Patents
Literature
46 results about "Duodenoscopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
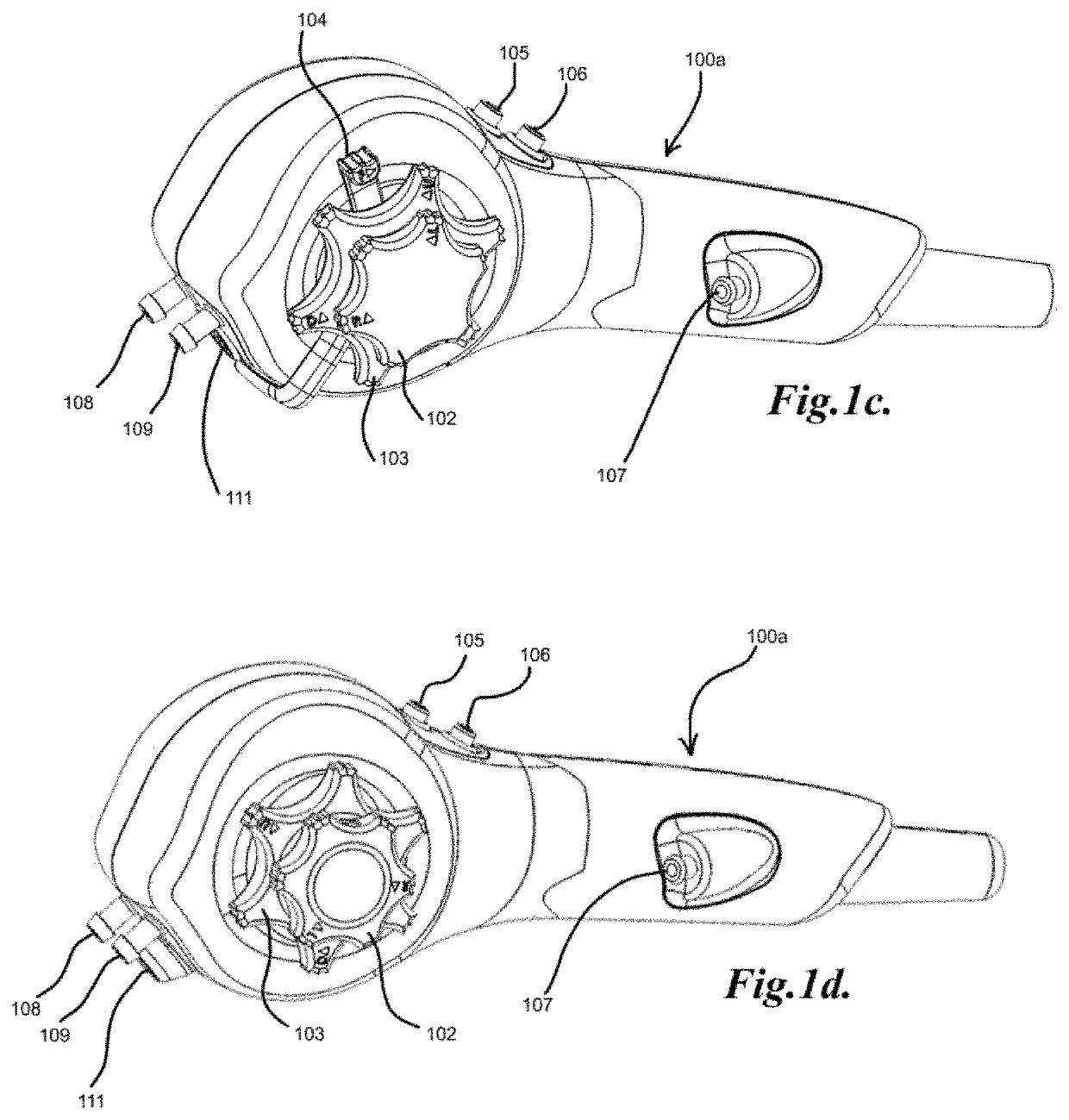
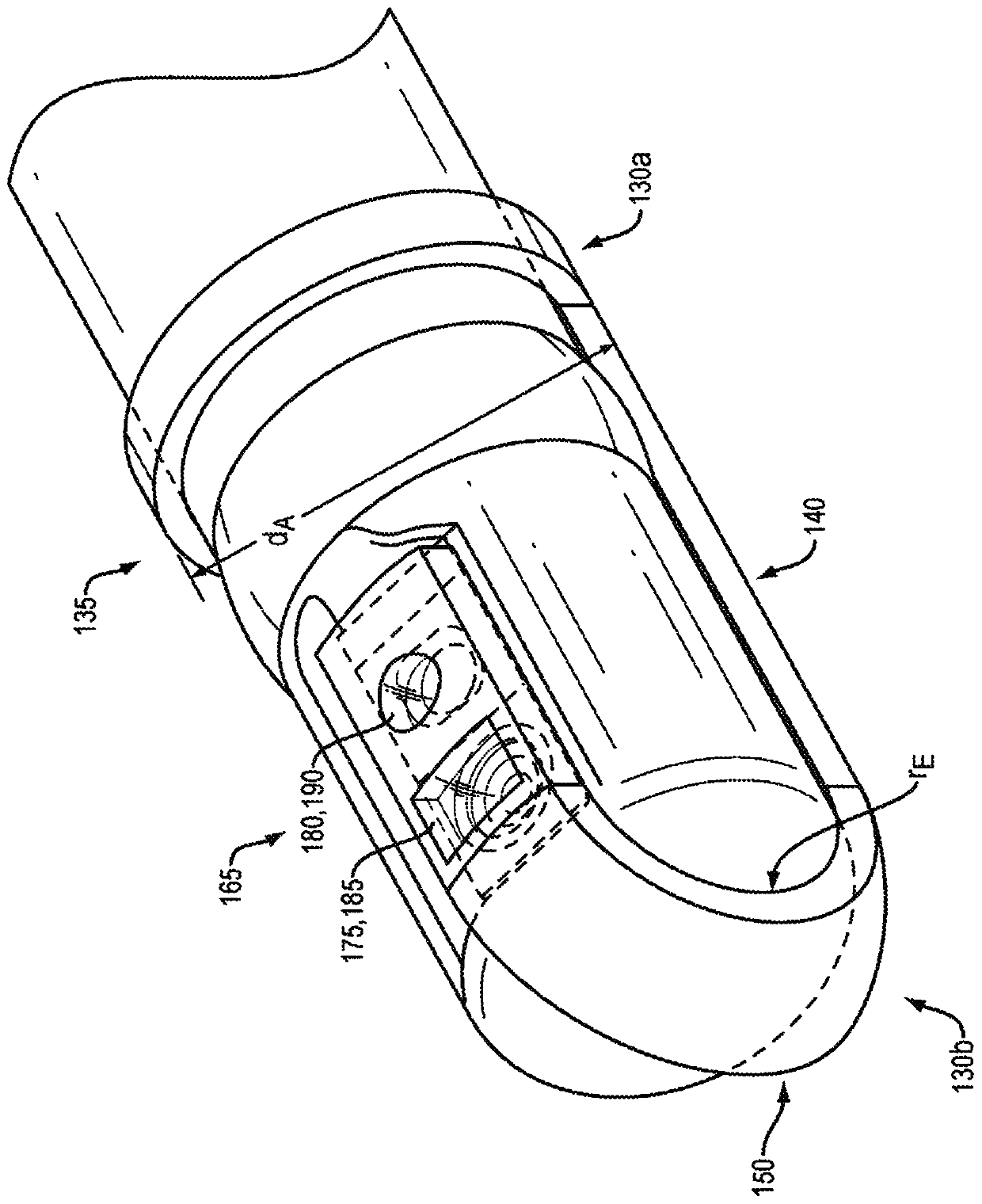
Flexible endoscopes designed for direct insertion through the mouth in the upper gastrointestinal tract for visual examination, biopsy, and treating lesions of the interior of the proximal portion of the small intestine from pylorus to the jejunum (i.e., duodenum). Duodenoscopes usually consist of a flexible outer sheath, a lighting system, and a working channel for catheters and operative devices.
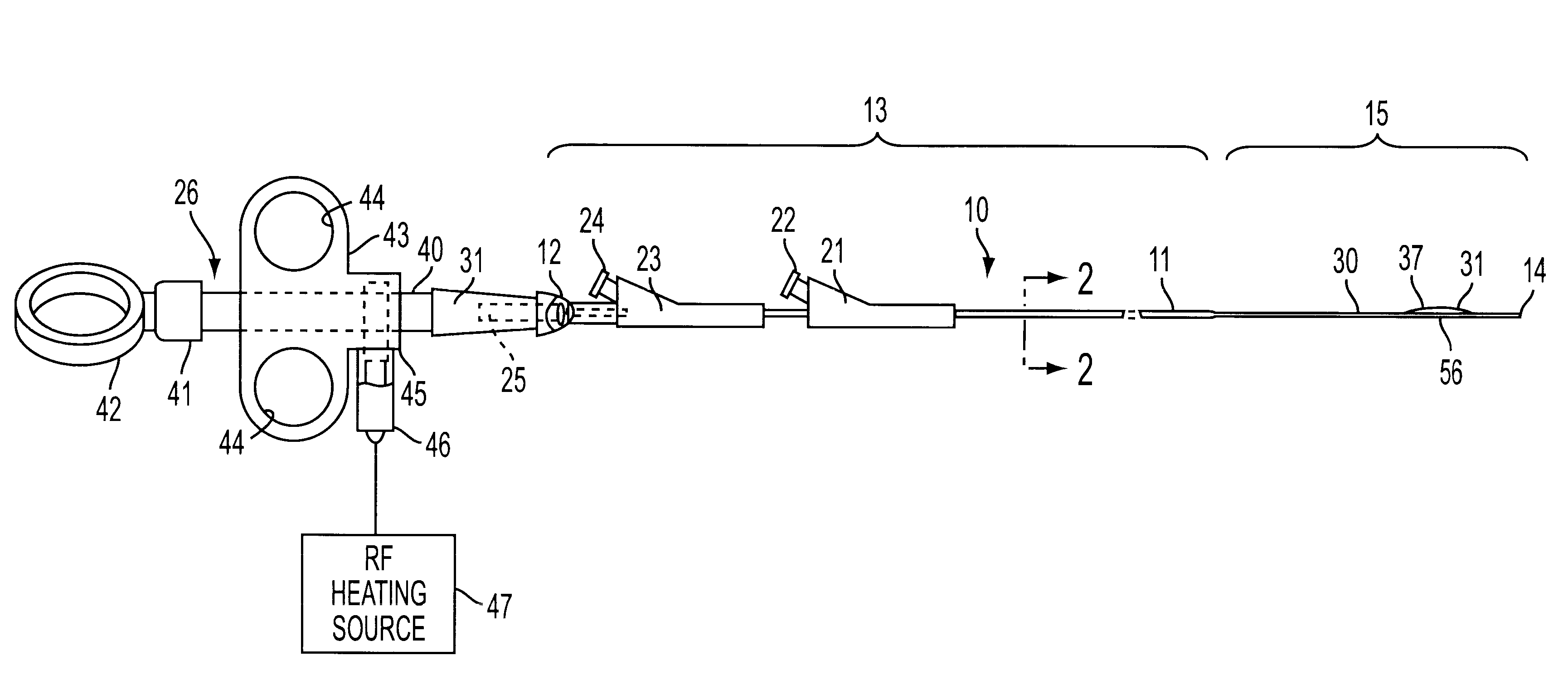
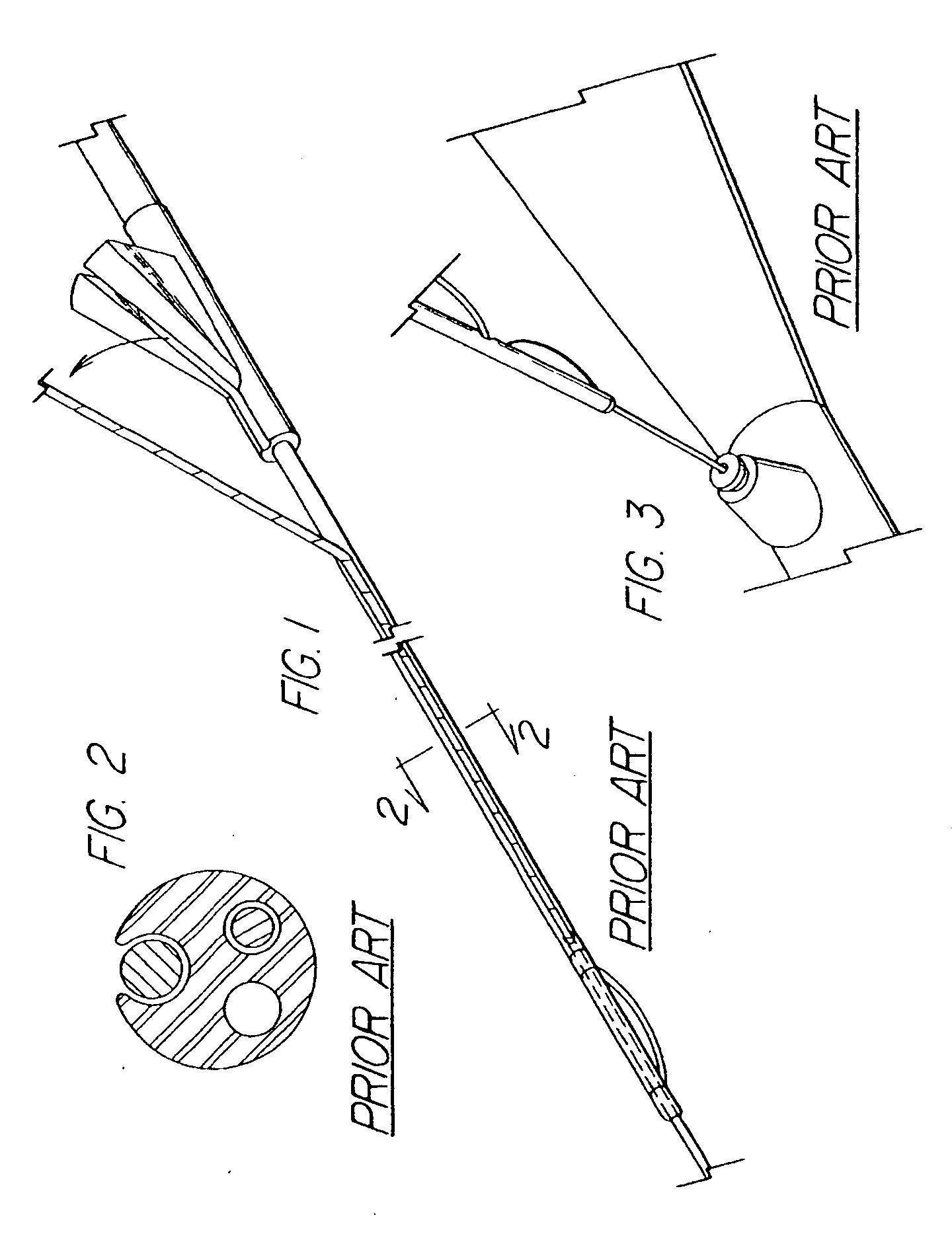
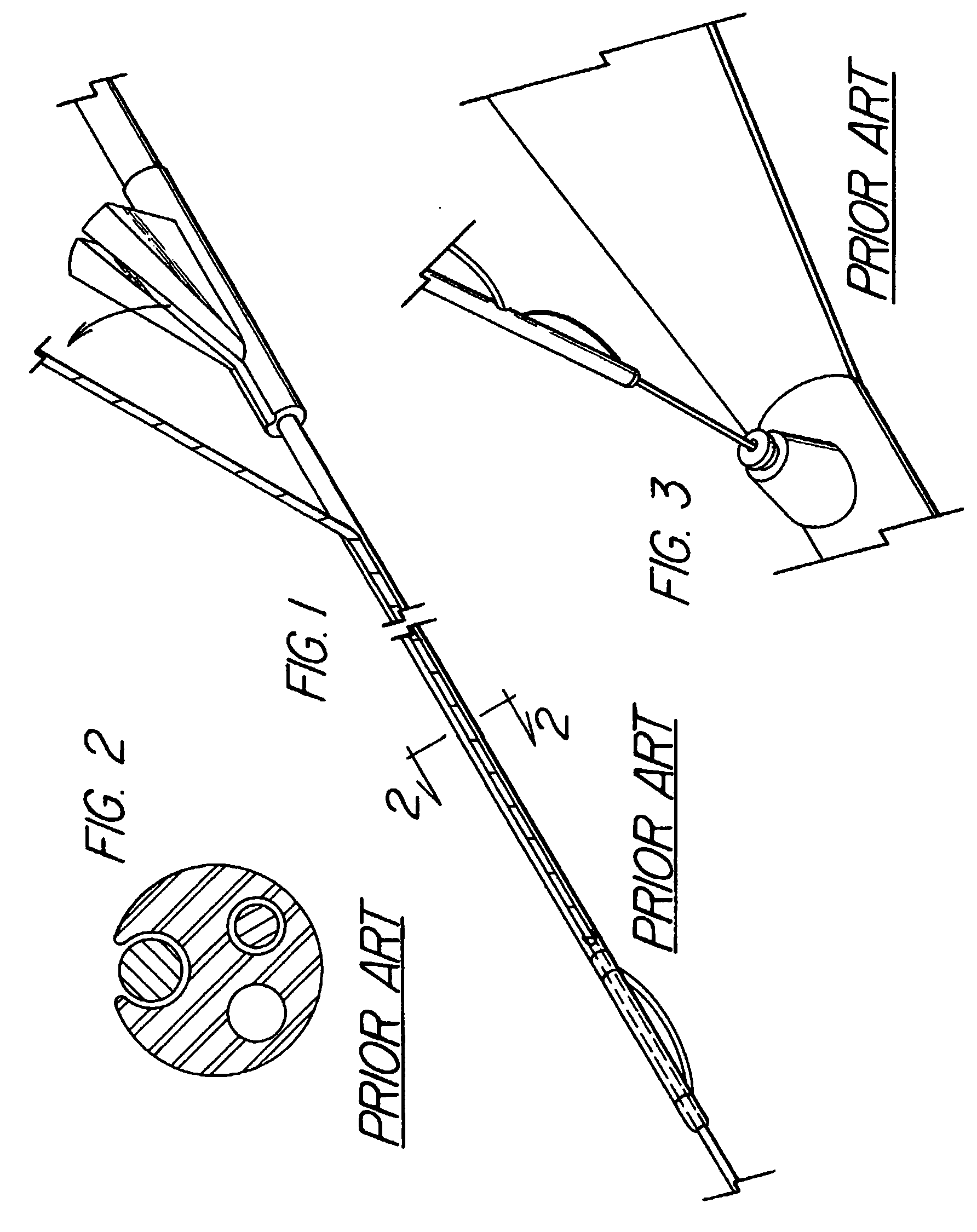
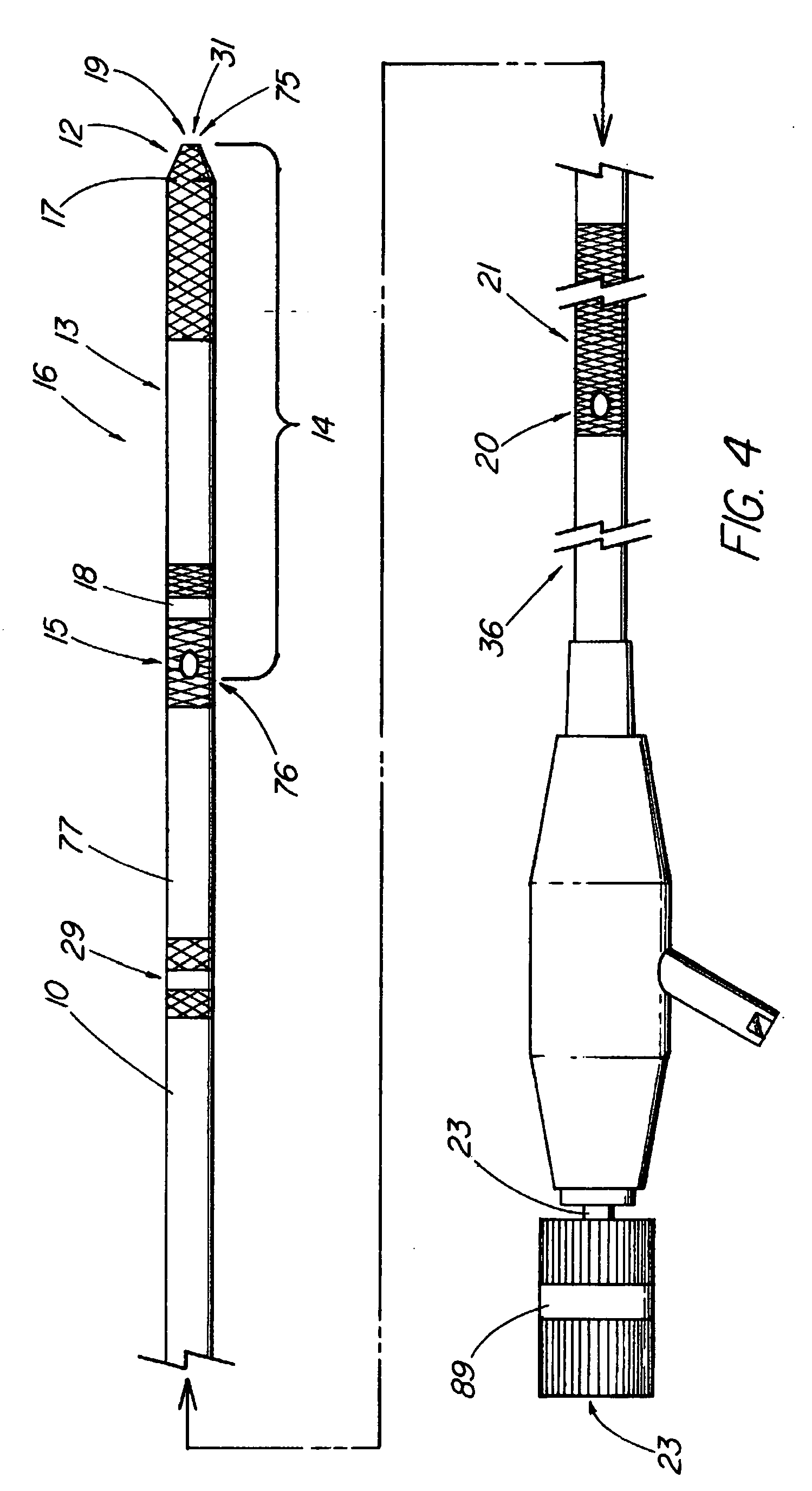
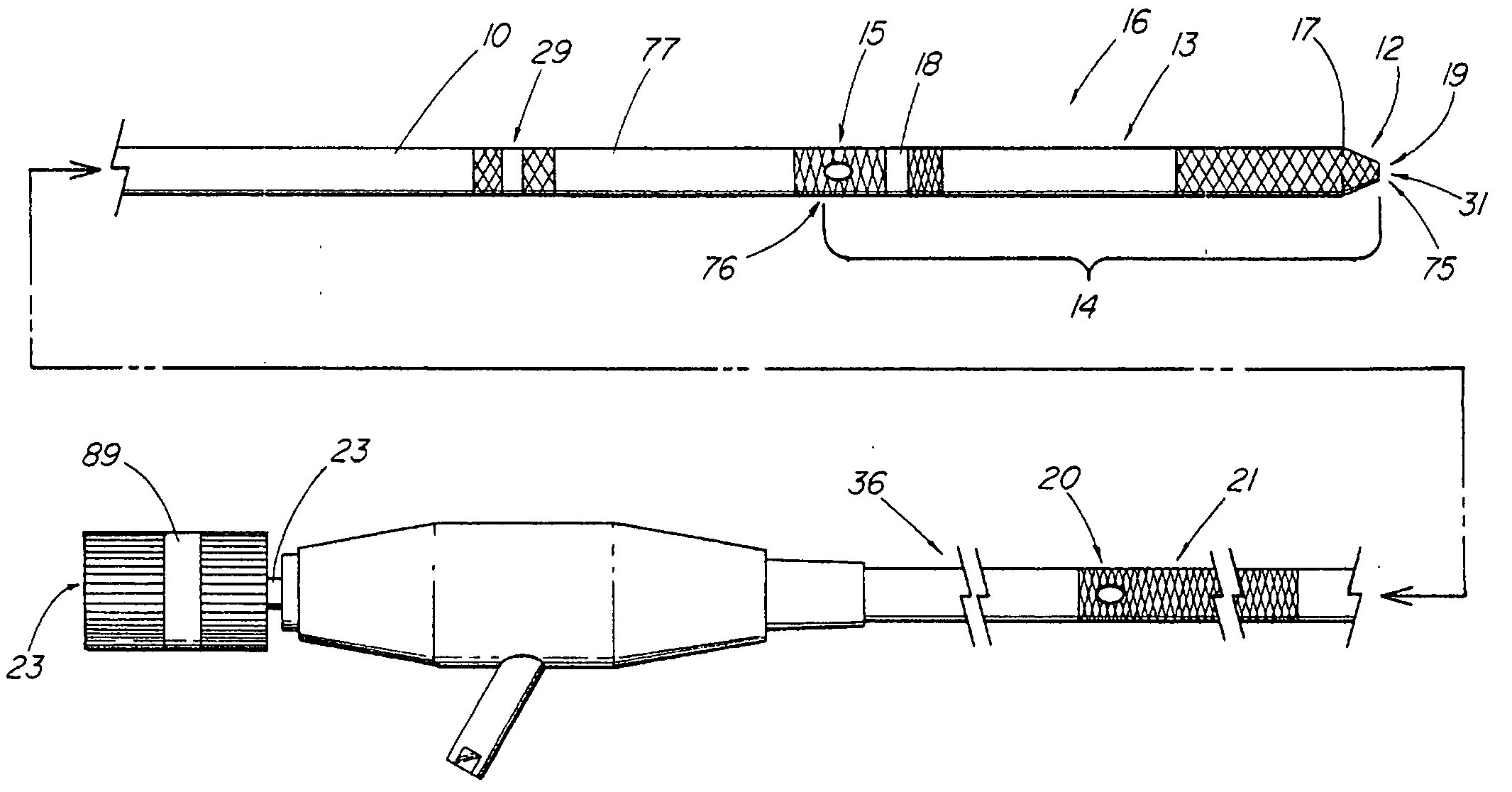
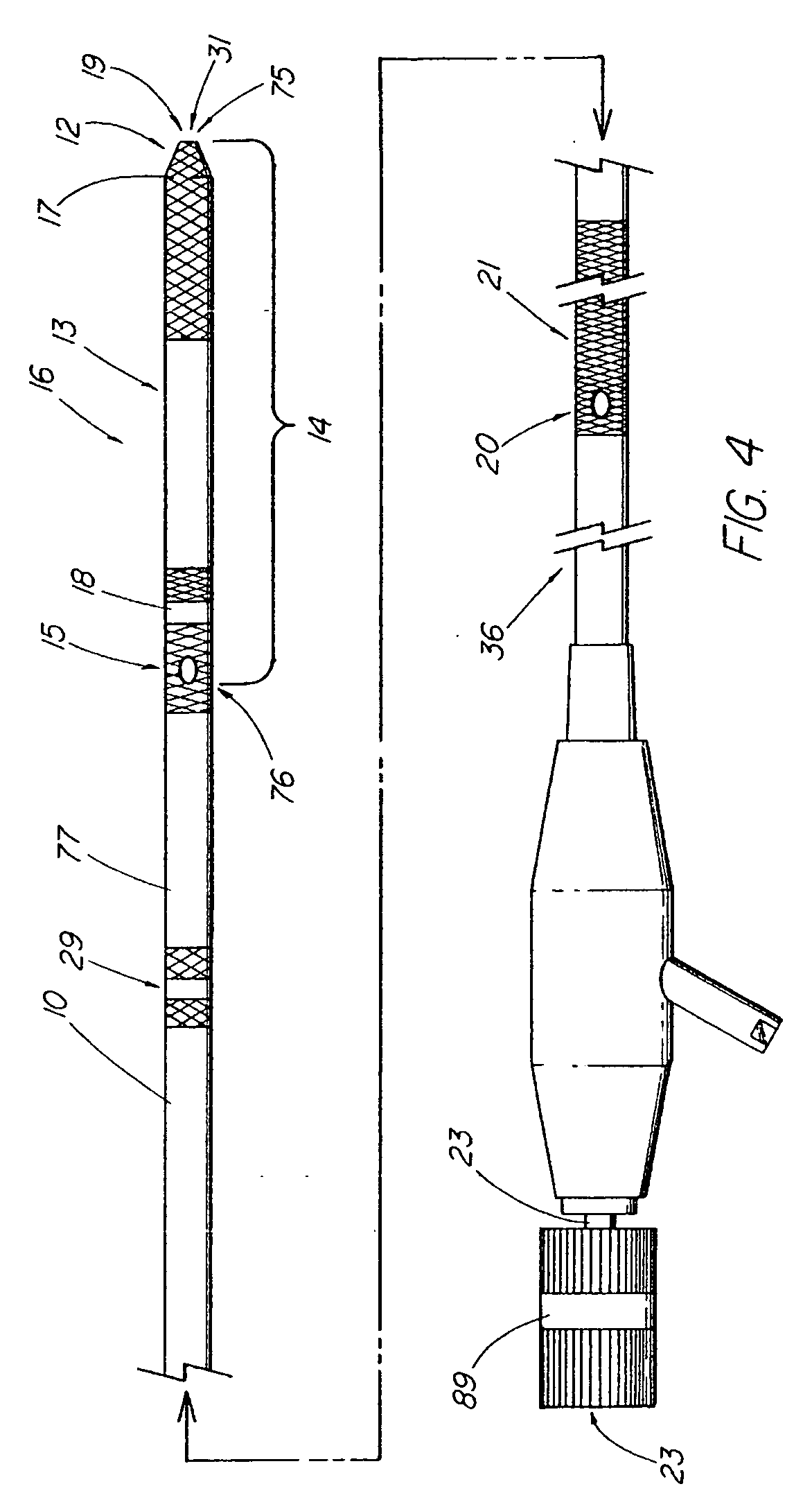
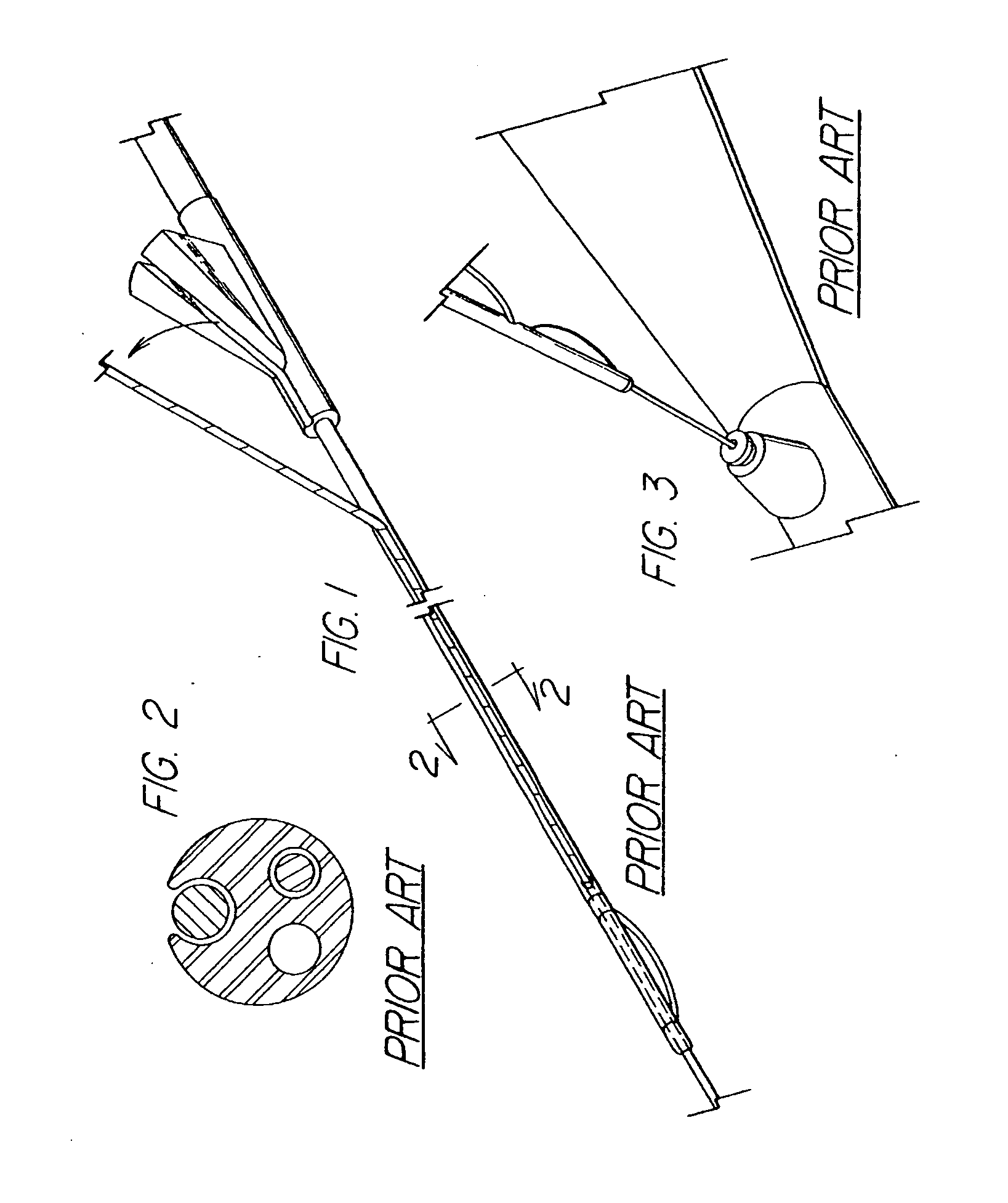
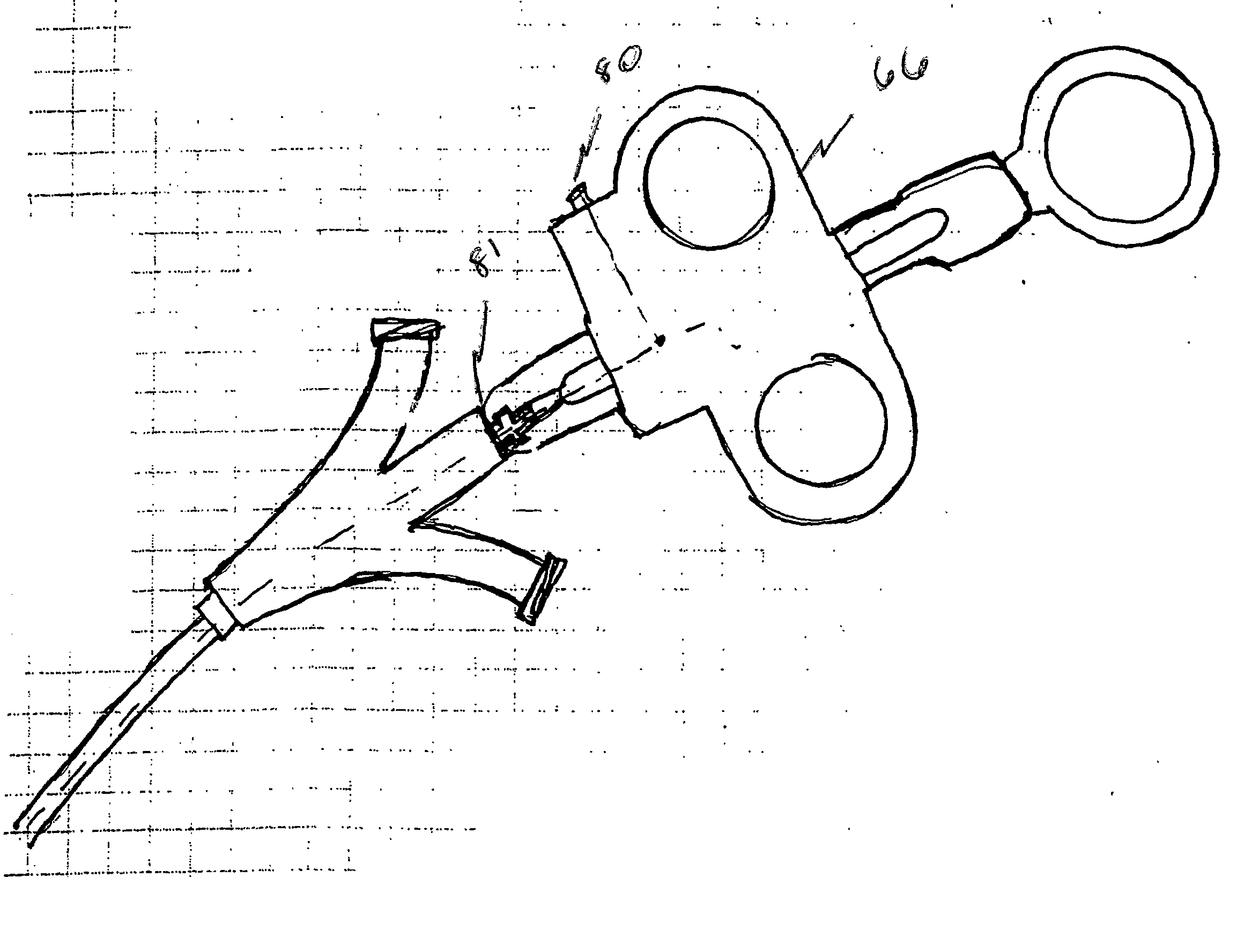
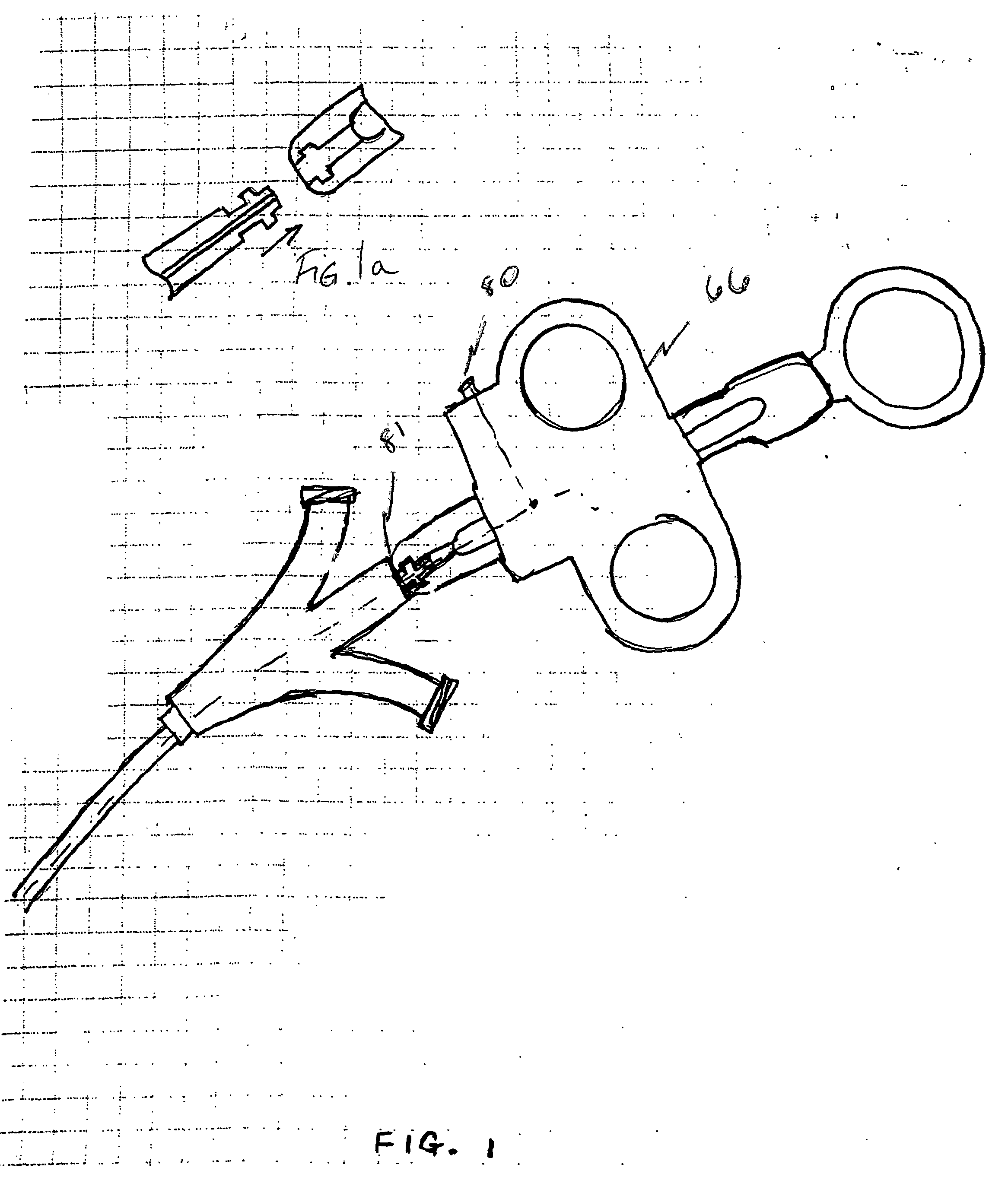
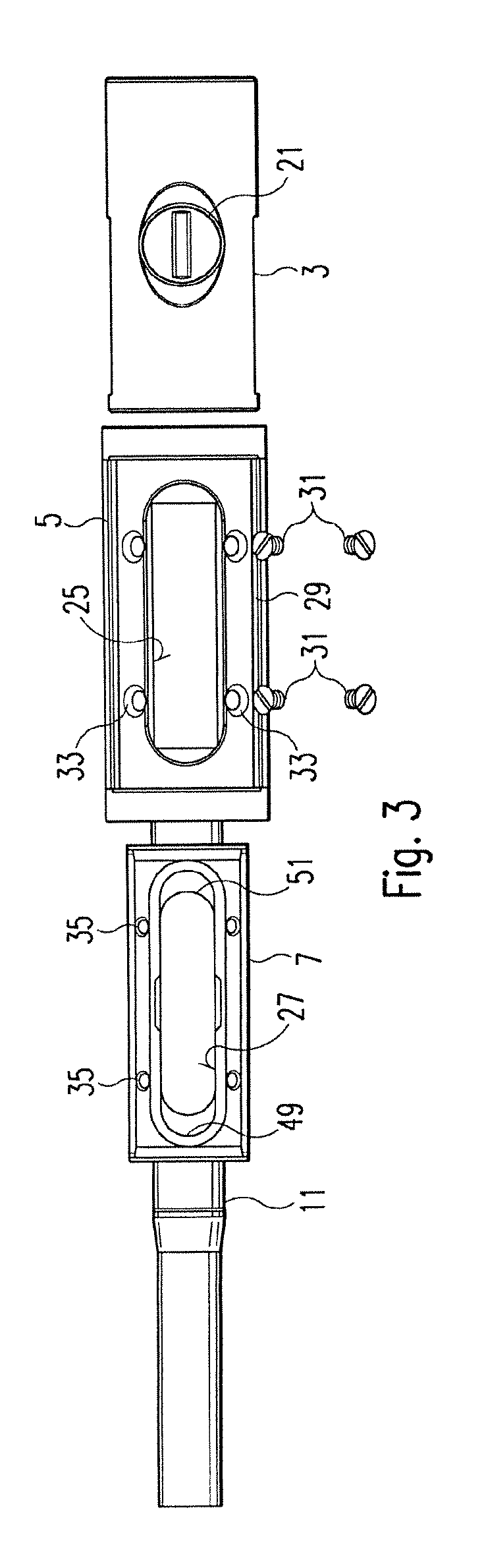
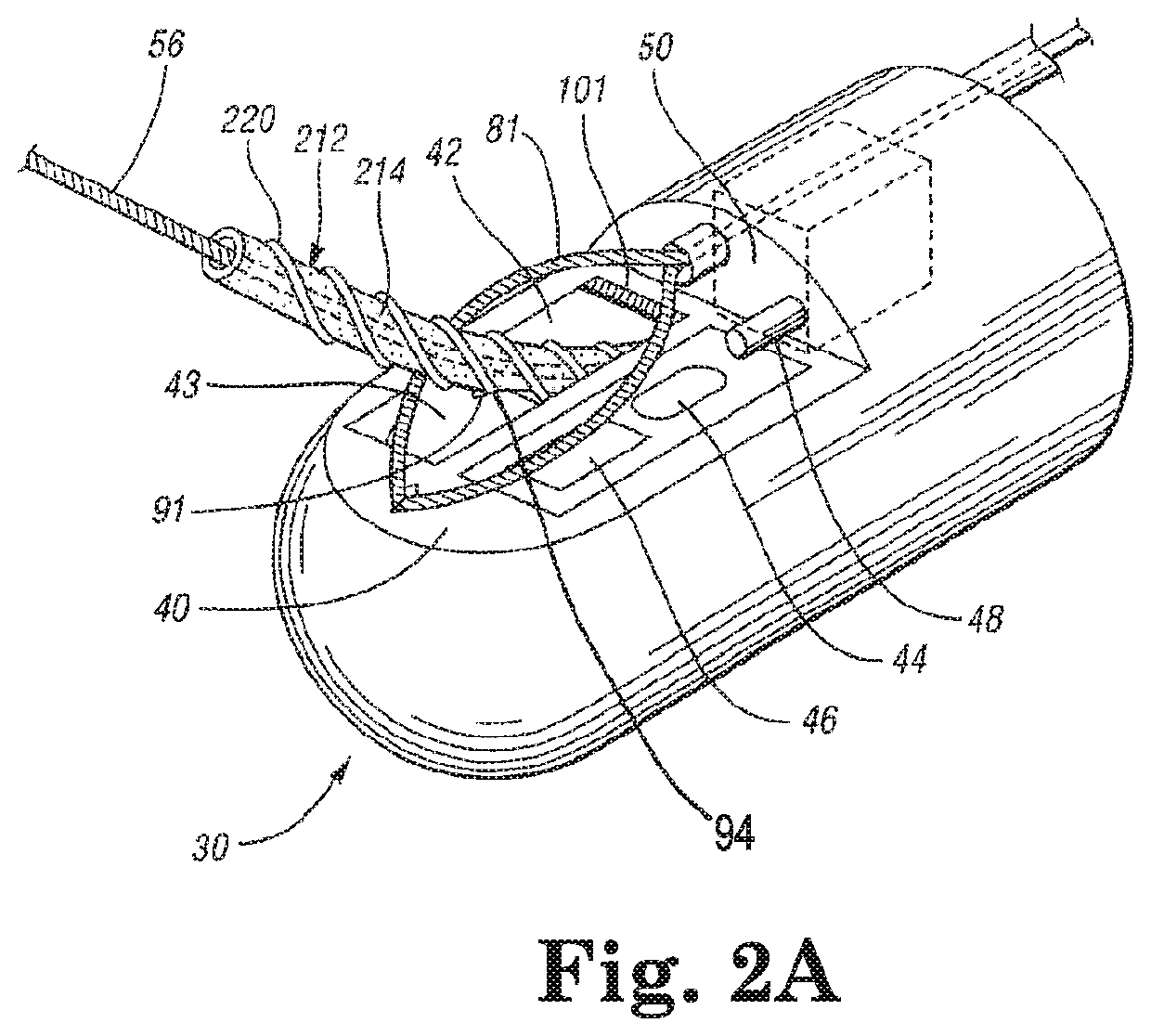
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
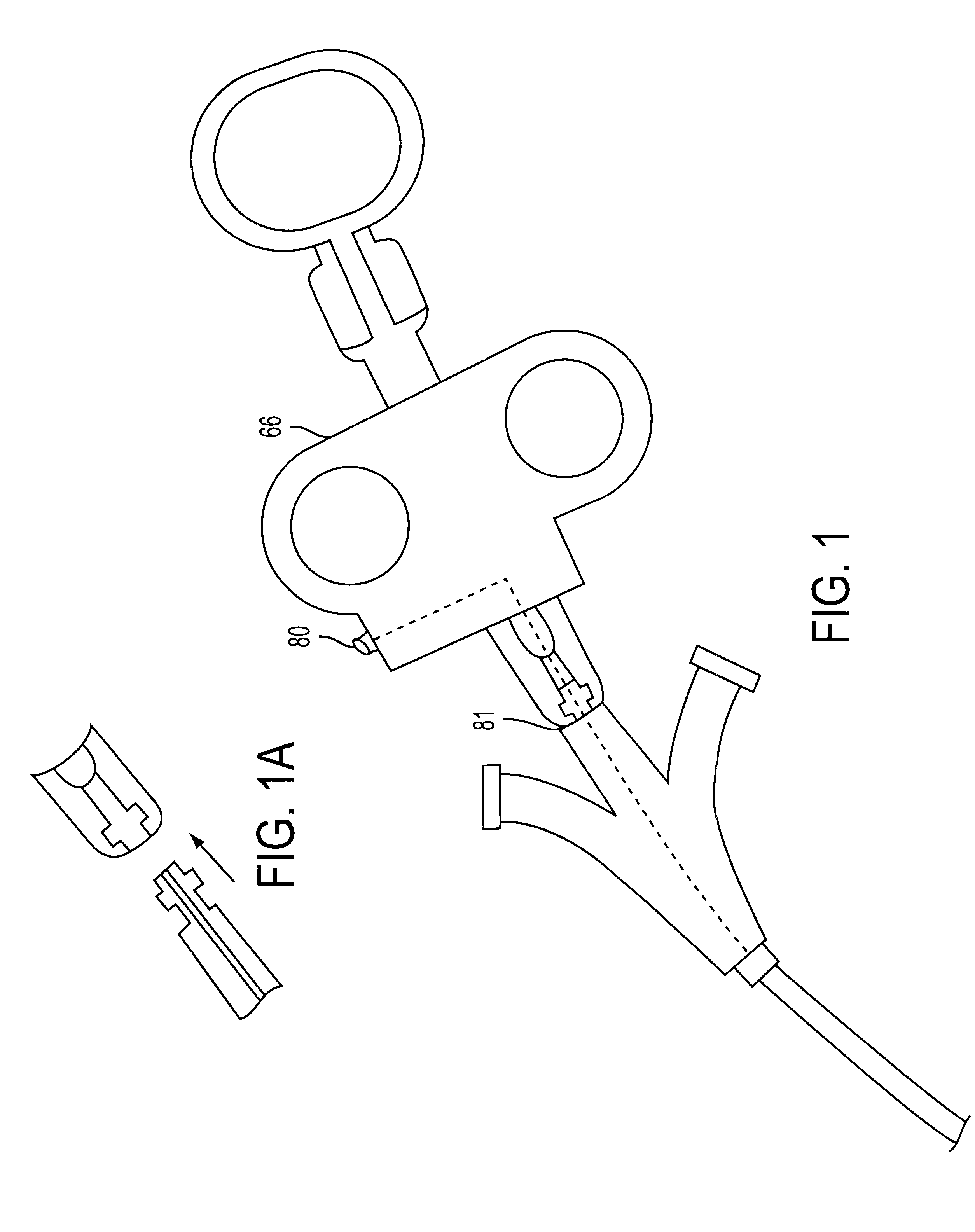
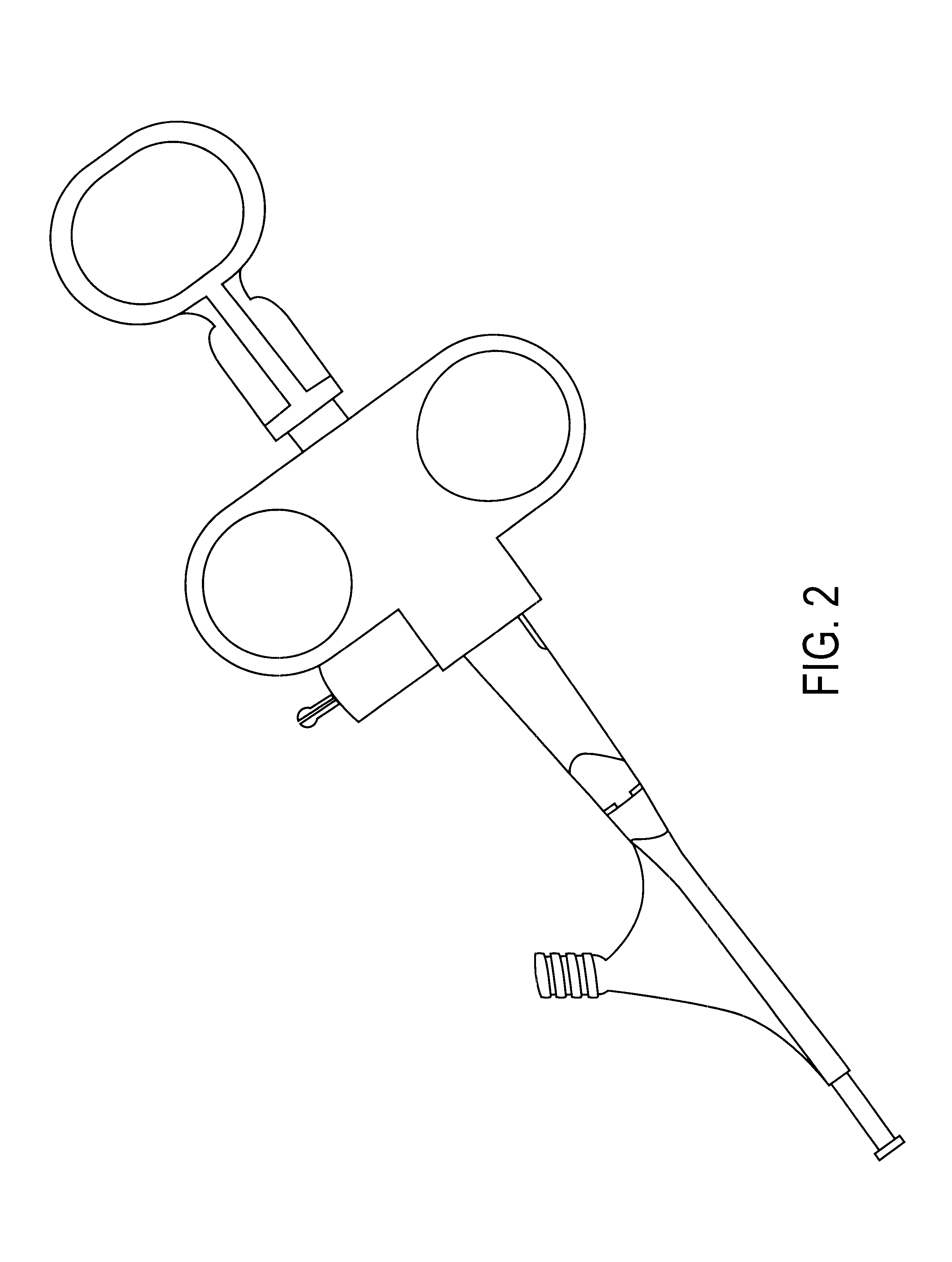
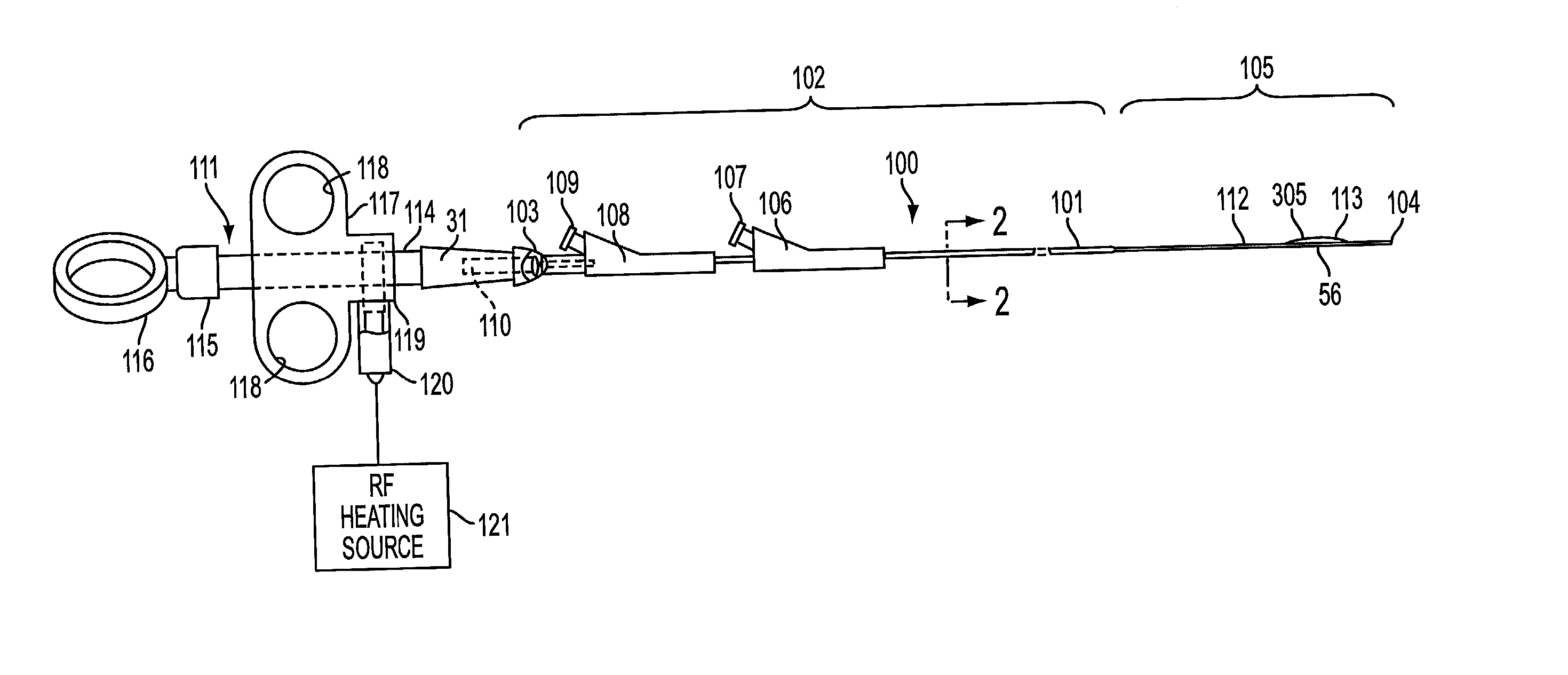
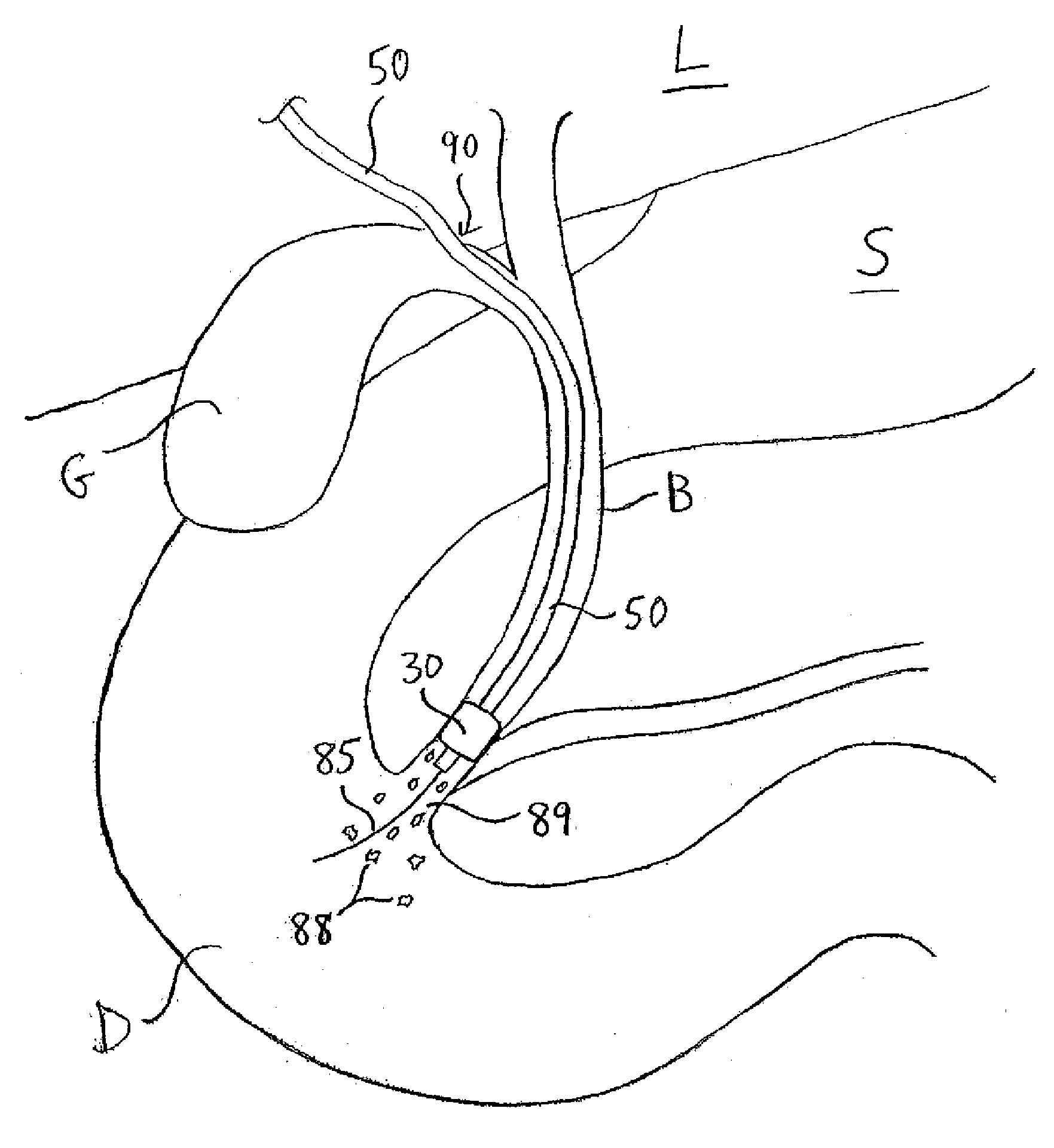
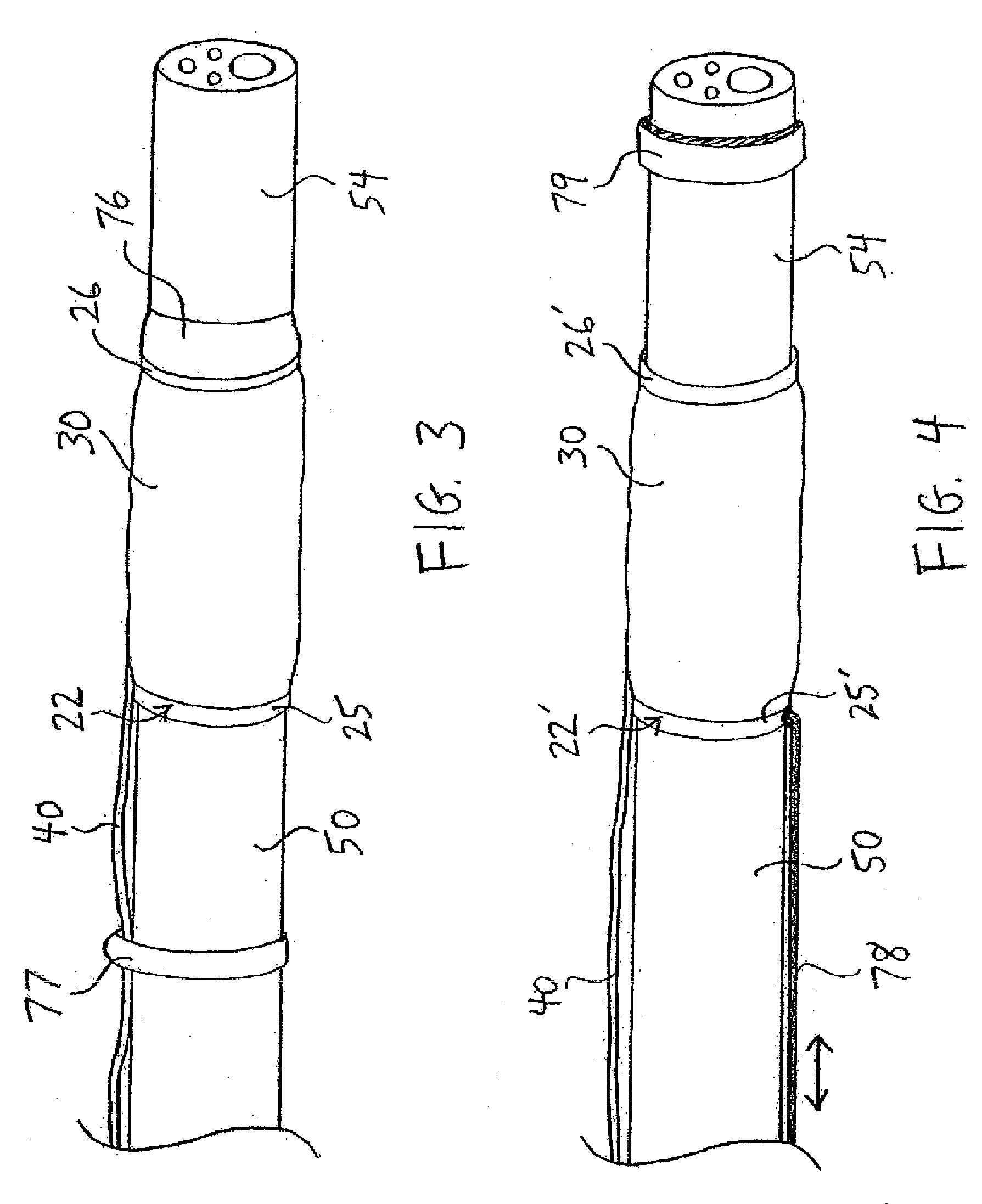
System and method for introducing multiple medical devices
ActiveUS20050059990A1Timely controlSatisfy safety performance requirementsStentsGuide needlesDilatorBiliary tract
A method and apparatus for introducing a first elongate medical device and short wire guide that are coupled together into a work site and remotely disconnecting them within the work site such that a secondary device comprising a catheter member can be introduced over the wire guide to the work site, and / or a second wire guide can be introduced to the work site via a passageway of the primary access device. A separating member may be provided to remotely separate the wire guide from the elongate medical device. A system of indicia, such as radiopaque or viewable markers, permits the operator to monitor the relative alignment of the devices within the work site to determine when uncoupling has occurred. In one example of the method, a wire guide and primary access device (e.g., a sphincterotome) is coupled to the wire guide and introduced via a duodenoscope into the biliary system. After performing a first medical operation, the devices are uncoupled with the wire guide being left within the biliary system such that a secondary access device, such as a balloon, biopsy device, stent delivery catheter, dilator, etc., can be introduced to perform a second medical operation without a traditional over-the-wire exchange being required. In another example of the method, a prosthesis, such as a valve or stent, is placed within the work site coupled to a wire guide which is remotely disconnected within the work site and a secondary device, such as a dilation balloon or second prosthesis, is introduced into the work site after the first delivery system is removed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
System and method for introducing multiple medical devices
