Patents
Literature
67results about How to "Minimal trauma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
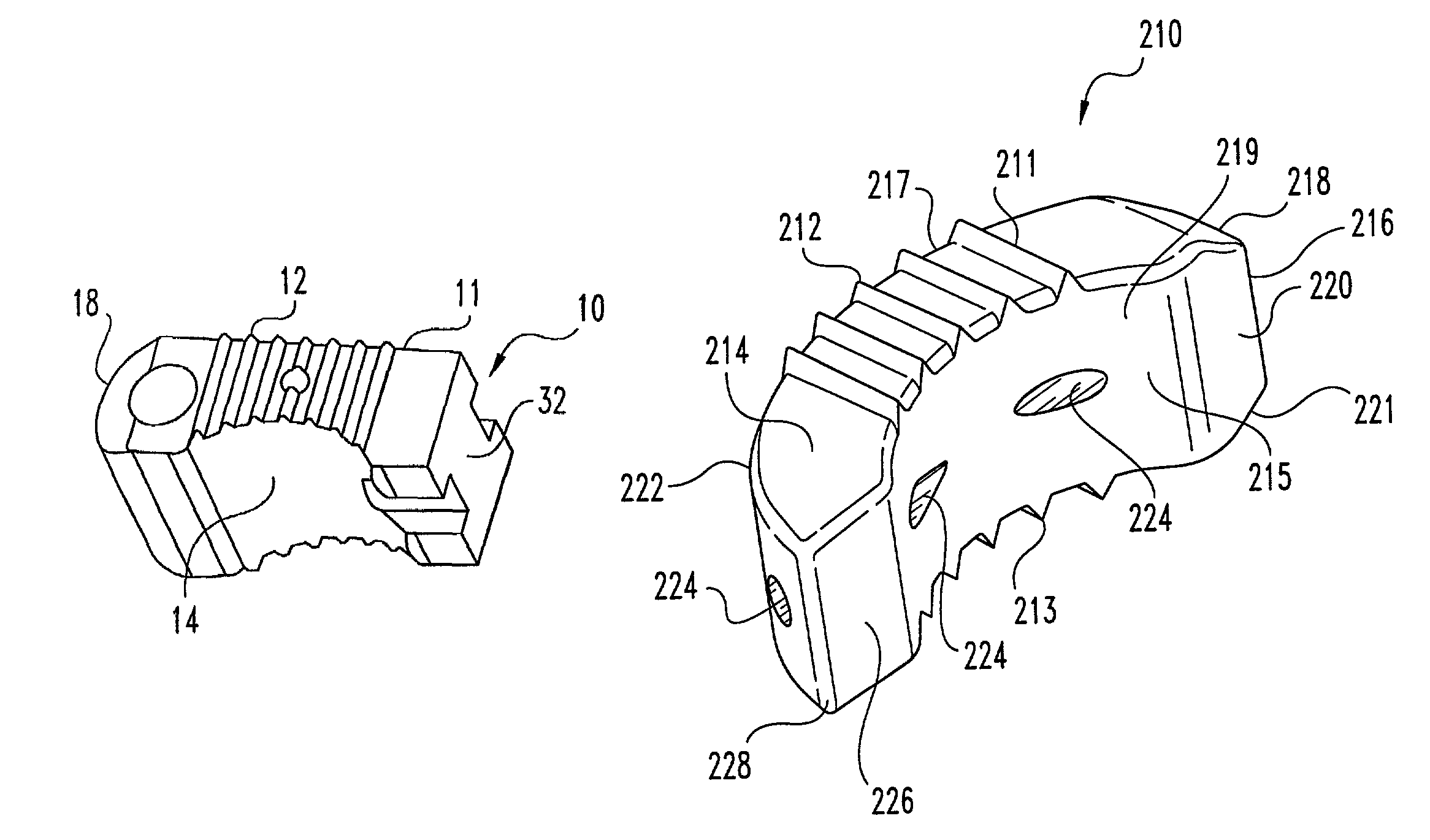
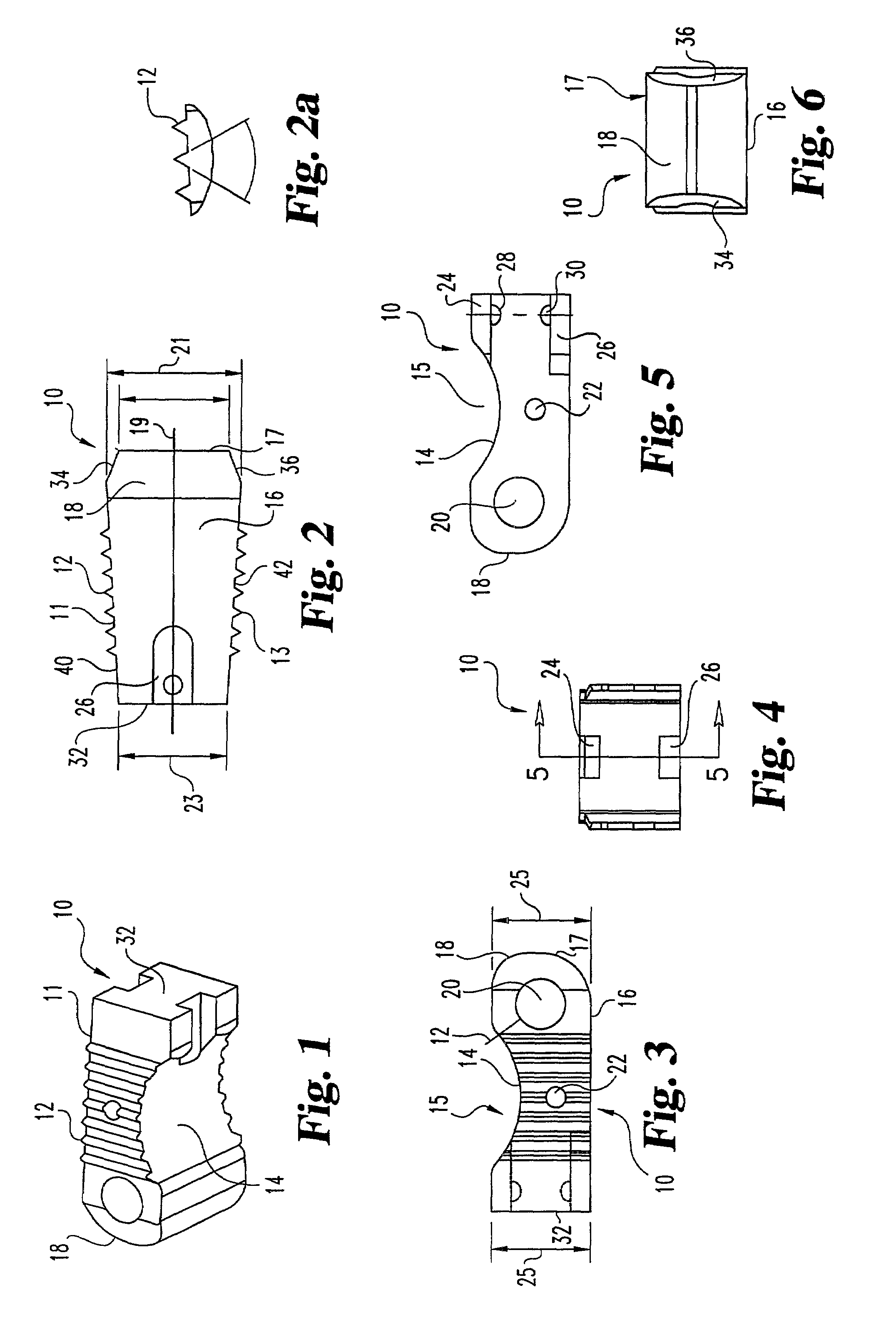
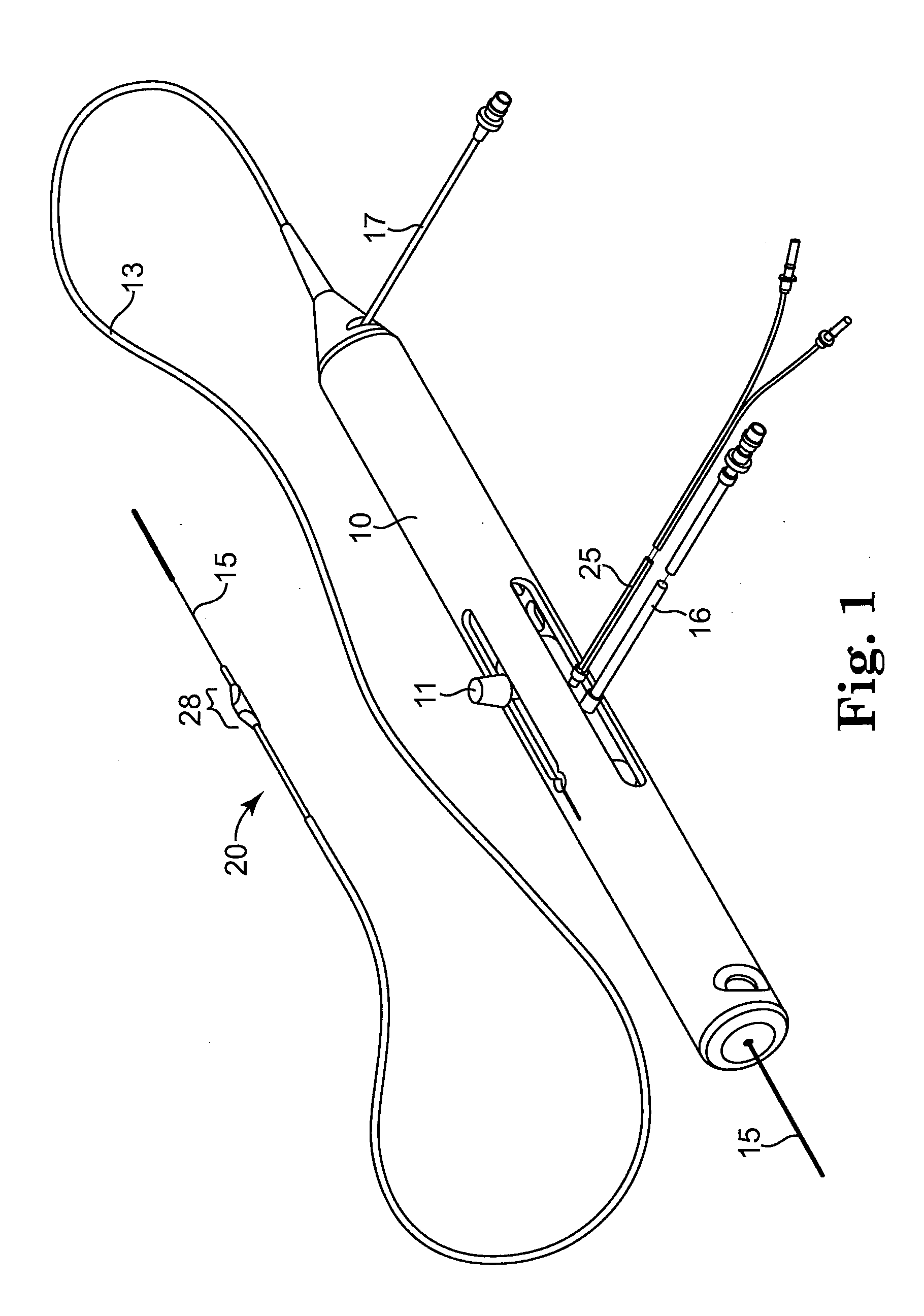
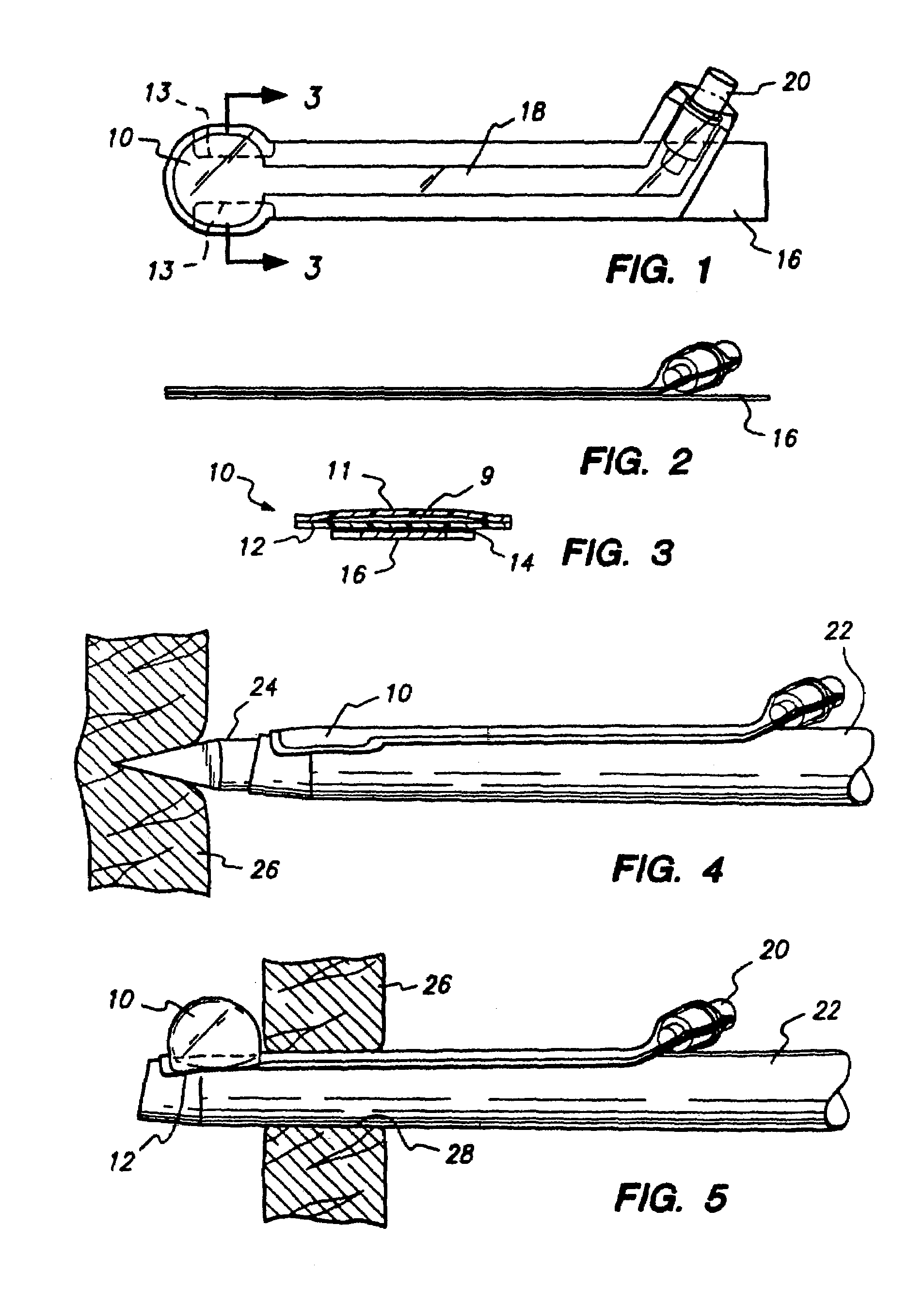
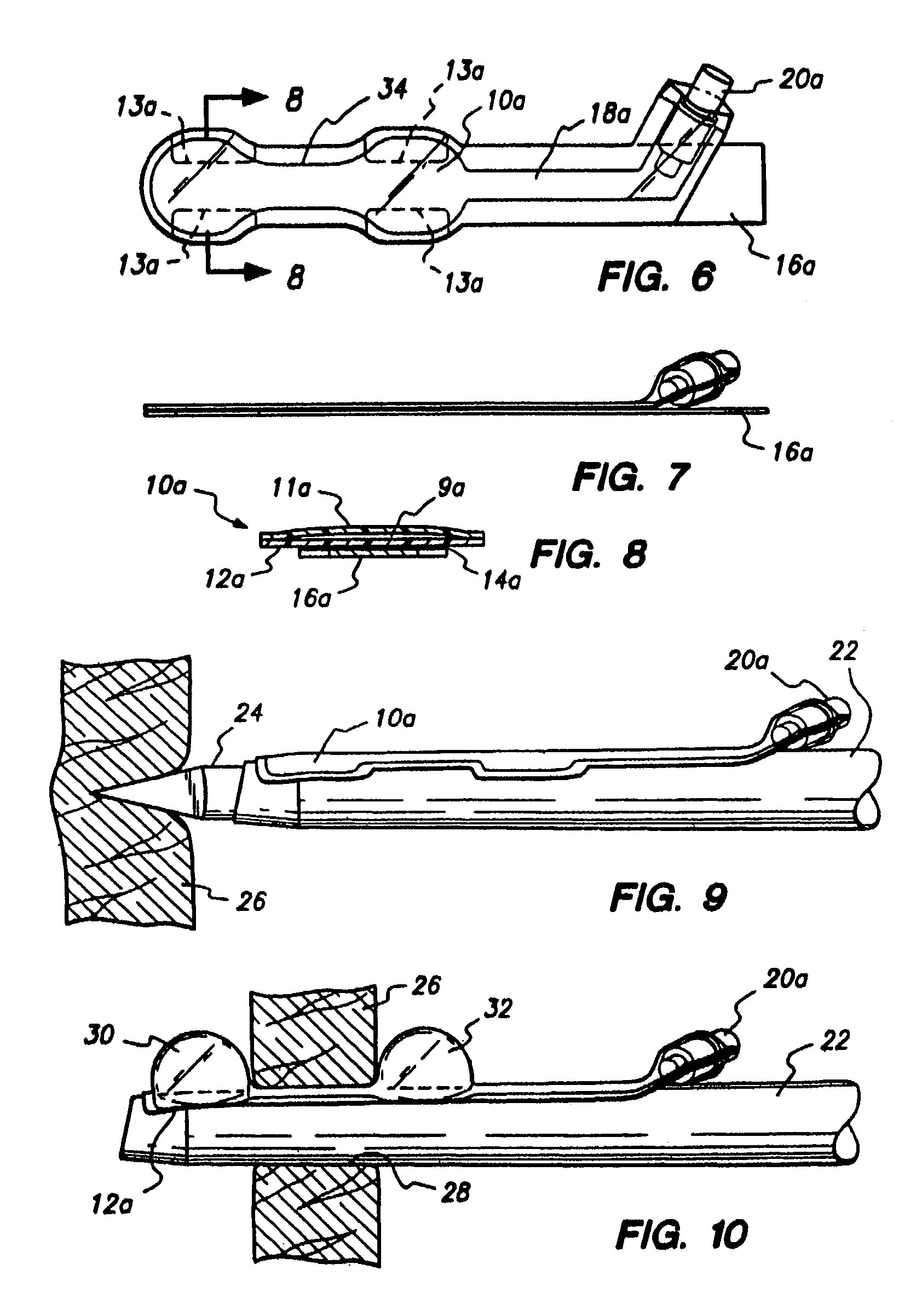
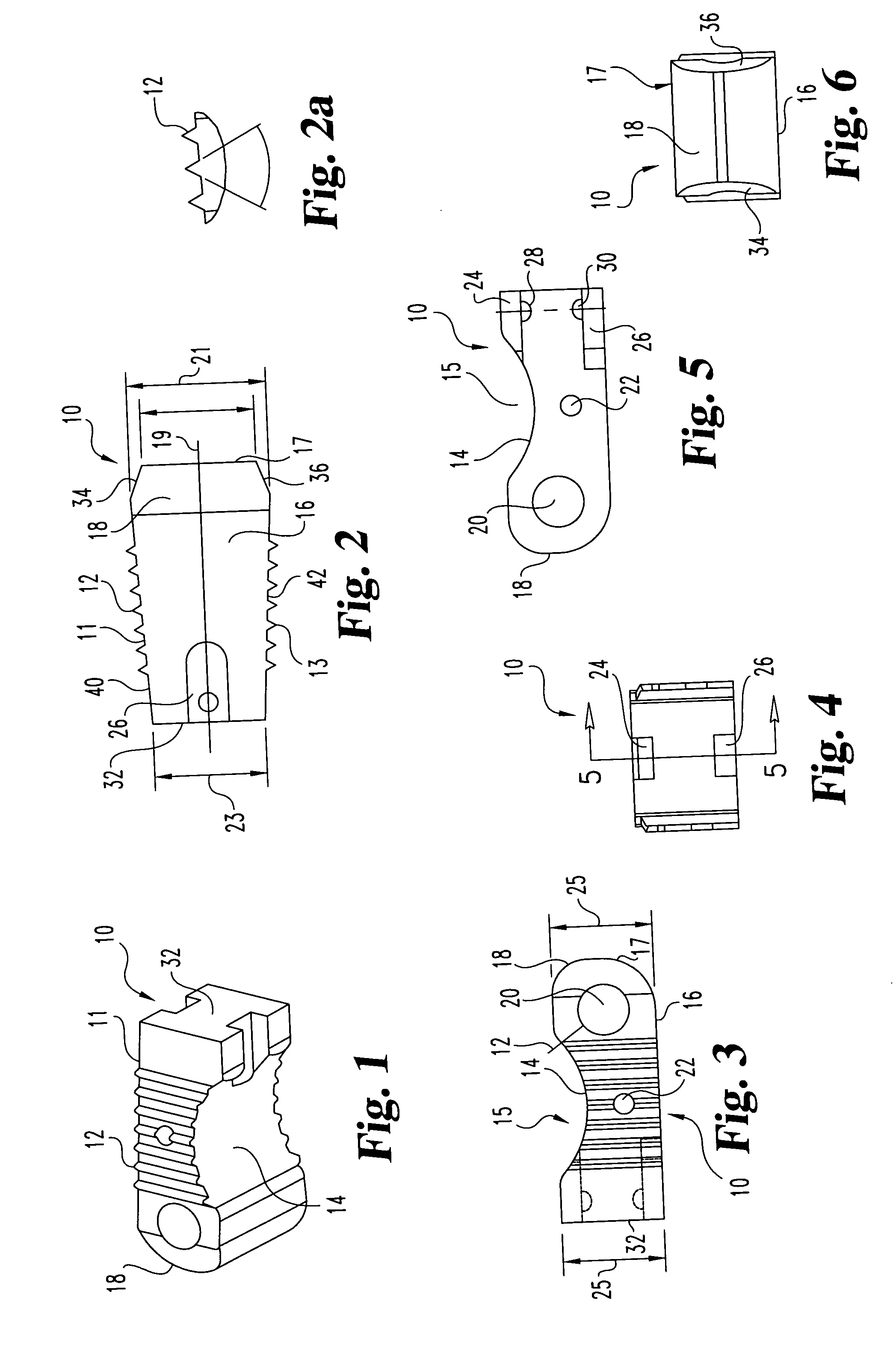
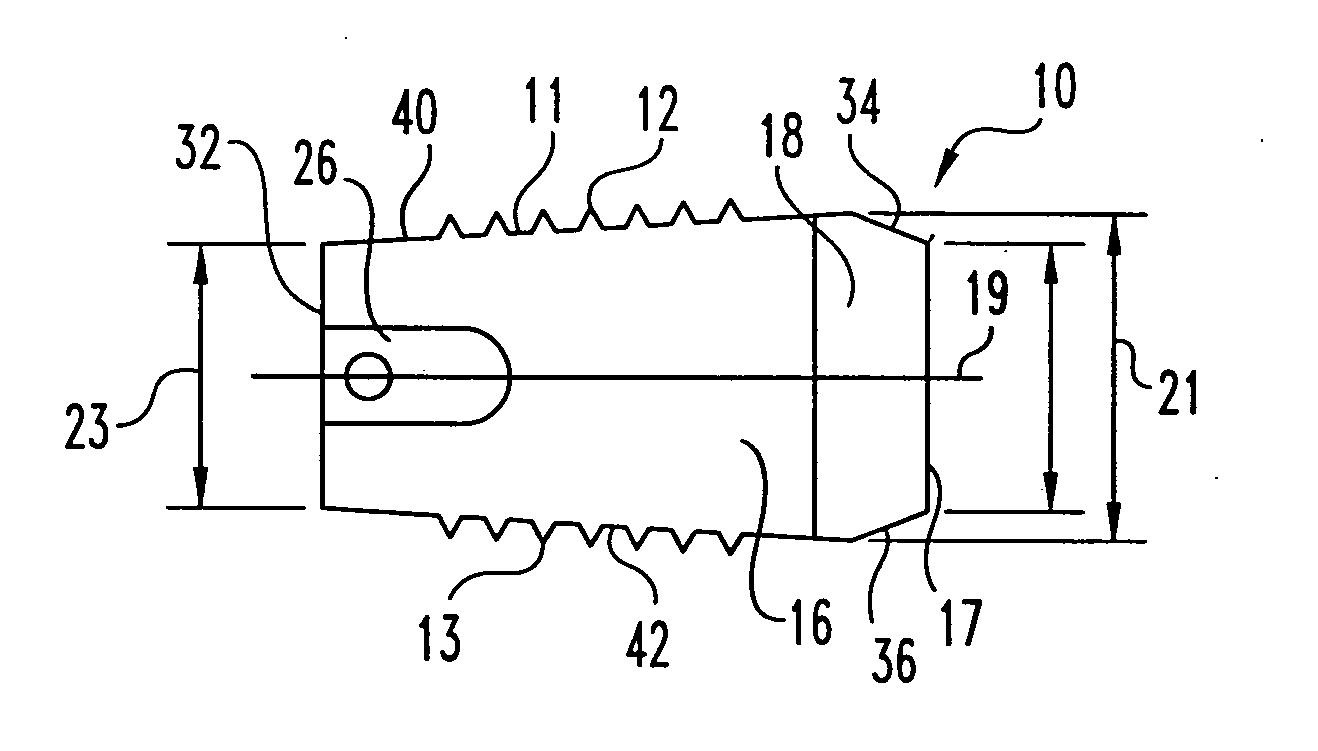
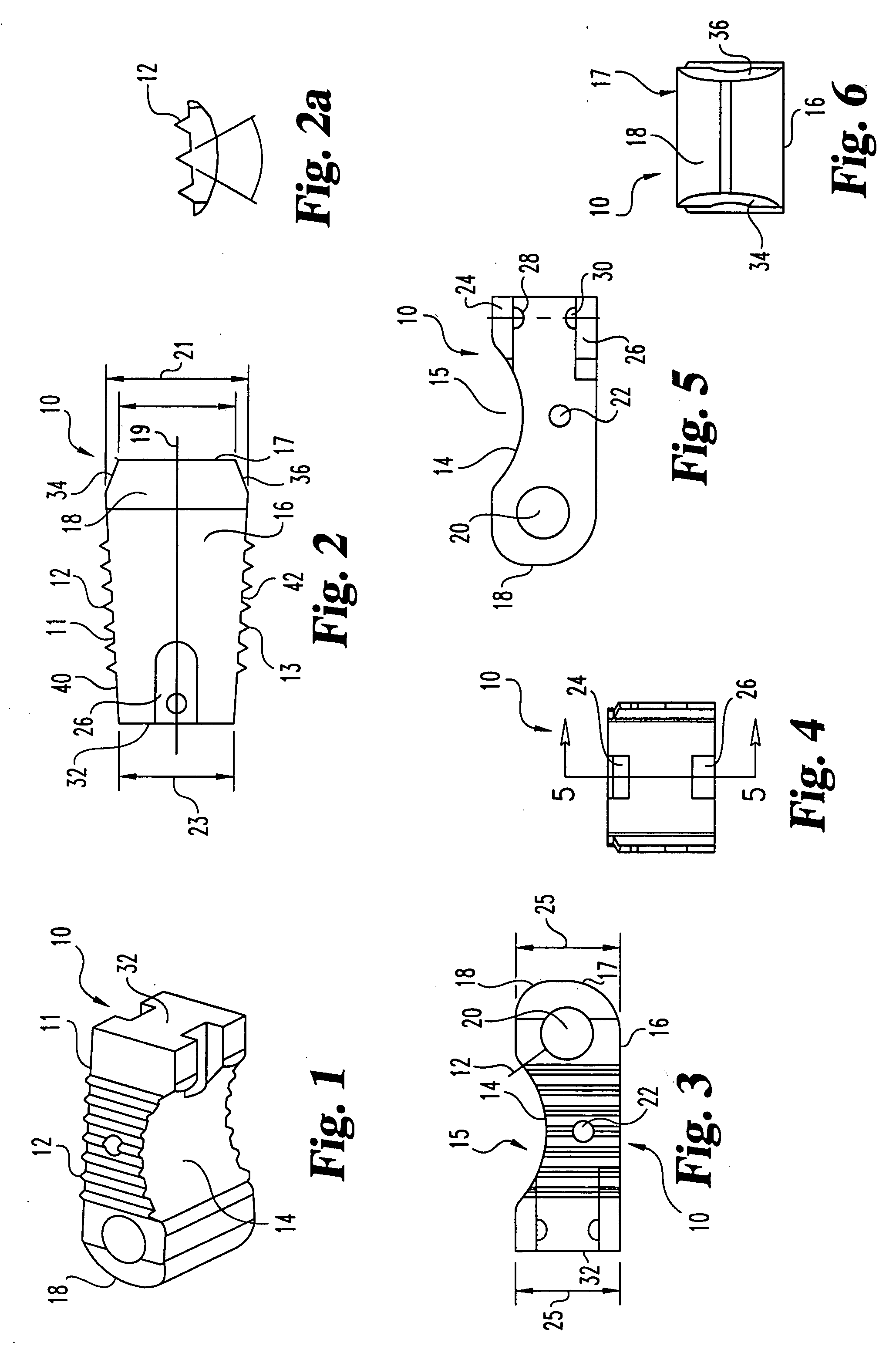
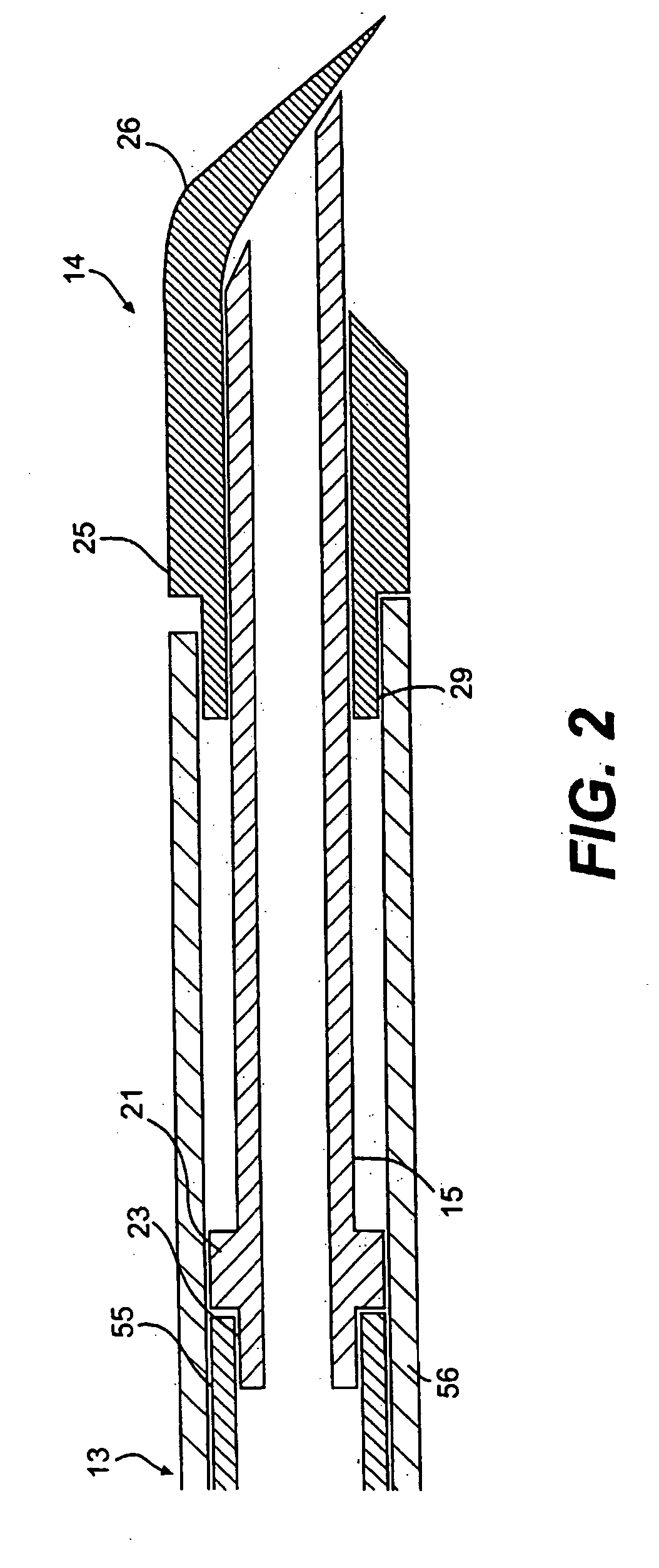
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS7479160B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineDonor bone
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Eccentric abrading head for high-speed rotational atherectomy devices
ActiveUS20080306498A1Improve abilitiesMinimal traumaCannulasExcision instrumentsStenotic lesionRotational axis
