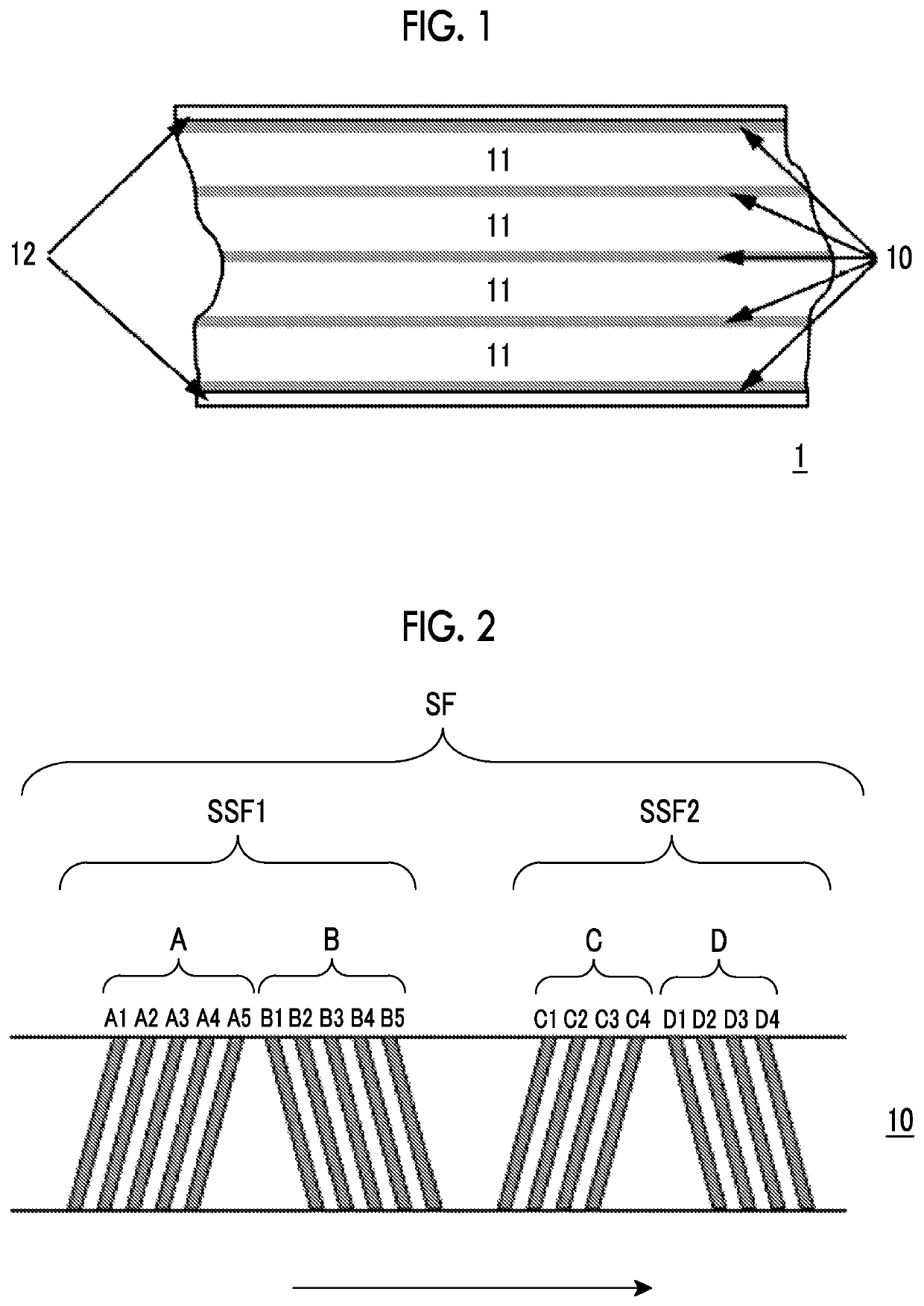
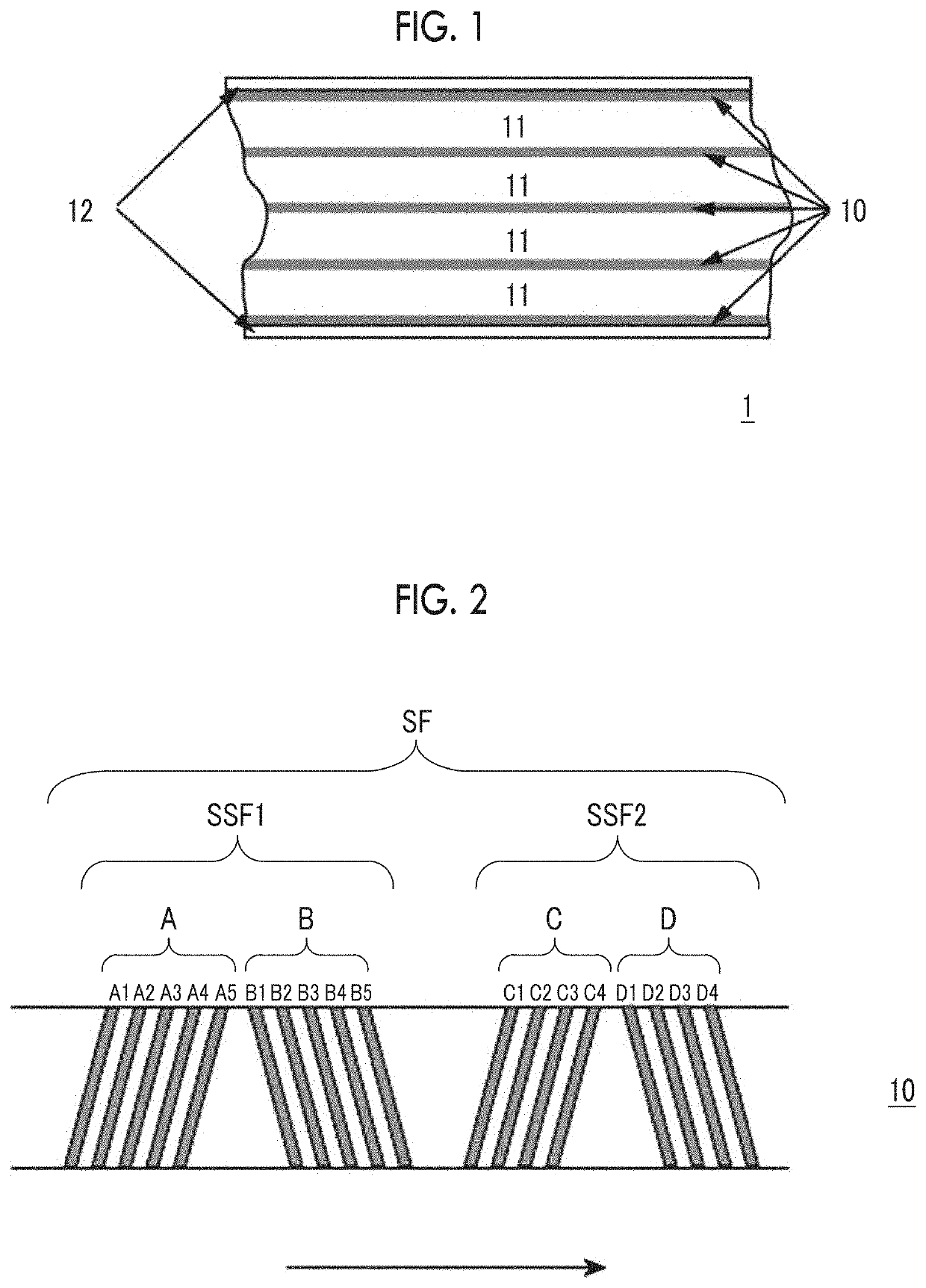
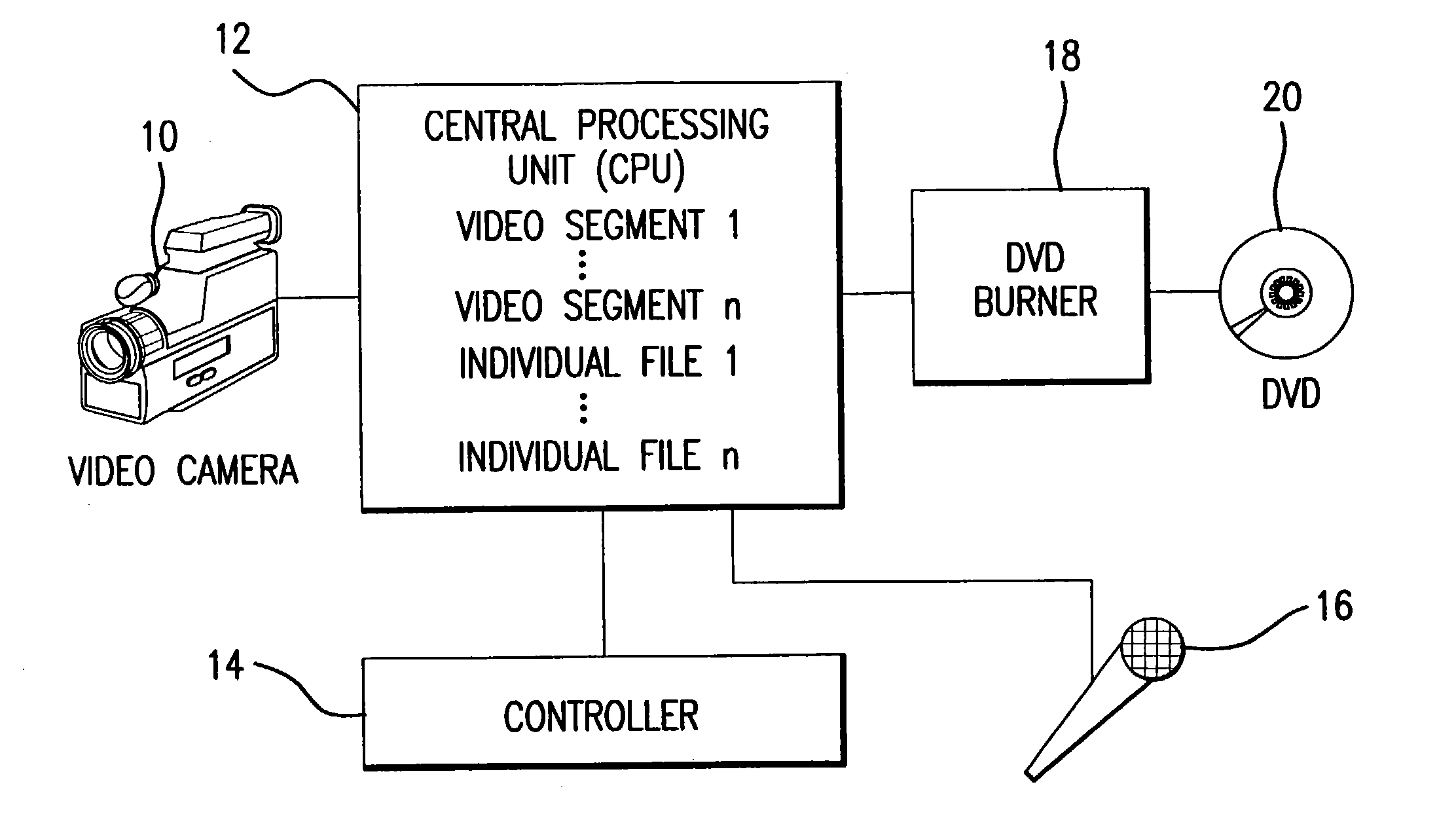
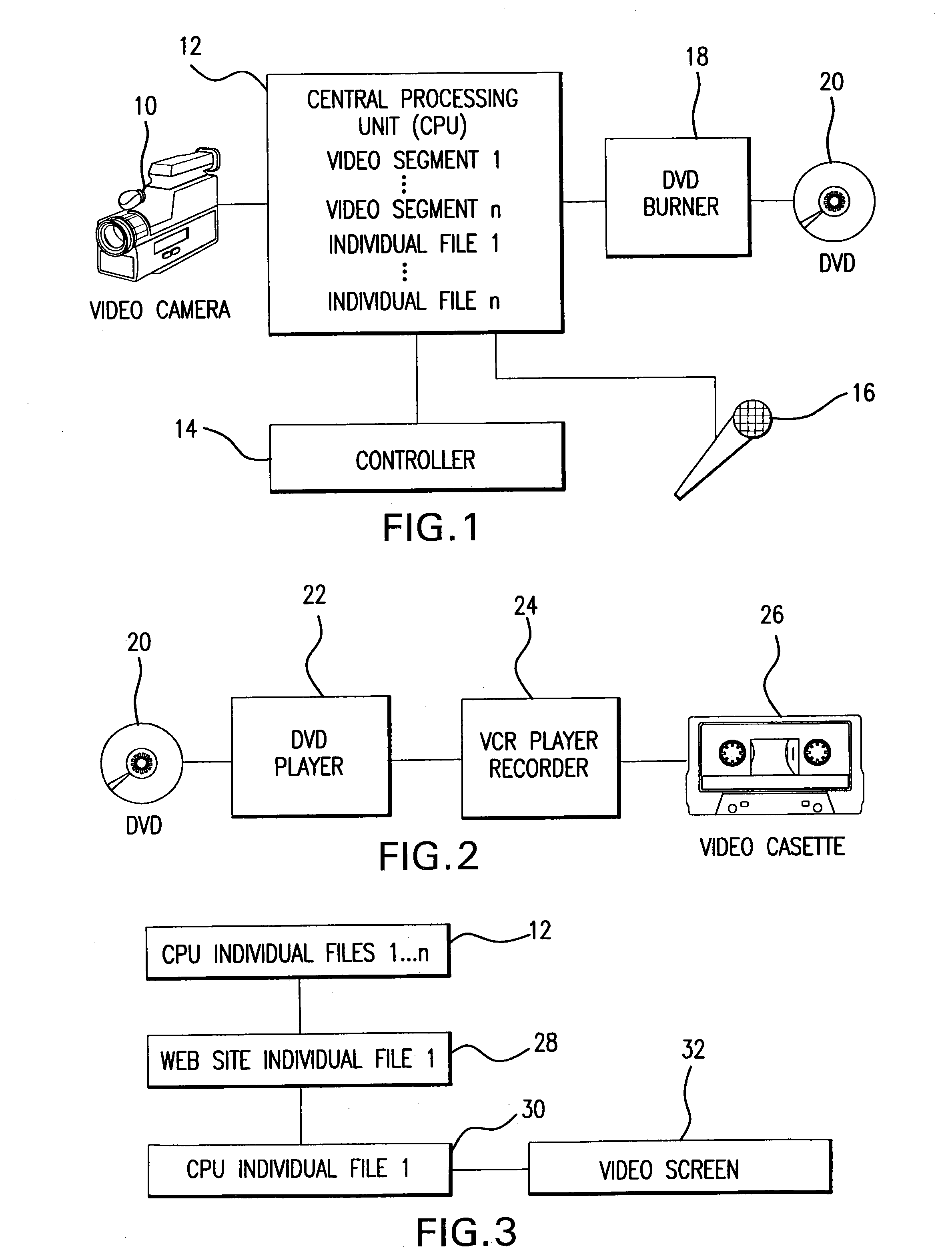
Patents
Literature
233 results about "Cassette tape" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Compact Cassette, Compact Audio Cassette or Musicassette (MC), also commonly called the cassette tape or simply tape or cassette, is an analog magnetic tape recording format for audio recording and playback.It was developed by Philips in Hasselt, Belgium, and introduced in September 1963. Compact Cassettes come in two forms, either already containing content as a prerecorded cassette ...
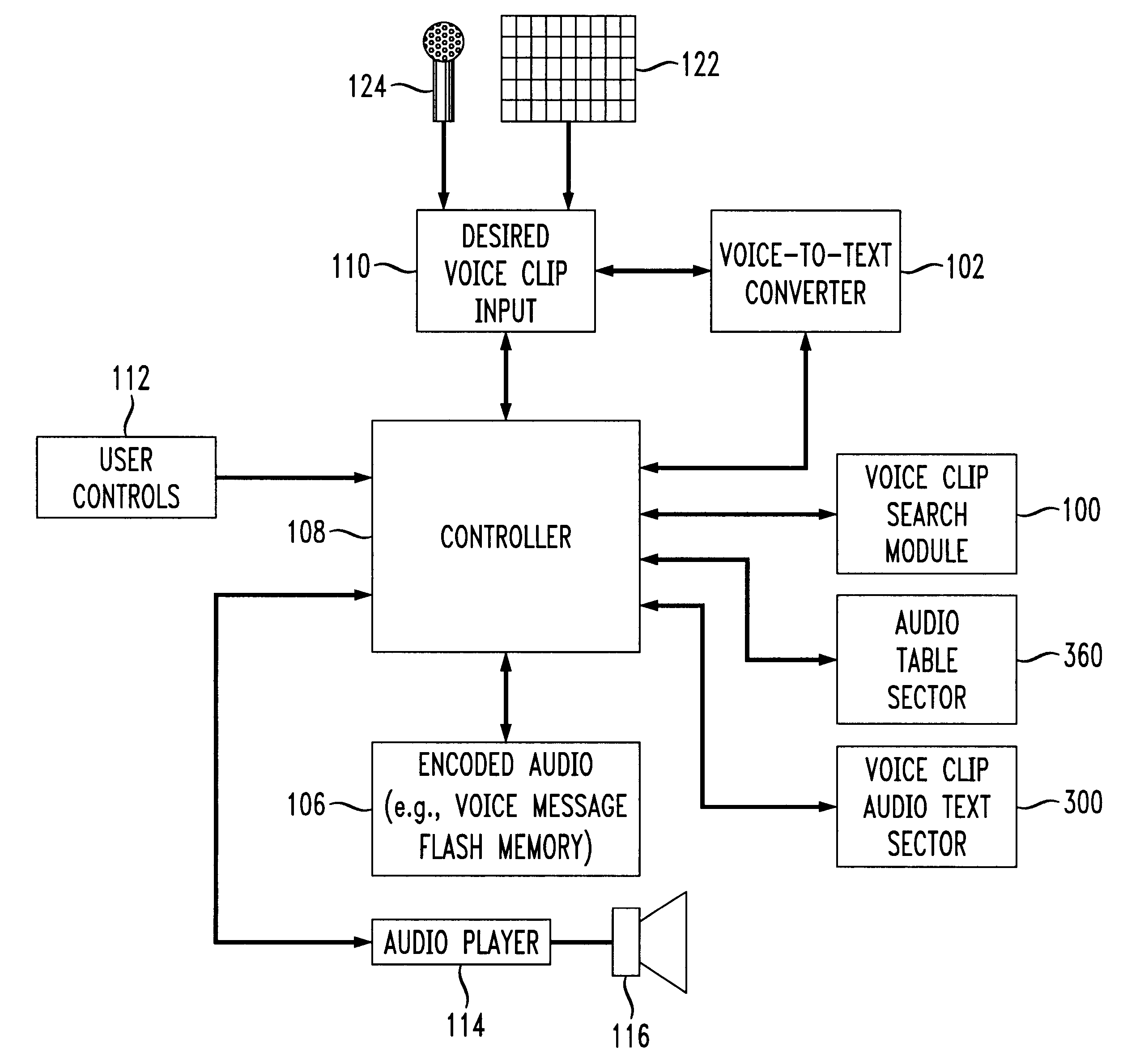
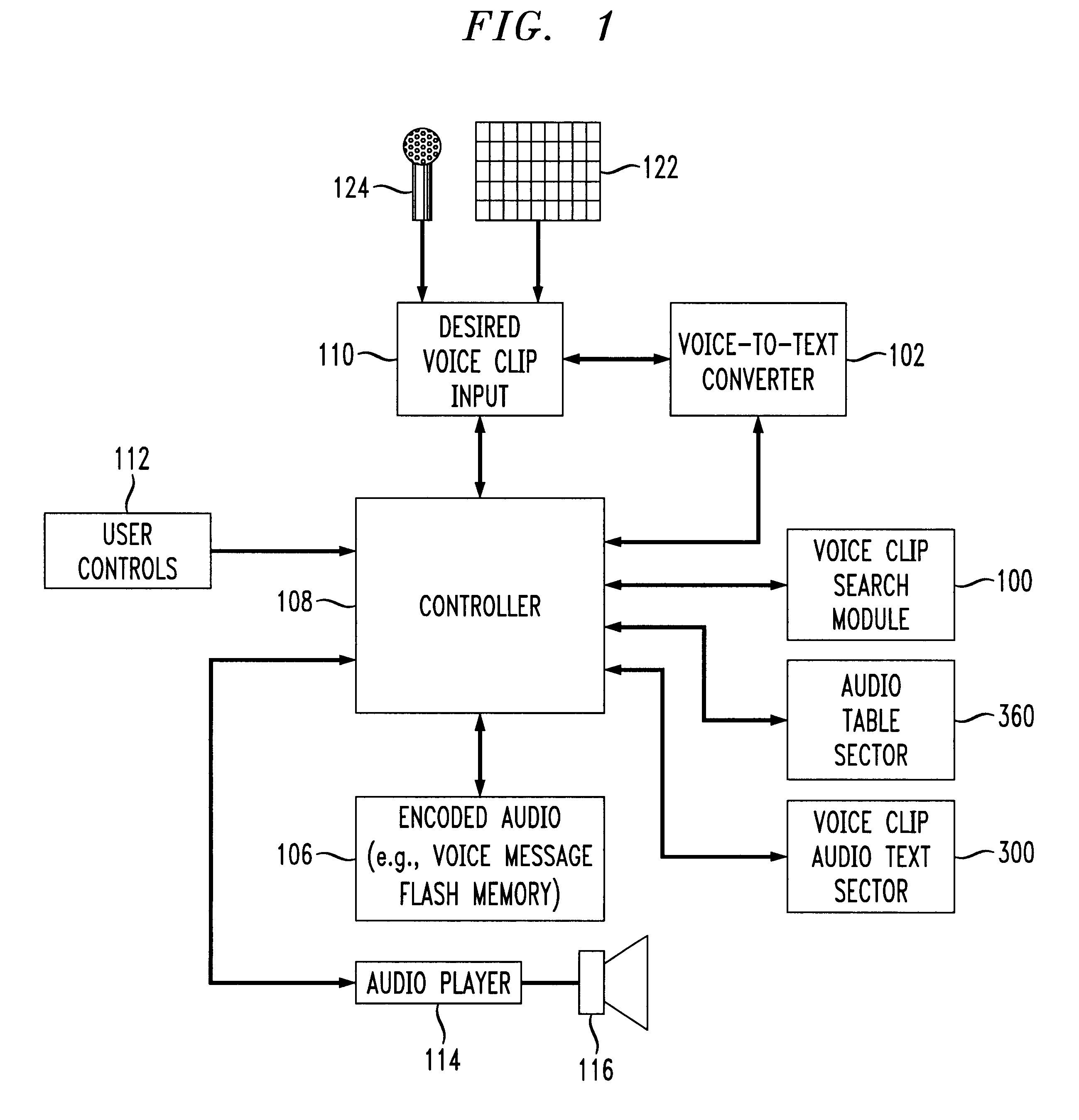
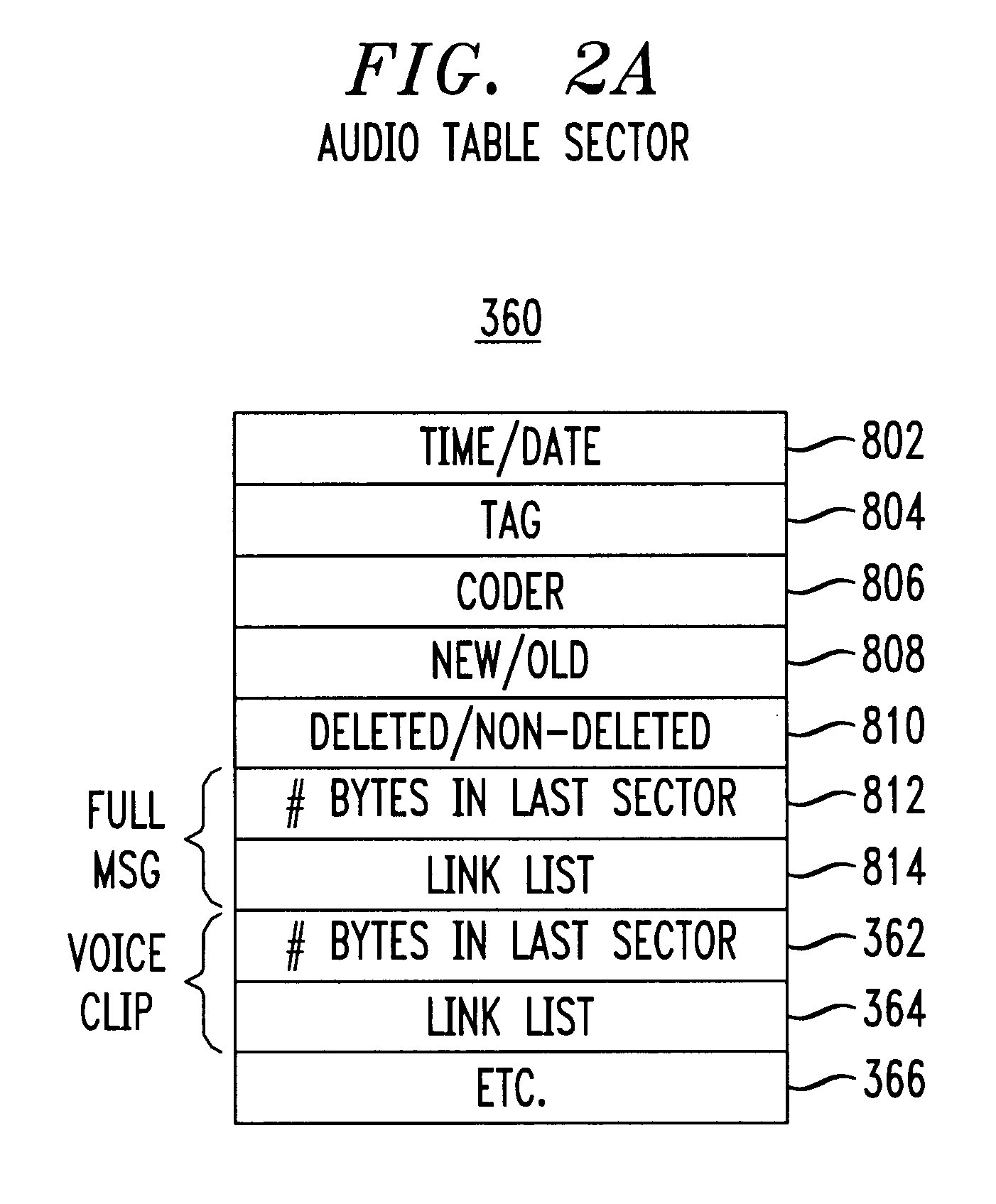
Voice clip search
InactiveUS6697796B2Television system detailsData processing applicationsDigital videoHard disc drive
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
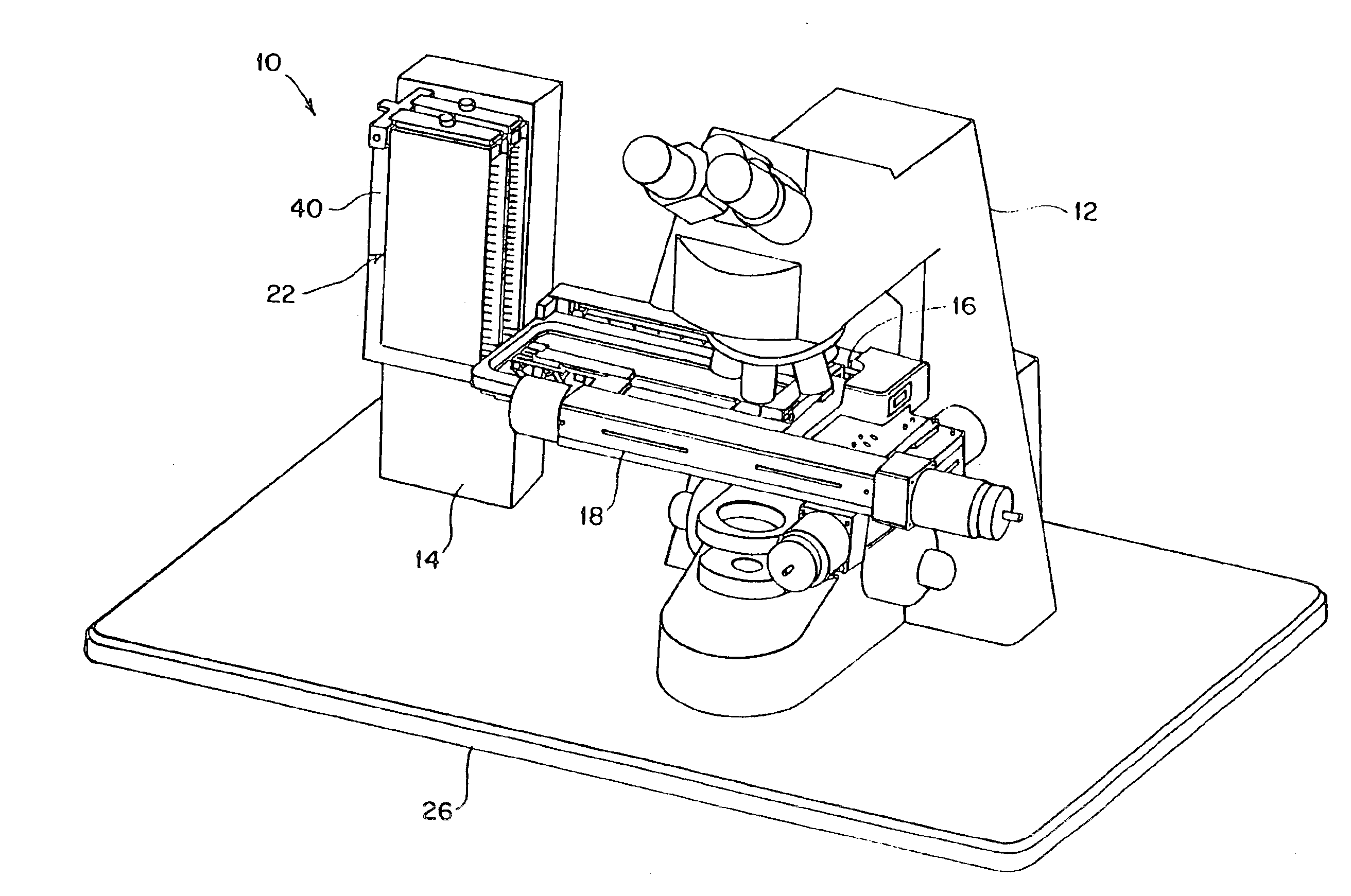
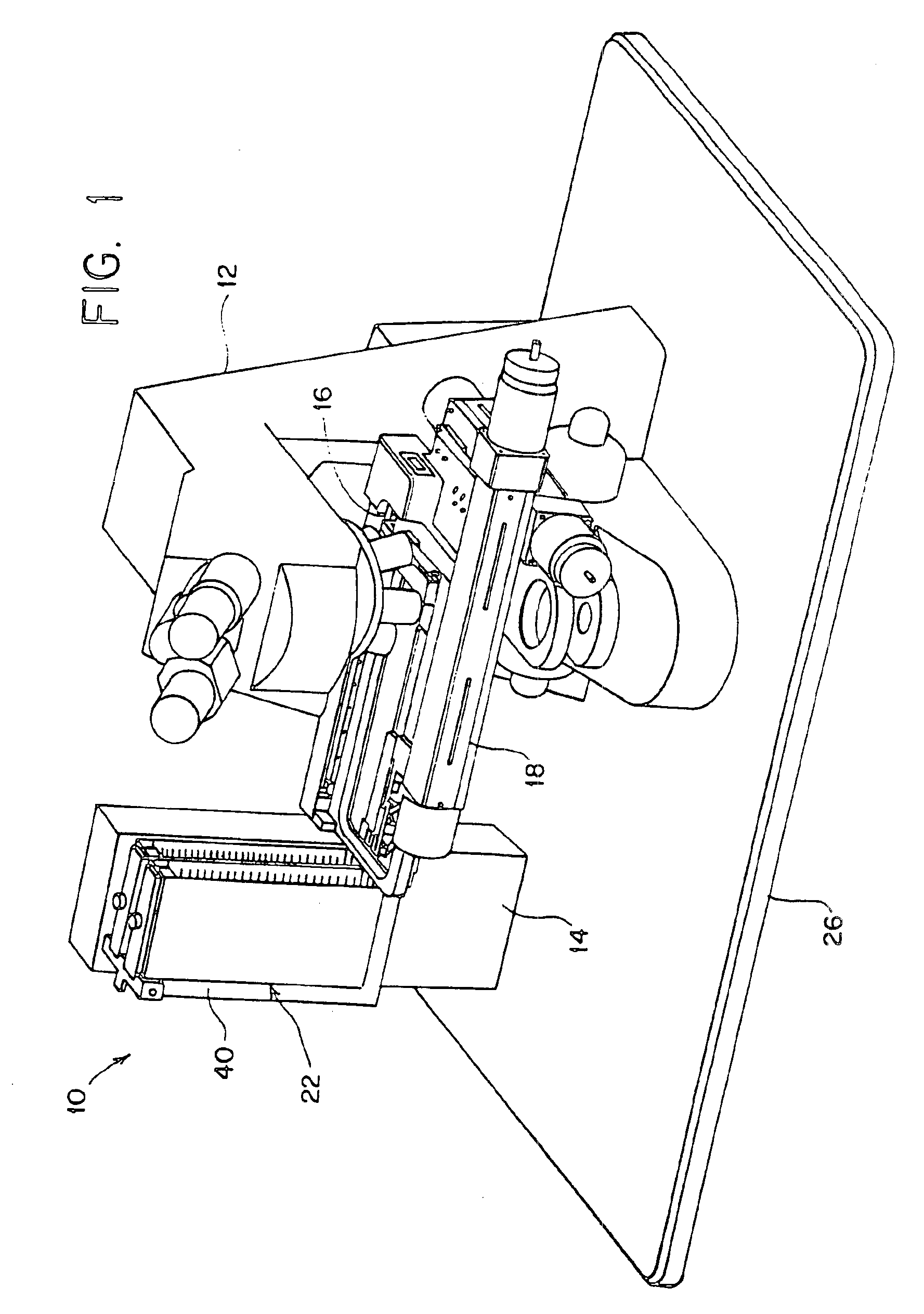
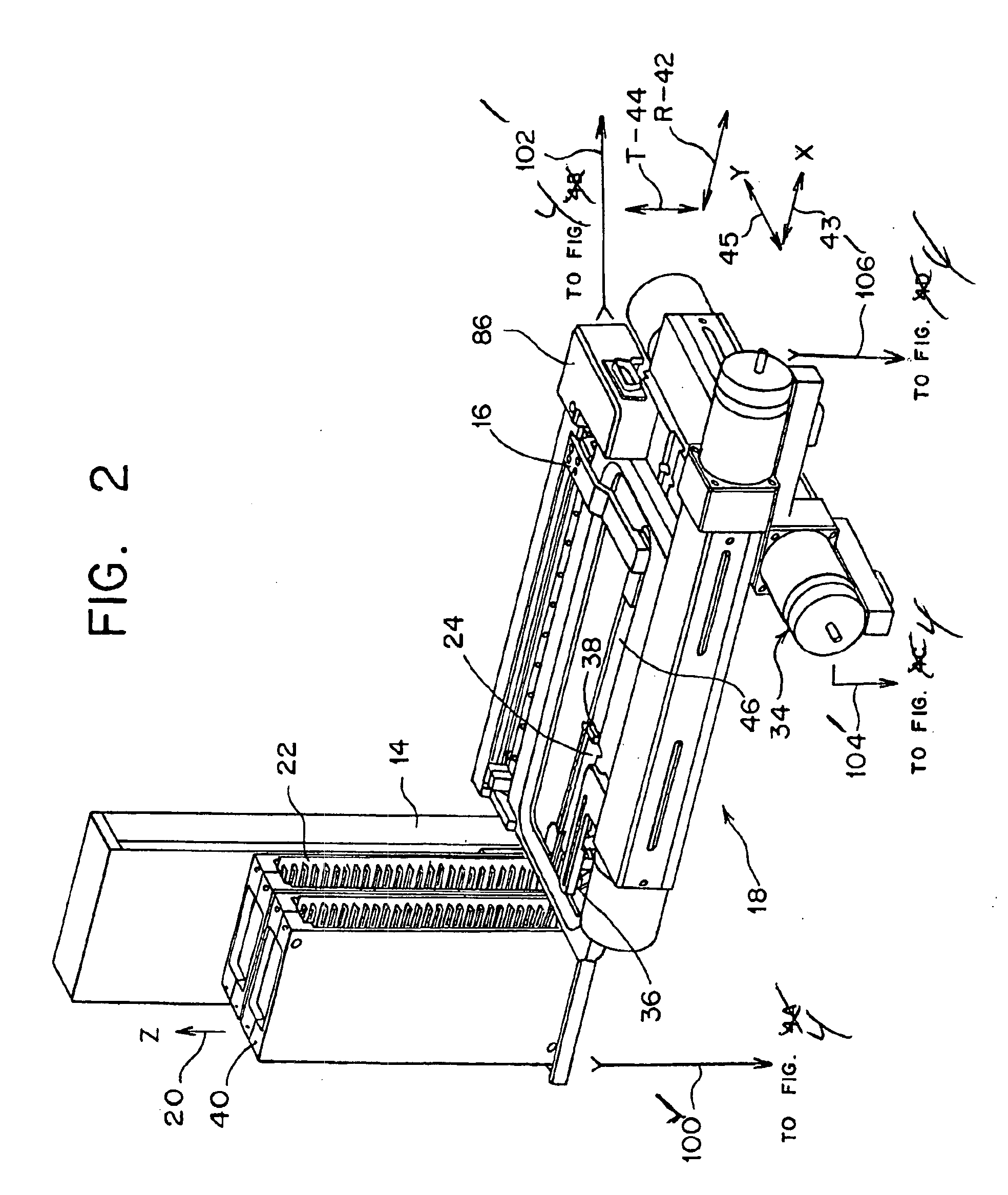
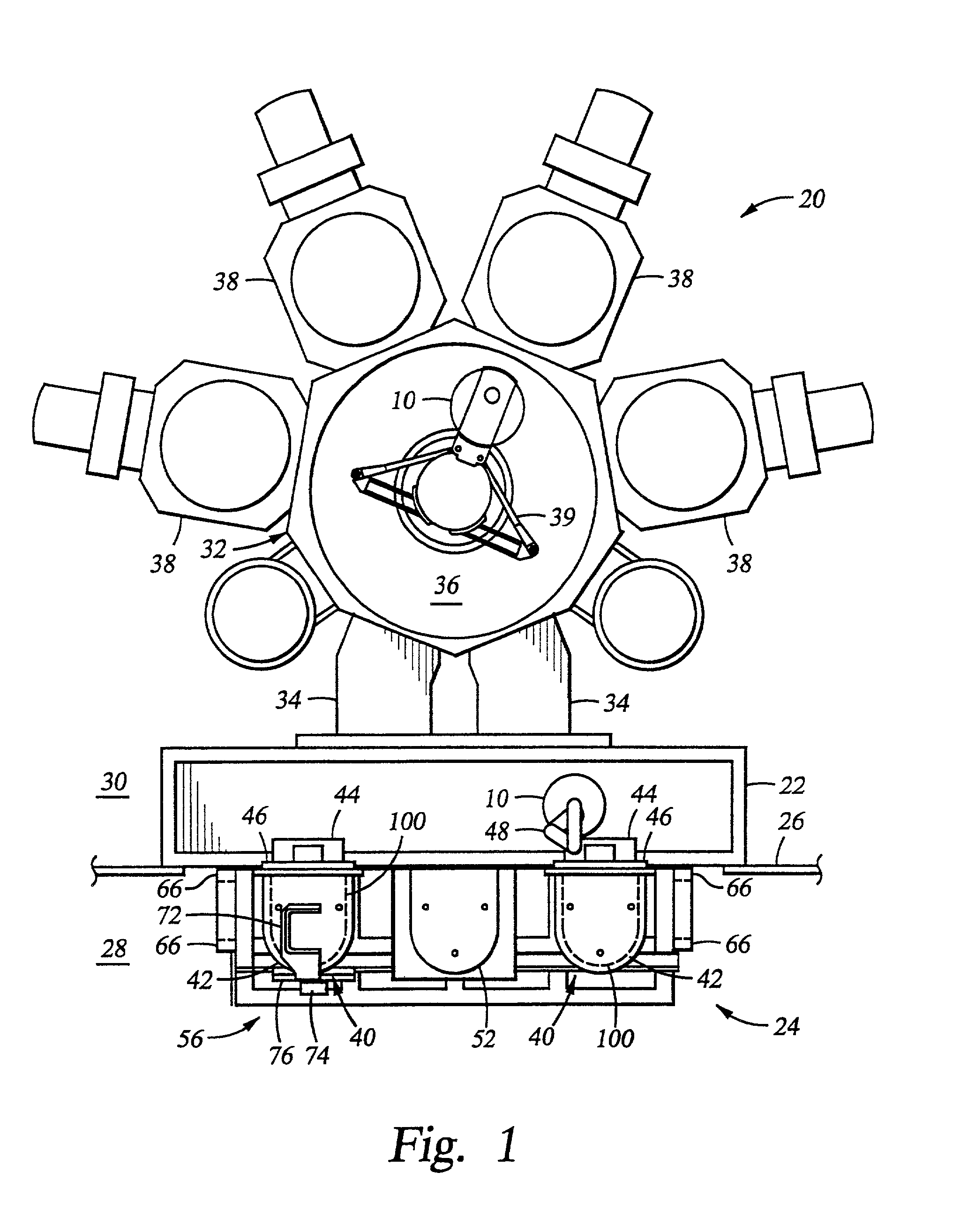
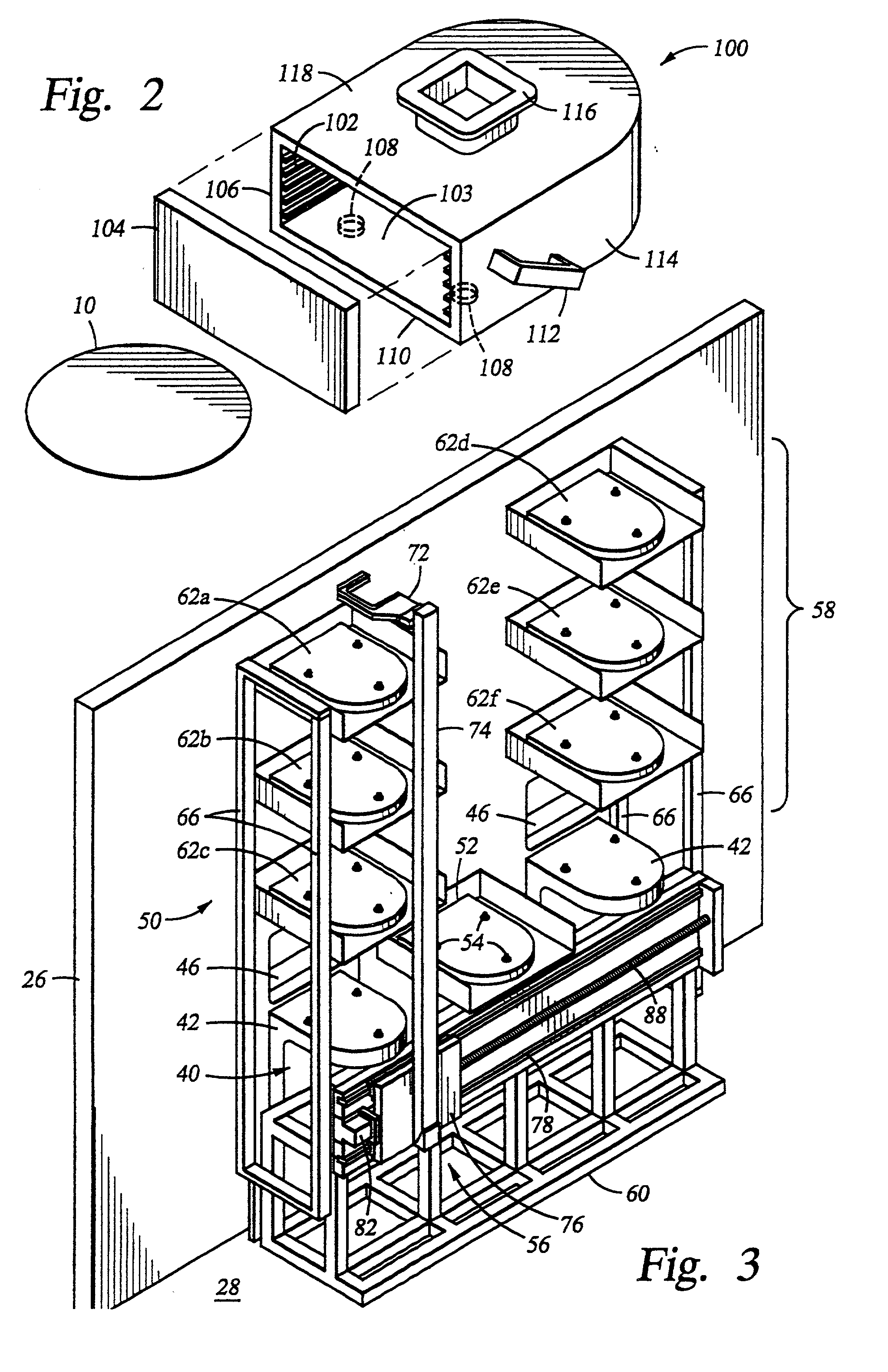
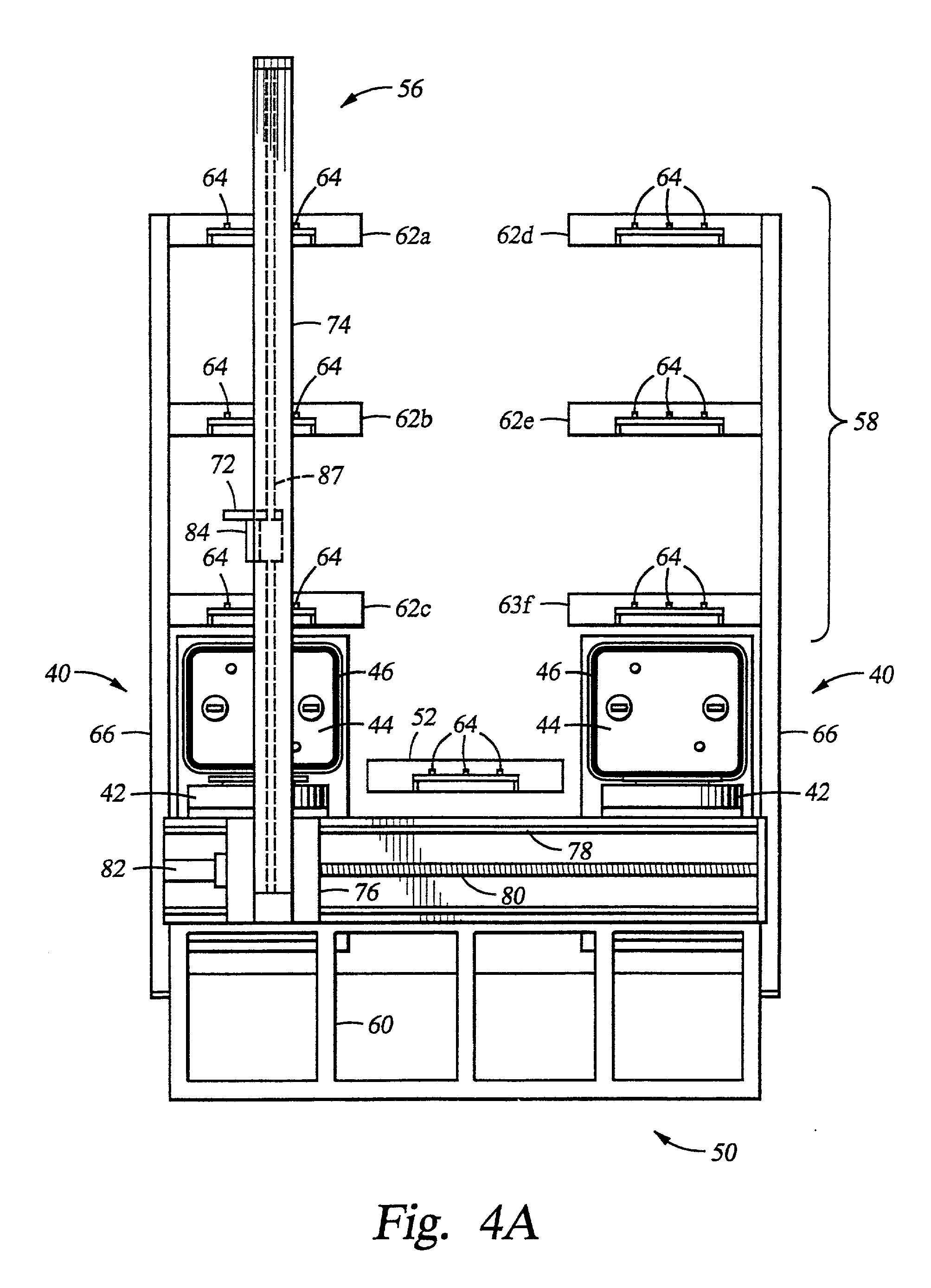
Automated slide loader cassette for microscope
InactiveUS6847481B1Enhance intrinsic valuePrecise positioningArticle unpackingMicroscopesMicroscope slideMagnetic tape
The slide handler is an instrument that automatically transfers glass microscope slides from a cassette or magazine to a motorized microscope stage and then returns the slide back into the second cassette. The use of this instrument permits the unattended computer control, measurement and inspection of specimens mounted to the slides. Full modular integration of the system components allows for the slide handler instrument to be utilized with any microscope. The instrument system has a minimum of three components; namely a slide cassette indexer, an XY-stage, and a slide exchange arm. The indexer, the arm and the XY-stage are connected together and integrated into one unitary modular instrument that can be moved from one microscope to another.
