Patents
Literature
2272 results about "Optical disc drive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Optical disc drives that are no longer in production include CD-ROM drive, CD writer drive, combo (CD-RW/DVD-ROM) drive, and DVD writer drive supporting certain recordable and rewritable DVD formats (such as DVD-R(W) only, DVD+R(W) only, DVD-RAM only, and all DVD formats except DVD-R DL). As of 2015, DVD writer drive supporting all existing recordable and rewritable DVD formats is the most common for desktop PCs and laptops. There are also the DVD-ROM drive, BD-ROM drive, Blu-ray Disc combo (BD-ROM/DVD±RW/CD-RW) drive, and Blu-ray Disc writer drive.
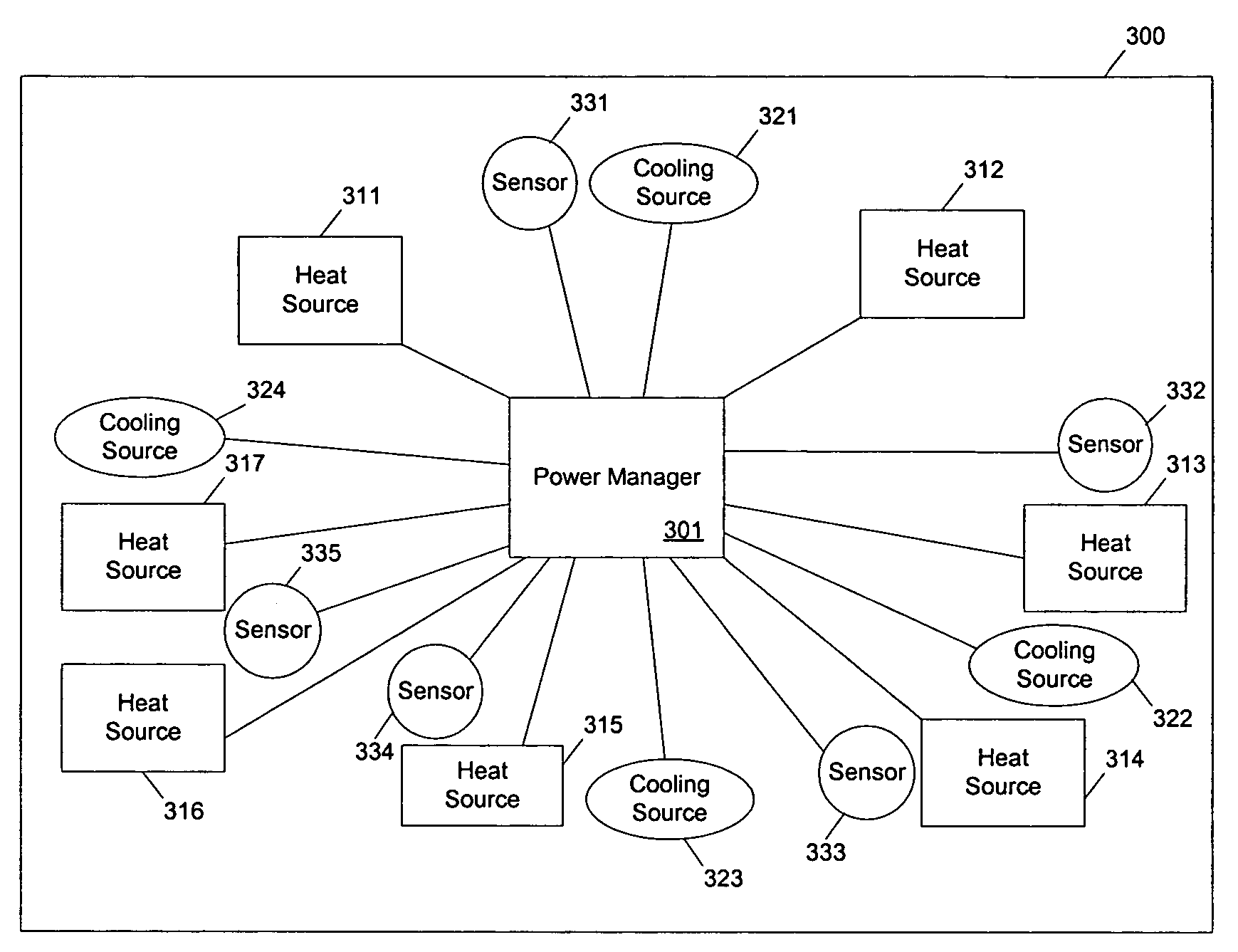
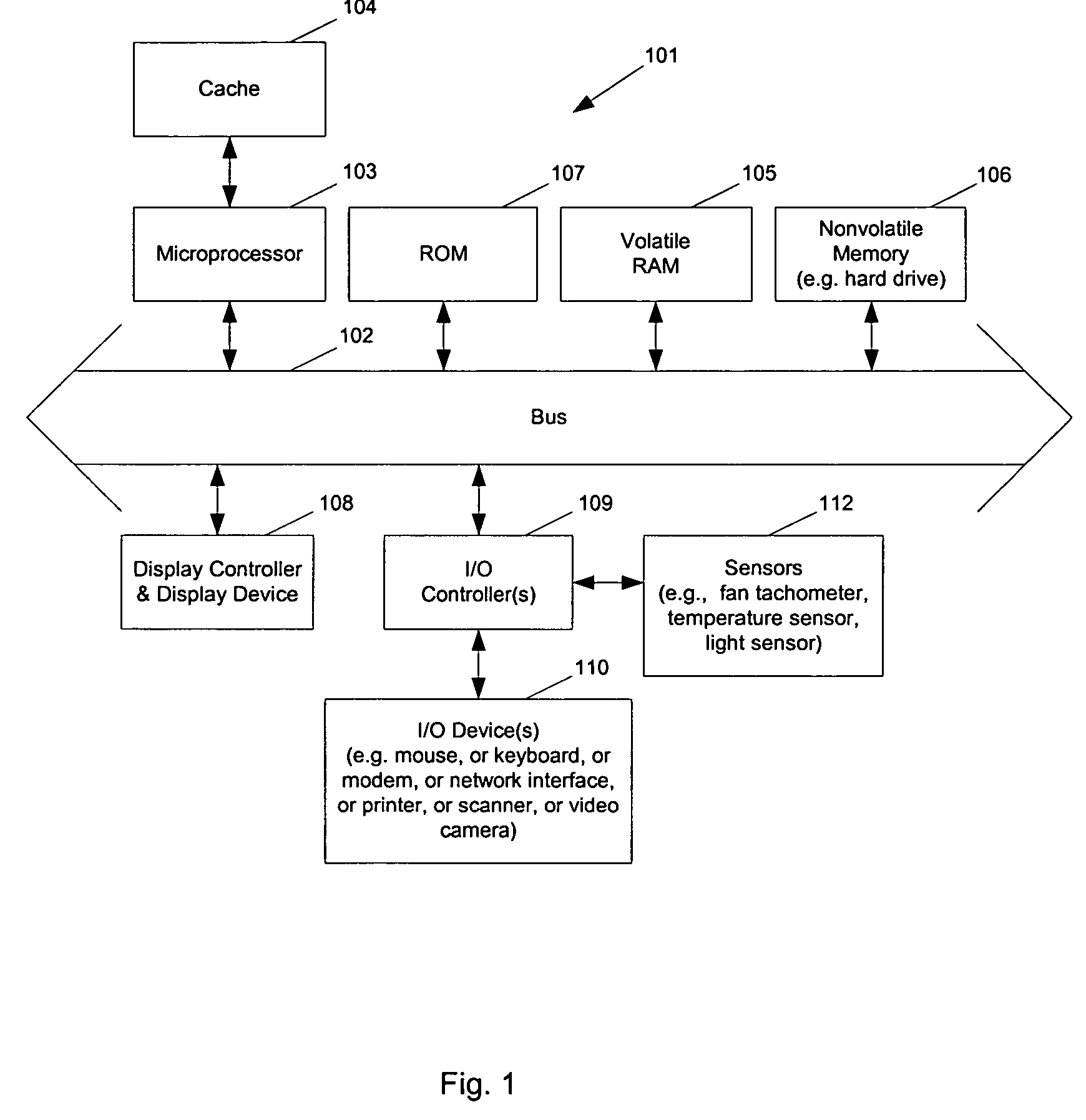
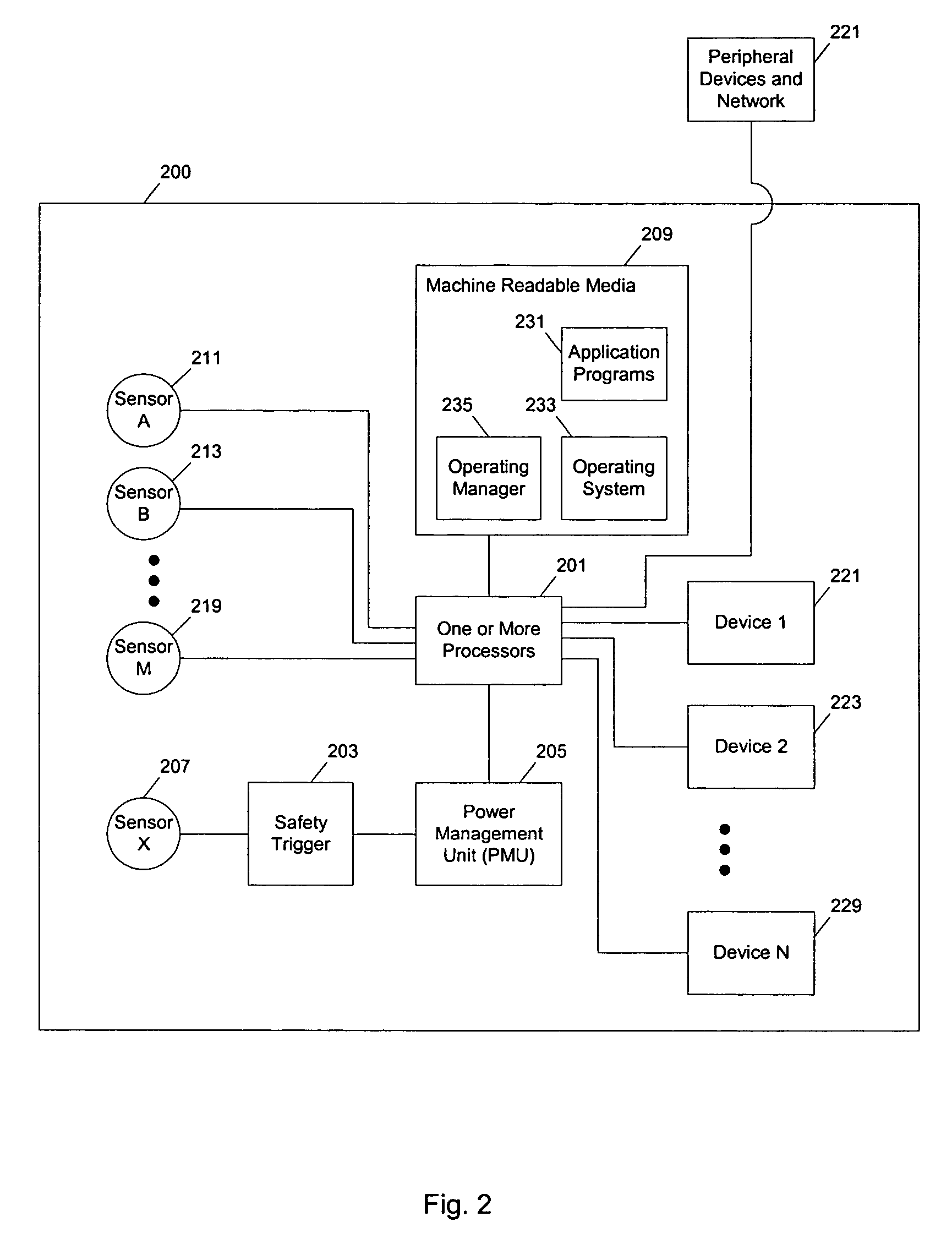
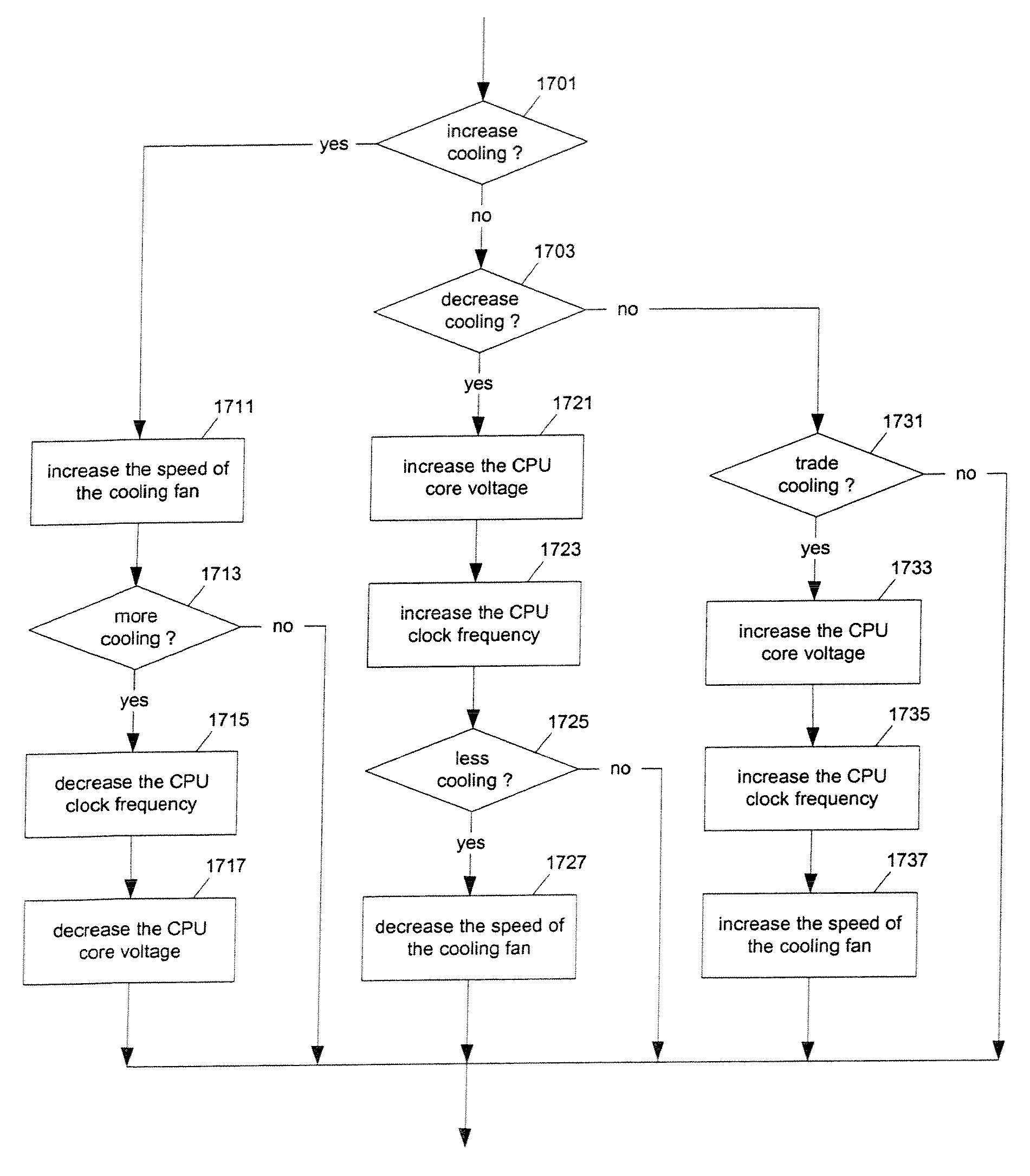
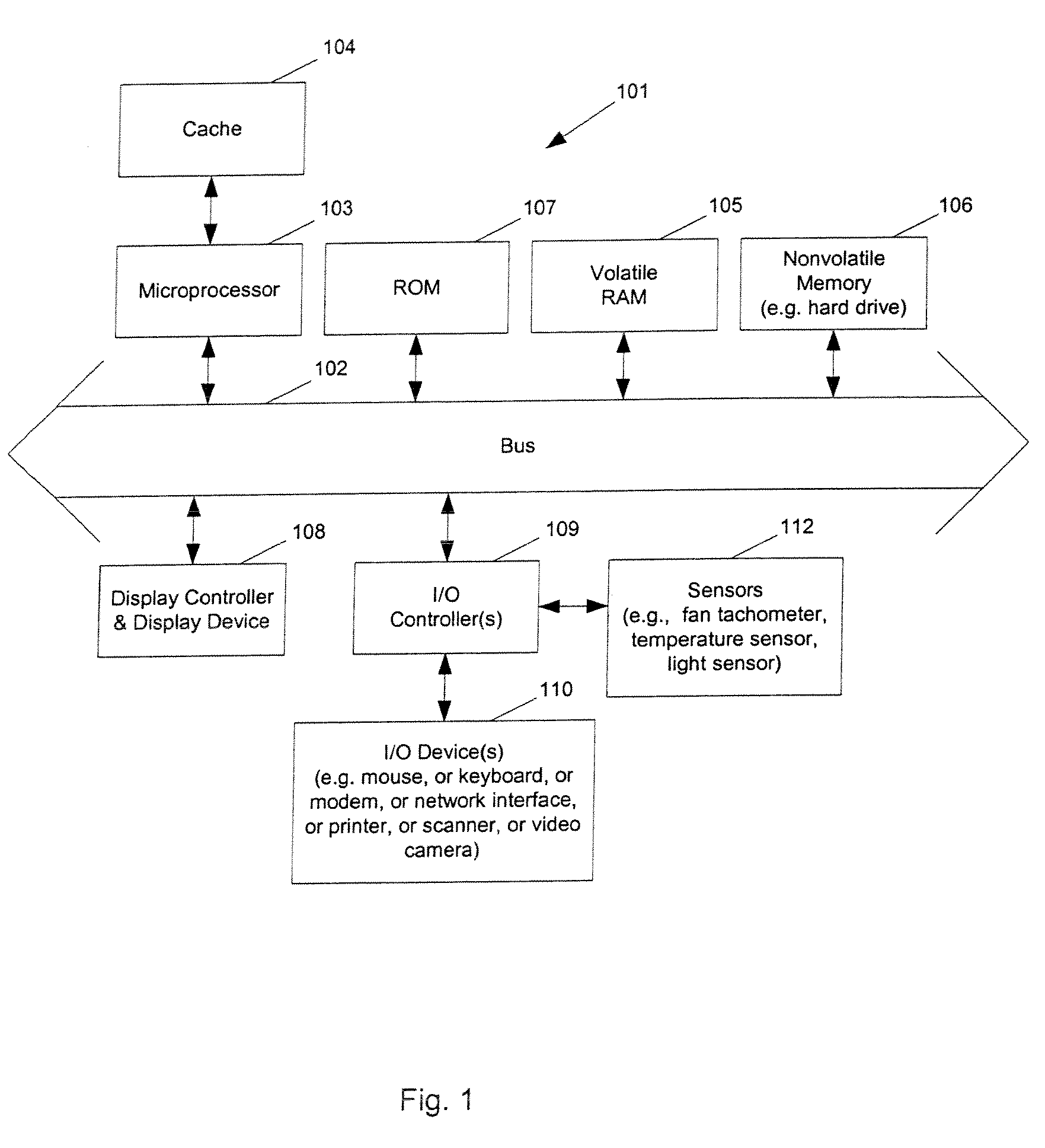
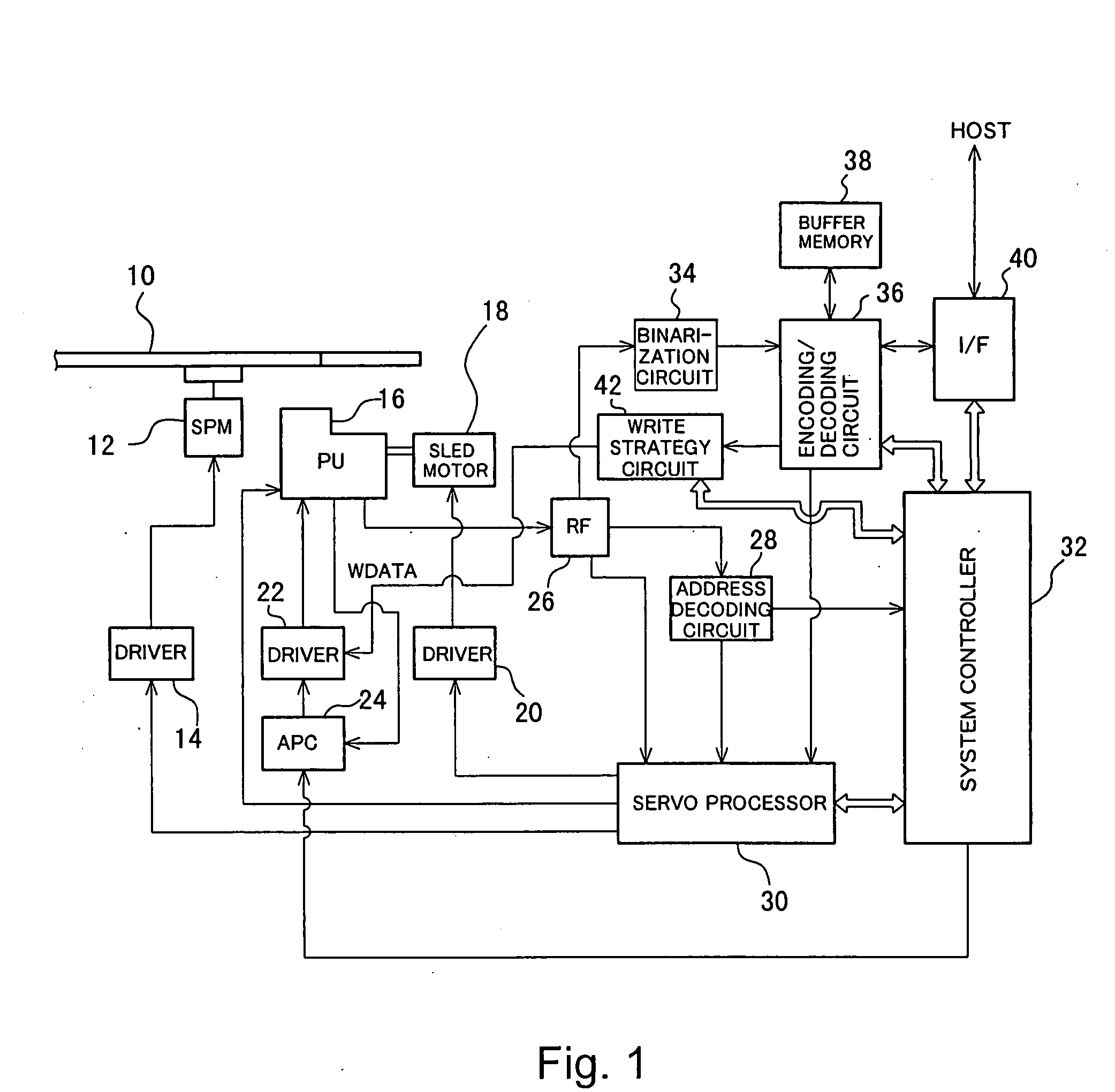
Methods and apparatuses for controlling the temperature of a data processing system
ActiveUS7451332B2Low heat generationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementHard disc driveHeat sensitive
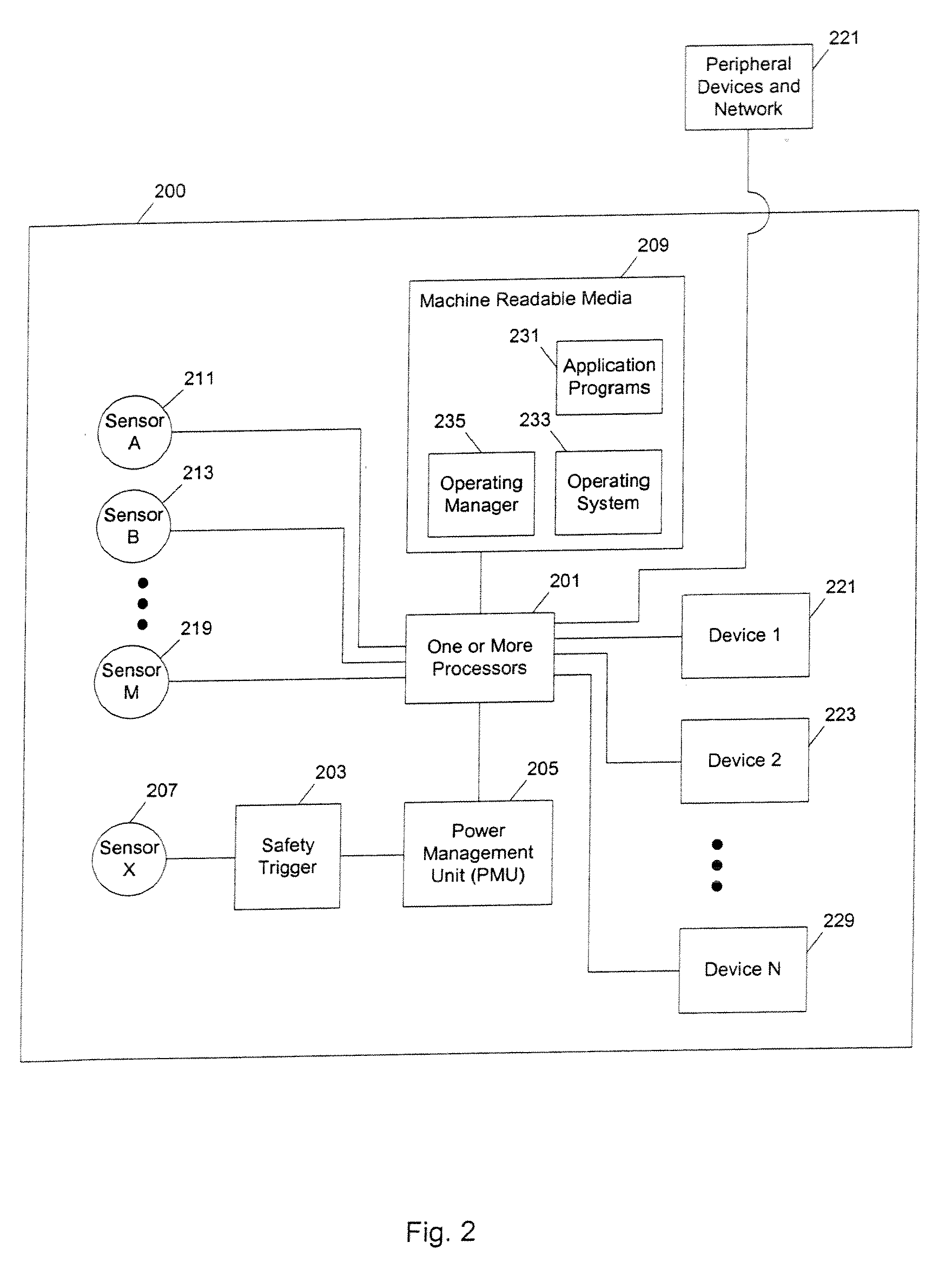
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
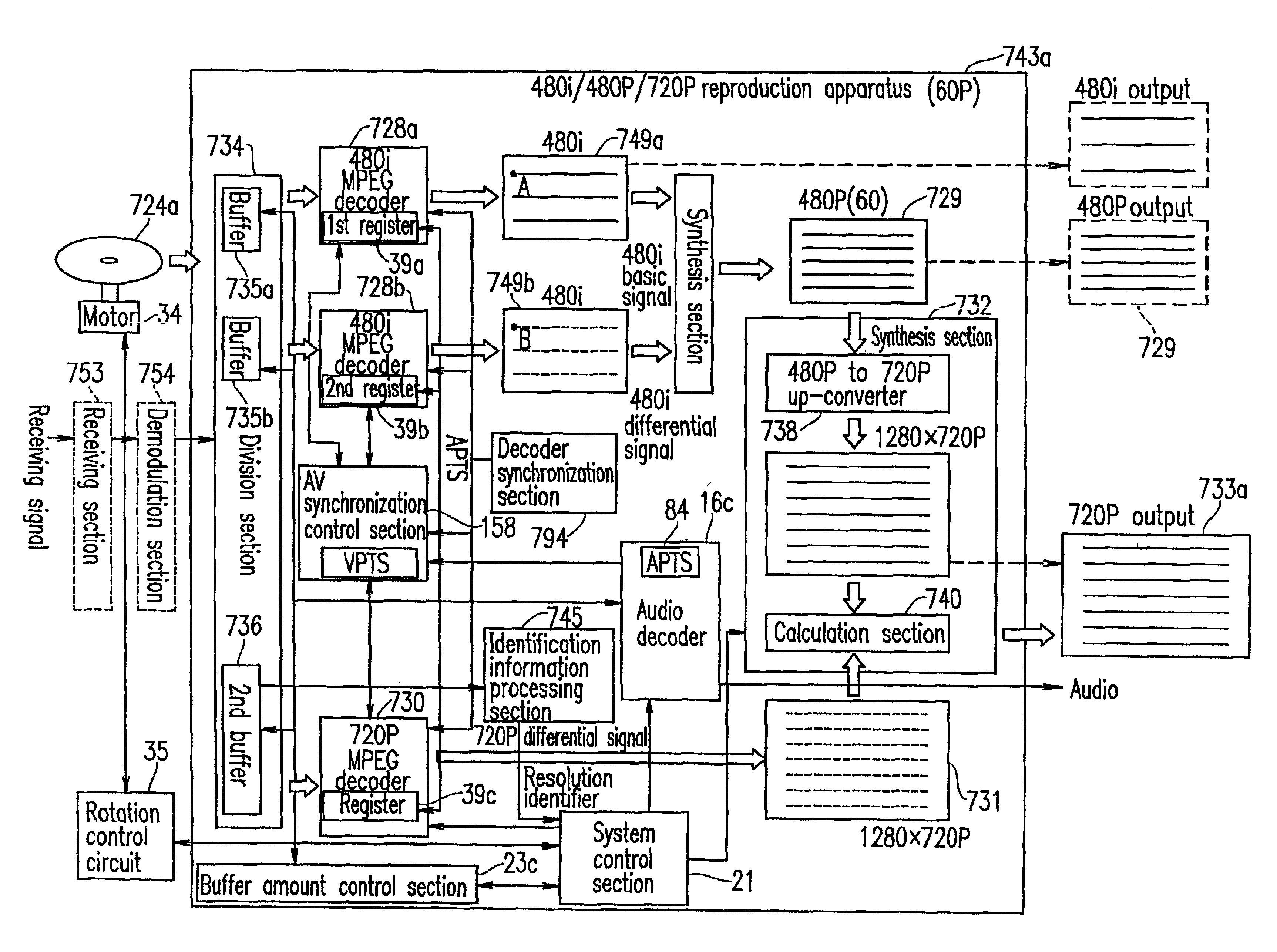
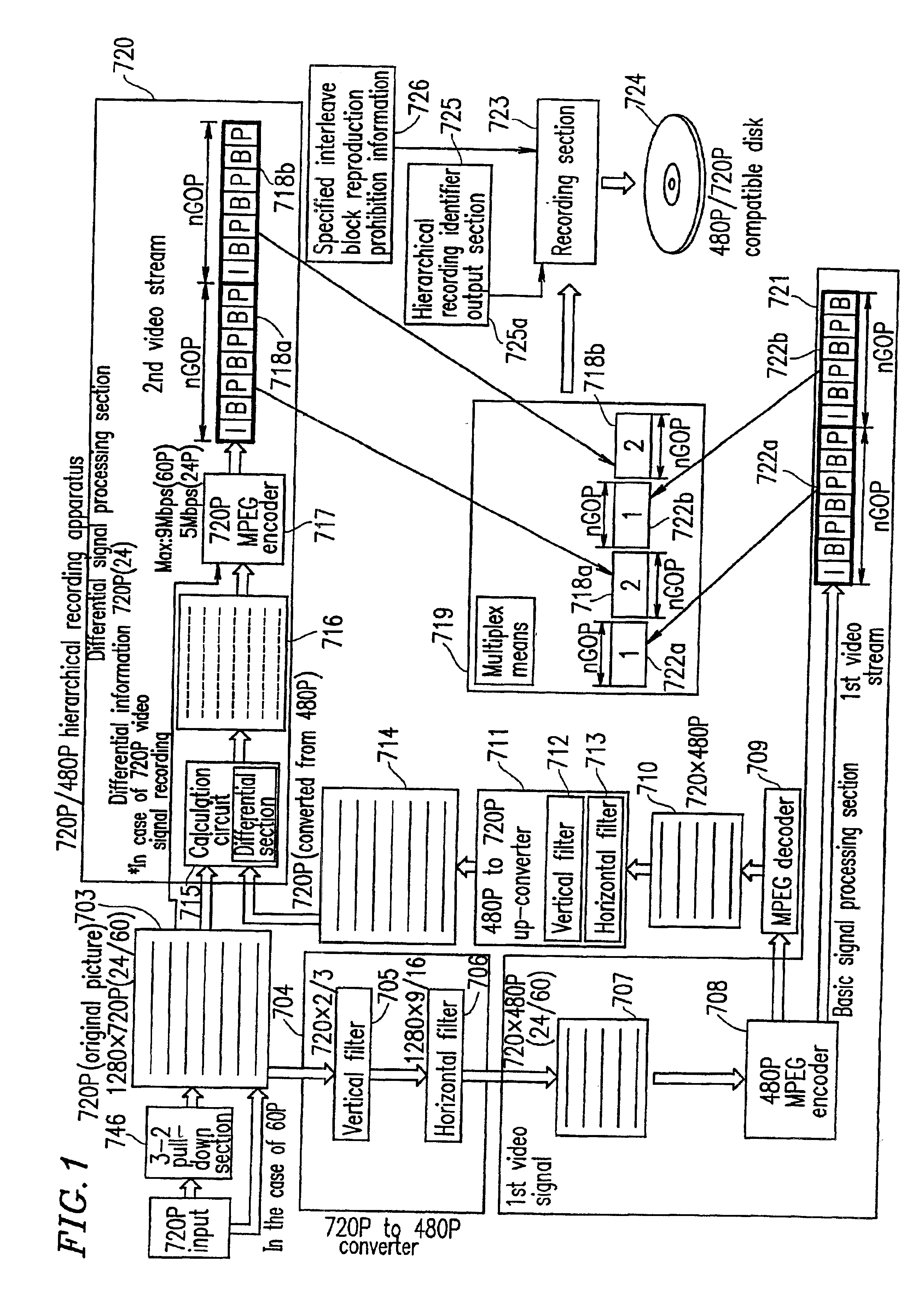
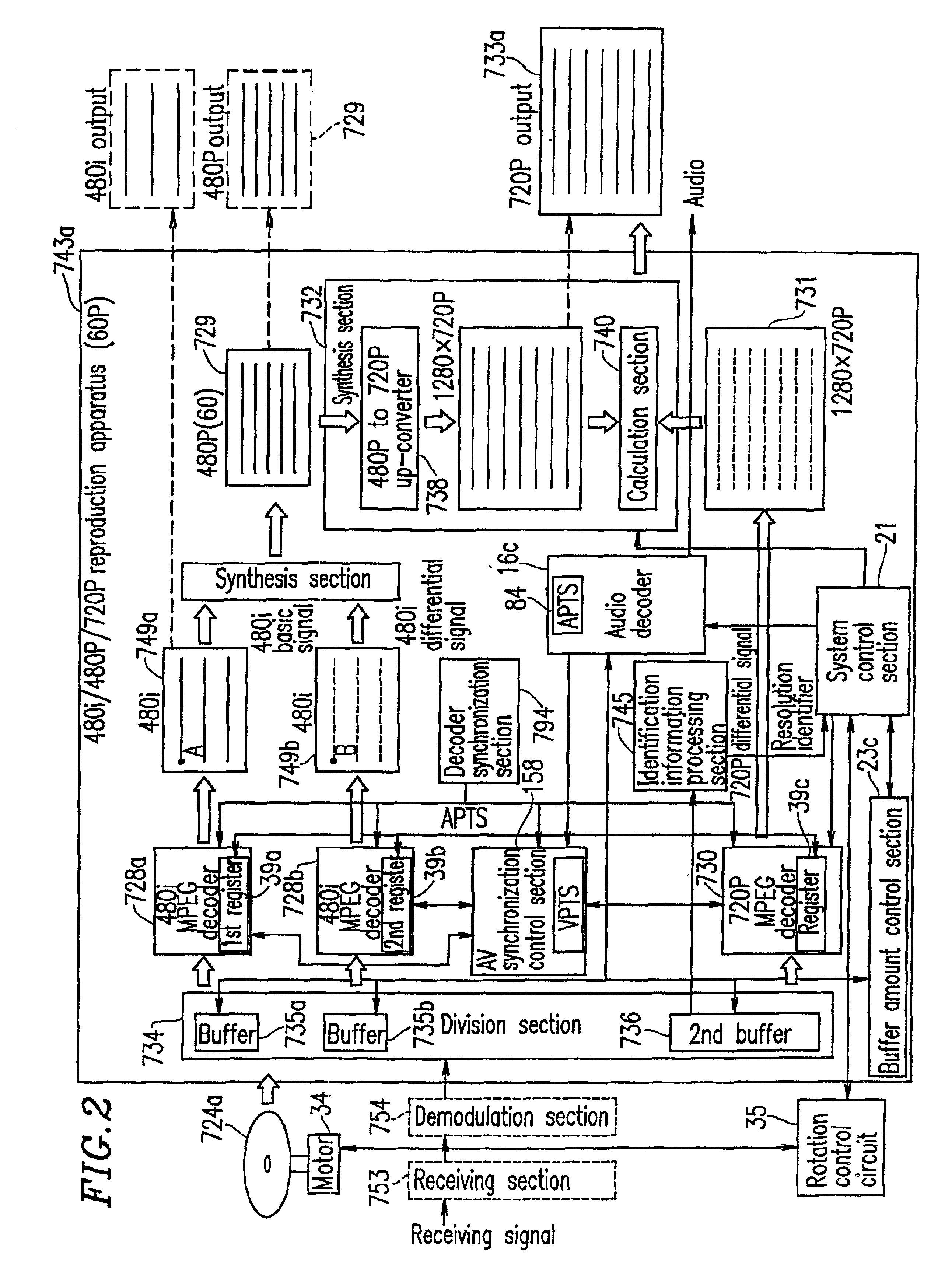
Optical disc for recording high resolution and normal image, optical disc player, optical disc recorder, and playback control information generator
InactiveUS6925250B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionMPEG encoding
The present invention has an objective of realizing compatibility of an optical disk having a high resolution video signal recorded thereon and a system for reproducing the optical disk, with a conventional system for producing a standard resolution video signal. A high resolution-video signal is divided by video division means into a main signal and a sub signal, and the main signal and the sub signal are MPEG-encoded. The stream of the main signal and the stream of the sub signal are divided into 1 GOP or more of frames. First interleave blocks 54 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the main signal and second interleave blocks 55 each including 1 GOP or more of the stream of the sub signal are recorded on an optical disk 1. A high resolution reproduction apparatus reproduces both the first and second interleave blocks to obtain a high resolution video output. A non-high quality picture reproduction apparatus reproduces only the first or second interleave blocks to obtain a standard resolution video output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatuses for operating a data processing system
