Patents
Literature
43 results about "Common Duct" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
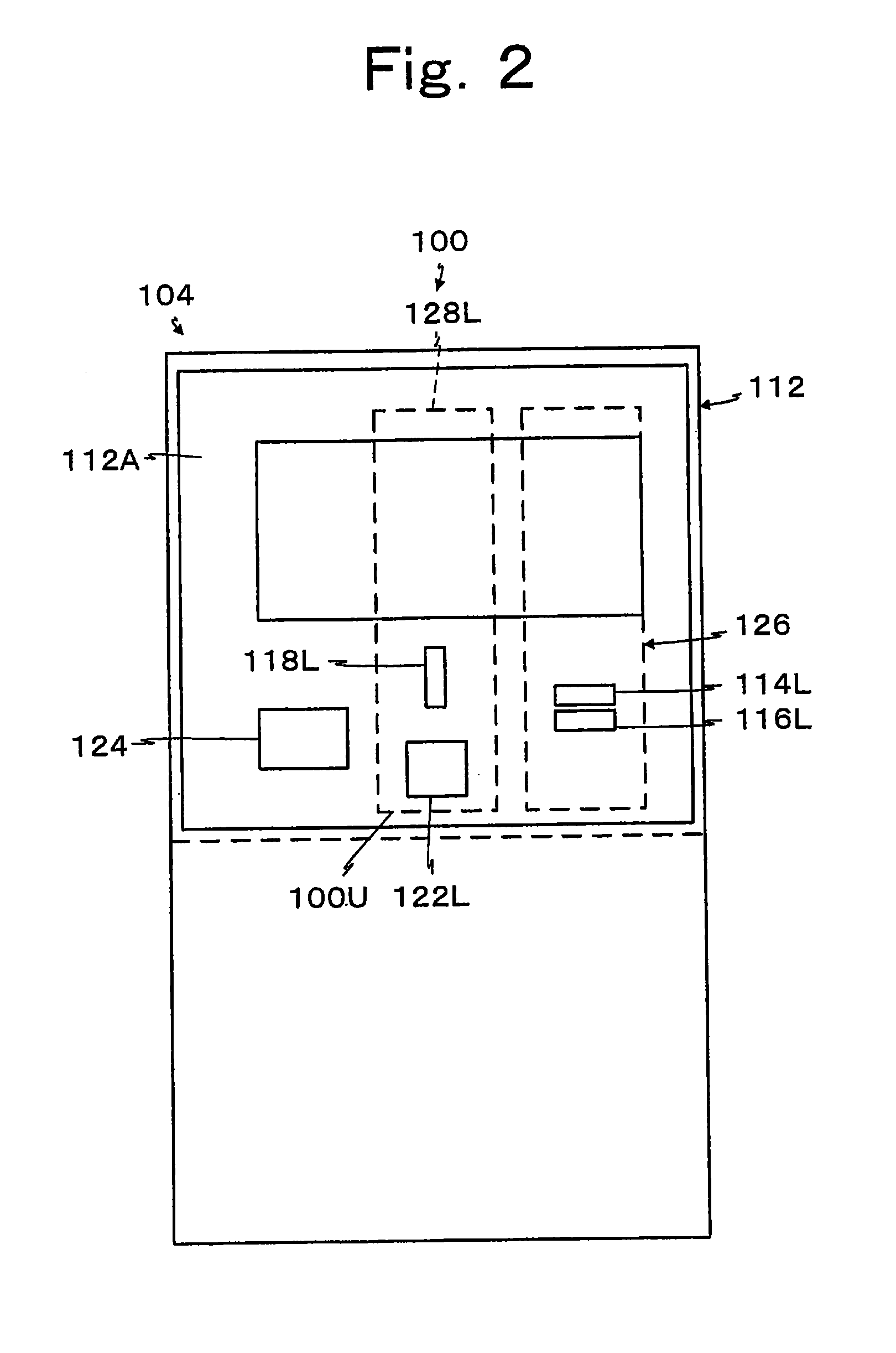
Four-stroke internal combustion engine with recuperator in cylinder head
InactiveUS6340013B1Prevent leakageQuick mixInternal combustion piston enginesCylinder headsThermal energyCommon Duct
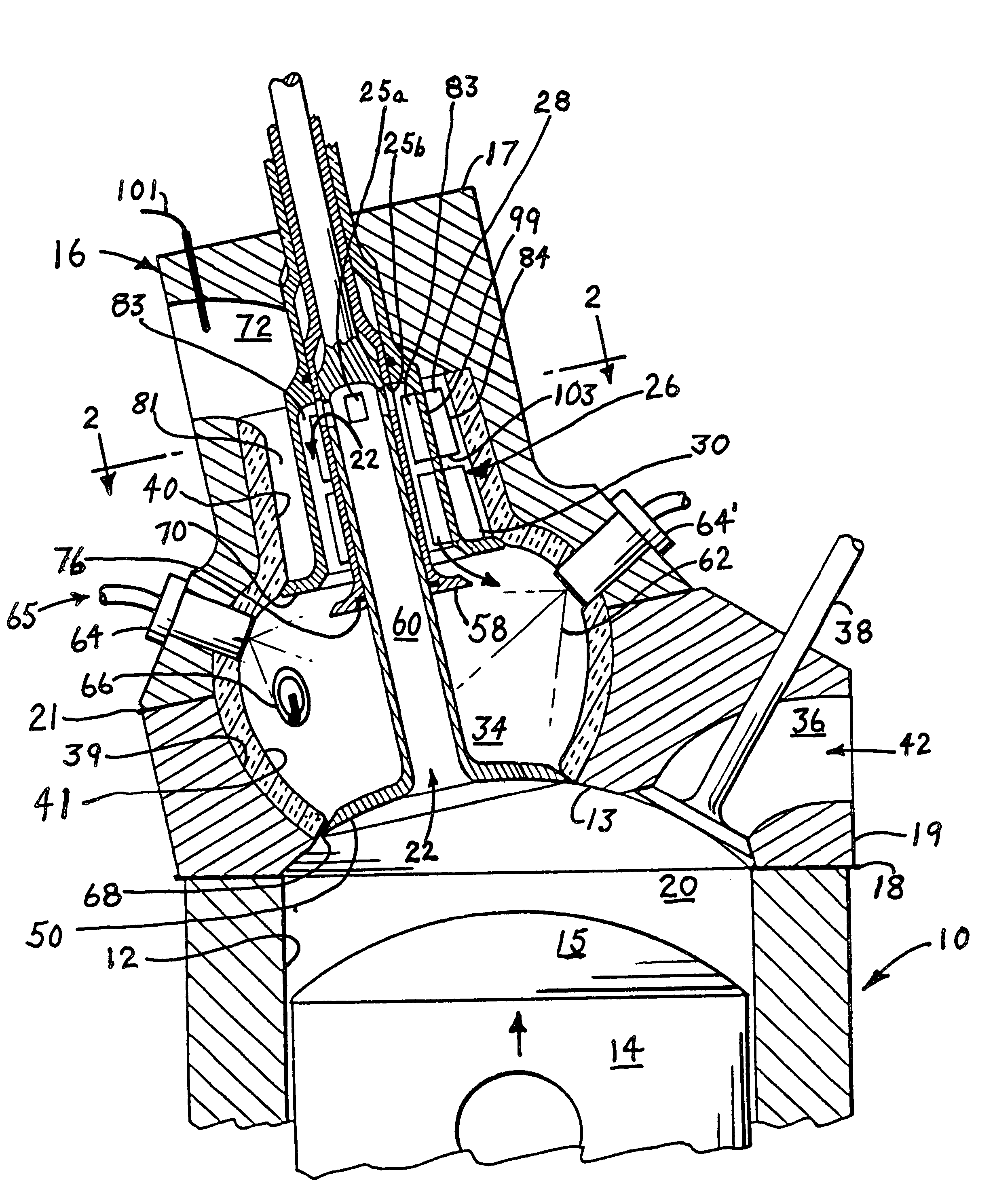
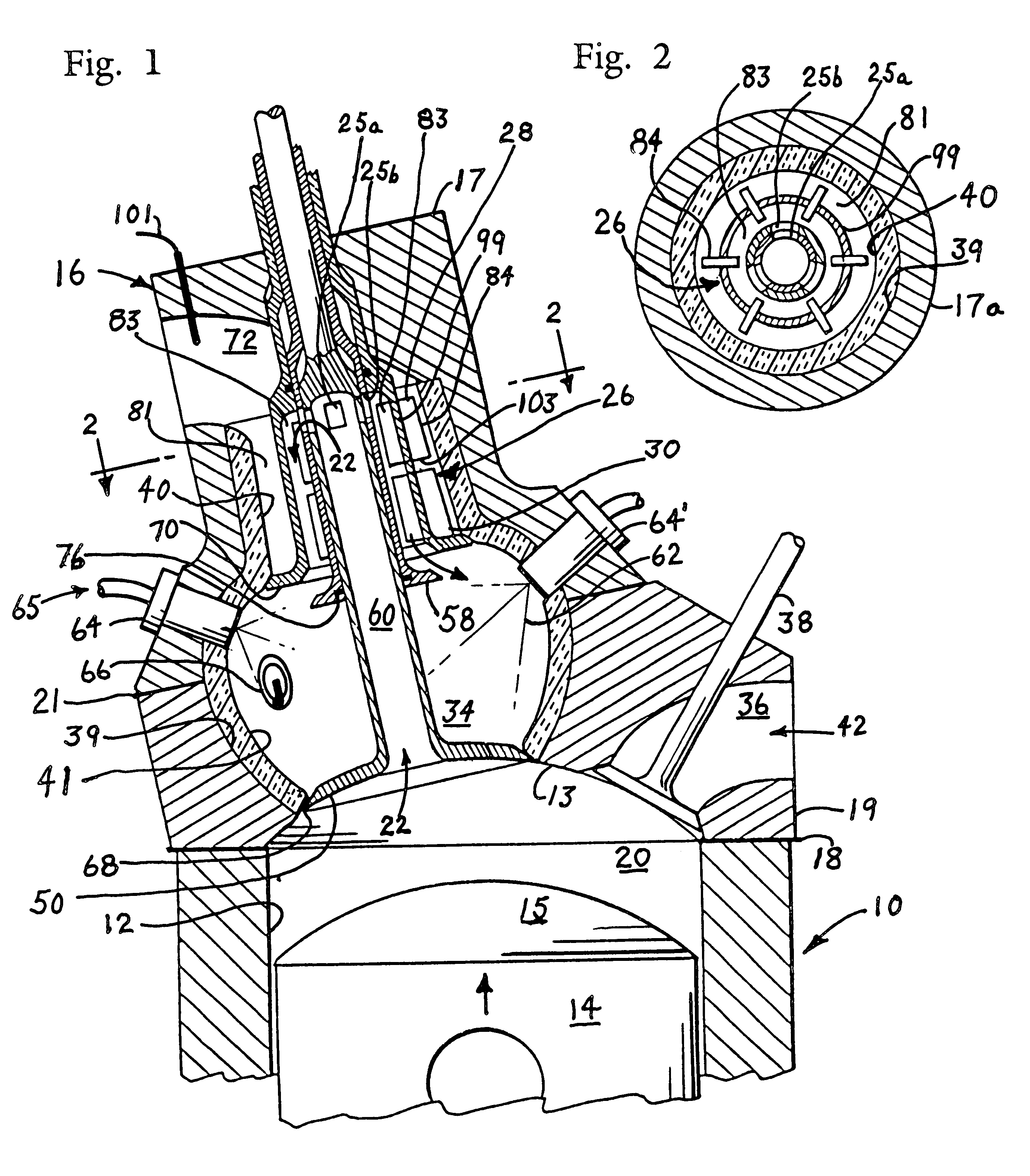
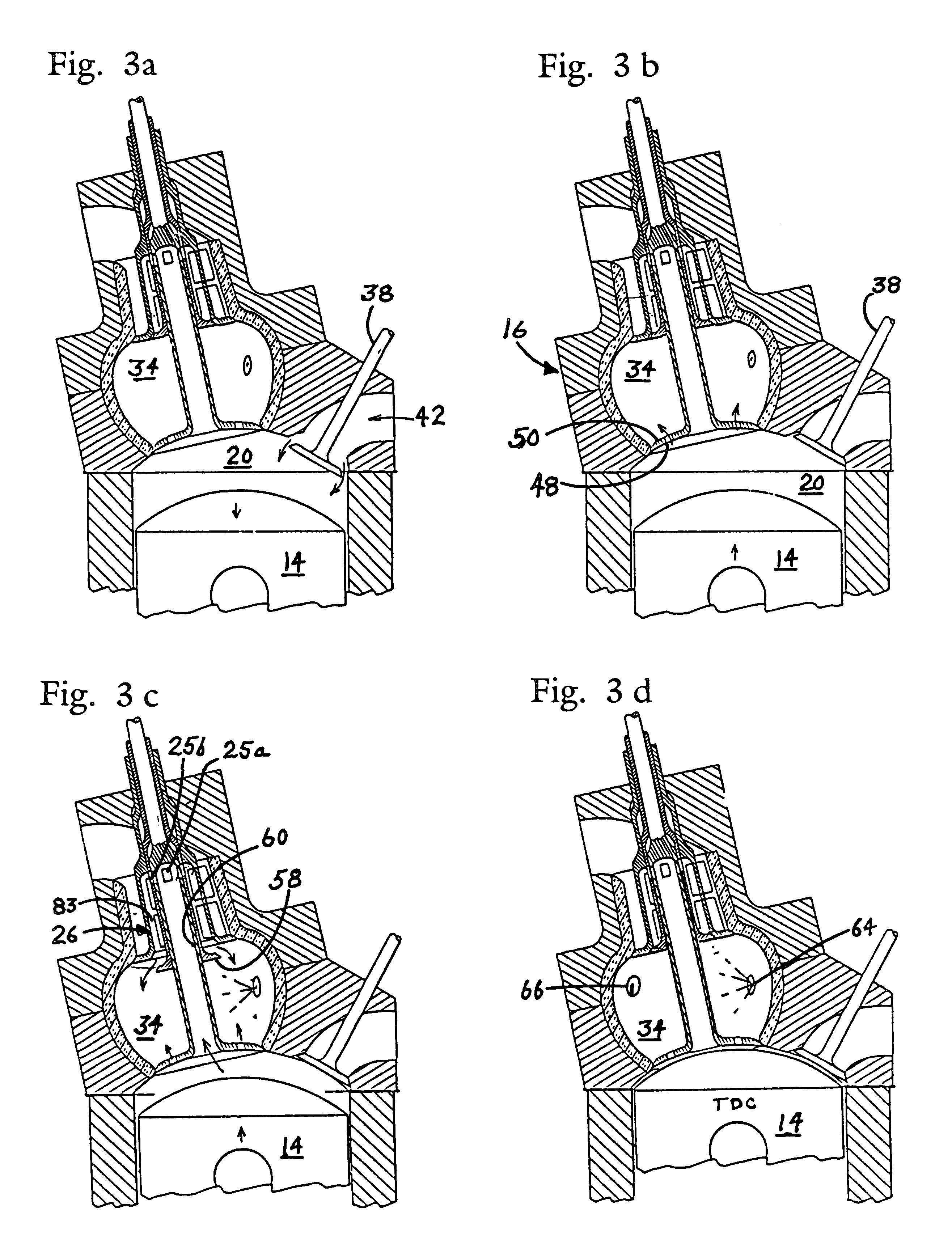
A recuperating four-stroke internal combustion engine obtains improves Carnot efficiency by use of a new and novel cylinder head which captures thermal energy normally thrown away in the exhaust and re-introduces it to the working cycle. This result, long sought by others, has been achieved by incorporating within the head a compact internal recuperative heat exchanger in series with a combustion chamber or pre-chamber. A recuperator-protecting valve segregates the recuperator from hot combustion gases until the gases reach maximum expansion in the cylinder. Recuperators of both common-duct and seperated-duct design are described, the separated duct recuperator permitting higher recuperator temperature and increased efficiency and a reduction in the number of valves necessary to control gas flow. A preferred embodiment employs four valves per cylinder unit, a separated duct recuperator, and an insulating liner that surrounds both the combustion chamber and the recuperator. A similar prototype recuperative engine has demonstrated that recuperation can reduce exhaust temperature as much as 600° Rankine below that attainable in an equivalent Otto Cycle engine.
Owner:BRITTON RICHARD BERKELEY
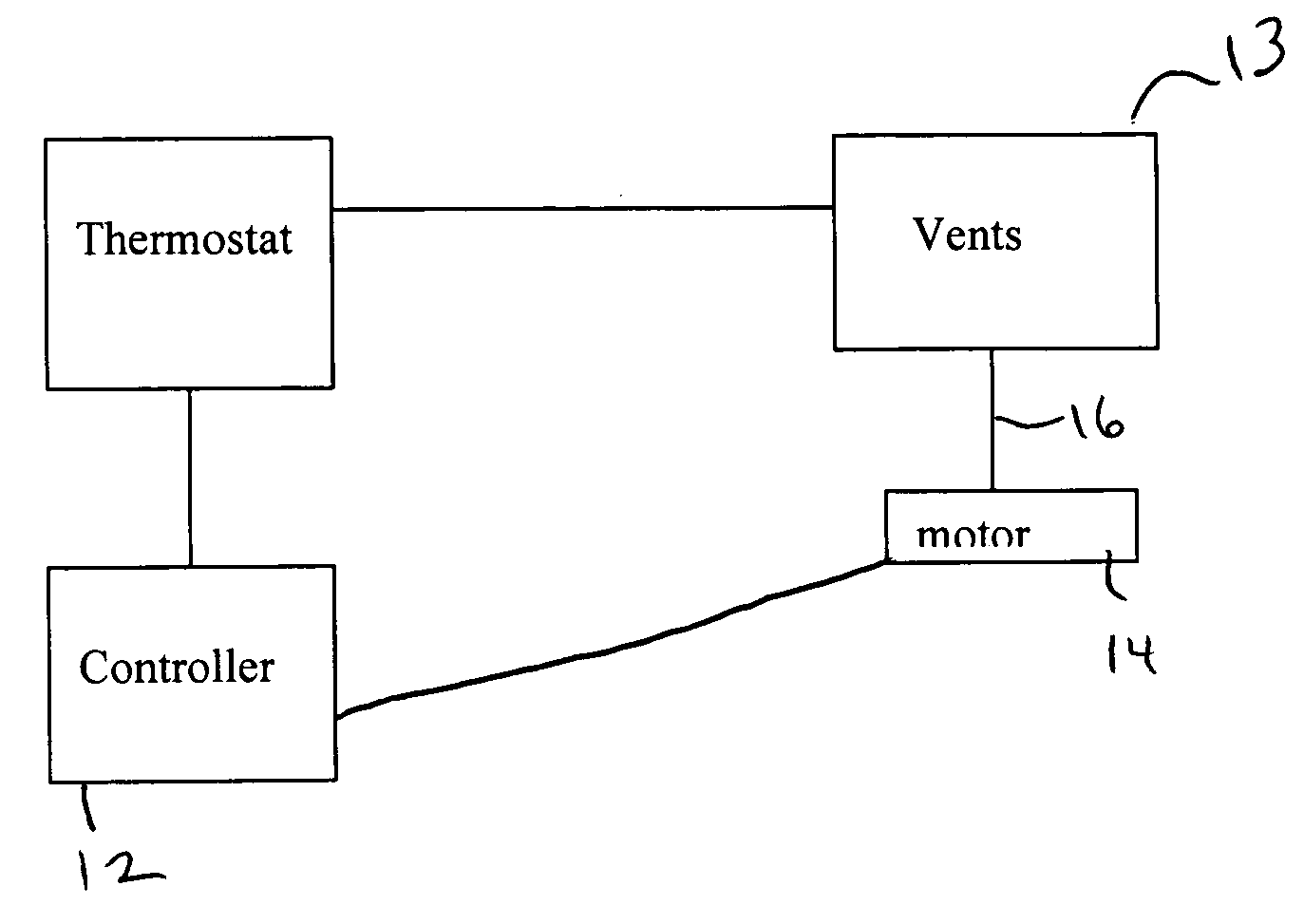
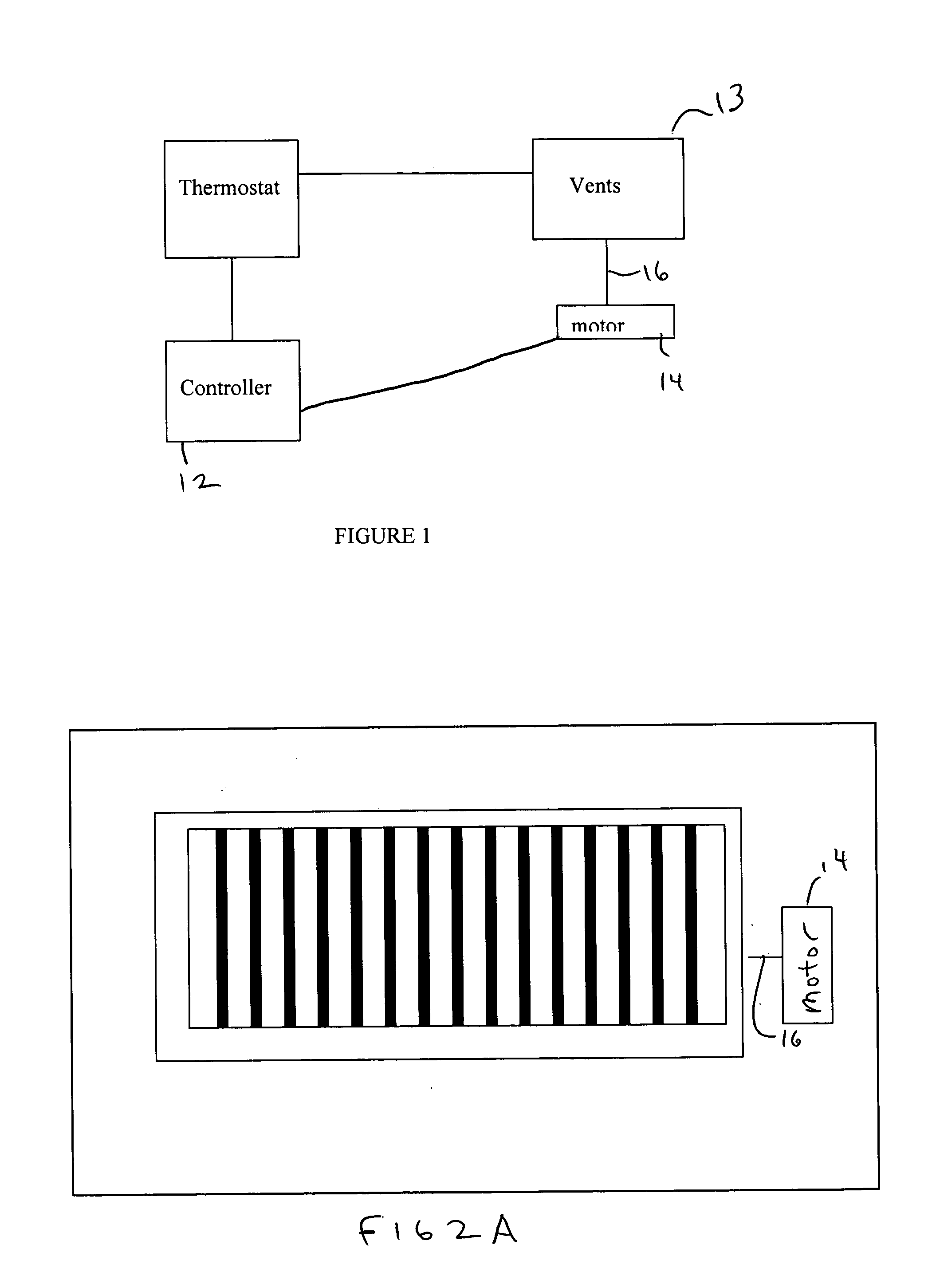
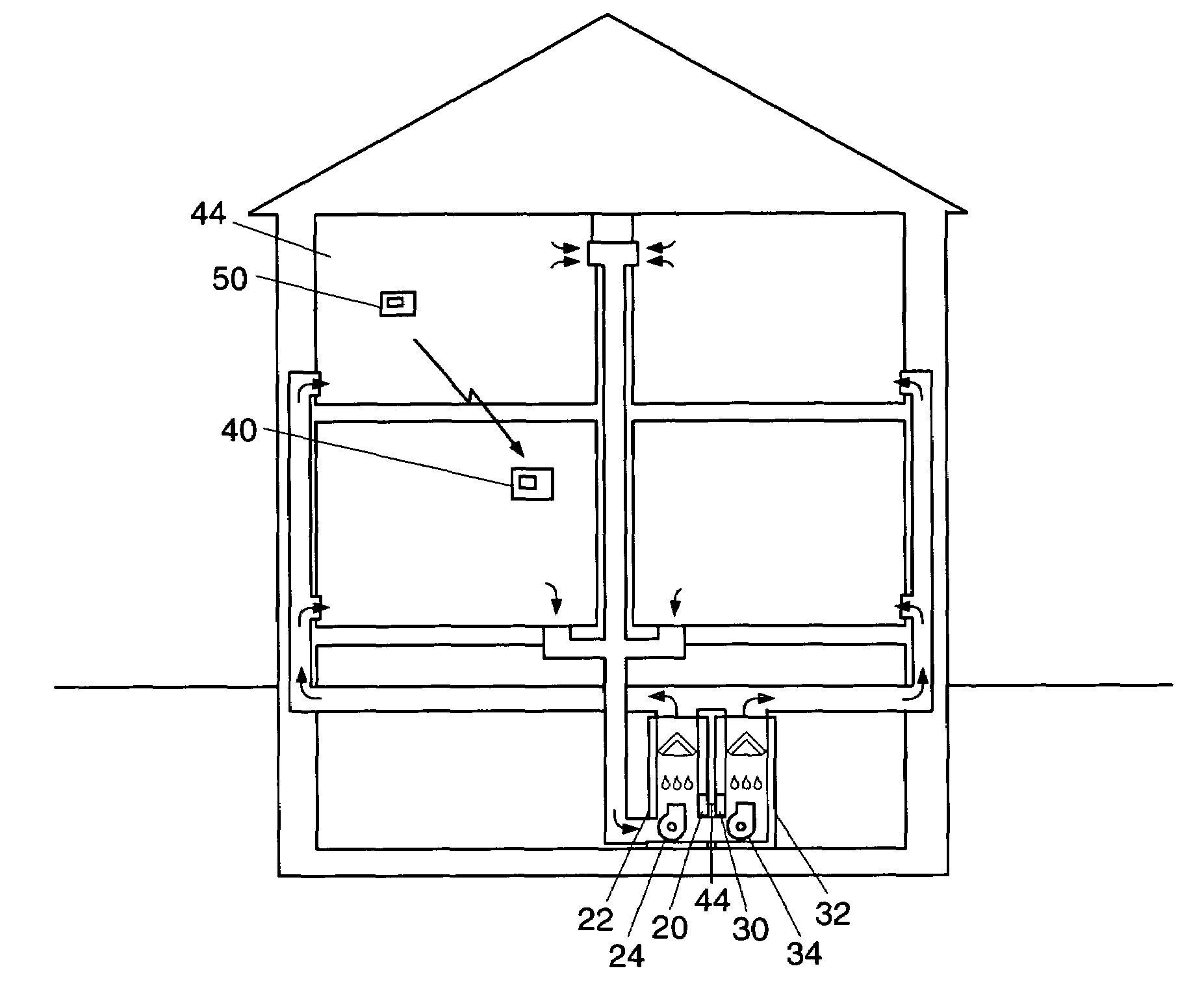
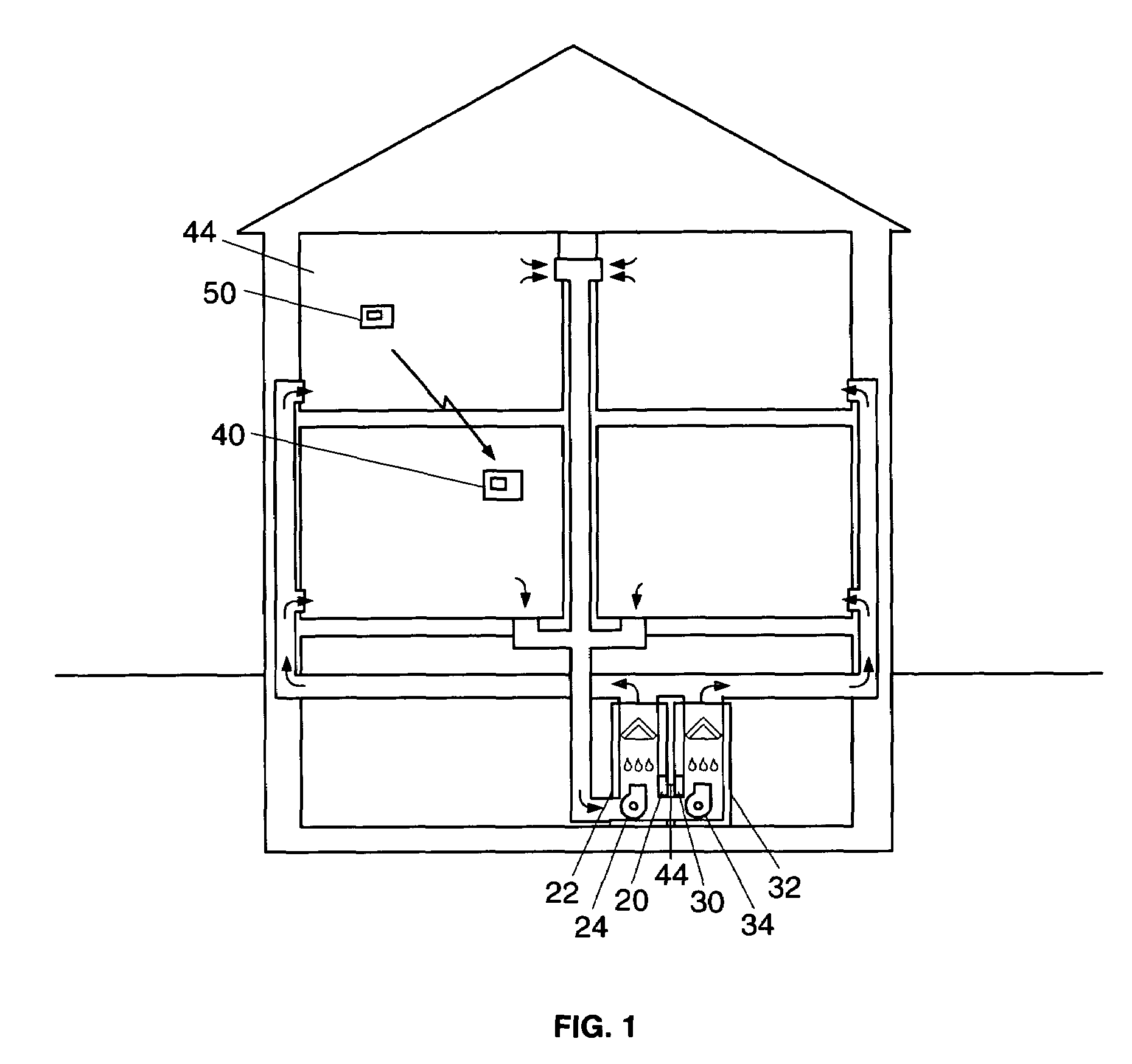
System for controlling a ventilation system
InactiveUS20050082053A1Mechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsCommon DuctControl of respiration
A central system wherein conditioned or heated air is supplied to a plurality of rooms to be air-conditioned through a common duct, the system comprising: means for generating conditioned air or heated air and forcibly supplying the air to a plurality of rooms; a vent control mechanism, corresponding to a vent in each room, for controlling a flow of the conditioned air from the common duct into corresponding room; a room remote controller, provided in each room, including a command signal to control the operation of the vent control.
