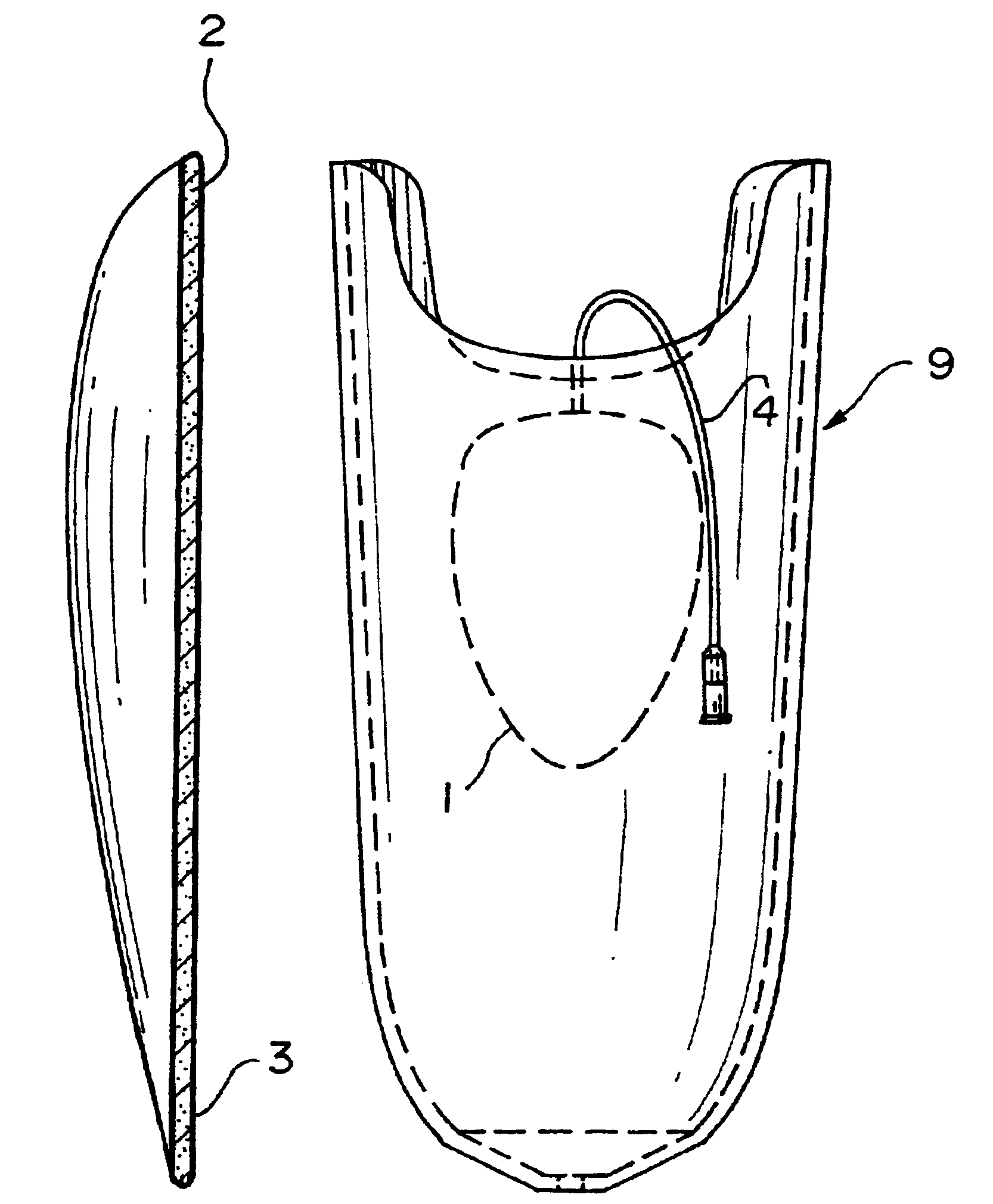
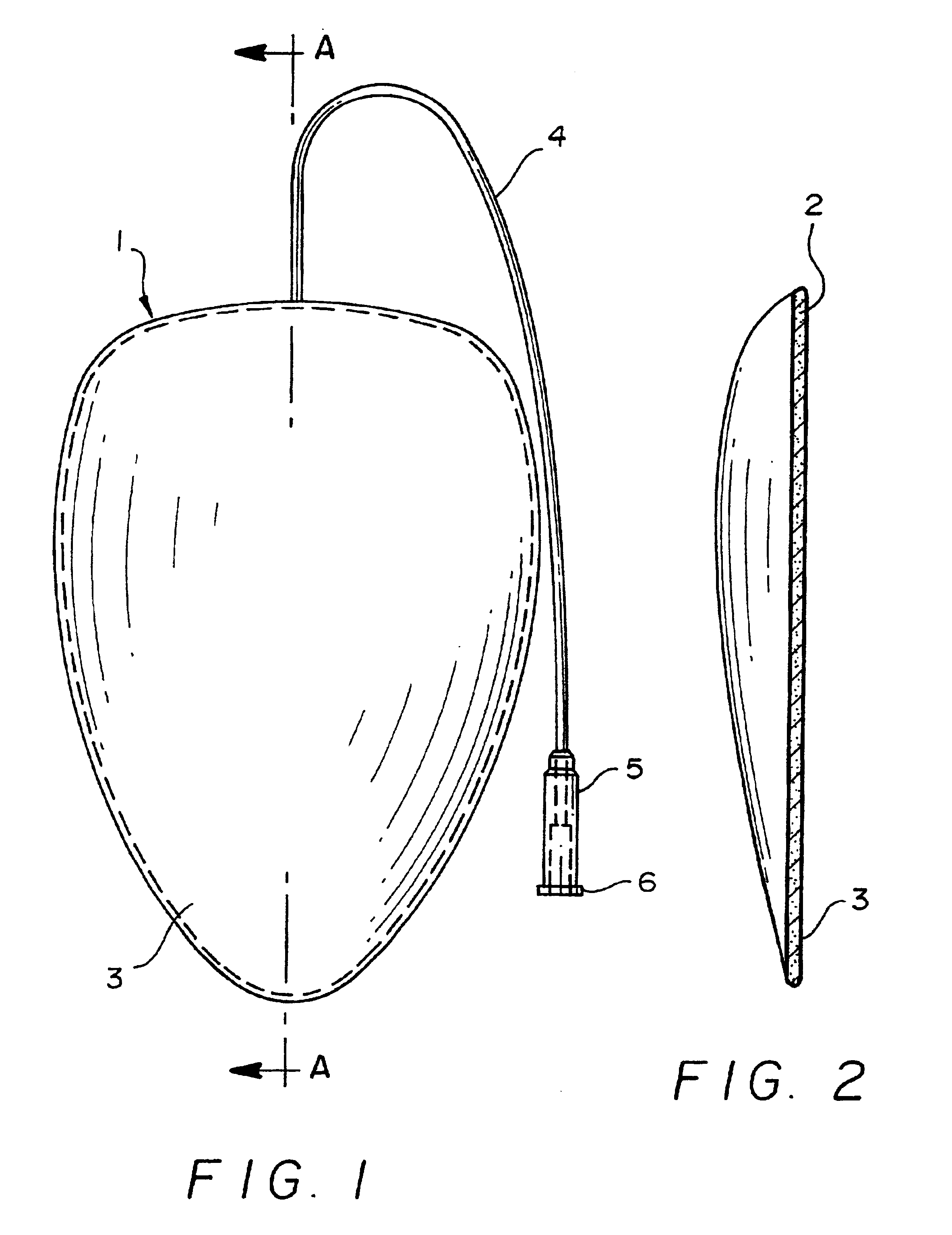
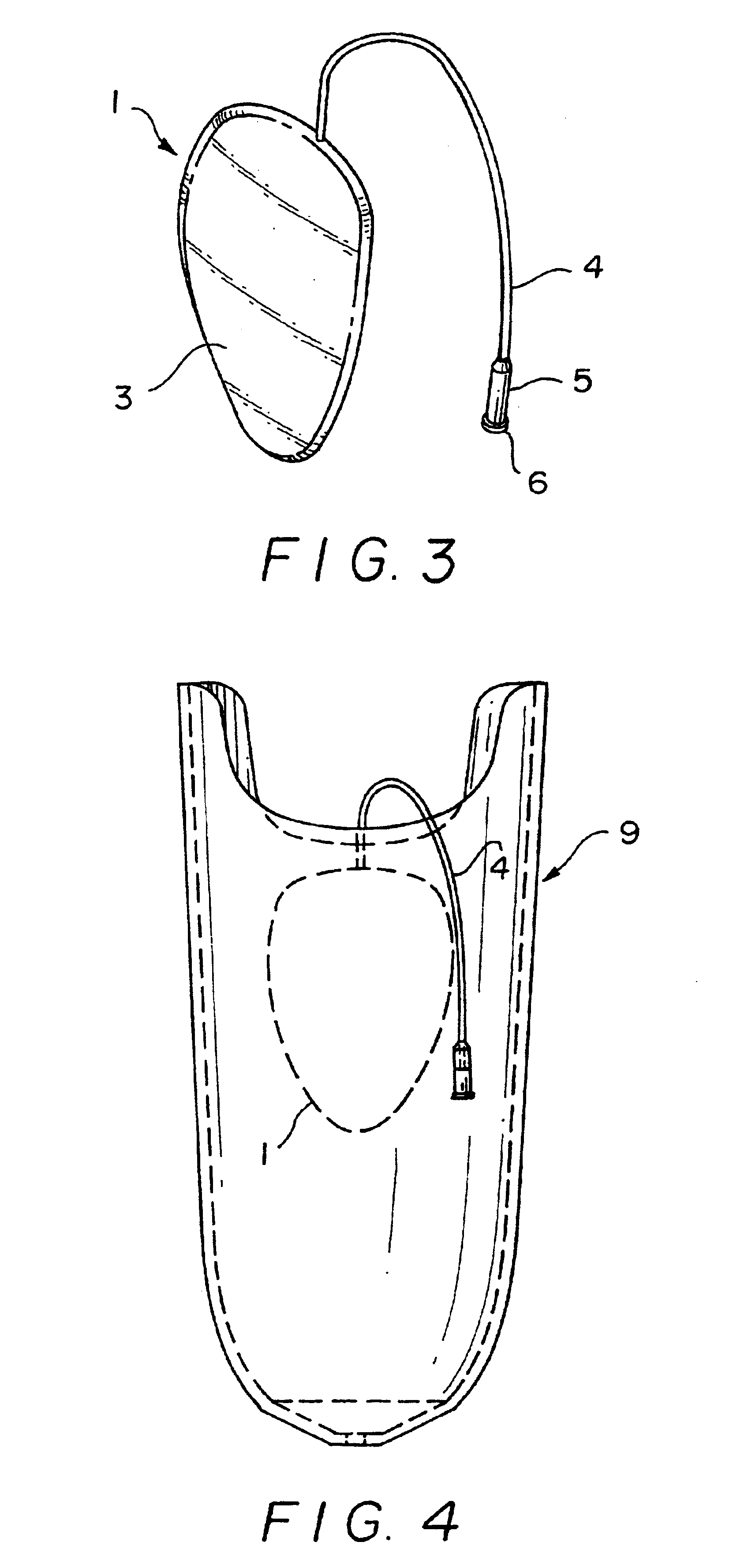
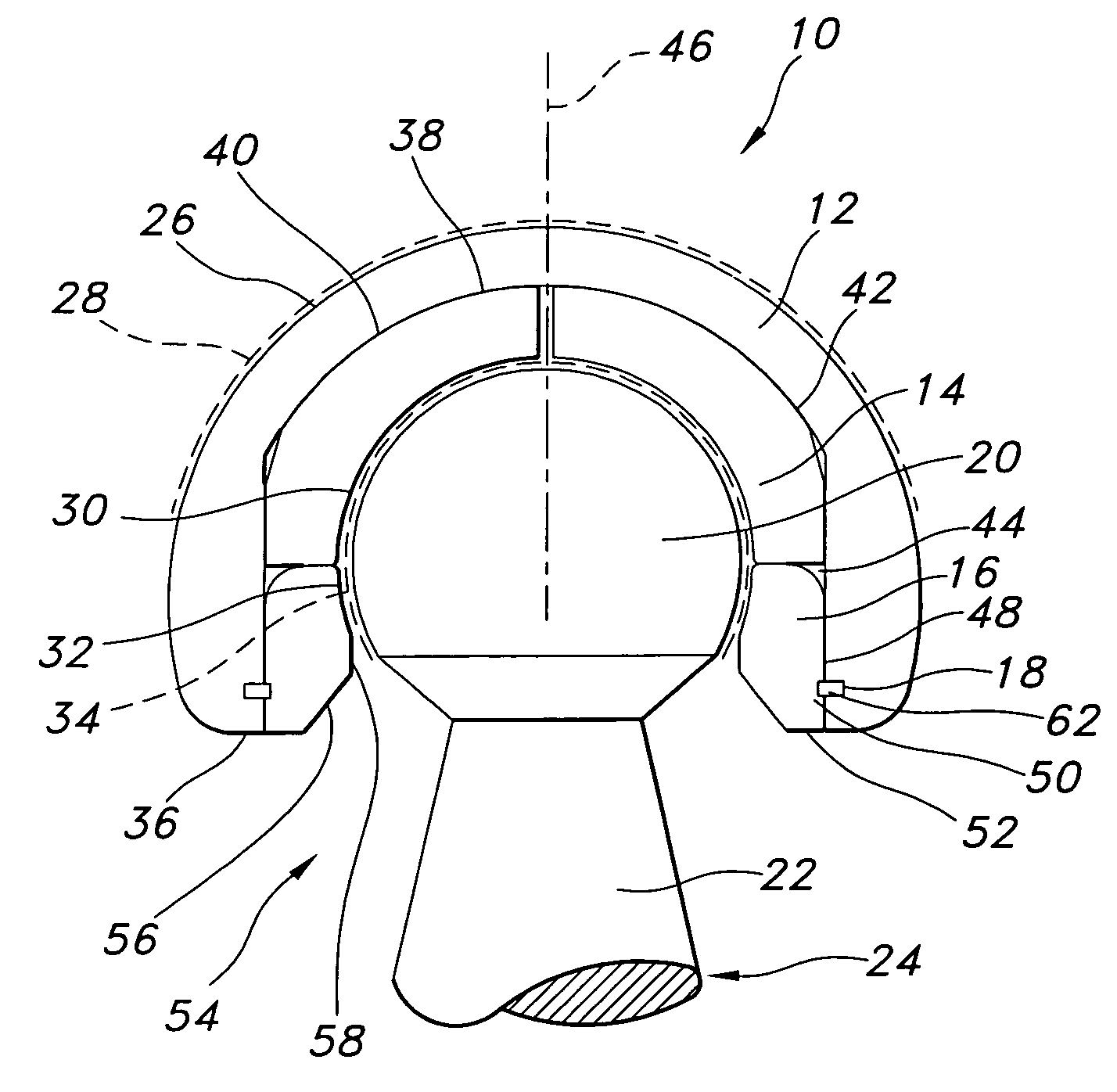
Patents
Literature
733 results about "Artificial limbs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
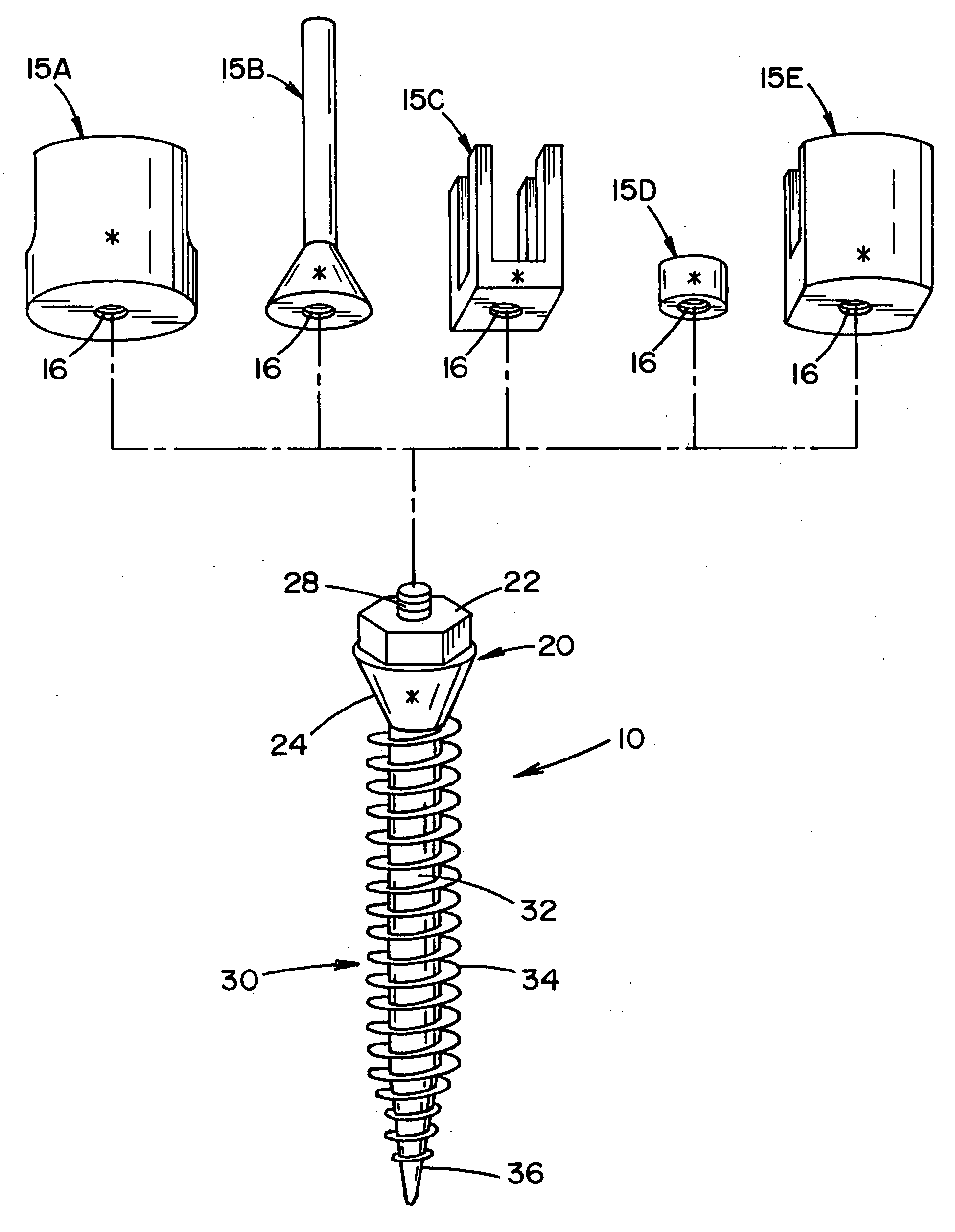
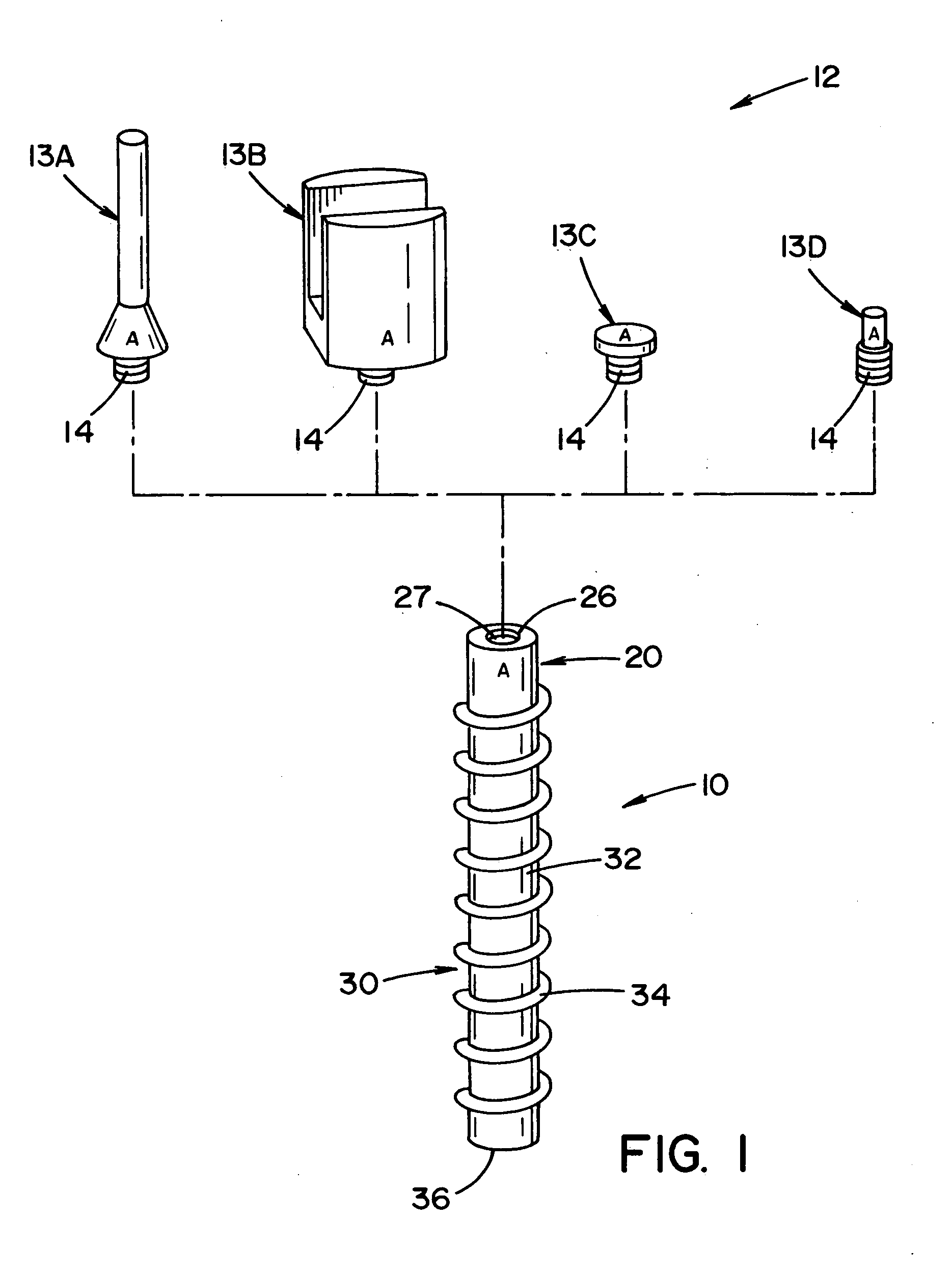
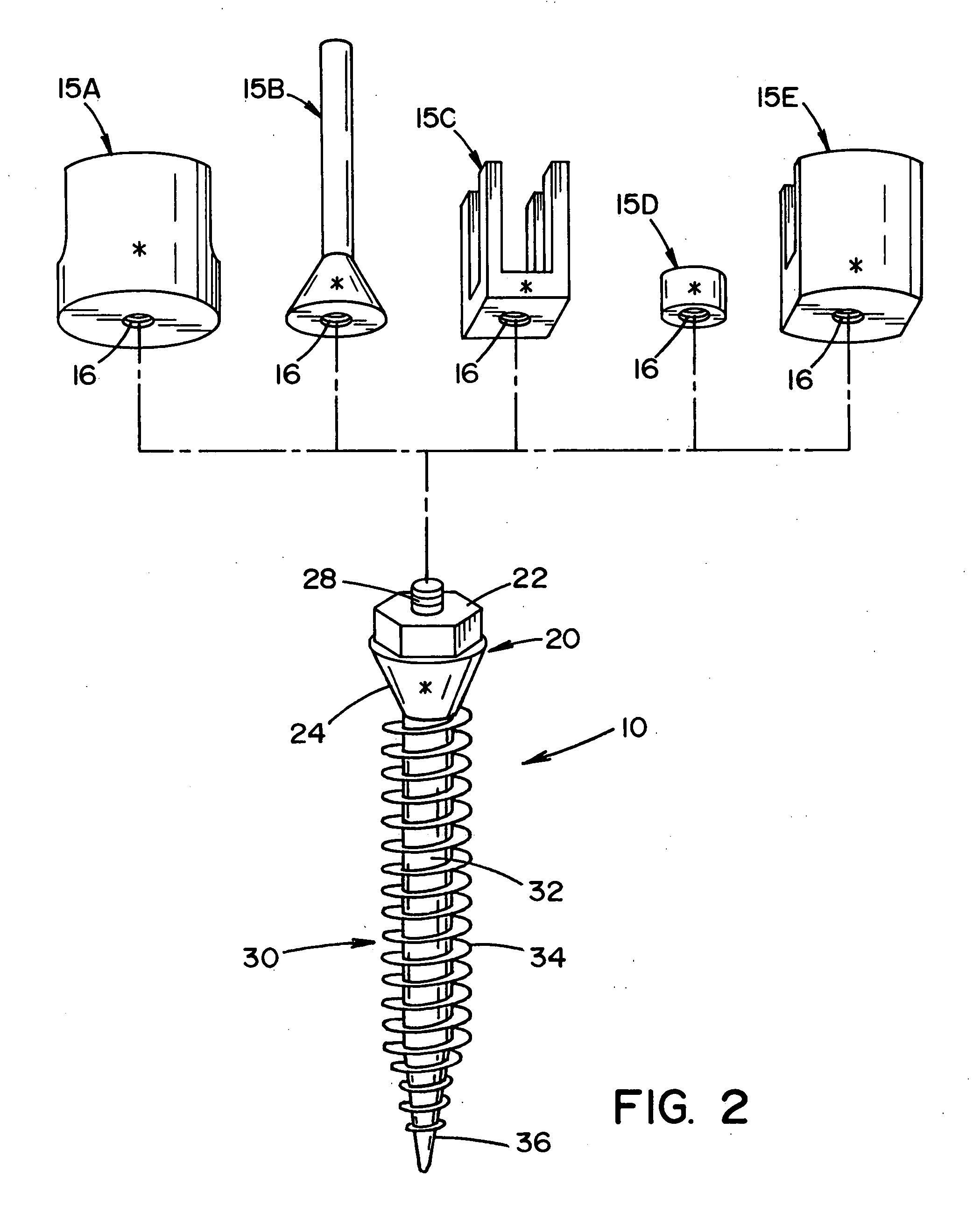
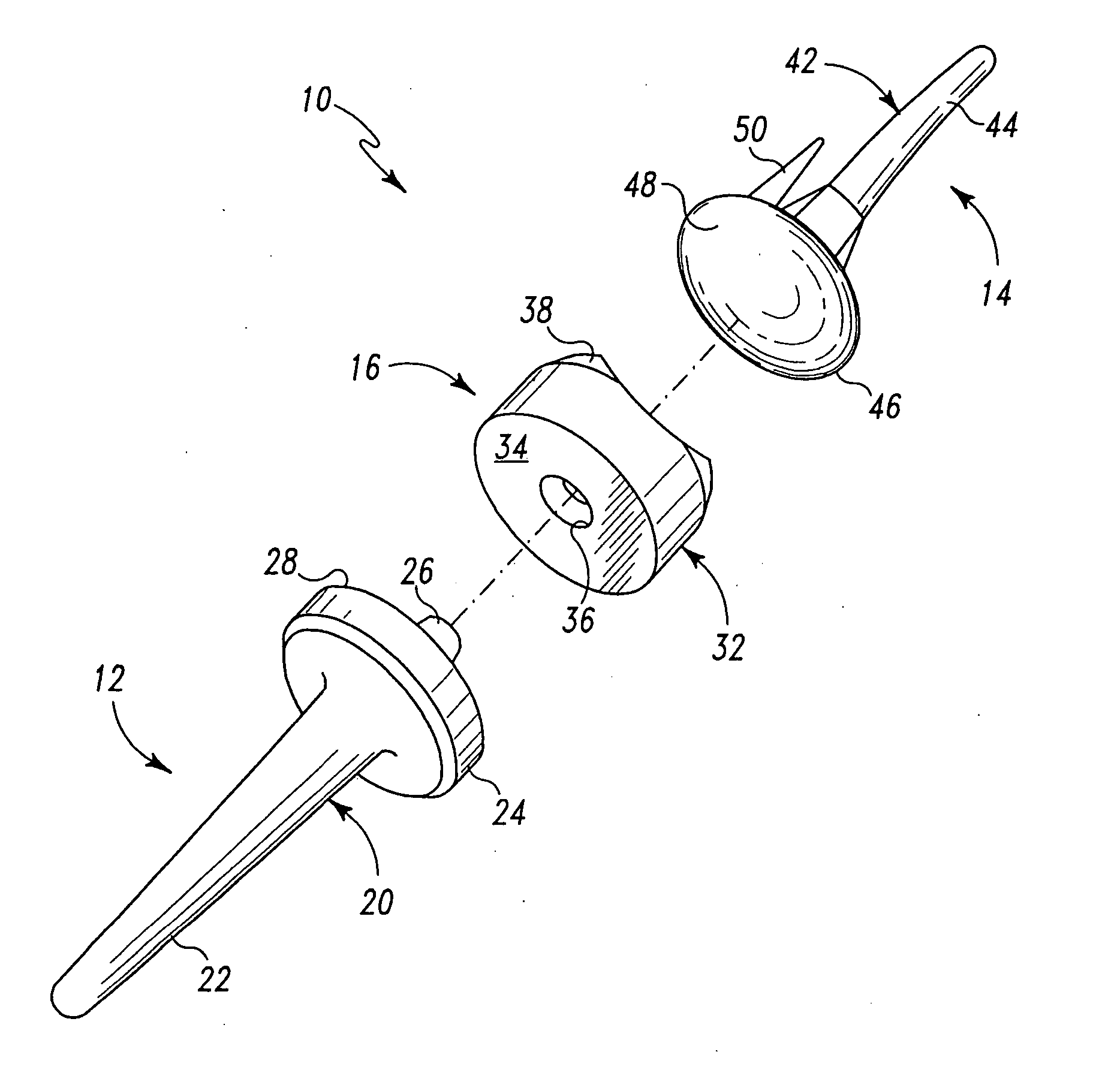
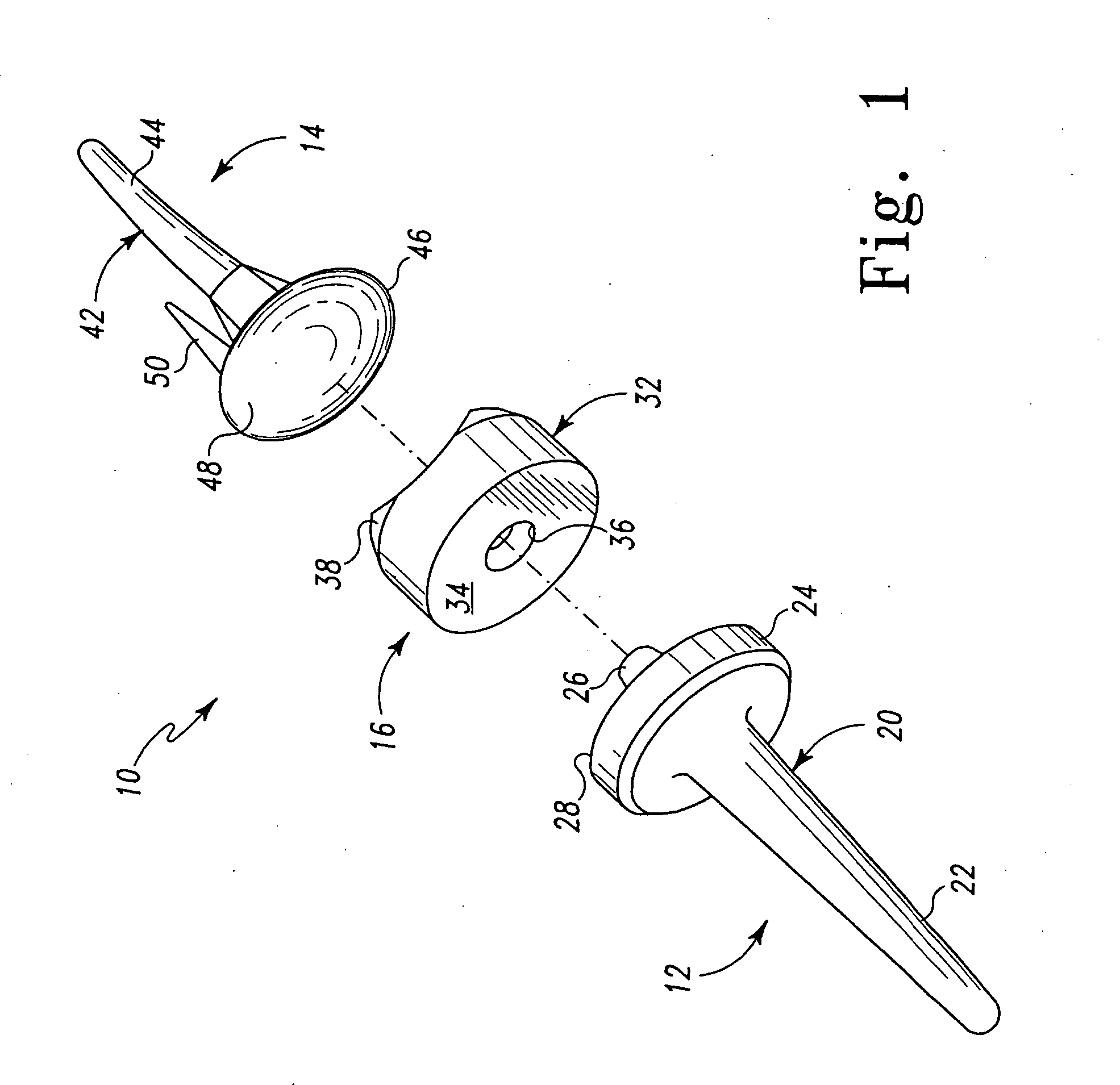
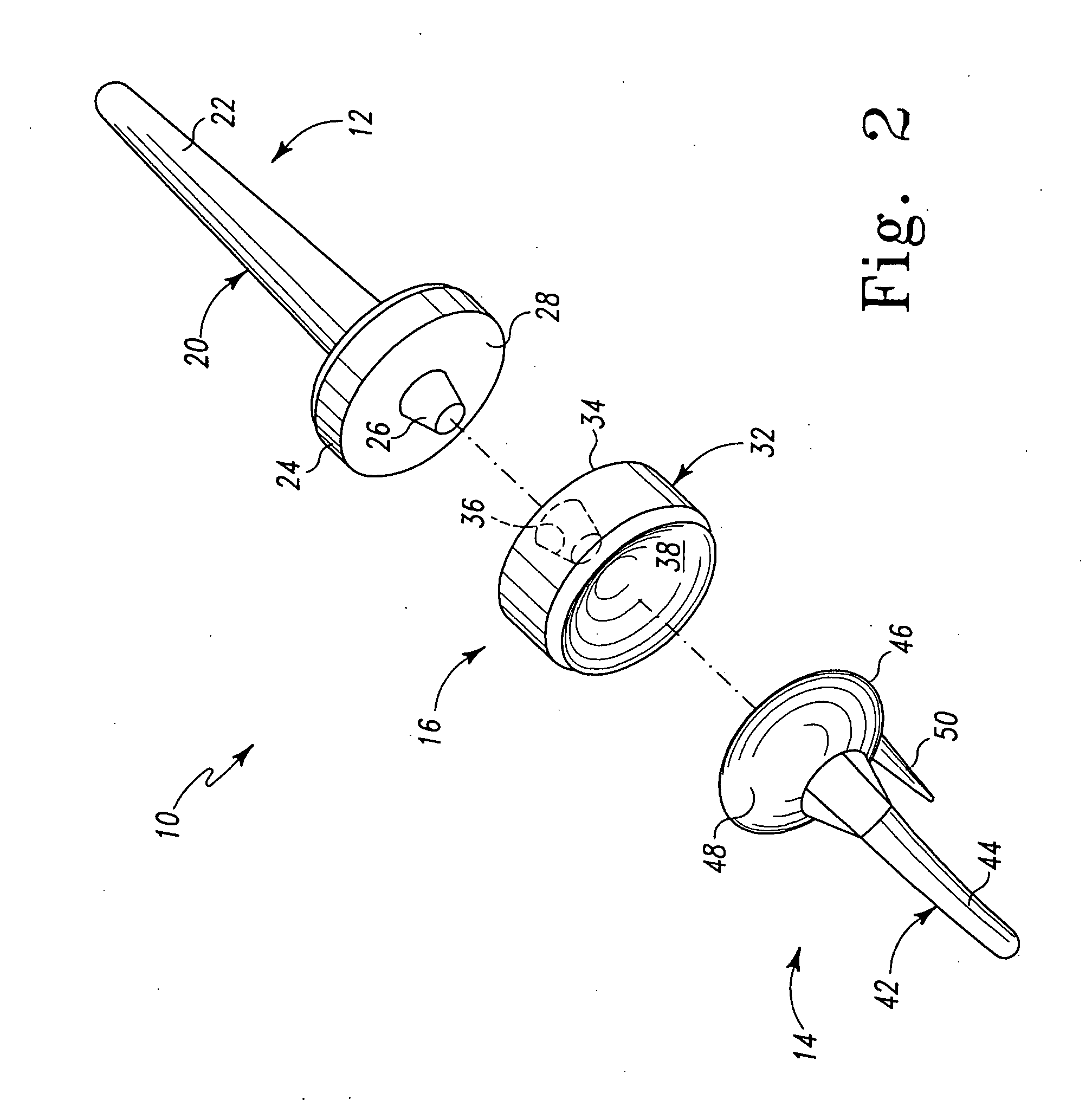
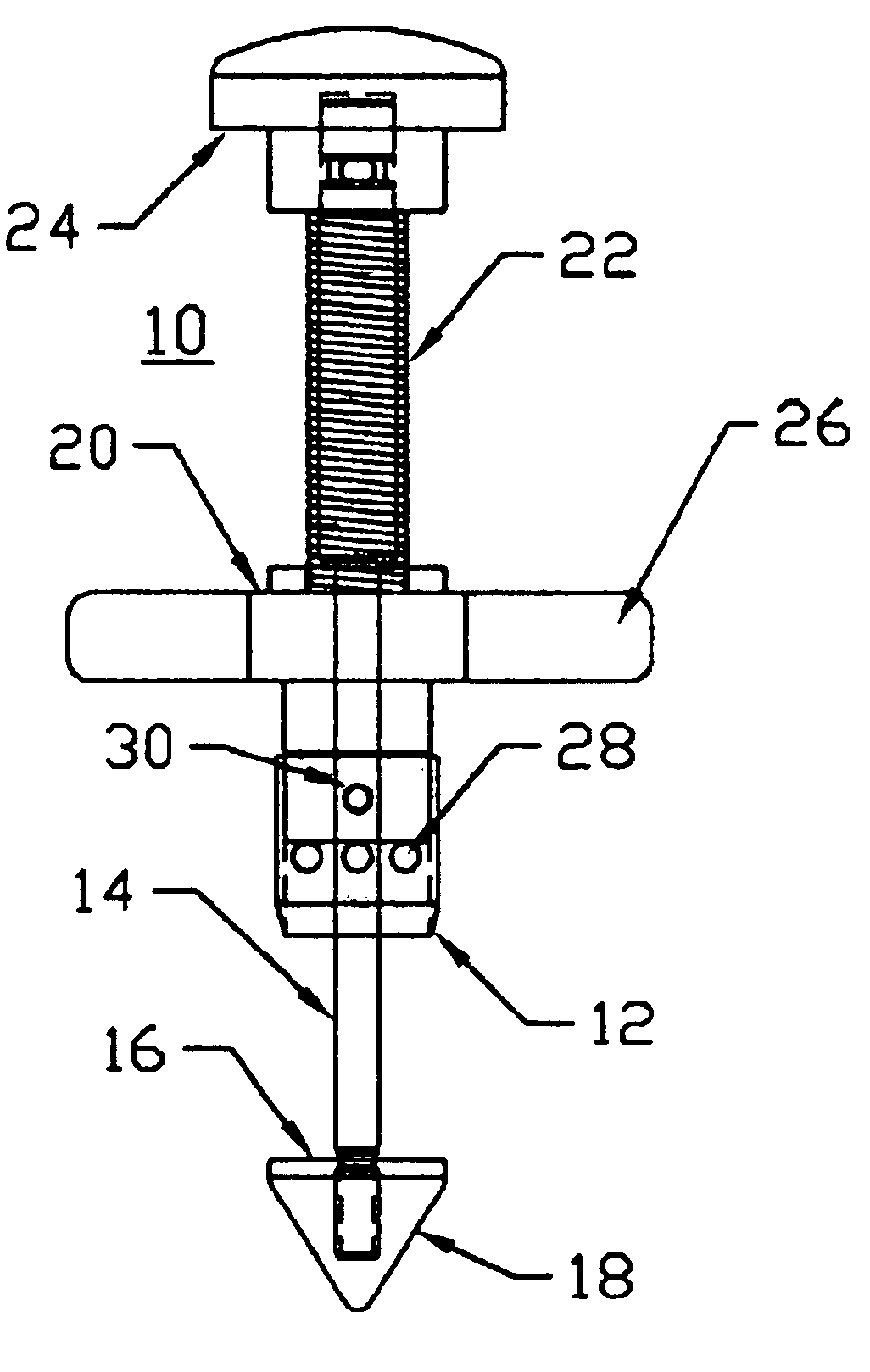
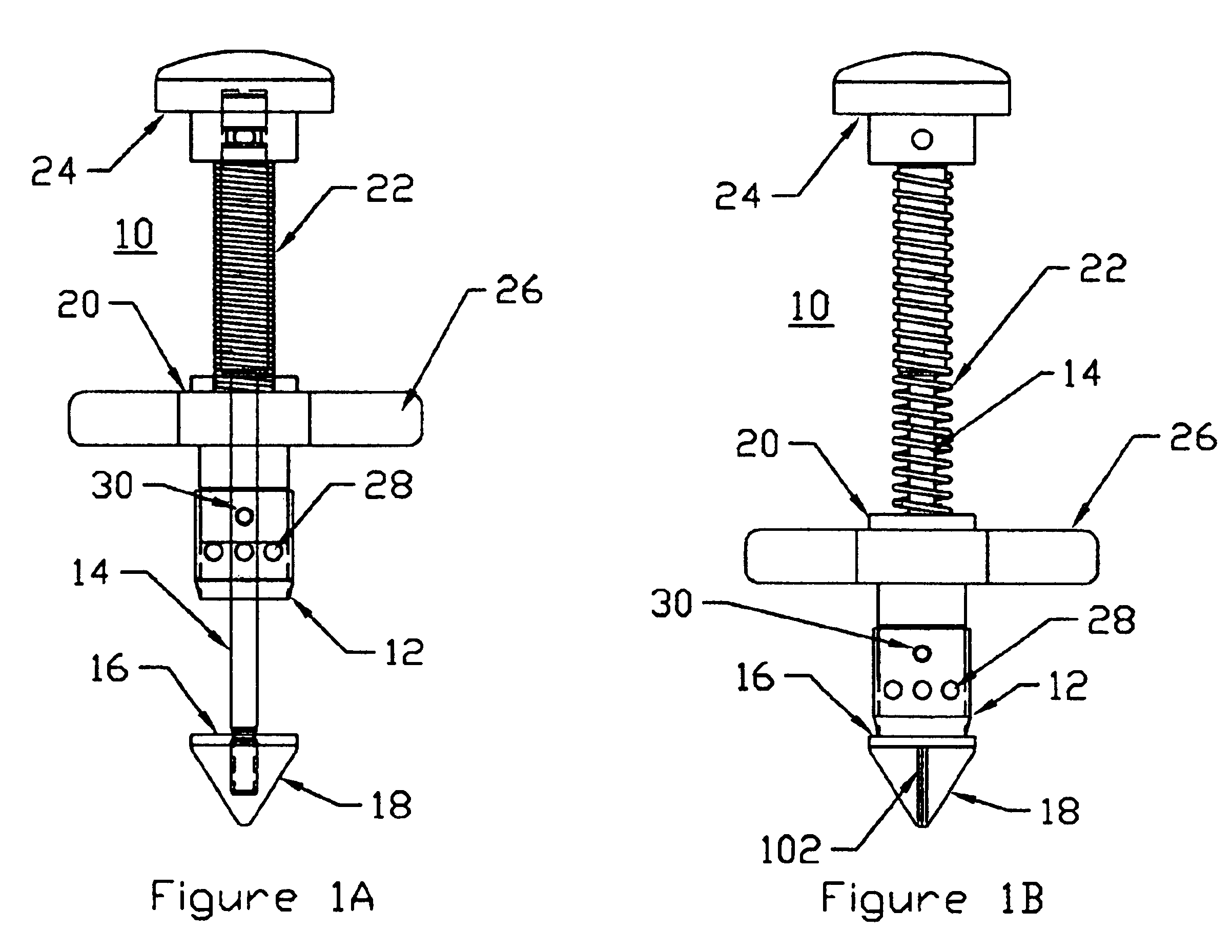
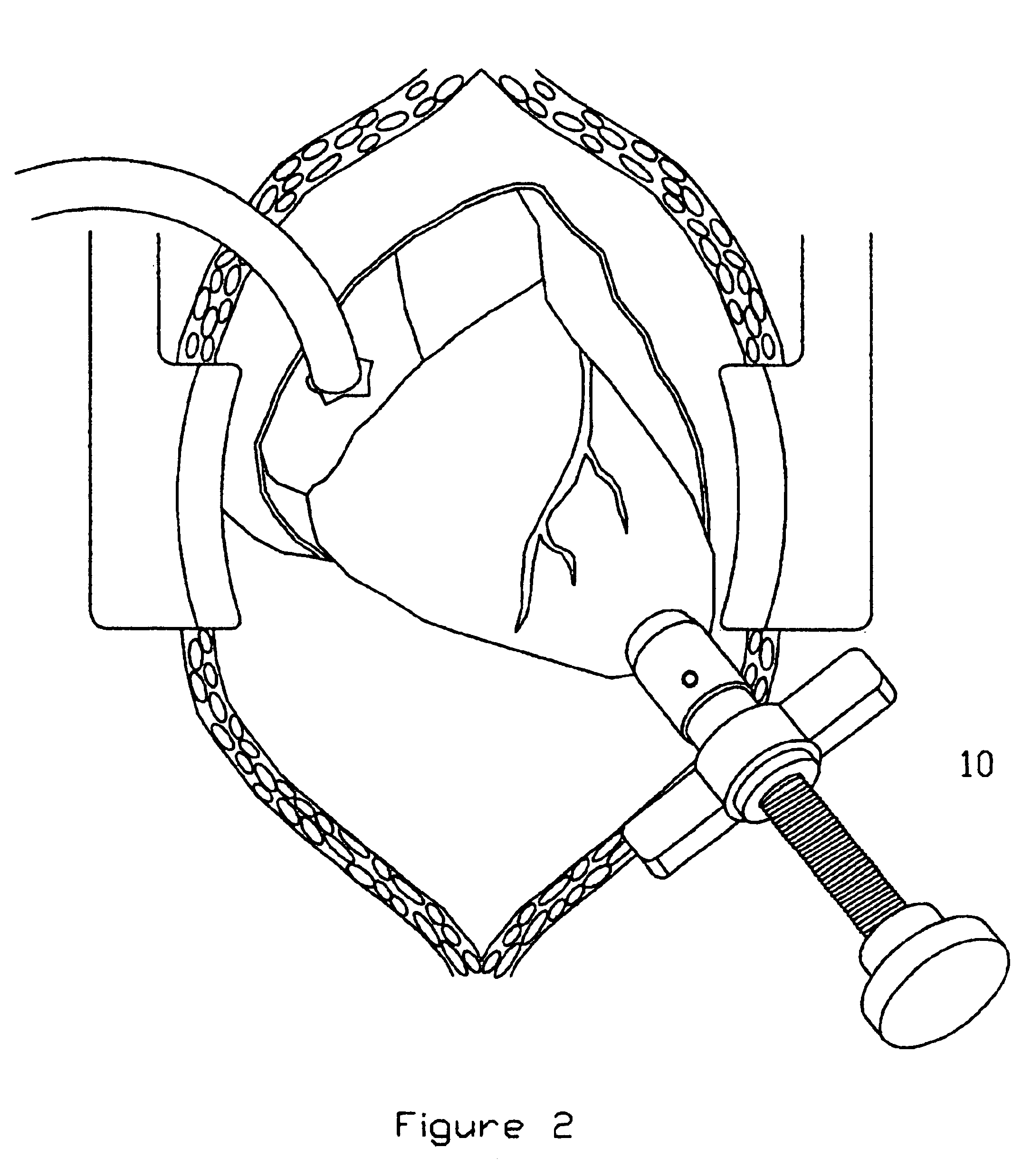
Bone anchor prosthesis and system
InactiveUS20050059972A1Easy to removeEasy to insertSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyMedicineProsthesis
A prosthetic screw system that includes a prosthetic screw for at least partial insertion into a bone and / or cartilage. The prosthetic screw includes a head and a lower portion connected to the head. The prosthetic screw system also includes a set of head-pieces that can be connected to the head of the prosthetic screw. The head-pieces have differing configurations that are designed to be connected to different types of components of a prosthetic system. The universal connection arrangement between the prosthetic screw and the set of head-pieces enables the prosthetic screw to be customized for connection with a variety of components of a prosthetic system. The head-pieces can alternatively or additionally include a mechanical and / or electrical mechanism that provides one or more substances (e.g., medicine and / or other biological agent, etc.) and / or electrostimulation to a surgical site.
