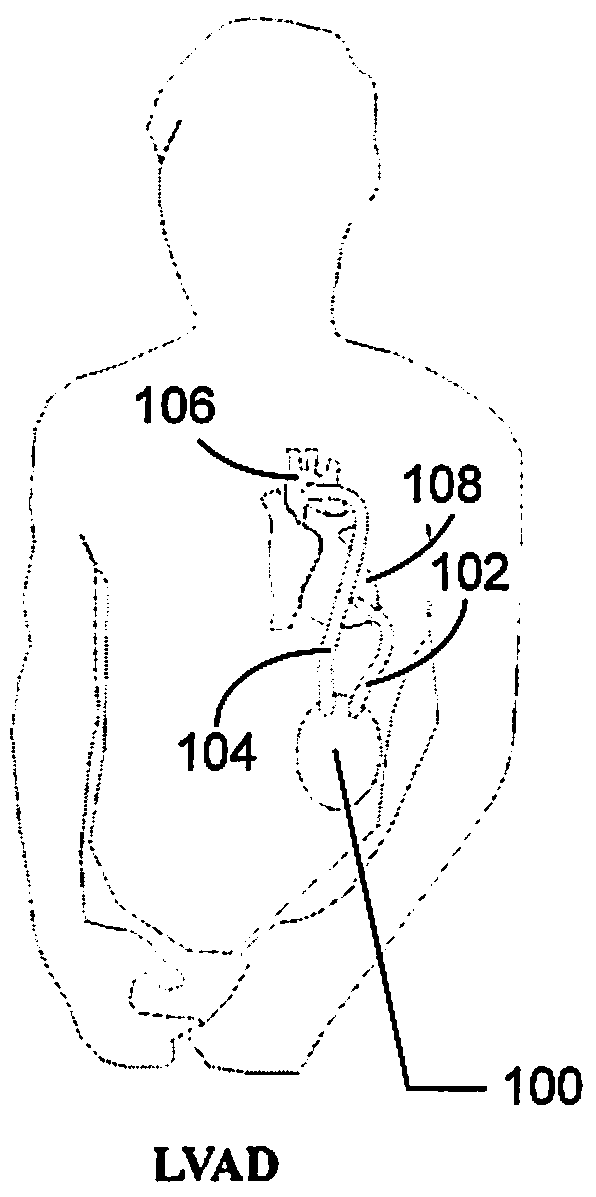
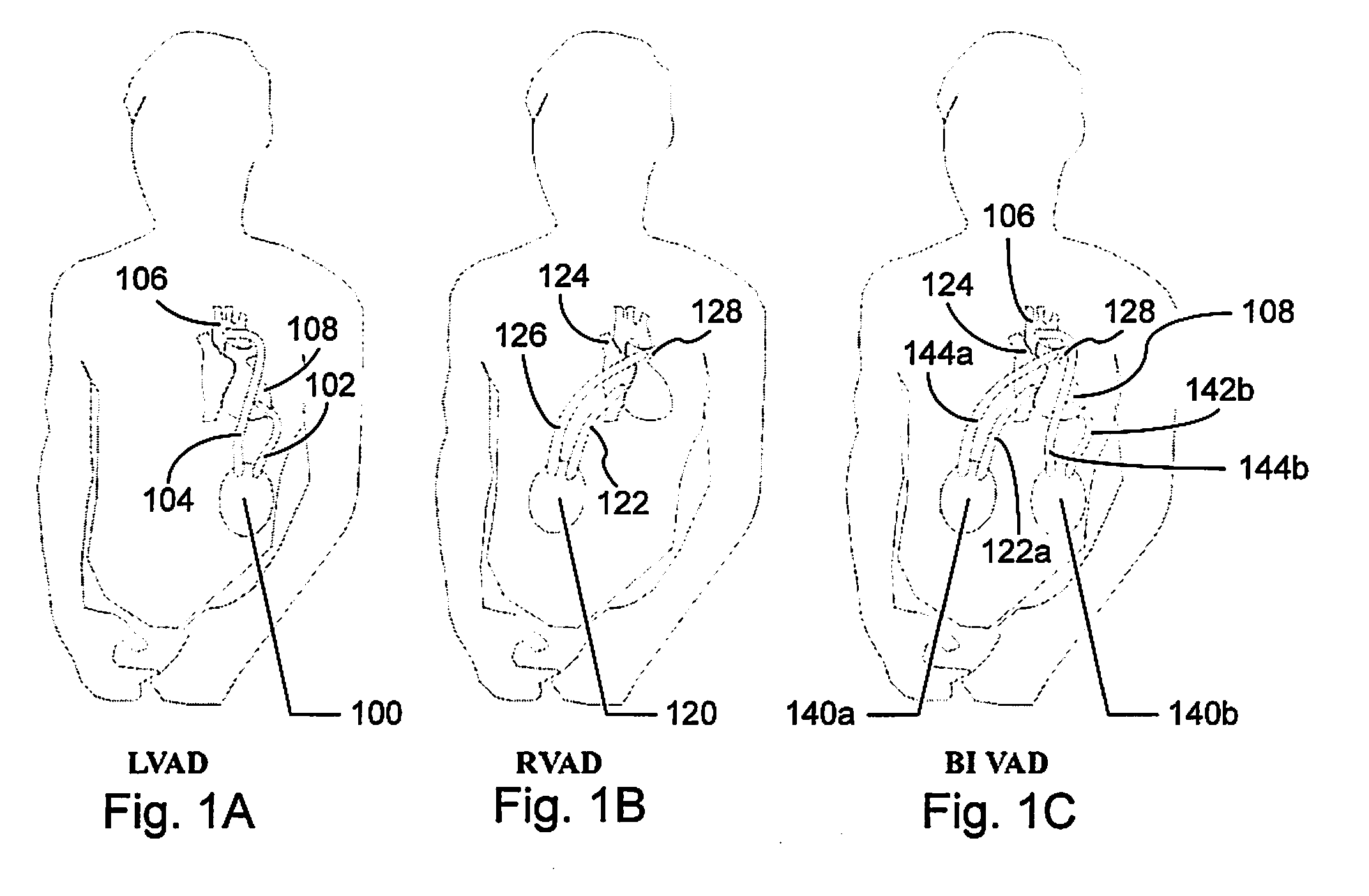
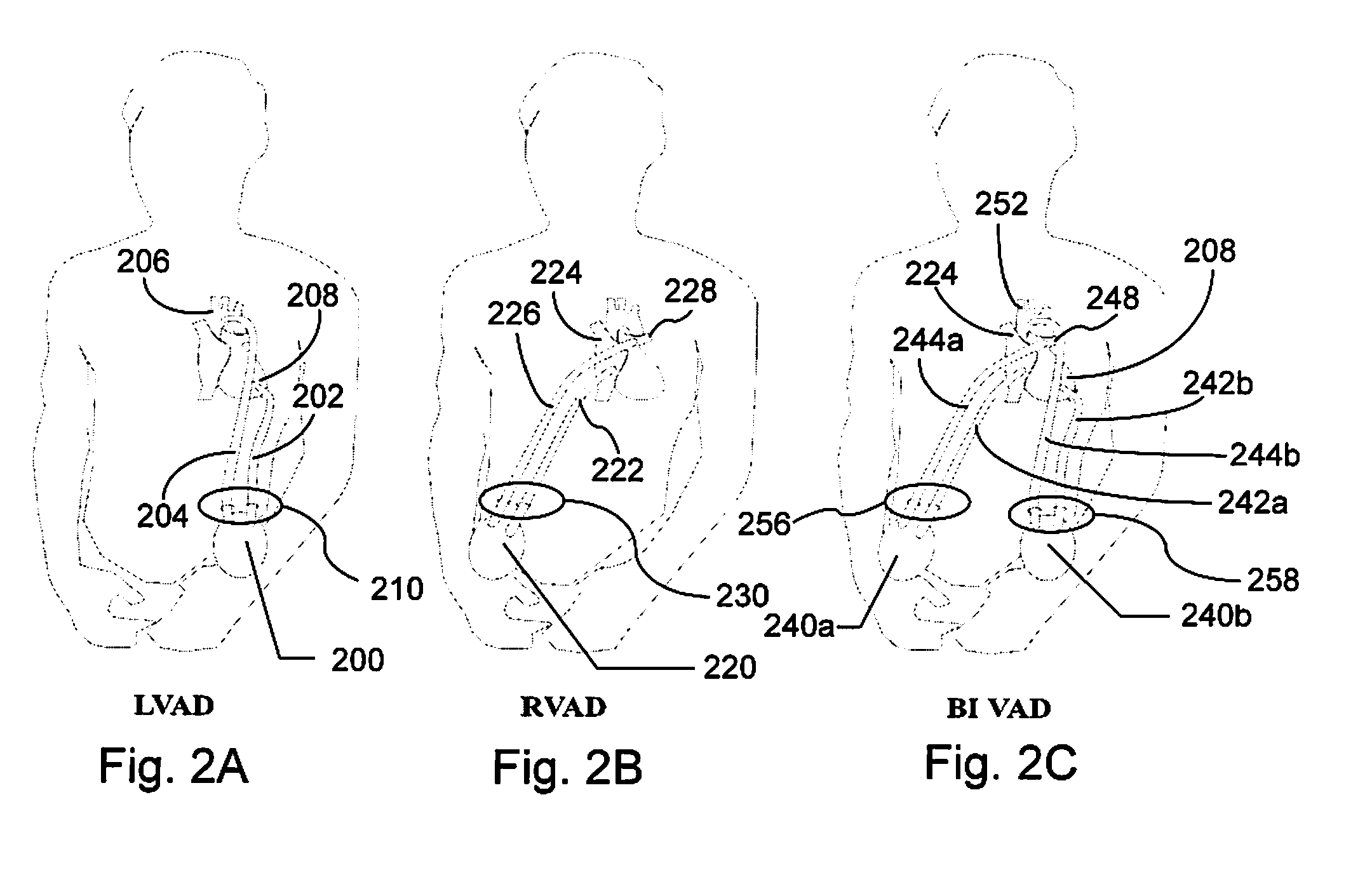
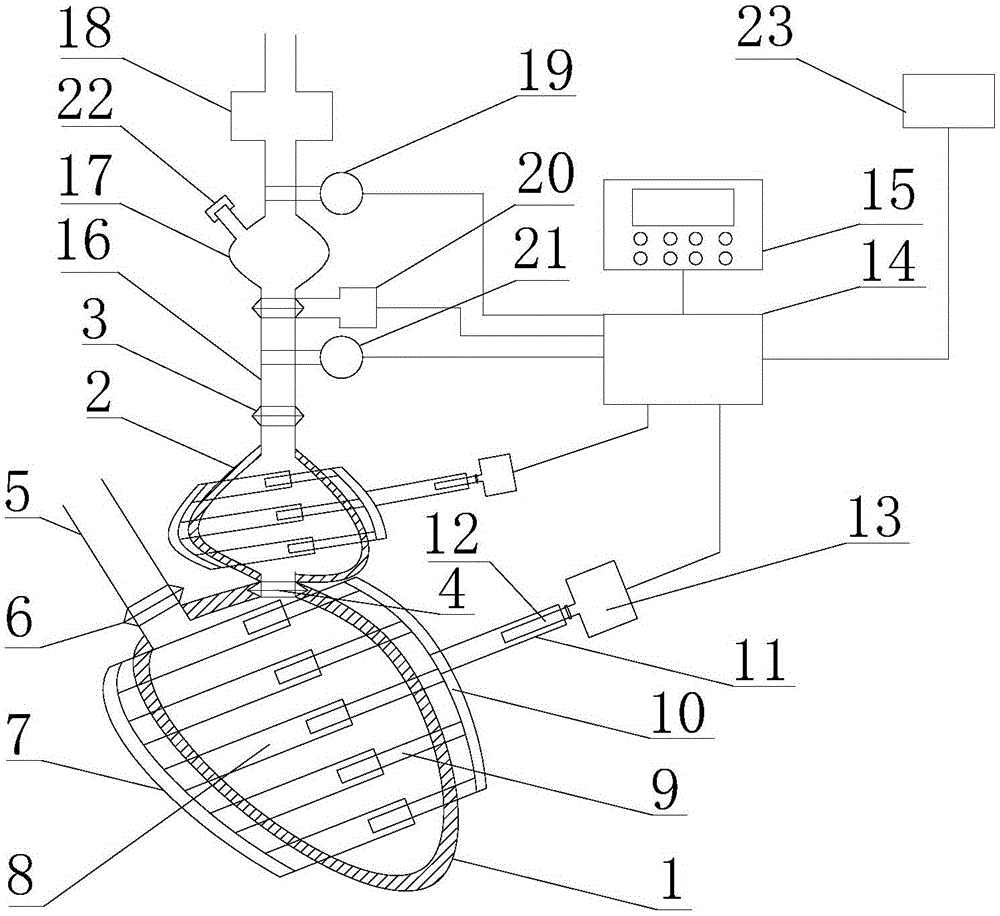
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Heart/circulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
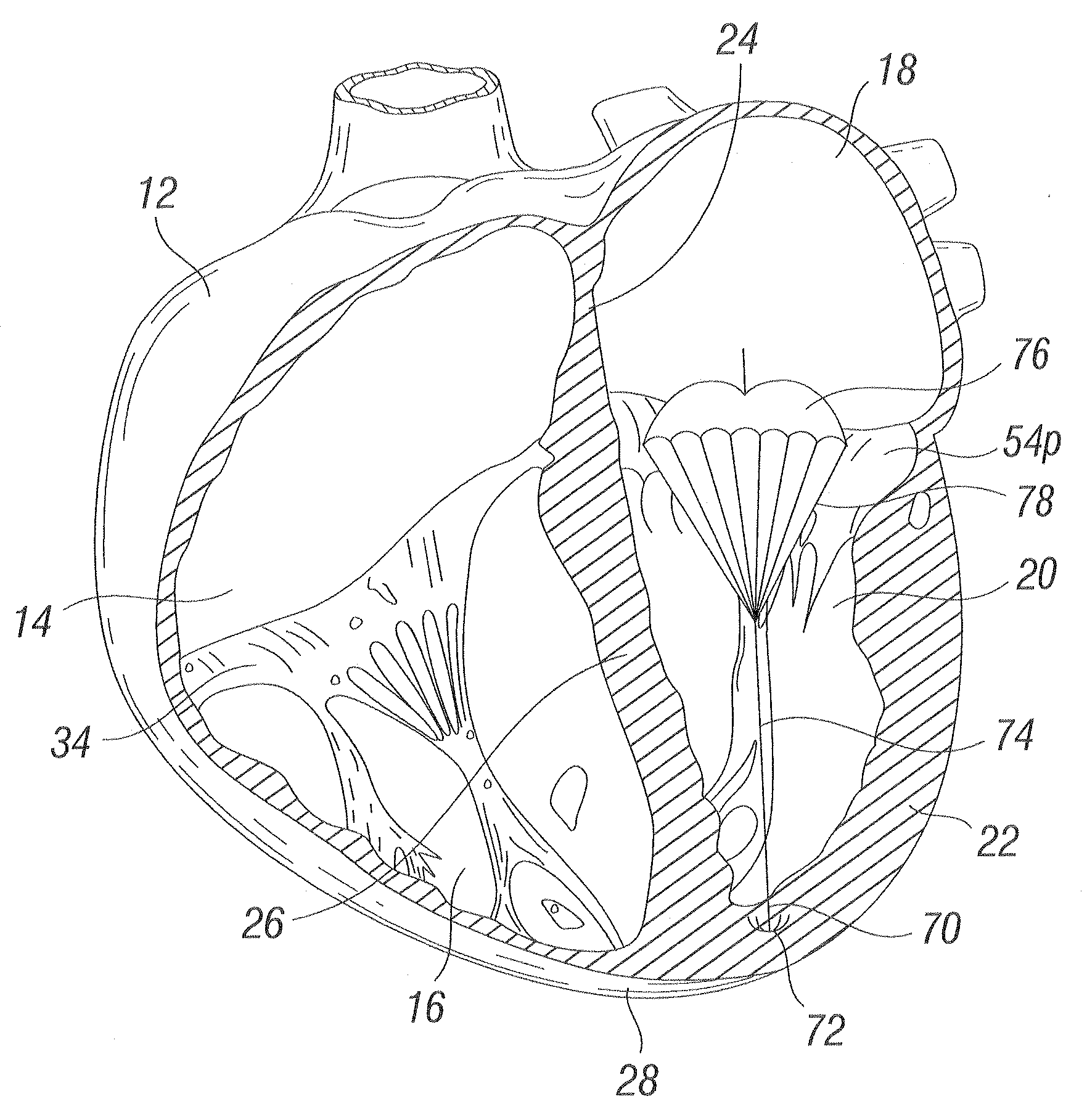
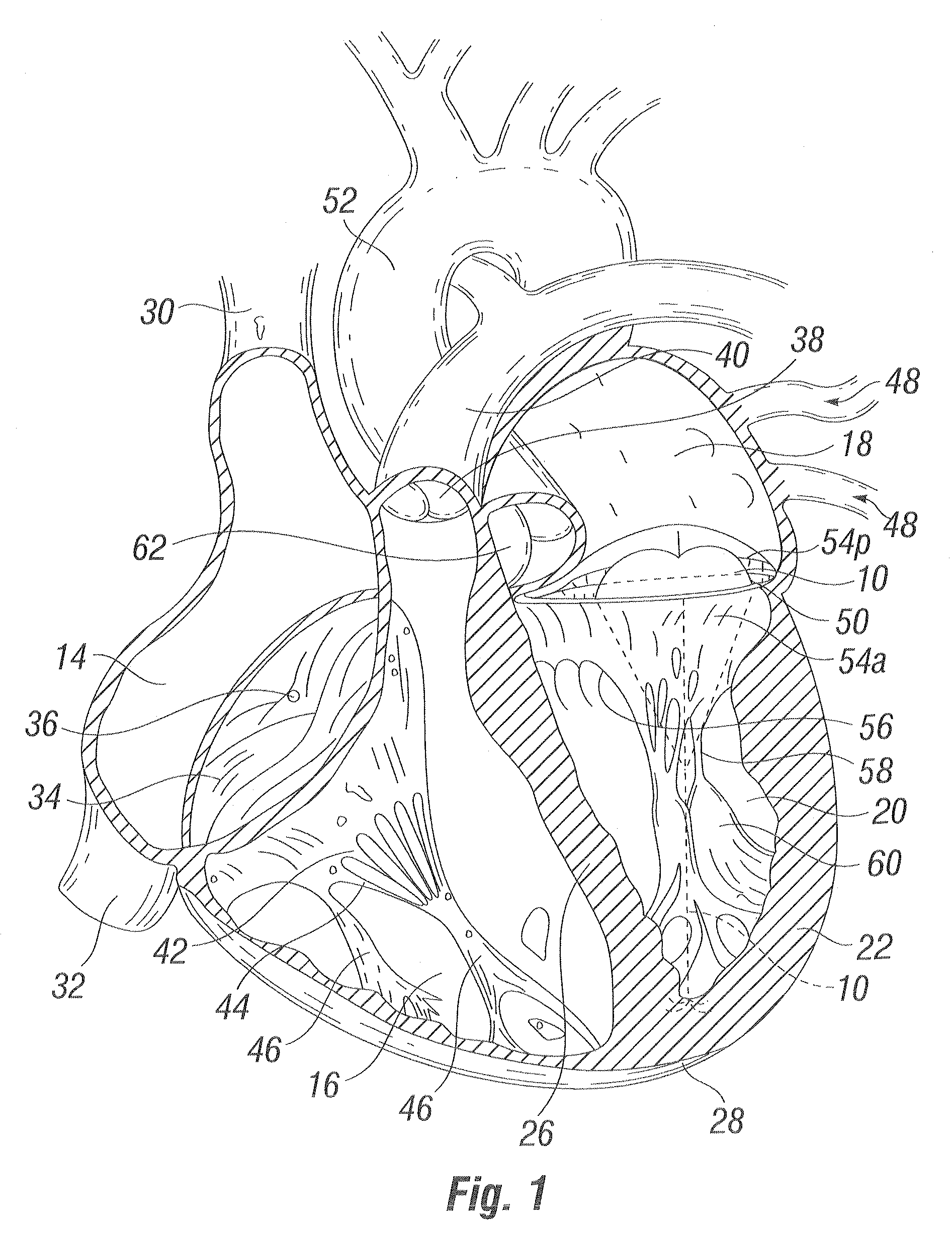
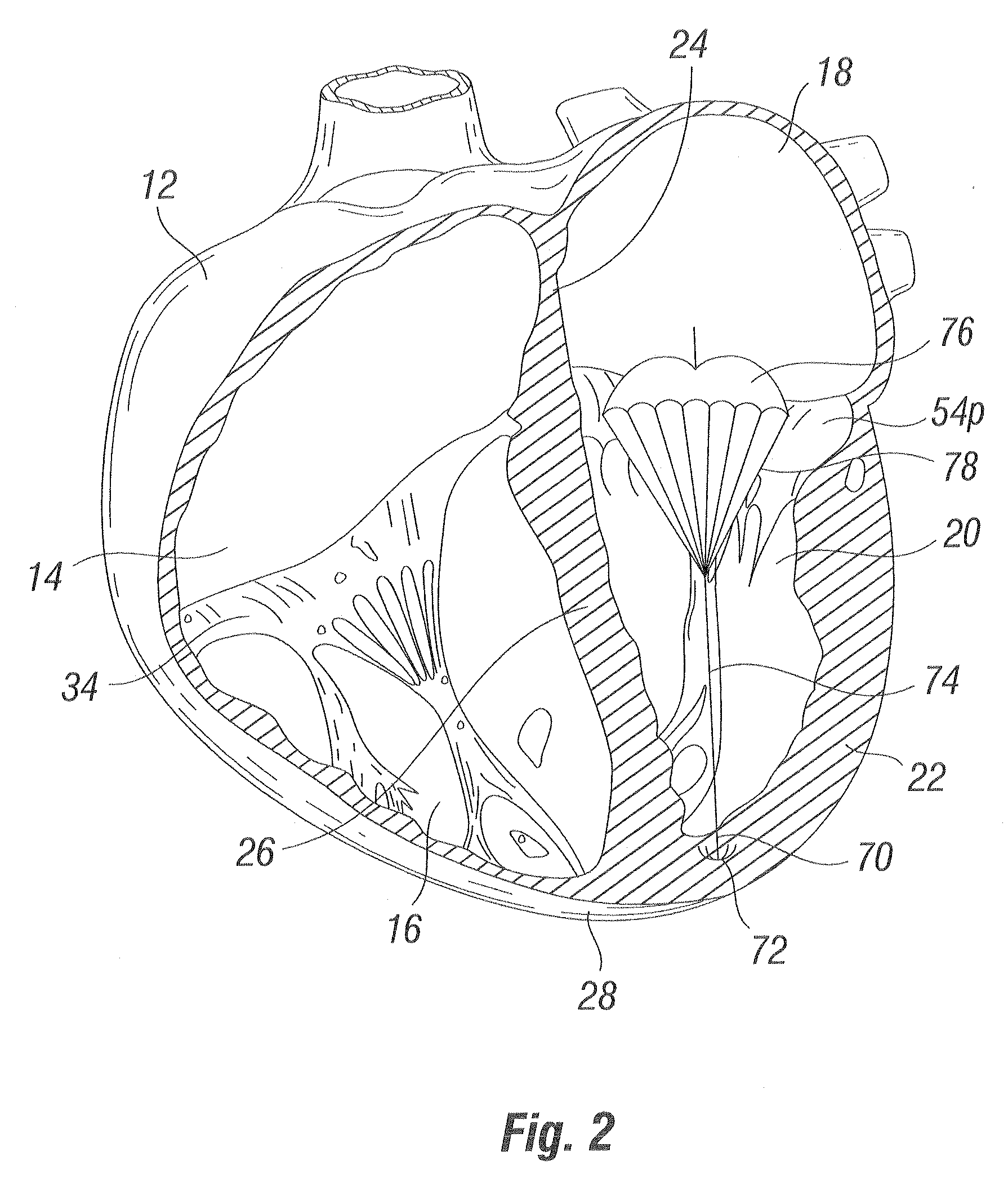
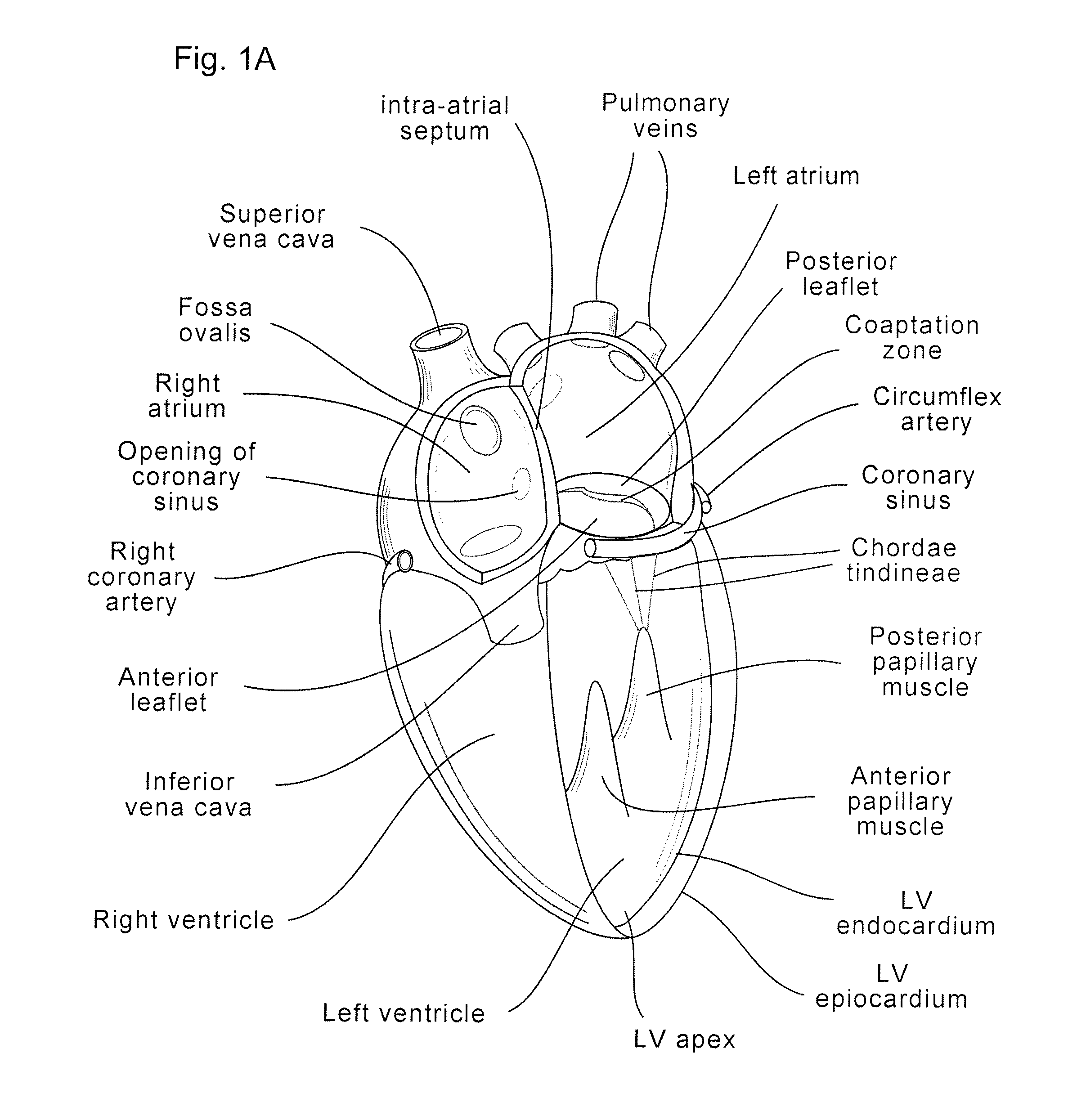
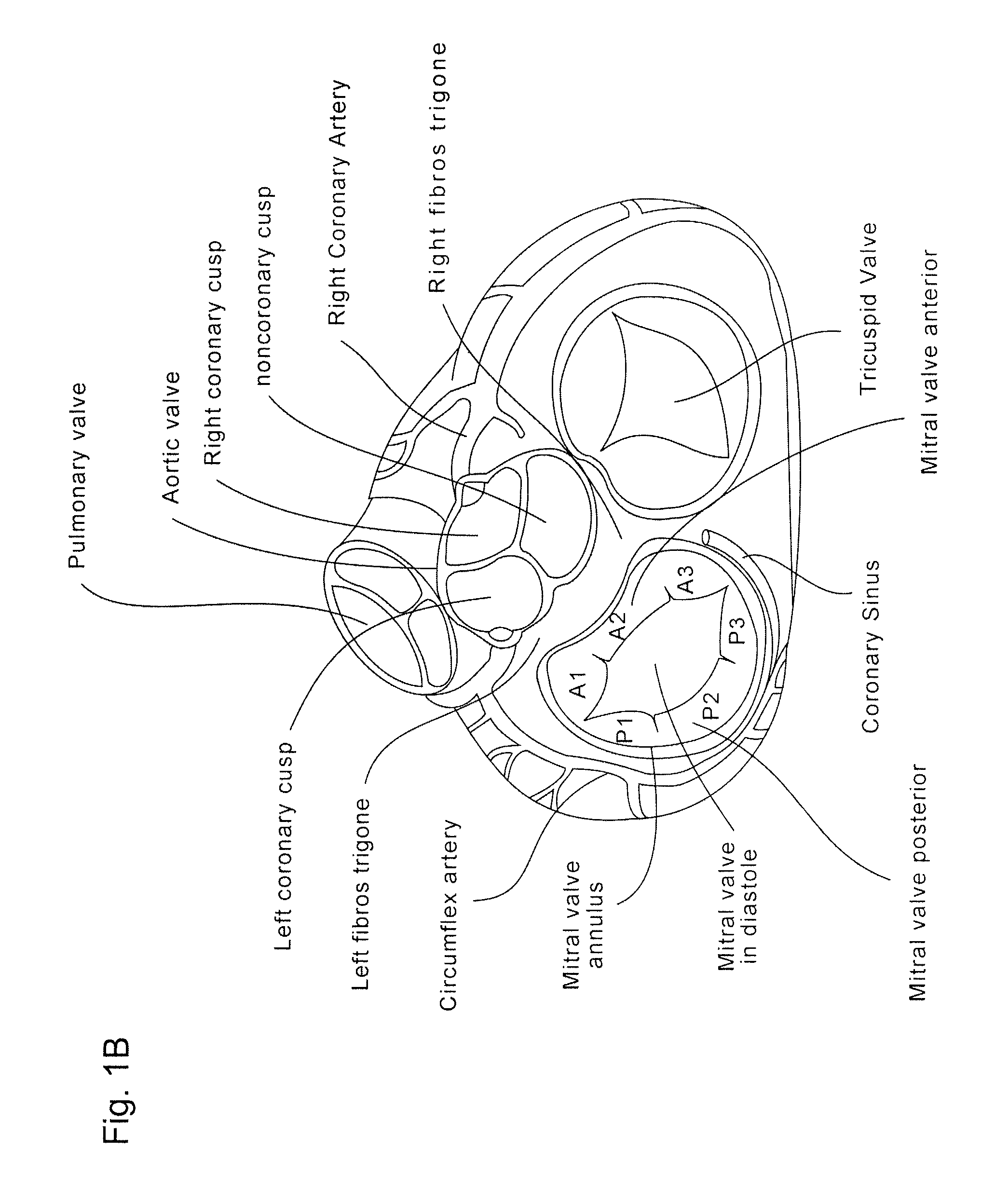
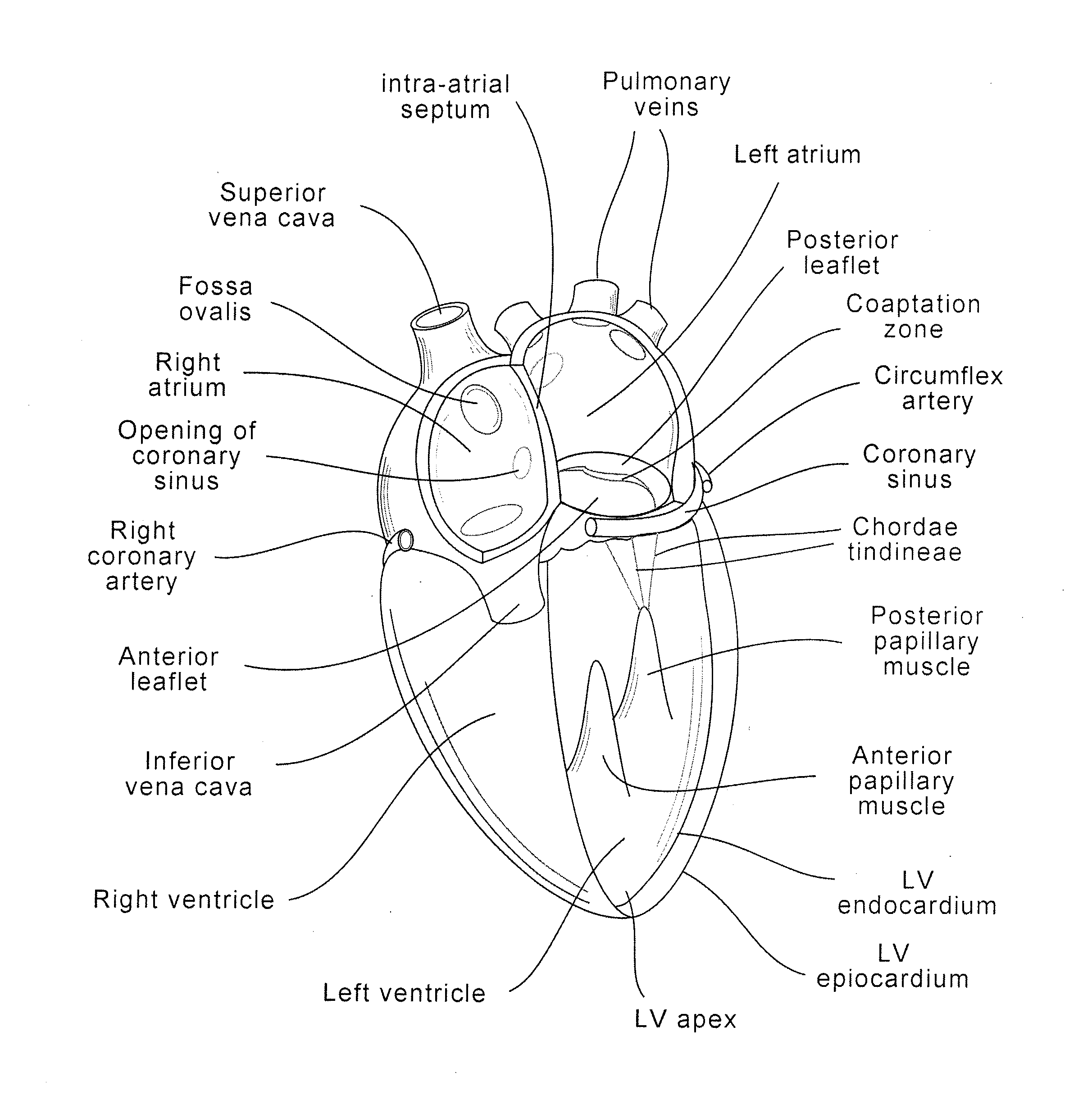
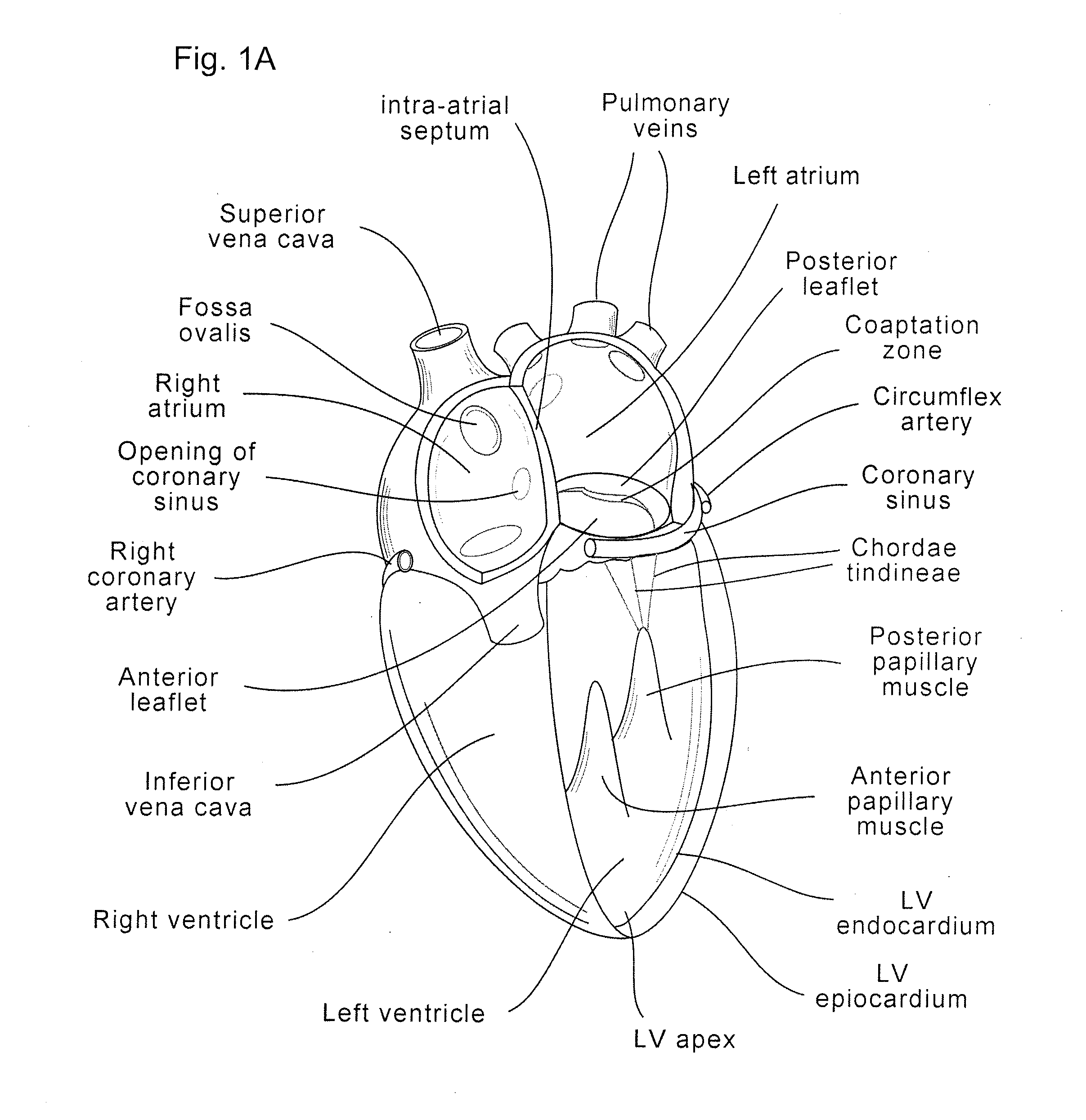
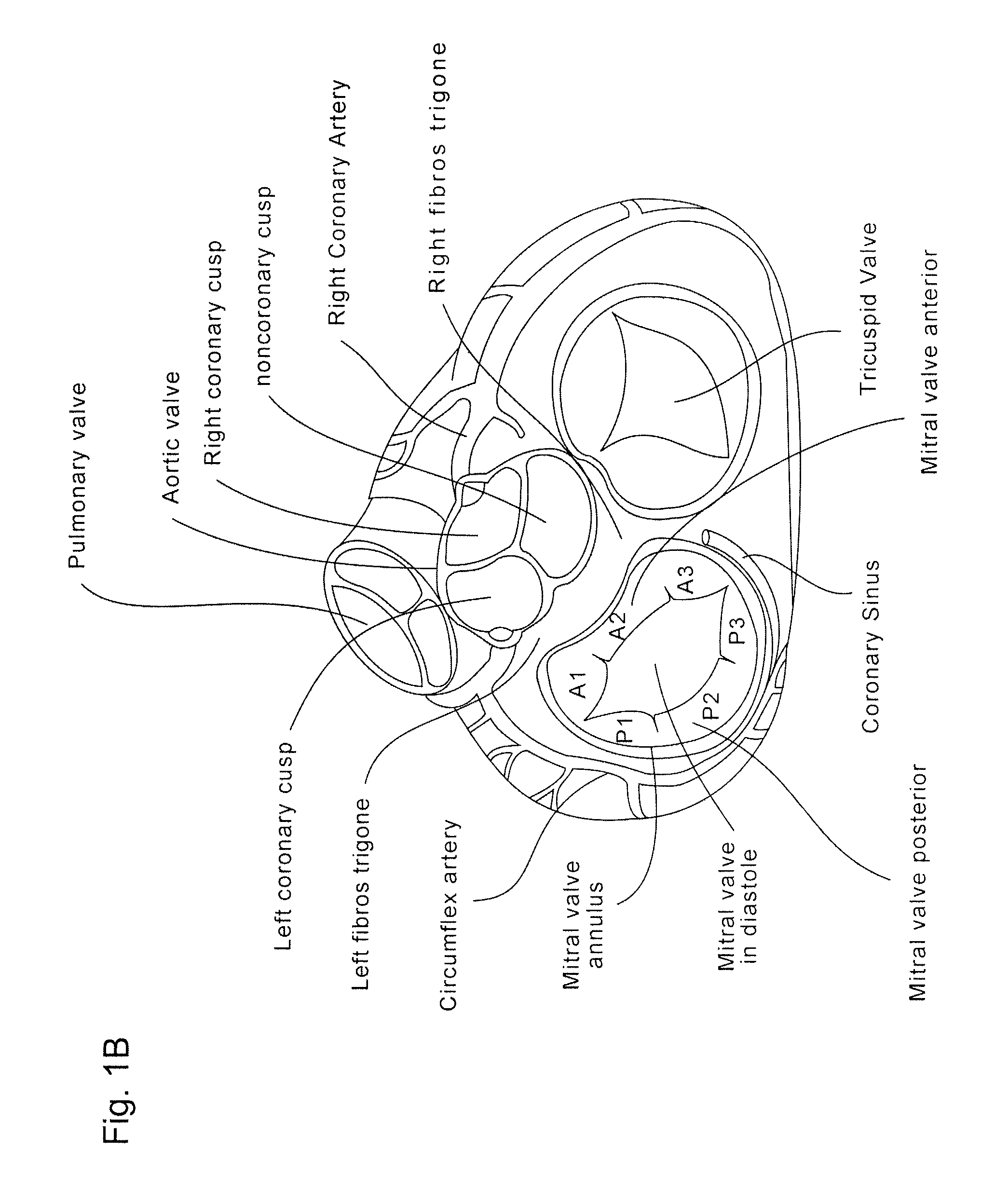
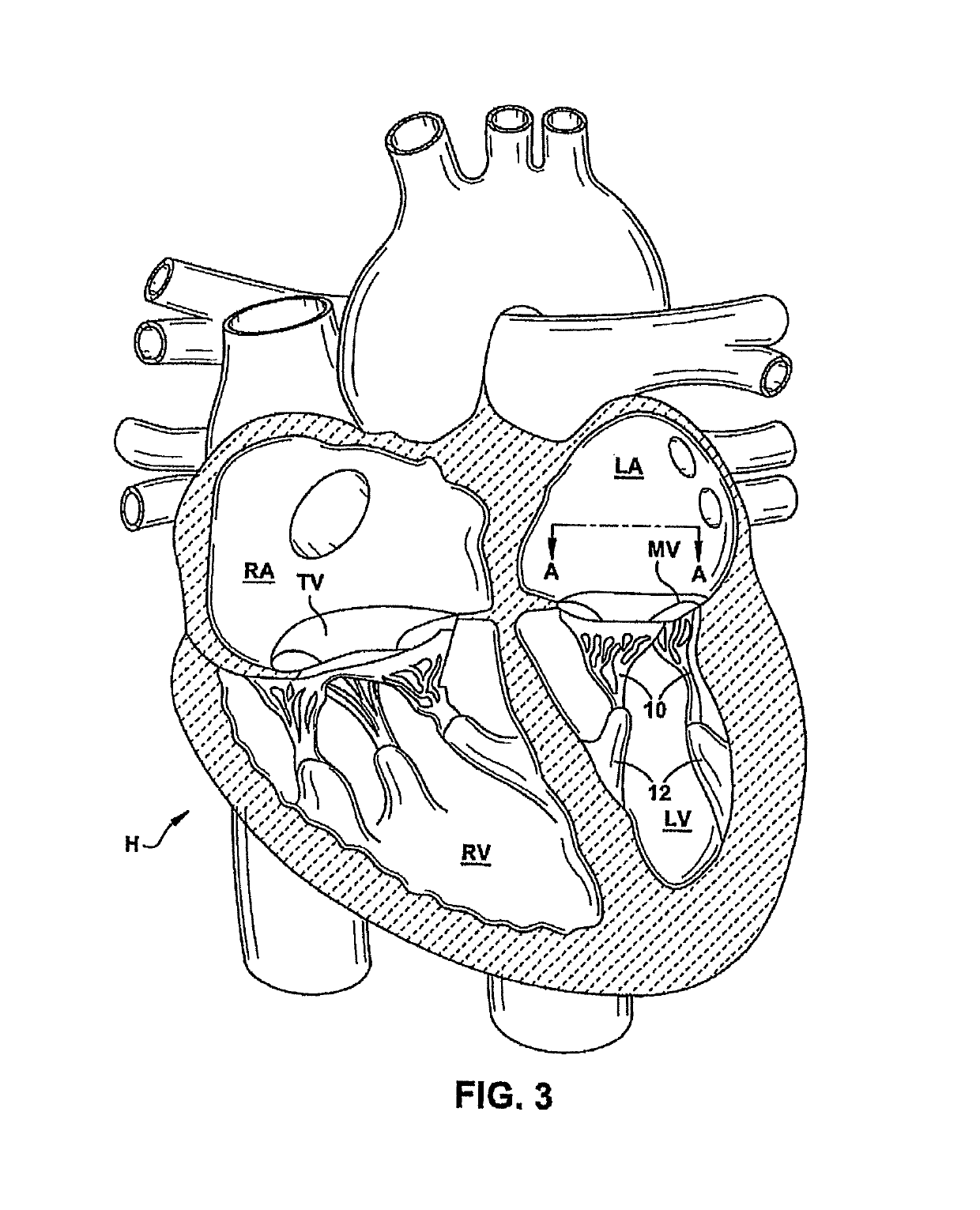
Device and method for improving heart valve function
ActiveUS20070270943A1Function increaseInhibit refluxSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac wallHeart chamber
The invention is device and method for reducing regurgitation through a mitral valve. The device and method is directed to an anchor portion for engagement with the heart wall and an expandable valve portion configured for deployment between the mitral valve leaflets. The valve portion is expandable for preventing regurgitation through the mitral valve while allowing blood to circulate through the heart. The expandable valve portion may include apertures for reducing the stagnation of blood. In a preferred configuration, the device is configured to be delivered in two-stages wherein an anchor portion is first delivered and the valve structure is then coupled to the anchor portion. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming an anchor portion wherein a disposable jig is used to mold the anchor portion into a three-dimensional shape for conforming to a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP +1
Coaptation enhancement implant, system, and method
ActiveUS8845717B2Safe and effective and operation of valveImprove sealingSuture equipmentsHeart valvesBody shapeCatheter
Implants, implant systems, and methods for treatment of mitral valve regurgitation and other valve diseases generally include a coaptation assist body which remains within the blood flow path as the leaflets of the valve move, the valve bodies often being relatively thin, elongate (along the blood flow path), and / or conformable structures which extend laterally from commissure to commissure, allowing the native leaflets to engage and seal against the large, opposed surfaces on either side of the valve body during the heart cycle phase when the ventricle contracts to empty that chamber of blood, and allows blood to pass around the valve body so that blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle during the filling phase of the heart cycle. Separate deployment of independent anchors near each of the commissures may facilitate positioning and support of an exemplary triangular valve body, with a third anchor being deployed in the ventricle. An outer surface of the valve body may accommodate tissue ingrowth or endothelialization, while a fluid-absorbing matrix can swell after introduction into the heart. The valve body shape may be selected after an anchor has been deployed, and catheter-based deployment systems may have a desirable low profile.