Owner:HALABI KHALID
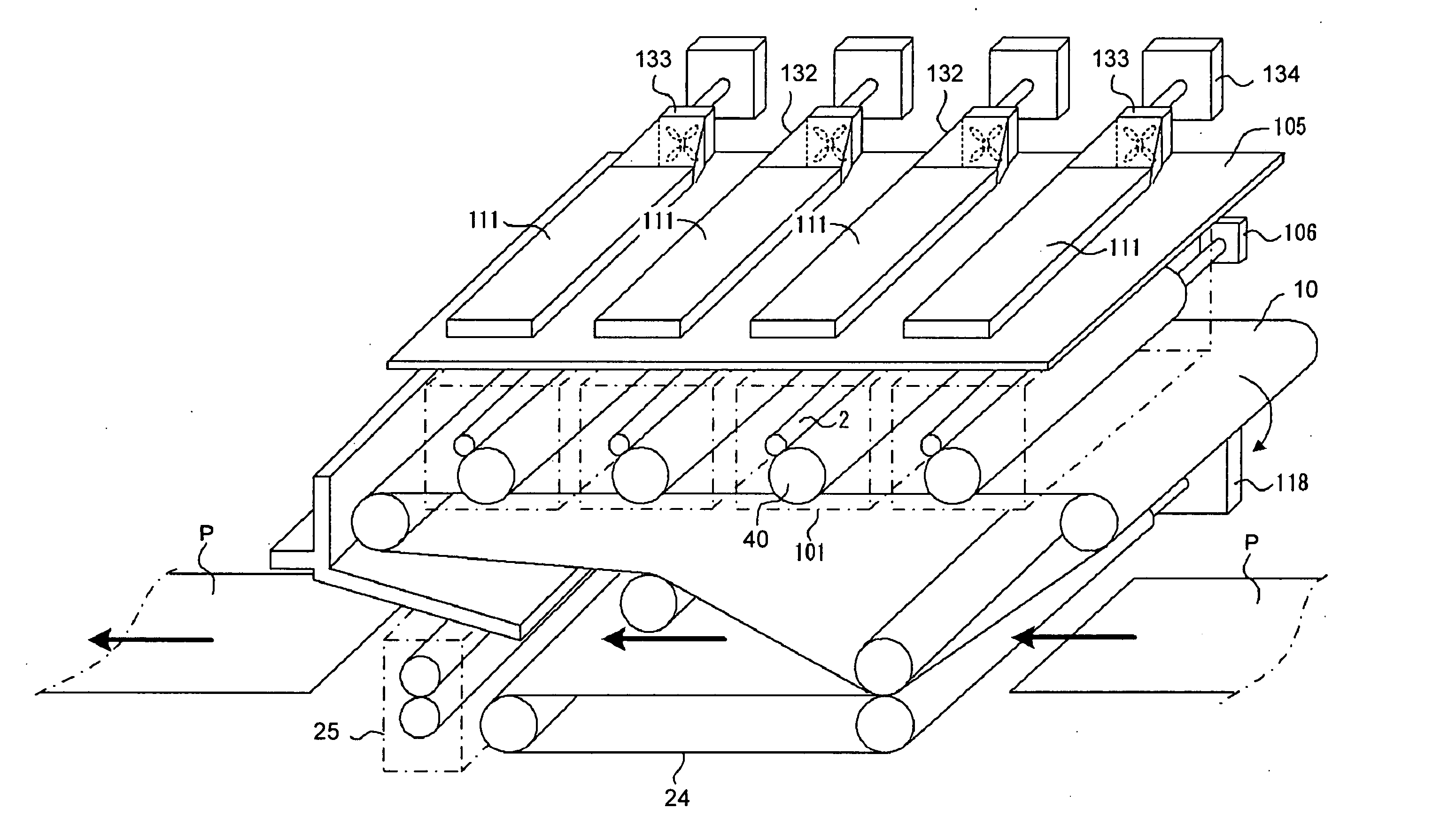
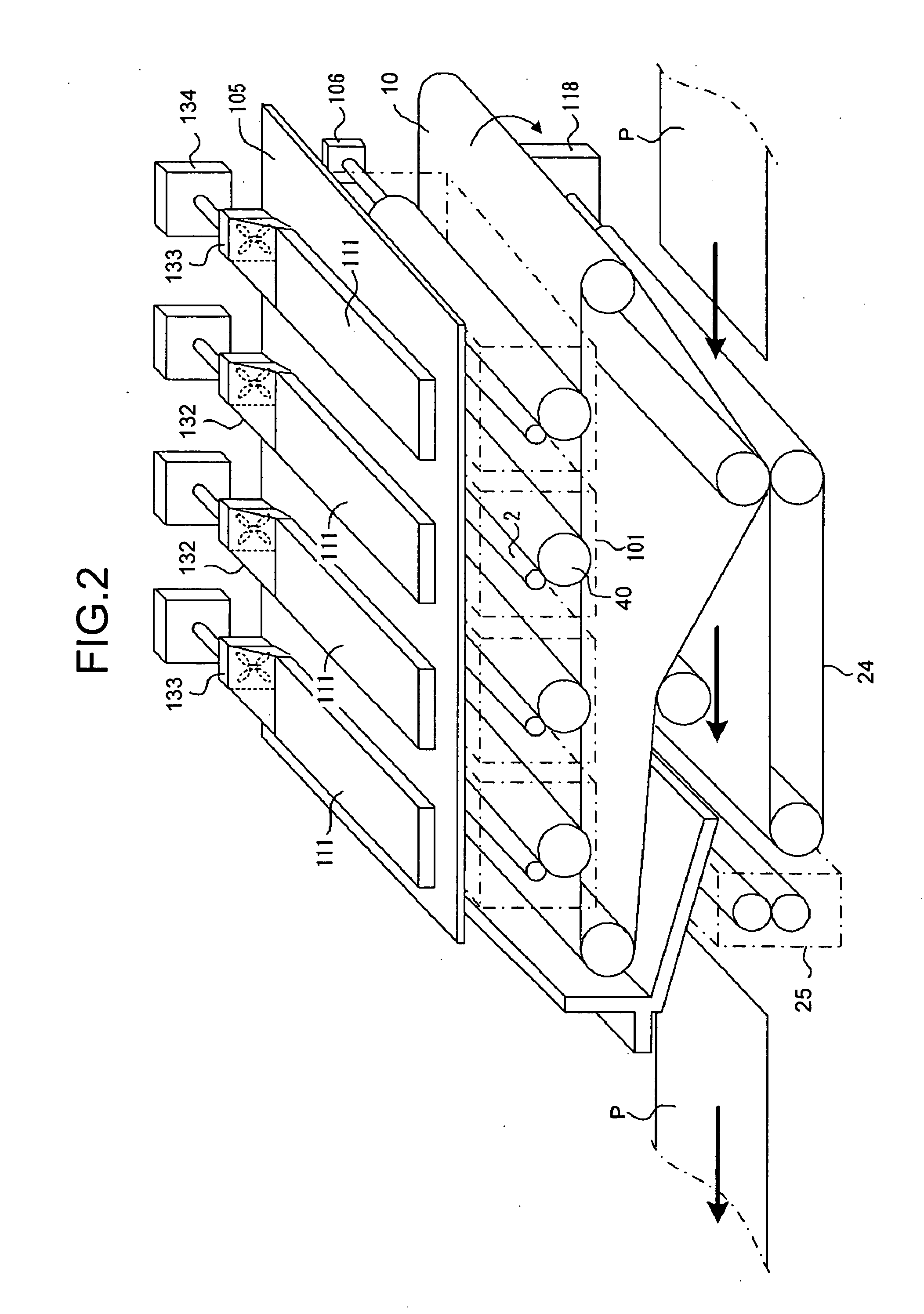
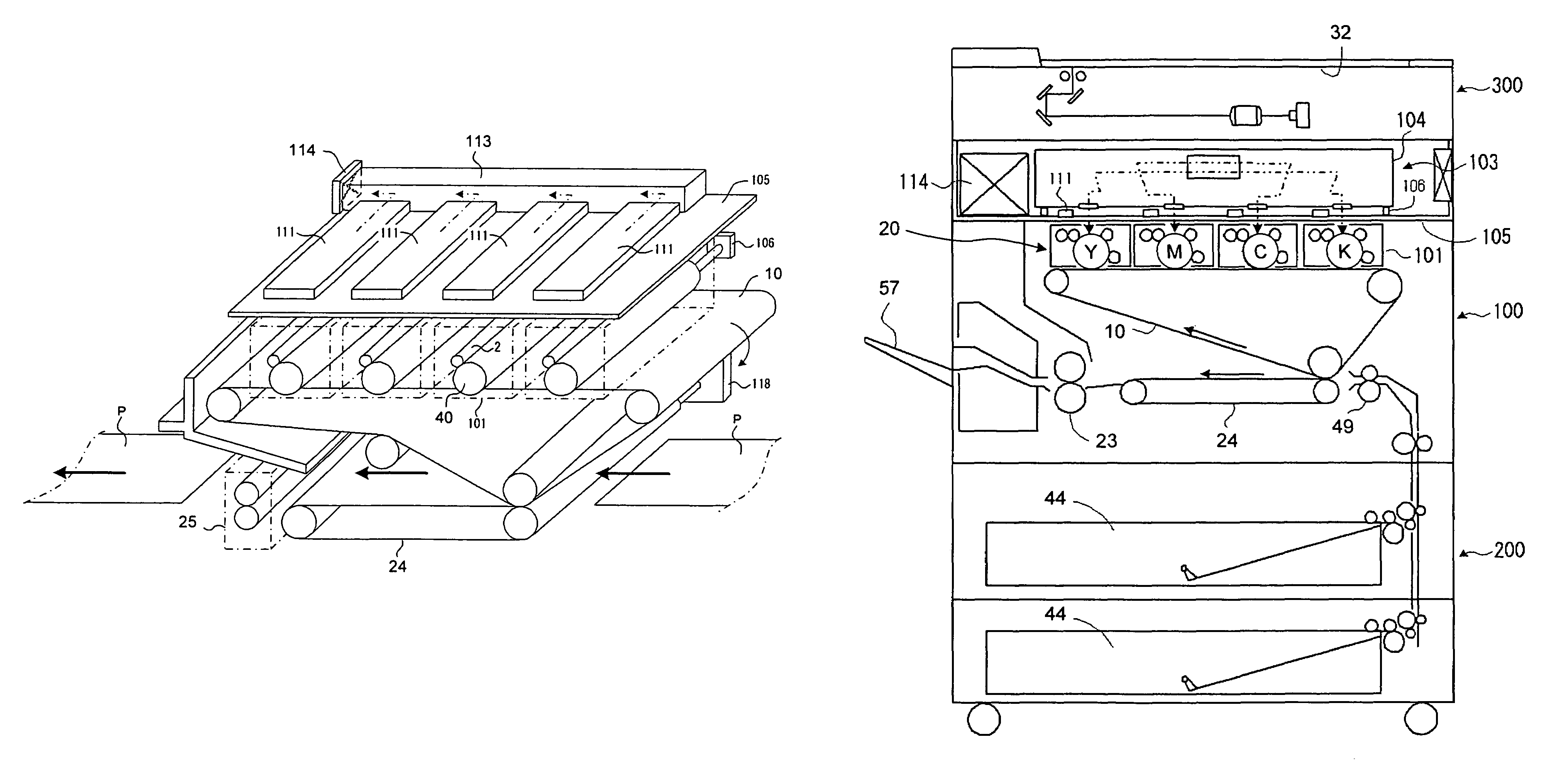
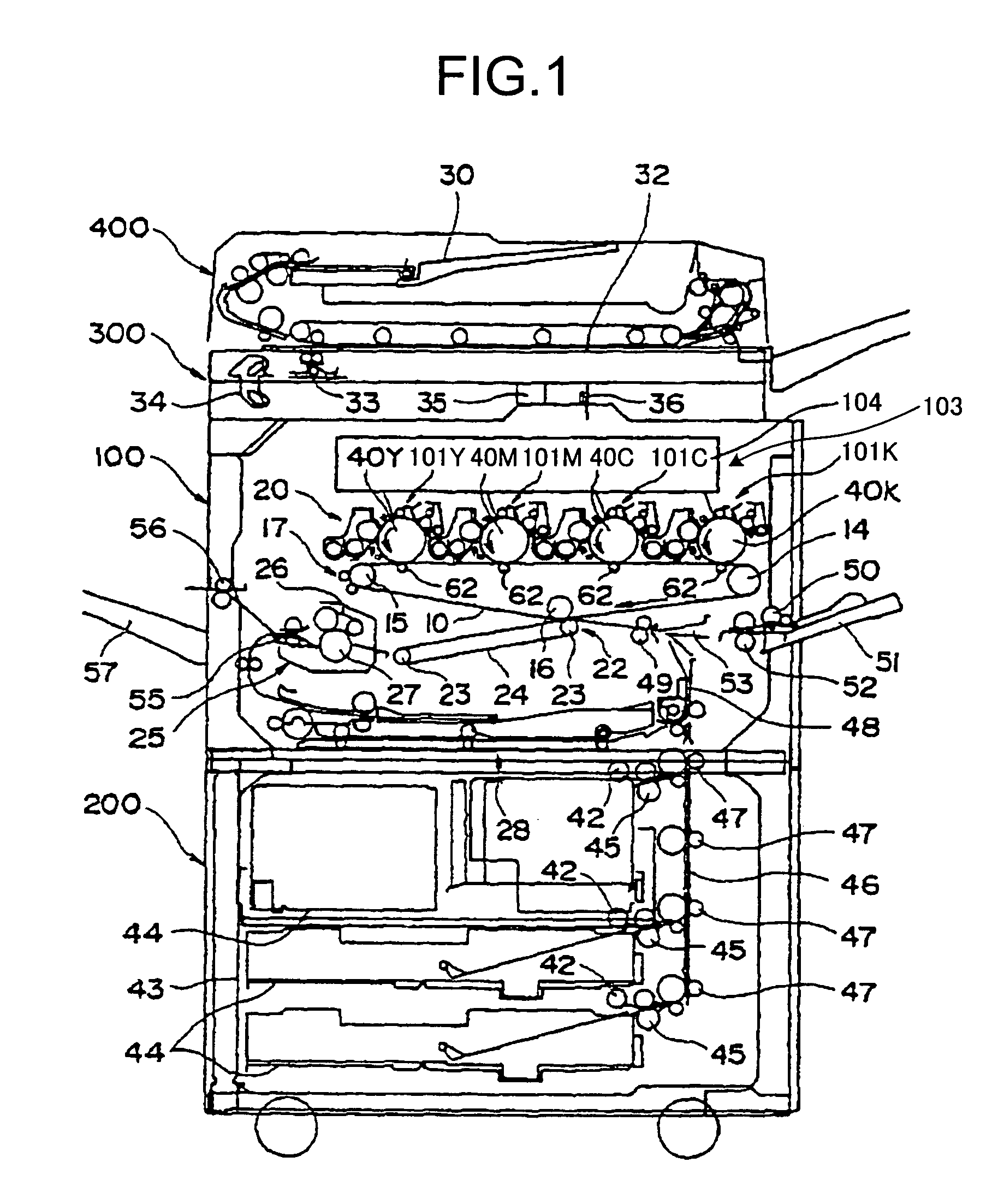
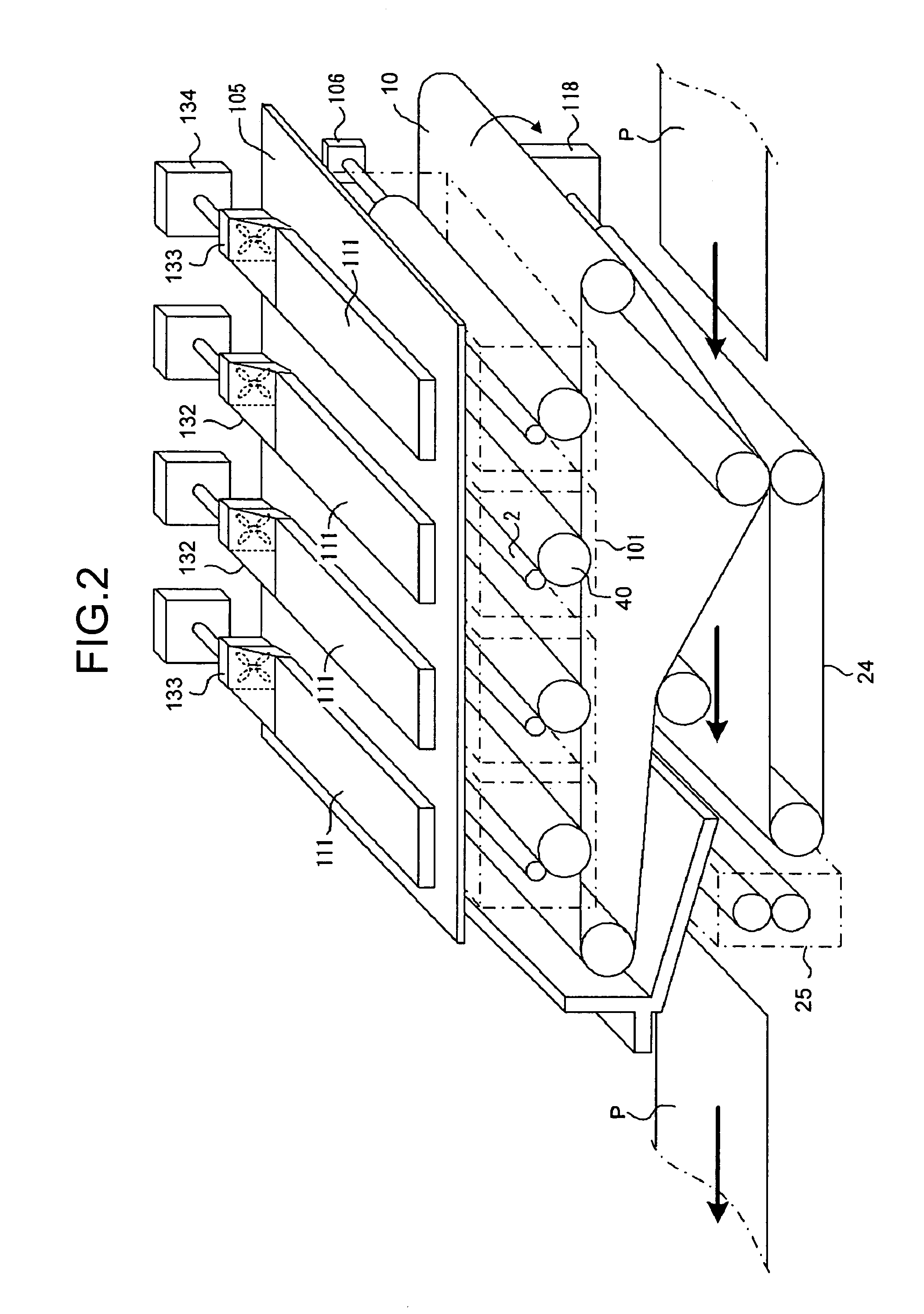
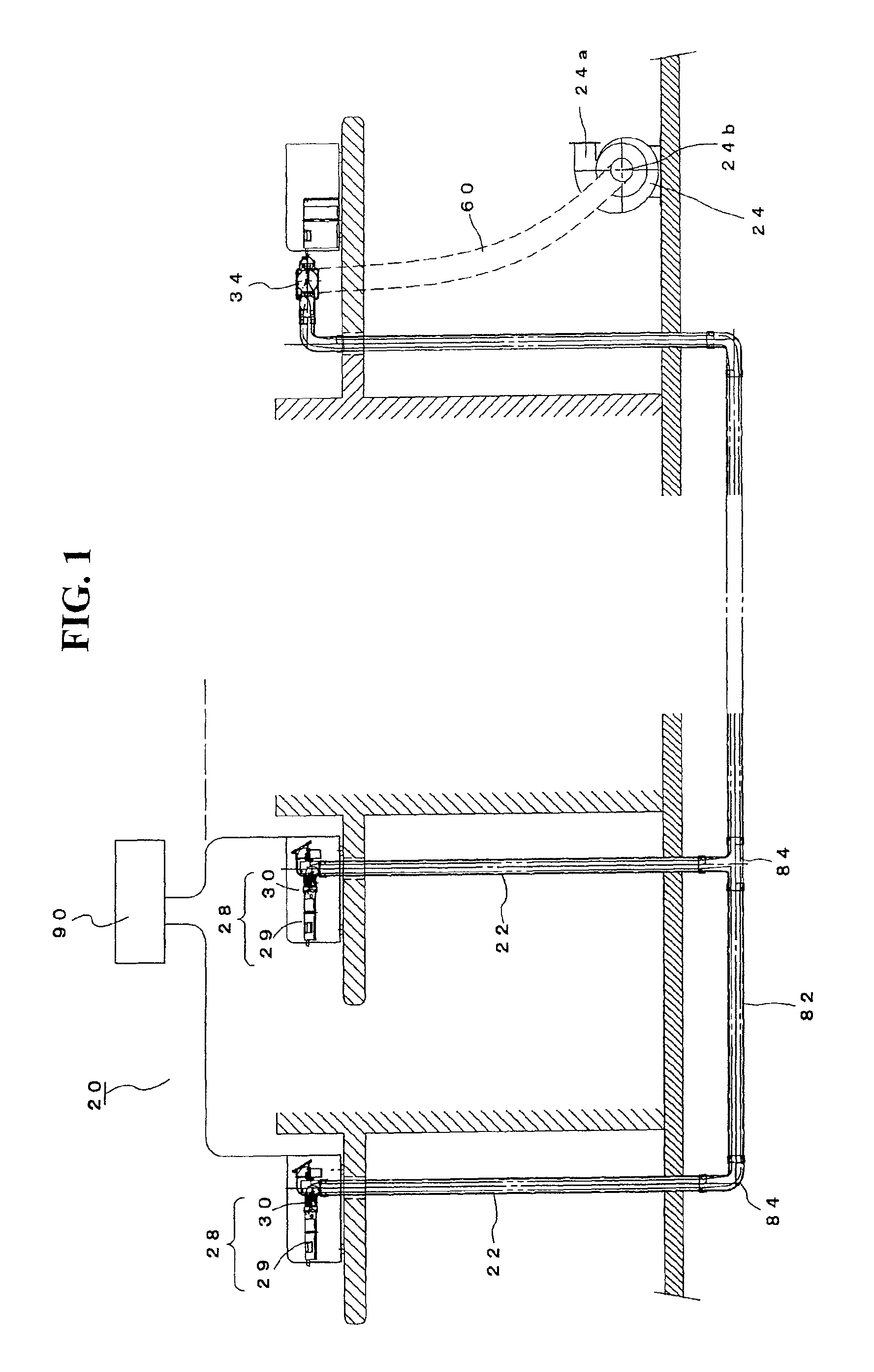
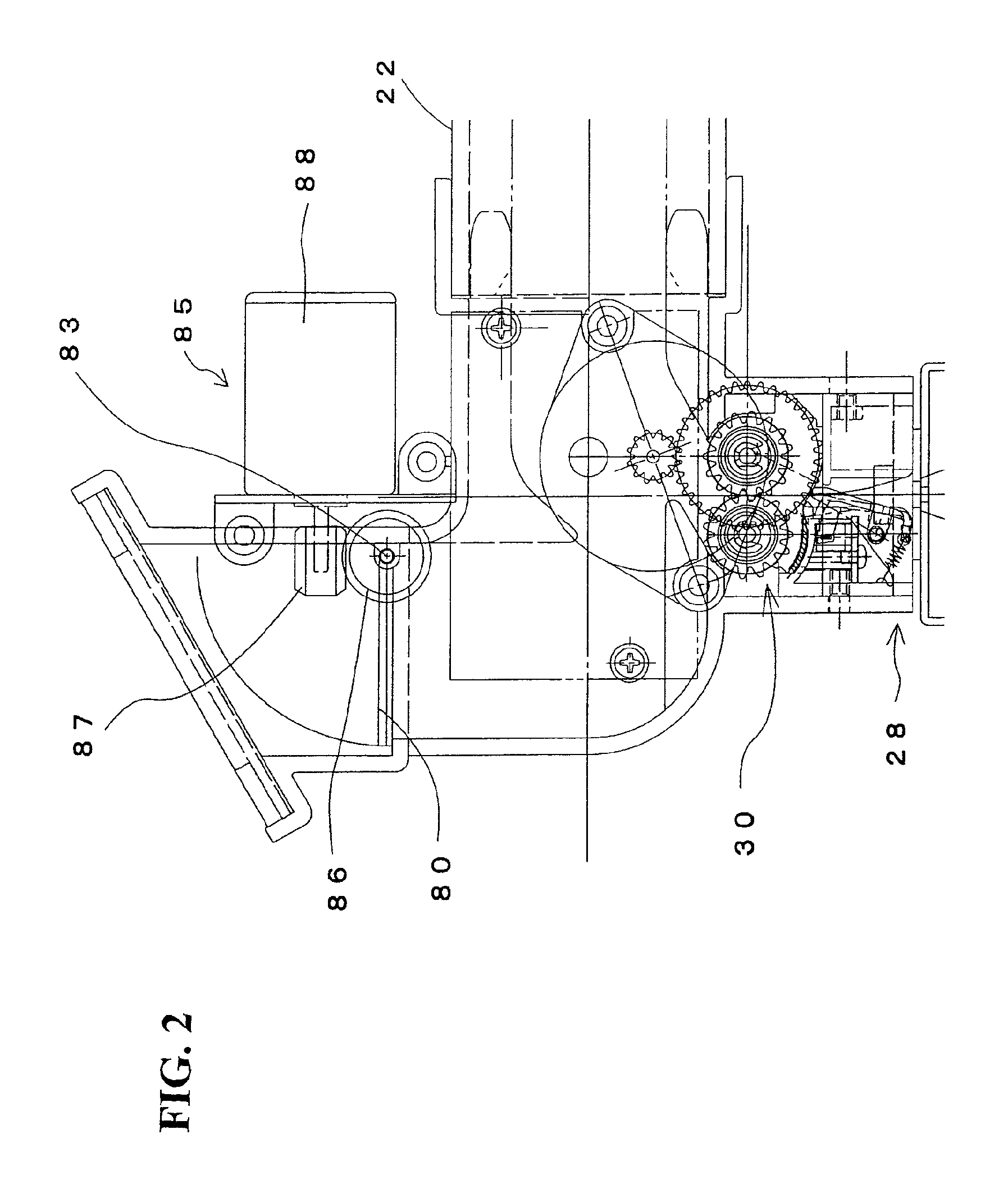
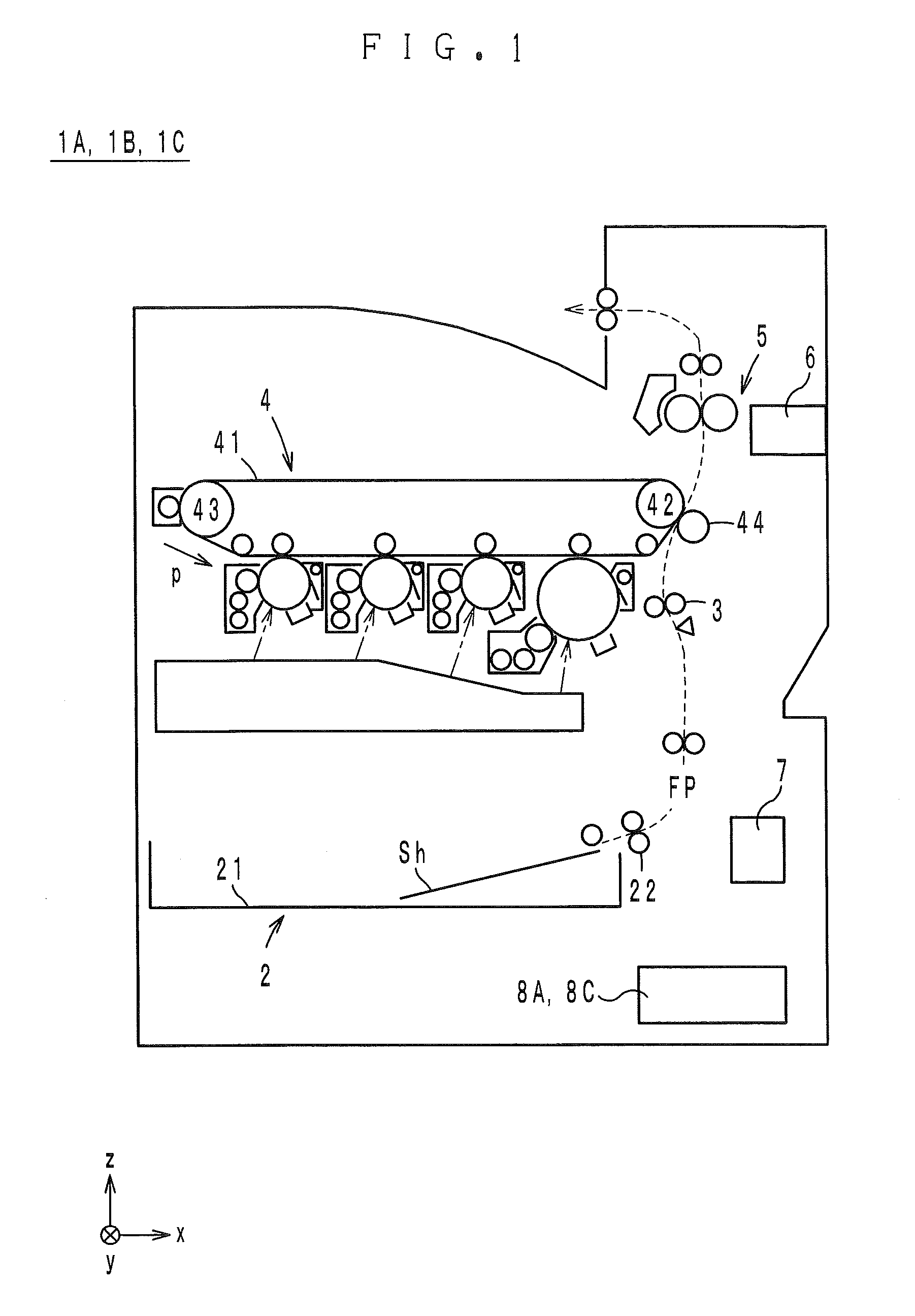
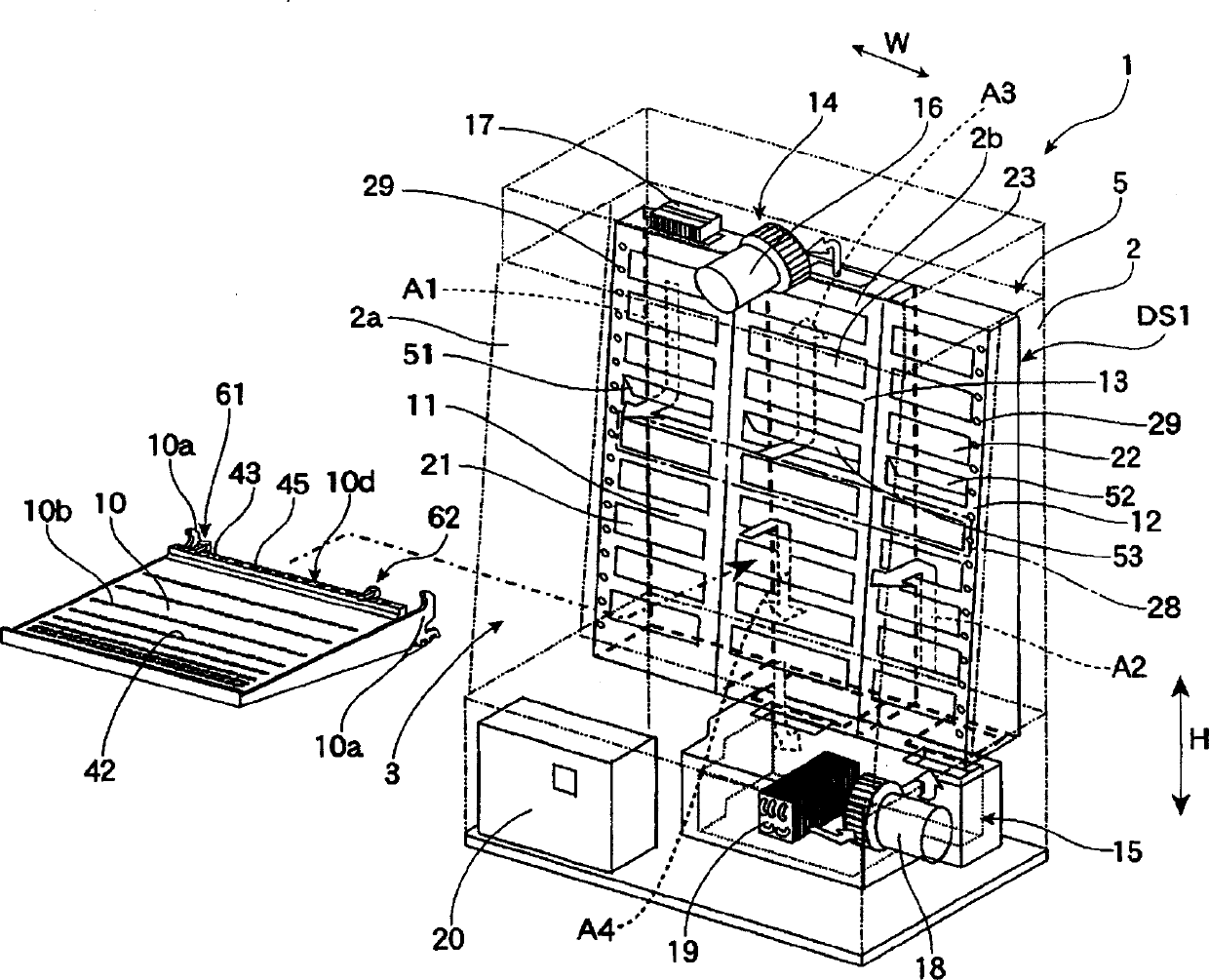
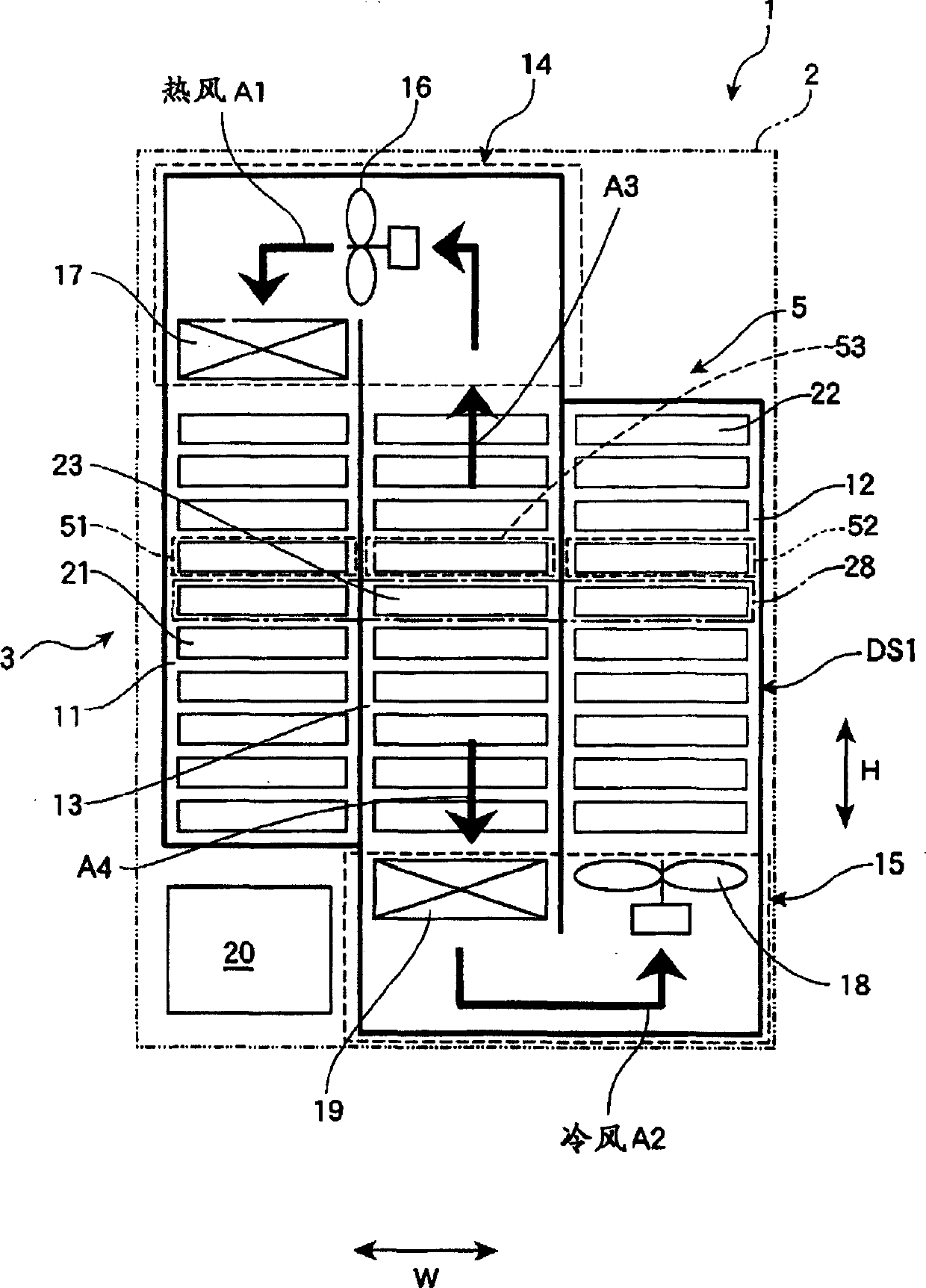
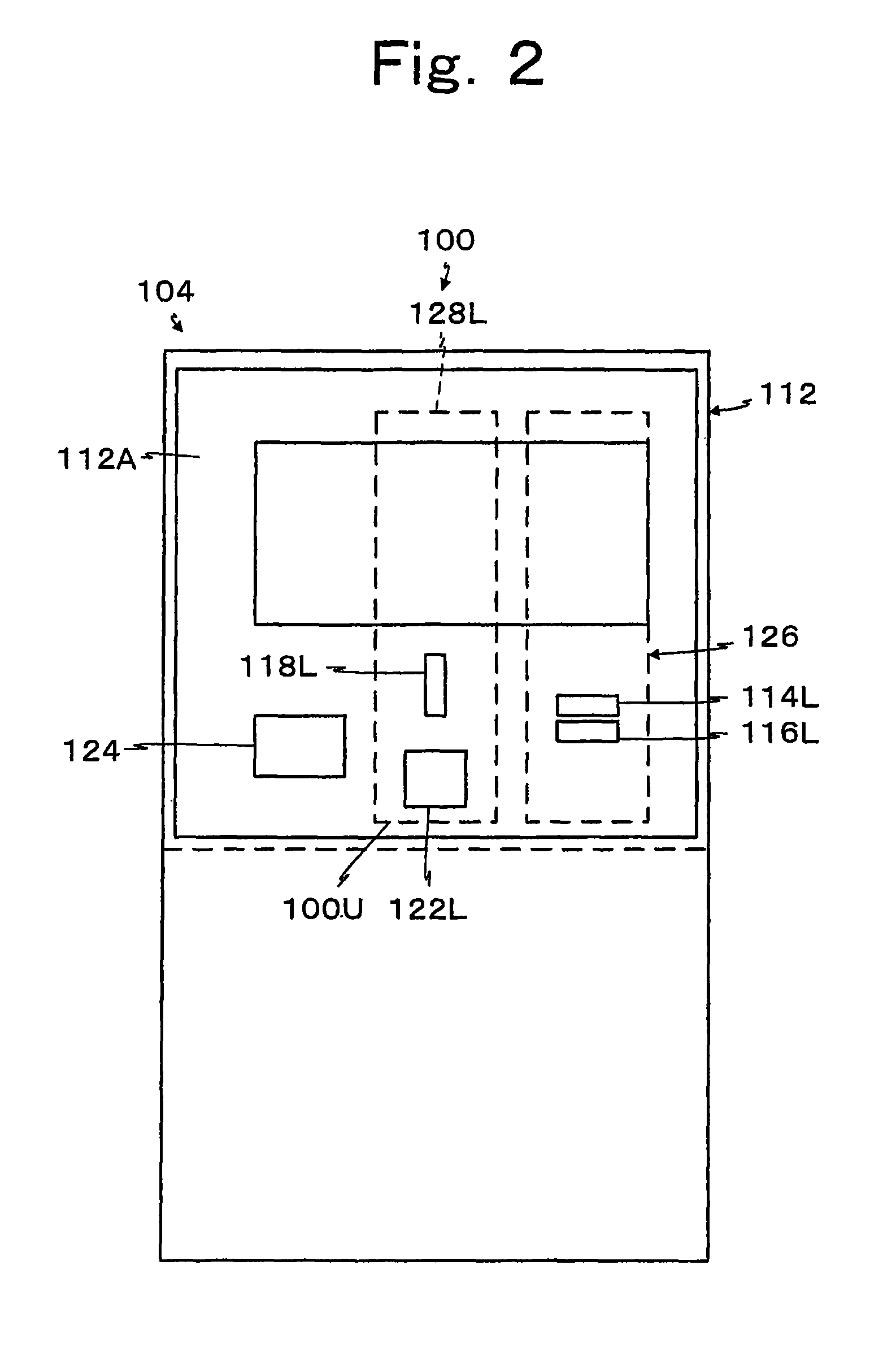
Image forming apparatus
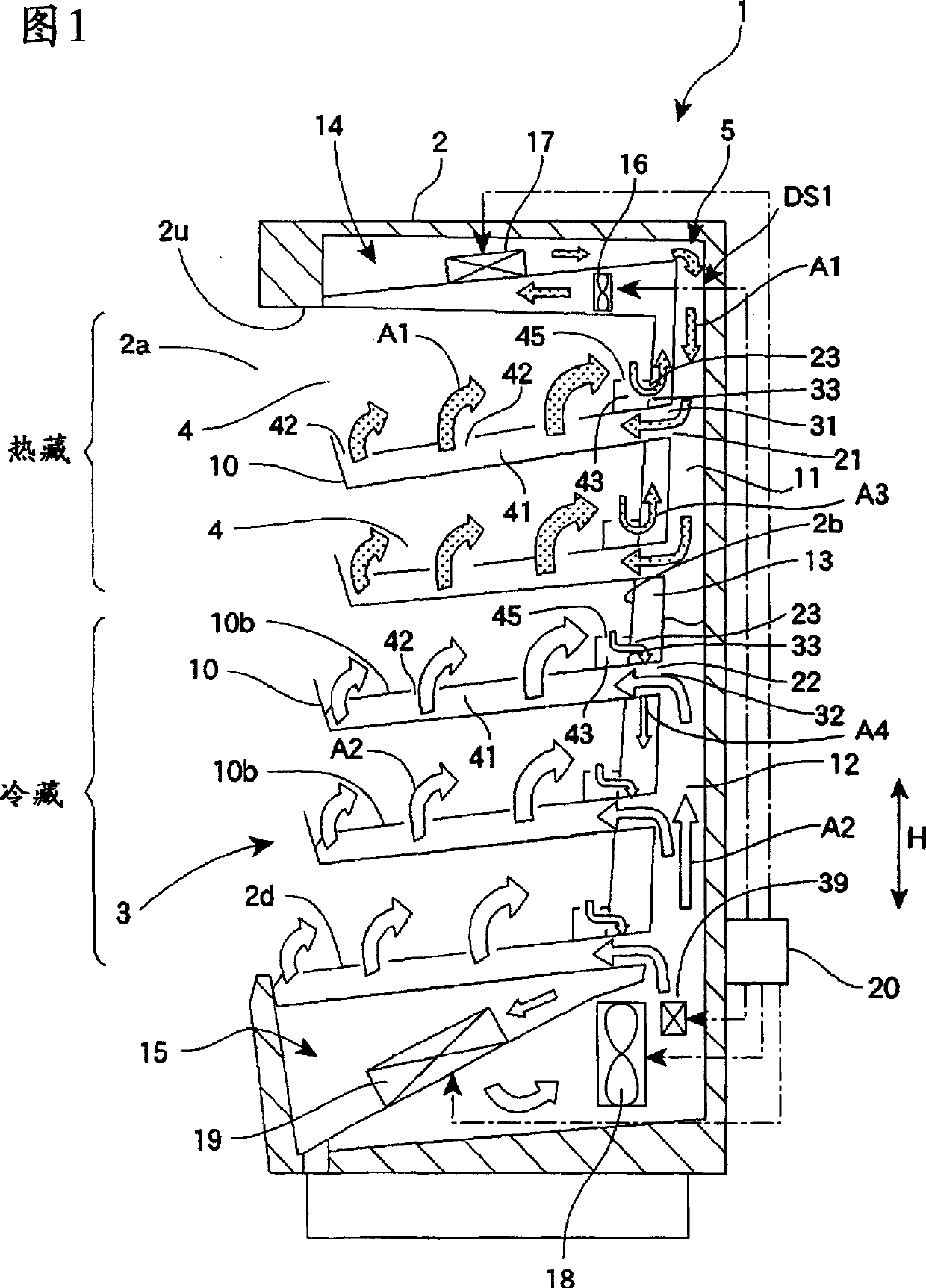
Heat exhaust holes are provided in a unit frame at positions just above respective imaging units. An exhaust fan causes air heated at developing elements to be exhausted outside an apparatus via heat exhaust ducts and a common duct. The heat exhaust holes are formed in different sizes depending on a position of the imaging unit. The closer the position of the imaging unit is, the larger the heat exhaust hole provided above the imaging unit is.
Owner:RICOH KK
Heat exhaustion apparatus and image forming apparatus using same
Heat exhaust holes are provided in a unit frame at positions just above respective imaging units. An exhaust fan causes air heated at developing elements to be exhausted outside an apparatus via heat exhaust ducts and a common duct. The heat exhaust holes are formed in different sizes depending on a position of the imaging unit. The closer the position of the imaging unit is, the larger the heat exhaust hole provided above the imaging unit is.
Owner:RICOH KK
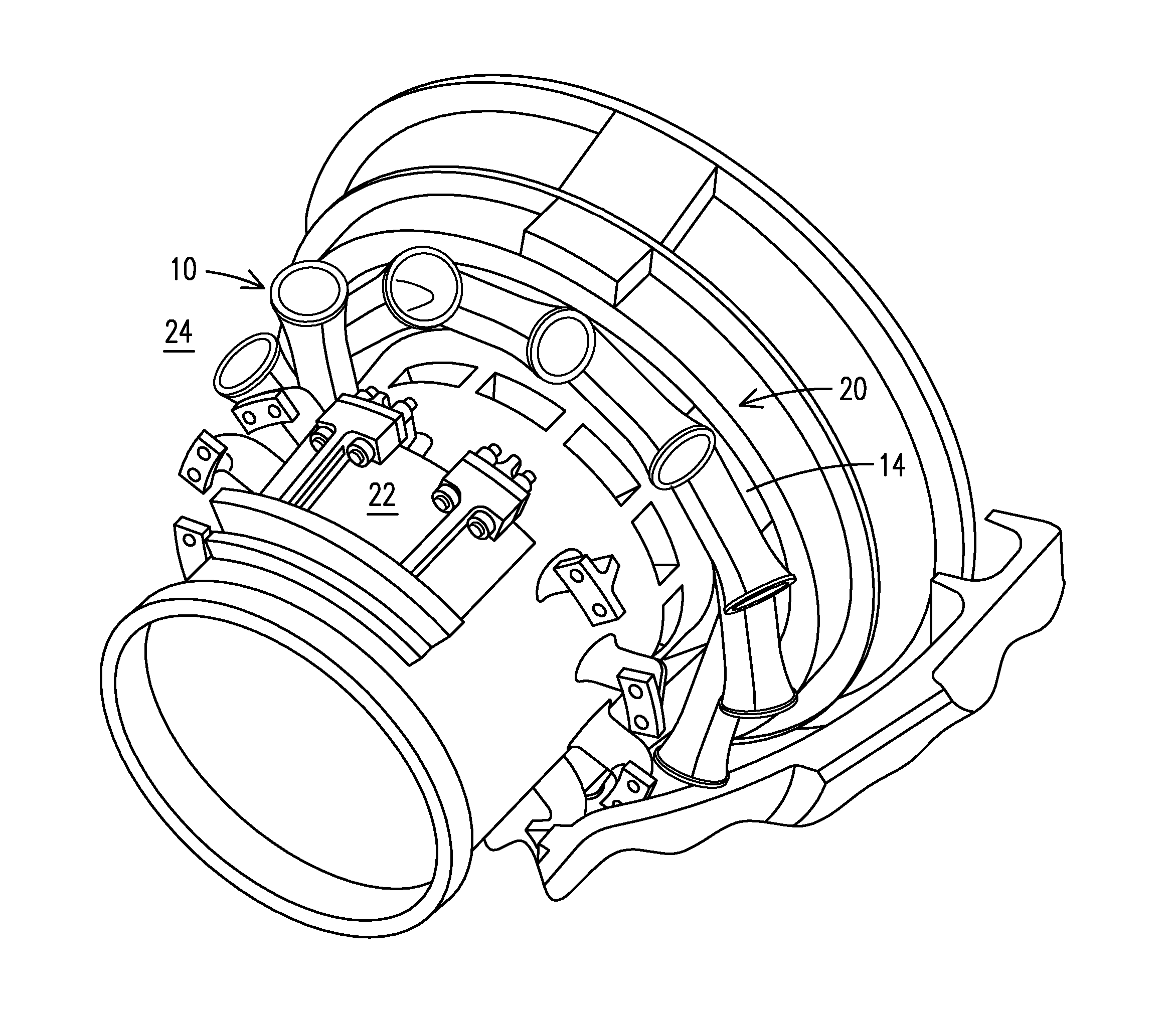
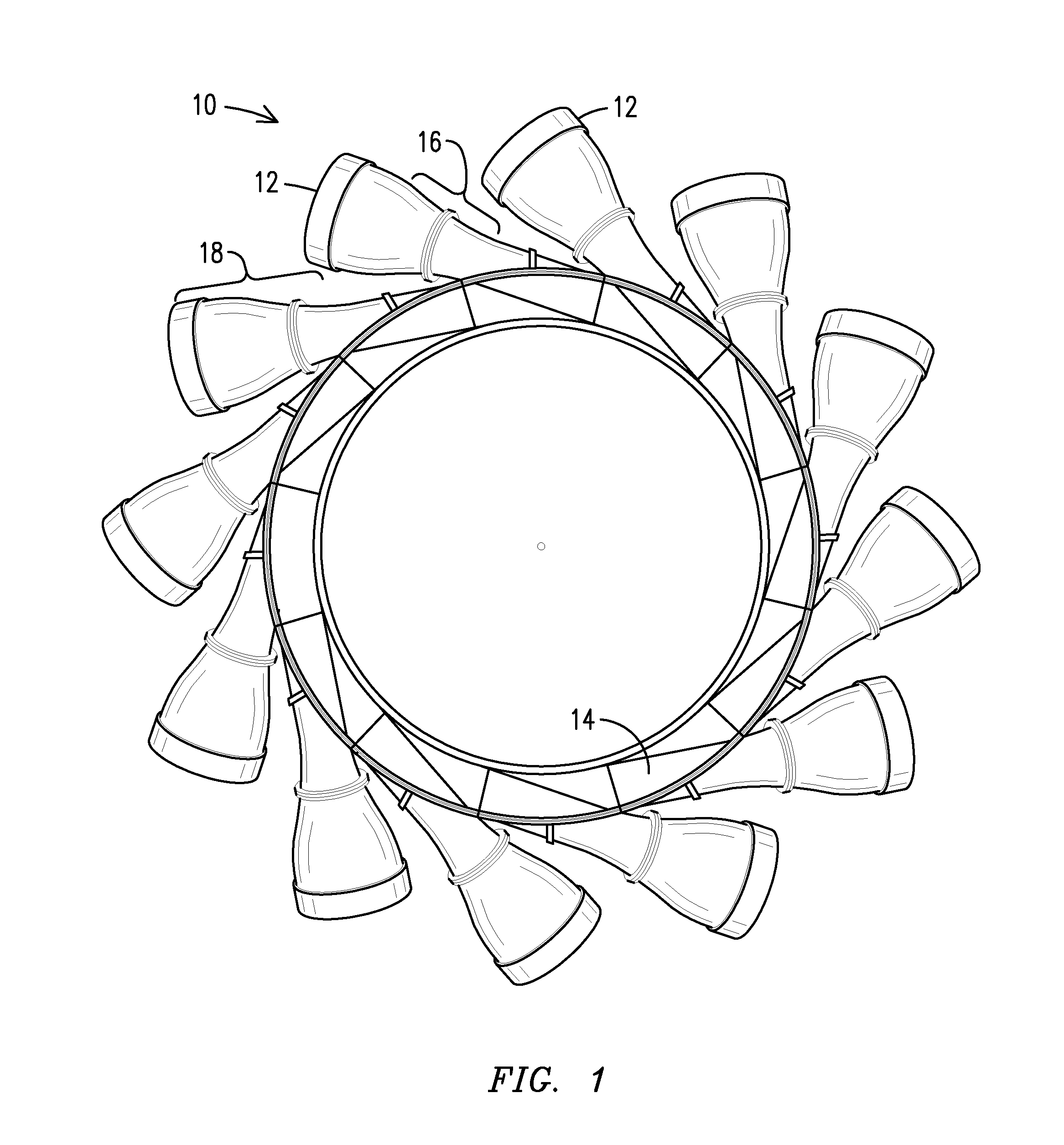
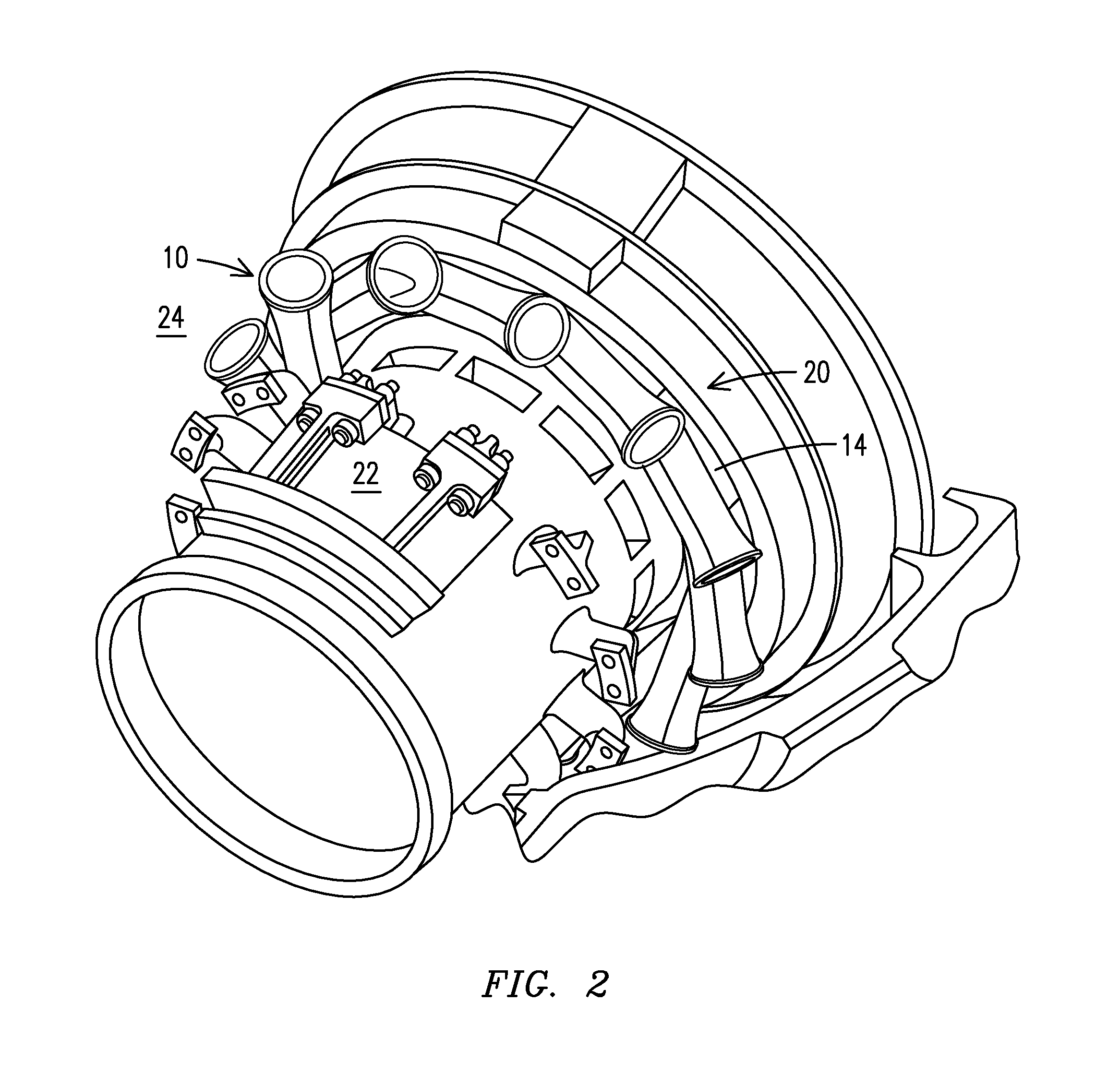
Gas turbine engine ducting arrangement having discrete insert
A ducting arrangement (10), including: a plurality of discrete ducts (18), each defining a flow path and configured to receive a flow of combustion gases from a respective combustor can, where the plurality of discrete ducts merge to form a common duct structure; and a throat insert (50) configured to define at least part of a junction of one of the discrete ducts and the common duct structure.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