Owner:SPINECO
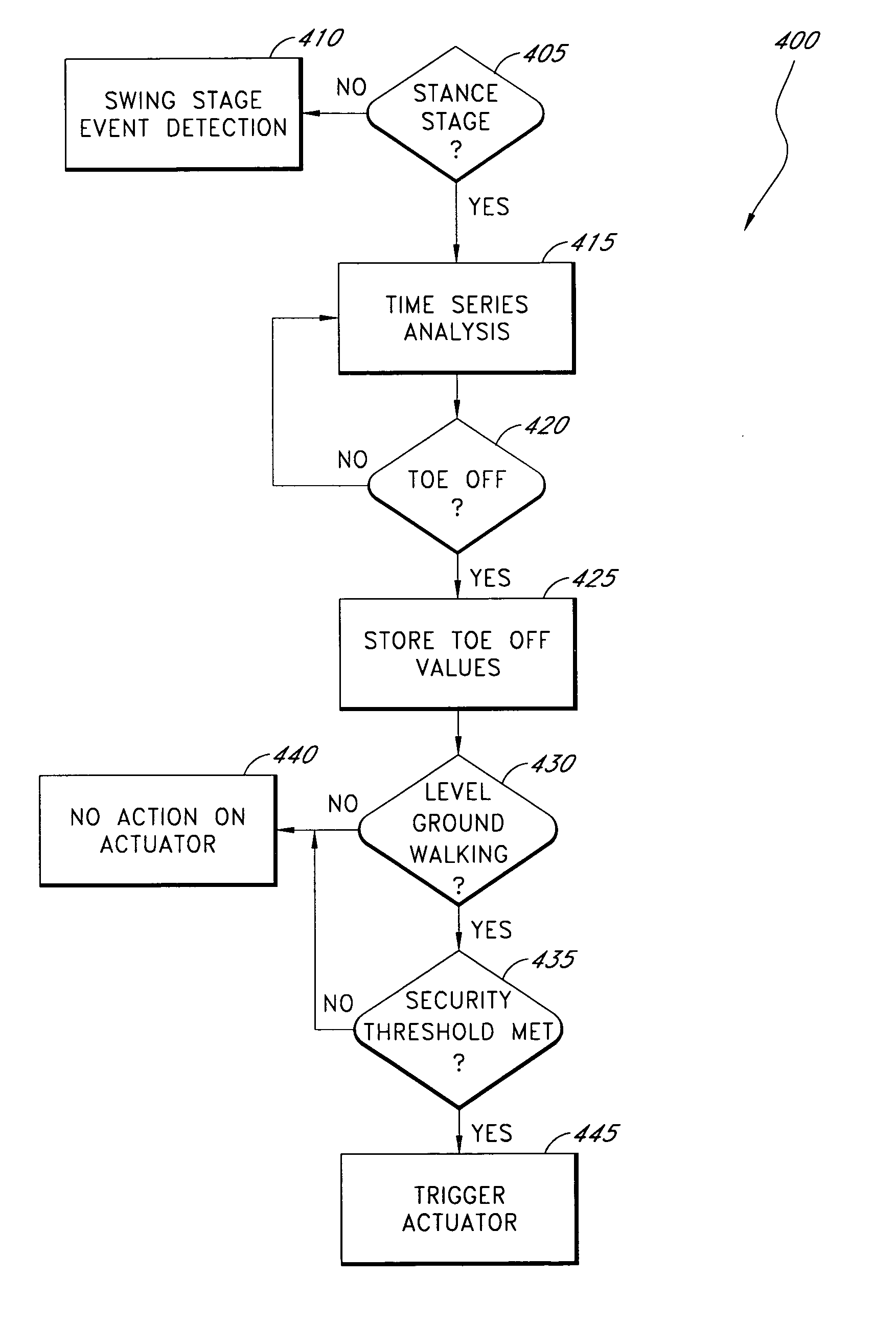
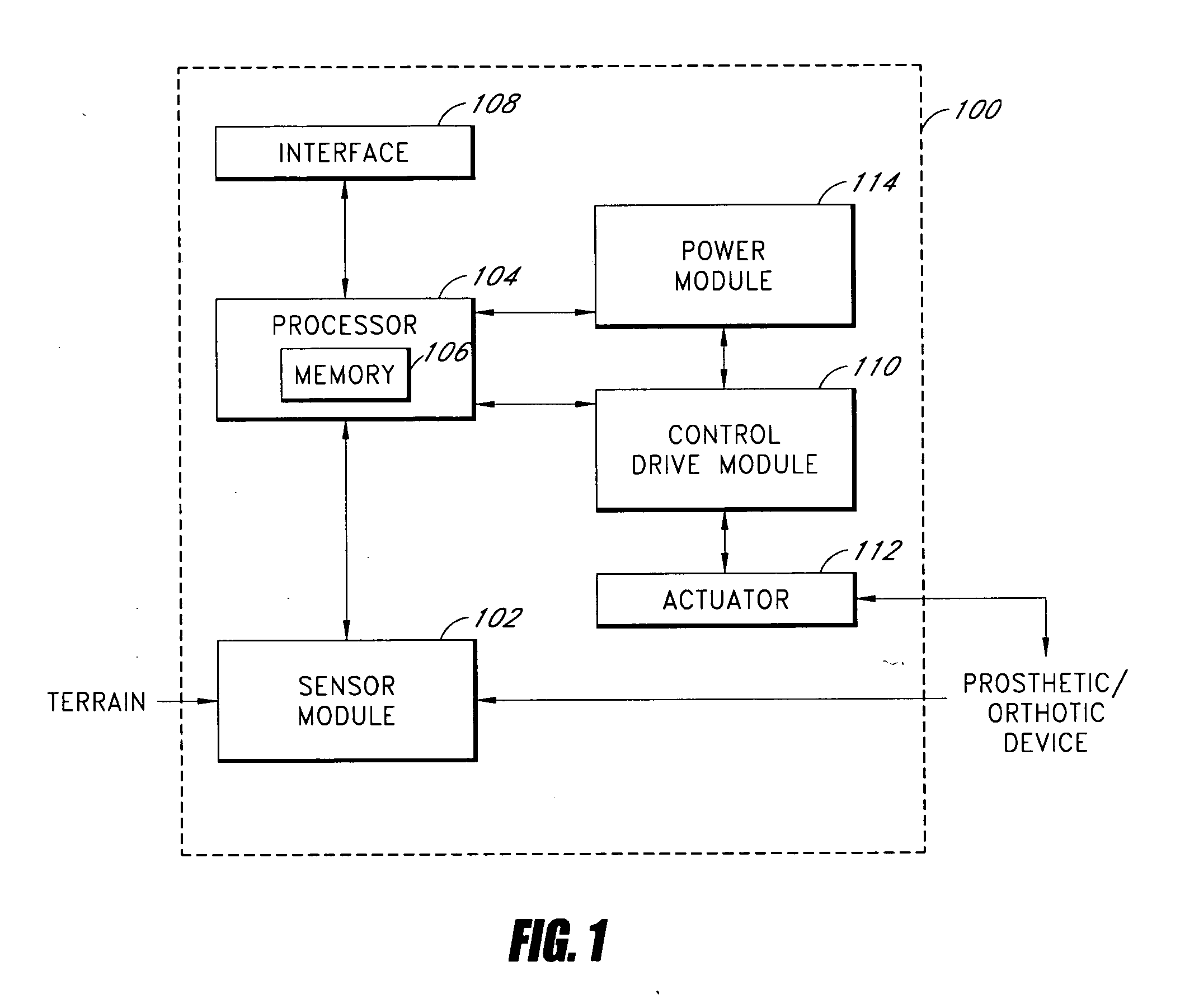
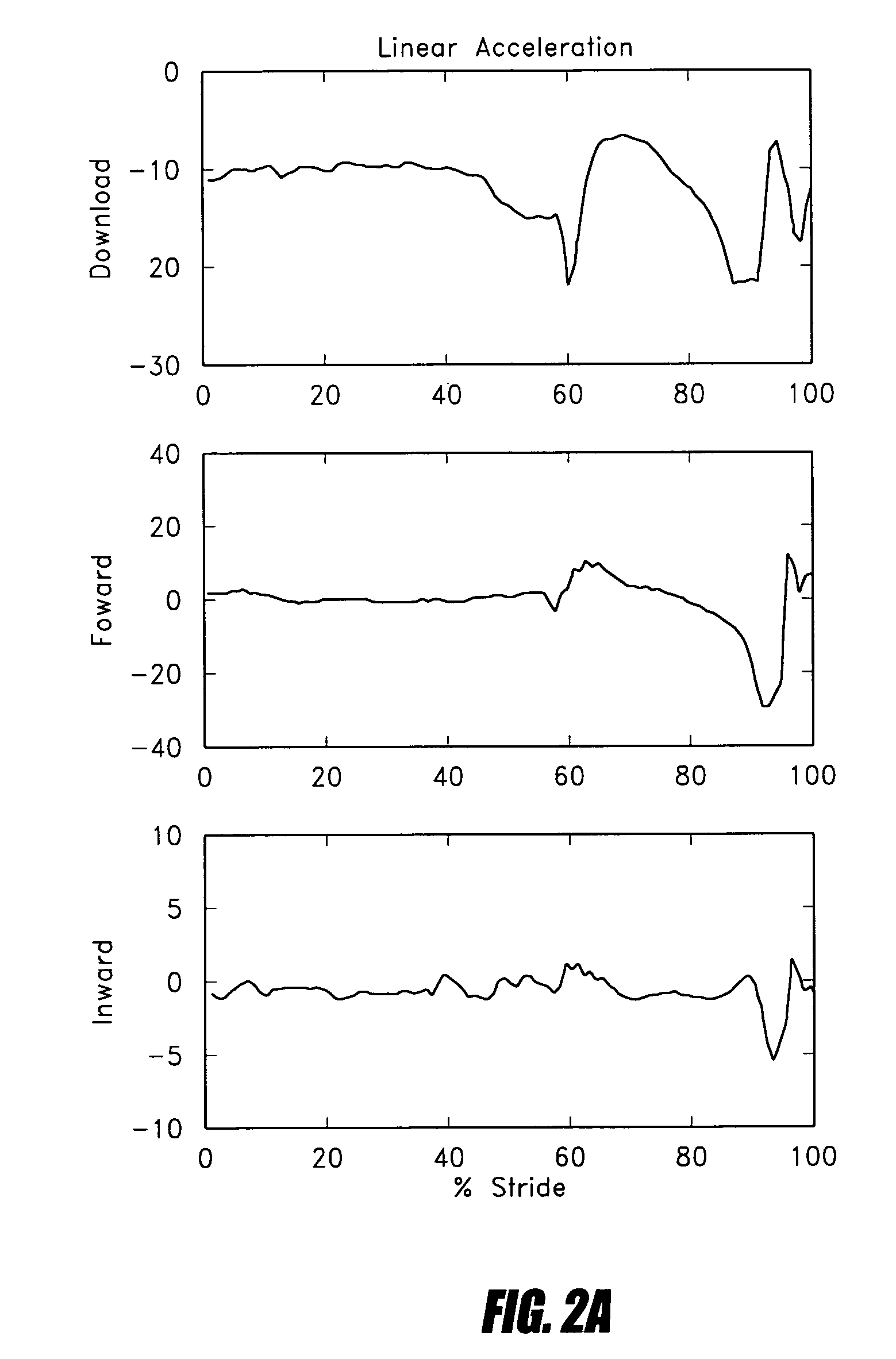
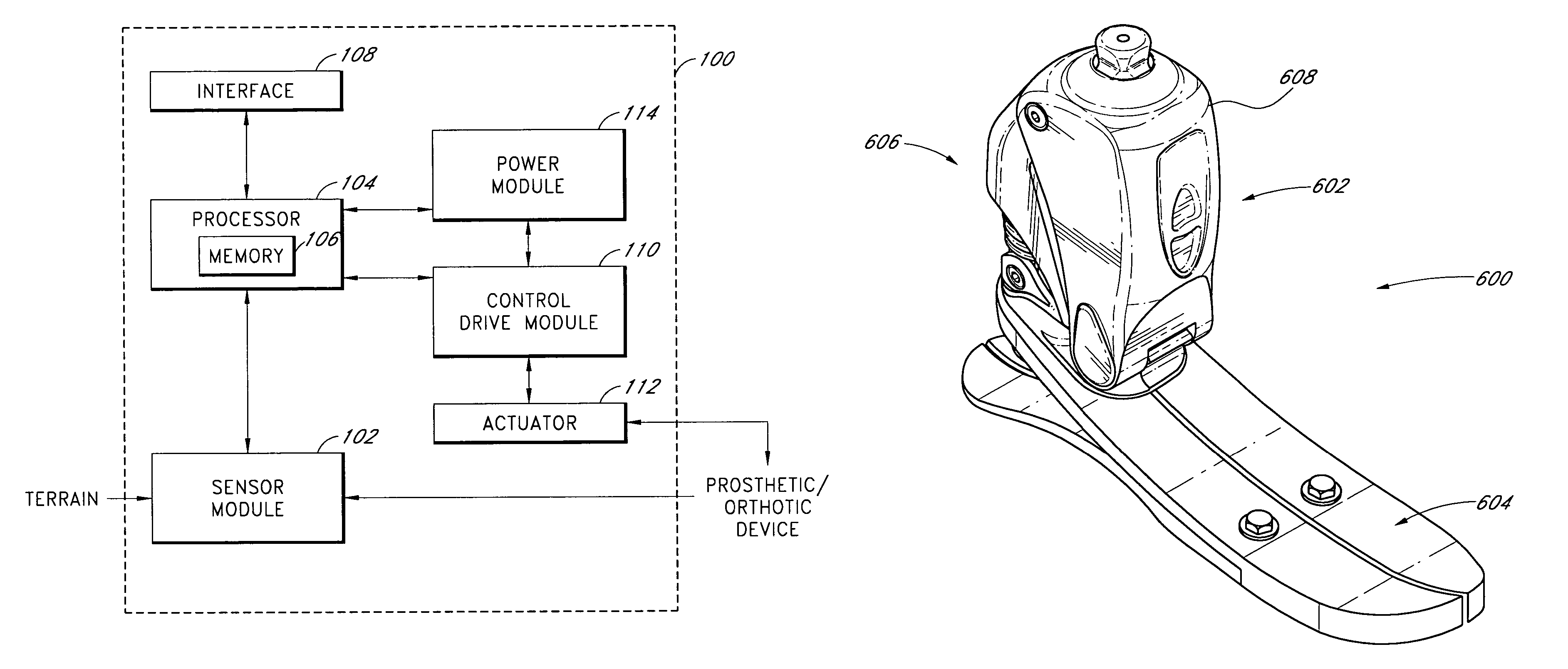
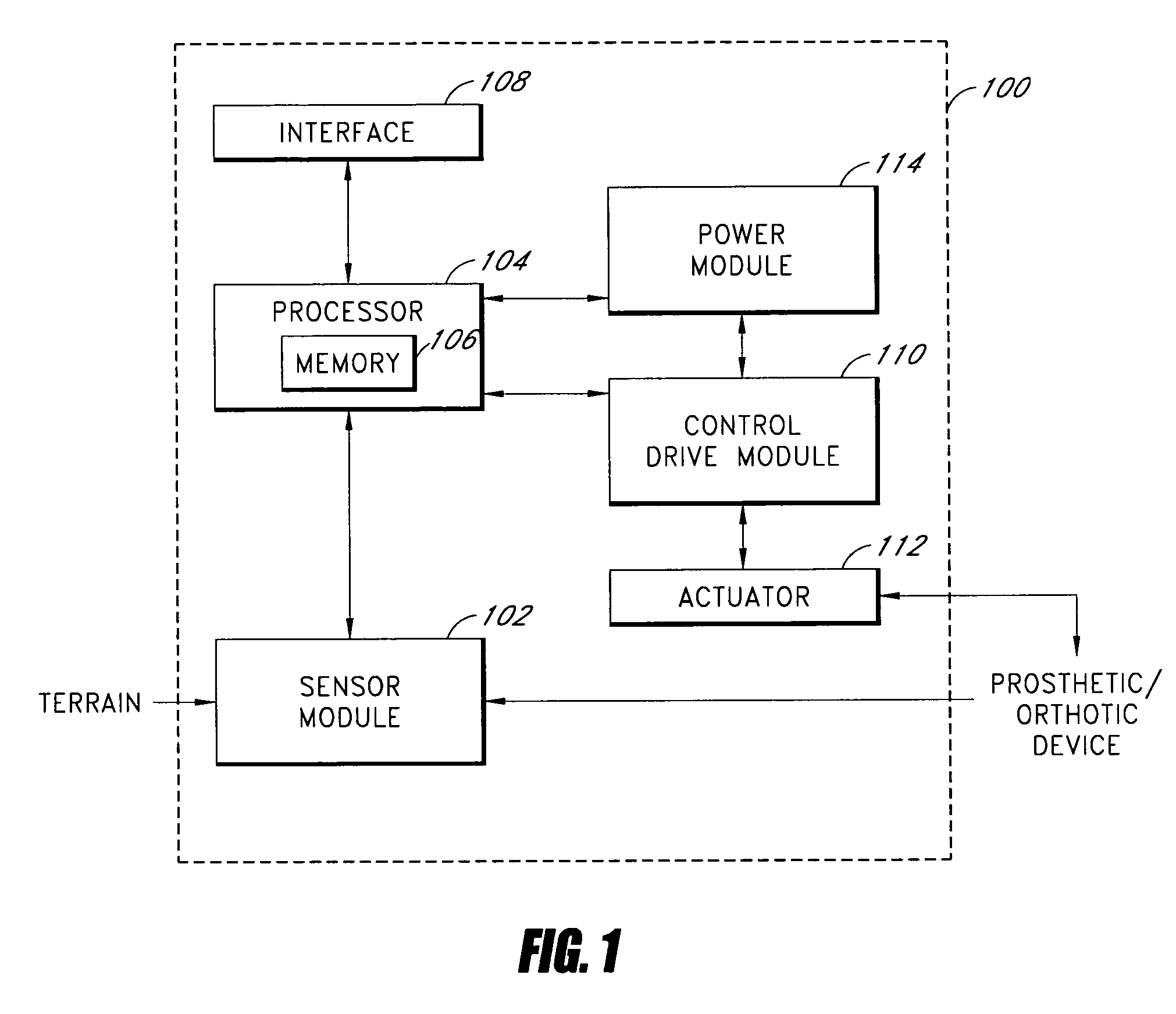
Systems and methods for processing limb motion
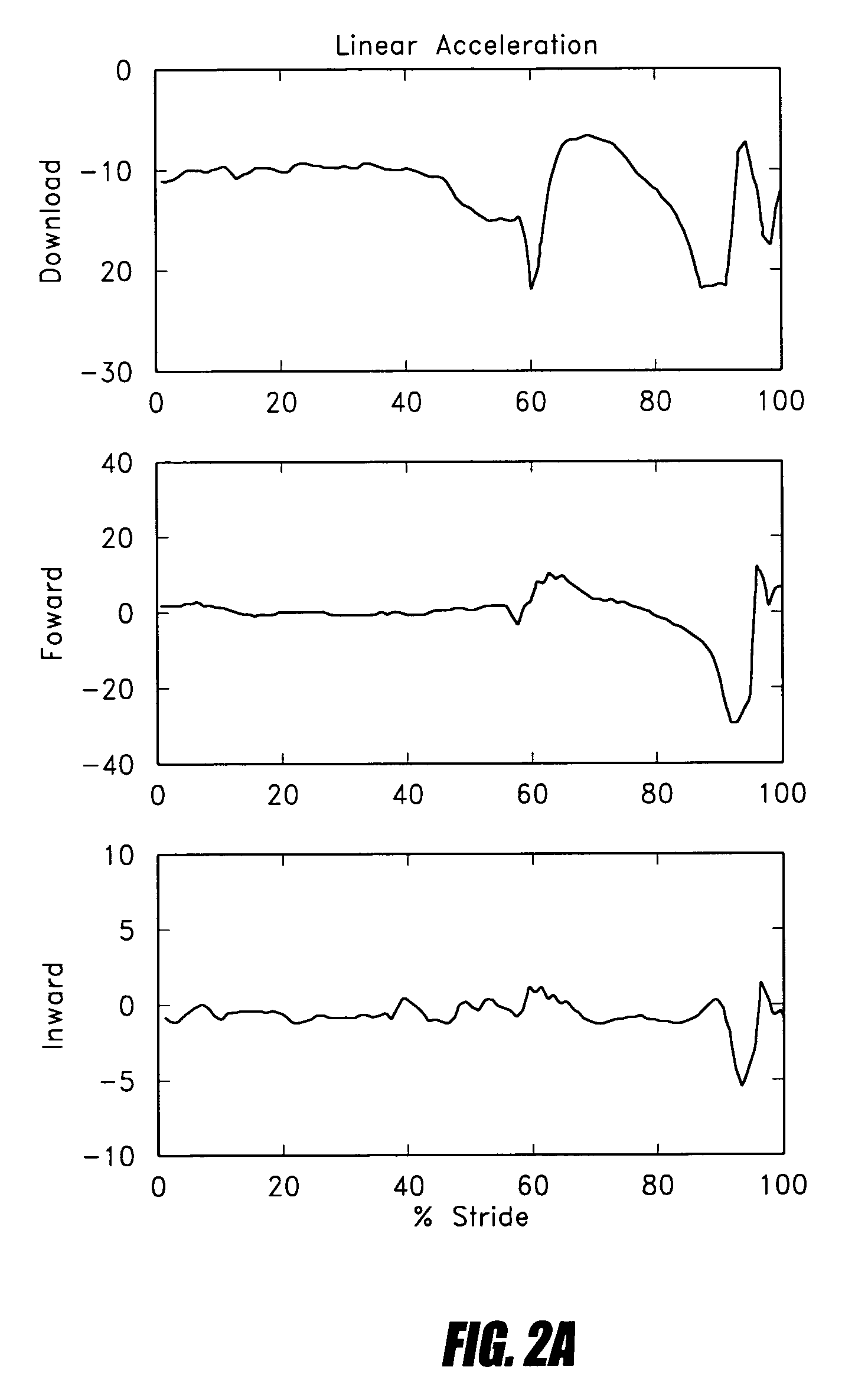
ActiveUS20060135883A1Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringArtificial limbsData set
Control systems and methods are disclosed for processing a time series of signals associated with the movement of a device associated with a limb. The time series of motion signals is filtered, such as thorough an autoregressive filter, and compared to stored data sets representing a limb-motion event and / or phase. In certain examples, a plurality of accelerometers generate the time series of motion signals based at least on acceleration measurements in three orthogonal directions and / or planes. The acceleration measurements may relate to the movement of an artificial limb, such as a prosthetic or orthotic device. Upon determining an event and / or phase of limb motion, the control system may trigger an actuator to appropriately adjust one or more prosthetic or orthotic joints.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Instrumentation and method for prosthetic knee
InactiveUS20050192588A1Shorten study timeImprove usabilityDiagnosticsSurgical sawsTibial boneFemoral bone
Instrumentation for guiding a surgeon in performing a unicompartmental knee replacement includes a tibial block having a guide, and a milling tool adapted to engage the guide, such that the surgeon can mill the desired tibial bone bed by directing the milling tool along the guide. Further including a femoral jig having a cutting slot, a guide, and a milling tool adapted to engage the guide, such that a surgeon can cut a portion of the femur through the slot, and mill the femoral bone bed by directing the milling tool about the guide. A femoral trial removal clamp facilitates in removing the femoral trial prosthesis, and a spreader compression clamp aids in compressing the final prostheses as the bone cement cures.
Owner:GARCIA DANIEL X
Modular knee prosthesis
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Device and method for tacking a prosthetic screen
Owner:TOOLS FOR SURGERY
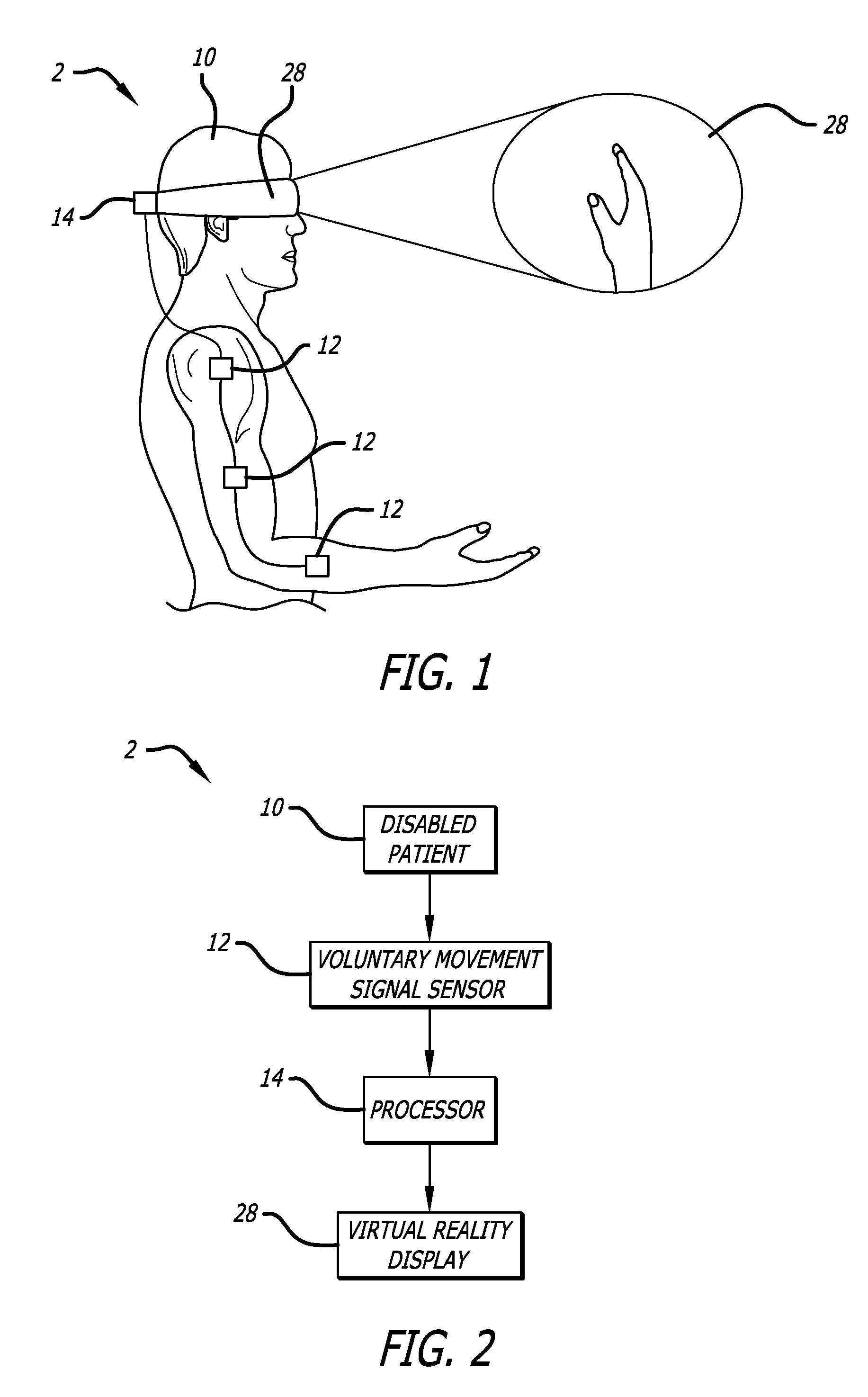
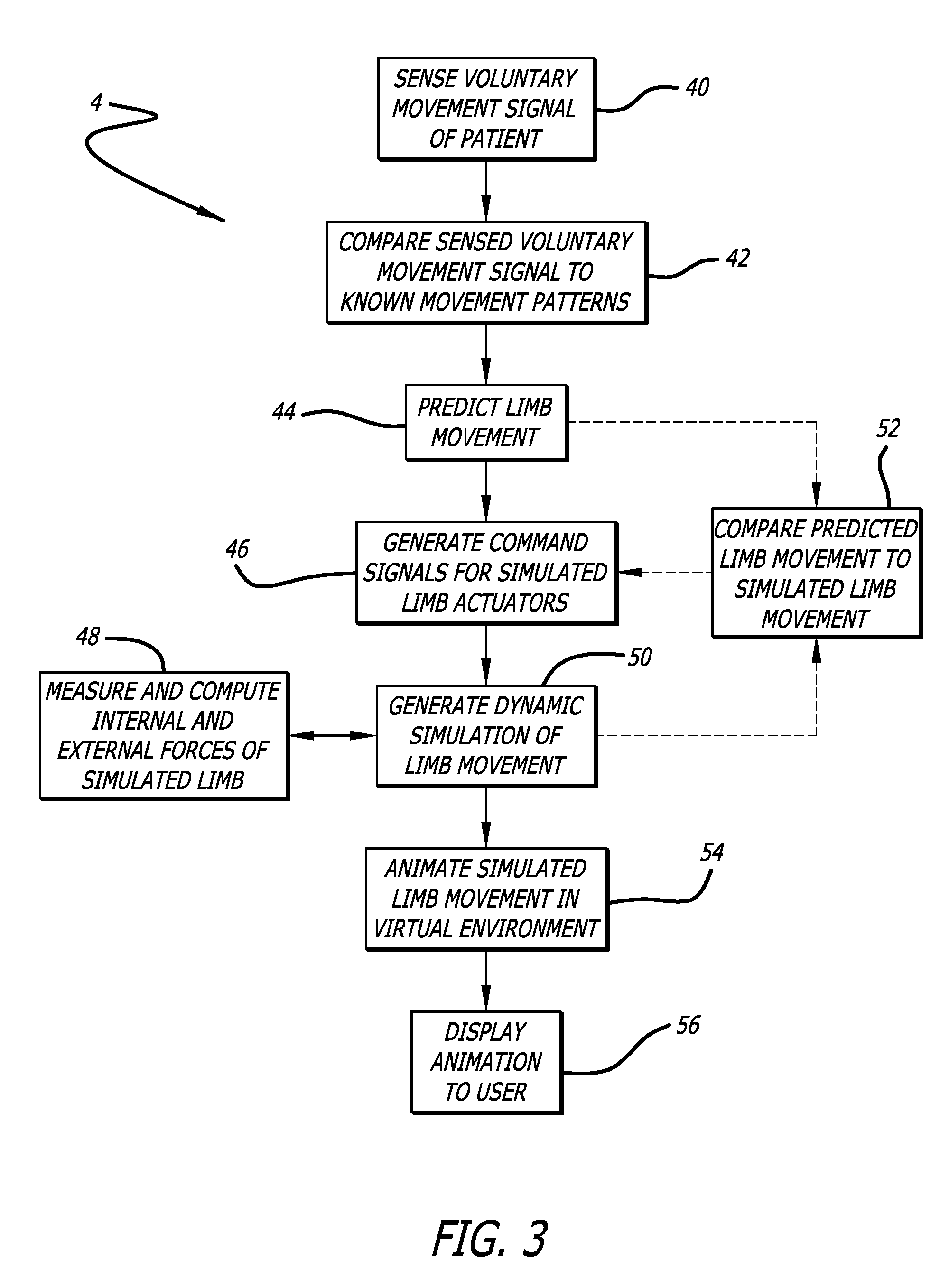
Method and system for training adaptive control of limb movement
InactiveUS20070016265A1Facilitate prescriptionImprove fitMedical simulationElectrotherapyPhysics basedAnimation
Disclosed are methods and systems for a virtual reality simulation and display of limb movement that facilitate the development and fitting of prosthetic control of a paralyzed or artificial limb. The user generates command signals that are then processed by the control system. The output of the control system drives a physics-based simulation of the limb that simulates the limb to be controlled. The computed movements of the model limb are displayed to the user as a 3D animation from the perspective of the user so as to give the impression that the user is watching the actual movements of his / her own limb. The user learns to adjust his / her command signals to perform tasks successfully with the virtual limb. Alternatively or additionally, the errors produced by the virtual limb and / or the responses of the user during the training process can provide information for adapting the properties of the control system itself.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Prosthetic joints with contained compressible resilient members
InactiveUS20050192674A1Improve protectionEliminate shear stressInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElastomerTotal knee replacement
In a total knee replacement (TKR), the use of a cushion element provides better wear characteristics than polyethylene (“poly”) alone. Since a metal-on-metal, metal-on-ceramic, or ceramic-on-ceramic articulating surface has better wear characteristics than metal on poly, the invention essentially provides cushioning for metal / ceramic-on-metal / ceramic joint replacements. It also allows the use of elastomers for their cushioning properties rather than their surface wear and tensile strength characteristics. The contained compressible elements could also be used as a cushion below polyethylene components, polyethylene over metal components, unicondylar knee replacements, patellar components, and prosthetic components for other parts of the body, including the hip, elbow, shoulder, wrist, and ankle.
Owner:ANOVA
Prosthetic Knee
A prosthetic knee for replacing the knee of a patient including: (a) a femoral component being coupable to a resected distal end of a femur of patient; (b) a tibial component being couplable to a resected proximal end of a tibia of the patient; and (c) an insert, wherein the femoral component and the tibial component articulate by way of the insert arrangable therebetween, and a curved articular surface of the insert is adapted to pivot with respect to a corresponding curved articular surface of the tibial component.
