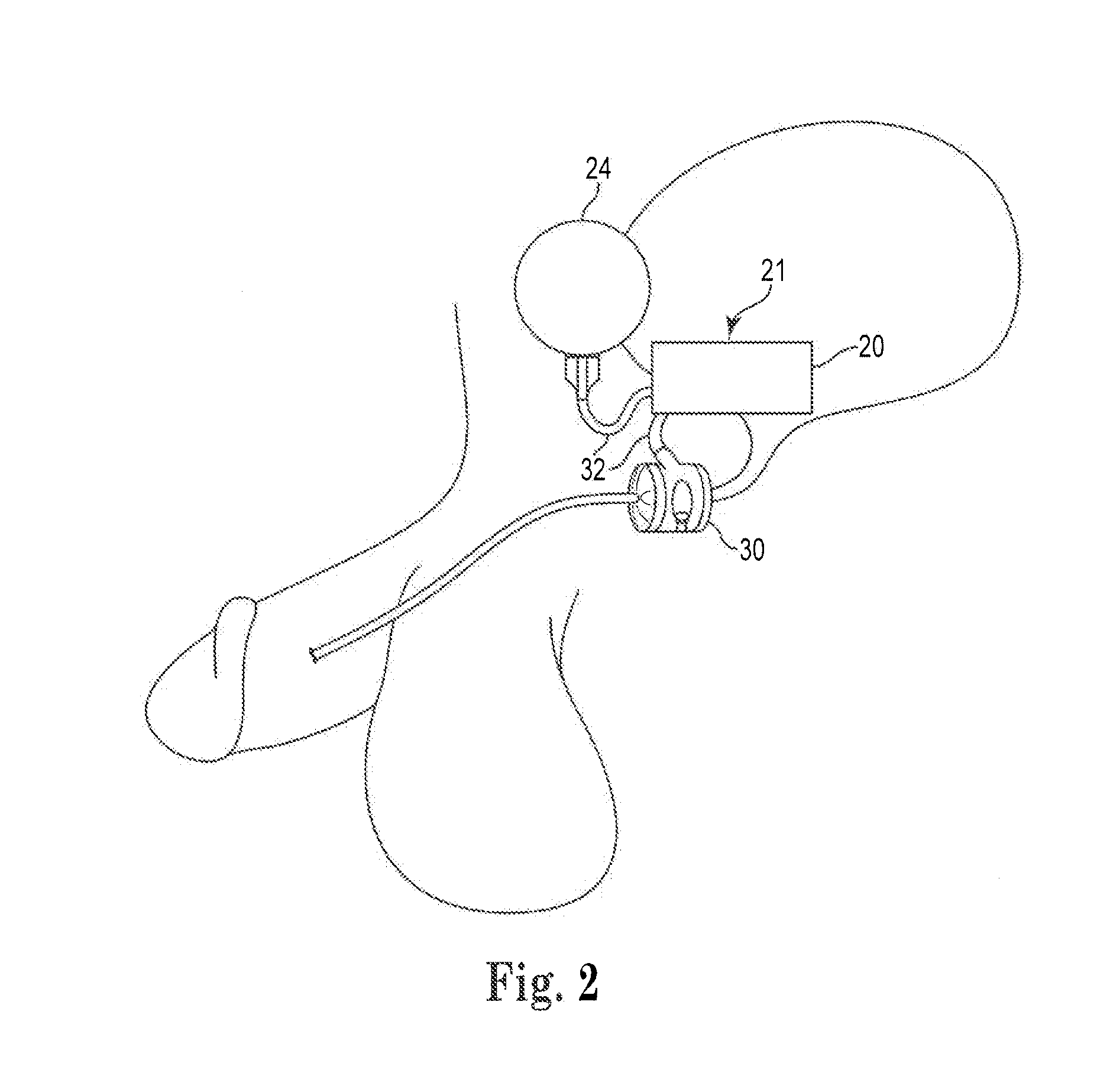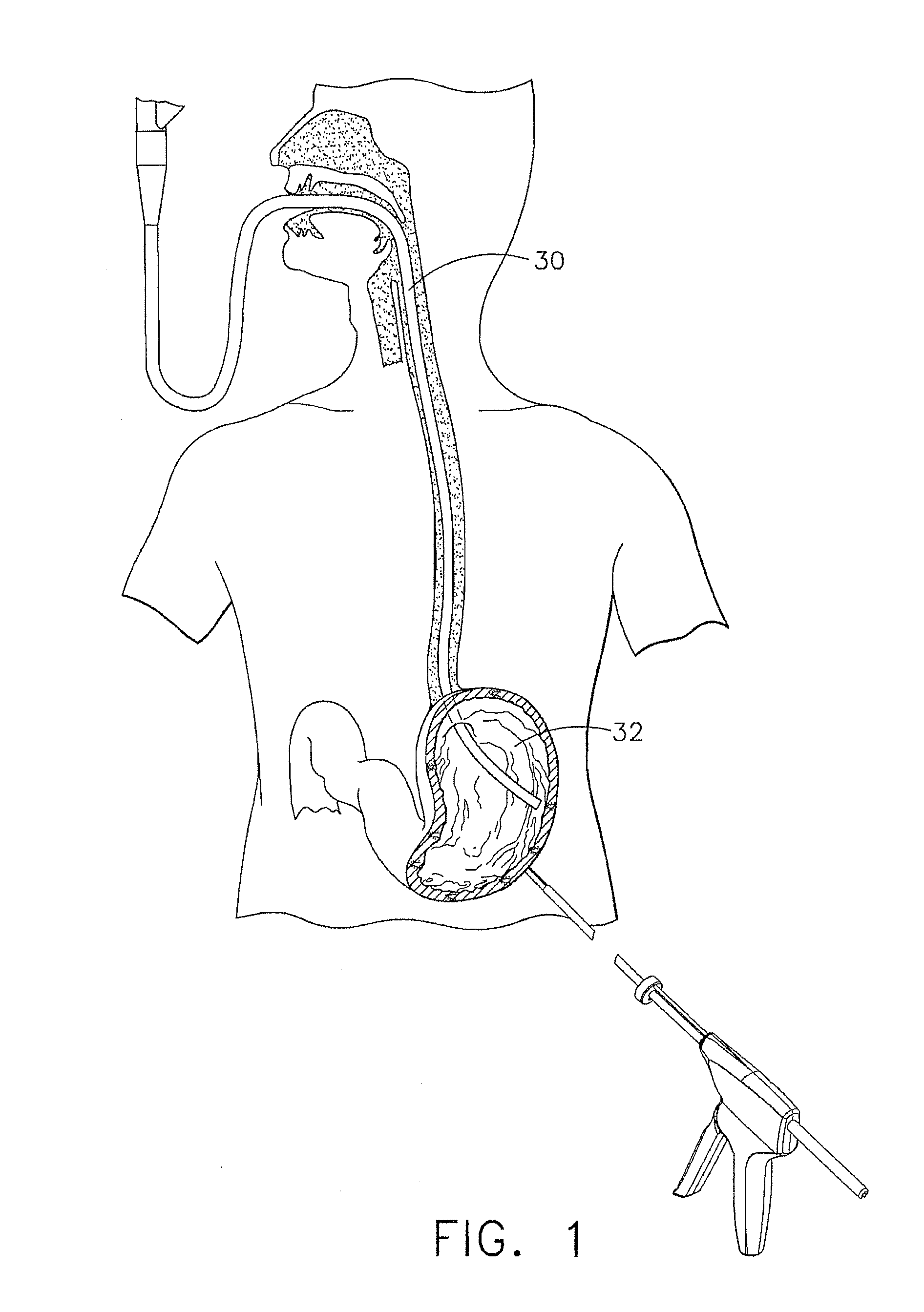Patents
Literature
201 results about "Sphincter of Oddi" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
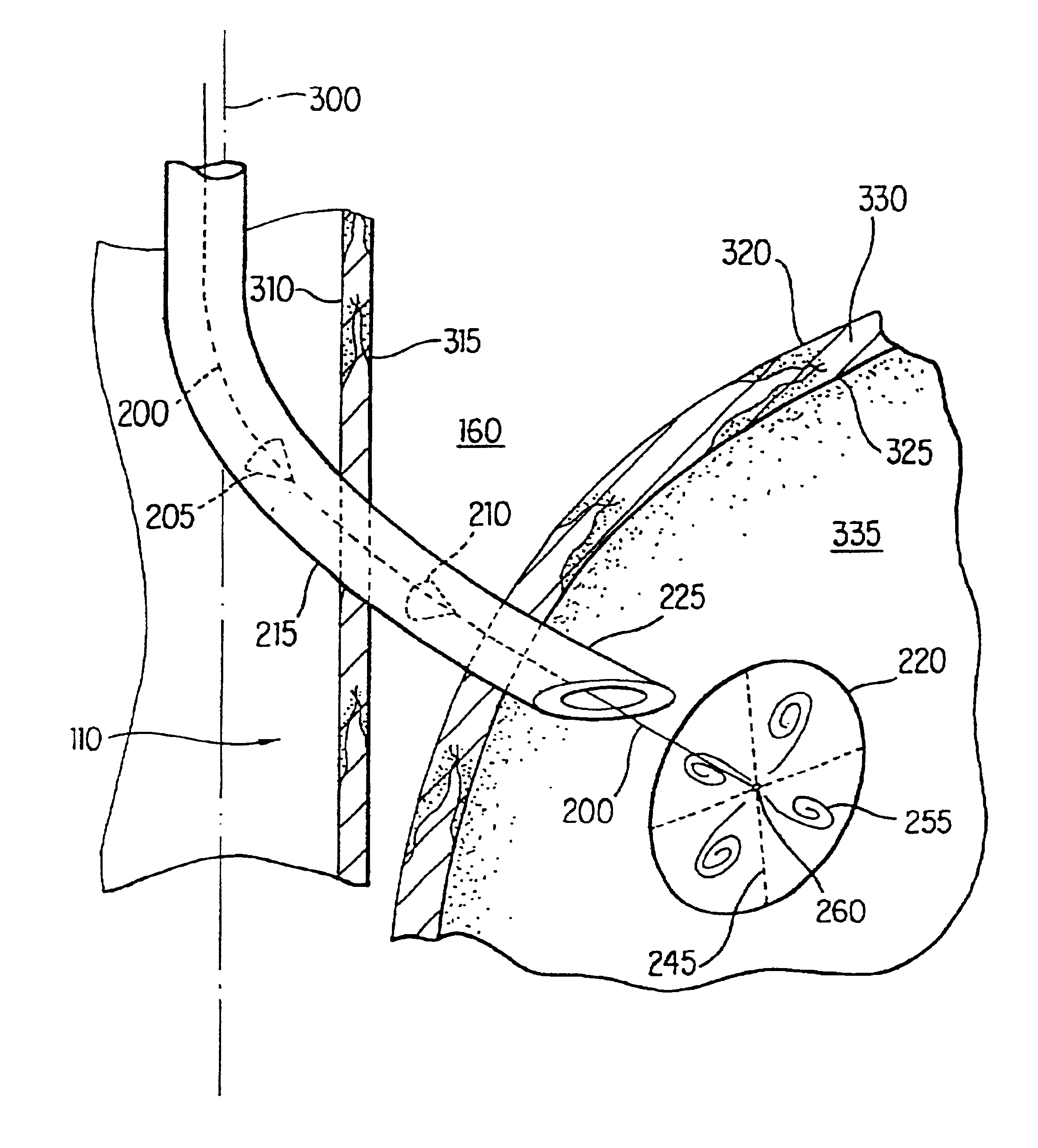
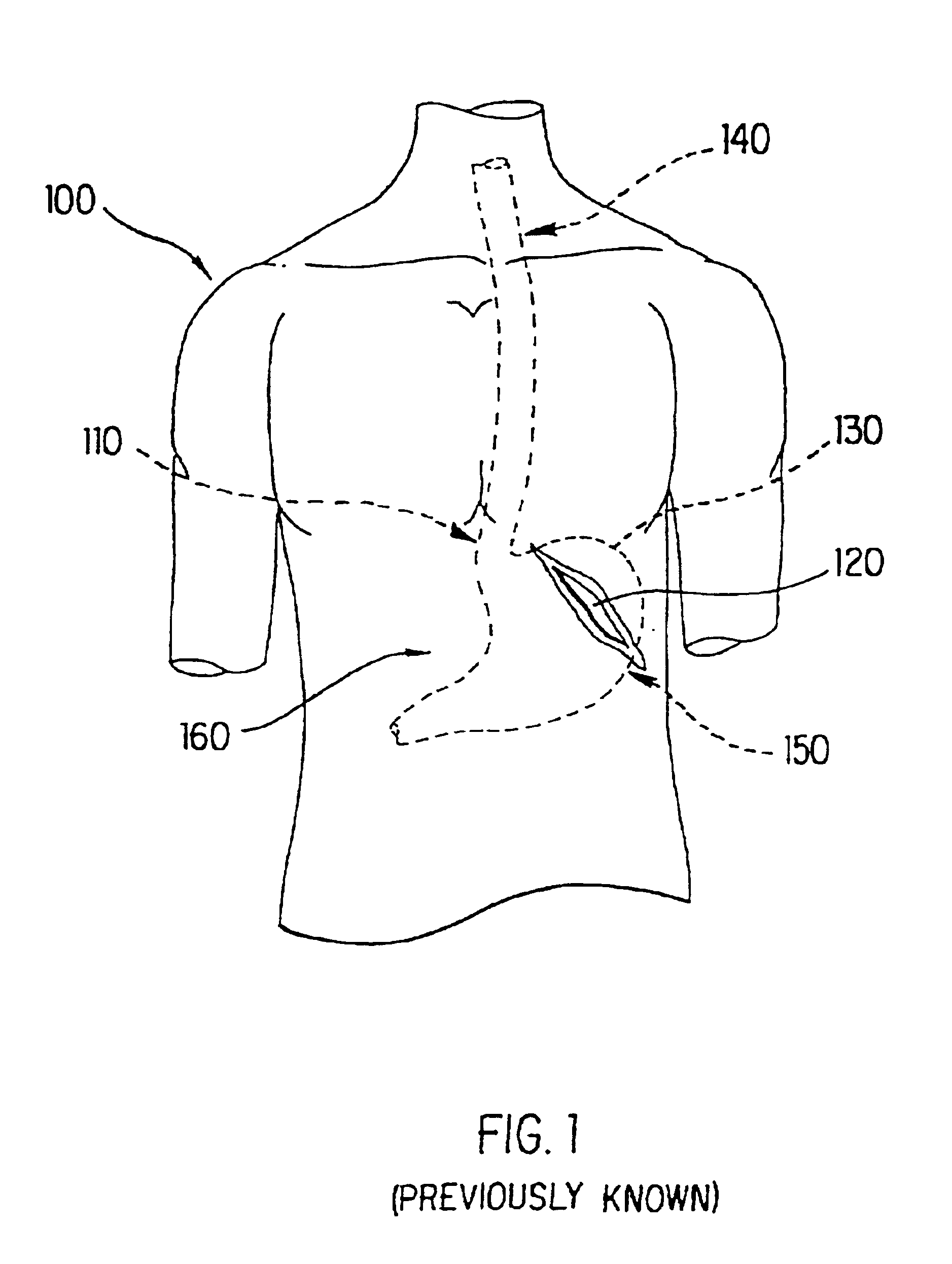
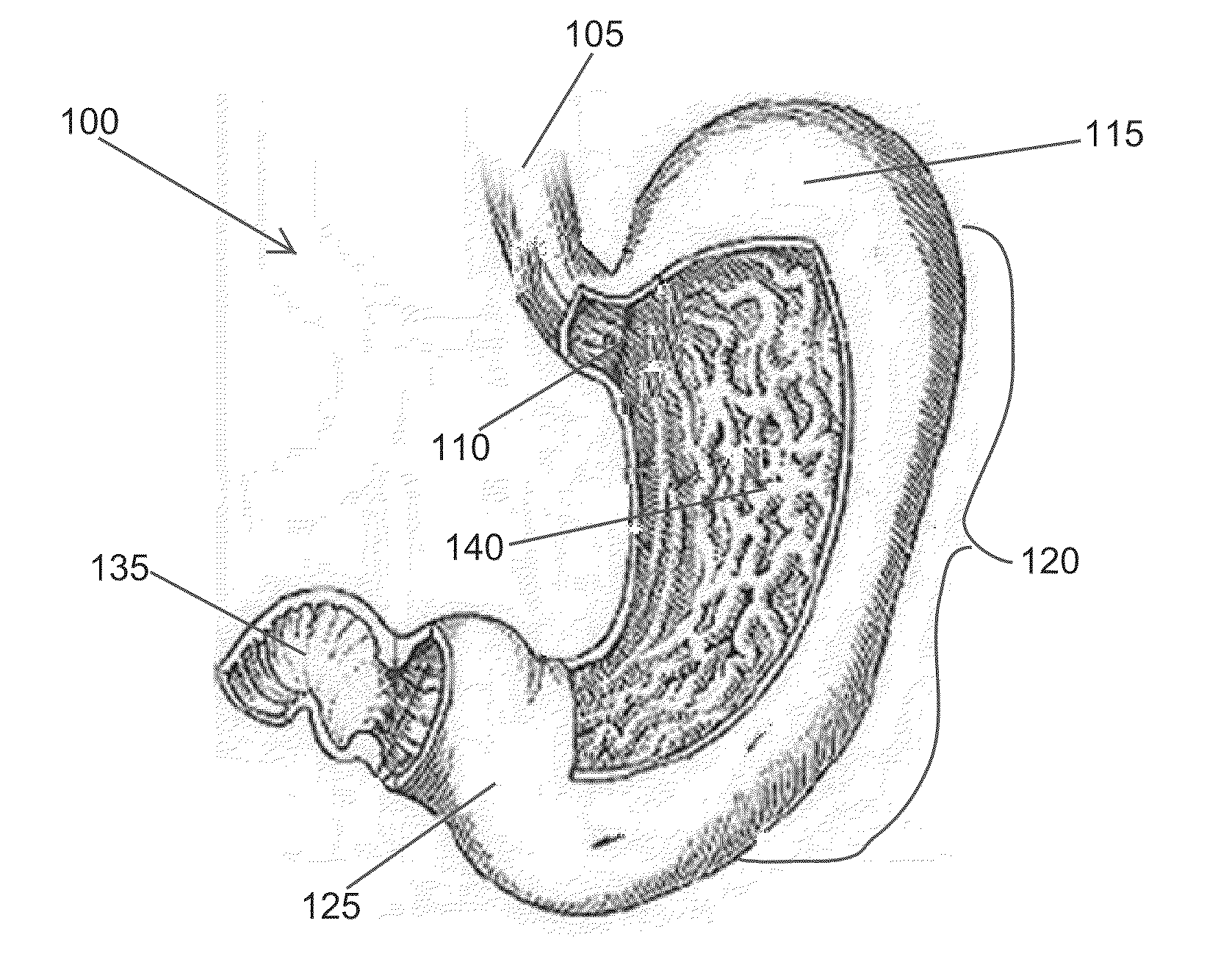
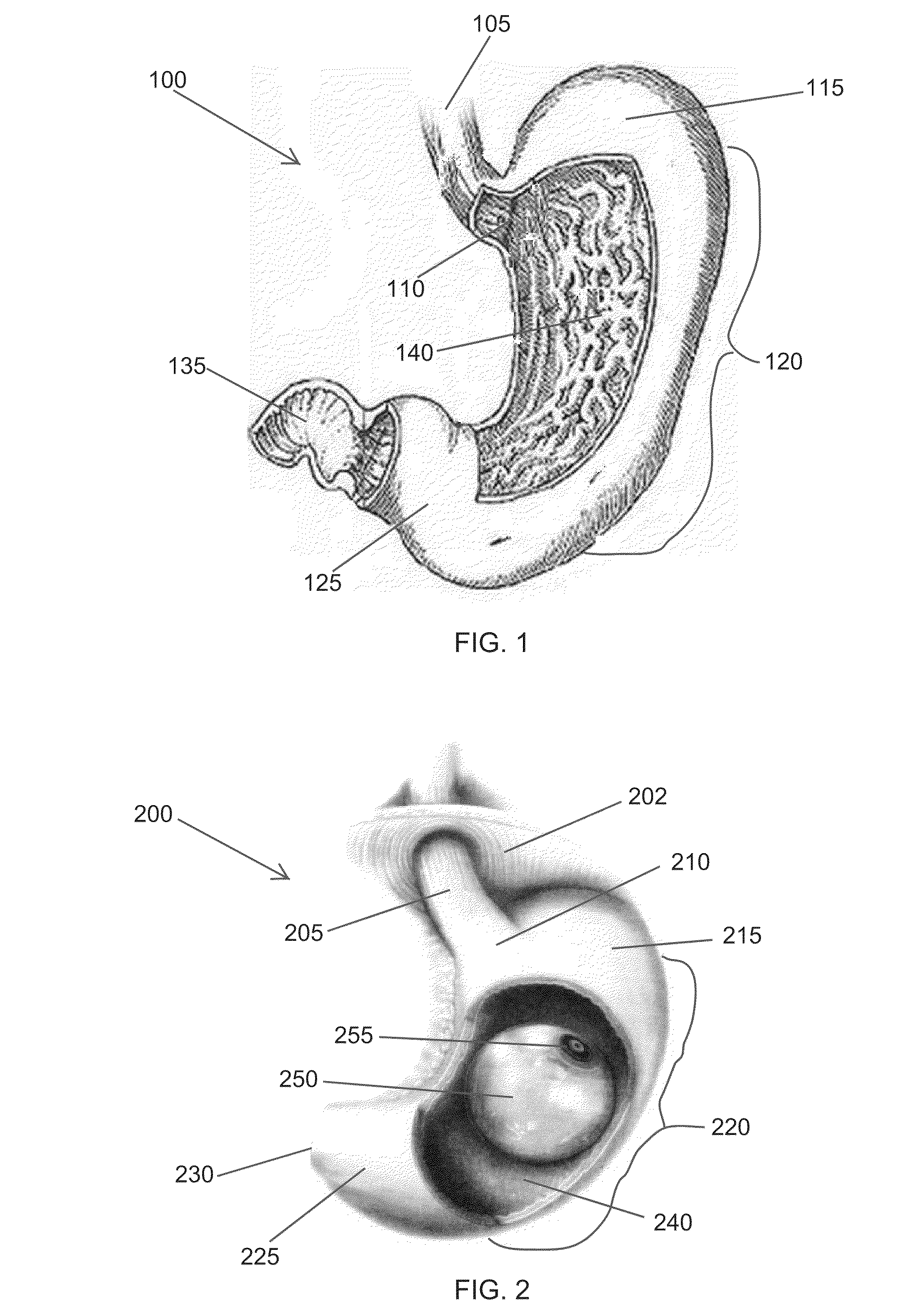
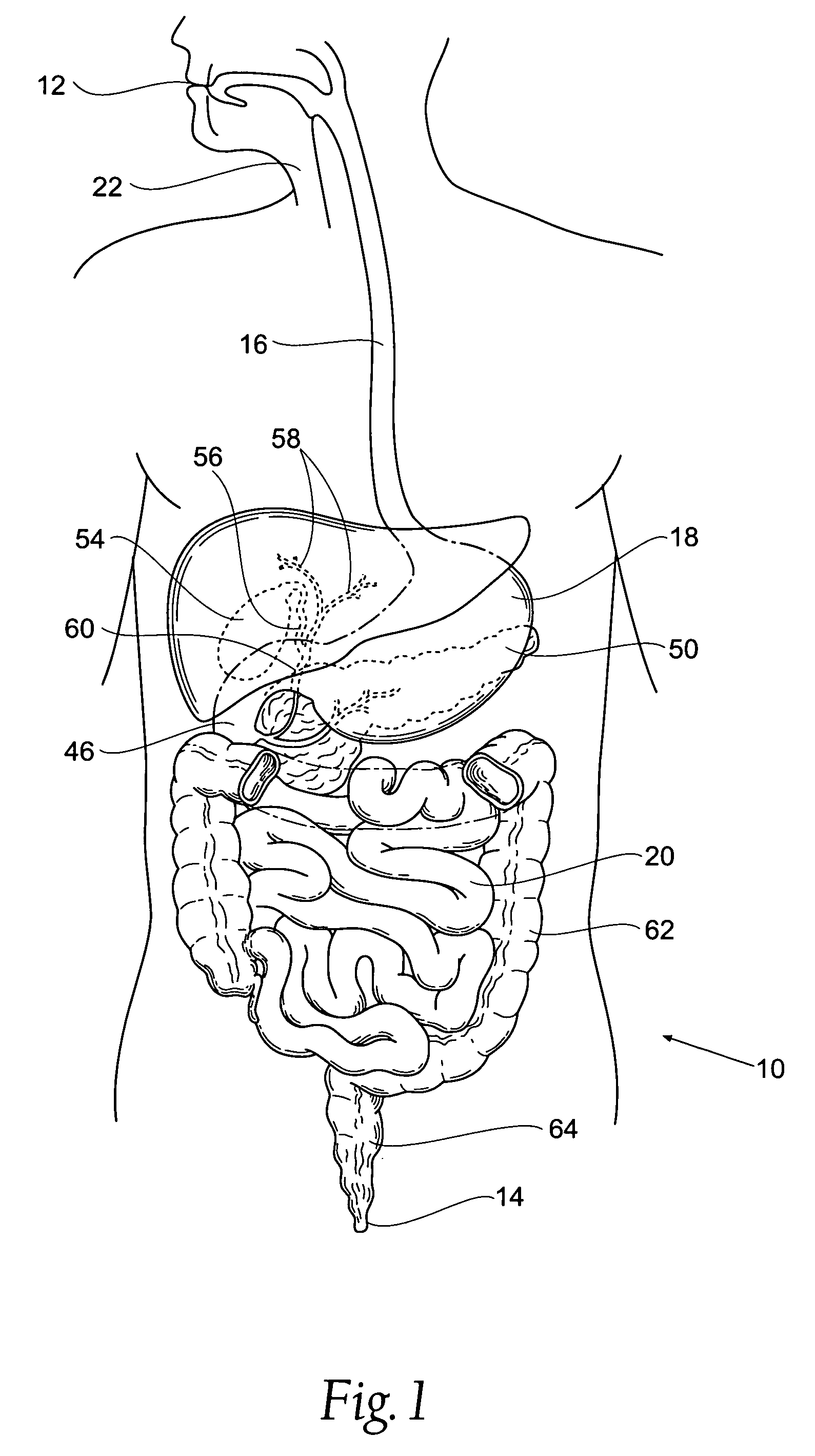
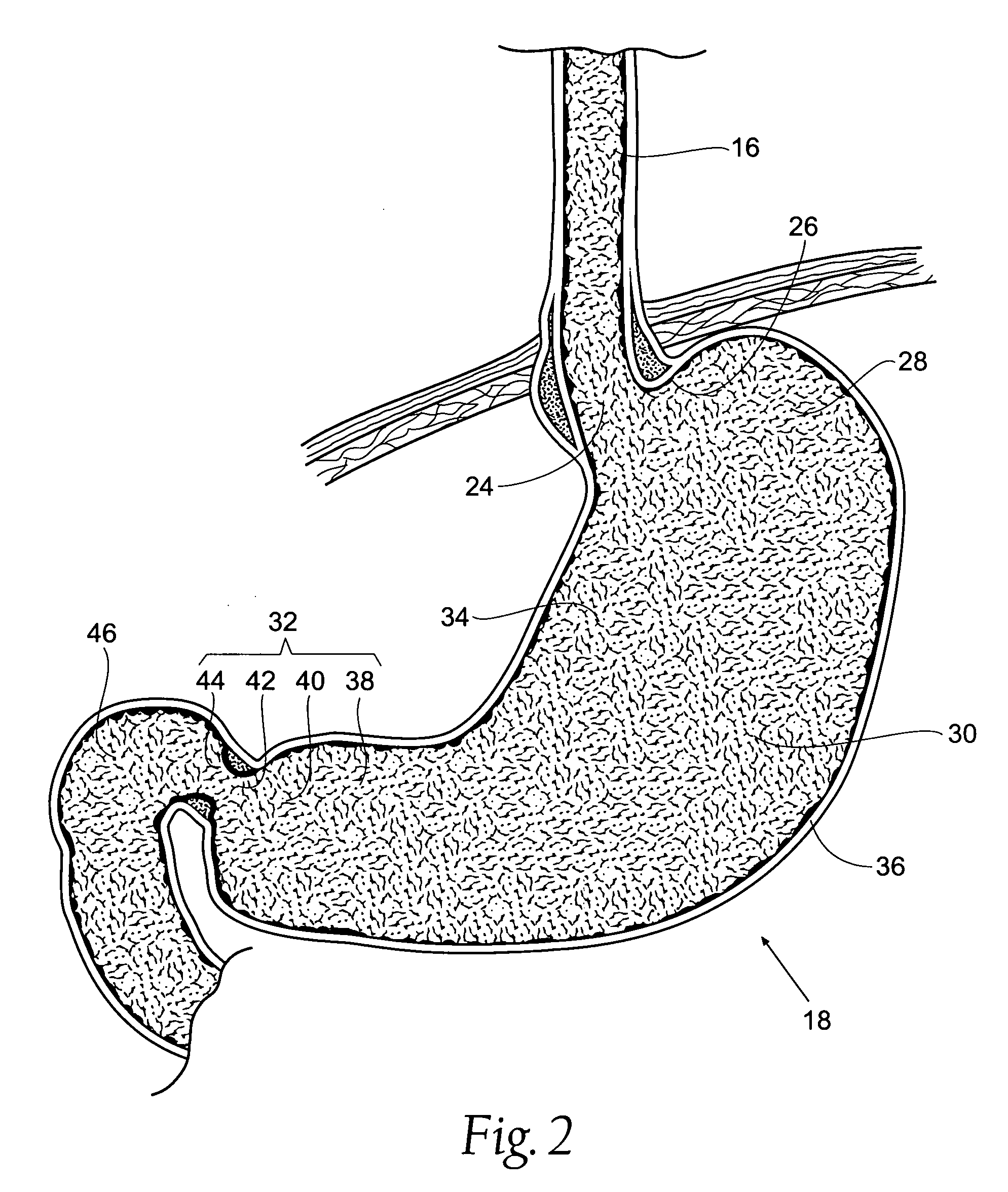
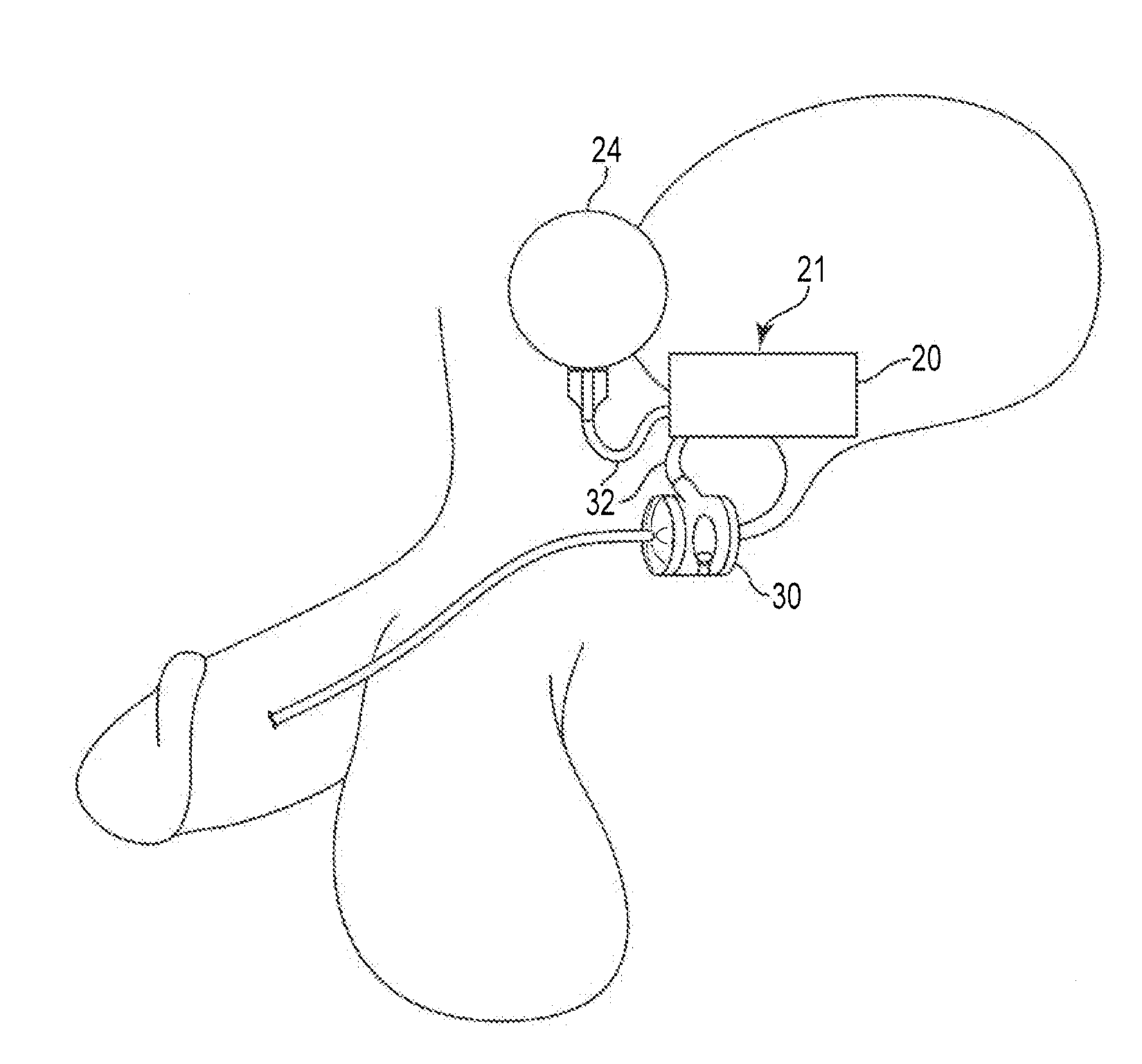
The sphincter of Oddi (also hepatopancreatic sphincter or Glisson's sphincter), abbreviated as SO, is a muscular valve that in some animals, including humans, controls the flow of digestive juices (bile and pancreatic juice) through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi. The sphincter of Oddi is relaxed by the hormone cholecystokinin via vasoactive intestinal peptide.
