Patents
Literature
202 results about "Real time multimedia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
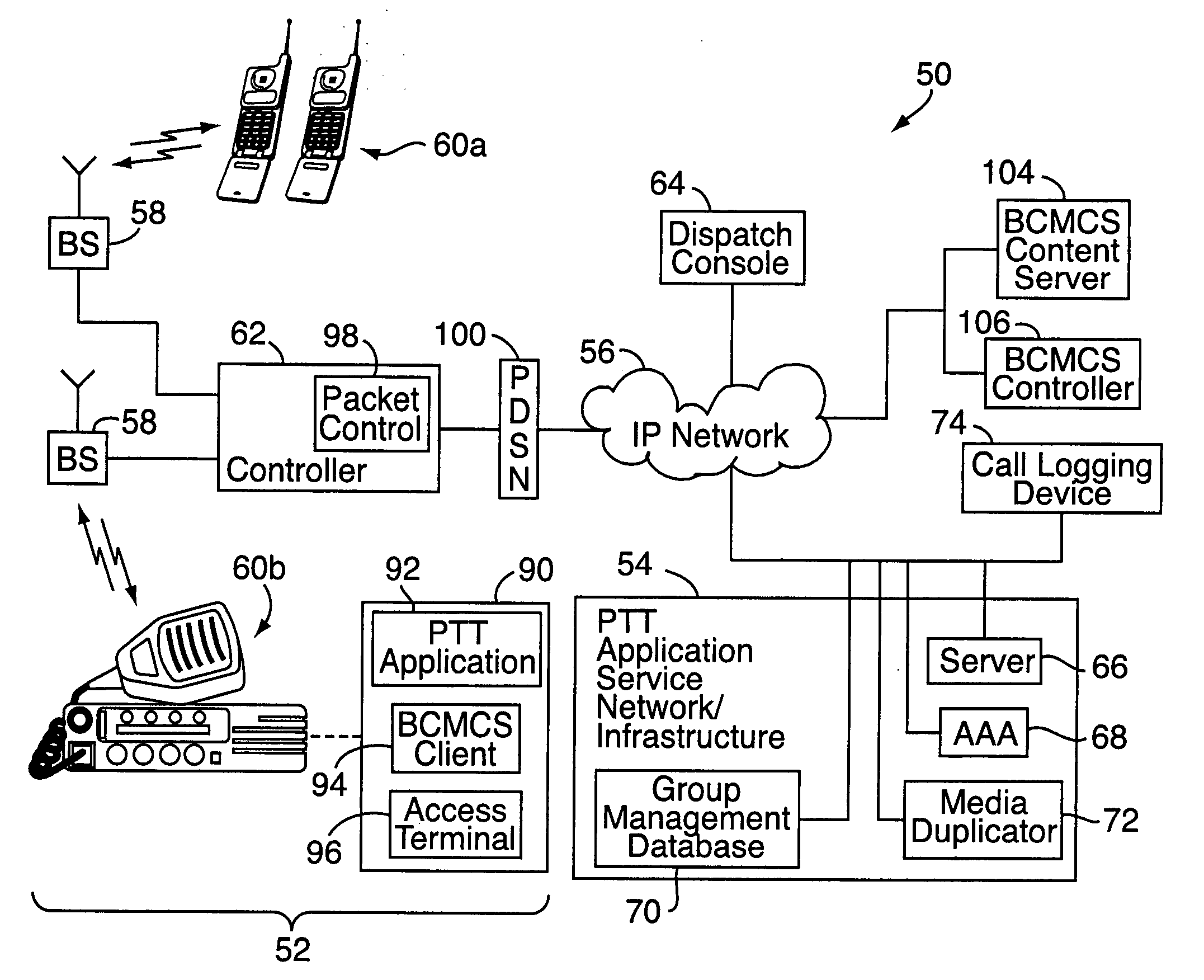
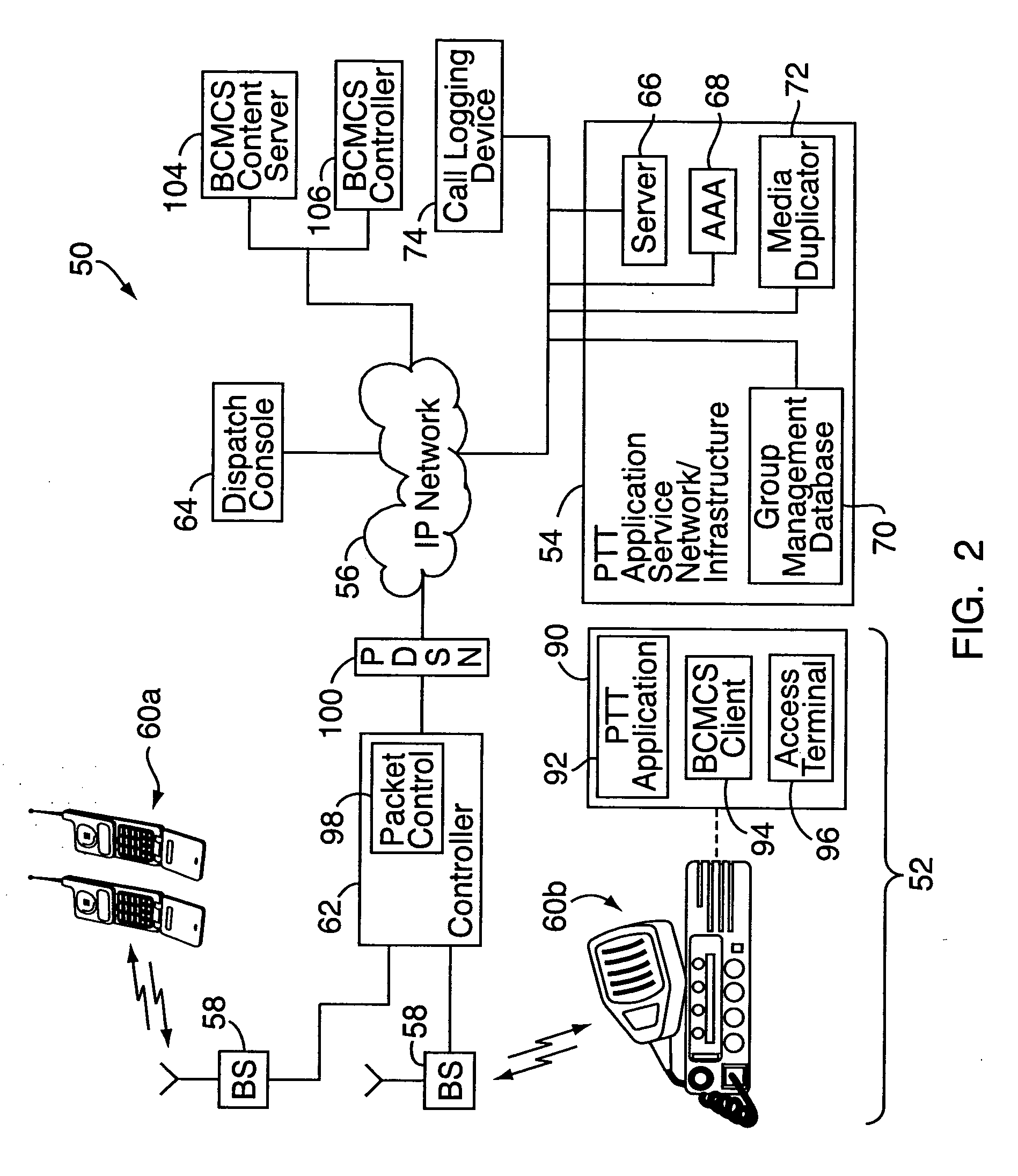
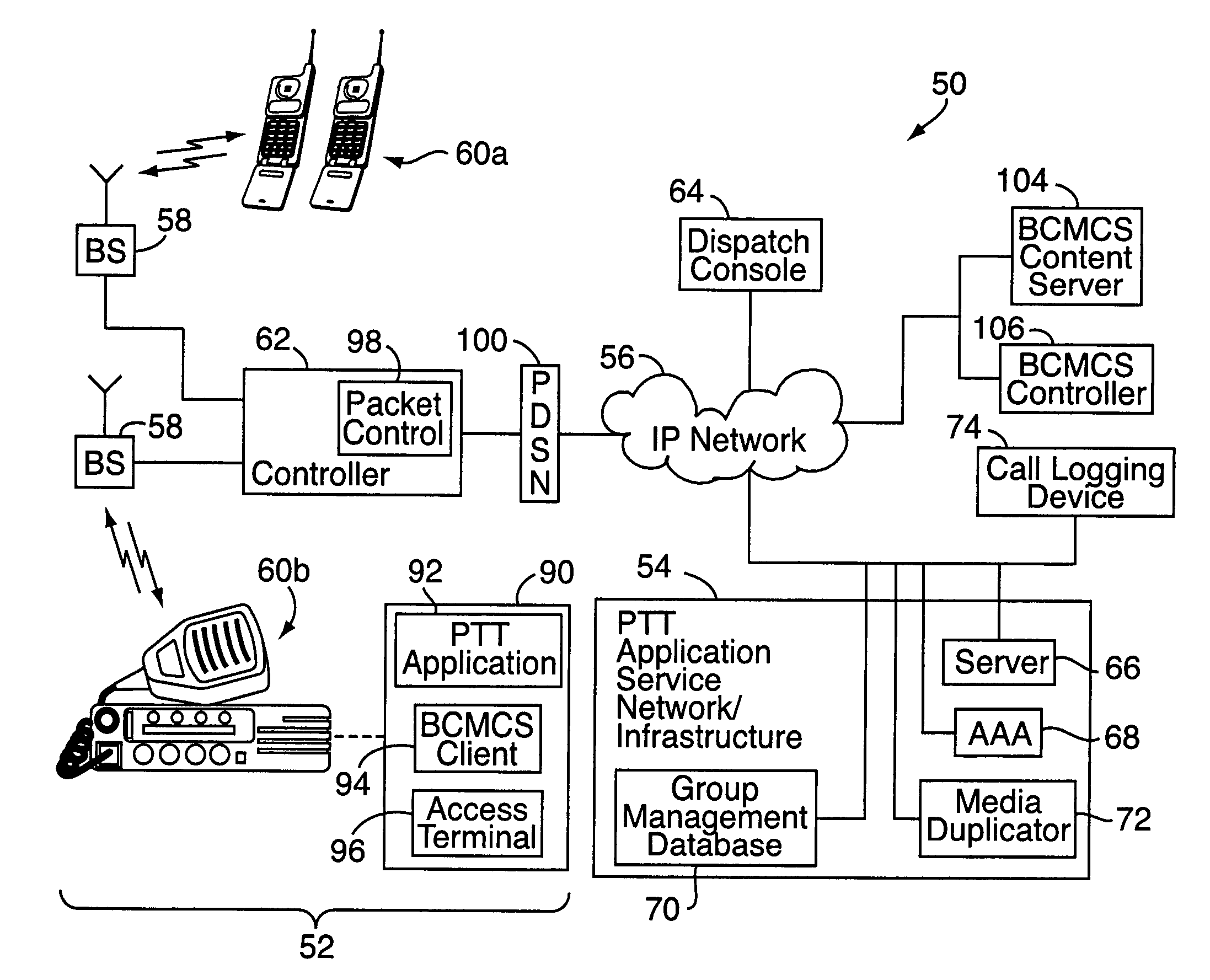
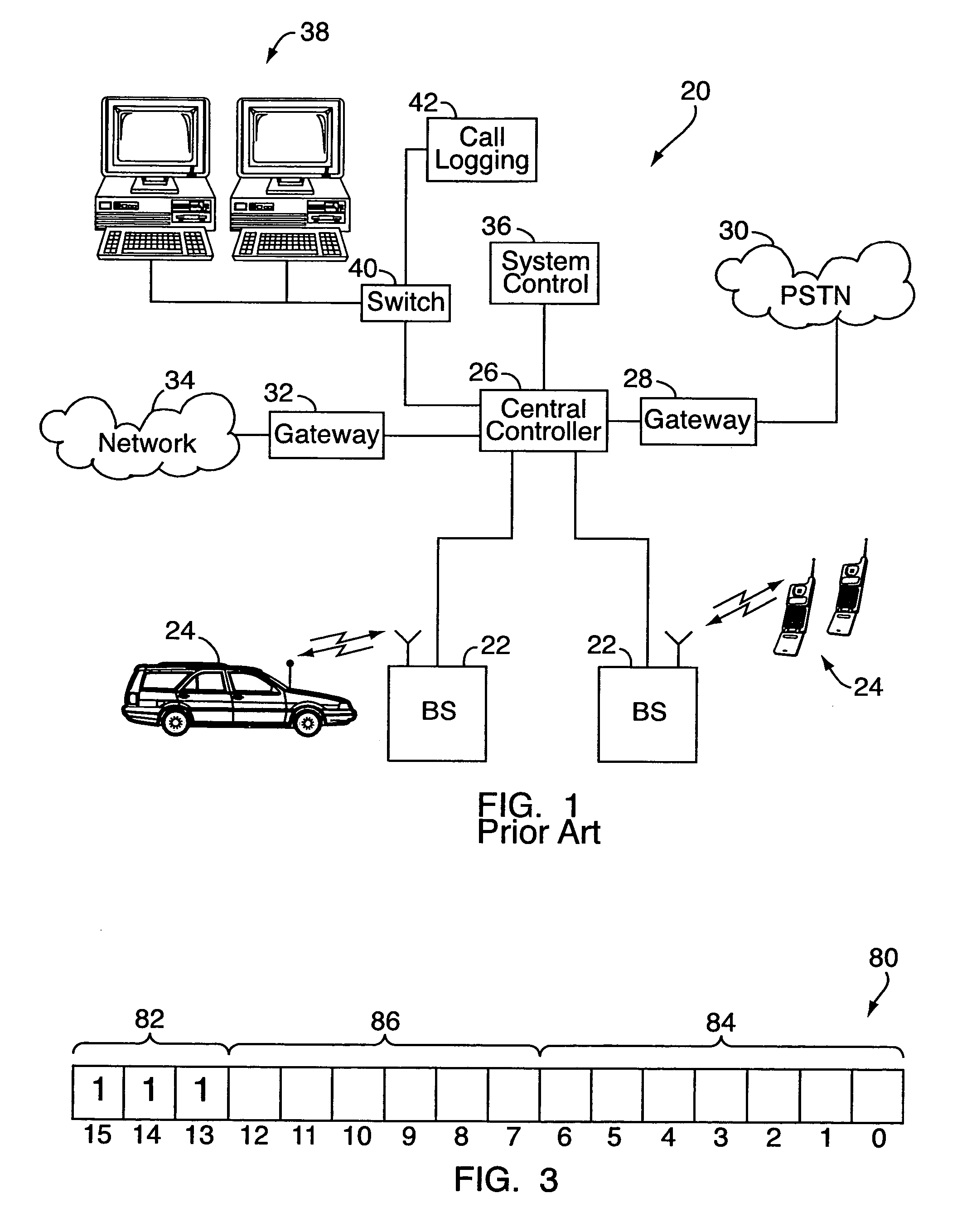
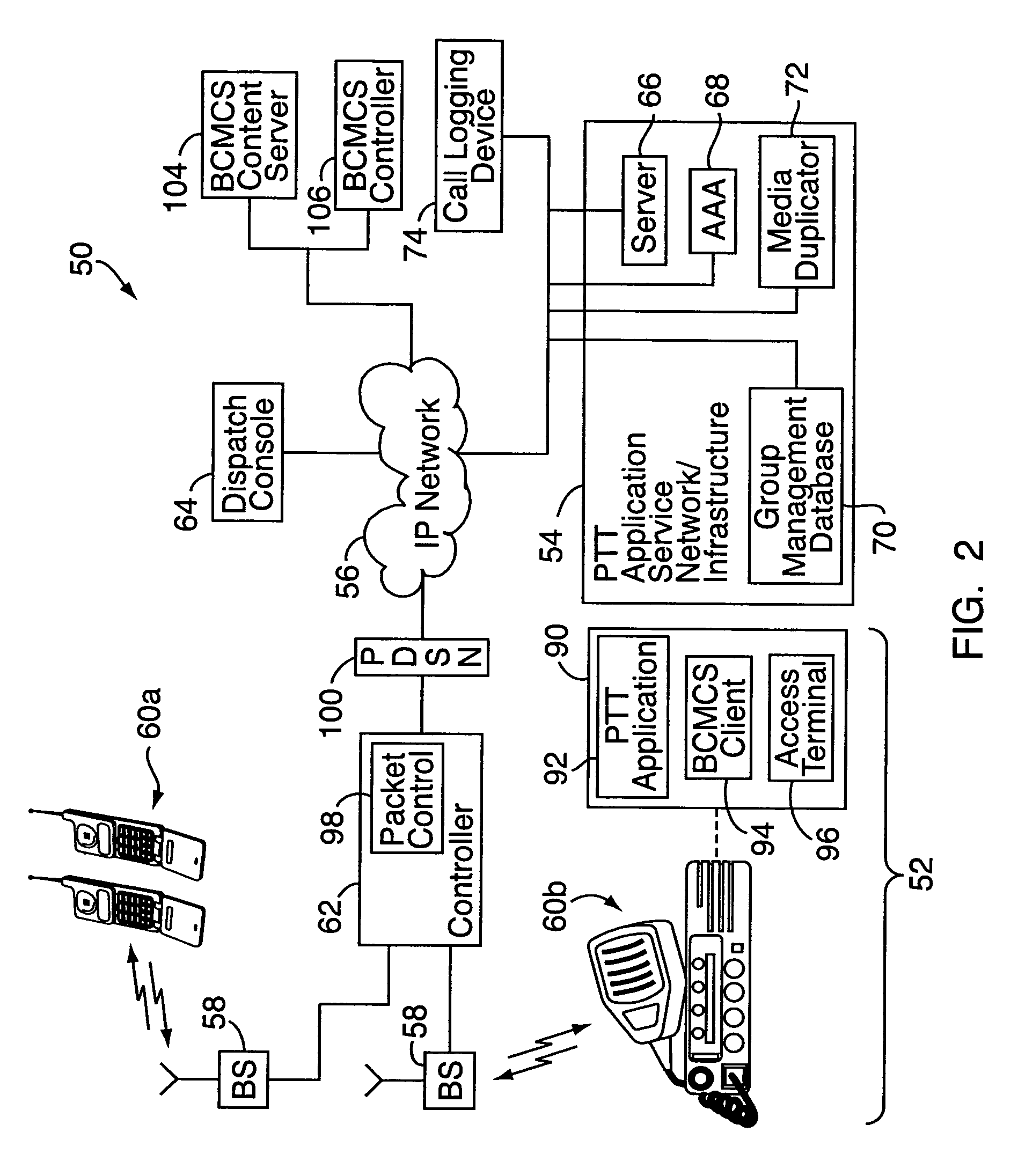
Push-to-talk group call system using CDMA 1x-EVDO cellular network
InactiveUS20070049314A1Reliable and fast transmissionShorten call setup timePower managementConnection managementRadio access networkPush-to-talk
A push-to-talk (“PTT”) group call system, for use as, e.g., a public safety wireless network, includes a CDMA-based 1x-EVDO radio access network operably connected to a PTT server over an IP network. The radio access network includes base stations for radio communications with a number of distributed mobile stations. In carrying out wireless communications, the group call system combines IP-based voice and other real-time multimedia services with the 1x-EVDO radio access network's Broadcast Multicast Service. This allows a number of users to receive the same copy of an IP-based media stream for point-to-multipoint, group transmissions. To reduce call setup times, the group call system uses “standing” call groups, which are ongoing group communication channels pre-established between the PTT server and authorized group users. Thus, mobile stations link to one or more standing call groups of interest upon power-up, prior to users speaking.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
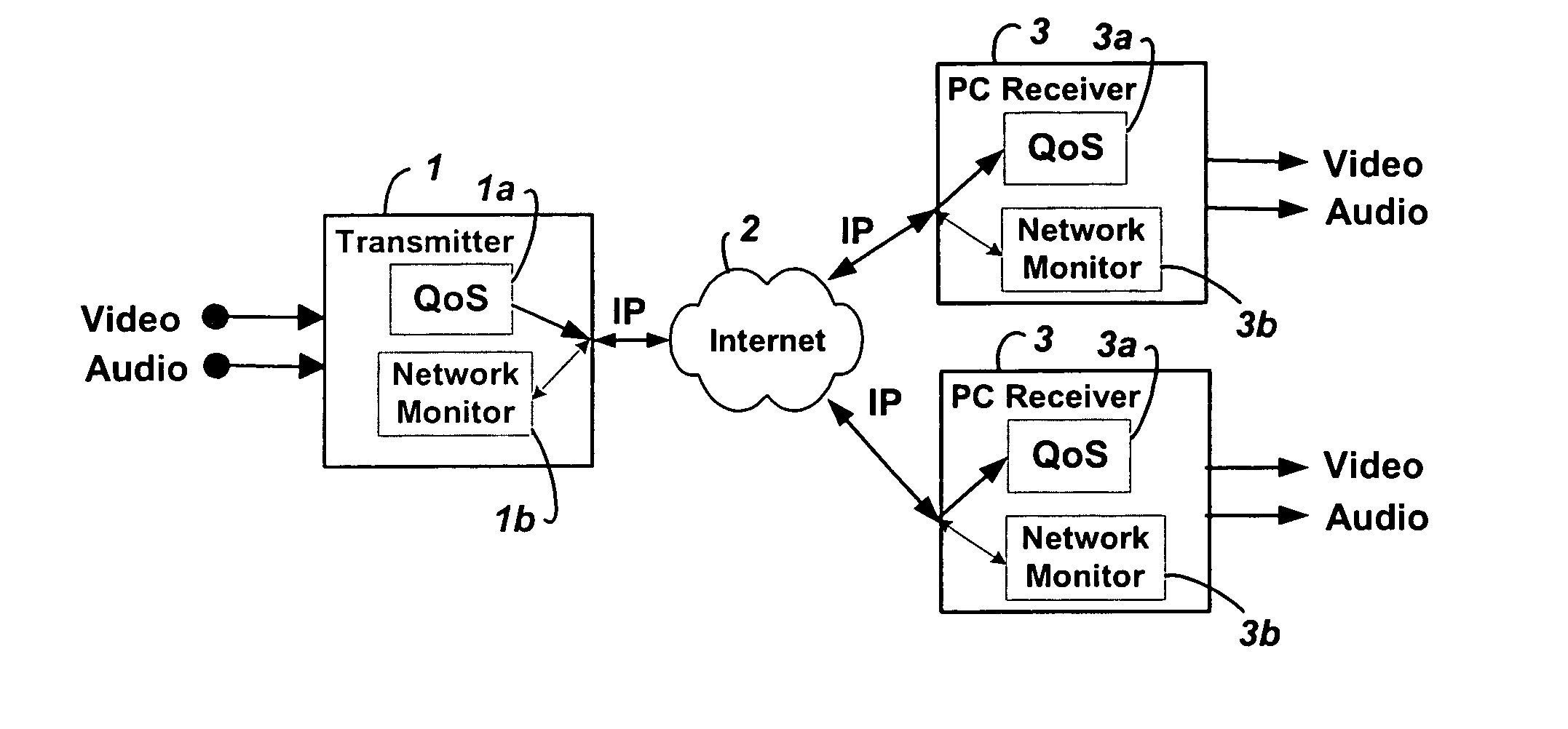
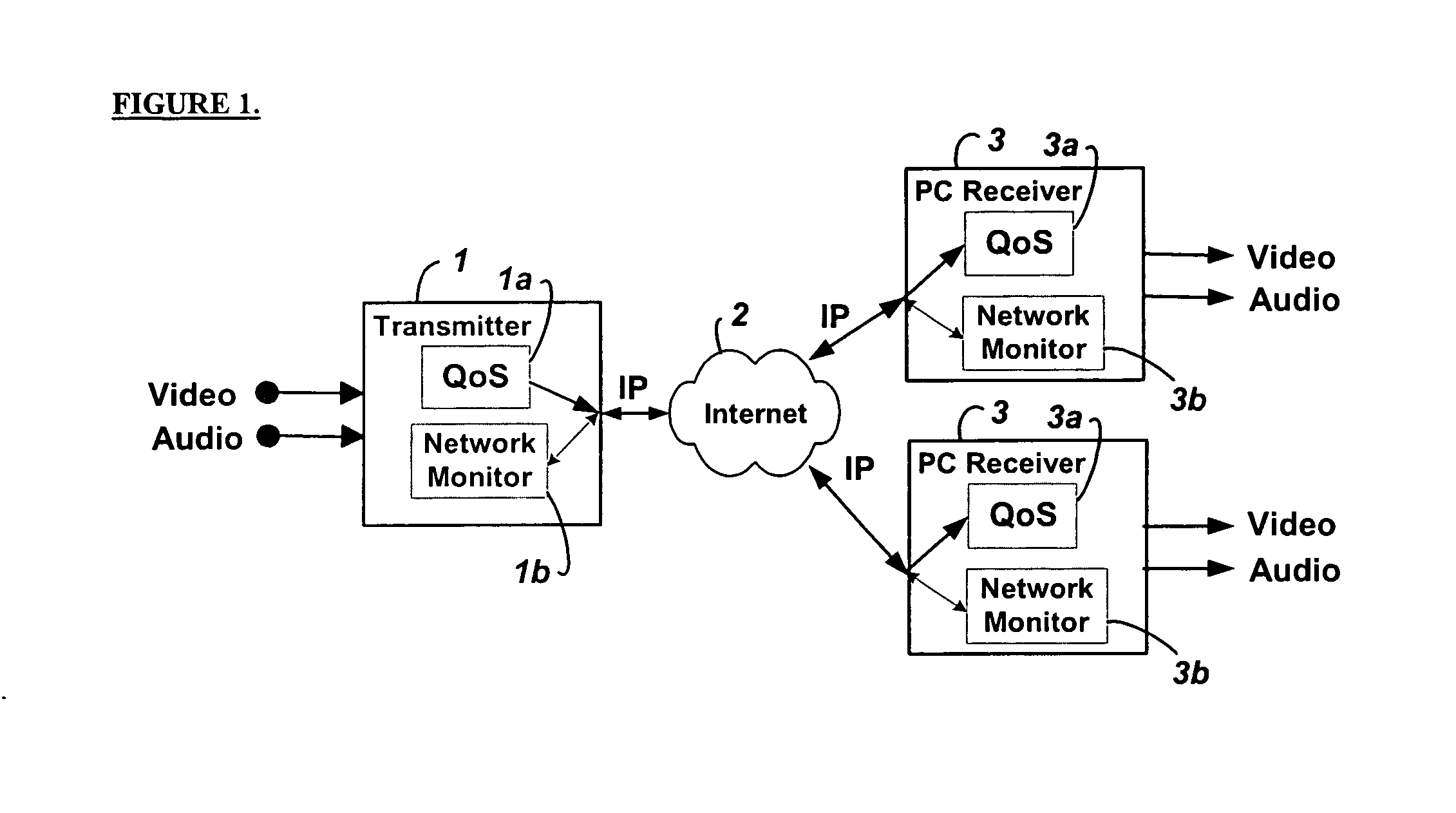
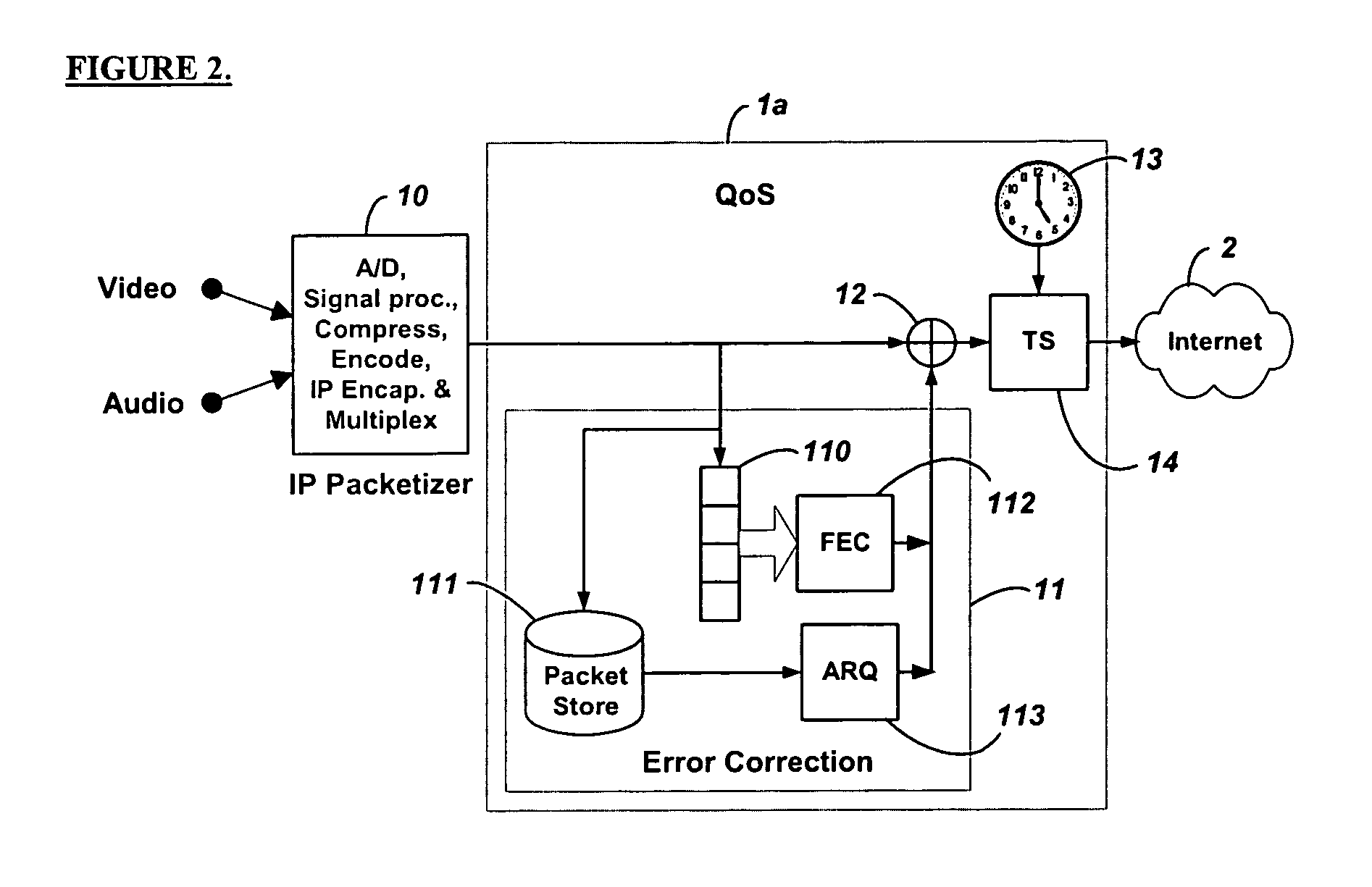
Method and system for providing site independent real-time multimedia transport over packet-switched networks
InactiveUS20060007943A1Minimal latency site-independenceAchieve independenceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData packTimestamp
Embodiments of the invention enable minimum latency site independent real-time video transport over packet switched networks. Some examples of real-time video transport are video conferencing and real-time or live video streaming. In one embodiment of the invention, a network node transmits live or real-tine audio and video signals, encapsulated as Internet Protocol (IP) data packets, to one or more nodes on the Internet or other IP network. One embodiment of the invention enables a user to move to different nodes or move nodes to different locations thereby providing site independence. Site independence is achieved by measuring and accounting for the jitter and delay between a transmitter and receiver based on the particular path between the transmitter and