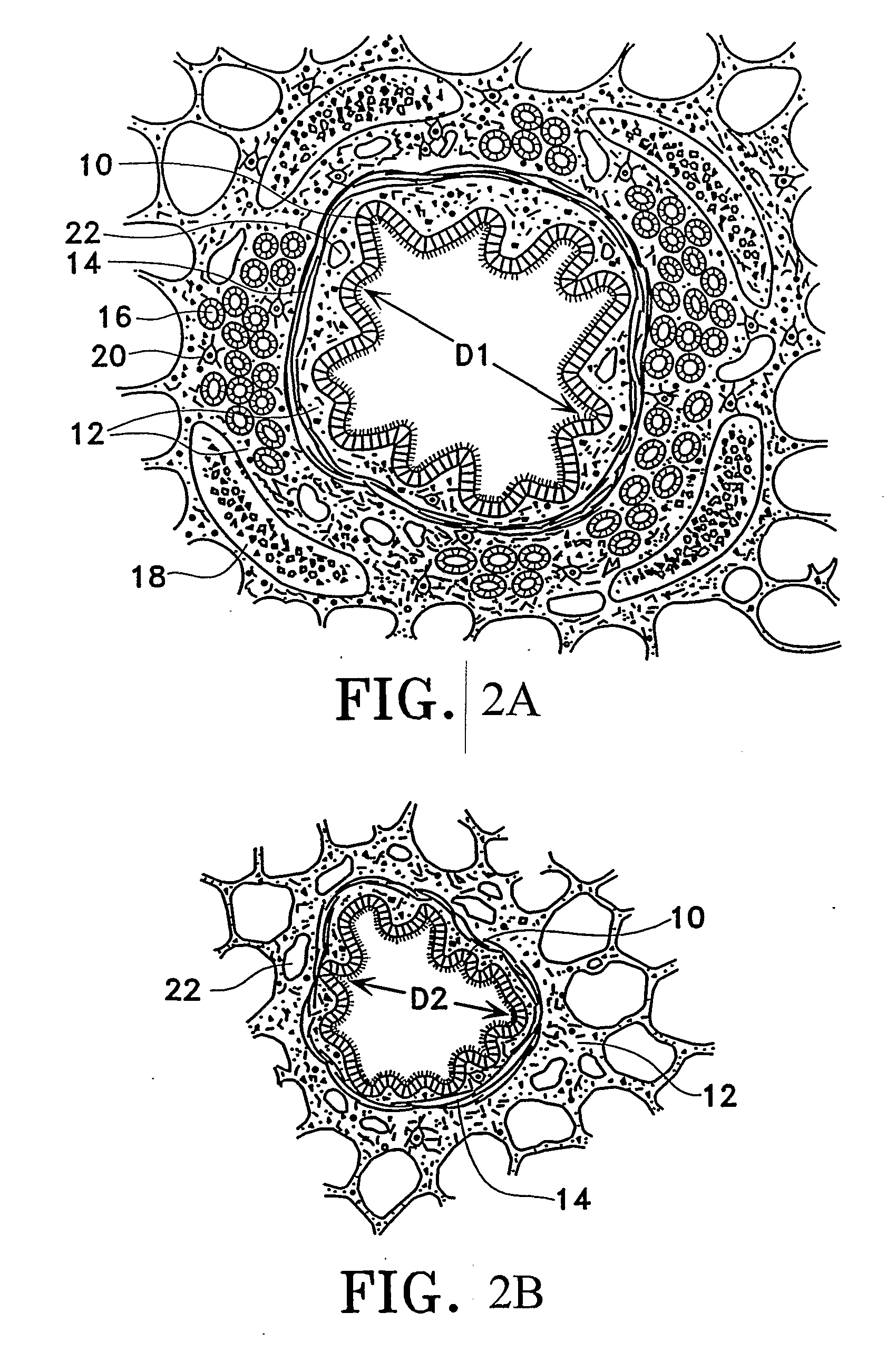
Patents
Literature
714 results about "Gain factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The amplification factor, also called gain , is the extent to which an analog amplifier boosts the strength of a signal . Amplification factors are usually expressed in terms of power .
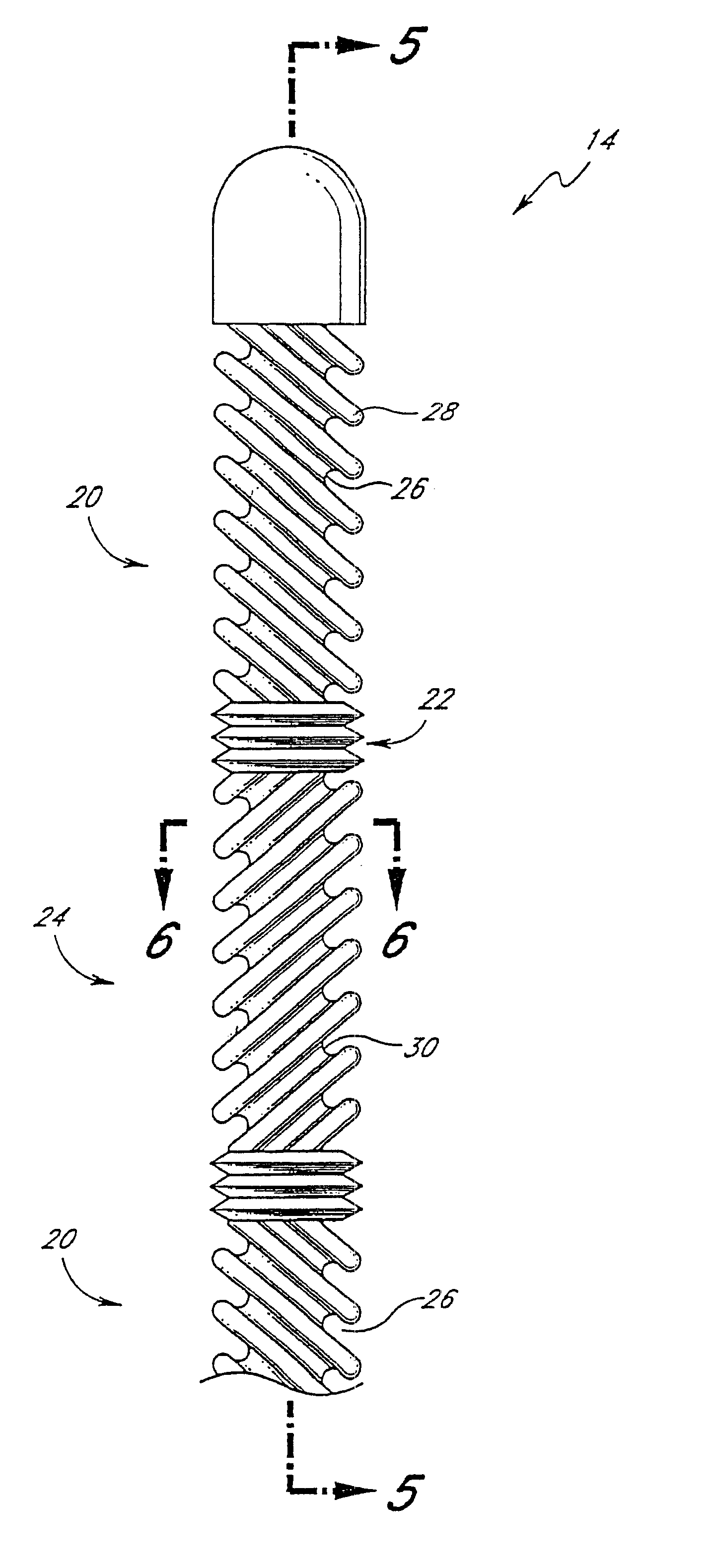
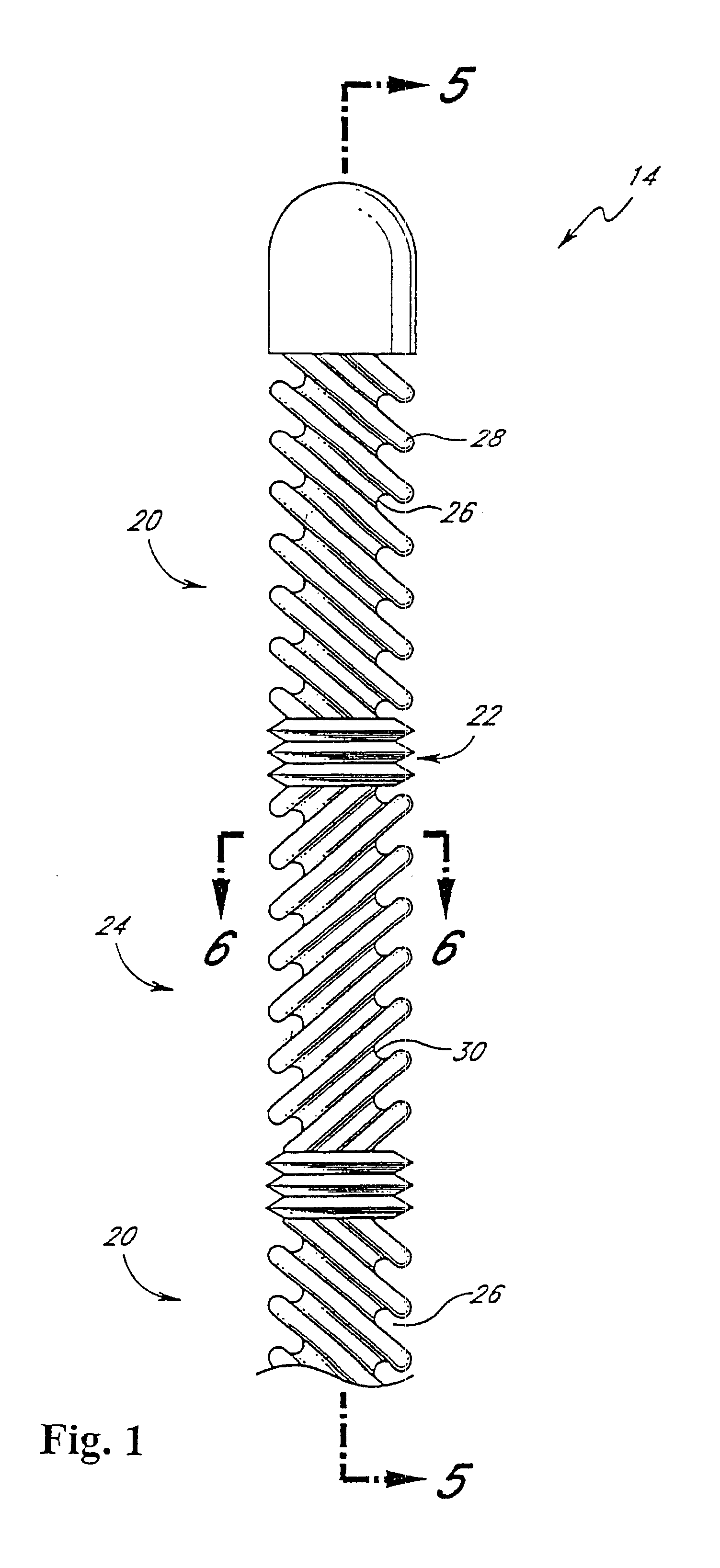
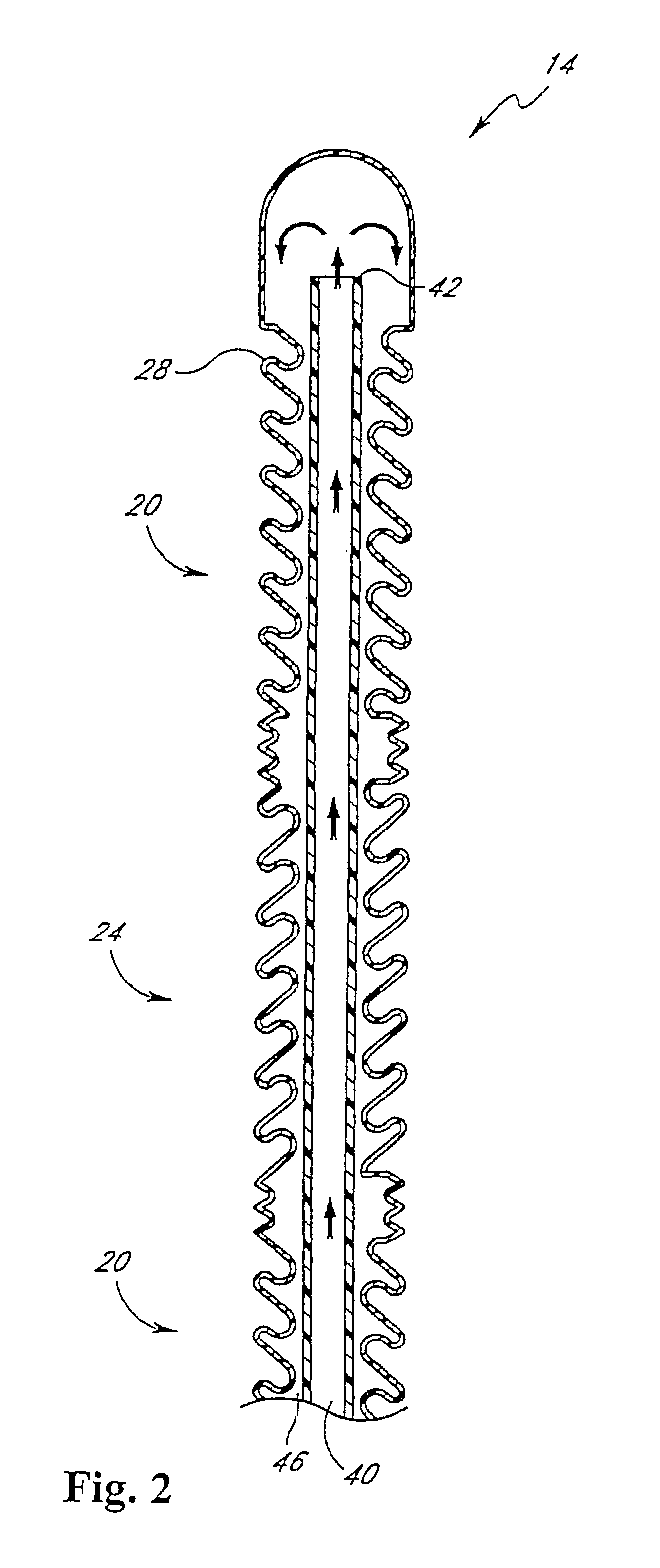
Micropressors, devices and methods for use in analyte monitoring systems
ActiveUS20060063218A1Reduce lag timeImprove usabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSensorsAnalyteMonitoring system
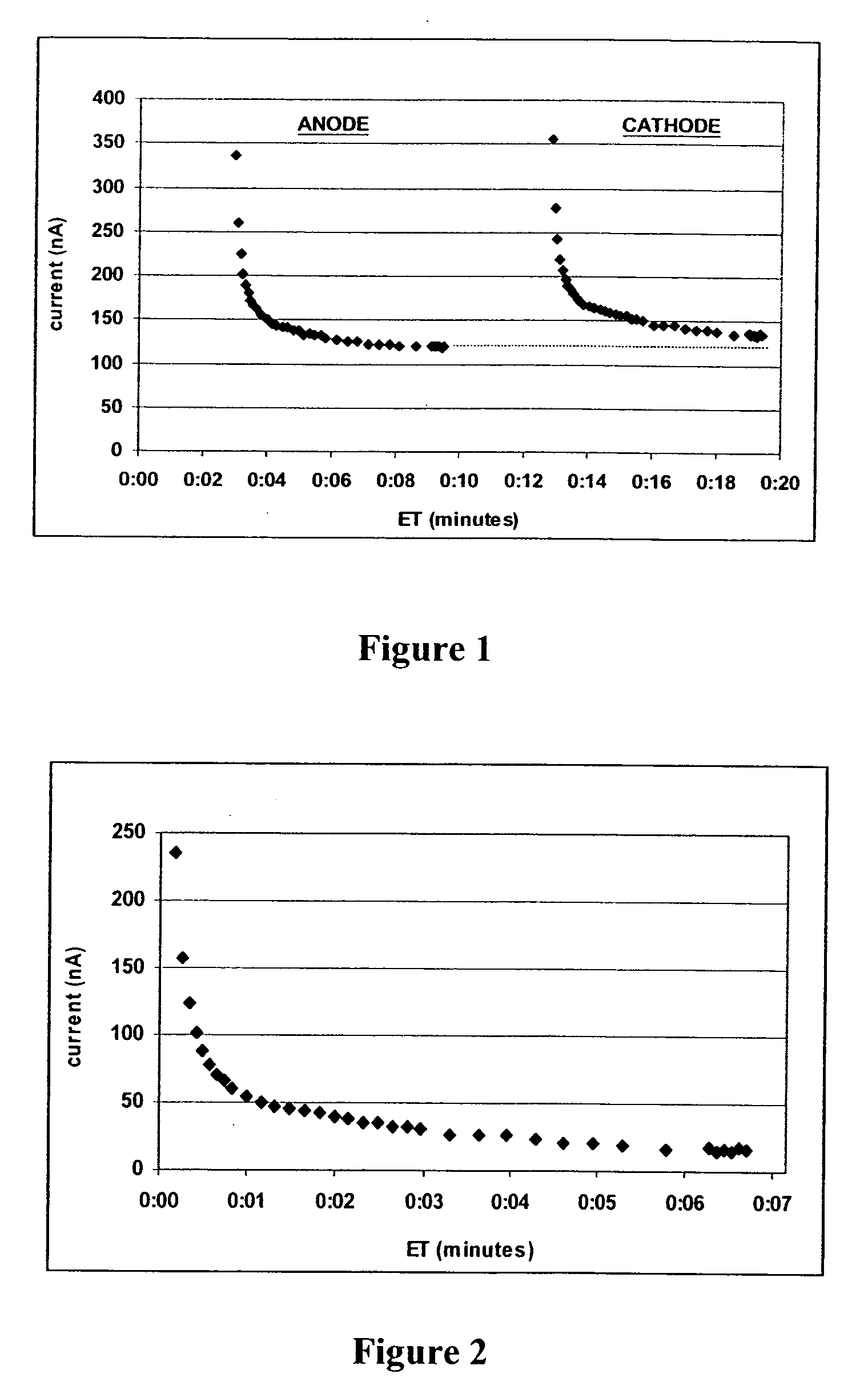
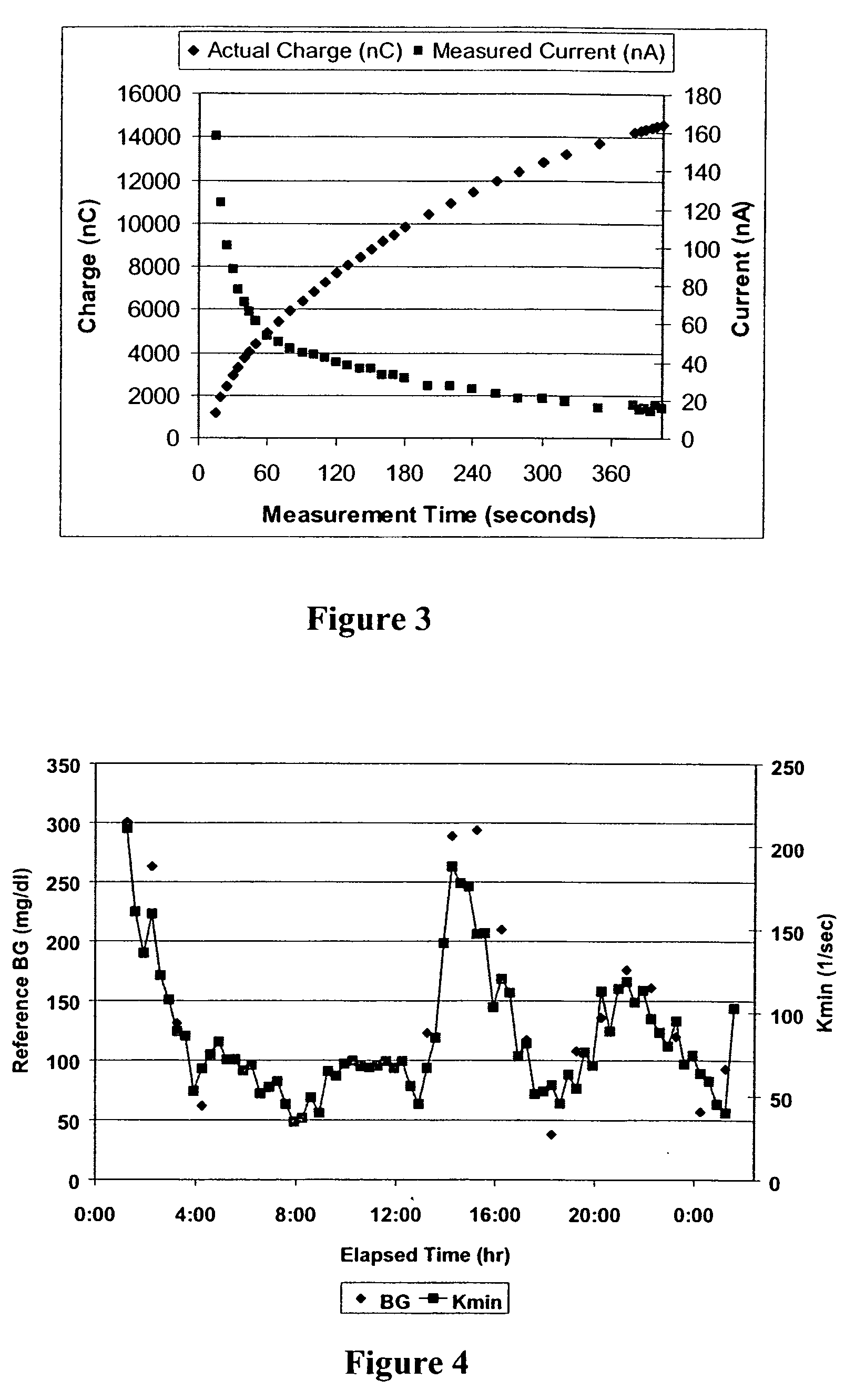
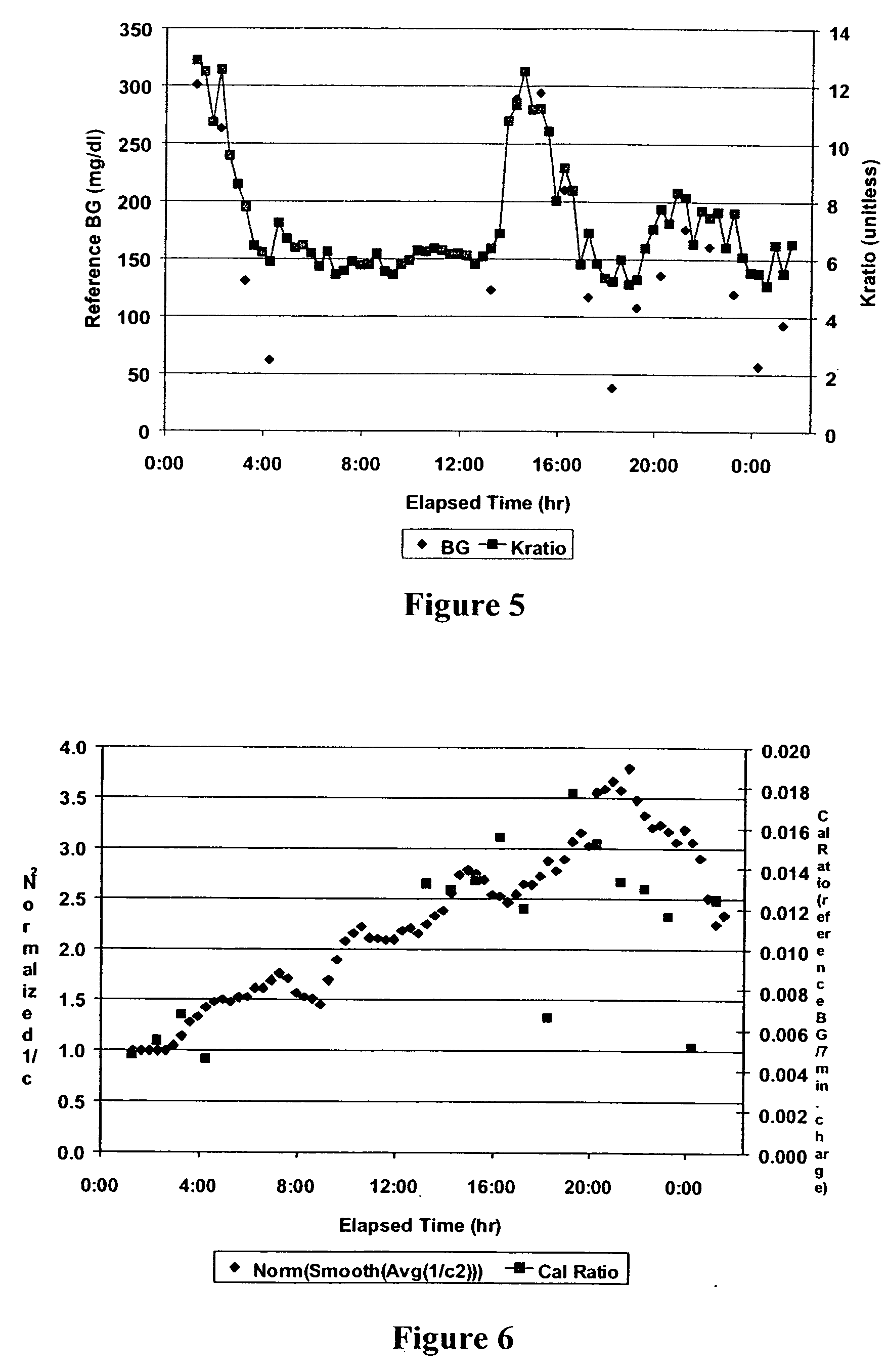
The present invention comprises one or more microprocessors programmed to execute methods for improving the performance of an analyte monitoring device including prediction of glucose levels in a subject by utilizing a predicted slower-time constant (1 / k2). In another aspect of the invention, pre-exponential terms (1 / c2) can be used to provide a correction for signal decay (e.g., a Gain Factor). In other aspects, the present invention relates to one or more microprocessors comprising programming to control execution of (i) methods for conditional screening of data points to reduce skipped measurements, (ii) methods for qualifying interpolated / extrapolated analyte measurement values, (iii) various integration methods to obtain maximum integrals of analyte-related signals, as well as analyte monitoring devices comprising such microprocessors. Further, the present invention relates to algorithms for improved optimization of parameters for use in prediction models that require optimization of adjustable parameters.