Owner:RICHARDSON RODNEY LAN WALTER
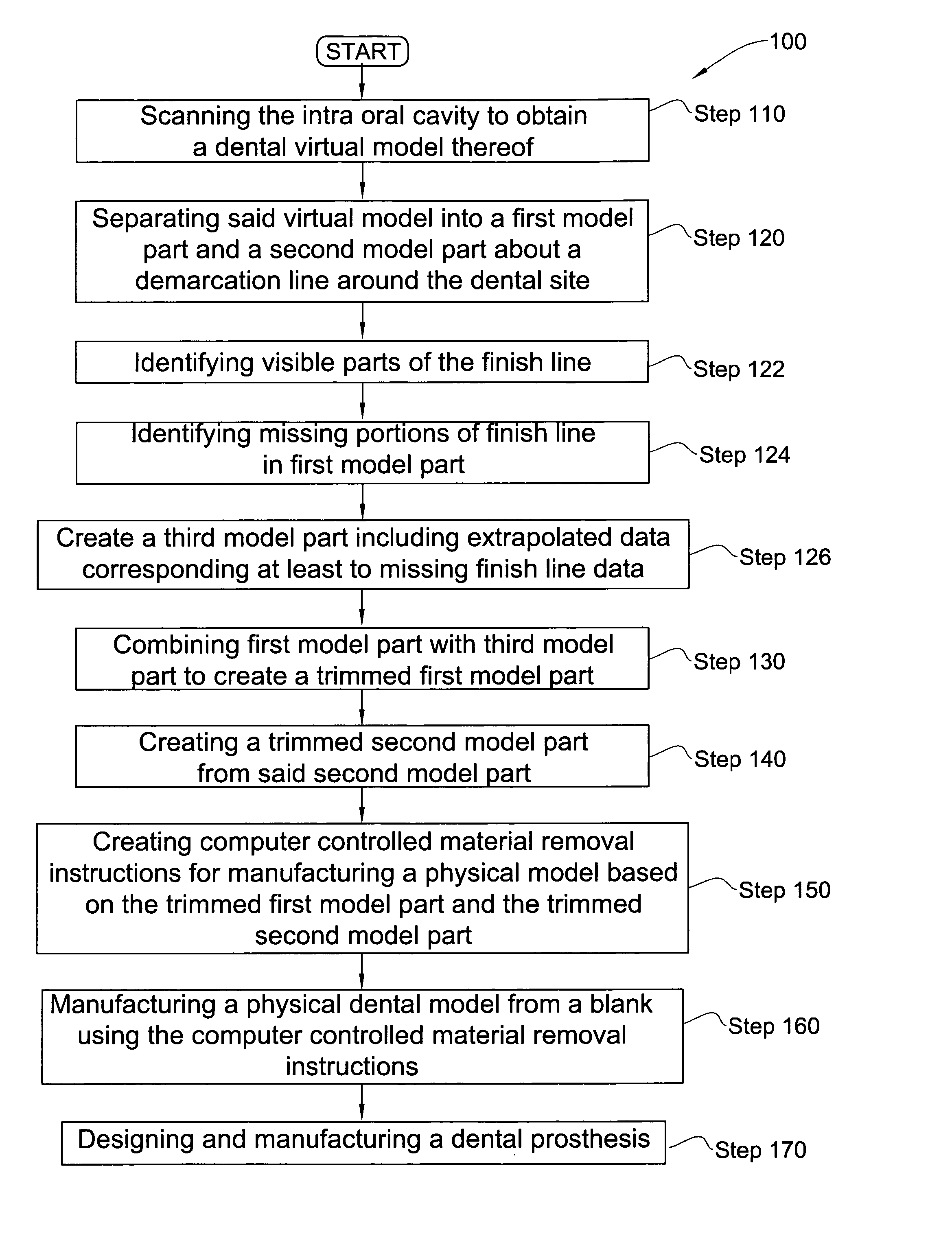
Method for manipulating a dental virtual model, method for creating physical entities based on a dental virtual model thus manipulated, and dental models thus created
A 3D virtual model of an intra oral cavity in which at least a part of a finish line of a preparation is obscured is manipulated in virtual space by means of a computer or the like to create, recreate or reconstruct finish line data and other geometrical corresponding to the obscured part. Trimmed virtual models, and trimmed physical models, can then be created utilizing data thus created. The virtual models and / or the physical models may be used in the design and manufacture of copings or of prostheses.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
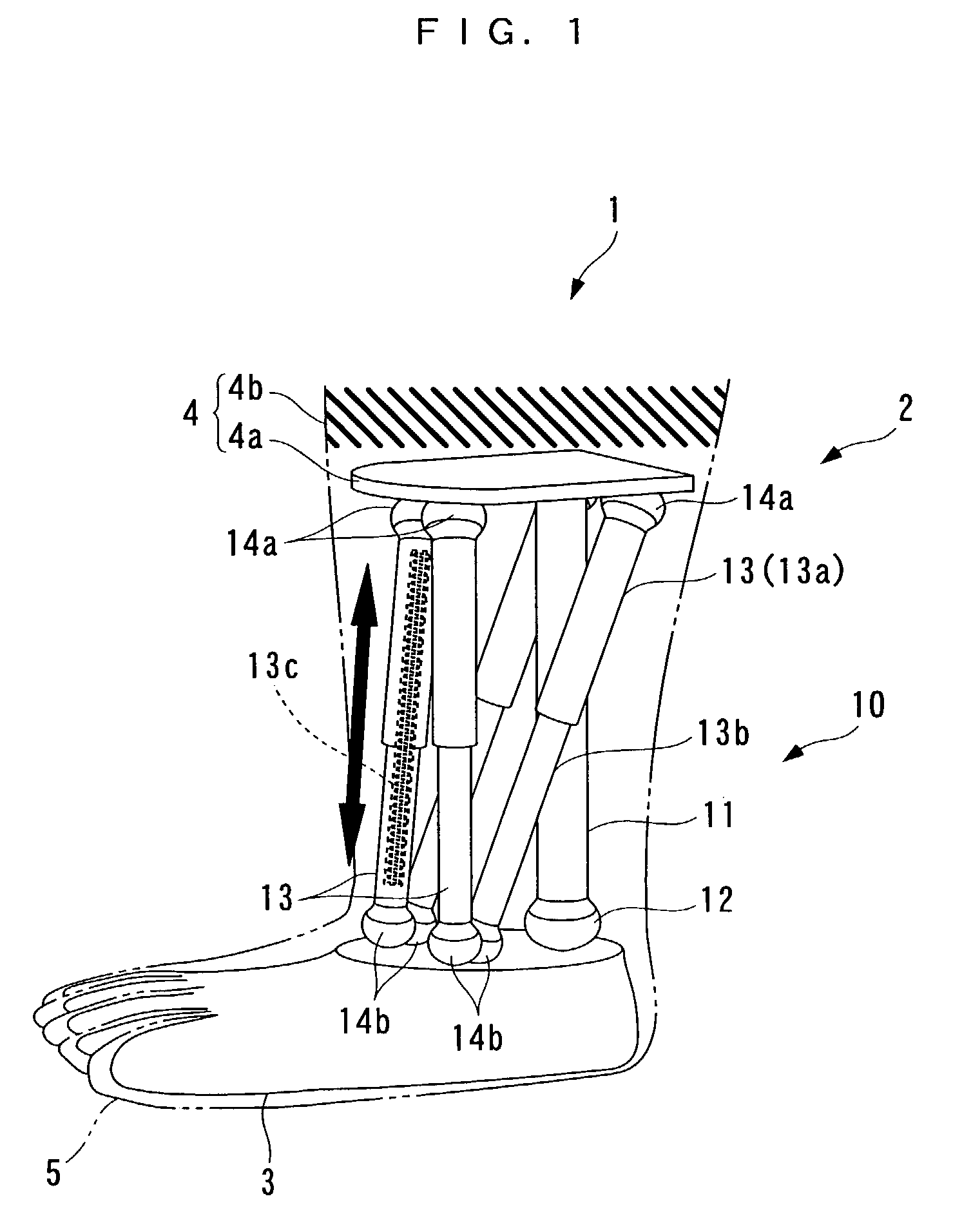
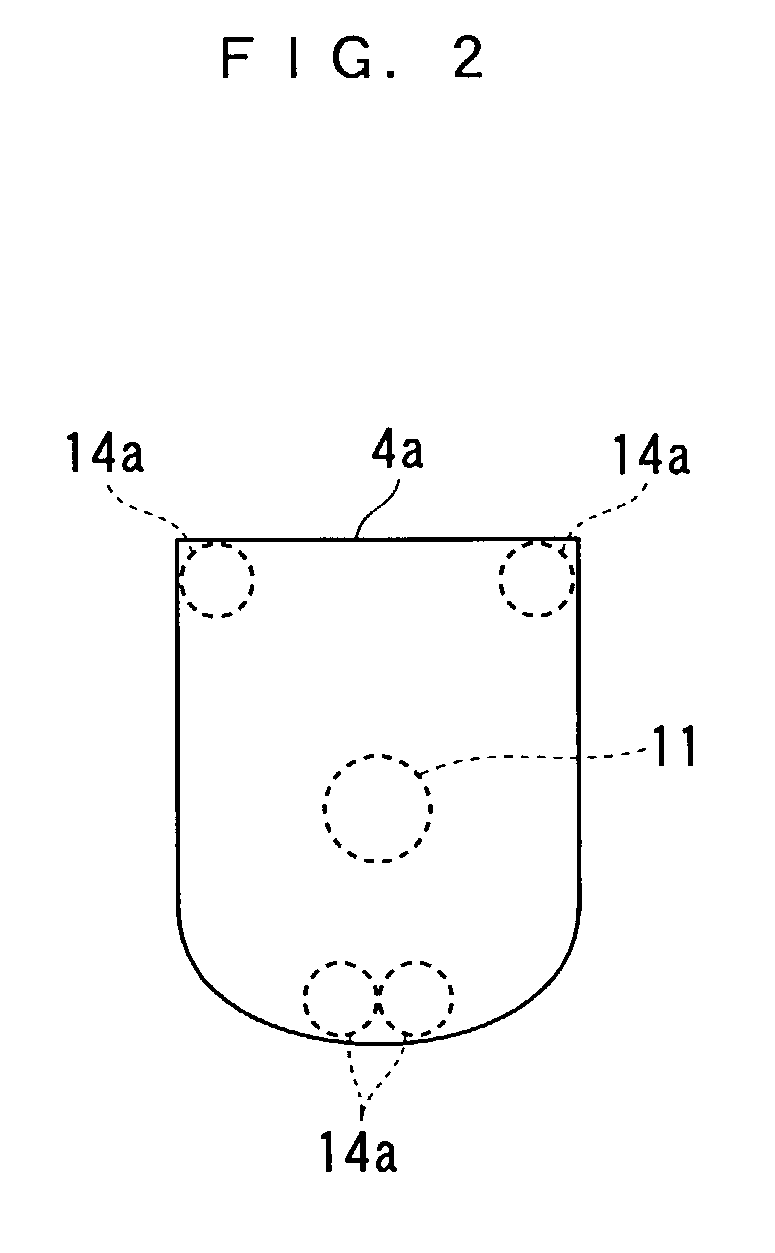
Parallel linkage and artificial joint device using the same
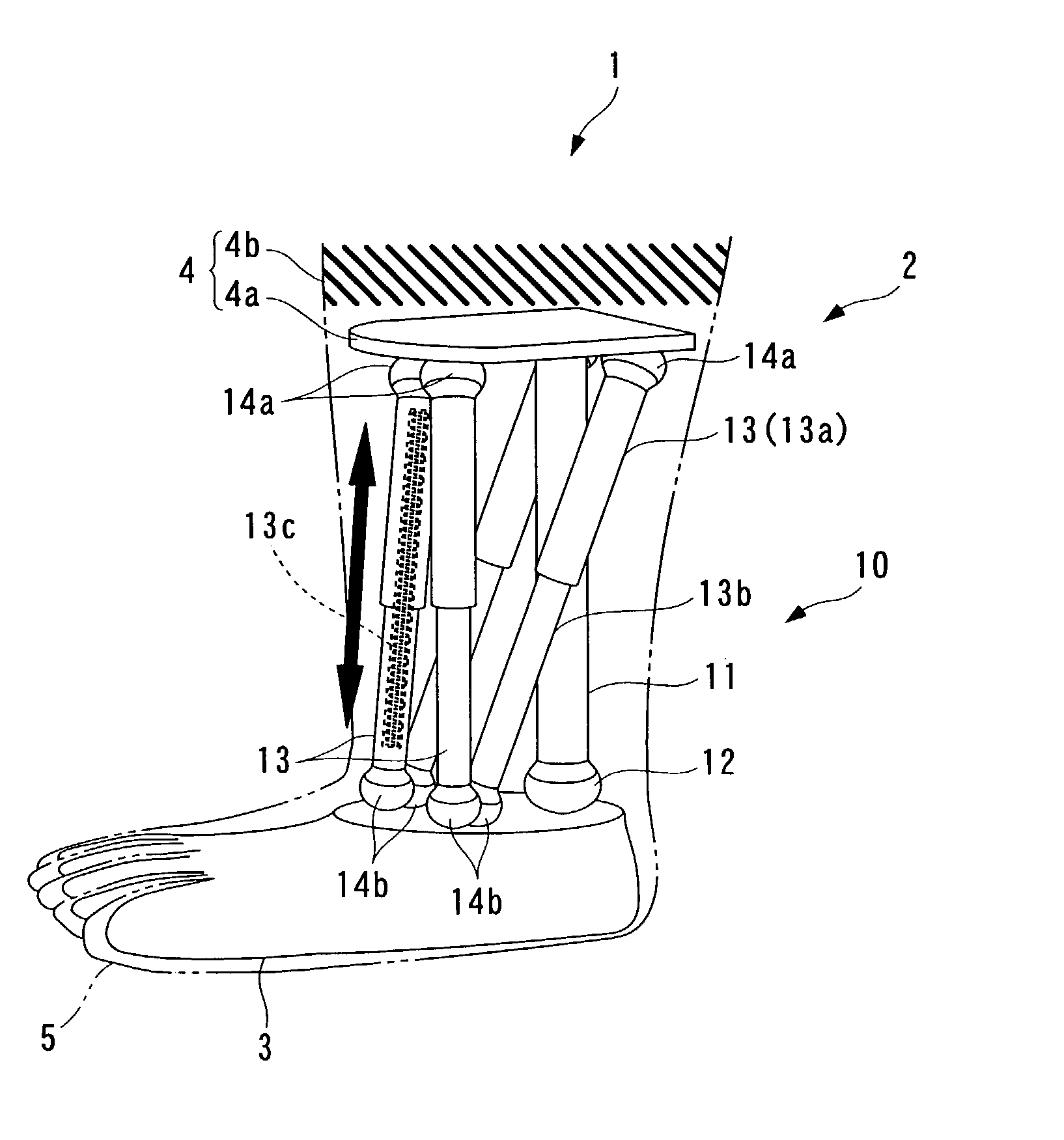
InactiveUS7118601B2Reduce the burden onReduce wearProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsArtificial jointsEngineering
There are provided an artificial joint device that can realize an artificial limb enabling twisting motion without a drive source, and when with the drive source, reduce the size and costs of the device, and a parallel linkage that can realize the device. The linkage connects a foot portion and a mounting plate spaced from each other. A fixed link has one end fixed to the plate, and the other end connected to the foot portion via a ball joint, making the angle of the fixed link relative to the foot portion changeable in any direction. Expansible links extend between the foot portion and the plate in an expansible / contractible manner and each have opposite ends connected to the plate and the foot portion via respective upper and lower ball joints, making respective angles thereof relative to the foot portion and the plate changeable in any direction.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Systems and methods for processing limb motion
ActiveUS7811333B2Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerData set
Control systems and methods are disclosed for processing a time series of signals associated with the movement of a device associated with a limb. The time series of motion signals is filtered, such as thorough an autoregressive filter, and compared to stored data sets representing a limb-motion event and / or phase. In certain examples, a plurality of accelerometers generate the time series of motion signals based at least on acceleration measurements in three orthogonal directions and / or planes. The acceleration measurements may relate to the movement of an artificial limb, such as a prosthetic or orthotic device. Upon determining an event and / or phase of limb motion, the control system may trigger an actuator to appropriately adjust one or more prosthetic or orthotic joints.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Positioning and buffering device for artificial knee joint
A positioning and buffering device of a knee joint for artificial limb is disclosed. The device comprises a knee cap head, an interlinking device including two arch plates, a buffering device including an interlinking rod, an interlinking support and a hydraulic cylinder; a spring device having a spring and a spring support; and a knee cap body module. The knee cap body is used to connect to the thigh and the lower edge of the knee cap body is for connection to the shank and the leg bottom portion. By means of the interlinking rod and the linking support, when the leg is stretched or is standing, a pressure exerted changes the angle between the interlinking rod and the interlinking support such that the knee joint is at a fixed position, the shank will not bent or knee down and the buffering device will produce a buffering and shock absorbing effect.
Owner:CHENG CHIA PAO
Wrist prosthesis
A wrist prosthesis has first, second, and third components that in one form are a radial component, a metacarpal component, and a bearing component. The bearing component is non-fixed or non-stationary relative to one of the radial component and the metacarpal component when the wrist prosthesis is assembled such as when implanted into a patient. As such, in one form a rotational joint or union is provided on the radial component and the bearing component. The bearing component is thus free to rotationally ride on the radial component, preferably 360° thereabout. Distal the radial component, the bearing component includes an articulation surface. The metacarpal component includes an articulation surface that is complementary to the articulation surface of the bearing component. In this manner, the metacarpal component correspondingly moves relative to the bearing component. The bearing component is preferably made of a polymer such as polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
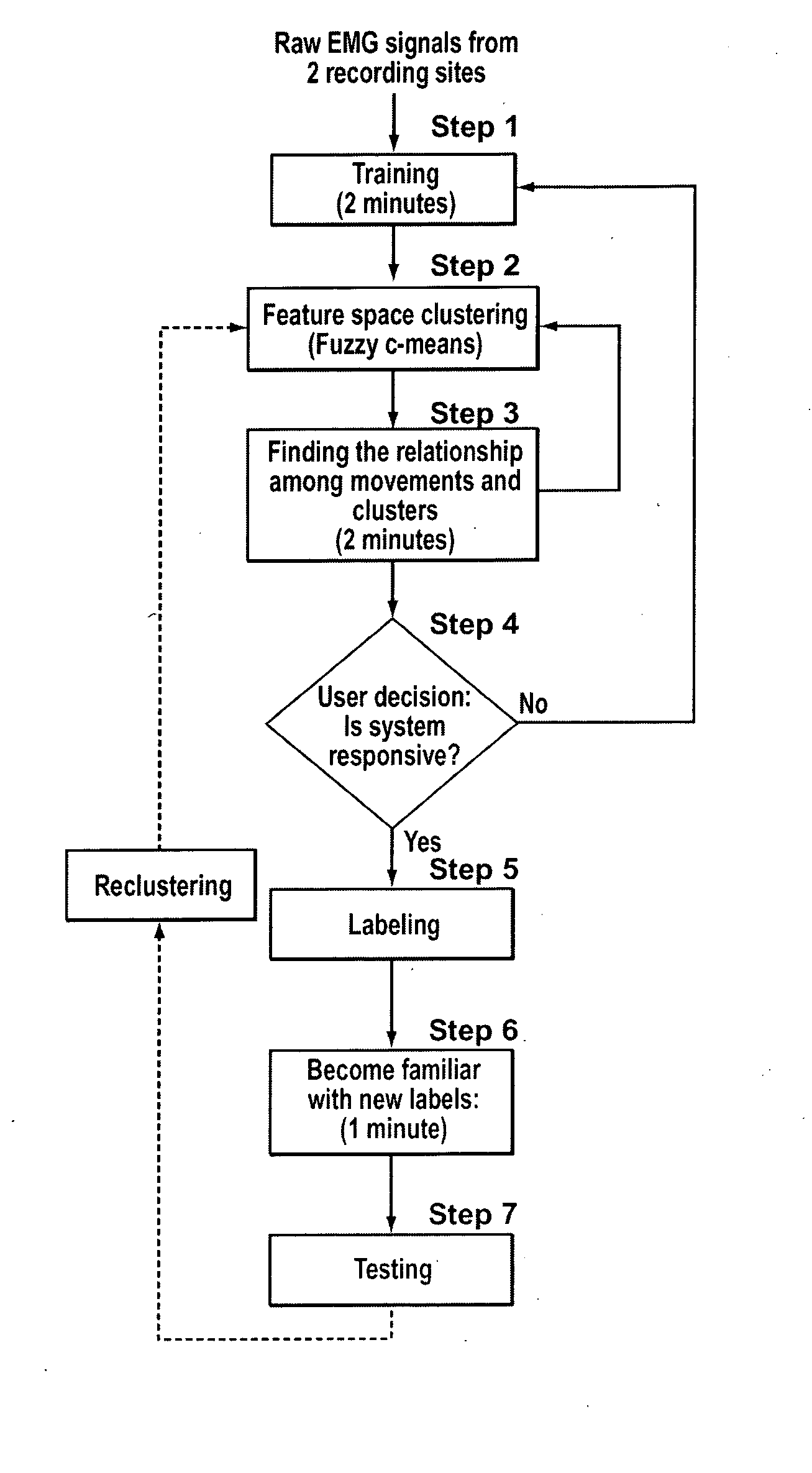
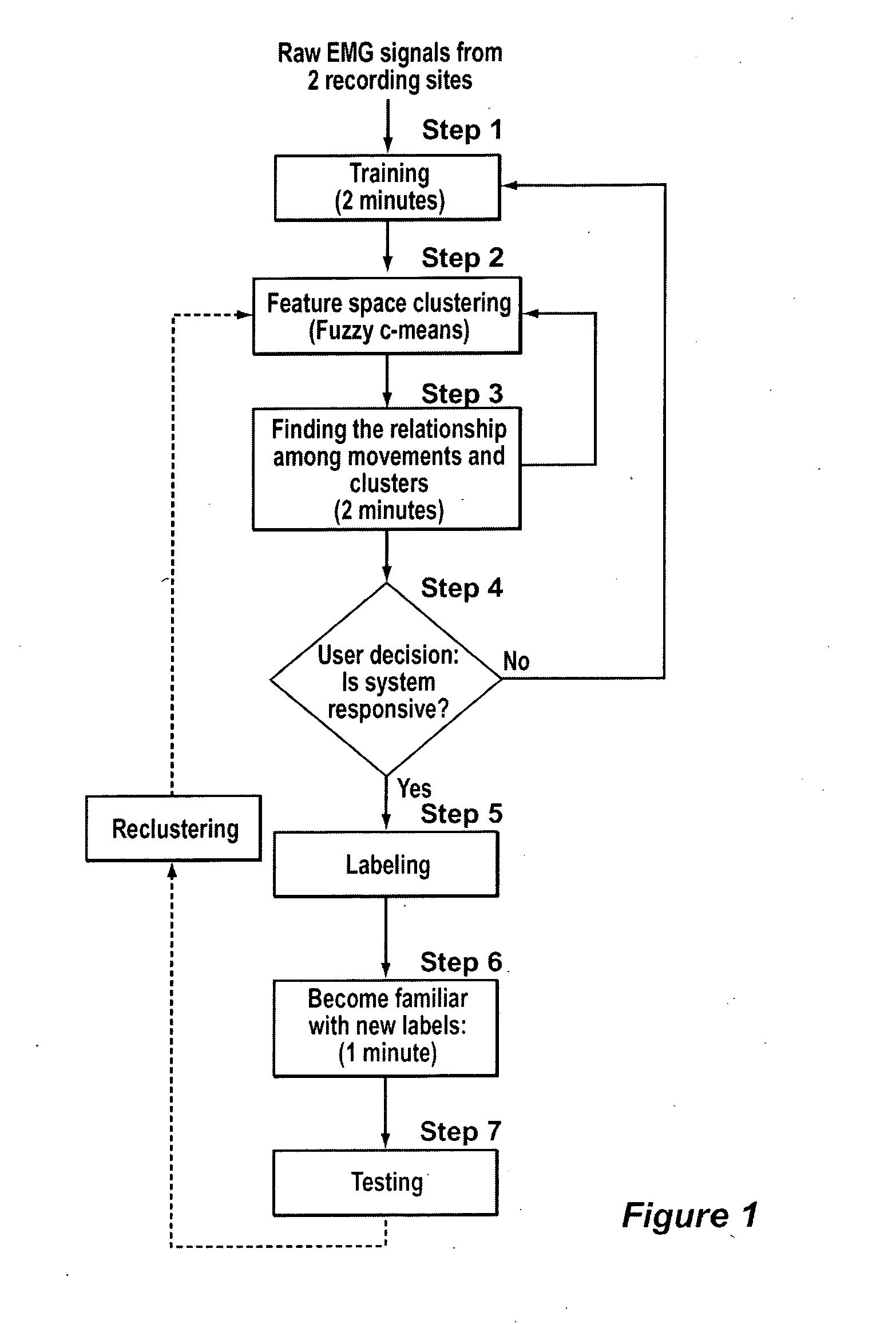
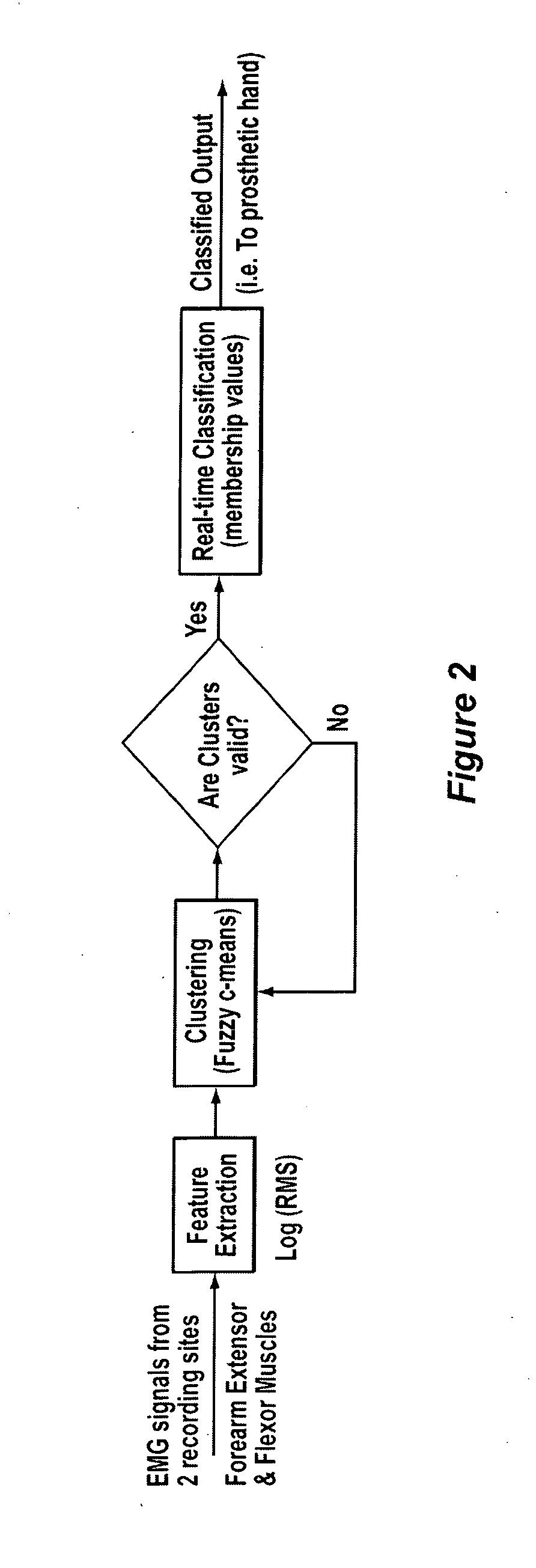
Method, system and apparatus for real-time classification of muscle signals from self-selected intentional movements
InactiveUS20080058668A1Improve abilitiesEasy to operateMedical data miningElectromyographyMuscle contractionSelf training
A new method, system and apparatus is provided that enables muscle signals that correspond to muscle contractions to be mapped to one or more functions of an electronic device such as a prosthetic device or gaming apparatus. Muscle signals are classified in real-time from self-selected intentional movements. A self-training protocol allows users to select and label their own muscle contractions, and is operable to automatically determine the discernible and repeatable muscle signals generated by the user. A visual display means is used to provide visual feedback to users illustrating the responsiveness of the system to muscle signals generated by the user.
