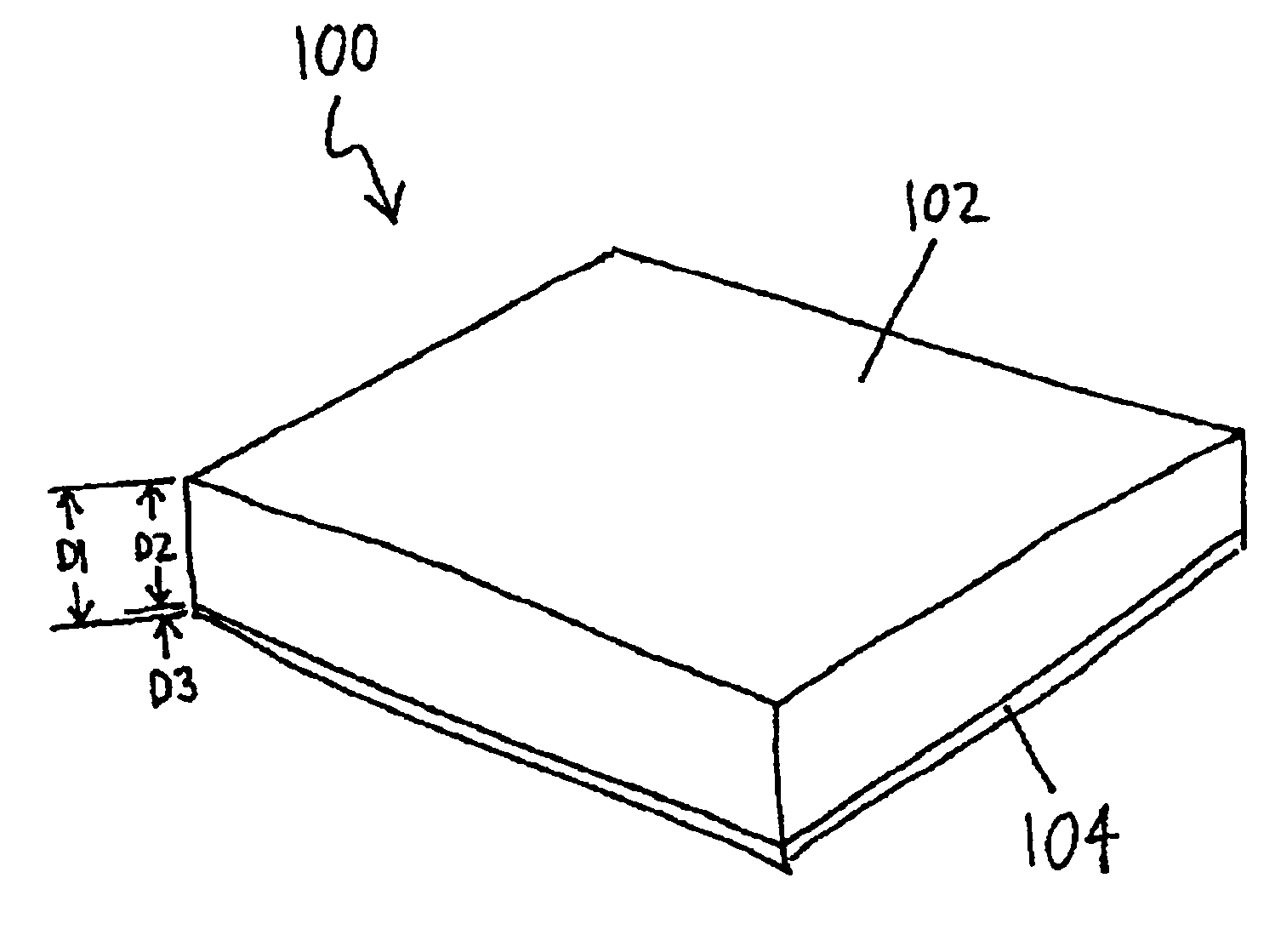
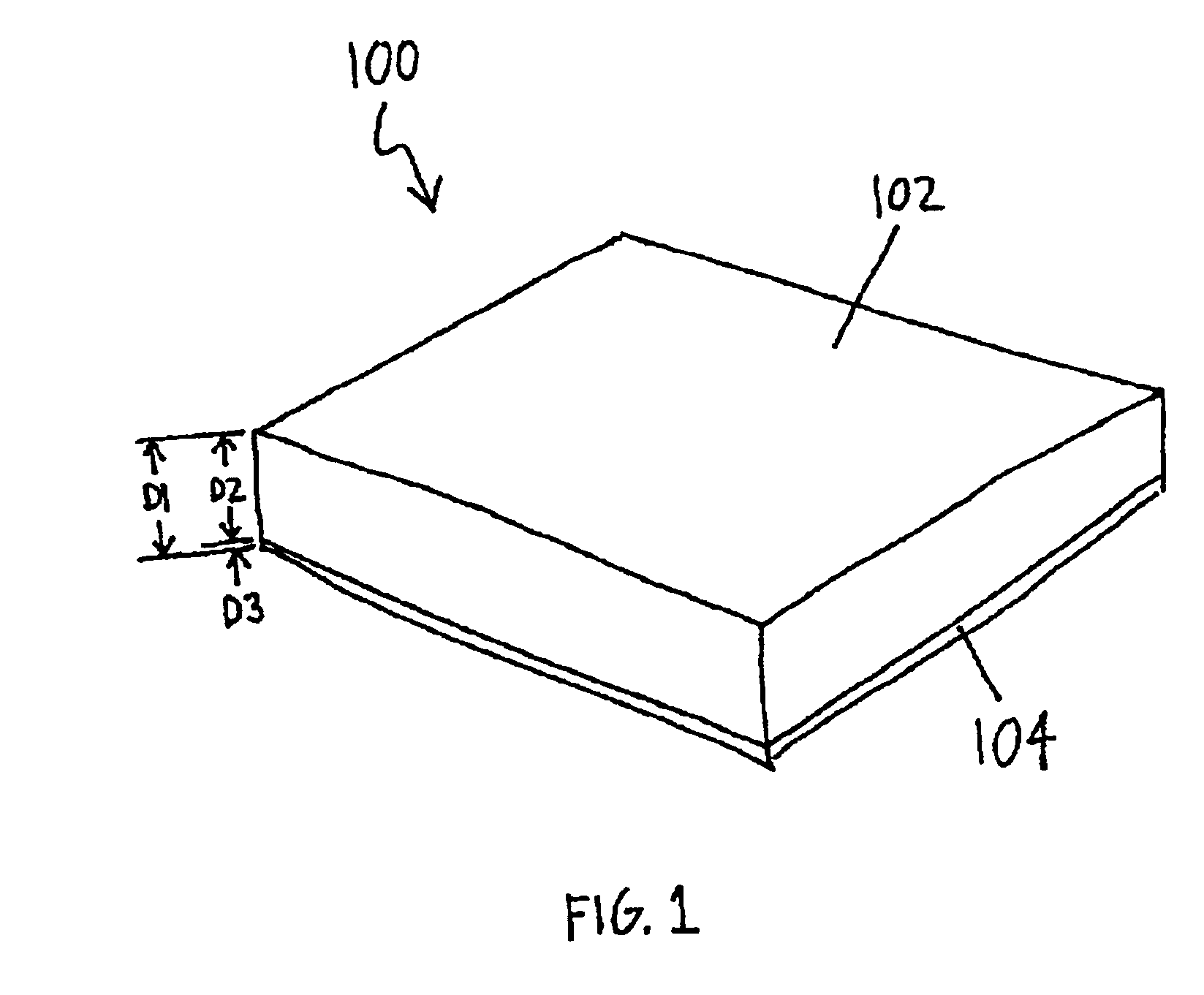
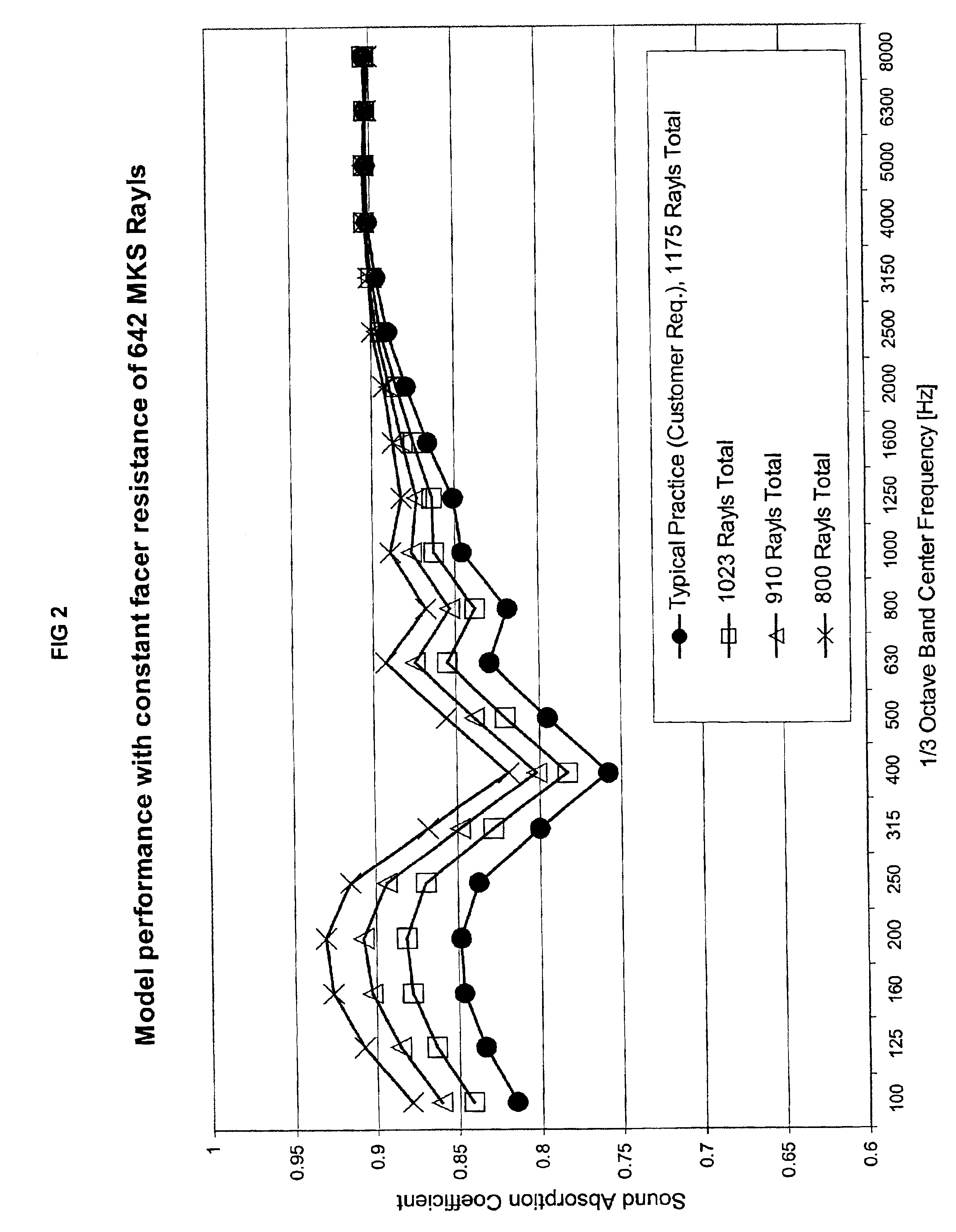
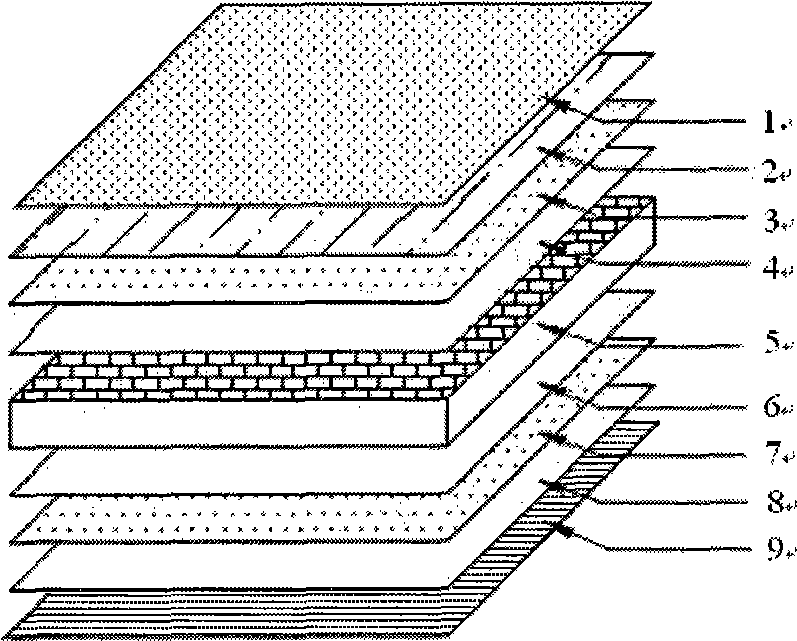
Patents
Literature
459 results about "Acoustic absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
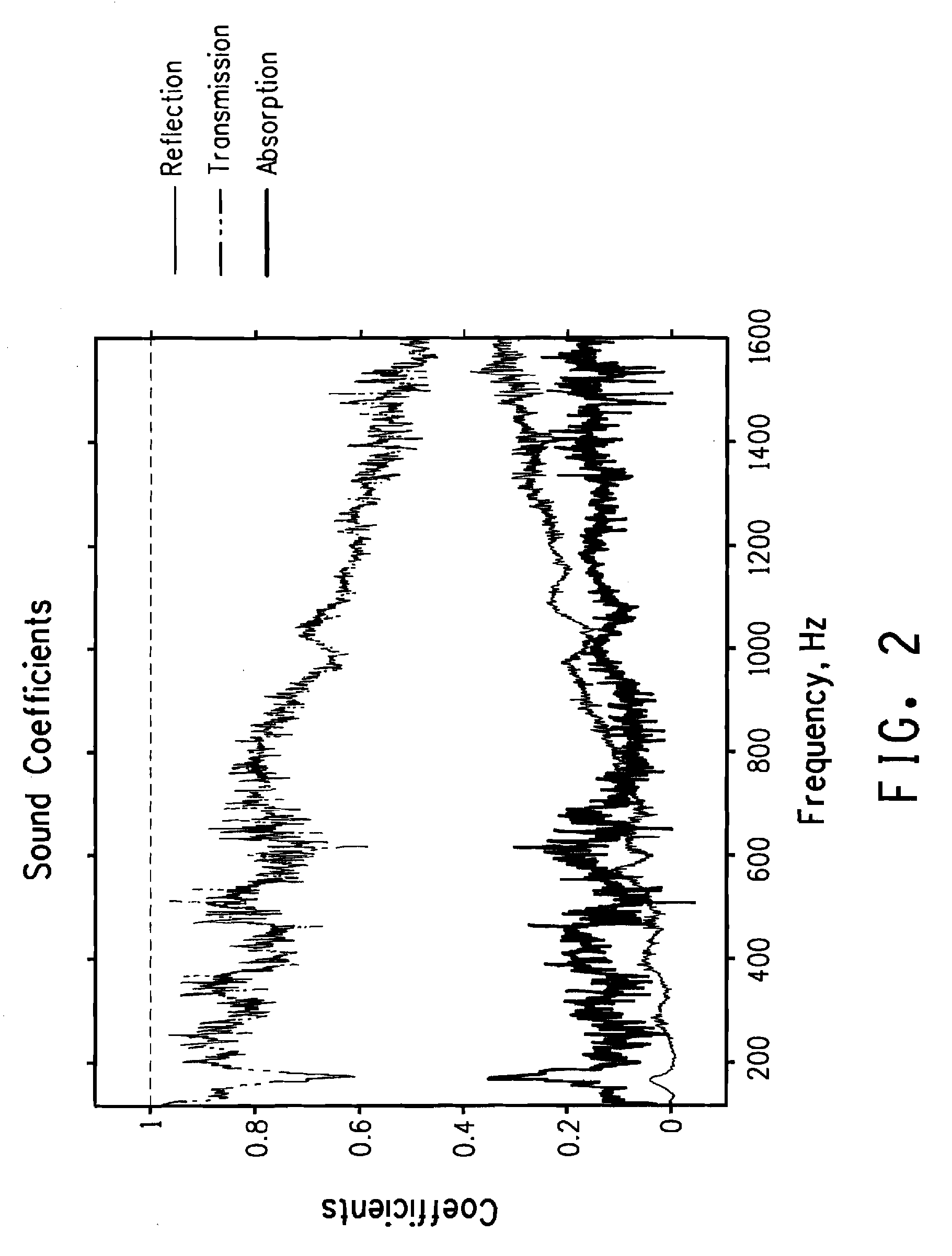
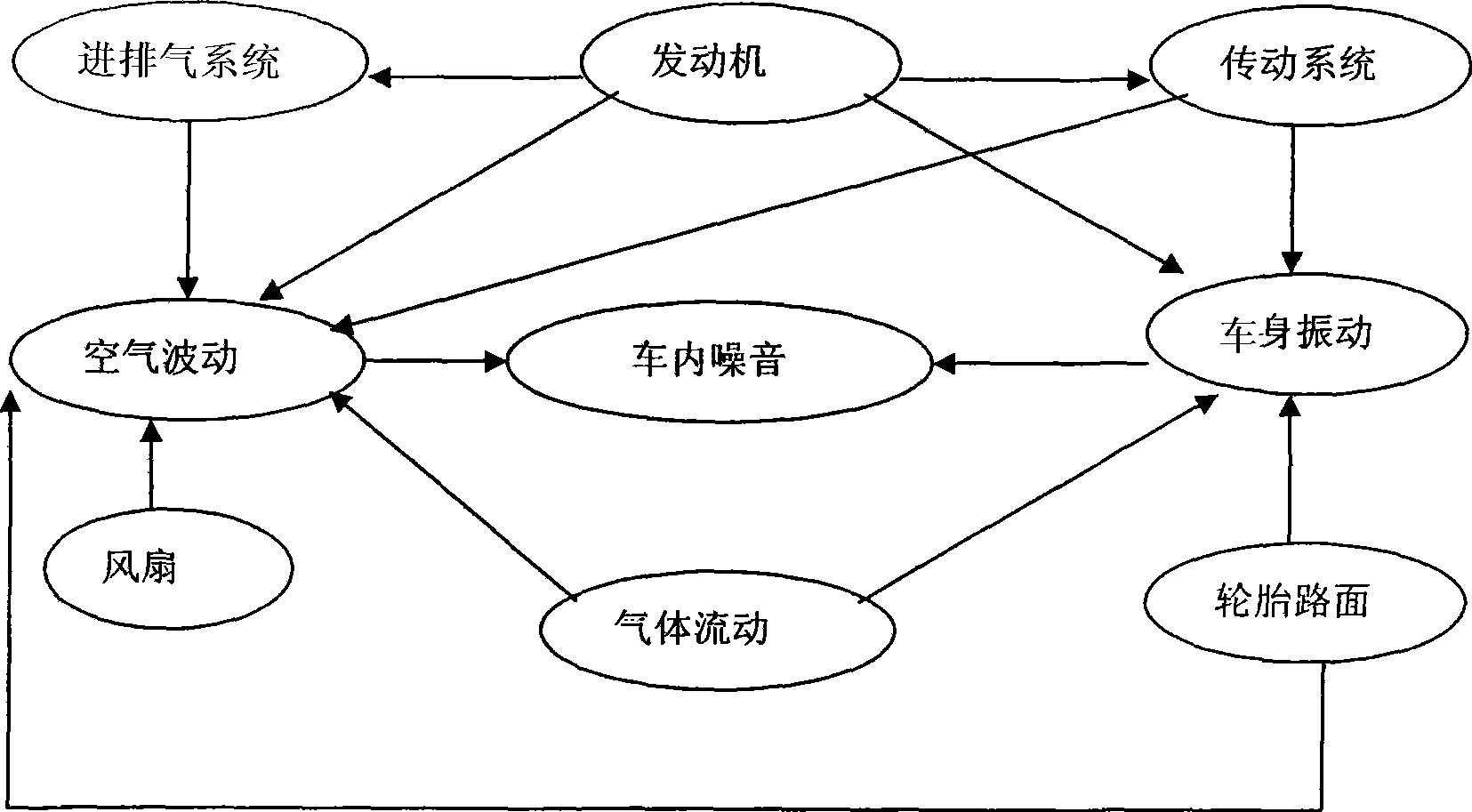
Acoustic absorption refers to the process by which a material, structure, or object takes in sound energy when sound waves are encountered, as opposed to reflecting the energy. Part of the absorbed energy is transformed into heat and part is transmitted through the absorbing body.