Owner:LUDL ELECTRONICS PRODS
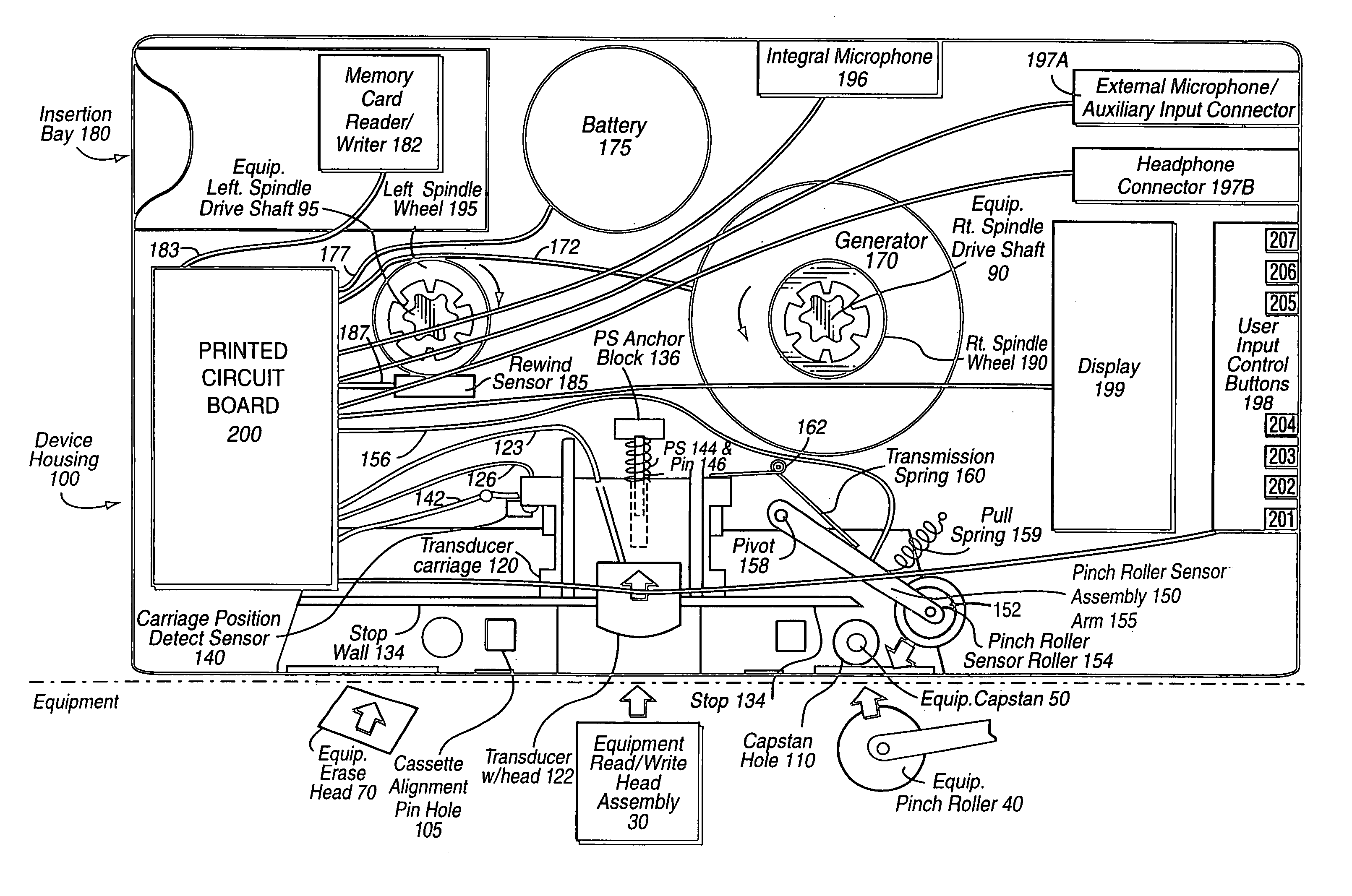
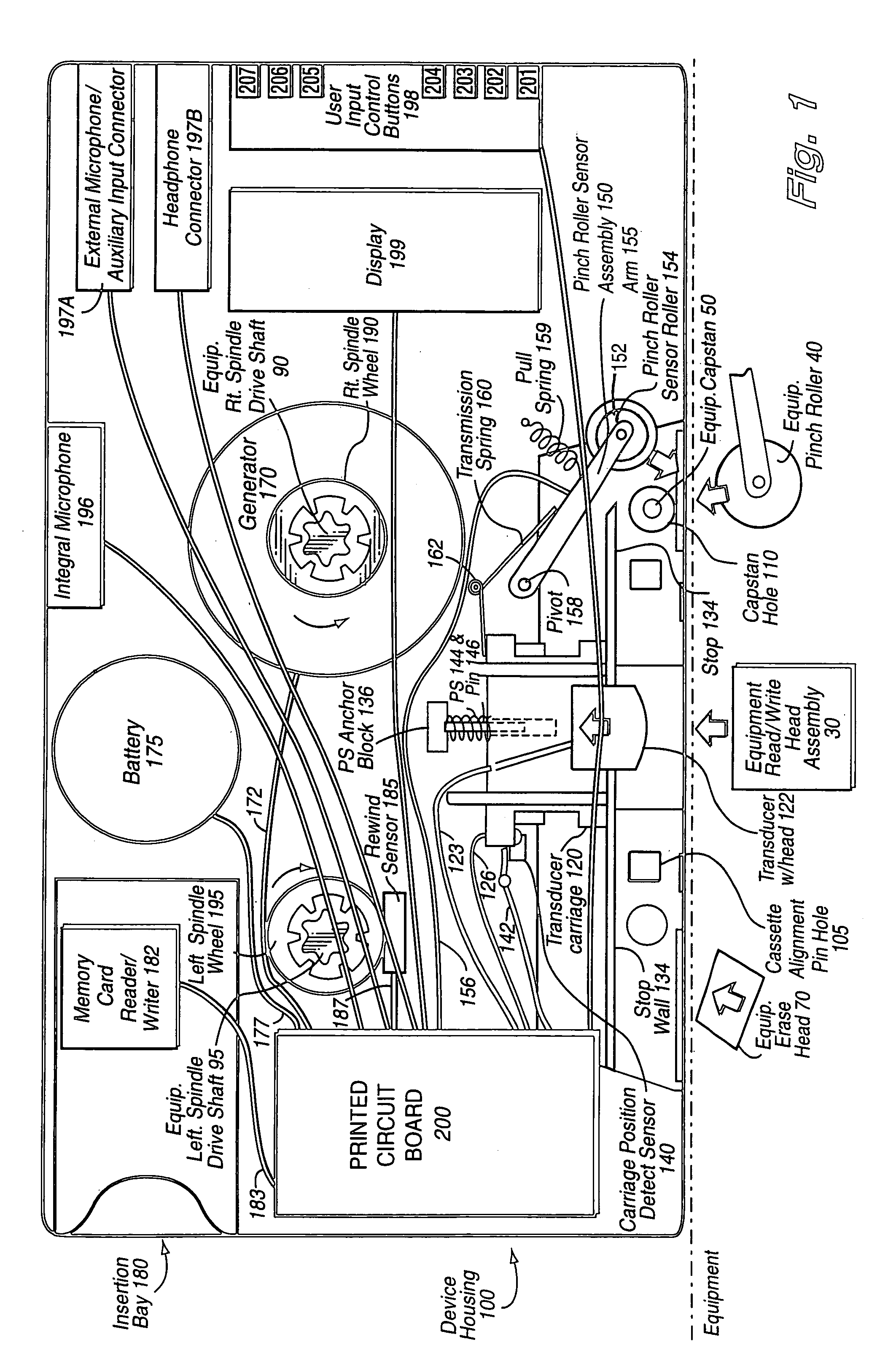
Audio cassette emulator
InactiveUS6941180B1Saving positionSaving stateApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageThe InternetMultiple sensor
A device of the same general physical size and shape as a standard audio cassette tape, but which accepts digital information from any of a variety of sources—including for example: Internet transmission, a digital computer, or memory cards (especially digital memory cards)—and plays this digital information through any, for example, standard audio tape cassette player. The device operates by converting the digital representation of the sound into magnetic signals which are presented to the read / write head of the cassette player equipment. The device allows the user of the cassette player to regulate the audio playback using conventional equipment controls such as: START, STOP, REWIND, FAST REWIND, FORWARD, FAST FORWARD, etc. In one exemplary implementation, the device has the same general physical dimensions of a standard audio cassette; at least one digital processor; and a slot into which electronic media such as, for example, memory cards, smart cards having a processor and a memory embodied thereon and other memory media may be inserted. Converter circuitry converts data stored in digital memory to an analog signal which is magnetically coupled to the read head of the equipment. Numerous sensors detect changes in at least one of the tape equipment mechanisms in the audio cassette emulator.
