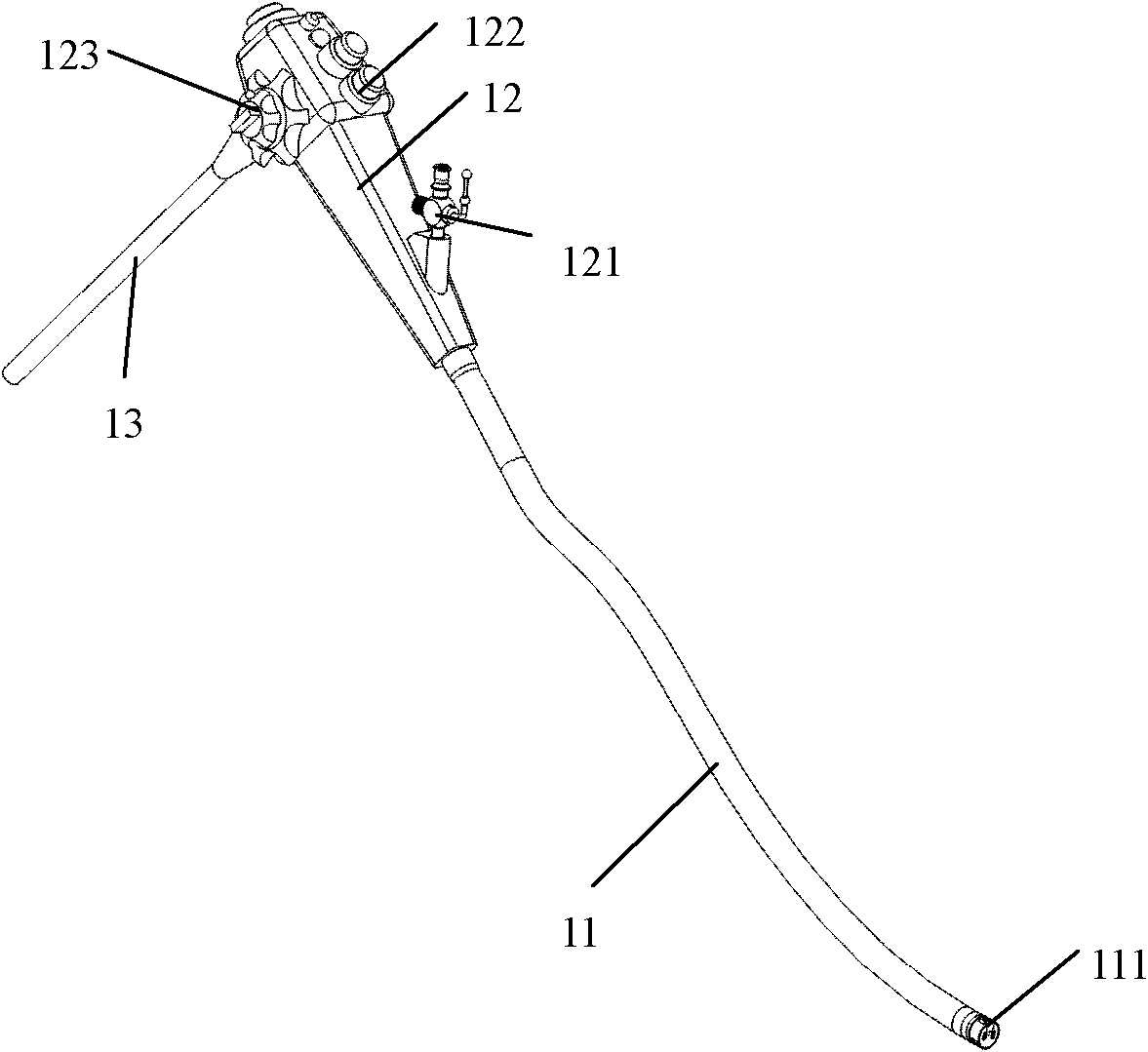
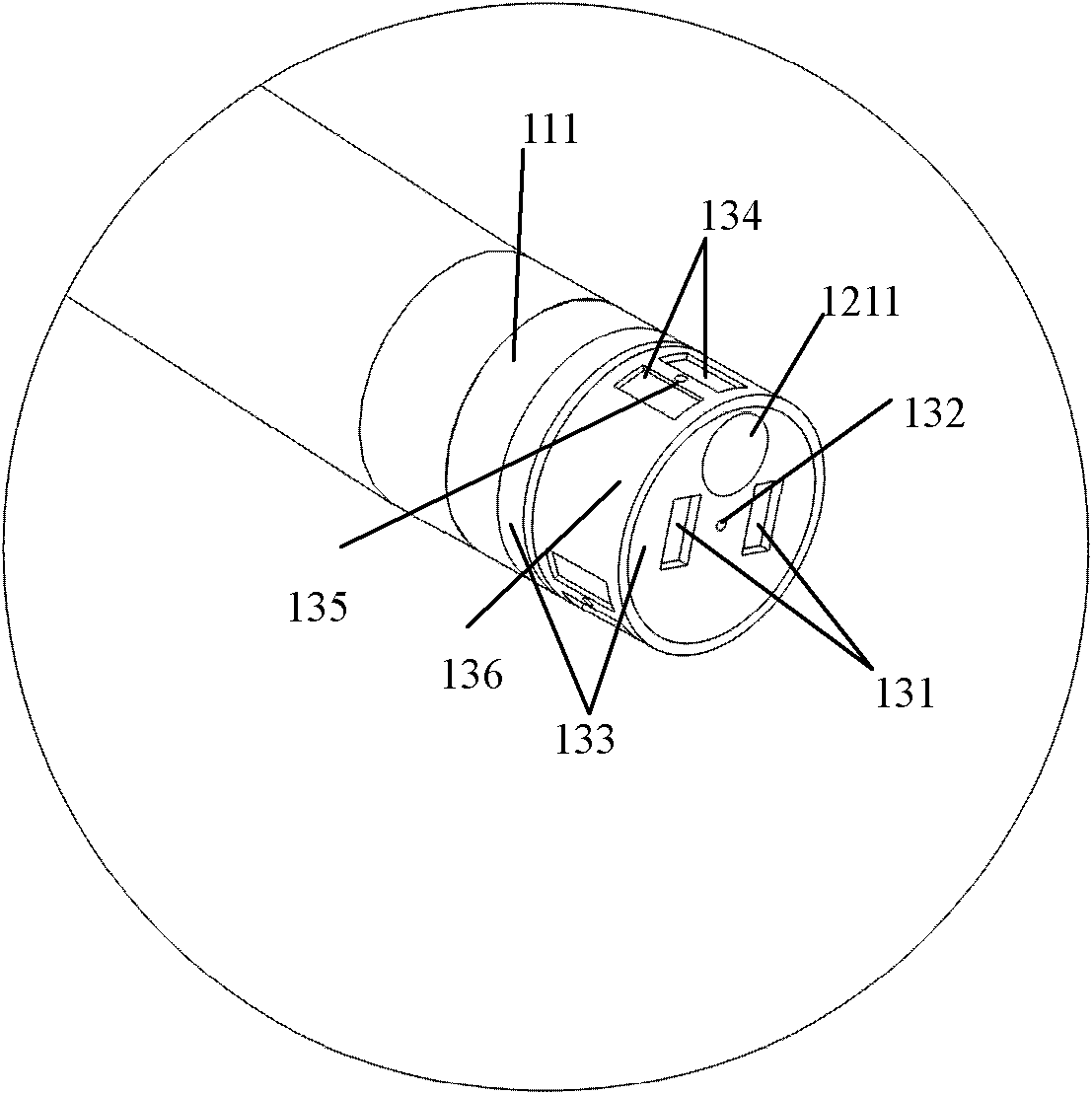
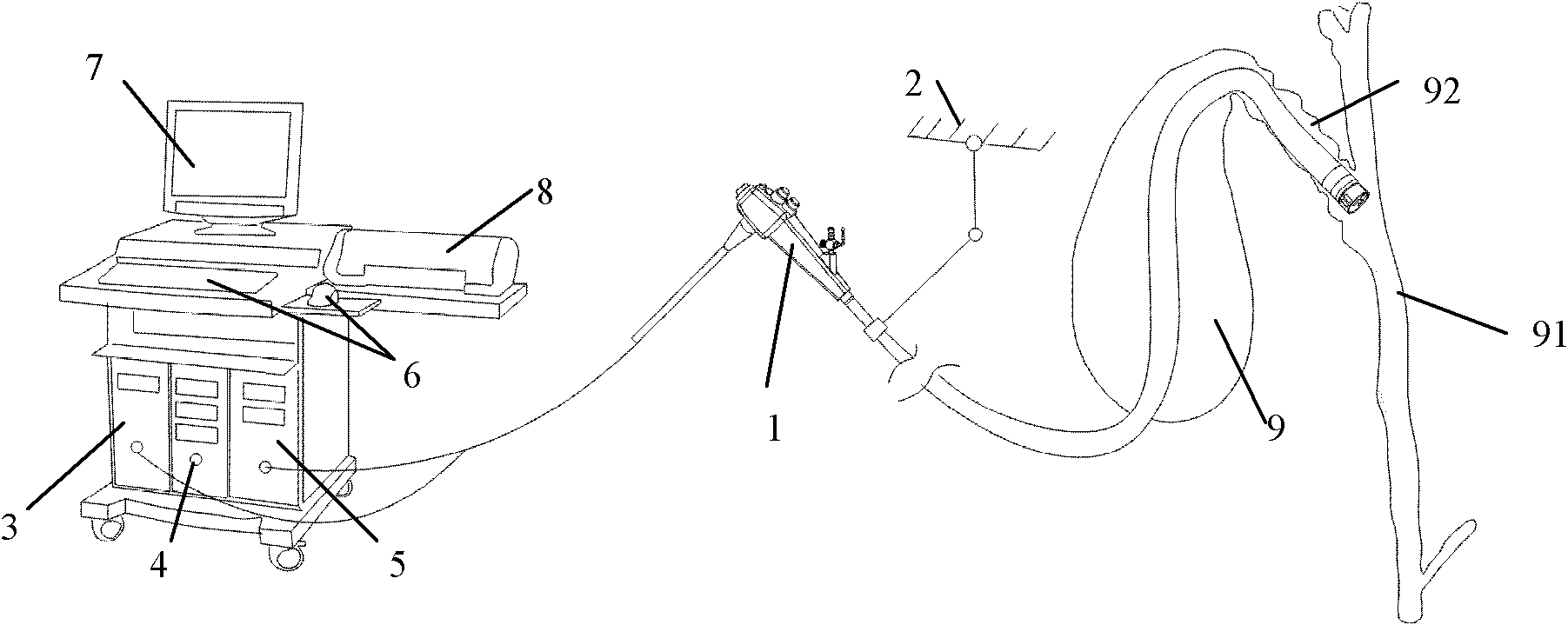Patents
Literature
88 results about "Common bile duct dilatation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Very rare deformities of the common bile duct are cystic dilations (4 cm), choledochoceles (cystic dilation of the ampula of Vater (3–8 cm), and biliary atresia.
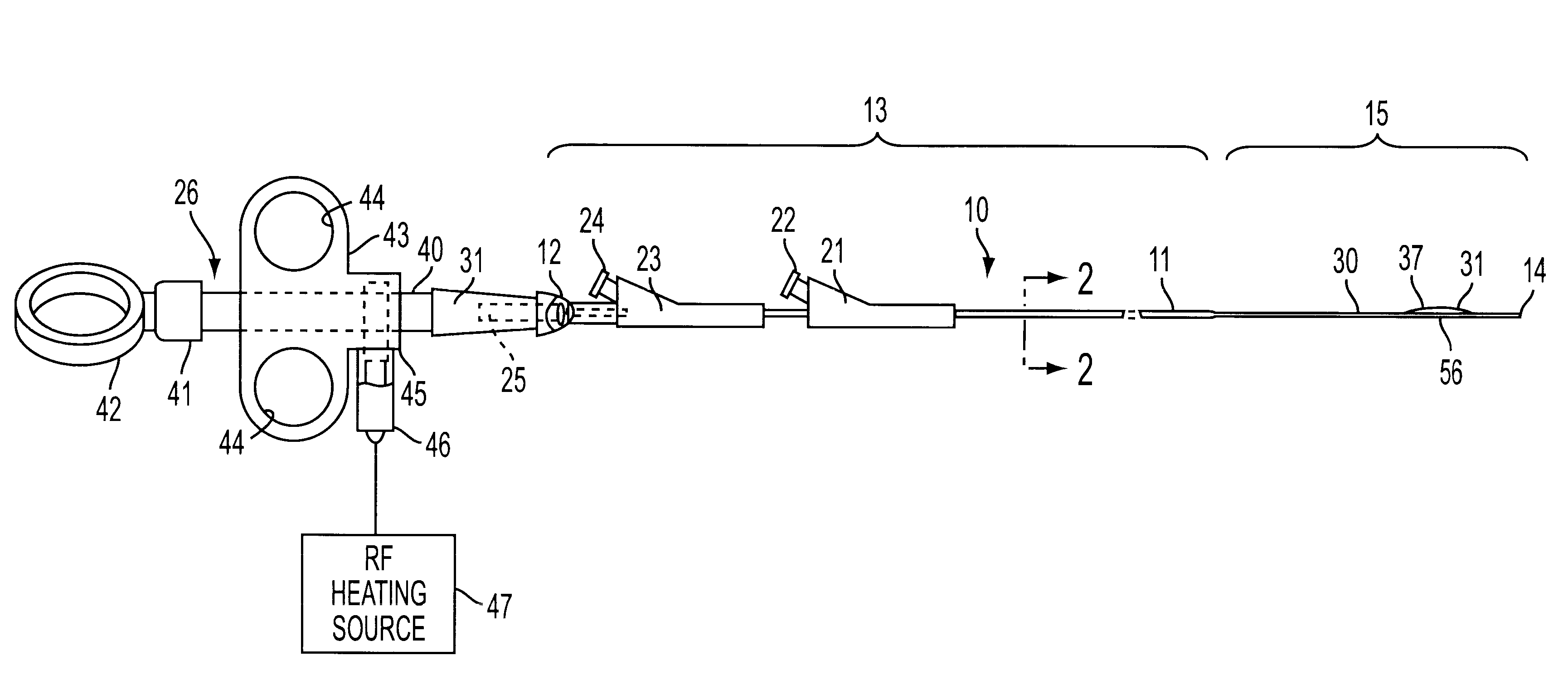
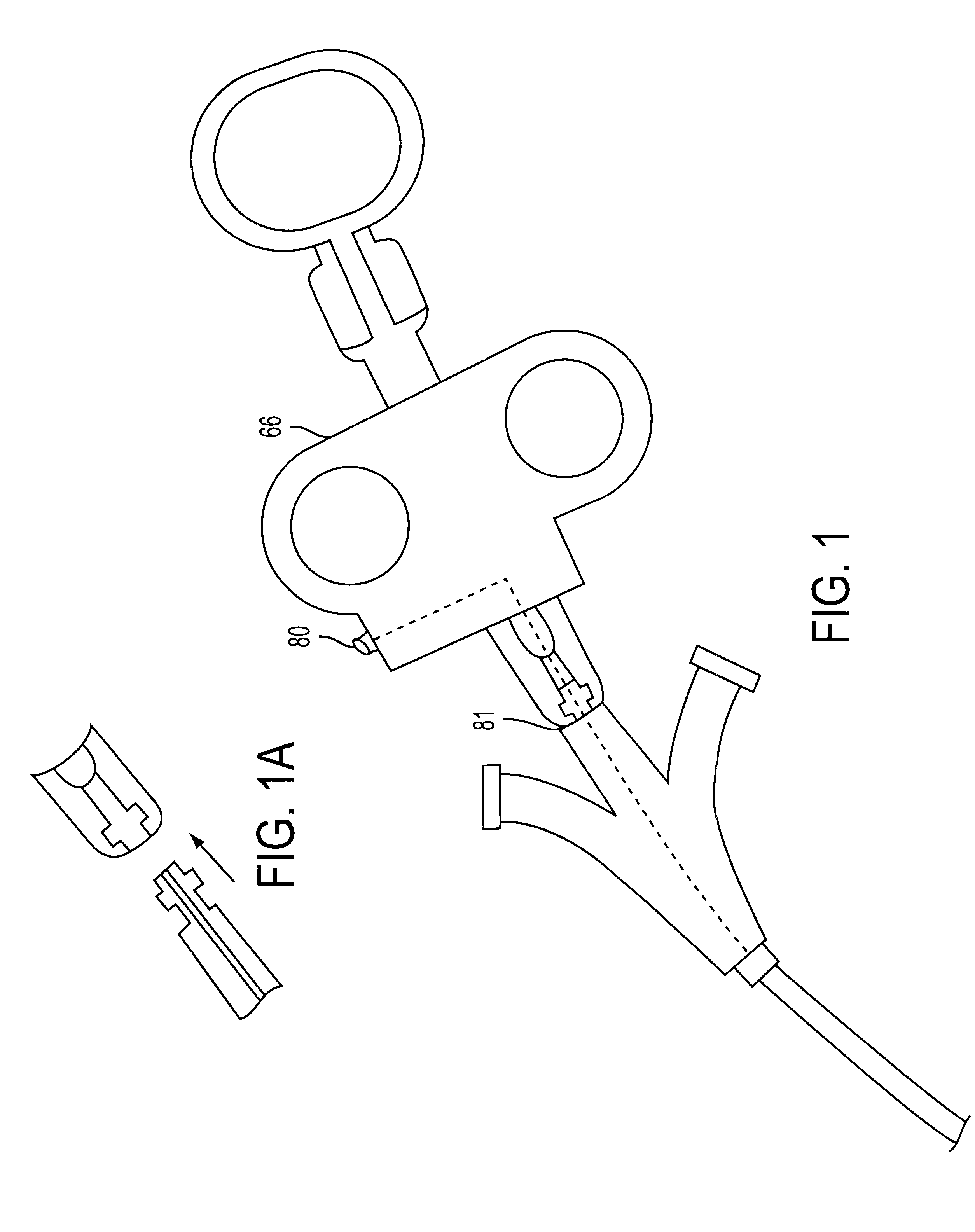
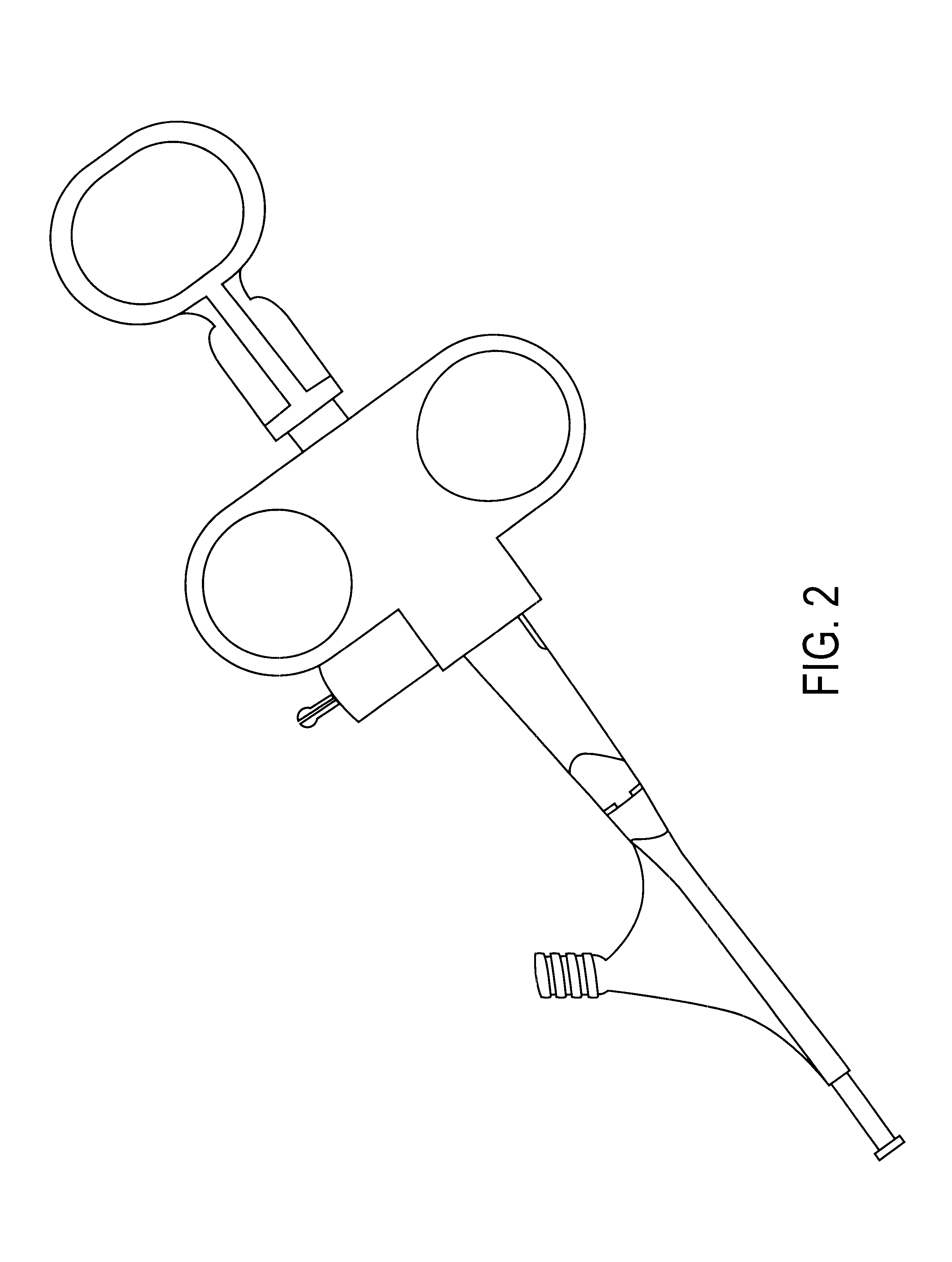
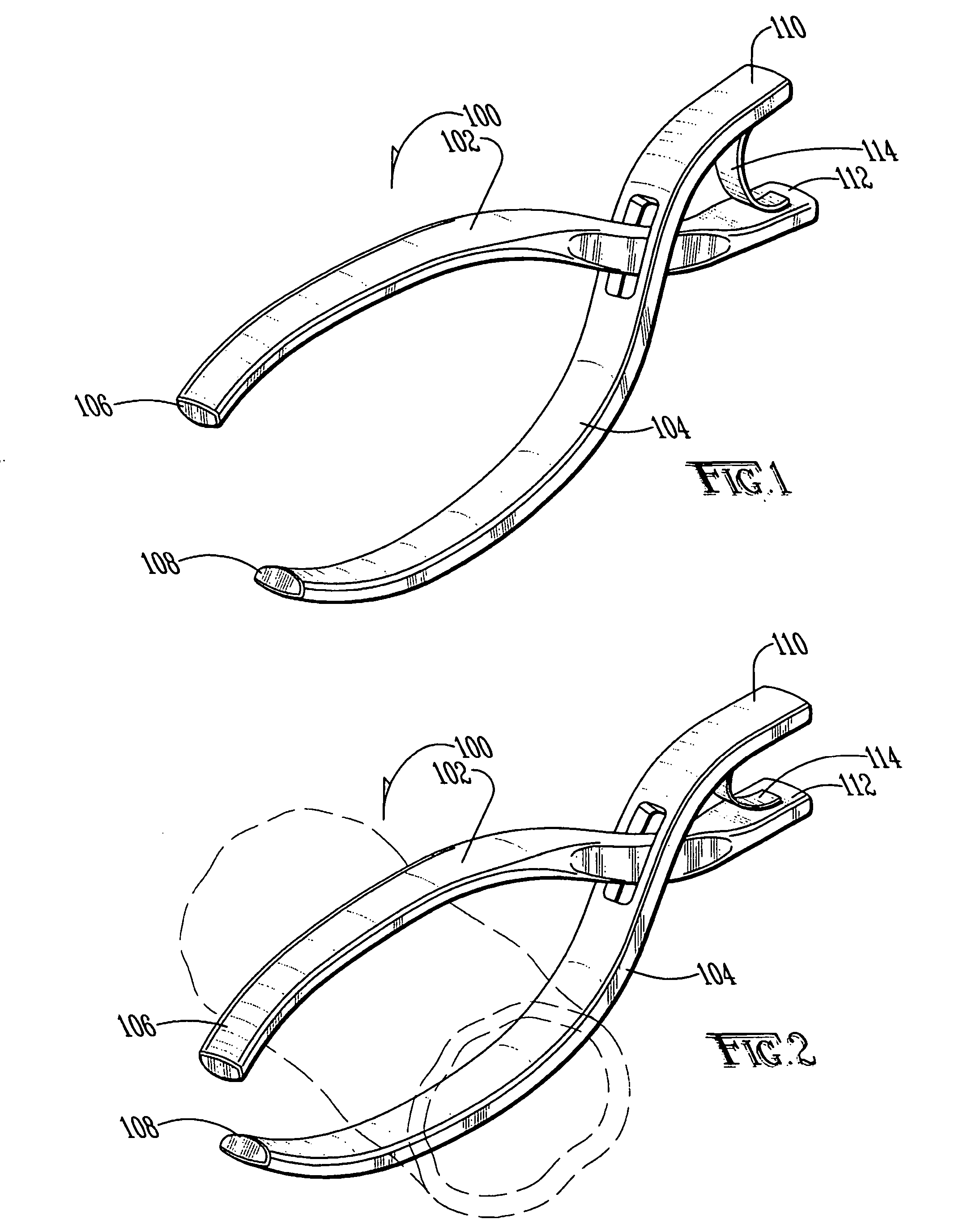
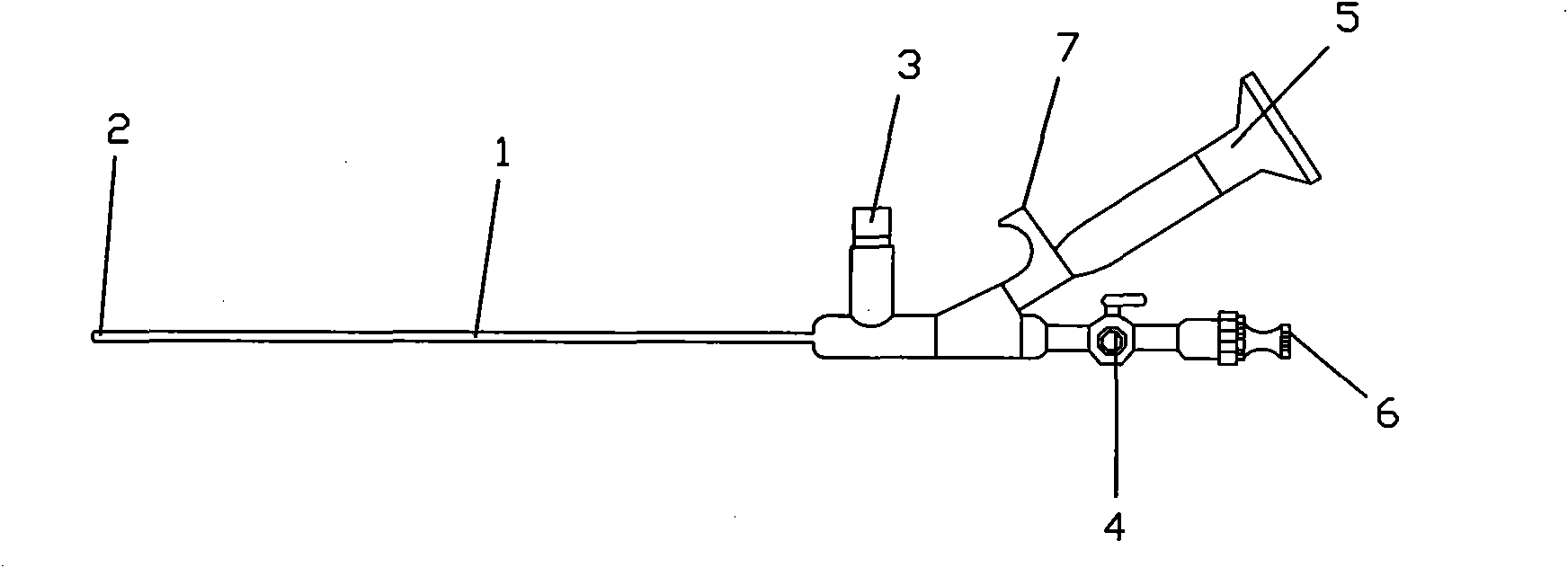
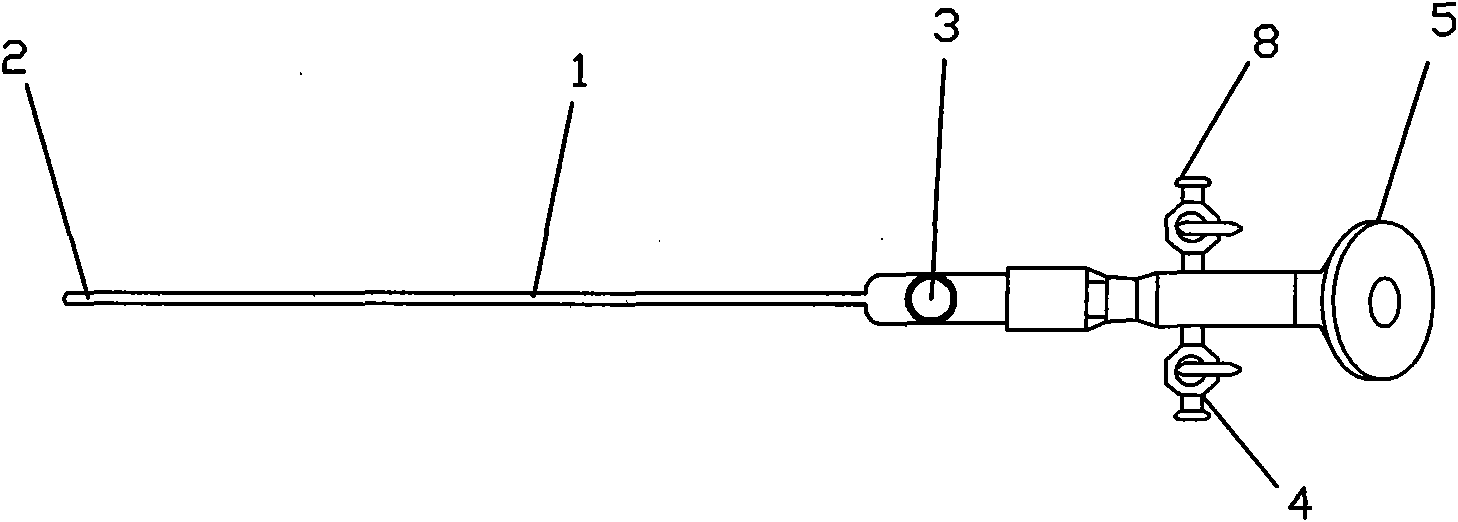
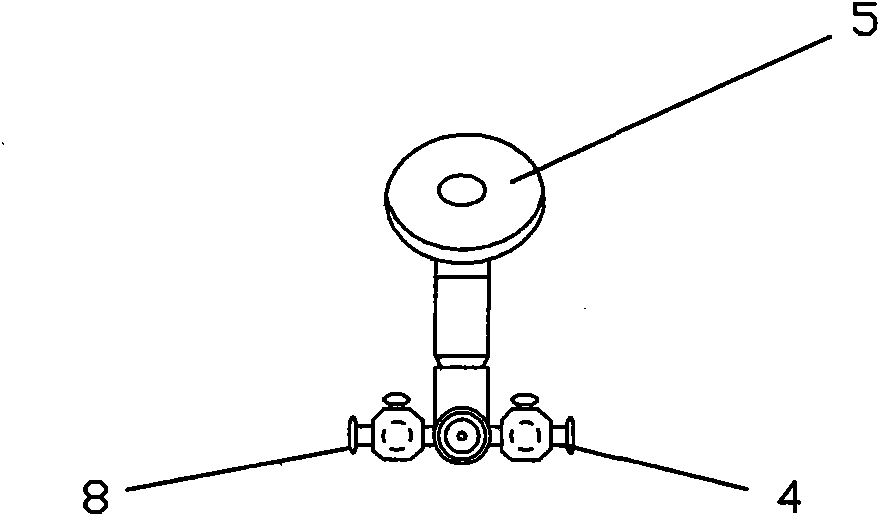
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