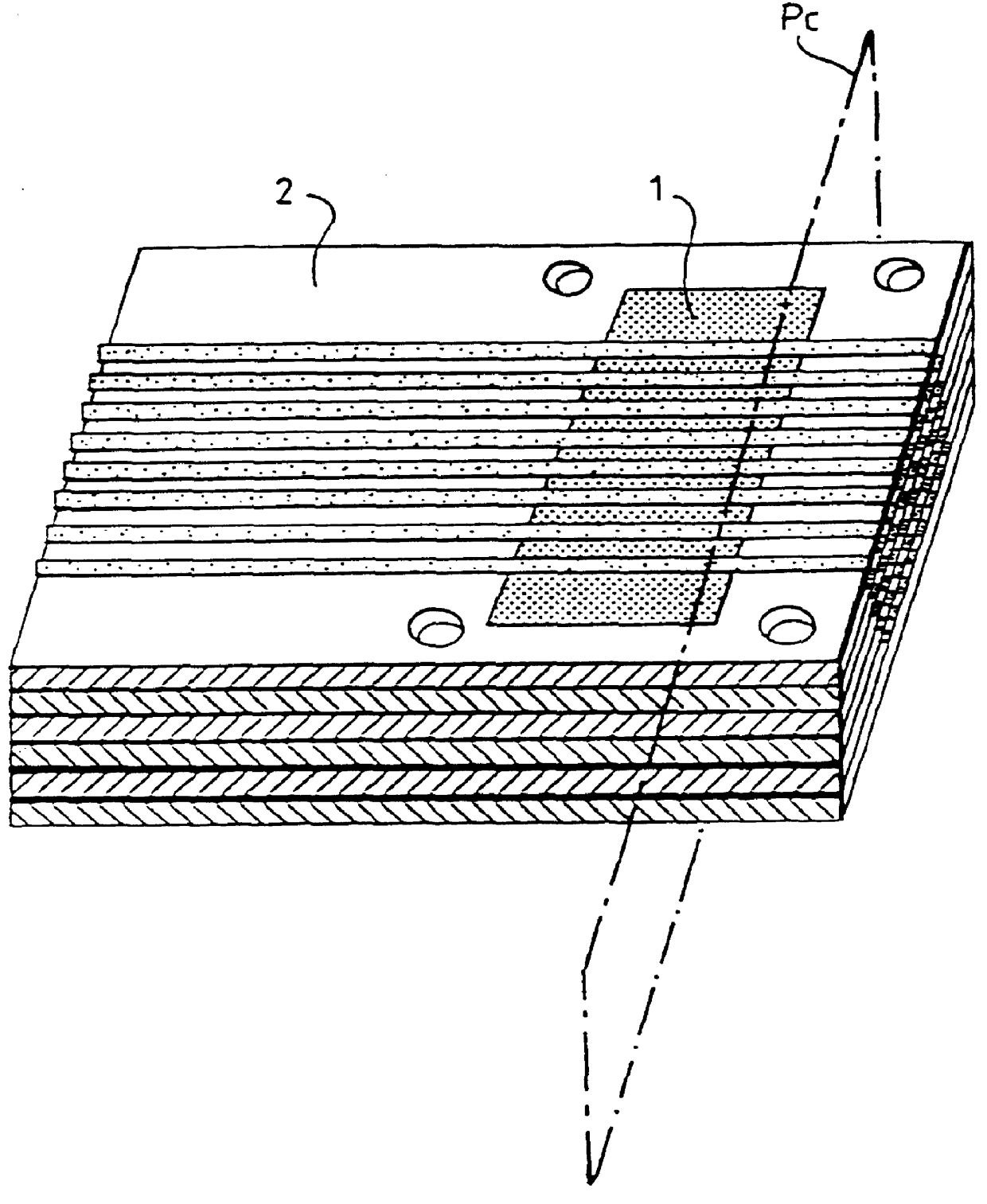
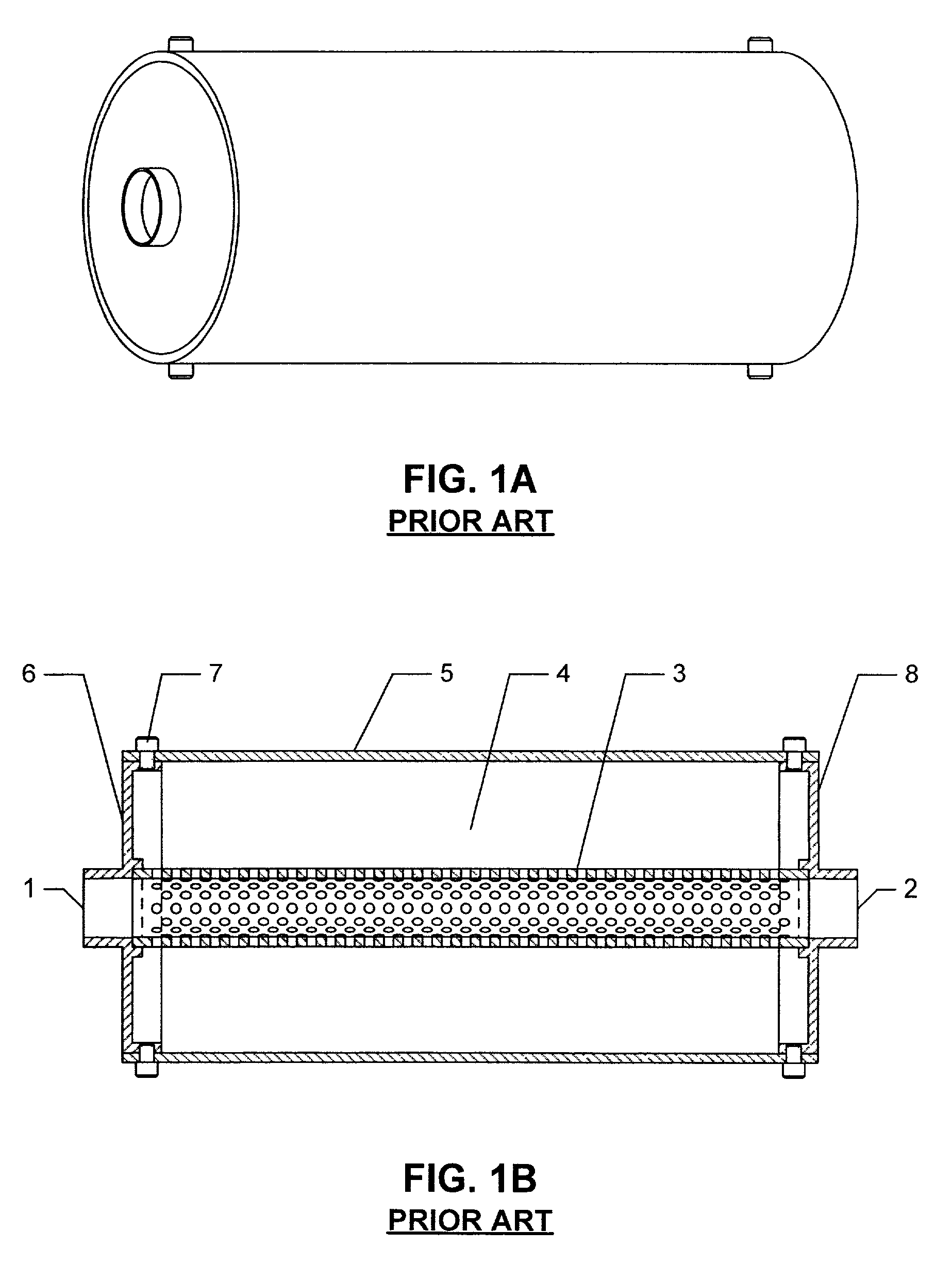
Miniature MEMS condenser microphone packages and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20100183181A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesLine/current collector detailsAcoustic absorptionMems microphone
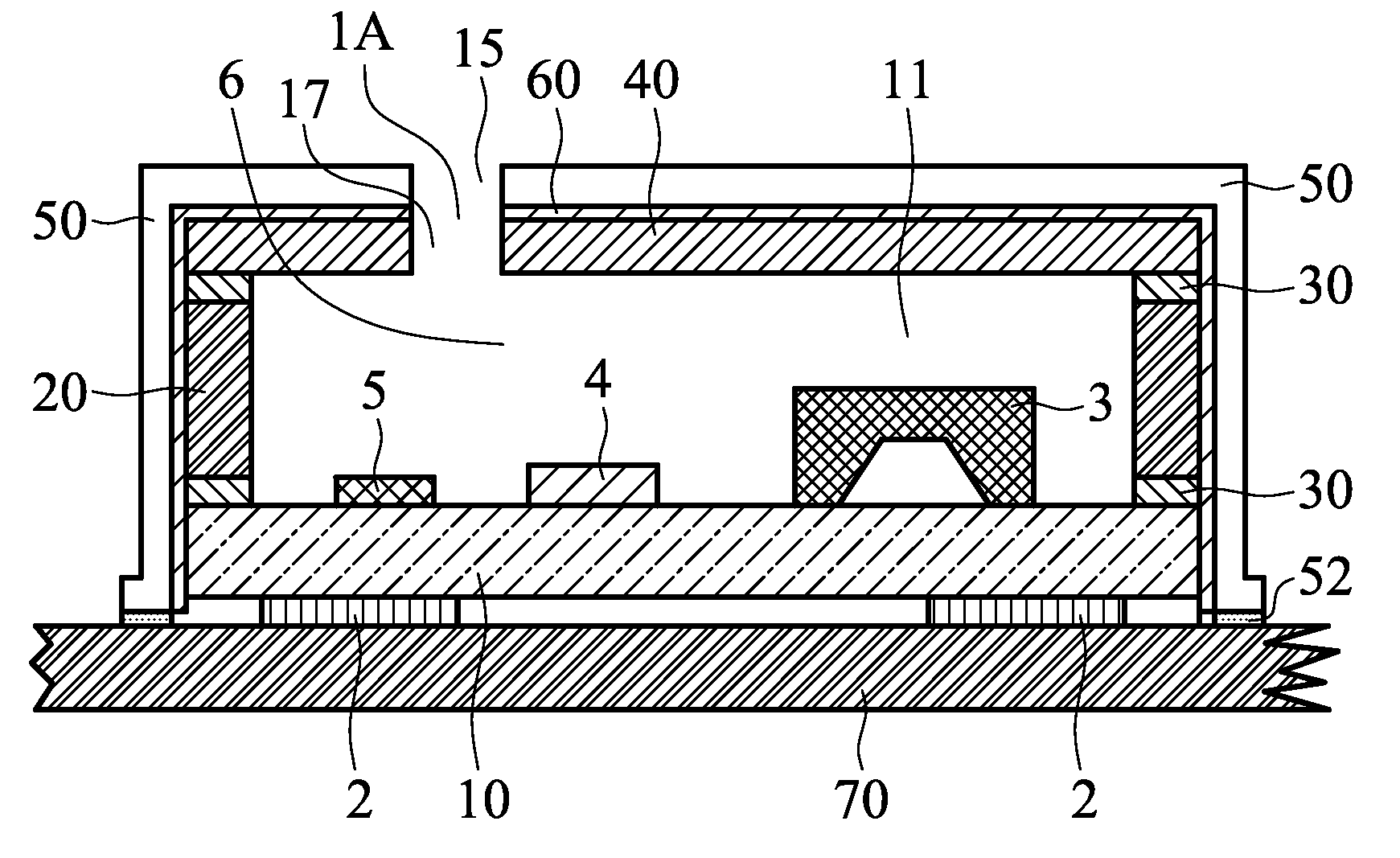
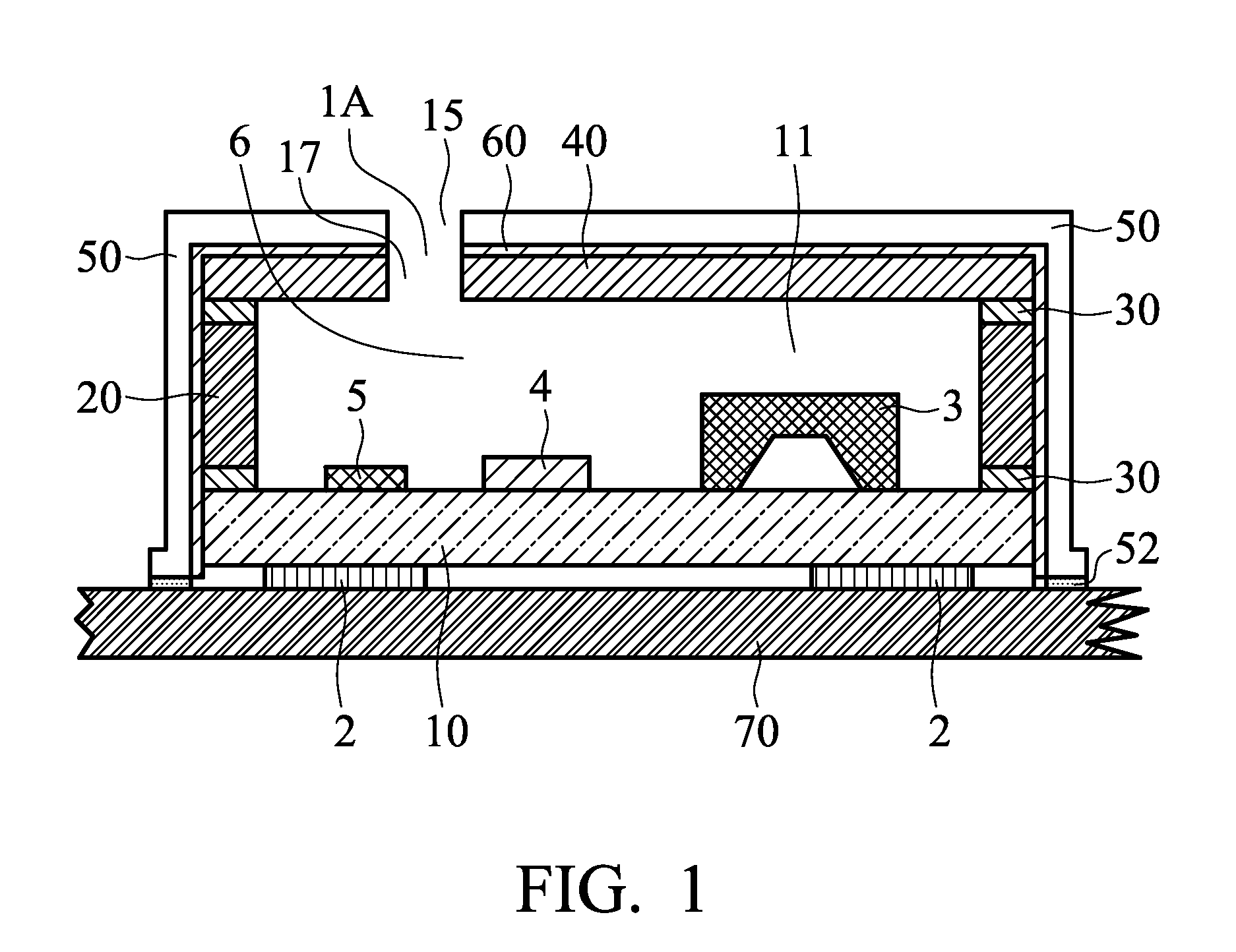
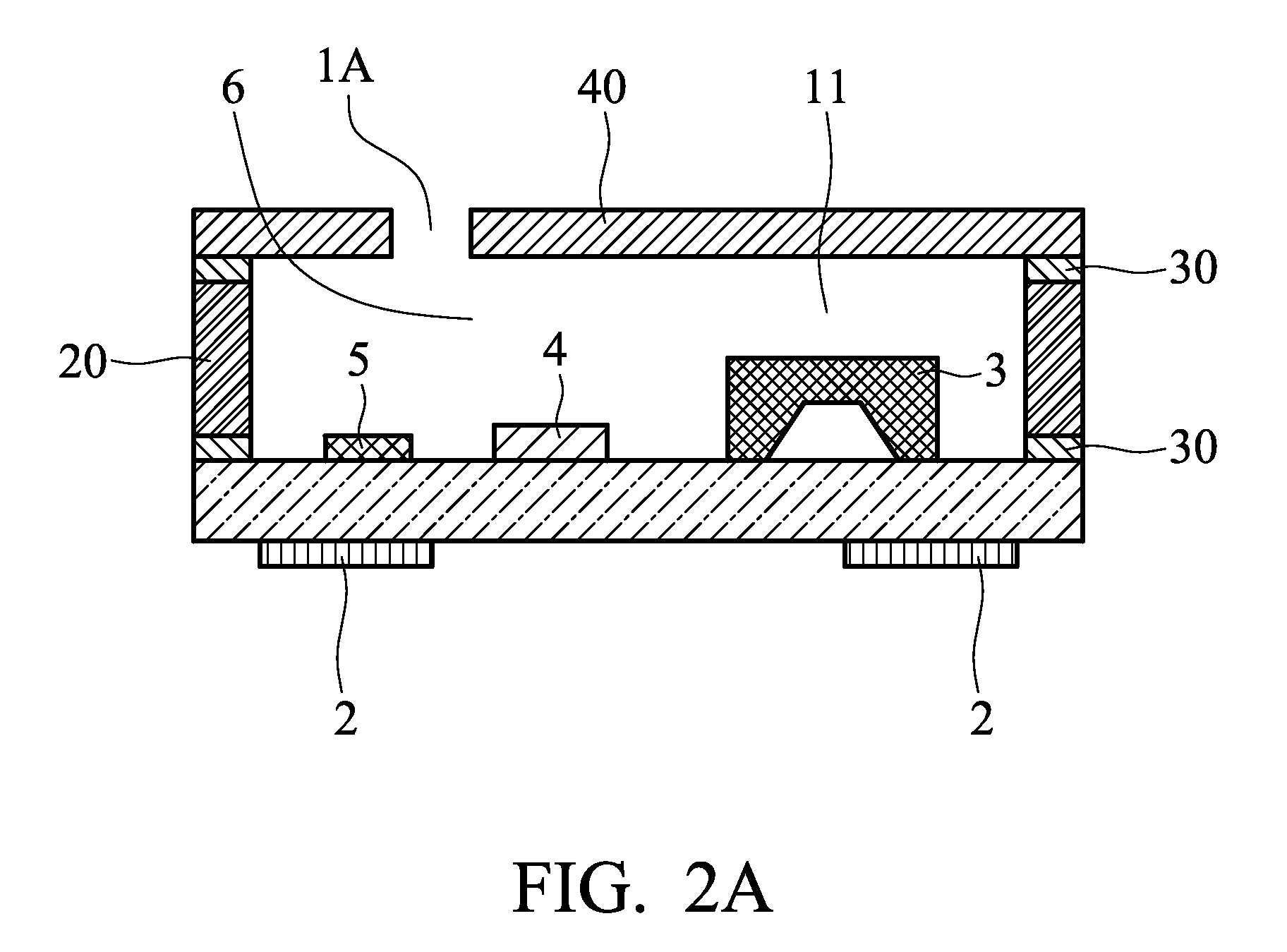
MEMS microphone packages and fabrication methods thereof are disclosed. A MEMS microphone package includes a cavity that houses a MEMS sensing element, an IC chip and other passive elements supported by a common substrate. The cavity is formed by a top cover member, a housing wall surrounds and supports the top cover member and the common substrate supports the housing wall. A conductive casing encloses and surrounds the cavity, and is electrically connected to a common analog ground lead on a PCB board. The top cover member and the housing wall are non-conductive. And the conductive casing is not connected directly to the ground leads of the package. An acoustic absorption layer is sandwiched between the conductive casing and the cavity which is formed by the top cover member, the housing wall and the substrate.
Owner:NEOMEMS TECH INC WUXI CHINA
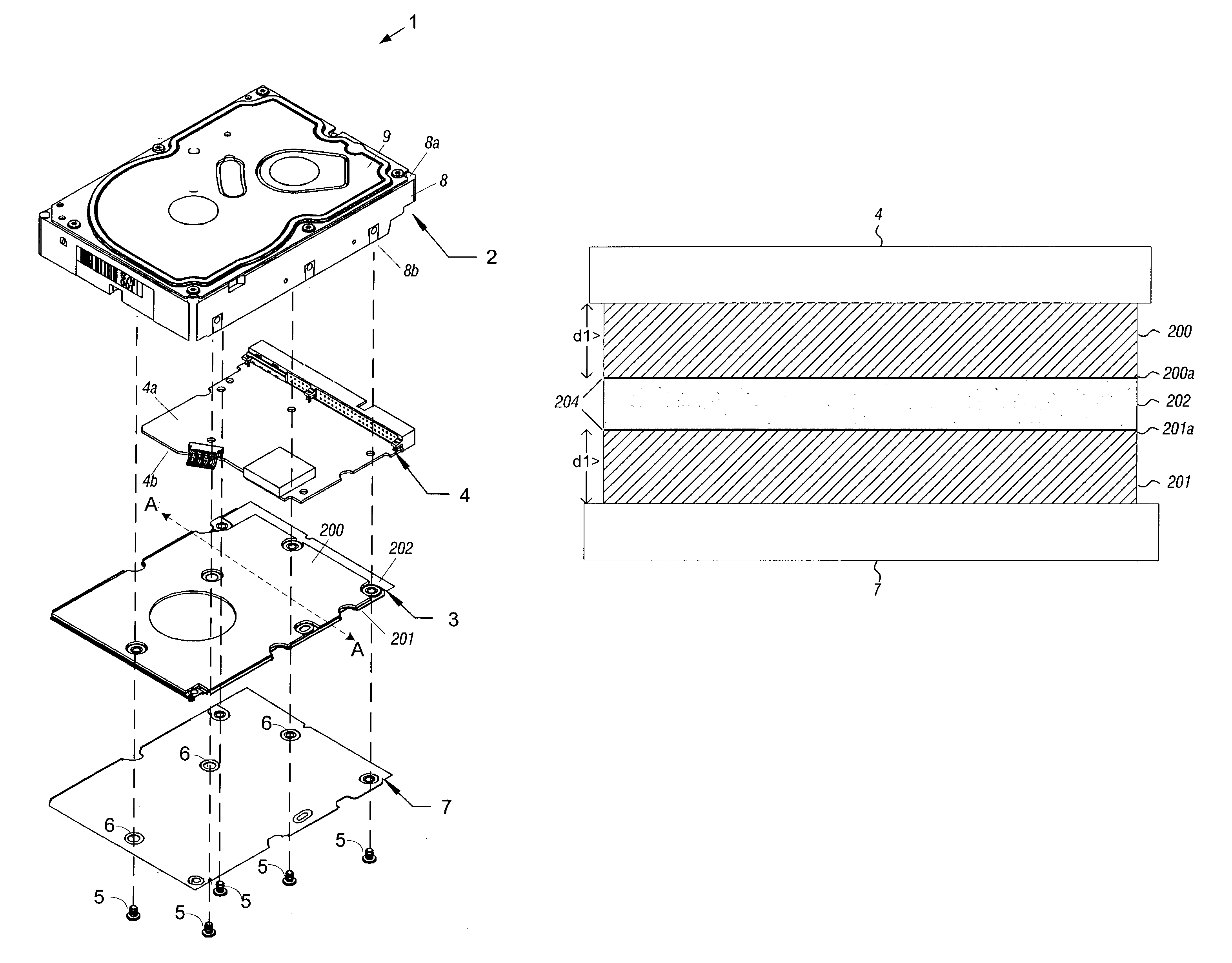
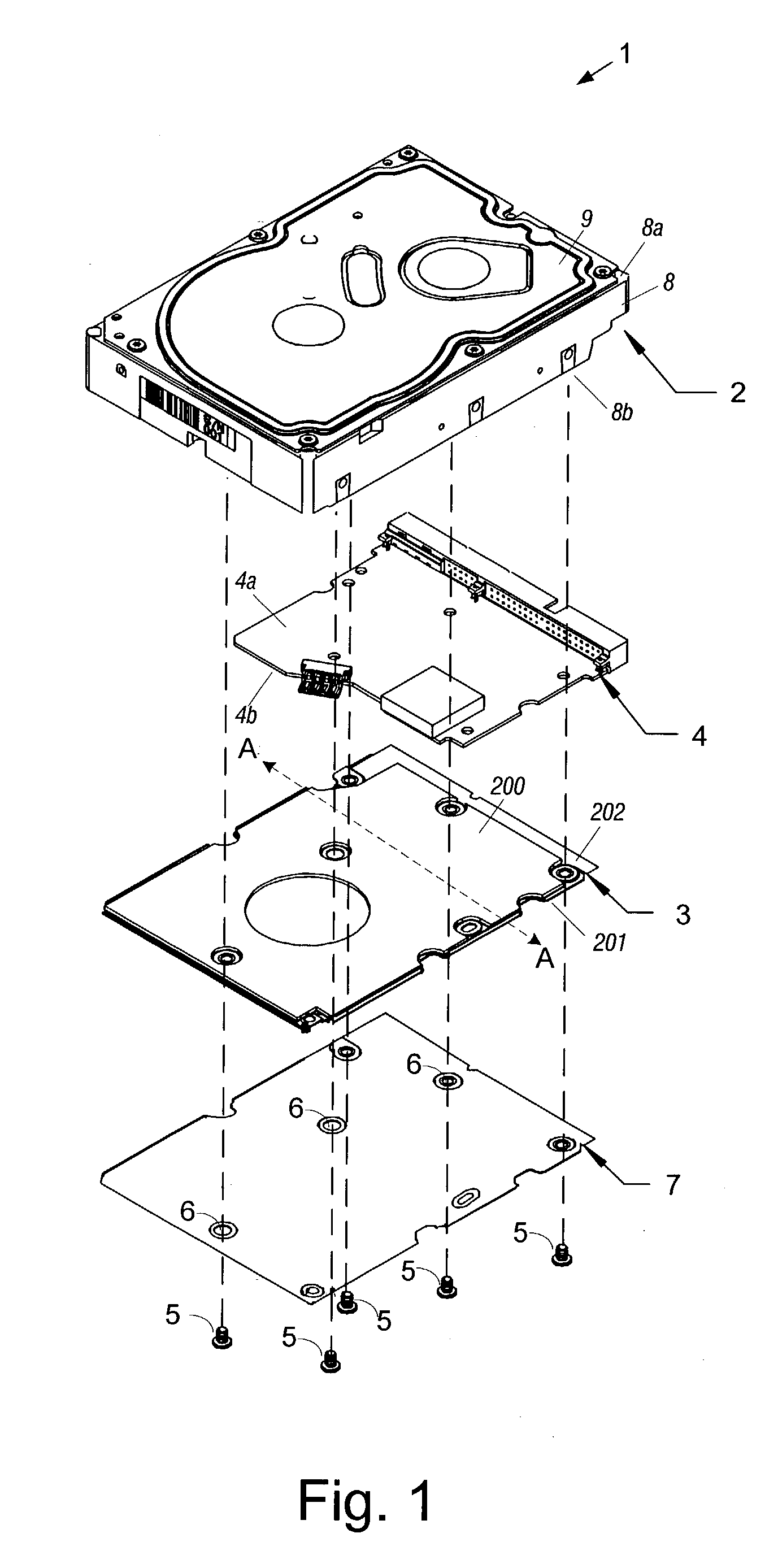
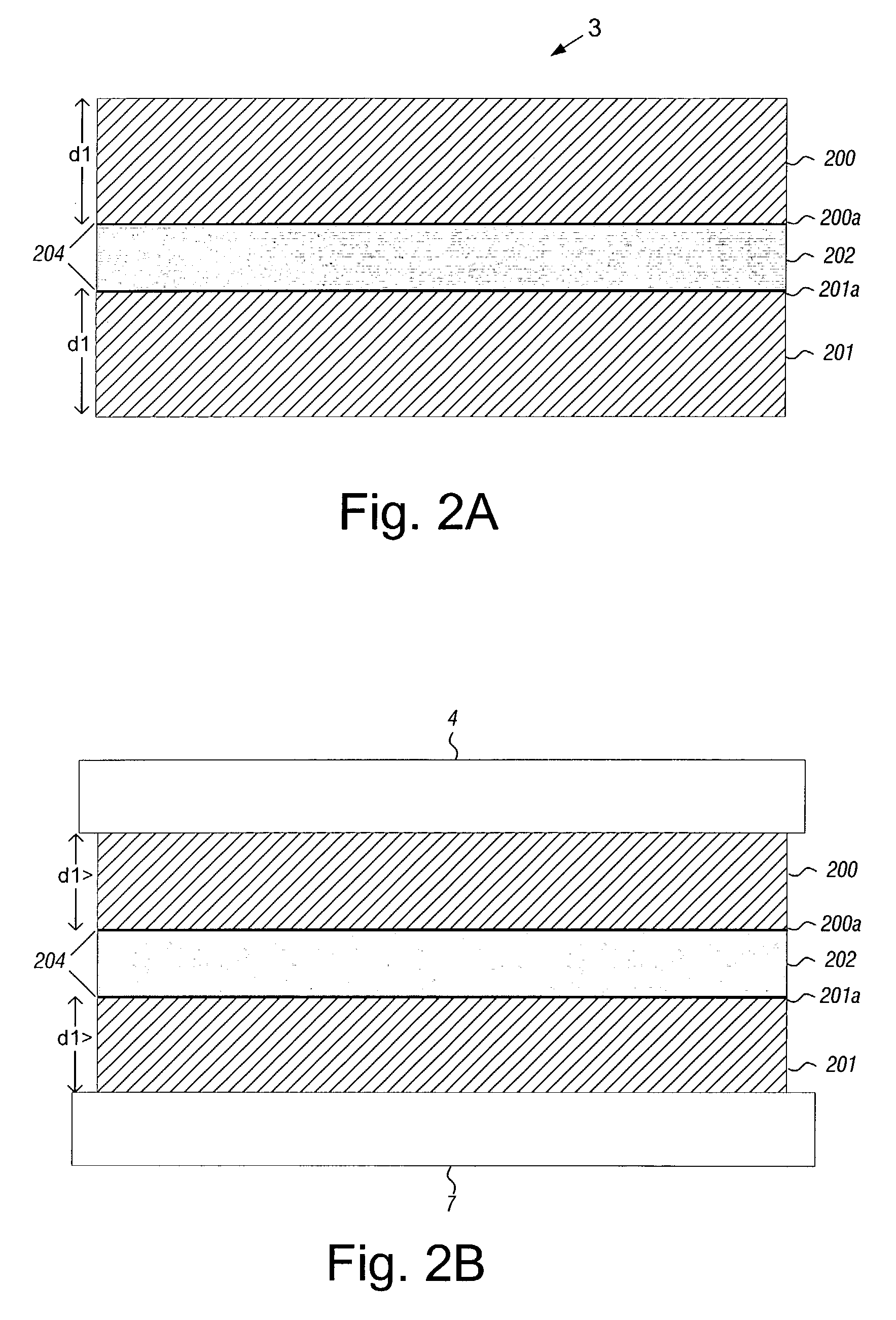
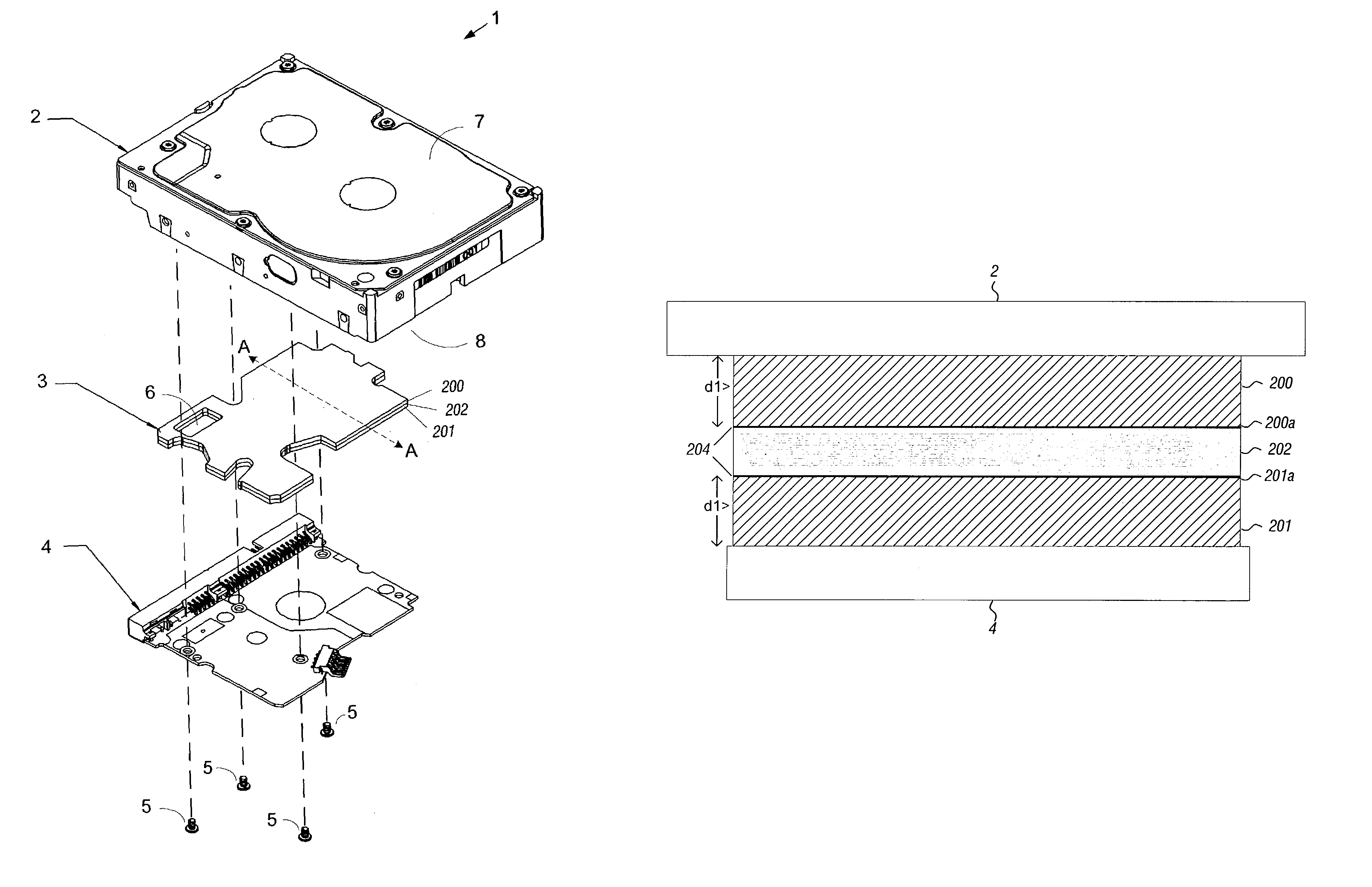
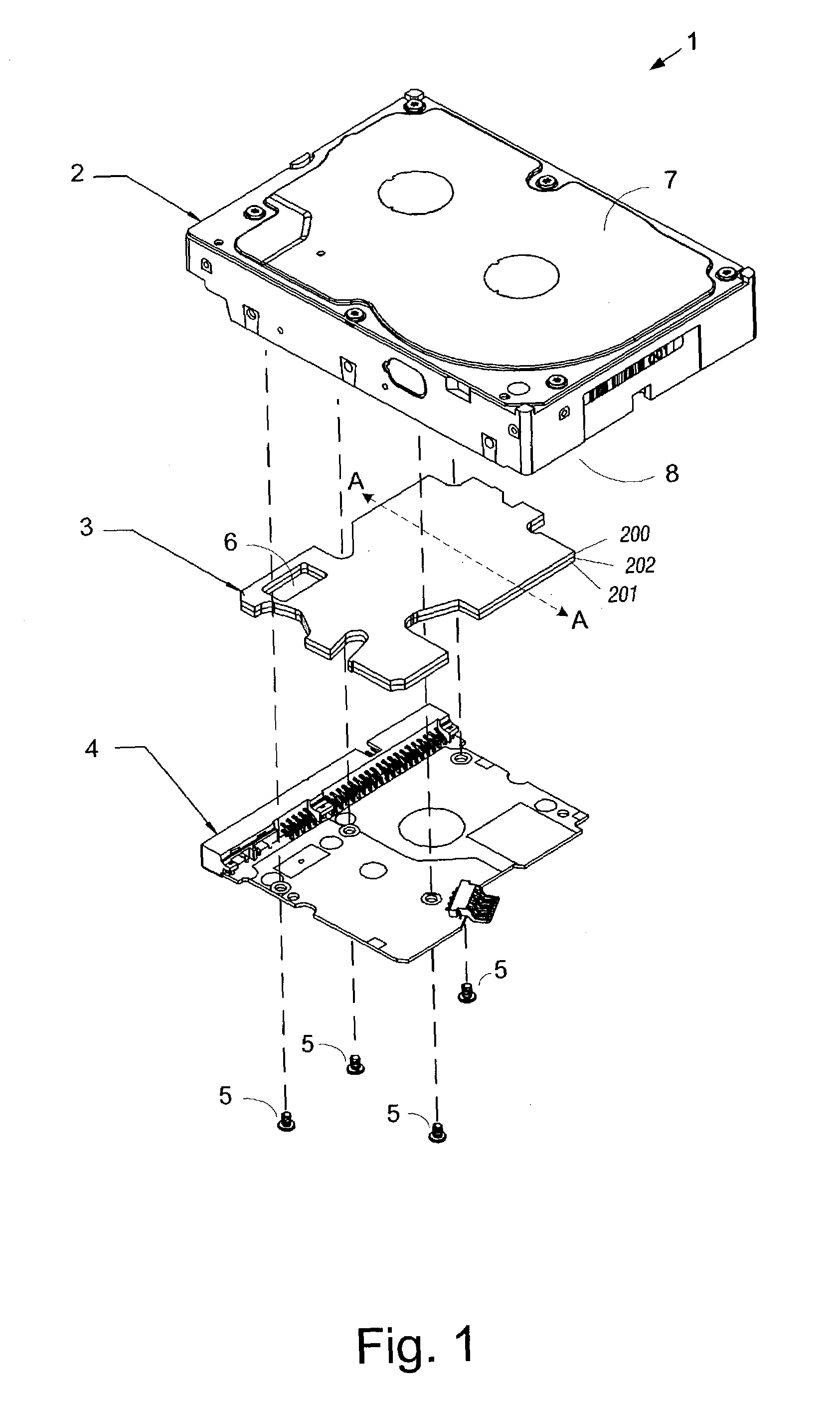
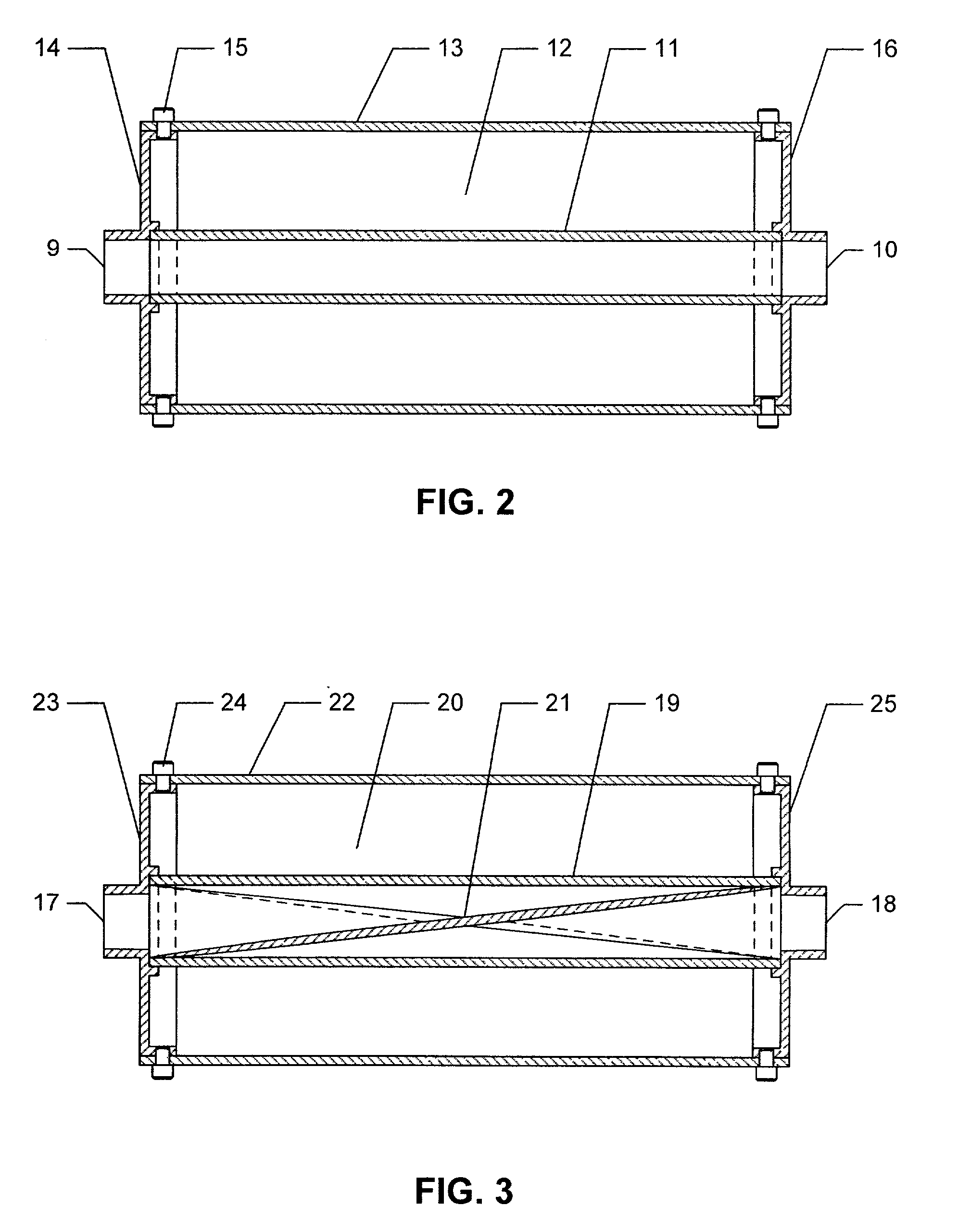
Disk drive having an acoustic damping shield assembly with an acoustic barrier layer
InactiveUS6958884B1Carrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersAcoustic absorptionEngineering
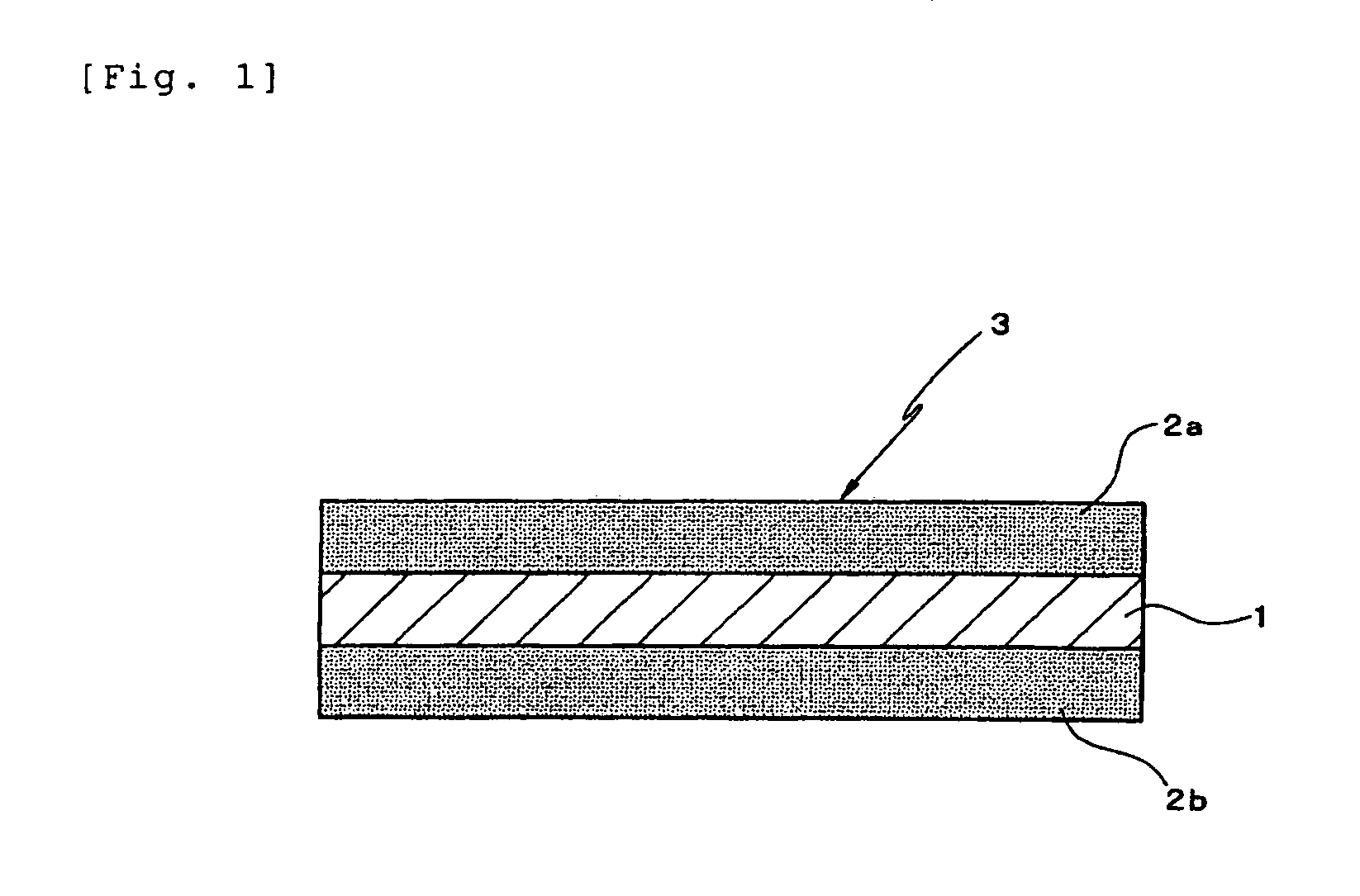
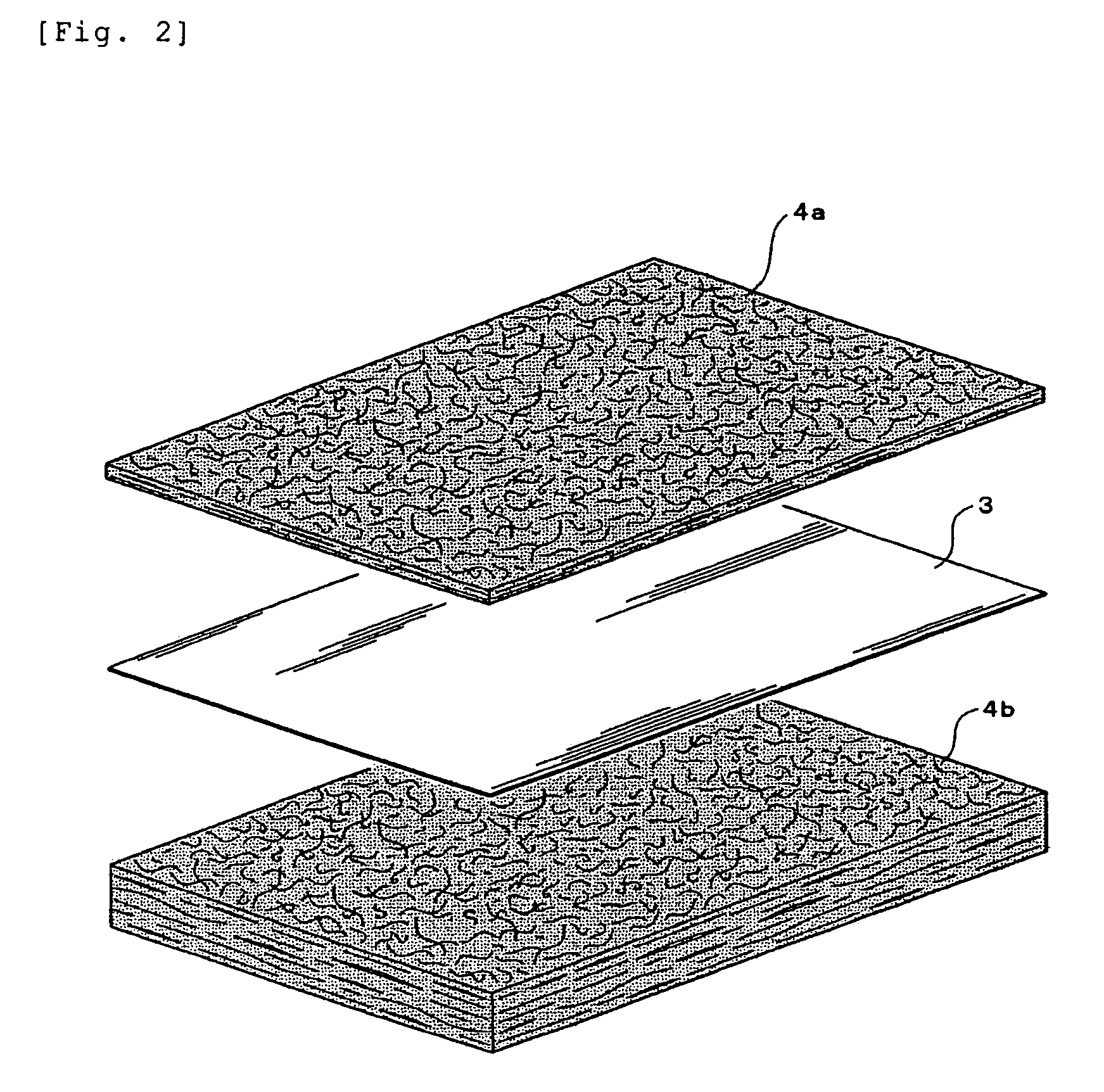
A disk drive that includes a head disk assembly (HDA) comprising a base having a top base surface and a bottom base surface, and a top cover secured to the top base surface; a printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) in communication with the HDA and comprising a first PCBA surface and a second PCBA surface wherein the first PCBA surface faces the bottom base surface; and a bottom cover fastened to and substantially covering the bottom base surface. The invention further includes an acoustic damping shield assembly placed between the bottom cover and the second PCBA surface, wherein the acoustic damping shield assembly comprises first and second acoustic absorption layers having major surfaces; an acoustic barrier layer placed in between the major surfaces; and the major surfaces and the acoustic barrier layer are fixed in a stacked relationship.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive having an acoustic damping assembly with an acoustic barrier layer