Owner:FISCHER ADDISON M
Remote accessible programming
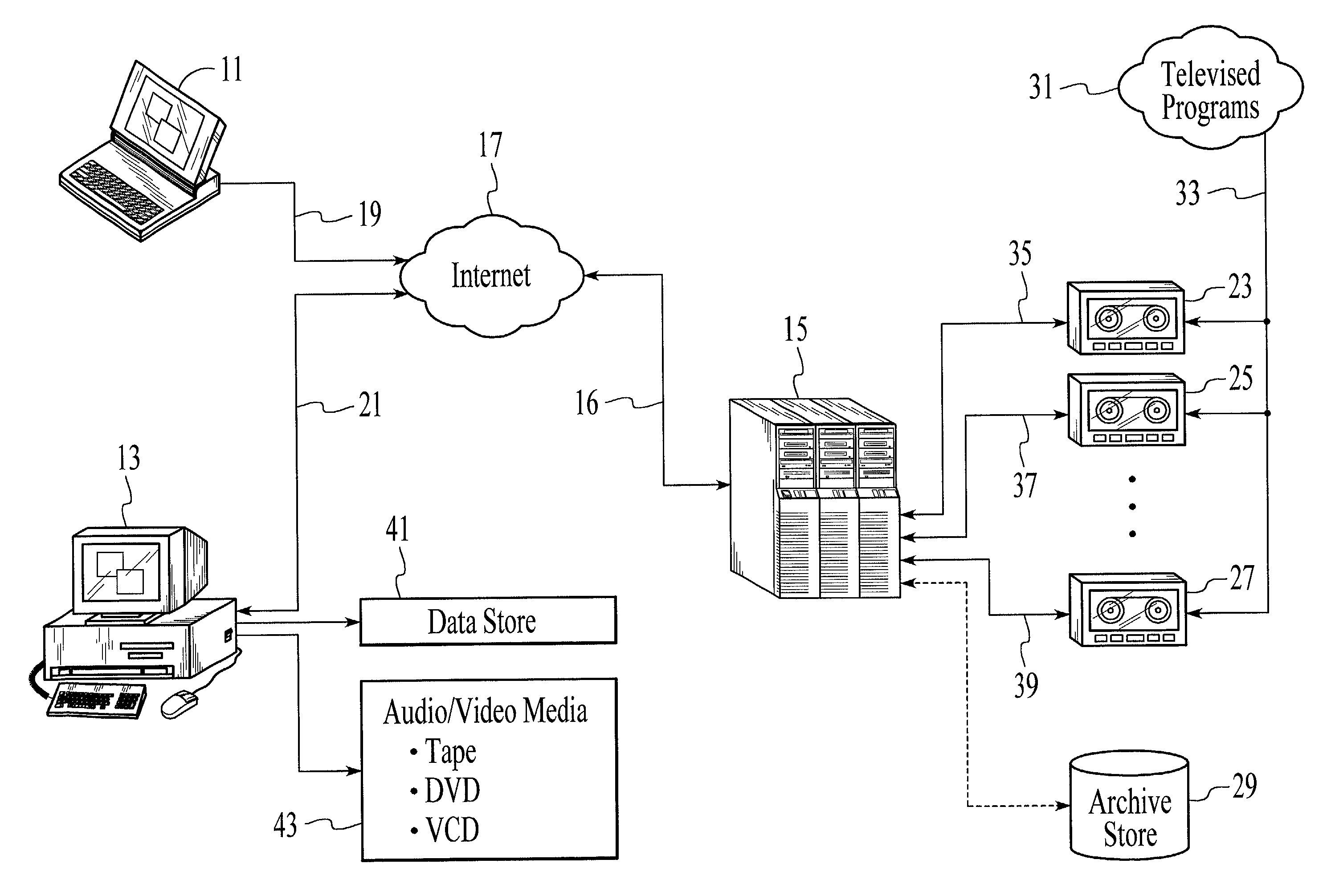
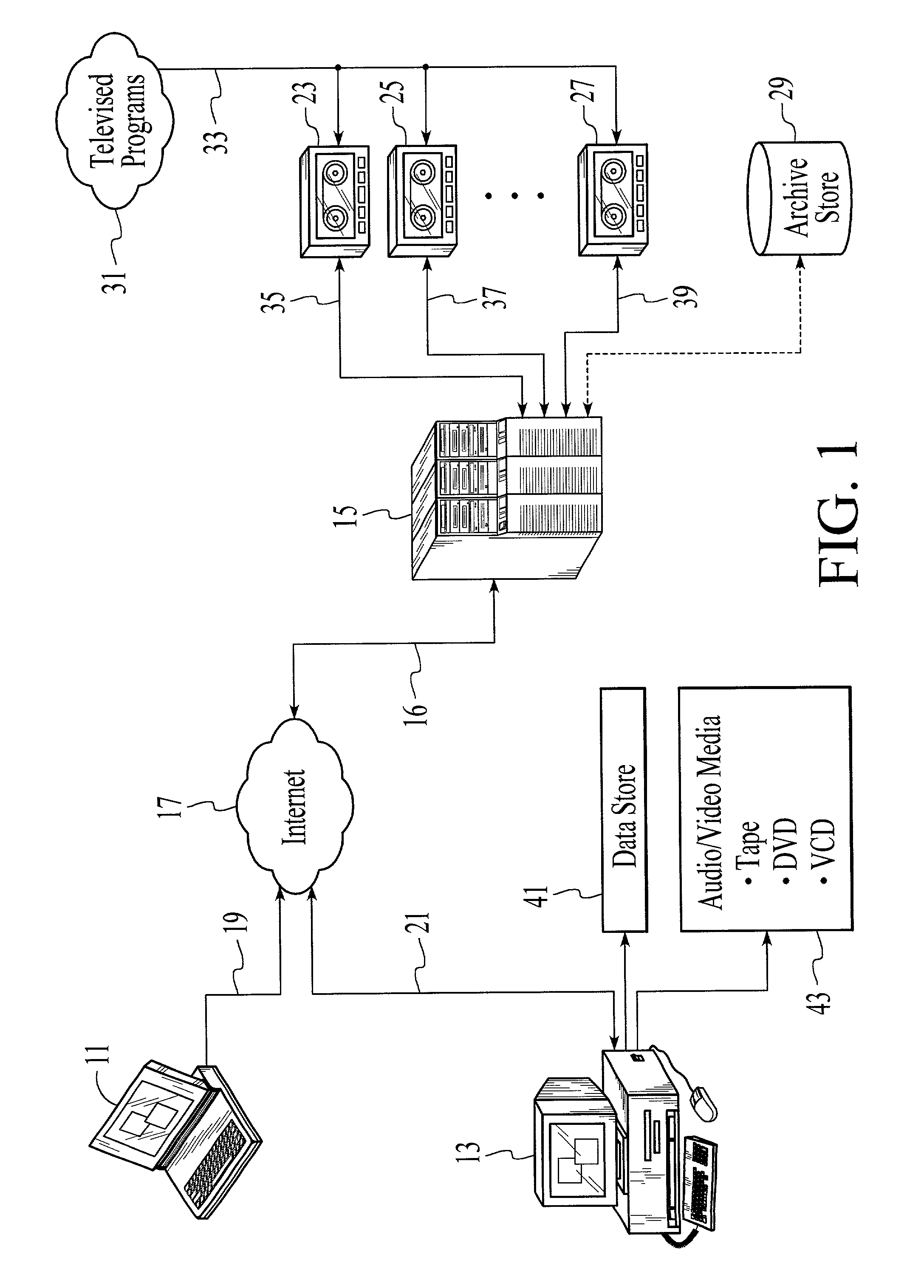
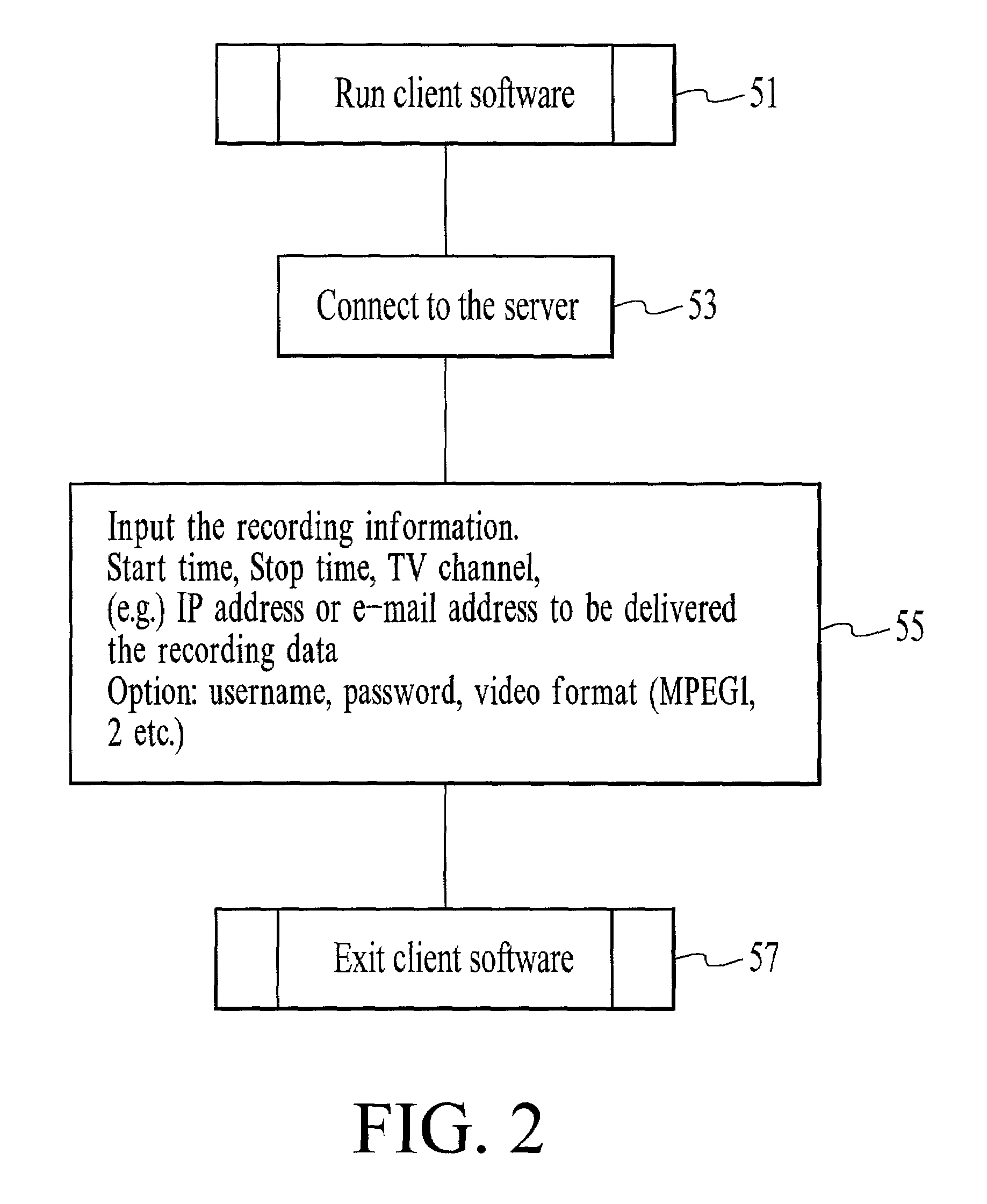
A local user issues recording instructions via the Internet to a remote computing device. The remote recording device records broadcast programs available to it according to the received recording instructions, and compresses and encodes the recorded program into a specified media format. The file holding the encoded broadcast program may be subdivided into multiple smaller files before being moved into another computer specified by the user and accessible via the Internet. The remote computing device may receive recording instruction via a pulse telephone and may be incorporated into existing video cassette recorders.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
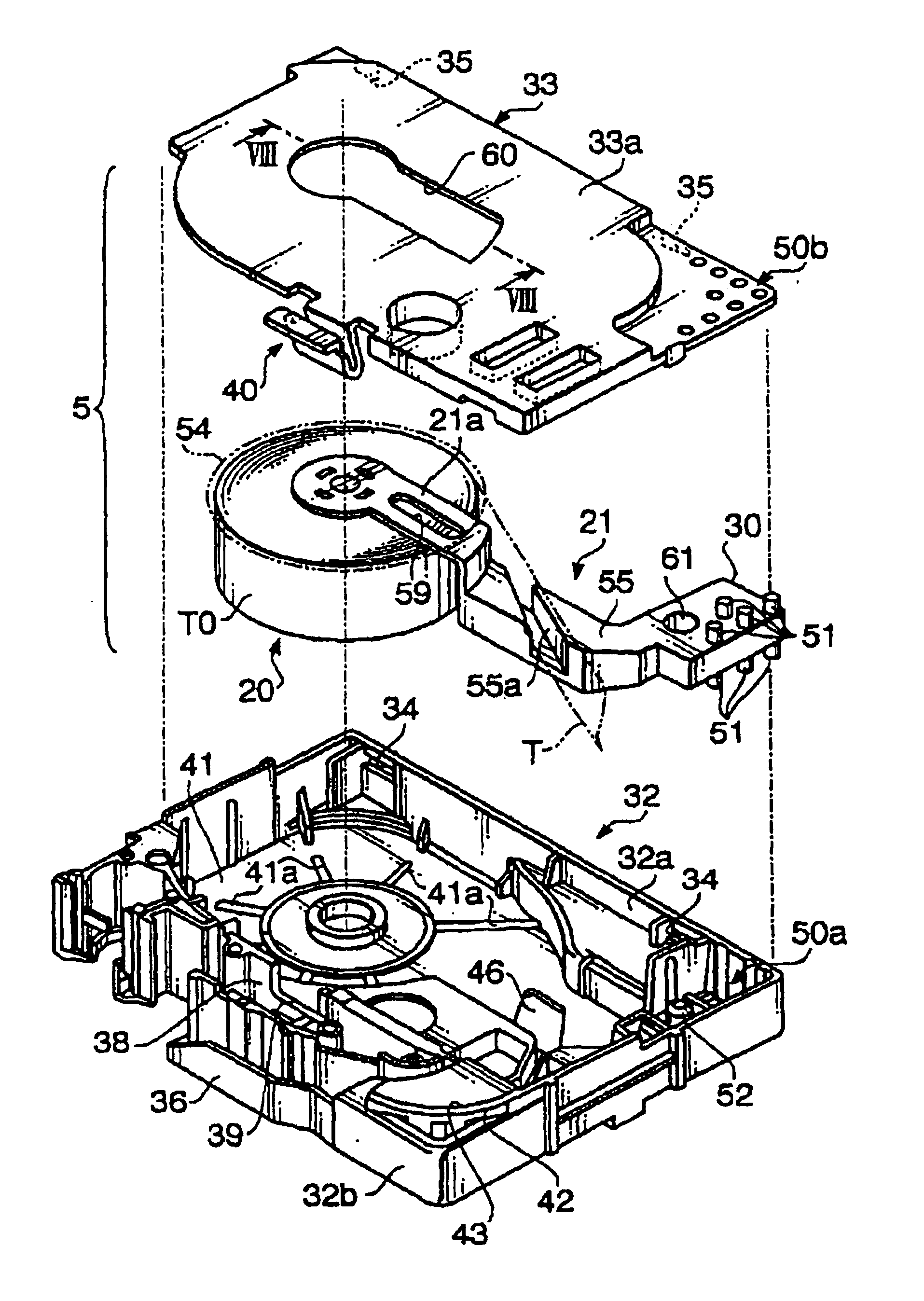
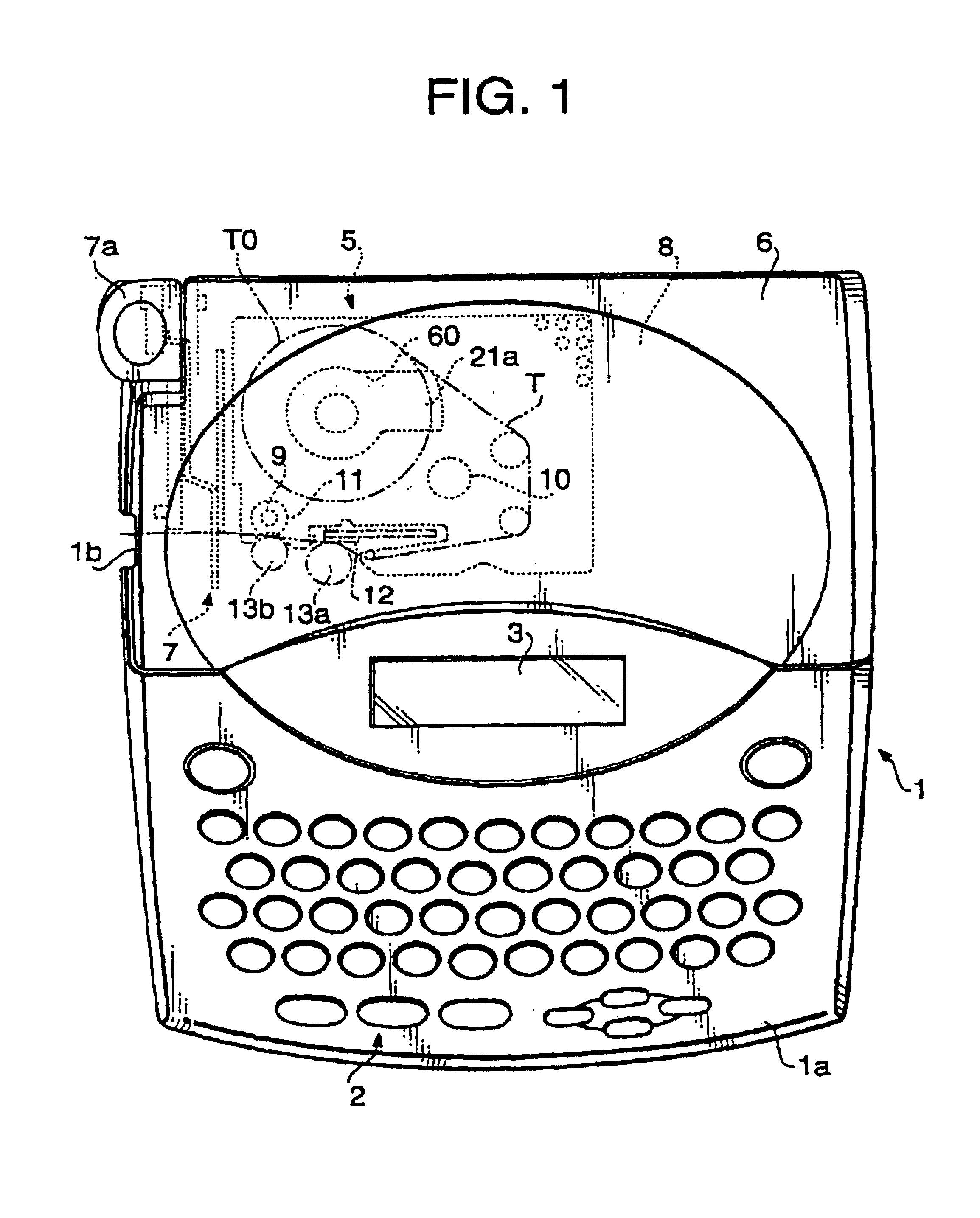
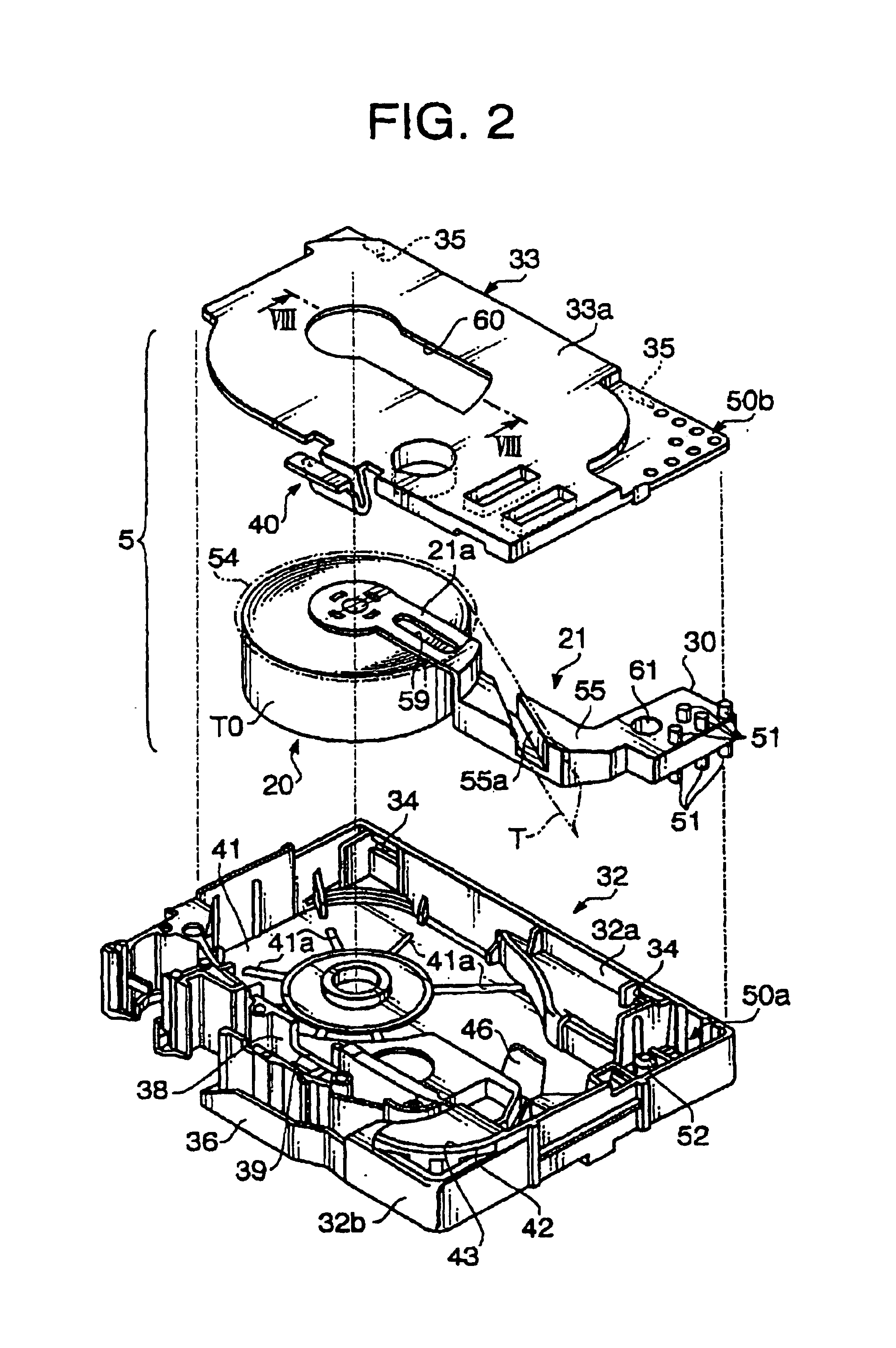
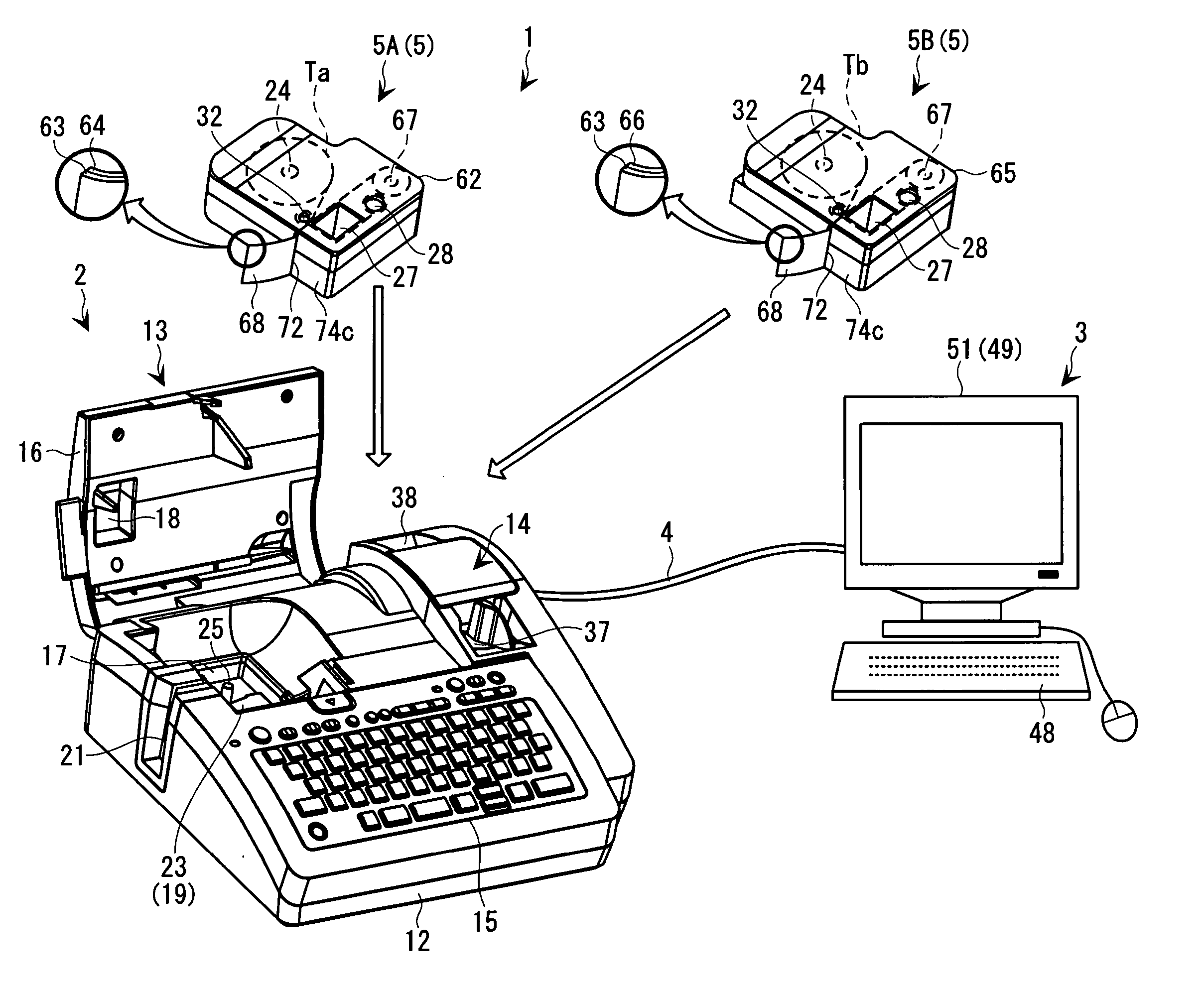
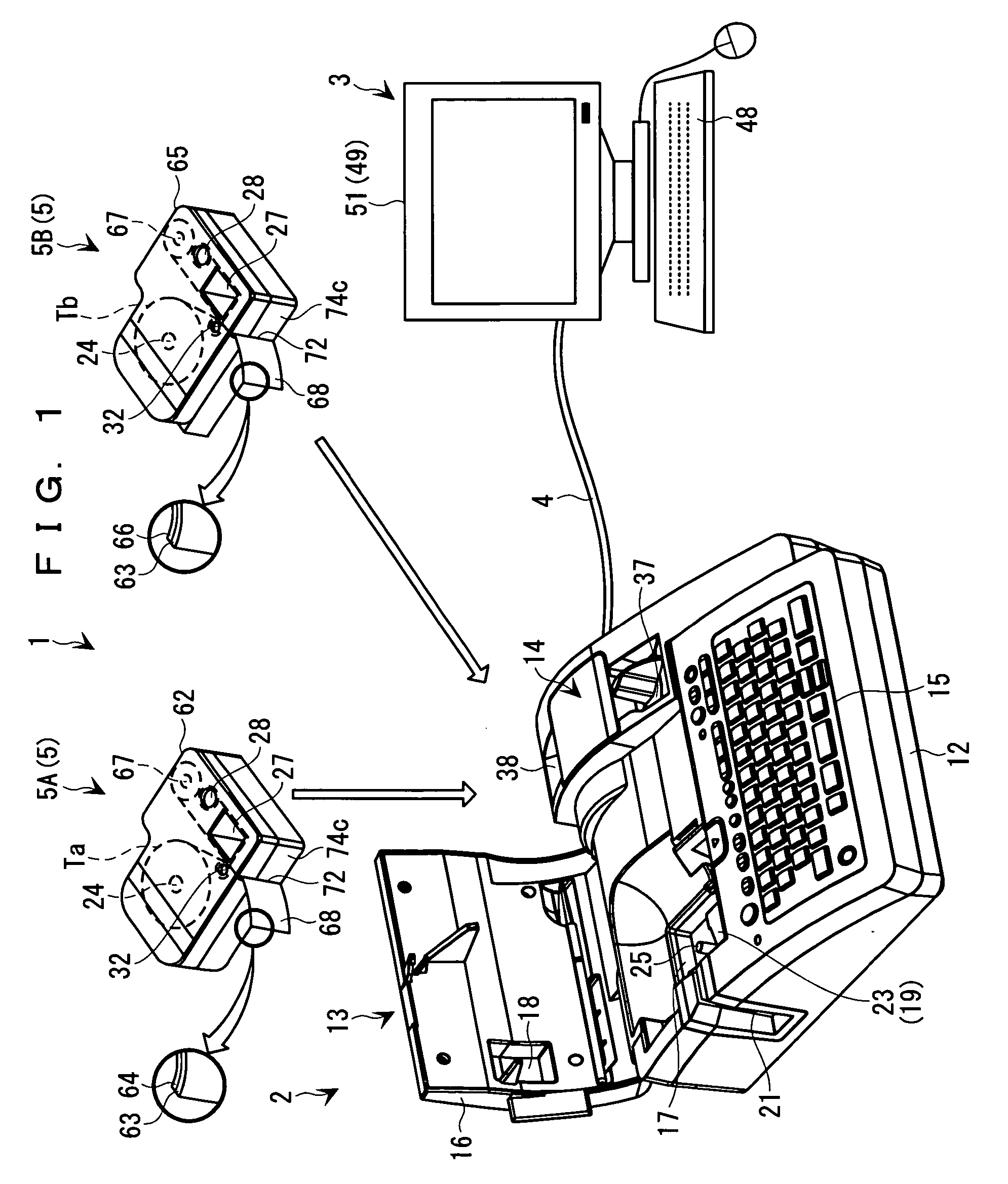
Tape cassette and tape unit
InactiveUS6955318B2Erroneous loadingPicture changing apparatusInking apparatusMagnetic tapeCassette tape
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Audio cassette emulator with cryptographic media distribution control
InactiveUS7436957B1Saving positionSaving stateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDistribution controlThe Internet
A device of the same general physical size and shape as a standard audio cassette tape, but which accepts digital information from any of a variety of sources—including for example: Internet transmission, a digital computer, or memory cards (especially digital memory cards)—and plays this digital information through any, for example, standard audio tape cassette player. The device operates by converting the digital representation of the sound into magnetic signals which are presented to the read / write head of the cassette player equipment. The device allows the user of the cassette player to regulate the audio playback using conventional equipment controls such as: START, STOP, REWIND, FAST REWIND, FORWARD, FAST FORWARD, etc. The device has the same general physical dimensions of a standard audio cassette; at least one digital processor; and a slot into which electronic media such as, for example, memory cards, smart cards having a processor and a memory embodied thereon and other memory media may be inserted. Numerous sensors detect changes in at least one of the tape equipment mechanisms in the audio cassette emulator. Various cryptographic techniques are described for protecting the unauthorized distribution of audio information.
