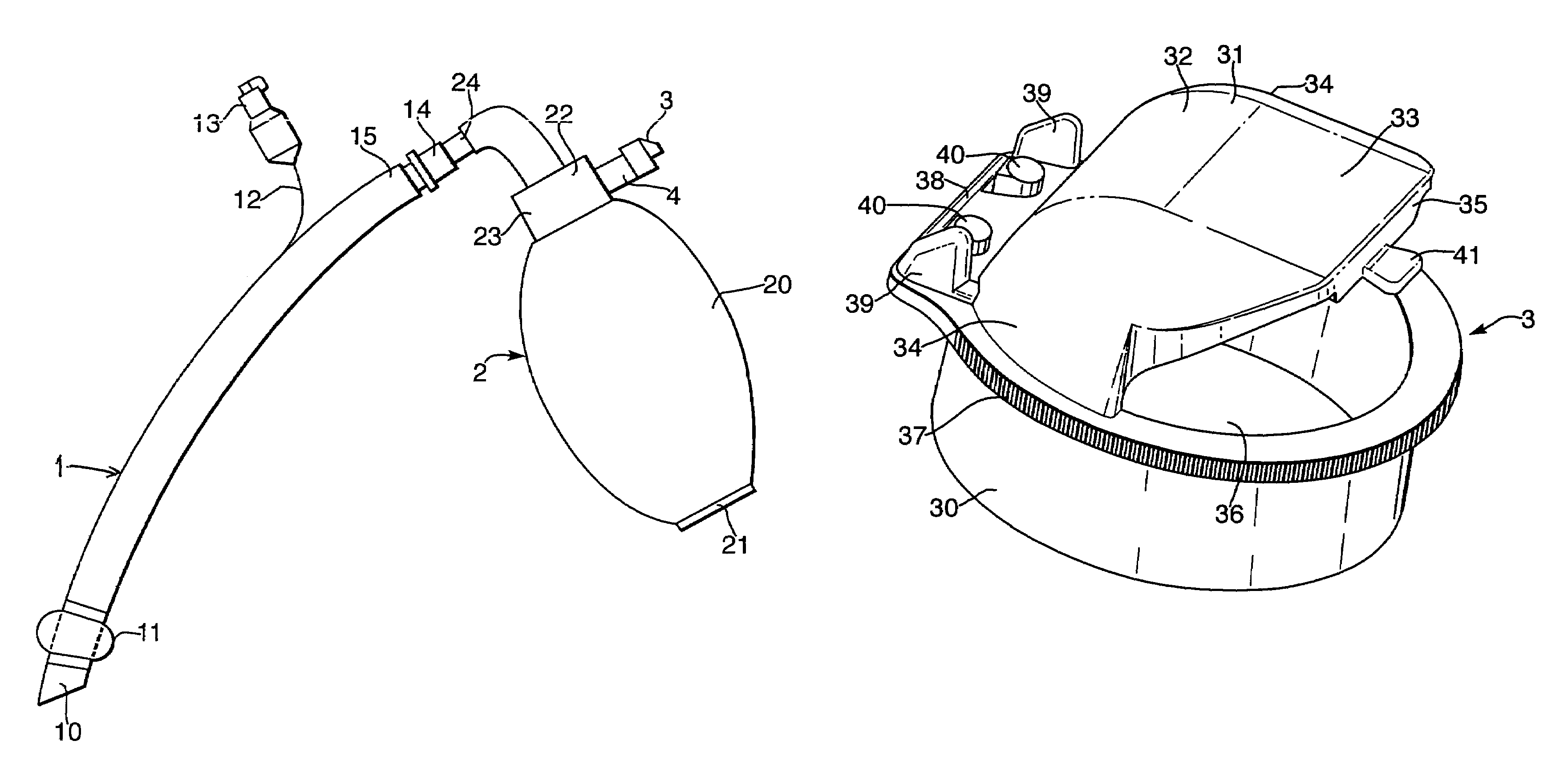
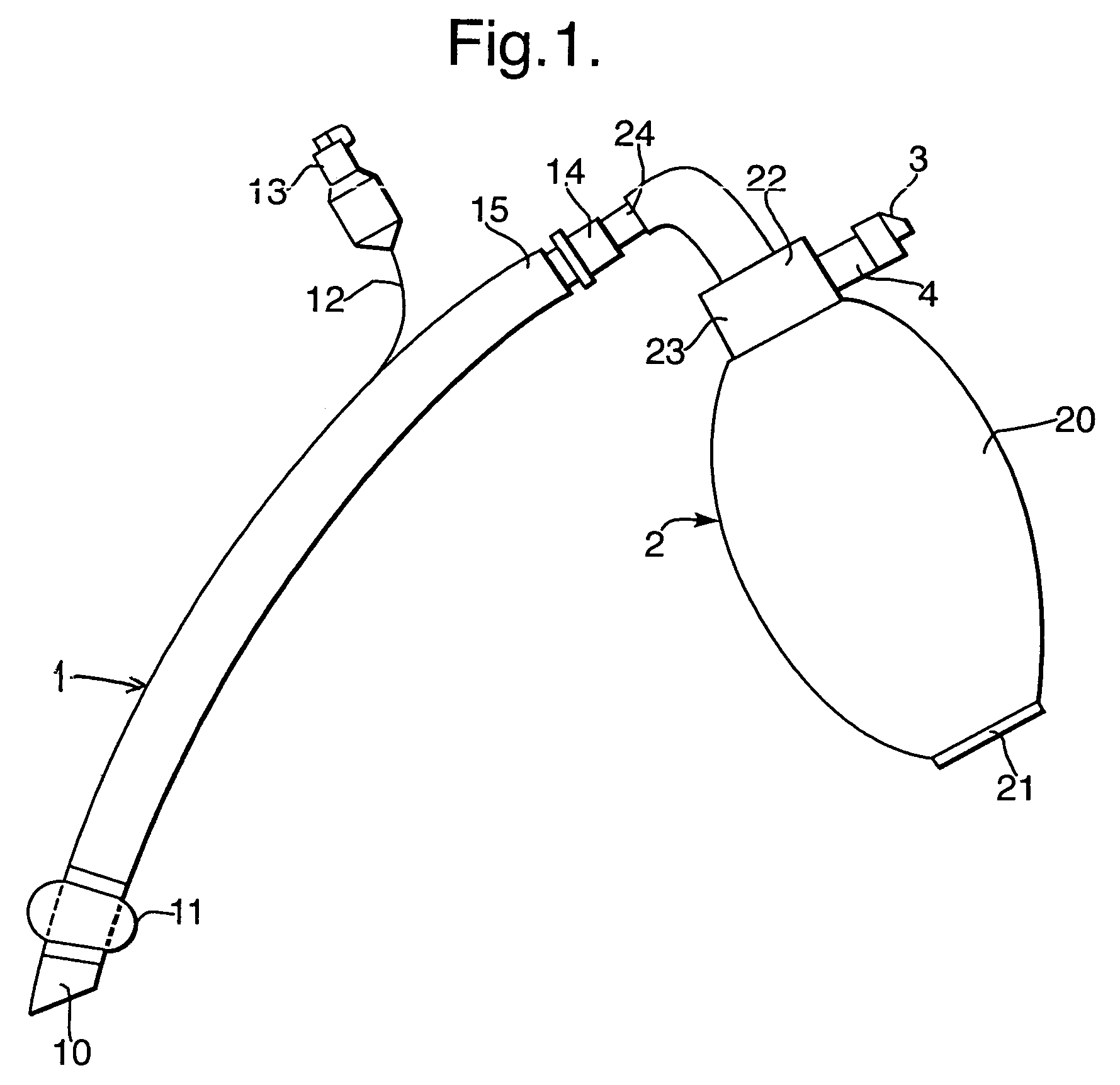
Manually-operable resuscitators
A manually-operable resuscitator operable also to inject medication into air being supplied to a patient. The resuscitator has a resiliently compressible air bag having an inlet and an outlet. The inlet has a one-way valve through which air passes into the bag from the atmosphere and a patient valve through which air flows in passing from the bag to the patient. The patient valve has a one-way valve member through which air flows in passing from the bag to the patient. The patient valve also has a passage extending from the atmosphere to the interior thereof adjacent to the one-way valve member and upstream thereof through which medication can be injected into the air as it passes from the bag to the one-way valve member.
Owner:FLYNN STEPHEN
Electric resuscitator mode control devices and methods thereof
The invention discloses a mode control device and a method thereof for an electric respirator, the device comprises: a motor; a motor control part, which controls the rotational speed of the motor; a crank link mechanism, which can be rotatablely connected with the motor by a connecting shaft, and the crank link mechanism is connected with a piston. The rotational speed of the motor is constantly changed by the motor control part, thus ensuring the piston to have the constant speed. The device adopts the control algorithm to ensure the running speed of the piston to be