Patents
Literature
44 results about "Nerve bundle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
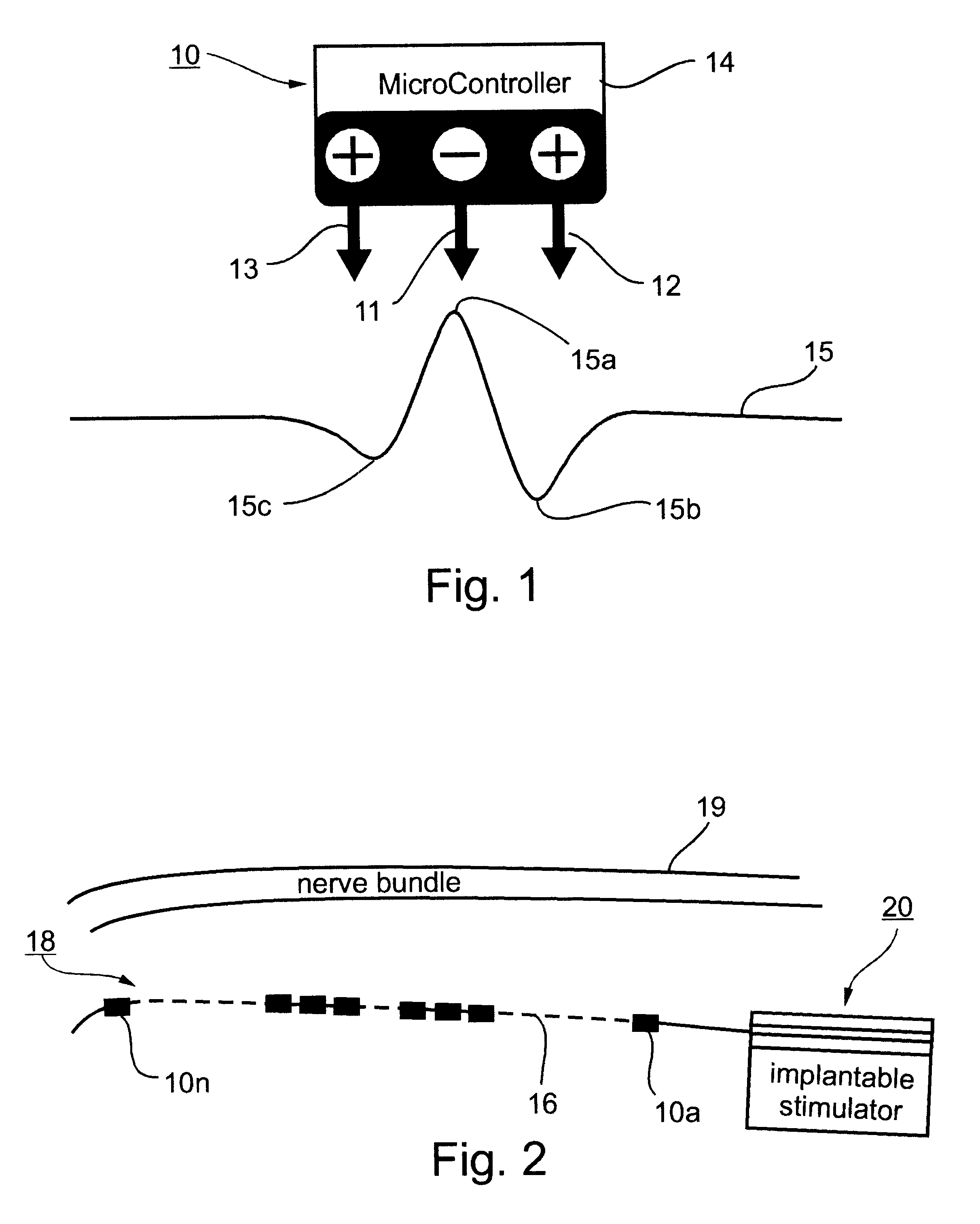
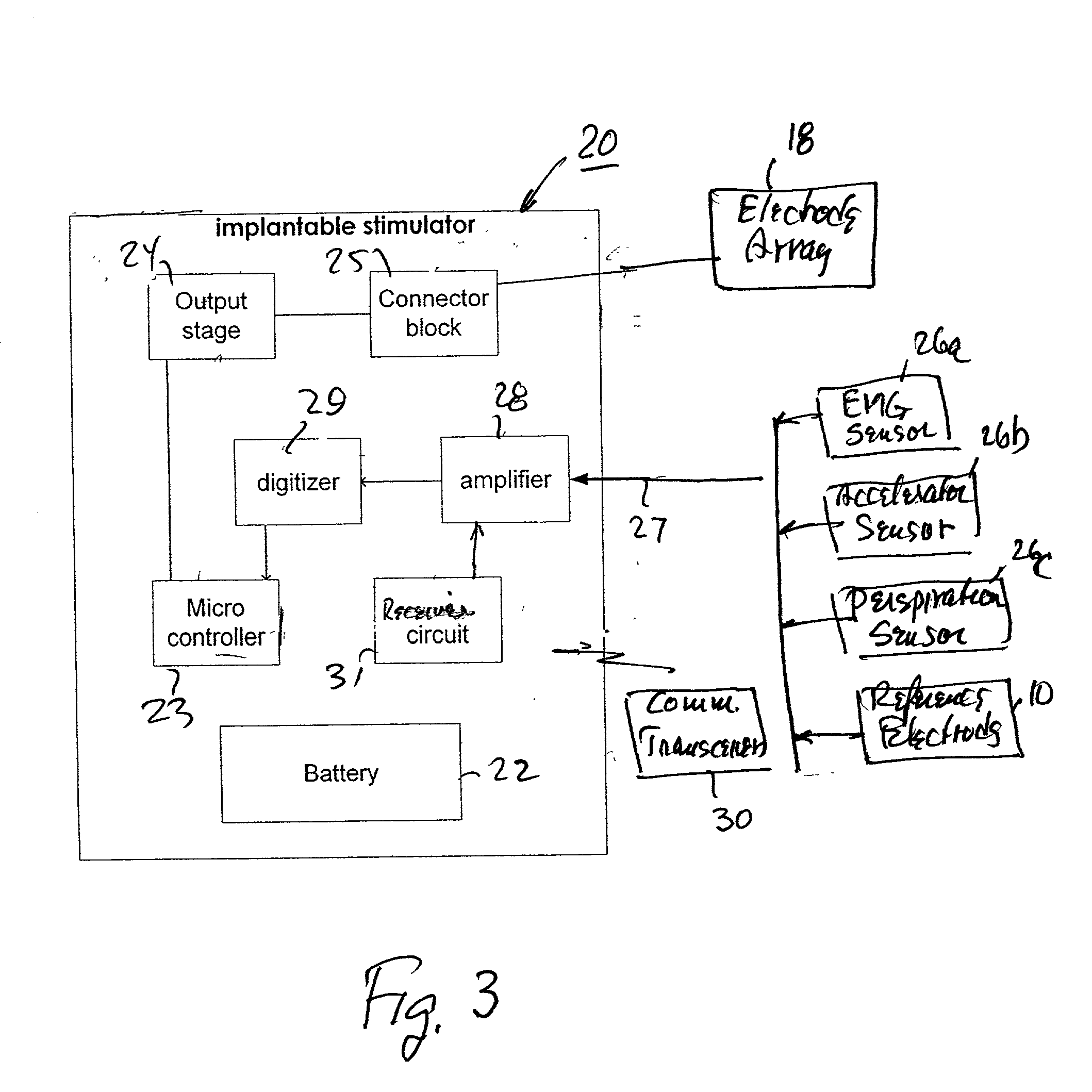
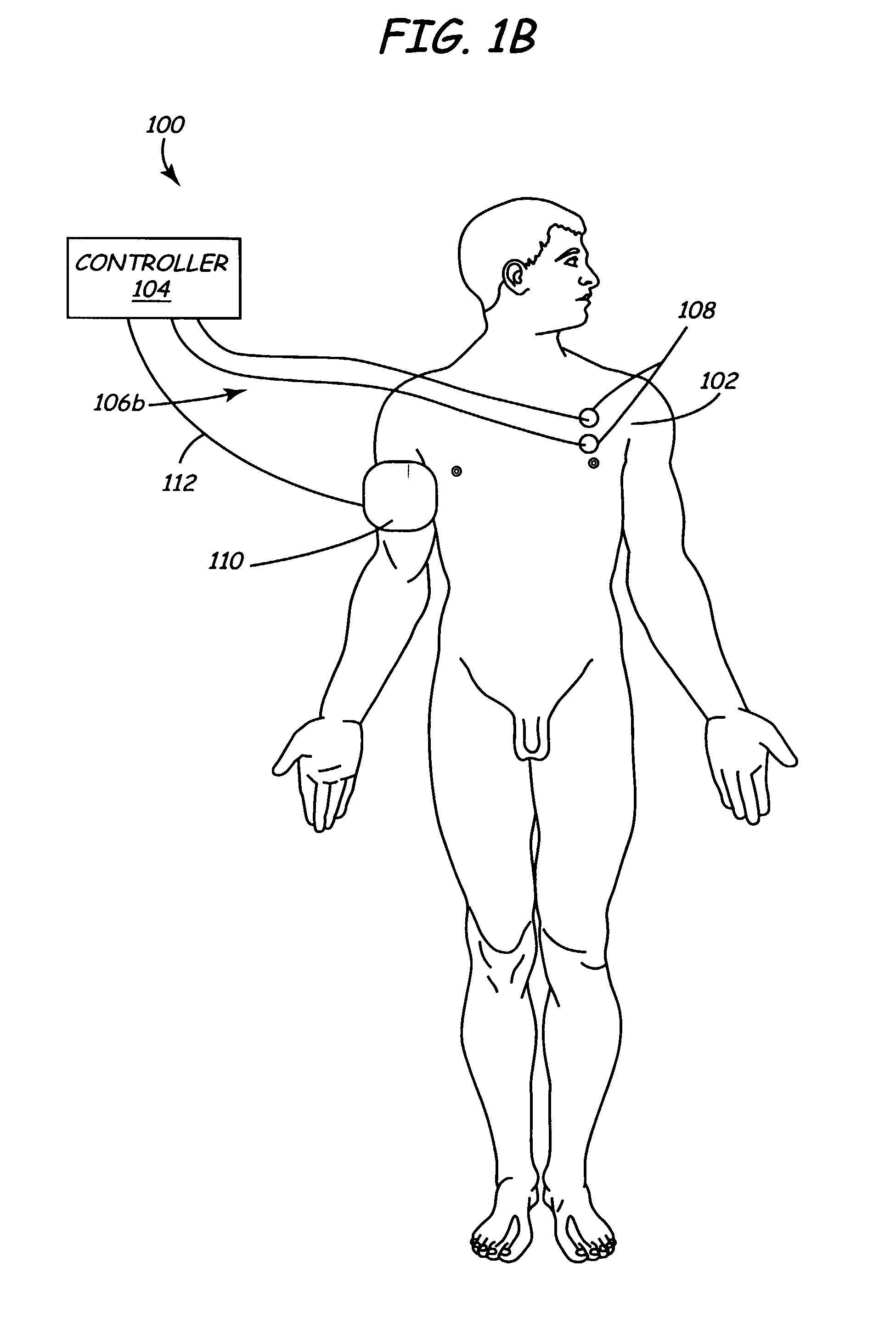
Method and apparatus for electrically stimulating the nervous system to improve ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions
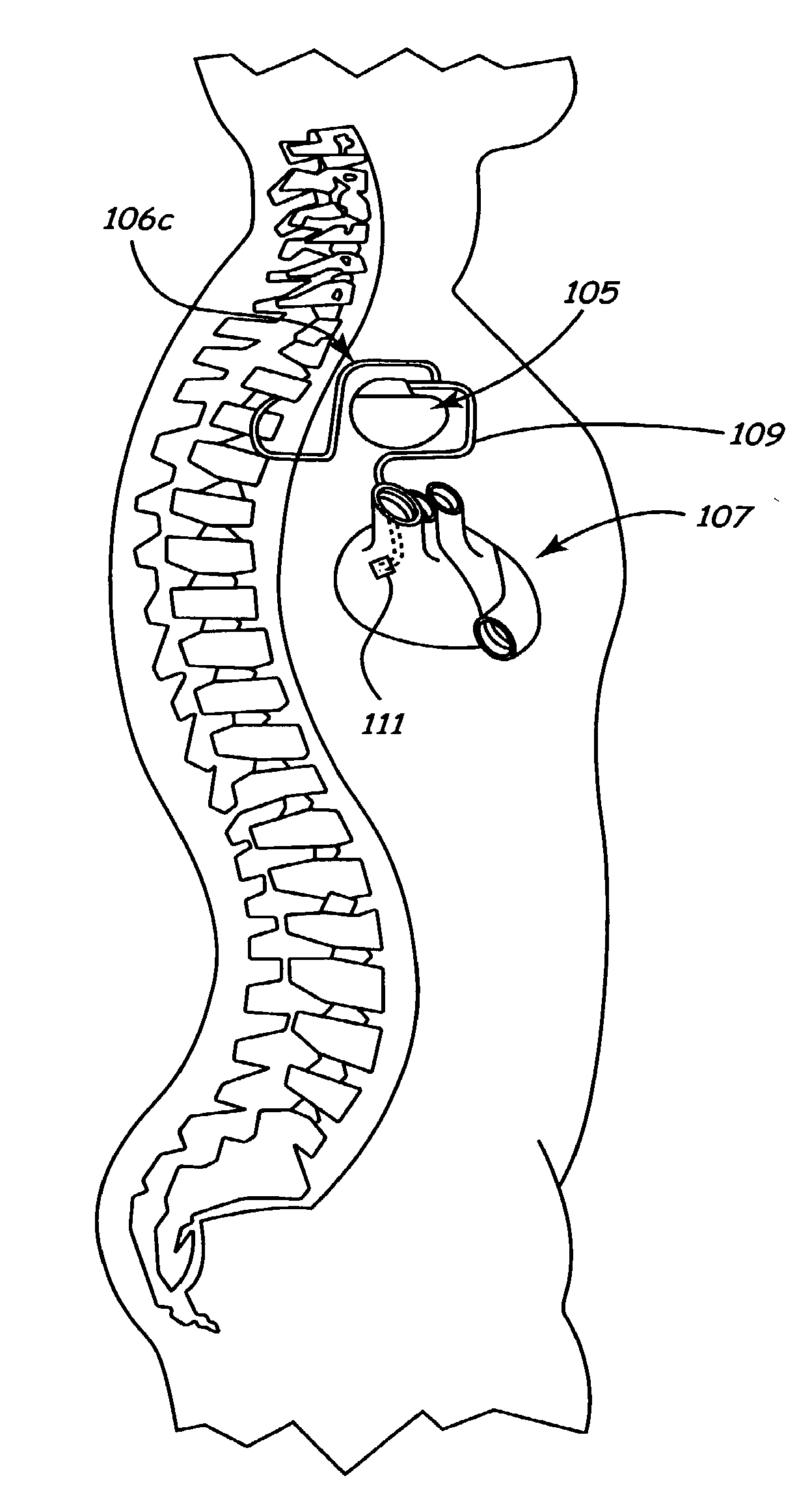
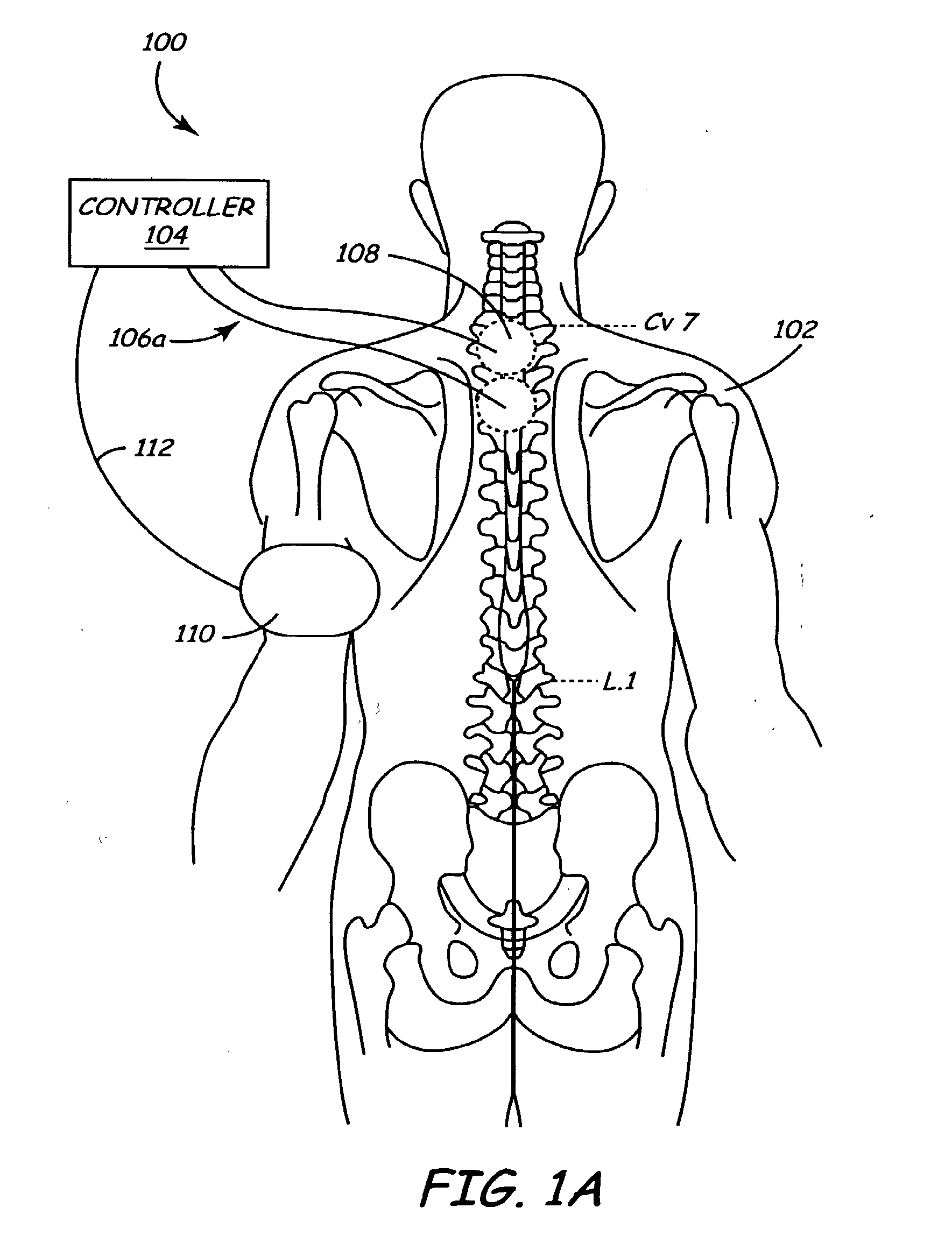
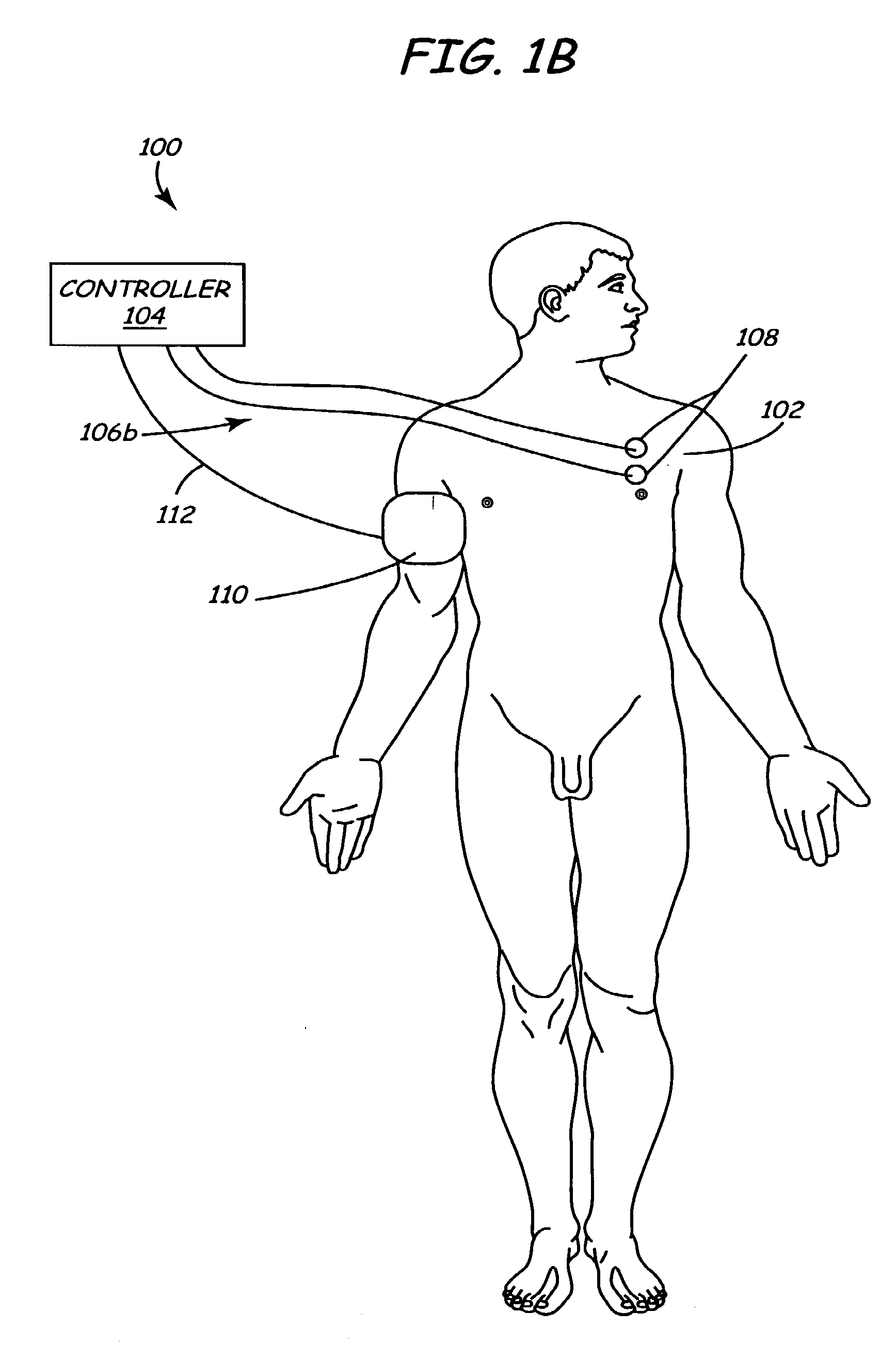
A method and apparatus are used to provide therapy to a patient experiencing ventricular dysfunction or heart failure. At least one electrode is located in a region associated with nervous tissue, such as nerve bundles T1-T4, in a patient's body. Electrical stimulation is applied to the at least one electrode to improve the cardiac efficiency of the patient's heart. One or more predetermined physiologic parameters of the patient are monitored, and the electrical stimulation is adjusted based on the one or more predetermined physiologic parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
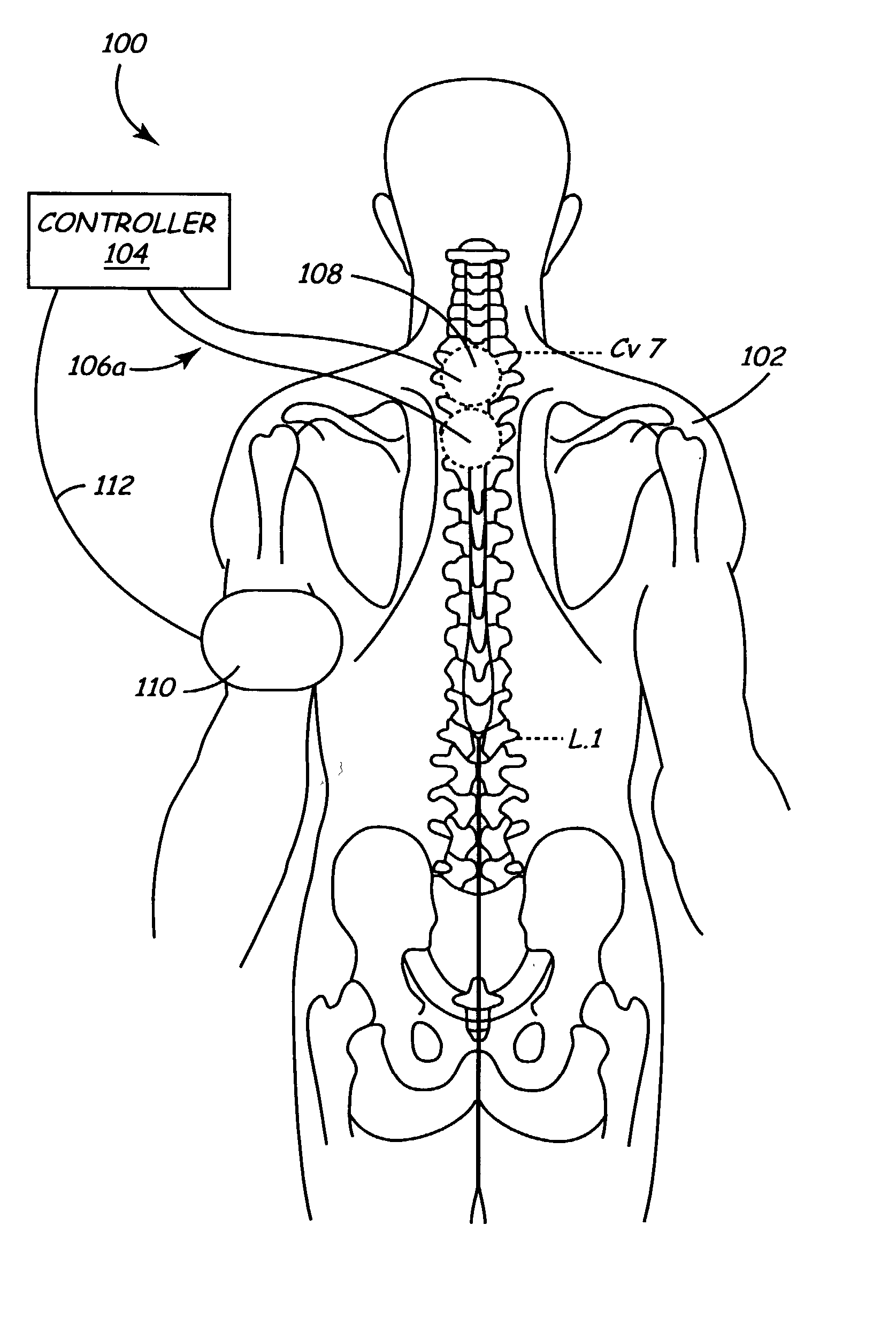
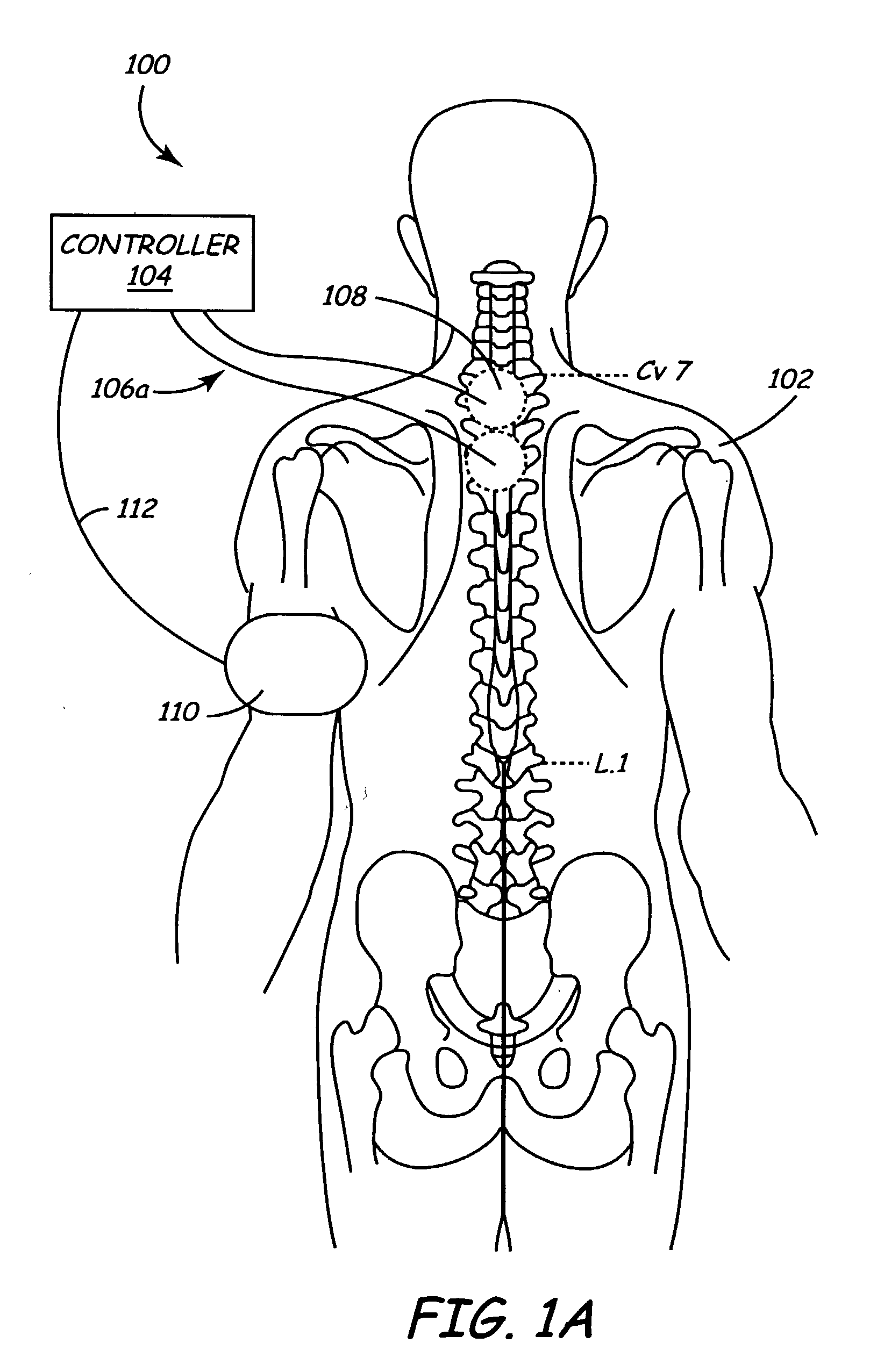
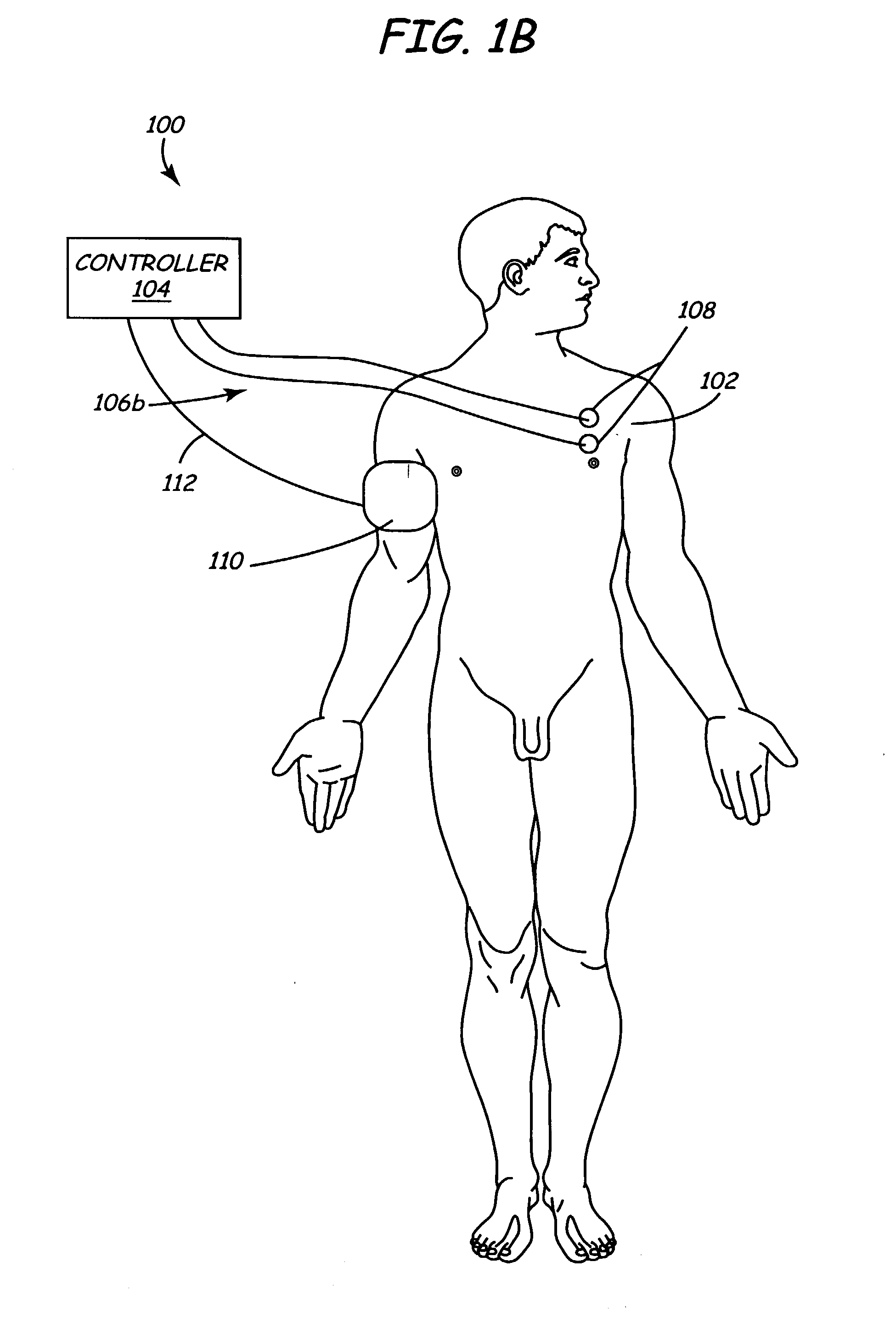
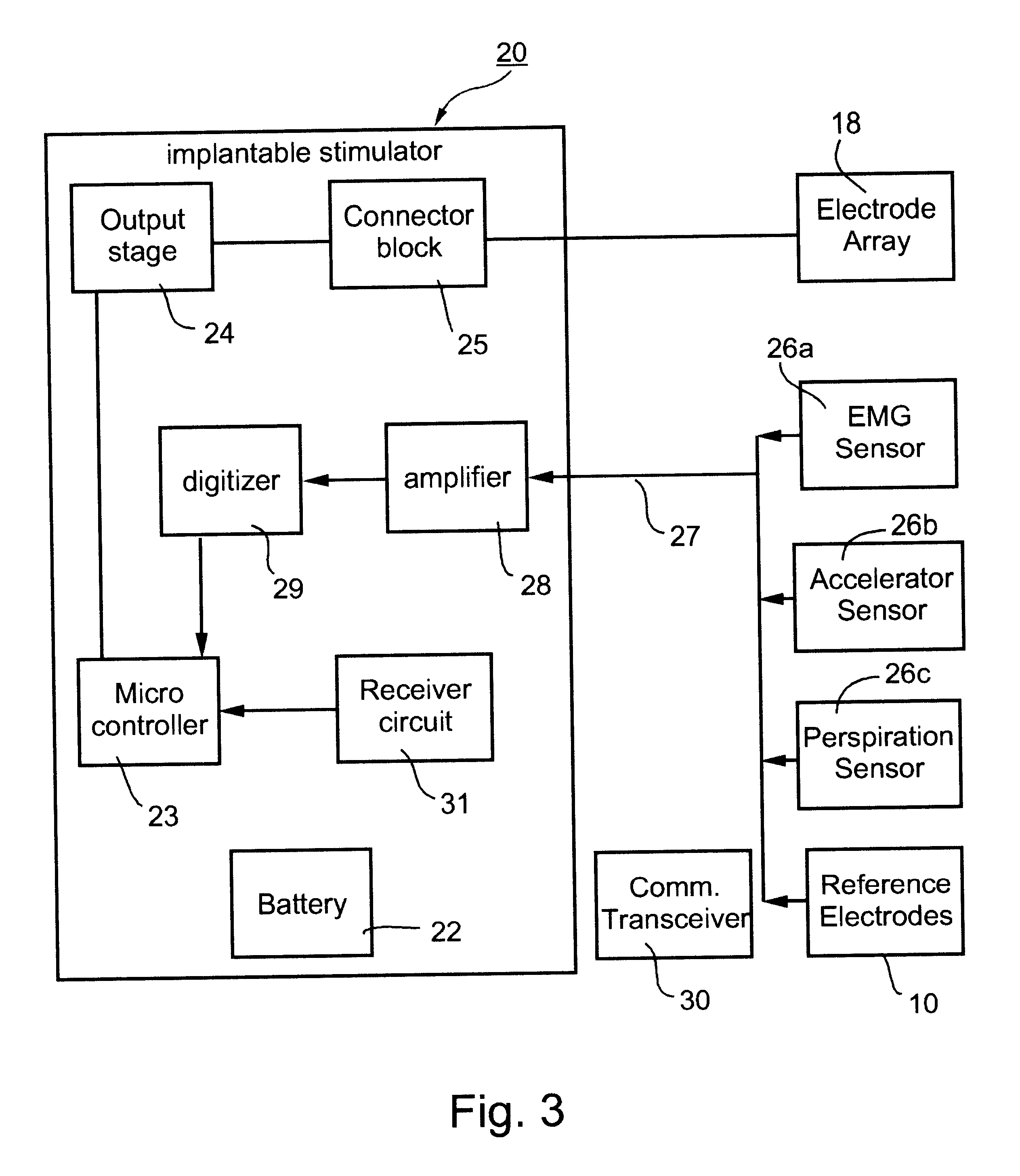
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
InactiveUS6600954B2Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
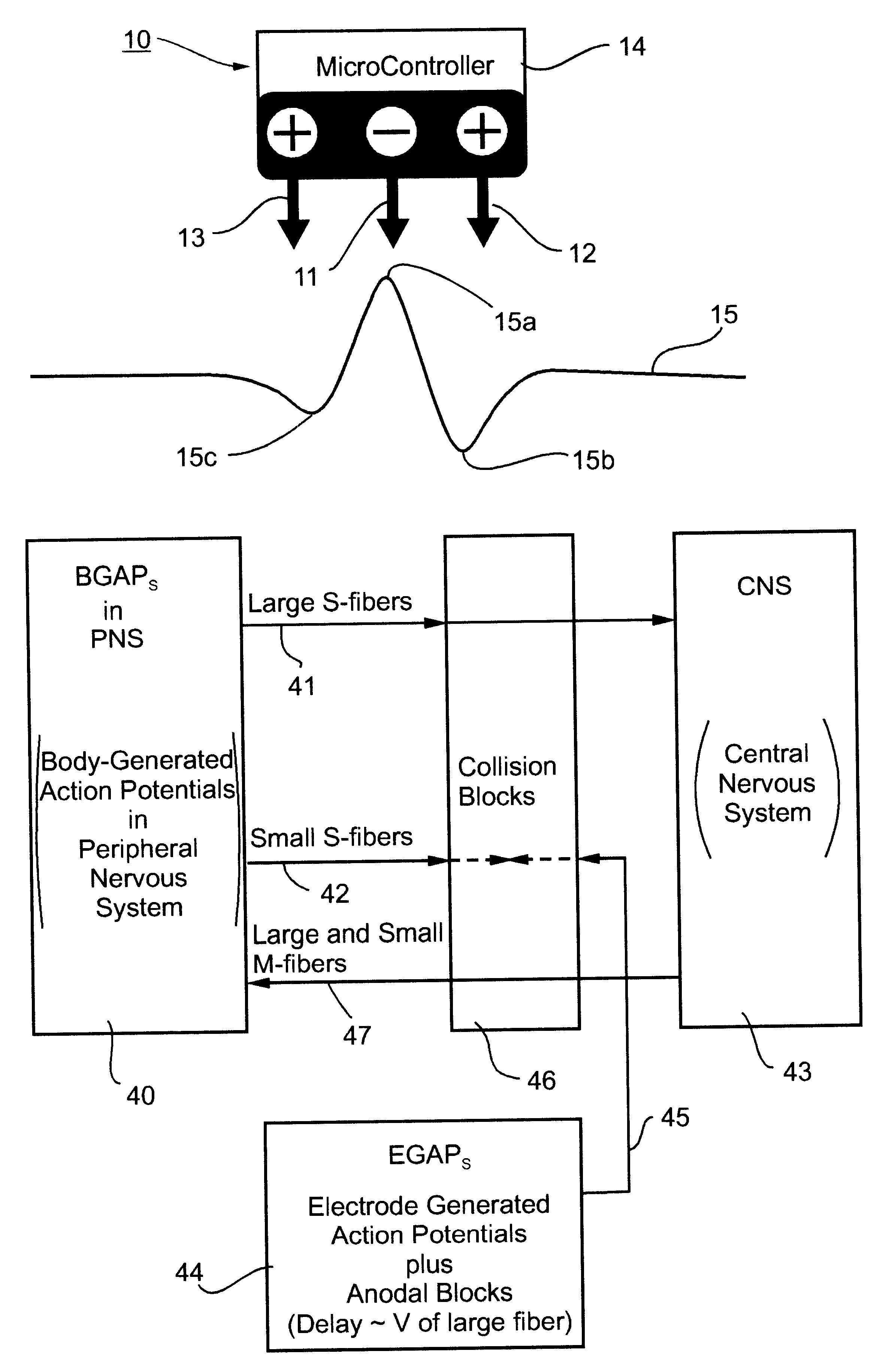
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
InactiveUS20020099419A1Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems, methods, and devices using stretchable or flexible electronics for medical applications