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
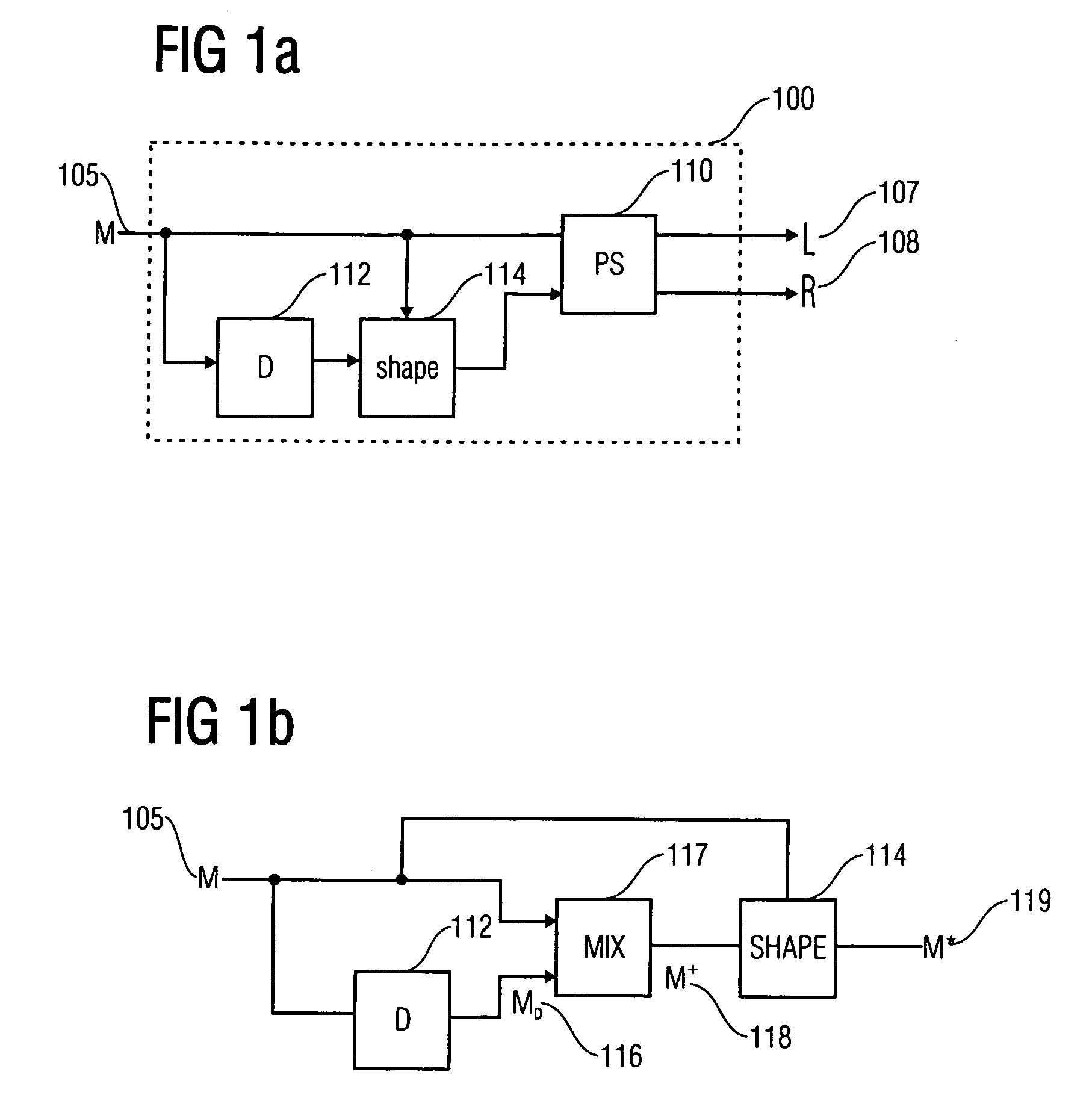
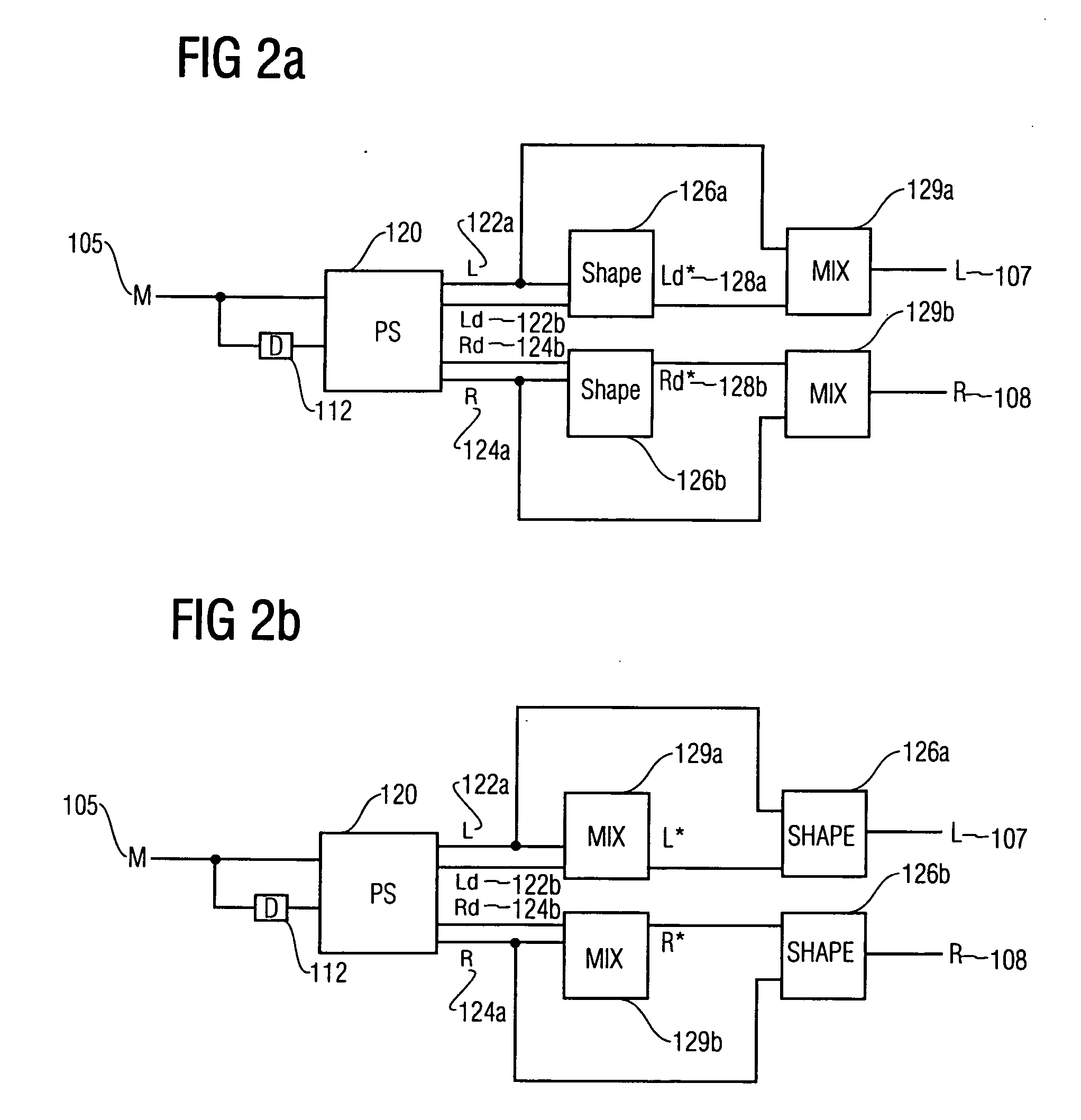
Envelope shaping of decorrelated signals
ActiveUS20060239473A1Avoid introducingEffective shapingSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsFrequency spectrumDistortion
The envelope of a decorrelated signal derived from an original signal can be shaped without introducing additional distortion, when a spectral flattener is used to spectrally flatten the spectrum of the decorrelated signal and the original signal prior to using the flattened spectra for deriving a gain factor describing the energy distribution between the flattened spectra, and when the so derived gain factor is used by an envelope shaper to timely shape the envelope of the decorrelated signal.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +1
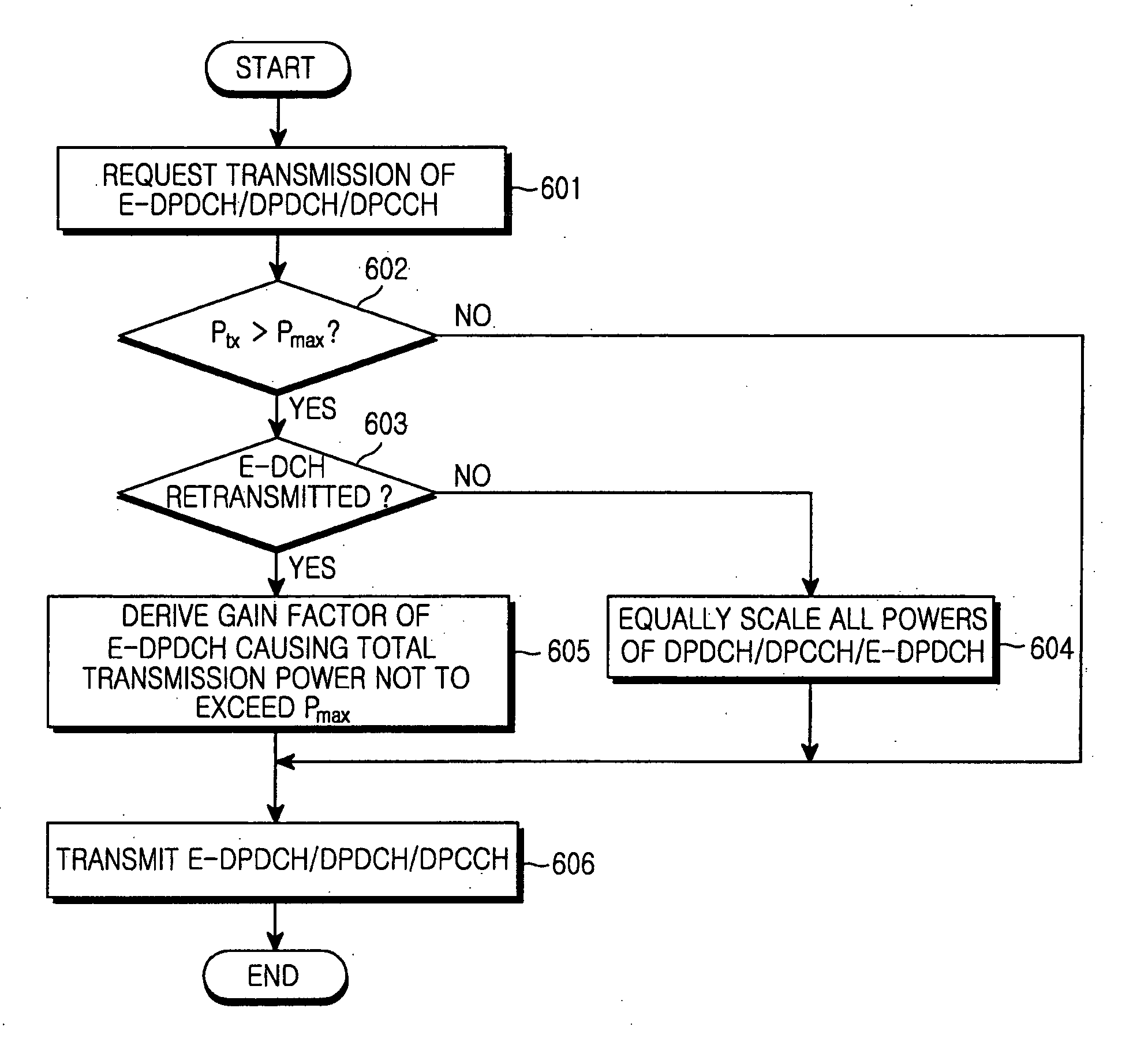
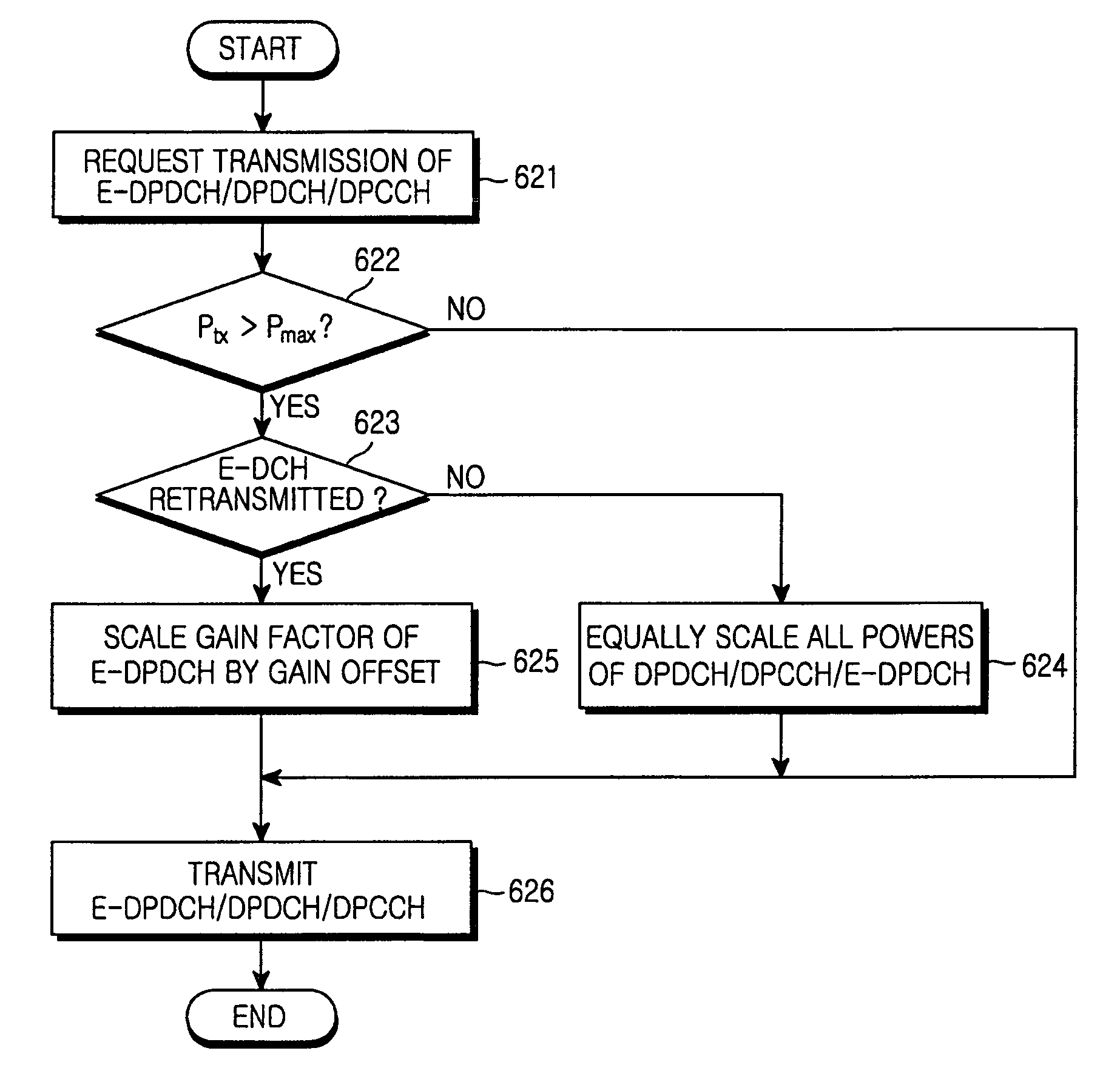
Method and apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting enhanced uplink service
ActiveUS20060003787A1Effective controlReduce transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTransmitted powerControl channel
A method and an apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting an enhanced uplink service are provided. A Transport Format Combination (TFC) selector determines TF information for data to be transmitted through a first data channel not supporting Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) and a second data channel supporting HARQ, and determines gain factors for the first and second data channel, and first and second control channel carrying control information for the first and second data channel. The gain factors are input to a physical channel transmission controller, and the physical channel transmission controller reduces the gain factor for the second channel if total transmit power required for transmission of the channels exceeds the predetermined maximum allowed power. A gain scaler adjusts transmit powers of the channels using the scaled gain factor and gain factors for the first data channel, the first control channel and the second control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
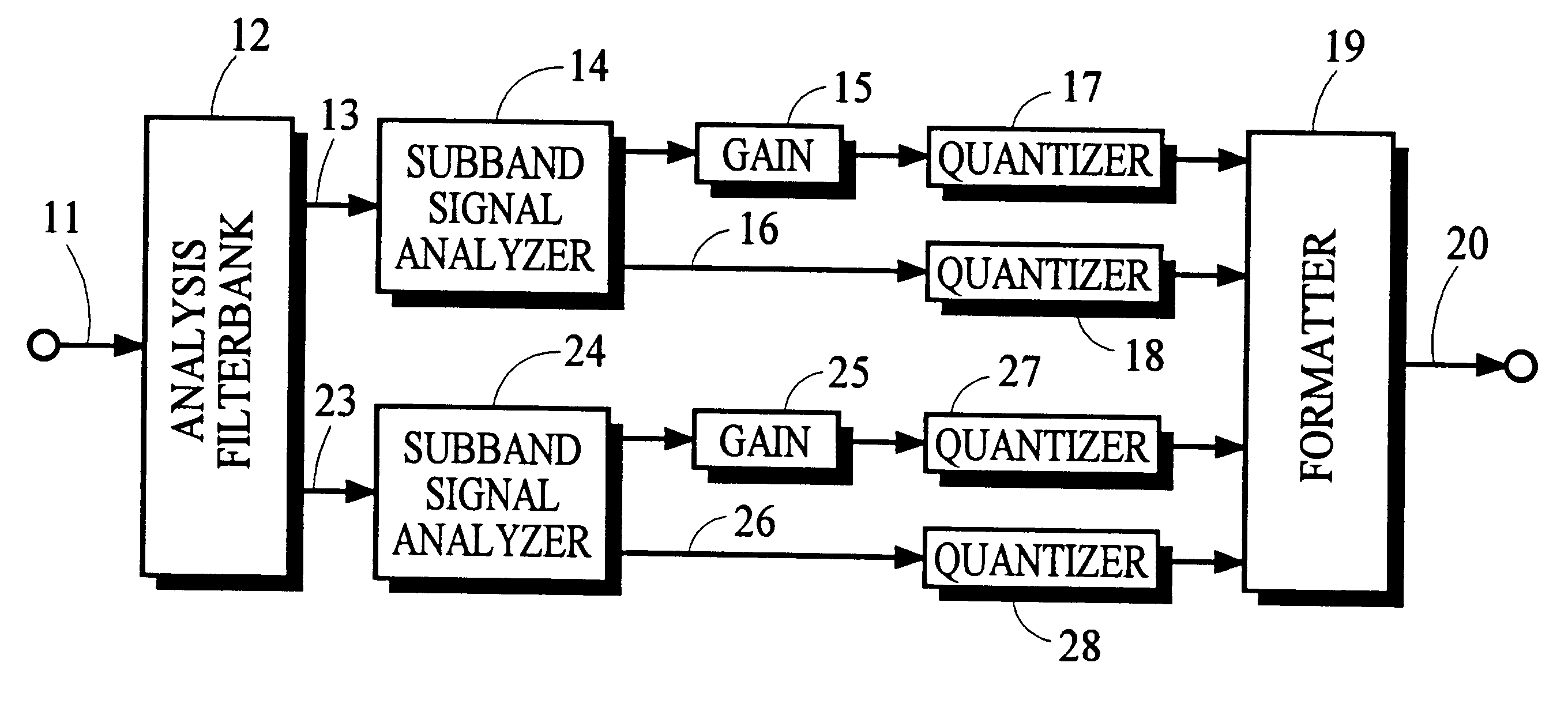
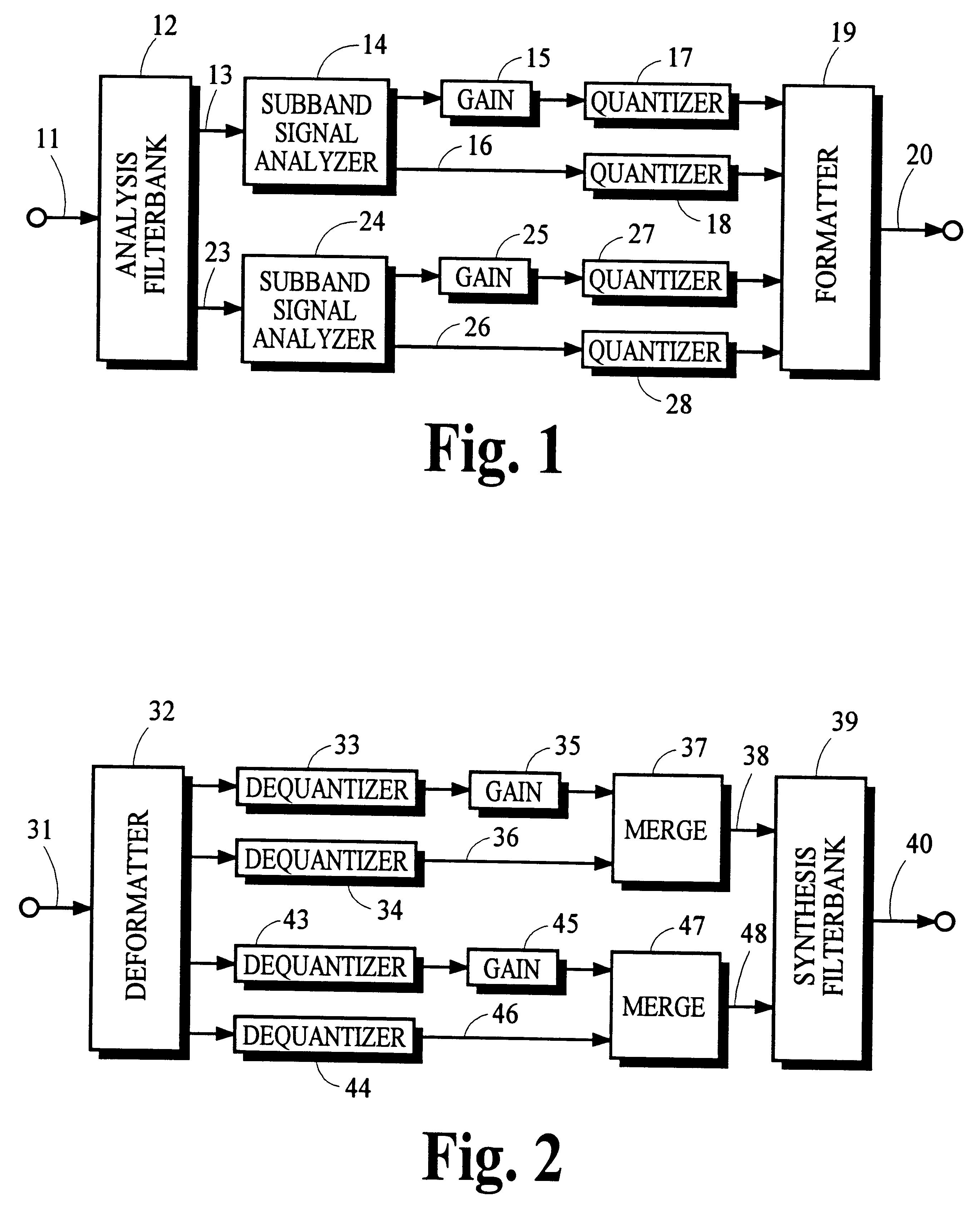
Using gain-adaptive quantization and non-uniform symbol lengths for improved audio coding
InactiveUS6246345B1Good coding gainEfficient executionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNormal densityIntra-frame
Techniques like Huffman coding can be used to represent digital audio signal components more efficiently using non-uniform length symbols than can be represented by other coding techniques using uniform length symbols Unfortunately, the coding efficiency that can be achieved by Huffman coding depends on the probability density function of the information to be coded and the Huffman coding process itself requires considerable processing and memory resources. A coding process that uses gain-adaptive quantization according to the present invention can realize the advantage of using non-uniform length symbols while overcoming the shortcomings of Huffman coding. In gain-adaptive quantization, the magnitudes of signal components to be encoded are compared to one or more thresholds and placed into classes according to the results of the comparison. The magnitudes of the components placed into one of the classes are modified according to a gain factor that is related to the threshold used to classify the components. Preferably, the gain factor may be expressed as a function of only the threshold value. Gain-adaptive quantization may be used to encode frequency subband signals in split-band audio coding systems. Additional features including cascaded gain-adaptive quantization, intra-frame coding, split-interval and non-overloading quantizers are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for determining the effective thermal mass of a body or organ using a cooling catheter
A method and apparatus is provided for determining an effective thermal mass of a patient. The effective thermal mass is employed to determine a gain factor used in a feedback control system controlling patient temperature. The method begins by inducing hypothermia or hyperthermia in at least a selected portion of the patient with a device having a heat transfer surface. Next, power is transferred between the device and the patient. A change in temperature over time, which arises in the selected portion of the patient, is measured while performing the step of inducing hypothermia or hyperthermia. Finally, an effective thermal mass is calculated based on the measured power and the measured temperature change over time.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
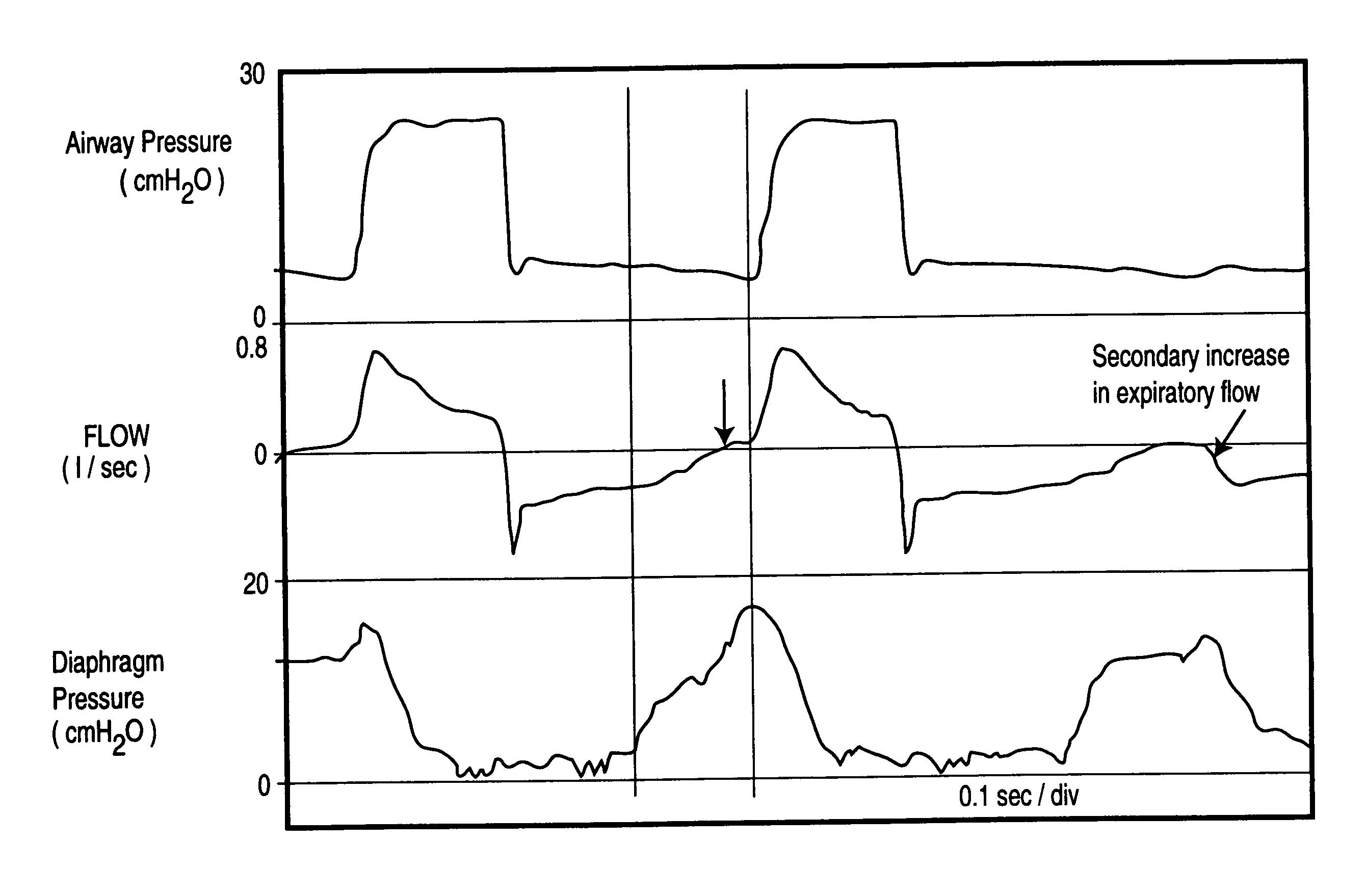
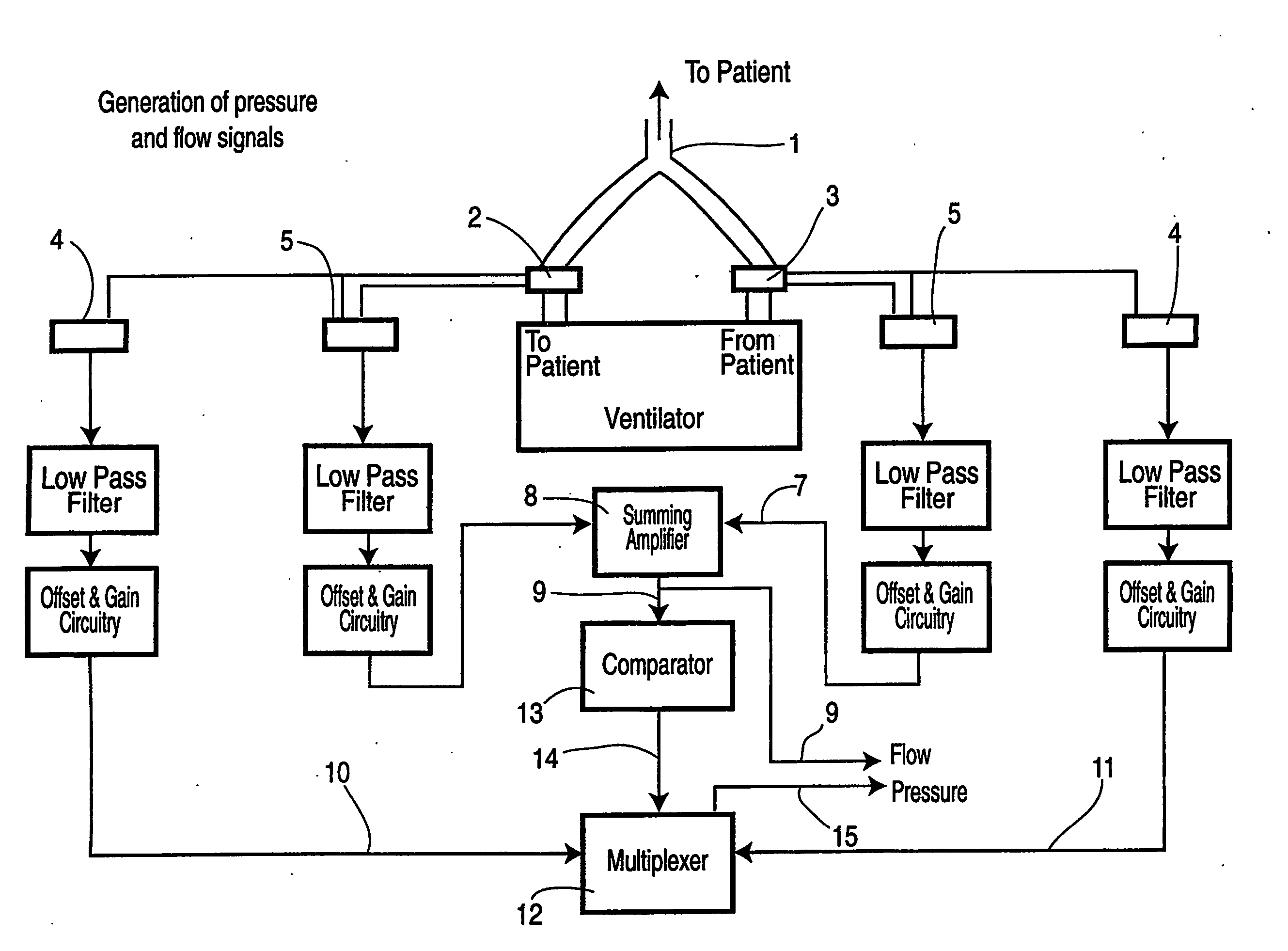
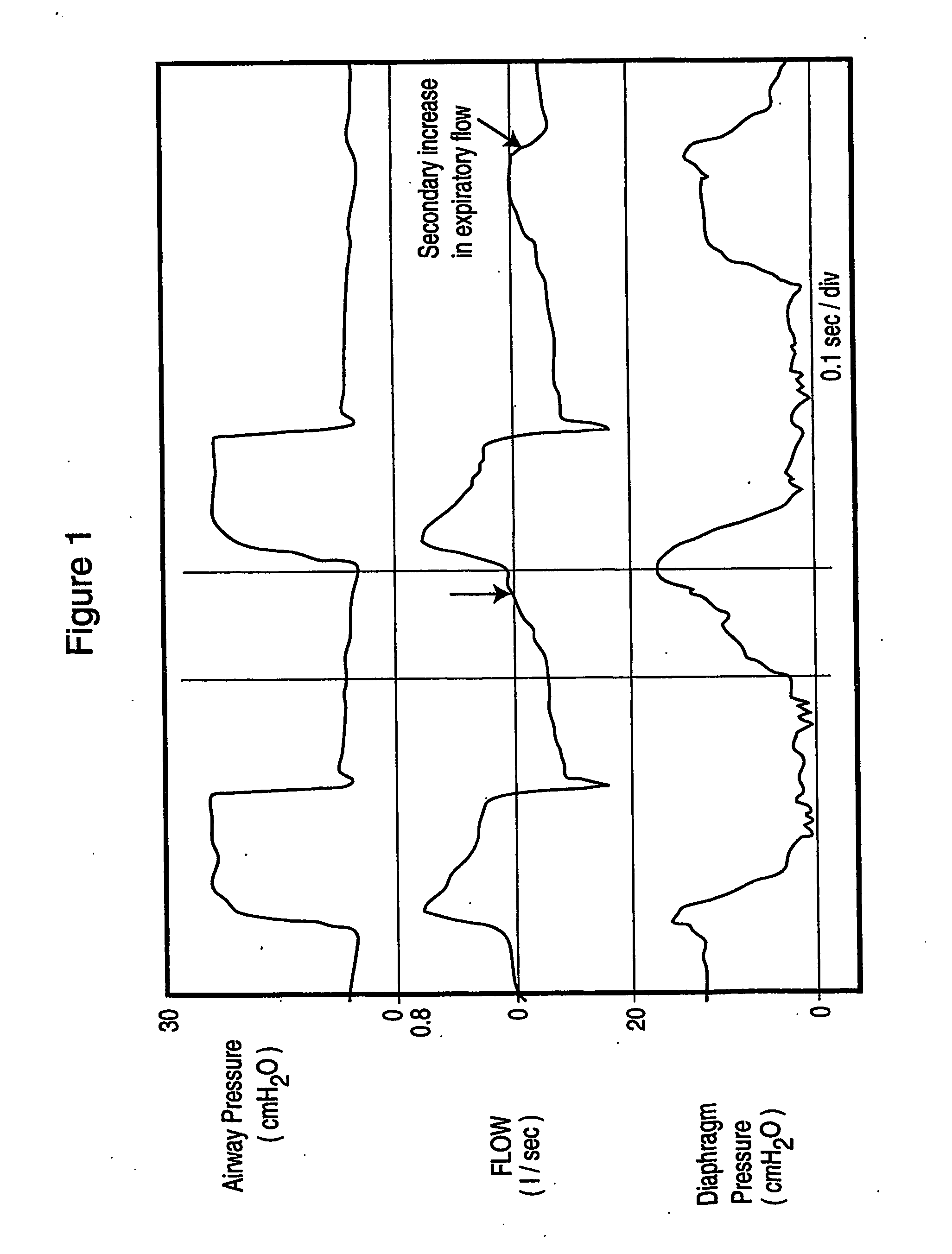
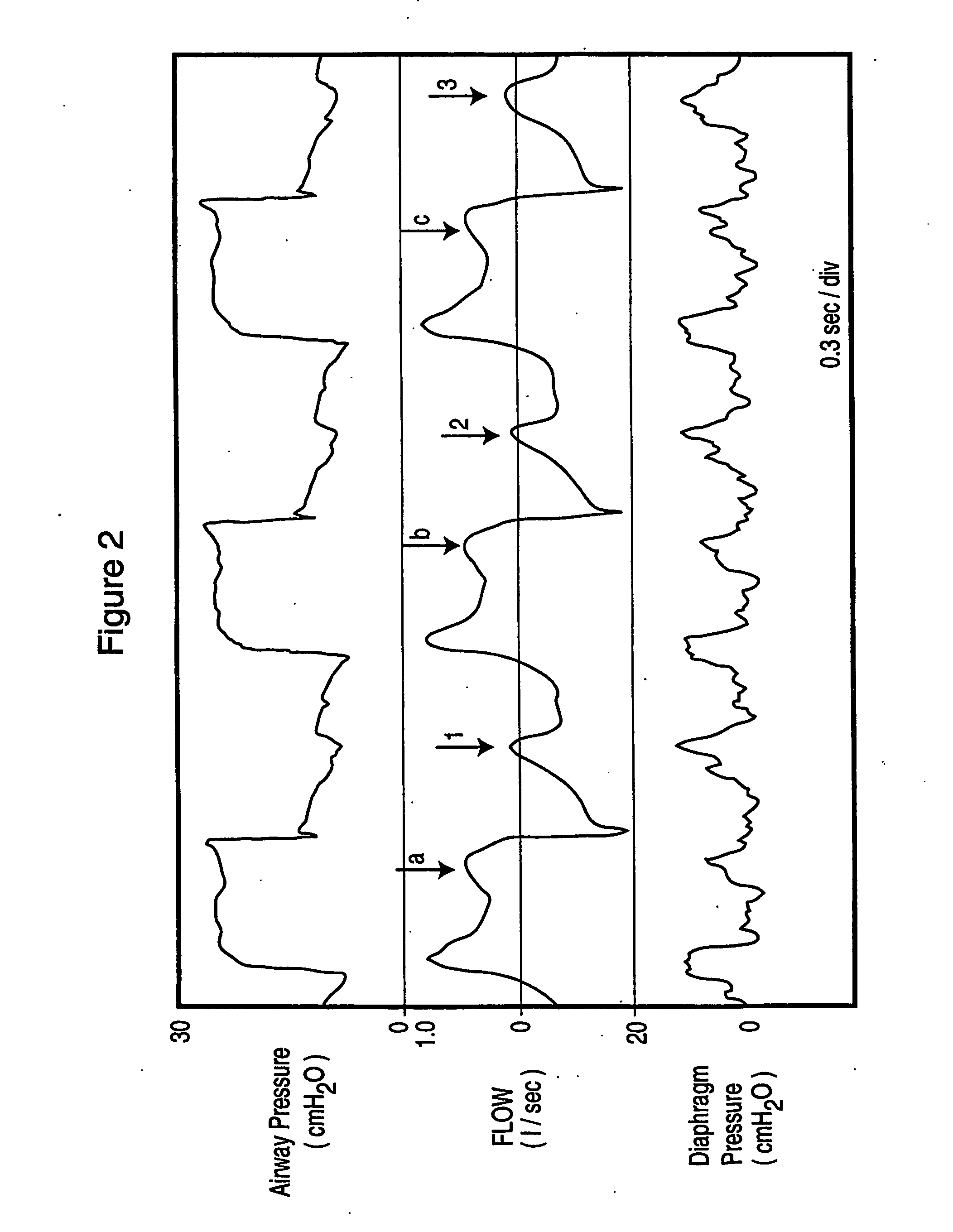
Method and device for monitoring and improving patient-ventilator interaction
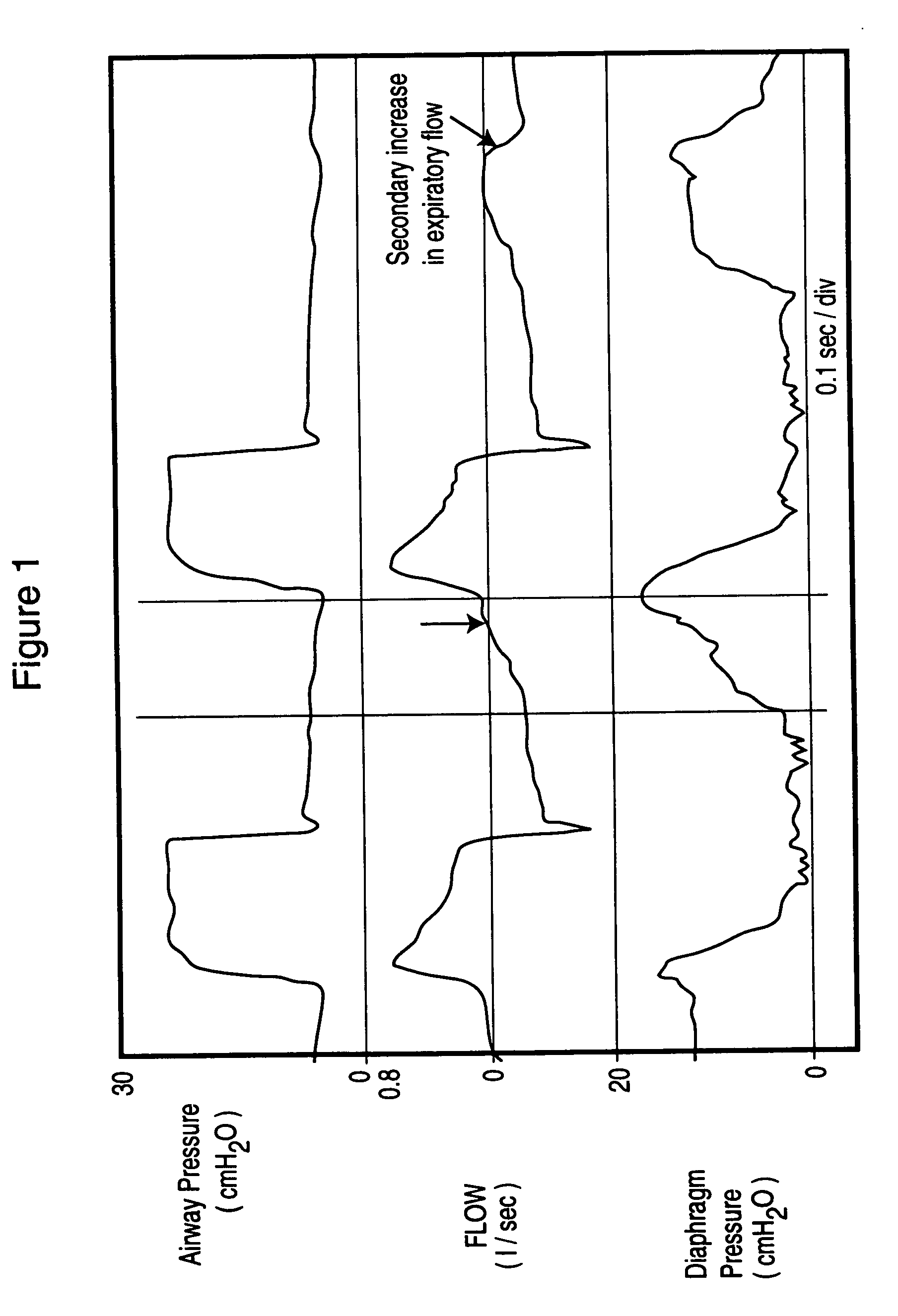
InactiveUS20040050387A1Increase uncertaintySharp changeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringAirway pressures
Method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the time onset (Tonset) and end (Tend) of patient inspiratory efforts. A composite pressure signal is generated comprising the sum of an airway pressure signal, a gas flow pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kf) to a signal representing gas flow rate and a gas volume pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kv) to a signal representing volume of gas flow. Kf and Kv values are adjusted to result in a desired linear trajectory of composite pressure signal baseline in the latter part of the exhalation phase. The current composite pressure signal is compared with (i) selected earlier composite pressure signal values and / or (ii) value expected at current time based on extrapolation of composite pressure signal trajectory at specified earlier times and / or (iii) the current rate of change in the composite pressure signal with a selected earlier rates of change. The differences obtained by the comparison are compared with selected threshold values. Tonset is identified when at least one of the differences exceeds the threshold values.