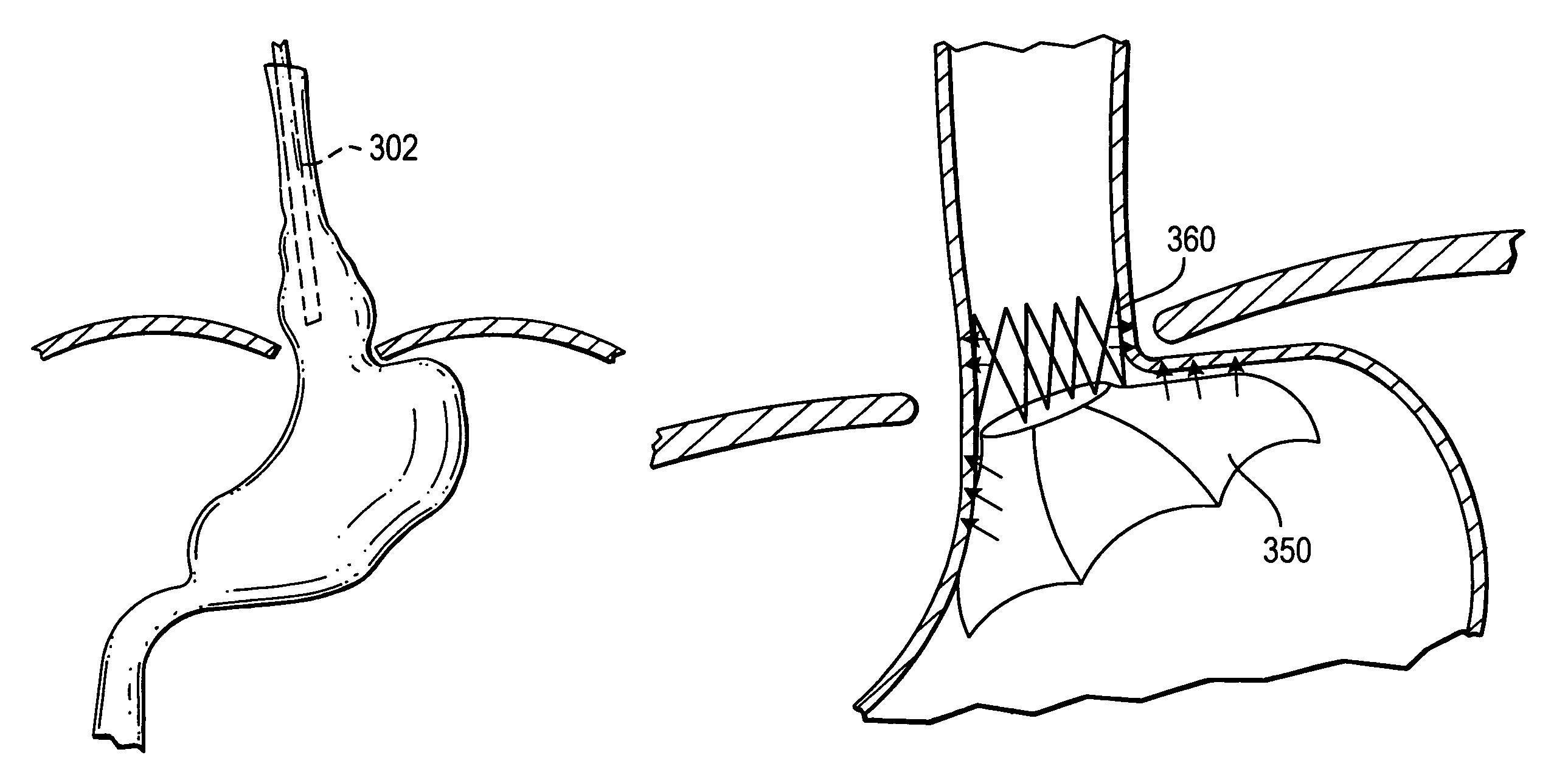
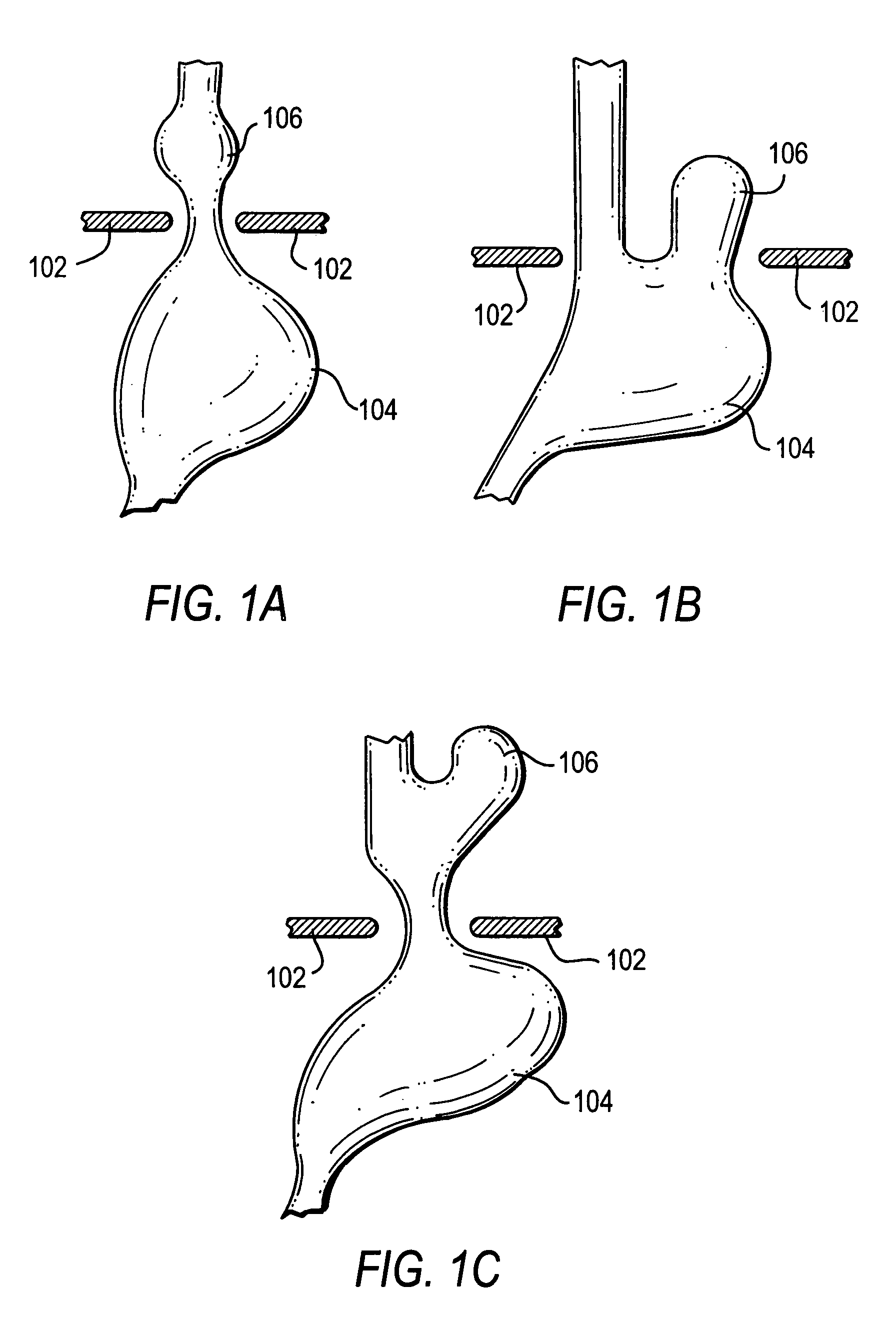
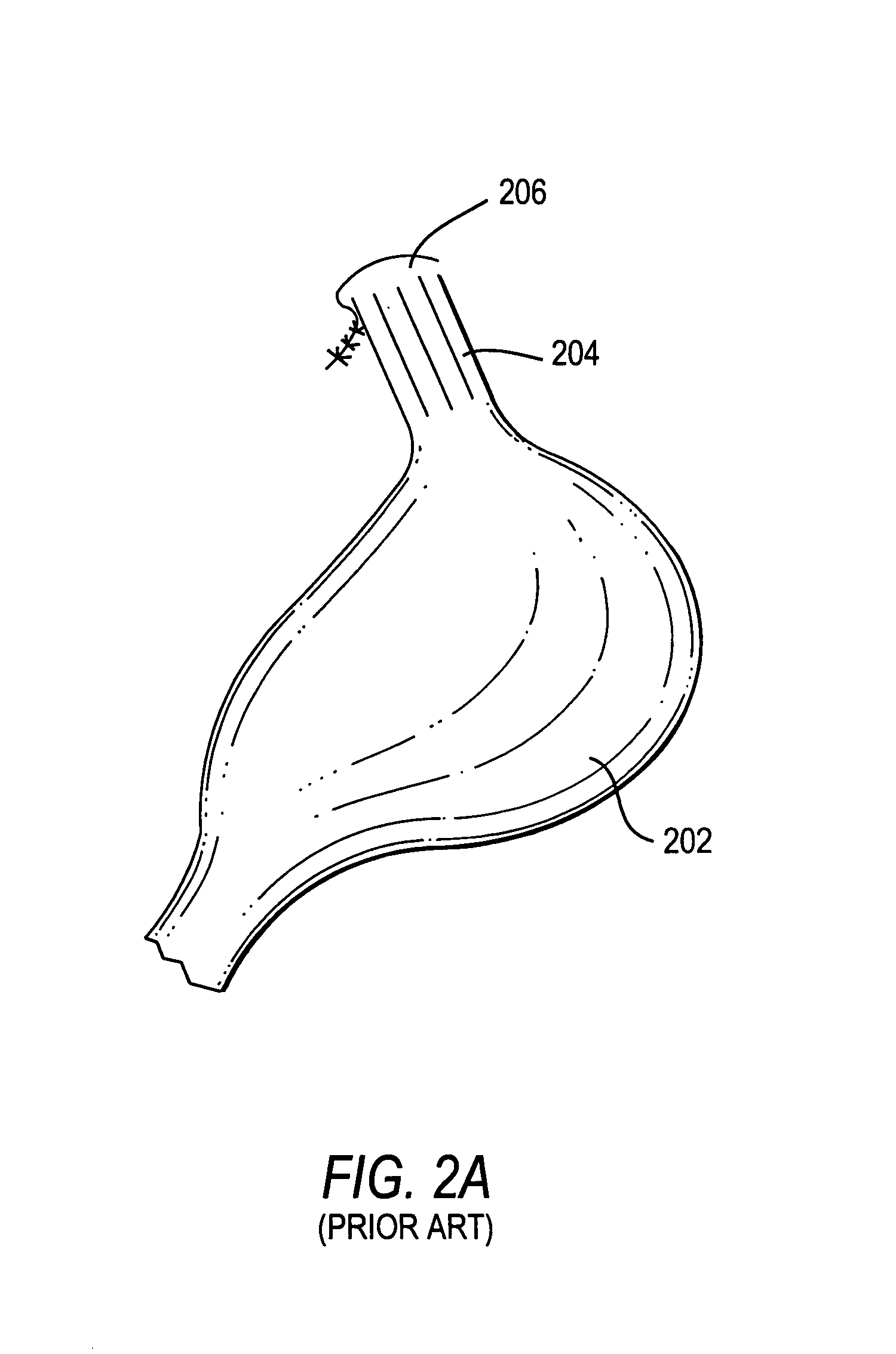
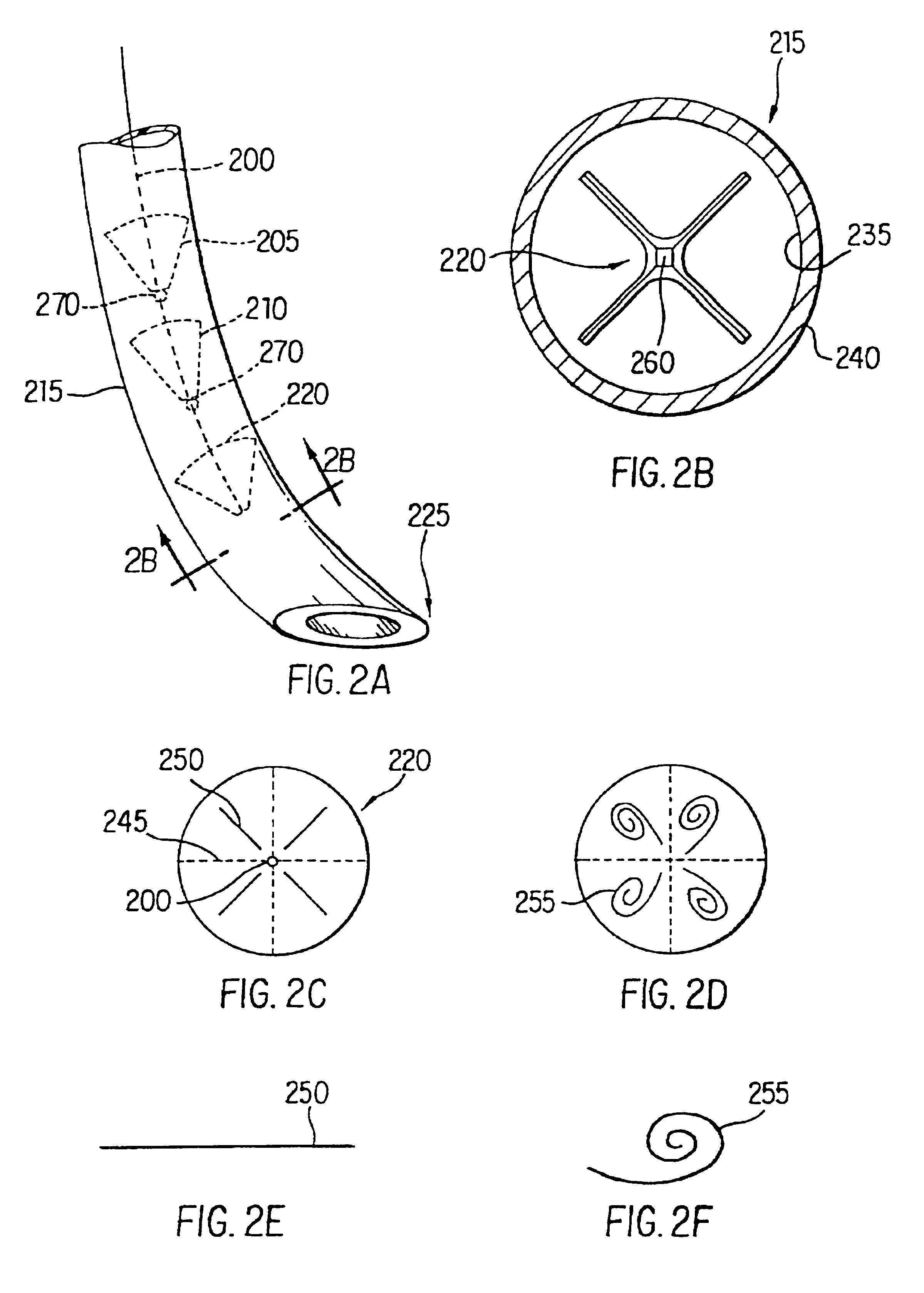
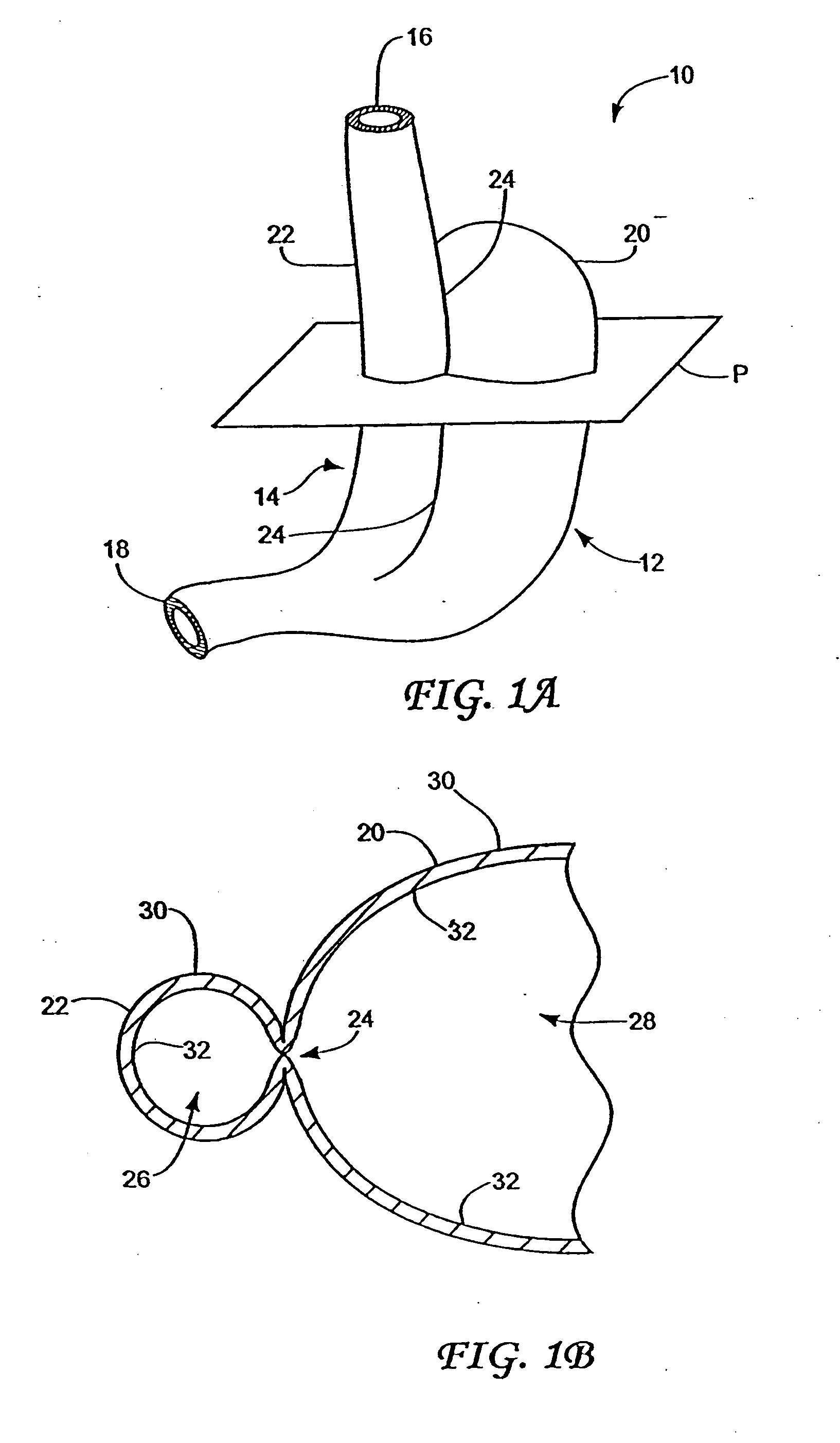
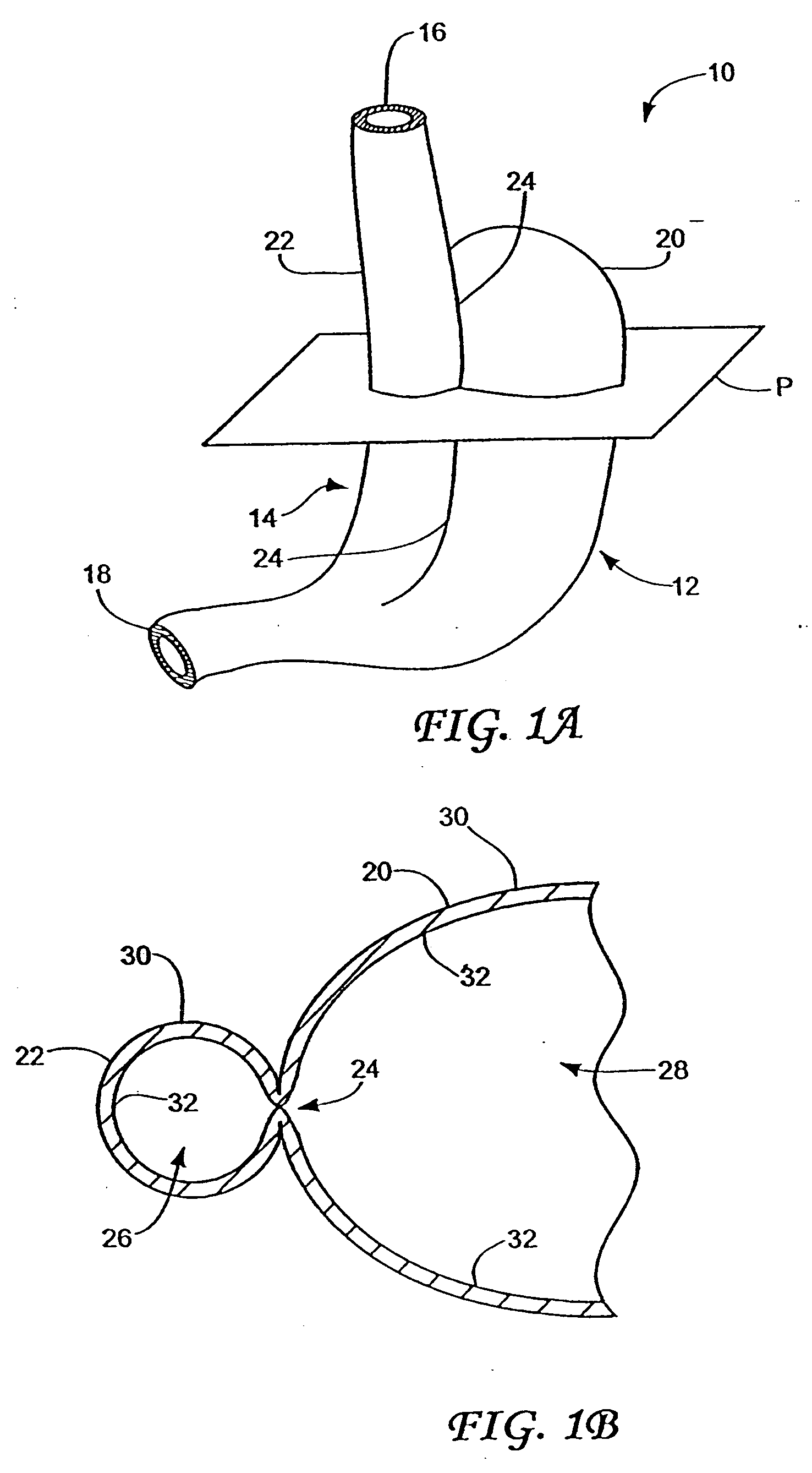
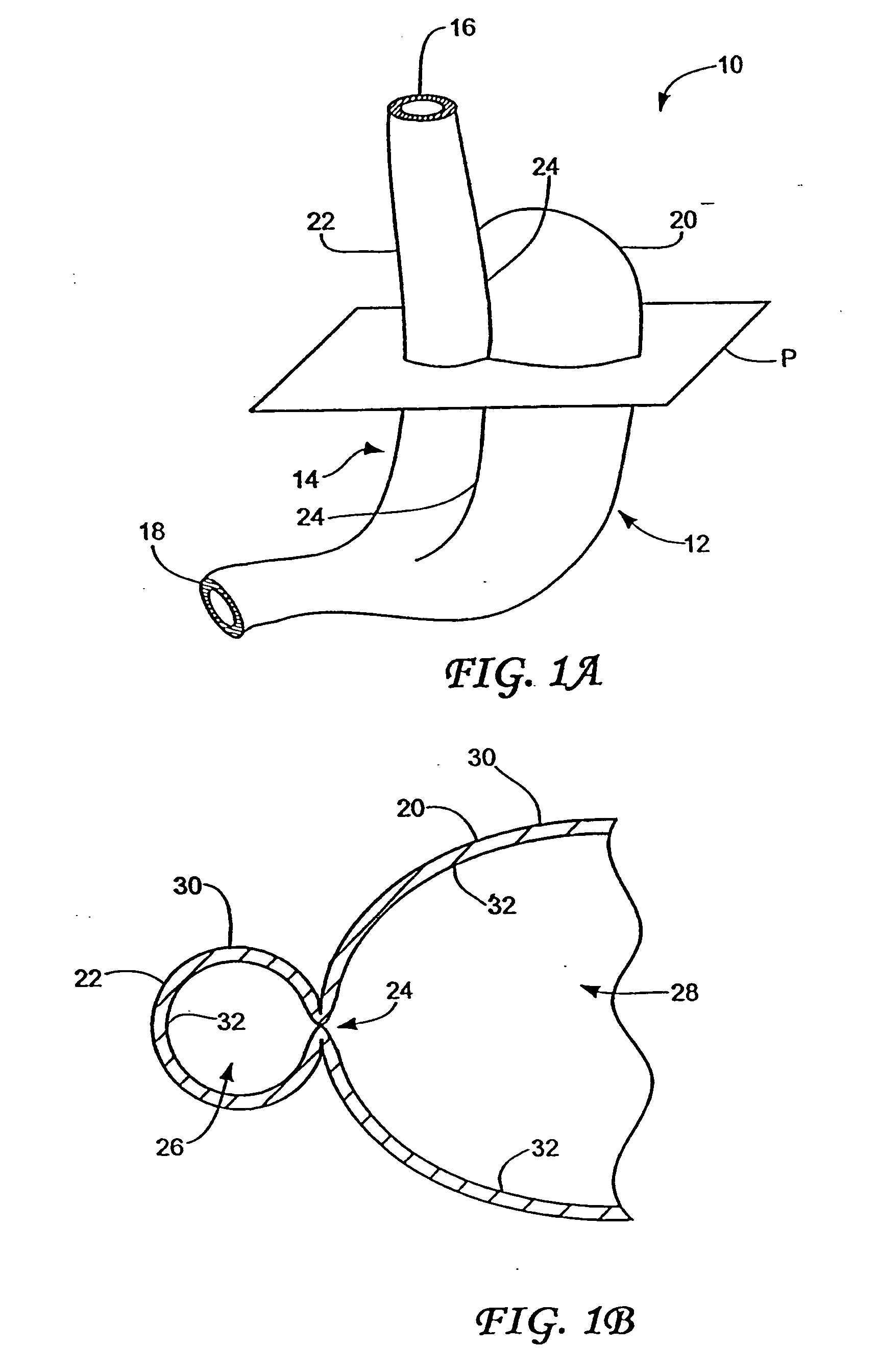
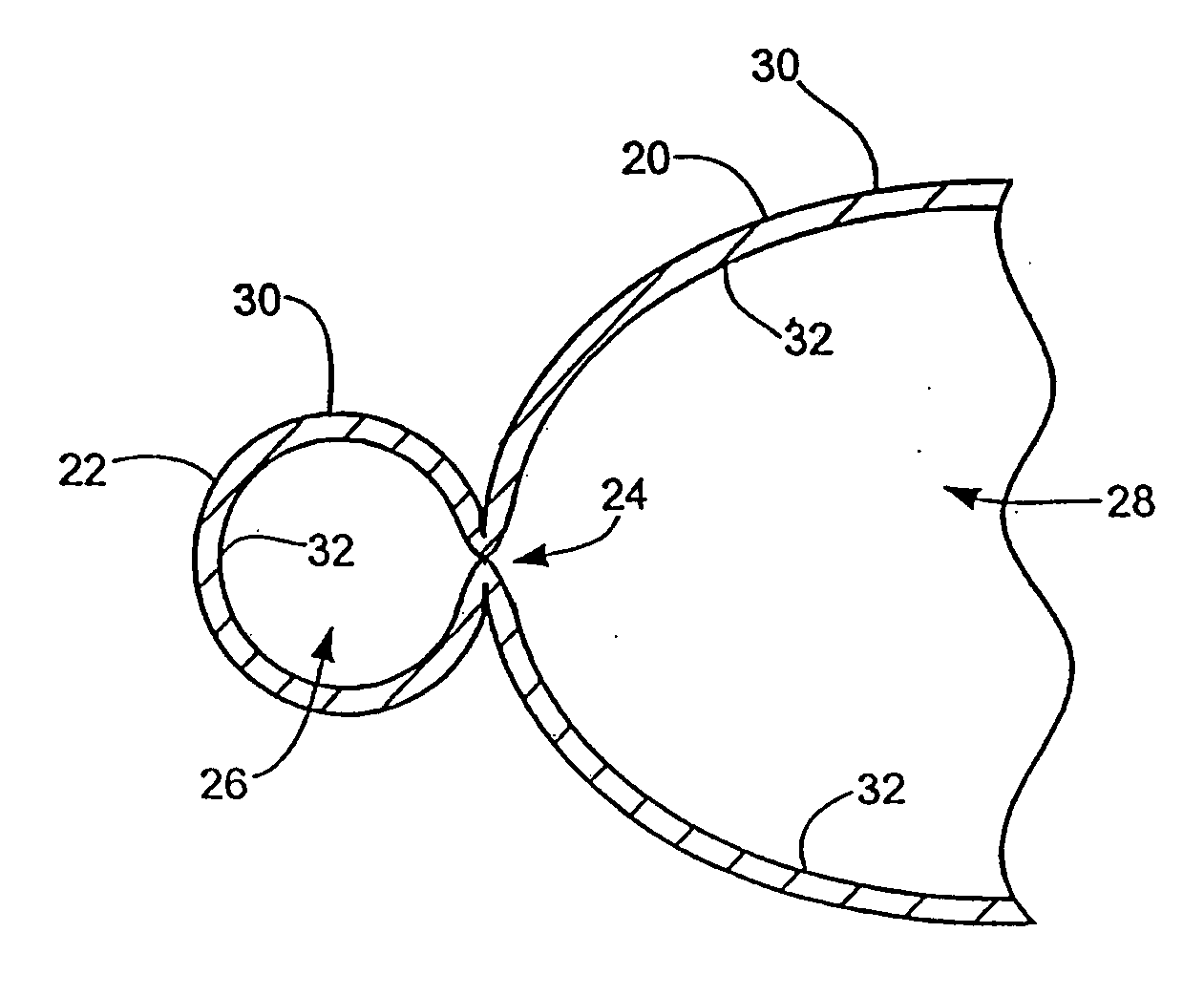
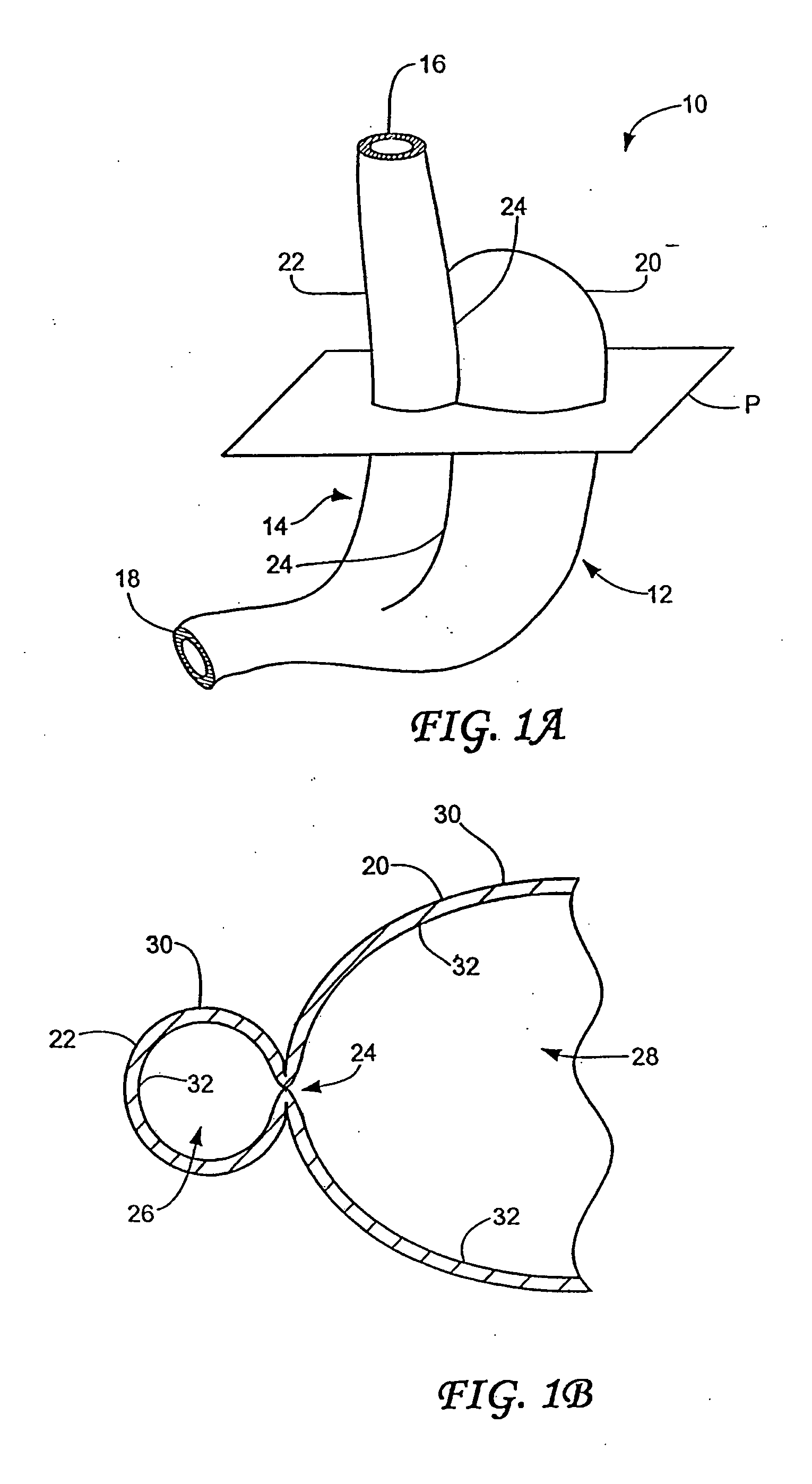
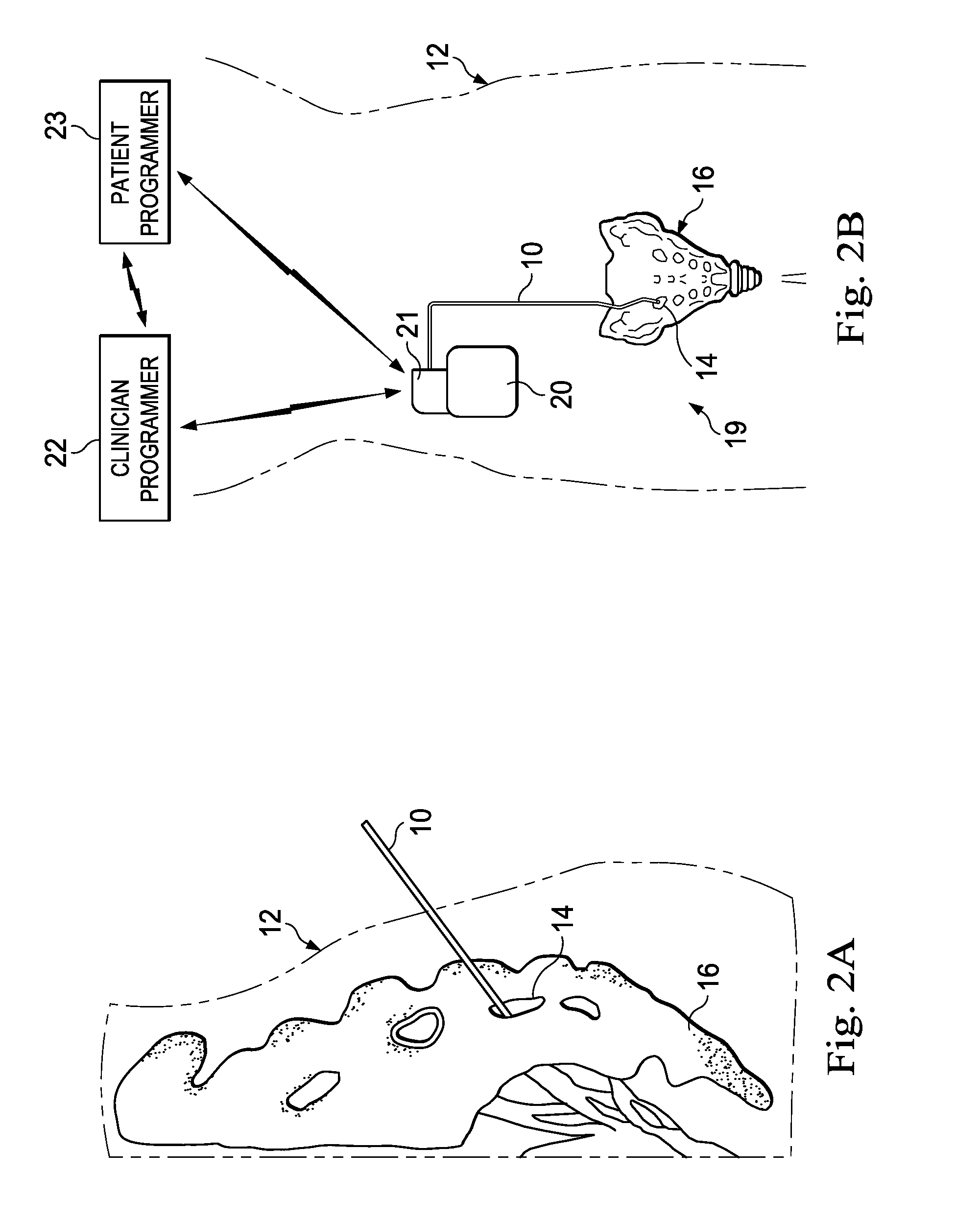
Methods and apparatus for improving the function of biological passages
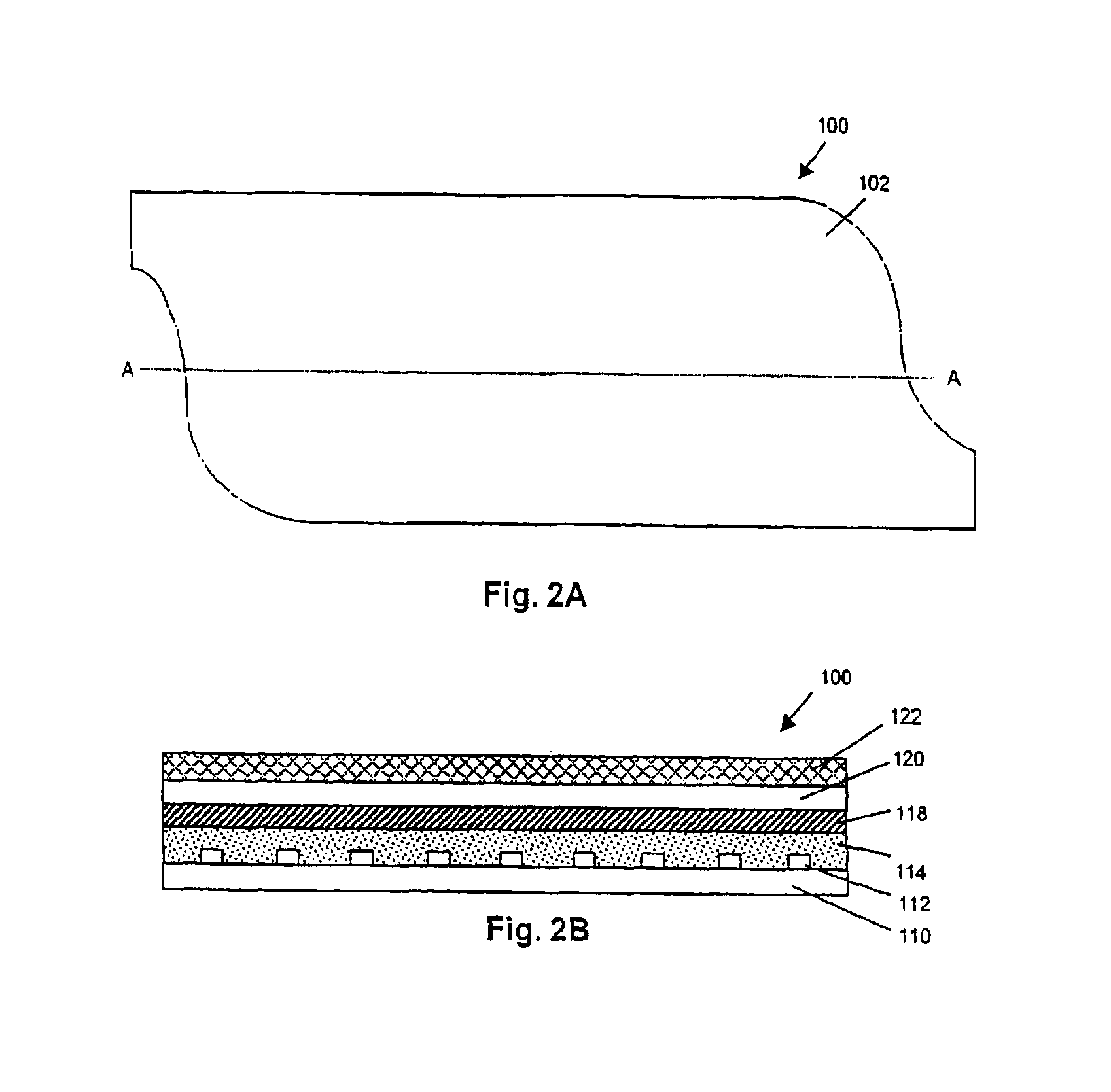
ActiveUS6960233B1Reduces the hiatal herniaStrengthens the function of the lower esophageal sphincterTubular organ implantsInsertion stentEsophageal wall
Several methods and apparatus are available for treating patients that suffer from both gastro-esophageal reflux disorder and hiatal hernias. In order to treat these patients, an endoscopic probe may be used to push the herniated stomach below the diaphragm. In some embodiments, a two-part stent comprising a funnel stent and a reverse stent may be deployed to prevent a future re-herniation of the stomach and to reduce the annulus of the lower esophageal sphincter. In some embodiments, a reverse stent with perforating barbs may be deployed, in which the barbs penetrate the esophageal wall and attach to the diaphragm. In some embodiments, the crus muscles may be sutured together to reduce the hiatus size and a reverse stent may be deployed to reduce the annulus of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Owner:TORAX MEDICAL
Surgical instruments for treating gastro-esophageal reflux
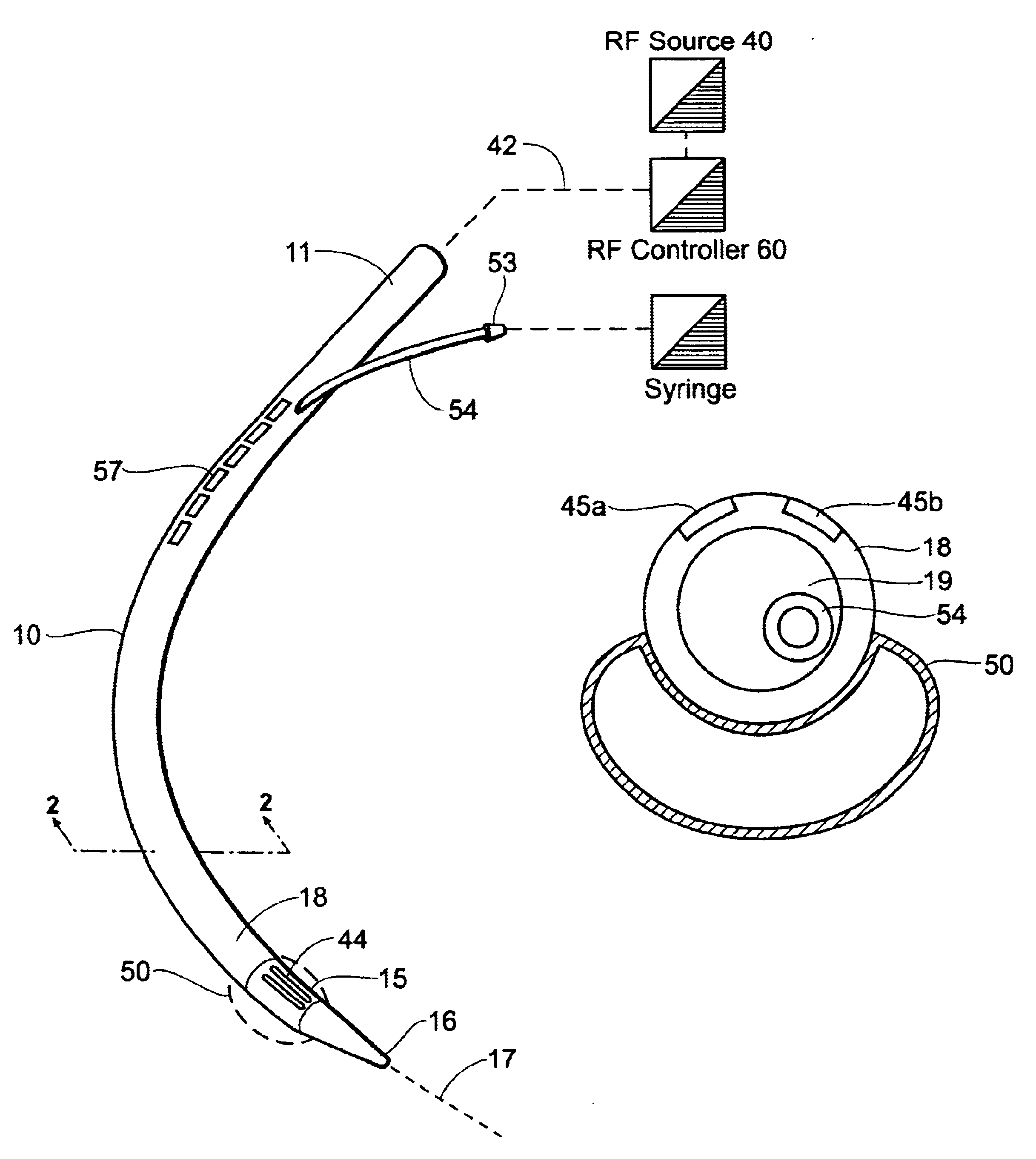
InactiveUS6740082B2Augment objectInexpensive and disposableElectrotherapyEndoscopesSensor arrayFiber
Instruments for thermally-mediated treatment of a patient's lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to induce an injury healing response to thereby populate the extracellular compartment of walls of the LES with collagen matrices to altere the biomechanics of the LES to provide an increased intra-esophageal pressure for preventing acid reflux. A preferred embodiment is a bougie-type device for trans-esophageal introduction that carries conductive electrodes for delivering Rf energy to walls of the LES (i) to induce the injury healing response or (ii) to "model" collagenous tissues of the LES by shrinking collagen fibers therein. Typically, an Rf source is connected to at least one conductive electrode that may be operated in a mono-polar or bi-polar fashion. A sensor array of individual sensors is provided in the working end. A computer controller is provided, which together with feedback circuitry, is capable of full process monitoring and control of: (i) power delivery; (ii) parameters of a selected therapeutic cycle, (iii) mono-polar or bi-polar energy delivery, and (iv) multiplexing of current flow between various paired electrodes. The controller can determine when the treatment is completed based on time, temperature, tissue impedance or any combination thereof.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Method and apparatus for endoscopic repair of the lower esophageal sphincter