Owner:HOLLAND BLOORVIEW KIDS REHABILITATION HOSPITAL
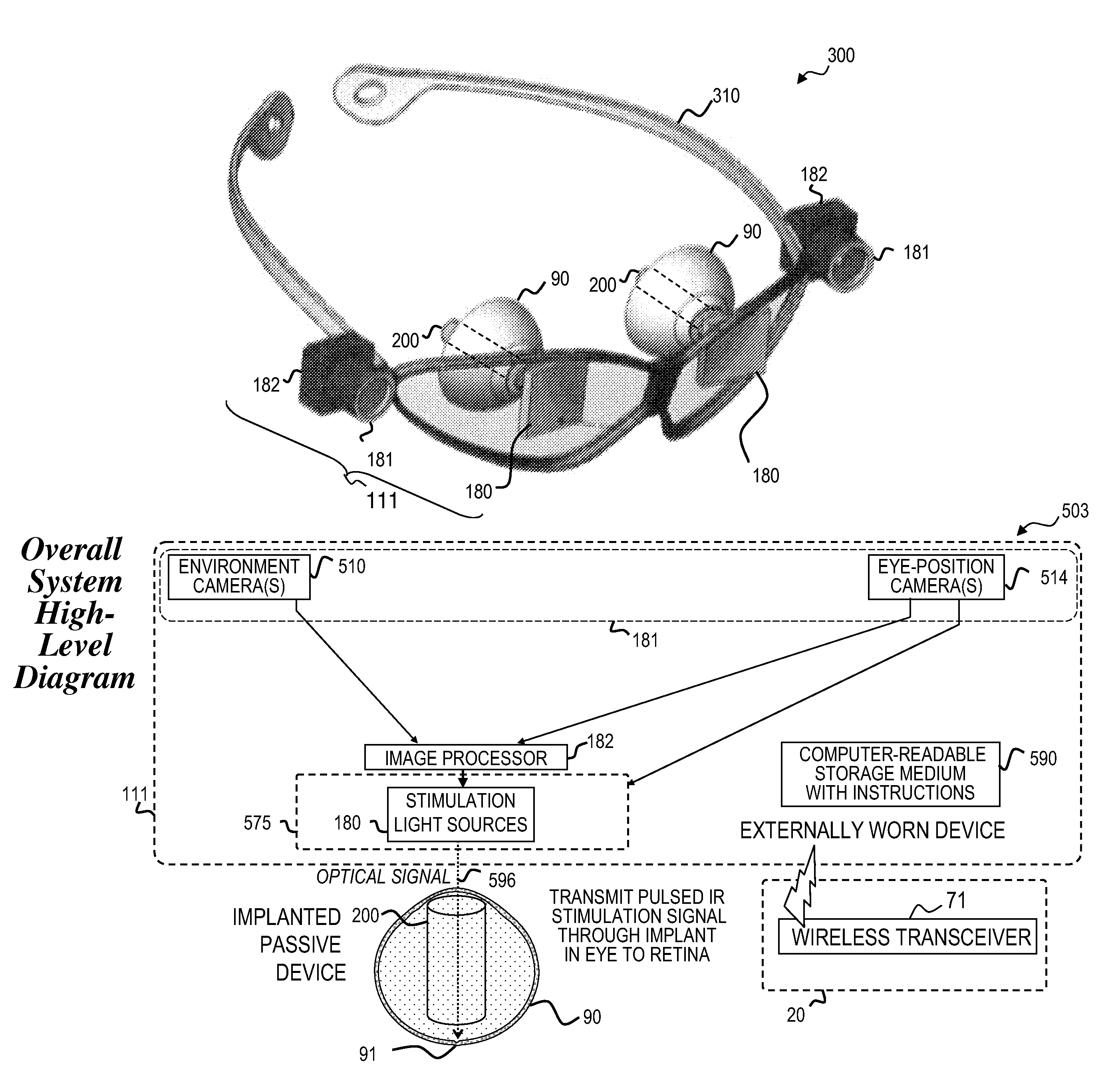
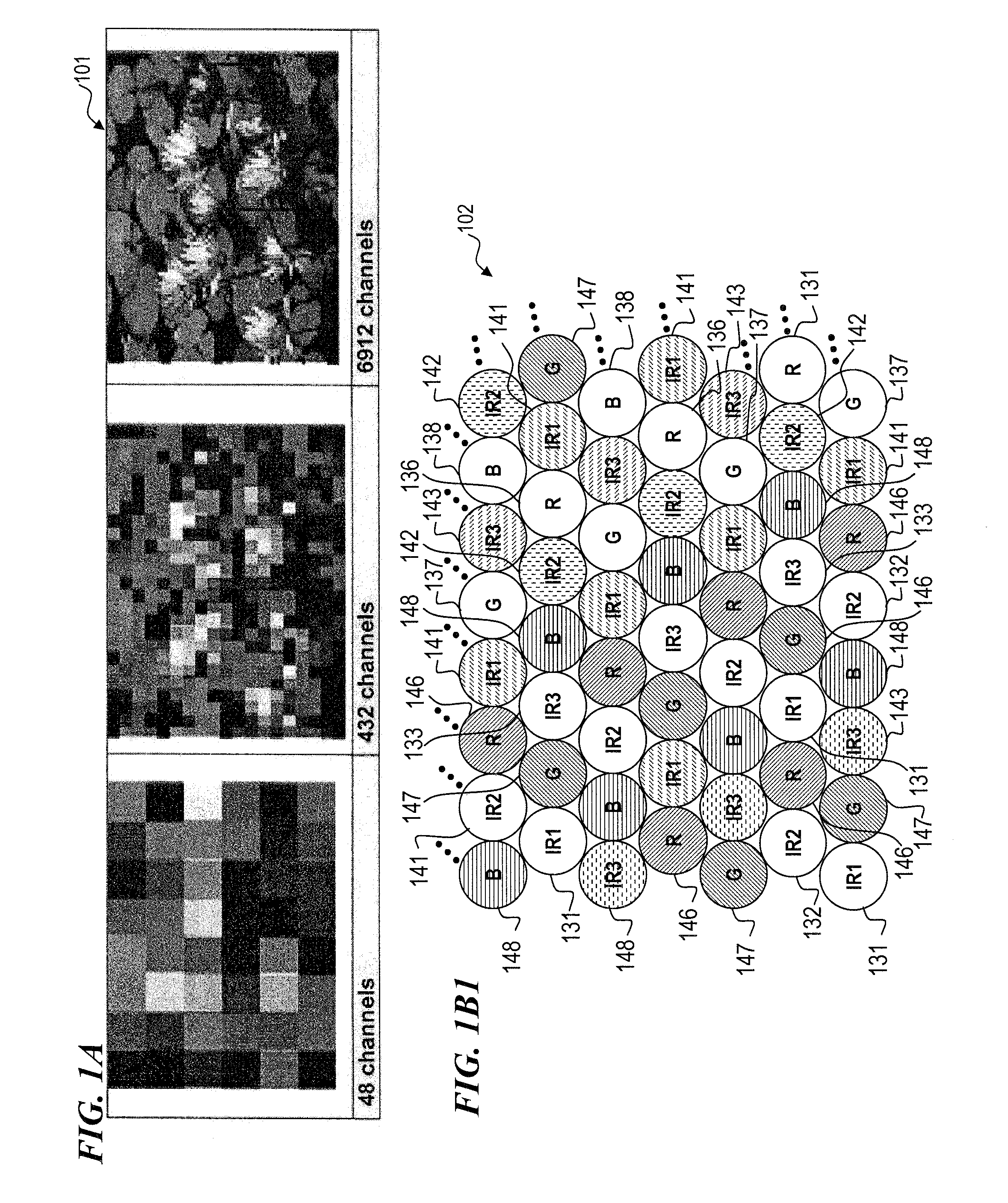
Eye-tracking visual prosthetic and method
An improved prosthesis and method for stimulating vision nerves to obtain a vision sensation that is useful for the patient that has lost vision due to AMD, RP, and other diseases. The invention utilizes infrared light to cause action potentials in the retinal nerves similar to those which result from rods and cones stimulated by visible light in healthy retinas. In some embodiments, the invention provides a prosthesis that generates a stimulation pattern of infrared light from an external stimulator array through the eye and focusing the stimulation pattern of infrared light on the retina, especially the fovea. Some embodiments the invention provides improved resolution down to a group of nerves, or even the individual nerve level, with sufficient energy density so as to cause a desired action potential.
Owner:NUROTONE MEDICAL LTD
Osmotic membrane and vacuum system for artificial limb
InactiveUS6974484B2Prevent air leakageReduce pressureAbsorbent padsBaby linensWater vaporPerspiration
A system for removing perspiration from a residual limb inserted in a prosthesis comprising an nonporous prosthesis socket, a porous thin sheath adjacent the socket, a nonporous liner adjacent the sheath, an osmotic membrane adjacent the liner allowing water vapor to pass from the limb but preventing liquid from passing to the limb, a nonporous seal that prevents air leakage between the residual limb and the socket; and, a vacuum source to reduce the pressure in a space between the limb and socket. A method of removing perspiration from a residual limb in a prosthesis.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Assistive clothing
ActiveUS7918808B2Precise alignmentRapidly and inexpensivelyProgramme controlInput/output for user-computer interactionNormal appearancePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An apparatus and process for empowering those in wheelchairs and others with loss of limb control to walk, climb stairs, sit in ordinary chairs, use normal bathroom facilities and stand at normal height with their peers. It also provides a means to speed rehabilitation of the injured and a means to deliver more comfortable and effective prostheses while providing superior physical therapy without draining professional resources which includes new simulation and training means. Most of the apparatus is worn under normal clothing allowing them to enjoy a normal appearance. Additional advancements include improved actuator design, user interface, visual means and advanced responsive virtual reality.
Owner:SIMMONS JOHN C
Vacuum pump with shock absorption and controlled rotation for prosthetic devices
ActiveUS20050240282A1Positive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesReciprocating motionPump chamber
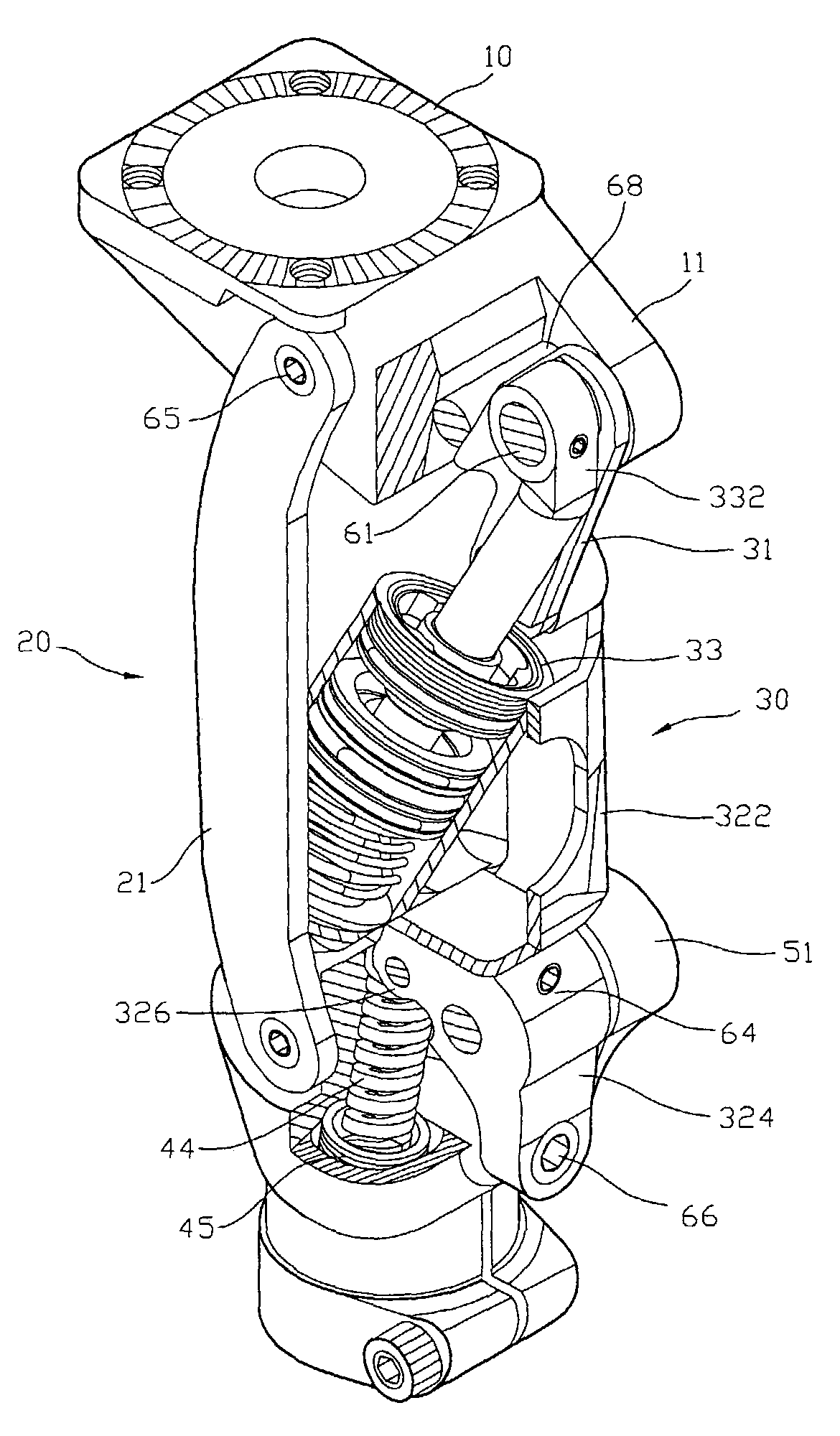
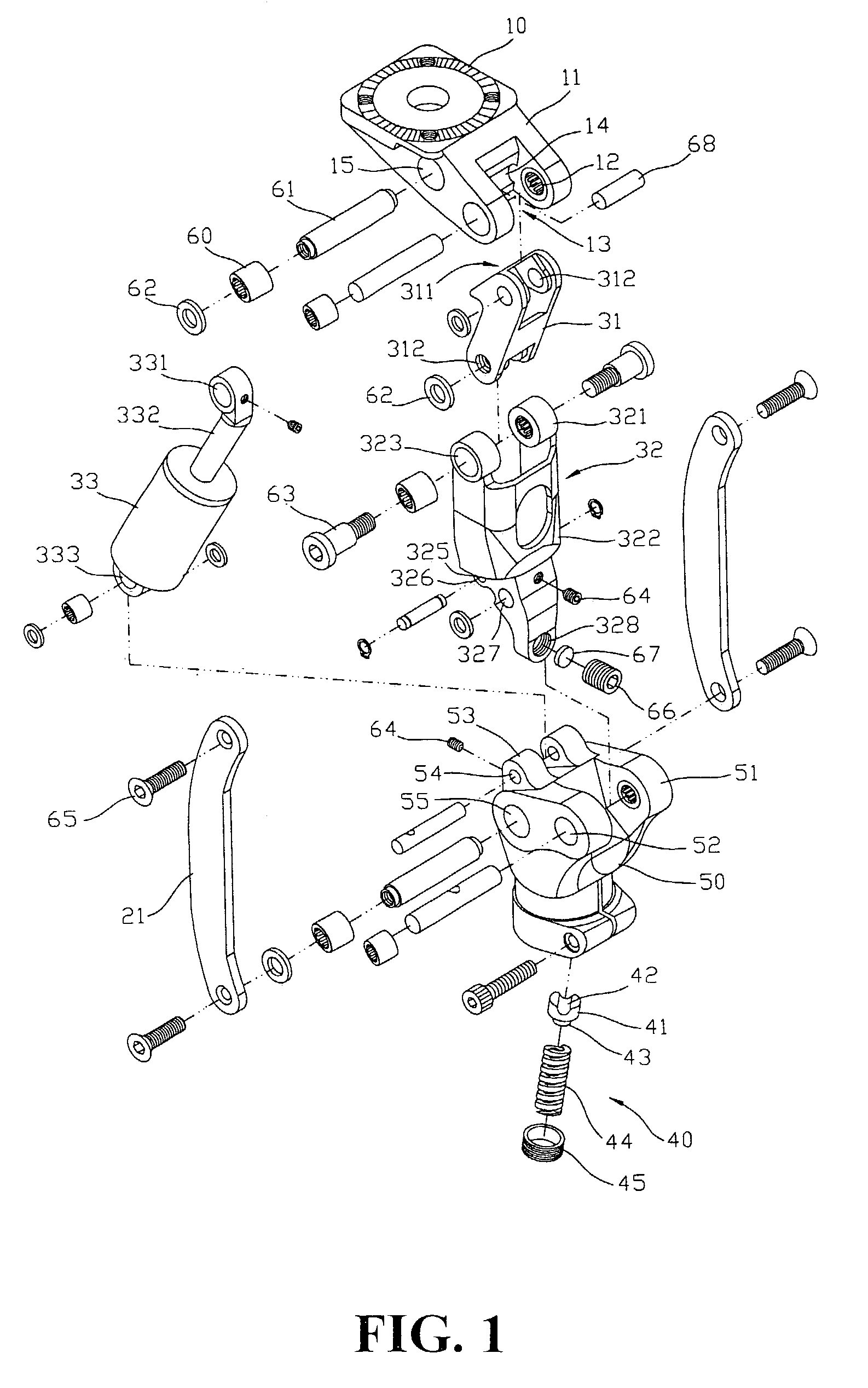
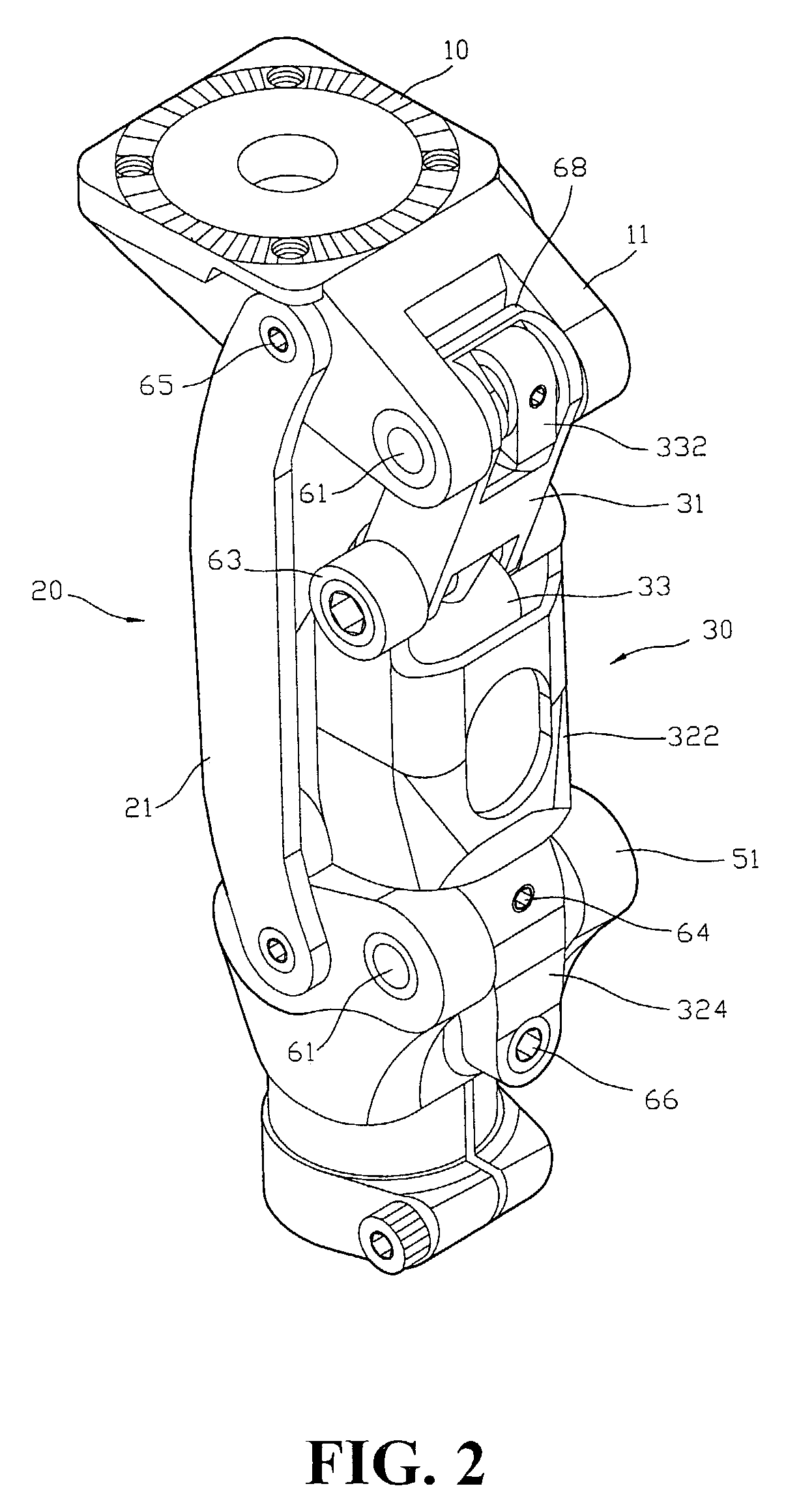
A vacuum pump having shock absorption and controlled rotation for use in an artificial limb. The pump includes a housing having a first chamber, and a shaft configured to be received by and to reciprocate within the first chamber, the housing and shaft forming a pump chamber. A piston may be coupled to the shaft and positioned within the pump chamber, and intake and exhaust ports are fluidly coupled to the pump chamber. Rotational structure is mounted with respect to the pump to provide controlled rotation of the shaft relative to the housing, and shock absorption structure is included within the pump to provide shock absorption for the shaft. Both a pneumatic spring and a mechanical spring element may be provided for the shock absorption structure. An optional adapter couples the shaft to the pylon of an integral pylon prosthetic foot.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
Systems and methods for actuating a prosthetic ankle based on a relaxed position