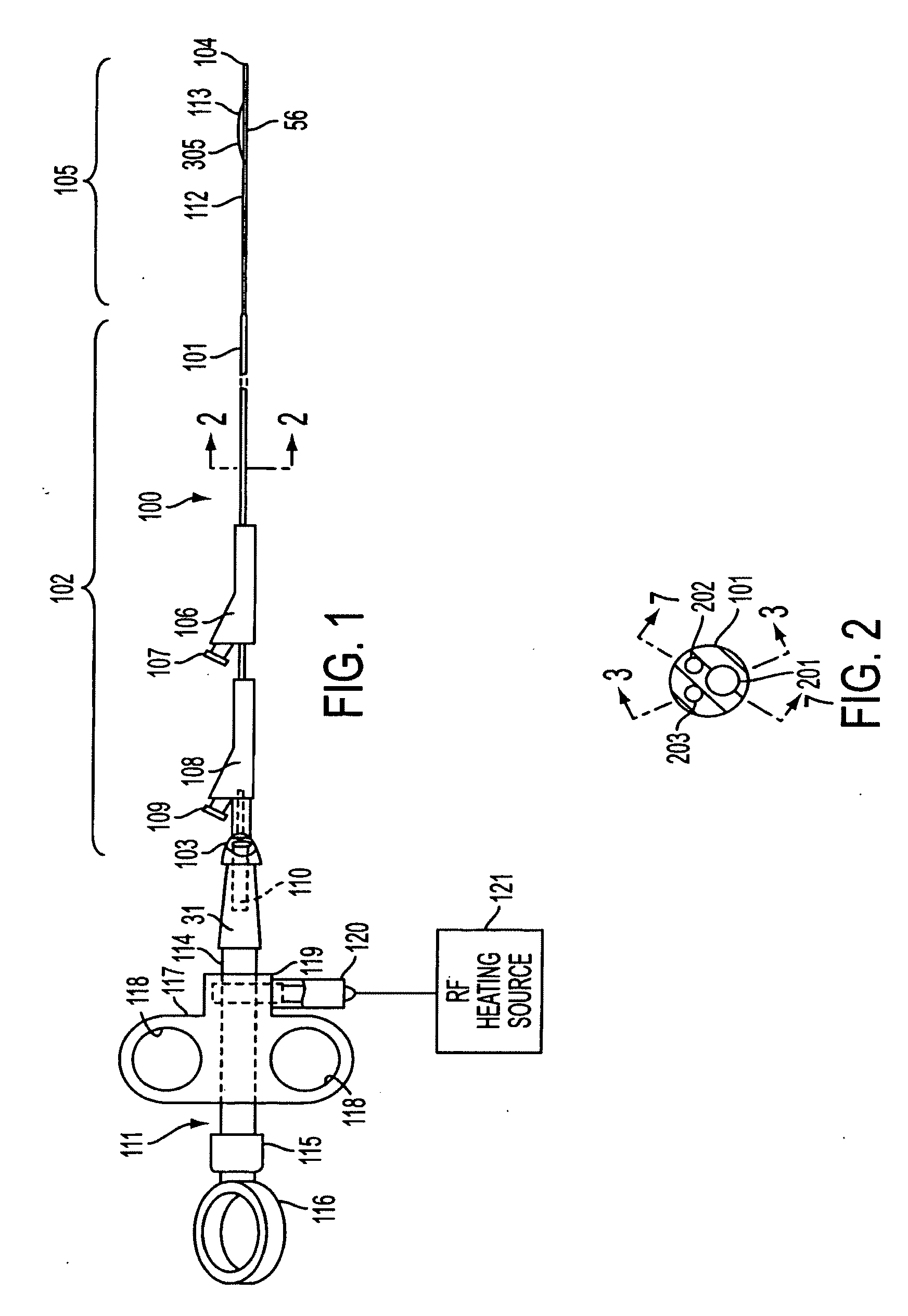
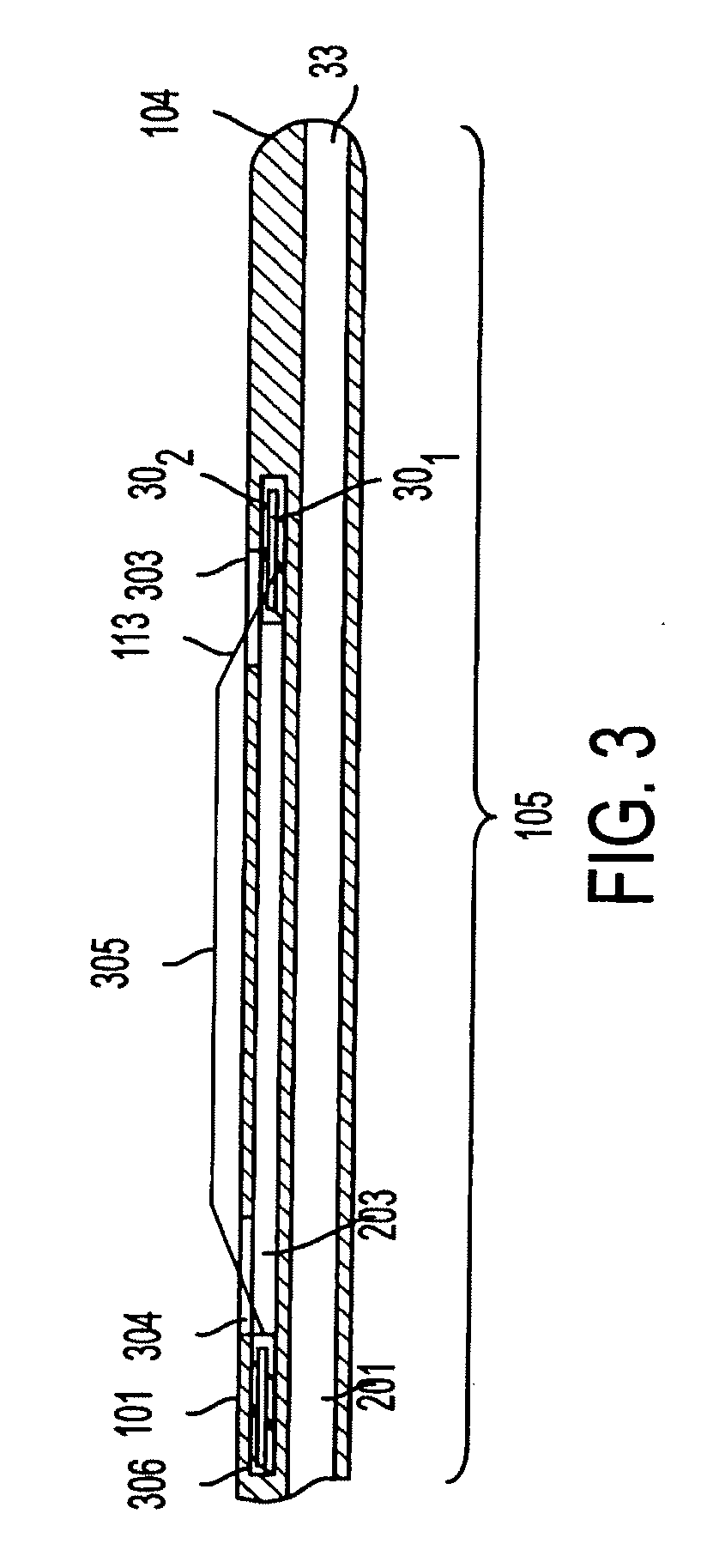
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
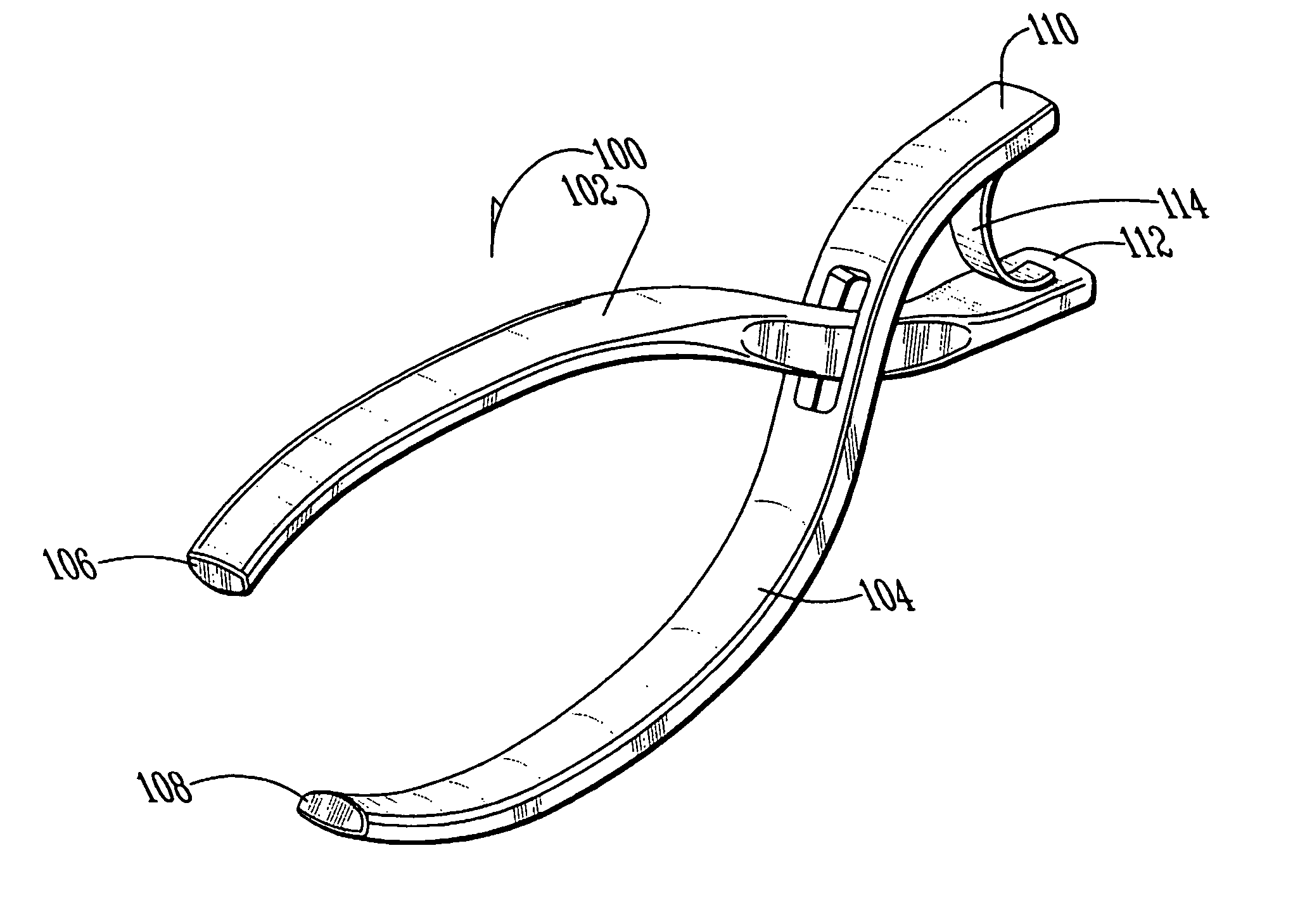
Surgical marker clip and method for cholangiography
A surgical marker clip and method for enhancing the safe performance of a cholangiography and cholecystectomy is disclosed. The clips are configured to frictionally engage the outer surface of the duct and are retained in place by light clamping force without damaging the duct. Placement of the clips allows a physician to visually isolate the common bile duct from the cystic duct during laparoscopic procedures which reduces bile duct injury typically caused by misidentification or visual misperception of the anatomy during the procedure.