Owner:POLARES MEDICAL INC
Coaptation enhancement implant, system, and method
ActiveUS20120197388A1Mal-coaptation is mitigatedImprove valve functionSuture equipmentsBone implantBody shapeAbdominal cavity
Implants, implant systems, and methods for treatment of mitral valve regurgitation and other valve diseases generally include a coaptation assist body which remains within the blood flow path as the leaflets of the valve move, the valve bodies often being relatively thin, elongate (along the blood flow path), and / or conformable structures which extend laterally from commissure to commissure, allowing the native leaflets to engage and seal against the large, opposed surfaces on either side of the valve body during the heart cycle phase when the ventricle contracts to empty that chamber of blood, and allows blood to pass around the valve body so that blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle during the filling phase of the heart cycle. Separate deployment of independent anchors near each of the commissures may facilitate positioning and support of an exemplary triangular valve body, with a third anchor being deployed in the ventricle. An outer surface of the valve body may accommodate tissue ingrowth or endothelialization, while a fluid-absorbing matrix can swell after introduction into the heart. The valve body shape may be selected after an anchor has been deployed, and catheter-based deployment systems may have a desirable low profile.
Owner:POLARES MEDICAL INC
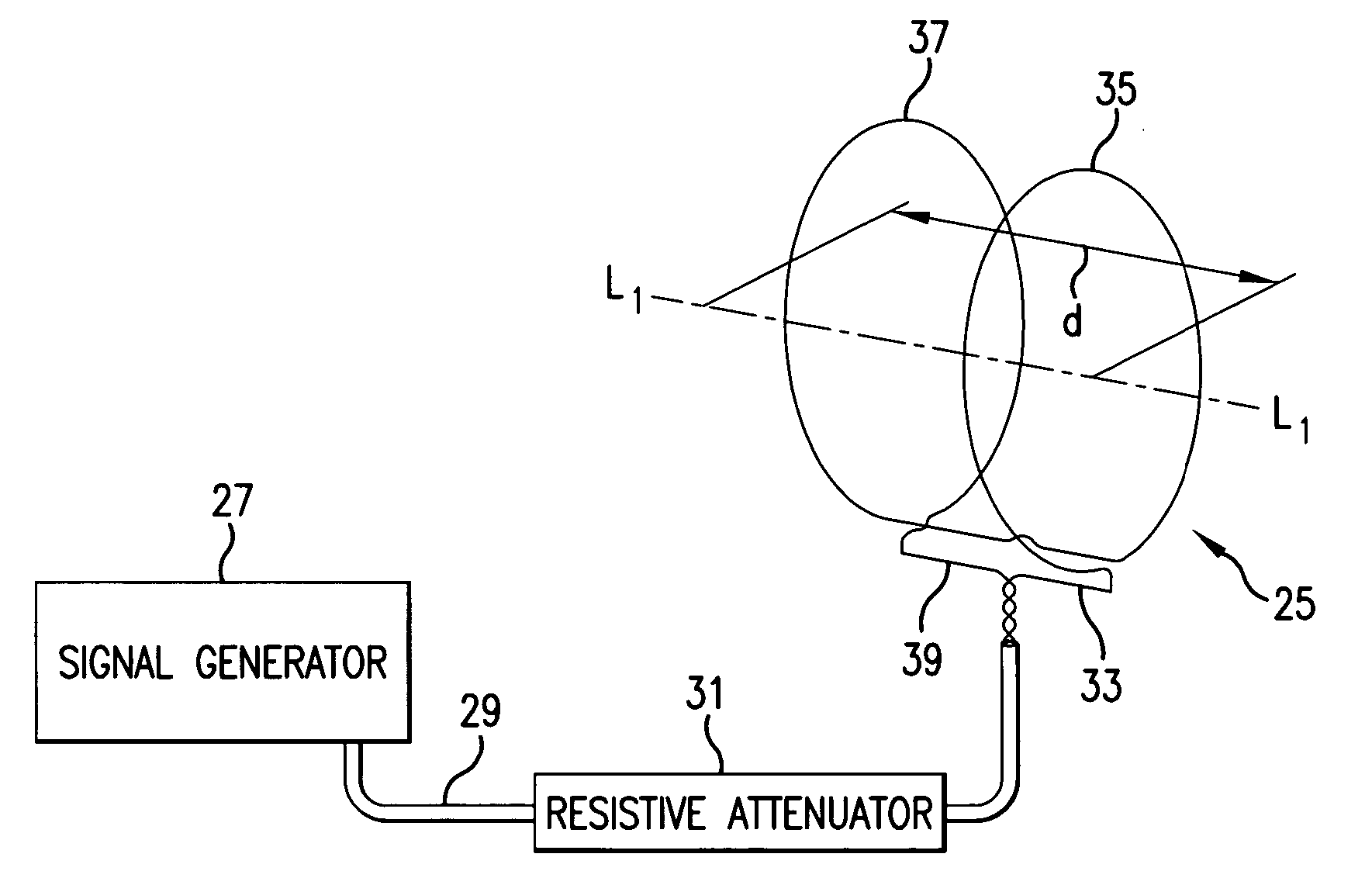
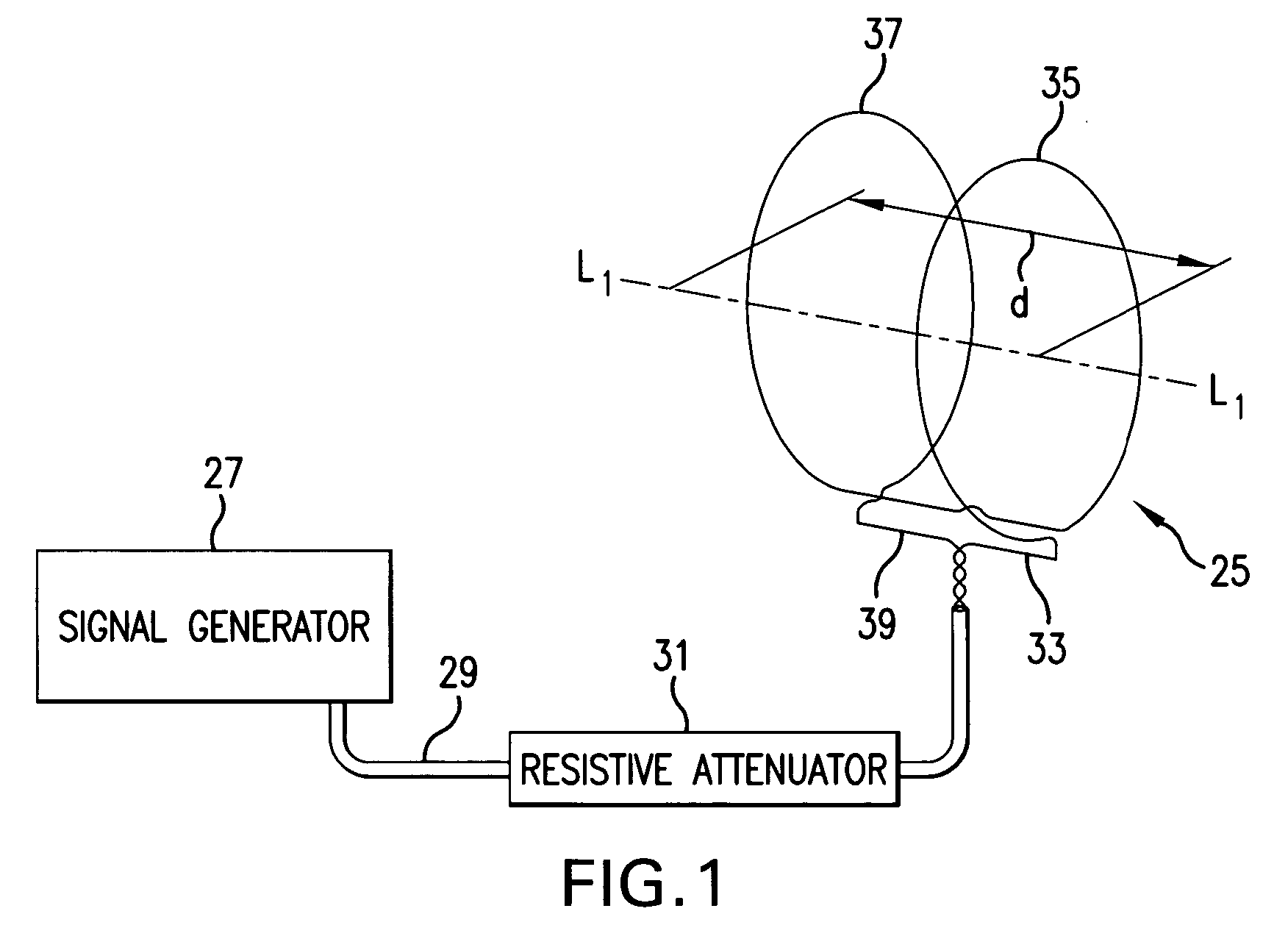
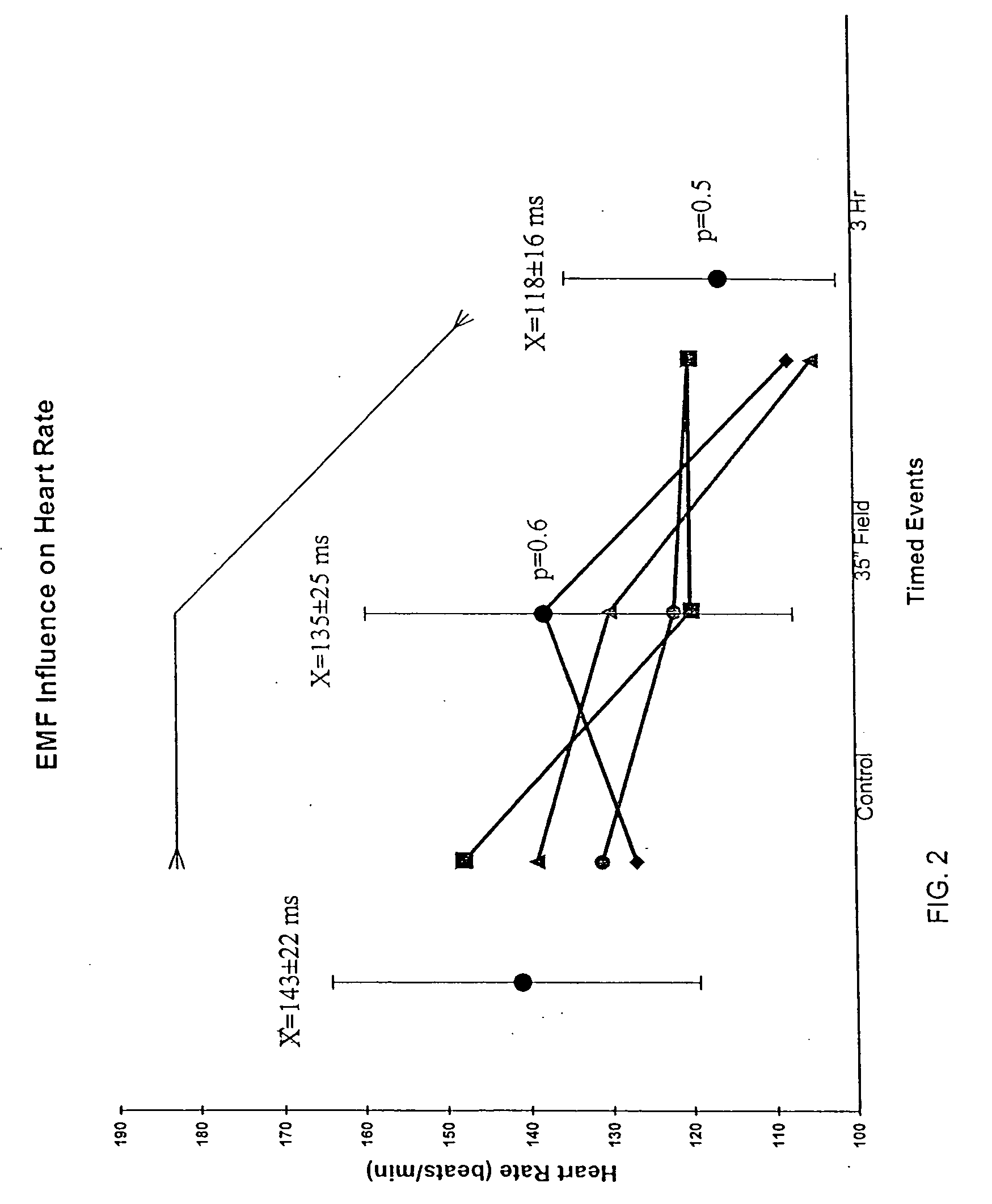
Cardioelectromagnetic treatment
ActiveUS20050080459A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsImplanted deviceHeart/circulation
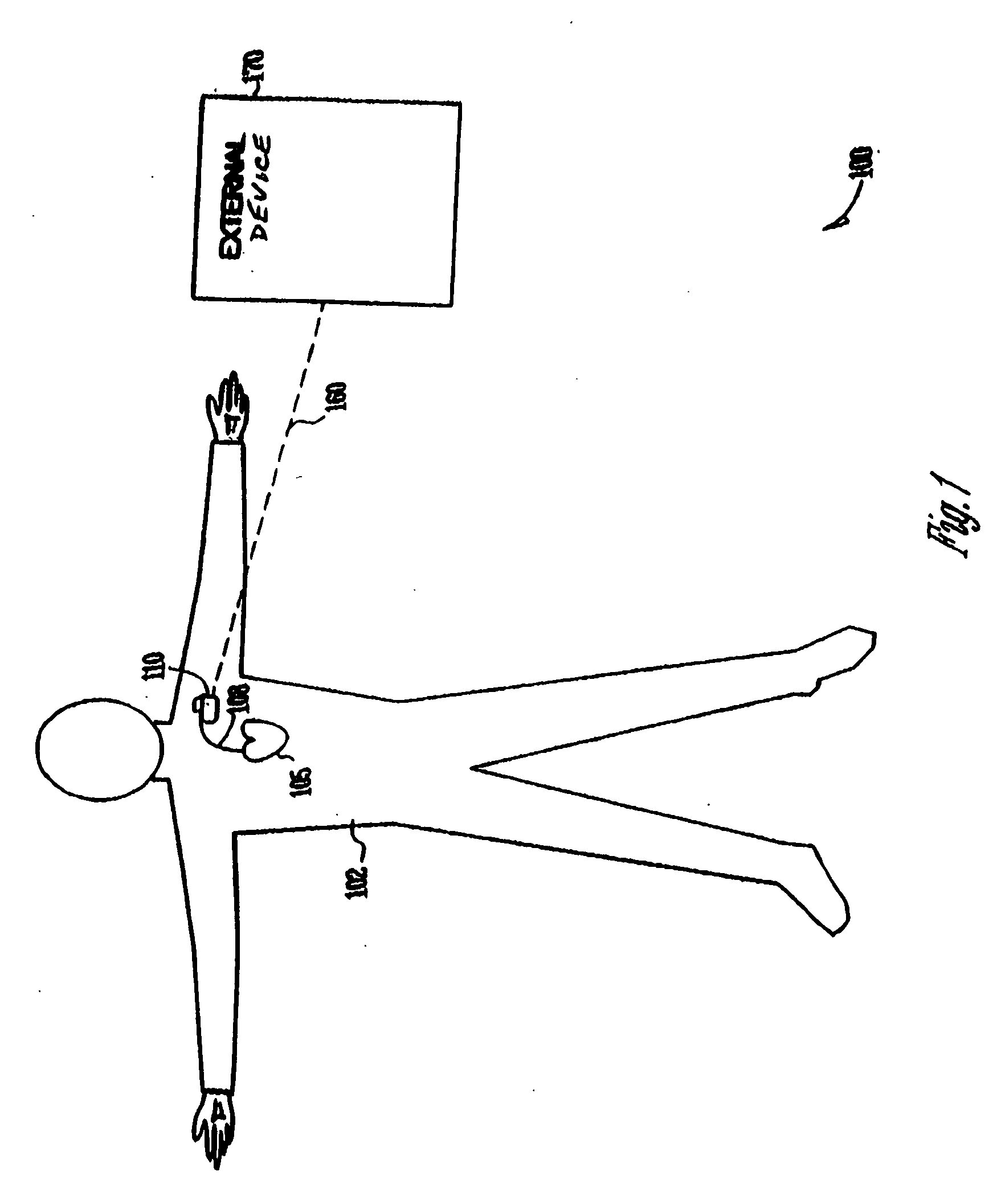
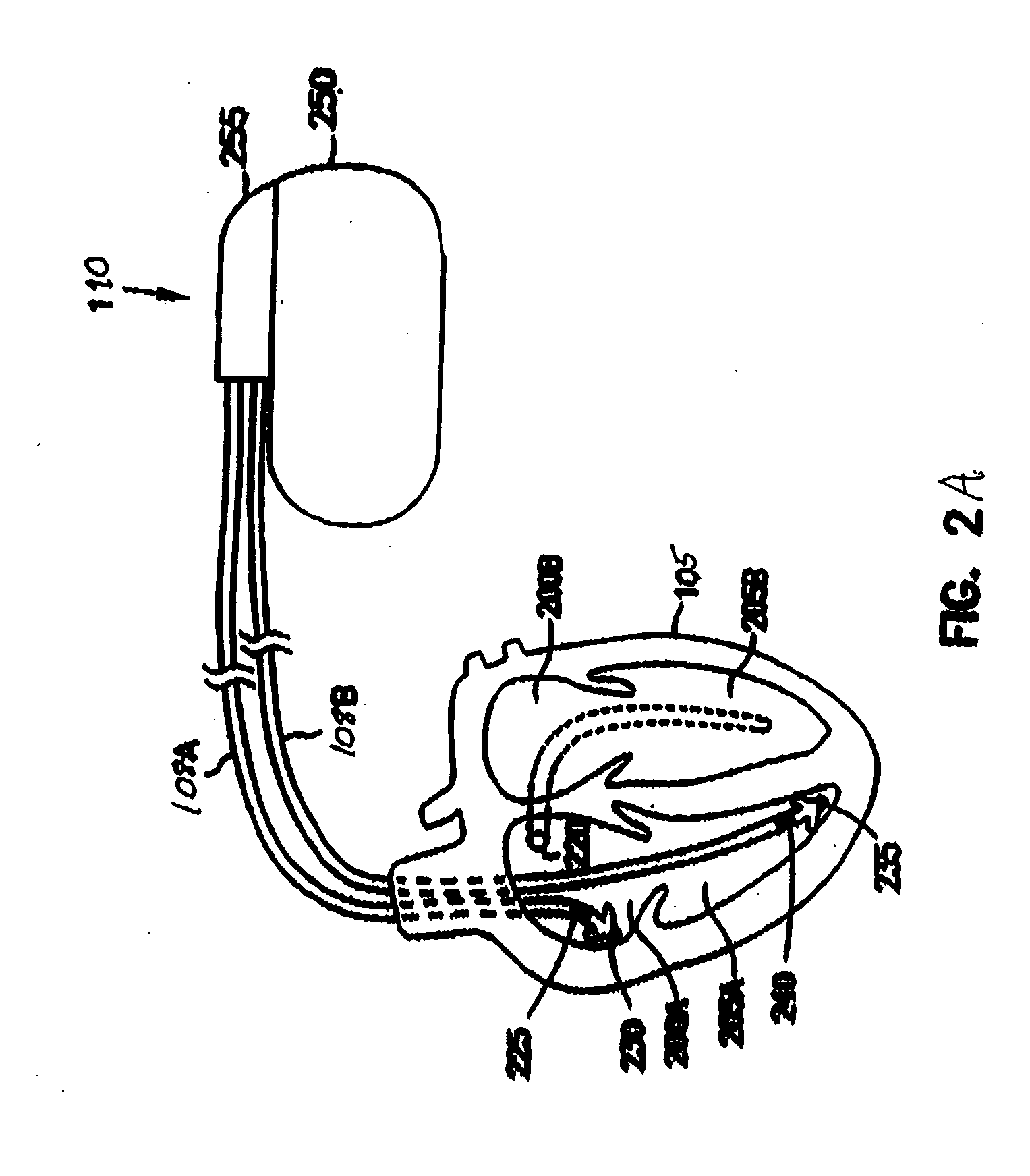
A method of treatment or prophylaxis of a disease state or a condition ameliorated or prevented by electromagnetic field application. A person having or susceptible to such disease state or condition is subjected to electromagnetic fields having a frequency between zero and about 200 Hertz. The diseased state or condition may include diseased heart valves, an enlarged heart, circulatory blockage, coronary insufficiencies, and ischemia. The treatment may be administered non-invasively or invasively. An implantable device for invasively administering the treatment may include at least one component emitting electromagnetic fields having a frequency between zero and about 200 Hertz. The component may include at least one inductor.