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for electrically stimulating the nervous system to improve ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions
ActiveUS20100016919A1Improve heart functionImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesNervous systemHeart disease
A method and apparatus are used to provide therapy to a patient experiencing ventricular dysfunction or heart failure. At least one electrode is located in a region associated with nervous tissue, such as nerve bundles T1-T4, in a patient's body. Electrical stimulation is applied to the at least one electrode to improve the cardiac efficiency of the patient's heart. One or more predetermined physiologic parameters of the patient are monitored, and the electrical stimulation is adjusted based on the one or more predetermined physiologic parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
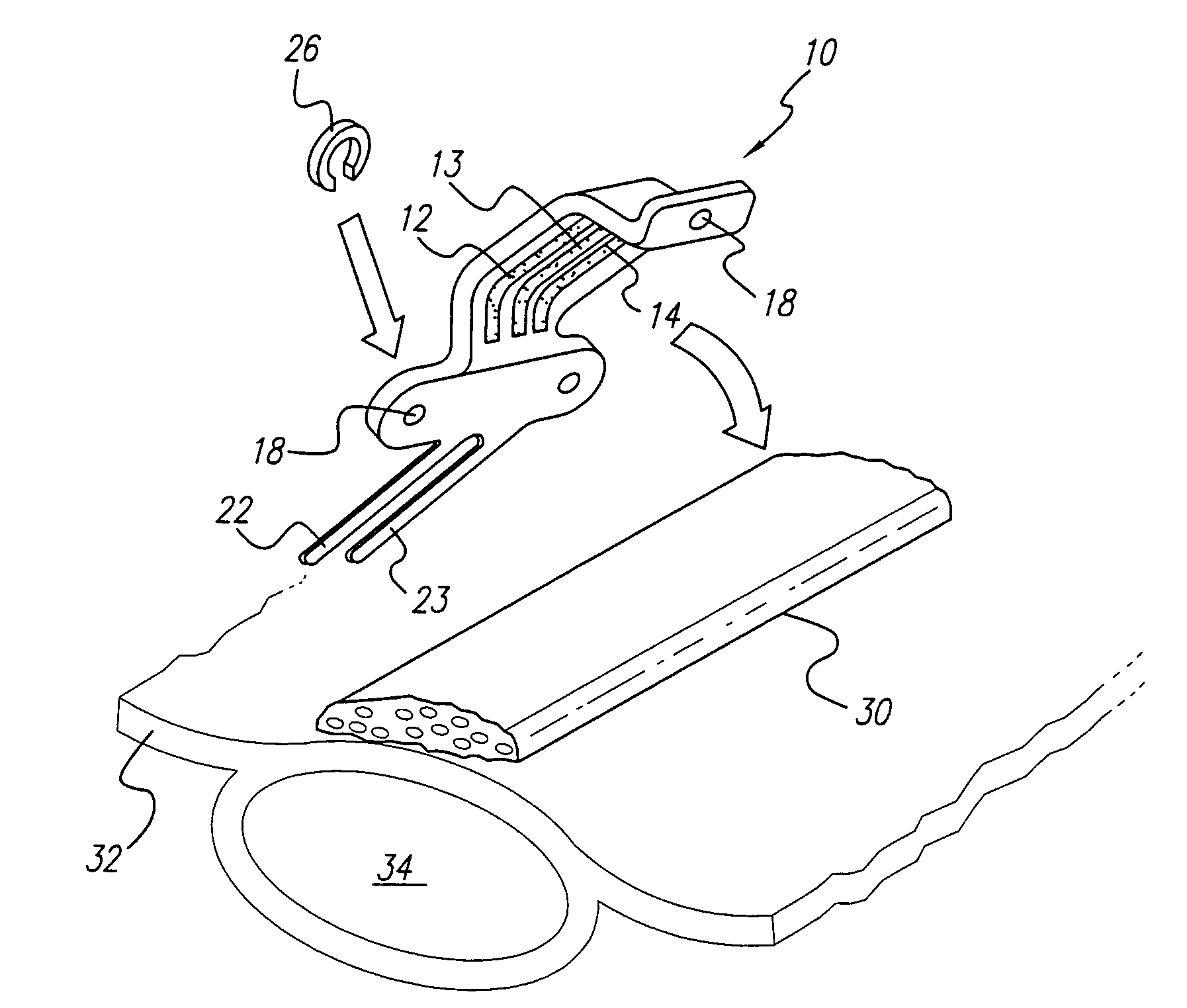
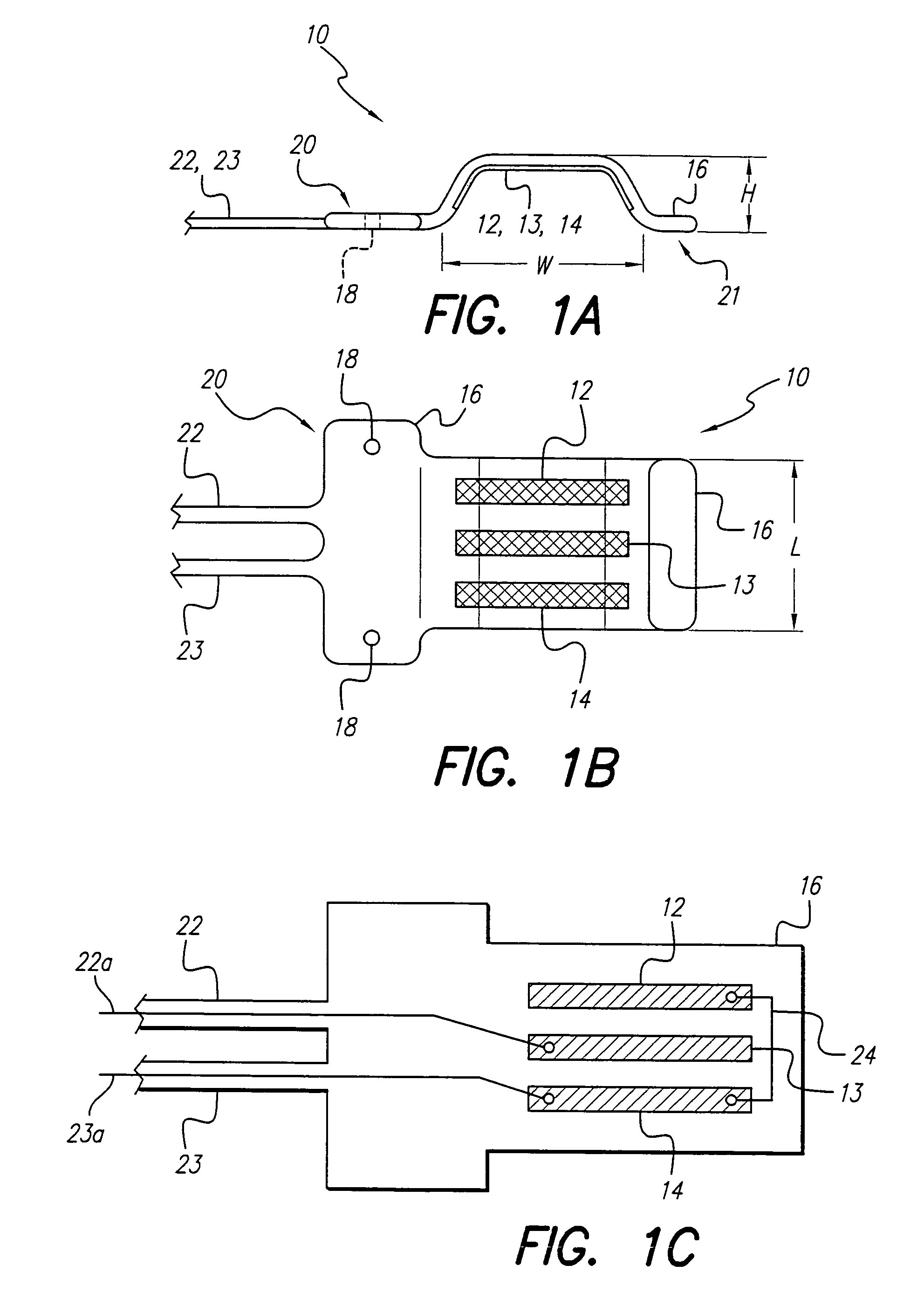
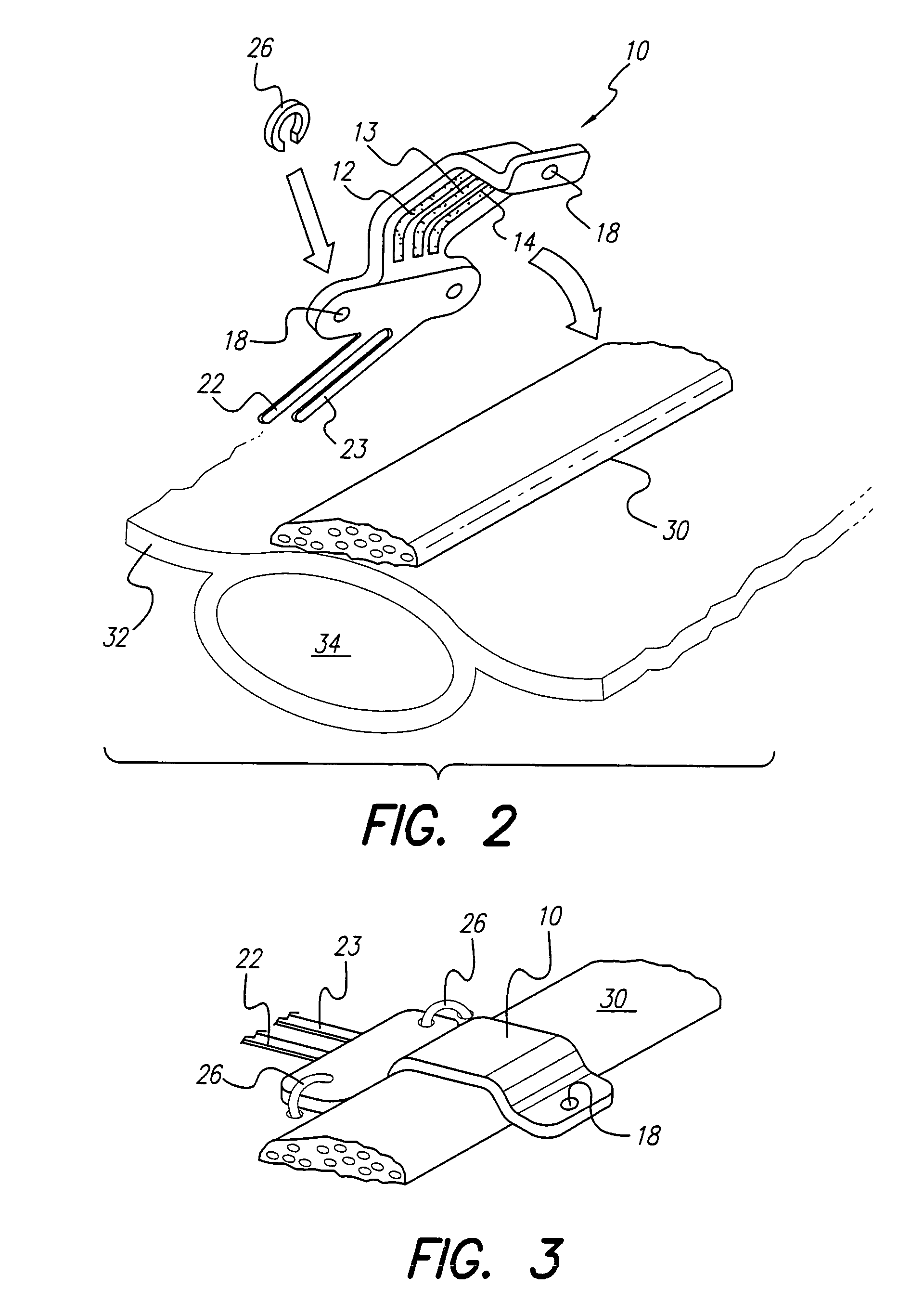
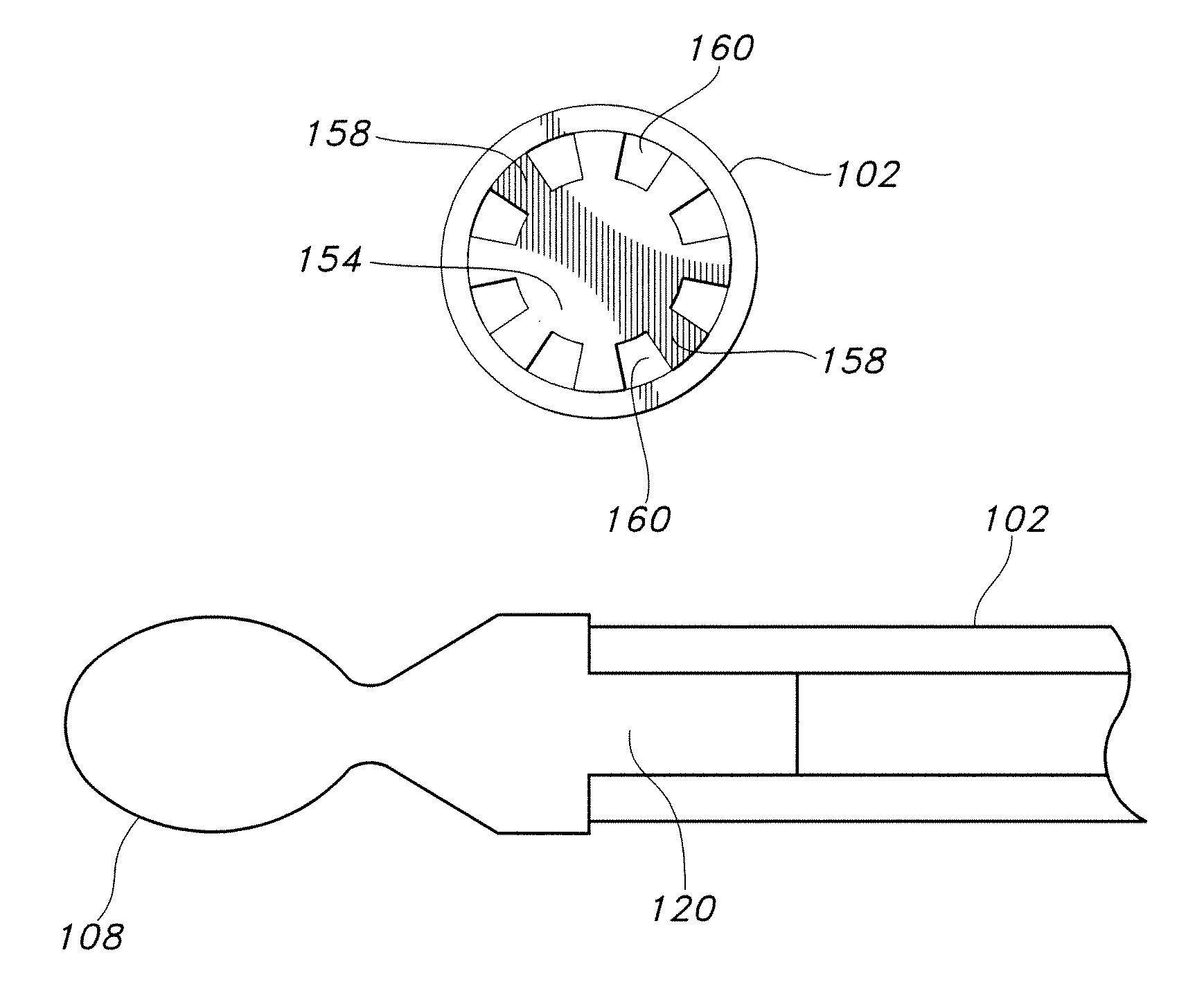
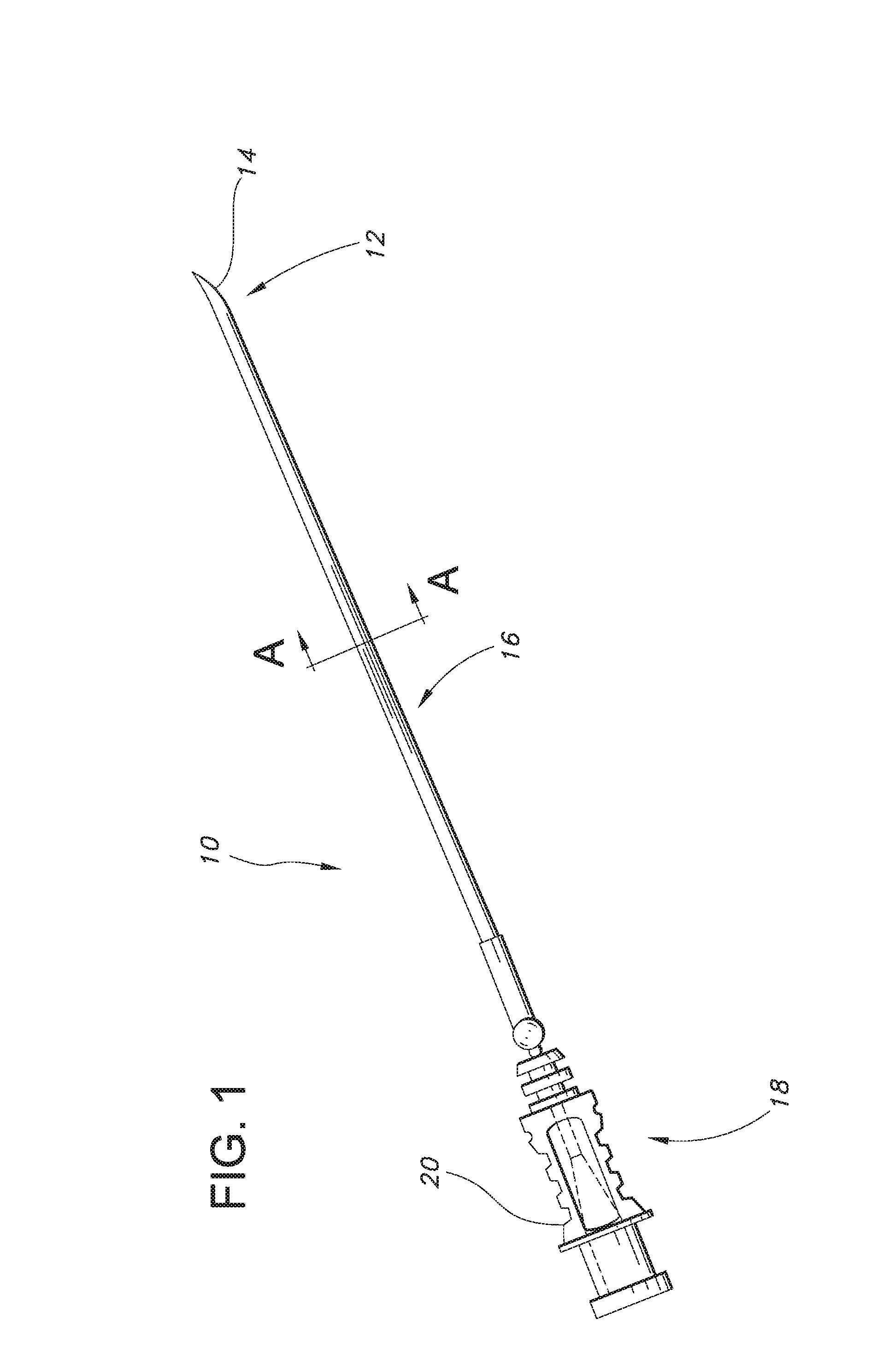
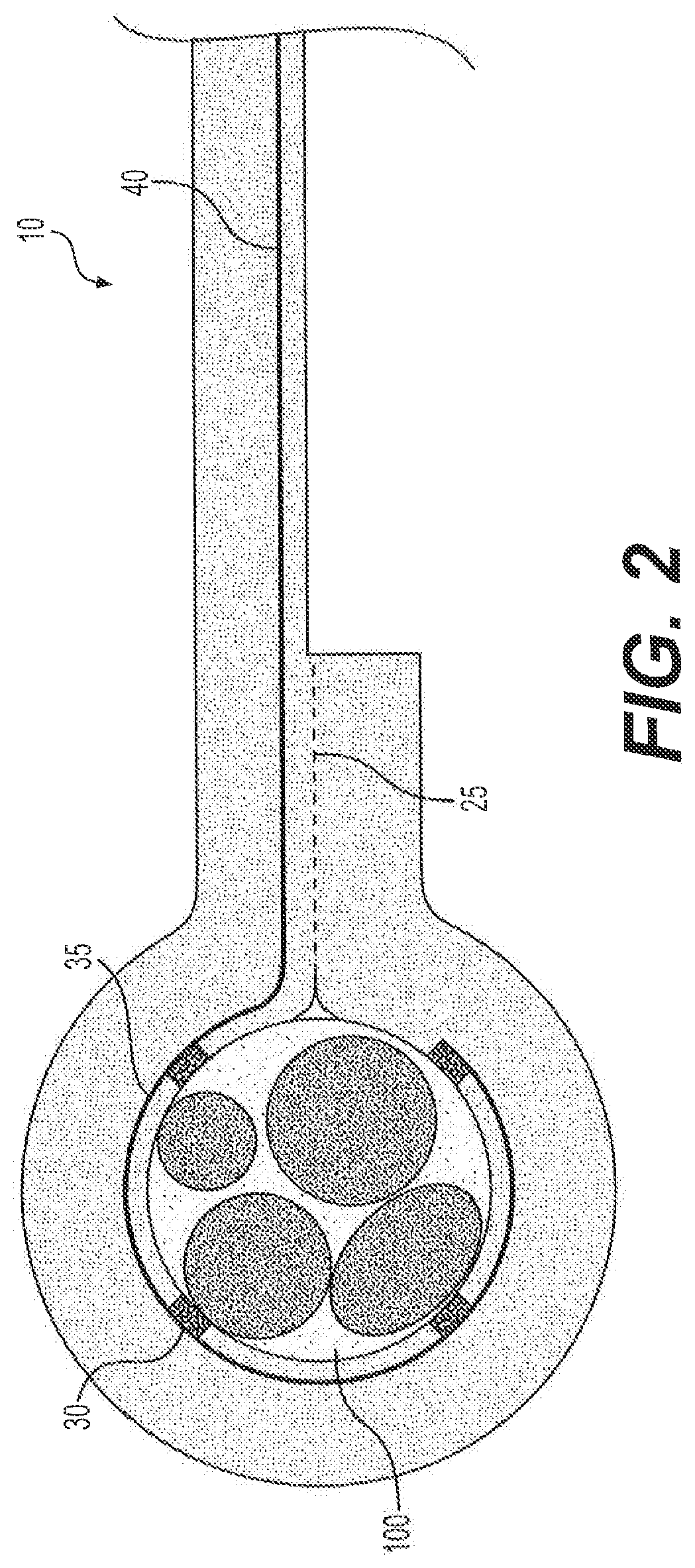
Curved paddle electrode for use with a neurostimulator
ActiveUS7006875B1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringSexual impotenceNeurovascular bundle
A curved paddle electrode allows the electrode to be placed over a relatively flat or oval shaped nerve bundle attached to fascia tissue without having to separate the nerve bundle from the fascia tissue. The electrode includes at least one suture hole that allows the electrode to be held in place over the nerve bundle through a clip-on stitch, or equivalent. In one embodiment, the curved paddle electrode provides a tripolar electrode configuration that allows three spaced-apart