ActiveUS20100117579A1Balance performanceShorten speedDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlHard disc driveThermistor
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
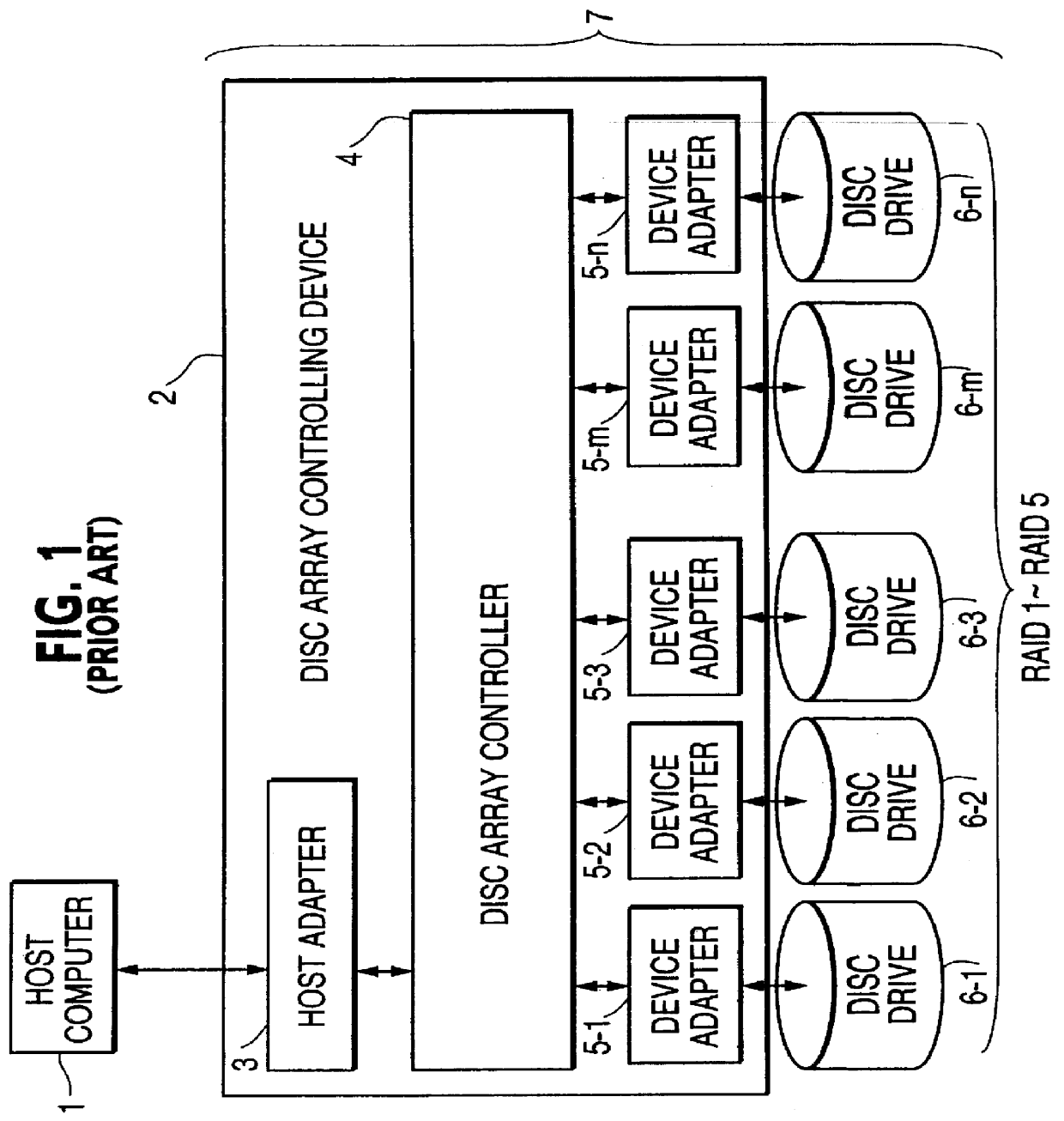
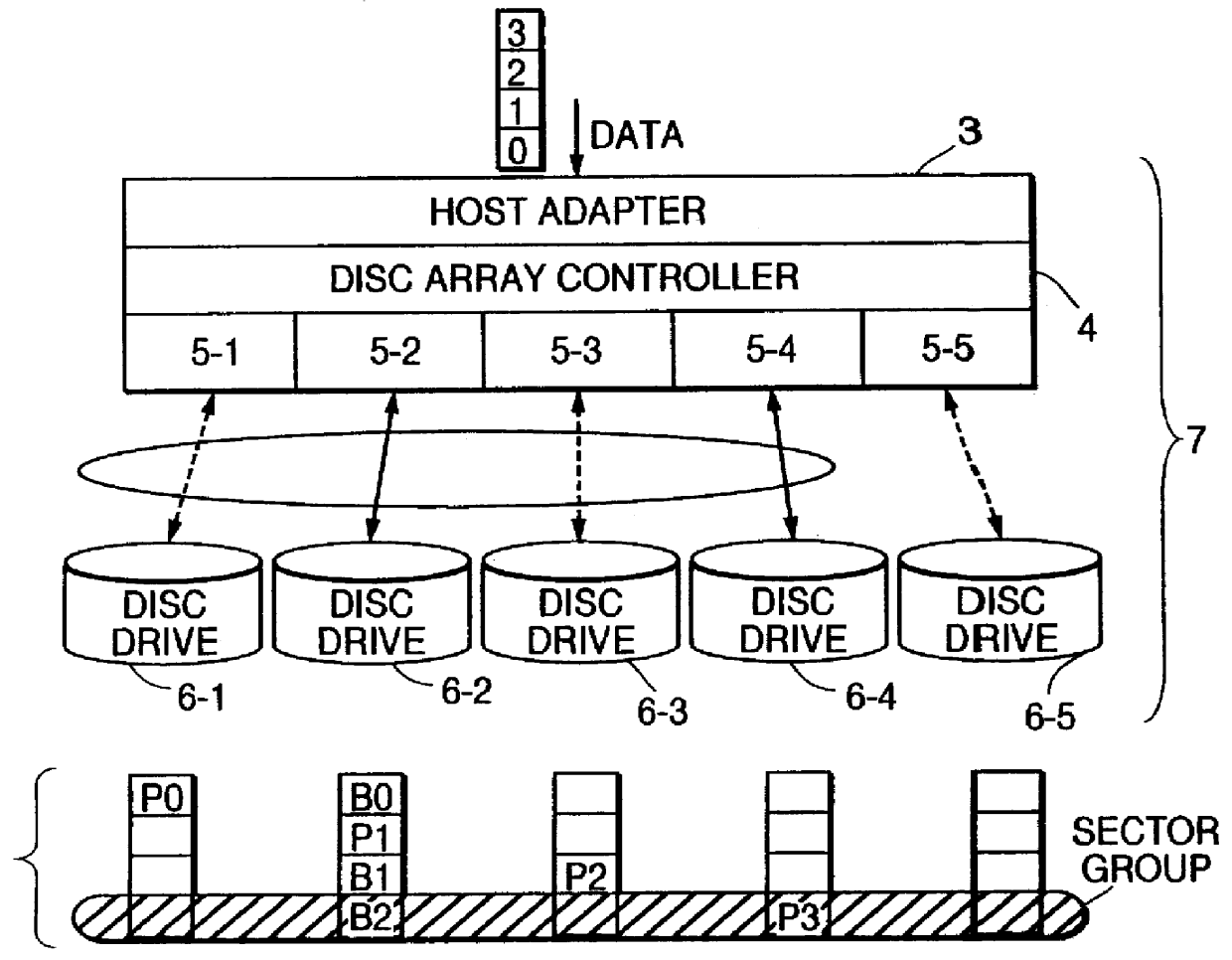
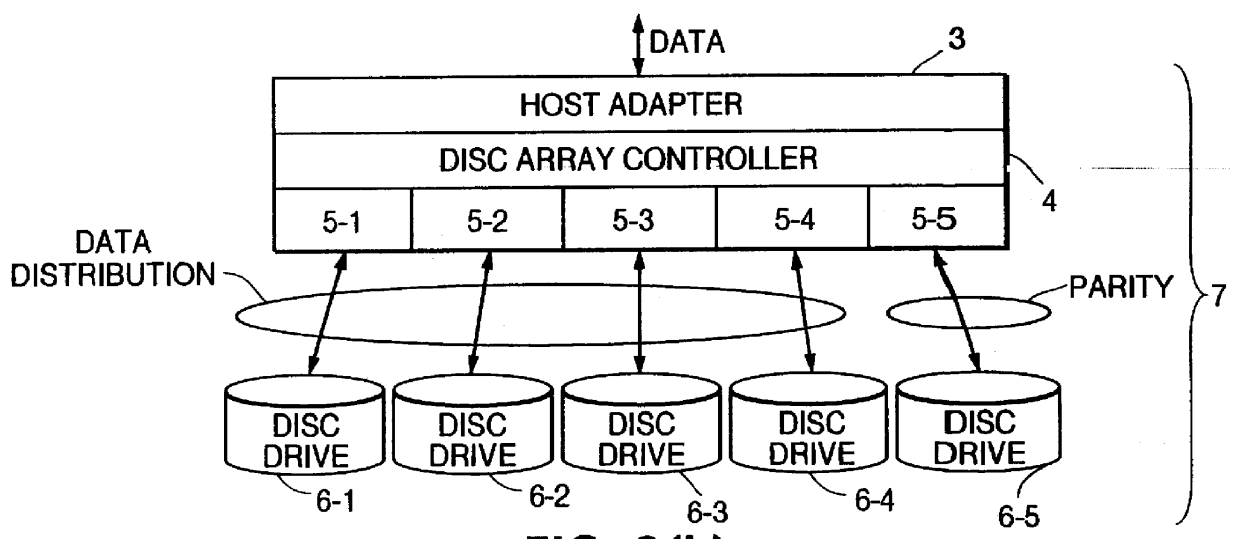
Disc array apparatus checking and restructuring data read from attached disc drives
The present invention relates to a disc array apparatus assuring that even if contradiction is detected in matching of parity data during a read parity check, correct host data is Restructured and can always be transferred to the host. The disc array apparatus of the present invention is particularly applicable to disc drives in the RAID configuration. For example, in a disc array apparatus of the present invention implementing RAID level 3, the disc array apparatus adds CRC data to data transferred from a host computer, divides the data, generates parity from the divided data, and stores the data and the parity data into the disc drives. During a read operation, the disc array apparatus of the present invention executes a read parity check. If contradiction is detected between the parity data stored in the disc drives and the parity data generated during the read parity check, the disc array controller sequentially assumes, one disc drive at a time, that one of the disc drives is storing erroneous data, restructures the host data from the divided data and parity data of the disc drives other than the disc drive storing erroneous data for each assumption, and executes a CRC check on the restructured host data for each assumption. Restructured host data is determined to be correct host data when the CRC check detects no error. The principle of the present invention is also implemented in other RAID levels, and using data such as time or counter value, to determine and restructure erroneous data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
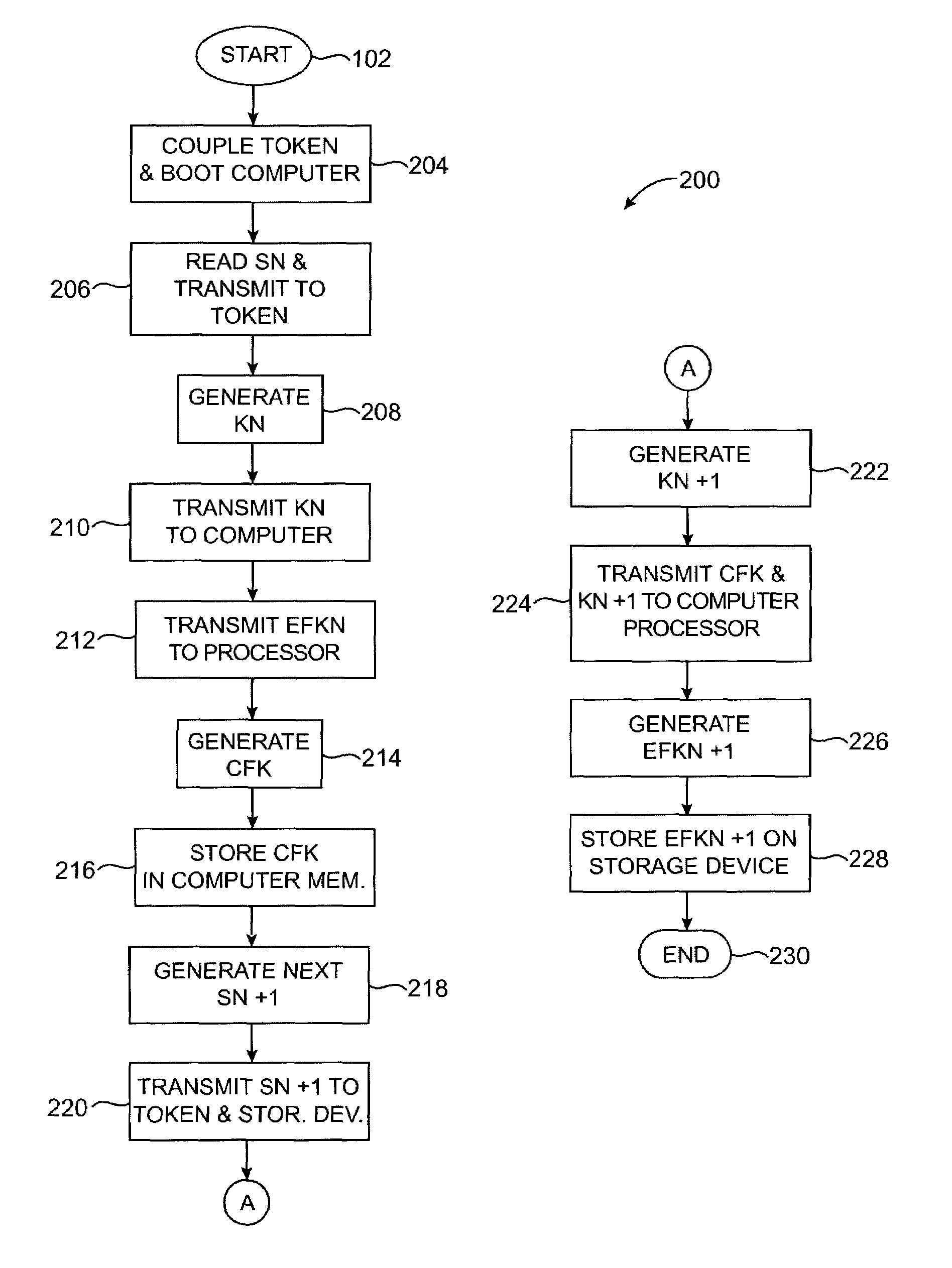
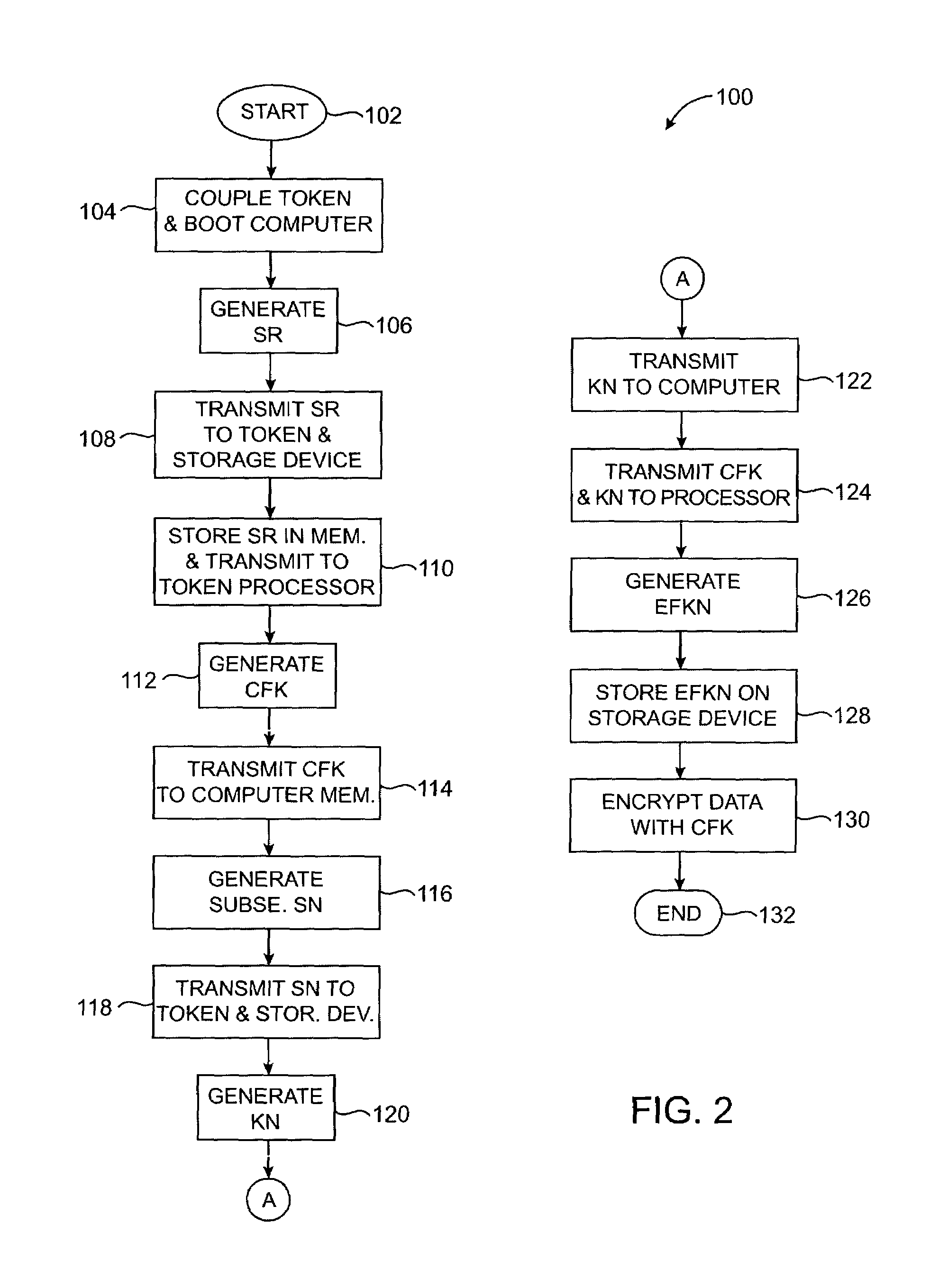
Method and system for controlling access to data stored on a data storage device
ActiveUS7191344B2Allow accessKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveData storing
A system and method of data encryption and decryption for controlling access to a data storage device such as a hard disk drive or optical drive is provided. The invented method utilizes data encryption and decryption techniques, combined with a token device, to control access to data stored on the data storage device.