A method and apparatus for introducing a first elongate medical device and short wire guide that are coupled together into a work site and remotely disconnecting them within the work site such that a secondary device comprising a catheter member can be introduced over the wire guide to the work site, and / or a second wire guide can be introduced to the work site via a passageway of the primary access device. A system of indicia, such as radiopaque or viewable markers, permit the operator to monitor the relative alignment of the devices within the work site to determine when uncoupling has occurred. In one example of the method, a wire guide and primary access device (e.g., a sphincterotome) is coupled to the wire guide and introduced via a duodenoscope into the biliary system. After performing a first medical operation, the devices are uncoupled with the wire guide being left within the biliary system such that a secondary access device, such as a balloon, biopsy device, stent delivery catheter, dilator, etc., can be introduced to perform a second medical operation without a traditional over-the-wire exchange being required. In another example of the method, a prosthesis, such as a valve or stent, is placed within the work site coupled to a wire guide which is remotely disconnected within the work site and a secondary device, such as a dilation balloon or second prosthesis, is introduced into the work site after the first delivery system is removed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
System for introducing multiple medical devices
InactiveUS20050070794A1Timely controlSatisfy safety performance requirementsStentsGuide needlesDilatorBiliary tract
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
System and method for introducing a prosthesis
InactiveUS20050070821A1Timely controlSatisfy safety performance requirementsStentsGuide needlesDilatorBiliary tract
A method and apparatus for introducing a first elongate medical device and short wire guide that are coupled together into a work site and remotely disconnecting them within the work site such that a secondary device comprising a catheter member can be introduced over the wire guide to the work site, and / or a second wire guide can be introduced to the work site via a passageway of the primary access device. A system of indicia, such as radiopaque or viewable markers, permits the operator to monitor the relative alignment of the devices within the work site to determine when uncoupling has occurred. In one example of the method, a wire guide and primary access device (e.g., a sphincterotome) is coupled to the wire guide and introduced via a duodenoscope into the biliary system. After performing a first medical operation, the devices are uncoupled with the wire guide being left within the biliary system such that a secondary access device, such as a balloon, biopsy device, stent delivery catheter, dilator, etc., can be introduced to perform a second medical operation without a traditional over-the-wire exchange being required. In another example of the method, a prosthesis, such as a valve or stent, is placed within the work site coupled to a wire guide which is remotely disconnected within the work site and a secondary device, such as a dilation balloon or second prosthesis, is introduced into the work site after the first delivery system is removed.