Owner:YRT
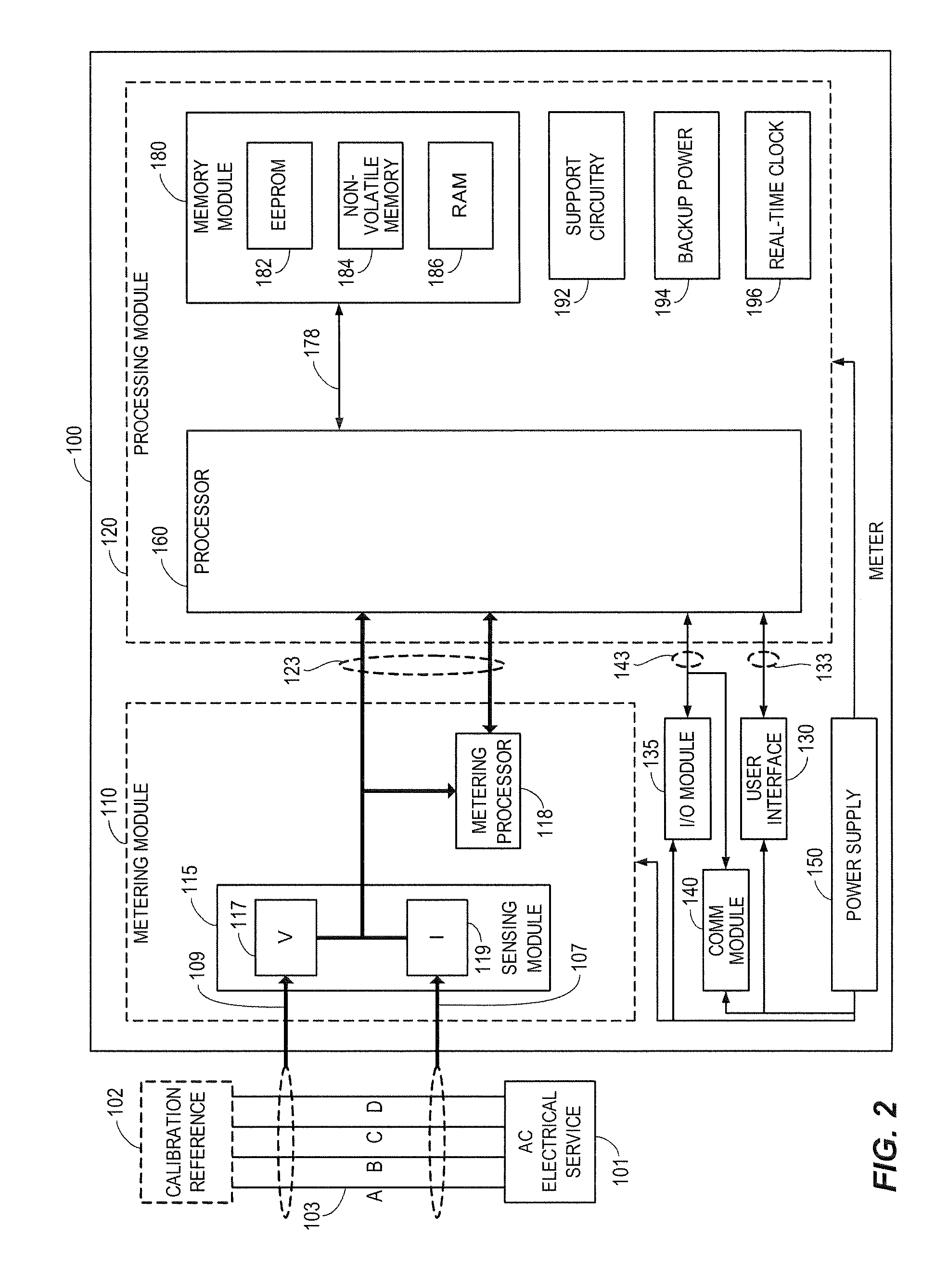
Intelligent Electronic Device with Board-Range High Accuracy
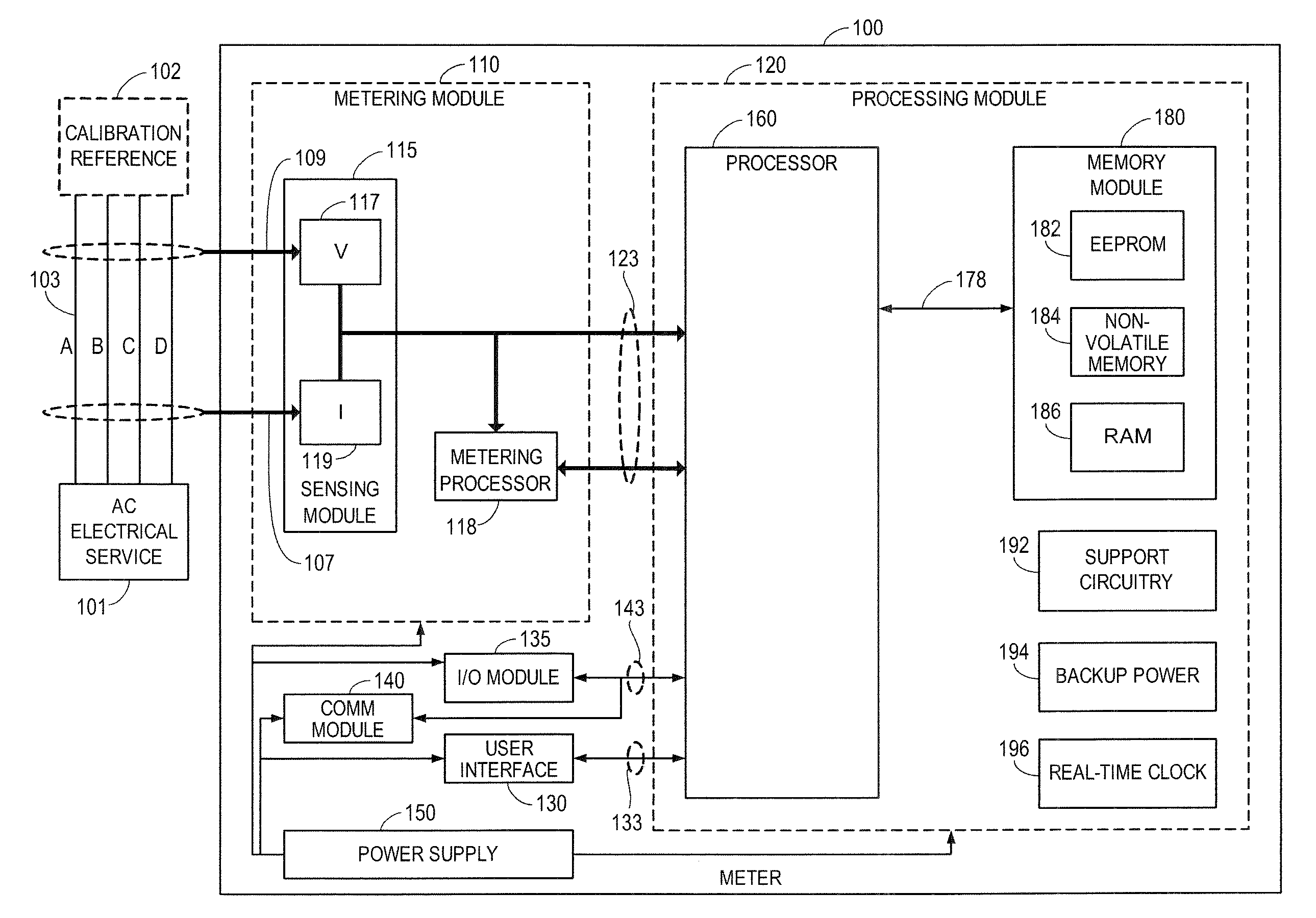
ActiveUS20080172192A1Improve overall utilizationImprove accuracyElectric devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectricityEngineering
A method and apparatus provides high-accuracy measurements of an electrical parameter across a broad range of parameter input values. In one embodiment, an intelligent electronic device (IED), e.g., a digital electrical power and energy meter, with a plurality of independently-adjustable gain factors measures a parameter, and calculates and stores calibration factors associated with known values of the measured parameter. The IED or meter applies the stored calibration factors when measuring unknown values of the measured parameter, to improve the accuracy of the measurement.
Owner:ELECTRO INDUSTRIES GAUGE TECH
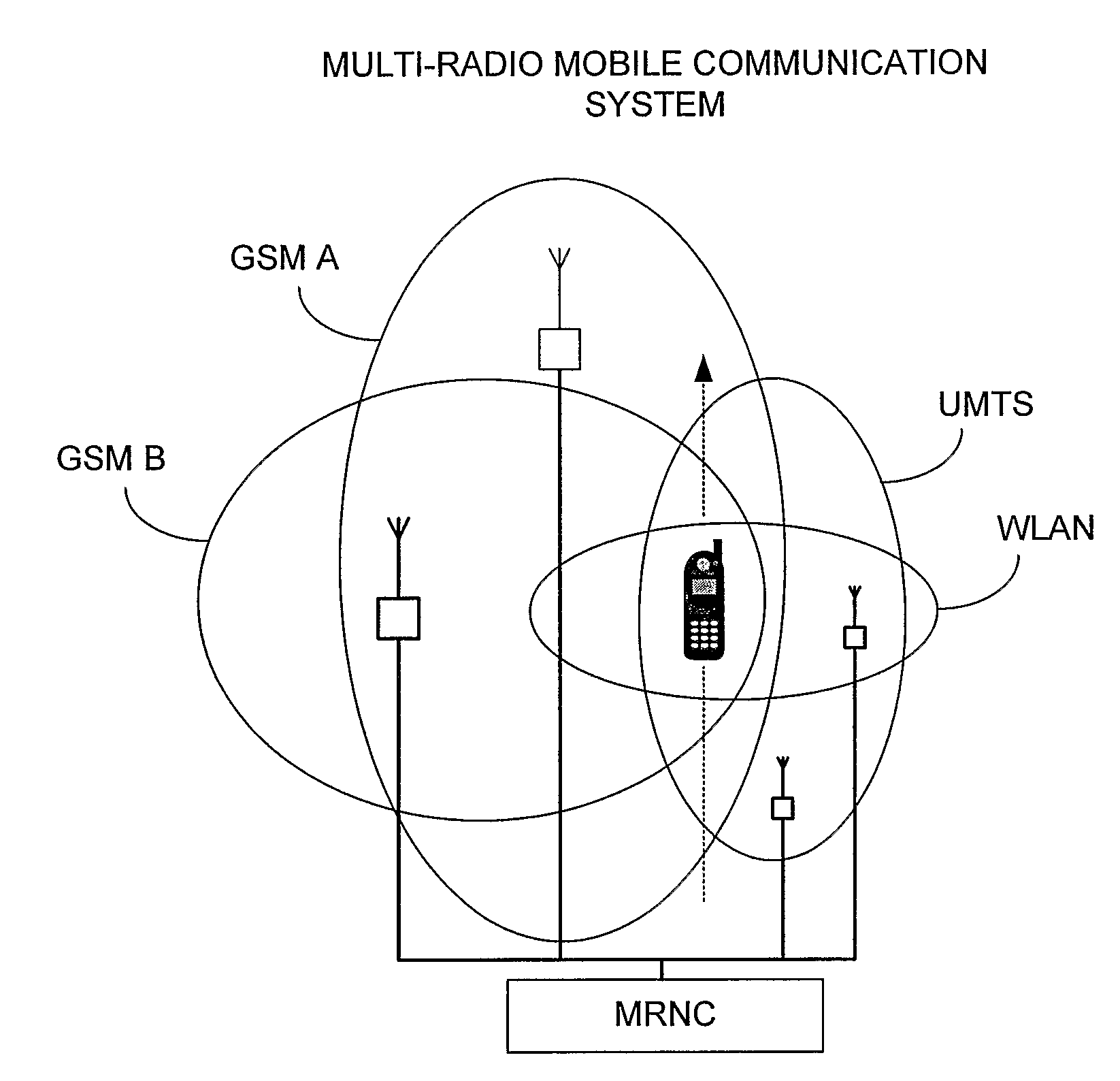
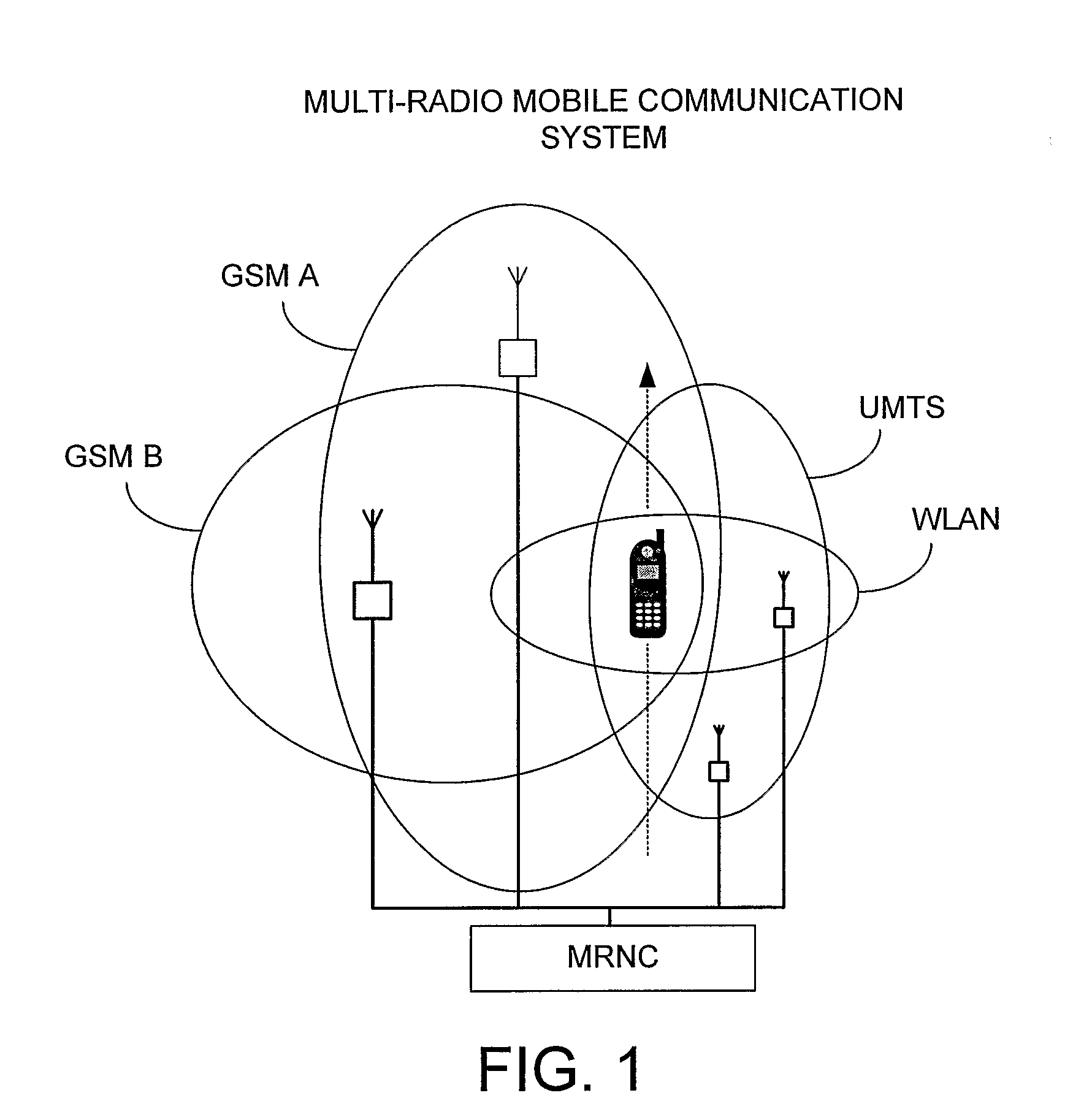
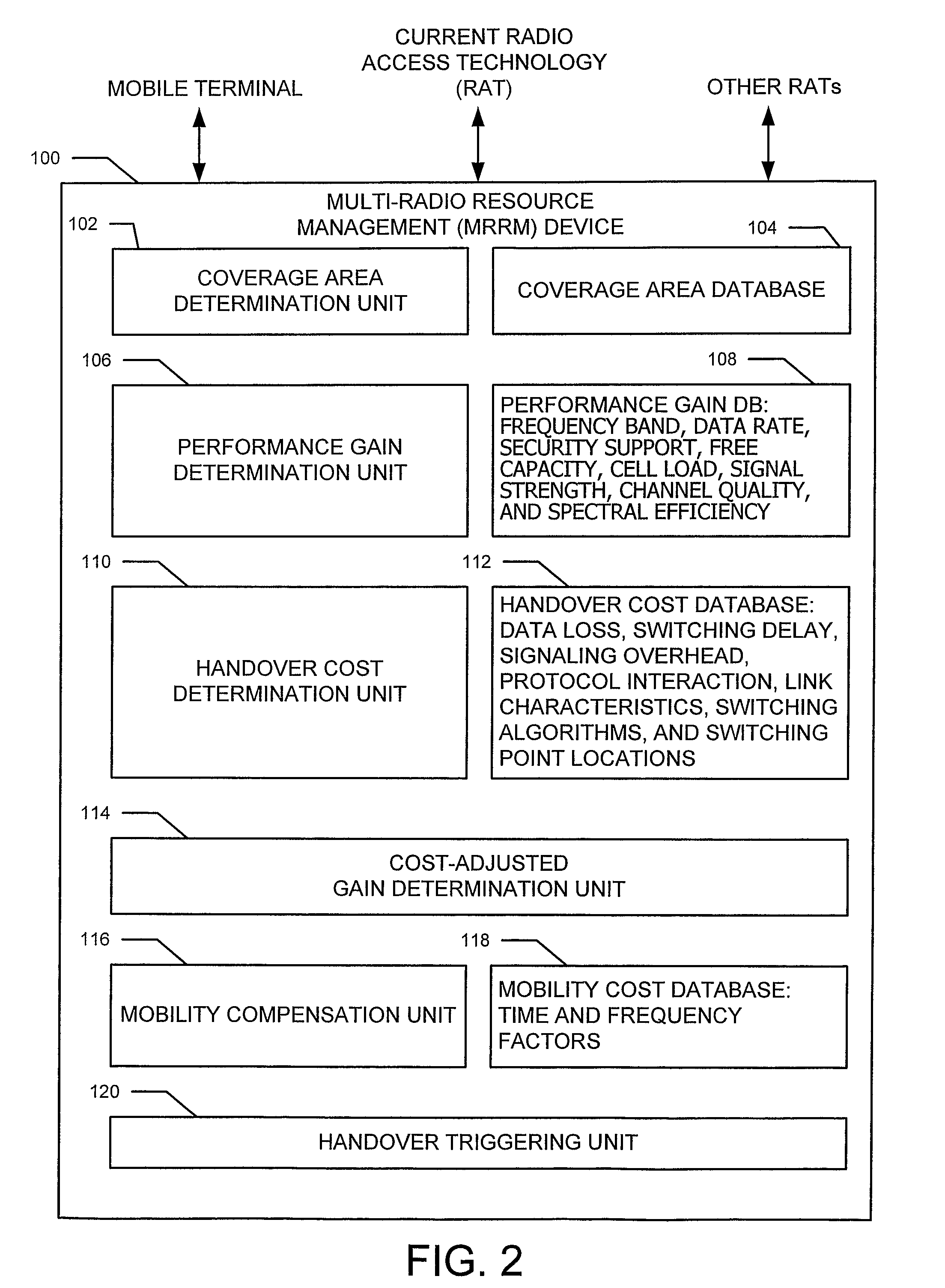
Technique for controlling handovers within a multi-radio wireless communication system
InactiveUS20090017823A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationRadio access technologyCommunications system
A technique is provided for use by a Multi-Radio Management Resource (MRRM) component of a multi-radio wireless communication system for controlling the handover of a mobile terminal between different radio access technologies (RAT). In one example, all suitable RATs having coverage areas currently covering the location of a mobile terminal are identified. The performance gain that might be achieved via a handover to one of the other RATs is then determined by the MRRM based on various performance gain factors. Handover costs that will be incurred as a result of the handover are also explicitly calculated. Then, a cost-adjusted gain is determined by the MRRM based on the performance gain and the handover costs. A handover is only triggered by the MRRM if the cost-adjusted gain exceeds a minimum threshold. The speed and trajectory of the mobile terminal may also be considered.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Multimode optical fibre communication system
InactiveUS20070009266A1Convenient calibrationManual exchangesAutomatic exchangesOptical radiationCommunications system
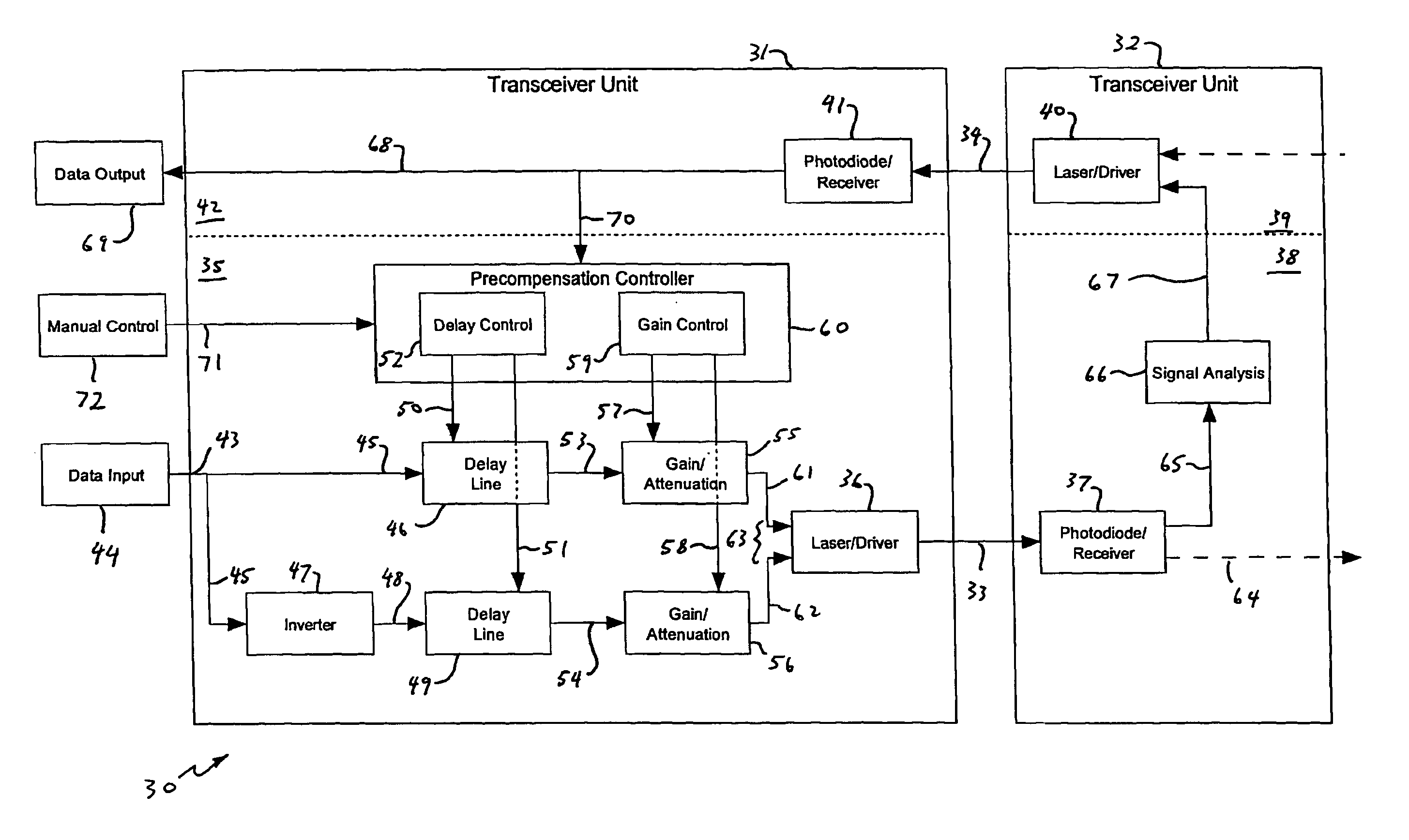
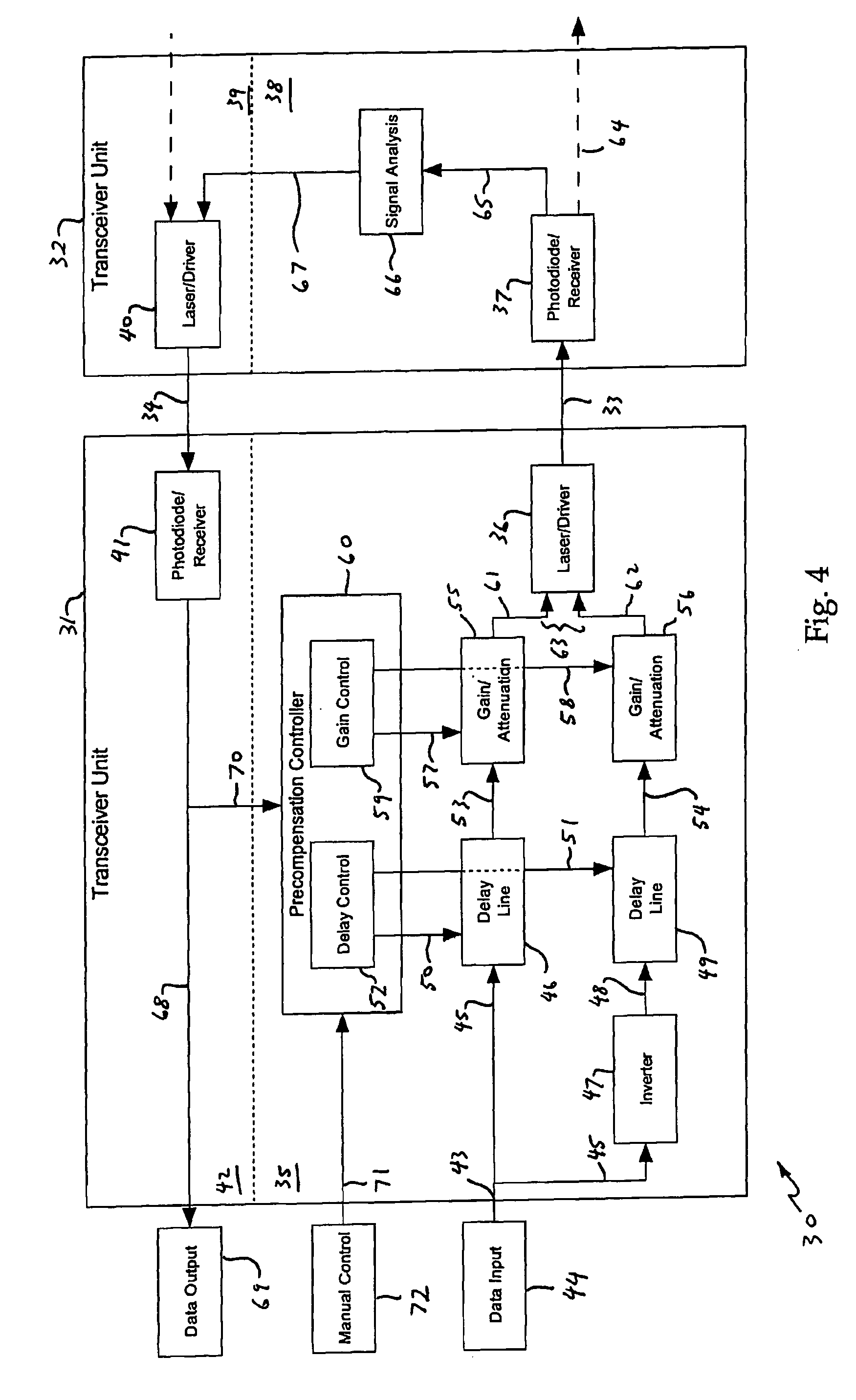
A multimode optical fibre communications system, and in particular to a system in which non-linearities in the propagation of the signal through a multimode optical communications channel degrade the signal presented to the receiver. The system includes an optical transmitter unit for connection to a multimode optical fibre transmission link. The transmitter unit has a data input for receiving an input data signal, a data signal processing circuit and a source of optical radiation. The data signal processing circuit is arranged to receive the input data signal from the data input and to provide a processed data signal to the source of optical radiation and the source of optical radiation is arranged to generate from this an optical signal for transmission by a multimode optical fibre. The data processing circuit is arranged to provide from the input data signal a non-inverted data signal and an inverted data signal, receive a control signal for controlling the generation of the processed data signal, apply a controllable delay in accordance with the control signal to at least one of the non-inverted and inverted data signals, and combine the non-inverted and inverted signals after the application of the controllable delay(s) and gain factor(s) to generate the processed data signal.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
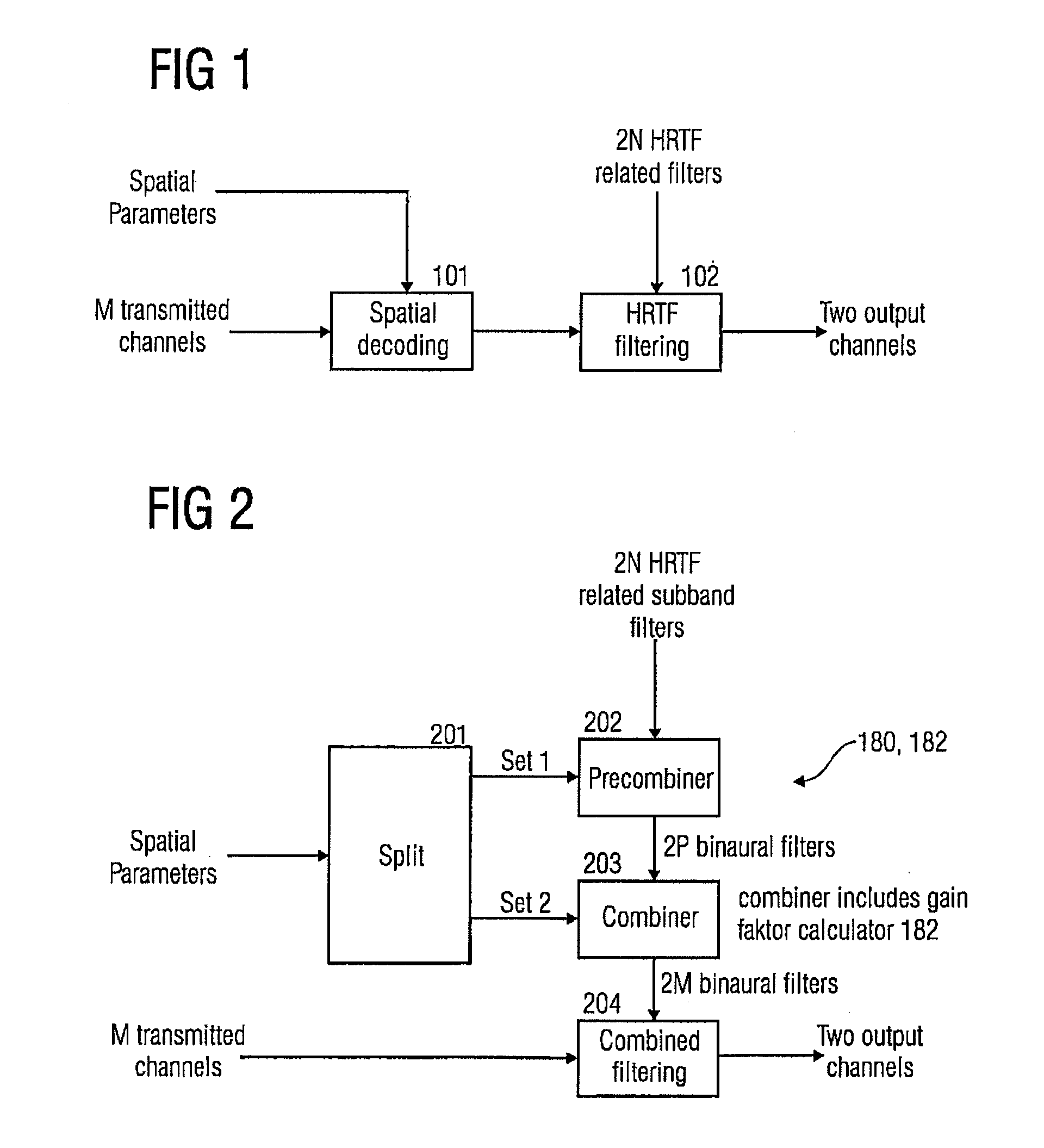
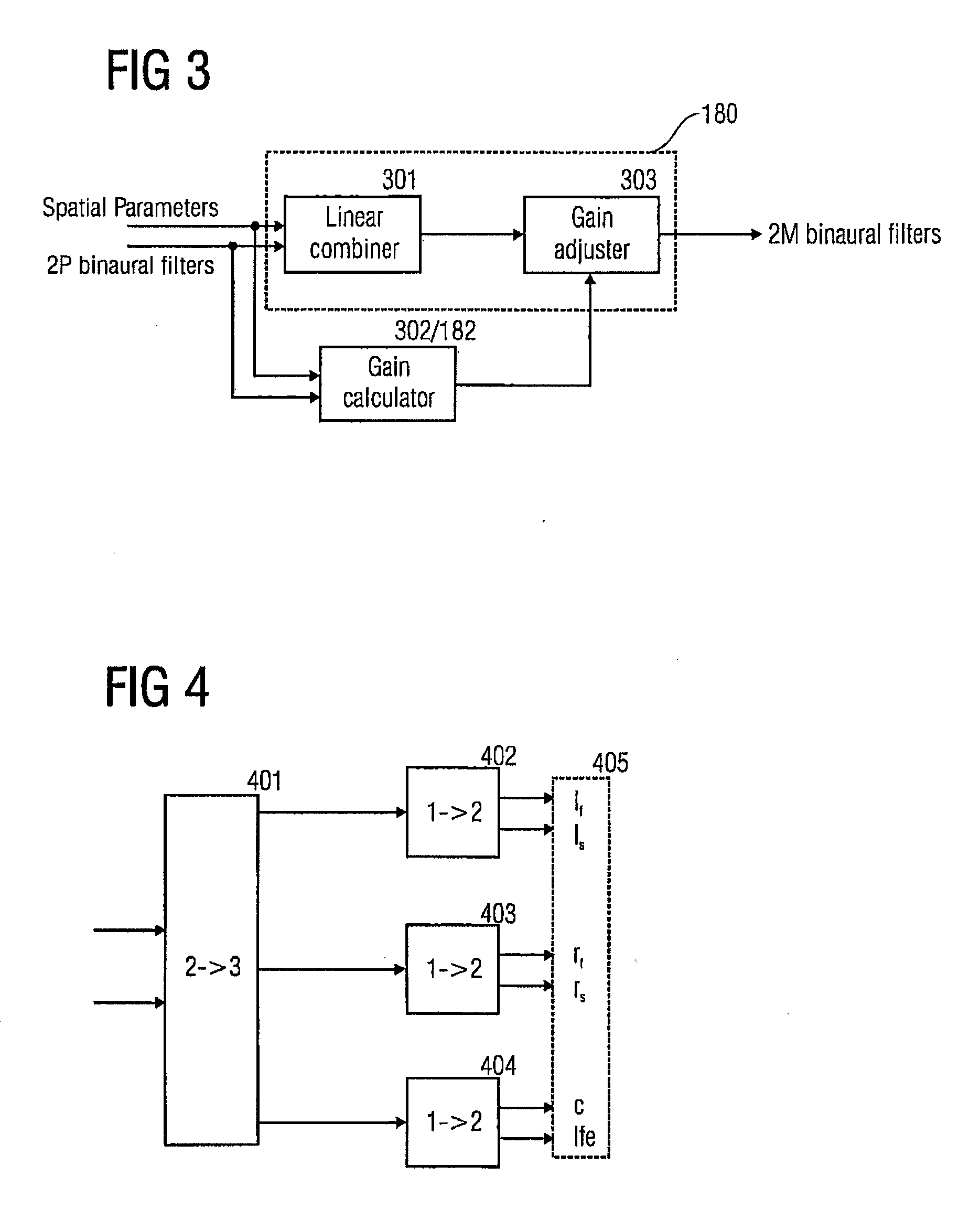
Binaural multi-channel decoder in the context of non-energy conserving upmix rules
ActiveUS20070280485A1Reducing and eliminating energy-errorEasy to useSpeech analysisCode conversionVocal tractComputer science
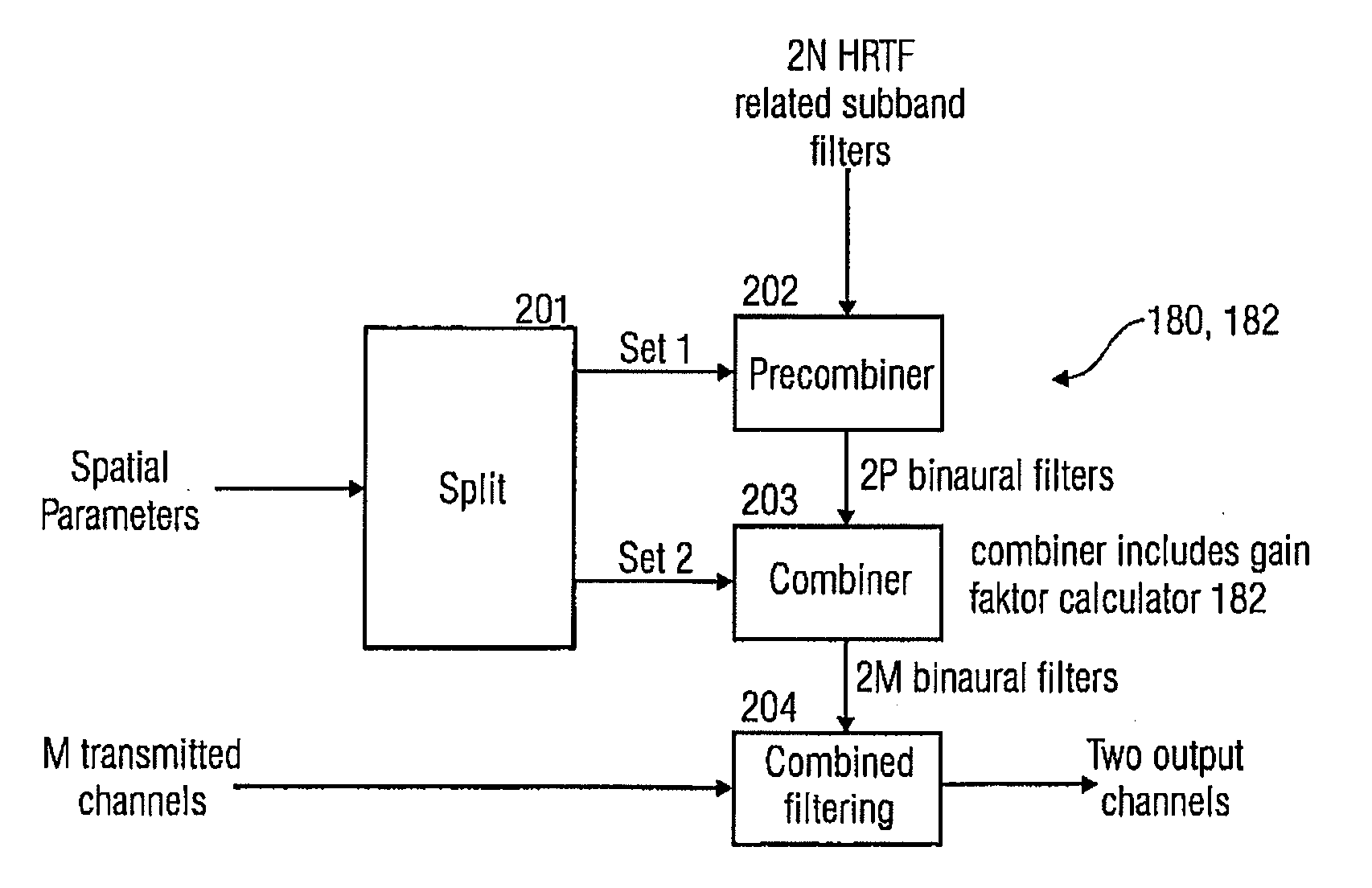