receiver independent of site location. The transmitter inserts timestamps and sequence numbers into packets and then transmits them. A receiver uses these timestamps to recover the transmitter's clock. The receiver stores the packets in a buffer that orders them by sequence number. The packets stay in the buffer for a fixed latency to compensate for possible network jitter and / or packet reordering. The combination of timestamp packet-processing, remote clock recovery and synchronization, fixed-latency receiver buffering, and error correction mechanisms help to preserve the quality of the received video, despite the significant network impairments generally encountered throughout the Internet and wireless networks.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
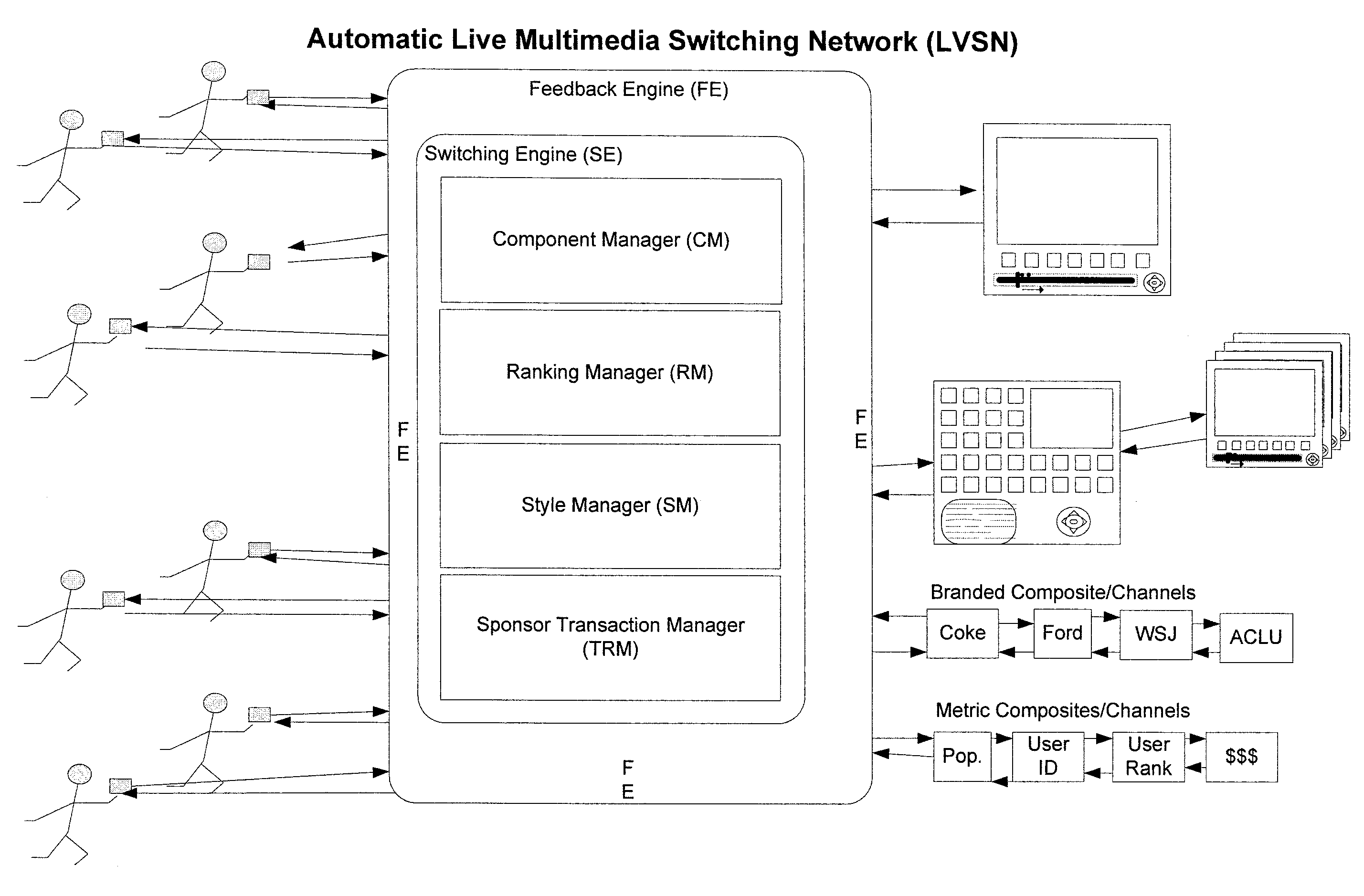
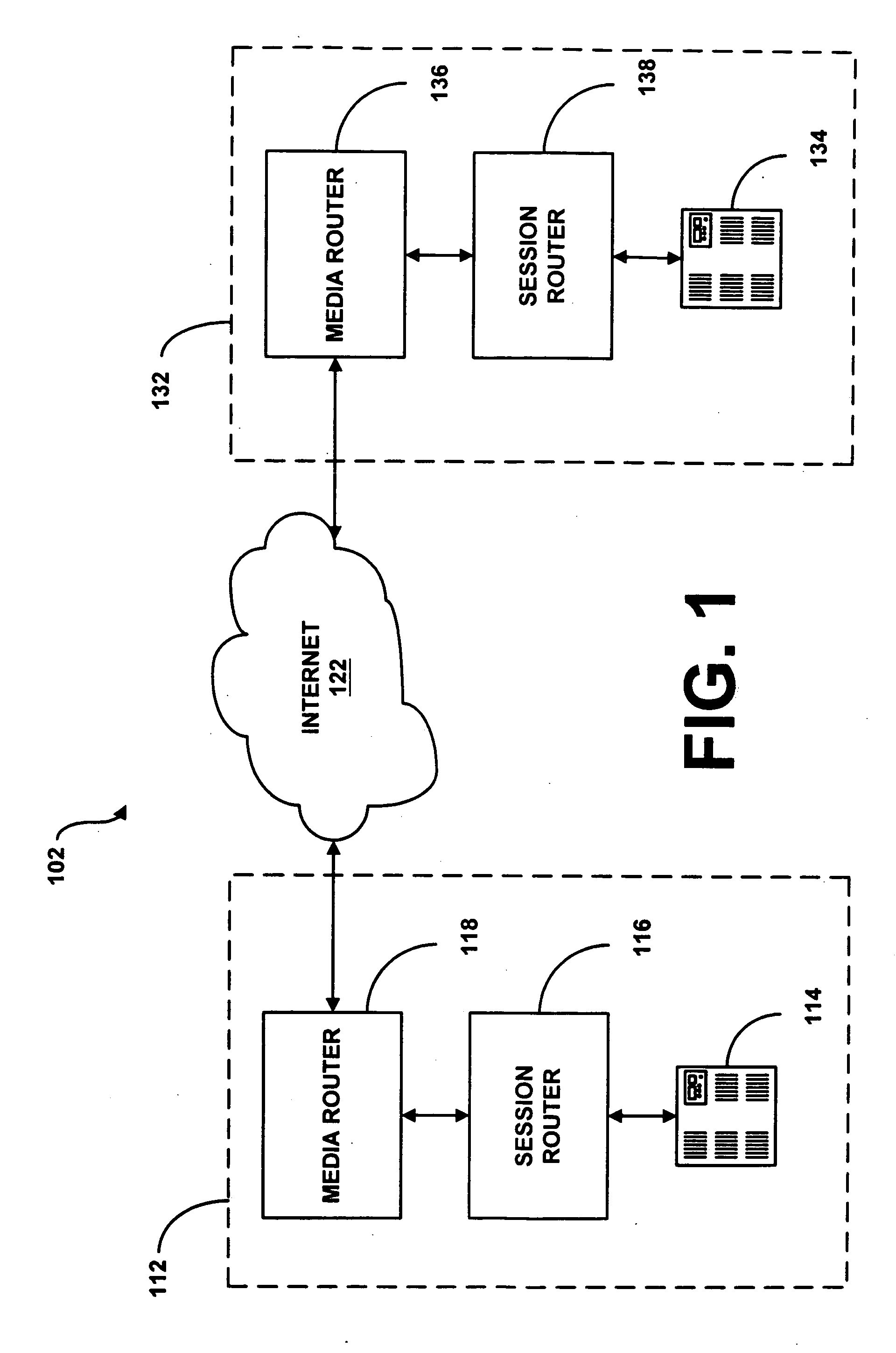
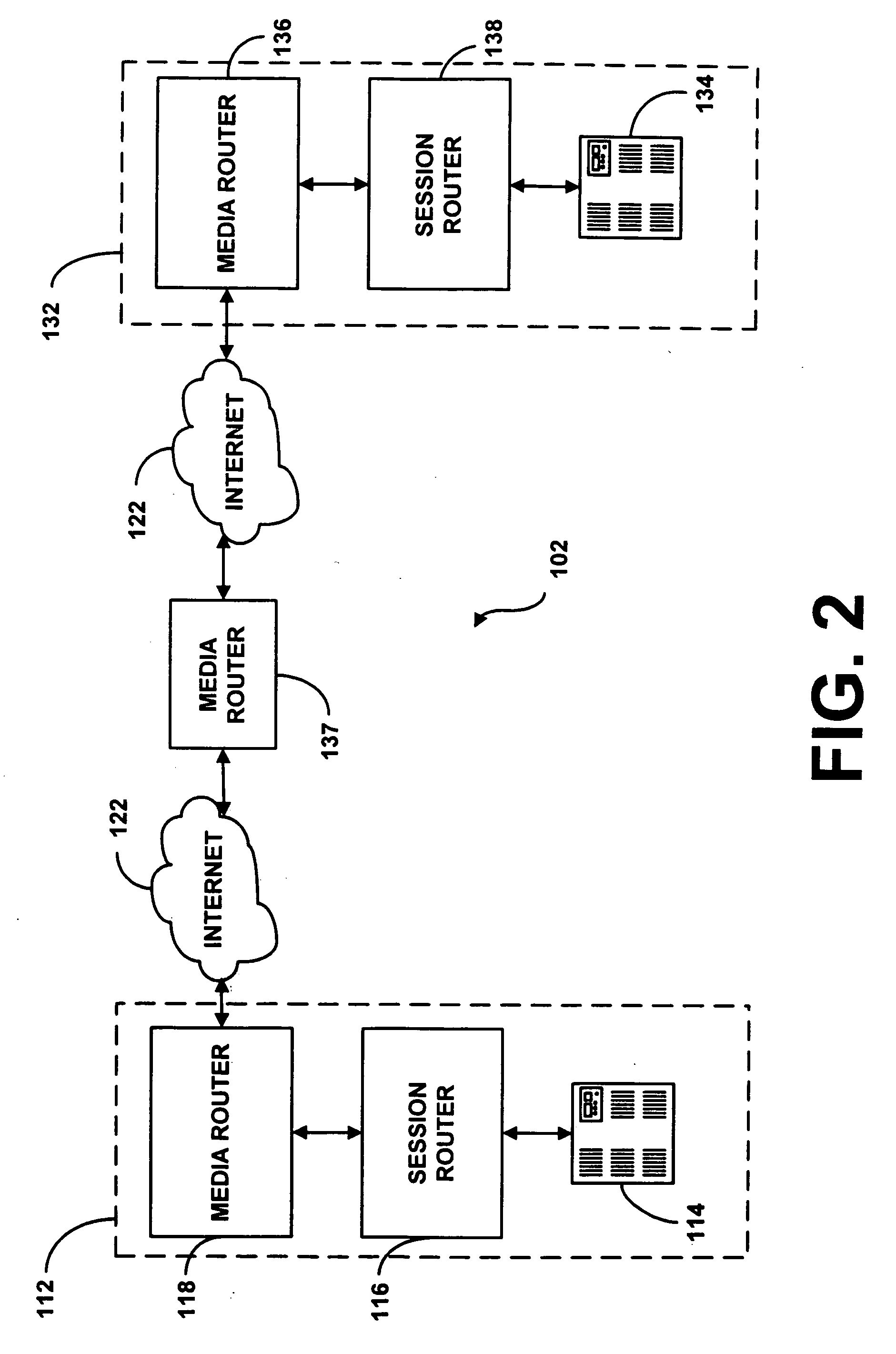
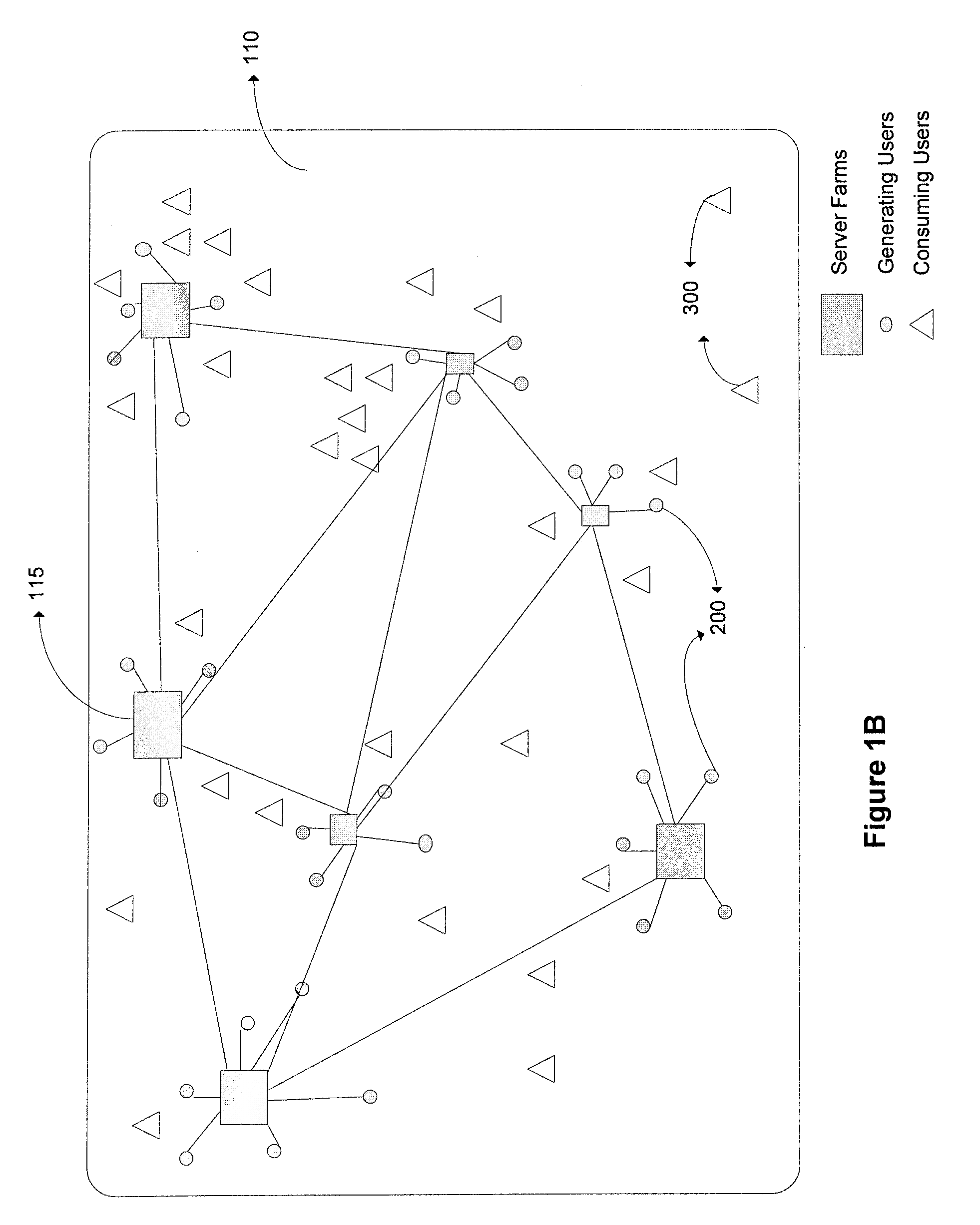
Distributed live multimedia switching mechanism and network
InactiveUS20090089352A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionNetwork methodMultimedia
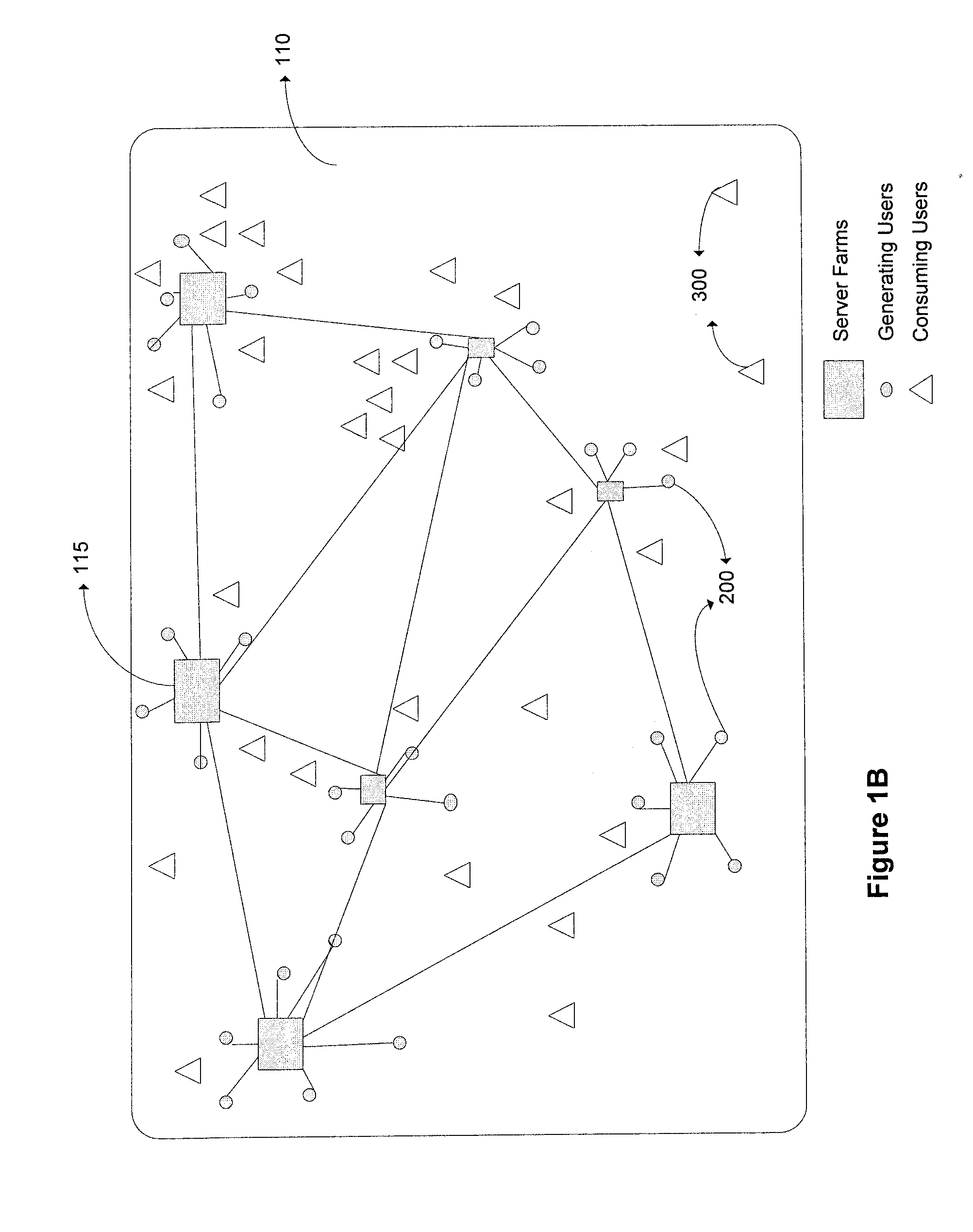
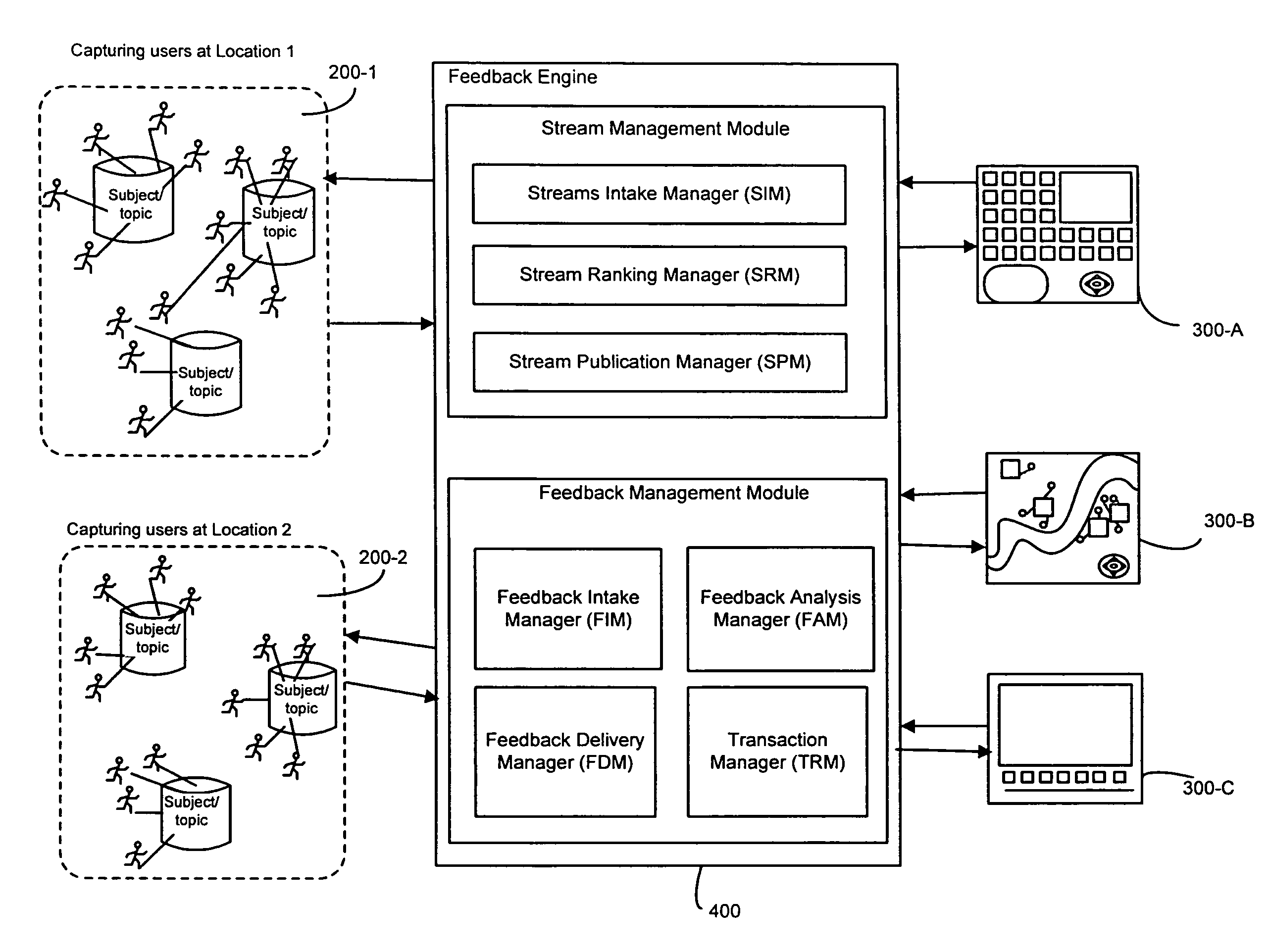
Methods and systems for controlling switching of multimedia content captured from a plurality of locations via one or more capturing devices include obtaining multimedia content that identify a type of content being captured and / or location of capture. The captured multimedia content is processed and the multimedia content conforming to search preference is presented to the receiving devices in substantial real-time. Feedback regarding the presented multimedia content is received from receiving devices. Switching of certain multimedia content presented at the receiving devices is enabled in substantial real-time based on the feedback, so that each of the receiving devices is presented with a dynamic subset of the multimedia content based on the changes in content obtained from capturing devices, the feedback obtained from the receiving devices and search preference.
Owner:OATH INC
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
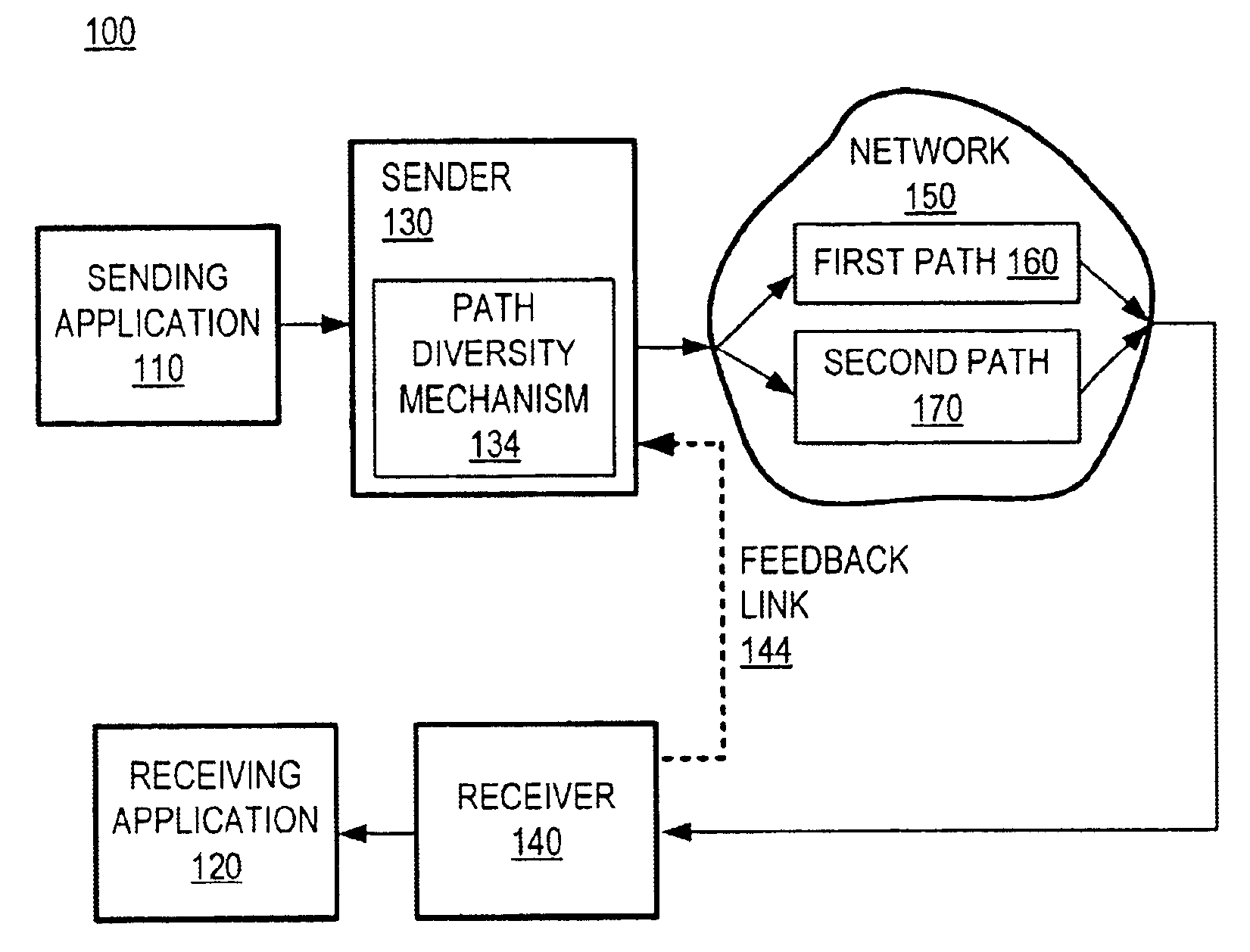
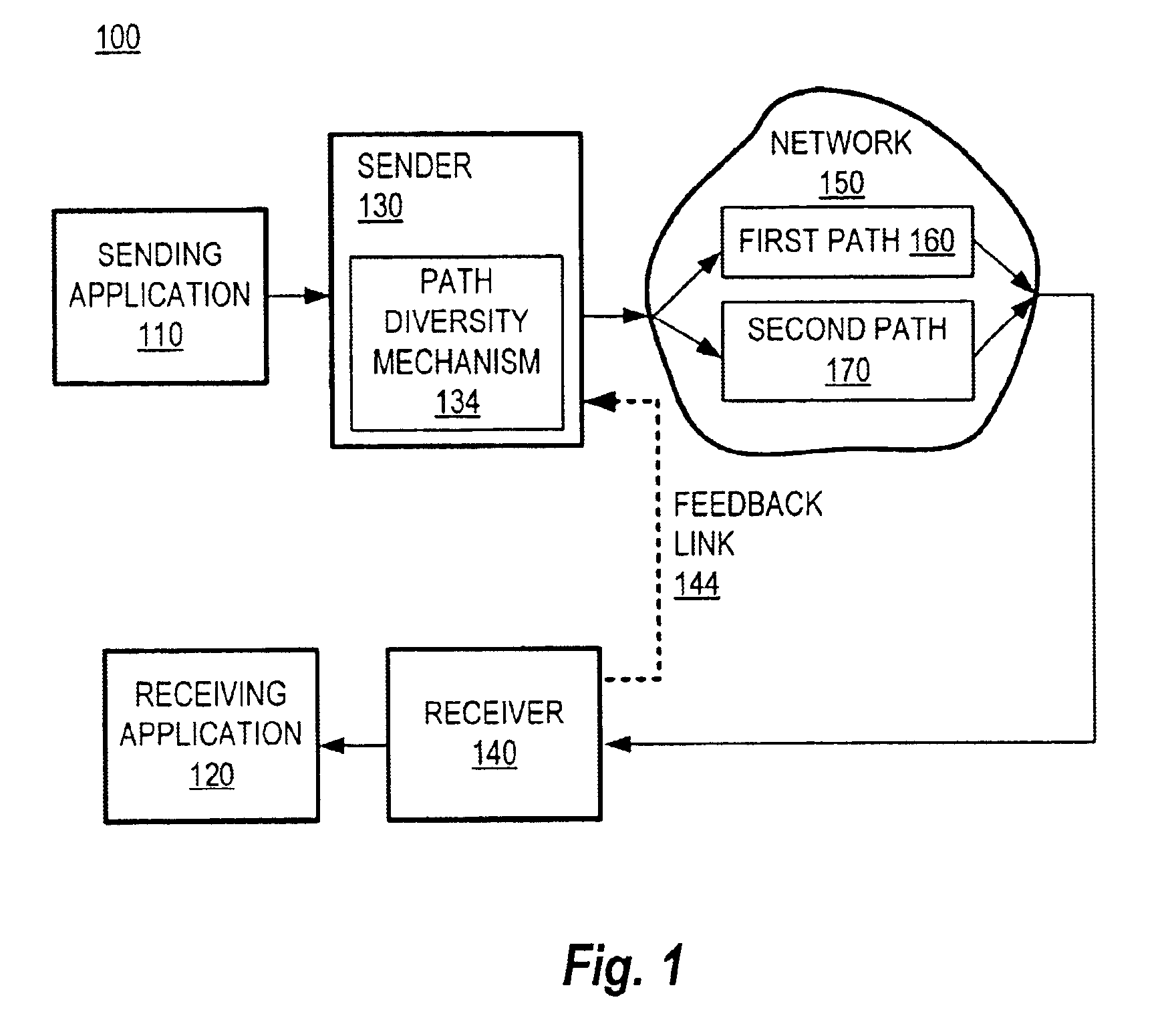
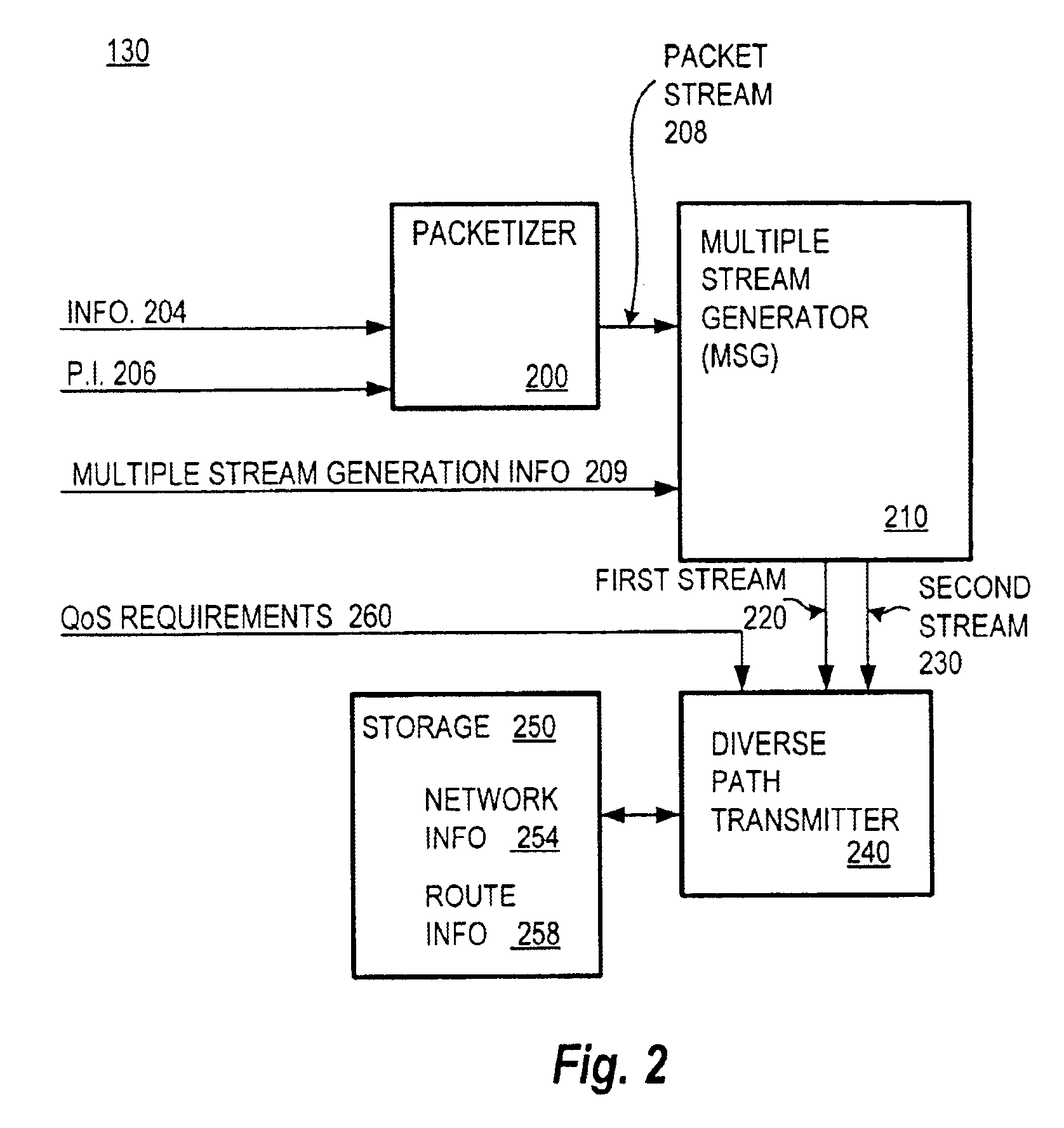
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
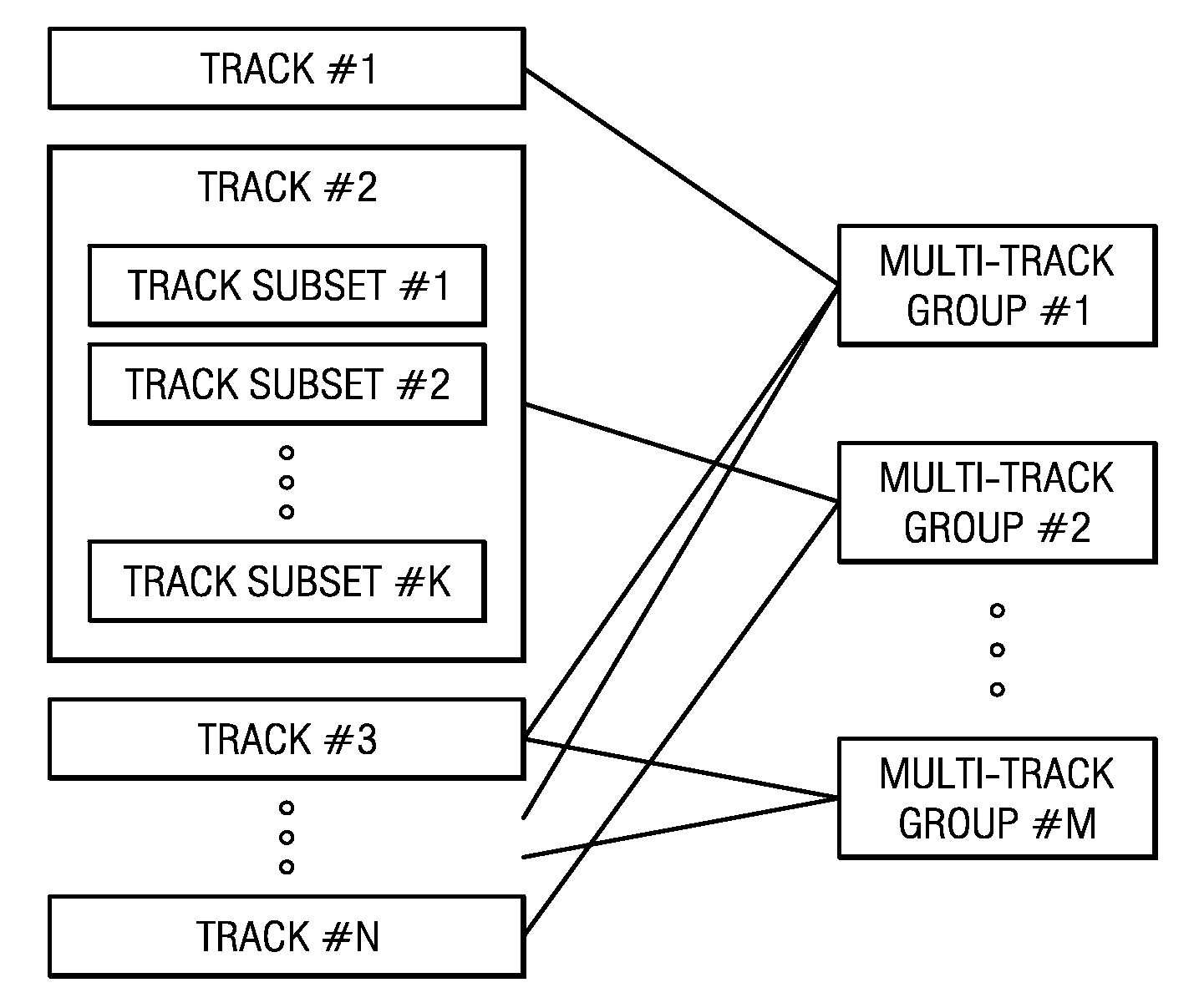
Method and Apparatus For Track and Track Subset Grouping
A method comprises storing real-time multimedia data in a plurality of tracks and / or track subsets; and identifying one or more multi-track groups, each multi-track group being associated with a relationship among one or more of the plurality of tracks and / or track subsets.