Owner:DUFF MICHAEL
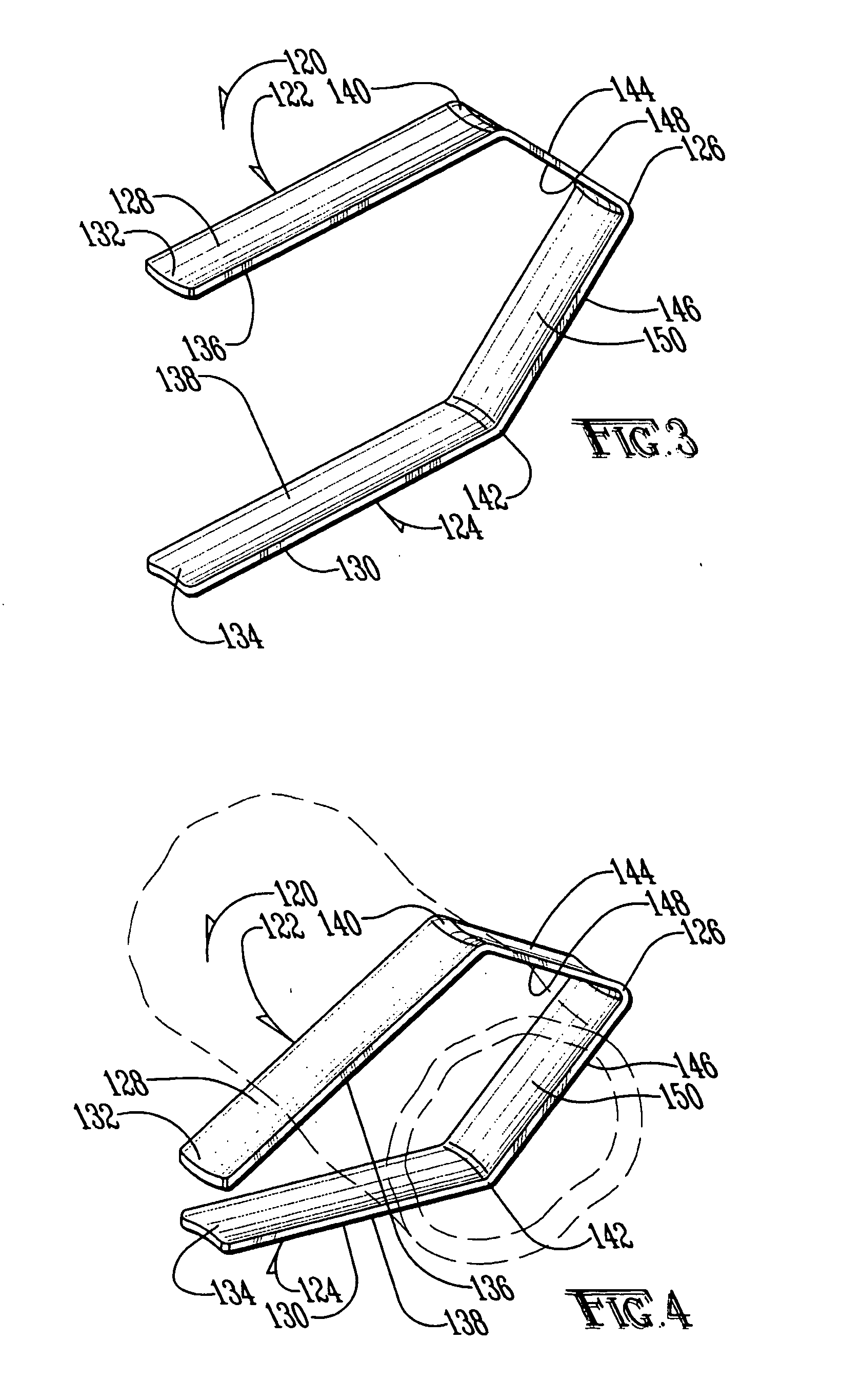
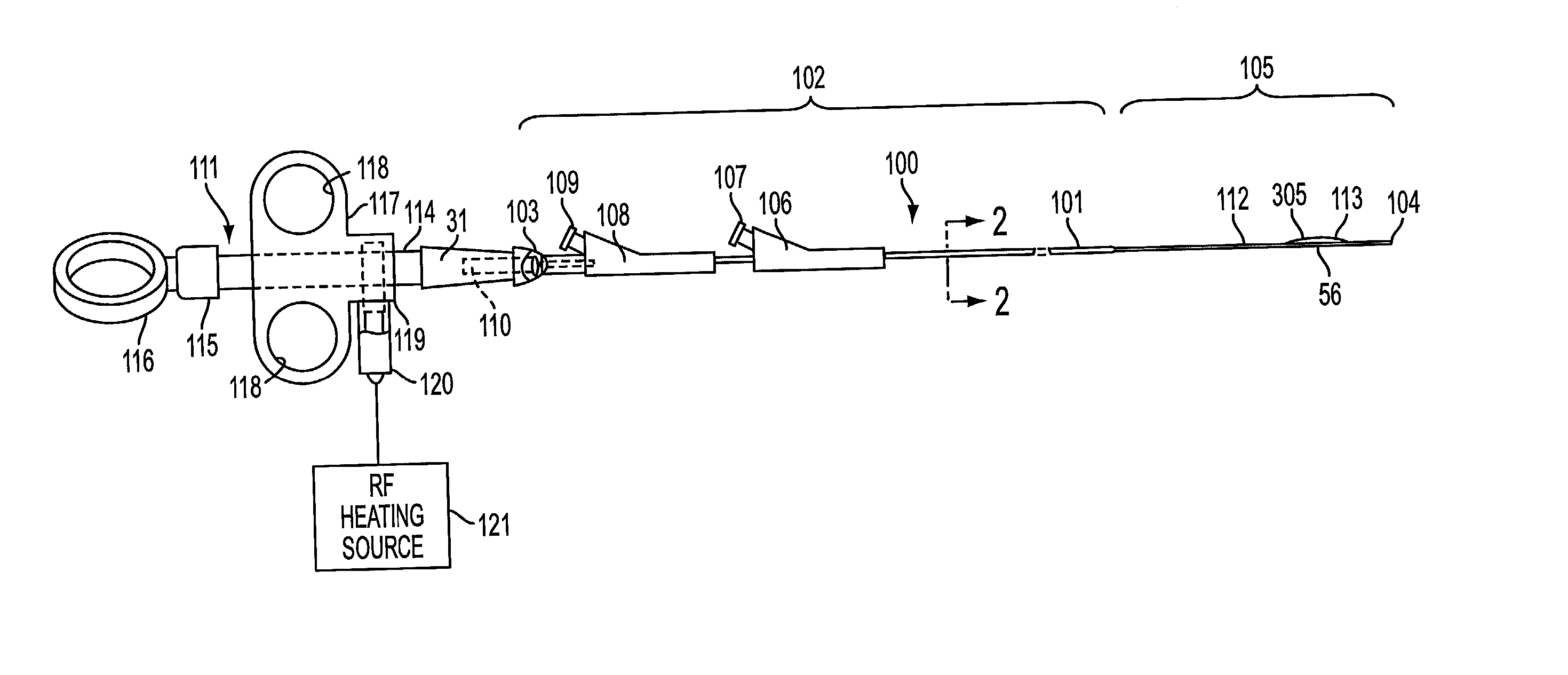
Method and apparatus for measuring and controlling blade depth of a tissue cutting apparatus in an endoscopic catheter
InactiveUS20030060842A1Surgical needlesDiagnostic markersPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Techniques for gall bladder stimulation
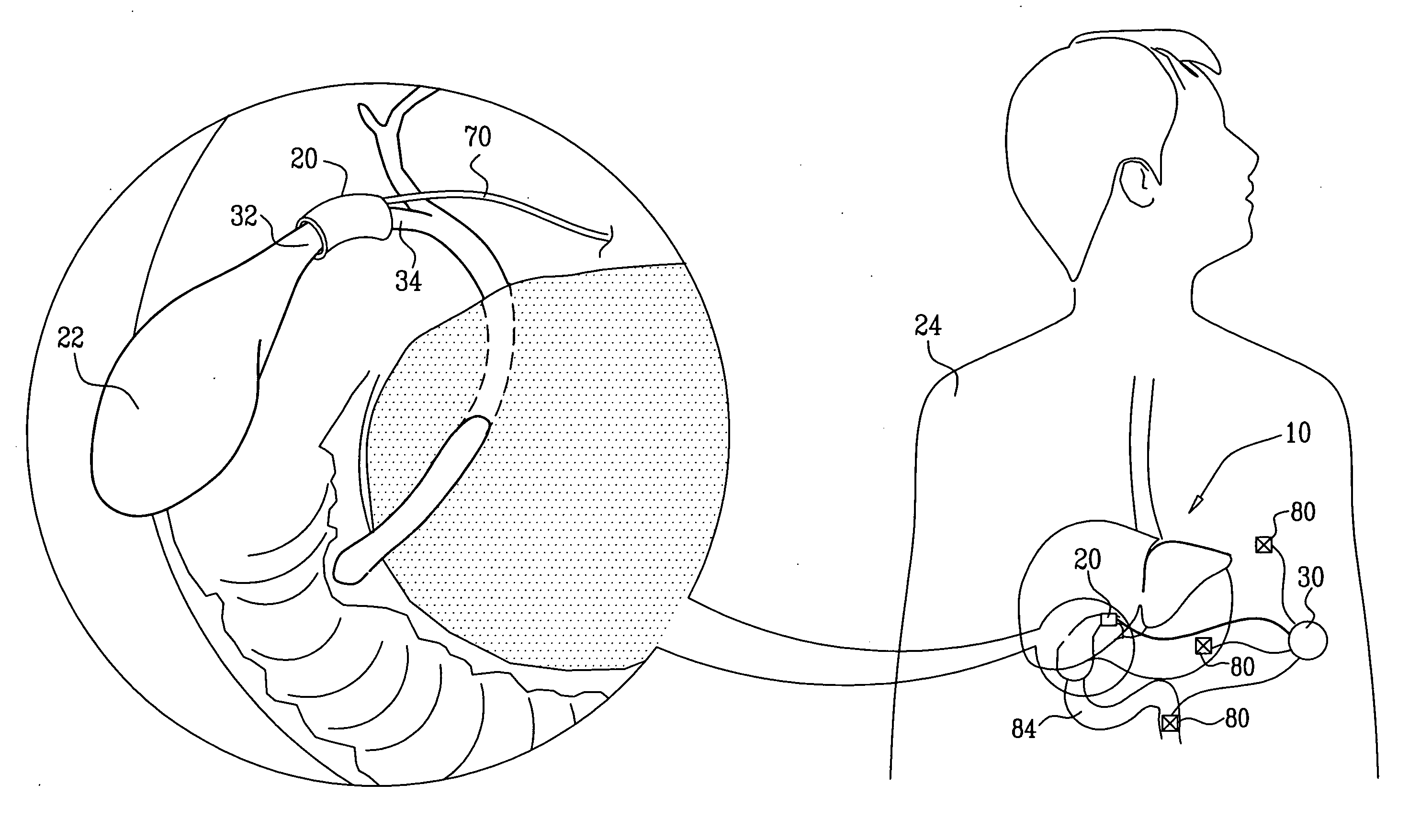
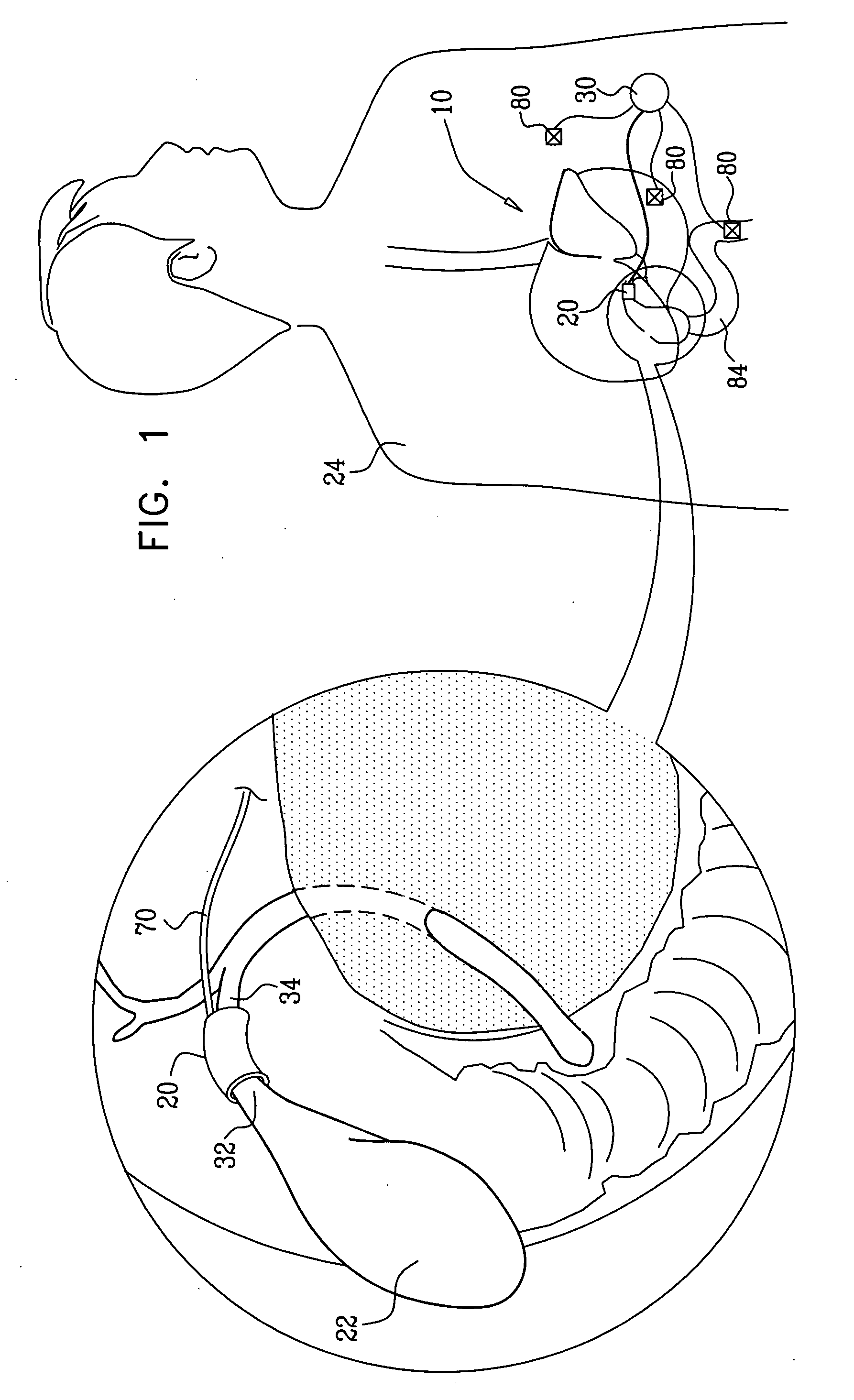
Apparatus for treating a patient is provided, including an electrode device, which is configured to be placed in a vicinity of at least one gall bladder site of the patient selected from the group consisting of: a gall bladder, a neck of the gall bladder, a cystic duct, a hepatic duct, a common hepatic duct, a bile duct, a common bile duct, sensory fibers of the gall bladder, and a hepatic port. The apparatus further includes a control unit, which is configured to drive the electrode device to apply a current to the site, and to configure the current to induce weight loss of the patient. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
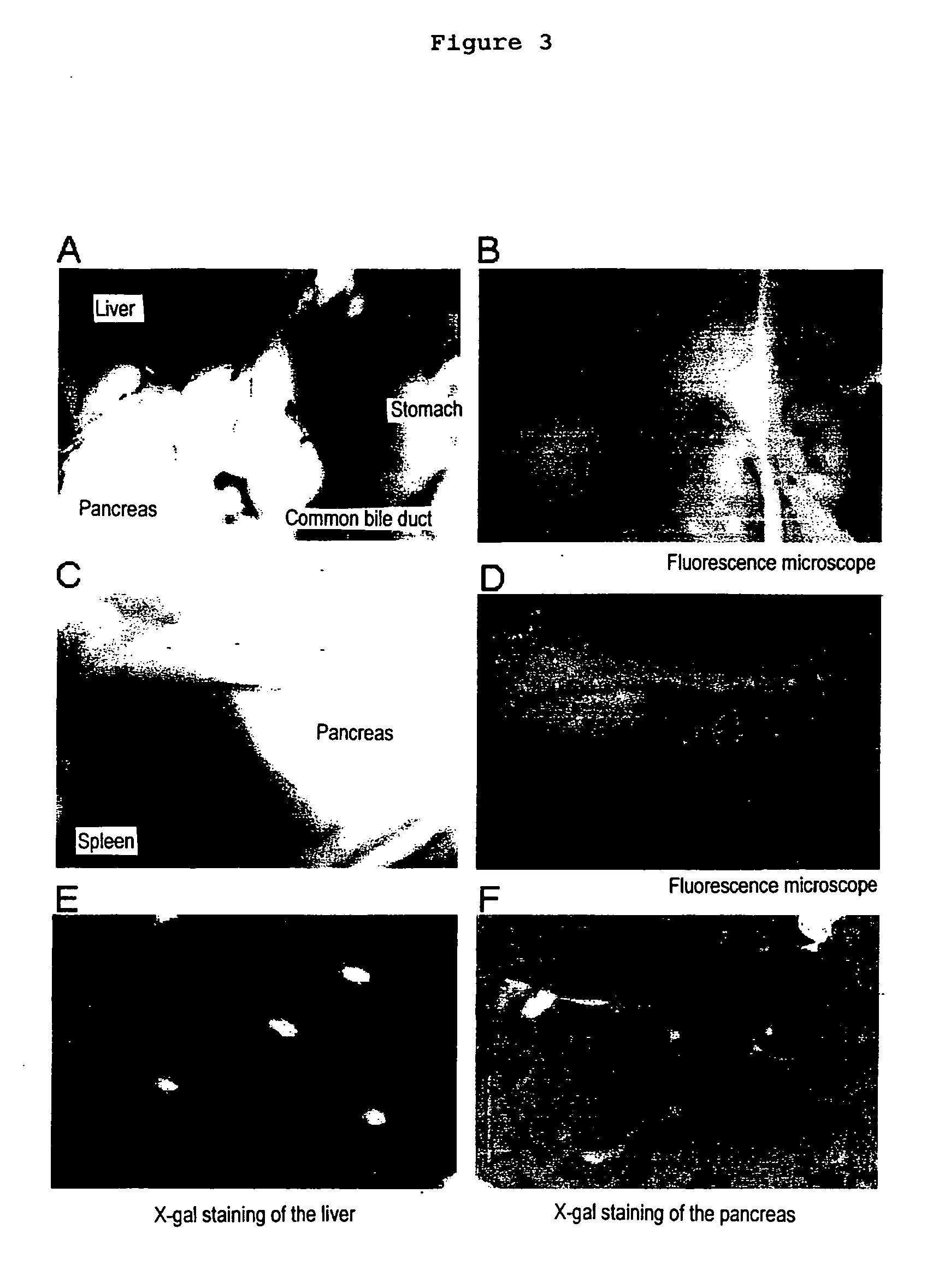
Induction of the formation of insulin-producing cells via gene transfer of pancreatic beta-cell-associated transcriptional factor
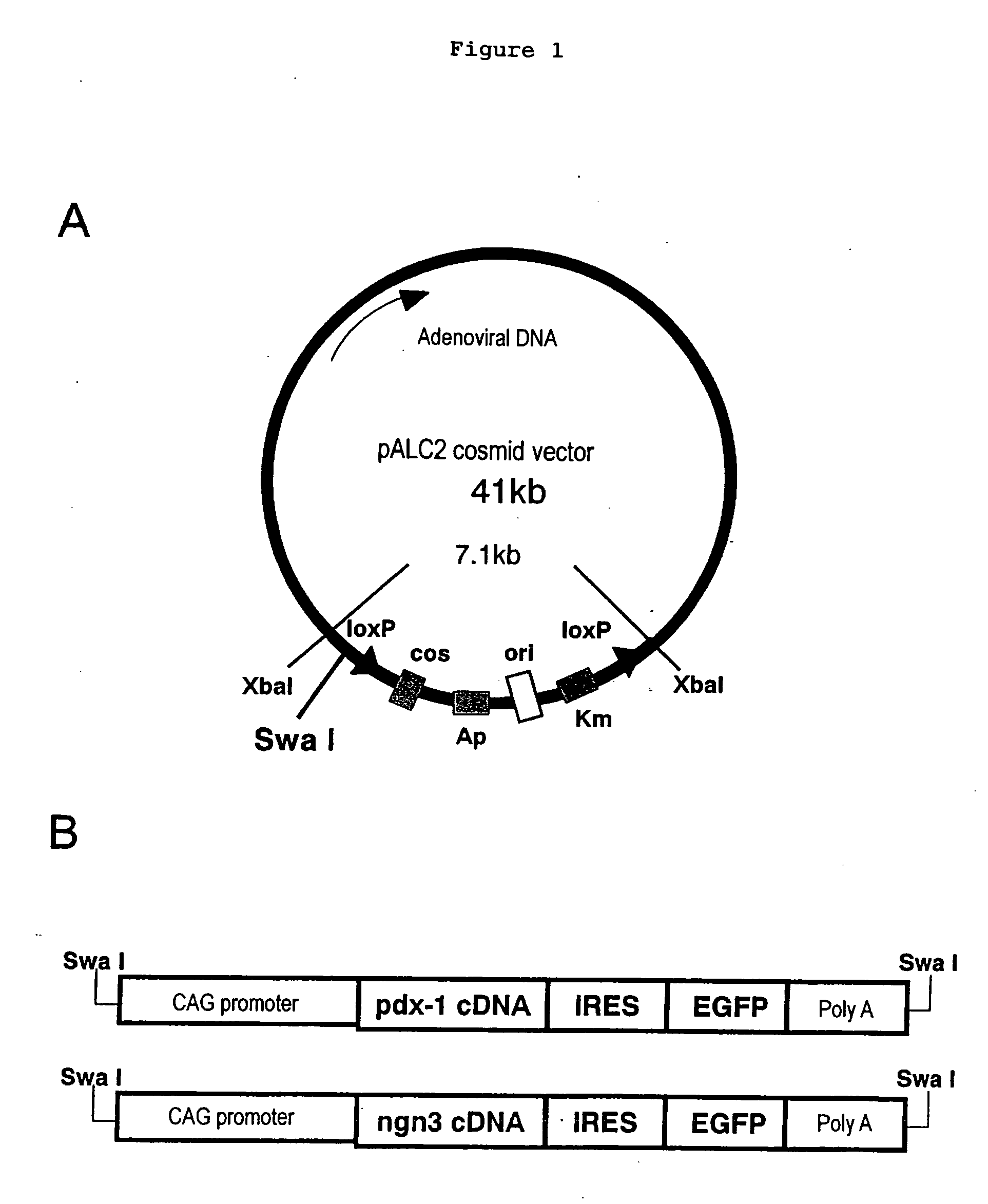
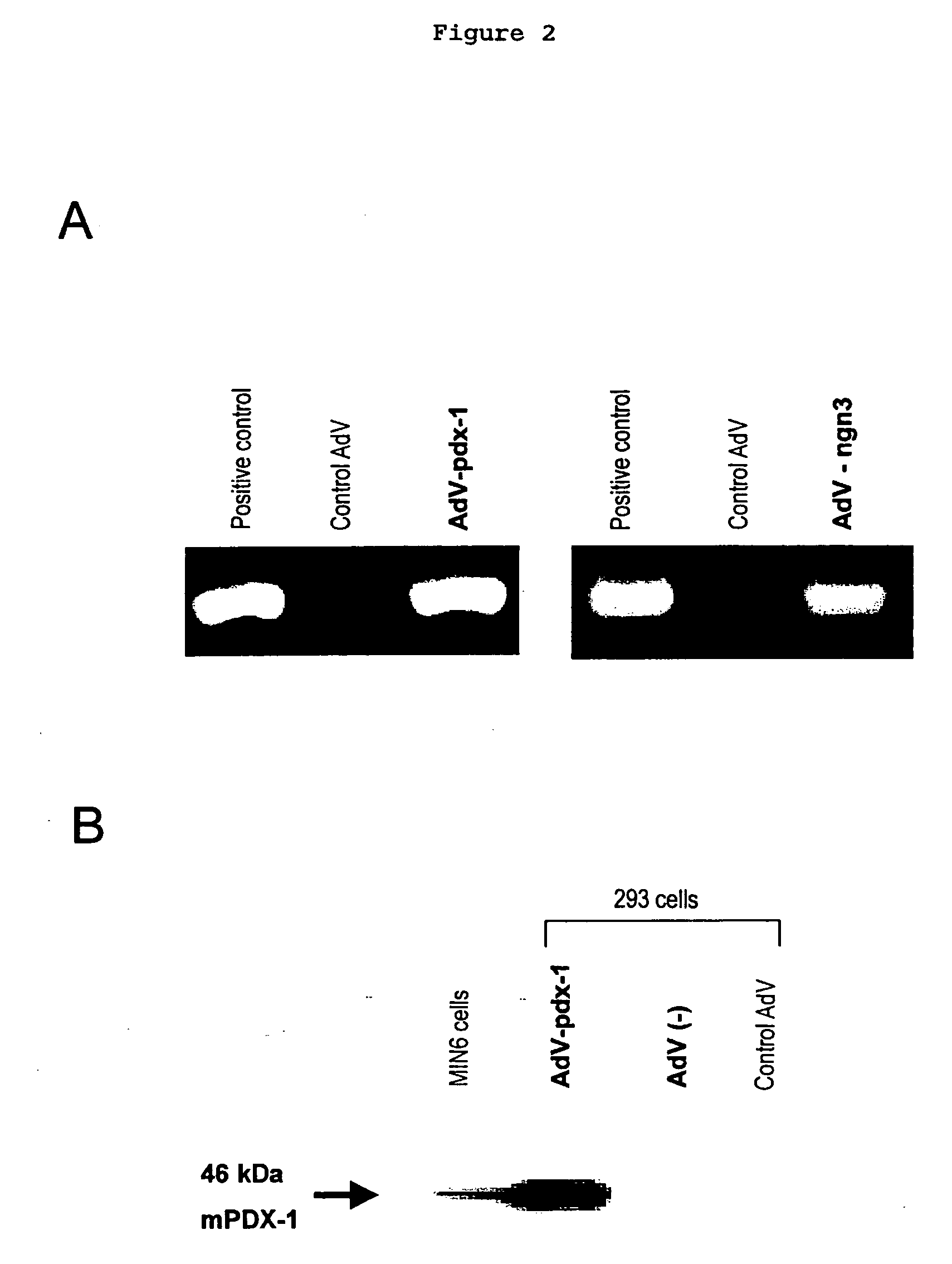
The present invention provides a method of inducing the formation of insulin-producing cells which comprises transferring a pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene into the pancreas to induce the formation of insulin-producing cells. The pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene is transferred into the pancreatic tissue stem cells by the ICBD injection without ligating the common bile ducts and thus the formation of insulin-producing cells is induced. In the present invention, pdx-1, neurogenin3, etc. are used as such pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene and an adenoviral vector with the use of the Cre-loxP recombination system, etc. is used as a vector for transferring the pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene into the pancreas. The method of the invention enables regeneration therapy for diabetes mellitus by inducing the formation of insulin-producing cells.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
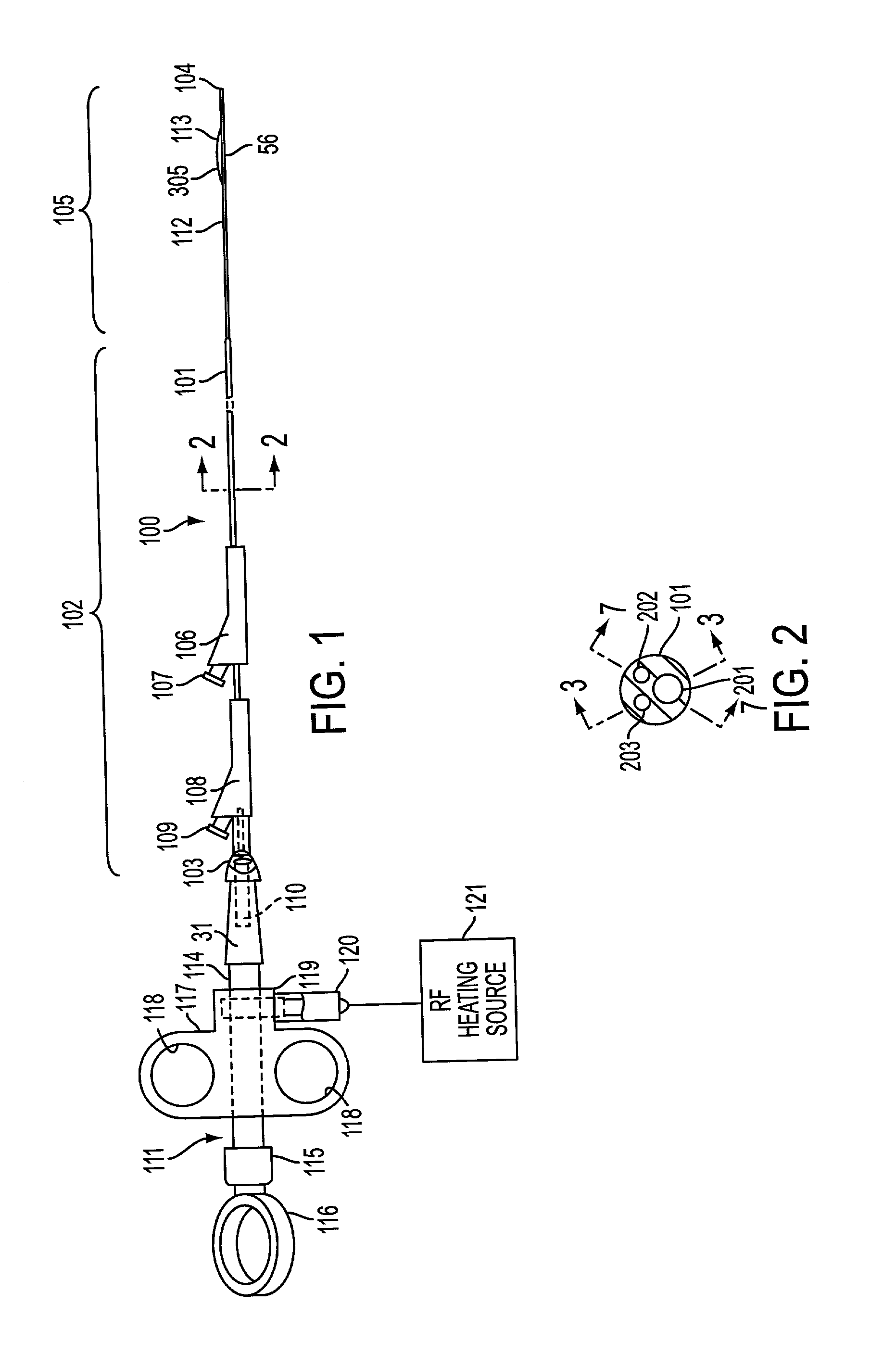
Method and Apparatus for Measuring and Controlling Blade Depth of a Tissue Cutting Apparatus in an Endoscopic Catheter
InactiveUS20090005637A1Precise depth controlProviding resistance to movementSurgical needlesEndoscopesPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
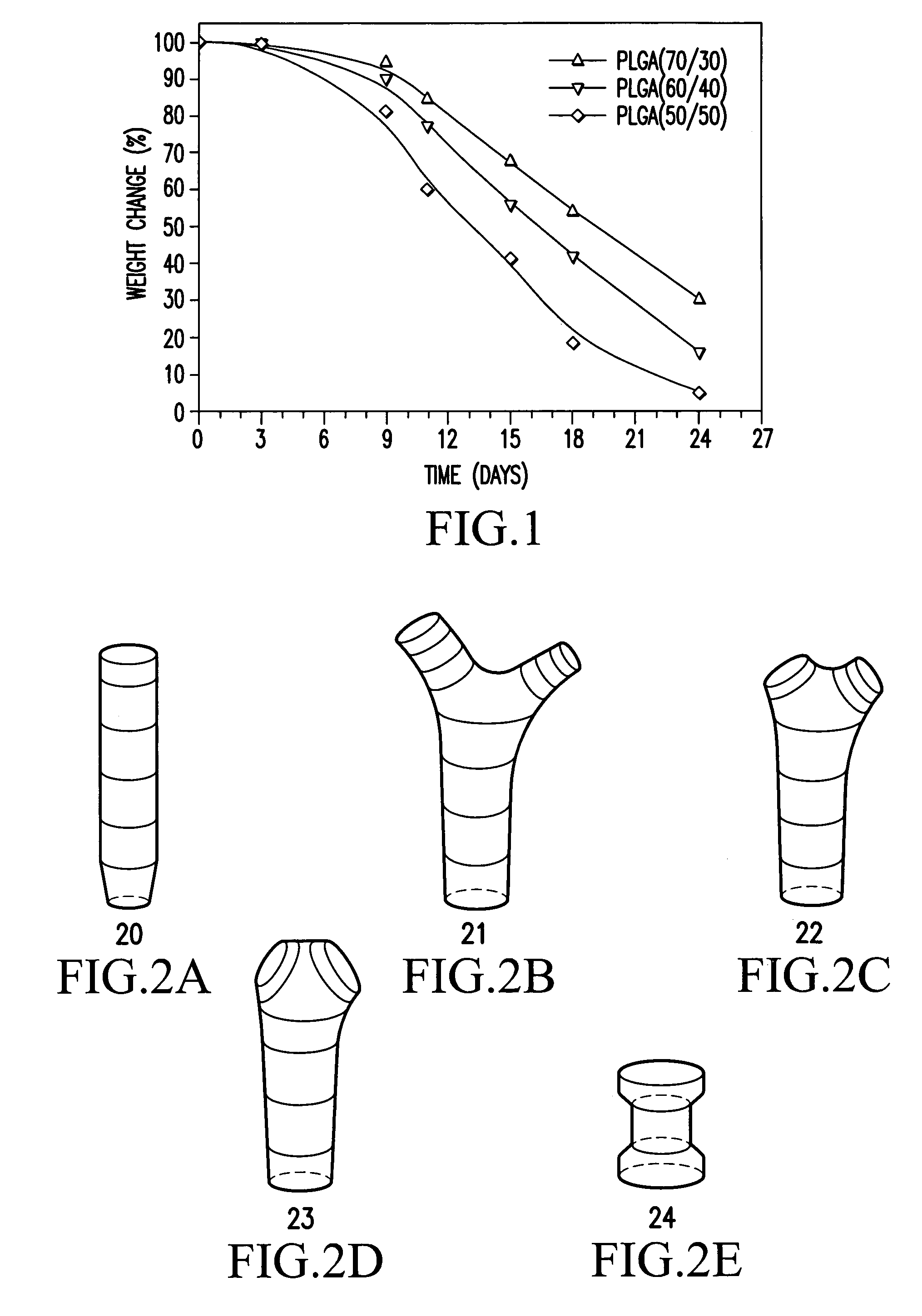
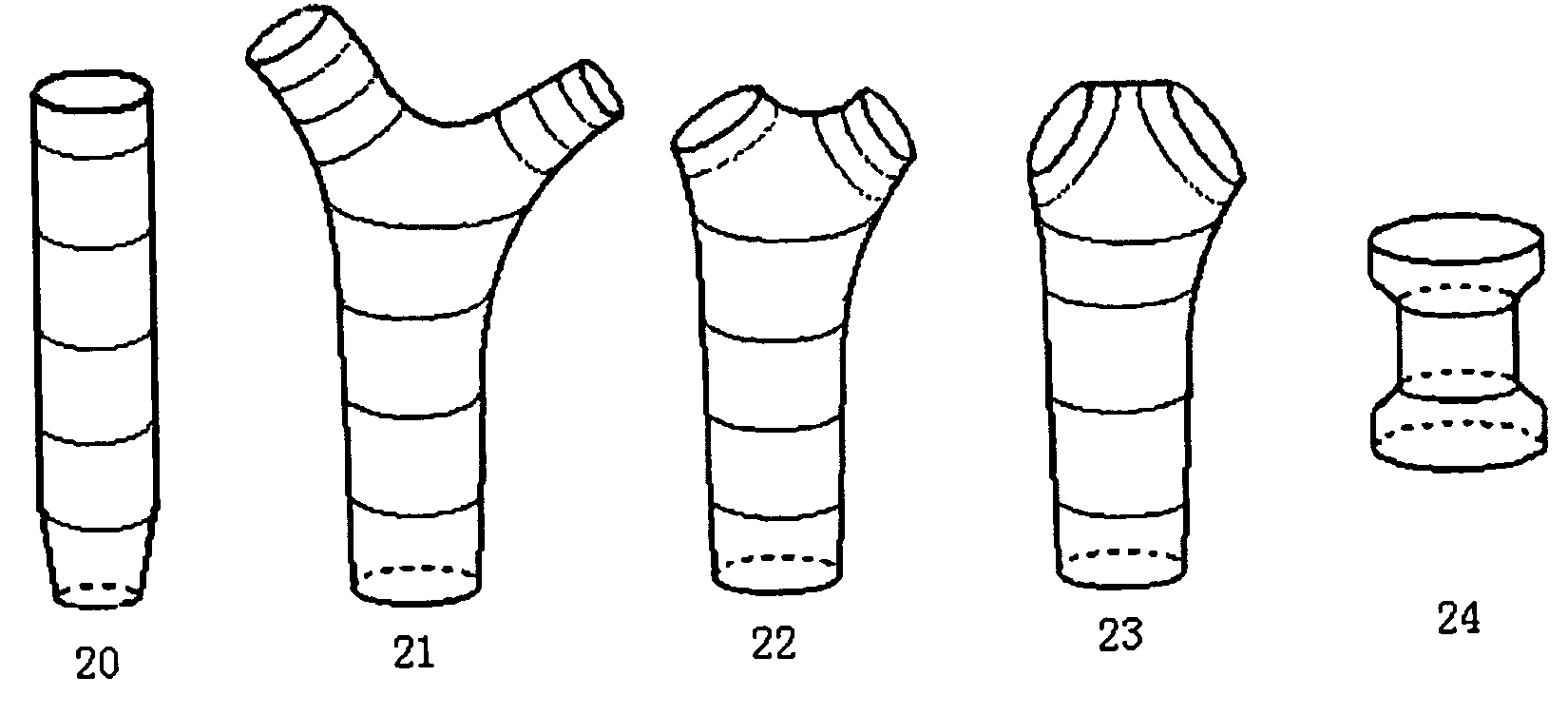
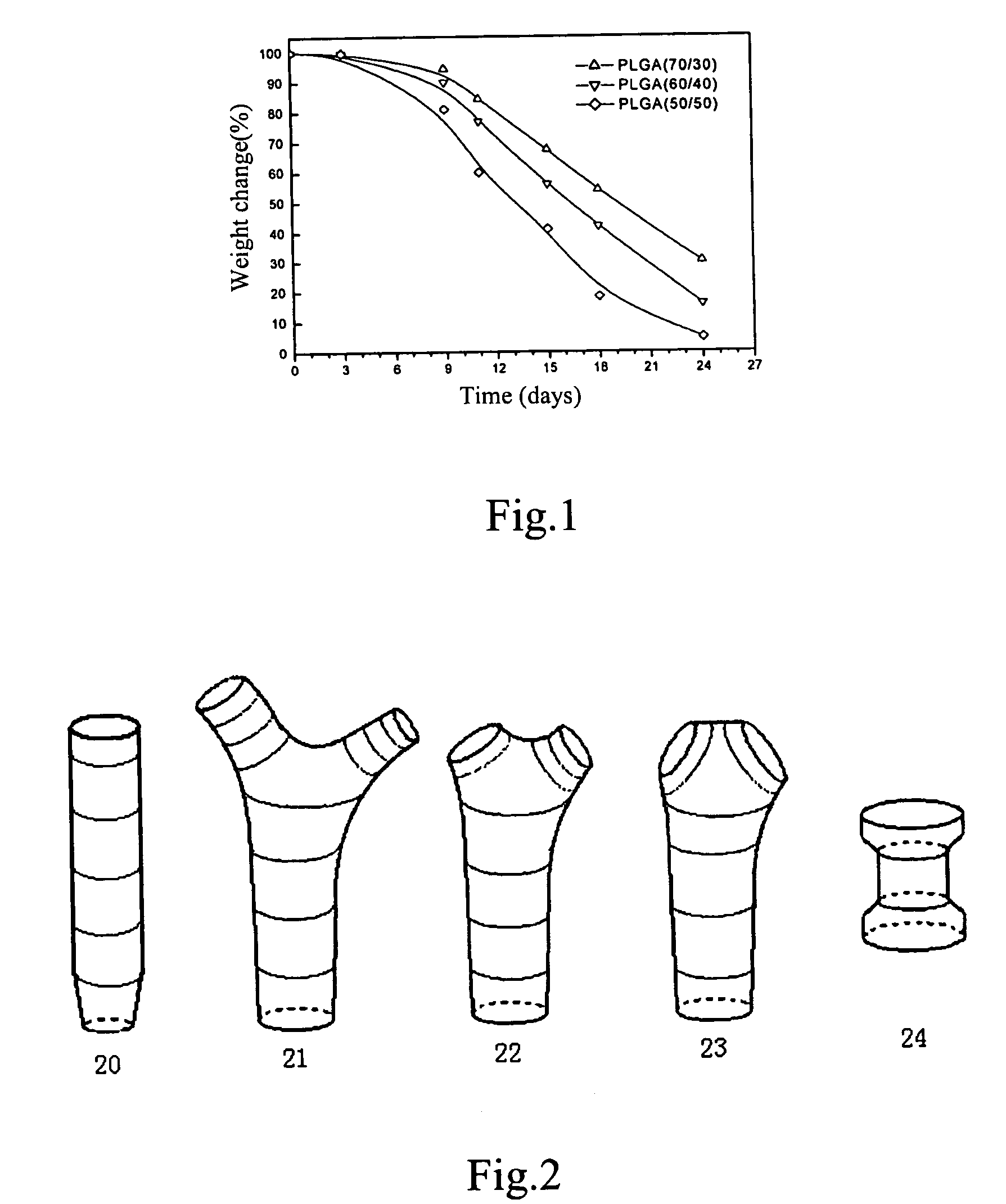
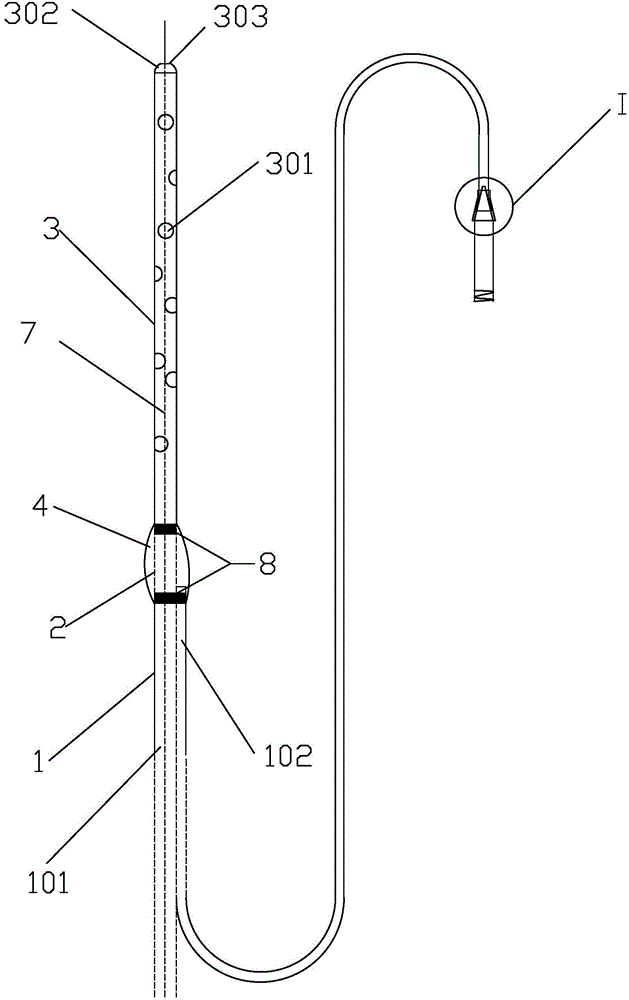
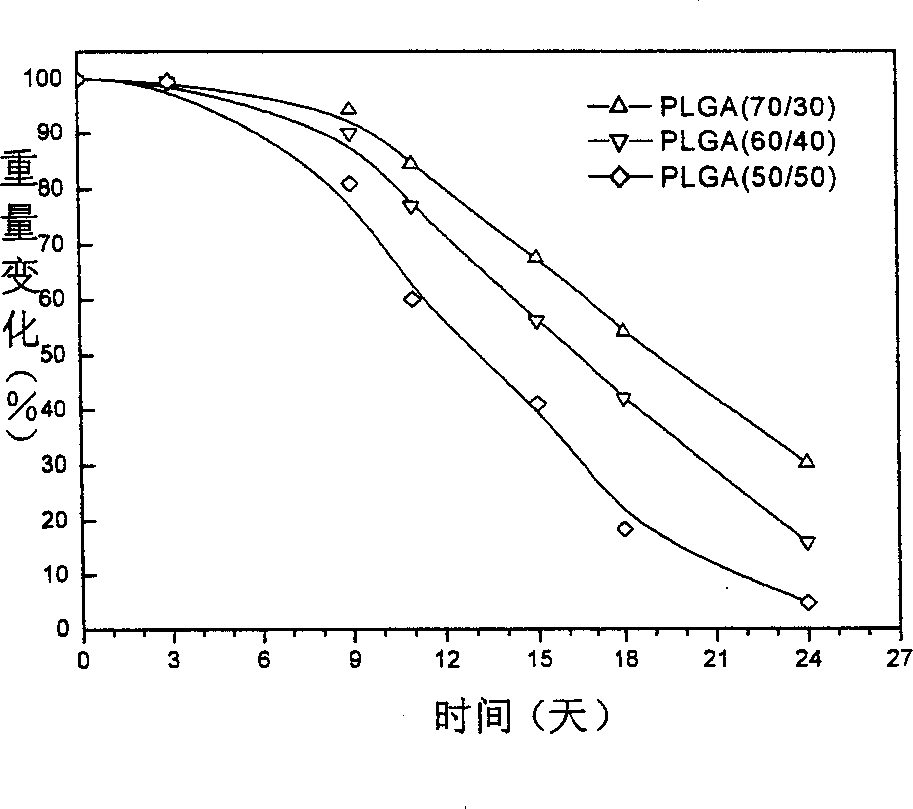
Biodegradable common bile duct stent and the method for preparing thereof
InactiveUS7094260B2Easy to sutureAvoid it happening againBile ductsBlood vesselsSurgical operationLarynx structure
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biodegradable common bile duct stent and the method for preparaing thereof
InactiveUS20050010280A1Conveniently sutured in operationAvoid it happening againBile ductsBlood vesselsSurgical operationLarynx structure
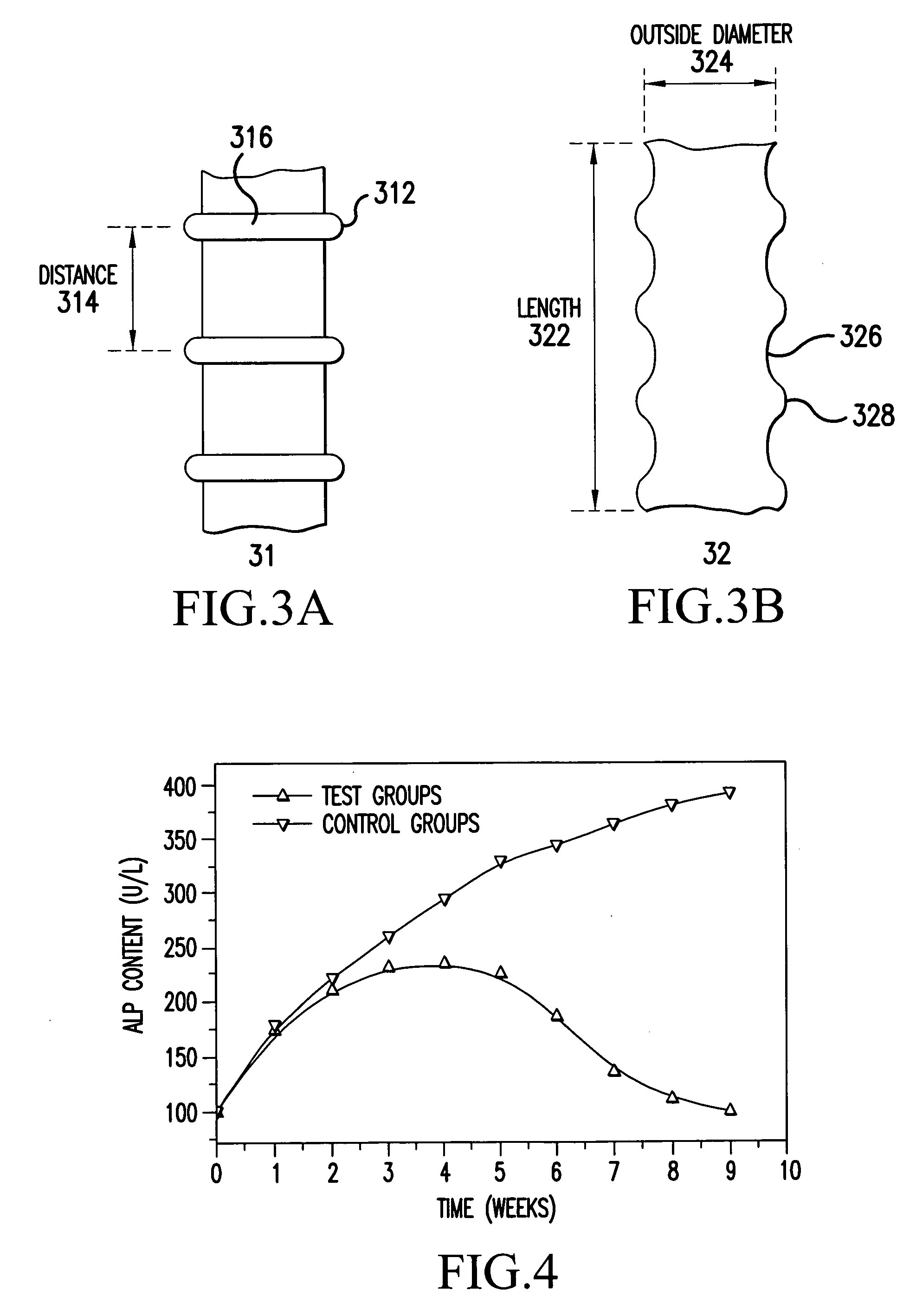
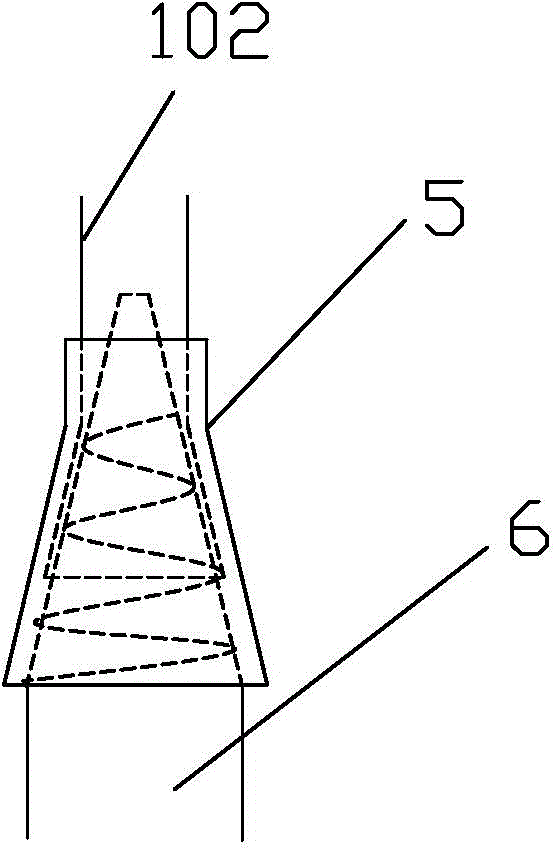
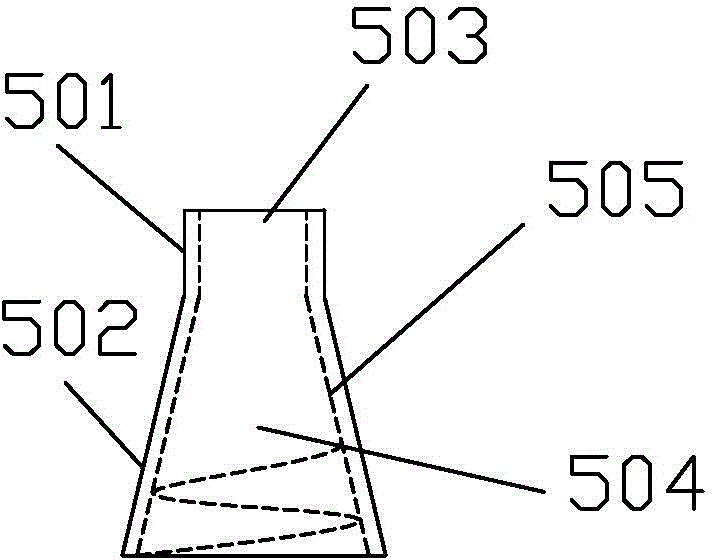
A biodegradable common bile duct stent and the method for preparing thereof are provided. The stent is made of biodegradable polymeric material with incorporation of X-ray opaque components. The stent adapt to anatomic shape of CBD or it can be sutured together with the wall of the bile duct. After placing in the duct, it maintains its position and does not slip. The circular tube of the stent being suitably sized and having multiple ring-shaped protruding rims at the outer wall and / or with larynx structure, leakage and outflow of the bile are thereby prevented. The process for manufacturing the stent comprises the following steps: (1) mixing and pelletizing of biodegradable polymer, X-ray opaque components and processing additives; (2) injection molding or extrusion-blowing followed by polishing of the exterior surface. In surgical operation on bile duct, the stent can replace the T-tube which is conventionally used to support the duct and guide bile drainage. It can reduce the time required for surgical operation and treatment, reduce possible complications and can be degraded and eliminated as the incision heals and the CBD regains its normal functions.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Design method of pipe holder capable of bearing micro radioactive particles
The invention relates to the technical field of medical apparatuses, in particular to a method for designing a pipe support capable of bearing miniature radioactive particle sources, wherein the pipe support is mainly used for internal radiation treatment of intermediate and late pancreatic cancer and malignant bile duct stenosis. The method can optimally design a concrete structure of the pipe support capable of bearing the miniature radioactive particle sources by utilizing natural cavities (including a common bile duct, a main pancreatic duct, an accessory pancreatic duct and so on) on the circumference of the pancreatic head of a human body. The method comprises: S1, designing the outside diameter of the support, the inside diameter of drainage cavities, the length of the support and so on; S2, selecting different support materials according to a clinic radiation planning, and selecting whether to apply materials with different shielding materials to seal a radiation window; and S3, designing the inside diameter of a particle channel, the dimension of the radiation window and interval arrangement. The method realizes the aims of precise positioning, precise planning and precise treatment, and achieves optimum internal radiation treatment effect.