A multi-channel decoder for generating a binaural signal from a downmix signal using upmix rule information on an energy-error introducing upmix rule for calculating a gain factor based on the upmix rule information and characteristics of head related transfer function based filters corresponding to upmix channels. The one or more gain factors are used by a filter processor for filtering the downmix signal so that an energy corrected binaural signal having a left binaural channel and a right binaural channel is obtained.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
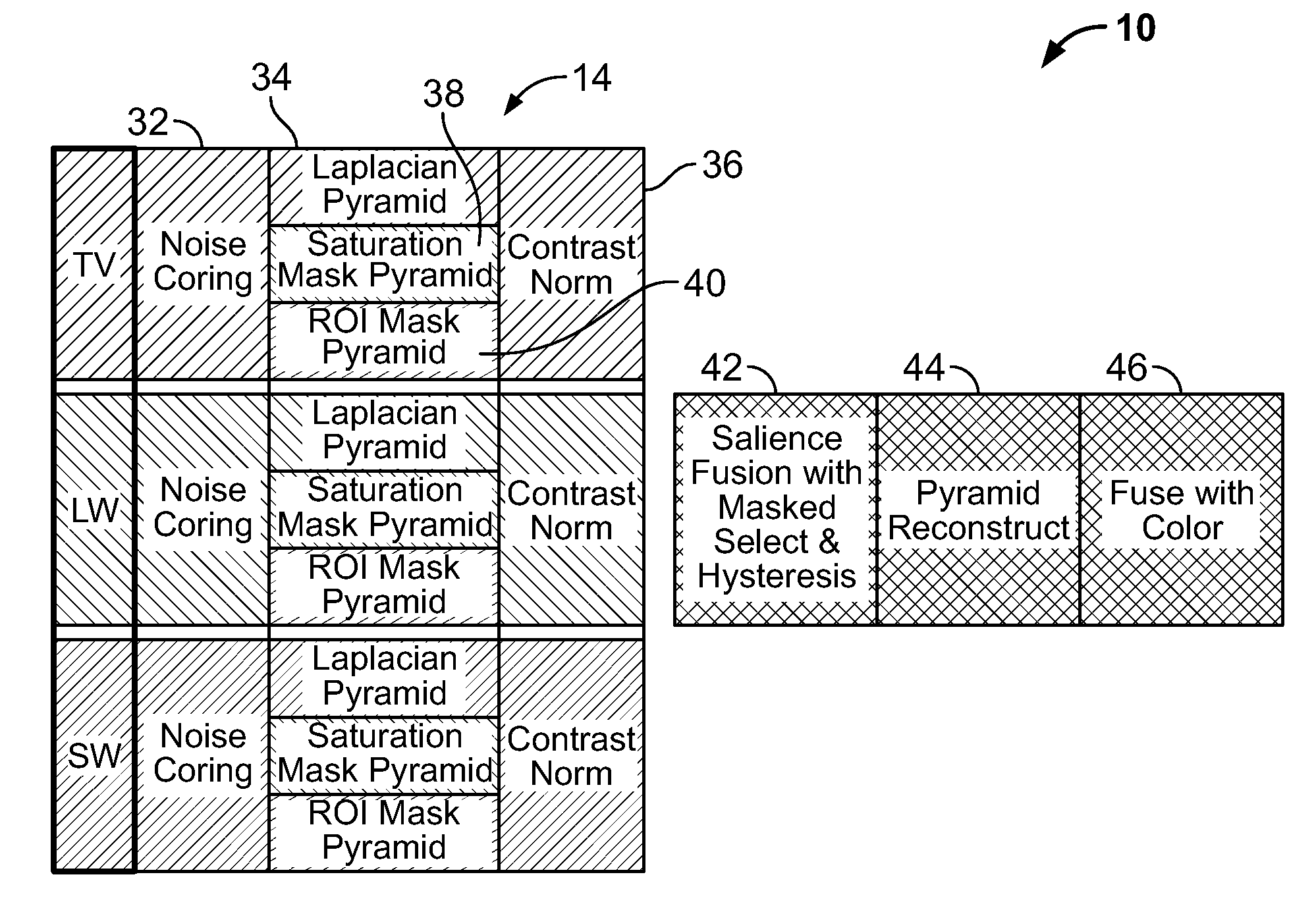
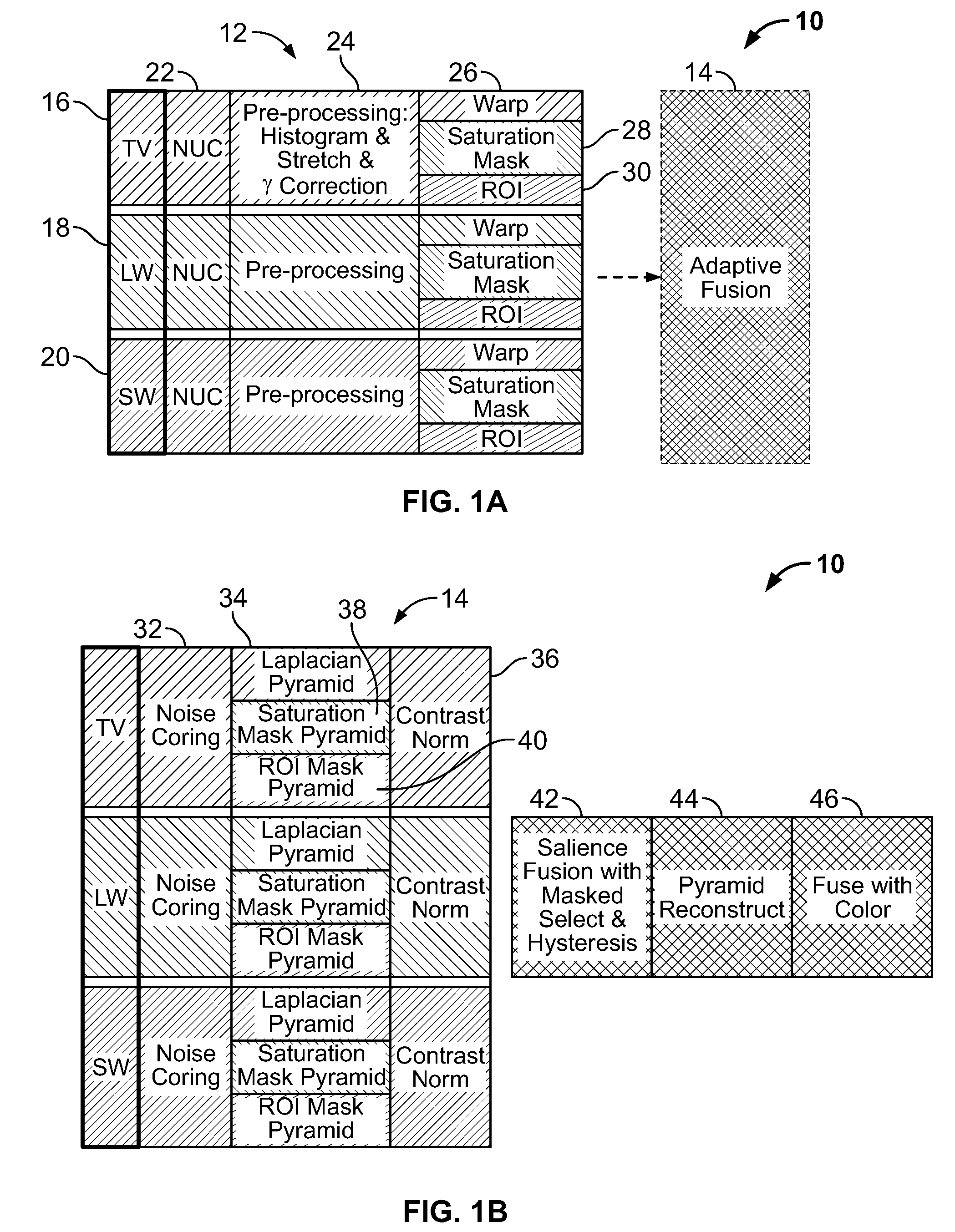
Multi-scale multi-camera adaptive fusion with contrast normalization
ActiveUS20090169102A1Reduce flickering artifactReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMulti cameraEnergy based
A computer implemented method for fusing images taken by a plurality of cameras is disclosed, comprising the steps of: receiving a plurality of images of the same scene taken by the plurality of cameras; generating Laplacian pyramid images for each source image of the plurality of images; applying contrast normalization to the Laplacian pyramids images; performing pixel-level fusion on the Laplacian pyramid images based on a local salience measure that reduces aliasing artifacts to produce one salience-selected Laplacian pyramid image for each pyramid level; and combining the salience-selected Laplacian pyramid images into a fused image. Applying contrast normalization further comprises, for each Laplacian image at a given level: obtaining an energy image from the Laplacian image; determining a gain factor that is based on at least the energy image and a target contrast; and multiplying the Laplacian image by a gain factor to produce a normalized Laplacian image.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
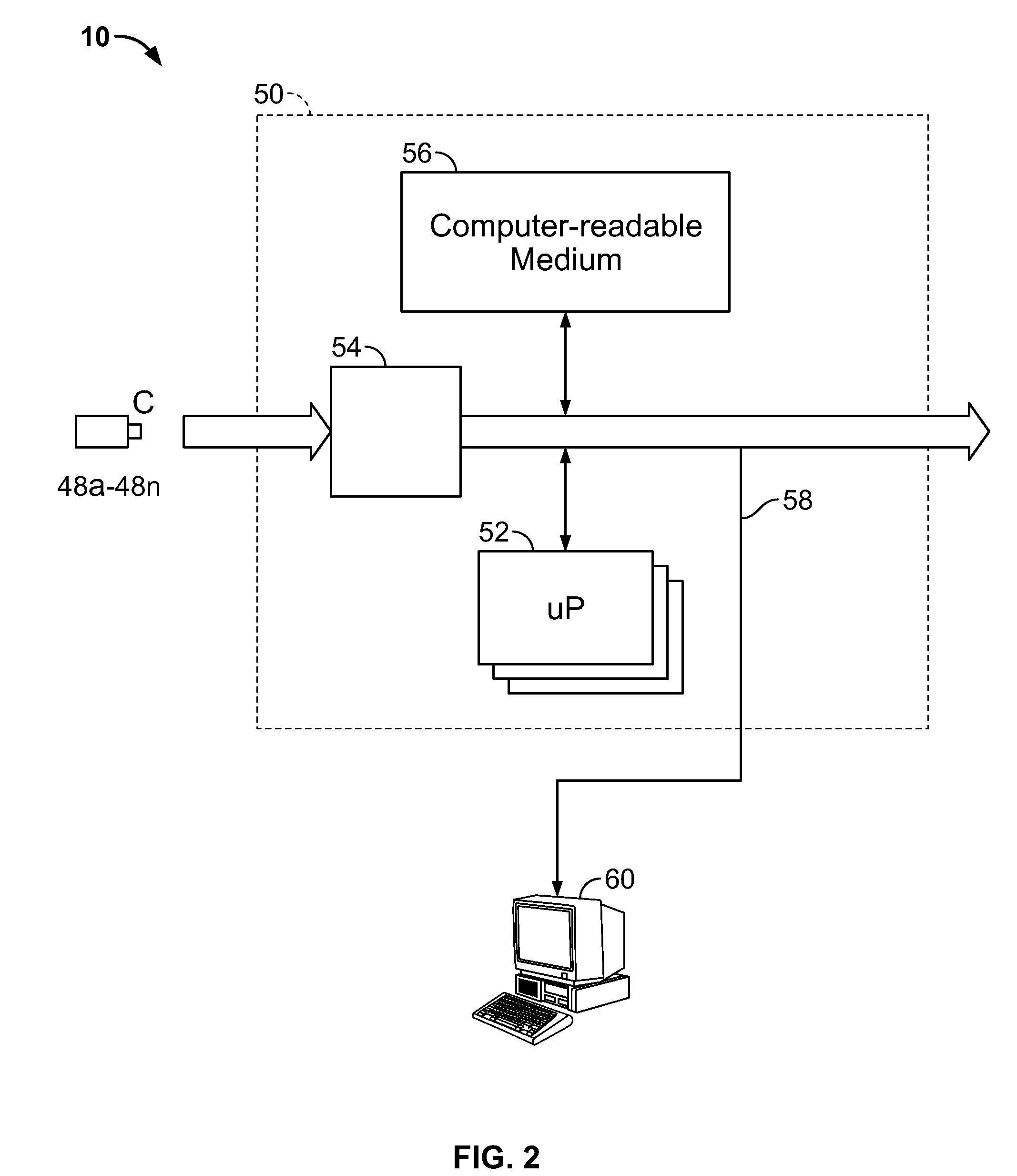
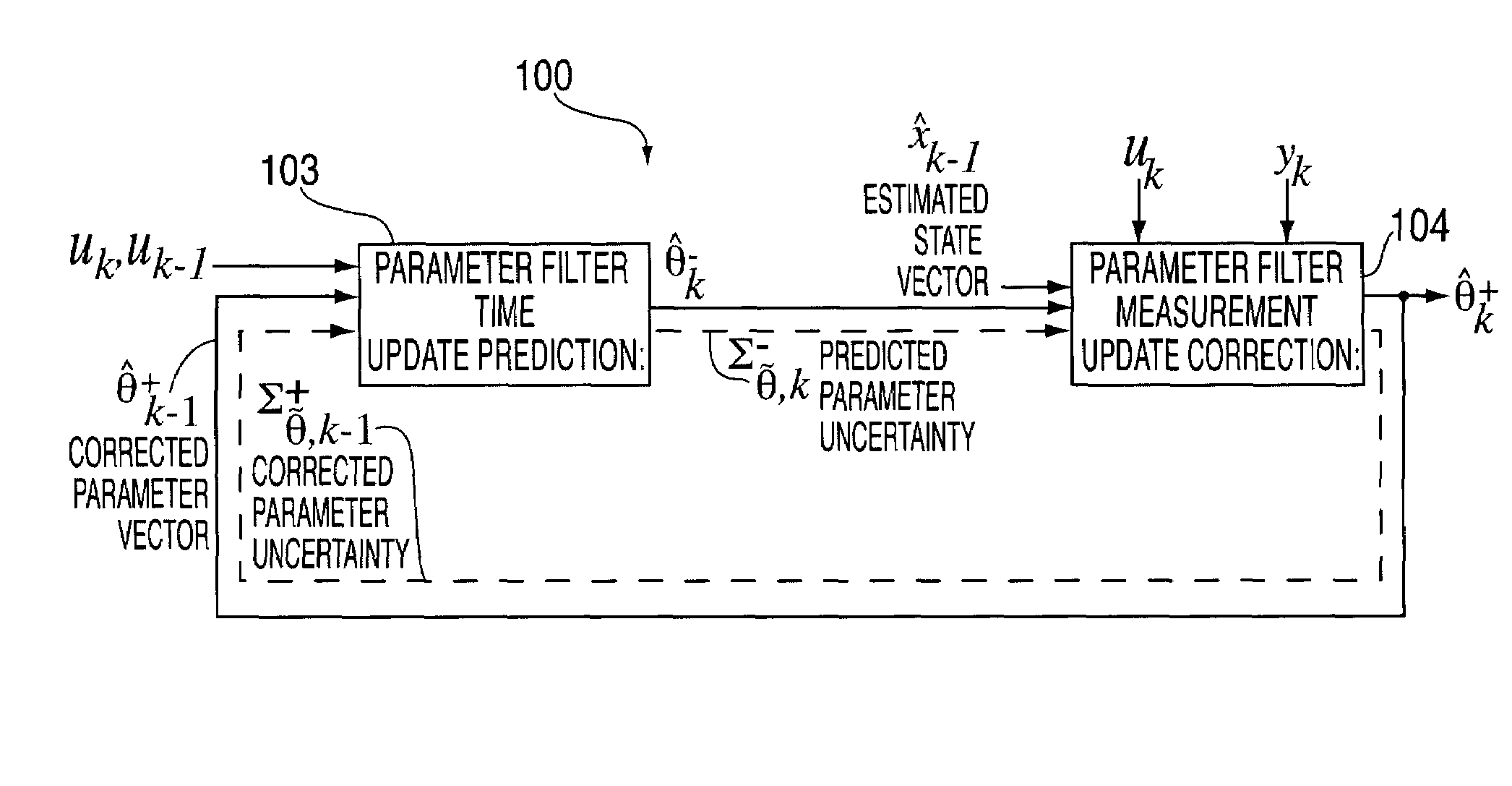
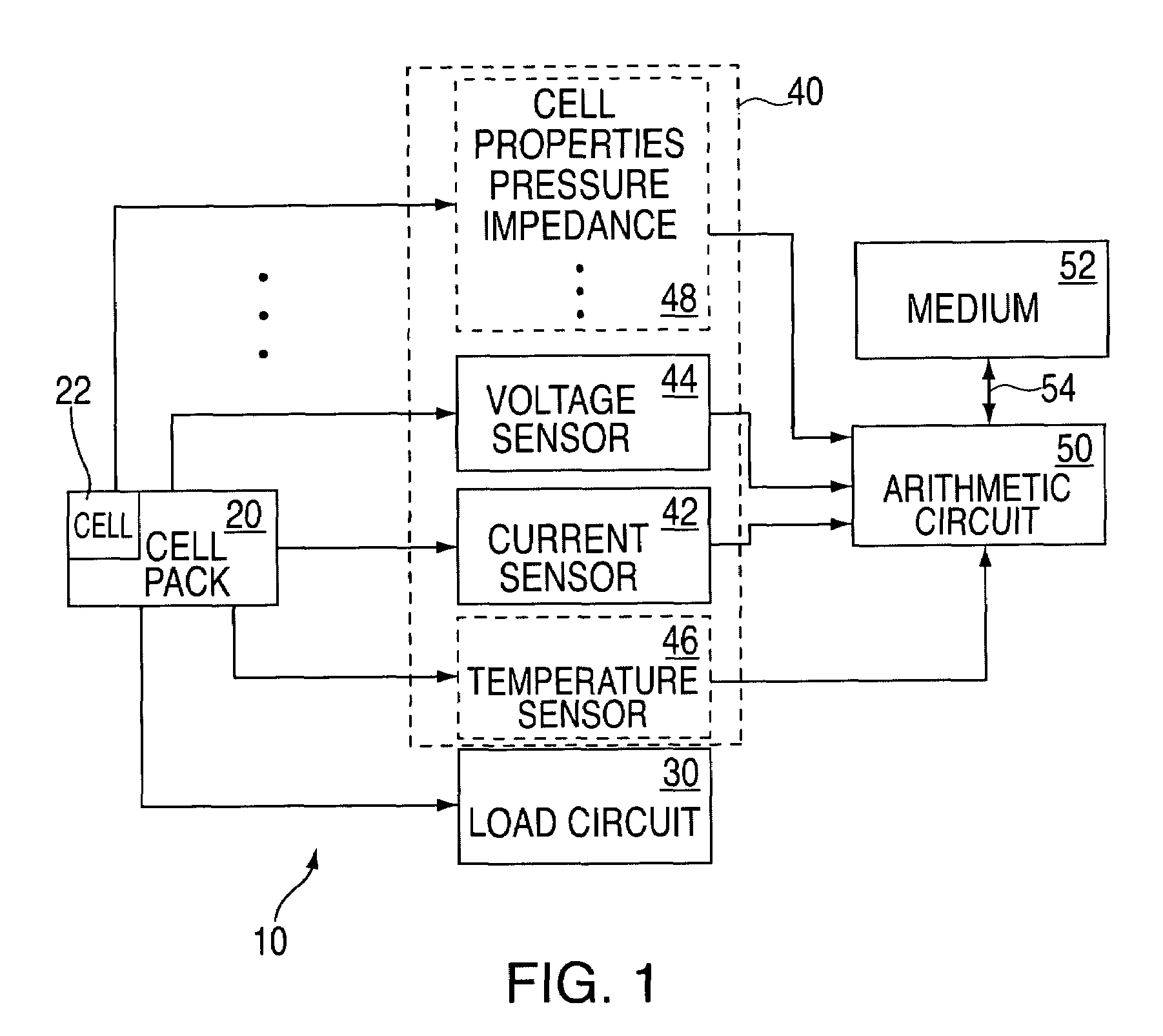
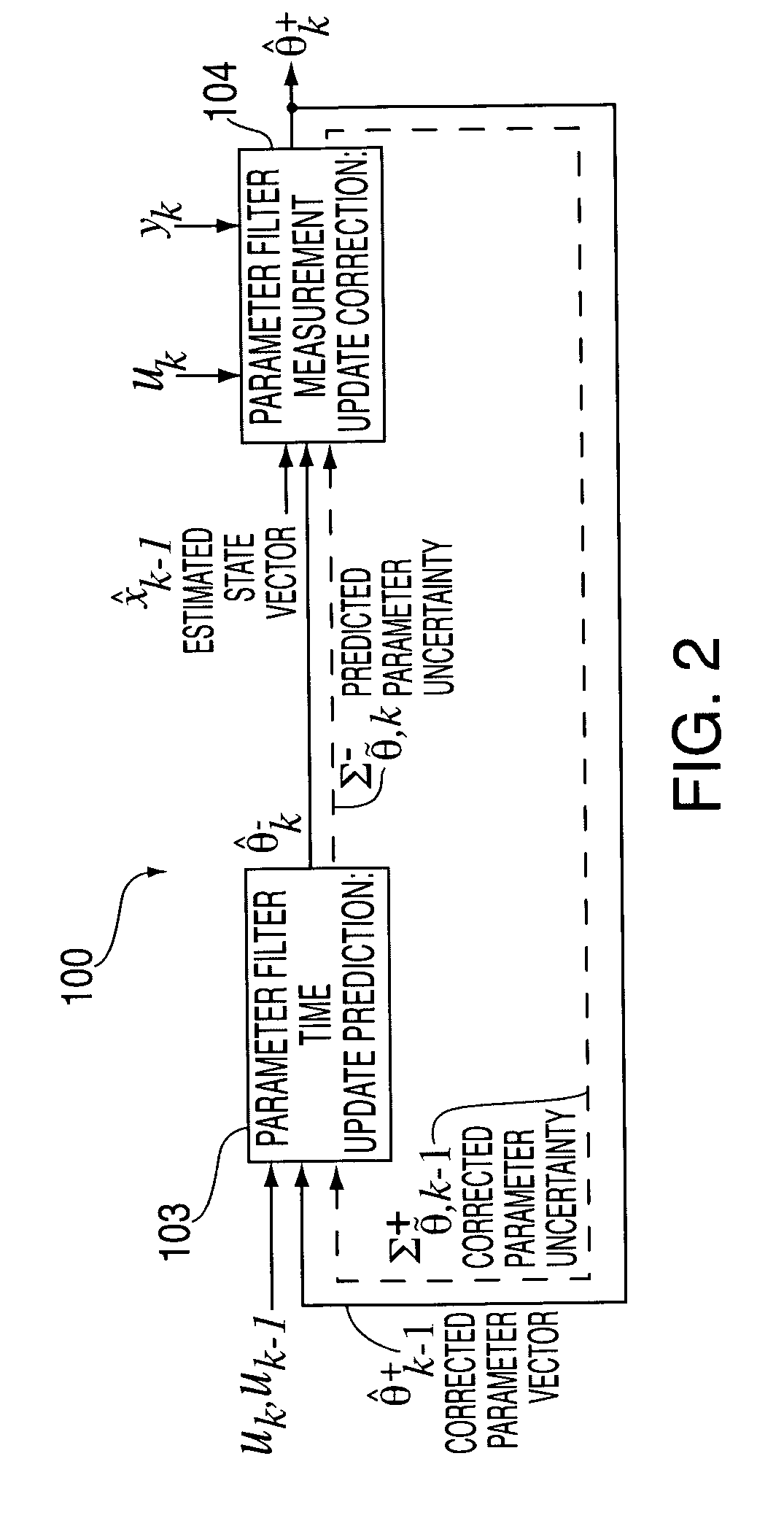
Method and system for battery parameter estimation
ActiveUS7315789B2Batteries circuit arrangementsCurrent/voltage measurementEstimation methodsCell based
Methods and systems for predicting a cell capacity associated with a cell of an electrochemical cell system are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, the method determines a first predicate cell capacity of the cell of the electrochemical cell system. The method further includes measuring a voltage of the cell to obtain a measured voltage. The method further includes determining a corrected predicted cell capacity of the cell based on the first predicted cell capacity, the measured voltage, and a gain factor.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
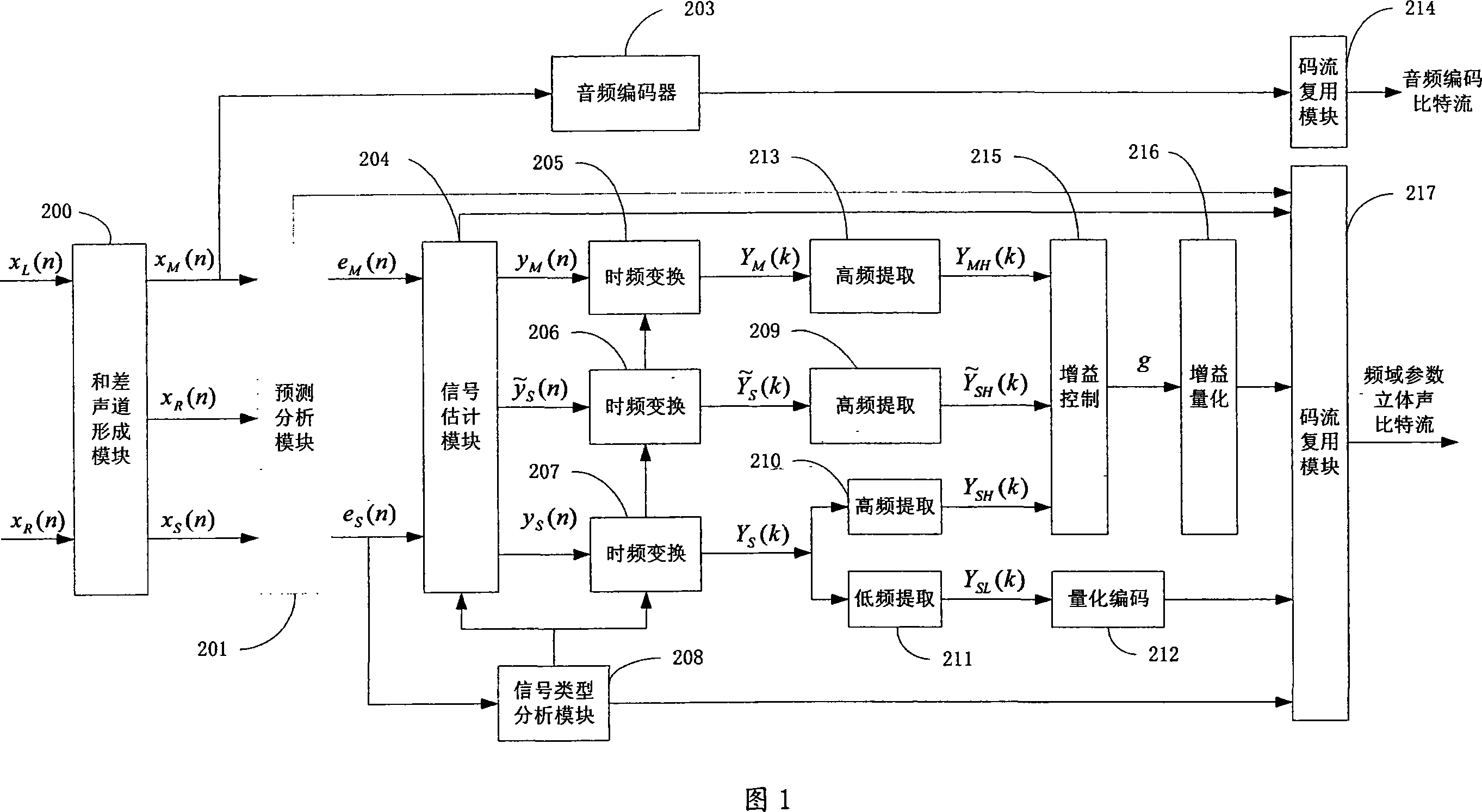
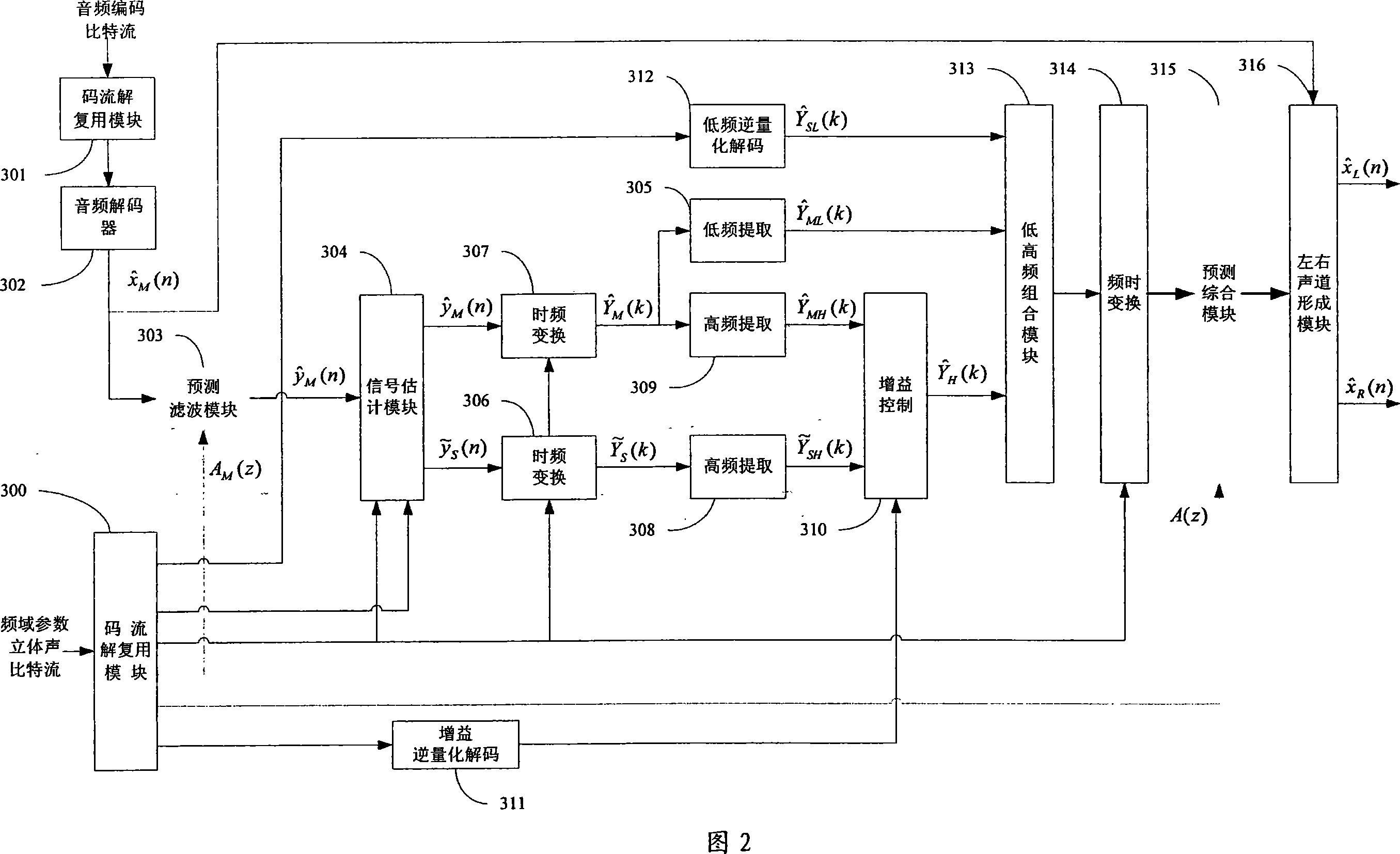
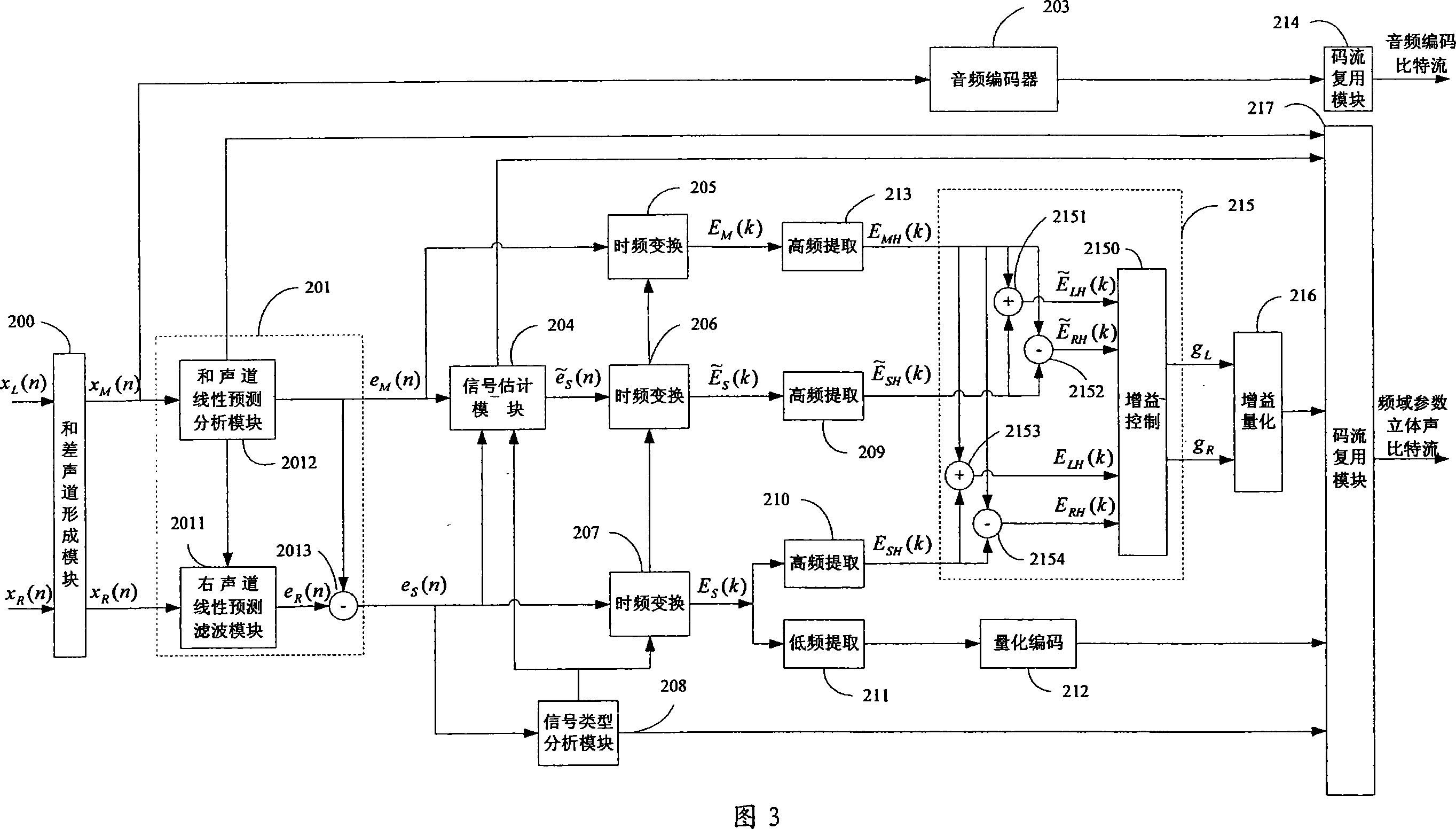
Efficient configurable frequency domain parameter stereo-sound and multi-sound channel coding and decoding method and system
InactiveCN101067931AImprove compression efficiencyEnsure consistencySpeech analysisDecoding methodsFrequency conversion
This invention provides a method and a system for coding / decoding frequency domain parameter stereos and multiple tracks, which converts signals of right and left tracks to a residual signal of a sum-difference tack and a residual signal of an estimated difference track, carries out time frequency conversion to residual signals of the estimated difference track, the original difference track and the original sum track to pick up the HF component and low frequency component of the residual signal of the original difference track, which is coded in quantization to utilize the HF component to get estimated residual RF component of the right and left tracks and gets the original residual RF component of the right and left tracks to be controlled in gain to get a gain coefficient of the difference of the two tracks and coded in quantization and finally multiplexes the coded data and edge information to get a frequency domain parameter stereo bit stream.