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy device having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with at least one flexible eccentric enlarged abrading head attached thereto. In other embodiments, the eccentric abrading head is not flexible or partially flexible. At least part of the eccentric enlarged cutting head has a tissue removing surface—typically an abrasive surface. In certain embodiments, the abrading head will be at least partially hollow. When placed within an artery against stenotic tissue and rotated at sufficiently high speeds the eccentric nature of the enlarged cutting head causes the cutting head and drive shaft to rotate in such a fashion as to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter substantially larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged cutting head. Preferably the eccentric enlarged cutting head has a center of mass spaced radially from the rotational axis of the drive shaft, facilitating the ability of the device to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter substantially larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged cutting head when operated at high speeds.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Robotic guided endoscope
ActiveUS9125556B2Level accuracyReduce traumaEndoscopesComputerised tomographsSurgical robotEngineering
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
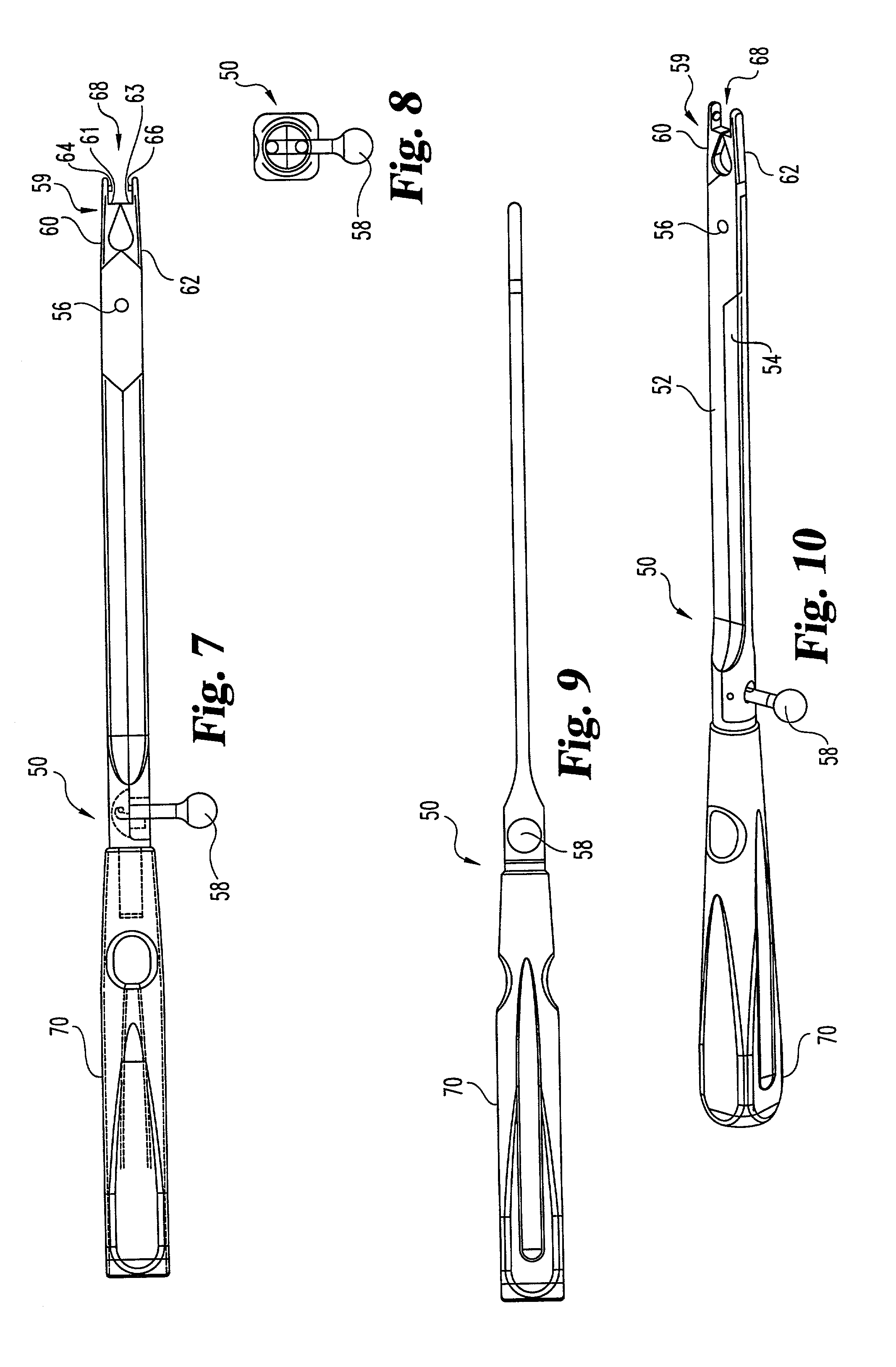
Handle and articulator system and method
InactiveUS20070135733A1Ergonomically improvedSimple wayMedical devicesCatheterDental ArticulatorsDistal portion
The invention includes an assembly having a handle for articulating an articulator in an ergonomically improved manner. The handle can be adapted to articulate a distal portion of the articulator when squeezed. The handle can have at least one accessible attachment mechanism useful for reattachably attaching the articulator and the handle during a medical procedure. The invention also includes methods of making and using such a handle.