parallel electrode contacts to be positioned transverse to a target nerve bundle. Such electrode configuration allows bipolar or tripolar stimulation to occur. Other embodiments employ less or more than three electrode contacts. A preferred application of the curved paddle electrode is for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED), where the electrode is placed over the neurovascular bundle attached to the rectal fascia tissue near the rectum.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
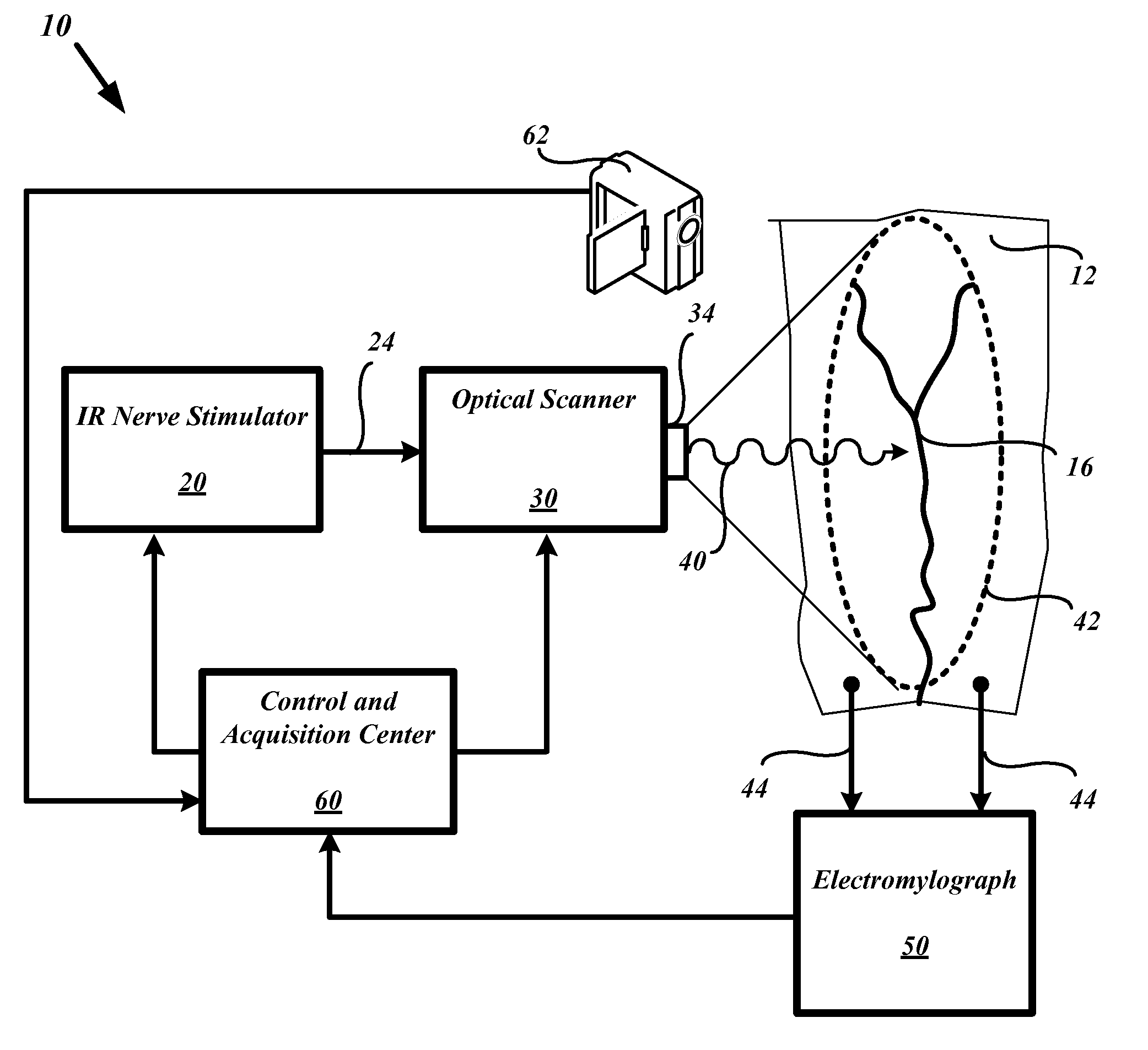
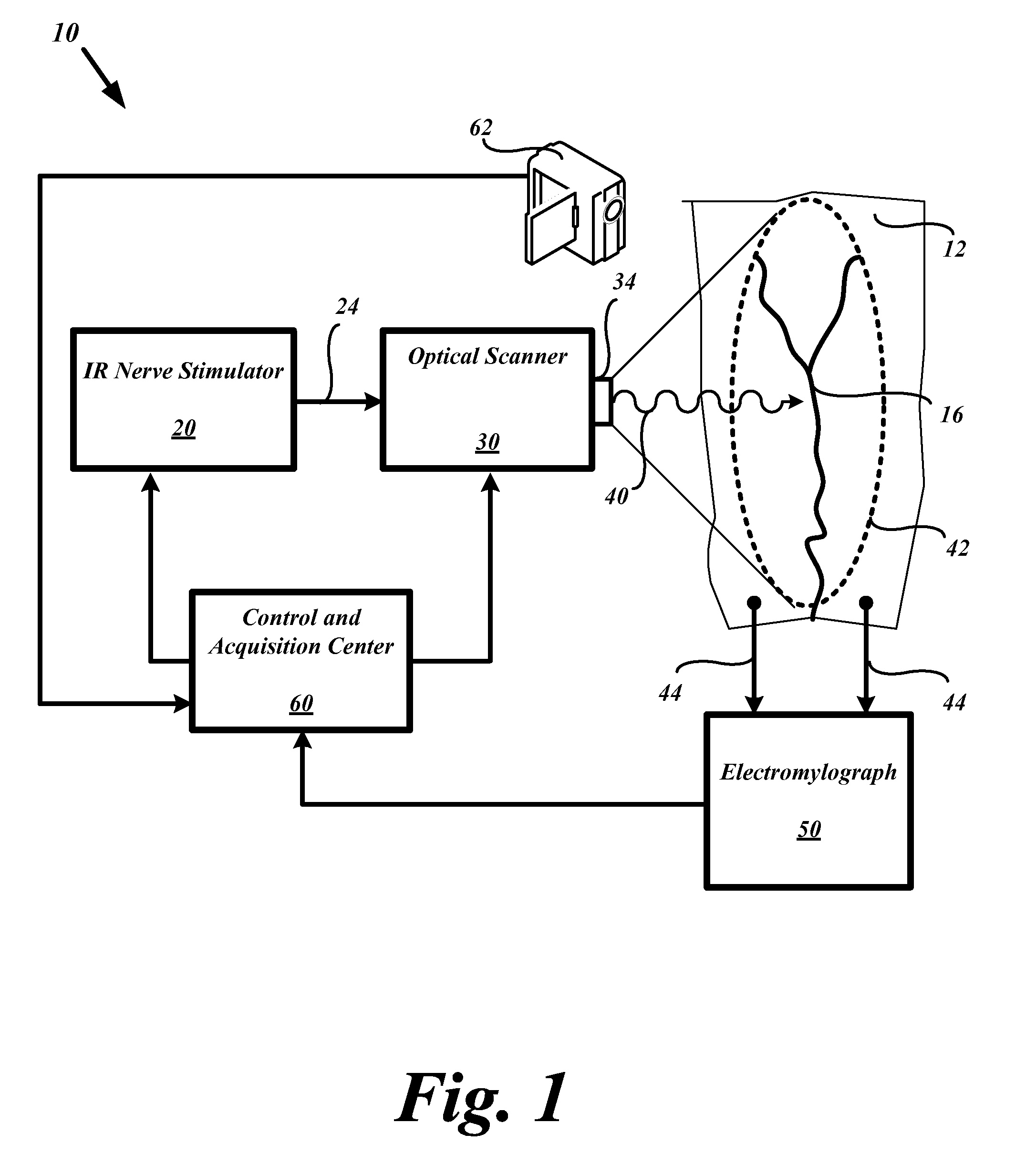
System and methods for nerve response mapping
InactiveUS20090088660A1Risk minimizationMaximize functionalityDiagnostics using lightElectromyographyMuscle tissueNEUROLOGIC REACTION
Systems and methods are described to detect and anatomically map the location of active nerves or nerve bundles before, during, or after surgical procedures. The optical-based system supports and provides for methods to stimulate nerves in a non-electrolytic manner to activate or stimulate nerves within muscular tissue within the surgical field so that a given nerve's anatomical location or level of functional activity may be made contemporaneously apparent to the surgeon or operating personnel in the form of a neural activity map. The neural activity map provides for mapping of nerve location and classifying the mapped nerves by functional levels. The contemporaneously presented neural activity map enables the surgeon or operating personnel to initially plan a neural muscular surgery before undertaking incisions, or modify the surgical procedure based upon the updated neural mapping of the surgical region of interest.