Owner:SISVEL INT
Apparatus and methods for real-time multimedia network traffic management & control in wireless networks
InactiveUS20100318652A1Facilitate real-time network managementEasy to manufactureMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionReal-time webNetwork management
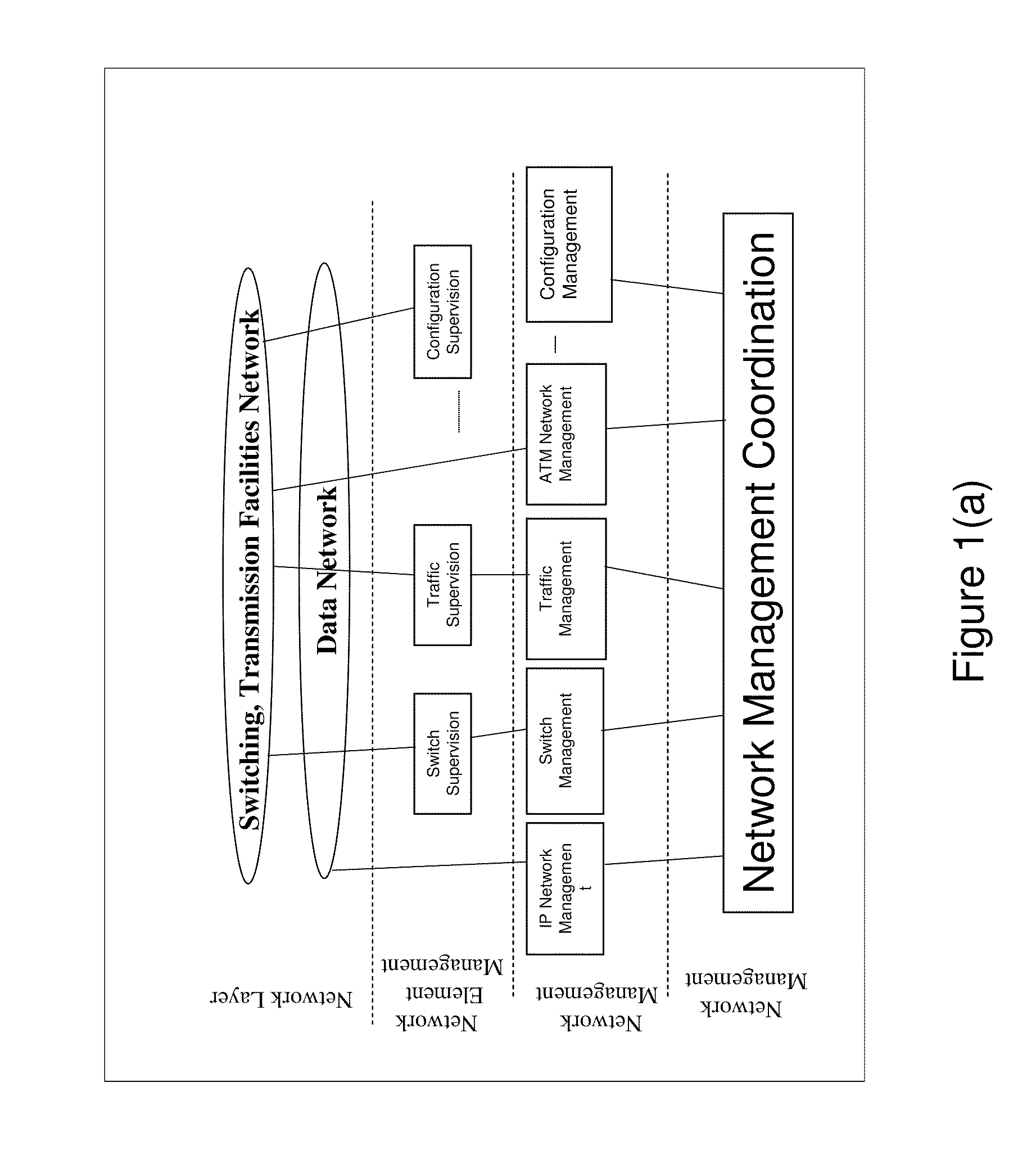
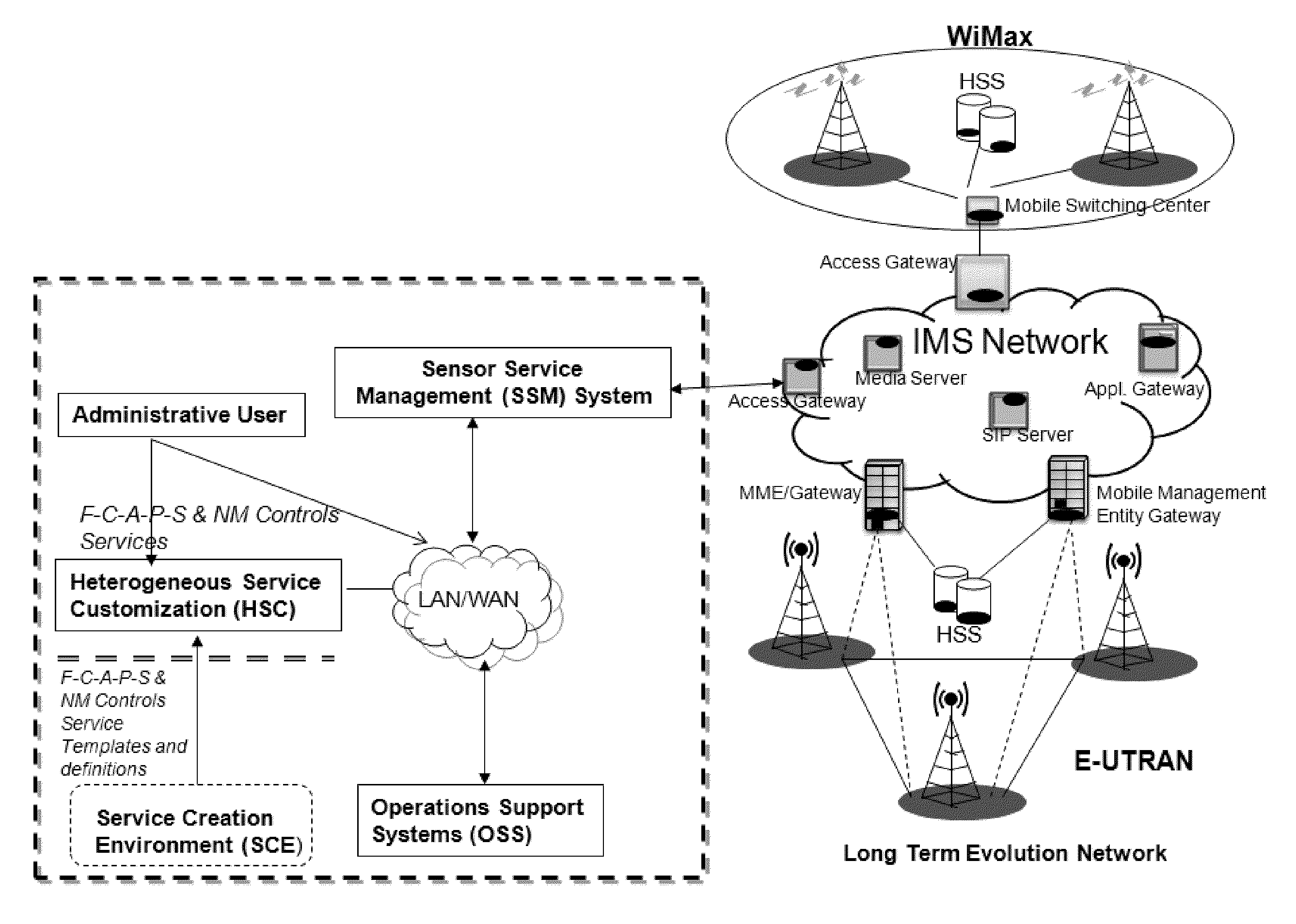
The invention is directed to network management systems and methods that provide substantially real-time network management and control capabilities of multimedia streaming traffic in telecommunications networks. The invention provides pre-emptive and autonomous network management and control capabilities, and may include shared intelligence of embedded systems—Heterogeneous Sensor Entities (HSE) and the Sensor Service Management (SSM) system. HSEs are distributed real-time embedded systems provisioned in various network elements. HSEs performs fault, configuration, accounting, performance and security network management functions in real-time; and real-time network management control activations and removals. SSM facilitates automated decision making, rapid deployment of HSEs and real-time provisioning of network management and control services. The service communication framework amongst various HSEs and the SSM is provided by the Heterogeneous Service Creation system. The proposed network management procedure provides real-time network management and control capabilities of multimedia traffic in wireless networks and clusters of independent networks respectively.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
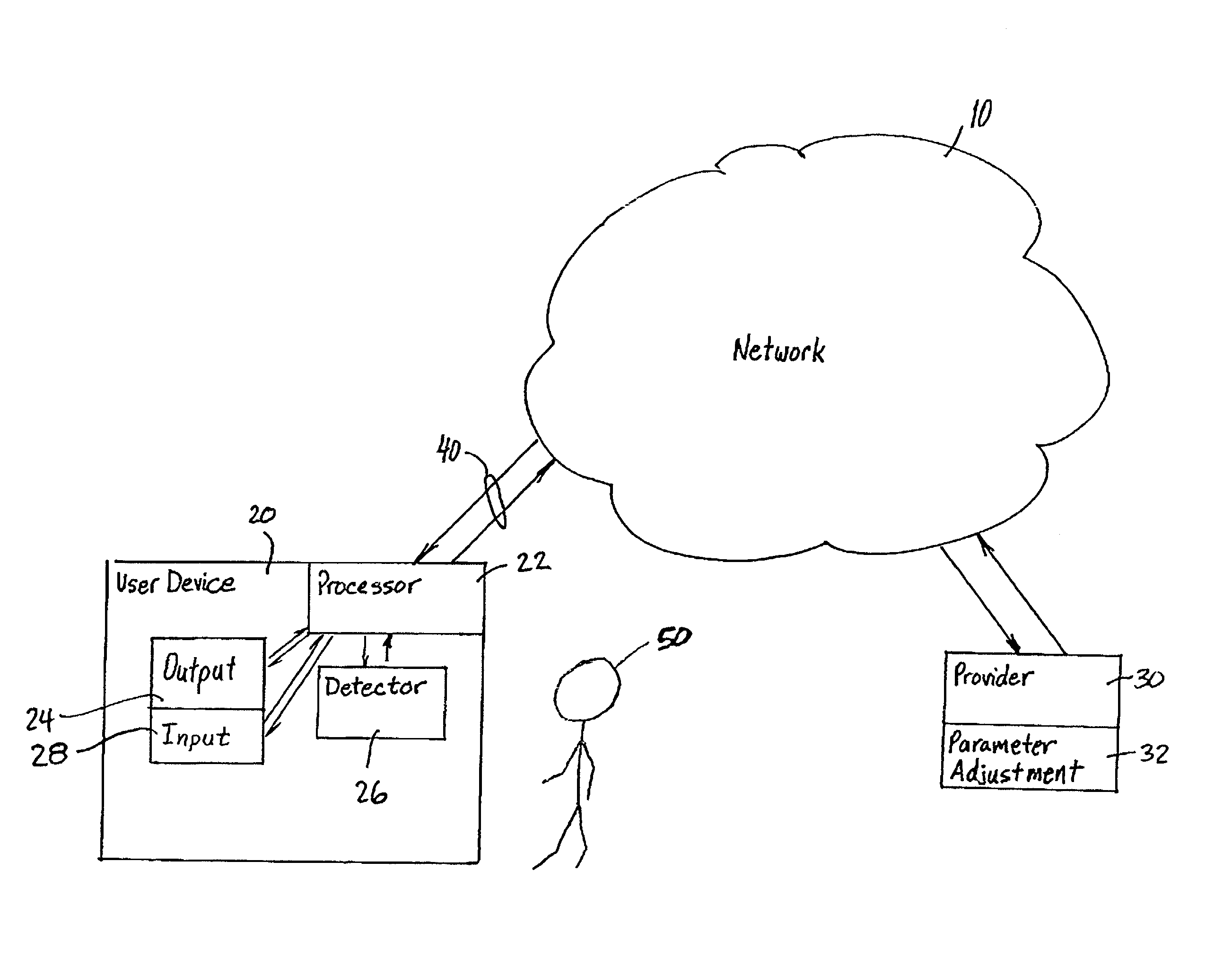
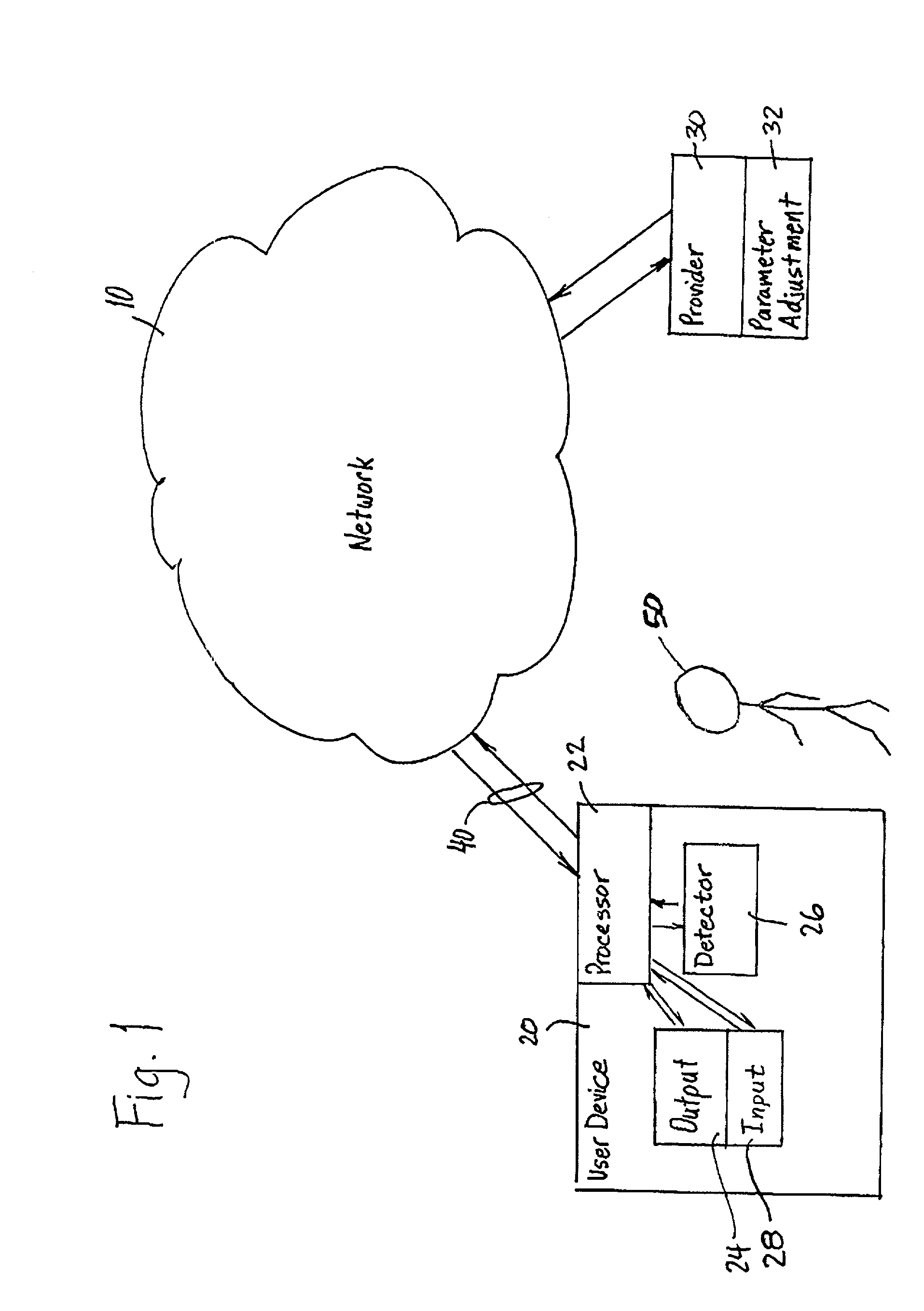
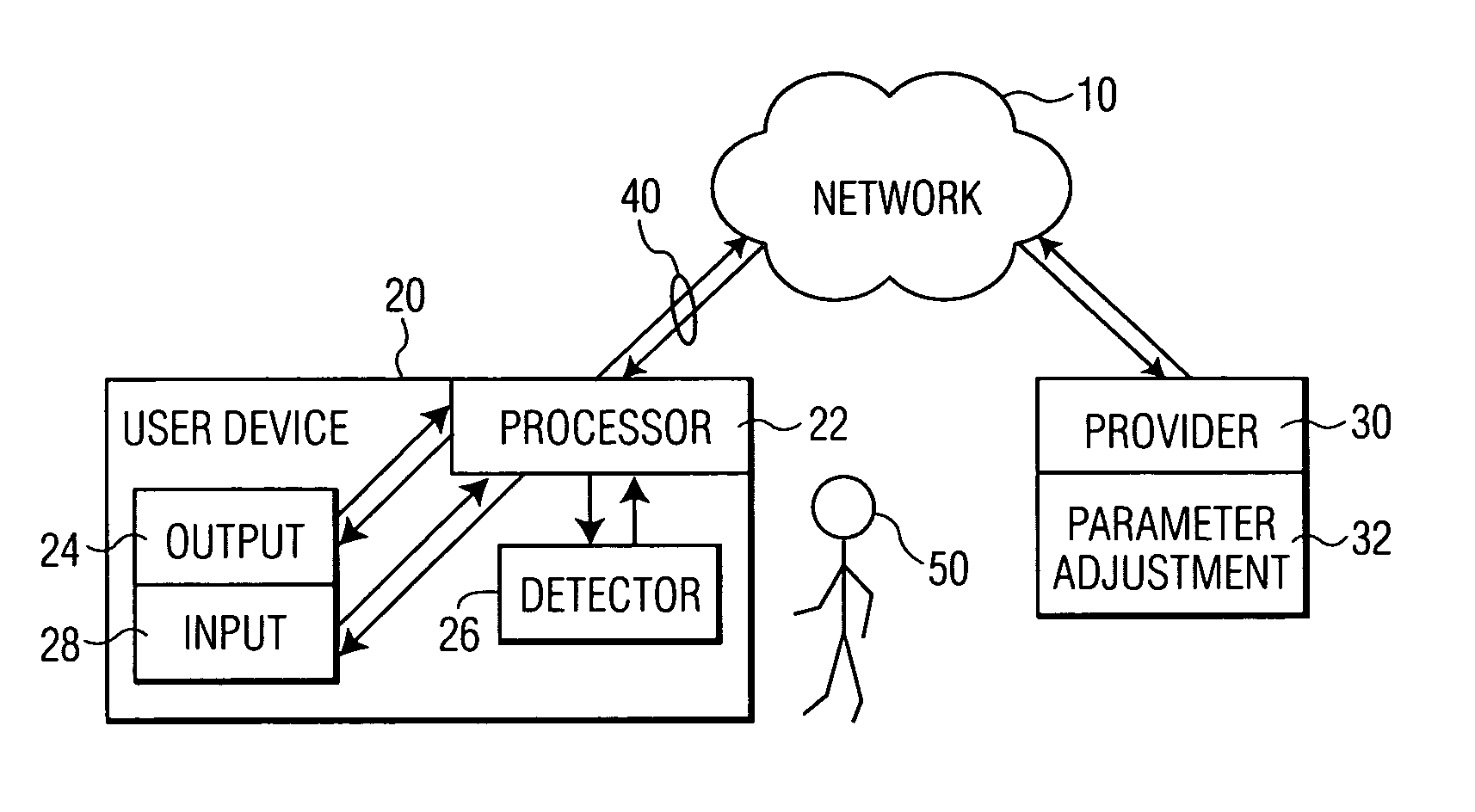
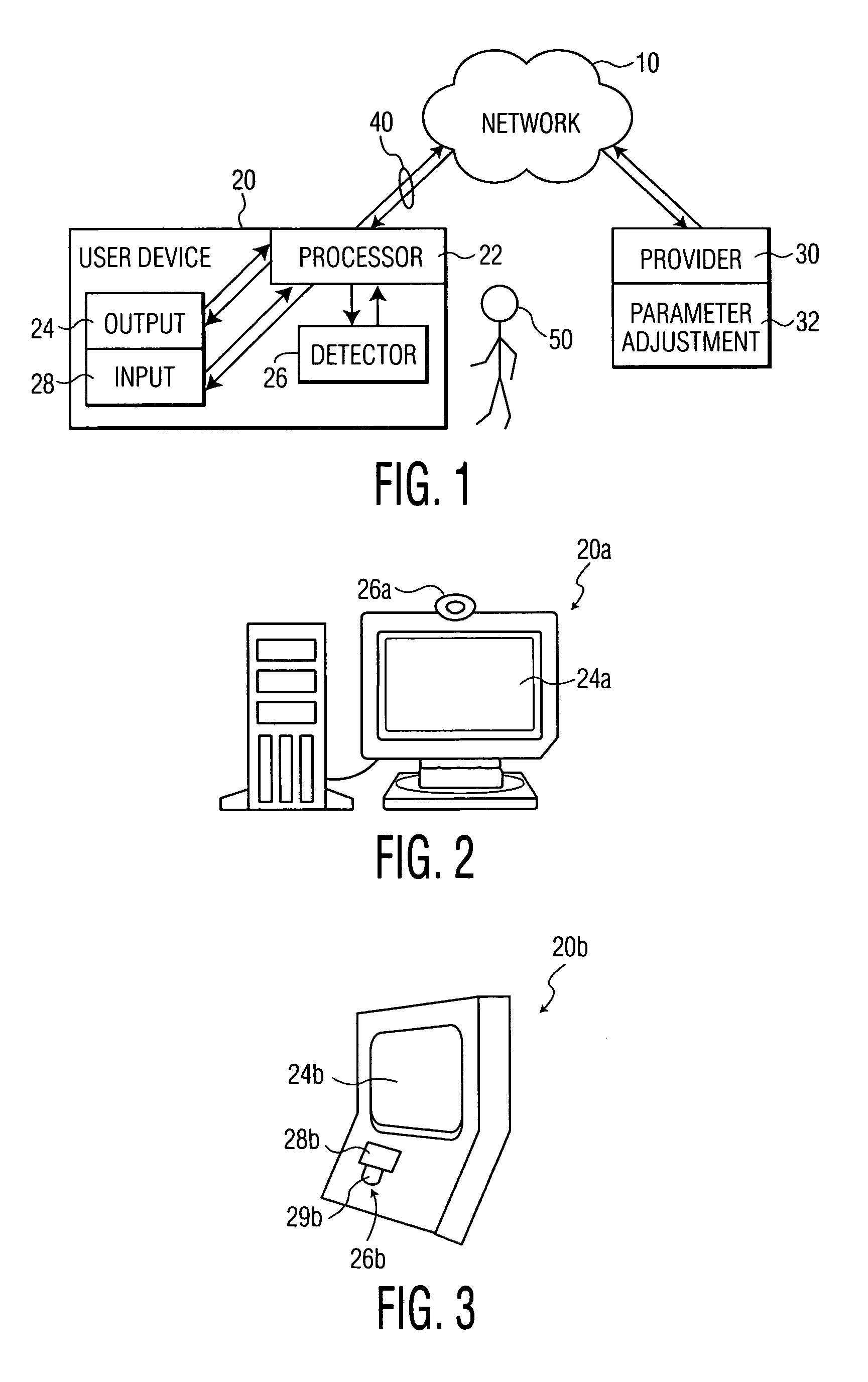
InactiveUS20030052911A1Reduce data transfer rateMoreData processing applicationsImage analysisUser deviceQuality level
A method for transmitting a stream of multi-media content from provider server to a user device includes transmitting multi-media content from the provider server to the user device via a communication network and outputting the multi-media content from the user device to a user via an output on the user device such that the multi-media content is delivered from the provider server to the user in real-time. A degree of attention that the user directs to the output of the user device is continuously determined during the transmission and a parameter adjusting module at the provider server adjusts a parameter of the multi-media content in response to the degree of attention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
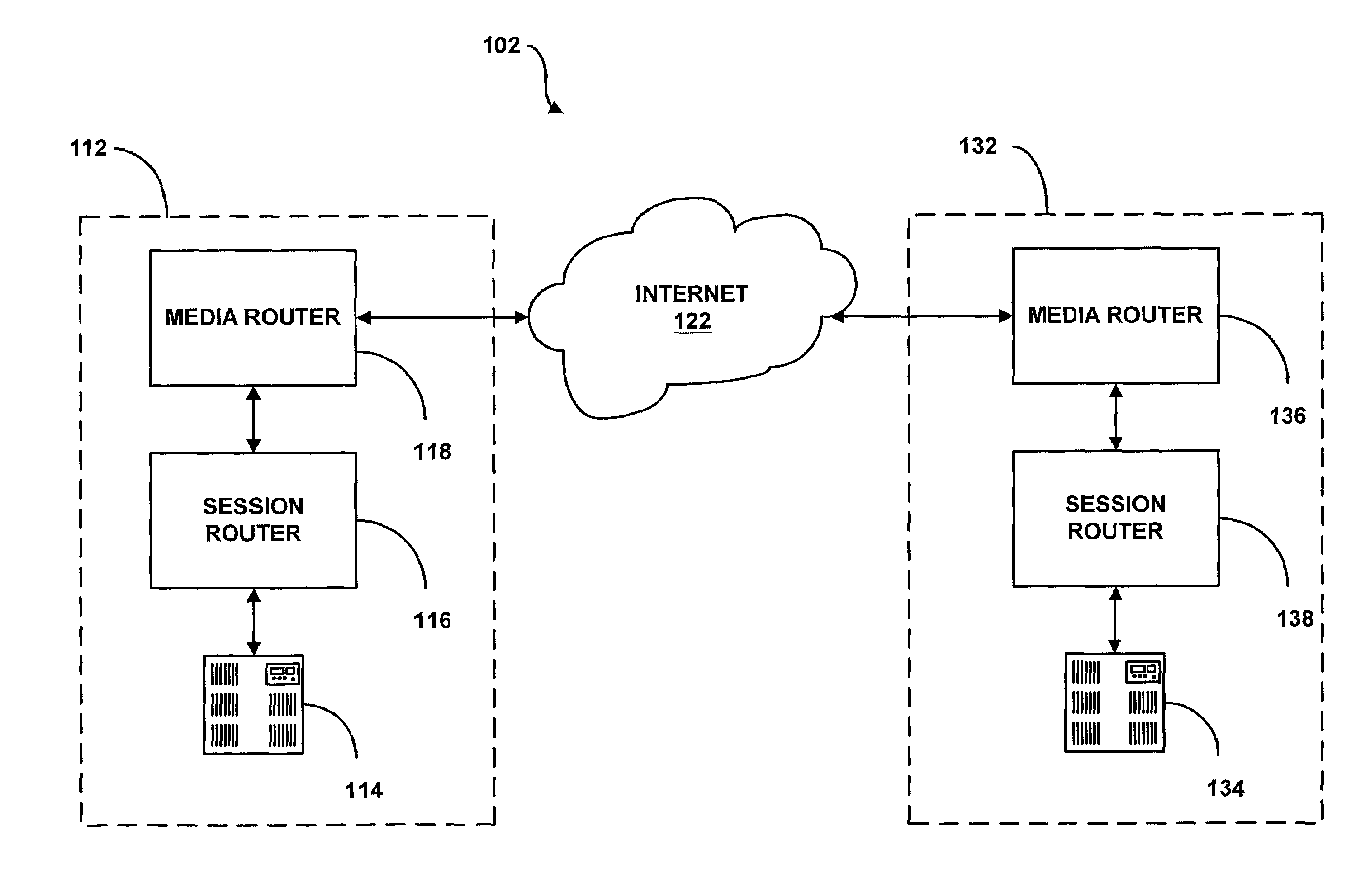
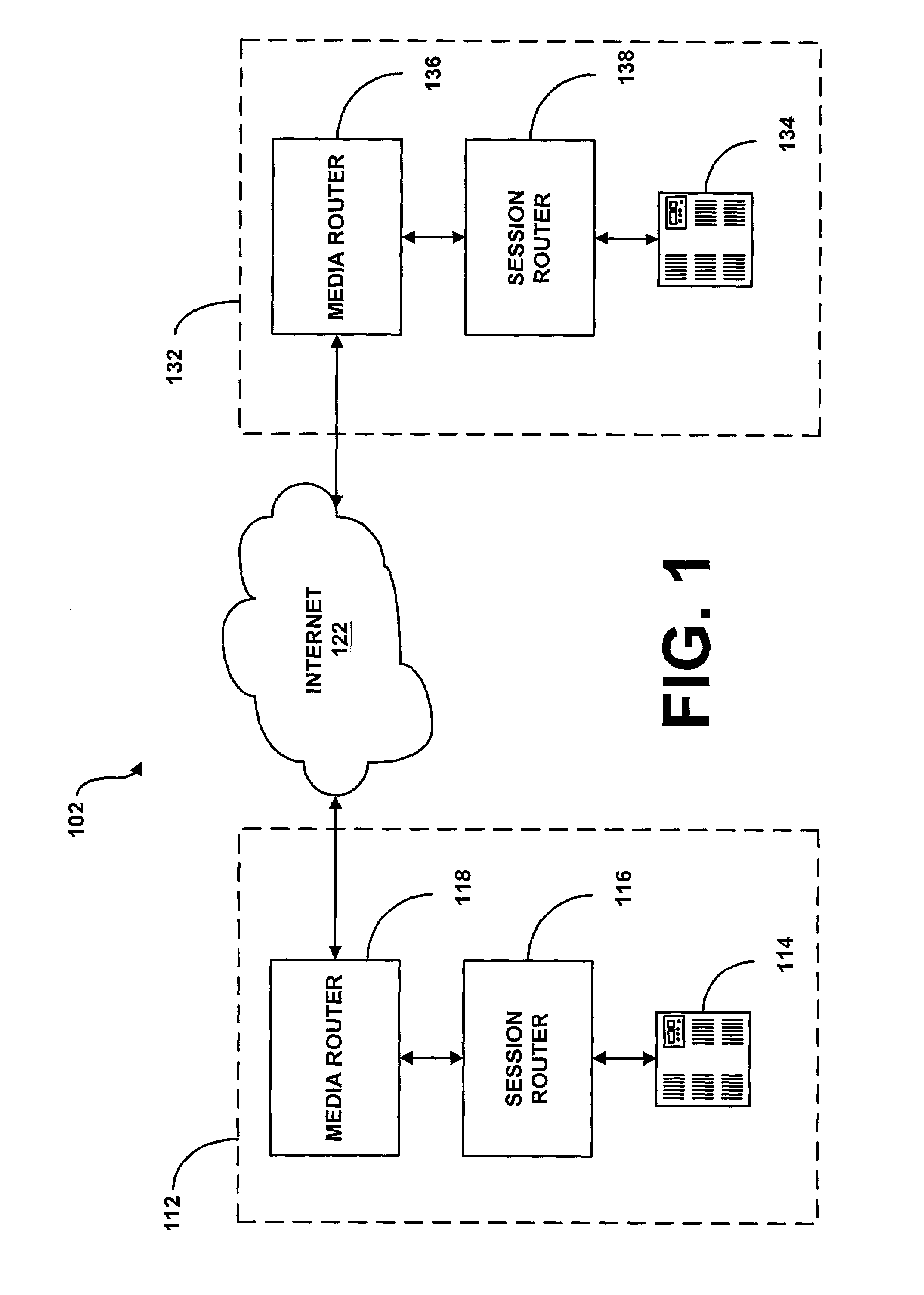
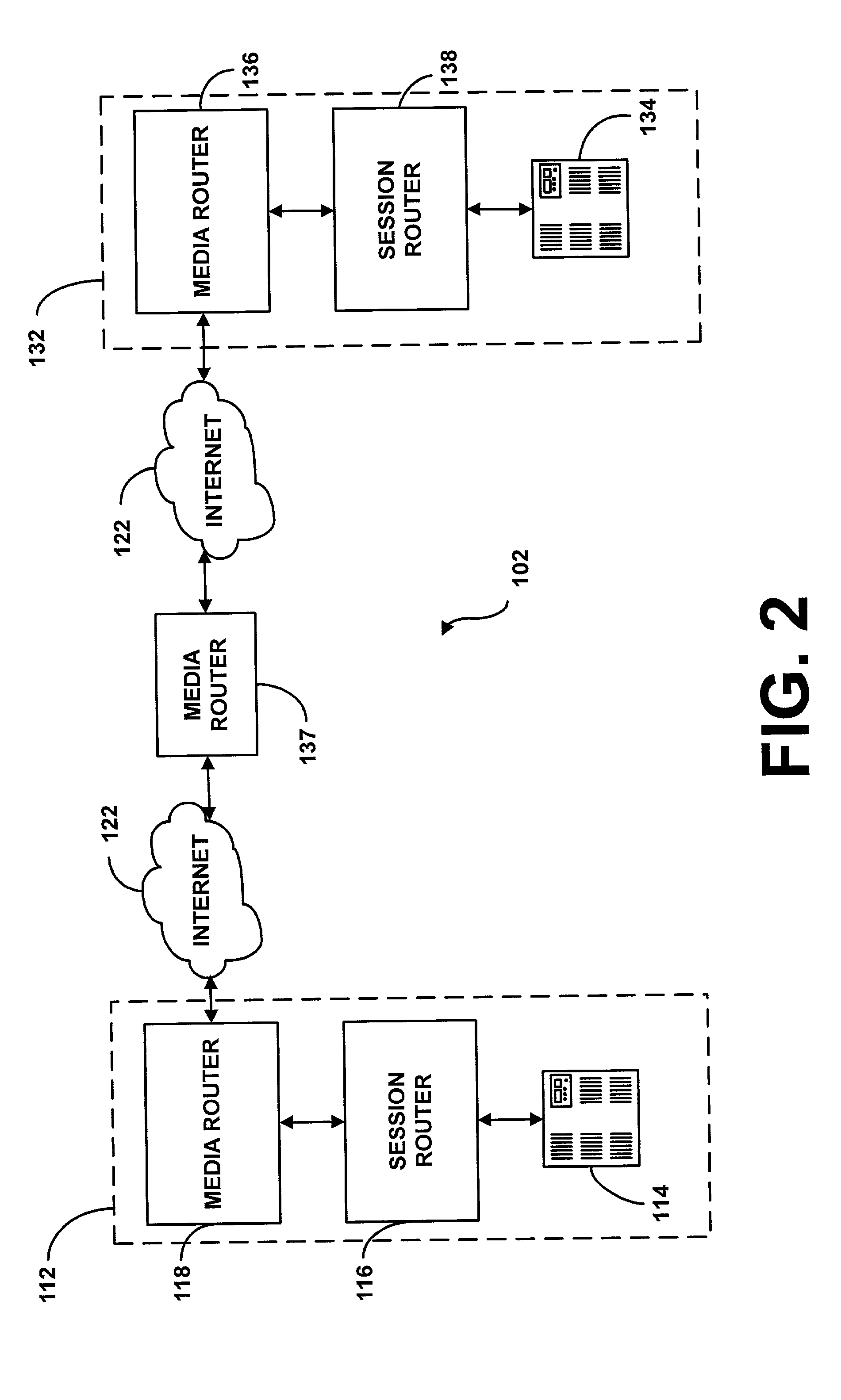
System and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time multi-media flows
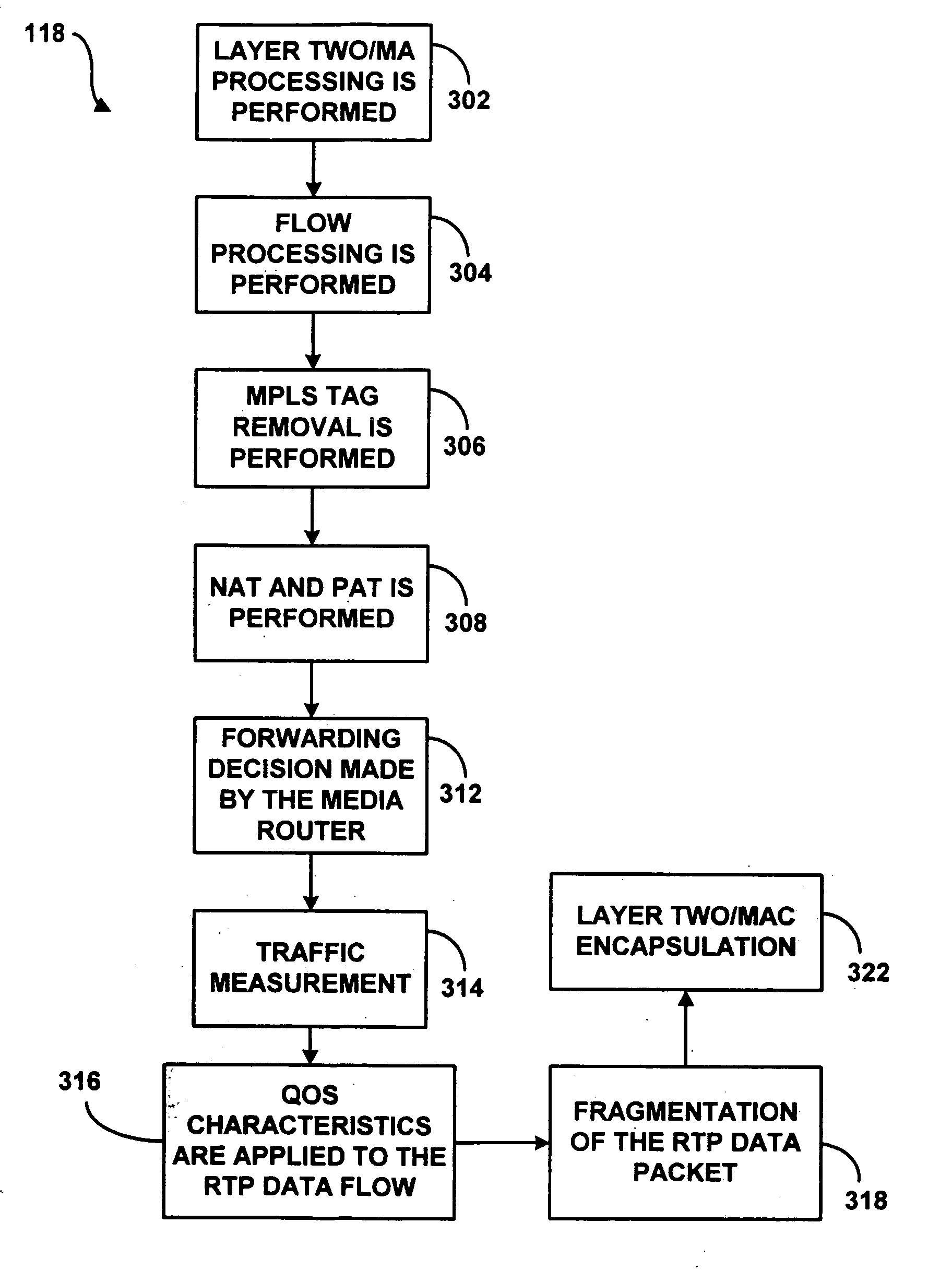
A system and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time transport protocol (RTP) multi-media flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor configured by the software. The processor is configured to perform the steps of, performing flow processing on a data packet received at a first endpoint, from a second endpoint, removing a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) tag from the data packet, translating a source address and destination address of the data packet, and determining a forwarding destination if more than one destination address of the data packet is provided.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
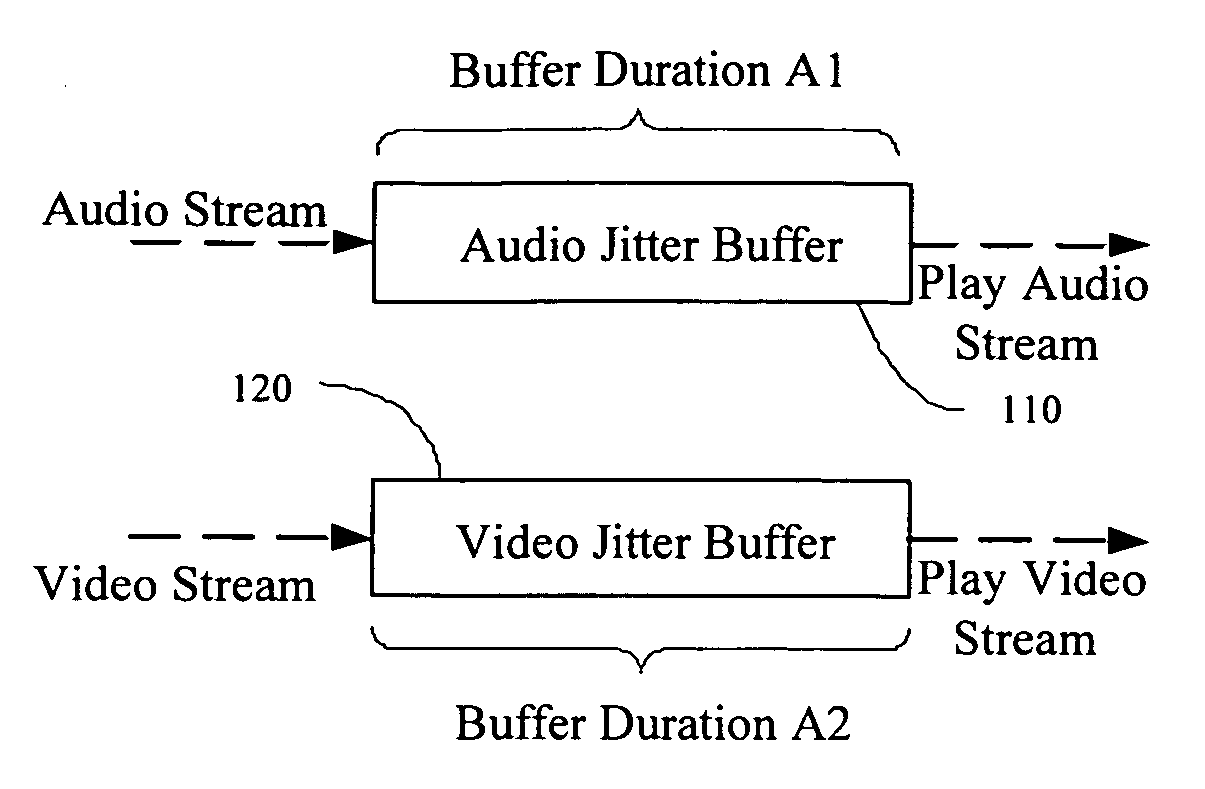
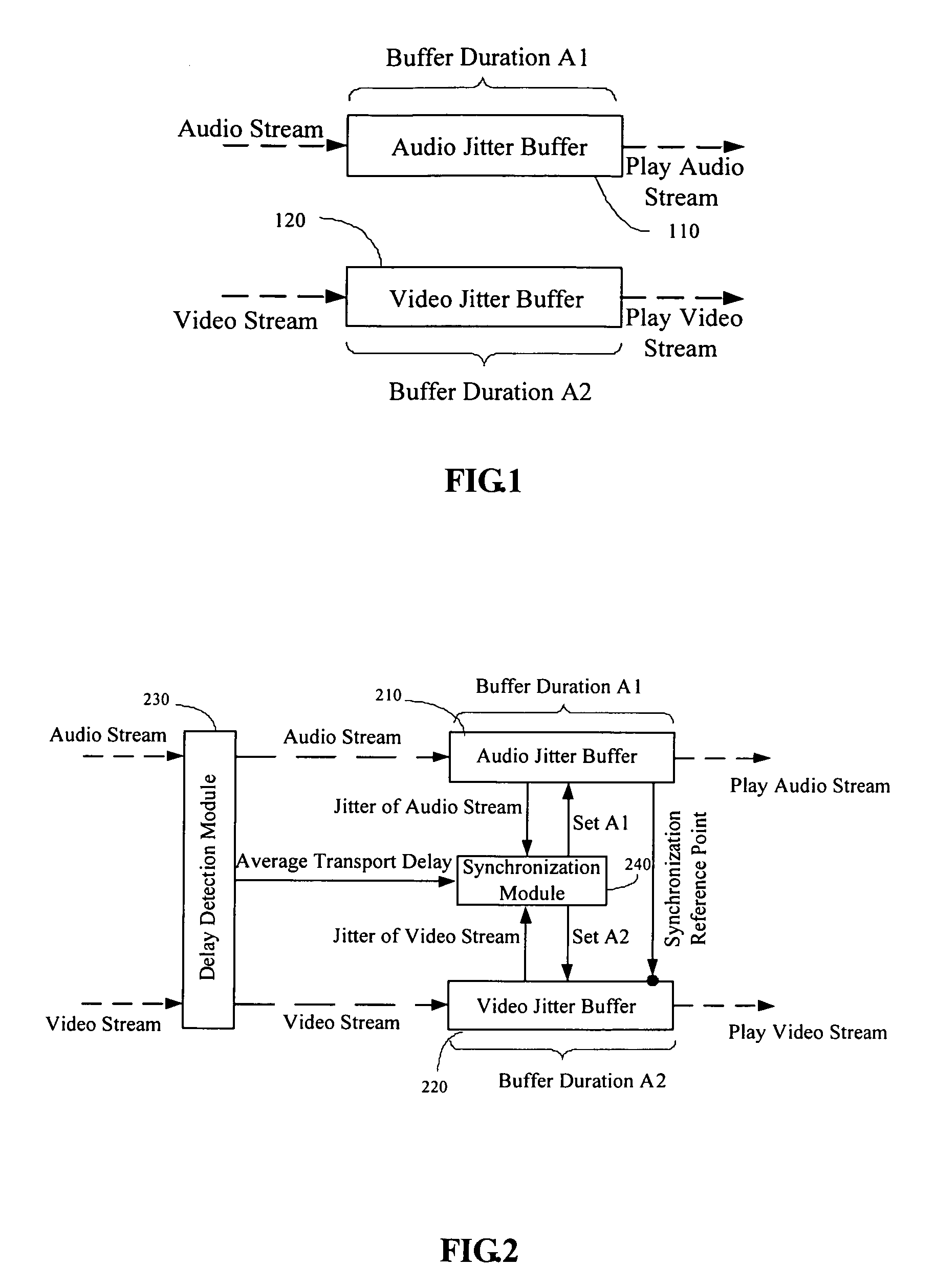
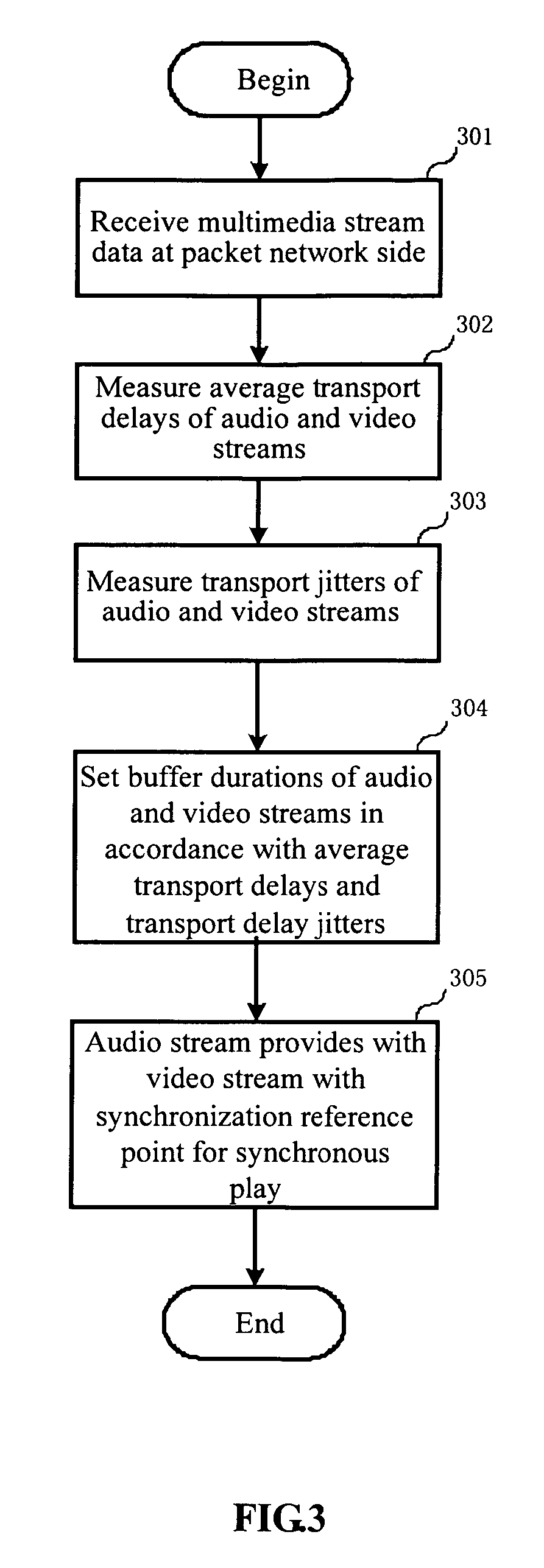
Method and device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over packet network
ActiveUS20070081562A1Transport resistantHigh precisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexTransport delayTransmission latency