Owner:HERAEUS MATERIALS
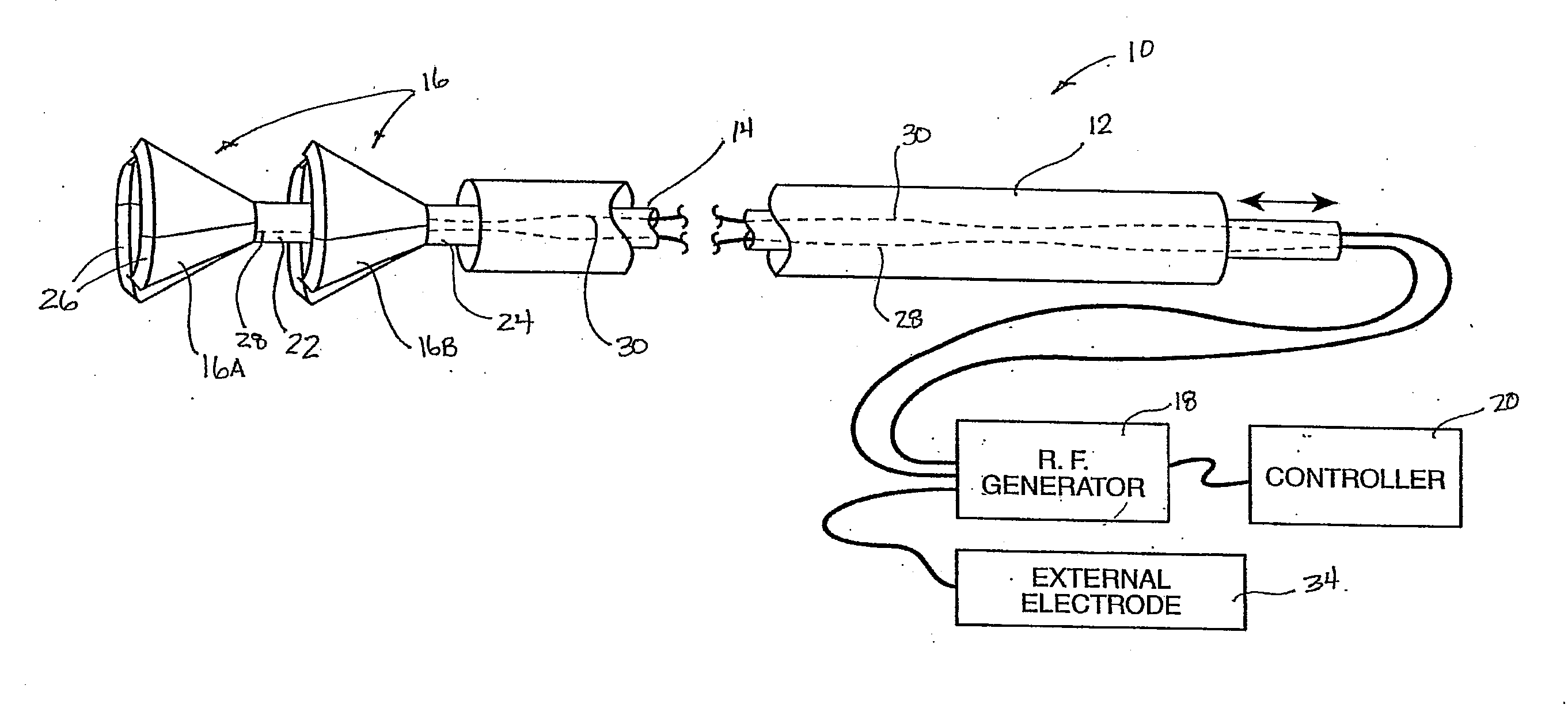
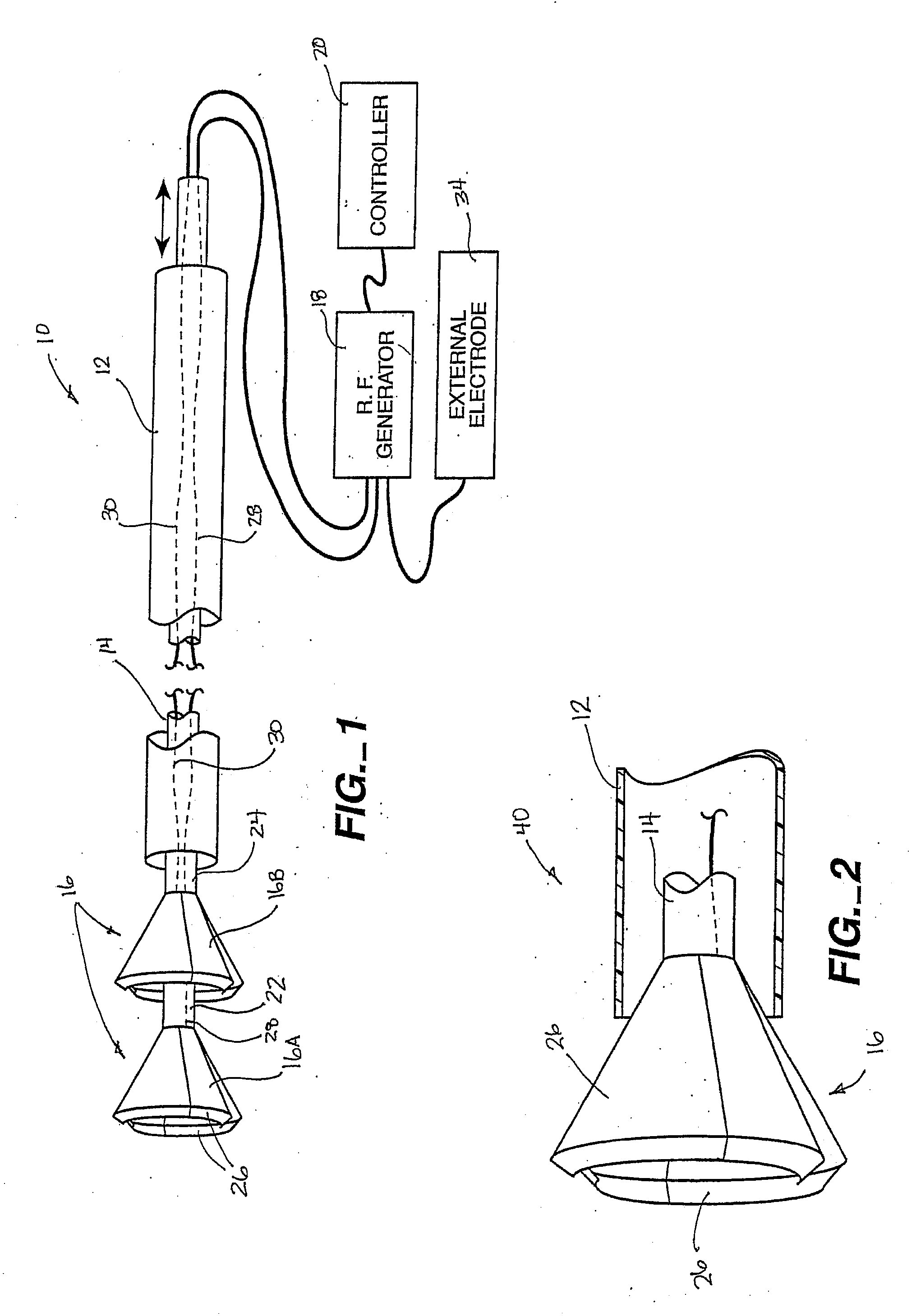
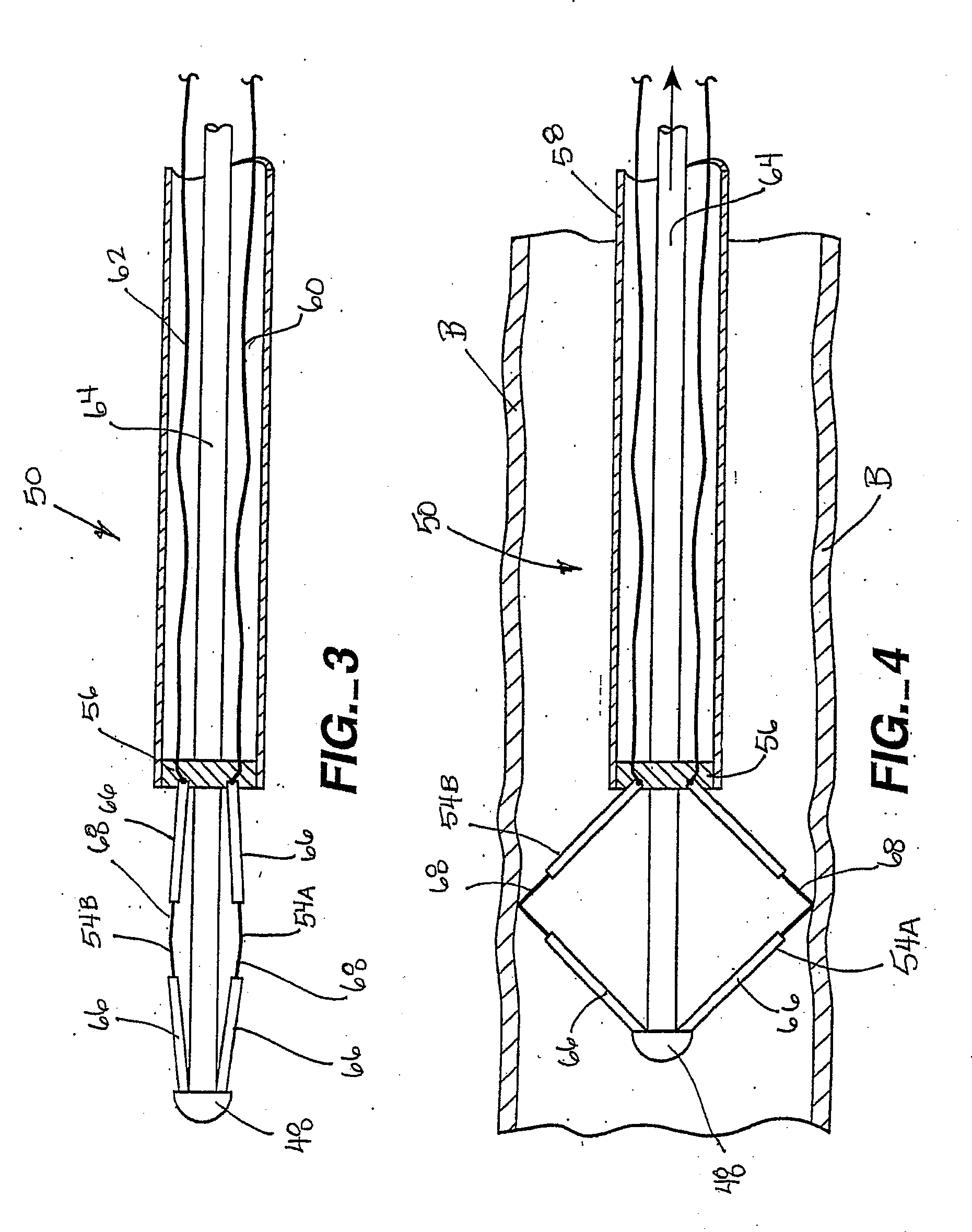
Expandable electode devices and methods of treating bronchial tubes
InactiveUS20070106296A1Minimal traumaAlteration of coefficientElectrotherapyDilatorsBronchial tubeObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Methods are provided for treating collapsed bronchial tubes found in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, such as asthma. The method includes heating the bronchial tube to cause tissue in the wall of the bronchial tube to undergo a structural transformation effective to render the wall capable of supporting a non-collapsed lumen. The procedure effectively reinforces the structural integrity of the bronchial tube wall and thereby prevents the lumen from collapsing.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for anchoring laparoscopic instruments