Owner:VERATHON
Surgical forceps
InactiveUS20130144313A1Comfortable and easy to maintainEnhanced surface contactFallopian occludersSurgical forcepsAnatomical structuresLymphatic vessel
This application presents a bifurcated, optimally-angled surgical forceps. In one example, this surgical forceps may enable a more natural maneuver for initial clamping of the vas deferens through the scrotal skin. This may be more comfortable for users and easier to maintain, and may provide greater tactile surface contact between the thumb and vas deferens. This device also may provide the surgeon with an entire segment of vas deferens upon which the vasectomy may be performed, thus reducing the need for frequent repositioning of instruments. The device may also be applied to other surgical procedures that may benefit from the features of the device and where a section of a tubular anatomical structure may need clamping at two points along its length. Examples include blood and lymphatic vessels, ducts of the digestive system, and large nerves or nerve bundles.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Digital stereotaxic manipulator with interfaces for use with computerized brain atlases
InactiveUS20060052689A1Least possible damageClear locationSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer monitorImage resolution
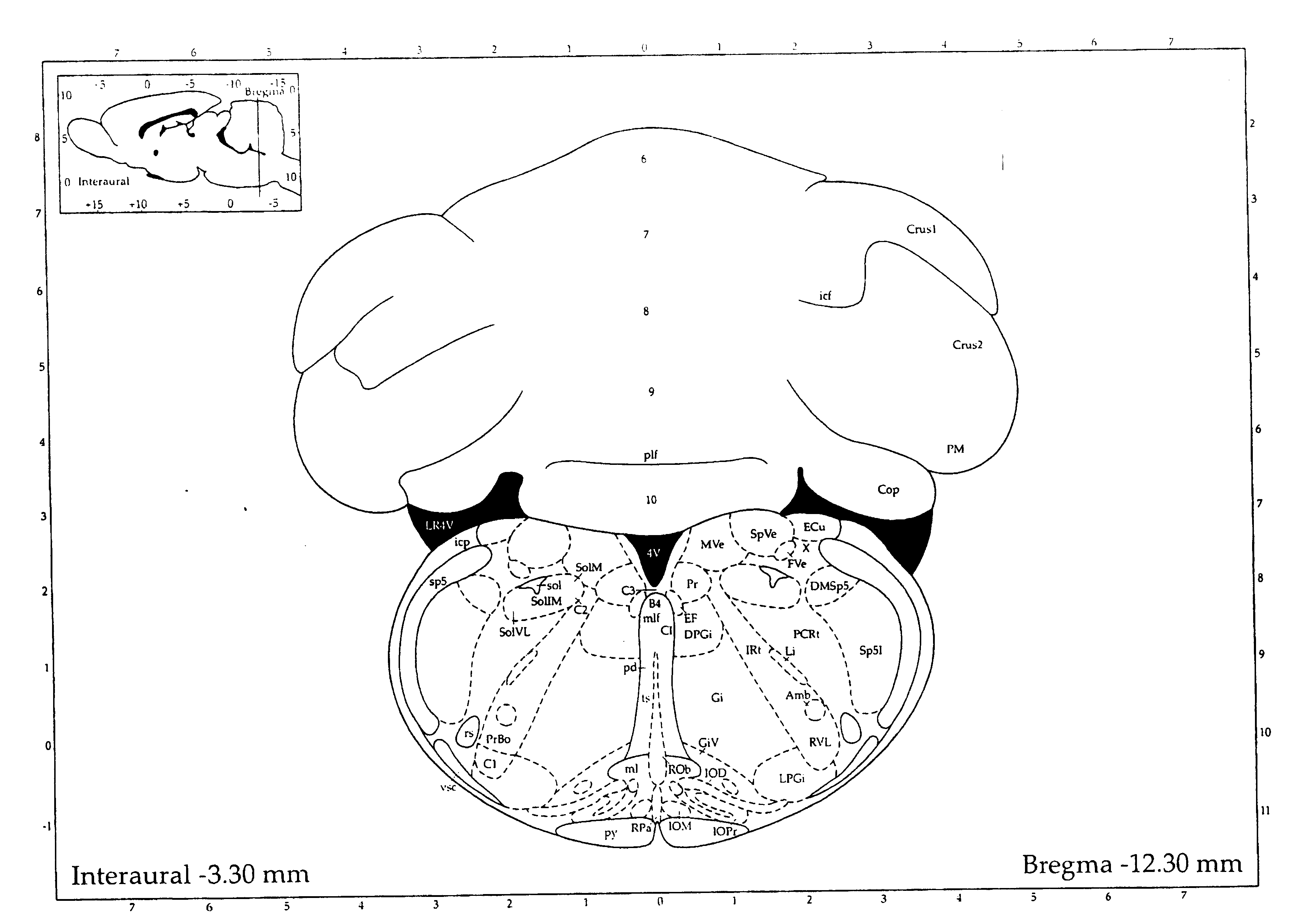
A system is disclosed that allows stereotaxic procedures being performed on lab animals to interact, on a “live” or “real-time” basis, with information that has been compiled in stereotaxic brain atlases. For example, during an invasive procedure, a researcher can see, on a cross-sectional brain map displayed on a full-sized computer monitor, the location and travel of an instrument tip, indicated by means such as a bright blinking cursor or icon. If desired, important brain structures (such as major nerve bundles) can been prominently labeled and / or colored, to clearly indicate their locations, and help the researcher ensure that they are avoided. This system can be provided by coupling a digital stereotaxic manipulator to a dedicated controller with touch-screen capability, and coupling the PLC processor to a computer having a monitor screen that is large enough to display a brain map with good resolution. Alternately, the digital stereotaxic manipulator can be coupled directly to a computer, via an interface card or other device.
Owner:SCOUTEN CHARLES W +2
Process and apparatus for soft tissue manipulation
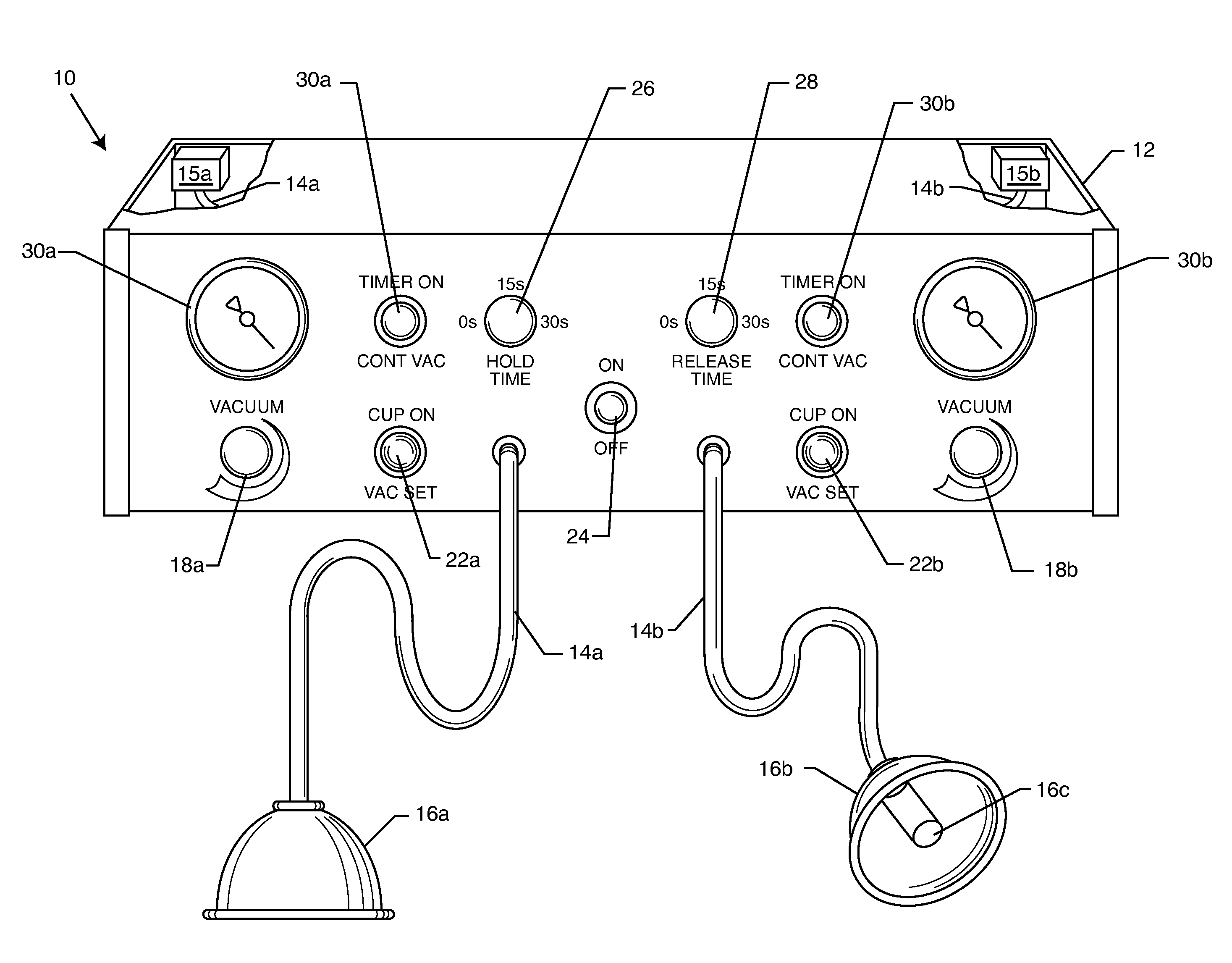
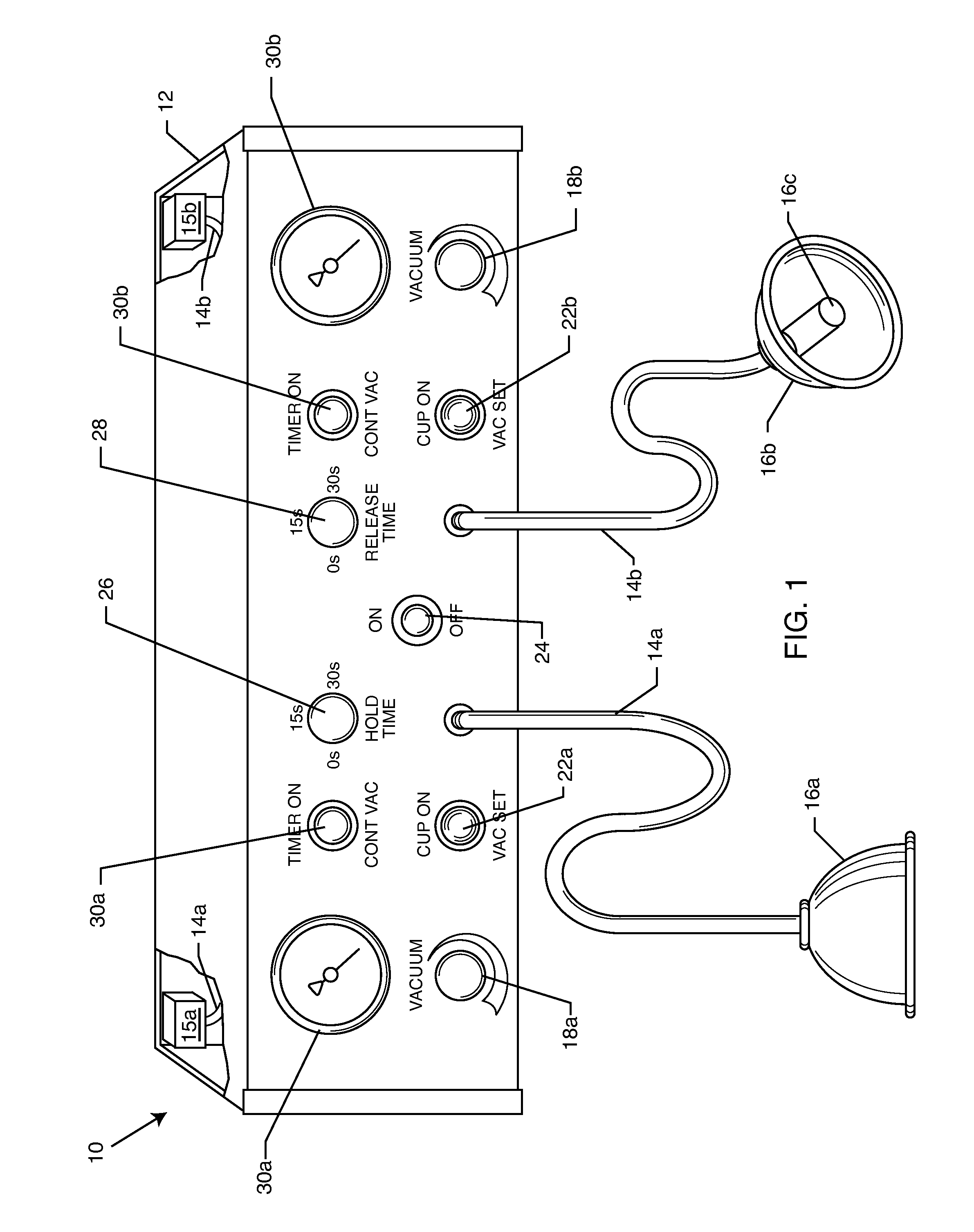
A vacuum pump apparatus for neurovascular restructuring of soft tissue includes at least two vacuum pumps connected to separate vacuum suction cups. The vacuum pumps are independently adjustable to a certain level of vacuum, as well as, hold time and release time. The vacuum suction cups are applied to areas of soft tissue that have suffered trauma or are otherwise causing pain. The vacuum action acts to lift and separate fascia and muscle tissue to allow for proper blood flow and alleviation of compression on nerve bundles.
Owner:BROOKS RONALD J
Method and apparatus for electrically stimulating the nervous system to improve ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions
ActiveUS8417334B2Improve heart functionImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesNervous systemHeart disease
A method and apparatus are used to provide therapy to a patient experiencing ventricular dysfunction or heart failure. At least one electrode is located in a region associated with nervous tissue, such as nerve bundles T1-T4, in a patient's body. Electrical stimulation is applied to the at least one electrode to improve the cardiac efficiency of the patient's heart. One or more predetermined physiologic parameters of the patient are monitored, and the electrical stimulation is adjusted based on the one or more predetermined physiologic parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Extraluminal balloon dissection
InactiveUS20060106414A1Shorten predeploymentShorten balloonBalloon catheterCannulasVeinLymphatic vessel
The present invention provides balloon dissection apparatus and methods of use in which an elongate balloon is utilized to dissect along a region that follows a naturally existing path alongside a vessel or structure, such as an entry, a vein, a lymphatic vessel, the traches, the esophagus, or even a nerve bundle.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP +1
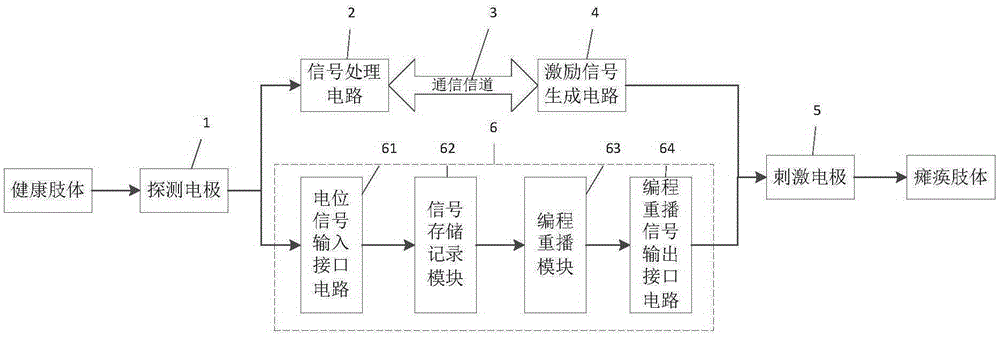
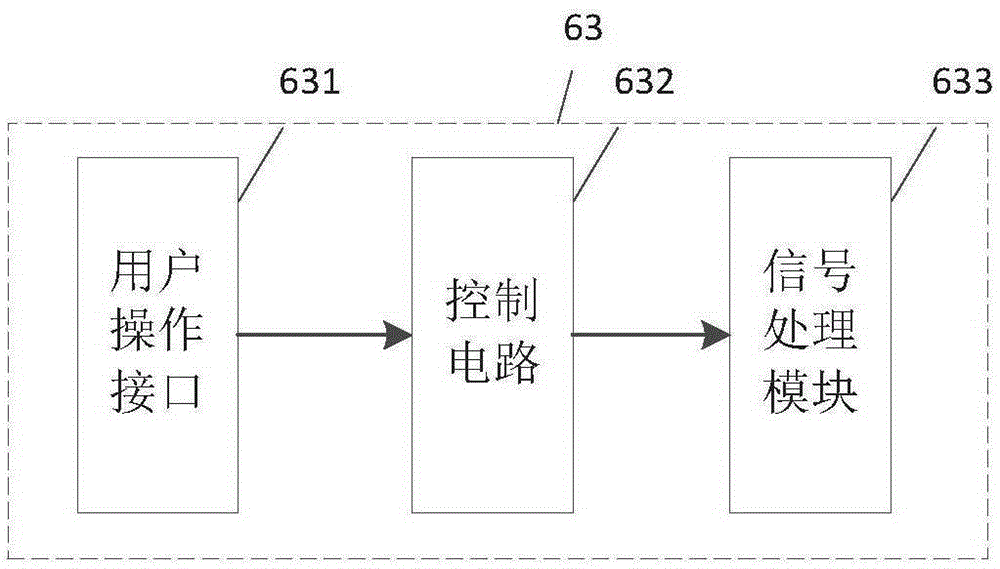
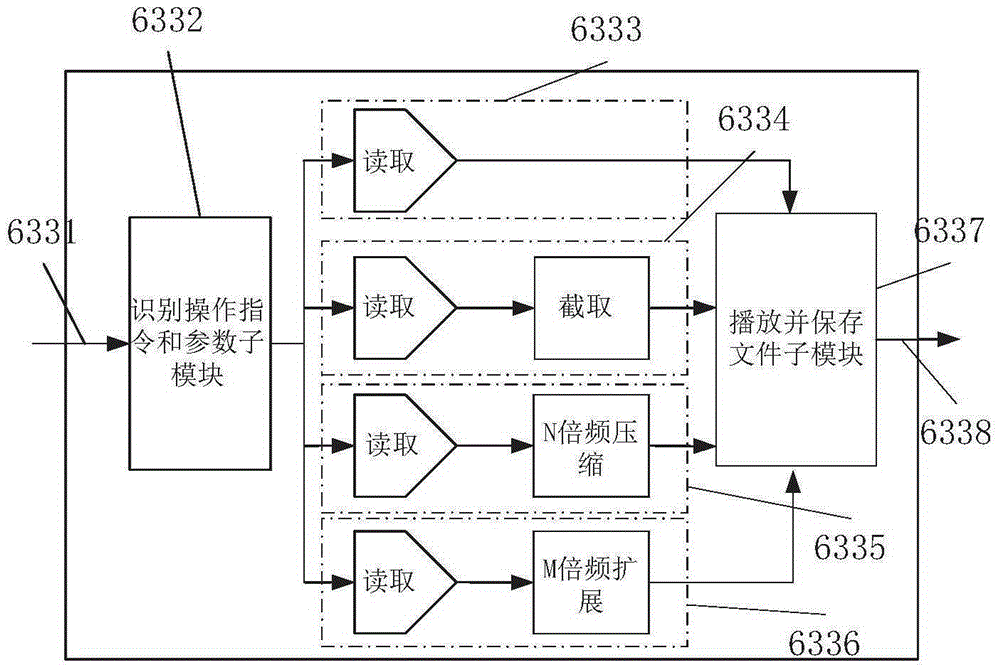
Implantable electrostimulation limb movement function regulation device
ActiveCN105311749AAchieve movementHigh control sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVoltage pulseSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses an implantable electrostimulation limb movement function regulation device. A body surface detecting electrode is adopted to collect body surface myoelectric action potential signals during movement at a site corresponding to a healthy limb, the body surface myoelectric action potential signals are amplified and filtered by a signal processing circuit, pulse amplitude modulation technology is utilized to modulate the body surface myoelectric action potential signals onto high-frequency carriers, high-frequency signals after being modulated are applied onto an in-vitro coil to generate a high-frequency electromagnetic field, the in-vitro coil is coupled on a coil of an in-vivo implantable electrode to generate high-frequency voltage, stimulating voltage pulse is formed after amplitude detection, the stimulating voltage pulse is applied onto an in-vivo electrode contacting with a controlled nerve bundle, and action potential is excited in the nerve bundle so as to realize movement of a paralytic limb. The body surface electrode is pasted on the healthy limb to acquire movement related myoelectric signals, so that the device has the advantage of non-intrusion; the in-vivo implantable electrode is adopted for functional electrostimulation, so that the device has the advantages of low stimulation voltage, high control sensitivity and high selectivity.