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
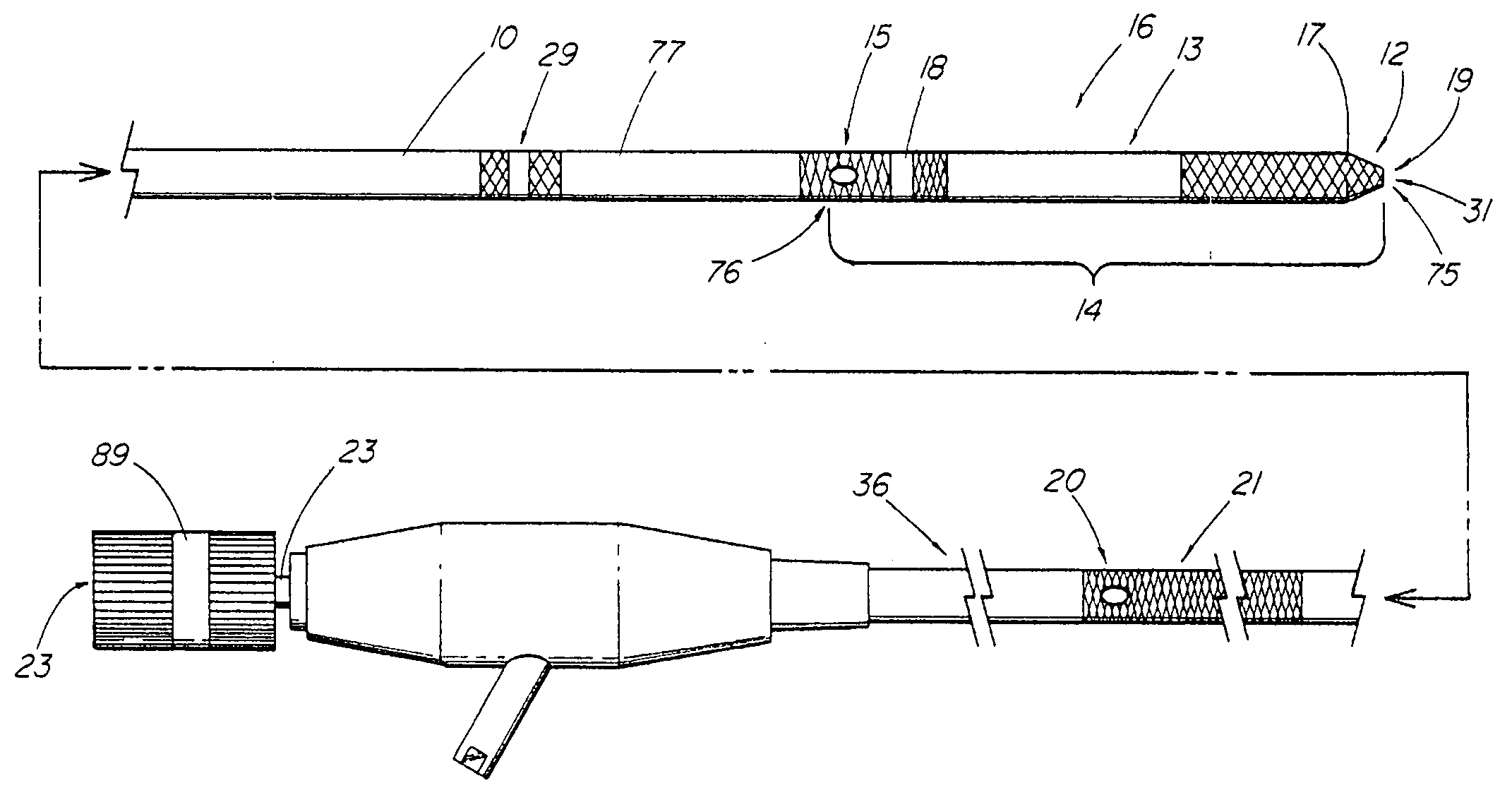
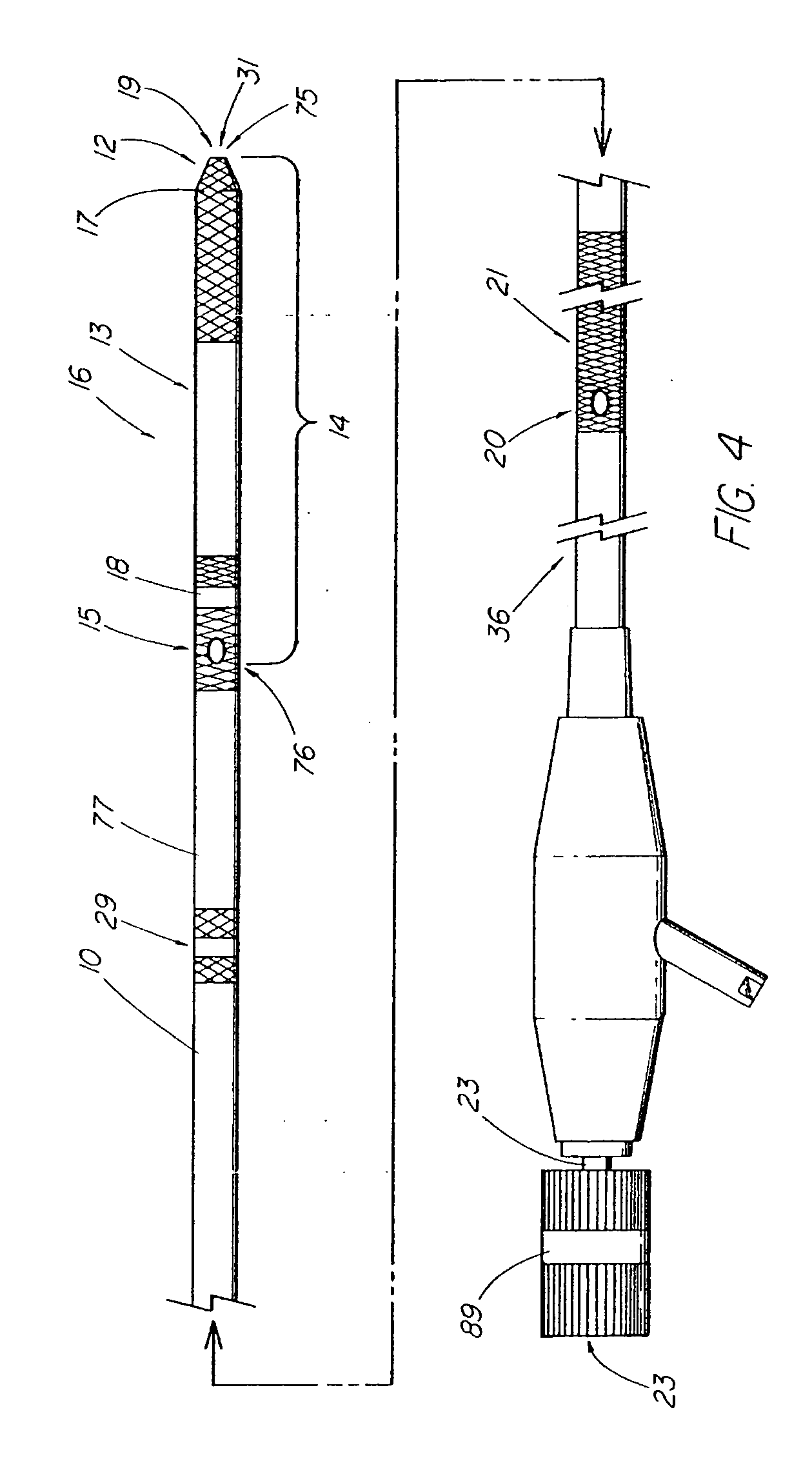
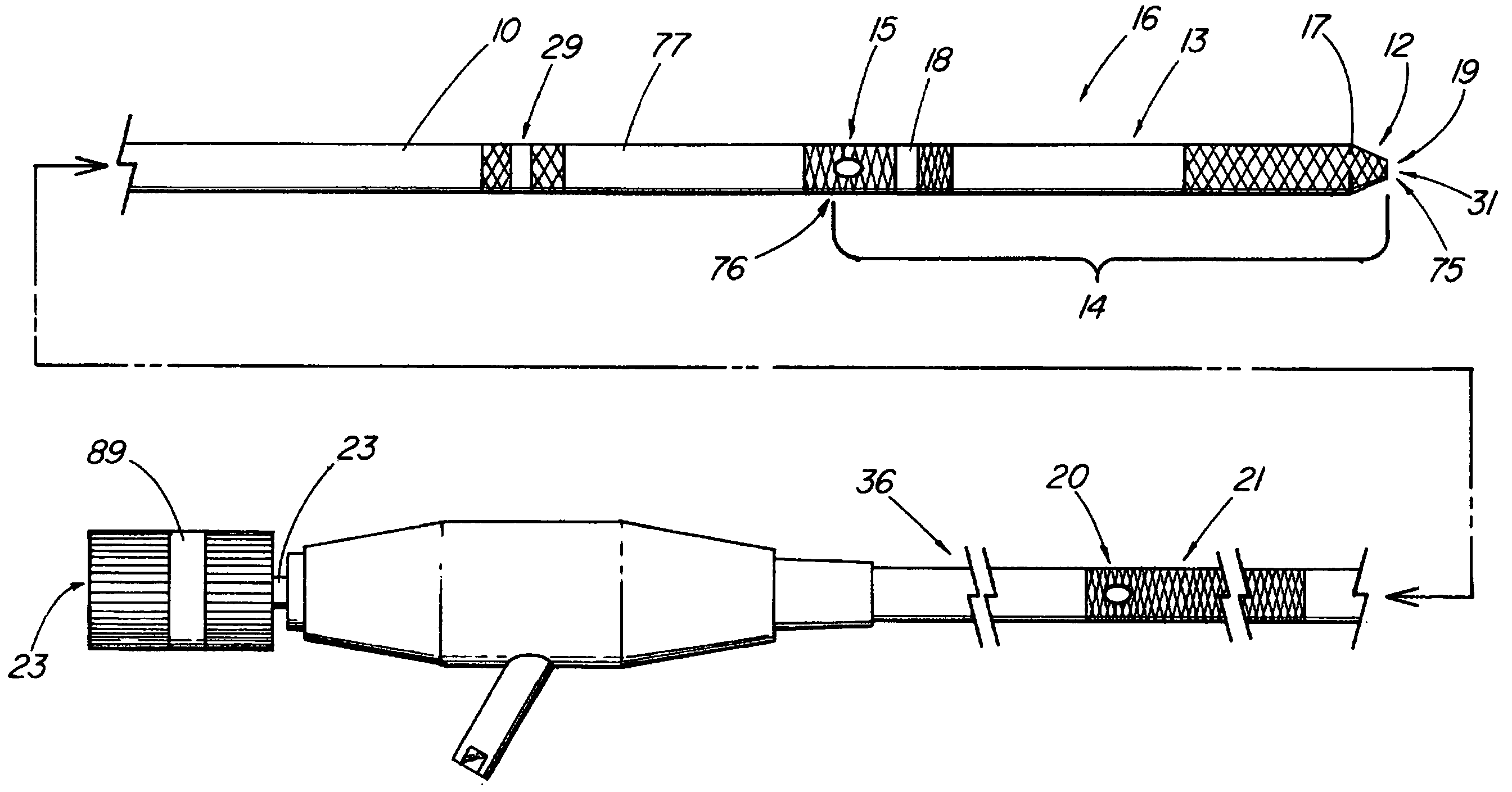
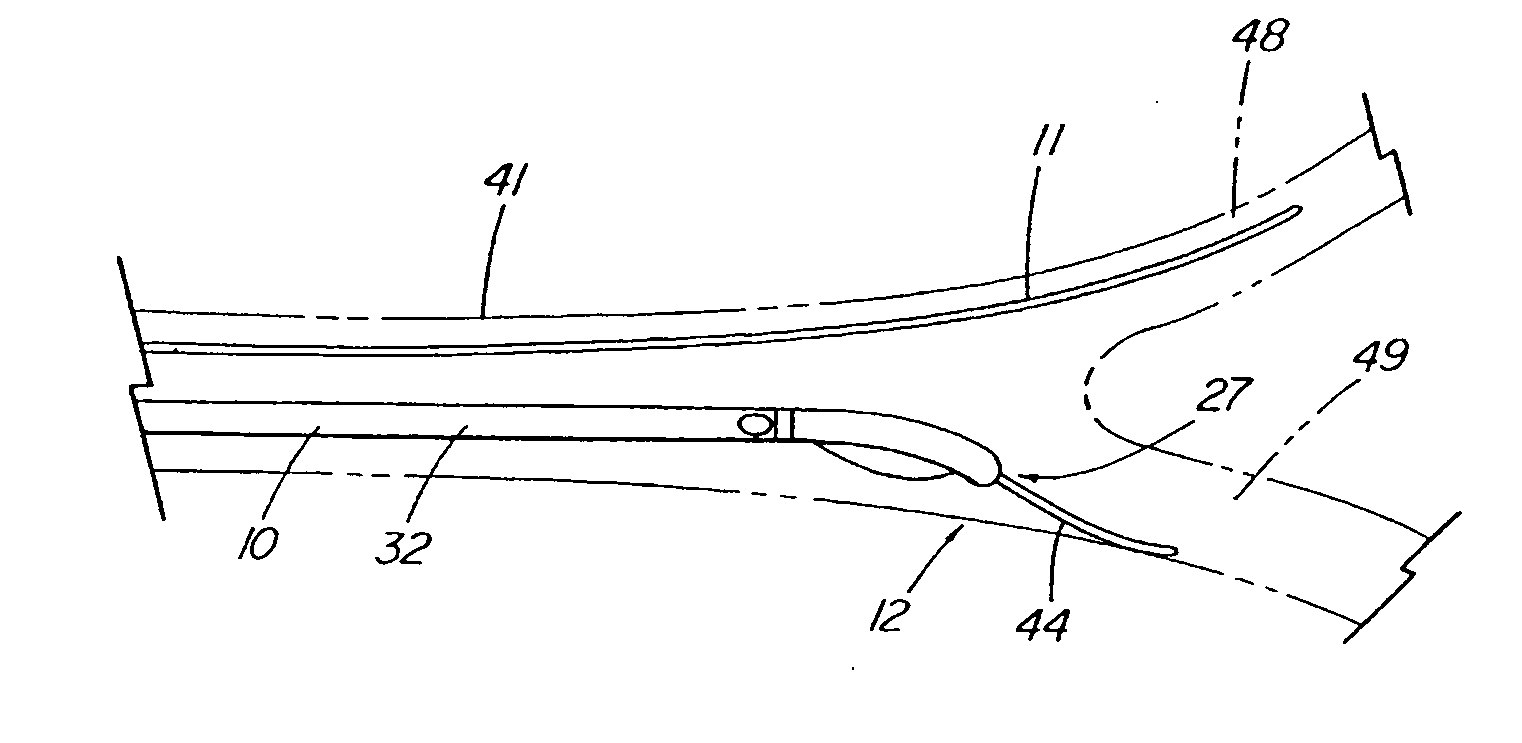
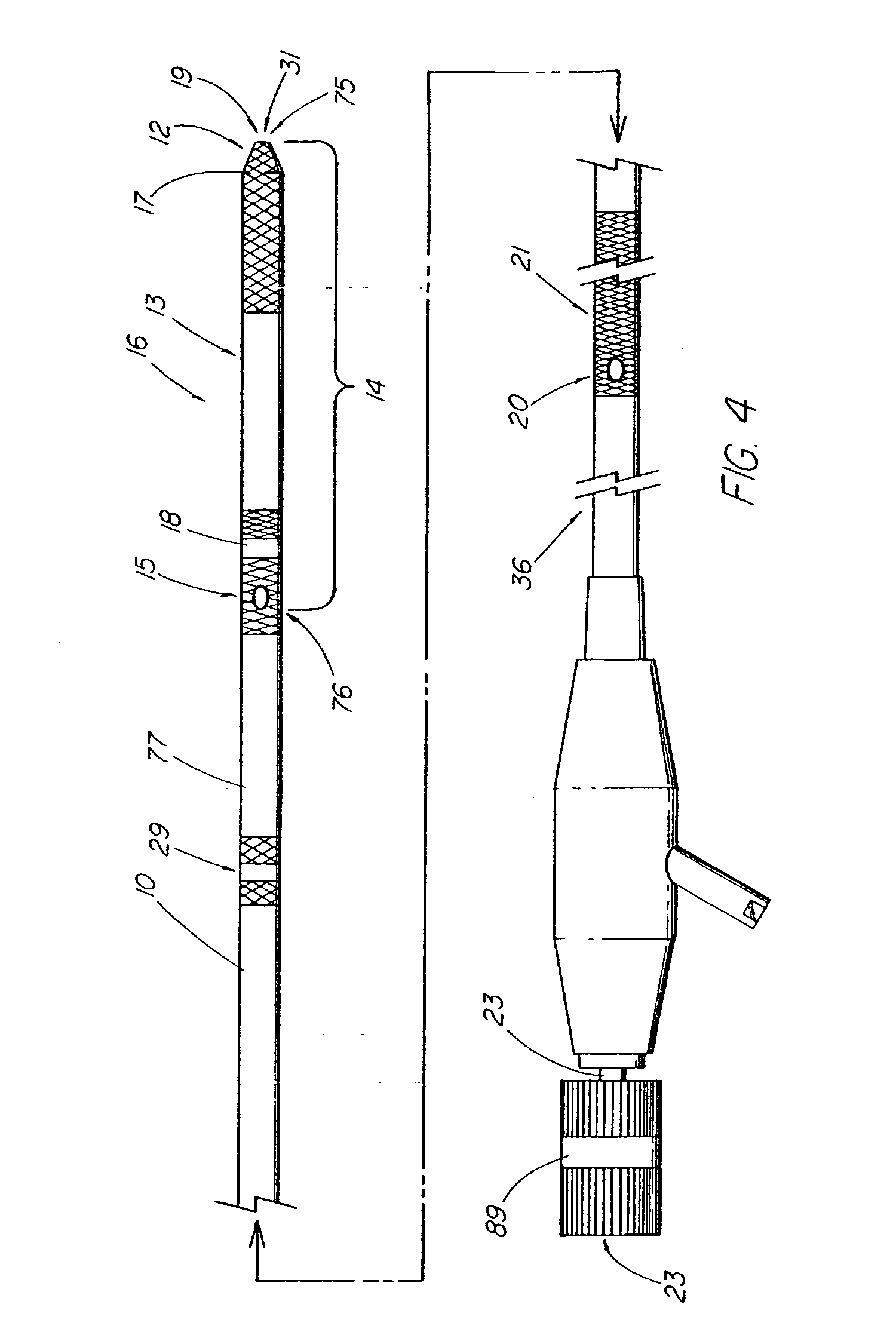
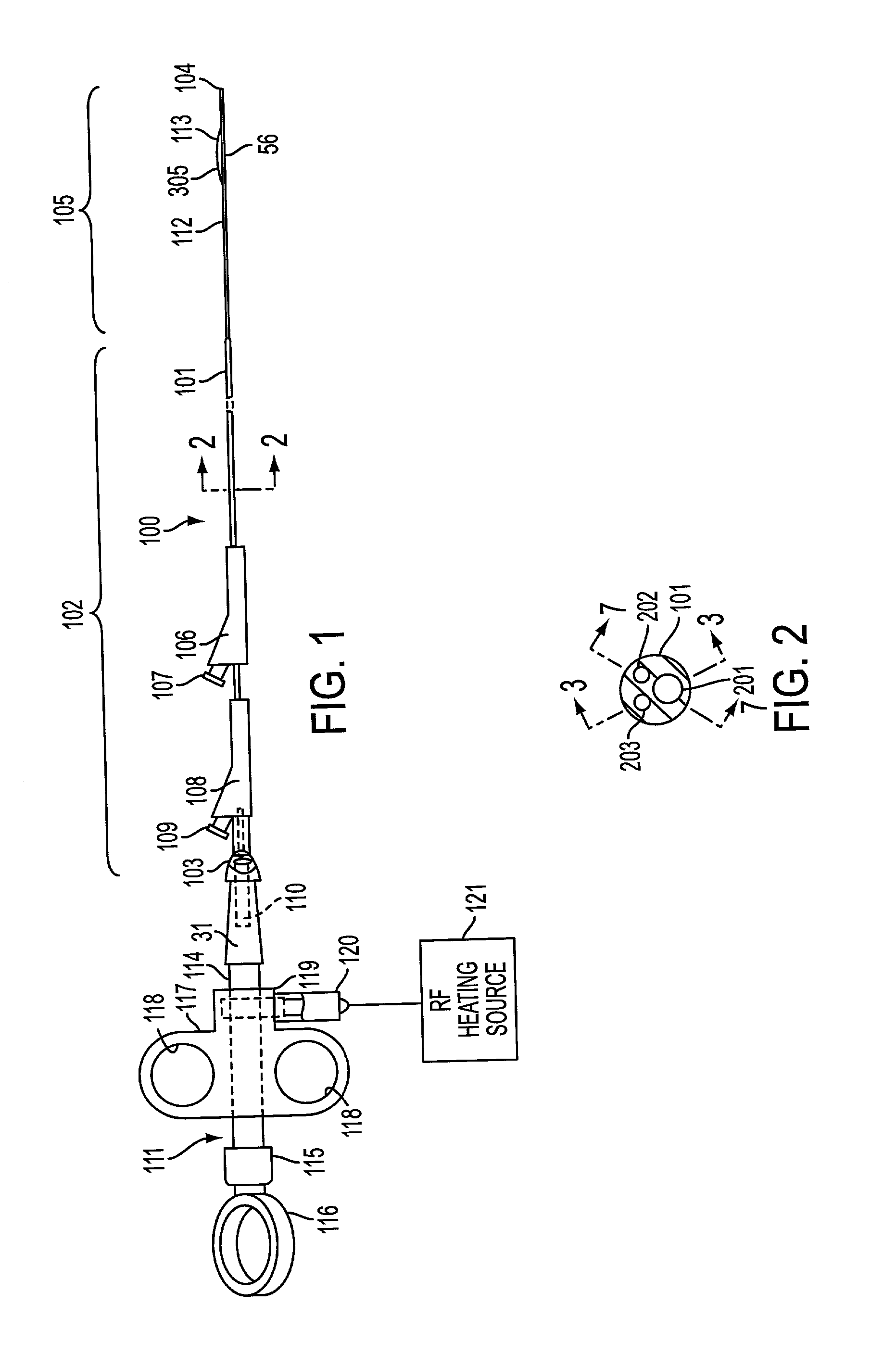
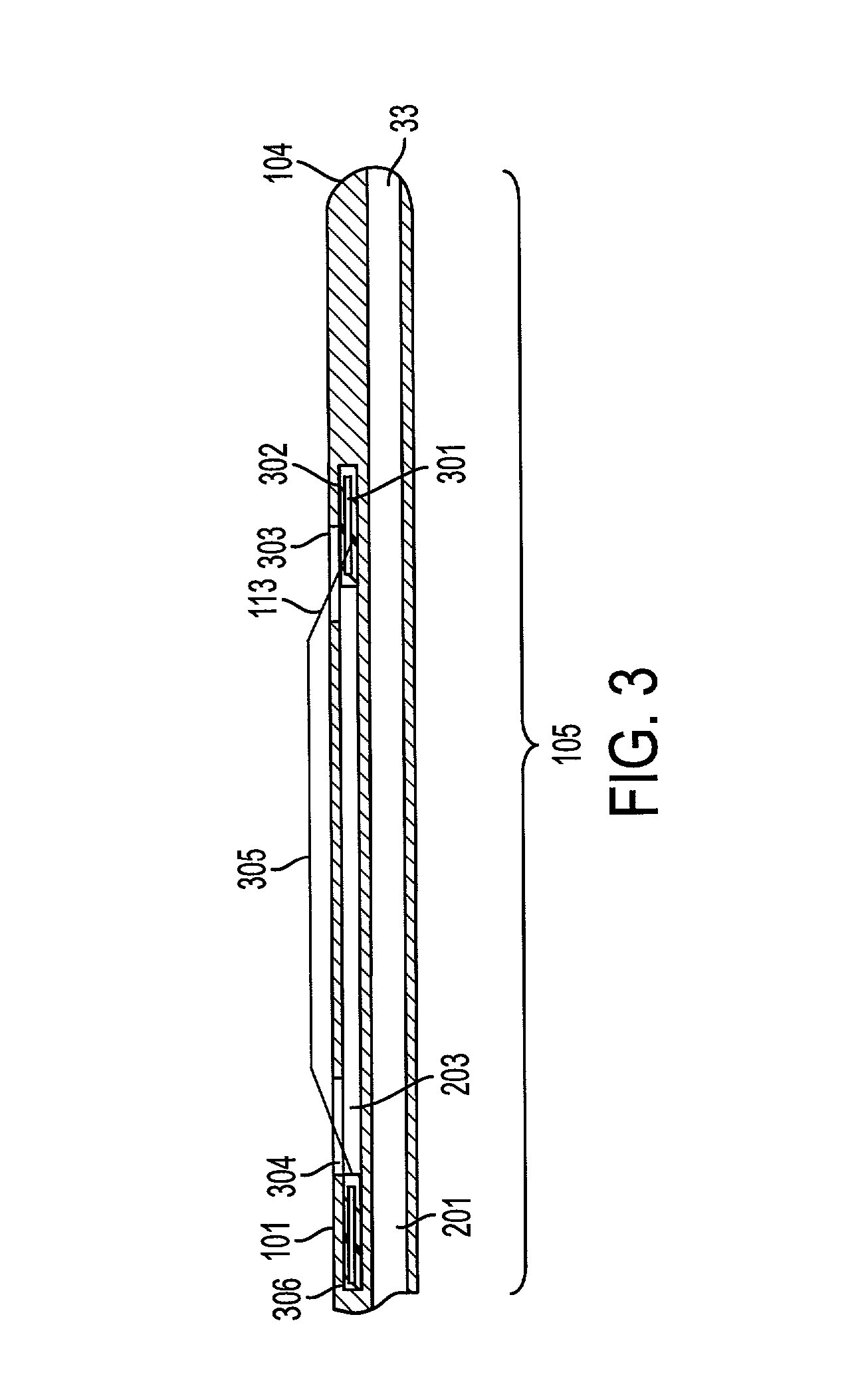
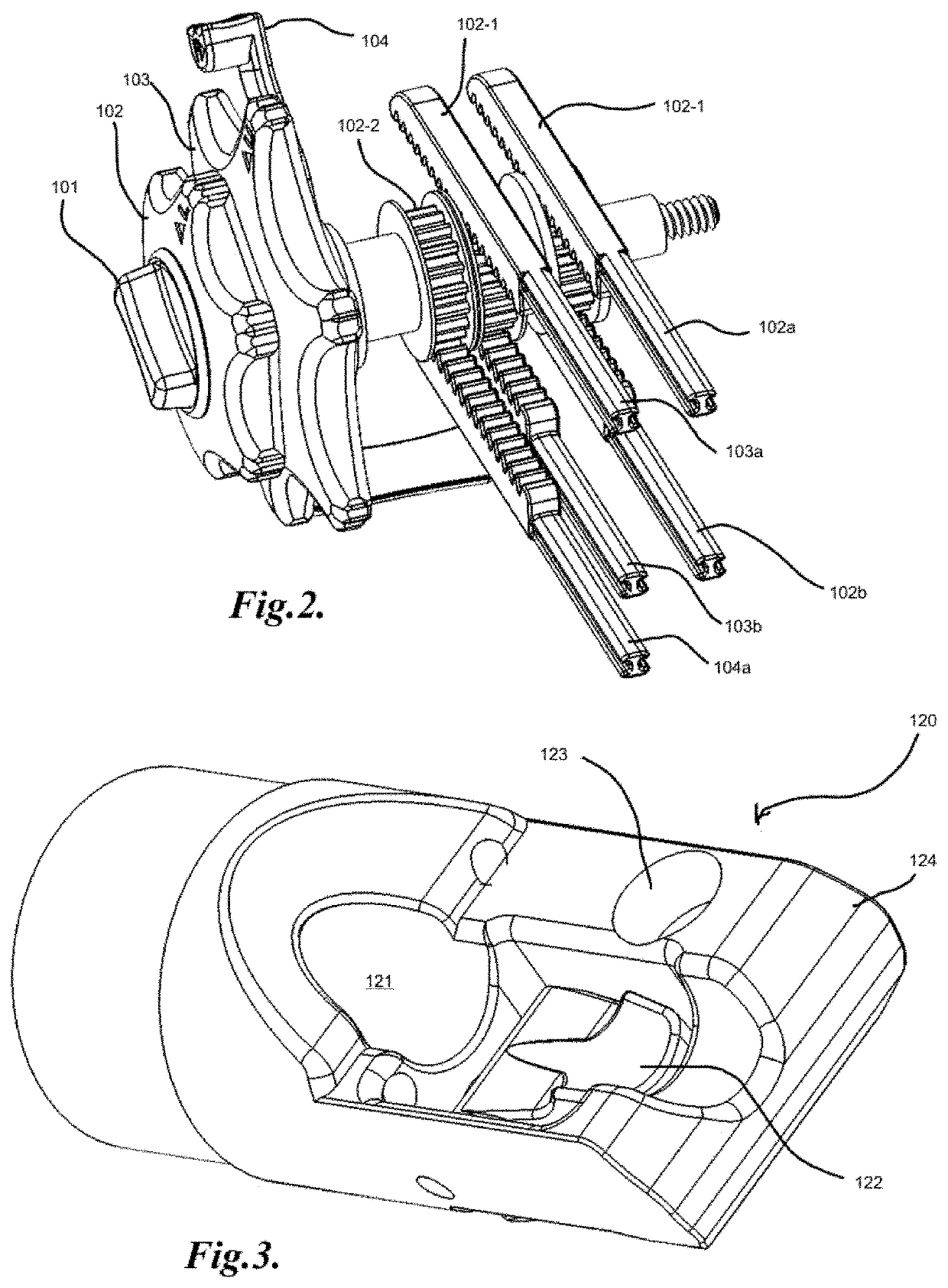
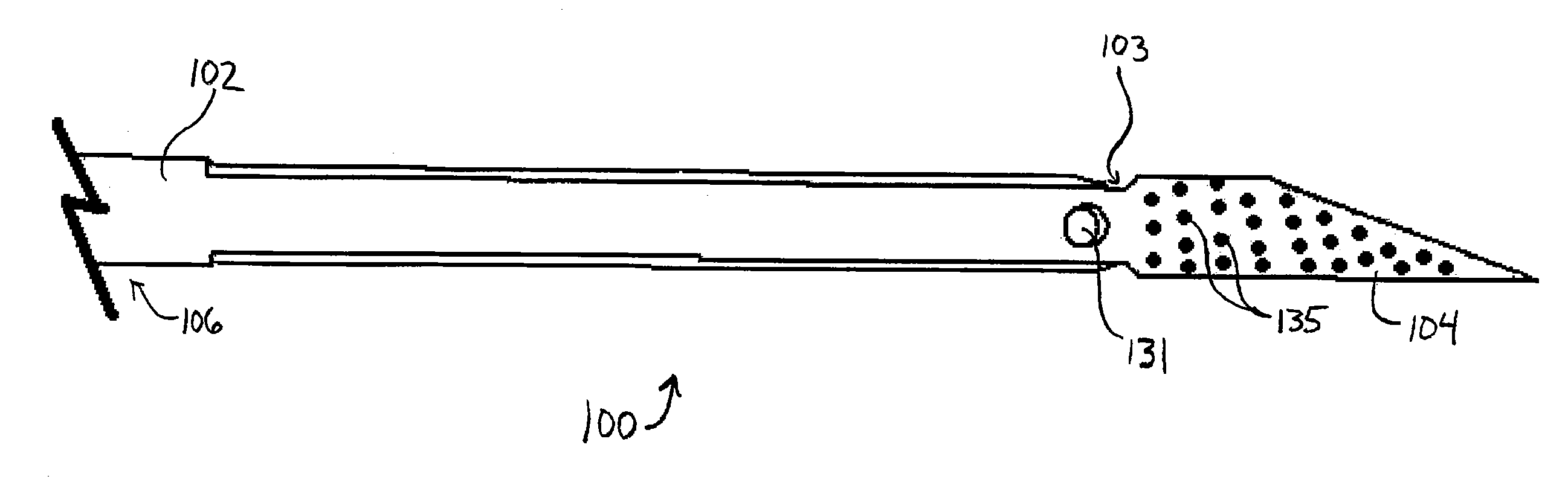
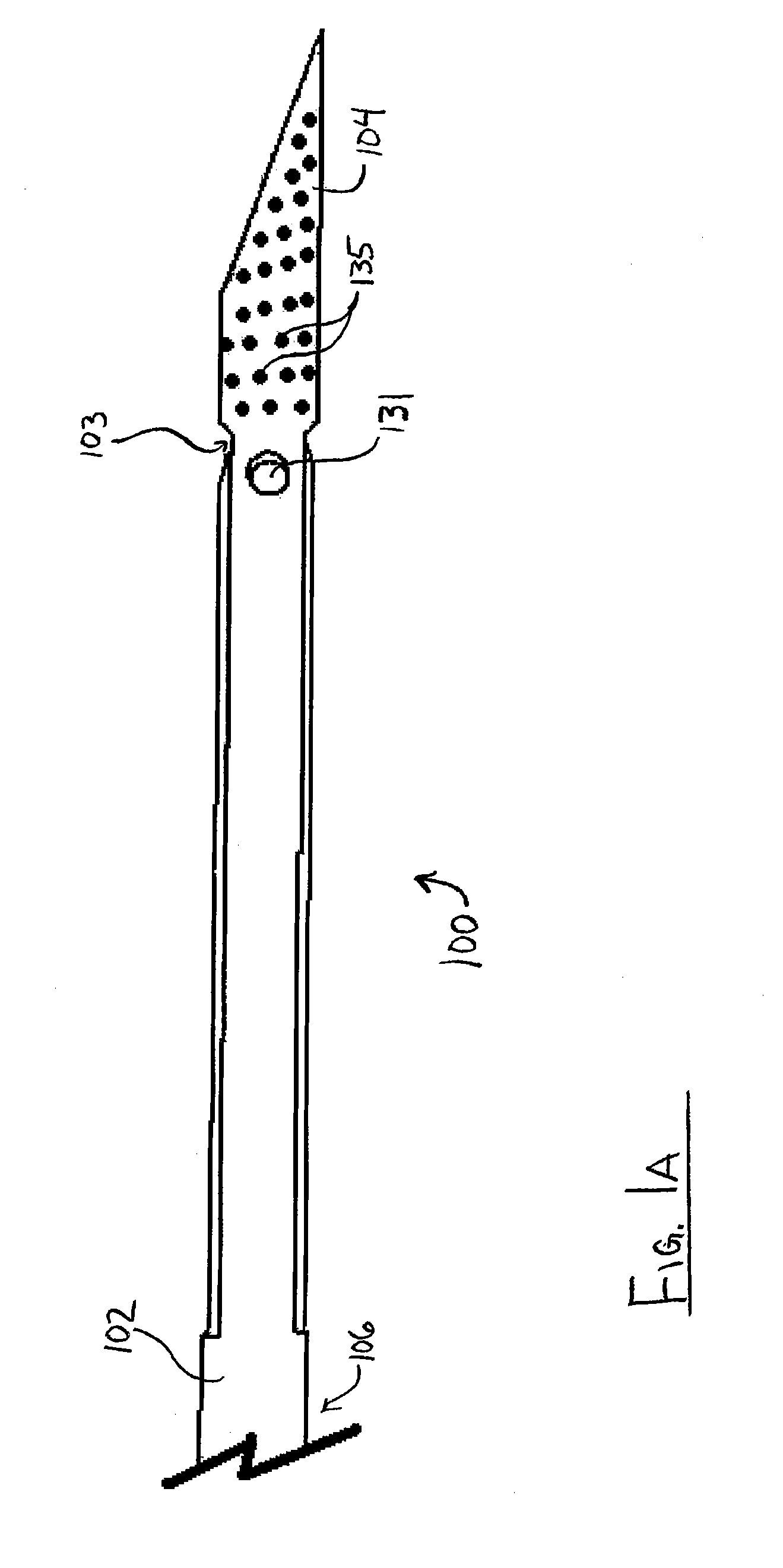
Method and apparatus for measuring and controlling blade depth of a tissue cutting apparatus in an endoscopic catheter
InactiveUS20030060842A1Surgical needlesDiagnostic markersPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Balloon cuff
The present invention provides a balloon cuff comprising an attachment structure adapted to be disposed around an exterior surface of an endoscope, and a balloon coupled to the attachment structure. An inflation means is in fluid communication with the balloon. The balloon has a deflated state suitable for insertion into a body passage and an inflated state suitable for urging stone fragments along the body passage. Optionally, an intraductal shock wave lithotripsy procedure may be performed through the working lumen of the first endoscope while the balloon cuff is disposed, either inflated or deflated, about the exterior surface of the first endoscope. The first endoscope and balloon cuff may be used alone to remove stone fragments, or alternatively, may be used in conjunction with a second endoscope, such as a duodenoscope, having a working lumen sized to received the first endoscope having the balloon cuff disposed thereon.
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
Steerable sphincterotome and methods for cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy
The present invention relates to methods and devices for performing endoscopic cannulation, papillotomy and sphincterotomy and similar procedures. According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and similar procedures are accomplished by advancing the device into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the device exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the device to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Due to inconsistencies in, for example, the sphincterotome, anatomy, and endoscope manipulation, it is difficult to accurately and consistently position the sphincterotome for proper cannulation. The steerable sphincterotome of the present invention allows the physician to control the position of the distal tip of the device independently of the endoscope and adjust for inconsistencies in the device and the anatomy. According to the present invention, the handle to which the cutting wire is attached is freely rotatable relative to the catheter. The handle, secured to the cutting wire but rotatable relative to the shaft of the catheter, provides a mechanism to rotate the wire, transmitting the force to rotate the device tip. With the handle rotating independently of the shaft at the proximal end, the force can be applied directly to the distal tip without twisting the entire shaft. Also a rotation lock to maintain the orientation of the tip and / or a rotation marking, to indicate the amount of rotation may be included.