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for adhering tissue to one another. In an embodiment of the present invention the two tissues to be joined, for example the lower esophagus and the fundus of the stomach, are first placed adjacent to one another. Next a first restraint is placed near the outside surface of one of the tissues and a second restraint is placed near the outside surface of the other tissue. An irritant is then placed between the two adjacent tissues. The restraints, and consequently the tissue surfaces, are then drawn together. As the touching irritated tissue surfaces heal they will become bonded to one another and their need for the mechanical fastening of the restraints, to secure them together, will be diminished.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
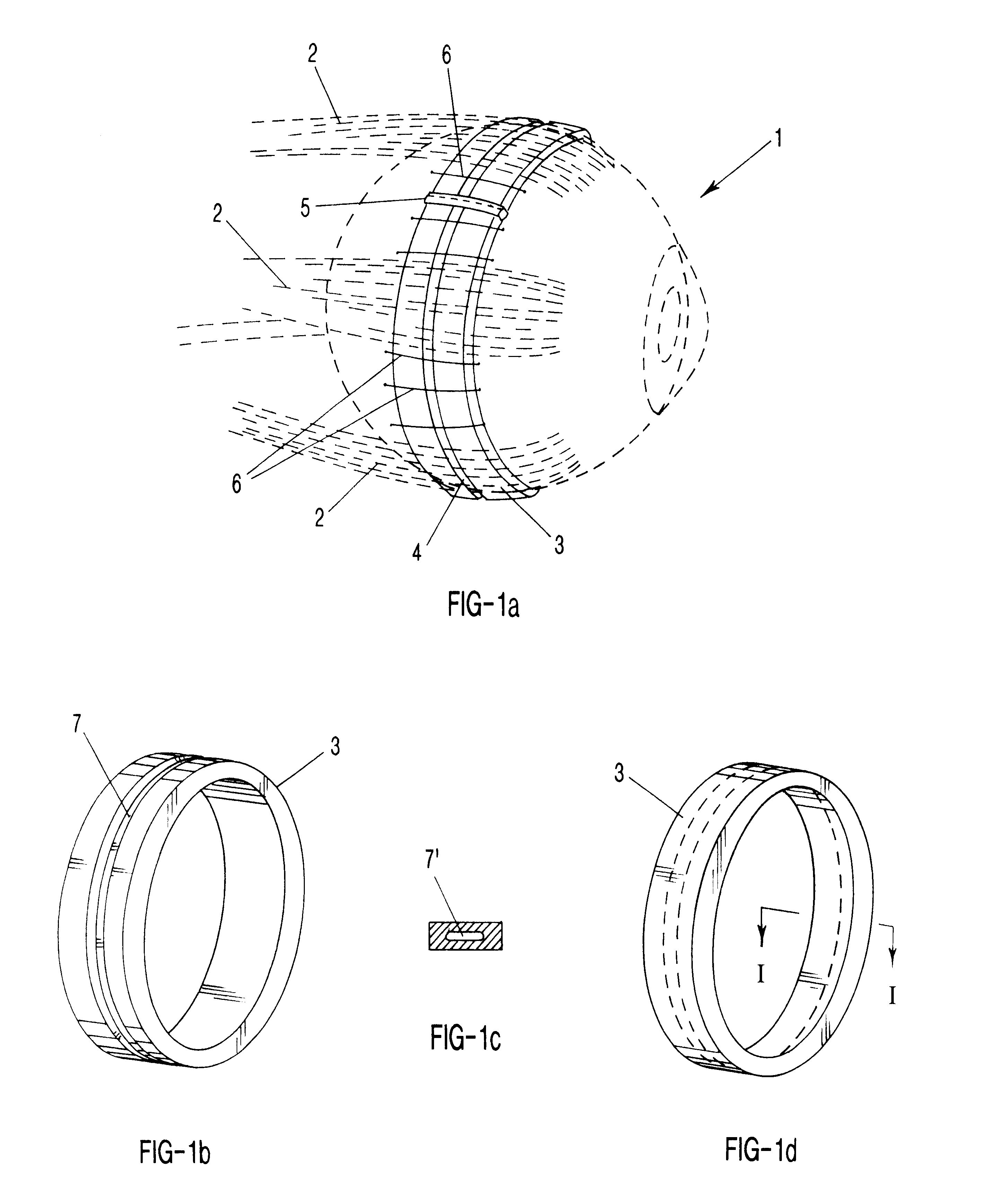
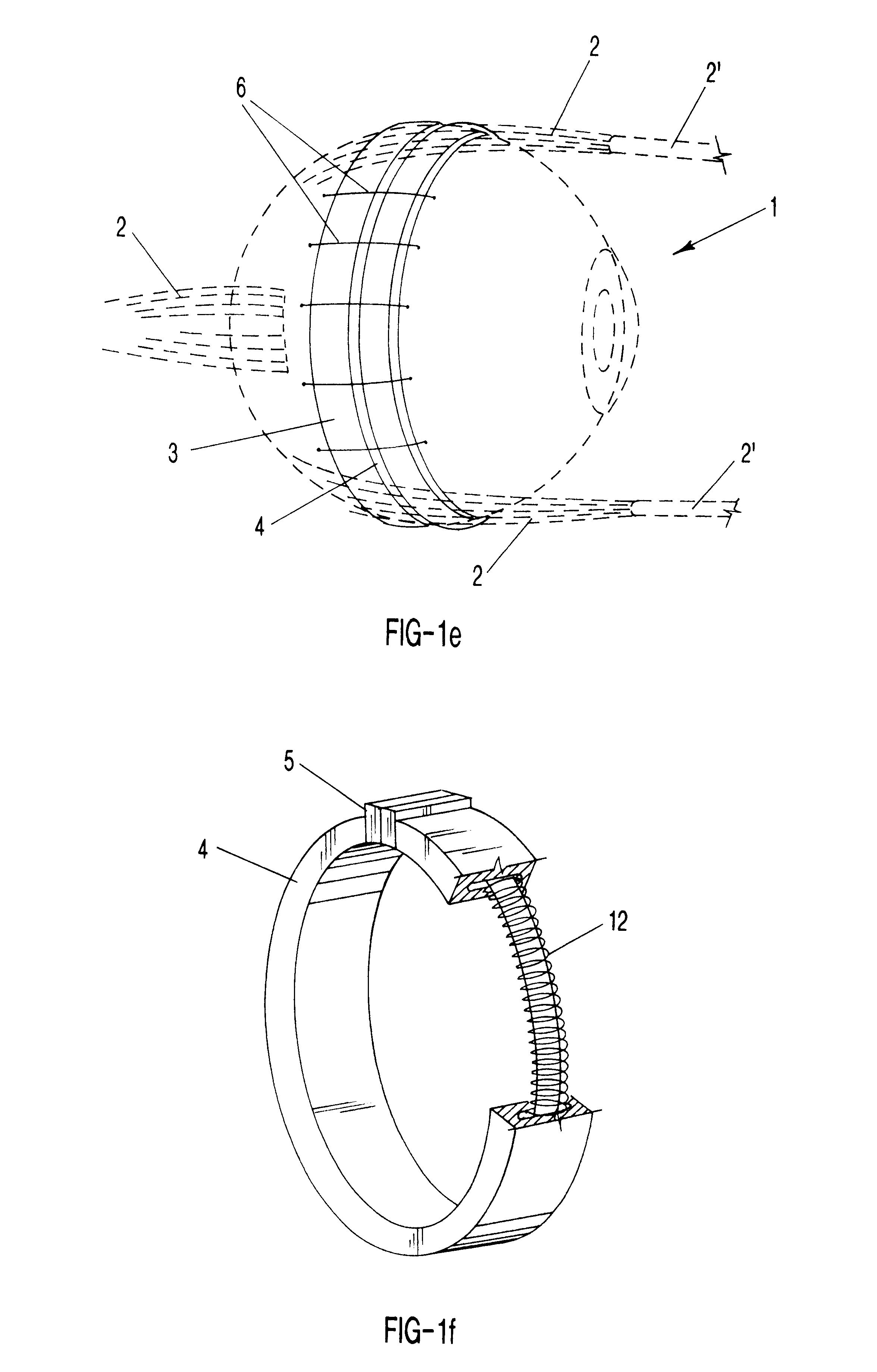
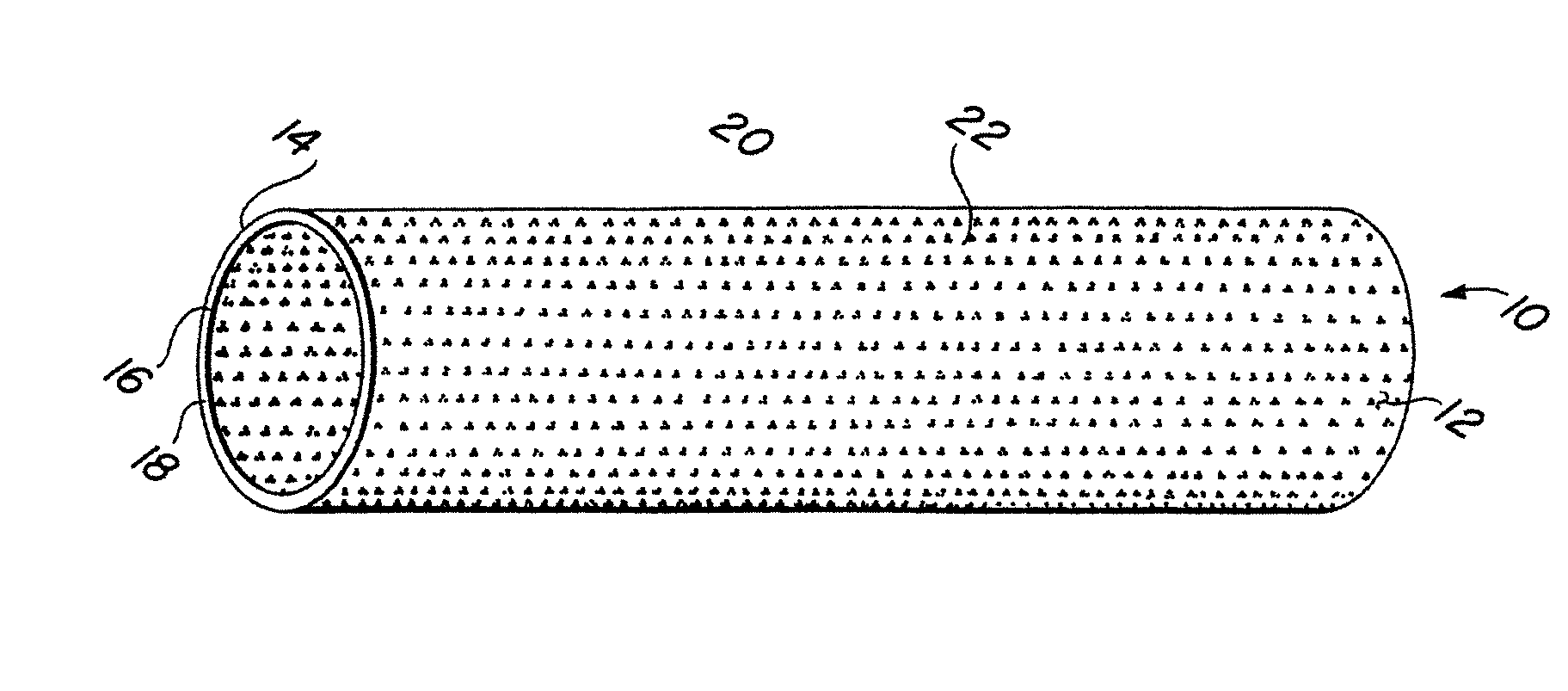
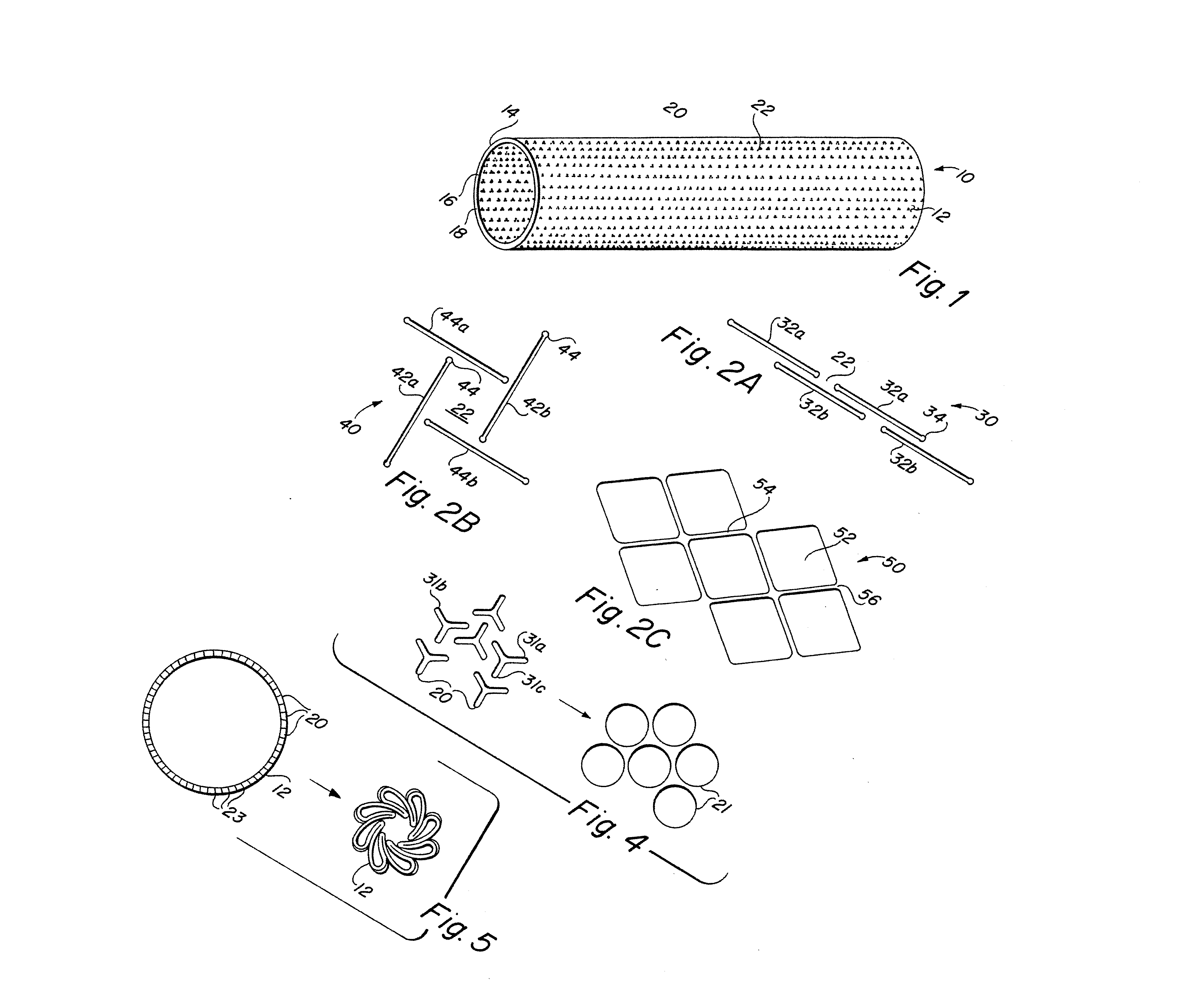
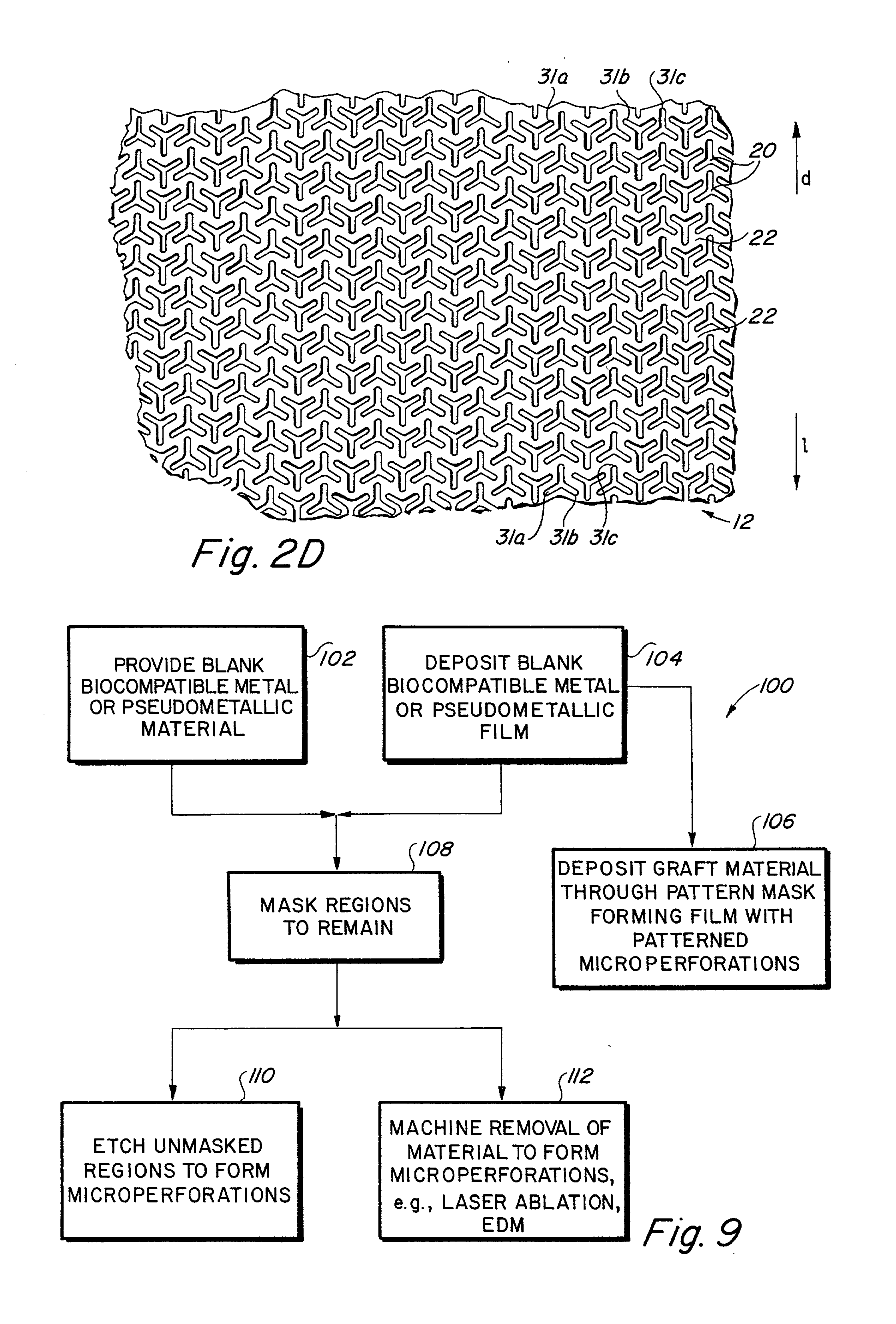
Self-supporting metallic implantable grafts, compliant implantable medical devices and methods of making same
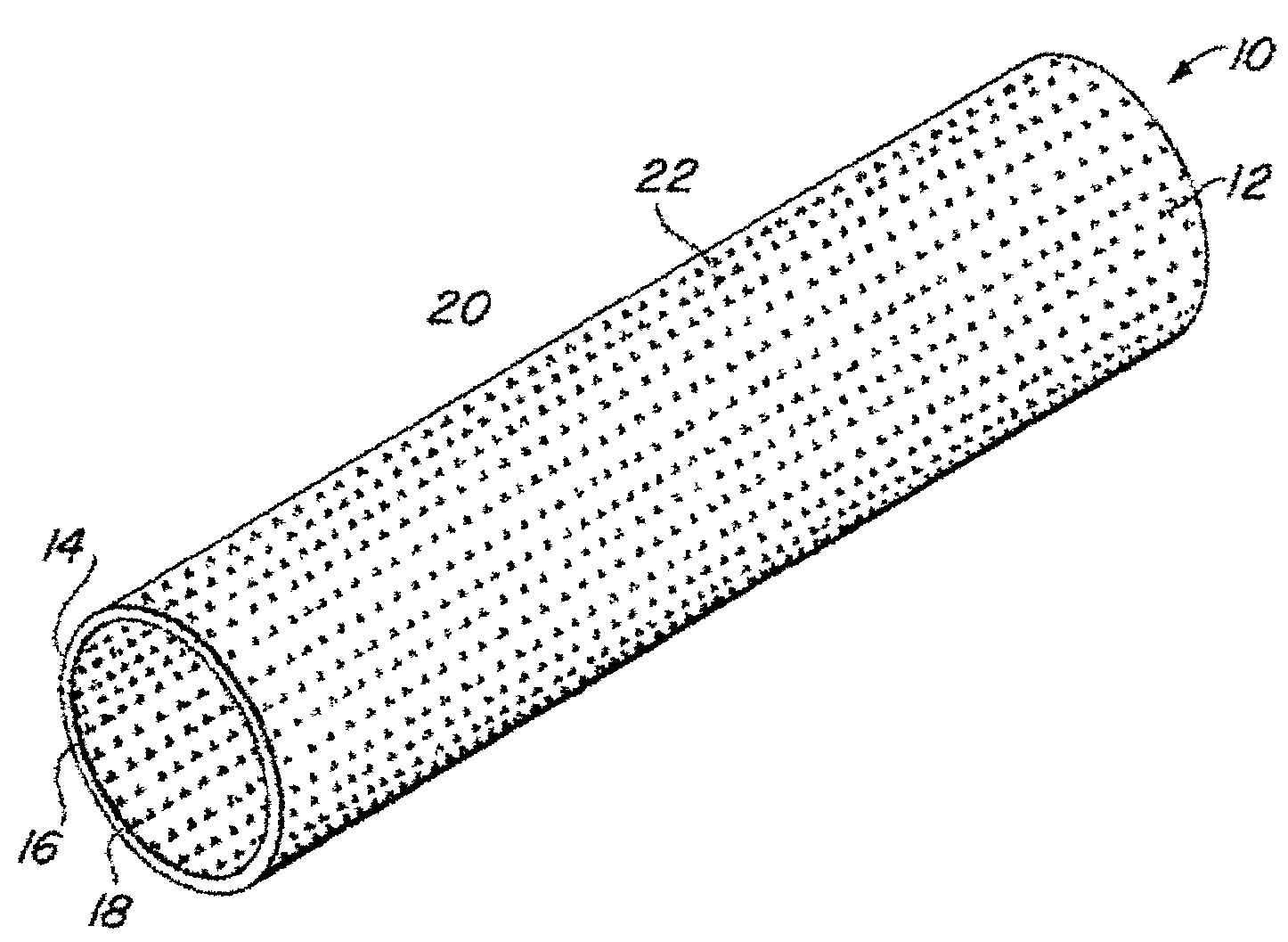
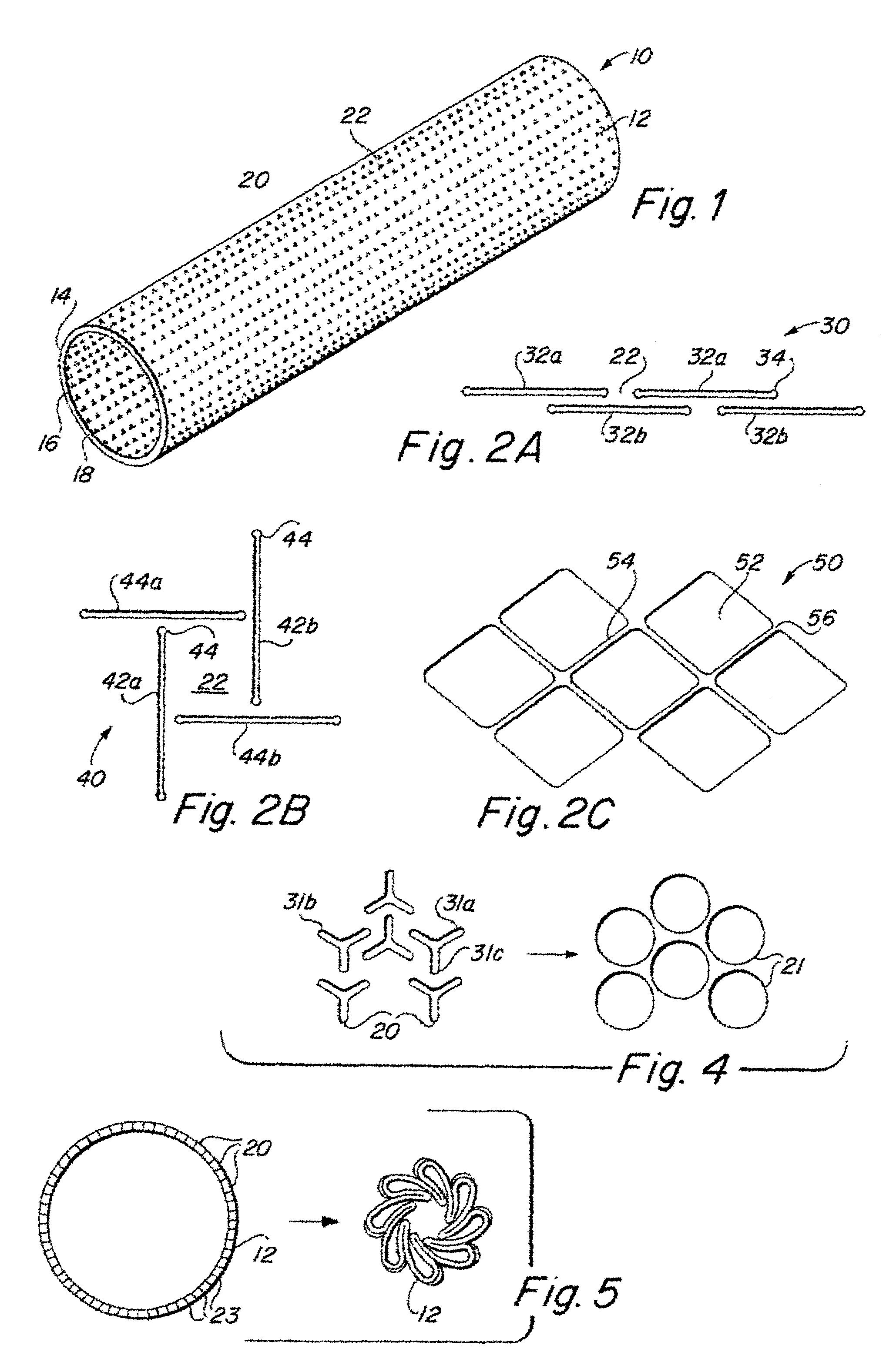
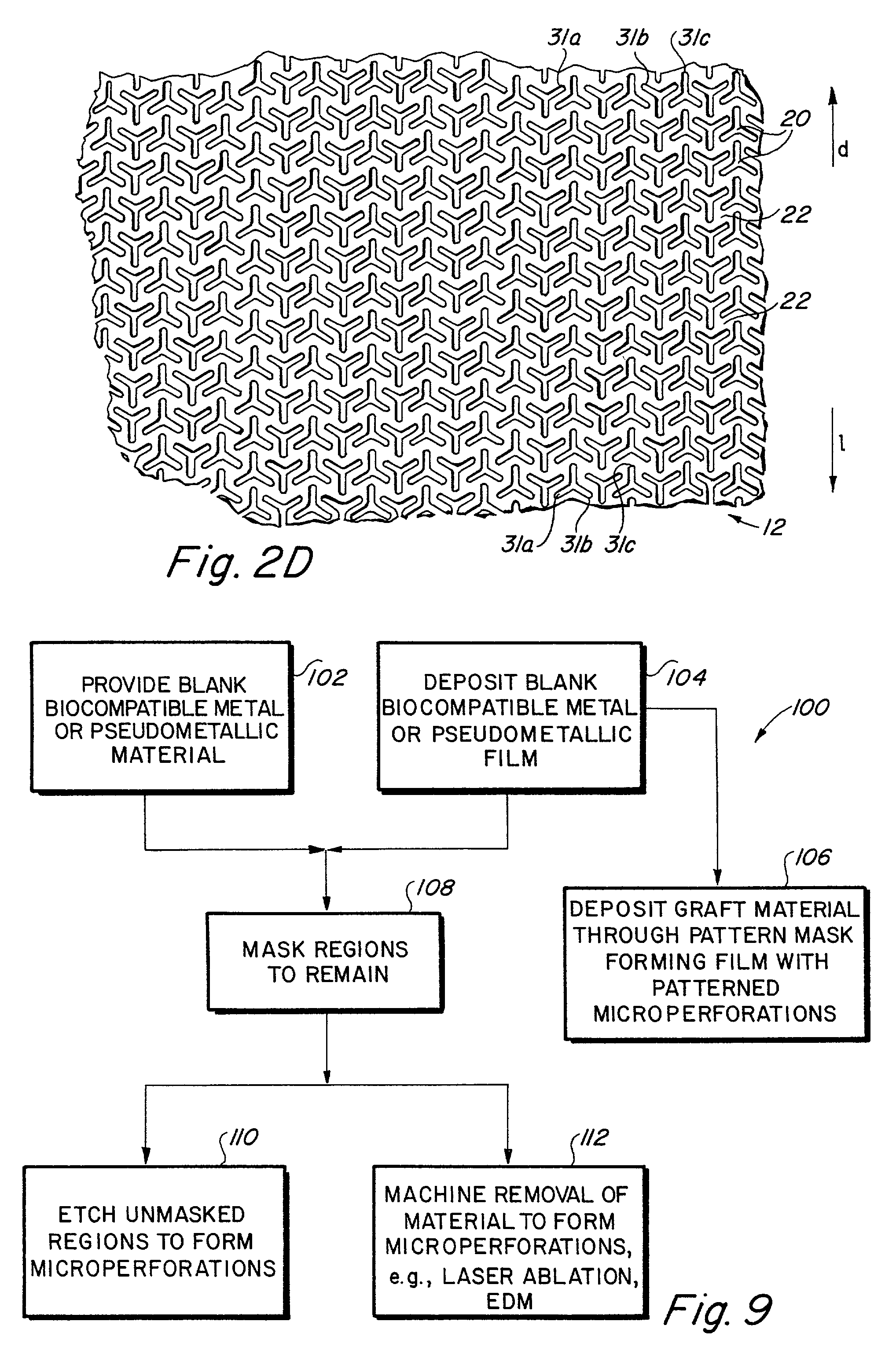
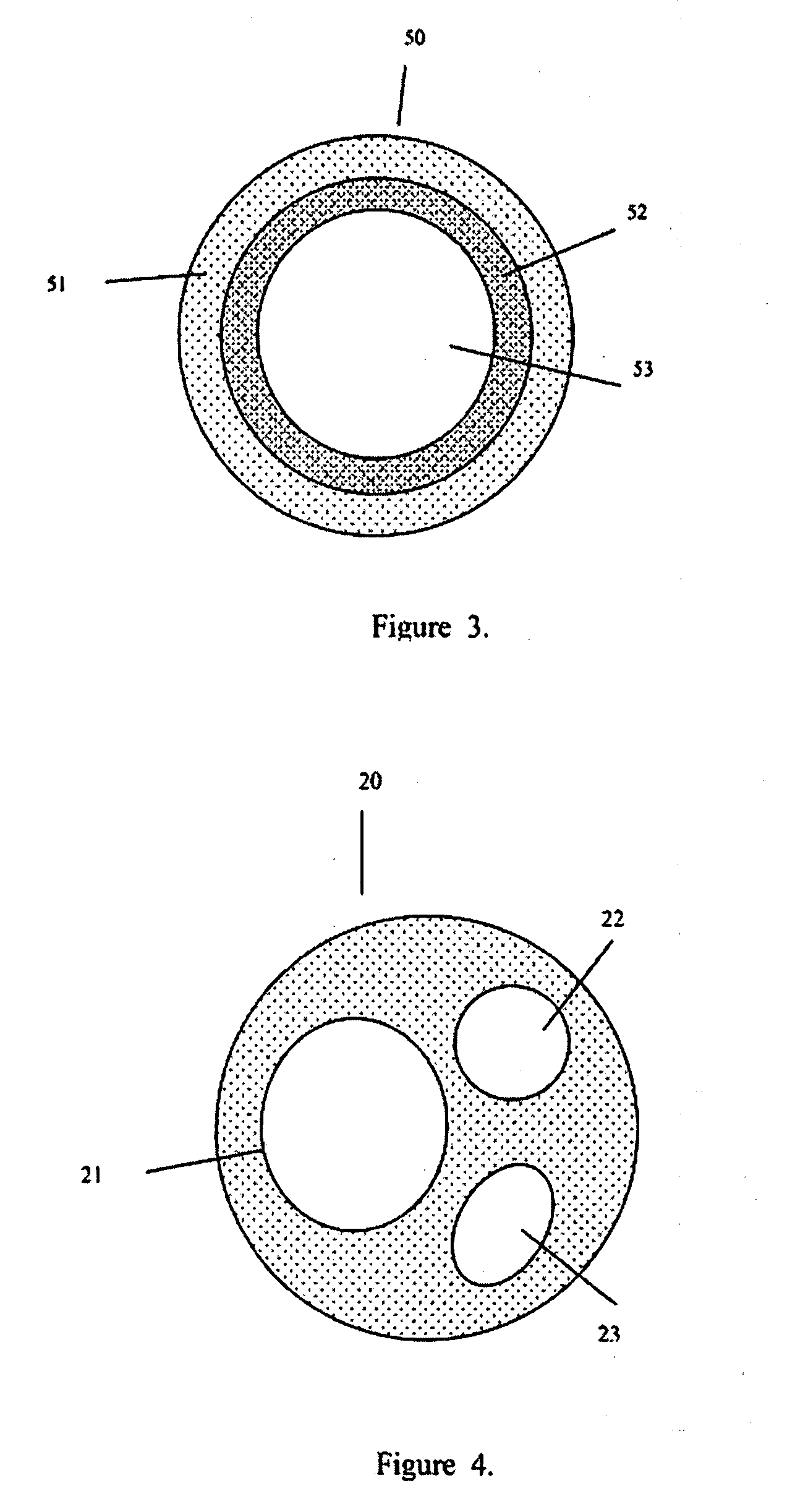
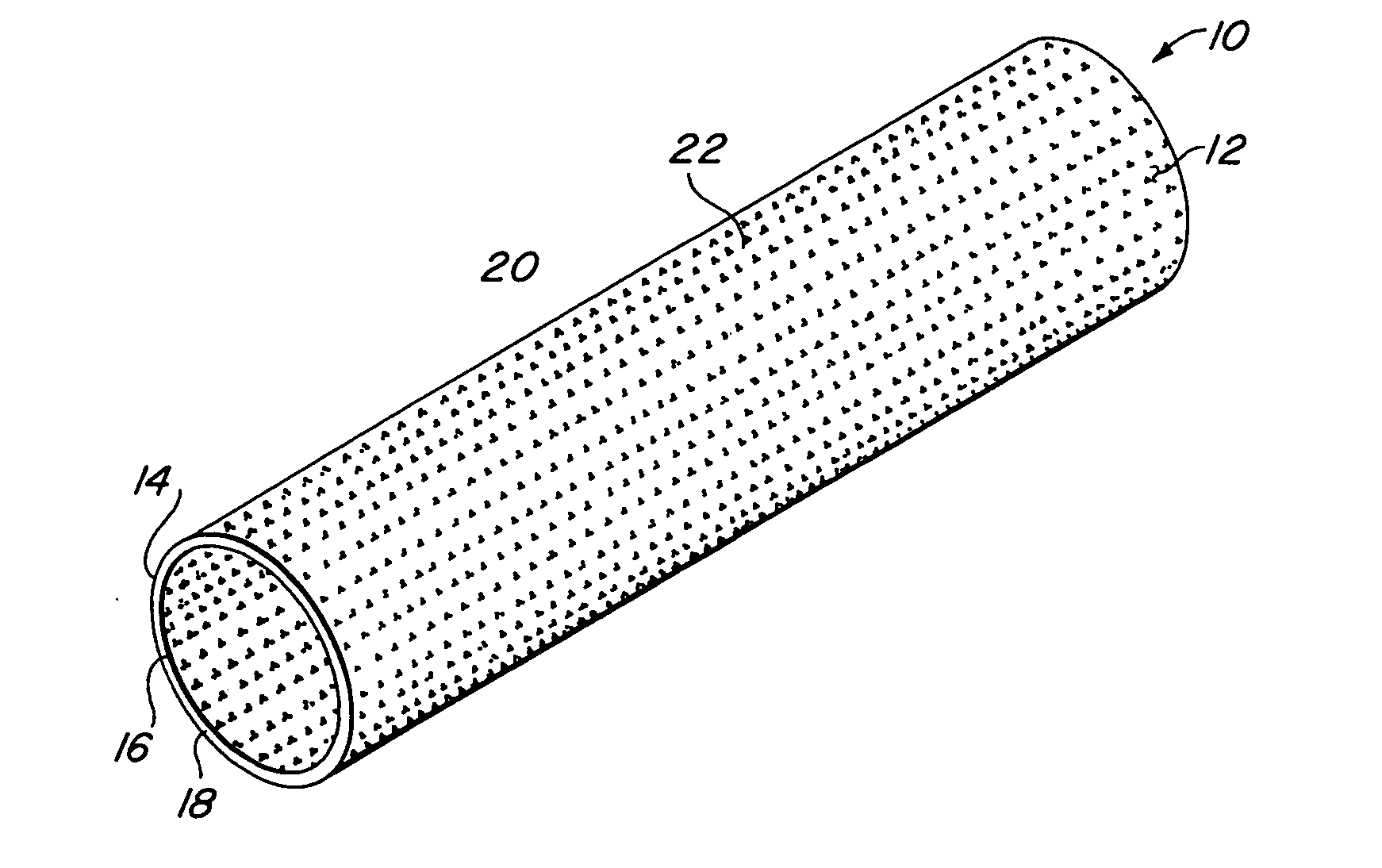
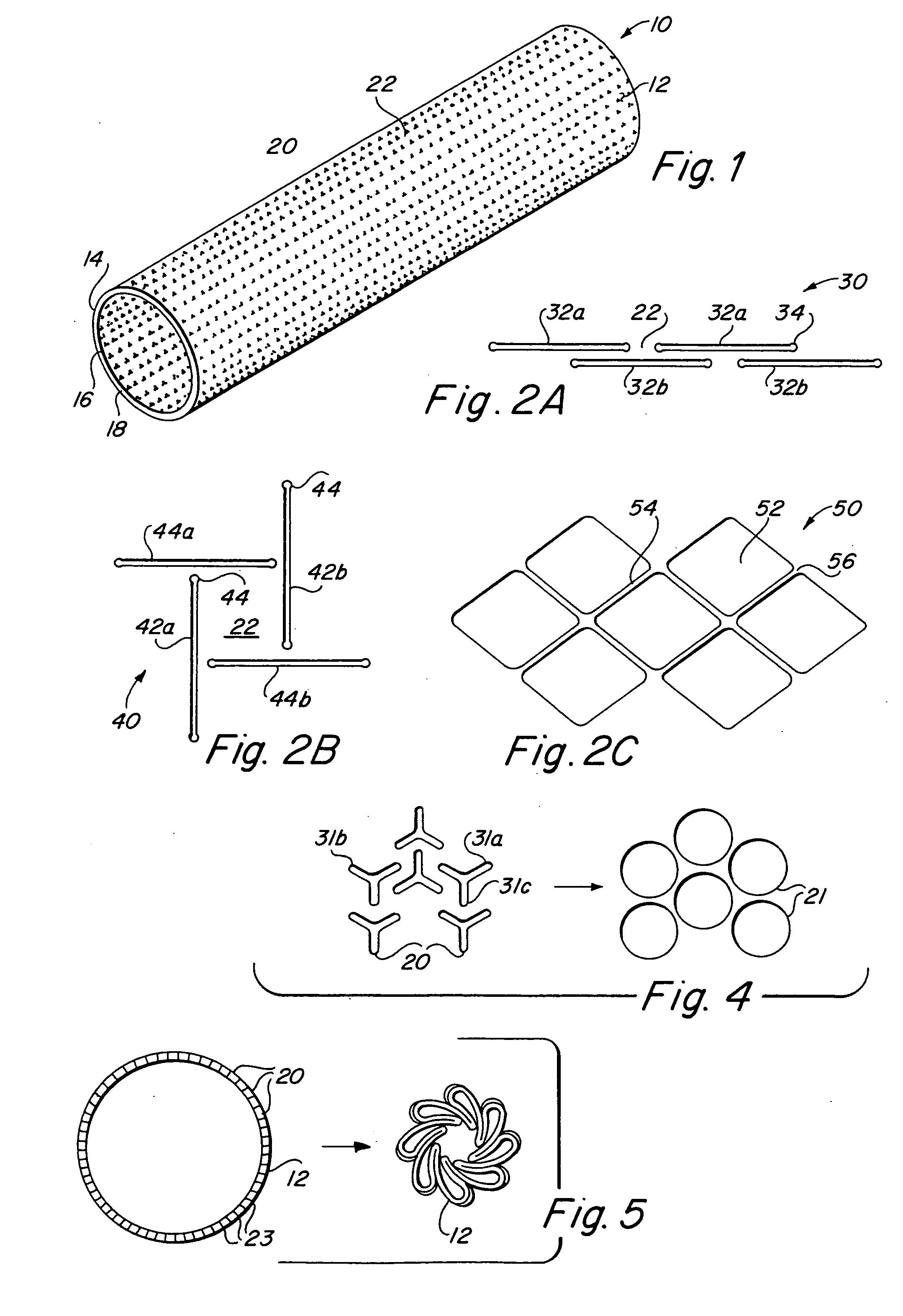
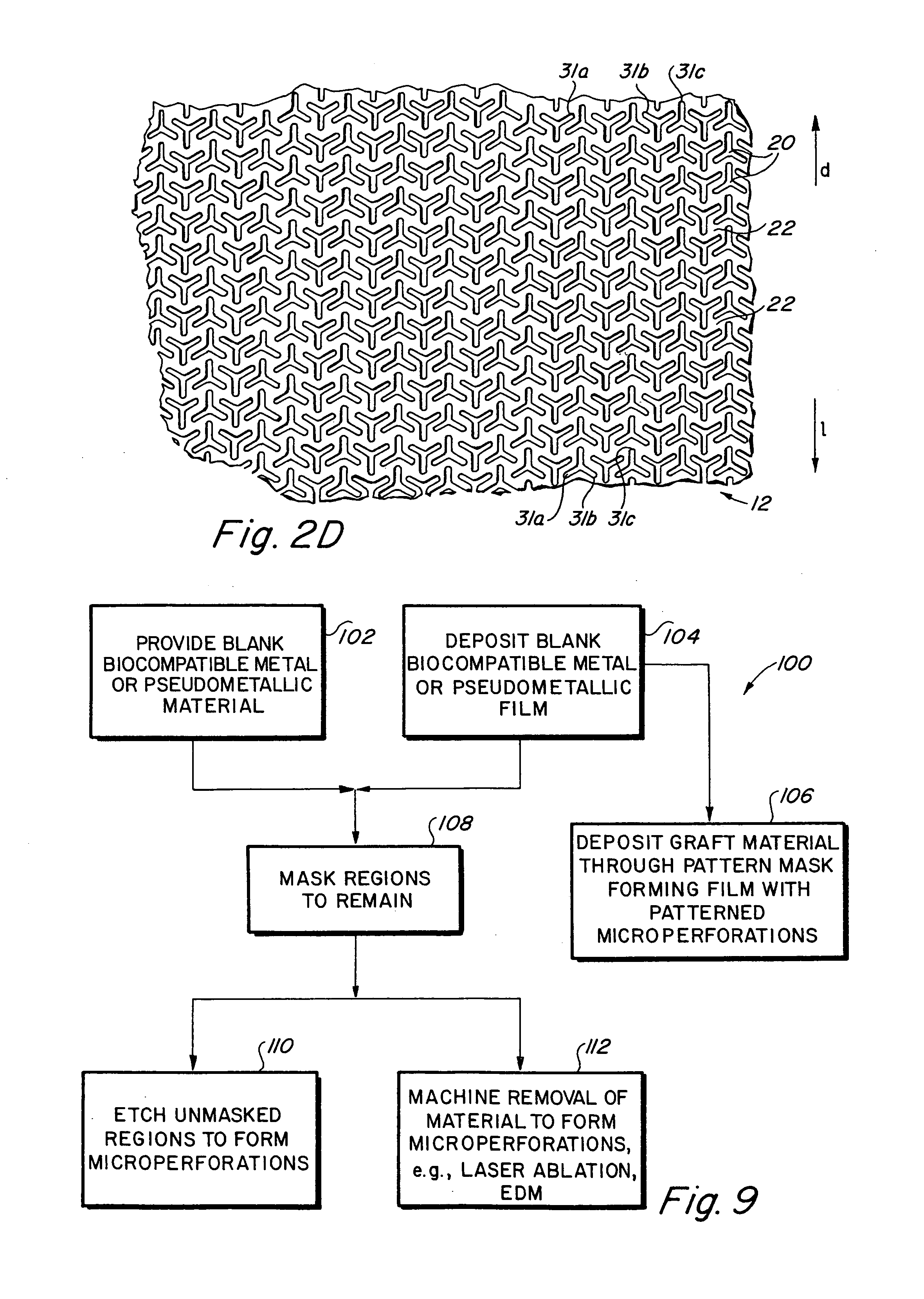
Implantable medical grafts fabricated of metallic or pseudometallic films of biocompatible materials having a plurality of microperforations passing through the film in a pattern that imparts fabric-like qualities to the graft or permits the geometric deformation of the graft. The implantable graft is preferably fabricated by vacuum deposition of metallic and / or pseudometallic materials into either single or multi-layered structures with the plurality of microperforations either being formed during deposition or after deposition by selective removal of sections of the deposited film. The implantable medical grafts are suitable for use as endoluminal or surgical grafts and may be used as vascular grafts, stent-grafts, skin grafts, shunts, bone grafts, surgical patches, non-vascular conduits, valvular leaflets, filters, occlusion membranes, artificial sphincters, tendons and ligaments.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
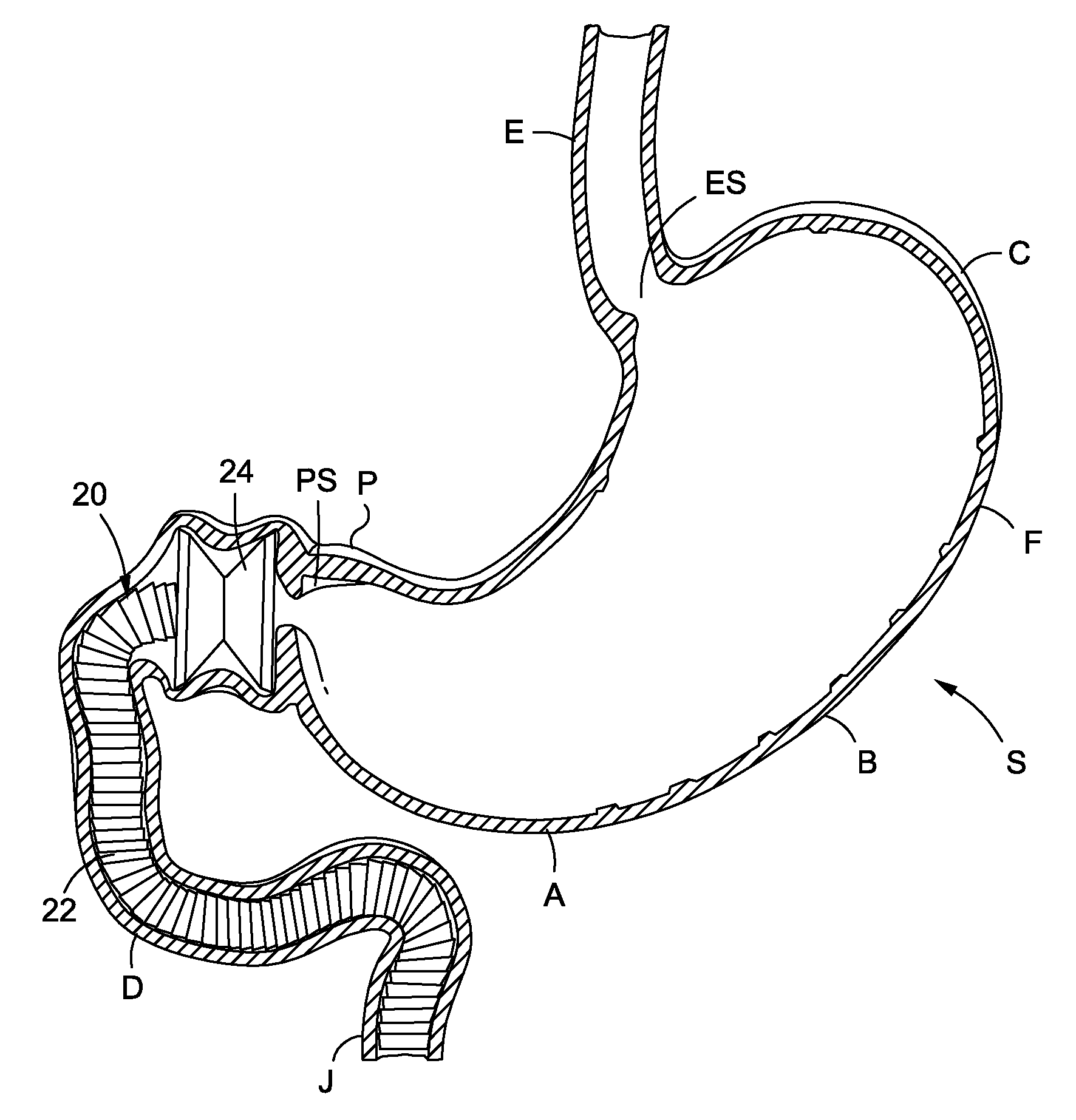
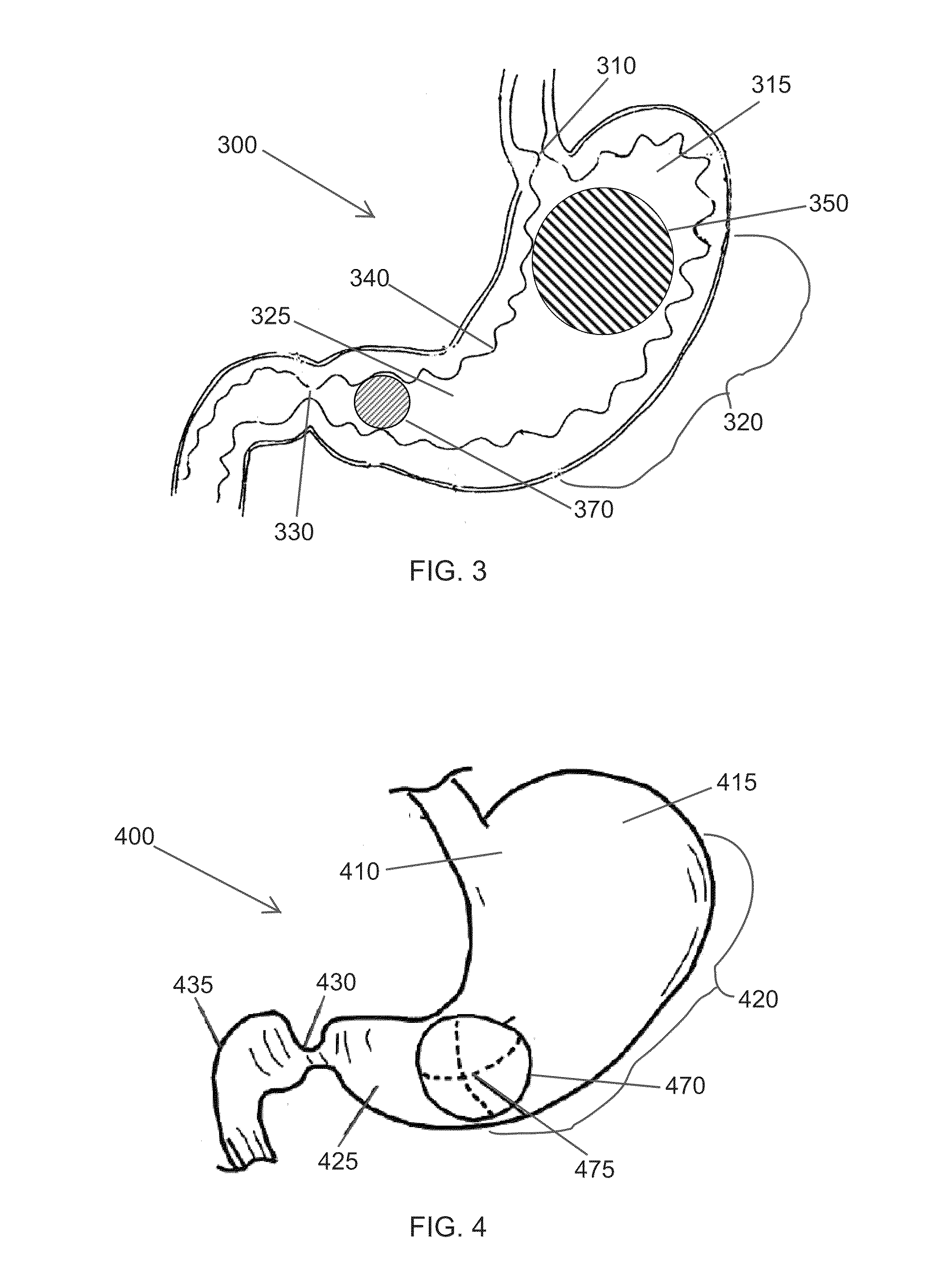
Obesity treatment tools and methods
Various obesity treatment tools and methods are described herein, as well as treatments for other gastric-related diseases, e.g., GERD. Treatment includes reducing the size of the stomach pouch to limit the caloric intake as well as to provide an earlier feeling of satiety. This may be done by creating a smaller gastric pouch within the stomach directly from the interior of the stomach itself. The smaller pouches may be made through the use of individual anchoring devices, rotating