Owner:路筝
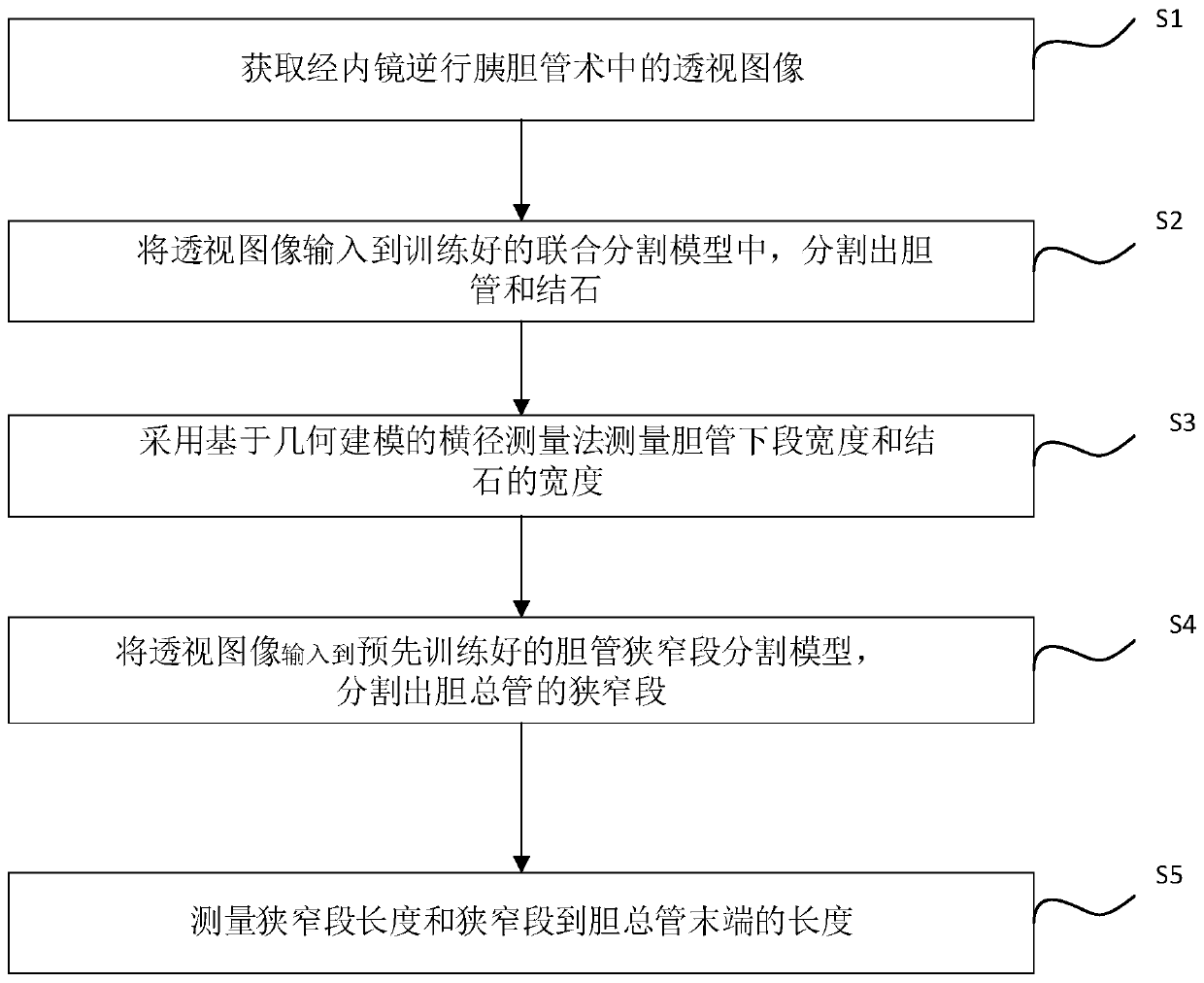
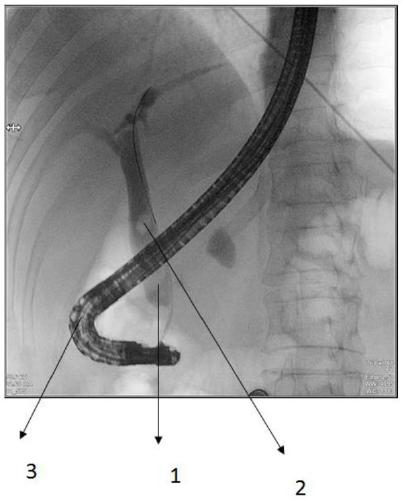
Auxiliary diagnosis and measurement method and system in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
The invention discloses an auxiliary diagnosis and measurement method in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining a perspective image inendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; s2, inputting the perspective image into a trained joint segmentation model, and carrying out segmenting to obtain a bile duct and a calculus; s3, measuring the width of the lower section of the bile duct and the width of the calculus by adopting a transverse diameter measurement method based on geometric modeling; s4, inputting the perspective imageinto a pre-trained bile duct narrow segment segmentation model, and segmenting a narrow segment of the common bile duct; and S5, measuring the length of the narrow section and the length from the narrow section to the tail end of the common bile duct. According to the invention, the joint segmentation model is established through a neural network to identify bile ducts and calculi; the narrow section of the common bile duct is segmented through the bile duct narrow section segmentation model, then the size of bile duct calculi, the width of the lower section of the bile duct, the length of the bile duct narrow section and the length from the bile duct narrow section to the bile duct tail end are measured, and a doctor can be assisted in diagnosing the bile duct calculi and bile duct narrowness through the measurement result.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Novel three-dimensional electronic choledochoscope system and use method thereof
ActiveCN102058387AEasy to findReasonable and effective treatment planGastroscopesOesophagoscopesBiliary tractBladder cavity
The invention belongs to medical instruments, and in particular relates to a novel three-dimensional electronic choledochoscope system for reconfiguring a three-dimensional image by using a multi-CCD (Charge Coupled Device) array, which comprises a soft electronic choledochoscope, a processing host computer, a light source host computer and a work station assembly, wherein the processing host computer, the light source host computer and the work station assembly are connected with the soft electronic choledochoscope; the three-dimensional soft electronic cystoscope enters a gall bladder cavity through a small cut at the bottom of the gall bladder and can enter the biliary tract through a small cut on the bile duct wall, then turns into the bile duct through better flexibility and control, and then enters the common bile duct for detecting the condition of the common bile duct; the multi-CCD array module at the tip part of a choledochoscope working end part is used for finely scanning the common bile duct, even the intrahepatic bile duct to obtain a three-dimensional image of the choledochoscope cavity; and a doctor treats the gall bladder pathological change according to the three-dimensional image.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAODAN MEDICAL INSTR TECH
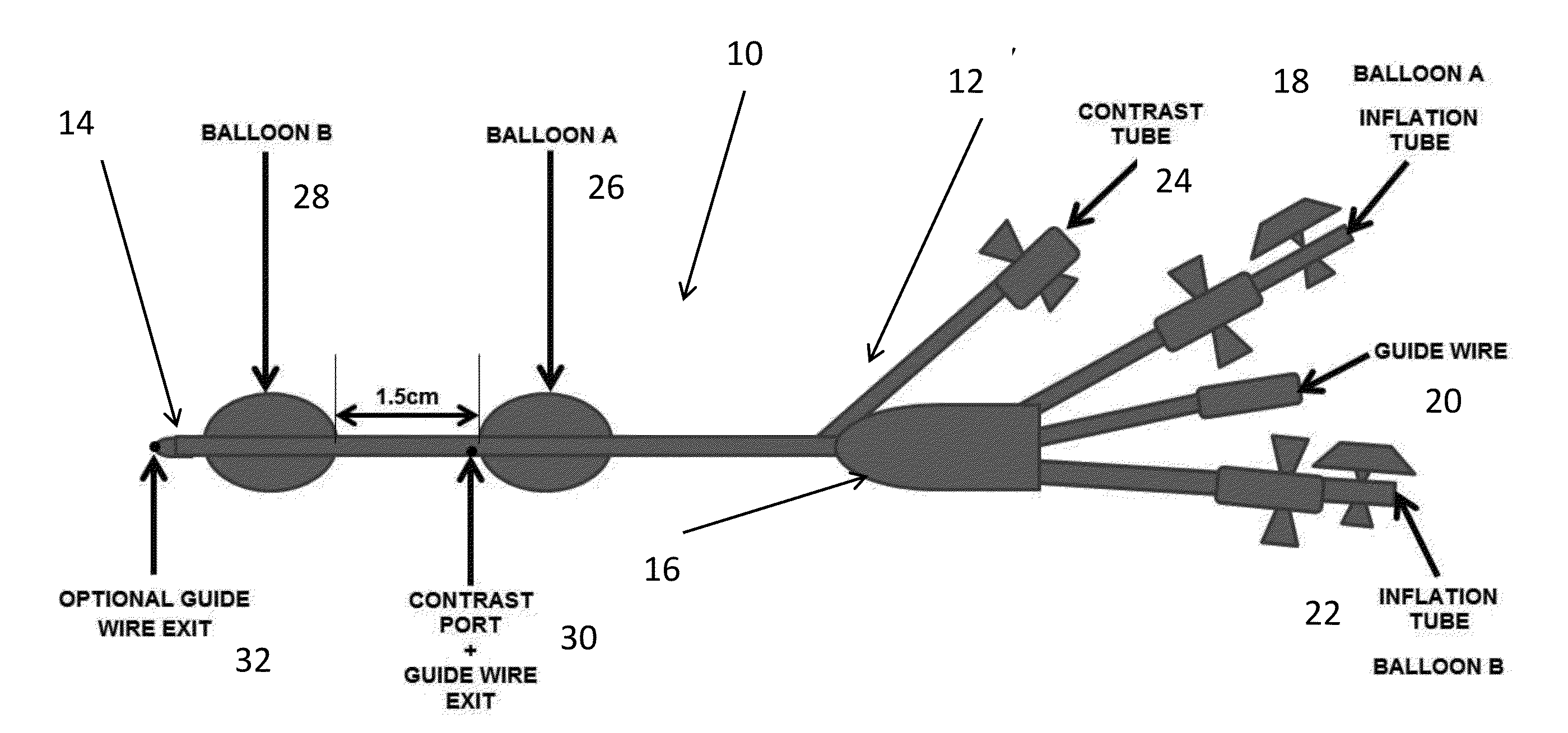
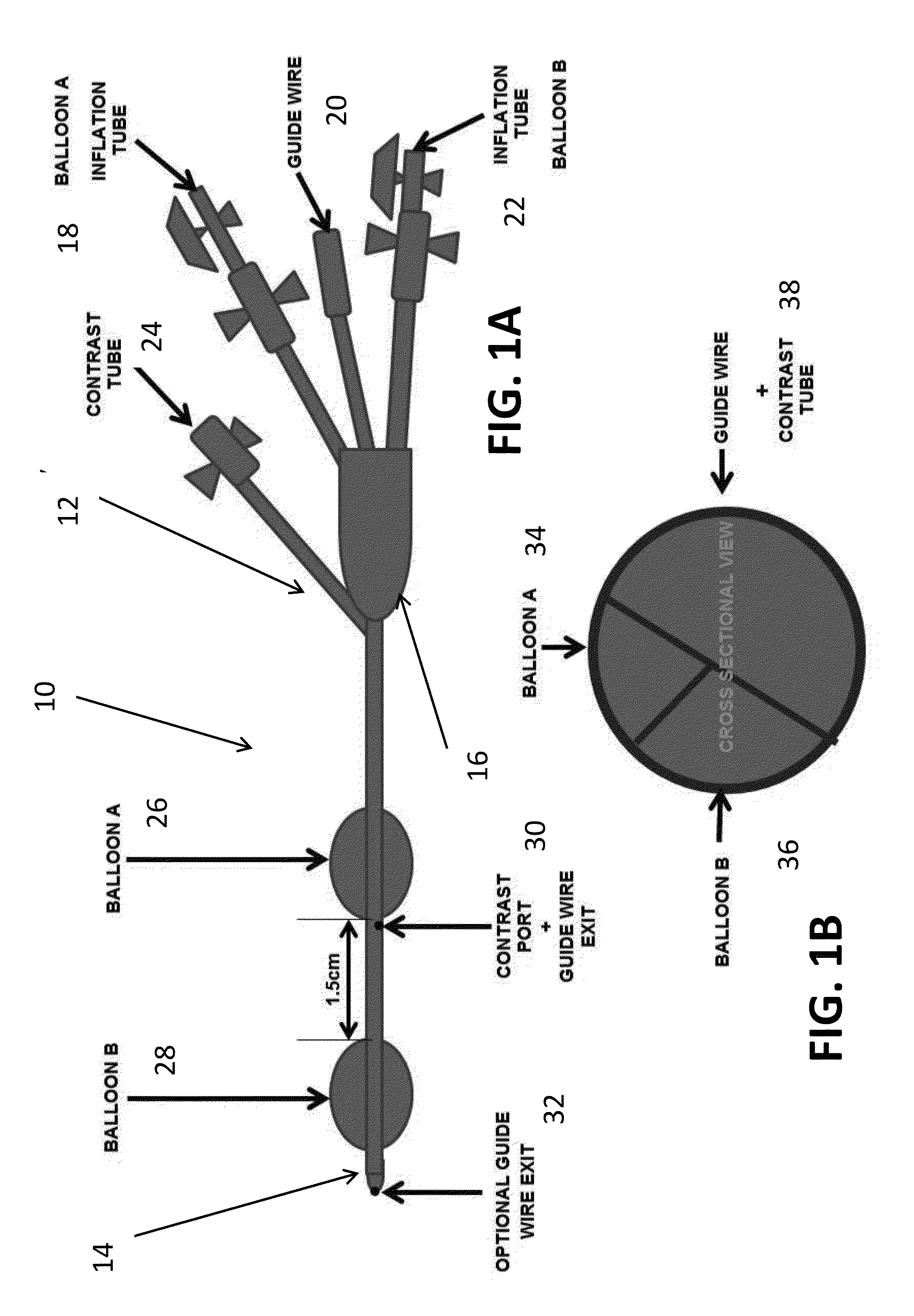
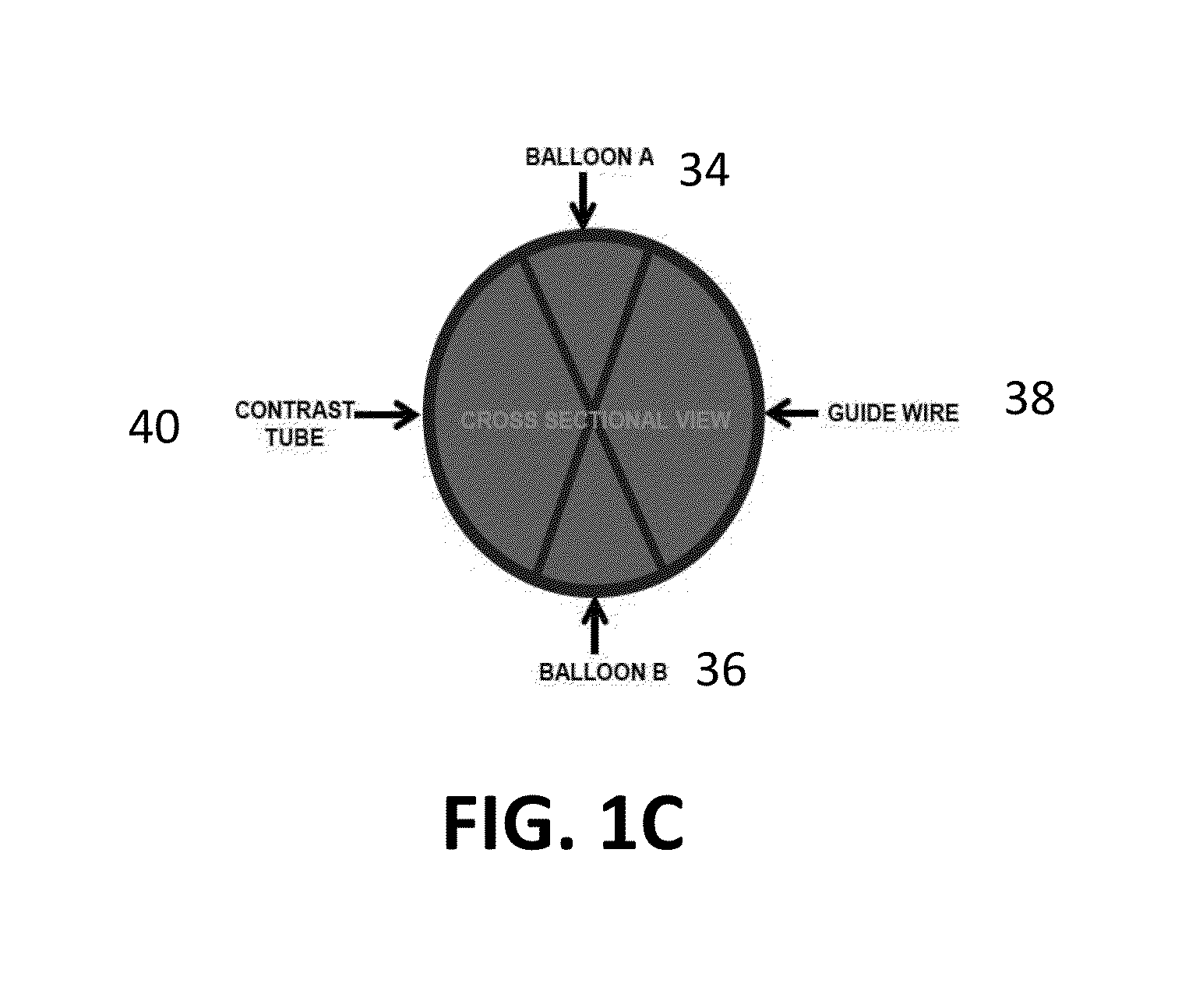
Dual Balloon Biliary Stone Extraction Device
InactiveUS20150150572A1Good choiceFacilitating its cannulationBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterGene deliveryBiliary epithelium
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for selective guide wire cannulation of a bile duct, removal of biliary calculi, and delivering hydrodynamic gene delivery are also provided. There is provided a method for straightening the terminal common bile duct to allow biliary calculi to be removed, assisting in creation of a gastoejunostomy, and selective guidewire cannulation. A method for isolating a segment of biliary epithelium for hydrodynamic gene delivery is also provided, in which a segment of the bile duct is isolated and plasmids (oncogenic or therapeutic) are injected under pressure to allow entry into cholangiocytes. There is also provided a method for isolating the cystic duct or left / right intrahepatic ducts to allow the insertion of a guide wire and subsequent therapy. A single catheter platform may be used to perform the above procedures.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
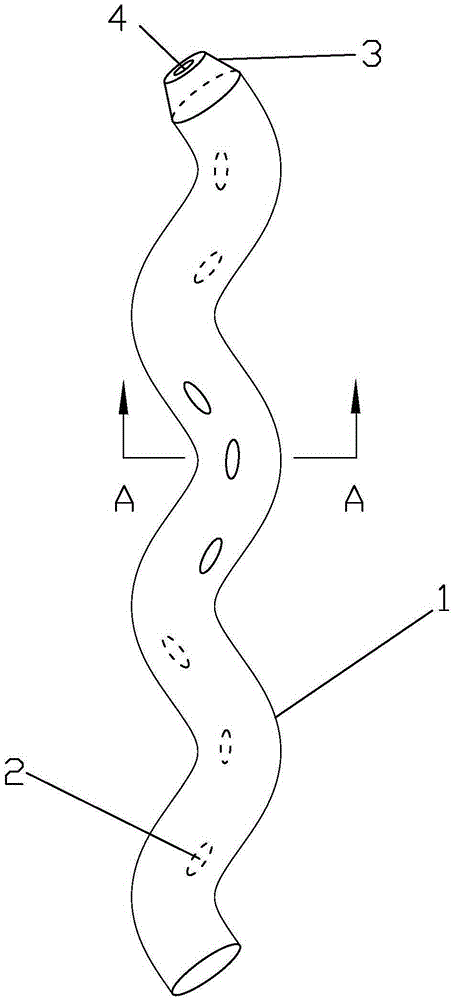
Spiral internal biliary drainage tube
The invention discloses a spiral internal biliary drainage tube, which comprises a spiral tube, wherein a plurality of through holes I are arranged on the outer wall of the spiral tube; the spiral tube is 7-11cm long, the spiral tube is 1-2mm in inner diameter, the spiral tube is 4-5mm in outer diameter, the spiral tube includes 2-5 cycles and the spiral tube is 5-8.5Fr in pipe diameter. The spiral tube disclosed by the invention has an anti-sliding function, and the spiral internal biliary drainage tube is low in probability of internal displacement or takeoff; the drainage tube is capable of preventing biliary wall mucosa from being adsorbed on and from blocking the through holes I and is conducive to the drainage of infectious thick bile; the bile is discharged into duodena through the through holes I and the inner cavity of the spiral tube, and the bile also flows out through an inner cavity formed by the spiral tube; the main body of the spiral tube has an effect on compressing stones in common bile duct; the drainage tube, when preventing the stones in the common bile duct from displacing, can bring about a friction effect on the stones through the sidewall thereof, so that the volume of the stones is diminished to create conditions for secondary stone removal through ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