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
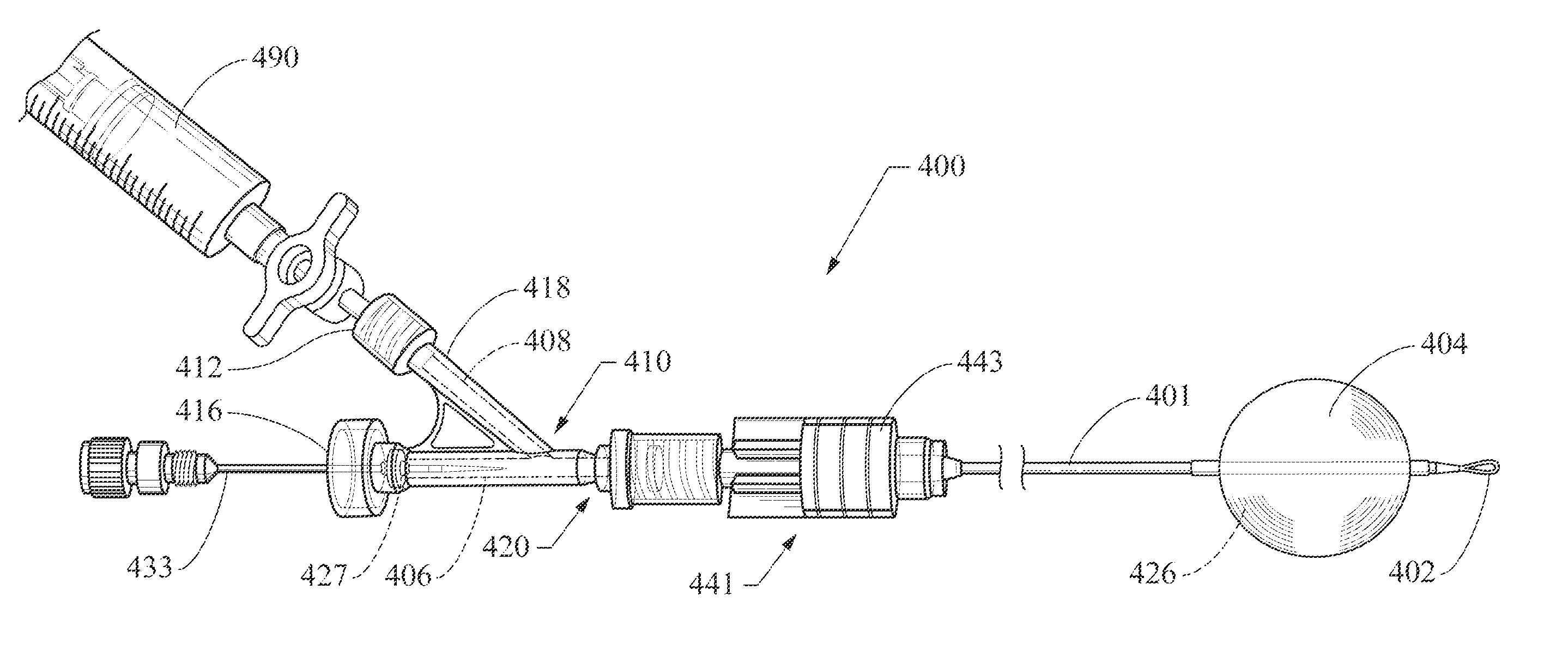
Balloon catheter with detachable hub, and methods for same
A balloon catheter may include a distal anchoring balloon and a proximal hub that is removable from the catheter body. The catheter body may include a valve structure providing for maintaining the balloon in an inflated state during and after removal of the proximal hub. The valve preferably is constructed such that removal of the hub provides a low-profile proximal catheter end that will allow that proximal catheter end to pass through an endoscopic surgical device such as, for example, through an accessory channel of a standard duodenoscope and / or an ultra-slim endoscope / cholangioscope, facilitating a scope-exchange for use during, for example, a cholangioscopy or pancreatoscopy procedure. A method useful for scope exchange and / or introducing another elongate surgical device may utilize a balloon catheter with a distal anchoring balloon and a proximal hub that is removable from the catheter body.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method and Apparatus for Measuring and Controlling Blade Depth of a Tissue Cutting Apparatus in an Endoscopic Catheter
InactiveUS20090005637A1Precise depth controlProviding resistance to movementSurgical needlesEndoscopesPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
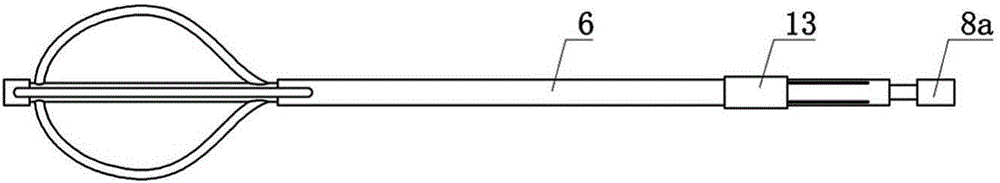
Sheathed Duodenoscope
ActiveUS20160227988A1Avoid stray lightAvoid light interferenceGastroscopesOesophagoscopesBiopsy forcepsEndoscope
A sheathed endoscope, includes: an endoscope and a disposable component. The disposable compartment protects the inner and outer surfaces of the endoscope. The disposable compartment includes: a cap of endoscope tip in the distal end of endoscope, a disposable tube for biopsy forceps, and an outside sheath capsule for endoscope shaft. The tip cap connects the sheath capsule and the disposable tube for biopsy forceps. There are multiple windows set on the lateral side of endoscope tip, wherein pills containing transparent fluid are placed somewhere in between of the tip cap and the distal end of endoscope. The pills will be crushed by co-fraction of the tip cap and the distal end of endoscope, to release the transparent fluid to fill in the space formed between the tip cap and the distal end of the endoscope. This disposable sheath compartment in the invention will cover all surfaces of the endoscope with disposable material, preventing contaminations on endoscope during endoscopy, meanwhile there is anti-glaring design, to prevent producing of glaring in the space formed between the tip cap and the distal end of endoscope.