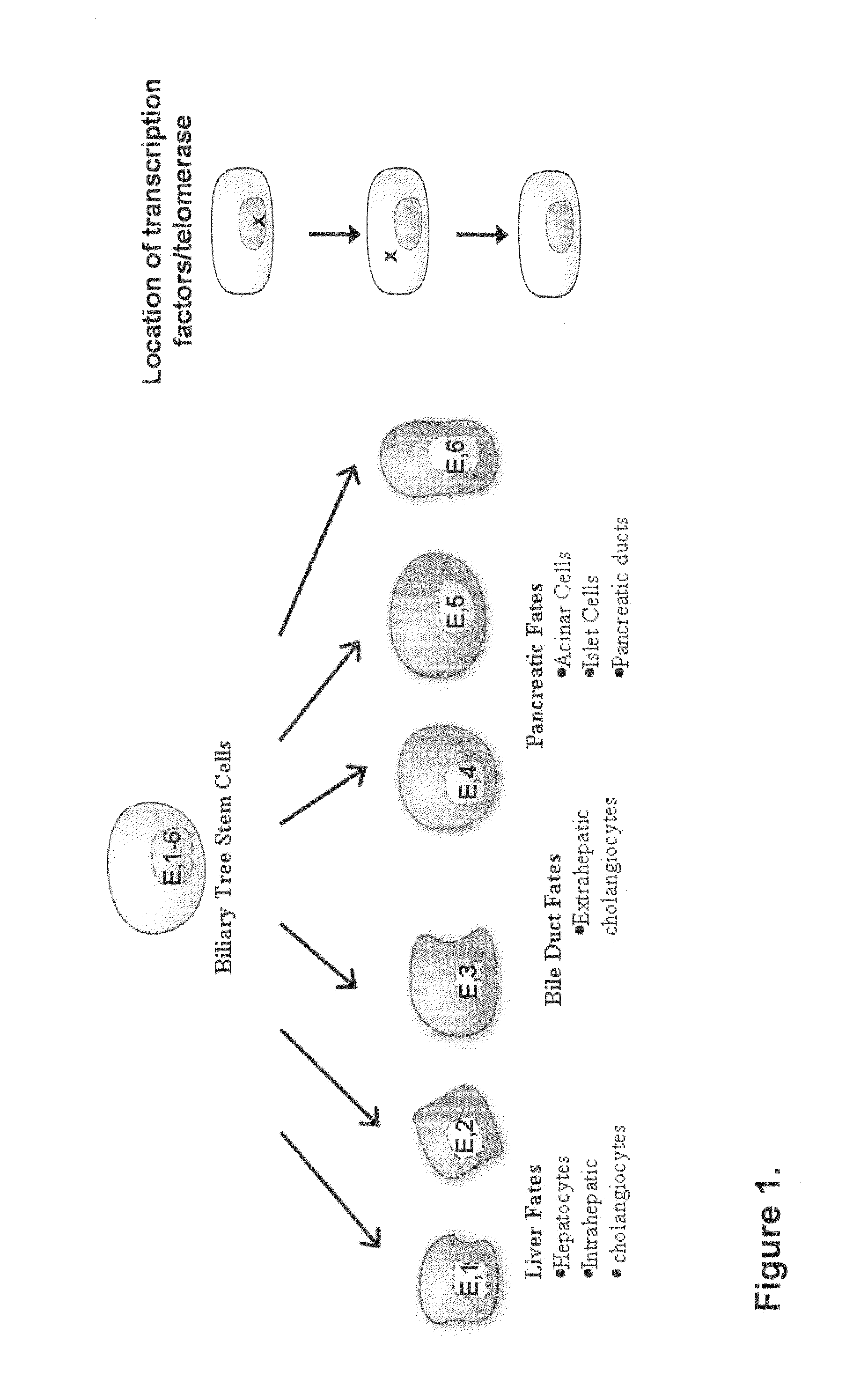
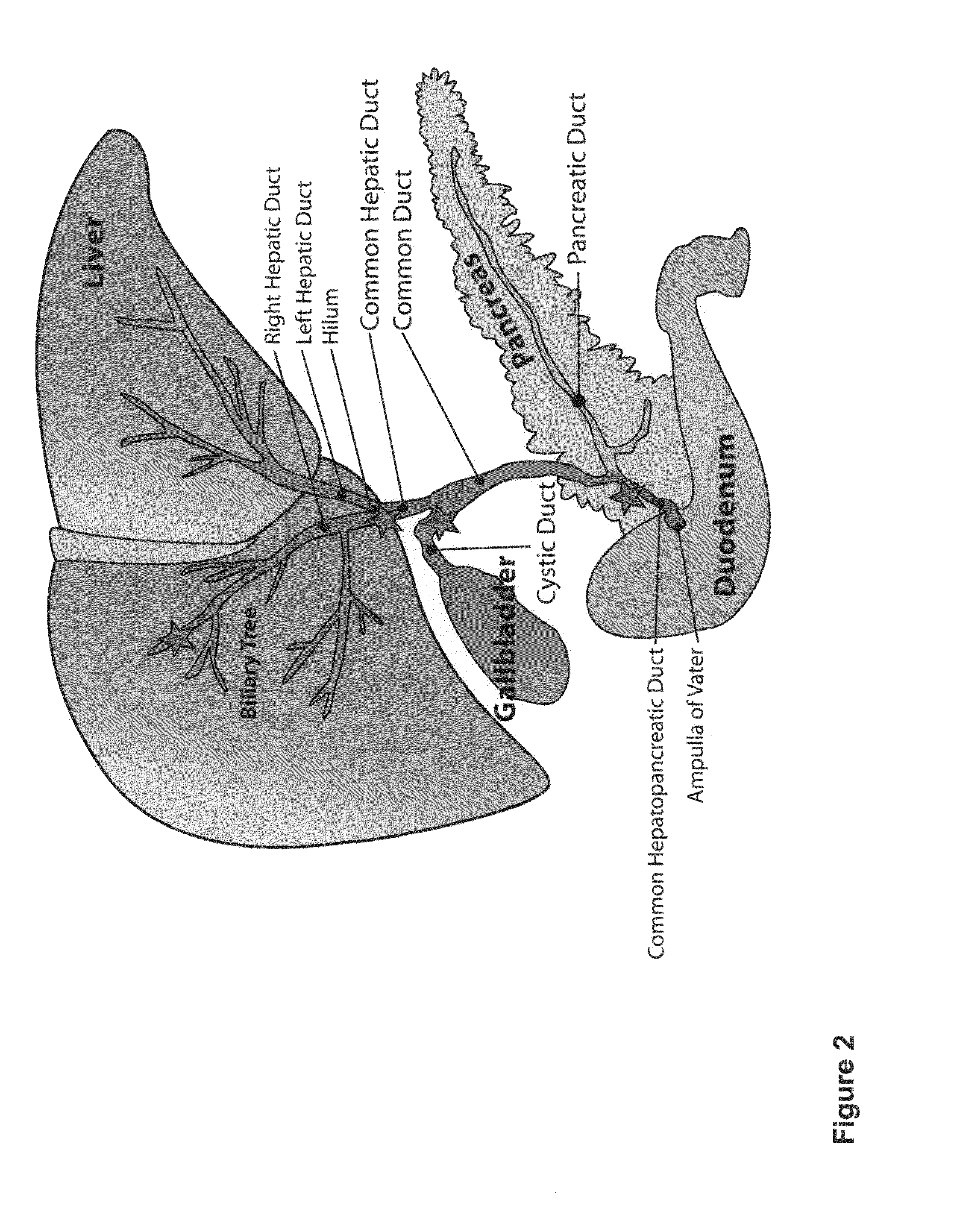
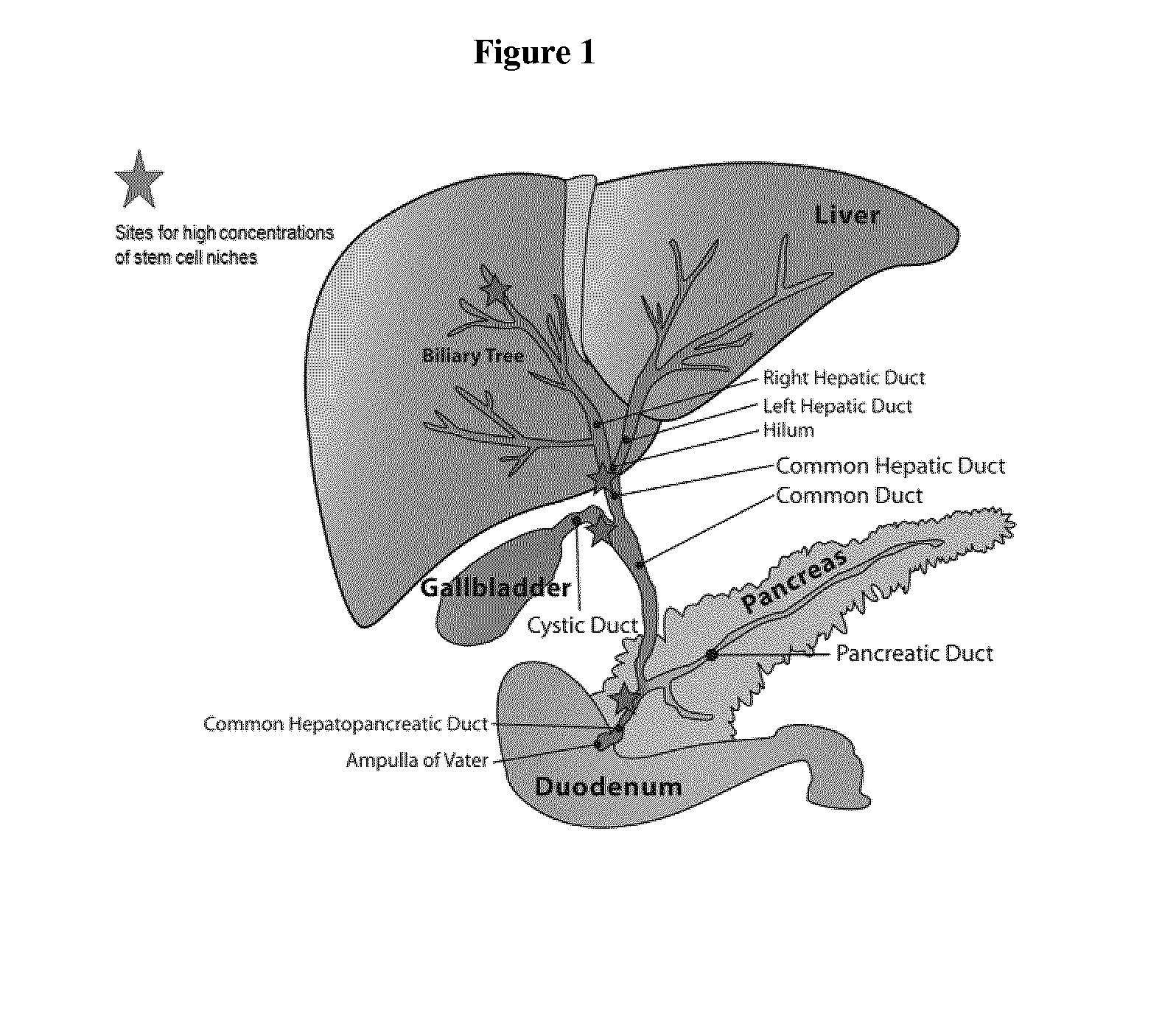
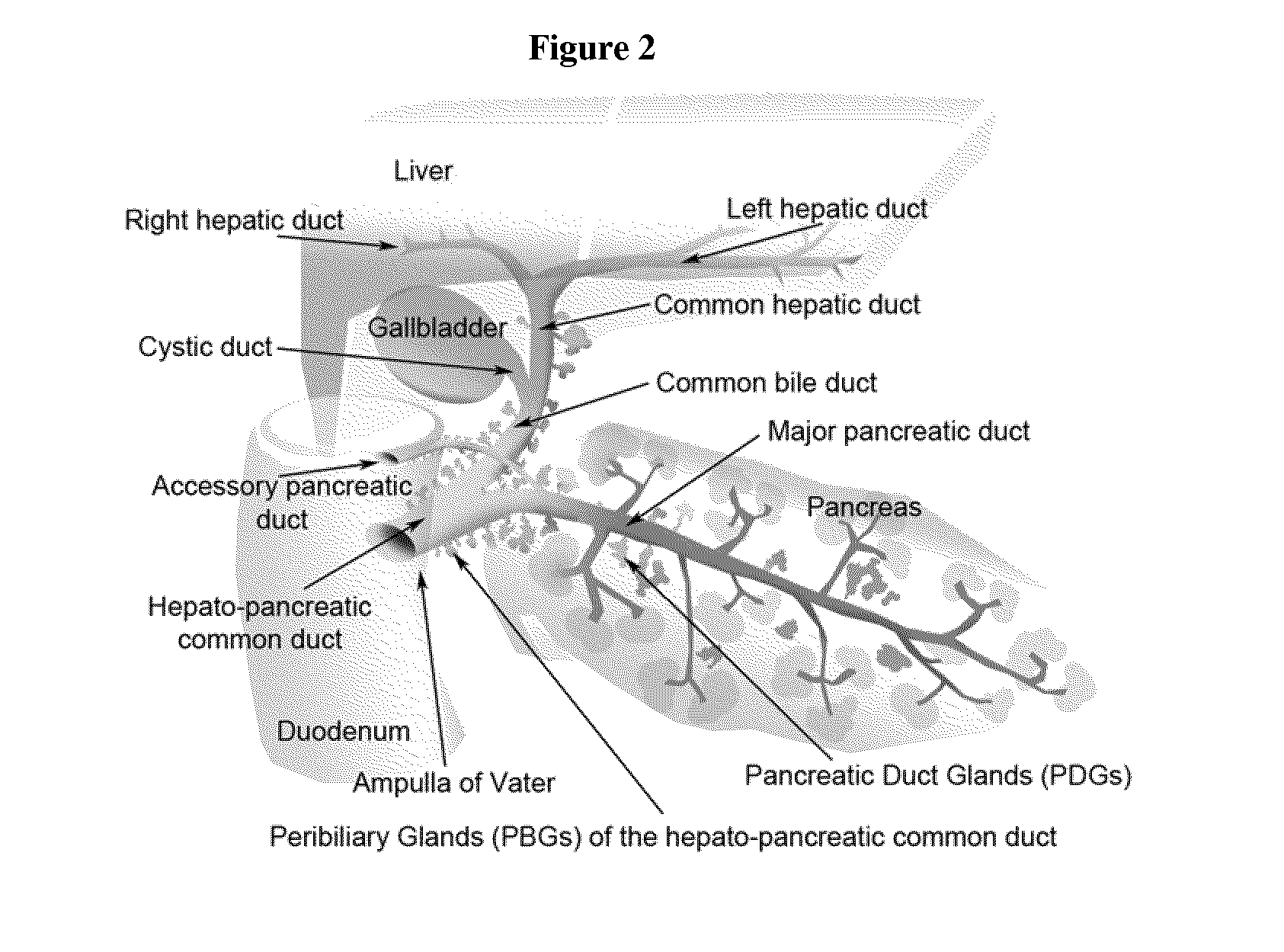
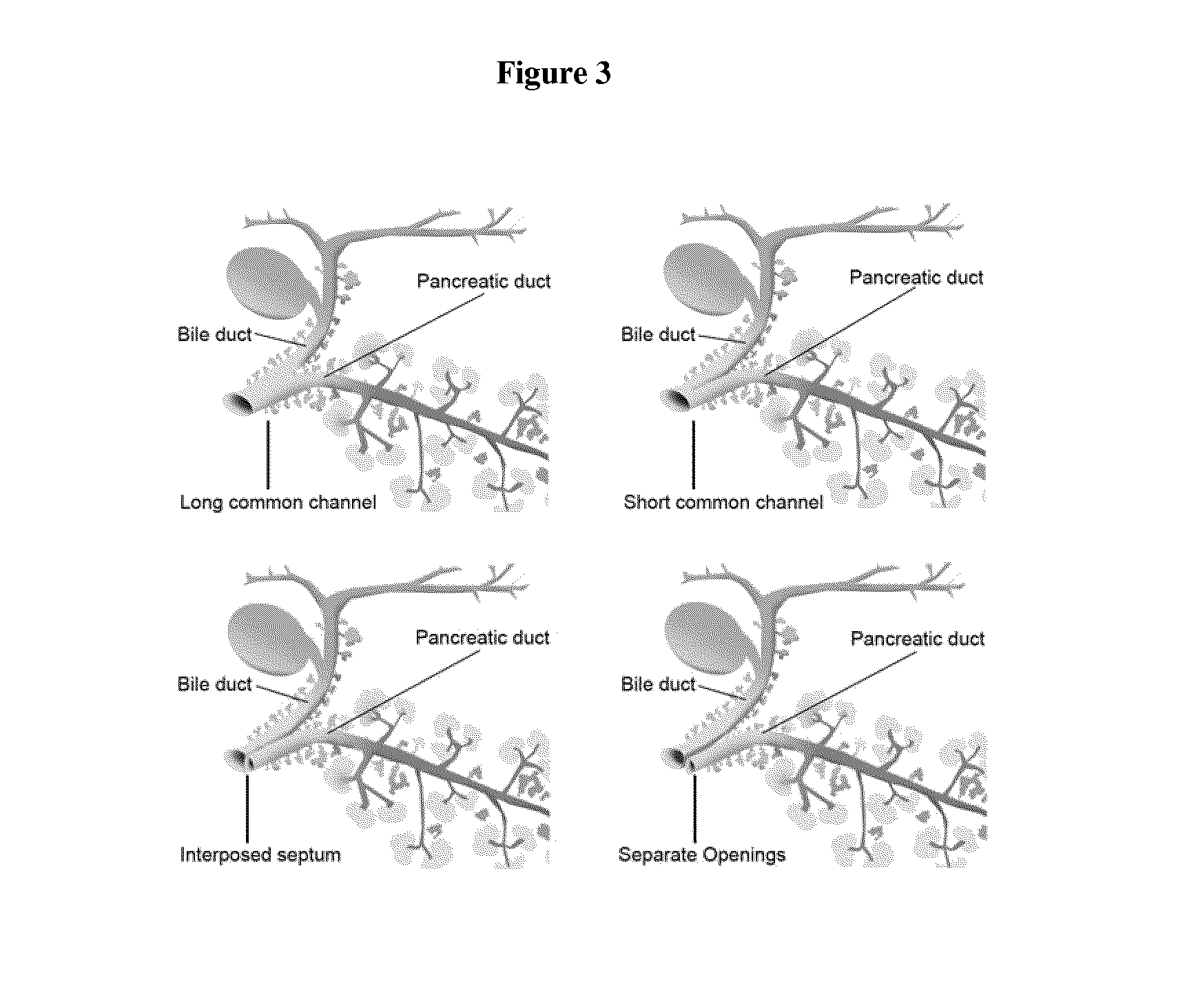
Multipotent stem cells from the extrahepatic biliary tree and methods of isolating same
PendingUS20110135610A1Differentiate faster and moreBiocideHepatocytesPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
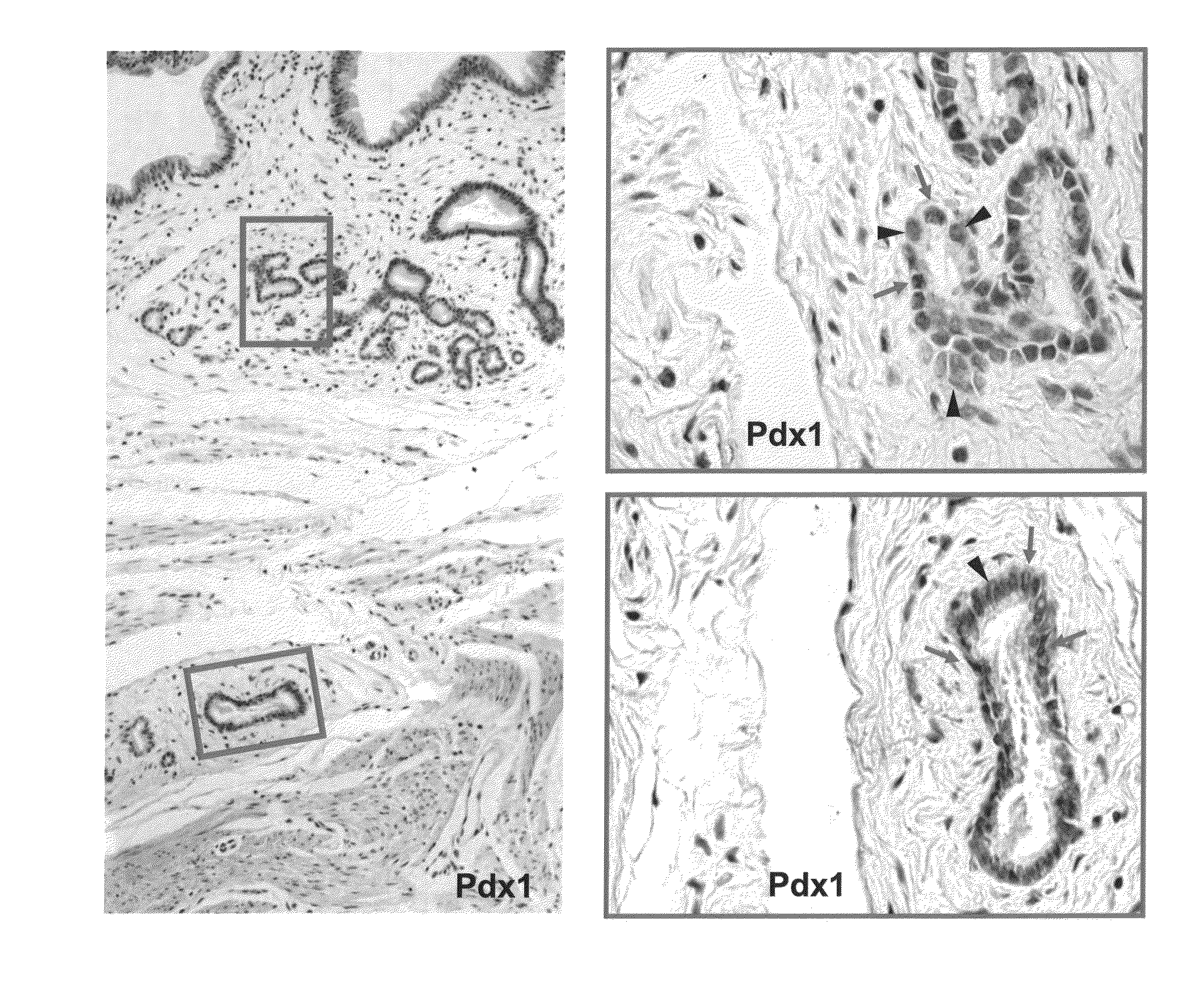
The present invention relates to a multipotent stem cell, multipotent cell populations, and an enriched multipotent cell population, each found in fetal, neonatal, pediatric, and adult biliary tree tissue and up to 72 hours post mortem (although preferentially, within 10 hours post mortem) and capable of maturing into multiple endodermal tissues that include liver, biliary and pancreatic tissues. The multipotent stem / progenitor cell and cell populations are found in peribiliary glands, and progenitors descending from them are present throughout the biliary tree including in the gallbladder. High numbers of the peribiliary glands are found in the branching locations of the biliary tree such as hilum, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, common duct, common hepato-pancreatic duct and gallbladder. Related multipotent cells, multipotent cell populations and their descendent progenitors are found throughout the biliary tree including in the gall bladder, which does not have peribiliary glands. Compositions comprising same, methods of identifying and isolating same, maintaining same in culture, expanding same in culture and differentiating or lineage restricting the same in vitro or in vivo to hepatic, biliary or pancreatic fates (e.g., as hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and / or pancreatic islet cells) are also provided. Methods of using the multipotent cells and / or multipotent cell populations are also provided.
Owner:SAPIENZA UNIV DE ROMA +1
Intravascular catheter capable of improving surface lubrication and preparation method for same