Owner:FISCHER ADDISON M
Apparatus and method of displaying recording
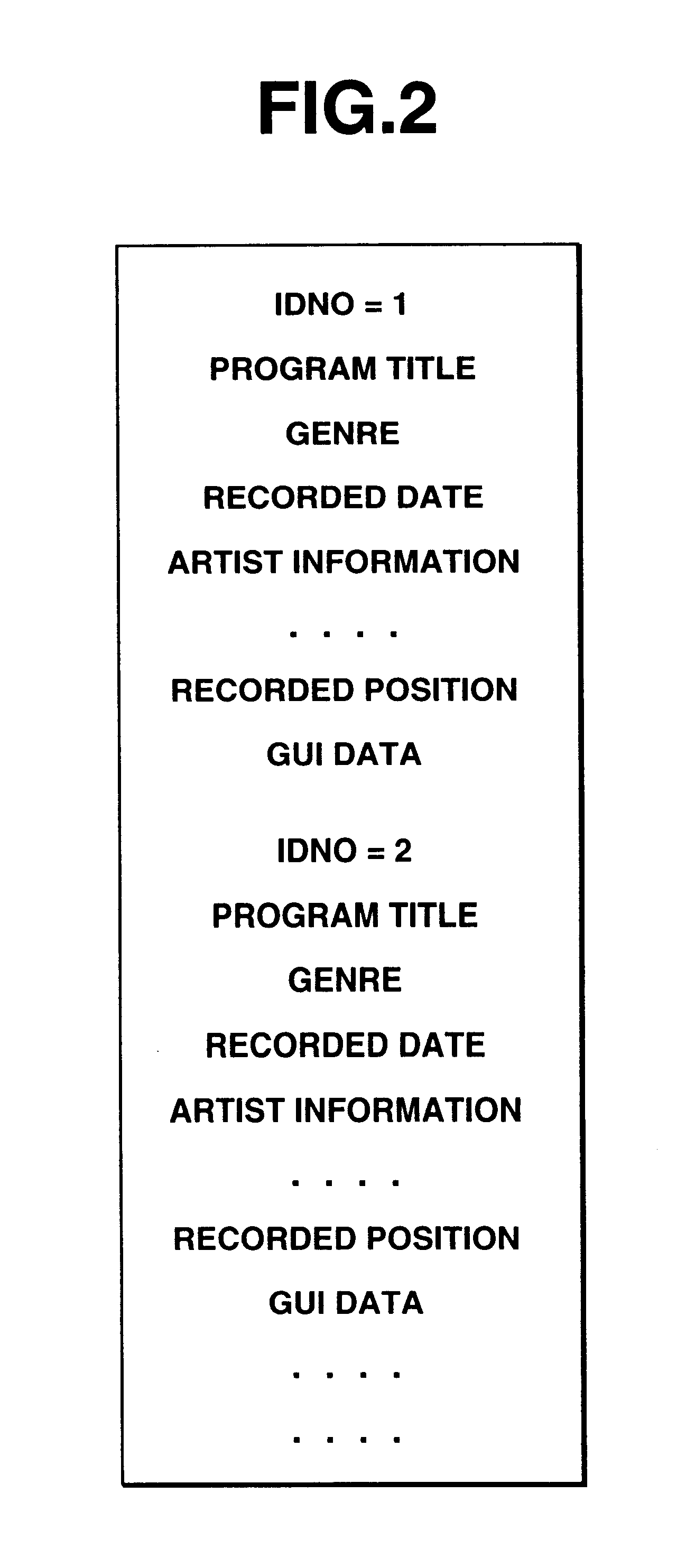
InactiveUS6289169B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareMagnetic tape
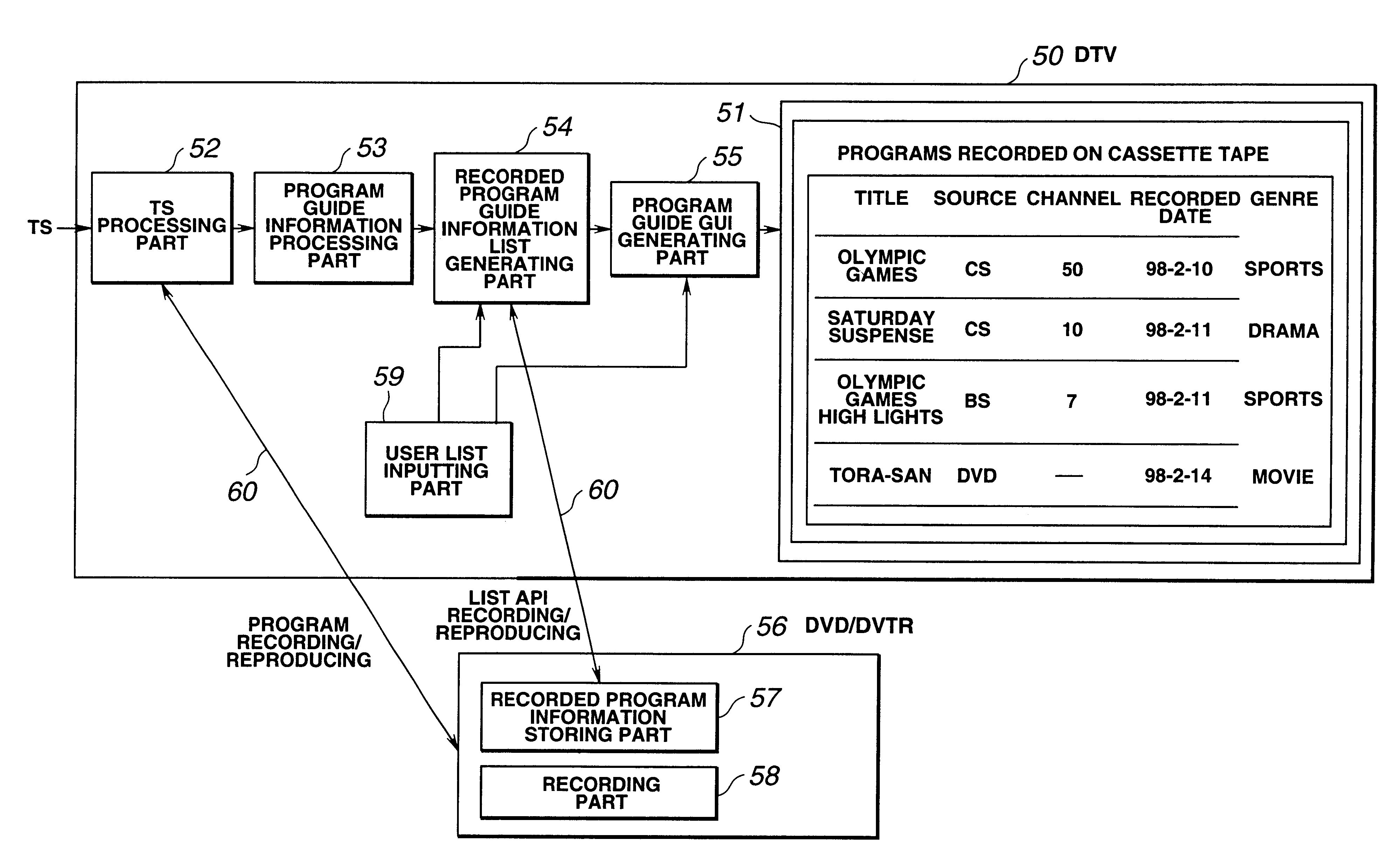
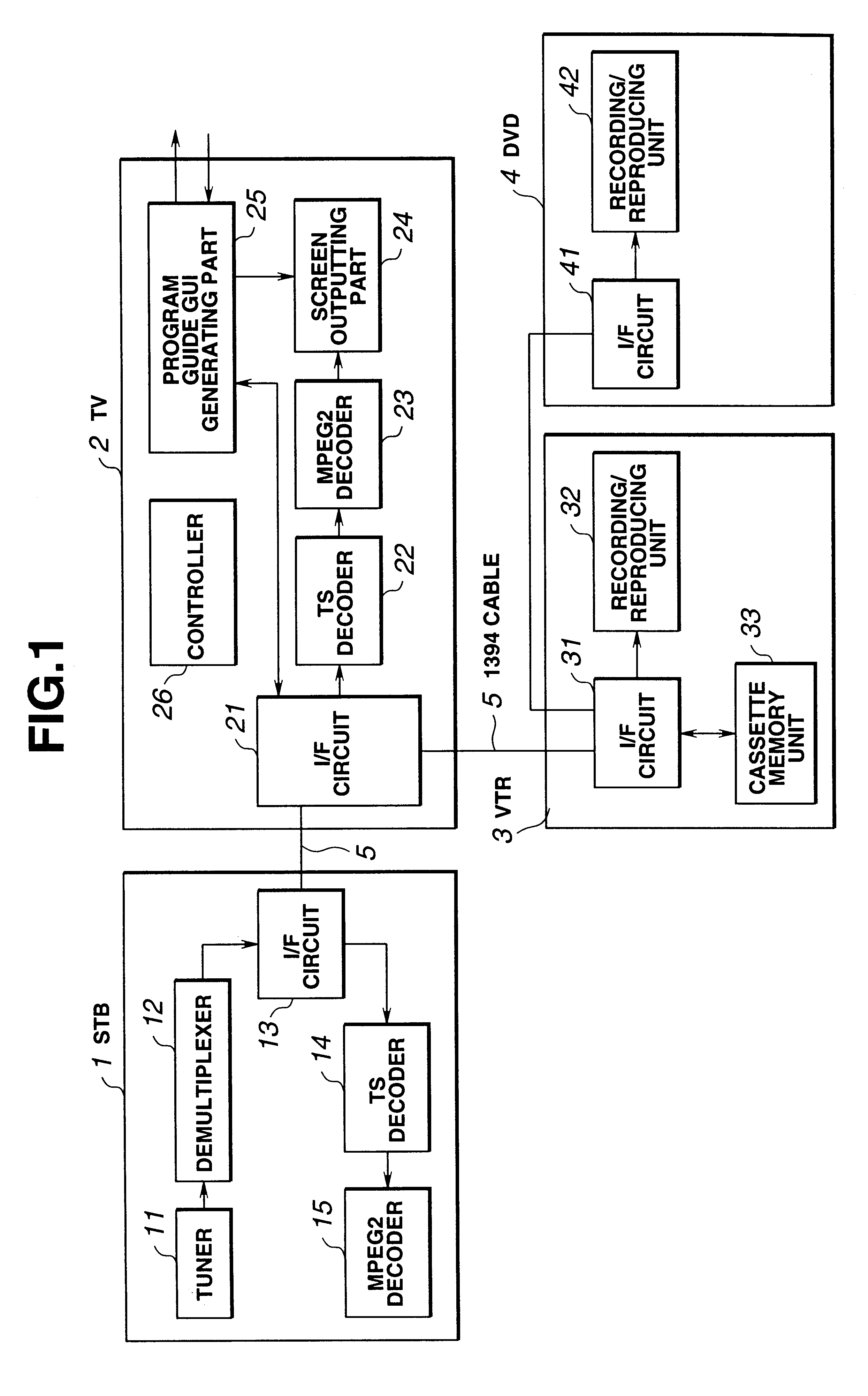
A controller makes a demultiplexer select a transport stream corresponding to user's operation, and supplies it to a VTR through an I / F circuit. The I / F circuit of the VTR gives the transport stream to a recording / reproducing unit for recording, and transmits EIT data to a TV to supply them to a program guide GUI generating part. The GUI generating part generates GUI data based on the inputted EIT data, and makes them stored in a cassette memory using a cassette memory unit of the VTR. At the time of reproduction, GUI data read by the cassette memory unit is supplied to the program guide GUI generating part, and a program guide display of programs recorded on a cassette tape is displayed. In this manner, guide information on programs recorded on a cassette tape is automatically displayed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Feeding mechanism auto-adjusting to load for use in automatic high-security destruction of a mixed load, and other feeding systems
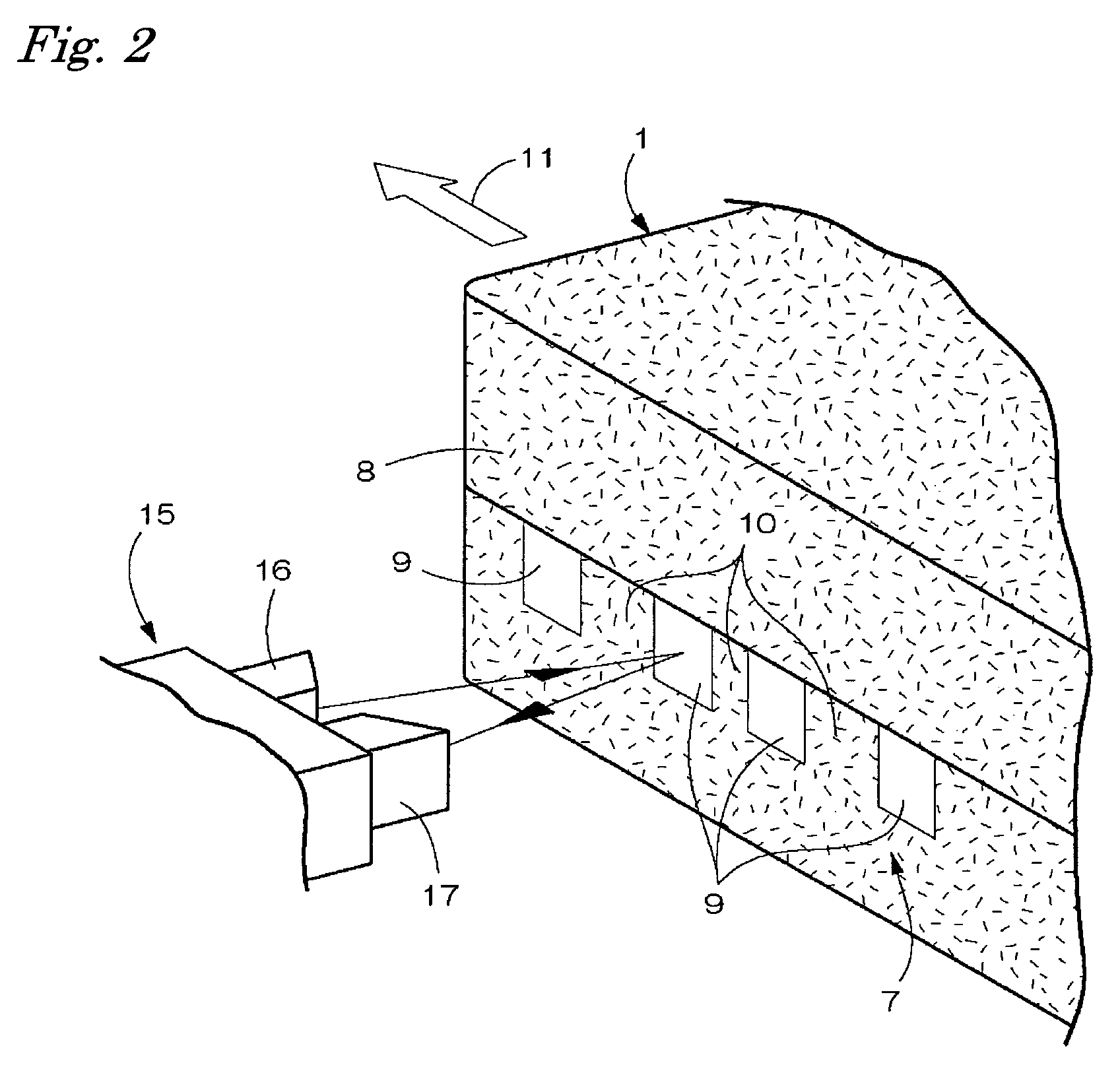
A inventive feeding mechanism continuously feeds and continuously subjects to shredding, cutting, recycling, sorting, or other processing, a load consisting of a mixture of different-thickness materials, such as a mixture of paper, compact disks (CDs), cassette tapes, videotapes, etc. The auto-adjusting feeding mechanism is useable in high-security destruction, food processing, recycling, sorting, processing, and other applications.
Owner:CASTRONOVO CHARLES A
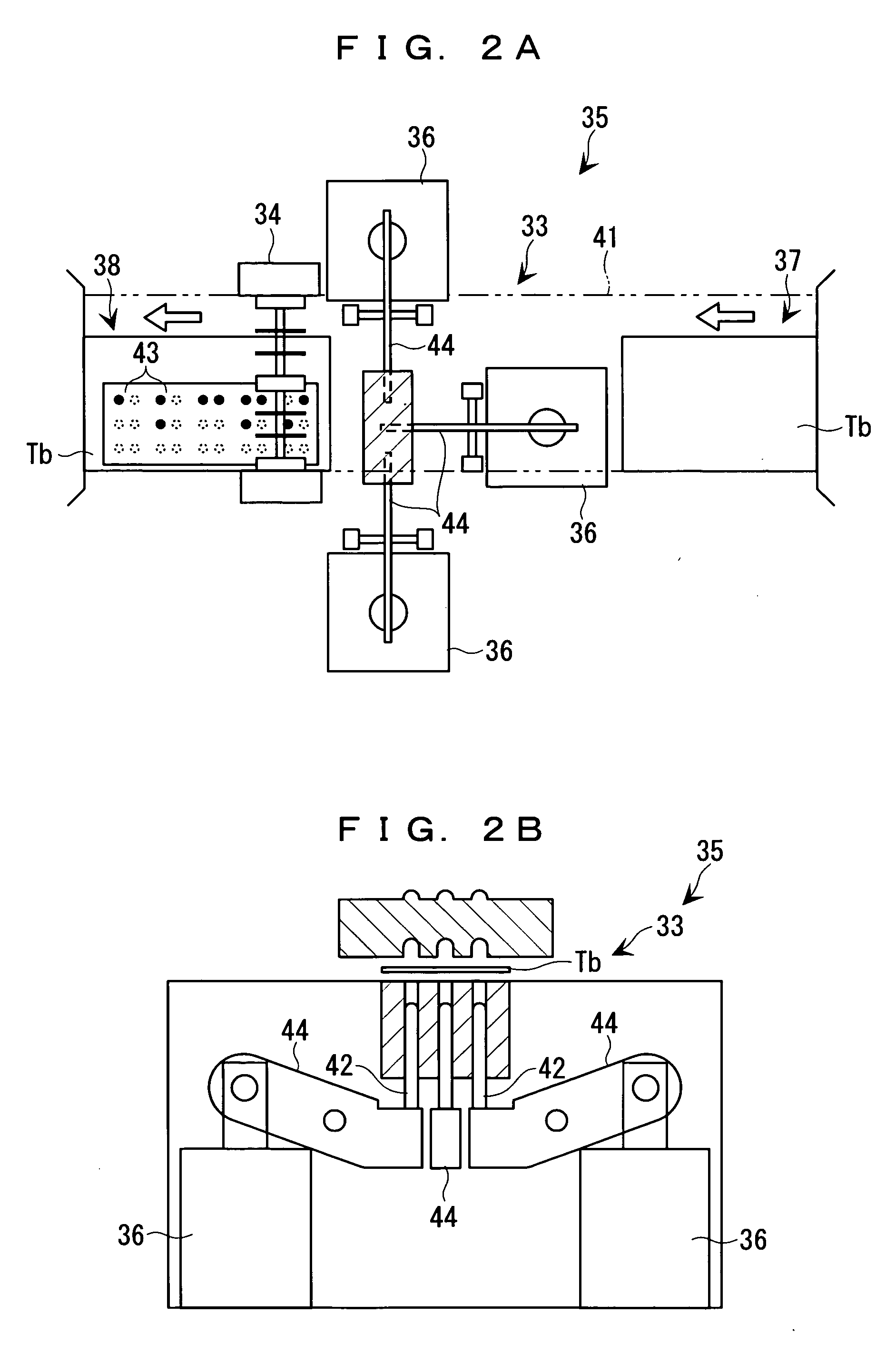
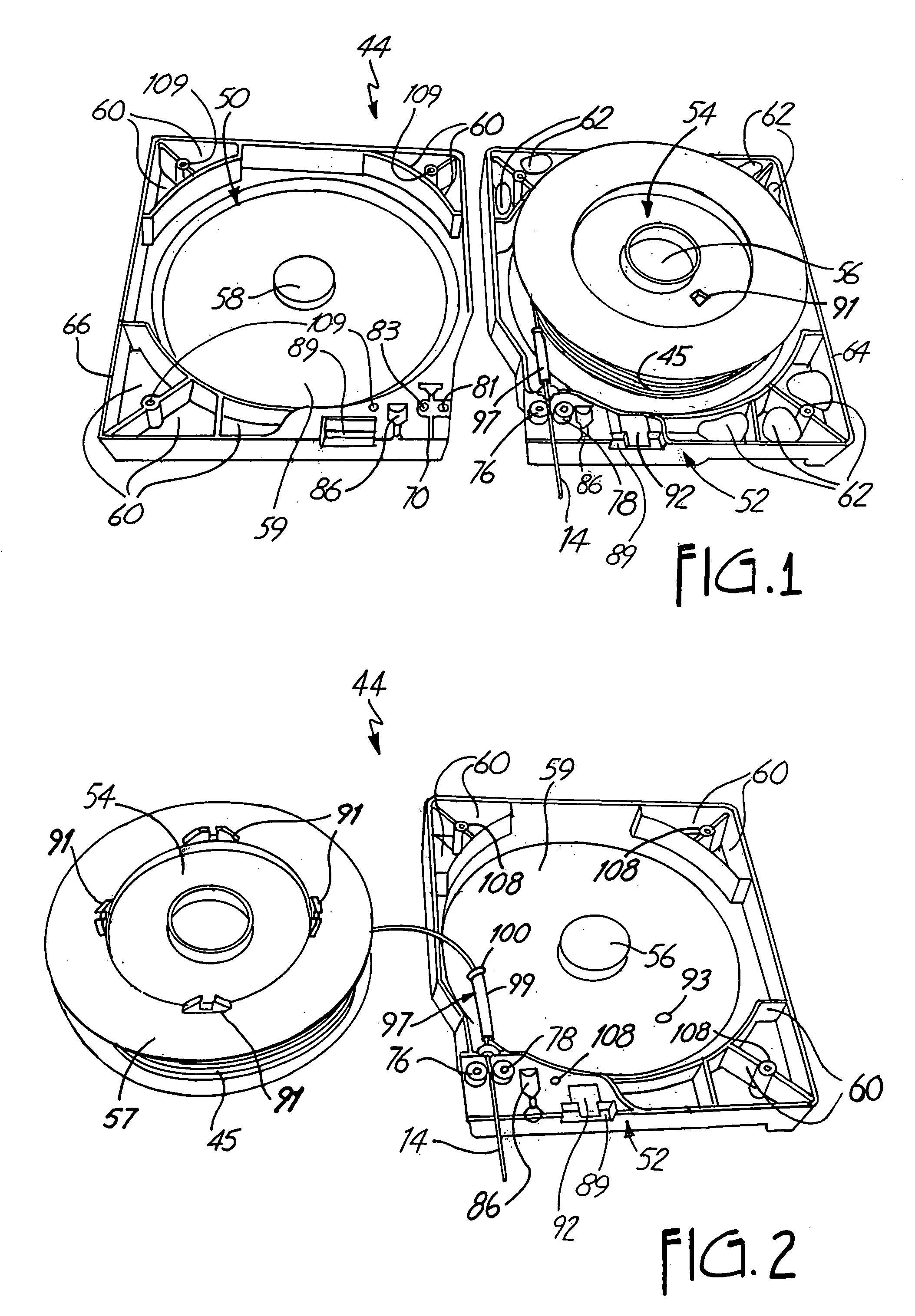
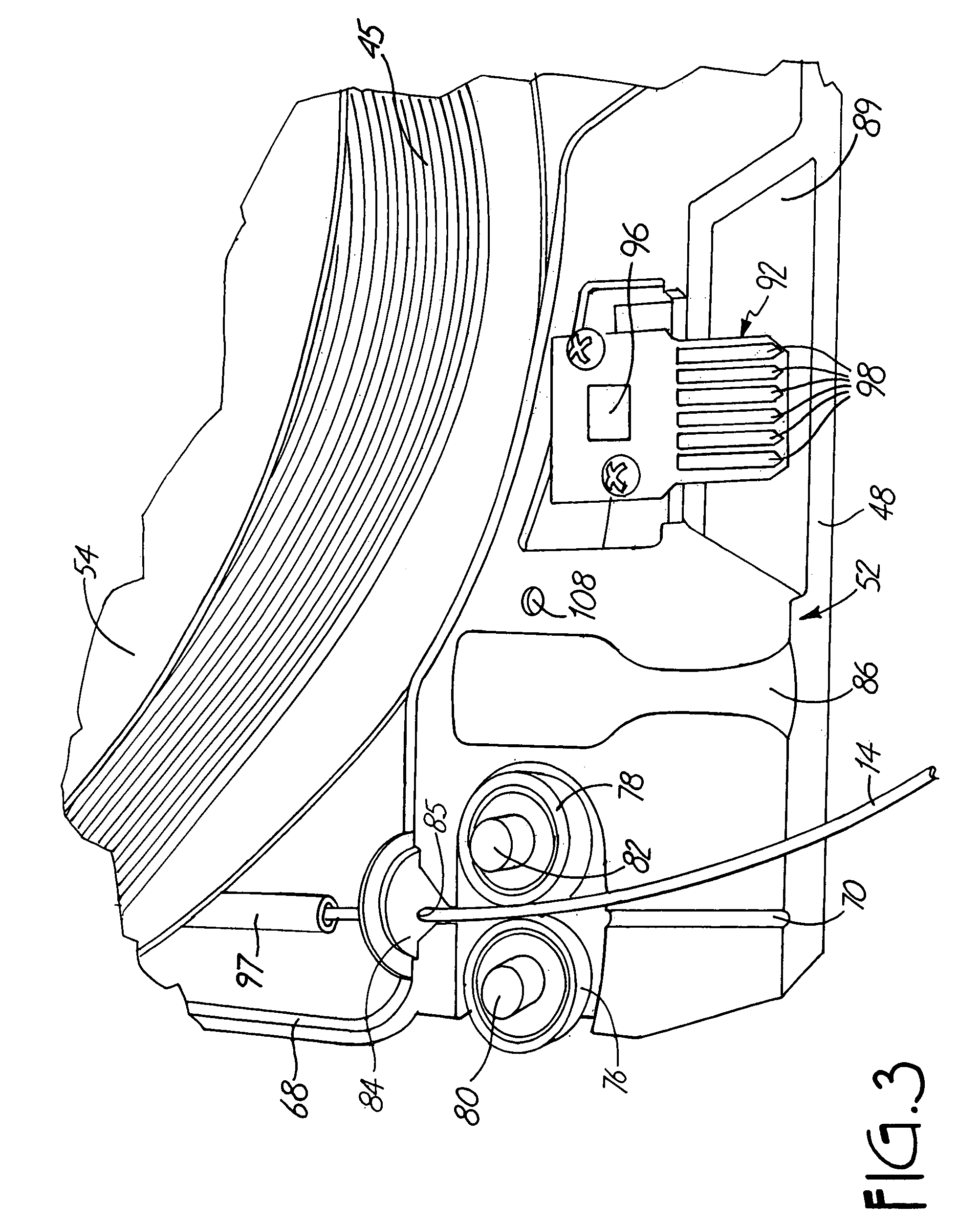
Tape cartridge and tape processing apparatus on which tape cartridge is detachably mounted
InactiveUS20060088802A1Easy to understandEnabling useTypewritersOther printing apparatusMagnetic tapeEngineering
A tape cartridge includes a process tape to be subjected to tape processing and a cartridge casing in which the process tape is accommodated and which has a plurality of outer wall faces making a contour of the cartridge casing, and is detachably mounted on a tape processing apparatus. The tape cartridge is handled in a state in which a feeding end of the process tape is slightly projected from a tape feeding port formed in one of the outer wall faces of the cartridge casing. One or more outer wall faces other than the one outer wall face of the cartridge casing have braille placed thereon serving as content indications.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Cassette device for reliable filament delivery
ActiveUS7063285B1Reduce failurePrevents tangling of the filamentContainers for annular articlesFilament handlingEngineeringFlange
A cassette for use in delivering a continuous length of filament provides improved reliability by employing means for preventing tangling of the filament in the cassette. The cassette has a substantially closed housing defining a chamber in which a spool is rotatably mounted, and a path from the chamber to an exit orifice. A length of filament is wound around the spool and has a free strand positioned in the path. The filament strand is advanced along the path and delivered through the exit orifice by a means for advancing. Tangling is prevented by locking the spool during transport of the cassette to maintain a tight wind, and by guiding the filament strand along a snag-free path as it is withdrawn from the cassette. In the exemplary embodiments, a removable pin locks a flange or hub of the spool, and the filament strand is withdrawn through a tubular guide member.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
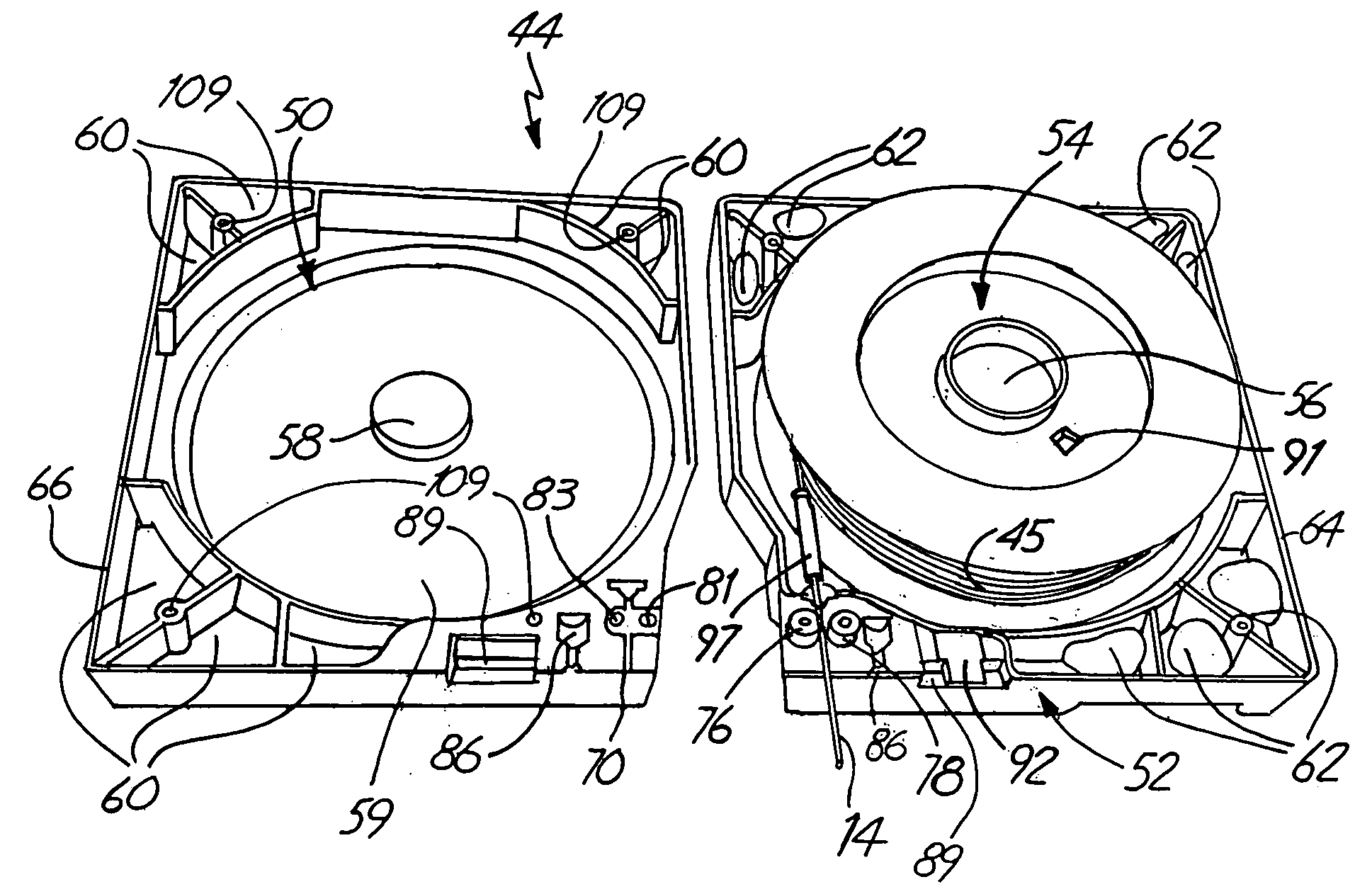
Magnetic tape cartridge
InactiveUS7287715B2Type differenceIncreased costPicture changing apparatusRecord information storageMagnetic tapeMagnetic cartridge
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Surgical cassette
ActiveUS20070107490A1Easy to identifyTesting/calibration apparatusEye surgeryMagnetic tapeEngineering
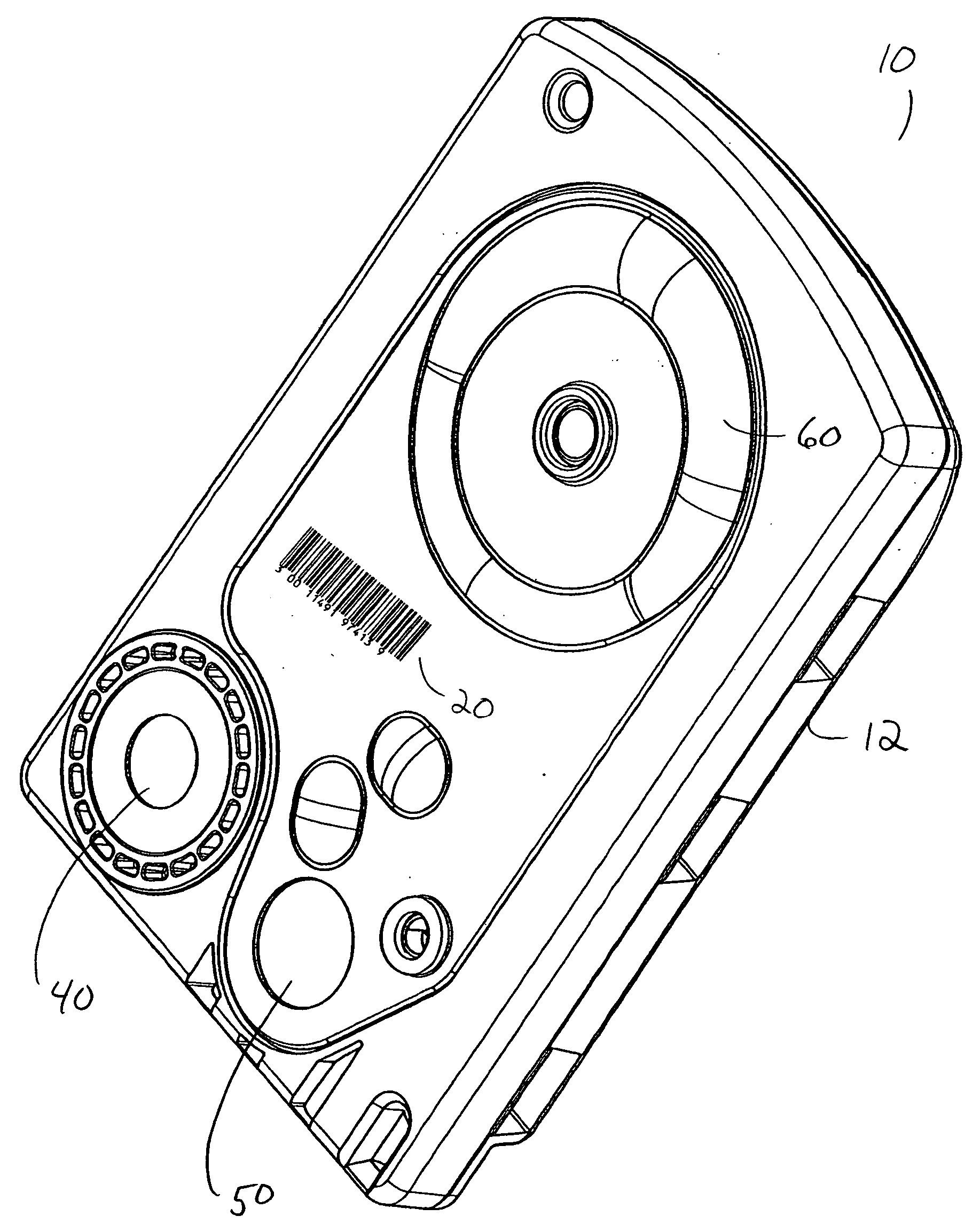
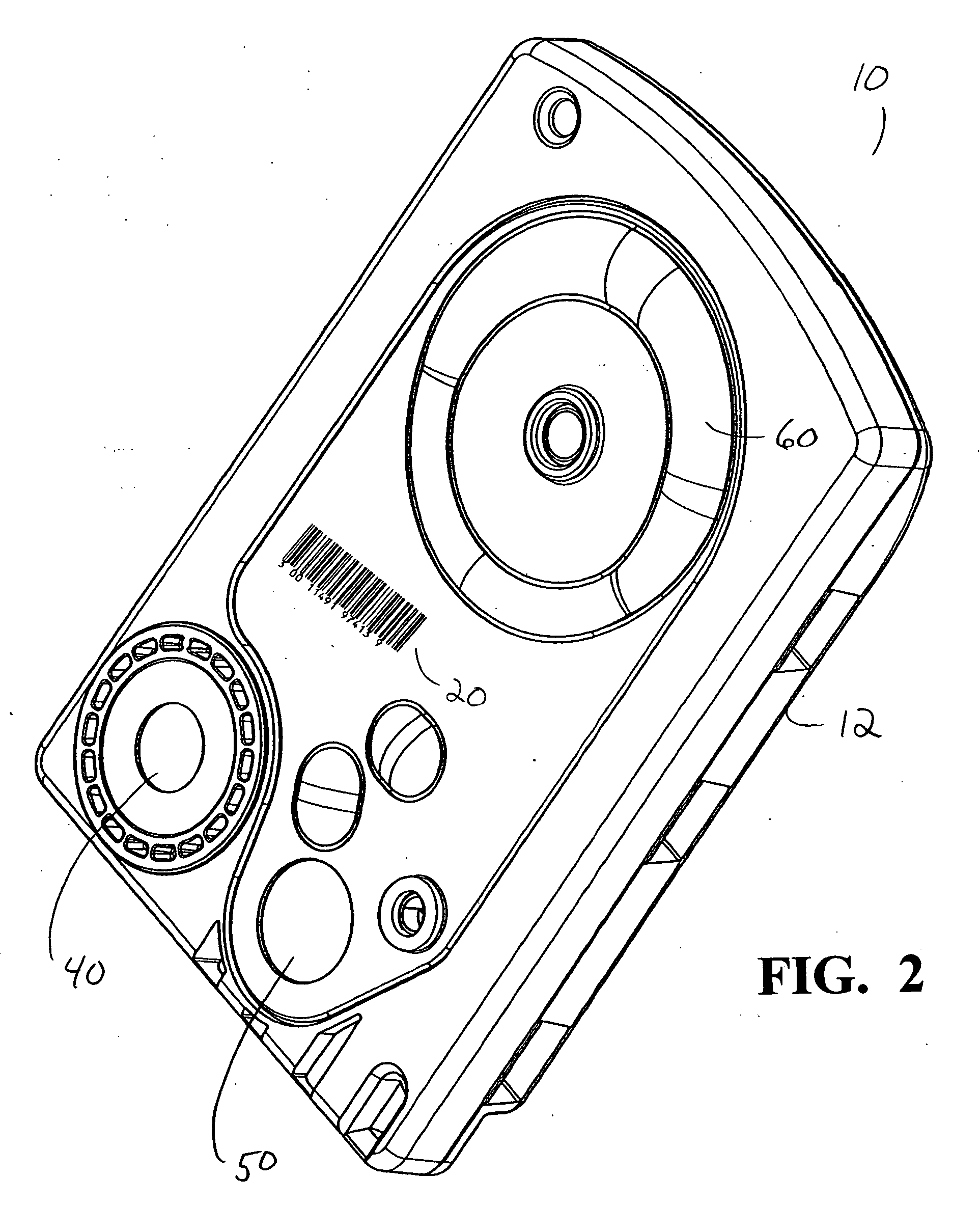
A surgical system and cassette, the cassette having an identification method that is specific to the cassette. Suitable methods include bar coding or Radio Frequency Identification (“RFID”). Cassette information that may be encoded include features such as lot number and performance characteristics, such as pressure sensor calibration data, flow and pressure data and any other performance characteristics of the cassette captured during testing of the cassette at manufacture.