Owner:NANJING SHENQIAO MEDICAL EQUIP
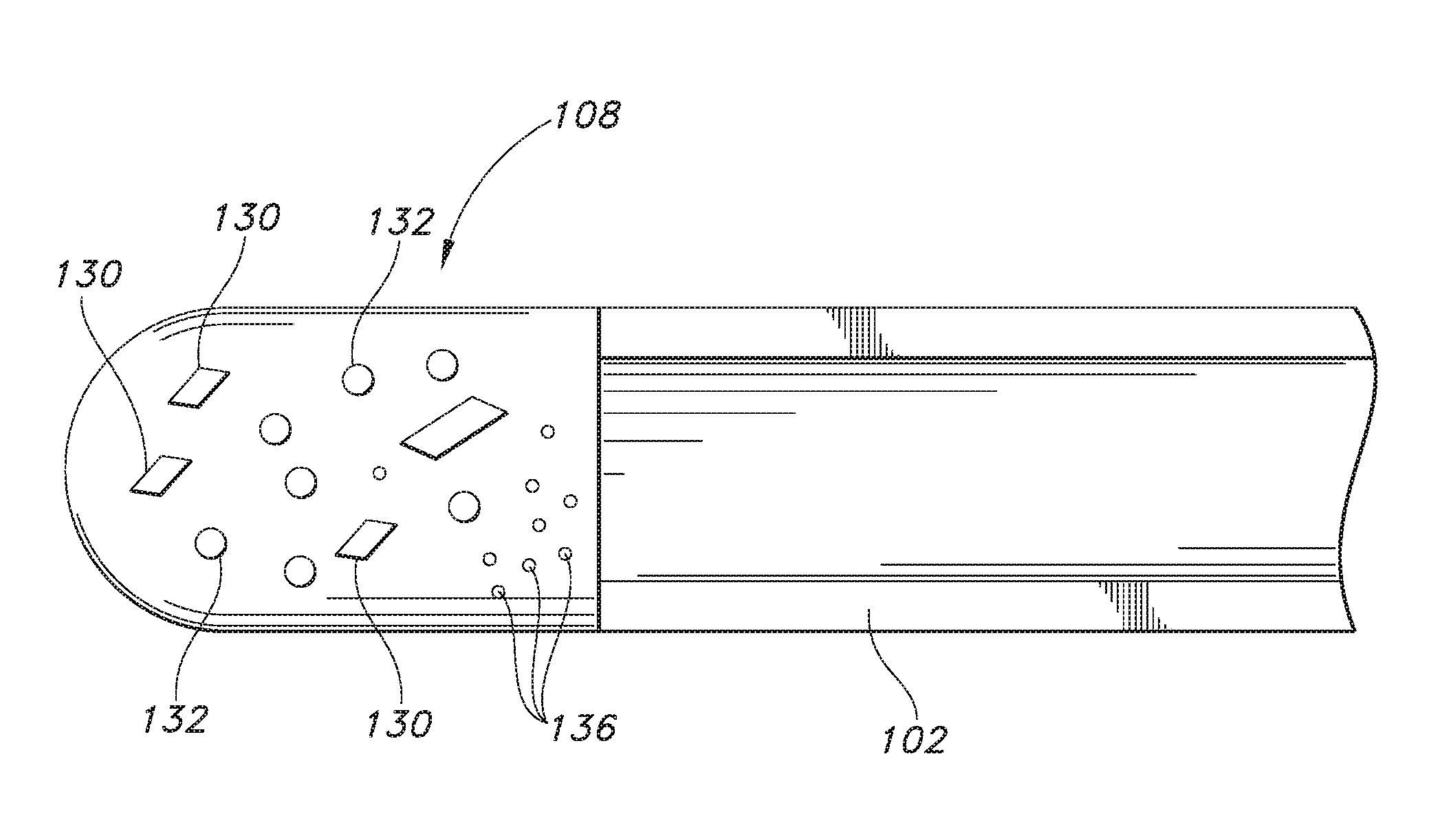
Echogenic nerve block apparatus and system
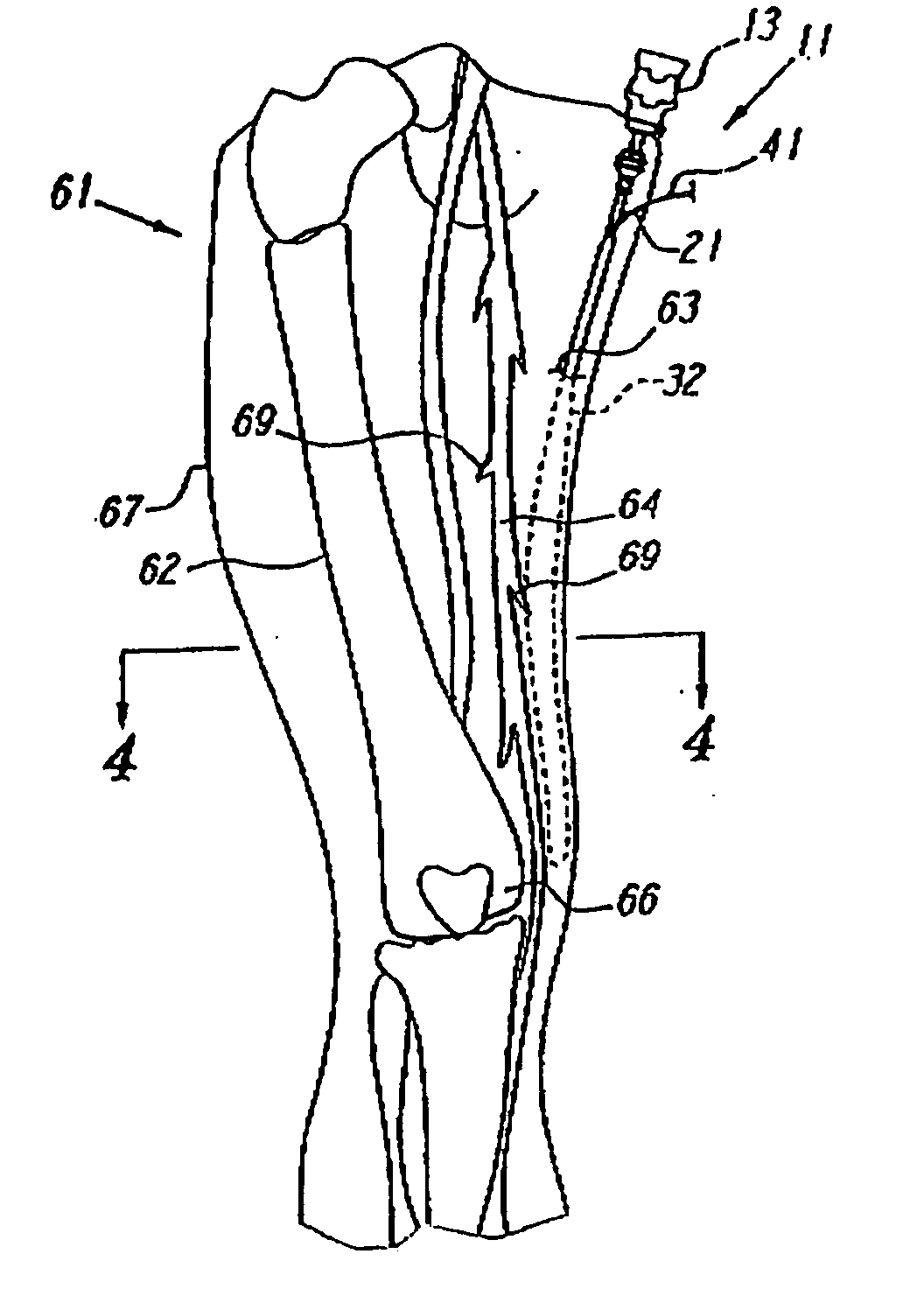
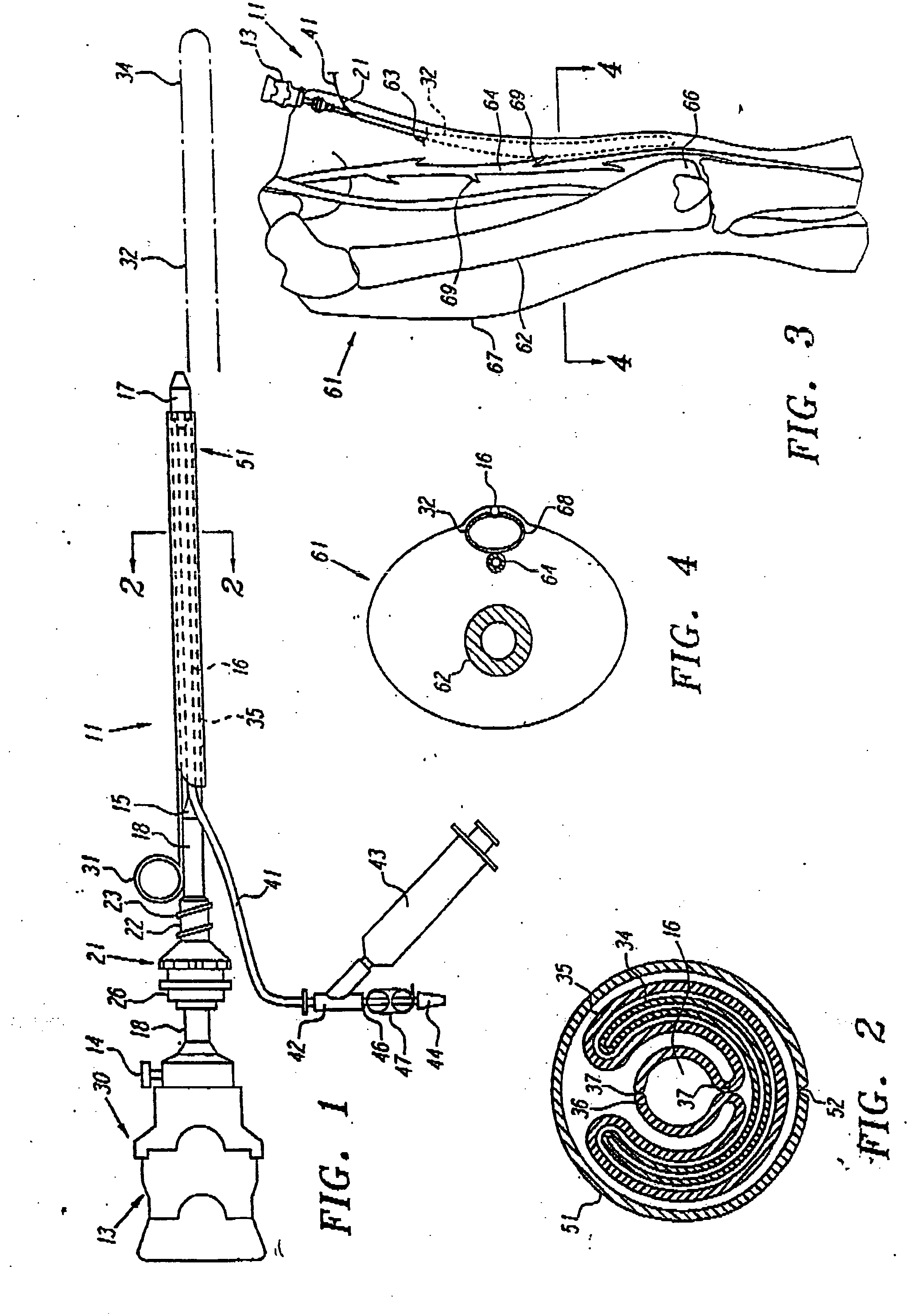
An apparatus for performing a nerve block procedure, the apparatus being composed of an echogenic needle or an echogenic soft tissue tunneling device and an echogenic catheter configured for controlled delivery of a medication. The apparatus may further include a sheath such that at least one of the needle or tunneling device and sheath is echogenic. The present invention also encompasses a system for performing a nerve block procedure, the system includes introducing an echogenic needle in the general area of a nerve bundle, positioning the echogenic needle adjacent the nerve bundle utilizing sonic imaging techniques, introducing an echogenic catheter configured for controlled delivery of a fluid through the echogenic needle, withdrawing the echogenic needle, positioning the echogenic catheter adjacent the nerve bundle utilizing sonic imaging techniques, and delivering fluid to the nerve bundle through the echogenic catheter.
Owner:AVENT INC
Nerve graft and nerve graft system using same
ActiveCN106822993AImprove match rateImplement category guidanceTissue regenerationProsthesisGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factorDisease
The invention provides a nerve graft and a nerve graft system using the same, and relates to the technical field of medical engineering. The nerve graft provided by the invention comprises a sensory nerve bundle passage, a moving nerve bundle passage and a mixed nerve bundle passage; all nerve bundle passages are matched with the nerve bundles of the corresponding sections of normal nerve, and are respectively filled with NGF (nerve growth factor), GDNF (glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor), and NGF and GDNF. The nerve graft provided by the invention is matched with the nerve section to be restored in appearance; the inside nerve bundle passage trend is also precisely matched with the nerve bundle to be restored. Secondly, different nerve nutrition factors are respectively loaded in the nerve graft; the promotion and the direction guide can be performed for the nerve bundles with different functions; the matching rate of the nerve graft and the receptor nerve can be improved; the classified guidance on different nerve bundles can be realized; the nerve restoration effect is improved. In addition, the invention also provides the nerve graft system using the nerve graft so as to treat complicated nerve defect diseases and patients.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +2
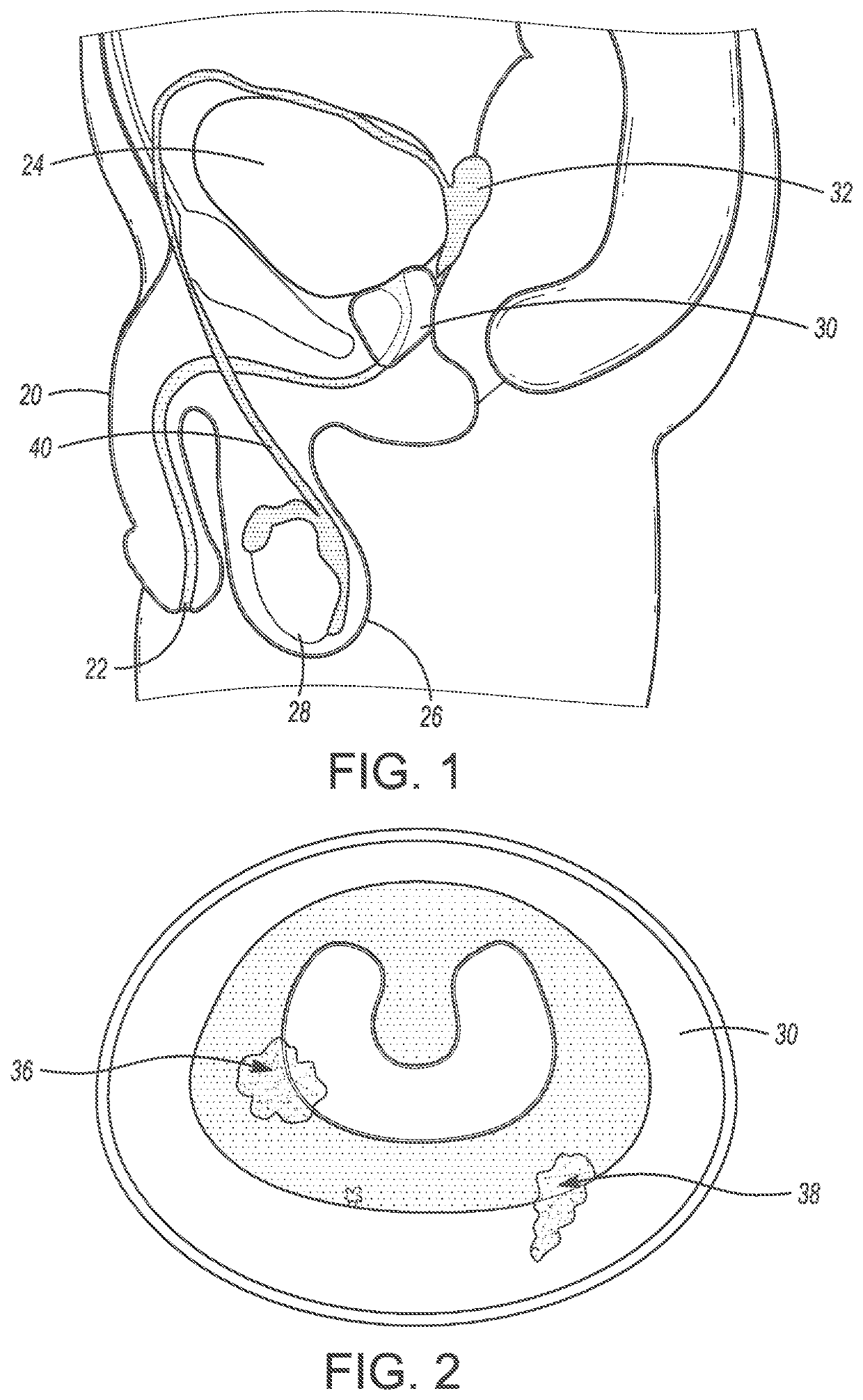
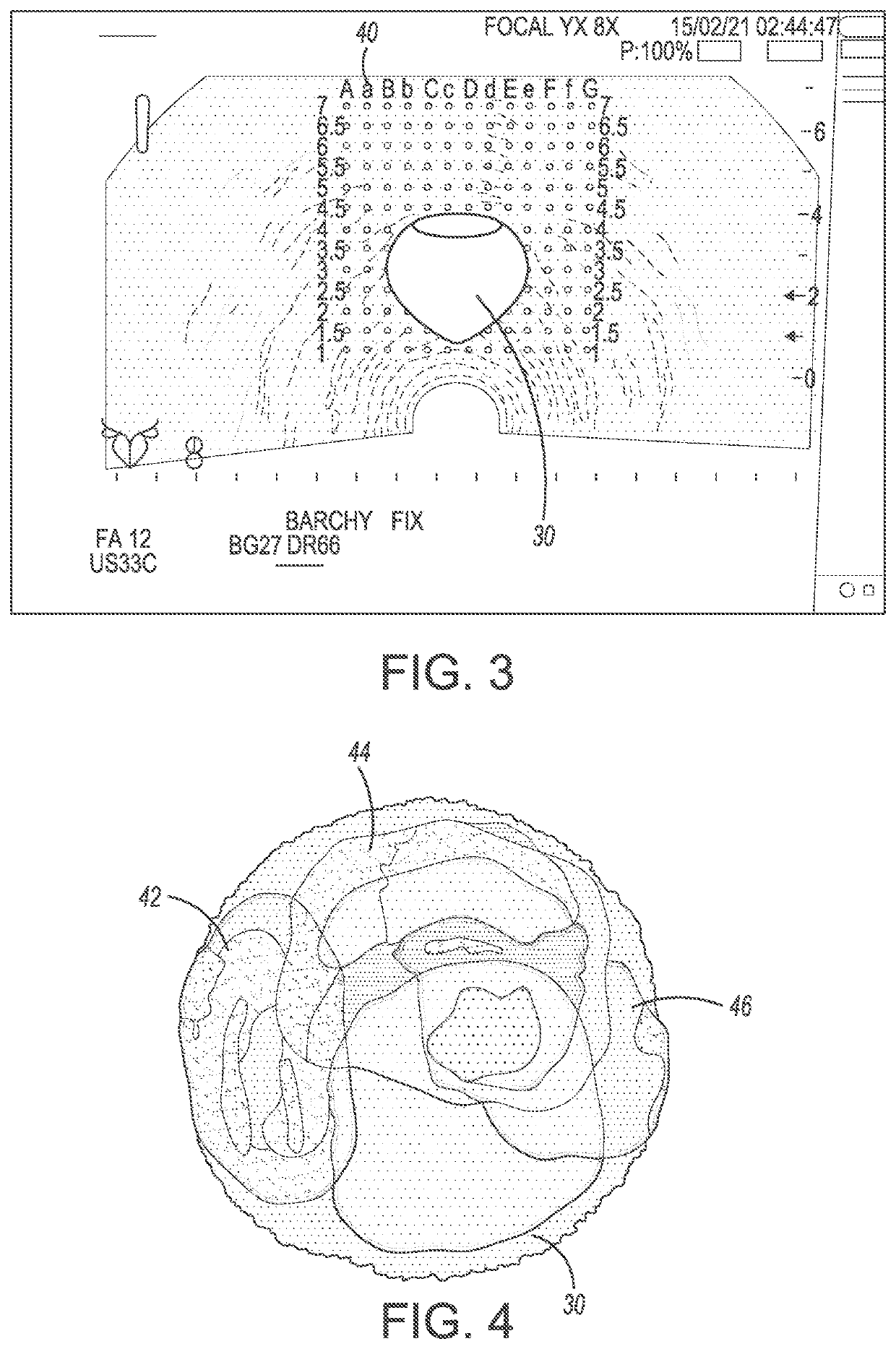
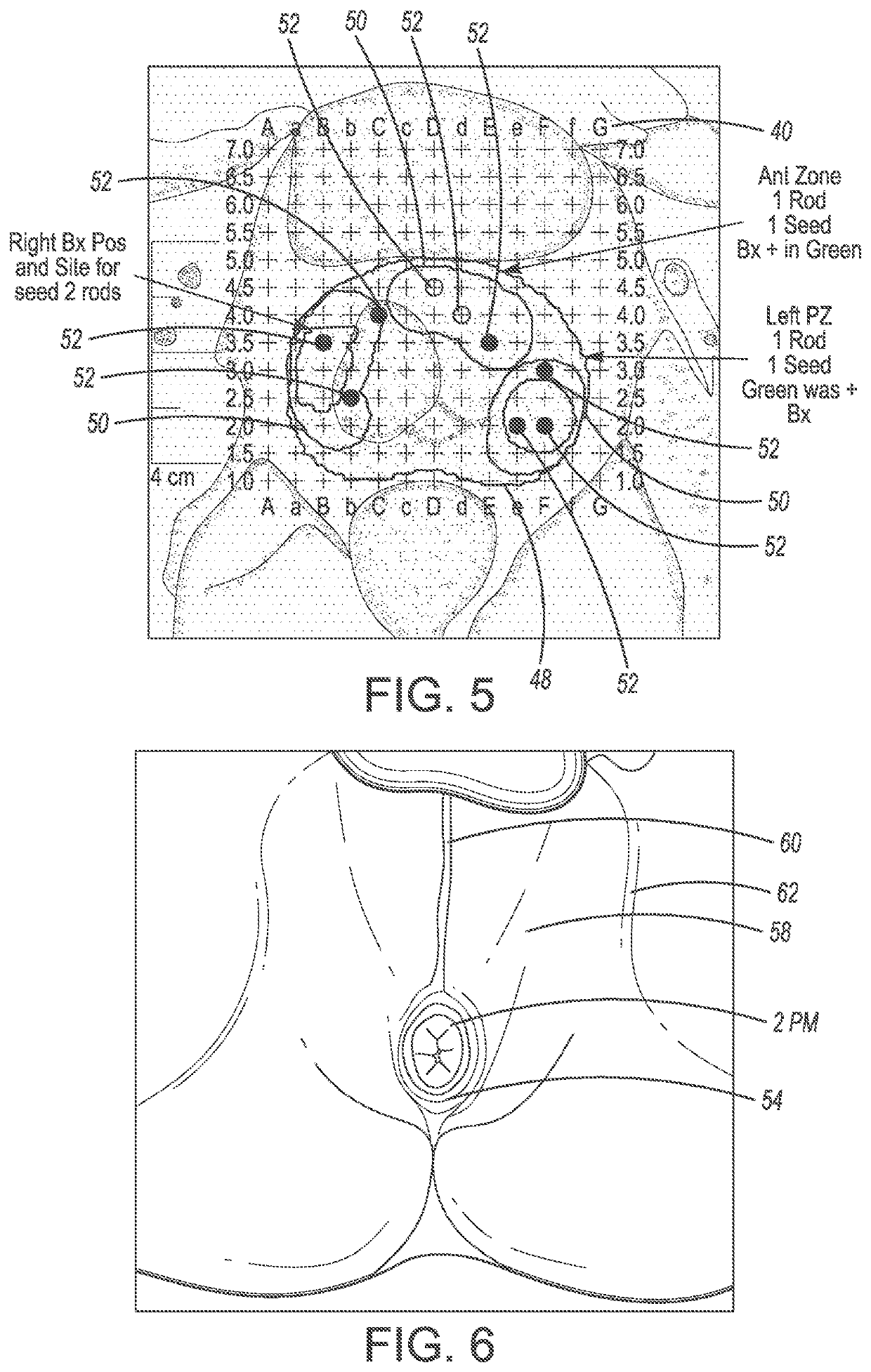
System and method for prostate treatment under local anesthesia
A system and method for prostate cancer treatment under local anesthesia includes creating a superficial skin and subcutaneous block in a perineal area of a patient by administering a first anesthetizing agent; creating a deep nerve block under ultrasound guidance by administering a second anesthetizing agent, the second anesthetizing agent infiltrating cavernosal nerve bundle tissue and periprostatic space; and ablating prostate tissue. The office-based method, statistical models and computer generated treatment plans identify and ablate prostate tissue containing cancer through or via the perineum while preserving prostate function, and critical anatomical structures. Multiple technologies are integrated and processed to deliver a safe treatment procedure, under local anesthesia by integrating the information of magnetic resonance imaging and planning the ablative treatment using algorithms that ensure maximal precision in both killing cancerous tissue and preserving healthy tissue along with its corresponding function.