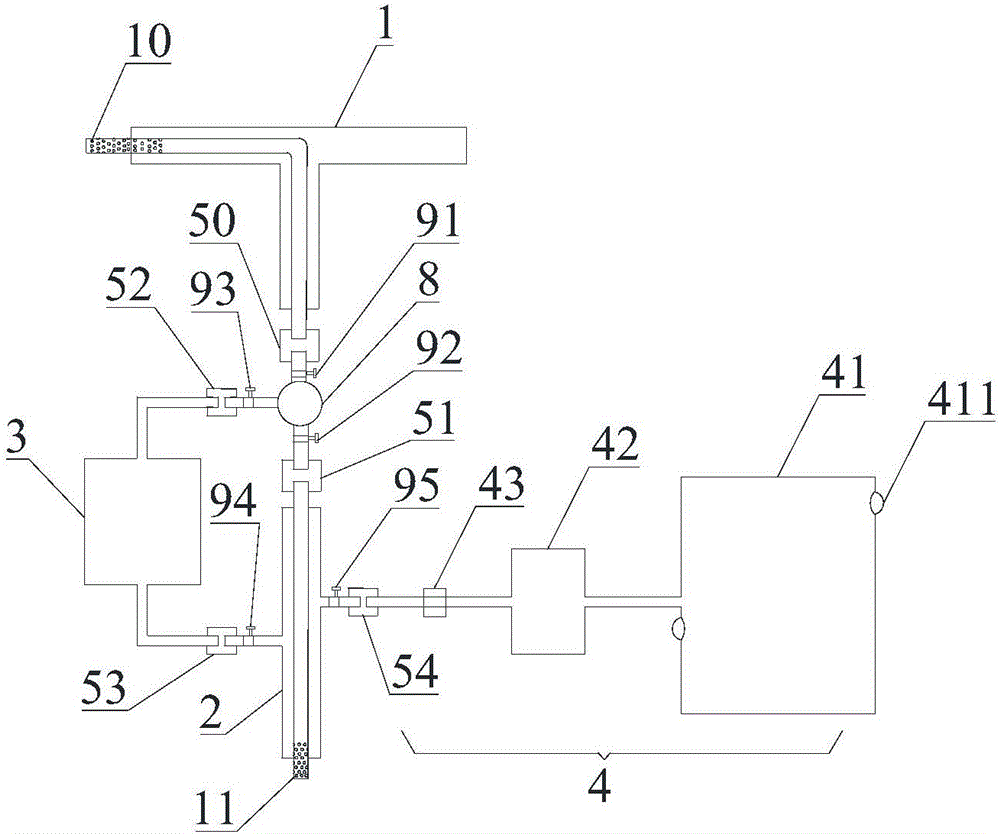
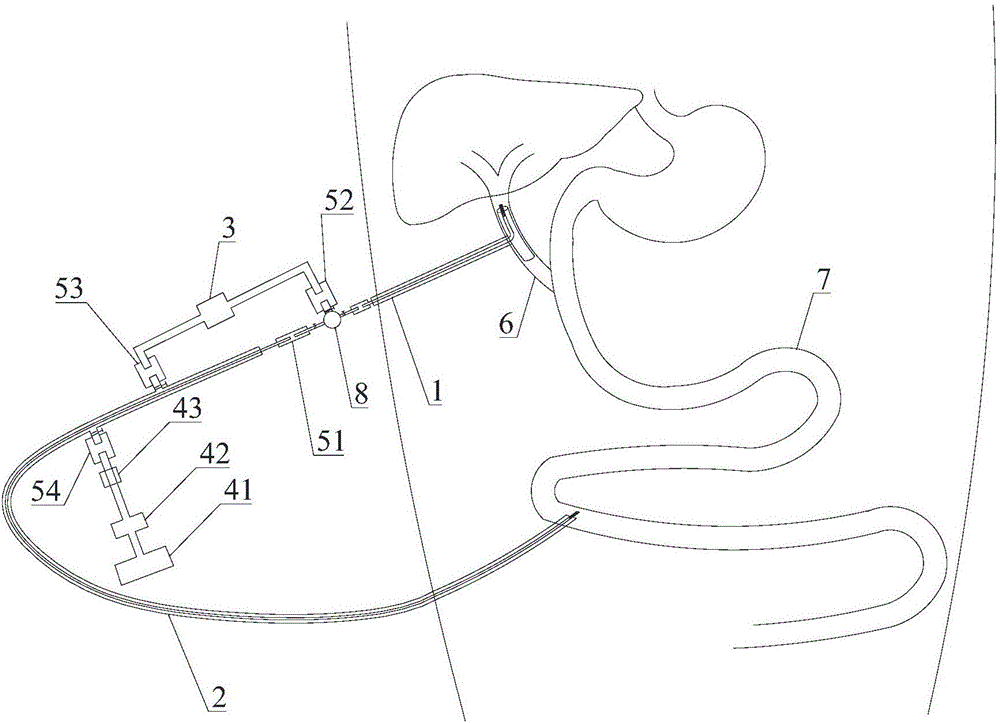
Selectable bile recycling and bypassing enteral nutrition device and use method thereof
PendingCN106798962AAvoid churnPromote recoveryWound drainsMedical devicesBiliary tract diseaseCommon Duct
The invention relates to a selectable bile recycling and bypassing enteral nutrition device and a use method thereof. The device comprises a drainage pipe used for draining bile from a common bile duct to the terminal and a bypassing pipe for returning the bile back to a jejunum in vivo, wherein the first end of the drainage pipe is placed in the common bile duct, the second end of the drainage pipe communicates with the first end of the bypassing pipe, and the second end of the bypassing pipe is placed into the jejunum. The bypassing pipe is used for returning the bile back to the enteric canal, the problem that a large number of bile losses due to long-term cathetering after surgery on biliary diseases is avoided, and thus a patient can recover well after the surgery; a bypassing heating bag is used for warming the bile, and the discomfort of the patient due to the fact that the processed bile returning back to the enteric canal has relatively low temperature is avoided; the drainage pipe, the bypassing pipe, the bypassing heating bag and a nutrient solution adding component are detachable, and can be selectively assembly according to the disease state and need of the patient; the bypassing pipe is connected with the nutrient solution adding component used for enteral nutrition treatment, thus being convenient for supplying the nutrition solution to the patient.
Owner:吴雪松 +1
Hepatic lobule-like bioreactor
ActiveCN102114275AWith liver metabolism functionGood mass transfer functionOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsCapillary networkCommon Duct
The invention discloses a hepatic lobule-like bioreactor, which belongs to the field of biomedical equipment. A nanofiber scaffold network is arranged in a shell of the bioreactor, an intrahepatic fibrovascular network, a bile capillary network, upper hepatic bile ducts, lower hepatic bile ducts, a common bile duct, and hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts are distributed in the whole nanofiber scaffold network, and the bile capillary network is distributed at the peripheries of the hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts; the upper hepatic bile ducts and the lower hepatic bile ducts are communicated through the common bile duct; bile capillaries in the bile capillary network are provided with more than two bile capillary epidermal cell inlets; the hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts are provided with more than two hepatic cell injection ports; the intrahepatic fibrovascular network is provided with a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet; and the bile capillary epidermal cell inlets, the hepatic cell injection ports, the liquid inlet, the liquid outlet and an outlet at the lower end of the common bile duct pass through the shell. The hepatic lobule-like bioreactor truly simulates the structure of hepatic lobule, realizes the functions of metabolic detoxification, excretion and the like of livers, and is superior to the conventional bioreactor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for dispersing stagnated liver qi for promoting bile flow and applications thereof
InactiveCN104173937ASignificant effectDigestive systemSulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsSalvia miltiorrhizaBiliary tract
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for dispersing stagnated liver qi for promoting bile flow and applications thereof. The composition is prepared from the following Chinese herbal medicine raw materials in parts by weight by decocting with water and extracting: 10-15 parts of radix bupleuri, 25-36 parts of polygonum cuspidatum, 12-18 parts of curcuma aromatica, 10-15 parts of radix aucklandiae, 10-15 parts of melia toosendan, 7-11 parts of radix scutellariae, 25-36 parts of flos lonicerae, 10-15 parts of rhizoma cyperi, 10-15 parts of semen raphani, 10-15 parts of corydalis yanhusuo, 10-15 parts of rhubarb, 25-36 parts of dandelion, 25-36 parts of christina loosestrife herb, 7-11 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, 5-8 parts of mirabilite, 10-15 parts of fructus aurantii immaturus, 25-36 parts of folium isatidis, 25-36 parts of herba artemisiae, and 10-15 parts of magnolia officinalis. The composition disperses stagnated liver qi for promoting bile flow, regulates qi to alleviate pain, diminishes inflammation and removes urinary calculus, and can be applied to the treatment of acute cholecystitis, infection of biliary tract, common bile duct and gallstone.
Owner:QINGDAO MUNICIPAL HOSPITAL
Water bag type gall external drainage tube
InactiveCN104800959APrevent prolapseStrong tensionBalloon catheterUpper gastrointestinalBiliary tract
