Patents
Literature
983results about "Apparatus for flat record carriers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
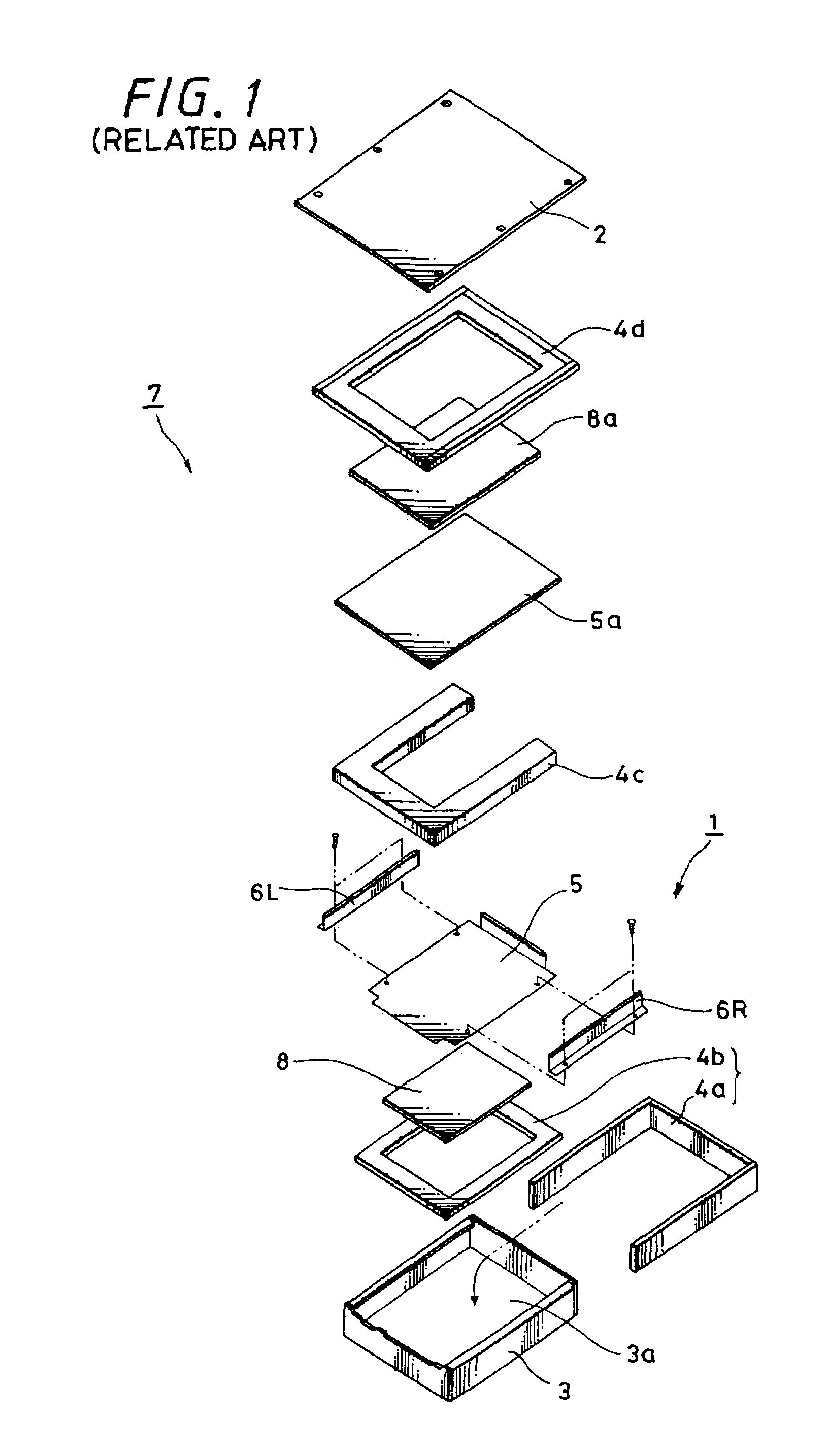
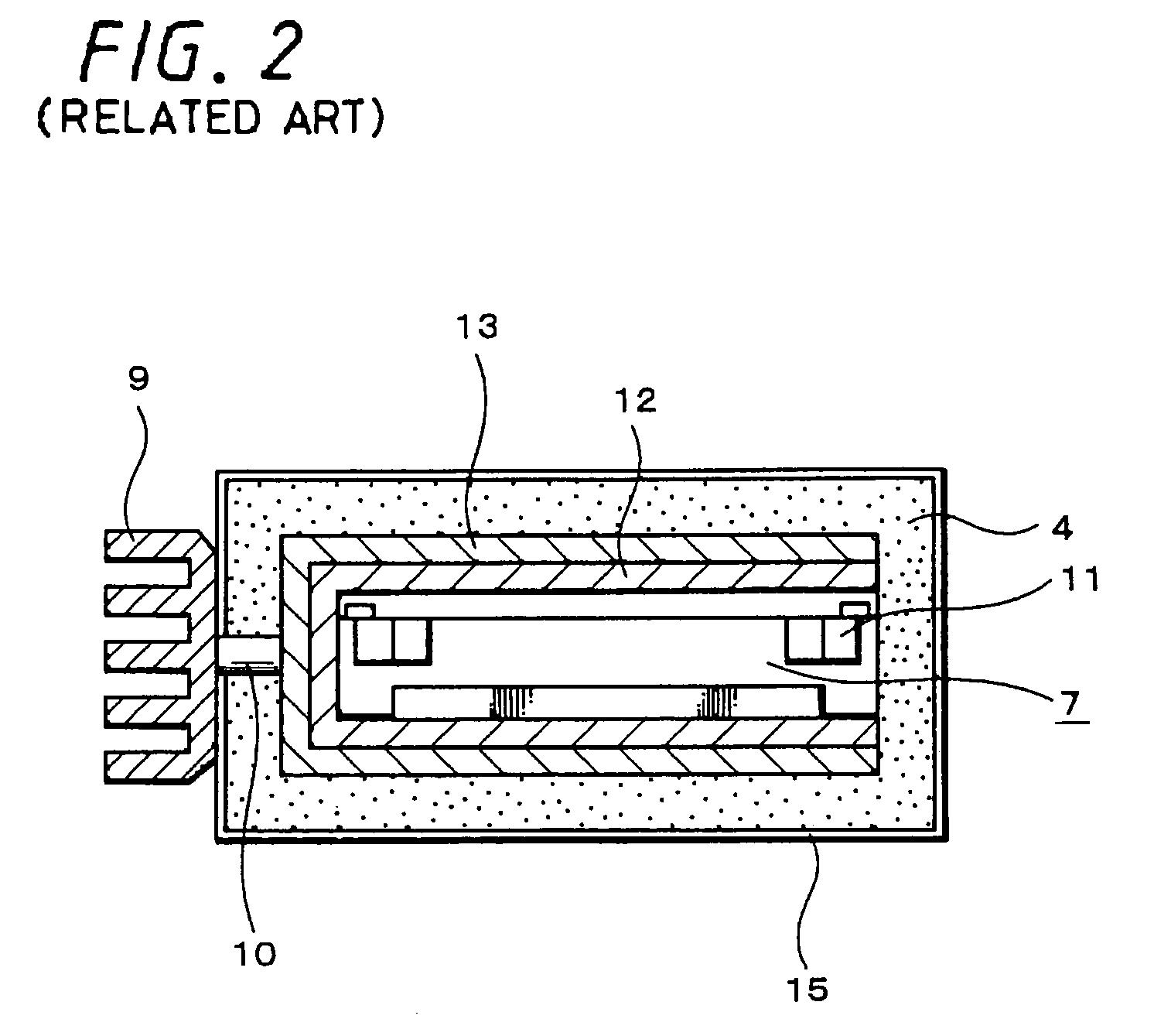
Programmable magnetic data storage card
ActiveUS7044394B2Reduce financial riskSimple and inexpensive and effectiveAcutation objectsApparatus for flat record carriersMicrocomputerComing out
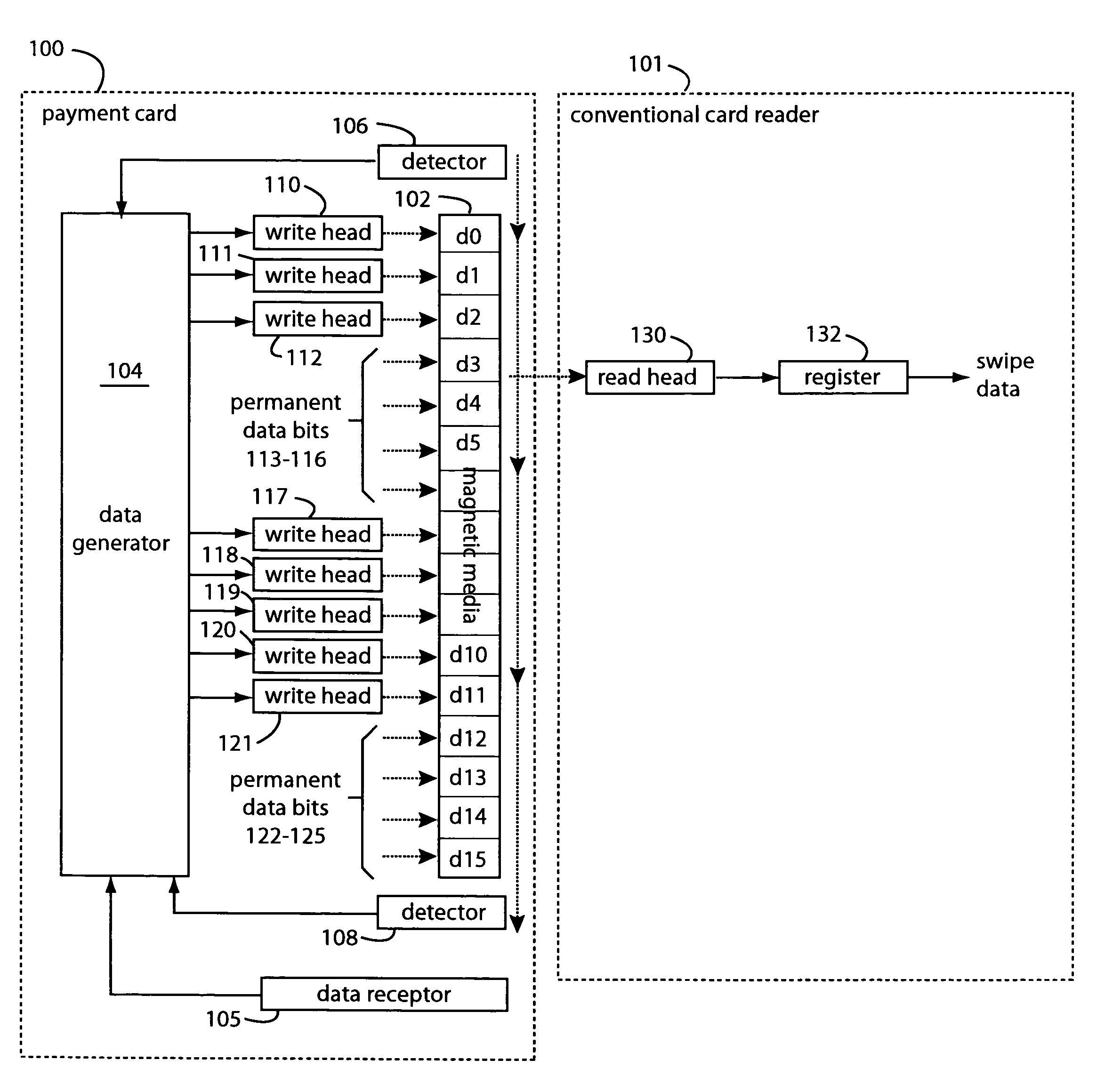
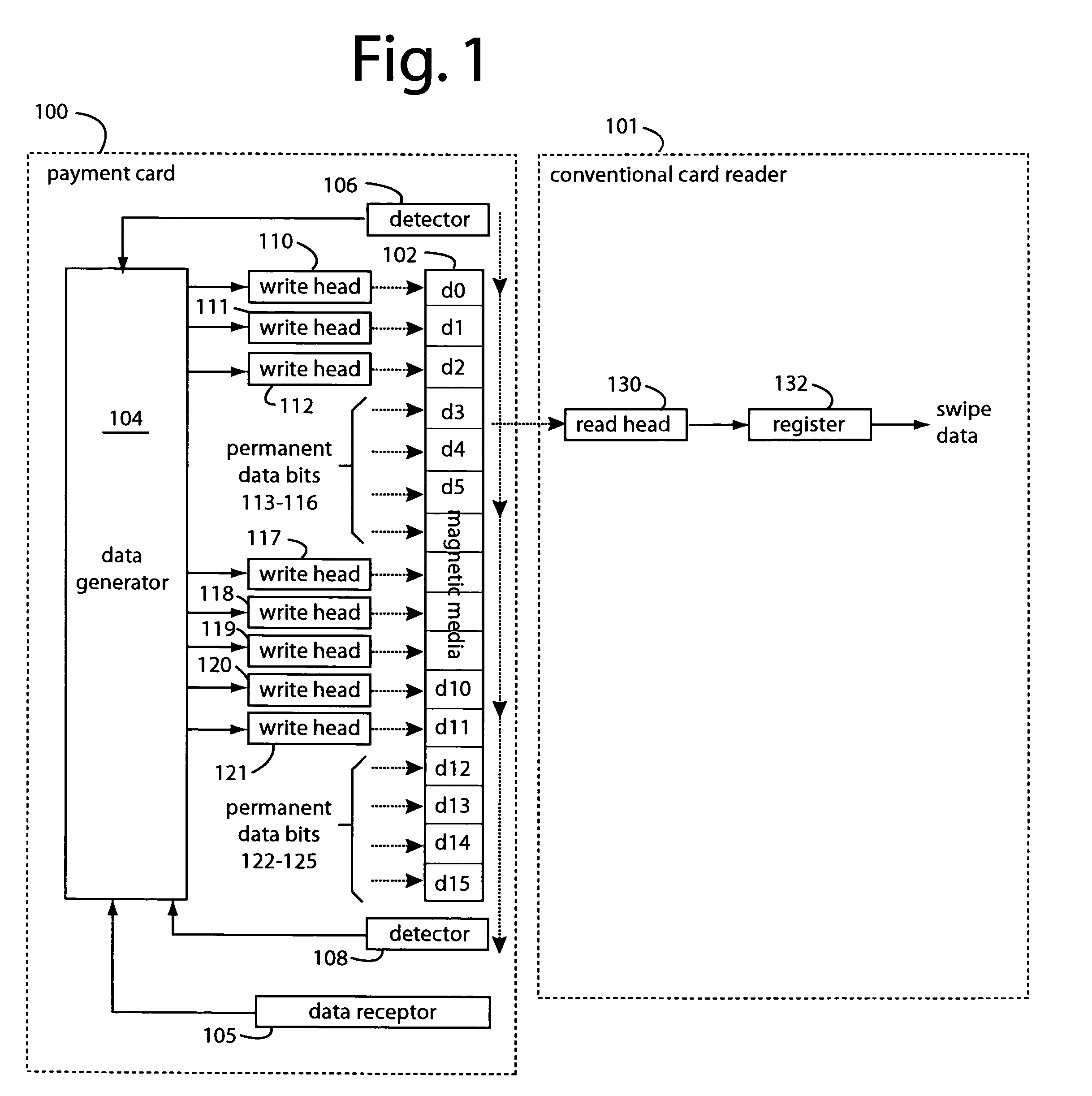
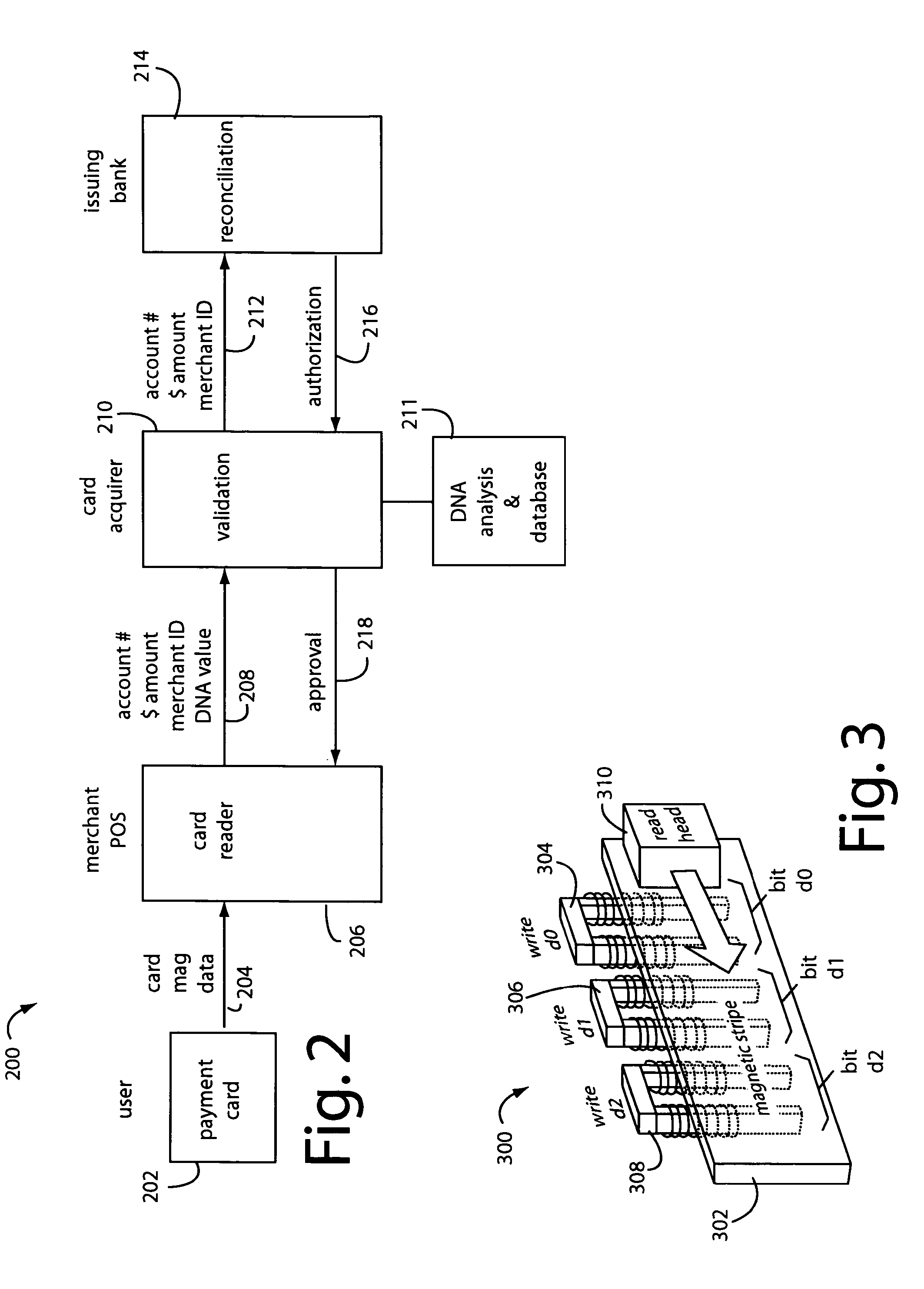
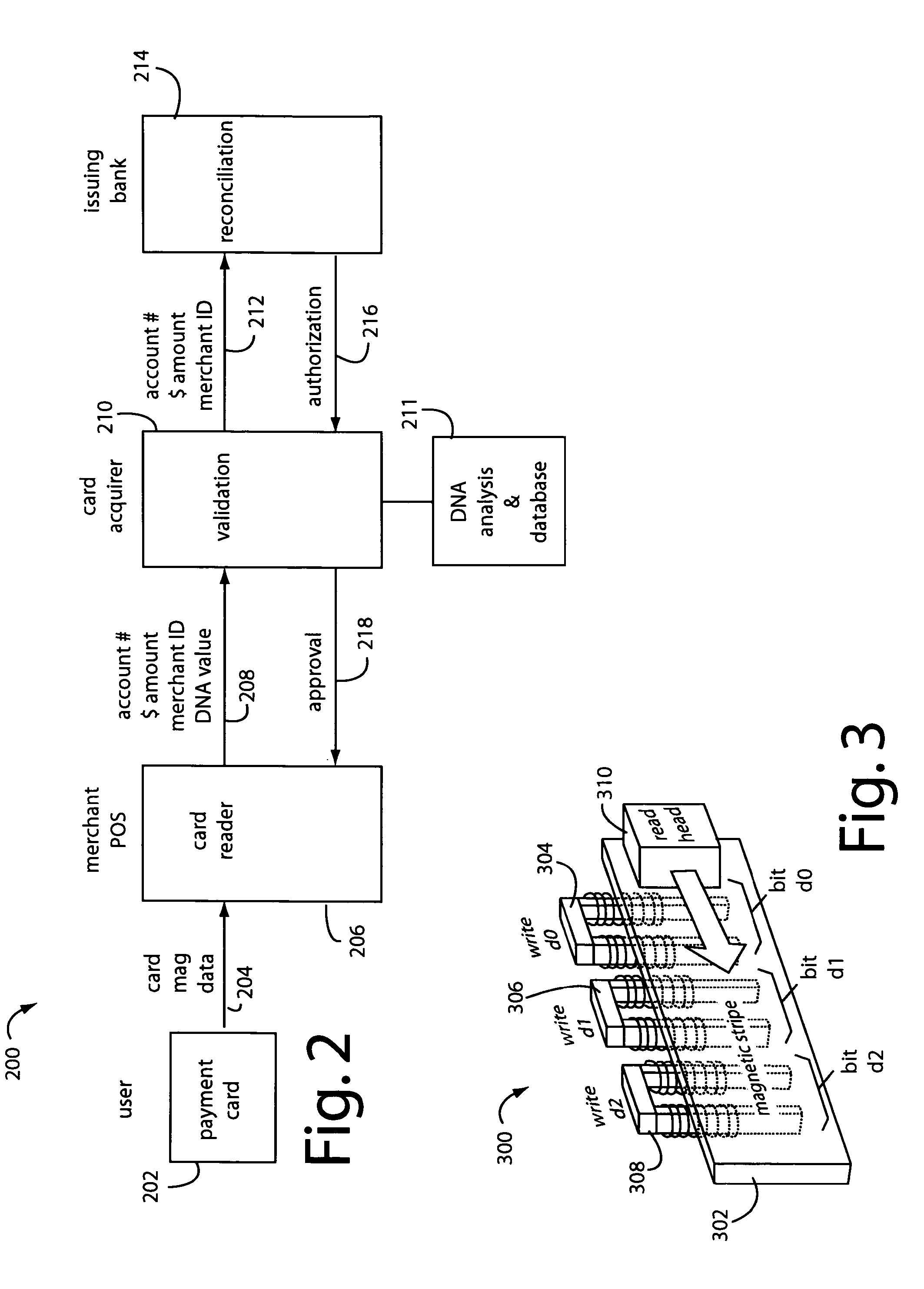
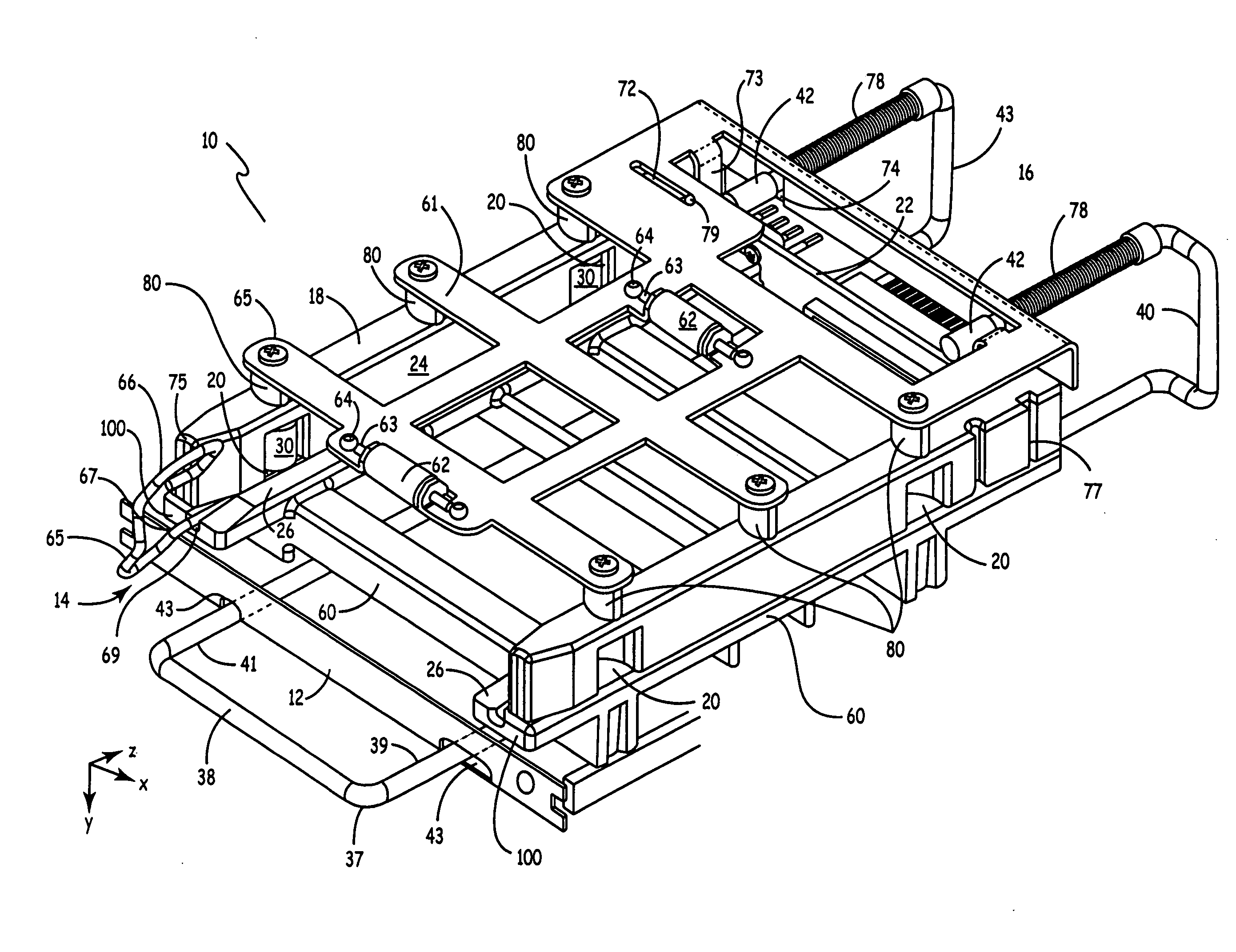
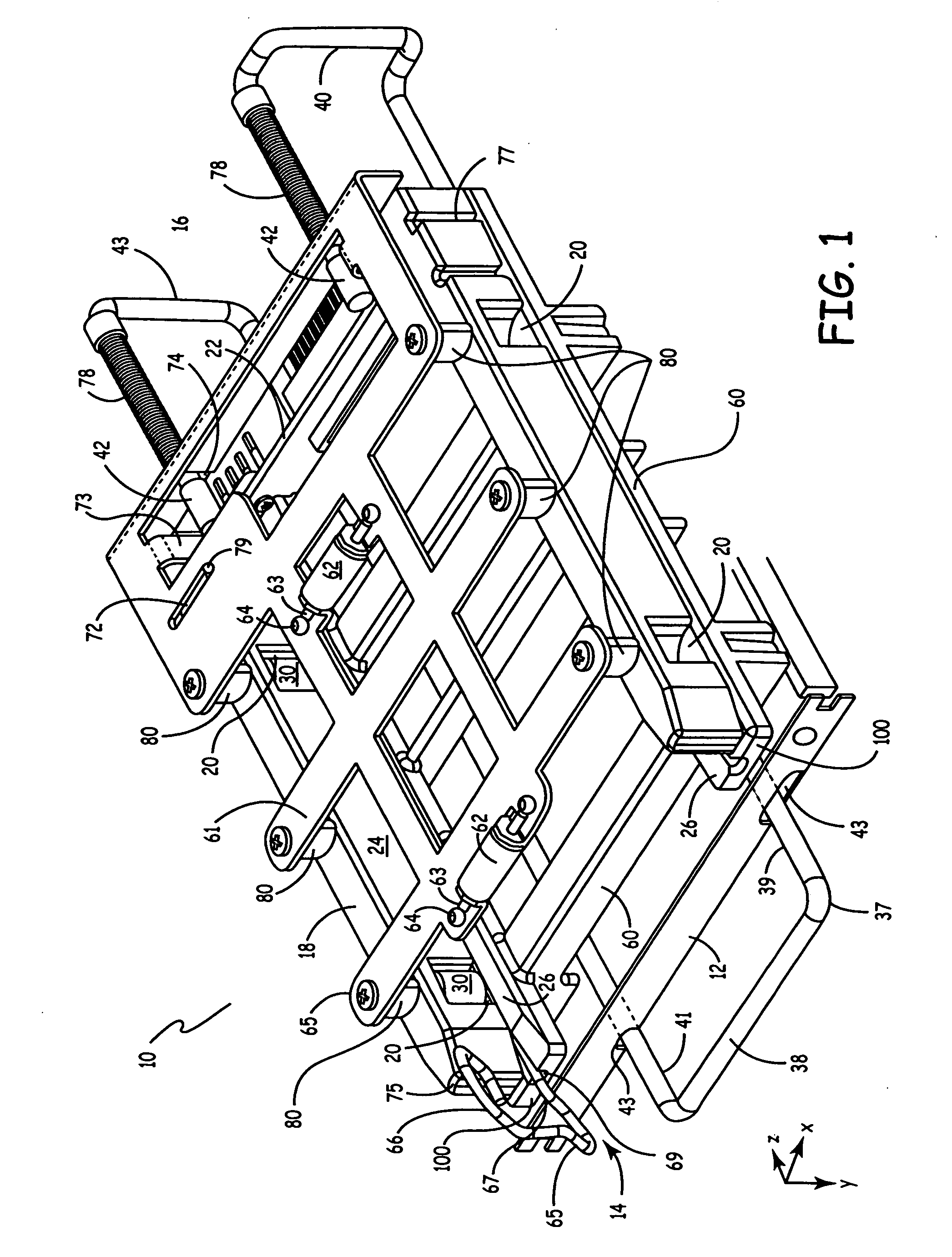
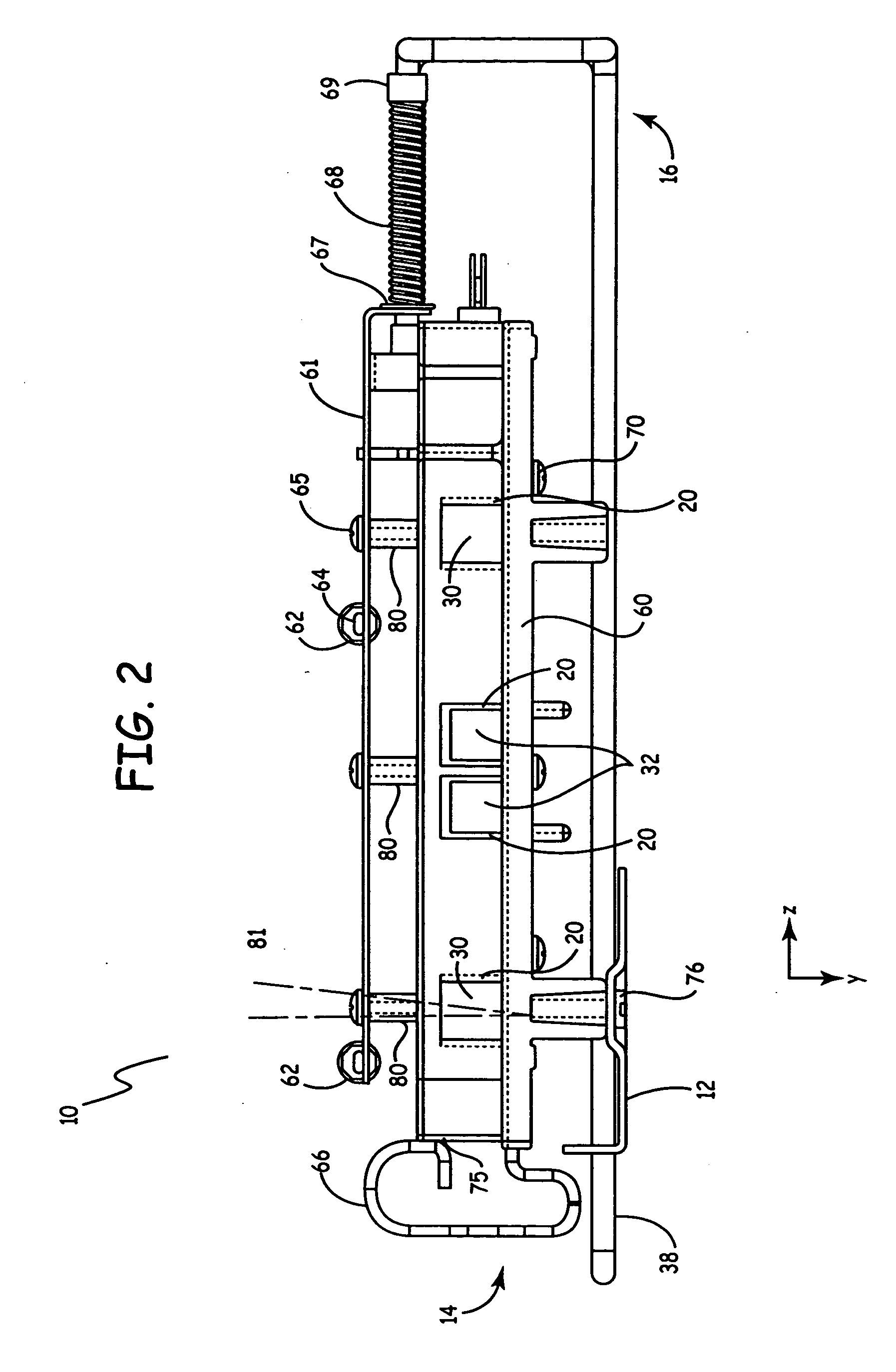
A payment card comprises a plastic card with a magnetic stripe for user account data. Internal to the plastic card, and behind the magnetic stripe, a number of fixed-position magnetic write heads allow the user account data to be automatically modified. For example, a data field that counts the number of times the card has been scanned is incremented. A payment processing center keeps track of this usage-counter data field, and will not authorize transaction requests that come out of sequence. For example, as can occur from a magnetic clone of a card that has been skimmed and tried later. A card-swipe detector embedded in the plastic card detects each use in a scanner, and it signals an internal microcomputer which changes data bits sent to the write heads. Once scanned, the payment card can also disable any reading of the user account data for a short fixed period of time.