A method for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network, in which the multimedia includes a first stream and a second stream which are buffered and played through buffers. The method includes: measuring average transport delays of the first and second streams; measuring transport delay jitters of the first and second streams; and calculating a delay difference between the first and second streams which corresponds to the average transport delays and the transport delay jitters of the first and second streams, and setting buffer durations. A device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network is also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
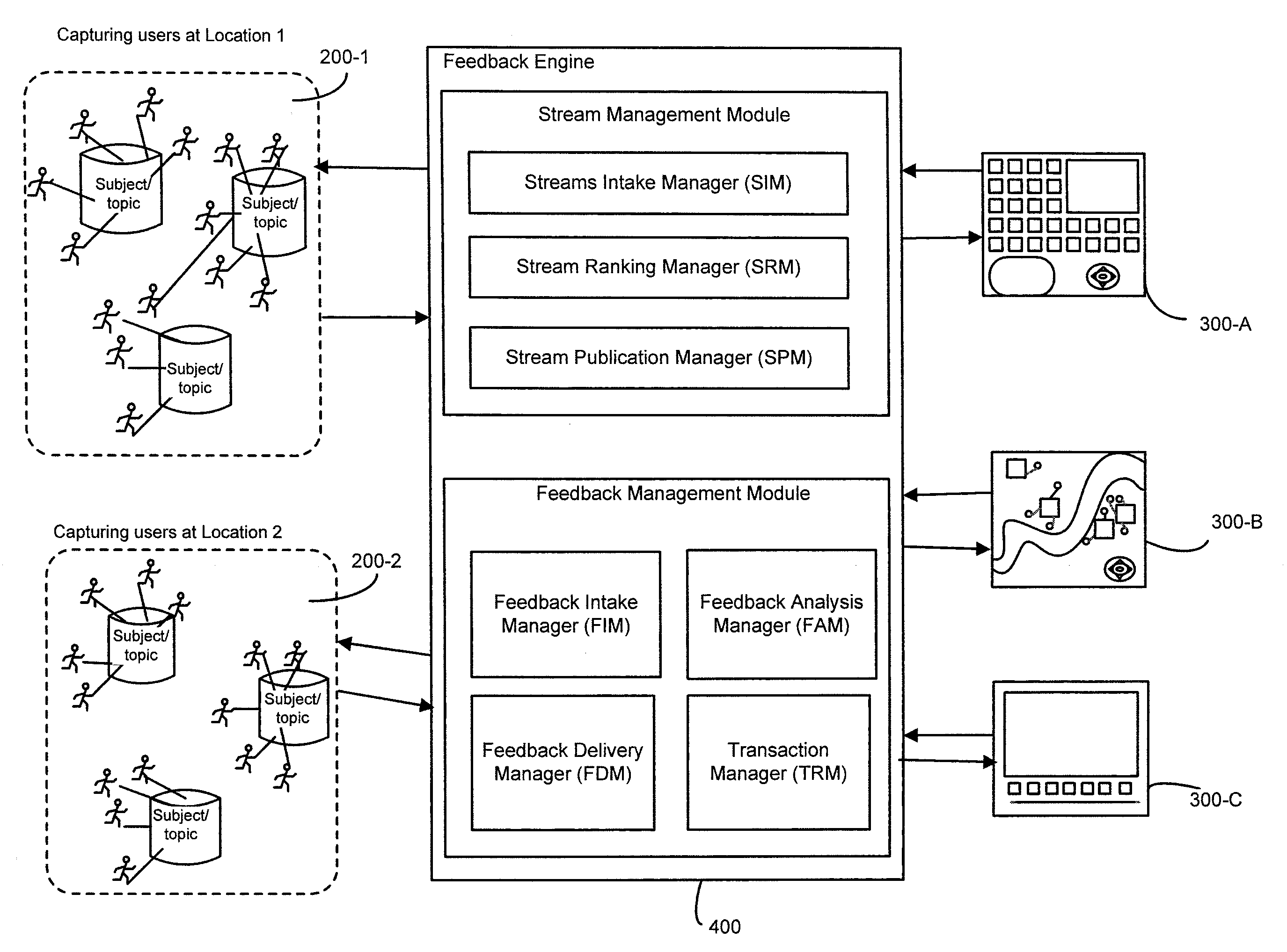
Distributed live multimedia capture, feedback mechanism, and network
ActiveUS20090089294A1Provide feedbackTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionNetwork methodReal time multimedia
Methods and systems for processing multimedia content captured from a plurality of locations via one or more capturing devices include obtaining multimedia content from one or more capturing devices. The capturing devices identify a type of content being captured and / or location of capture. An interest type for multimedia content is obtained from a consuming user. The multimedia content from the capturing devices are searched based on the interest type of the consuming user. A subset of the multimedia content conforming to the interest type is presented in substantial real-time at the receiving devices of the consuming users. Feedback regarding the presented multimedia content is obtained from consuming users and communicated to the capturing devices in substantial real-time so as to influence future capture of multimedia content.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
User attention-based adaptation of quality level to improve the management of real-time multi-media content delivery and distribution
InactiveUS7284201B2Reduce data transfer rateMoreImage analysisData processing applicationsUser deviceEngineering
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus and methods for real-time multimedia network traffic management and control in wireless networks
InactiveUS8868725B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksWireless mesh networkNetwork management
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Forward error correction for burst and random packet loss for real-time multi-media communication
ActiveUS20090193314A1Less powerFlexibility of deploymentError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionMissing dataPacket loss
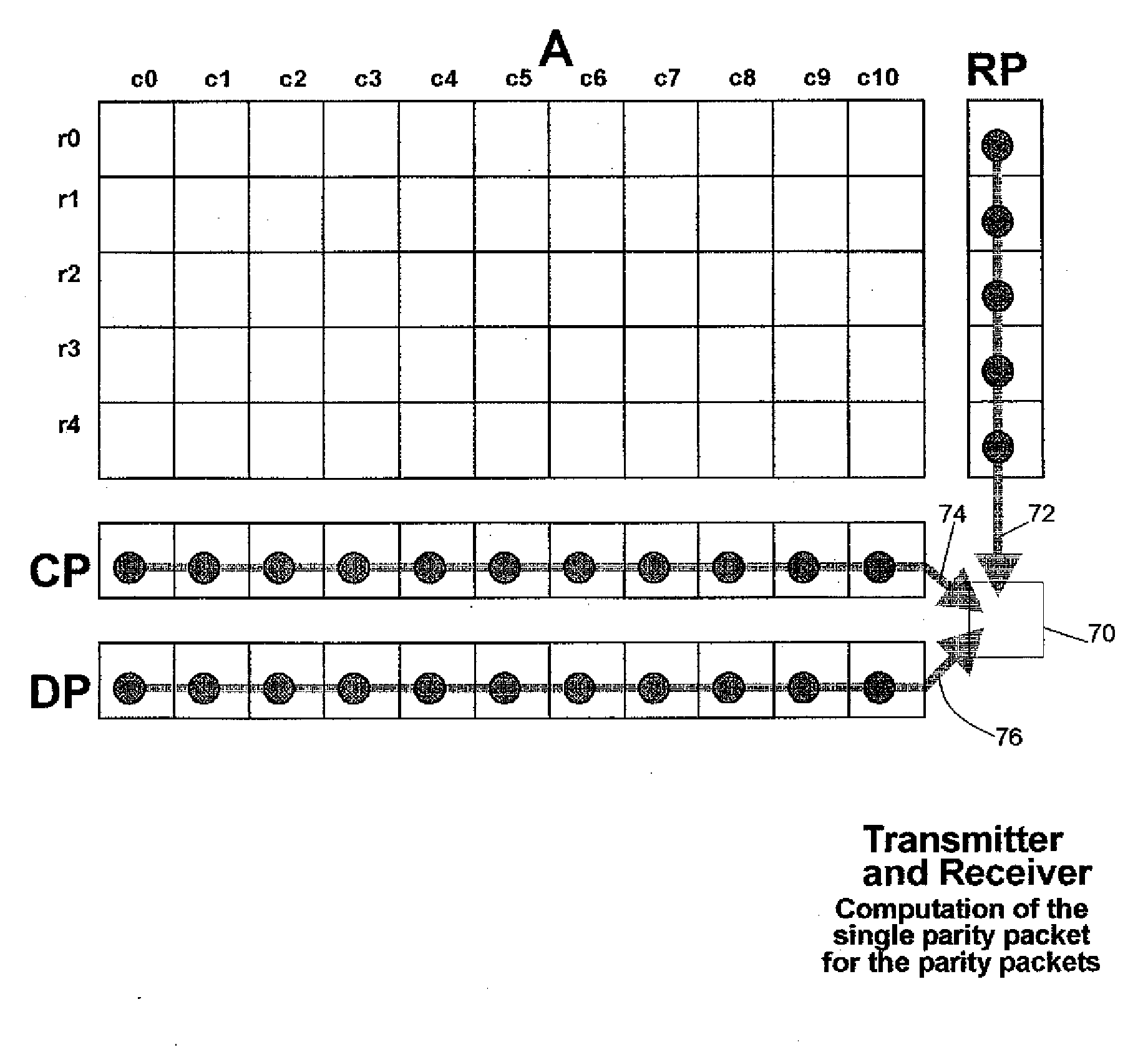
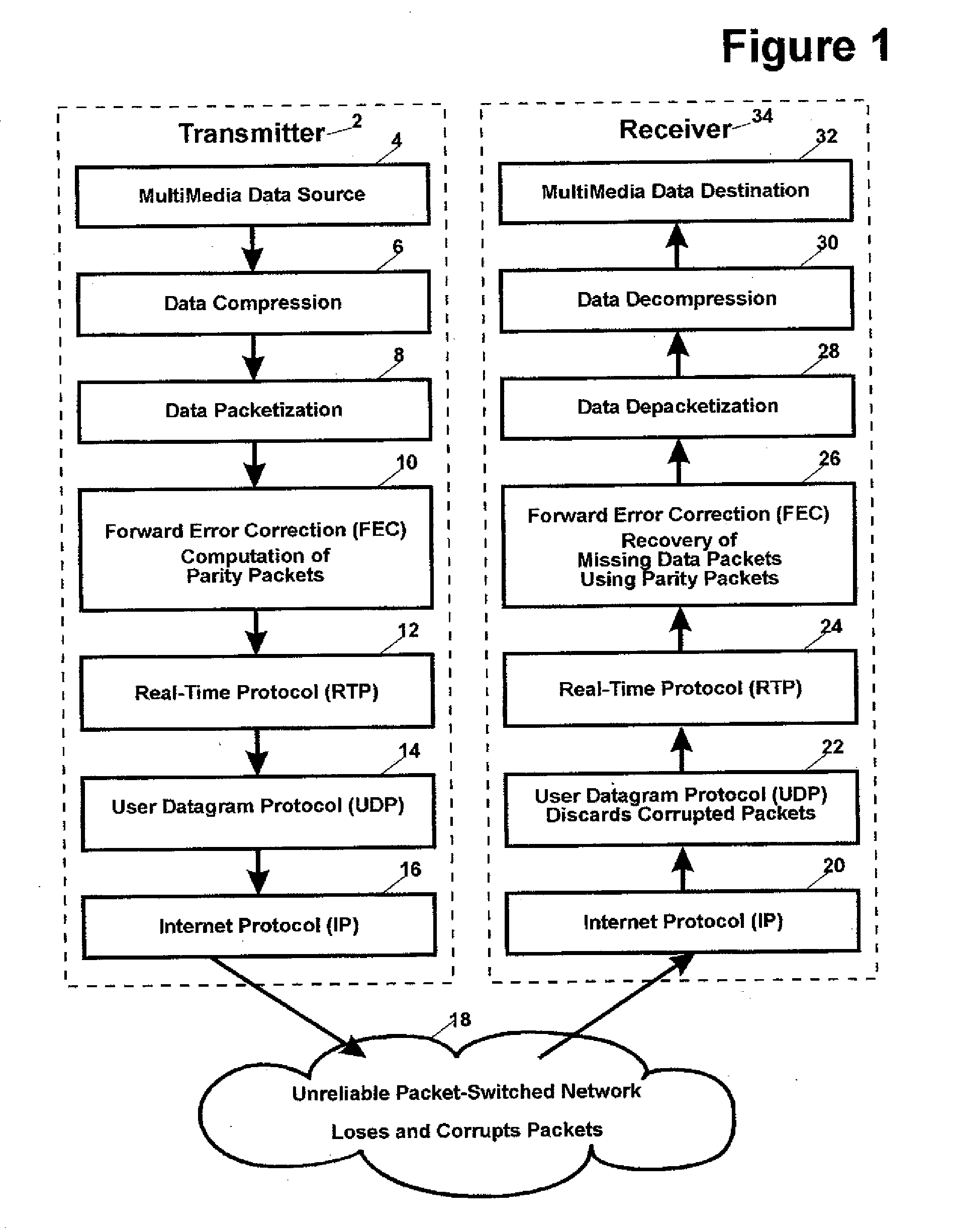
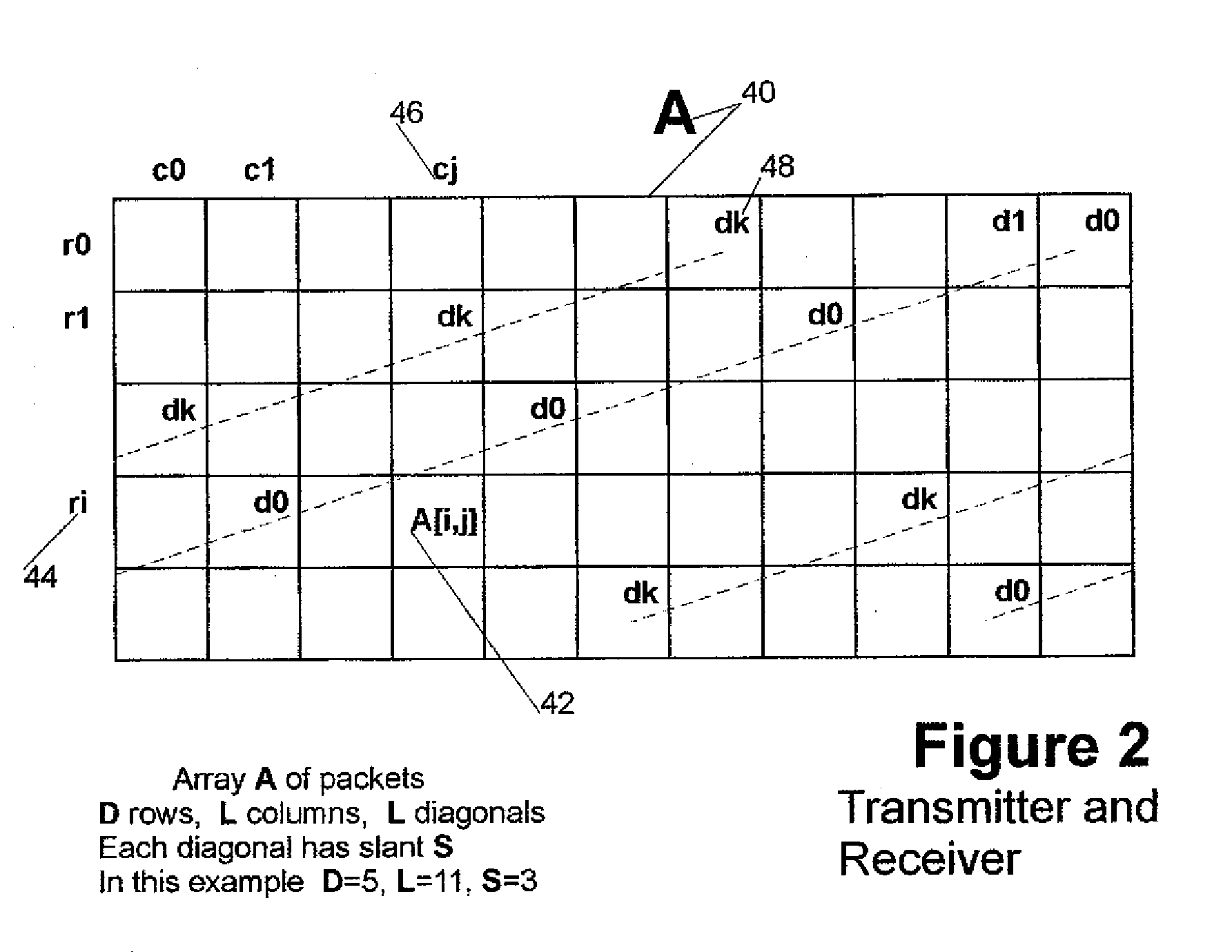
This invention relates generally to a packet recovery algorithm for real-time (live) multi-media communication over packet-switched networks, such as the Internet. Such multi-media communication includes video, audio, data or any combination thereof. More specifically, the invention comprises a forward error correction (FEC) algorithm that addresses both random and burst packet loss and errors, and that can be adjusted to tradeoff the recoverability of missing packets and the latency incurred. The transmitter calculates parity packets for the rows, columns and diagonals of a block of multi-media data packets using the exclusive or (XOR) operation and communicates the parity packets along with the multi-media data packets to the receiver. The receiver uses the parity packets to recover missing multi-media data packets in the block. The FEC algorithm is designed to be able to recover long bursts of consecutive missing data packets. If some parity packets are missing, they too can be recovered using an extra single parity packet, so that they can be used to recover other missing data packets. The invention applies to both one-way real-time streaming applications and two-way real-time interactive applications, and to both wired and wireless networks. The invention retains backwards compatibility with existing standards governing FEC for professional video over IP networks.
Owner:NEVION EURO
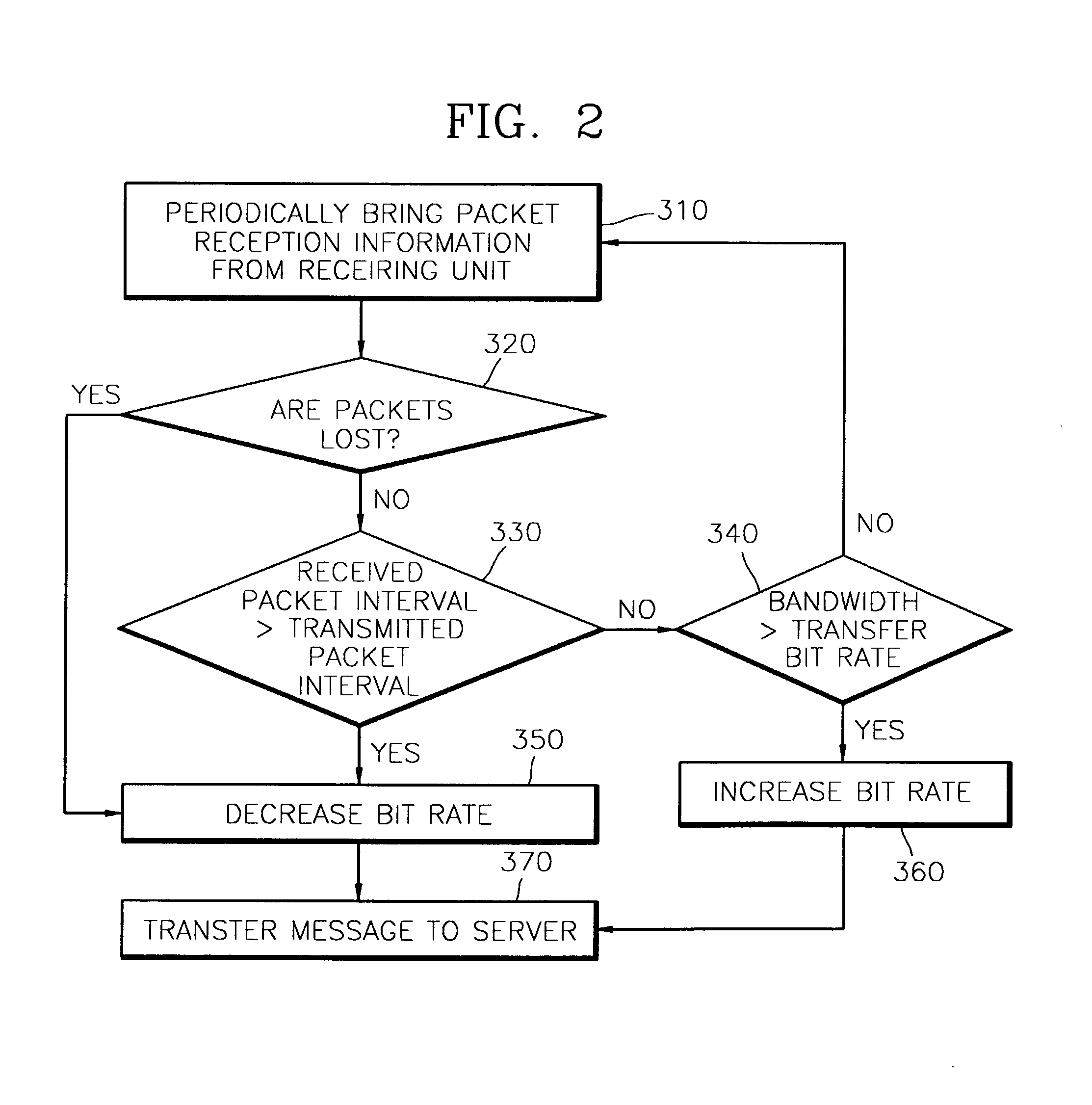
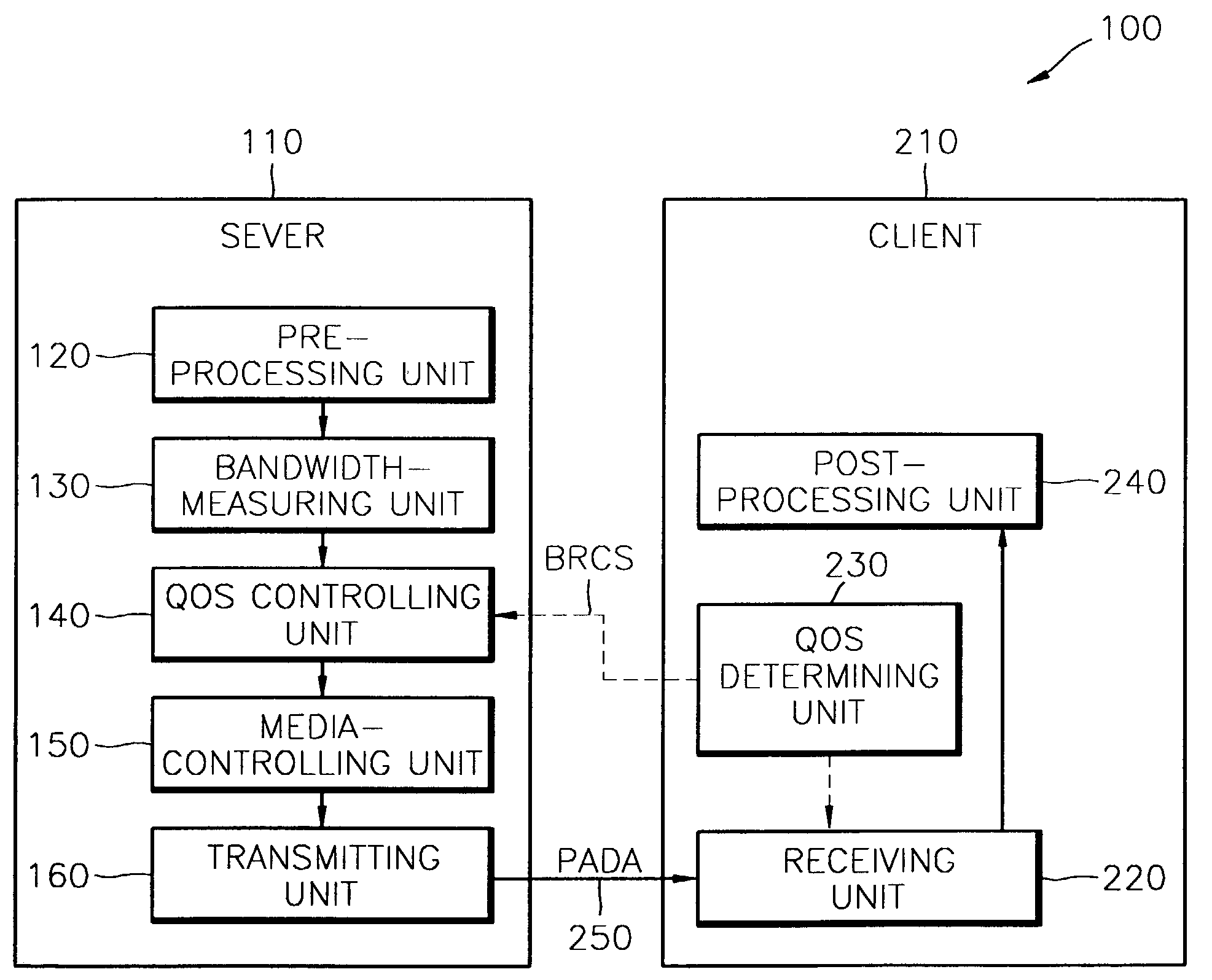
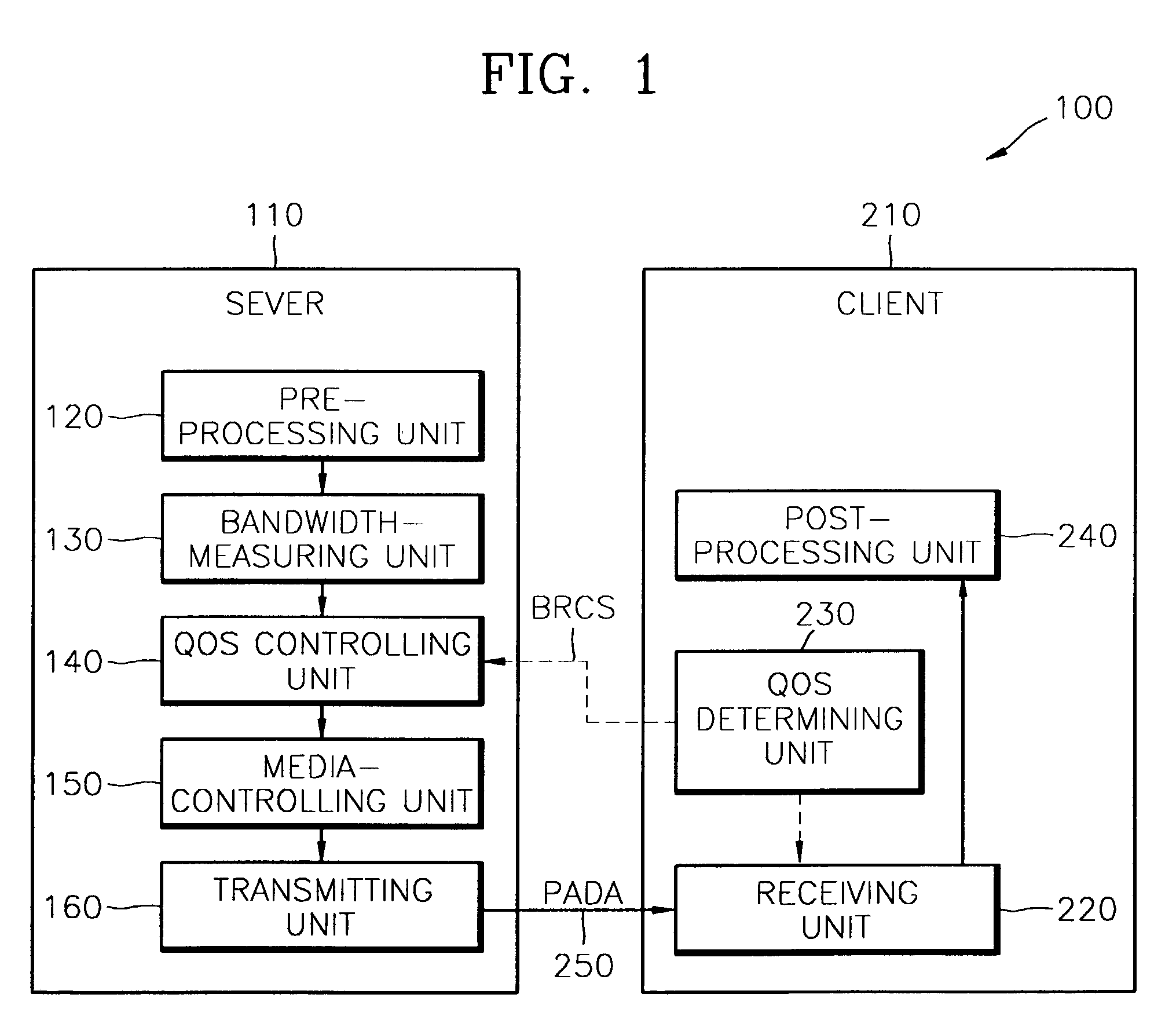
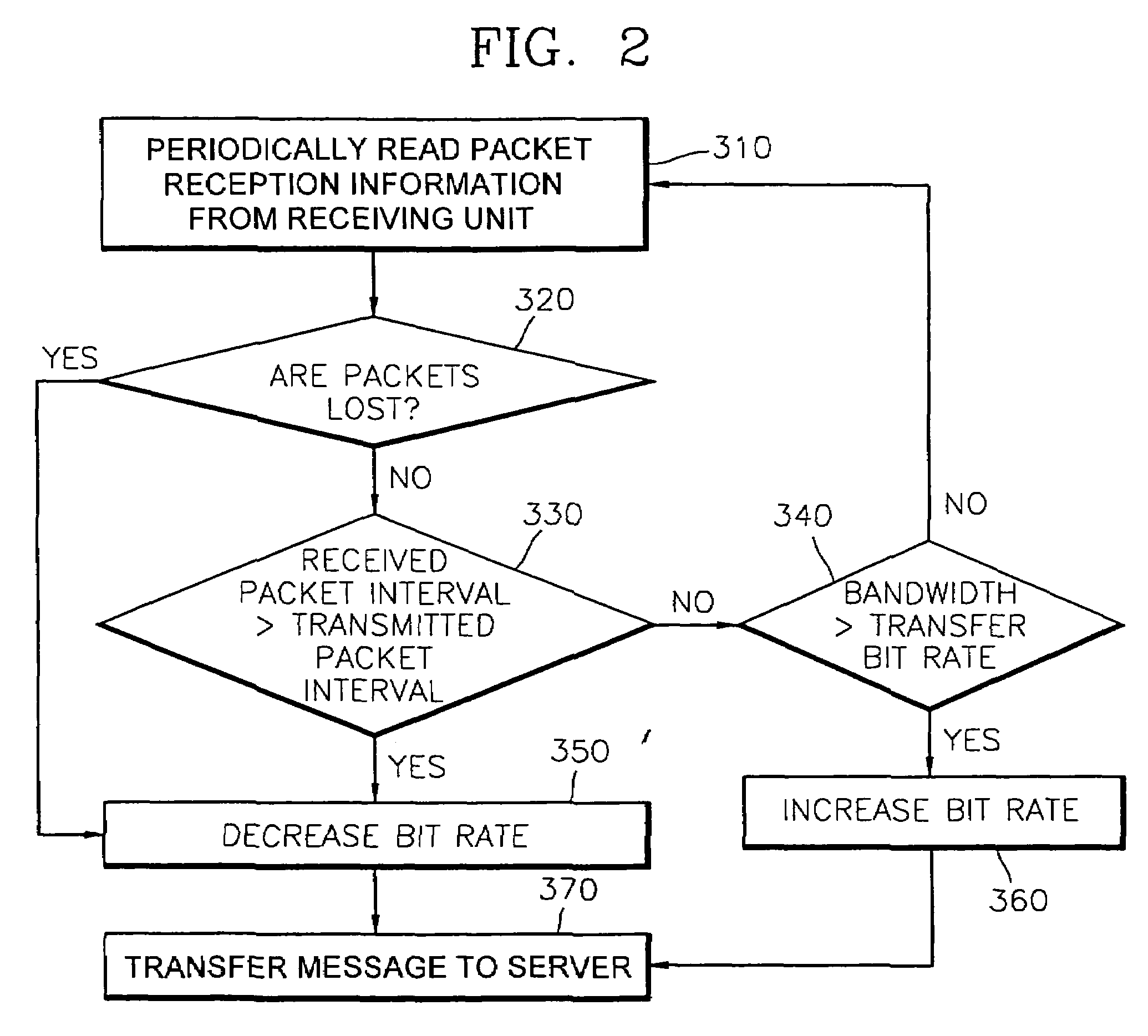
System and method of network adaptive real-time multimedia streaming
