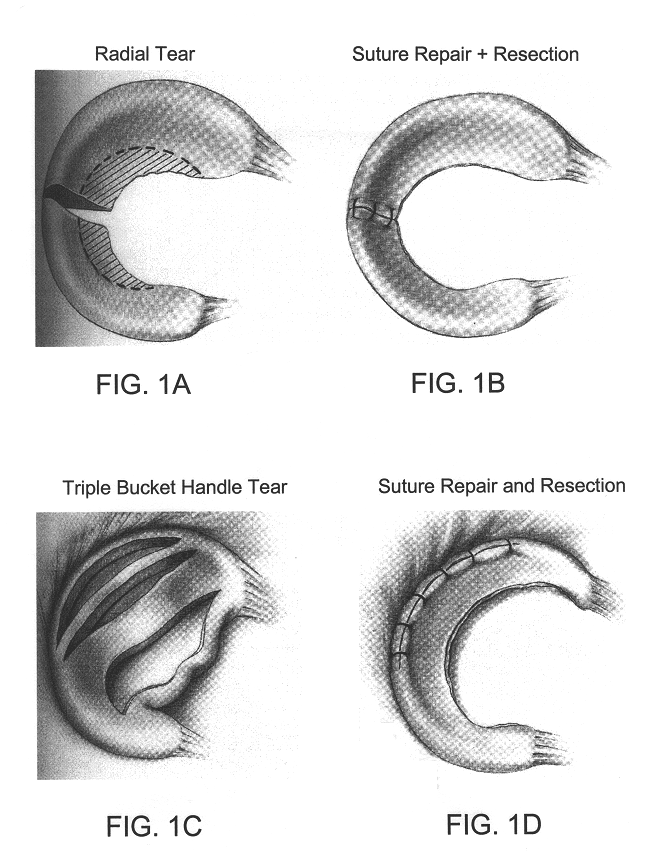
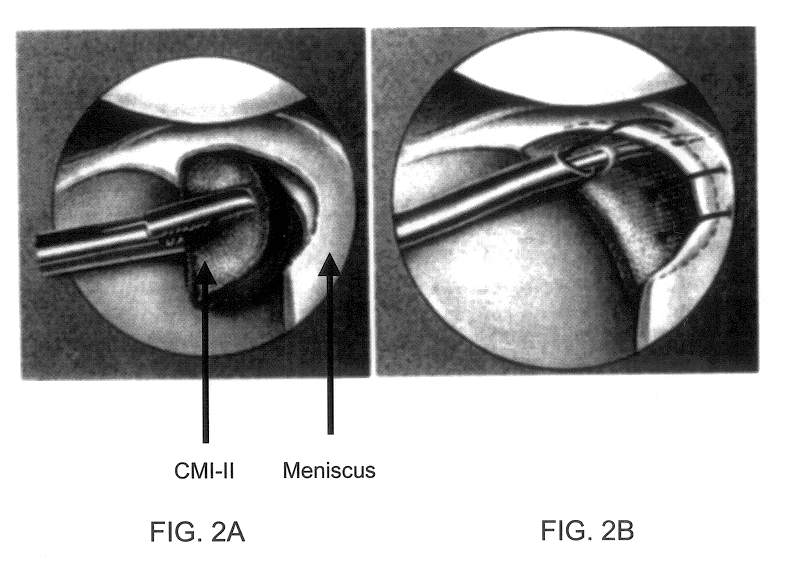
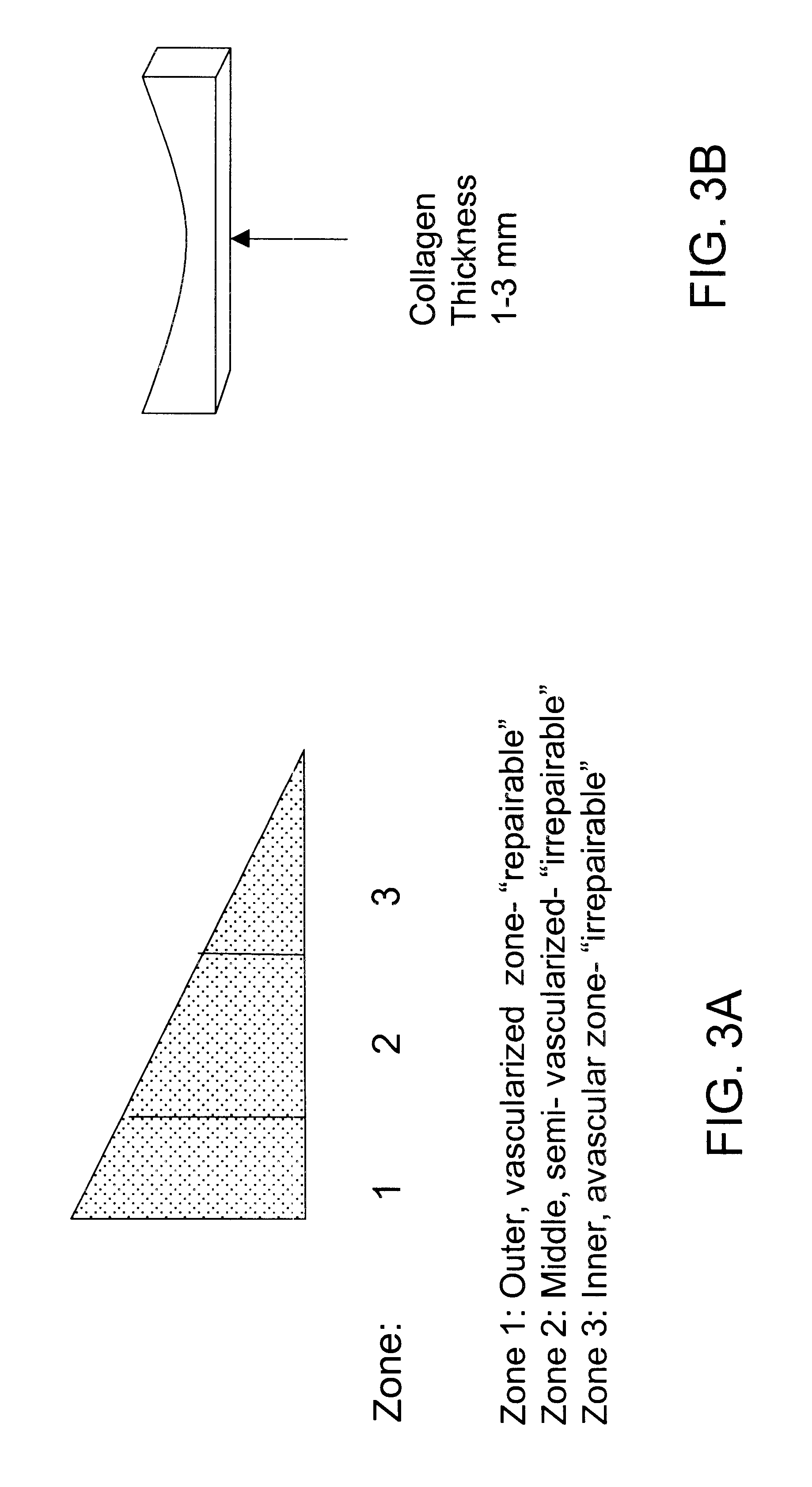
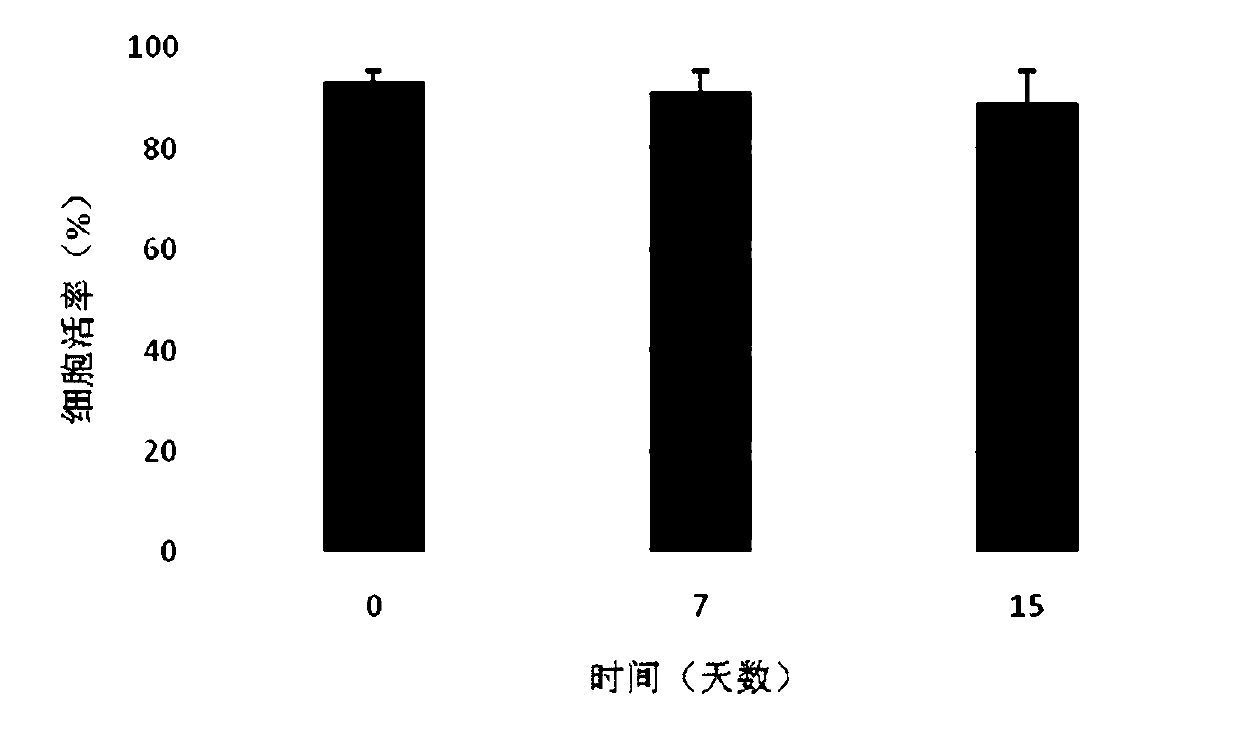
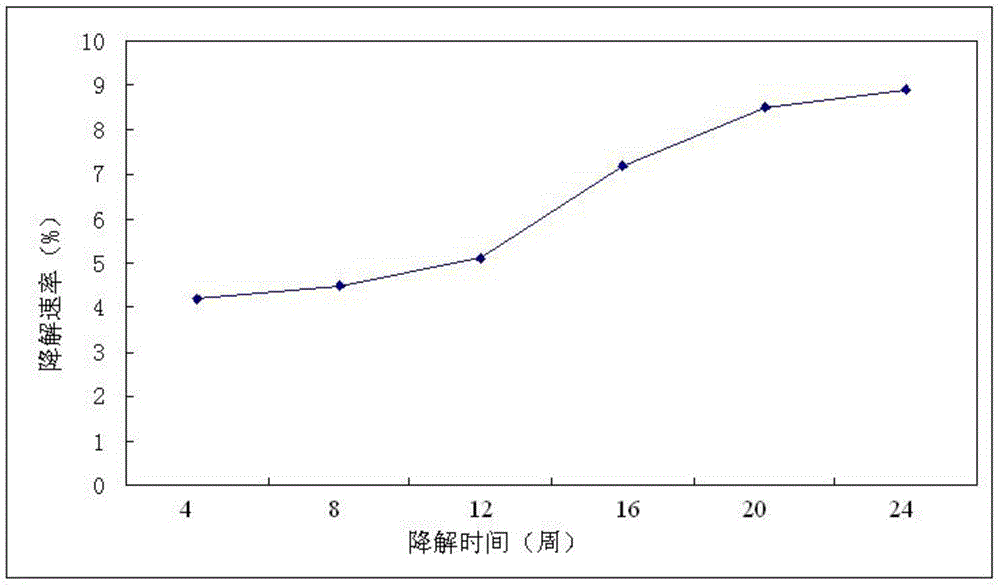
Patents
Literature
97 results about "Cartilage lesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment of articular cartilage lesions in the knee remains a challenge for the practising orthopaedic surgeon. A wide range of options are currently practised, ranging from conservative measures through various types of operations and, recently, use of growth factors and emerging gene therapy techniques.