Owner:AUTHENEX
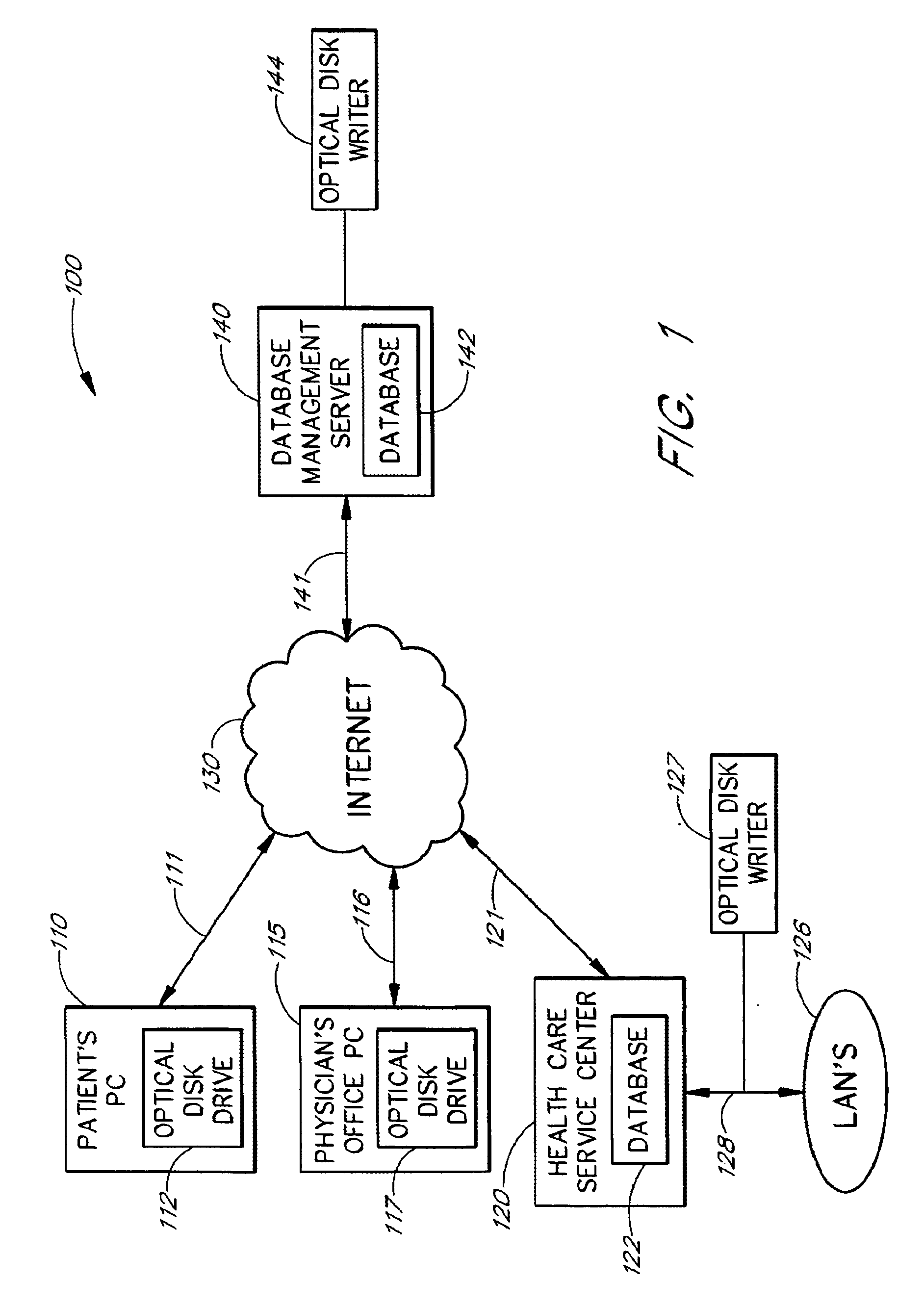
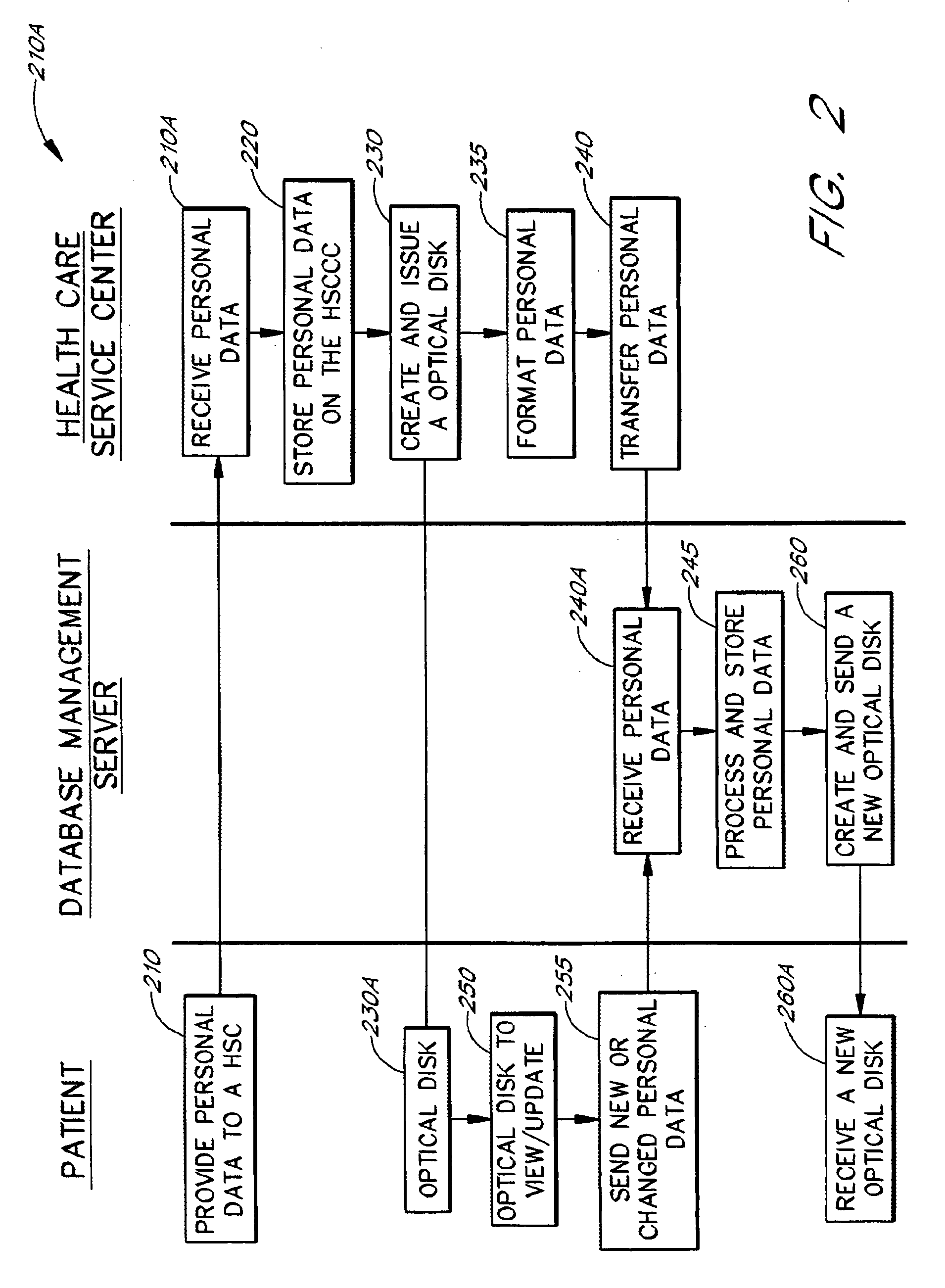
Personal information system
Owner:DATCARD SYST
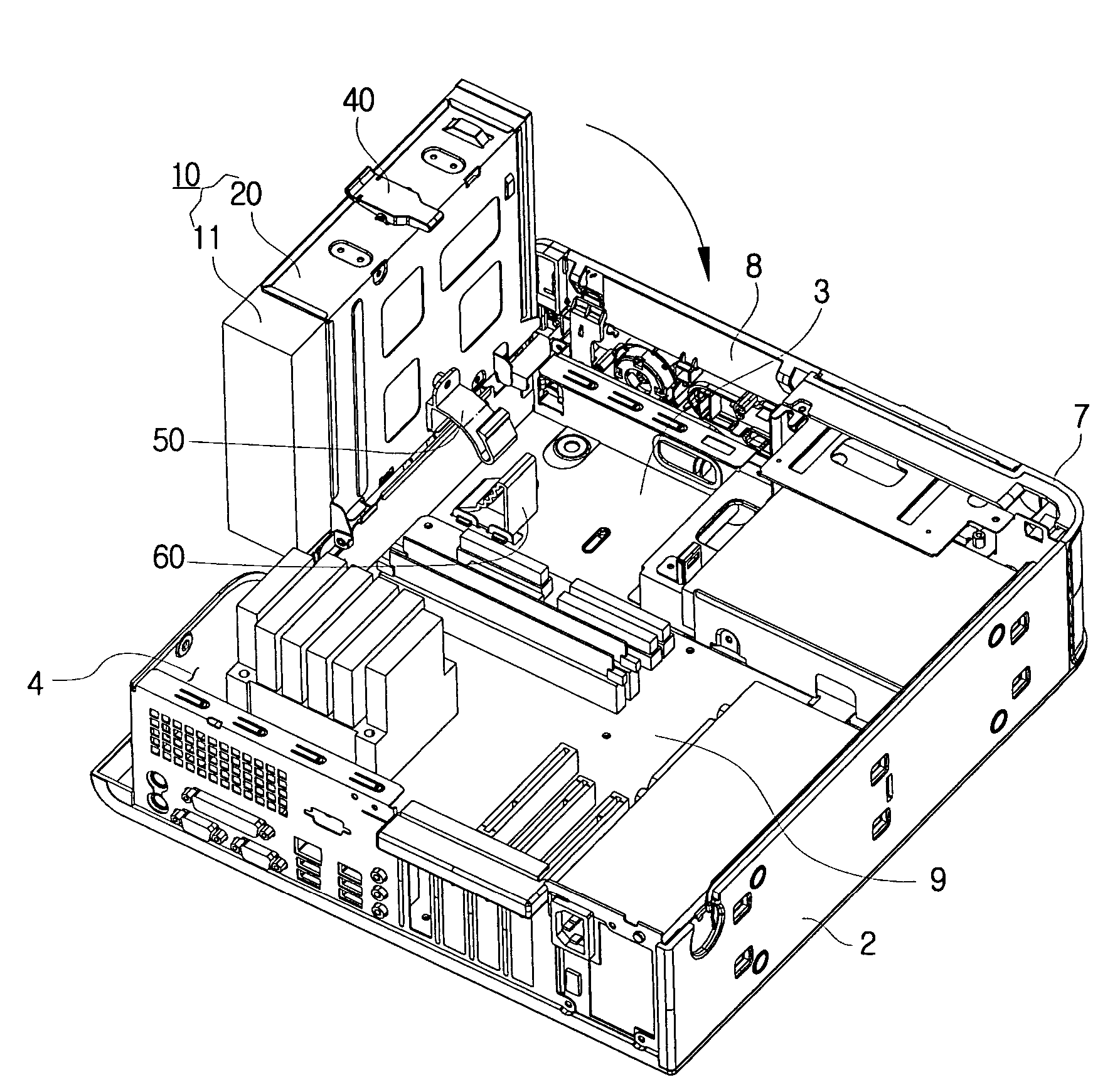
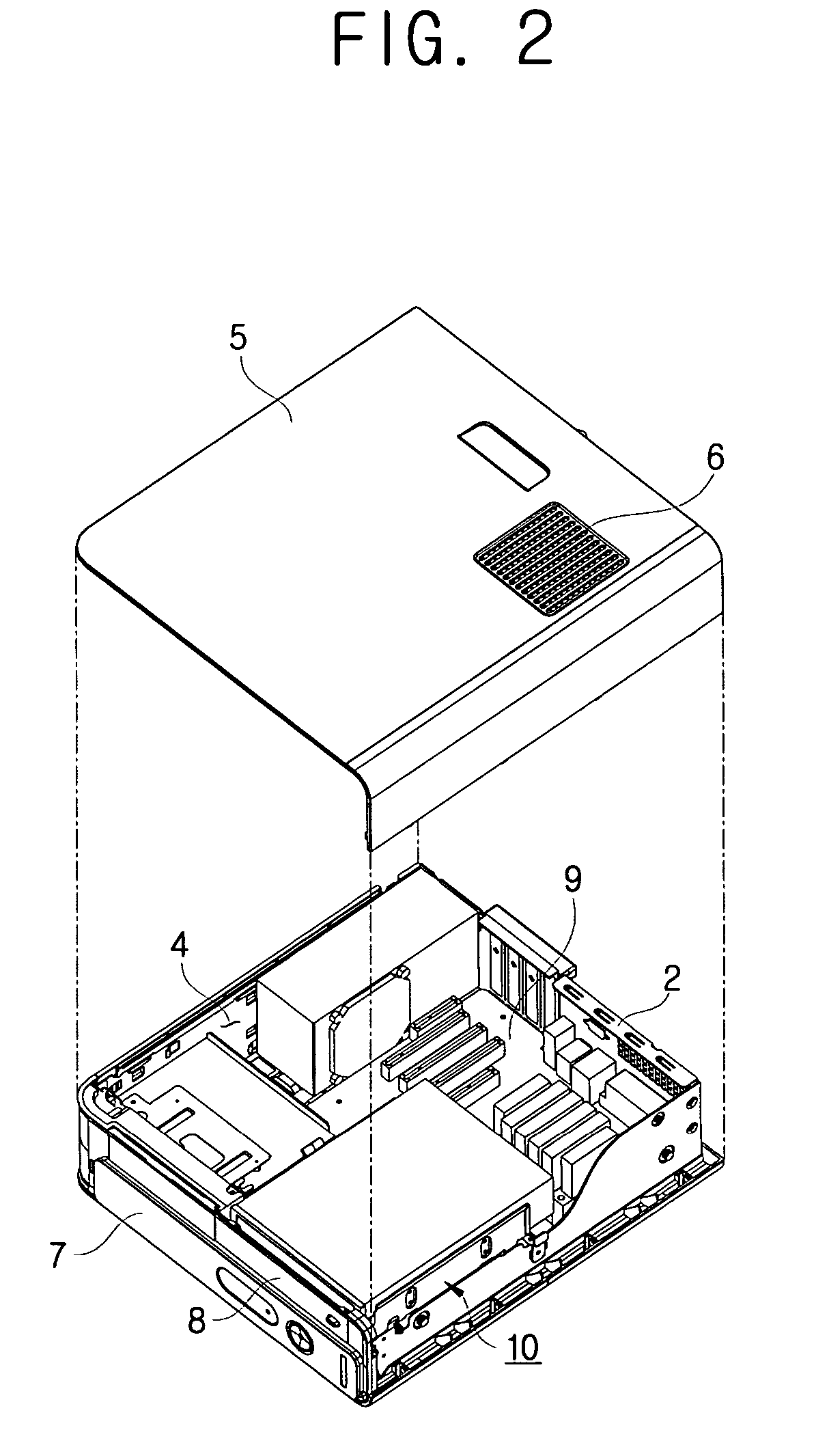
Optical disk drive assembly that is rotatable with respect to a computer casing
InactiveUS7257827B2Carrier constructional parts dispositionDigital data processing detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A computer comprising: a main body casing accommodating a plurality of hardware components and comprising an entrance opening on a first side thereof; an optical disk drive assembly combined to the main body casing to rotate relative to the main body casing; and a hinge unit provided on a side of the entrance opening of the main body casing, and supporting the optical disk drive assembly to enable the optical disk drive assembly to rotate between an accommodated position where the optical disk drive assembly is accommodated in the main body casing and an ejected position where the optical disk drive assembly is ejected out of the main body casing through the entrance opening. Such a computer is easy for disassembling and assembling when the user repairs or upgrades because an optical disk drive assembly rotates between the accommodated position and the ejected position.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
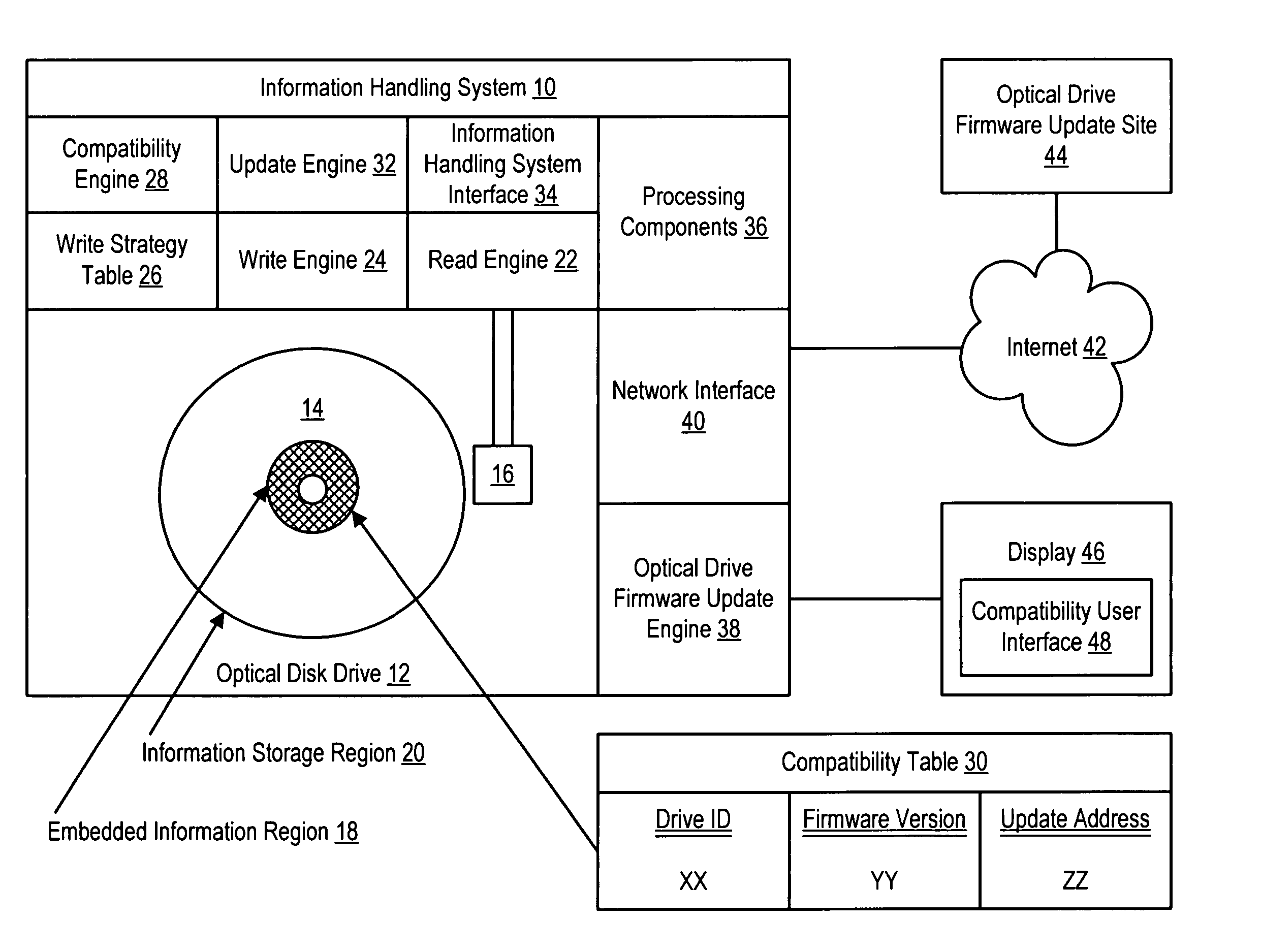
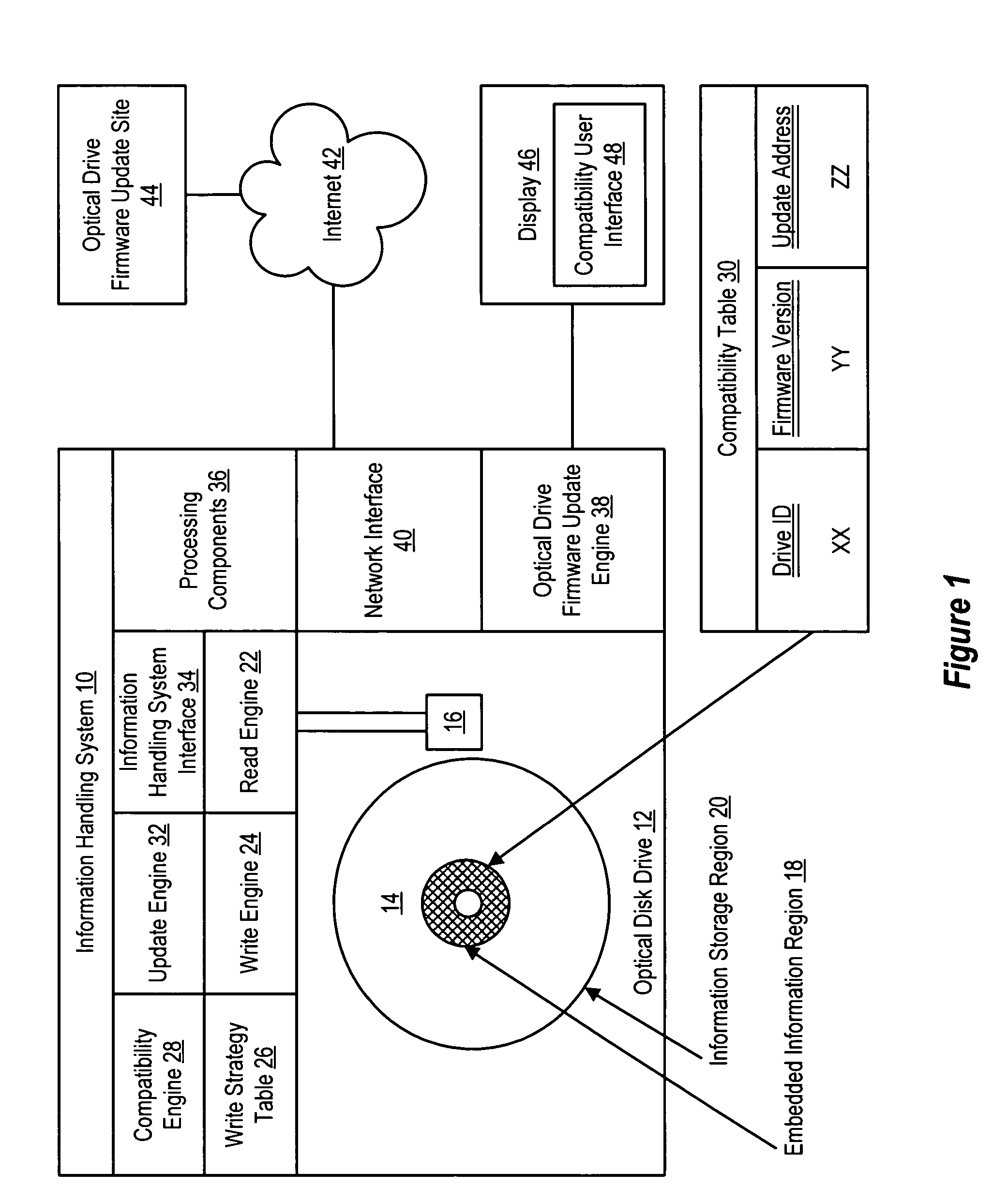
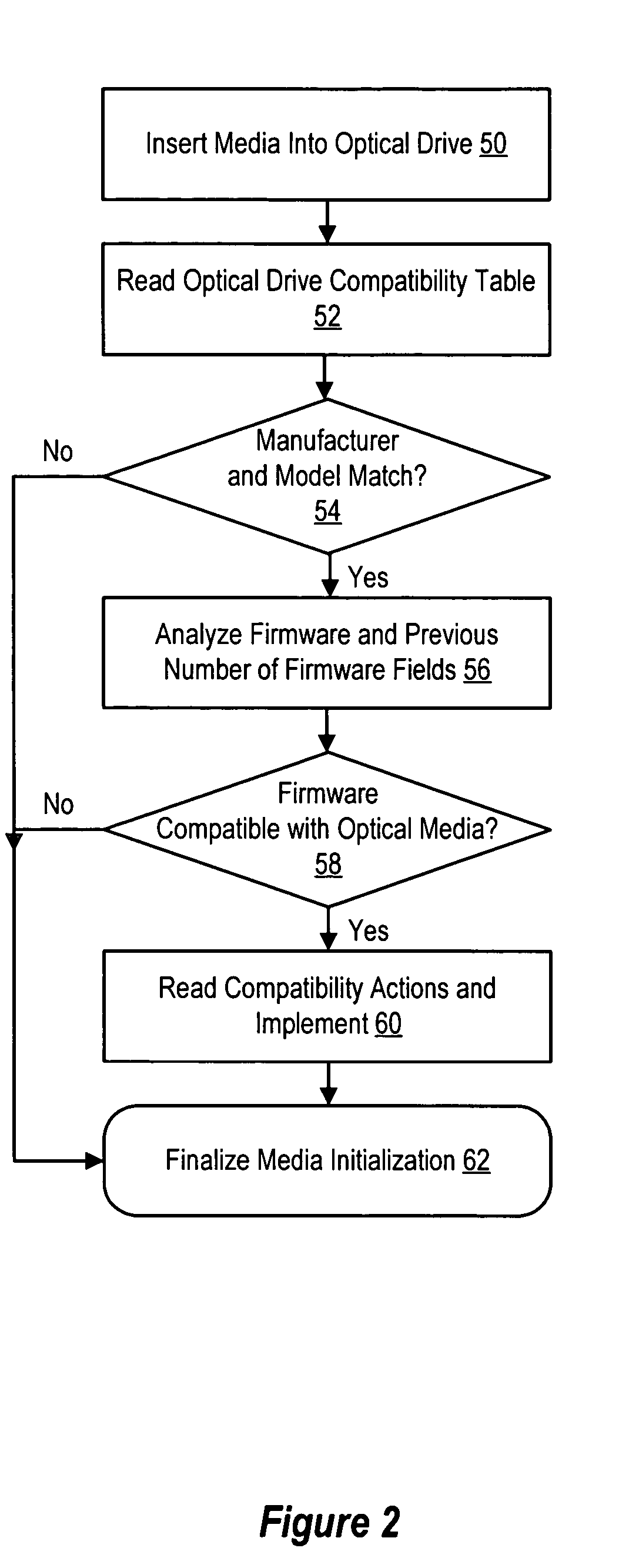
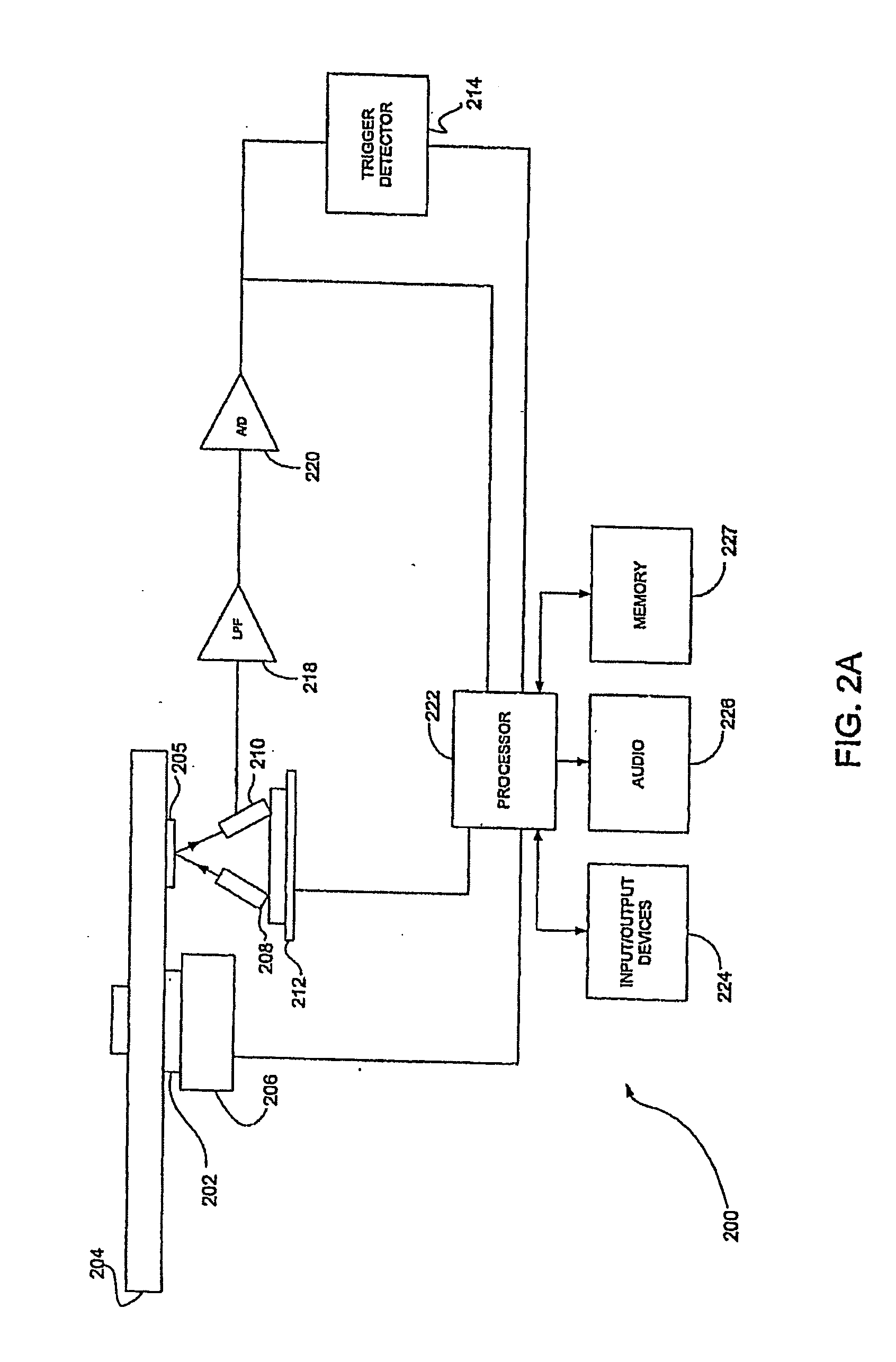
System and method for embedding optical drive compatibility information in optical media
ActiveUS7391694B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsCombination recordingRecord information storageFirmware versionComputer compatibility
Compatibility information embedded in an optical medium modifies actions allowed by predetermined non-compatible optical disc drives on the optical medium, such as optical disc drives that may suffer damage if certain actions are performed on the optical medium. For instance, a compatibility engine of the optical disc drive applies compatibility information read from an optical medium to determine restrictions to impose on the use of the optical medium, such as restricting the optical disc drive from writing to the optical medium, reading from the optical medium or performing any operations until an update to the optical disc drive firmware is performed either automatically or by display of a compatibility user interface at an information handling system associated with the optical disc drive. In one embodiment, the compatibility information identifies incompatible optical disc drives and firmware versions by unique identifiers.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +2
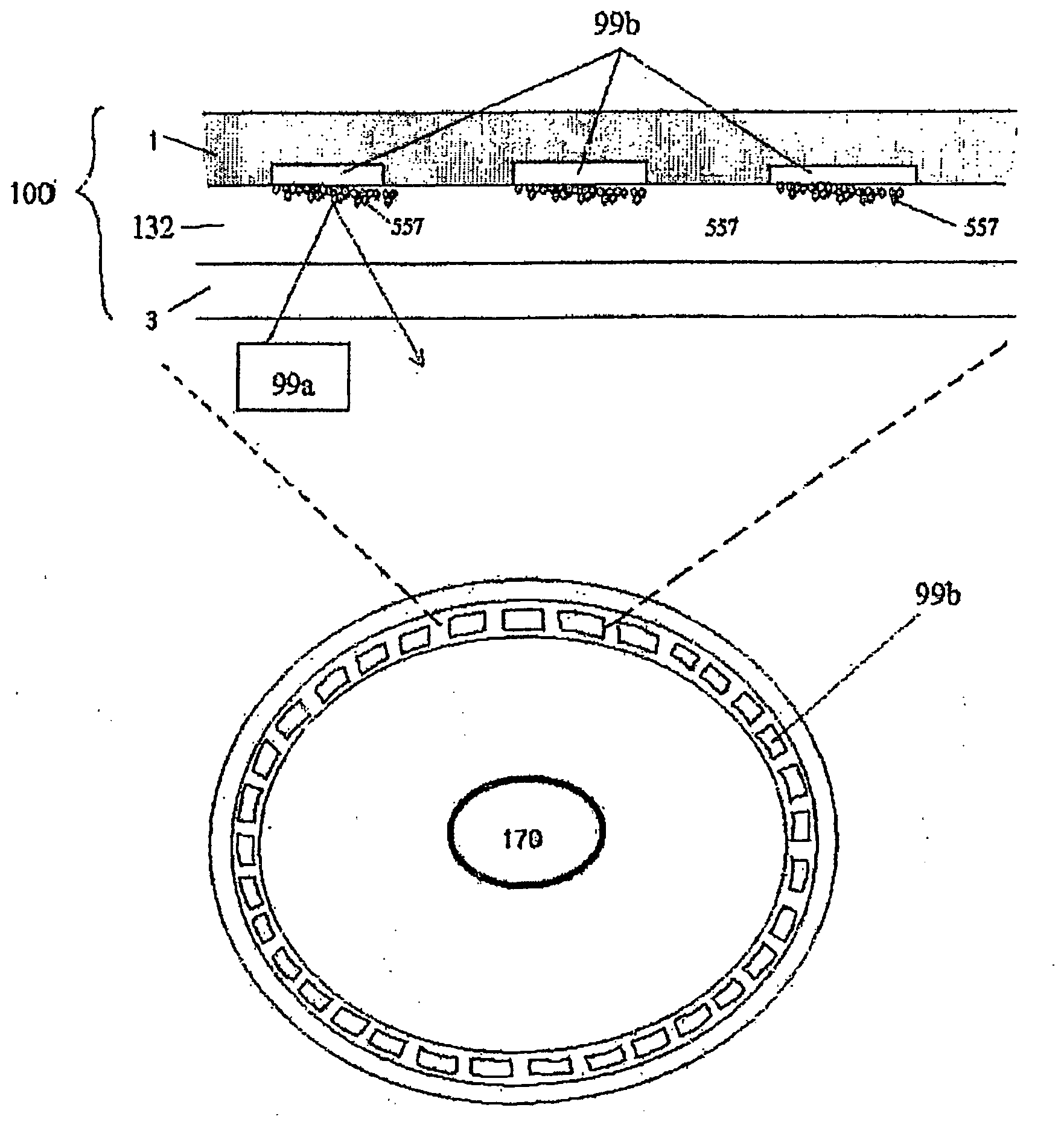
Bio disc, bio-driver apparatus, and assay method using the same
ActiveUS20100234237A1Increase surface areaHigh sensitivityValve arrangementsMicrobiological testing/measurementRecordable CDCD-ROM
A bio-disc device including new valve control means and fluid movement system, a bio-driver apparatus in which a controller disc including a controller for the bio-disc is installed, and an assay method using the same, which are suitable for labs-on-a-chips for various diagnostic assays, nucleic acid hybridization assays, and immunoassays, are provided. The bio-driver apparatus is compatible with general optical discs, including audio CDs, CD-Rs, game CDs, DVDs, etc., and the assay method is compatible with general optical disc drivers, including CD-ROMs, DVD players, etc. Thus, the bio-driver apparatus and the assay method offer and economical and convenient alternative to existing products. In addition, the bio-driver apparatus can be readily and easily applied in connection with a computer for remote diagnosis via the Internet.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
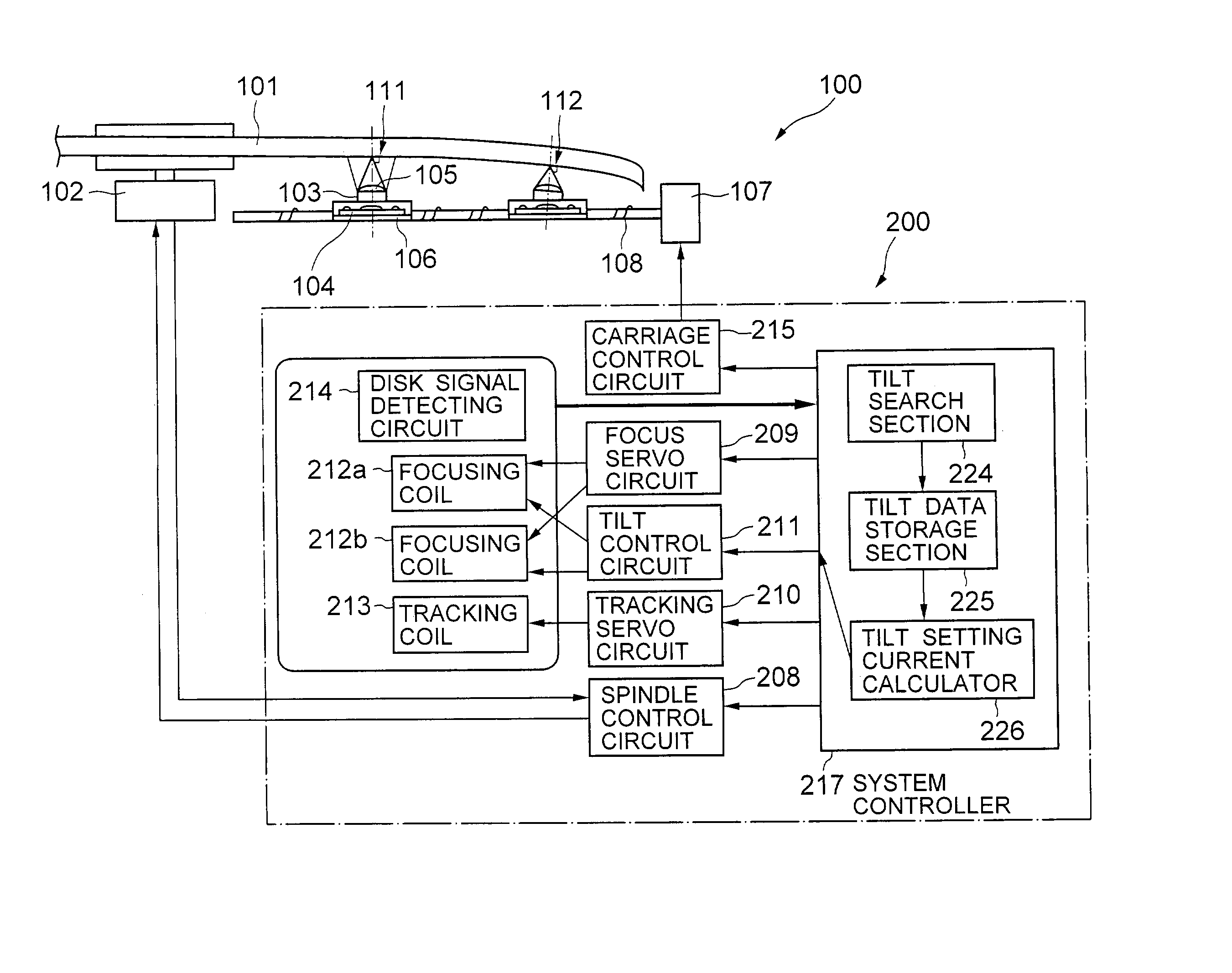
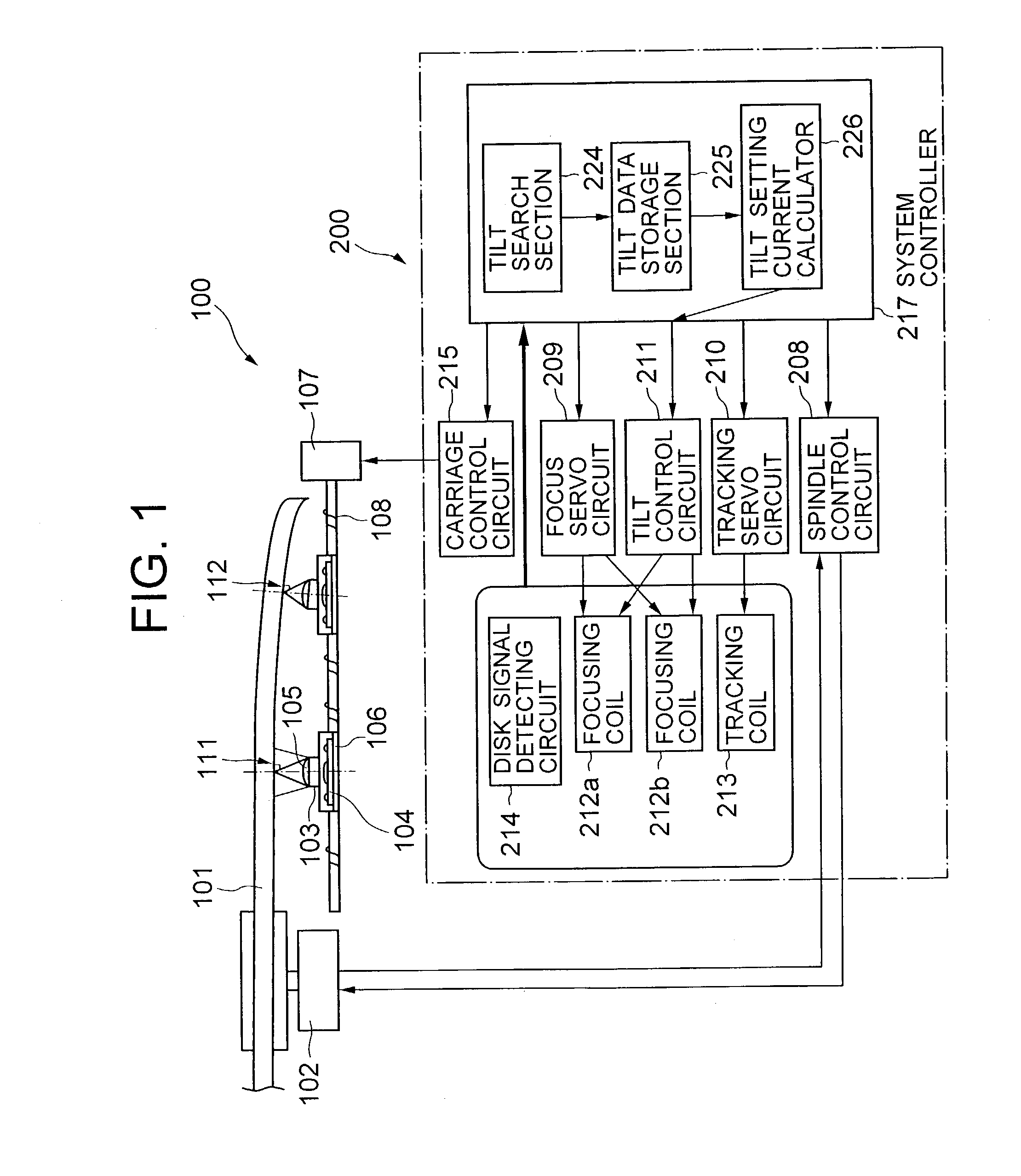
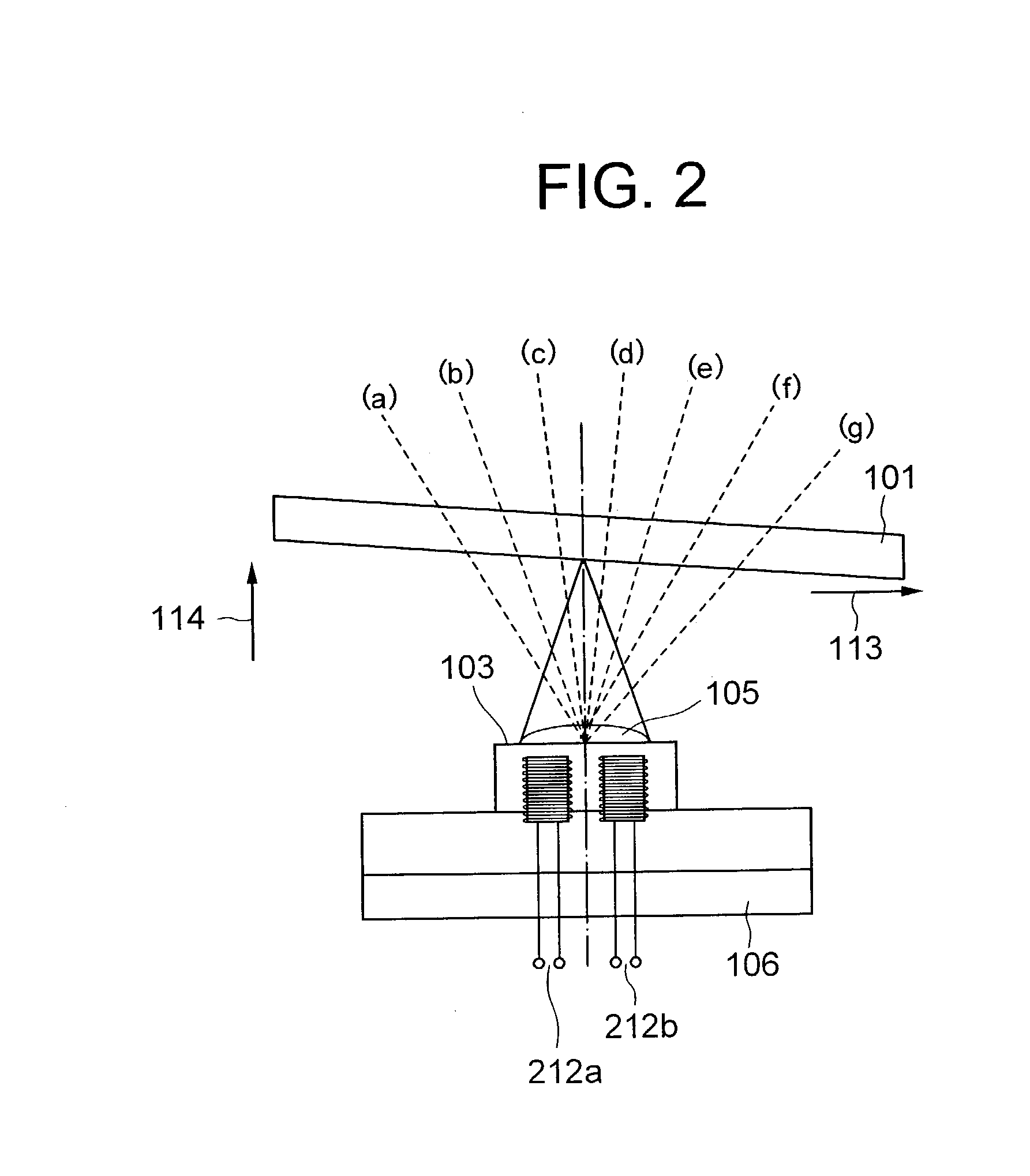
Optical disk drive having a tilt compensator
InactiveUS20030179665A1Accurate compensationCombination recordingRecord information storageRadial positionOptical disc drive
A tilt compensator in an optical disk drive detects an optimum tilt setting of the objective lens with respect to a reference plane of the optical head, which allows the optical head to obtain an optimum characteristic of a disk signal at a specified radial position of an optical disk. The optimum tilt setting is corrected at a desired track of the optical disk by using a difference between a first tilt angle of the reference plane with respect to the optical disk measured at the specified radial position and a second tilt angle of the reference plane measured at a desire track of the optical disk. The disk signal is a RF signal, a jitter of the encoded RF signal, a tracking error signal or a wobble signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical disk drive, its optical recording control method and data processing apparatus