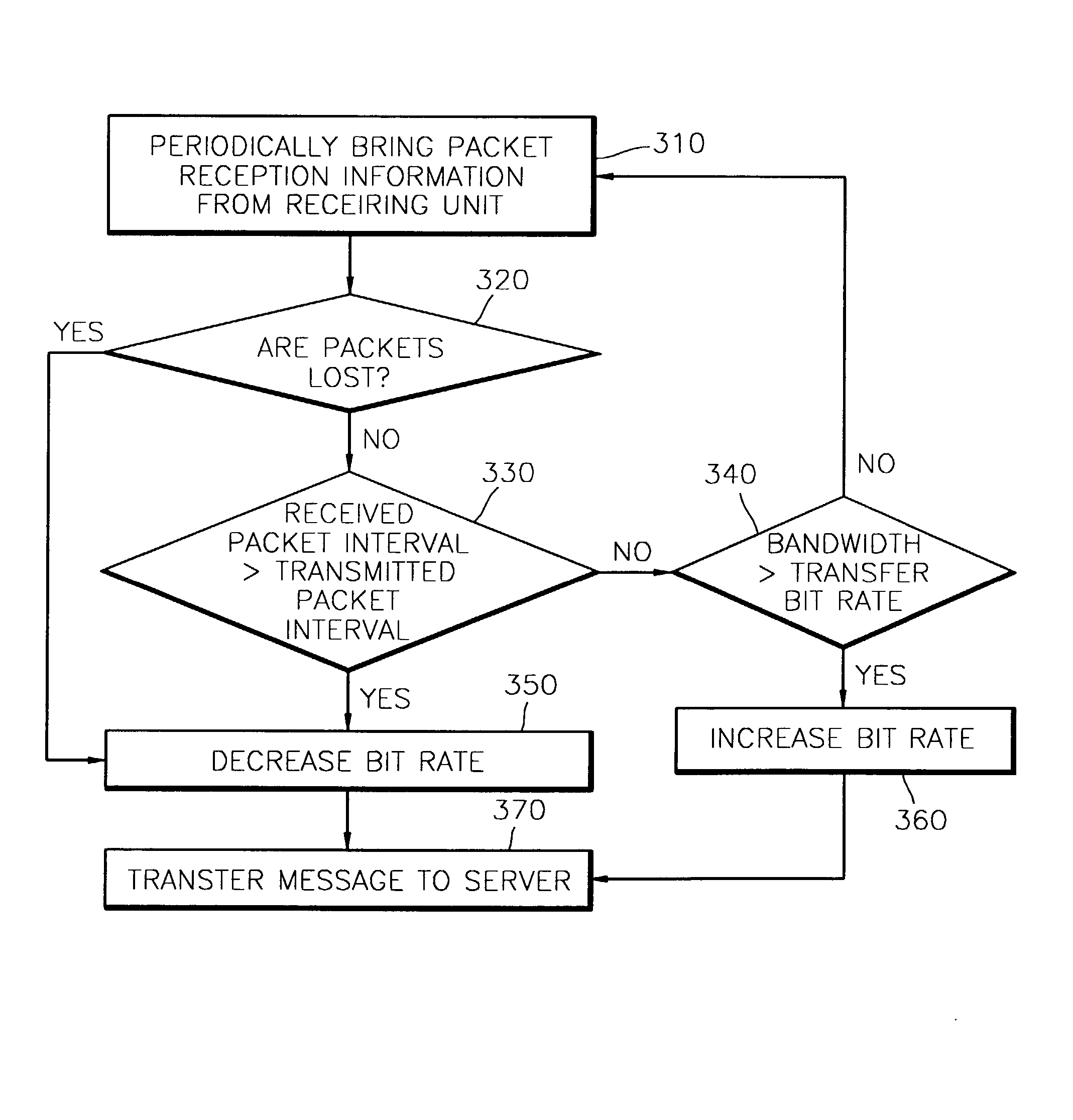
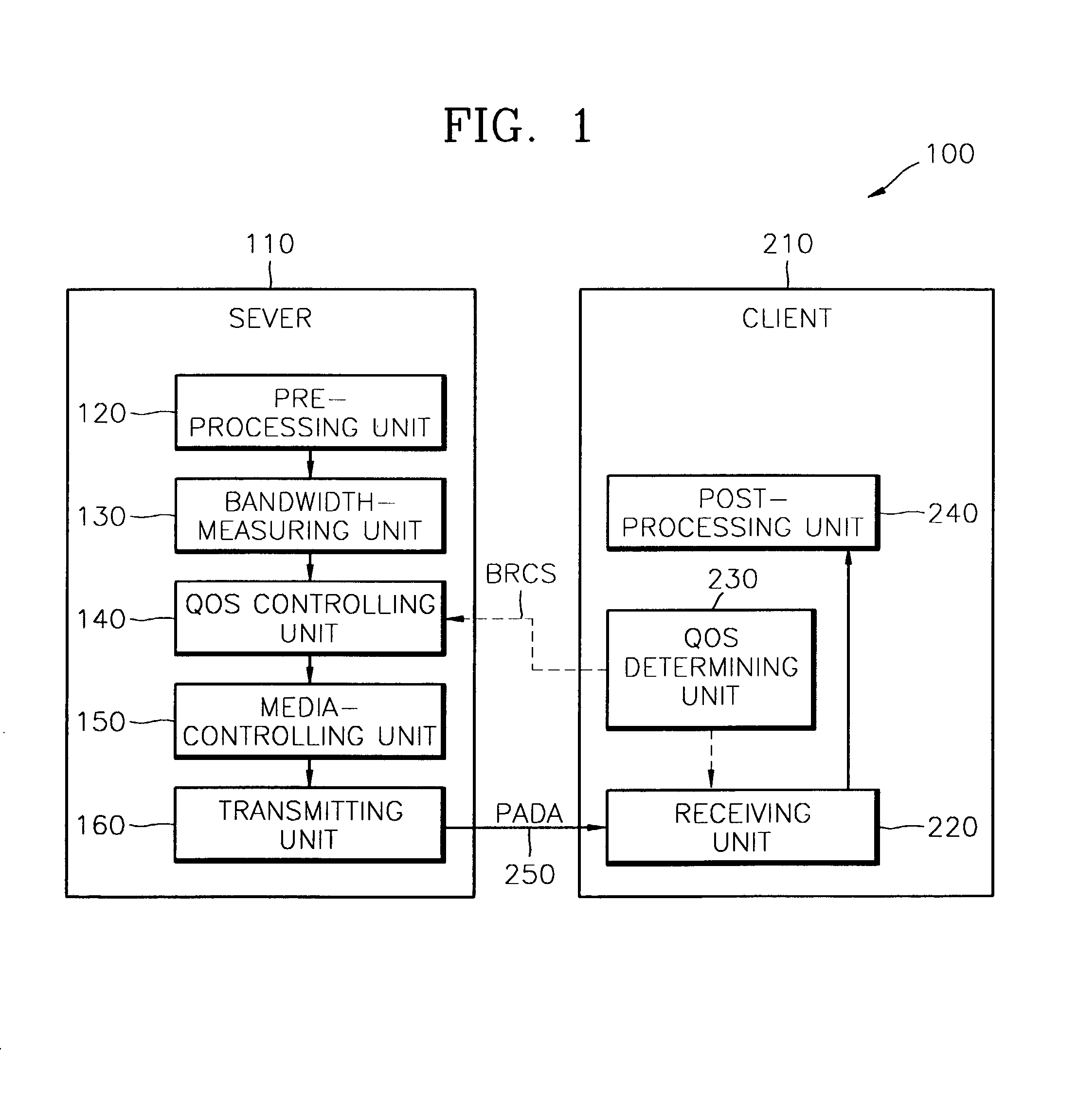
A system and method of network adaptive real-time multimedia streaming, in which a receiving bit rate of a packet that is received from a client is monitored, and the monitoring result is fed back to a streaming server, and a transfer bit rate of a packet that is transmitted by the streaming server are provided. The streaming system includes a streaming path on which packetized data are streamed, a streaming server for transmitting the packetized data at a first bit rate through the streaming path in response to a control signal, and a client for receiving the packetized data at a second bit rate according to the state of the streaming path, comparing the first bit rate with the second bit rate and generating the control signal corresponding to the comparison result. The first bit rate is controlled in response to the control signal. The size of packets and an interval between the packets are controlled by the first bit rate. The state of the network is sensed, and thus the transfer bit rate can be automatically controlled according to the state of the network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Audio-video packet synchronization at network gateway
InactiveUS7043749B1Increase or decrease a device transmission delayPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision conference systemsAudio frequencyCommunication device
A method and apparatus for synchronizing sound and images in a real-time multimedia communication, such as an audio-video telephone call, through a network gateway, when the source and / or the destination of the audio signals, and optionally also the video signals, are from and / or to separate audio and video communication devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
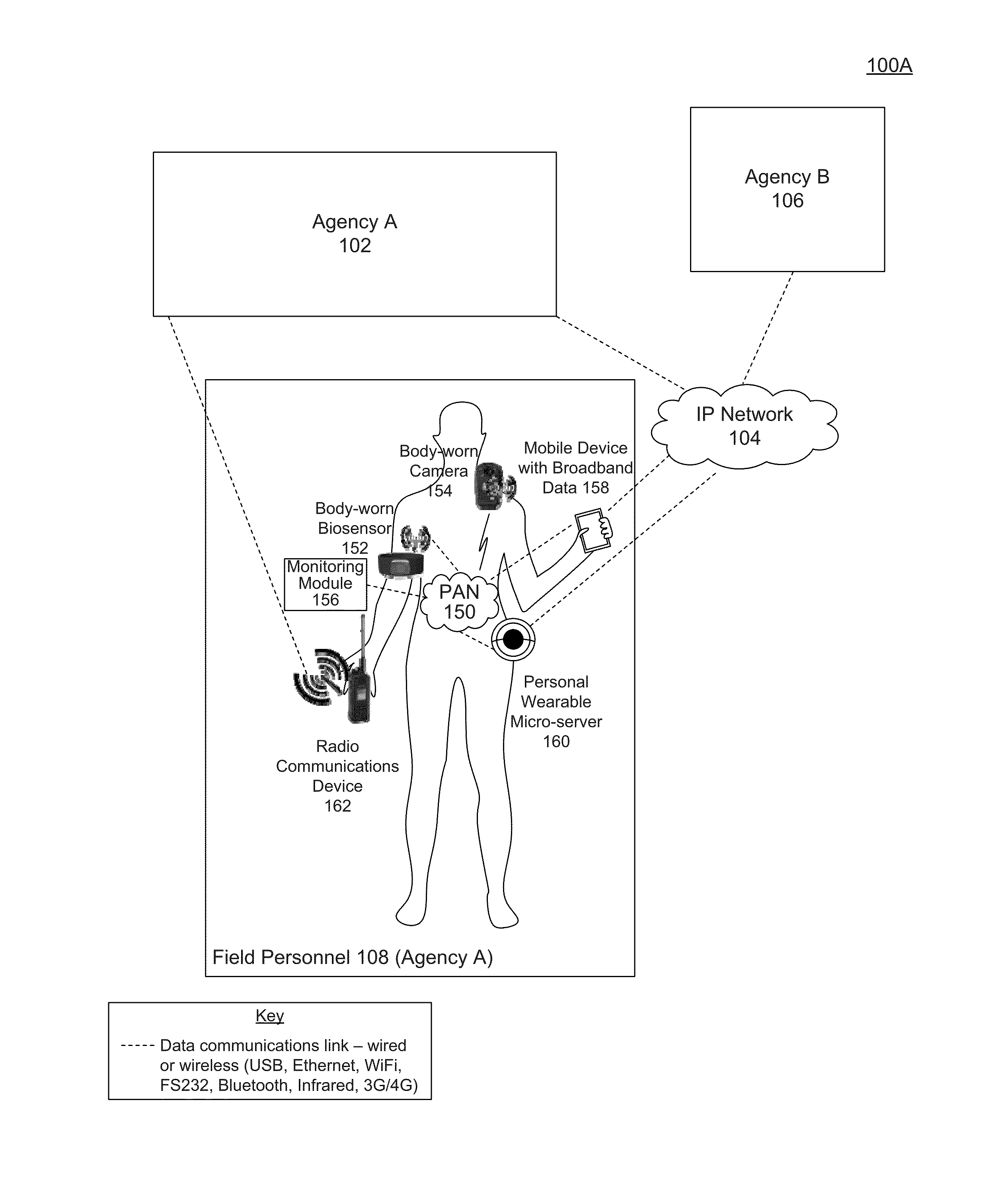
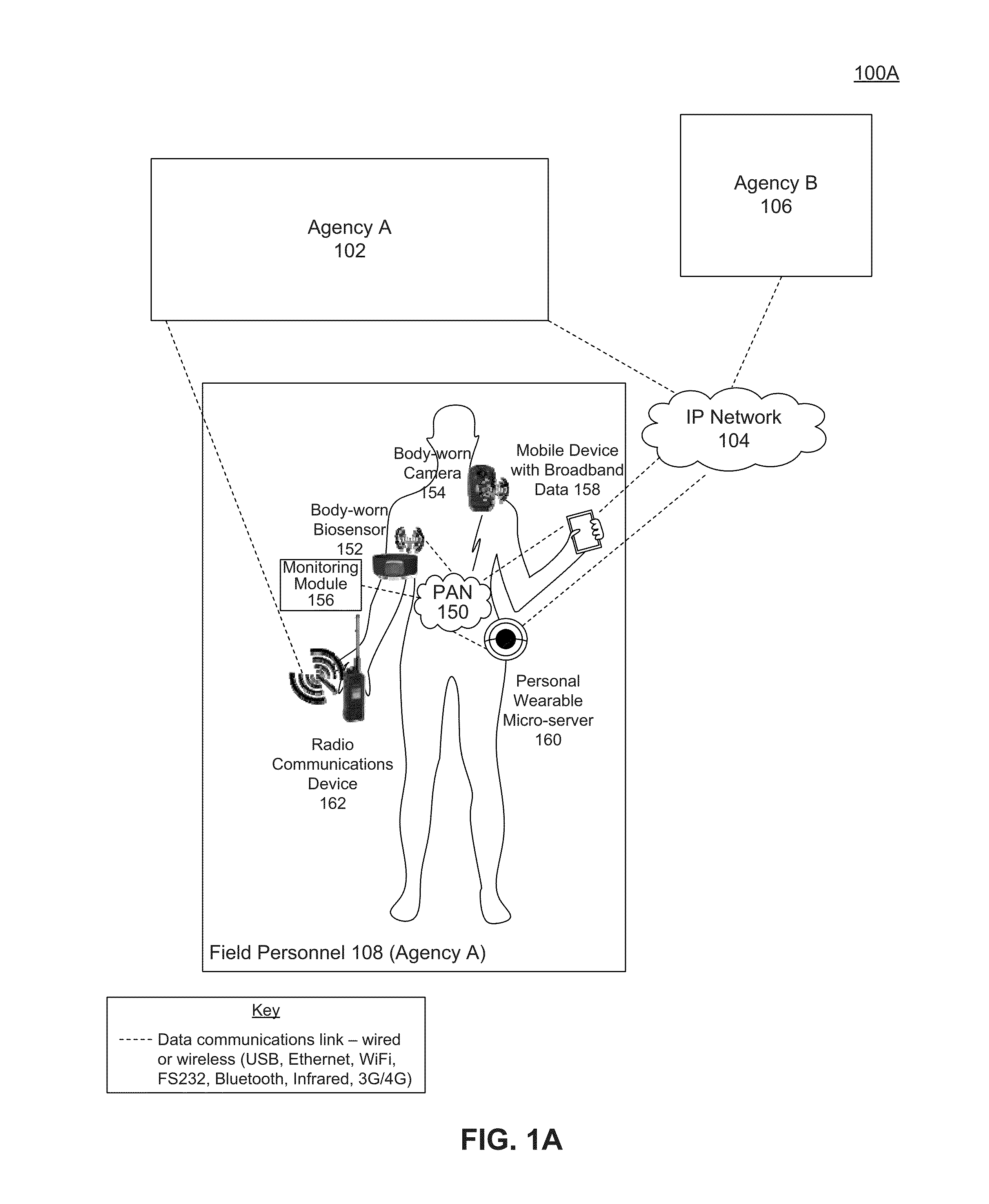
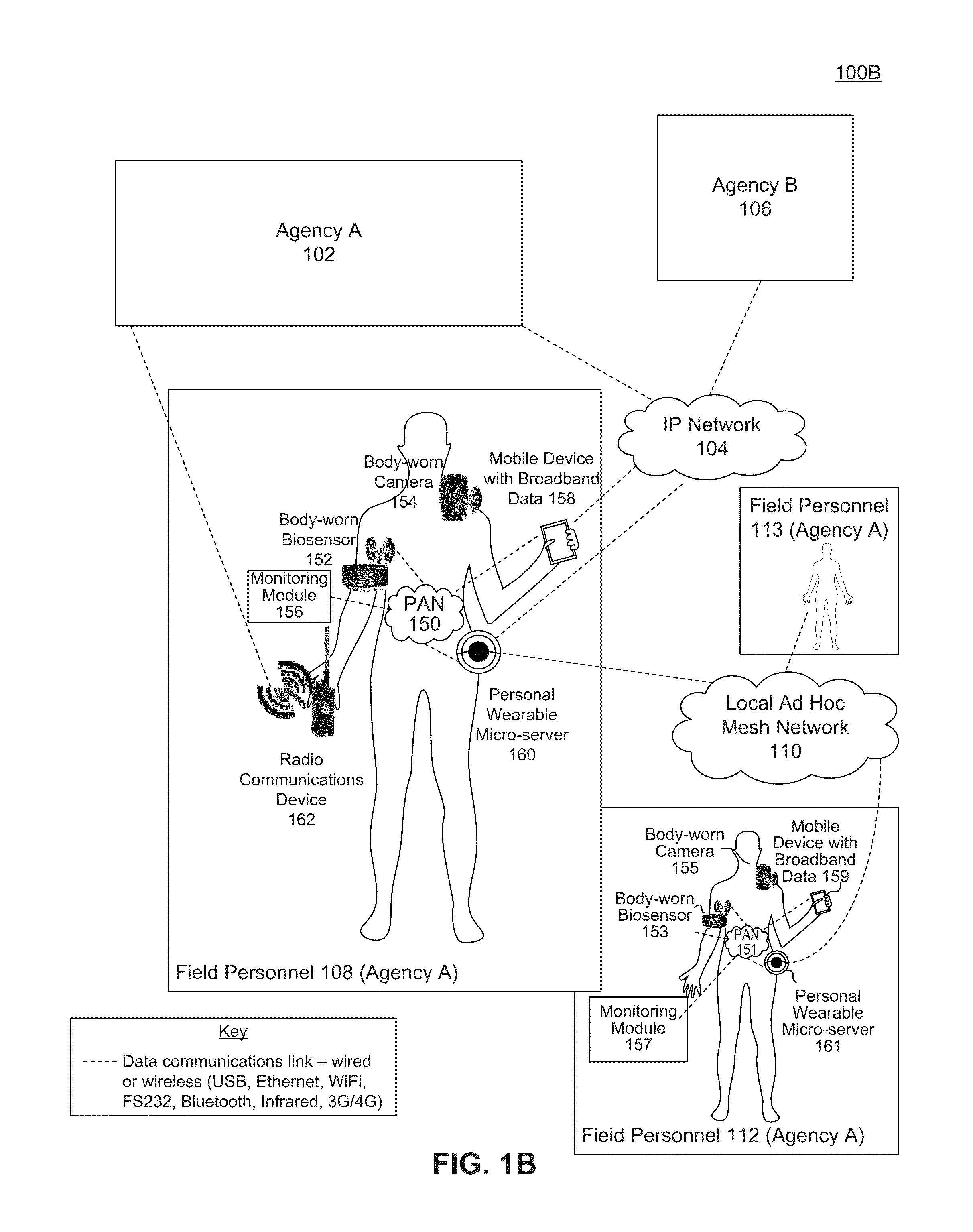
System and method for biosensor-triggered multimedia collaboration
Embodiments include a system, method, and computer program product for using a biosensor worn by a user to trigger an event and activate a camera worn by the user to begin streaming and / or recording video data. The biosensor trigger also initiates a real time multimedia collaboration session with the user wearing the biosensor and one or more designated parties. Through an interoperability gateway device, a voice communications device of the user is bridged with voice communications devices of the designated parties, and the video data is electronically transmitted to the designated parties. Thus, the designated parties may have real time voice communications among each other and with the user, and the designated parties may also view the video data in real time. Embodiments also determine when an event has ended and deactivates the camera worn by the user.
Owner:MUTUALINK INC
Distribution of Session Keys to the Selected Multiple Access Points Based on Geo-Location of APs
ActiveUS20080031194A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsKey issuesGeolocation
In the public WLAN systems, reliable user re-authentication for mobility support is an essential step. However, re-authentication during handoff procedures causes long handoff latency which deteriorates the quality of service specifically for real-time multimedia applications. One possible solution is to authenticate the Mobile Node (MN) in advance with all the neighboring Access Points (APs) and distribute the Session Keys to them. However, the key issue is how to optimally and efficiently select the neighboring APs. In the preferred embodiments, we propose a system that takes into account the user current “Geo-Location”, “Mobility Pattern” and “Application Running on MN”; estimates the “Expected Mobility Zone” (EMZ) and selects an appropriate set of candidate APs corresponding to the MN's geo-location. The EMZ may comprise of APs belonging to “Intra-domain”, “Inter-domain” or “Inter-technology Networks” (e.g., WLAN, WiMAX, and Cellular etc). The system assumes that not only the Mobile Nodes but also the Fixed Nodes (APs or Base Stations) are capable of knowing their Geo-Location Coordinates X, Y, Z. This capability may come either by integrating GPS receiver or through any other alternate, state of the art or future positioning technologies in the APs.