The invention discloses a water bag type gall external drainage tube. The water bag type gall external drainage tube comprises a drainage tube section I, a drainage tube section II and a drainage tube section III which are communicated in sequence, wherein a ball bag thin film sleeves the outer wall of the drainage tube section II; the cross section of the ball bag thin film is in a plum blossom shape; the drainage tube section I is internally provided with a pipeline I communicated with the drainage tube section II and a pipeline II communicated with the ball bag thin film; the other end of the pipeline II is connected with a pipe by a cap and the other end of the pipe is connected with a three-way valve; the cap is provided with a cylindrical head part and a circular-platform-shaped tail part; the small end of the circular-platform-shaped tail part is fixedly connected with the cylindrical head part. The water bag type gall external drainage tube has higher tension and is prevented from being released; the water bag type gall external drainage tube is suitable for common bile ducts with different diameters; the water bag type gall external drainage tube has no damages to bile duct mucosa, duodenal papilla and upper gastrointestinal tract mucosa when being put in or taken out; the water bag type gall external drainage tube can be prevented from displacement and the obstruction of the biliary tract is not caused.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Biodegradable common bile duct built-in carriage and its making method
The invention is a kind of main bile duct inner bracket which can be decomposed biologically and the manufacturing method. It is made up from biology-decomposed molecular material and added in the developable ingredient by the X radial. It uses the anatomy shape of the main bile duct or can be sealed with the duct wall, it can locate precisely and will not glide. The tube of the bracket has enough size, and the outer wall have several orbicular heave. It can be throat shape which can prvent the leakage of bile. The manufacturing process includes: (1) blending the biology-decomposed molecular with X-radial developing ingredient and assistant and makes them into particles. (2) carries on injection shaping, and the shape decoration. It can replace the T tube in bile duct operation.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Novel percutaneous transhepatic and transcystic duct choledochoscopy system
The invention discloses a novel percutaneous transhepatic and transcystic duct choledochoscopy system. The system includes a percutaneous transhepatic piercing sheath, a rigid choledochoscope, a flexible common bile duct sheath, a soft choledochoscope, a camera host, a monitor, and a light source host; the rigid main body of the rigid choledochoscope passes through a channel of the percutaneous transthoracic piercing sheath, the flexible common bile duct sheath passes through a rigid apparatus channel of the rigid choledochoscope, and the soft main body of the soft choledochoscope passes through the inside of the flexible common bile duct sheath; a rigid ocular lens input end of the ridig choledochoscope and the soft ocular lens input end of the soft choledochoscope are respectively connected to the camera host, and the camera host is connected with the monitor. The system has the advantages that the system can solve the diseases of gallstones and common bile duct stones in one time, can better clean the stones, and avoid the risks and burdens brought by the two operations to the patients, at the same time, the patient's pain is reduced, the postoperative complications are few, andthe use is convenient and reliable.
Owner:夏医君
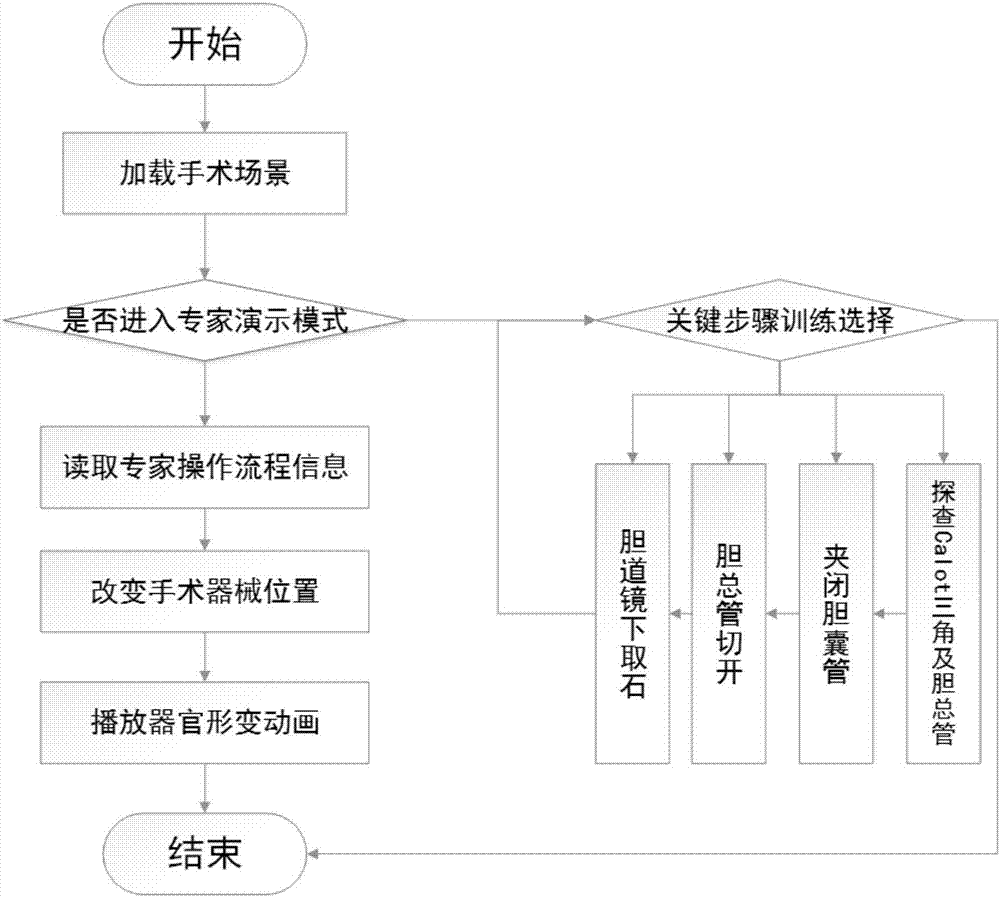
Virtual laparoscopic common bile duct exploration training method and system
InactiveCN107240344ASolve the problem of a single training model for exploratory surgeryGood for repeated trainingEducational modelsCommon bile duct stonePhysical model
The invention discloses a virtual laparoscopic common bile duct exploration training system which comprises the following modules: a physical modeling module, a random gall-stone generation module, an expert demonstration module and a stepped training module, wherein the physical modeling module is used for generating a human body model and various surgical instruments needed by virtual laparoscopic surgery; the random gall-stone generation module is used for randomly generating common bile duct stones; the expert demonstration module is used for playing stored expert operating information; and the stepped training module is used for training key operating procedures.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Biliary tract exploration method and device based on superfine endoscope
The invention provides a biliary tract exploration method and device based on a superfine endoscope. The biliary tract exploration method is characterized by comprising the following steps that a conical guide head is fixedly connected, and the superfine endoscope is mounted in an inserted mode; the superfine endoscope is put into the duodenum descending part; the conical guide head is fixed to the open position of duodenal papilla; a guide wire is inserted, and the superfine endoscope is brought into the common bile duct and the common hepatic duct by the guide wire; an annular surrounding saccule is opened through inflation, and an outer sleeve is fixed; the guide wire and the superfine endoscope are taken out and the outer sleeve is dwelled to form a stable biliary tract exploration channel. The biliary tract exploration device comprises the guide wire, a duodenoscope and the superfine endoscope and is characterized by further comprising the conical guide head, wherein the conical guide head is arranged at the front end of the superfine endoscope and is fixedly connected with the superfine endoscope, the annular surrounding saccule and a traction wire are arranged at the front portion of the outer sleeve, the superfine endoscope and the guide wire are inserted into the outer sleeve and enter the common bile duct, and the annular surrounding saccule is opened through inflation to fix the outer sleeve so as to form the biliary tract exploration channel.