InactiveUS6891786B2Make the starting of the recording opeIncrease speedCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsConstant linear velocityLight beam
In an optical disk drive, an OPC is performed prior to a start of recording of an optical disk by accessing a power calibration area of the disk with a light beam emitted by a light source while the disk is rotated at a constant linear velocity. An optimum recording power for the light source during the recording is determined based on results of the OPC. A highest linear velocity of linear velocities is changed to a next highest linear velocity for a controlled velocity of a disk rotation device during a subsequent OPC. It is detected whether the OPC and the determination are normally performed after one of the linear velocities is set. The controlled velocity during the recording is set to an angular velocity corresponding to the one of the linear velocities at which the OPC and the determination are normally performed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Slim type optical disc drive
InactiveUS6910218B2Easy to carryEasy constructionCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersOptical pickupPrinted circuit board
In a slim type optical disc drive, an optical pickup unit and an optical pickup transport assembly are installed on a main base disposed in a housing having a lower case and an upper case. A spindle motor is mounted on a tray so as to slide in and out of the housing. A spindle motor printed circuit board is mounted on the tray, and a main printed circuit board is fixed to the lower case. A flexible printed circuit connects the spindle motor and main printed circuits boards. The tray includes a table which supports the spindle motor, and side frame bars located at sides of the tray and spaced apart from the table. A pair of guide ribs are arranged in the housing to guide the movement of the table. In the slim type optical disc drive, only the spindle motor is disposed on the tray.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for improved seek performance and stability in a header-included land/groove optical disc
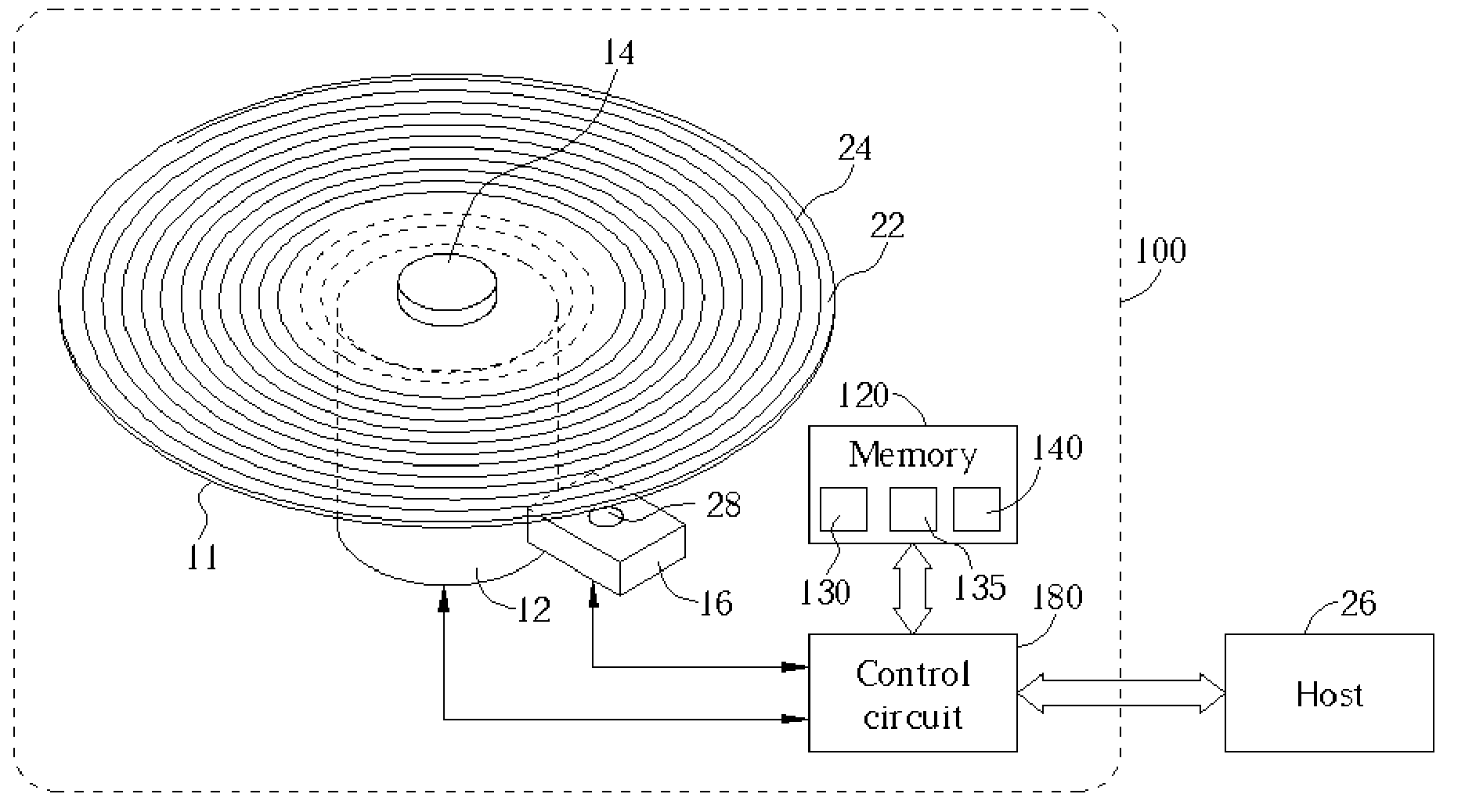
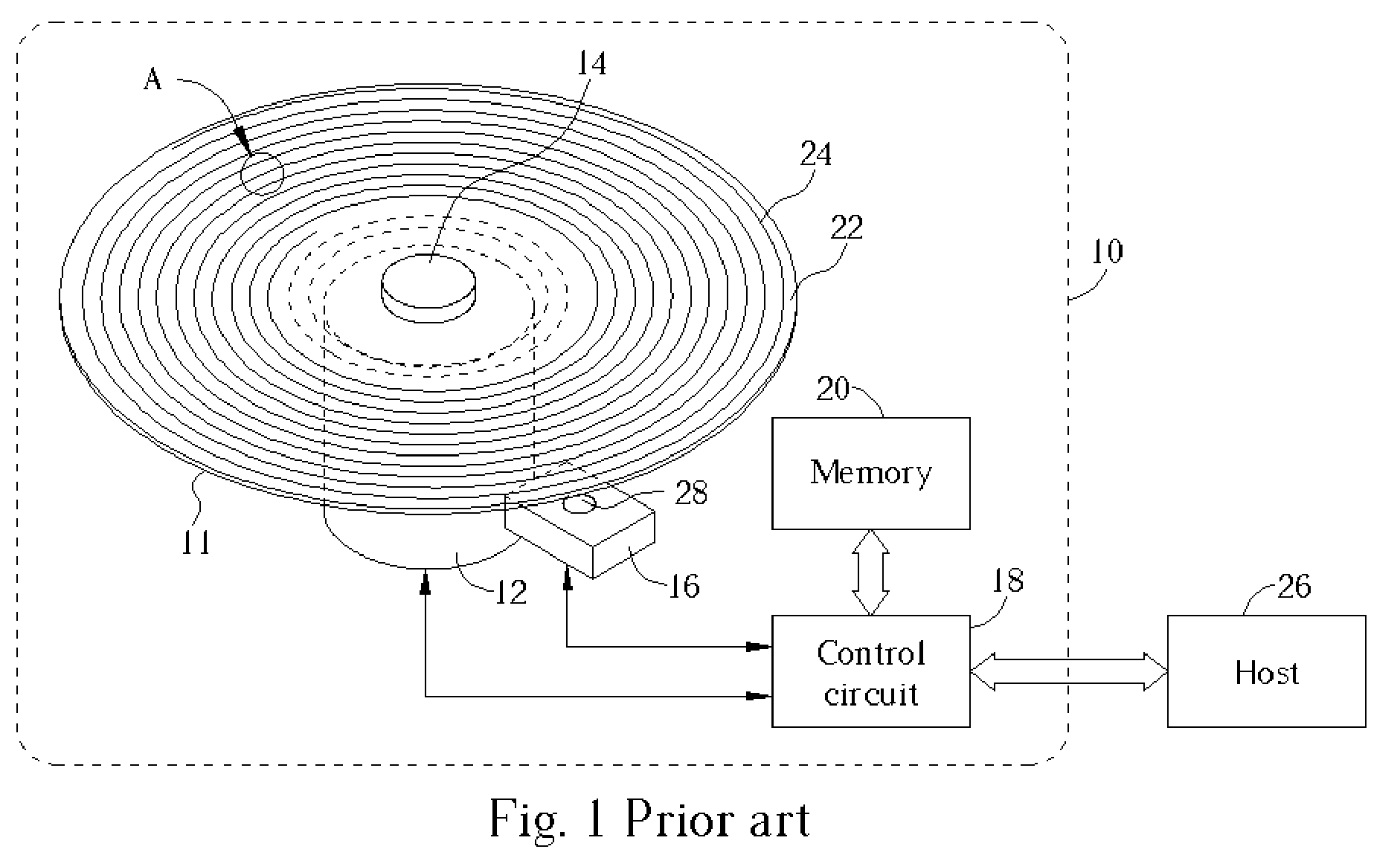
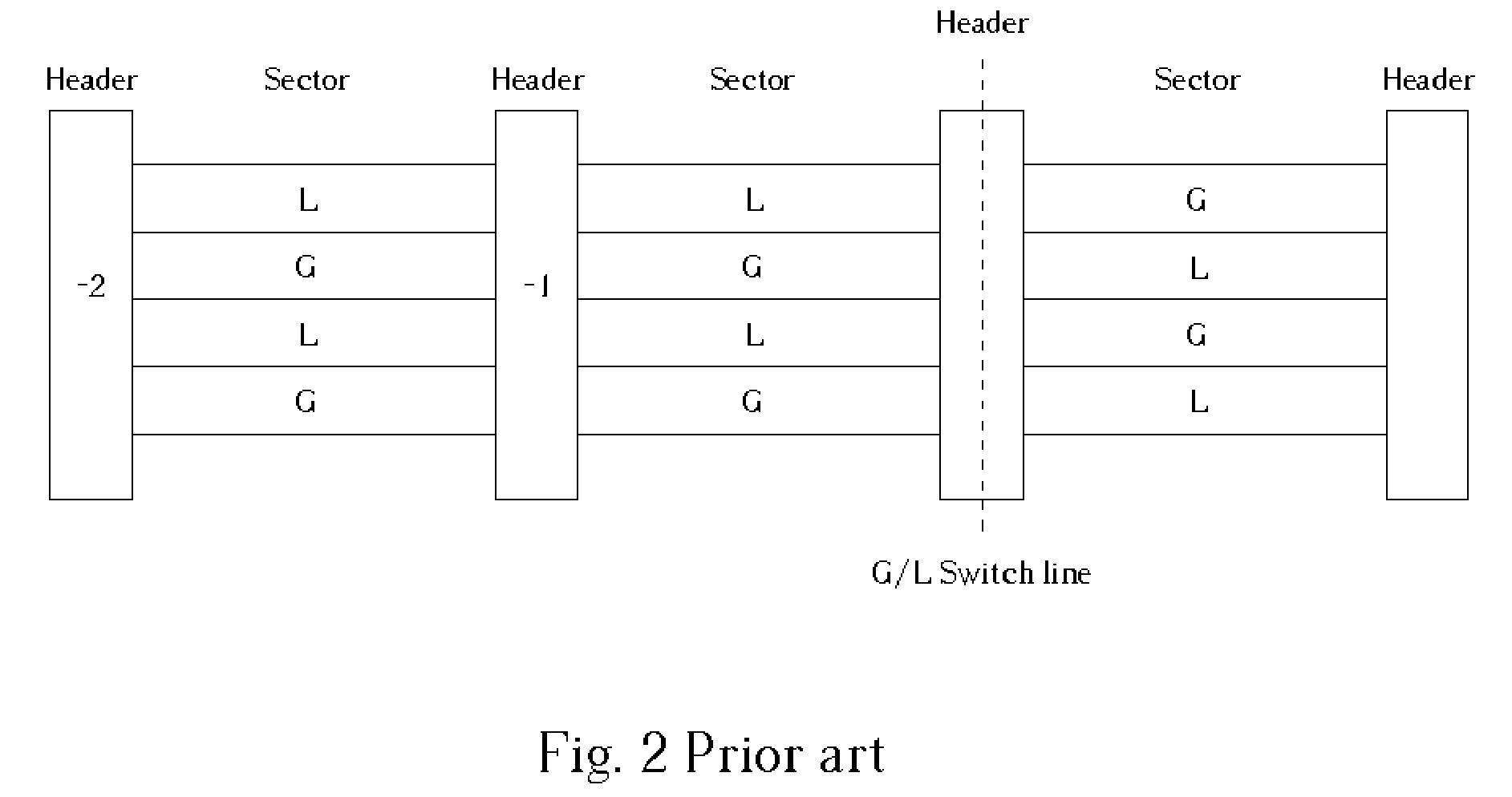
InactiveUS20050157603A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityRecord information storageGroove/land recordingEngineeringControl circuit
An optical disc drive utilized for transferring data to and / or from a header-included land / groove optical disc includes a motor, a spindle, a focusing lens, a laser, a pickup head, a memory, and a control circuit. A header position signal is utilized as a mask to eliminate false track readings produced by passing headers in a track count signal, improving track count and allowing more precise control over the accelerative and braking radial forces applied to the pickup head during a jump. Additionally, the memory includes computer code to delay initiating and / or ending a jump when passing headers may interfere with normal seek operations and may prevent some jumps in the immediate vicinity of an upcoming G / L Switch Line.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Arrangement of subtrays in a main tray of an optical disc drive apparatus
InactiveUS6031811ARecord information storageOptical recording/reproducingEngineeringOptical disc drive
An optical disc drive apparatus including a main tray having a stack of subtrays mounted thereon and movable between withdrawn and inserted positions. When the main tray is moved to the inserted position, the subtrays stacked thereon are held at a stand-by position and a selected one of the subtrays is ready to be drawn towards a loaded position so that an optical disc resting on the selected one of the subtrays can be clamped in position and optically read out. When an optical disc resting on one of the subtrays other than the uppermost subtray then held at the loaded position is desired to be removed or replaced, not only can such one of the subtray be returned from the loaded position to the stand-by position, the main tray is allowed to withdraw from the inserted position back to the withdrawn position carrying such one of the subtrays and the subtray or subtrays positioned immediately thereabove while leaving the subtray or the subtrays positioned above such one of the subtrays at the stand-by position, so that such one of the subtrays can readily be exposed to the outside for removal or replacement of the optical disc resting thereon.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