Owner:ALCON INC
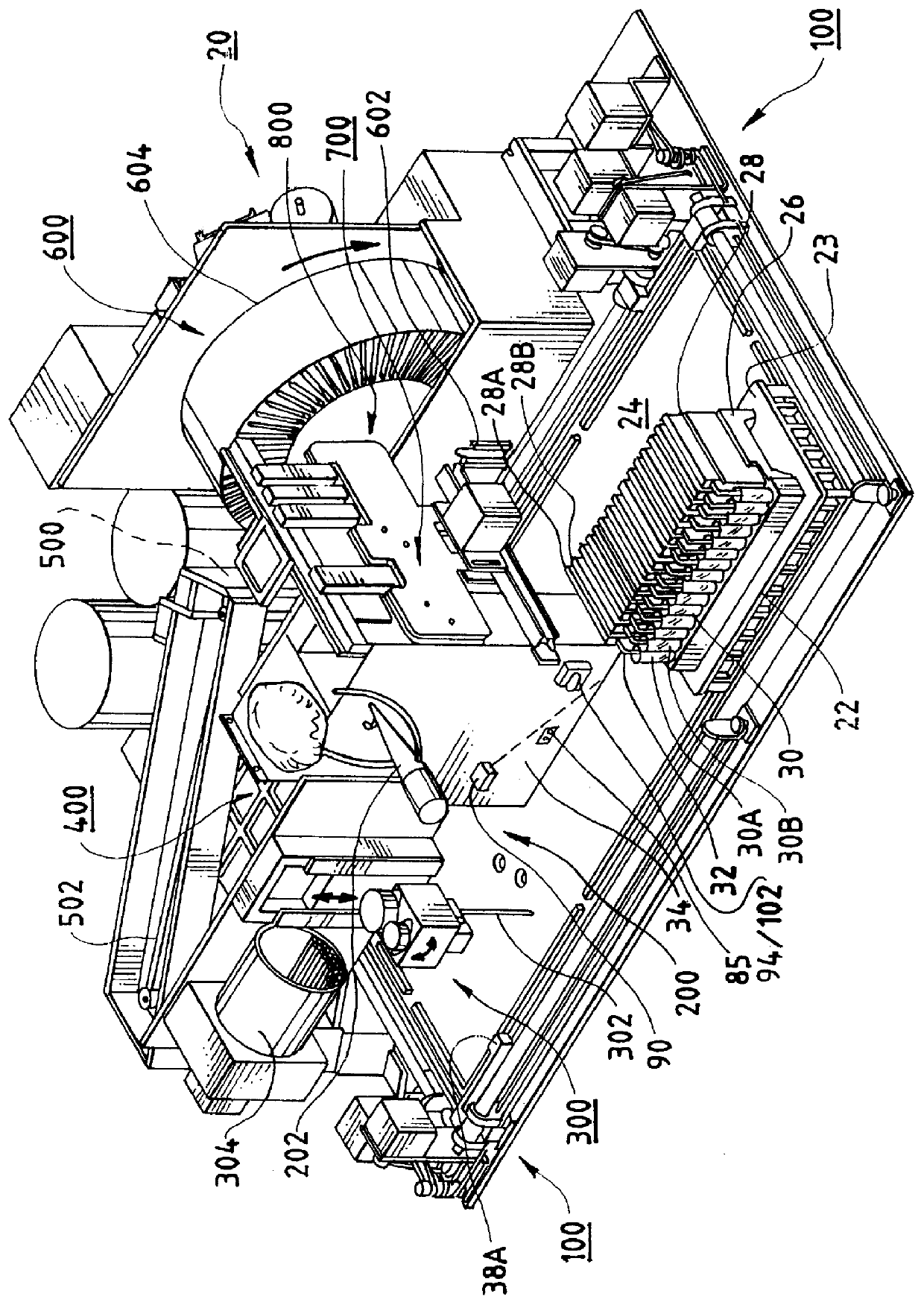
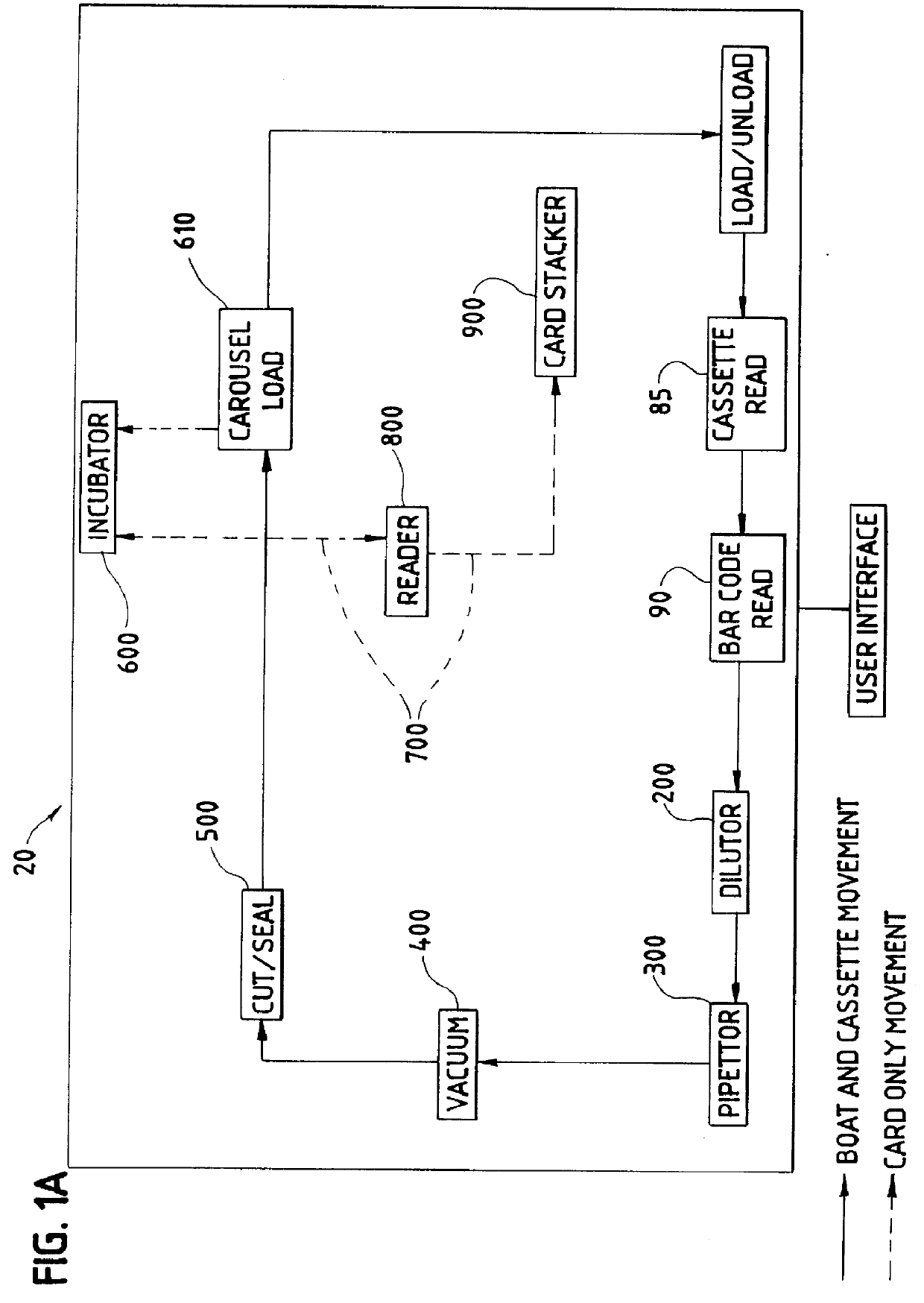
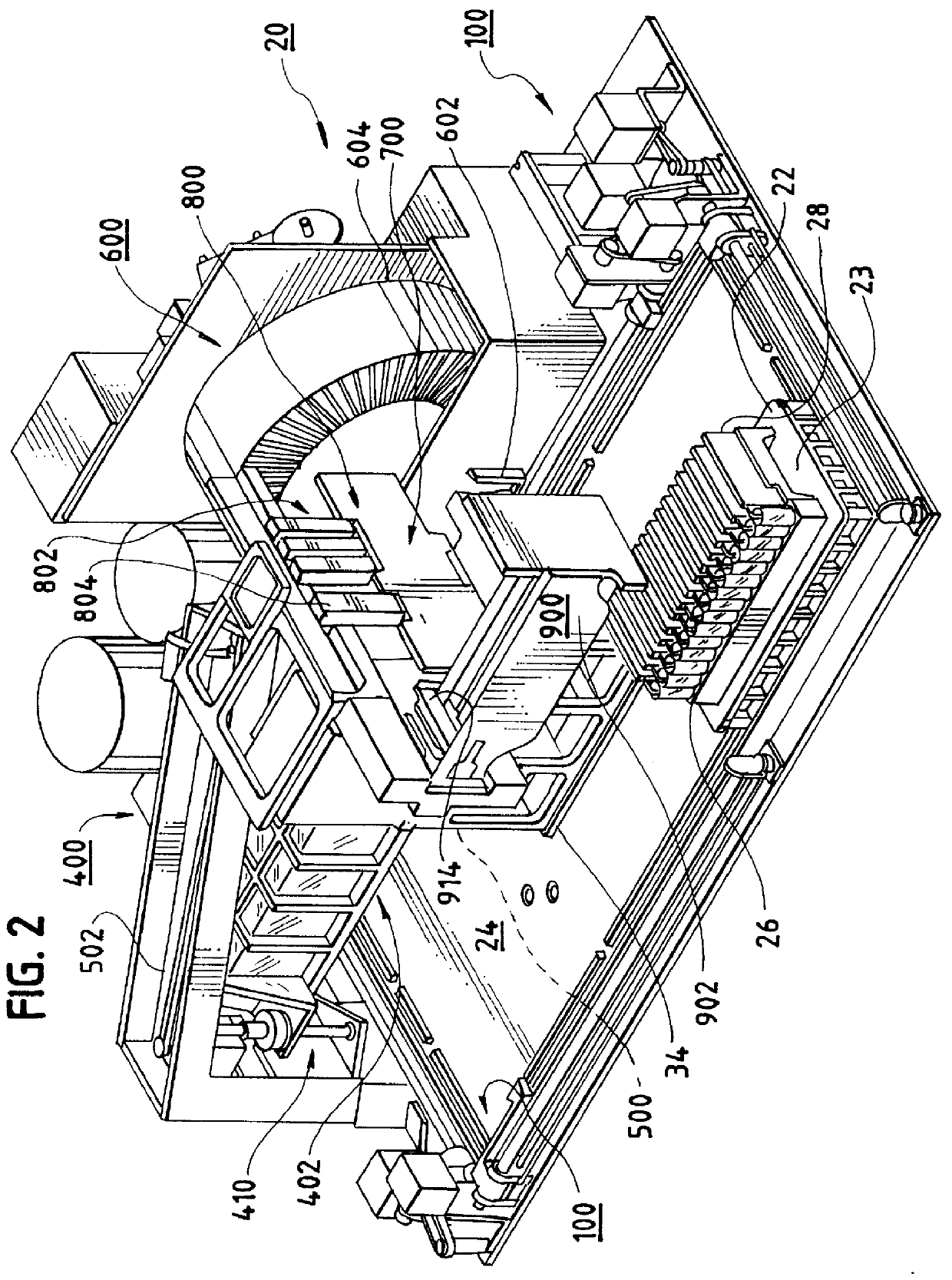
Incubation station for test sample cards
InactiveUS6024921ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReciprocating motionTest sample
Test sample cards containing biological samples are moved through an analytical instrument past a card detection device and detected by the device. The card detection device has an actuator that reciprocates relative to a housing between first and second positions. The actuator has a surface that comes into contact with the card as the card is moved past the device. The actuator carries an optical interrupt flag which is used in conjunction with an optical sensor placed in proximity to the actuator. When the card comes into contact with the actuator, the actuator is moved from the first position to the second, or retracted position. This action moves the flag relative to the optical sensor, triggering the optical sensor and a detection of the card. In one possible embodiment, multiple cards are placed in a cassette for movement around the instrument. The cassette has a number of slots for the cards, one card per slot. Each card has placed thereon indicia such as bar codes that are used for identification purposes by the instrument. The card detection device, in addition to performing the detection functions for each of the cards, also rocks the cards within the cassette slots so as to place the bar codes or other indicia into a better position for reading by a bar code reader or other appropriate reading device for the indicia.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
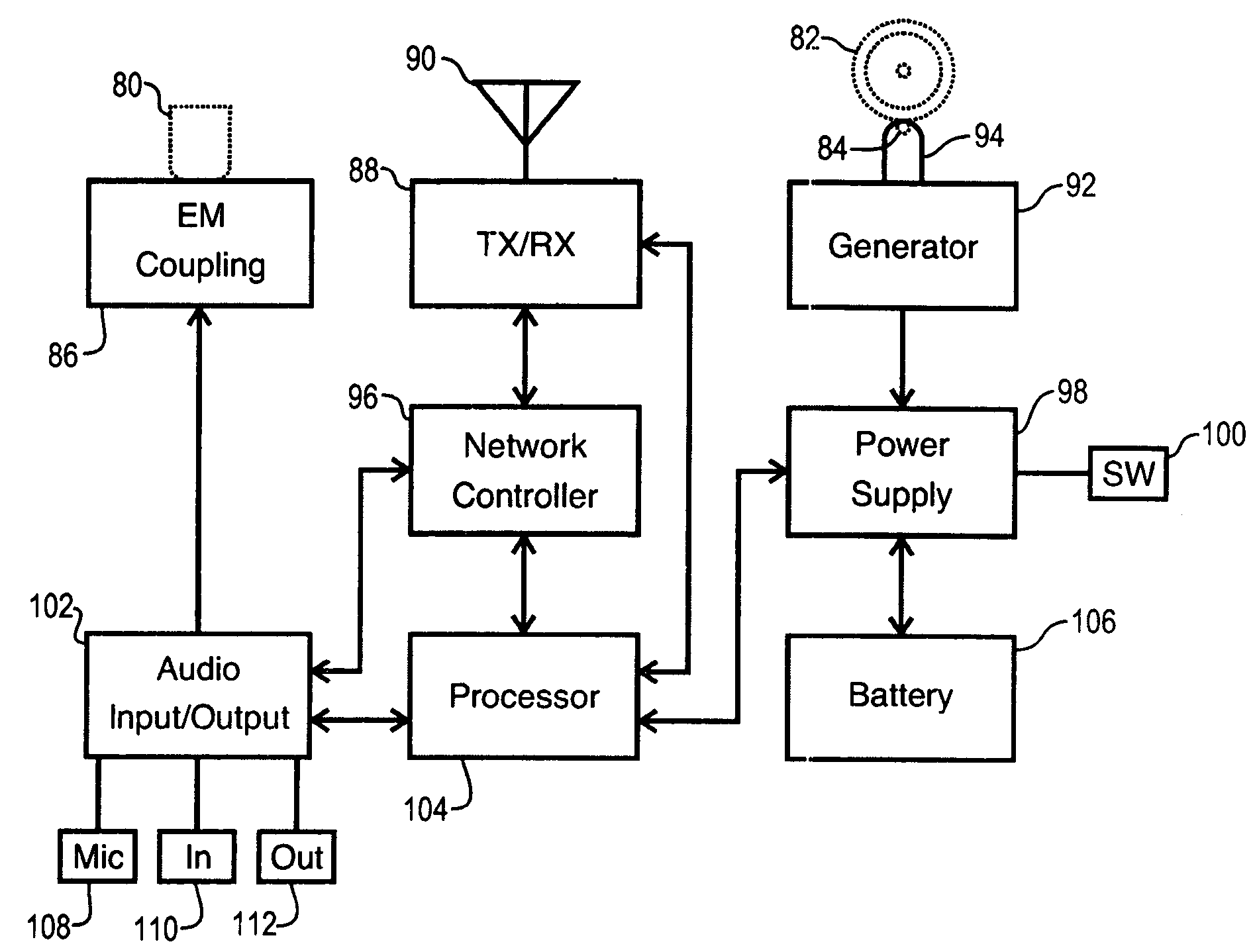
Network interface cassette adapter and method
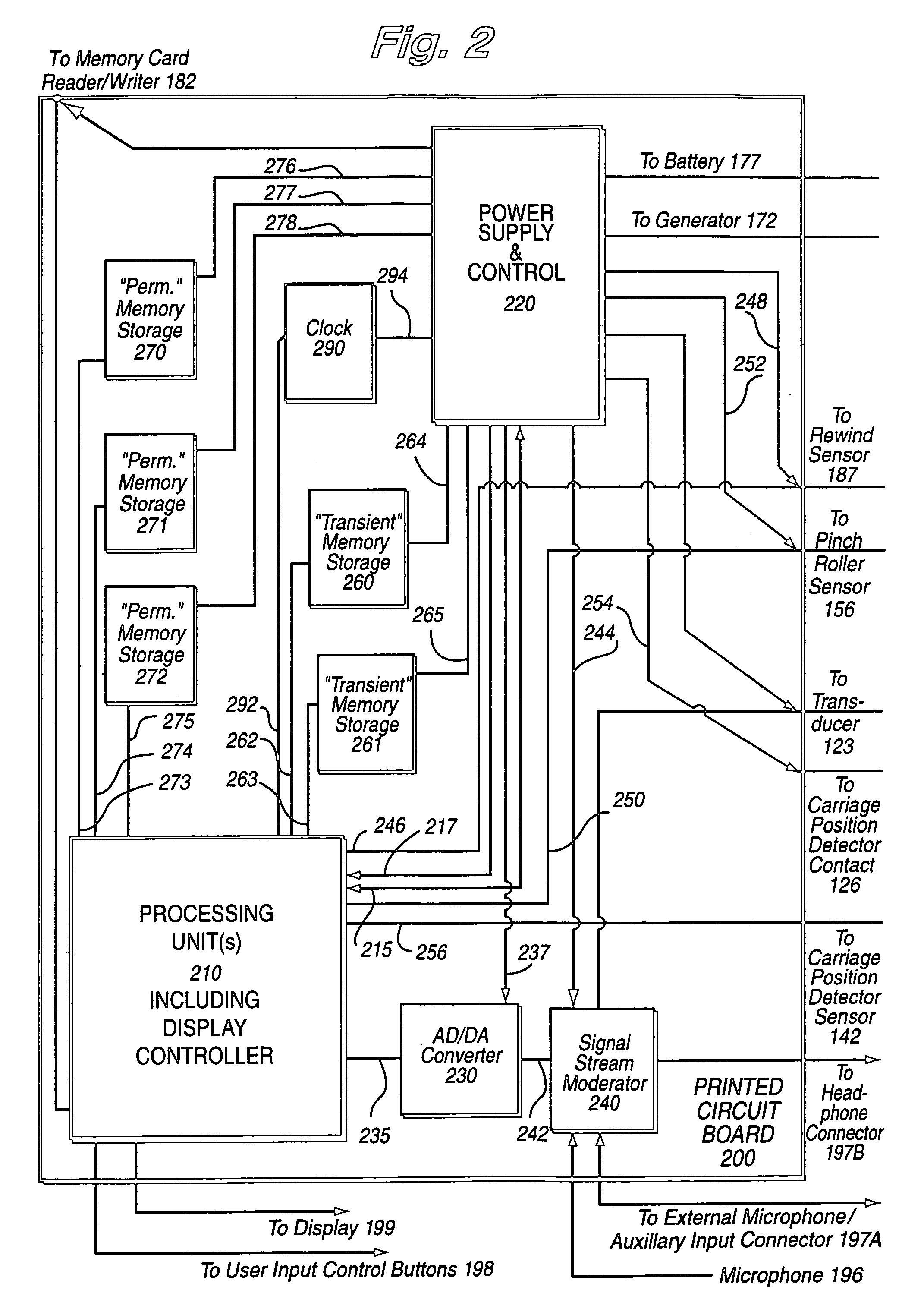
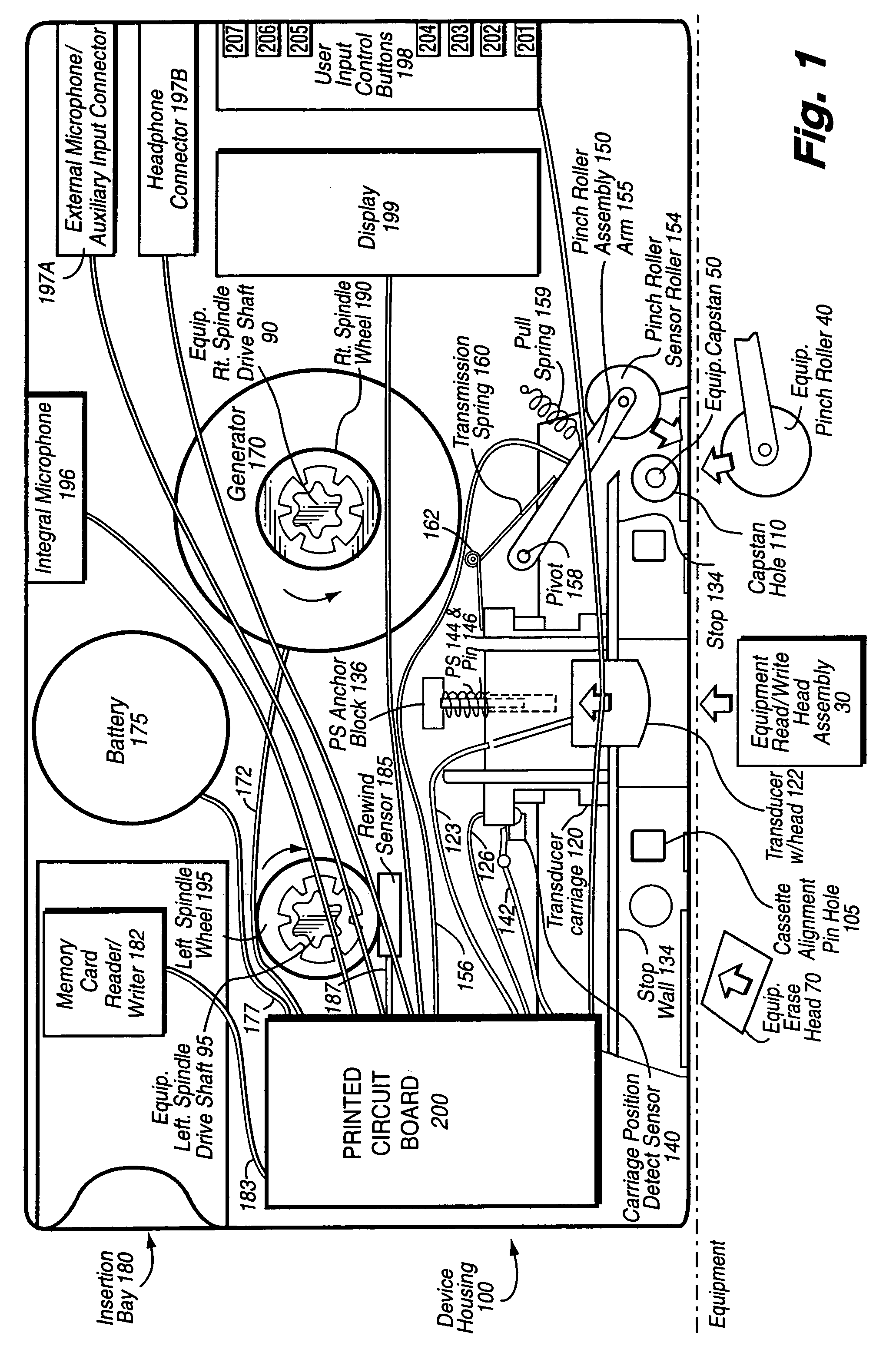
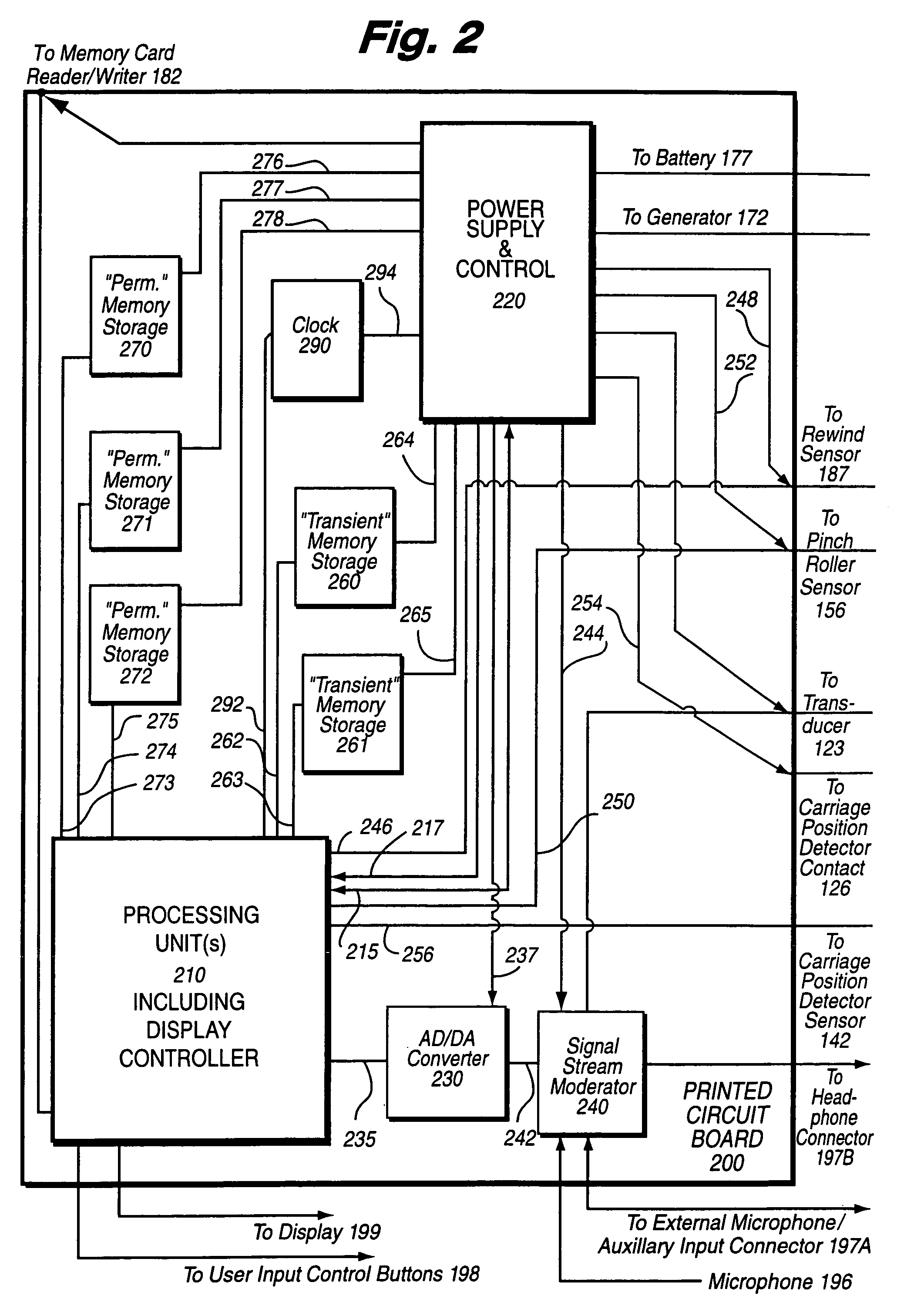
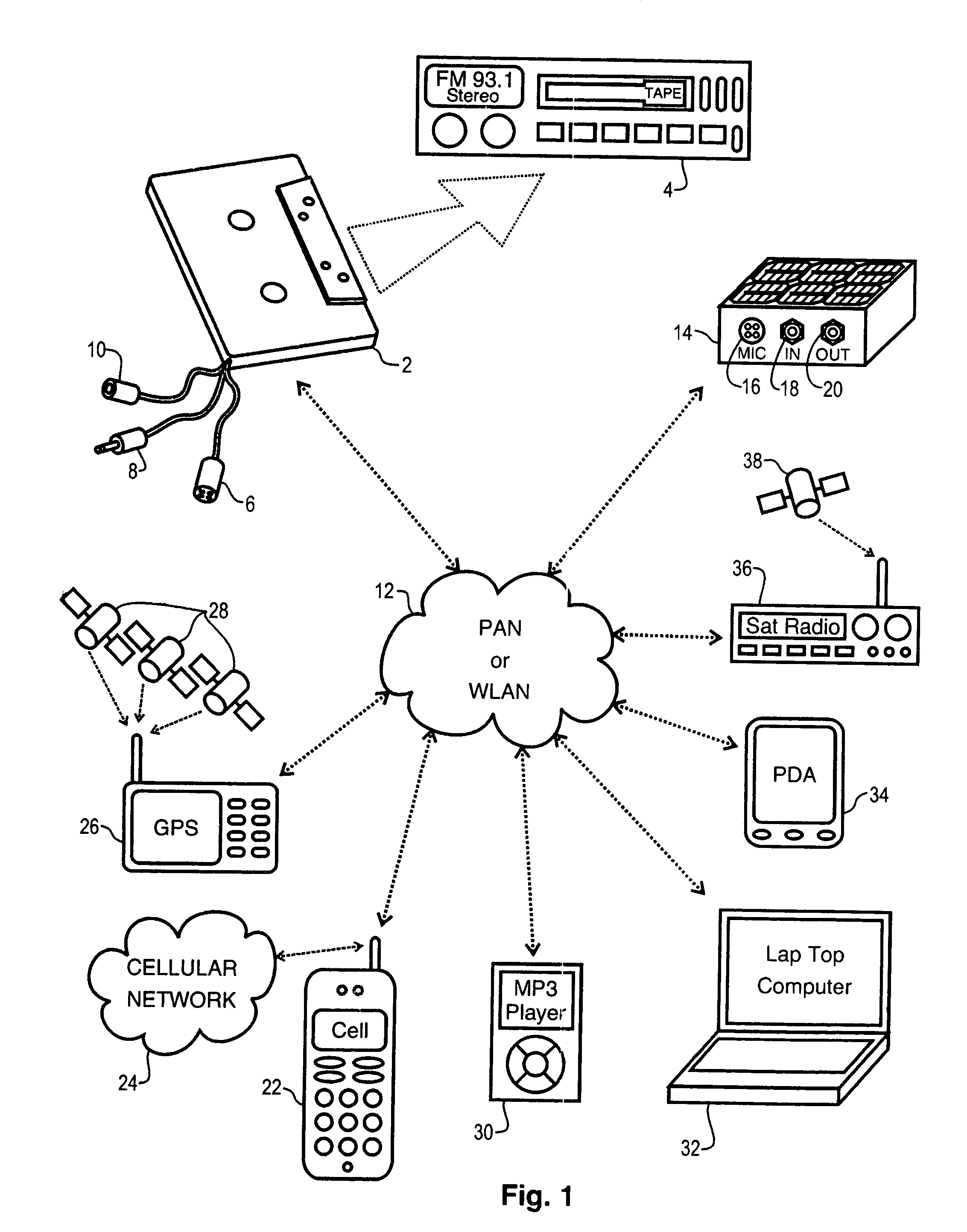
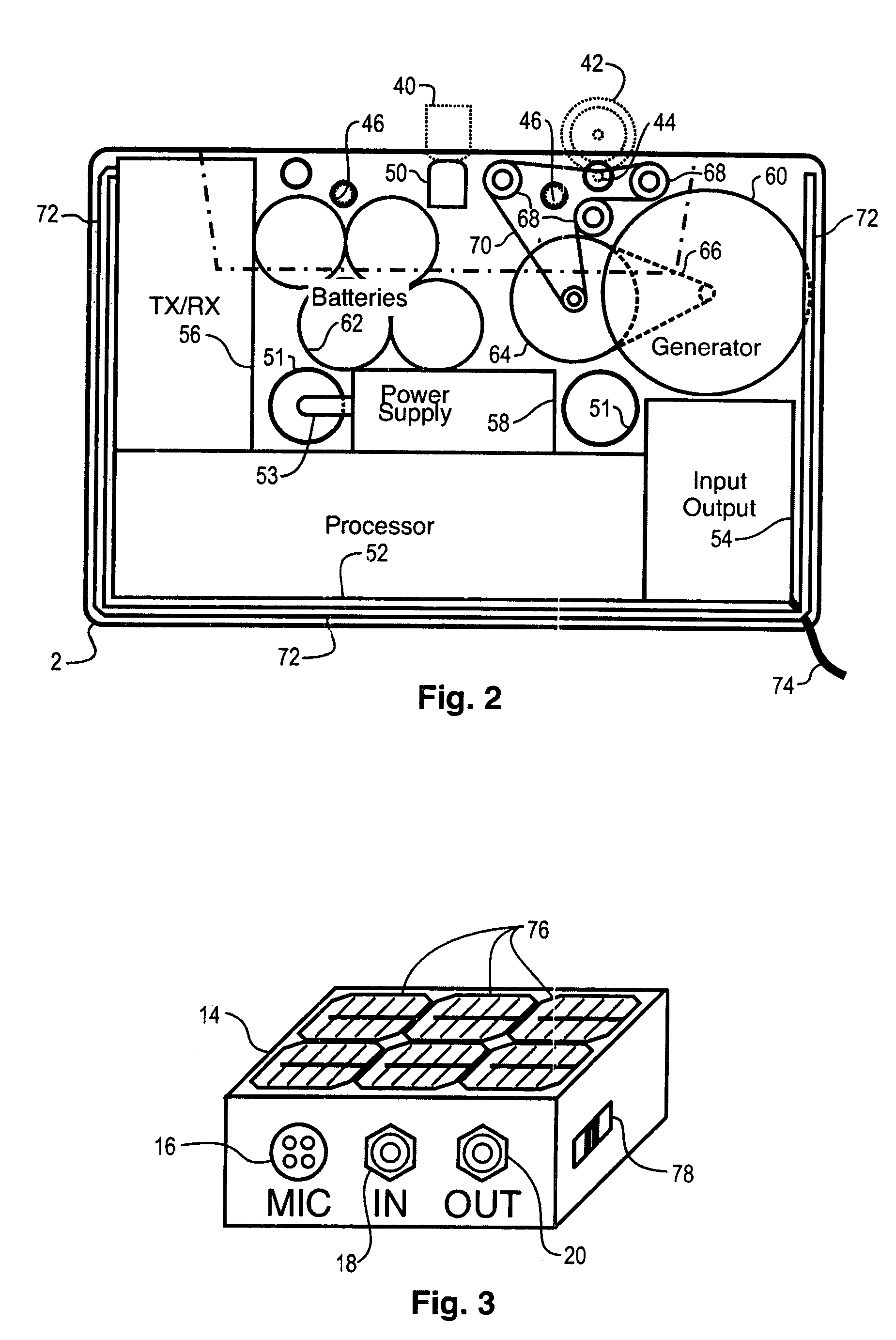
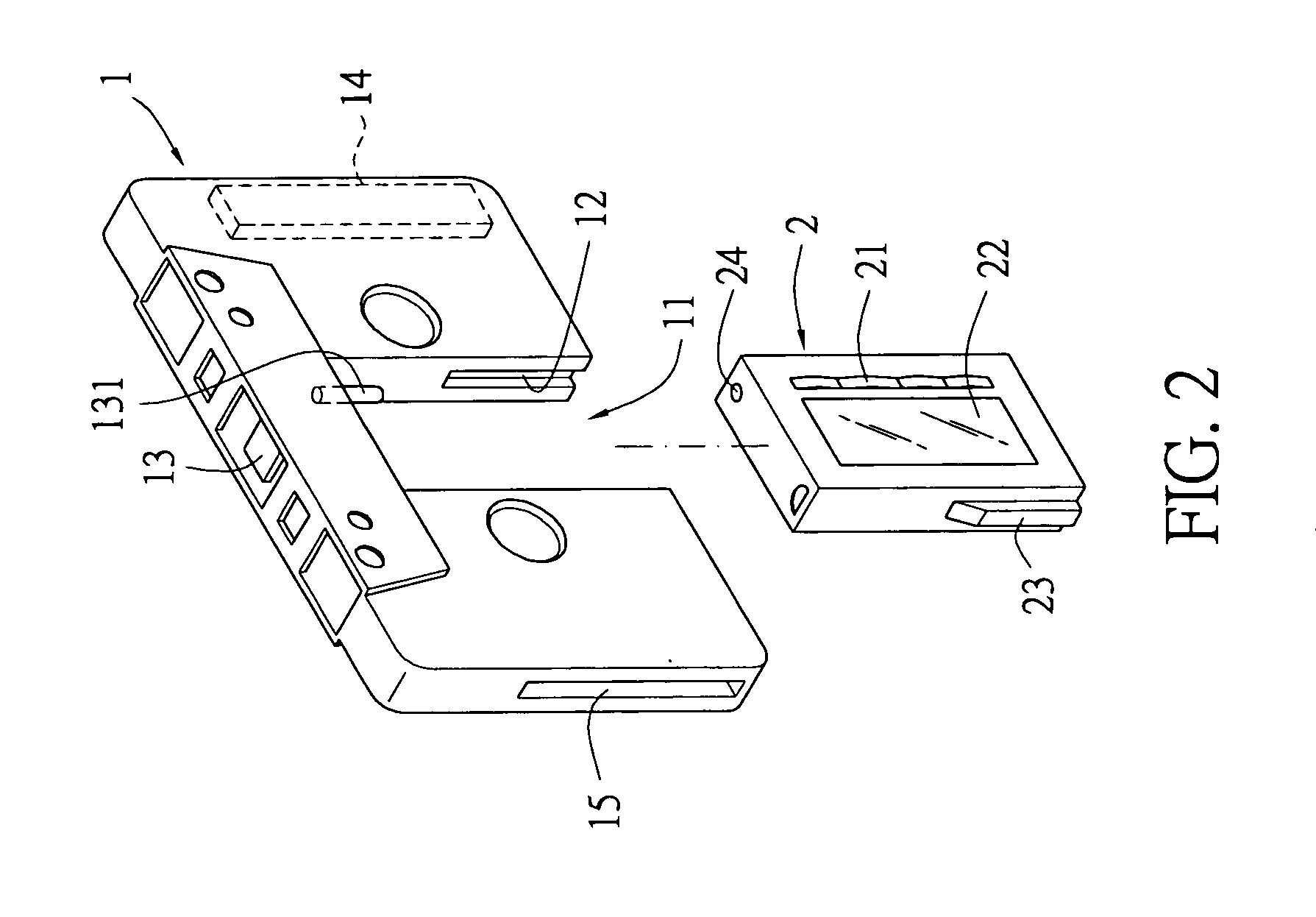
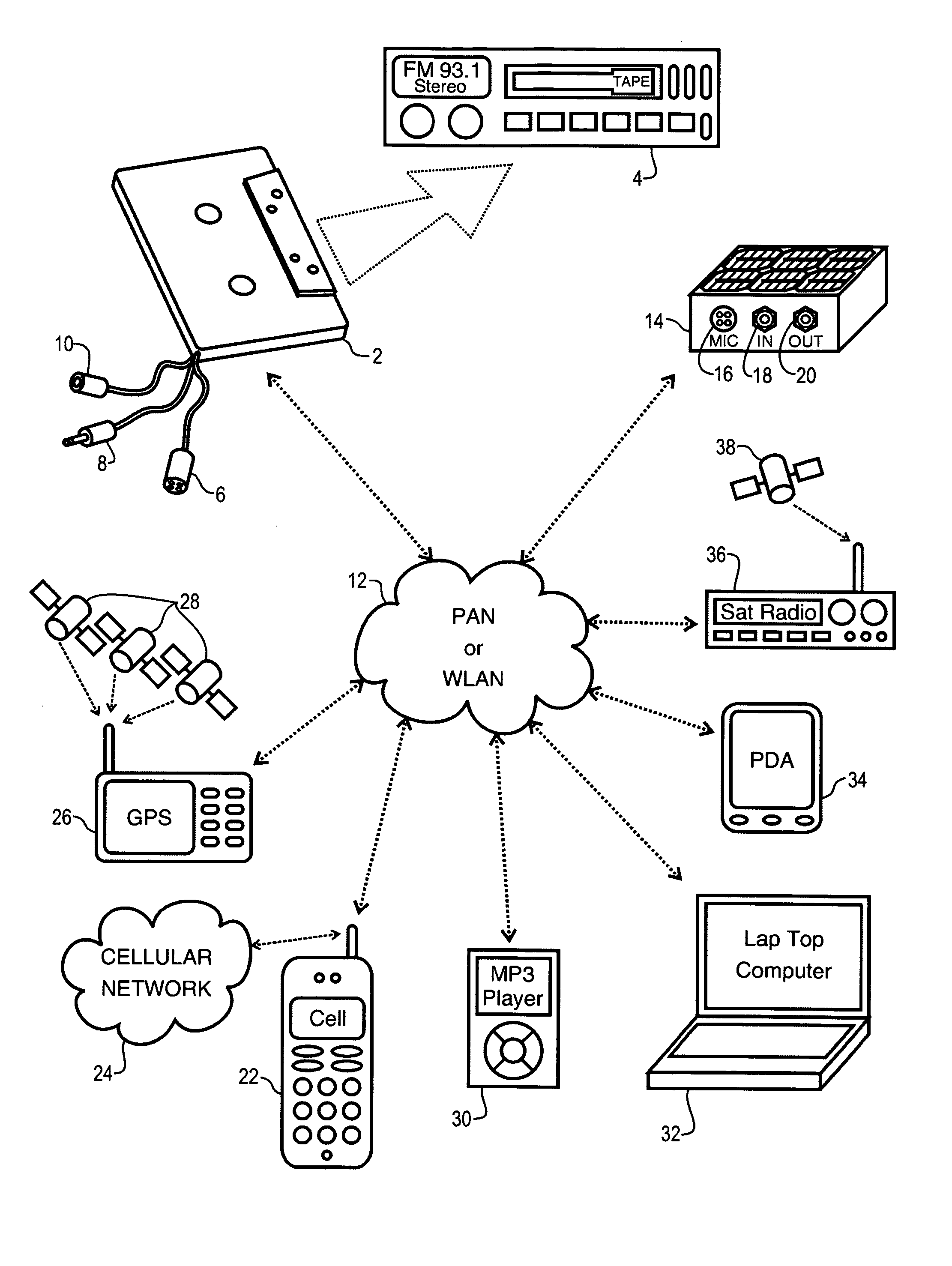
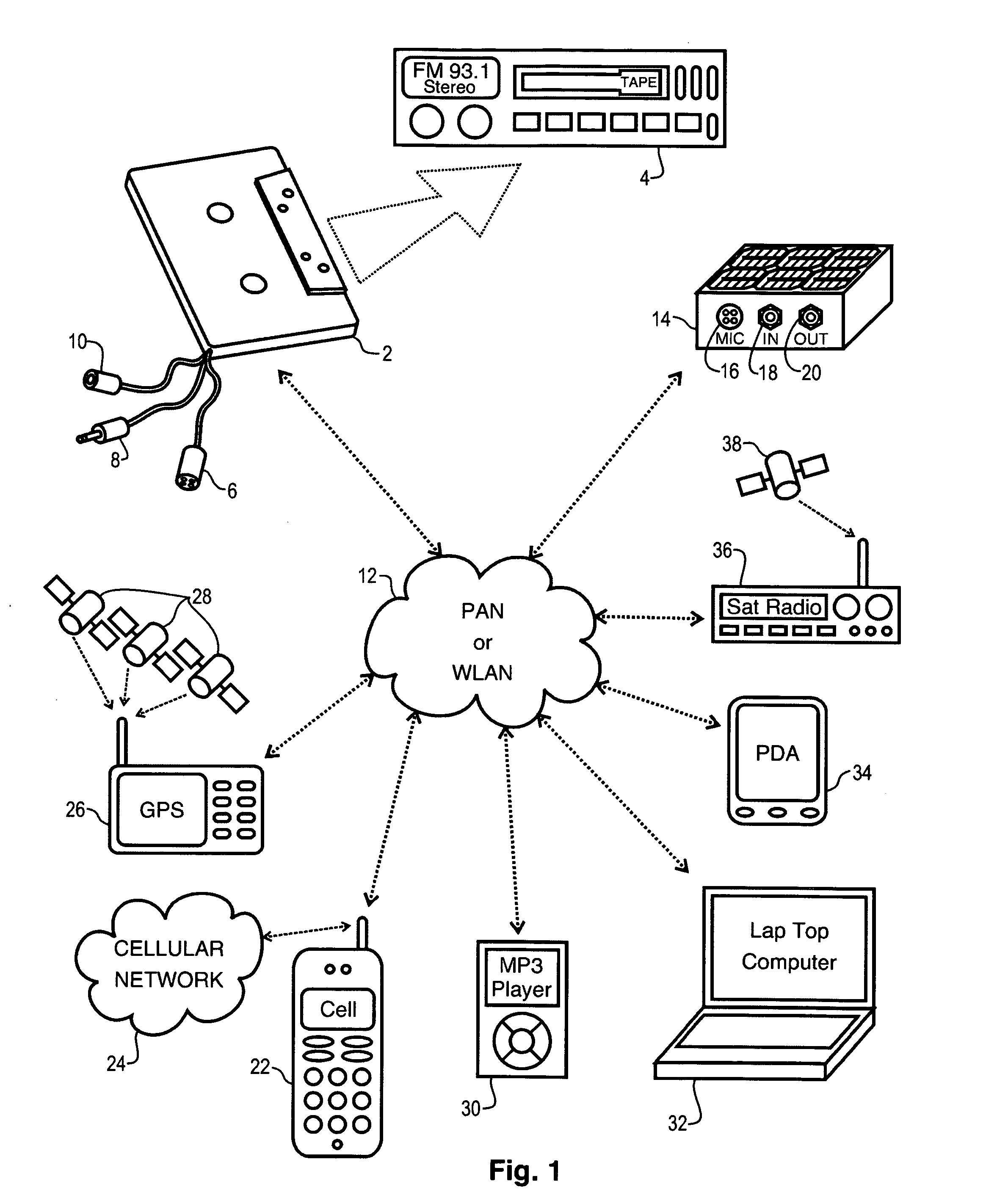
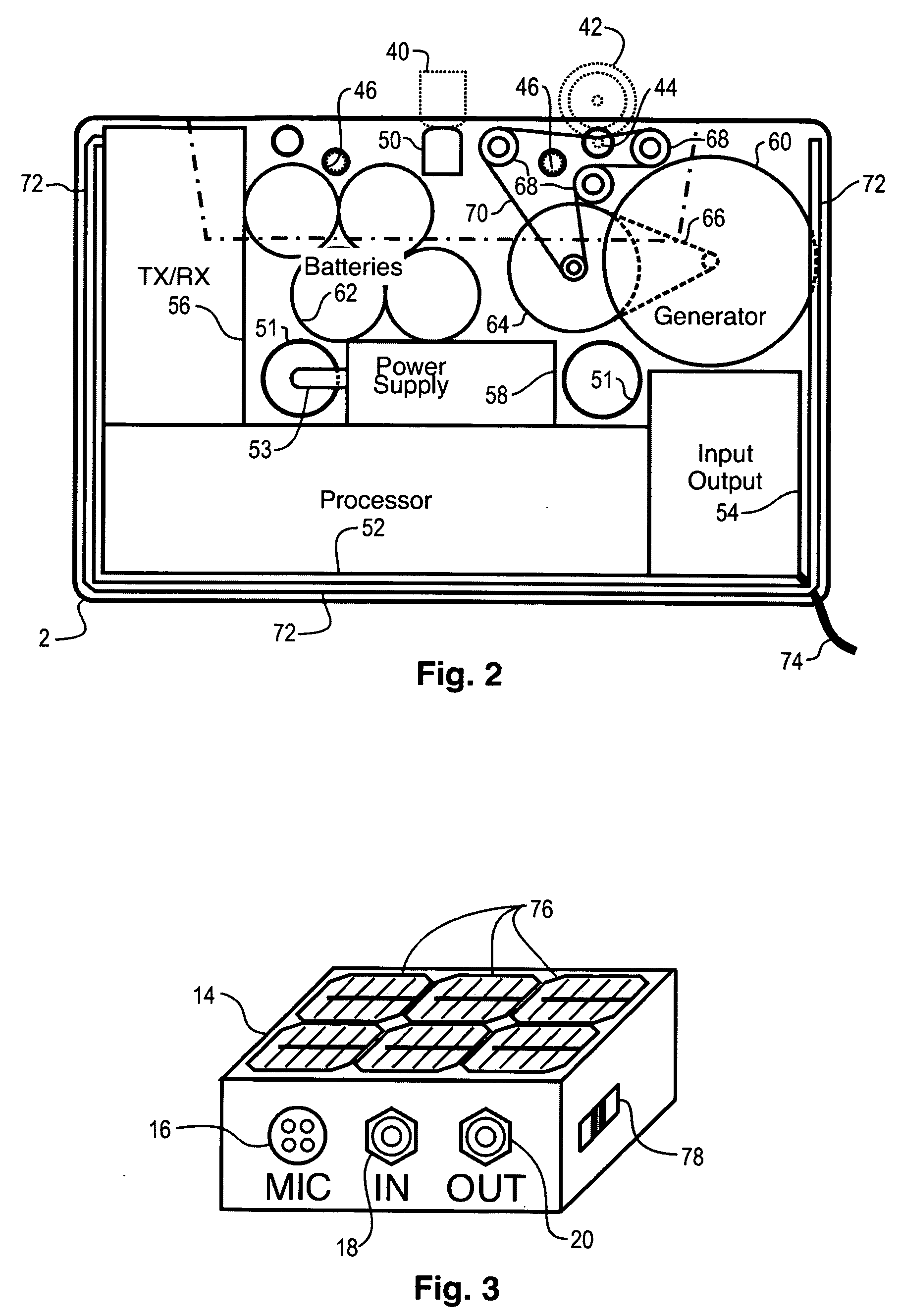
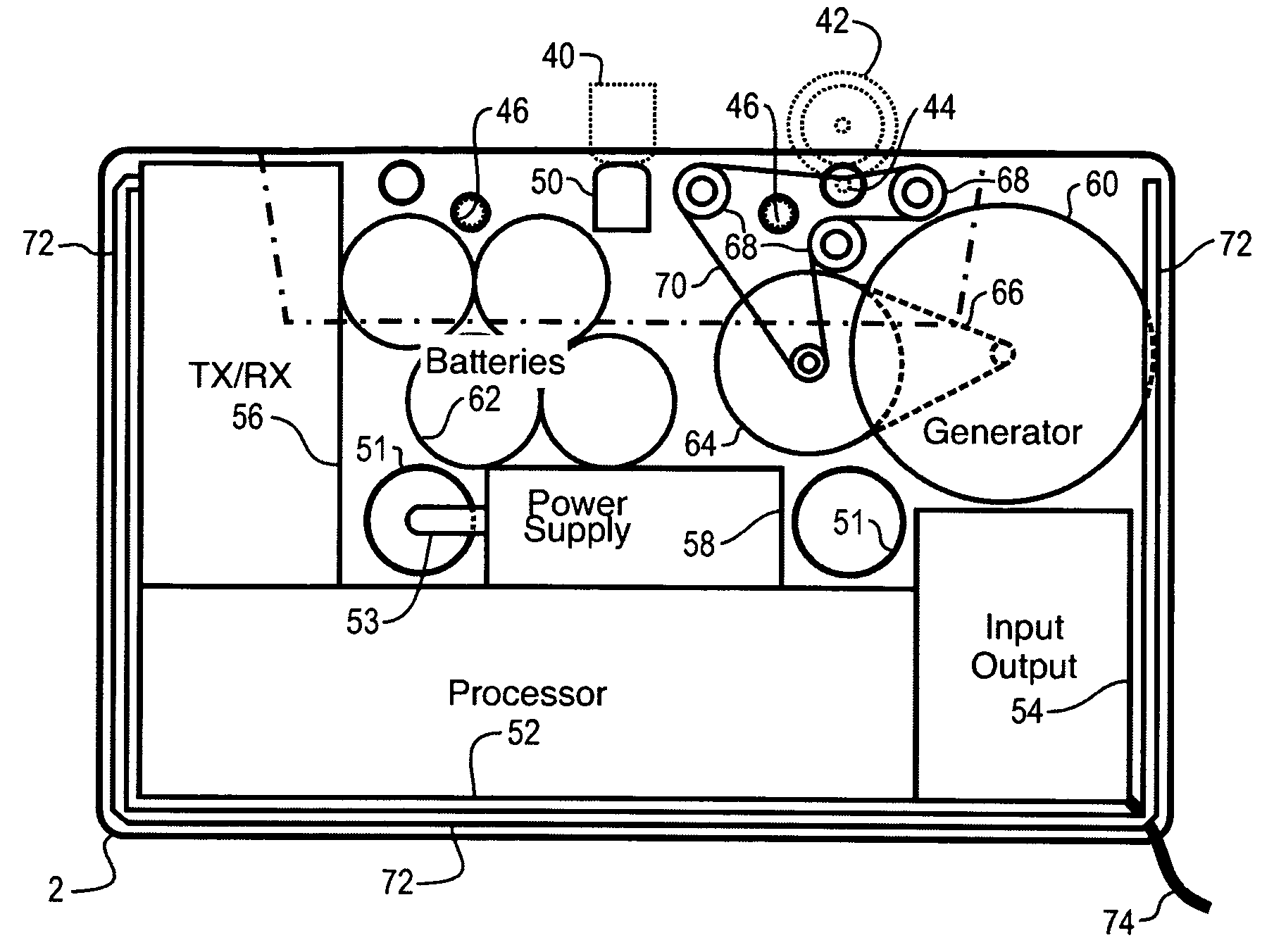
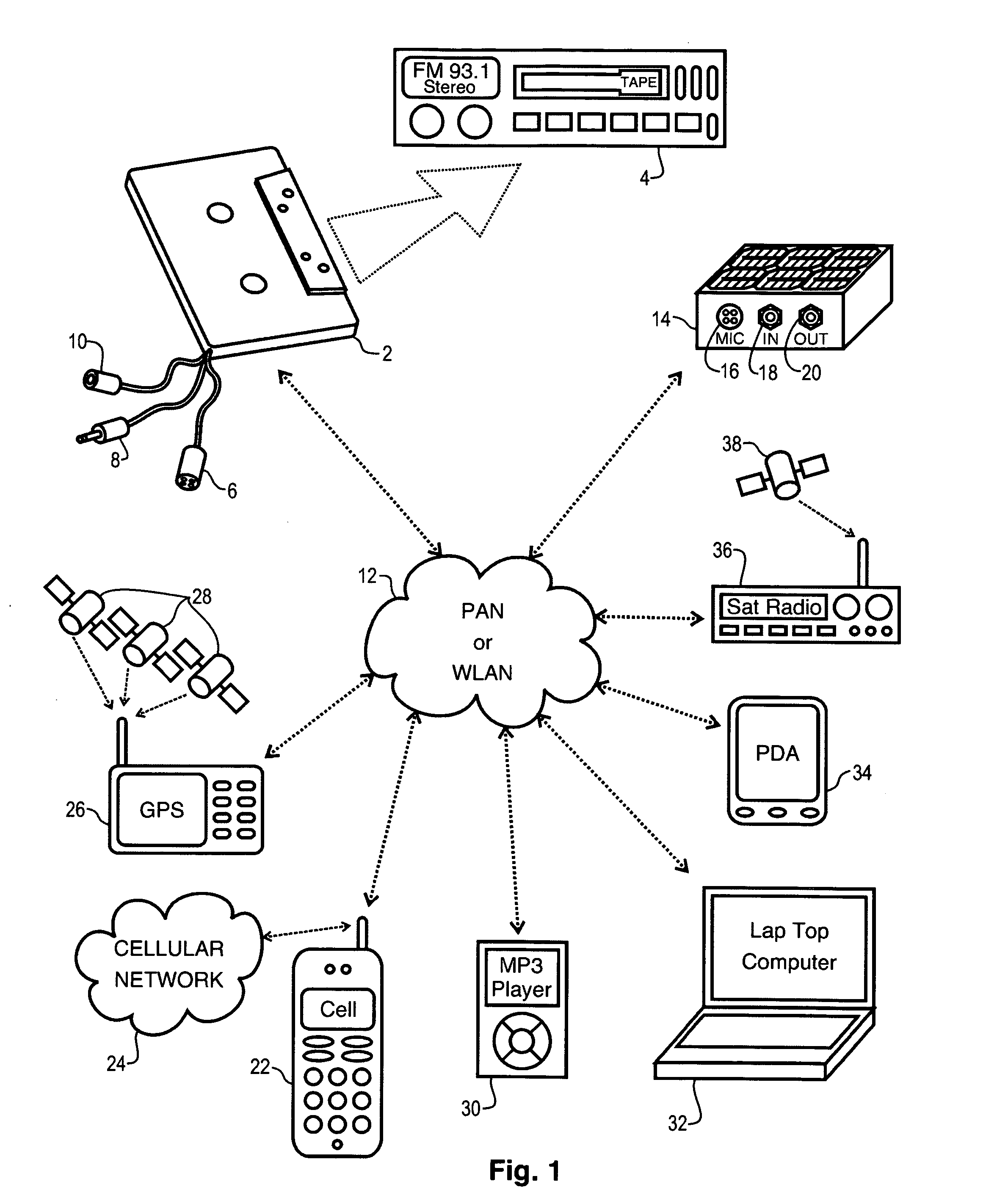
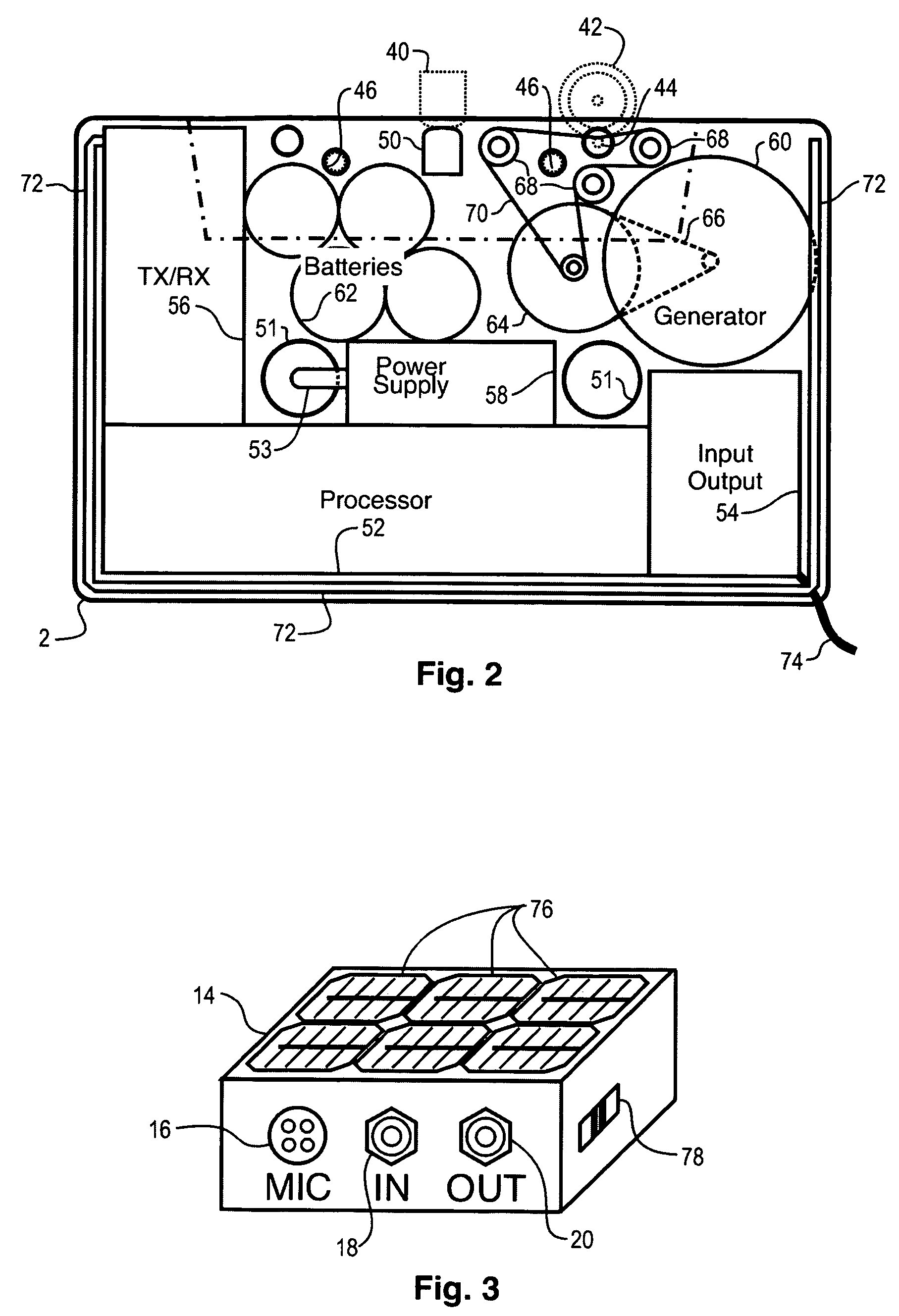