Owner:刘时助
Hepatic lobule-like bioreactor
InactiveUS8735143B2Good curative effectImprove performanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary networkCommon bile duct dilatation
The present invention provides a hepatic lobule-like bioreactor. The bioreactor includes a nanofiber scaffold enclosed within a housing. An intrahepatic fibrous vascular network, a bile capillary network, upper hepatic bile ducts, lower hepatic bile ducts, a common bile duct connecting the upper and the lower hepatic bile ducts, and collagen fibrous microchannels for hepatocytes surrounded by the bile capillary network are distributed throughout the nanofiber scaffold. Bile capillaries in the bile capillary network are provided with two or more inlet ports for biliary epithelial cells. The collagen fibrous microchannels for hepatocytes are provided with two or more inlet ports for hepatocytes. The intrahepatic vascular network is provided with a liquid inlet port and a liquid outlet port. These ports extend through the housing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mouse islet separation and purification method
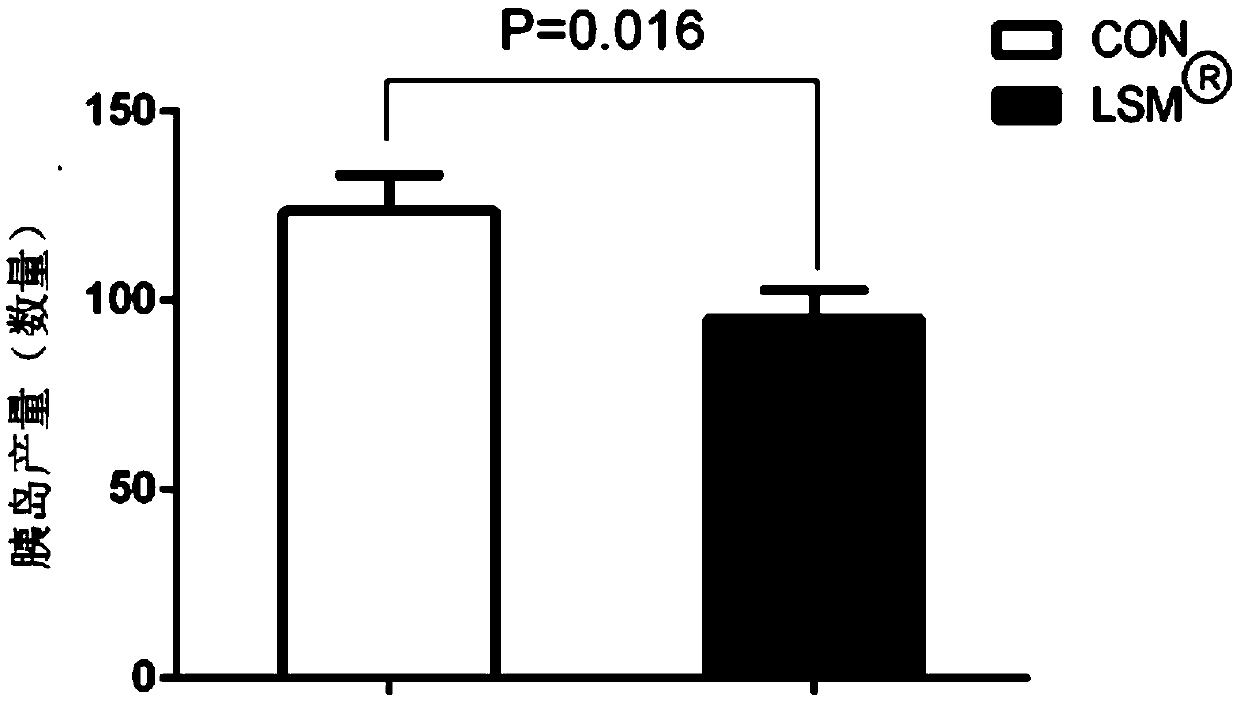
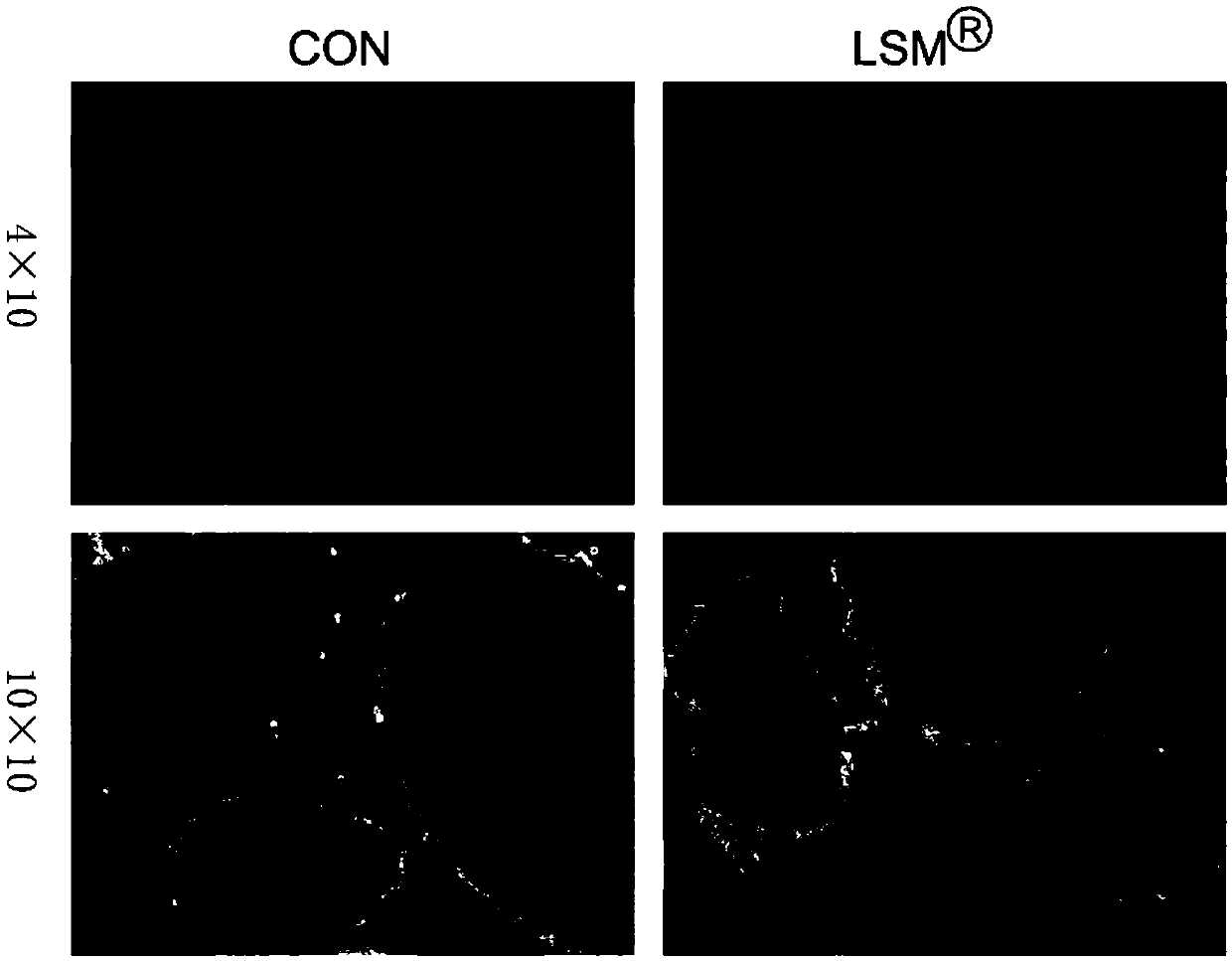
ActiveCN105368771AGood yieldHigh purityVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsPurification methodsStaining
The invention discloses a mouse islet separation and purification method. A self-made puncture needle is adopted to reversely puncture a common bile duct and inject collagenase V to digest a pancreatic gland, and inslets are separated and purified by using the combination of density gradient medium centrifugation and manual sorting. Inset density is identified by dithizone staining, and inset activity is identified by AO / PI staining. Inset functionality is detected by a glucose stimulated insulin release experiment. By using the method to extract islets on a large scale, time can be greatly saved, the puncture success rate can be increased, and Ficoll400 formulation time and price can be reduced. In addition, all the yield, purity, activity and function of islets obtained by purification are relatively good, and the method is simple, fast, cheap and efficient.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
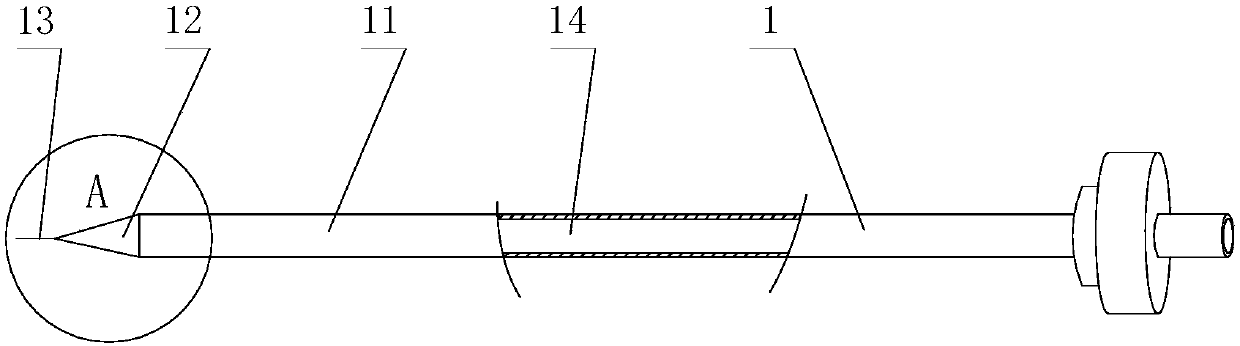
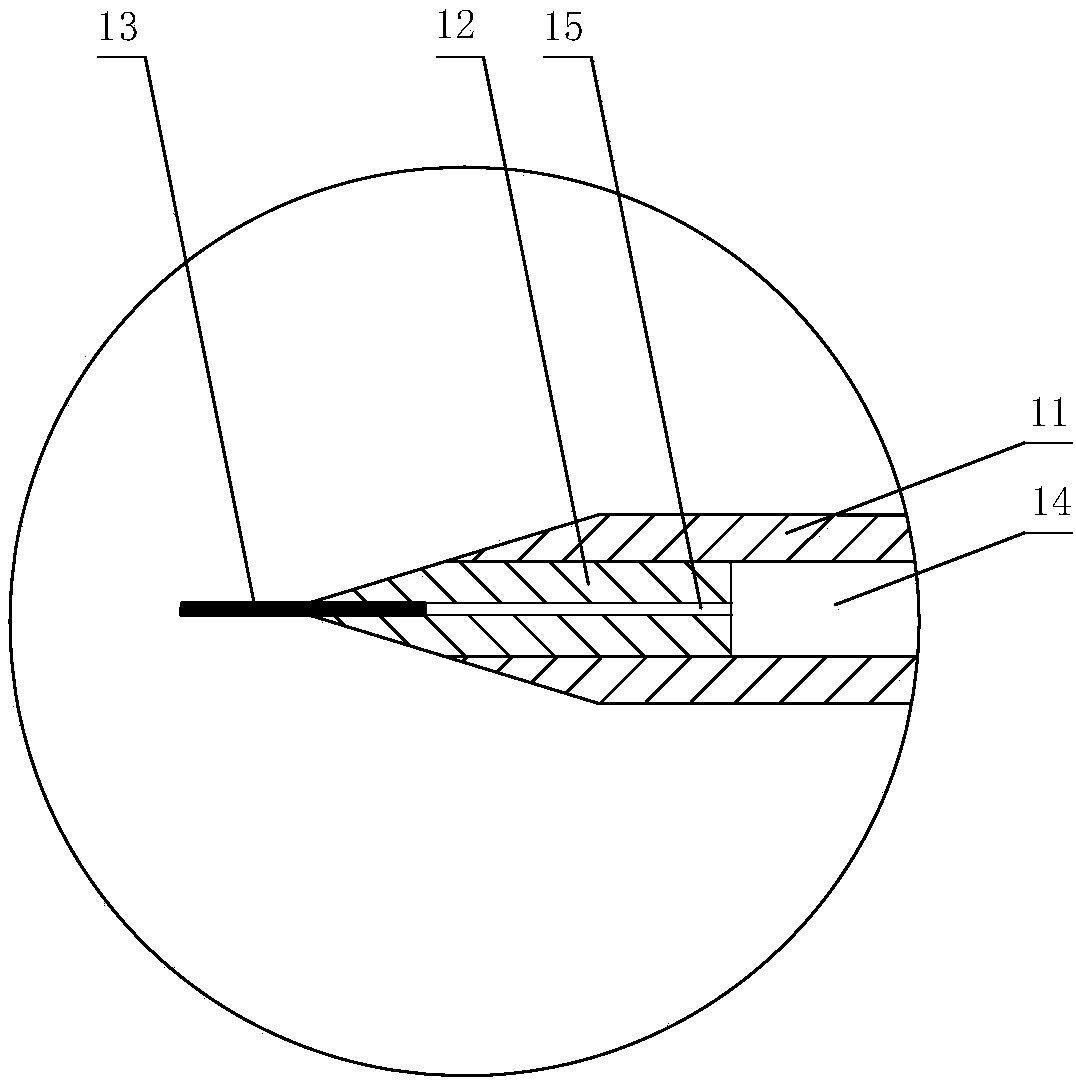
Laparoscope and common bile duct exploration T tube introducer
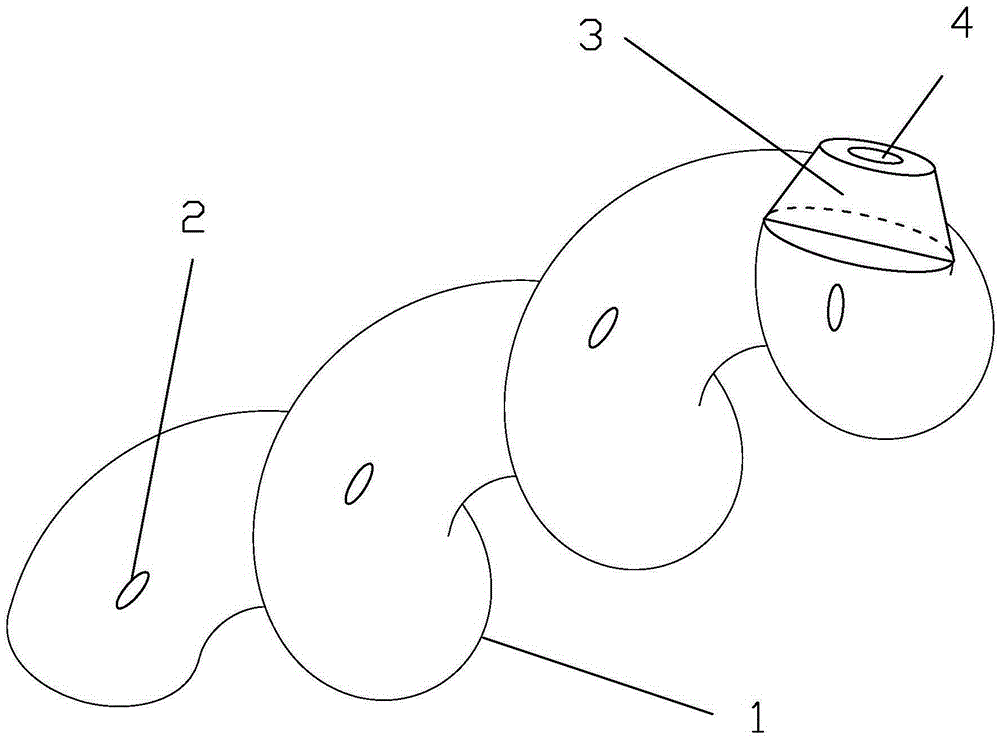
InactiveCN104174108ARelieve painShorten operation timeGuide needlesOuter CannulaCommon bile duct dilatation
The invention relates to a laparoscope and common bile duct exploration T tube introducer, which comprises a holding handle (1), a T tube control external sleeve (2), a T tube staff gauge (12) arranged at an introducing end, an inner half-tube-shaped support frame (3), a sliding sealing groove (4) at the side wall of the external sleeve, a T tube positioning support frame (10) and a sliding air-tight seal pad (11), wherein a T tube locking and unlocking clamp (5) and a T tube locking and unlocking key (6) are arranged on the inner half-tube-shaped support frame (3), a T tube release elastic key (7) controls and is connected with a release connecting rod (8), a T tube release spring (9) is positioned at the tail end of the release connecting rod (8), a T tube abdomen external drainage end is positioned and locked in the T tube locking and unlocking key (6), a T tube introducing drainage (in a common bile duct) section is positioned in the T tube positioning support frame (10), and the inner half-tube-shaped support frame (3) is locked and stored in the T tube control external sleeve (2). The T tube orientation and detection are completed in one step, a T tube is unlocked, released and introduced for drainage in real time, the operation time is shortened, and the pain of a patient is reduced.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
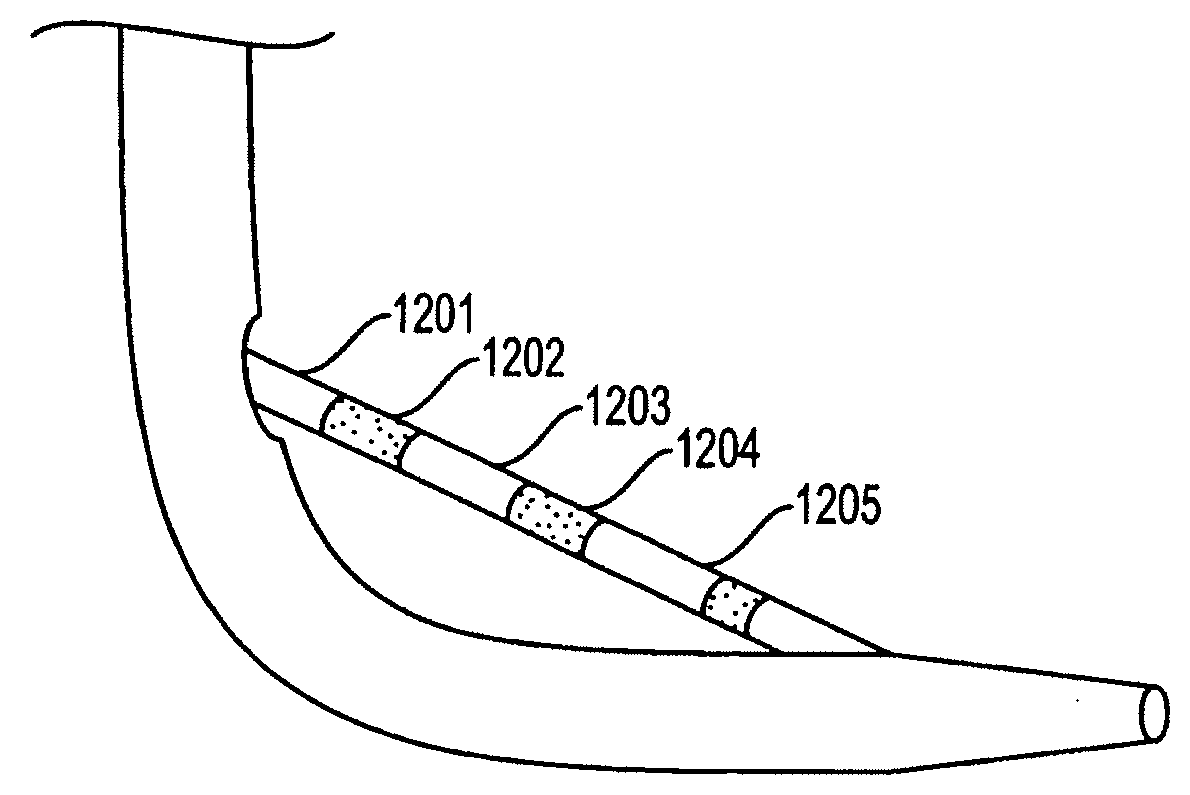
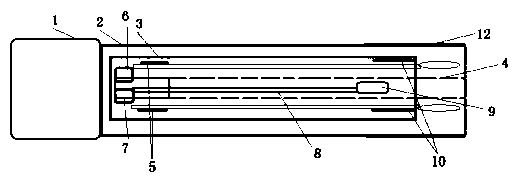
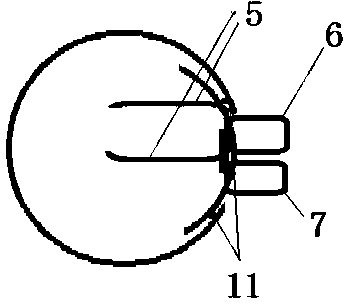
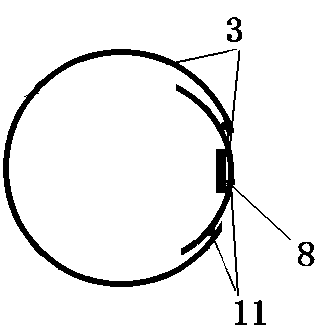
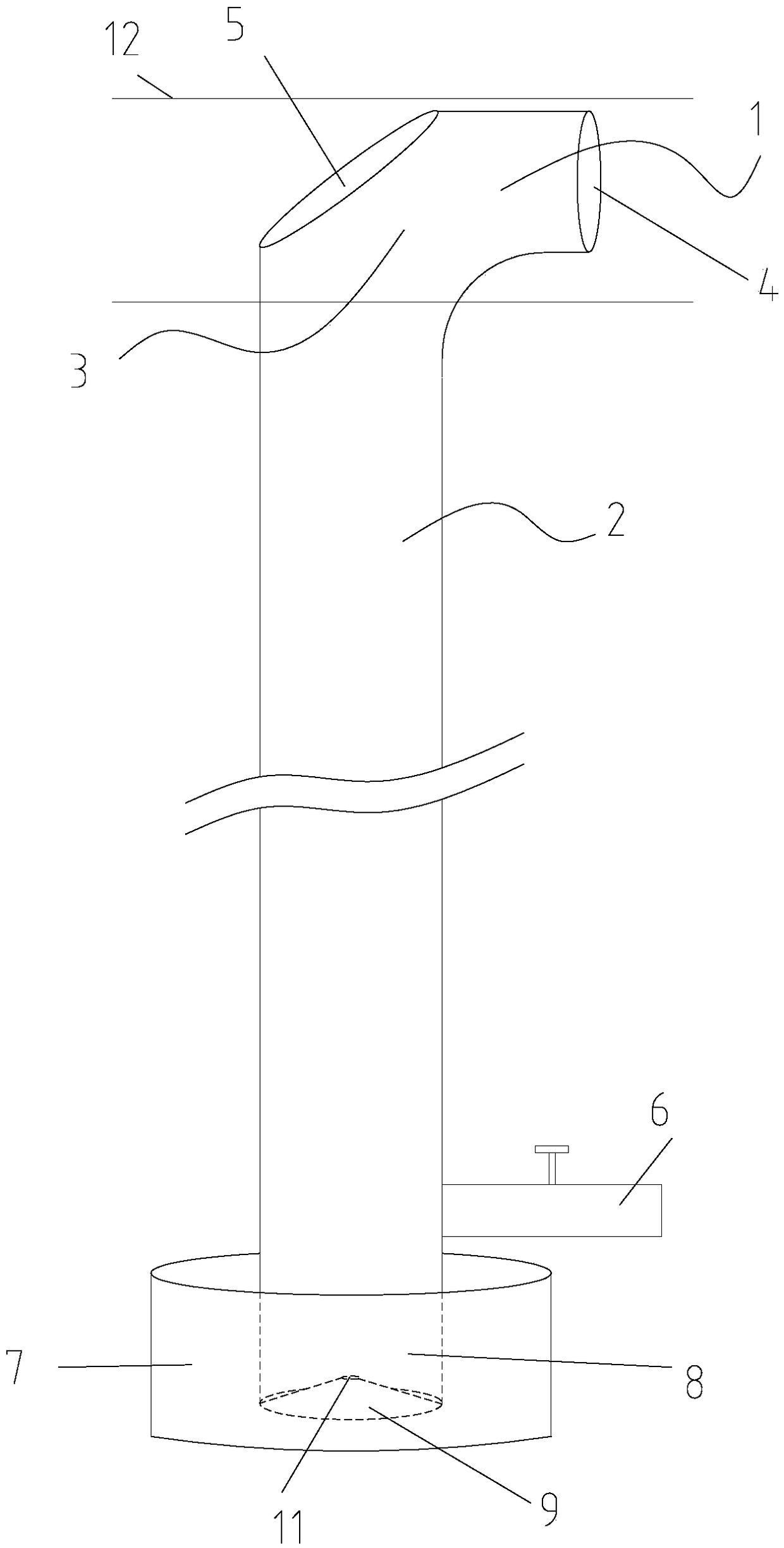
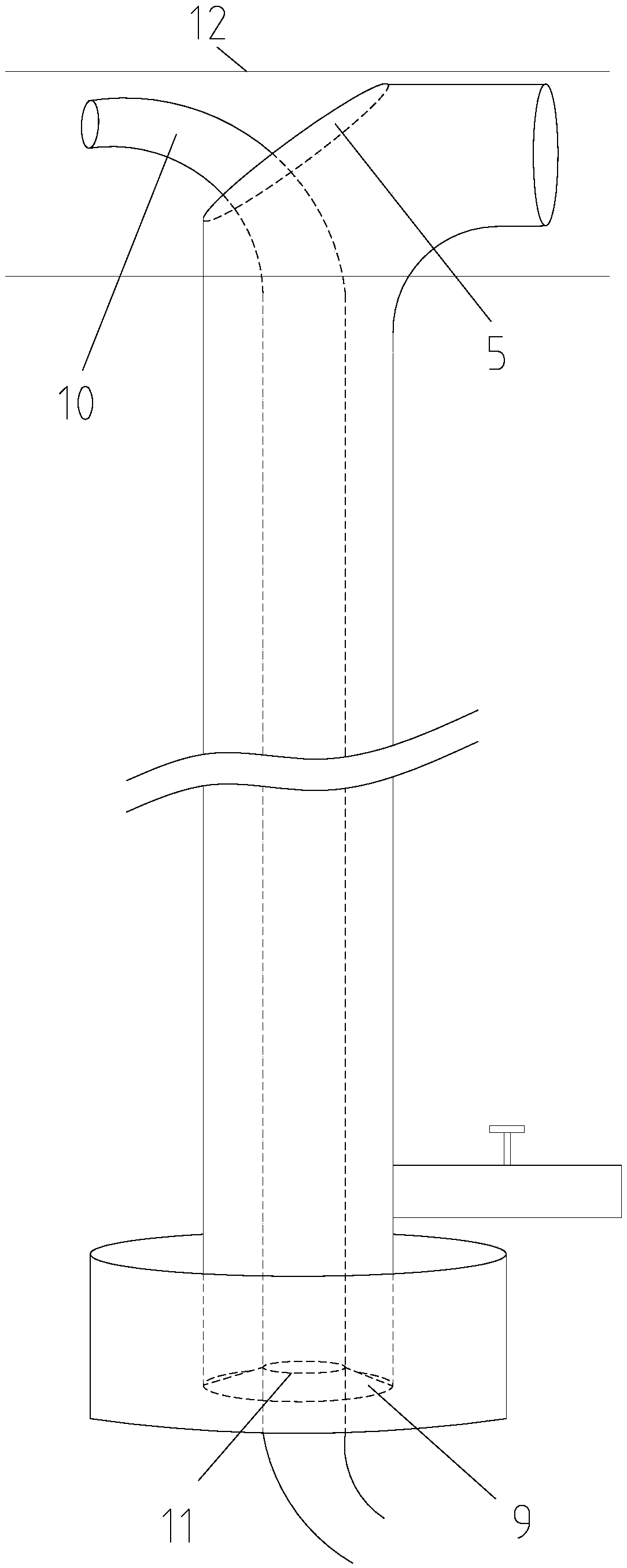
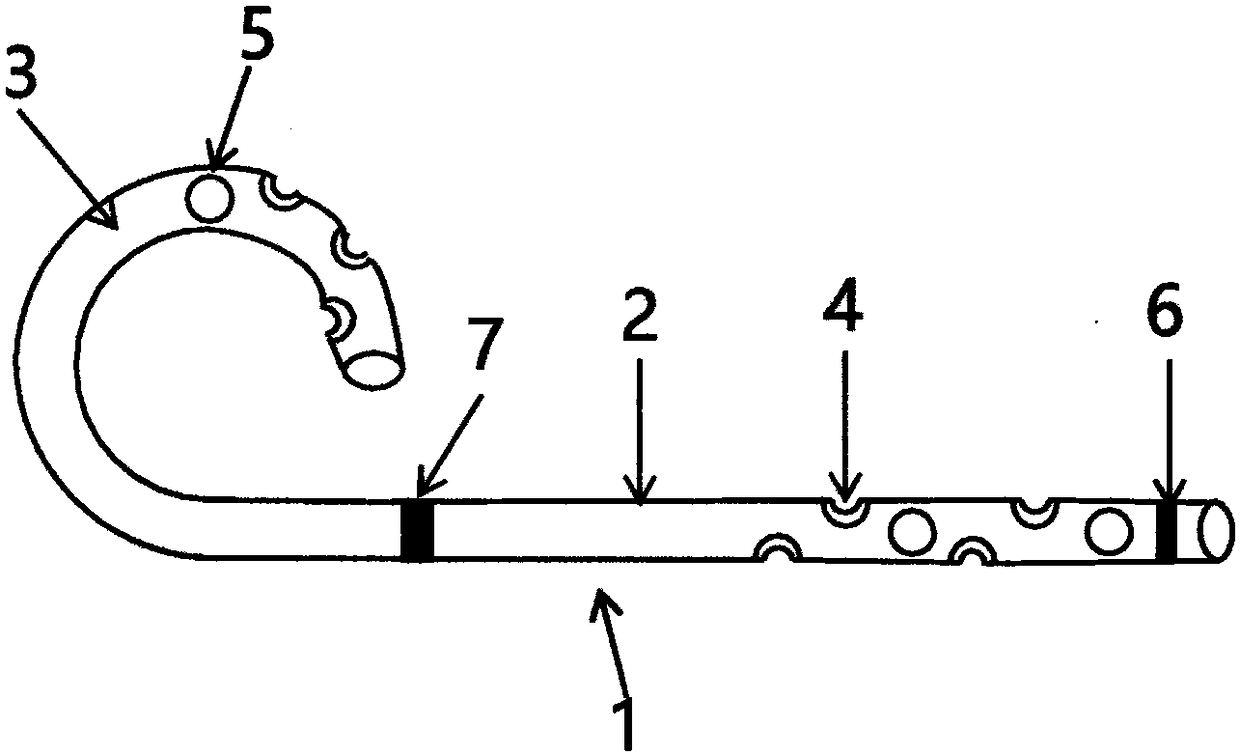
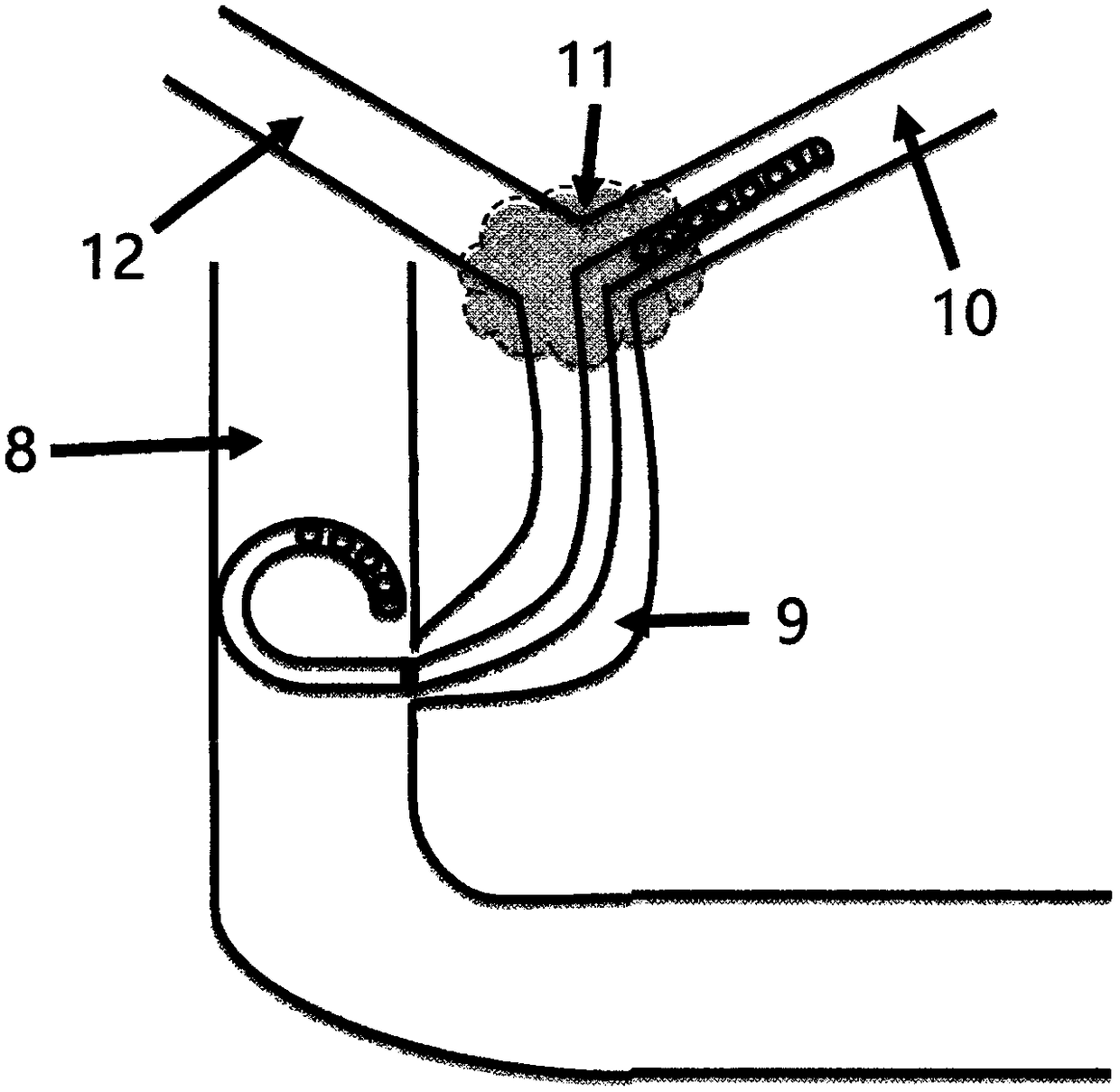
Common bile duct exploring sheath duct
The invention discloses a common bile duct exploring sheath tube, which is characterized in that: the sheath tube comprises a horizontal tube located at the head of the sheath tube and a vertical tube. The horizontal pipe and the vertical pipe are communicated with each other through an elbow pipe. An end of the horizontal pipe remote from the elbow pipe is provided with an opening. The outer edgeof the elbow pipe is provided with a through hole along the pipe wall. The outer wall of the vertical pipe is provided with a water outlet joint. A base is arranged one end of the vertical pipe far away from the elbow pipe. The base is provided with a channel communicating with the vertical pipe. An anti-reflux pad is arranged on the inner wall of the channel. The anti-reflux cushion is providedwith an elastic hole for the choledochoscope to pass through. After the invention enters the common bile duct, the pneumoperitoneum and the laparoscopic video can be closed, thereby avoiding the complications caused by the long-term pneumoperitoneum and the loss of the laparoscopic system. A suction tube is connecte with that water outlet connector, so that infectious bile, irrigation fluid, sediment-like calculus and biliary mud can be expel from the body, and the complications caused by the above substances entering the abdominal cavity can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