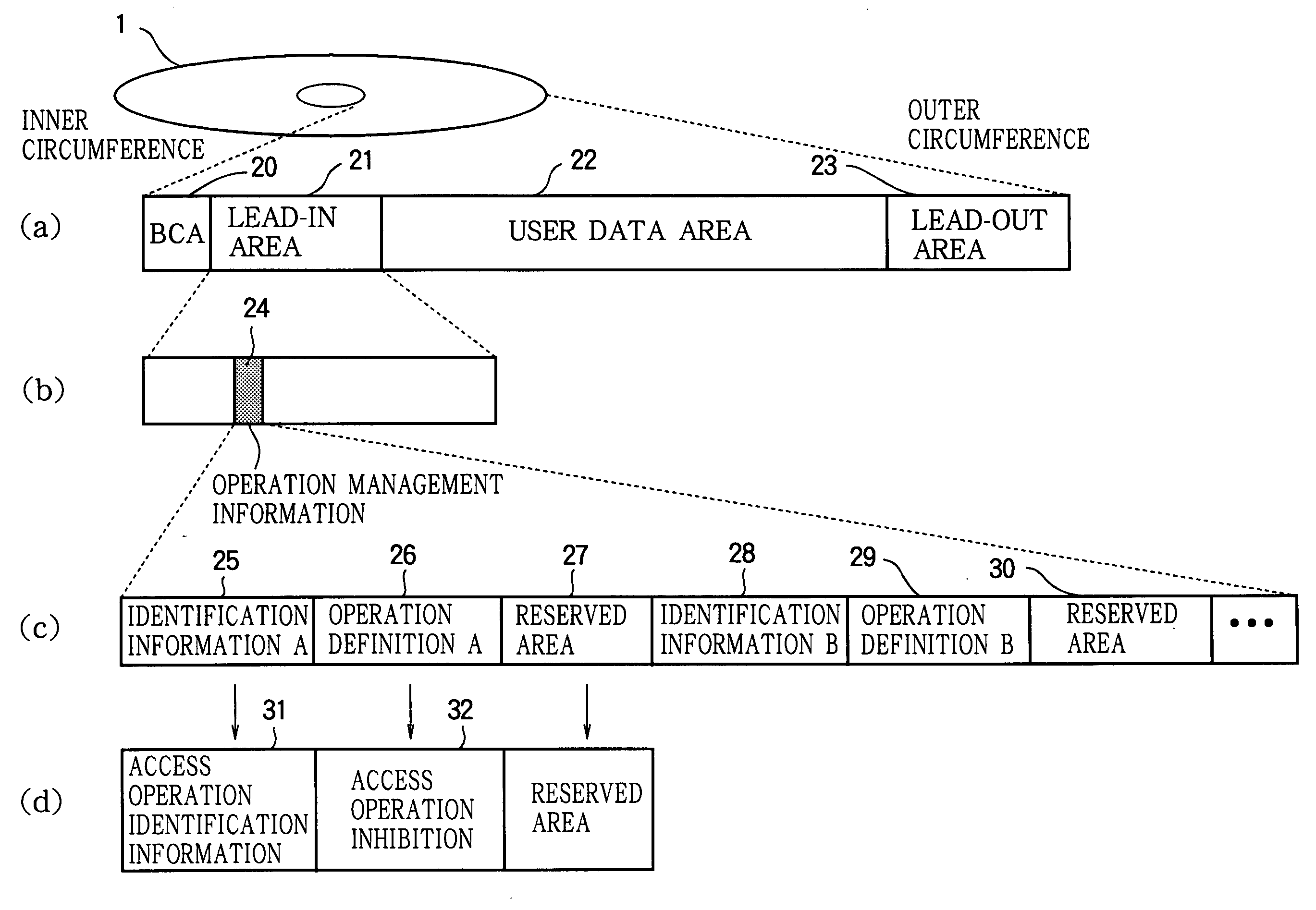
Optical Disc, Optical Disc Driving Apparatus, Optical Disc Driving Method, Data Processing Apparatus, and Optical Disc Recording/Reproducing Apparatus
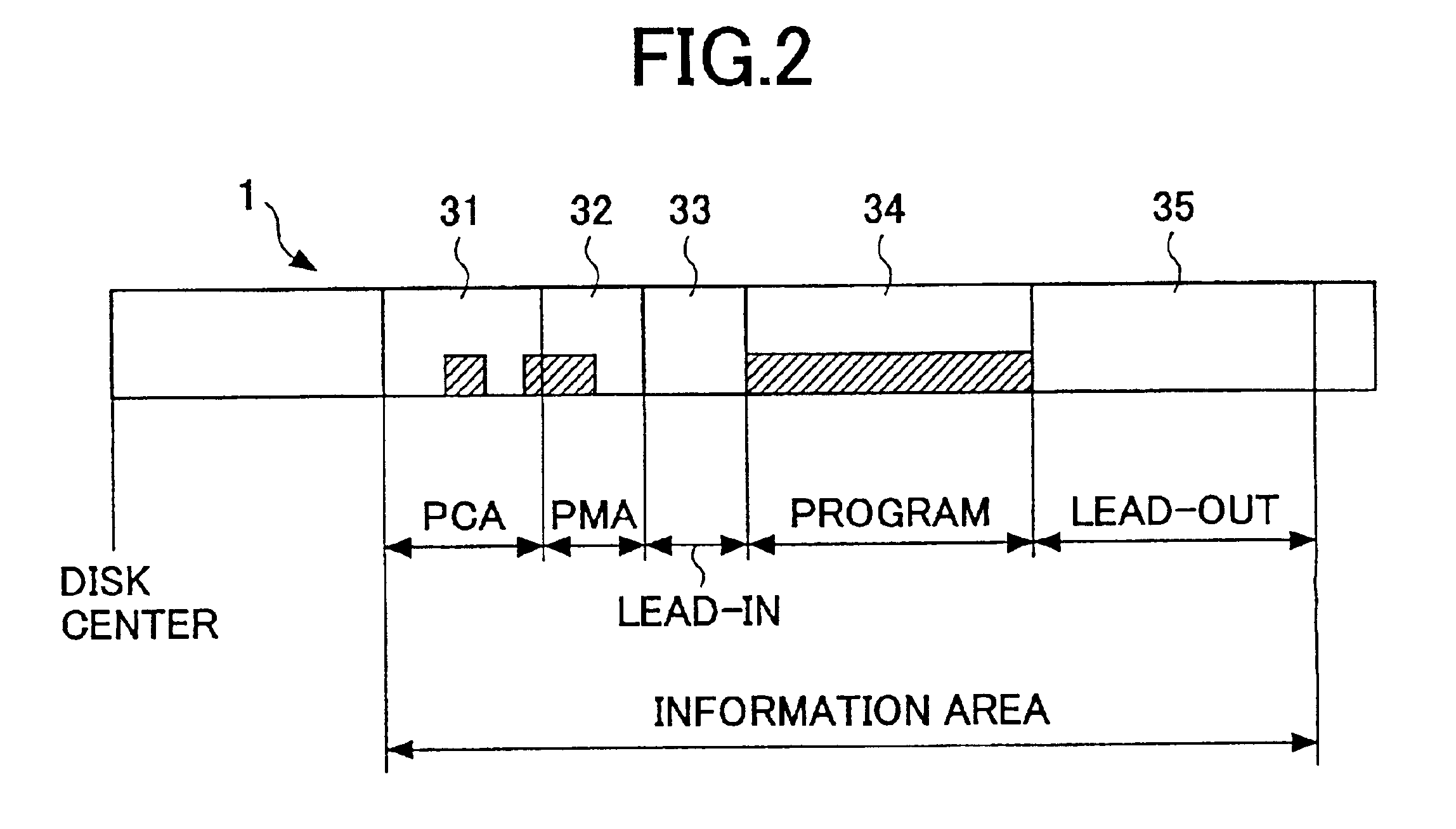
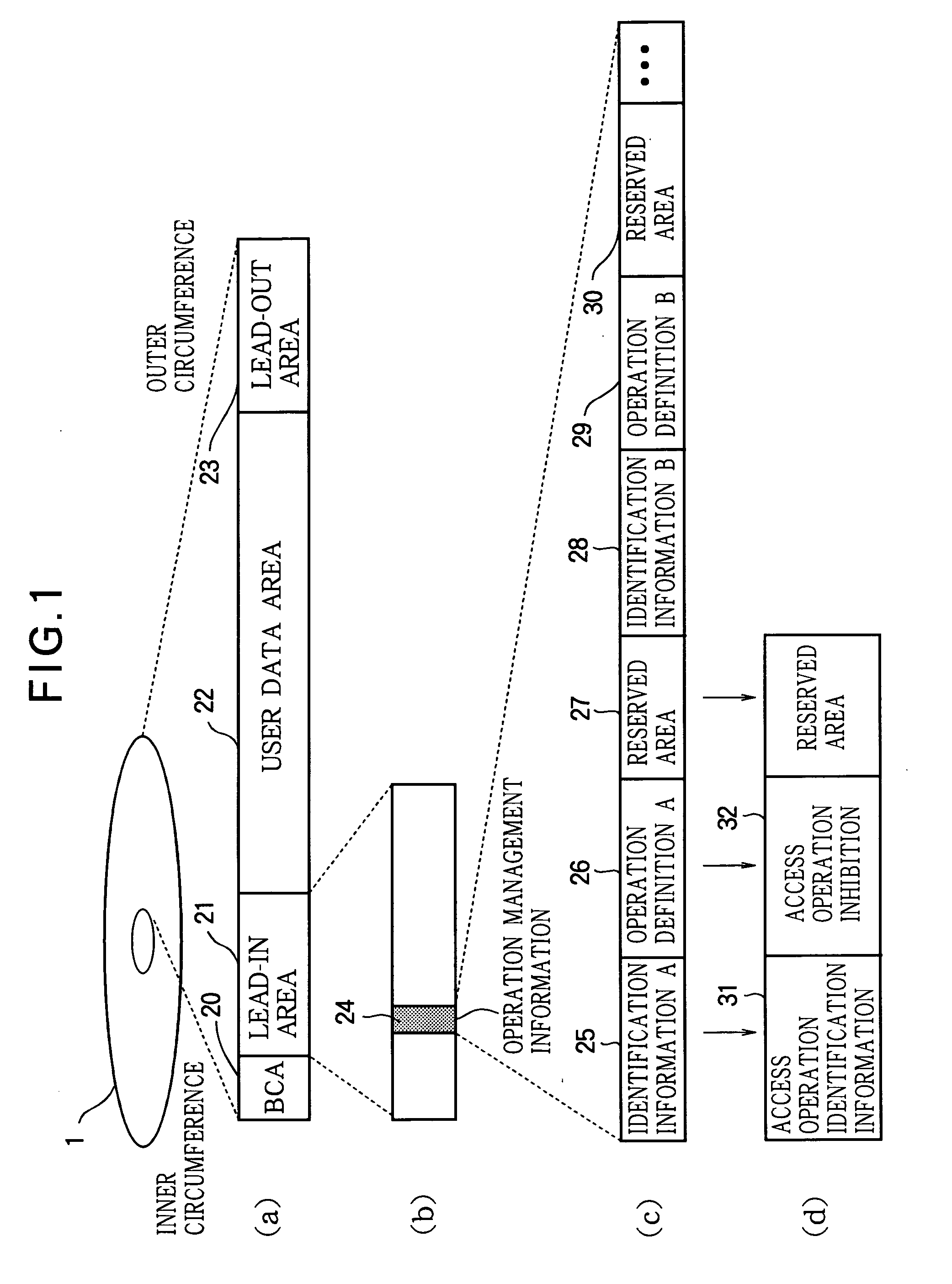
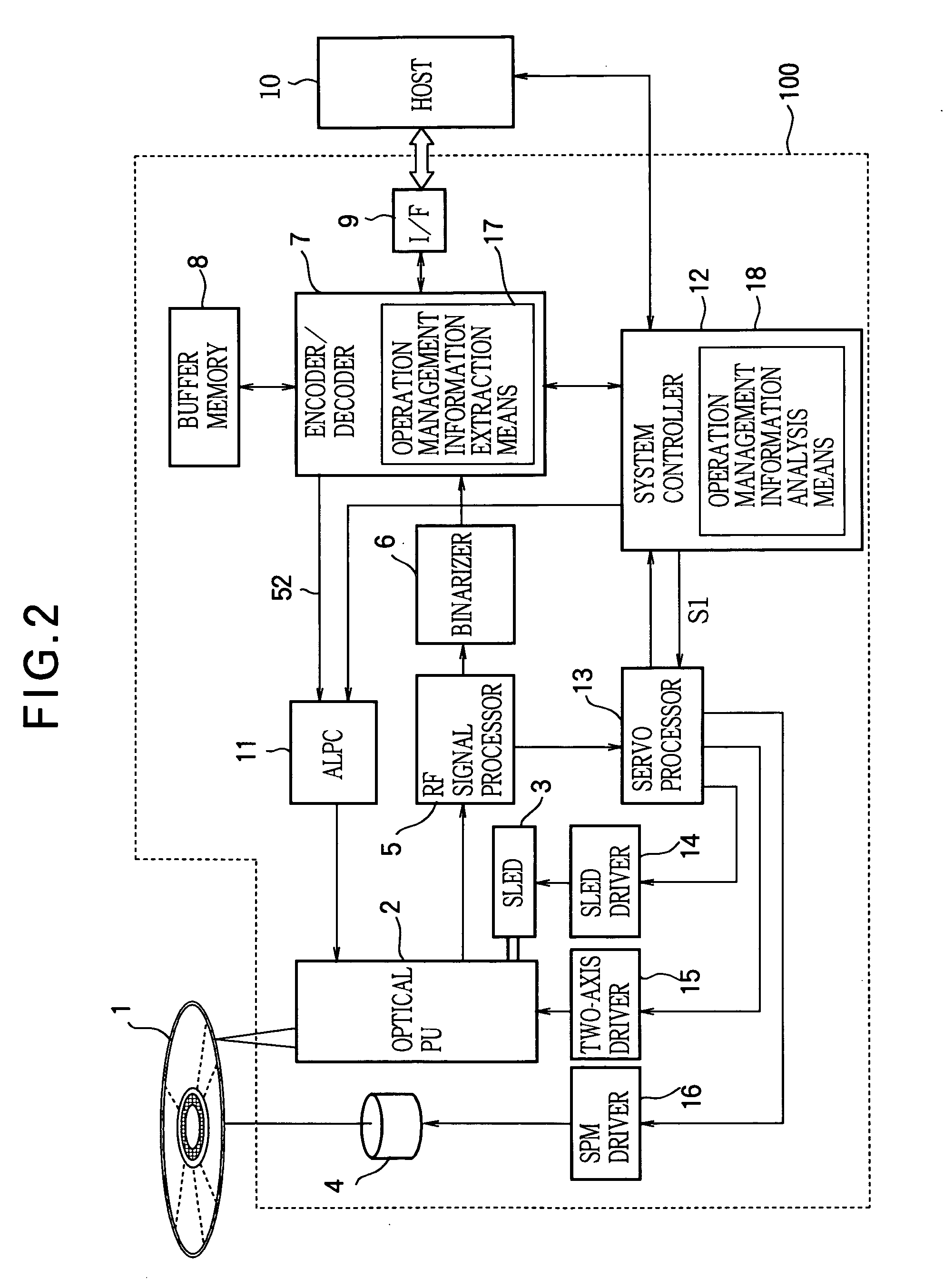
By avoiding the problem that in a hybrid optical disc with a standard-density recording area and a high-density recording area, an optical pickup designed to be suitable for the standard-density recording area cannot operate as desired in the high-density recording area and may cause a malfunction, damage to the disc drive or optical disc is prevented and optimal control is enabled. Access operation identification information such as reproducing identification information 225 indicating whether or not information recorded in the user data area 222 of the optical disc can be reproduced under the reproducing conditions of the optical disc driving apparatus is recorded in the lead-in area 222. The optical disc driving apparatus reads this type of access operation identification information, compares it with access operation identification information possessed by the optical disc driving apparatus, and if they do not correspond, does not carry out access operations by the optical head to the user data area 222, because reproducing or recording compatibility with the optical disc 201 is lacking.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Clock generating apparatus and method in optical storage system
ActiveUS20060197564A1High resolutionPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorSignal correctionOptical storage
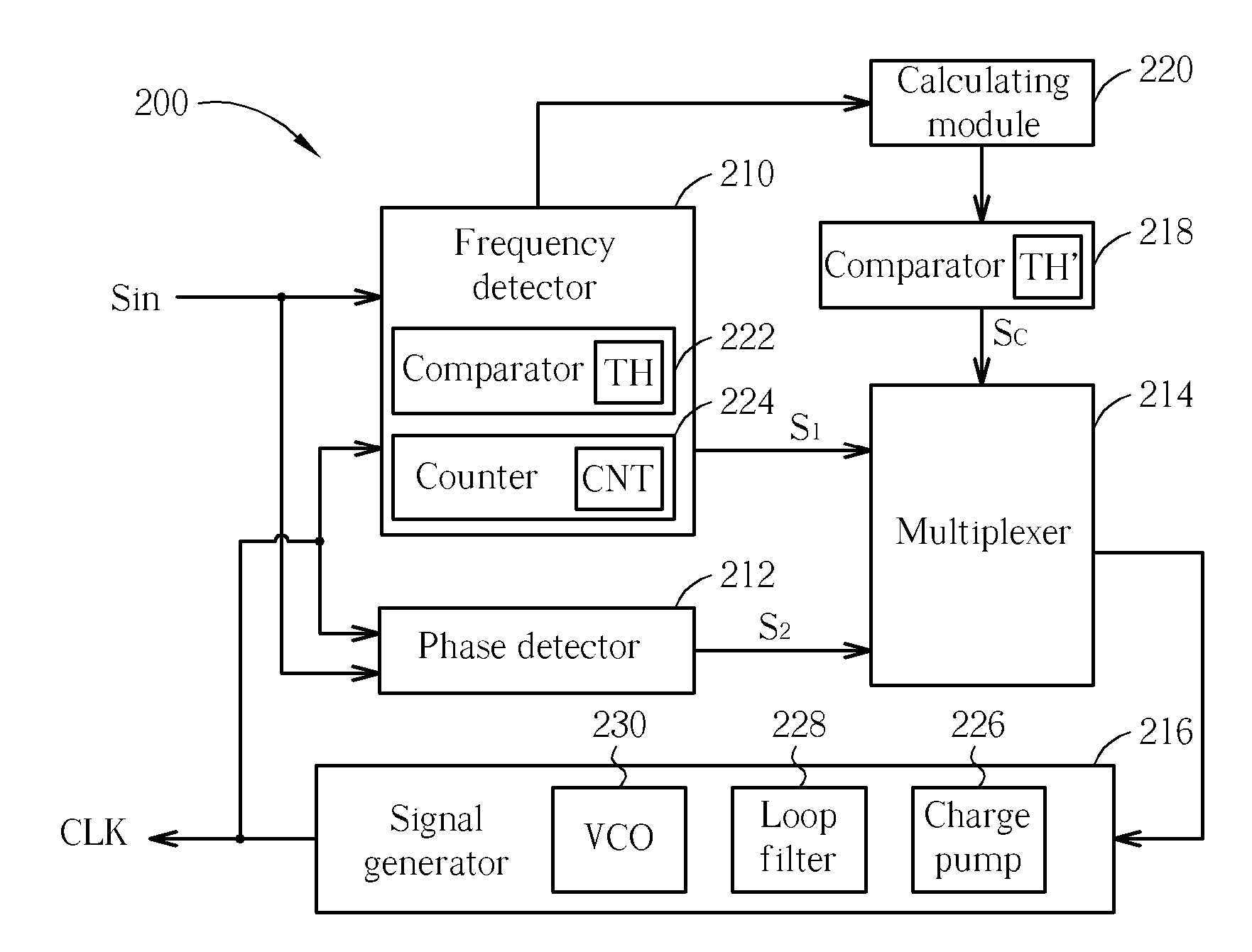
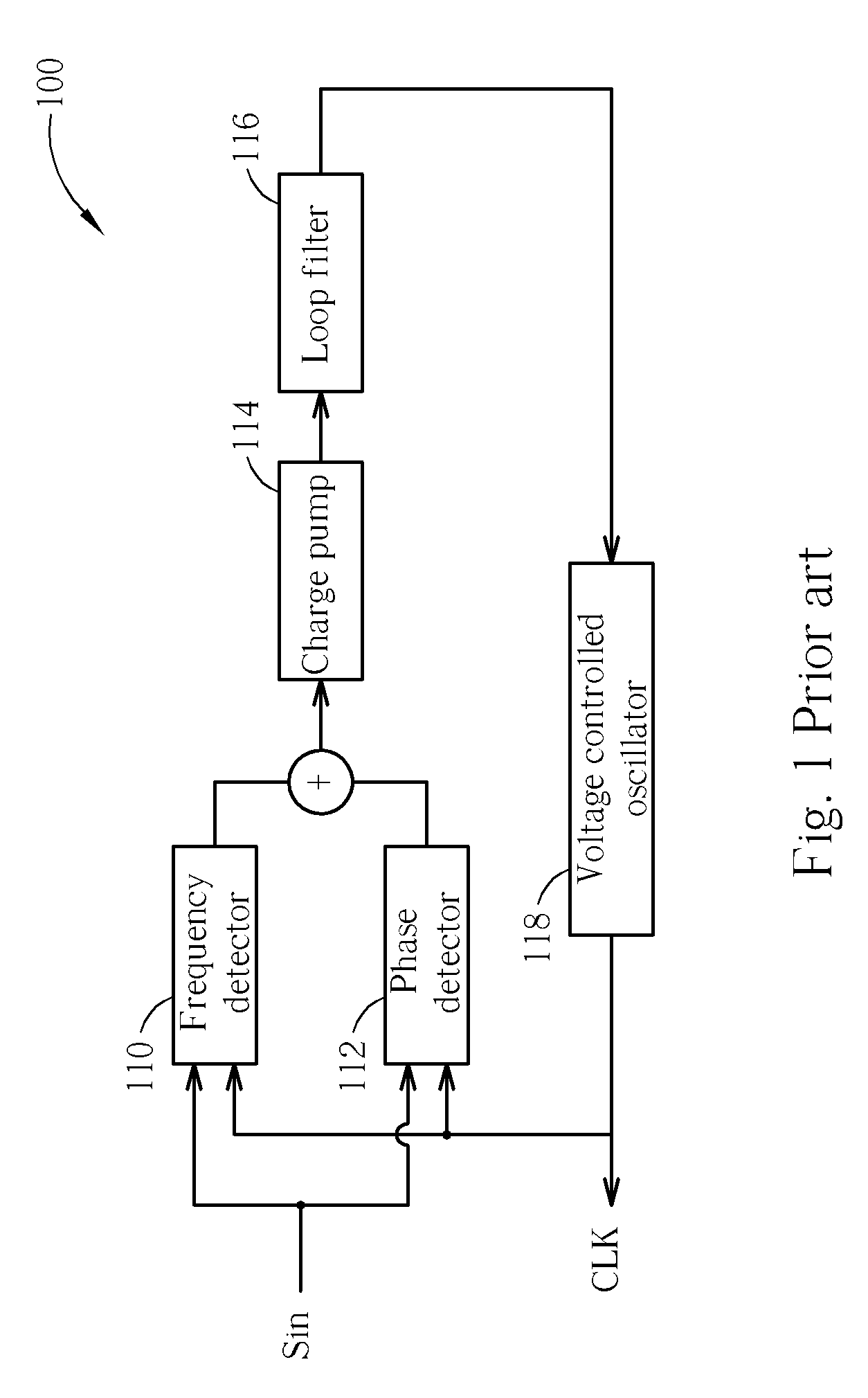
A clock generating apparatus and clock generating method of an optical disc drive for calibrating a clock signal according to an input signal. The clock generating apparatus includes a frequency detector for detecting sampling times in a duration when the clock signal samples an interval between two synchronization patterns of the input signal, and for generating a first adjusting signal according to the sampling times, and a signal generator electrically coupled to the frequency detector for calibrating the clock signal according to the first adjusting signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
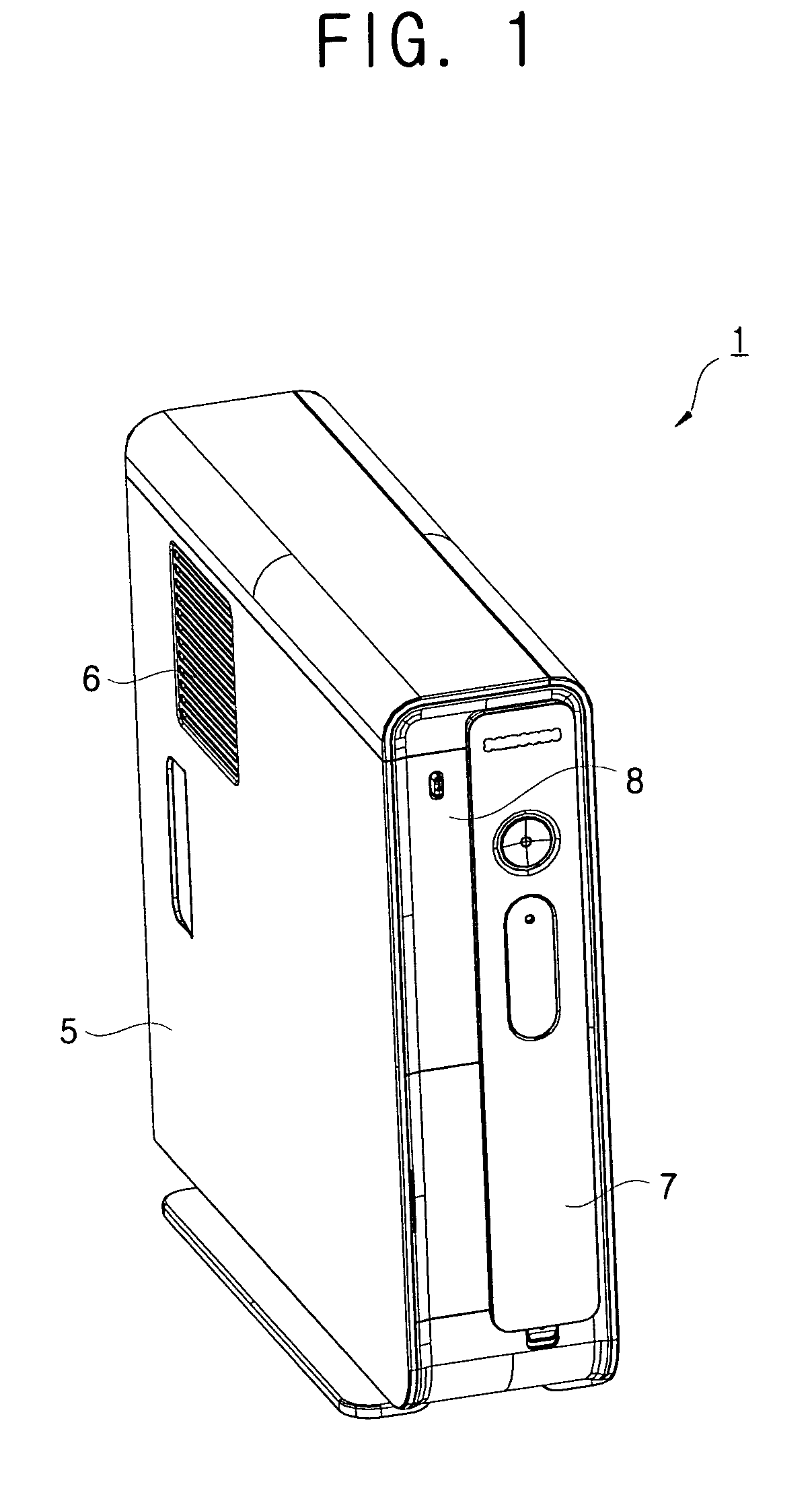
Optical disc driver enclosure
InactiveUS6909047B2Easy to disassembleCarrier constructional parts dispositionInstallation of lighting conductorsRear quarterEngineering
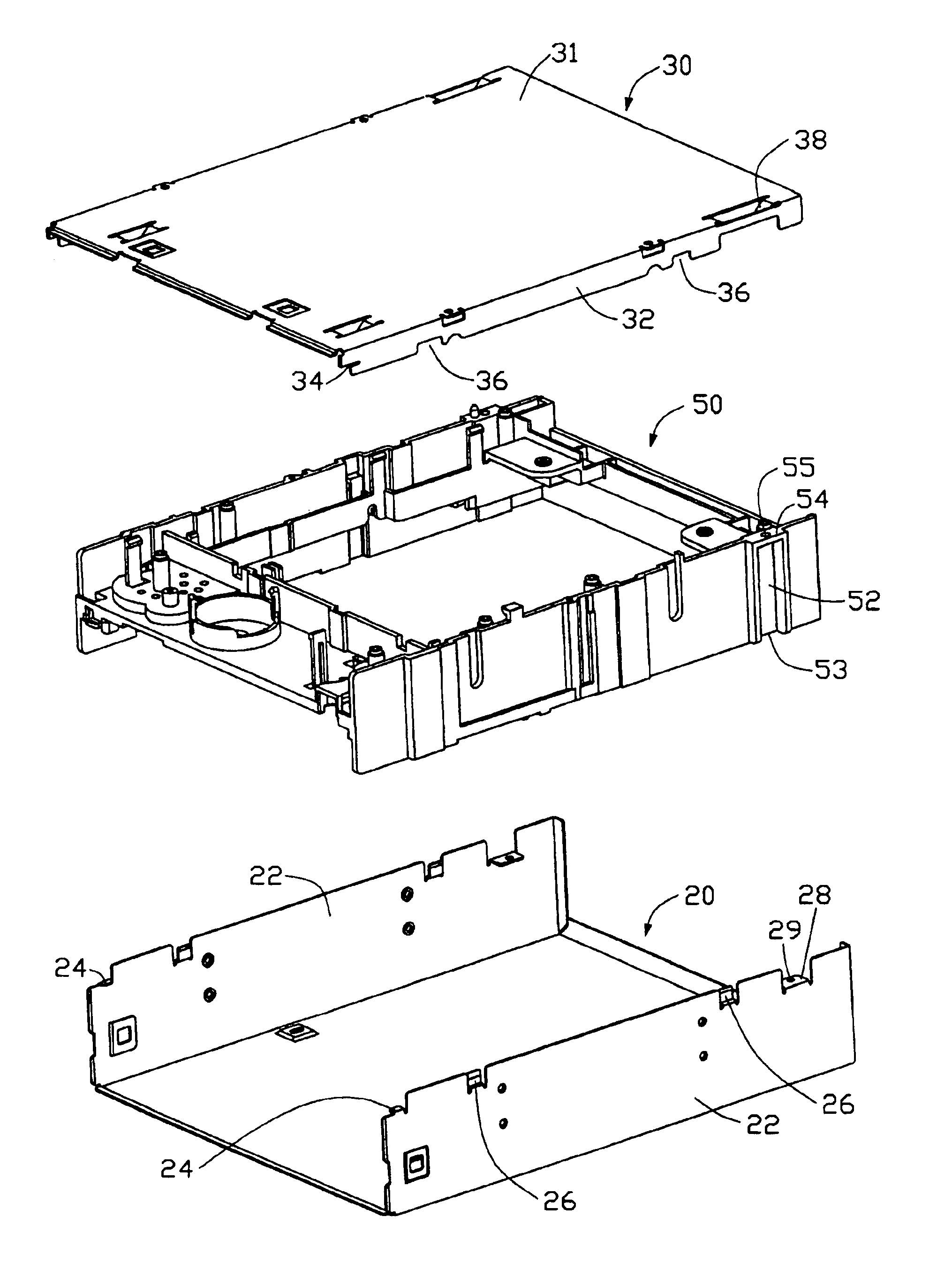
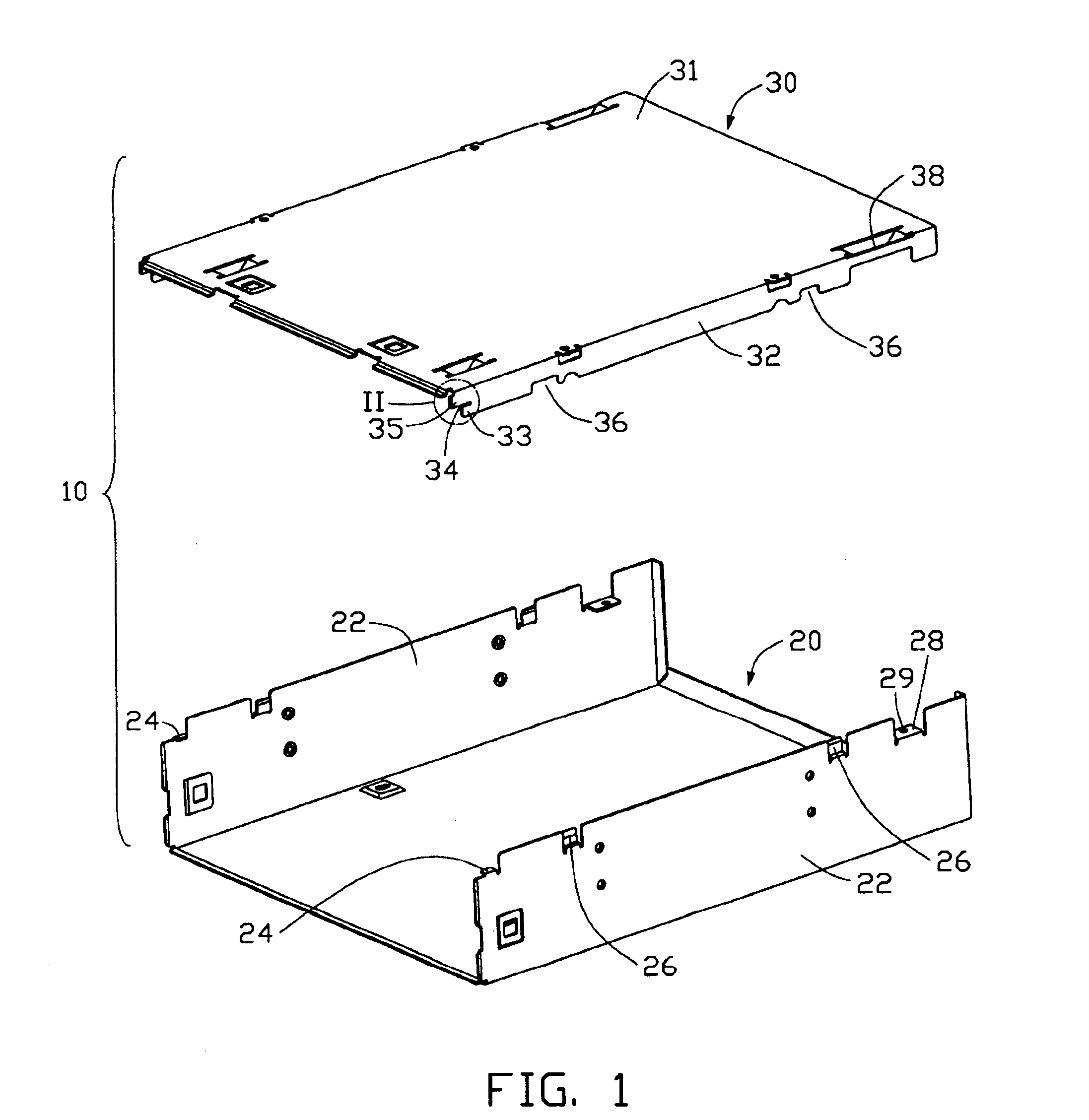
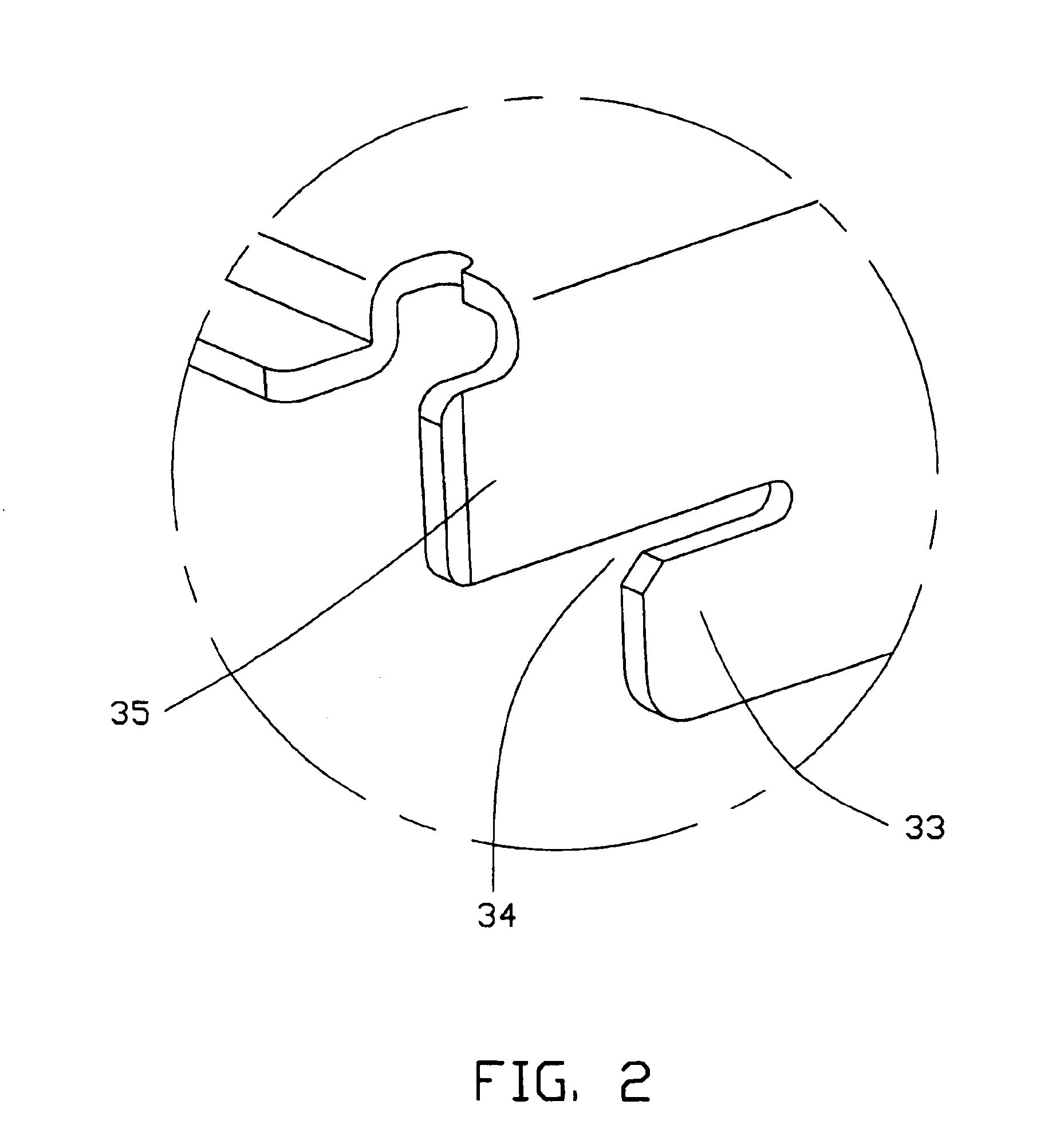
An optical disc drive enclosure (10) includes a first cover (20) and a second cover (30). The first cover has a bottom plate and two first side plates (22). A locating plate (24) extends inwardly from a front upper edge of each first side plate, and two protrusion plates (26) are formed on an upper edge of each first side plate. The second cover has a top plate (31) and two second side plates (32). A locating slot (34) is formed at a front end of each second side plate, and can engage with the corresponding locating plate. Two cutouts (36) are defined in each second side plate. During assembly, the locating slots engage with the locating plates, with the second cover at an angle to the first cover. The second cover is then rotated downwardly so that the cutouts engage with the protrusion plates and the second side plates are clipped between the first side plates and the protrusion plates. The first cover and the second cover can then be fixed together by a pair of screws (59).
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method for variably controlling data read speed in optical disc drive
InactiveUS20050105885A1Shorten the time periodImprove data reading speedTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareOptical disc drive
A method is provided for variably controlling a data read speed in an optical disc drive. The method includes determining whether or not a read command has been issued; if the determining step determines that the read command has been issued, examining additional information associated with the read command; and variably controlling a data read speed for an optical disc according to the additional information.