Owner:FITBIT INC
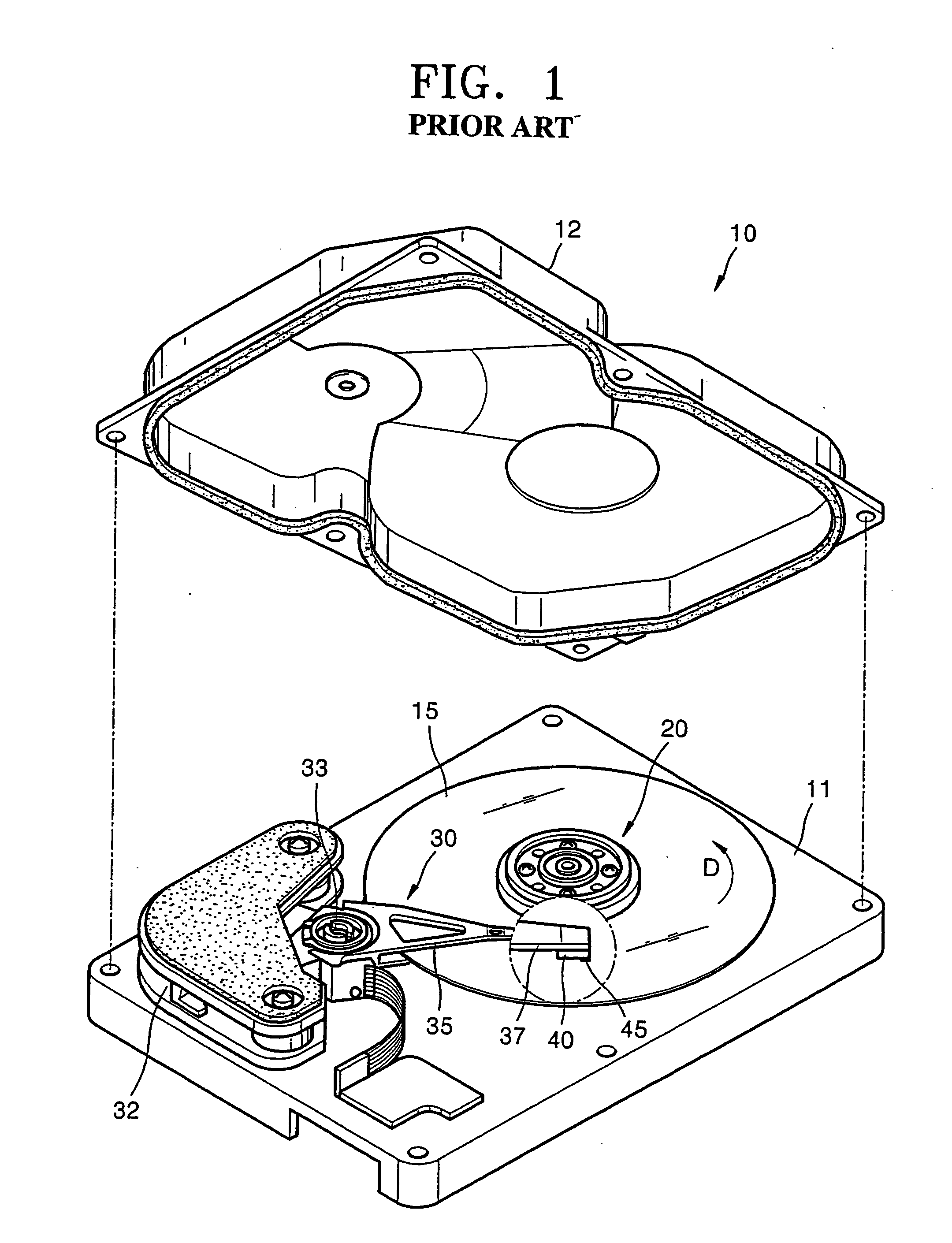
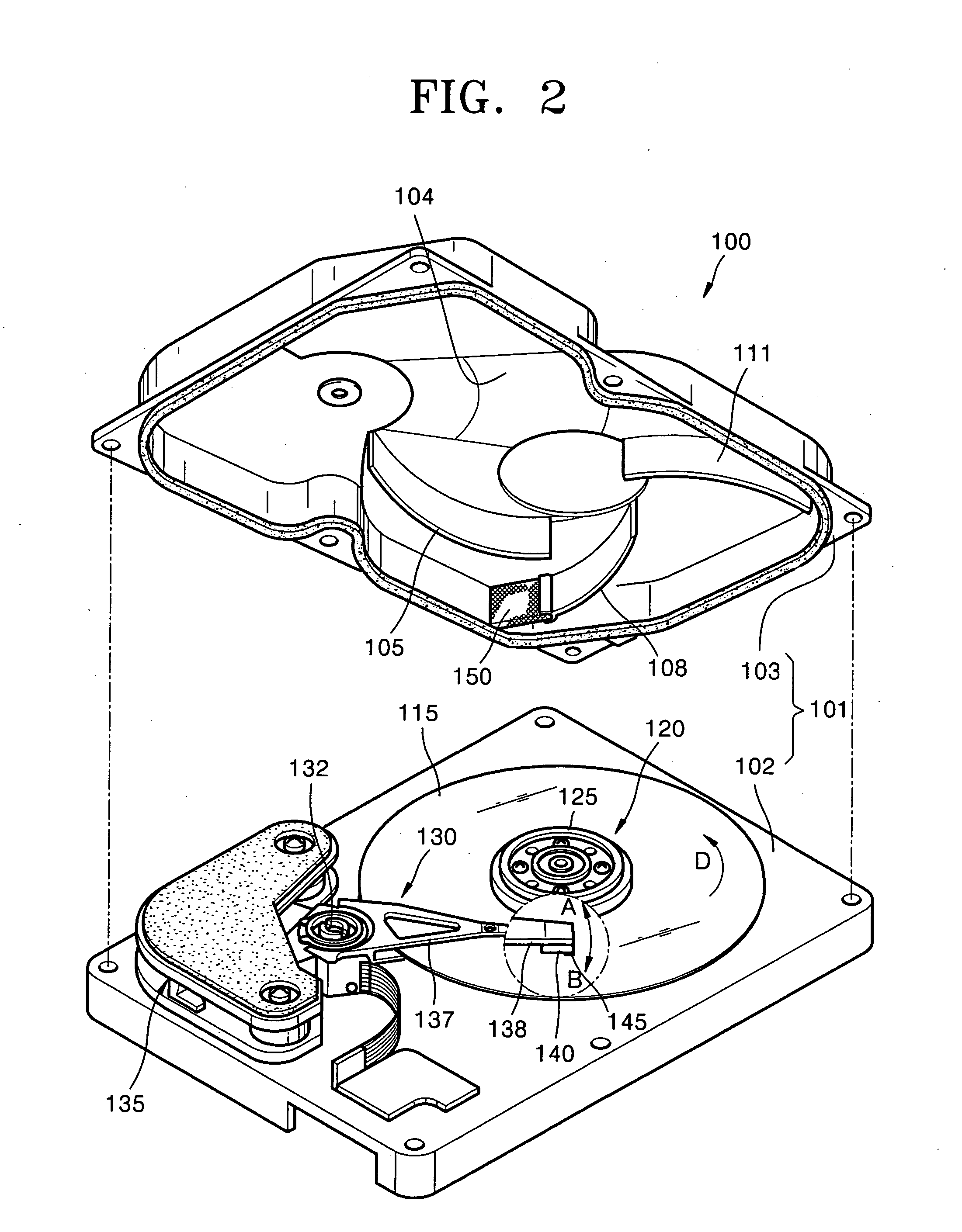
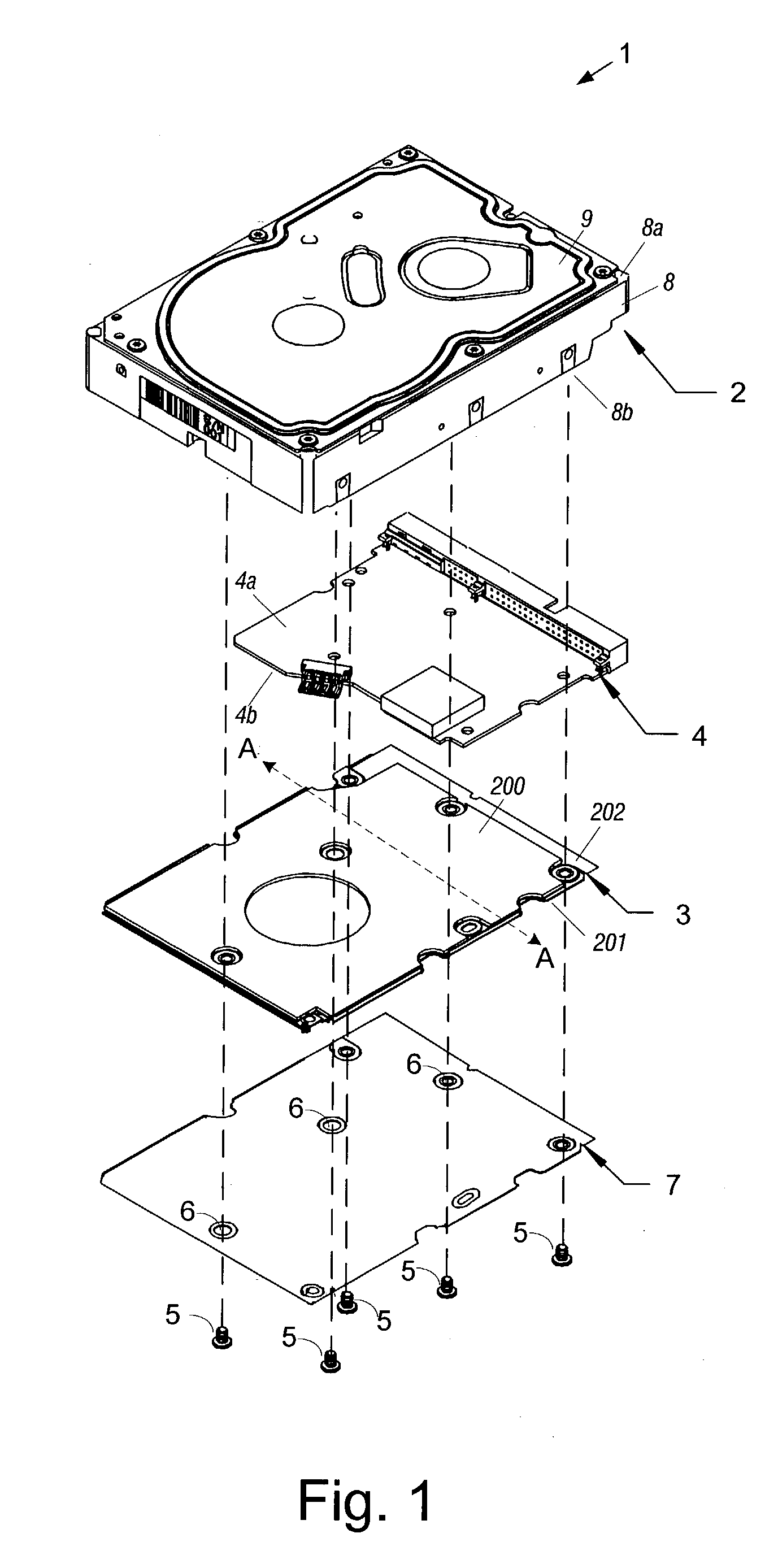
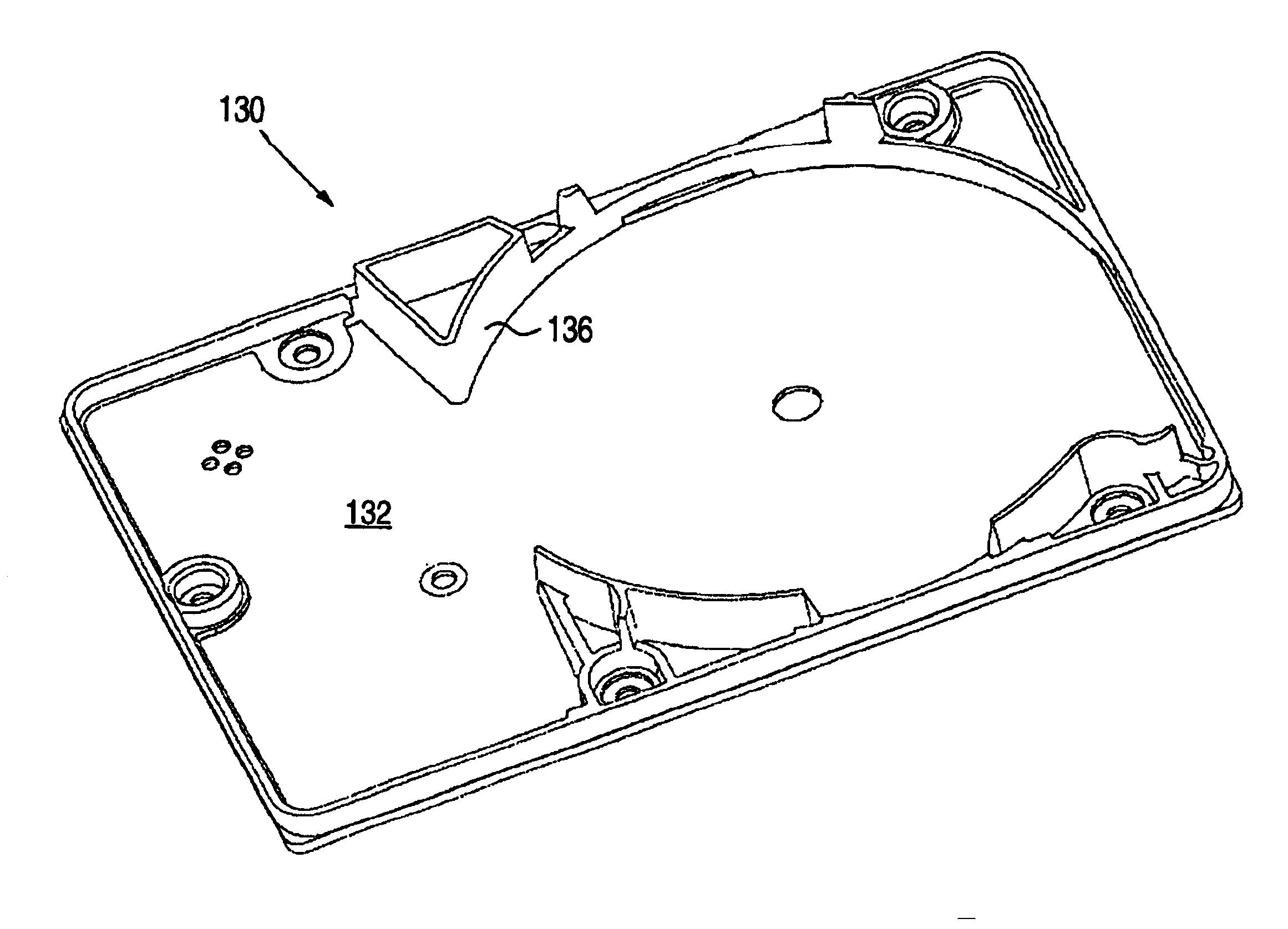
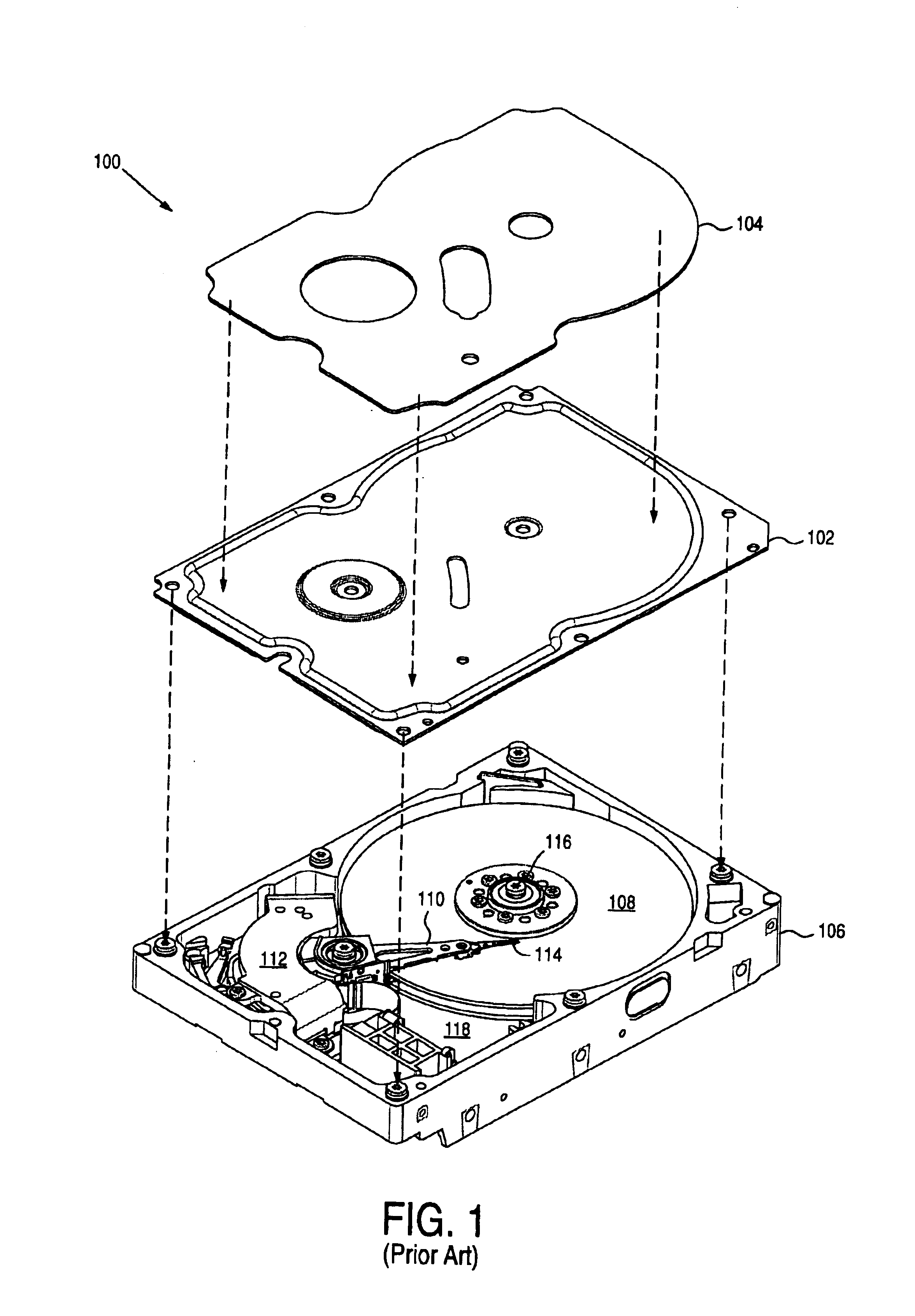
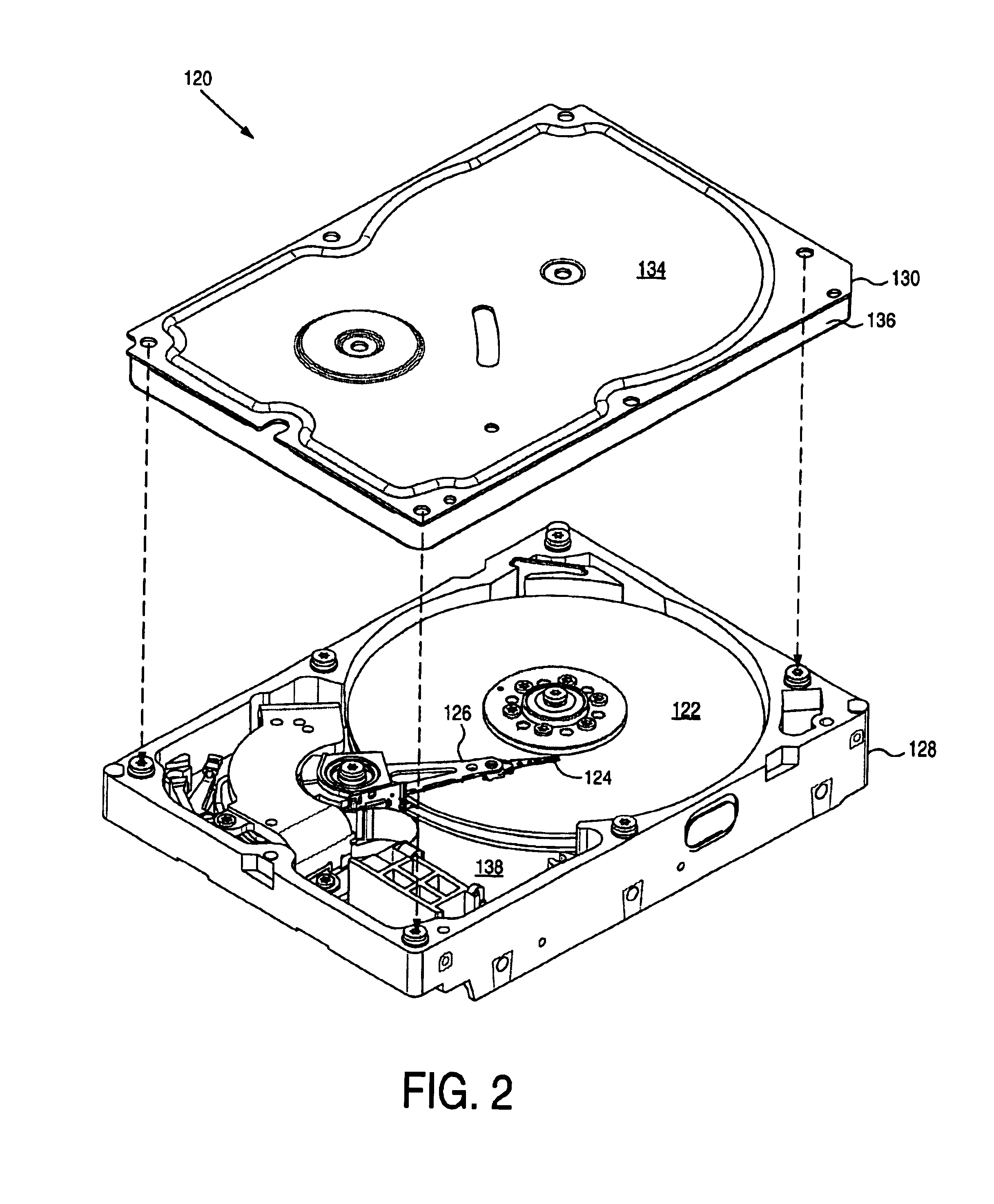
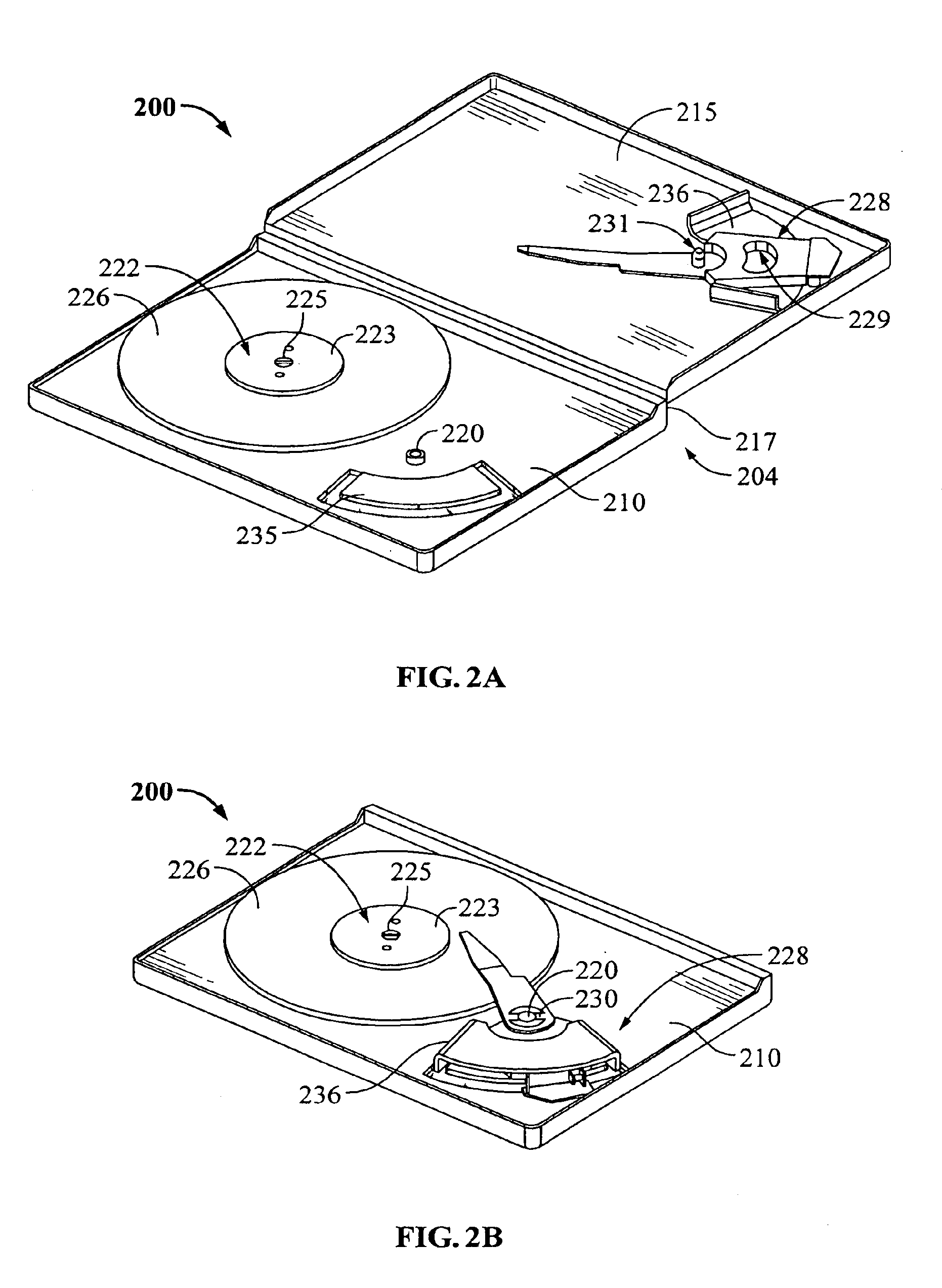
Hard disk drive
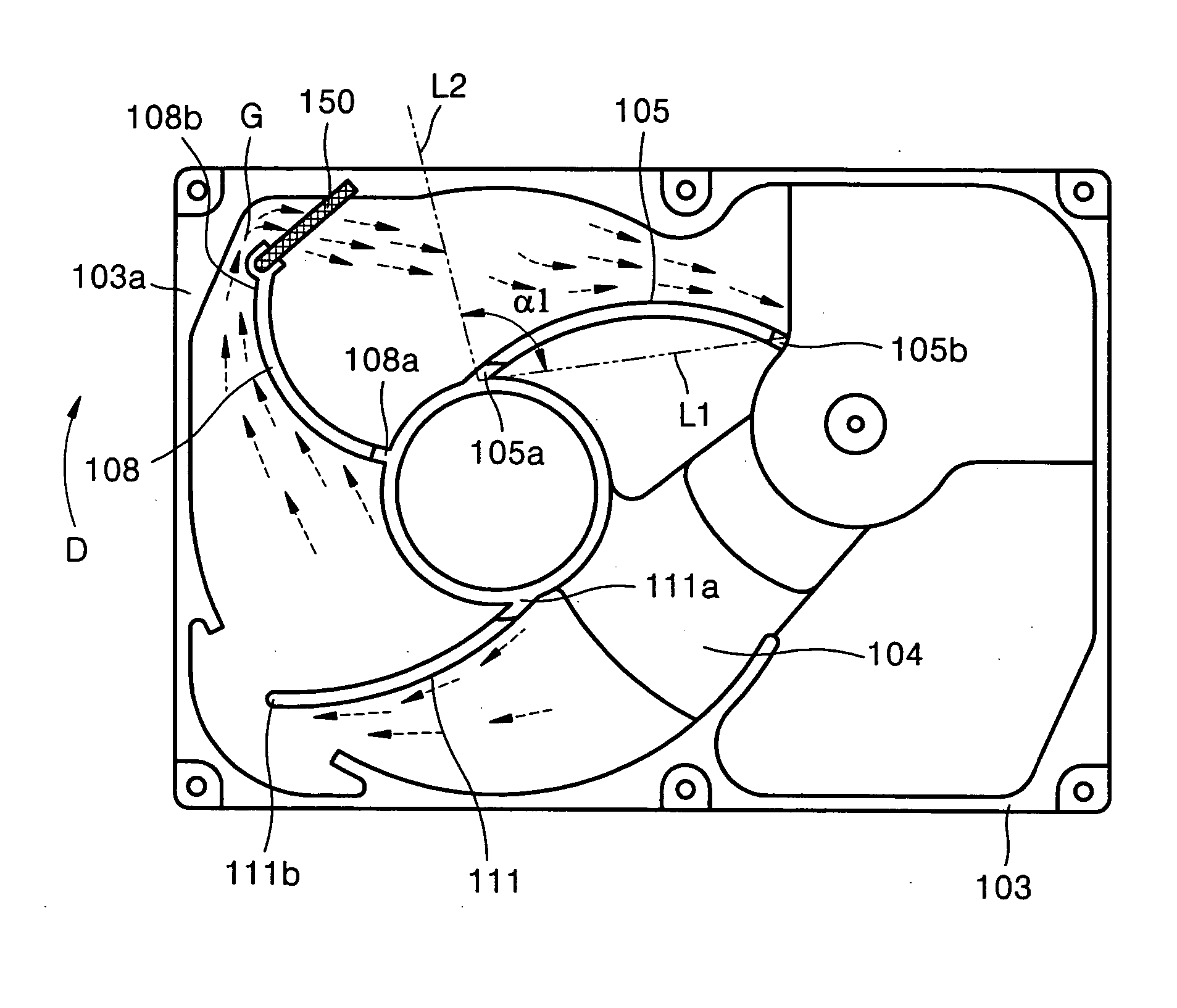
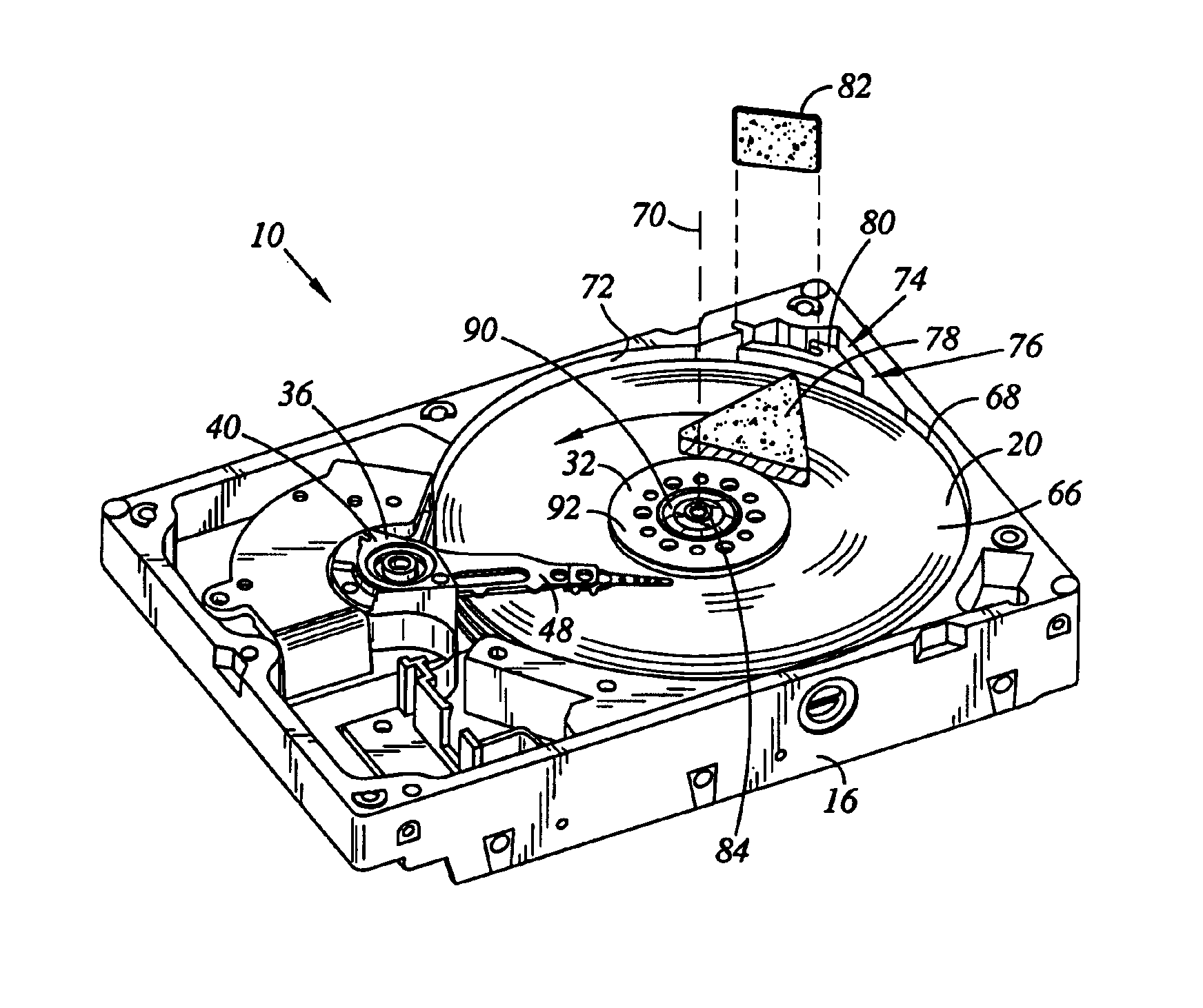
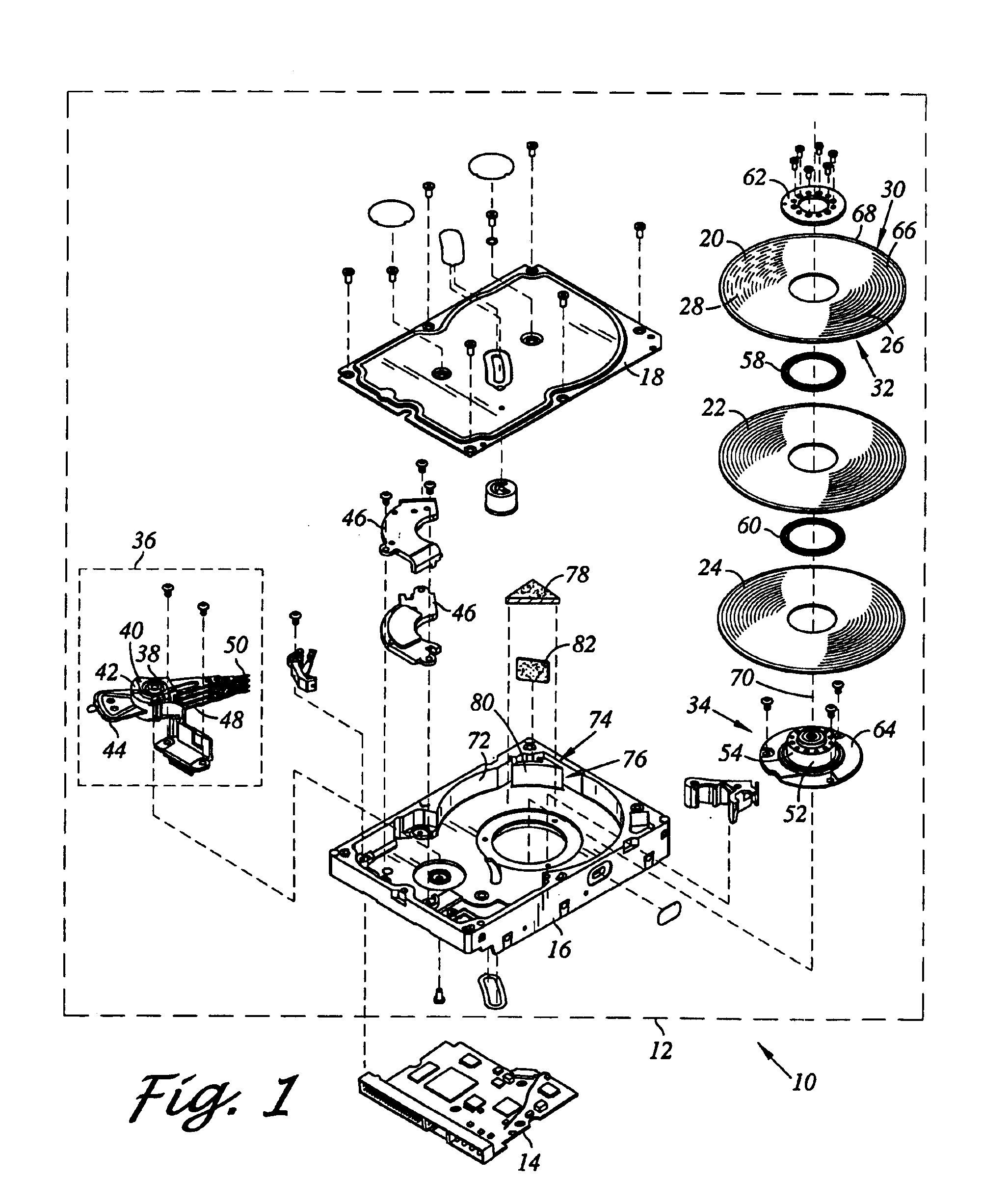
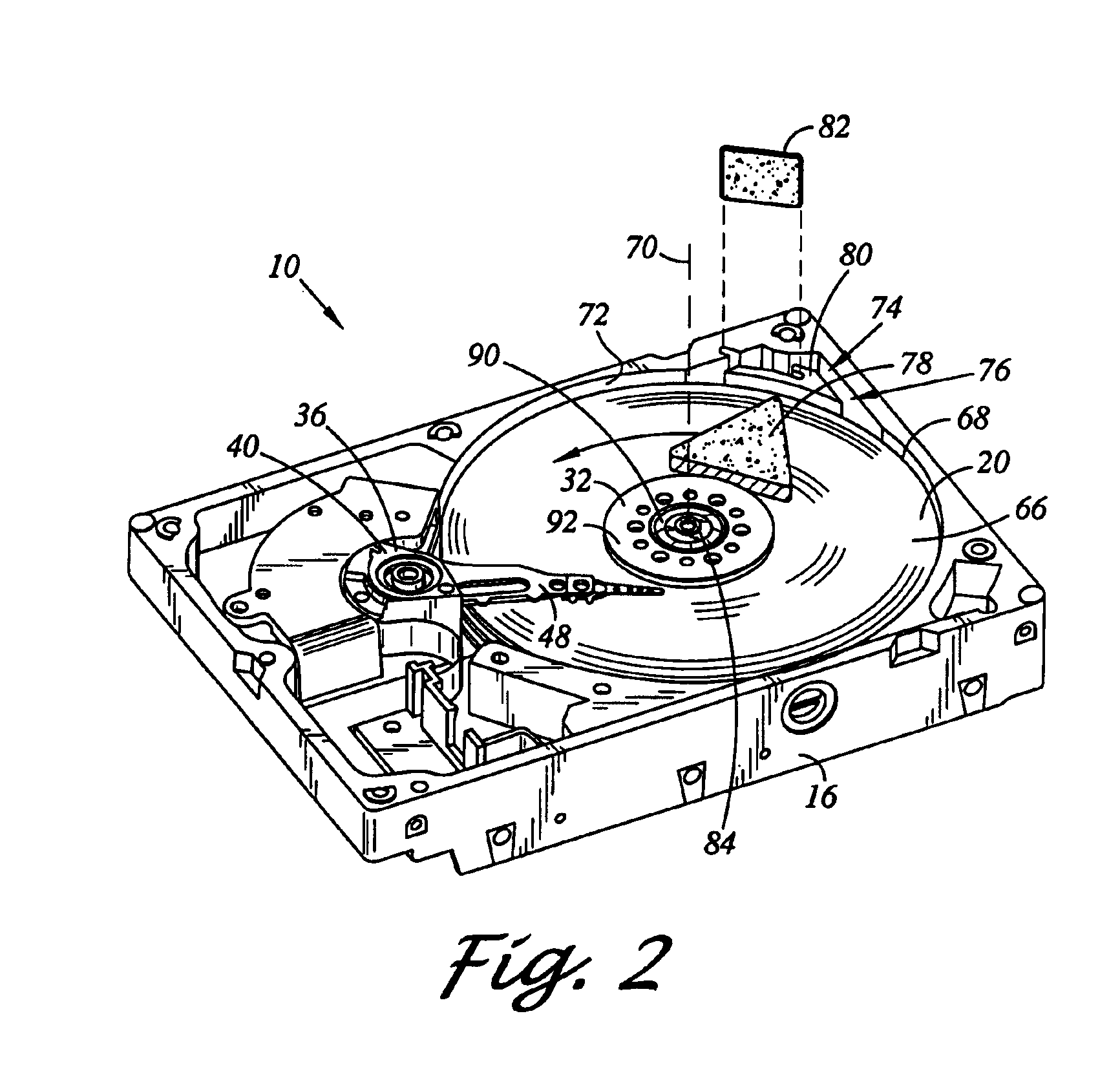
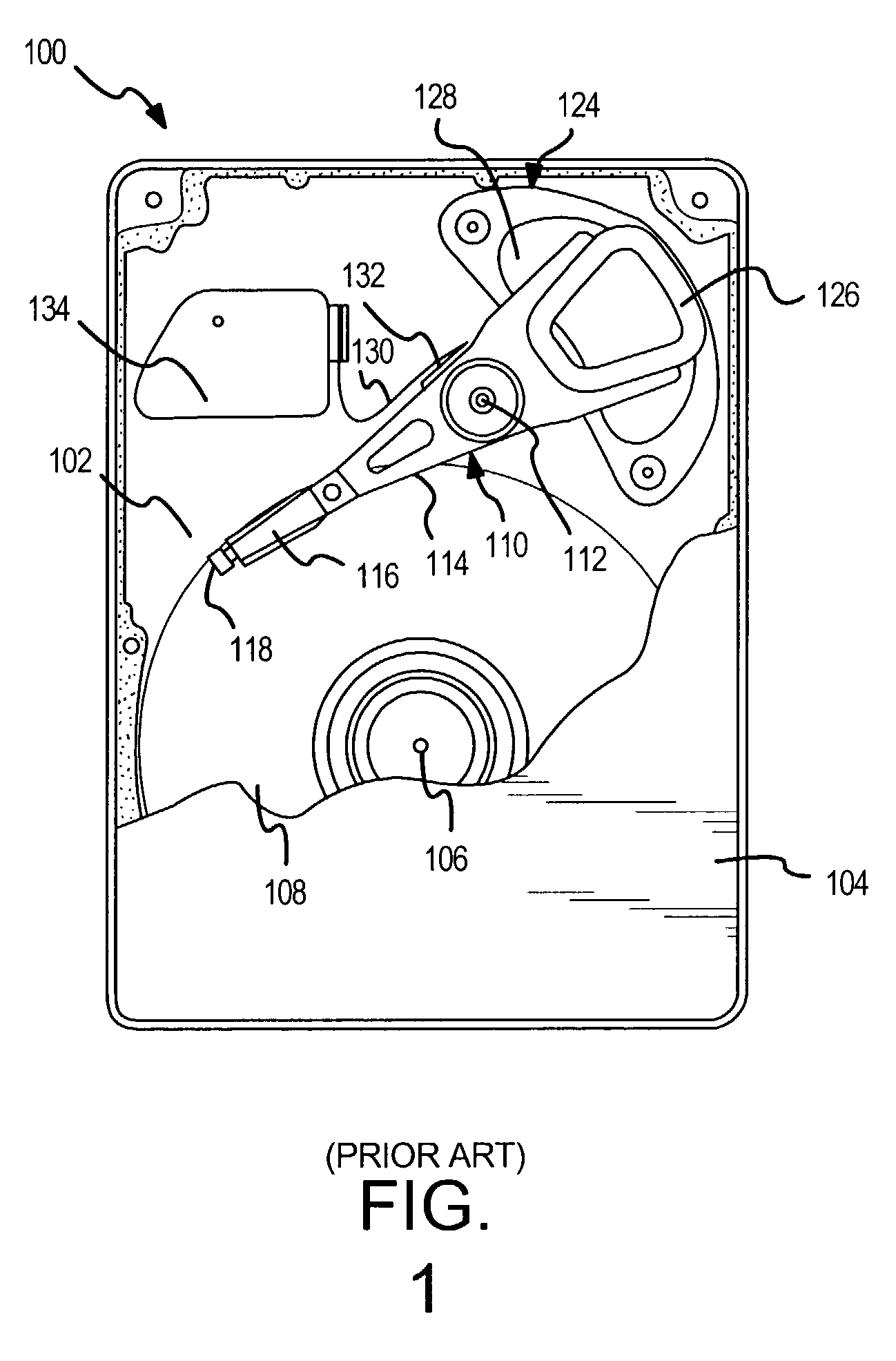
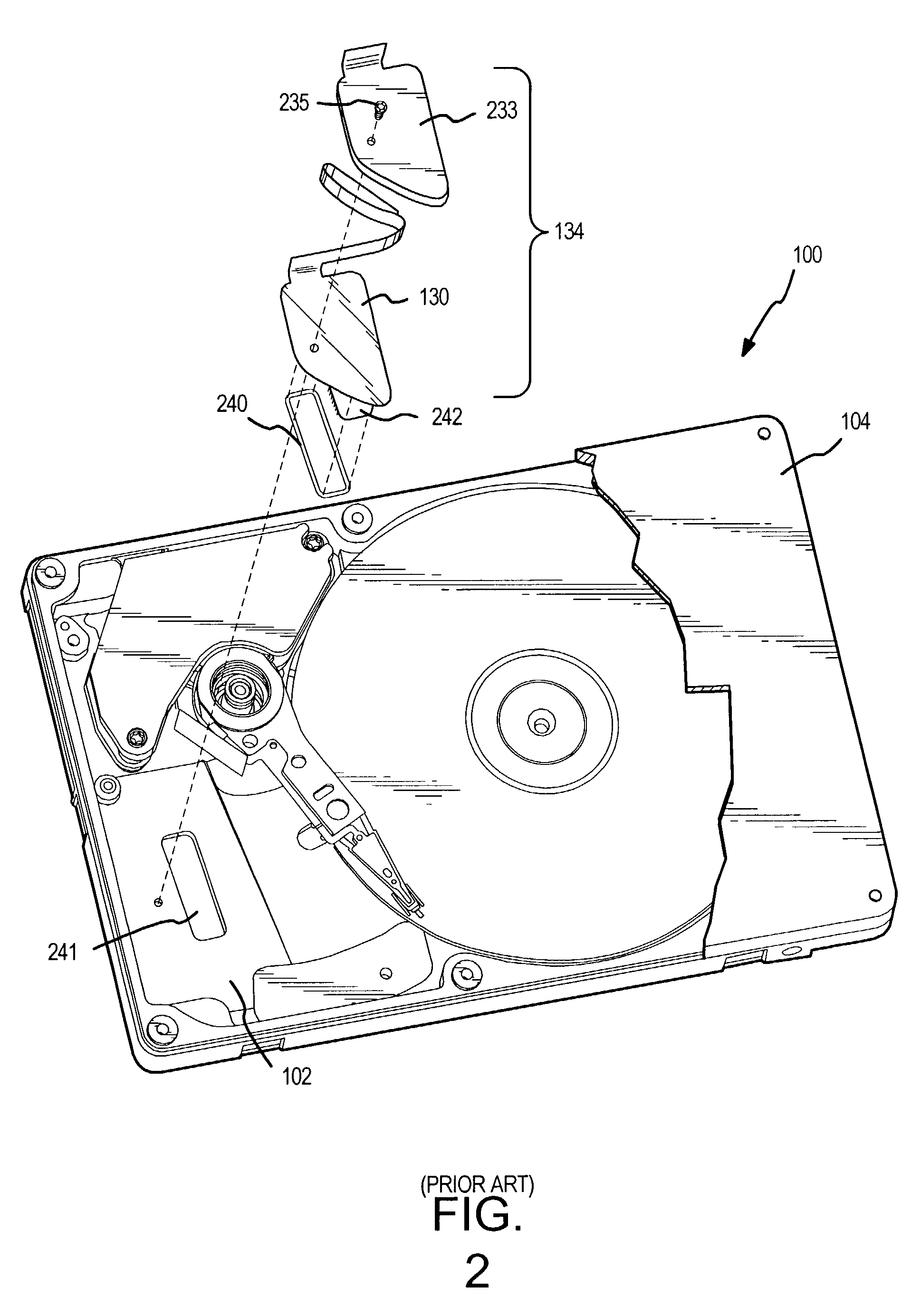
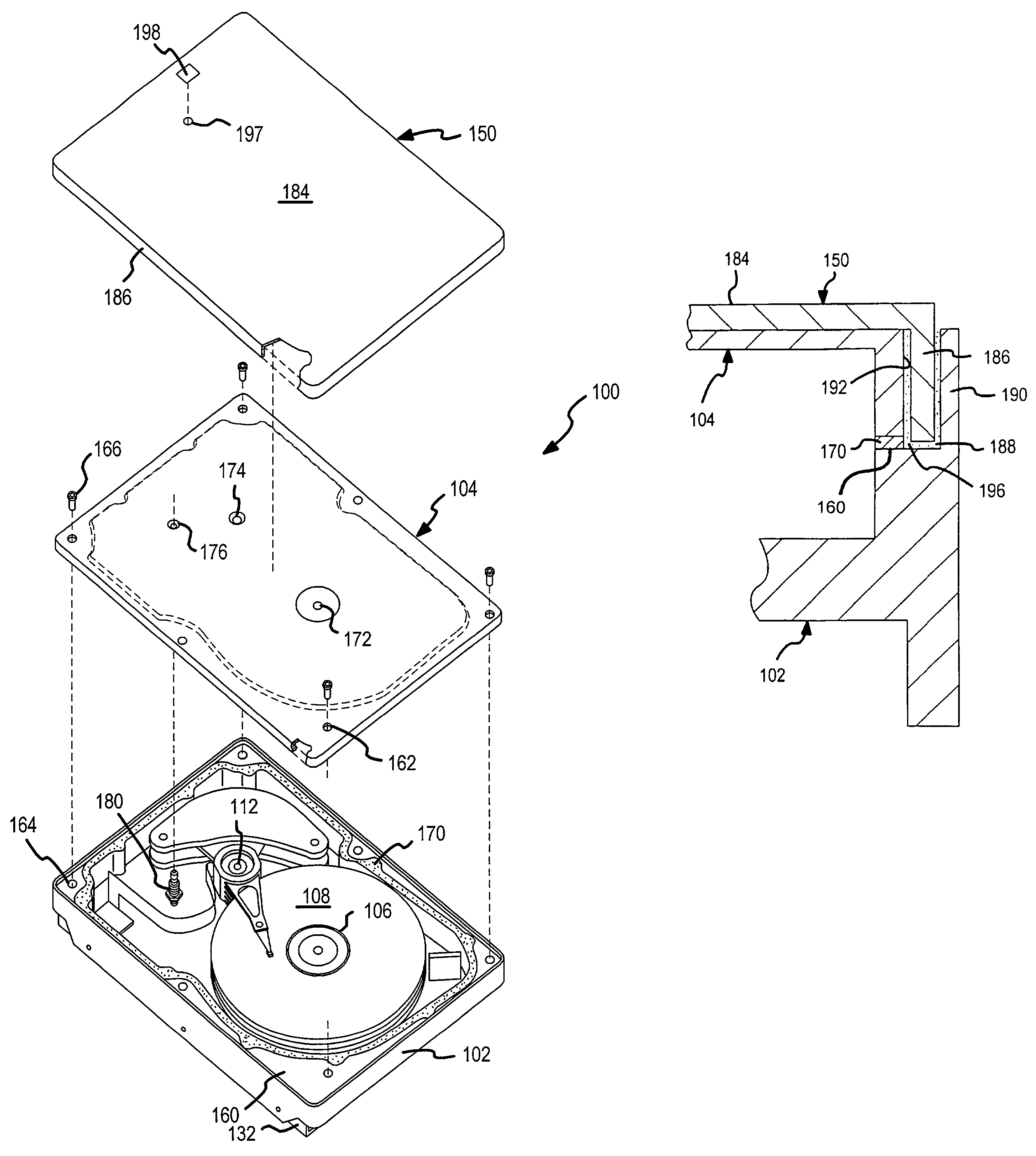
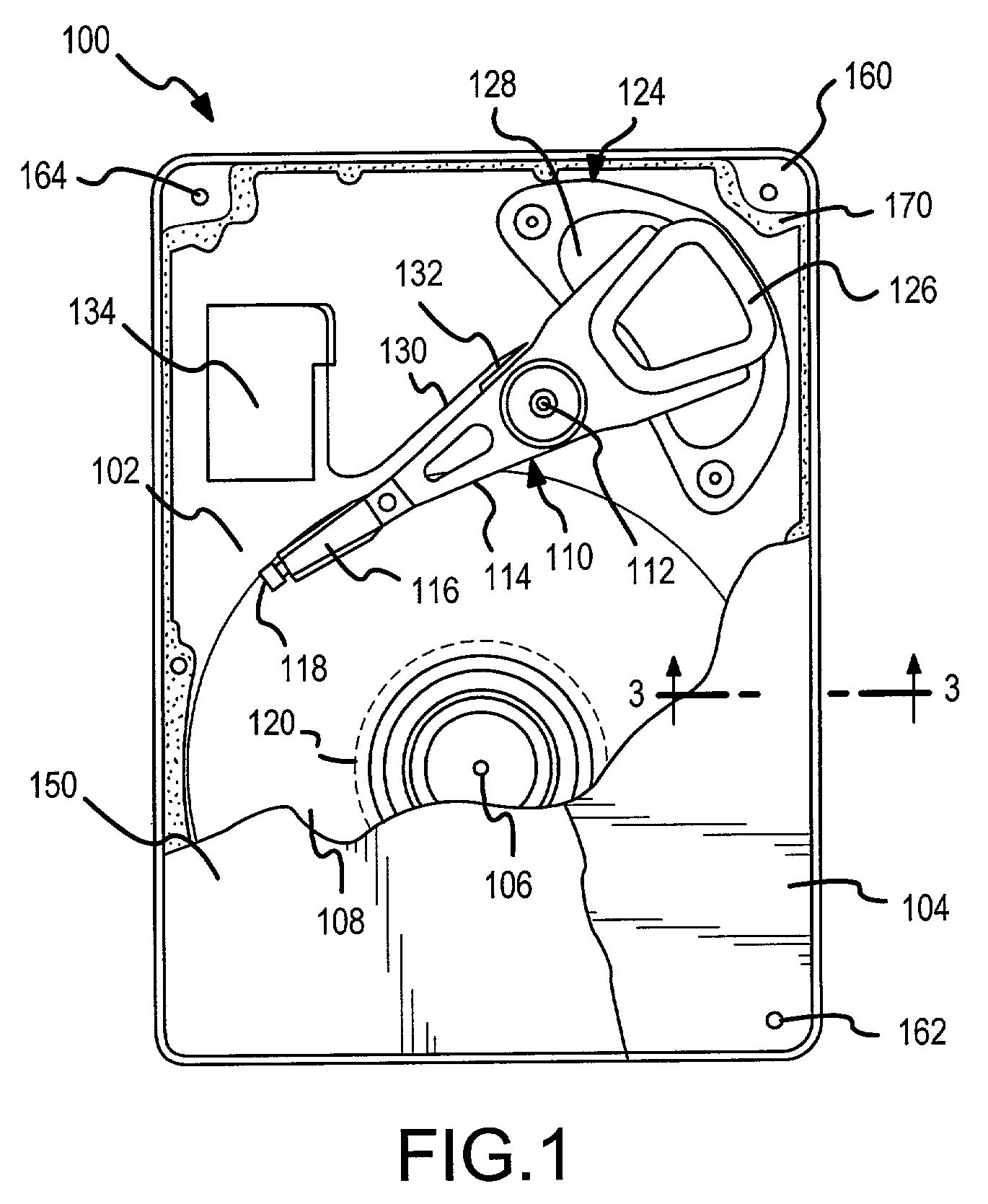
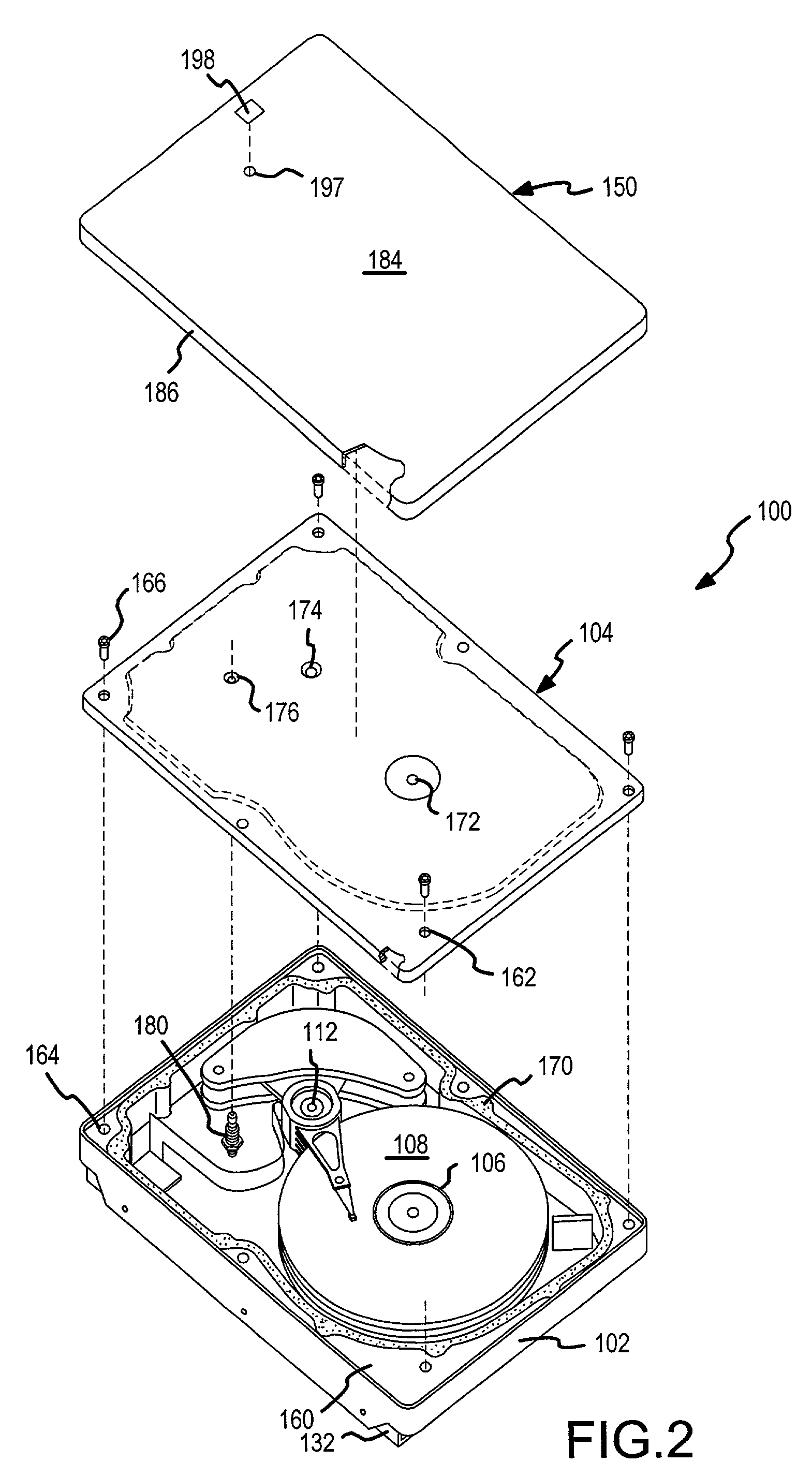
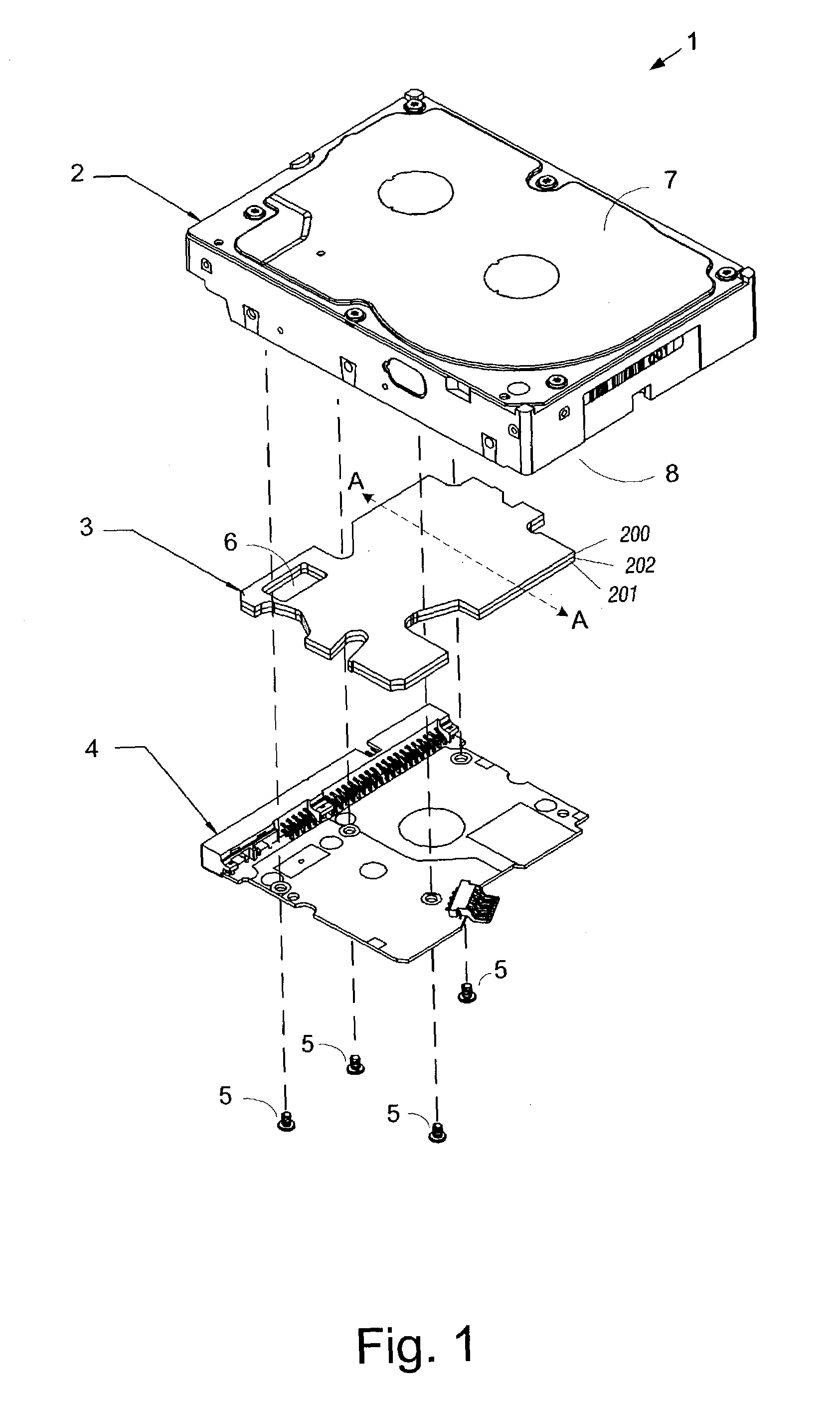
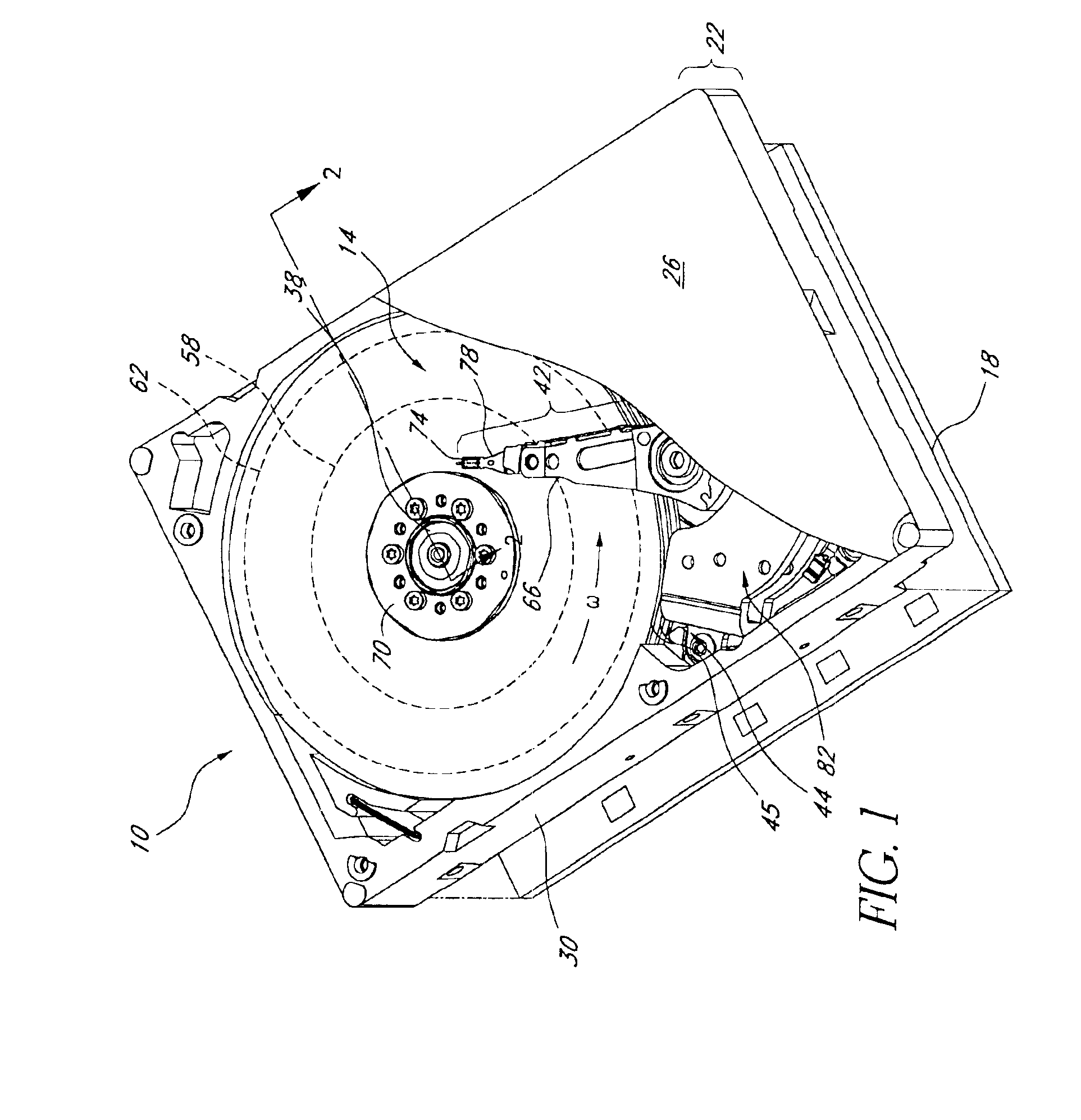
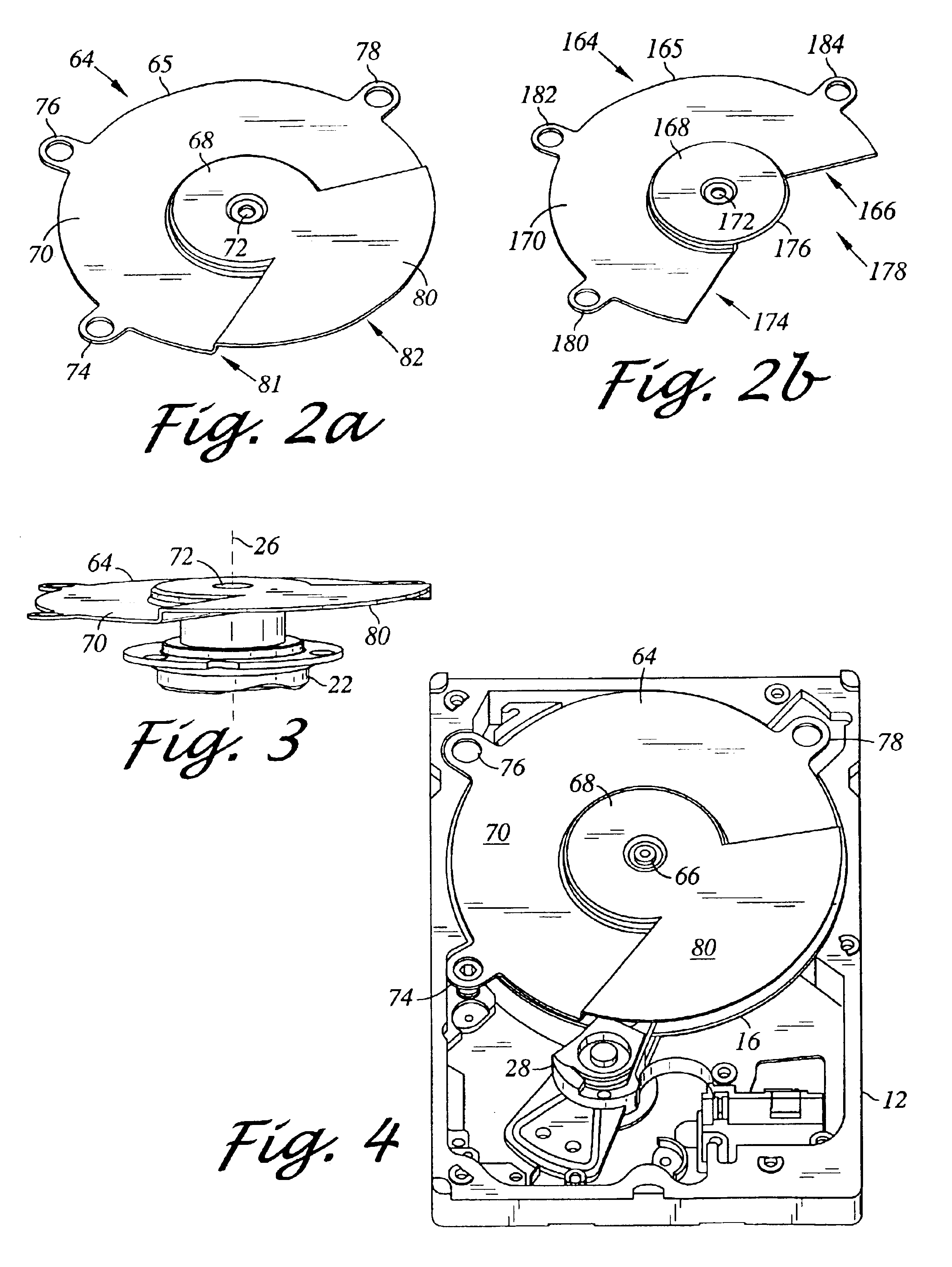
A hard disk drive having a housing with a base and a cover connected to each other, a spindle motor connected to the base, a disk mounted on the spindle motor and rotating with respect to the base, and an actuator rotatably connected to the base and supporting a slider with a magnetic head mounted on a front end thereof. The magnetic head writes and / or reads data to and / or from the disk. The hard disk drive also has a blade protruding from a surface of the base and / or a portion of the cover facing the disk. The blade guides an air flow caused by rotation of the disk toward an outer edge of the disk.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
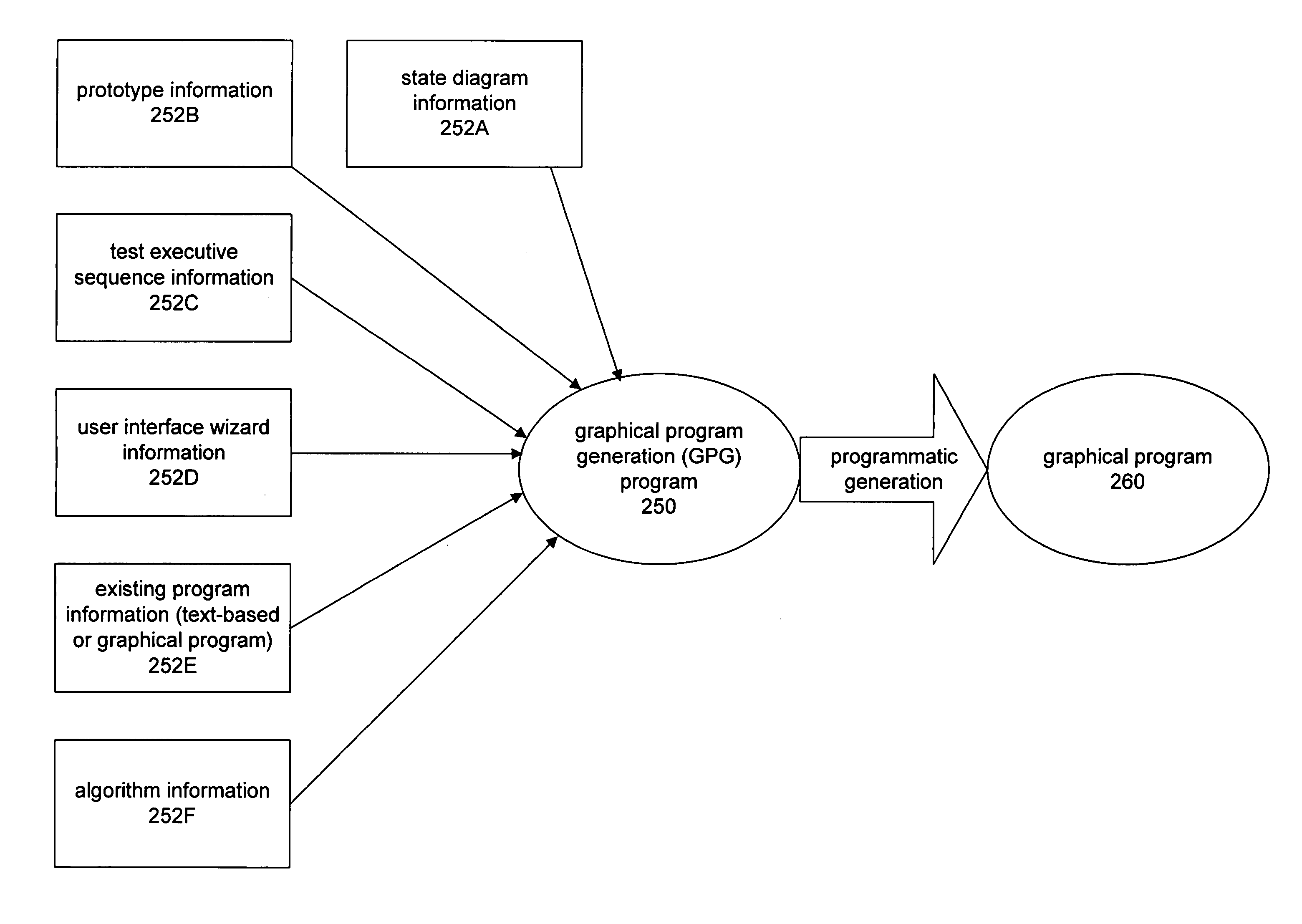
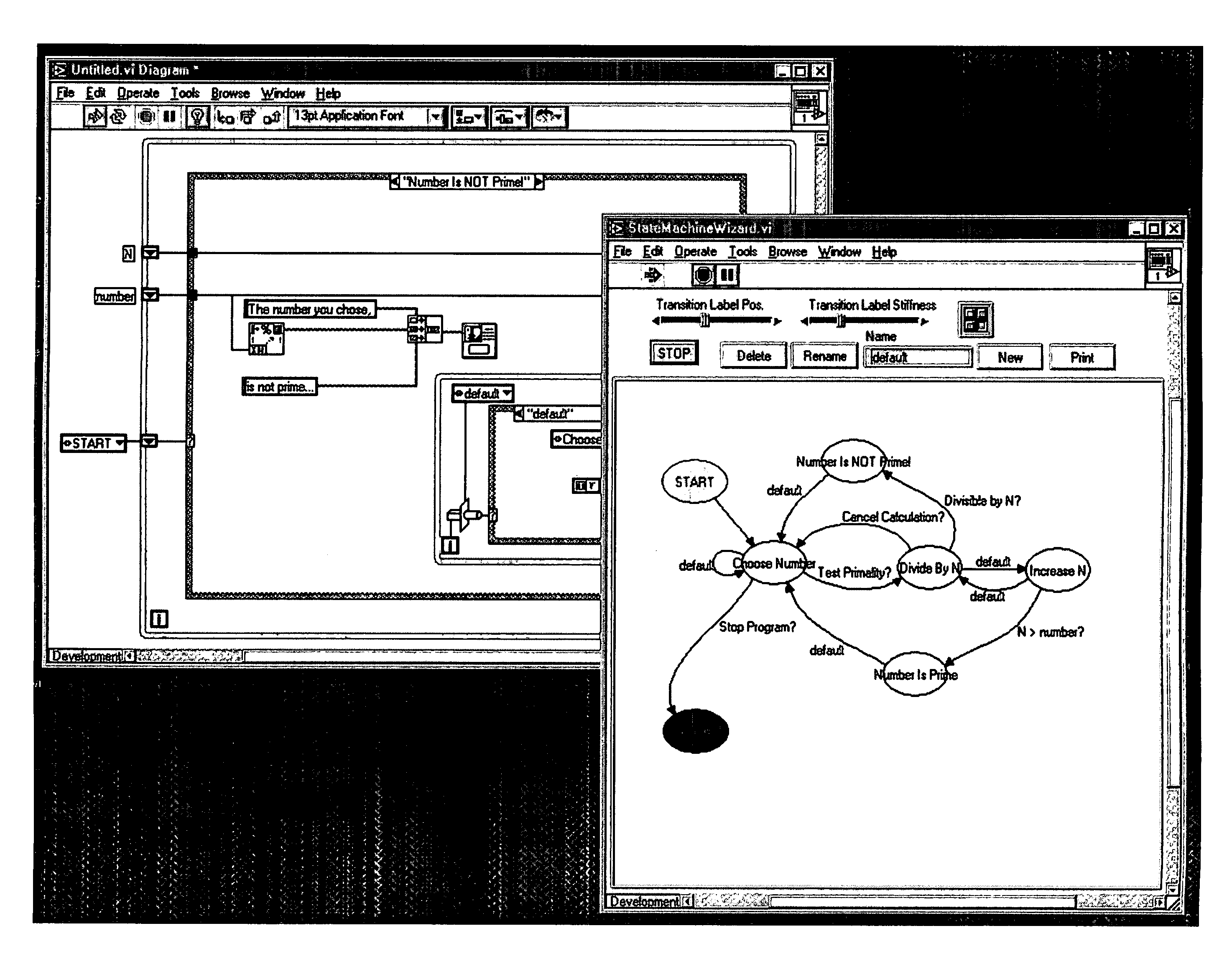
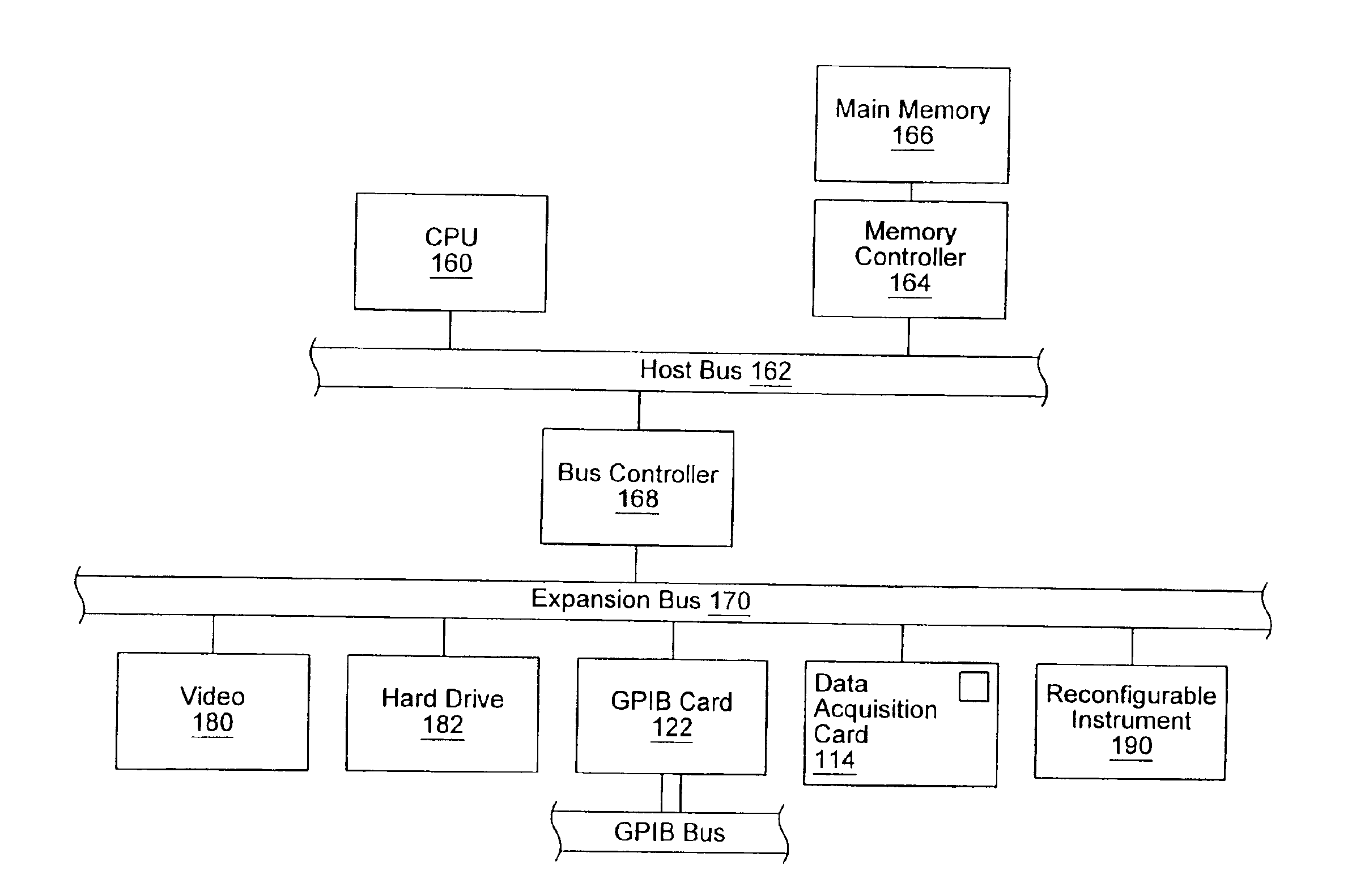
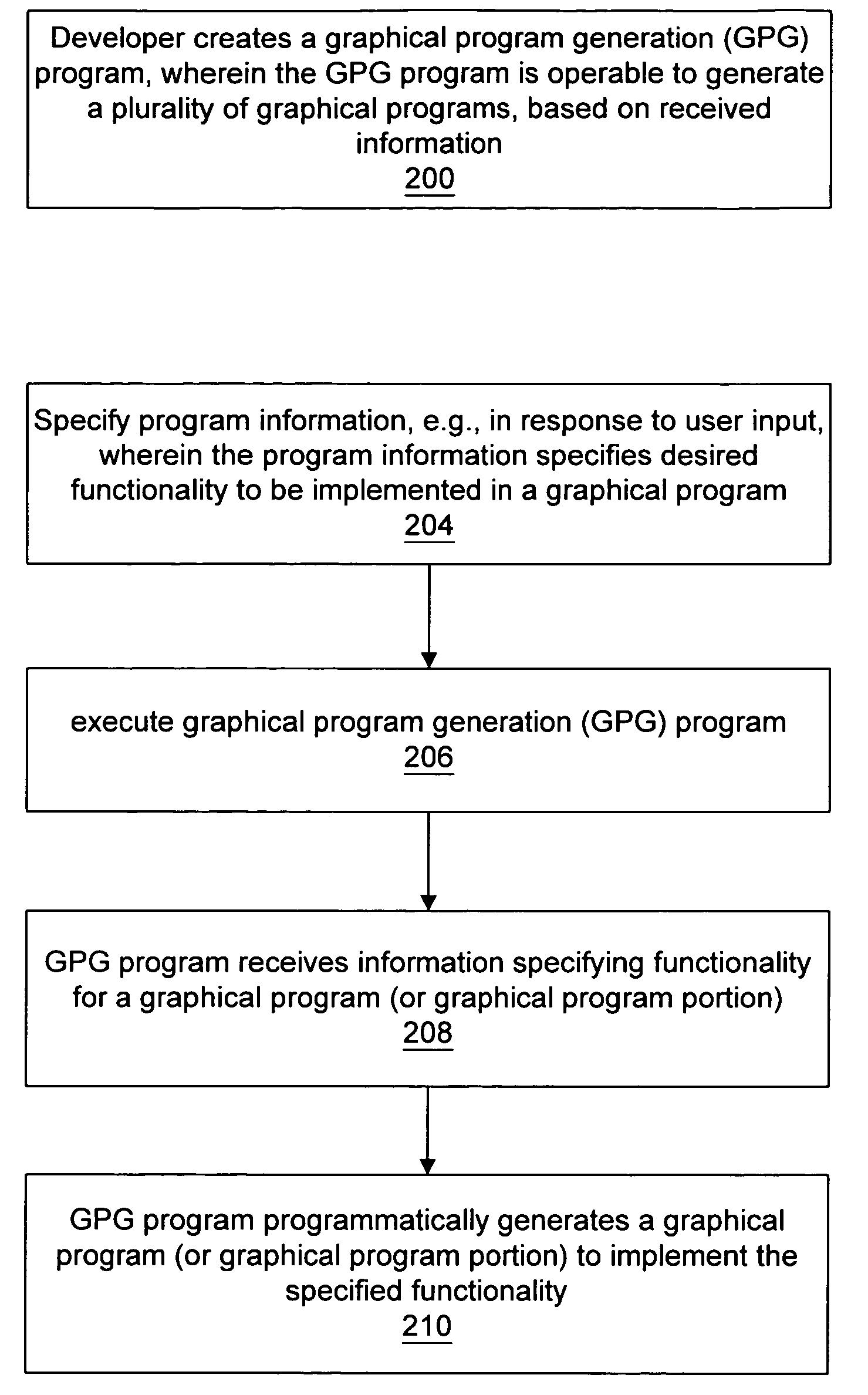
System and method for programmatically generating a graphical program in response to program information
InactiveUS7210117B2Easy retrievalFacilitate re-creationProgramme controlData processing applicationsGraphicsComputer science