constant, thus realizing the ventilation with the constant flow rate, overcoming the discomfort of a patient caused by the constant change of the flow rate, leading the patient to effectively carry out the gas exchange and improving the control precision.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
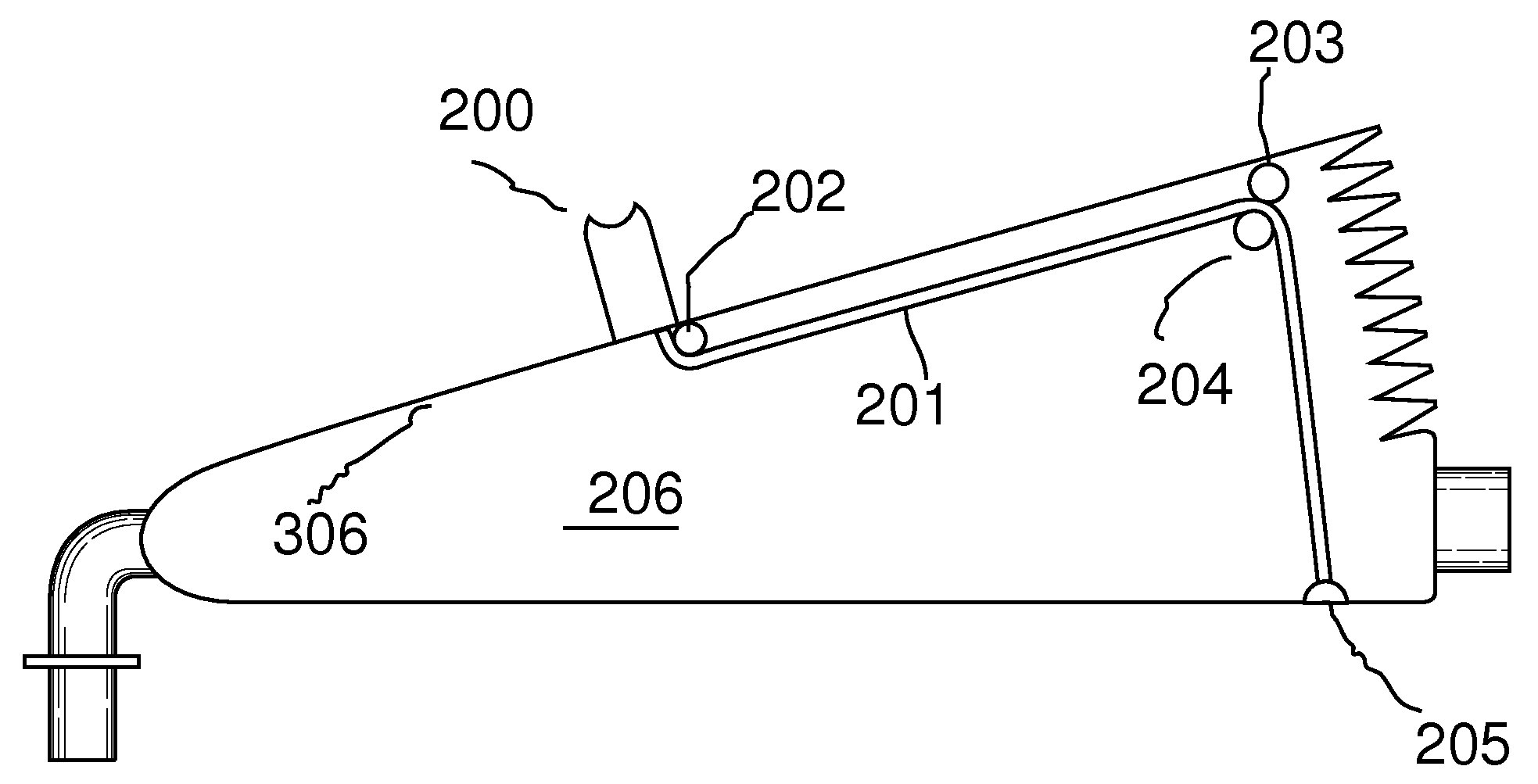
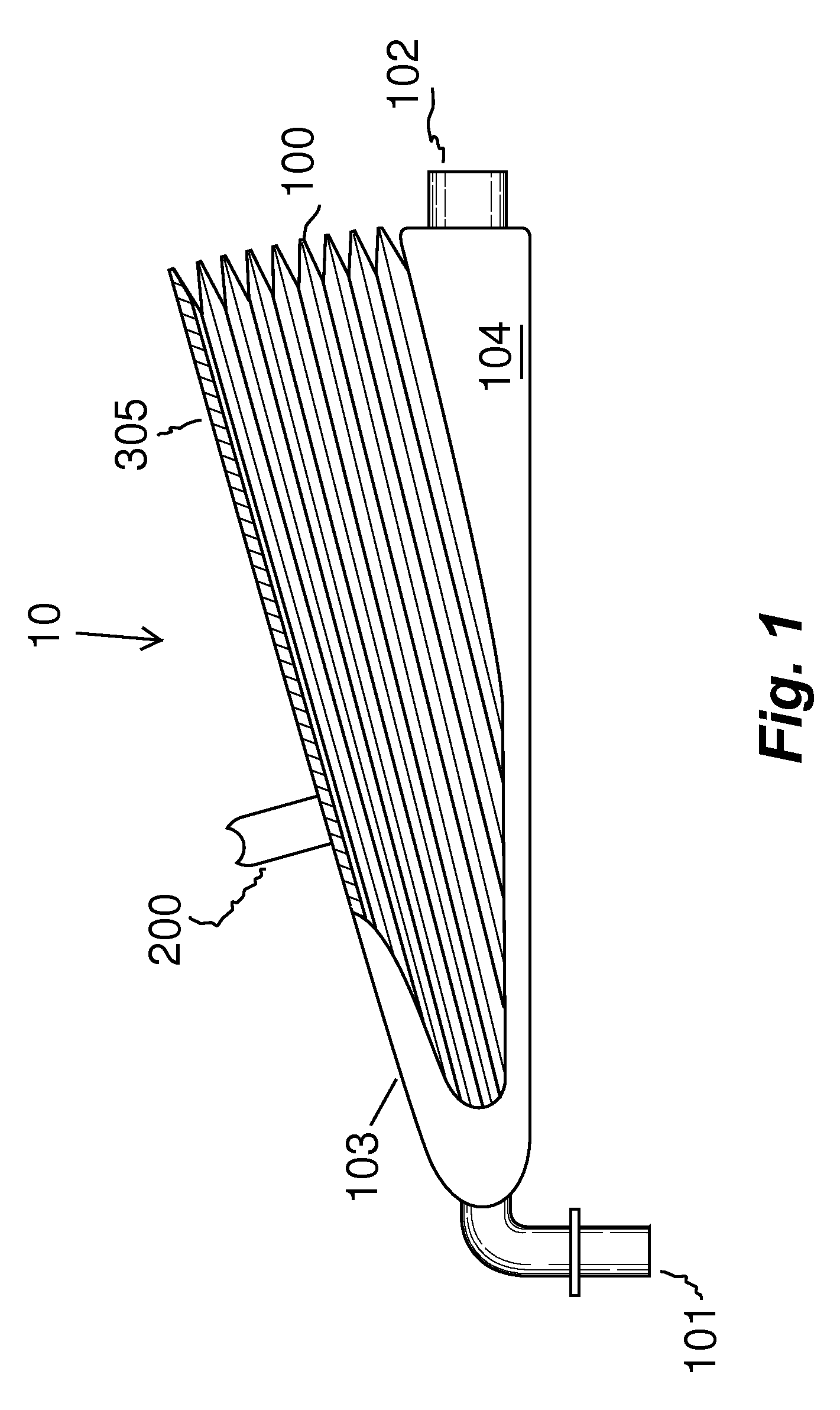
Manual emergency resuscitator with pre-defined volume control
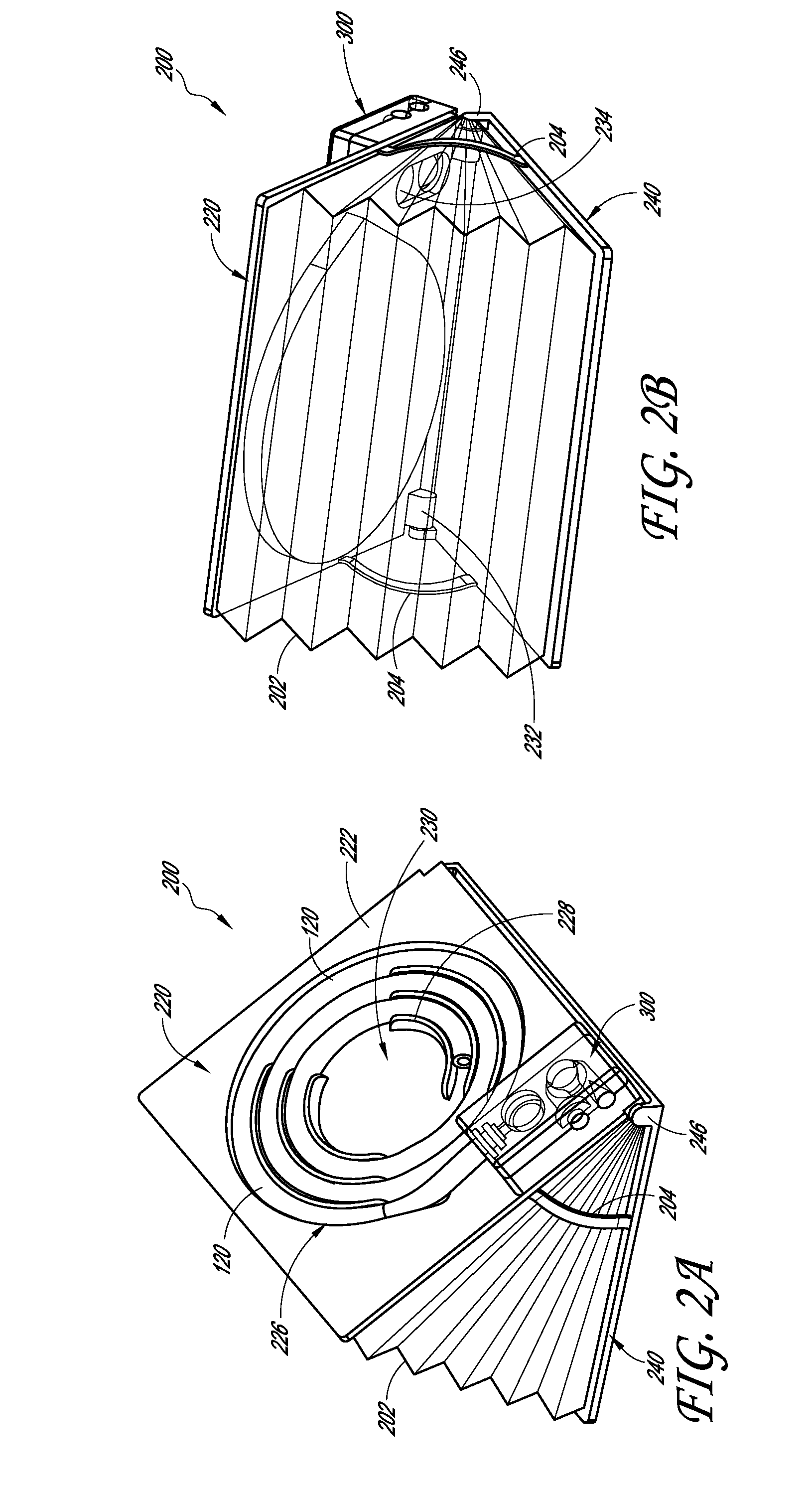
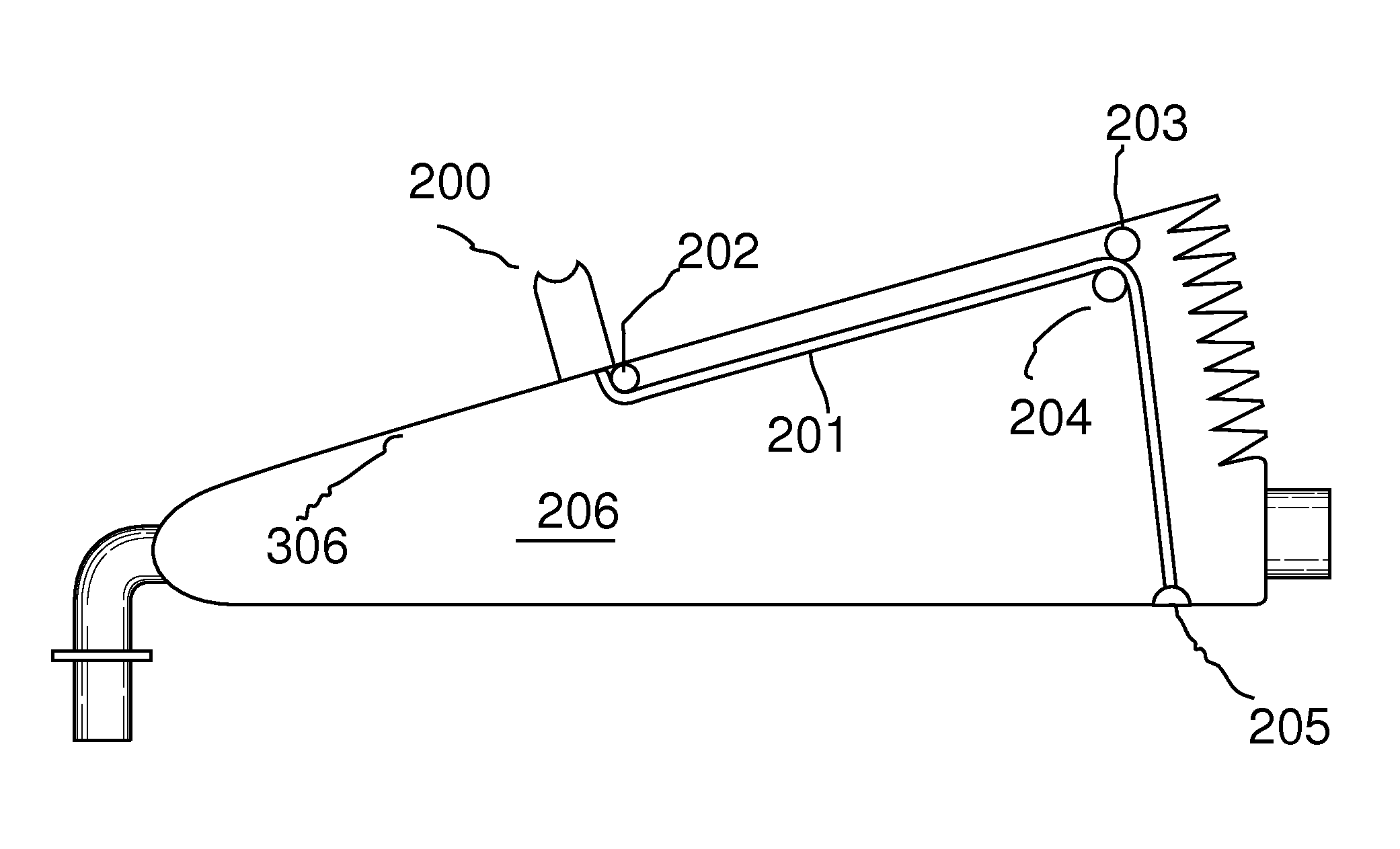
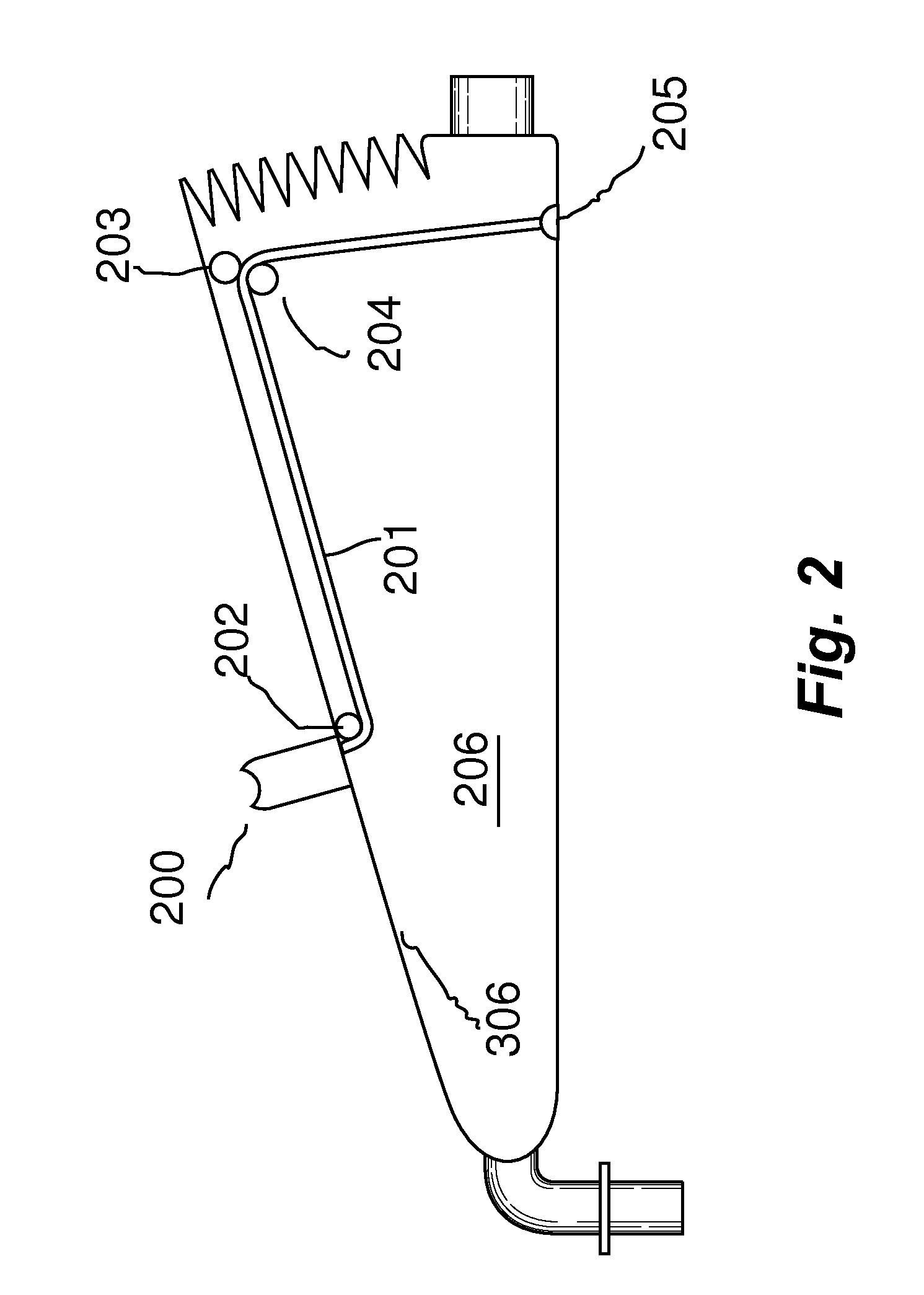
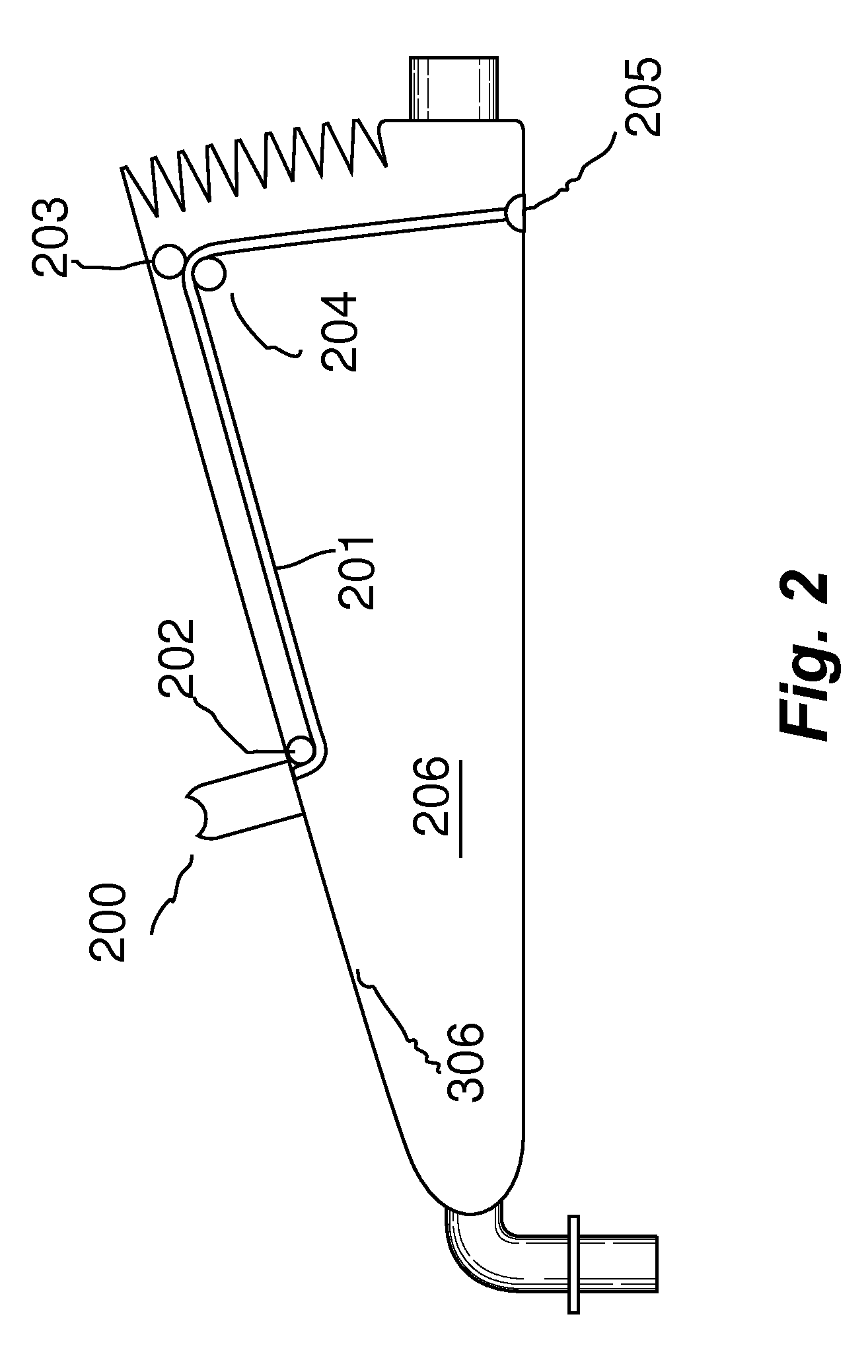
ActiveUS20130092166A1Accurate volumeRespiratorsMedical devicesMechanical engineeringFull Term Infant
A manual emergency resuscitator uses a volume control system having pre-defined setting to accommodate patients of different sizes. An upper plate 305 is attached to a front hinge assembly 103 and a lower housing assembly is attached to the front hinge assembly. The lower housing assembly defines the lower portions of an accordion chamber 206. A selection void 300 is defined within the upper plate 305, with the selection void further defined by voids indexed to a closed position, infant position, child position and an adult position. A volume selector cord 201 has a first end attached to a volume selector, with the volume selector contained within the selection void. Placing the volume selector into one of the predefined positions regulates the amount of air delivered by the resuscitator.