Systems and methods for sensing actuating a prosthetic ankle are disclosed. In one example, the system, such as an actuated prosthetic ankle joint, detects that the user has moved to a relaxed position, such as sitting, reclining, crawling, or leaning. In response, the actuated prosthetic ankle joint actively adjusts the angle between the members of the ankle to a relaxed state. The system may further detect when the user has moved to exit the relaxed position, and may actively adjust the angle between the members of the ankle to an exit state.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Prosthetic stent graft for treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm
A prosthetic stent graft including a trunk with a vascular graft bifurcated into two flow channels. The flow channels have a first taper angle, decreasing area along its length between the bifurcation point and an outlet. A leg section of the stent graft includes a tubular vascular graft. An inlet of the leg section has a deployed diameter at least about the same size or larger than a deployed diameter of the outlet of the flow channels. The leg section has its own taper angle, preferably less than or about equal to, and more preferably about equal to the taper angle of the flow channel. The deployed diameter of the leg section inlet is preferably about the same size or larger than the deployed diameter of the flow channels adjacent the bifurcation point of the trunk section, and the deployed diameter of flow channel outlets are preferably about the same size or smaller than the deployed diameter of the leg section at an equal distance from the leg section inlet as the outlet is from bifurcation point. Also provided according to the present invention is a method of in situ stent graft sizing for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS6863677B2Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
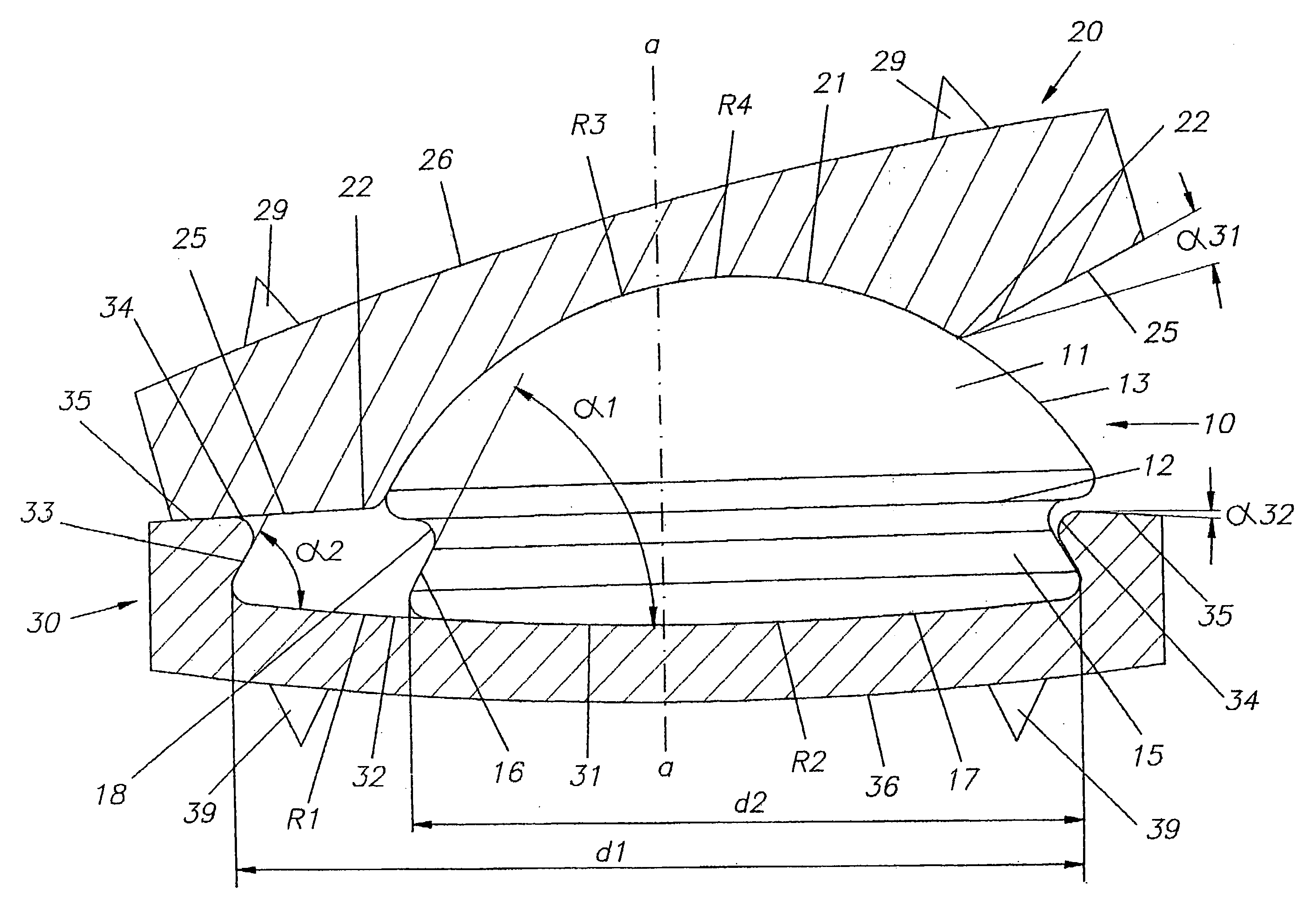
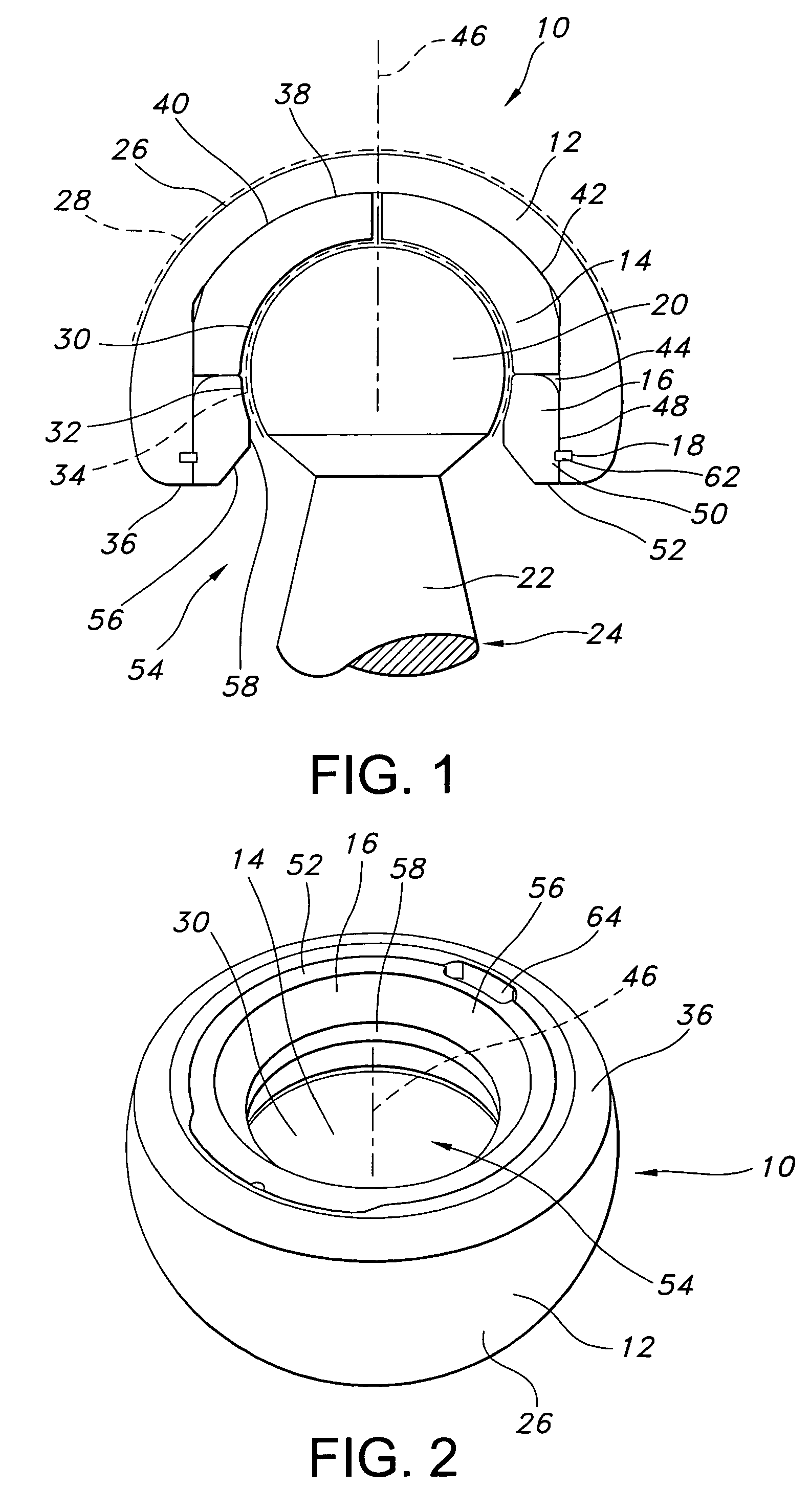
Intervertebral prosthesis
InactiveUS20060069437A1Improve distributionAvoid damageSpinal implantsProsthesisBiomedical engineering
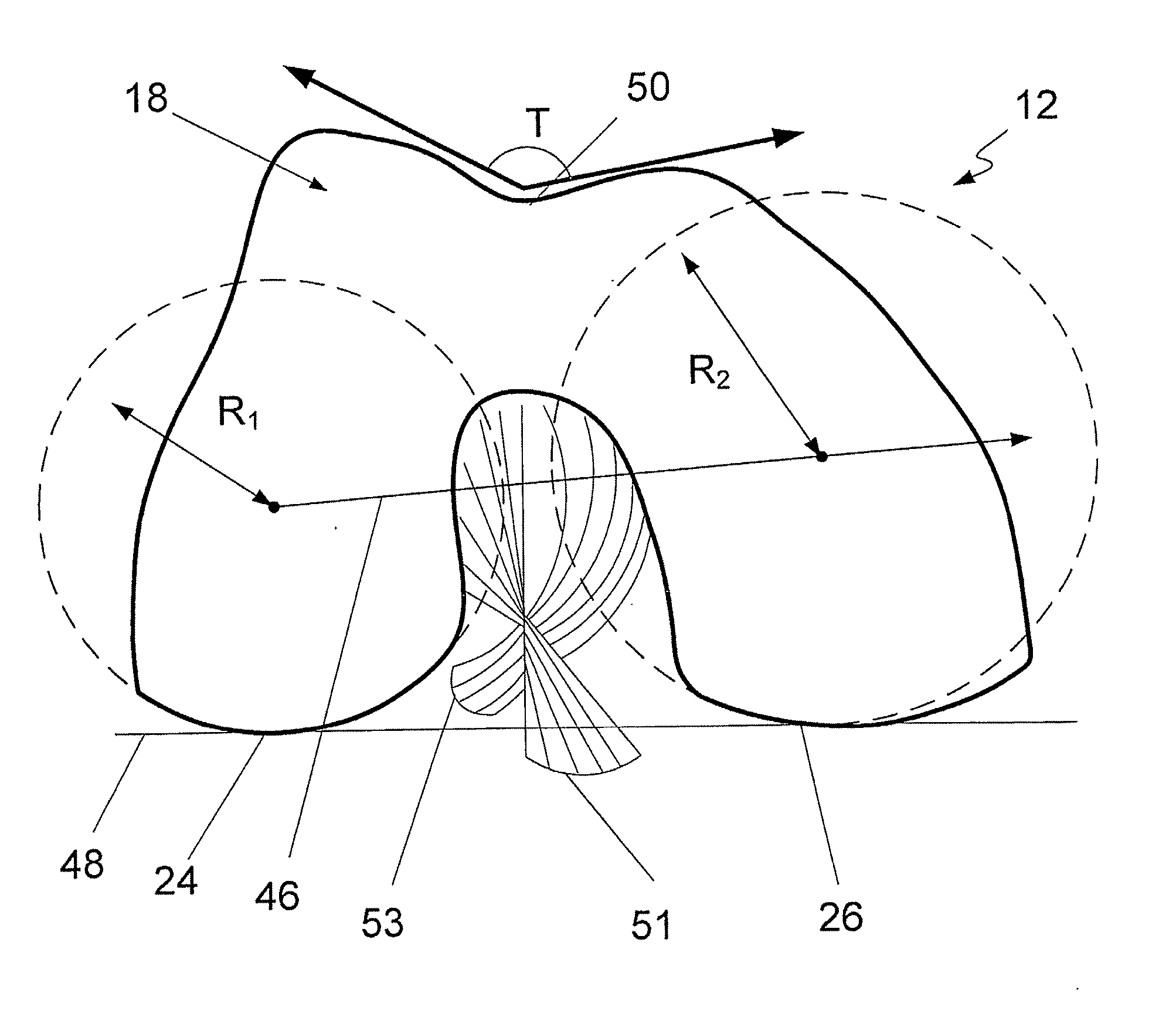
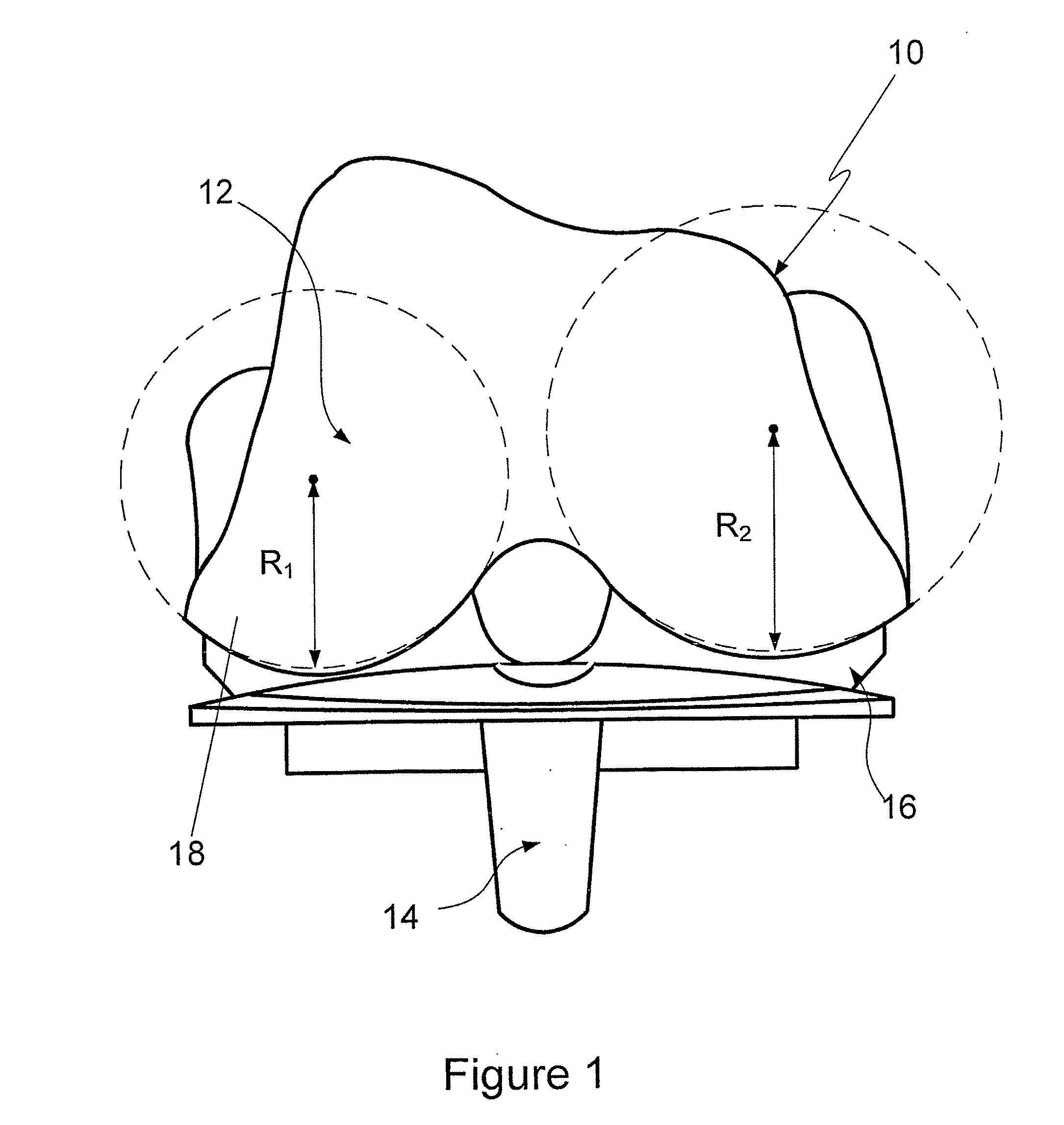
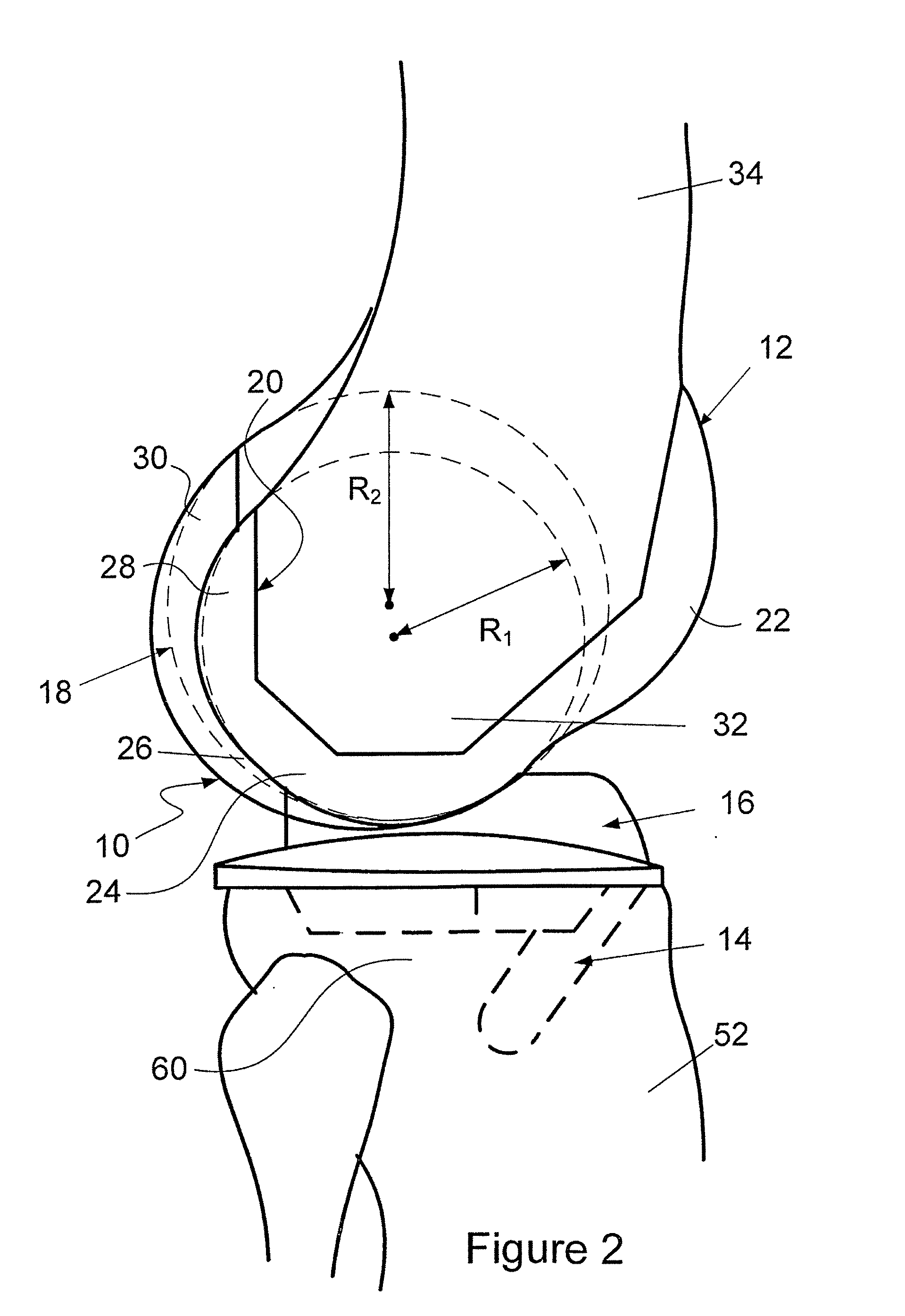
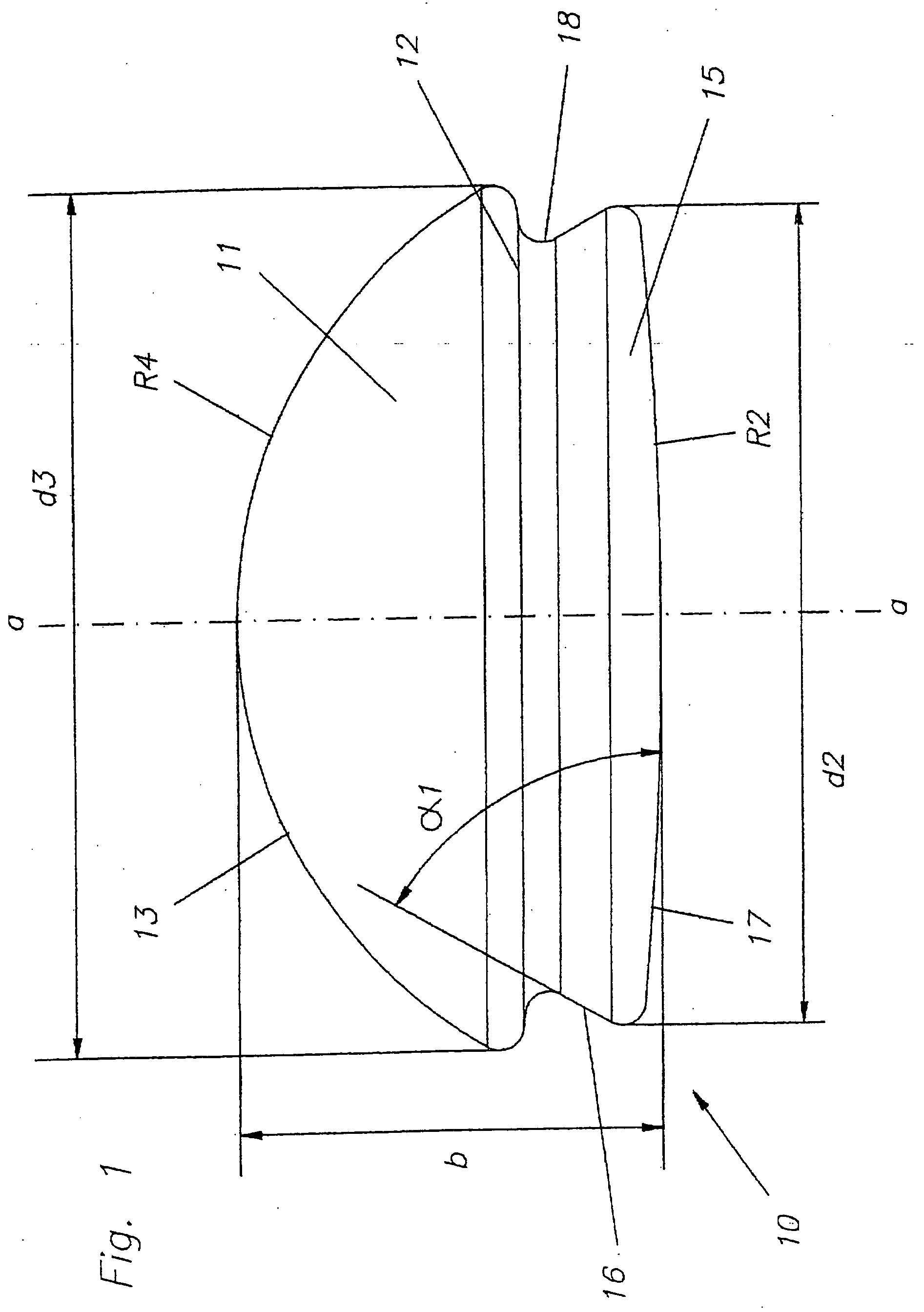
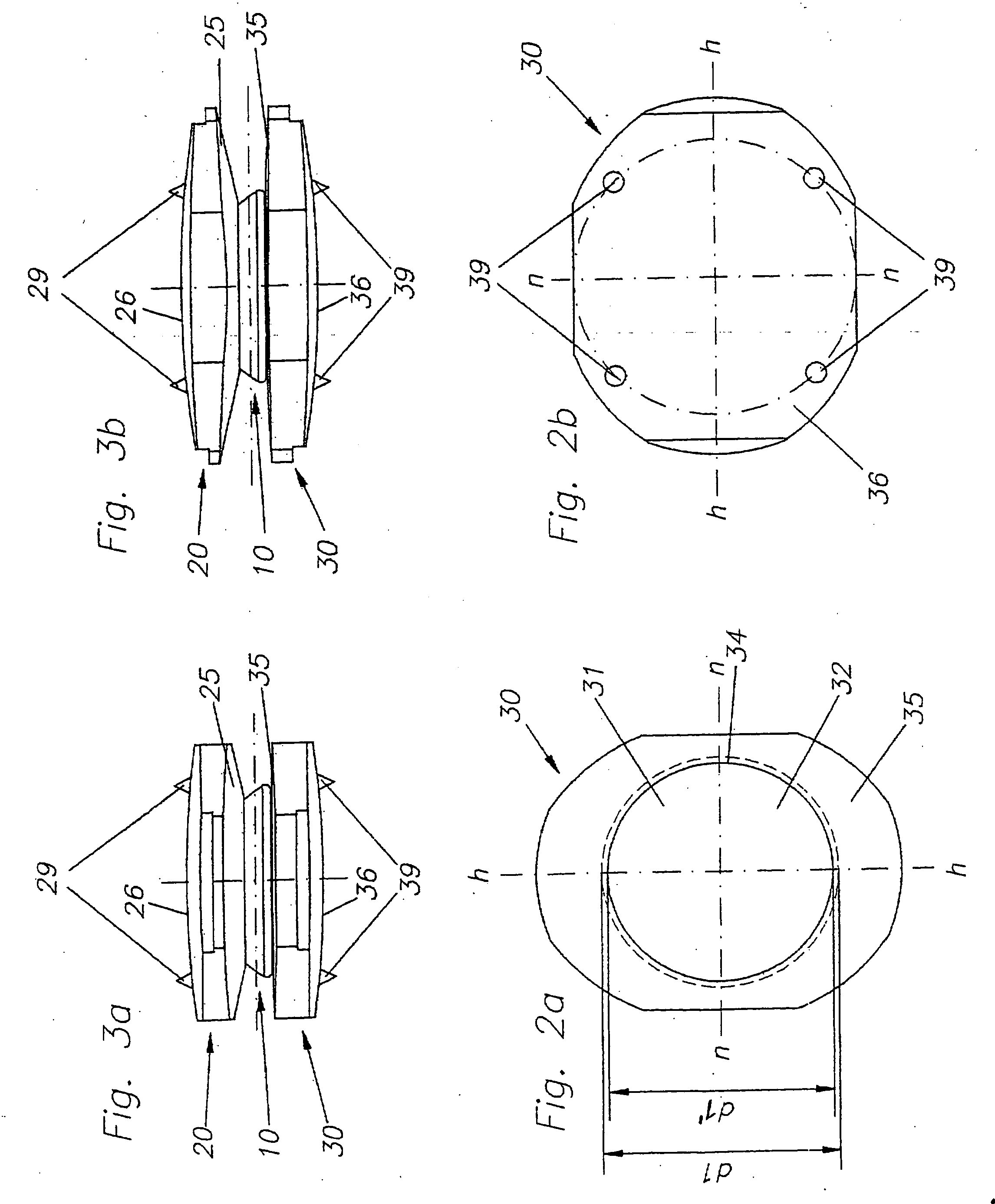
The invention concerns an intervertebral prosthesis comprised of a first prosthetic end plate (20) and a second prosthetic end plate (30) as wall as a prosthetic core (10) located between the first prosthetic end plate (20) and the second prosthetic end plate (30), wherein the first prosthetic end plate (20) has a hemispherical shaped recess (21) with a radius (R3), in which a hemispherical segment (11) of the prosthetic core (10) engages, and wherein the second prosthetic end plate (30) has an essentially planar recess (31), in which an essentially flat segment (15) of the prosthetic core (10), connected to the hemispherical segment (11), engages, wherein the essentially flat segment (15) of the prosthetic core (10) is slideably moveable in the essentially planar recess (31).
Owner:WEBER HELMUT
Walking aid exoskeleton rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN101810533ACompact designLarge range of joint rotationChiropractic devicesWalking aidsHuman bodyRehabilitation engineering
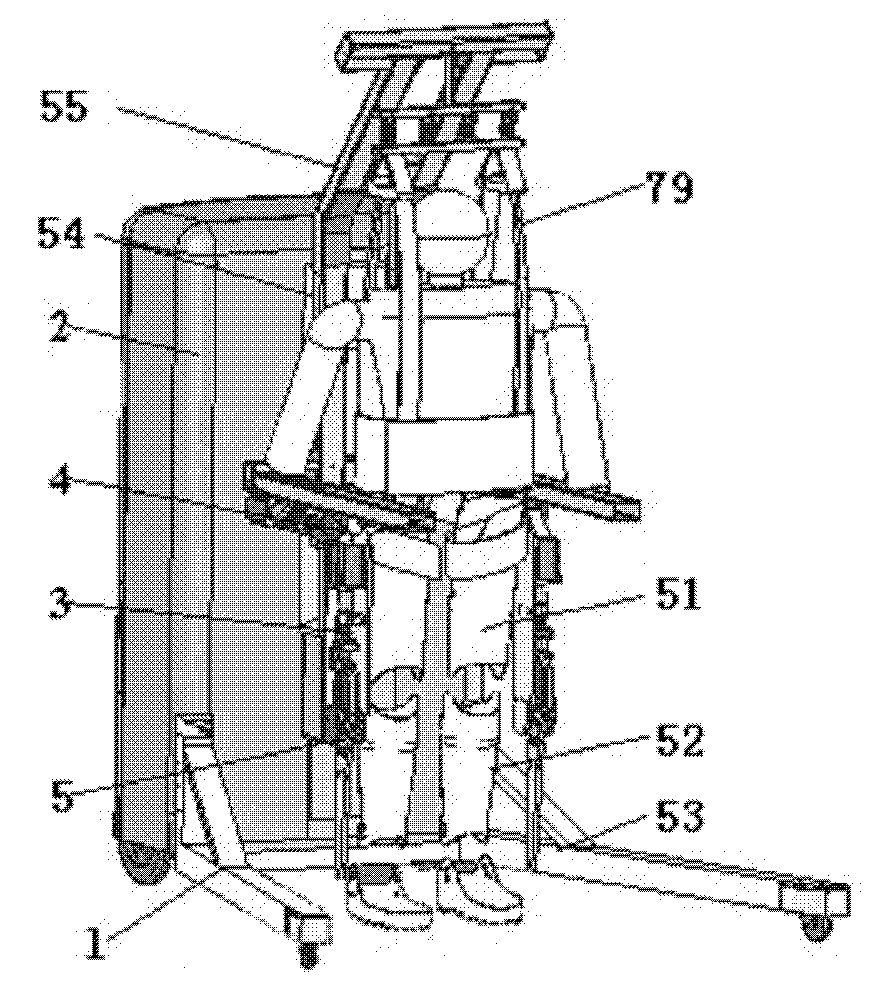
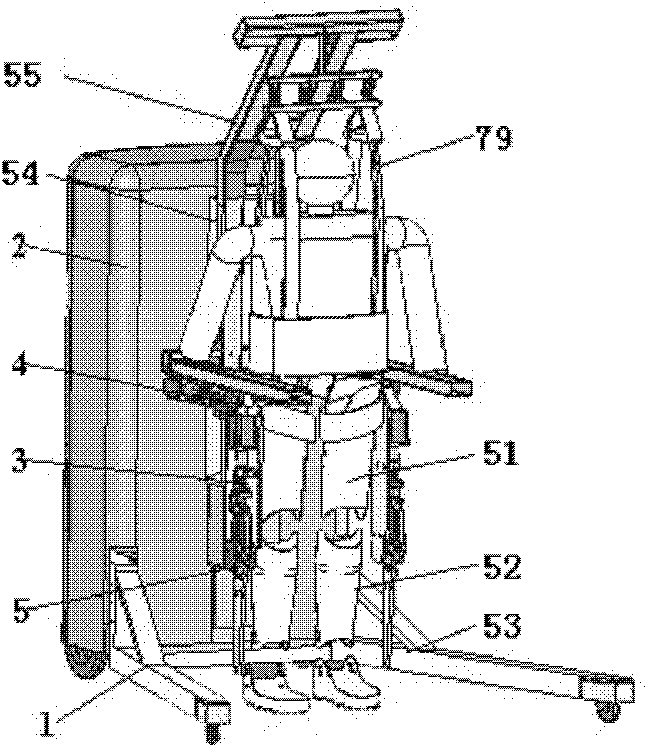
The invention discloses a walking aid exoskeleton rehabilitation robot in the technical field of rehabilitation engineering, which comprises a mobile auxiliary mechanism, a control mechanism and an exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism, wherein the mobile auxiliary mechanism is connected with the exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism, and the control mechanism is connected with the mobile auxiliary mechanism and the exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism respectively. The exoskeleton prosthesis mechanism has compact design structure and large rotation range of each joint, and can meet the requirement on actual motion of a human body. By adopting a servo motor to drive, the control precision is high, and the output torque is large; and the mobile auxiliary mechanism rotates under the driving of the servo motor, can freely move, and has higher climbing capacity and movement speed. The height of the mobile auxiliary mechanism is adjusted to be applied to people with different heights. When the patient undergoes gait rehabilitation training, the human gravity center is actively adjusted to accord with the characteristics that the human body is fluctuated along with alternative gait. The mobile auxiliary mechanism also can support the human body, prevent people from tumbling in walking, and guarantee the whole stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