Owner:HITACHI LG DATA STORAGE KOREA
Secure media distribution in a wager gaming system
ActiveUS20080153588A1Preventing executionApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesComputer hardwareAuthorization
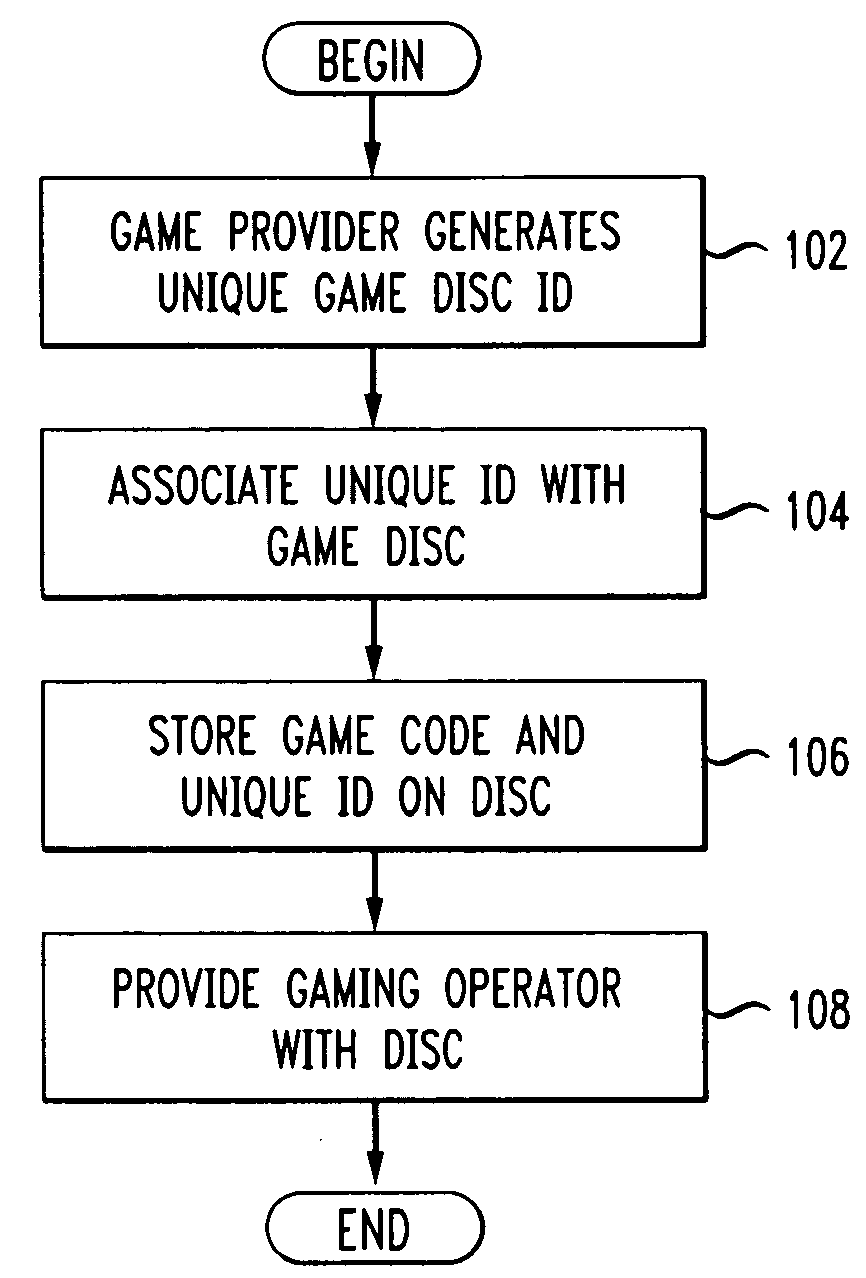
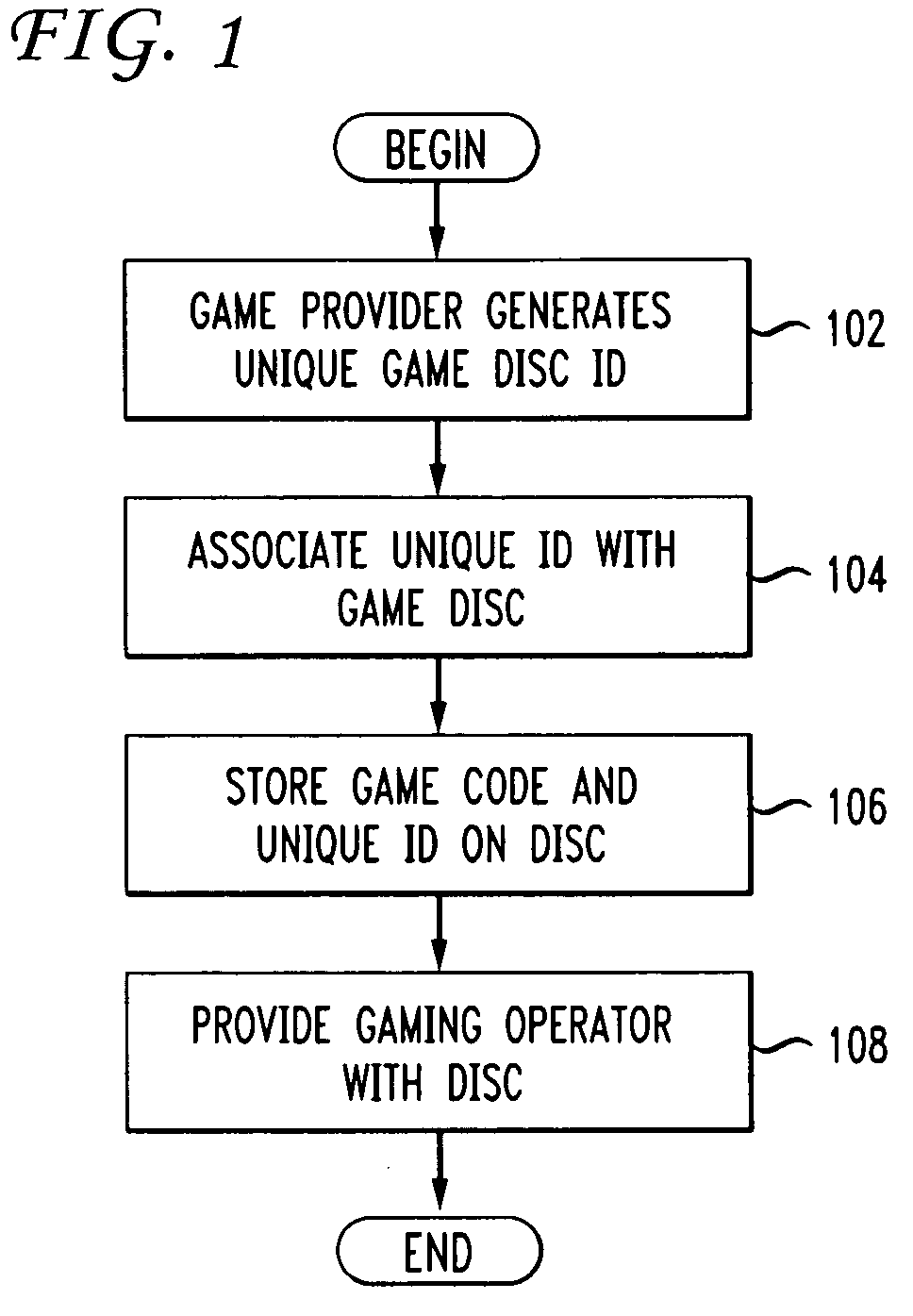
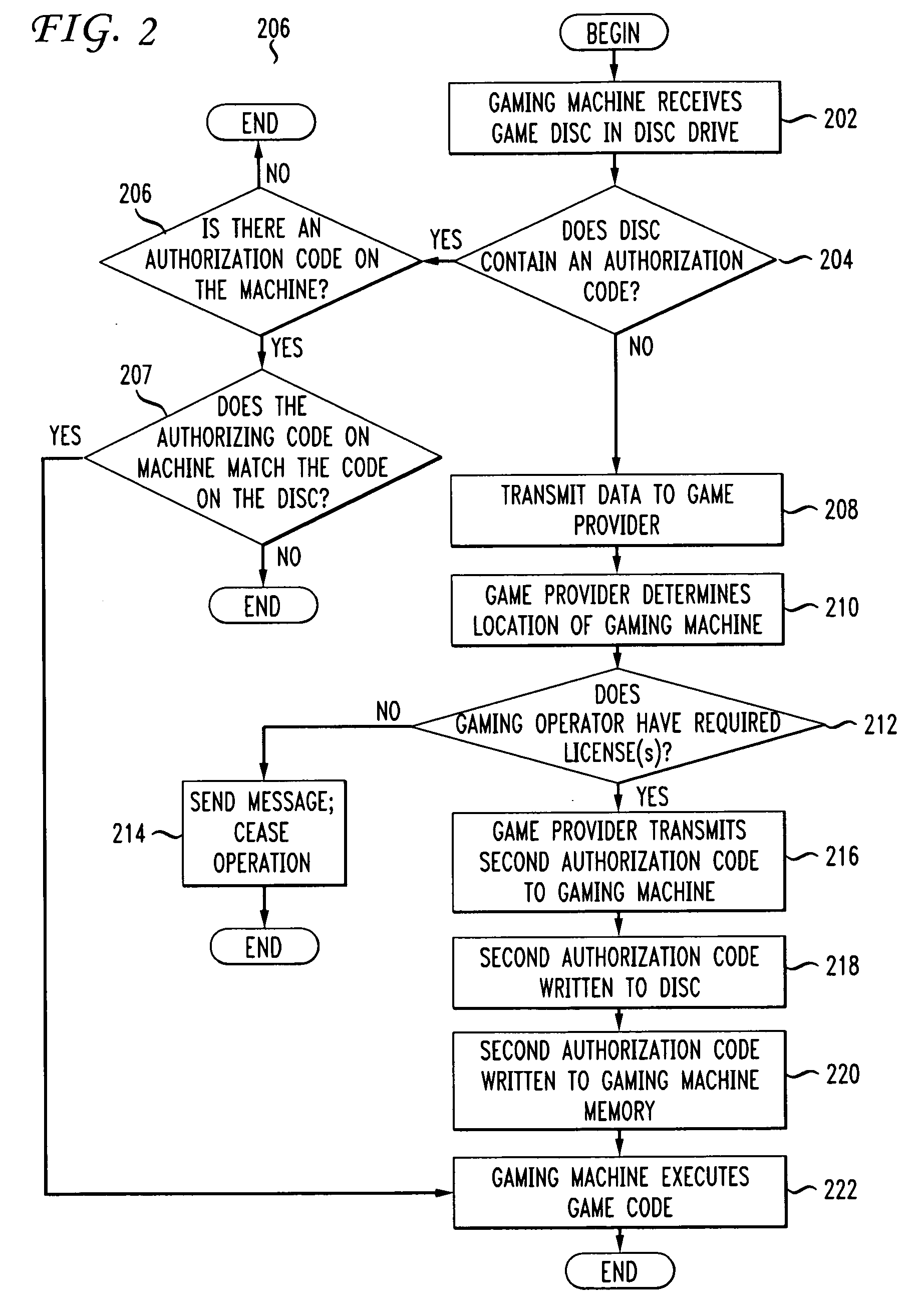
Novel wager gaming systems, machines, and methods for ensuring that wager game code on a game disc executes on an authorized wager gaming machine are described. To prevent an unauthorized copy of a wager game disc or other storage medium is not able to execute on a gaming machine, the machine checks whether an authorization code has been previously written to the disc. If the disc does not have a code, the gaming machine generates a first segment of an authorization code which is used, along with other data, by a game provider to generate a final authorization code. This is done after the game provider verifies that the machine operator has permission, such as a license, to execute that game code contained on that specific disc. The final authorization code is transmitted to the gaming machine, equipped with a writeable optical disc drive, where it is written or “burned” onto the game disc. At this stage the game disc is tied to or associated with the gaming machine and can execute on that machine.
Owner:IGT
Optical disc system having improved circuitry for performing blank sector check on readable disc and method for operating same
InactiveUS6069857AReduce sensitivityImprove accuracyCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsControl signalHemt circuits
An optical disc drive system is employed in conjunction with a storage medium having a plurality of data sectors each provided with a header and a data storage area. The system includes a data detection device for retrieving stored data from the storage medium and outputting a data signal, an amplifier for providing a variable gain to the data signal and outputting an amplified data signal, a detector that is responsive to the amplified data signal for evaluating a predetermined one of the sectors to ascertain whether the storage area is blank, and an automatic gain control circuit producing a gain control output for controlling the gain of the amplifier. The control circuit has a first mode and a second mode, the first mode being active during retrieval of the header and the second mode being active during retrieval of the data storage area. The system is further provided with a sampling device for sampling the gain control output during retrieval of the stored data in a respective one of the storage areas containing previously stored data. The sampling device outputs results of the sampling, and a fixed gain control circuit is responsive to the results of the sampling for outputting a fixed gain control signal. The fixed gain control signal is applied to the amplifier during evaluation of the predetermined one of the sectors.
Owner:DISCOVISION ASSOC
Method and system for psychological treatment by brain stimulation of the psychologically disordered object
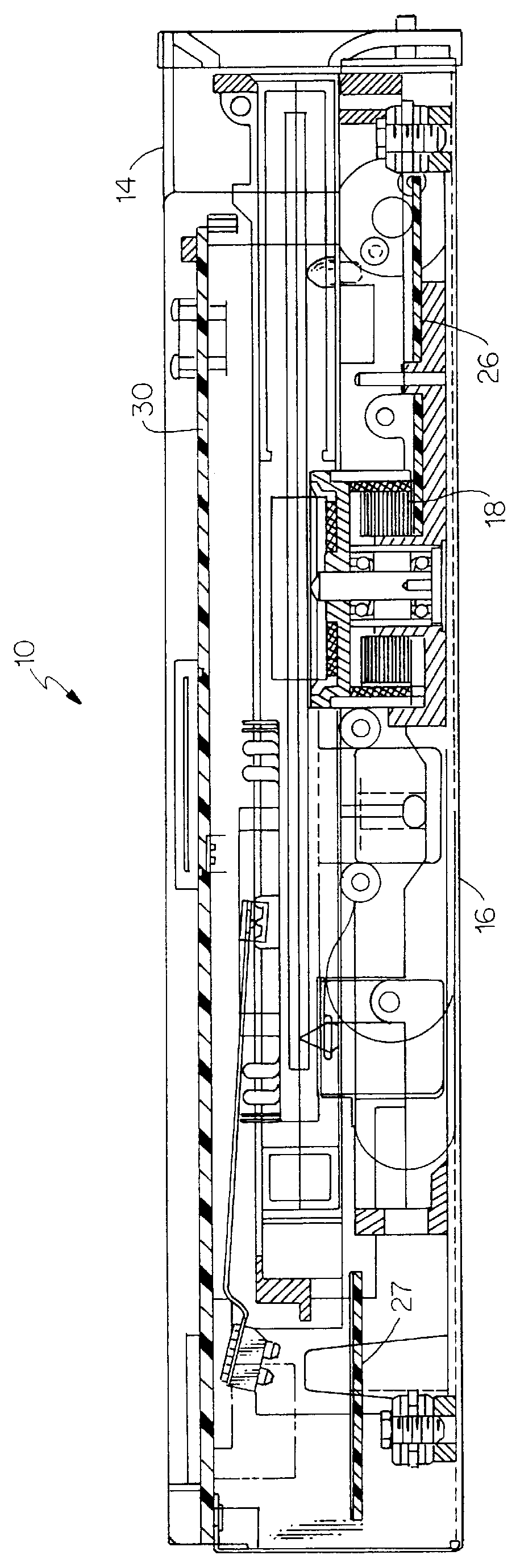
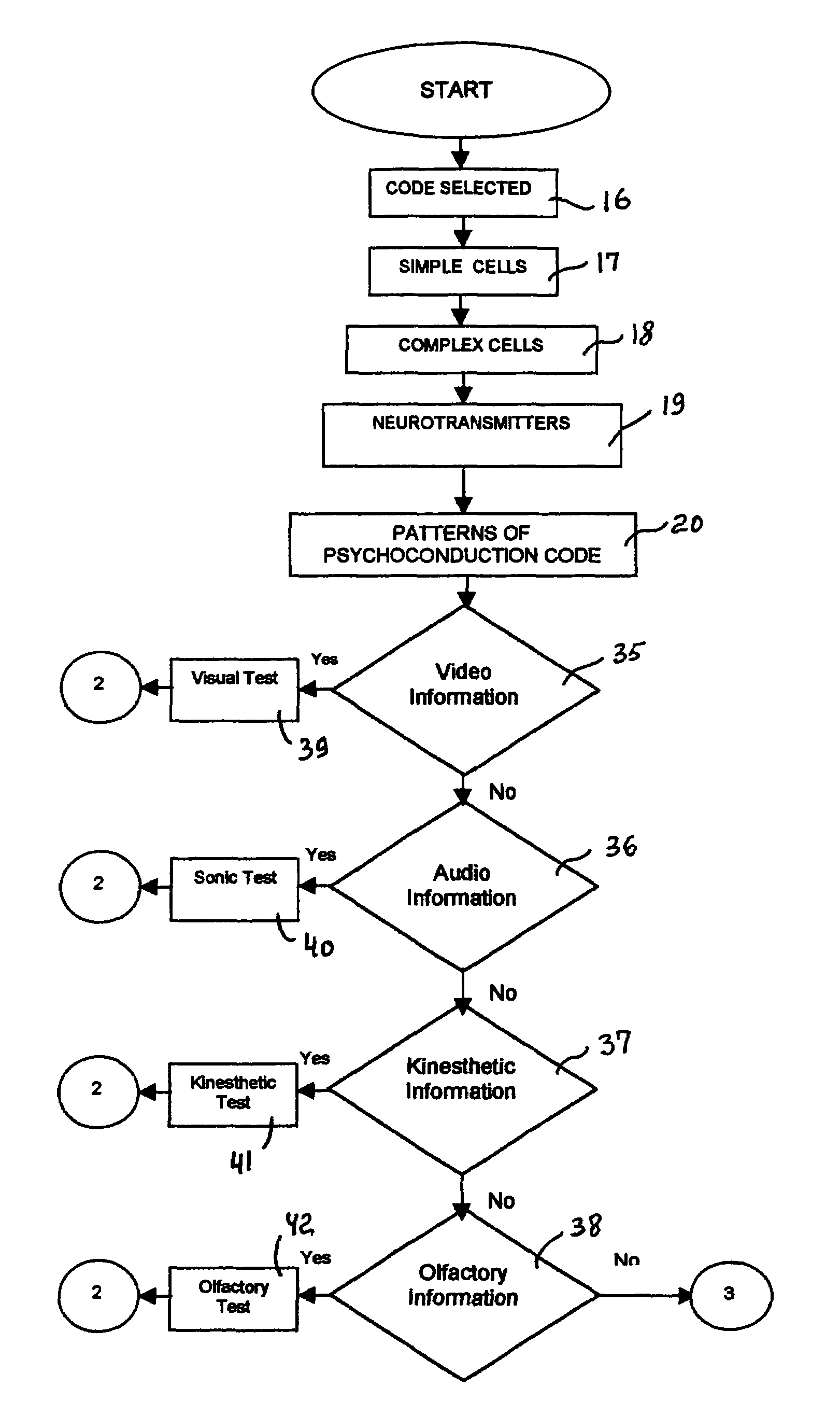
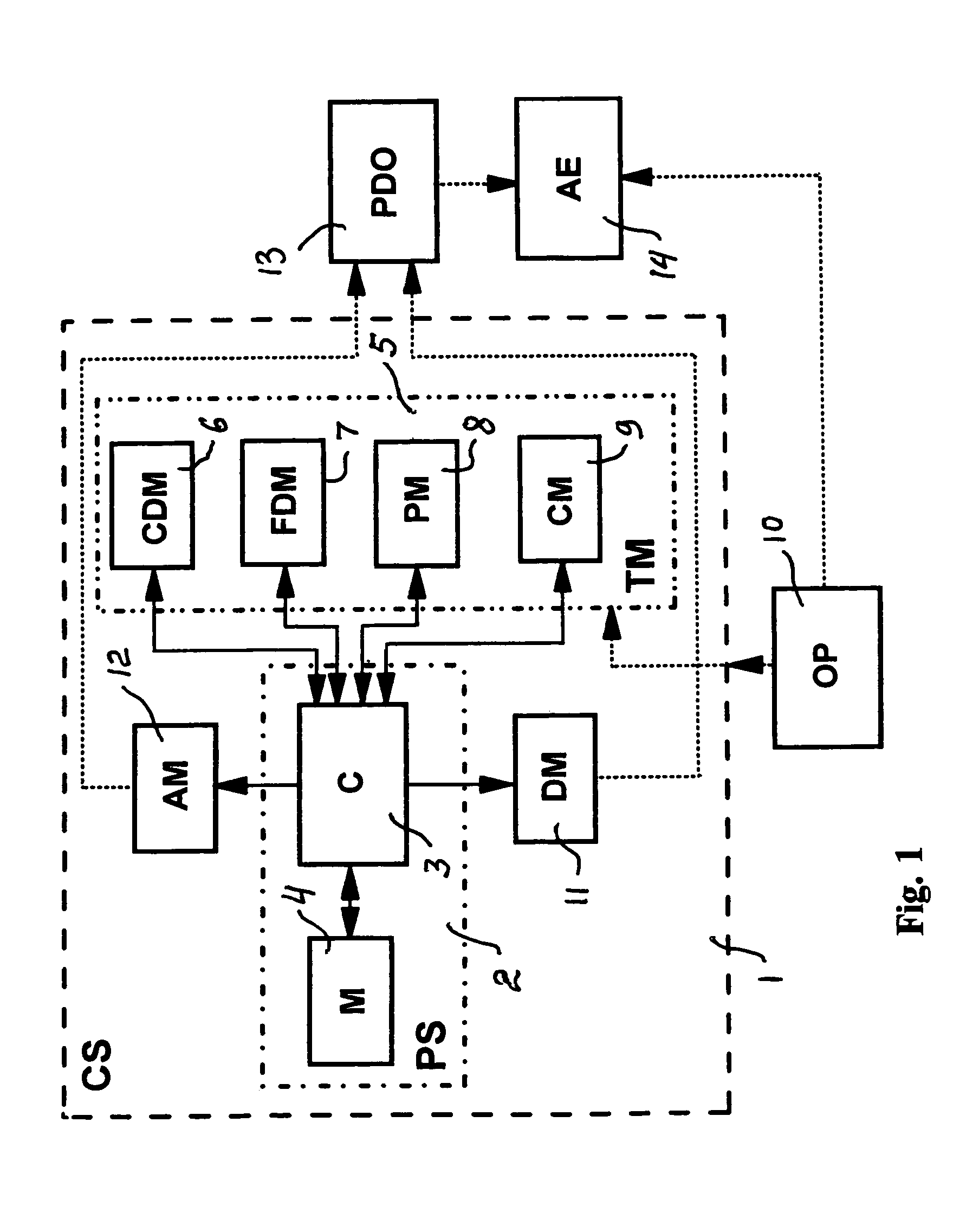
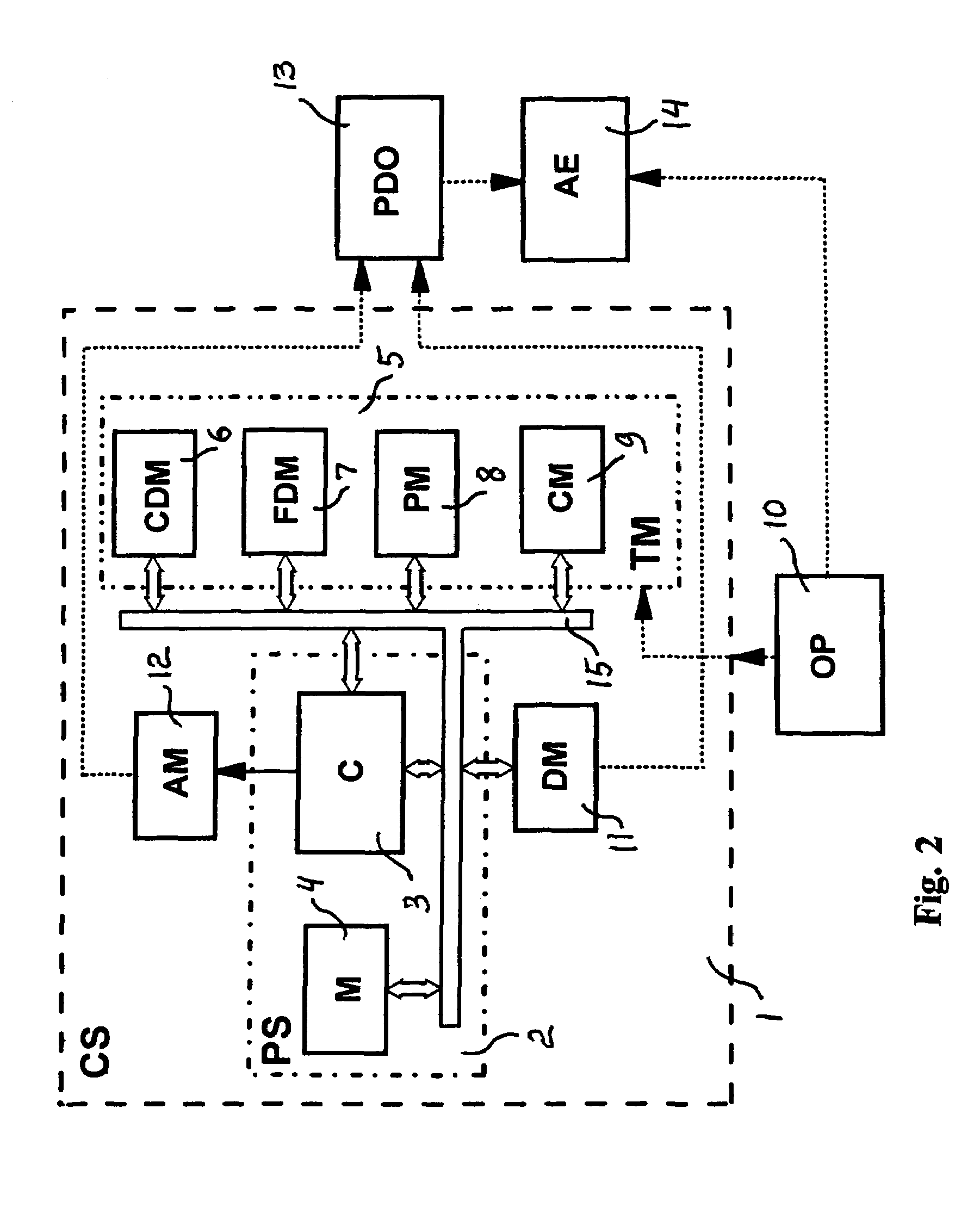
InactiveUS7400927B1Improved brain psychological treatmentElectrotherapyDiagnosticsDisplay deviceLoudspeaker
The method and system for psychological treatment by brain stimulation of the psychologically disordered object provide a possibility to stimulate the simple cells to assist the complex cells, and / or replace the complex cells in order to correctly perform the assigned command. An improved method includes the steps providing a creation of the psychoconduction code based on the simplified symbols, which by the audio, video, kinesthetic and / or olfactory stimulation simple cells to correct or replace the complex cells. An improved system comprises a controlling system comprising a processing system, including a controller and a memory, and a terminal device comprising at least one of a compact disk driver, a floppy disk driver, a printer and a control panel. Also, the improved system comprises an auxiliary equipment and a display connected to the controller, which is connected to the speaker(s).
Owner:LITVIN CHESTER
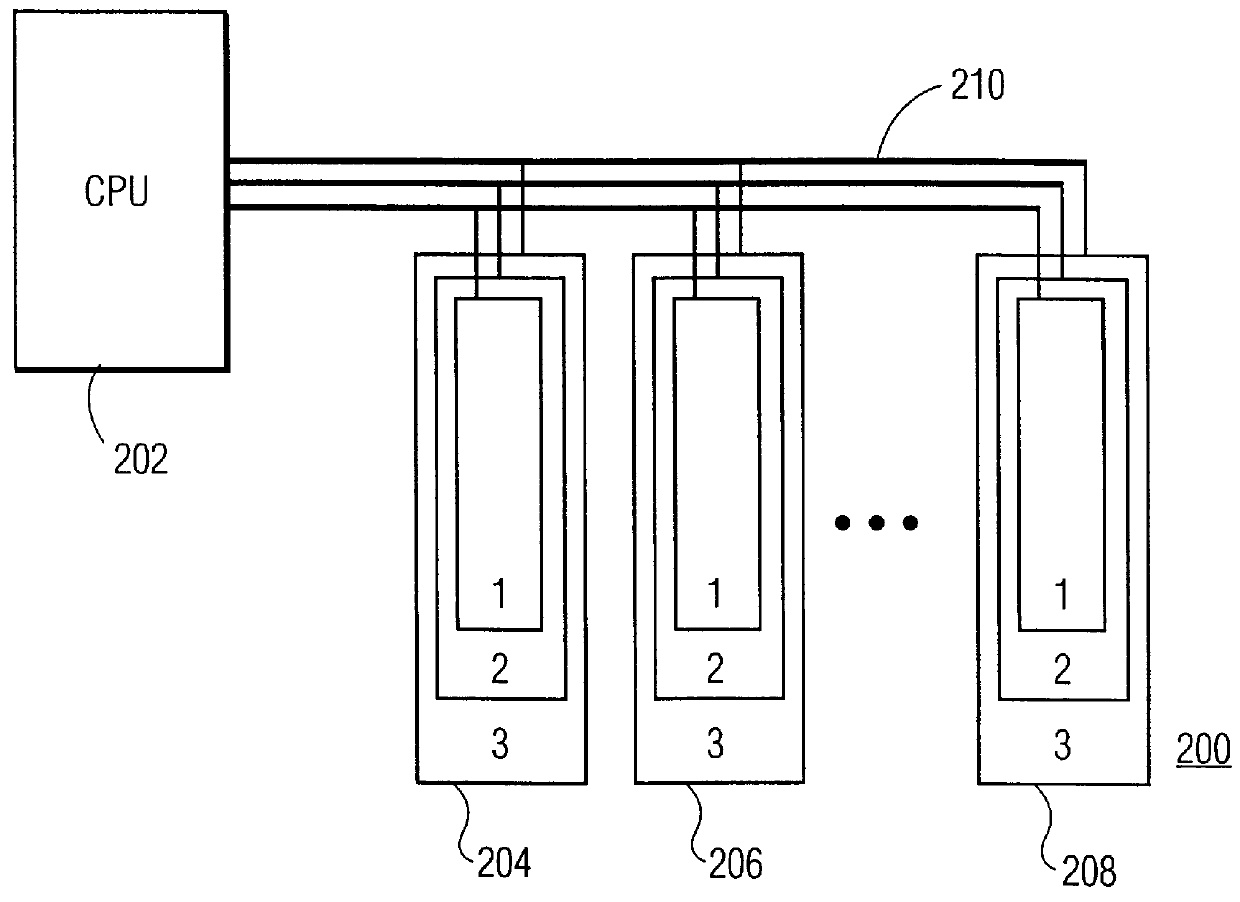
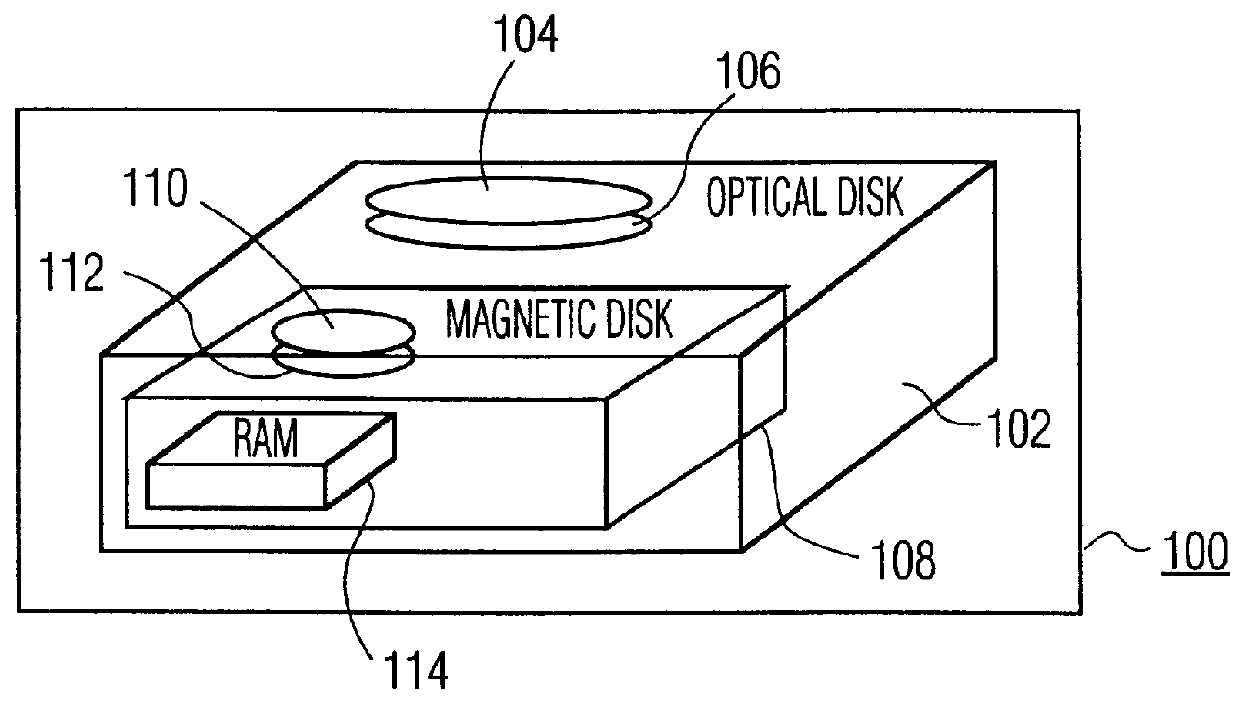
Memory system having magnetic disk drive implemented as cache memory and being integrated with optical disk drive in a hierarchical architecture
InactiveUS6070226ALower latencyUnacceptable latencyInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemData treatment
A data processing system with an optical disk drive is provided with a magnetic disk drive as a cache. The magnetic disk drive is physically integrated with the optical disk drive. A semiconductor RAM is provided as a further cache for the magnetic disk drive and is physically integrated therewith.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Calibration of tracking error signal gain in a tracking servo system
InactiveUS20020110057A1Filamentary/web record carriersRecord information storagePeak valueSignal gain
A calibration for a tracking error signal gain in a tracking servo system of an optical disk drive is presented. The calibration determines the peak-to-peak tracking error signal when the tracking servo system is open, calculates a gain factor in response to the peak-to-peak tracking error signal, and calculates a new tracking error signal gain based on the tracking error signal gain and the gain factor. New tracking error signal gains are calculated until the gain factor is approximately one.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