Owner:凯为半导体科技(上海)有限公司
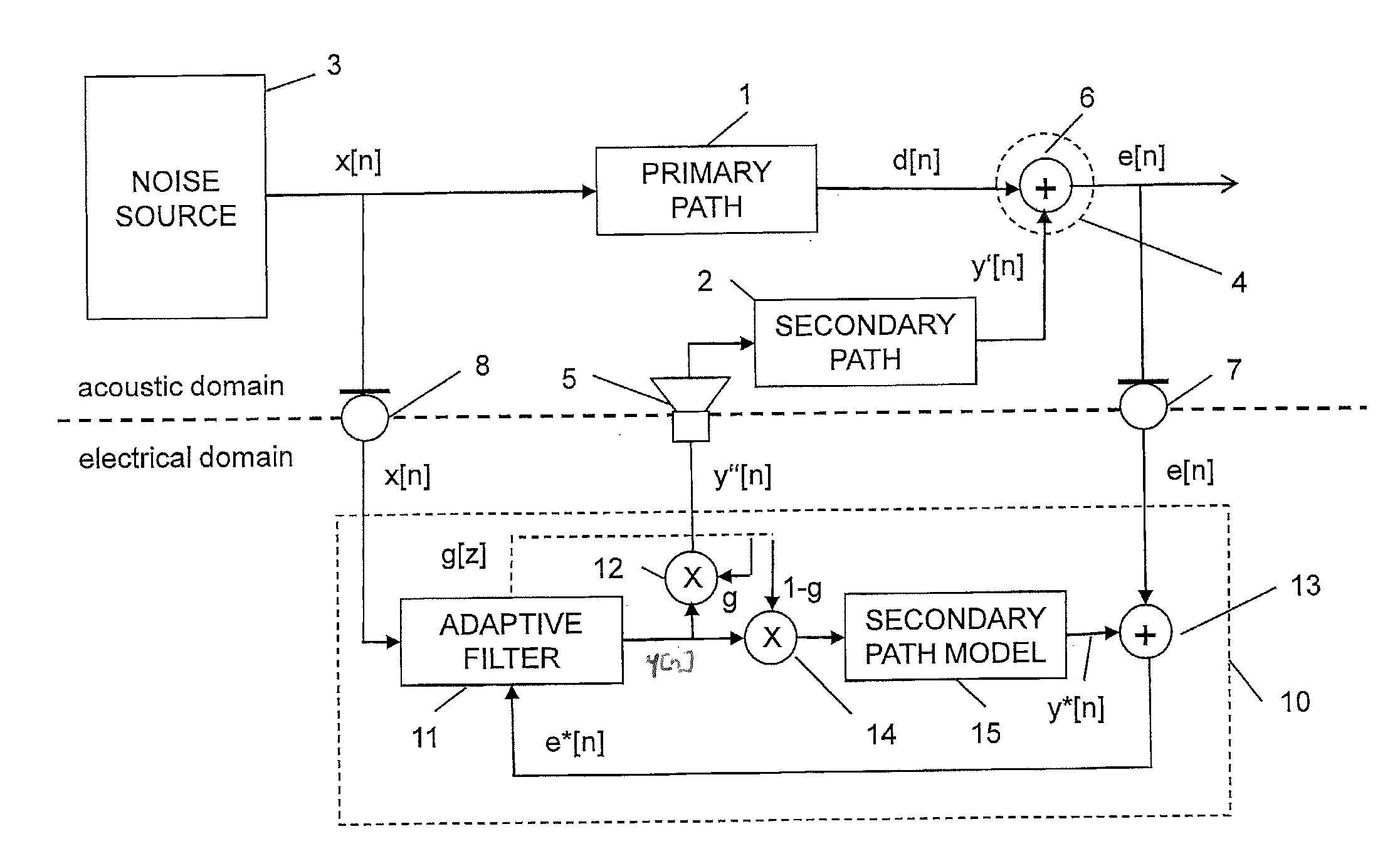
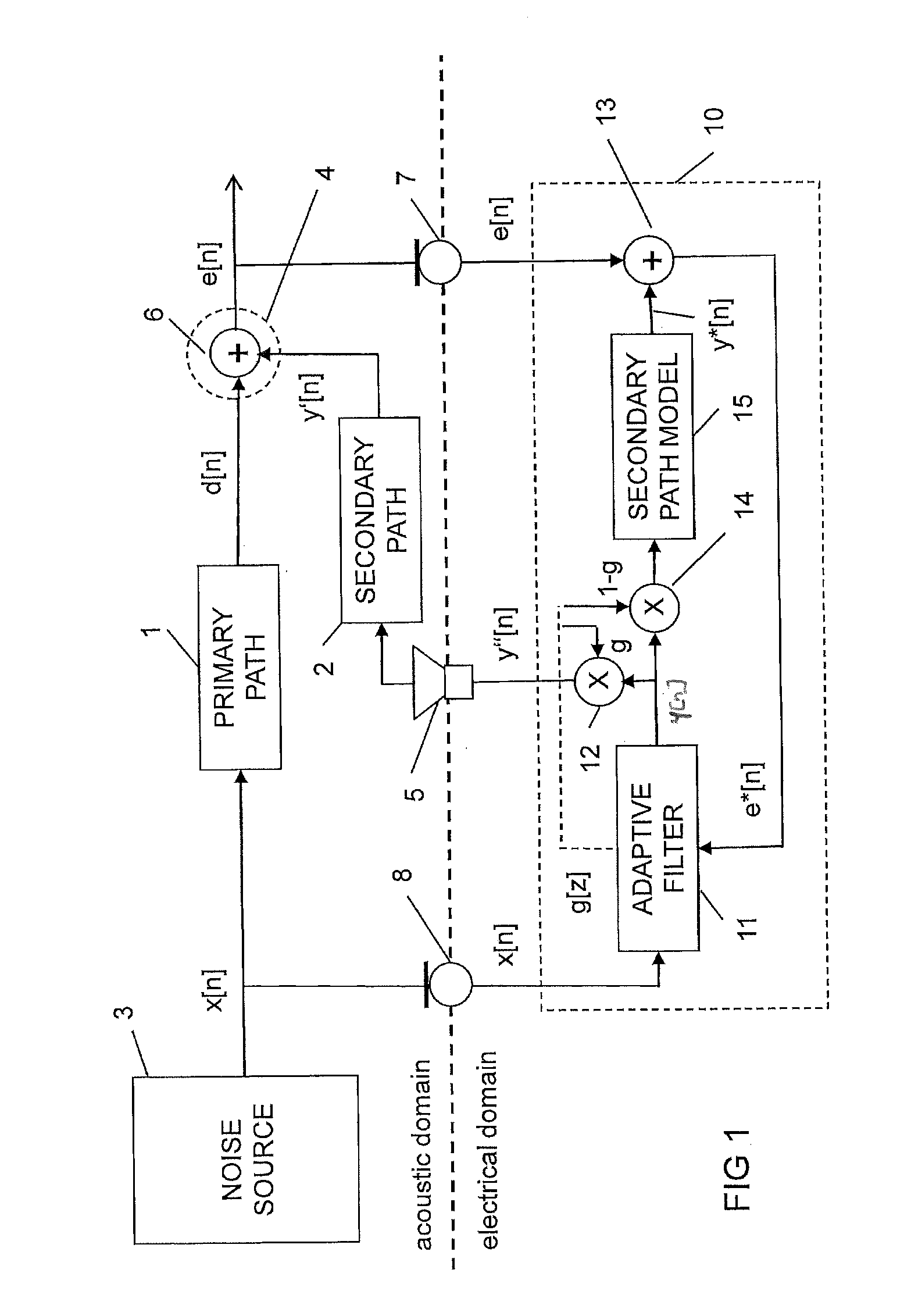
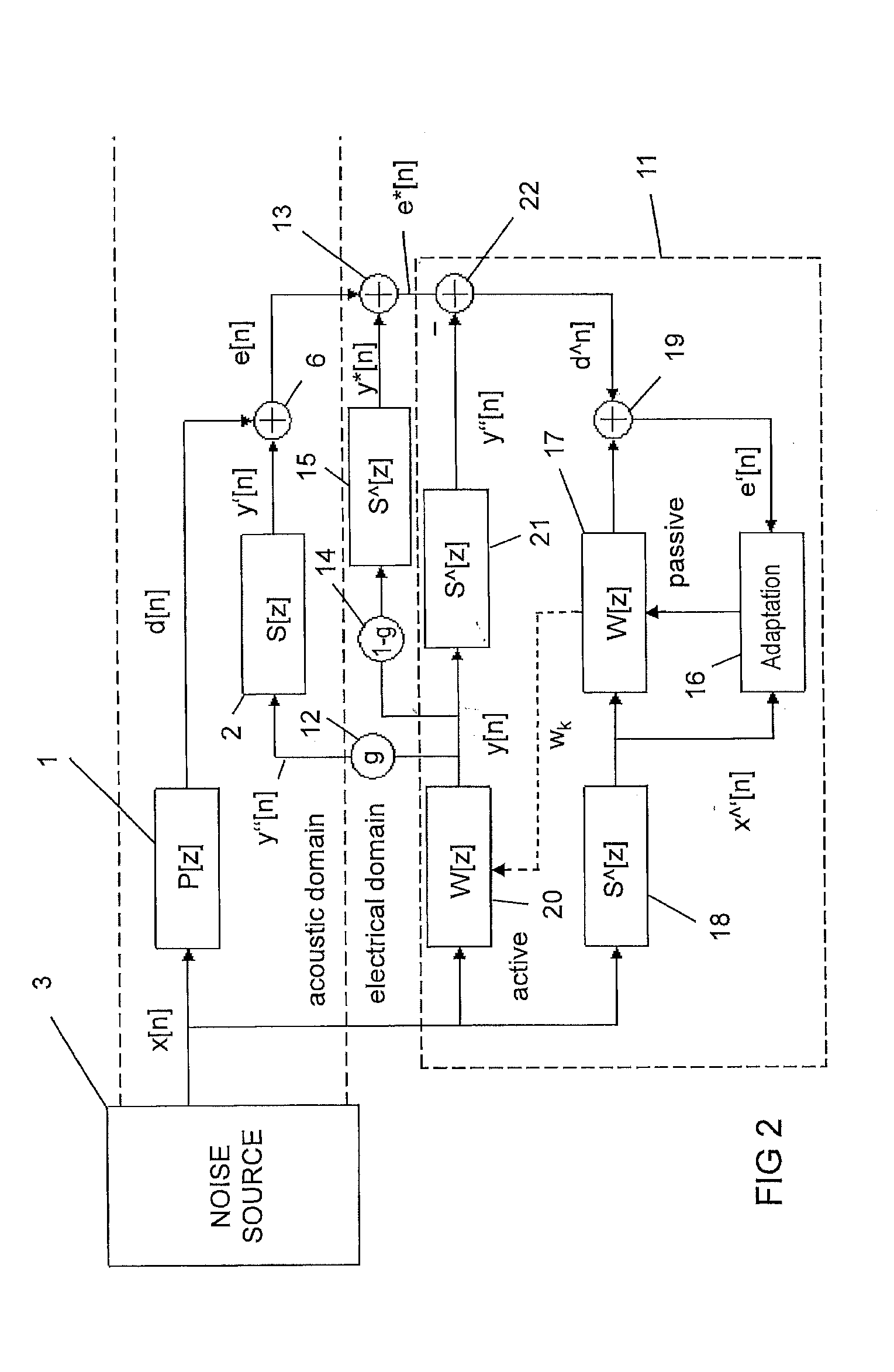
Adaptive noise control
ActiveUS20110305347A1Reduce the required powerEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlAdaptive filter
Adaptive noise control for reducing power of an acoustic noise signal radiated from a noise source to a listening position comprises providing an electrical reference signal correlated with the acoustic noise signal; filtering the electrical reference signal with an adaptive filter to provide an electrical output signal; multiplying the electrical output signal of the adaptive filter by a gain factor to provide a first electrical compensation signal; filtering and multiplying the electrical output signal of the adaptive filter by the inverse of the gain factor to provide a second electrical compensation signal, the second gain factor being equal to 1 subtracted by the first gain factor; radiating the first electrical compensation signal to the listening position with an acoustic transducer; sensing a residual electrical error signal at the listening position; adding the second electrical compensation signal to the electrical error signal to provide a compensated error signal; and adapting filter coefficients of the adaptive filter as a function of the compensated error signal and the reference signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
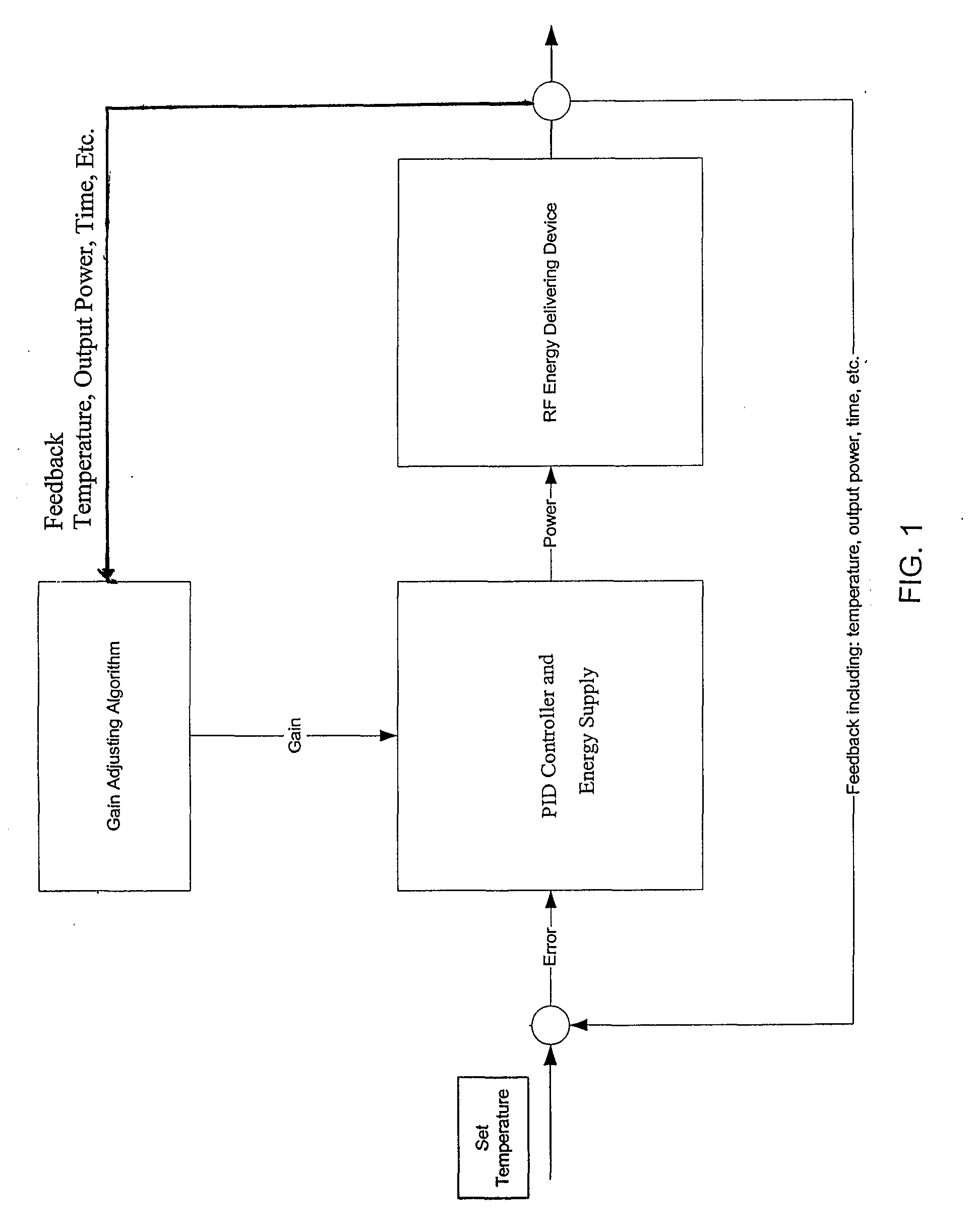
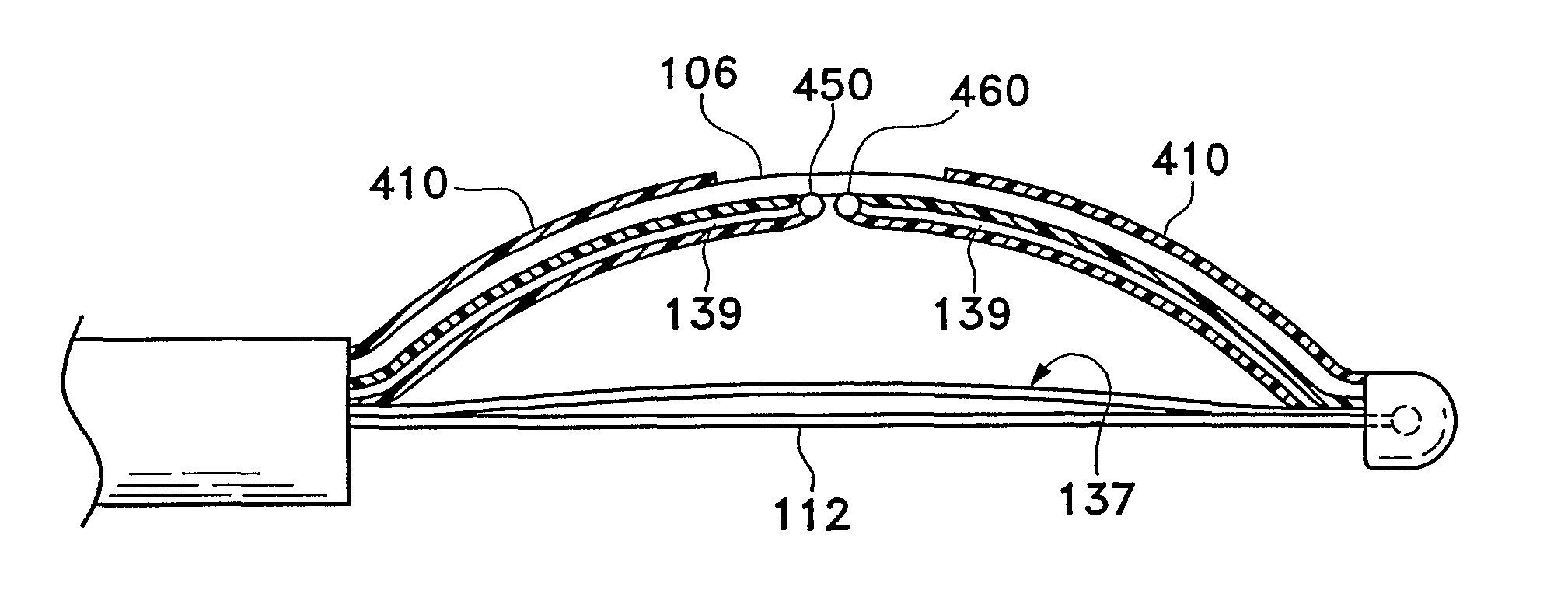
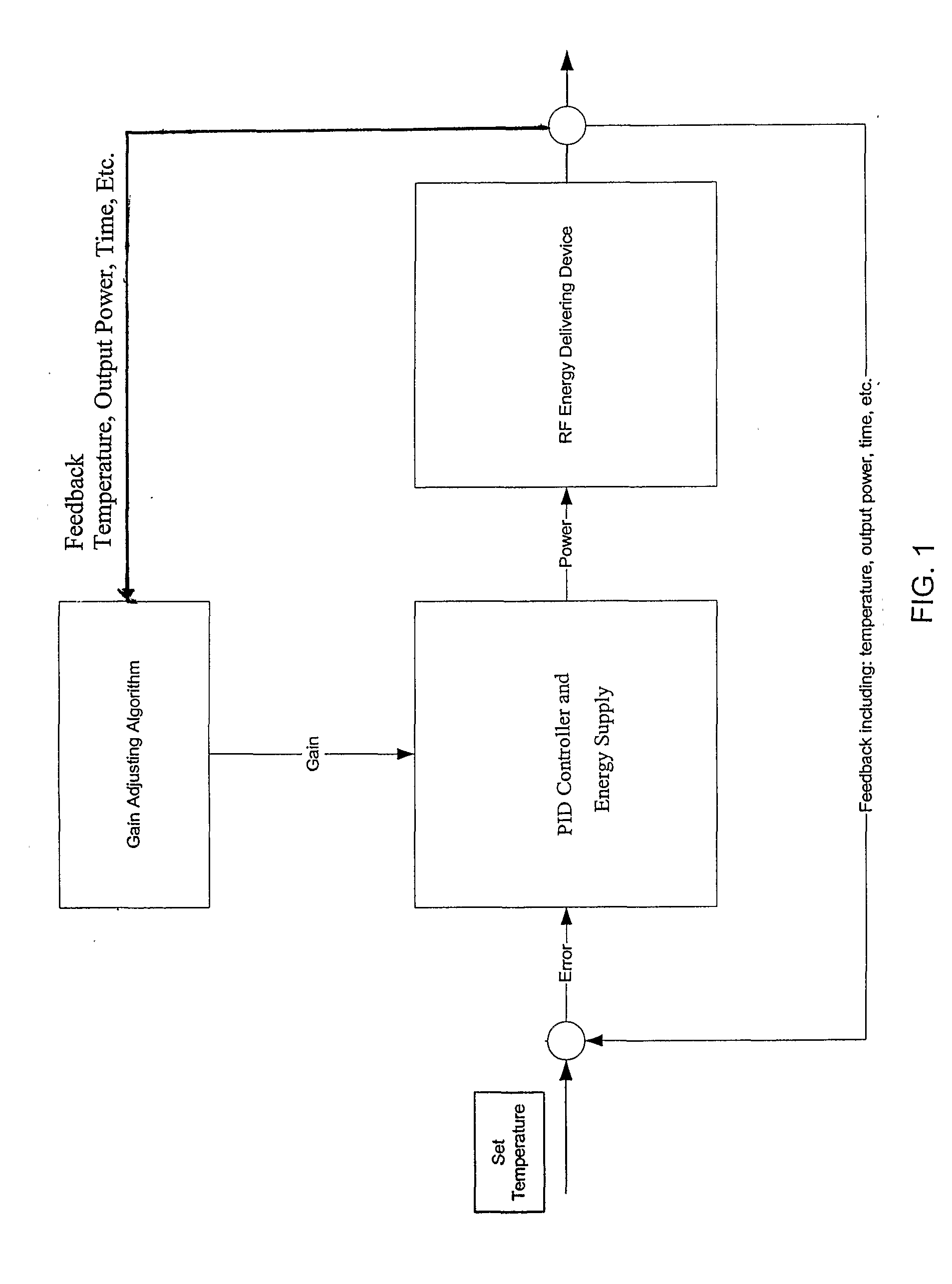
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247726A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pii+1=Pi+G(αei+βei-1+γei-2) where α, β and γ are preset values and a is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and 7 is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and device for monitoring and improving patient-ventilator interaction
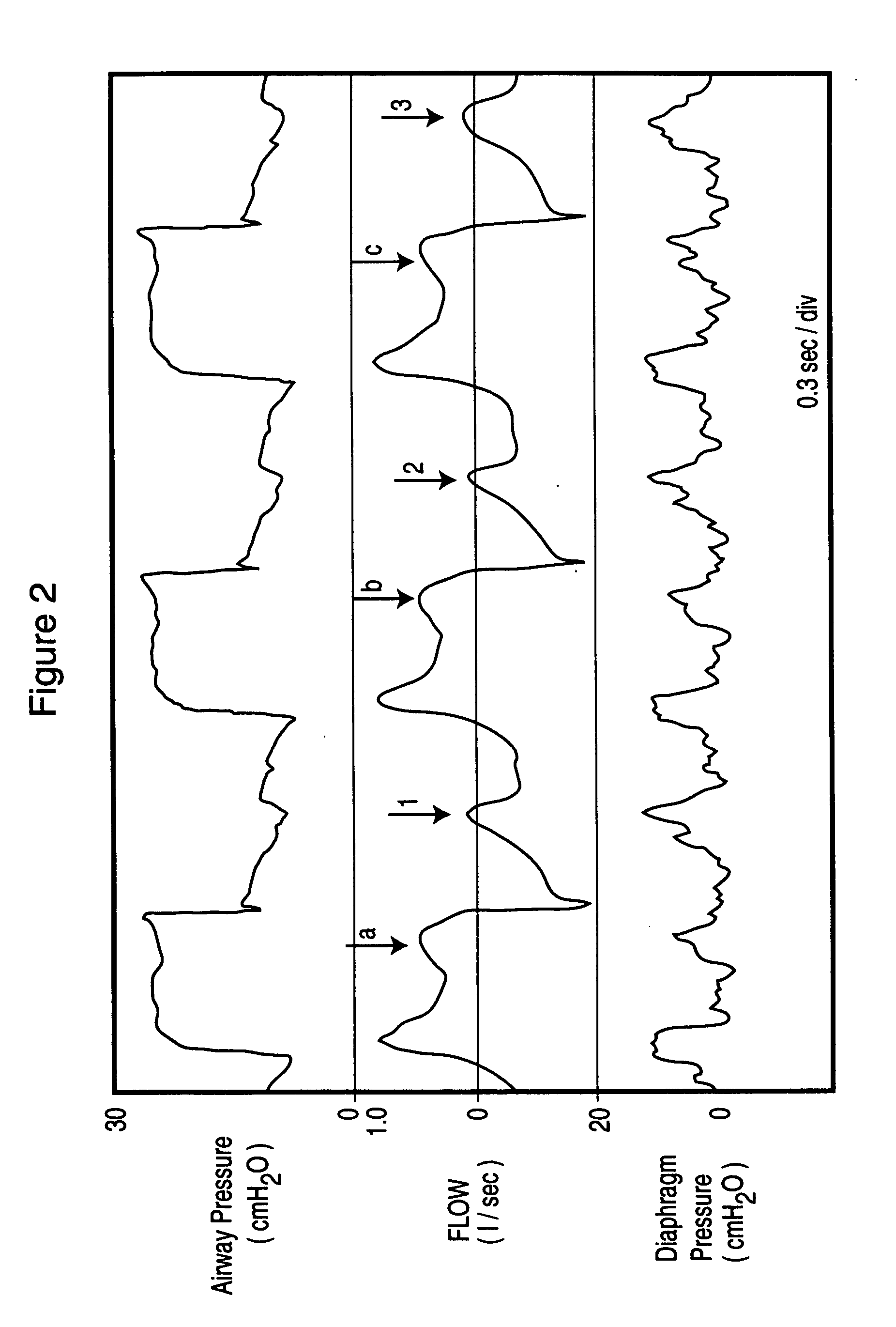
InactiveUS20060249148A1Error minimizationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
Method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the time onset (Tonset) and end (Tend) of patient inspiratory efforts. A composite pressure signal is generated comprising the sum of an airway pressure signal, a gas flow pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kf) to a signal representing gas flow rate and a gas volume pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kv) to a signal representing volume of gas flow. Kf and Kv values are adjusted to result in a desired linear trajectory of composite pressure signal baseline in the latter part of the exhalation phase. The current composite pressure signal is compared with (i) selected earlier composite pressure signal values and / or (ii) value expected at current time based on extrapolation of composite pressure signal trajectory at specified earlier times and / or (iii) the current rate of change in the composite pressure signal with a selected earlier rates of change. The differences obtained by the comparison are compared with selected threshold values. Tonset is identified when at least one of the differences exceeds the threshold values.