A system and method for programmatically generating a graphical program or a portion of a graphical program in response to receiving program information is disclosed. During execution of a graphical program generation (GPG) program, the GPG program receives program information specifying functionality of the graphical program to be generated. In one embodiment the program information does not specify specific nodes in the graphical program or connections among the nodes. In response to the program information, the GPG program programmatically generates a graphical program (or graphical program portion) that implements the specified functionality.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Audio cassette emulator
InactiveUS6941180B1Saving positionSaving stateApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageThe InternetMultiple sensor
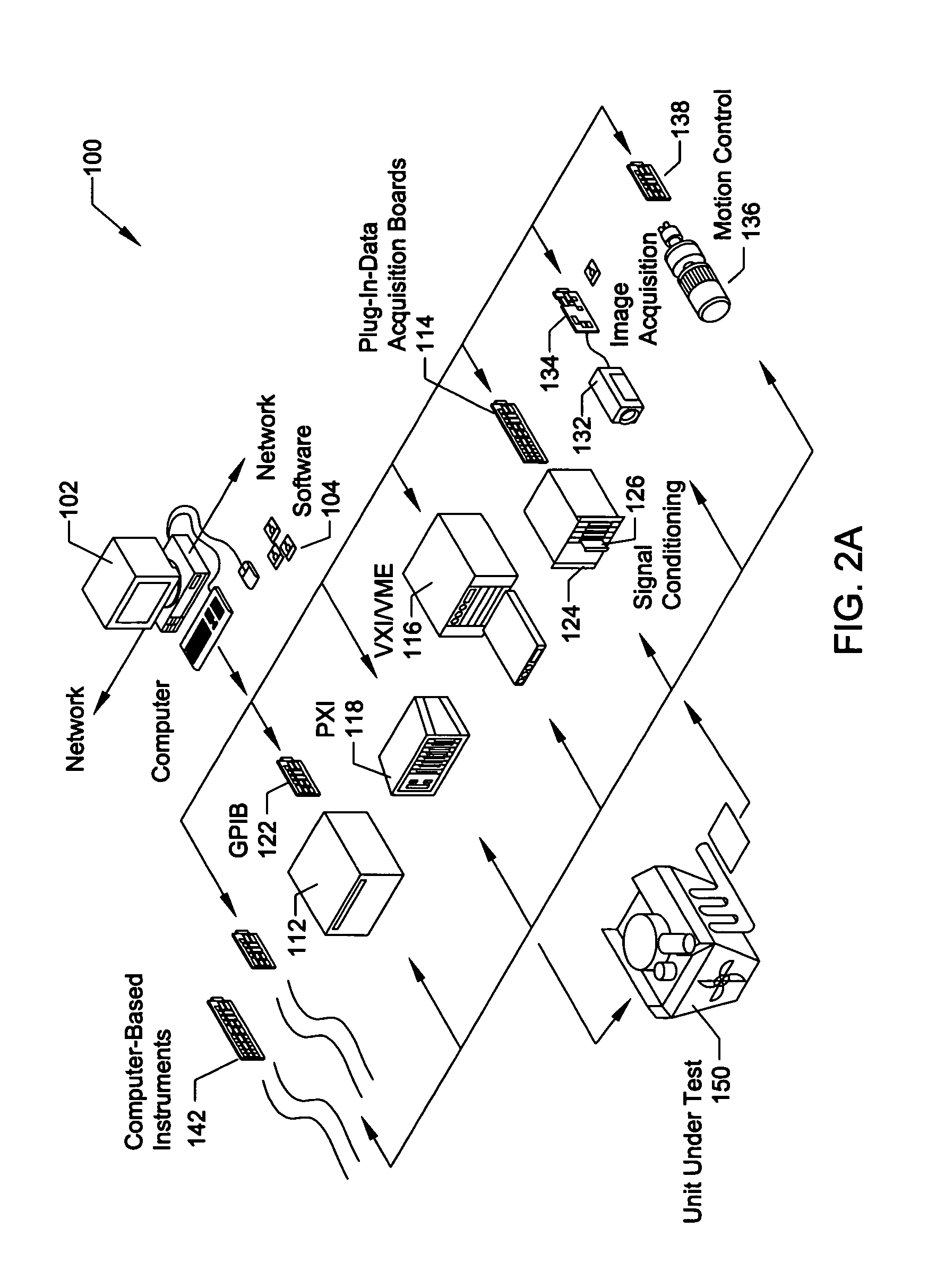
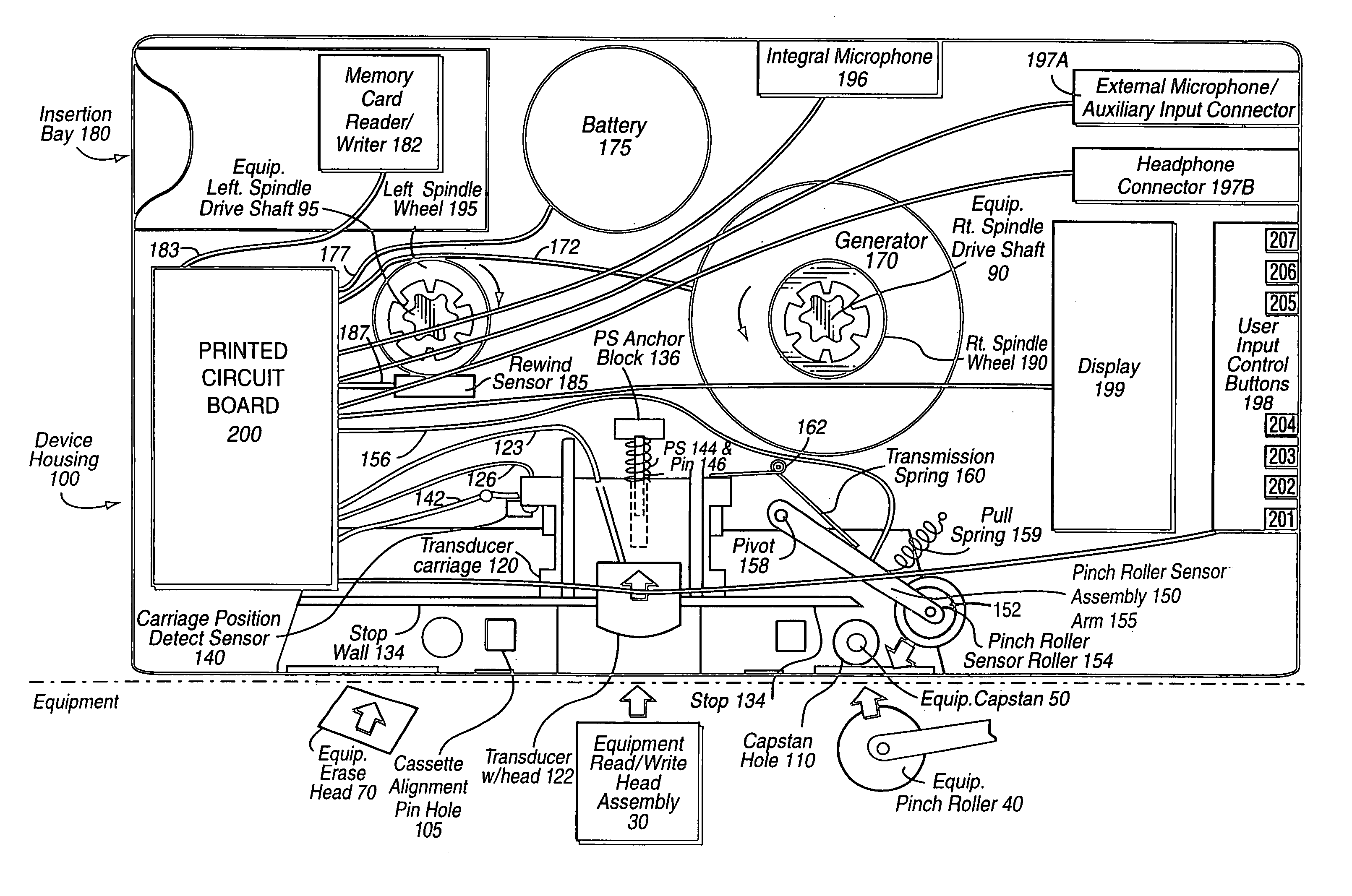
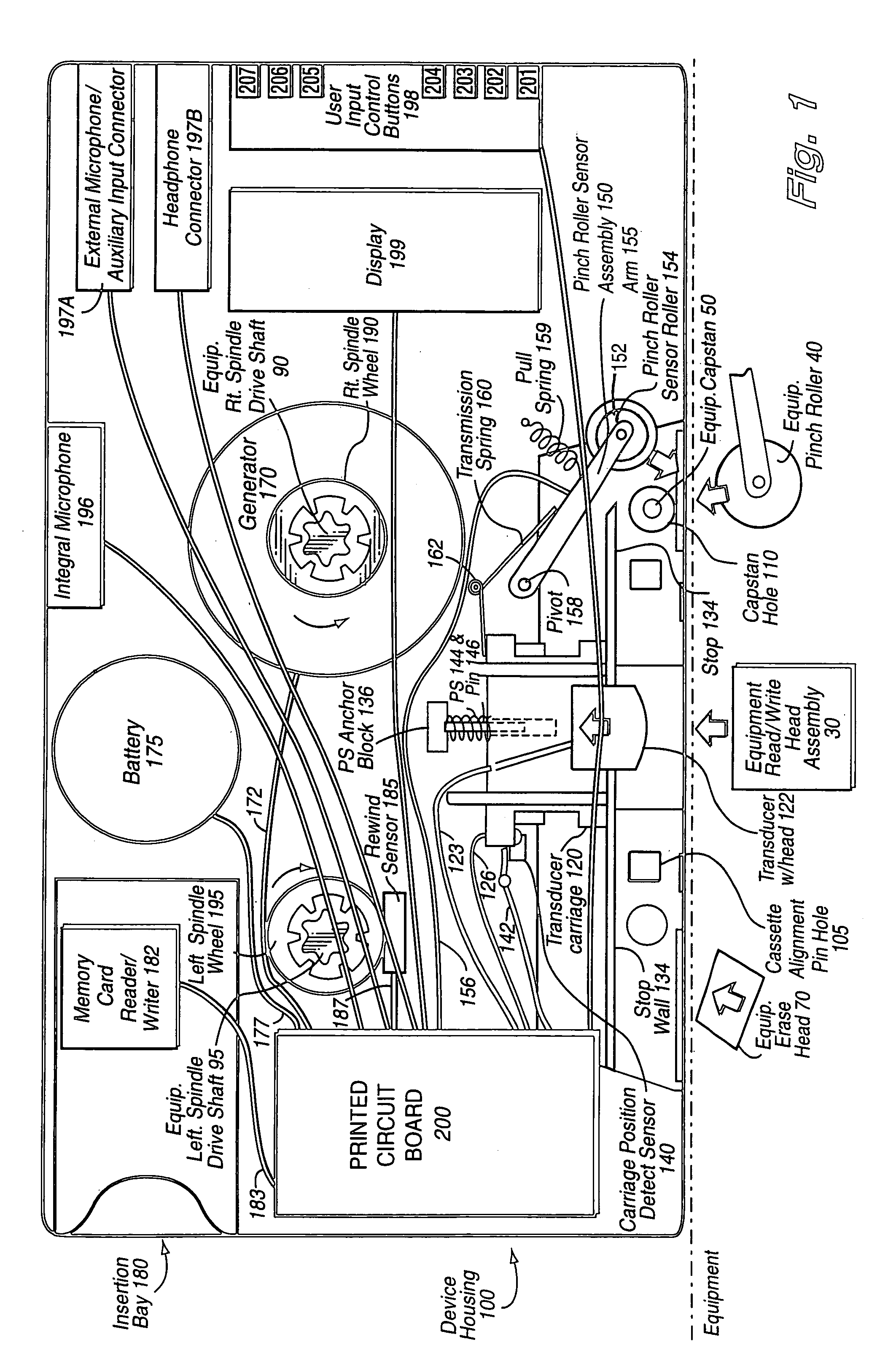
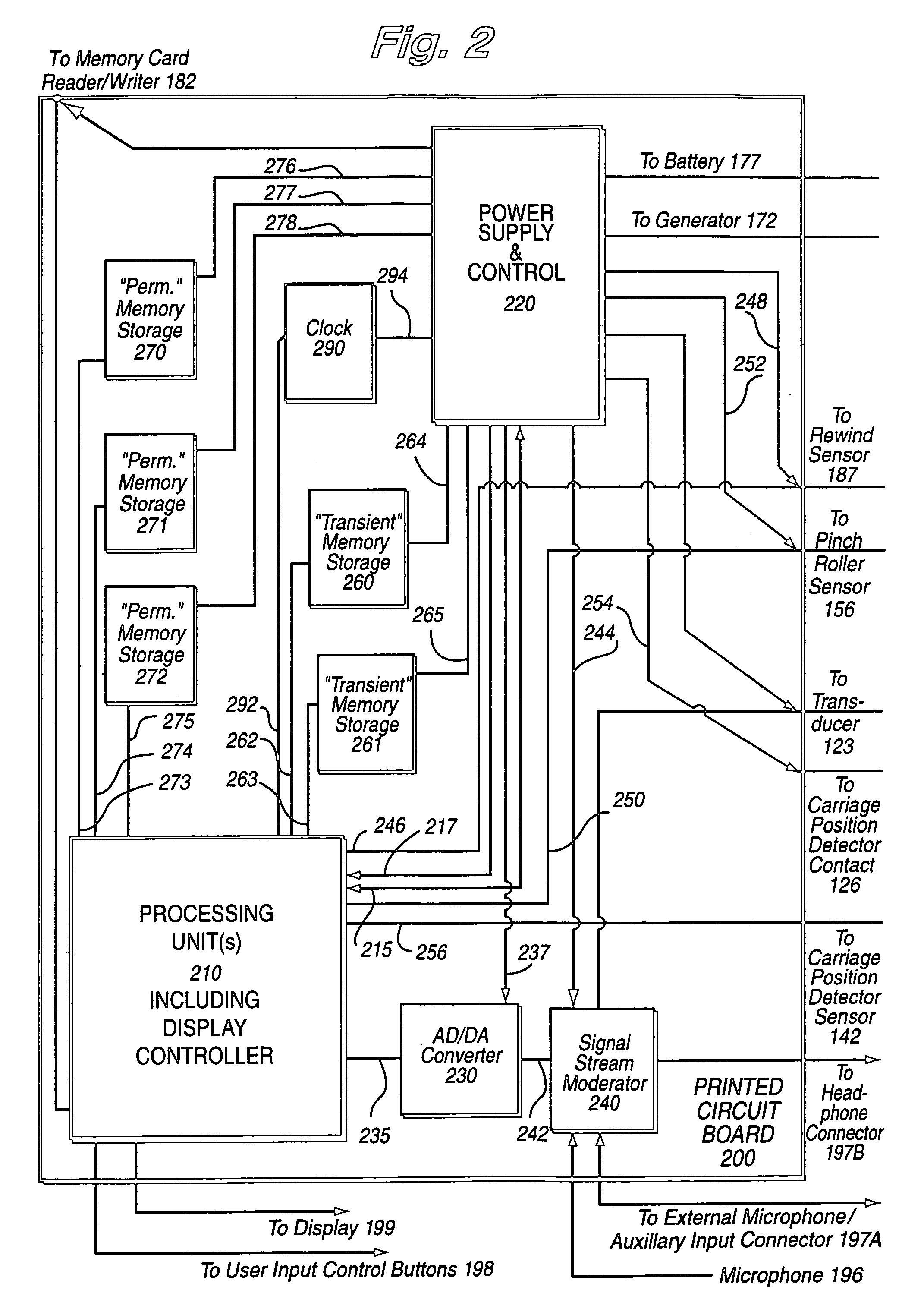
A device of the same general physical size and shape as a standard audio cassette tape, but which accepts digital information from any of a variety of sources—including for example: Internet transmission, a digital computer, or memory cards (especially digital memory cards)—and plays this digital information through any, for example, standard audio tape cassette player. The device operates by converting the digital representation of the sound into magnetic signals which are presented to the read / write head of the cassette player equipment. The device allows the user of the cassette player to regulate the audio playback using conventional equipment controls such as: START, STOP, REWIND, FAST REWIND, FORWARD, FAST FORWARD, etc. In one exemplary implementation, the device has the same general physical dimensions of a standard audio cassette; at least one digital processor; and a slot into which electronic media such as, for example, memory cards, smart cards having a processor and a memory embodied thereon and other memory media may be inserted. Converter circuitry converts data stored in digital memory to an analog signal which is magnetically coupled to the read head of the equipment. Numerous sensors detect changes in at least one of the tape equipment mechanisms in the audio cassette emulator.