The invention discloses an intravascular catheter capable of improving surface lubrication. The intravascular catheter capable of improving surface lubrication is characterized in that an intravascular catheter made from a polyurethane material is used as a matrix, and a layer of poly-p-xylylene film is coated on the outmost layer. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the intravascular catheter capable of improving surface lubrication simultaneously. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cracking the poly-p-xylylene film into poly-p-xylylene active monomers by using an inert gas as a carrier, then realizing coating for the layer of poly-p-xylylene film on the outmost layer of the intravascular catheter by virtue of a vapour deposition method; because the poly-p-xylylene film rapidly forms a layer of lubrication film with water, the intravascular catheter is excellent in lubrication effect, and the lubrication degree is 10-100 times than that of a common catheter. Therefore, injuries on vascular tissues during catheter insertion are reduced, the occurrence of complications is prevented, the platelet adhesiveness is greatly reduced, and the thrombosis is reduced; the intravascular catheter capable of improving surface lubrication is an upgrade and update product for intravascular catheters.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHUNMEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Dual recycling-type coin changer
InactiveUS20110281513A1Small distanceEfficient processingApparatus with change-givingCoin countersCommon DuctEngineering
A compact recycling coin changer device for simultaneously serving a plurality of users includes a housing with a plurality of coin inlet and outlet slots. Individual coin lift units deliver coins for sorting and distributing to common coin denomination hoppers are arranged in parallel rows. A common duct, centrally located in the housing, can receive released coins from the hoppers and deposit them on a common coin-distributing device that operatively interconnects with the respective coin outlets, for example on opposite exterior housing walls. The coin changer device can be operatively associated with the dispensing of products, for example at a gas station or other retail outlets.