Owner:JACOBSON RESONANCE ENTERPRISES
Non-invasive monitoring of hemodynamic parameters using impedance cardiography
InactiveUS6161038AImprove accuracySimple processCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationLeft Ventricular Ejection TimeHarmonic
PCT No. PCT / SG97 / 00013 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 8, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 8, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 7, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 37591 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 16, 1997A method and apparatus for determination of heart rate, heart stroke volume, heart stroke volume, and cardiac output from thoracic bioimpedance signals and electrocardiograms. A unique bioimpedance electrode arrangement is employed, and the bioimpedance signals are corrected for gain-phase-frequency distortion through the use of sinusoidal test signals through the measuring or detection electrodes to identify distortions and correct for same during actual measurements. Time-derivative bioimpedance signals are employed, the power spectrum calculated, and a novel autoconvolution procedure used to emphasize the heart rate harmonic. Breath waves and other signals not indicative of the patient's cardiocycles are removed. Left ventricular ejection time is derived from the bioimpedance signals, and an improved version of Kubicek's equation is employed to derive heart stroke volume and thus cardiac output.
Owner:RHEO GRAPHIC PTE
Intracardiac impedance and its applications
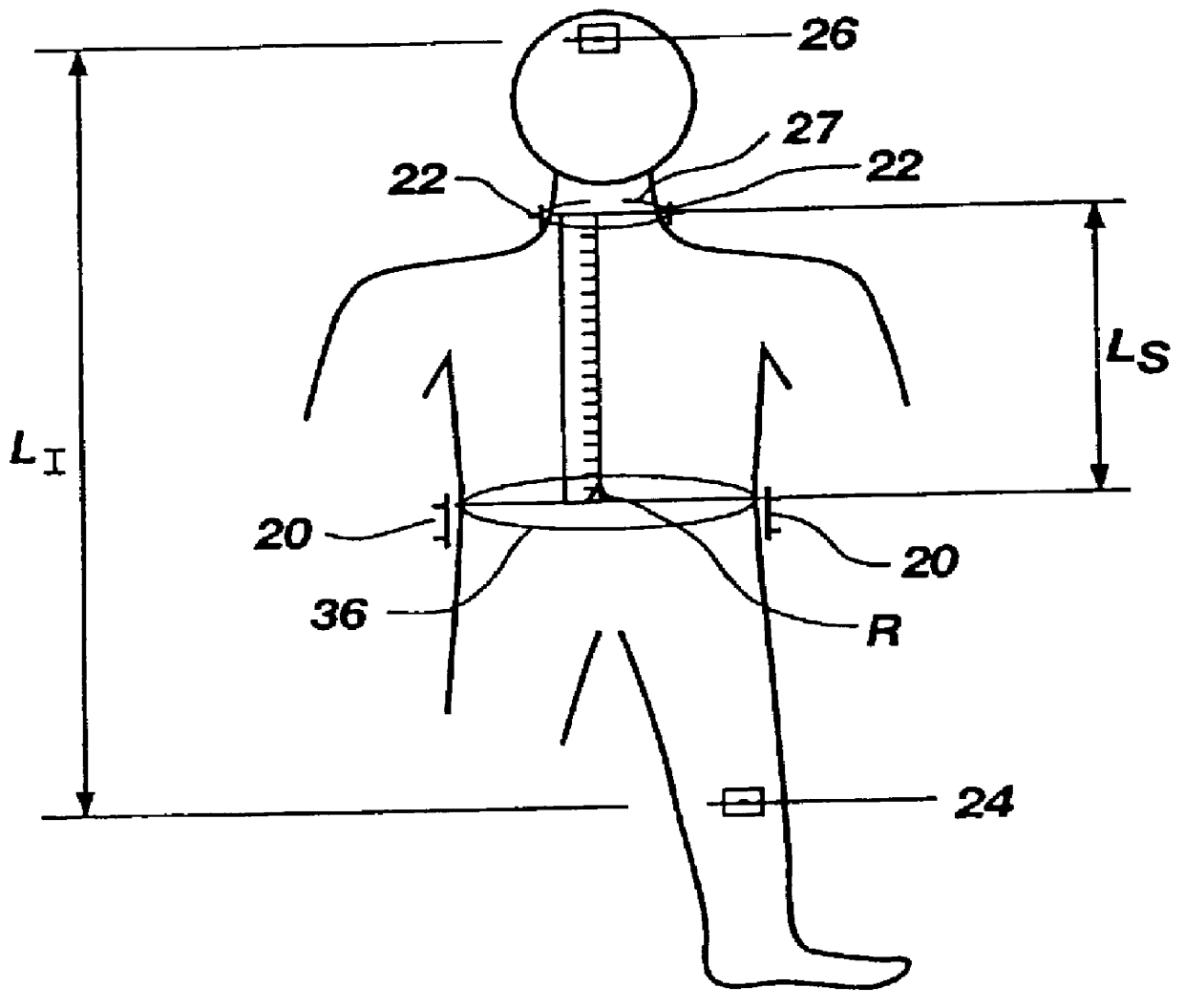
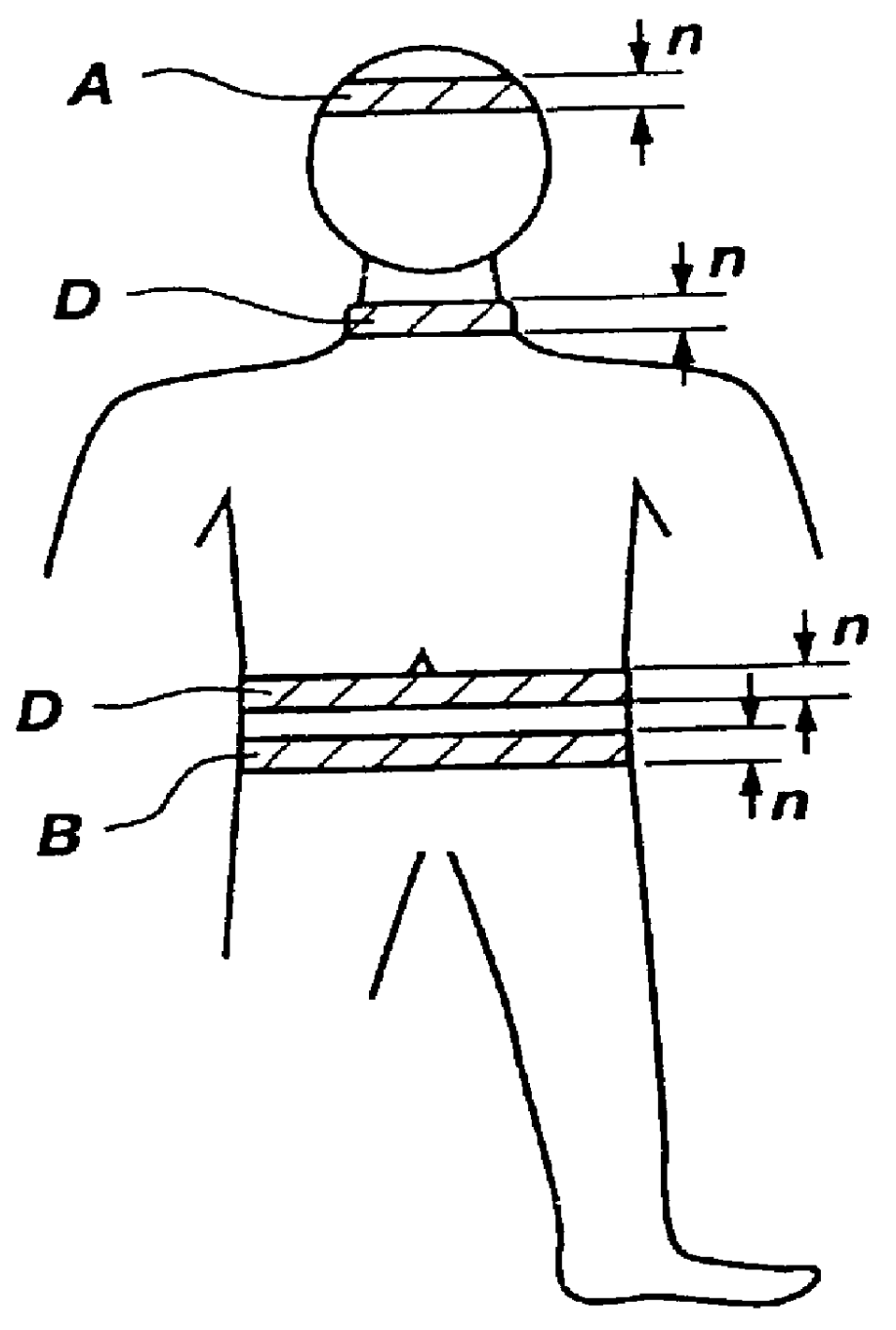
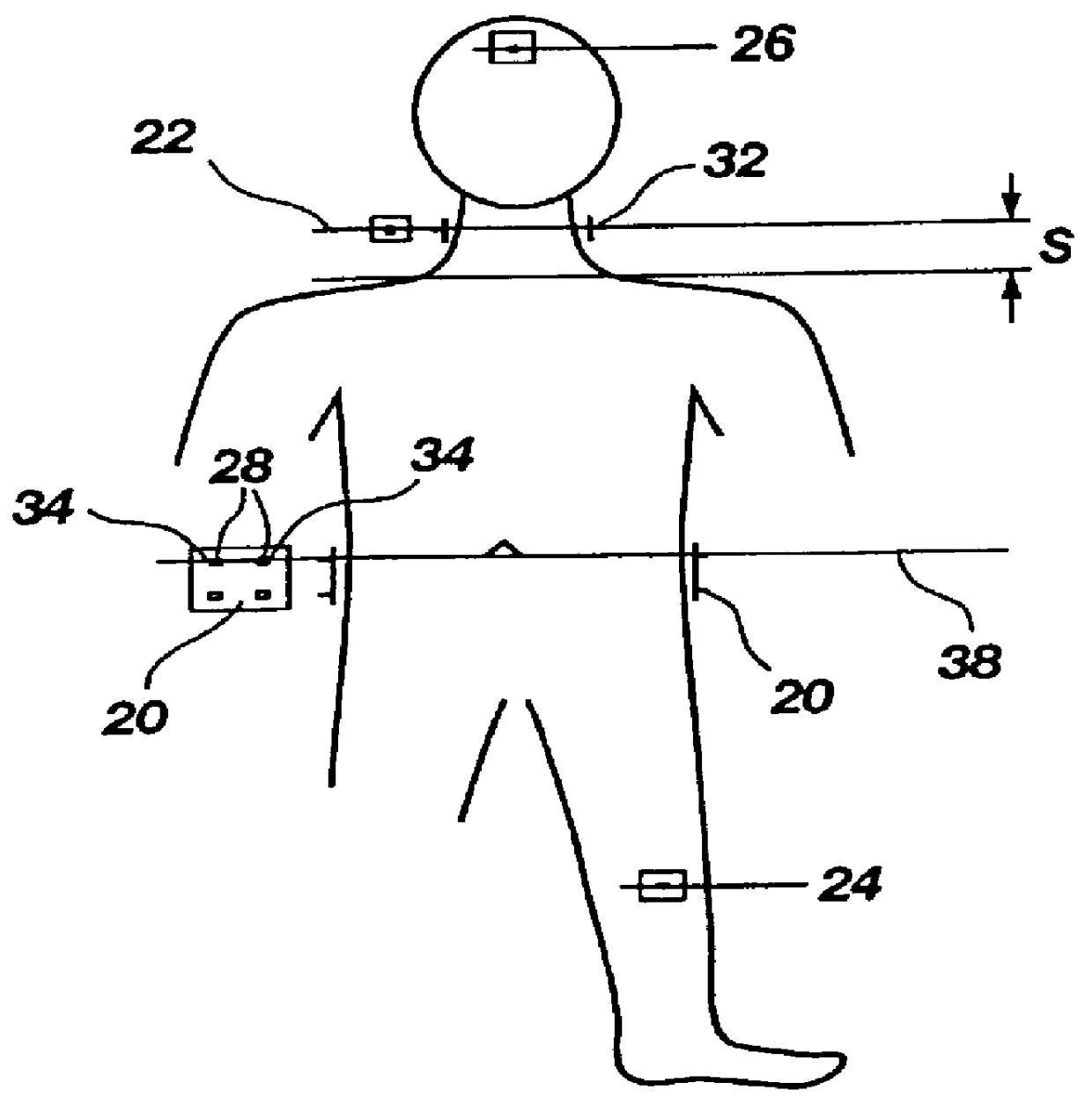
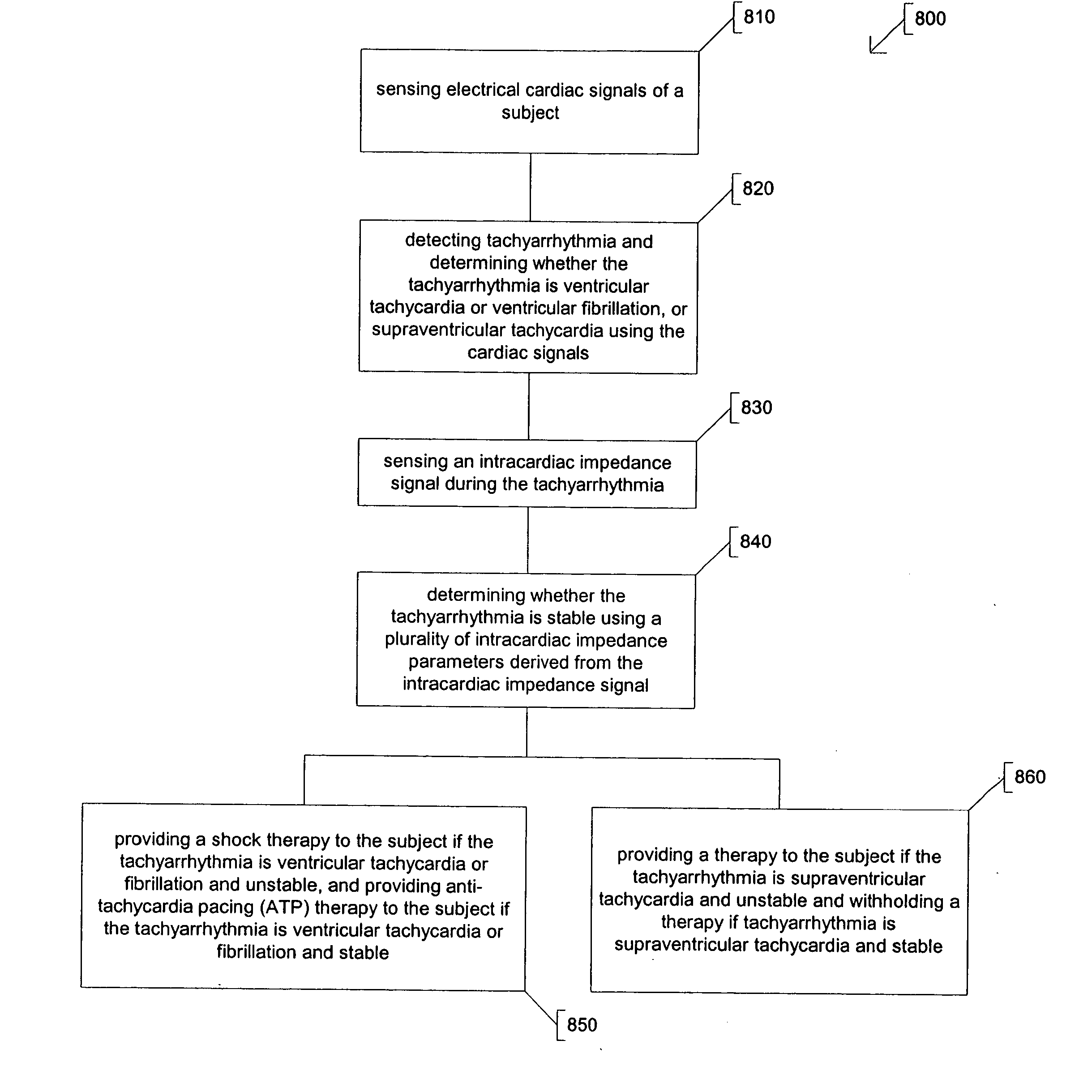
InactiveUS20070043394A1Heart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac cycle
A system to measure intracardiac impedance includes implantable electrodes and a medical device. The electrodes sense electrical signals of a heart of a subject. The medical device includes a cardiac signal sensing circuit coupled to the implantable electrodes, an impedance measurement circuit coupled to the same or different implantable electrodes, and a controller circuit coupled to the cardiac signal sensing circuit and the impedance measurement circuit. The cardiac signal sensing circuit provides a sensed cardiac signal. The impedance measurement circuit senses intracardiac impedance between the electrodes to obtain an intracardiac impedance signal. The controller circuit determines cardiac cycles of the subject using the sensed cardiac signal, and detects tachyarrhythmia using cardiac-cycle to cardiac-cycle changes in a plurality of intracardiac impedance parameters obtained from the intracardiac impedance signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
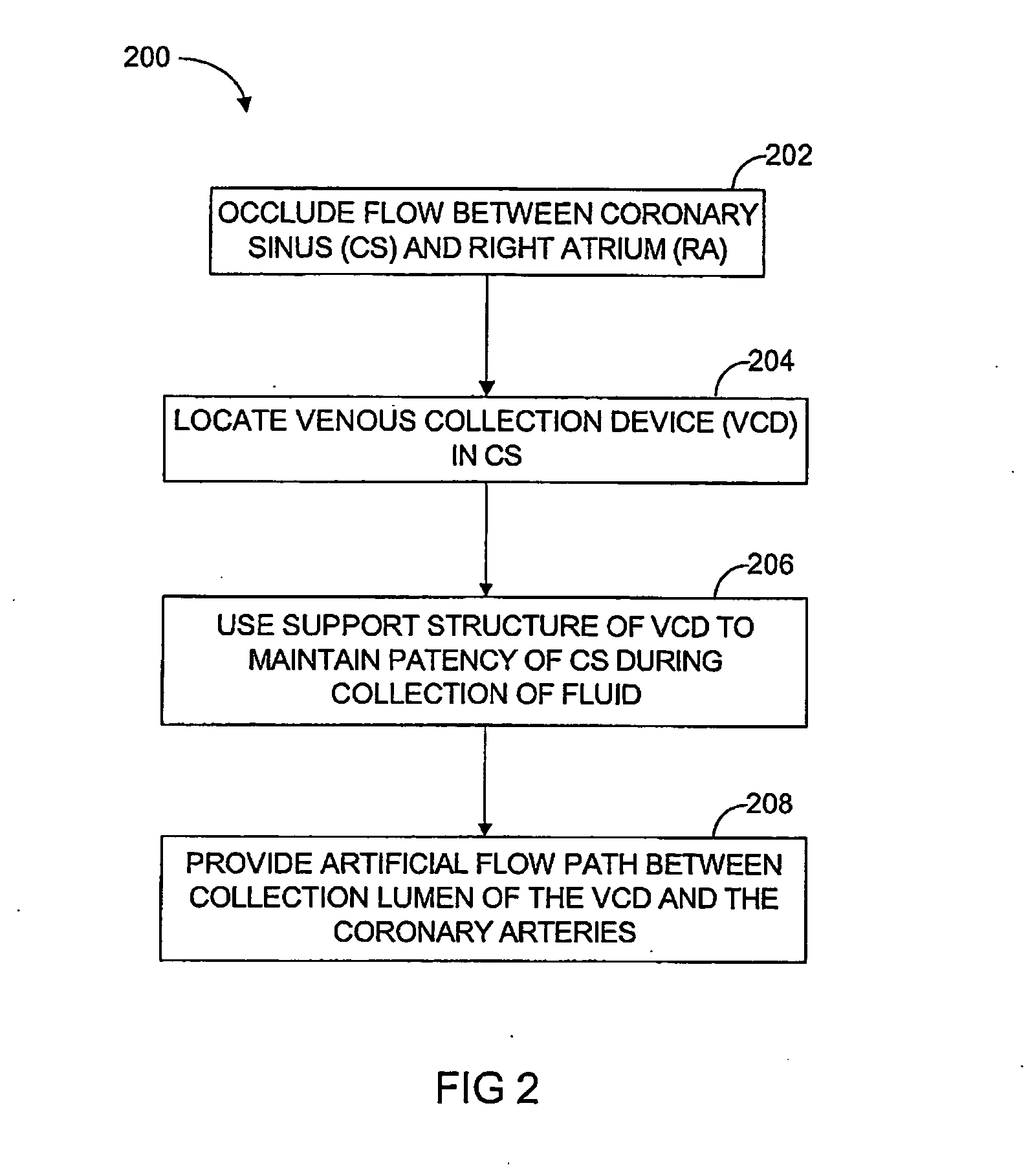
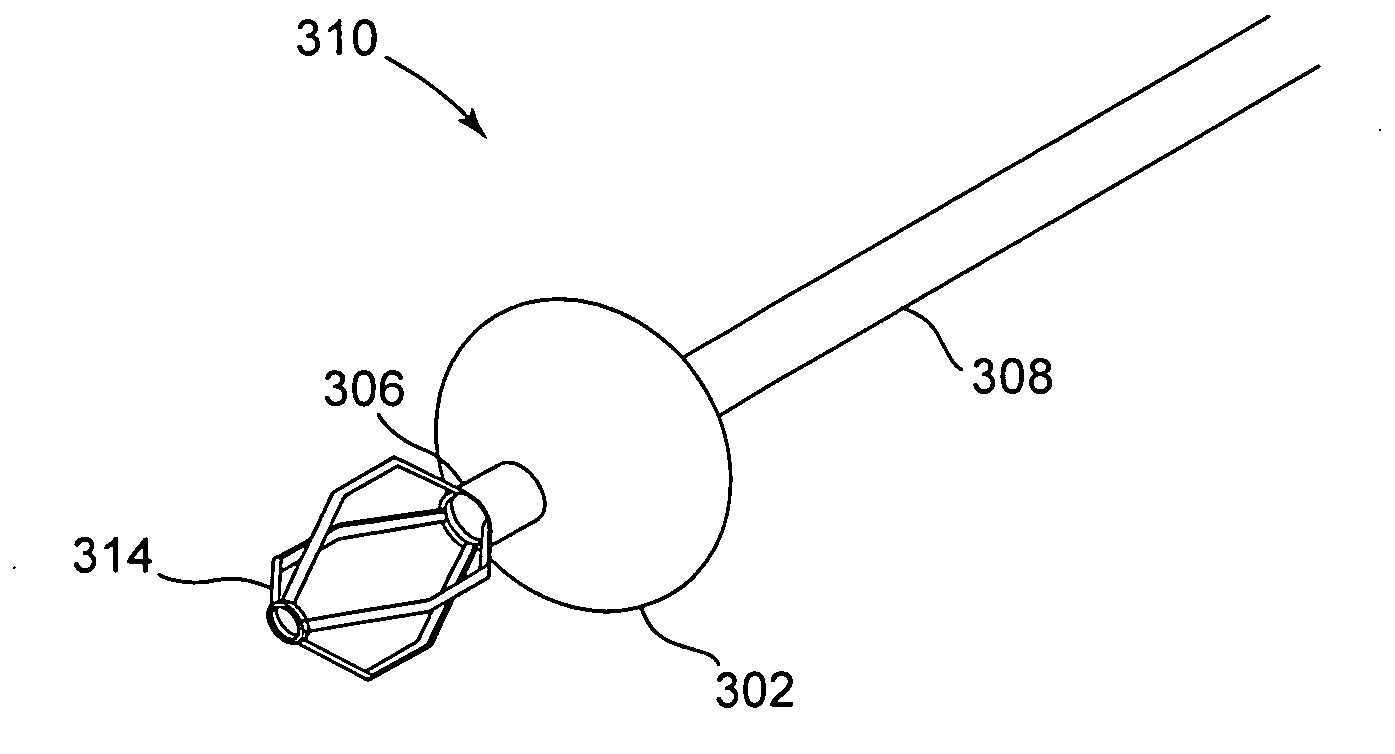
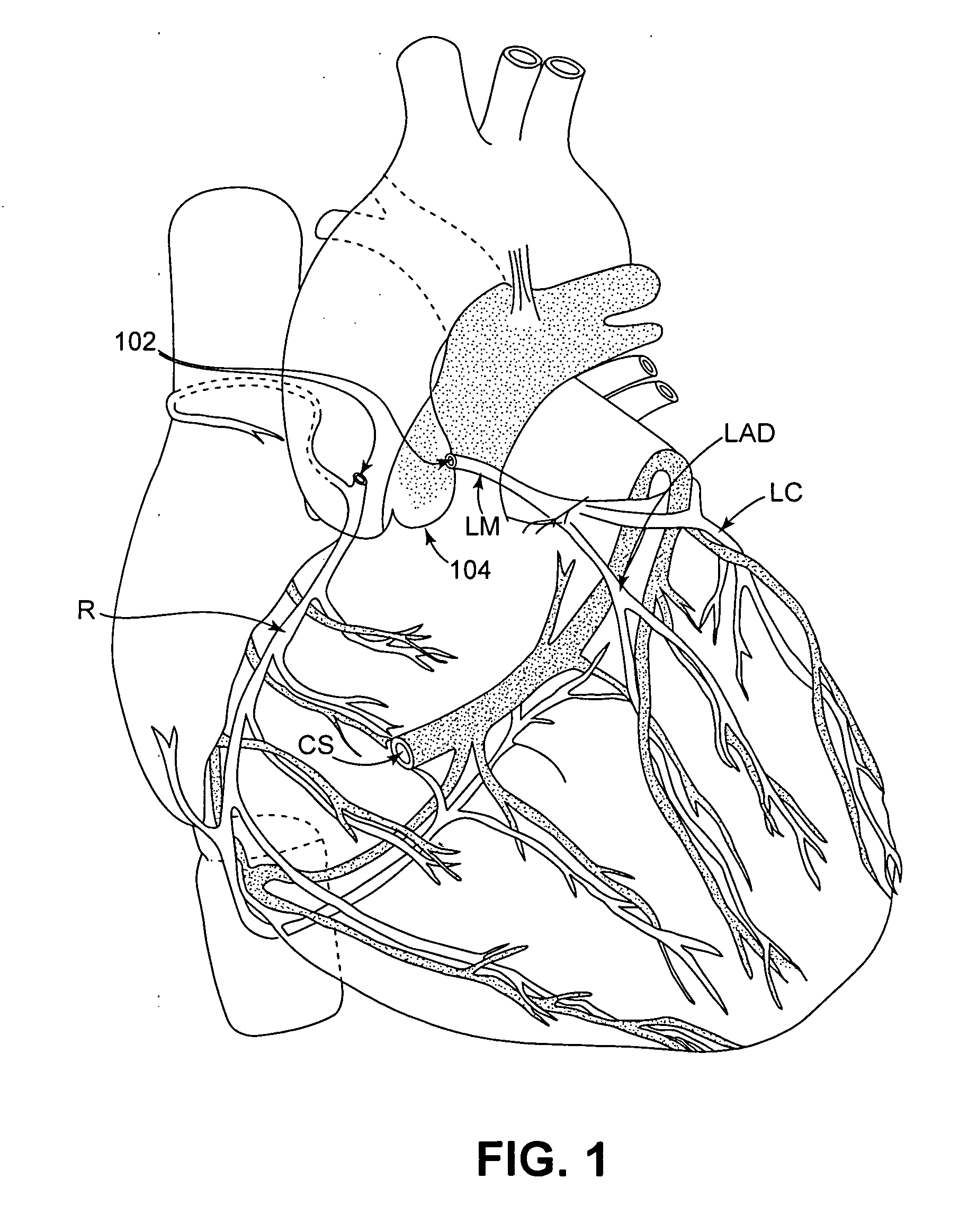
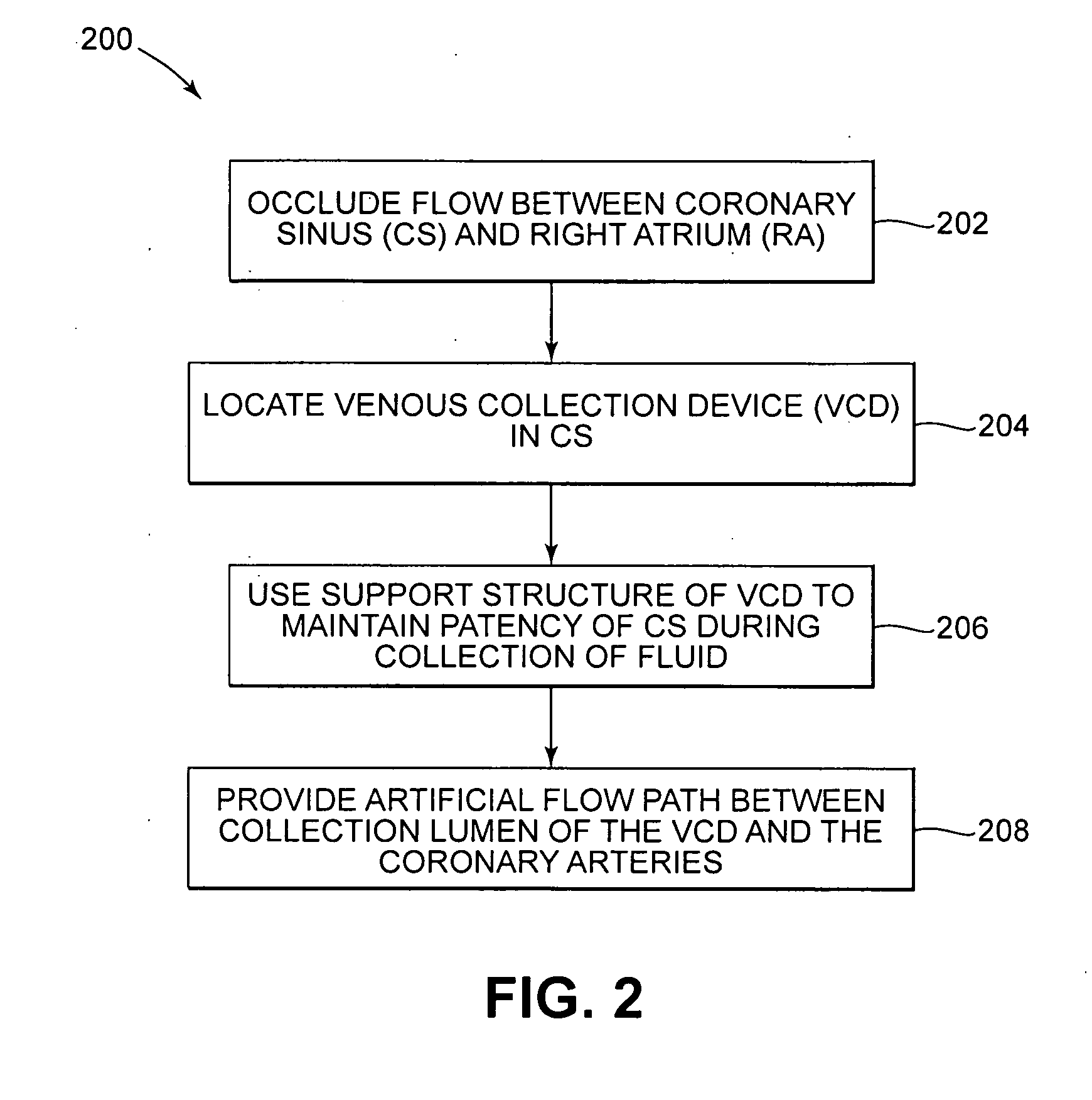
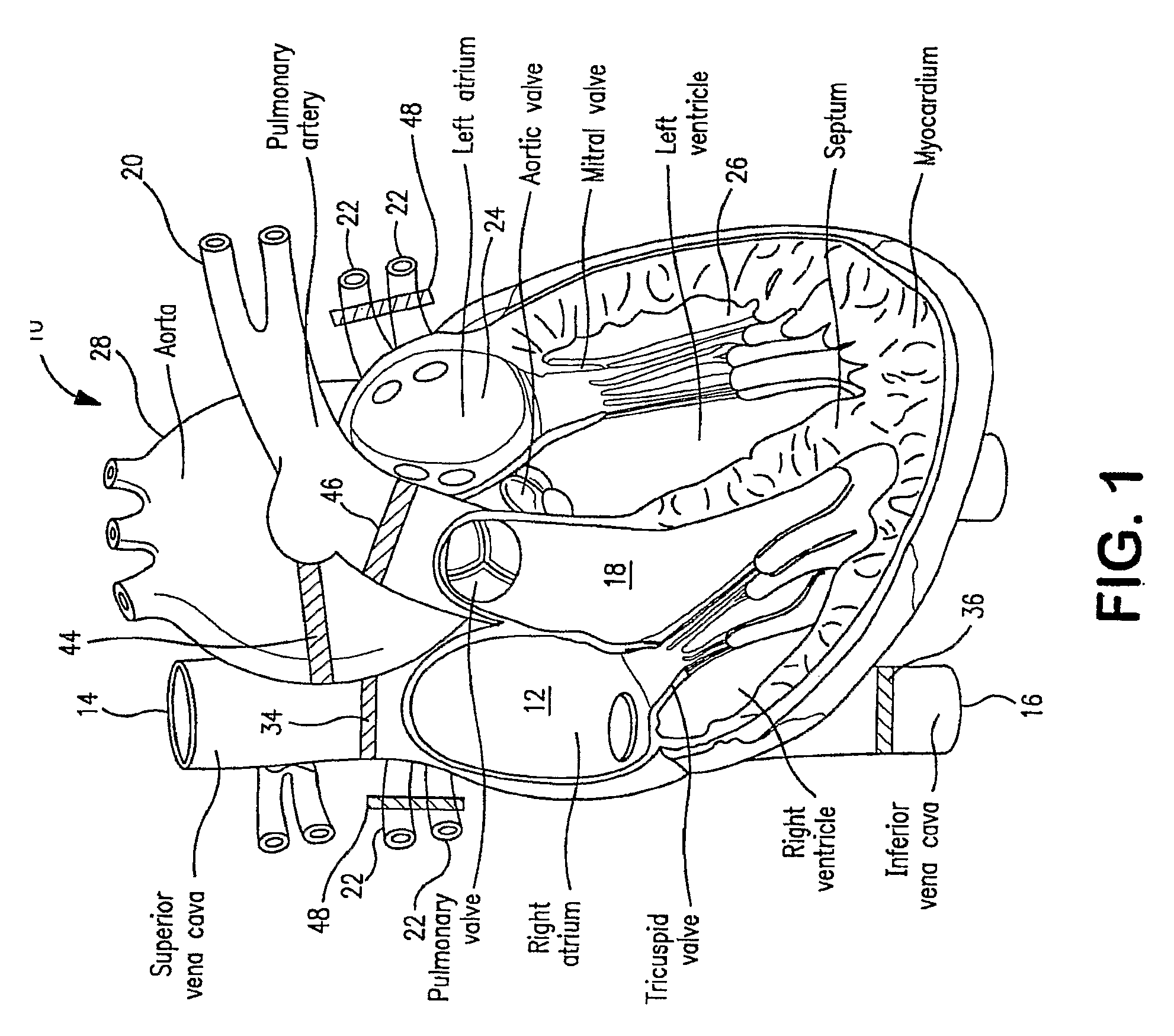
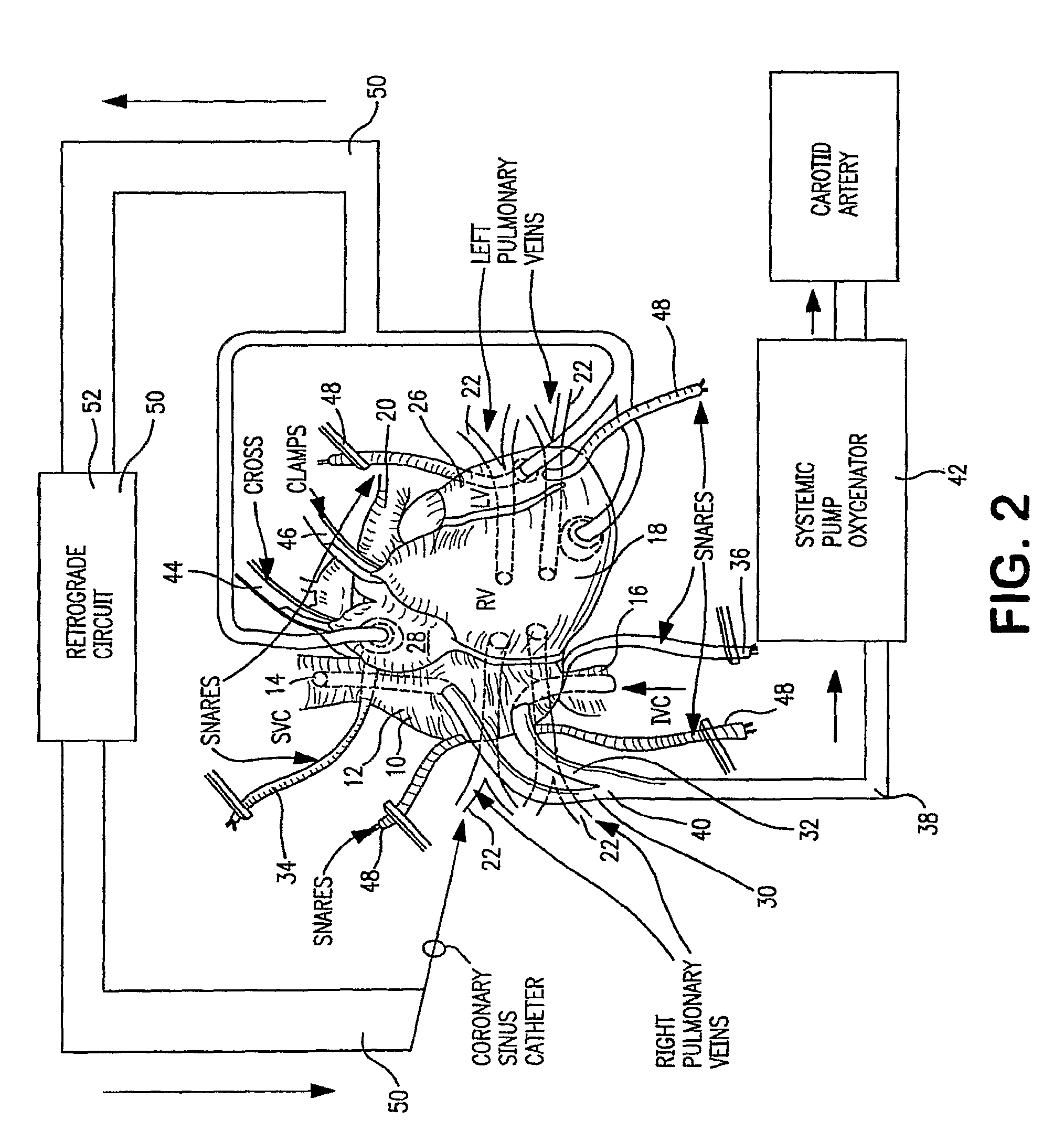
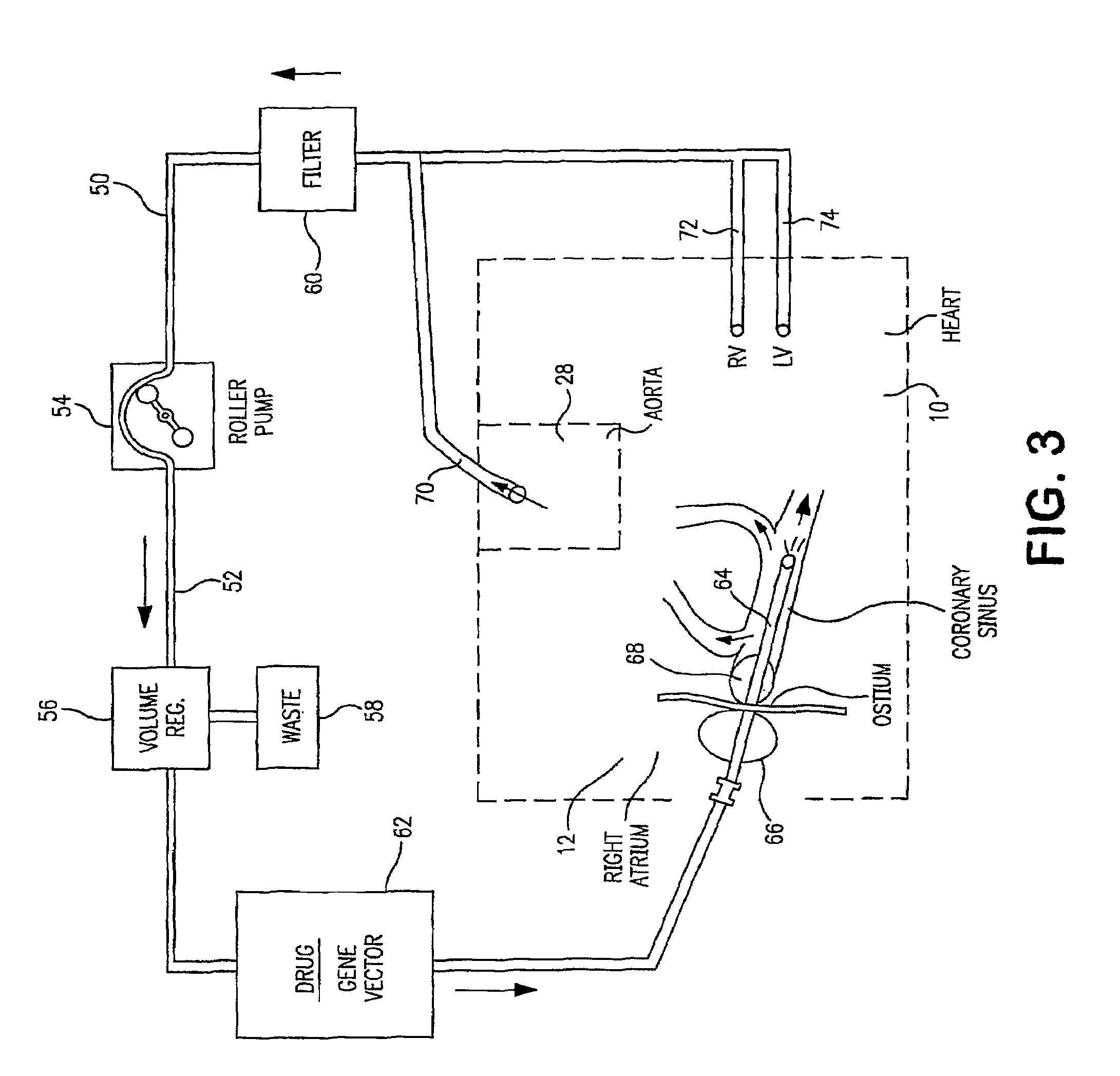
Isolating cardiac circulation
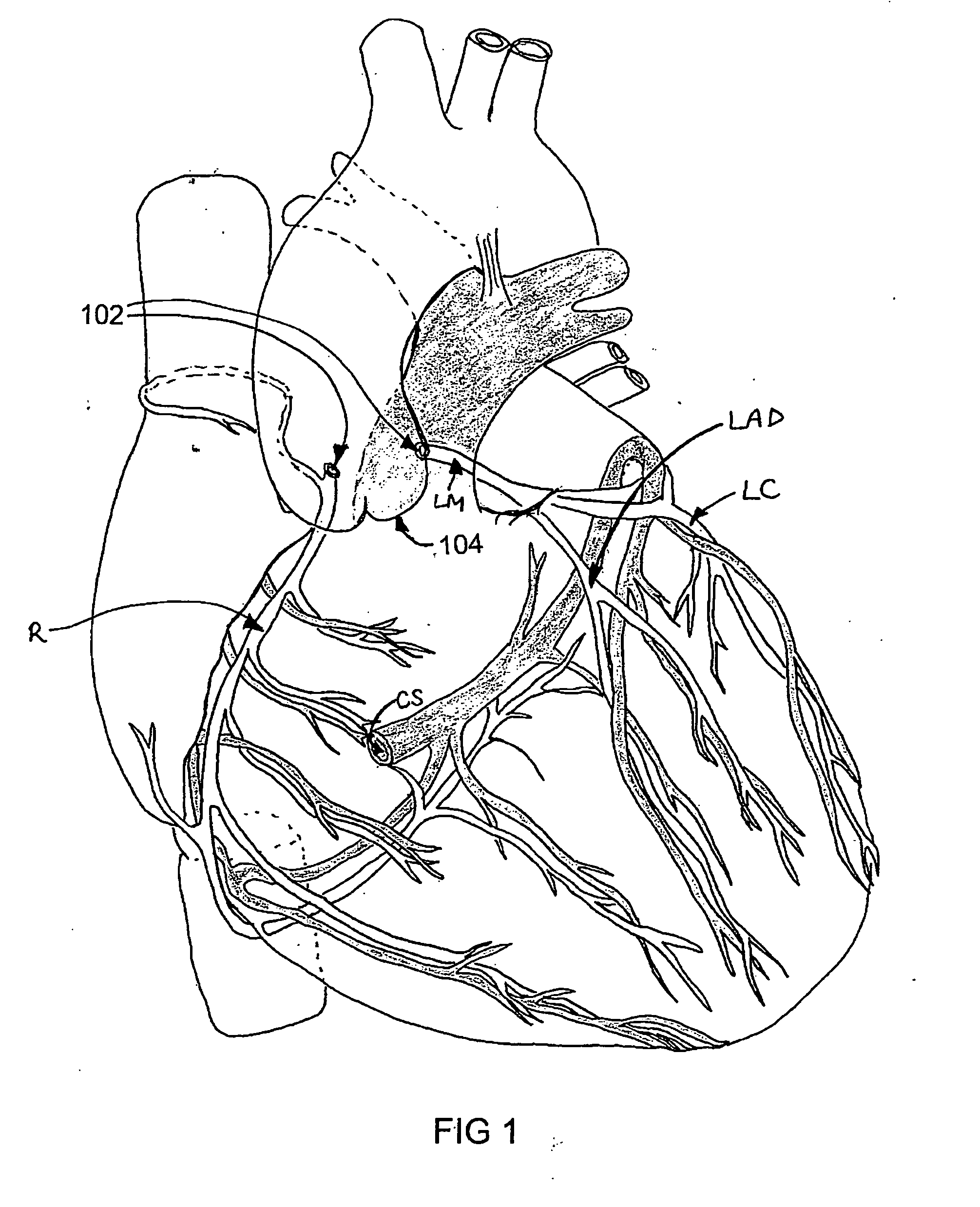
In a method for substantially isolating cardiac circulation from systemic circulation, flow between the coronary sinus and the right atrium is occluded. A venous collection device having a collection lumen and a support structure is located in the coronary sinus. The support structure is used to maintain patency of the coronary sinus during collection of fluid through the collection lumen. An artificial flow path is provided between the collection lumen and the one or more coronary arteries, thus isolating the cardiac circulation. According to the method, cardiac pumping for systemic circulation can be maintained during isolation of the cardiac circulation.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