Owner:SMARTBLATE LLC
Catheter with Seal Layer
A catheter assembly for locating an object of interest (e.g., an anatomical region such as a muscle, nerve bundle, etc.) is provided. The catheter assembly includes a catheter having a catheter body defining a proximal end and a distal end; a transducer located at the distal end of the catheter; one or more transducer wires extending from a proximal end of the transducer towards the proximal end of the catheter; and a length of tubing surrounding the catheter, the transducer, and the one or more transducer wires, wherein the length of tubing has a proximal portion and a distal portion, wherein the proximal portion surrounds the one or more transducer wires and the distal portion surrounds the transducer, wherein the proximal portion includes a conductive filler.
Owner:AVENT INC
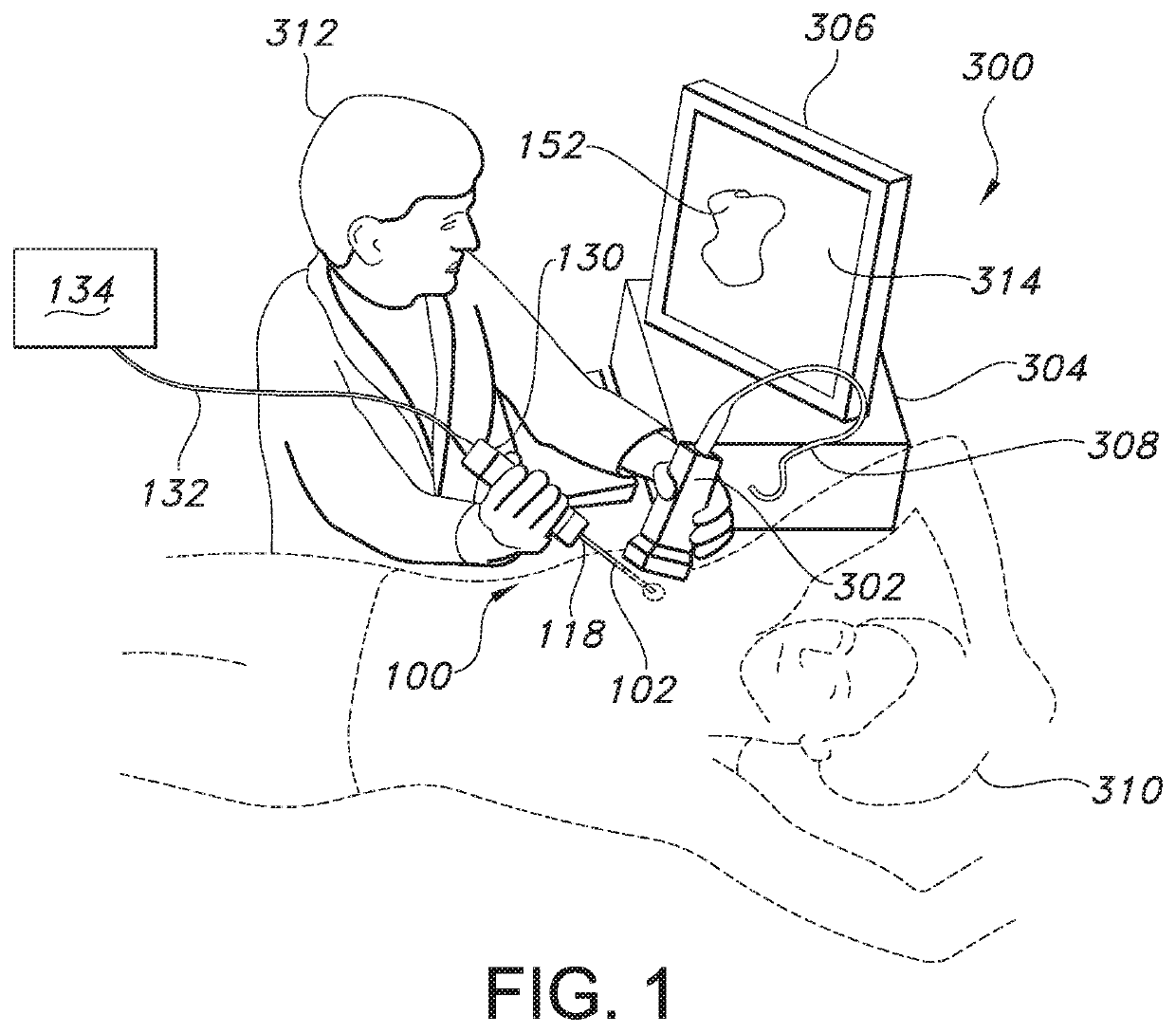
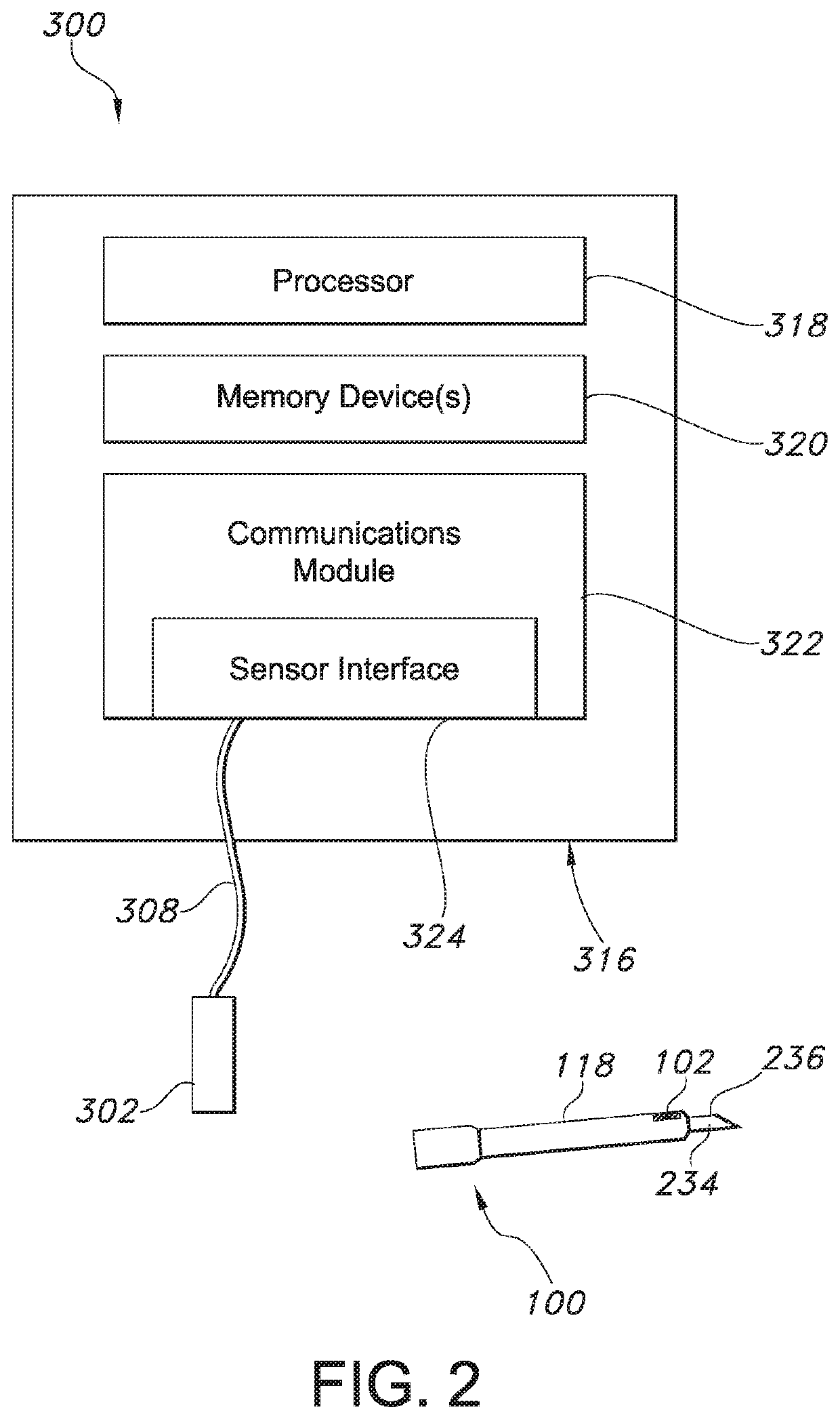
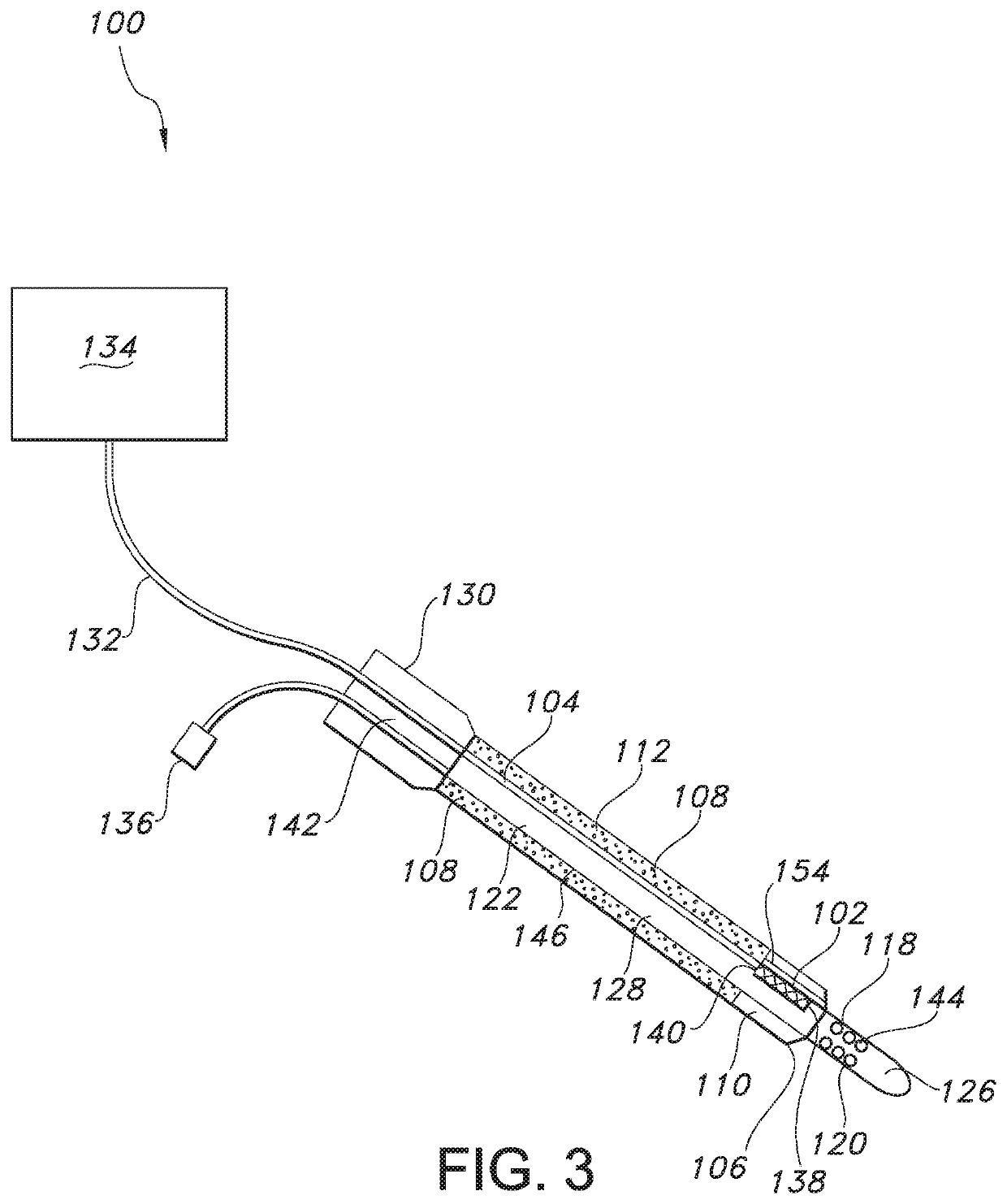
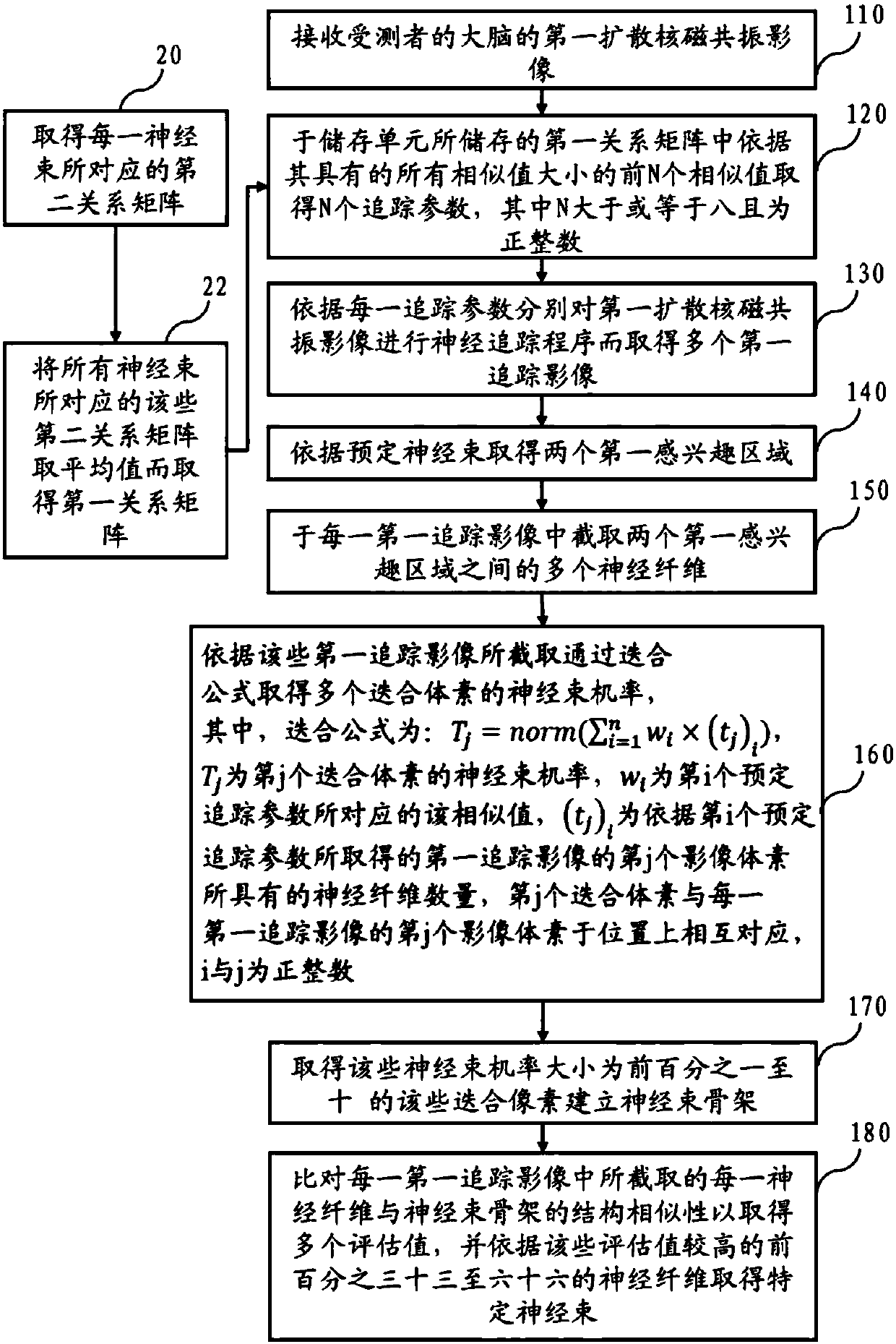
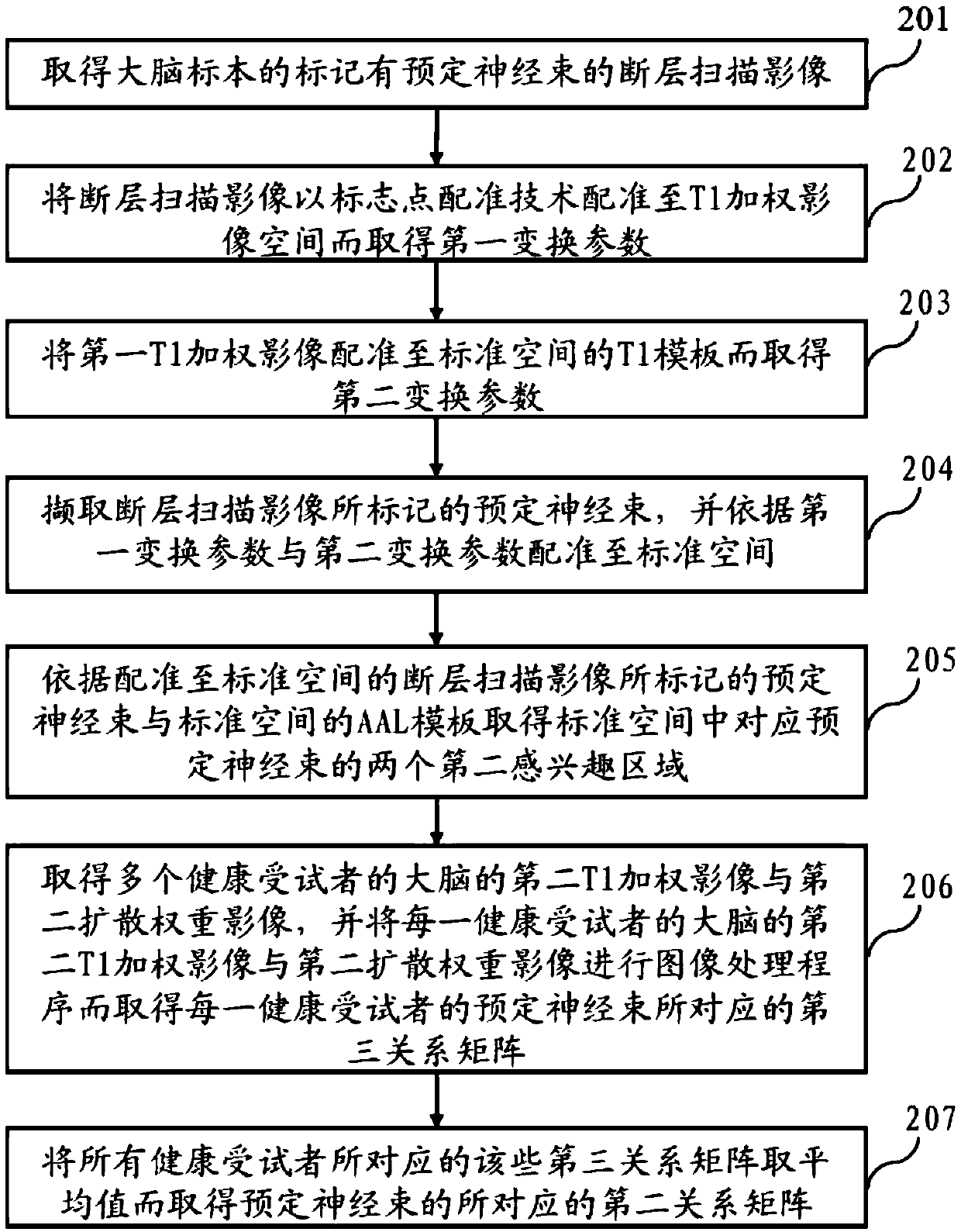
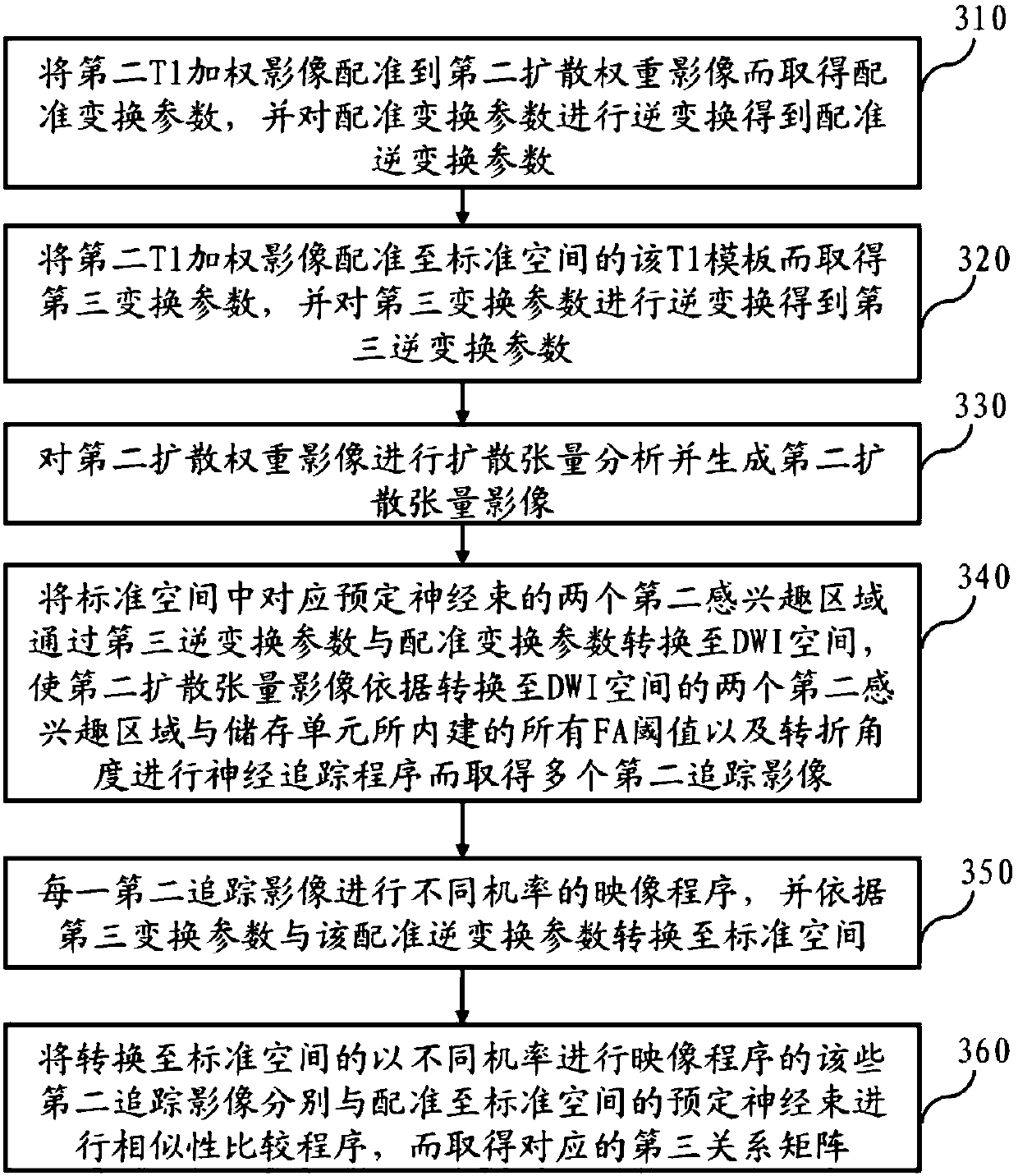
Method for nerve tracking, non-transitory computer readable medium and apparatus
ActiveCN109741290AIncreased sensitivityImprove navigation performanceImage analysisPattern recognitionNerve fiber bundle
The invention discloses a method for nerve tracking, a non-temporary computer readable medium and equipment. The method includes performing a neural tracking procedure on the diffusion nuclear magnetic resonance image of the brain of the subject through a plurality of verified better tracking parameters to obtain a plurality of first tracking images; intercepting a plurality of nerve fibers between the two first regions of interest from each first tracking image; and establishing a nerve bundle skeleton from the nerve fibers intercepted by the plurality of first tracking images according to asuperposition program, and finally selecting a plurality of nerve fibers with a structure similar to that of the nerve bundle skeleton to obtain a specific nerve bundle of the tested person. Accordingly, the method for nerve tracking, non-transitory computer-readable medium, and apparatus may be used to achieve improved sensitivity to nerve tracking, and contribute to improving effects of pre-operative assessment and intra-operative navigation.