Owner:ASAHI SEIKO CO LTD
HVAC twinning control
ActiveUS7377120B2Mechanical apparatusAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesMicrocomputerCommon Duct
Owner:COPELAND COMFORT CONTROL LP
Spiral internal biliary drainage tube
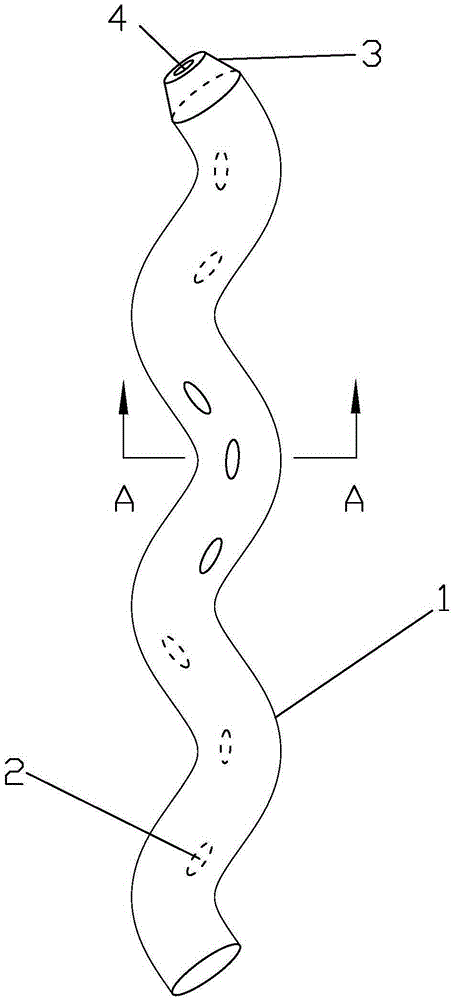
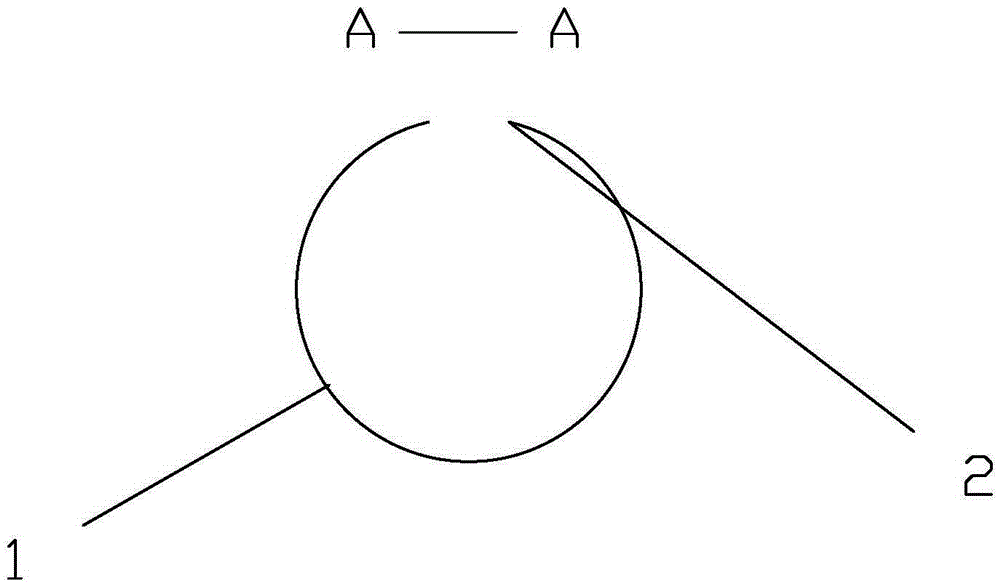
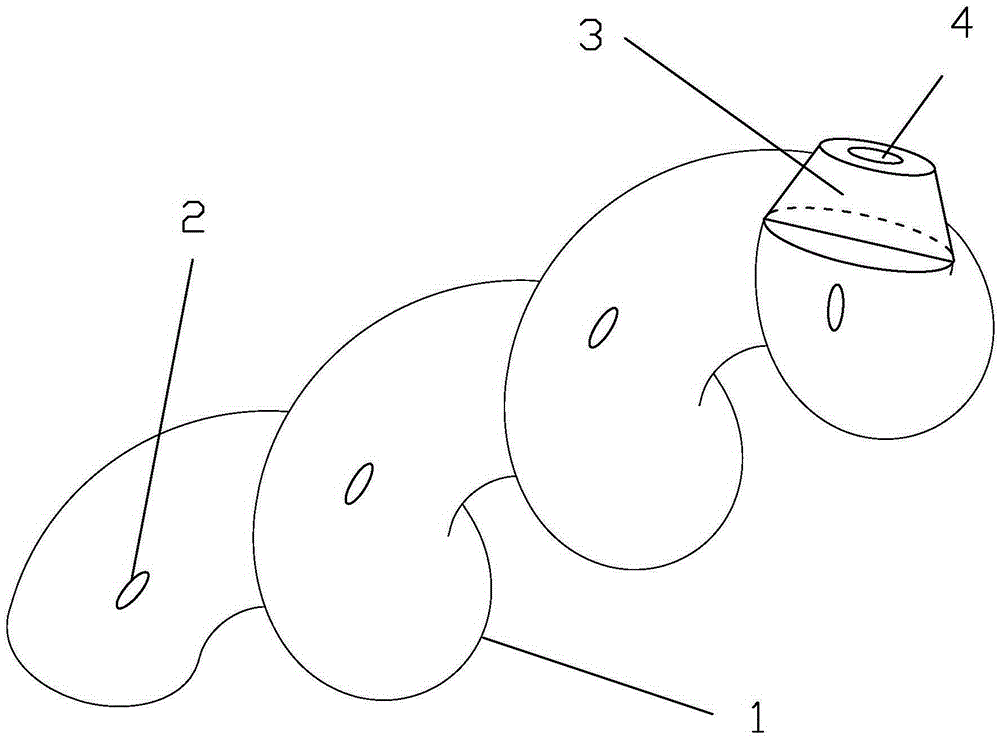
The invention discloses a spiral internal biliary drainage tube, which comprises a spiral tube, wherein a plurality of through holes I are arranged on the outer wall of the spiral tube; the spiral tube is 7-11cm long, the spiral tube is 1-2mm in inner diameter, the spiral tube is 4-5mm in outer diameter, the spiral tube includes 2-5 cycles and the spiral tube is 5-8.5Fr in pipe diameter. The spiral tube disclosed by the invention has an anti-sliding function, and the spiral internal biliary drainage tube is low in probability of internal displacement or takeoff; the drainage tube is capable of preventing biliary wall mucosa from being adsorbed on and from blocking the through holes I and is conducive to the drainage of infectious thick bile; the bile is discharged into duodena through the through holes I and the inner cavity of the spiral tube, and the bile also flows out through an inner cavity formed by the spiral tube; the main body of the spiral tube has an effect on compressing stones in common bile duct; the drainage tube, when preventing the stones in the common bile duct from displacing, can bring about a friction effect on the stones through the sidewall thereof, so that the volume of the stones is diminished to create conditions for secondary stone removal through ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Method of treating pancreatic and liver conditions by endoscopic-mediated (or laparoscopic-mediated) transplantation of stem cells into/onto bile duct walls of particular regions of the biliary tree
ActiveUS20140301985A1Engraftment can be facilitatedAvoids ectopic cell distributionBiocideDigestive systemCommon DuctProgenitor
A method of repairing diseased or dysfunctional pancreas or liver is provided. The method involves preparation of a suspension of stem cells and / or progenitor cells such as biliary tree stem cells, hepatic stem cells, pancreatic stem cells or their descendants, committed progenitor cells, from healthy tissue of the patient or of the biliary tree of a non-autologous donor and engrafting the cells into the wall of bile ducts near to the organ to be treated. The graft consists of stem cells or progenitors that are admixed with biomaterials and, optionally, with cytokines and / or native epithelial-mesenchymal cells appropriate for the maturational lineage stage of the cells to be engrafted. The cells are specifically introduced to the hepato-pancreatic common duct of the subject for treatment of pancreatic conditions or to the bile duct wall near to the liver for treatment of liver conditions and allowed to migrate to the pancreas or to the liver and expand and then rebuild part or the entirety of the diseased or dysfunctional organ.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA +2
Selectable bile recycling and bypassing enteral nutrition device and use method thereof
PendingCN106798962AAvoid churnPromote recoveryWound drainsMedical devicesBiliary tract diseaseCommon Duct
The invention relates to a selectable bile recycling and bypassing enteral nutrition device and a use method thereof. The device comprises a drainage pipe used for draining bile from a common bile duct to the terminal and a bypassing pipe for returning the bile back to a jejunum in vivo, wherein the first end of the drainage pipe is placed in the common bile duct, the second end of the drainage pipe communicates with the first end of the bypassing pipe, and the second end of the bypassing pipe is placed into the jejunum. The bypassing pipe is used for returning the bile back to the enteric canal, the problem that a large number of bile losses due to long-term cathetering after surgery on biliary diseases is avoided, and thus a patient can recover well after the surgery; a bypassing heating bag is used for warming the bile, and the discomfort of the patient due to the fact that the processed bile returning back to the enteric canal has relatively low temperature is avoided; the drainage pipe, the bypassing pipe, the bypassing heating bag and a nutrient solution adding component are detachable, and can be selectively assembly according to the disease state and need of the patient; the bypassing pipe is connected with the nutrient solution adding component used for enteral nutrition treatment, thus being convenient for supplying the nutrition solution to the patient.
Owner:吴雪松 +1
Hepatic lobule-like bioreactor
ActiveCN102114275AWith liver metabolism functionGood mass transfer functionOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsCapillary networkCommon Duct
The invention discloses a hepatic lobule-like bioreactor, which belongs to the field of biomedical equipment. A nanofiber scaffold network is arranged in a shell of the bioreactor, an intrahepatic fibrovascular network, a bile capillary network, upper hepatic bile ducts, lower hepatic bile ducts, a common bile duct, and hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts are distributed in the whole nanofiber scaffold network, and the bile capillary network is distributed at the peripheries of the hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts; the upper hepatic bile ducts and the lower hepatic bile ducts are communicated through the common bile duct; bile capillaries in the bile capillary network are provided with more than two bile capillary epidermal cell inlets; the hepatic cell collagen fiber microducts are provided with more than two hepatic cell injection ports; the intrahepatic fibrovascular network is provided with a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet; and the bile capillary epidermal cell inlets, the hepatic cell injection ports, the liquid inlet, the liquid outlet and an outlet at the lower end of the common bile duct pass through the shell. The hepatic lobule-like bioreactor truly simulates the structure of hepatic lobule, realizes the functions of metabolic detoxification, excretion and the like of livers, and is superior to the conventional bioreactor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
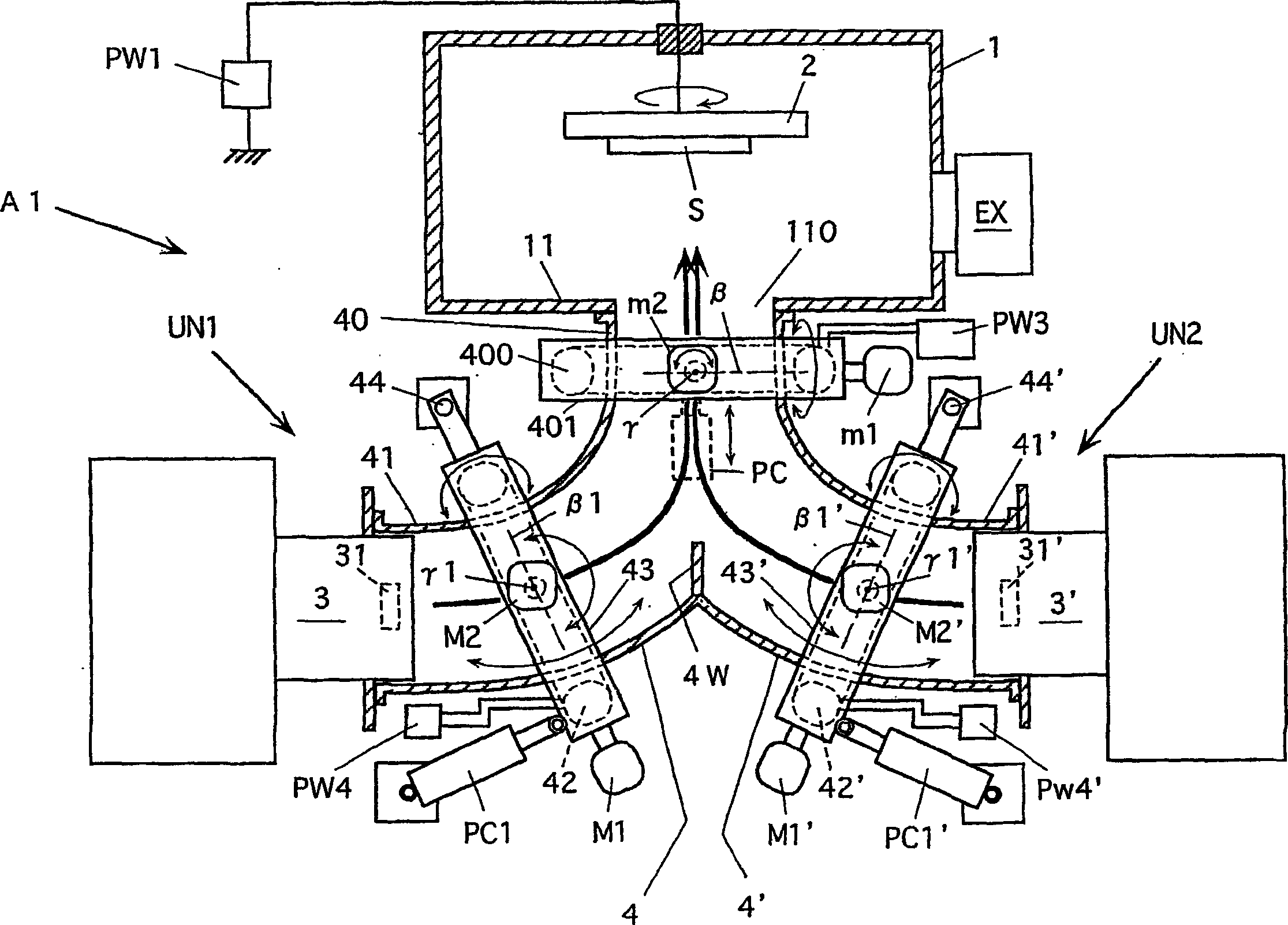
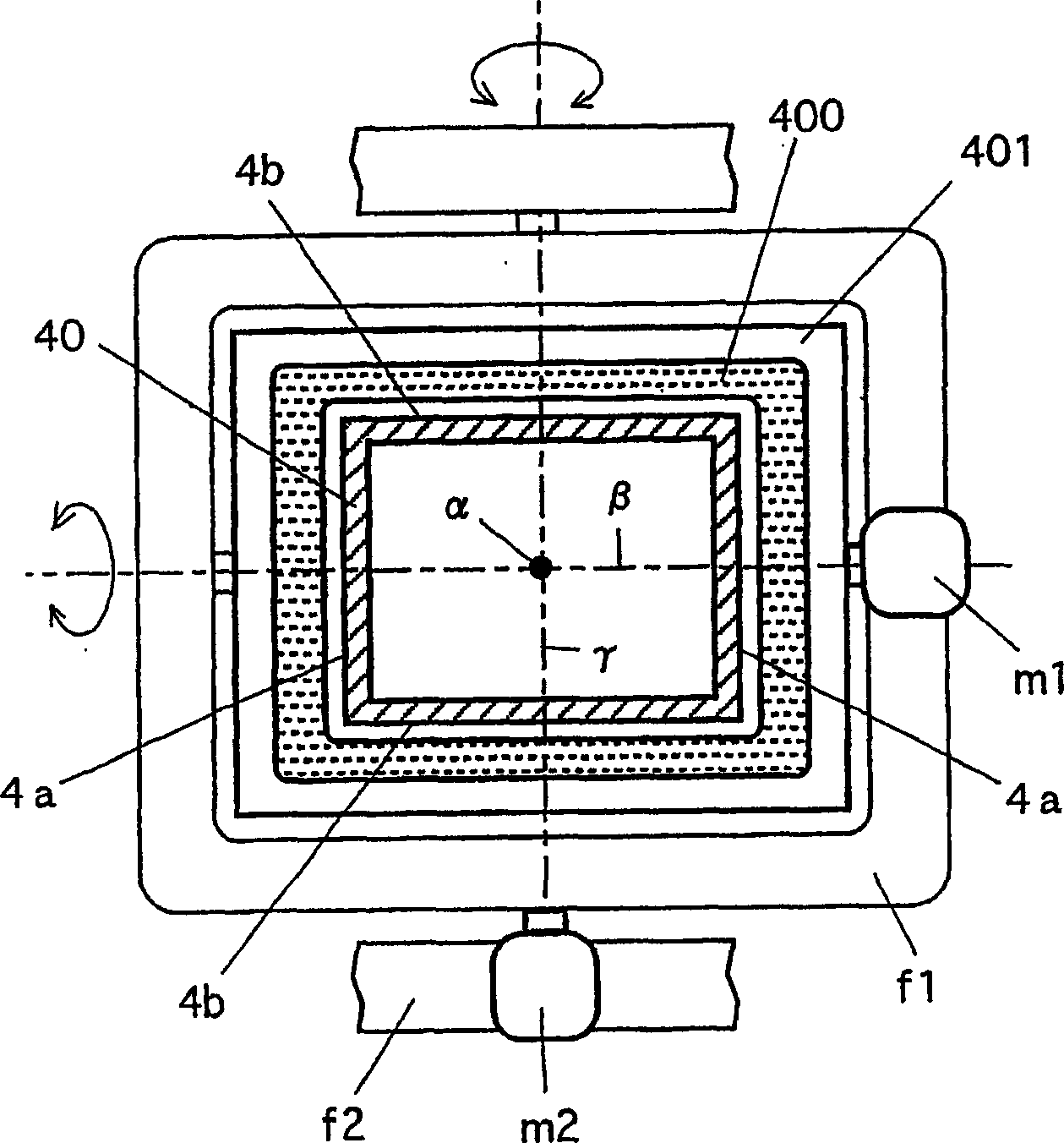
Deflection magnetic field type vacuum arc vapor deposition device
InactiveUS20070023282A1Quality improvementDesired structureCellsElectric discharge tubesProduction rateCommon Duct
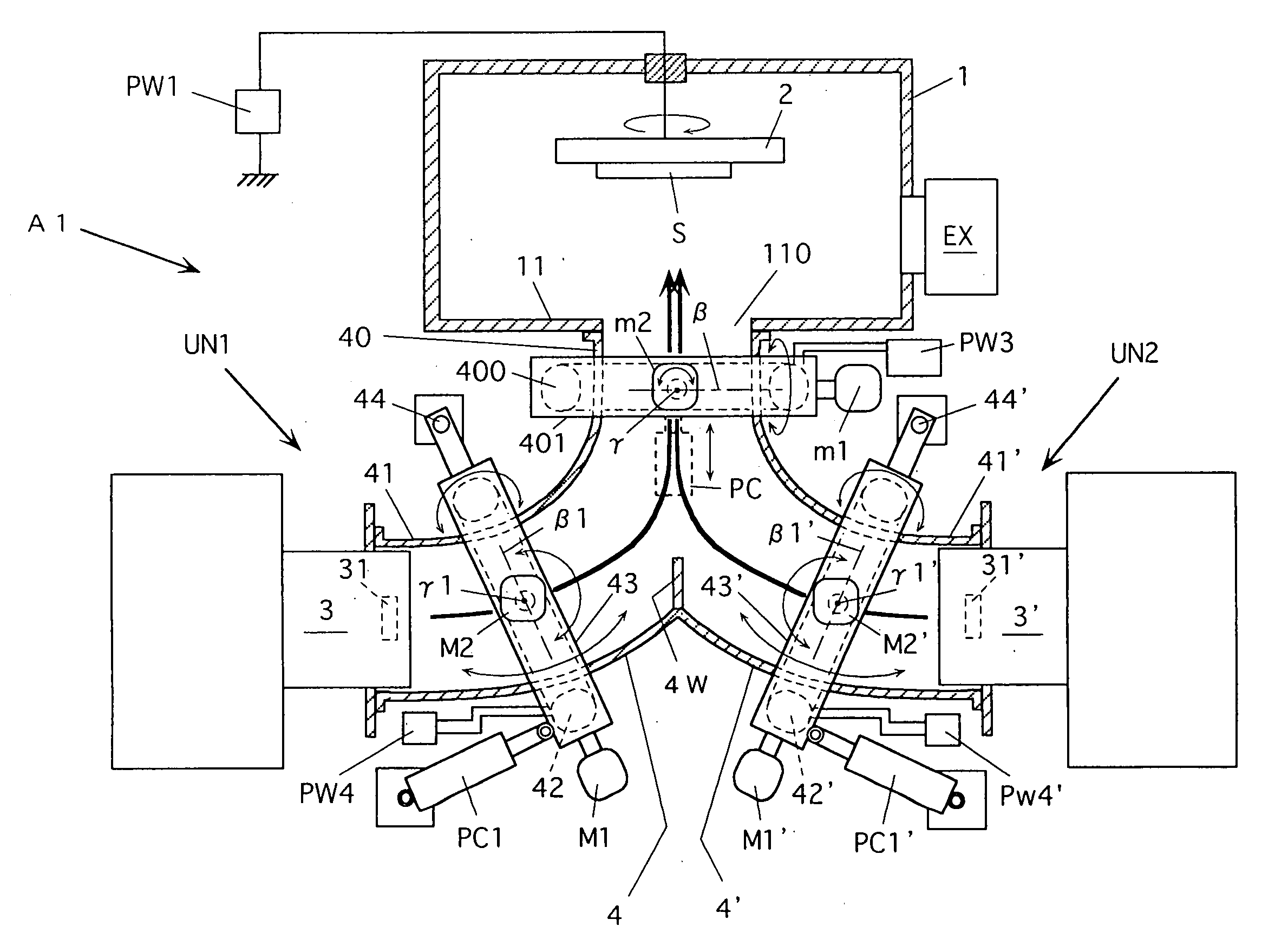
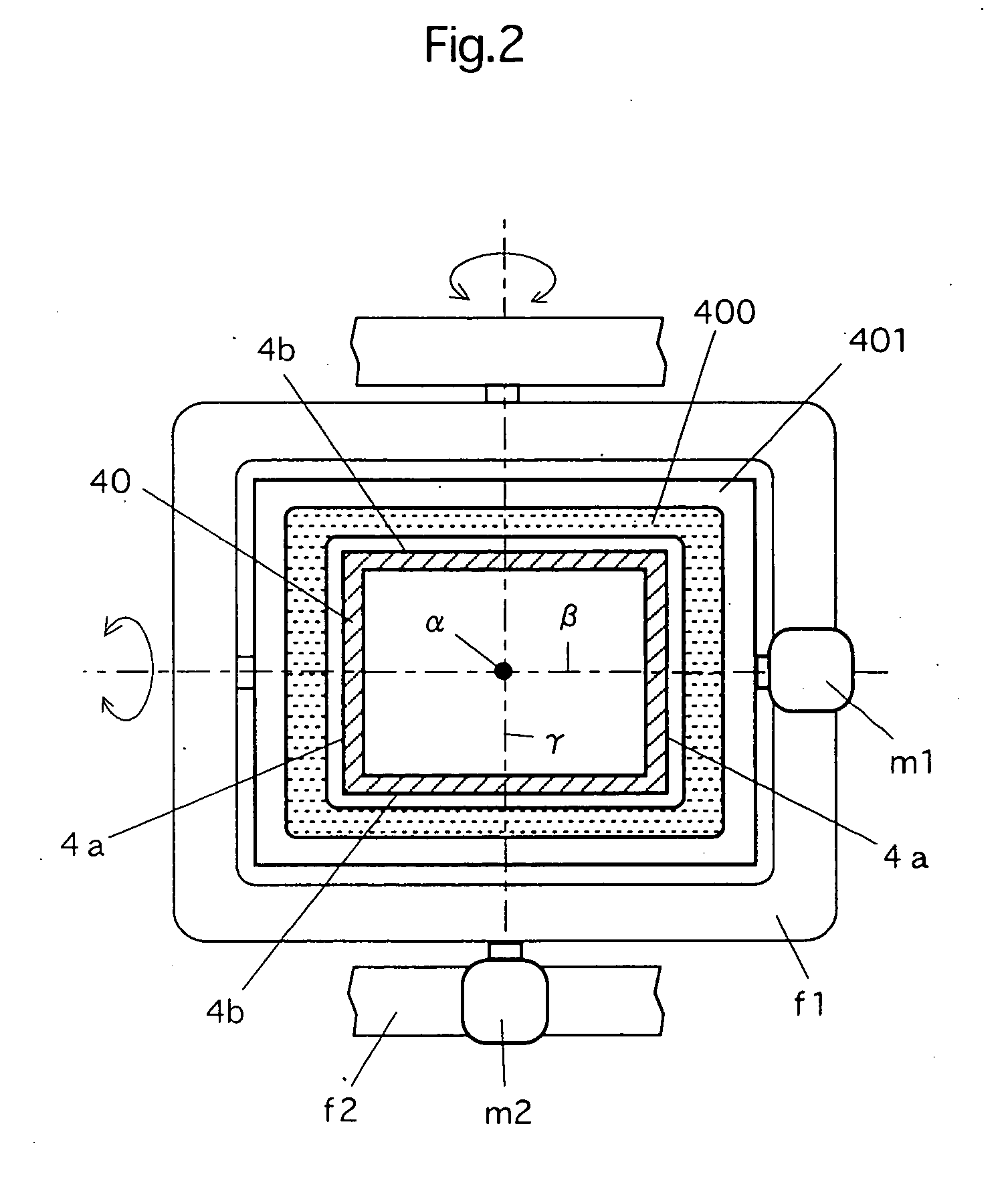
A vacuum arc vapor deposition apparatus of a deflection field type includes a plurality of vapor deposition units (UN1, UN2) each including a vapor source (3, 3′) and a curved filter duct (4, 4′) provided with deflection field forming coils (400, 42 or 42′). The ducts (4, 4′) have duct ends opposed to the deposition target holder (2) and formed together to provide a common duct end (40). The vapor source (3, 3′) is arranged on the other end (41, 41′) of each duct. The coil (400) is arranged for the common duct end (40), and one magnetic field forming coil (42, 42′) is arranged for each of the ducts. An adjusting device (motors m1, m2 and drive device PC, motors M1, M2 and drive device PC1, motors M1′, M2′ and drive device PC1′) for adjusting a state of arrangement is arranged for each coil. This vacuum arc vapor deposition apparatus can form a thin film of good quality having a desired structure on the deposition target with good productivity.