Owner:YRT
Control system and process for application of energy to airway walls and other mediums
InactiveUS20060247727A1Improve conductivityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingControl systemEngineering
The present invention includes a system for delivering energy to an airway wall of a lung comprising an energy delivering apparatus and a PID controller having one or more variable gain factors which are rest after energy deliver has begun. The energy delivering apparatus may include a flexible elongated member and a distal expandable basket having at least one electrode for transferring energy to the airway wall and at least one temperature sensor for measuring temperature. The PID controller determines a new power set point base on an error between a preset temperature and the measured temperature. The algorithm can be Pi+1=Pi+G(αei+βei−1+γei−2) where α, β and γ are preset values and α is from 1 to 2; β is from −1 to −2; and γ is from −0.5 to 0-5. In another variation, the controller is configured to shut down if various measured parameters are exceeded such as, for example, energy, impedance, temperature, temperature differences, activation time and combinations thereof. Methods for treating a target medium using a PID algorithm are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Extreme chirped/stretched pulsed amplification and laser
InactiveUS7095772B1Efficiently externally compressedIncrease powerExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor amplifier structureChirped pulse amplificationFiber Bragg grating
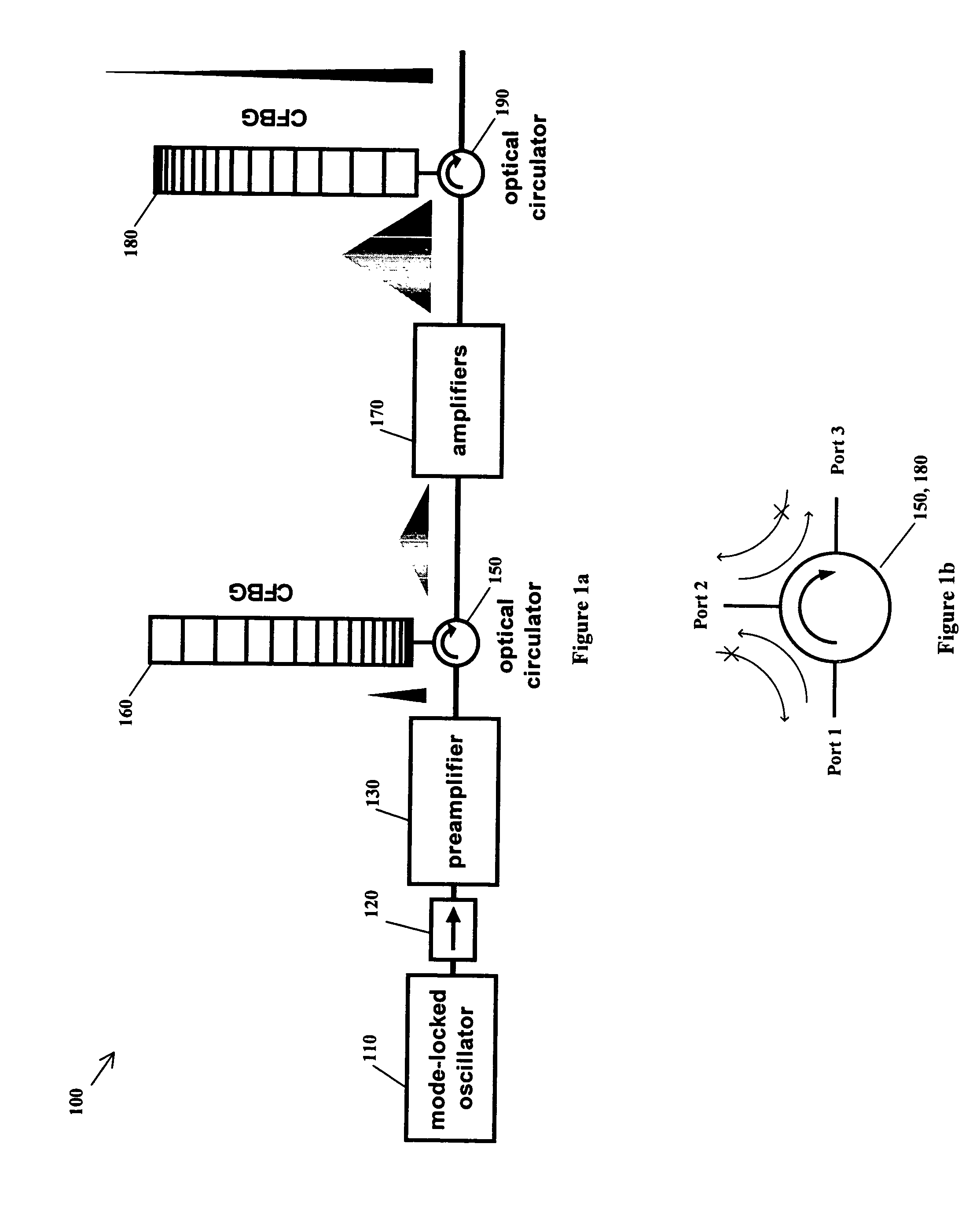
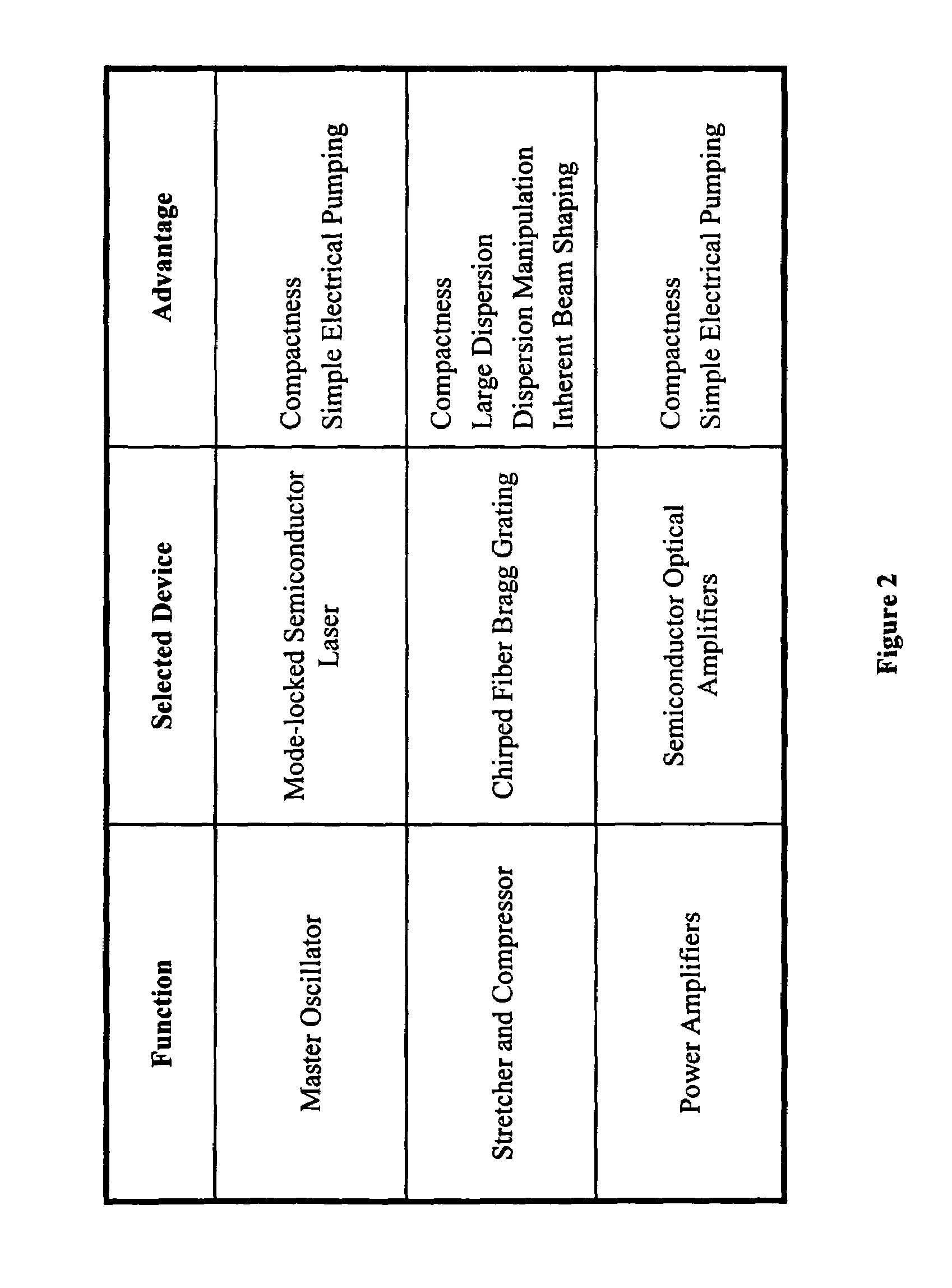
Methods, devices and systems for generating ultrashort optical linear chirped pulses with very high power by amplifying the pulses so that their temporal duration is longer than the storage time of the amplifying medium. The additional gain factor is related to the ratio of the storage time to the stretched pulse. A preferred embodiment connects a mode locked laser source that generates optical pulses whose duration is stretched with a chirped fiber Bragg grating. Embodiments include methods, devices and systems causing an extreme chirped pulse amplifier (XCPA) effect in an oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system
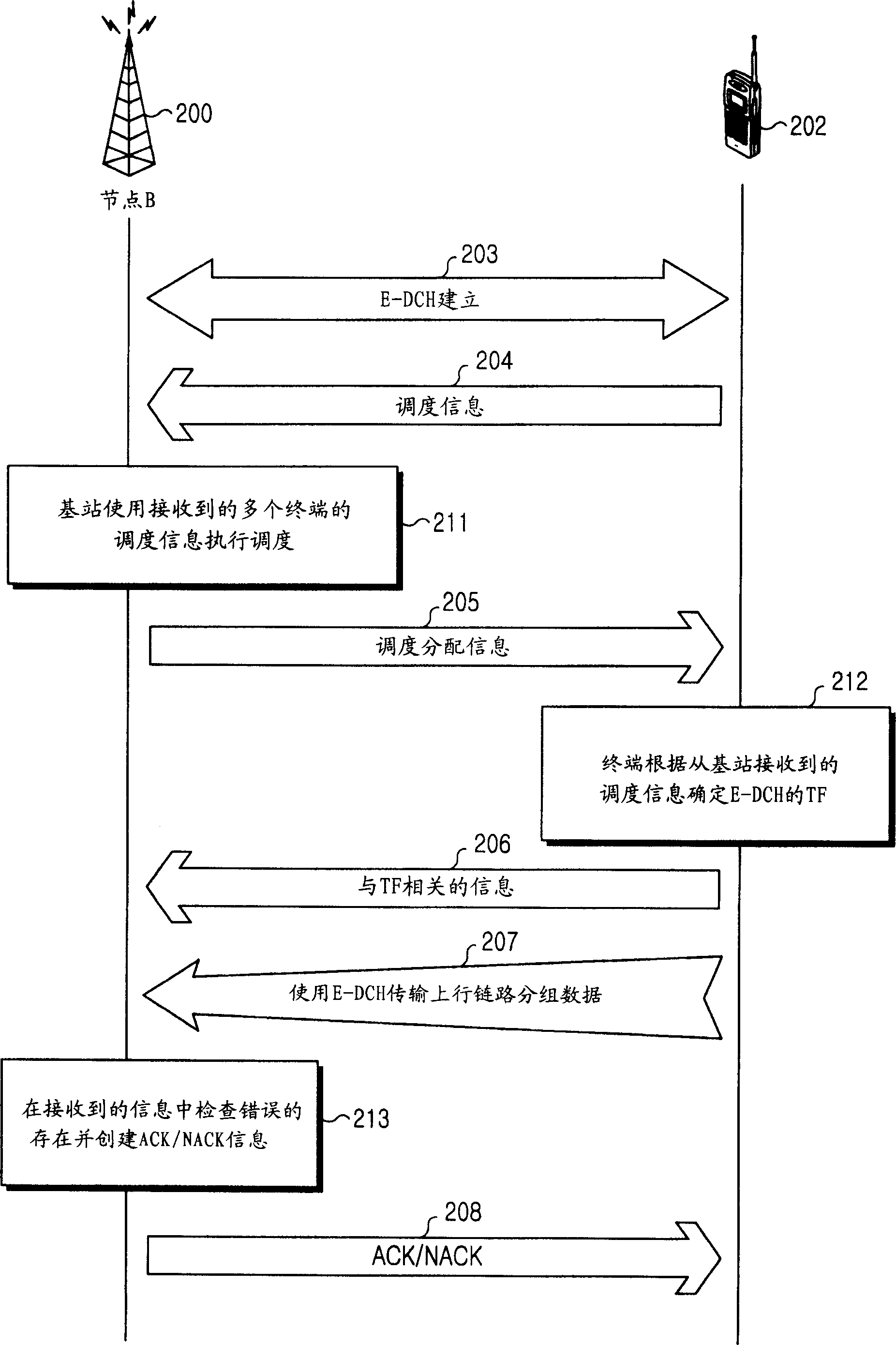
ActiveCN1716837AReduce transmit powerReduced transmit power factorEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmitted powerControl channel
A method and an apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting an enhanced uplink service are provided. A Transport Format Combination (TFC) selector determines TF information for data to be transmitted through a first data channel not supporting Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) and a second data channel supporting HARQ, and determines gain factors for the first and second data channel, and first and second control channel carrying control information for the first and second data channel. The gain factors are input to a physical channel transmission controller, and the physical channel transmission controller reduces the gain factor for the second channel if total transmit power required for transmission of the channels exceeds the predetermined maximum allowed power. A gain scaler adjusts transmit powers of the channels using the scaled gain factor and gain factors for the first data channel, the first control channel and the second control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Class-D amplifier having high order loop filtering
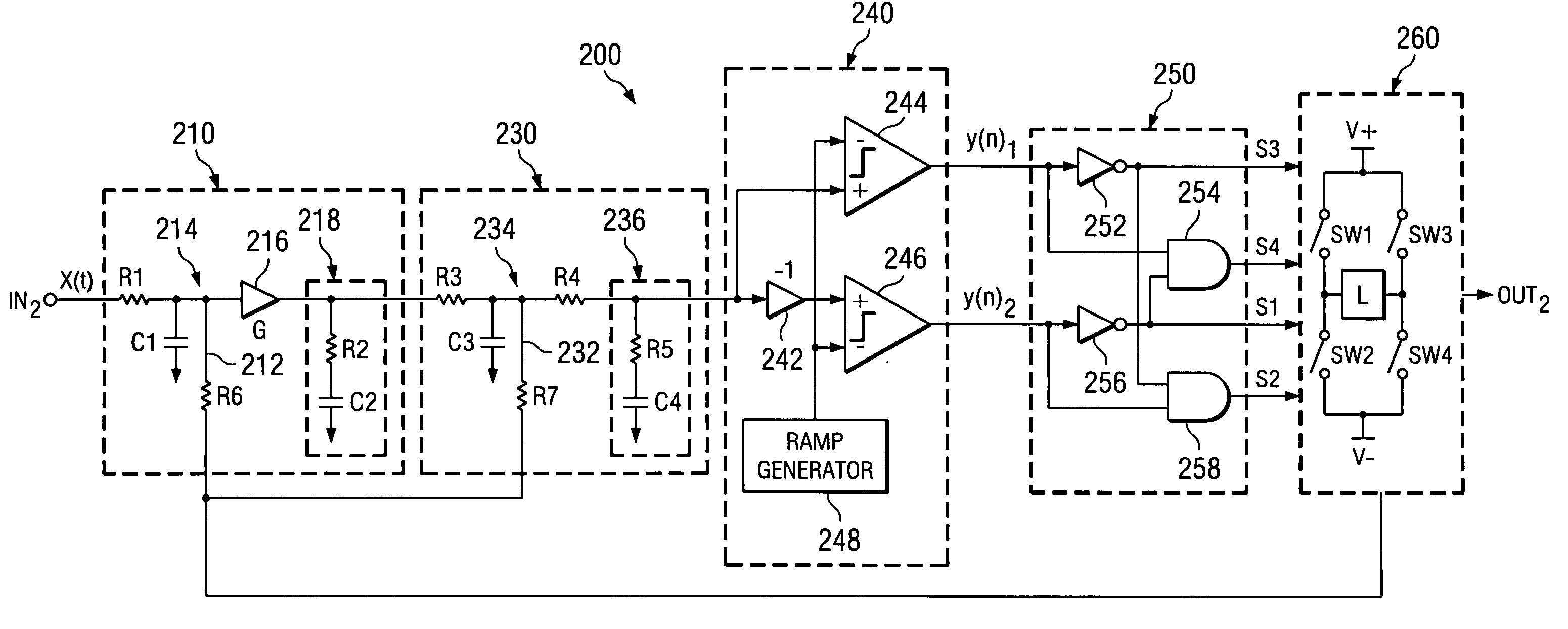
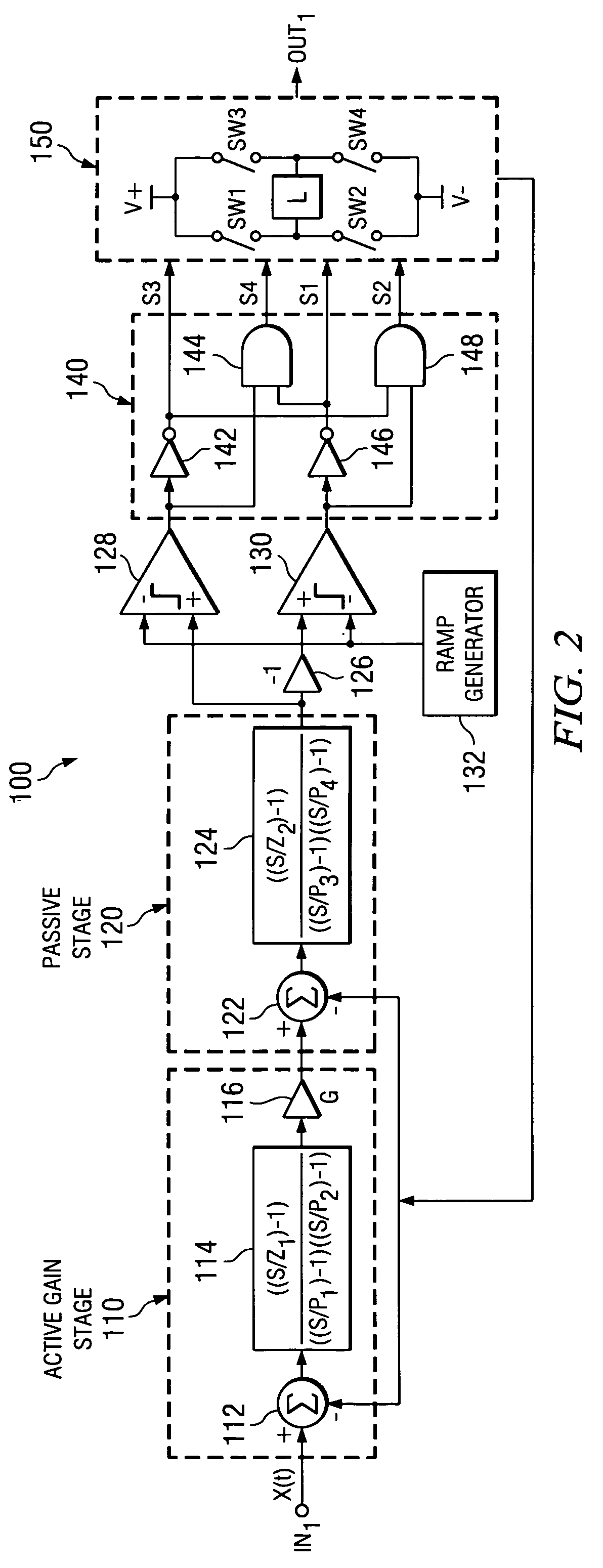
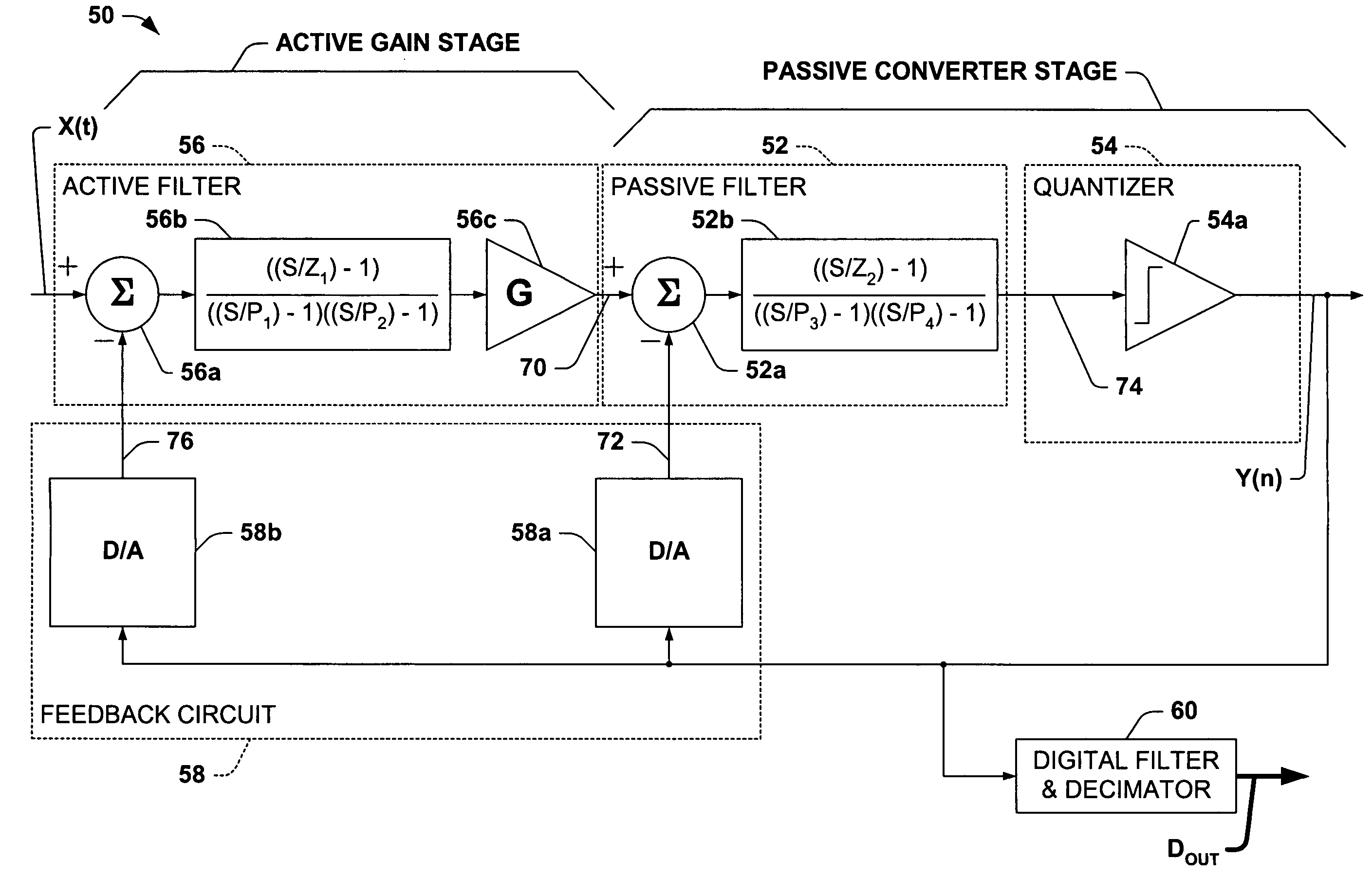
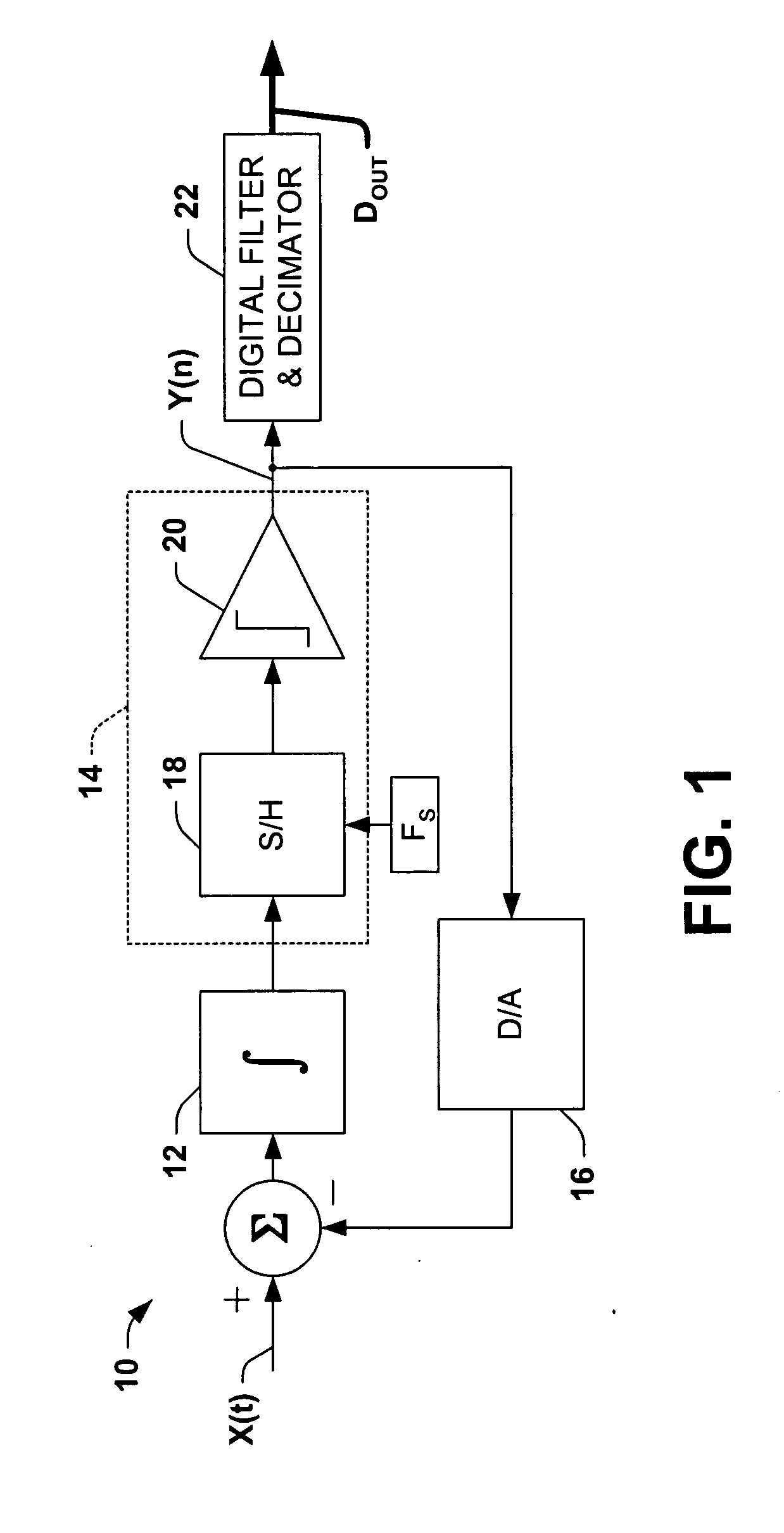
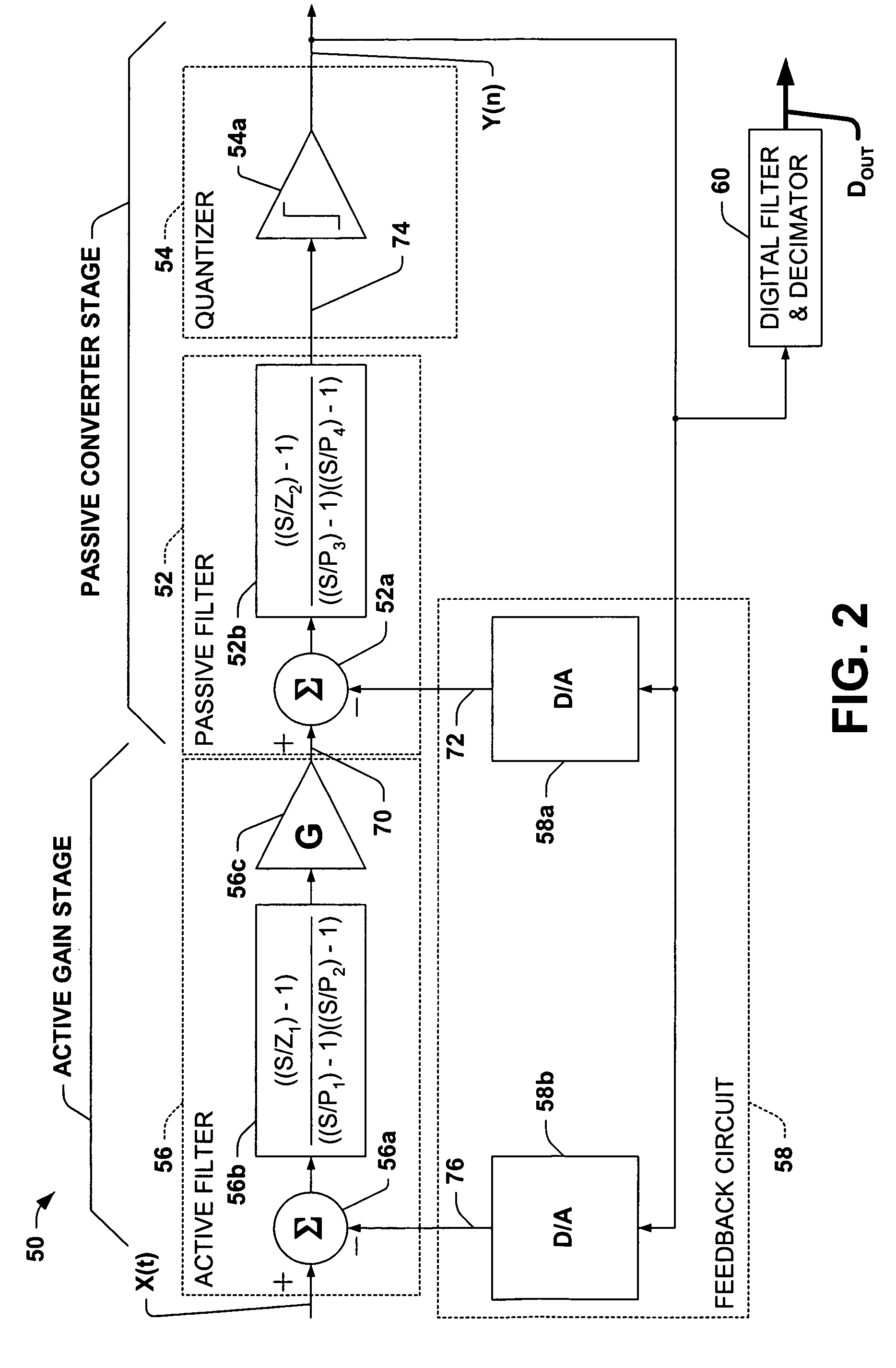
InactiveUS20060044057A1High SNDR performanceImprove PSRRNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorLow-pass filterClass-D amplifier
An amplifier having an active and passive gain stage connect to a load for driving a load according to a system analog input. A first embodiment of the amplifier in accordance with the present invention includes a logic network connected between a comparator network and a switching system, wherein the comparator network connects to the passive gain stage. Specifically, the active gain stage may include an active filter connected to receive an analog or digital input and provide a difference between the analog or digital input and the feedback signal relative to the gain factor of a gain unit connected to the active filter. The passive gain stage includes a passive filter. The logic network generates at least one switching signal which controls the switching system that includes at least one switching device to selectively provide power to the load. An output signal from the switching system provides output for the amplifier and is fed back to the active gain stage. In another embodiment, the output is a two-level signal and the passive and active filters are second order low pass filters, where the gain factor is about 25 or more. In yet another embodiment, the gain factor is approximately 250. Moreover, the amplifier may include a digital delta-sigma modulator connected to supply a two level input.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
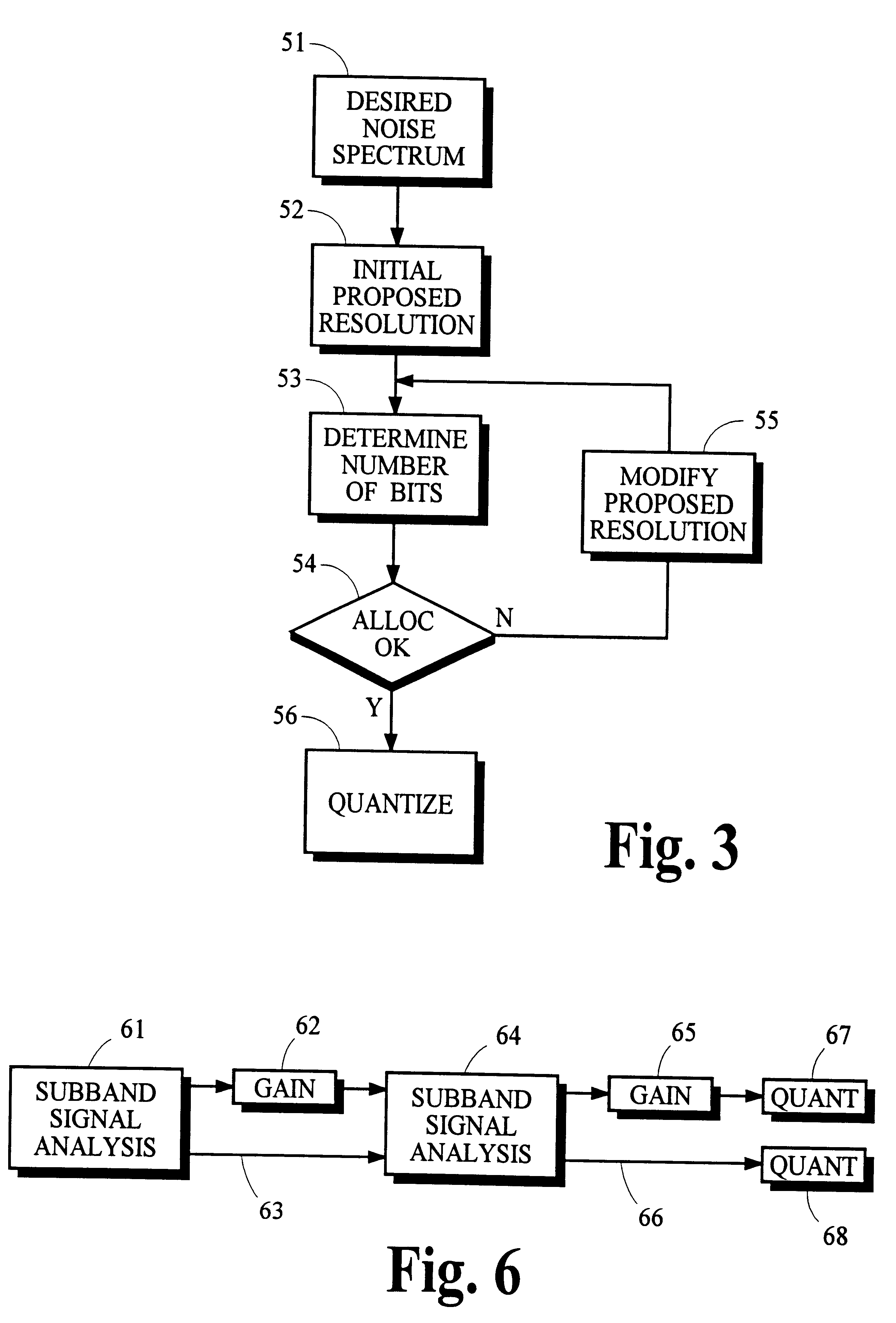
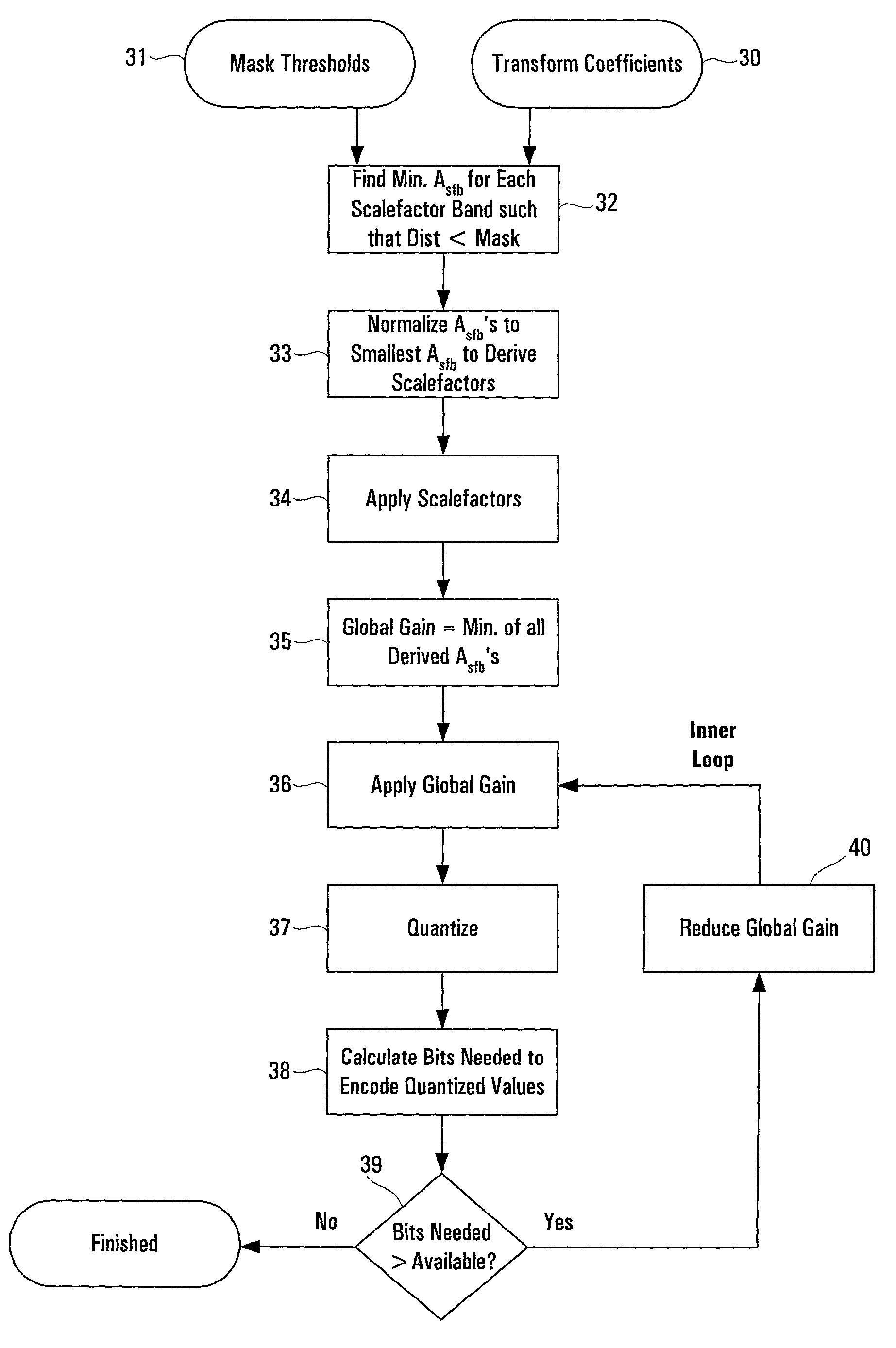
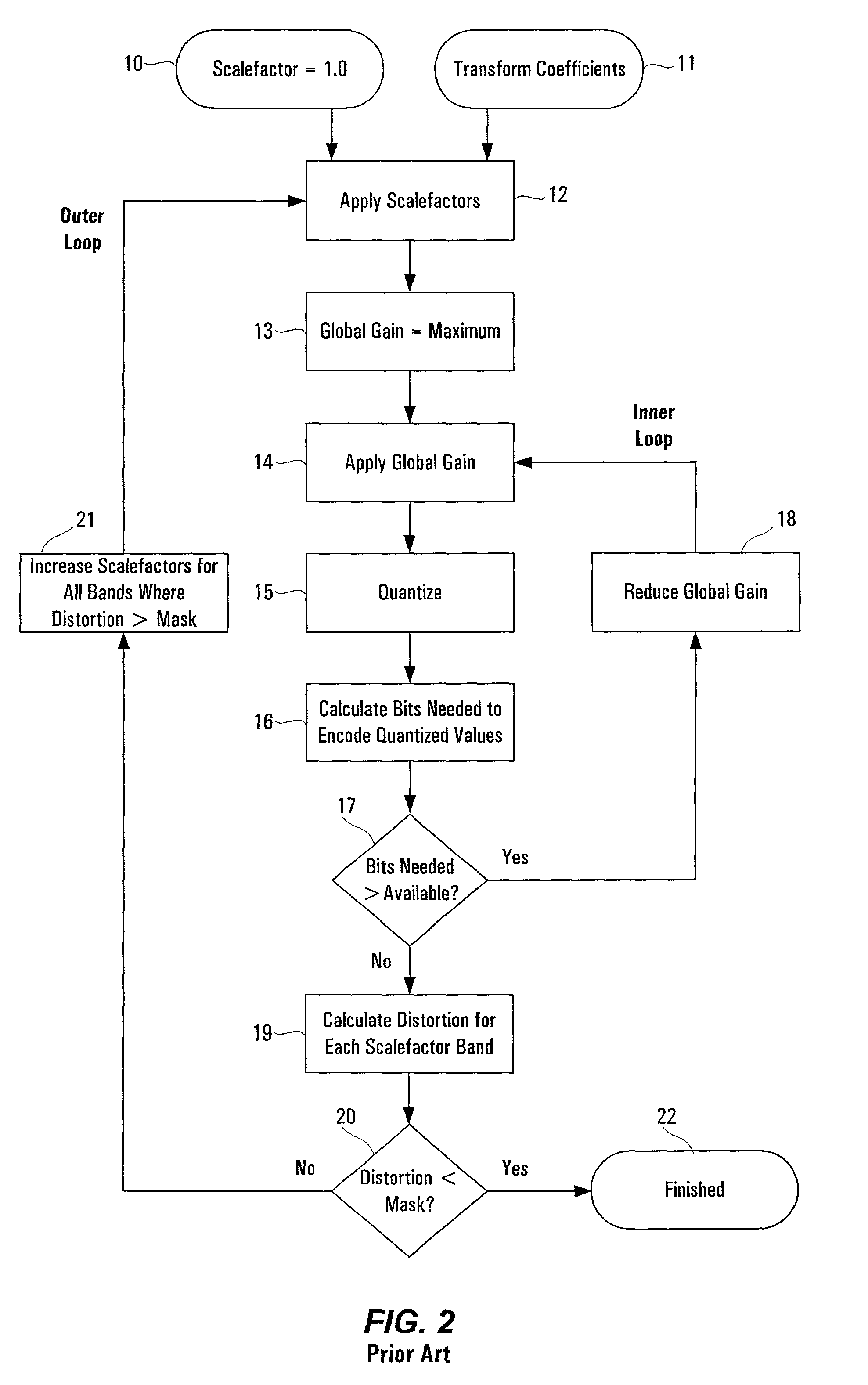
Feedforward prediction of scalefactors based on allowable distortion for noise shaping in psychoacoustic-based compression