Owner:SHENYANG SHENDA ENDOSCOPE
Medical anchor device
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
ERCP auxiliary manipulator device
InactiveCN105030332AHigh precision speedHigh position controlDiagnosticsSurgeryX-rayFunctional diversity
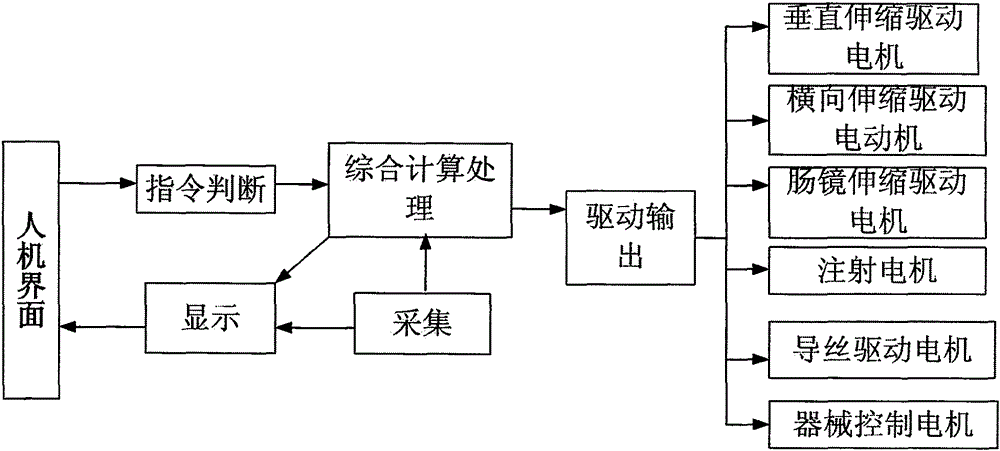
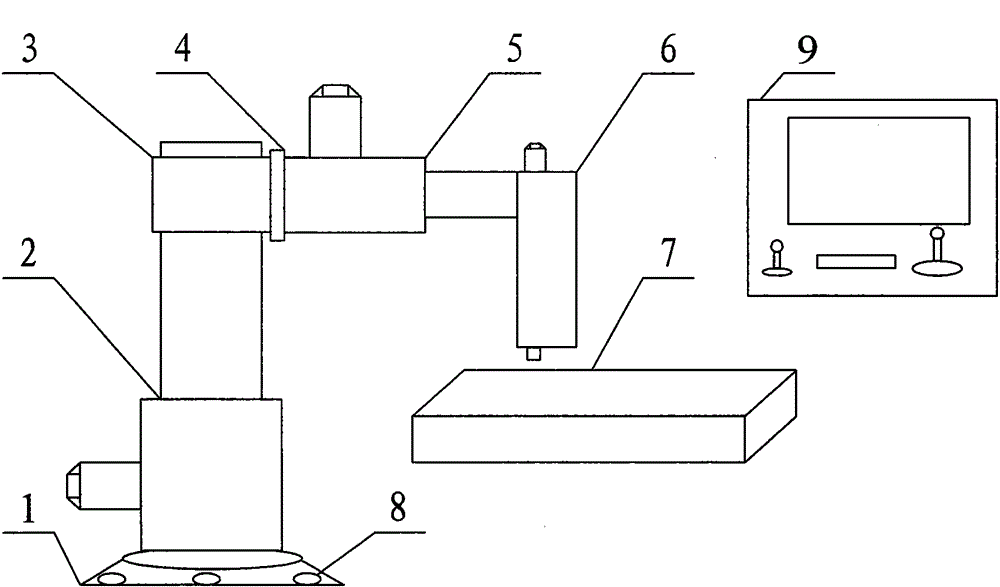
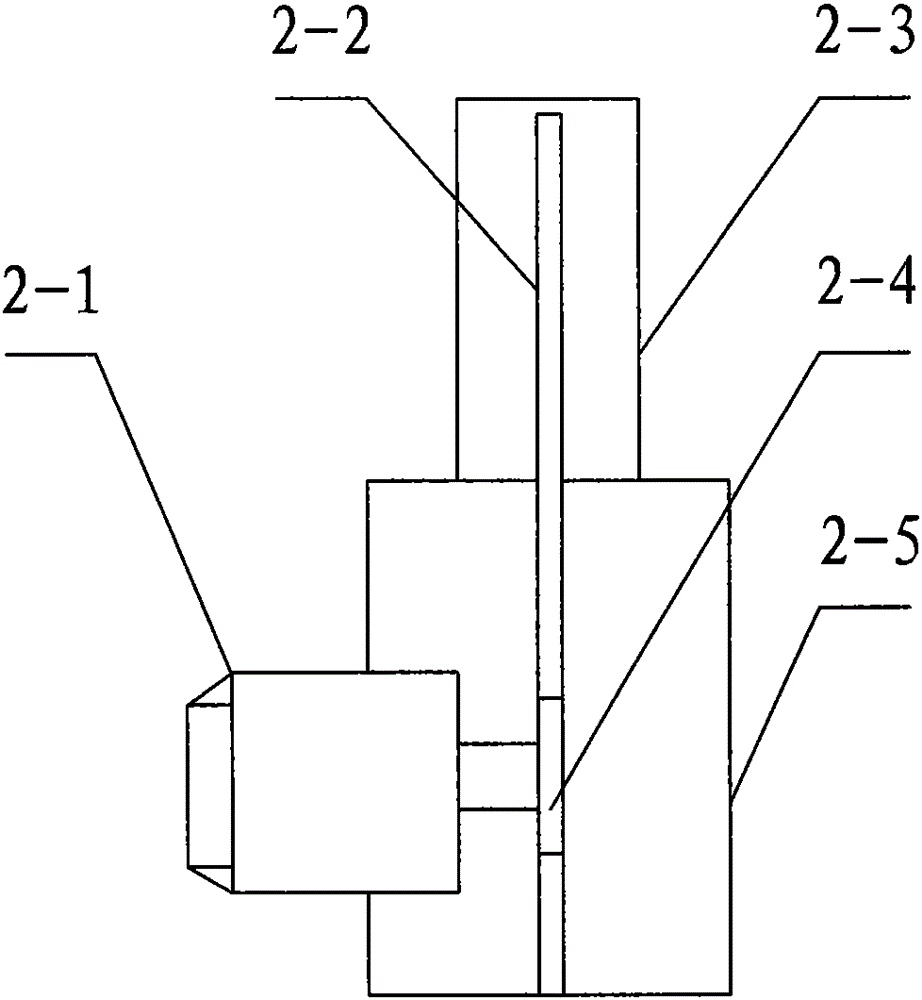
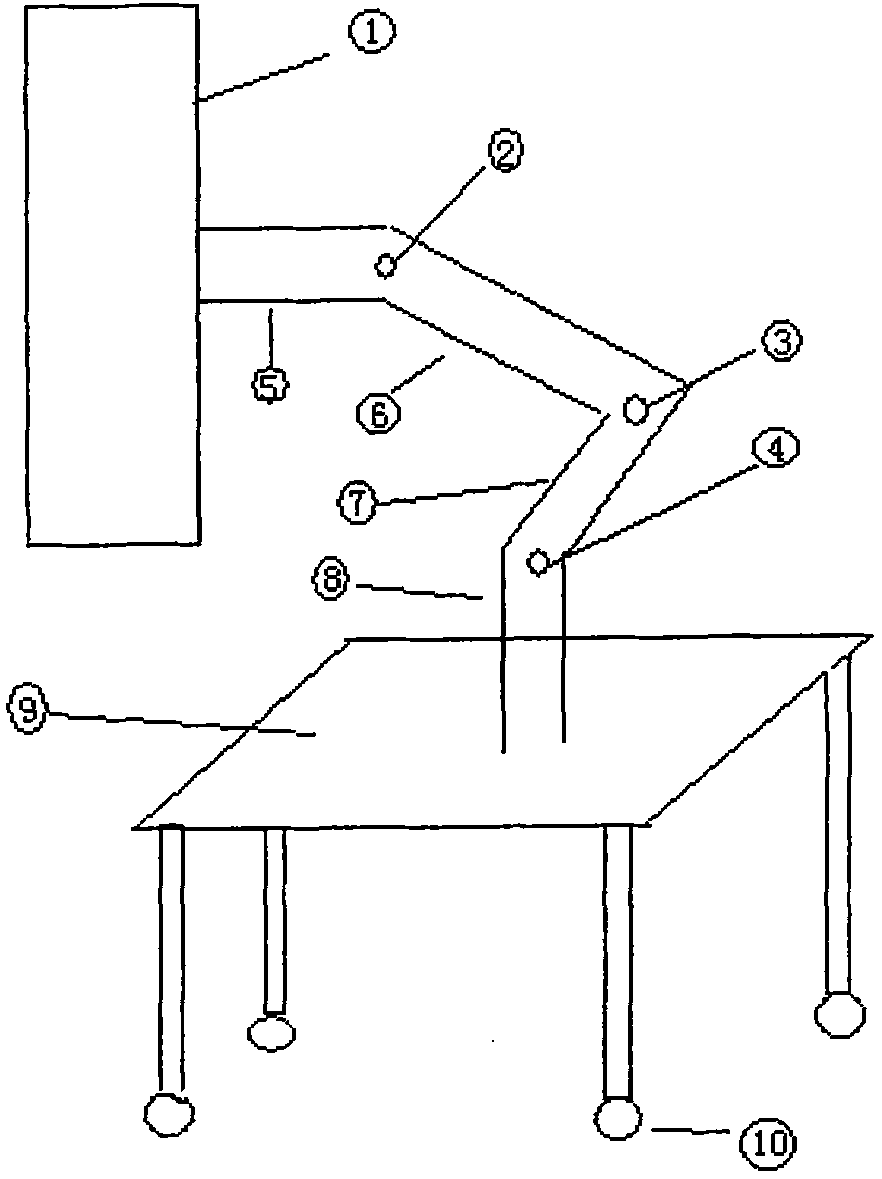
The invention provides an ERCP auxiliary manipulator device. The ERCP auxiliary manipulator device comprises a base, a vertical retractor device, a hoop, a connecting flange, a horizontal retractor device, aduodenoscope control box, an operating table, foundation bolts and a control device, wherein the base is fixed on the ground through the foundation bolts; the upper end of the base is provided with the vertical retractor device, the top end of the vertical retractor device is provided with the hoop; the horizontal retractor device is arranged on the hoop through the connecting flange; the duodenoscope control box is arranged at the other end of the horizontal retractor device; and the control device is connected with the ERCP auxiliary manipulator device body through a special cable. According to the ERCP auxiliary manipulator device, through the arrangement of the vertical retractor device, the horizontal retractor device and the duodenoscope control box, the adjustment is accurate, so that the operation is simple, the control is convenient, and the ERCP auxiliary manipulator device is safe and reliable, thus the functional diversity is perfected, and further, the success rate of an operation is improved, and the damage to health of medical staff caused by X rays is avoided.
Owner:郑步峰
Balloon catheter with detachable hub, and methods for same
A balloon catheter (400) may include a distal anchoring balloon (404) and a proximal hub (410) that is removable from the catheter body. The catheter body may include a valve structure (420) providing for maintaining the balloon in an inflated state during and after removal of the proximal hub. The valve preferably is constructed such that removal of the hub provides a low-profile proximal catheter end that will allow that proximal catheter end to pass through an endoscopic surgical device such as, for example, through an accessory channel of a standard duodenoscope and / or an ultra- slim endoscope / cholangioscope, facilitating a scope- exchange for use during, for example, a cholangioscopy or pancreatoscopy procedure. A method useful for scope exchange and / or introducing another elongate surgical device may utilize a balloon catheter with a distal anchoring balloon and a proximal hub that is removable from the catheter body.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) auxiliary mechanical arm device
The invention relates to an ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) auxiliary mechanical arm device which is a machinery automation device for assisting in completing various treatment operations based on ERCP. The ERCP auxiliary mechanical arm device is designed according to duodenoscope and various instruments, the duodenoscope is placed in a descending part of a duodenum, the duodenoscope and / or an assistant device is fixed on corresponding positions, remote control of movement of a mechanical device is realized by a control system, and operations of intubatton, radiography, stone removal, and the like are finished. Therefore, the damage of X ray to the health of medical staff in the process of curing patients is avoided. In the mechanical arm device, each button of the duodenoscope and various related devices are firmly fixed so that various operations with endoscopes are accurately completed, and in addition, the automation control technology is applied so that medical staff can control with long distance so as to avoid the damage of the X ray.
Owner:曹罡 +2
Three-endoscopic joint microinvasive gallbladder-protected lithotomy