A network interface cassette for coupling signals between a wireless network and a tape head in a cassette tape player. The network interface cassette includes an enclosure that is conformed to the cassette tape form factor. It contains a transceiver that converts base band signals for radio frequency communications within the wireless network. It also contains a network controller that is coupled to communicate the base band signals with the transceiver. The network controller converts digital audio signals to and from the base band signals. There is an audio processor that converts the digital audio signals to analog audio signals. A coupling means converts the analog audio signals to magnetic audio signals. The coupling means is aligned to couple the magnetic audio signals to the tape head. A power supply with batteries and a generator driven from the cassette player capstan are provided. A wireless user interface adapter is provided to couple microphone and audio signals to the apparatus. Plural communications requests are processed, and include a priority scheme to manage resource contention.
Owner:THE SOURCE
Cassette having elastomeric clamping ribs
A cassette having a molded flow channel contained on an elastomeric sheet that is bonded or mechanically attached to a rigid substrate. A surgical console contains a cassette receiving area having a pump head with rollers that are mounted radially from the axis of rotation of the pump motor and compress the elastomeric flow channels against the rigid substrate. The cassette is held in place against the pump head by a latching mechanism that draws the cassette against the pump head. The periphery of the elastomeric sheet contains a raised ridge or boss integrally formed as part of the elastomeric sheet at or near the area(s) of the elastomeric sheet that is / are subject to high transient or static pressures. The ridge allows the elastomeric sheet to be firmly pressed against the cassette receiving portion of the surgical console, yet still allow the cassette to be drawn against the pump head. The firm engagement of the sheet ridge against the cassette receiving portion of the surgical console helps to ensure that the elastomeric sheet does not become dislodged when the cassette is exposed to high transient pressures.