ActiveUS6954329B1Apparatus for flat record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersAcoustic absorptionEngineering
A disk drive that includes a head disk assembly (HDA) having a disk drive base, and a printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) in communication with the HDA. The invention further includes an acoustic damping assembly placed between the disk drive base and the PCBA. The acoustic damping assembly includes first and second acoustic absorption layers having major surfaces, an acoustic barrier layer placed in between the major surfaces, and the major surfaces and the acoustic barrier layer are fixed in a stacked relationship.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
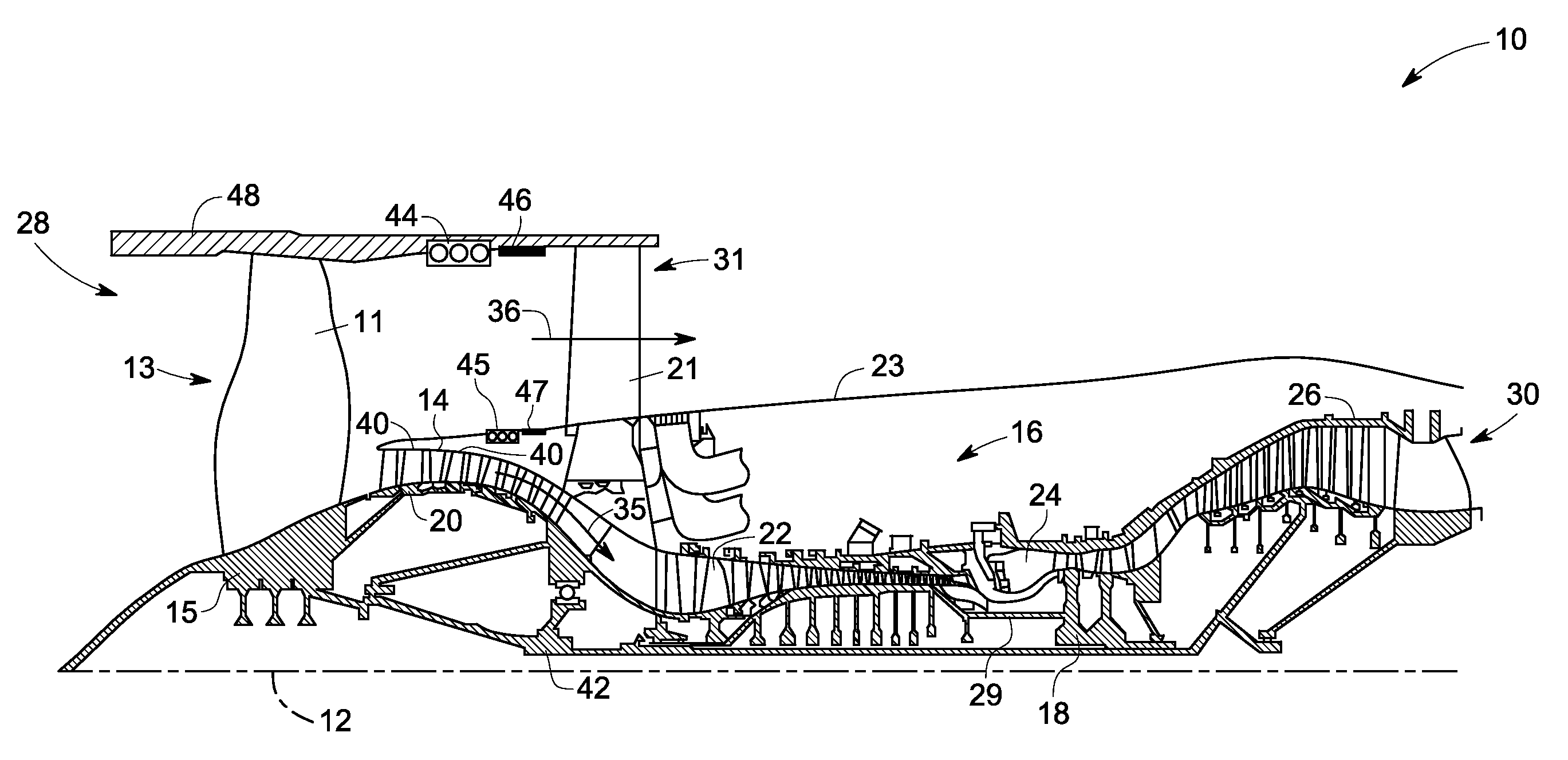
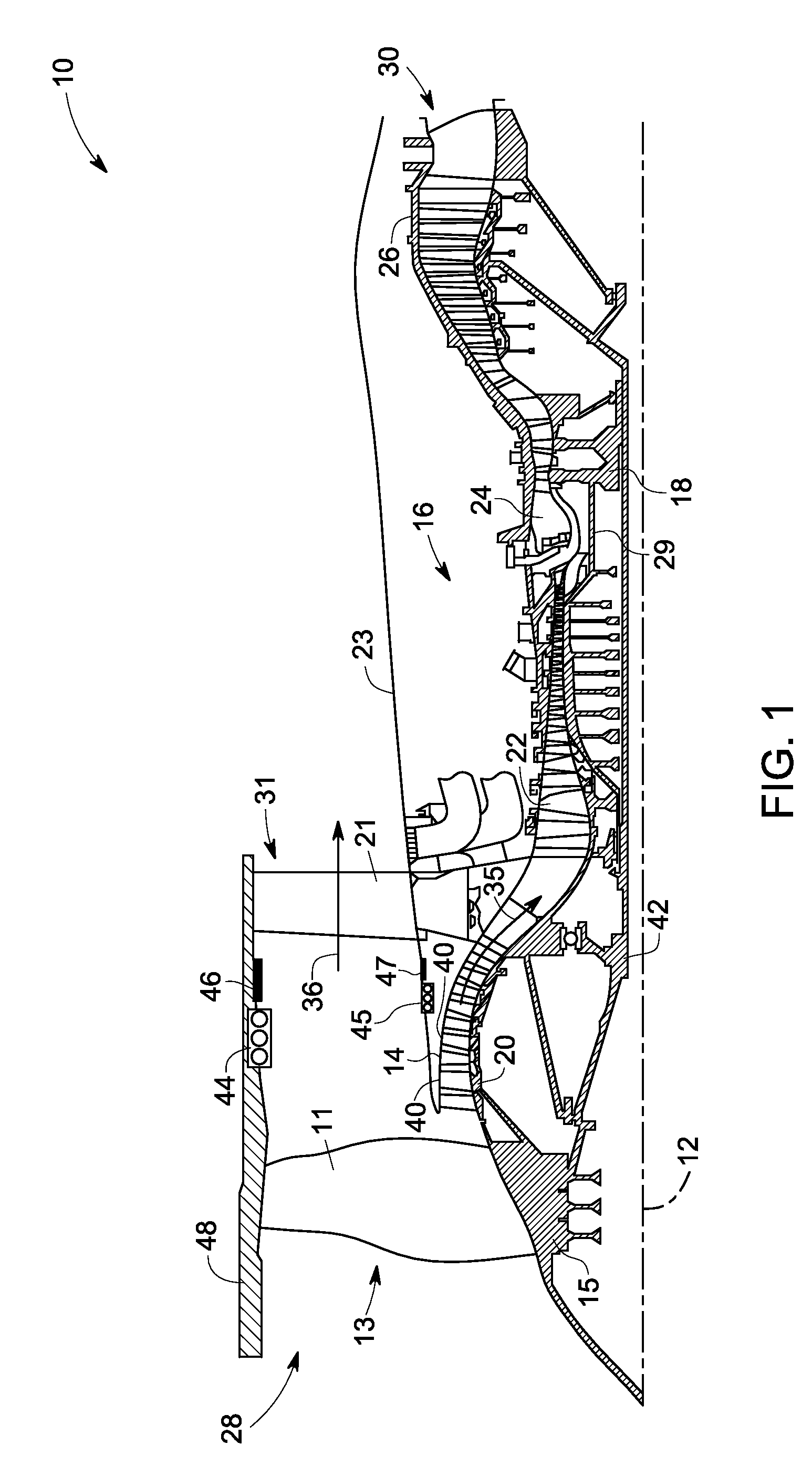
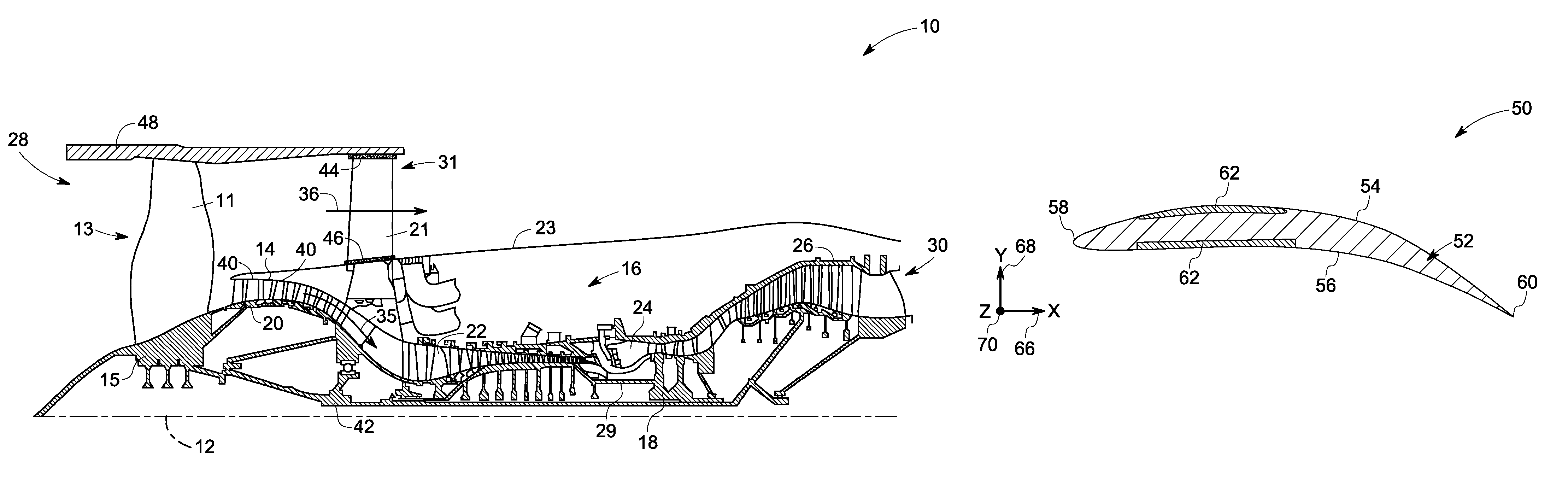
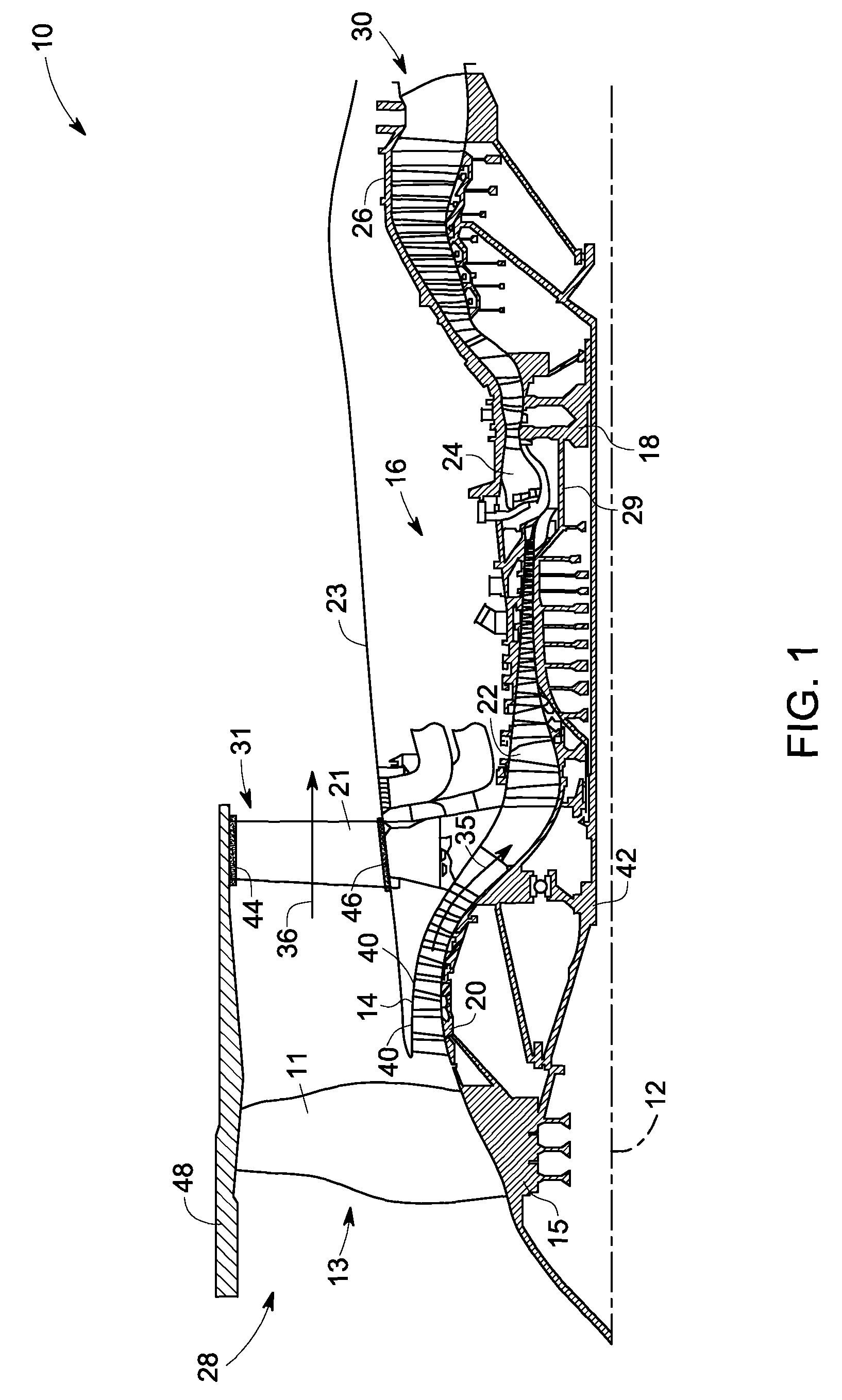
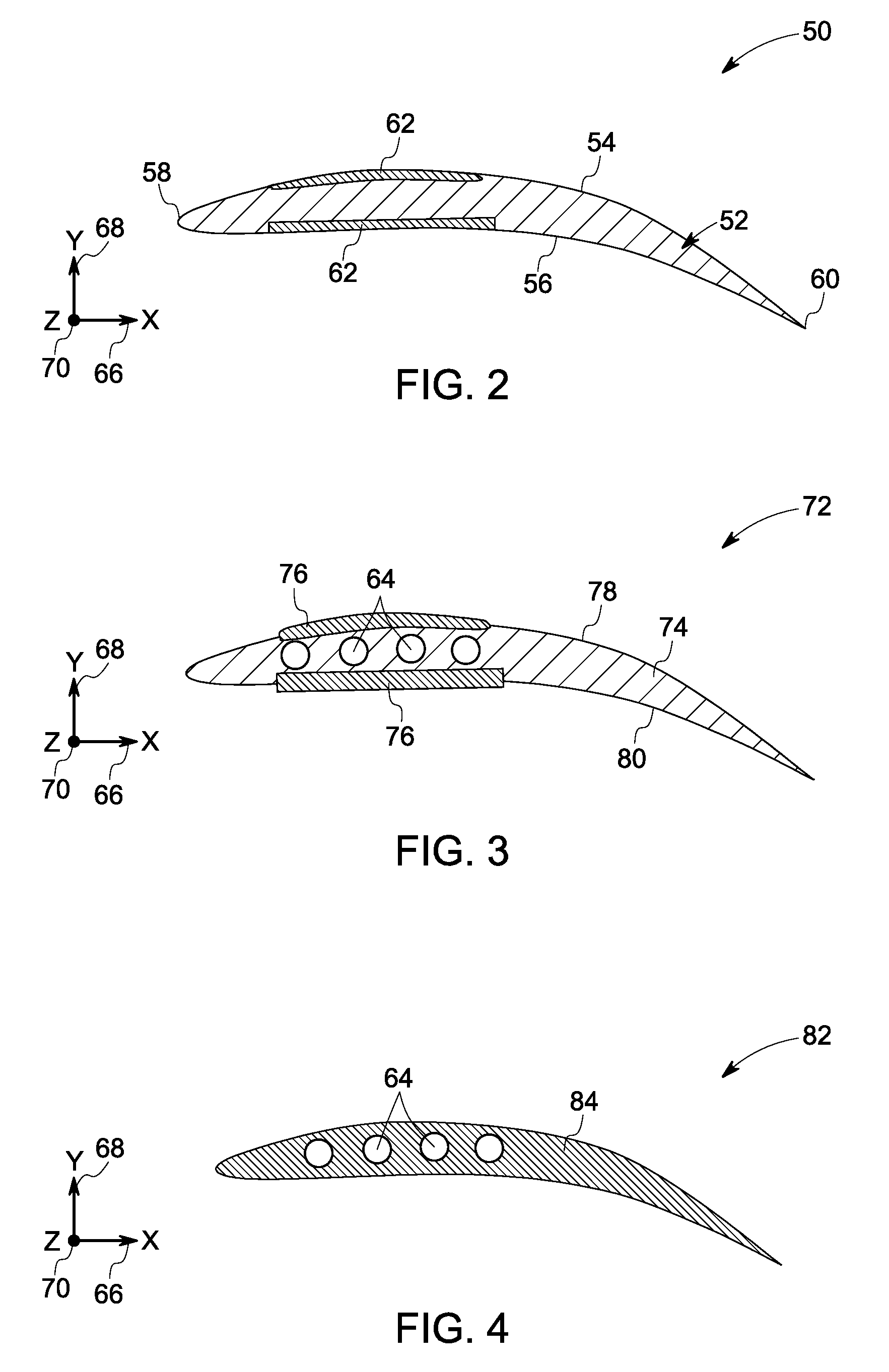
Combined acoustic absorber and heat exchanging outlet guide vanes
ActiveUS20090317238A1Improve heat transfer performanceImprove sound absorptionPump componentsEngine fuctionsSurface coolingAcoustic absorption
An outlet guide vane assembly for turbomachines is provided. The outlet guide vane assembly comprises one or more outlet guide vanes, wherein each of the one or more outlet guide vanes comprises a first surface and a second surface, and wherein the one or more outlet guide vanes are disposed between an inner wall and an outer wall of an engine and a surface cooler layer disposed on at least a portion of the first surface, the second surface, or both of the one or more outlet guide vanes, wherein the surface cooler layer comprises a metal foam, a carbon foam, or a combination thereof, wherein the metal foam, the carbon foam or the combination thereof is configured to augment heat transfer and enhance acoustic absorption.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Acoustical ceiling tiles
InactiveUS6877585B2Simple and inexpensiveImprove performanceCeilingsWallsAcoustic absorptionEngineering