Owner:NISSIN ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
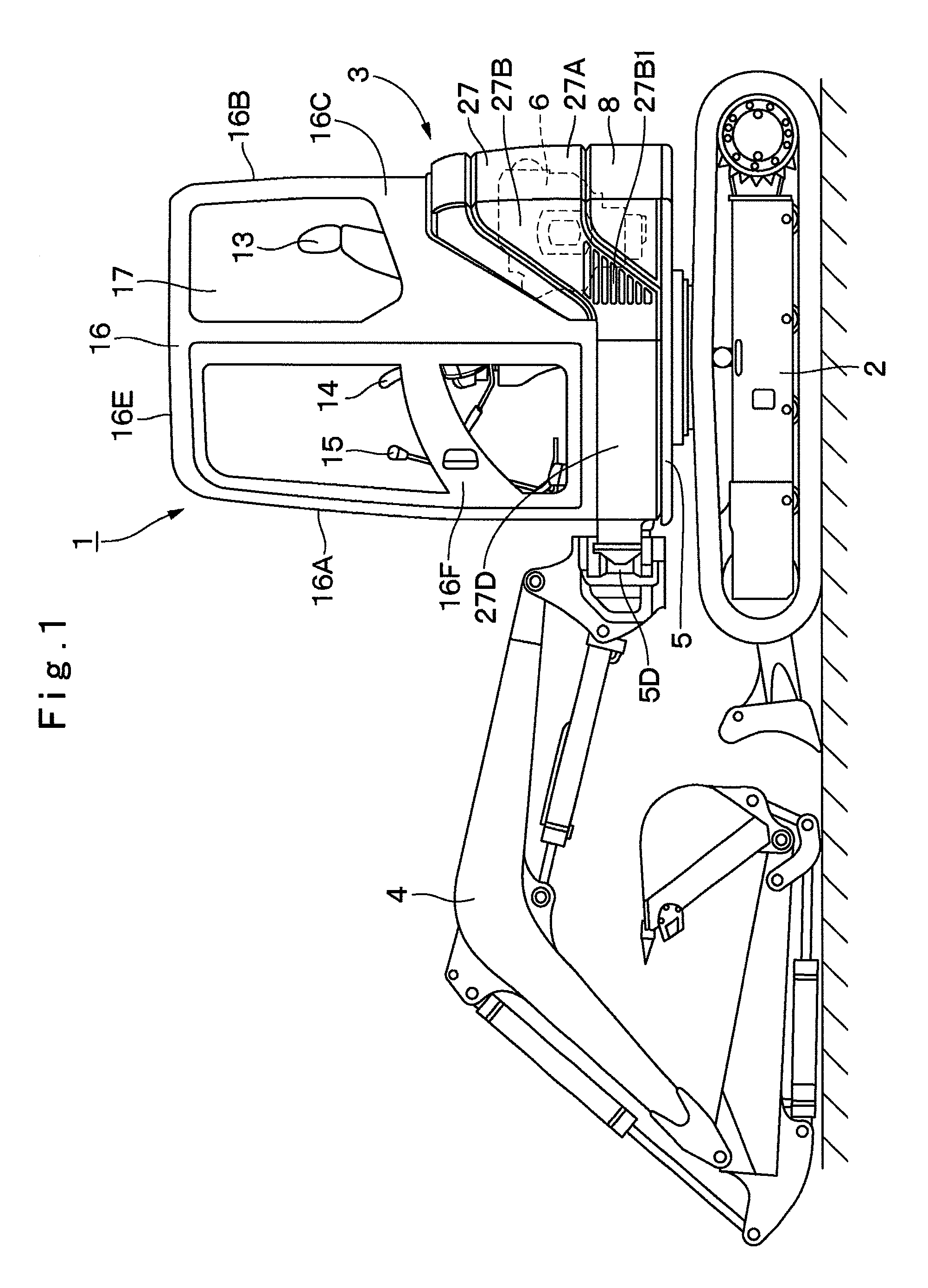
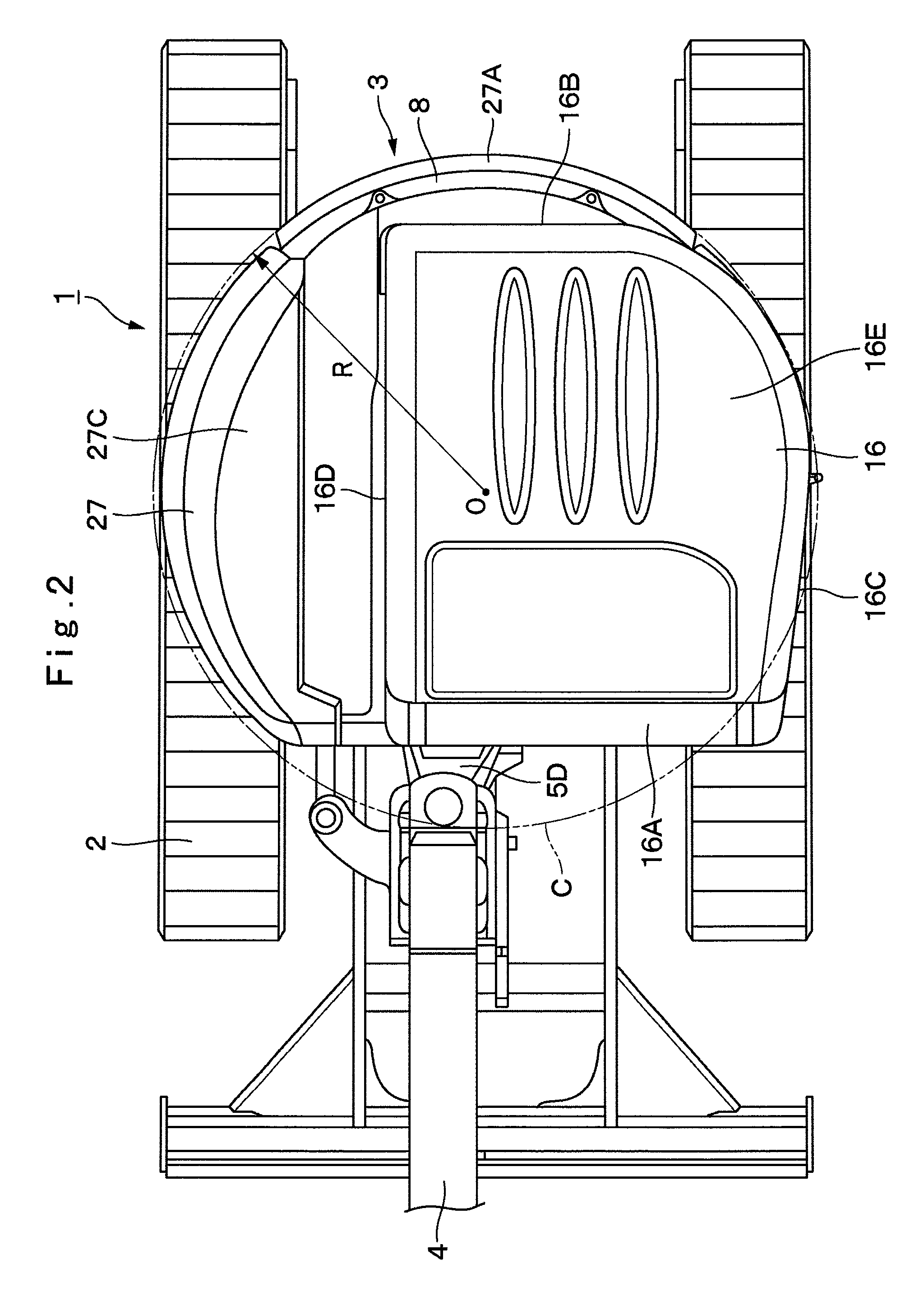
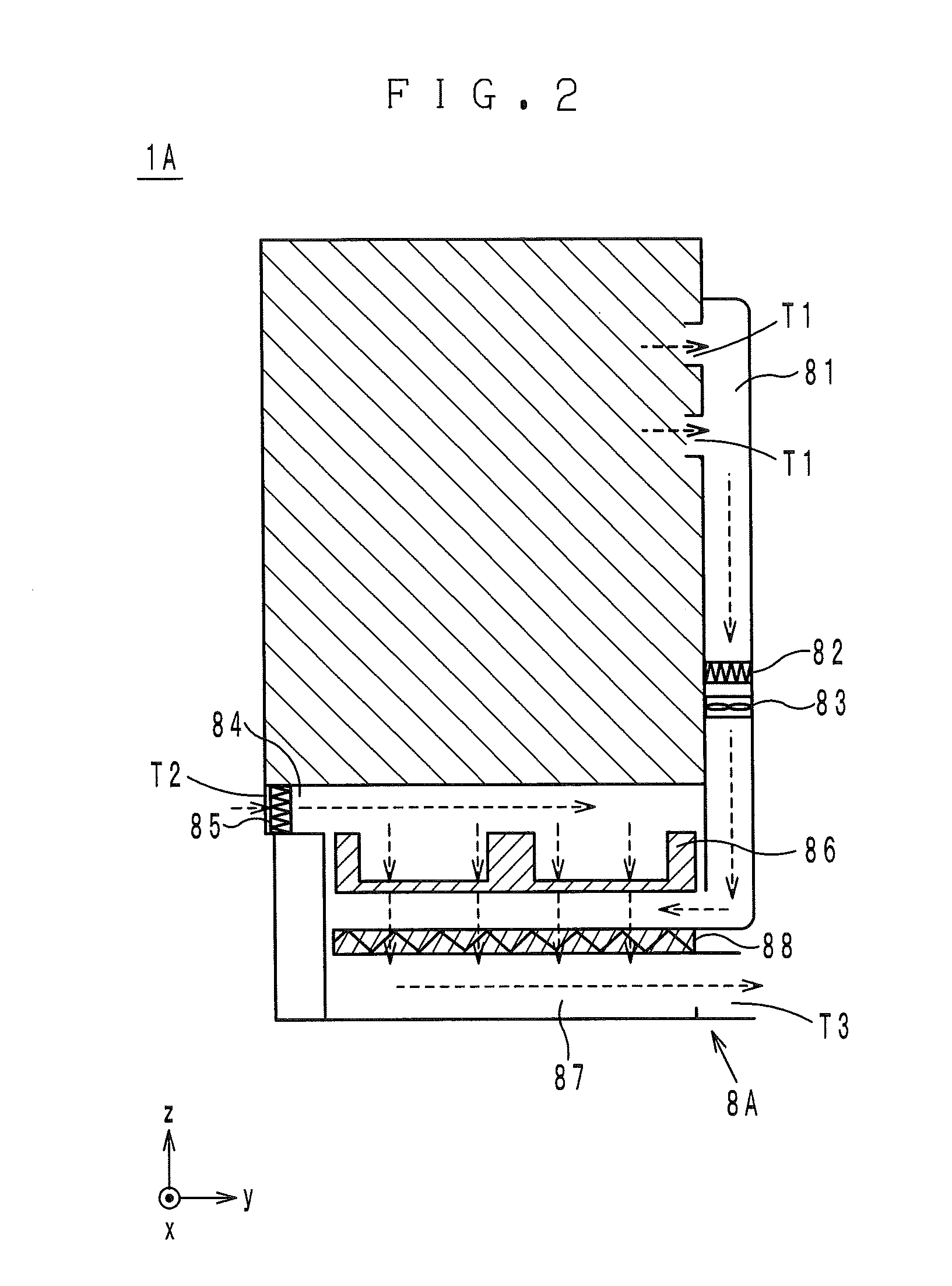
Construction machine
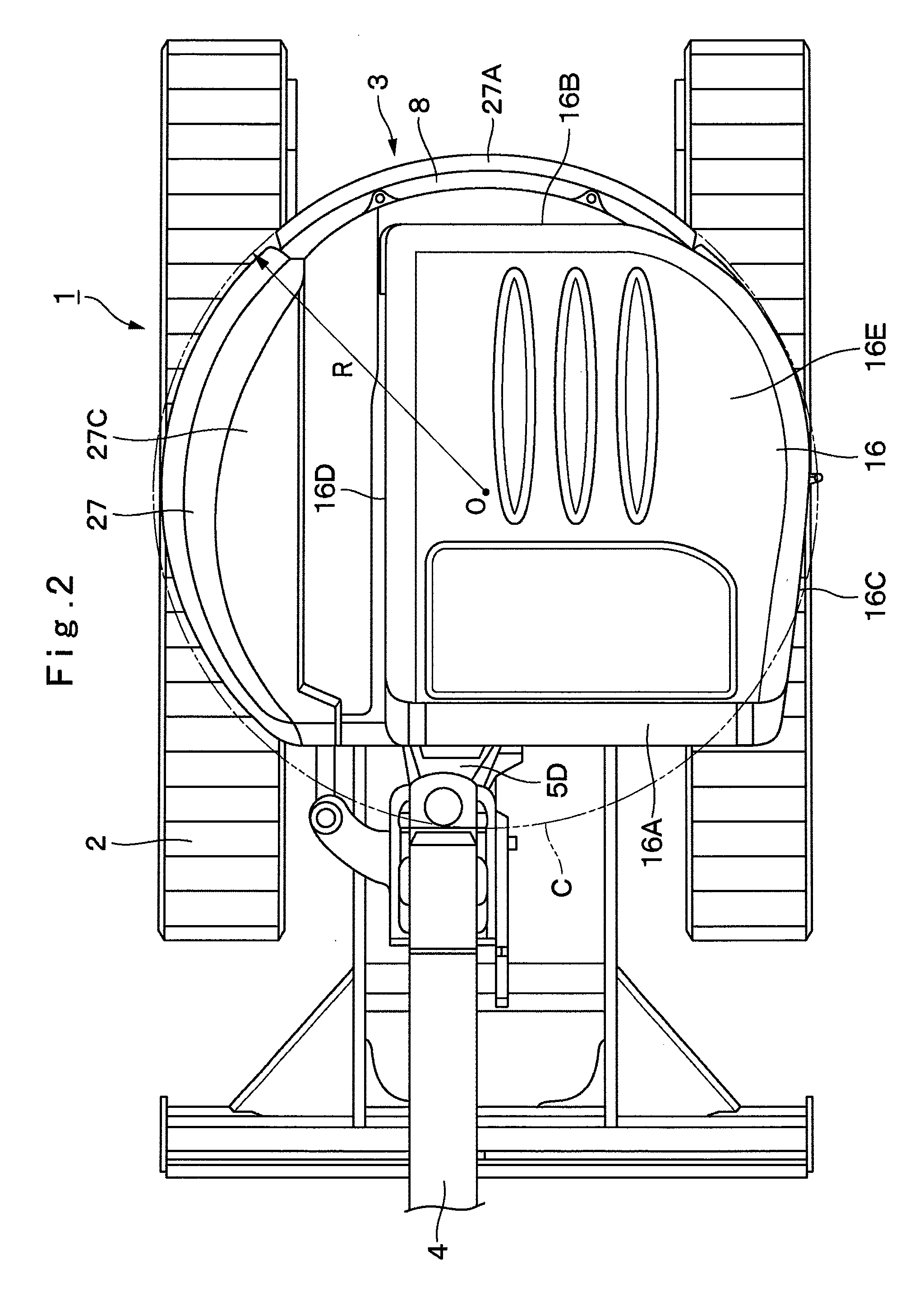
ActiveUS8616619B2Great suctionLimited spaceVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesCommon DuctUltimate tensile strength
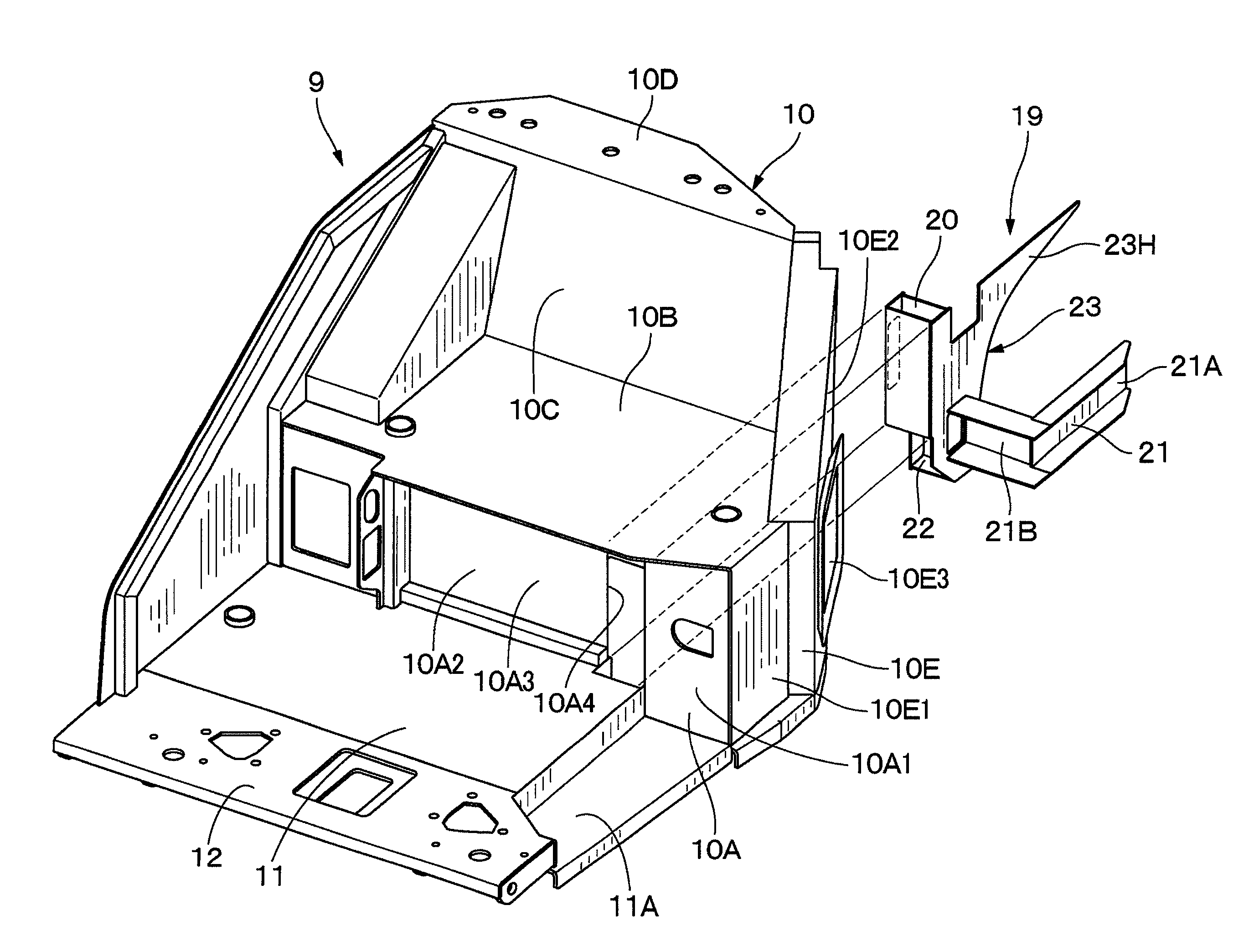
A suction duct (19) provided in a floor member (9) comprises an internal air duct portion (20) connected to the internal air inlet port (10A3), an external air duct portion (21) connected to an external air inlet port (10E3), and a common duct portion (22) for connecting the internal air duct portion (20) and the external air duct portion (21) to a blower fan 18B suction side of an air conditioner unit (18). The suction duct is constructed to form a hollow column (23) having a hollow closed section structure with the internal air duct portion and the common duct portion formed integrally in the upper and lower directions. Therefore, the hollow column formed of the hollow closed section structure can increase strength of the floor member as a strong column while circulating internal air between the internal air inlet port and the air conditioner unit.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
HVAC twinning control
ActiveUS20070068179A1Mechanical apparatusAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesCommon DuctMicrocomputer
A control is provided for a first HVAC unit that is coupled to a common duct shared with at least one other HVAC unit. The control comprises a twinning connection for communication with at least a second control of another HVAC unit, and a voltage signal applied to the twinning connection. The control further comprises a switching means for switching the voltage signal to ground. A microcomputer for monitoring the twinning connection and for controlling the switching means is configured to actuate the switching means to switch the voltage at the twinning connection to ground for a predetermined time period to communicate a blower speed for the first HVAC unit. The microcomputer monitors the twinning connection to sense the duration that the voltage at the twinning connection is being conducted to ground, and responsively controls the speed of the first HVAC blower according to the prescribed blower speed corresponding to the sensed duration.
Owner:COPELAND COMFORT CONTROL LP
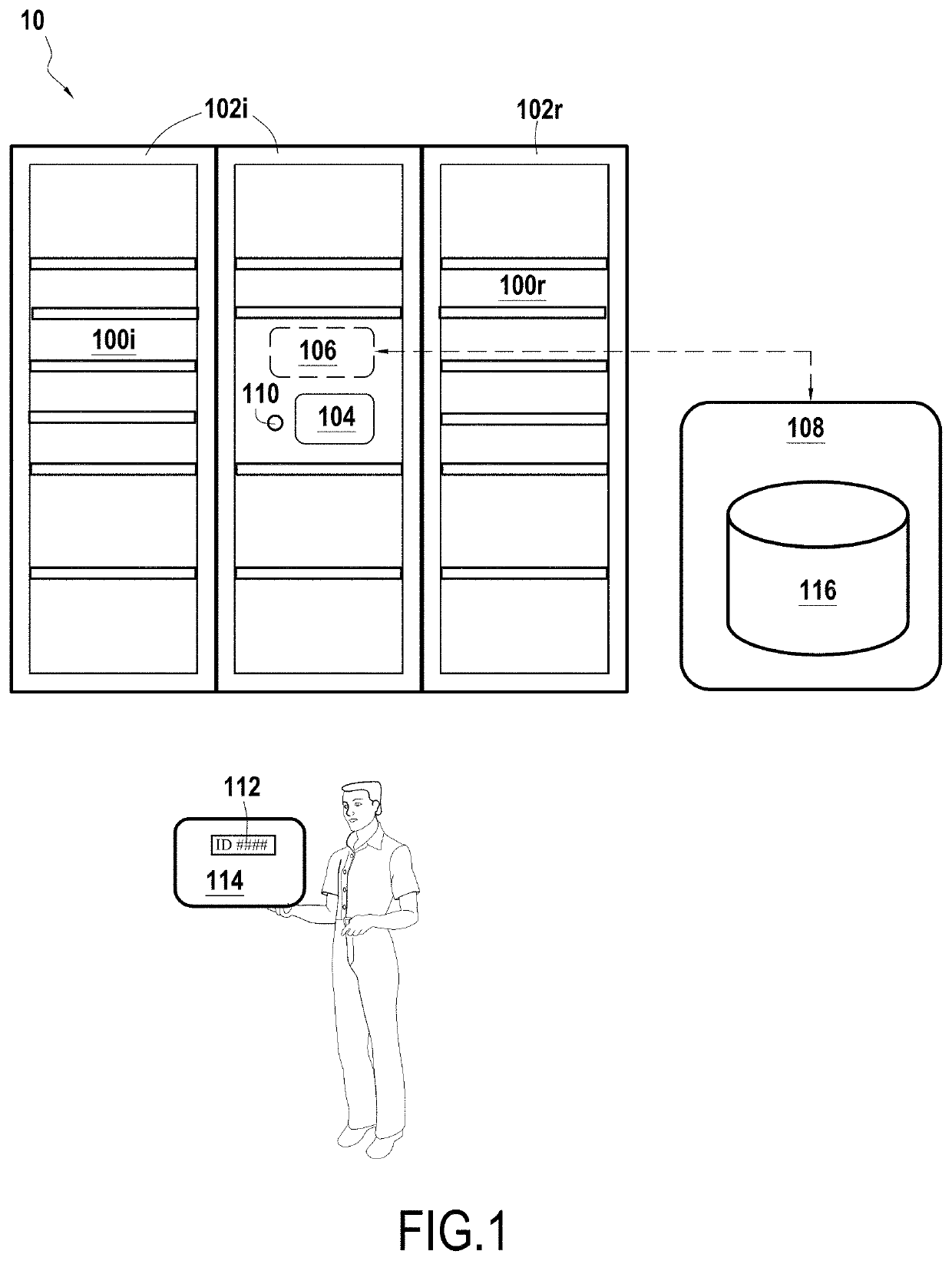
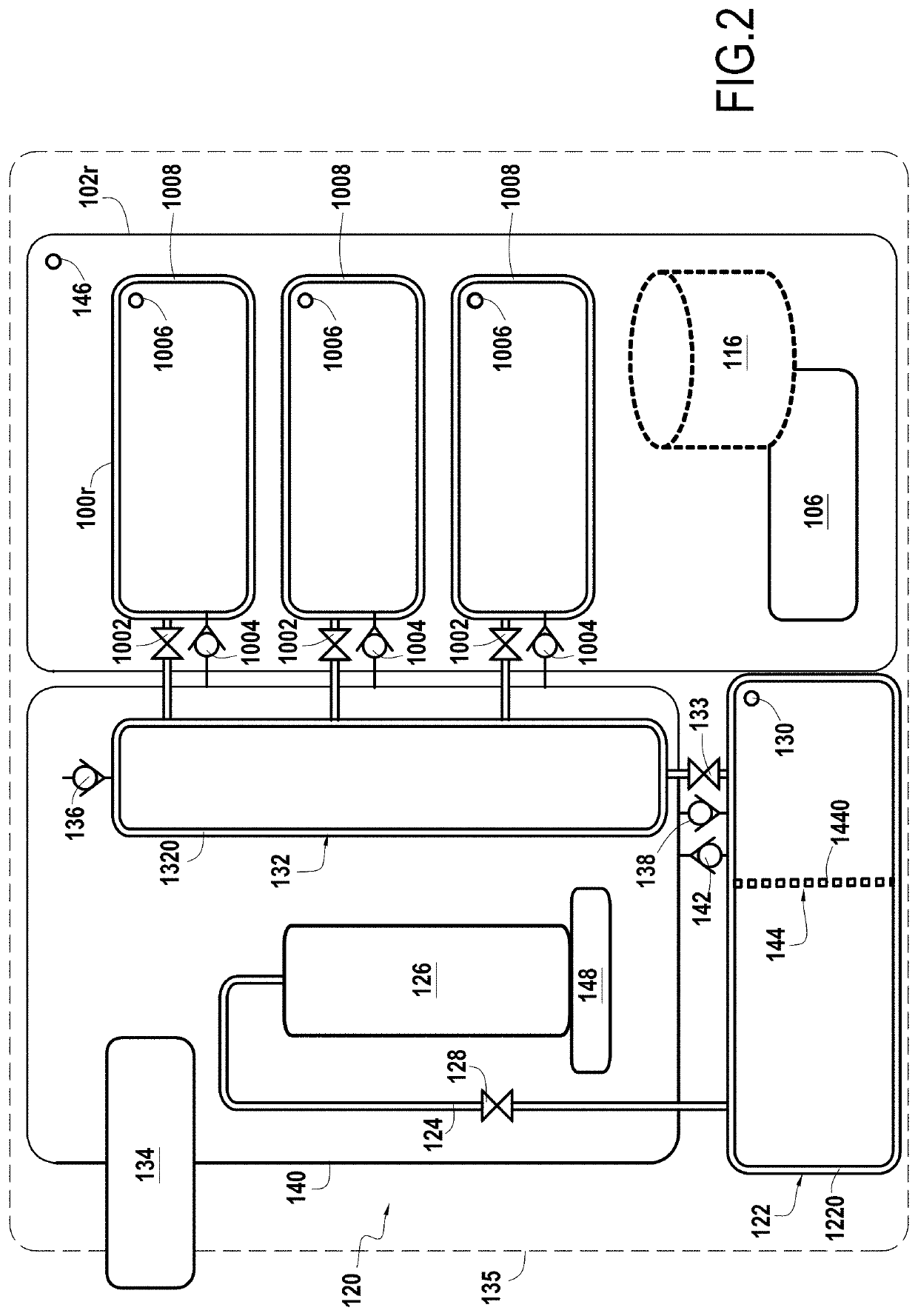
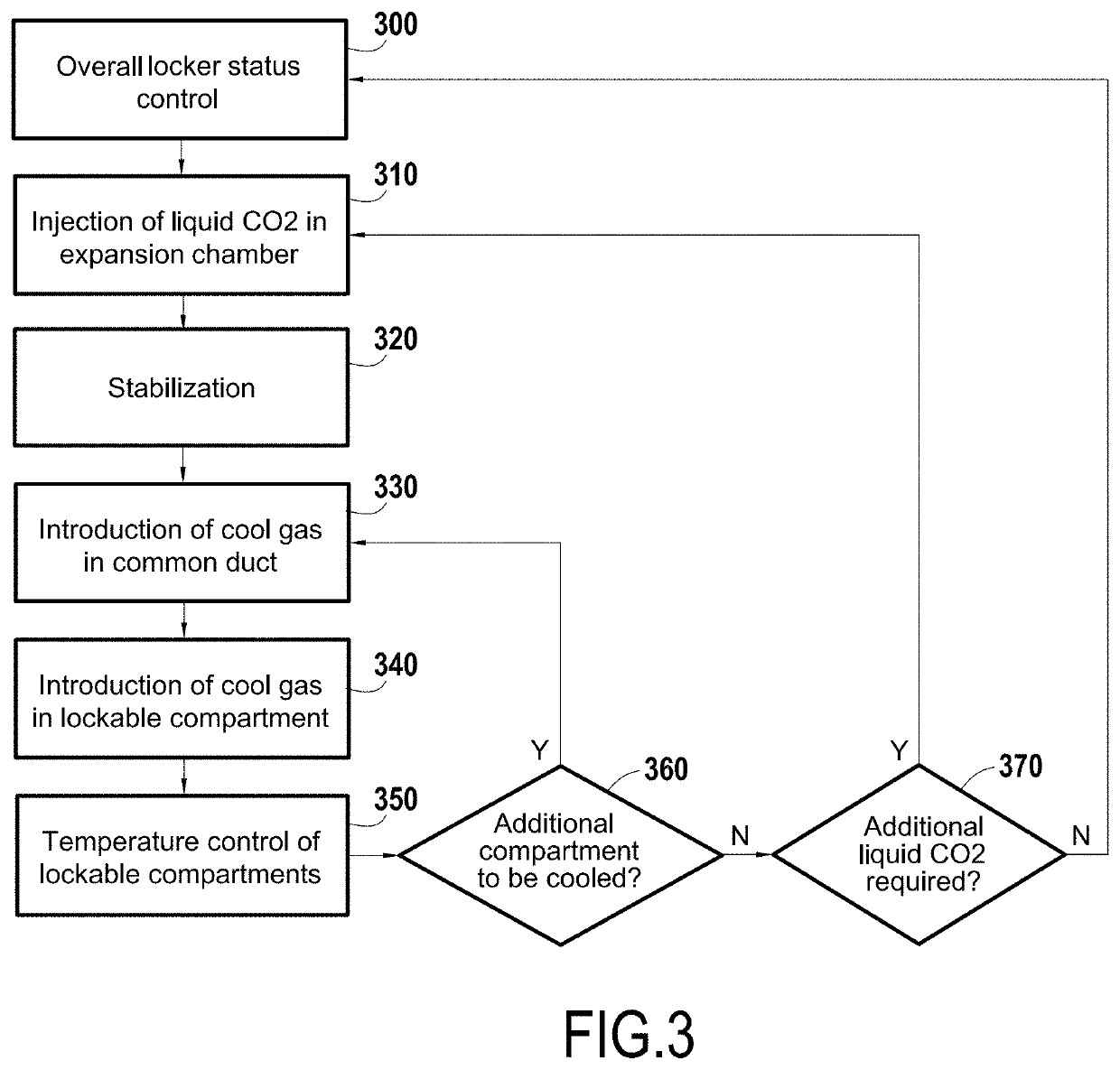
Locker system for delivery of heat sensitive products
ActiveUS20200158414A1Concentrate moreRapid coolingLighting and heating apparatusBuilding locksCommon DuctCool storage
A locker system for delivering heat sensitive products comprising a plurality of lockable compartments including at least one refrigerated lockable compartment, a control unit for controlling said plurality of lockable compartments, a cooling device comprising an expansion chamber receiving liquid CO2from a reserve of liquid CO2 and delivering gaseous CO2 in each of said refrigerated lockable compartments through at least one common duct, and an extraction system to avoid excessive concentration of CO2 in a building where the locker system is located.