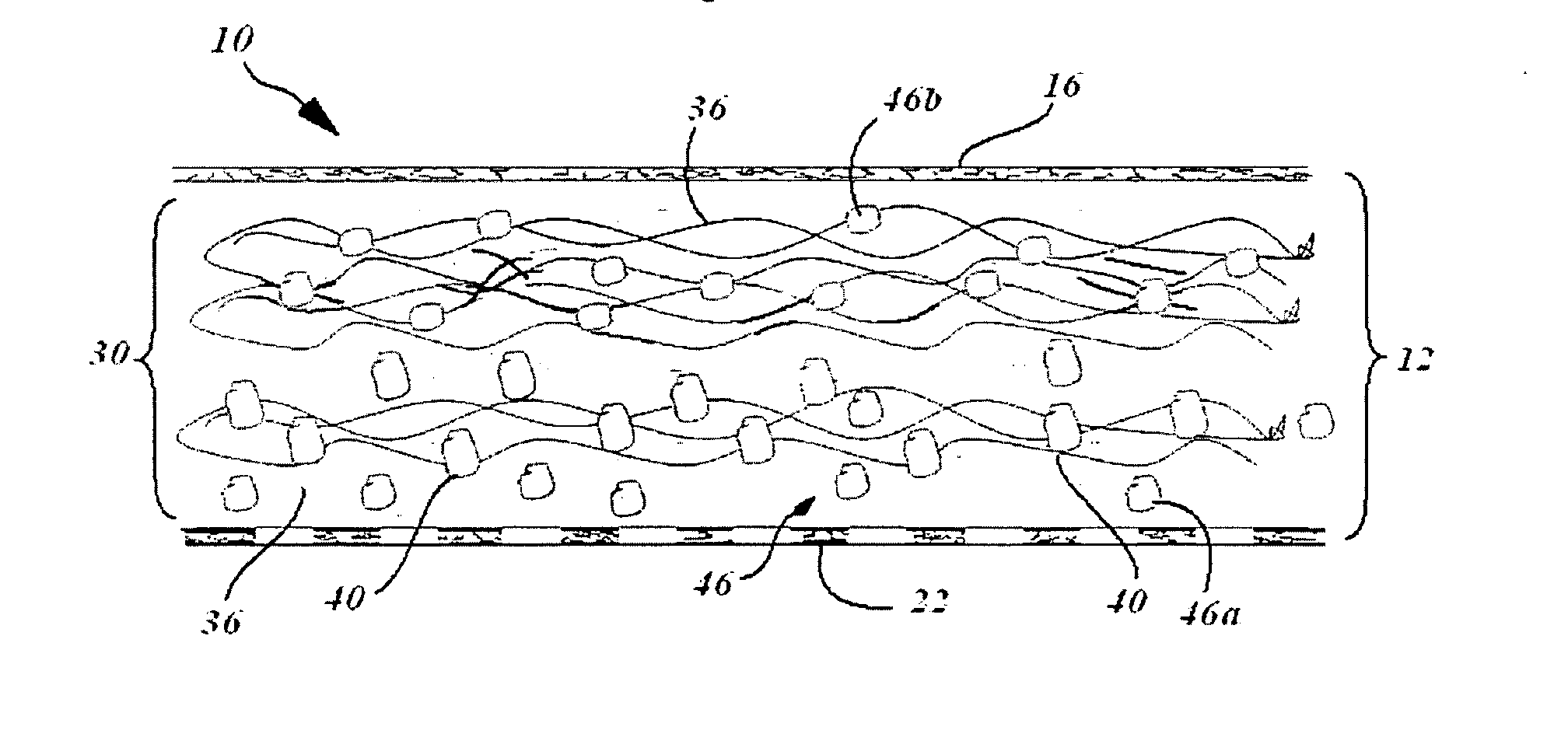
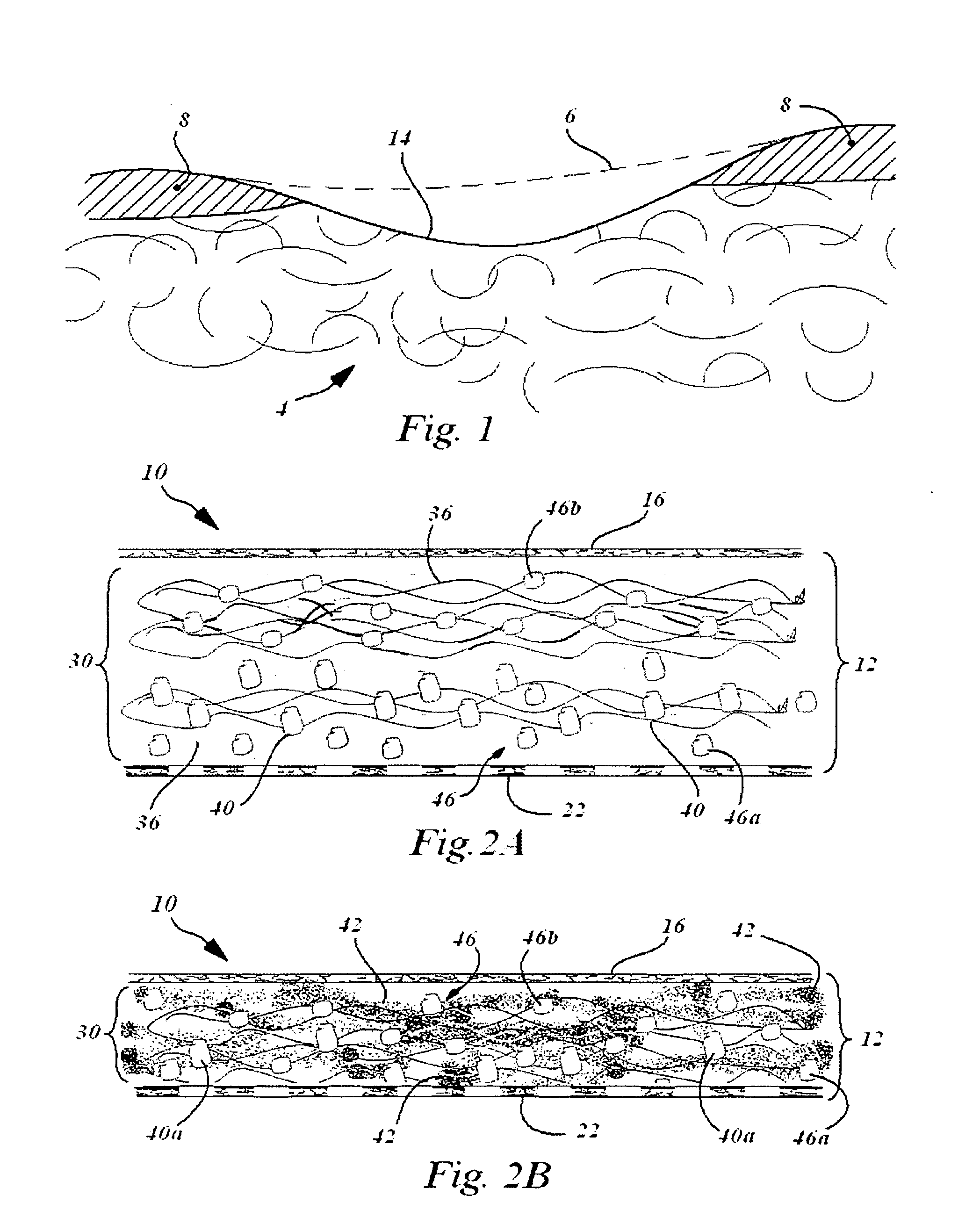
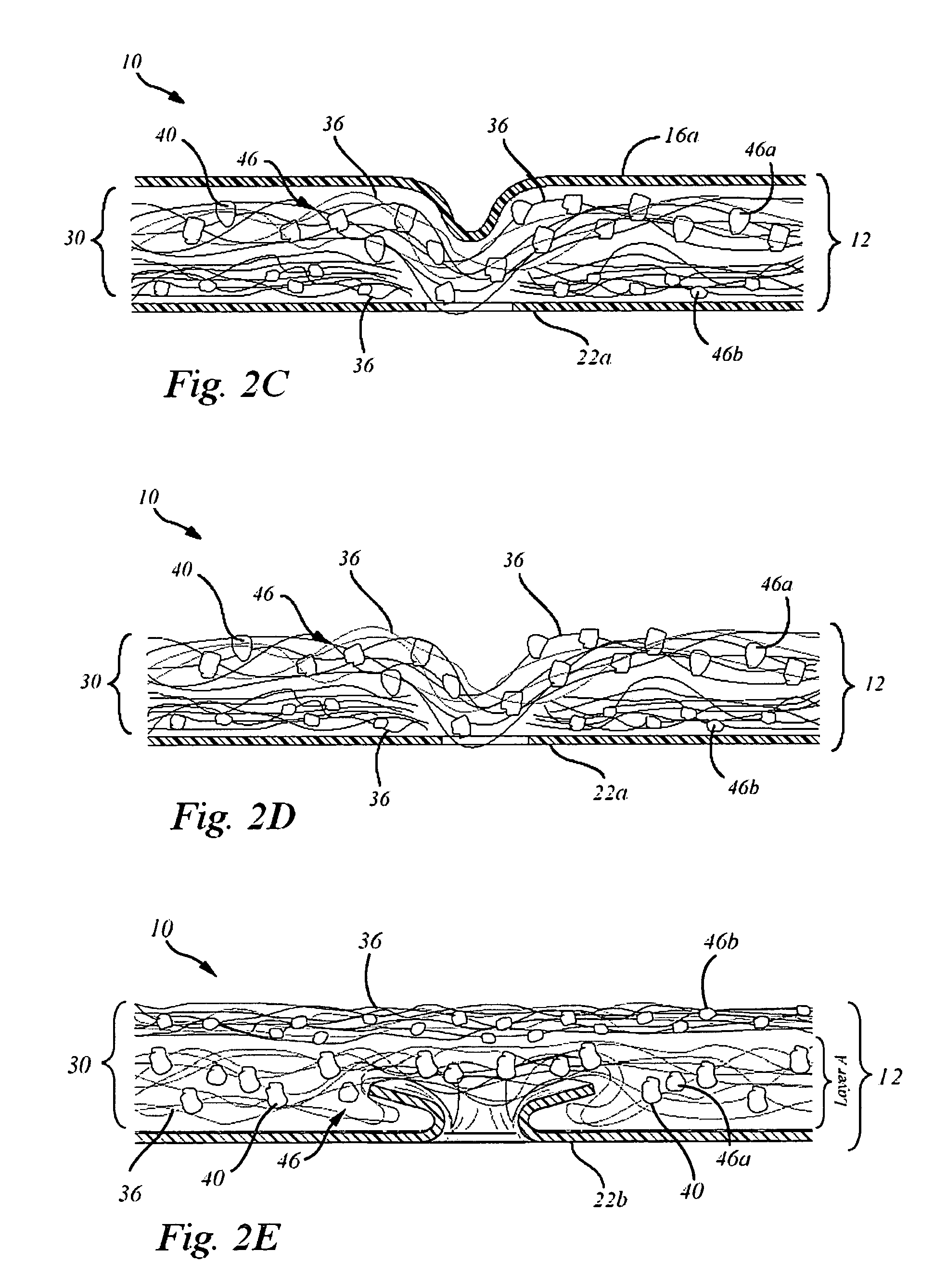
Compositions for regeneration and repair of cartilage lesions
InactiveUS6511958B1Increase ratingsImprove repair qualitySuture equipmentsPowder deliveryMedicineCartilage lesion
Disclosed is a cartilage repair product that induces both cell ingrowth into a bioresorbable material and cell differentiation into cartilage tissue. Such a product is useful for regenerating and / or repairing both vascular and avascular cartilage lesions, particularly articular cartilage lesions, and even more particularly mensical tissue lesions, including tears as well as segmental defects. Also disclosed is a method of regenerating and repairing cartilage lesions using such a product.
Owner:ZIMMER ORTHOBIOLOGICS
Regeneration of articular cartilage damaged by grade I and II osteoarthritis by means of the intraarticular application of a mixture of sodium hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate in a gel vehicle
Methods of treating osteochondral lesions by the intraarticular application of a mixture of sodium hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate are disclosed.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method for preparing and implanting a cartilage construct to treat cartilage lesions
Neo-cartilage constructs for growth and surface coating for the de novo formation of a superficial cartilage layer. A method for generation of the neo-cartilage and the neo-cartilage construct. A method for repair and restoration of the injured, damaged, diseased or aged cartilage into its full functionality and for treatment of injured or diseased cartilage by implanting the neo-cartilage construct between two layers of biologically acceptable sealants.
Owner:TAKAGI IND CO LTD +1
Acellular matrix implant for treatment of cartilage lesions, injuries and defects
InactiveUS20060083728A1Provide protectionPeptide/protein ingredientsJoint implantsMedicineAcellular matrix
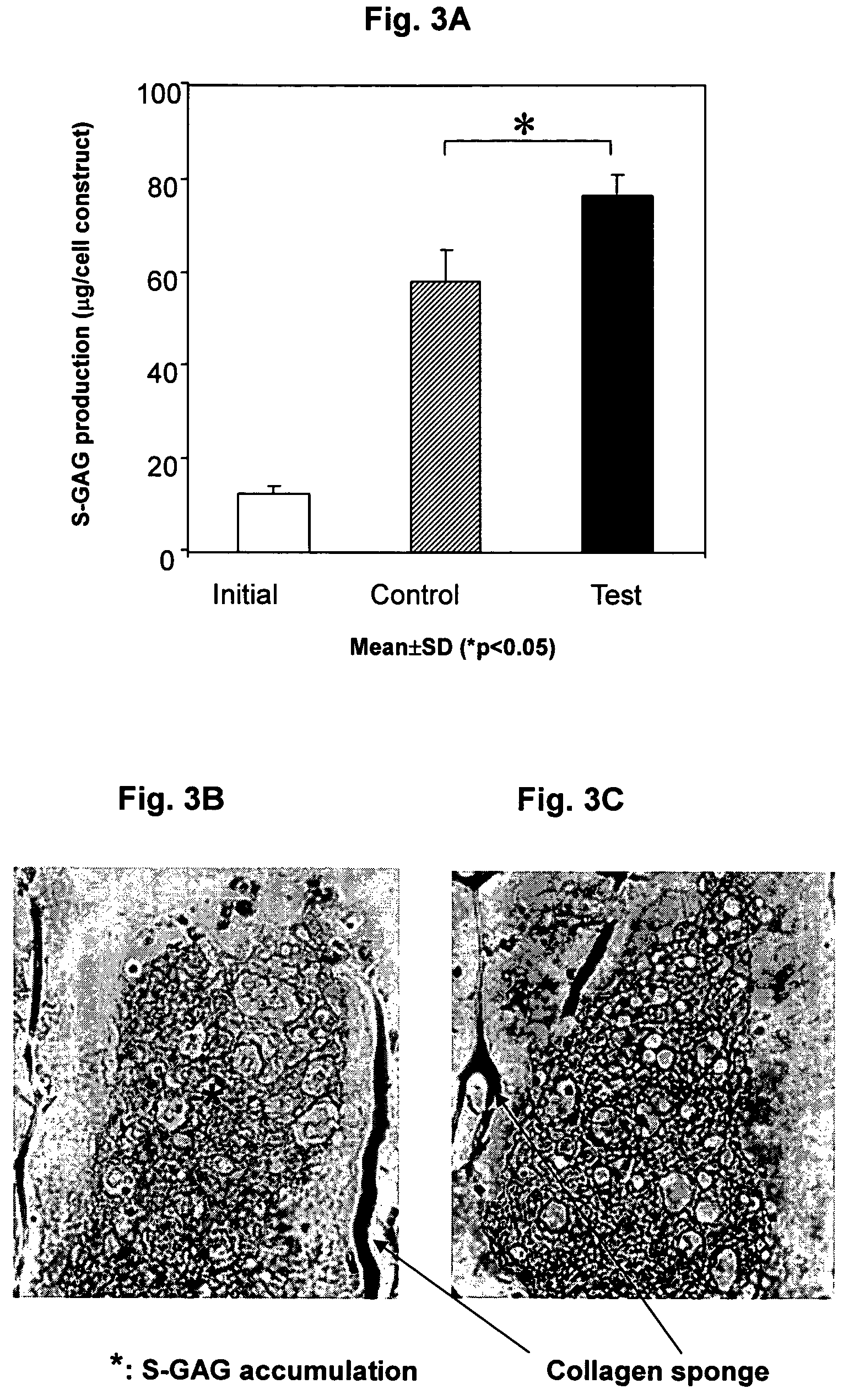
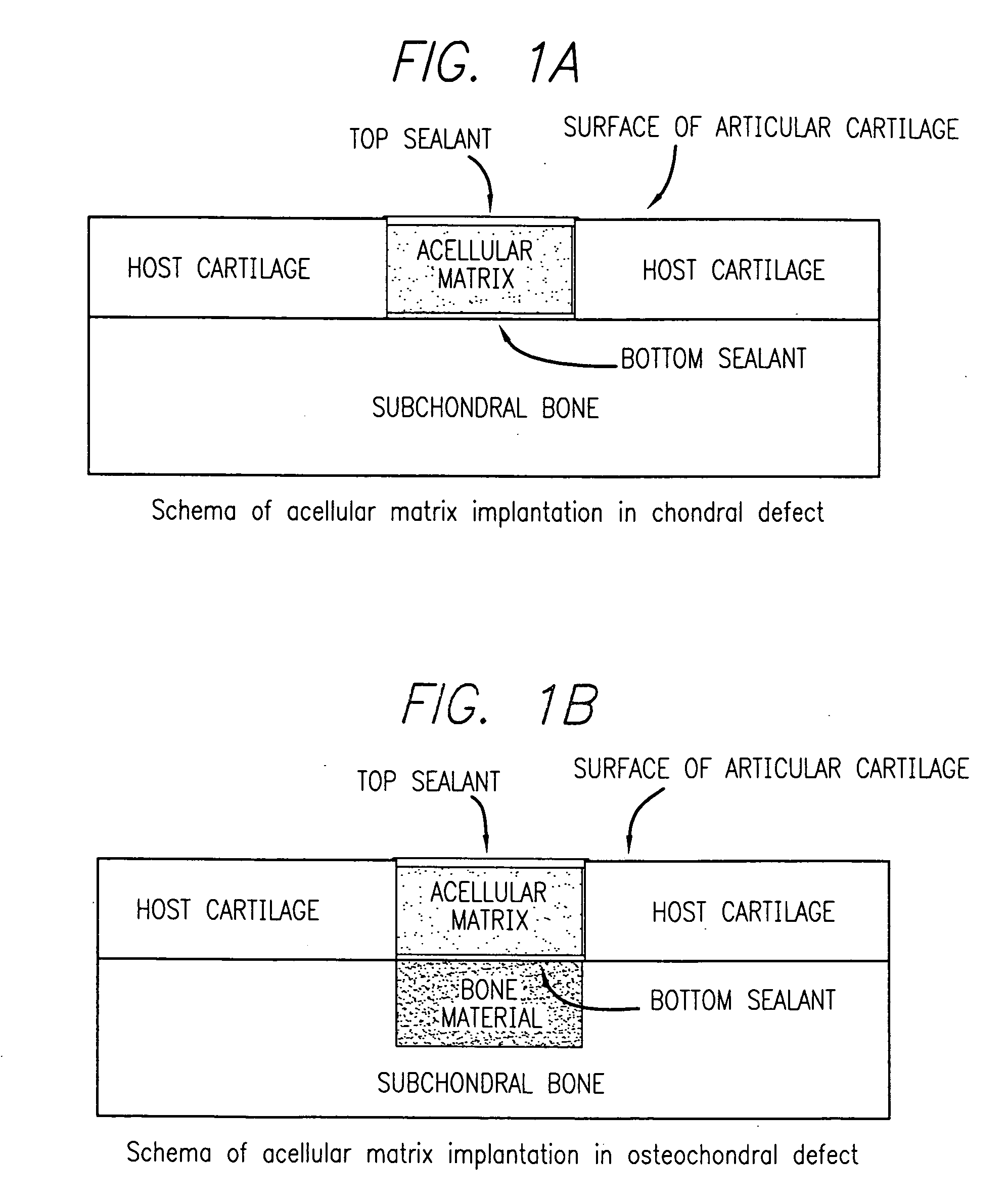
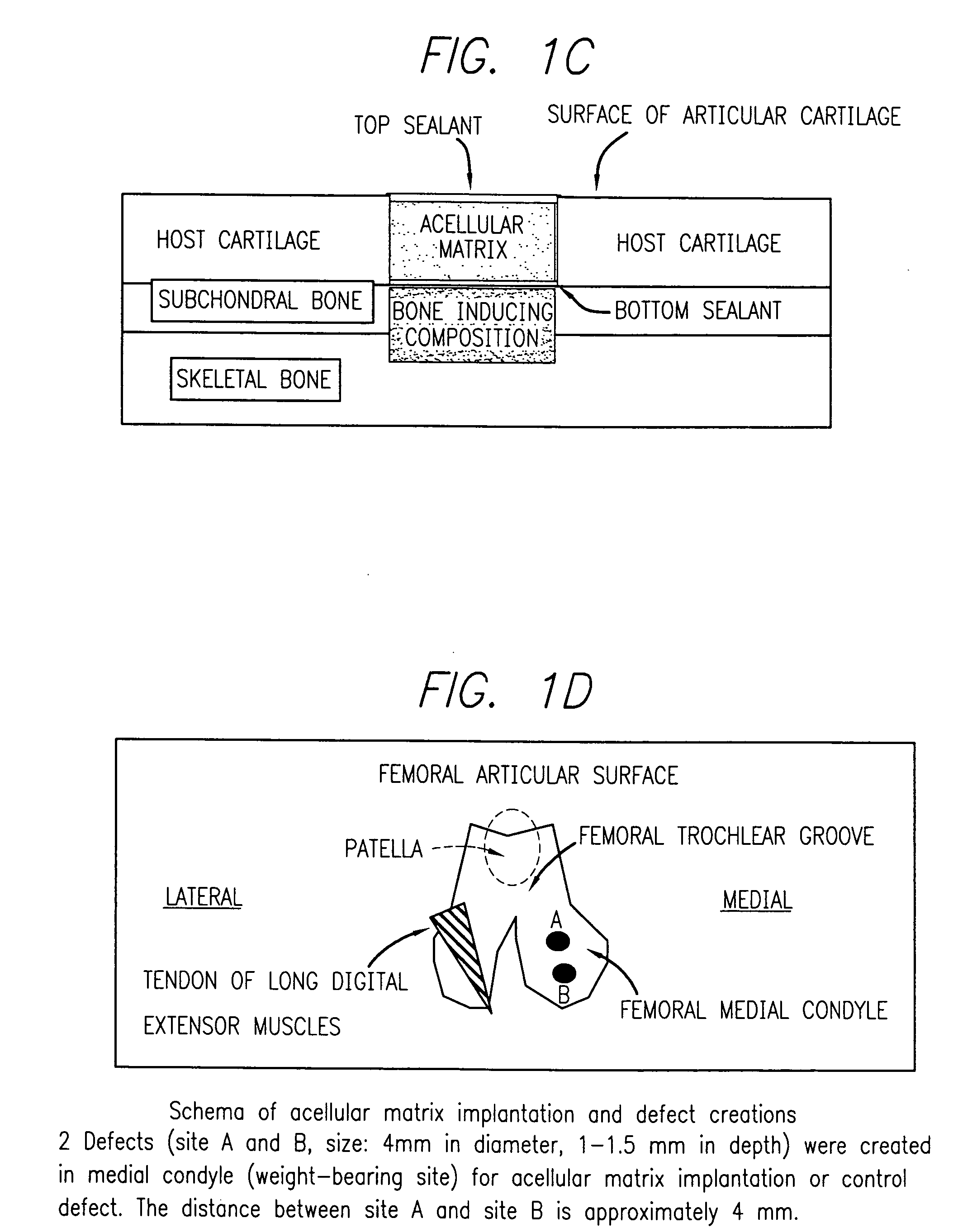
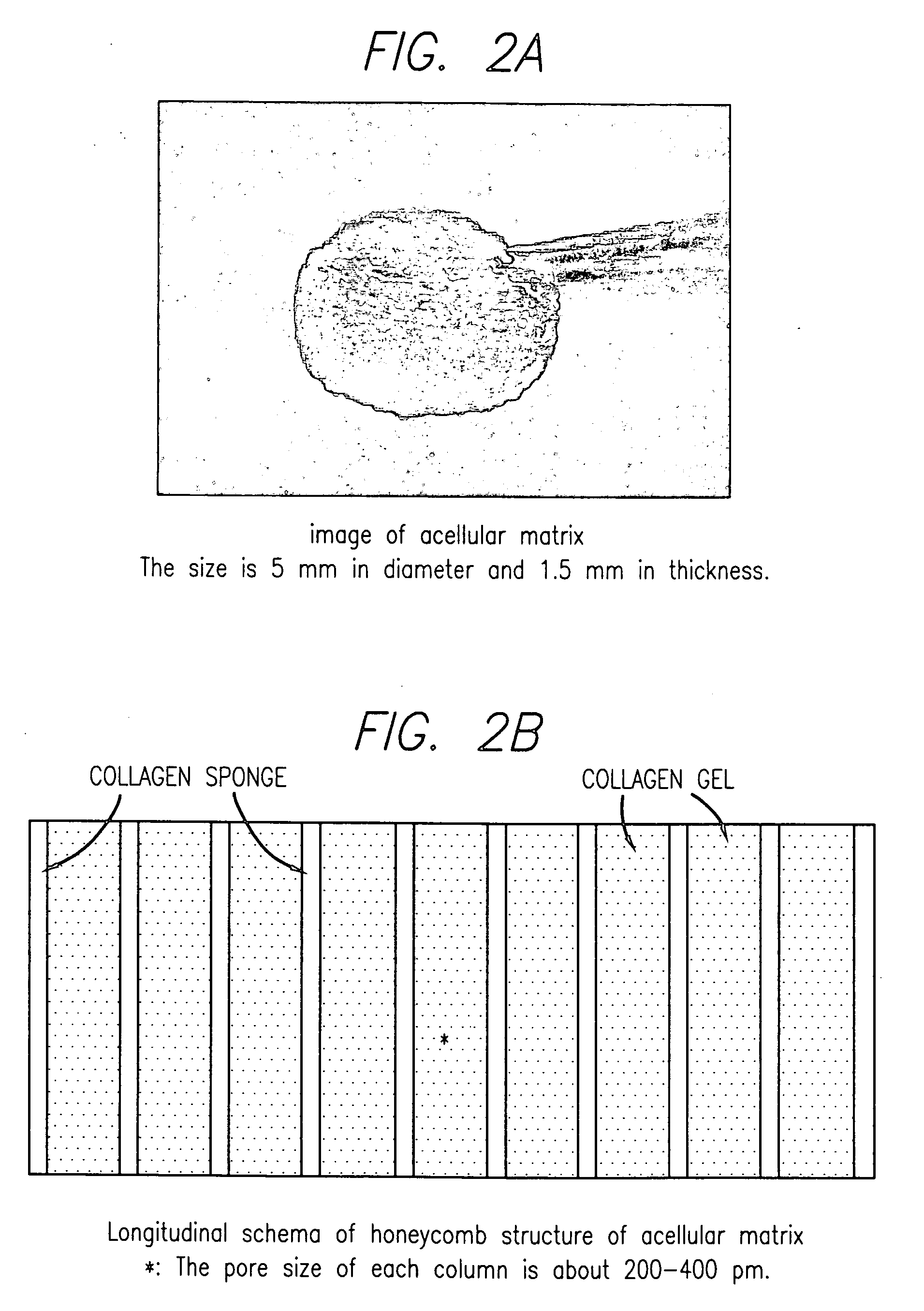
An acellular matrix implant for treatment of defects and injuries of articular cartilage, bone or osteochondral bone and a method for treatment of injured, damaged, diseased or aged articular cartilage or bone, using the acellular matrix implant implanted into a joint cartilage lesion in situ and a bone-inducing composition implanted into an osteochondral or bone defect. A method for repair and restoration of the injured, damaged, diseased or aged cartilage or bone into its full functionality by implanting the acellular matrix implant between two layers of biologically acceptable sealants and / or the bone-inducing composition into the osteochondral bone or skeletal bone defect. A method for fabrication of the acellular matrix implant of the invention. A method for preparation of bone-inducing composition.
Owner:KUSANAGI AKIHIKO +2
In situ system for intra-articular chondral and osseus tissue repair
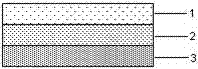
Disclosed is a device and method which provide a surgical therapy for in situ treatment and repair of intra-articular cartilage lesions and / or defects. The device is an implantable laminate cartilage repair patch which is bio-compatible and physiologically absorbable. The cartilage repair patch has a first outer cell occlusive layer; a second outer, cell porous layer adapted to be disposed proximate a subchondral bone wound site; and a cartilagenic matrix disposed between the first and second layers. The cartilagenic matrix is a sink for diffusion of autologous stem cells and includes chemical components promoting generation of hyaline-like cartilage in the presence of the autologous stem cells. The method of the present invention provides the autologous compositions, which when used in combination with the repair patch provides a therapeutic system to regenerate replacement hyaline-like intraarticular cartilage.
Owner:LABE MEDIDOM