A method of encoding a digital signal, particularly an audio signal, which predicts favorable scalefactors for different frequency subbands of the signal. Distortion thresholds which are associated with each of the frequency subbands of the signal are used, along with transform coefficients, to calculate total scaling values, one for each of the frequency subbands, such that the product of a transform coefficient for a given subband with its respective total scaling value is less than a corresponding one of the distortion thresholds. In an audio encoding application, the distortion thresholds are based on psychoacoustic masking. The invention may use a novel approximation for calculating the total scaling values, which obtains a first term based on a corresponding distortion threshold, and obtains a second term based on a sum of the transform coefficients. Both of these terms may be obtained using lookup tables. The total scaling values can be normalized to yield scalefactors by identifying one of the total scaling values as a minimum nonzero value, and using that minimum nonzero value to carry out normalization. Encoding of the signal further includes the steps of setting a global gain factor to this minimum nonzero value, and quantizing the transform coefficients using the global gain factor and the scalefactors.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
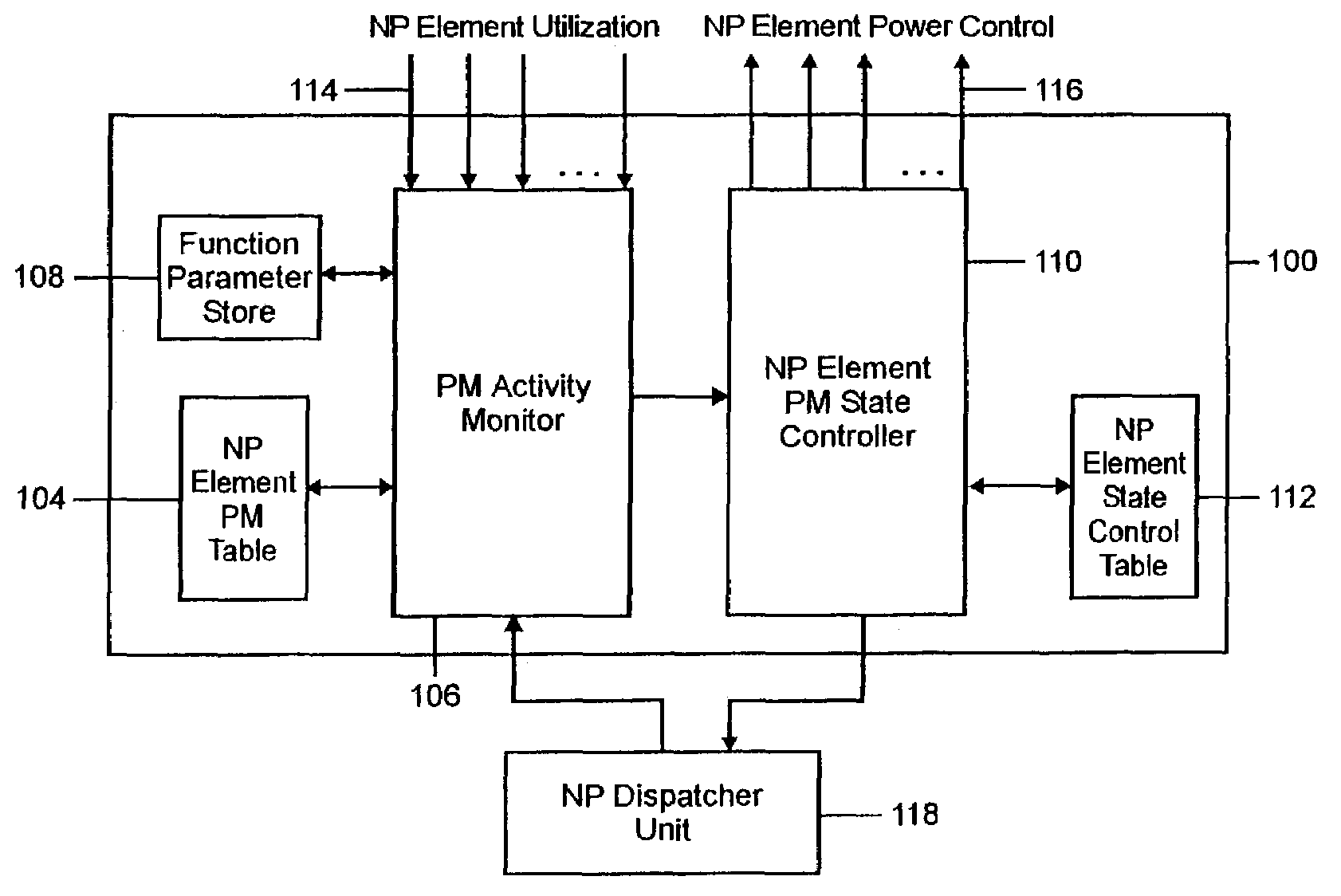
Network processor power management
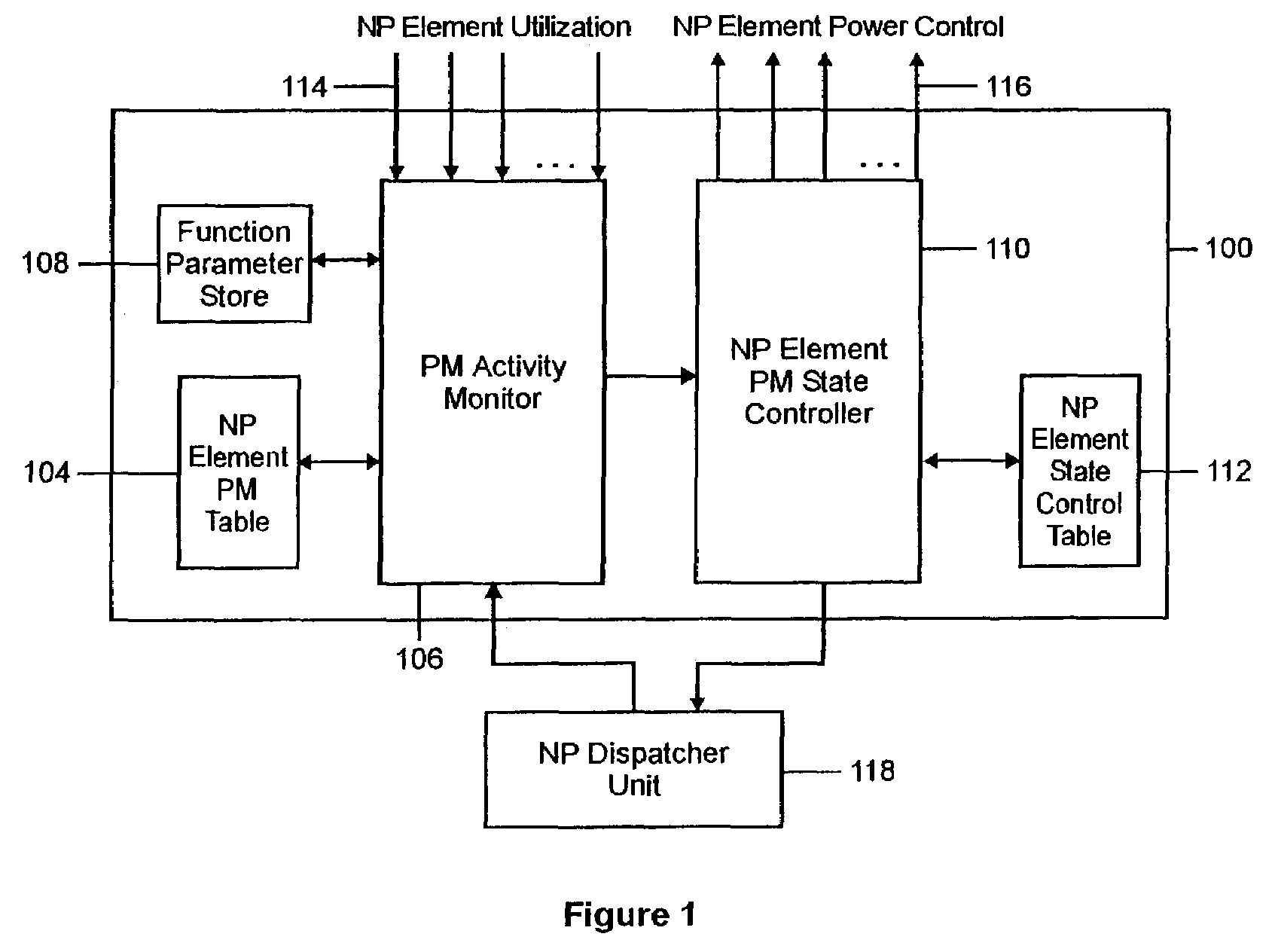
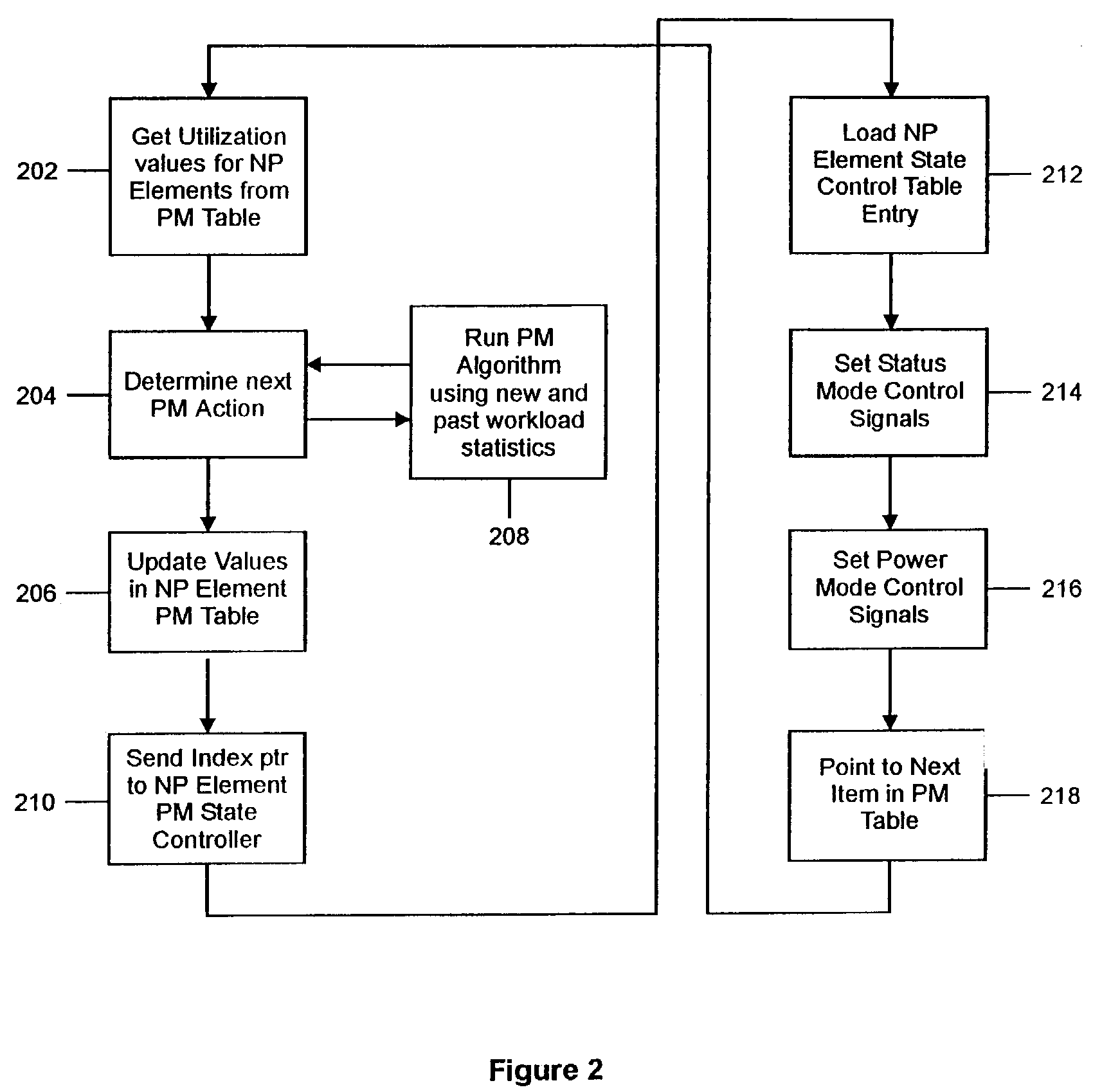
InactiveUS7337334B2Control power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringSystems designEngineering
A programmable state machine is incorporated into the core of a network processor (NP) to monitor the utilization of different processing elements in the NP and to control the power state of each element as a function of past and predicted utilization. The state machine can be used to control a centralized power management control unit or to control a distributed power management unit where each processing element includes its own state machine. The function of the power management state machine can be implemented in any combination of software and / or hardwired logic, depending on the system design requirements. The monitoring and control are implemented through the use of a power management state change algorithm. The determination of the power state of a processing element accommodates interdependencies between the elements. It also makes adjustments in gain factors in response to actual performance and utilization of the network processor.
Owner:IBM CORP
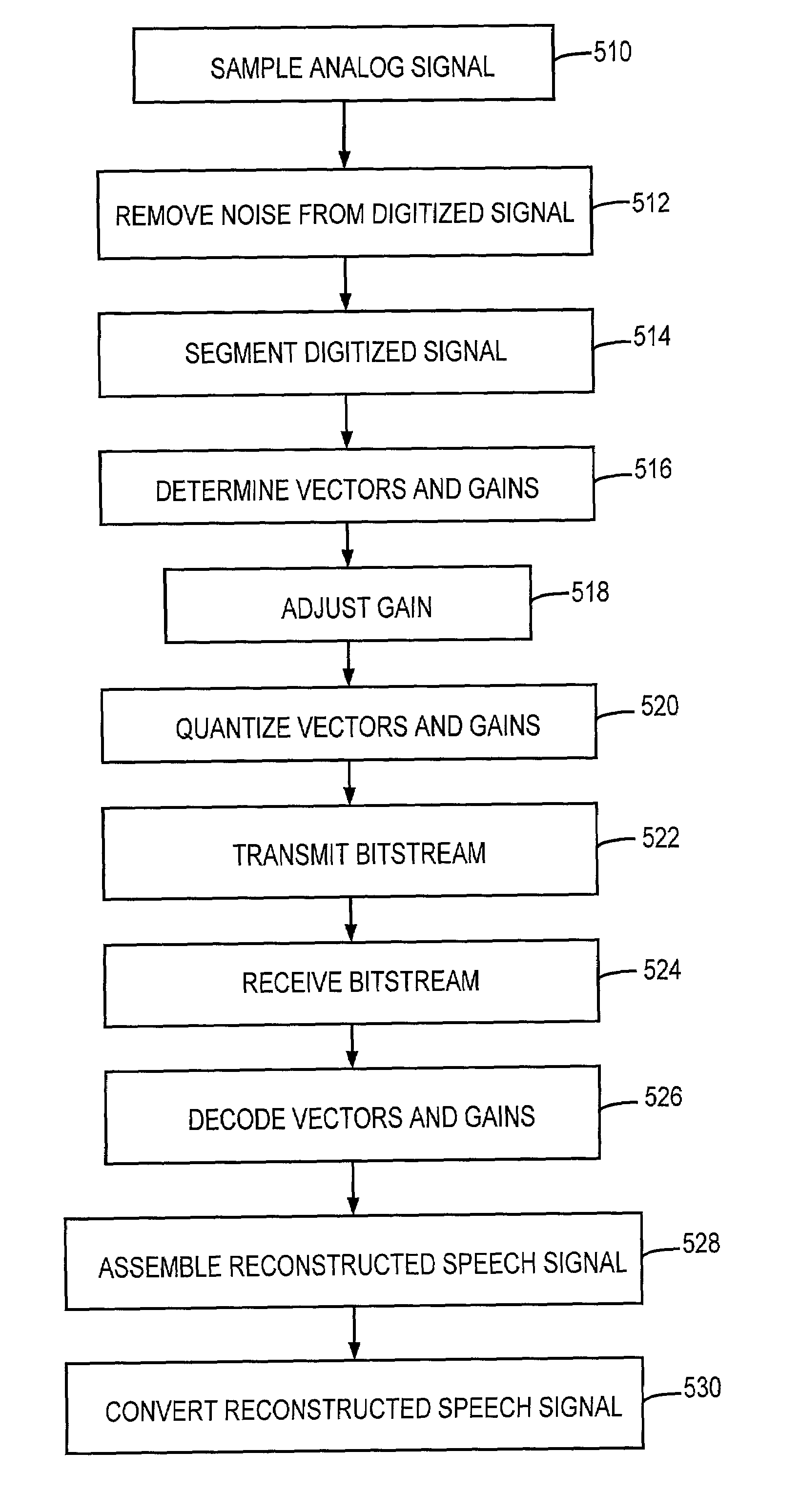
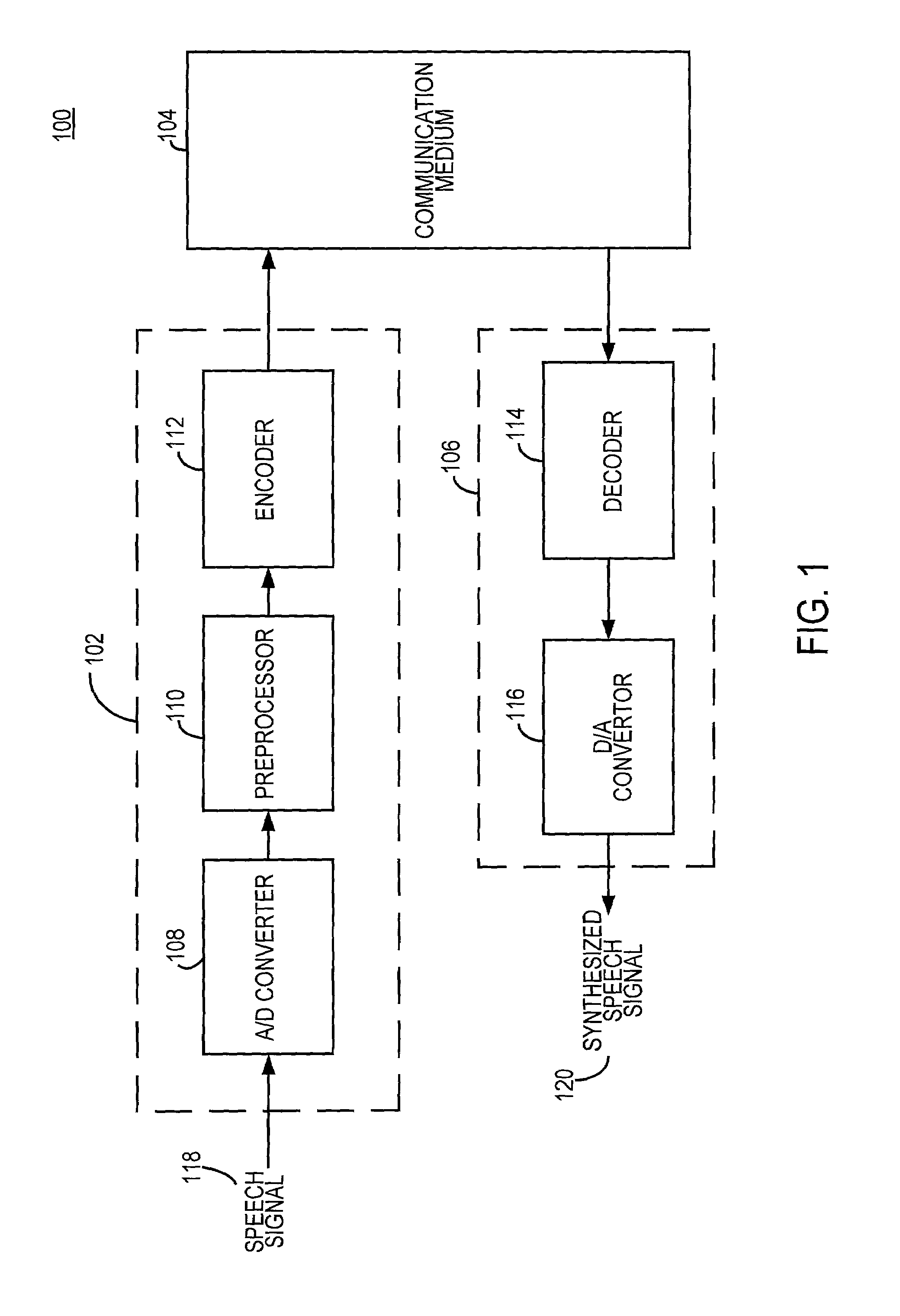
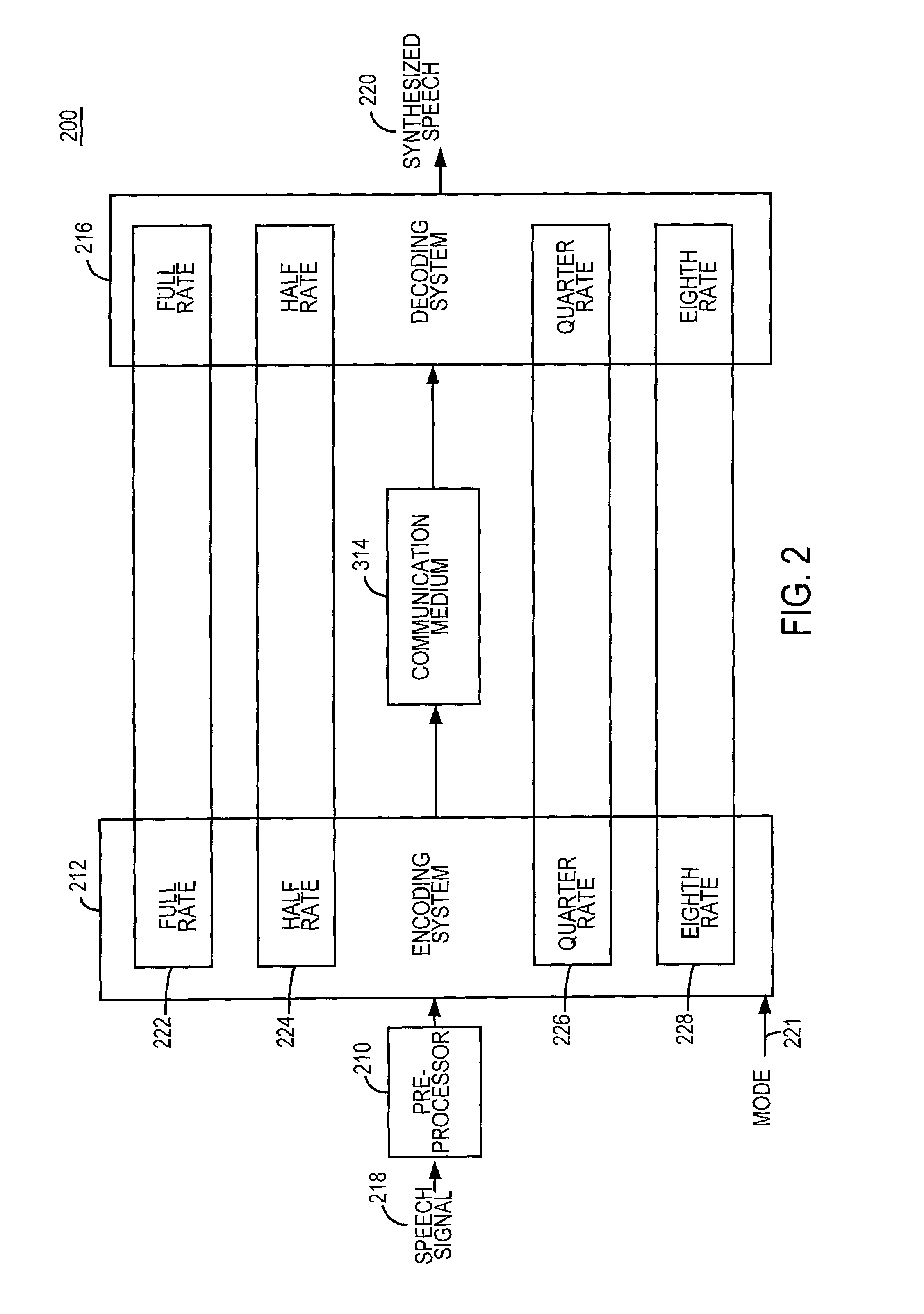
Speech coding system with time-domain noise attenuation
InactiveUS7020605B2Suppress noiseReduce background noiseSpeech analysisAnalog-to-digital converterBackground noise
A speech coding system is provided with time-domain noise attenuation. The speech coding system has an encoder operatively connected to a decoder via a communication medium. A preprocessor processes a digitized speech signal from an analog-to-digital converter. Speech coding systems are used to encode and decode a bitstream. Gains from the speech coding are adjusted by a gain factor Gf that provides time-domain background noise attenuation.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC +1
Method and apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting enhanced uplink service
ActiveUS7447516B2Effective controlPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTransmitted powerControl channel
A method and an apparatus for data transmission in a mobile telecommunication system supporting an enhanced uplink service are provided. A Transport Format Combination (TFC) selector determines TF information for data to be transmitted through a first data channel not supporting Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) and a second data channel supporting HARQ, and determines gain factors for the first and second data channel, and first and second control channel carrying control information for the first and second data channel. The gain factors are input to a physical channel transmission controller, and the physical channel transmission controller scales-down the gain factor for the second channel if total transmit power required for transmission of the channels exceeds the predetermined maximum allowed power. A gain scaler adjusts transmit powers of the channels using the scaled gain factor and gain factors for the first data channel, the first control channel and the second control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low radiation wireless communicator
InactiveUS20100056210A1Reduce usageReduce amountPower managementSubstation equipmentData limitationsModem device
A wireless communicator, including a modem operable to transmit and receive voice communication phone calls, a power amplifier coupled with the modem operable to dynamically apply a variable gain factor to voice communications transmitted by the modem, to produce an appropriate power output, and a controller coupled with the modem including a radiation monitor operable to monitor the power output of the power amplifier, the controller being operable to restrict operation of the modem, based on data provided by the radiation monitor, when the cumulative power output produced by the power amplifier exceeds a pre-designated daily cumulative power limit.