Owner:QUADIENT TECH FRANCE
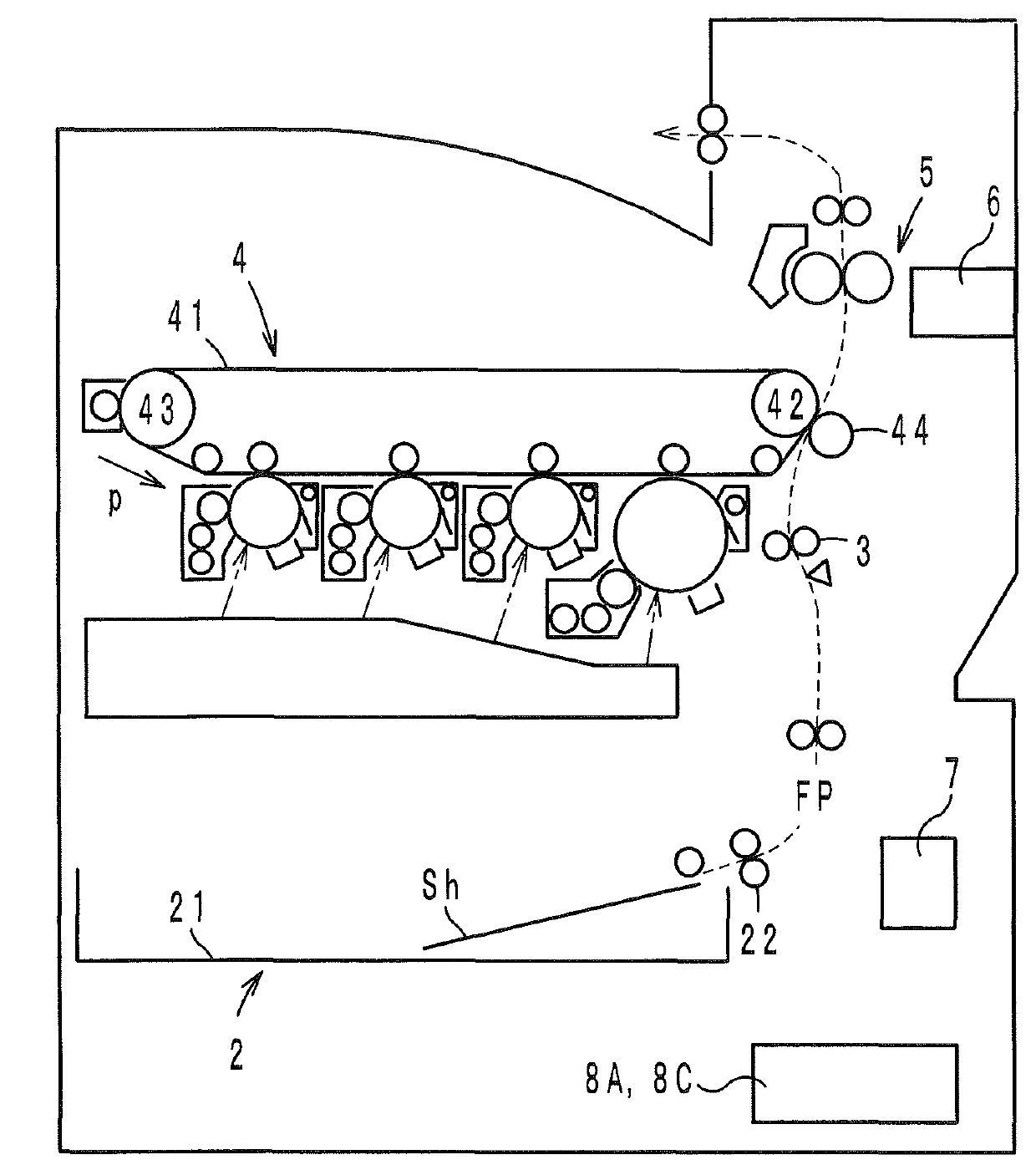
Paper sheet conveyance method and paper sheet conveyance device with common blower duct
An equipment for conveying sheet-shaped members, including a plurality of blower ducts being arranged in parallel; a common duct connected to outlets of the blower ducts; an air stream unit for generating air streams in the blower ducts; a plurality of sheet feeding units respectively connected to the blower ducts, the sheet feeding units feeding sheet-shaped members into the blower ducts; a plurality of open / close valves respectively provided to the blower ducts, the open / close valves opening and closing the blower ducts; a drive section for respectively driving the open / close valves; a collecting unit provided to a terminal end of the common duct, the collecting unit collecting the sheet-shaped members conveyed; and a control section for controlling the drive section.
Owner:MARS ENG
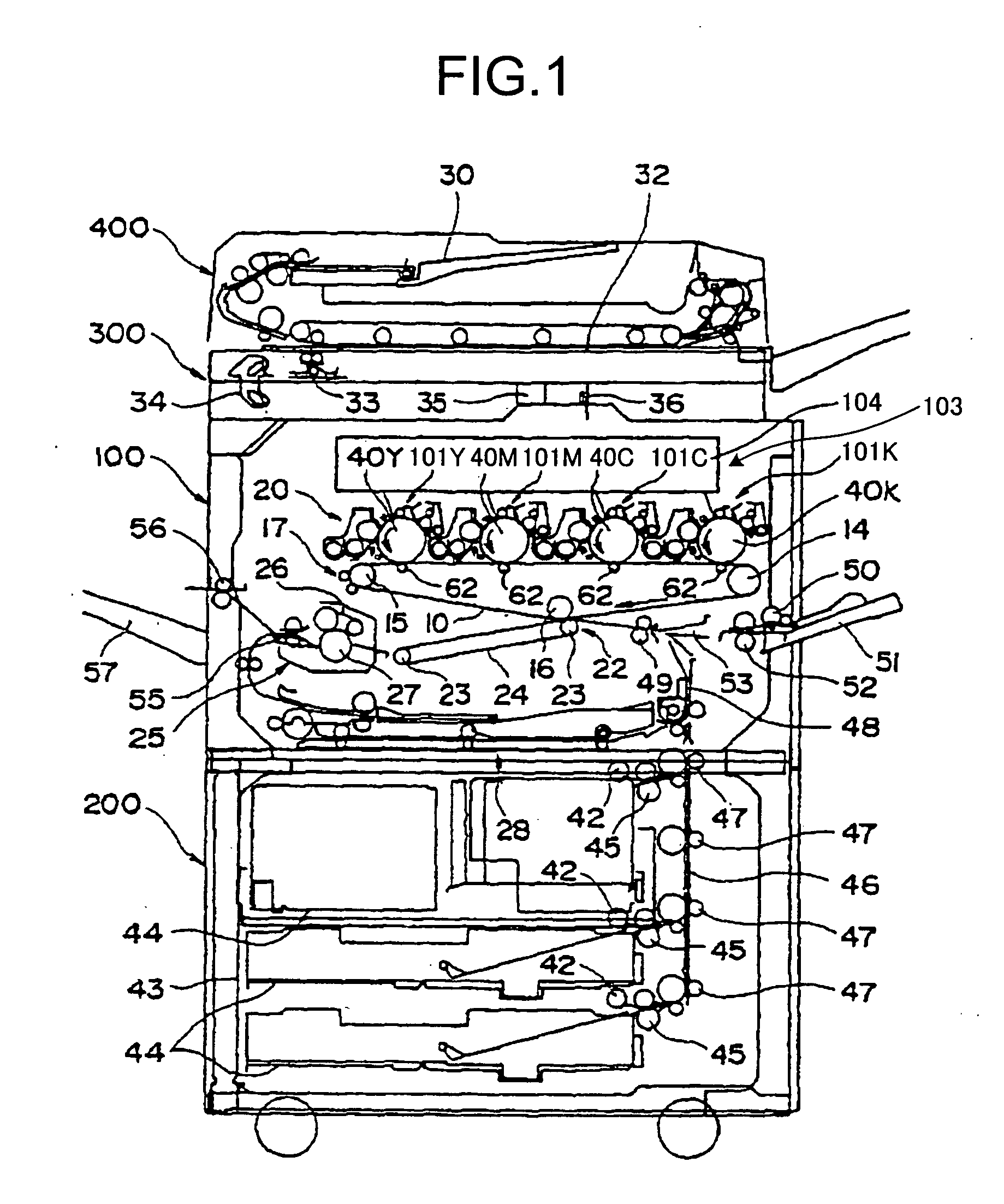
Image forming apparatus
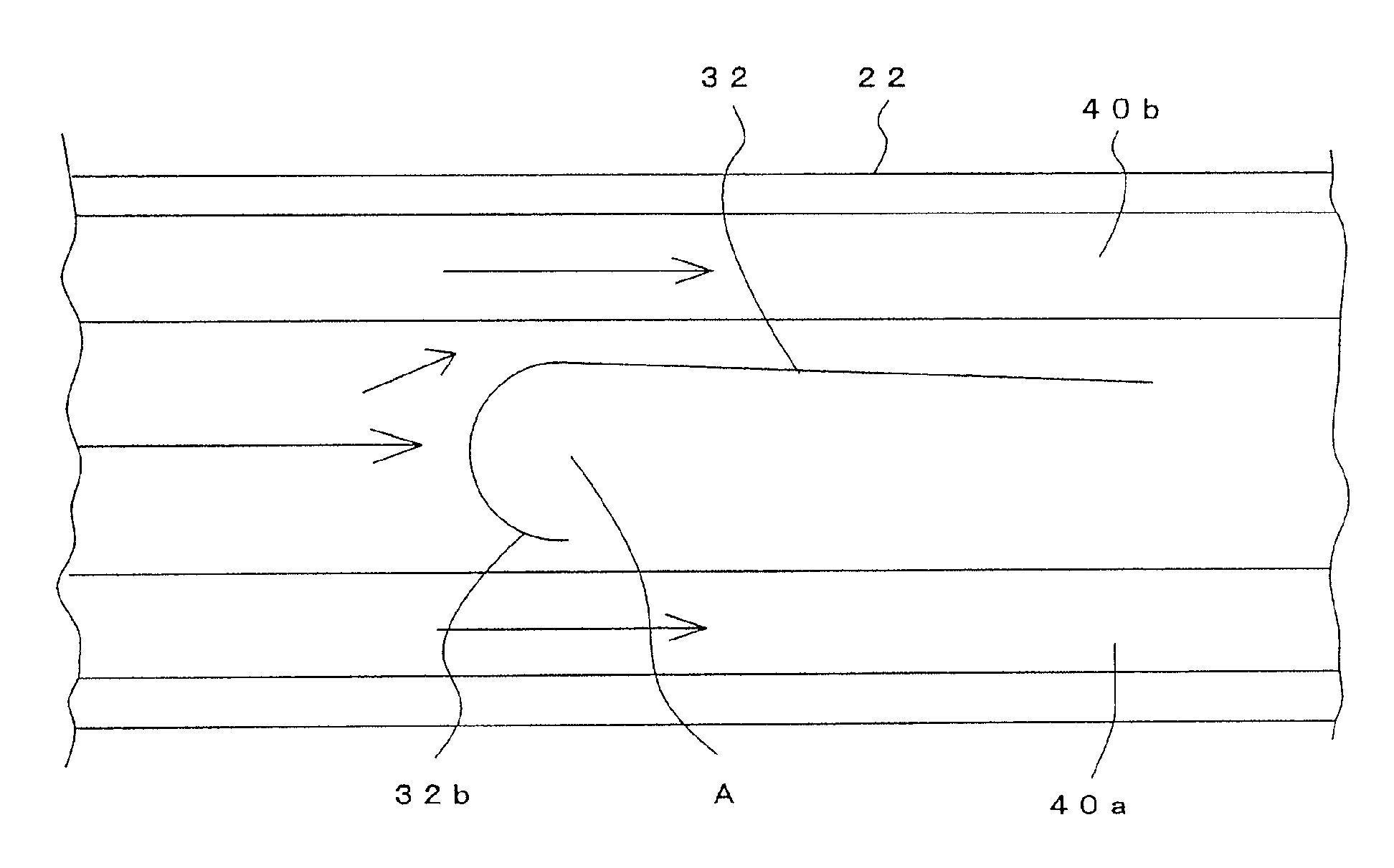
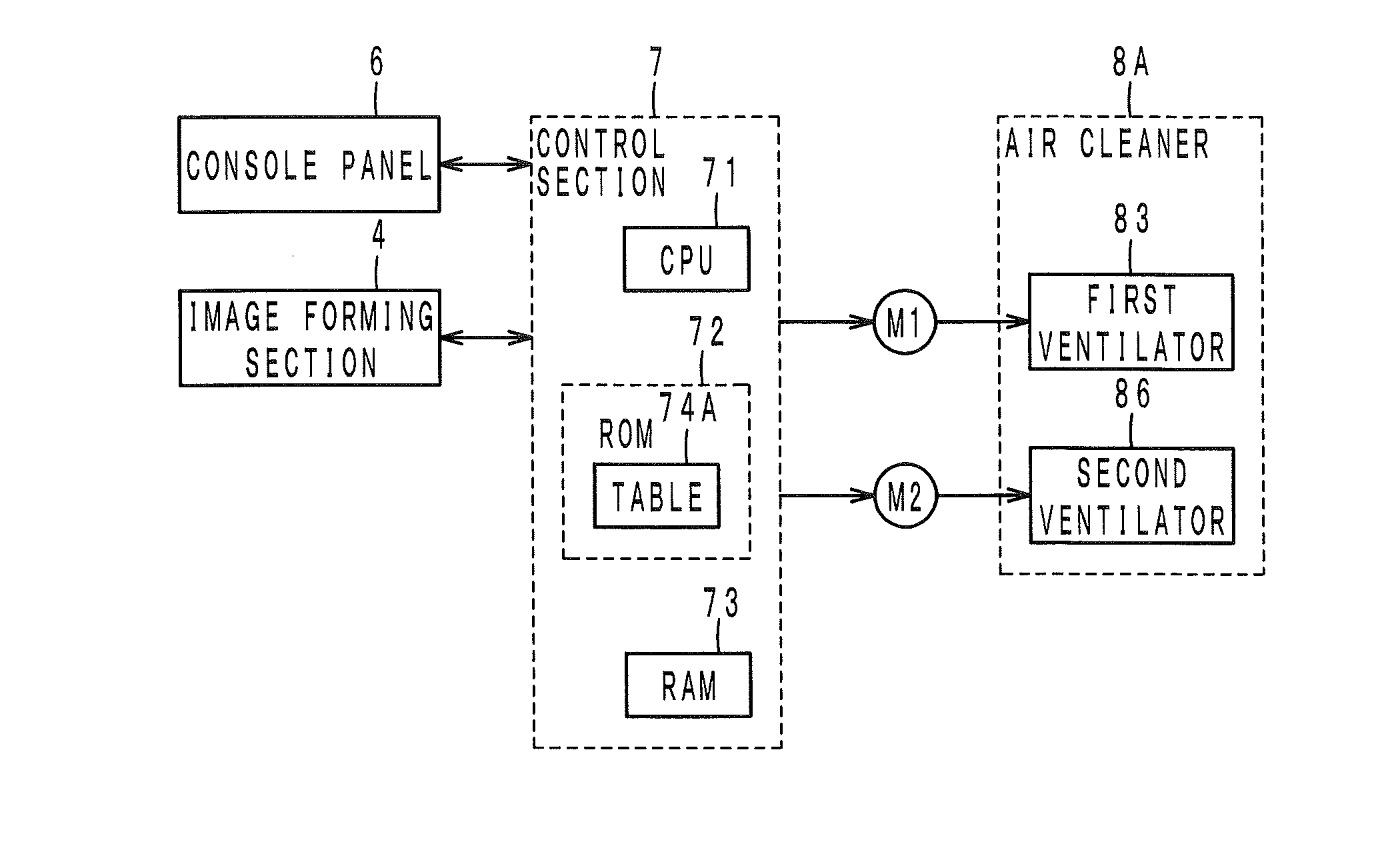
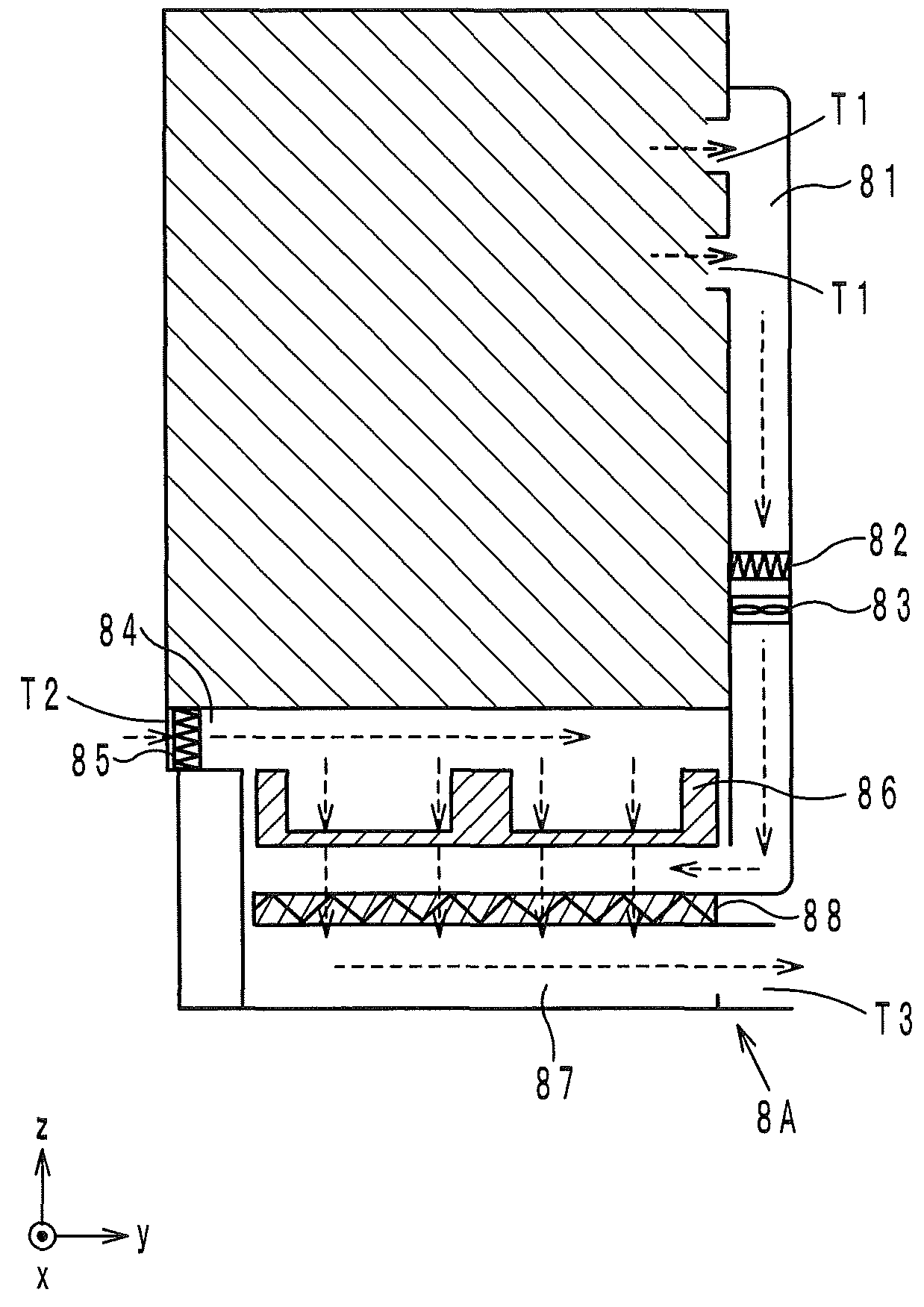
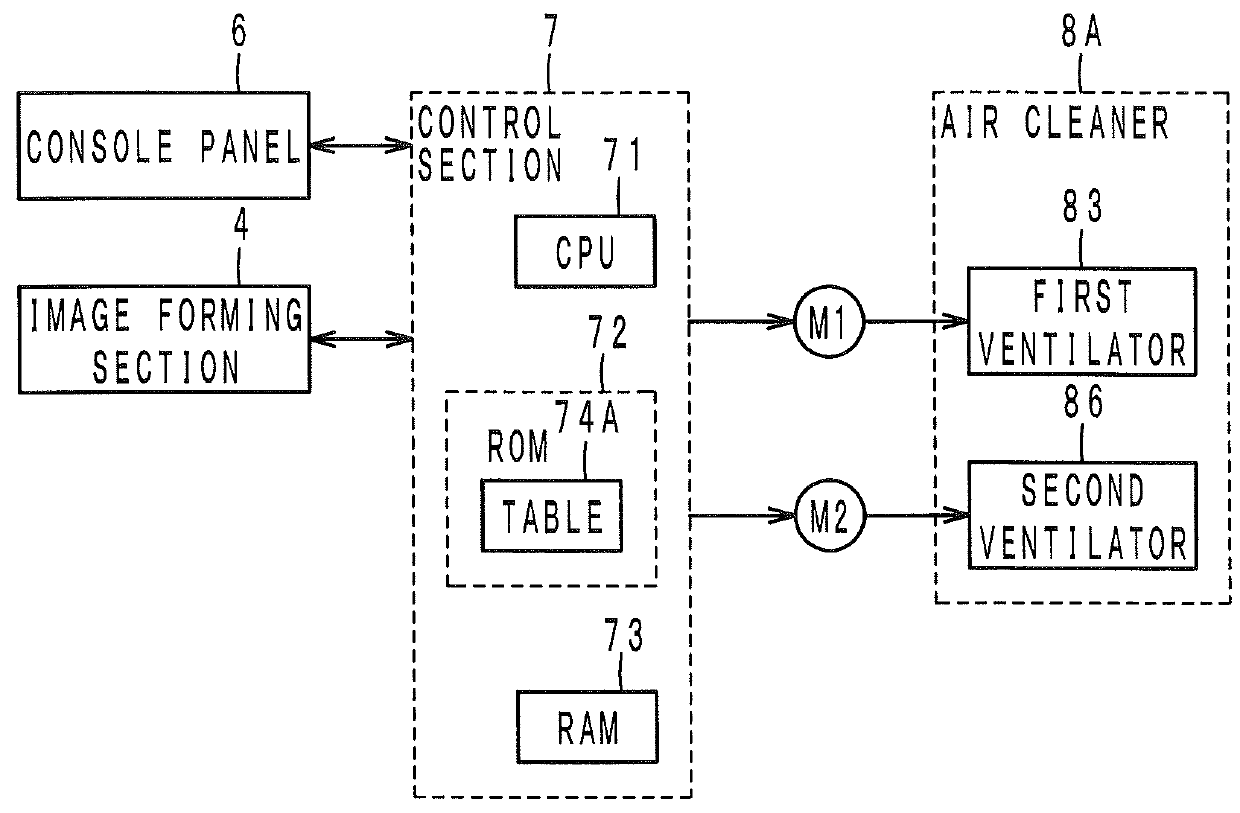
InactiveUS20160004218A1Increase pressureConstant flowElectrographic processCommon DuctImage formation
An image forming apparatus having: an inside-air duct having a first inlet to an inside of the image forming apparatus; a first ventilator provided in the inside-air duct; an outside-air duct having a second inlet to an outside of the image forming apparatus; a common duct into which the inside-air duct and the outside-air duct are merged; a second ventilator provided in at least one of the outside-air duct and the common duct; a filter provided in the common duct; and a control section that retrieves information indicative of an flow rate in the inside-air duct and increases a pressure produced by the second ventilator based on the retrieved information such that an flow rate in the outside-air duct is substantially constant with respect to an increase of the flow rate in the inside-air duct.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Construction machine
ActiveUS20130017048A1Great suctionLimited spaceVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesCommon DuctUltimate tensile strength
A suction duct (19) provided in a floor member (9) comprises an internal air duct portion (20) connected to the internal air inlet port (10A3), an external air duct portion (21) connected to an external air inlet port (10E3), and a common duct portion (22) for connecting the internal air duct portion (20) and the external air duct portion (21) to a blower fan 18B suction side of an air conditioner unit (18). The suction duct is constructed to form a hollow column (23) having a hollow closed section structure with the internal air duct portion and the common duct portion formed integrally in the upper and lower directions. Therefore, the hollow column formed of the hollow closed section structure can increase strength of the floor member as a strong column while circulating internal air between the internal air inlet port and the air conditioner unit.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Common bile duct exploring sheath duct
The invention discloses a common bile duct exploring sheath tube, which is characterized in that: the sheath tube comprises a horizontal tube located at the head of the sheath tube and a vertical tube. The horizontal pipe and the vertical pipe are communicated with each other through an elbow pipe. An end of the horizontal pipe remote from the elbow pipe is provided with an opening. The outer edgeof the elbow pipe is provided with a through hole along the pipe wall. The outer wall of the vertical pipe is provided with a water outlet joint. A base is arranged one end of the vertical pipe far away from the elbow pipe. The base is provided with a channel communicating with the vertical pipe. An anti-reflux pad is arranged on the inner wall of the channel. The anti-reflux cushion is providedwith an elastic hole for the choledochoscope to pass through. After the invention enters the common bile duct, the pneumoperitoneum and the laparoscopic video can be closed, thereby avoiding the complications caused by the long-term pneumoperitoneum and the loss of the laparoscopic system. A suction tube is connecte with that water outlet connector, so that infectious bile, irrigation fluid, sediment-like calculus and biliary mud can be expel from the body, and the complications caused by the above substances entering the abdominal cavity can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
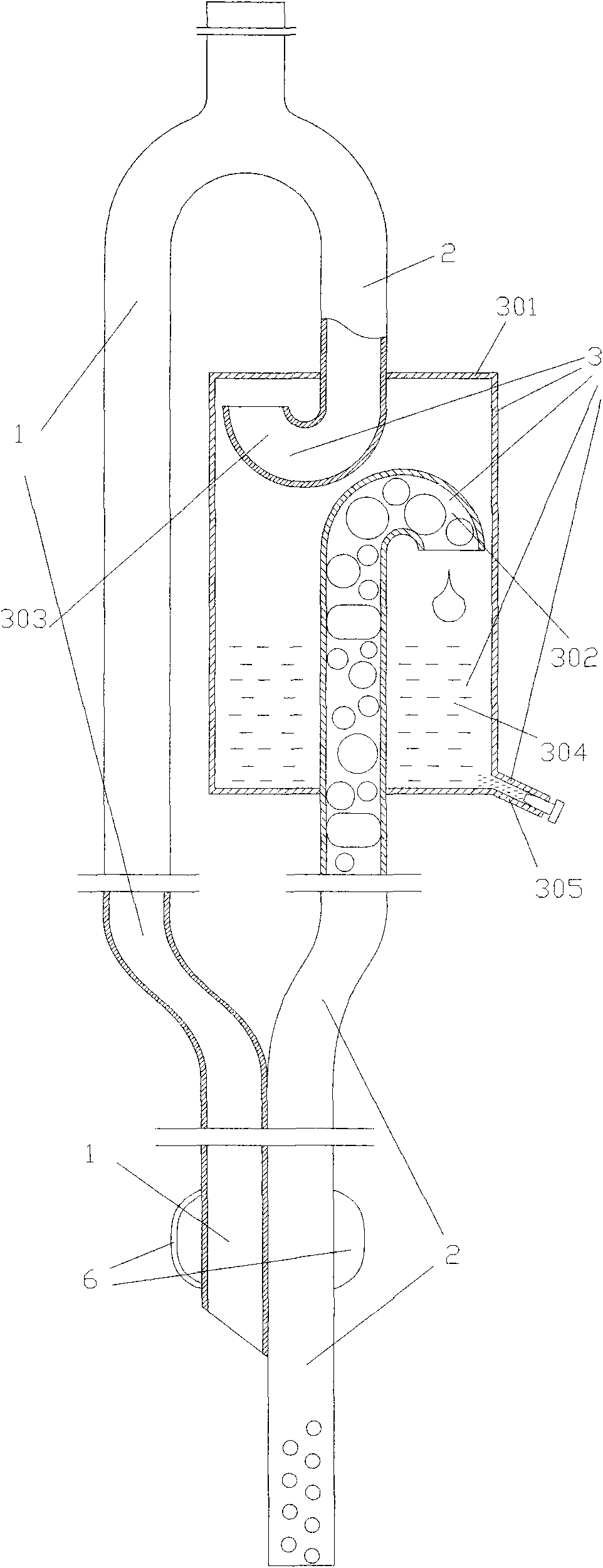
Duct system and receiving device
InactiveCN1705855AImprove heat exchange efficiencyLow thermal efficiencyShow cabinetsLighting and heating apparatusCold airCommon Duct
A duct system has a first duct guiding warm air downward from a warm air production source provided in an upward position and having warm air-feeding openings in the middle of the first duct, a second duct guiding cold air upward from a cold air production source provided in a downward position and having cold air-feeding openings in the middle of the second duct, and a third duct for connecting the warm air production source and the cold air production source and having recovery openings in the middle of the third duct. The duct system is a simple duct system where warm air and cold air can be independently fed and recovered through the common duct. As a consequence, a receiving device, such as a showcase, that is compact and has high heat exchange efficiency can be provided.