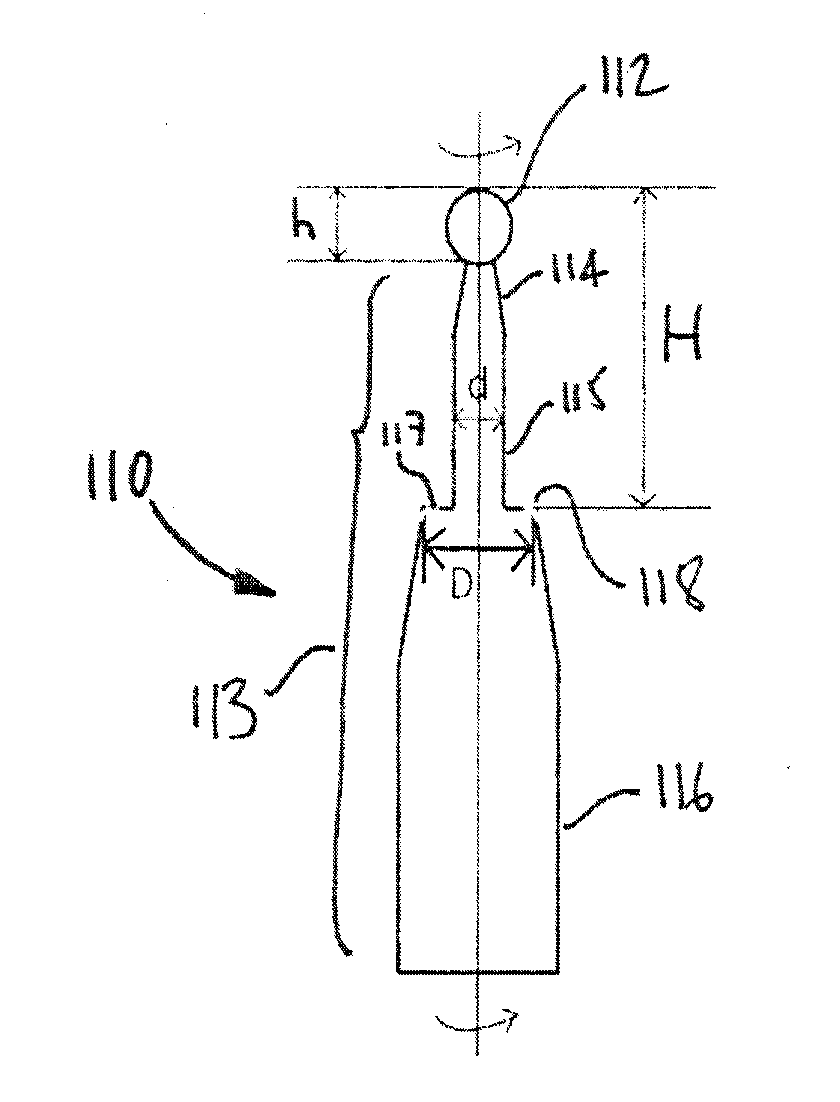
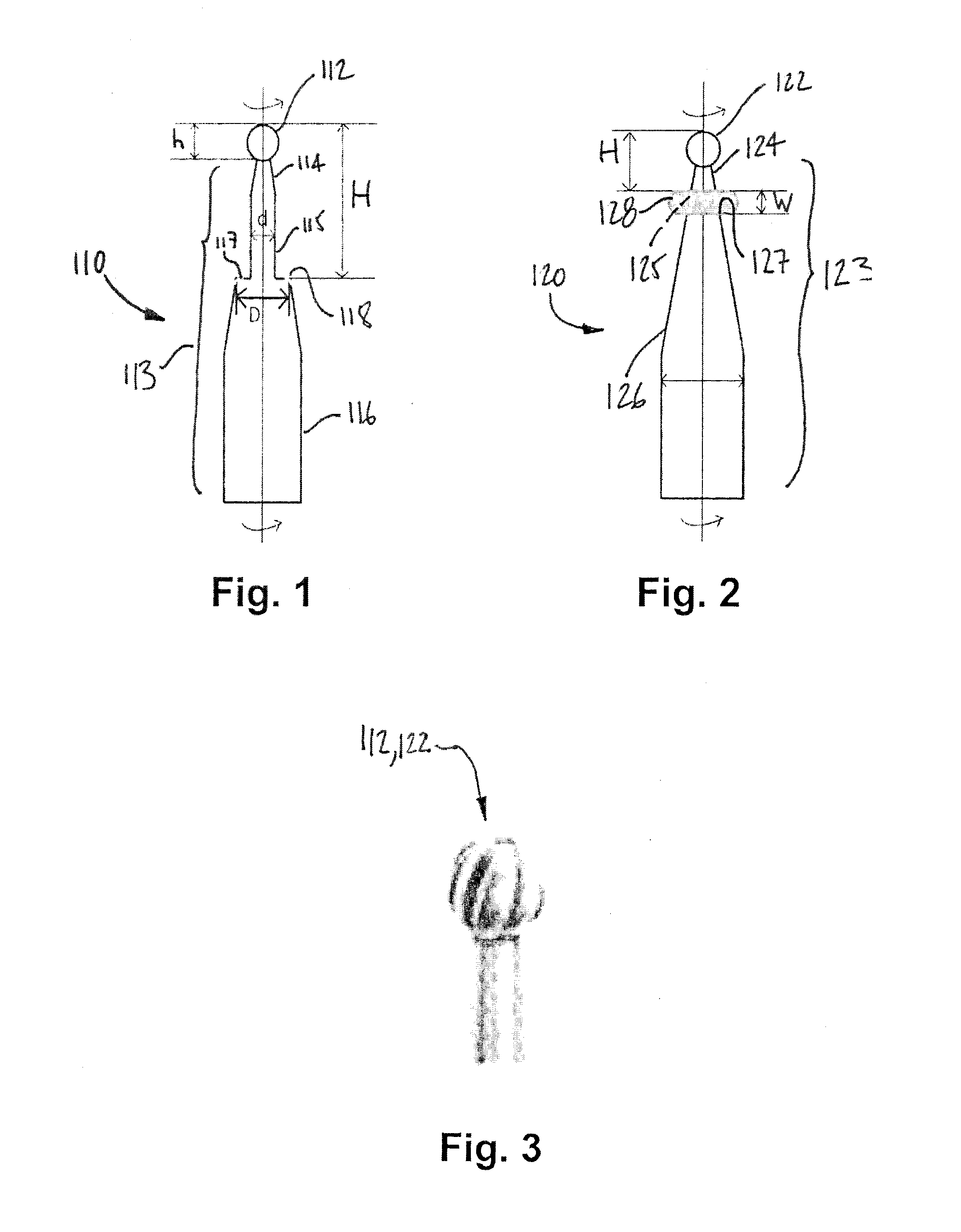
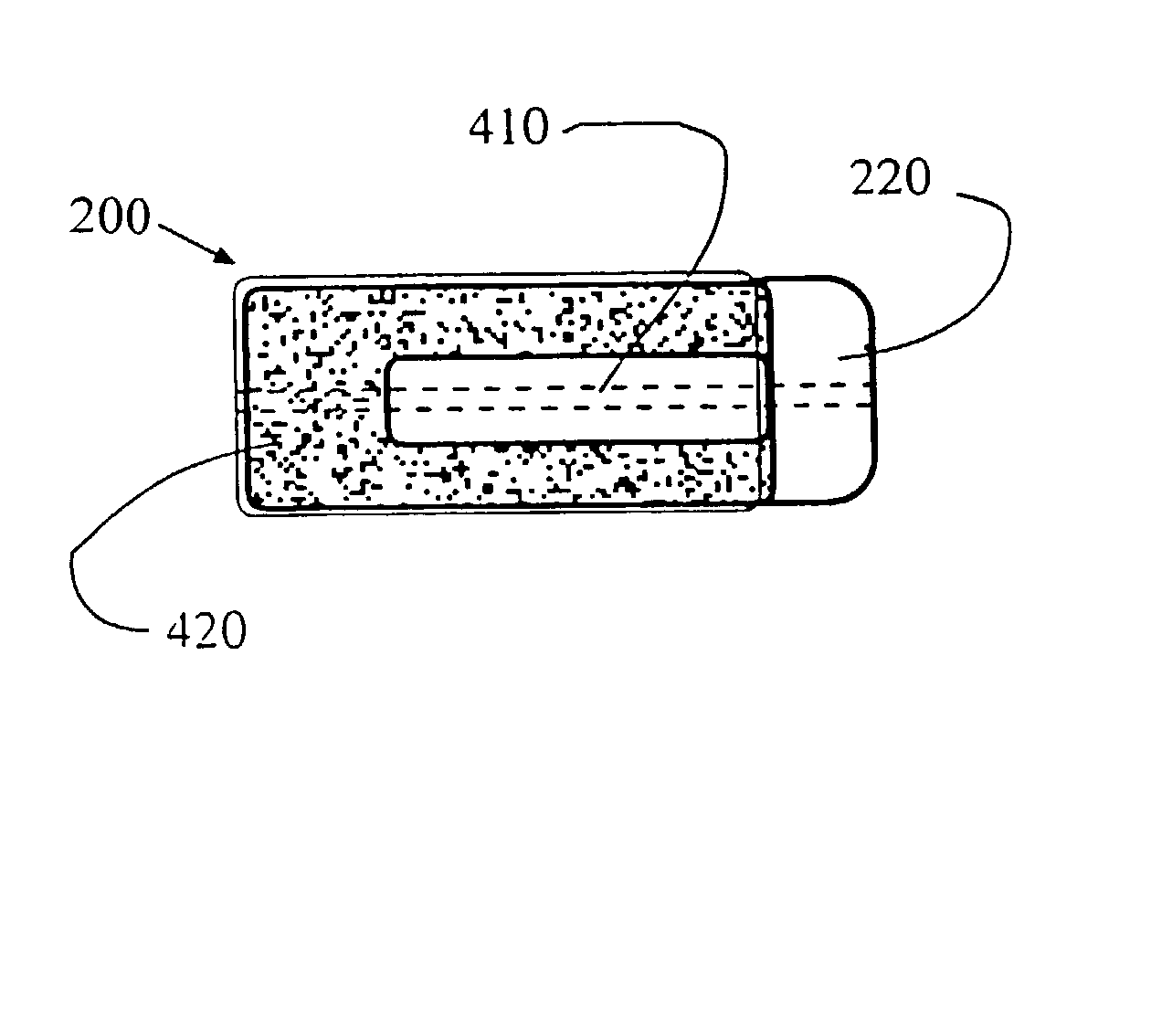
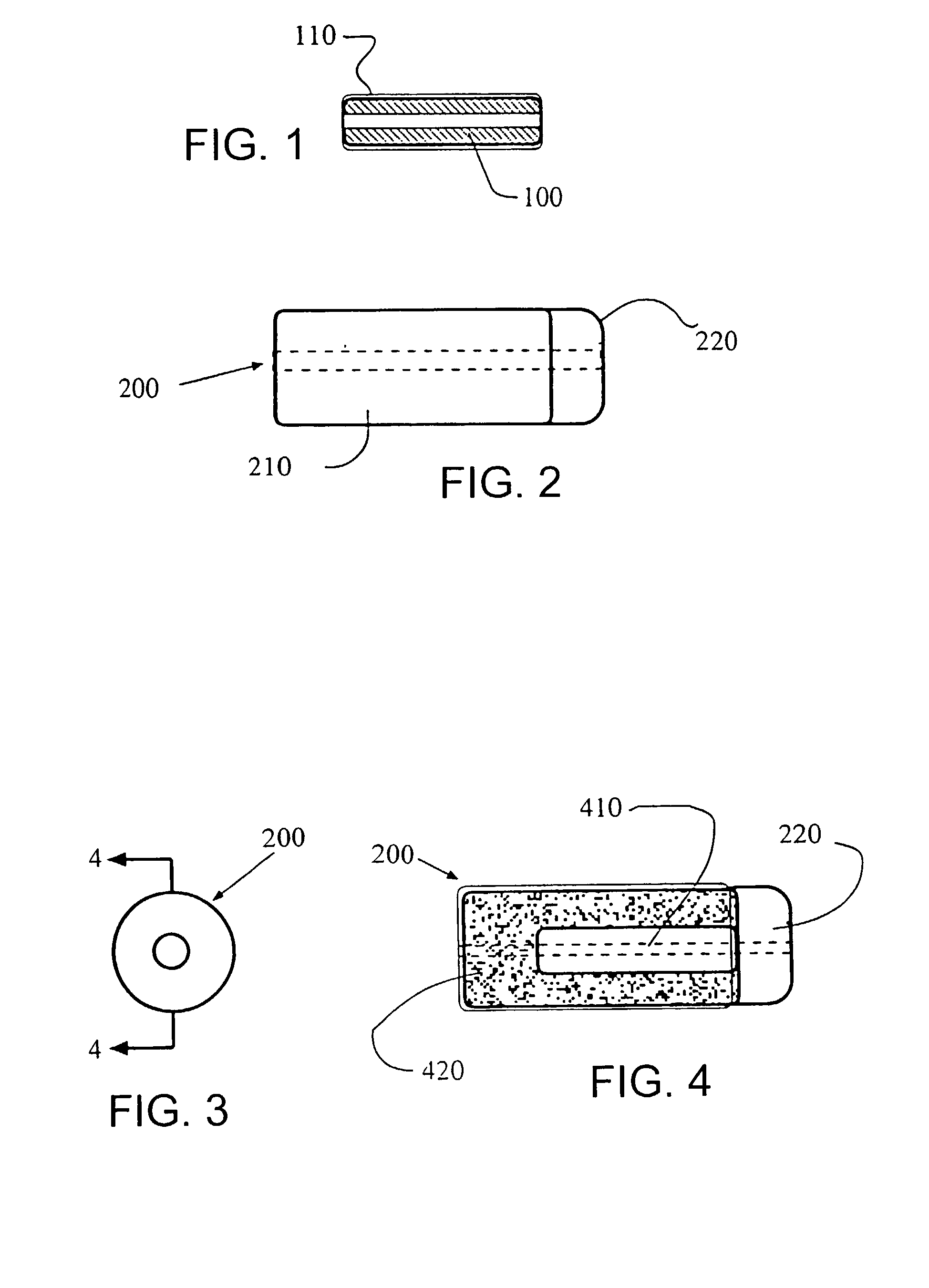
Drill burr and method for performing holes in subchondral bone to promote cartilage repair
A method for performing holes in subchondral bone to promote cartilage repair comprises selecting a drill burr having a drilling head and an axial stop, as a function of the distance between the tip of the drilling head and the axial stop and of a desired depth to reach a desired subchondral bone marrow compartment of a patient; drilling a hole through a base of a cartilage lesion with the drill burr to reach the desired subchondral bone marrow compartment of the patient; abutting the base of the cartilage lesion defining a periphery of the hole with the axial stop while drilling; and withdrawing the drill burr from the hole; whereby the hole has the desired depth and reaches the desired subchondral bone marrow compartment to promote cartilage repair.
Owner:POLYVALOR LP
Composition for treatment of articular cartilage damage
InactiveUS7459307B2Good effectEasy to operateBiocideSkeletal disorderCellular componentArticular pain
Disclosed herein is a composition for the treatment of articular cartilage damage or loss or defect. The composition for the treatment of articular cartilage injury of the present invention includes (i) cellular components separated, proliferated, and / or differentiated from the umbilical cord blood, (ii) a culture medium; and (iii) a biocompatible polymer. The composition has very superior ability of proliferation and differentiation and easier to be collected and acquired.
Owner:MEDIPOST +1
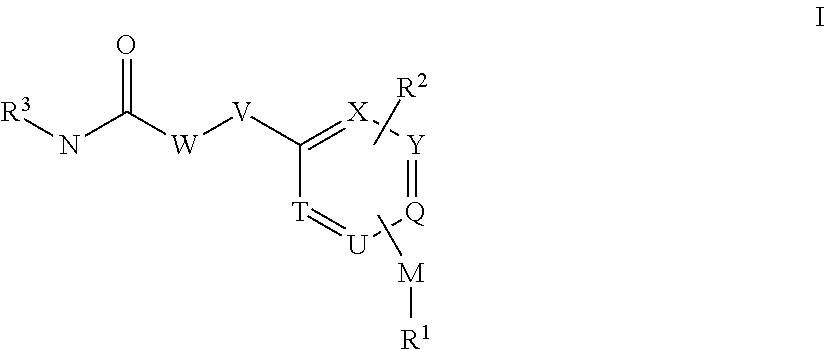
Ddr2 inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis
InactiveUS20150225369A1Less side effectsImprove stabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryCartilage lesionDepressant
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula I and in particular medicaments comprising at least one compound of the formula I for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathophysiological states in the triggering of which DDR2 is involved, in particular for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of osteoarthritis, hepatocirrhosis, traumatic cartilage injuries, pain, allodynia or hyperalgesia.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Articular cartilage graft and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103920190AAvoid allergiesLower immune responseJoint implantsCell-Extracellular MatrixCartilage lesion
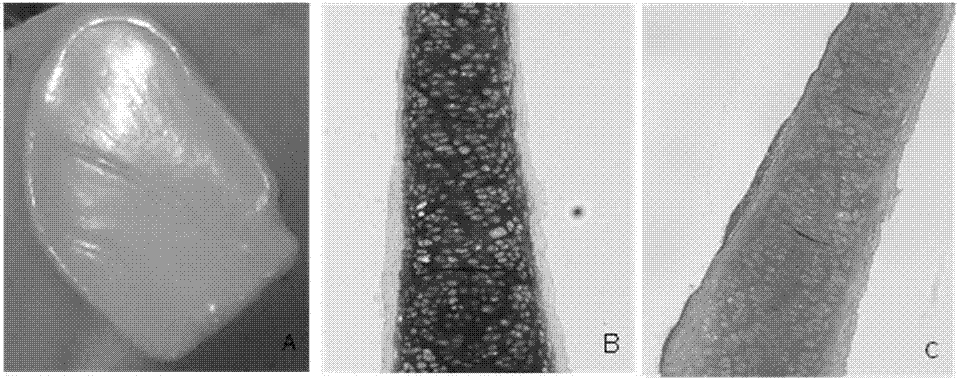
An articular cartilage graft and a preparation method thereof are provided. The prepared articular cartilage graft is composed of a superficial layer, a middle layer and a deep layer from outside to inside; the thickness, shape and size of each layer are all matched with a cartilage injury part, and thus preoperative shaping is not required; after grafting, the articular cartilage graft has layer distribution corresponding to distribution of each layer of surrounding normal cartilages, is conducive to intercellular signal transmission, transduction and regulation, and can be better integrated with surrounding normal cartilage tissues; the articular cartilage graft has structure characteristics consistent with those of the natural cartilages, the collagen type II content is gradually decreased from the superficial layer to the deep layer, the GAG content is increased gradually from the superficial layer to the deep layer, and compression resistance and wear resistance are good; and chondrocytes in the cartilage graft are wrapped with an extracellular matrix, have low immunogenicity, allow generation of immunologic rejection to be avoided after grafting, can survive for a long term and exert functions, and improve cartilage repair long-term curative effects.
Owner:西安博鸿生物技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for treating osteochondral pathologies
InactiveUS20020188353A1Promote growthCost effectiveBone implantSurgical needlesPorous substrateArticular surfaces