Isolating cardiac circulation
In a method for substantially isolating cardiac circulation from systemic circulation, flow between the coronary sinus and the right atrium is occluded. A venous collection device having a collection lumen and a support structure is located in the coronary sinus. The support structure is used to maintain patency of the coronary sinus during collection of fluid through the collection lumen. An artificial flow path is provided between the collection lumen and the one or more coronary arteries, thus isolating the cardiac circulation. According to the method, cardiac pumping for systemic circulation can be maintained during isolation of the cardiac circulation.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
Ablation systems including insulated energy transmitting elements
Ablation systems comprise a support body, an energy transmitting element supported by the support body and an insulating member covering a portion of the support body and energy transmitting member. Ablation energy is transmitted from an uncovered, exposed portion of the energy transmitting element. The insulating member may be a distal portion of an introducer sheath. An open segment may be provided in the distal portion to expose a portion of the energy transmitting element. When used in cardiac ablation therapy, for example, the insulating member decreases the amount of ablation energy dissipated in the blood circulating through the heart and thermally insulates the energy transmitting member and the tissue at the ablation site, enabling better control of the ablation process. An inflatable balloon or an expandable web may be provided coupled to the distal portion of the sheath behind the open segment to provide further insulation of the energy transmitting element and of the tissue around the ablation site. In another embodiment, ablation catheters incorporate an insulating member such as the inflatable balloon, expandable web or a cover. Methods of ablating tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ablation systems including insulated energy transmitting elements
Ablation systems comprise a support body, an energy transmitting element supported by the support body and an insulating member covering a portion of the support body and energy transmitting member. Ablation energy is transmitted from an uncovered, exposed portion of the energy transmitting element. The insulating member may be a distal portion of an introducer sheath. An open segment may be provided in the distal portion to expose a portion of the energy transmitting element. When used in cardiac ablation therapy, for example, the insulating member decreases the amount of ablation energy dissipated in the blood circulating through the heart and thermally insulates the energy transmitting member and the tissue at the ablation site, enabling better control of the ablation process. An inflatable balloon or an expandable web may be provided coupled to the distal portion of the sheath behind the open segment to provide further insulation of the energy transmitting element and of the tissue around the ablation site. In another embodiment, ablation catheters incorporate an insulating member such as the inflatable balloon, expandable web or a cover. Methods of ablating tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Heart valve sealing devices and delivery devices therefor