Owner:上海爱谨人工智能科技有限公司
Echogenic Nerve Block Apparatus and System
Owner:AVENT INC
Identification of ligands that enable endocytosis, using in vivo manipulation of neuronal fibers
InactiveUS20060280724A1Efficient transportAvoiding and minimizingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberOrthodontic ligature
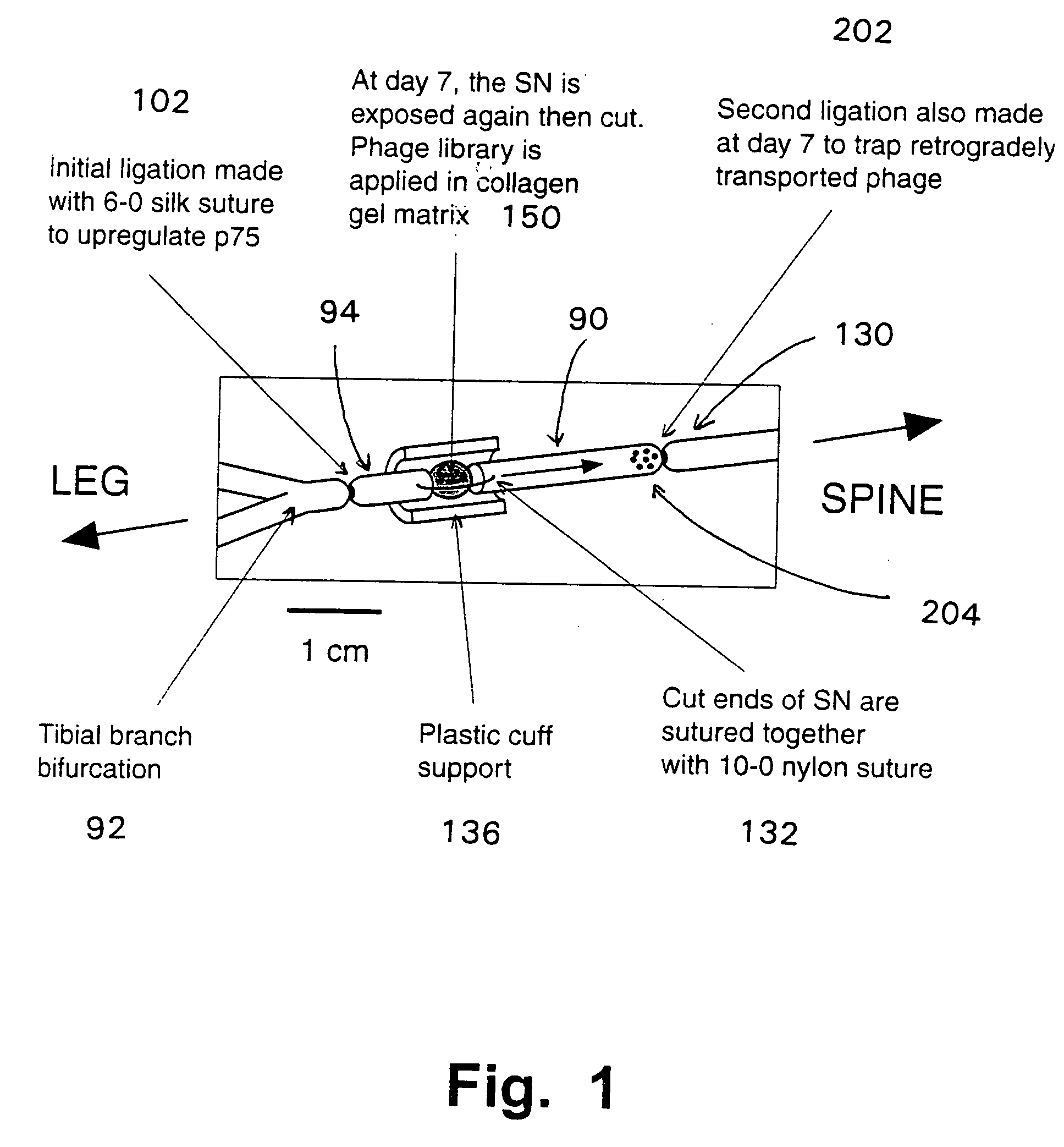
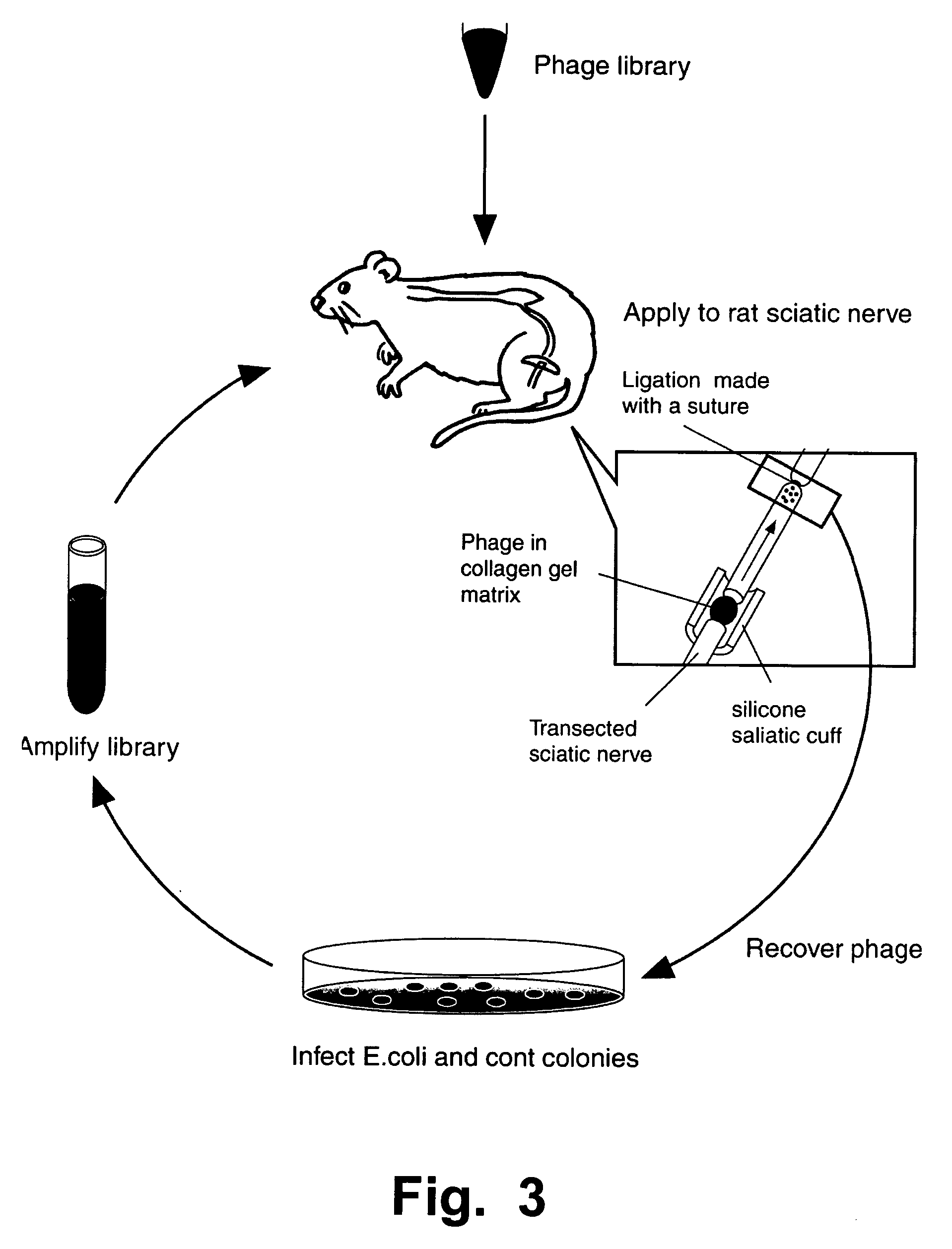
In vivo screening is used to identify and isolate ligands that drive endocytosis (internalisation) of molecules into animal cells. These ligands can transport passenger molecules (drug or diagnostic compounds, genetic vectors, etc.) into targeted classes of cells. A population of candidate ligands, such as a phage display or combinatorial library, is placed in a rat leg, in contact with a sciatic nerve bundle, and a ligature is tightened around the same nerve bundle at the hip. After a delay, to enable ligands that bind to endocytotic receptors on the nerve fibers to be internalised and transported within the fibers, fiber segments are harvested from the ligature site in the hip. Ligands that entered the harvested nerve segments can be isolated, sequenced, reproduced, etc. If desired, rats can be transformed to express human endocytotic receptors, to allow selection of ligands that will be transported into targeted human cells.
Owner:FERGUSON IAN +1
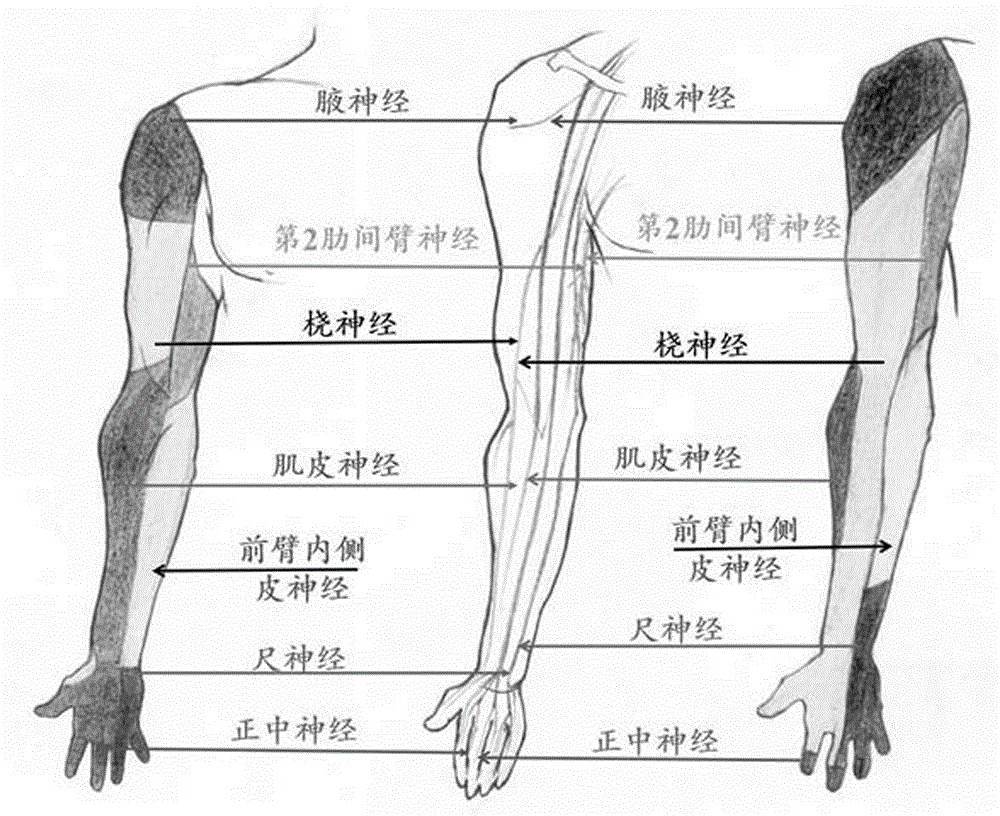
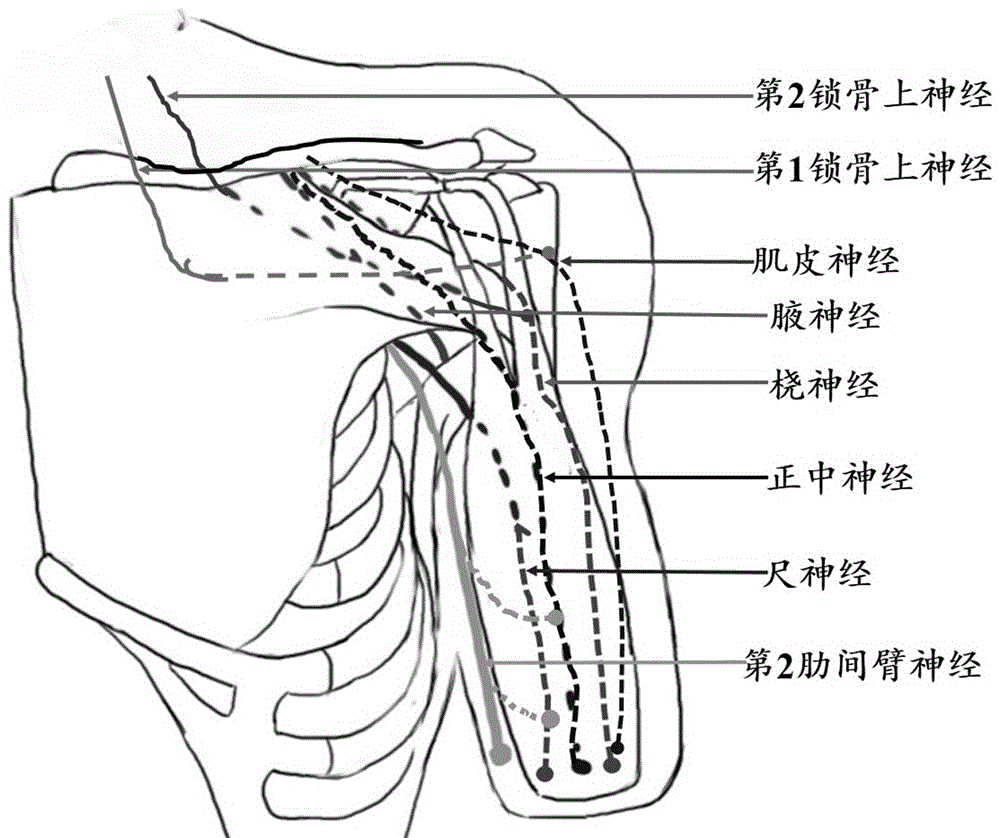
Method for reconstructing sensory nerve functions of amputation upper limbs and method for sensory nerve and artificial limb interfaces
InactiveCN105769396AFeeling resolvedThe technical method is simpleProsthesisSomesthetic areaPlexus brachialis
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing sensory nerve functions of amputation upper limbs and a method for reconstructing sensory nerve and artificial limb interfaces.The method for reconstructing the sensory nerve functions of the amputation upper limbs includes steps of separating sensory branches of various nerve bundles of remaining brachial plexus nerves of amputation patients and connecting the nerve sensory branches with sensory nerves in target sensory regions; adding different sensory sensors into nerve artificial limbs, timely transmitting external stimulation in contact with the artificial limbs to the target sensory regions of the limbs of the amputees by the aid of a stimulation input process and further transmitting the external stimulation in contact with the artificial limbs to sensory center regions of the brains of the amputees by the aid of the reconstructed target sensory regions of the limbs.The methods have the advantages that the brachial plexus nerves remained after the upper limbs of the amputation patients are amputated are connected into the selected target sensory regions, sensory innervation regions of the limbs can be reconstructed in the target sensory regions by the brachial plexus nerves, the limb sensory functions lost due to amputation can be reconstructed, and accordingly interfaces functions of remaining limb sensory and multifunctional nerve artificial limb sensory can be implemented.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nerve fiber model for quality control of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109157218AImprove the simulation effectNo toxicityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFiberImaging quality
The invention discloses a nerve fiber model for quality control of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging and a preparation method thereof. The model comprises a magnetic resonance compatible container,agarose gel placed in the container and orderly arranged electrospun fibers having a channel structure immobilized in the agarose gel, wherein the mass concentration of the agarose gel is 1-2%, and the outer diameter of the duct of the electrospun fiber with the duct structure is 1-20 microns, and that pipe is filled with water. The spinning fibers with the channel structure are fixed in the agarose gel according to the spatial distribution of the main nerve bundles of the human brain in the human brain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Making method of sandwich-type composite membrane stent
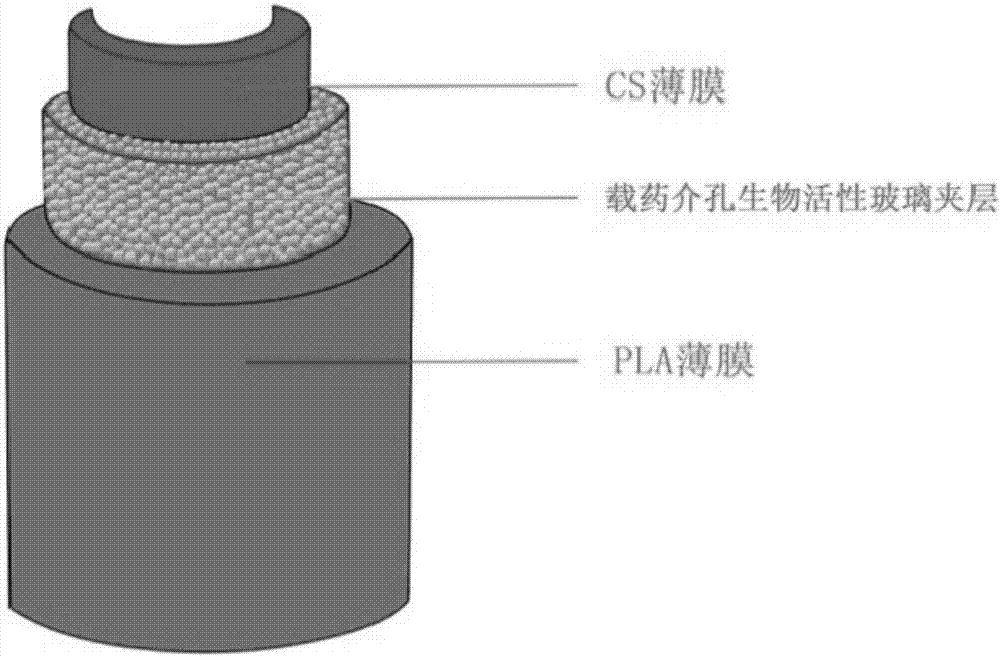
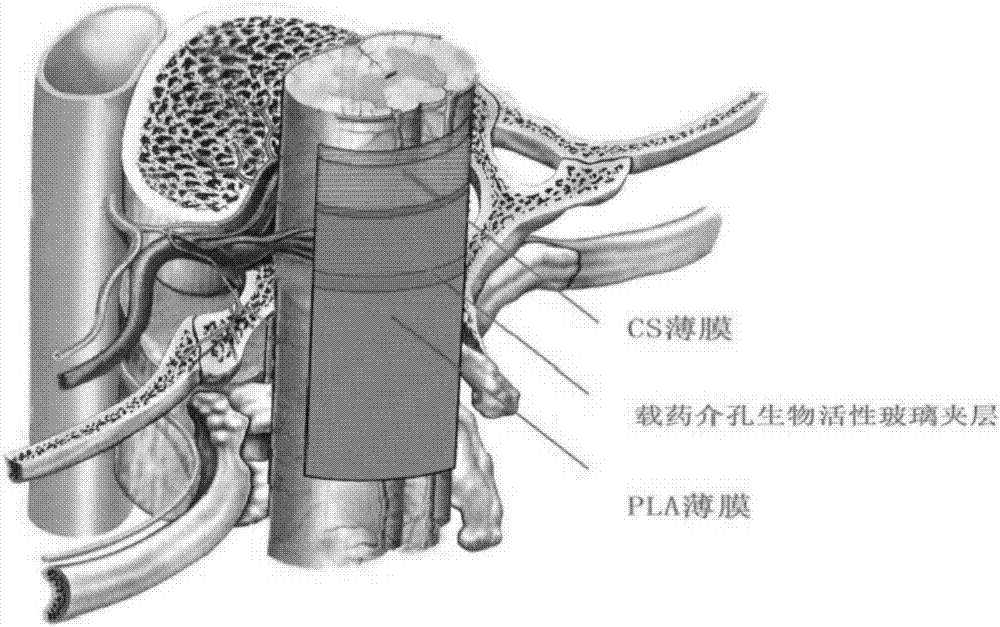
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a sandwich-type composite membrane support, constructing a polylactic acid / bioactive glass / chitosan sandwich-type composite membrane carrier loaded with biologically active factors; comprising the following steps: Mesoporous bioactive glass with active factors, chitosan membrane loaded with seed cells as the outer sealing layer, sandwich layer and inner controlled release and stem cell scaffold layer; 2) The sandwich layer of bioactive glass loaded with bioactive factors is covered on the polymer On the lactic acid film, the chitosan membrane loaded with seed cells was covered on the bioactive glass layer to construct a sandwich composite membrane carrier. To solve the problem that a single nerve bundle that has been damaged (but not dead) cannot be repaired and treated by the existing technology; the existing drug-loading system cannot achieve the directional release of the drug and cannot guarantee the high concentration of the damaged local factors.