Systems and methods are described for treating osteochondral pathologies. An implantable prosthesis for treating osteochondral pathologies includes: a porous substrate; and a substance positioned within the porous substrate that is elutable with regard to the porous substrate. The systems and methods provide advantages because a baited route is provided to attract mesenchymal stem cells from the cancellous bone underlying the articular surfaces up to chondral lesions within the joint, thereby promoting the growth of chondrocytes in the area of the chondral lesions.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
Articular cartilage repair
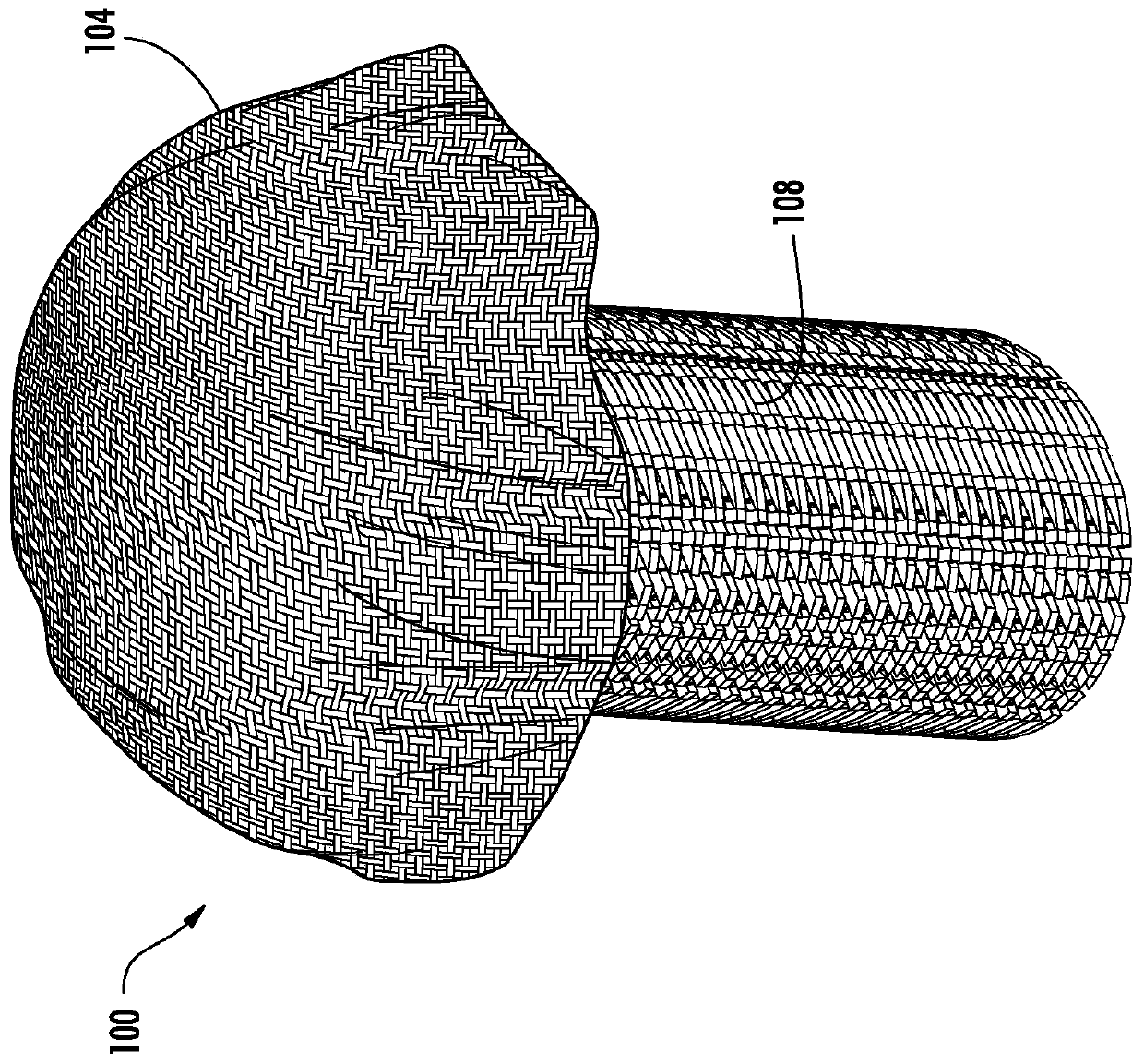
ActiveCN109789020AEnsure full thicknessEnsure consistencyBone implantSkeletal disorderPorous substrateStent replacement
An implant is configured for repair and regeneration of cartilage lesions. The implant includes a three-dimensional woven textile scaffold and a three-dimensional rigid, porous substrate. The scaffoldis bonded to the substrate such that the substrate supports the scaffold. The substrate is configured to be inserted into bone tissue including cartilage lesions such that the substrate and the scaffold replace the bone tissue including the cartilage lesions. The substrate and scaffold are further configured such that after the substrate and the scaffold have replaced the bone tissue including the cartilage lesions, the substrate and scaffold promote growth and integration of new bone tissue into the implant.
Owner:CYTEX THERAPEUTICS
Cell gel preparation for treating articular cartilage injury and use thereof, and used gel solution for maintaining activity of cryopreserved cells
InactiveCN108670946AGood biocompatibilityHigh activityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryHigh cellGel preparation
The invention discloses a cell gel preparation for treating articular cartilage injury and a use thereof, and a used gel solution for maintaining the activity of cryopreserved cells. The formula of the cell gel preparation comprises, according to the volume percentage, 50% to 95%, of the gel solution and 5% to 50% of a compound electrolyte cell resuspension, and per milliliter of the cell gel preparation contains 0.5*10<5>-2*10<7> cells. The gel solution includes the following components by mass and volume: 1 to 50 mg of a high molecular material stabilizer, 0.1 to 1 mg of chondroitin sulfate,5 to 50 mg of human serum albumin, 30 to 150 [mu]l of glycerol, 1 to 30 [mu]l of DMSO, and 700 to 900 [mu]l of a compound electrolyte injection liquid or amino acid injection liquid or normal salineinjection liquid. The gel preparation has good biocompatibility and can be directly stored at low temperature for a long time and maintain high cell viability, and does not require traditional liquidnitrogen cryopreservation; the cell gel preparation after resuscitation can maintain cell biological characteristics and functions and high survival rate in a joint cavity, and can be used in treatment of articular cartilage injury.
Owner:TIANJIN AMCELLGENE ENG
Biological material suitable for the therapy of osteoarthrosis, ligament damage and for the treatment of joint disorders
The present invention regards a biological material comprising: a) a liquid carrier comprising a viscous solution containing at least one natural and / or semisynthetic polysaccharide, and having a Dynamic viscosity measured at 20° C. and at shear rate of D=350 s−1, comprised between 100 and 250 c Poise and / or a Kinematic viscosity comprised between 99 and 248cSt (measured at the same conditions); b) a culture of mesenchymal stem cells, and / or c) a platelet-rich hemo-derivative. This type of material in form of viscous liquid is particularly suitable for the therapy of osteoarthrosis, ligament damage, in particular tendon and cartilage damage) and may be administered intra-articularly, intradermally or directly applied in situ without altering the properties of the mesenchymal stem cells and / or platelets contained therein.