probes, or volume reduction devices. A pyloroplasty procedure may also be performed to render the pyloric sphincter incompetent. A gastric bypass procedure may additionally be performed using atraumatic magnetic anastomoses devices so that sugars and fats are passed directly to the bowel while bypassing the stomach. Many of these procedures may be done in a variety of combinations. Treatment may create enforced behavioral modifications by discouraging the ingestion of high-caloric foods.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Injectable hollow tissue filler
The present invention comprises a plurality of injectable hollow particulate fillers suspended in a biocompatible fluid carrier to significantly improve the clumping resistance and injectability of the composition. The hollow particulate fillers have a lower effective density and are able to suspend in the carrier without precipitation. The loss of skin volume as a result of aging, diseases, weight loss, and injury can lead to uneven skin surface (e.g. wrinkle, etc.). The uneven skin can be repaired by injecting appropriate amount of hollow fillers underneath the skin. Some cases of urinary incontinence occur when the resistance to urine flow has decreased excessively. Continence is restored by injecting the present invention to the urethra tissue to increase resistance to urine outflow. Similarly, the present invention allows for the control of gastric fluid reflux by submucosal injections of the fillers to the esophageal-gastric and gastric-pyloric junction. For patients with vesicoureteral reflux, it can be treated by injection of the present invention into patients' ureteral tissue. This invention can also be used to repair defective or inadequately functioning muscles of the anal sphincter by administering an effective amount of injectable hollow fillers into the defect or anal sinuses.
Owner:CHU JACK FA DE
Compliant implantable medical devices and methods of making same
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
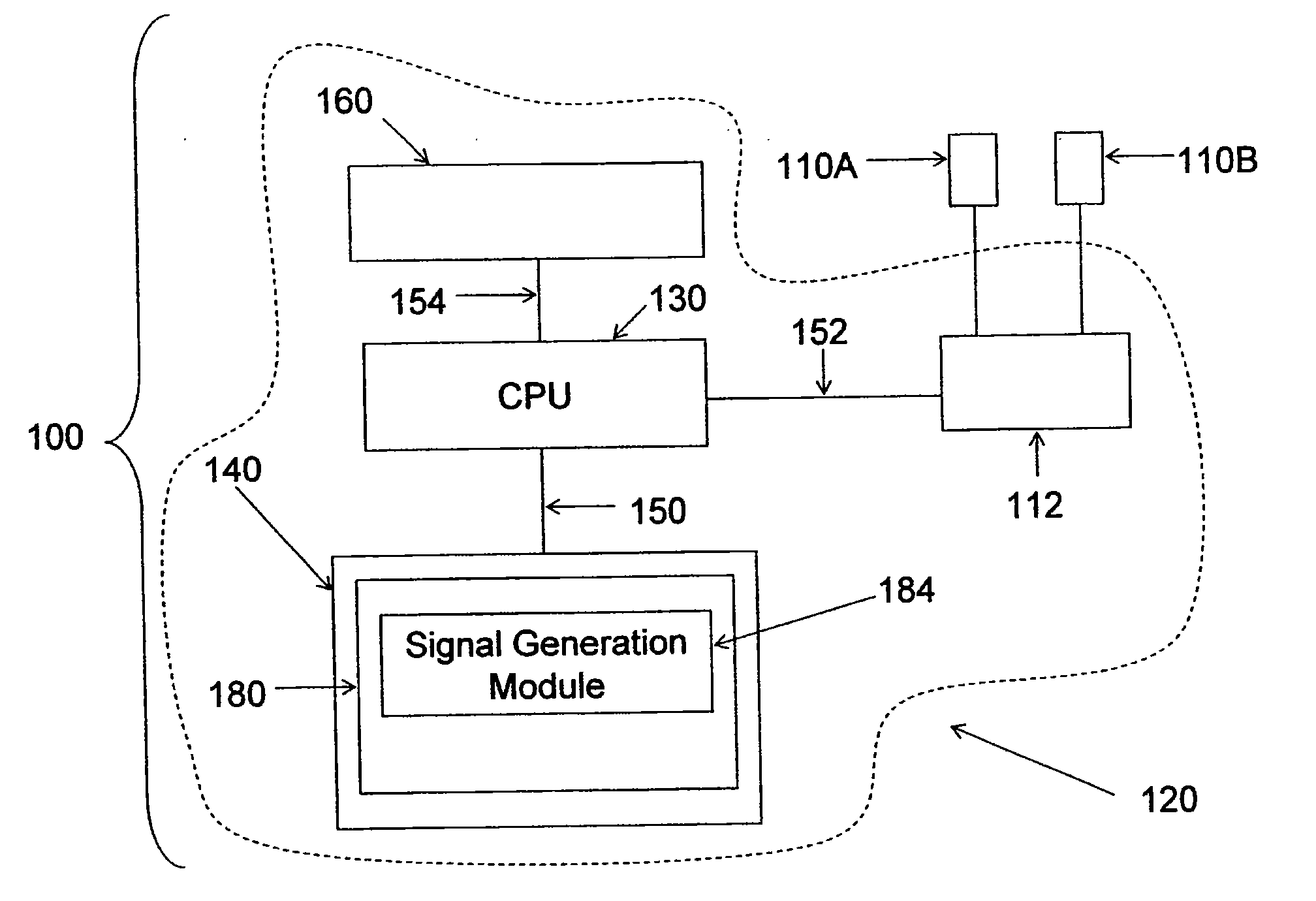
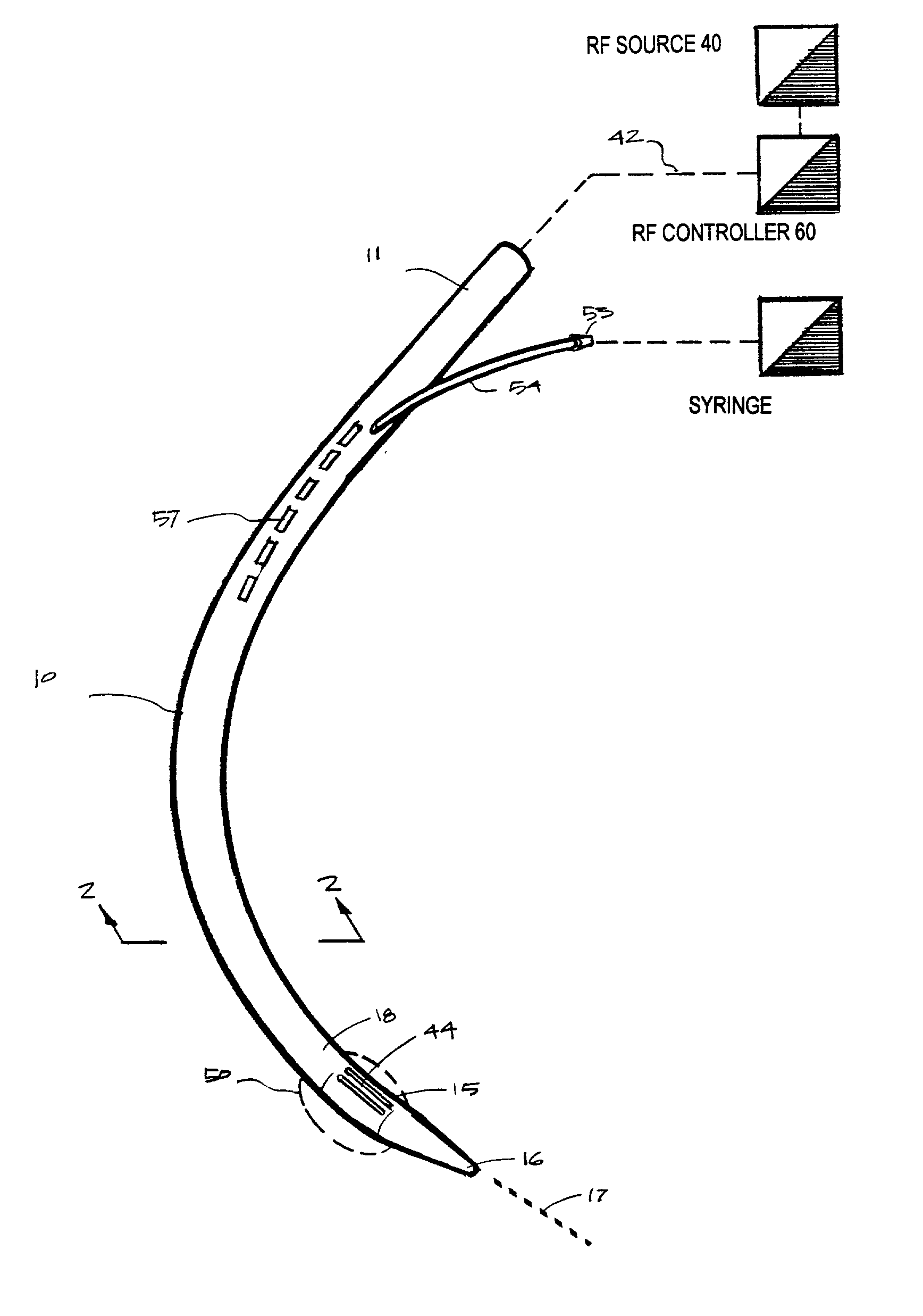
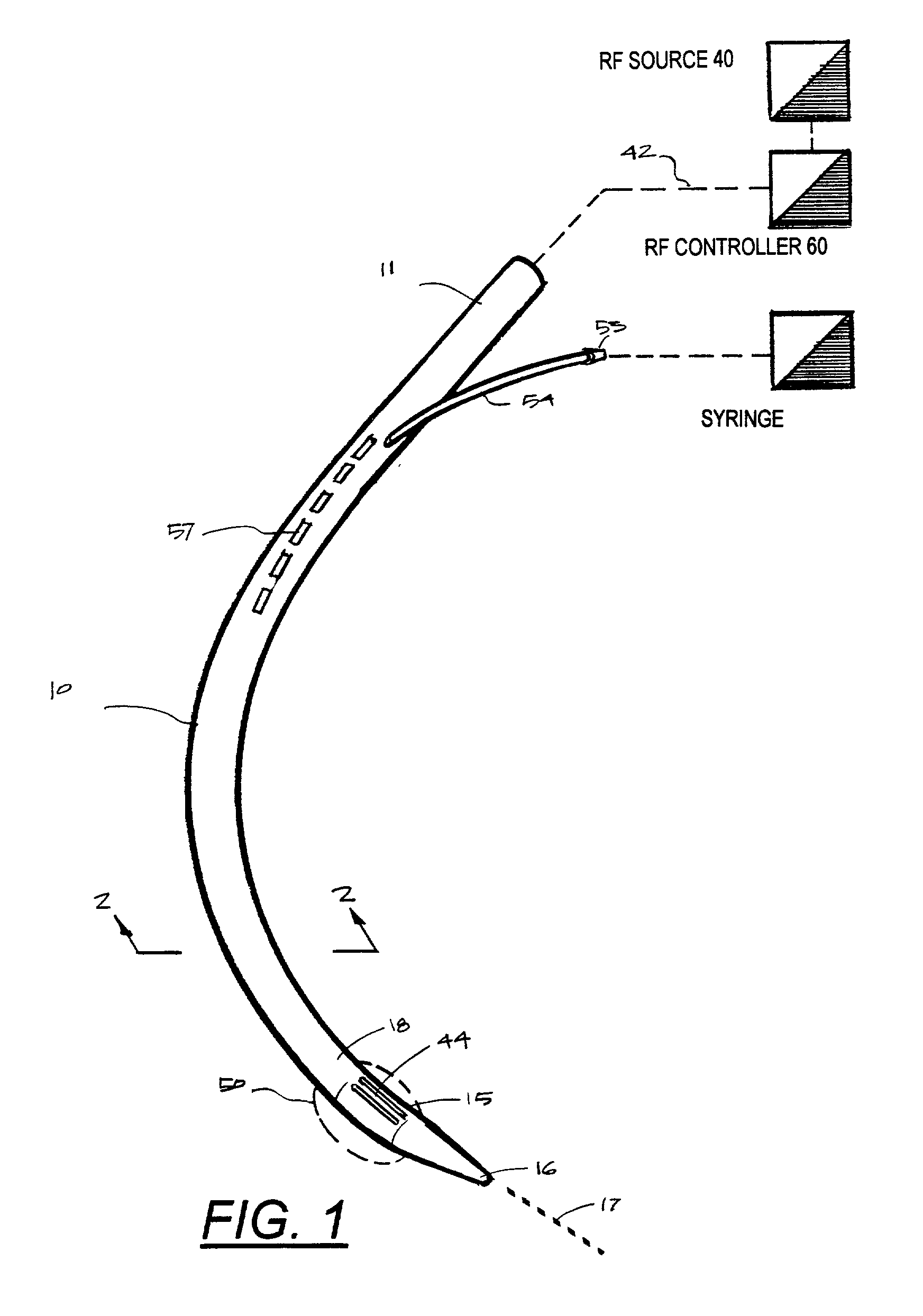
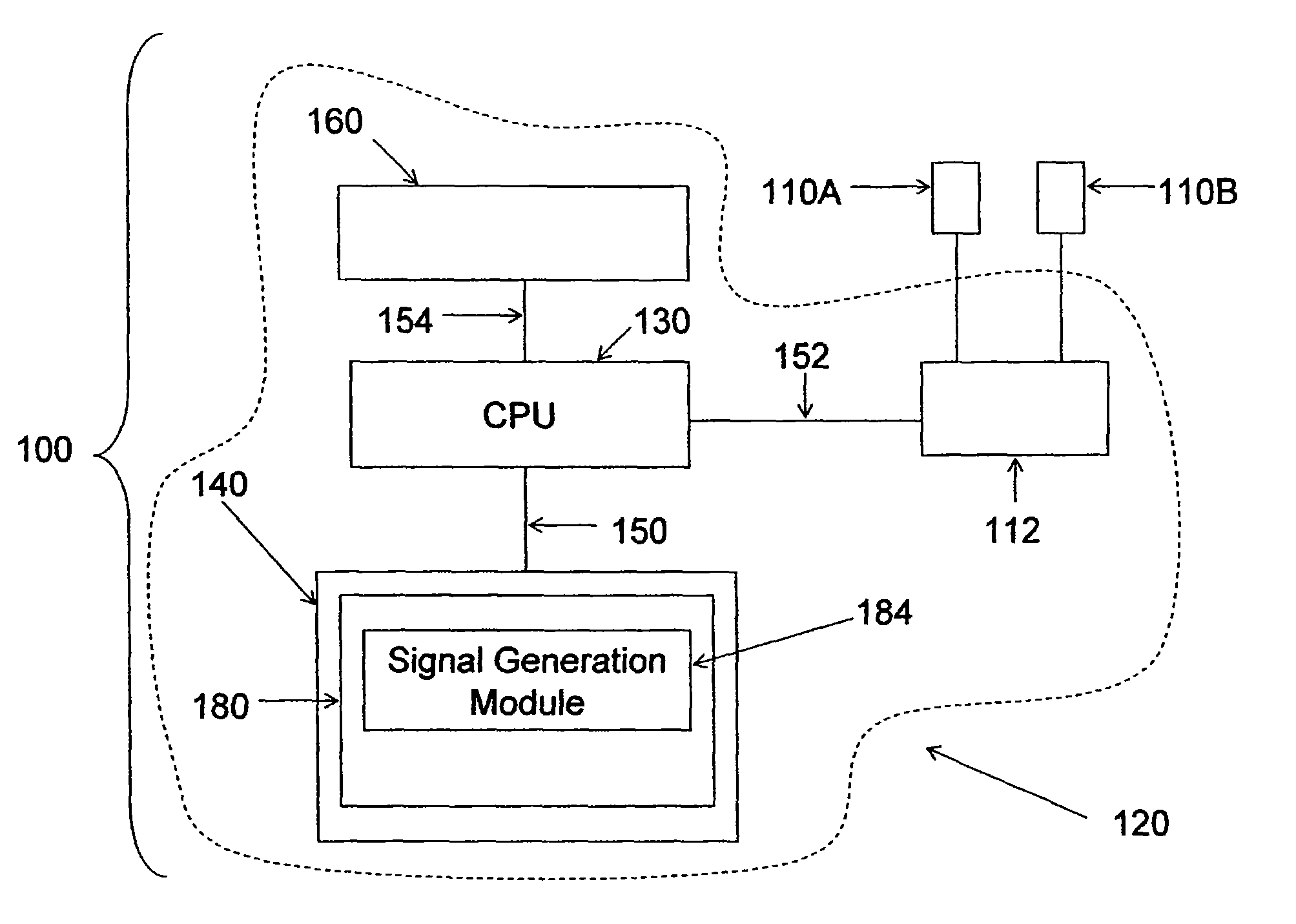
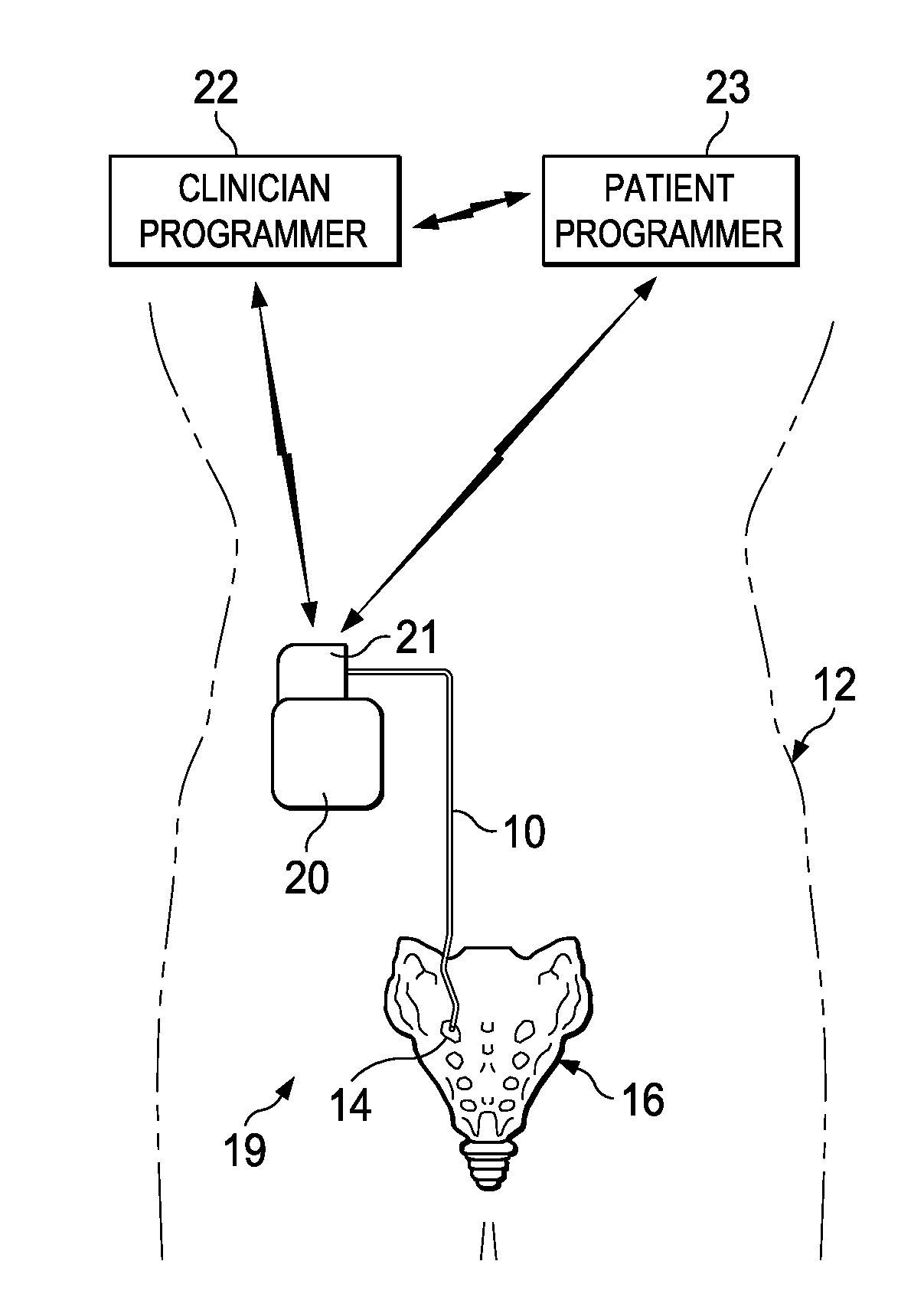
Device and implantation system for electrical stimulation of biological systems
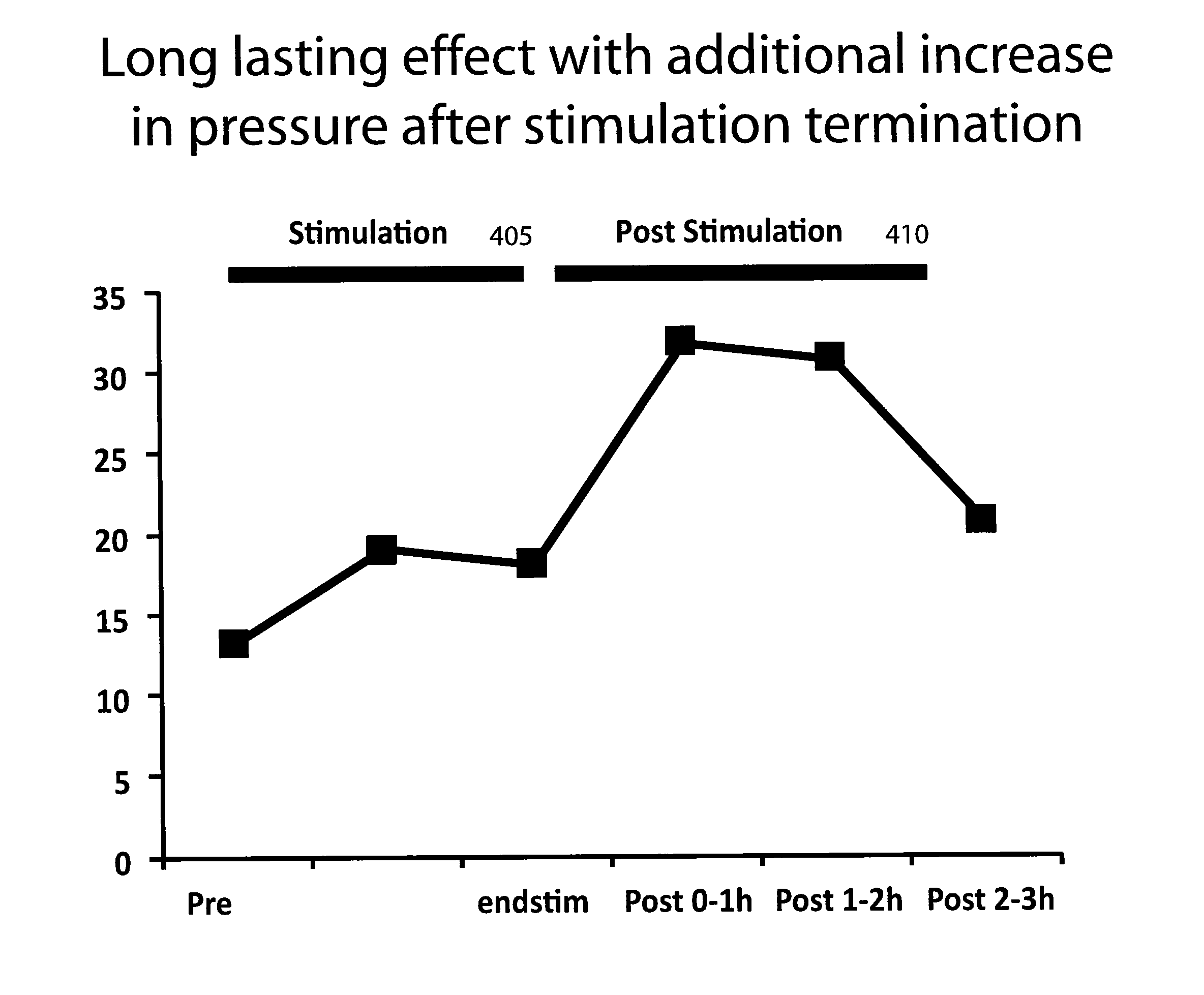
ActiveUS20110307027A1Increase pressureKeep the pressureImplantable neurostimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPhysical therapy
The present specification discloses devices and methodologies for the treatment of GERD. Individuals with GERD may be treated by implanting a stimulation device within the patient's lower esophageal sphincter and applying electrical stimulation to the patient's lower esophageal sphincter, in accordance with certain predefined protocols. The presently disclosed devices have a simplified design because they do not require sensing systems capable of sensing when a person is engaged in a wet swallow and have improved energy storage requirements.