Degradable radioactive biliary stent and method for producing the same
The invention relates to a radioactive bile duct support which can be degraded, used to treat cancer, wherein it is formed by the common bile duct support woven from NiTi alloy lines and the degradable belly film made from radioactive material covering the support. And its production comprises (1), using NiTi alloy lines to weave the bile duct support; (2), plating belly layer on the support, emerging it in crosslinker; (3), freezing and drying; (4), before using, using epoxyethane gas to disinfect it. The invention can treat and restrain the membrane increment and cancer growth, without hurting normal organism. And the epoxyethane, dope and chitose of carrier can be degraded.
Owner:六安市济民医药科技有限公司
Choledochoscope for removing calculi
InactiveCN102309306AImprove stone extraction efficiencyStone extraction is easySurgeryEndoscopesBiliary tractCommon bile duct dilatation
The invention relates to a choledochoscope for removing calculi from intrahepatic bile duct, the calculi from extrahepatic bile duct and postoperative residual calculi, keeping a gall bladder and taking out calculi of gall bladder in surgery (including endoscopic surgery and open surgery). The choledochoscope for removing calculi comprises a choledochoscope body, wherein a choledochoscope tip is formed at the first end of the choledochoscope body; the second end of the choledochoscope body is connected with a cold light source interface, a water inlet interface, a camera interface and an operation passage entrance; a hollow cavity structure is formed on the back part of the choledochoscope body; the hollow cavity structure is communicated with the cold light source interface, the water inlet interface, the camera interface and the operation passage entrance. Compared with the prior art, the choledochoscope for removing the calculi is connected with a camera through the camera interface, so that the choledochoscope for removing the calculi can treat the calculi in first-level, second-level and third-level bile ducts and even part of fourth-level bile ducts, and calculi in a common bile duct (particularly the middle lower section) and the gall bladder efficiently and quickly on a television screen or a computer screen through an operation passage and the calculi removal efficiency is high.
Owner:顾思平
'J' type biliary stent for drainage of high biliary obstruction
PendingCN108451677AImprove practicalityAvoid displacementStentsMedical devicesInsertion stentBiliary obstructions
The invention provides a 'J' type biliary stent for drainage of high biliary obstruction, which comprises: a bile duct part arranged in a common bile duct and an intestinal part arranged in a duodenum. The intestinal part is integrally connected with the bile duct part. A large 'C' type structure is formed in the intestinal part. By arranging the bile duct part and the intestinal part and settingthe intestinal part as a large 'C' type structure, the intestinal part can form a 'C' type ring at the descending part of duodenum, which effectively avoids the situations of movement of the long frame for drainage of high-level biliary obstruction to the bile duct and slip of the duodenum. As a result, the drainage effect is more stable and reliable, and the practicability of the 'J' type biliary stent for drainage of high biliary obstruction is improved. The manufacture is simple, which facilitates the popularization and application in the market.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
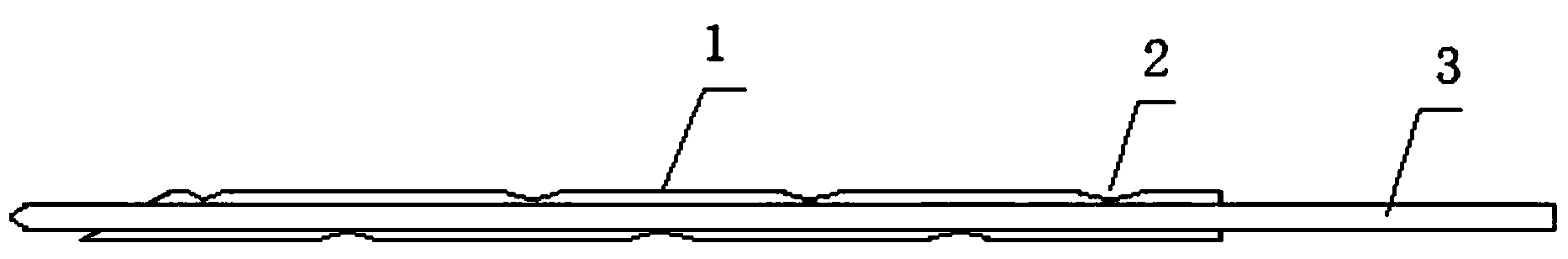
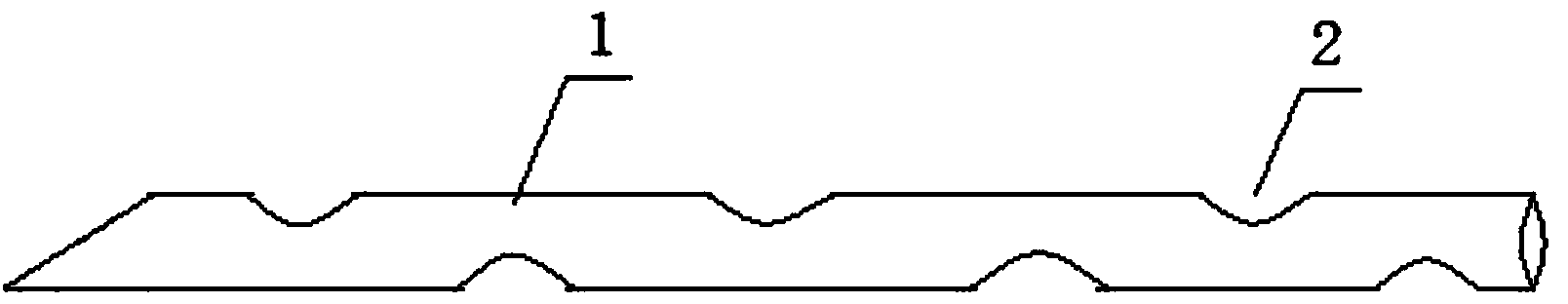
Biliary tract inner support drainage tube
InactiveCN103816602AAdequate drainageReduce complicationsGuide wiresBiliary tractCommon bile duct dilatation
The invention relates to a biliary tract inner support drainage tube and belongs to medical apparatuses and instruments. The biliary tract inner support drainage tube comprises a support drainage tube and a guiding wire placed in the support drainage tube. One end of the support drainage tube is in an oblique-face shape. Side through holes are evenly distributed in the tube wall of the support drainage tube. The support drainage tube and the guiding wire are used for replacing a T-shaped tube for being used in operative treatment of a patient with choledocholithiasis, after the choledocholith is fully taken out, the primary suture of the common bile duct is carried out without placing the traditional T-shaped tube, so operation time is shortened, operation difficulty is lowered, operation equipment cost is lowered, patient hospital staying time is shortened, hospital staying cost is lowered, postoperative complications are reduced, the patient can be recovered quickly, what is more important, the support drainage tube can be excreted out of the body along with excrement in about one week after operation, so that the patient does not need to suffer from the pain caused by long-term T-shaped tube retention, a series of complications caused by T-shaped tube placing are completed avoided, scars after operation become small, and accordingly the operation becomes more minimally invasive. If the biliary tract inner support drainage tube can be used widely and clinically, great benefit will be brought to the patient.
Owner:李瑞斌
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com