The invention discloses a three-mirror combined minimally invasive gallbladder-preserving stone removal operation, which relates to medical equipment and is used to solve the problem that the existing stone removal mesh basket will touch the inner wall of the gallbladder, and the operation process is prone to pain, trauma, bleeding, and cannot collect gallbladder stones. , flushing, imaging and expansion in one. It includes a stone extraction basket, a choledochoscope, a laparoscope, and a duodenoscope. The stone extraction basket includes a catheter, a hollow guide head positioned at the left end of the catheter, and a wire basket positioned on the guide head. The wire basket includes at least 2 first net baskets, at least 2 second net baskets, the conduit includes outer tubes, sliding tubes, inner tubes and sliding couplings arranged from outside to inside, the sliding couplings include first terminals, second The terminal is used to connect the coupling shaft of the first terminal and the second terminal. The retractable mesh basket design prevents the stone extraction mesh basket from touching the inner wall of the gallbladder. There is no pain, trauma, or bleeding during the operation, and it can integrate gallbladder stone extraction, washing, imaging, and expansion.
Owner:南宁博锐医院有限公司
Endoskop, insbesondere duodenoskop fur die mutter-baby-cholangioskopie
InactiveUS20070118016A1Improve mobilityAvoid disadvantagesSurgeryEndoscopesDuodenoscopesFirst insertion
An endoscope, in particular a duodenoscope, for mother-baby cholangioscopy, having a working canal that runs in or on a shaft of the endoscope and includes an outlet opening distally on the endoscope head, so that the working canal includes at least a first insertion opening, which lies in an area of the shaft far from the proximal end of the endoscope.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
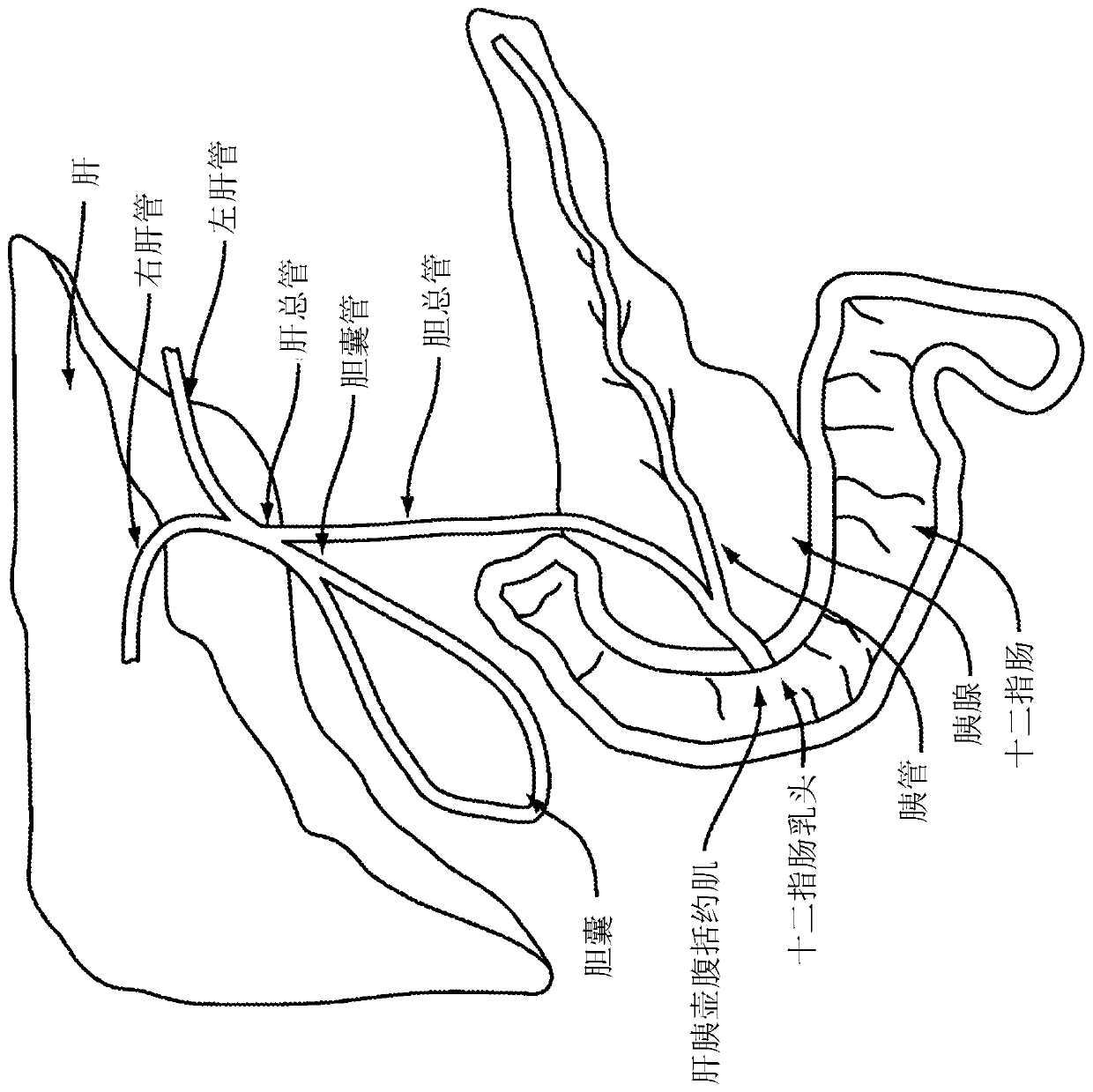
Biliary tract exploration method and device based on superfine endoscope
The invention provides a biliary tract exploration method and device based on a superfine endoscope. The biliary tract exploration method is characterized by comprising the following steps that a conical guide head is fixedly connected, and the superfine endoscope is mounted in an inserted mode; the superfine endoscope is put into the duodenum descending part; the conical guide head is fixed to the open position of duodenal papilla; a guide wire is inserted, and the superfine endoscope is brought into the common bile duct and the common hepatic duct by the guide wire; an annular surrounding saccule is opened through inflation, and an outer sleeve is fixed; the guide wire and the superfine endoscope are taken out and the outer sleeve is dwelled to form a stable biliary tract exploration channel. The biliary tract exploration device comprises the guide wire, a duodenoscope and the superfine endoscope and is characterized by further comprising the conical guide head, wherein the conical guide head is arranged at the front end of the superfine endoscope and is fixedly connected with the superfine endoscope, the annular surrounding saccule and a traction wire are arranged at the front portion of the outer sleeve, the superfine endoscope and the guide wire are inserted into the outer sleeve and enter the common bile duct, and the annular surrounding saccule is opened through inflation to fix the outer sleeve so as to form the biliary tract exploration channel.
Owner:刘时助
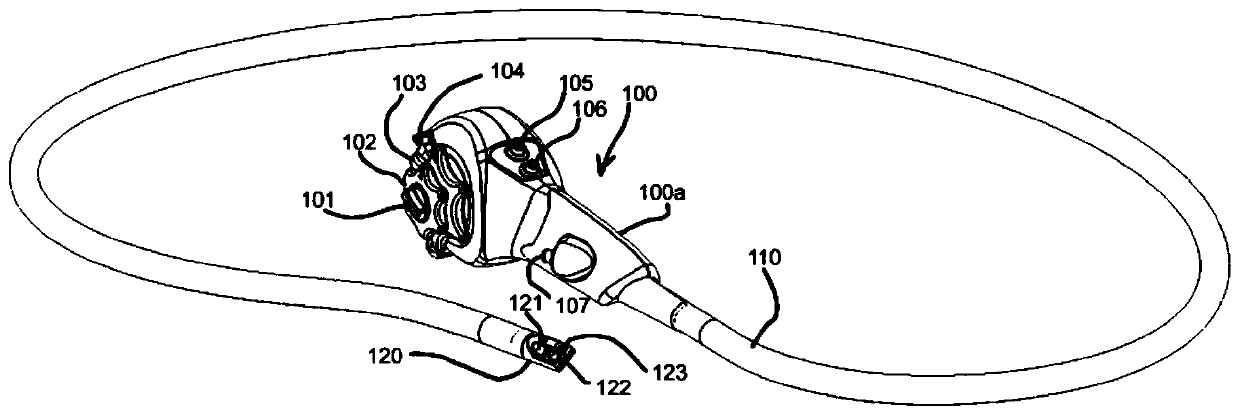
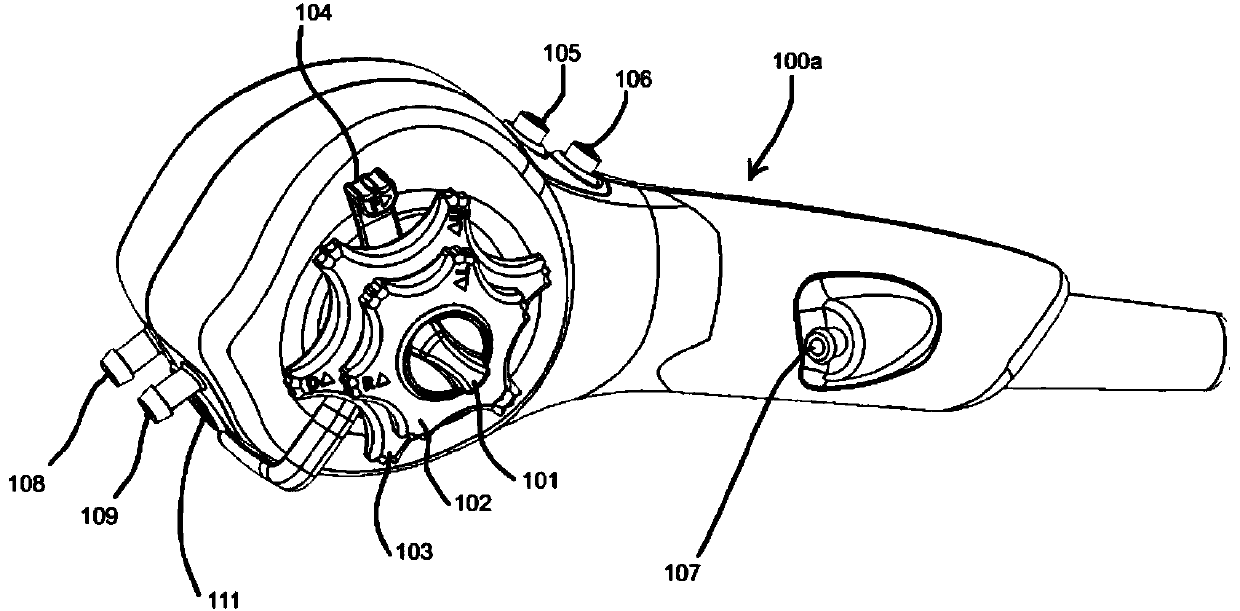
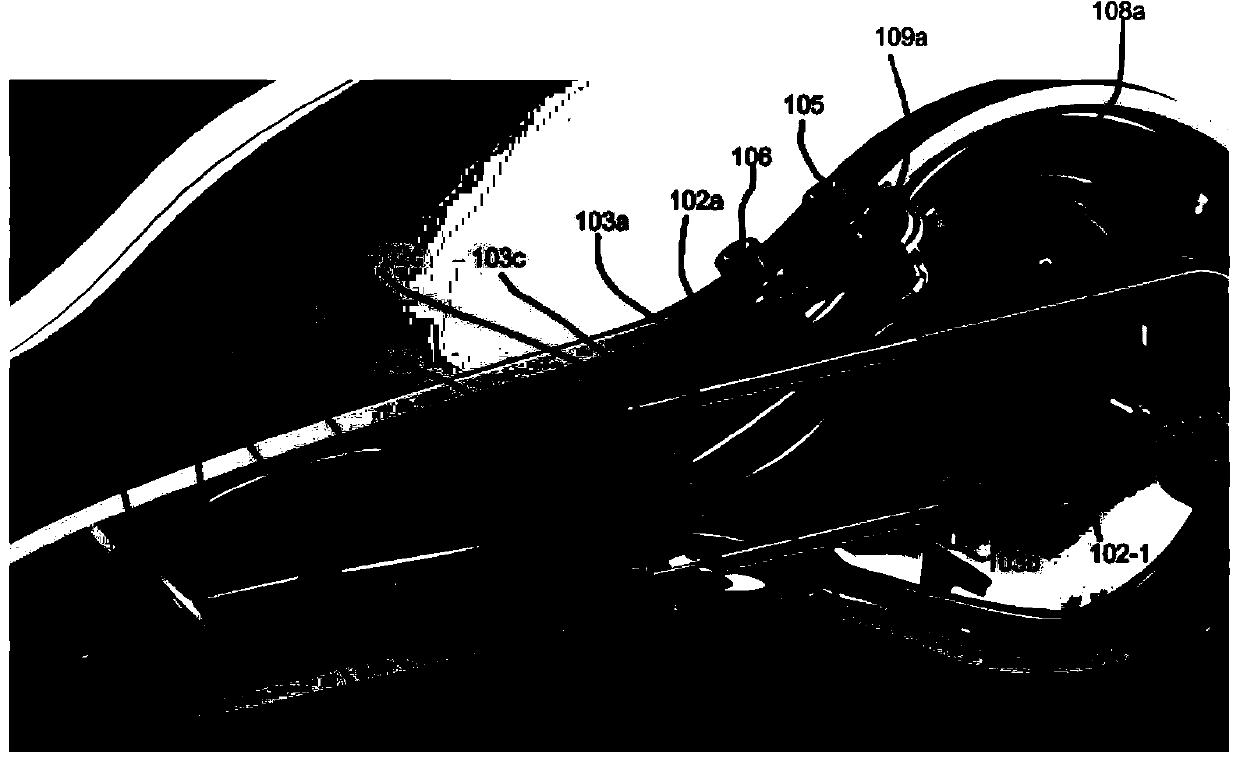
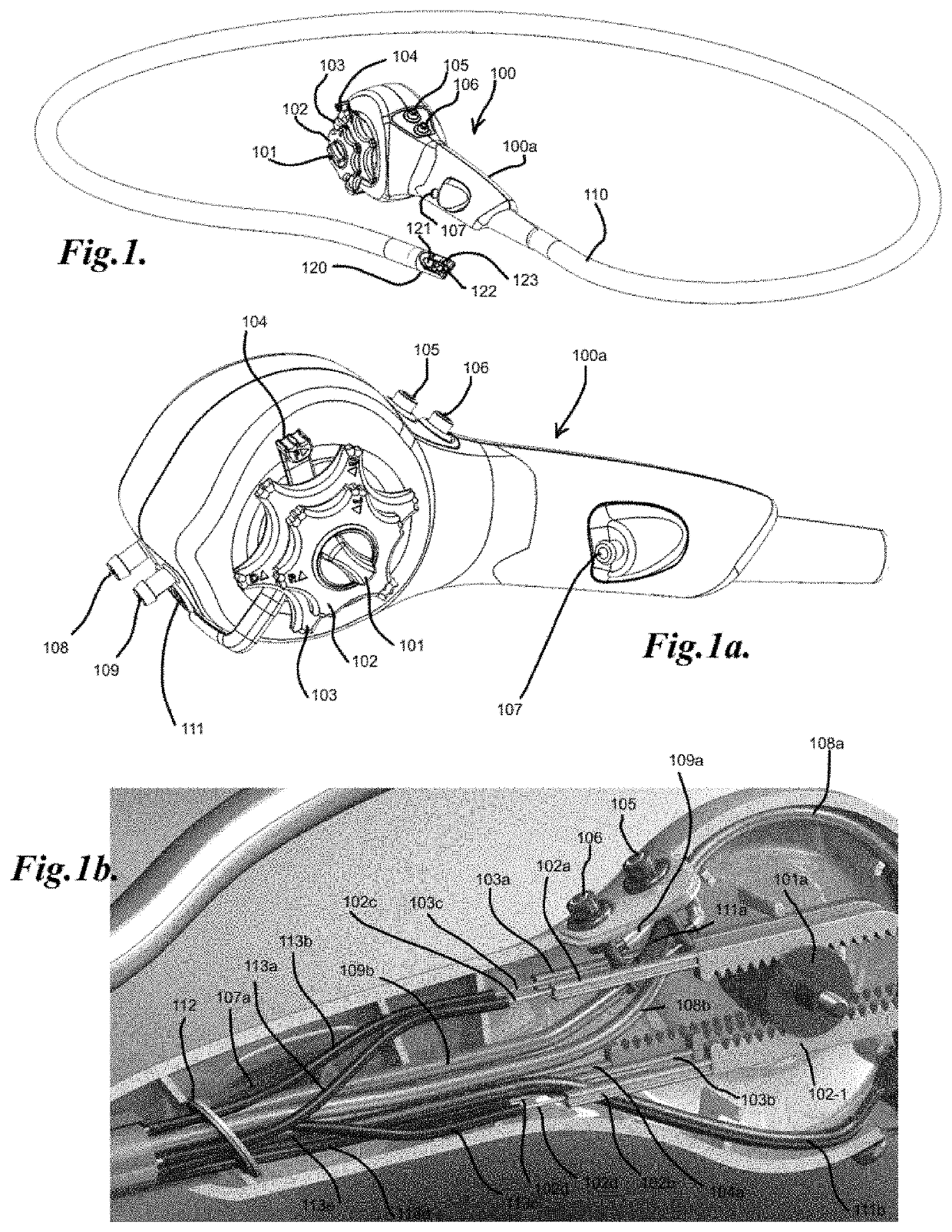
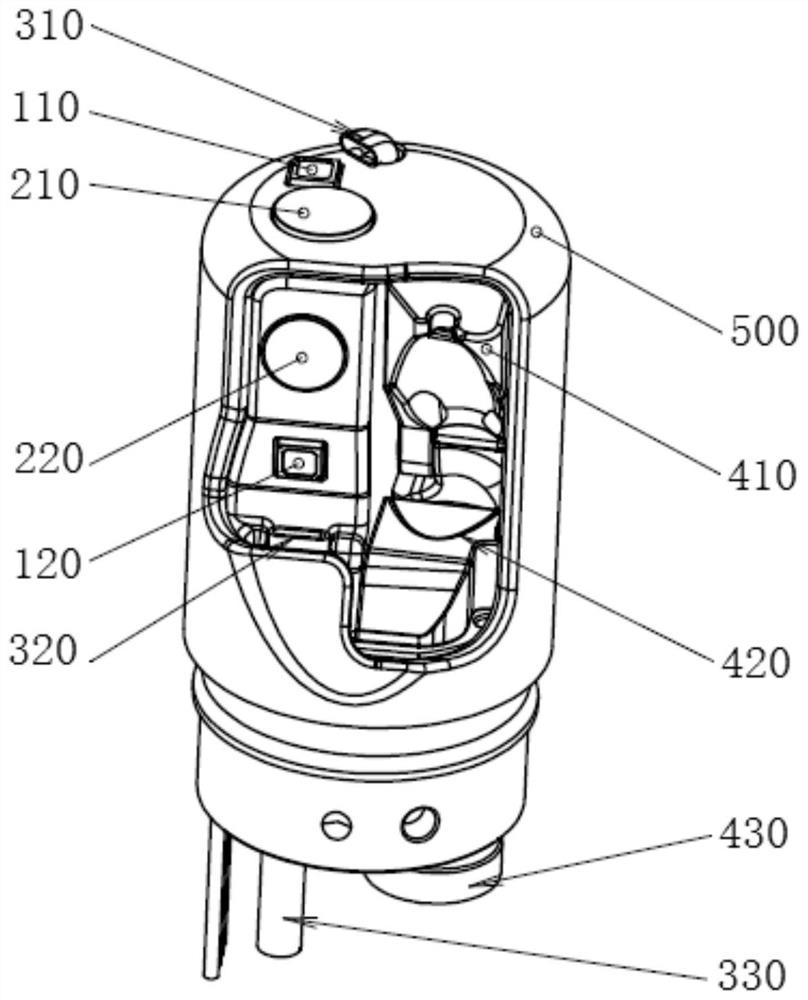
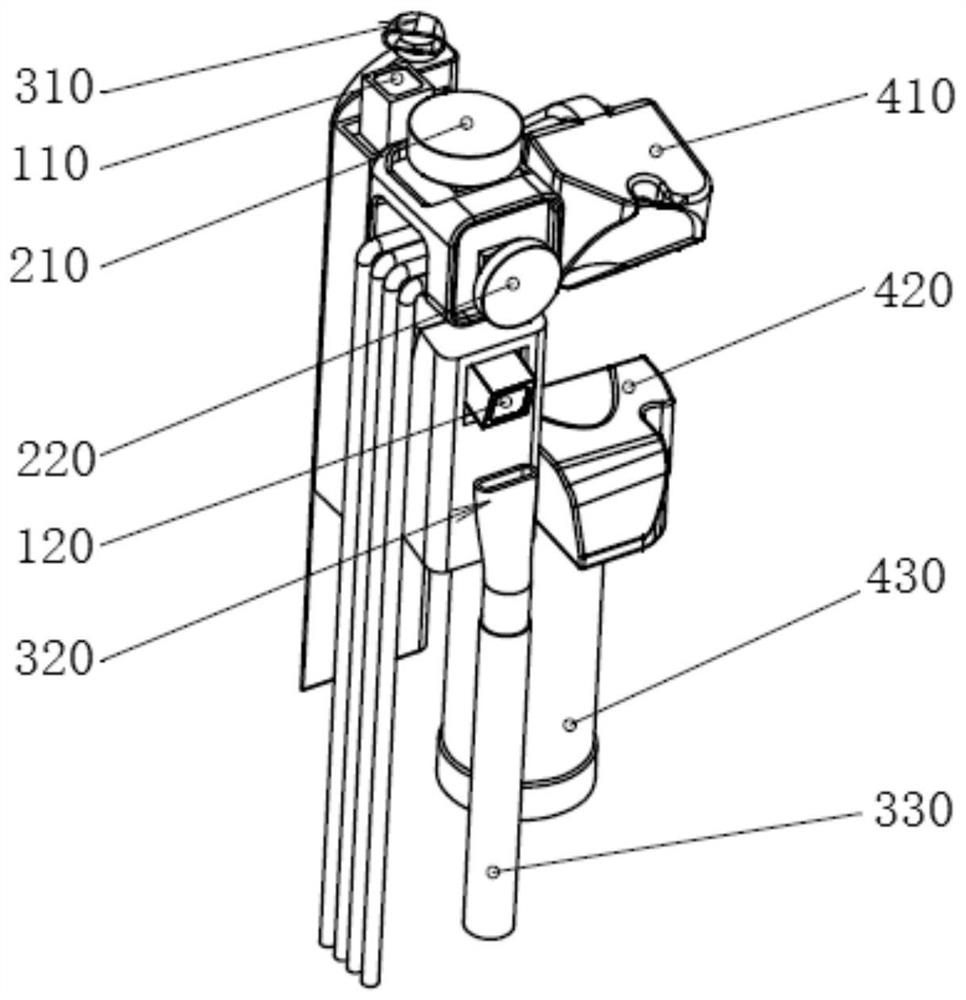
Devices and methods for internal imaging
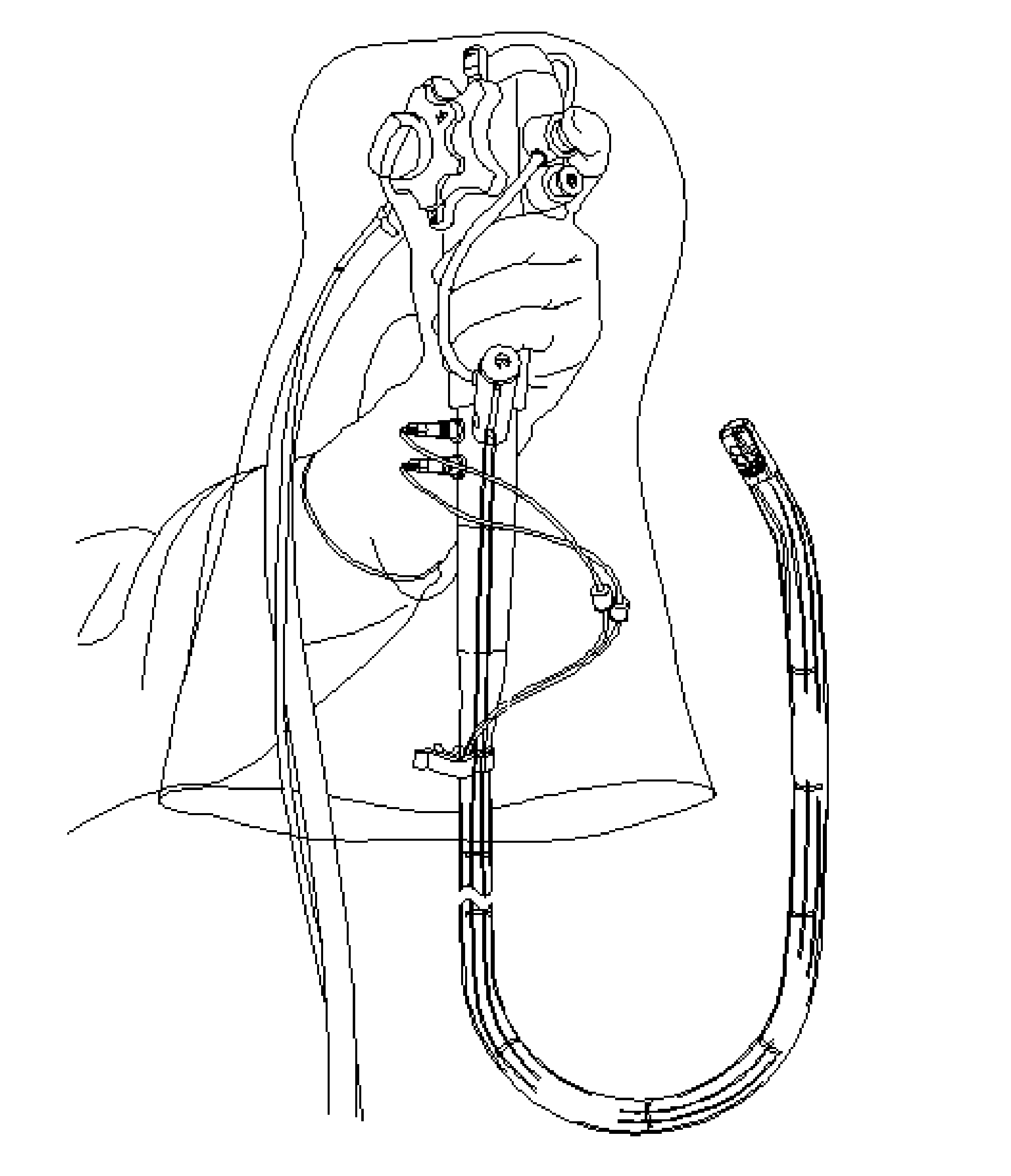
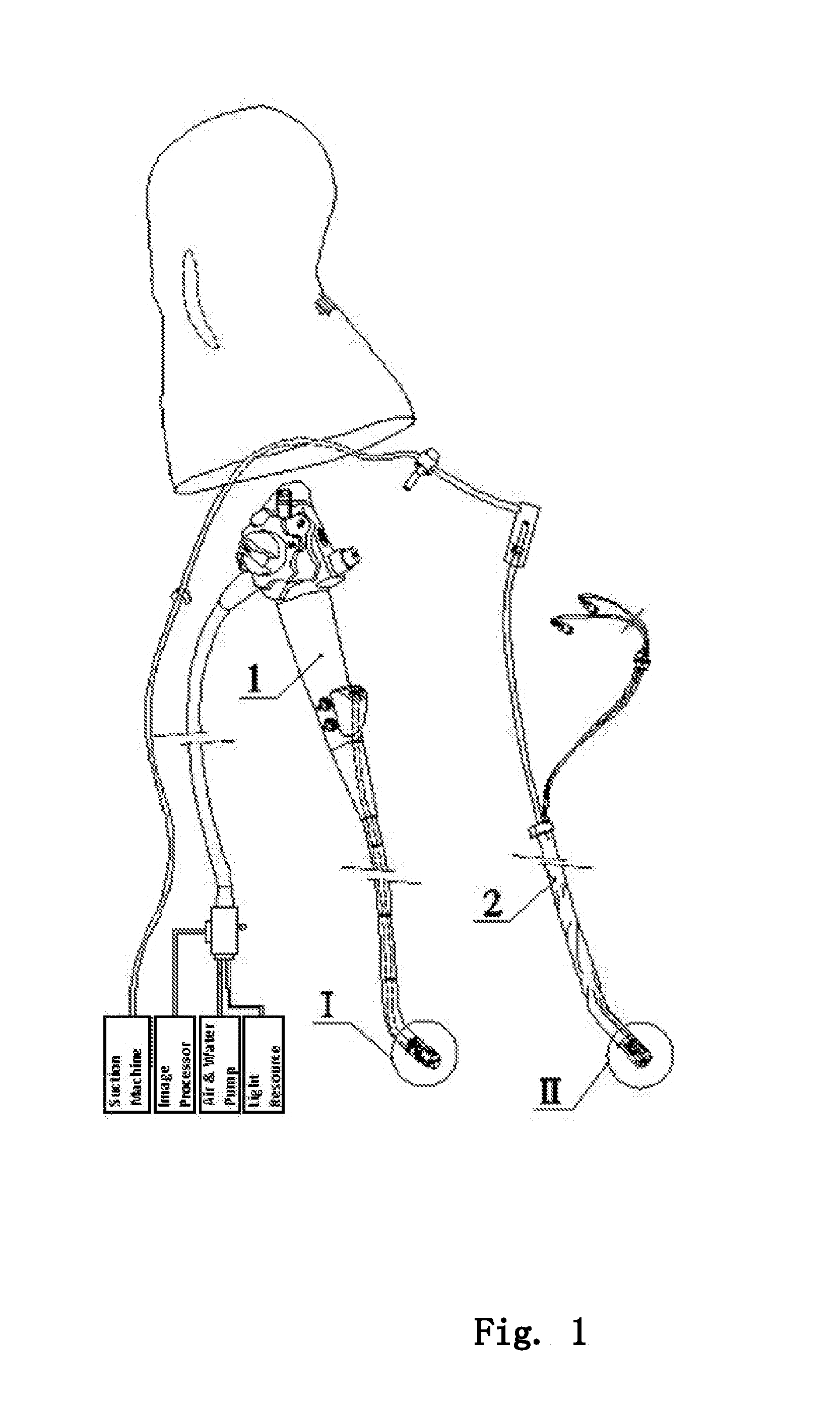
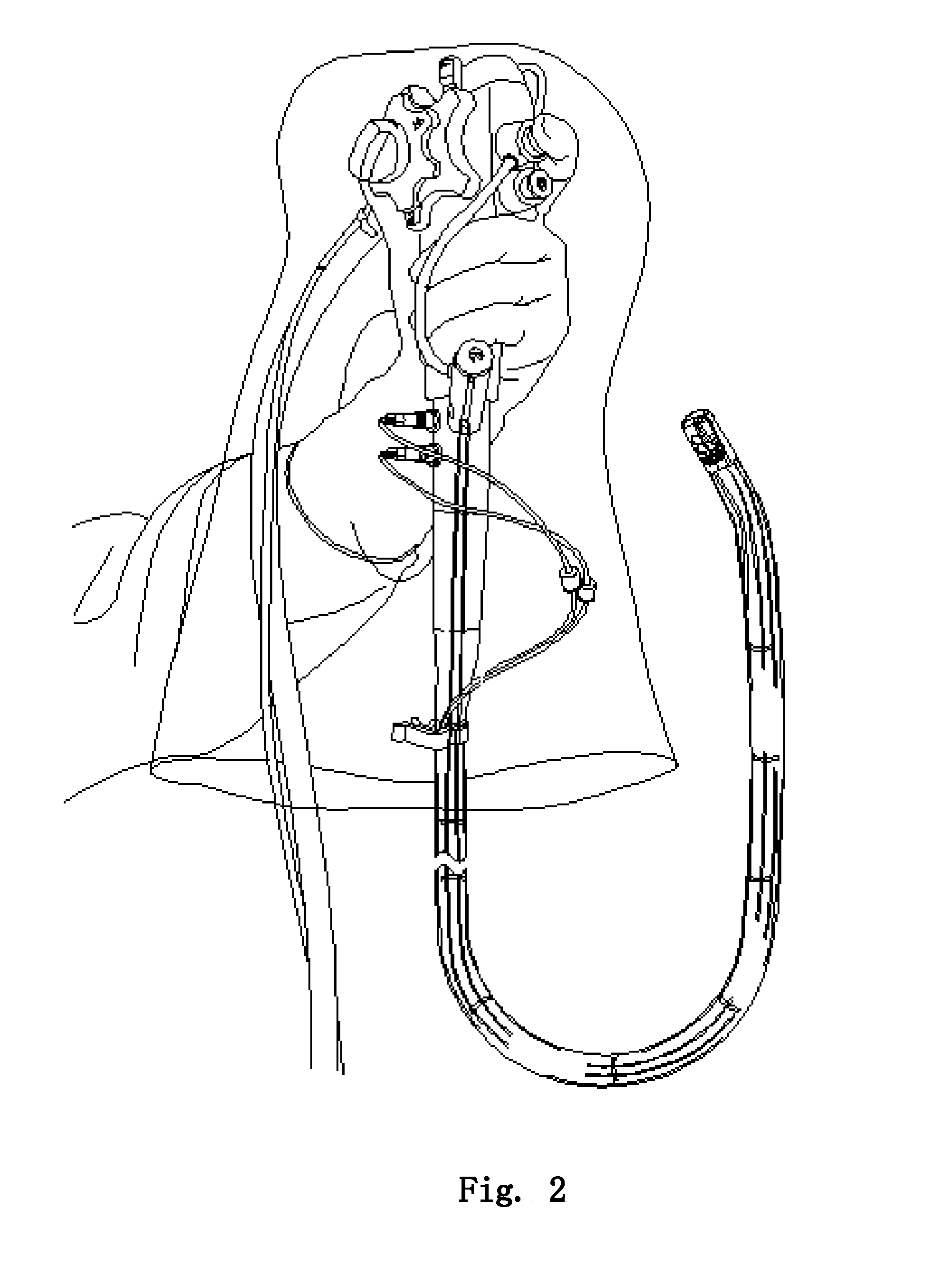
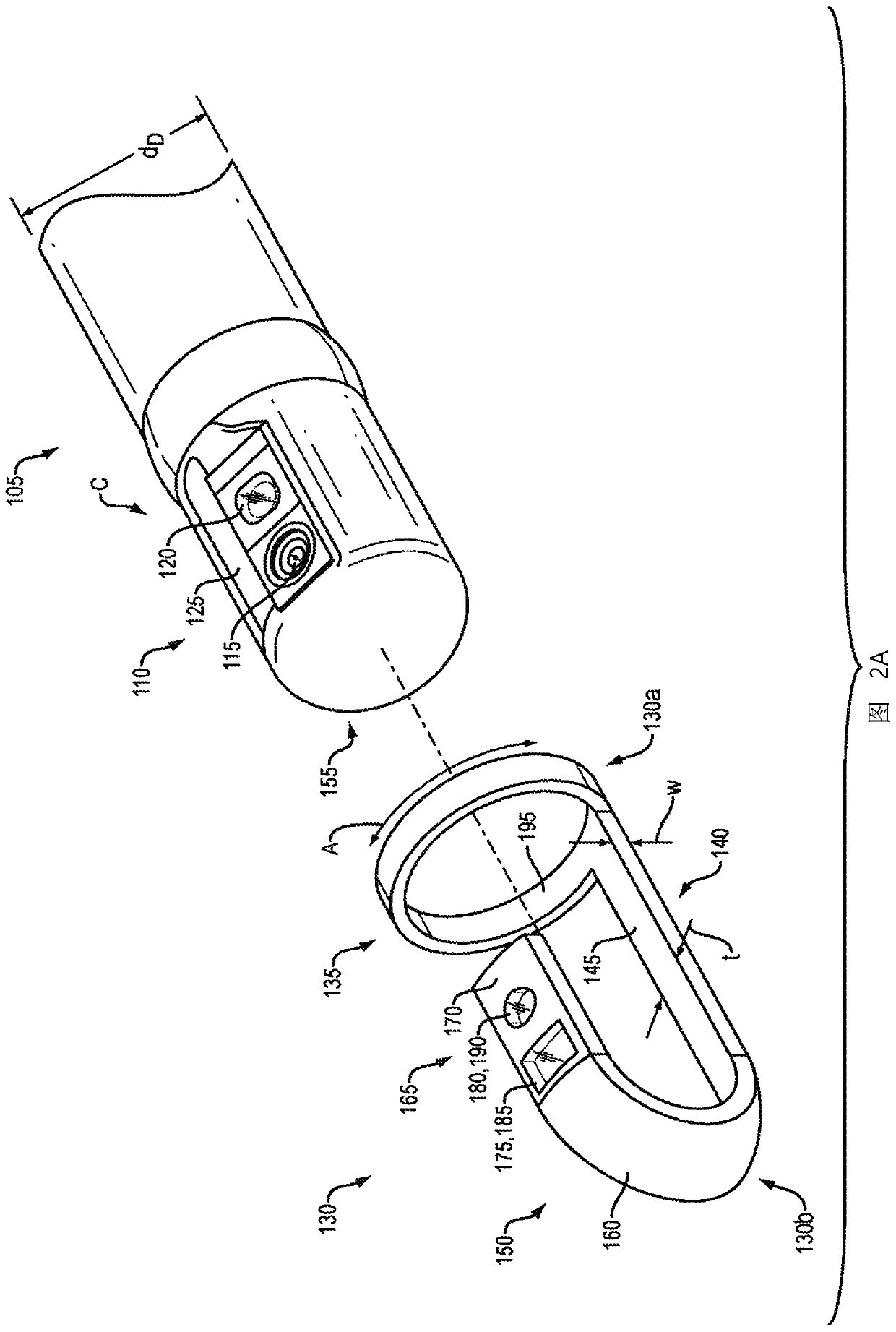
The invention relates to devices and methods for visualizing and / or interacting with internal body tissues. More particularly, the present invention relates to endoscopic methods and devices for visualizing and / or interacting with the gastrointestinal and / or pancreaticobiliary systems, such as with one use or disposable devices, such as with duodenoscopes. A device for visualizing and / or interacting with internal body tissues may generally include a handpiece, a distal assembly, and / or a connecting conduit. A plurality of conduits and / or channels may span through the connecting conduit from the handpiece to the distal assembly, and may, for example, carry fluid / gas connections, electrical / sensor connections, such as for a camera, mechanical connections and / or carry medical devices througha working channel. The device may also reduce the needs associated with reusable devices such as for reducing risks associated with improper sterilization.