Owner:PEARCE RICHARD S
Manually-operable resuscitators
A manually-operable resuscitator operable also to inject medication into air being supplied to a patient. The said resuscitator has a resiliently compressible air bag having an inlet and an outlet. The inlet has a one-way valve through which air passes into the bag from the atmosphere and a patient valve through which air flows in passing from the bag to the patient. The patient valve has a one-way valve member through which air flows in passing from the bag to the patient. The patient valve also has a passage extending from the atmosphere to the interior thereof adjacent to the one-way valve member and upstream thereof through which medication can be injected into the air as it passes from the bag to the one-way valve member.
Owner:FLYNN STEPHEN
Device having manual resuscitation and suction capabilities
InactiveUS20150352303A1Reduce and prevent problemShorten operation timeTracheal tubesRespiratory apparatusCatheterEngineering
Disclosed is a resuscitator including a valve assembly having a check valve arranged within a valve body, the valve body defining a gas passageway therethrough, the valve body including a first inlet, a second inlet and a first outlet, wherein the second inlet and the first outlet are axially aligned, and the first inlet is axially perpendicular to both the second inlet and the first outlet, and wherein the valve is arranged within the valve body between the second inlet and the first outlet in axial alignment with the second inlet and the first outlet; a compressible bag in fluid communication with the first inlet; a suction device removably attached to the second inlet; and an endotracheal tube removably attached to the first outlet. The suction device includes a tube arranged to be advanced through the valve and into the endotracheal tube such that the endotracheal tube can be suctioned without having to detach the endotracheal tube from the valve body.
Owner:GODWIN GRANT
Carbon dioxide indicating apparatus, particularly, disk-like carbon dioxide indicating apparatus
Carbon dioxide indicator for receiving gas containing carbon dioxide and for providing a visible indication of the presence of carbon dioxide in the gas, the indicator includes a connector for removably connecting the indicator to a source of gas containing carbon dioxide and which connector is for communicating at least a portion of such gas to the indicator. The carbon dioxide indicator may be a disk indicator and the connector may be a male luer or a locking male luer. The carbon dioxide indicator may include removable ultraviolet radiation shielding permitting the carbon dioxide indicator to be preassembled to a patient's respiratory or breathing circuits or to a resuscitator.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL CONSUMABLES LLC
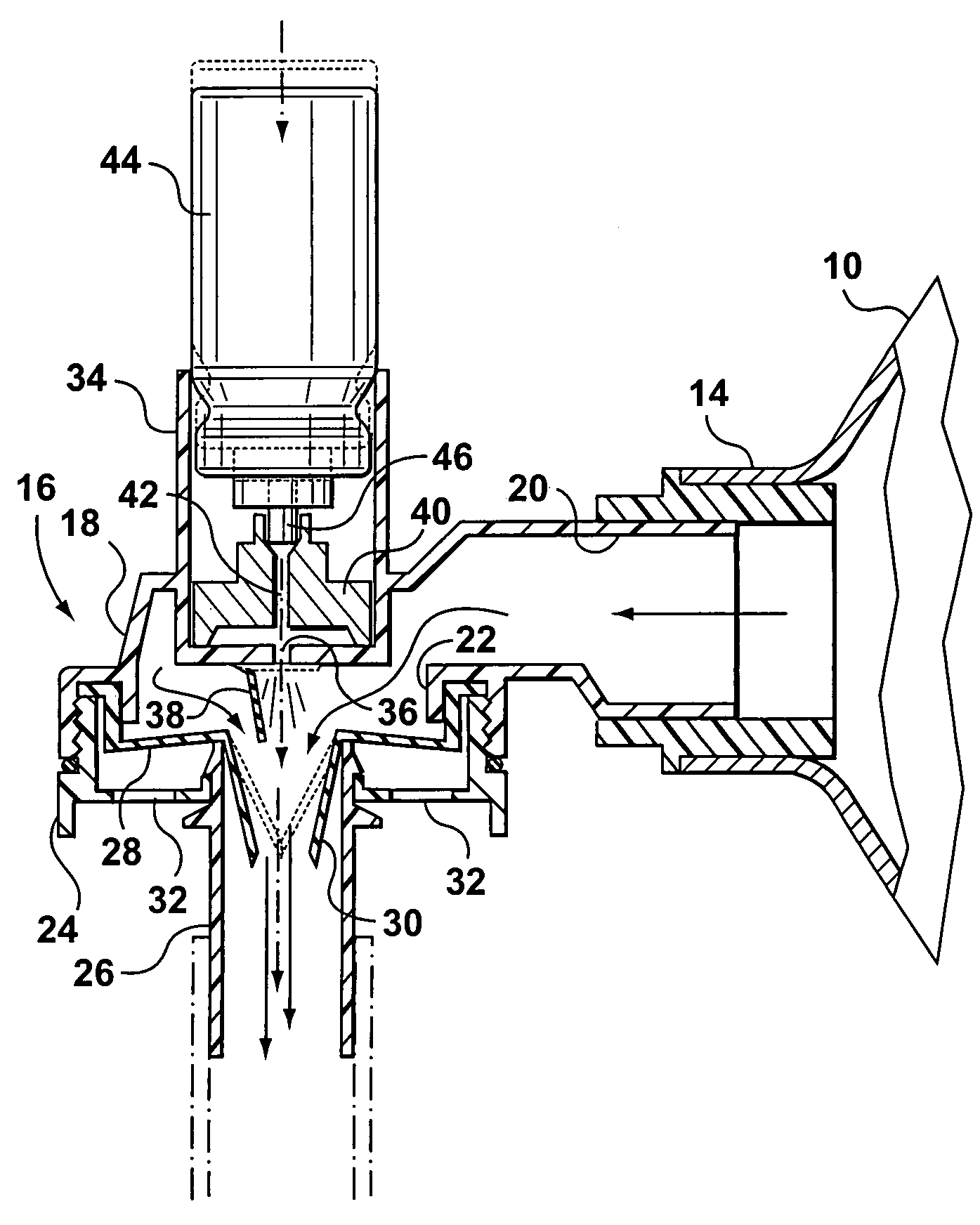
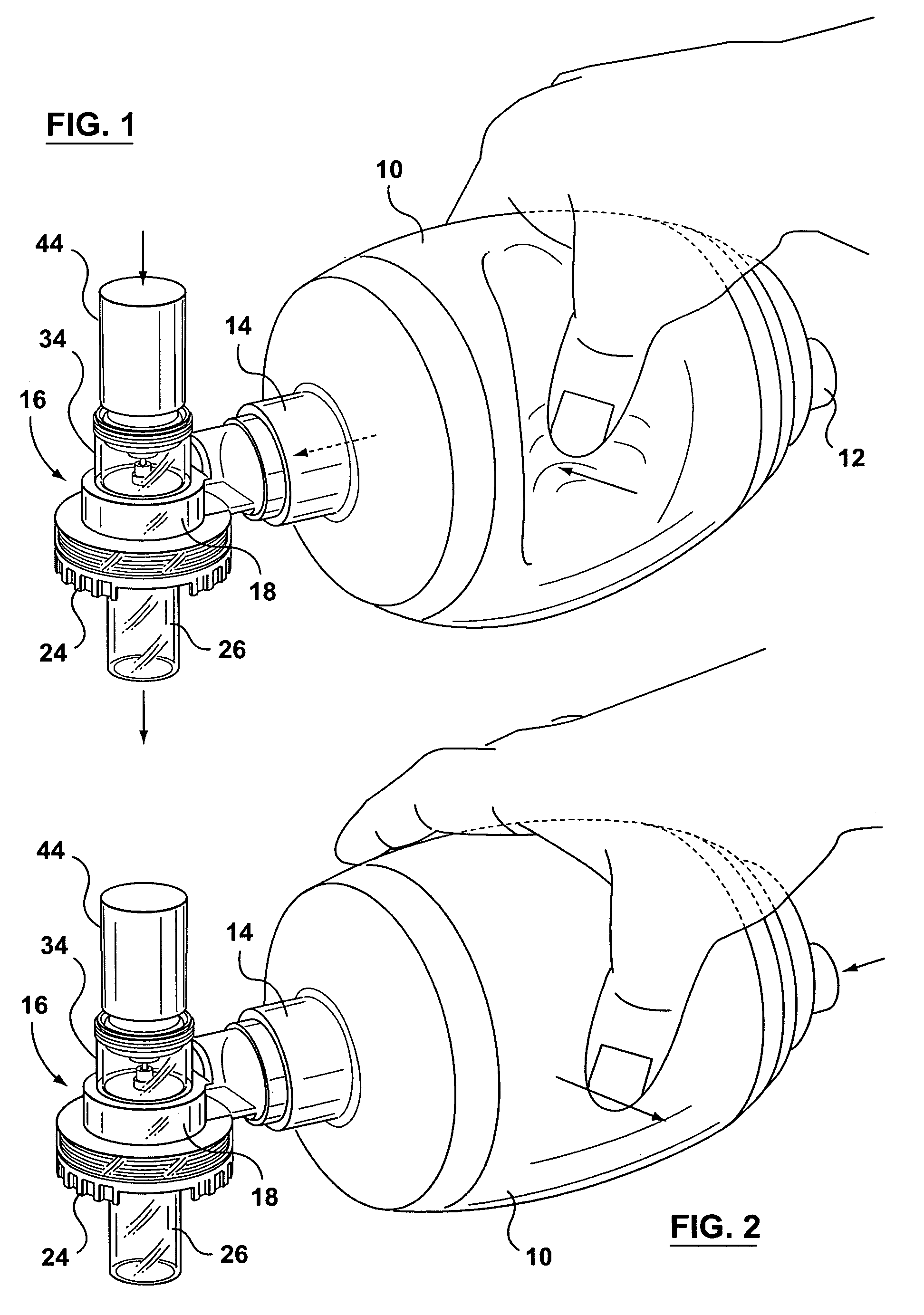
Gas Pressure Intensifier System for use with a Ventilator or Resuscitator
InactiveUS20090032020A1Reduce the temperatureReduce pressureRespiratorsElectrotherapyEnergy sourceIntermediate pressure
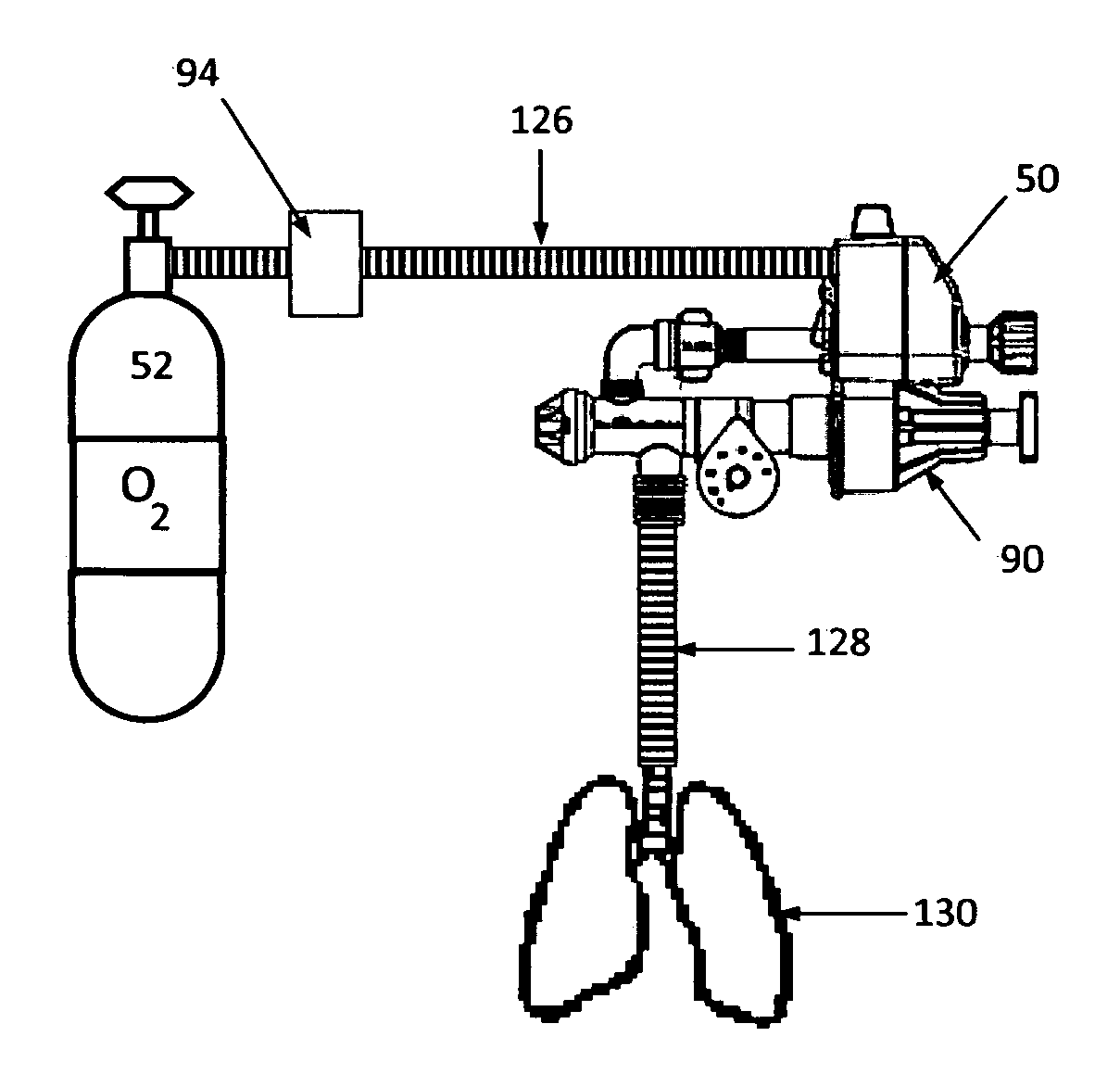
The present invention is directed to a system for supplying gas to a pneumatic logic controlled system such as ventilator or resuscitator. The system produces a high pressure gas stream and a low pressure gas stream from an intermediate gas pressure source. The intermediate pressure source could be any oxygen supply including a chemical oxygen generator or compressor. The high pressure gas stream has the water removed from the gas stream. The high pressure gas provides an energy source to the pneumatic logic of the ventilator or a resuscitator. The output flow of the pneumatic logic is used to control the flow of the low pressure gas by means of a proportional flow control valve. The proportional flow control valve combines the signal gas flow from the pneumatic control logic and the low pressure gas.