Owner:无锡市锡山人民医院
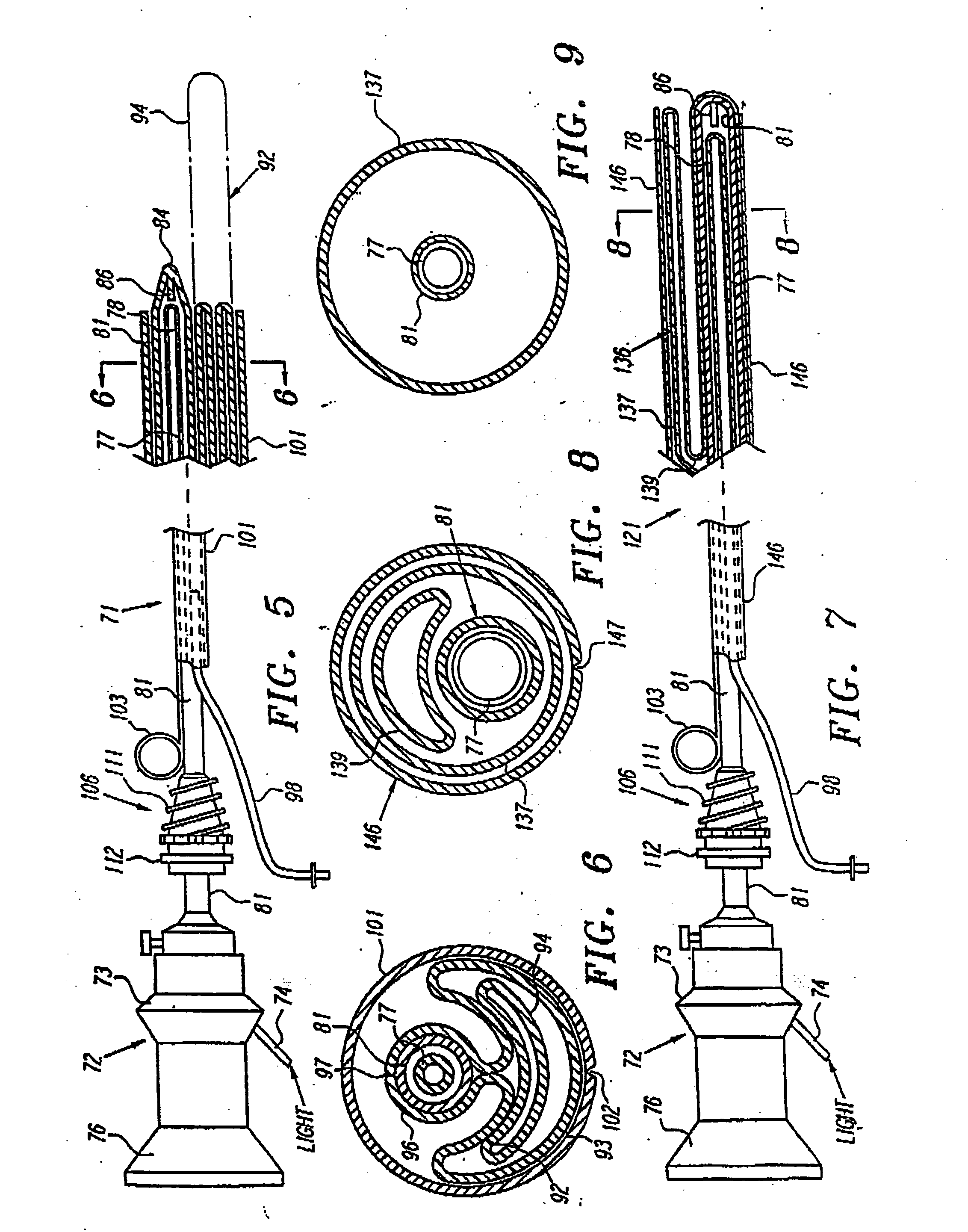
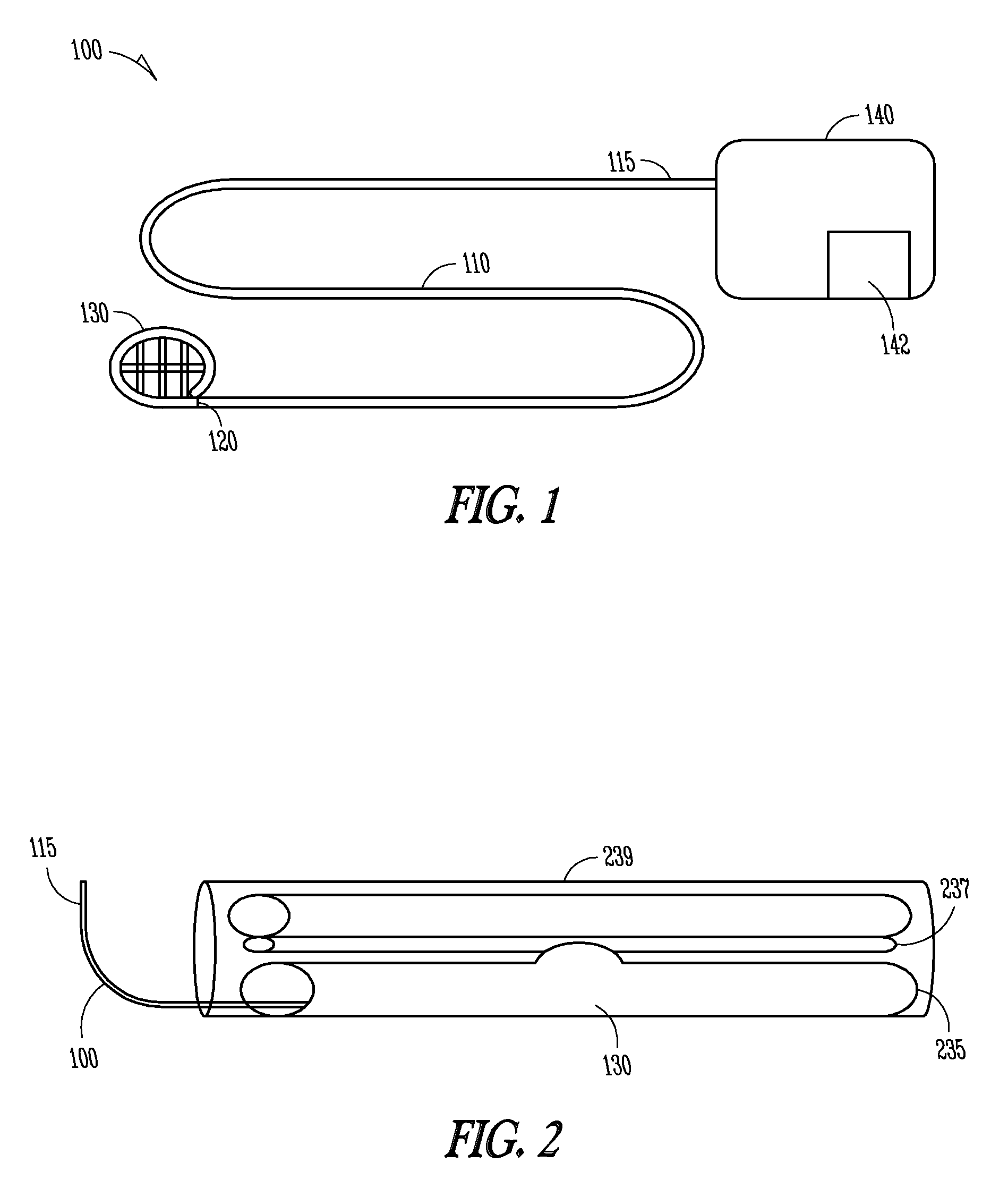
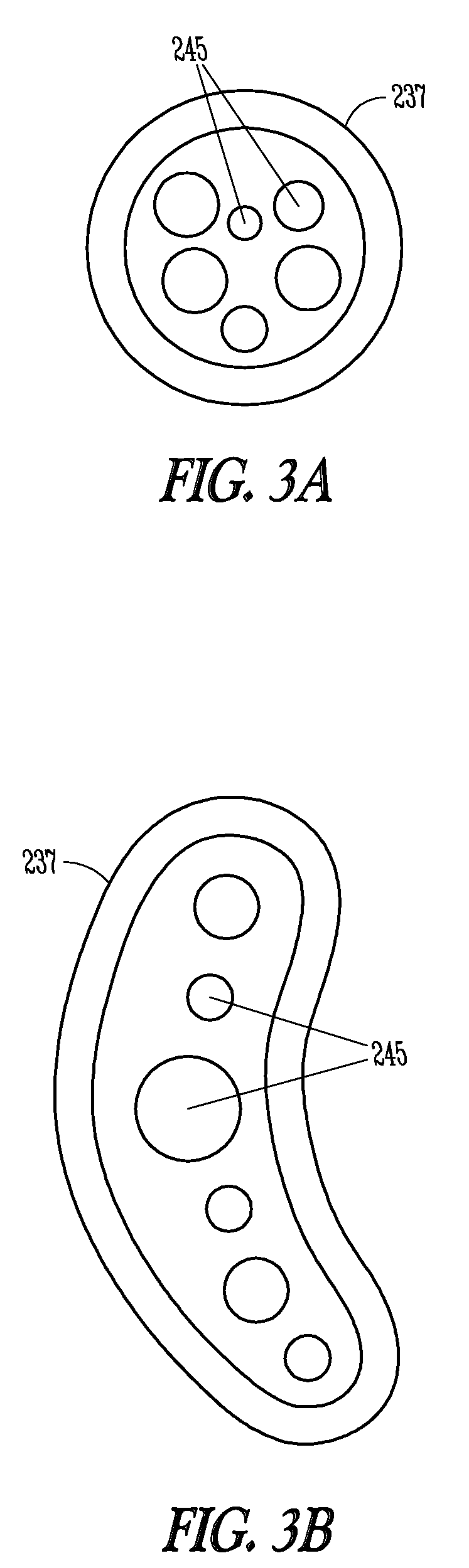
Extraneural cuff with flexible interconnects for stimulation and recording
PendingUS20210205622A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorPhysical therapy
An electrode system for neuromodulation and for recording of signals indicative of nerve activity is provided. The system can include a plurality of electrodes provided on a flexible, non-conductive substrate. The substrate can be rolled into a cuff for encircling a nerve bundle of a patient. The plurality of electrodes on the cuff can be interconnected using flexible conductors provided on the substrate. In one implementation, the electrodes can be interconnected using conductors that have spring-like configuration. Flexibility of the conductors allows the cuff to expand and contract with the nerve without causing excessive stress / strain at the nerve-cuff interface.
Owner:GALVANI BIOELECTRONICS LTD
Transvascular reshaping lead system
ActiveUS7979141B2Increase the usable areaReducing a threshold bias for stimulating the nerve trunkSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesLead systemBiological activation
A system for selective activation of a nerve trunk using a transvascular reshaping lead is provided. One aspect of this disclosure relates to a system for spreading nerve bundles in a nerve trunk. The system includes a lead adapted to be chronically implanted in a blood vessel proximate a nerve trunk, and having an expandable portion adapted to be expanded to reshape the blood vessel to an elongated shape and to reshape the nerve trunk into an elongated shape to spread nerve bundles of the nerve trunk. The system also includes a plurality of electrodes and an implantable device coupled to the lead, where an electrical signal is delivered from the implanted medical device to one of the plurality of electrodes to transvascularly deliver neural stimulation from the electrode to at least one of the nerve bundles of the nerve trunk. Other aspects and embodiments are provided herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate nerve regeneration devices
InactiveUS20090209983A1Easy to catchEasy to handleBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsAbsorbable polymersMetabolite
Nerve regeneration devices are provided with improved rates of axonal regeneration, and methods for their manufacture are also disclosed. The devices are formed from a biocompatible, absorbable polymer, known as poly-4hydroxybutyrate. Growth factors, drugs, or cells that improve nerve regeneration may be incorporated into the devices. The devices are administered by implantation preferably without the use of sutures. In one aspect, the device is in the form of a wrap that can be used easily to capture the severed nerve bundle ends during surgery, and formed into a conduit in situ. If desired, the edges of the wrap can be melted together to seal the conduit, and hold it in place A major advantage of the device is that it does not need to be removed after use since it is slowly degraded and cleared by the patient's body, yet remains functional in situ beyond the time required for nerve regeneration, and helps exclude scar tissue. The device also degrades in a cell-friendly manner, and does not release highly acidic or inflammatory metabolites. Furthermore, the device is flexible, strong, does not crush the regenerating nerve, is easy to handle, reduces surgical time by eliminating the need to harvest an autologous graft, and allows the surgeon to repair the nerve without a prolonged delay.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Device to prevent brachial plexus injury during childbirth
InactiveUS20060074364A1Quick installationRestricts lateral movementRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObstetricsShoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia occurs most frequently during the birth of large infants, where the shoulders remain impacted, and lateral traction on the fetal neck with evulsion of the brachial plexus may cause brachial plexus injury. The idea is to prevent excessive lateral bending of the infant's head, its ensuing stress, and damage to the brachial nerve bundle. This invention consists of a special head brace, which limits the lateral movement of the baby's head with respect to the clavicle, and can be quickly mounted when required by the specific medical situation. Its design in two sections provides a snug fit, regardless of the infant's head size, and permits its installation in the little time available to complete the birth process.
Owner:KLEIN STEVEN +1
Method for detecting nerve bundle protein NF155 and NF186 antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid
InactiveCN112230002AAccurate detectionHigh detection sensitivityImmunoglobulin superfamilyBiological material analysisViral infectionNeurotensin
The invention discloses a method for detecting neurotensin NF155 and NF186 antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid, which comprises the following steps: S1, plasmid construction: respectively connecting target genes NF155 and NF186 with a carrier to obtain target plasmids; s2, transfecting 293T cells with the plasmids obtained in the step S1 to obtain viruses; s3, infecting 293T cells with thevirus obtained in the step S2 to obtain transfected cells; and S4, detecting antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid by using the transfected cell expression protein. Proper plasmids are constructed and transfected into cells, a special culture medium is adopted for screening, and after a stable expression effect is generated, whether corresponding antibodies exist or not is accurately detected according to the combination of the corresponding antibodies in serum or cerebrospinal fluid and expression proteins of the antibodies, so that the detection sensitivity and accuracy are improved.
Owner:成都海默云因医学检验实验室有限公司
Living body nerve scaffold with central perfusion system and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN110960732AIncrease cell densityHigh activityNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsPerfusion CultureBlood vessel
The invention provides a living body nerve scaffold with a central perfusion system and a manufacturing method of the living body nerve scaffold. The living body nerve scaffold is manufactured by three-dimensionally culturing a nerve bundle in vitro with a lumen structure, modifying endothelial cells on the inner wall of the lumen of the nerve bundle, and manufacturing under the condition of perfusion culture. In the perfusion culture process, the shear stress of a fluid can improve the activity of endothelial cells, construction of vascularized nerve tracts is facilitated, and therefore localblood supply of the nerve tracts in the early stage after the nerve tracts are implanted into the body is improved. Meanwhile, the shear stress of the fluid can promote proliferation and differentiation of the neural stem cells, and perfusion culture can enable the nerve tracts to obtain more sufficient nutrient supply and reduce the concentration of metabolic wastes in a cell growth environment,so that the nerve tracts with higher cell density are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An implantable nerve signal blocking device
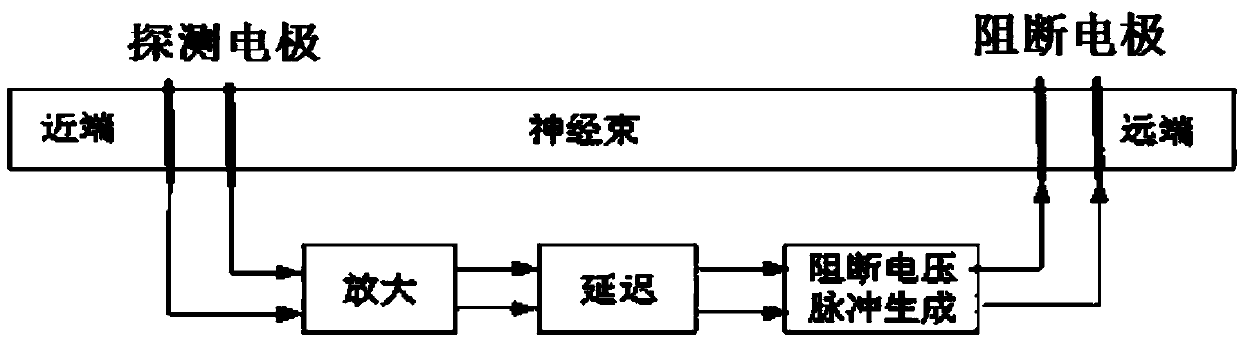
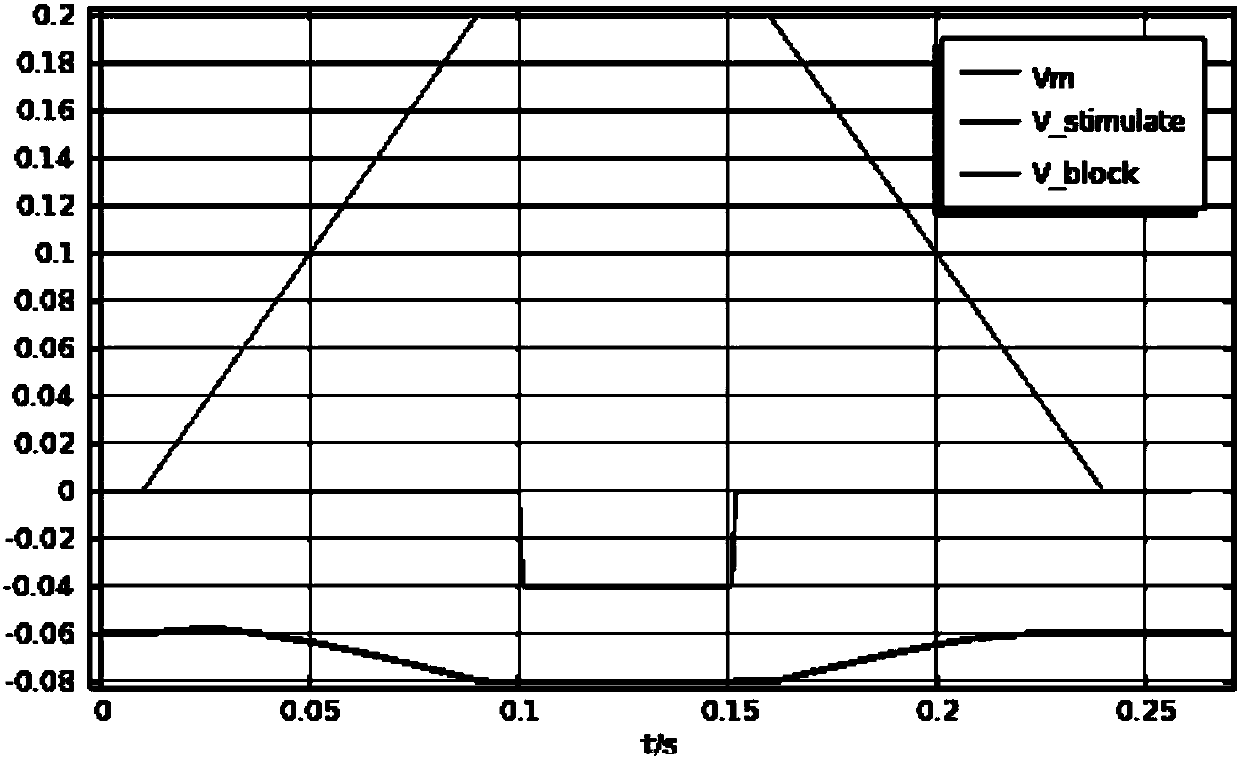
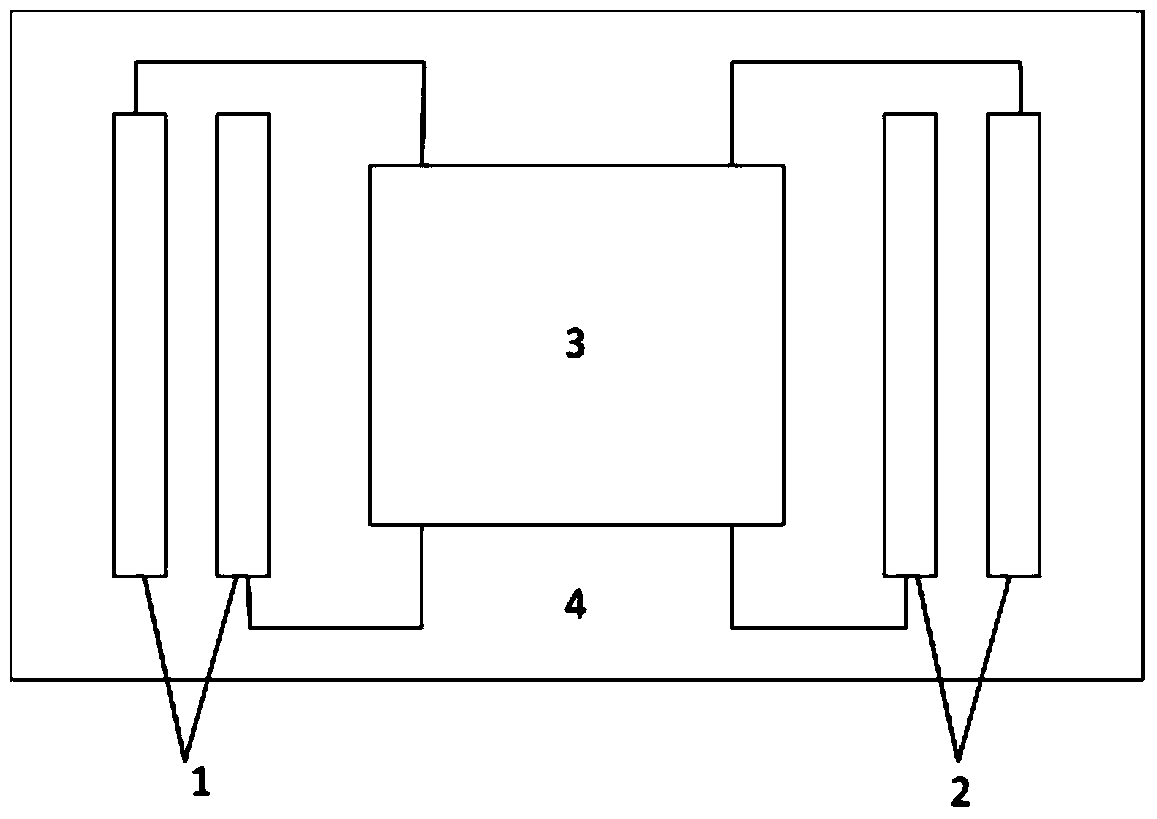
ActiveCN105310680BEliminate crampsEliminate pain sensationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineNeuron
An implantable nerve signal blocking device proposed by the present invention includes a flexible curled substrate, a first kraft electrode, a second kraft electrode, and a signal processing module arranged on the surface of the flexible curled substrate. The first Kraft electrode is placed at the source or proximal end of the nerve bundle that sends out the signal, and the second Kraft electrode is placed at the distal end of the nerve bundle. Use the first Kraft electrode to detect the motor nerve impulse signal that causes muscle spasm or the sensory nerve action potential signal that causes pain, amplify it, and perform necessary adjustments on the amplified signal according to the propagation speed of the action potential in the neuron Delay and reverse, so that it can appear on the second Kraft electrode before the action potential reaches the "intercept" site, so as to realize the cancellation of the action potential signal in the nerve segment where the block is applied, so as to eliminate muscle spasm or pain sense of purpose.
Owner:NANJING SHENQIAO MEDICAL EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com