InactiveUS7235064B2Low profileAvoid high forceEar treatmentCannulasAbdominal cavitySurgical department
A balloon anchor provides for the anchoring of a surgical instrument, such as conventional trocar sheath, within a puncture opening formed by a trocar. When used on a trocar sheath, the anchor is secured to the smooth outer surface of the sheath for extension through the puncture opening as the trocar within the sheath forms the opening. Adhesive or mechanical means are provided to secure the balloon the instrument. No modification to the structure of the instrument is required. Once in place within the opening, the balloon is inflated to the interior of the tissue to anchor the instrument in place. Certain embodiments also provide for inflation of the balloon within and / or to the exterior of the opening.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Apparatus and methods for entering cavities of the body
InactiveUS20060063965A1Minimal traumaOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryGeneral surgeryBody Regions
A cannula assembly provides access to an interior body region. The cannula assembly defines a lumen having a distal region. The lumen includes a bend in the distal region to guide deployment in the body region. A closure assembly can be provided to open and close the cannula assembly to fluid flow.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Obesity treatment tools and methods
InactiveUS20070118159A1Convenient treatmentMinimal traumaSuture equipmentsStapling toolsDiseasePyloric sphincter
Various obesity treatment tools and methods are described herein, as well as treatments for other gastric-related diseases, e.g., GERD. Treatment includes reducing the size of the stomach pouch to limit the caloric intake as well as to provide an earlier feeling of satiety. This may