A valve repair device for repairing a native heart valve of a patient includes a pair of clasps, where each clasp is configured to attach to native valve leaflet. The ends of the pair of clasps can move away from one another to a partially open position when the native valve leaflets open during a diastolic phase of a cardiac cycle, and the ends of the pair of clasps can move toward one another when the native valve leaflets close during a systolic phase of a cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
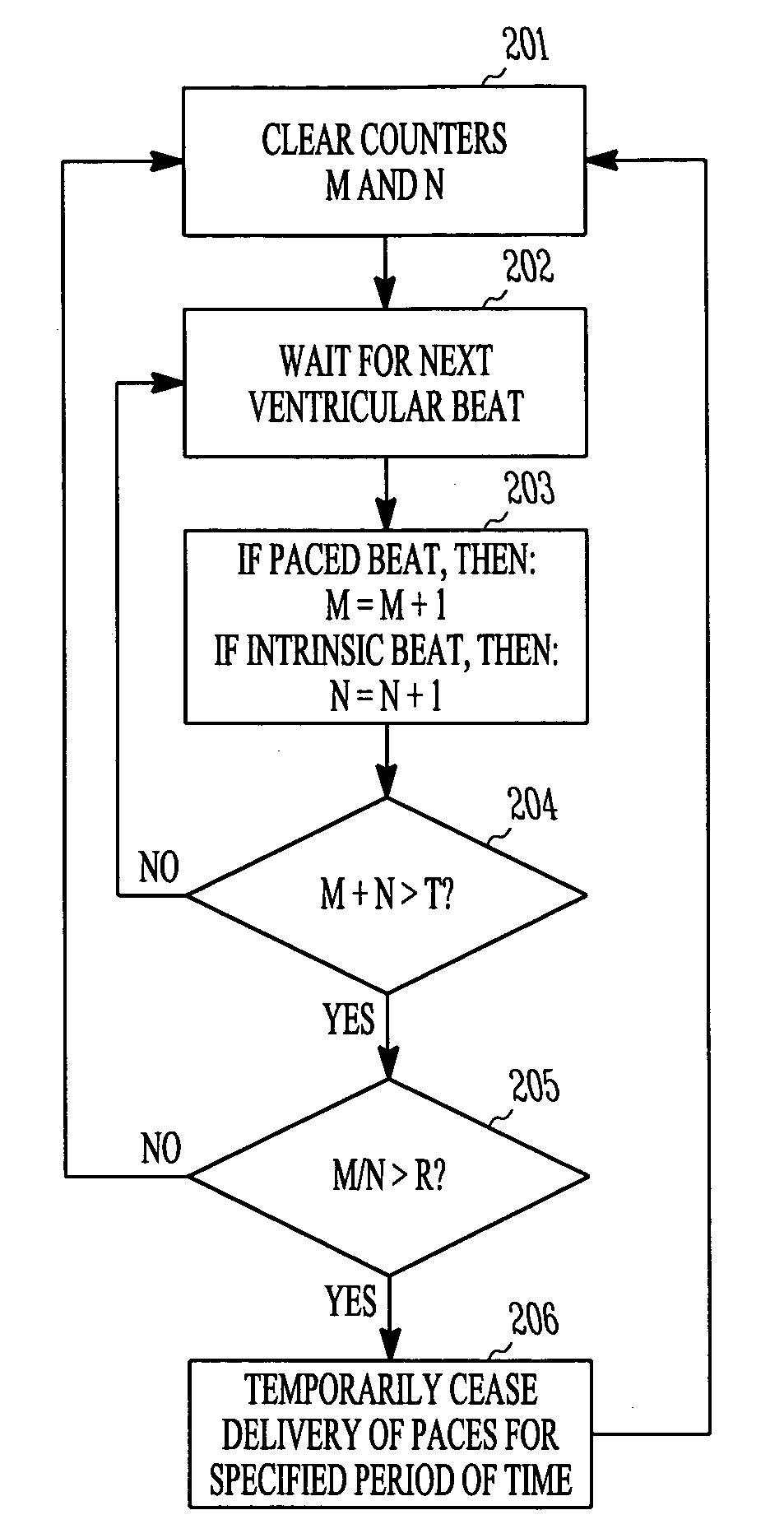
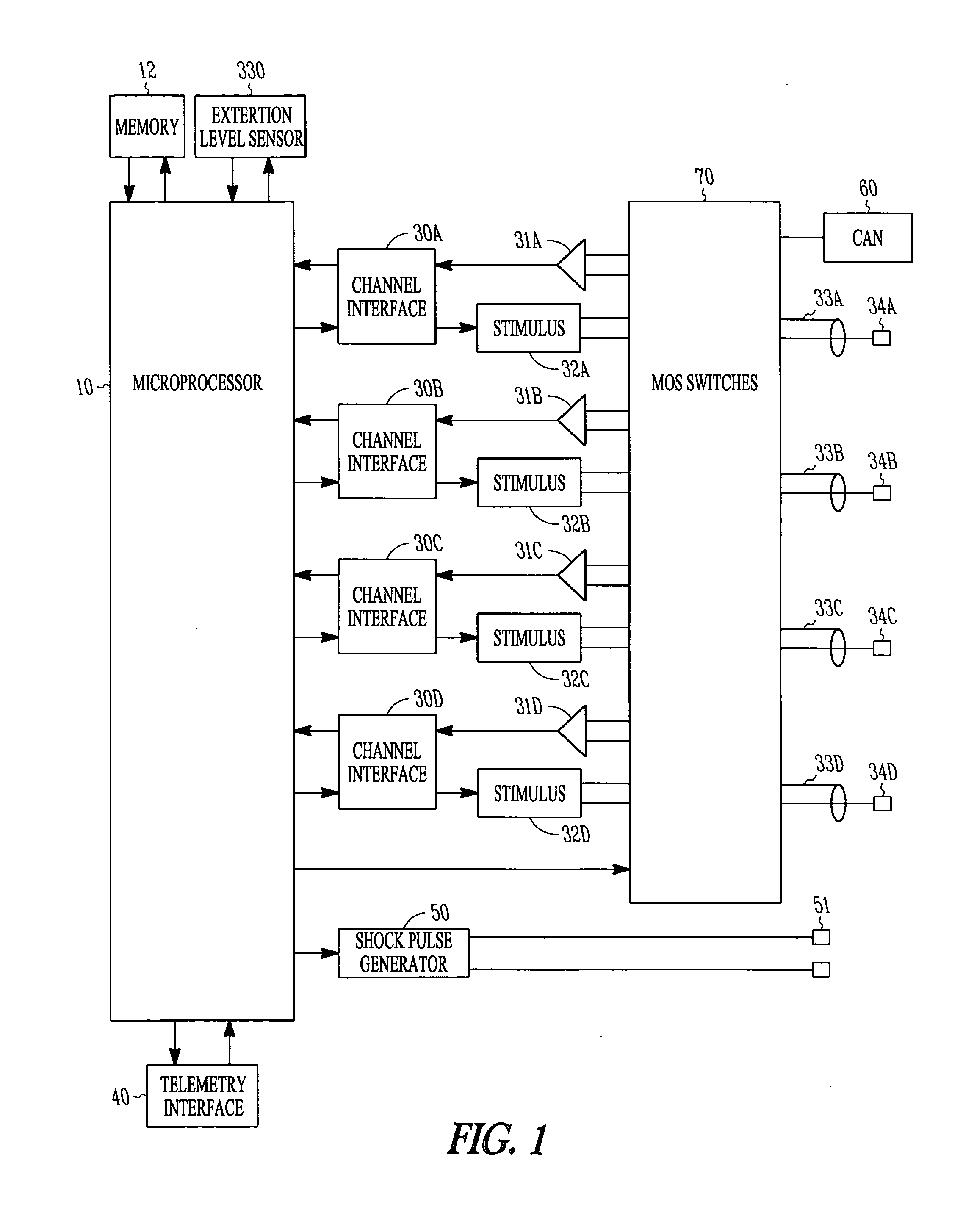
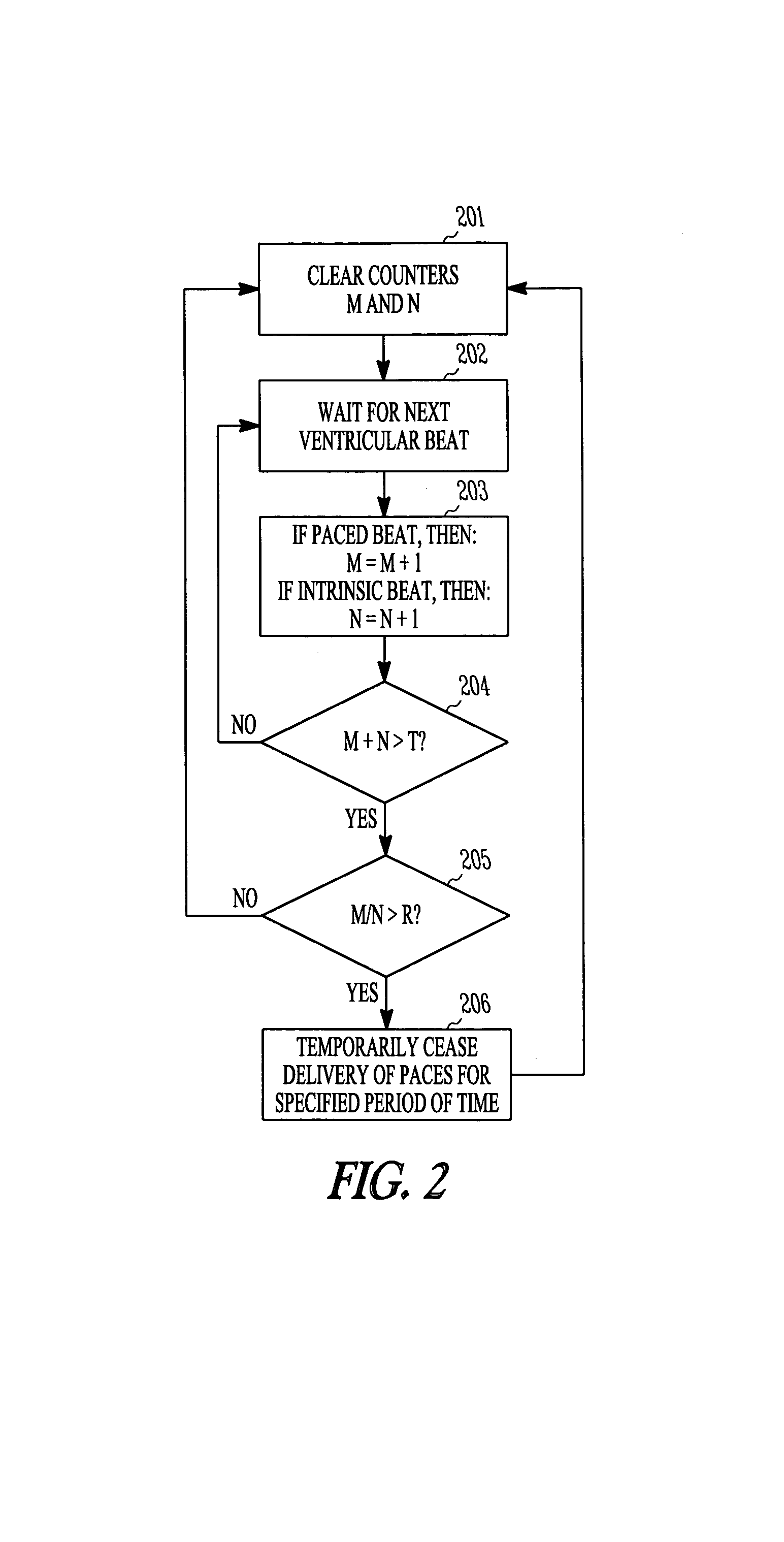
Pacing method and device for preserving native conduction system
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apex to aorta cannula assembly
ActiveUS7524277B1Reduce thrombosisEnsure sealing performanceBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesCannula insertionThrombus
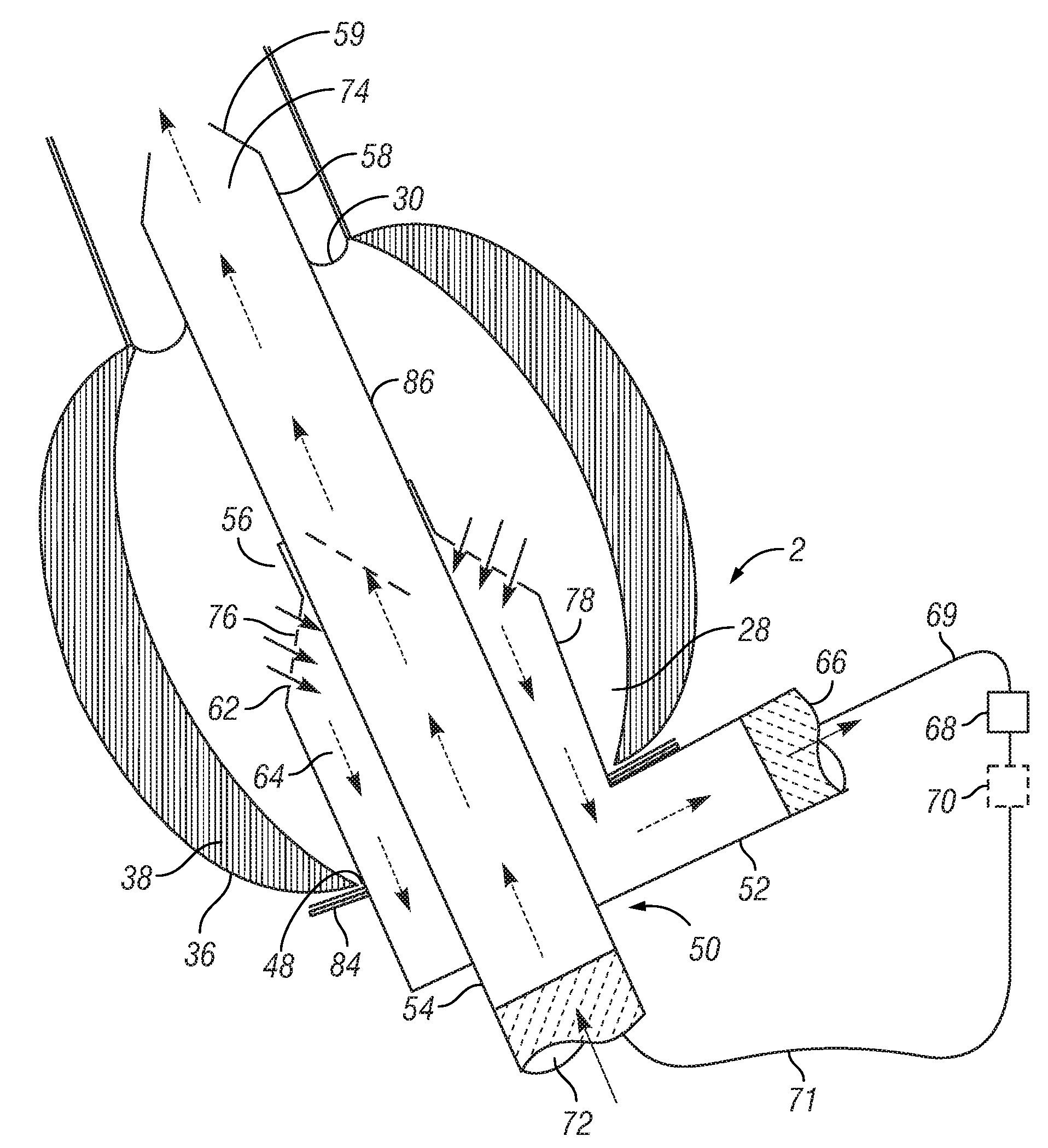
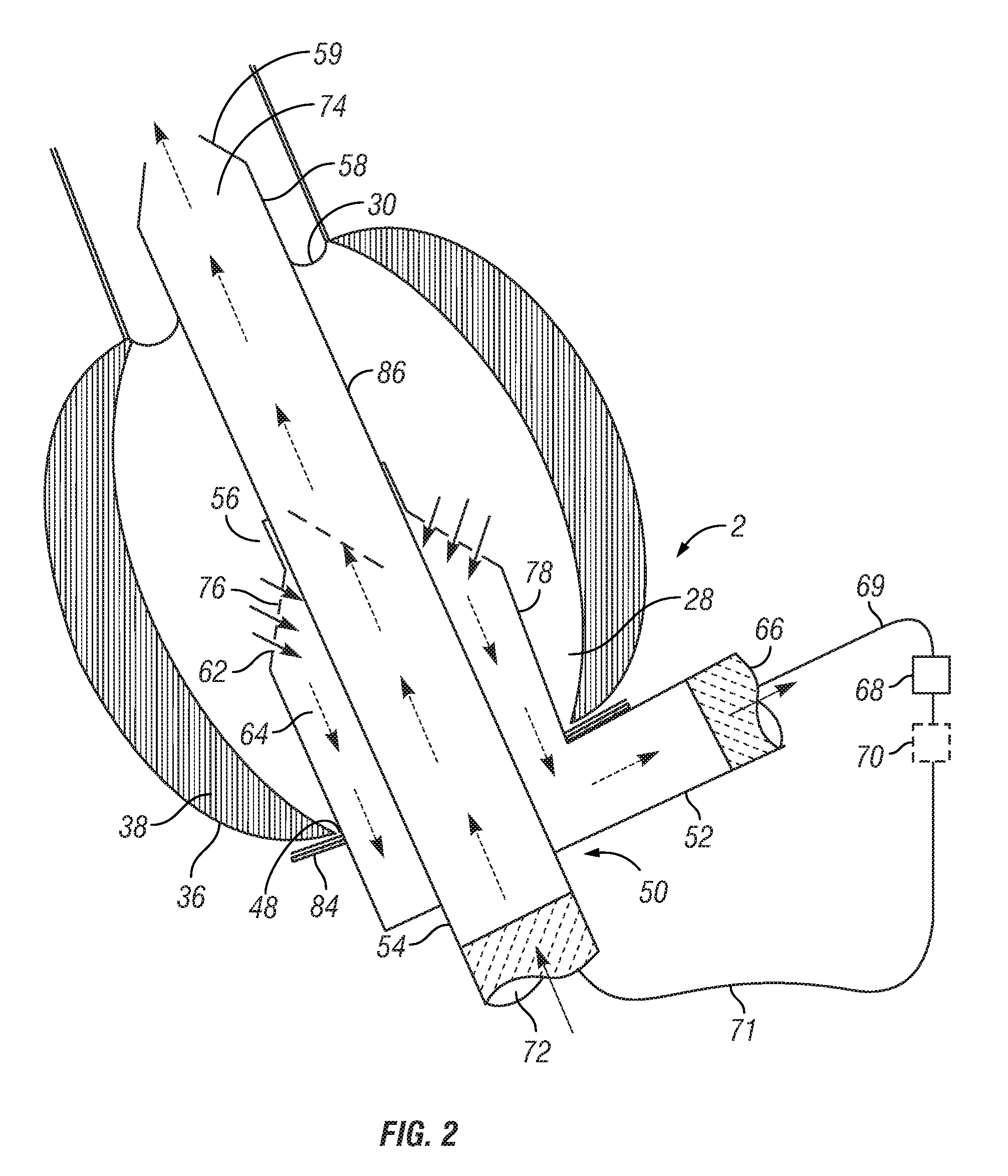
An apparatus, system, and method for assisting a heart in circulating blood that has been damaged, for example, by a myocardial infarction. In at least one aspect, an apparatus, system, and method are used for inserting a single cannula assembly comprising at least an inner and outer cannula into the left ventricle, advancing the inner cannula portion of the cannula assembly past the aortic valve, and into the aorta without requiring a secondary cannula insertion through an external portion of the aorta. In another aspect, an intraventricular assistant device (IVAD) having a motor and impeller can be inserted directly into the heart, such as in the left ventricle. The IVAD uniquely provides a pump within the heart through a single insertion that can reduce thrombosis and lessen the complexities typically associated with such efforts.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
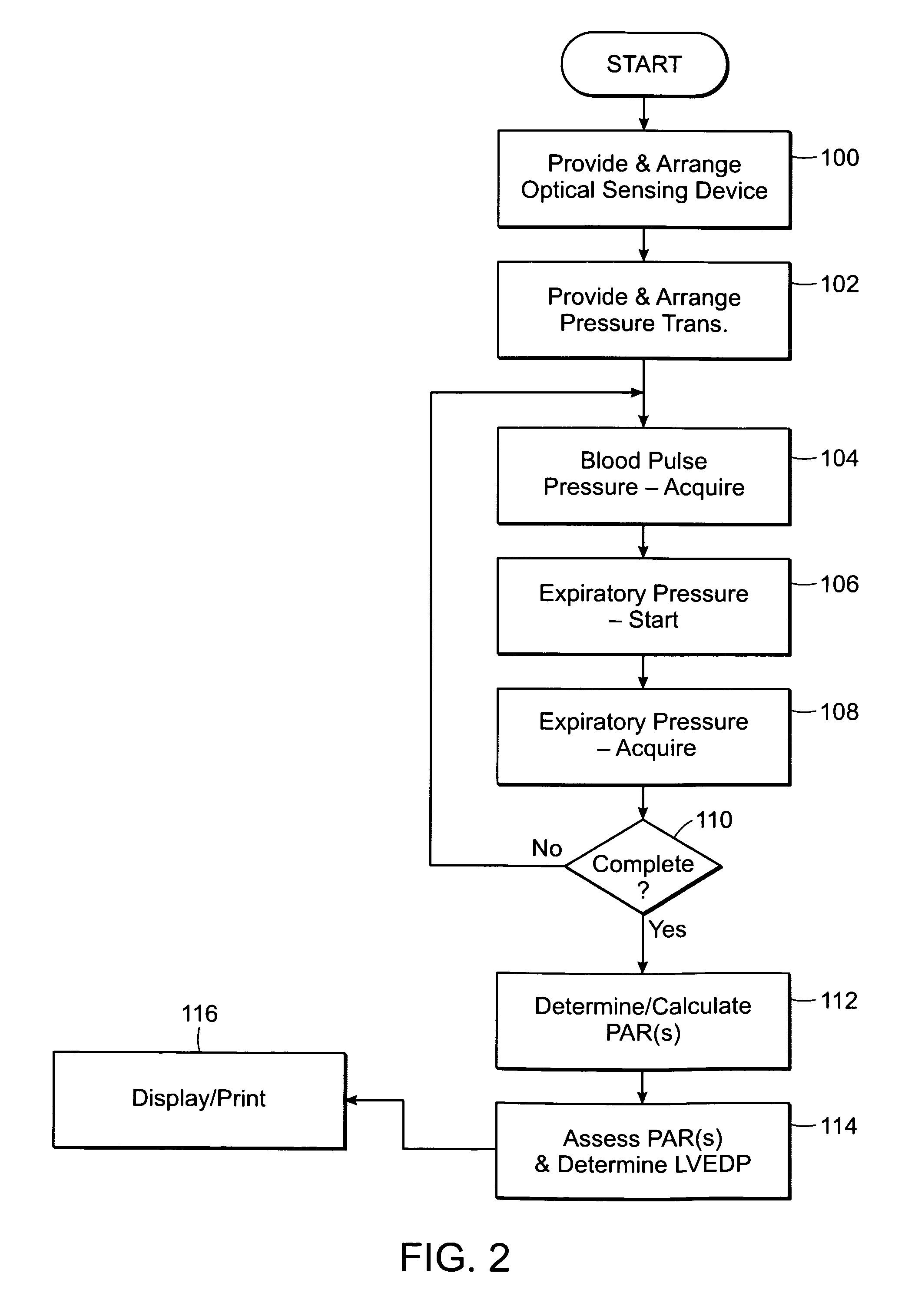
Non-invasive methods and systems for assessing cardiac filing pressure
ActiveUS20110245691A1Improve accuracyCentral arterial stiffnessEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterTransducerHeart/circulation
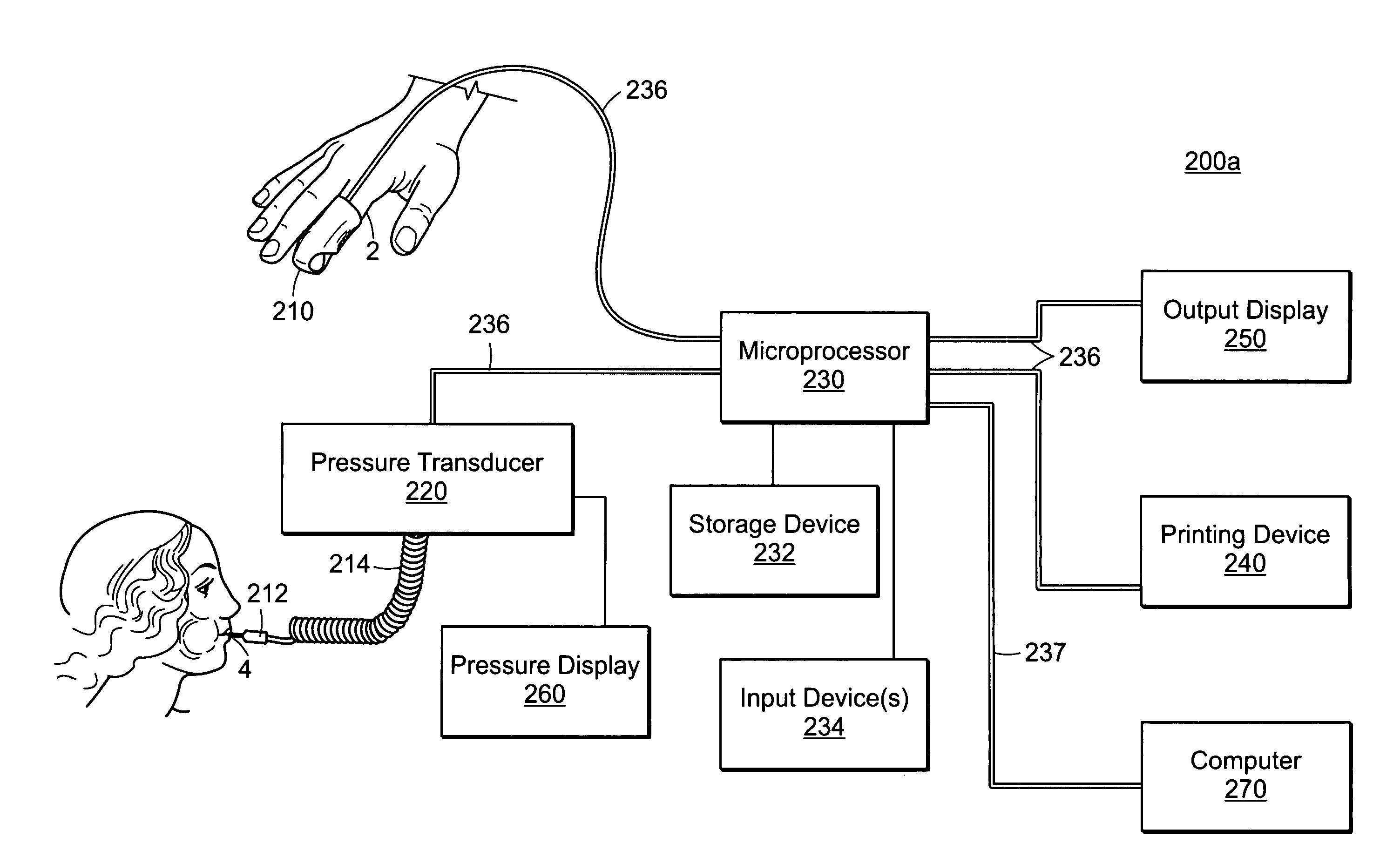
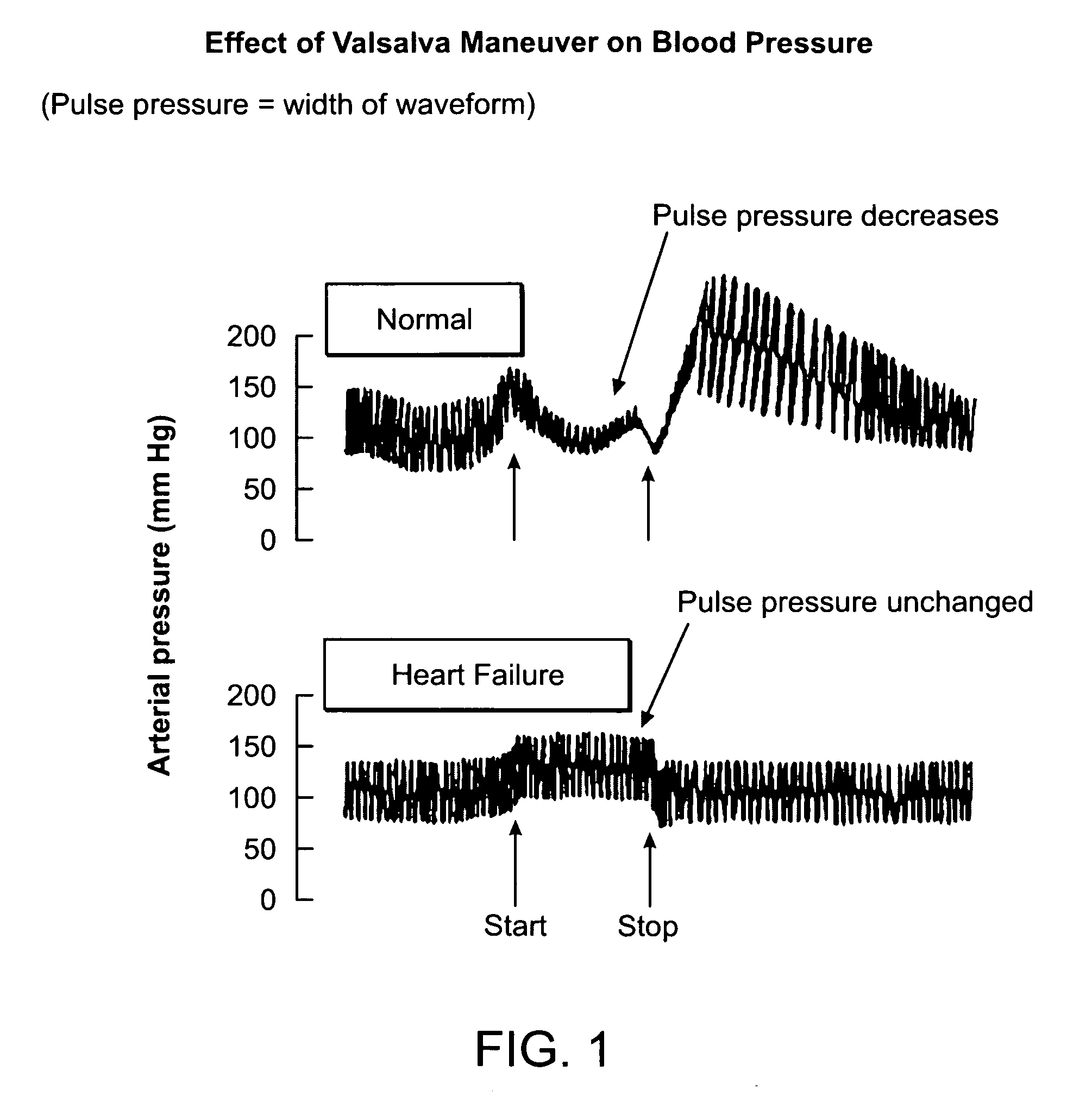
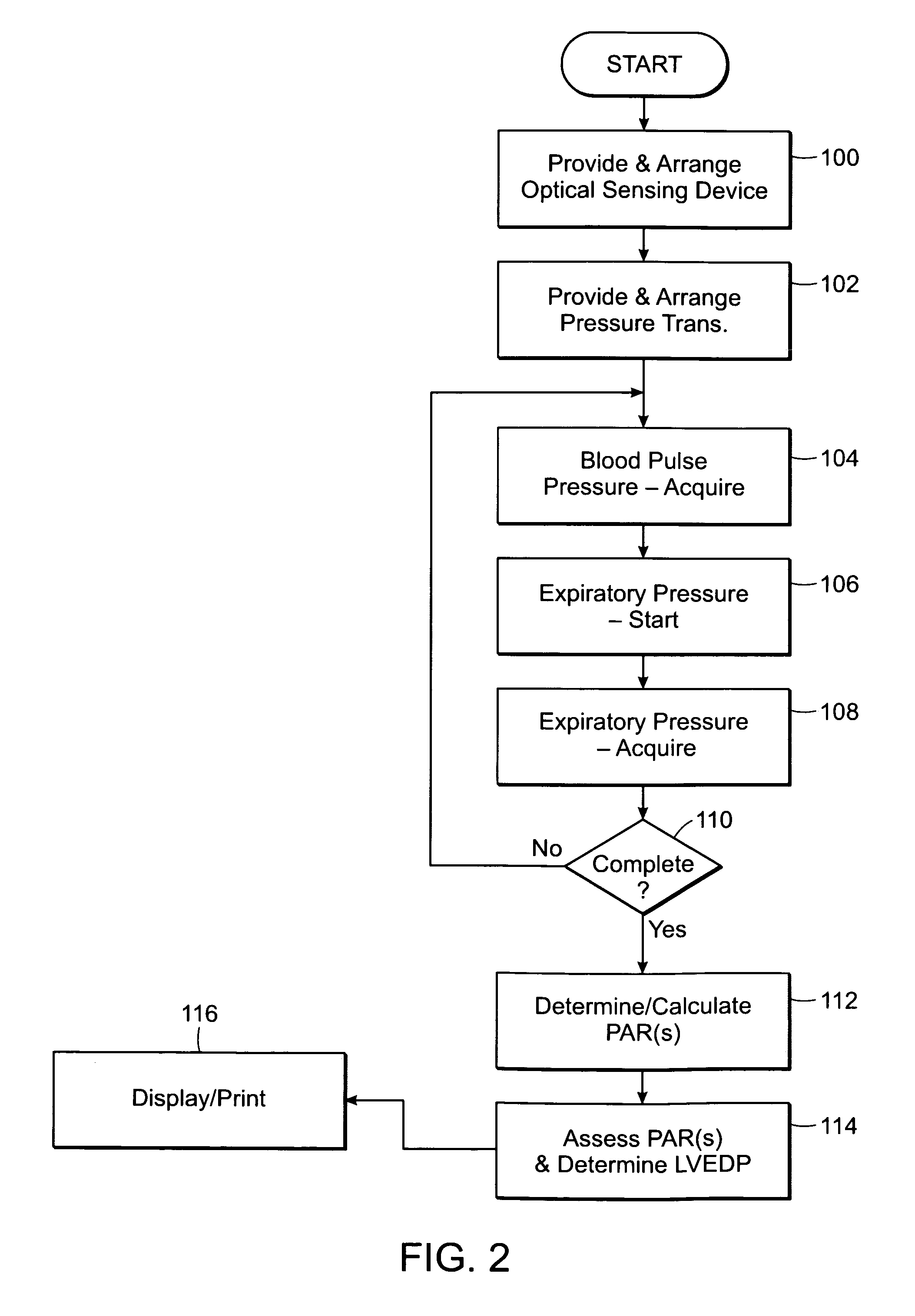
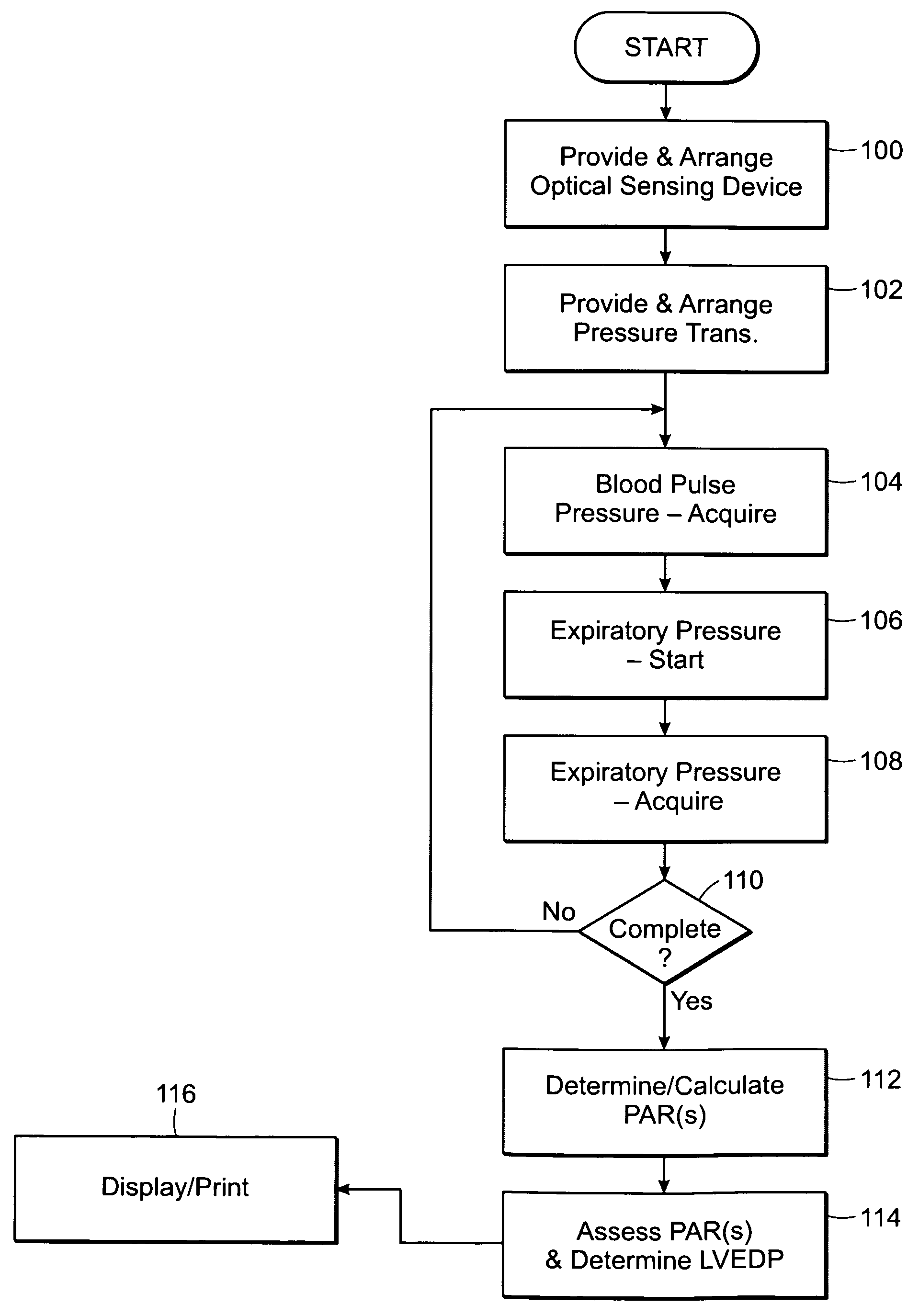
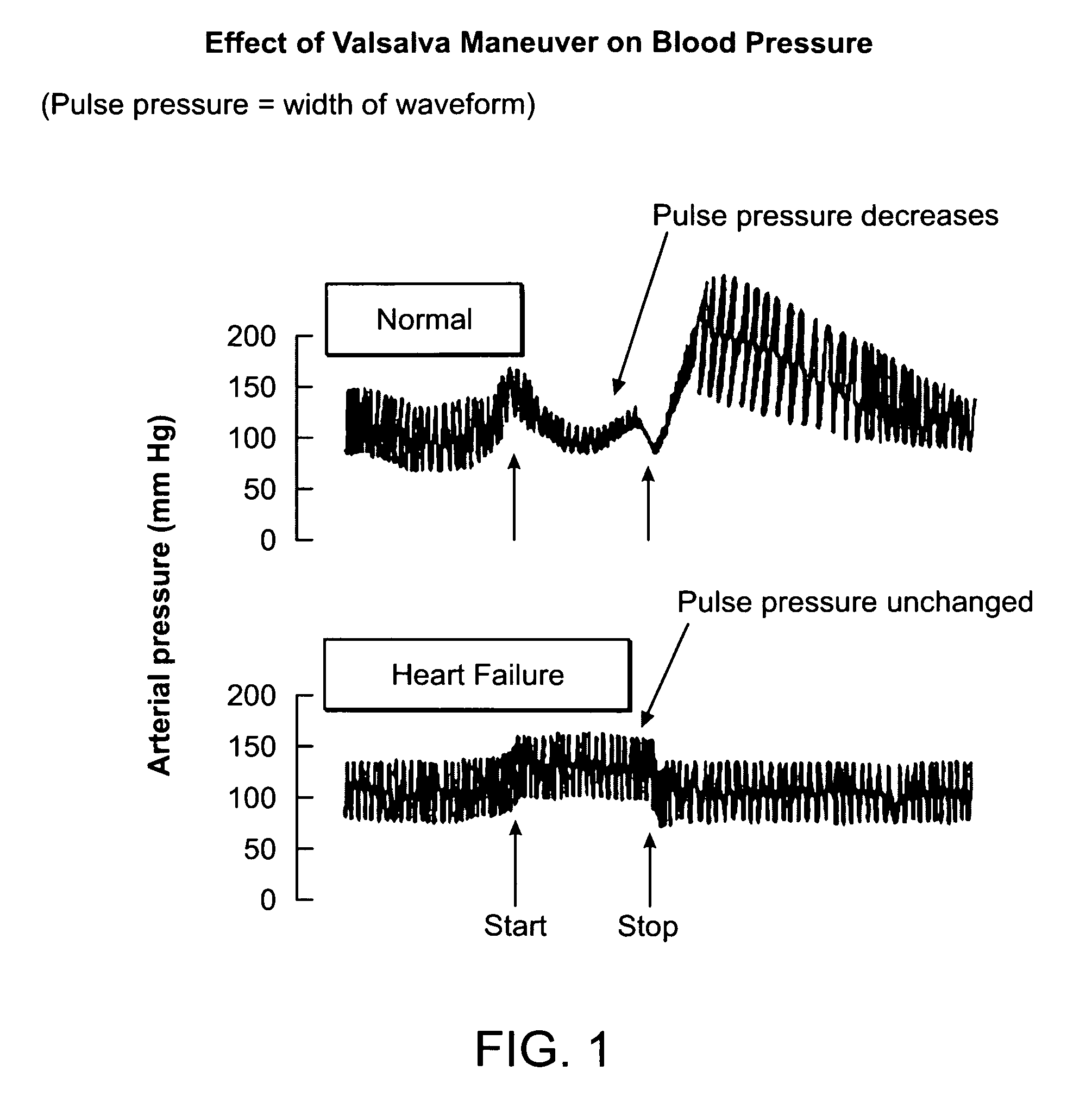
Featured are methods and systems for assessing cardiac filing pressure non-invasively. Such methods include, inter alia, arranging a photoplethysmography (PPG) transducer on a finger of a patient and fluidly coupling a pressure transducer to the patient's mouth so that the pressure transducer measures expiratory pressure. The PPG transducer provides an output of a pulse volume signal of cardiac circulatory flow. Such methods also including determining a pulse amplitude ratio, using the pulse volume near the end of the expiratory effort and a baseline pulse volume, and assessing the pulse amplitude ratio so as to determine a filing pressure condition for the heart of the patient.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Device for cardiocirculatory assistance
InactiveUS7367959B2Efficient and effective haematic flowImprove reliabilityFlexible member pumpsMedical devicesInterior spacePositive pressure
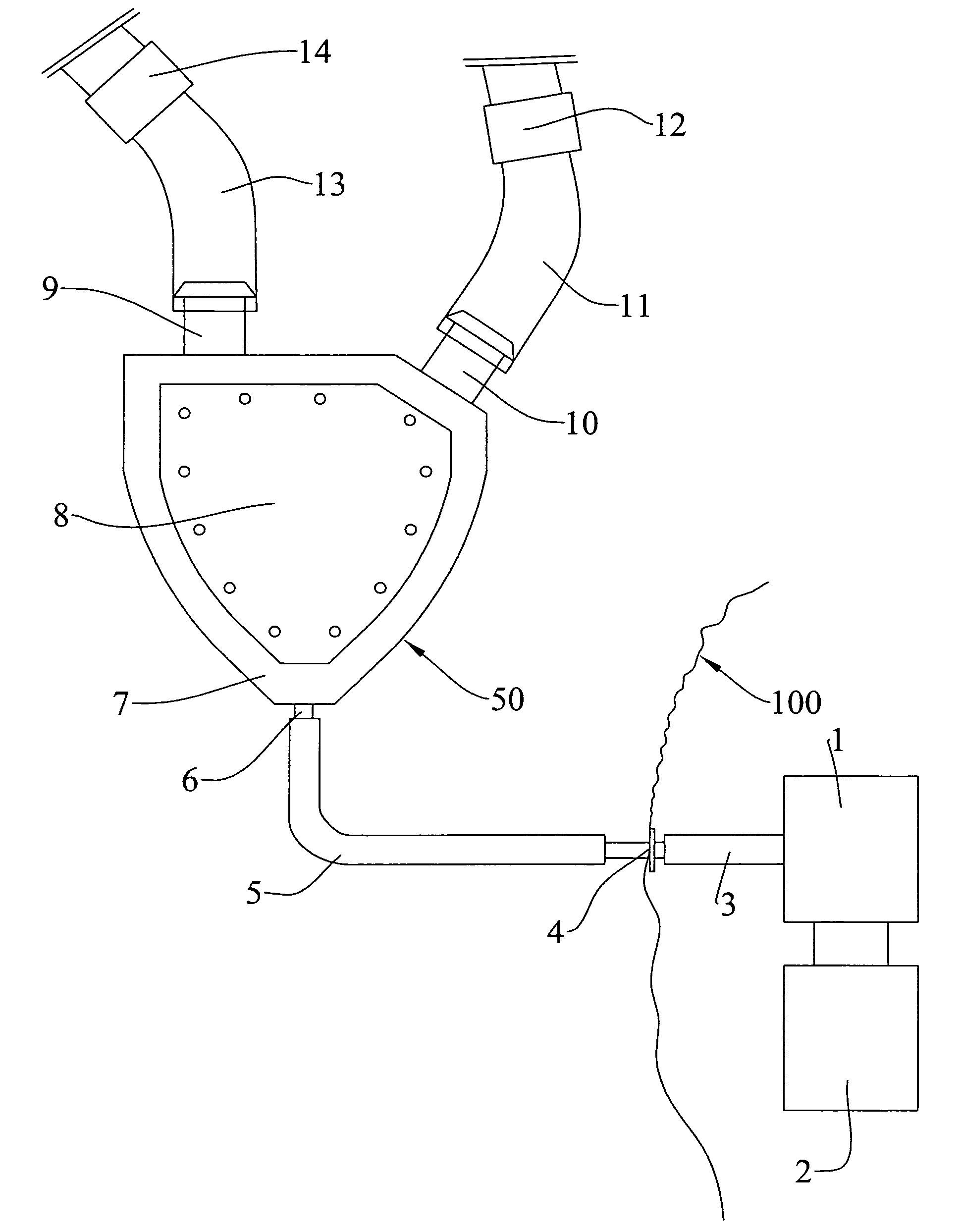
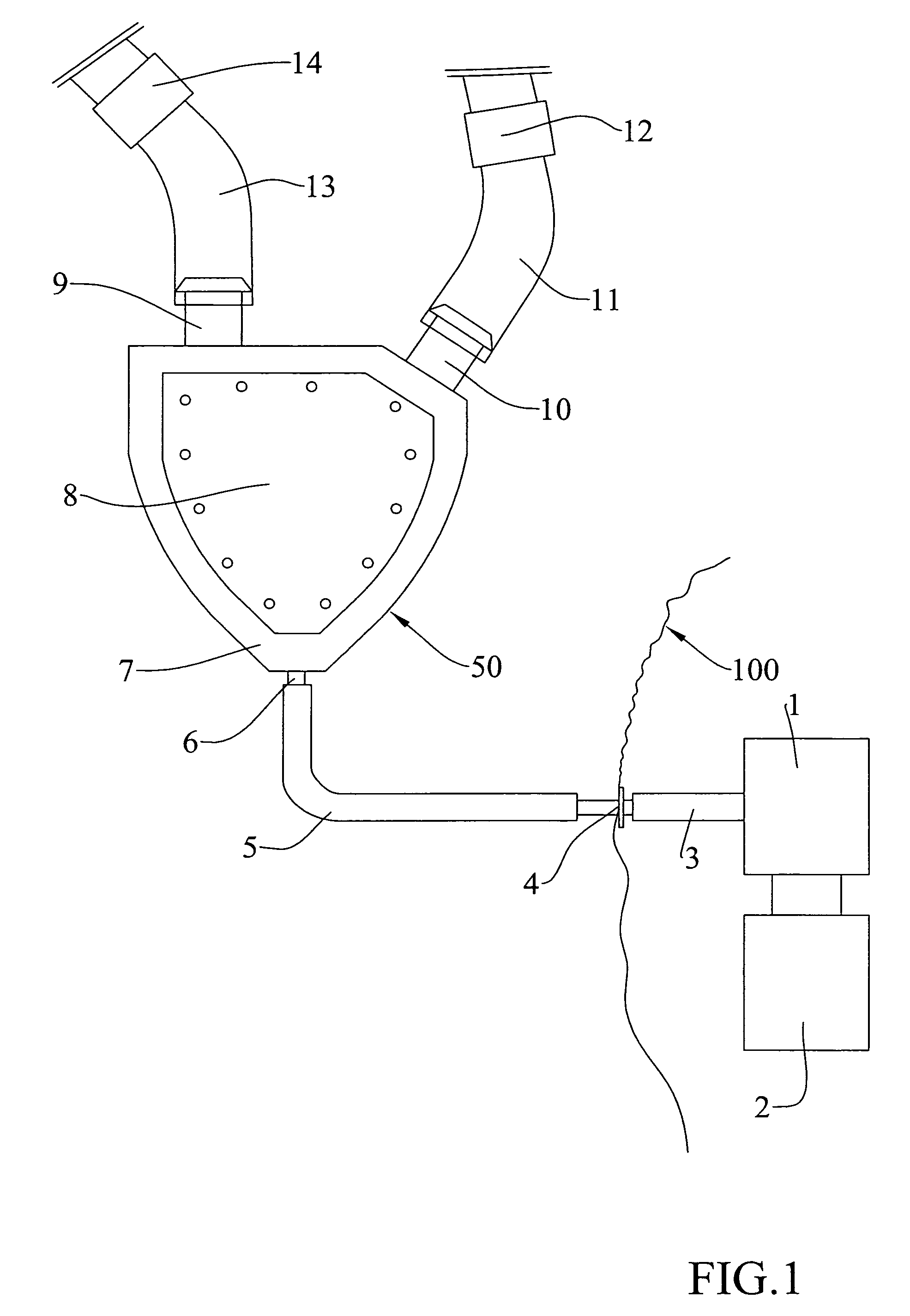
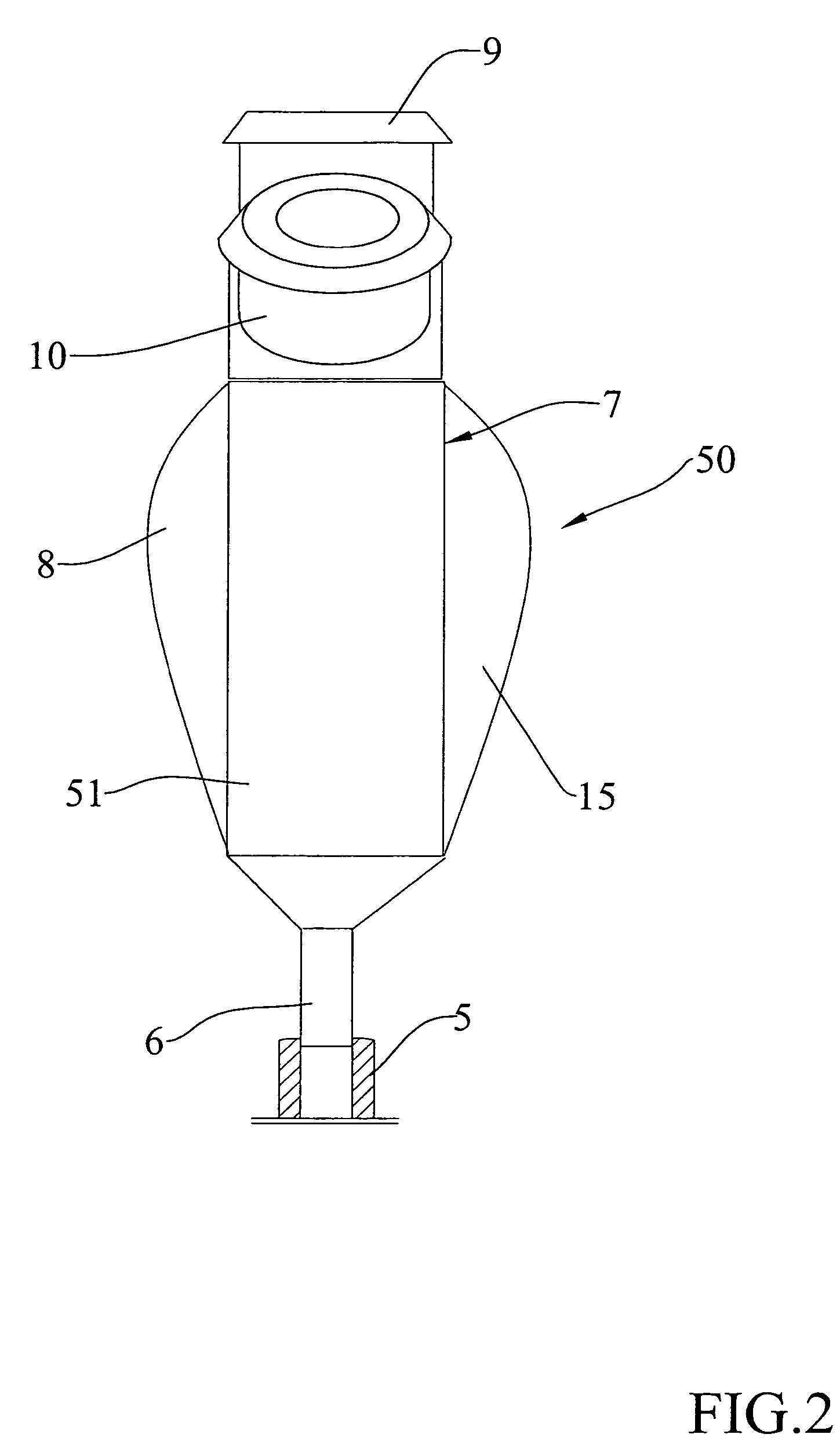
A device for cardiocirculatory assistance, also named a ventricular assist device, includes a haematic pump (50) with a pump body (7) having an inner space (21) defined by a rigid structure (51) and a pair of mobile membranes (16, 17) alternately driven in opposite directions by alternately positive pressure and negative pressure gas supplied to recesses (19, 20) surrounding the two membranes by means of an external pneumatic force generating unit (1). This device achieves excellent operation results while maintaining a reduced size and reduced weight.