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC +1
Adaptive data rate streaming in a peer-to-peer network delivering video content
ActiveUS20110258322A1Increased bit rate consumptionIncrease consumptionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData rateSelf adaptive
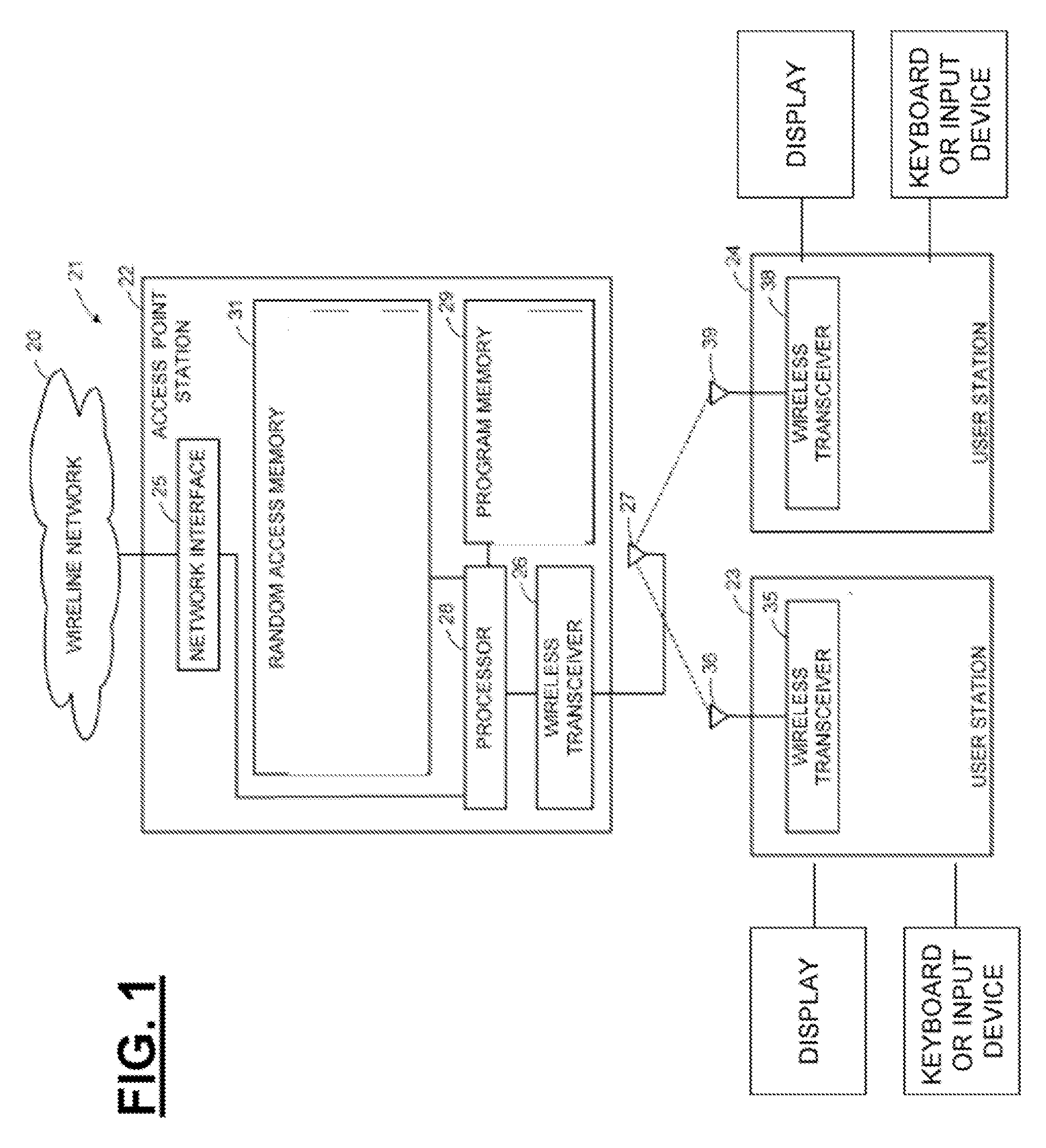
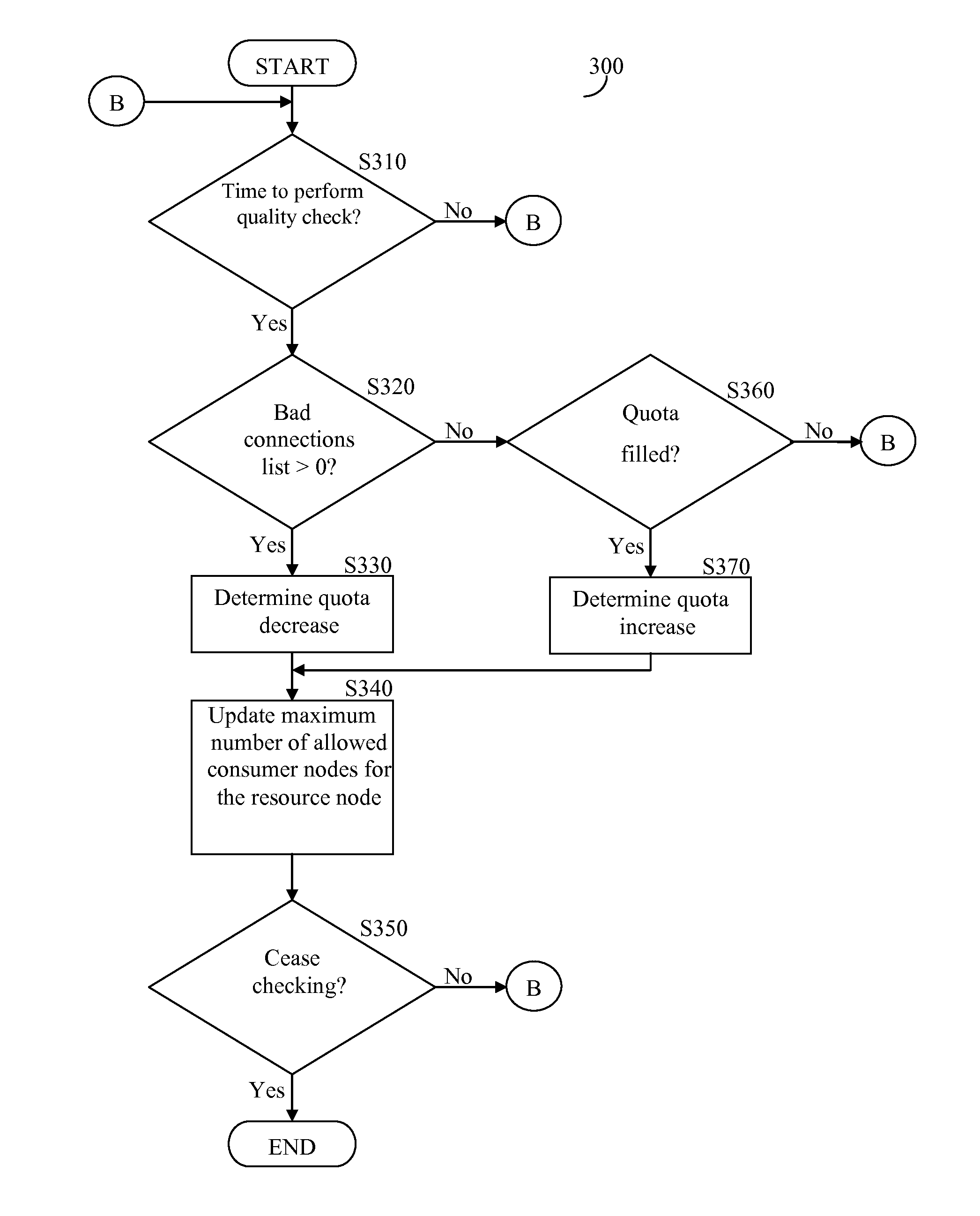
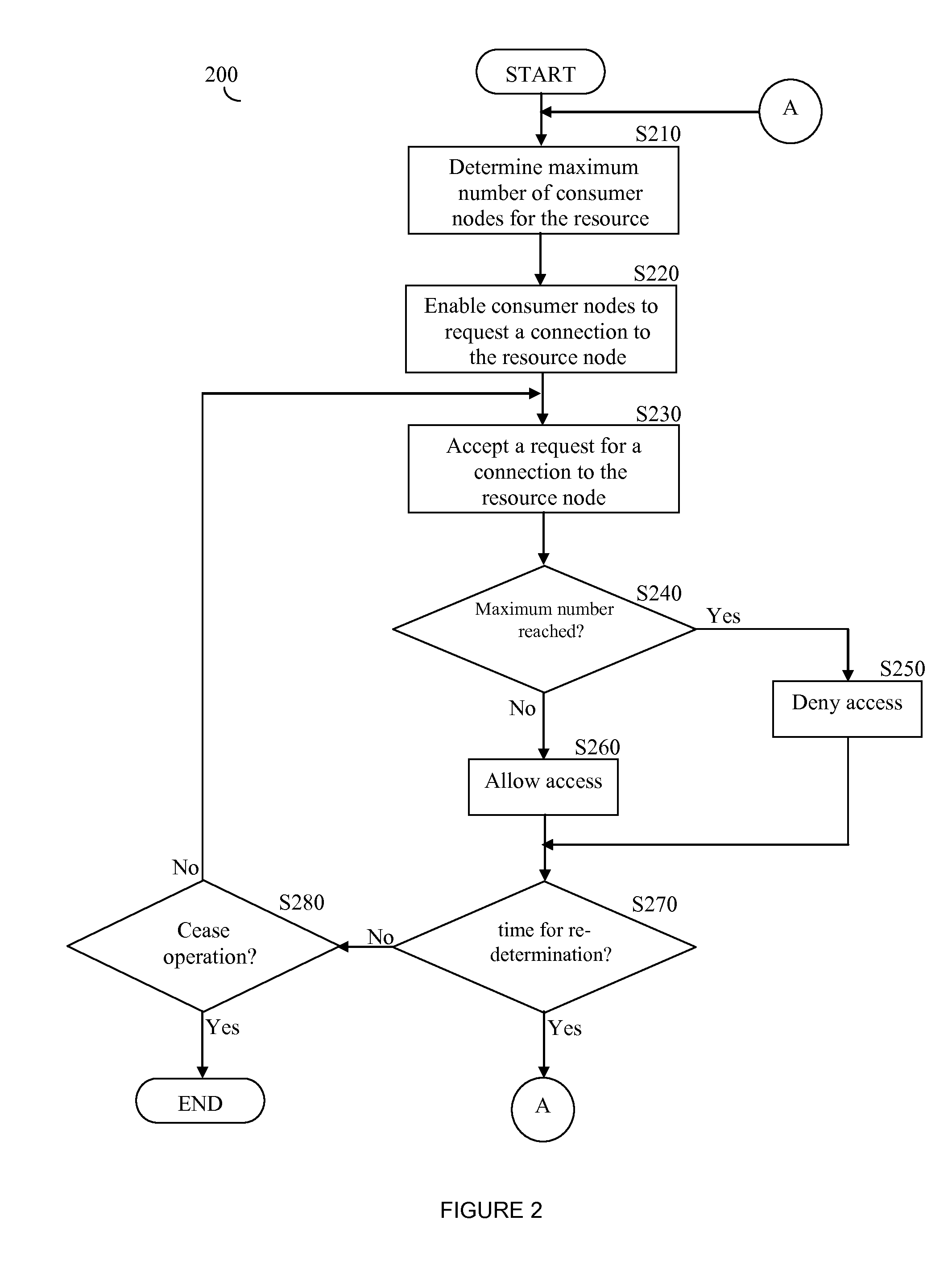
A method for increasing bit-rate consumed by a consumer node in a real-time peer-to-peer (P2P) network delivering real-time multimedia content. The method comprises determining desirability to switch to a higher bit-rate consumption respective of a current bit-rate consumption; sending requests to resource nodes of the P2P network for supply of additional bandwidth to support a difference between the higher bit-rate consumption and the current bit-rate consumption; connecting to at least one resource node of the P2P network that can supply the additional bandwidth, thereby increasing bit-rate consumption; determining whether there are connection problems due to the increase in bit-rate consumption; and consuming from the at least one resource node the current bit-rate in addition to the additional bandwidth when no connection problems occur and it is established that the consumer node is capable of handling the higher bit-rate consumption of the real-time multimedia content.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
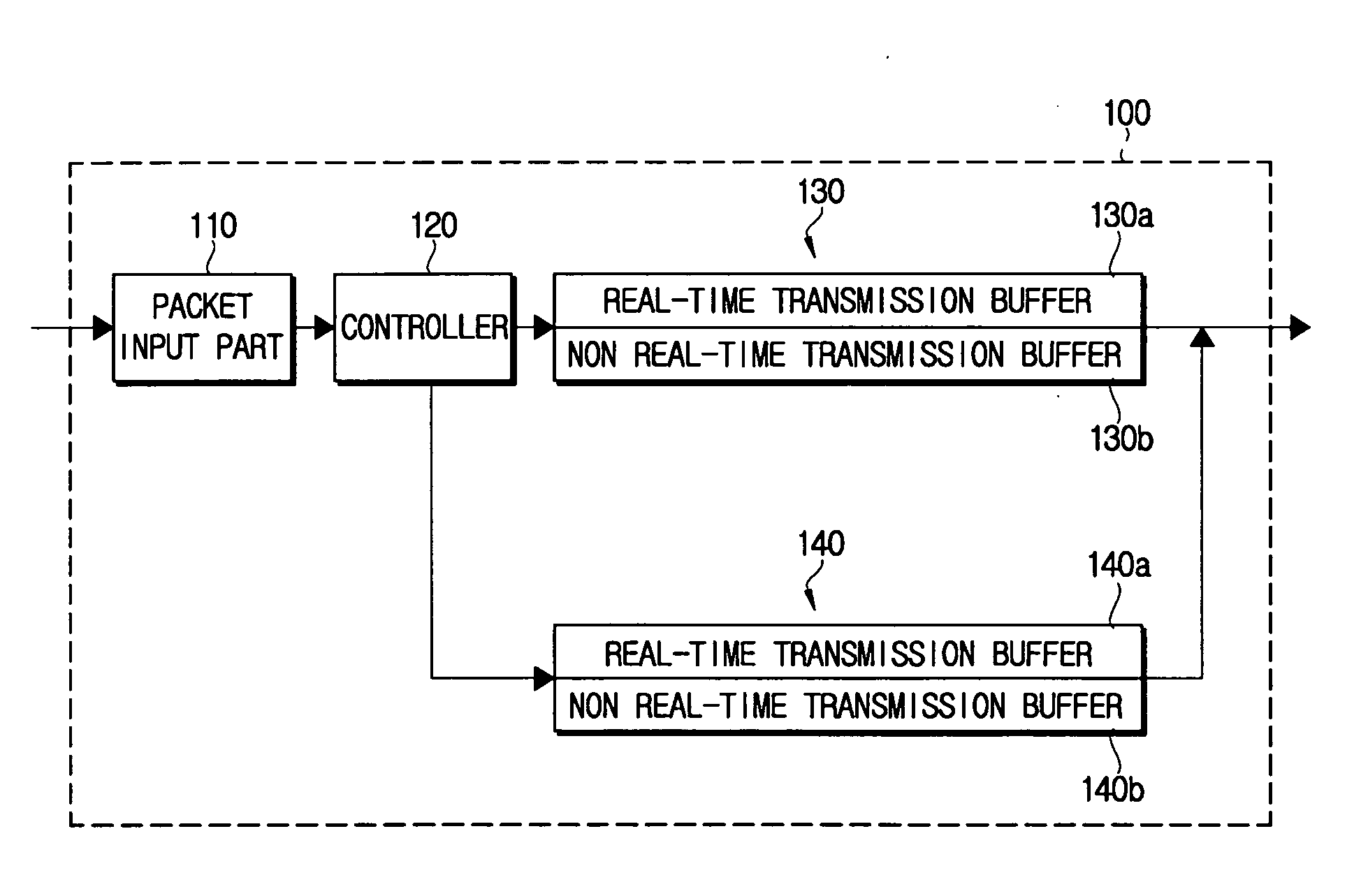
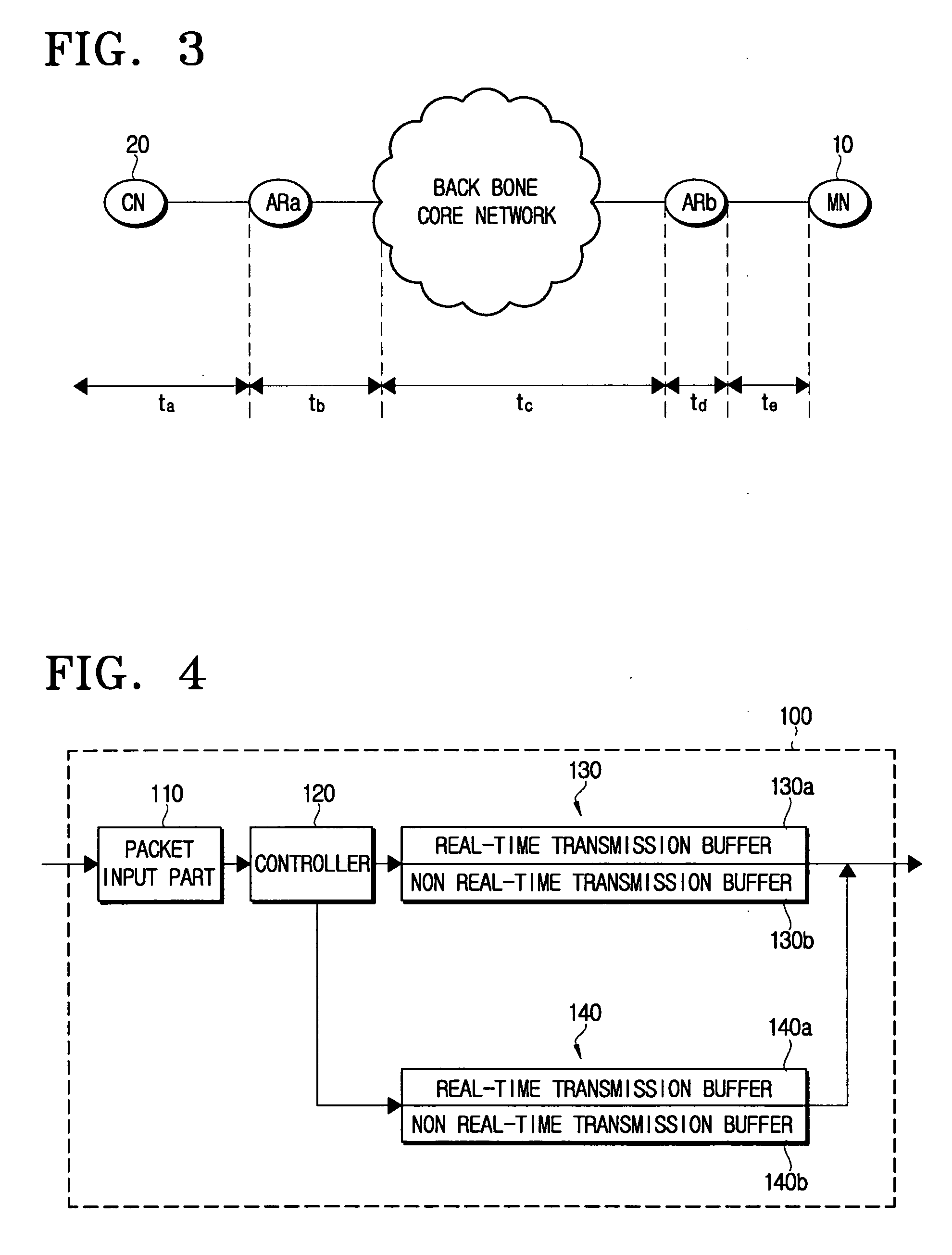
Access network device for managing queue corresponding to real time multimedia traffic characteristics and method thereof
ActiveUS20050232154A1Efficient managementSave resourcesOther printing matterError preventionAccess networkTraffic characteristic
A queue management method of an access network device includes receiving a packet, determining feasibility of a packet transmission within a delivery deadline allowed from a destination if the received packet is for real-time transmission, storing the packet in the transmission queue and transmitting the packet in sequential order of the storage when the packet transmission within the delivery deadline is feasible, and dropping the packet instead of storing the packet in the transmission queue when the packet transmission is determined infeasible. Accordingly, resources required for the packet transmission are saved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Distributed live multimedia capture, feedback mechanism, and network
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
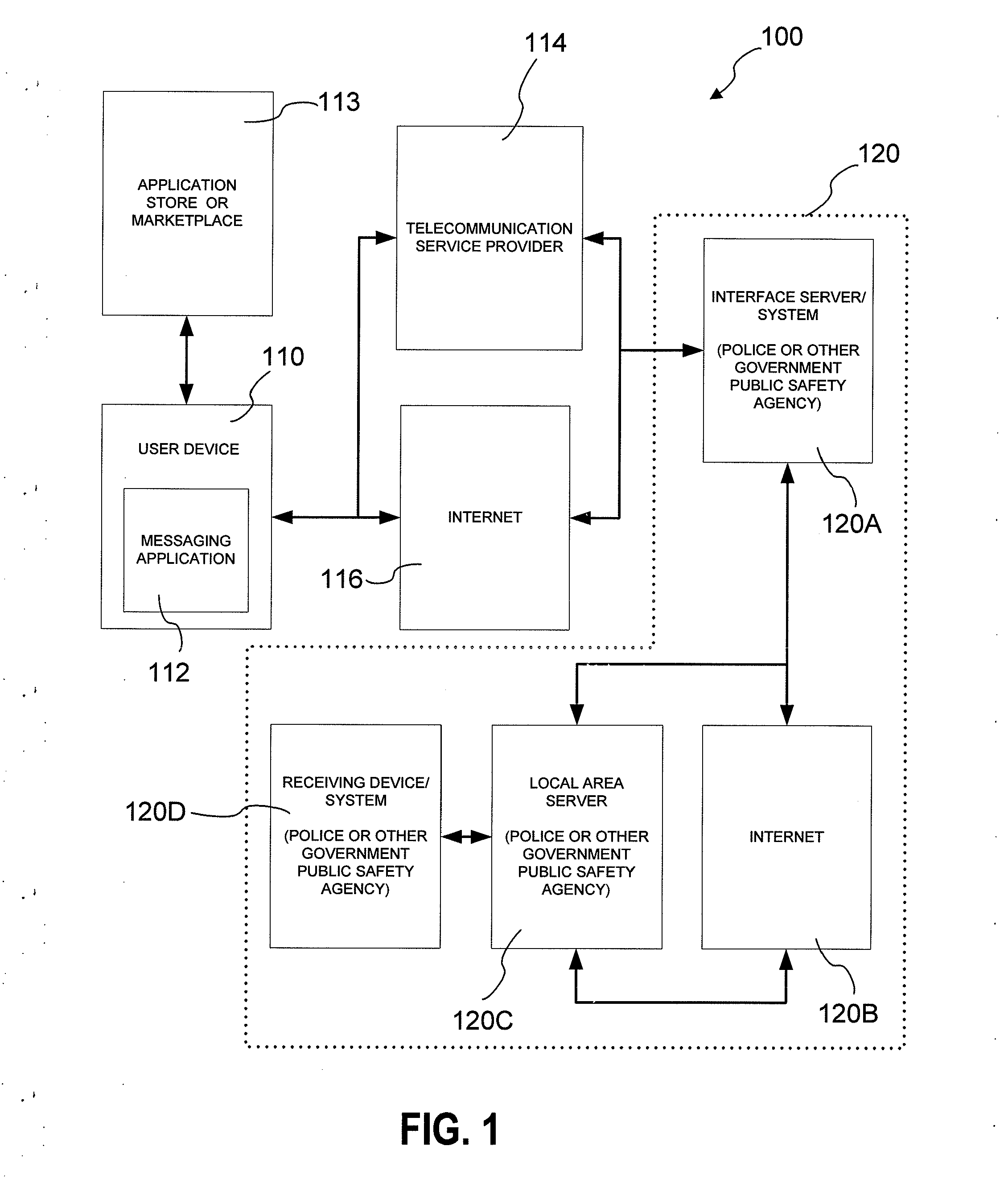
Method and system for communicating information associated with an incident and/or emergency situation
InactiveUS20140057590A1Service provisioningEmergency connection handlingDisplay deviceLocation based information
A computer-implemented method and system for communicating real-time multi-media information associated with an emergency situation. The method may include providing a device having a dedicated button and / or at least one displayed selectable icon on a display of the device. The button and / or the icon may be associated with indicating an emergency situation. After pushing of the button or selection of the at least one selectable icon by the user in the emergency situation, the method may include automatically preparing, by the device, a message to send, the message including one or more of user identification information, user contact information, and / or location-based information; automatically sending, by the device, the message to a receiving system of a government public safety agency; automatically activating video and / or audio recording features of the device; and automatically transmitting, by the device, real-time video, audio, and / or location-based information to the government public safety agency.