Owner:ALCON INC
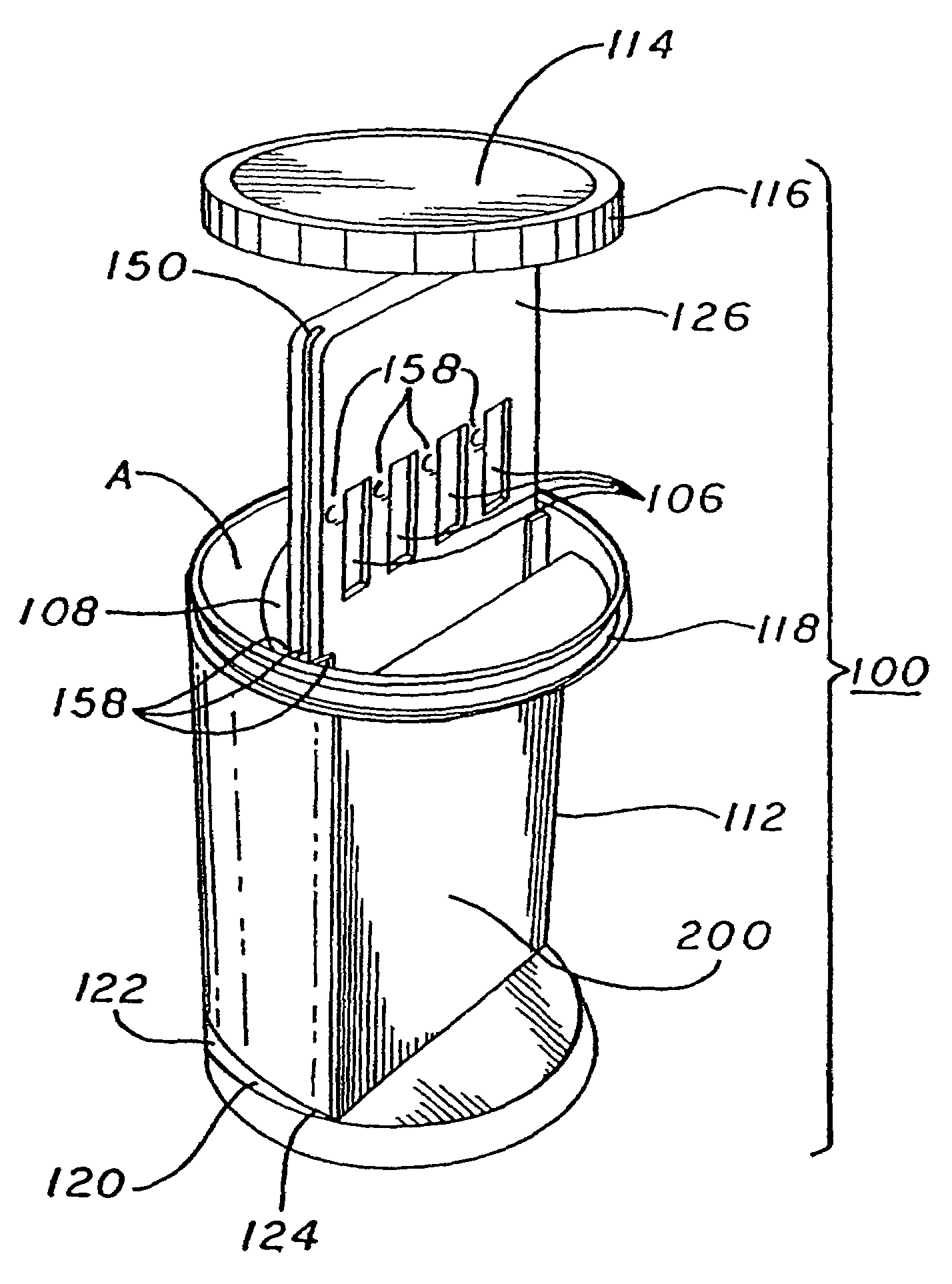
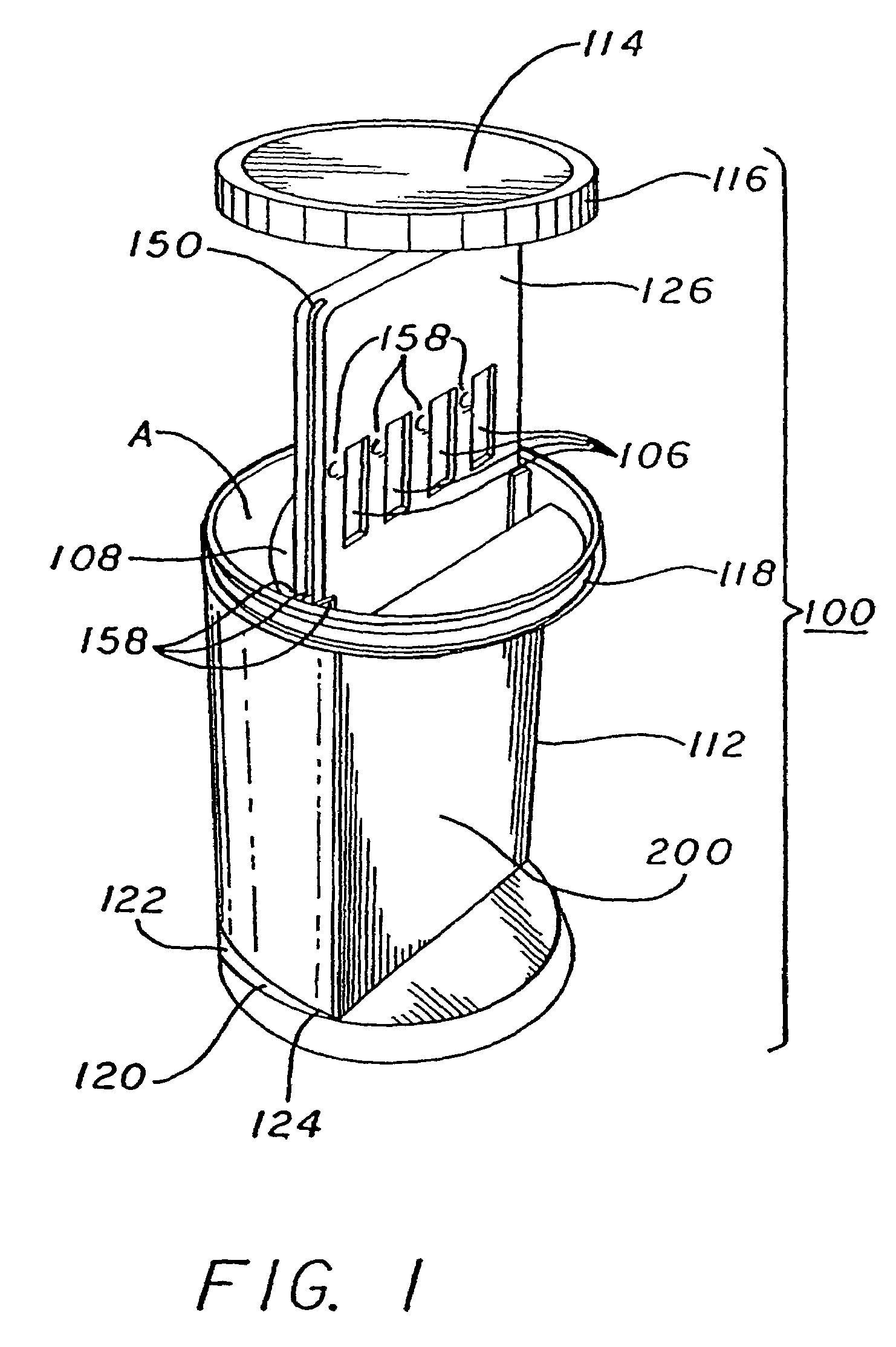
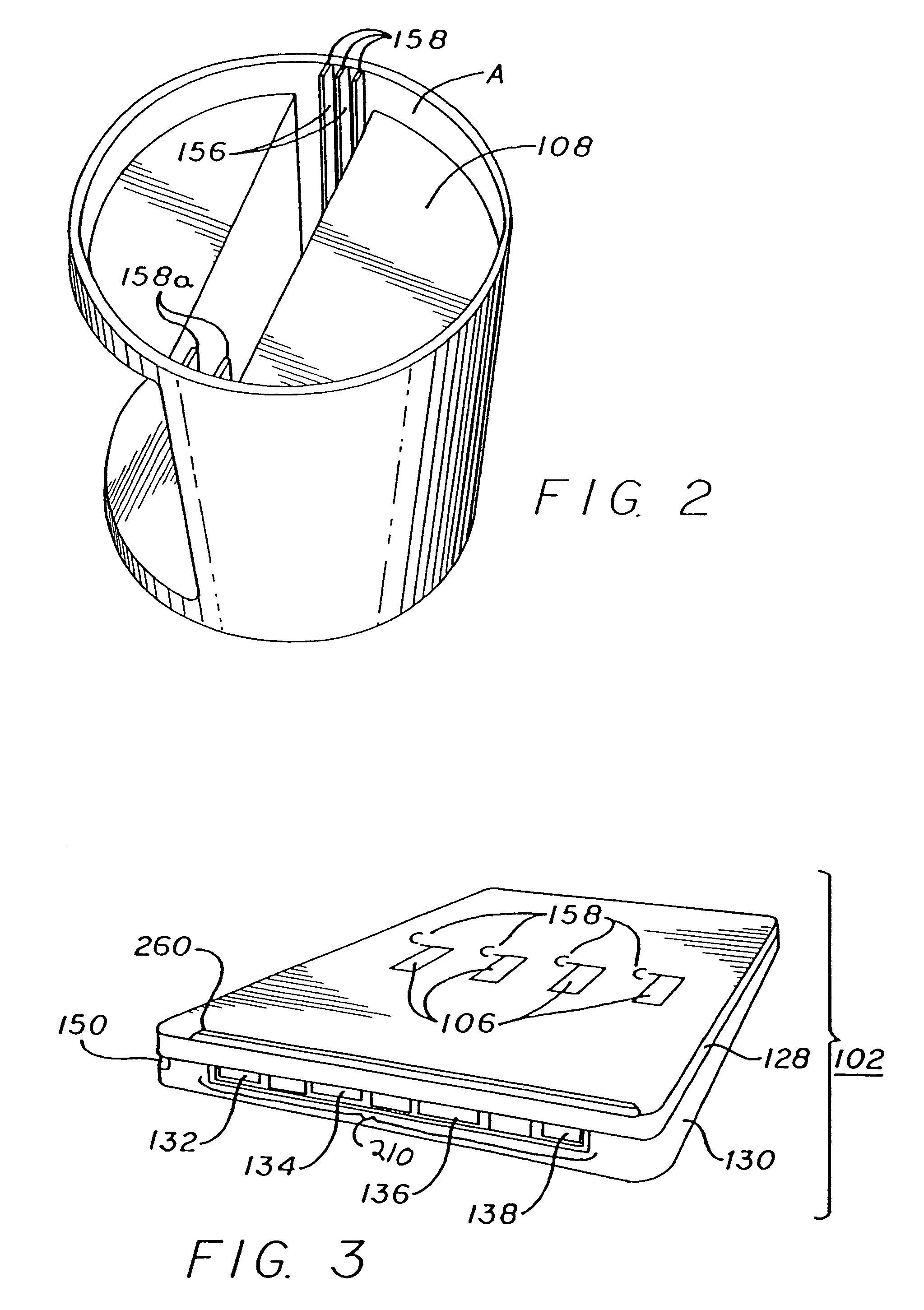
Slide-in cassette for a cup for testing of drugs of abuse
InactiveUS7244392B1Cut off available spaceEase of use and stabilityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMagnetic tapeHermetic seal
A specimen cup (100) has slide-in cassette (102) hermetically sealed in a chamber (104), with a outer partition being transparent. The cassette comprised chemical test strips (106) used to provide testing of drugs of abuse or other chemical or biological substances. The cassette is designed to draw urine up from the front bottom of the cup, thereby reduces the amount of urine required to perform the test. Further the cassette is designed to form isolated test channels through the use of strategically placed vertical and horizontal bars which are hermetically sealed. The cup further comprises a spill prevention flap or float (108) and an optionally enlarged sample collection portion (110) for its operation. The windows of the test cassette are covered with transparent fluid-resistant plate to prevent urine from accidentally spill onto the strips.
Owner:ABBOTT RAPID DIAGNOSTICS INT UNLTD
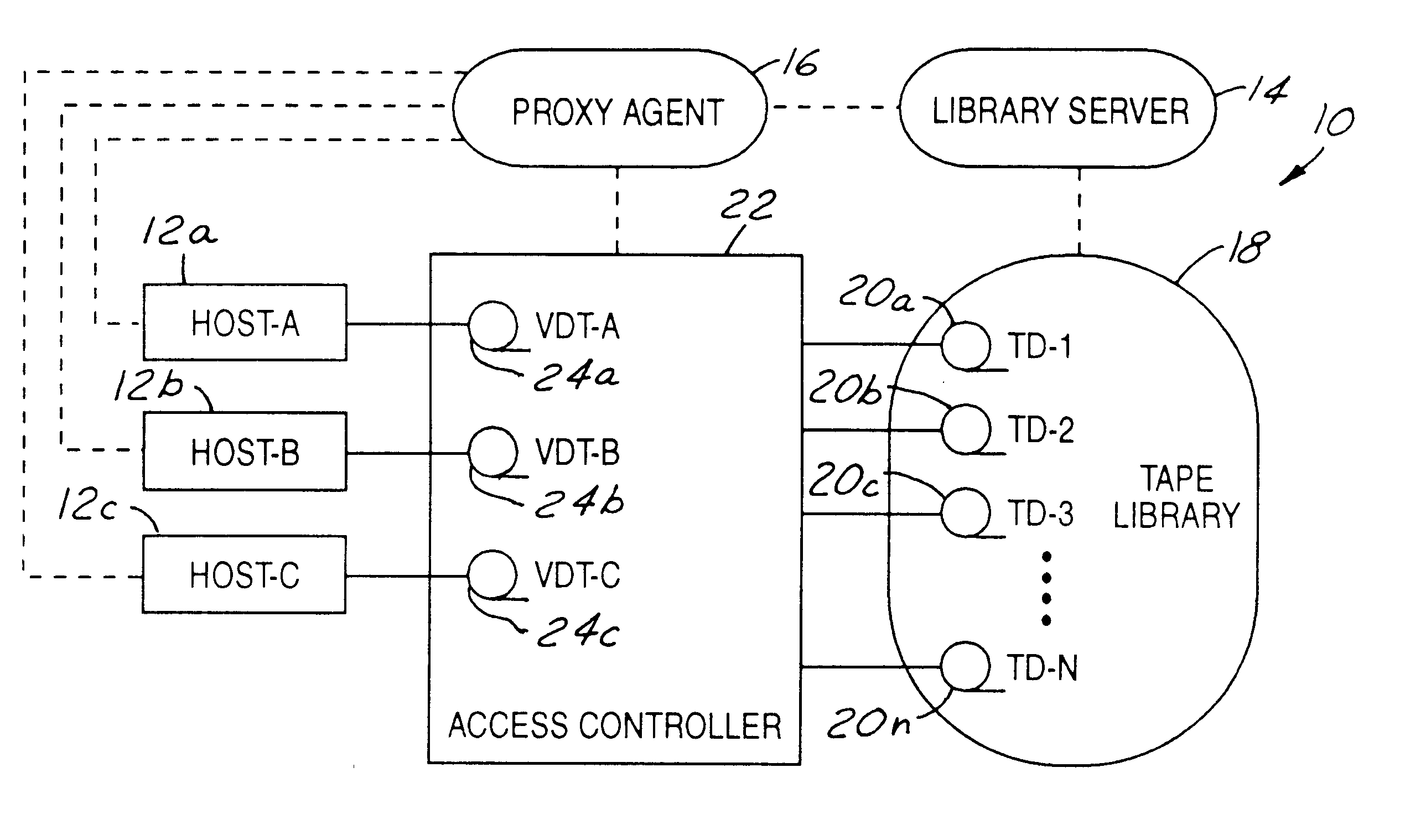
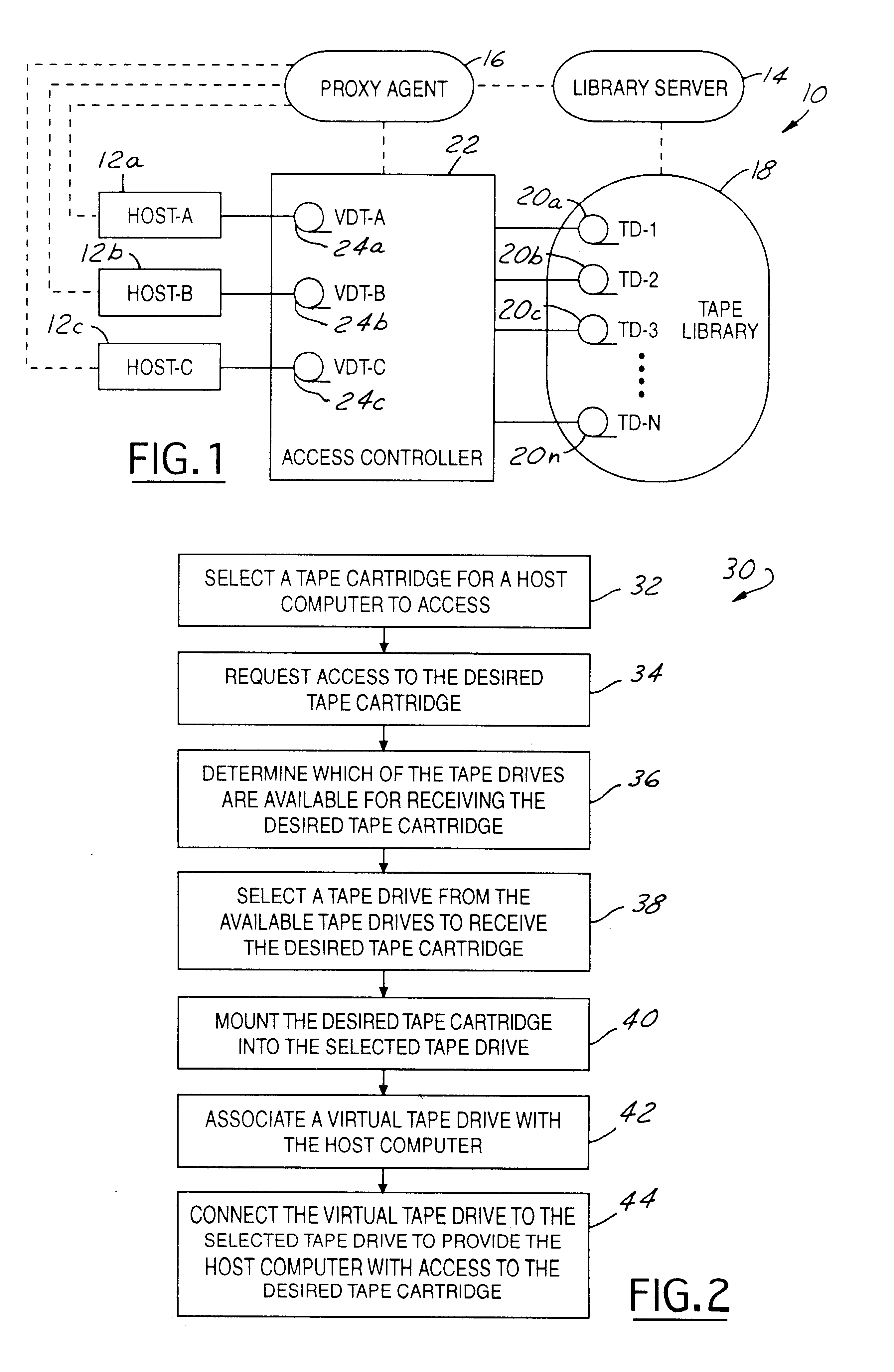
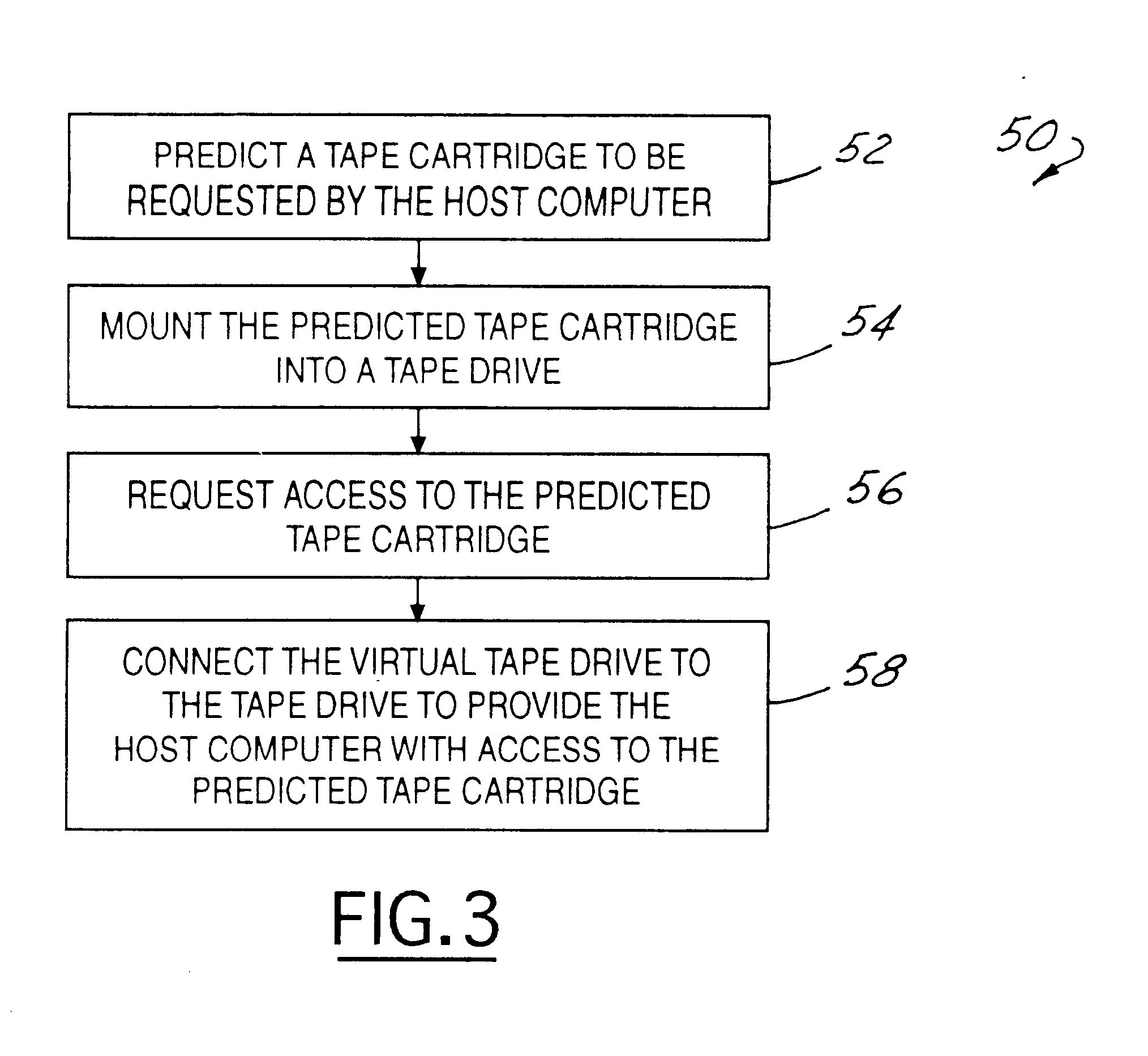
Method and system for dynamically selecting tape drives to connect with host computers
InactiveUS6842841B1Reduce configurationReduce the time required for installationFlat record carrier combinationsInput/output to record carriersMagnetic tapeEngineering
A method and system for connecting a host to a tape drive for accessing a tape cartridge in a data storage system having a tape library provided with cartridges and tape drives includes the host requesting a desired cartridge to access. In response to the request, a proxy agent queries the library to determine which of the tape drives are available to receive the desired cartridge. The proxy agent then selects a tape drive from the available tape drives to receive the desired cartridge. The desired cartridge is then mounted into the selected tape drive. An access controller then connects a virtual tape drive associated with the host to the selected tape drive to provide the host with access to the desired cartridge. The selected tape drive may be selected as a function of its location with respect to the storage location of the desired cartridge. While the host computer is accessing the desired cartridge, the access controller may simultaneously connect another virtual tape drive associated with a second host to another tape drive to provide the second host with access to a different cartridge.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
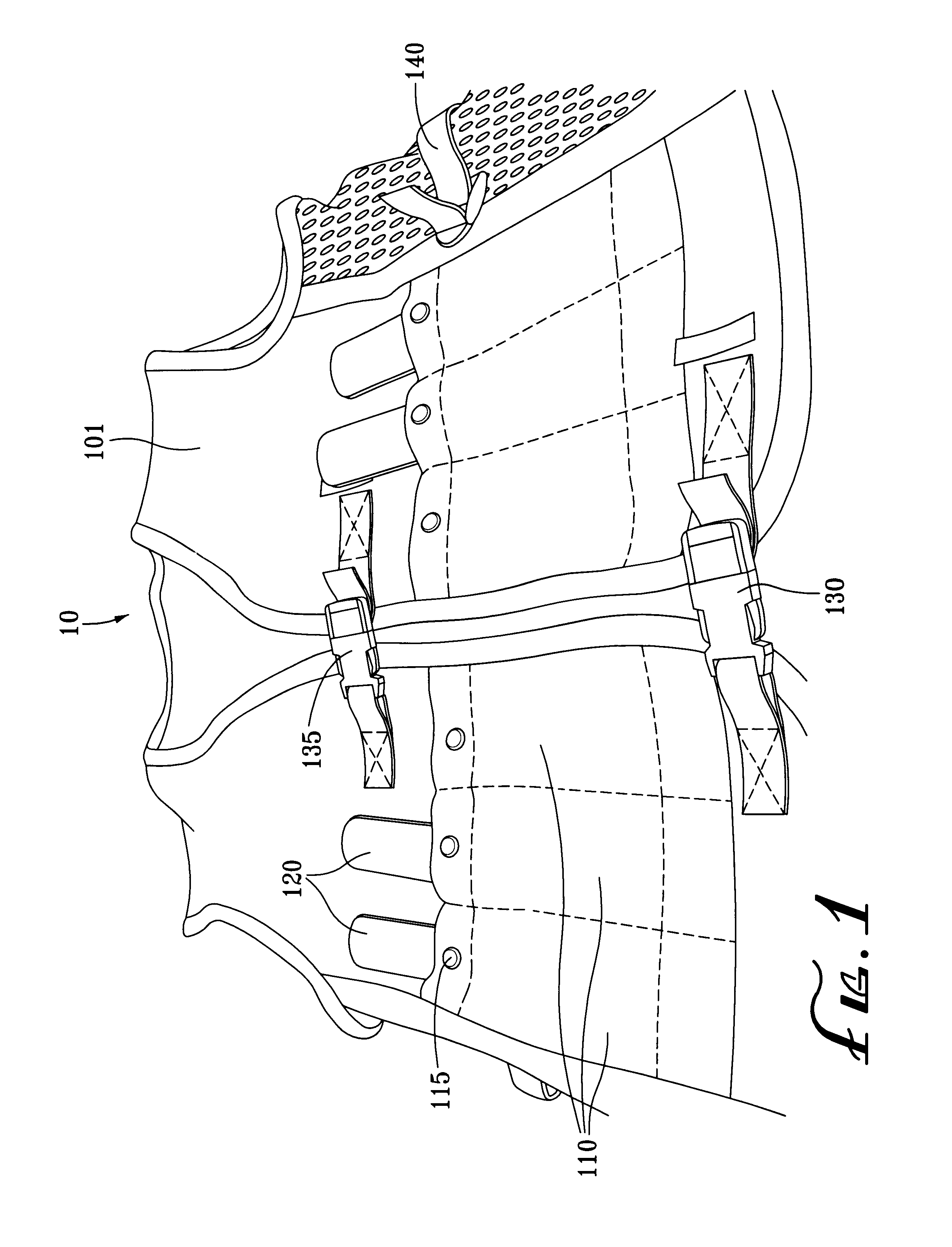
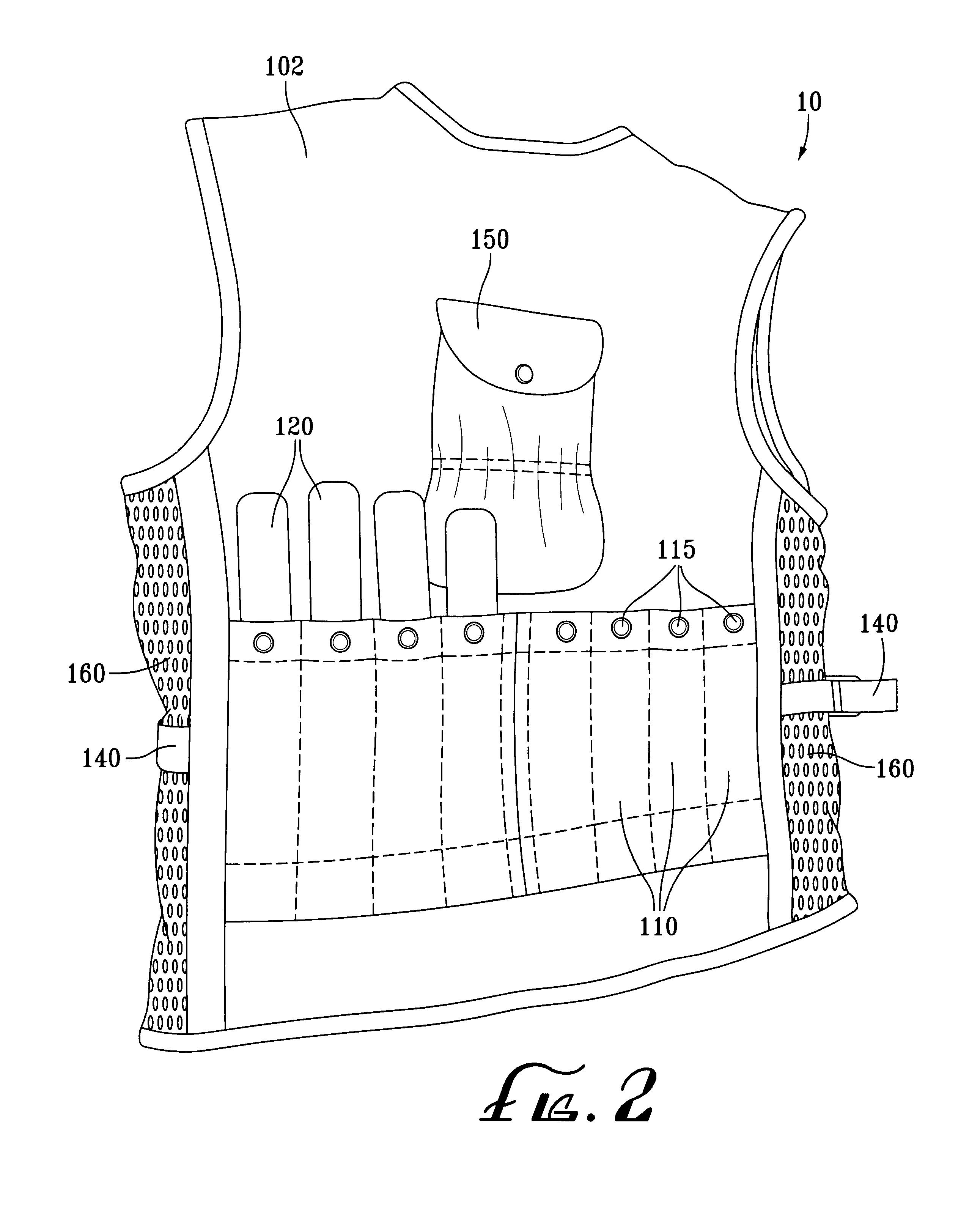
Method of wearing weighted training vest while listening to audio equipment
A weighted exercise vest is adapted for wearing on the upper body of a person. The vest has front and rear compartments in which multiple weights may be inserted. The compartments securely hold the weights therein when the wearer is engaged in physical activity. The weight-containing compartments, according to one or more embodiments of the invention, are formed as elongated tubular ribs or pockets and are located across the back, front or sides of the vest. The vest, in a particularly preferred embodiment, also includes a single pocket advantageously located on the upper back portion of the vest, sized to fit other equipment, such as a portable CD or cassette tape player. The outer surface of the weight-containing compartments or pockets is made from elastic material or includes elastic lining or bands to snugly hold the weights or other equipment inserted therein. In a certain embodiments of the invention, the vest has air-pervious panels, for example on the left and right sides, to allow for air circulation between the body of the wearer and the vest.