Owner:GLOSTER
Deflection magnetic field type vacuum arc vapor deposition device
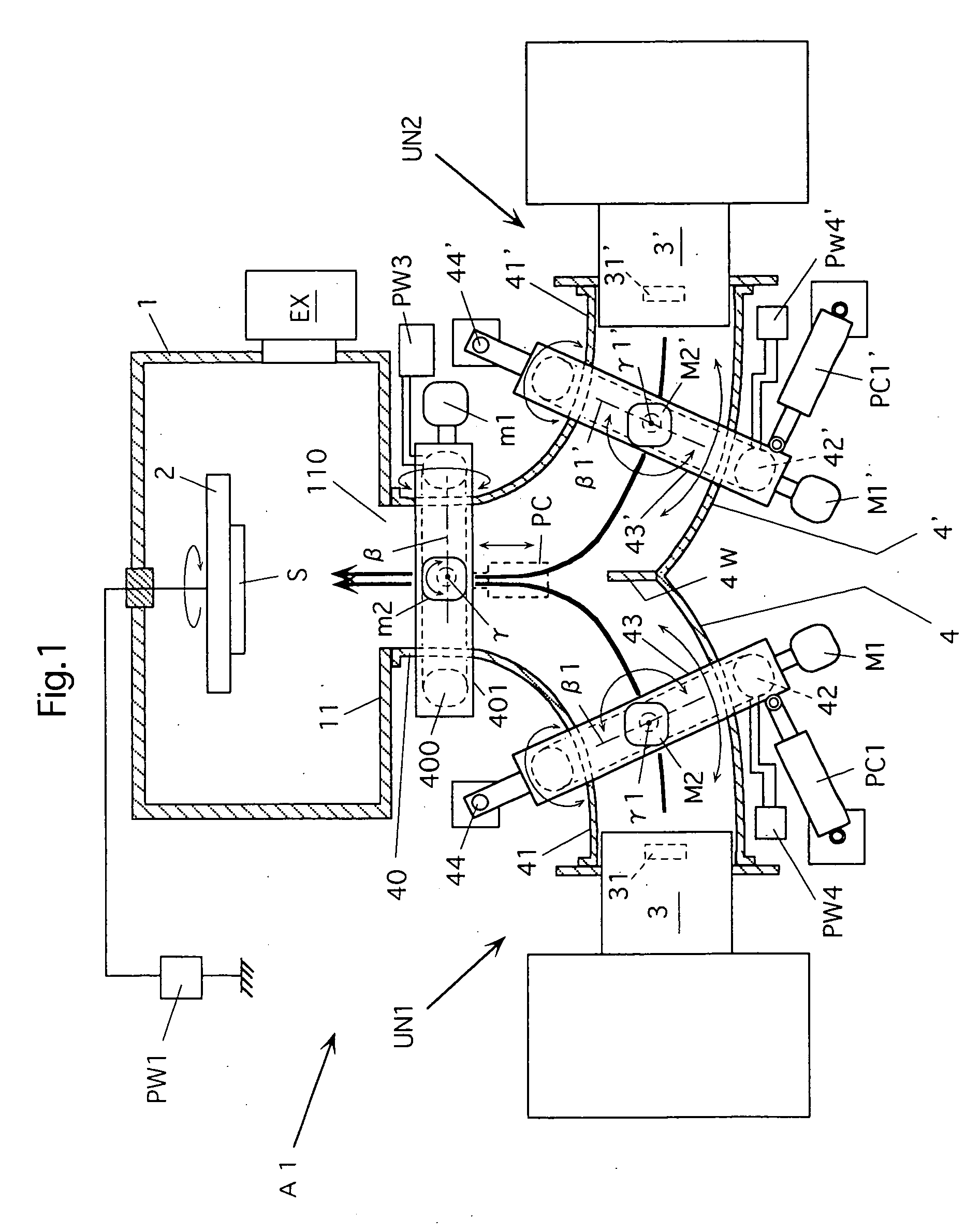
A deflection magnetic field type vacuum arc vapor deposition device has vapor deposition units (UN1, UN2) and these units include evaporation sources (3, 3'), and curved filter ducts (4, 4') having magnetic field forming coils (400, 42, 42') annexed thereto. The ducts (4, 4') are formed with a common duct end (40) facing a film forming subject article support holder (2), and the vapor sources (3, 3') are installed on the opposite ends (41, 41') of the ducts. The common coil (400) is installed at the duct end (40), and another magnetic field forming coil (42, 42') is installed for each duct. Installation state adjusting device (motor (m1, m2), driving device (PC), motor (M1, M2), driving device (PC1), motor (M1', M2'), and driving device (PC1')) is installed for each coil. This vapor deposition device is capable of efficiently forming a high quality thin film of desired construction on the film forming subject article.
Owner:NISSIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
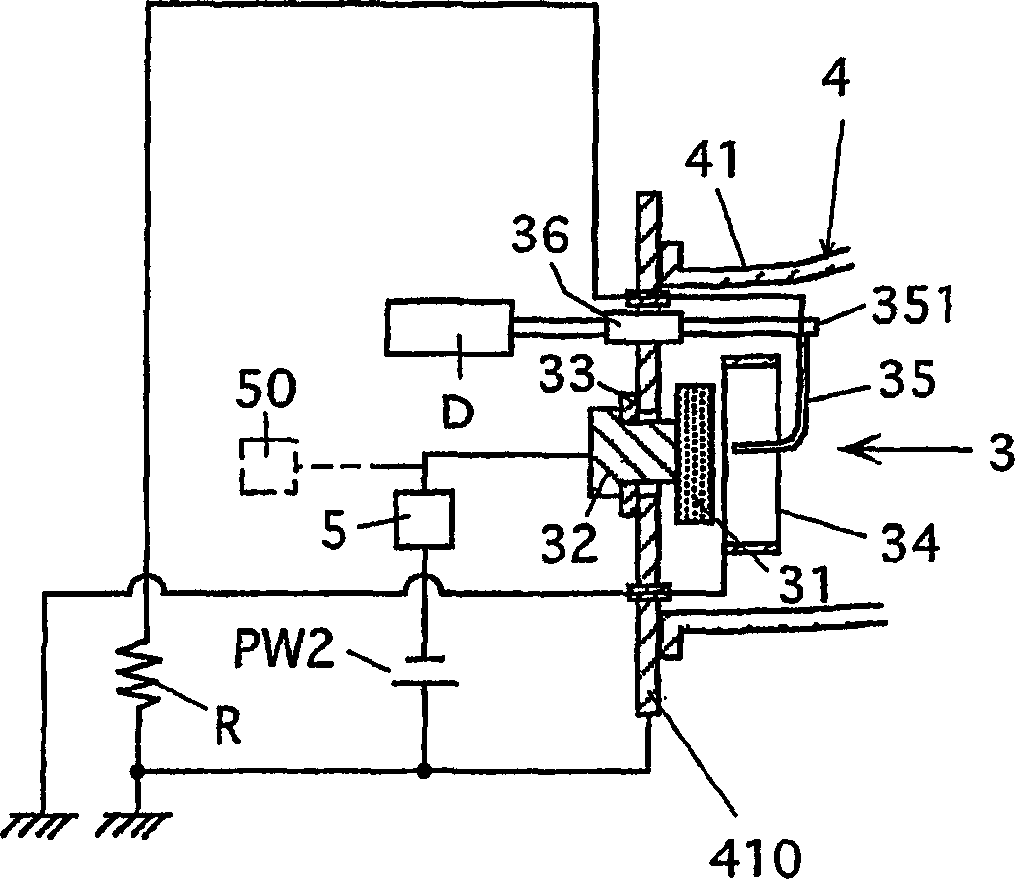
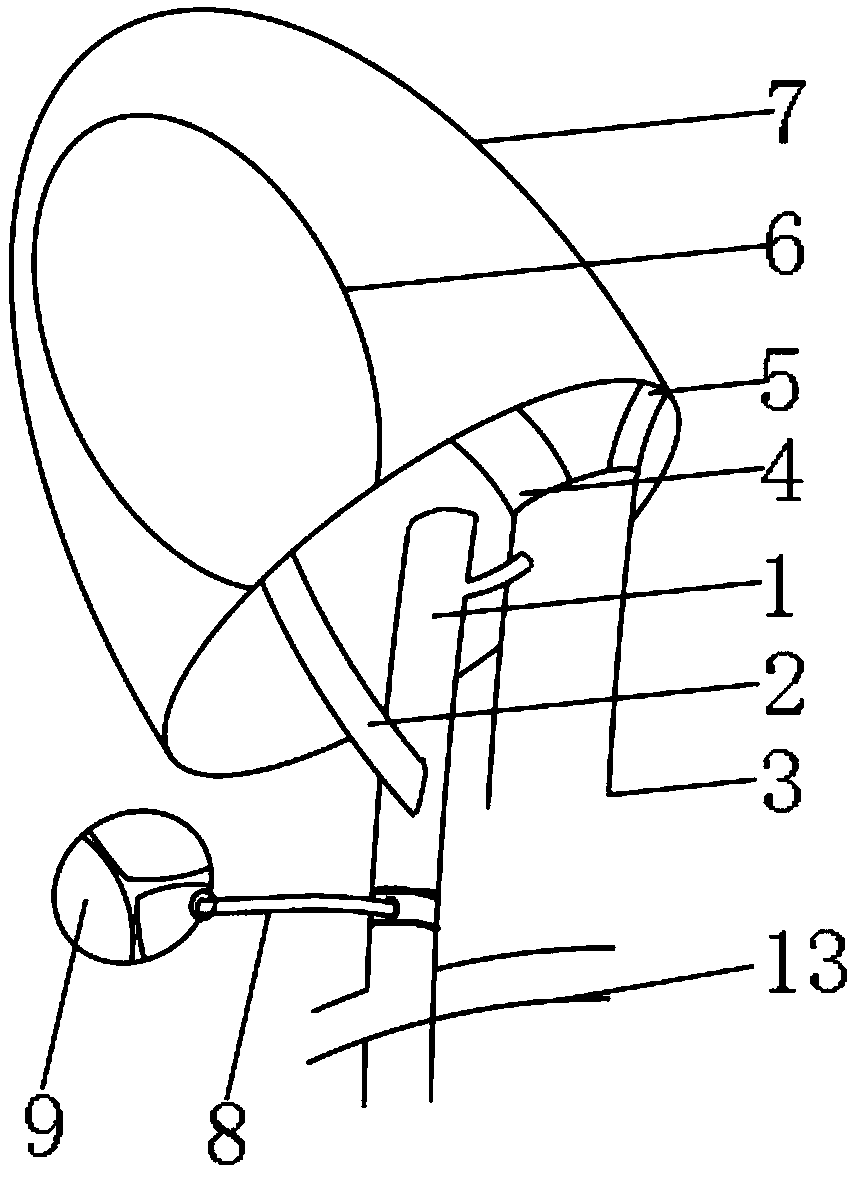
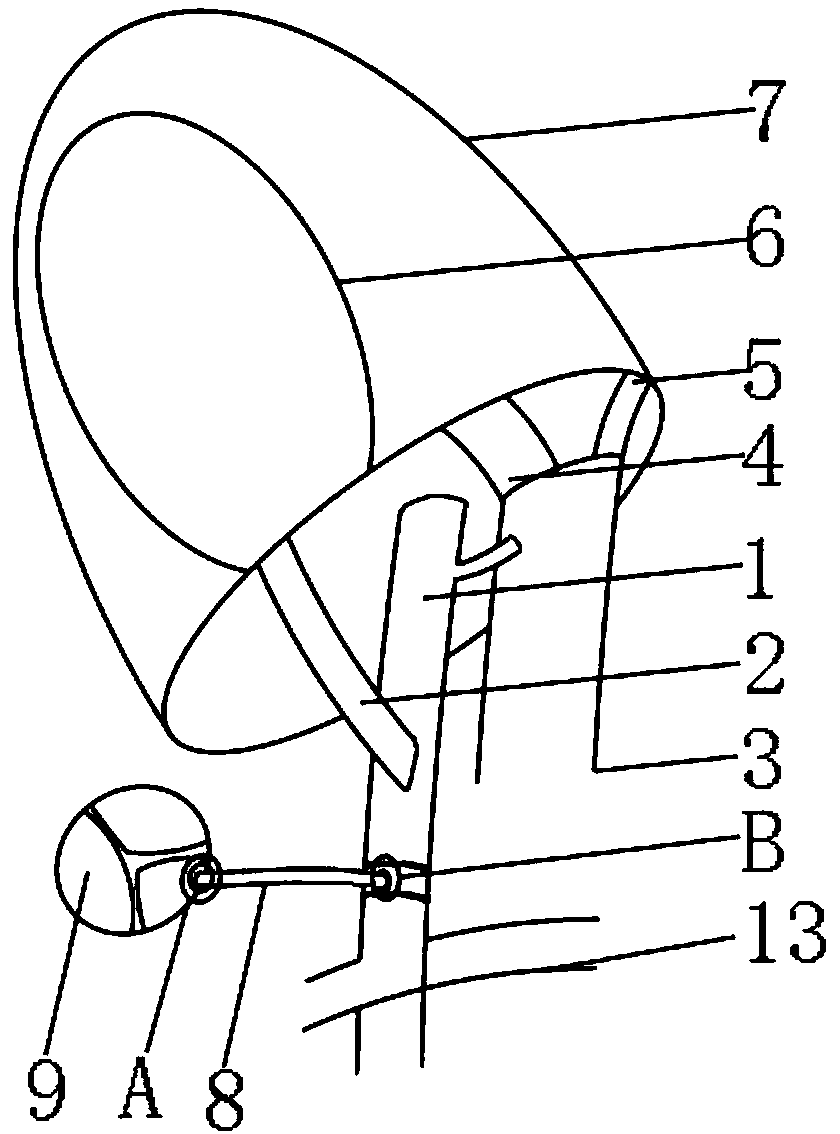
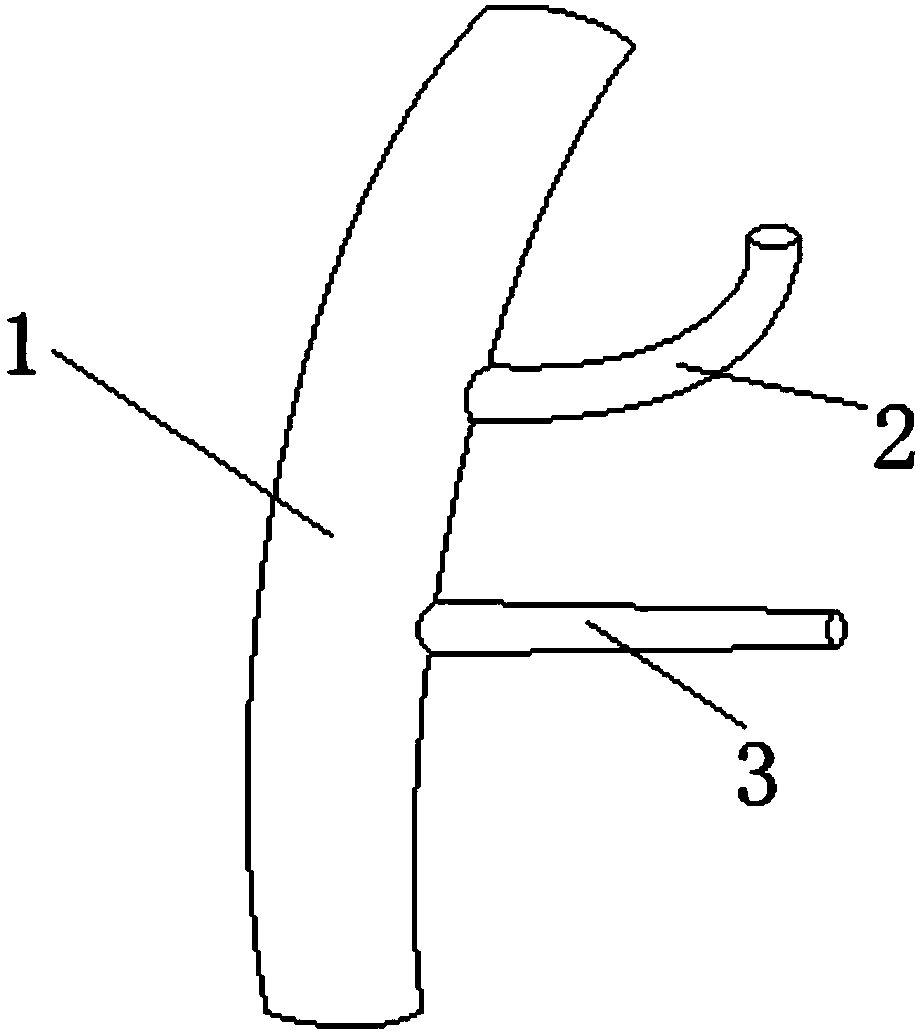
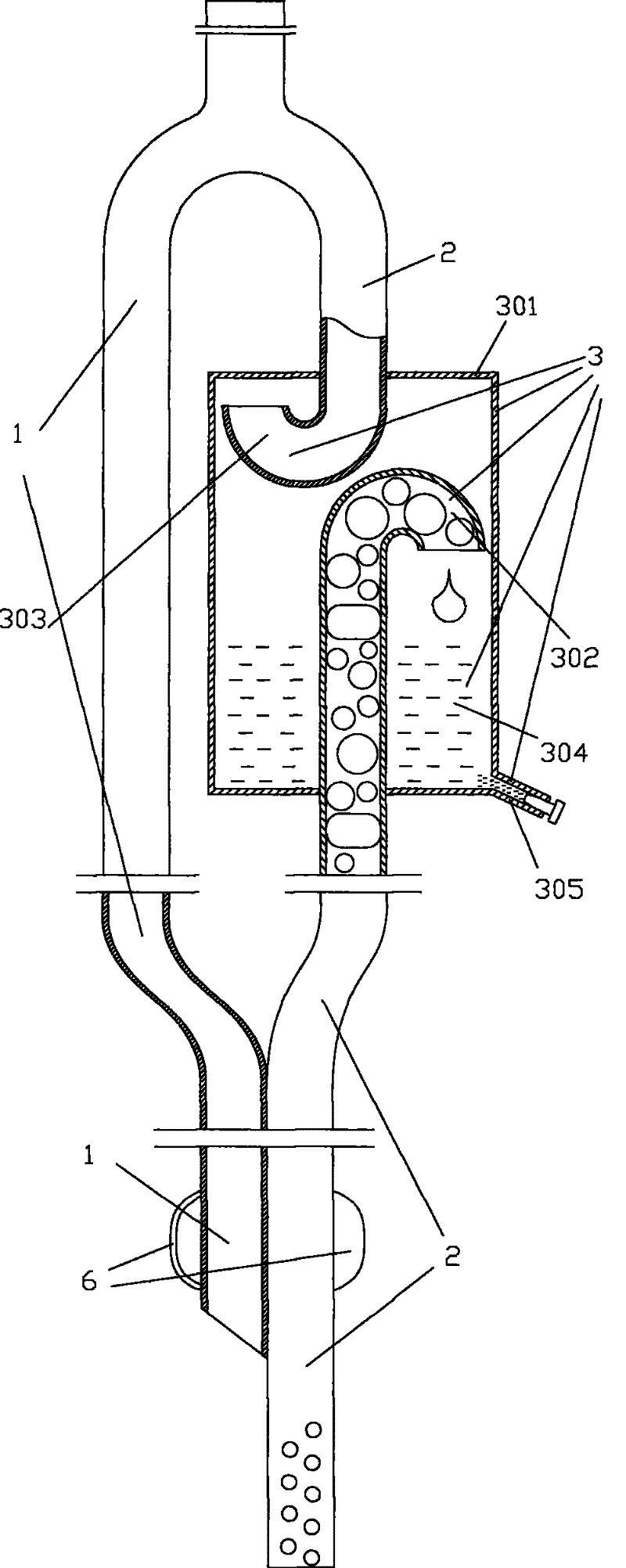
Tracheal cannula with function of automatically eliminating phlegm and automatic phlegm eliminating system using same
The invention discloses a tracheal cannula with function of automatically eliminating phlegm, which comprises two ventilation ducts, namely an air inlet and outlet duct (1) and a special exhaust duct(2); and the special exhaust duct (2) is provided with a phlegm eliminating device (3). The invention also discloses an automatic phlegm eliminating system comprising the tracheal cannula with the function of automatically eliminating phlegm. The air inlet and outlet duct (1) and / or the special exhaust duct (2) of the tracheal cannula with the function of automatically eliminating phlegm are respectively connected with a respirator (5) or are integrated into a common duct and then connected with the respirator (5). The tracheal cannula has the function of automatically sucking the phlegm, greatly lightens the work load of medical care personnel, reduces the alarm frequency of an artificial respirator, relieves the pain of the patient due to phlegm sucking, and has low cost and great marketand social values.
Owner:刘春江
Dual recycling-type coin changer
InactiveUS8430224B2Efficient processingInexpensive and compactApparatus with change-givingCoin countersCommon DuctEngineering
A compact recycling coin changer device for simultaneously serving a plurality of users includes a housing with a plurality of coin inlet and outlet slots. Individual coin lift units deliver coins for sorting and distributing to common coin denomination hoppers are arranged in parallel rows. A common duct, centrally located in the housing, can receive released coins from the hoppers and deposit them on a common coin-distributing device that operatively interconnects with the respective coin outlets, for example on opposite exterior housing walls. The coin changer device can be operatively associated with the dispensing of products, for example at a gas station or other retail outlets.
Owner:ASAHI SEIKO CO LTD
Novel biliary obstructive liver fibrosis model
The invention discloses a novel biliary obstructive liver fibrosis model, which comprises a common bile duct. One end of the common bile duct is provided with a cystic duct; one side of the cystic duct is provided with proper hepatic artery; the upper end of the cystic duct is provided with a gallbladder main body; one side, close to the cystic duct, of one end of the common bile duct is providedwith a pressure drain tube; one end of the pressure drain tube is provided with a tricuspid valve; and a first inner concave clasp is arranged between the tricuspid valve and the pressure drain tube.According to the novel biliary obstructive liver fibrosis model disclosed in the invention, the common bile duct can maintain certain stable inner pressure, clinical obstructive liver fibrosis can bewell simulated, a more effective animal model is provided for treatment of the disease, the pressure of the bile in the liver main body can be controlled, long-term feeding is facilitated, the pathological mechanism and the curative effects of drugs and the like can be observed, and the biliary obstructive liver fibrosis model brings better application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF MEDICINE & HEALTH SCI
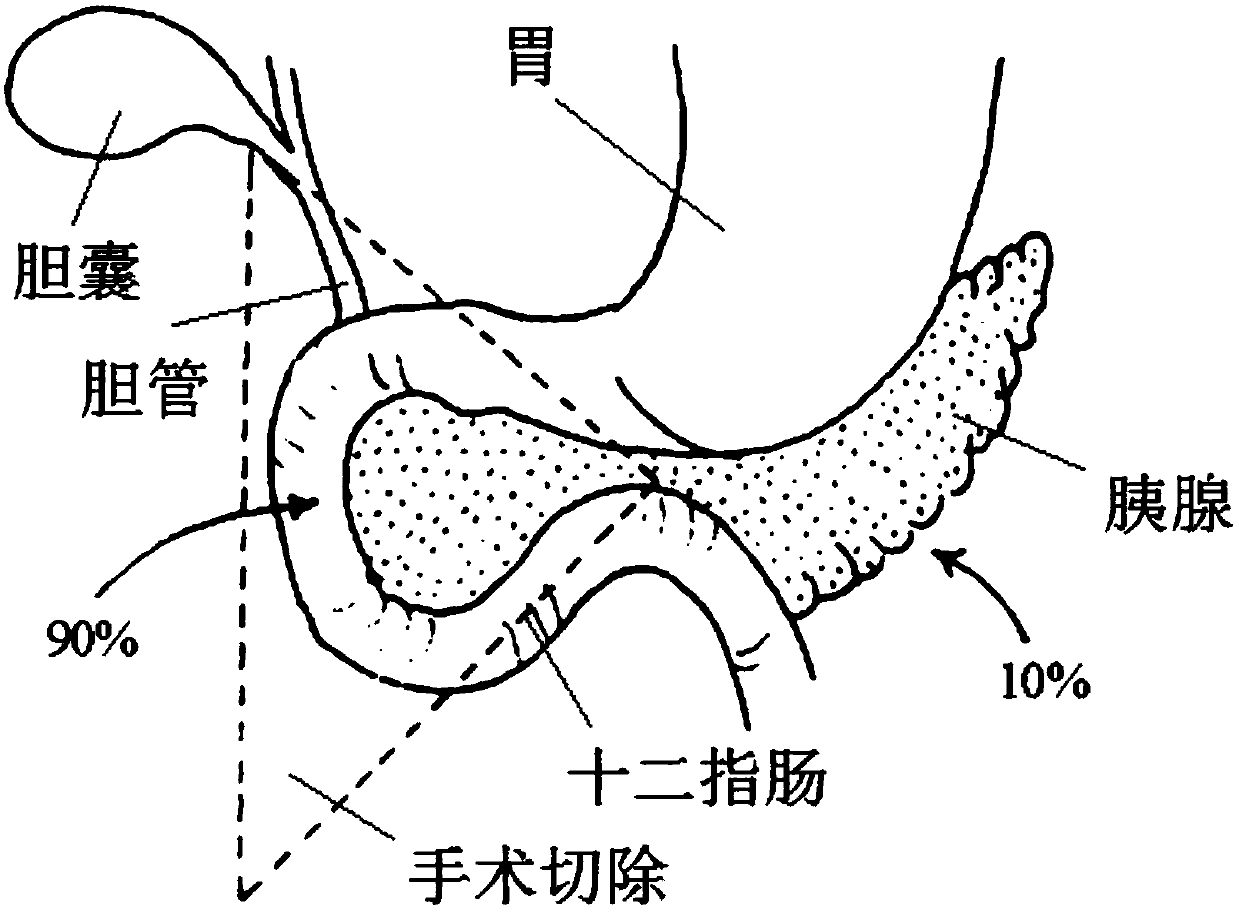
Gastrointestinal Connectors for Gastrointestinal Reconstruction in Duodenectomy
The invention discloses a digestive tract connector for reconstructing a digestive tract in duodenectomy. The digestive tract connector is used for anastomosing of a pancreatic gland, a common bile duct, a stomach and an empty intestine when the digestive tract is reconstructed in the duodenectomy, and comprises a connector main body, wherein the connector main body has a pipe-shaped appearance; one end of the connector main body is relatively large and the other end of the connector main body is relatively small; the relatively large end of the connector main body is anastomosed with the stomach of a human body; the relatively small end of the connector main body is anastomosed with the empty intestine of the human body; a bile duct anastomosing tube and a pancreatic gland anastomosing tube are arranged on a side wall of the connector main body; one end of the bile duct anastomosing tube is communicated with the connector main body and the other end of the bile duct anastomosing tube is anastomosed with the bile duct of the human body. One end of the pancreatic gland anastomosing tube is communicated with the connector main body and the other end of the pancreatic gland anastomosing tube is anastomosed with the pancreatic gland of the human body. According to the digestive tract connector disclosed by the invention, the anastomosing of the pancreatic gland, the common bile duct, the stomach and the empty intestine can be rapidly finished, the surgery time is shortened and injuries to patients in surgeries are reduced.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Image forming apparatus
An image forming apparatus having: an inside-air duct having a first inlet to an inside of the image forming apparatus; a first ventilator provided in the inside-air duct; an outside-air duct having a second inlet to an outside of the image forming apparatus; a common duct into which the inside-air duct and the outside-air duct are merged; a second ventilator provided in at least one of the outside-air duct and the common duct; a filter provided in the common duct; and a control section that retrieves information indicative of an flow rate in the inside-air duct and increases a pressure produced by the second ventilator based on the retrieved information such that an flow rate in the outside-air duct is substantially constant with respect to an increase of the flow rate in the inside-air duct.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Systems for collecting and recycling winding waste
Device for collecting the scraps produced by a spooler both for "dust removal" and for the pieces of yarn, wherein the spooling units are served by single aspirators that individually equip each spooling unit, and are each equipped with a separating filter for the dust and for the pieces of yarn, which collects both materials. All of the filters are connected through a common duct to a common suctioning filter for collecting the spooling scraps that, periodically treating an individual filter at a time, discharges and receives without selection the material retained by such individual filters.
Owner:SAVIO MACCHINE TESSILI
Tracheal cannula with function of automatically eliminating phlegm and automatic phlegm eliminating system using same
The invention discloses a tracheal cannula with function of automatically eliminating phlegm, which comprises two ventilation ducts, namely an air inlet and outlet duct (1) and a special exhaust duct (2); and the special exhaust duct (2) is provided with a phlegm eliminating device (3). The invention also discloses an automatic phlegm eliminating system comprising the tracheal cannula with the function of automatically eliminating phlegm. The air inlet and outlet duct (1) and / or the special exhaust duct (2) of the tracheal cannula with the function of automatically eliminating phlegm are respectively connected with a respirator (5) or are integrated into a common duct and then connected with the respirator (5). The tracheal cannula has the function of automatically sucking the phlegm, greatly lightens the work load of medical care personnel, reduces the alarm frequency of an artificial respirator, relieves the pain of the patient due to phlegm sucking, and has low cost and great market and social values.
Owner:刘春江
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com