Owner:KLEINBECK THOMAS RAYMOND
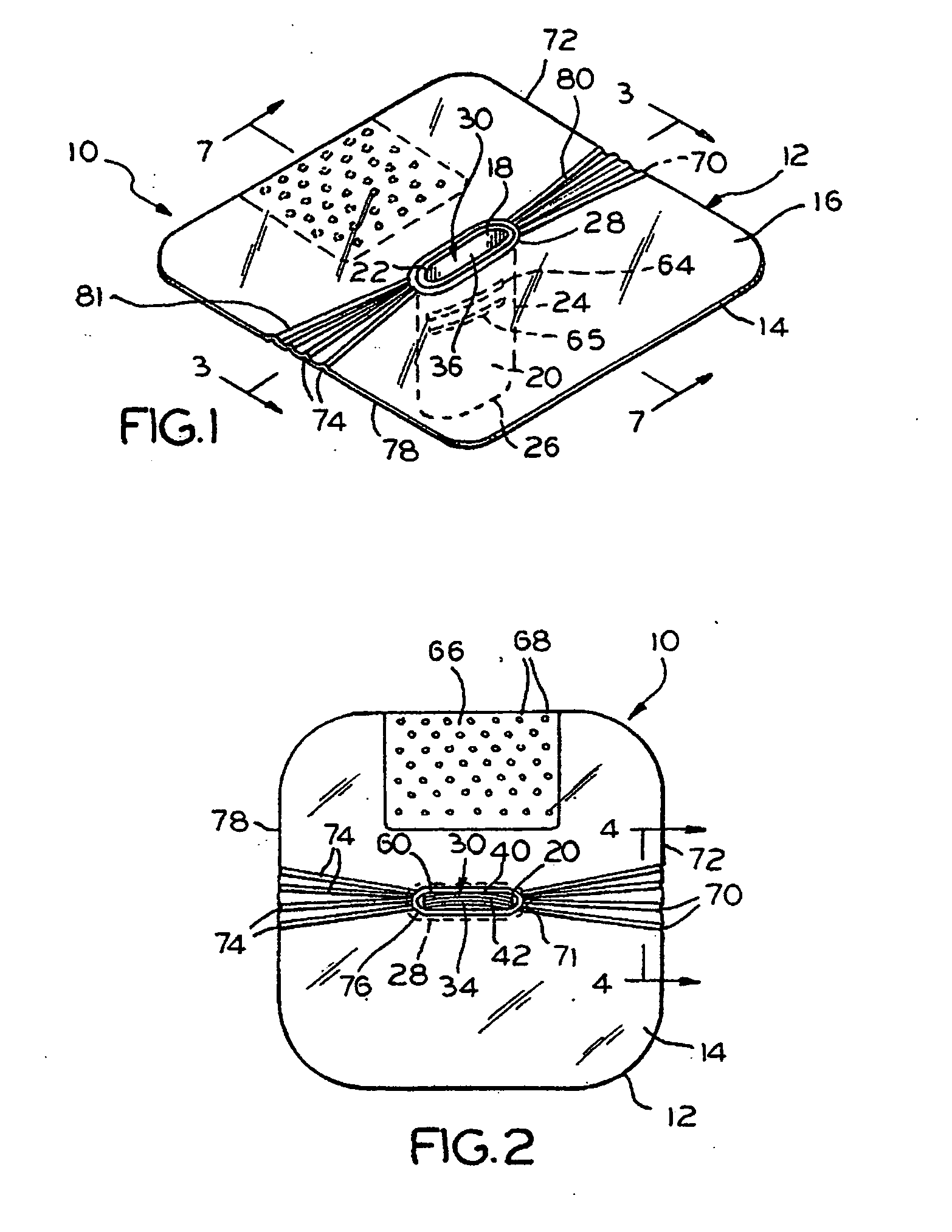
Mouth-to-mouth resuscitator device
A mouth to mouth resuscitator device for use by a rescuer for resuscitating a victim, the device comprising a sheet of flexible material having a top surface and an undersurface, the sheet forming a mouth opening, a hollow substantially rigid tube having an external surface, a first end, a second end and a tube length between the first and second ends, a tube passage aligned at least in part with the mouth opening, the tube extending from the undersurface of the sheet to the second end and a self closing one-way valve located within the tube passage to restrict flow from the second end to the first end of the tube and to allow flow from the first end to the second end when a rescuer exhales air into the mouth opening, wherein the external surface of the tube forms at least one recess at a location along the tube length, the recess for receiving a victim's teeth.
Owner:WESTFALL MARK D
Manual emergency resuscitator with pre-defined volume control
ActiveUS8936024B2Accurate volumeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A manual emergency resuscitator uses a volume control system having pre-defined setting to accommodate patients of different sizes. An upper plate 305 is attached to a front hinge assembly 103 and a lower housing assembly is attached to the front hinge assembly. The lower housing assembly defines the lower portions of an accordion chamber 206. A selection void 300 is defined within the upper plate 305, with the selection void further defined by voids indexed to a closed position, infant position, child position and an adult position. A volume selector cord 201 has a first end attached to a volume selector, with the volume selector contained within the selection void. Placing the volume selector into one of the predefined positions regulates the amount of air delivered by the resuscitator.
Owner:PEARCE RICHARD S
Method, device, and apparatus for measuring cardiopulmonary resuscitation compression depth, and storage medium
ActiveCN109223503AQuality assuranceExact referenceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationClassical mechanicsMulti axis
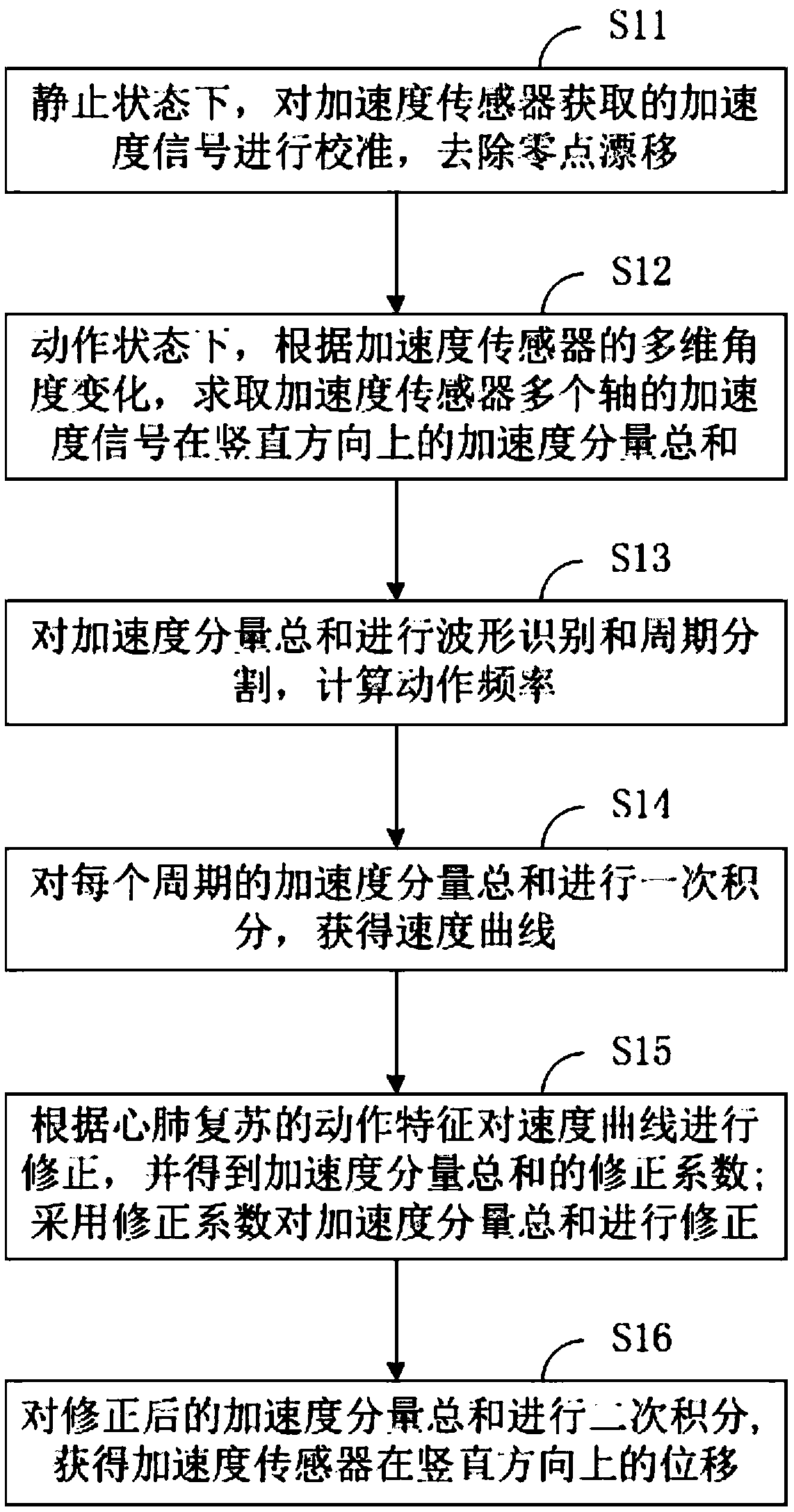
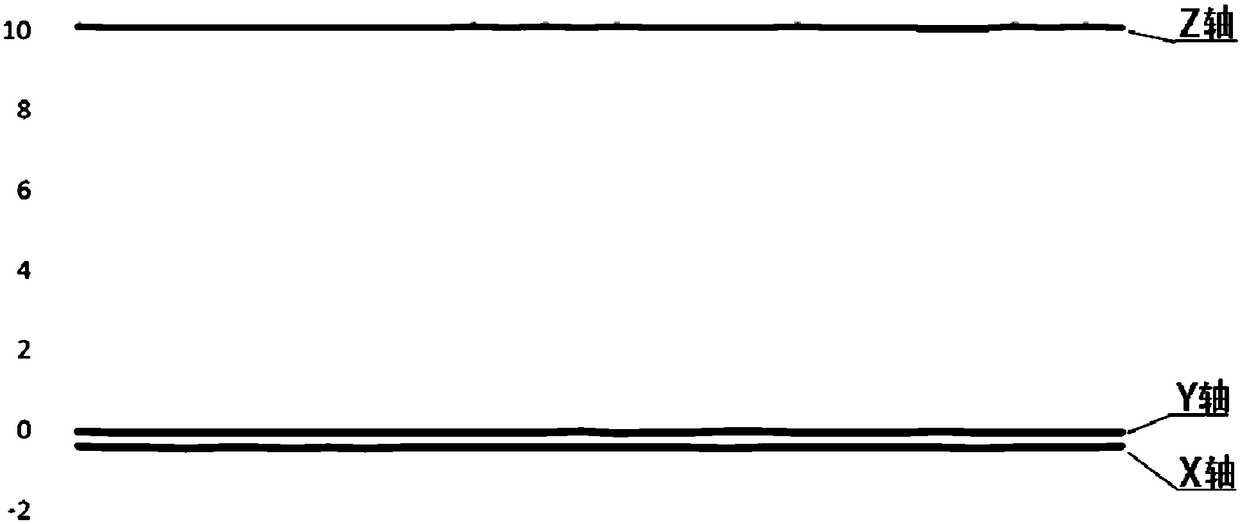
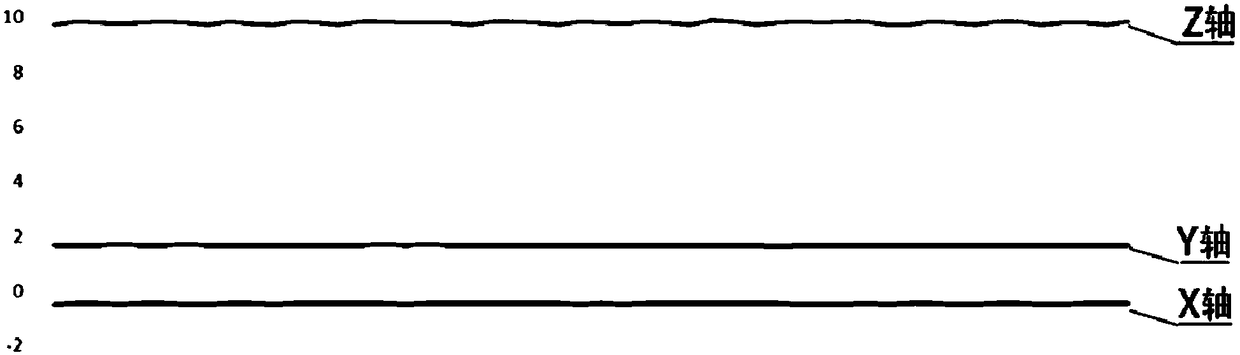
A method, a device, and an apparatus for measuring cardiopulmonary resuscitation compression depth, and a storage medium are disclosed. The method comprises the following steps of: calibrating an acceleration sensor in a stationary state; the vertical acceleration components of the multi-axis acceleration signal are summed up according to the multi-dimensional angle change of the acceleration sensor in the operation state. Obtaining a velocity curve by first integrating the sum of acceleration components of each period; the velocity curves were modified according to the motion characteristicsof CPR, and the summation of acceleration components was modified by the obtained correction coefficients. The displacement of the acceleration sensor is obtained by performing a second integration onthe sum of the corrected acceleration components. The method obtains the displacement of the acceleration sensor, namely the pressing depth of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation through the secondaryintegration through the correction of the acceleration sensor and the twice-corrected acceleration signal obtained by the comprehensive correction method based on the correction of the velocity curve,thus providing more accurate reference and assistance for the resuscitator of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation and ensuring the quality of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Owner:深圳市智城华业科技有限公司