Owner:A N B TECH
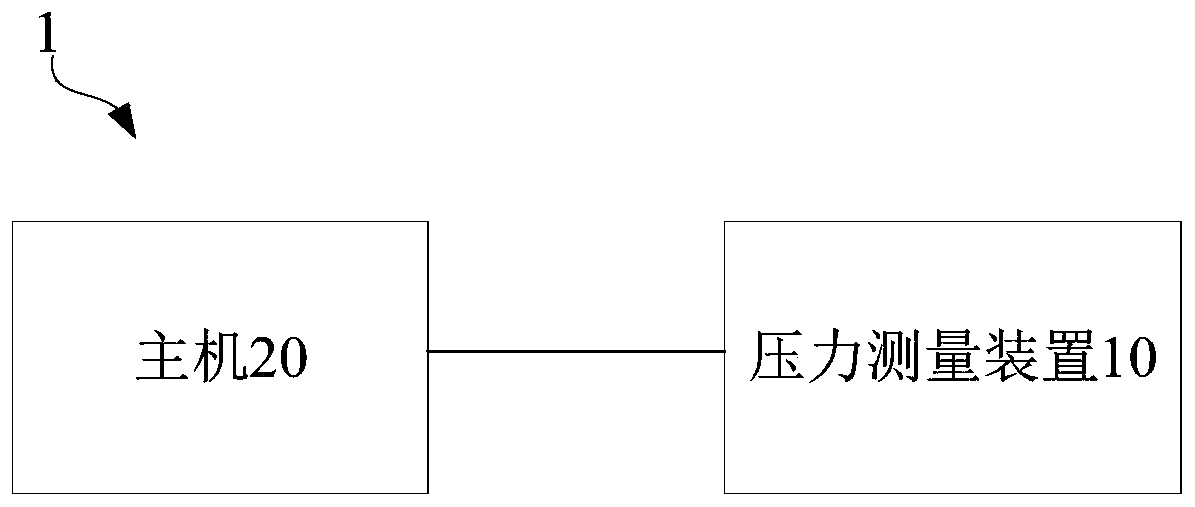
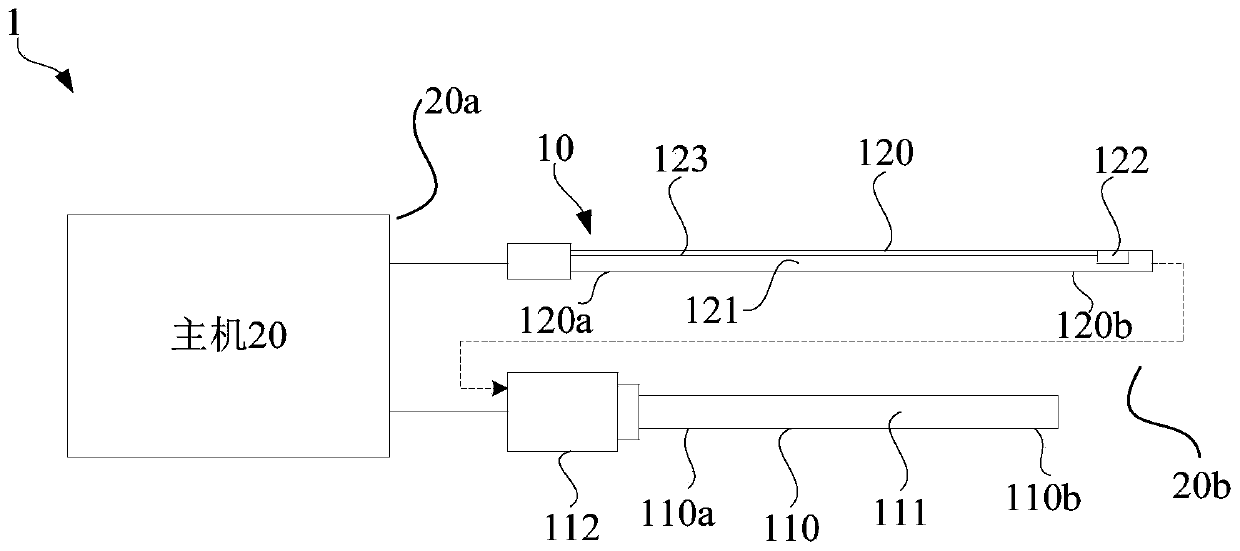
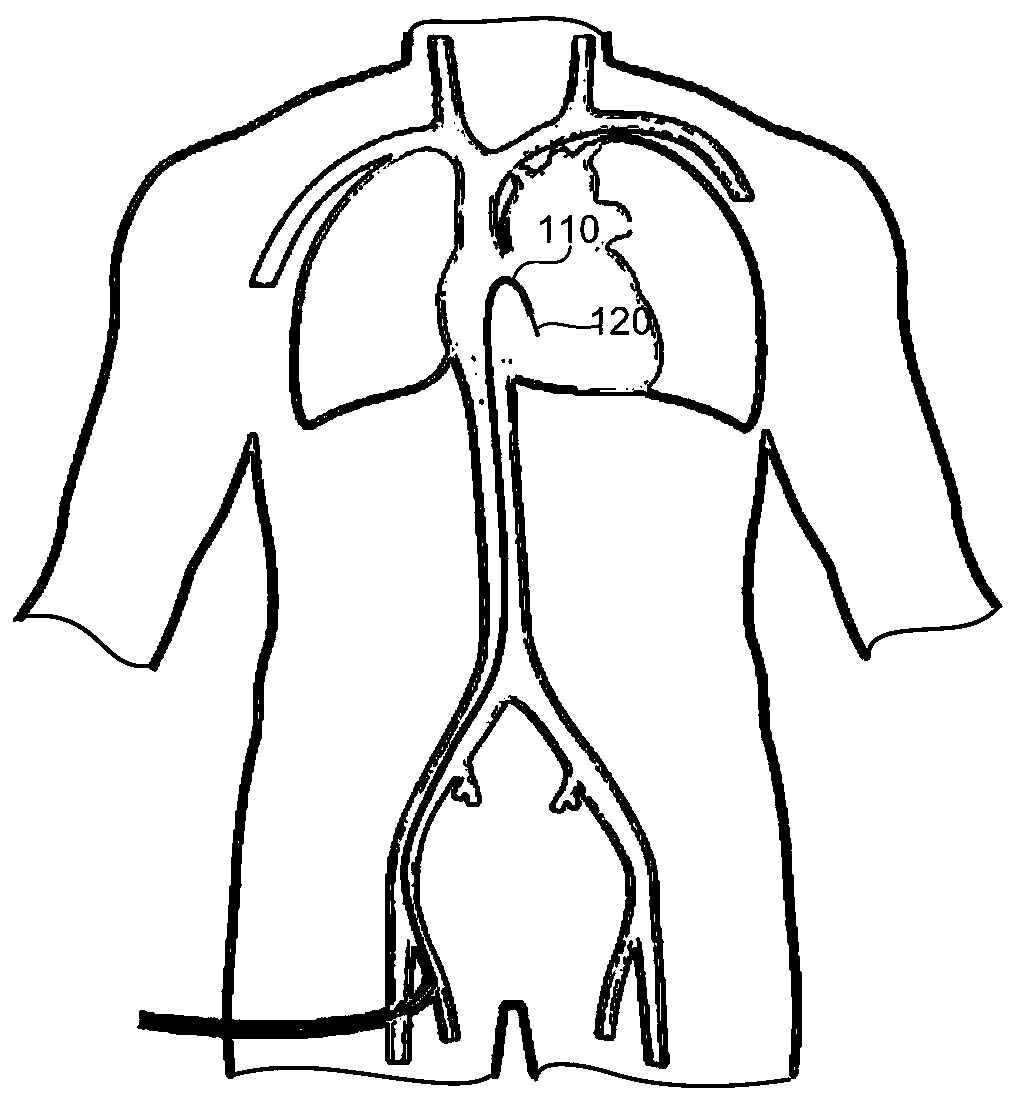
System and method for tracking cardiac cycle event by using blood pressure
The invention relates to a system for tracking a cardiac cycle event by using blood pressure. The system comprises a pressure measuring device and a host, wherein the pressure measuring device is configured to measure the pressure close to the proximal side in a blood vessel and the pressure far away from the proximal side in the blood vessel respectively and generate a first pressure signal and asecond pressure signal; the host is connected with the pressure measuring device and receives the first pressure signal and the second pressure signal; the host distinguishes various cardiac cycles based on the first pressure signal and the second pressure signal, calculates the ratio of the pressure value of the second pressure signal to the pressure value of the first pressure signal corresponding to the pressure value of the second pressure signal to obtain a pressure ratio value and generates a target pressure waveform; the host acquires a target derivative waveform based on the target pressure waveform, and determines a target period in any cardiac cycle based on the target derivative waveform, and thus, an average value of the corresponding pressure ratio value in the target periodis obtained; and the target period is a period in which the derivative value of the target derivative waveform in the cardiac cycle changes within a preset numerical range.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSIGHT MED CO LTD
Device and method for connecting a blood pump without trapping air bubbles
An apparatus and a method for connecting medical tubing or any other type of fluidic circuit conduits (e.g., cannulae) to a ventricular assist device (“VAD”) or any other pumping device used for blood pumping during cardiac circulatory support for vascular surgery. The apparatus and the method prevent air bubbles from entering a cardiac circulatory support system when connecting cannulae to a VAD that may later enter the blood stream of a patient during cardiac surgery, and also provide for purging any air bubbles that may have entered the cardiac circulatory support system during a cannulae-VAD connection.
Owner:VITALMEX INT DE C V
In-vitro minimally invasive bionic circulation assistance system and control method thereof
InactiveCN106237409AOvercome the disadvantage of slow switching speedCirculatory blood flow is equalOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesHeart/circulationArtificial Ventricle
The invention provides an in-vitro minimally invasive bionic circulation assistance system and a control method thereof, and relates to the field of heart assistance circulation. The system comprises an artificial heart ventricle and an artificial atrium, the artificial atrium is connected with a blood inlet tube, the blood inlet tube is provided with a one-way valve, the artificial heart ventricle is connected with the artificial atrium through an artificial atrioventricular valve and connected with a blood outlet tube through an artificial aortic valve, and the outer wall of the artificial ventricle and the outer wall of the artificial atrium are provided with a first diastolic and systolic device and a second diastolic and systolic device respectively. By arranging the diastolic and systolic devices on the outer wall of the artificial ventricle and the outer wall of the artificial atrium respectively, the artificial ventricle and the artificial atrium are diastolic and systolic or systolic and diastolic simultaneously, switching is quickly completed in a short time through the mechanical acting force, and then a real heart circulation system is simulated; the defect that the states of hydraulic driving are switched slowly is overcome.
Owner:ANHUI TONGLING BIONIC TECH CO LTD
Cardiocirculatory aiding device
InactiveUS20070004960A1Simple processMaximum performance guaranteeIntravenous devicesBlood pumpLeft ventricular sizeBlood pump
Cardiocirculatory aiding device, as hematic pumping device able to aid the right or left ventricular or biventricular of the human body, characterised by being supplied by gas pneumatic energy, in which: i) the variation of pressure generator device systems is intended for being placed outside of the human body; ii) the pumping device of the blood (P), is conceived to be installed inside of the human body; iii) the two said devices (i,ii) are connected with at least one tubular duct of transmission of said gas, passing from the inside of the human body to the external of the same; iv) said pumping device of the blood (P) being driven by the variation of pneumatic pressure in said duct by means of two opposite expansible and retractable lungs that compress a central chamber body elastically yielding by pulses in order to cause, by means of two ducts respectively of blood entry and blood exit with unidirectional valves, the pumping of the blood.
Owner:ABM HEART TECH
Method and medical apparatus for measuring pulmonary artery blood flow
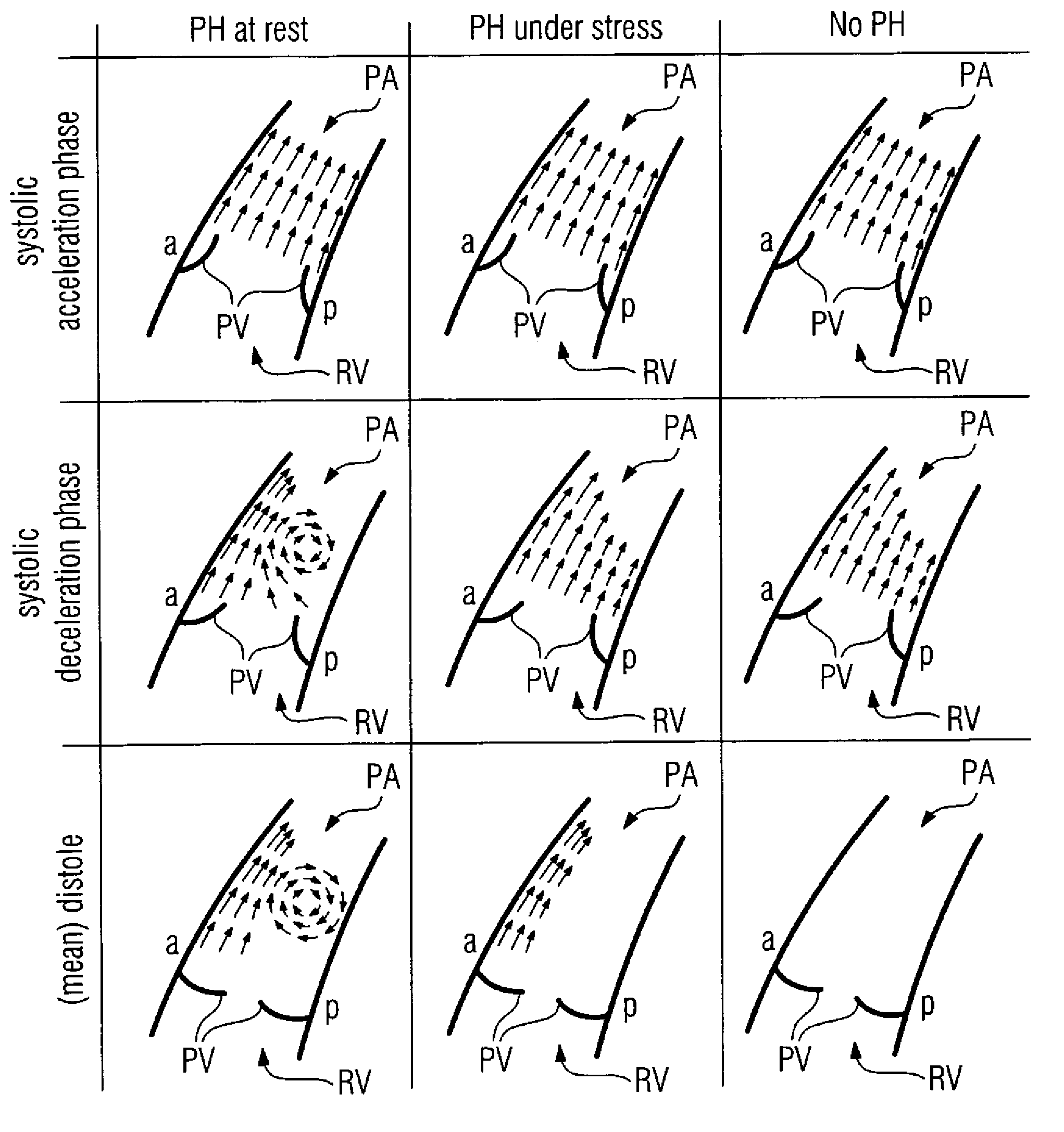
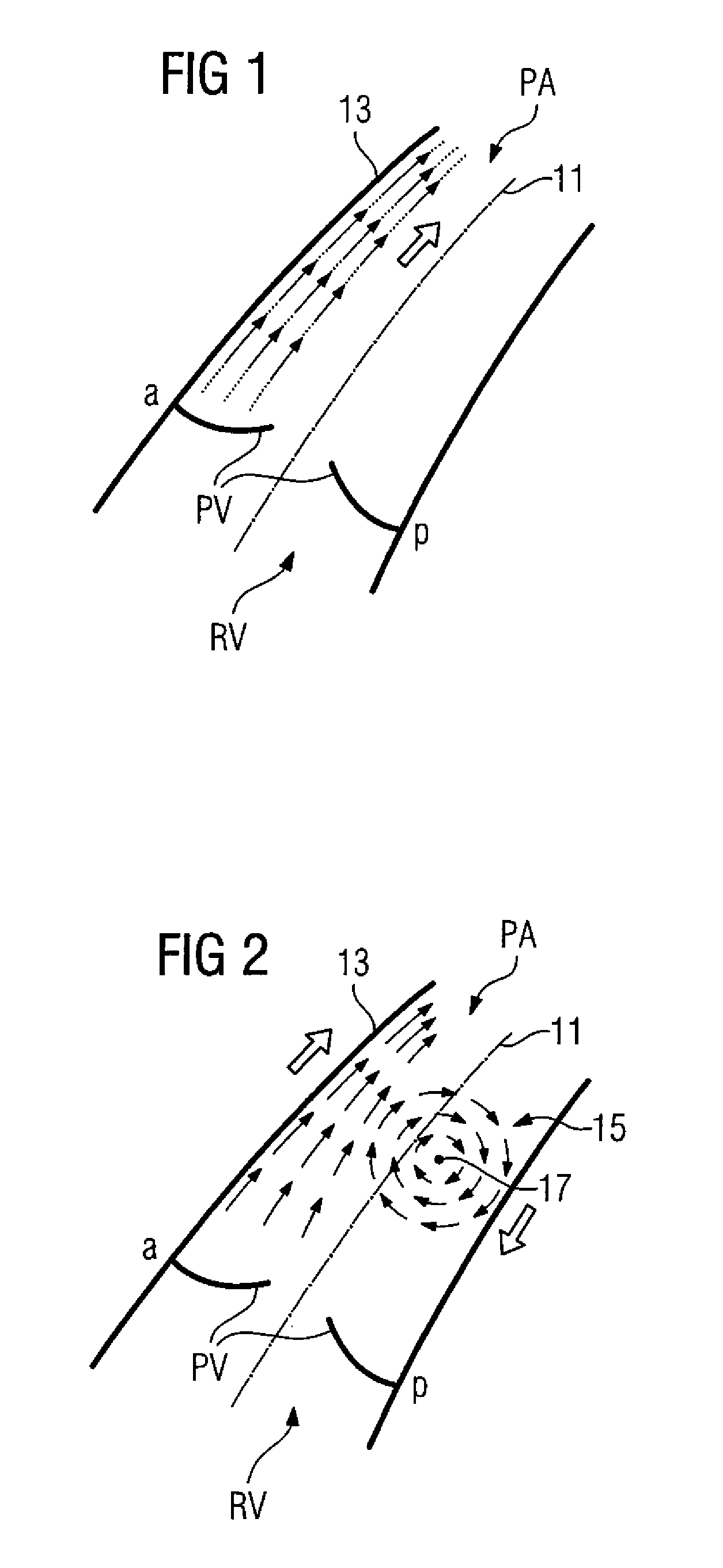
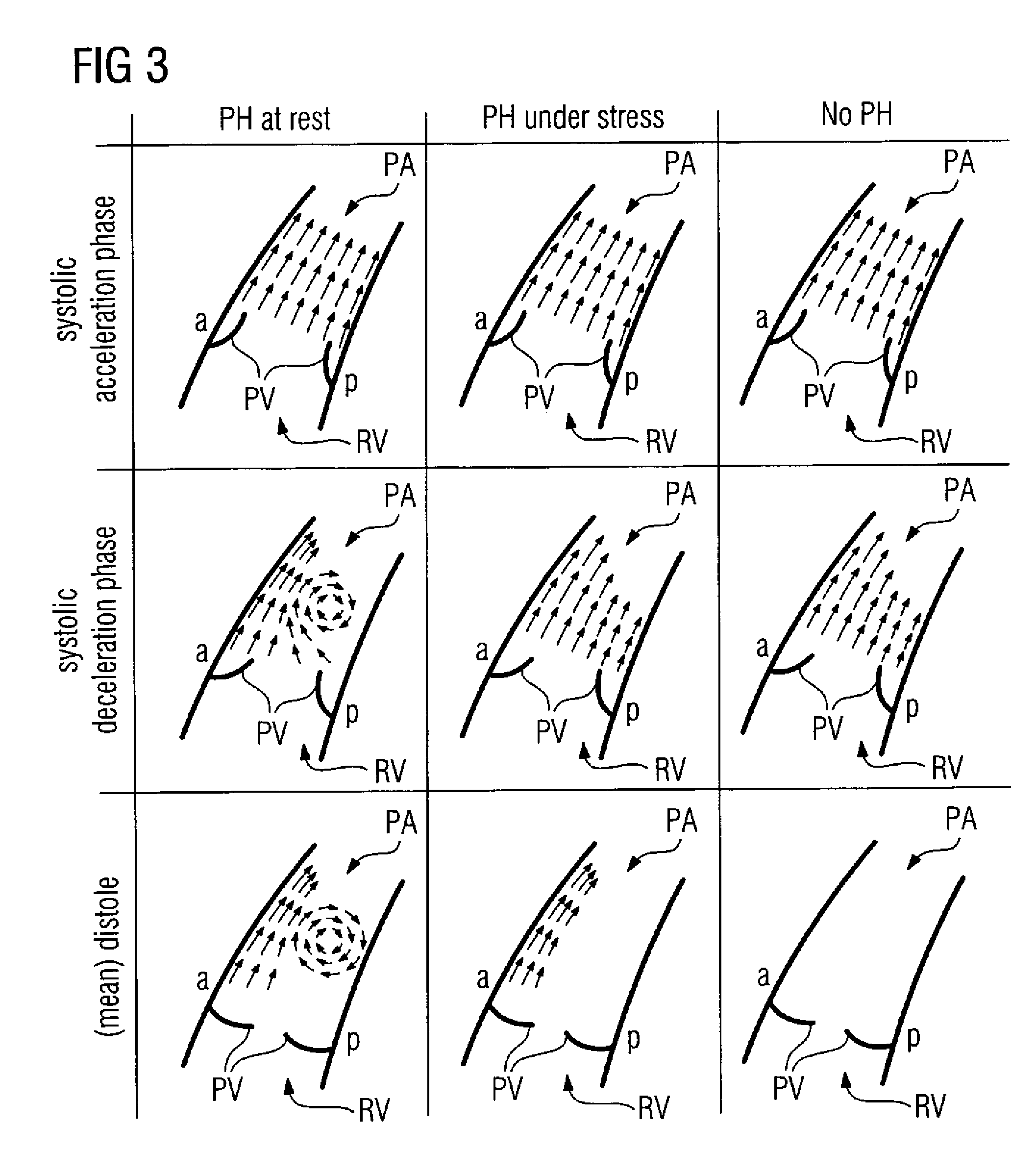
ActiveUS8050737B2Reliable supportImprove securityBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsCardiac cycleHeart/circulation
In a method and apparatus for examination and evaluation of a blood flow in a pulmonary artery of a patient, measurement data are recorded, from which at least a part of the blood flow in the pulmonary artery is able to be re-constructed at least two-dimensionally in a plane defined by a longitudinal axis of the pulmonary artery and by an anterior-posterior direction, including at least at several diastolic points in time in the course of a heart cycle, after a closure of the pulmonary valve. The number of diastolic points for which an asymmetry in relation to the longitudinal axis of the pulmonary artery in the anterior-posterior direction exists is determined. A measure is then determined that characterizes how long, after the closure of the pulmonary valve, the aforementioned asymmetry exists.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for Assessing The Functional Condition Of Cardiovascular System
InactiveUS20080287811A1Easy to optimizeEasy to operateEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterNervous systemCardiac cycle
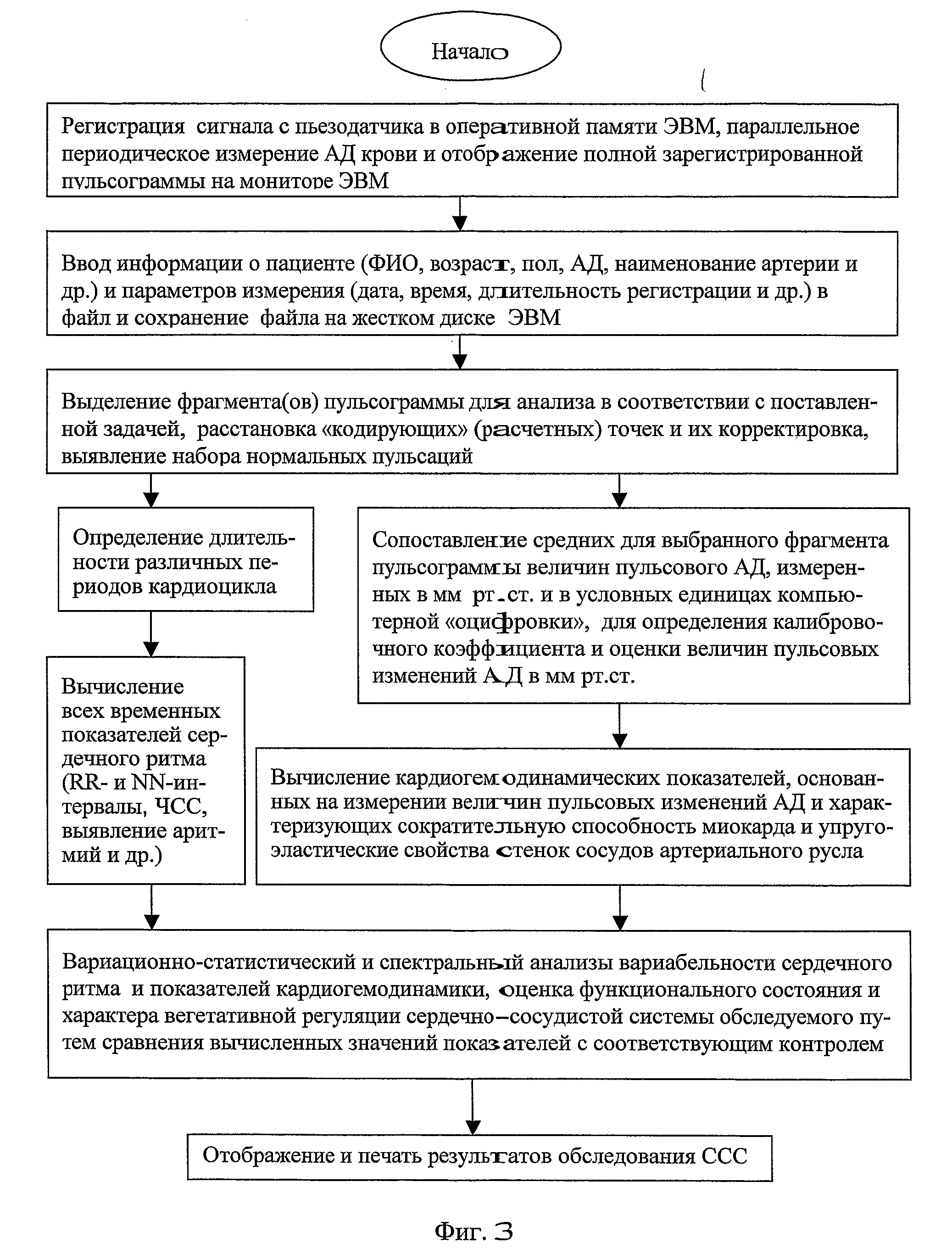
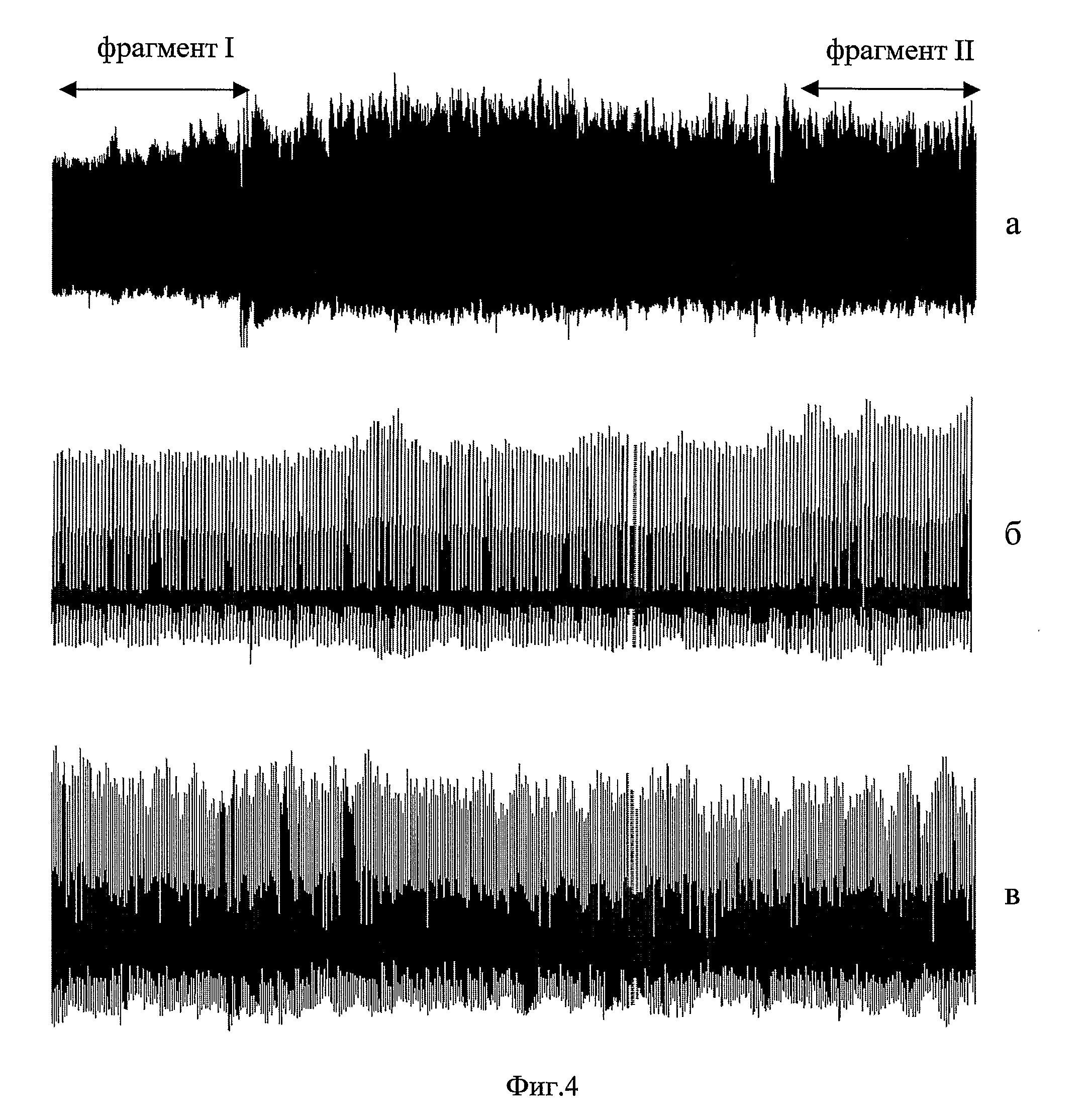
The invention relates to medicine, namely: to cardiology, and may be used for assessment of functional condition of the human cardiovascular system (CVS) and the character of its control by the autonomic nervous system and other regulatory systems of the homeostasis. A method of non-invasive examination of the human CVS was developed, the method enabling to continuously, during a necessary period of time and quite simply with the aid of a computer and a piezoceramic tranducer (FIG. 3), record differential sphygmograms (FIG. 4) and by these sphygmograms using the method of determining the “coding” points to perform express-analysis simultaneously of two main pulse characteristics: a) rhythmicity and b) pulse oscillation of the arterial pressure (AP). The automatic disposition of the “coding” points in the averaged graph of the cardiocycle and their additional visual correction (FIG. 5) guarantee precision of determining the amplitude-temporal parameters at each recognised normal pulsation of a selected pulsogram fragment. By this fragment, the cardiac rhythm and all the amplitude-temporal cardiohemodynamic parameters will be measured and analysed, the parameters characterising the left ventricle myocardium contractile capacity as well as the resilient-elastic properties of the arterial bed vessel walls. For this purpose, the conventional units of the computer “digitizing” will be calibrated and transformed into accepted units of the blood AP measurement (mm Hg) and then, by means of integrating by respective areas of the cardiocycle graphs, the values of the blood AP pulse increment will be determined for different stages of the cardiac cycle. The continuous monitoring of the pulsogram parameter changes provides fulfillment of spectral analysis of the cardiac rhythm variability as well as of the selected cardiohemodynamic parameters. By results of the statistical and spectral analyses of the measured parameters' variability, the functional condition and the character of the subject's CVS vegetative regulation will be assessed by comparing the obtained values with the average statistical numerical values of these same parameters established for the CVS of groups of people who were selected as control subjects. The results may be used for resolving the problems of differential diagnosis of the cardiovascular diseases under clinical conditions, for individual examination of patients as well as for performing an operative medical checkup of health condition in various groups of population.