Owner:FISCHER ADDISON M
System and method for programmatically modifying a graphical program in response to program information
InactiveUS7000190B2Easy retrievalFacilitate re-creationProgramme controlData processing applicationsGraphicsApplication software
A system and method for programmatically generating and modifying graphical programs, in response to receiving program information. The program information may specify functionality of the graphical program or graphical program portion. During execution of a graphical program generation (GPG) program, the GPG program may be operable to receive the program information. In response to the program information, the GPG program may programmatically generate a graphical program (or graphical program portion) that implements the specified functionality. Thus, the GPG program may generate different graphical programs, depending on the program information received. The GPG program may have any of various purposes or applications. In some embodiments, the GPG program may be a program or application which a user utilizes to construct or characterize a computational process. In response to the specified computational process, the GPG program may programmatically generate a graphical program to implement the computational process. In other embodiments, the GPG program may be a program or application that directly aids the user in creating a graphical program. In addition to these examples, a GPG program may receive any other type of information and programmatically generate a graphical program based on the received information. After programmatically generating the graphical program, the GPG program may receive subsequent program information specifying a modification to the graphical program and may programmatically modify the graphical program based on the program information.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
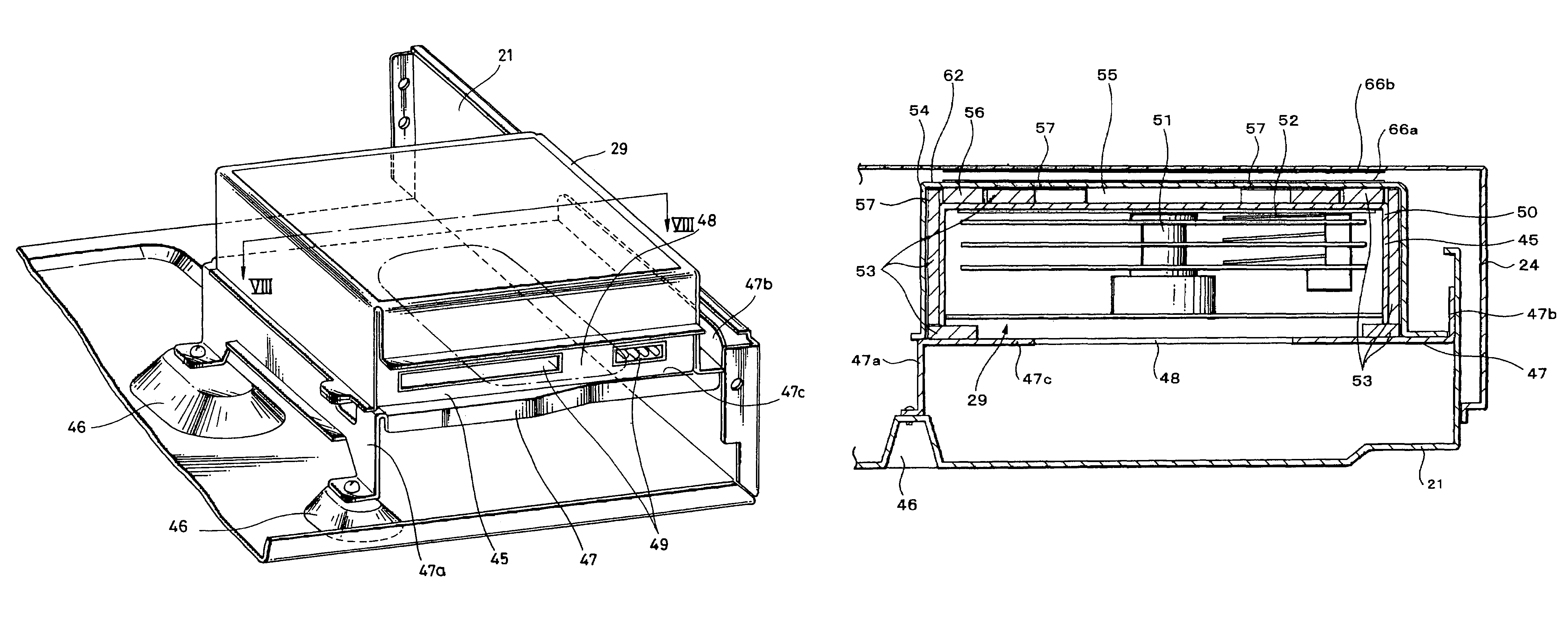
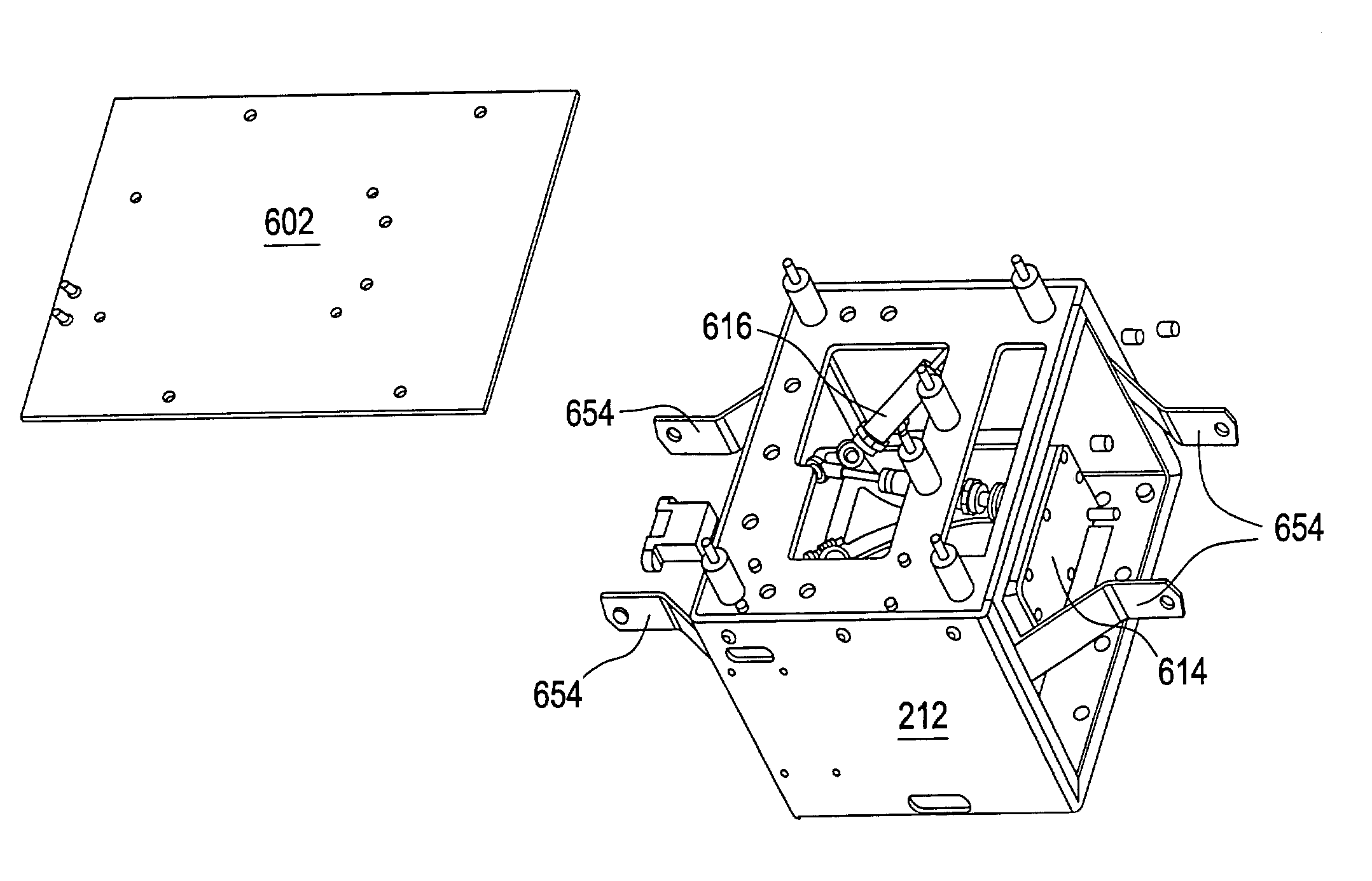