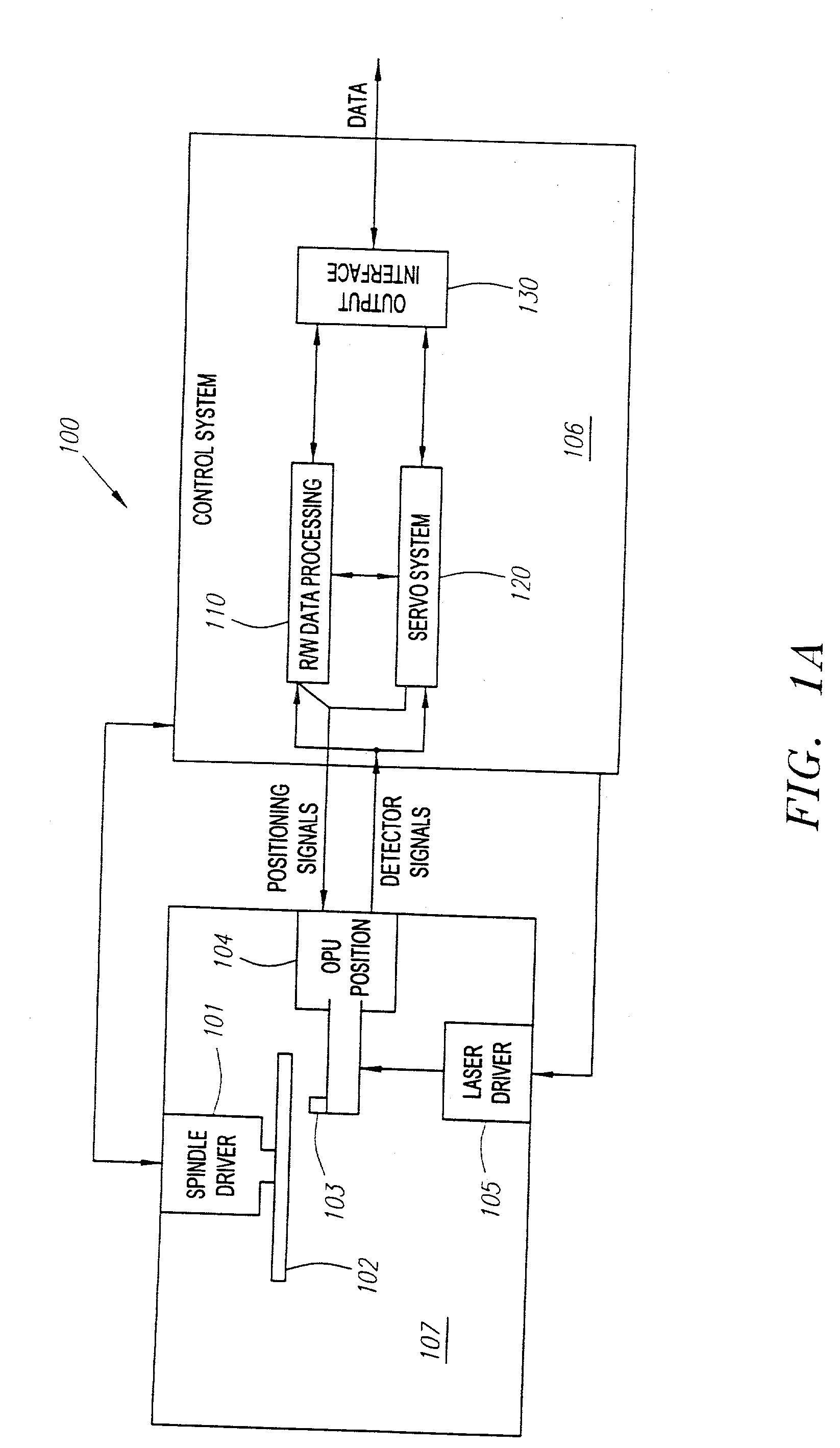
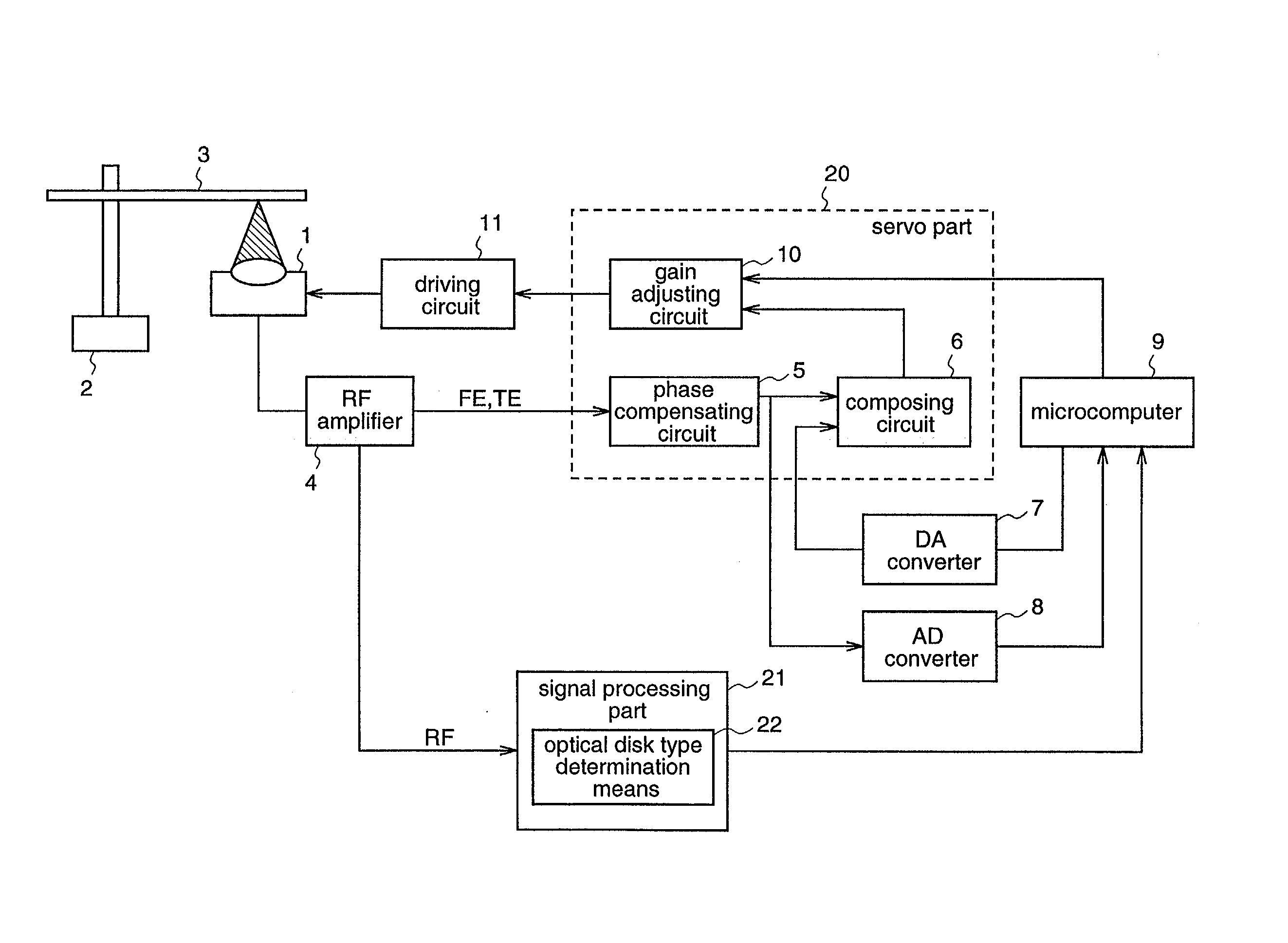
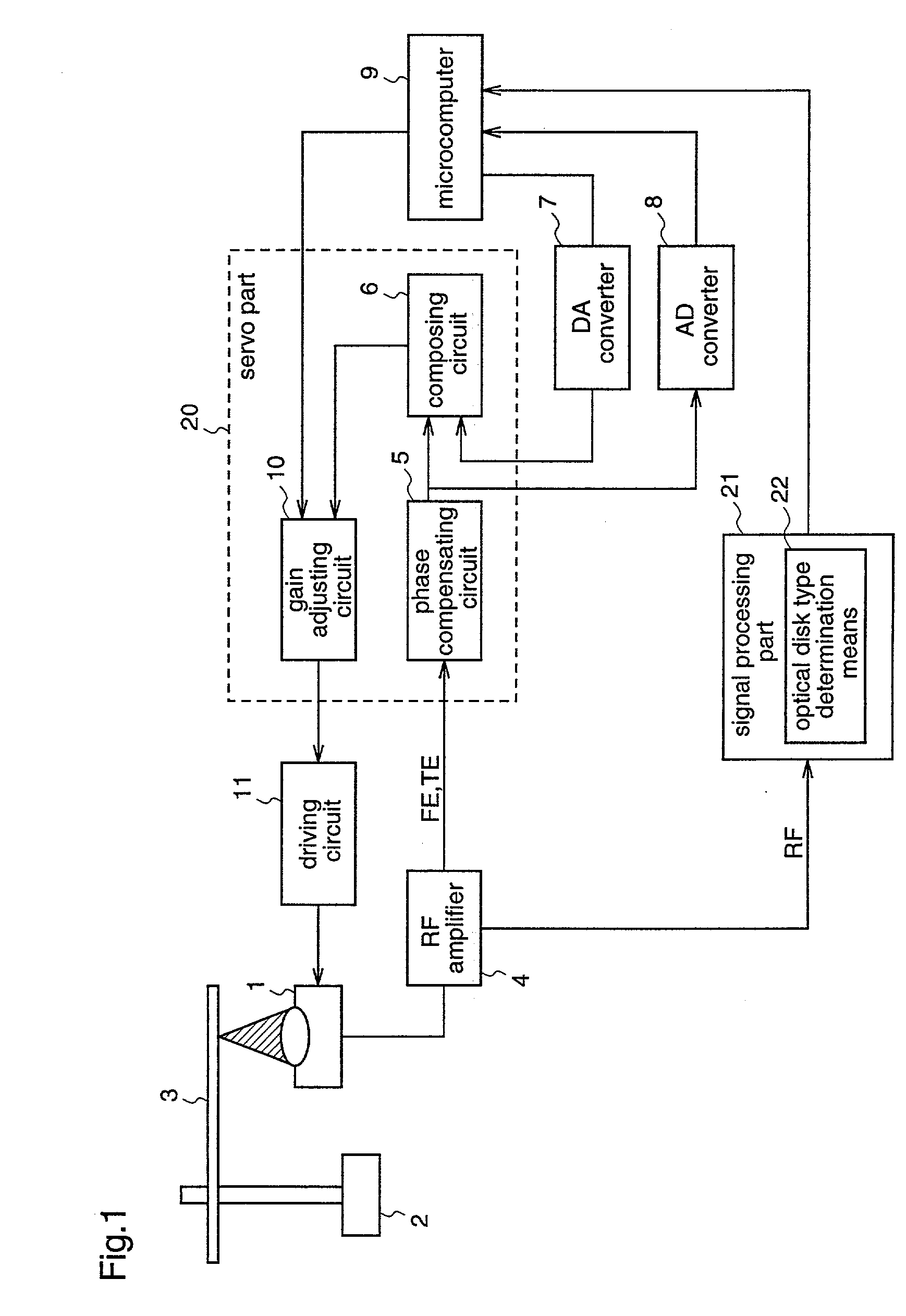
Optical disc drive
InactiveUS20020105865A1Combination recordingInformation arrangementOptical pickupRecordable compact disc
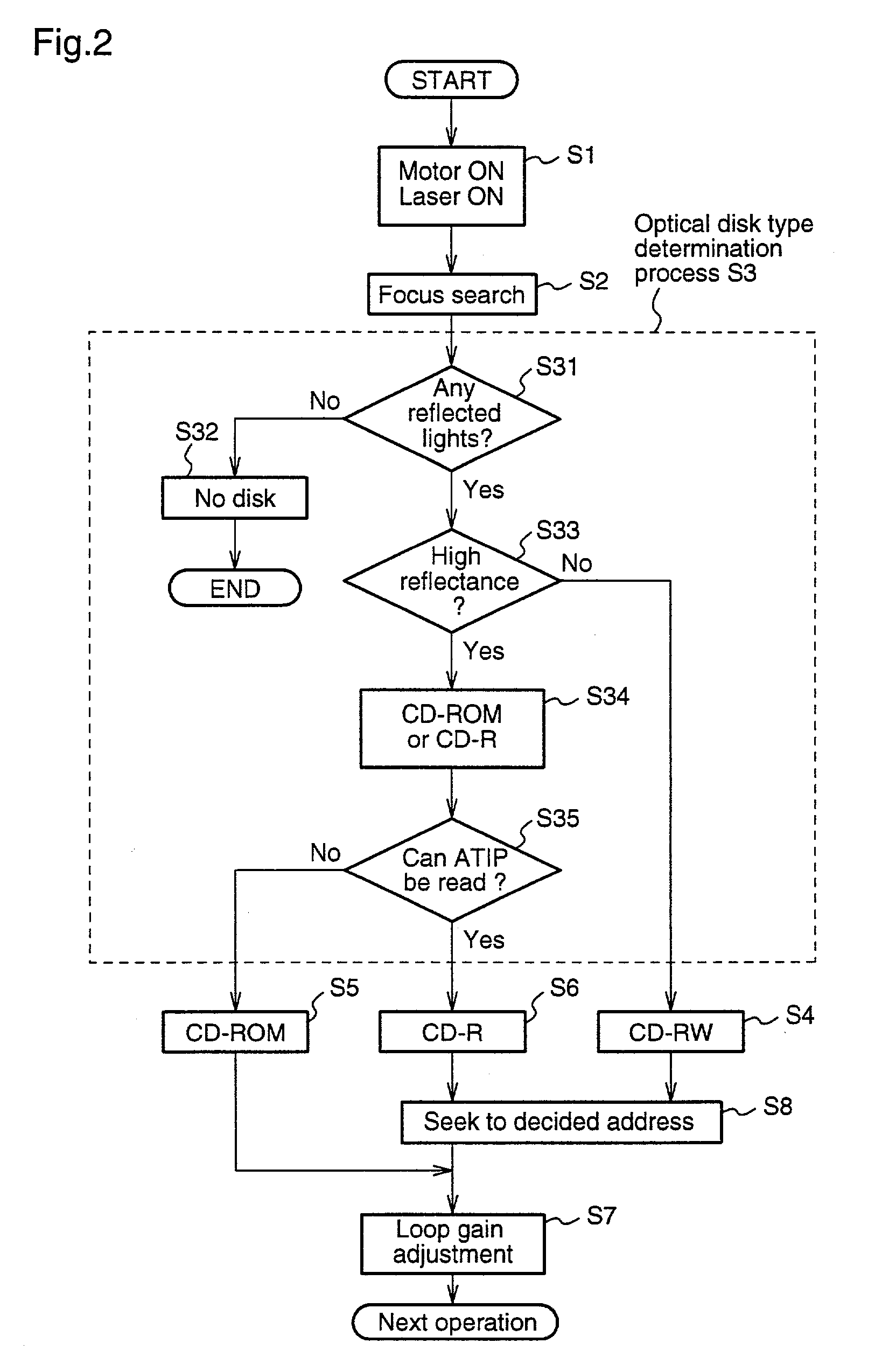
The present invention relates to loop gain adjustment of a focus / tracking servo in an optical disk apparatus, and provides an optical disk apparatus which can make the loop gain adjustment converge normally even in an optical disk in which prerecorded areas and recorded areas are mixed, and further which always has a stable servo system even when a gain is significantly varied due to changes in the disk state. When an inserted optical disk is determined to be a recordable optical disk by an optical disk type determination means 22, an optical pickup 1 is made seek a previously set area, thereby performing the loop gain adjustment. Further, when a gain is varied during the operation, a gain adjusting means 10 changes over a gain adjustment value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical disk drive and method for recording data
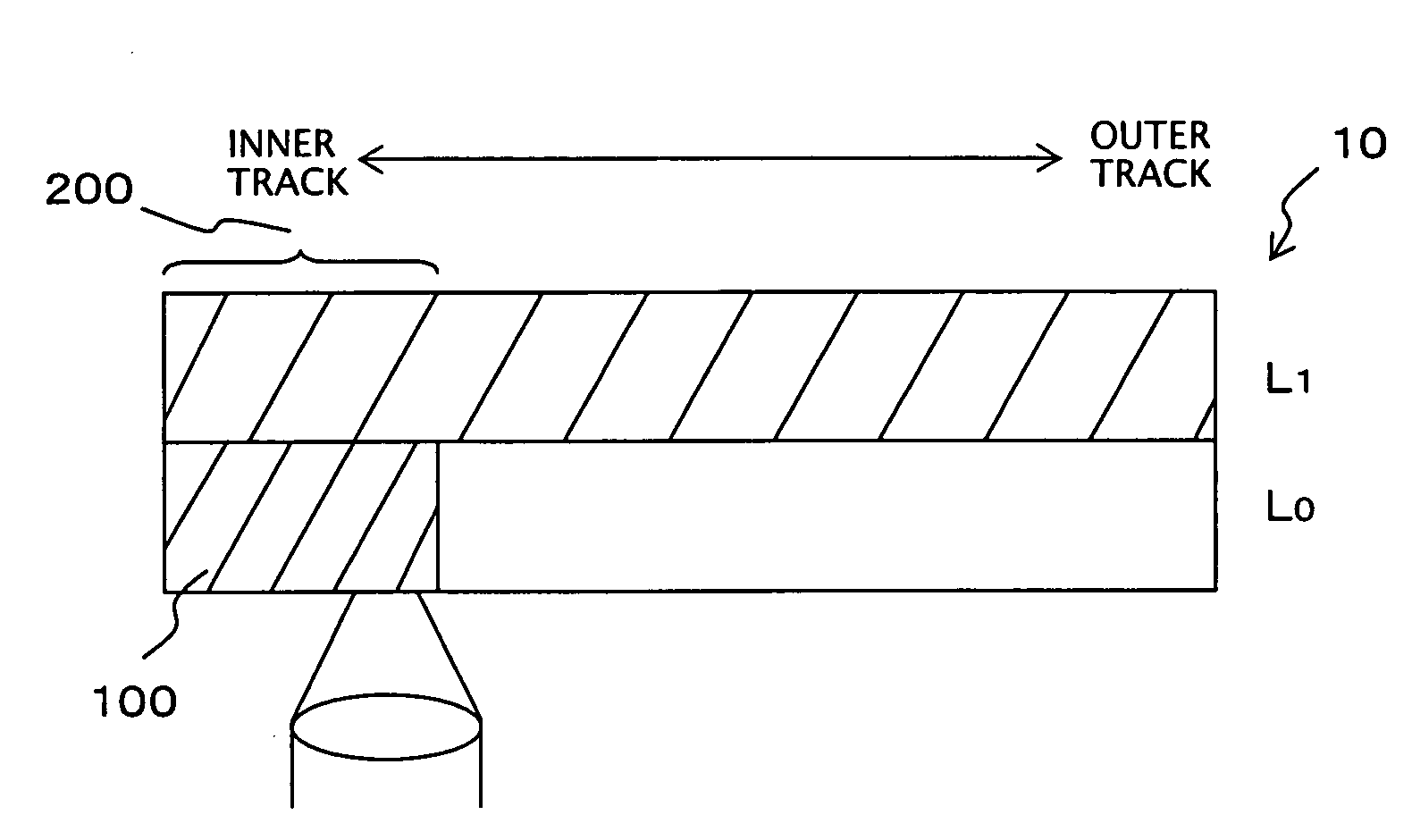
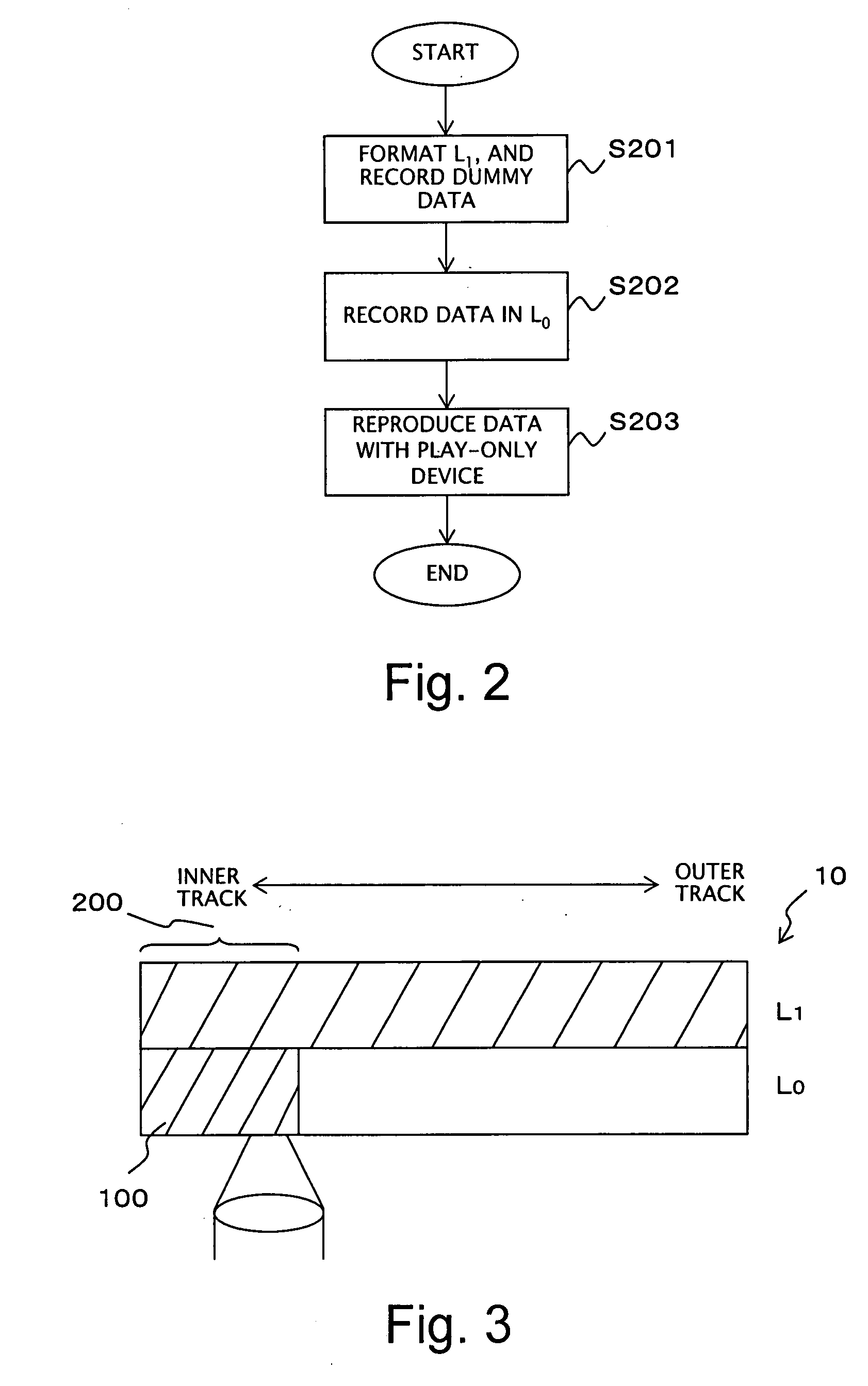
InactiveUS20070253307A1Reduce processing timeMechanical record carriersRecord information storageDummy dataData recording
Recording of data into a multilayer optical disk and reliable reproduction of the data are enabled. When user data are recorded on a multilayer optical disk having a first layer L0 and a second layer L1, the second layer L1 is formatted beforehand, to thus record dummy data. Subsequently, the user data are recorded into the first layer L0. Even after completion of recording of the user data at some point in the first layer L0, an area of the second layer L1 located immediately above or below a recorded area of the first layer L0 remains in a recorded state at all times. Compatibility with a play-only disk is maintained, and the play-only drive can reproduce the user data immediately after recording of the data.
Owner:TEAC CORP
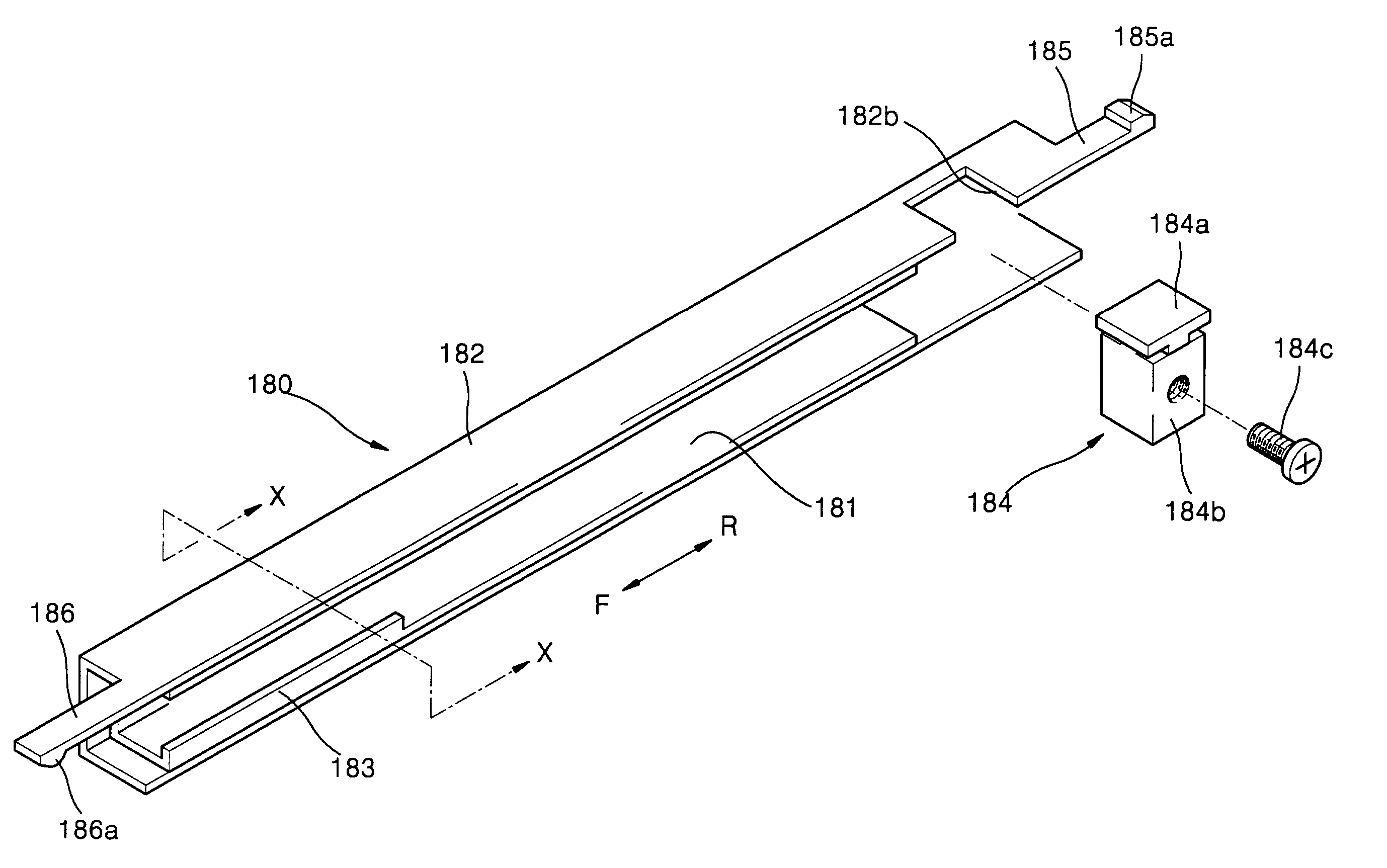
Tray guide mechanism for an optical disc drive
InactiveUS7020884B2Avoid verticalPrevent horizontal vibrationRecord information storageRecord carrier contruction detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tray guide mechanism for an optical disc drive guides a backward and forward movement of a tray installed to slide into and out of a housing made of a lower case and an upper case. The tray guide mechanism includes guide rails installed to slide into and out of both sides of the upper case, a guide rail supporting unit installed at both sides of the lower case, to prevent the guide rails from deviating from a backward and forward moving path, and rail combiners formed at both sides of the tray in a moving path of the tray, and combined with the guide rails to slide into the guide rails. The tray guide mechanism also includes a forward moving distance limiting unit to limit a moving distance of the tray and the guide rails in a direction to which the tray and the guide rails project to prevent the tray from detaching from the housing. The tray guide mechanism also includes vertical and horizontal restrainers to prevent vertical and horizontal movement of the tray. The guide rails are shaped such that the rail combiners are inserted thereinto, and includes rails which slide into and out of the rail combiners while remaining in contact with the rail combiners. The guide rails also include rail covers which are fixed to outer sides of the rails and slide into and out of the lower case while being in contact with the lower case. The tray guide mechanism is configured such that a guide rail is installed in contact with a rail and a rail cover, and thus is strengthened to firmly support the tray and is installed in a narrow space of the compact optical disc drive. Also, the tray guide mechanism includes the vertical and horizontal restrainers that prevent vertical and horizontal vibration or swaying of the tray.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical disc having a reduced planar thickness
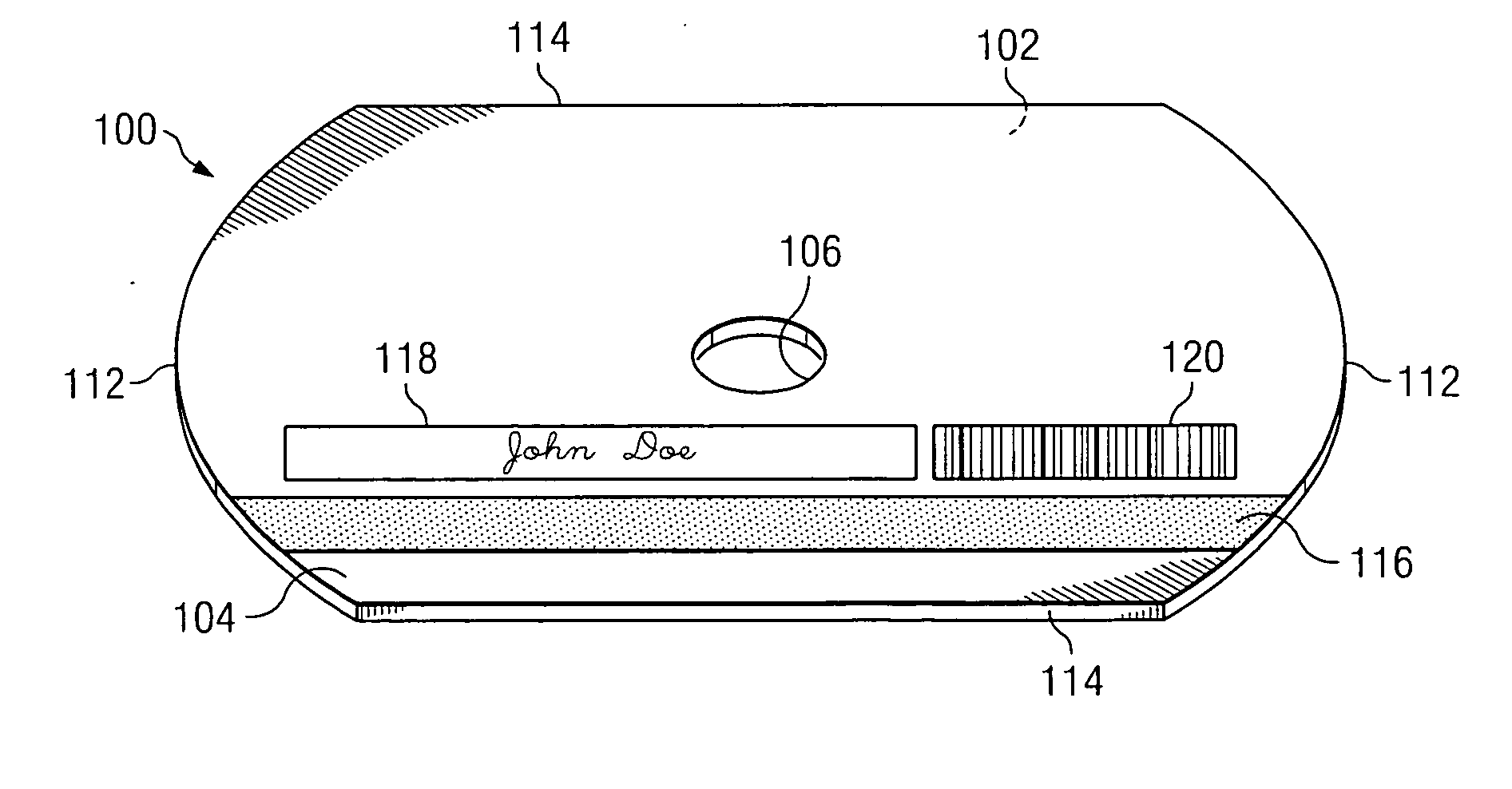
InactiveUS20060198281A1Reduced planar thicknessLittle and no reduction in readabilityAccessories for auxillary signalsInformation arrangementEngineeringOptical disc drive
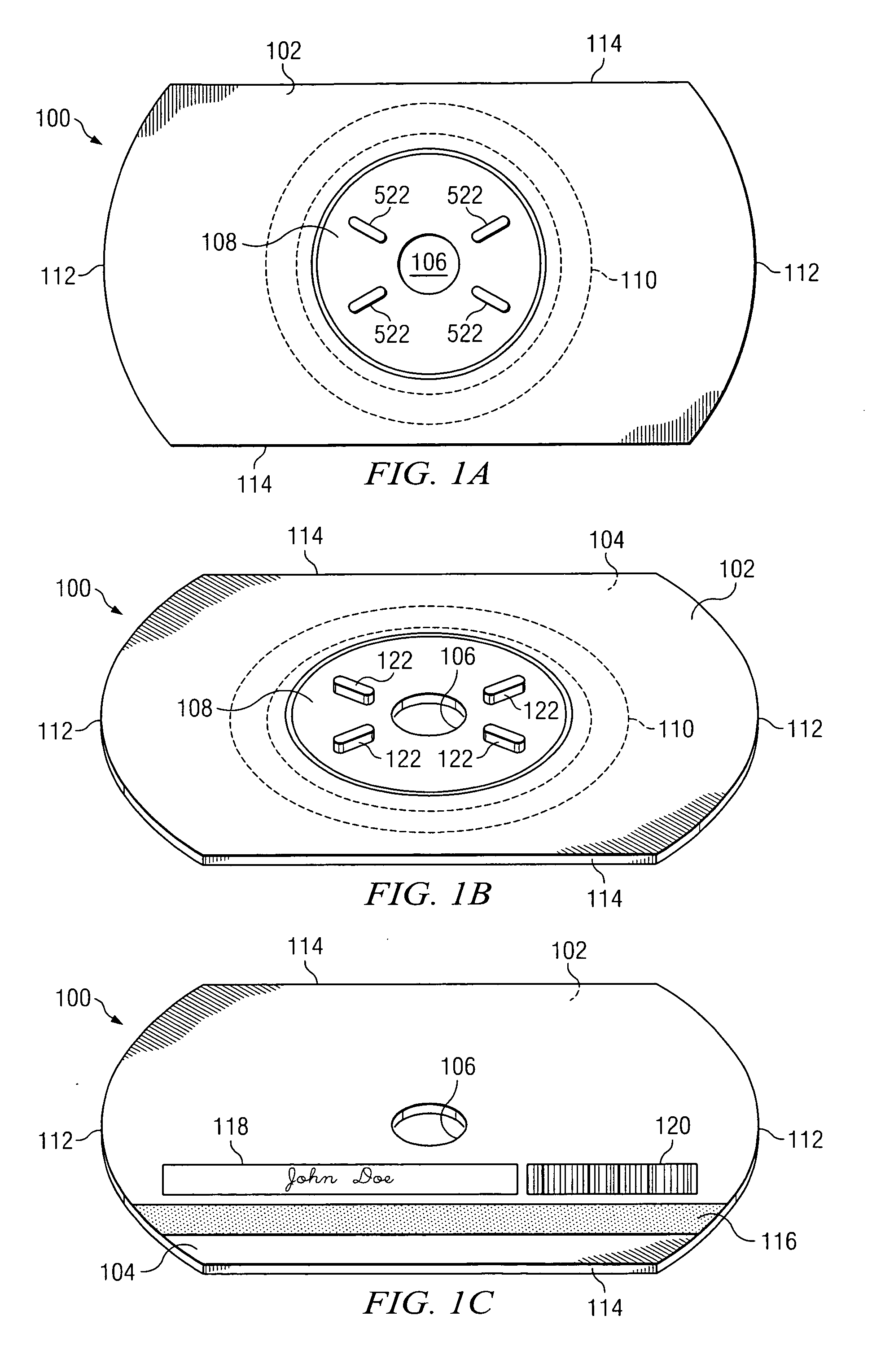
In accordance with the teachings of the present invention, an optical disc having a reduced planar thickness is provided. In accordance with a particular embodiment of the present invention, the optical disc includes a central clamping area that defines a central aperture operable to be engaged by a spindle mechanism of an optical disc drive, an optically-readable data storage area substantially surrounding the central clamping area, the optically-readable data storage area having a planar thickness of less than 1.20 mm, and one or more stacker elements coupled to, or integral with, the central clamping area, the stacker elements configured to increase the thickness of the central clamping area above the planar thickness of the optically-readable data storage area. In particular embodiments, the optical disc may further include a magnetic stripe disposed upon one surface of the optical disc.