Owner:FIDIA FARM SPA
Manufacturing method of tissue engineered cartilage
InactiveCN1565647AEasy to obtainGood biocompatibilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCartilage cellsAlpha-tricalcium phosphate
The invention belongs to tissue engineering field, and discloses a manufacturing method of tissue engineered cartilage comprising needed degradable porous biological ceramic materials. The invention composite generates cartilage tissue by inorganic biological bracket materials(alpha tricalcium phosphate porous ceramic materials) and tissue cell(cartilage cell) to restore articular cartilage injury. The invention can realize functional restoration of cartilage injury and has a considerate clinical practice prospect.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Preparation method and application of targeted chondrocyte exosome
InactiveCN113018265AAvoid damageInhibition of catabolismOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticKnee JointCartilage lesion
The invention provides a preparation method of a targeting chondrocyte exosome. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing an exosome carrier, preparing a targeting cartilage exosome, and preparing miRNA-140 wrapped by the targeting cartilage exosome. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the miRNA medicine is delivered with treatment potential, high efficiency and tissue specificity for treating osteoarthritis, the application of the miRNA-140 wrapped by the targeting exosome in the medicine for treating osteoarthritis is mainly utilized, in an osteoarthritis animal model of a rat, the expression of MMP-13 can be inhibited by injecting the miRNA-140 into a knee joint cavity, the damage of cartilage matrix can be obviously improved, the cartilage damage process of an osteoarthritis animal model is delayed, and the cartilage protection effect is achieved, and therefore, the exosome is used for transporting miRNA-140 in a targeted manner, degradation of cartilage tissues can be slowed down, and the effect of inhibiting catabolism of cartilage matrix is achieved, so that the damage of articular cartilage is controlled, and cartilage repair is promoted.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Anatomical composite three-dimensional scaffold tissue engineering cartilage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104623735AUnique anisotropic alignment structureGood biomechanical propertiesProsthesisMicrosphereCartilage lesion
The invention relates to an anatomical composite three-dimensional scaffold tissue engineering cartilage and a preparation method thereof. According to the anatomical composite three-dimensional scaffold tissue engineering cartilage, a scaffold is made of polycaprolactone-hydroxyapatite composite material; IGF-1 PLGA microspheres are carried on the scaffold; and the adding amount of the IGF-1 PLGA microspheres is 0.1%-2% of the weigh of the scaffold. The novel three-dimensional porous scaffold prepared by the method has good biocompatibility and biodegradability and is free of cytotoxicity, can be gradually degraded along with regeneration of normal cartilage tissues after being implanted into a living body, and is finally replaced with regenerated cartilage, so that the target of thoroughly healing cartilage injuries is reached.
Owner:HANGZHOU CITY XIAOSHAN DISTRICT TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICAL HOSPITAL
Method for producing cartilage cells induced to be differentiated from stem cells
PendingCN110300798AStable structureImprove expression levelSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood/immune system cellsCartilage cellsCord blood stem cell
Owner:伊普塞尔有限公司
Articular cavity inner injecting and administering preparations containing low-molecular-weight heparin or the low-molecular-weight heparin salt
The present invention provides an intra-articular injection administration preparation containing low molecular weight heparin or the salt, which is characterized in that the preparation contains the low molecular weight heparin or the salt. The present invention is characterized by anti-swelling, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and immune modulation of the low molecular weight heparin or the salt, the invention is used for intra-articular injection administration, which can significantly improve and treat the rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, synovitis and / or cartilage injury.
Owner:凌沛学
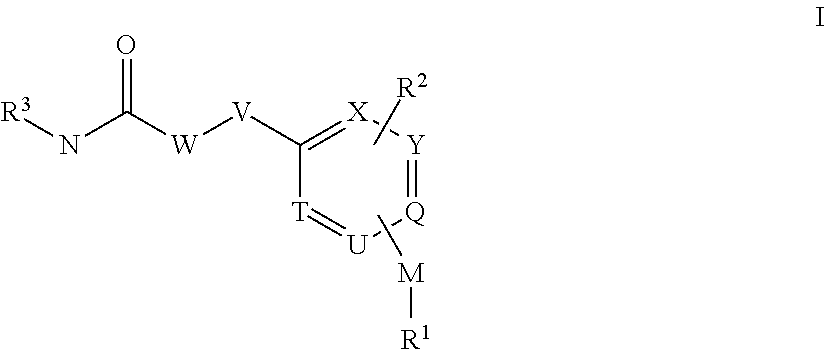
Acylguanidines for treating osteoarthritis
ActiveUS20150361037A1Less side effectsImprove stabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryCartilage lesionAcyl group
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula (I) and in particular to medicaments comprising at least one compound of the formula I for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathophysiological conditions in the triggering of which cathepsin D is involved, in particular for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of osteoarthritis, traumatic cartilage injuries, arthritis, pain, allodynia or hyperalgesia.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