Electronic apparatus and hard disk drive housing apparatus
InactiveUS7315447B2Effective radiationImprove reliabilityApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageHard disc driveHeat transmission
A system for mounting a hard disk drive inside an electronic apparatus in such a way that the hard disk drive is isolated from vibration and noise and heat generated by the hard disk dive is radiated to a cover of the electronic apparatus to prevent overheating. A foam heat transmission sheet is placed between the hard disk drive cover and an outer casing that is mounted to the electronic apparatus and far-infrared ray transmitting and receiving sheets are attached to the outside of the outer casing and to the inside of the cover of the electronic apparatus to transmit heat from the hard disk drive to the exterior of the apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
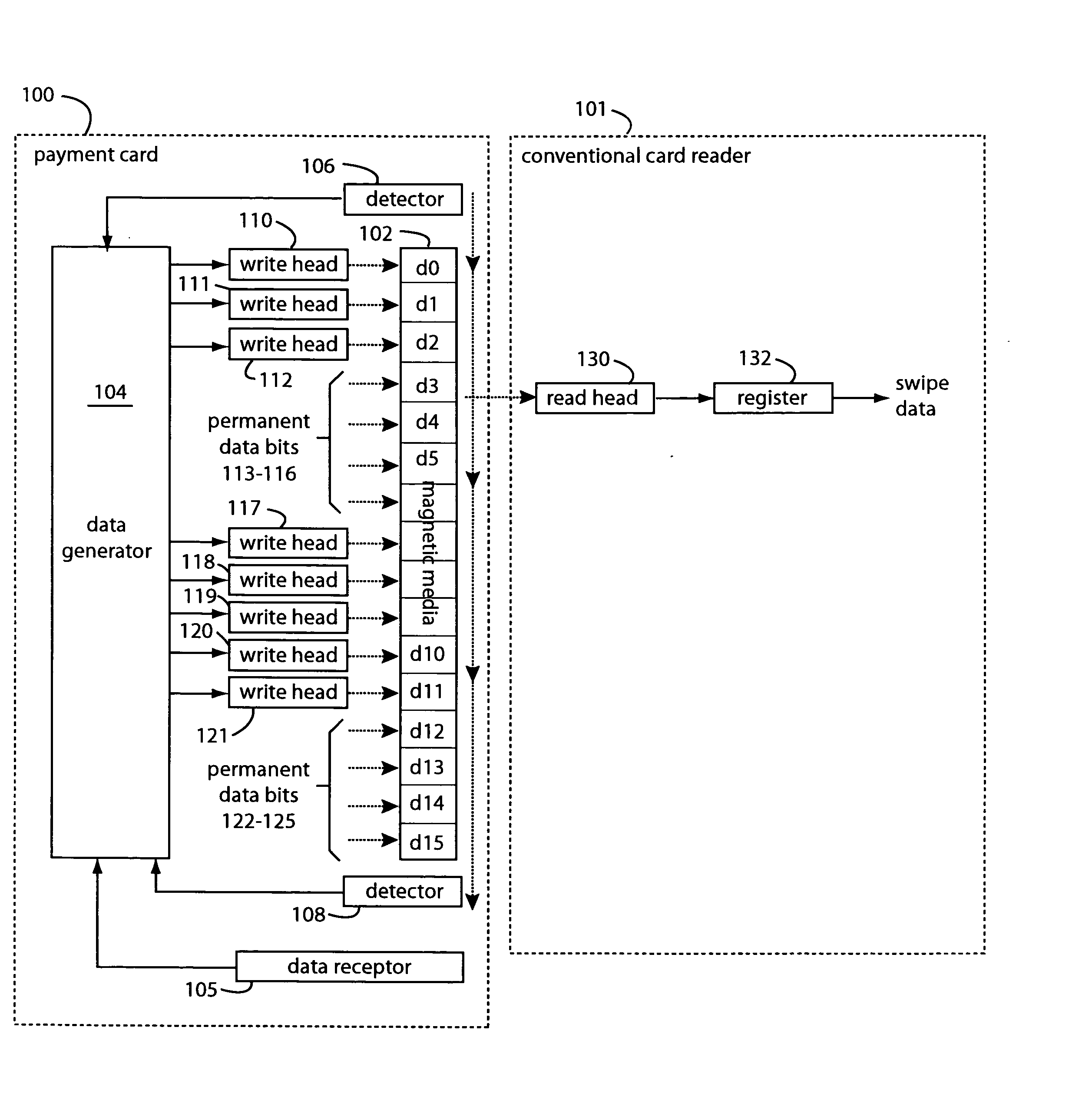
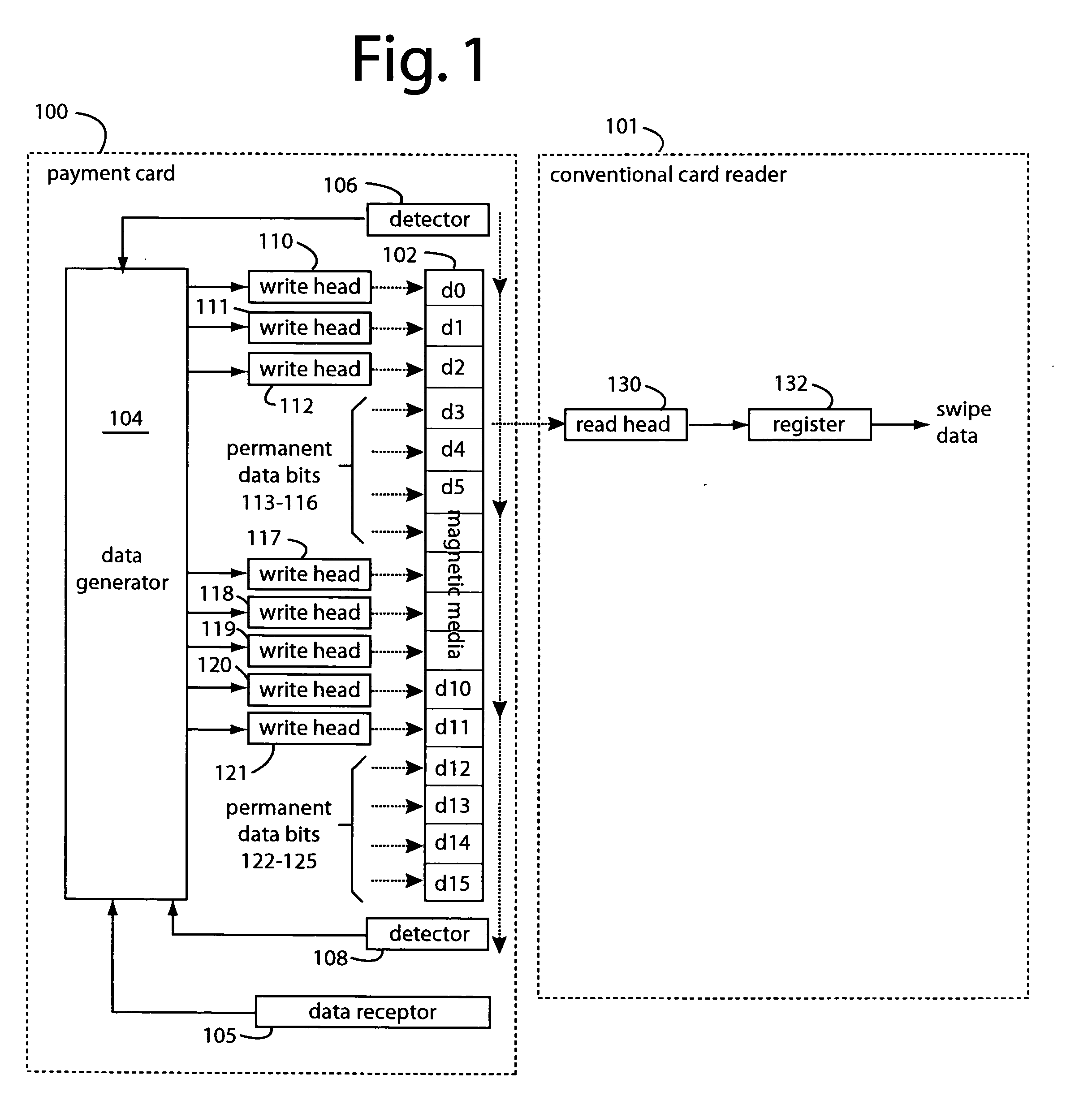
Programmable magnetic data storage card
ActiveUS20050133606A1Reduce riskSimple and inexpensive and effectiveAcutation objectsApparatus for flat record carriersComing outMicrocomputer
A payment card comprises a plastic card with a magnetic stripe for user account data. Internal to the plastic card, and behind the magnetic stripe, a number of fixed-position magnetic write heads allow the user account data to be automatically modified. For example, a data field that counts the number of times the card has been scanned is incremented. A payment processing center keeps track of this usage-counter data field, and will not authorize transaction requests that come out of sequence. For example, as can occur from a magnetic clone of a card that has been skimmed and tried later. A card-swipe detector embedded in the plastic card detects each use in a scanner, and it signals an internal microcomputer which changes data bits sent to the write heads. Once scanned, the payment card can also disable any reading of the user account data for a short fixed period of time.