Owner:OPTIVON
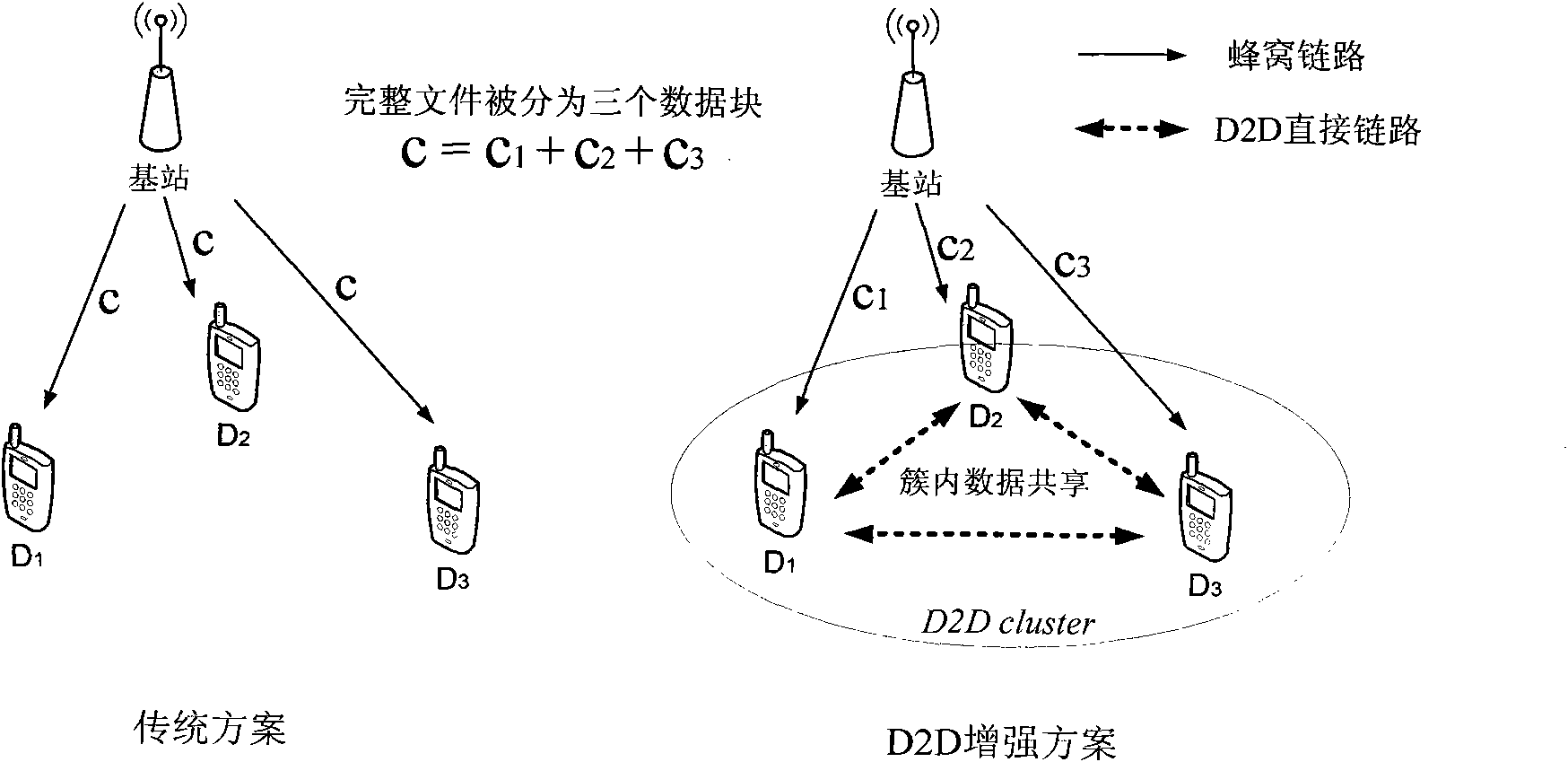
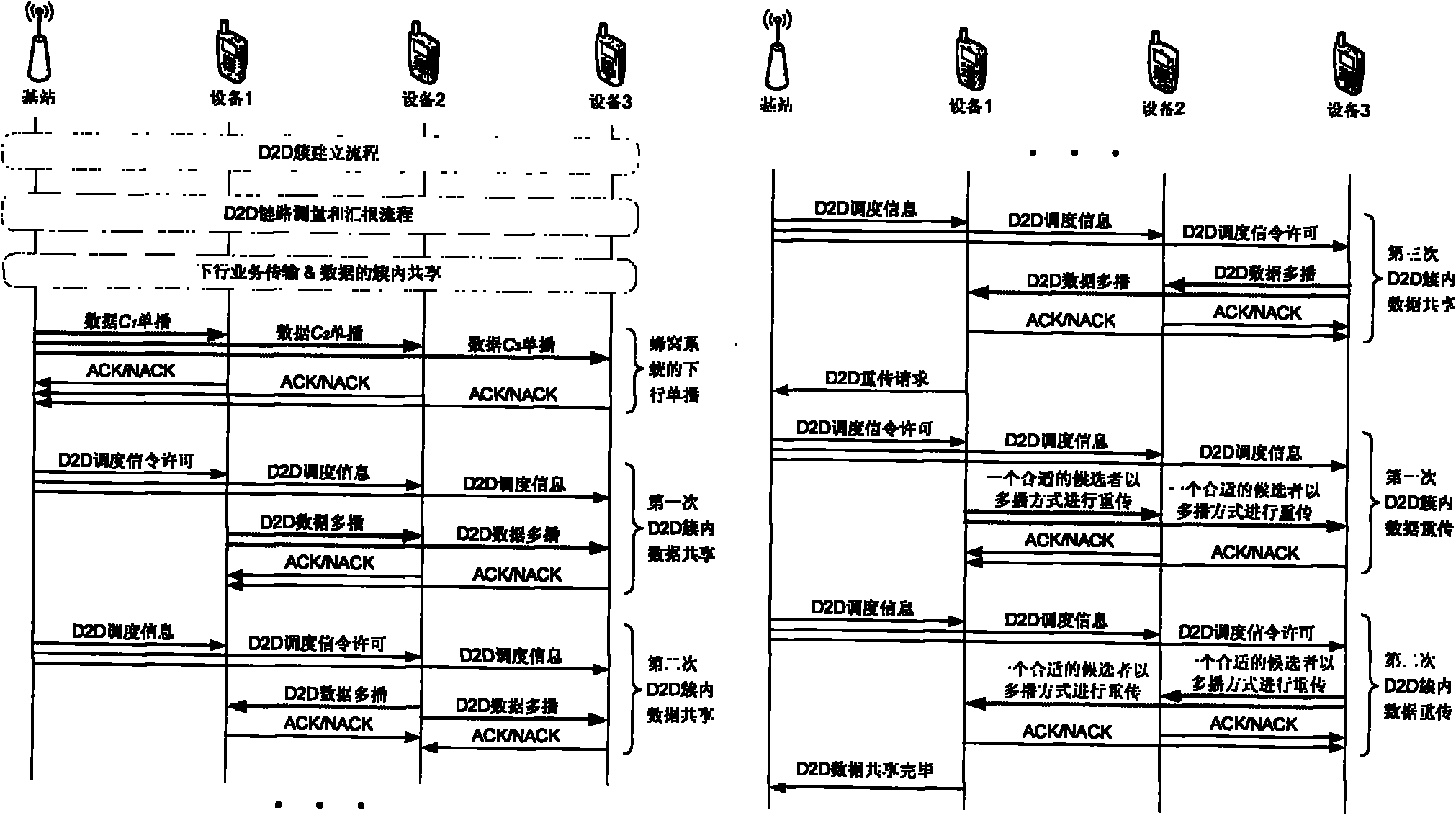
Device-to-device (D2D) cluster data sharing method under cellular environment
InactiveCN102340829AReduce the number of retransmissionsReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork packetSystem time
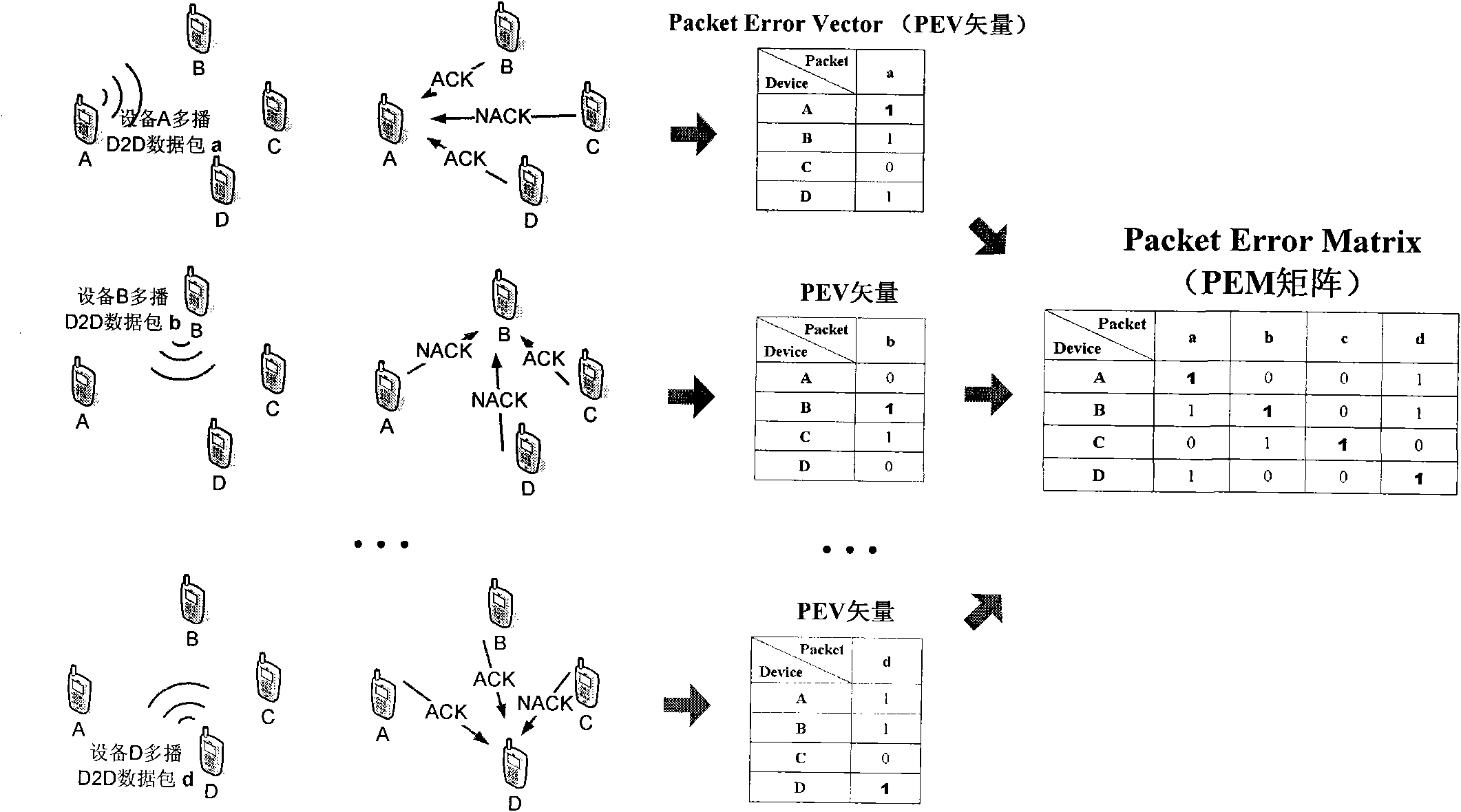
The invention discloses a device-to-device (D2D) cluster data sharing method under a cellular environment. The method comprises the following steps that: step1. before D2D cluster retransmission begins, each mobile equipment in the D2D cluster firstly acquires a packet error matrix (PEM) which belongs to the mobile equipment itself; step 2. a retransmission gain factor of the each mobile equipment in the D2D cluster is calculated; step 3. the mobile equipment with the highest retransmission gain factor is taken as a transmitter in the D2D cluster retransmission; step 4. the transmitter retransmits a data packet needed to be retransmitted in the cluster and updates the PEM of the each mobile equipment; step 5. if the updated PEM still contains a ''0'' element, the step 1 to the step 4 are repeated till the PEMs of all the mobile equipment in the D2D cluster are ''1'' matrixes. In the method of the invention, through effectively reducing retransmission times in the D2D cluster, related signaling costs of D2D communication under the cellular environment can be substantially saved and simultaneously system time delay can be shortened. The method is beneficial to realization of a real time multimedia service.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Method for transmitting real time multimedia datain ethernet network
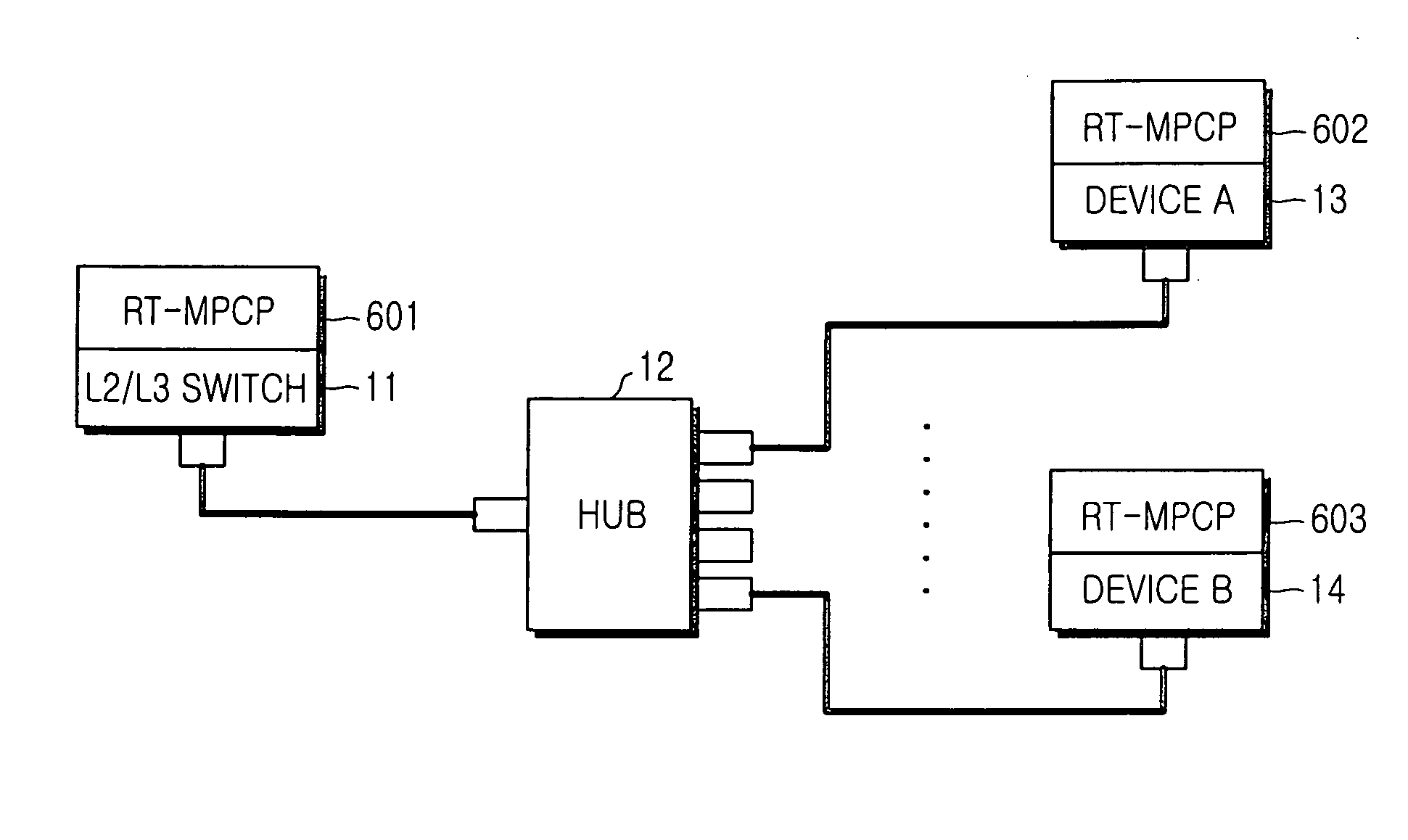
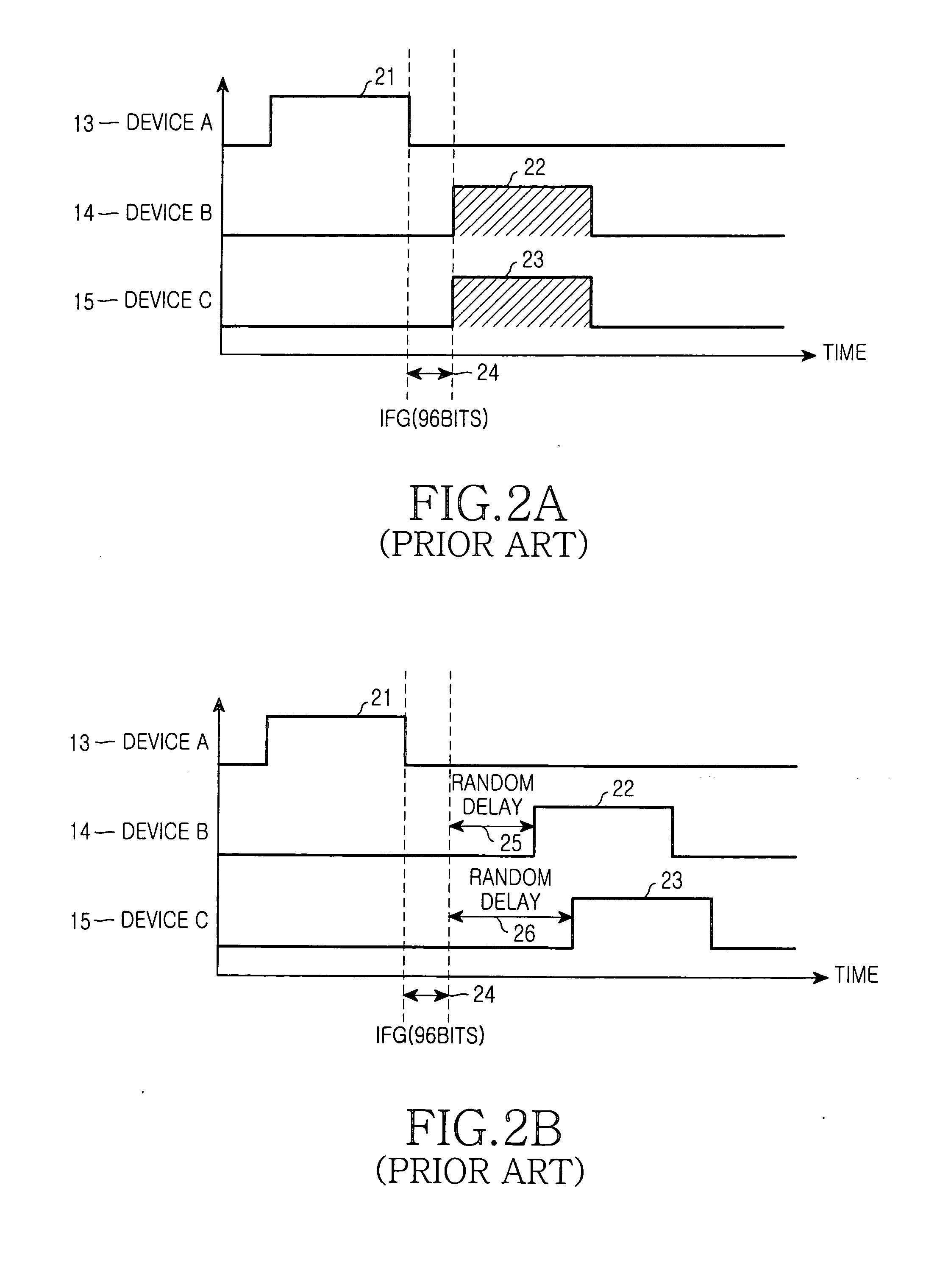
InactiveUS20050078682A1Delay the time of being blockedAvoid collisionStar/tree networksReal-time dataEthernet
A method for effectively implementing real time multimedia data transmission in an Ethernet network that operates in a CSMA / CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detect) scheme. Real time data gets priority over general data, and uses an MPCP (Multi-Point Control Protocol) of the IEEE 802.3ah EPON to prevent a collision from occurring in real time data transmission, and also prevents delay time variation. An RT-IFG (Real Time Inter-Frame Gap) is defined for real time data, shorter than an IFG, to give priority to the real time data over general Ethernet data. The MPCP is used for transmission of real time data without collision between the real time data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
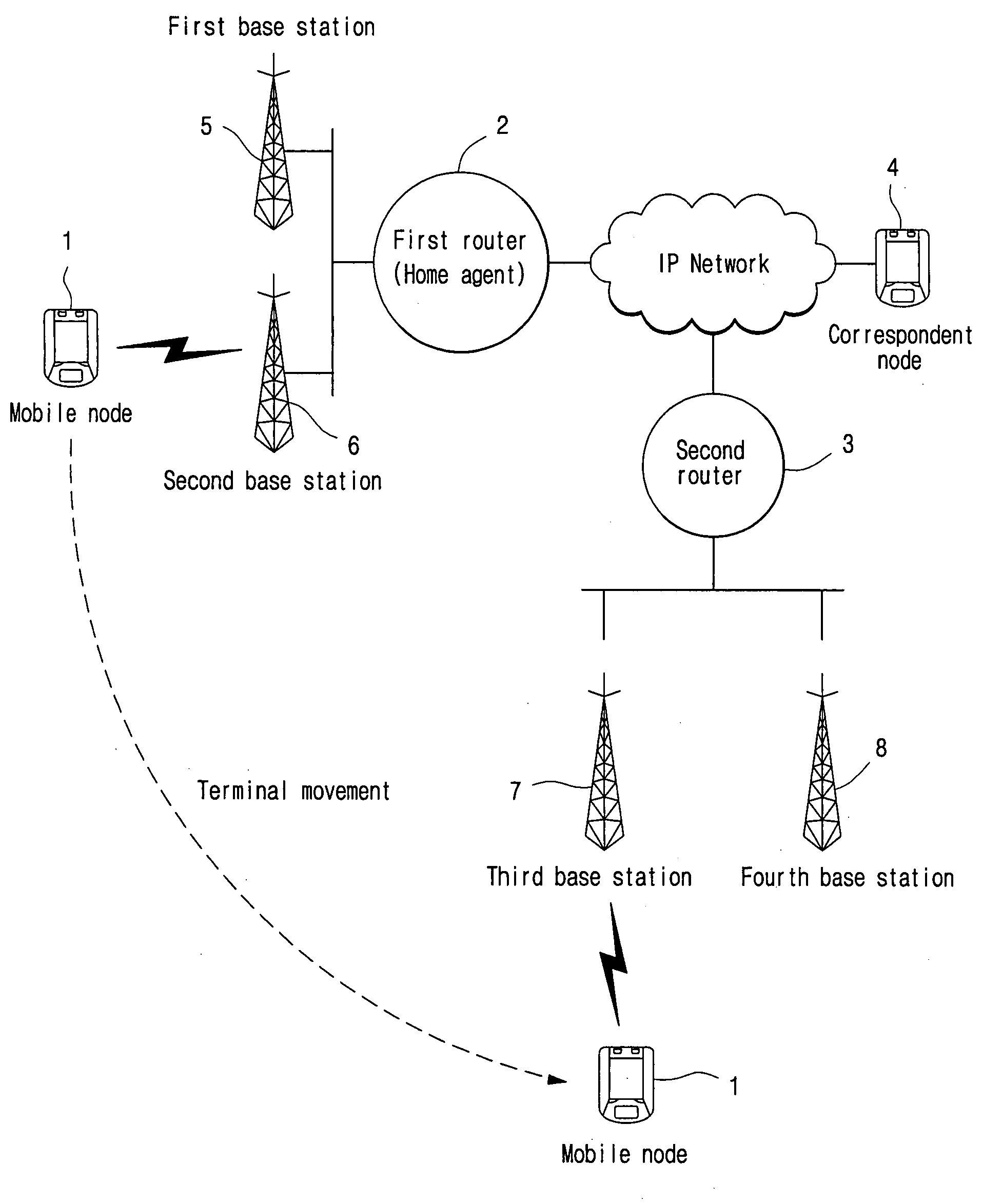
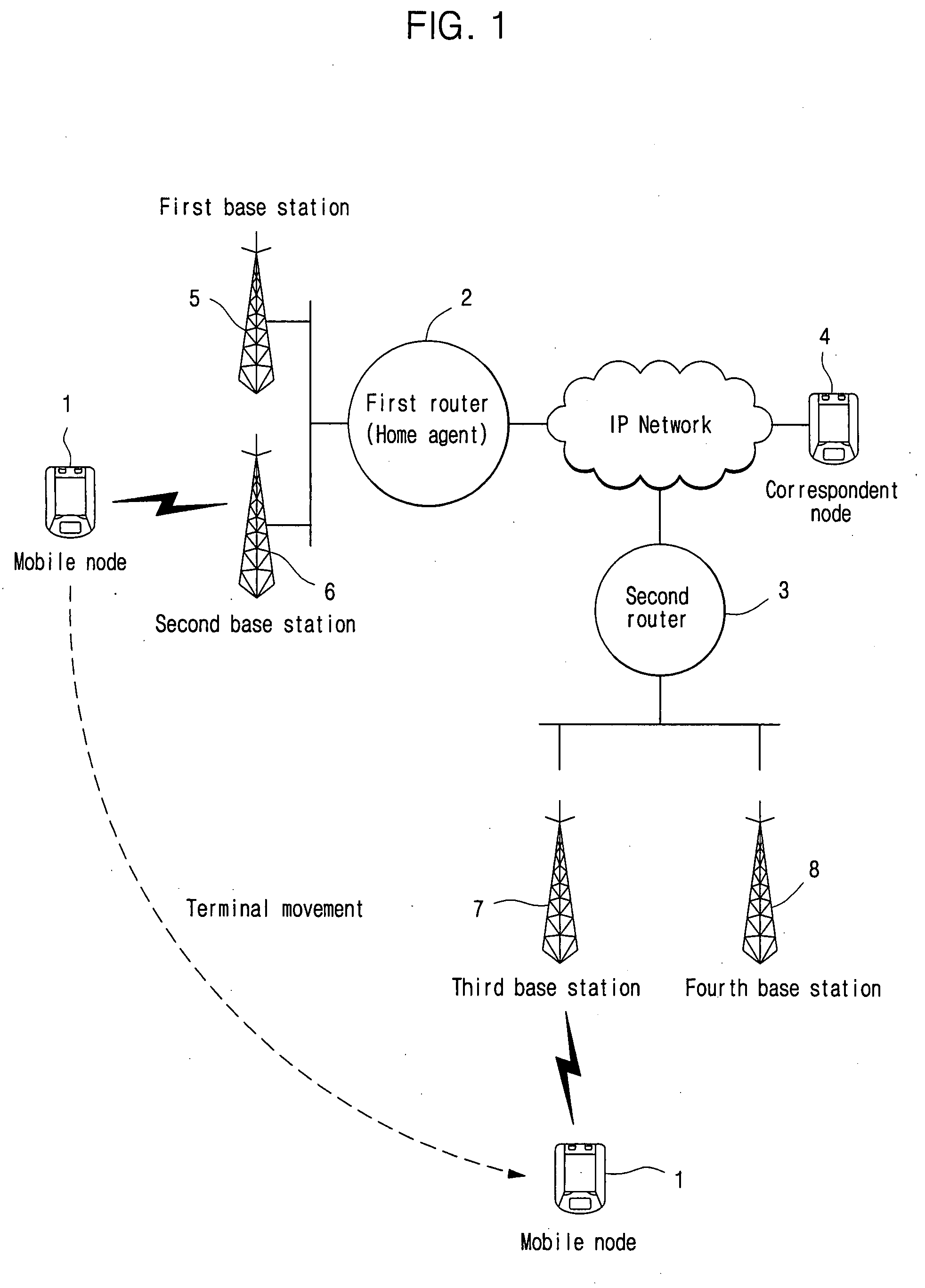
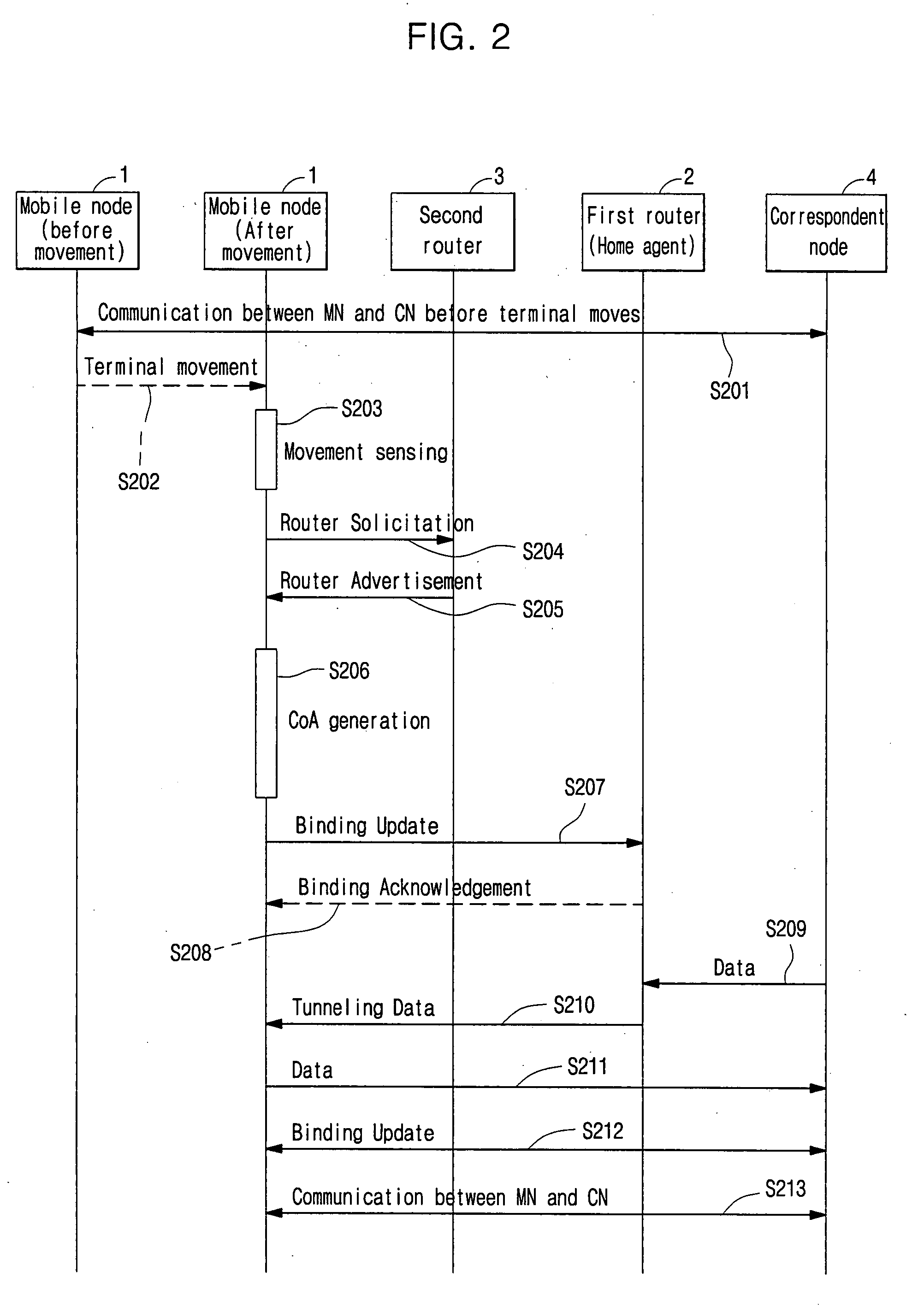
Apparatus and method for controlling layer 3 handover of mobile node
ActiveUS20070275726A1Faster handover of a mobile nodeAssess restrictionWireless network protocolsControl layerReporting state
A system and method for controlling layer 3 (L3) handover of a mobile node. A mobile Internet protocol (MIP) network includes a plurality of mobile nodes adapted to provide data service to a plurality of users, and a plurality of routers and a handover control system, the plurality of routers being adapted to provide data service to ones of the plurality of mobile nodes in coverage areas of a plurality of base stations managed by the plurality of routers, and to periodically report state information of the plurality of base stations and the plurality of routers to a handover control system, the handover control system being adapted to receive the state information of the plurality of base stations and the plurality of routers to produce a handover topology map, to map a current location of ones of the plurality of mobile nodes to the handover topology map to search for a plurality of target routers having a highest probability of handover of ones of the plurality of mobile nodes, and to transmit the state information of the searched plurality of target routers to the ones of the plurality of mobile nodes. Thus, the L3 handover time can be shortened to tens of ms or less, allowing for seamless real-time multimedia service even though a terminal moves.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Push-to-talk group call system using CDMA 1x-EVDO cellular network
InactiveUS7970425B2Reliable and fast transmissionShorten call setup timePower managementBroadcast transmission systemsRadio access networkPush-to-talk
A push-to-talk (“PTT”) group call system, for use as, e.g., a public safety wireless network, includes a CDMA-based 1x-EVDO radio access network operably connected to a PTT server over an IP network. The radio access network includes base stations for radio communications with a number of distributed mobile stations. In carrying out wireless communications, the group call system combines IP-based voice and other real-time multimedia services with the 1x-EVDO radio access network's Broadcast Multicast Service. This allows a number of users to receive the same copy of an IP-based media stream for point-to-multipoint, group transmissions. To reduce call setup times, the group call system uses “standing” call groups, which are ongoing group communication channels pre-established between the PTT server and authorized group users. Thus, mobile stations link to one or more standing call groups of interest upon power-up, prior to users speaking.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