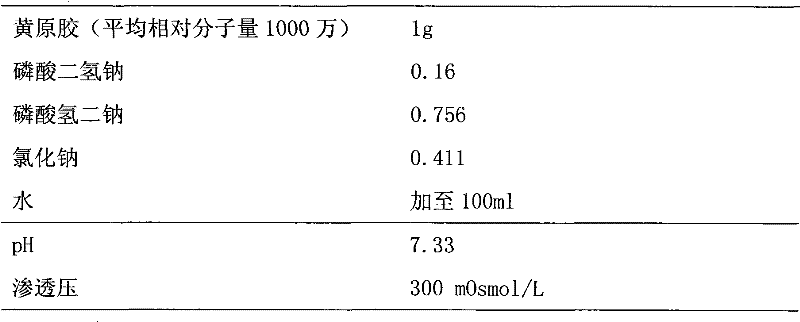
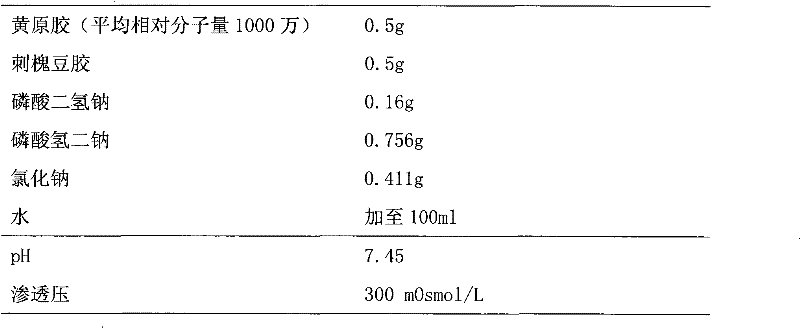
Xanthan-gum-containing pharmaceutical preparation for joint intracavity injection
ActiveCN101940587BIncrease viscosityViscosity recoveryOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderJoint cavityRheumatism
Owner:INST OF BIOPHARM OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane, and making method and application thereof
ActiveCN104368043AFlat surfaceSimple preparation processProsthesisSodium bicarbonateCartilage lesion
The invention discloses a making method of a collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane. The method comprises the following steps: 1, shearing a raw material pork leg tendon, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis, centrifuging, filtering, and dissolving to obtain an I type collagen solution; 2, neutralizing the I type collagen solution obtained in step 1 by using a 1M sodium bicarbonate solution; 3, pouring the neutralized I type collagen solution obtained in step 2 into a die, and drying at 30-40DEG C for 35-54h to form an I type collagen matrix membrane in the die; and 4, immersing the I type collagen matrix membrane obtained in step 3 in a 20-200[mu]g / mL parathyroid hormone related peptide solution, and incubating at 30-40DEG C for 0.5-2h to obtain the parathyroid hormone related peptide compounded I type collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane. The invention also discloses the collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane and an application thereof. The cartilage repairing membrane has certain adhesiveness to injured surfaces of cartilage, and is suitable for repairing cartilage injuries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINGYUE BIOTECH
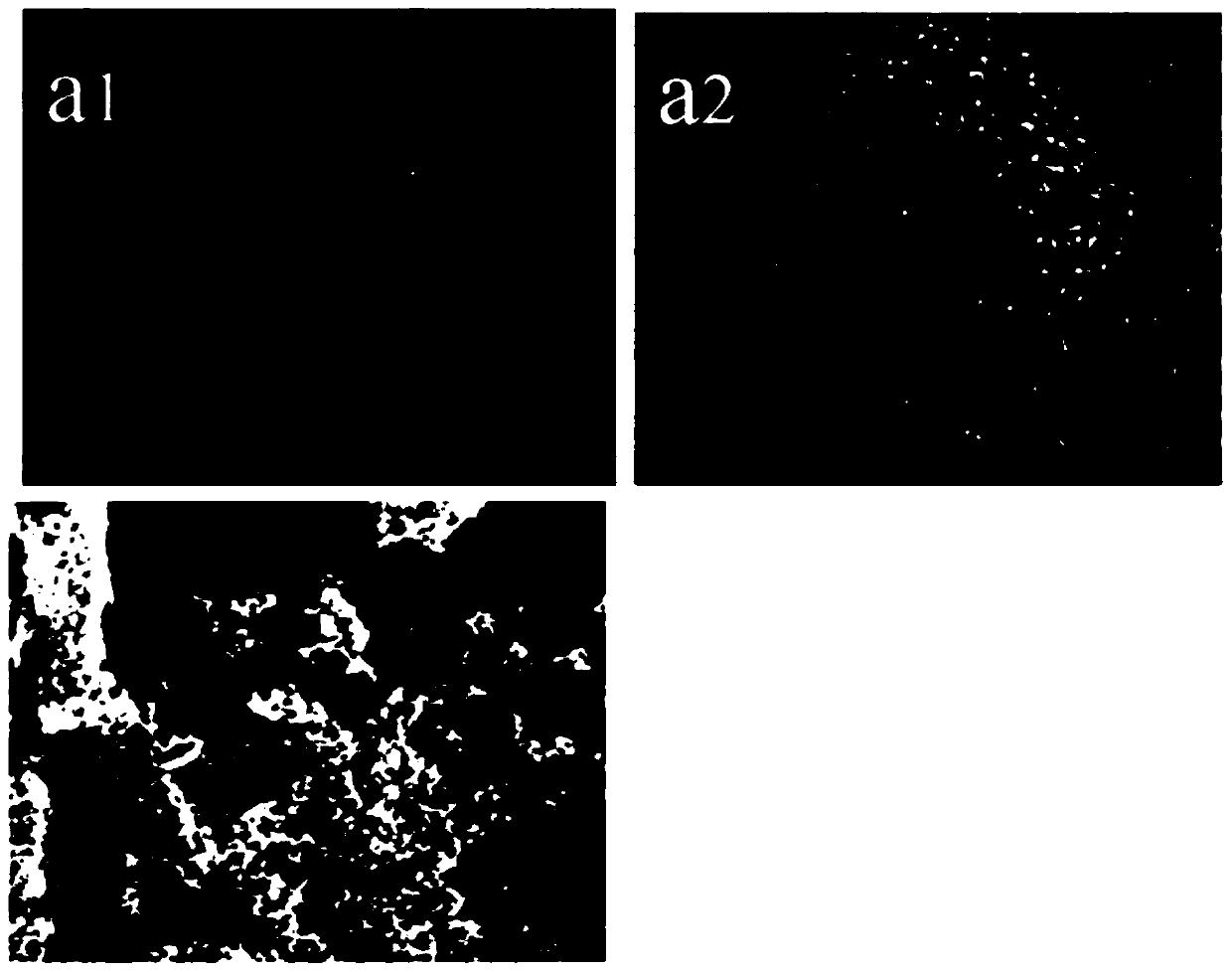
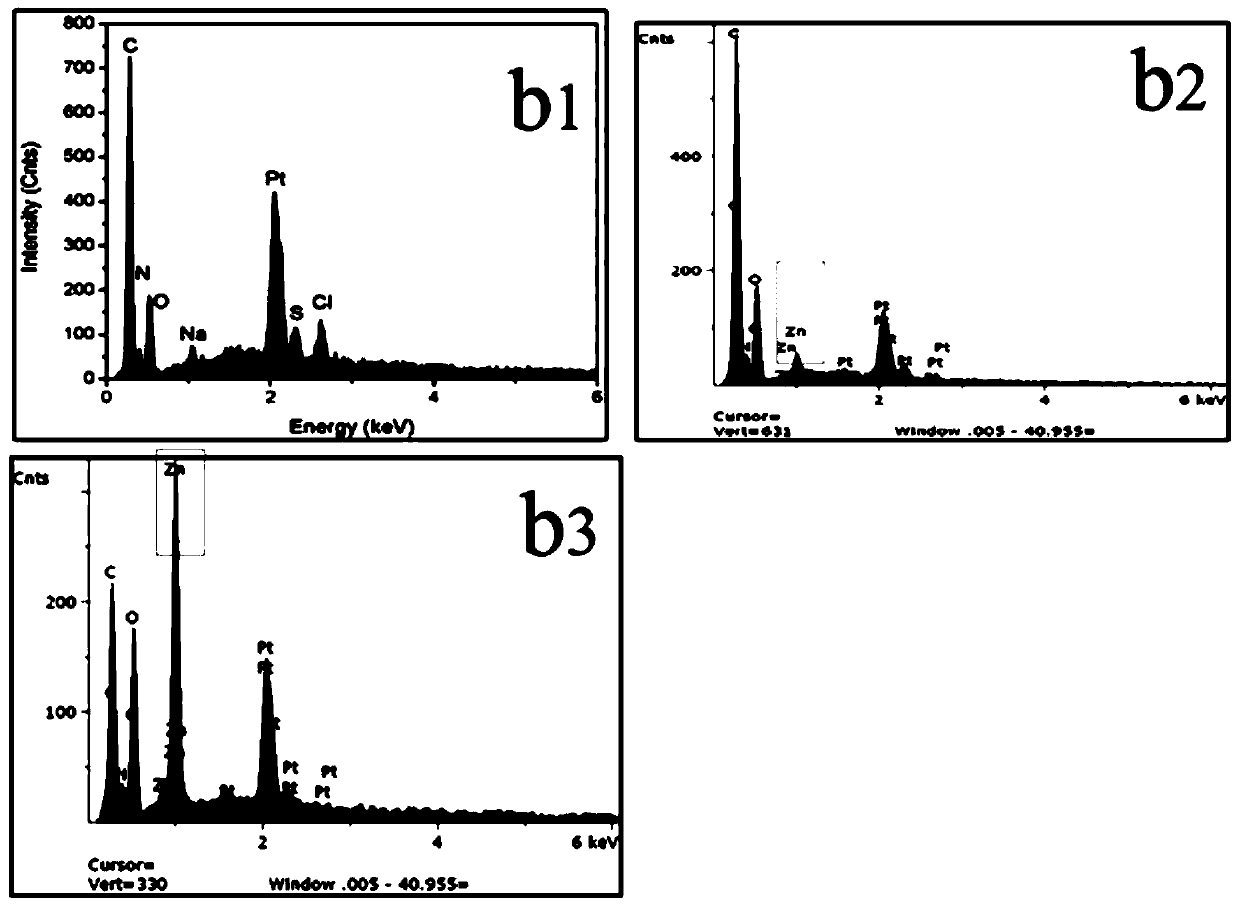
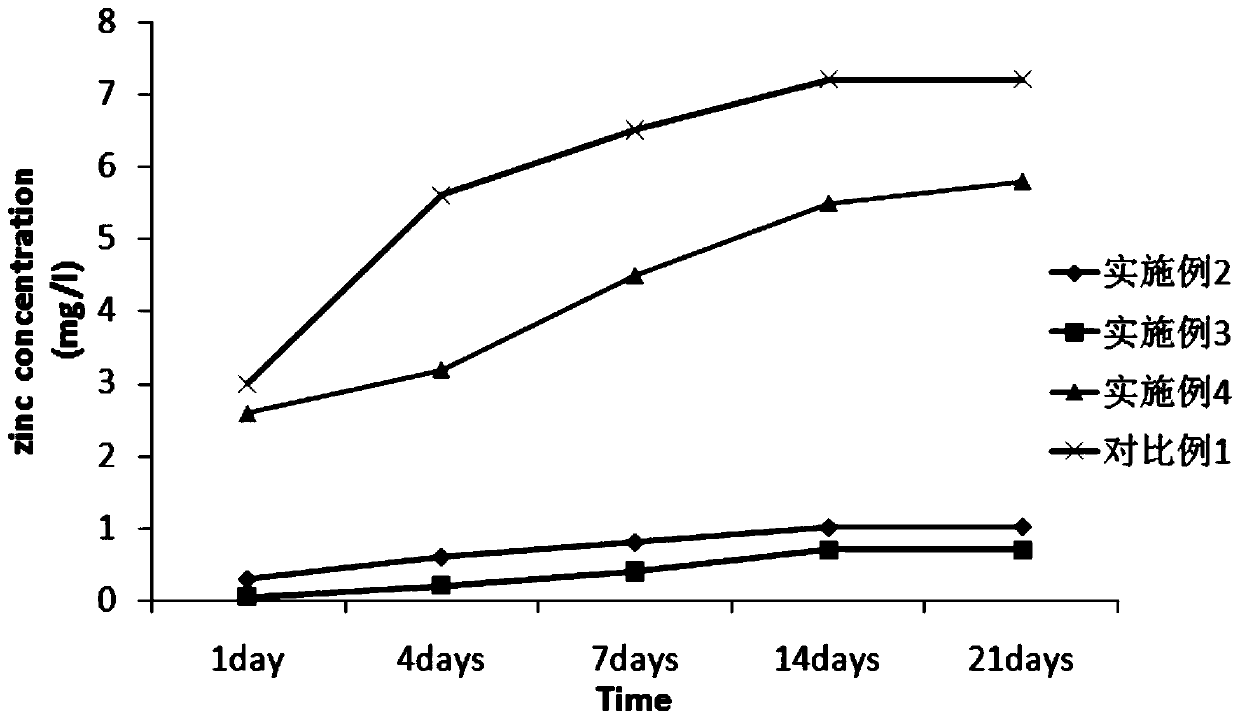
Preparation method of zin-ion-containing tissue engineering scaffold with anti-inflammatory function
ActiveCN111012949AGood tissue compatibilityImprove adhesionTissue regenerationProsthesisEnzymatic digestionFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zin-ion-containing tissue engineering scaffold with an anti-inflammatory function. The method comprises the following steps: separating Wharton's jelly from a human umbilical cord; preparing a pure Wharton's jelly scaffold through the processes of repeated low-temperature crushing, freeze thawing, gradient centrifugation, pancreatin digestion and elution, vacuum freeze compression drying and the like; performing induced deposition on the pure Wharton jelly scaffold in simulated body fluid containing zinc ions; putting the scaffold in an ammoniawater solution in a hydrothermal kettle and performing a gas-phase hydrothermal reaction; and then performing vacuum freeze drying to obtain the cartilage tissue engineering scaffold containing zincions. The tissue engineering scaffold prepared by the method not only has high histocompatibility but also can successfully load zinc ions and release the zinc ions through a slow release effect, so that macrophage polarization is regulated and an anti-inflammatory effect on cartilage injury in an inflammatory environment is realized; and stem cells can be induced to differentiate into chondrocytes; and a good internal immune environment is provided for cartilage repair.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods for repairing cartilage damage
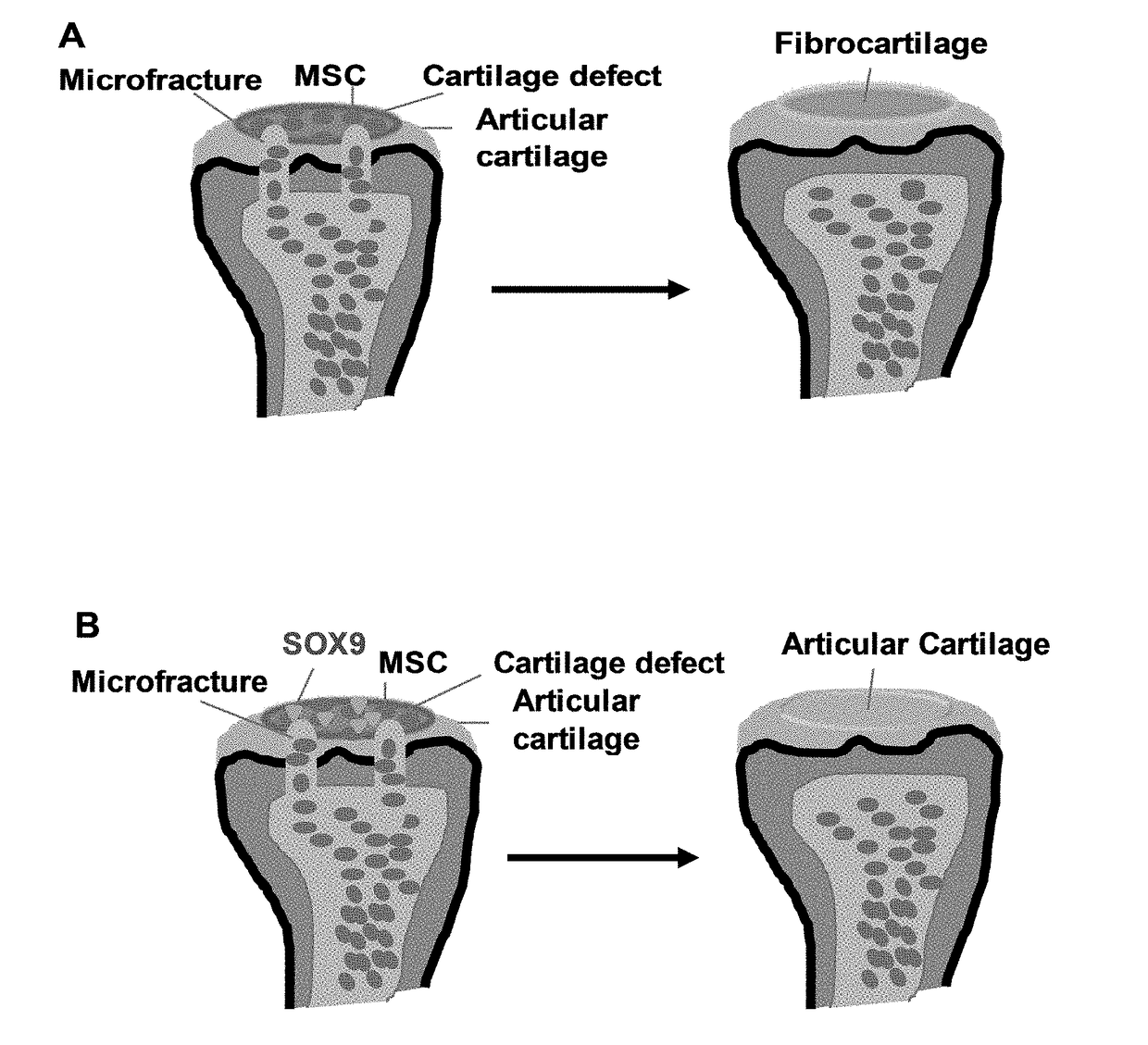
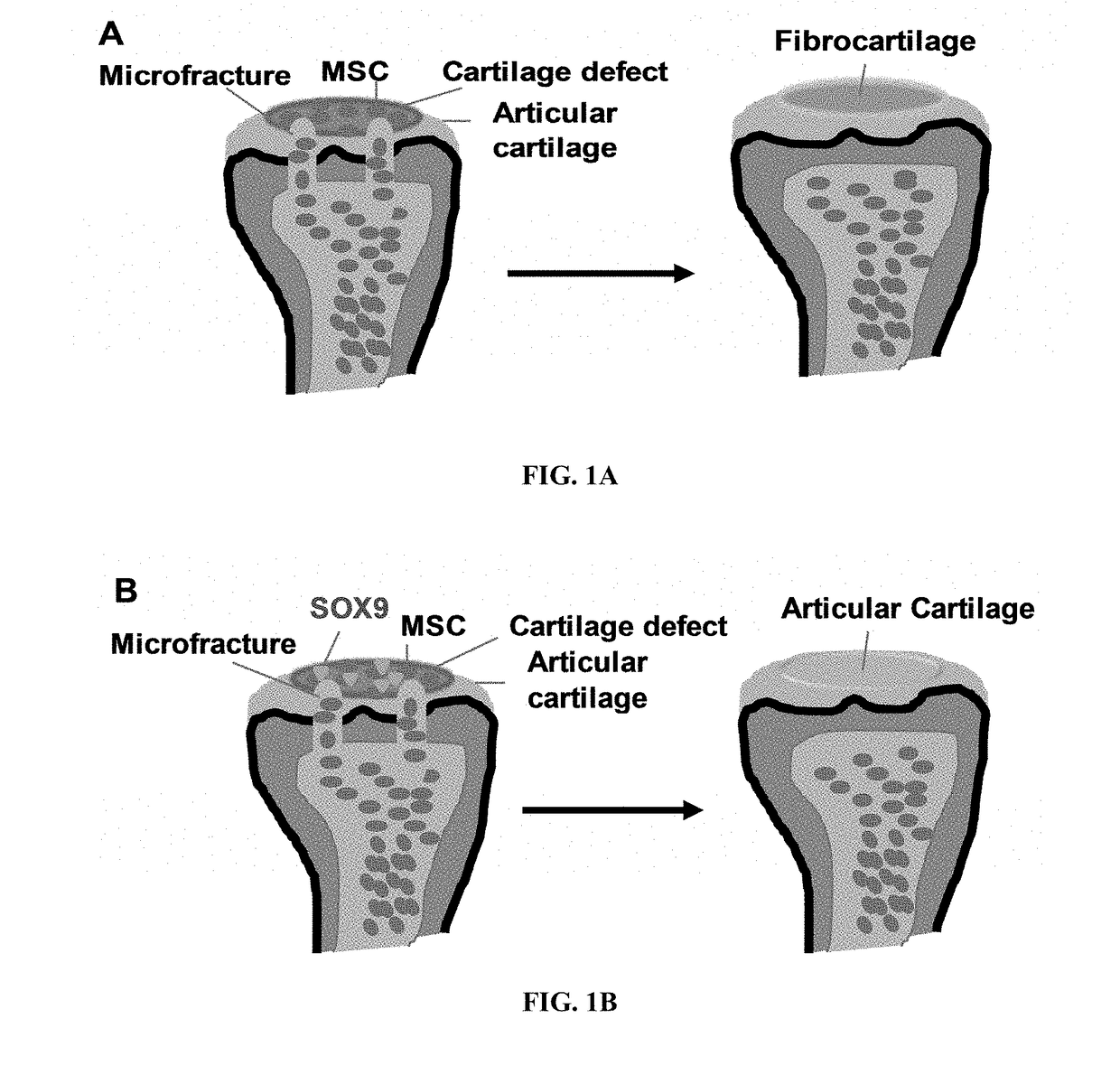
InactiveUS20170197011A1Improve permeabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineStimulation technique
A method for repairing cartilage damage comprising (a) creating a microfracture or performing other bone marrow stimulation techniques on a patient inflicted with cartilage damage; and (b) administering a composition to the microfracture, wherein the composition comprises an agent capable of regenerating organized hyaline cartilage.
Owner:VIVOSCRIPT
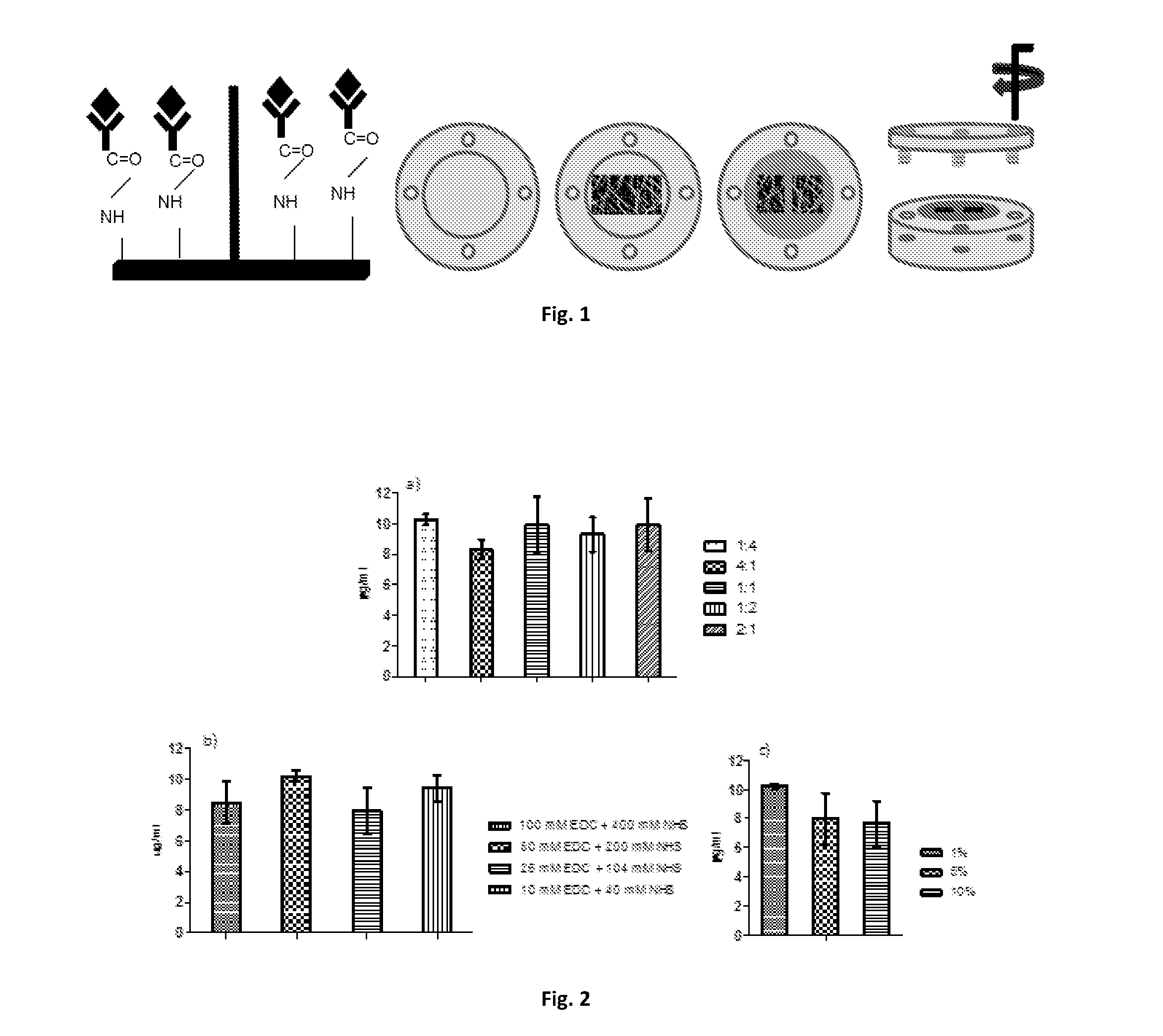
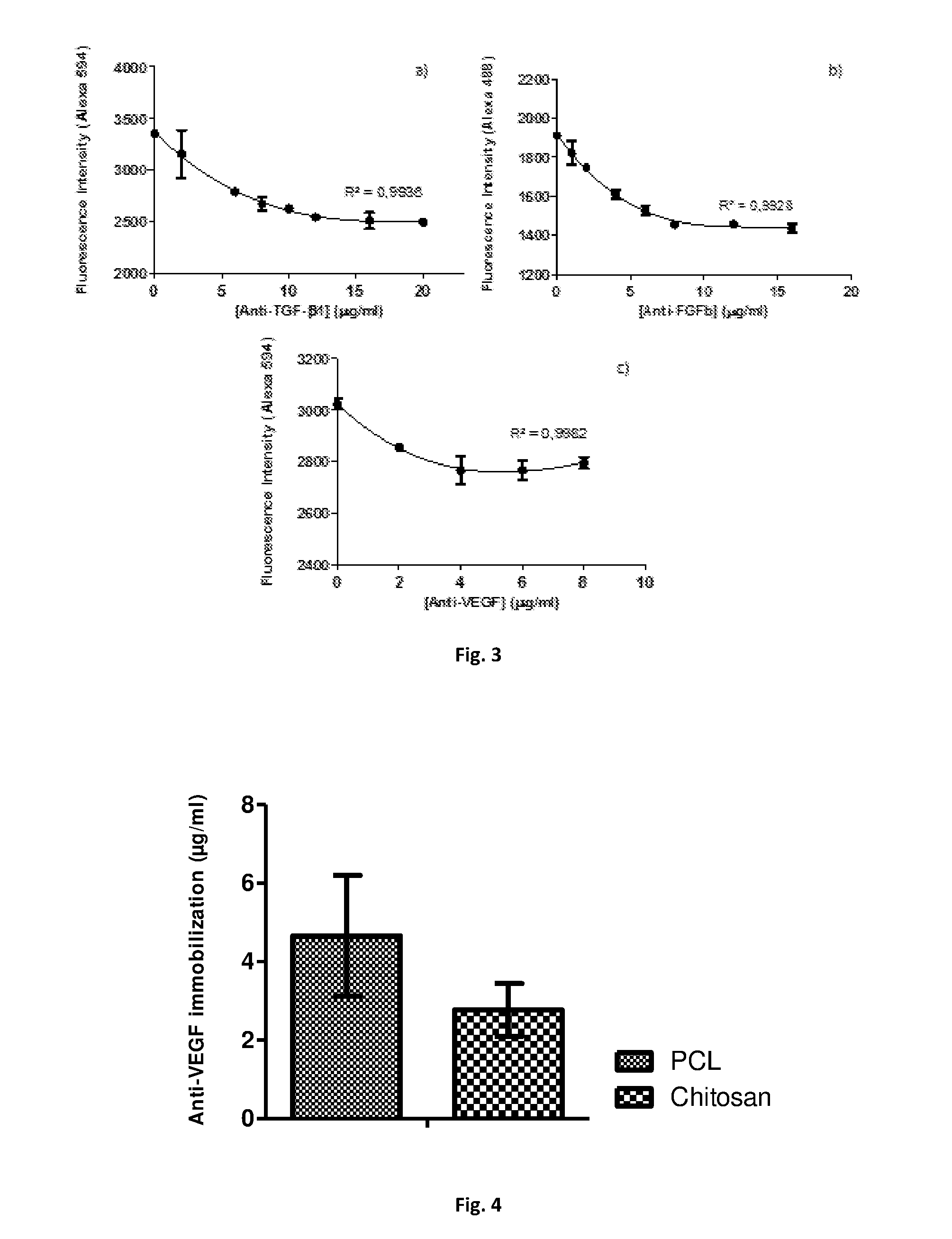
Polymeric substrates with immobilized antibodies and method of production thereof
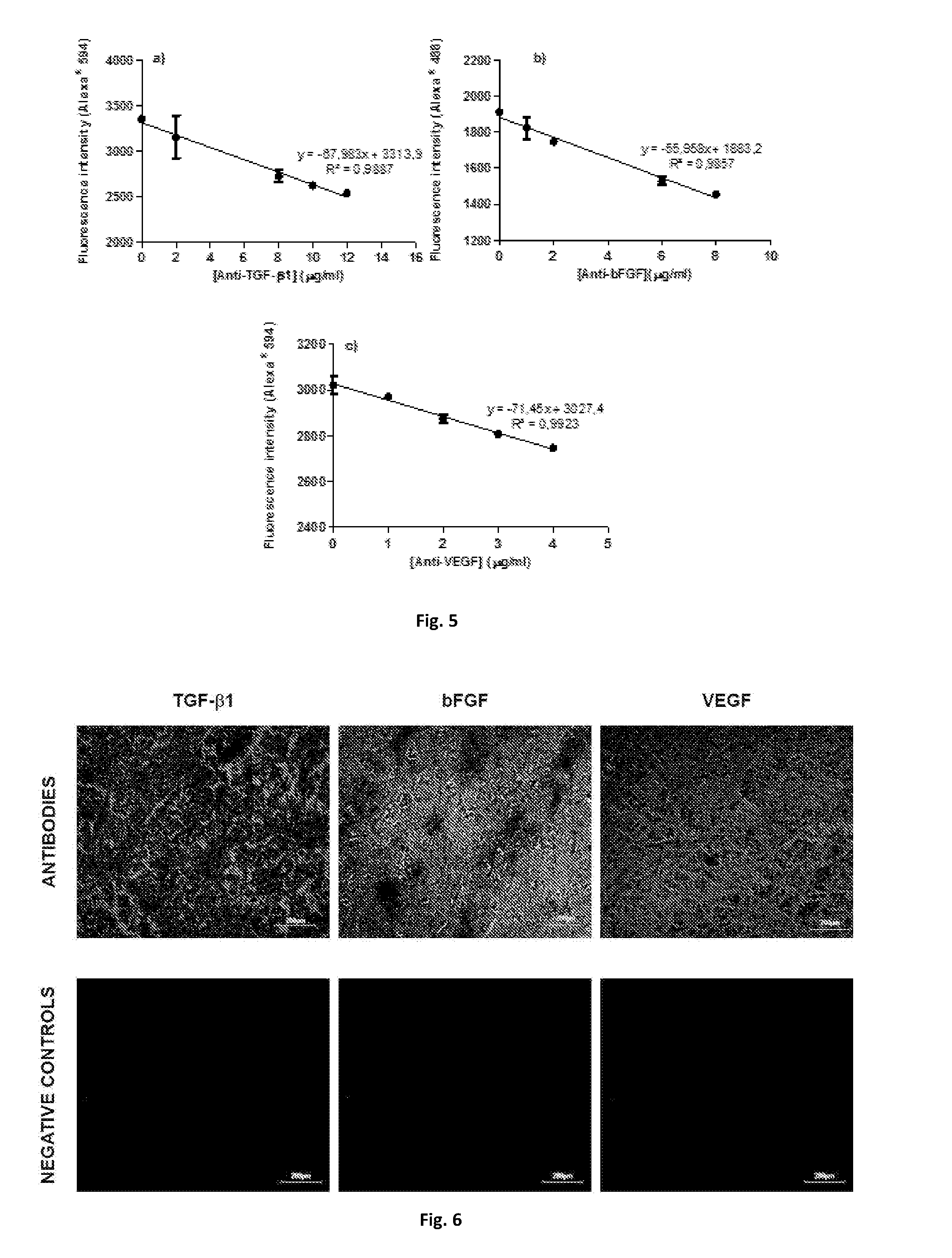
InactiveUS20170051050A1Immunoglobulins against growth factorsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCartilage lesionLigament structure
The present invention relates to biofunctional polymeric substrates product comprising immobilized antibodies that selective bind to antigens namely autologous growth factors and an inflammatory molecule, uses and method of production. The bio-functional polymeric substrate can be used in a quantification method of antigens namely soluble growth factors, inflammatory molecules and hormones or the biofunctional polymeric substrate can be used to isolate extracellular vesicules. The biofunctional polymeric substrate can be also used in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine approaches, namely in bone and cartilage lesions, esophageal lesions, periodontal ligament reconstruction and skin lesions regeneration or treatment.