Owner:FITBIT INC
Disk drive comprising control circuitry powered by a secondary voltage supplied by a center tap of a spindle motor during a normal operating mode
InactiveUS6876508B1Carrier constructional parts dispositionDriving/moving recording headsElectric machineOperation mode
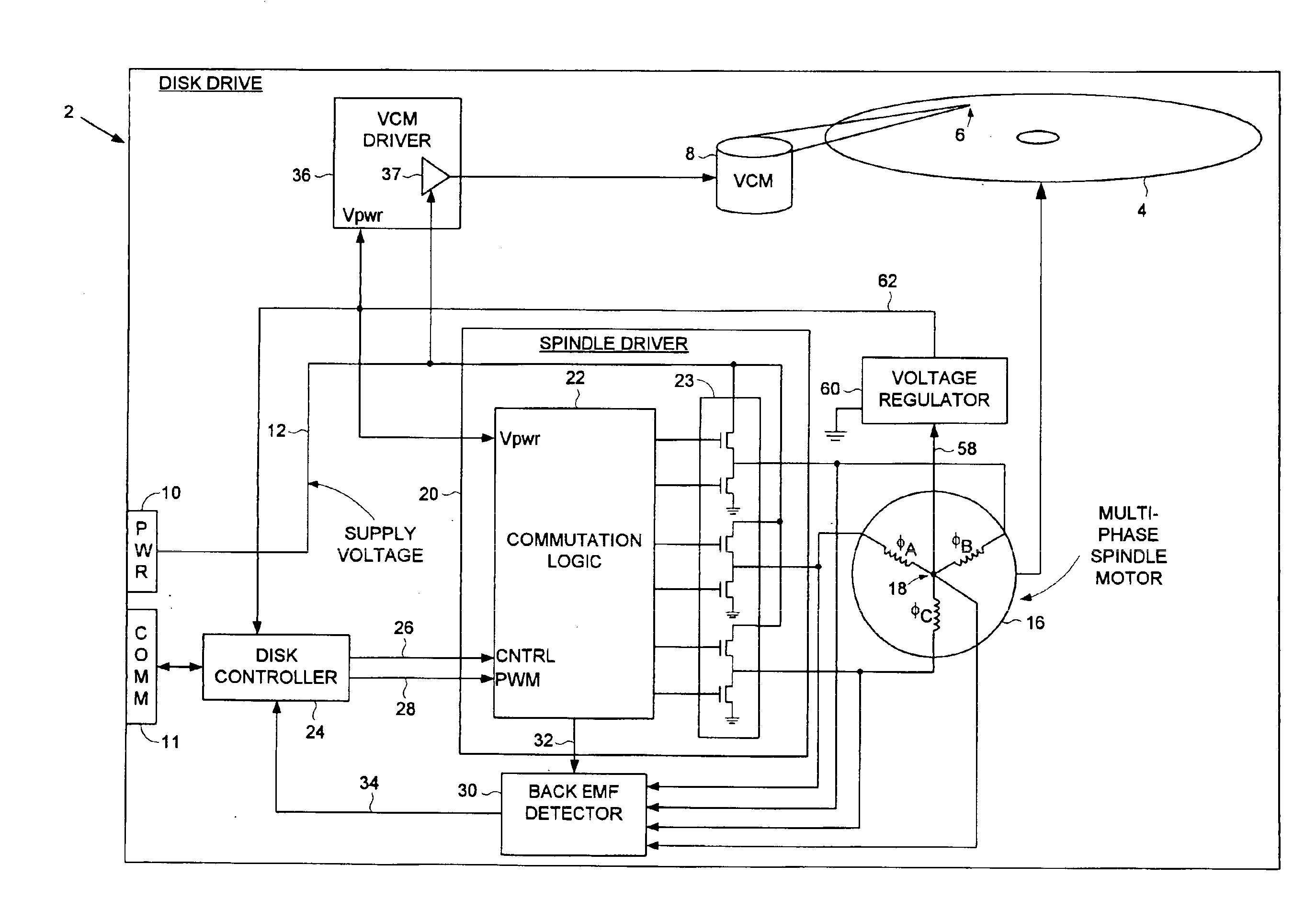
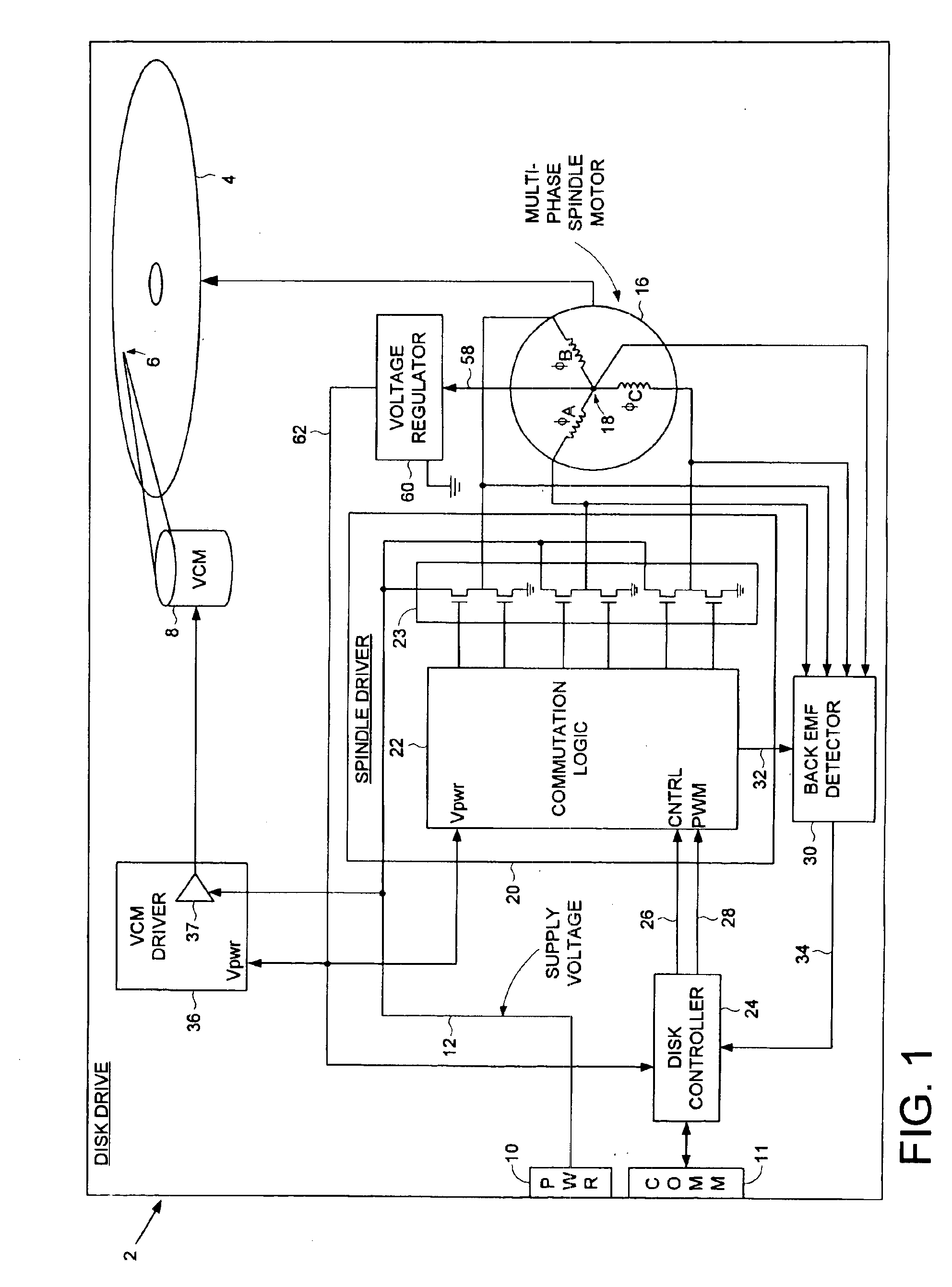
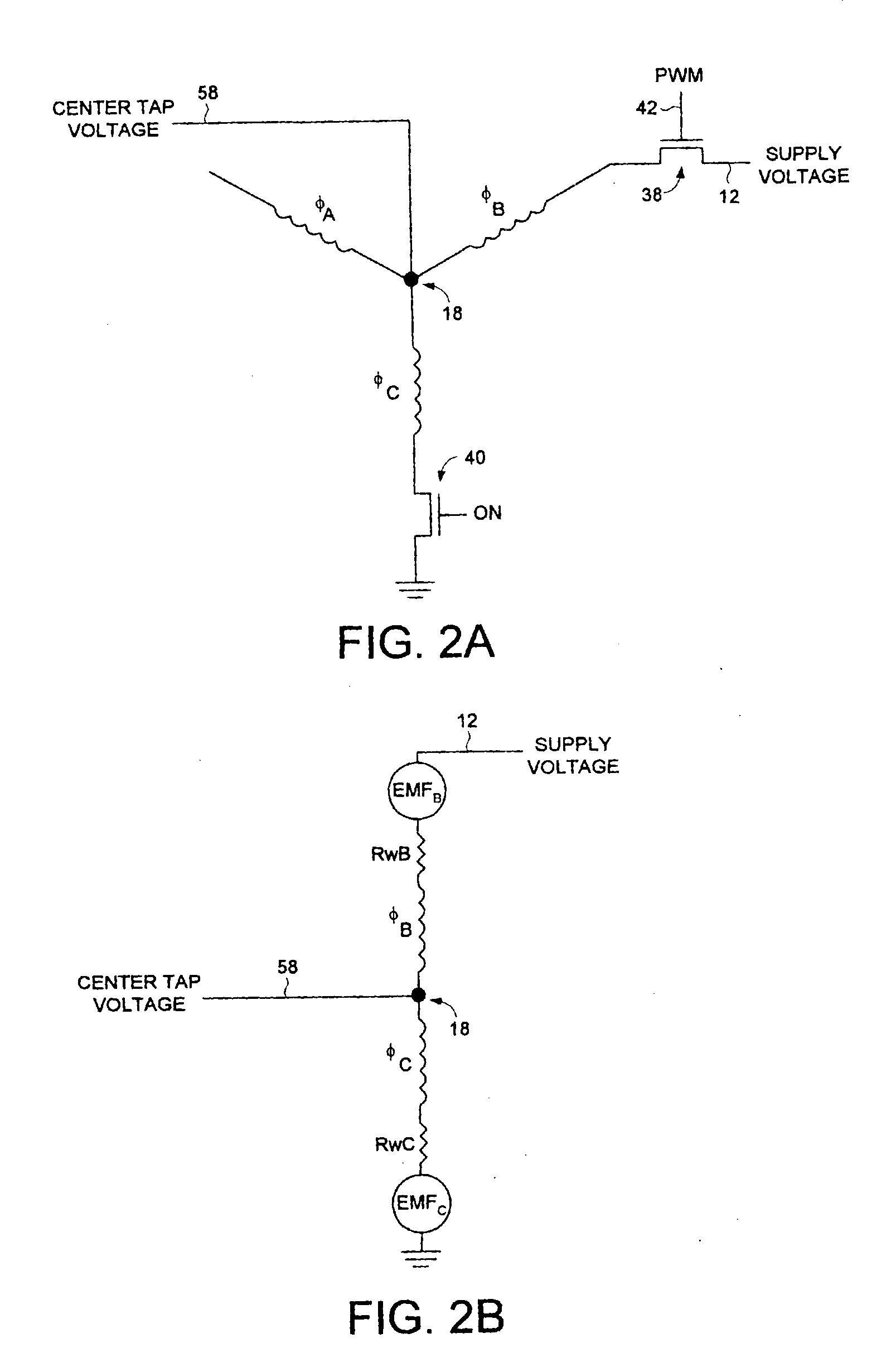
A disk drive is disclosed comprising an interface for receiving a supply voltage from a host computer and control circuitry for controlling at least one operation of the disk drive. The supply voltage is applied to the windings of a multi-phase spindle motor in a commutation sequence during a normal operating mode, and a secondary voltage supplied by a center tap of the windings is used to power the control circuitry during the normal operating mode.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for programmatically generating a second graphical program based on a first graphical program
InactiveUS7043693B2Improve performanceProgramme controlData processing applicationsProgramming languageGraphics
System and method for programmatically generating a second graphical program associated with a second programming development environment based on a first graphical program associated with a first programming development environment. The second graphical program may be generated programmatically, without relying on user input, or may prompt for user input to determine various options to use in generating the second graphical program. The second graphical program may implement the functionality of, or a portion of the functionality of, the first graphical program. The method preferably generates the second graphical program such that the second programming development environment is operable to treat the second graphical program identically to a graphical program interactively developed by a user using the second programming development environment. Thus, once the second graphical program has been generated, the user may use the second programming development environment to edit the second graphical program, execute the second graphical program, etc.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System and method for programmatically generating a graphical program in response to user input
InactiveUS7120876B2Simple taskEasy to specifyData processing applicationsApparatus for flat record carriersGraphicsUser input
A system and method for programmatically generating a graphical program or a portion of a graphical program in response to receiving user input. The user input may specify functionality of the graphical program or graphical program portion to be generated. In response to the user input, a graphical program (or graphical program portion) that implements the specified functionality may be programmatically generated. Thus, different graphical programs may be generated, depending on the user input received.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
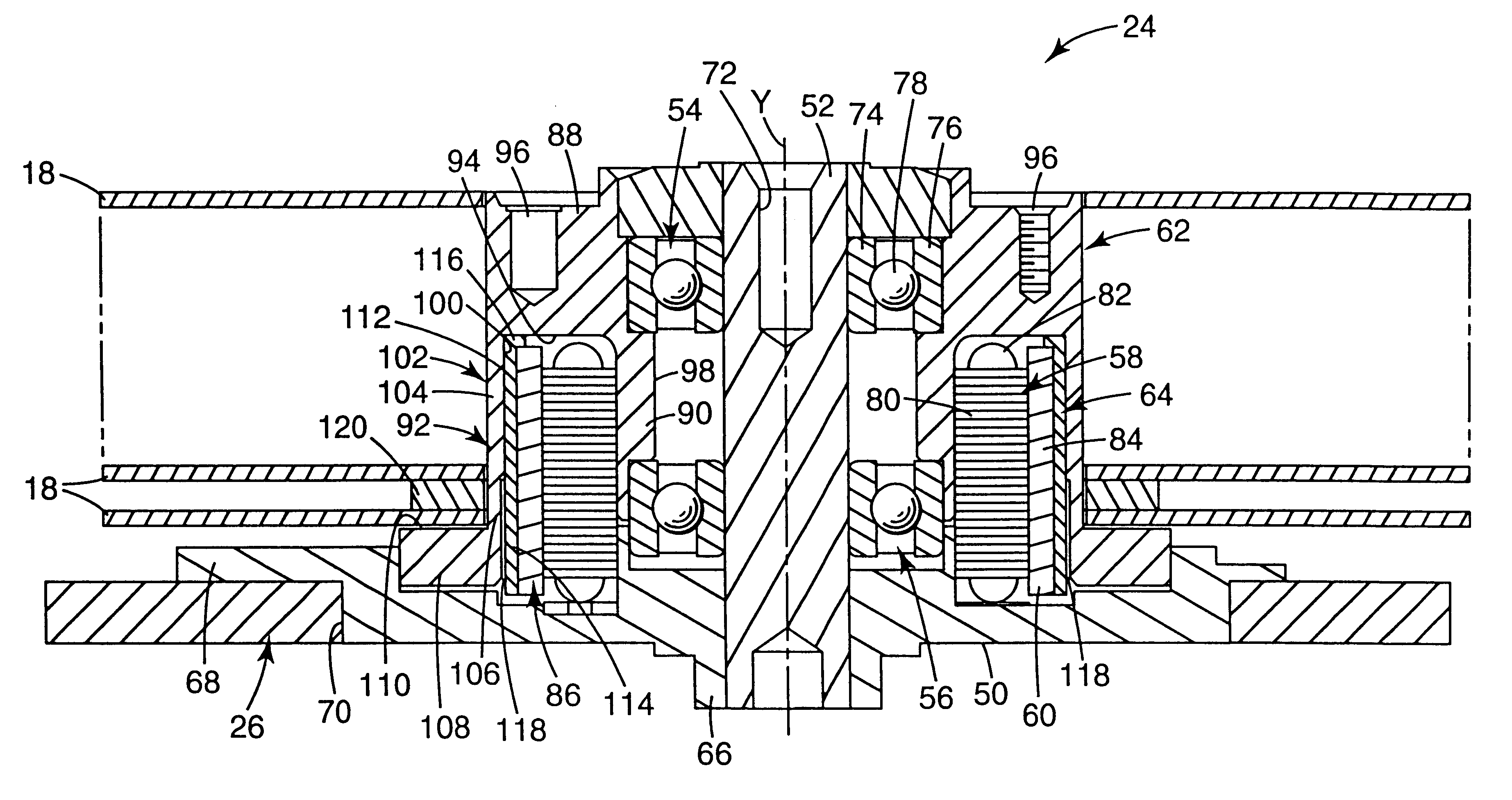
Disk unit and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS6867939B2Improve the operating environmentNot easily affectedApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageInformation processingEngineering
A disk unit, such as a magnetic disk unit, has a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, a heater, a Peltier element, etc. The disk unit heats and cools in accordance with temperature and humidity. The disk unit has a double-structure of outline comprising a first outline and a second outline surrounding said first outline, so that an internal environment is isolated from an external environment.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Portable hard disk drive
InactiveUS6891721B2Easy to installCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersHard disc driveAlloy
A portable disk drive in accordance with the present invention includes a housing made from aluminum alloy. The housing is provided with a front cover having a hook release button mounted thereon. The housing is provided with transparent side panels, which is illuminated when standby. A rear panel integrally formed with a supporting bracket on which a printed circuit board is mounted. The printed circuit board is mounted LED with respect to the transparent side panels. The supporting bracket is provided with a latch, which interlocks with a hook of the hook release button when the support bracket is inserted into the housing. When the portable hard disk drive is electrically connected, the LED illuminates the side panels.
Owner:HUANG CHENG YU
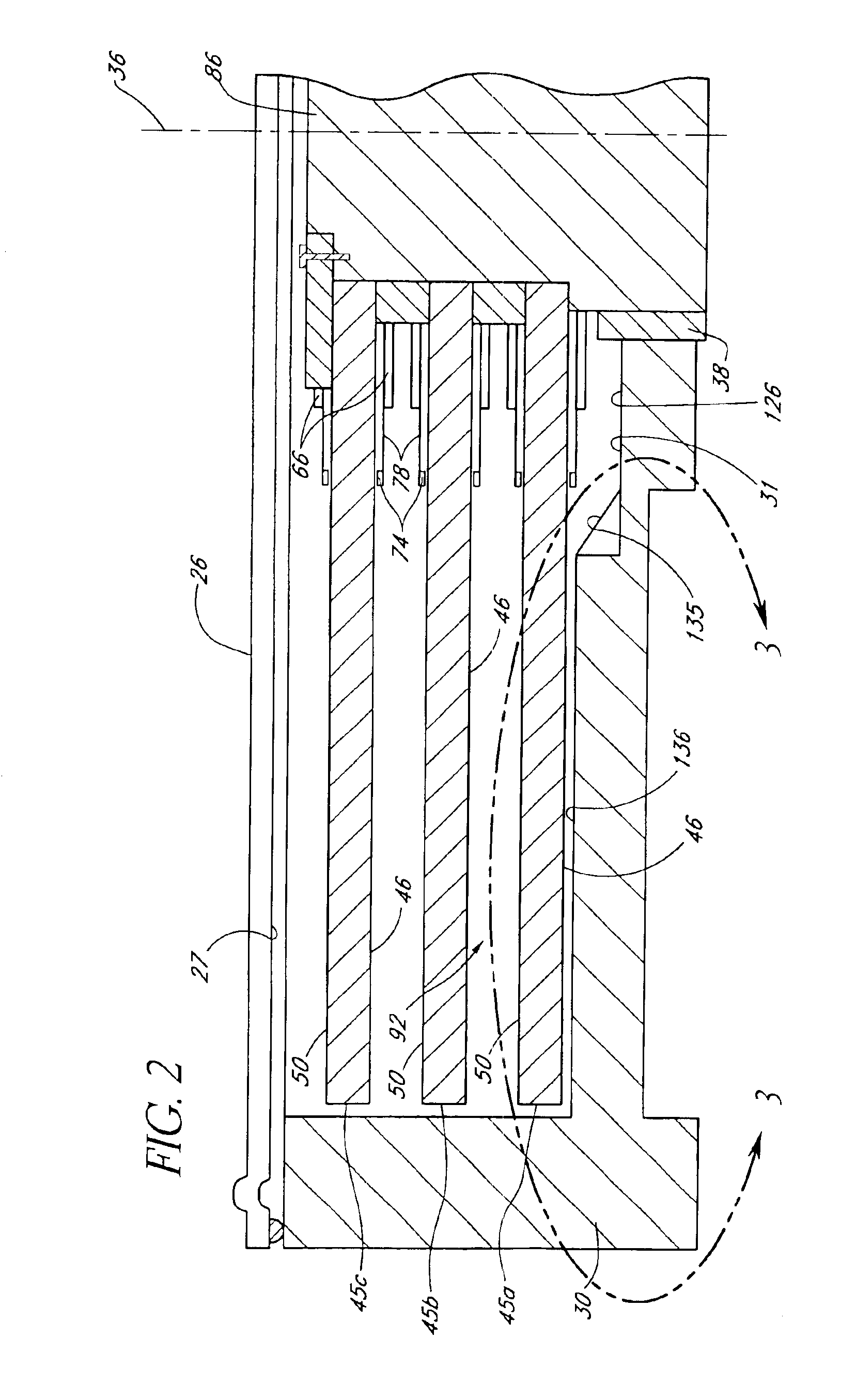
Disk drive including an airflow diverter element radially between spindle motor axis of rotation and cavity in shroud surface
InactiveUS6876514B1Reducing temperature influence on carrierApparatus for flat record carriersRotational axisDisk pack
A disk drive including a disk drive base and a cover attached to the disk drive base. The disk drive further includes a rotatable disk including a disk surface extending to an outer periphery. The disk drive further includes a spindle motor including an axis of rotation. The spindle motor is rotatably coupled to the disk drive base for rotating the disk about the axis of rotation. The disk drive further includes a shroud surface concentrically formed about and adjacent the outer periphery. The disk drive further includes a cavity formed in the shroud surface. The cavity extends to a cavity opening adjacent the outer periphery. The disk drive further includes an airflow diverter element extending from the cover towards the disk surface radially between the cavity opening and the axis of rotation for diverting disk rotation induced airflow adjacent the disk surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive having an acoustic damping shield assembly with an acoustic barrier layer
InactiveUS6958884B1Carrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersAcoustic absorptionEngineering
A disk drive that includes a head disk assembly (HDA) comprising a base having a top base surface and a bottom base surface, and a top cover secured to the top base surface; a printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) in communication with the HDA and comprising a first PCBA surface and a second PCBA surface wherein the first PCBA surface faces the bottom base surface; and a bottom cover fastened to and substantially covering the bottom base surface. The invention further includes an acoustic damping shield assembly placed between the bottom cover and the second PCBA surface, wherein the acoustic damping shield assembly comprises first and second acoustic absorption layers having major surfaces; an acoustic barrier layer placed in between the major surfaces; and the major surfaces and the acoustic barrier layer are fixed in a stacked relationship.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Read/write device, storage medium, driving method of read/write device, semiconductor laser life estimation method, program, program storage medium, and semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20050213436A1Shorten access timeDrive stabilityApparatus for flat record carriersHeads using thin filmsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEstimation methods