Owner:ROCKER DEBRA
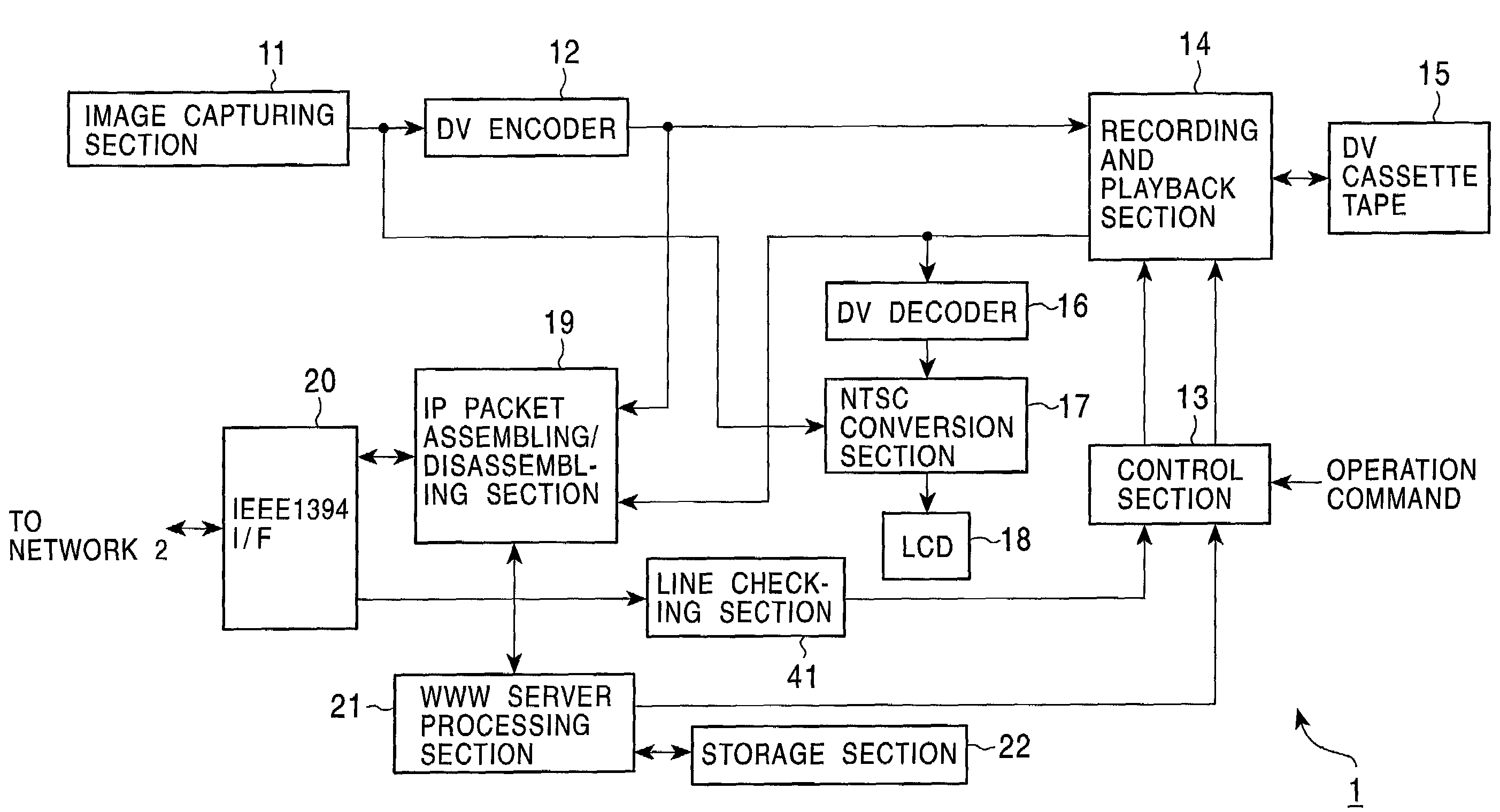
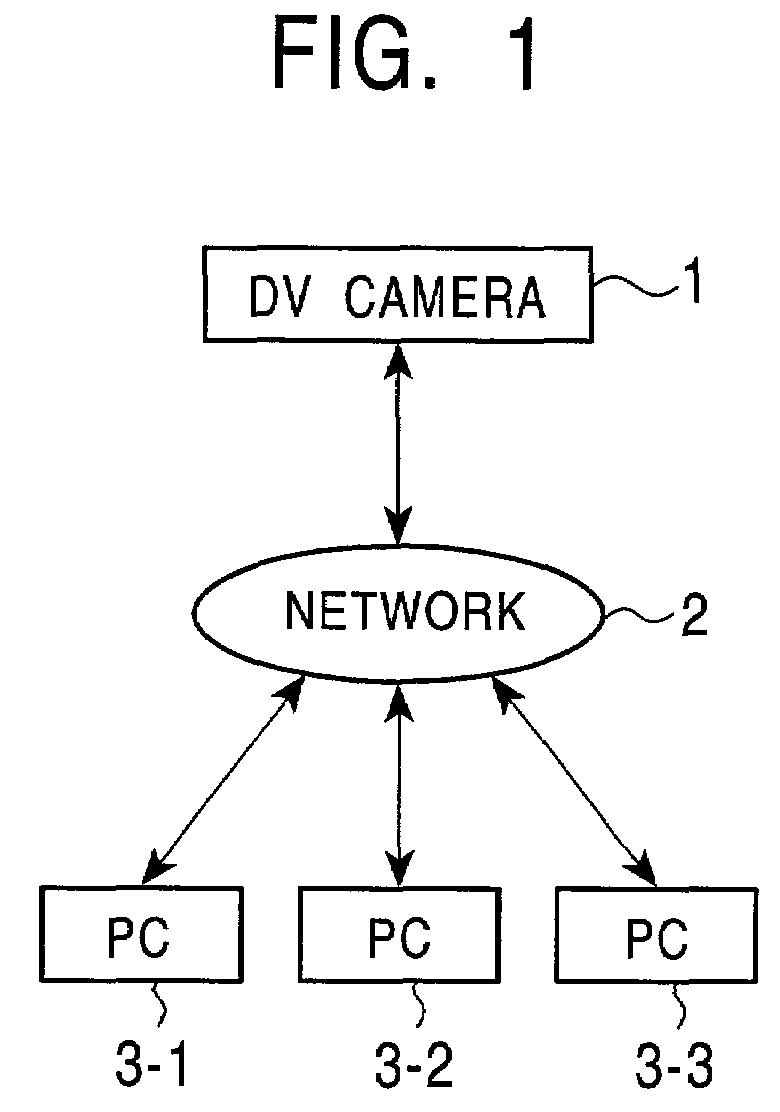
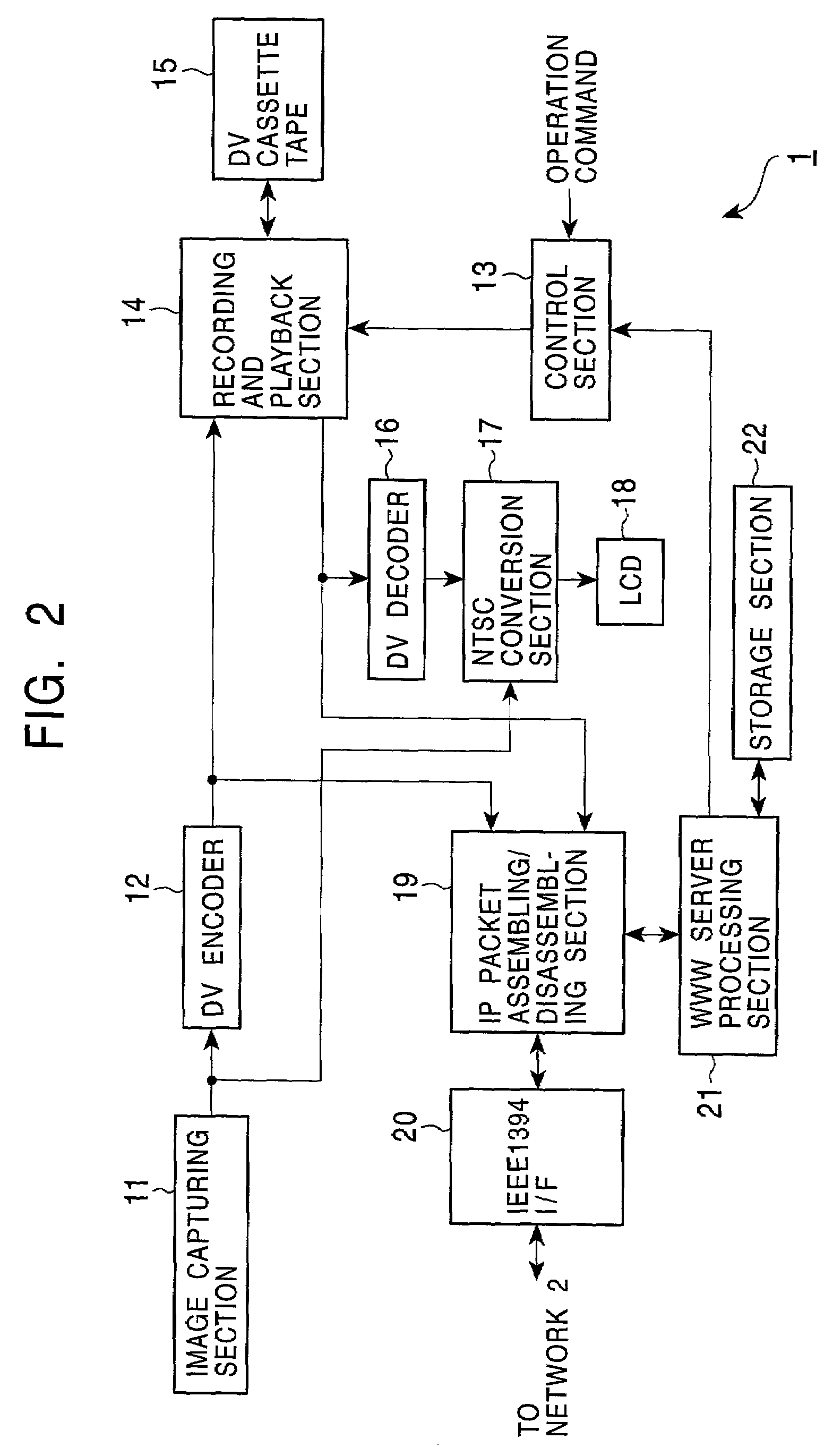
Network compatible image capturing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7256821B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoMagnetic tape
In order that a digital video (DV) camera function as a WWW server in a network, an image capturing section captures an image of a subject. A DV encoder encodes an image signal input from the image capturing section. A recording and playback section plays back DV data recorded in a DV cassette tape. An IP packet assembling / disassembling section assembles a DV signal input from the DV encoder, a DV signal input from the recording and playback section, or an HTML file input from a WWW server processing section into IP packets, and outputs them to an IEEE 1394 interface. The IEEE 1394 interface transmits, via the network, the IP packets input from the IP packet assembling / disassembling section to a personal computer which accessed the DV camera.
Owner:SONY CORP
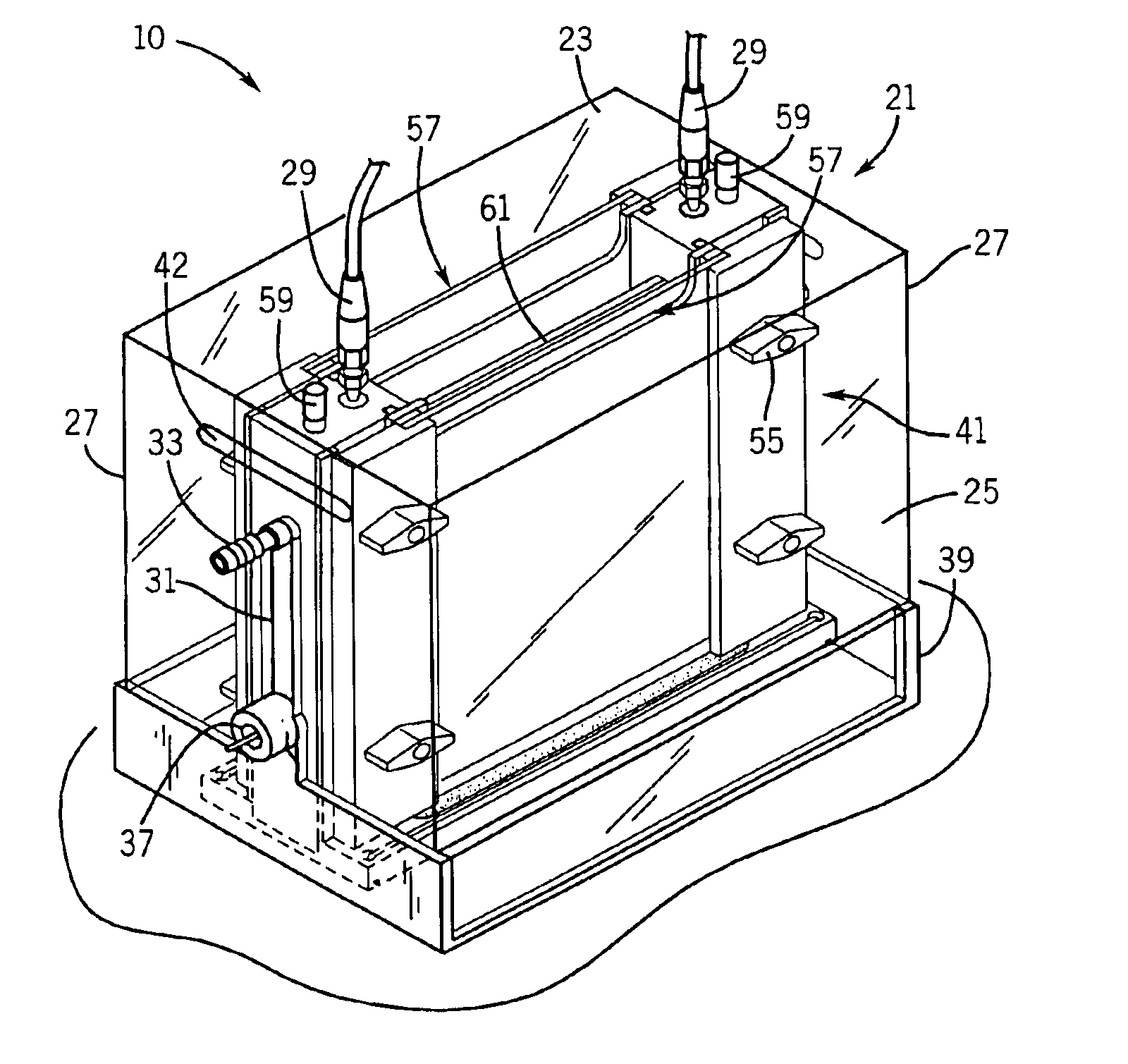
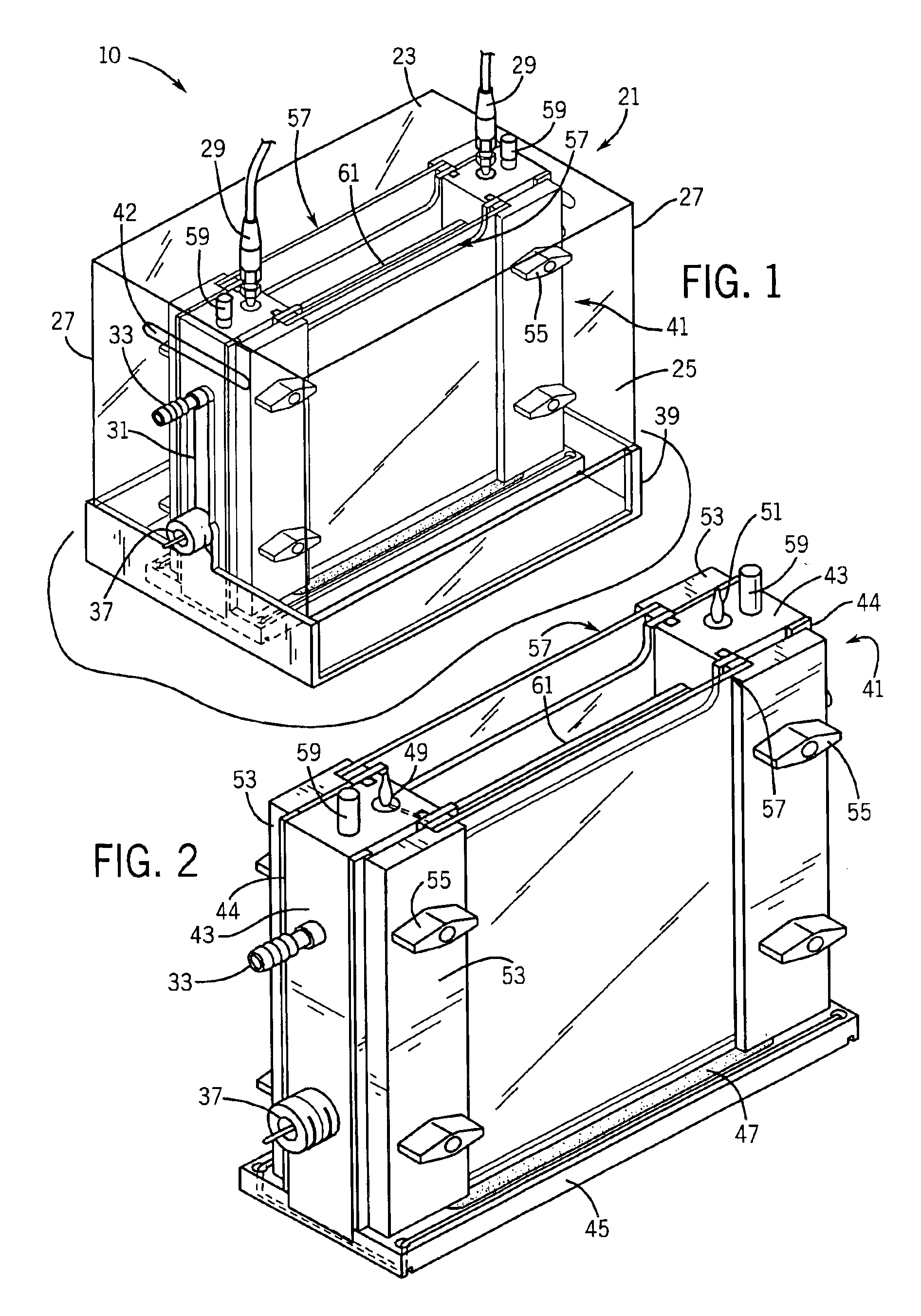
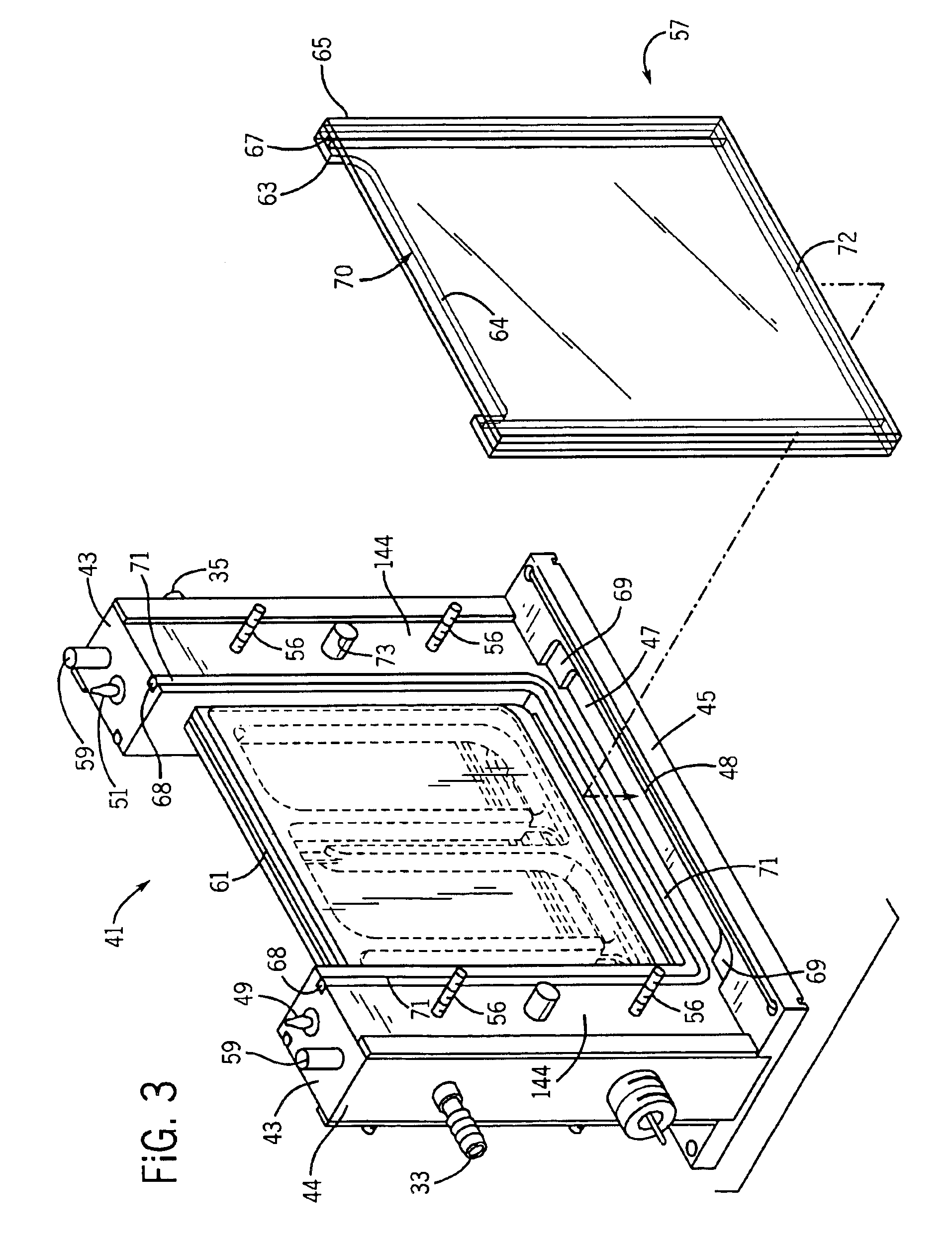
Vertical electrophoresis system
InactiveUS6942775B1Facilitate electrophoresisPrevent accidental contactSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisEngineering
A plugging medium is used to block the bottom opening of cassettes for vertical electrophoresis in order to facilitate filling the cassettes with separation media. Cassettes can be filled within a vertical electrophoresis system in which electrophoresis is conducted without further manipulation of the cassettes. The system includes a frame assembly mounted on a base containing a basin for plugging solution. The cassette is mounted to the frame assembly in a substantially vertical position such that a bottom opening of the empty cassette resides below the rim of the basin. The plugging solution (e.g. agarose gel) forms a plug within the bottom of the cassette to contain the separation medium.
Owner:OWL SEPARATION SYST
Apparatus for storing and moving a cassette
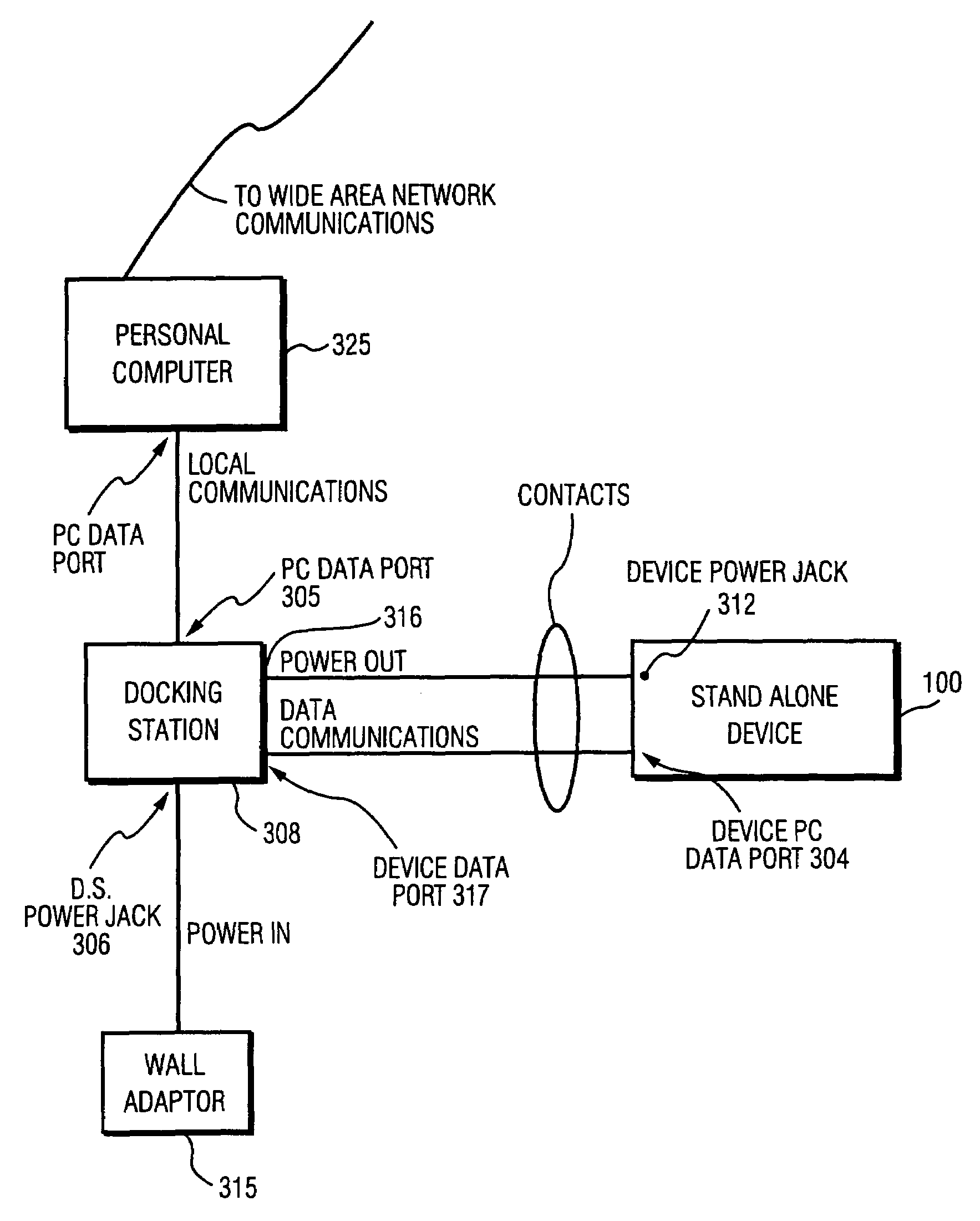
InactiveUS20010043849A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationDocking stationMagnetic tape
Owner:PERLOV ILYA +2
Gripper mechanism for tape cartridges
ActiveUS7002772B2Available for useRecord information storageAutomatic cassette changing arrangementsMagnetic tapeEngineering
A gripper mechanism for manipulating tape cartridges in a tape library system, the tape library system having a plurality of storage cells for removably storing a tape cartridge therein, each tape cartridge formed with engageable side slots located at side portions of the cartridge designed for retaining a respective cartridge in a respective storage cell and including a downward sloped lower front edge portion. The gripper mechanism includes a pair of gripping fingers actuated for respectively engaging a respective side slot located at a side portion of the cartridge for manipulating the cartridge, and including support members extending outward from the gripper mechanism at a lower portion thereof for engagement with the sloped lower front edge portion of the cartridge.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Conversion device of MP3
InactiveUS20050152231A1Record information storageMagazines/cassettes storageDevice formSignal transition
A conversion device includes a mounting device sized and shaped to fit in a cassette deck of a cassette tape player. The mounting device forms a cutoff zone defined by opposite side edges into which a playing device for compression / decompression, storage and playback of digital sounds is received. Slots are defined in the side edges of the cutoff zone and corresponding projections are formed in opposite sides of the playing device for slidably engaging the slots of the cutoff zone of the mounting device. A signal converter is provided between the playing device and mounting device for receiving MP3 signals from the playing device and converting the MP3 signals into signals recognizable by the cassette tape player.
Owner:YEH MING HSIANG
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200035265A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMagnetic materials for record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeRefractive index
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer has a servo pattern, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy measured regarding an in-plane direction of the magnetic layer and a refractive index Nz measured regarding a thickness direction of the magnetic layer is 0.25 to 0.40, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Network interface cassette adapter and method
A network interface cassette for coupling signals between a wireless network and a tape head in a cassette tape player. The network interface cassette includes an enclosure that is conformed to the cassette tape form factor. It contains a transceiver that converts base band signals for radio frequency communications within the wireless network. It also contains a network controller that is coupled to communicate the base band signals with the transceiver. The network controller converts digital audio signals to and from the base band signals. There is an audio processor that converts the digital audio signals to analog audio signals. A coupling means converts the analog audio signals to magnetic audio signals. The coupling means is aligned to couple the magnetic audio signals to the tape head. A power supply with batteries incorporates a spindle driven sensor means to control power and function selection within the device. A wireless user interface adapter is provided to couple microphone and audio signals to the apparatus. Plural communications requests are processed, and include a priority scheme to manage resource contention.
Owner:GENERAL WIRELESS OPERATIONS +1
Network interface cassette adapter and method
ActiveUS7120463B2Television system detailsSubstation speech amplifiersTransceiverDigital audio signals
A network interface cassette for coupling signals between a wireless network and a tape head in a cassette tape player. The network interface cassette includes an enclosure that is conformed to the cassette tape form factor. It contains a transceiver that converts base band signals for radio frequency communications within the wireless network. It also contains a network controller that is coupled to communicate the base band signals with the transceiver. The network controller converts digital audio signals to and from the base band signals. There is an audio processor that converts the digital audio signals to analog audio signals. A coupling means converts the analog audio signals to magnetic audio signals. The coupling means is aligned to couple the magnetic audio signals to the tape head. A power supply with batteries incorporates a spindle driven sensor means to control power and function selection within the device. A wireless user interface adapter is provided to couple microphone and audio signals to the apparatus. Plural communications requests are processed, and include a priority scheme to manage resource contention.
Owner:GENERAL WIRELESS OPERATIONS +1
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200211592A1Improve surface smoothnessReduce frequencyRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeMaterials science
Provided are a magnetic tape including: a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which a total thickness of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer has a servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured on a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy of the magnetic layer, measured in an in-plane direction and a refractive index Nz of the magnetic layer, measured in a thickness direction is 0.25 to 0.40, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20210020195A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMagnetic materials for record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeRefractive index
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
System for creating a personalized fitness video for an individual
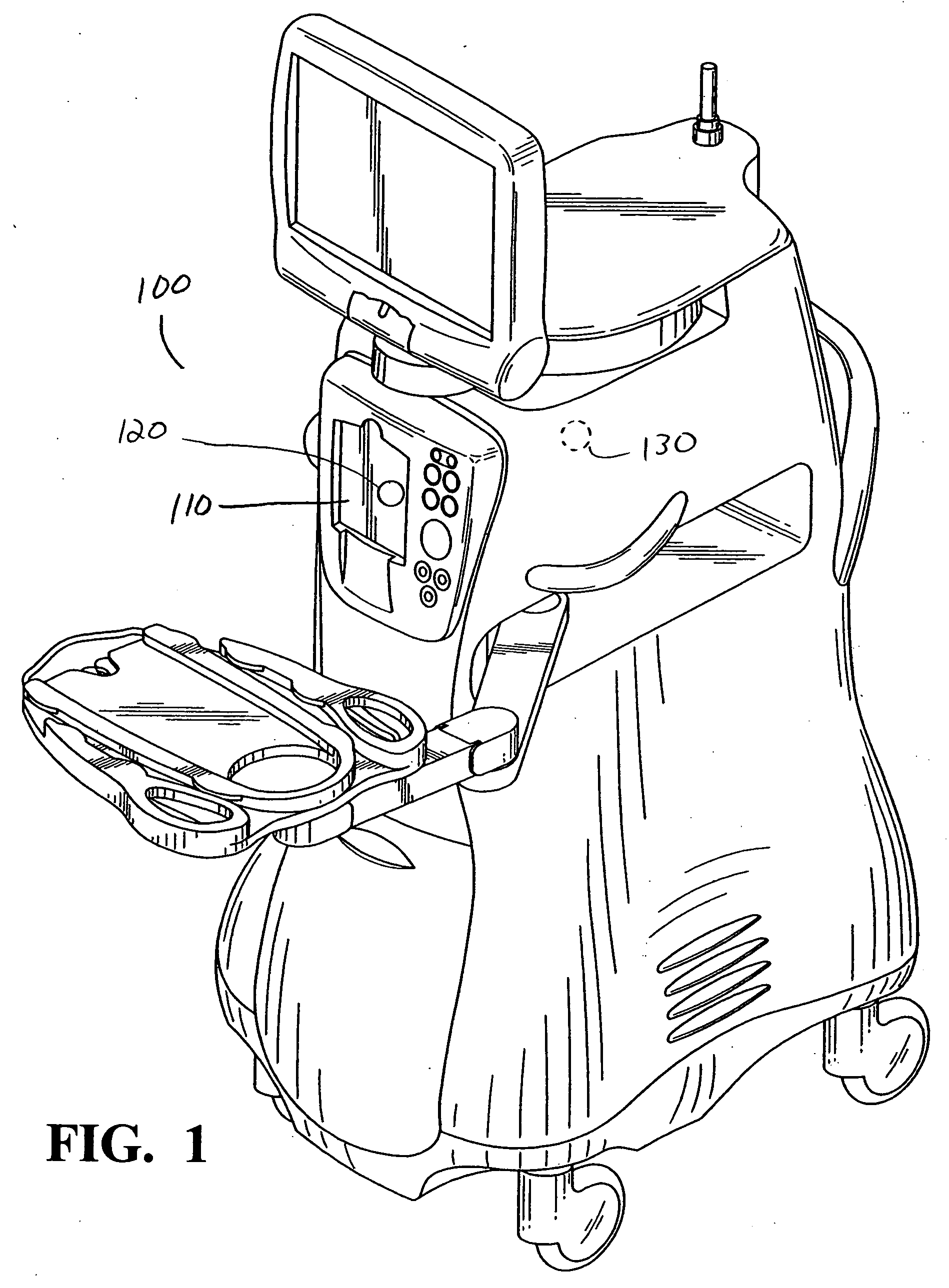
A physical fitness professional assesses an individual for whom a personalized fitness video is to be created with respect to flexibility, cardiovascular condition, body fat composition, muscular strength and condition, as well as other health conditions and limitations. Based on this assessment a specific fitness plan is determined and which includes a detailed workout program of specific exercises in at least one sequential arrangement. The physical fitness professional selects a plurality of video segments from a series of video segments stored in a computer wherein each selected video segment is a specific exercise of the detailed workout program and arranges the selected video segments into a sequence corresponding to the sequential arrangement of specific exercises of the specific fitness plan and records the same on a digital versatile disc or video cassette tape or makes the selected video segments of the specific fitness plan available on a secure web site.
Owner:DEMAS DONALD P
Surveillance system with digital tape cassette
InactiveUS20070217501A1Improve fault toleranceHigh speedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo monitoringMagnetic tape
A video surveillance system in which the compressed video is written to a digital tape cassette. The tape cassette includes an EEPROM, which holds directory information relating to the location of particular video on the tape, the identity of the tape, the identity of the video, and other key information relating to the video. The directory on the EEPROM permits rapid access to the video and redundancy of key data. In case of tape error, the tape automatically restores itself when inserted into the tape deck.
Owner:SECURITY WITH ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com