Owner:NESTEROV VLADIMIR PETROVICH +2
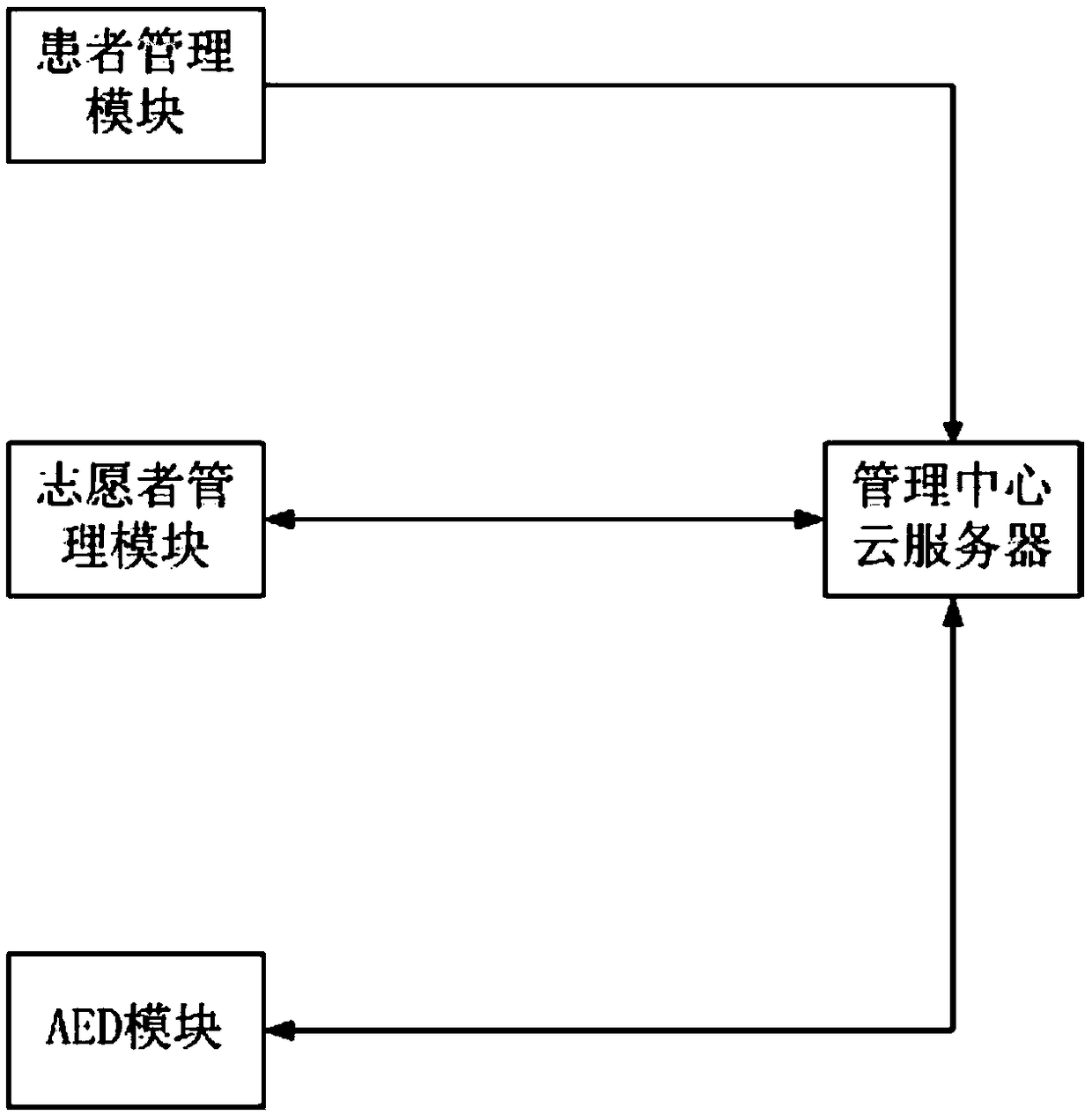
AED scheduling management system and AED scheduling management method
InactiveCN109273076ATemporarily maintain brain and heart circulation functionMaintain brain and heart circulationMedical communicationHealthcare resources and facilitiesApproaches of managementHeart/circulation
The invention discloses an AED scheduling management system and an AED scheduling management method. According to the invention, patients, volunteers and AEDs are subjected to unified management; whena patient calls for help, a plurality of volunteers and AEDs closest to the patient can be found, and navigation information can be provided, such that the volunteers and the AEDs can reach the position of the patient in the shortest time so as to improve the success rate of the treatment; particularly in the case of the multiple volunteers, the first volunteer can be instructed to directly reachthe position of the patient to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation so as to temporarily maintain the brain and heart circulation functions, and the second volunteer is notified to take the AED, andthen goes to the position of the patient so as to get the most rescue time for the patient; and the system has advantages of automated operation, unattended mode, intelligent scheduling and efficientoperation.
Owner:王冬梅
Endovascular apparatus for perfusing organs in a body
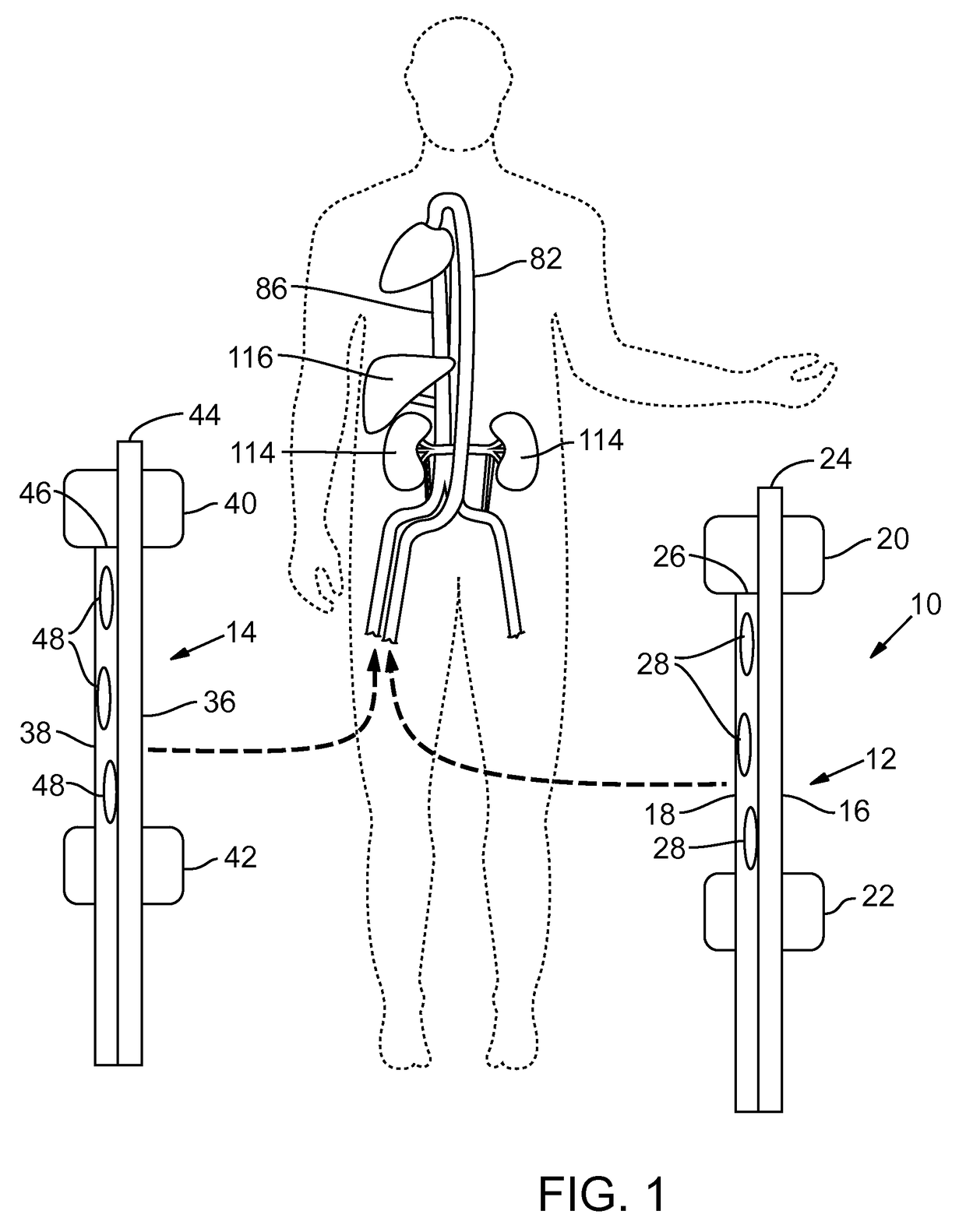
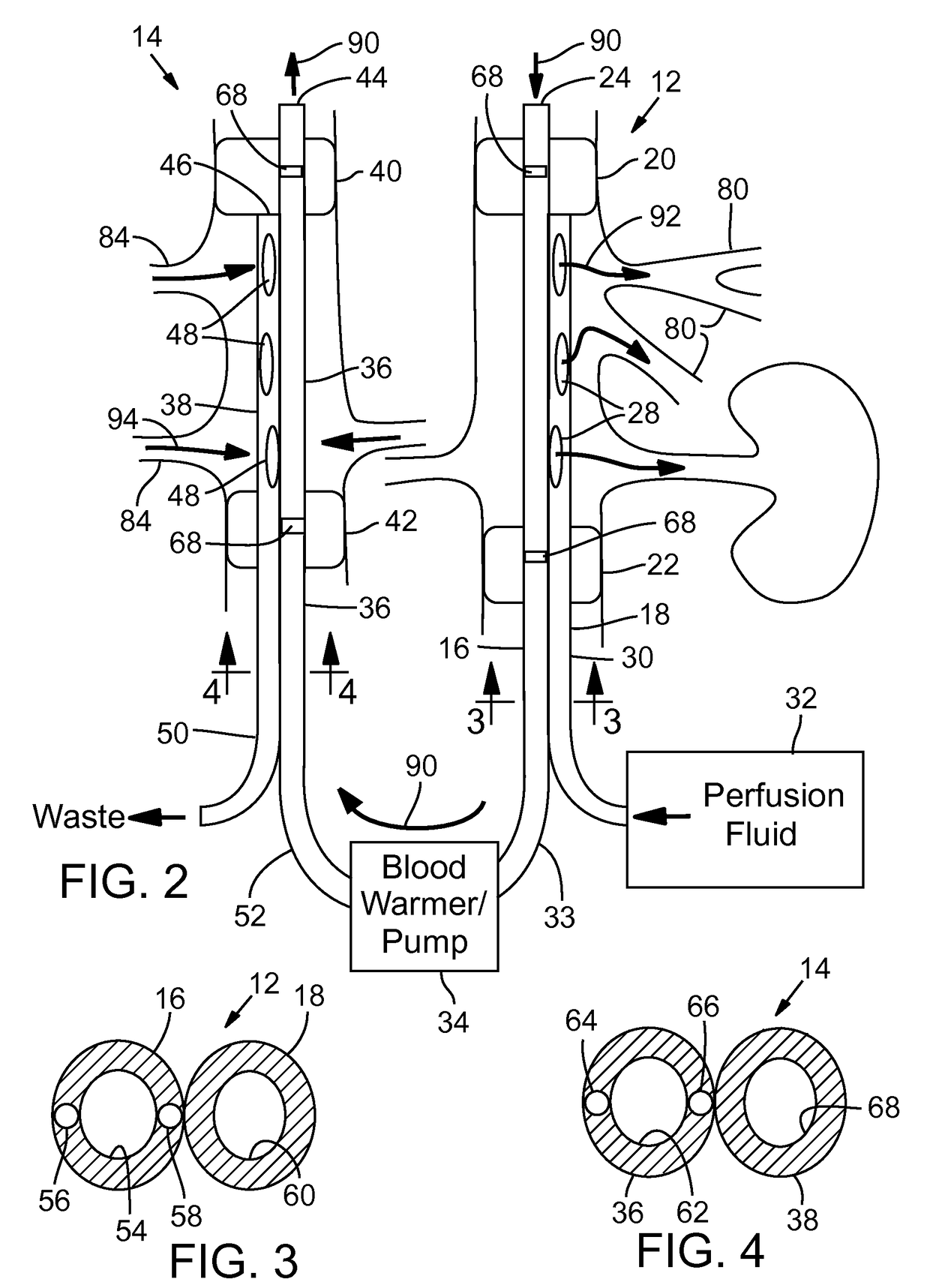
ActiveUS20170164605A1Minimizing warm ischemia timePreserve organ functionBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesHeart/circulationBlood circulating
In one representative embodiment, a method of perfusing organs in a patient's body is provided. The method comprises isolating the visceral arteries and the visceral veins from blood circulating through the patient's heart and perfusing the visceral arteries, the visceral veins, and the abdominal organs with a perfusion fluid that is fluidly separated from the blood circulating through the patient's heart. While the visceral arteries and the visceral veins are isolated, and the visceral arteries, the visceral veins, and the abdominal organs are being perfused, the patient's blood is allowed to continue to circulate through the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Non-invasive methods and systems for assessing cardiac filling pressure
ActiveUS9549678B2Improve accuracyCentral arterial stiffnessEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterHeart/circulationNon invasive
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
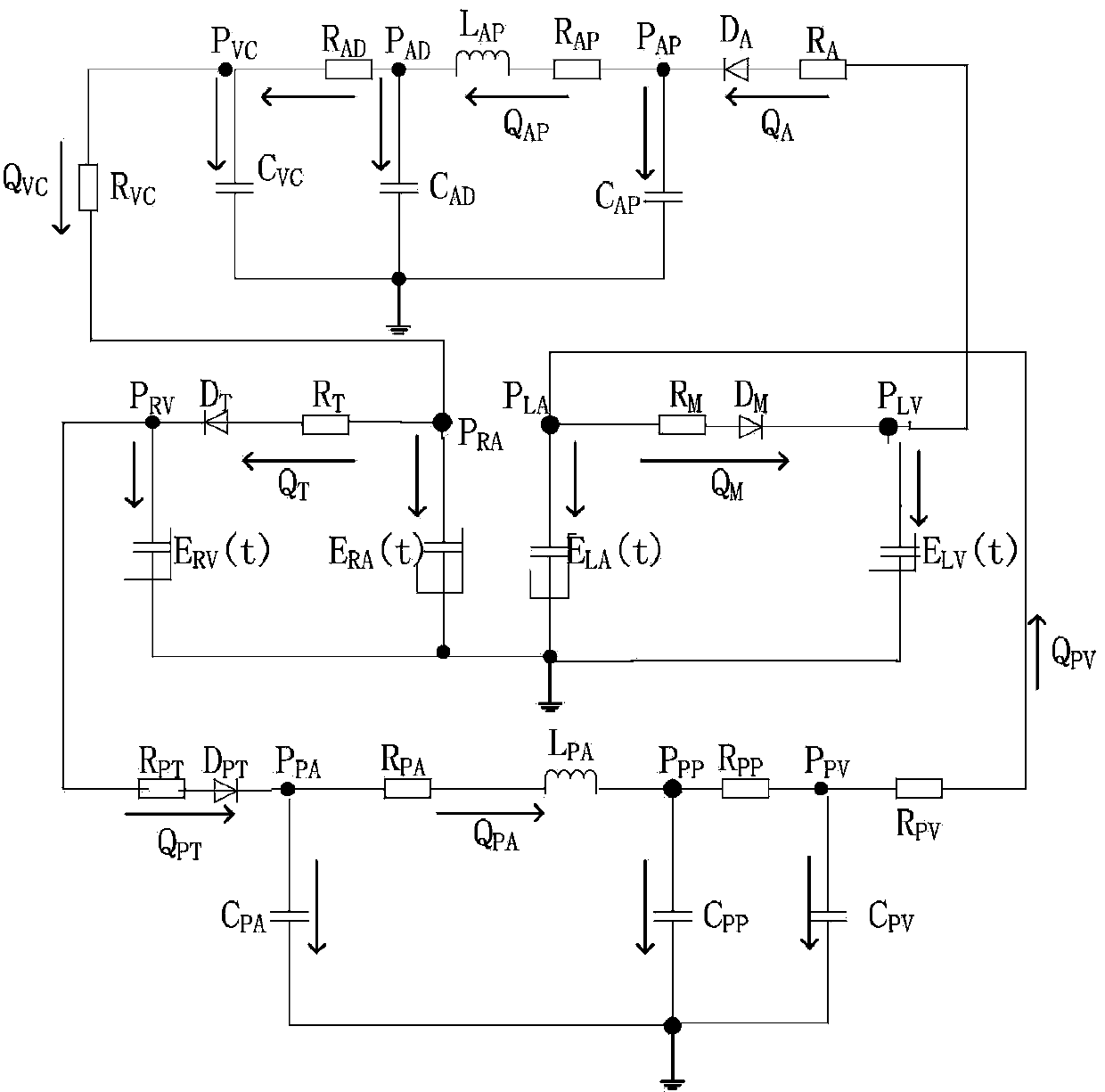
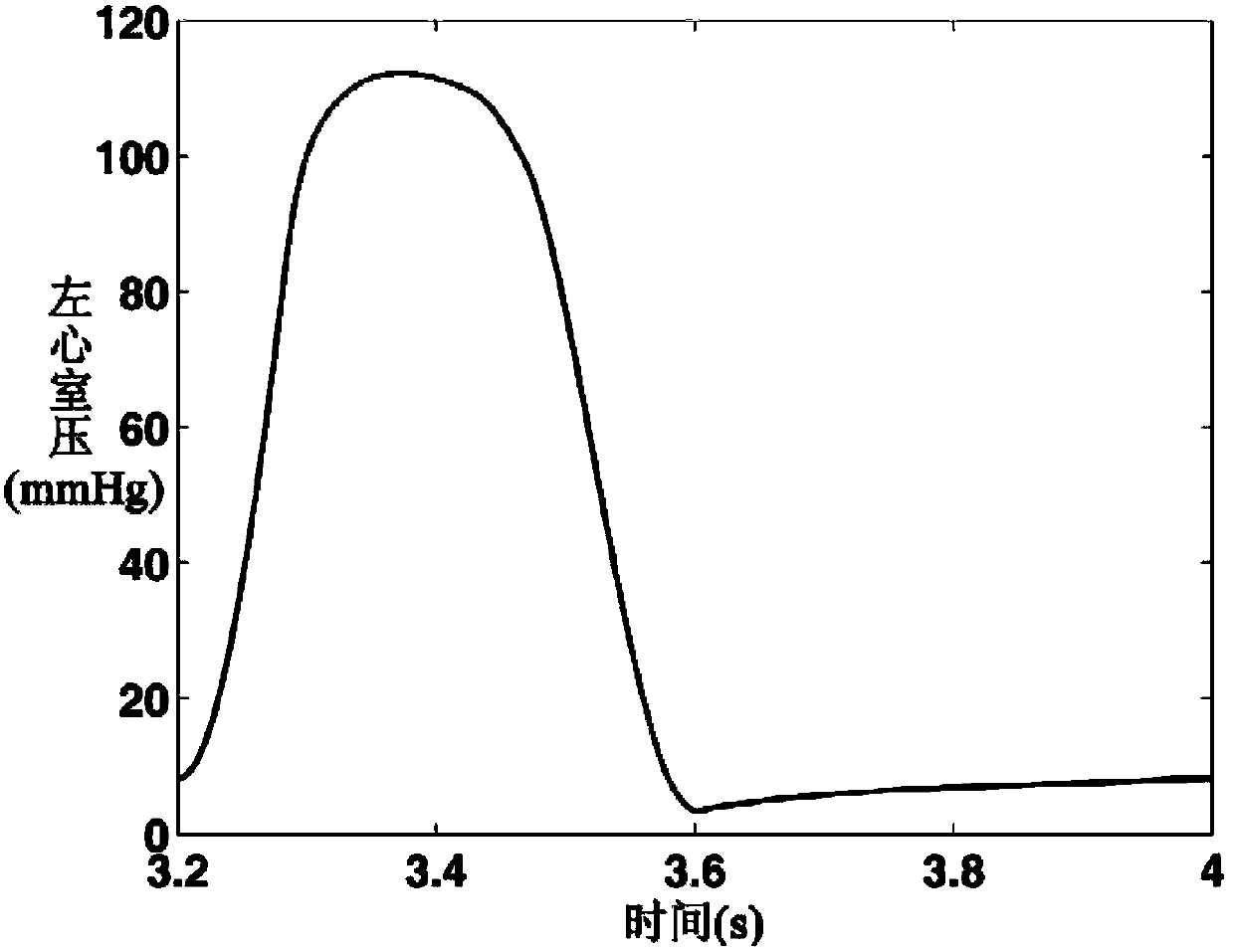
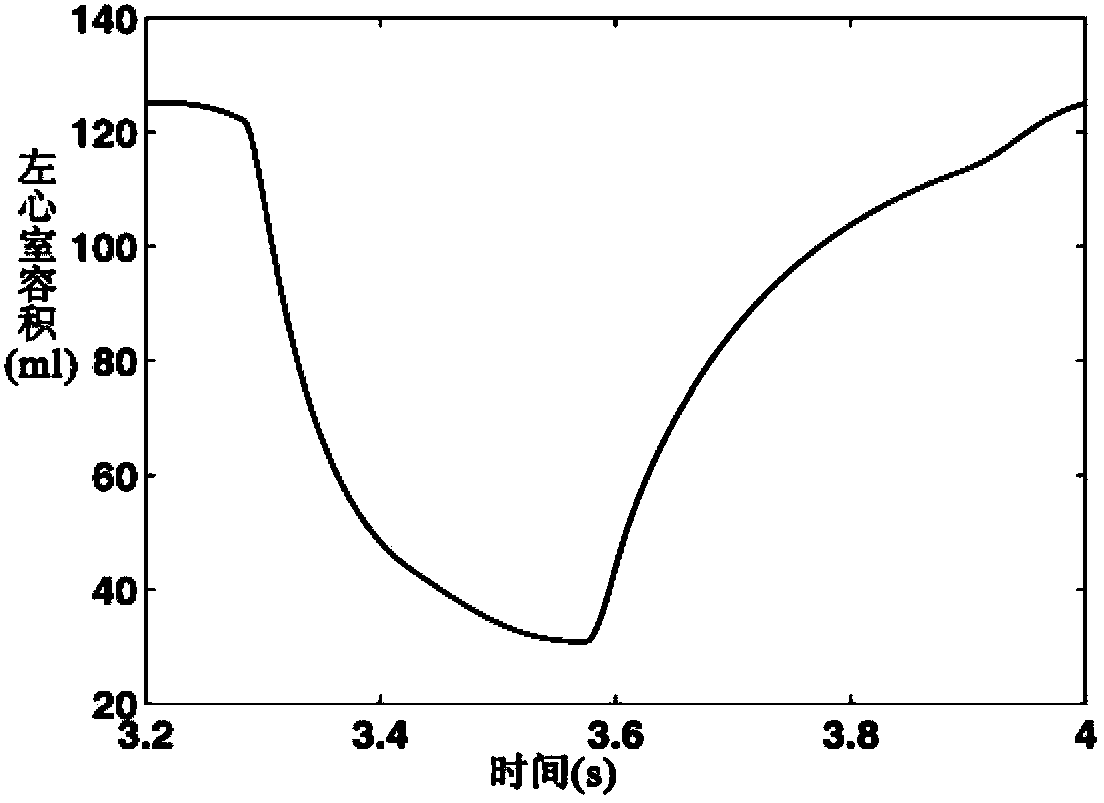
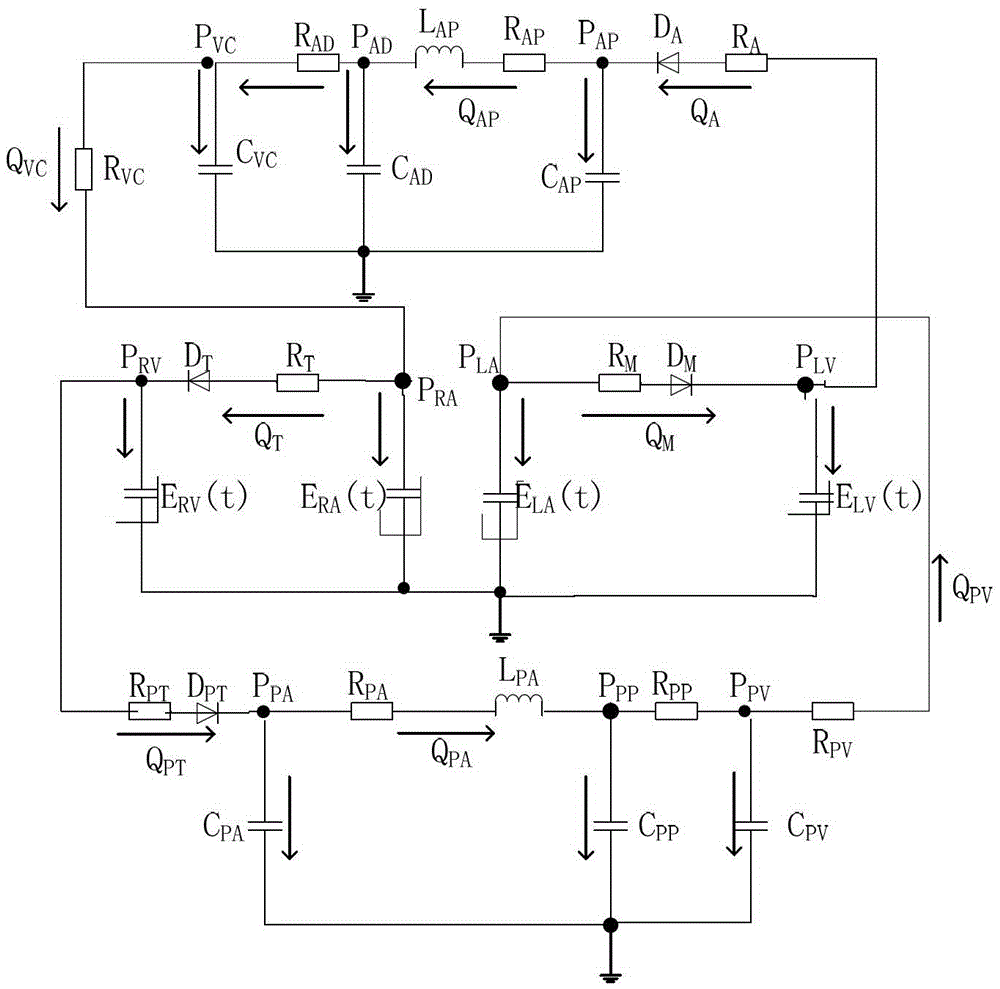
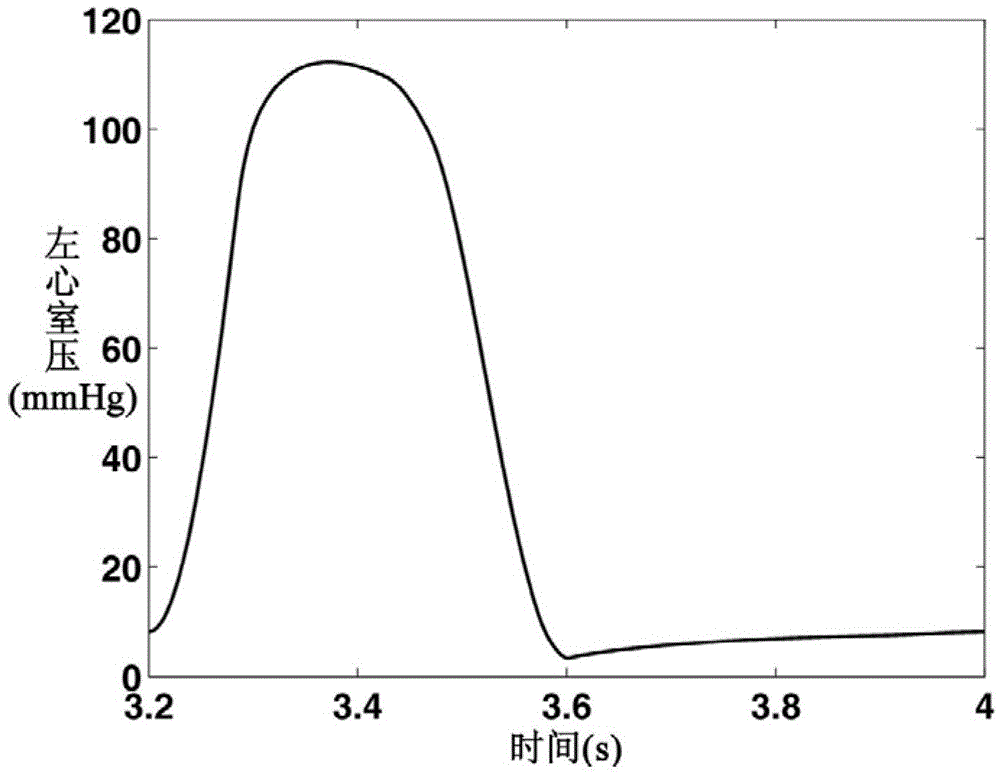
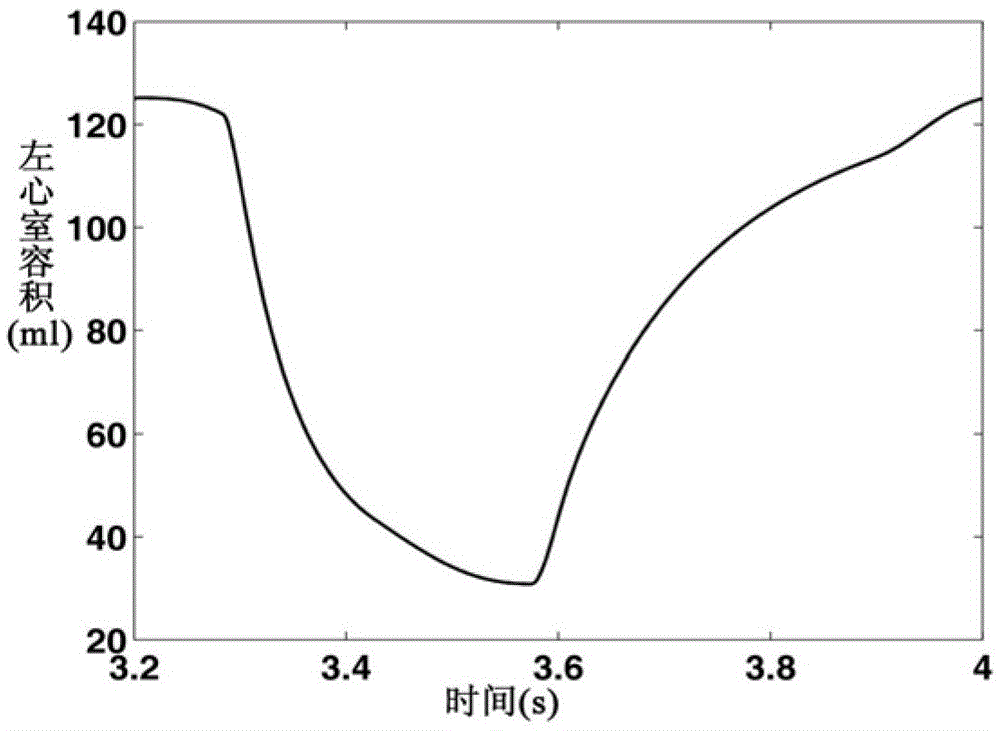
Digital simulation method for blood backflow caused by mitral valve insufficiency
InactiveCN103366072AShorten experiment timeLow costSpecial data processing applicationsTricuspid Valve InsufficiencyHeart/circulation
The invention relates to cardiovascular systems, in particular to a digital simulation method for blood backflow caused by mitral valve insufficiency. A, a four-cavity lumped parameter angiocarpy dynamic circuit model equivalent to lesser circulation system, a systemic circulation system, a left heart circulation system and a right heart circulation system is established according to the equivalent relation of hemodynamics parameters and circuit parameters; B, according to the circuit model established in the step A, an established dynamic circuit is analyzed through a state variable analysis method, and corresponding state equations are established for related nodes in the circuit; C, according to simulation needs, the corresponding parameters in the step A and the step B are set, the state equations are solved according to the circuit model arranged in the step A and the state equations arranged in the step B, and the time curve graphs of the nodes in the circuit are obtained; D, QM obtained in the step C is calculated, and the blood backflow amount VRM, the mitral valve forward output amount VFM and the mitral valve volume VM under the condition that the mitral valve insufficiency occurs are obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Cardiac targeted delivery of cells
InactiveUS8158119B2Efficient deliveryBiocideOther blood circulation devicesWhole bodyHeart/circulation
A method of delivering cardiac stem cell and treating damaged cardiac tissue is provided. The method involves isolation of subject's cardiac circulation from the subject's systemic circulation and perfusing a solution comprising stem cells into the cardiac circuit.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