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC
Obesity treatment tools and methods
InactiveUS20070118159A1Convenient treatmentMinimal traumaSuture equipmentsStapling toolsDiseasePyloric sphincter
Various obesity treatment tools and methods are described herein, as well as treatments for other gastric-related diseases, e.g., GERD. Treatment includes reducing the size of the stomach pouch to limit the caloric intake as well as to provide an earlier feeling of satiety. This may be done by creating a smaller gastric pouch within the stomach directly from the interior of the stomach itself. The smaller pouches may be made through the use of individual anchoring devices, rotating probes, or volume reduction devices. A pyloroplasty procedure may also be performed to render the pyloric sphincter incompetent. A gastric bypass procedure may additionally be performed using atraumatic magnetic anastomoses devices so that sugars and fats are passed directly to the bowel while bypassing the stomach. Many of these procedures may be done in a variety of combinations. Treatment may create enforced behavioral modifications by discouraging the ingestion of high-caloric foods.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
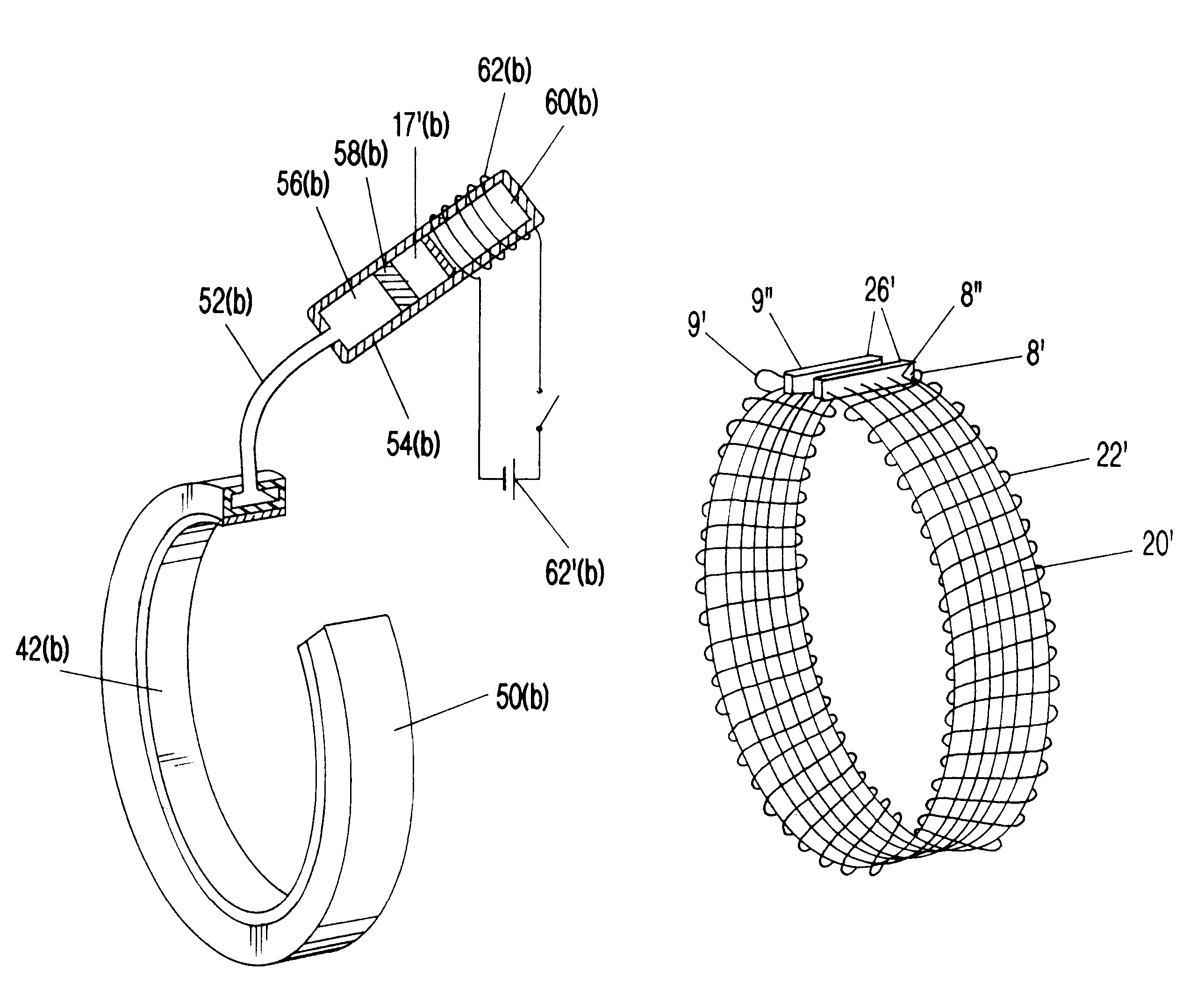
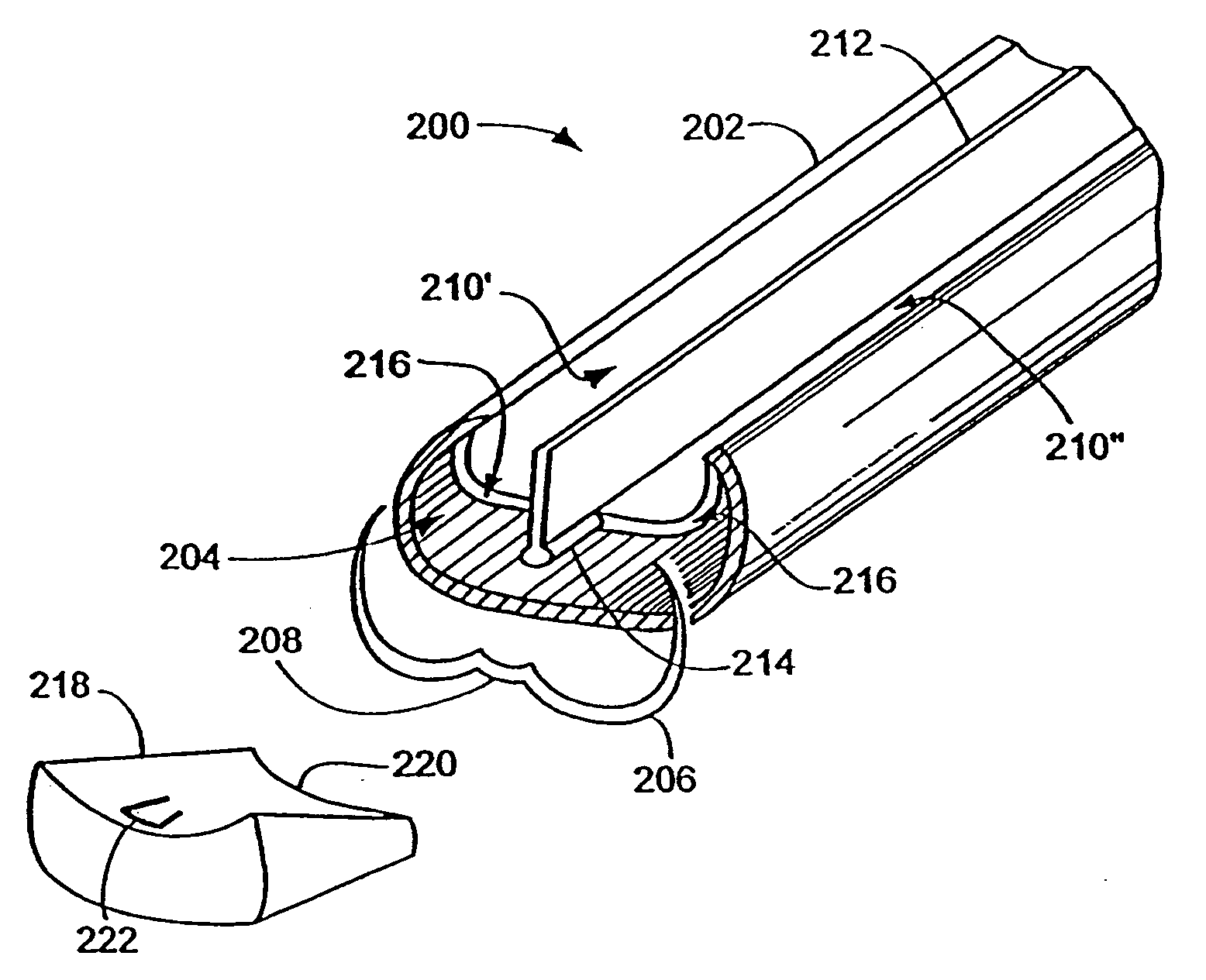
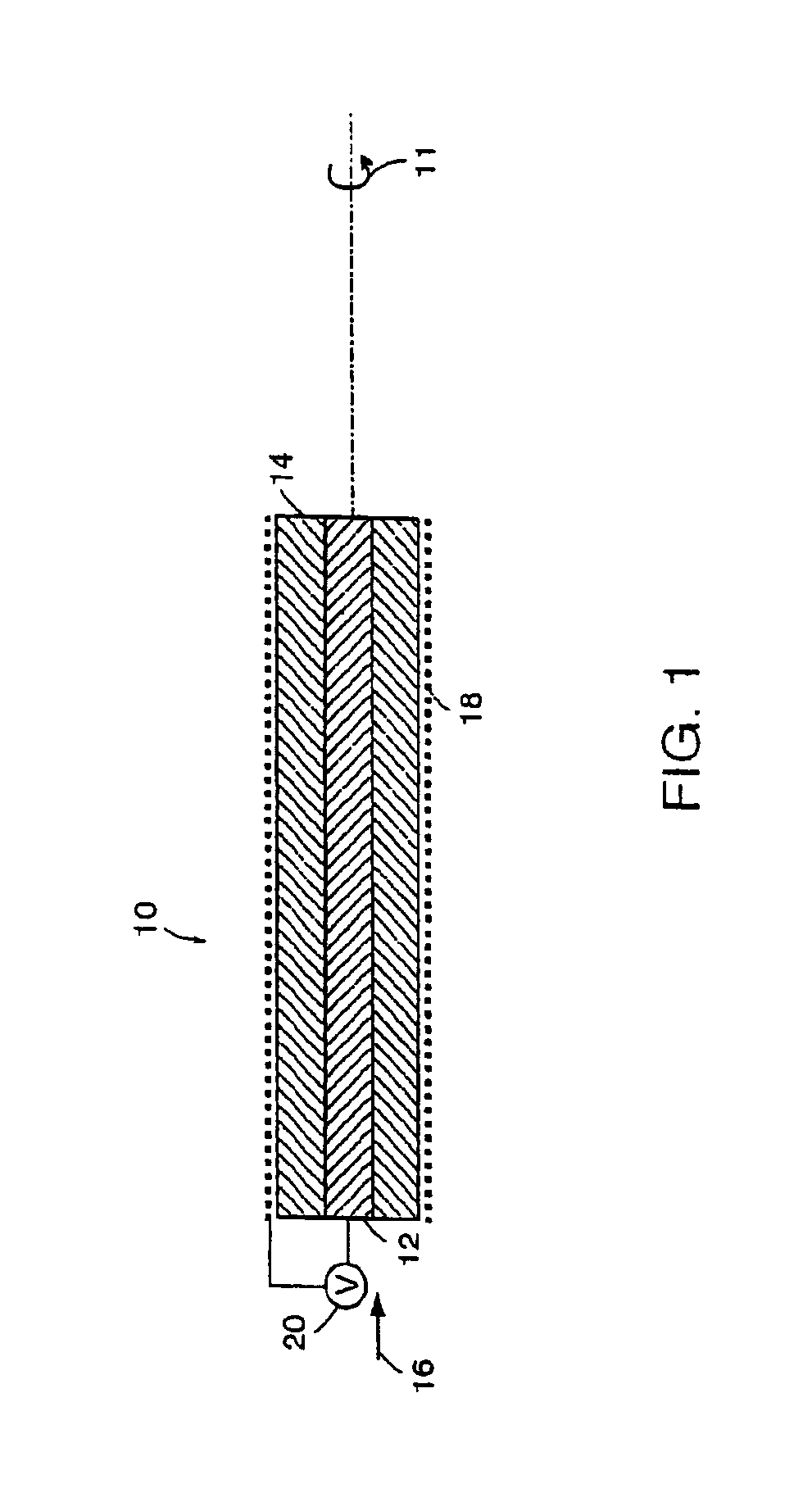
Electroactive polymer based artificial sphincters and artificial muscle patches
InactiveUS6921360B2Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunctionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryLower esophagusElectroactive polymer actuators
Provided are artificial muscle patches, which are adapted to be implanted adjacent a patient's heart, and artificial sphincter cuffs, which are adapted to be implanted around a body lumen, such as the urethra, the anal canal, or the lower esophagus. The devices of the present invention comprise: (a) one or more electroactive polymer actuators; and (b) a control unit for electrically controlling the one or more electroactive polymer actuators to expand or contract the devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device and implantation system for electrical stimulation of biological systems
ActiveUS20110295336A1Less energyImproved LES functionImplantable neurostimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPhysical therapy
The present specification discloses devices and methodologies for the treatment of diurnal GERD. Individuals with GERD may be treated by implanting a stimulation device within the patient's lower esophageal sphincter and applying electrical stimulation to the patient's lower esophageal sphincter, in accordance with certain predefined protocols. The presently disclosed devices have a simplified design because they do not require sensing systems capable of sensing when a person is engaged in a wet swallow and have improved energy storage requirements.
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC
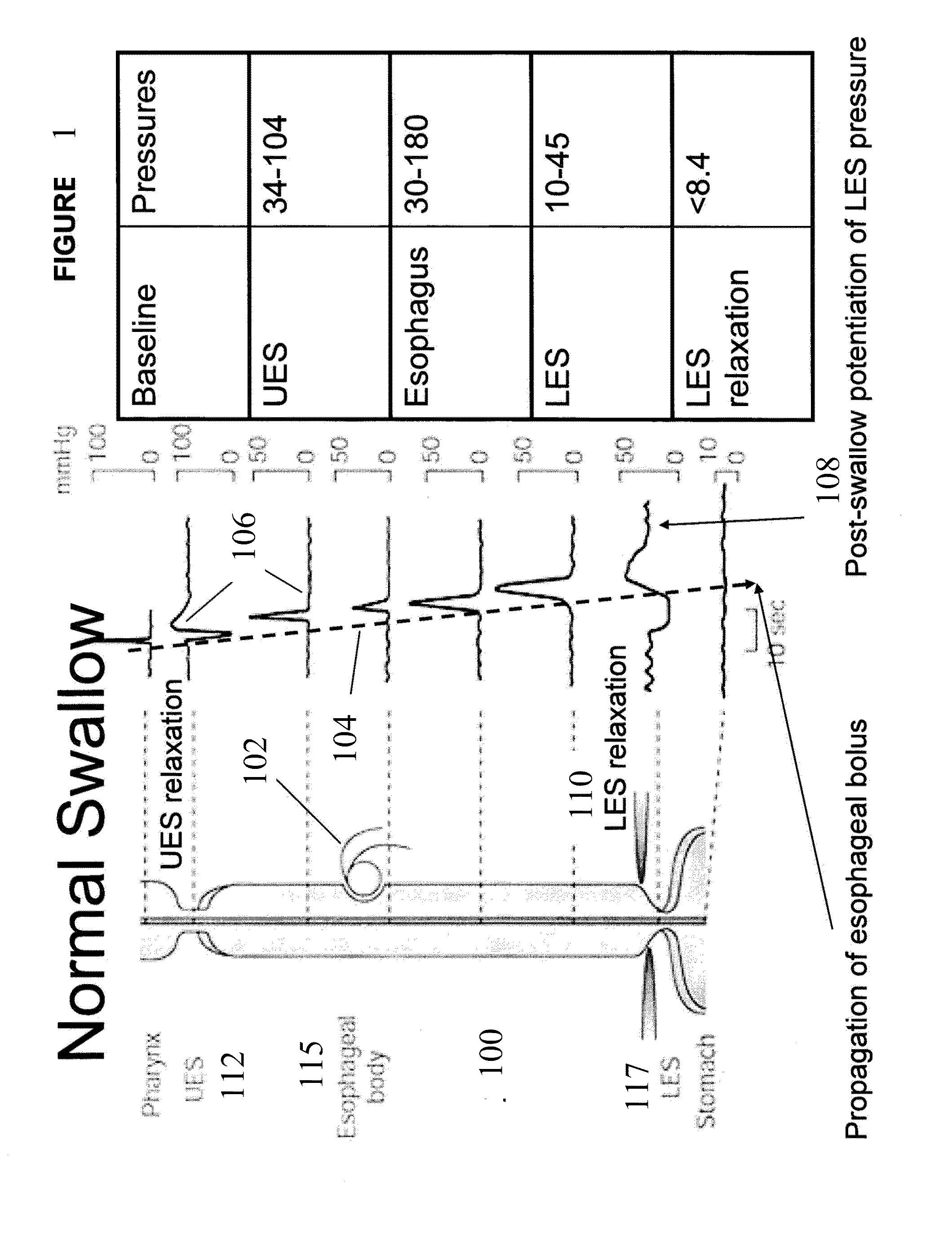
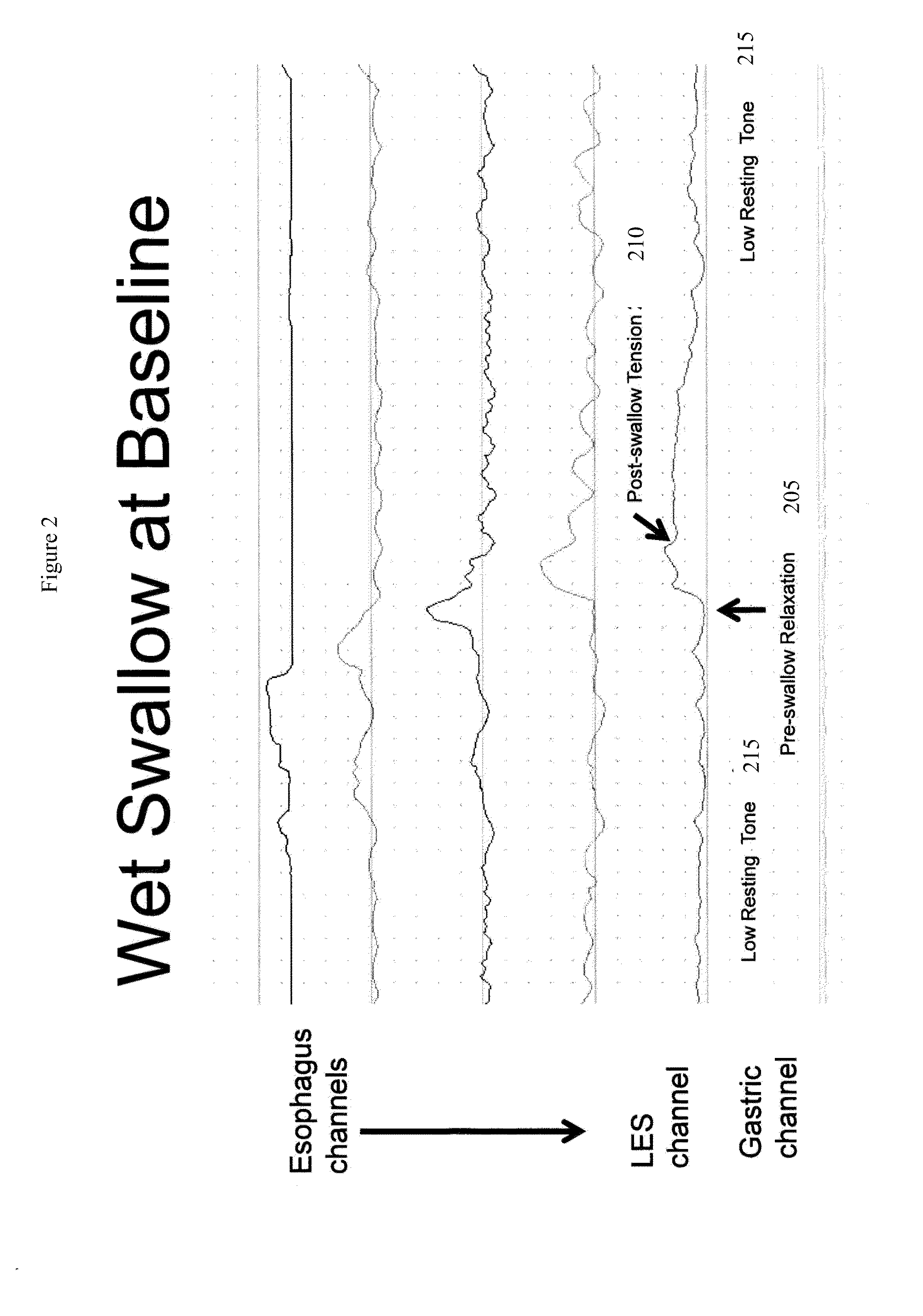
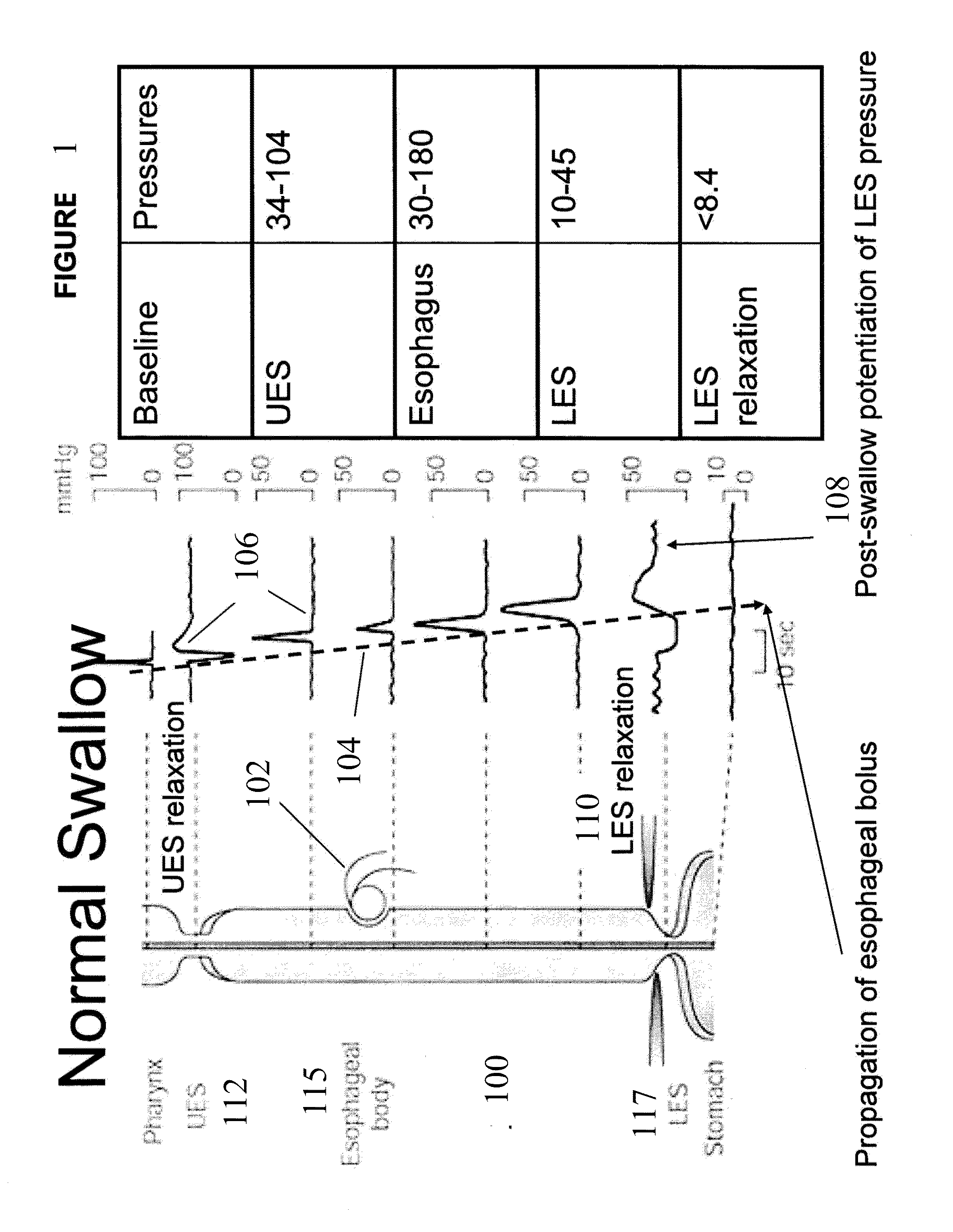
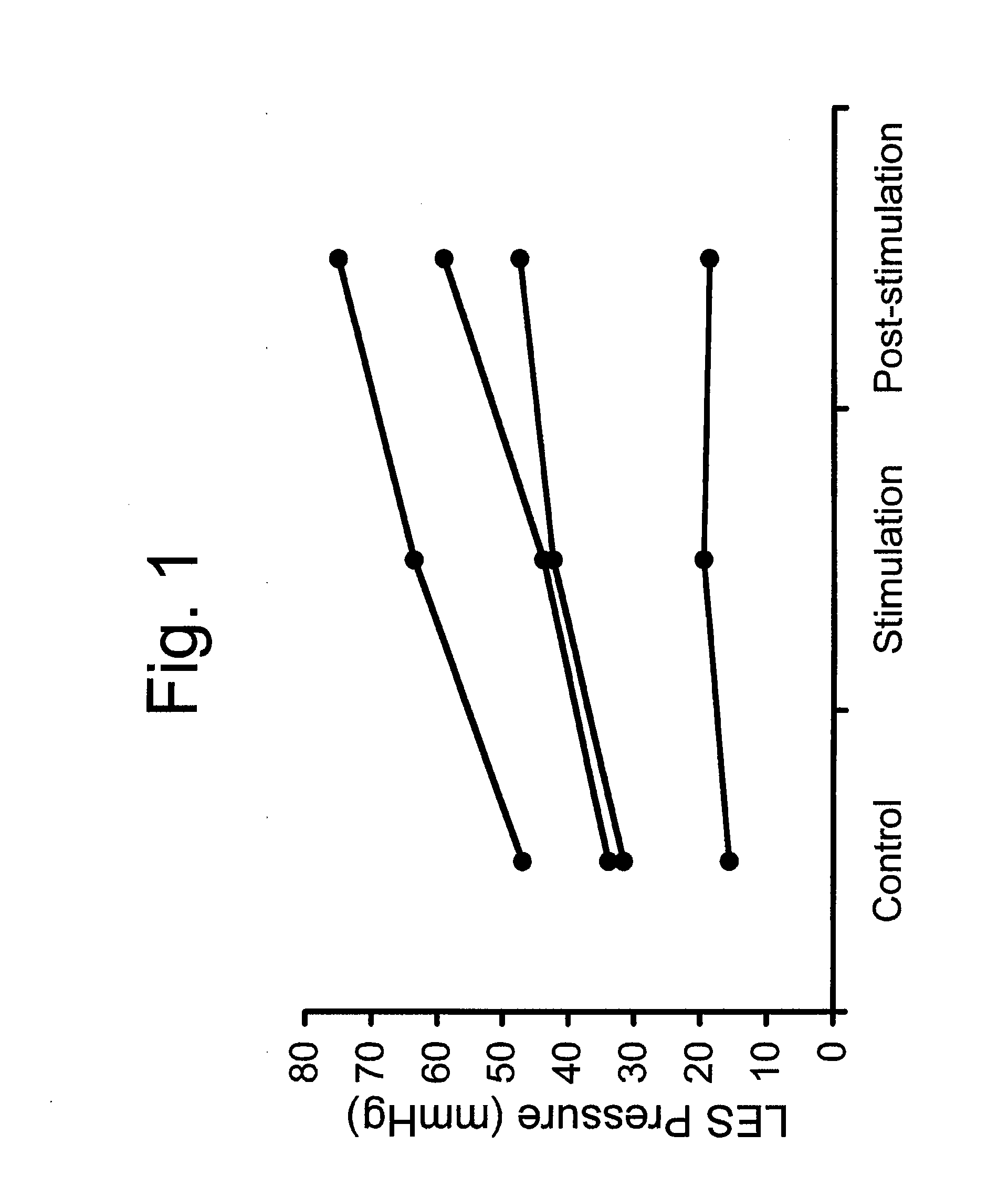
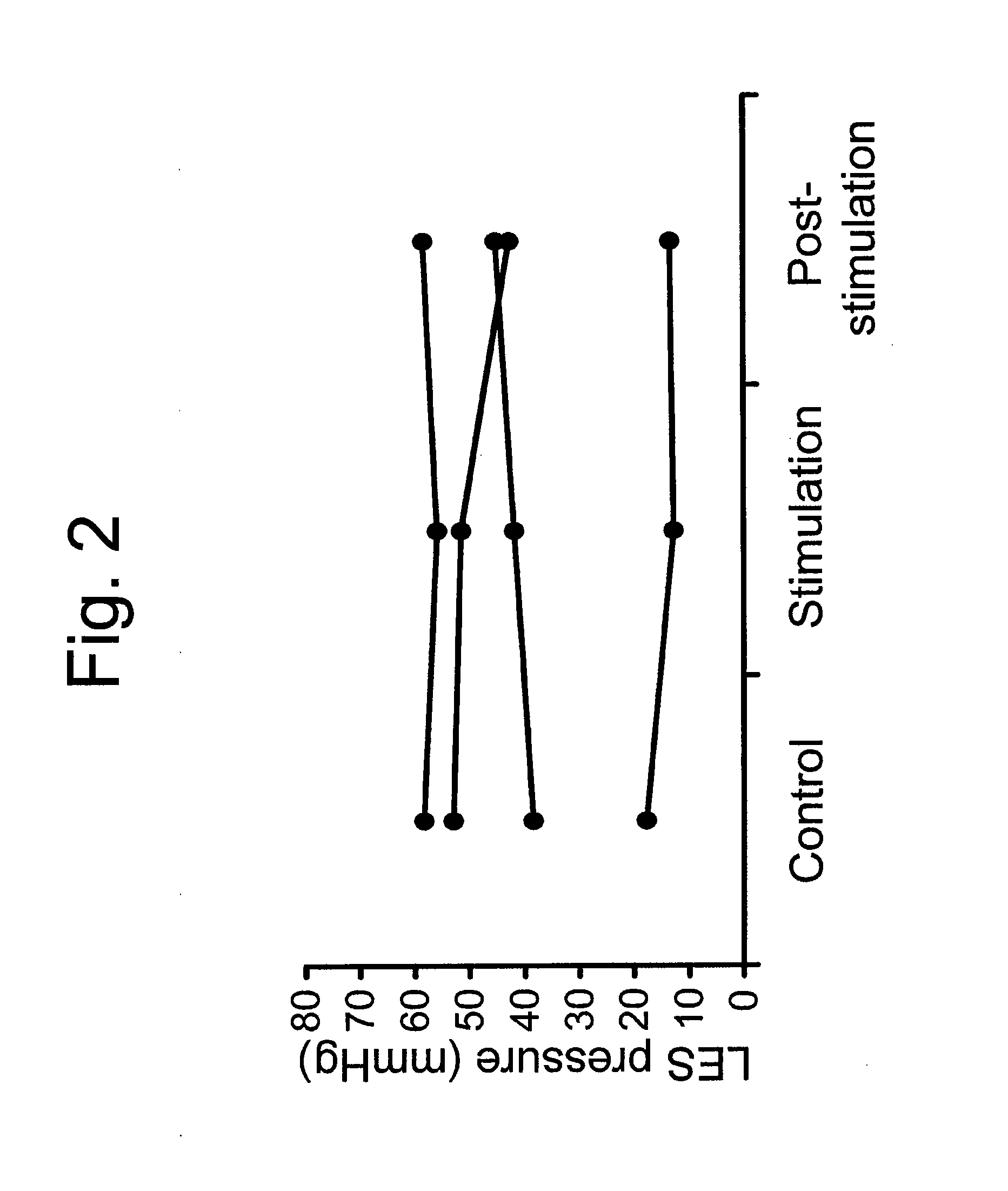
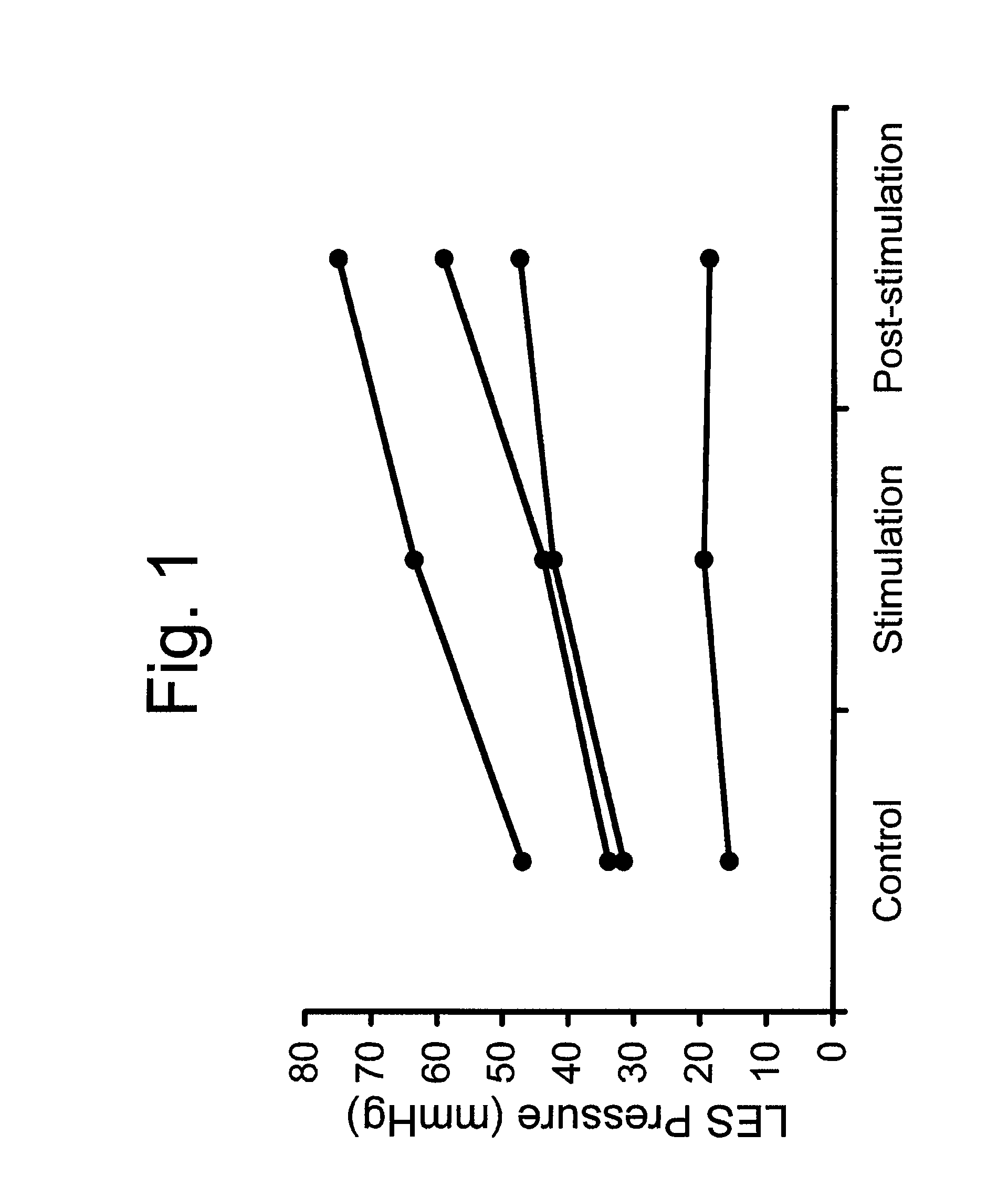
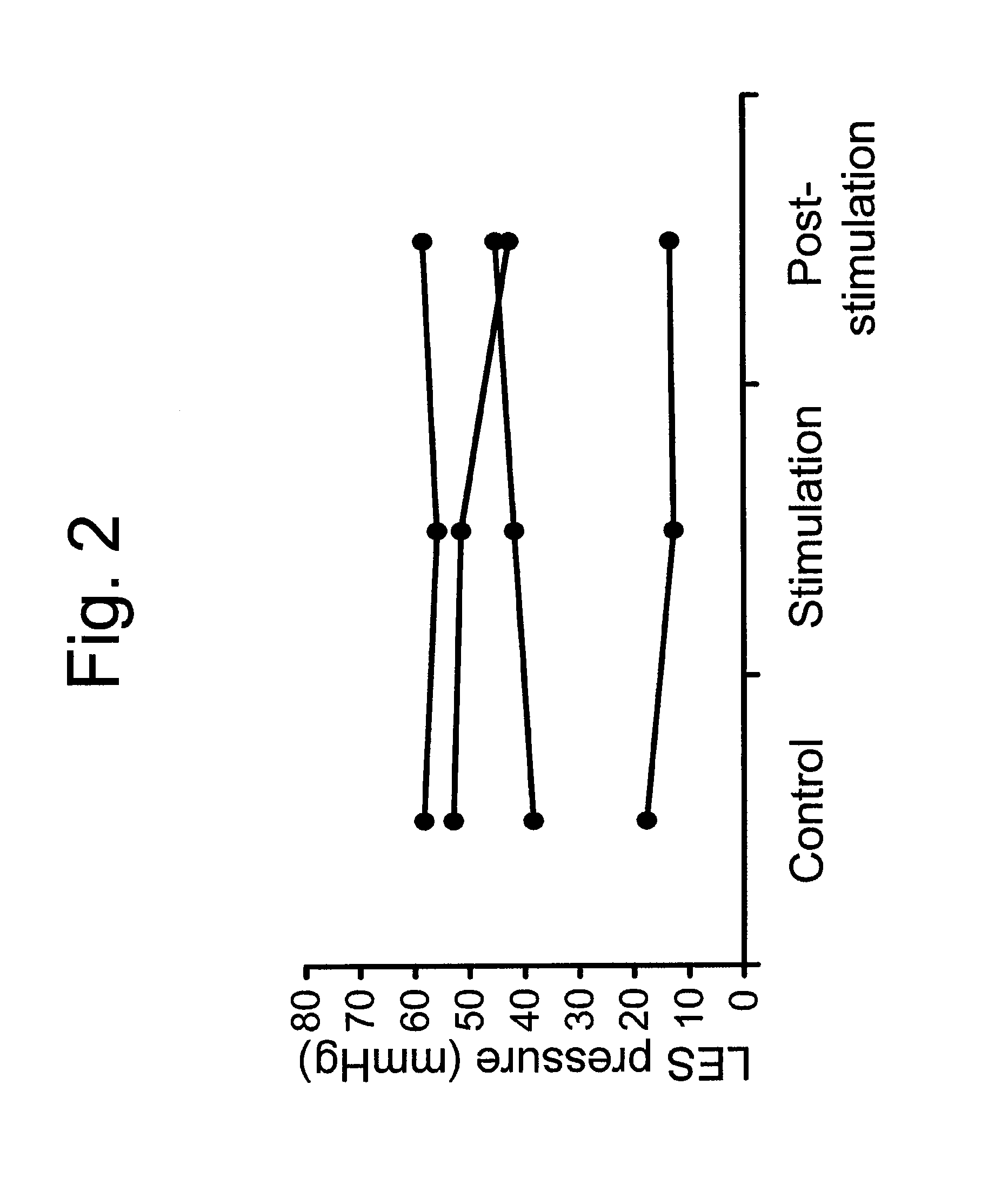
Use of electrical stimulation of the lower esophageal sphincter to modulate lower esophageal sphincter pressure
ActiveUS20090132001A1Decreasing esophageal pressureIncrease pressureElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineHigh frequency stimulation
The present invention describes methods and devices using low frequency electrical stimulation or neural high frequency stimulation to modulate lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure. The electrical stimulation may be delivered to the LES via one or more electrodes that is placed in contact with the LES tissue. The methods and devices are useful to treat a number of conditions or disease conditions, including for example, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC
Surgical instruments for treating gastro-esphageal reflux
Instruments for thermally-mediated treatment of a patient's lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to induce an injury healing response to thereby populate the extracellular compartment of walls of the LES with collagen matrices to altere the biomechanics of the LES to provide an increased intra-esophageal pressure for preventing acid reflux. A preferred embodiment is a bougie-type device for trans-esophageal introduction that carries conductive electrodes for delivering Rf energy to walls of the LES (i) to induce the injury healing response or (ii) to "model" collagenous tissues of the LES by shrinking collagen fibers therein. Typically, an Rf source is connected to at least one conductive electrode that may be operated in a mono-polar or bi-polar fashion. A sensor array of individual sensors is provided in the working end. A computer controller is provided, which together with feedback circuitry, is capable of full process monitoring and control of: (i) power delivery; (ii) parameters of a selected therapeutic cycle, (iii) mono-polar or bi-polar energy delivery, and (iv) multiplexing of current flow between various paired electrodes. The controller can determine when the treatment is completed based on time, temperature, tissue impedance or any combination thereof.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Surgical instrument for treating female urinary stress incontinence
InactiveUS20100198002A1High tensile strengthPrevents voiding dysfunctionAnti-incontinence devicesTissue remodelingUrethra
A suburethral sling device and method for treating female urinary stress incontinence which is anatomically configured to implant into the lower abdomen of a female in a manner providing support to mid-urethral and bladder neck sphincteric continence sites with the sling defining in part, mesh and tissue remodeling portions. The sling is deployed via a sling transfer instrument having distal and proximal ends with the instrument comprising in part a progressively curved shaft portion positioned between the distal and proximal ends. An insertion handle of the transfer instrument is secured to the curved metal shaft section guiding the shaft tip through the tissues of the abdomen in an anterior / posterior direction as well as a cephalad / caudad direction.