In a read / write device for writing and reading a storage medium by way of a heat assisted magnetic recording / reproduction scheme, the read / write device including an elevated slider provided with a semiconductor laser, provided is a heat dissipation mechanism for dissipating heat generated in the elevated slider to an outside of a housing of the read / write device. Further, the storage medium has a second heatsink layer formed of an Al film having a thickness of 50 μm, a backing layer, a heat barrier layer, a first heatsink layer, a magnetic recording layer, and a protection film on a glass substrate. With this arrangement, in a read / write device which performs a heat assisted magnetic recording and reproduction by a semiconductor laser provided on the elevated slider, the occurrence of malfunction due to temperature rises in the storage medium is prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
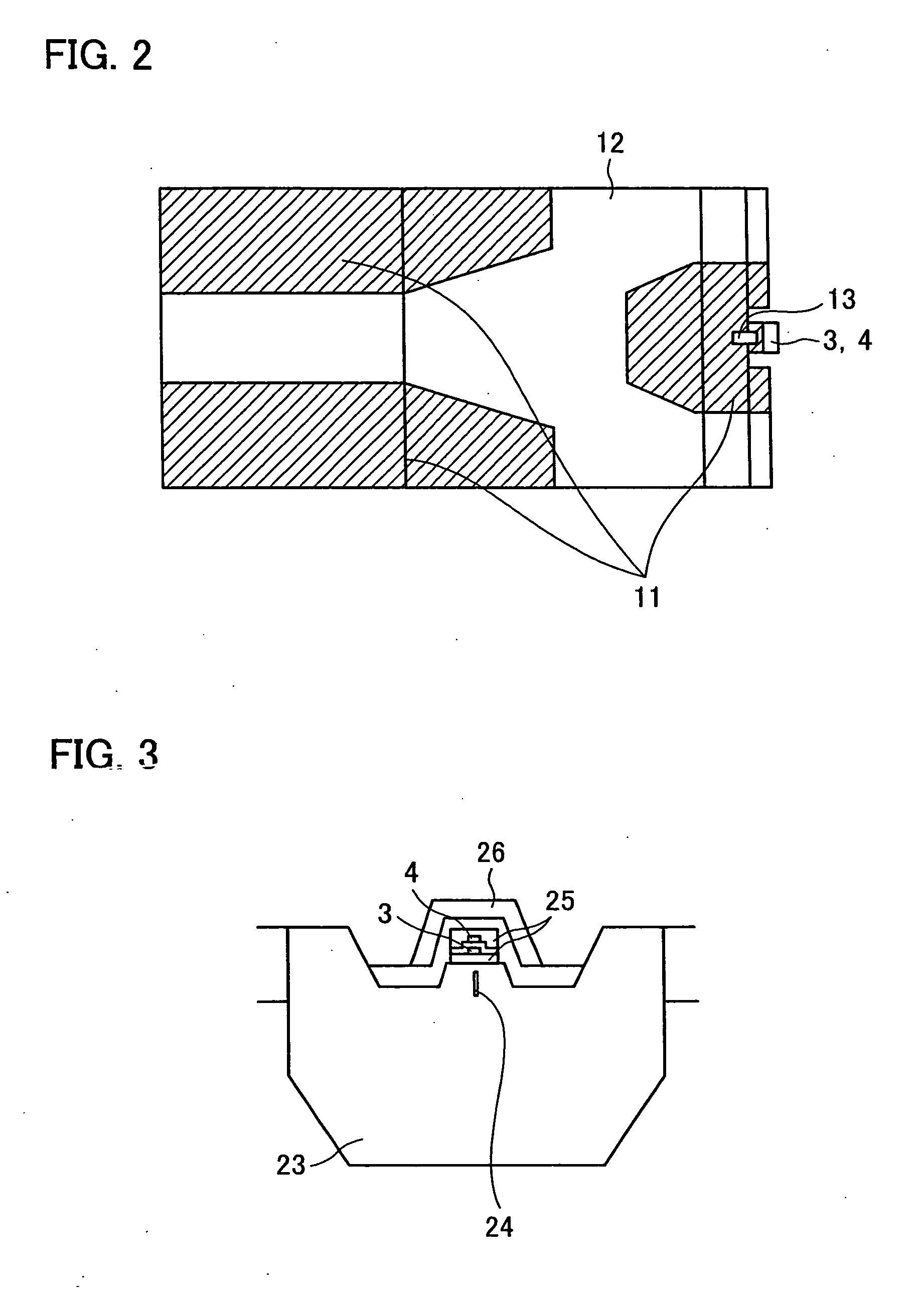
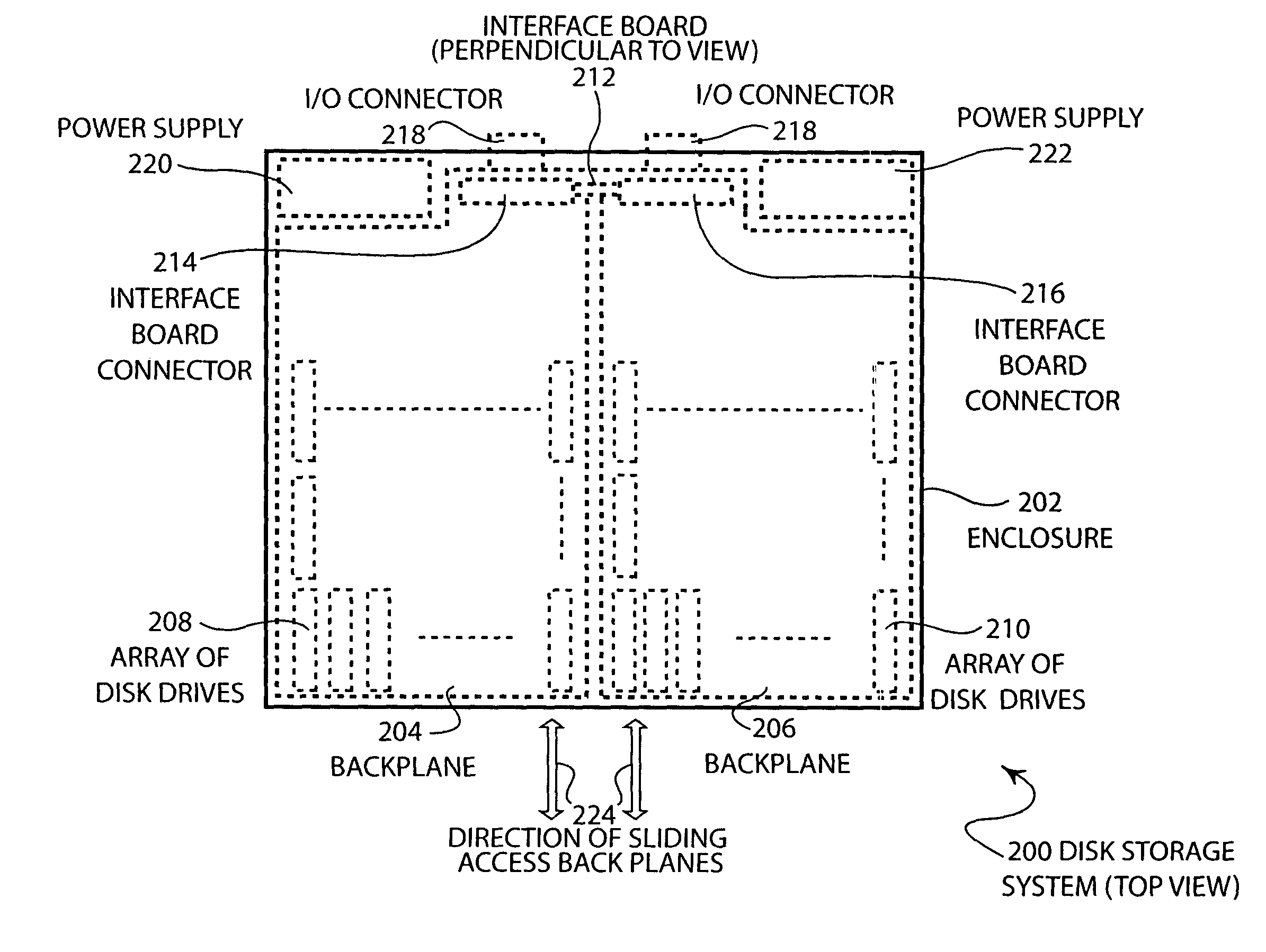
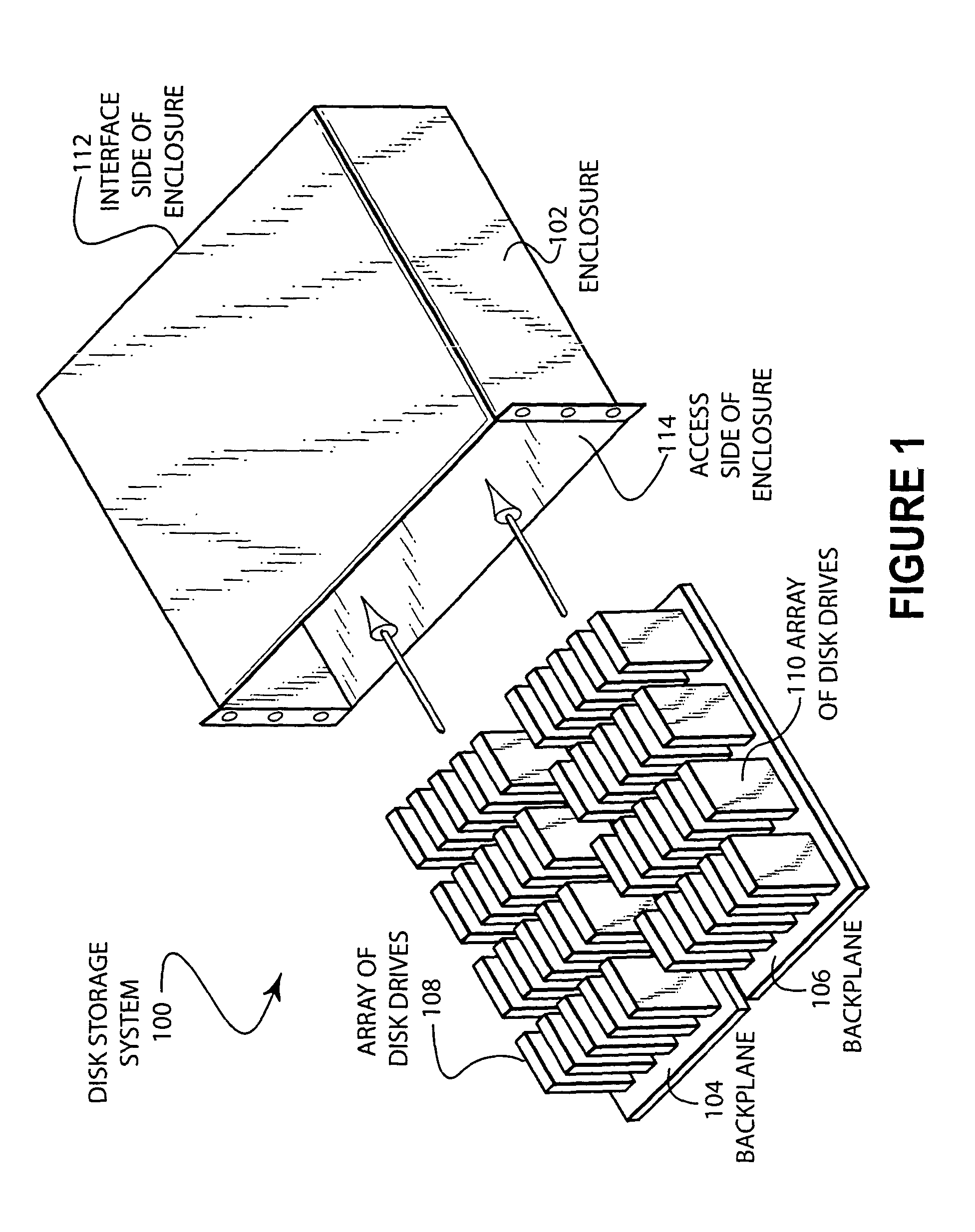
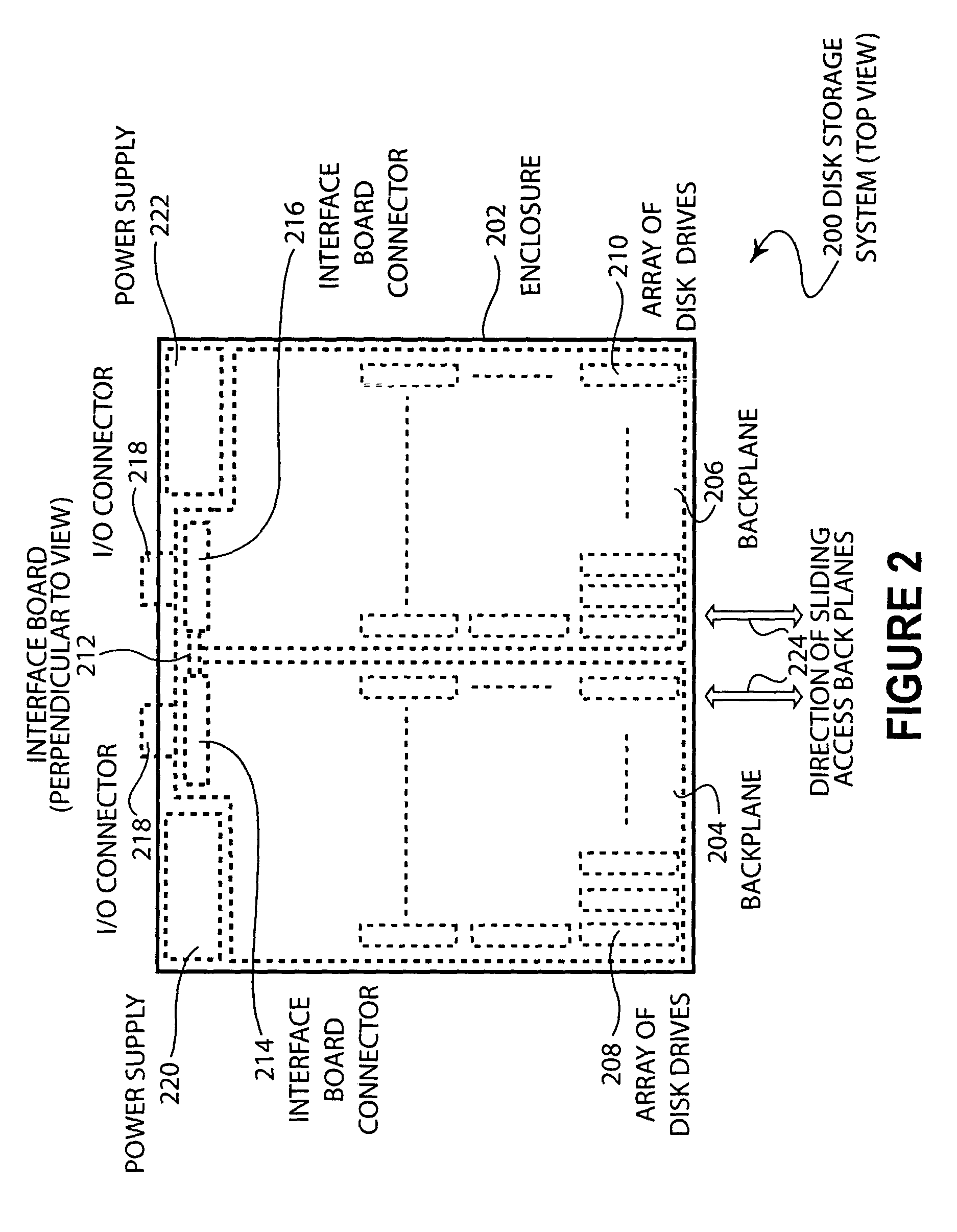
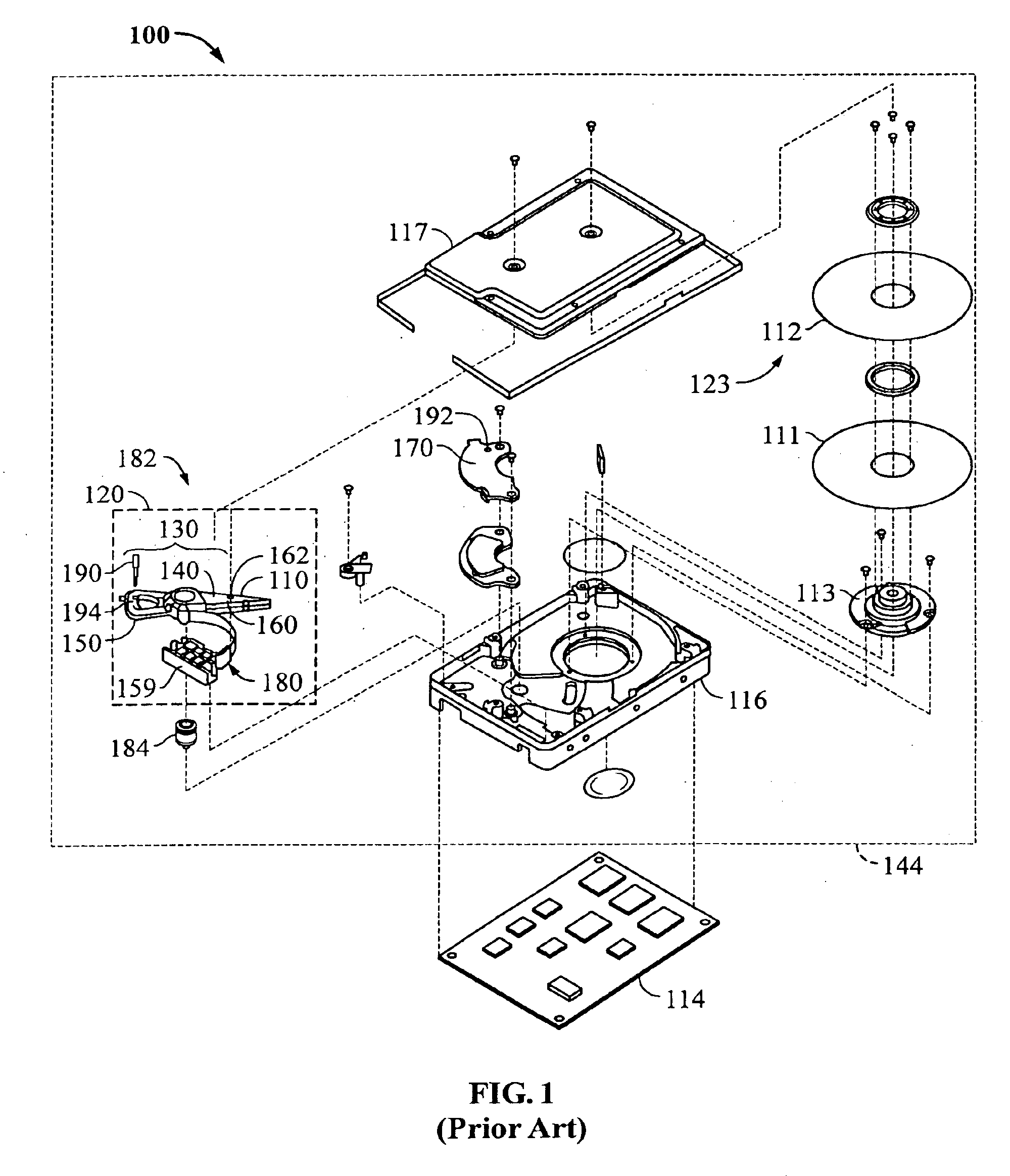
Disk storage system with removable arrays of disk drives
InactiveUS6987674B2Reduce in quantityHigh degree of symmetryCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersRAIDEmbedded system
Two sets of disk drives are mounted in a grid arrangement onto a backplane to form a removable multi-disk drive unit for a high capacity disk storage system. The removable units may be mounted into an enclosure that contains a RAID controller. The disk drives are mounted such that the longest edge of the disk drive is perpendicular to the plane of the backplane.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Disk drive comprising a cover shaped to improve radial and axial shrouding
InactiveUS6922308B1Easy to coverImproved shroudingApparatus for flat record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersElectric machineEngineering
A disk drive with improved shrouding is disclosed. The disk drive comprises a disk, a spindle motor for rotating the disk, a head, an actuator arm for actuating the head radially over the disk, a base, and a cover attached to the base to form a head disk assembly chamber. The cover comprises an inner surface and an outer surface, and a shroud extending axially from the inner surface into the head disk assembly chamber substantially enveloping the periphery of the disk, including at least part of the periphery coextensive with the actuator arm, to provide radial shrouding of the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
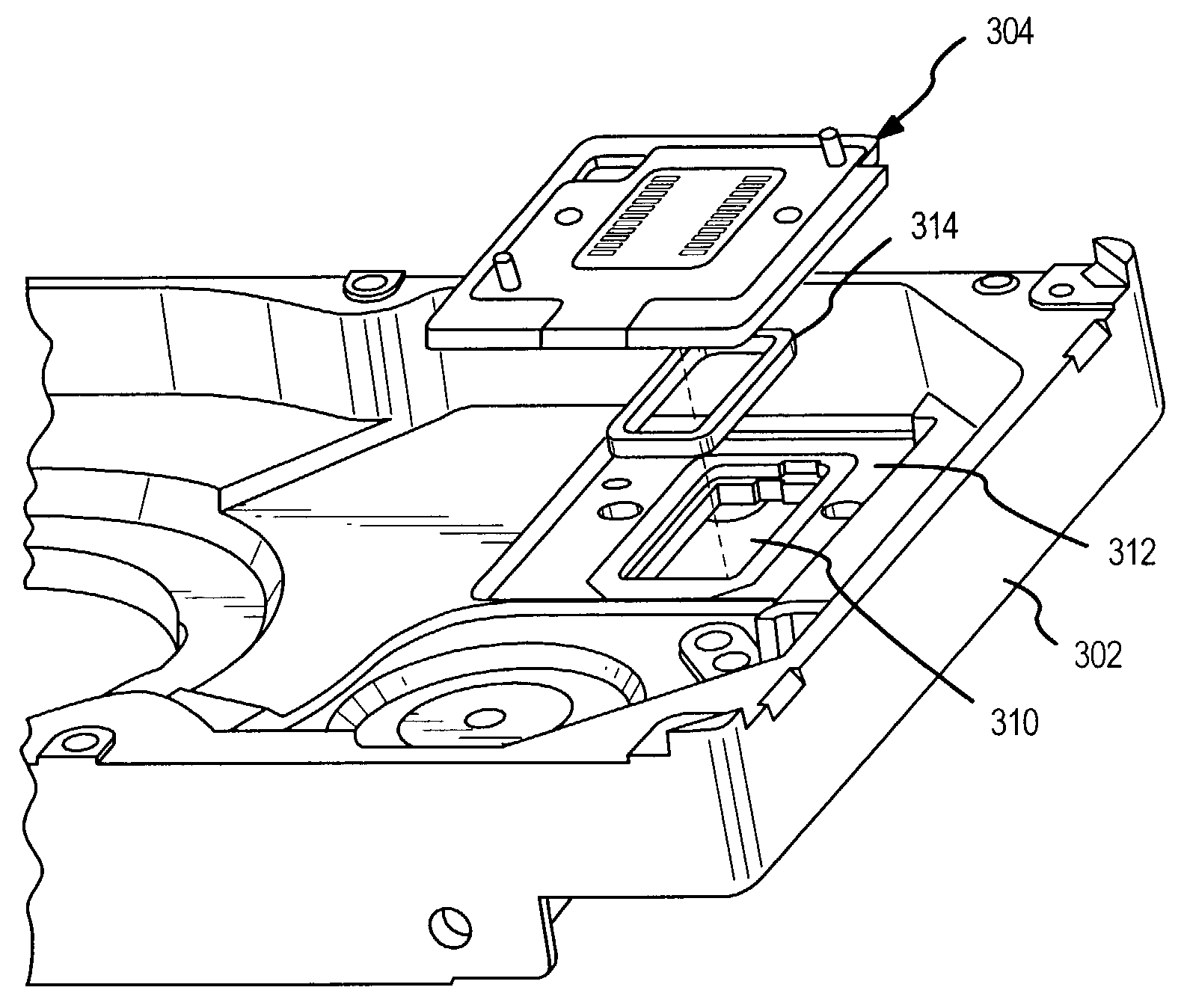
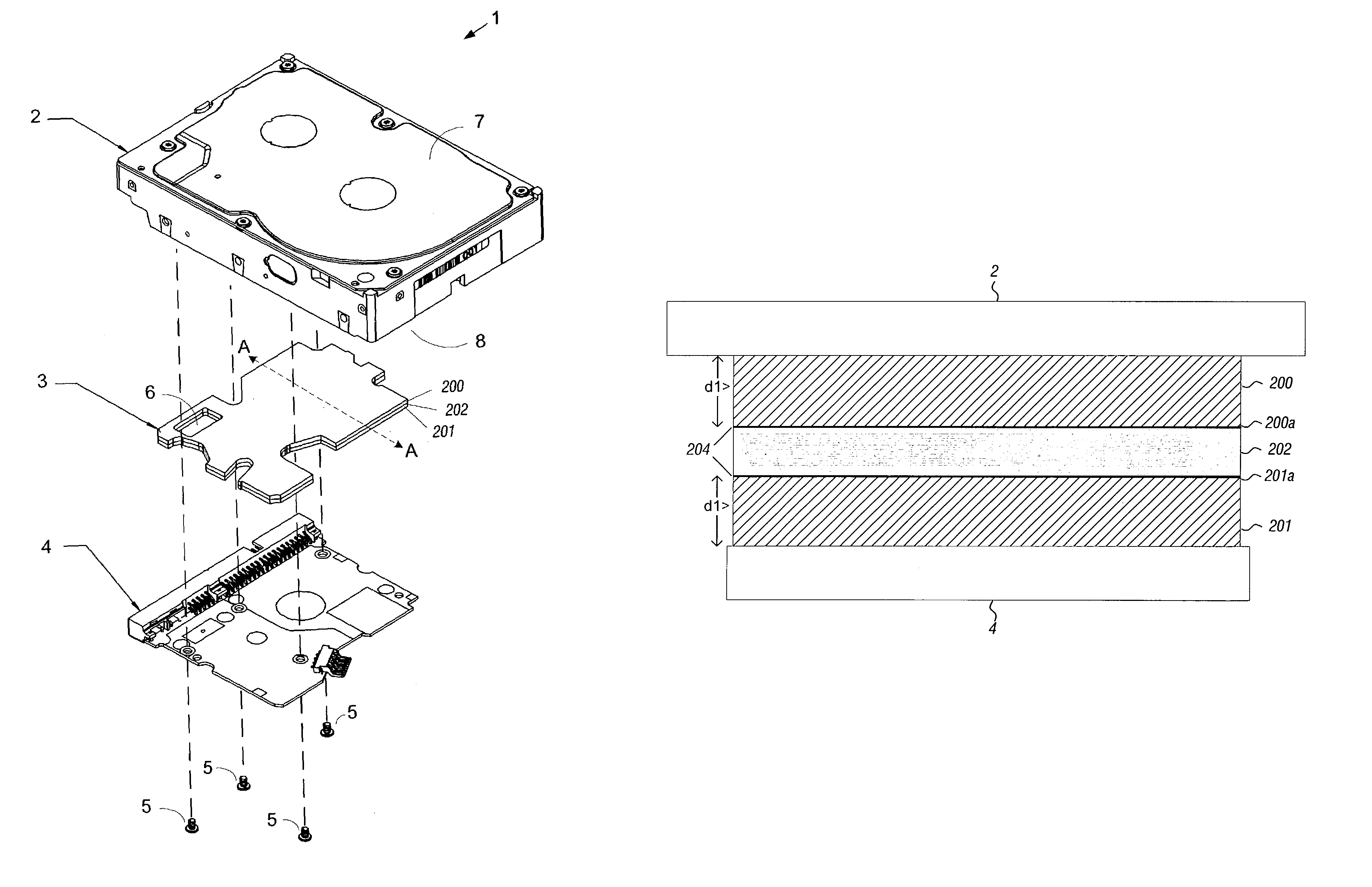
Bulkhead connector for low leak rate disc drives
InactiveUS6970322B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsCarrier constructional parts dispositionFlexible circuitsEngineering
A disc drive has a rotatable disc carried by a spindle motor and an actuator assembly with a read / write head. A base deck supports the spindle motor and the actuator assembly and defines a connector opening for transmitting electrical signals from the read / write head through the base deck to a printed circuit board attached to an exterior surface of the base deck. A bulkhead connector is adhesively affixed to the base deck to cover the connector opening. The bulkhead connector comprises a backing plate and a flex circuit bonded to the backing plate. The flex circuit extends across a top surface of the backing plate, wraps around one edge of the backing plate, and extends across a bottom surface of the backing plate.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Two-stage sealing of a data storage assembly housing to retain a low density atmosphere
ActiveUS7218473B2Stable operation of driveGuaranteed uptimeElectrical transducersCarrier constructional parts dispositionHermetic sealEngineering
A disc drive includes a base plate and a structural cover removably attached to the base plate to form an internal environment within the disc drive that is filled with a low density gas such as helium. A sealing cover is permanently attached to the base plate and the structural cover to form a hermetic seal for the low density gas. A first seal secured between the base plate and the removable structural cover permits short term operation of the disc drive with minimal leakage of the low density gas so that the drive can be tested prior to permanent attachment of the sealing cover.
Owner:SEAGATE SINGAPORE INT HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
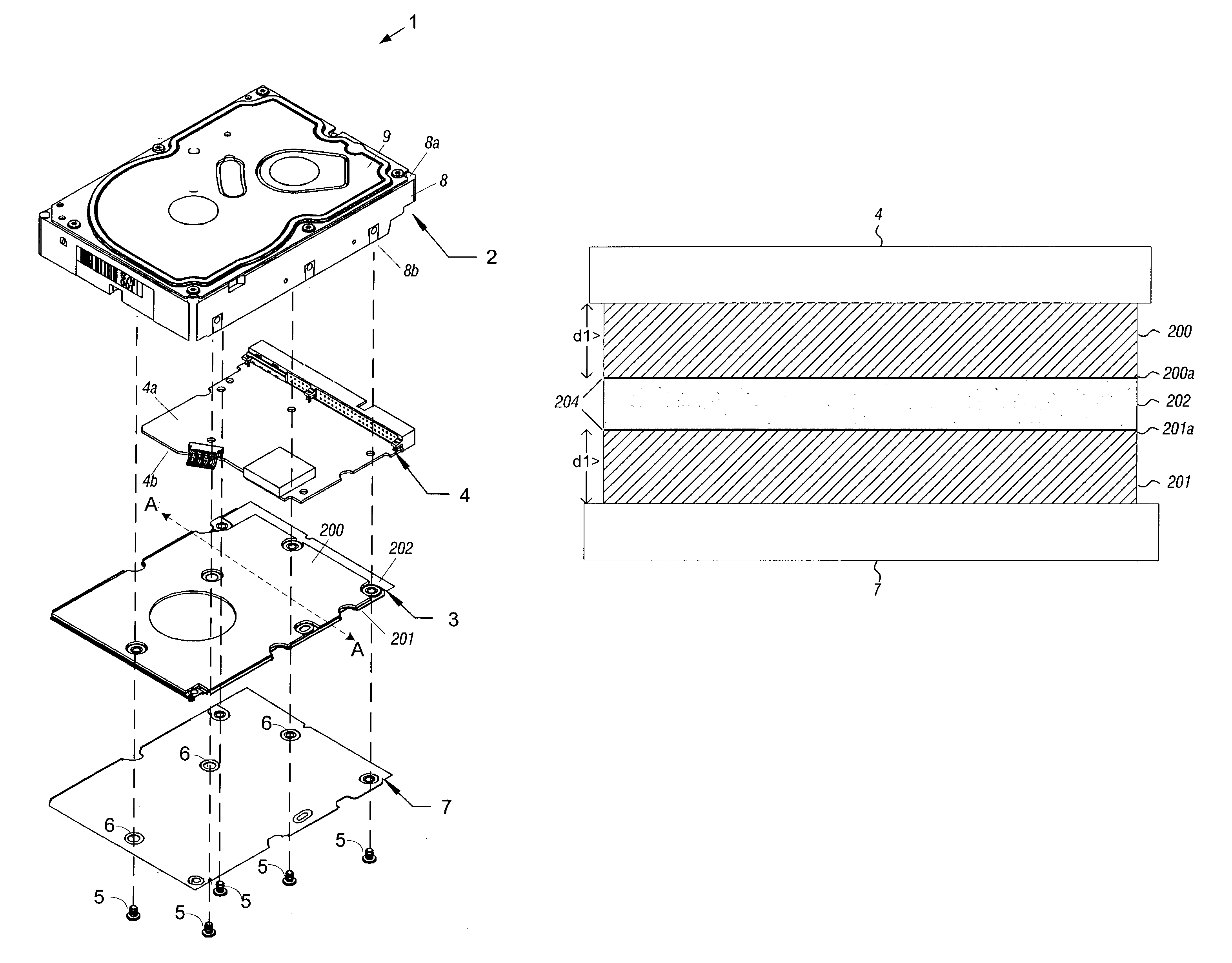
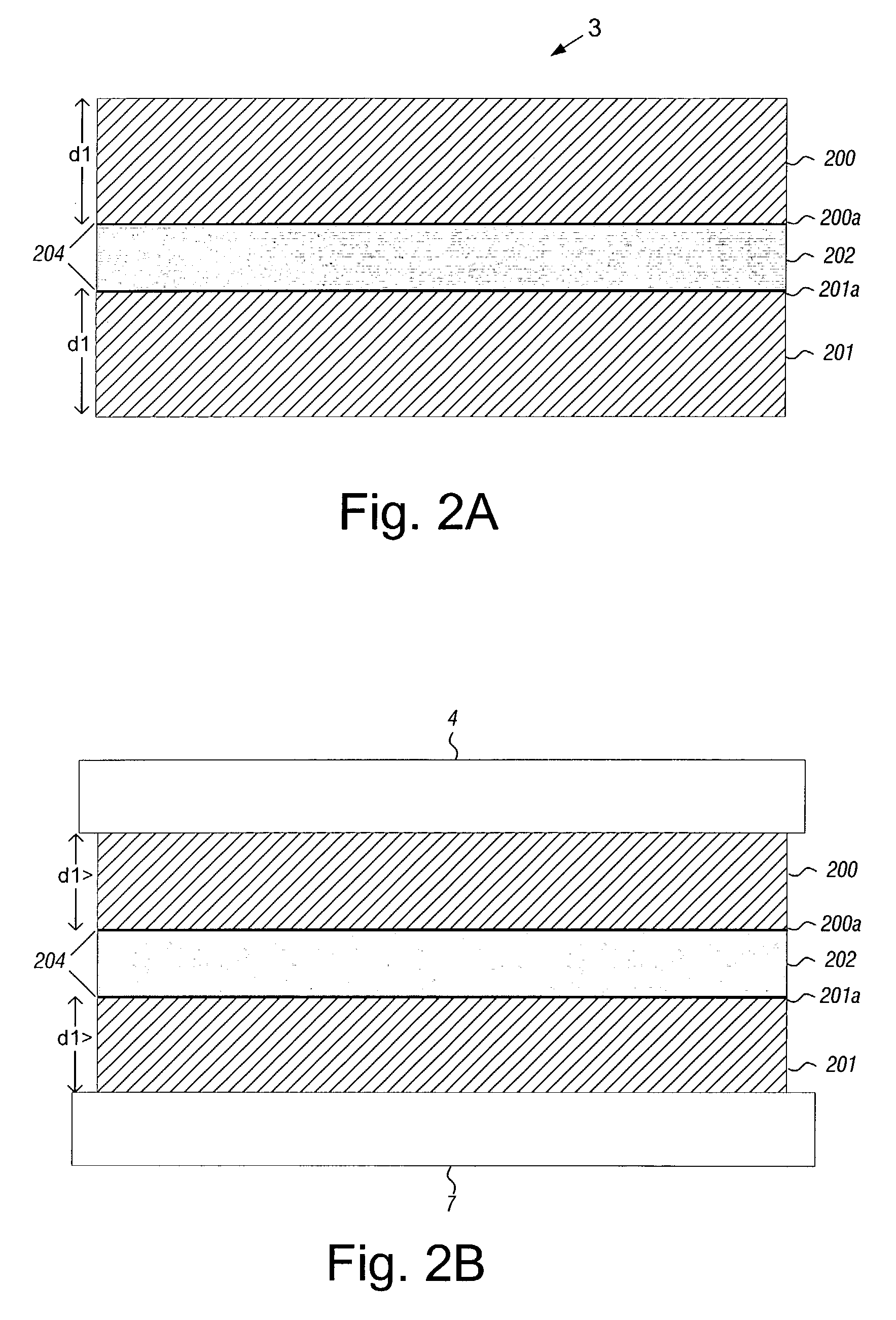
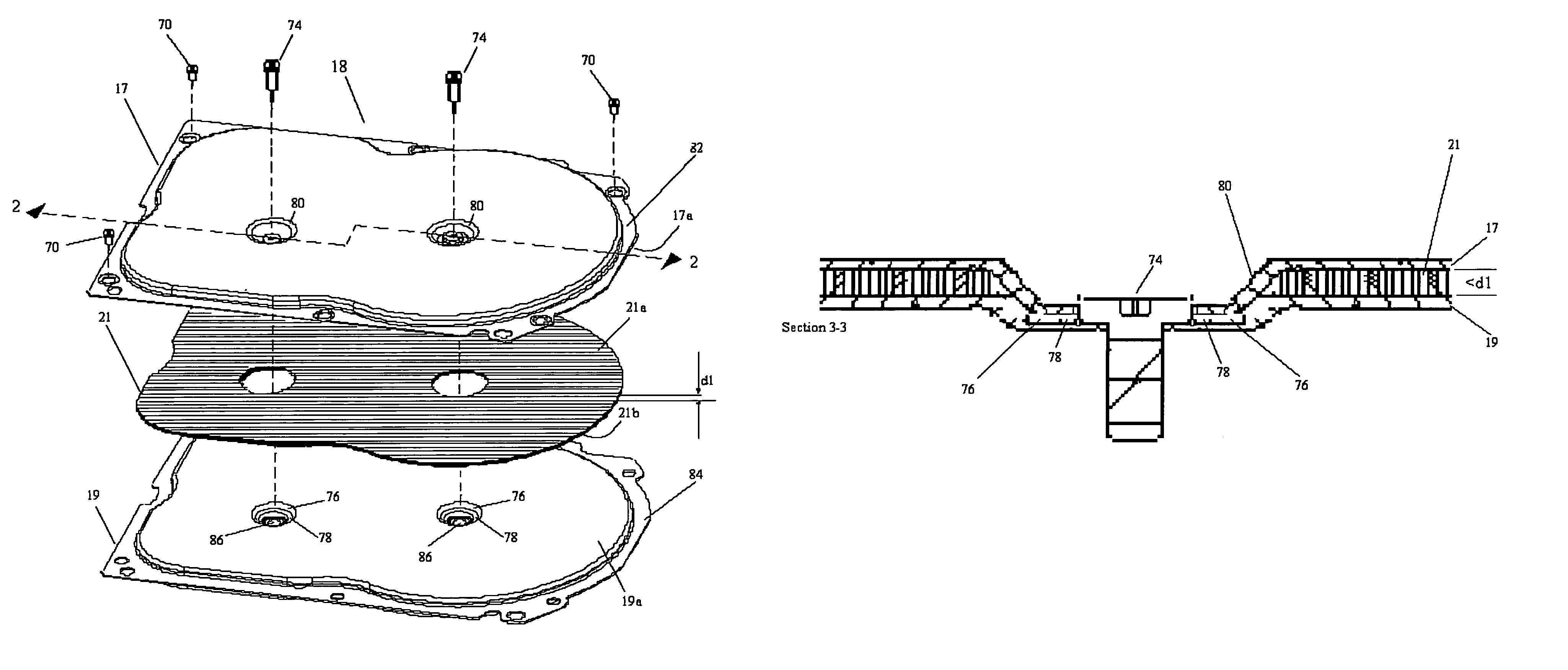
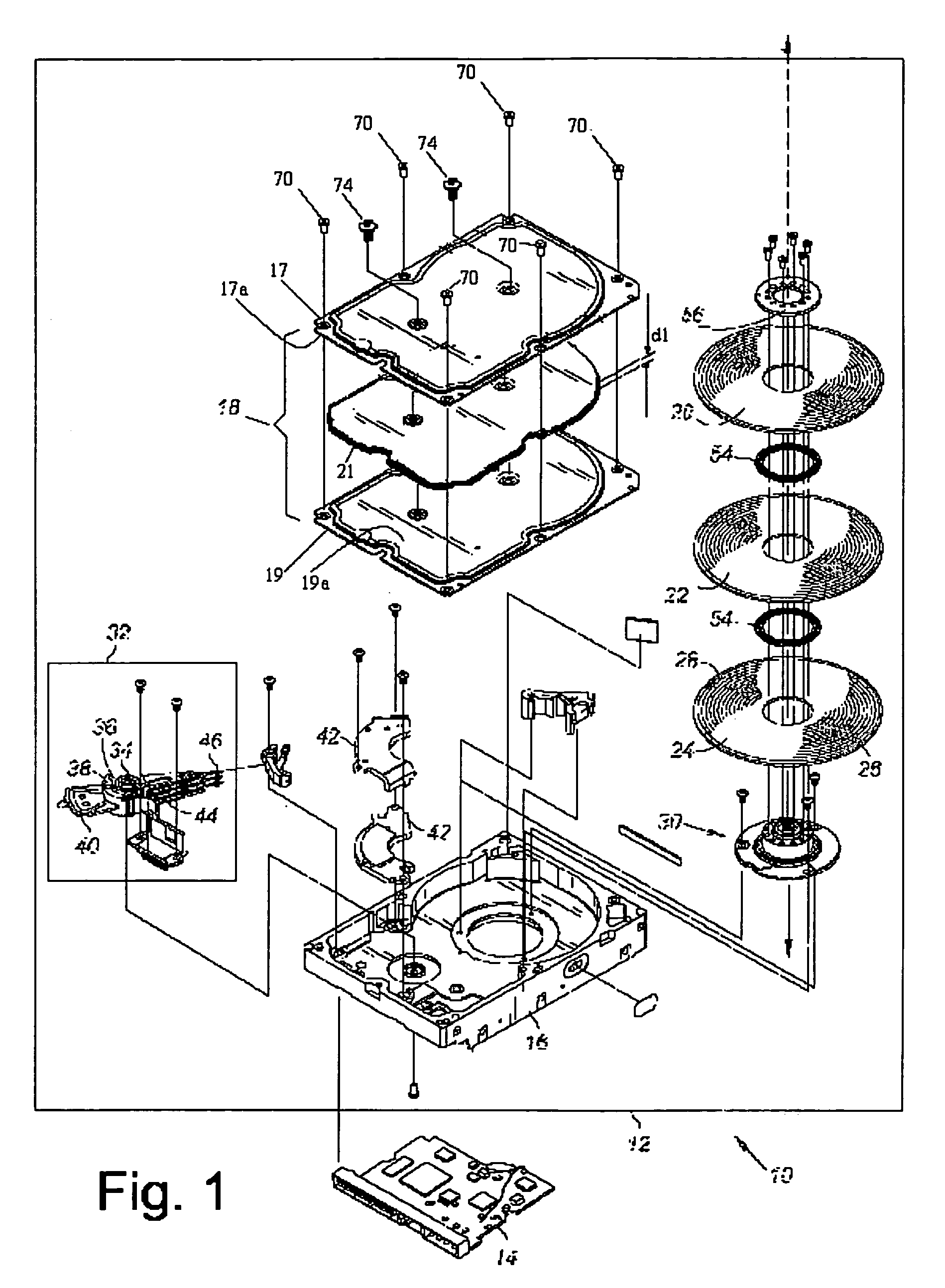
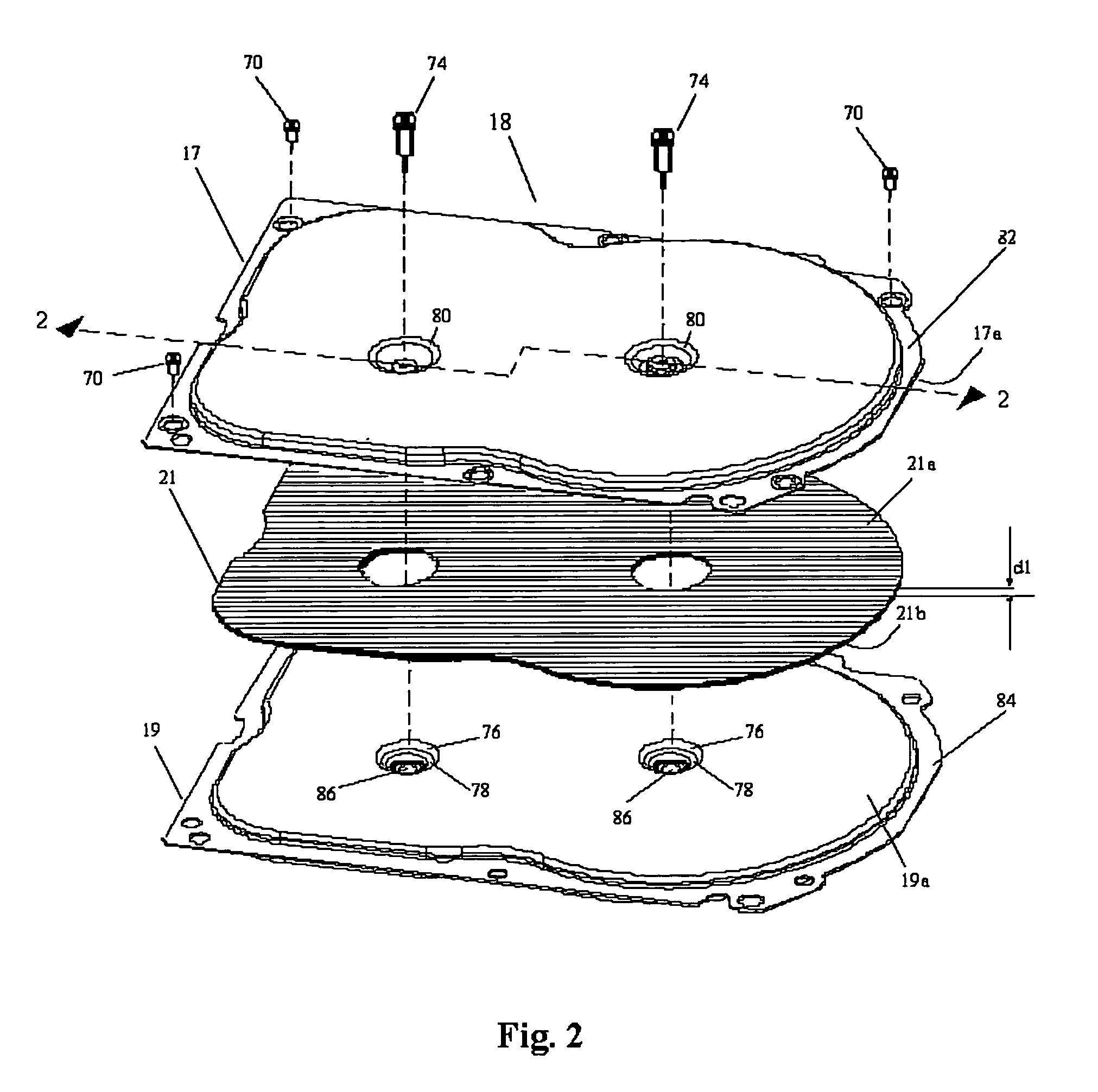
Disk drive having cover assembly which compresses a foam member between substantially planar rigid members
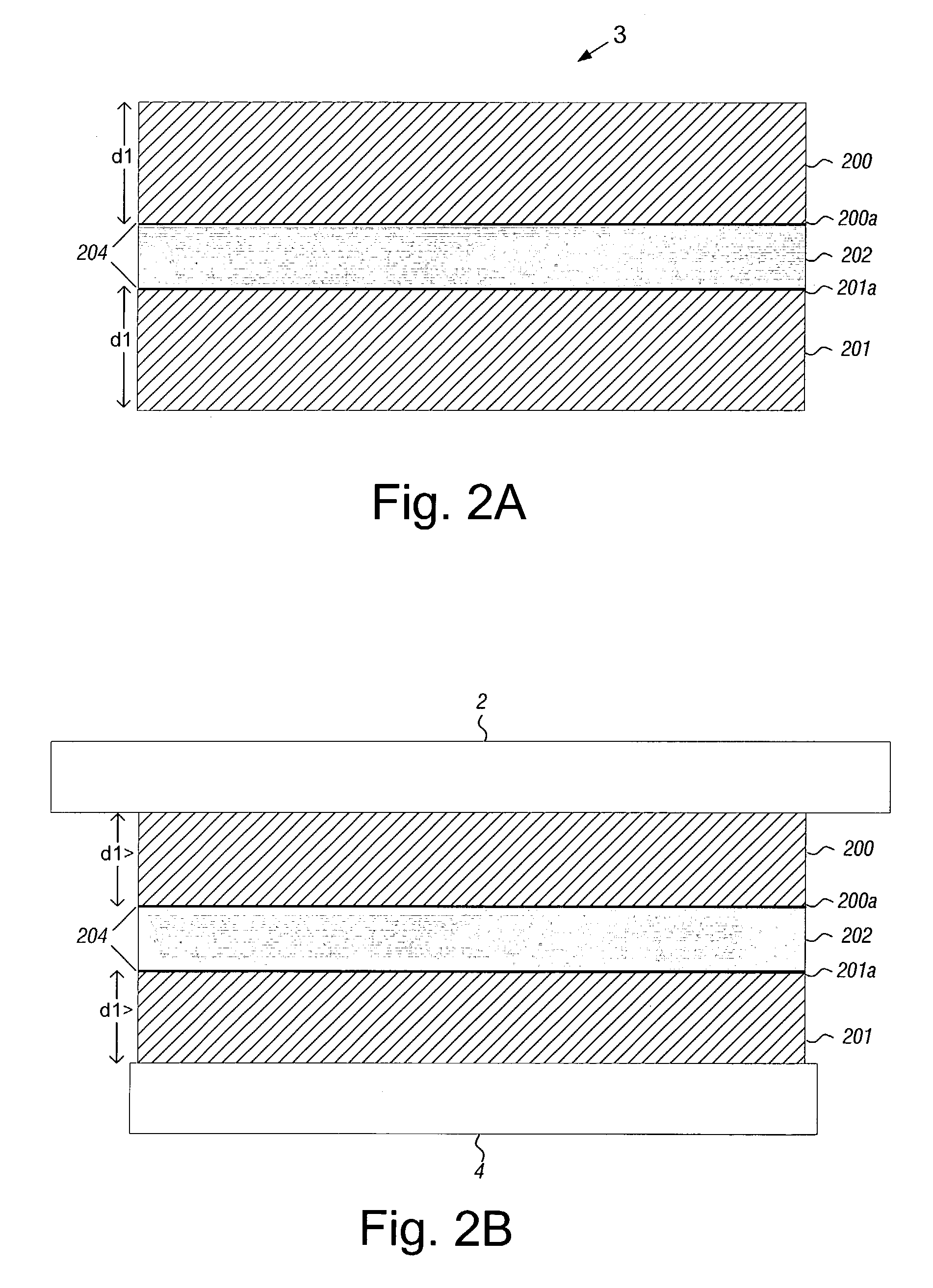
InactiveUS6950275B1Damping noiseCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersEngineeringCompression member
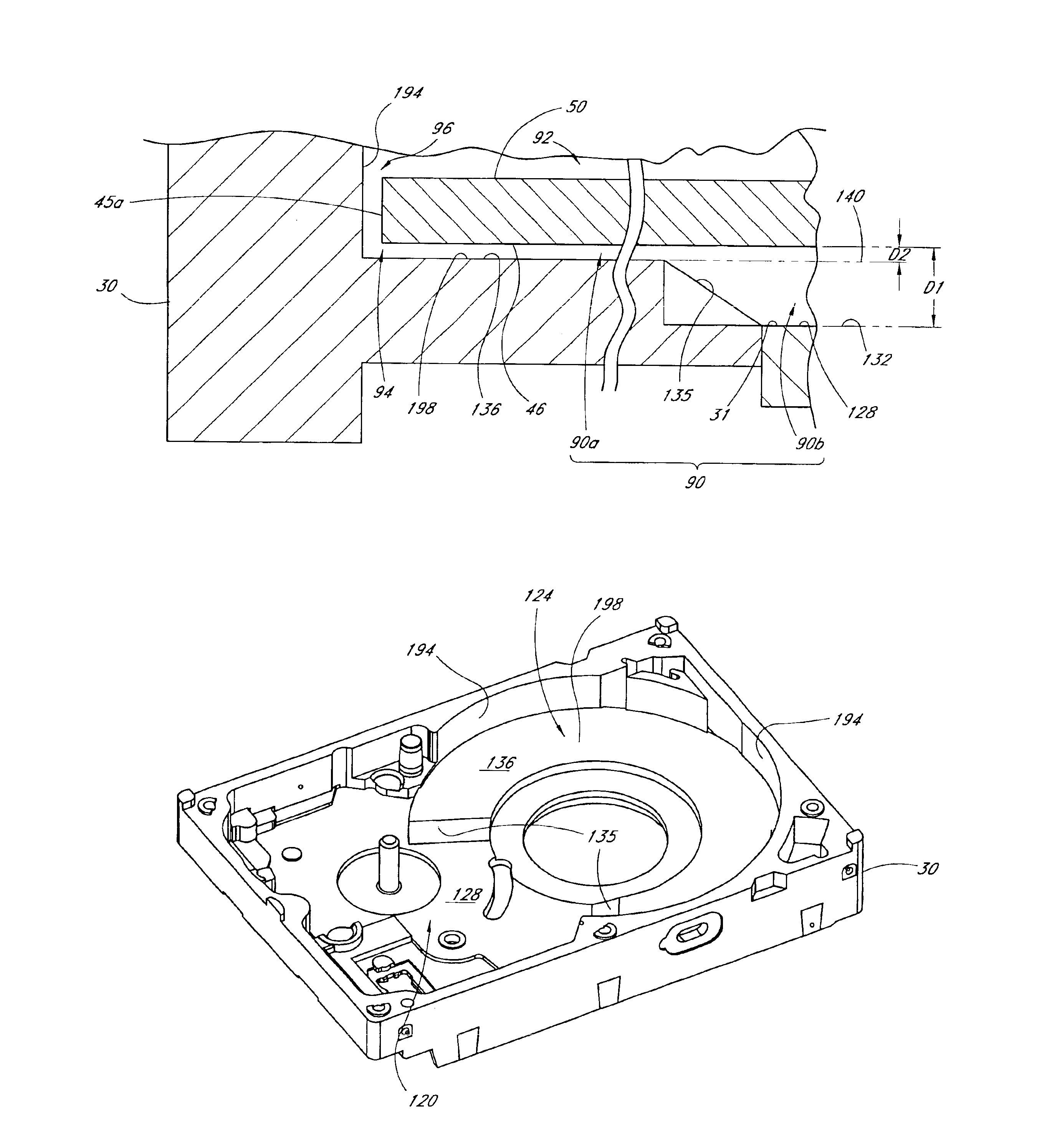
A disk drive including a head disk assembly in communication with a printed circuit board assembly, and further includes a disk drive base and a disk drive cover assembly collectively housing a head stack assembly and a data storage disk mounted on a spindle motor assembly for rotating the storage disk. The disk drive cover assembly further includes first and second substantially-planar rigid members having major surfaces, a compressible member of a foam composition placed in between the major surfaces wherein the compressible member is characterized by an unconstrained thickness d1, and wherein the major surfaces and the compressible member are fixed in a stacked relationship to compress the compressible member to a thickness less than d1. The head disk assembly further includes structure for fixing the disk drive cover assembly to the head stack assembly and the spindle motor assembly.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Protective apparatus for sensitive components
InactiveUS6967833B2Efficient and effectiveImprove efficiencyCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersHard disc driveStructural engineering
The present invention is directed to a protective apparatus for housing and protecting sensitive components disposed therein, such as a central processing unit (CPU) or a hard drive. The protective apparatus includes an outer casing, a fan panel, a connector panel, an internal box including the sensitive components and located within the outer casing, an internal housing contained within the internal box, and shock assemblies suspending the internal housing within the internal box.
Owner:INTEGRIAN
Disk drive having an acoustic damping assembly with an acoustic barrier layer
ActiveUS6954329B1Apparatus for flat record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersAcoustic absorptionEngineering
A disk drive that includes a head disk assembly (HDA) having a disk drive base, and a printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) in communication with the HDA. The invention further includes an acoustic damping assembly placed between the disk drive base and the PCBA. The acoustic damping assembly includes first and second acoustic absorption layers having major surfaces, an acoustic barrier layer placed in between the major surfaces, and the major surfaces and the acoustic barrier layer are fixed in a stacked relationship.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