Owner:SAFEVIEW MEDICAL LLC
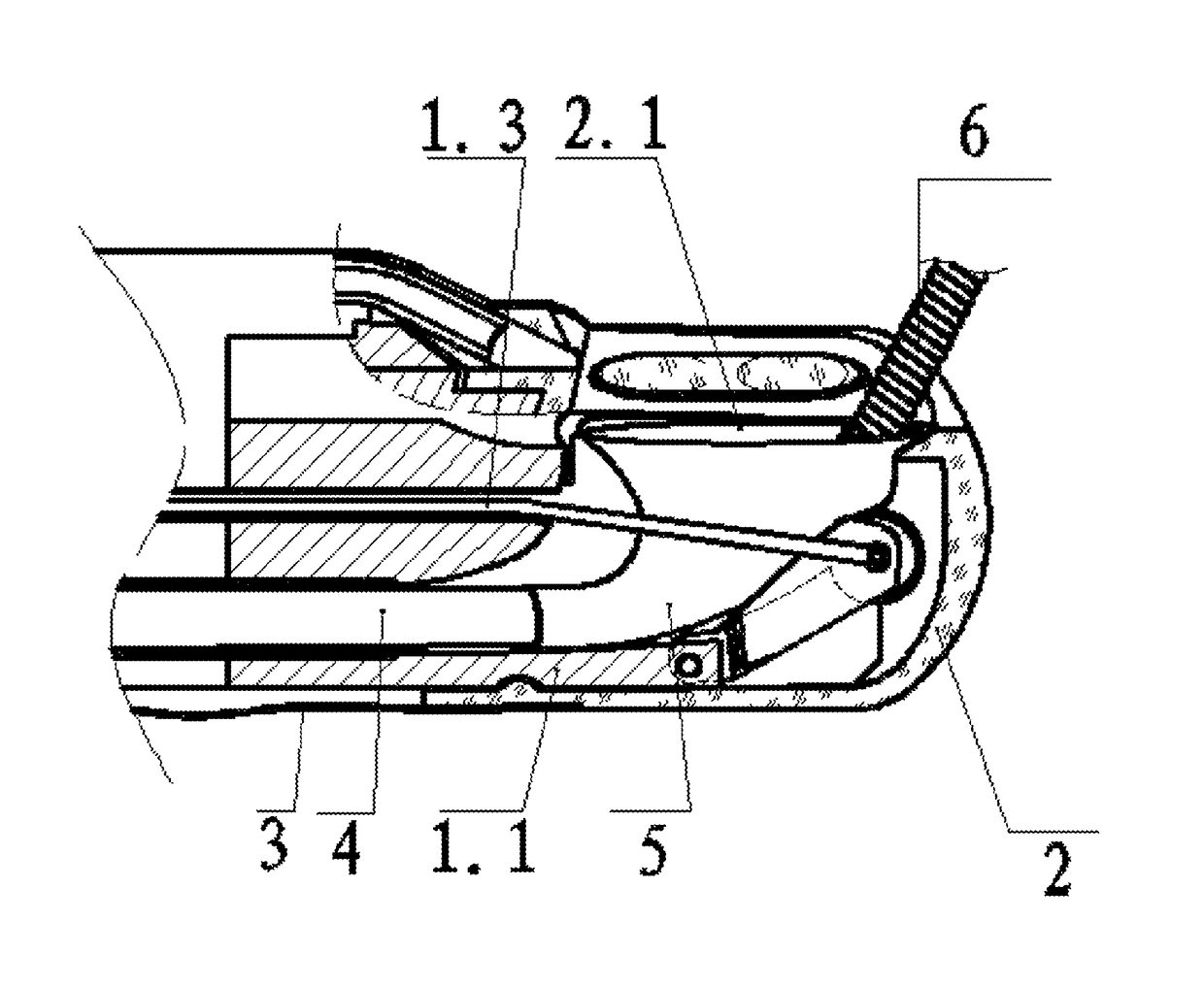
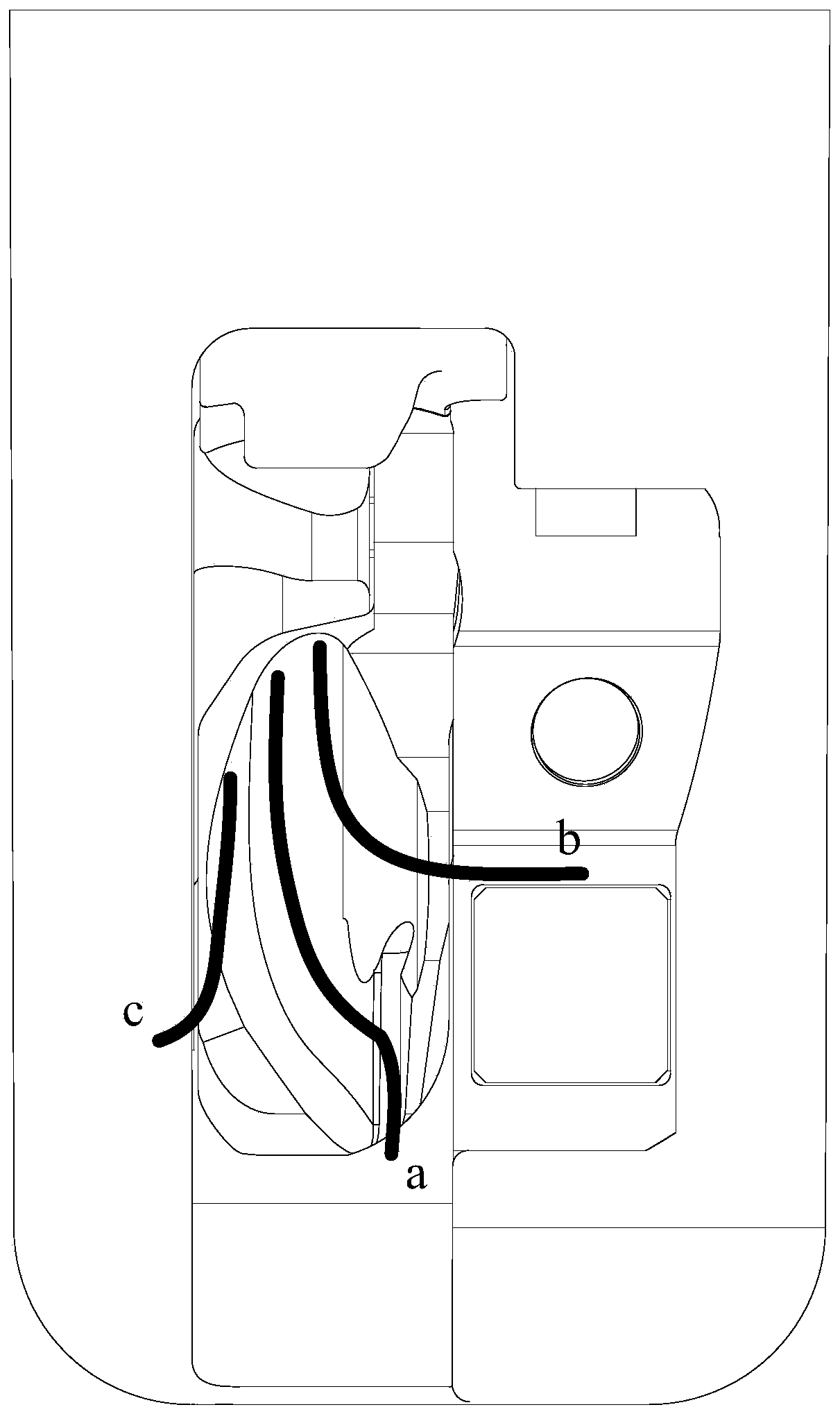
Duodenoscope Protected With Disposable Consumables
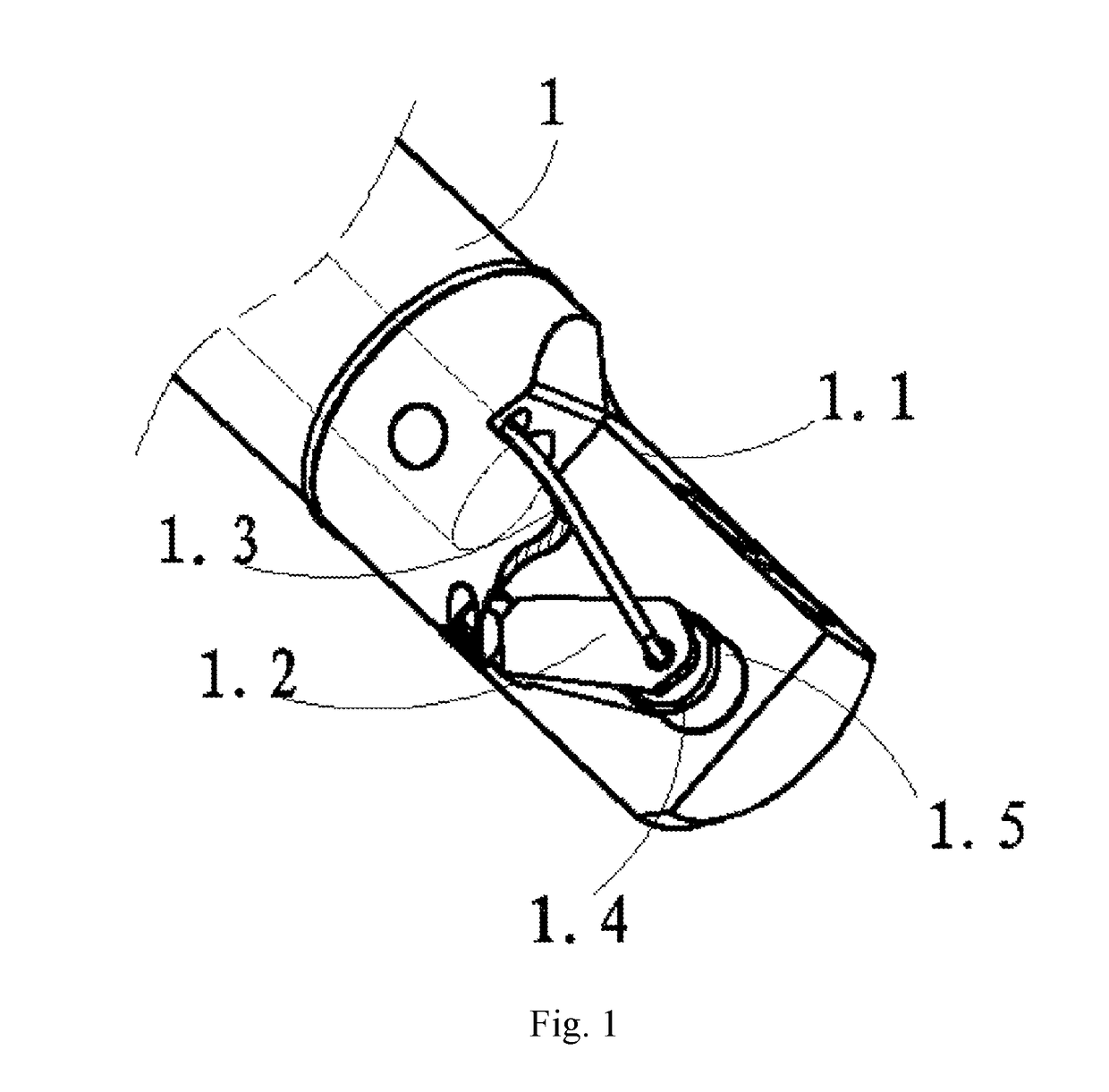
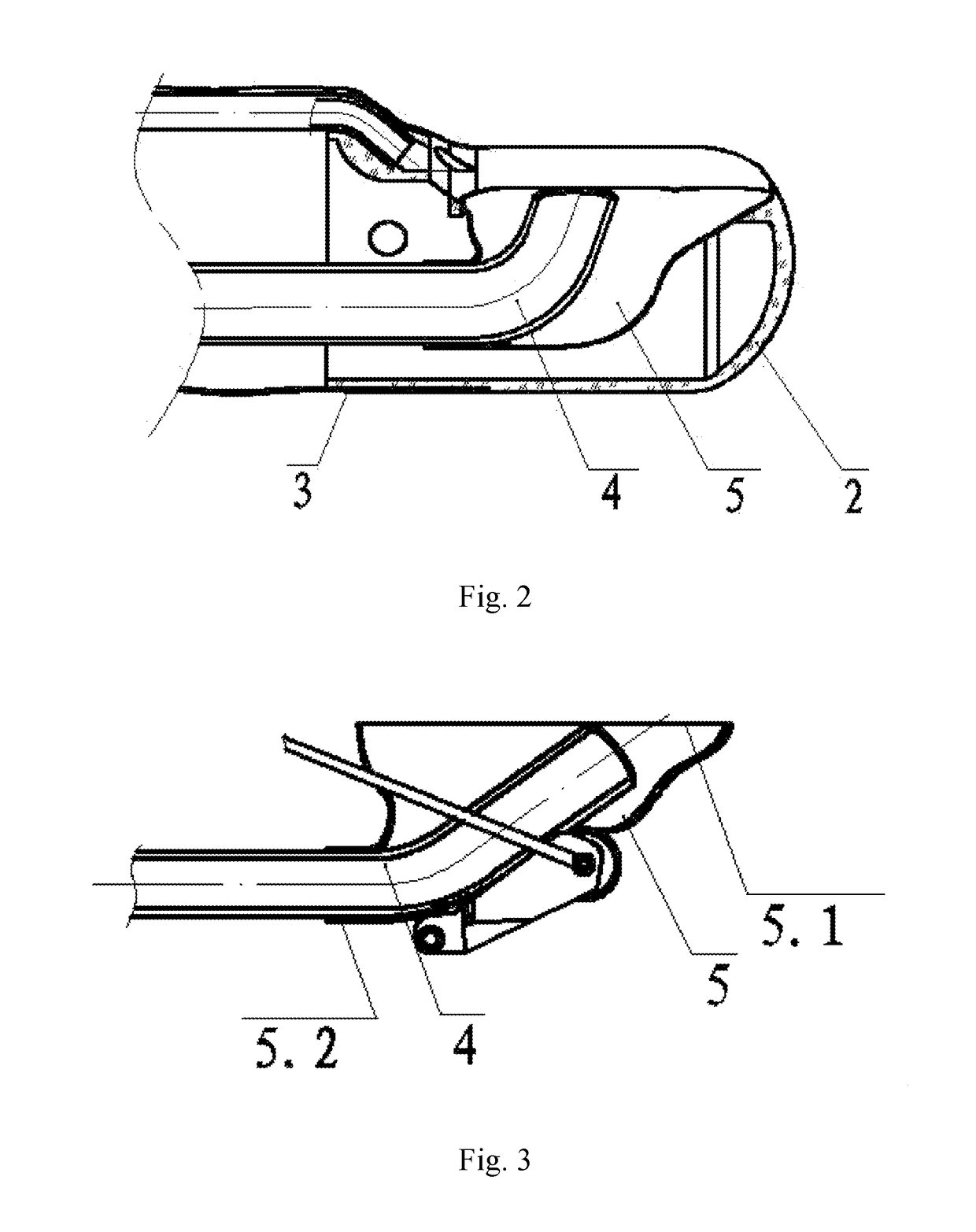
ActiveUS20170325666A1Reduce kinetic frictionAvoid cross infectionGastroscopesOesophagoscopesForcepsThin membrane
A duodenoscope protected with disposable consumables is provided. An insertion portion of a duodenoscope body (1) is covered with a cuff (3). A disposable forceps passage tube (4) is inserted into a tube of the duodenoscope body (1). A distal end of the duodenoscope body (1) is covered with an end cap (2) which is integrally connected to the cuff (3) and the disposable forceps passage tube (4). An elongated opening (2.1), which is of the same shape as the opening of a head end (1.1) of the duodenoscope body (1), is formed in a side face of the end cap (2). A forceps-lifting unit (1.2) is disposed in the head end (1.1) of the duodenoscope body (1). The end cap (2) is made of a transparent elastic material. A soft connection port (5) is disposed in the elongated opening (2.1) of the end cap (2). The soft connection port (5) is shaped like a smoking pipe and made of an elastic film. A large-orifice end of the soft connection port (5) is glued to the elongated opening (2.1) of the end cap (2), while a small-orifice end (5.2) thereof sleeves and is glued to a distal end of the disposable forceps passage tube (4). A pulley (1.4) is disposed on the head of the forceps-lifting unit (1.2), and a groove (1.5) is formed in the periphery of the pulley (1.4). The duodenoscope protected with disposable consumables can protect both the external surface of the duodenoscope and the internal surface of the tube.
Owner:SHENYANG SHENDA ENDOSCOPE
Hands-free mechanical manipulation of duodenoscope elevator during cleaning
ActiveUS20200100665A1Reduce labor intensiveReduce time-consumingToothed gearingsEndoscopesForcepsActuator
An endoscope cleansing accessory is described for use with an automatic endoscope reprocessing (AER) apparatus which utilizes the motive force provided by a flowing cleansing fluid already within the AER to actuate an actuator wheel of the endoscope during the cleansing process. The movement or actuation of the actuator wheel during cleansing in turn imparts a back and forth motion to an elevator platform or forceps raiser within the endoscope to loosen tissue and other particles that are then flushed out by the flowing cleansing fluid.
Owner:MEDIVATORS INC
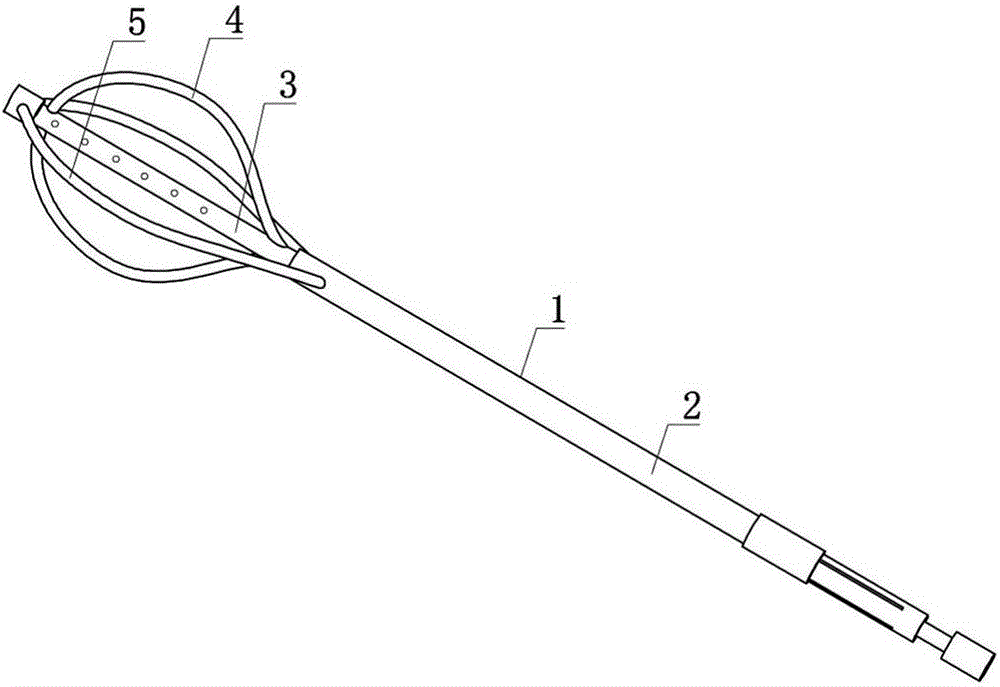
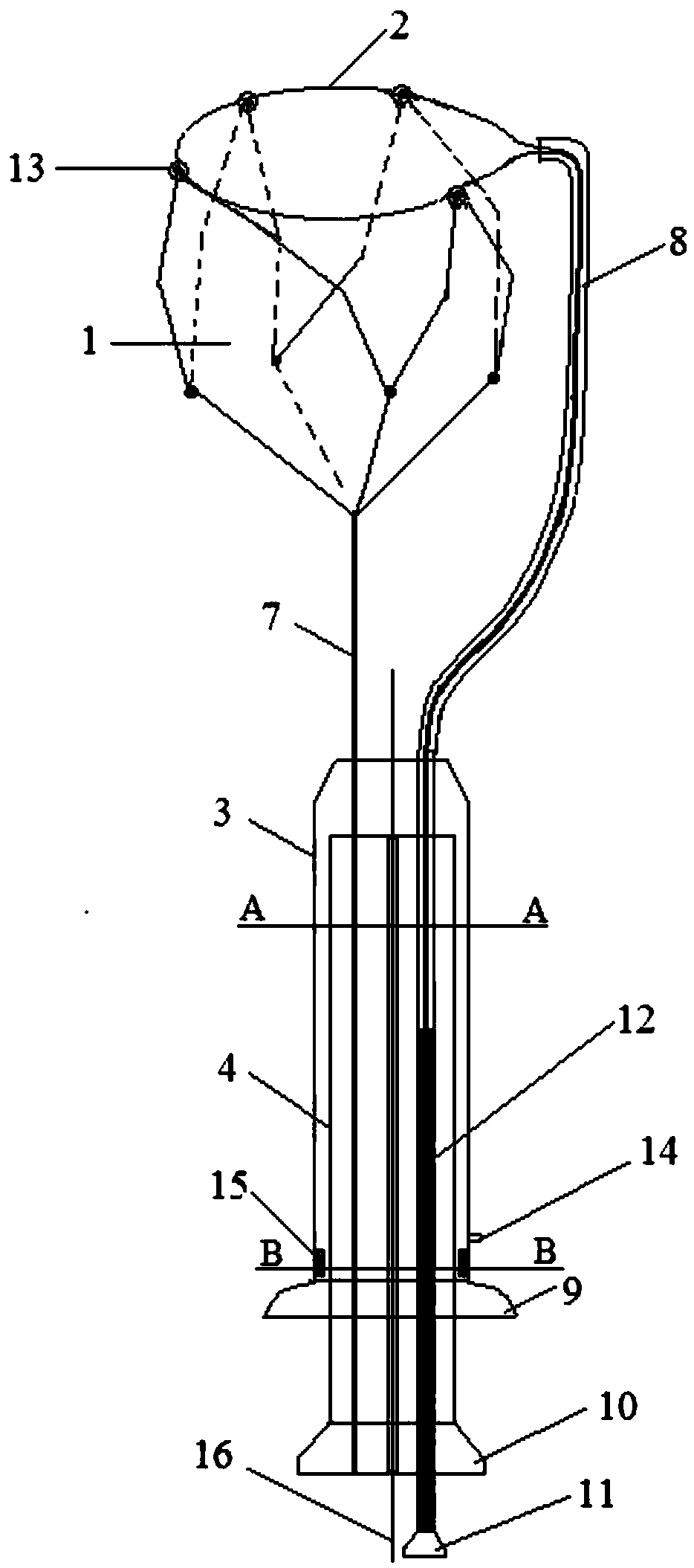
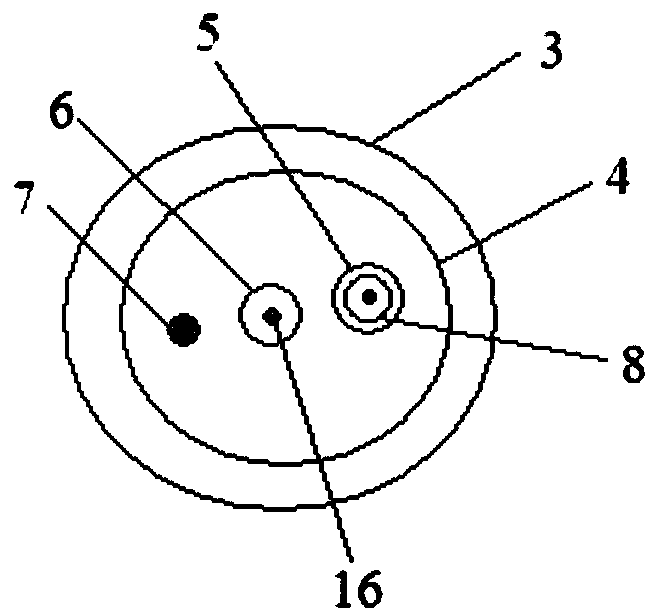
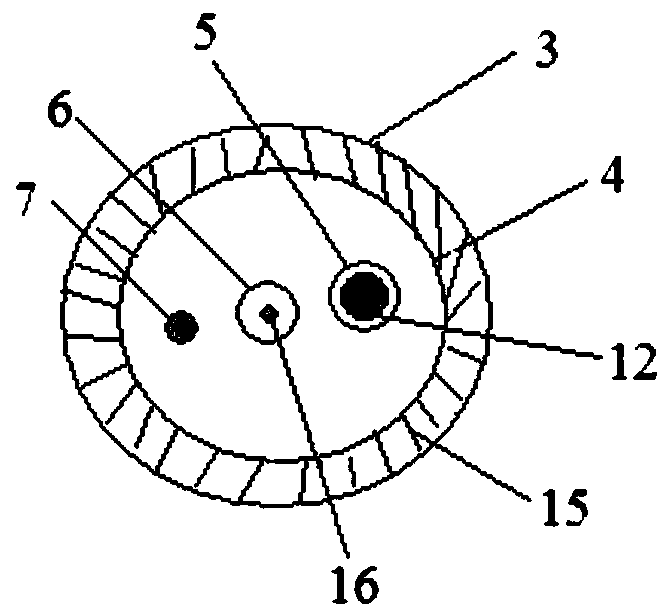
Cup-shaped calculus removal mesh basket
The invention relates to the technical field of medical apparatuses, and in particular to a cup-shaped calculus removal mesh basket. The device (the mesh basket) comprises a cup-shaped mesh basket body, a loop, an outer sleeve and an inner core pipe, wherein the inner core pipe covers a metal connecting rod of the cup-shaped mesh basket body; the inner core pipe, which is applied to a duodenoscope, is a dual-lumen tube which comprises a tube lumen I and a tube lumen II; a connecting rod of the loop passes through the interior of the tube lumen I, and a zebra lead passes through the interior ofthe tube lumen II; the inner core tube, which is applied to a choledochoscope, is a single-lumen tube which comprises a tube lumen I, and the connecting rod of the loop passes through the interior ofthe tube lumen I; the head end of the connecting rod is represented in an inverted L-shaped form; and the loop, which is represented in an O-shaped form, is connected to an opening of the cup-shapedmesh basket. The mesh basket provided by the invention can be widely popularized in such fields as endoscopic therapy of gall stones and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Duodenoscope
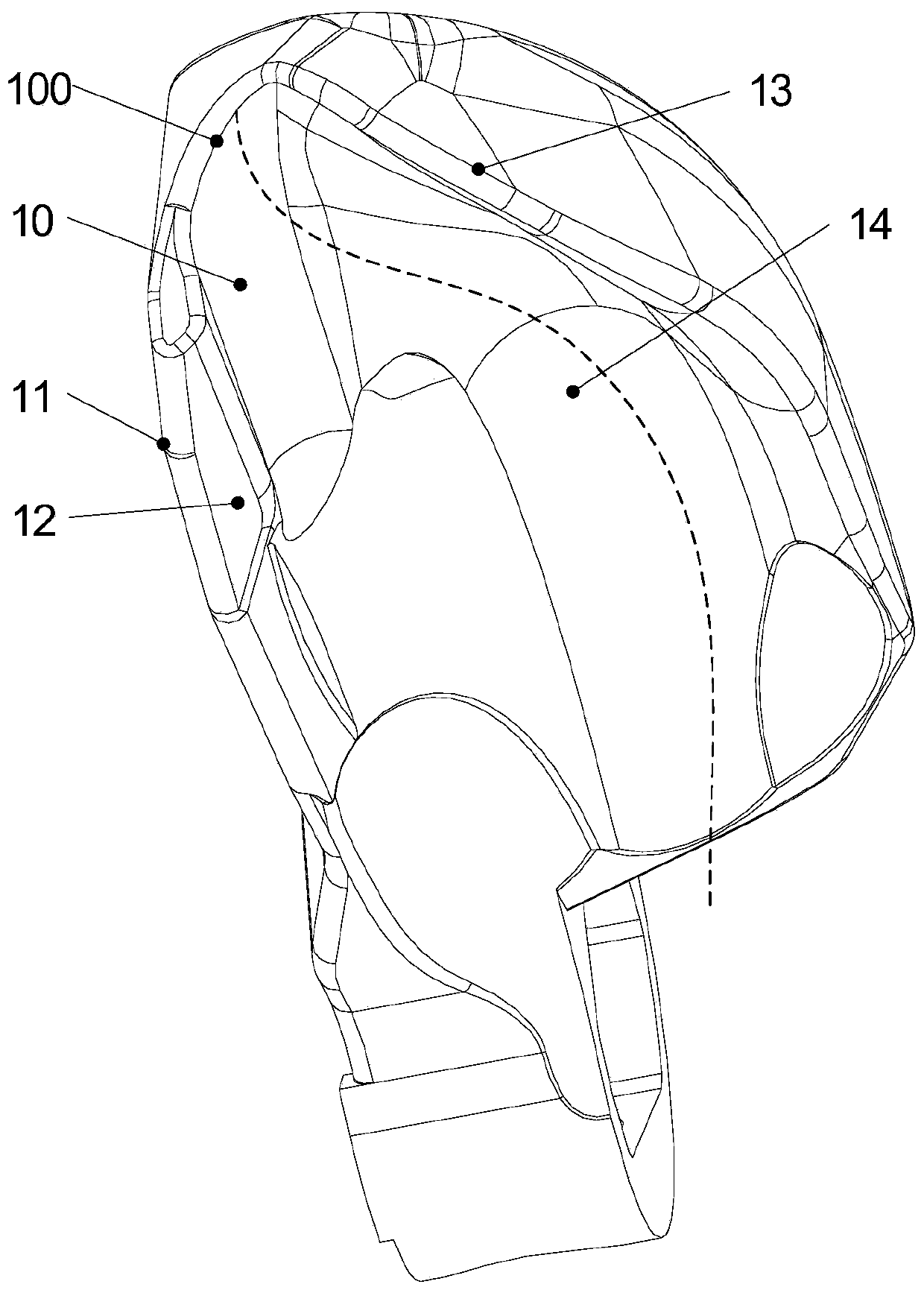
InactiveCN105433898AUnreliable solution to disinfectionImprove securityEndoscopesLaproscopesMicroorganismForceps
The invention discloses duodenoscope and belongs to the field of medical instruments. An observation system, a lighting system and an operation pipe opening are arranged on the side face of the head end of an insertion portion. A forceps lifter is arranged in the pipe opening and is in sliding connection with a steel wire rope in the axial direction. A gap between the steel wire rope and a pore matched with the steel wire rope is sealed through a rubber bellows. One end of the rubber bellows is bonded to the outside of the steel wire rope, and the other end of the rubber bellows is bonded to the inner wall of the pore matched with the steel wire rope. A fine monofilament is welded to the front end of the steel wire rope and connected with the forceps lifter. By means of the structure of the duodenoscope, the problem of unreliability of sterilization of duodenoscope caused by the fact that pollutants and microorganisms are brought into the duodenoscope in the traction process as a result of the axial gap between the steel wire rope and the pore is solved thoroughly, and huge security assurance is brought to doctors and patients.
Owner:SHENYANG SHENDA ENDOSCOPE +1
Devices and methods for internal imaging
InactiveUS20200015670A1Reduce contaminationReduce incidenceGastroscopesOesophagoscopesSingle-Use DeviceEngineering
The invention relates to devices and methods for visualizing and / or interacting with internal body tissues. More particularly, the present invention relates to endoscopic methods and devices for visualizing and / or interacting with the gastrointestinal and / or pancreaticobiliary systems, such as with one use or disposable devices, such as with duodenoscopes. A device for visualizing and / or interacting with internal body tissues may generally include a handpiece, a distal assembly, and / or a connecting conduit. A plurality of conduits and / or channels may span through the connecting conduit from the handpiece to the distal assembly, and may, for example, carry fluid / gas connections, electrical / sensor connections, such as for a camera, mechanical connections and / or carry medical devices through a working channel. The device may also reduce the needs associated with reusable devices such as for reducing risks associated with improper sterilization.