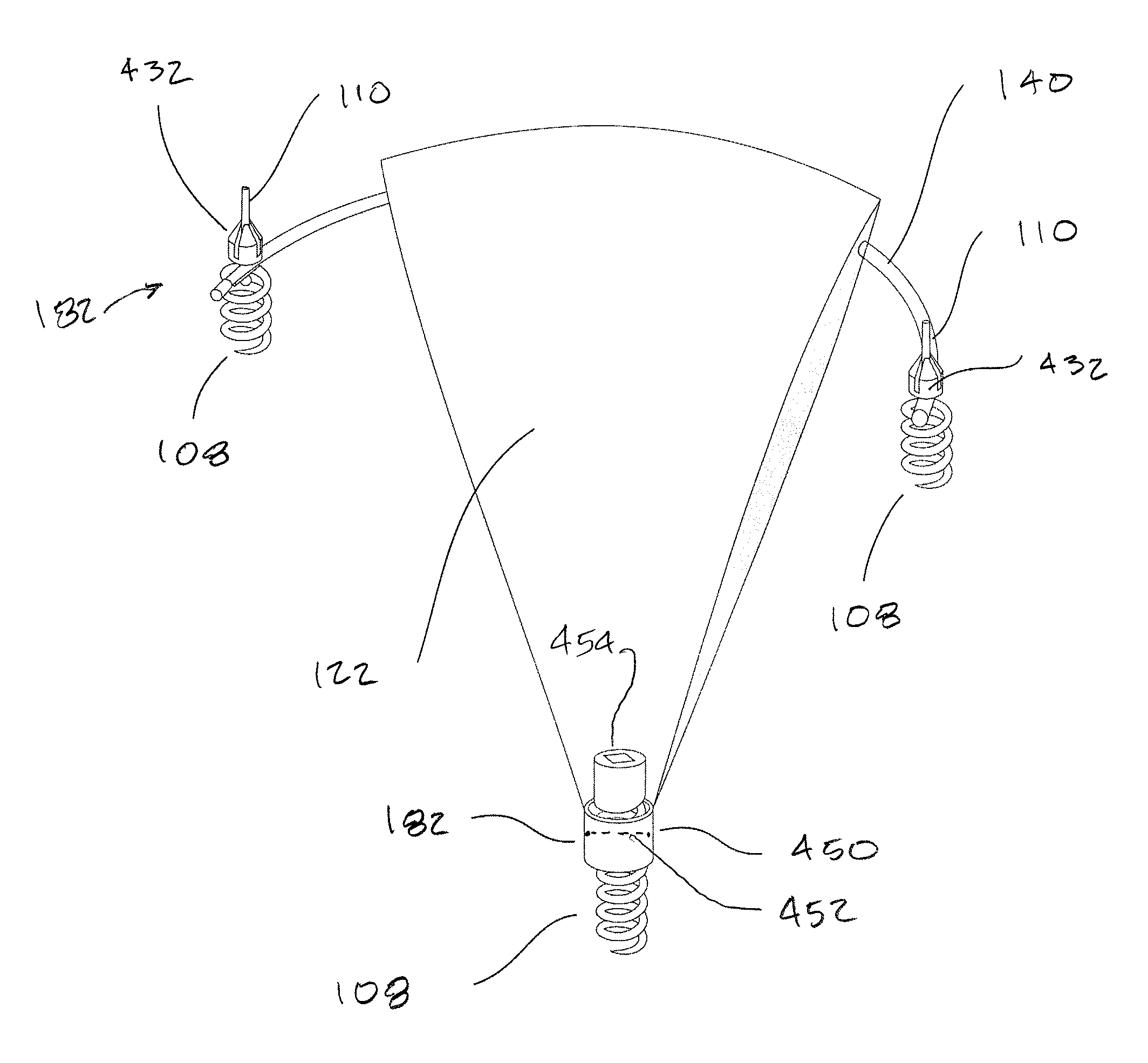
Device For Cardiocirculatory Assistance
ActiveUS20180117225A1Easy to manufactureEasy to implantFlexible member pumpsIntravenous devicesEngineeringHeart/circulation
A device for cardiocirculatory assistance constituting a pump for a blood flow includes a body, a pair of covers, and a pair of membranes. The device is provided with a circuit for the passage of a gas or gaseous fluid alternatively under pressure and depressurization so that a reciprocating pumping motion of the membranes is established.
Owner:PULSAHEART FINTECH LTD
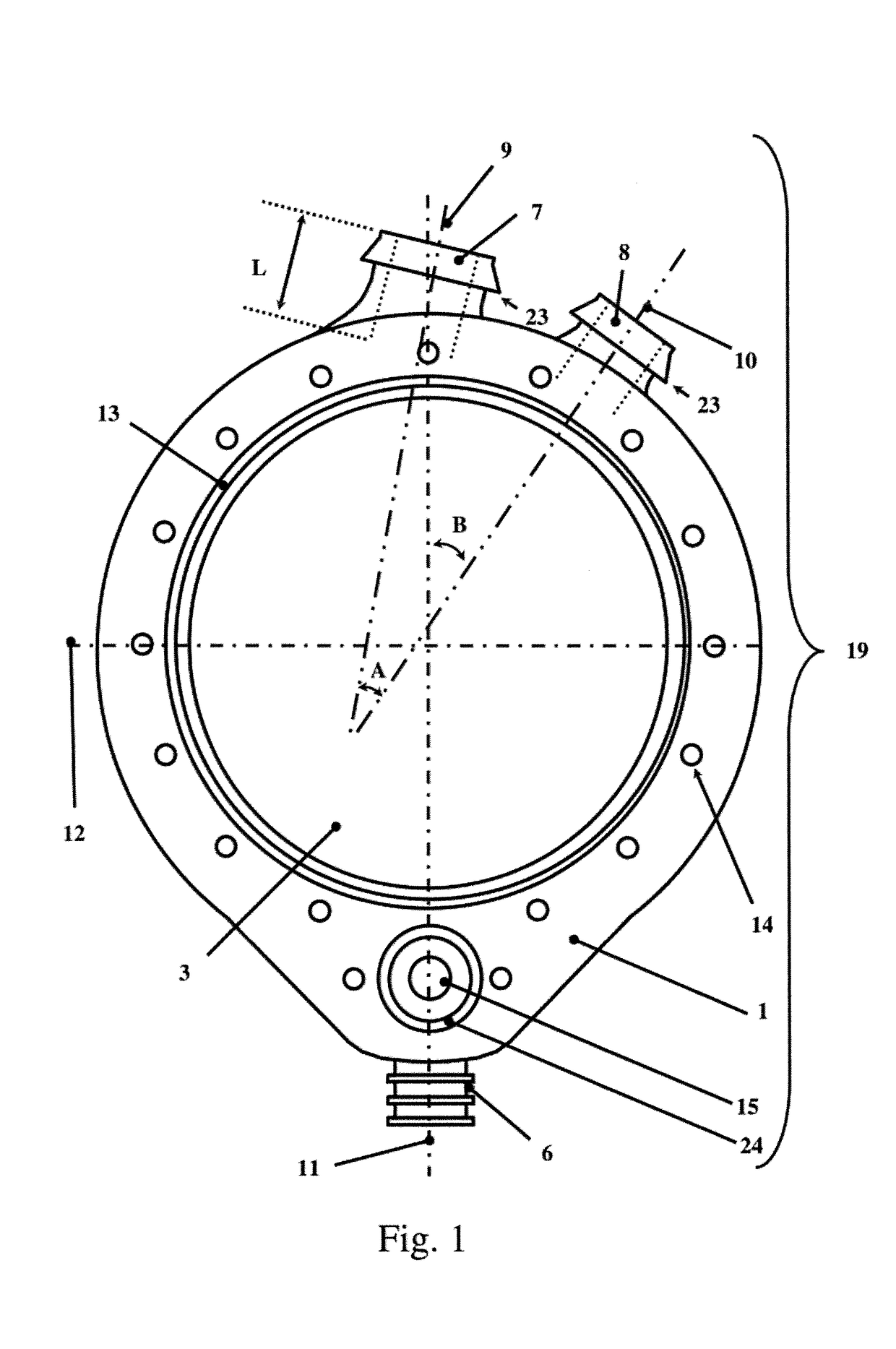
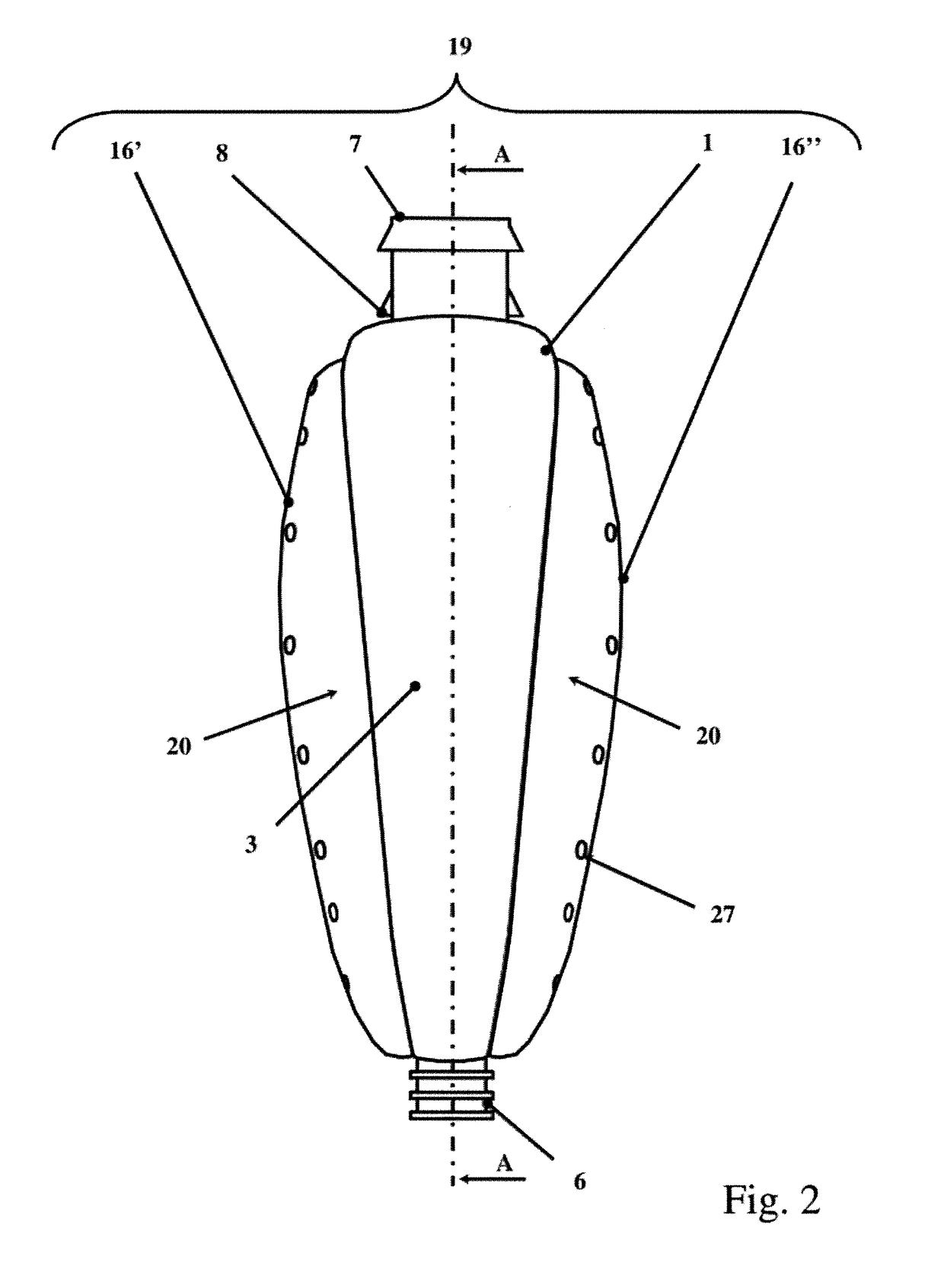
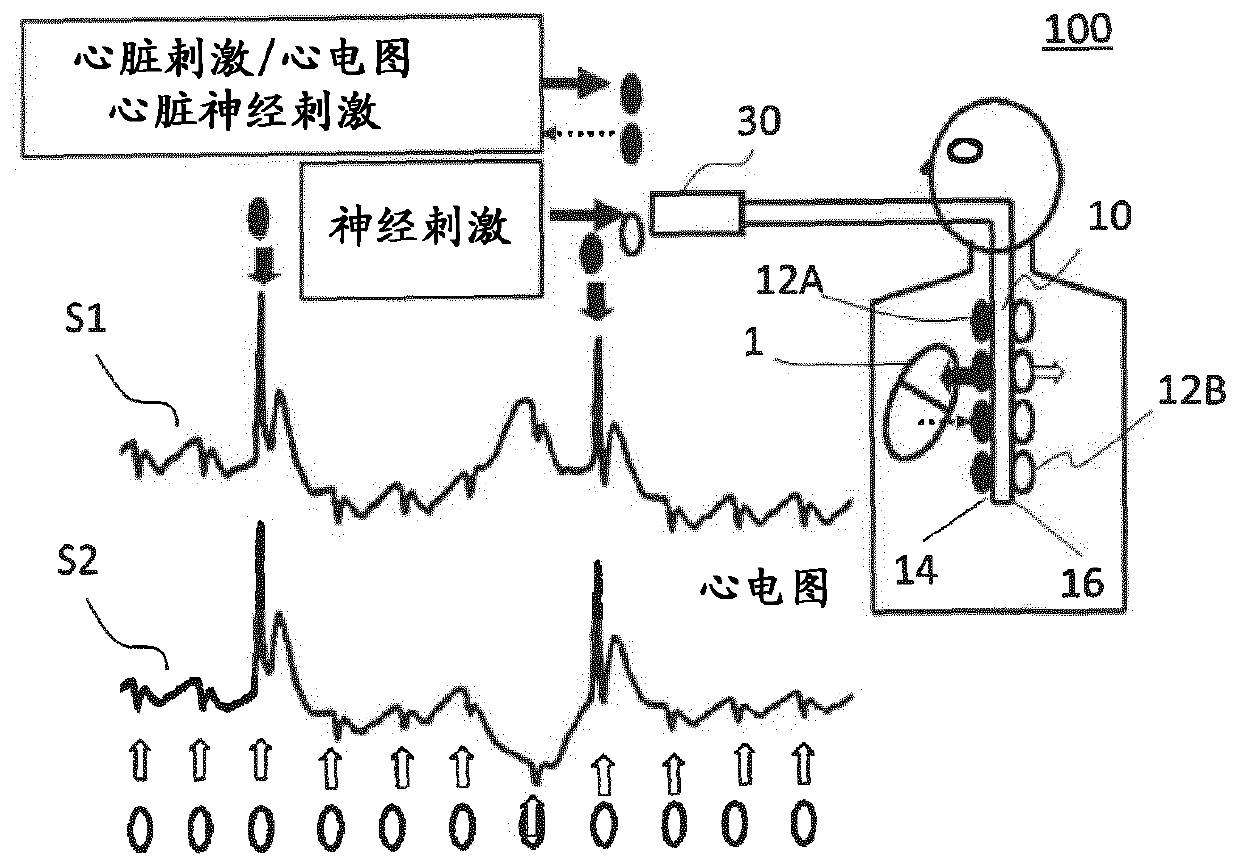
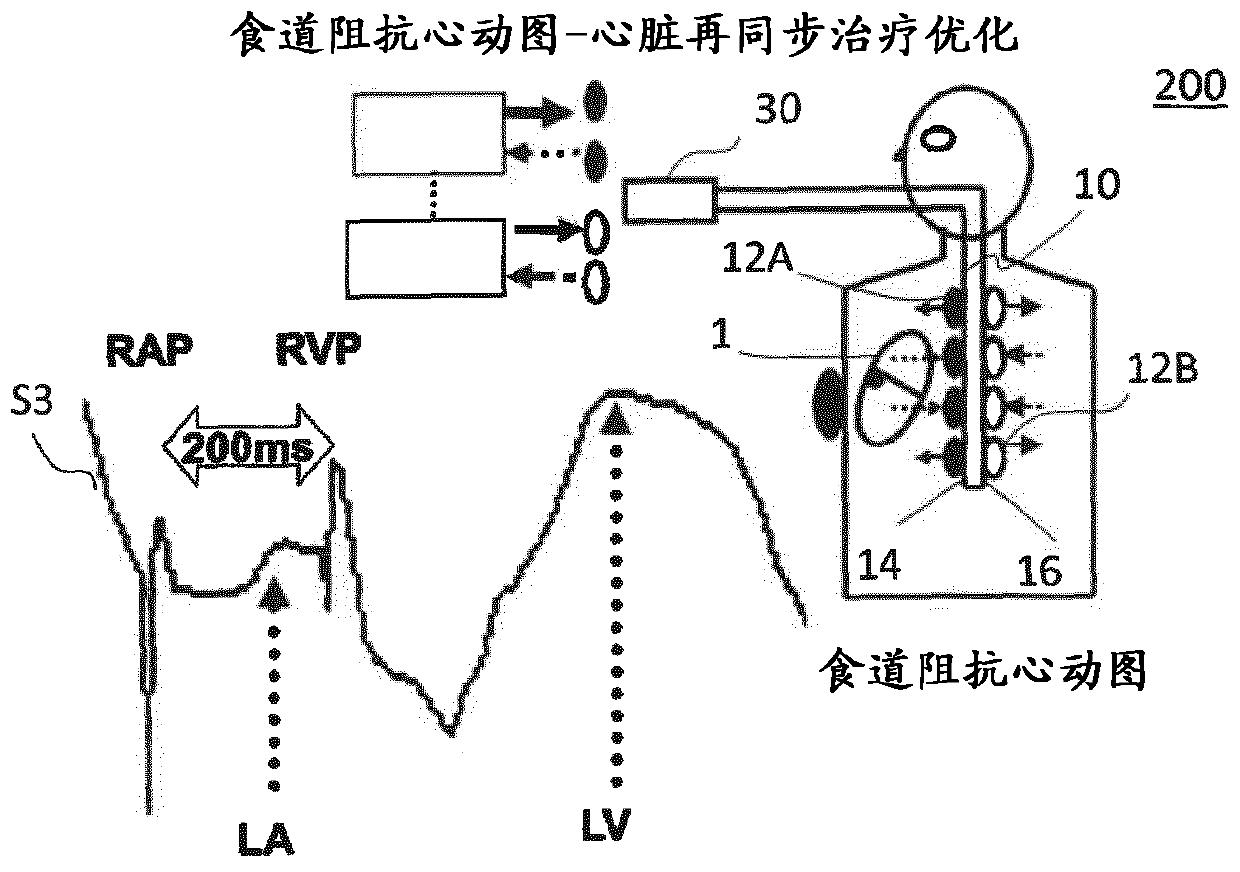
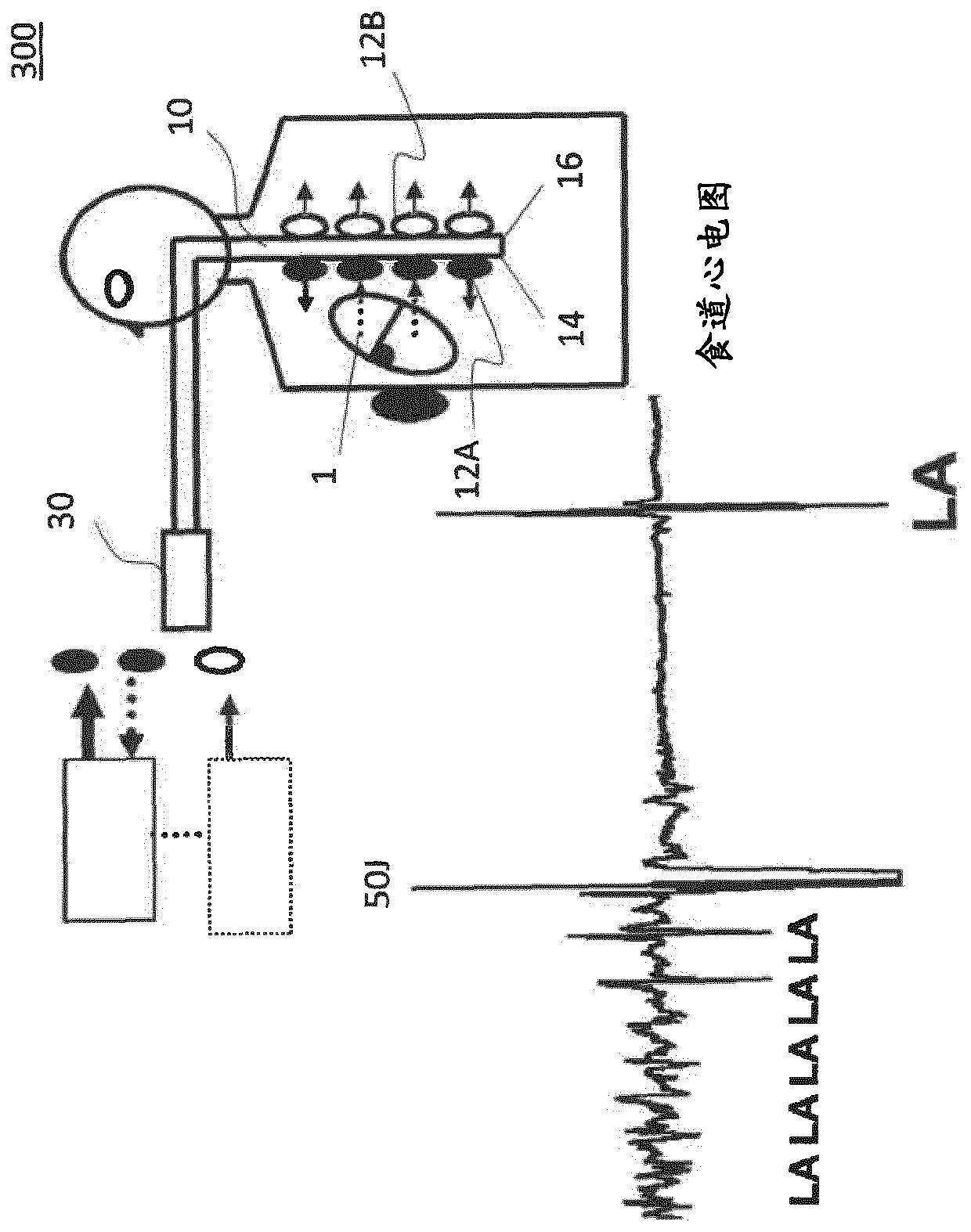
Oesophageal electrode probe and device for cardiological treatment and/or diagnosis
The invention relates to an oesophageal electrode probe (10) for bioimpedance measurement and / or for neurostimulation; a device (100) for transoesophageal cardiological treatment and / or cardiologicaldiagnosis; and a method for the open-loop or closed-loop control of a cardiac catheter ablation device and / or a cardiac, circulatory and / or respiratory support device. The oesophageal electrode probecomprises a bioimpedance measuring device for measuring the bioimpedance of at least one part of the tissue surrounding the oesophageal electrode probe. The bioimpedance device comprises at least onefirst and one second electrode, wherein the at least one first electrode (12A) is arranged on a side (14) of the oesophageal electrode probe facing towards the heart and the at least one second electrode (12B) is arranged on a side (16) of the oesophageal electrode probe facing away from the heart. The device (100) comprises the oesophageal electrode probe (10) and a control and / or evaluation device (30), which is configured for receiving a first bioimpedance measurement signal from the at least one first electrode (12A) and a second bioimpedance measurement signal from the at least one secondelectrode (12B), and comparing same, and generating a control signal on the basis of the comparison. The control signal can be a signal for the open-loop or closed-loop control of a cardiac catheterablation device and / or a cardiac, circulatory and / or respiratory support device.
Owner:XENIOS AG
Device and method for connecting a blood pump without trapping air bubbles
An apparatus and a method for connecting medical tubing or any other type of fluidic circuit conduits (e.g., cannulae) to a ventricular assist device (“VAD”) or any other pumping device used for blood pumping during cardiac circulatory support for vascular surgery. The apparatus and the method prevent air bubbles from entering a cardiac circulatory support system when connecting cannulae to a VAD that may later enter the blood stream of a patient during cardiac surgery, and also provide for purging any air bubbles that may have entered the cardiac circulatory support system during a cannulae-VAD connection.
Owner:VITALMEX INT DE C V
A digital simulation method of blood regurgitation in mitral regurgitation
InactiveCN103366072BShorten experiment timeLow costSpecial data processing applicationsNODALHeart/circulation
The invention relates to cardiovascular systems, in particular to a digital simulation method for blood backflow caused by mitral valve insufficiency. A, a four-cavity lumped parameter angiocarpy dynamic circuit model equivalent to lesser circulation system, a systemic circulation system, a left heart circulation system and a right heart circulation system is established according to the equivalent relation of hemodynamics parameters and circuit parameters; B, according to the circuit model established in the step A, an established dynamic circuit is analyzed through a state variable analysis method, and corresponding state equations are established for related nodes in the circuit; C, according to simulation needs, the corresponding parameters in the step A and the step B are set, the state equations are solved according to the circuit model arranged in the step A and the state equations arranged in the step B, and the time curve graphs of the nodes in the circuit are obtained; D, QM obtained in the step C is calculated, and the blood backflow amount VRM, the mitral valve forward output amount VFM and the mitral valve volume VM under the condition that the mitral valve insufficiency occurs are obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com