A system for improved sound absorption, including a substrate of porous insulation material and of a first air flow resistance, and a facing material attached to the substrate and of a second air flow resistance, wherein a total system resistance is a combination of the first and second air flow resistances, and wherein the total system resistance and the second air flow resistance are of relatively low values.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
Polyurethane multilayer composite sheet for automotive headliner and processing method thereof
InactiveCN101544083ASolve pollutionAvoid product qualitySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationSurface finishGlass fiber
The invention discloses a polyurethane multilayer composite sheet for an automotive headliner, which has a non-woven fabric layer, a first reinforcing glue film layer, a first reinforcing fiber layer, a first adhesive film layer, polyurethane foam board, a second adhesive film layer, a second reinforcing fiber layer, a reinforcing glue layer and a surface finish layer from bottom to top. The production method of the polyurethane multilayer composite sheet has the characteristics that: the use of the reinforcing glue films as a substitute of hot-melt adhesive powder simplifies production process, improves production efficiency and product quality, radically solves dust pollution in a production process, and improves the working environment of workers. The polyurethane multilayer composite sheets produced by the method can be used for fiber glass-free automotive roofs, biodegradable automotive roofs, light automotive roofs, and other high-quality automotive headliners; the introduction of reinforcing fiber mats in different forms enables the method to produce breathable automobile roofs, high acoustic absorption automotive roofs, high strength automotive roofs and other functional automotive headliners; and the sheet and the method fill a gap of the automotive headliner industry in China.
Owner:陈雅君
Acoustic attenuation panel for aircraft for engine nacelle
InactiveUS20110133025A1Weight optimizationOptimize sound absorption characteristicDe-icing equipmentsEfficient propulsion technologiesNacelleAcoustic absorption
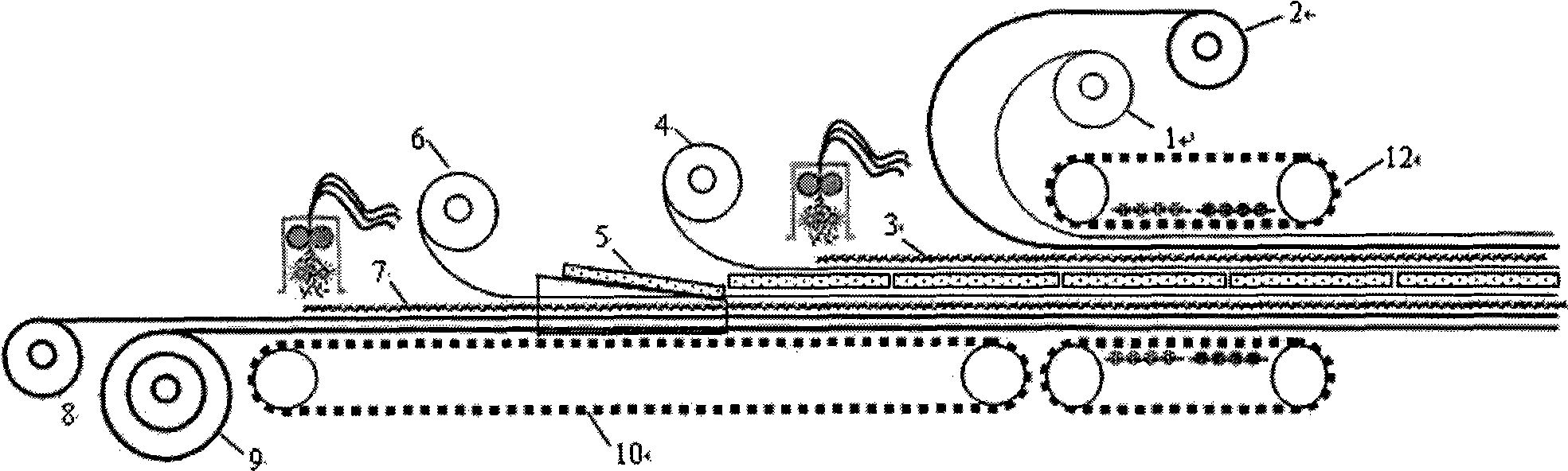
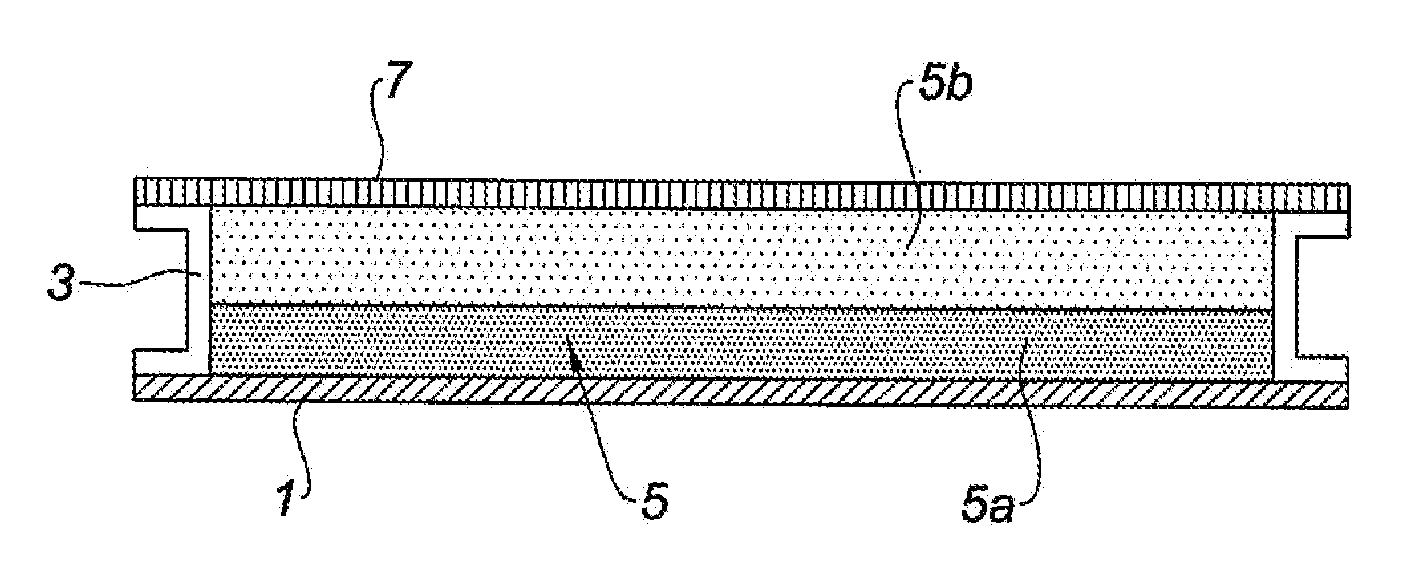
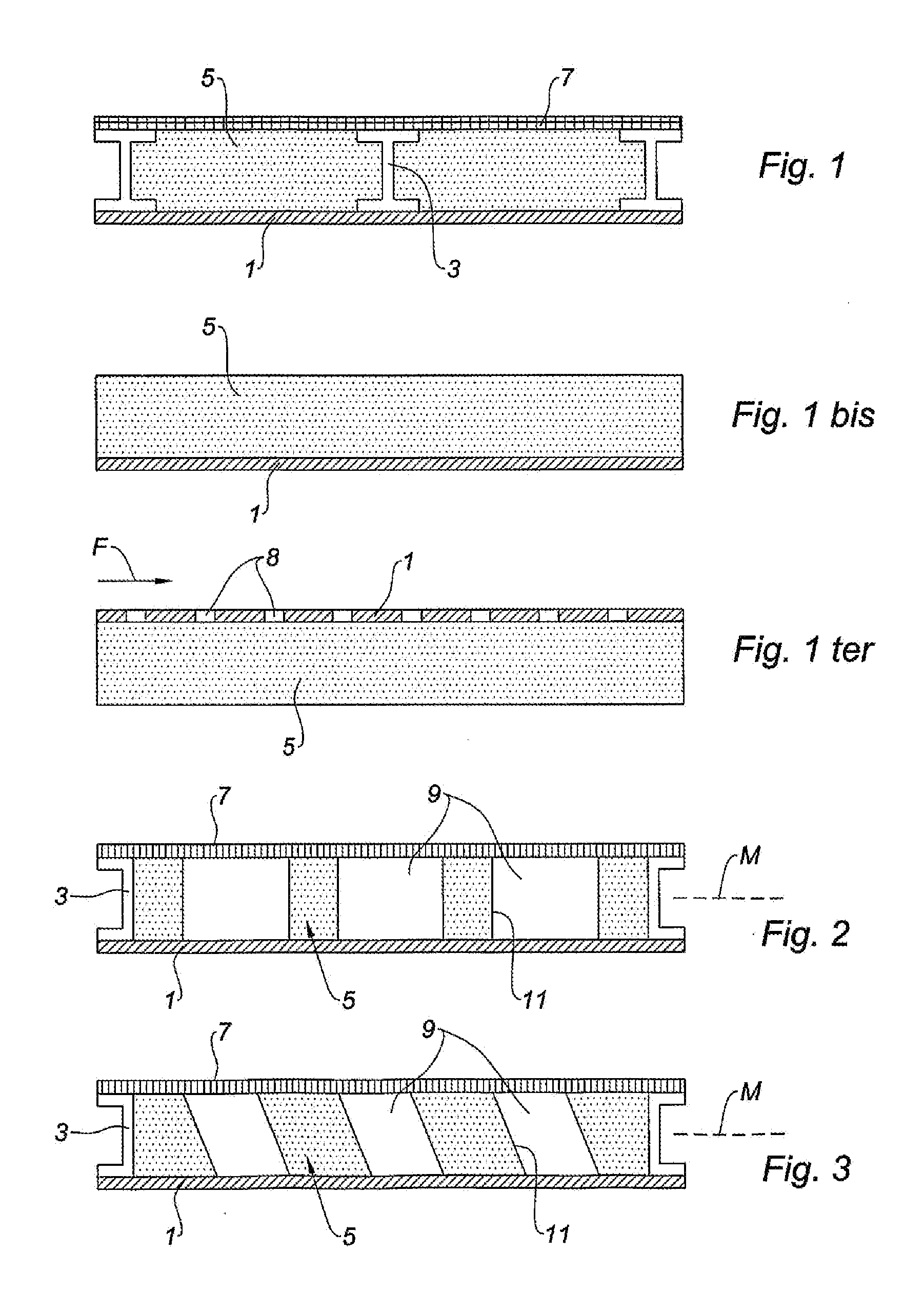
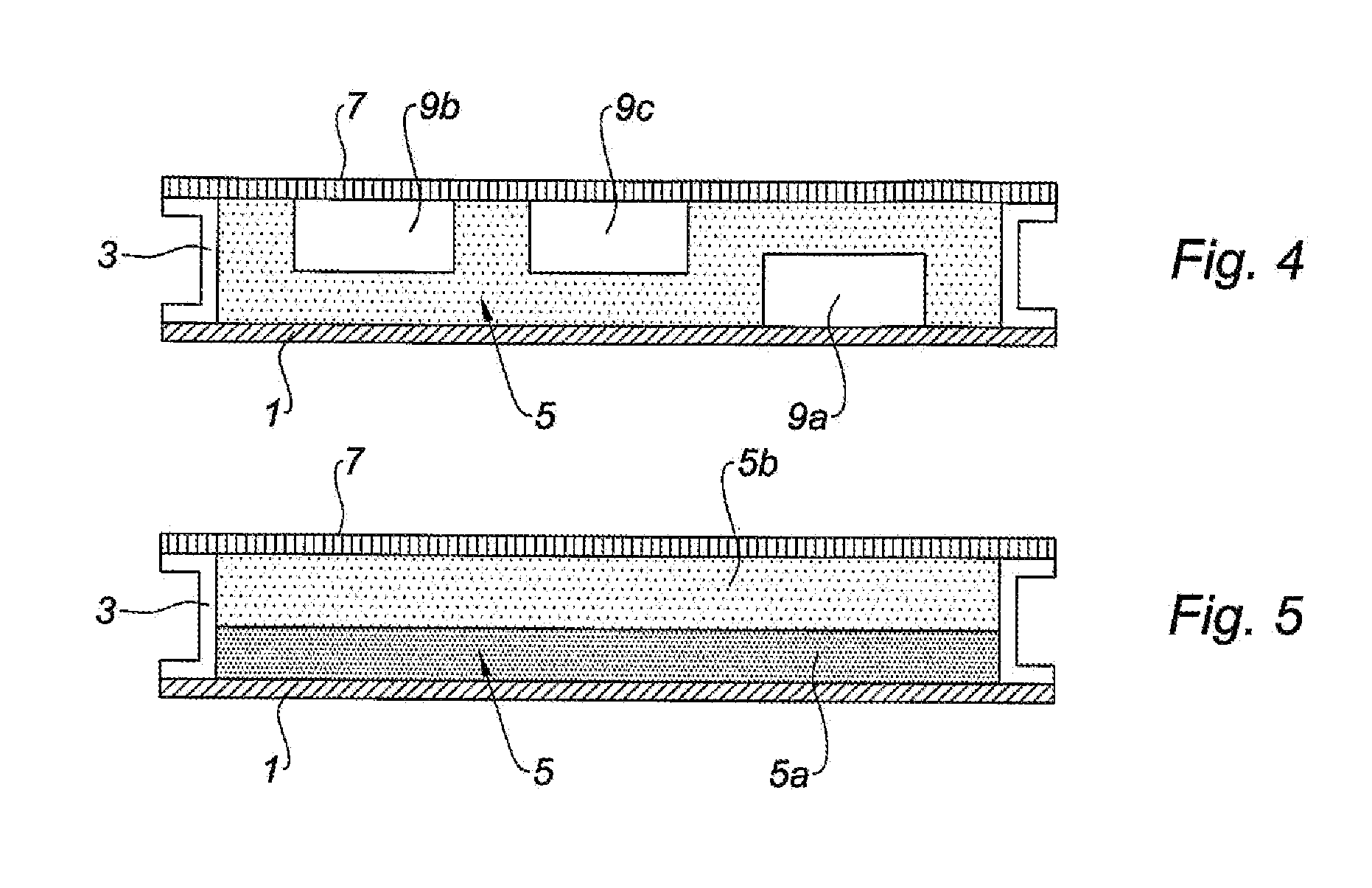
This acoustic attenuation panel for an aircraft engine nacelle comprises a structuring skin (1) and, by way of acoustic absorption material, a porous material (5) attached to this skin (1).