Owner:SAFEVIEW MEDICAL LLC
Duodenoscope
PendingCN113288032AImprove observabilityImprove work performanceGastroscopesOesophagoscopesOphthalmologyEngineering
The duodenoscope comprises a lens device, a lighting system, a water and gas spraying device, an operating mechanism and a control device, the lens device comprises a first lens and a second lens, and the first lens and the second lens are arranged at the top end and the first side face of the duodenoscope end respectively. The lighting system, the water and gas spraying device and the lens device are correspondingly arranged in a matched mode and integrated into an integral structure, and the integral structure and the operating mechanism are arranged on the second side face and the third side face of the duodenoscope end respectively and wrapped by a shell with a lateral opening. The control mechanism is in control connection with the lens device, the lighting system, the water and gas spraying device and the operation mechanism. According to the scheme, the forward lens is additionally arranged on the basis of the lateral lens of an existing duodenoscope, the core difficulty of realizing a multi-view-field endoscope structure is solved through optimized arrangement and integration of the structure, and the working performance of the duodenoscope is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AOHUA PHOTOELECTRICITY ENDOSCOPE
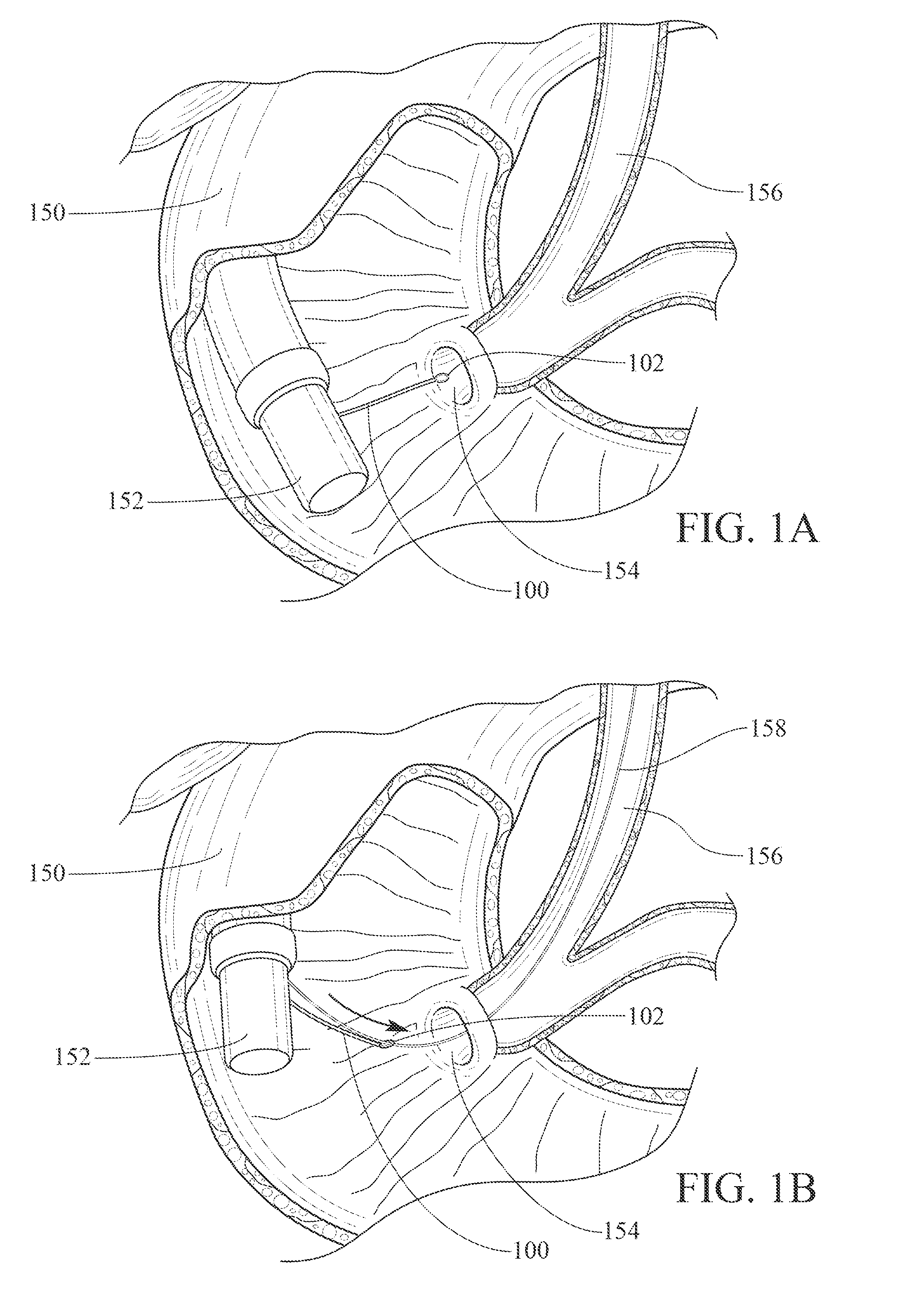
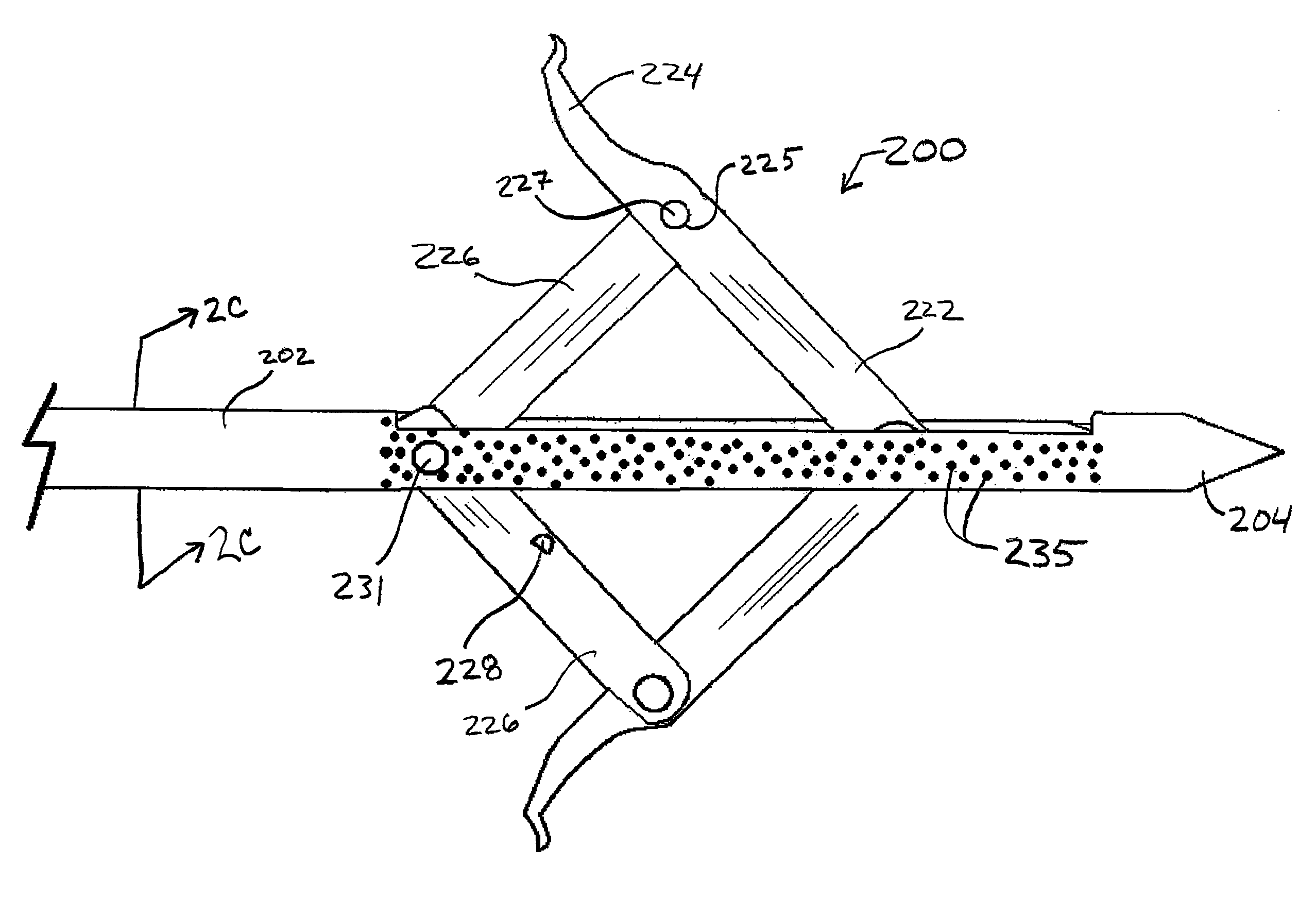
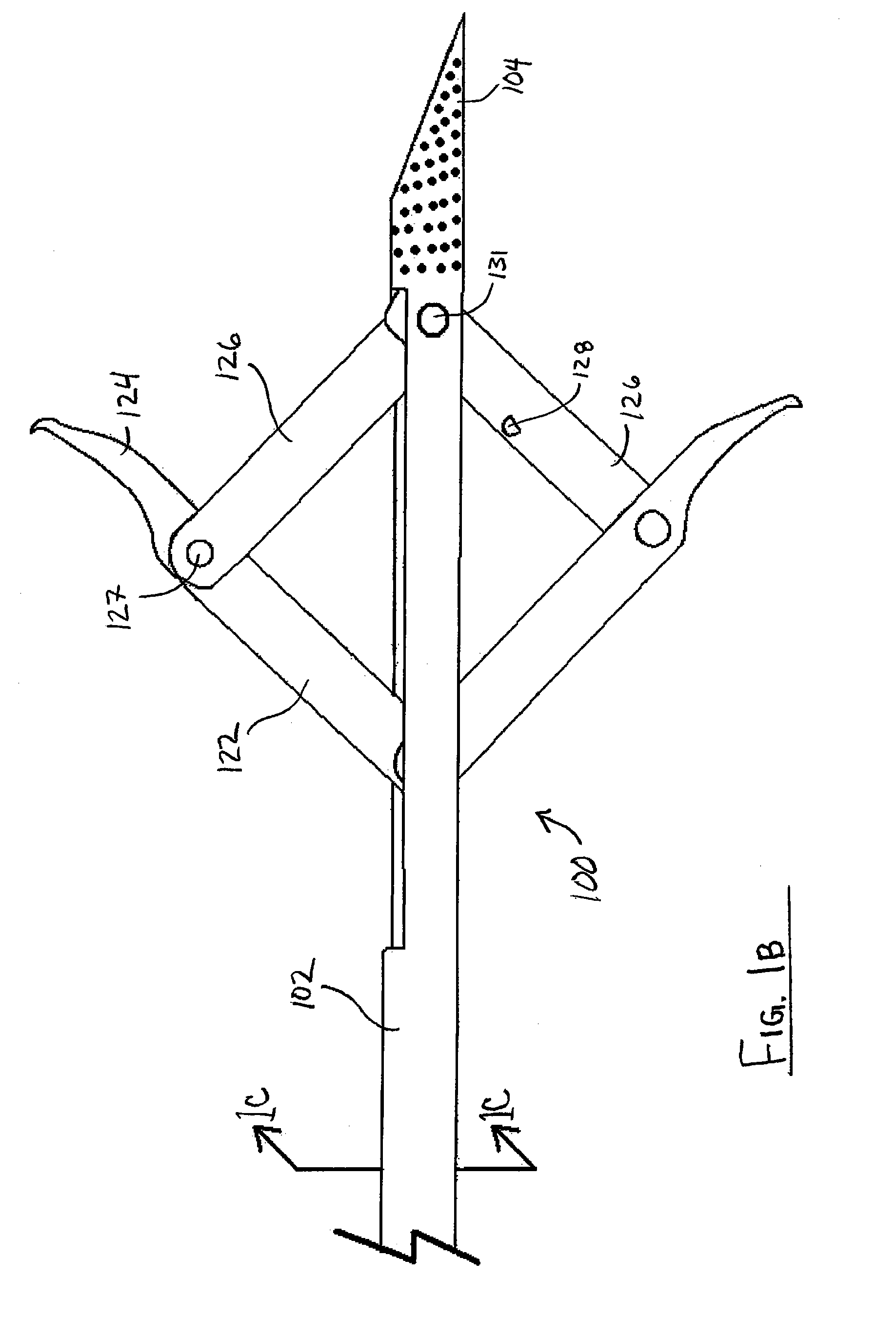
Medical anchor device
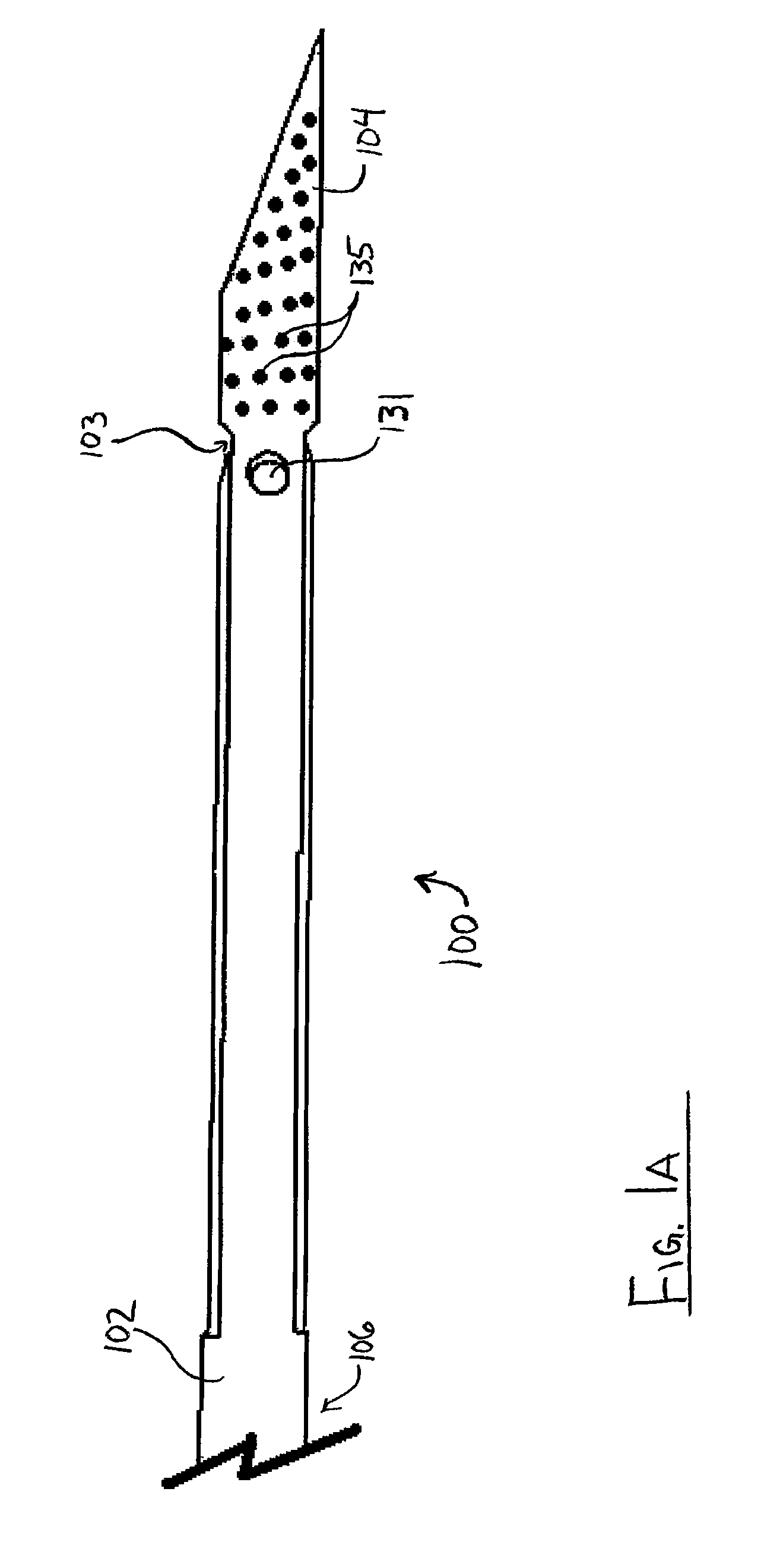
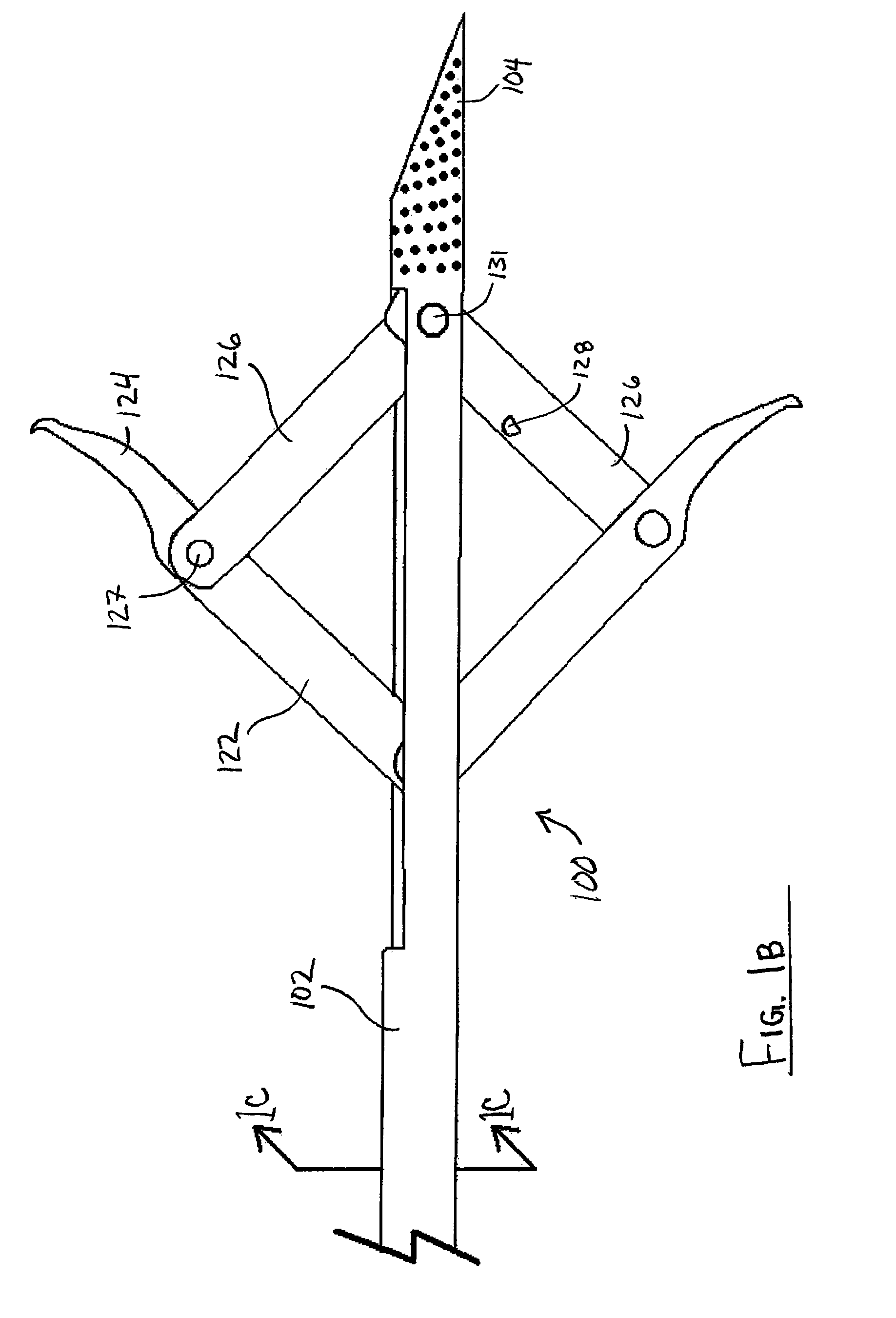
ActiveUS20110251642A1Avoid insufficient lengthSolve the lack of flexibilitySuture equipmentsEndoscopesFlexible endoscopeDistal portion
An endoscopically-deployable tissue-manipulation device including an elongate, generally tubular outer body having a proximal portion and a distal end portion that may be configured as sufficiently flexible to traverse the working channel of a flexible endoscope (e.g., side-viewing duodenoscope). The outer body may include an outer body lumen extending longitudinally between the proximal and distal portions. An anchoring structure of the device will include an elongate inner body that may extend through the outer body lumen and be configured to include a first linkage member attached to the inner body, a second linkage member that is pivotably attached to the first linkage member and to the outer body.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
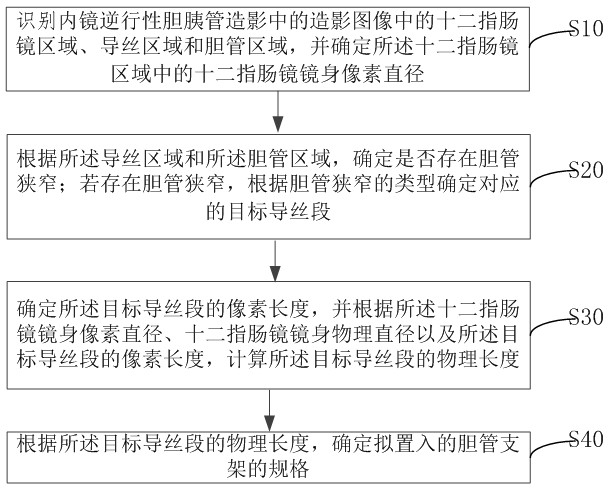
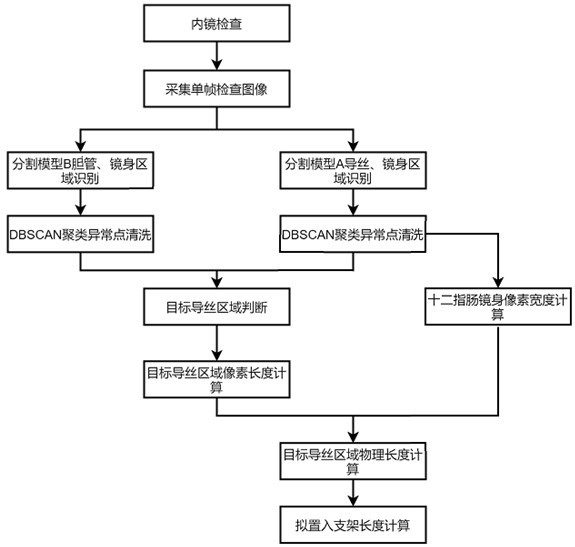
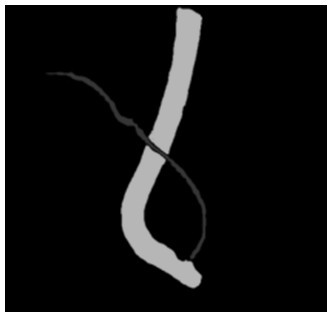
Bile duct stent specification selection method and device
ActiveCN114612475AReduce Radiation DamageImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisGuide wiresImage processing
The invention relates to the technical field of endoscopic image processing, in particular to a bile duct stent specification selection method and device.The method comprises the steps that a duodenoscope area, a guide wire area and a bile duct area in an angiography image in endoscopic retrograde bile duct angiography are recognized, and the duodenoscope body pixel diameter in the duodenoscope area is determined; according to the guide wire area and the bile duct area, whether bile duct stenosis exists or not is determined; if the bile duct stenosis exists, determining a corresponding target guide wire section according to the type of the bile duct stenosis; determining the pixel length of the target guide wire section, and calculating the physical length of the target guide wire section according to the pixel diameter of the body of the duodenoscope, the physical diameter of the body of the duodenoscope and the pixel length of the target guide wire section; according to the physical length of the target guide wire section, the specification of the bile duct stent to be implanted is determined. According to the invention, the accuracy of specification selection of the bile duct stent is improved, and the time of exposure of medical staff and patients to electromagnetic radiation in the ERCP operation process is shortened.
Owner:青岛美迪康数字工程有限公司 +1
Three-dimensional electronic duodenoscope system and use method thereof
ActiveCN102058383AImage based on goodReasonable and effective treatment planGastroscopesOesophagoscopesComputer moduleData transmission
The invention belongs to medical instruments, and relates to a three-dimensional electronic duodenoscope system for reconstructing a three-dimensional image by using a multi-CCD (Charge Coupled Device) array, which comprises a soft electronic duodenoscope. The soft electronic duodenoscope comprises a soft working end part, wherein the soft working end part is provided with a multi-CCD array module used for three-dimensionally scanning and shooting and displaying a full-view three-dimensional image and reconstructing a three-dimensional image of the duodenum, and the multi-CCD array module comprises at least one first CCD array arranged at the front end face of the first end part of the soft working end part and at least one second CCD array arranged on the surface of the excircle of the first end part of the soft working end part. Image information in the duodenum is obtained, the data is transmitted to a processing host computer for centrally processing and reconstructing so that the three-dimensional environment in the duodenum is reproduced, and the three-dimensional image in the duodenum has valuable significance on formulating the most reasonable effective processing scheme for doctors to observe internal pathological changes of the duodenum in multi-angle manner and research the environment of the duodenum.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAODAN MEDICAL INSTR TECH
Fluorophore imaging devices, systems, and methods for an endoscopic procedure
Fluorescent imaging systems for performing an endoscopic procedure, such as a retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedure may include a first light source for emitting light in the visible spectrum, or light in the near infrared (NIR) spectrum, or both. A light source bandpass filter may block the emitted light in the visible spectrum, or in the NIR spectrum, or both. A first sensor may be capable of detecting the light in the visible spectrum, or the light in the NIR spectrum, or both. A sensor bandpass filter may block the detected light in the visible spectrum, or in the NIR spectrum, or both. The first or a second light source, or the first or a second sensor, or combinations thereof, may be removably disposed on a duodenoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
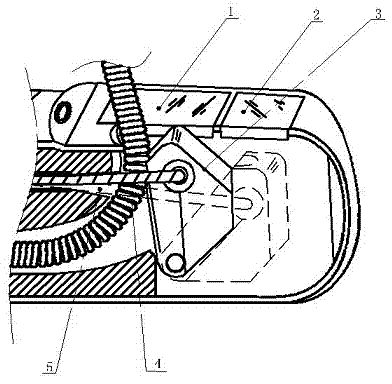
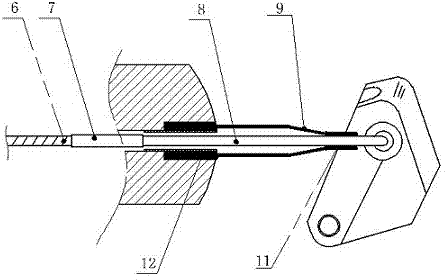
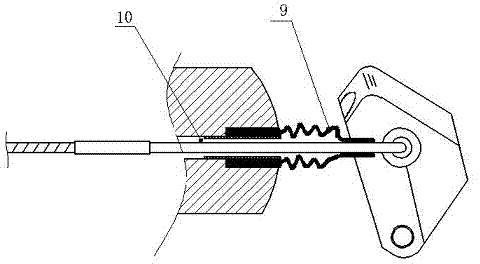
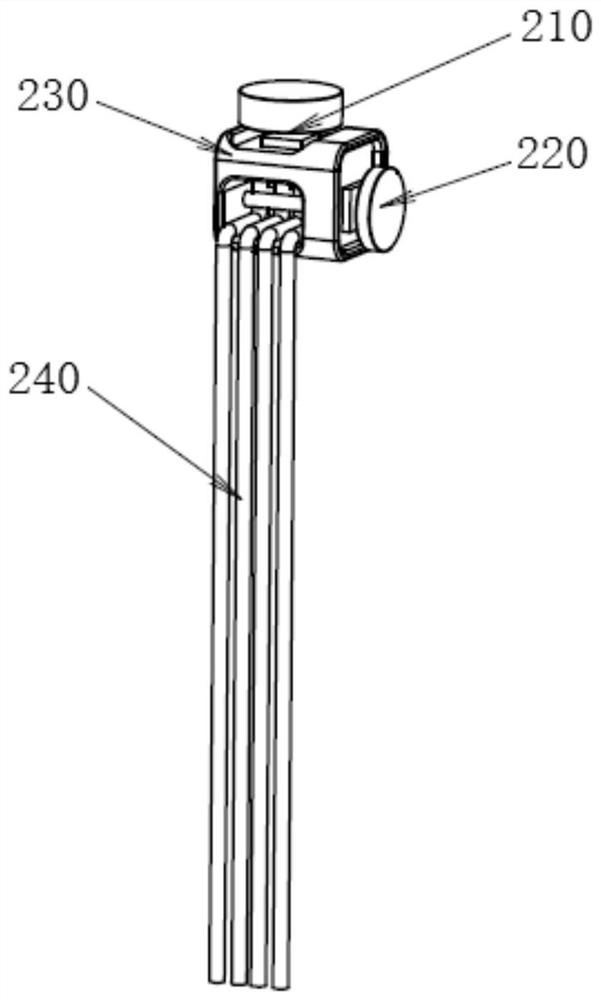
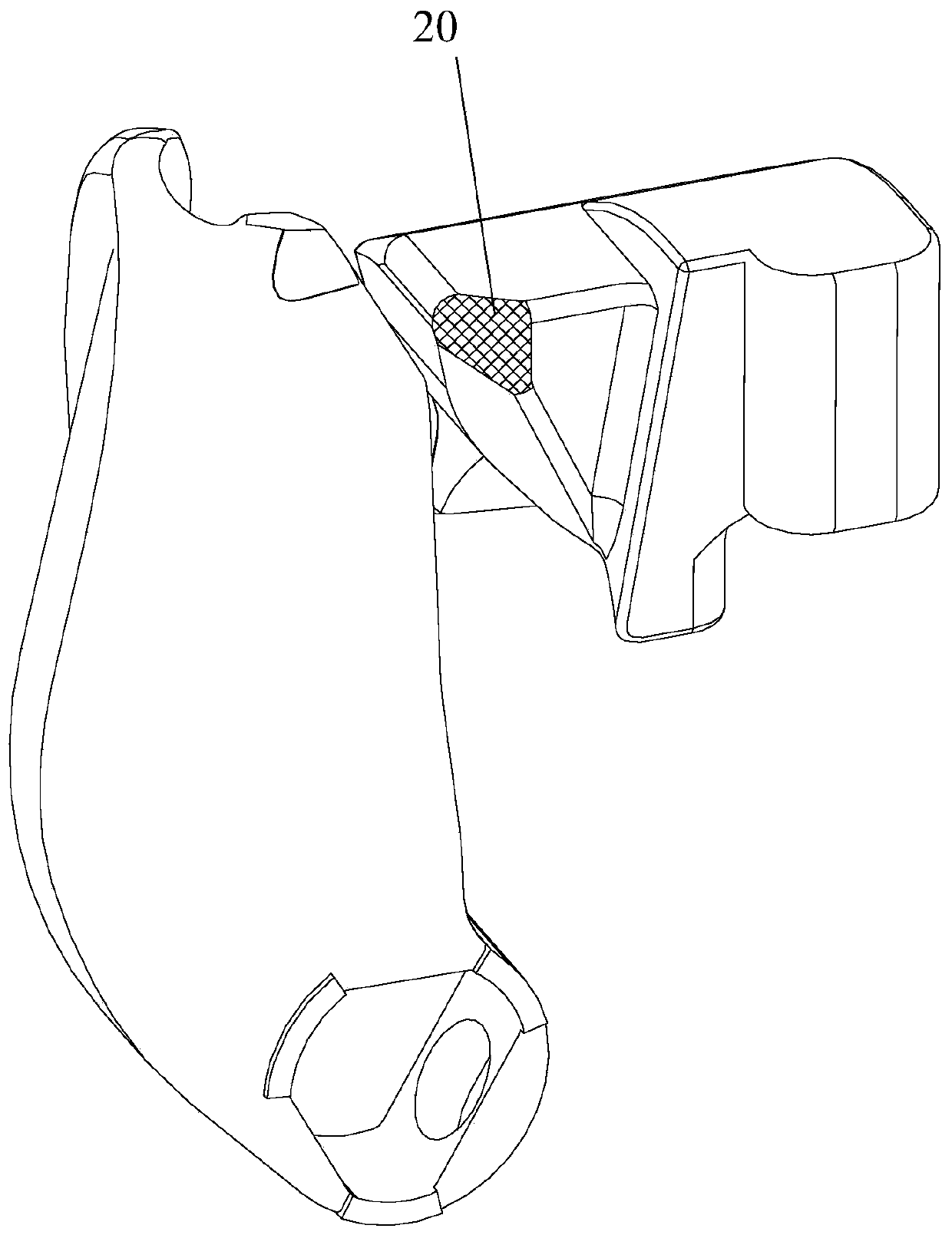
Endoscope forceps lifting device, endoscope head end and duodenoscope system
The invention discloses an endoscope forceps lifting device, an endoscope head end and a duodenoscope system. The bottom of the endoscope forceps lifting device is communicated with an instrument channel and is provided with a hinge part which is hinged to a endoscope head end seat; the top of the endoscope forceps lifting device is provided with a positioning groove matched with a positioned piece; and the side edge of the endoscope forceps lifting device is provided with a shearing edge and a guide surface, and the guide surface is positioned between the positioning groove and the shearing edge. In the lifting process of the endoscope forceps lifting device, the shearing edge can move close to the inner side surface of the head end seat so as to guide the positioned piece in the first deflection extending state to the guide surface, the guide surface can guide the positioned piece into the positioning groove, and the positioning groove can be matched with an abutting fixing piece toclamp and fix the positioned piece so as to achieve the purpose of preventing the positioned piece from coming out of papilla and moving into the papilla, and enabling the operation to go smoothly.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com