Owner:SUN DAVID
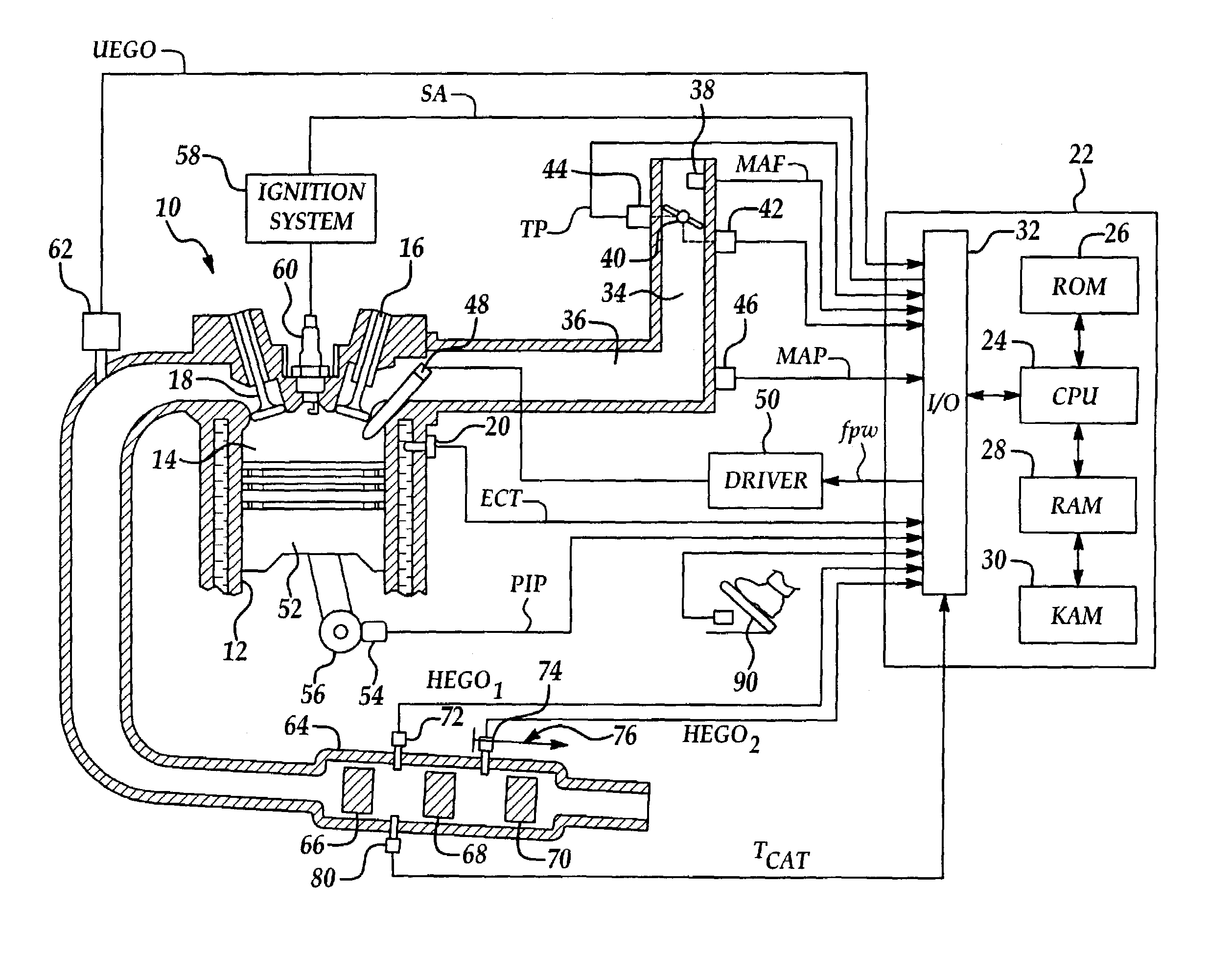
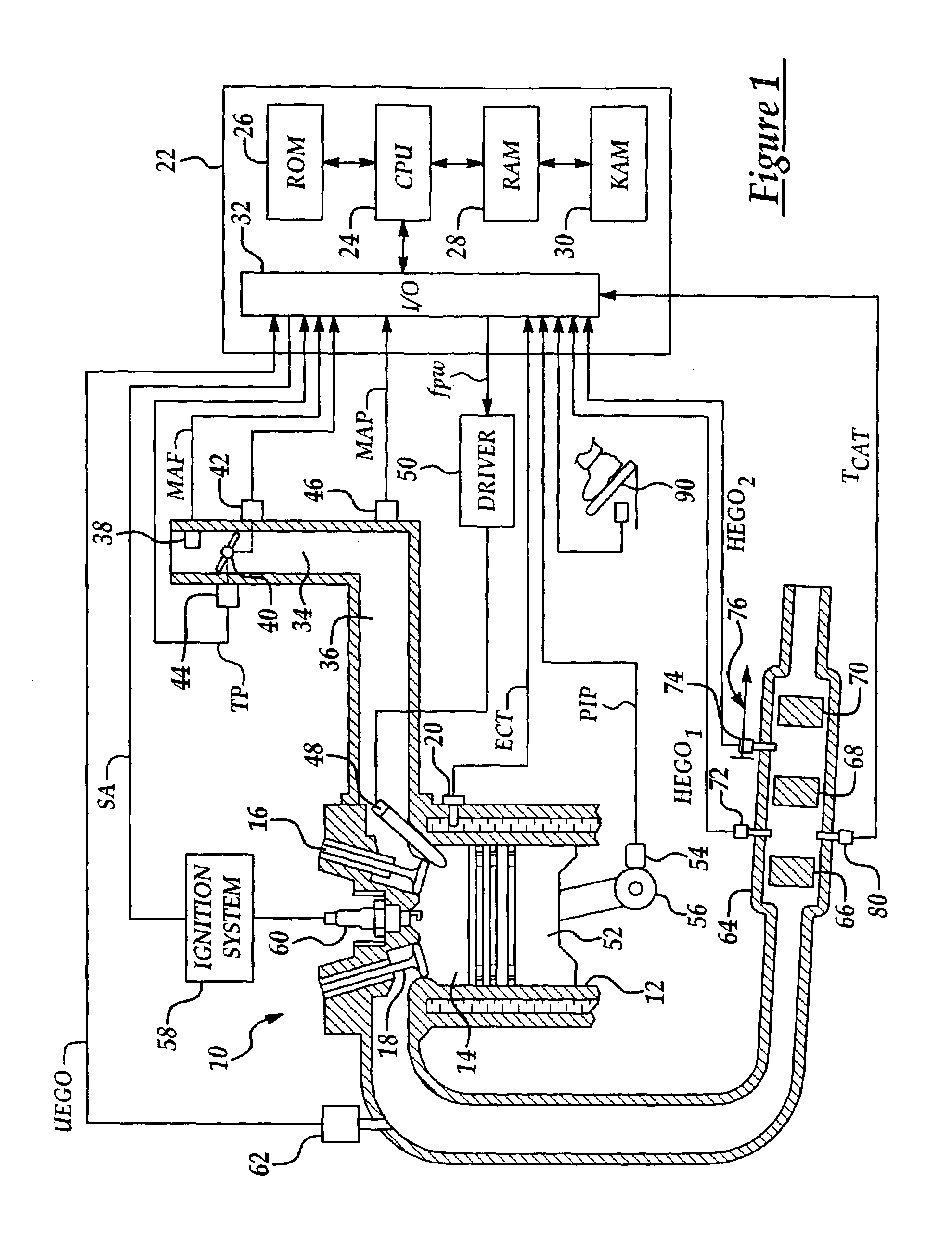
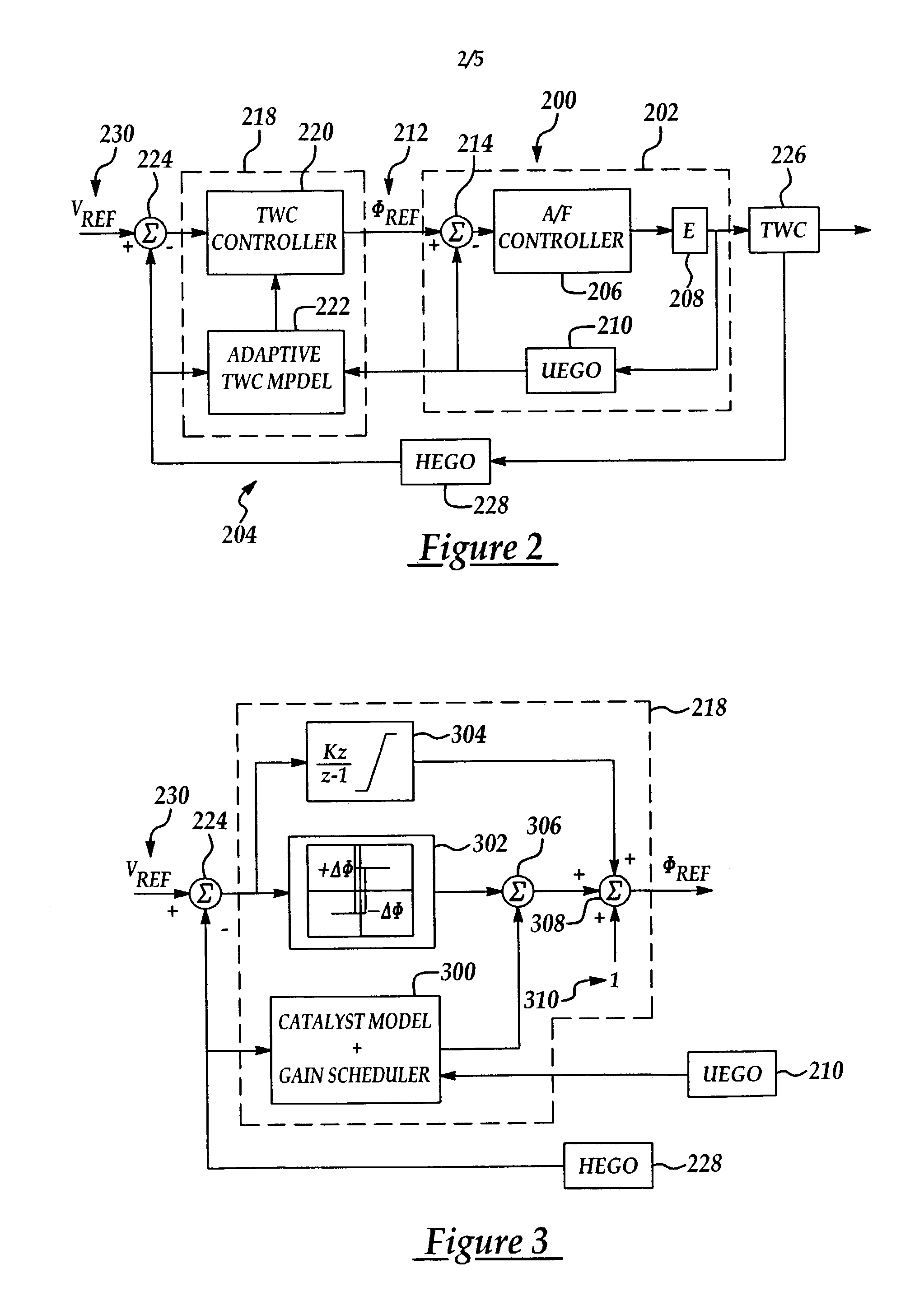
Fuel/air ratio feedback control with catalyst gain estimation for an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7000379B2Low costSaving weightElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesIntegratorFeedback control
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine for low emissions include an inner feedback control loop to control the engine fuel / air ratio with feedback provided by a first exhaust gas sensor and an outer feedback control loop that modifies the fuel / air ratio reference provided to the inner feedback control loop based on feedback signals provided by the first exhaust gas sensor and a second exhaust gas sensor. The fuel / air ratio reference signal controller adapts to the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst by modeling the catalyst as an integrator with an unknown gain and estimating the catalyst gain based on the first and second exhaust gas sensor signals. Using the estimated catalyst gain, an adaptive controller gain factor is determined and subsequently used to determine the fuel / air ratio reference signal provided to the fuel / air ratio controller of the inner feedback control loop.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
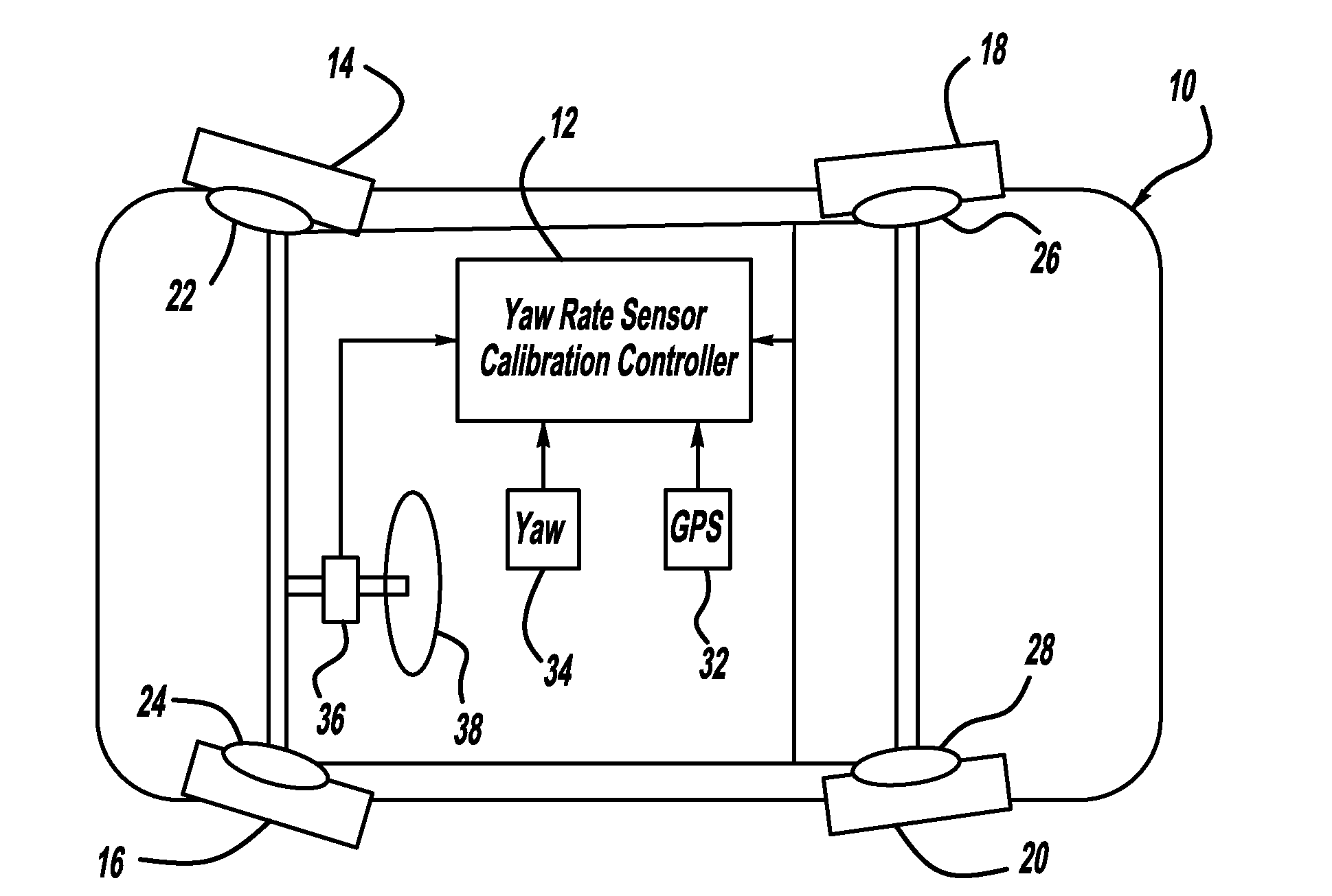
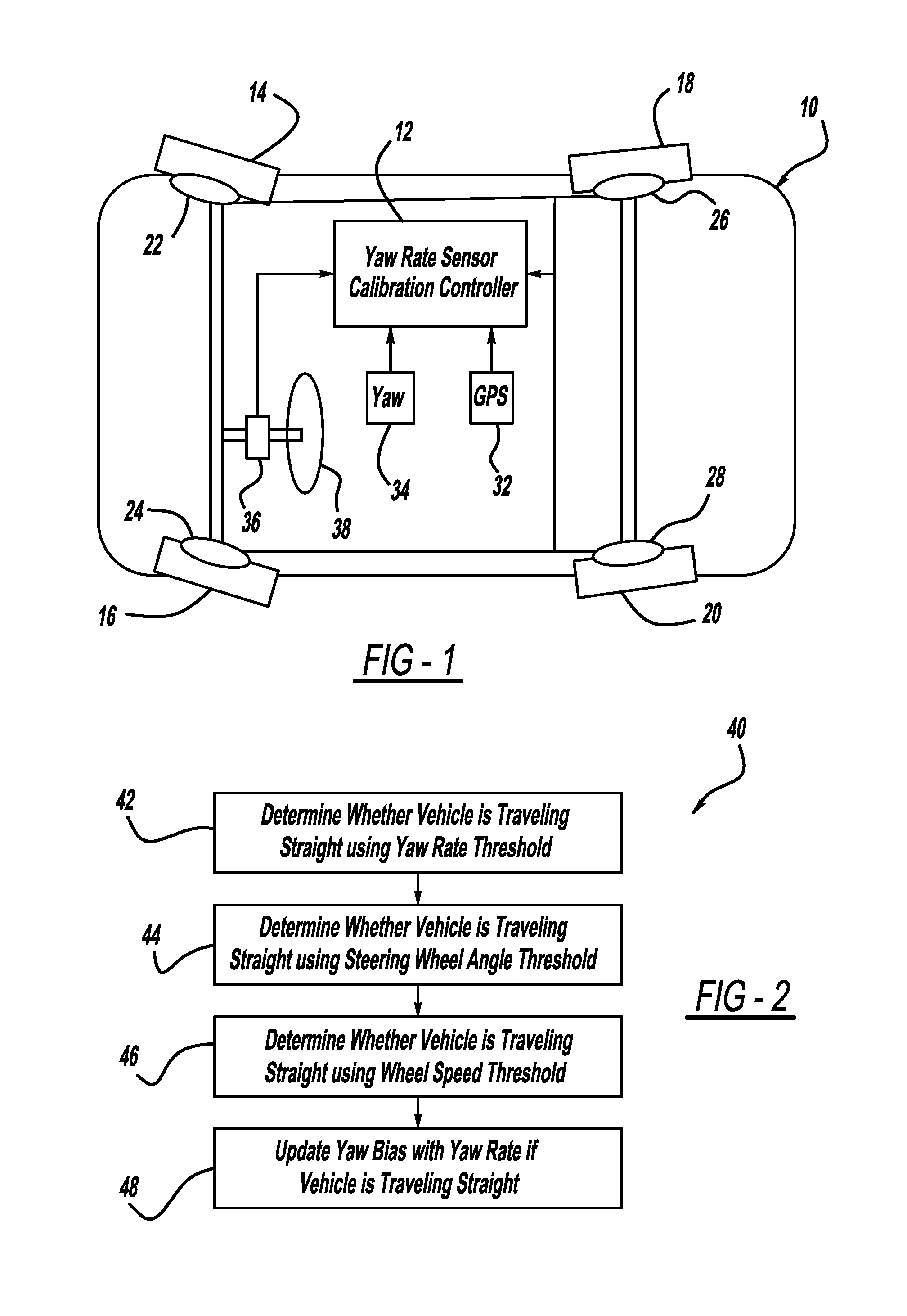
In-vehicle sensor-based calibration algorithm for yaw rate sensor calibration
A system and method for calibrating a vehicle heading sensor, such as a yaw-rate sensor, when GPS signals are not available using a bias update model that employs a bias gain factor. In order for the bias update model to be accurate, the vehicle should be traveling relatively straight. One embodiment of the present invention uses three thresholds to determine if the vehicle is traveling straight. These thresholds include a yaw-rate threshold, a steering wheel angle threshold and a wheel speed threshold. If all three of the thresholds indicate that the vehicle is traveling straight, then the update bias model can be used to calibrate the yaw-rate sensor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Continuous time fourth order delta sigma analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS20050116850A1Reduce adverse effectsWell formedDelta modulationA d converterGreek letter sigma
A fourth order delta sigma analog-to-digital converter is presented, comprising a passive delta sigma modulator including a passive filter, a quantizer, and a digital-to-analog converter in a first feedback loop, and an active filter having a large gain factor in a second feedback loop around the passive delta-sigma modulator.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
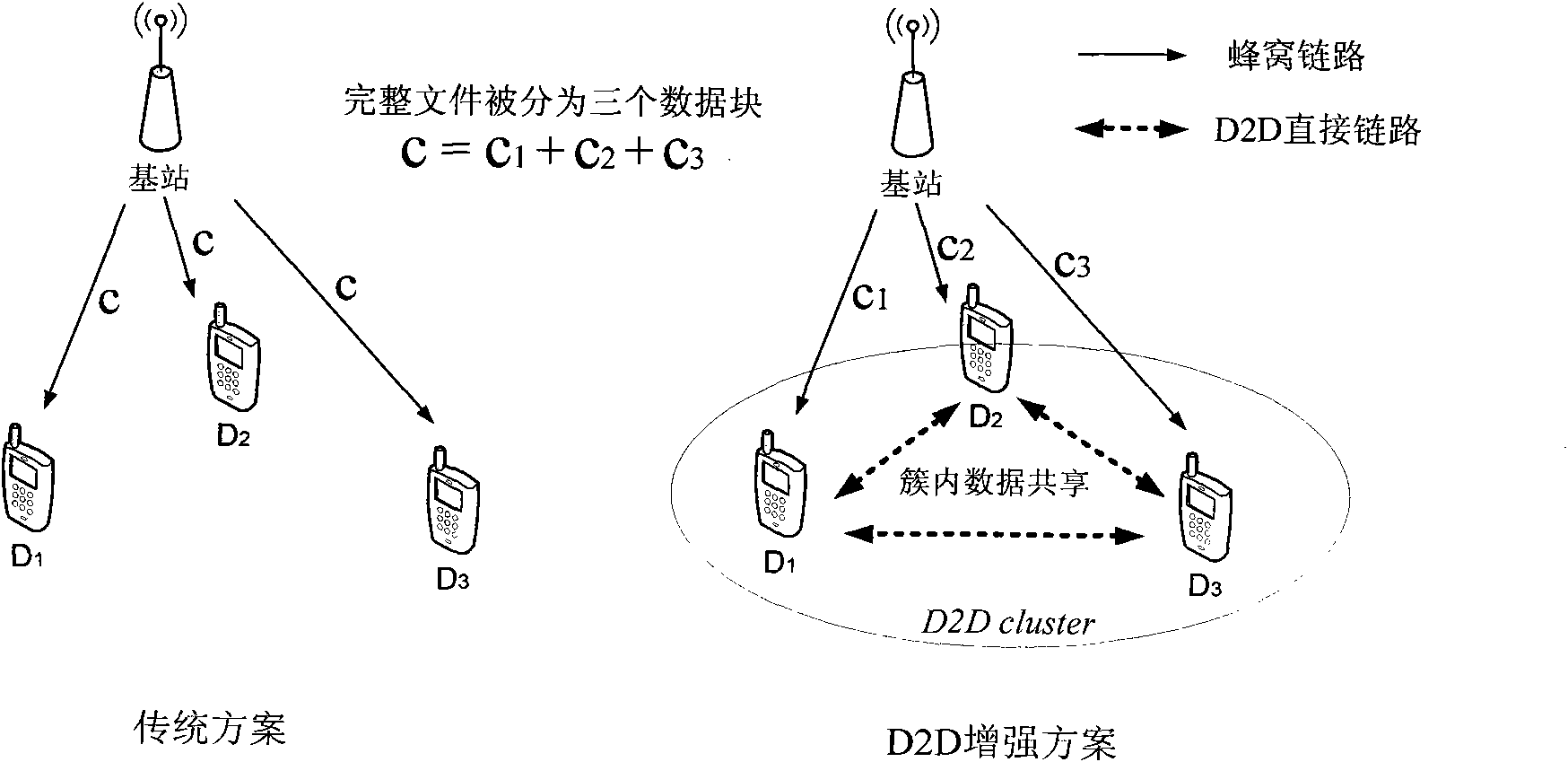
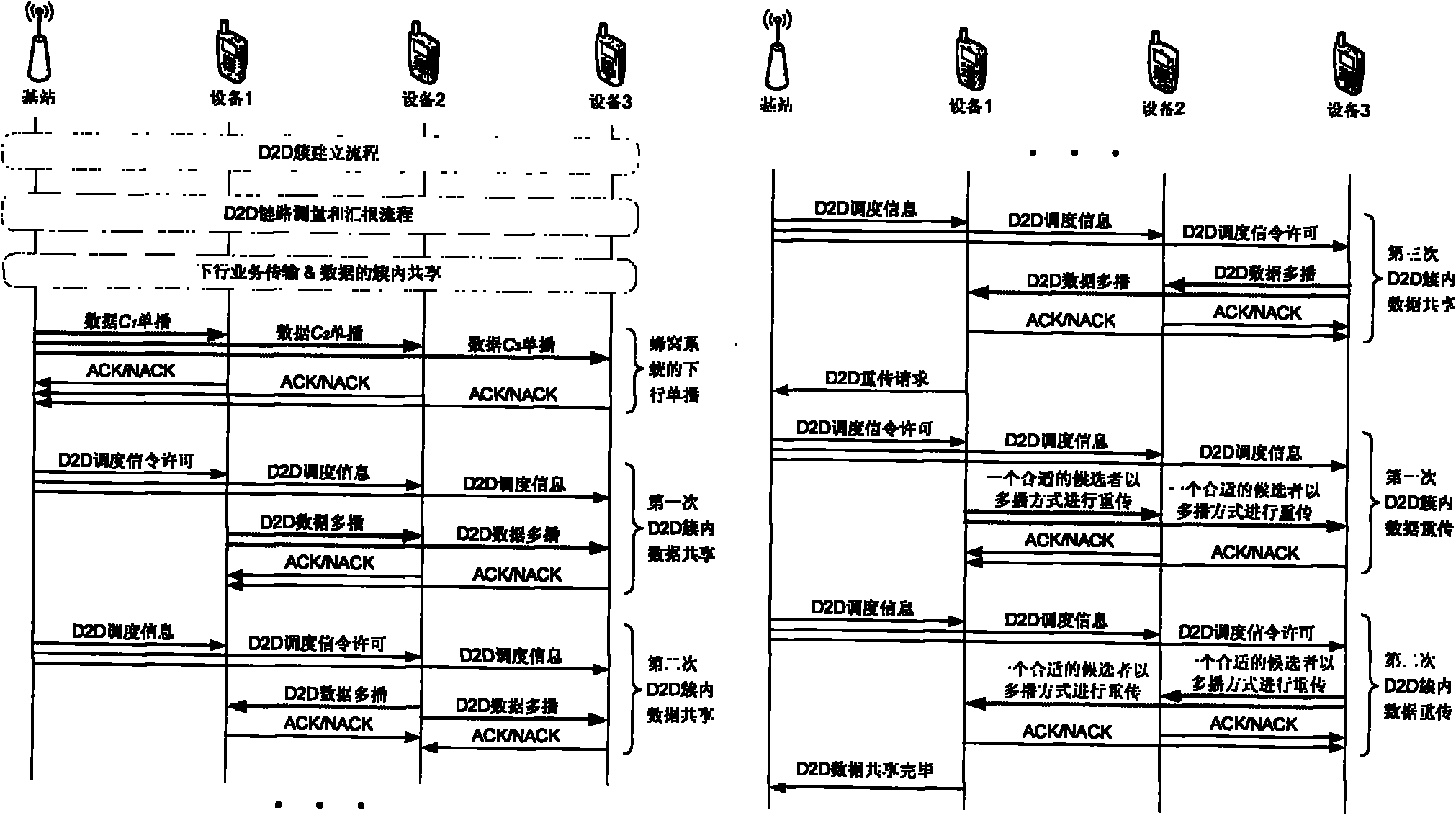
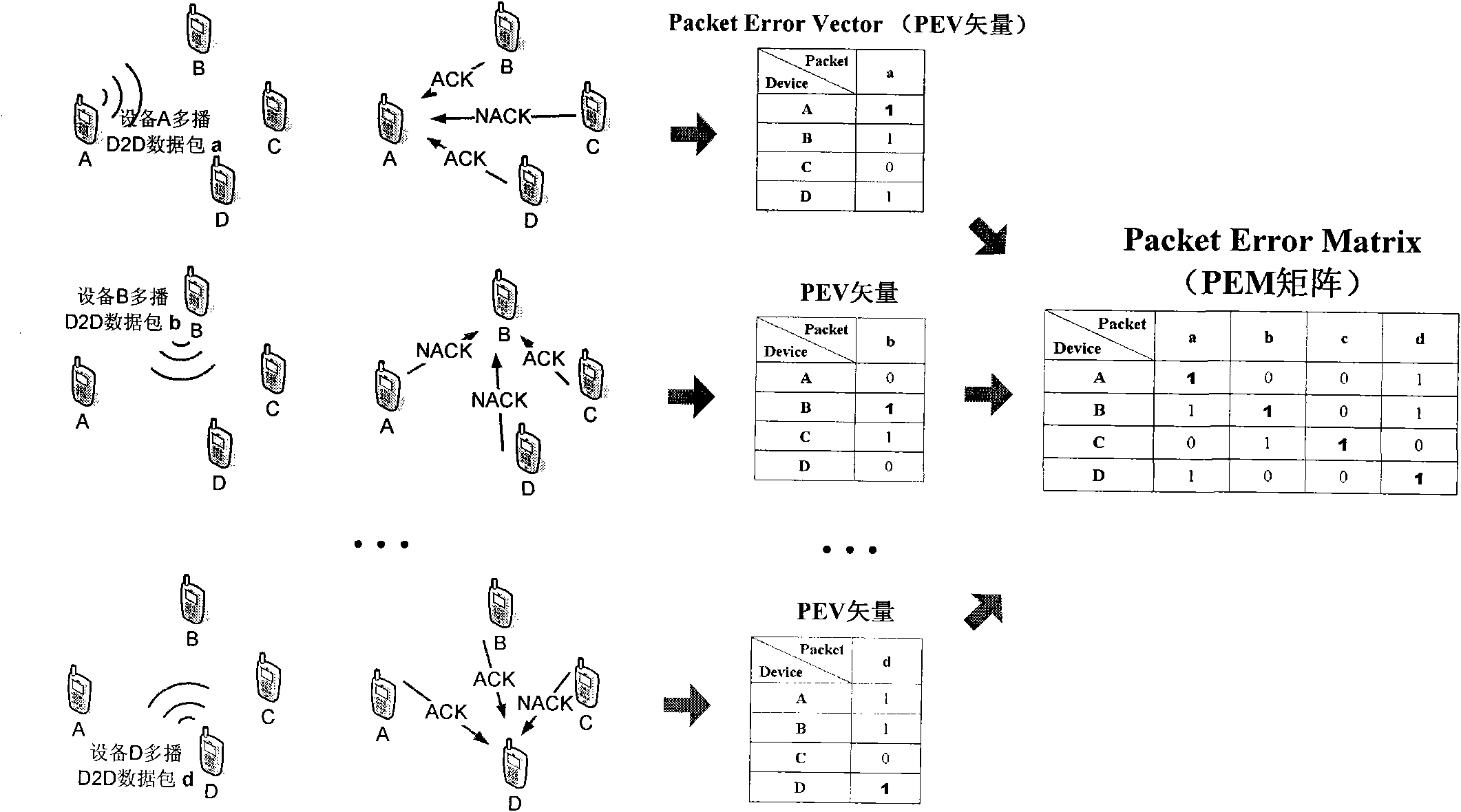
Device-to-device (D2D) cluster data sharing method under cellular environment
InactiveCN102340829AReduce the number of retransmissionsReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork packetSystem time
The invention discloses a device-to-device (D2D) cluster data sharing method under a cellular environment. The method comprises the following steps that: step1. before D2D cluster retransmission begins, each mobile equipment in the D2D cluster firstly acquires a packet error matrix (PEM) which belongs to the mobile equipment itself; step 2. a retransmission gain factor of the each mobile equipment in the D2D cluster is calculated; step 3. the mobile equipment with the highest retransmission gain factor is taken as a transmitter in the D2D cluster retransmission; step 4. the transmitter retransmits a data packet needed to be retransmitted in the cluster and updates the PEM of the each mobile equipment; step 5. if the updated PEM still contains a ''0'' element, the step 1 to the step 4 are repeated till the PEMs of all the mobile equipment in the D2D cluster are ''1'' matrixes. In the method of the invention, through effectively reducing retransmission times in the D2D cluster, related signaling costs of D2D communication under the cellular environment can be substantially saved and simultaneously system time delay can be shortened. The method is beneficial to realization of a real time multimedia service.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Speech enhancement method using voice existence probability
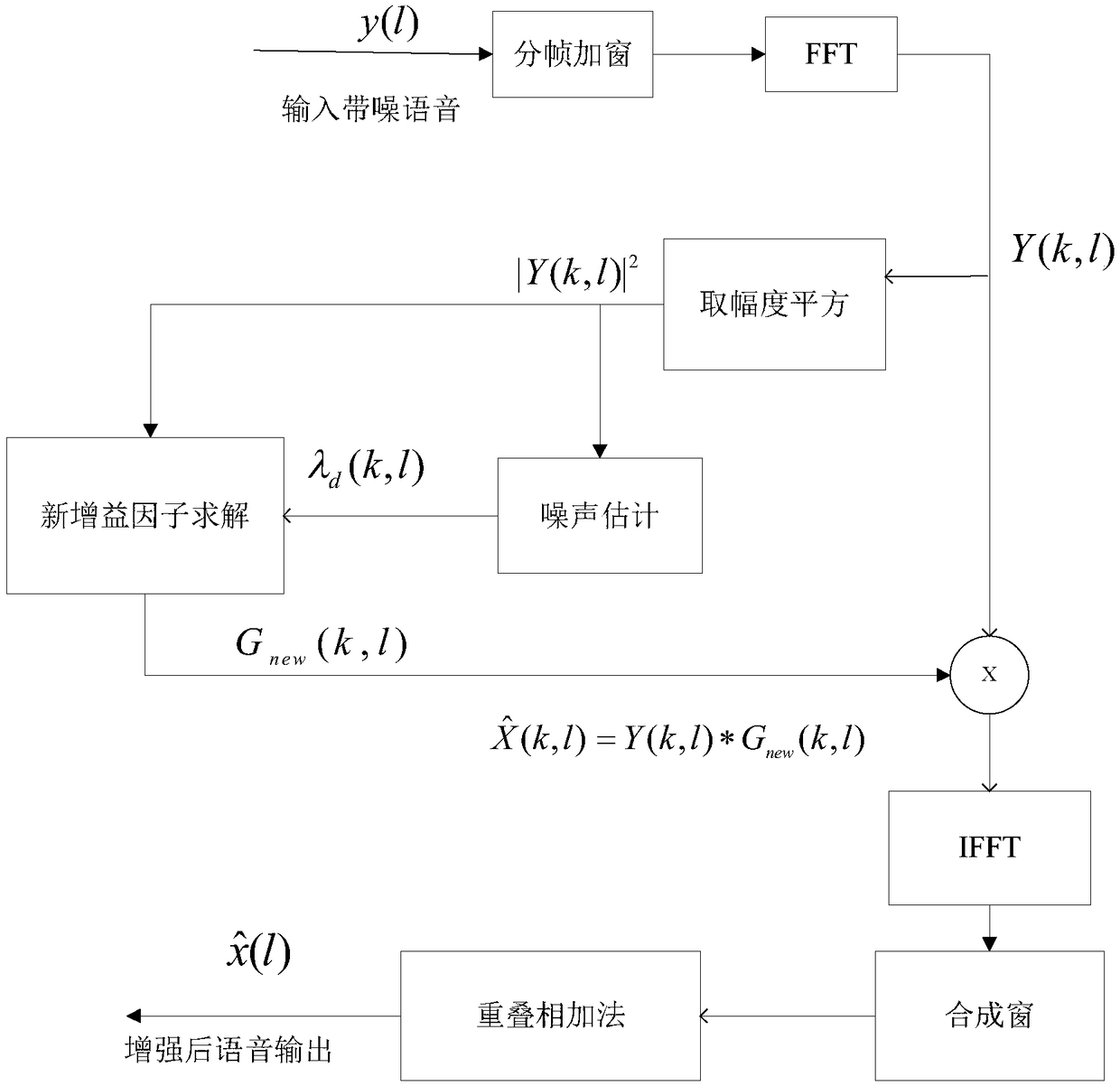
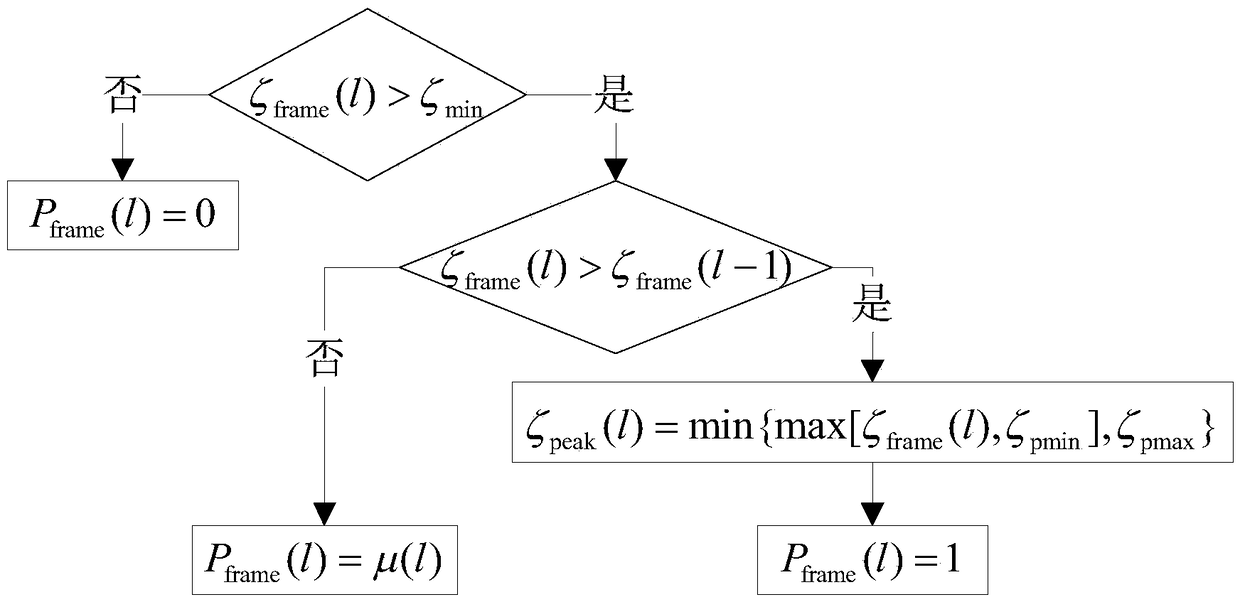
ActiveCN108831499AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce distortionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
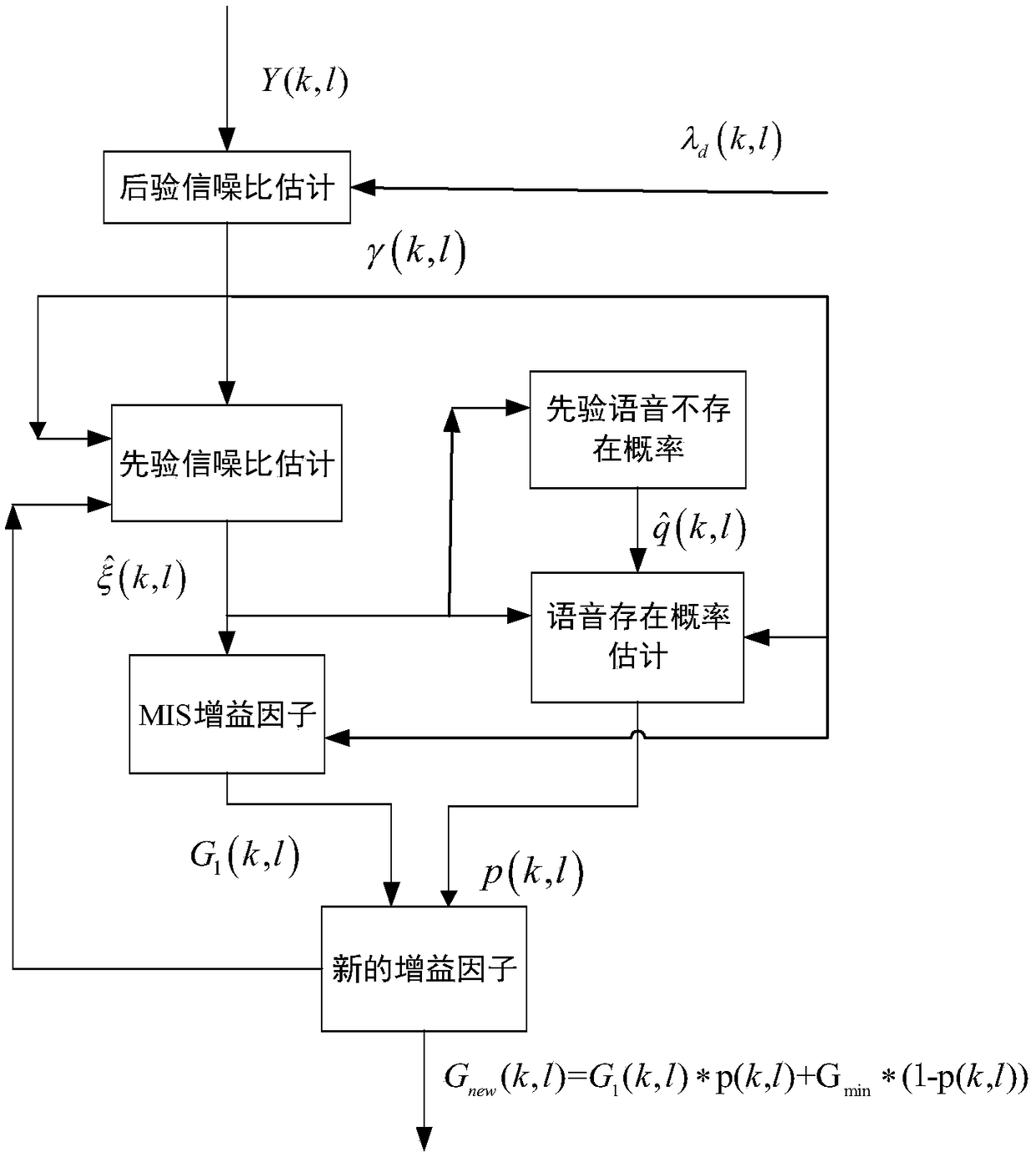
The invention discloses a speech enhancement method using a speech existence probability, after the processing of the invention, the speech quality is higher, and the noise reduction amount is larger.The method is realized by the following technical scheme that: on the basis of a MIS measure speech enhancement method, the speech existence probability is used, an inputted noisy speech is sampled,framed and windowed, and then a noisy speech spectrum is obtained through fast Fourier transform (FFT); the noise estimation of the obtained speech spectrum is carried out, based on a non-stationary noise minimum search algorithm of statistical information, the smoothing between front and back frame noise estimation values is carried out by using inter-frame correlation, and a noise power spectrumis estimated; at the same time, speech prior signal-to-noise ratio estimated values obtained in several front and back frames are smoothened; then the speech existence probability and a MIS measure gain factor are combined, the obtained noisy speech spectrum is multiplied by a new gain factor, and a spectrum of the enhanced speech is obtained; and the inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) is performed to obtain an enhanced time domain speech signal.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com