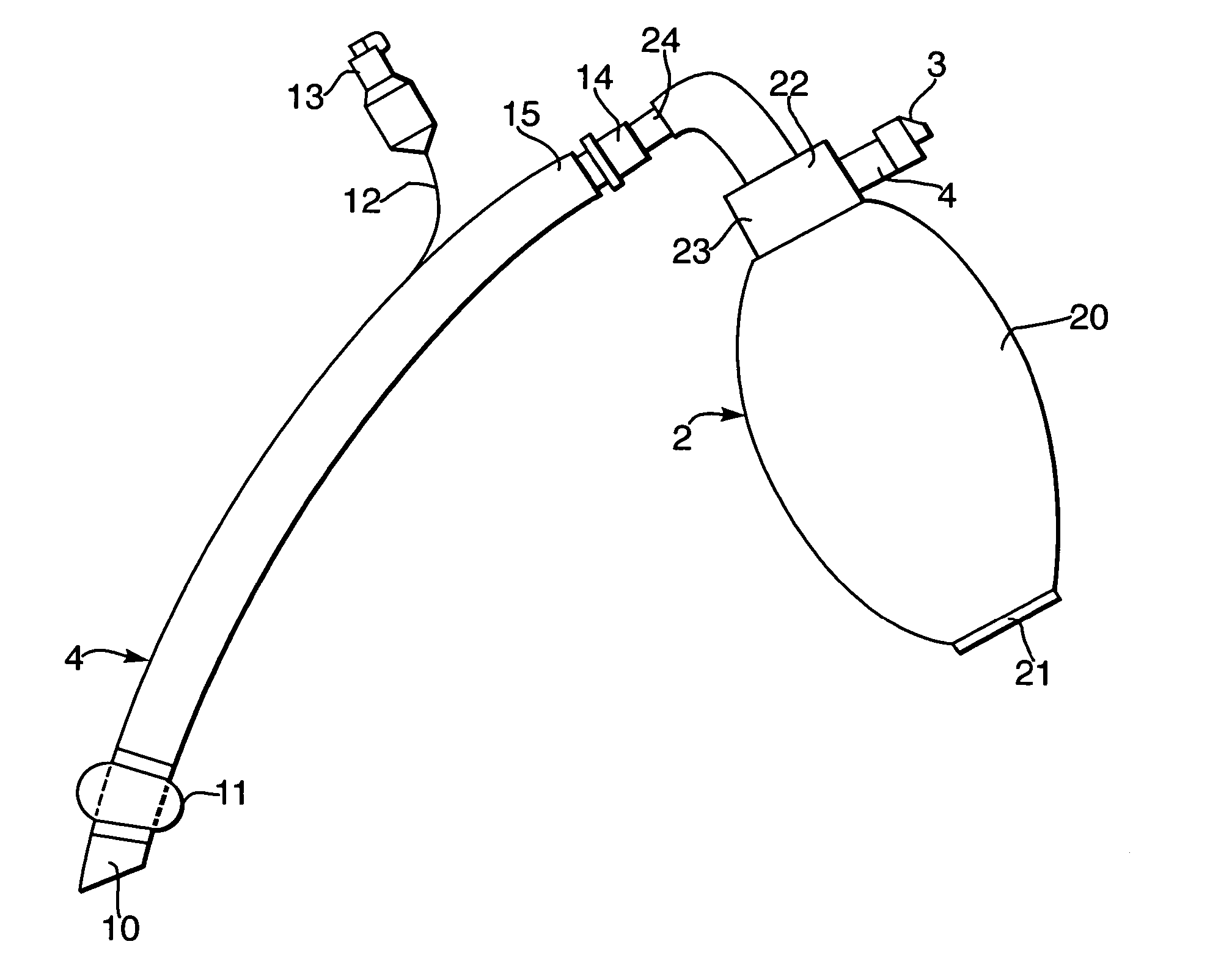
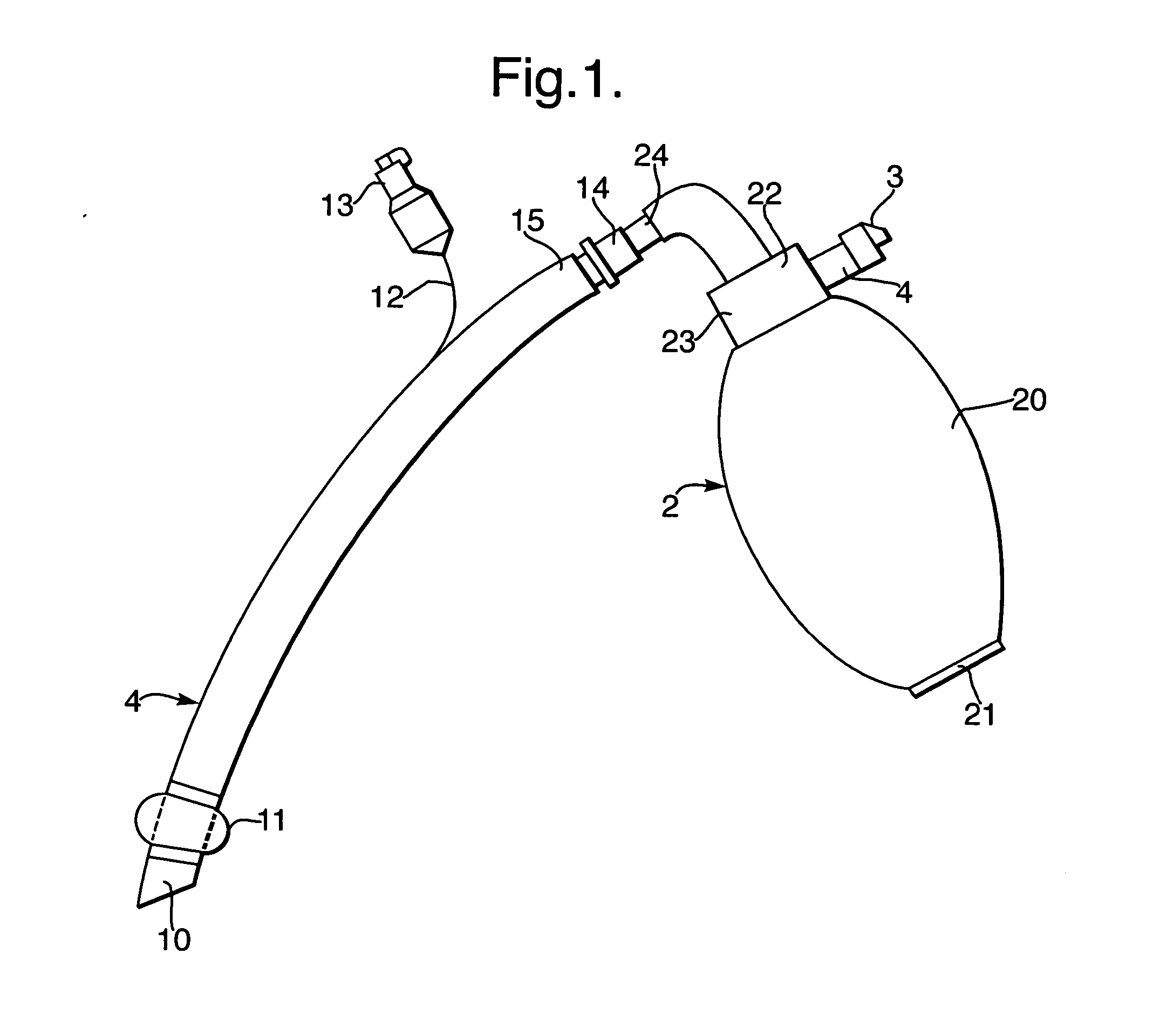
Breathing resuscitator
InactiveCN101816815ADoes not interfere with efficacySignificant progressSleep/relaxation inducing devicesEngineeringVALVE PORT
The invention relates to a breathing resuscitator which comprises an air bag, a pressure release valve, an air conveying pipe, a one-way valve and an air outlet member, wherein the air bag is capable of containing air and is provided with an air conveying port; the pressure release valve is connected to the air conveying port of the air bag; one end of the air conveying pipe is connected with the pressure release valve; the one-way valve is connected to the other end of the air conveying pipe; and the air output member is connected with the one-way valve; the pressure release valve is provided with an air release hole and is used for adjusting the pressure of air output from the air conveying port, the one-way valve is provided with an air outlet used for outputting air in the air conveying pipe, when the air bag is pressed and deformed, the air inside the air bag is output to the air conveying pipe through the air conveying port, and then is conveyed to the air outlet member through the air outlet of the one-way valve so as to be breathed by a patient. Therefore, the invention has the effects of applying medical inspection operation without interference.
Owner:GALEMED
Portable pen type thyrocricoid puncture device
InactiveCN101292893AEasy to carryEasy to useRespiratorsSurgical needlesRespiratorCricothyroid membrane
The present invention discloses a portable pen type cricothyroid membrane puncture outfit which comprises a puncture needle, a puncture needle guard tube, a sealing ring, a handle, a respirator or a resuscitator joint, etc. The puncture needle comprises a needle core, a sleeve and a puncture needle base. The puncture needle is arranged inside a cavity of the puncture needle guard tube. The needle core is fixed at the front end of the handle. The handle is a cavity structure. The sealing ring is arranged at the connected part of the puncture needle guard tube and the handle. The back end of the handle is equipped with the respirator or the resuscitator joint which is spliced with the puncture needle base. The puncture outfit of the present invention has the advantage that the equipments required by cricothyroid membrane puncture are combined together and are designed in the form of a pen, which is convenient for carrying and is easy to use.
Owner:SHANDONG YIHE MEDICAL TECH
Resuscitation device with onboard processor
A resuscitator has a patient airway interface device, a bag, a flow passage coupled between the bag and patient airway interface device, and a sensor assembly. The patient airway interface device may be a mask or an endotracheal tube. The sensor assembly has a display, at least one sensor coupled to the flow passage and configured to provide a measurement of at least one parameter, and a processor coupled to the display and the at least one sensor. The processor is configured to receive the measurement from the sensor and provide information on the display based on the received measurement. The information may include a current breath rate, a pressure-vs-time curve, and guidance to the user to assist in achieving a target breath rate.