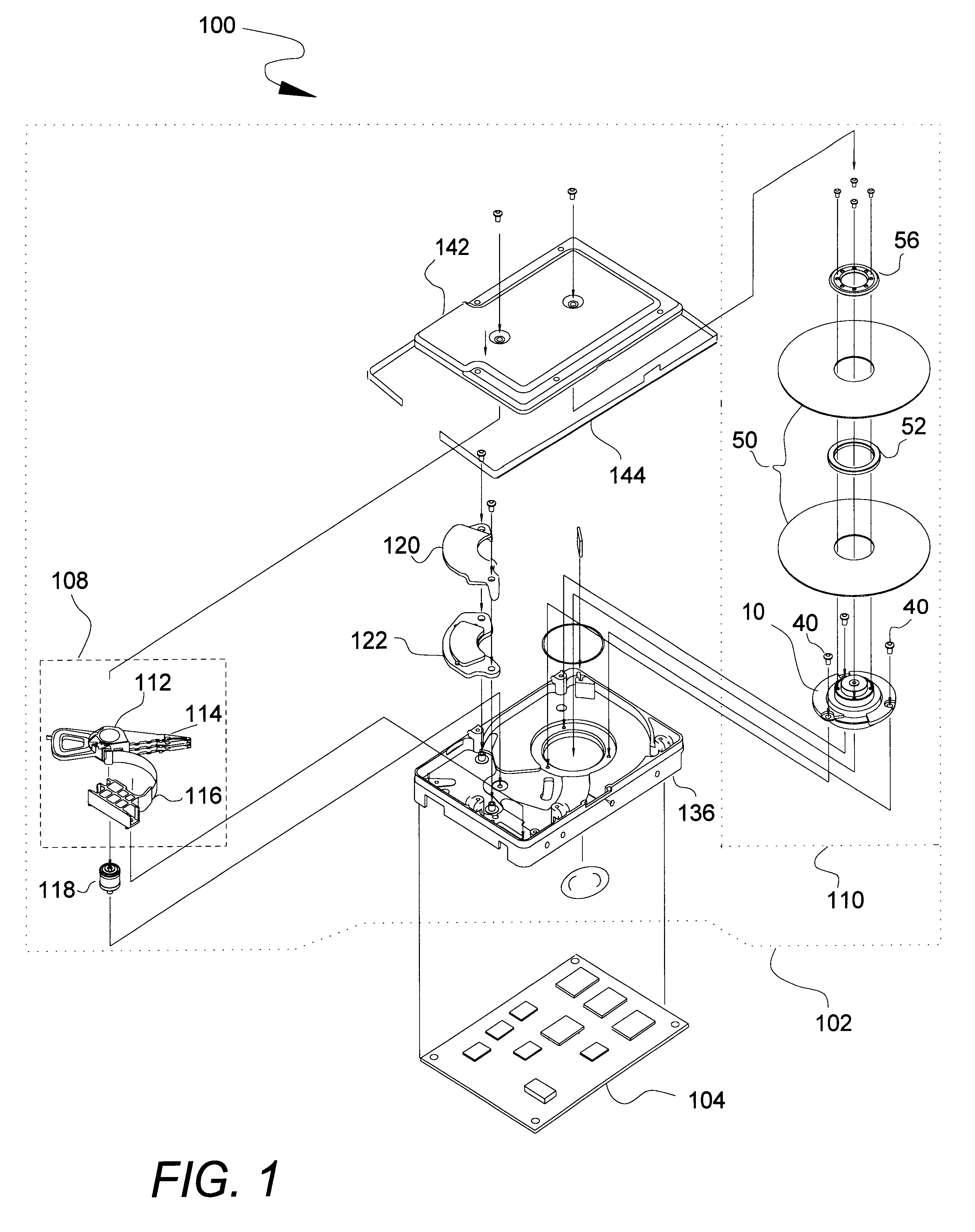
Disk drive having a head disk assembly enclosure including insert molded components
InactiveUS6900961B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsApparatus for flat record carriersEngineeringElectric motor
Disclosed is disk drive having a molded head disk assembly enclosure including insert molded components and methods for manufacturing the same. In one aspect, the invention may be regarded as a disk drive having a molded enclosure including a base, a cover, and a coupling mechanism to couple the base to the cover. A pivot is insert molded into the base. A first portion of a spindle motor is insert molded into the base. A second portion of a spindle motor is attached to the first portion to form the spindle motor. Further, a disk is mounted to the spindle motor and a head stack assembly having a coil portion is pivotally coupled to the pivot.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
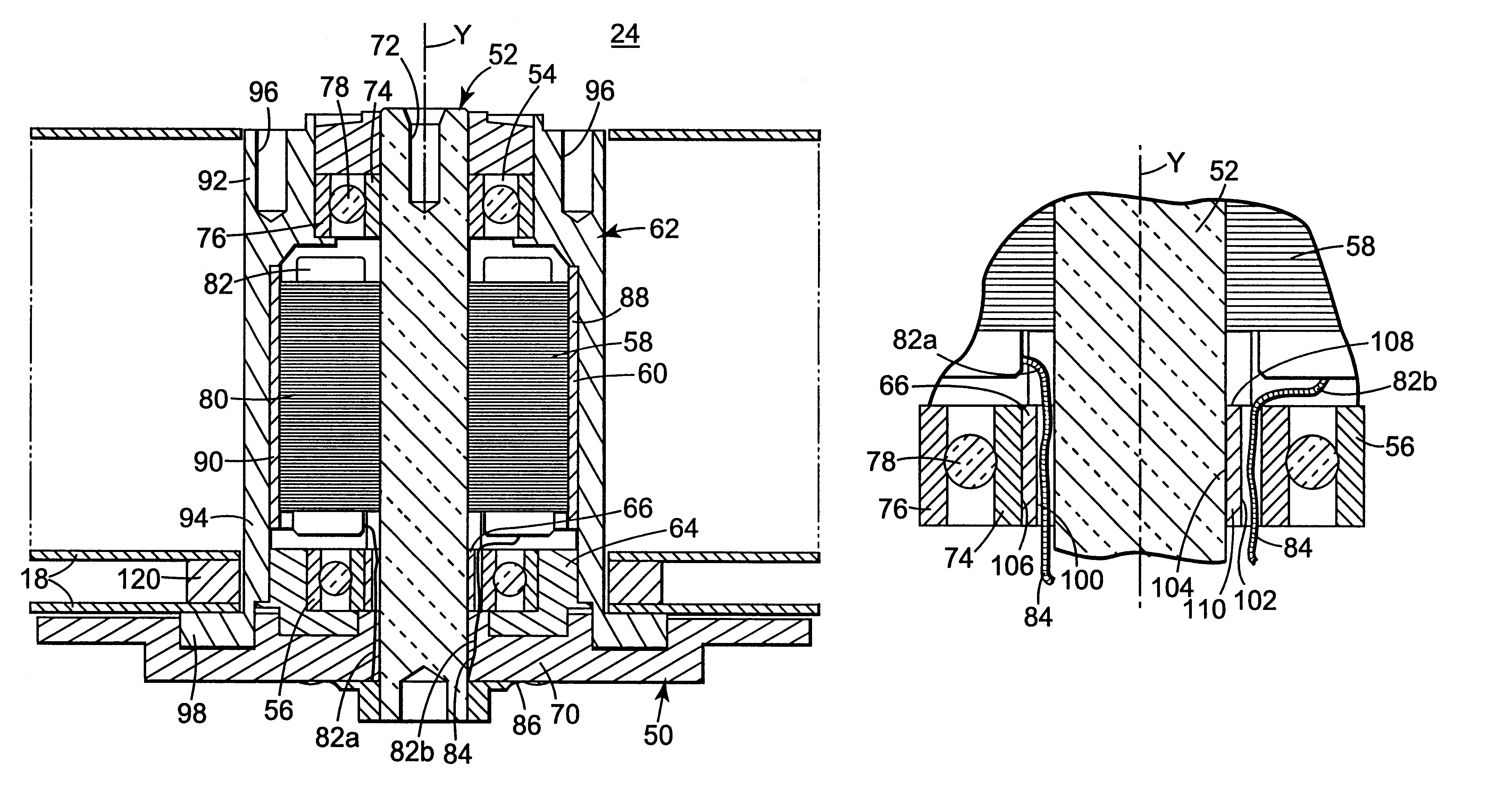
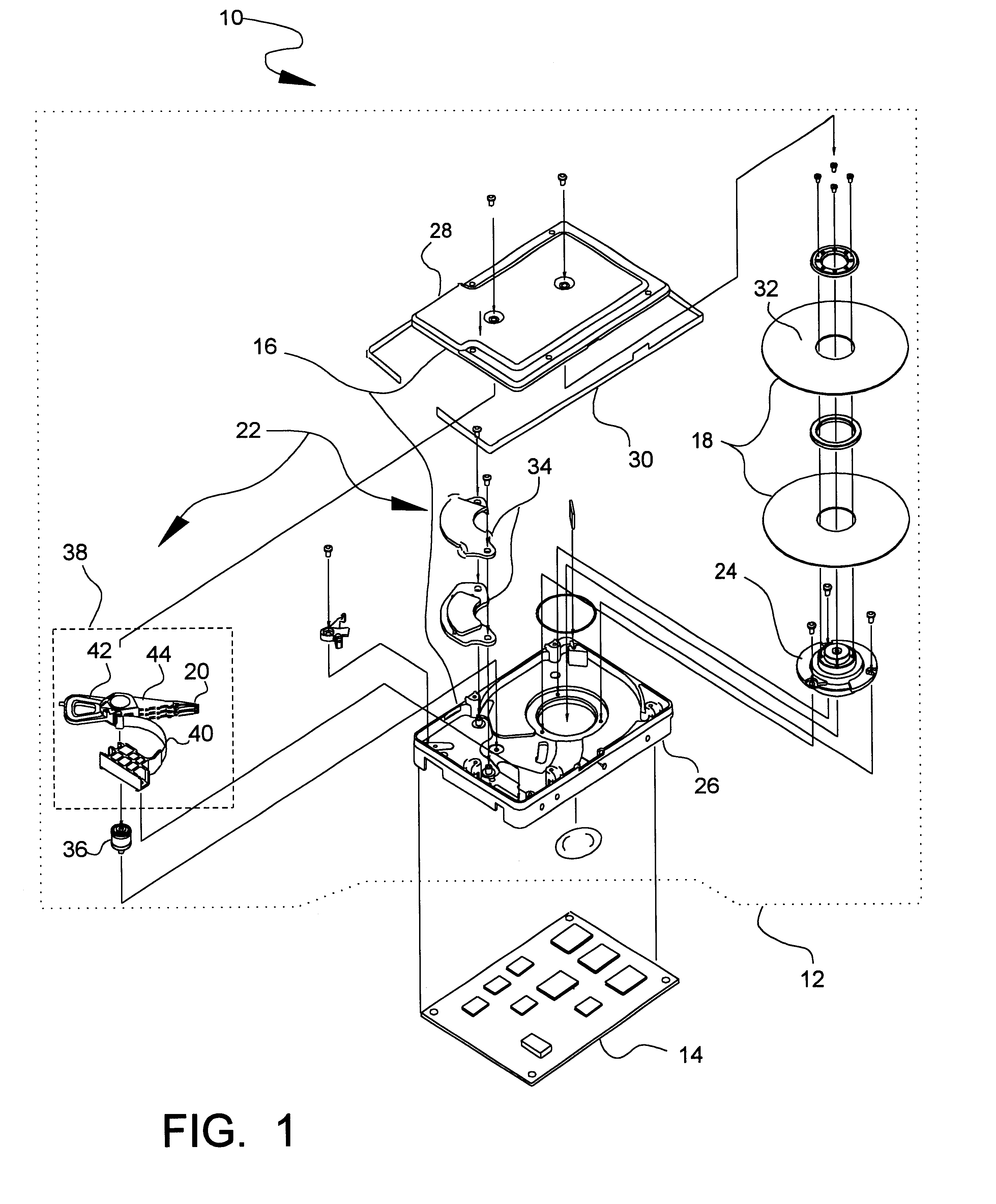
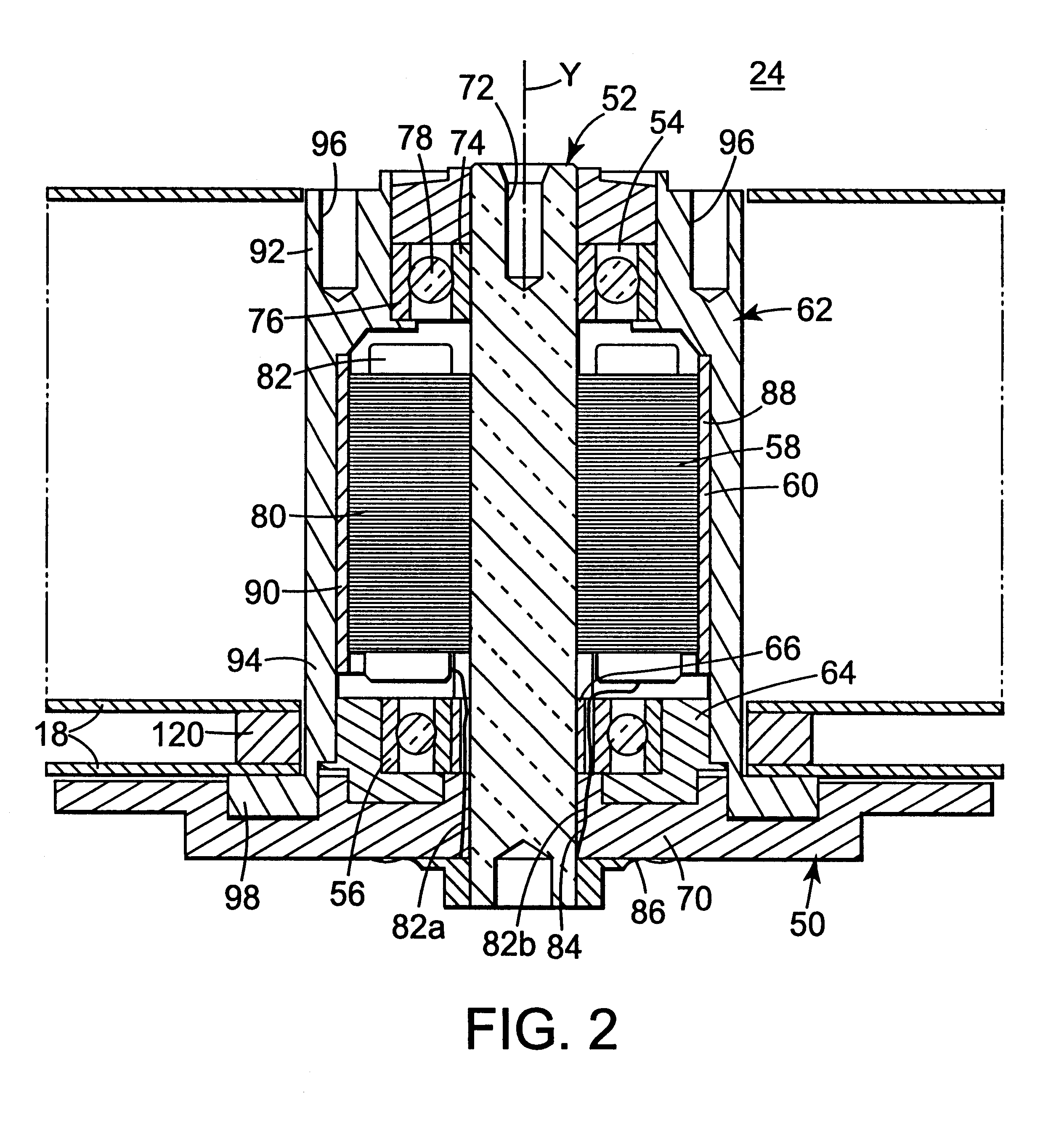
Disk drive spindle motor with wire guide insert
InactiveUS6215616B1Carrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A spindle motor for a disk drive includes a shaft, an upper bearing, a lower bearing, a stator, a hub and wire guide body. The upper bearing surrounds the shaft. The lower bearing surrounds the shaft, is spaced-apart from the upper bearing, and includes an inner race. The stator surrounds the shaft between the upper bearing and the lower bearing, and includes a stator wire extending from a stator core. The hub is concentrically positioned about the stator. The wire guide body is secured between the shaft and the lower bearing, and includes a generally cylindrically shaped surface and a channel. The channel is sized to receive the stator wire and is formed adjacent to the cylindrically shaped surface such that the channel opens into at least one of the shaft and the inner race.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Hard drive test fixture
InactiveUS20050109131A1Carrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersEngineeringTest fixture
The present invention is a method and apparatus for testing electrical or optical devices. The invention includes a test fixture having a base component, a first rail and a second rail coupled to the base component, a top component coupled to the first and second rails, and an interposer coupled to the first and second rails.
Owner:BENCHMARK ELECTRONICS SUZHOU
Aerodynamic base design for TMR reduction
InactiveUS6891696B1Apparatus for flat record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A disk drive includes an enclosure having a cover and a base, a spindle motor assembly, a disk, and an arcuate raised portion on the base. The disk is mounted on a hub of the spindle motor assembly and has a first surface and a second surface. The first surface is proximate the base and is spaced apart from the base by a first clearance distance. The arcuate raised portion on the base is spaced apart from the disk by a second clearance distance. The second clearance distance is less than the first clearance distance. At least a portion of the disk is superposed over the arcuate raised portion.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive with reduced thermal expansion induced disk slip
InactiveUS6185067B1Carrier constructional parts dispositionMagnetic circuit rotating partsThermal dilatationEngineering
A spindle motor for a disk drive includes a shaft, an aluminum hub, a bearing, a magnetic steel back iron, and a magnet. The hub includes an axial wall having an inner surface. The back iron has an upper portion and a lower portion. The hub is concentrically position about the shaft such that the inner surface extends along a direction of a longitudinal axis defined by the hub. The bearing is positioned between the hub and the shaft. The back iron is secured to the hub such that the upper portion abuts the inner surface, whereas the lower portion is spaced-apart radially from the inner surface, thereby forming a single gap between the back iron and the hub. Finally, the magnet is attached to the back iron such that an axial length of the magnet is substantially coextensive with an axial length of the back iron.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drives and host devices including a resetable shock sensor
InactiveUS6975476B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsApparatus for flat record carriersEngineeringMobile device
Disclosed herein are disk drives and mobile host devices that include a resetable shock sensor. A mobile host device may include a memory device configured to receive a shock event signal and a shock sensor. The shock sensor may be coupled to the memory device and is configured to generate the shock event signal. The shock sensor includes a fixed portion, and a movable portion responsive to shock events. The movable portion is configured to remain out of contact with the fixed portion until the mobile host device is subjected to a shock event greater than a predetermined magnitude and to contact and remain in contact with the fixed portion and to generate the shock event signal after the mobile host device is subjected to a shock event greater than the predetermined magnitude.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Hard disk system having a hard disk unit and a conversion unit for connection to a host device
InactiveUS7333328B2Easy to useCarrier constructional parts dispositionInput/output to record carriersEngineeringTransducing Unit
A large capacity HDD is handled as a portable recording medium. In a state where a portable hard disk (PHD) unit is mounted on a cradle, data is written and read between the PHD unit and a host device. By having a first engagement section on the side of the PHD unit and a second engagement section on the side of a mounting section of the cradle mutually engaged while the PHD unit is mounted on the mounting section, a state where the PHD unit is mounted on the mounting section is maintained.
Owner:SONY CORP
Disk drive having a disk plate body attached to a fixed spindle shaft of a spindle motor
InactiveUS6888697B1Apparatus for flat record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionElectric machineEngineering
A disk drive includes an enclosure including a disk drive base and a disk drive cover, a disk for storing data, a spindle motor attached to the disk drive base, the spindle motor for rotating the disk and including a fixed spindle shaft defining a longitudinal axis, and a disk plate attached to the disk drive base. The disk plate includes a plate body extending radially above the disk and spaced-apart longitudinally from the disk. The plate body is attached to the fixed spindle shaft.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Popular searches
Payment architecture Record carriers used with machines Electric digital data processing Verifying markings correctness Fluid-dynamic spacing of heads Protective measures for recording heads Reducing physical parameters of carriers Cooling/ventilation/heating modifications Visual/graphical programming Specific program execution arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com