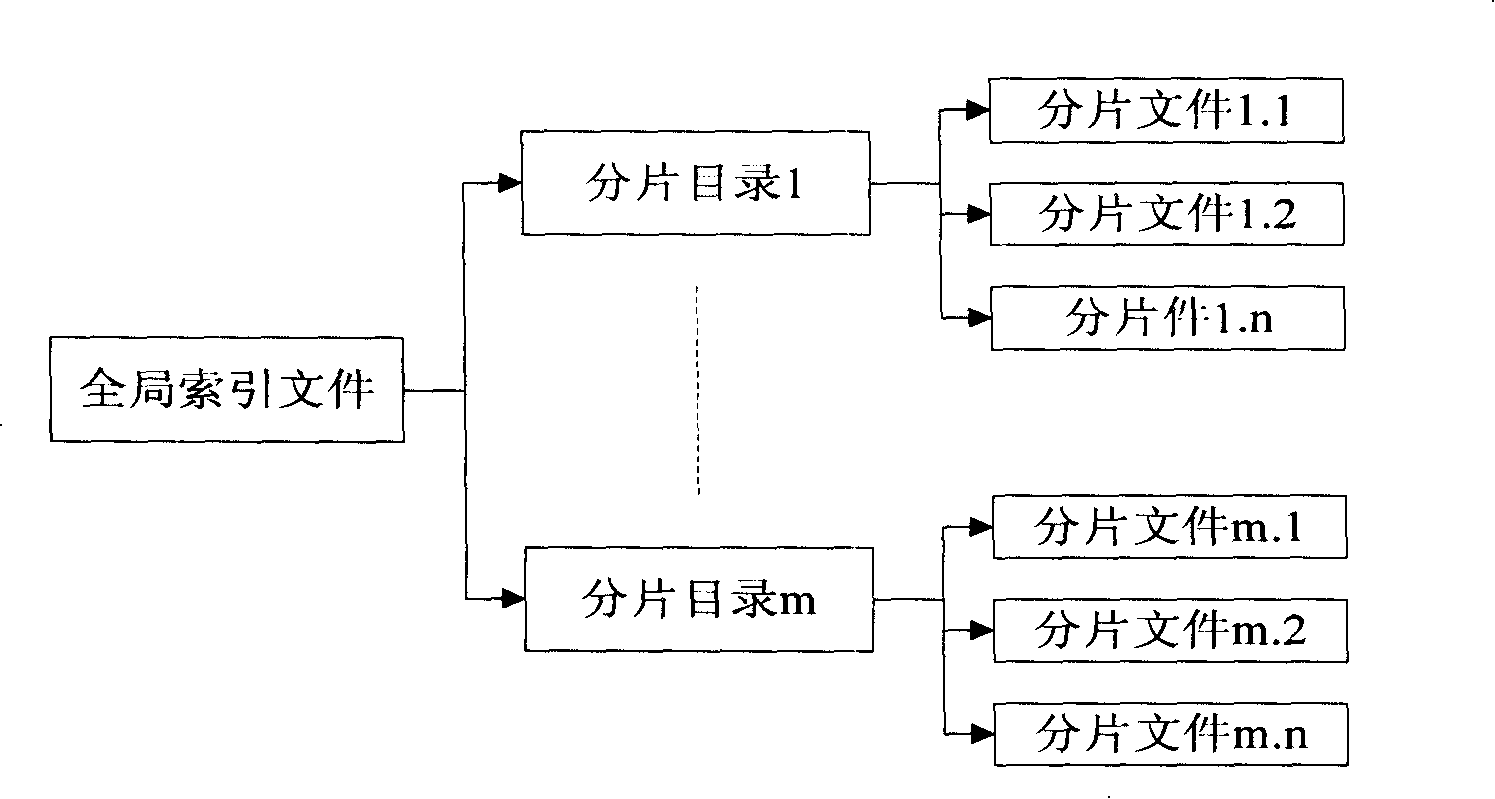
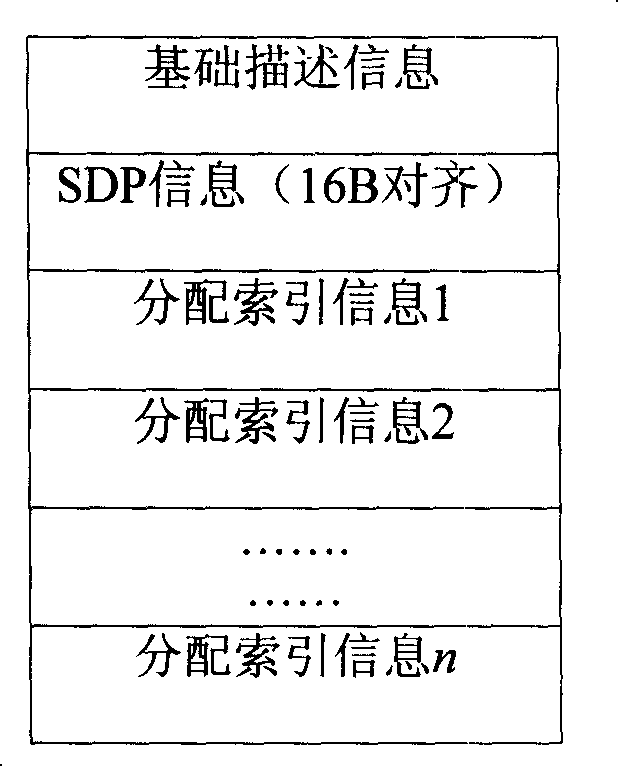
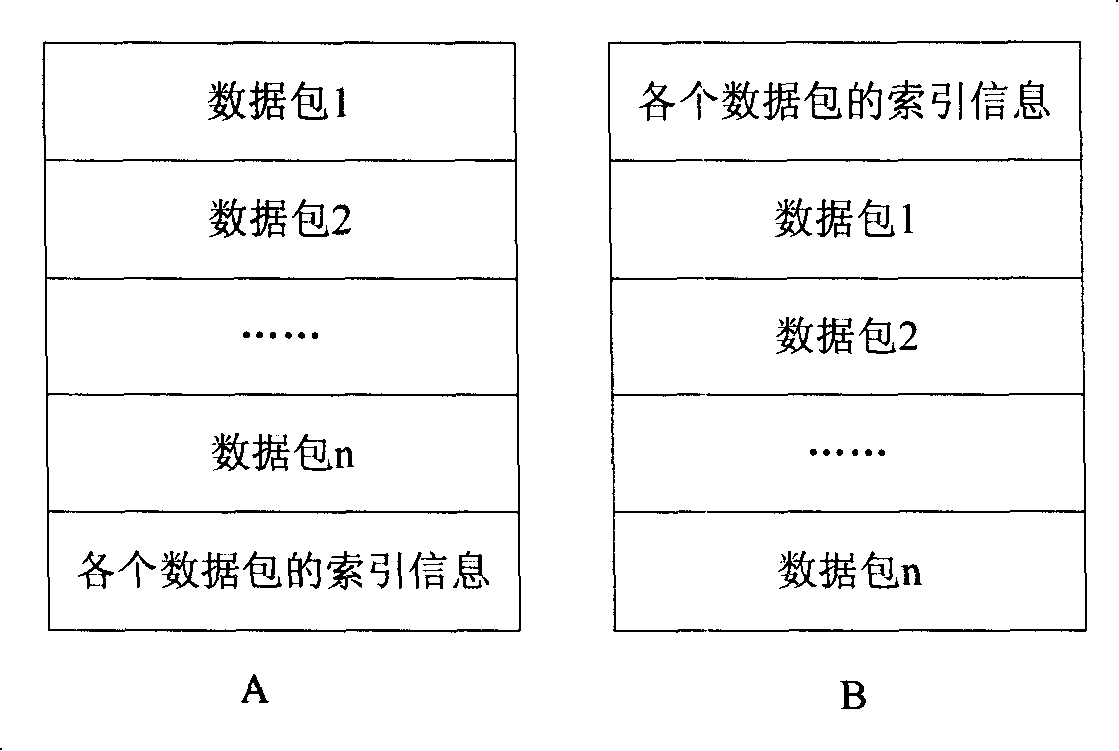
A storage and playing method for real time multimedia image information
InactiveCN101193273ASimple storage formatCutting costsCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingTwo-way working systemsNetwork packetDatabase
The invention discloses a method for real-time storing and playing multimedia image information. The method for storing includes the following steps: (a) a slicing base directory is established according to names of stored files, and a global index file is established in the slicing base directory; information of a session description protocol in a multimedia file and index information of a slicing file are stored in the global index file, the session description protocol is called as SDP information for short hereinafter; (b)according to the regulation recorded in the index information of the slicing file in the global index file, a directory of the slicing file is established; and (c) the slicing file is established under the directory of the slicing file, and the slicing file includes the index information of each media data packet and the content of each data packet. The method for playing utilizes the global index and a slicing index to position the data packet so as to carry out the operation of playing. By adopting the method in the invention, the storage of file has simple format with small difficulty for implementation, and the cost of the storage device is saved; meanwhile, the experience and feeling of users on the media program is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
System and method of network adaptive real-time multimedia streaming
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multimedia data sharing method, system and state judgment server
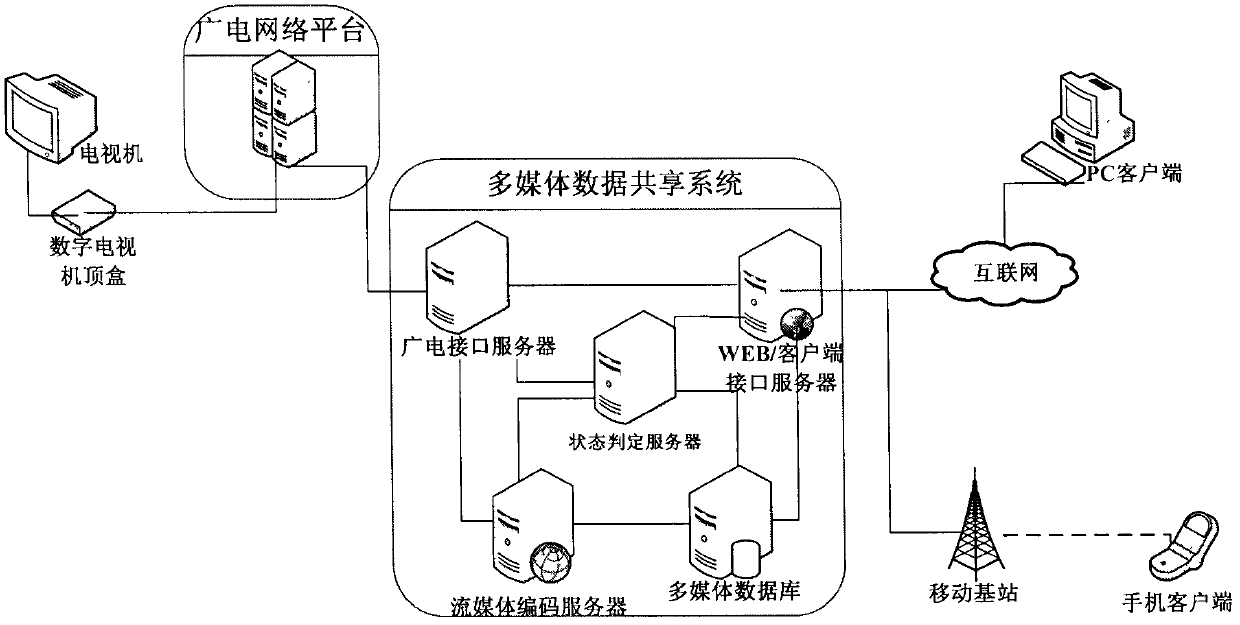
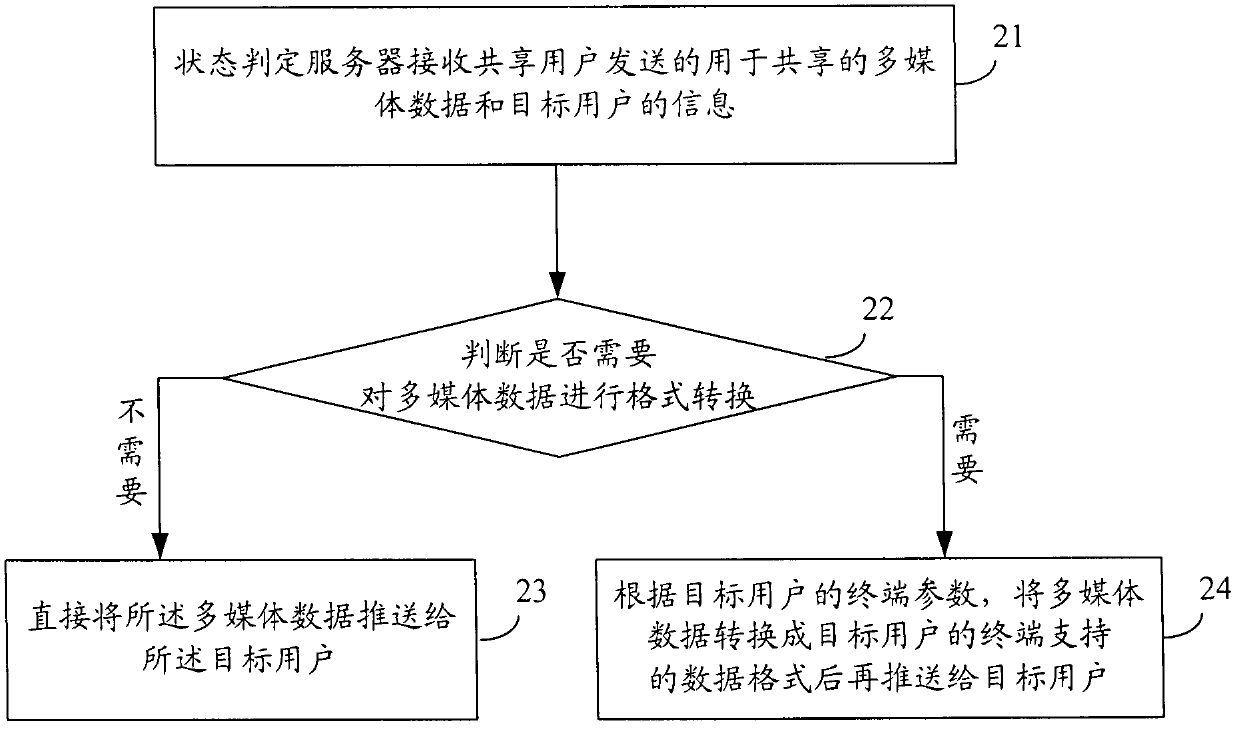
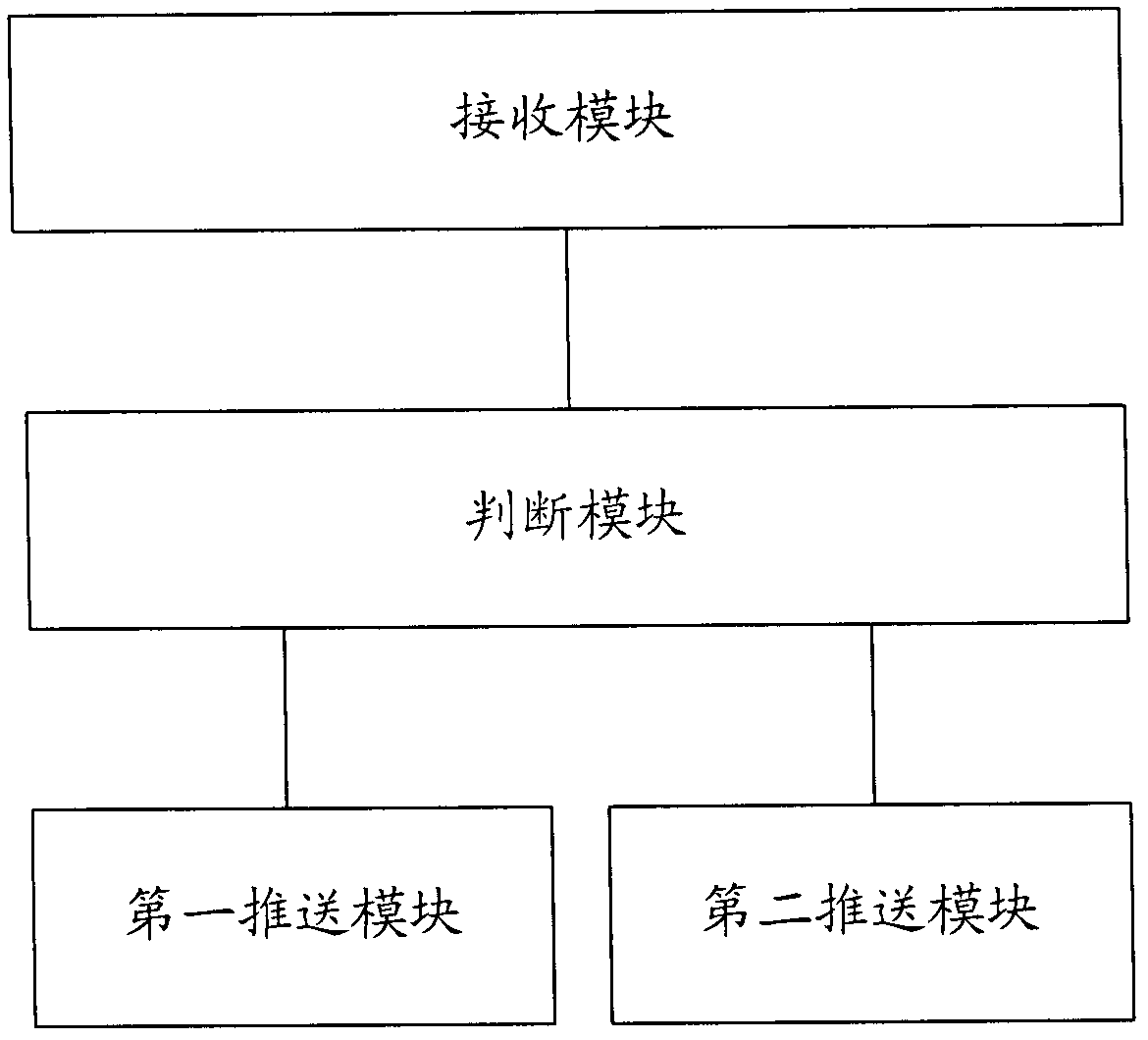
The invention provides a multimedia data sharing method, system and state judgment server. The method comprises the steps that: the state judgment server receives sharing multimedia data and object user information sent by a sharing user; the state judgment server judges whether to carry out format conversion according to the user state of the sharing user and the object user, wherein the user state comprises an logging-in state and terminal parameters, and the logging-in state is used for presenting that the user logs-in from a broadcasting television network, a telecommunication network or an internet; when the multimedia data does not need format conversion, the multimedia data is directly pushed and transmitted to the object user; and when the multimedia data needs format conversion, the multimedia data is converted into data format supported by a terminal of the object user according to the terminal parameters of the object user, and then pushed and transmitted to the object user. According to the invention, simple, convenient and real-time multimedia data sharing among different network terminals can be realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP GUANGDONG CO LTD
System and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time multi-media flows
InactiveUS20060187927A1Data switching by path configurationAutomatic exchangesTransceiverMulti protocol
A system and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time transport protocol (RTP) multi-media flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor configured by the software. The processor is configured to perform the steps of, performing flow processing on a data packet received at a first endpoint, from a second endpoint, removing a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) tag from the data packet, translating a source address and destination address of the data packet, and determining a forwarding destination if more than one destination address of the data packet is provided.
Owner:ACME PACKET
Distributed live multimedia monetization mechanism and network
InactiveUS20090089162A1AdvertisementsSelective content distributionNetwork methodReal time multimedia
Methods, systems and computer readable media for managing monetization of live multimedia content include receiving multimedia content from capturing devices in substantial real-time. The capturing devices identify a type of content being captured or location of capture. One or more promotional media from the multimedia content are identified. The identified promotional media is matched with one or more promotional advertisements. The identified promotional media is integrated with the one or more promotional advertisements to generate a composite multimedia stream and the composite multimedia stream is presented to receiving devices in substantial real-time as well as over time. Monetization revenue based on interactions at the receiving devices is tracked. The monetization revenue depends on monetization criteria associated with the promotional media of the multimedia content.
Owner:OATH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com