Owner:ASSOC FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF TISSUE ENG & CELL BASED TECH & THERAPIES A4TEC
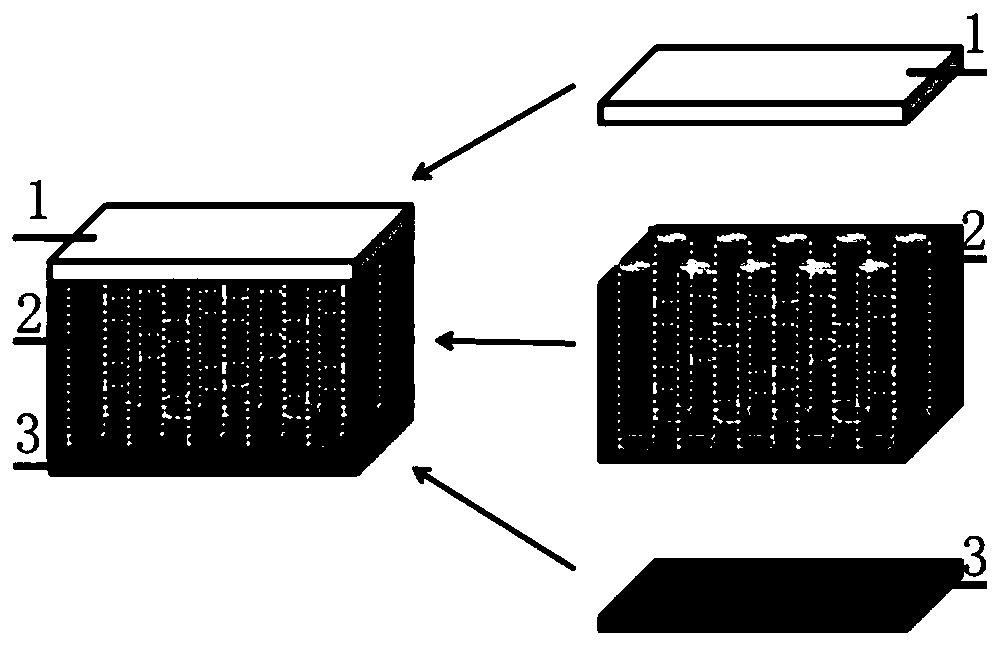
Bionic multilayer collagen support for cartilage repair and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN111249529APromote recruitmentGood biocompatibilityBone implantJoint implantsCartilage lesionImmunogenicity
The invention relates to medical materials, particularly relates to the field of cartilage injury regeneration and mainly discloses a bionic multilayer collagen support for cartilage repair and a preparation method therefor. The support product disclosed by the invention has a multilayer three-dimensional space structure; through lowering of immunogenicity of materials and multilayer stacked design of a dense layer, a porous layer and a barrier layer, collecting of in-vivo cells is promoted, and exogenous-cell-free biomaterial induced in-vivo cartilage regeneration is achieved; and a regeneration policy is optimized, so that the support is applicable to the treatment and regeneration of the cartilage repair.
Owner:GUANGDONG GENERAL HOSPITAL
Biological material suitable for the therapy of osteoarthrosis, ligament damage and for the treatment of joint disorders
The present invention regards a biological material comprising: a) a liquid carrier comprising a viscous solution containing at least one natural and / or semisynthetic polysaccharide, and having a Dynamic viscosity measured at 20° C. and at shear rate of D=350 s−1, comprised between 100 and 250 c Poise and / or a Kinematic viscosity comprised between 99 and 248 cSt (measured at the same conditions); b) a culture of mesenchymal stem cells, and / or c) a platelet-rich hemo-derivative. This type of material in form of viscous liquid is particularly suitable for the therapy of osteoarthrosis, ligament damage, in particular tendon and cartilage damage) and may be administered intra-articularly, intradermally or directly applied in situ without altering the properties of the mesenchymal stem cells and / or platelets contained therein.
Owner:FIDIA FARM SPA
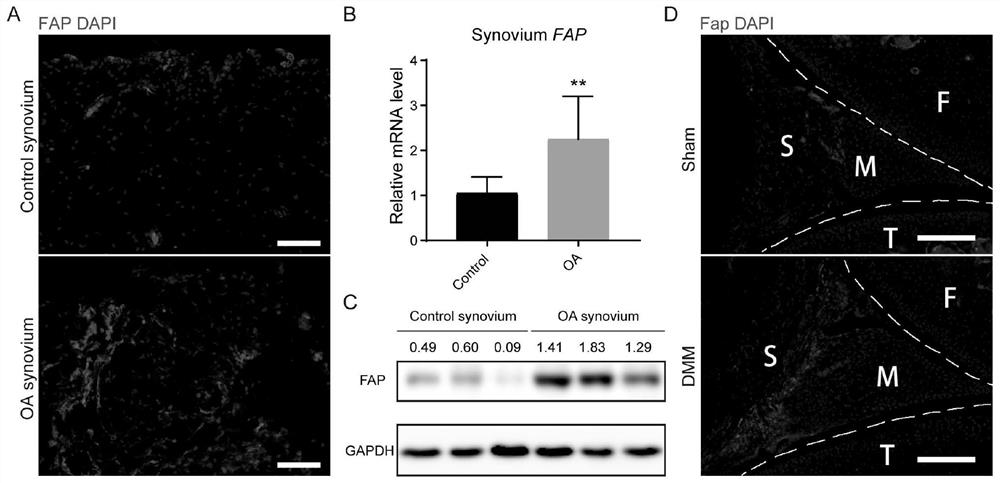
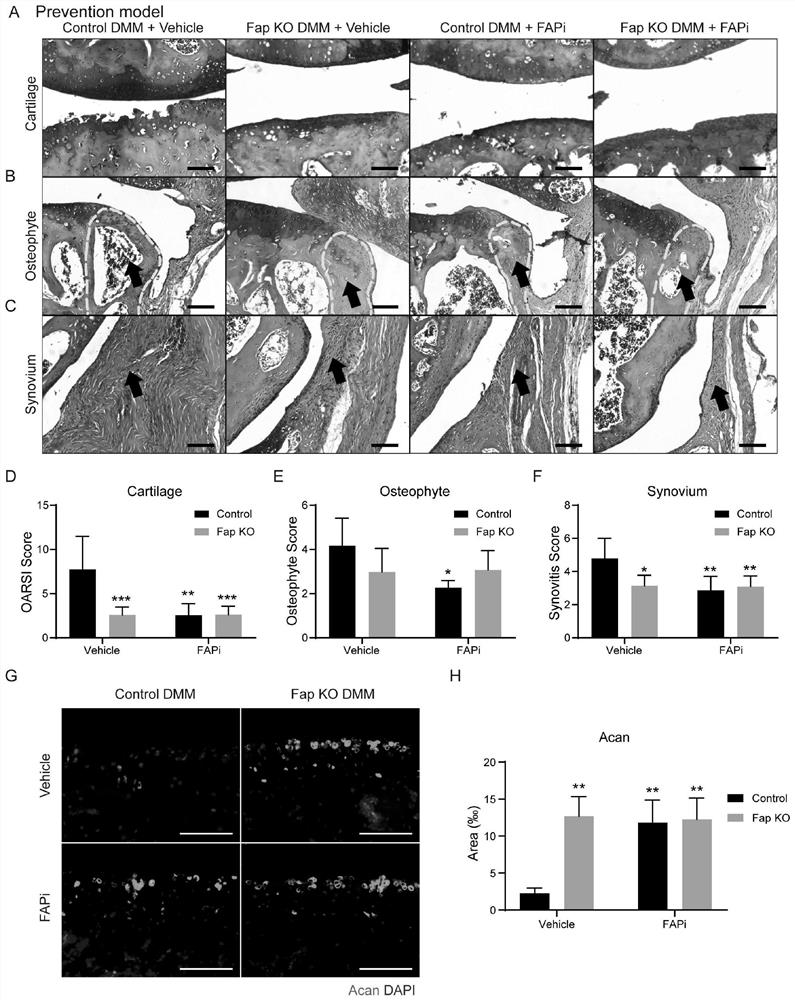
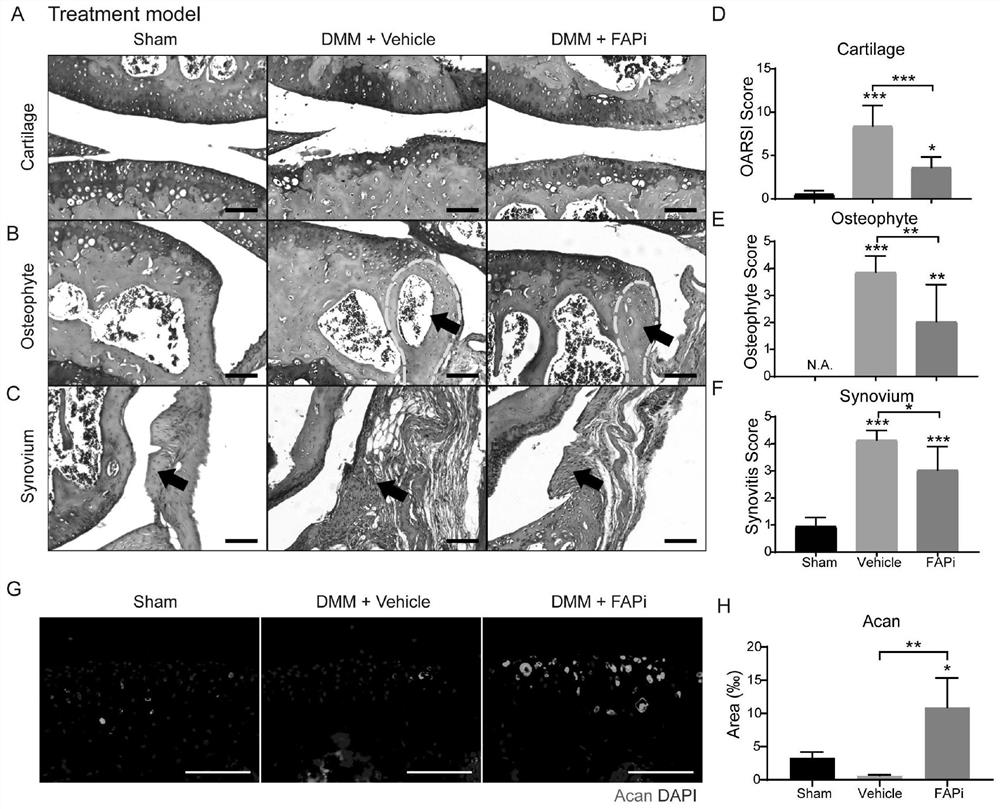
Application of fibroblast activation protein (Fap) as drug target in treatment of osteoarthritis (OA)
PendingCN112522388APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacometricsCartilage lesion
The invention provides application of fibroblast activation protein (Fap) as a target in screening drugs for treating osteoarthritis (OA) or inhibiting cartilage injury or osteophyte generation or synovitis. The invention also provides application of an Fap gene as a target in screening drugs for treating OA or inhibiting cartilage injury or osteophyte generation or synovitis. The invention also provides application of a targeted Fap inhibitor in preparation of drugs for treating OA or inhibiting cartilage injury or osteophyte generation or synovitis. The invention also provides application ofosteolectin (Oln) in preparation of drugs for treating OA or inhibiting cartilage injury or osteophyte generation or synovitis. It is found that Fap is highly expressed in synovial membrane of OA, cartilage injury, osteophyte generation, synovitis and cartilage aggregation protein polysaccharide loss of mouse OA can be relieved by inhibiting Fap through genetics and pharmacology, and both an Fapsmall-molecule inhibitor and an endogenous protein inhibitor Oln can treat the OA.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