Owner:ODONNELL PAT D
Vaginal operation method for the treatment of anal incontinence in women
ActiveUS20110015474A1Reduce riskLow placementSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesFecal incontinenceVagina
There is disclosed a method for treating anal incontinence in women. The method comprises accessing the rectum or colon or anus though an incision in the vagina and implanting a powered restriction device on the rectum, colon or anal sphincter. There are also disclosed methods for energizing and controlling the restriction device.
Owner:FORSELL PETER
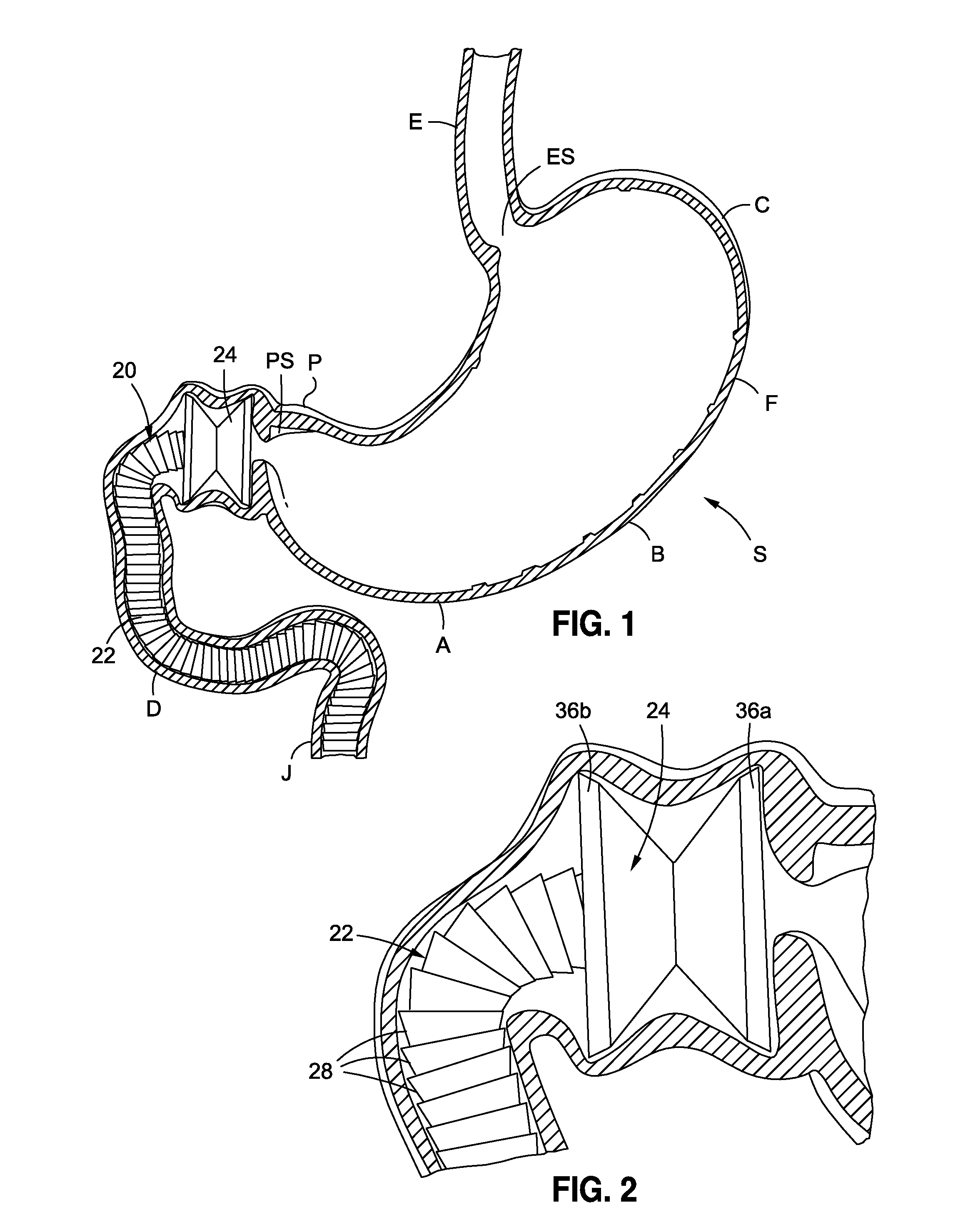
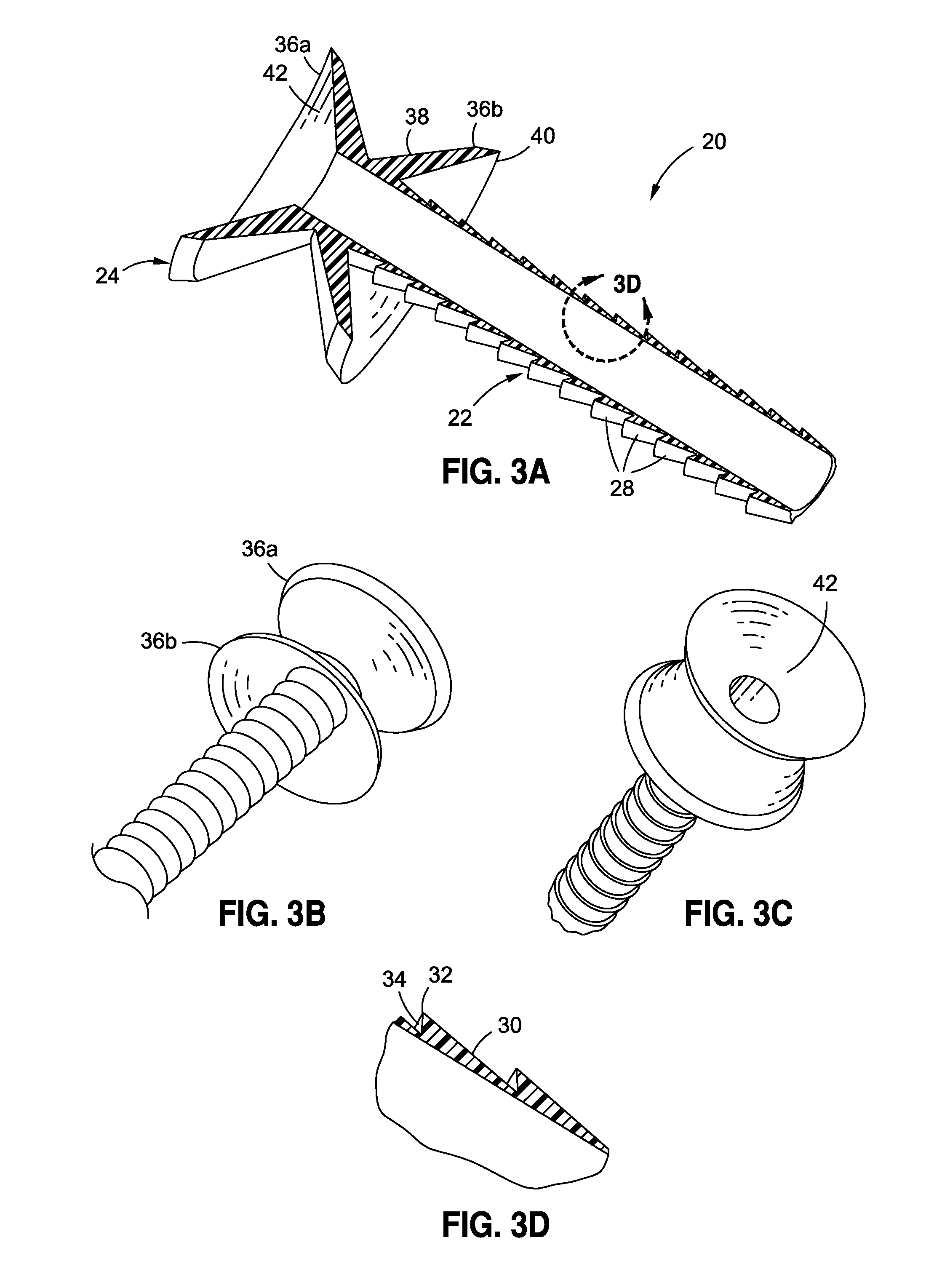
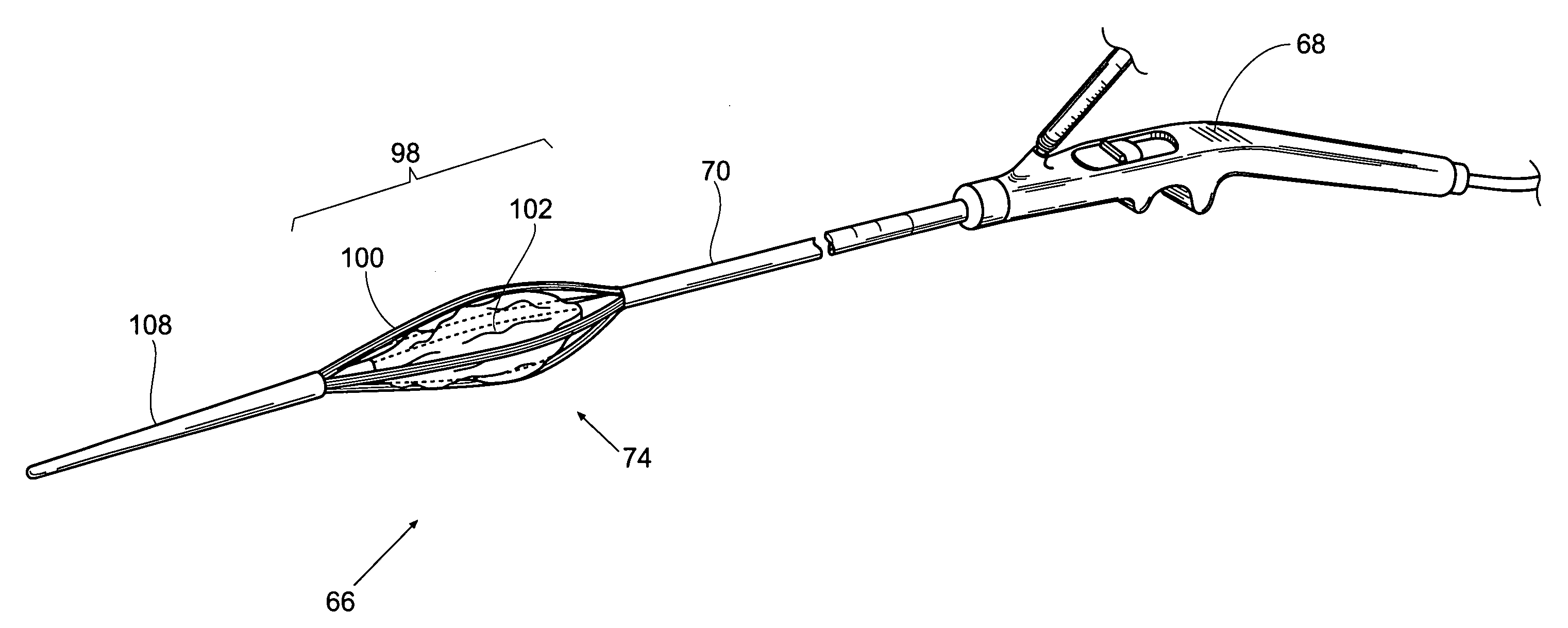
Anchored non-piercing duodenal sleeve and delivery systems
InactiveUS20120095483A1Easy to disassembleSimple structureObesity treatmentWound clampsGastric emptyingPyloric sphincter
An intragastric implant for obesity treatment is disclosed. The device delays digestion by providing a duodenal sleeve, and may also slows gastric emptying by limiting flow through the pyloric sphincter. The implant includes an elongated axially-compressible duodenal sleeve having a non-tissue-piercing anchor on a proximal end sized to lodge within the duodenal bulb. The anchor may have oppositely-directed anchoring flanges to resists migration in both directions. The sleeve may also have barbed ribs to resist proximal movement back up into the stomach. A method of implant includes collapsing / compressing the device and transorally advancing it through the esophagus to be deployed within the duodenum. A dissolvable jacket may constrain the implant for delivery and naturally dissolve upon implant. Removal of the implant may occur in the reverse.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
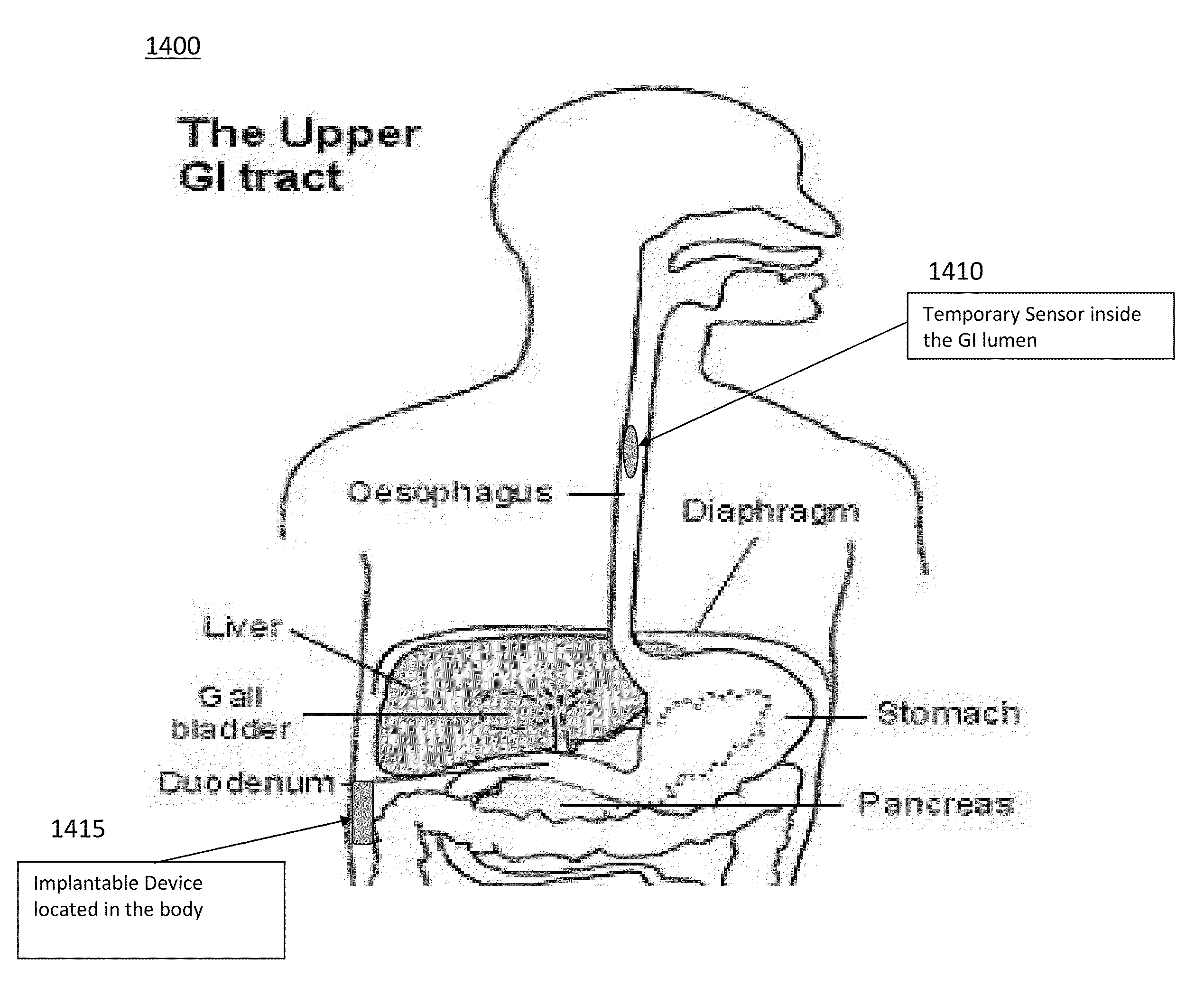
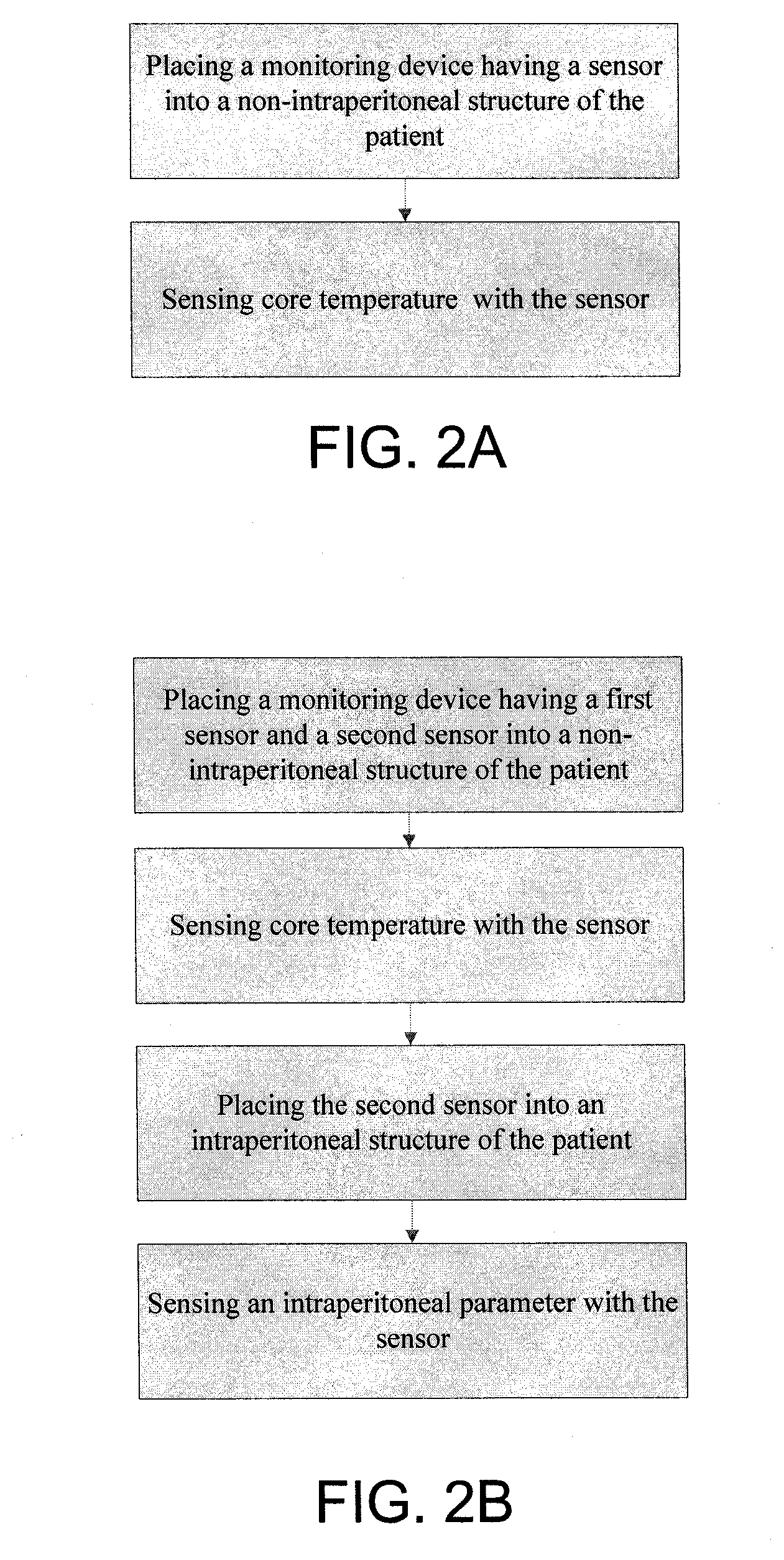
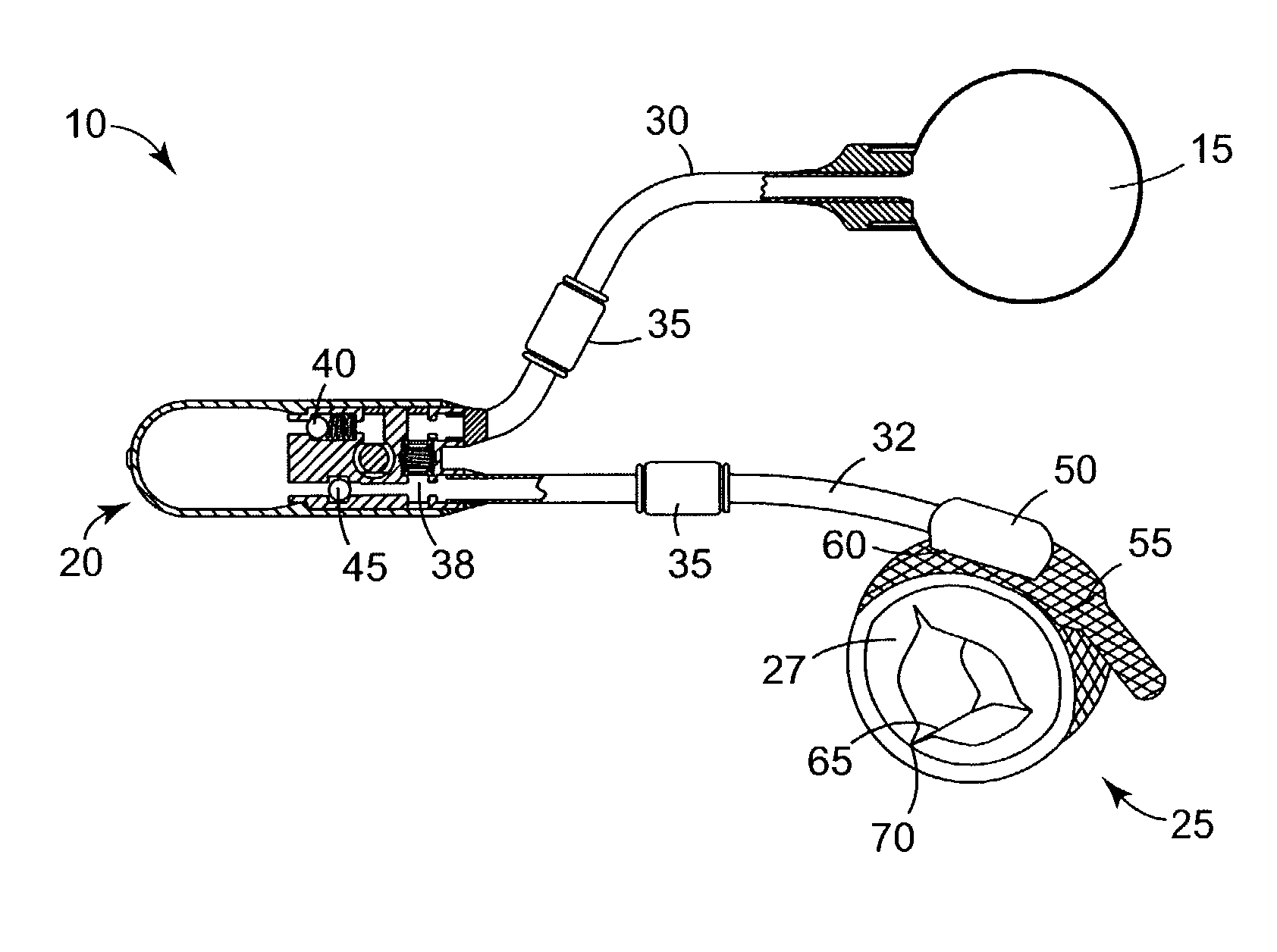
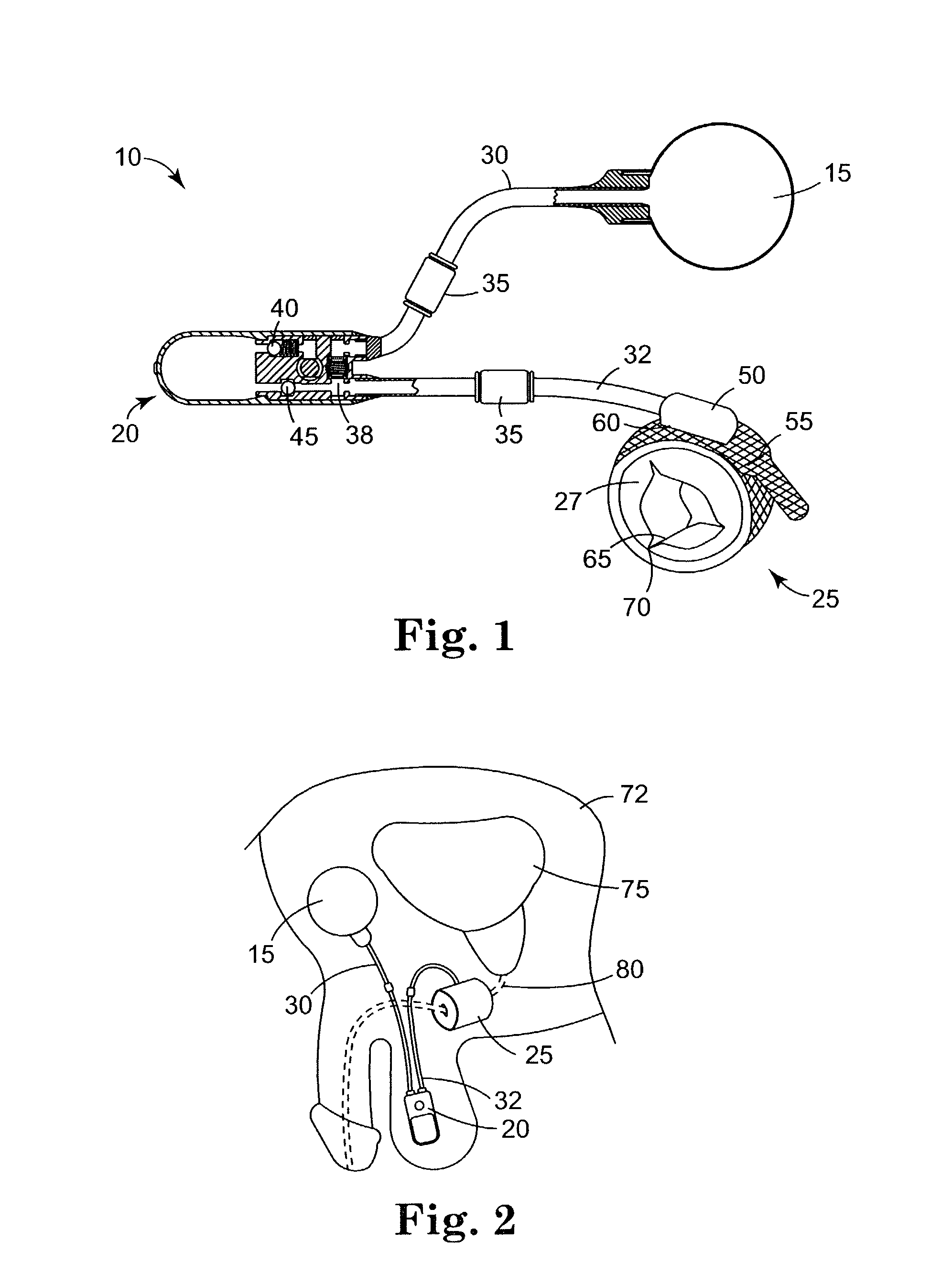
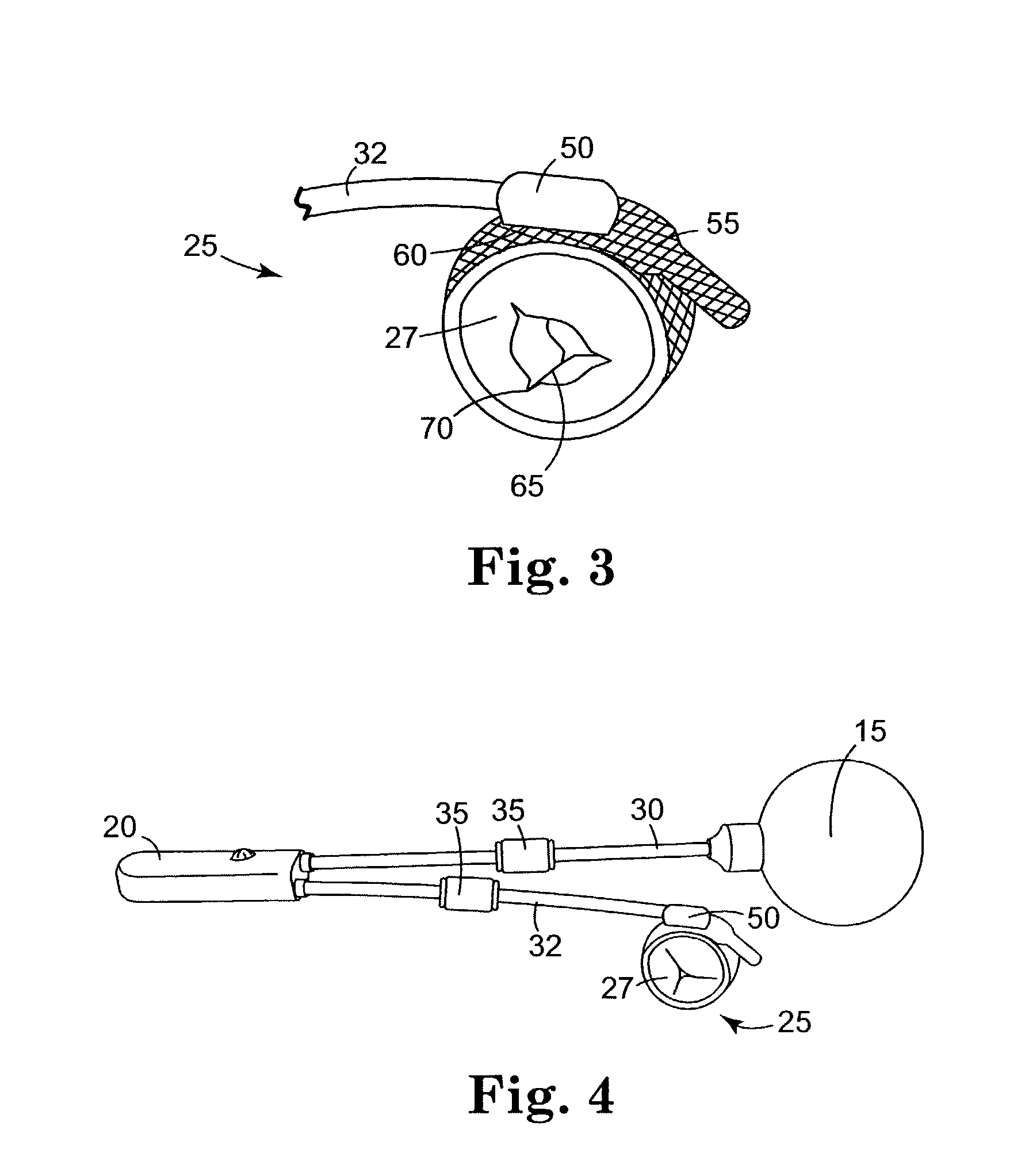
Devices and Methods for Monitoring Core Temperature and an Intraperitoneal Parameter
Methods and apparatus for monitoring core temperature of a patient receiving intraperitoneal hypothermia or hyperthermia are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is placing a monitoring device having a sensor into a non-intraperitoneal cavity of a patient. The non-intraperitoneal cavity can be a urethra, a rectum, an anal sphincter, a stomach, an esophagus, the peripheral vasculature, or a vagina, for example. Another feature is sensing core temperature of the patient with the sensor.