Owner:ENXNET
Sensor system and methods for improved quantitation of environmental parameters
InactiveUS20050111328A1Improve functionalityCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsNoise levelPhotodetector
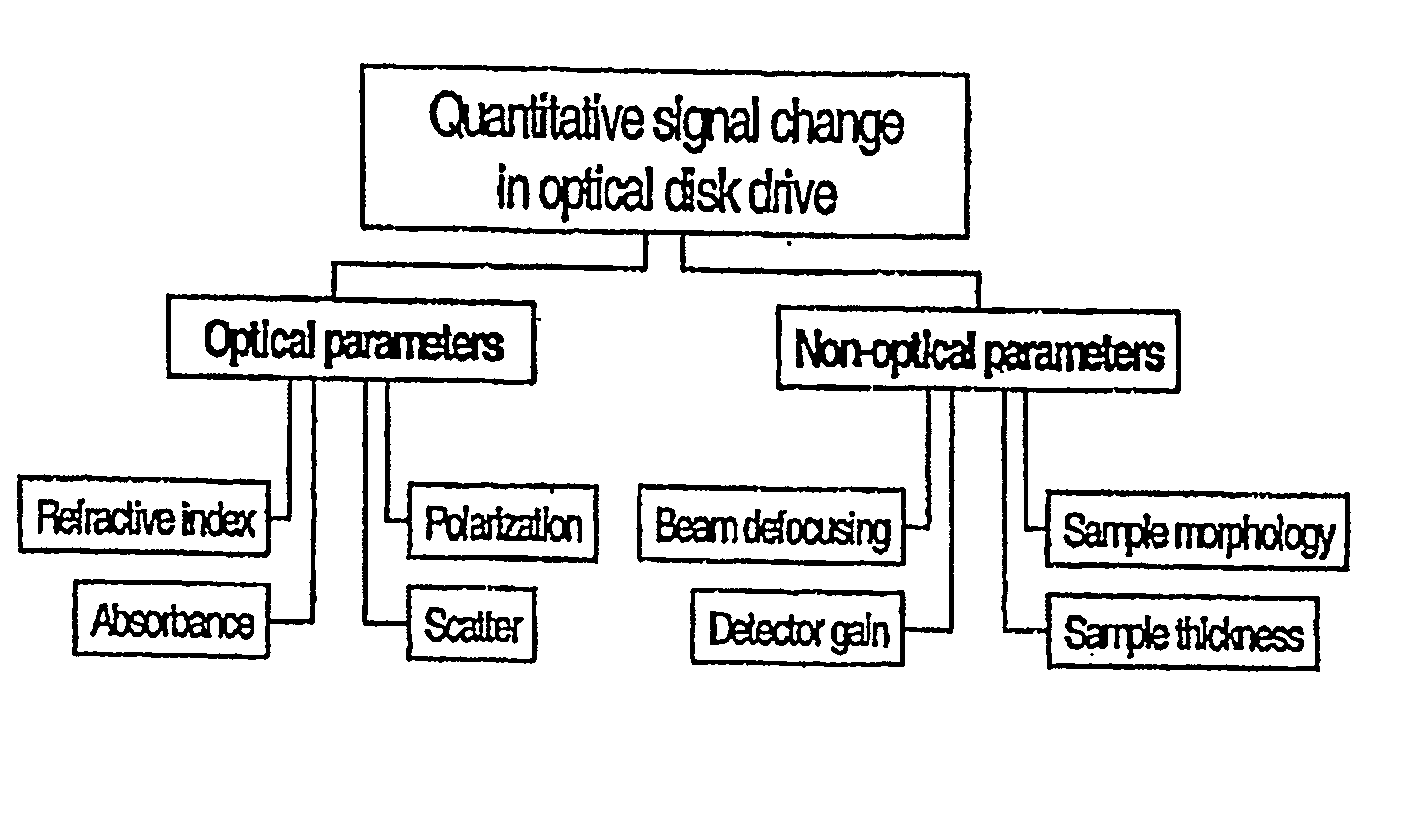
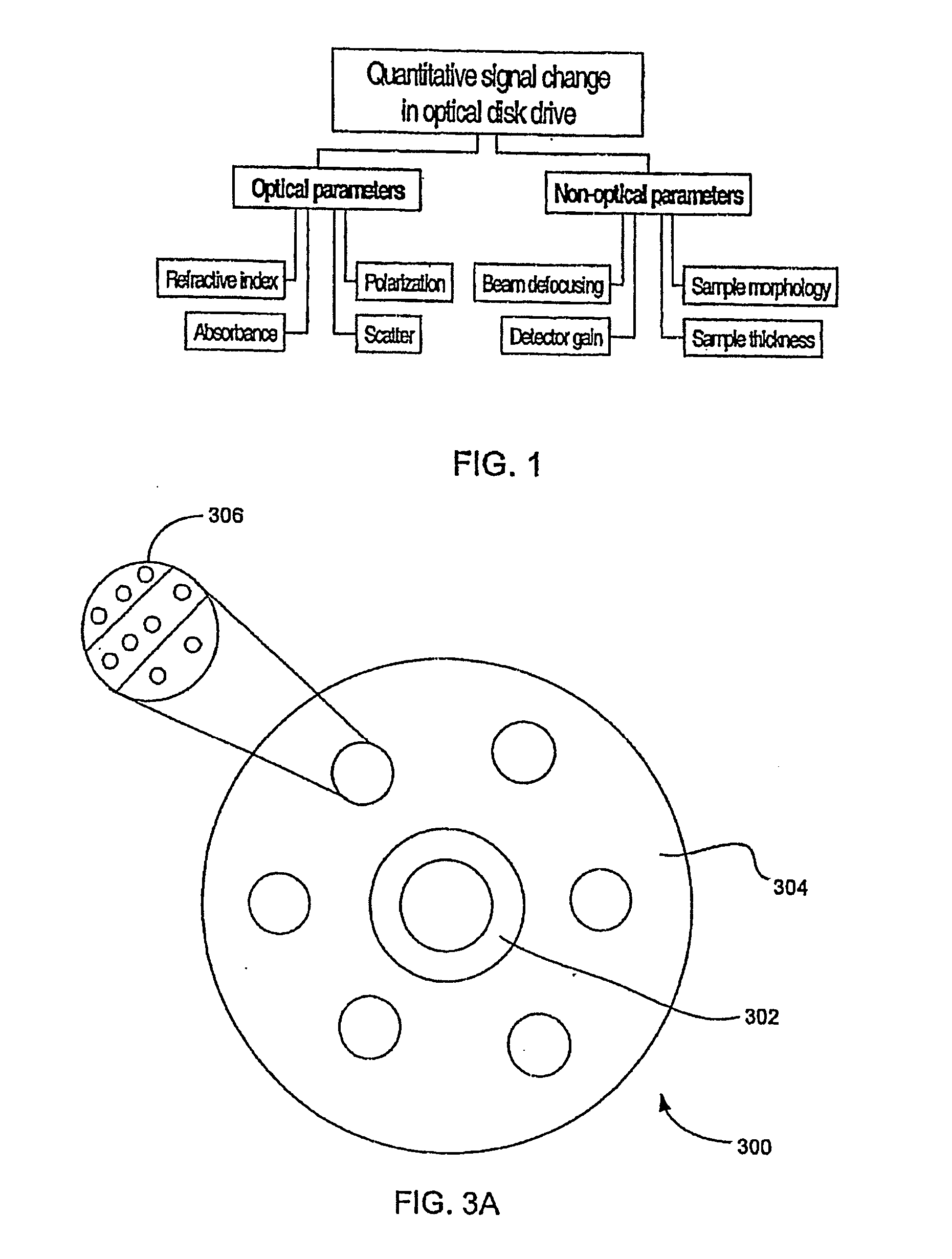
A system and method employing optical disk drives for quantitative analysis of chemical and biochemical parameters, in which sensor materials disposed on an optical disk are responsive to physical, chemical, biochemical, and other parameters in the environment. The light interacts with the sensor materials when the light propagates through the sensor material, reflects off the optical media's reflective layer, and propagates back through the sensor region. The interacted light is captured by a photodetector, which outputs a response analog signal, for example, an analog voltage signal, which is indicative of a condition of the environment to which the sensor materials have been exposed. The system includes software algorithms which cause the laser source and optical detector to move to a specified location or logical block address of the disk, measure the optical signal during disk rotation, display a map of the sensor material response, and reduce the noise level in the measured signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
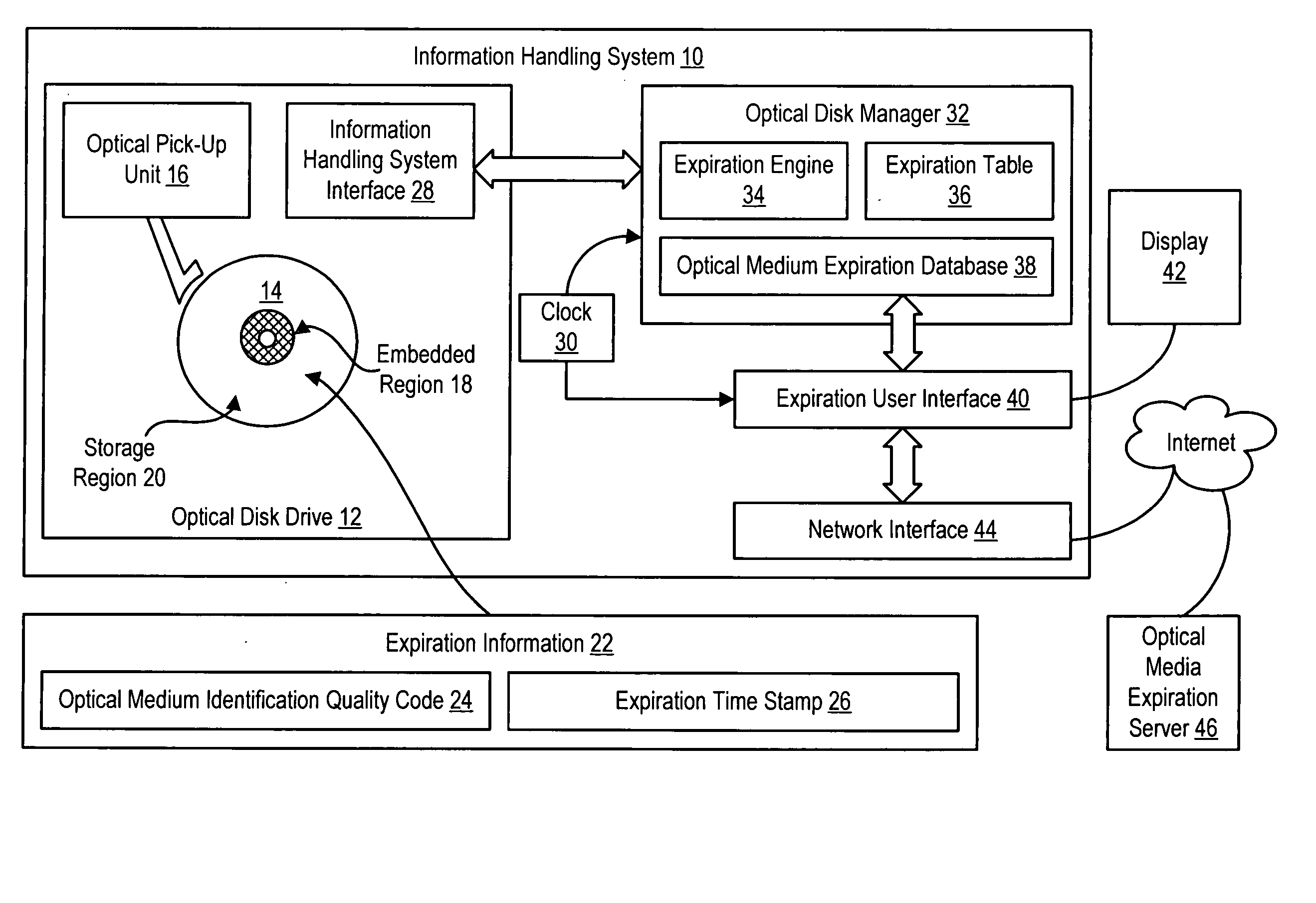
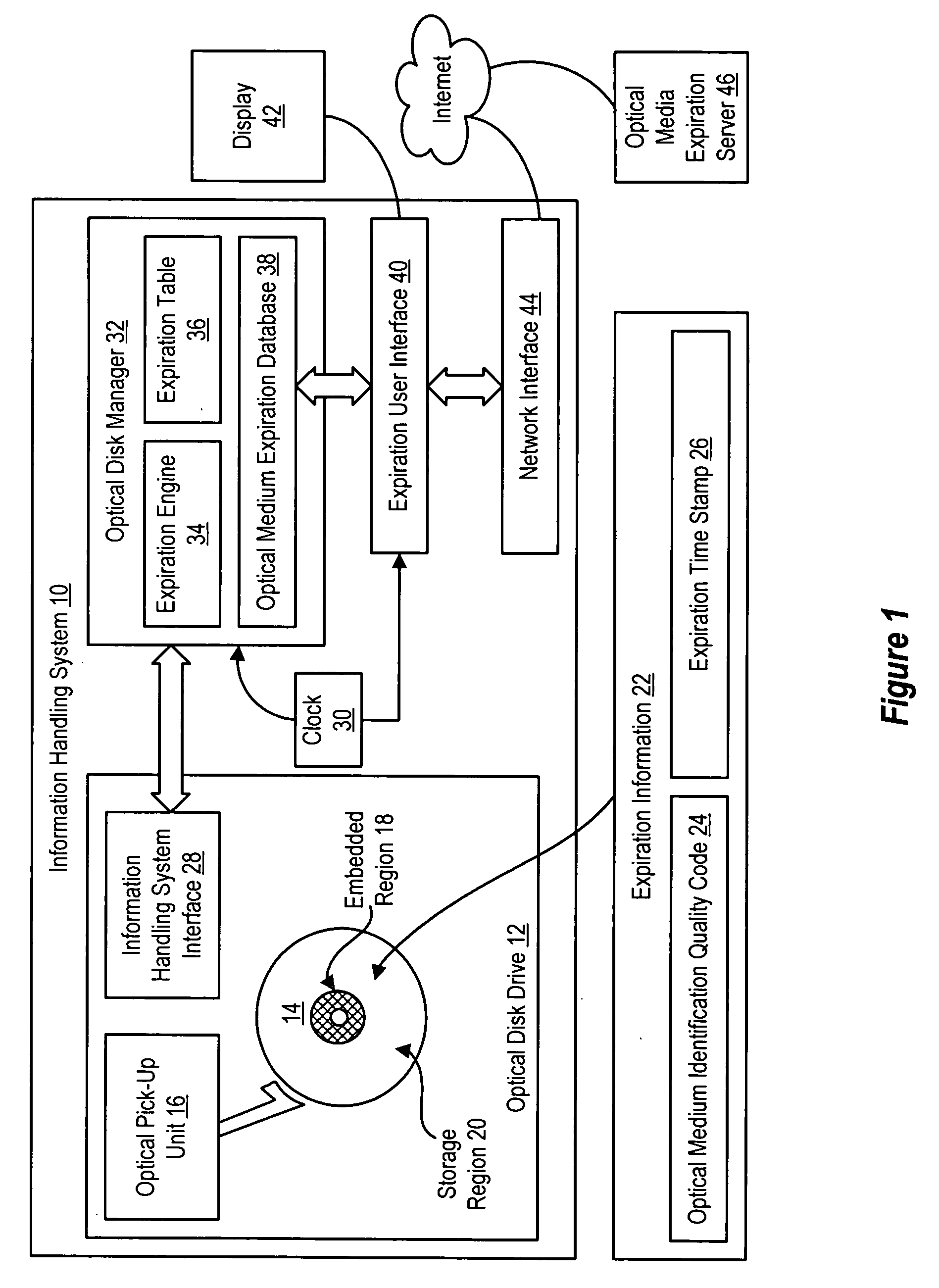
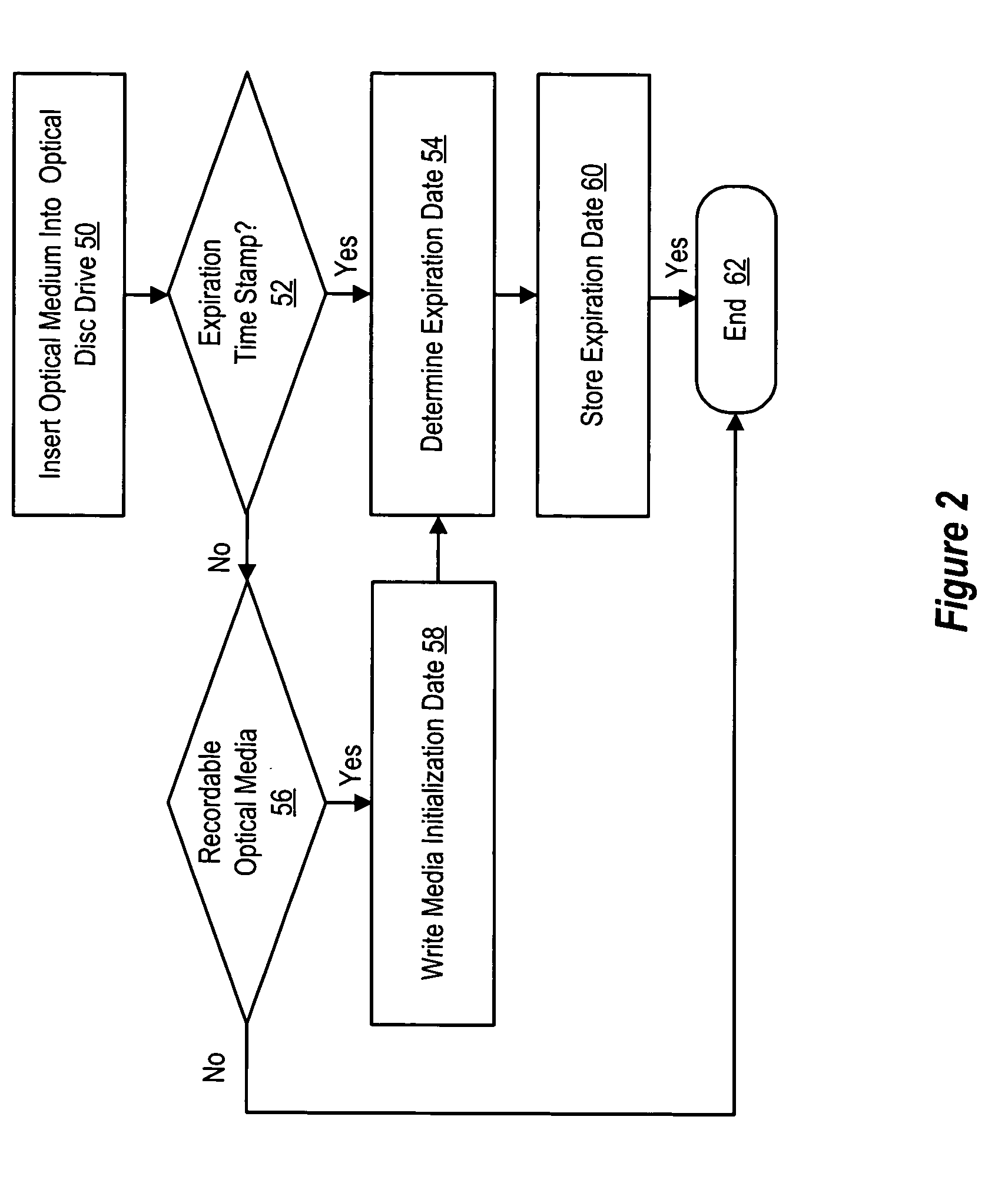
System and method for optical media information storage life tracking
ActiveUS20060023595A1Improve reliabilityUsers' confidence is enhancedChildren cyclesAccessories for auxillary signalsCompact discInformation processing
Expiration information stored on an optical medium is applied to determine an expiration date of the optical medium that provides a predetermined reliability of information archived on the optical medium, such as a predetermined acceptable defect level of the information at the expiration date. An expiration engine associated with an information handling system or optical disc drive determines the expiration date from one or more factors, such as the manufacture date of read-only optical media, the initialization date of recordable optical media, a quality rating associated with a defect growth rate over time of the optical media, and a desired reliability. In one embodiment, the expiration engine writes expiration information to the optical media, such as a date stamp at initialization of a recordable optical medium. Alternatively, an expiration date is stored on an information handling system to provide expiration warnings a predetermined time before the expiration date.
Owner:DELL PROD LP +2
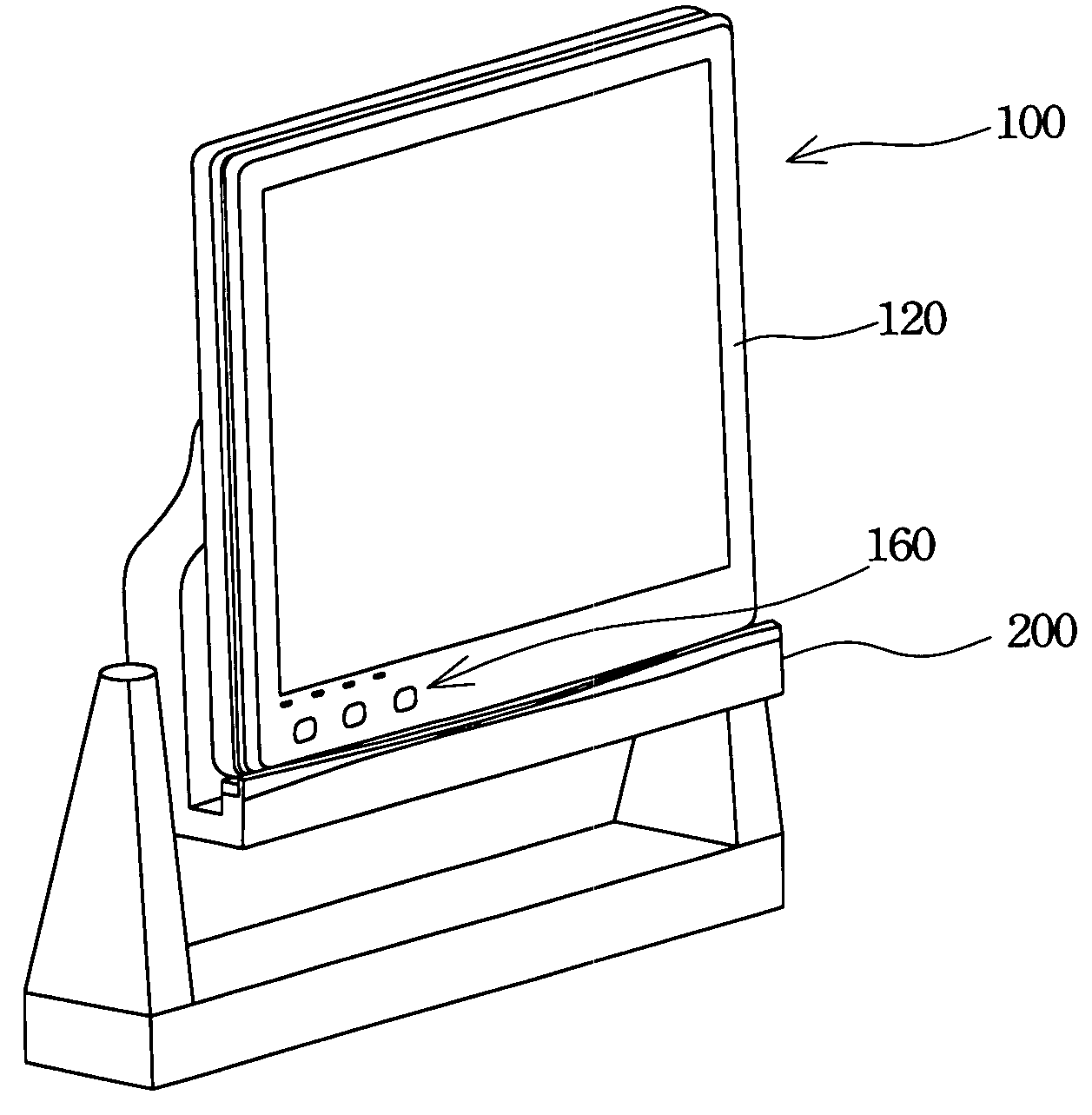
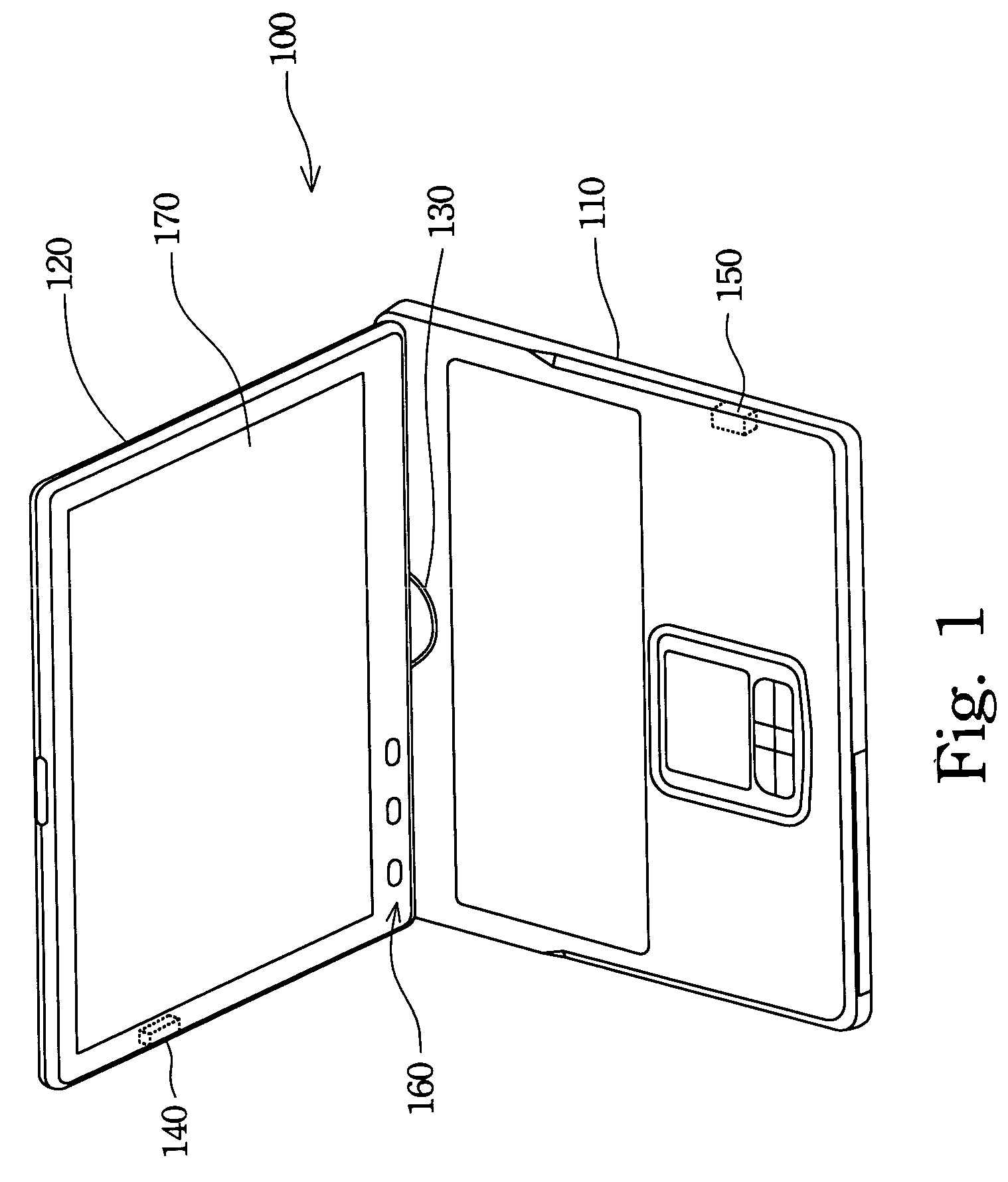
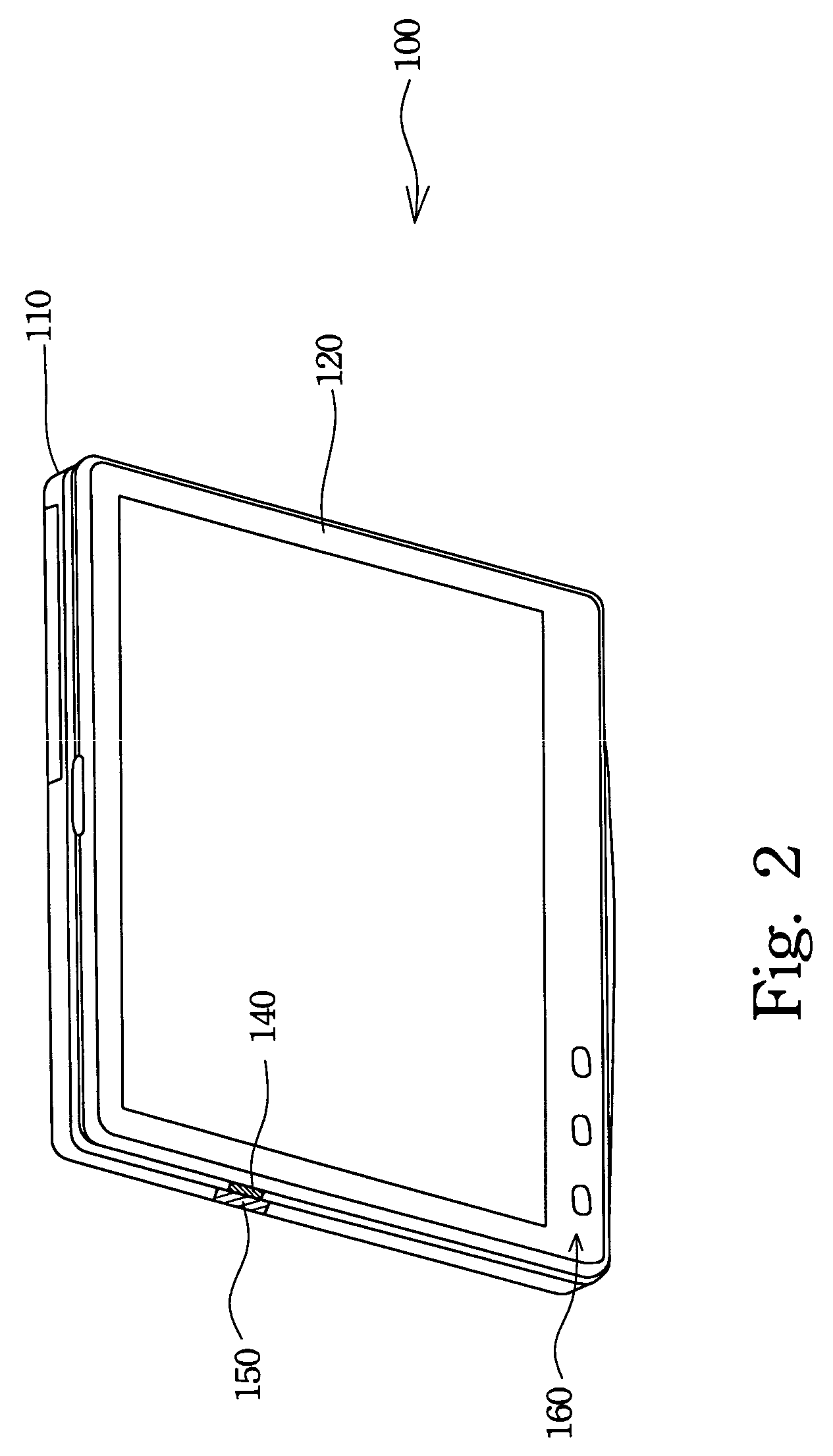
Liquid crystal display with optical disk drive control functions
InactiveUS7148877B2Extend effectively application scopeReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display with optical disk drive control functions is described. The liquid crystal display is utilized in a notebook / tablet dual-purpose computer. The liquid crystal display has a liquid crystal display panel, a plurality of control buttons, and an option determining device. The control buttons can directly control the optical disk drive to play an optical disk content on the liquid crystal display panel after the control functions of the control buttons are set by the option determining device. The option determining device is capable of switching within predetermined working functions of the liquid crystal display. The computer is capable of playing the optical disk content as a central processing unit thereof shuts down. The option determining device further includes an option controller and an option inductor to switch the liquid crystal display to a handwriting input panel and set the functions of the control buttons.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com