be done by creating a smaller gastric pouch within the stomach directly from the interior of the stomach itself. The smaller pouches may be made through the use of individual anchoring devices, rotating probes, or volume reduction devices. A pyloroplasty procedure may also be performed to render the pyloric sphincter incompetent. A gastric bypass procedure may additionally be performed using atraumatic magnetic anastomoses devices so that sugars and fats are passed directly to the bowel while bypassing the stomach. Many of these procedures may be done in a variety of combinations. Treatment may create enforced behavioral modifications by discouraging the ingestion of high-caloric foods.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
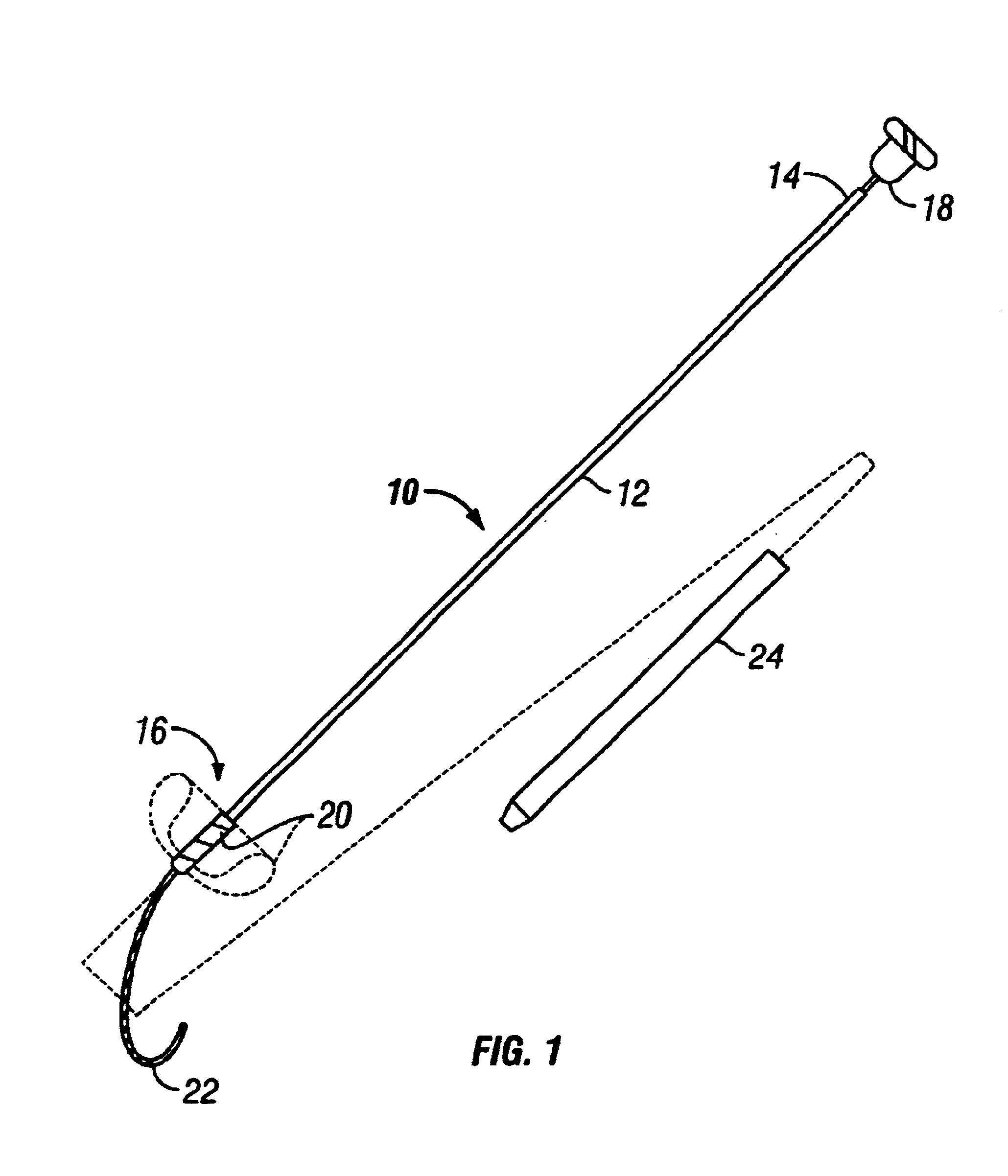
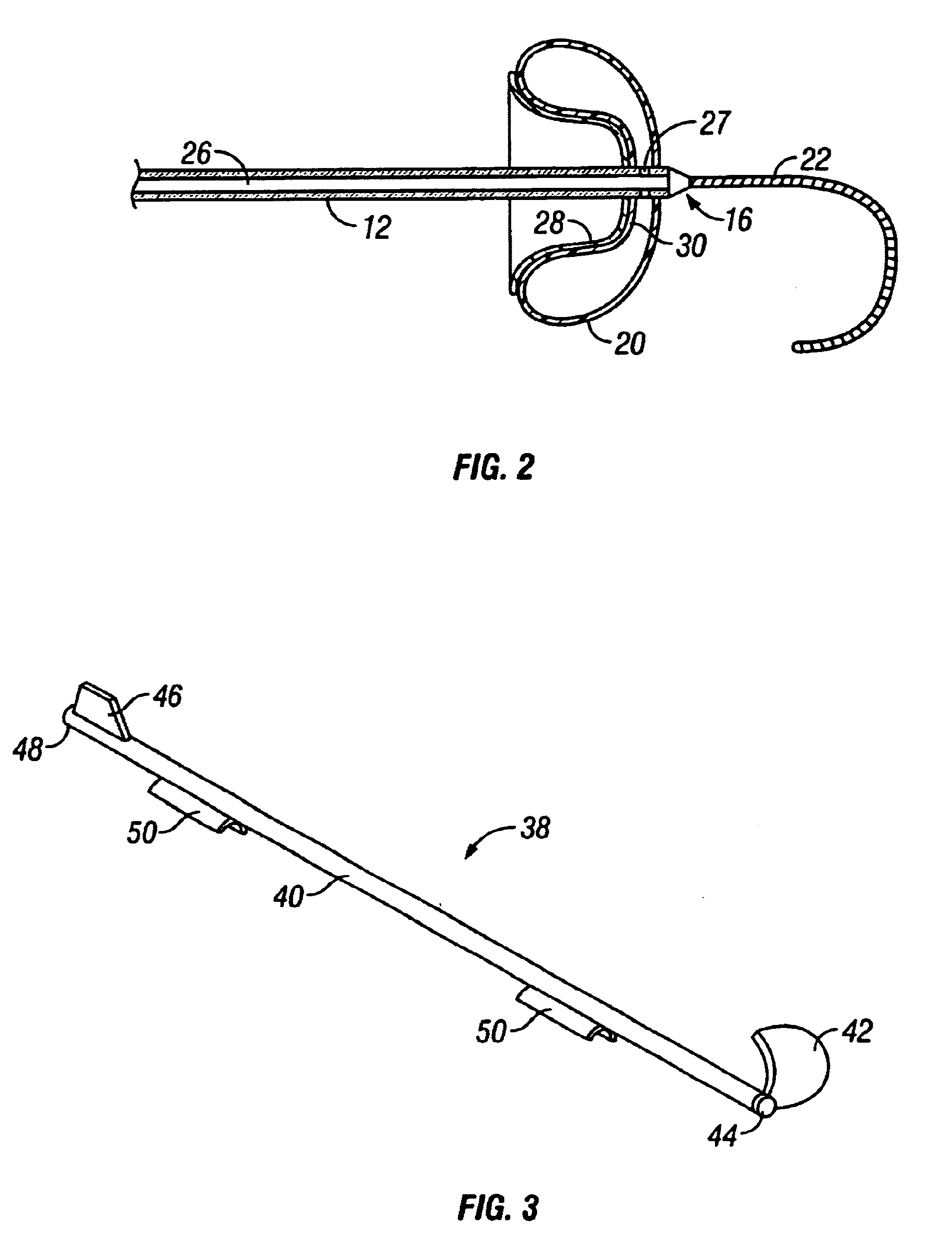
Methods and apparatus for forming anastomotic sites