Owner:VELOMEDIX
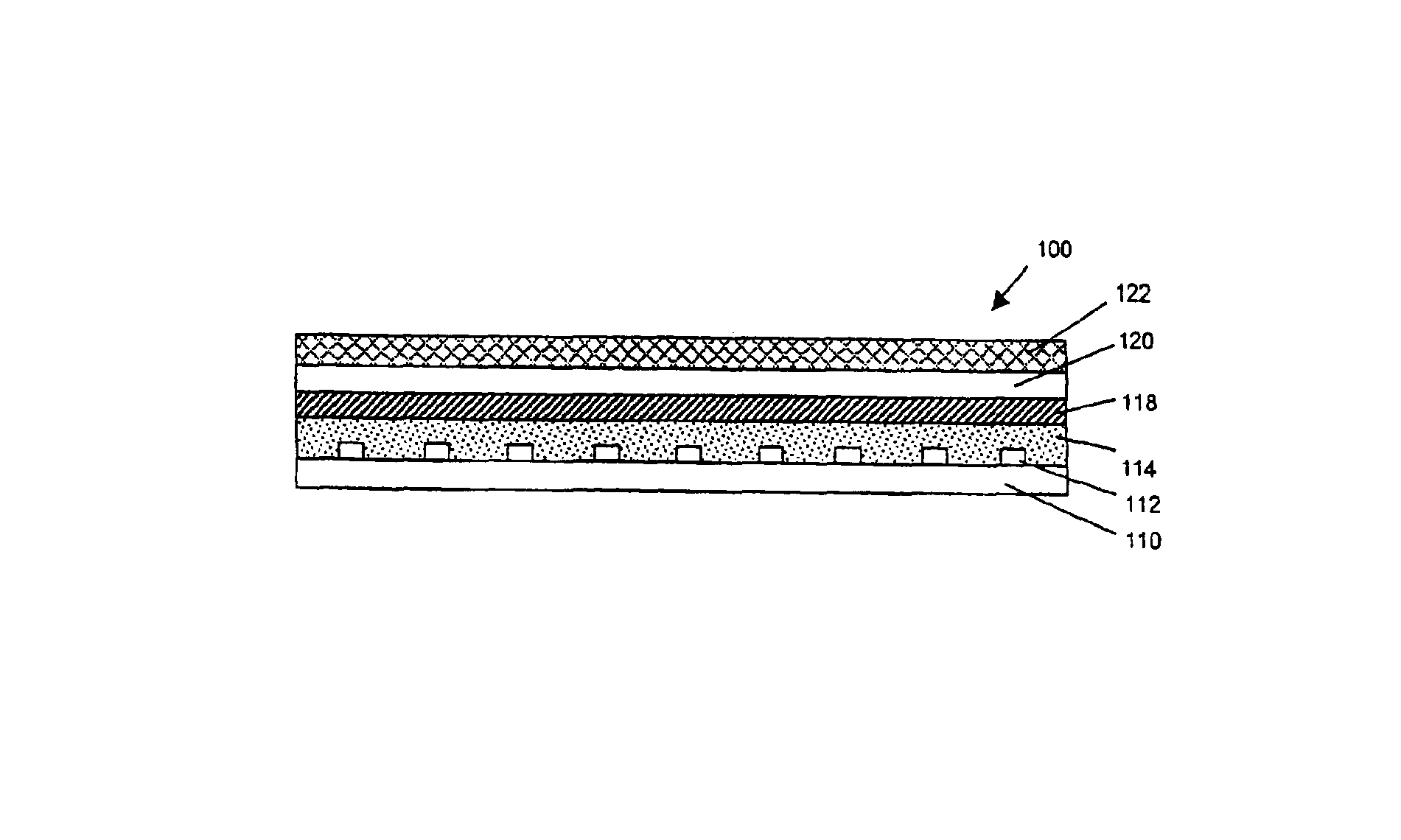
Parylene coated components for artificial sphincters
InactiveUS7011622B2Prevent and inhibit wearPrevent and inhibit and abrasionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryParylene coatingVacuum chamber
This invention provides an artificial sphincter including a component coated on at least one contacting surface with a polymeric material, the polymeric coating adapted to expand and return to an original configuration and to prevent or inhibit wear or abrasion of the contacting surface. The polymeric material is parylene in some embodiments. The component adapted for inflation and deflation may be a cuff formed from silicon and adapted to surround a urethra or a rectum. Also provided by the present invention is a method of depositing a coating to a surface of an inflatable component by providing a vacuum chamber system having an inner chamber positioned within an outer chamber. At least one coating material is introduced into at least one of the inner and outer chambers to deposit a coating onto an exposed surface of the component. This invention also provides methods of masking portions of surfaces of an inflatable component to prevent a coating from being deposited on the masked portion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Use of electrical stimulation of the lower esophageal sphincter to modulate lower esophageal sphincter pressure
The present invention describes methods and devices using low frequency electrical stimulation or neural high frequency stimulation to modulate lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure. The electrical stimulation may be delivered to the LES via one or more electrodes that is placed in contact with the LES tissue. The methods and devices are useful to treat a number of conditions or disease conditions, including for example, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC
Obesity treatment tools and methods
Various obesity treatment tools and methods are described herein, as well as treatments for other gastric-related diseases, e.g., GERD. Treatment includes reducing the size of the stomach pouch to limit the caloric intake as well as to provide an earlier feeling of satiety. This may be done by creating a smaller gastric pouch within the stomach directly from the interior of the stomach itself. The smaller pouches may be made through the use of individual anchoring devices, rotating probes, or volume reduction devices. A pyloroplasty procedure may also be performed to render the pyloric sphincter incompetent. A gastric bypass procedure may additionally be performed using atraumatic magnetic anastomoses devices so that sugars and fats are passed directly to the bowel while bypassing the stomach. Many of these procedures may be done in a variety of combinations. Treatment may create enforced behavioral modifications by discouraging the ingestion of high-caloric foods.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Obesity treatment tools and methods
Various obesity treatment tools and methods are described herein, as well as treatments for other gastric-related diseases, e.g., GERD. Treatment includes reducing the size of the stomach pouch to limit the caloric intake as well as to provide an earlier feeling of satiety. This may be done by creating a smaller gastric pouch within the stomach directly from the interior of the stomach itself. The smaller pouches may be made through the use of individual anchoring devices, rotating probes, or volume reduction devices. A pyloroplasty procedure may also be performed to render the pyloric sphincter incompetent. A gastric bypass procedure may additionally be performed using atraumatic magnetic anastomoses devices so that sugars and fats are passed directly to the bowel while bypassing the stomach. Many of these procedures may be done in a variety of combinations. Treatment may create enforced behavioral modifications by discouraging the ingestion of high-caloric foods
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Implantable digestive tract organ
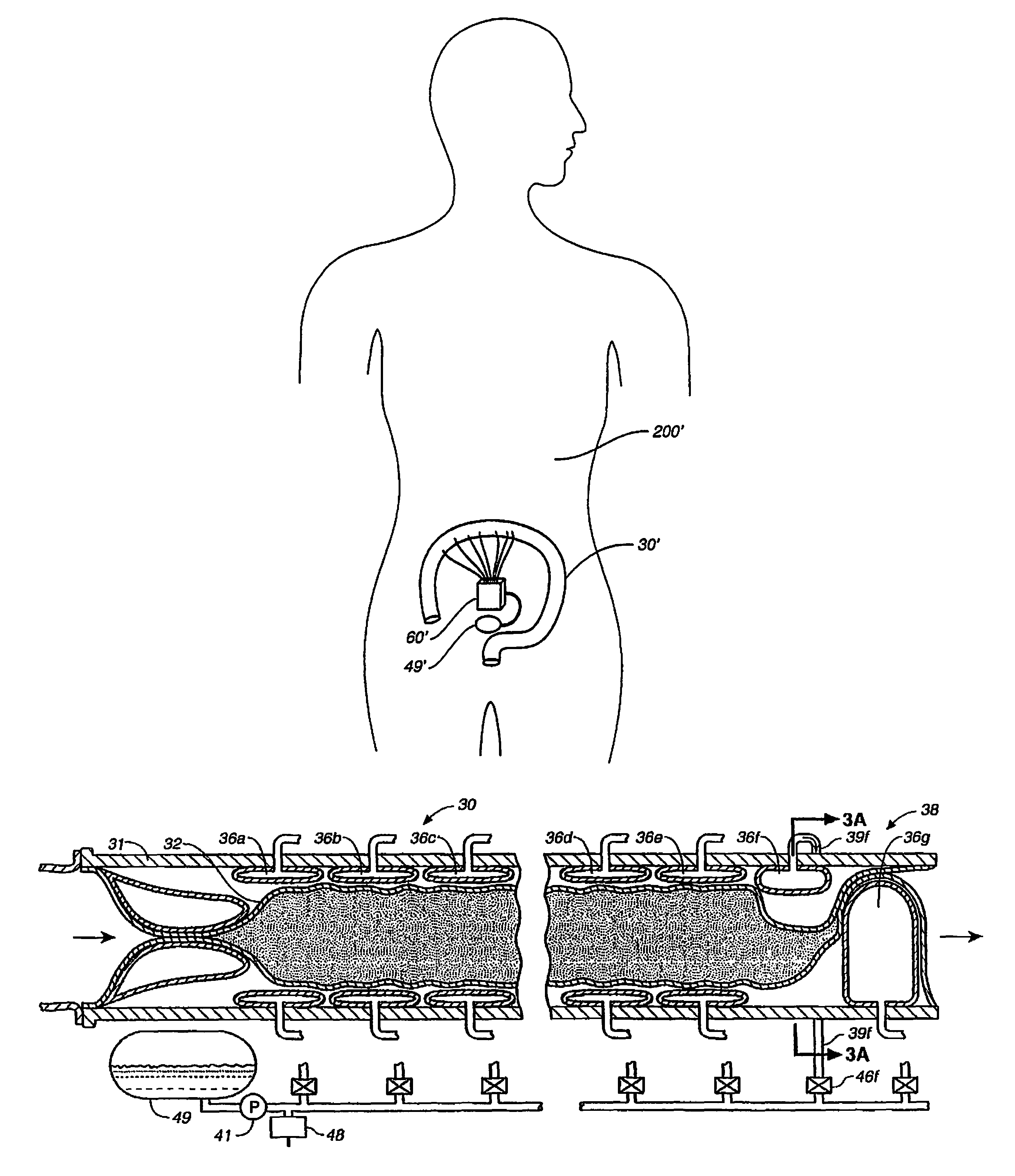
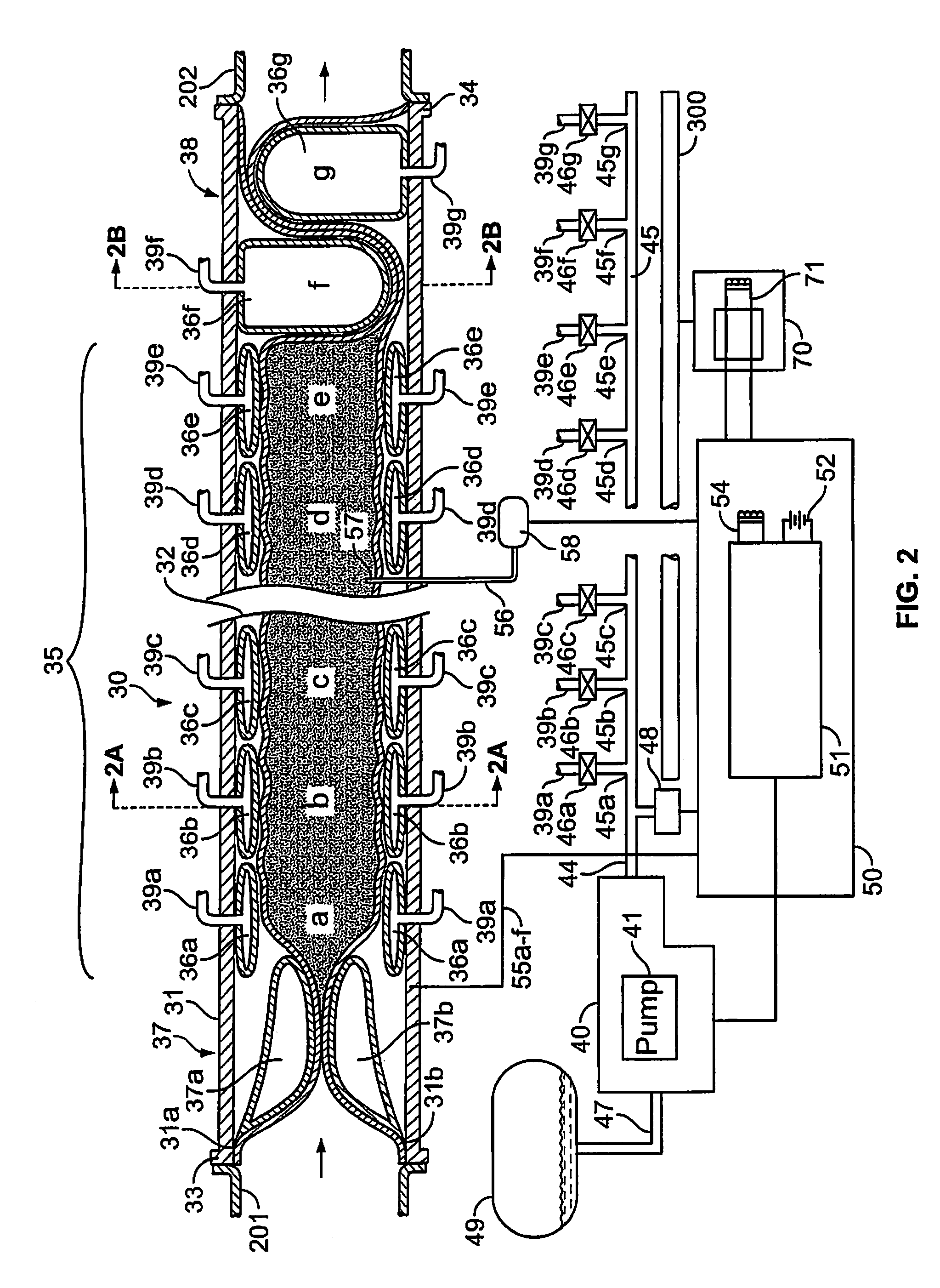
An implantable digestive organ is provided for the transport of materials through the digestive tract and in one particular application to an artificial large bowel for replacing all or part of a colon or large bowel. The prosthetic organ of one embodiment includes an outer support structure, an expandable member or members located within the outer support structure, and a flexible inner member forming a conduit for the passage of material. The flexible inner member is located within the outer member and the expandable member or members are located between the inner member and the outer support structure. The expandable members are expanded and contracted, or inflated and deflated to provide a pumping action that pumps the material through the organ. The prosthesis may also include valves or sphincters at the entrance and / or exit points of the organ where material moves into and out of the prosthesis. An implantable pump unit may be included for inflating and deflating the expandable members according to a desired sequence.
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
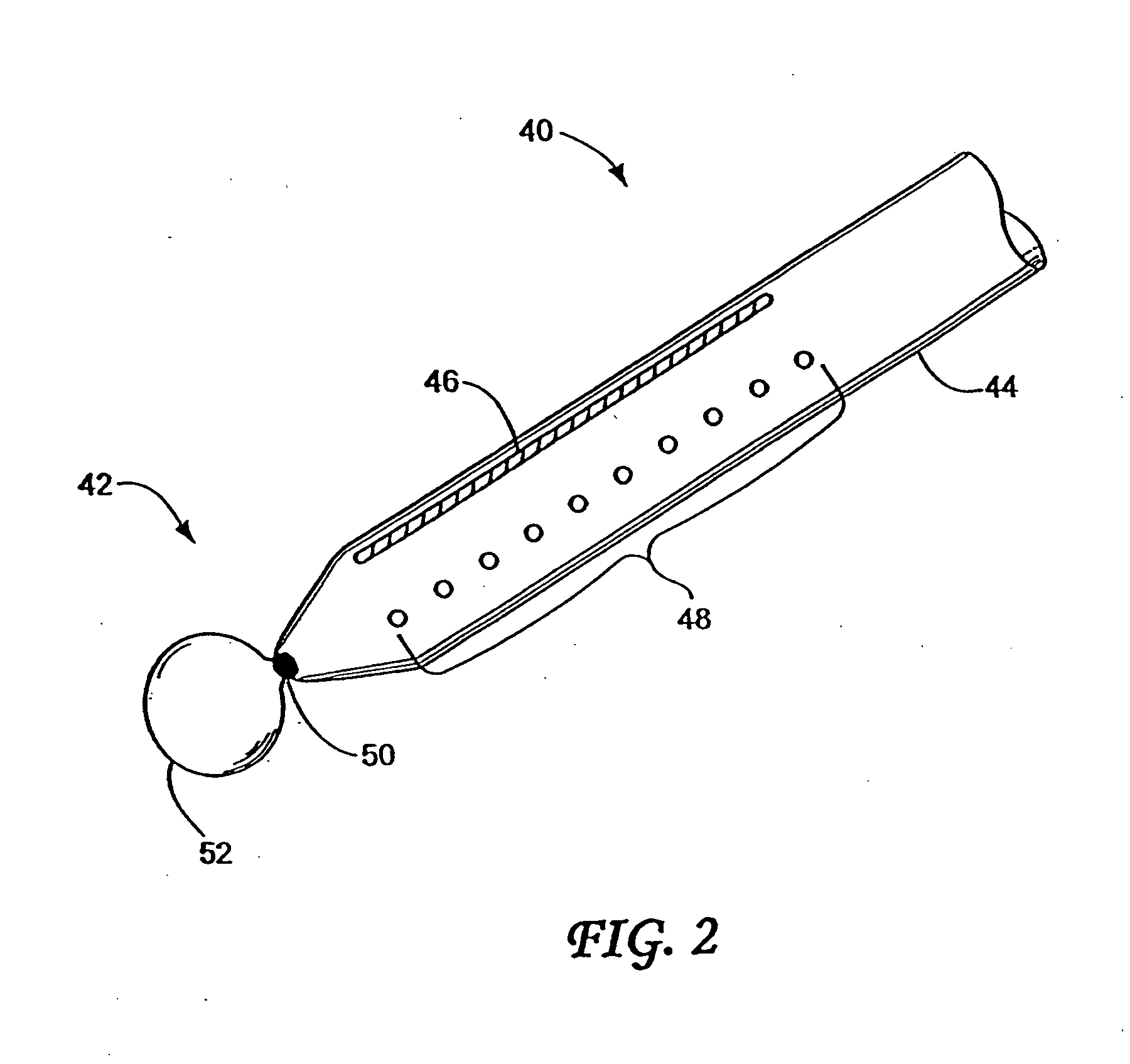
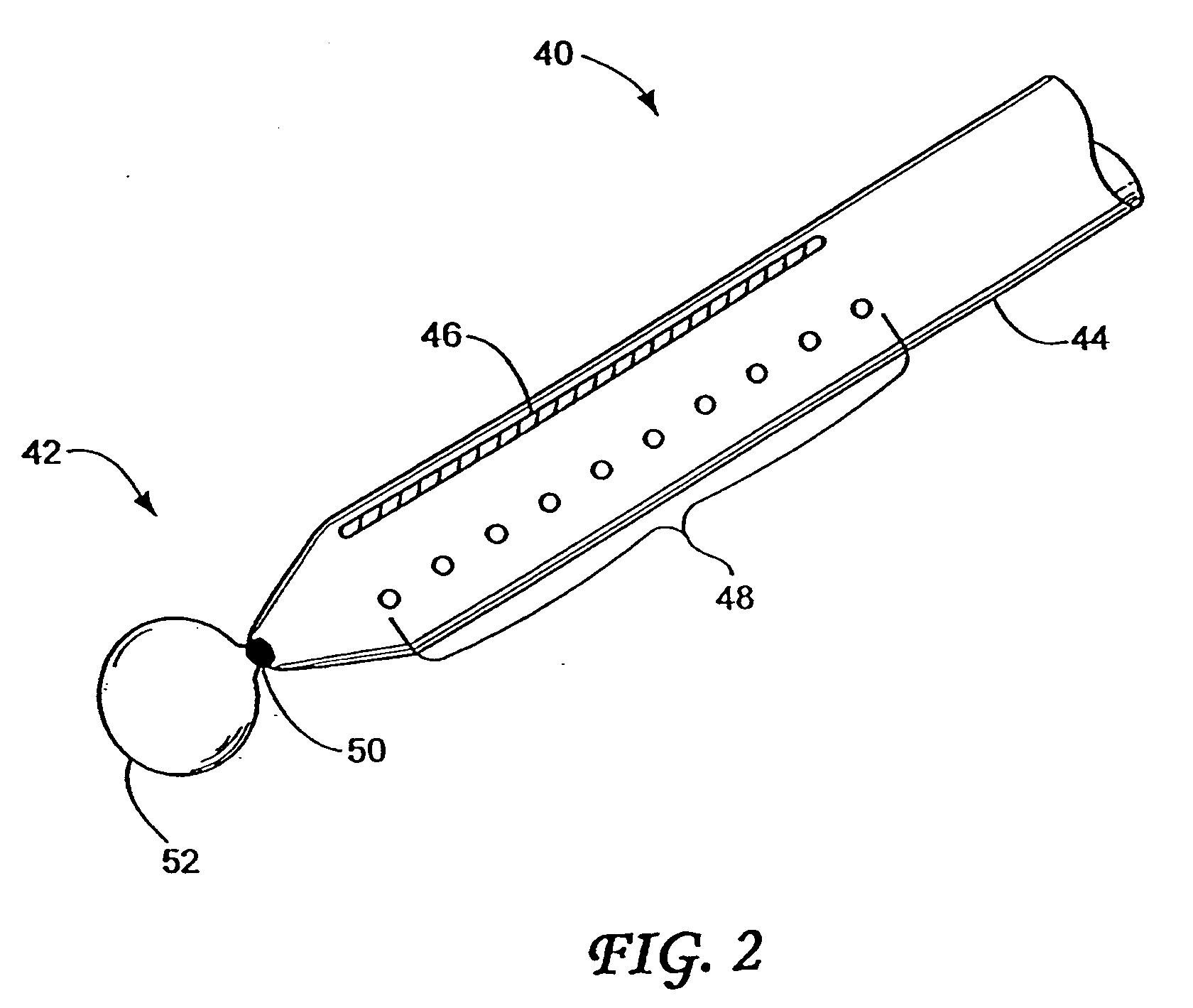