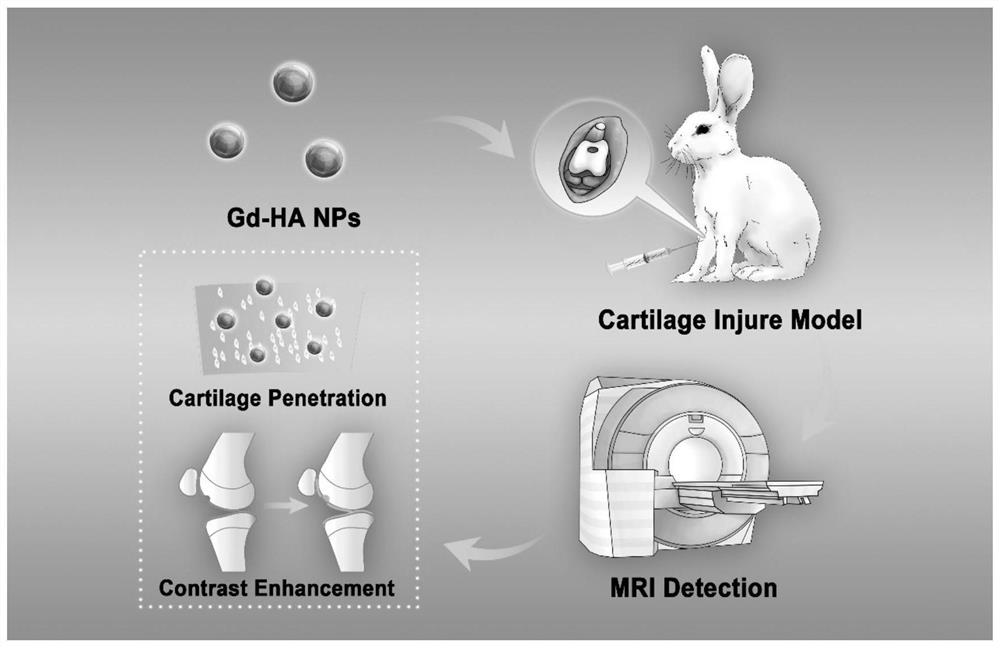
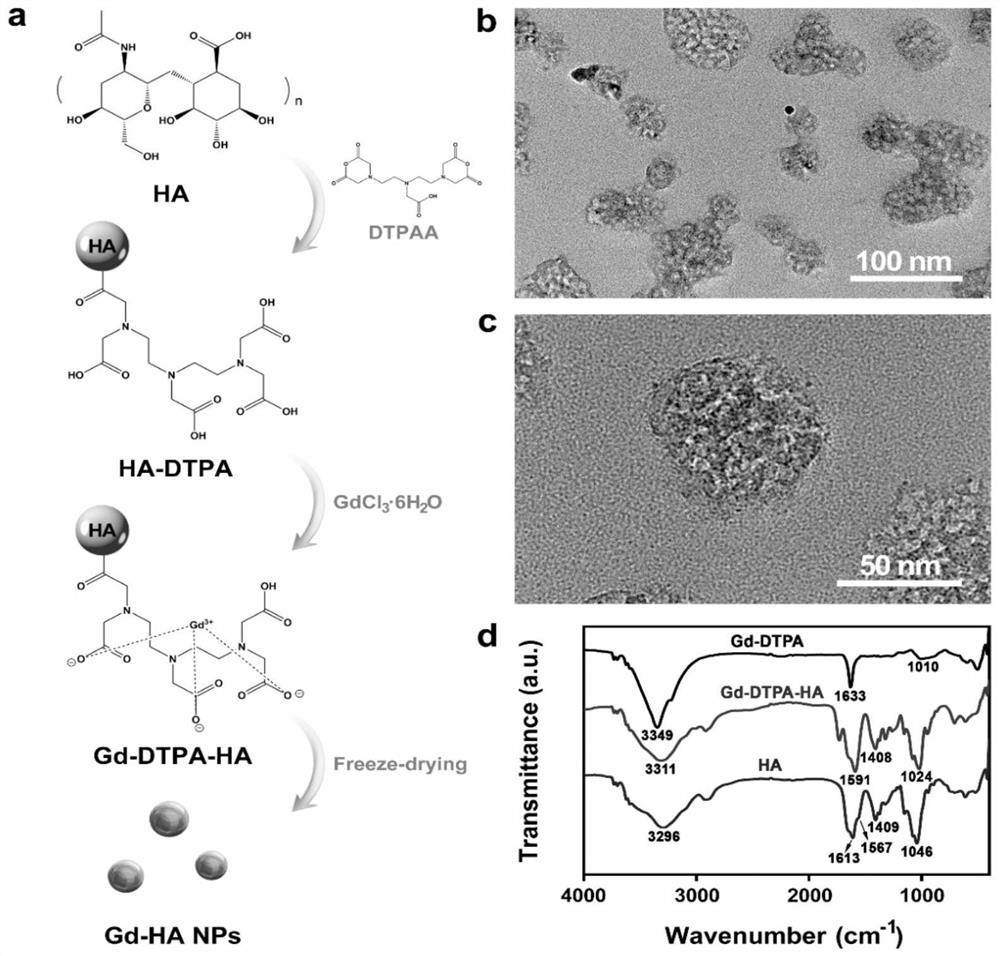
Targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent for articular cartilage injury as well as preparation and application of targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent
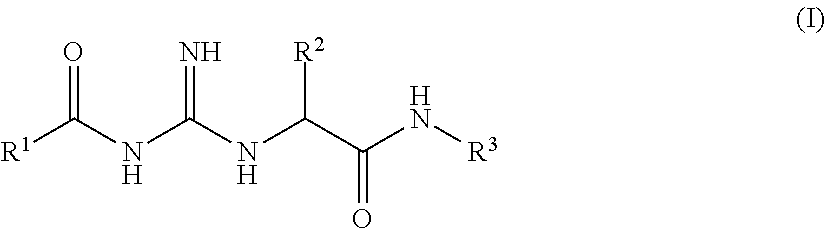
InactiveCN113440626AImprove permeabilityHigh precisionNanomagnetismEmulsion deliveryExtracellular matrix bindingCell-Extracellular Matrix
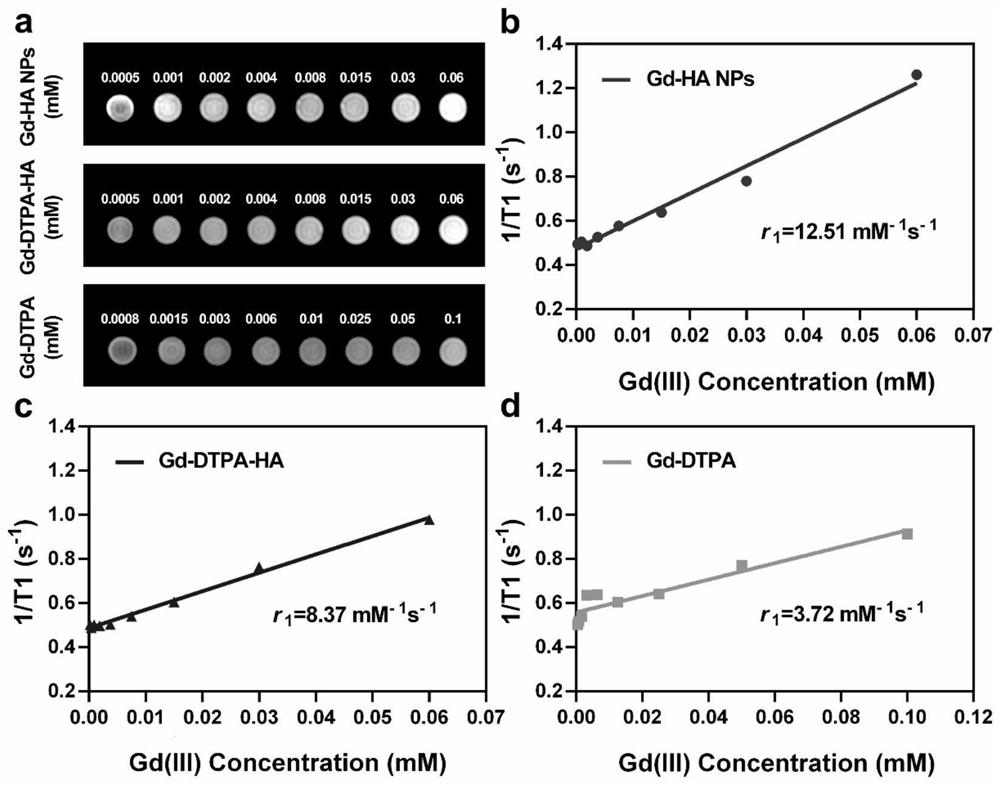
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and relates to a targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent for articular cartilage injury as well as preparation and application of the targeted nano magnetic resonance contrast agent. The structure of the contrast agent is HA-DTPA-Gd, hyaluronic acid HA and gadolinium ions Gd (III) are linked through diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid DTPA, and the molecular structural formula of the contrast agent is shown in the formula (I). The contrast agent can be injected through an articular cavity, the size of the contrast agent is nanoscale, nanoparticles are combined with an extracellular matrix of a cartilage defect area based on the surface effect of the nanoparticles, specific aggregation in the cartilage injury area is easier, the enhancement degree of a focus area after MRIT1 weighted delay enhancement is more obvious than that of a clinical gadolinium-containing contrast agent, and therefore the cartilage injury focus can be accurately and visually displayed; improvement of accuracy and safety of clinical treatment is facilitated, the curative effect of a knee joint cartilage injury treatment mode is evaluated, and prognosis of a patient is evaluated.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
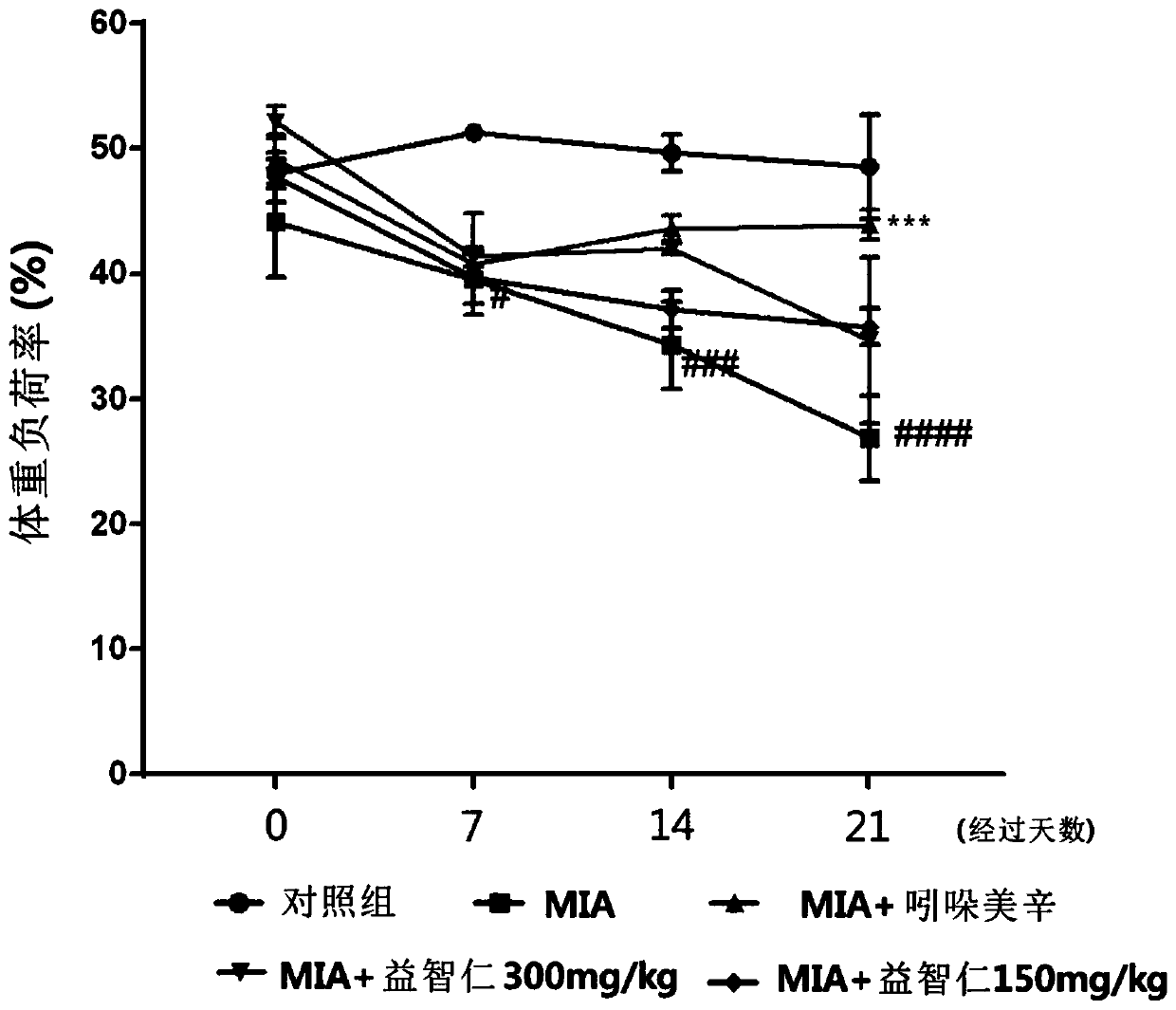
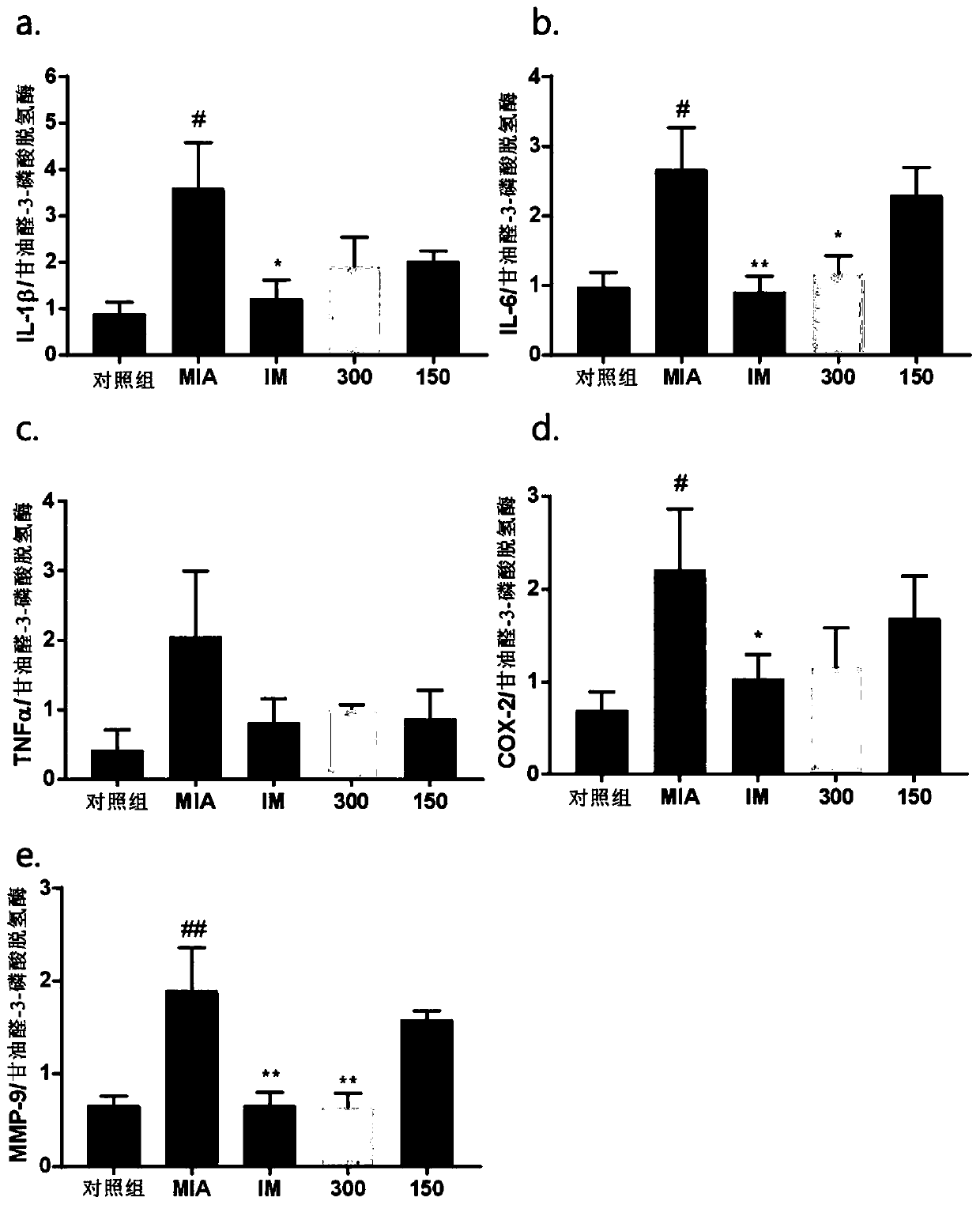
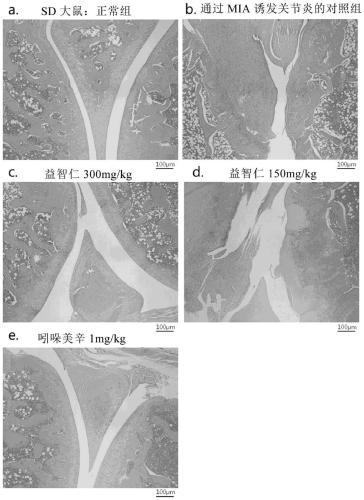
Composition containing alpinia oxyphylla extract as active ingredient for prevention, alleviation, or treatment of osteoarthritis
InactiveCN111093398AReduce expressionGood for restoring cartilage damageDispersion deliverySkeletal disorderWhite blood cellCartilage lesion
Owner:KOREA INST OF ORIENTAL MEDICINE
Scaffold with adhesive for articular cartilage repair
PendingUS20210161672A1Enhances cell attachmentIncreased proliferationJoint implantsSubchondral boneCartilage lesion
An injury or defect in articular cartilage is treated with a matrix implant that is applied above a barrier composition. The polymer-containing barrier composition is applied to the bottom of a cartilage lesion. The barrier composition can block migration of cells, blood, or other material from subchondral bone into the cartilage lesion.
Owner:OCUGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com