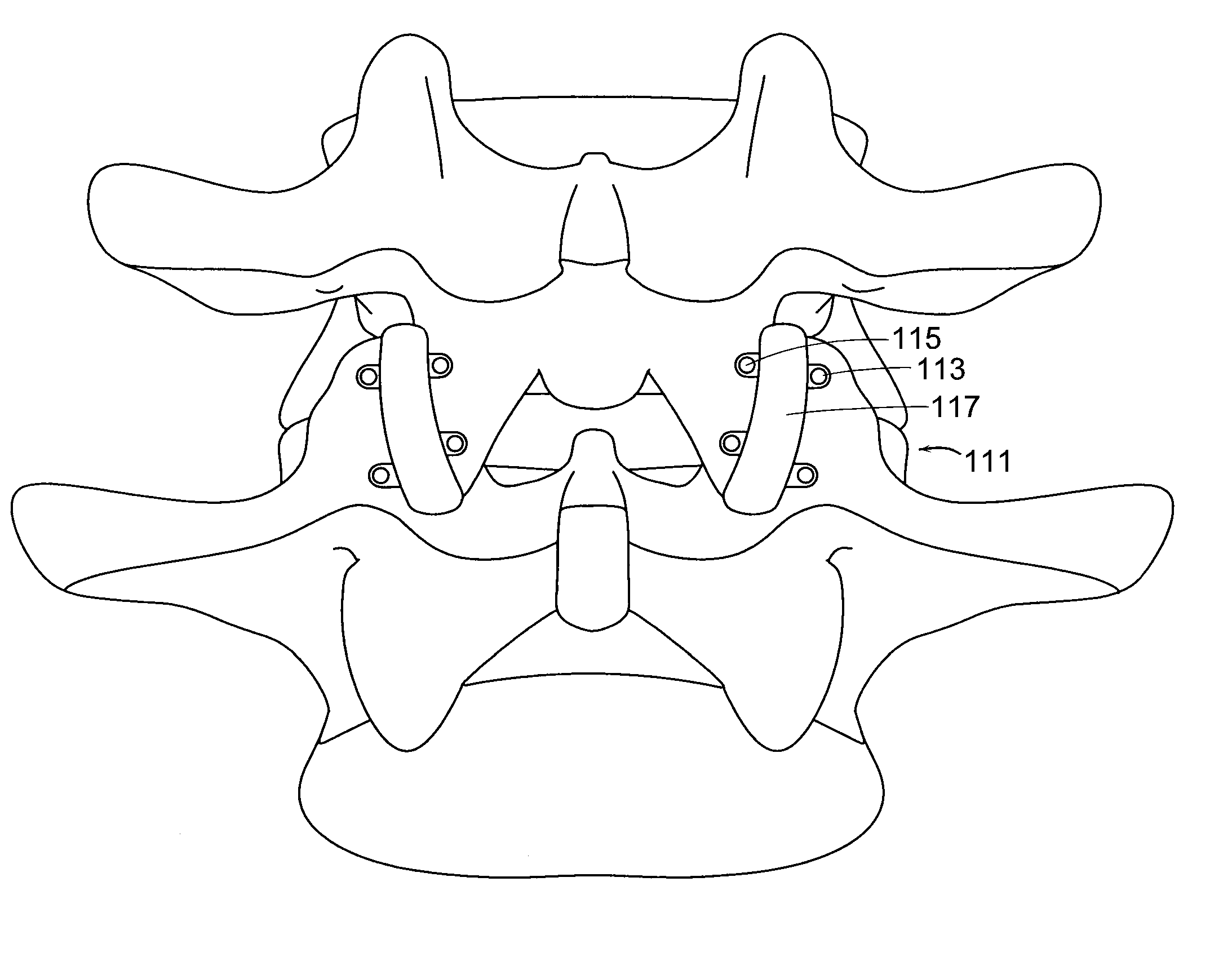
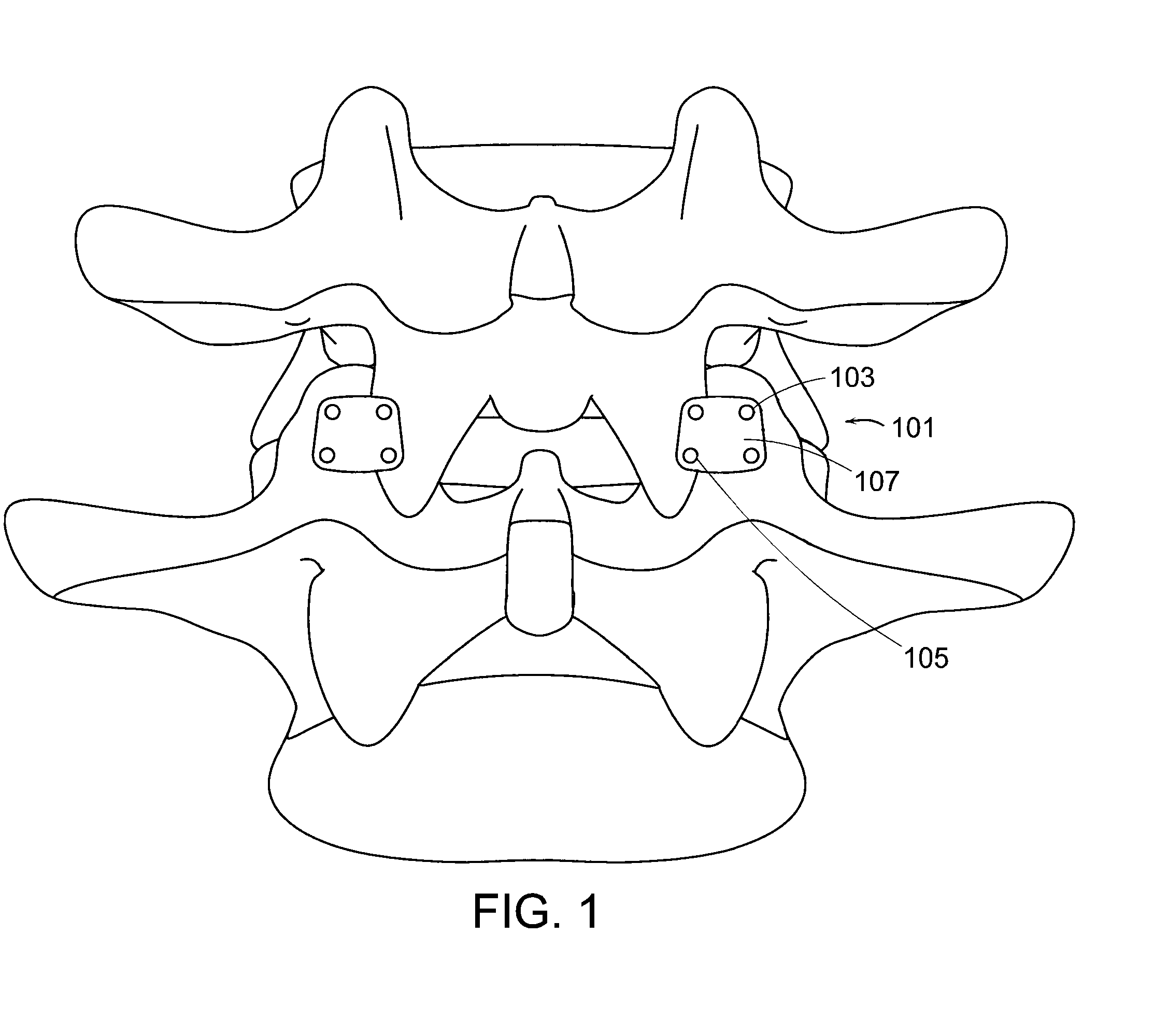
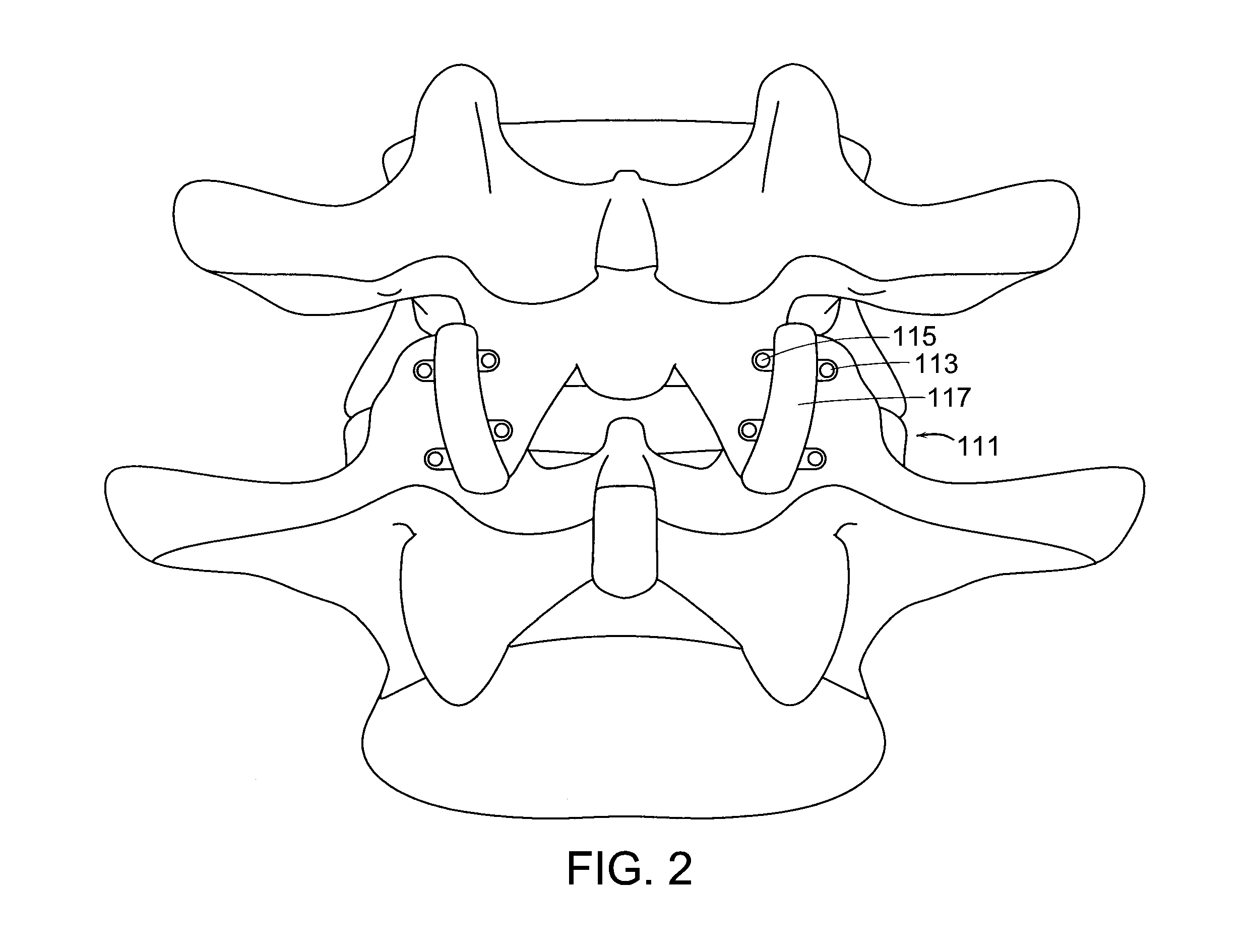
Prosthetic Facet Joint Ligament
InactiveUS20060259142A1Restore joint functionalityRelief the painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLigament structureSacroiliac joint
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
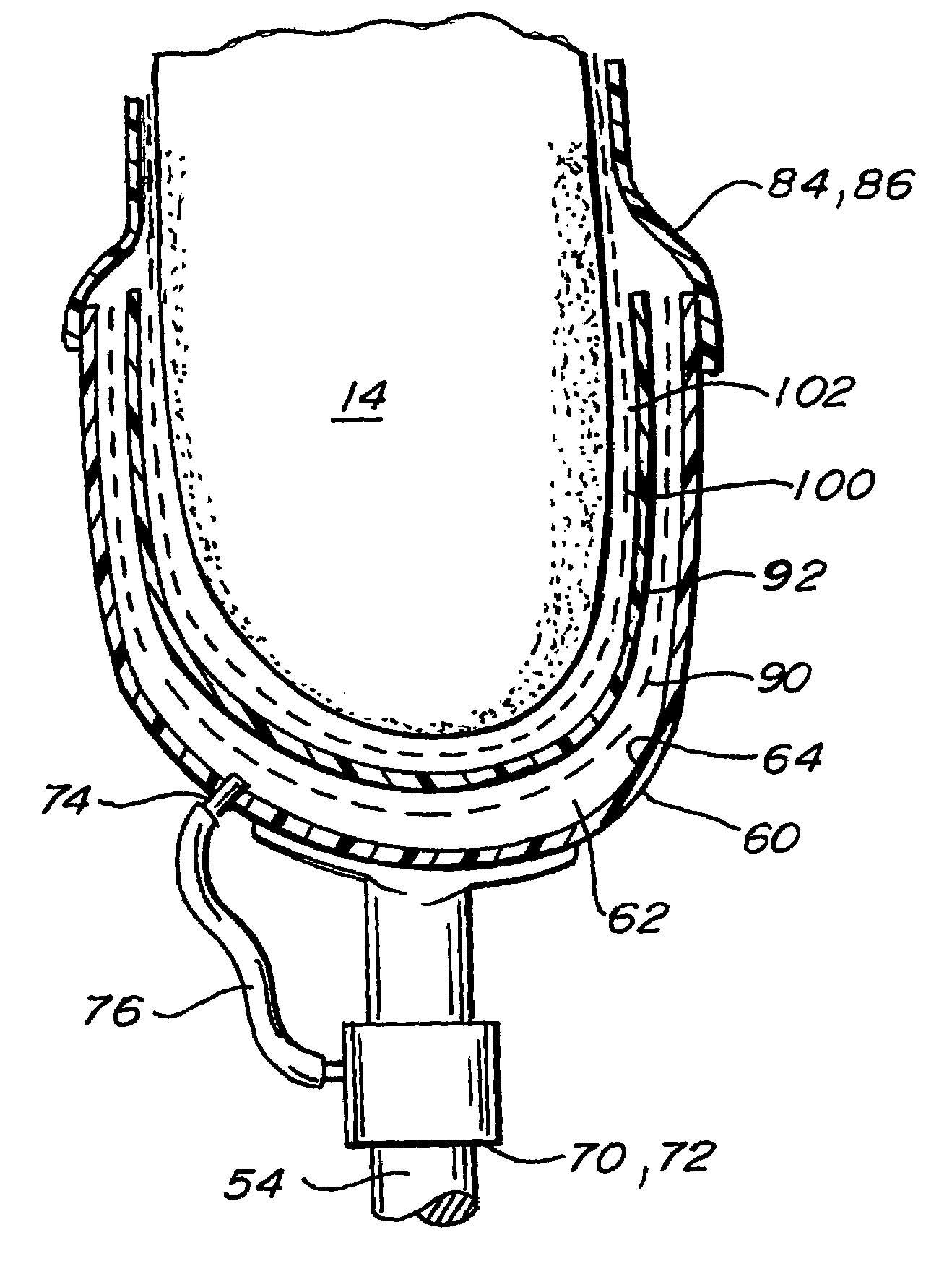
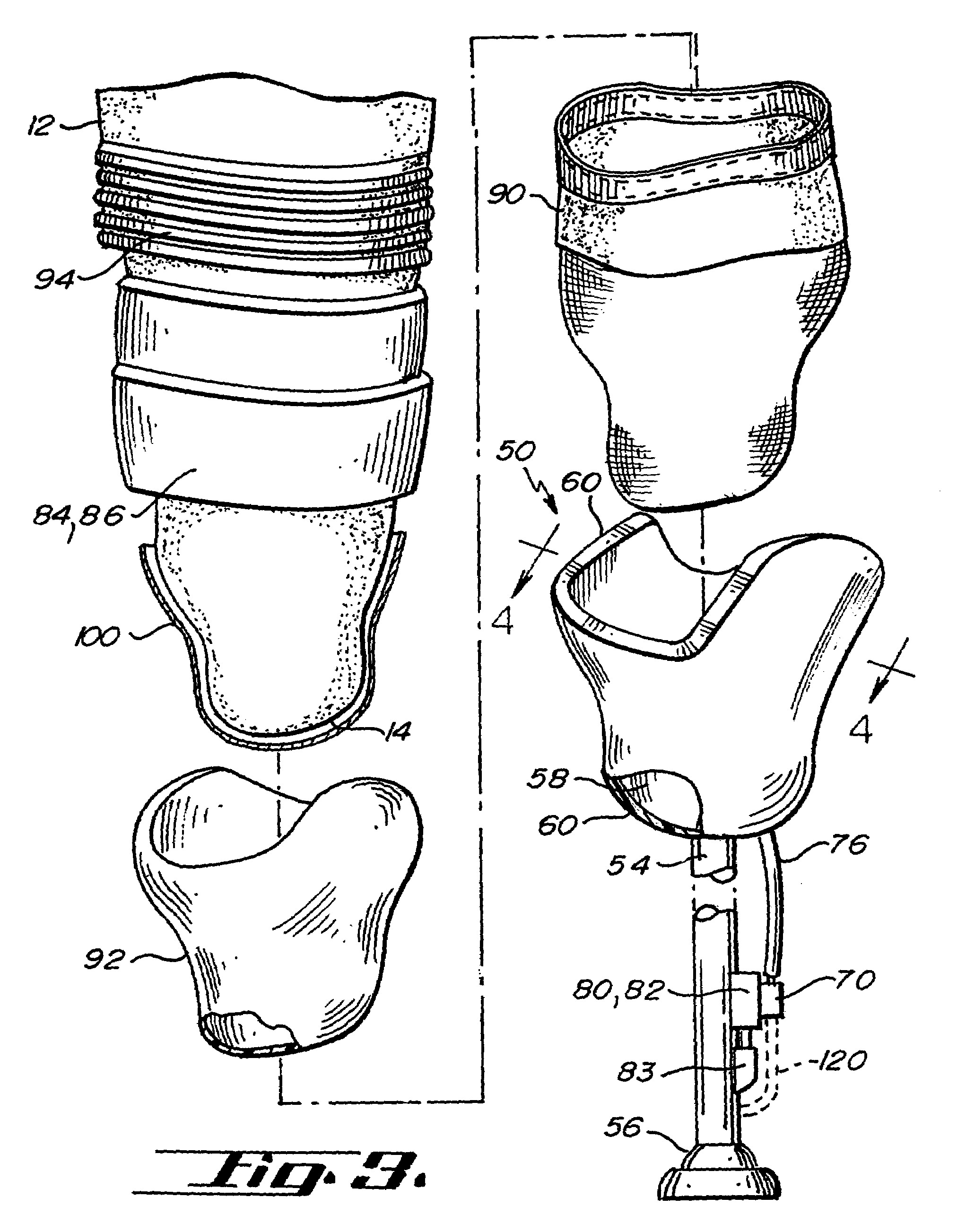
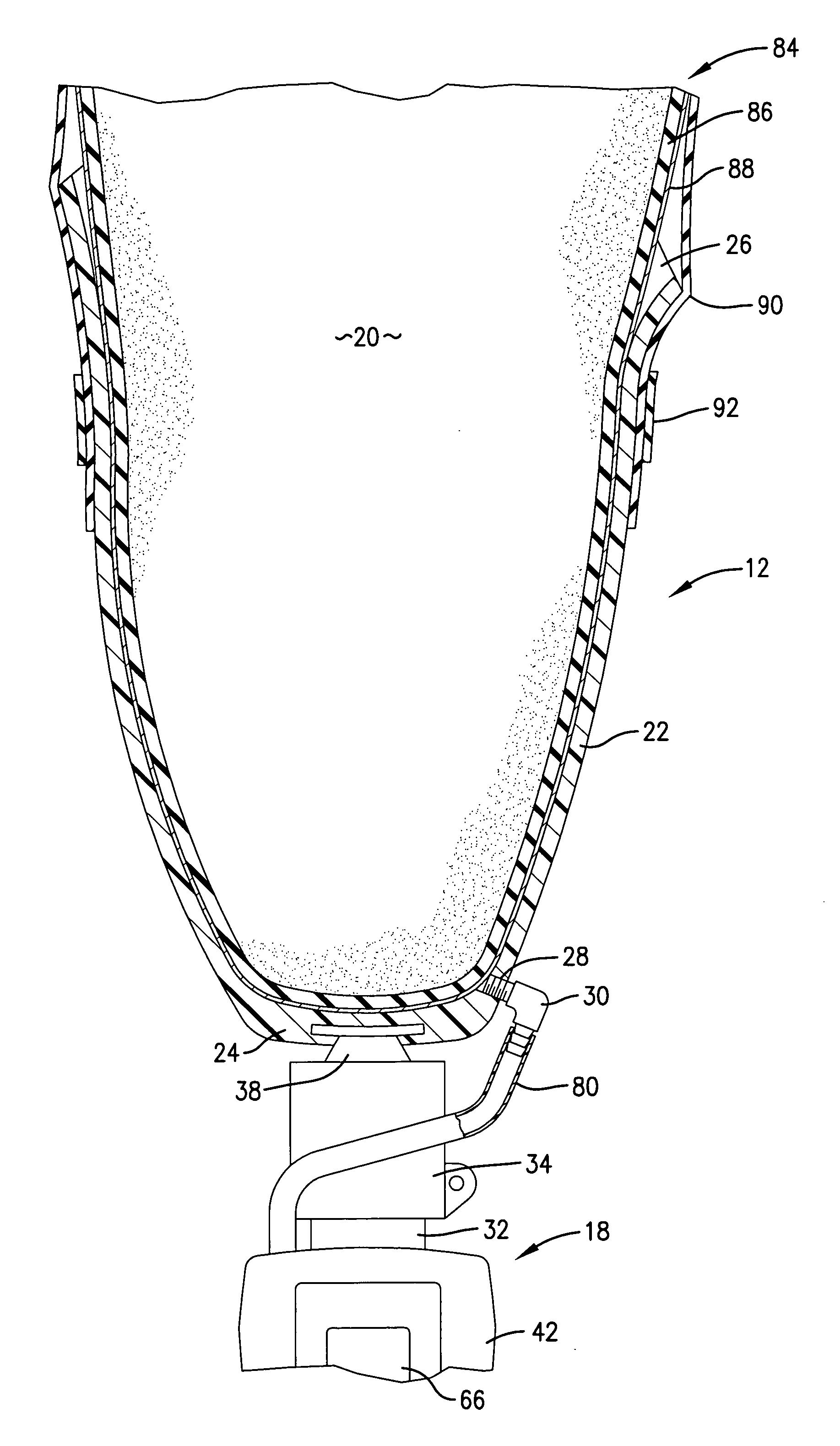
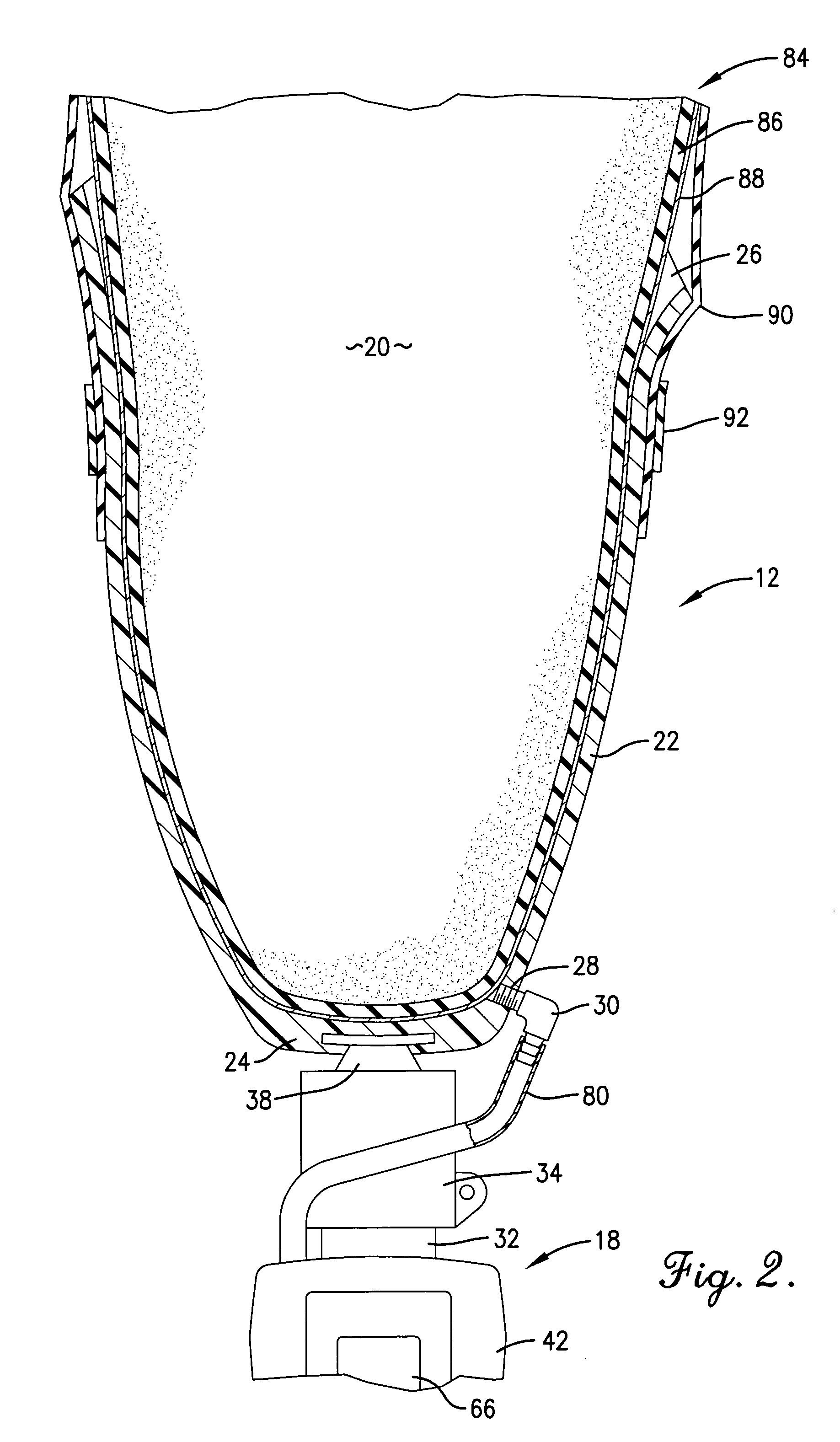
Artificial limb socket containing volume control pad
A volume control pad is provided for use in the socket of an artificial limb. The volume control pad has a core surrounded by a flexible shell. The core includes super absorbent polymer particles which form a gel Upon the addition of water thereto. The volume control pad includes a tube for the introduction of water into the core portion of the pad. The volume control pad provides a simple and inexpensive means for adjusting the conformance of the socket around the residual limb from an initial swollen condition to a further point in time in which the swelling has diminished.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Prostheses
InactiveUS6986792B2Reduce wearIncreasing or at least not compromising ability of the shell/linerJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral stemWear resistance
Bipolar prostheses which include various structures and other techniques for optimizing material wear and mechanical strength properties. Such prostheses feature, for example, improved resistance to polyethylene wear while also reducing potential for dislocation of the femoral stem from the prosthesis. Such techniques and structures include varying wear resistance and mechanical strength treatment in various components of the prostheses or portions of those components as desired to improve, accentuate or optimize wear performance and dislocation reduction, locking ring structural features, structures for retaining locking rings in the bipolar prosthesis shell, and structures for limiting or reducing movement or rotation of locking rings and liners in bipolar prosthesis shells.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Passive electro-magnetically damped joint
InactiveUS20090192619A1Improving cosmetic appearanceEasy to walkJoint implantsArtificial legsElectrical resistance and conductanceControl system
The present invention comprises an apparatus, system and method utilizing a passive electro-magnetically damped joint for prosthetics or orthotics. Such as system may be controlled through changing the resistive nature of the circuit in which a braking or damping mechanism can sufficiently replicate and augment biomechanical movement. This may be accomplished through electronic circuitry means only, or through the use of intelligent control through a microprocessor and dynamic ambulation replication algorithms.
Owner:ORTHOCARE INNOVATIONS
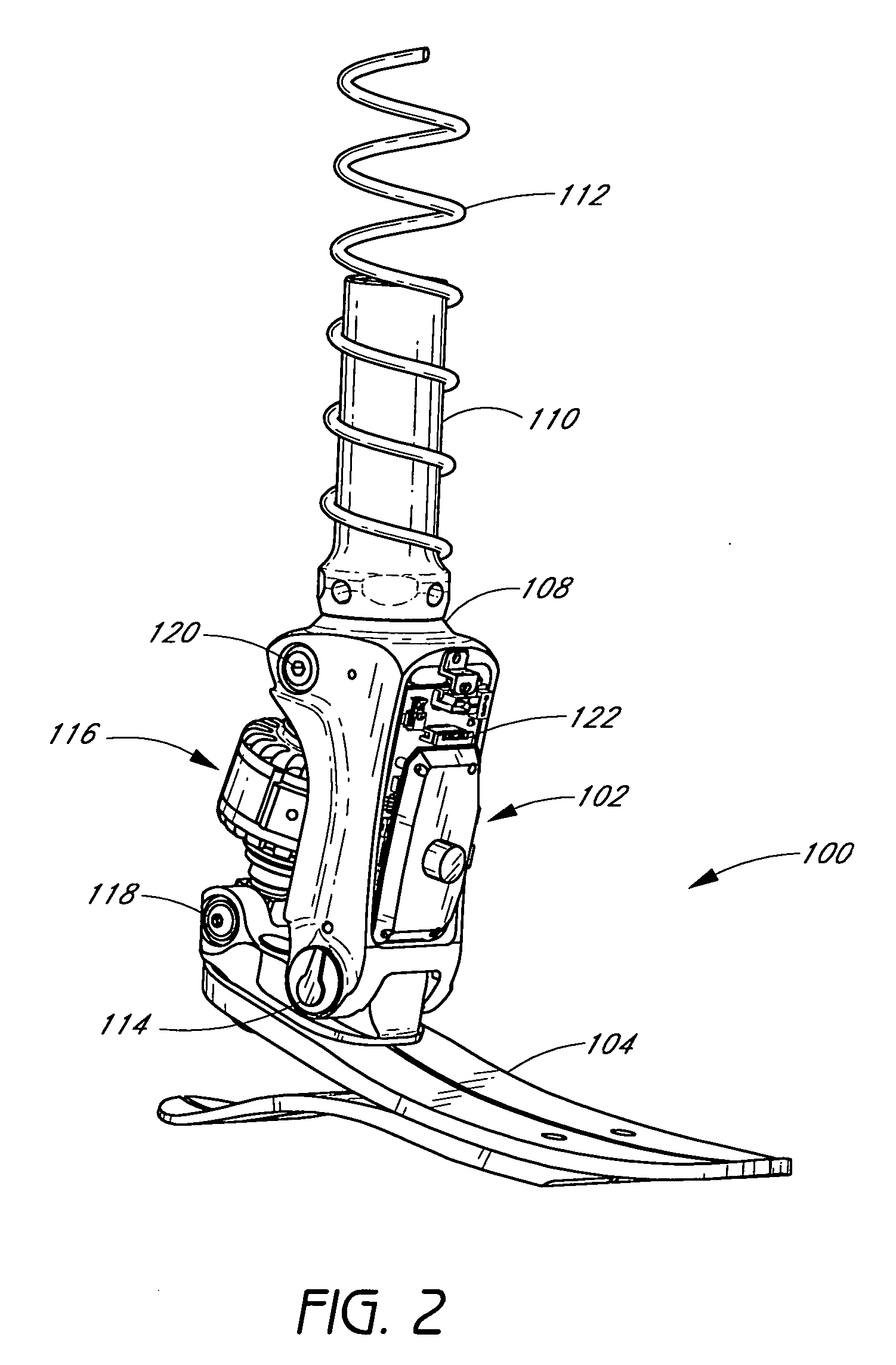
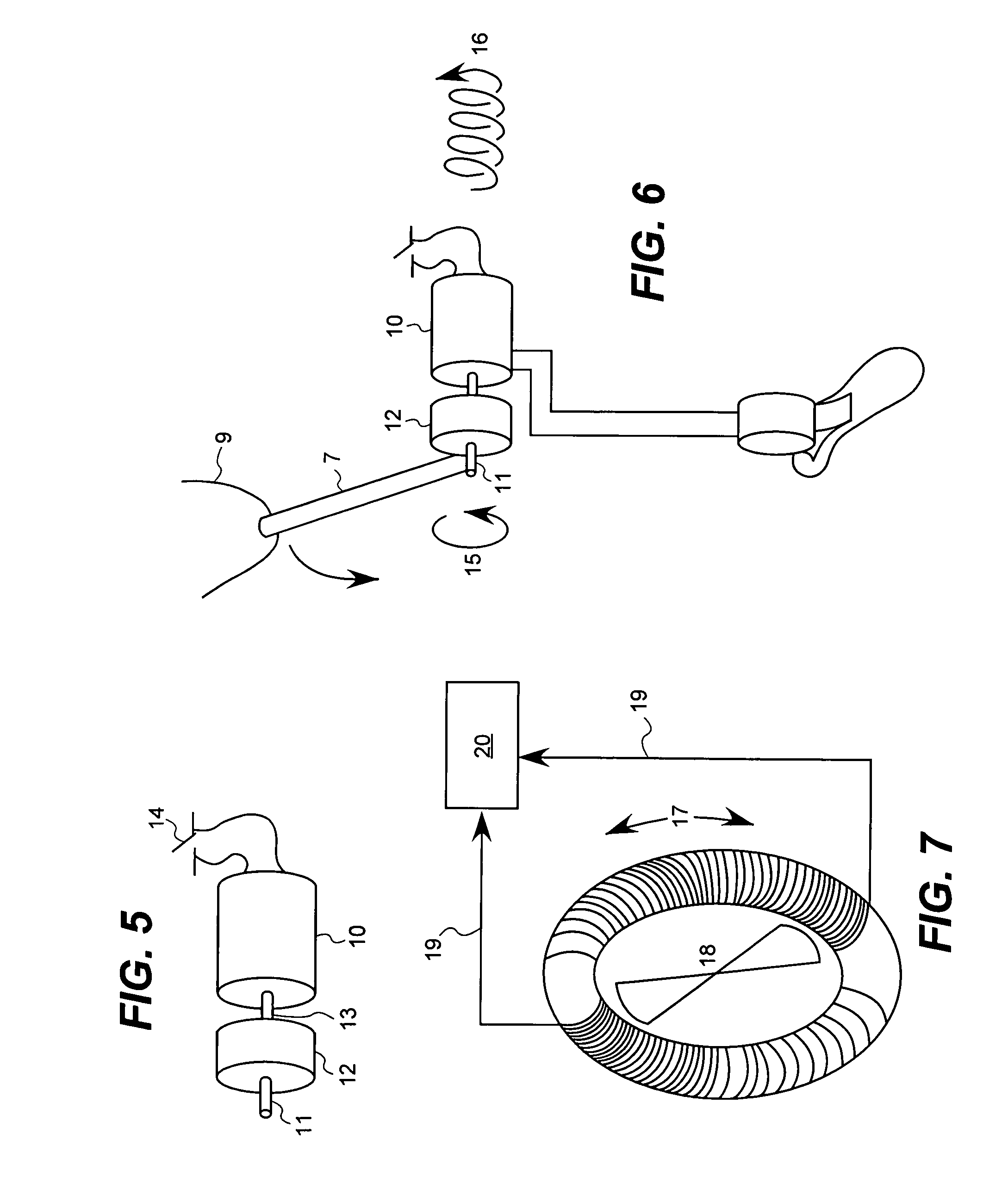
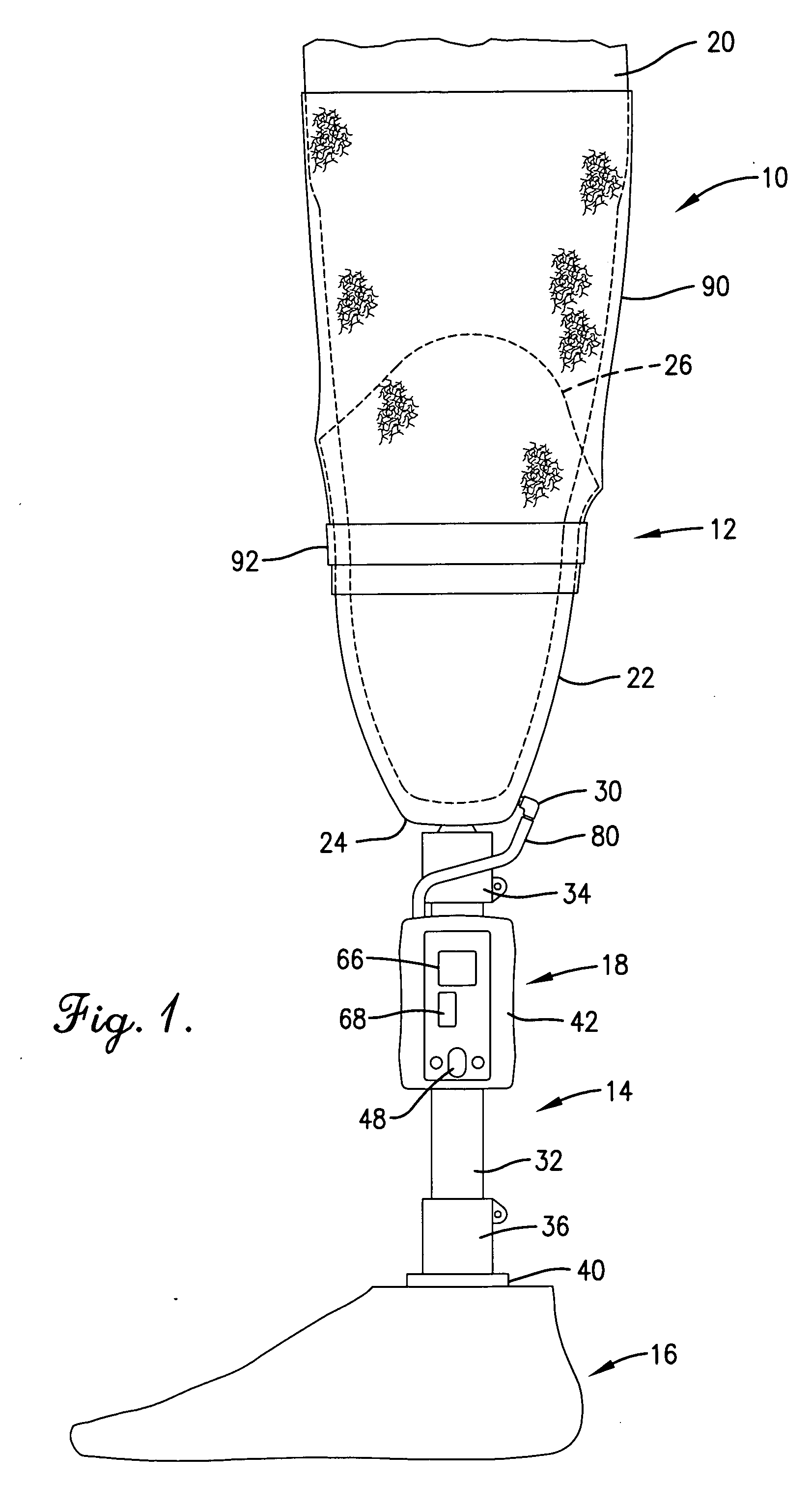
Artificial limb assembly having microprocessor-controlled vacuum pump
A vacuum-assist artificial limb assembly (10) is provided having a socket (22) for receiving a residual limb (20). The assembly (10) includes an on-board vacuum pump and control assembly (18) with a selectively operable vacuum pump (72) controlled by a microprocessor (44). The microprocessor (44) is also connected with an on-off switch (48), pressure adjust buttons (68), a pressure read-out (66), and an alarm (70). In use, a pressure transducer (74) in communication with the interior of socket (22) and coupled with microprocessor (44) monitors negative pressure conditions within the socket, and the microprocessor (44) operates pump (72) in response to transducer pressure signals. In this manner, the vacuum-assist operation of assembly (10) is essentially automatic.