Owner:SAFRAN NACELLES
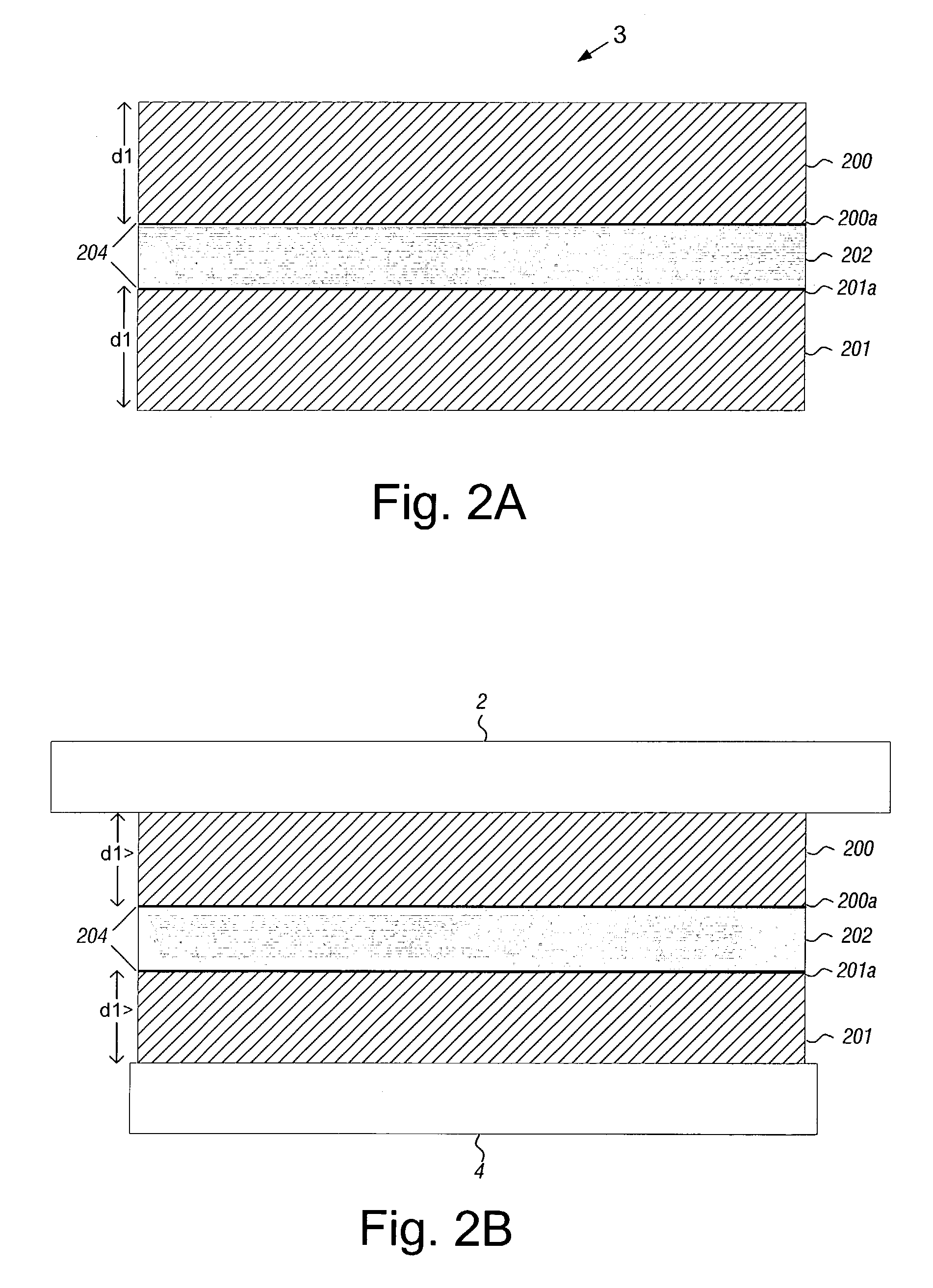
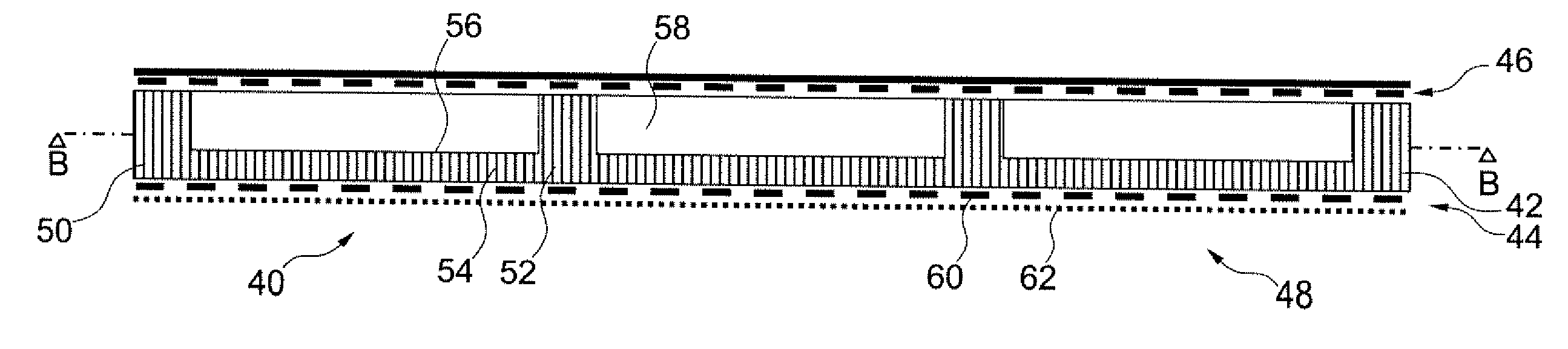
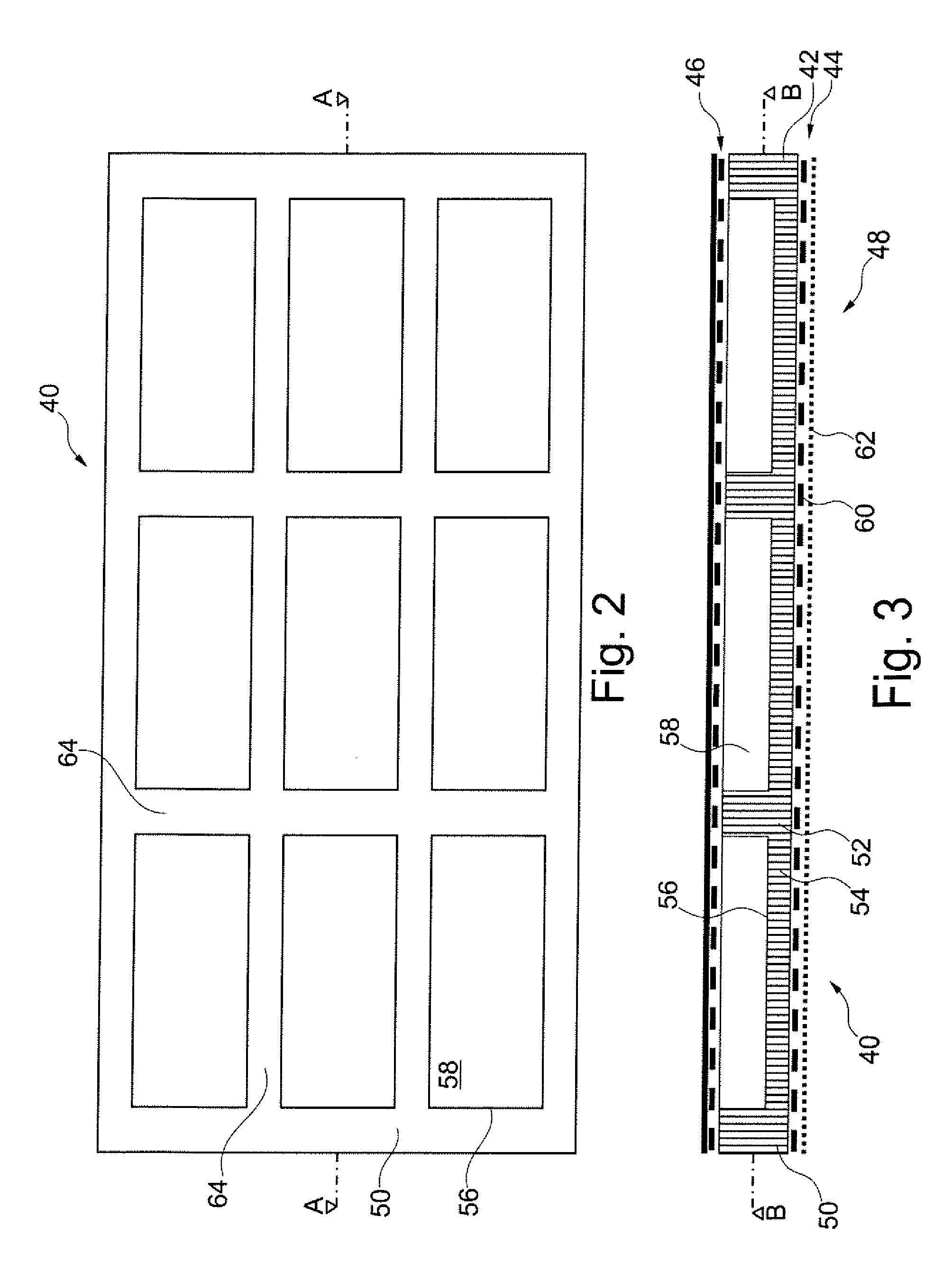
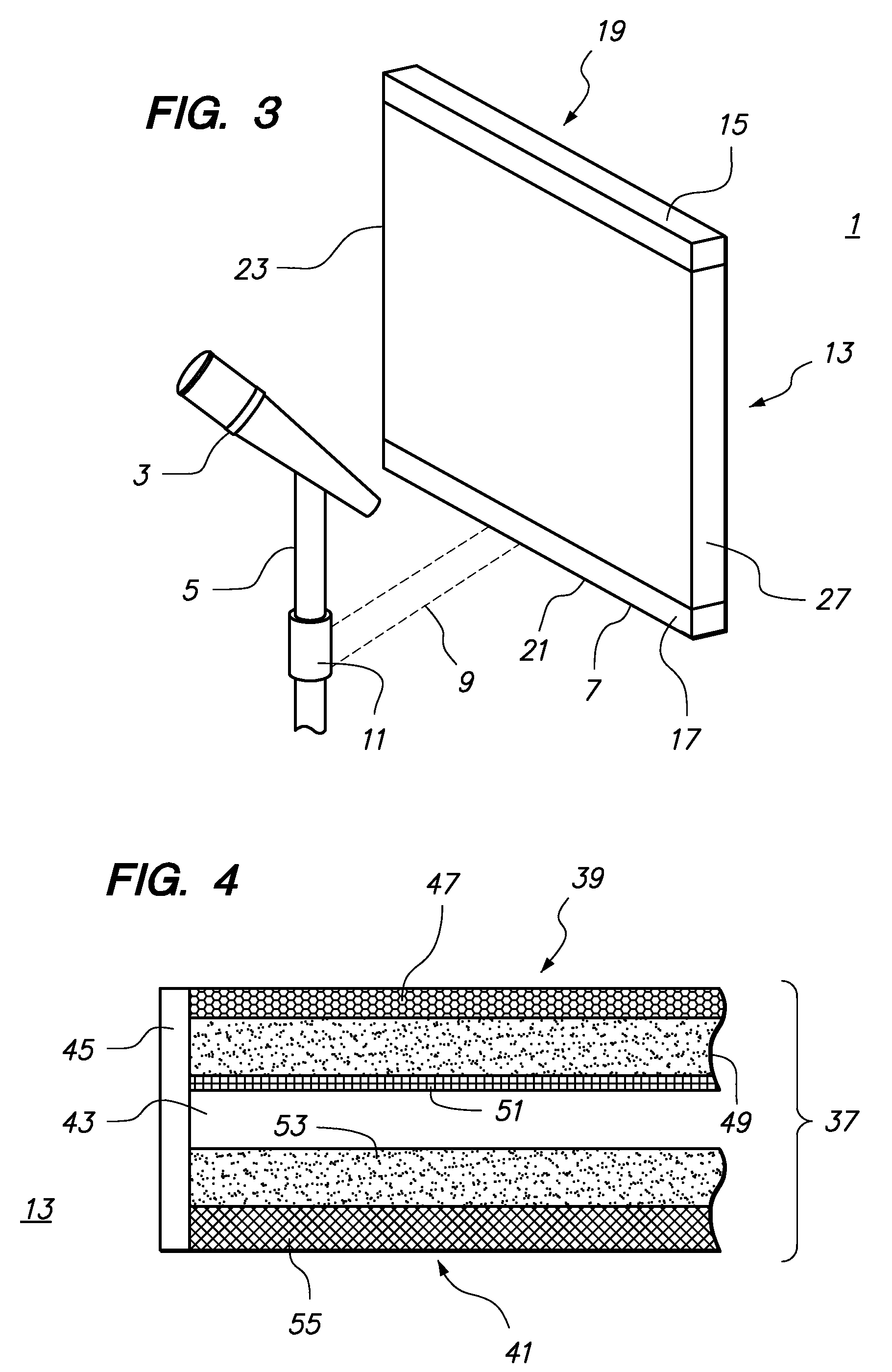
Acoustic absorption system for an aircraft airframe
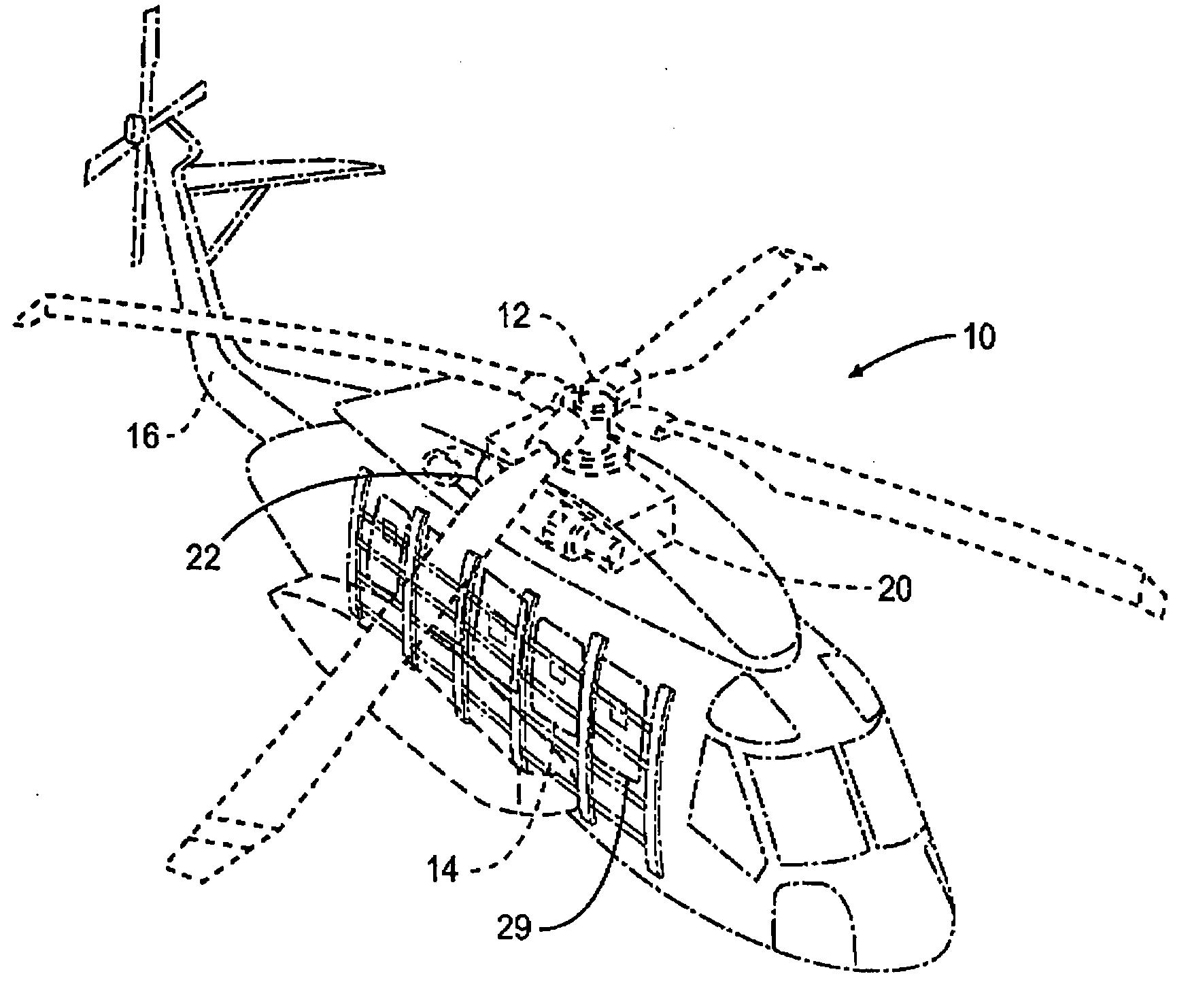
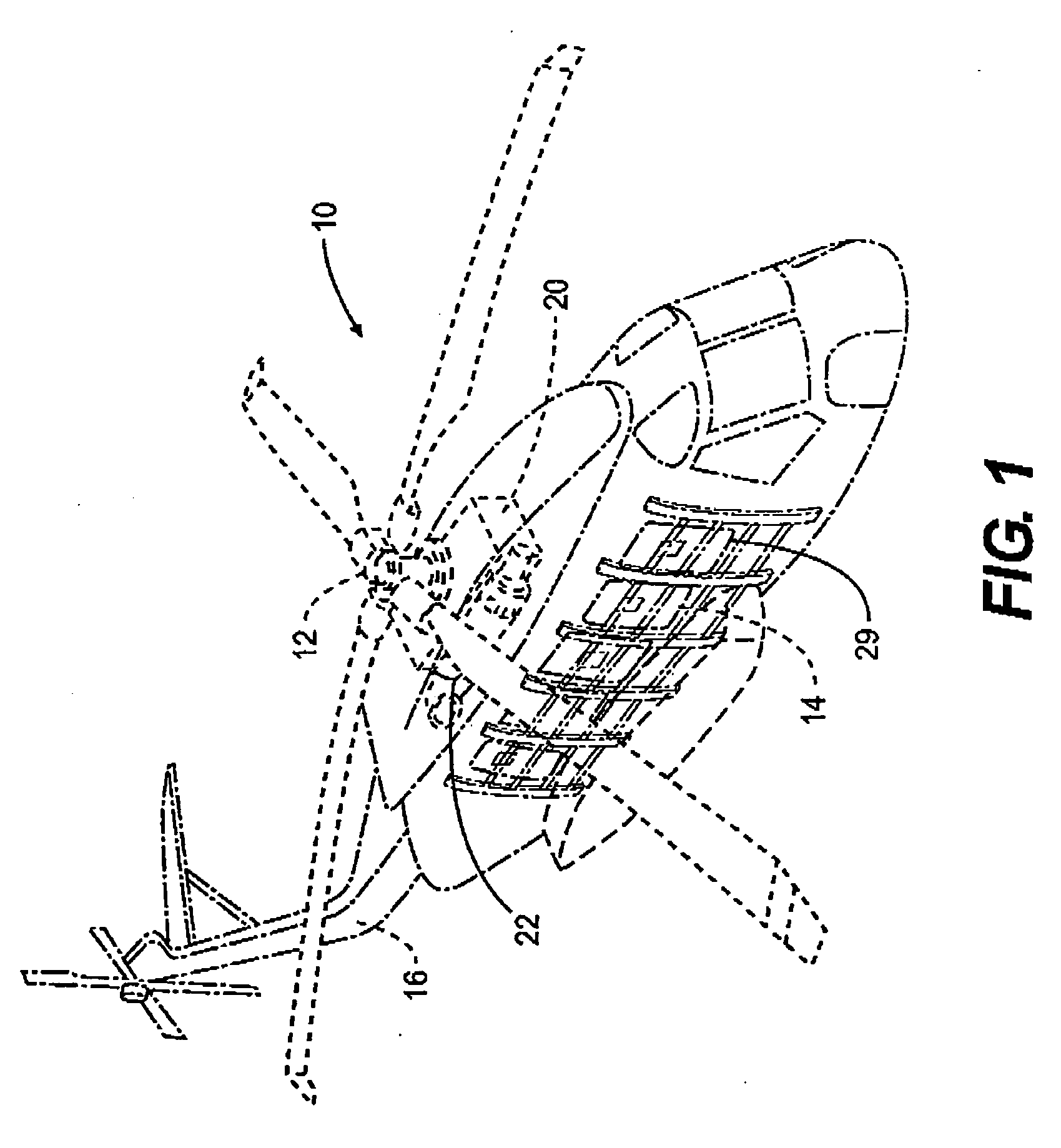
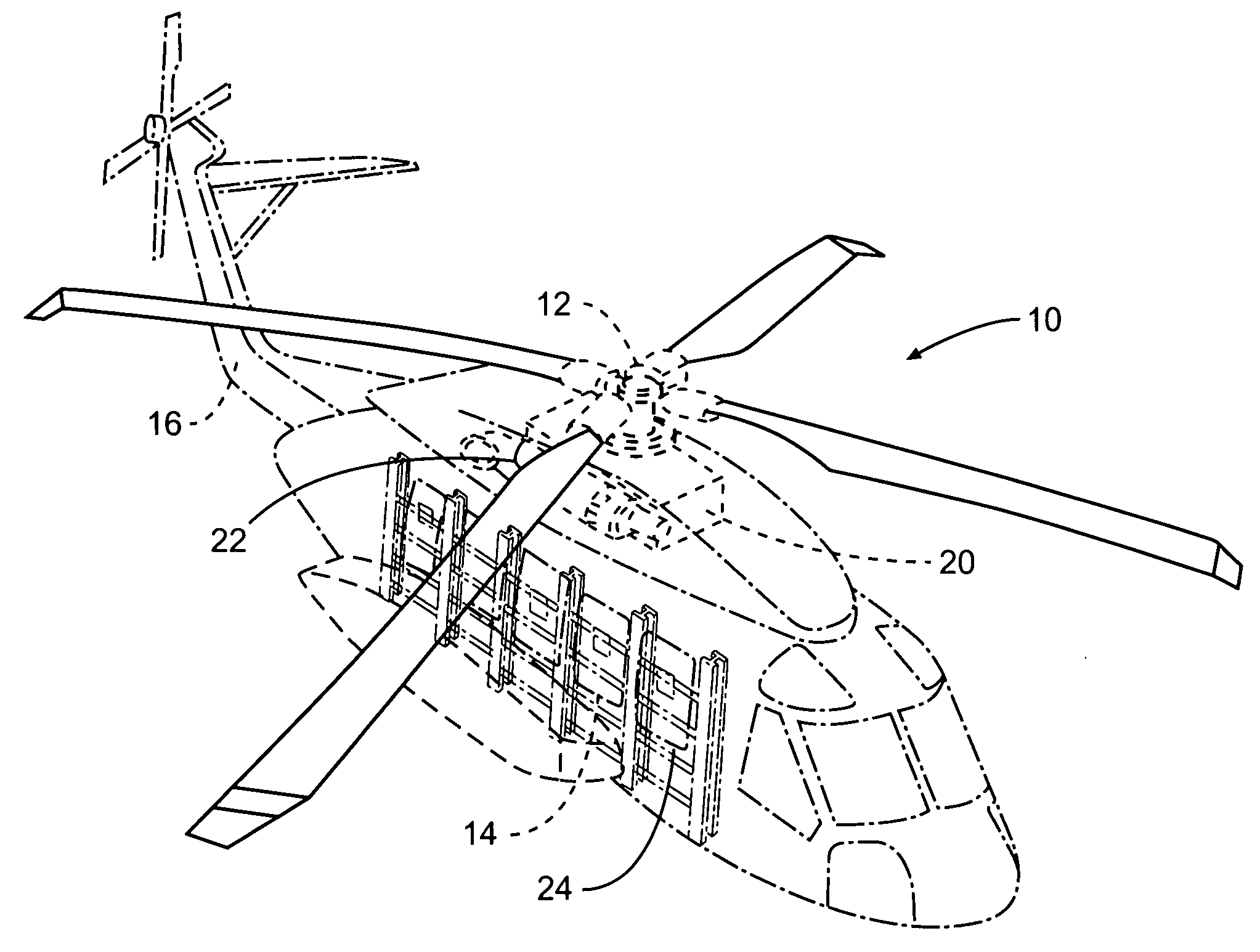
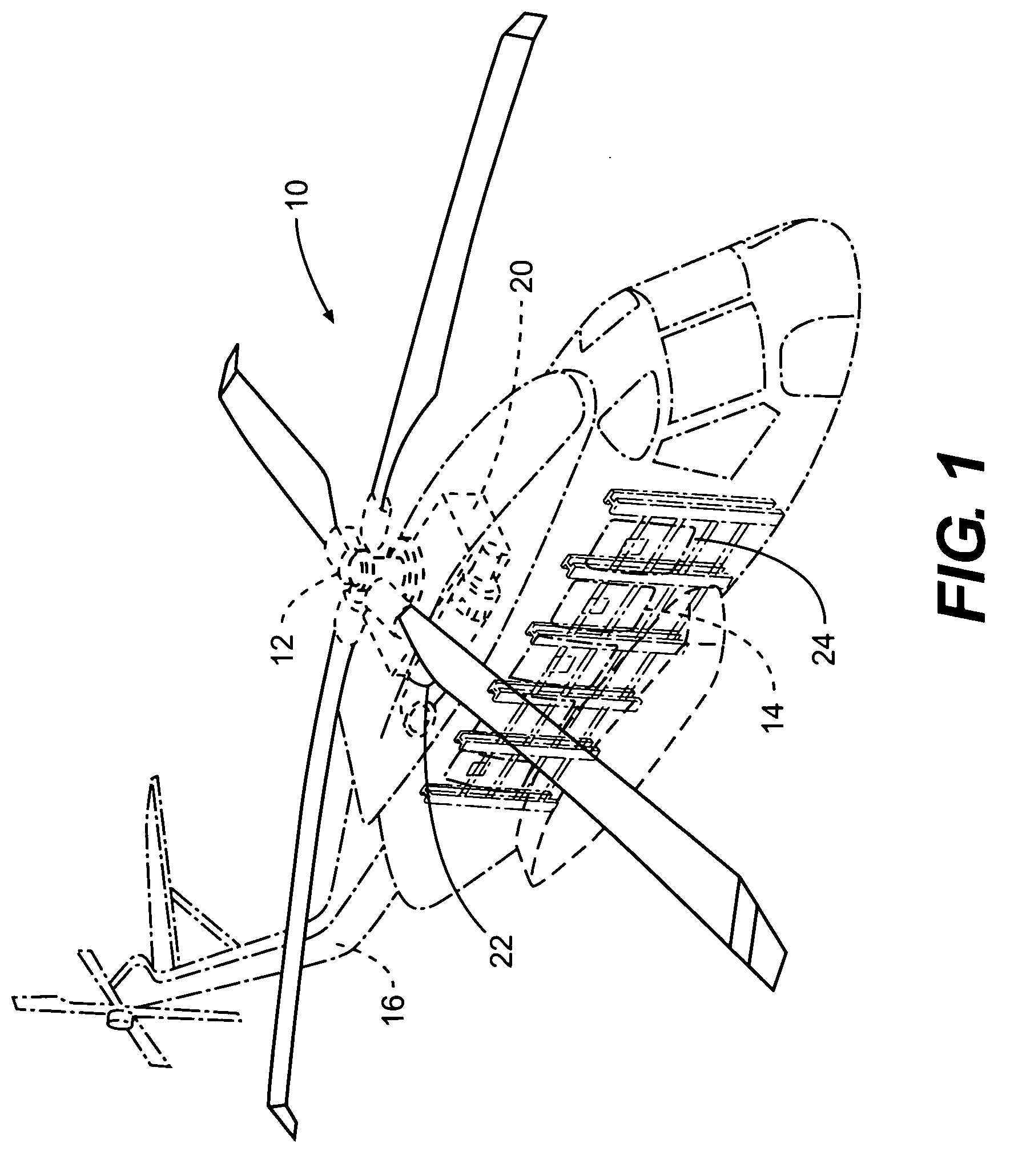
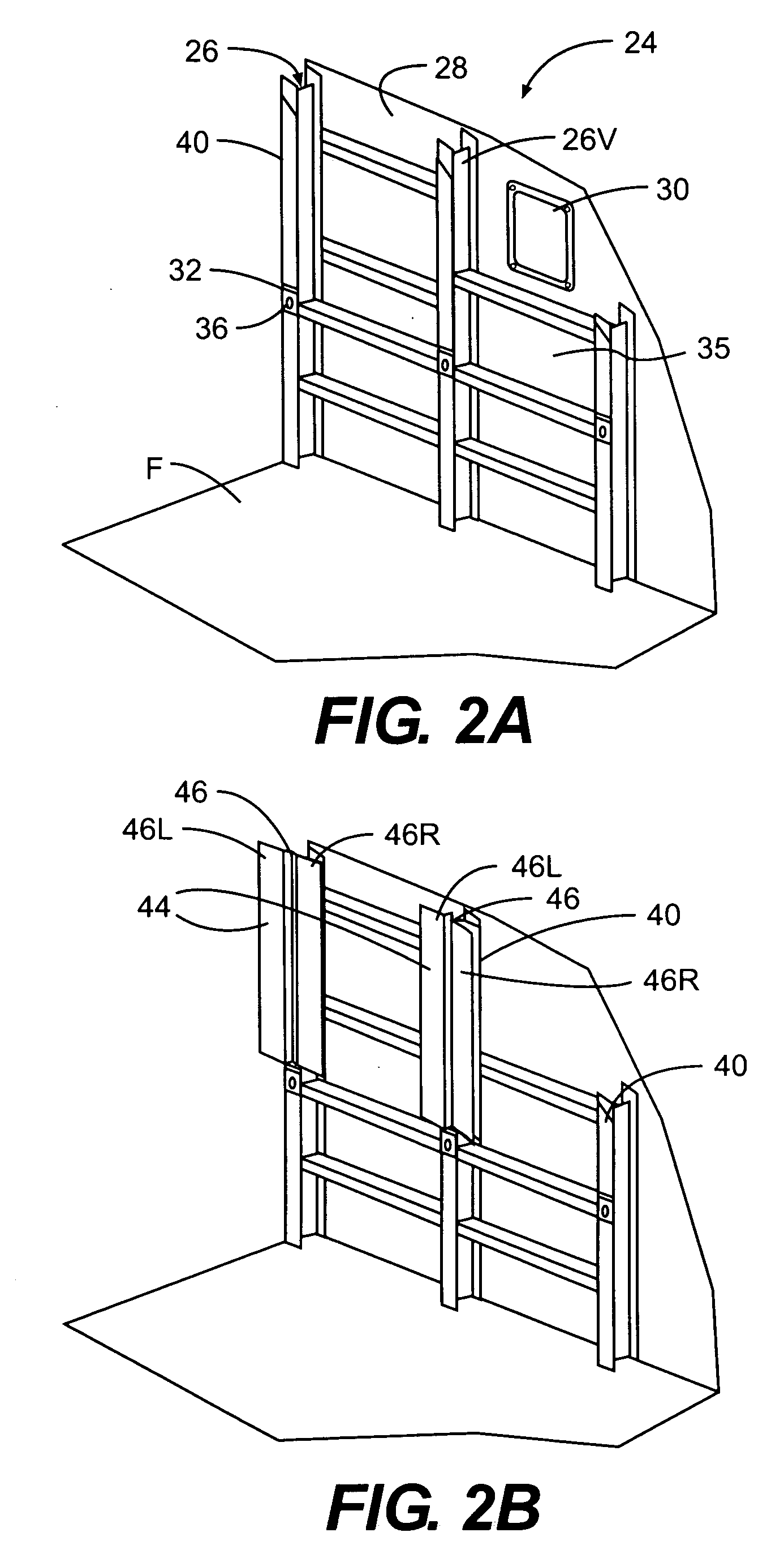
An acoustic absorption system fills each frame void within an airframe section with a close fitting foam portion. A mass barrier layer is adhered over the foam portions and to a multitude of frame members. The mass barrier layer is a contiguous layer adhered across the multitude of frame members to seal the airframe frame voids to make use of mass-air-mass principles to reduce flanking path leakage around the foam portions.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
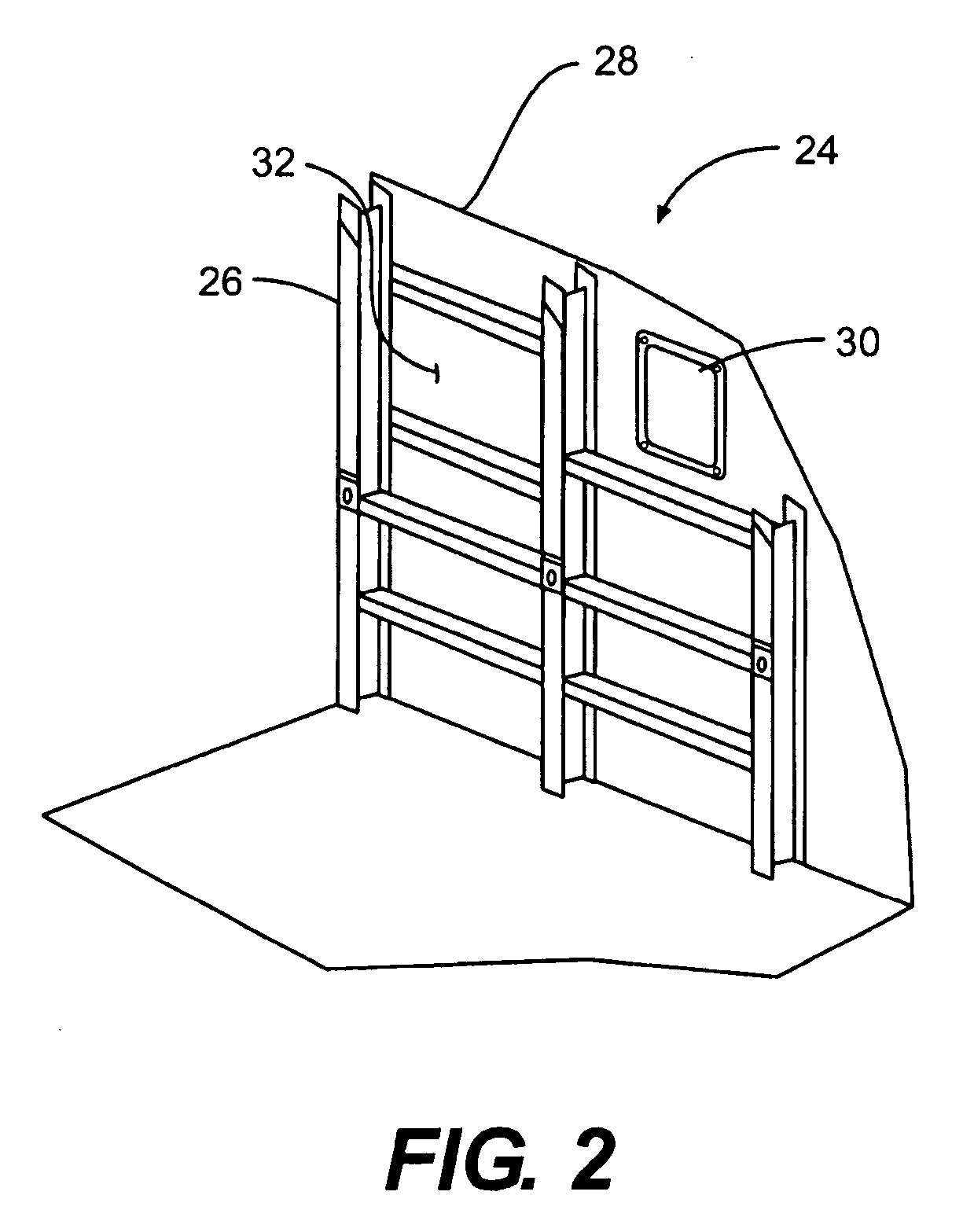
Method and framework for suspending acoustic absorption medium
A quickly erectable framework for supporting a curtain includes at least two standards. Each standard includes a shaft having a capital end and a base end, the base end. A clevis bracket affixed to the capital end of each standard suspends at least one curtain track configured, when the framework is in its erected state, to span horizontally an interspace between the two standards, the track being affixed to each of the capital ends by means of the clevis bracket. A plurality of trolleys is each configured to transit along the track while suspending an edge of a curtain. At least one edge scissor assembly is affixed at opposite ends to span the interspace between the standards. Each scissor assembly includes a plurality of scissor arms hingedly connected to one another.