Owner:SUNMED GRP HLDG LLC
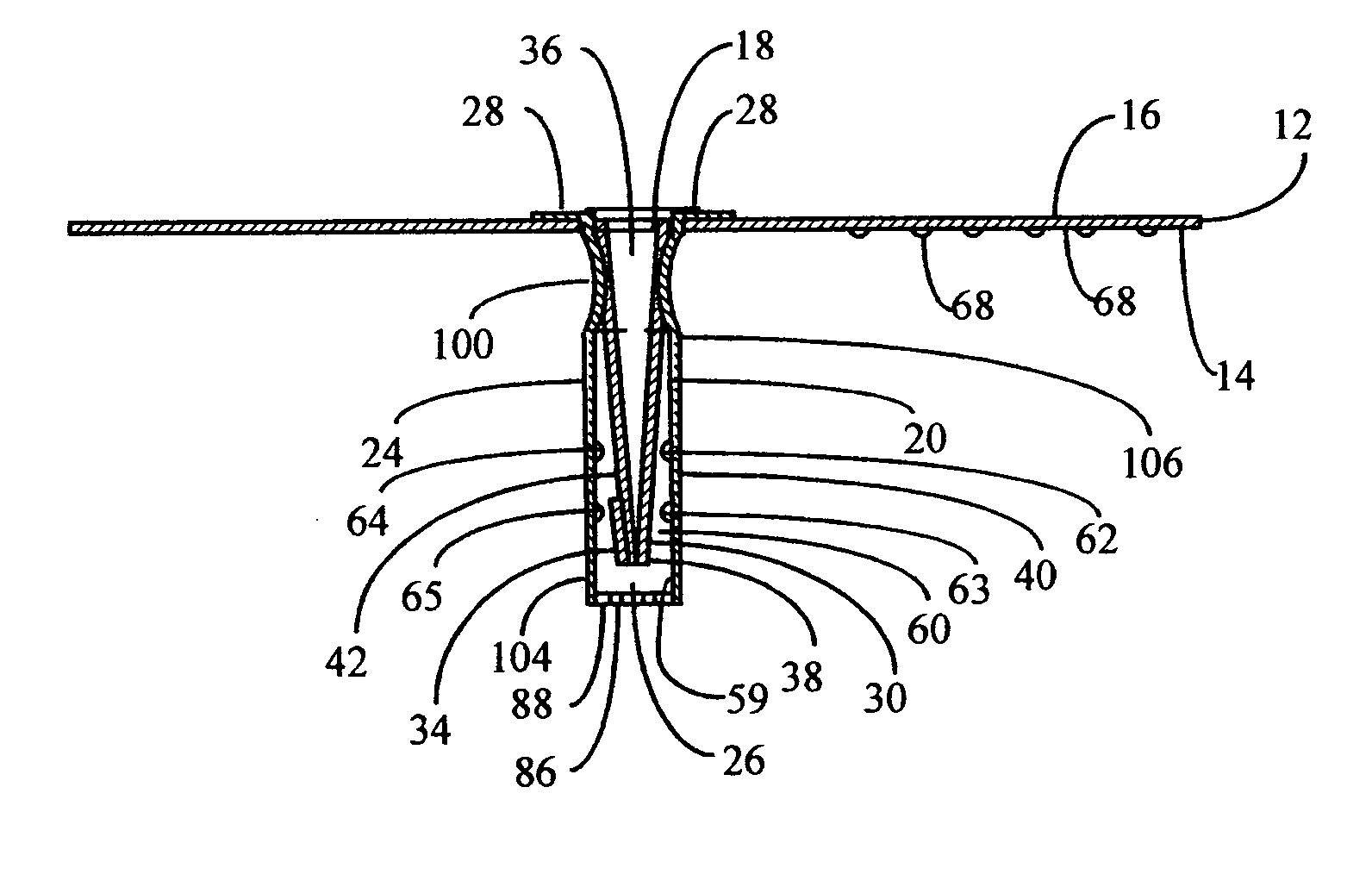
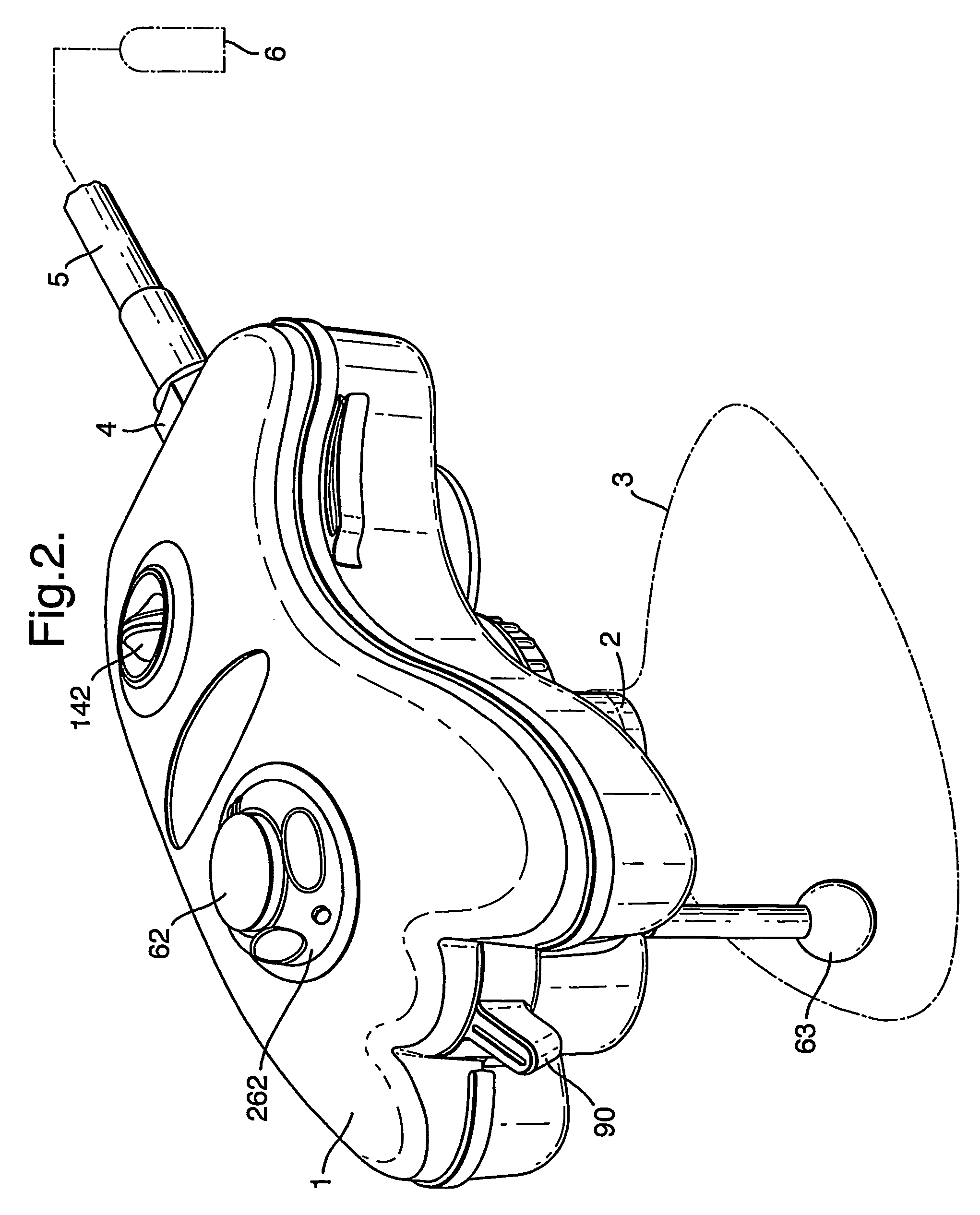
Resuscitators
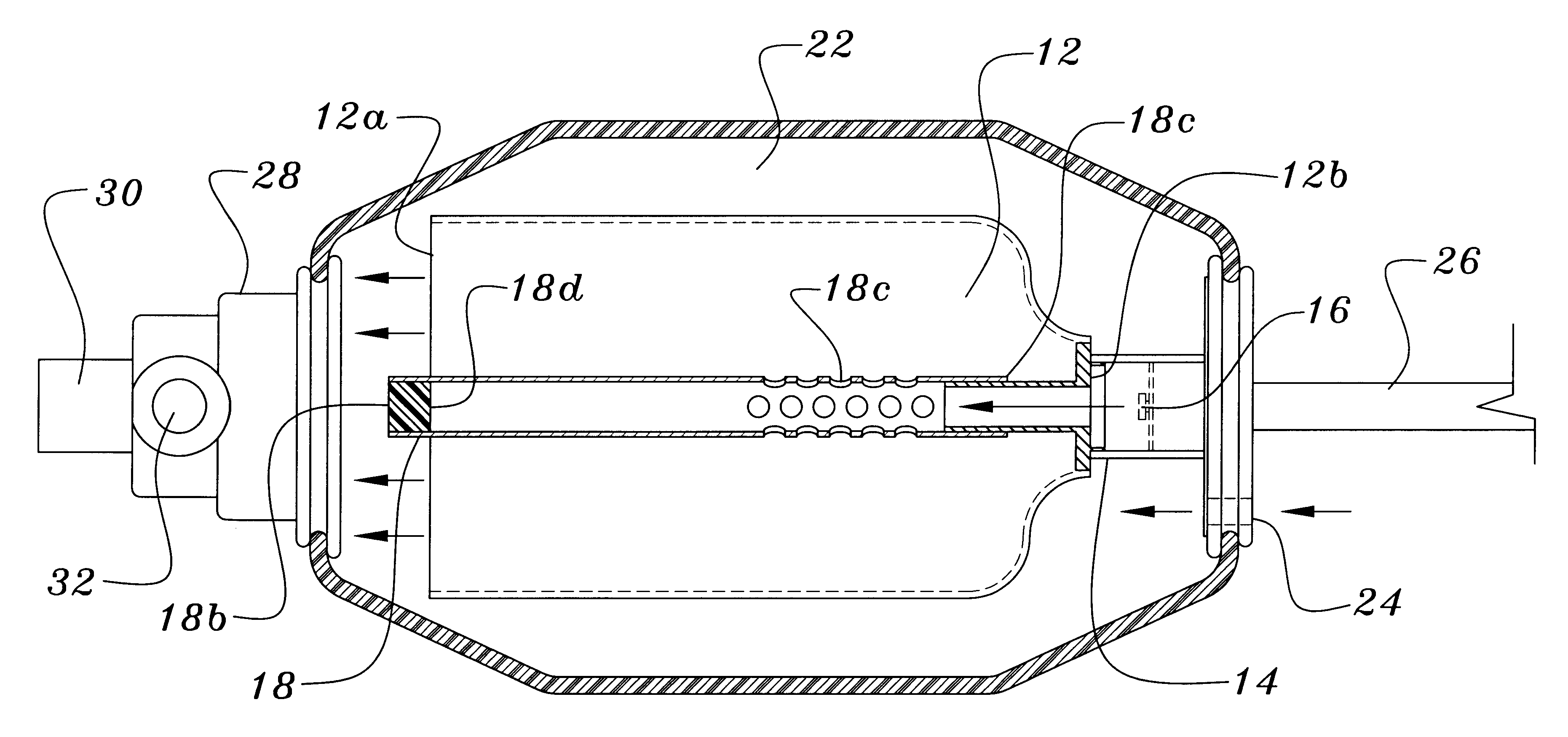
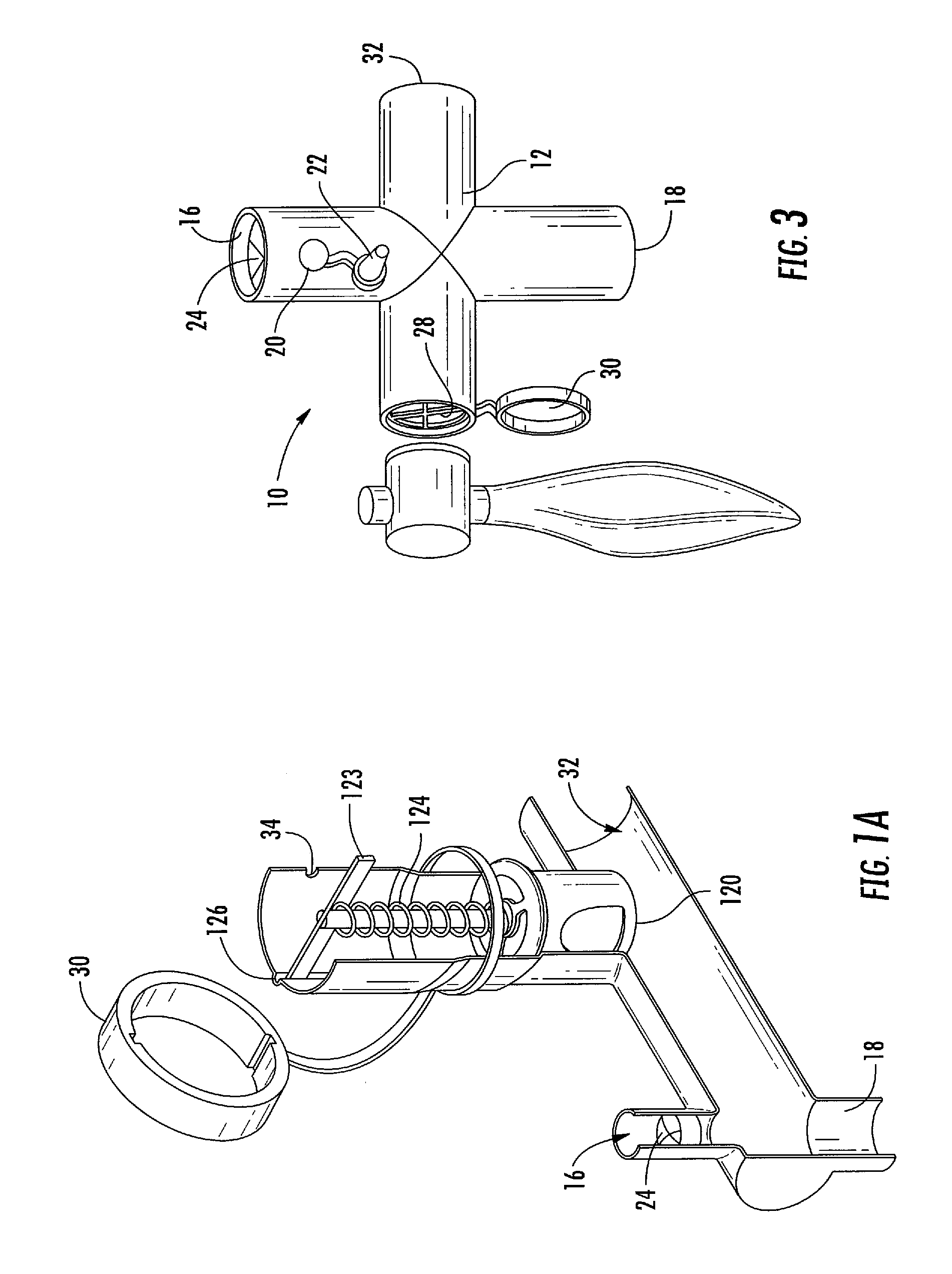
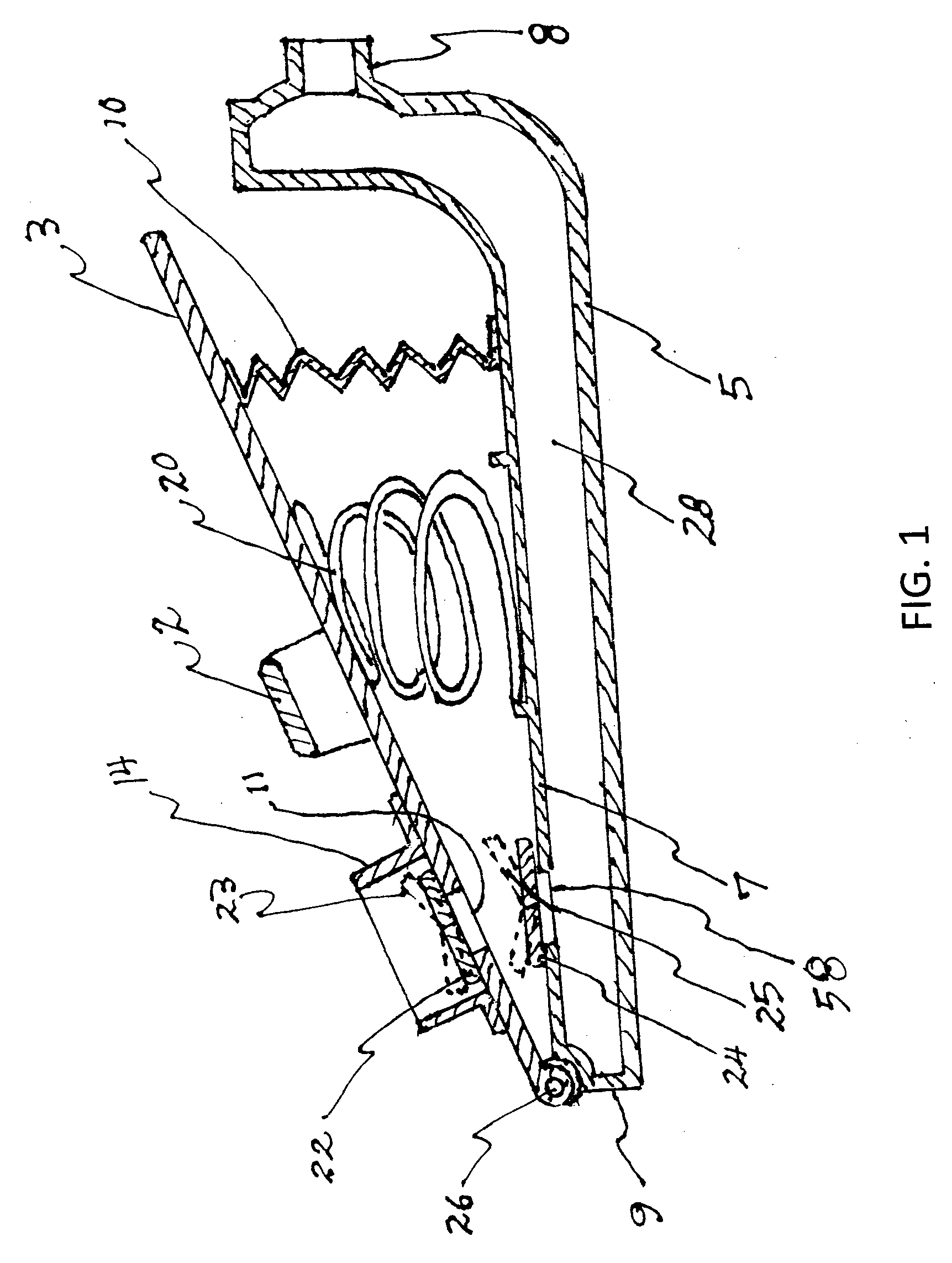
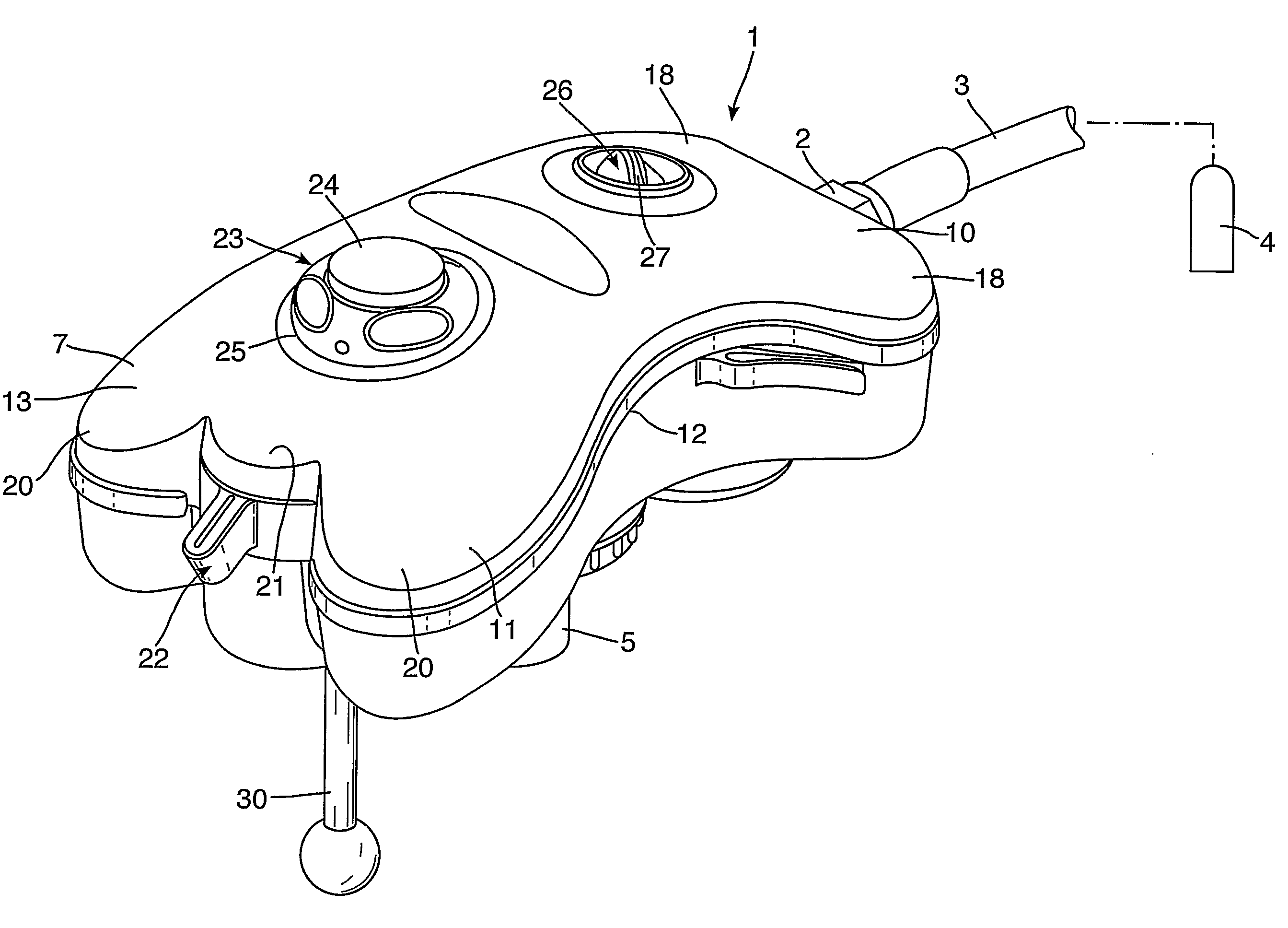
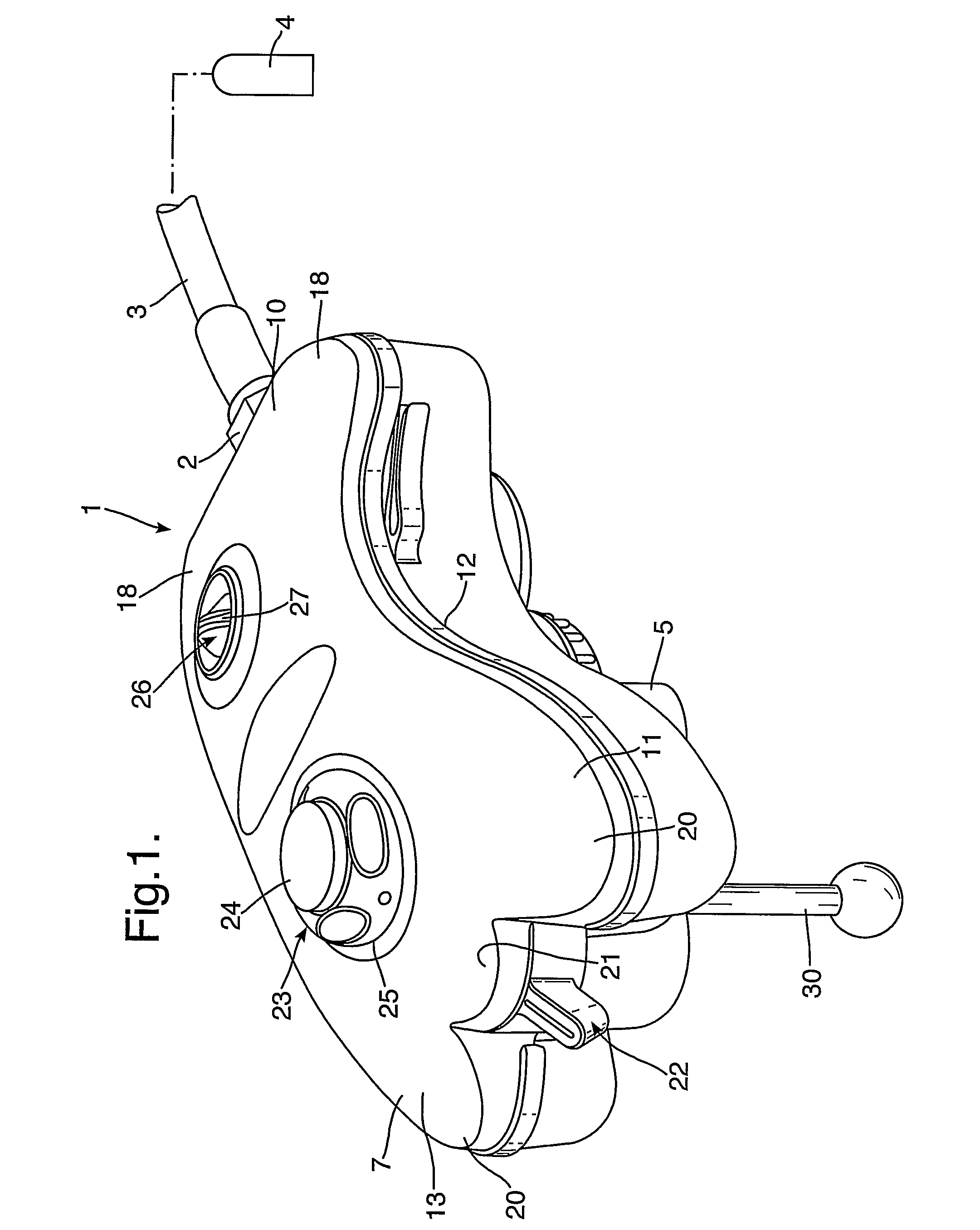
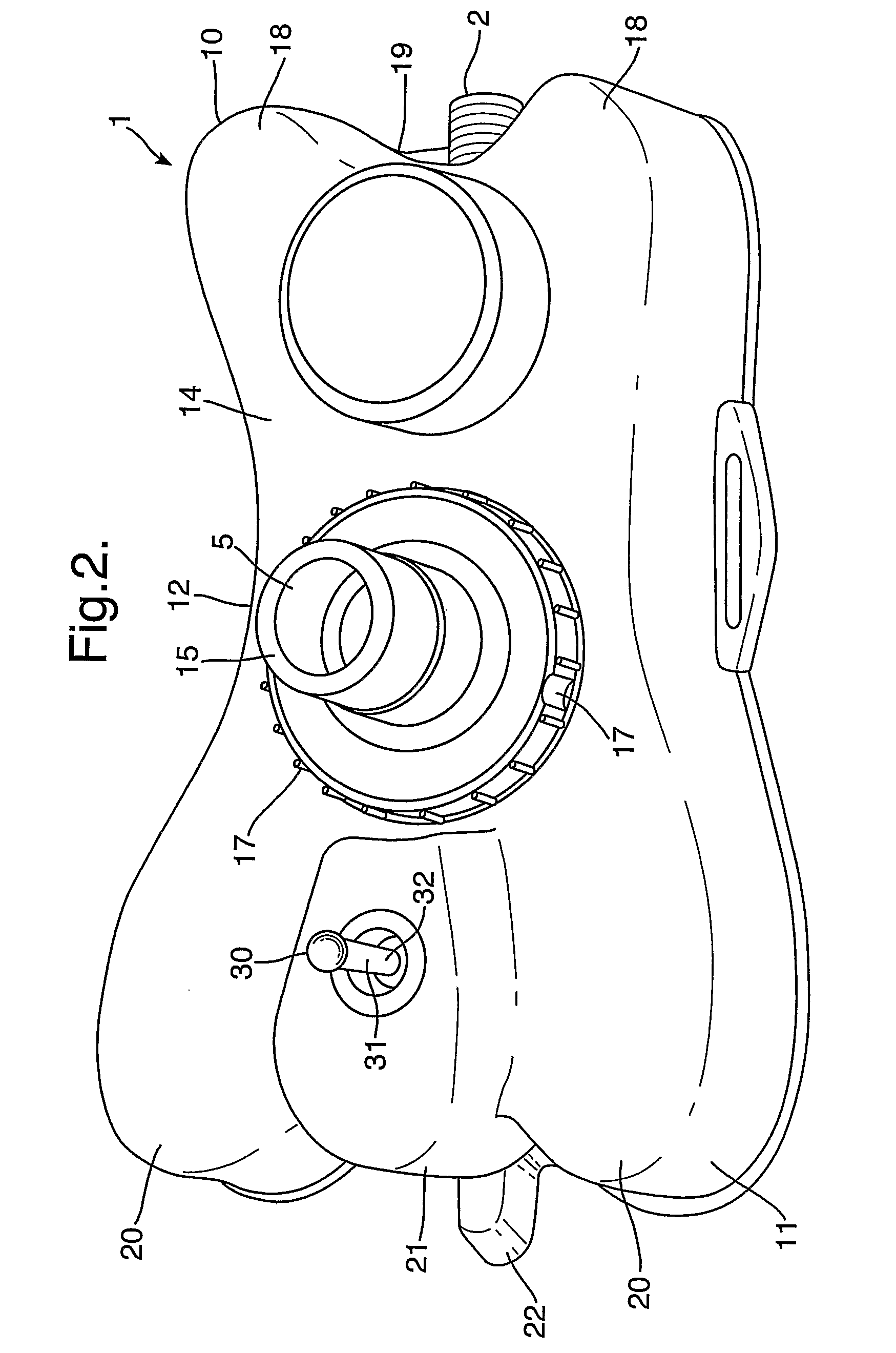
A resuscitator has two separate, spaced controls (23) and (30) both of which can be actuated manually to open a valve (100) and deliver a breathing cycle of a maximum timed duration to a patient. One control (23) has a button (24) on the top (13) of the unit (1), which is pushed in to actuate. A ring (25) surrounds the button (24) and has cam profiles (122) that engage with cam pins (120) on the button to push and hold it down when rotated. The other control (30) is on the underside surface (14), facing the patient and adjacent the gas outlet (5). This control includes a toggle lever (31), which can be displaced laterally in two different planes to open the valve (100).