Method and apparatus for measuring and controlling blade depth of a tissue cutting apparatus in an endoscopic catheter
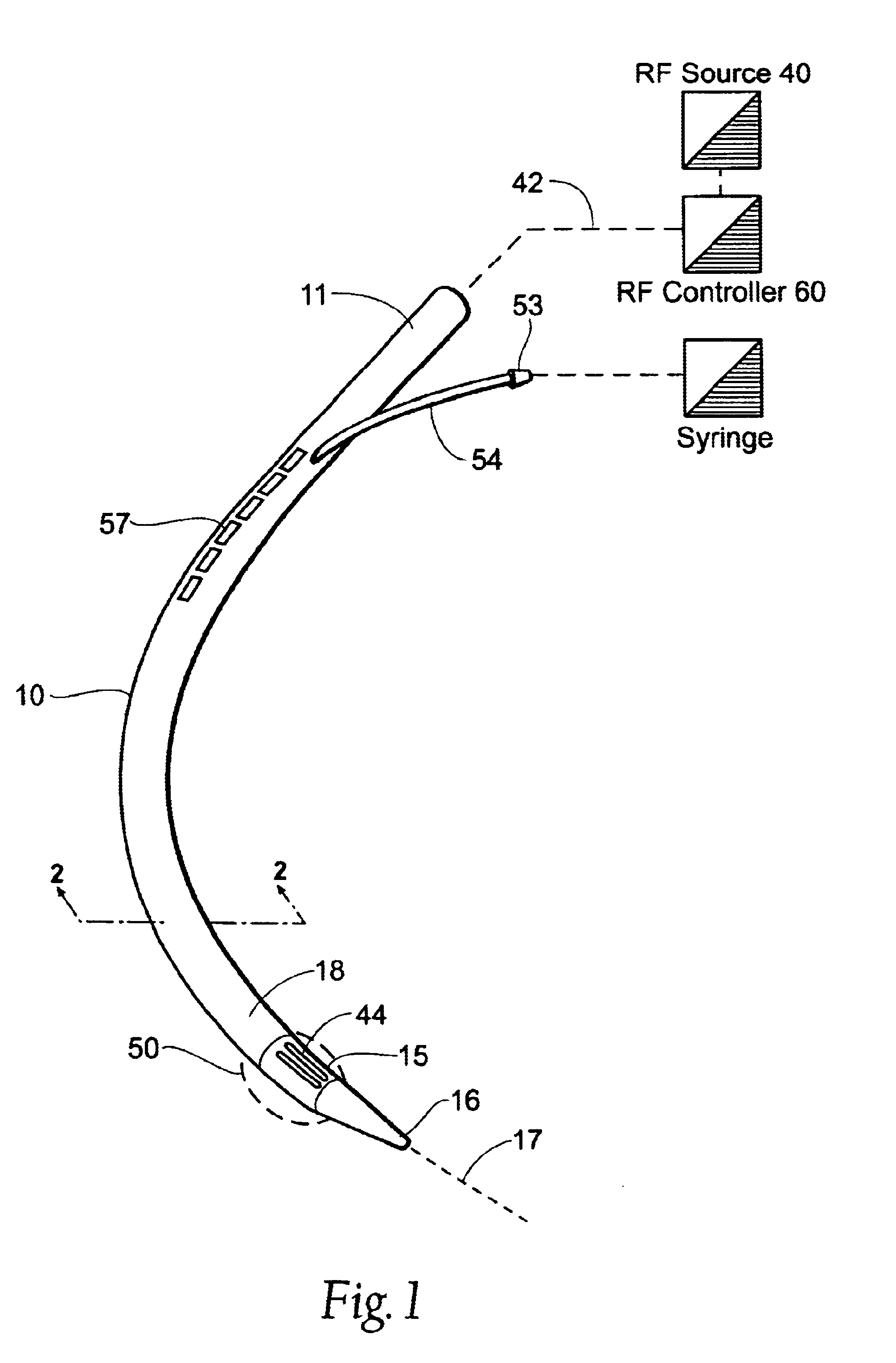
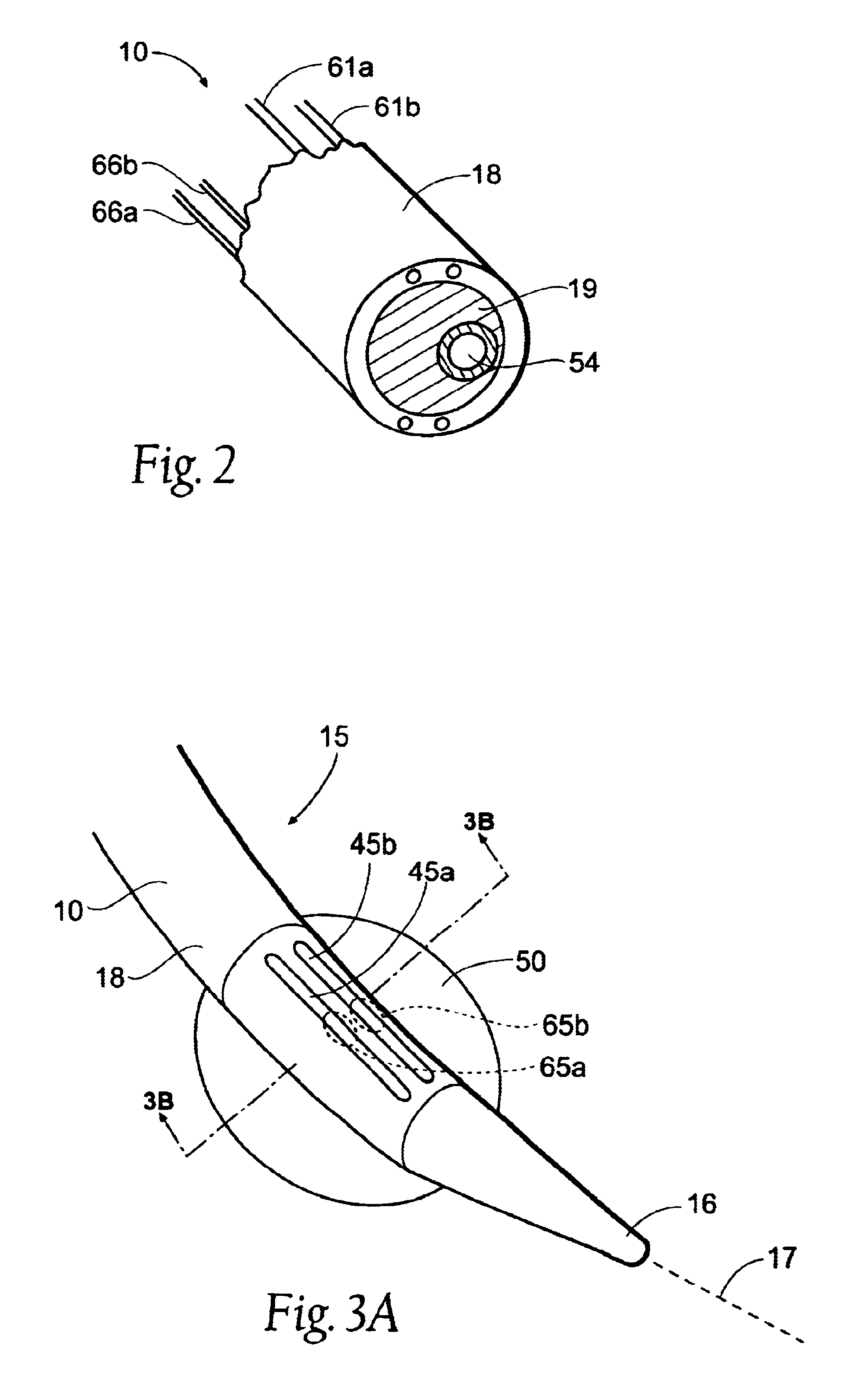
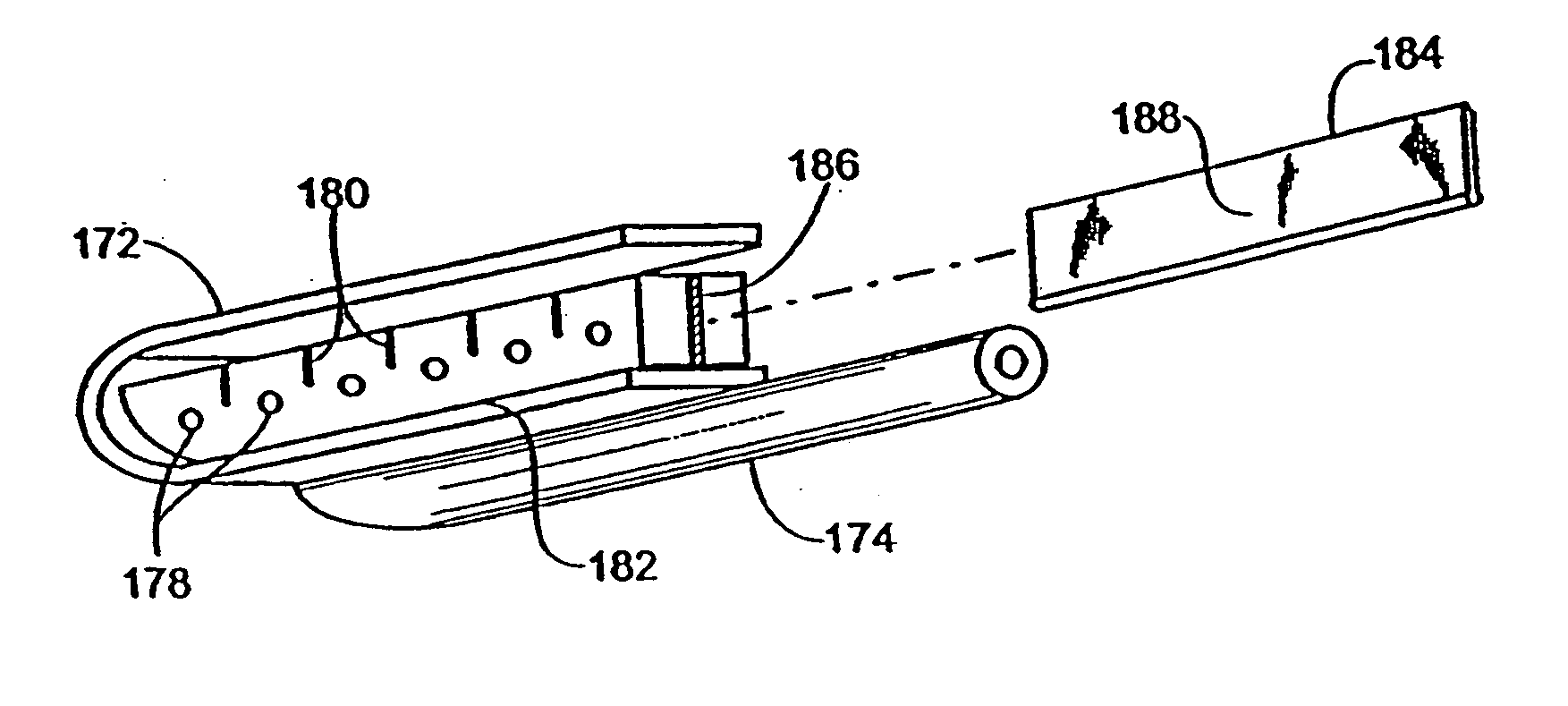
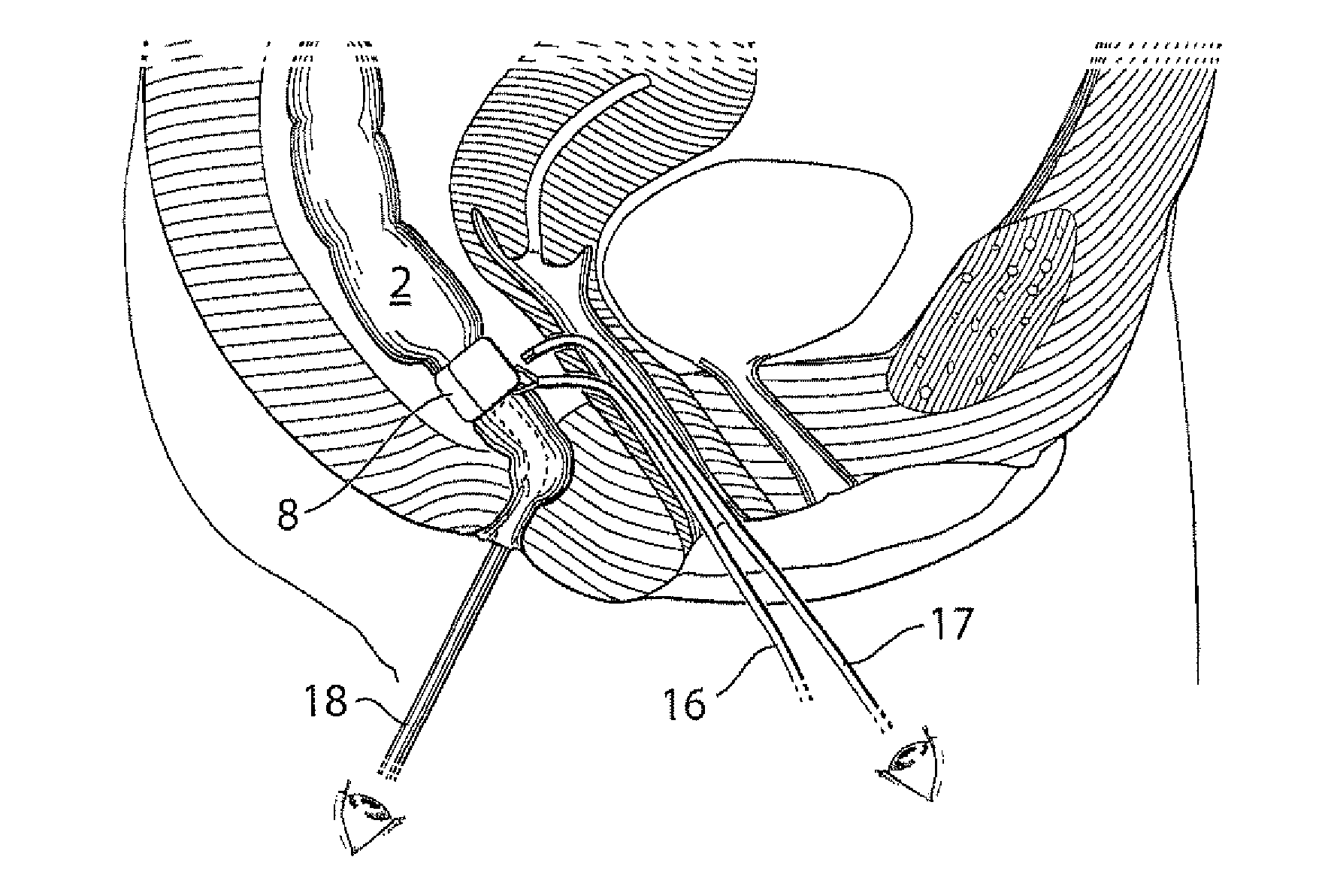
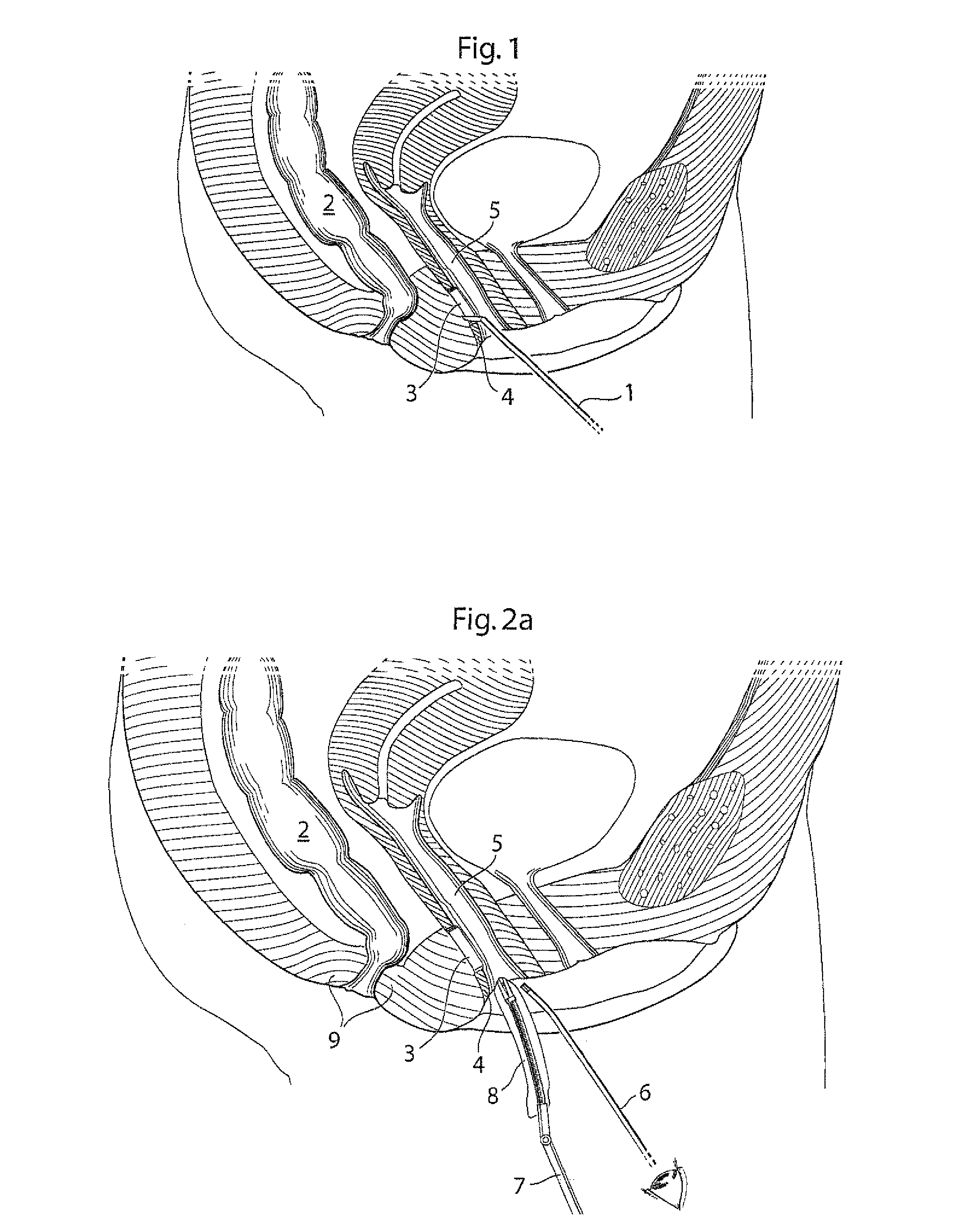
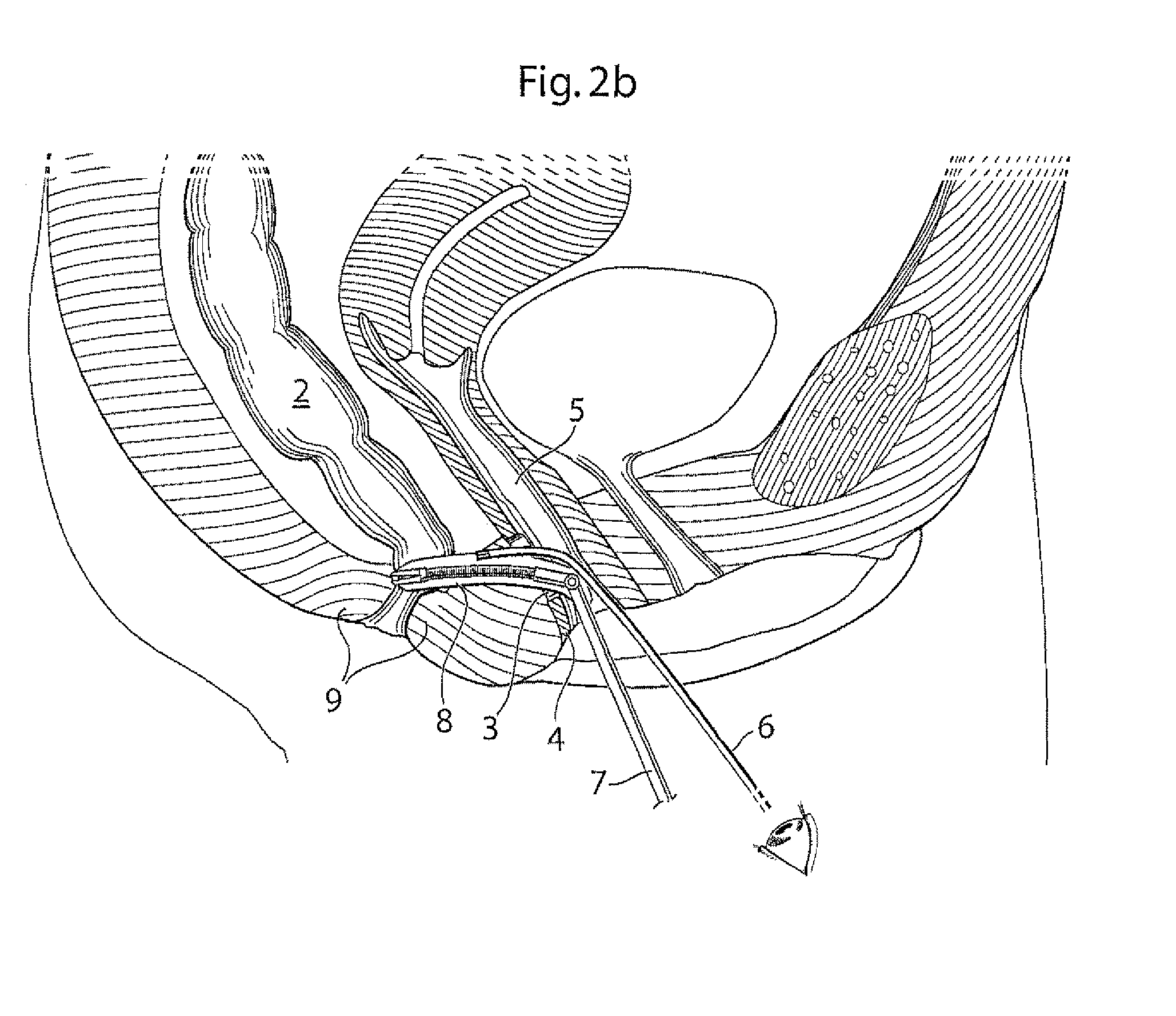
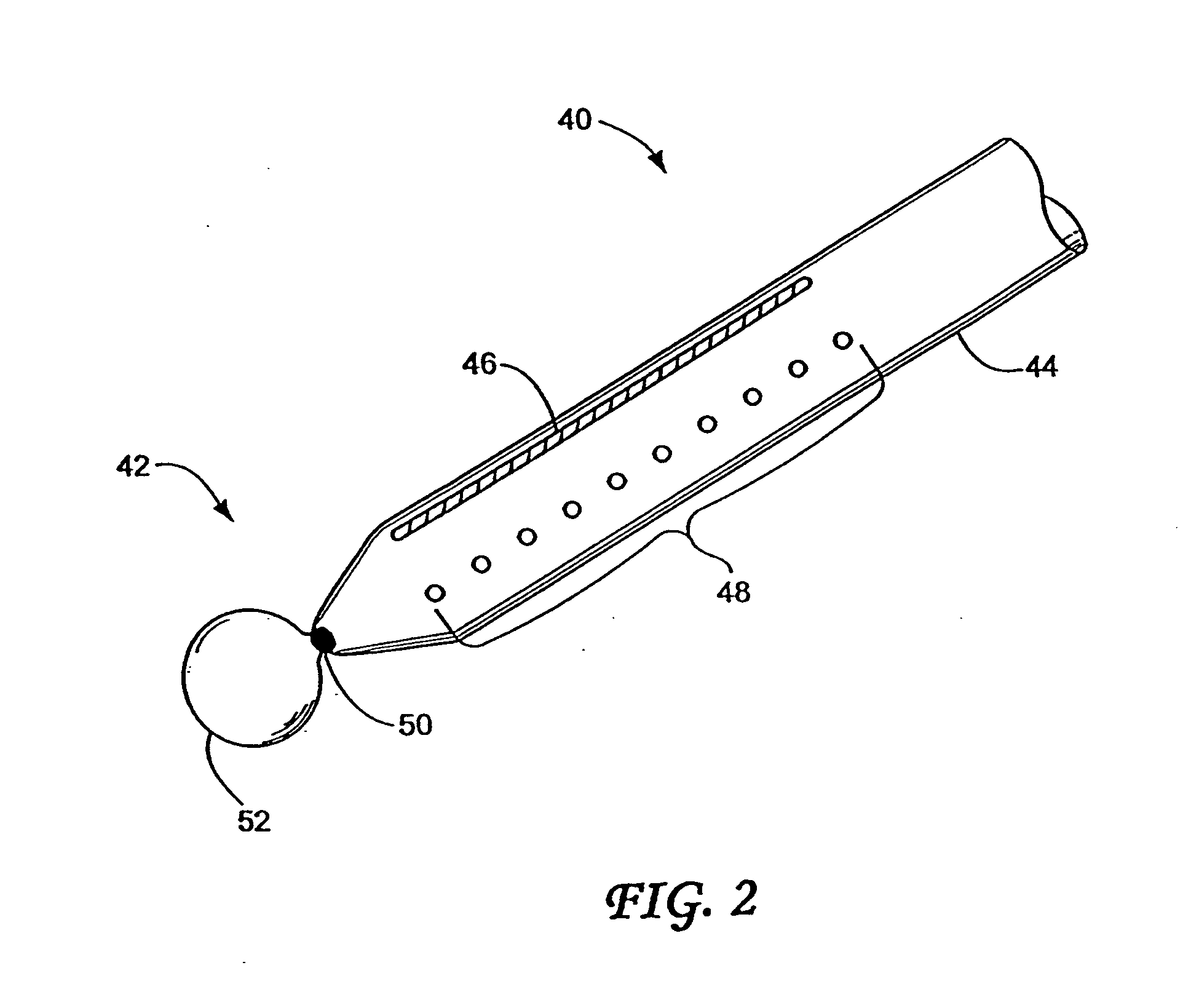
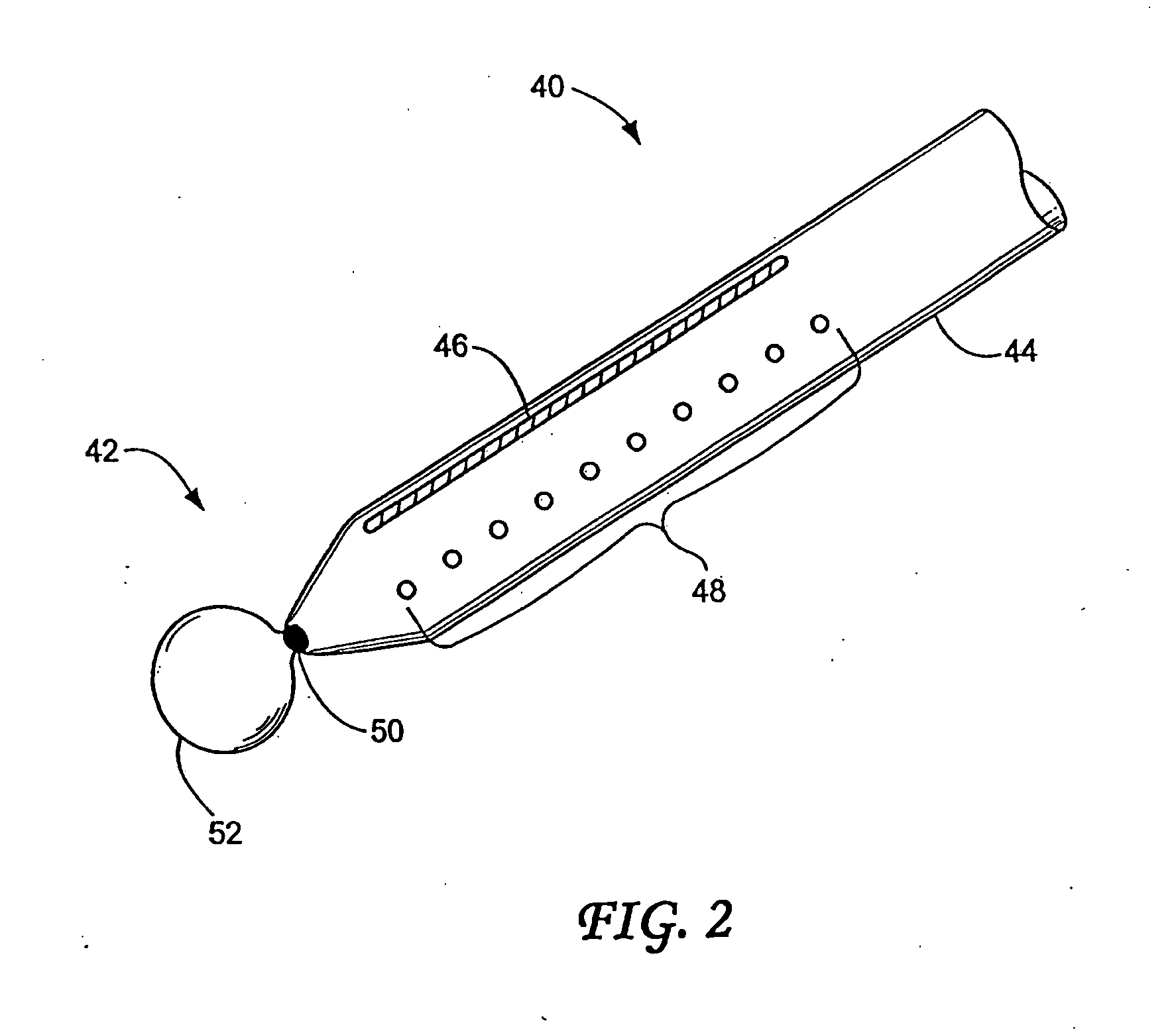
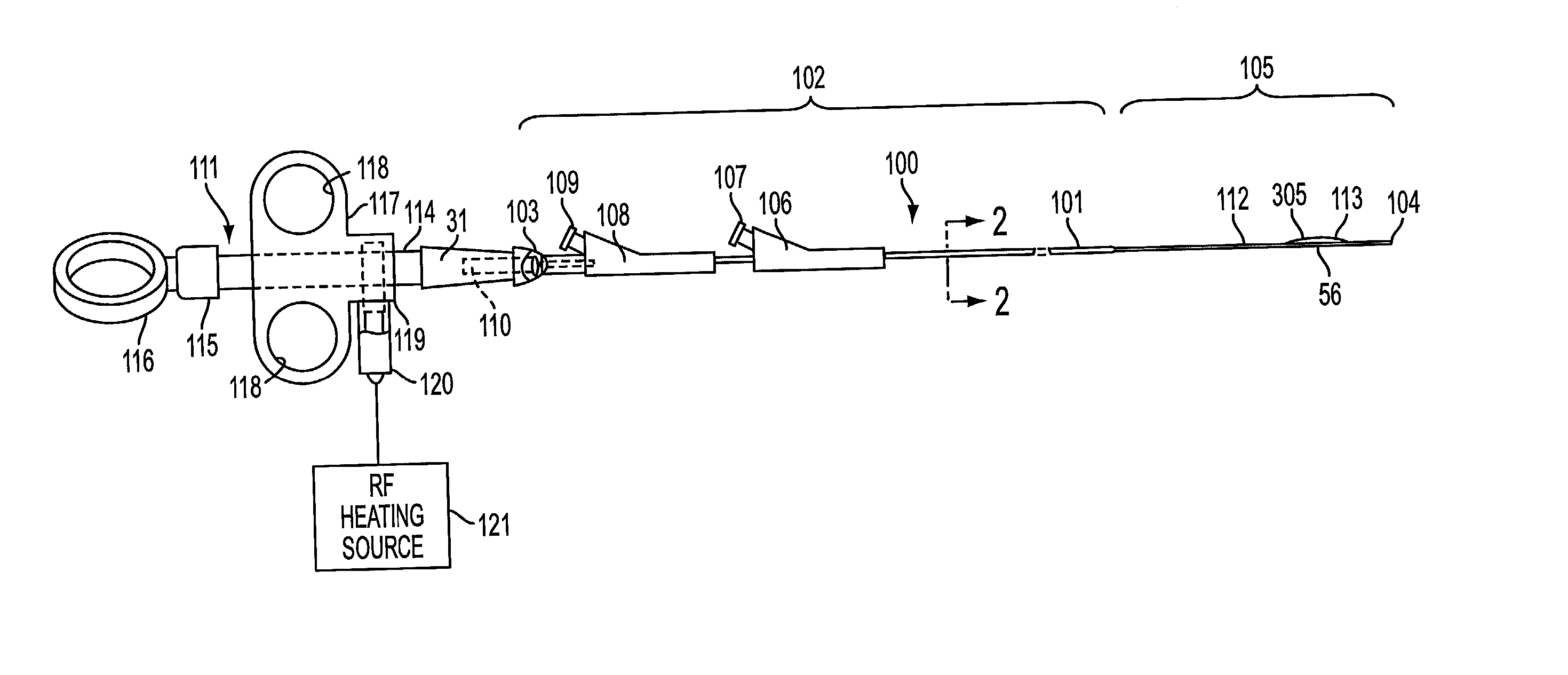
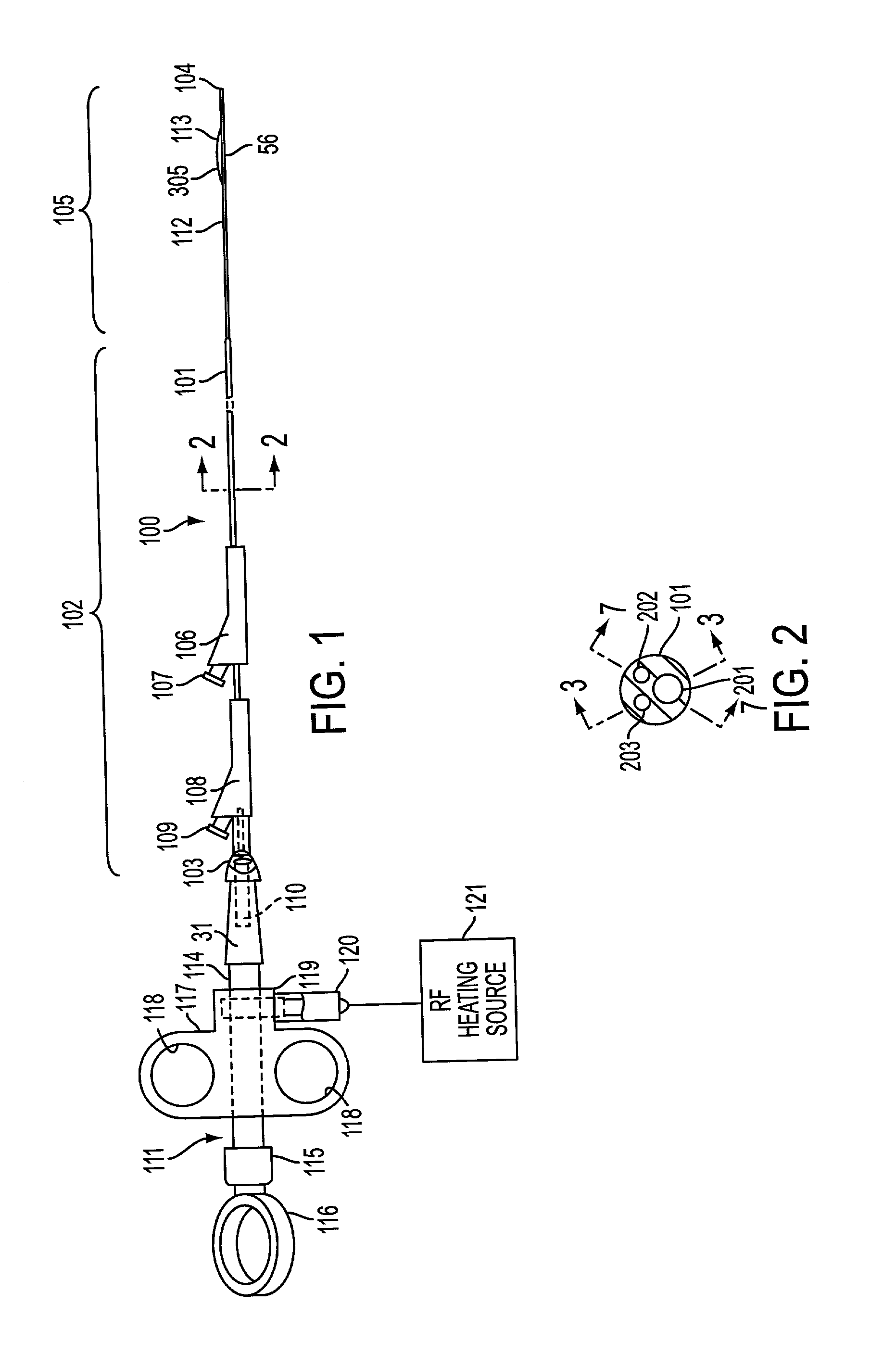
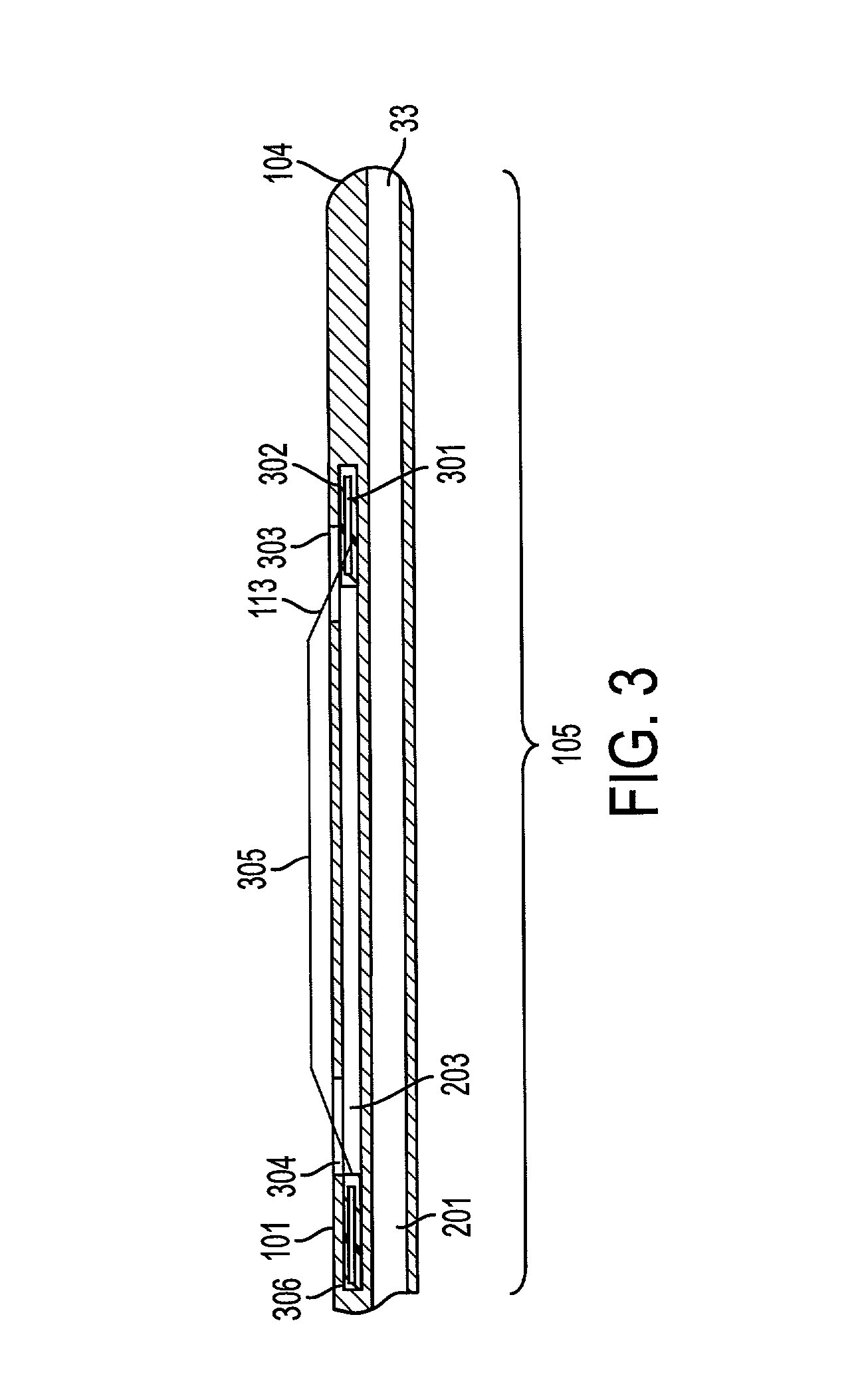
InactiveUS20030060842A1Surgical needlesDiagnostic markersPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
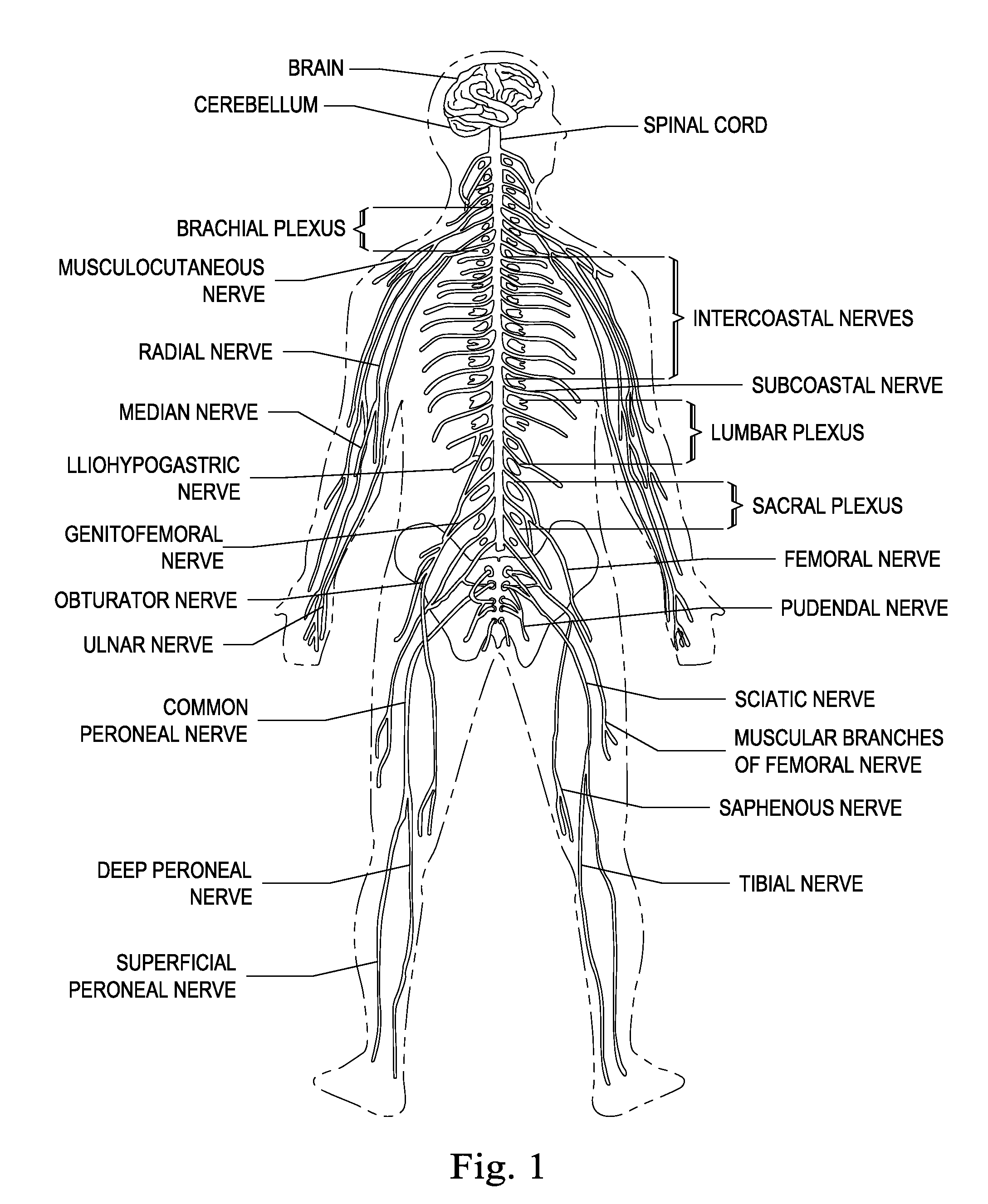
Methods, systems and devices for determining optimal placement for pudendal nerve stimulation lead using patient feedback
ActiveUS20150134027A1Good curative effectLoss of efficacySpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMotor actionSacral nerve stimulation
The present disclosure involves a method of measuring a physiological feedback from a patient in response to electrical stimulation. A stimulation parameter of a sacral nerve stimulation therapy is ramped up. The sacral nerve stimulation therapy includes electrical pulses generated by a pulse generator based on programming instructions received from an electronic programmer. The electrical pulses are delivered to a patient via a stimulation lead that is implanted in the patient. Via an anal electrode device that is at least partially inserted inside an anal canal of the patient, a compound motor action potential (CMAP) is measured from an anal sphincter of the patient while the stimulation parameter of the sacral nerve stimulation therapy is being ramped up. A stimulation threshold is determined based on the measured CMAP.
Owner:CIRTEC MEDICAL CORP
High specific gravity intragastric device
The teachings are directed to an intragastric device comprising a flexible and expandable bladder having a predetermined shape upon expansion for contacting the antrum of the stomach of a subject. The device is designed to avoid passage of any part of the device beyond the pylorus and lower esophageal sphincter while the bladder is expanded during use. In these embodiments, the bladder can contain a high specific gravity material when expanded; wherein, the high specific gravity material contributes to an in vivo specific gravity of the device that ranges from about 1.2 g / ml to about 2.1 g / ml and functions to direct the device to the pyloric antrum of the subject during use of the device. Moreover, these embodiments can include a filling material comprising a biocompatible fluid component and a hydrogel component to make the device substantially leakproof and contribute to the in vivo specific gravity of the device.
Owner:HANCOCK JOHN
Self-supporting metallic implantable grafts, compliant implantable medical devices and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070250156A1Give flexibilityFacilitating transmural endothelializationStentsBlood vesselsSurgical GraftMetallic materials
Implantable medical grafts fabricated of metallic or pseudometallic films of biocompatible materials having a plurality of microperforations passing through the film in a pattern that imparts fabric-like qualities to the graft or permits the geometric deformation of the graft. The implantable graft is preferably fabricated by vacuum deposition of metallic and / or pseudometallic materials into either single or multi-layered structures with the plurality of microperforations either being formed during deposition or after deposition by selective removal of sections of the deposited film. The implantable medical grafts are suitable for use as endoluminal or surgical grafts and may be used as vascular grafts, stent-grafts, skin grafts, shunts, bone grafts, surgical patches, non-vascular conduits, valvular leaflets, filters, occlusion membranes, artificial sphincters, tendons and ligaments.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Systems and methods for treating obesity and other gastrointestinal conditions
InactiveUS20090118699A1Reduce morbidityIncrease satietyElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsReflexREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:RESPIRATORY DIAGNOSTICS
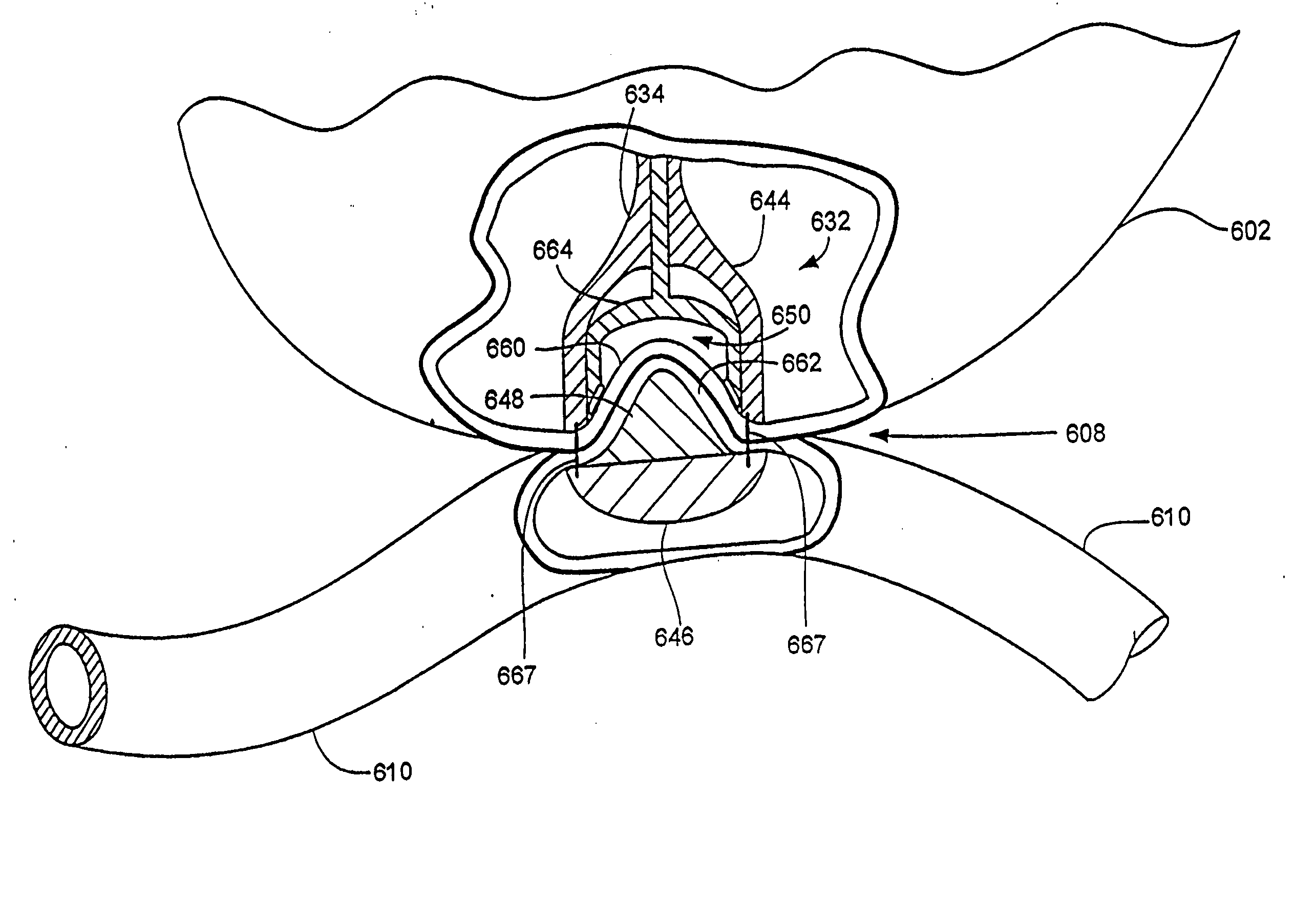
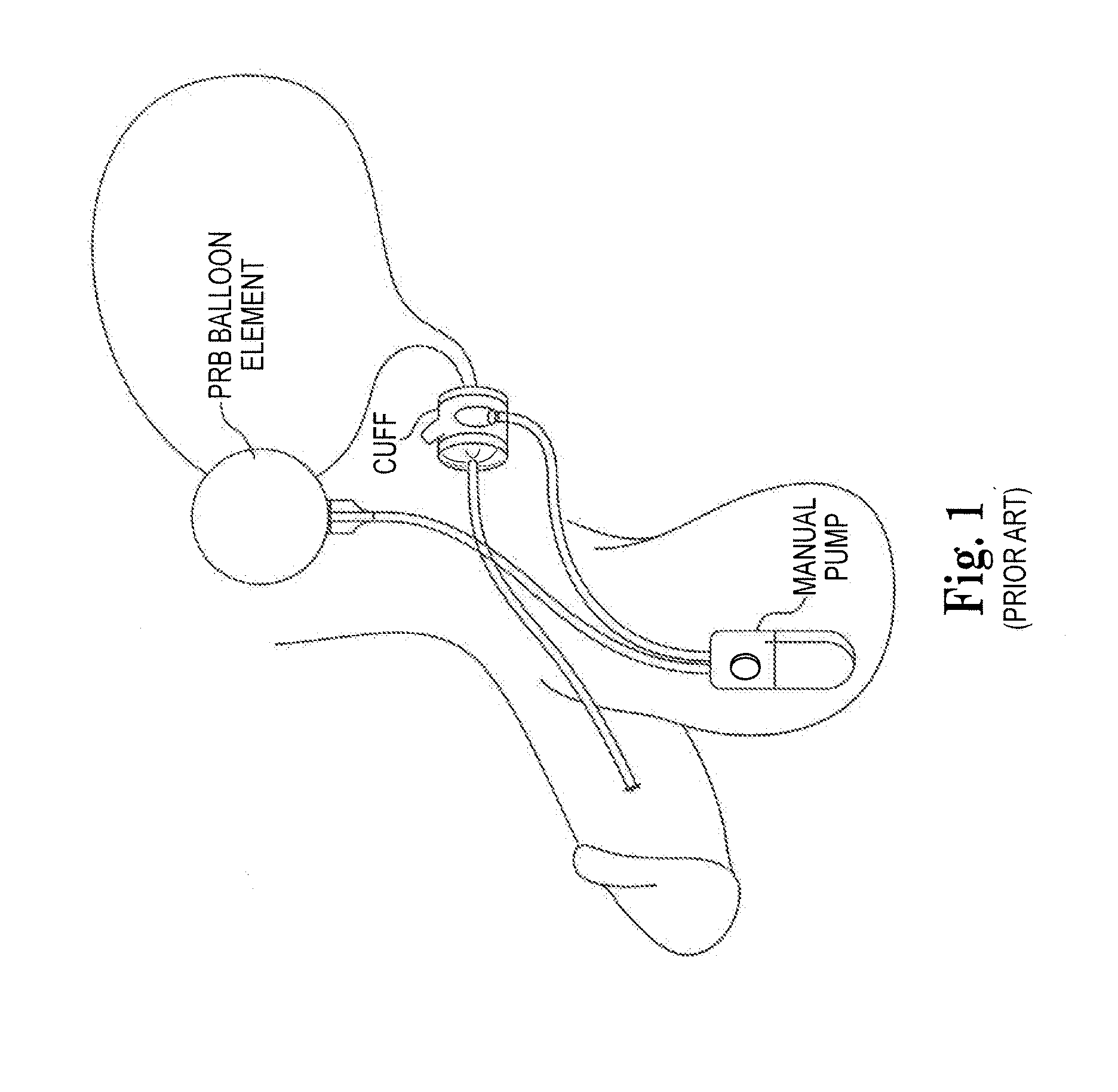
Artificial Sphincter System and Method
The present invention provides an artificial sphincter employing an easily controlled electro-mechanical pump system. The artificial sphincter includes an inflatable cuff, a control pump fluidly coupled to the inflatable cuff, and an electro-mechanical pump system. The inflatable cuff is adapted to surround a urethra or rectum of the patient to facilitate continence. An inflation element or balloon can be included to further control pressure to the cuff.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device for insufflating the interior of a gastric cavity of a patient
InactiveUS20090023984A1Preventing insufflationSuture equipmentsGastroscopesGastric cavityPERITONEOSCOPE
A method for laparoscopically preventing insufflation of the small bowel during gastric procedures includes applying an obstruction member at the pyloric sphincter to block the passage of gas from the gastric cavity into the small bowel and insufflating the gastric cavity.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com