Owner:FORREST SOUND PROD
Acoustically absorbent ceiling tile having barrier facing with diffuse reflectance
InactiveUS20090173570A1Improving acoustic absorptionImproving light reflectanceCeilingsConstruction materialBrickAcoustic absorption
An acoustically absorbent ceiling tile includes a core of acoustically absorbing material having two major surfaces, and a facing for covering the core on at least one major surface. The facing comprises a porous flash spun plexifilamentary film-fibril sheet having a coherent surface and comprising a plurality of pores having a pore diameter between about 100 nm and about 20,000 nm and a mean pore diameter of less than about 20,000 nm. The facing has highly diffuse reflectance of light, and a reflectance of greater than about 86%. The use of the facing improves the acoustic absorption of ambient sound at frequencies below about 1200 Hz. The facing provides a barrier to moisture and particles including microorganisms so that the ceiling tile is suitable for use in environments in which cleanliness is critical.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method and apparatus for improved noise attenuation in a dissipative internal combustion engine exhaust muffler
The use of fiber metal or similarly high flow resistance and high acoustic transparency material as a liner for traditional acoustically absorptive media in a dissipative muffler exhibits improved low frequency sound attenuation, reduces backpressure, and eliminates media entrainment or "blow-out" phenomenon which results in longer muffler life. The same class of materials may also be used to fashion an element that provides linear occlusion inside an otherwise line-of-sight type of muffler, where the occluding element provides improved impedance-matching acoustic absorption. Disclosed embodiments providing linear occlusion minimize traditional increases in muffler backpressure by incorporating helical, conical, and annular members in mufflers with round ducts. To maximize attenuation, a muffler according to the invention may feature both a fiber metal fill liner and a fiber metal linear occlusion element. Further, the liner that connects the inlet and outlet ports of the muffler may feature an offset, elbow, or turn that would simultaneously allow it to provide means for linear occlusion.
Owner:QUIET STORM
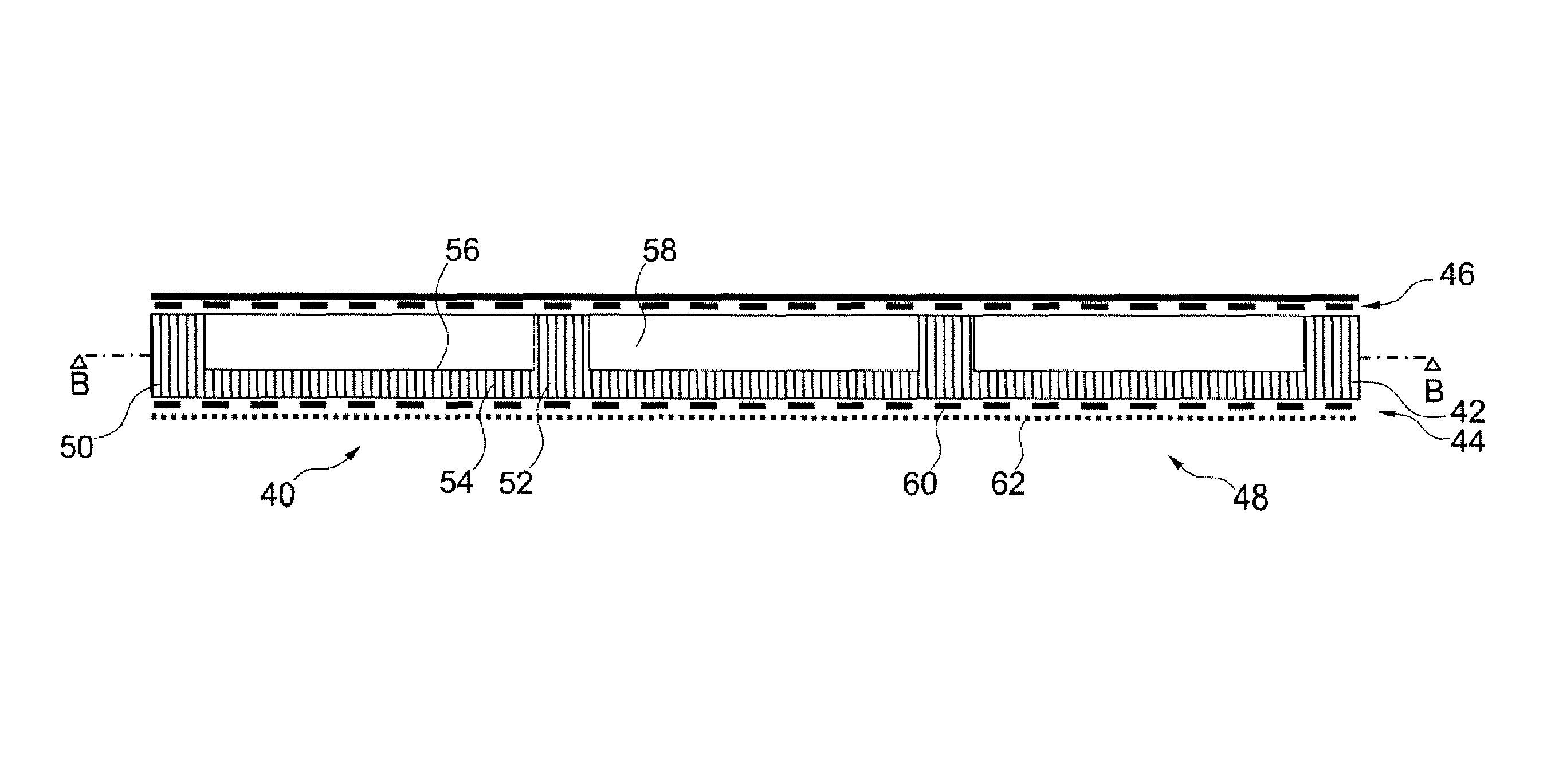
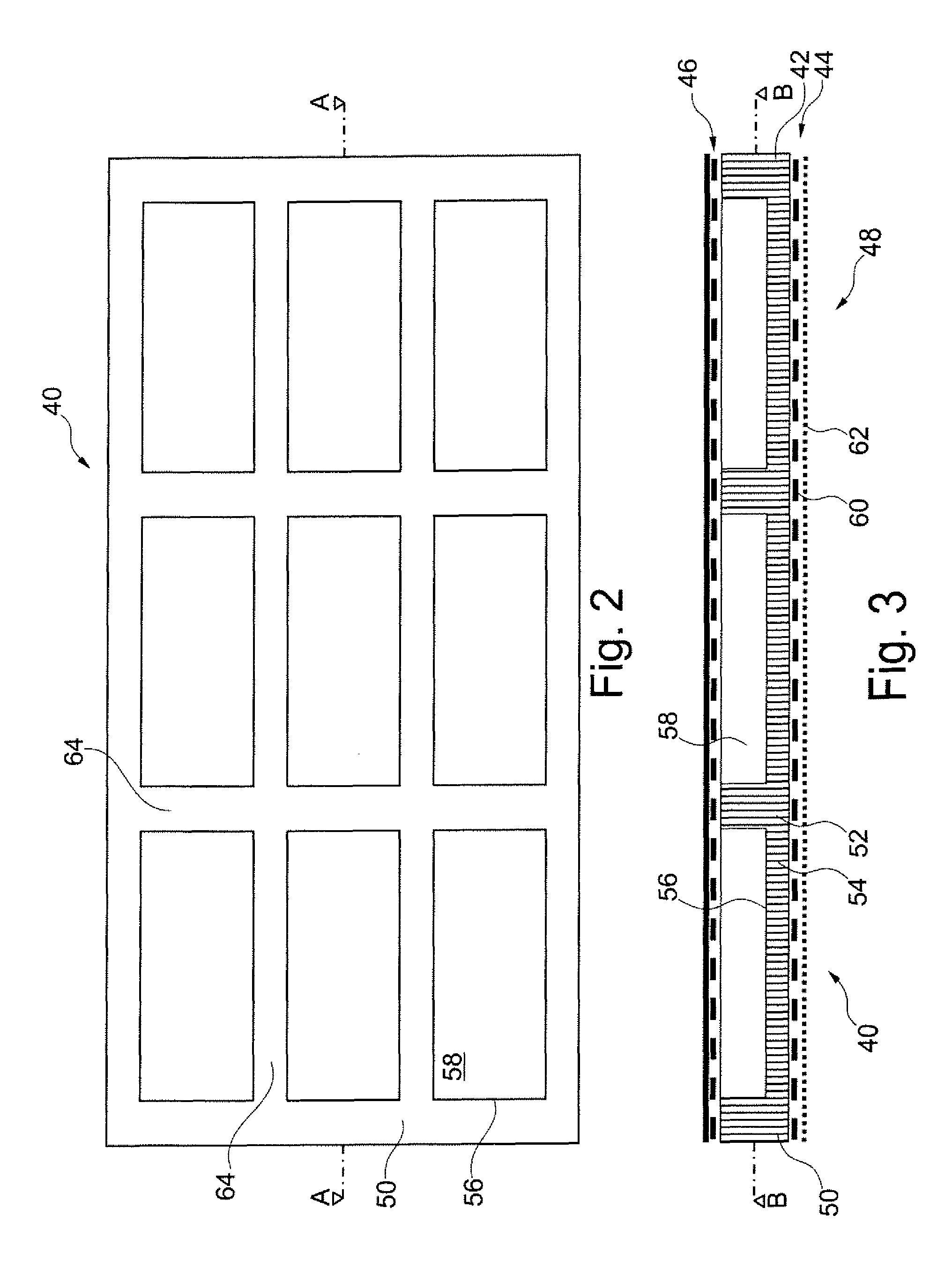
Aircraft cabin panel with core recesses for acoustic absorption
InactiveUS20100148001A1Good sound-absorbing propertiesEasy to adaptLayered productsFuselage insulationInterior spaceNacelle
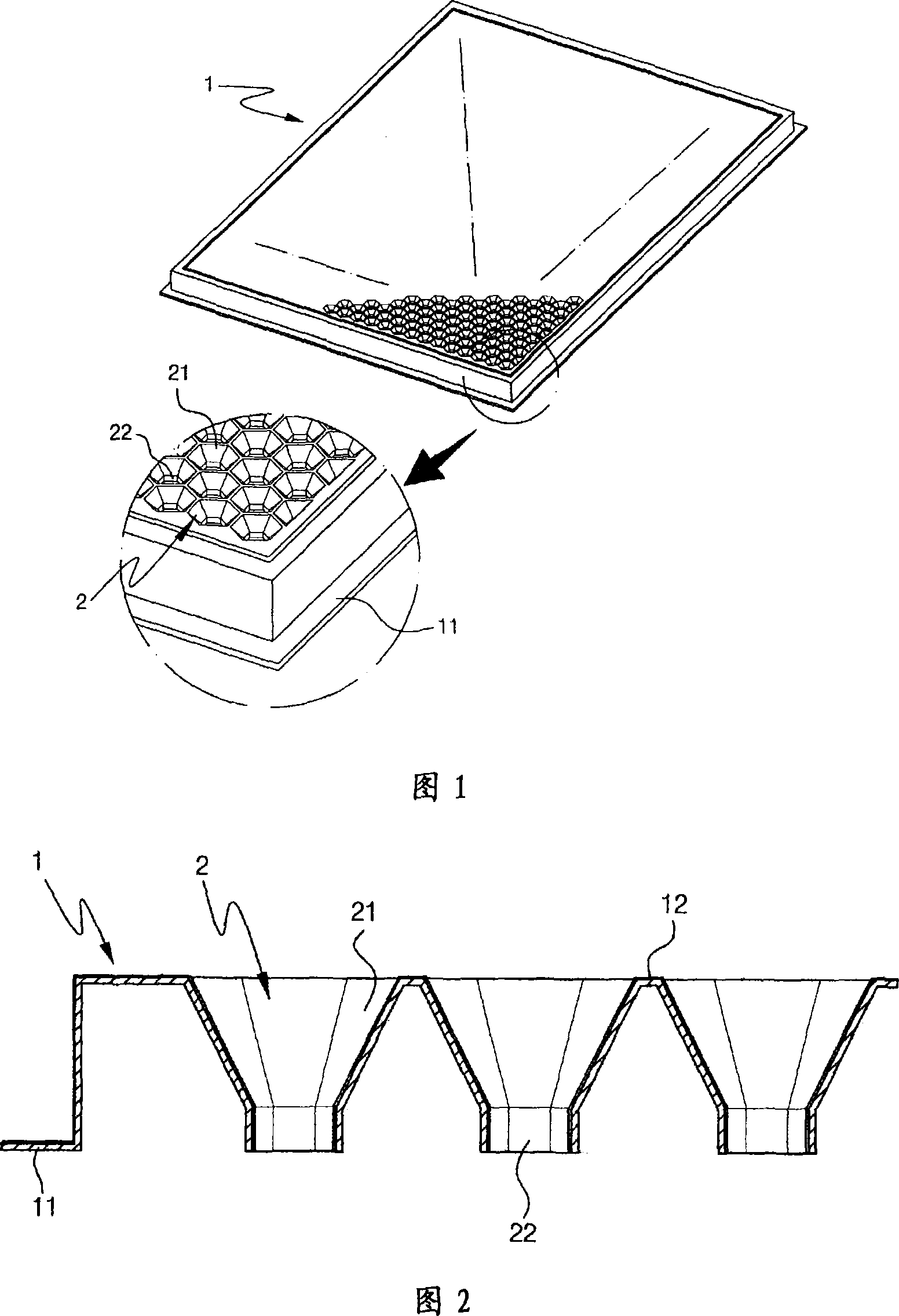
An aircraft cabin panel for acoustic absorption in an interior space includes a core layer, a first cover layer and a second cover layer. The first cover layer includes a space-enclosing first surface, and the second cover layer is arranged opposite the first cover layer. The first cover layer is acoustically transparent, and the core layer includes a honeycomb core with a plurality of tubular or honeycomb-like cells that are open throughout the thickness of the honeycomb core. The honeycomb core on the face pointing towards the first cover layer extends parallel to the first cover layer so as to be continuously throughout, and on the face pointing towards the second cover layer comprises recesses which extend over several cells. Absorbers are accommodated in the recesses.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Soundproofing material for vehicle
Owner:HOWA MASCH LTD
Decoration acoustic absorption sheet material of tripolite and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101428999AWith sound absorption and sound insulationMoisture-adjusting and anti-cleaning lotionFiberAcoustic absorption
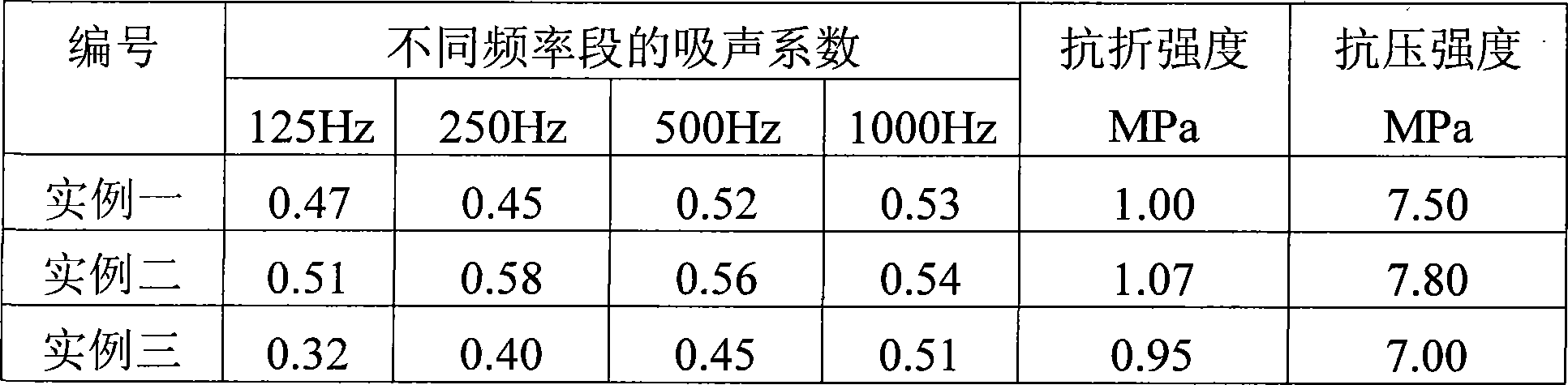
The invention discloses a diatomite decorative acoustic board, which belongs to the field of building material. The invention solves the problems that the prior porous acoustic material has low acoustical absorptivity to middle and low frequencies, a mineral wool acoustic board pollutes the environment and so on. The board consists of 70 to 80 weight percent of diatomite, 18 to 25 weight percent of gypsum, 1 to 3 weight percent of pigment, 0.9 to 1.5 weight percent of adhesive, and 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of fiber; the content of SiO2 in the diatomite is more than 85 percent, and the white content is more than 82; and the white content of the gypsum is more than 90 degrees. The method for preparing the board comprises the following steps: solid materials, namely the diatomite, the gypsum, the adhesive, the pigment and the fiber are added into a mortar mixer to be stirred for 20 to 30min, water which accounts for 1 to 1.5 times of the amount of the solid materials is added into the mixture after the mixture is stirred evenly to be prepared into uniform slurry, the slurry is cast into board molds with different specifications, and the mold stripping and drying are performed after 24h of maintenance. The board has functions of sound absorption and sound insulation, humidity conditioning and dewing prevention, fire resistance and flame retardation, thermal insulation, environmental protection, beautiful decoration, high strength, light mass, easy installation, convenient maintenance and so on, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:北京大地远通(集团)有限公司 +1
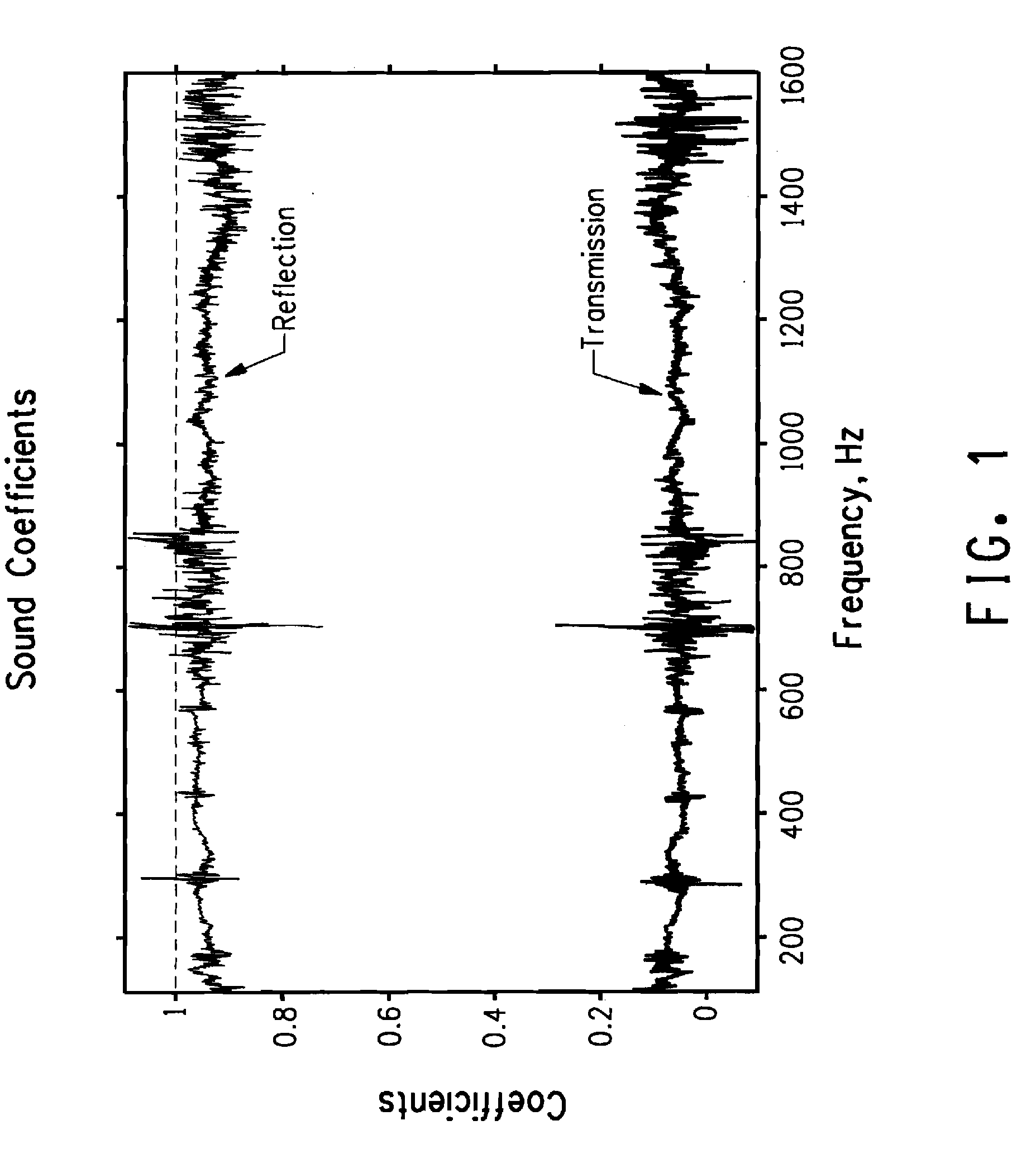
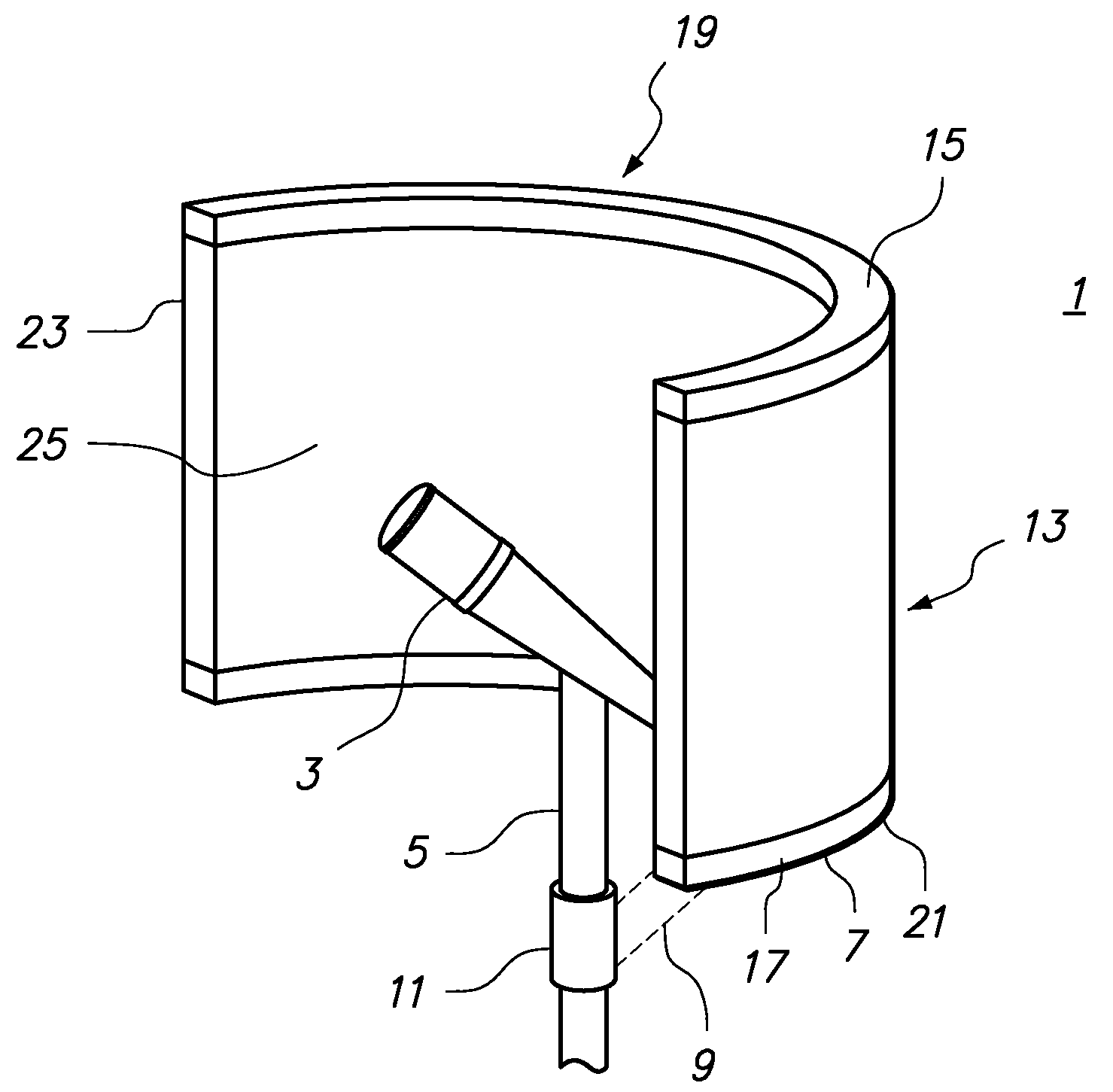
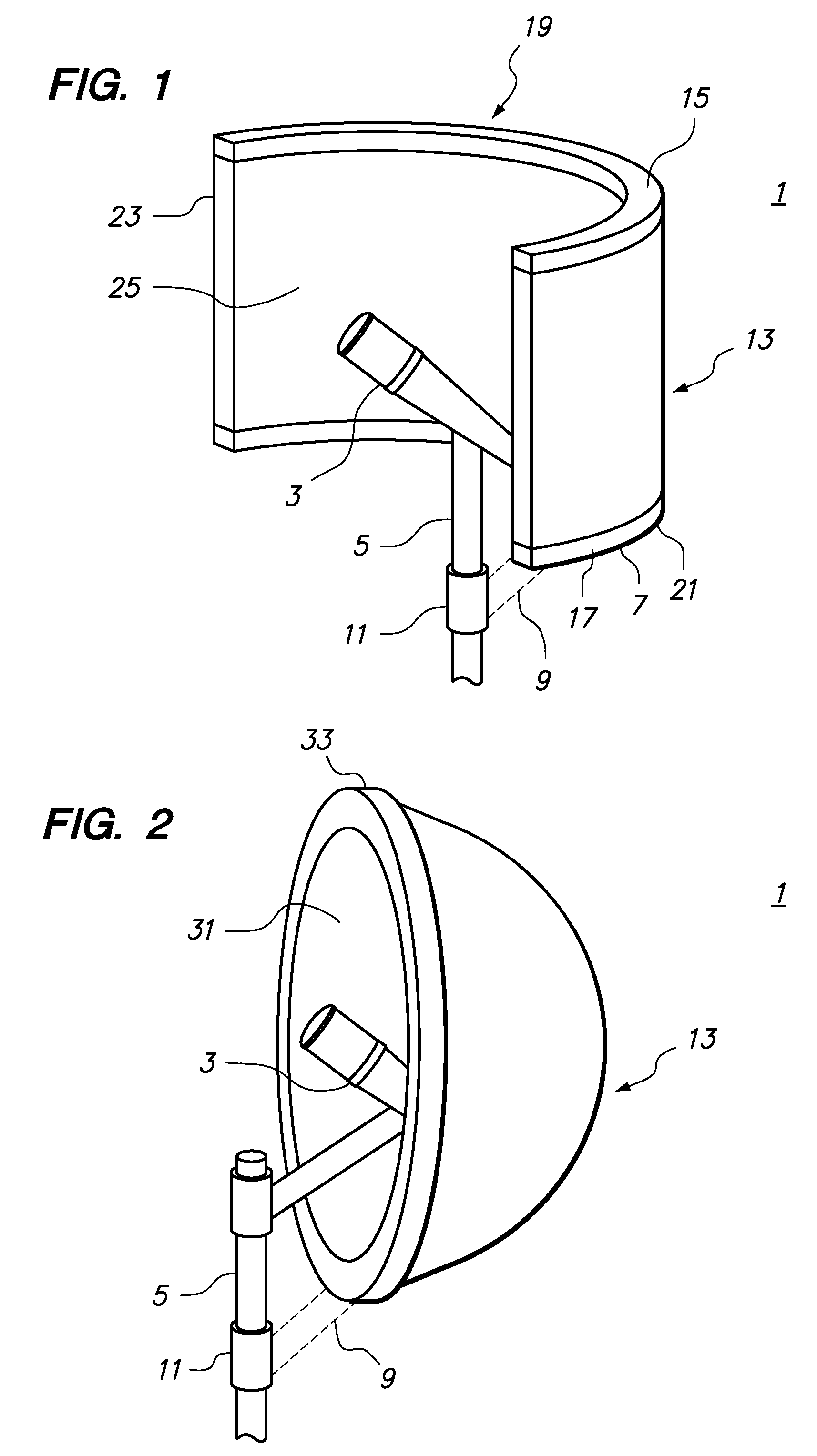
Method of making an acoustic probe
InactiveUS6044533AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAcoustic absorptionTransducer
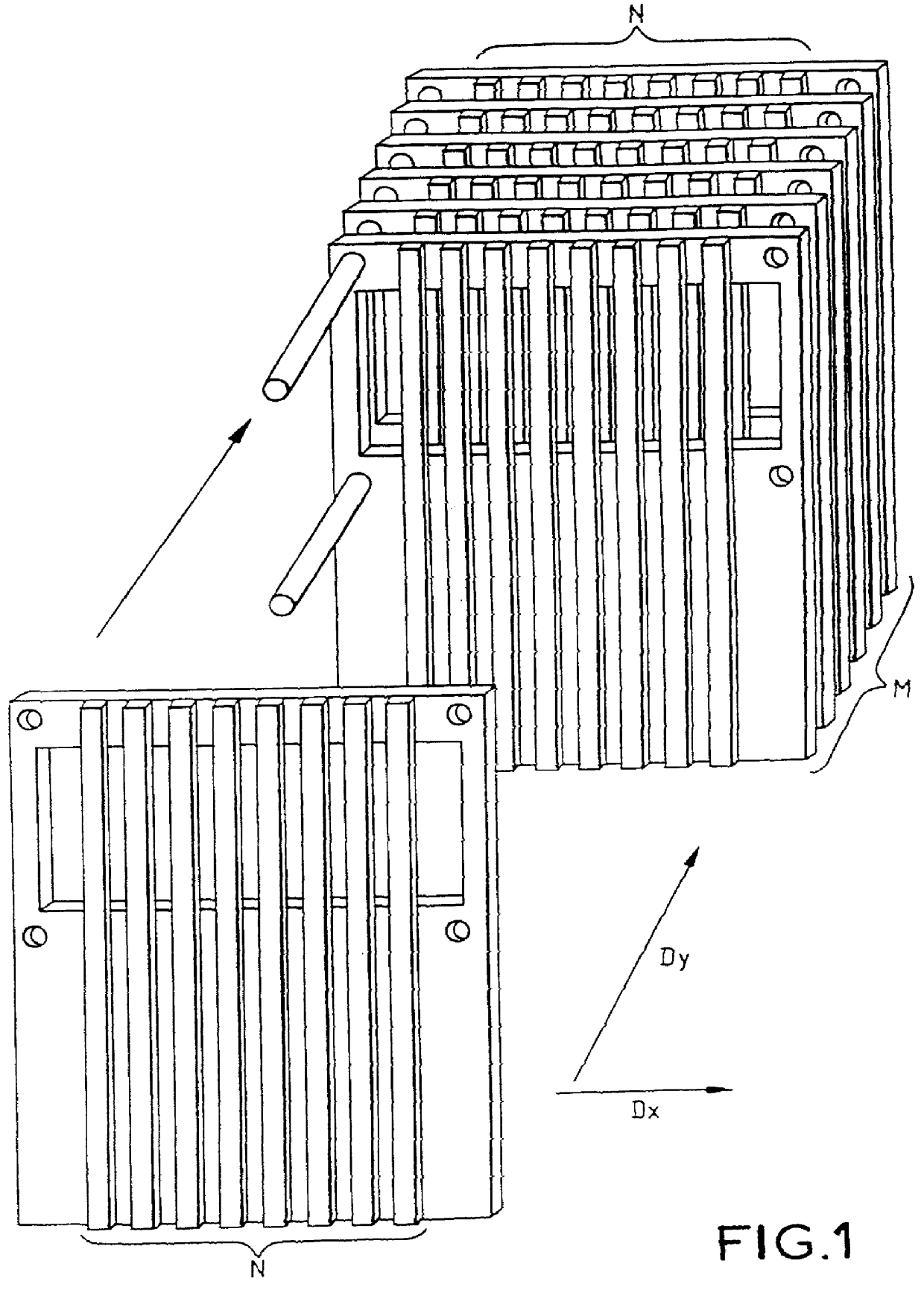
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 01650 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 2, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 2, 1997 PCT Filed Oct. 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 17145 PCT Pub. Date May 15, 1997An acoustic probe and a method for making the same. The probe includes a novel interconnection network consisting of two portions, i.e., a first portion in which MxN conductive paths have a section contacting MxN piezoelectric transducers and are arranged at a pitch (PN) in a direction (Dx) and at a pitch (PM) in direction (Dy) within the acoustic absorption material; and a second portion in which the MxN conductive paths are arranged on M dielectric substrates spaced apart at a pitch (P'M) and each provided with N paths are arranged at a pitch (P'N). A method for making the acoustic probe is also disclosed. The dielectric substrates may advantageously be flexible printed circuits optionally including chips.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Apparatus for Absorbing Acoustical Energy and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080302599A1High sensitivityReduce in quantityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesCeilingsAcoustic absorptionEngineering