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL INT
A cardiopulmonary resuscitation assisting device and a compression depth measurement method
PendingCN109172334AQuality assuranceExact referenceElectrotherapyHeart stimulationEngineeringCardiopulmonary resuscitation
The invention discloses a cardiopulmonary resuscitation assisting device and a compression depth measurement method. The auxiliary device comprises a base, a support rod, a sensor fixing platform, anangle adjusting platform, a camera, an infrared ranging sensor and a marking sticker. One end of the support rod is articulated with the base, and the other end is articulated with one end of the fixed platform of the sensor; the camera and the infrared ranging sensor are arranged on the angle adjusting platform; the angle adjusting platform is arranged at one end of the sensor fixed platform which is far away from the support bar and is articulated with the sensor fixed platform. The marking sticker is arranged at the test point in the cardiopulmonary resuscitation compression area. The invention calculates the pressing depth of cardiopulmonary resuscitation by measuring the distance and the angle of the infrared ranging sensor, and corrects the light of the infrared ranging sensor to reduce the influence of the ambient light on the ranging, so that the final result is more accurate. The invention can provide more accurate reference and assistance for cardiopulmonary resuscitation resuscitators, and ensure the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Owner:深圳市智城华业科技有限公司
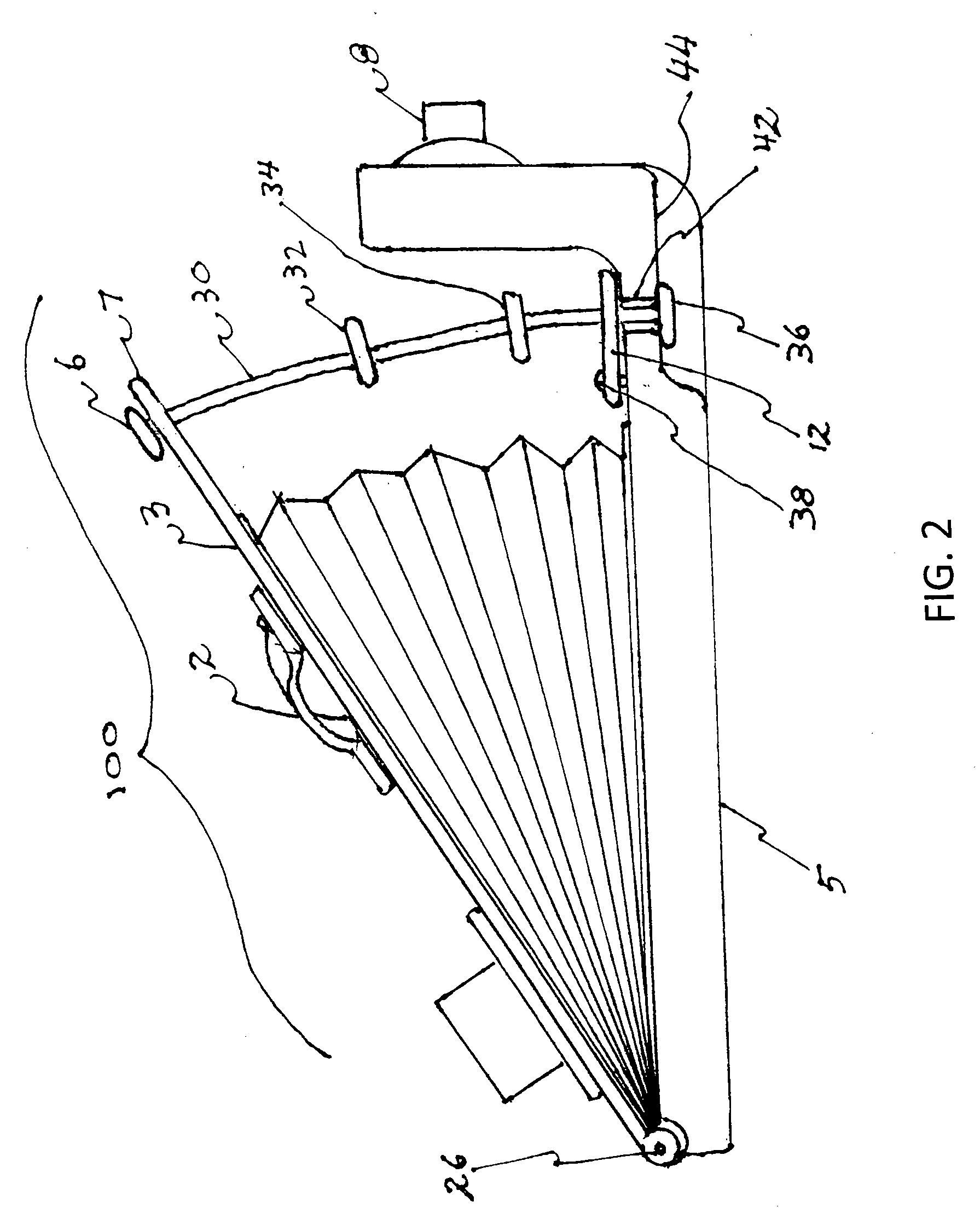
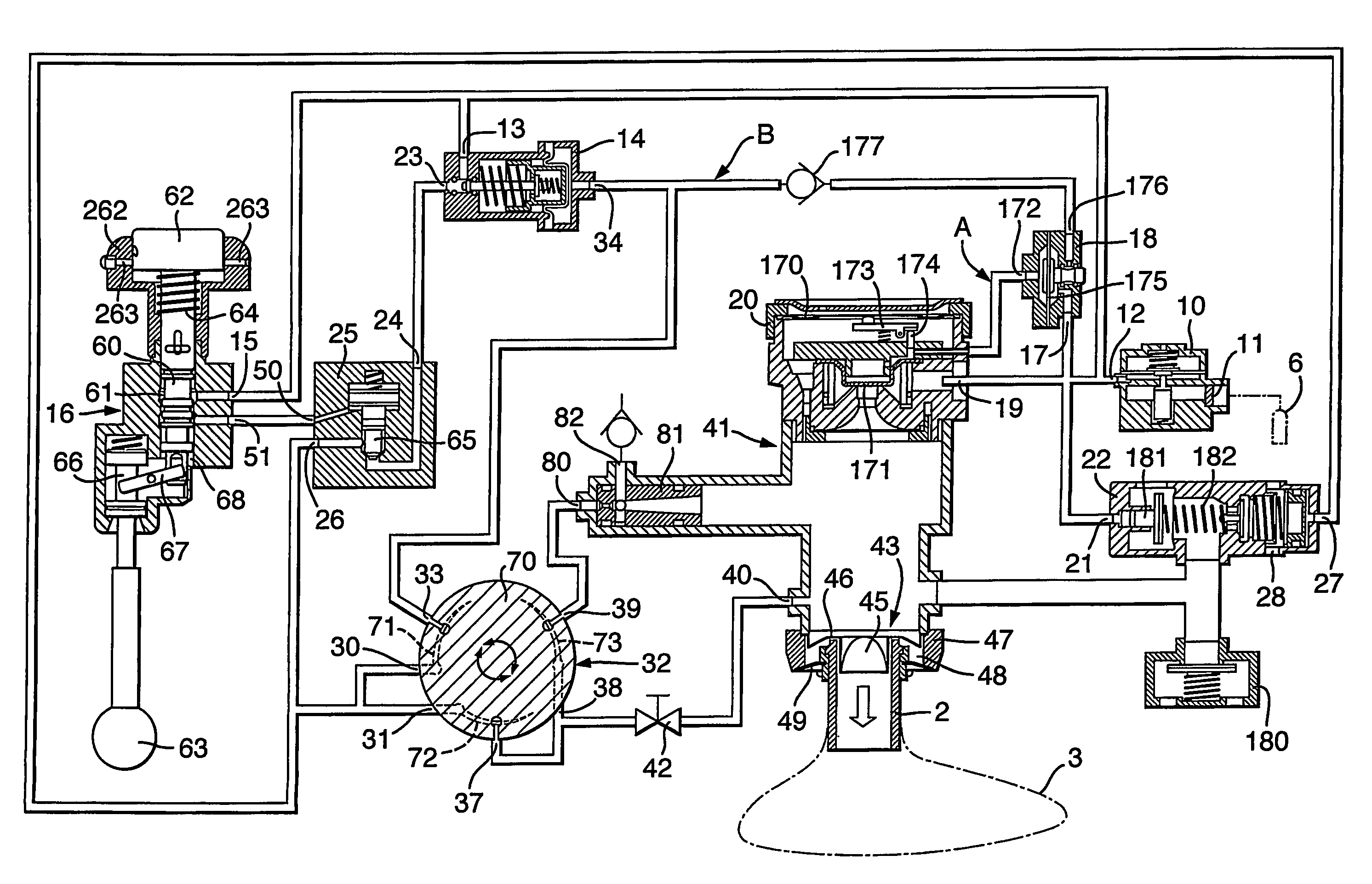
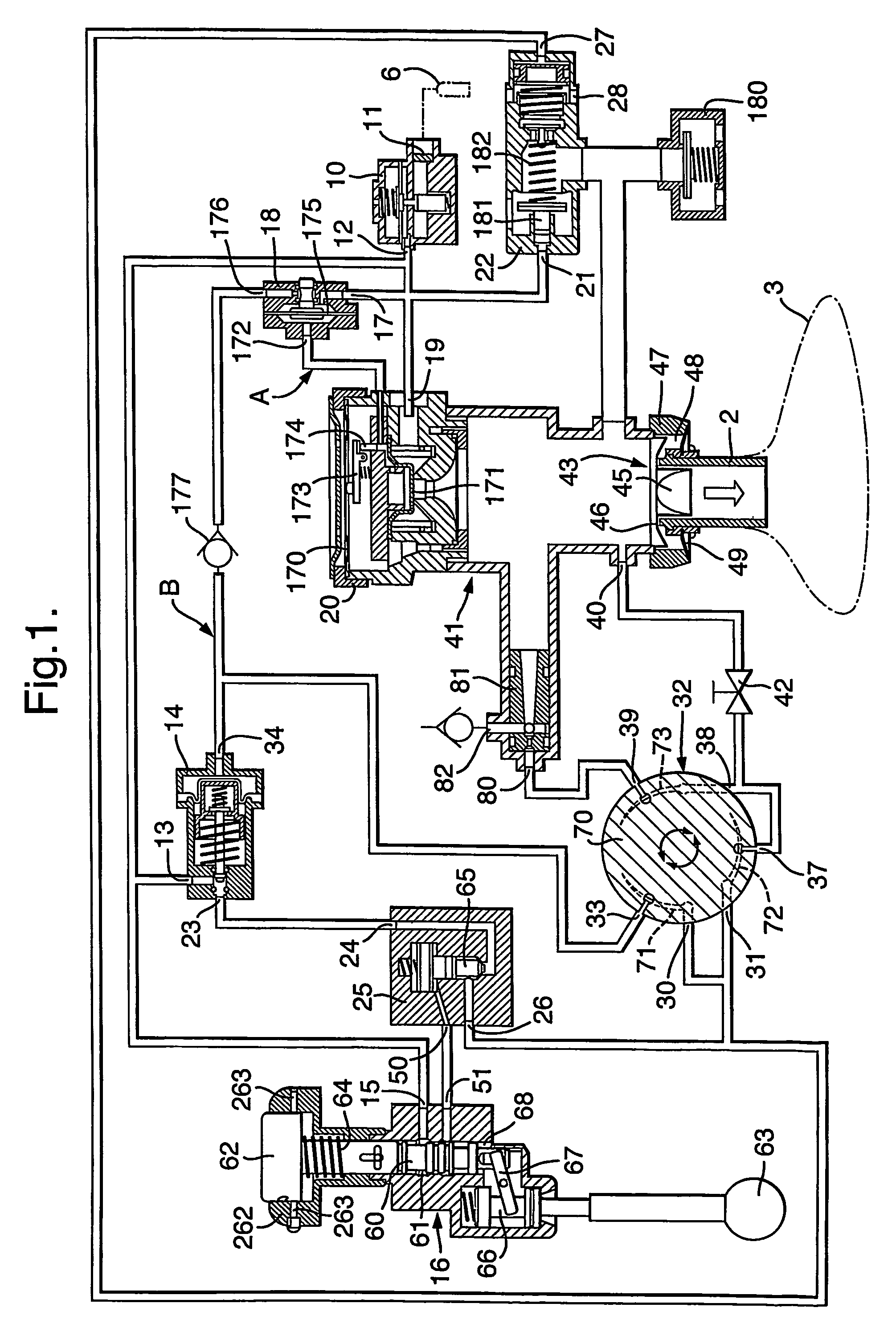
Resuscitators
A gas-powered resuscitator is operable either in a manual mode or an automatic mode. The resuscitator includes an oscillatory timing valve (14) having an outlet (23) connected to a bi-stable valve (25), the operation of which is piloted by a manual valve (16). The outlet (26) of the bi-stable valve (25) connects to the outlet (2) of the resuscitator via a rotatable control (32) and a patient valve (41). The outlet (26) of the bi-stable valve (25) also connects to the control inlet (34) of the timing valve (14). The manual valve (16) has a button (62) that can be pushed down manually in the manual mode or can be held down in the automatic mode by rotating a locking ring (262). The maximum duration of cycles is limited by operation of the timing valve (14), whether the resuscitator is operated manually or automatically.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com