Owner:JAEMS E & JOYCE E SMITH
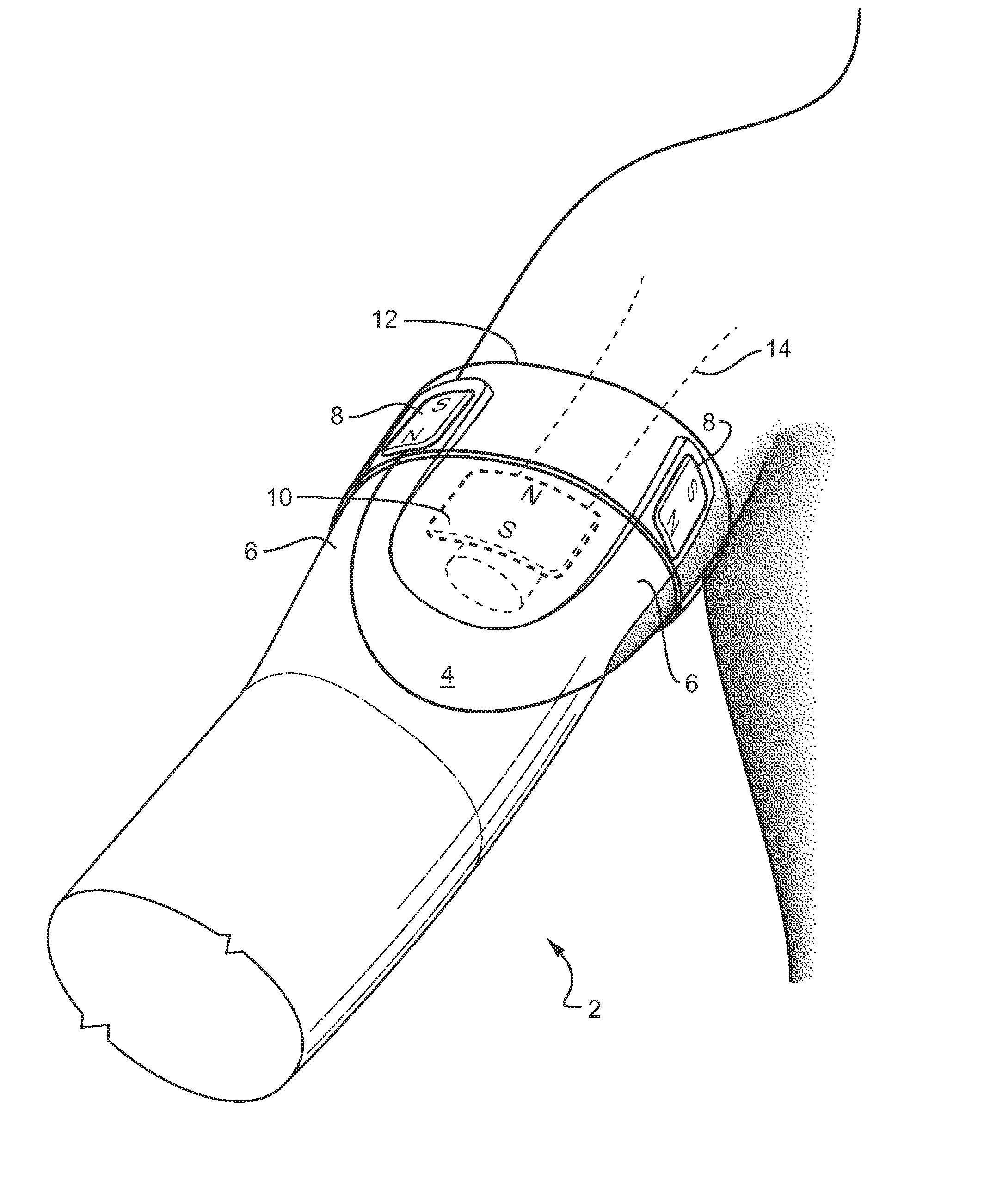
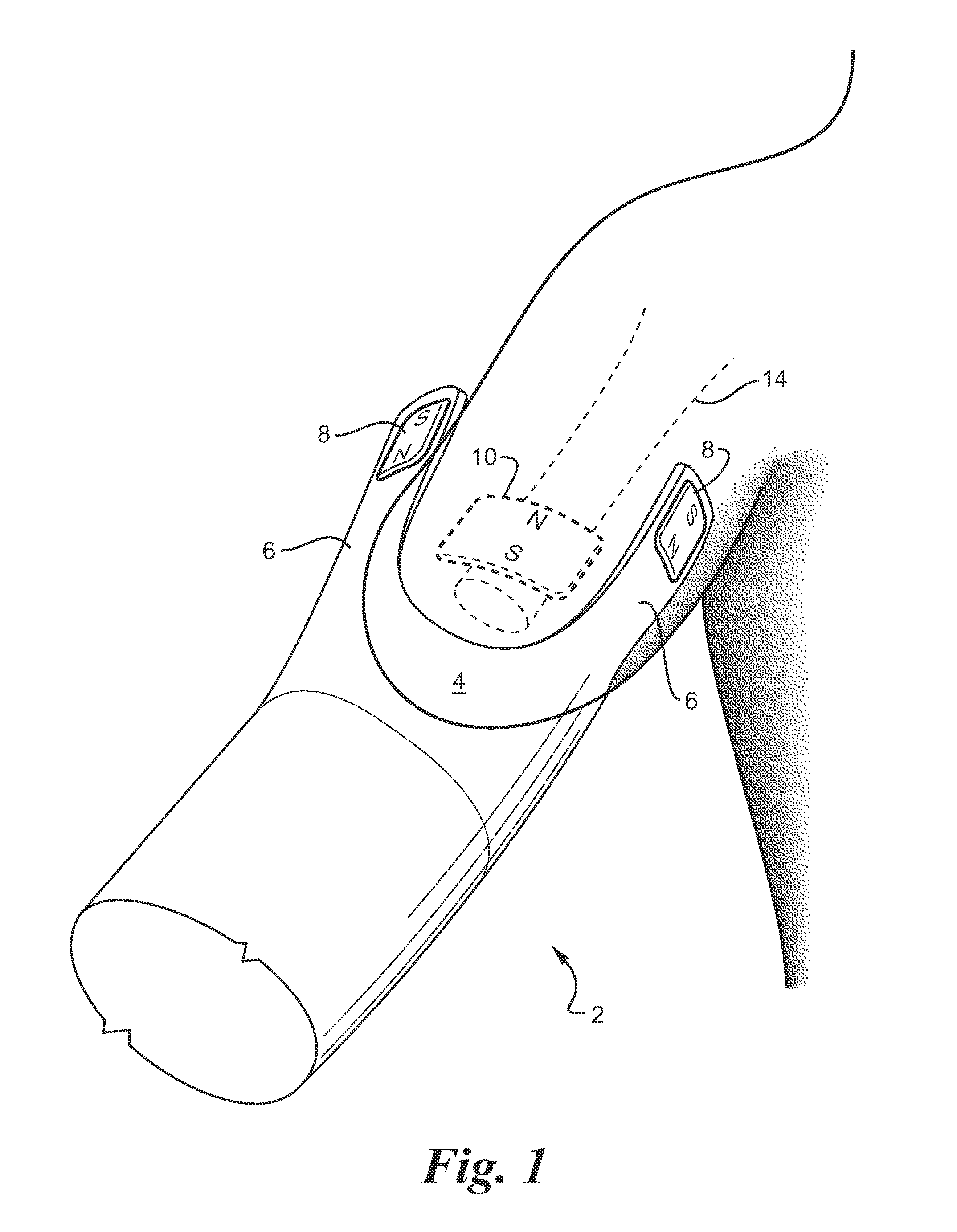
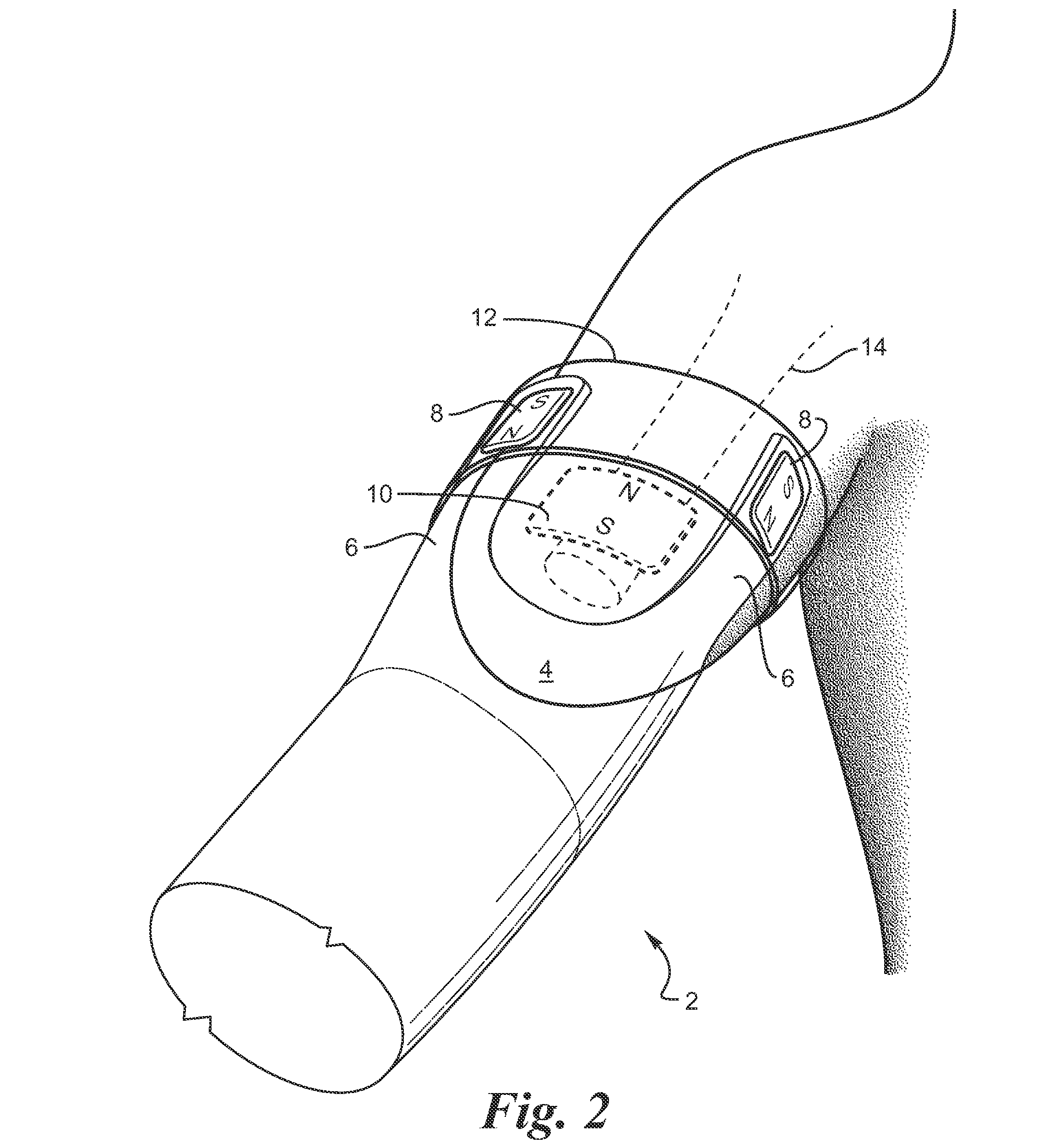
Strapless prosthetic arm
Permanent magnets or electromagnets or a combination of such magnets are provided to retain a prosthetic device on an extremity, such as an arm. The prosthesis utilizes the opposing forces, which are developed by virtue of like magnetic poles being in proximity to each other, to urge the prosthesis to remain attached to the extremity. The prosthesis is prevented from rotation by virtue of a centering force that is provided by an attachment magnet in the prosthesis being placed between two implanted magnets. A removable mounting ring is placed over the prosthesis straps to maintain them in proximity to the extremity.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
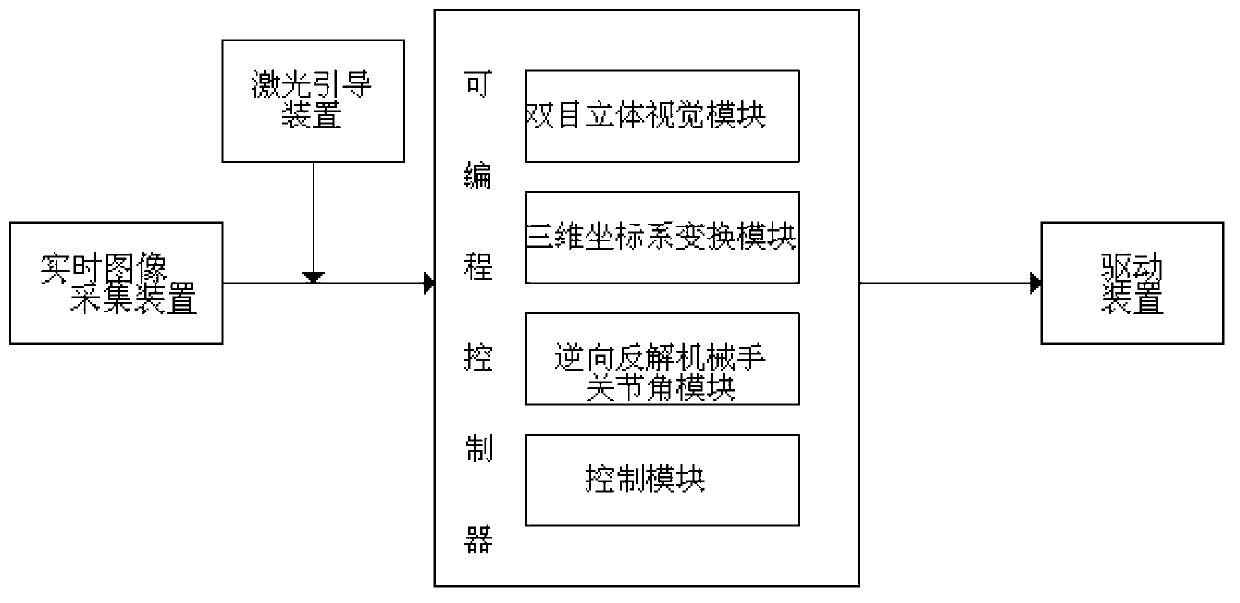
Man-machine interactive manipulator control system and method based on binocular vision
InactiveCN103271784AControl tension reductionImprove participationProgramme-controlled manipulatorProsthesisSystem transformationVisual perception
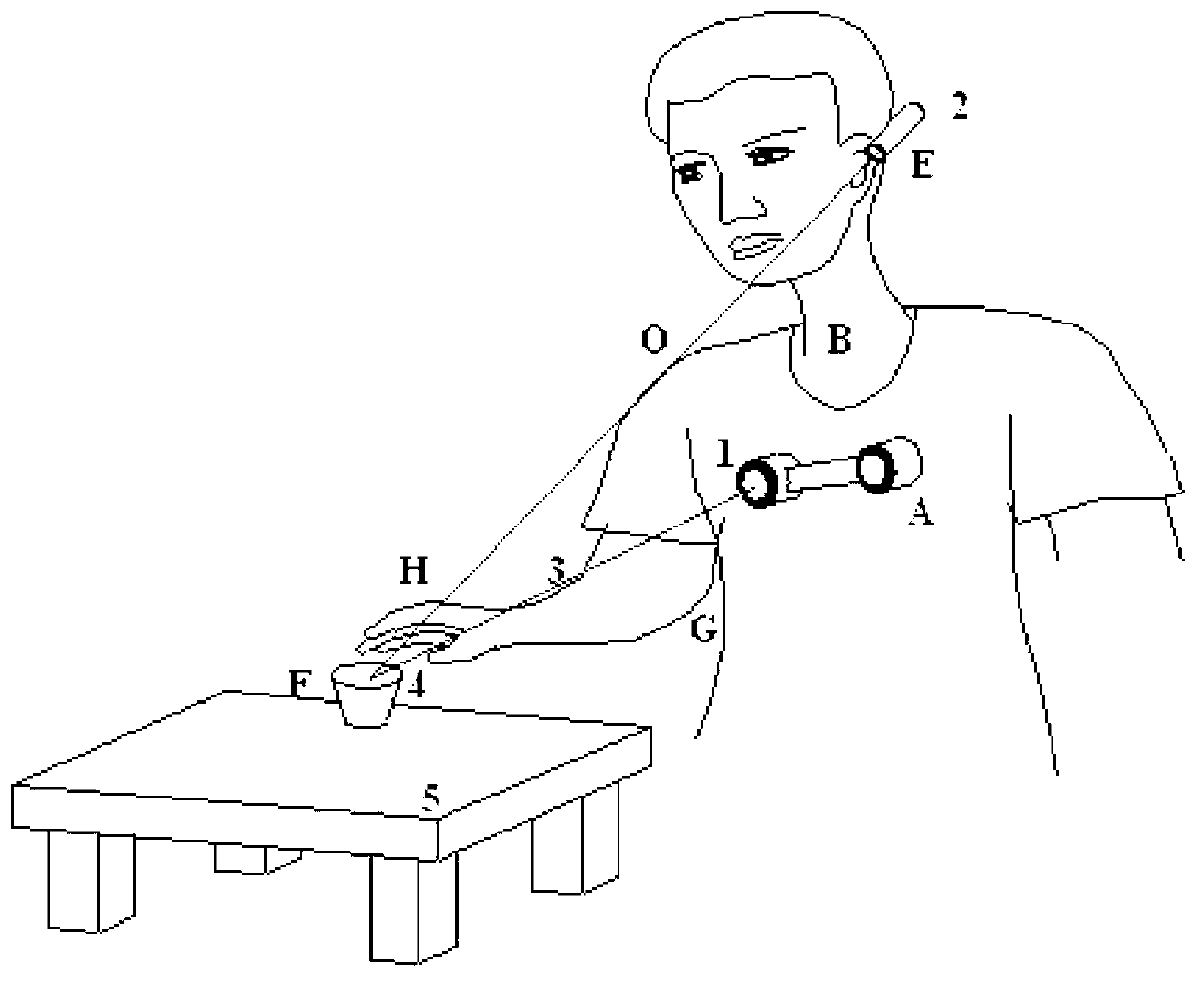
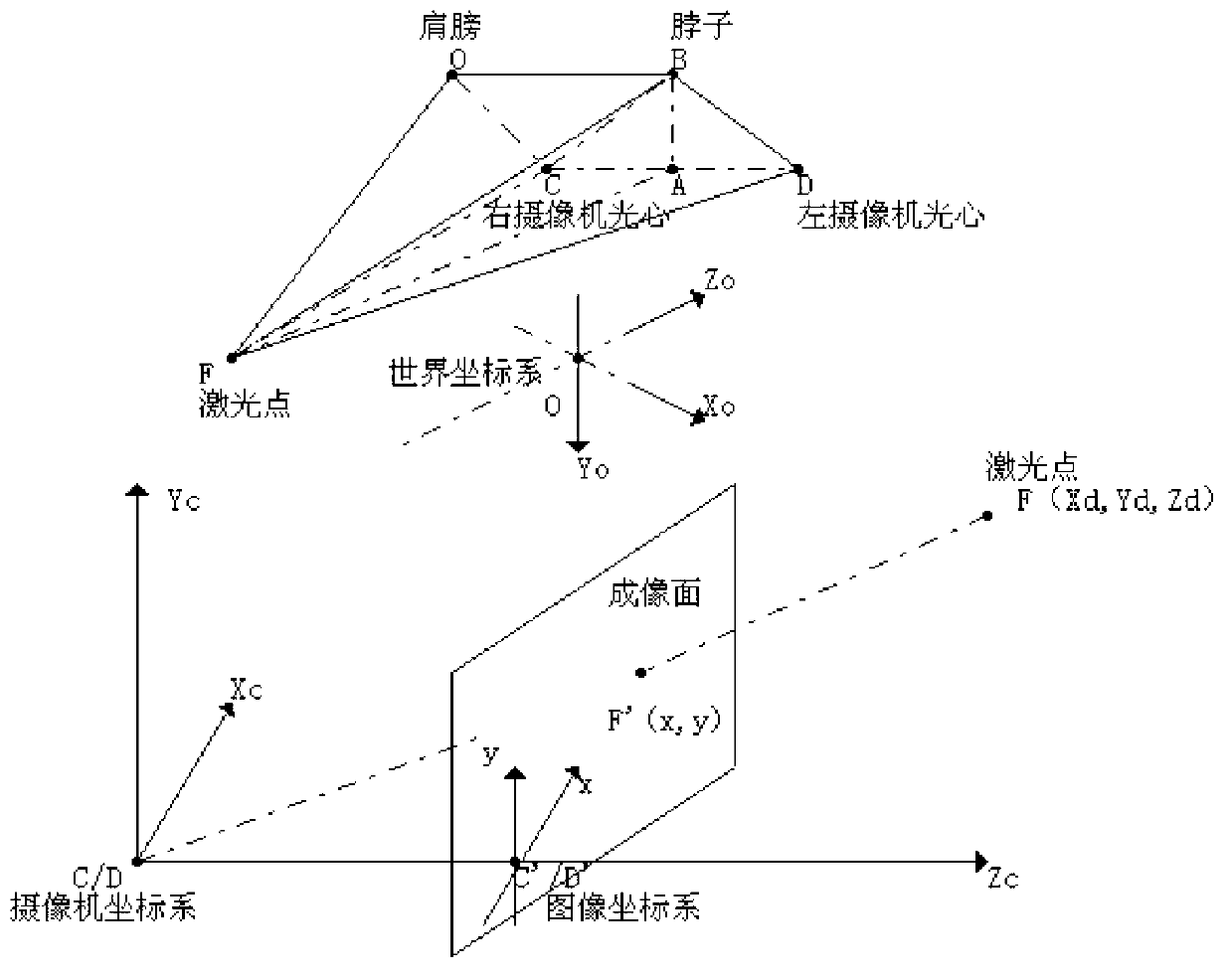
The invention discloses a man-machine interactive manipulator control system and method based on binocular vision. The man-machine interactive manipulator control system is composed of a real-time image collecting device, a laser guiding device, a programmable controller and a driving device. The programmable controller is composed of a binocular three-dimensional vision module, a three-dimensional coordinate system transformation module, an inverse manipulator joint angle module and a control module. Color characteristics in a binocular image are extracted through the real-time image collecting device to be used as a signal source for controlling a manipulator, and three-dimensional information of red characteristic laser points in a view real-time image is obtained through transformation and calculation of the binocular three-dimensional vision system and a three-dimensional coordinate system and used for controlling the manipulator to conduct man-machine interactive object tracking operation. The control system and method can effectively conduct real-time tracking and extracting of a moving target object and is wide in application fields such as intelligent artificial limb installing, explosive-handling robots, manipulators helping the old and the disabled and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com