An apparatus comprising a combination of a microphone and a composite acoustic panel. The composite acoustic panel comprises materials having different spectra of acoustic absorption. The materials may be integrated in a single layer or in a plurality of different layers.
Owner:SE ELECTRONICS INT
Aircraft cabin panel with core recesses for acoustic absorption
InactiveUS8336804B2Easy to adaptReduce interior noiseLayered productsFuselage insulationInterior spaceNacelle
An aircraft cabin panel for acoustic absorption in an interior space includes a core layer, a first cover layer and a second cover layer. The first cover layer includes a space-enclosing first surface, and the second cover layer is arranged opposite the first cover layer. The first cover layer is acoustically transparent, and the core layer includes a honeycomb core with a plurality of tubular or honeycomb-like cells that are open throughout the thickness of the honeycomb core. The honeycomb core on the face pointing towards the first cover layer extends parallel to the first cover layer so as to be continuously throughout, and on the face pointing towards the second cover layer comprises recesses which extend over several cells. Absorbers are accommodated in the recesses.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Combined surface cooler and acoustic absorber for turbomachines
ActiveUS20100155016A1Improve heat transfer performanceImprove sound absorptionFluid heatersExhaust apparatusSurface coolingAcoustic absorption
A surface cooler for turbomachines is provided. The surface cooler comprises an inner layer and an outer layer disposed adjacent to the inner layer and comprising a metal foam, a carbon foam, or a combination thereof, wherein the metal foam, the carbon foam or a combination thereof is configured to augment heat transfer and enhance acoustic absorption. Further, the outer layer comprises a plurality of fins, wherein the plurality of fins is configured to augment heat transfer and enhance acoustic absorption, and wherein the plurality of fins comprises metal foam, a carbon foam, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for improved noise attenuation in a dissipative internal combustion engine exhaust muffler
The use of fiber metal or similarly high flow resistance and high acoustic transparency material as a liner for traditional acoustically absorptive media in a dissipative muffler exhibits improved low frequency sound attenuation, reduces backpressure, and eliminates media entrainment or "blow-out" phenomenon which results in longer muffler life. The same class of materials may also be used to fashion an element that provides linear occlusion inside an otherwise line-of-sight type of muffler, where the occluding element provides improved impedance-matching acoustic absorption. Disclosed embodiments providing linear occlusion minimize traditional increases in muffler backpressure by incorporating helical, conical, and annular members in mufflers with round ducts. To maximize attenuation, a muffler according to the invention may feature both a fiber metal fill liner and a fiber metal linear occlusion element. Further, the liner that connects the inlet and outlet ports of the muffler may feature an offset, elbow, or turn that would simultaneously allow it to provide means for linear occlusion.
Owner:QUIET STORM
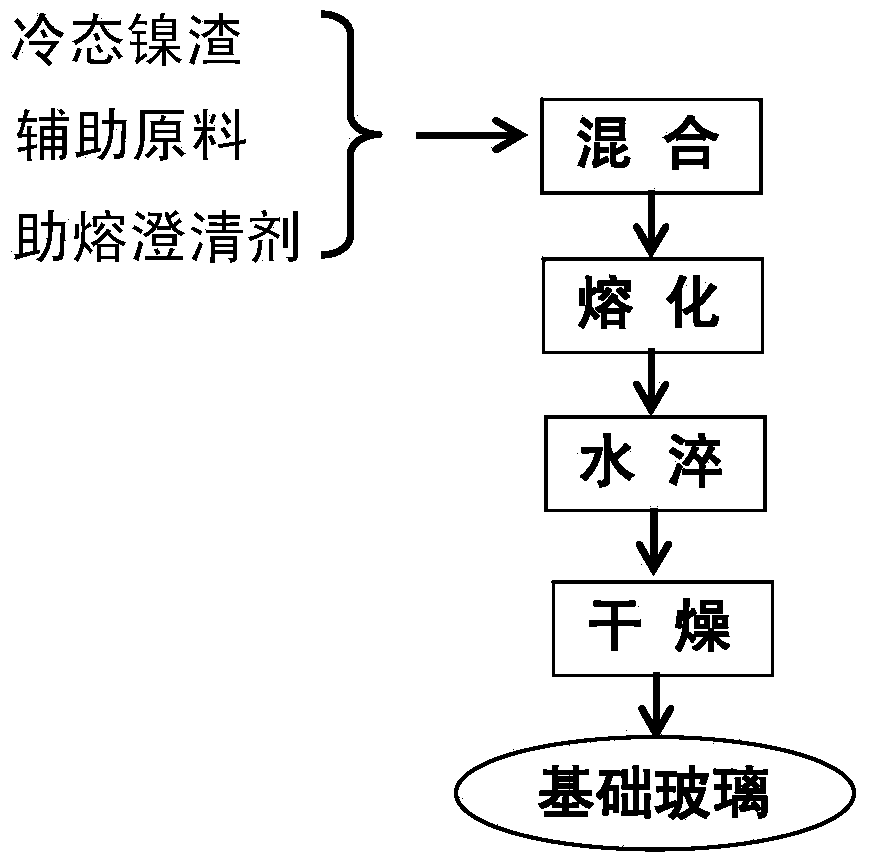
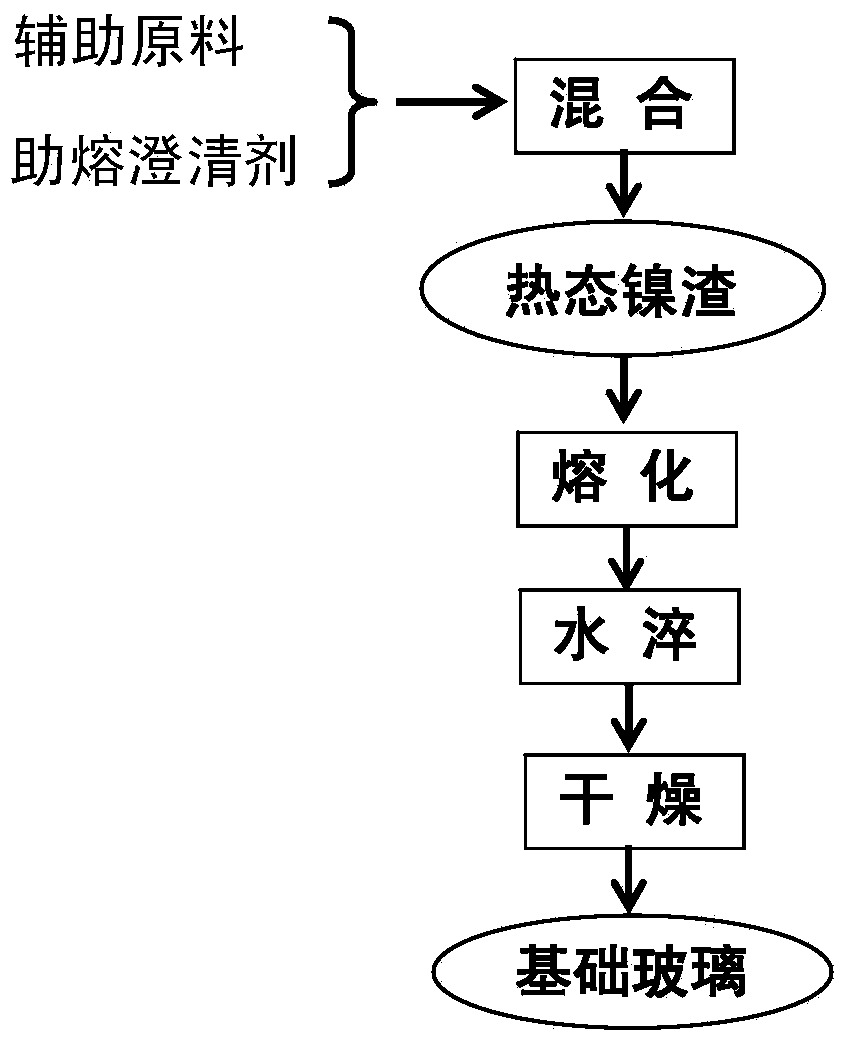
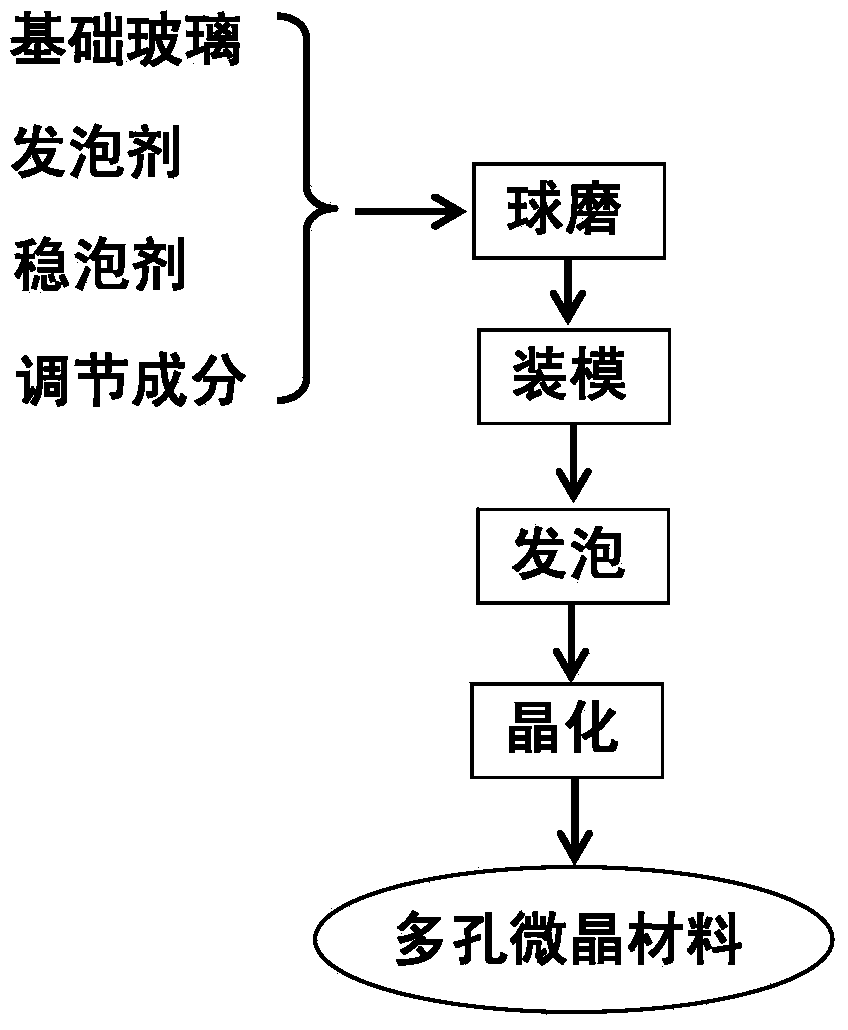
Nickel-slag porous microcrystalline material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nickel-slag porous microcrystalline material and a preparation method of the nickel-slag porous microcrystalline material. Smelting ferro-nickel waste residues are taken as main raw materials, and additives such as SiO2, CaCO3, Na2CO3, ZnO and K2CO3, and a clarifying agent are taken as auxiliary materials. The nickel-slag porous microcrystalline material disclosed by the invention is lightweight, insulating, abrasion-resistant, and resistant to acid and alkali corrosion, has good machinability, can be widely applied to heat insulation and preservation of a pipeline, a storage tank and a heat exchange system in the fields such as chemical engineering, metallurgy, architectural ornament, petroleum, mine and machinery, and a composite heat-insulation system and a soundproof and acoustic absorption system working under a special condition.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Macrocellular acoustic foam containing particulate additive
ActiveUS20050086823A1Avoid corrosionImprovement factorSound producing devicesDrying machinesParticulatesPolymer science
A cellular thermoplastic polyolefin foam comprising at least one particulate additive in admixture with a polymer matrix is disclosed, along with a process and foamable gel for manufacturing the same, wherein the polyolefin matrix comprises at least one polymer resin graft-modified with at least one polar group selected from the group consisting of acid, acid ester, and acid anhydride, and salts thereof. The invention facilitates the manufacture of macrocellular foams useful for acoustic absorption having increased amounts of particulate additives that provide certain desired properties difficult to achieve without the particulate additives, such as improved flame retardancy.
Owner:SEALED AIR U S
Acoustic absorption, noise insulation, thermal insulation, condensation resistant building material, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a construction material with the effects of sound absorption, sound insulation, heat preservation, anti-condensation, etc., a preparation method and the application thereof. The construction material consists of the following independent constituents: constituent I, constituent II and constituent III; wherein, the constituent I is a water-base interfacial agent; the constituent II mainly consists of the following constituents according to certain weight portion: 55 to 65 portions of plant fiber and 35 to 45 portions of caking agent; the constituent III is a sealing agent. The construction material of the invention is made of wood fiber by chemical treatment and the construction material is sprayed on the base surface of buildings, which has the effects of sound absorption, sound insulation, heat preservation and anti-condensation, fire protection, moulding prevention, etc. The construction material of the invention is completely suitable for being used on a base surface configuration of any building, such as arc form, waveform, etc., and also is suitable on large-scale public places needing sound absorption, sound insulation, heat preservation, anti-condensation, fire protection, etc. such as a gymnasium, a natatorium, an opera house, a cinema, an exhibition center, an airport, tunnel, an industrial factory building, a machinery room, etc.
Owner:傅梅
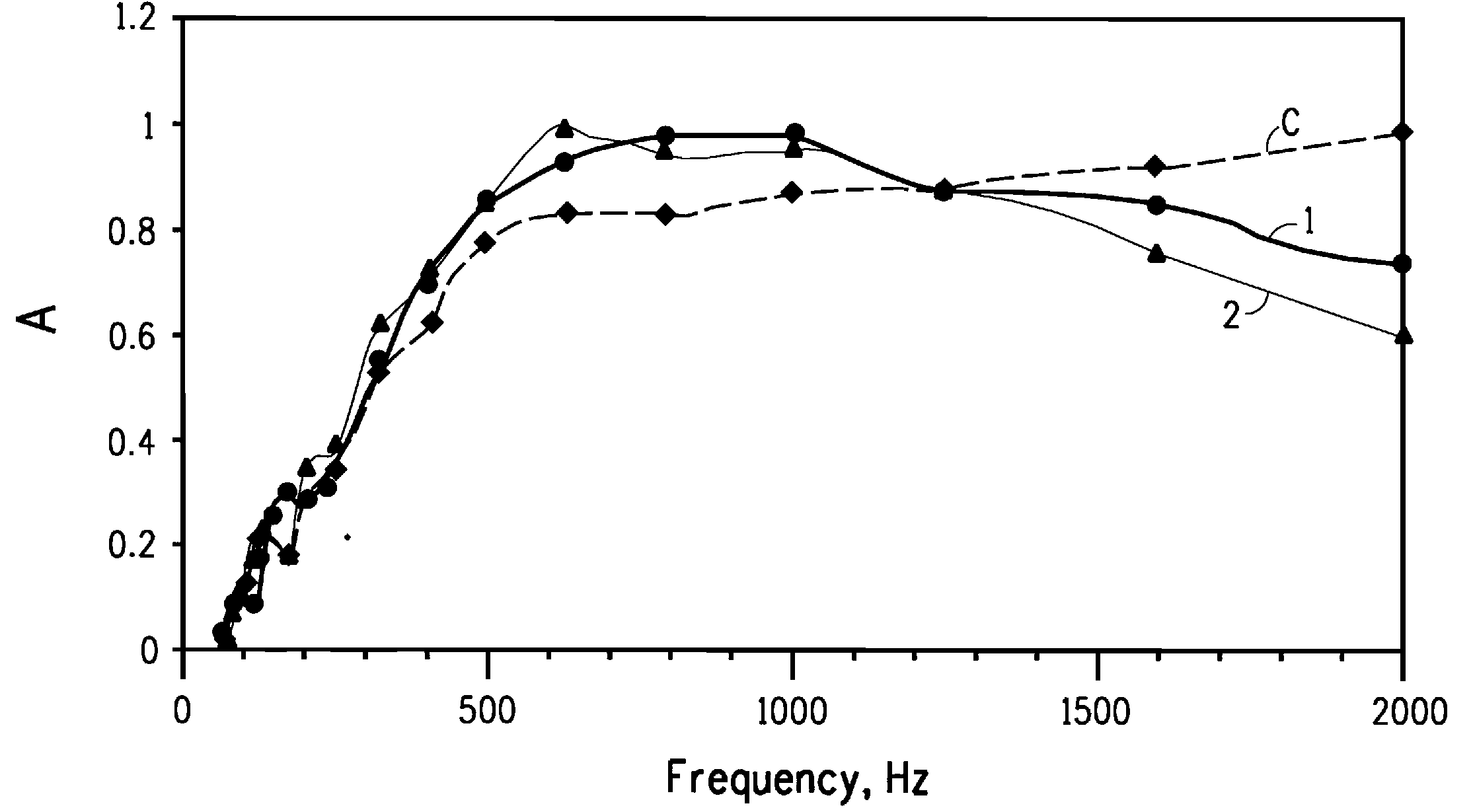
Porous rubber material member and full-frequency range vibration acoustical property analysis method thereof
ActiveCN102094922AFlat surfaceReduce resistance to movementSpringsSpecial data processing applicationsRubber materialAcoustic absorption
The invention relates to a porous rubber material member. The member comprises a thin covering layer and a hole sound absorption layer which are integrated and made of a rubber material, wherein holes of the hole sound absorption layer are blind holes. The hole condition of the porous rubber material member is different from that of the common porous sound insulation material; in order to exert a sound absorption function, air holes of the common porous material are open and intercommunicated, and sound absorption property is higher when the number of the air holes is larger; the blind holes are directly and vertically punched on a rubber plate, so the porous rubber material member is suitable for vibration reduction and sound insulation in an air medium, and meets the requirement of certain pressure resistance when underwater equipment works in a deep water area; movement resistance can be reduced because the porous rubber material member has smooth appearance; in addition, the hole sound absorption layer and the thin covering layer are combined to form a composite structure, so the porous rubber material member has high sound absorption and sound insulation properties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Passenger car floor with sound insulation and decrease of noise functions
ActiveCN101450642AInhibit sheddingPrevent water absorptionSuperstructure subunitsMetal layered productsHigh densityAcoustic absorption
The invention discloses a bus floor with acoustic insulation and damping functions, which is arranged at the back of a carriage, and comprises the following layers from the top down: a floor leather layer, a damping slab rubber layer, a bakelite board interlayer, a multilayer compound acoustic damping cotton layer, a steel plate layer and a self-crusting rubber-plastic sponge layer. A cavity is also arranged between the bakelite board interlayer and the multilayer compound acoustic damping cotton layer. The multilayer compound acoustic damping cotton layer comprises three layers from the top down, namely a porous sponge acoustic absorption layer, a high-density rubber-plastic sponge acoustic insulation layer and a self-adhesion damping acoustic insulation layer. The bus floor adopts sealing, acoustic absorption, acoustic insulation and vibration reduction to achieve the acoustic insulation and damping functions. After the floor is adopted, noise in a bus can be reduced, and environment in the carriage becomes more comfortable.
Owner:ZHONGTONG BUS HLDG
The sound-absorbing panel
InactiveCN101194077AGood sound absorptionEffective absorptionCovering/liningsSound proofingInterior spaceSection plane
Owner:金永玉
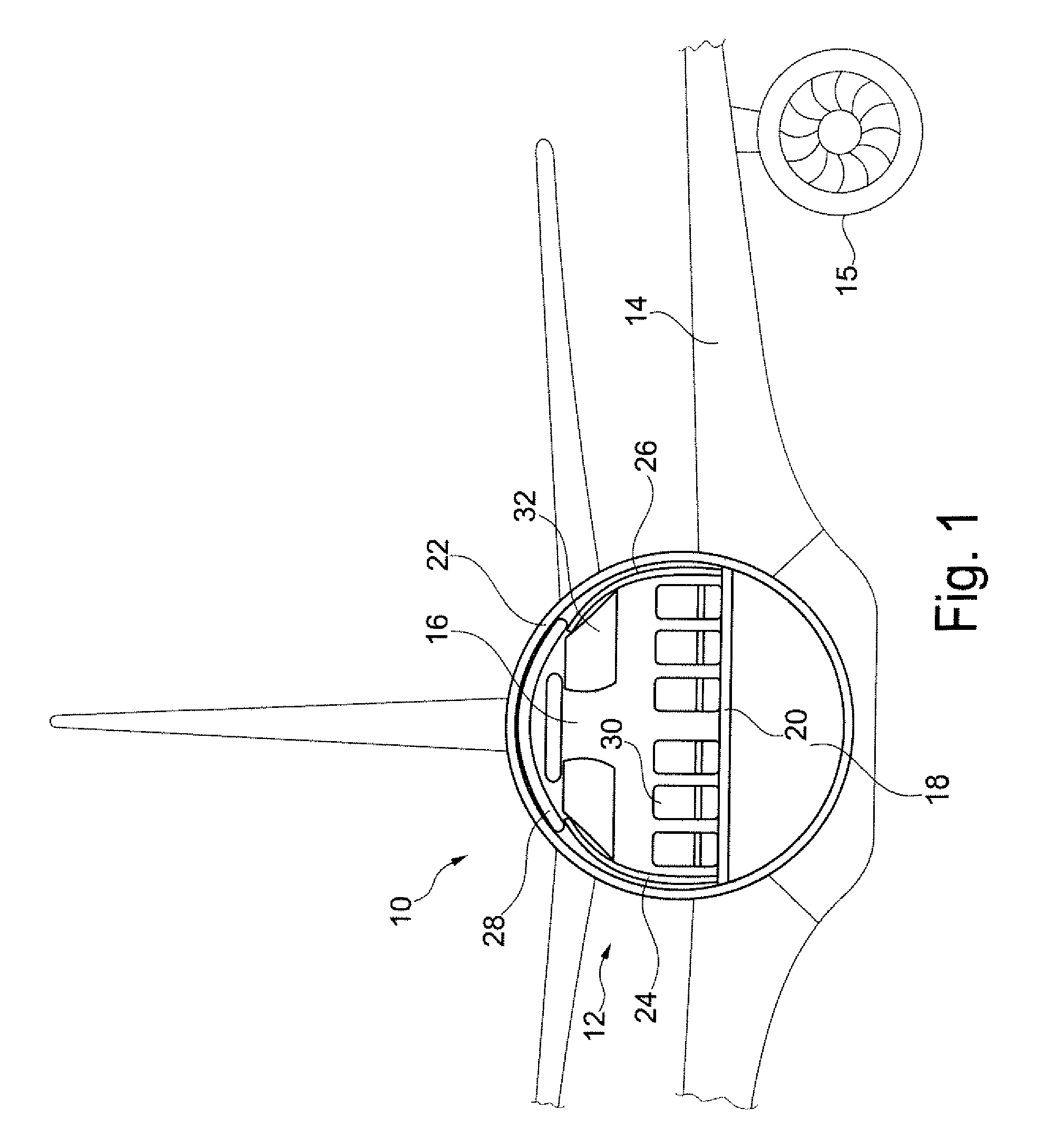
Tunable acoustic absorption system for an aircraft cabin
InactiveUS20080099609A1Improve sound absorptionPromote absorptionFuselage insulationAircraft floorsNacelleAcoustic absorption
A tunable acoustic absorption system according to the present invention includes an airframe batting area; a primary soundproofing blanket area; an interior trim panel area; and a hard trim area, which are layered over an aircraft outer skin. Specifically tailoring or “tuning” materials within each area to the particular aircraft acoustic signature achieves significant increases in acoustic absorption achieved over conventional generic sound treatments.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Combined acoustic absorber and heat exchanging outlet guide vanes
ActiveUS8333552B2Improve heat transfer performancePromote absorptionPump componentsEngine fuctionsSurface coolingAcoustic absorption
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Acoustic absorption polymer foam having improved thermal insulating performance
InactiveUS7018700B2Increase contentButtonsLayered productsLow-density polyethyleneAcoustic absorption
Polymer foams having a good balance of high sound absorption, low thermal conductivity and generally low water absorption are disclosed which are obtainable by perforating (i.e., hole punching) a polymer foam having a moderately large cell size (1.5 mm to 4 mm) and an open content not greater than 40 percent to increase the open cell content of the foam by at least about 10 percent relative to the non-perforated foam, the polymer foam matrix preferably made of a thermoplastic foam, such as a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) resin, a high melt strength (HMS) polypropylene resin (PP), or a blend of an HMS PP resin and an LDPE resin, optionally containing a cell size enlarging agent such as glycerol monostearate, an antioxidant, carbon black and / or flame retardant additives, using a volatile organic compound, e.g. isobutane, as blowing agent. These foams are useful for applications in which a combination of acoustic absorption, thermal insulation and possibly low water absorption is needed, such as outdoor, motor vehicle and marine applications. They exhibit a noise reduction coefficient greater than 0.3, a thermal conductivity not greater than 90 mW / m° K measured at an average temperature of 10° C. according to DIM52616 and a low (less than 10, such as less than 1.5, percent by volume) water absorption when measured according to EN 12088 at a 50° C. temperature gradient for an exposure test period of 14 days.
Owner:SEALED AIR U S
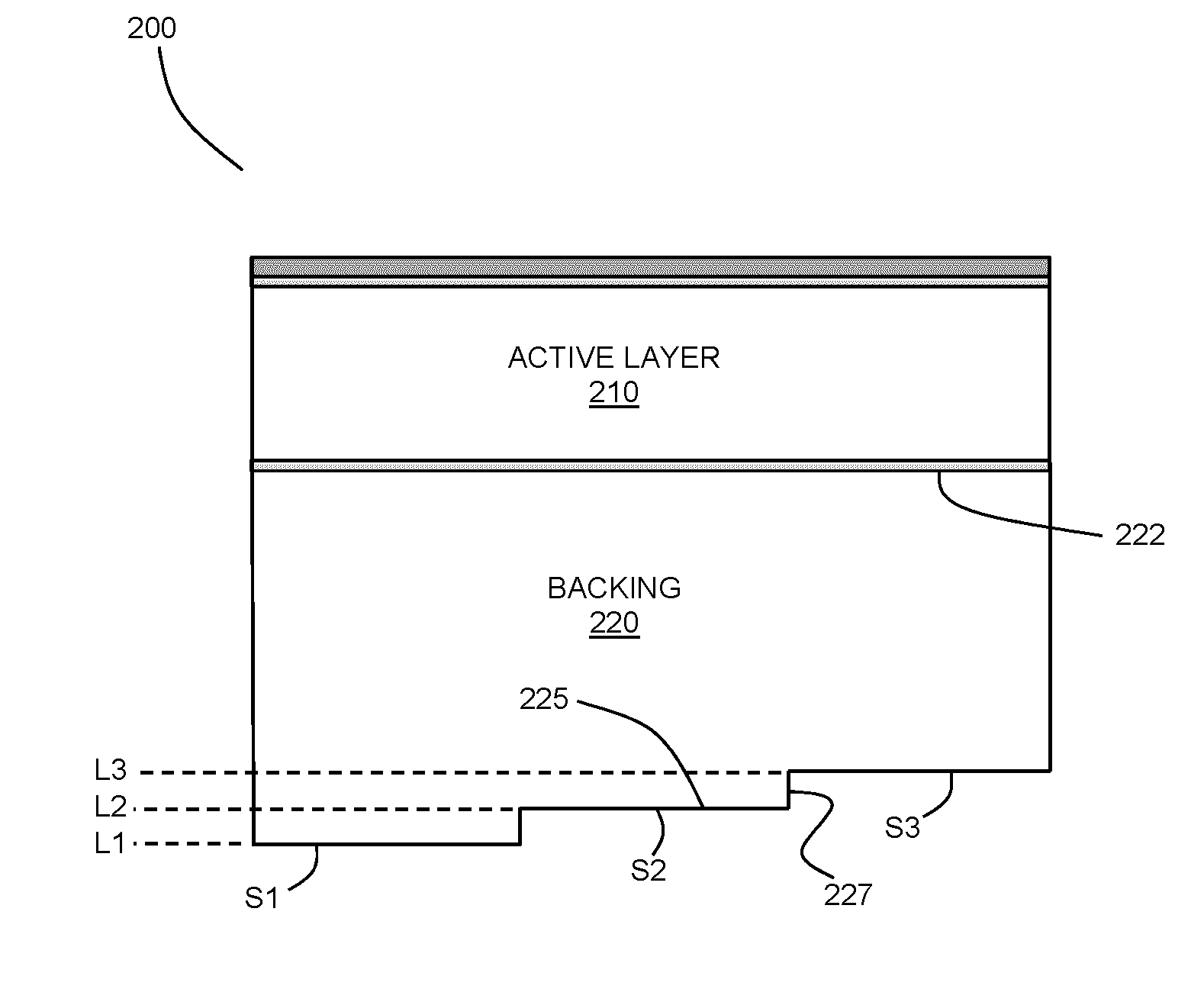
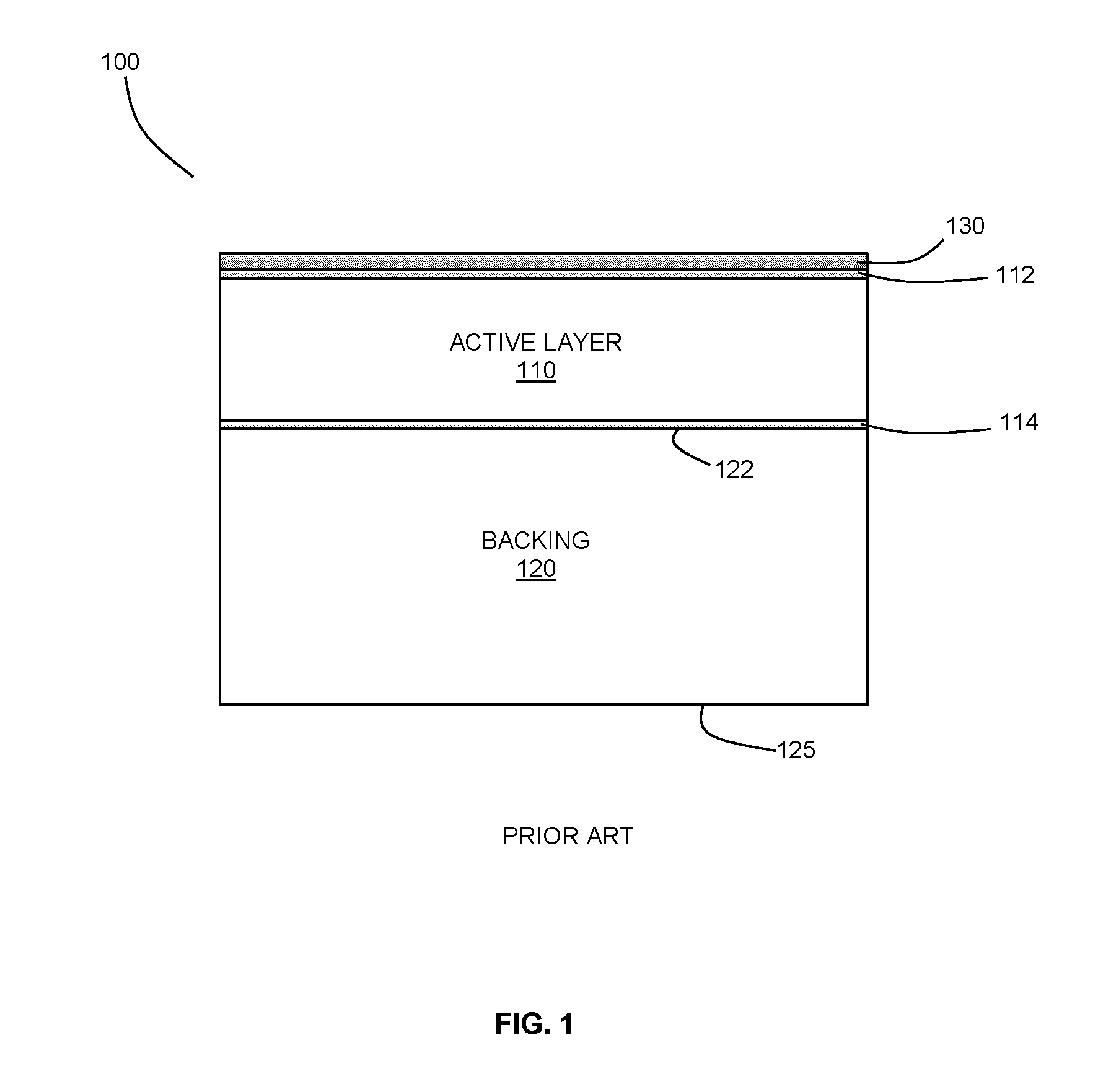
Ultrasonic transducer with backing having spatially segmented surface
ActiveUS20160296975A1Decreasing net amplitudeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationAcoustic absorptionUltrasonic sensor
Methods and devices are provided for suppressing reverberations within an ultrasound transducer with a backing whereby the backing may not sufficiently attenuate the acoustic energy by means of acoustic absorption and scattering alone. At least a portion of a surface of the backing is segmented into a plurality of levels defined by surface segments. The levels may be are spatially offset so that acoustic reflections from the segmented surface are spread out in time, thereby decreasing the net amplitude of the internally reflected waves as they interact with the piezoelectric layer. Adjacent (neighbouring) levels may be spatially offset by a longitudinal distance equaling approximately an odd number multiple of a quarter of an operational wavelength of the transducer, so that destructive interference occurs from acoustic waves reflected from adjacent levels. Various example configurations of segmented surfaces are described, and methods for selecting a profile of a segmented surface are provided.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
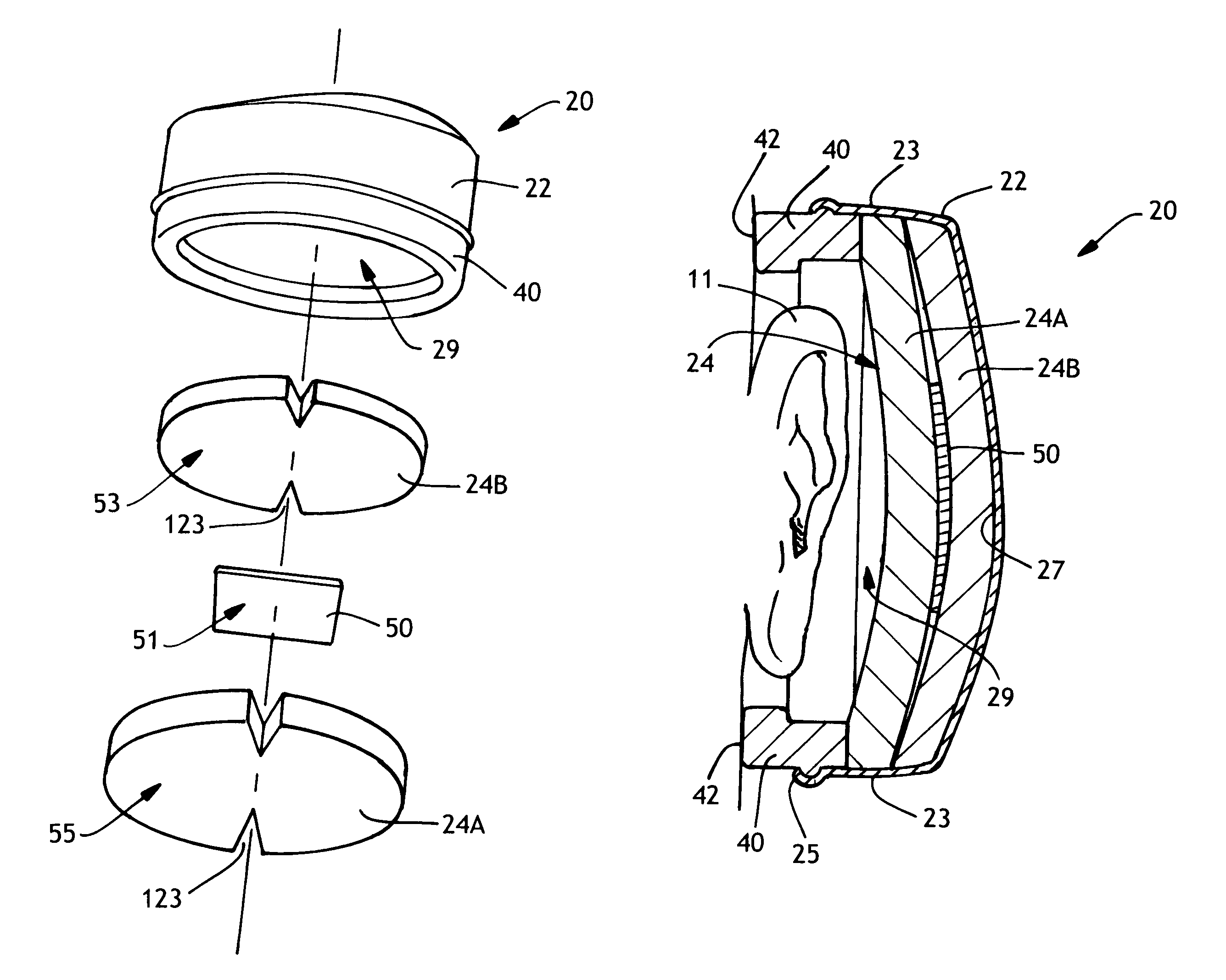
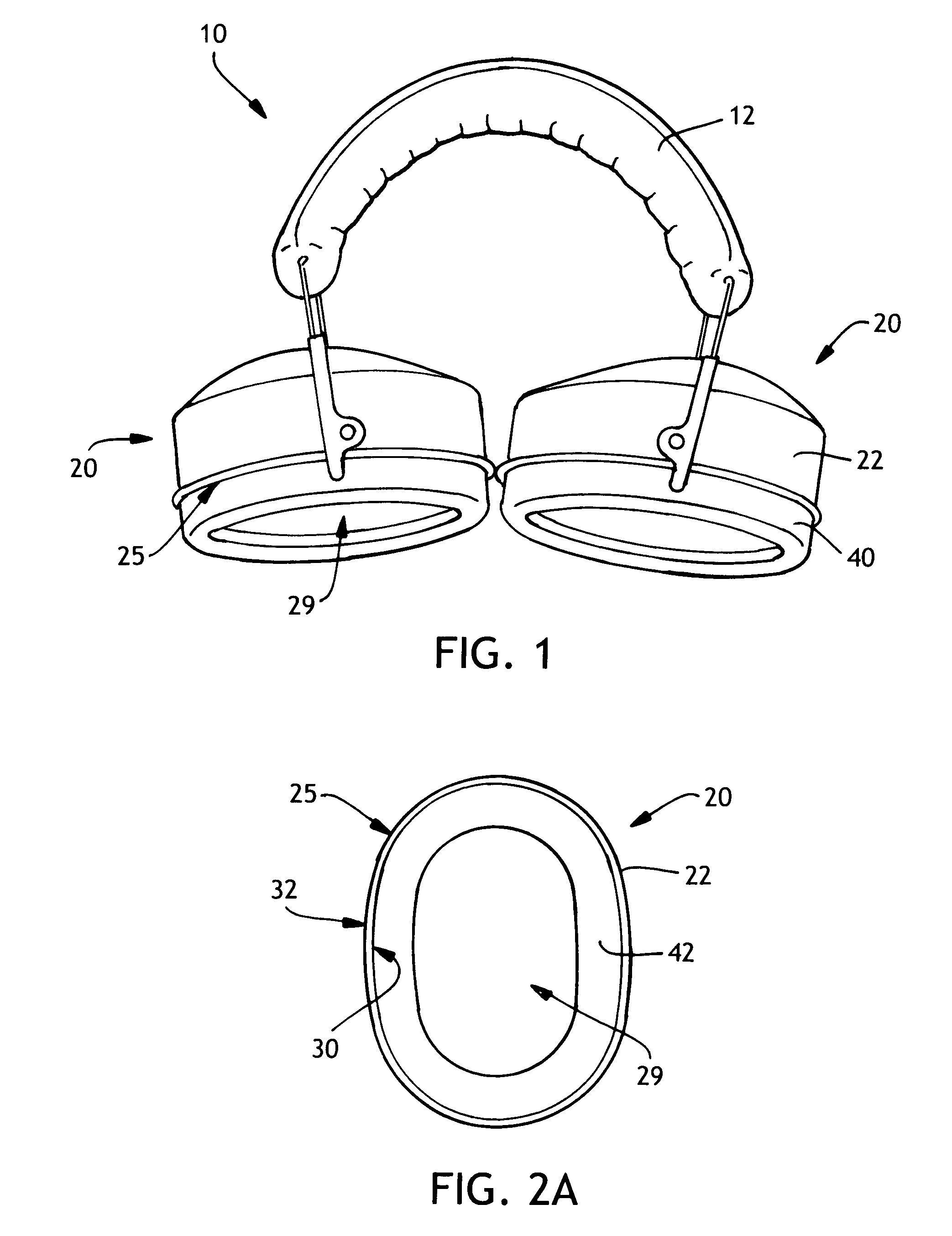
Hearing protection cap
InactiveUS7717226B2Improve protectionImprove sound attenuationEar supported setsEarmuffsAcoustic absorptionEngineering
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com