InactiveUS6712831B1Reduce distractionsForce can be appliedSuture equipmentsWound clampsEnd to side anastomosisThree vessels
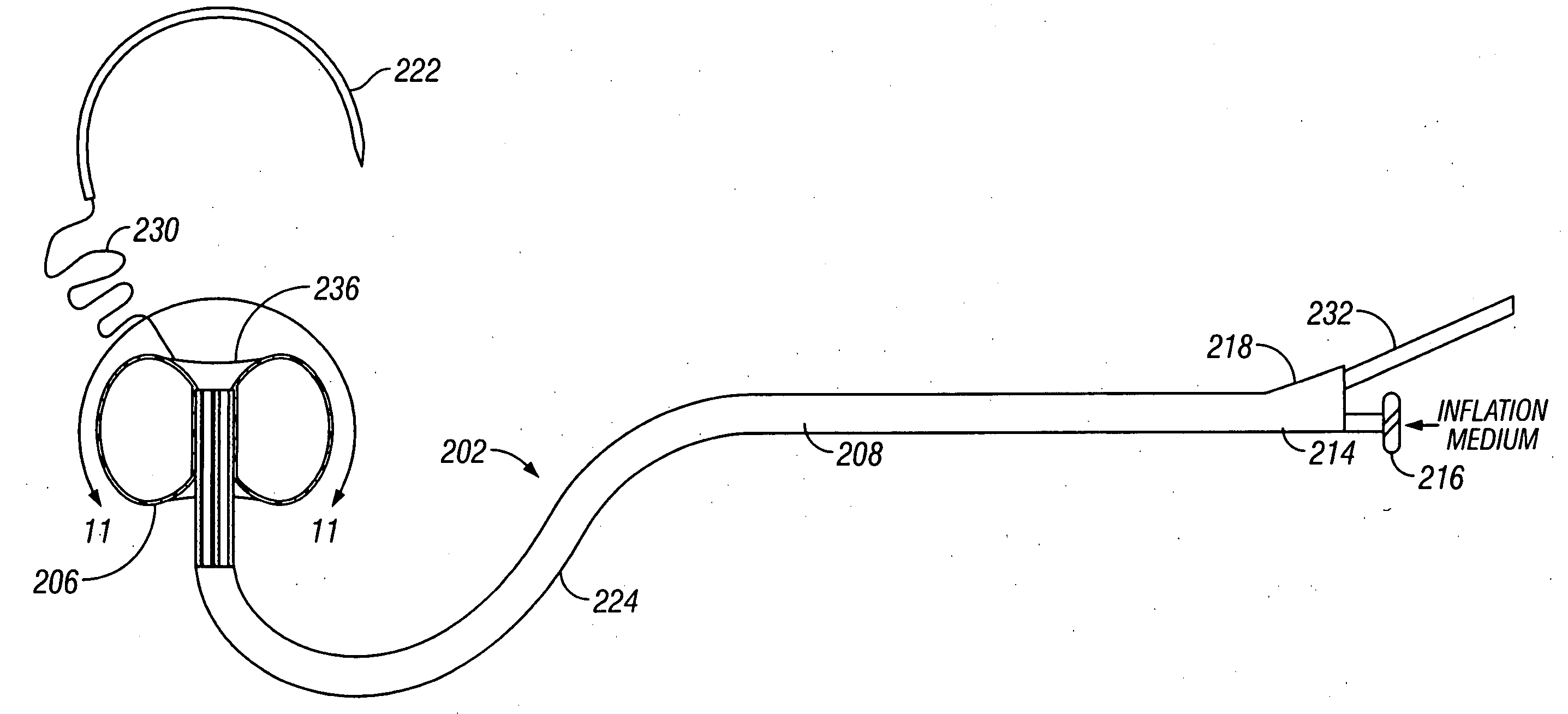
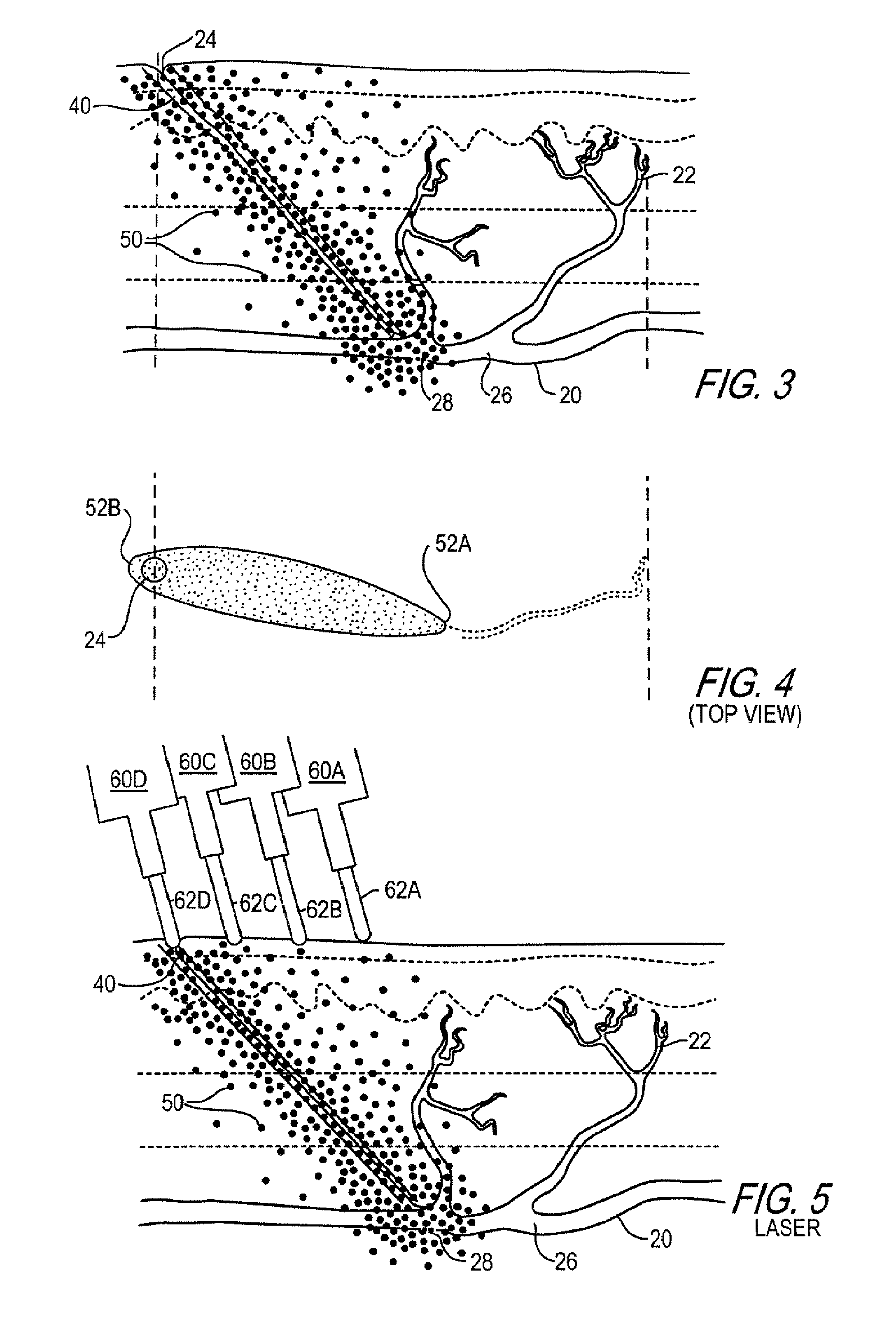
Apparatus and methods are provided for forming a working space on the interior wall of a blood vessel, such as the aorta. The working space is isolated from blood flow and permits creation of an anastomotic hole and subsequent suturing of the hole to form an end-to-side anastomosis, even while the heart is beating. The apparatus comprises tools including inflatable barriers, such as cup-shaped balloons, which engage the inner wall of the blood vessel with minimum trauma and maximum sealing. In a first embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a penetration at the site of the anastomotic attachment. In a second embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a second penetration axially spaced-apart from the site of the anastomotic attachment.
Owner:AARON V KAPLAN M D
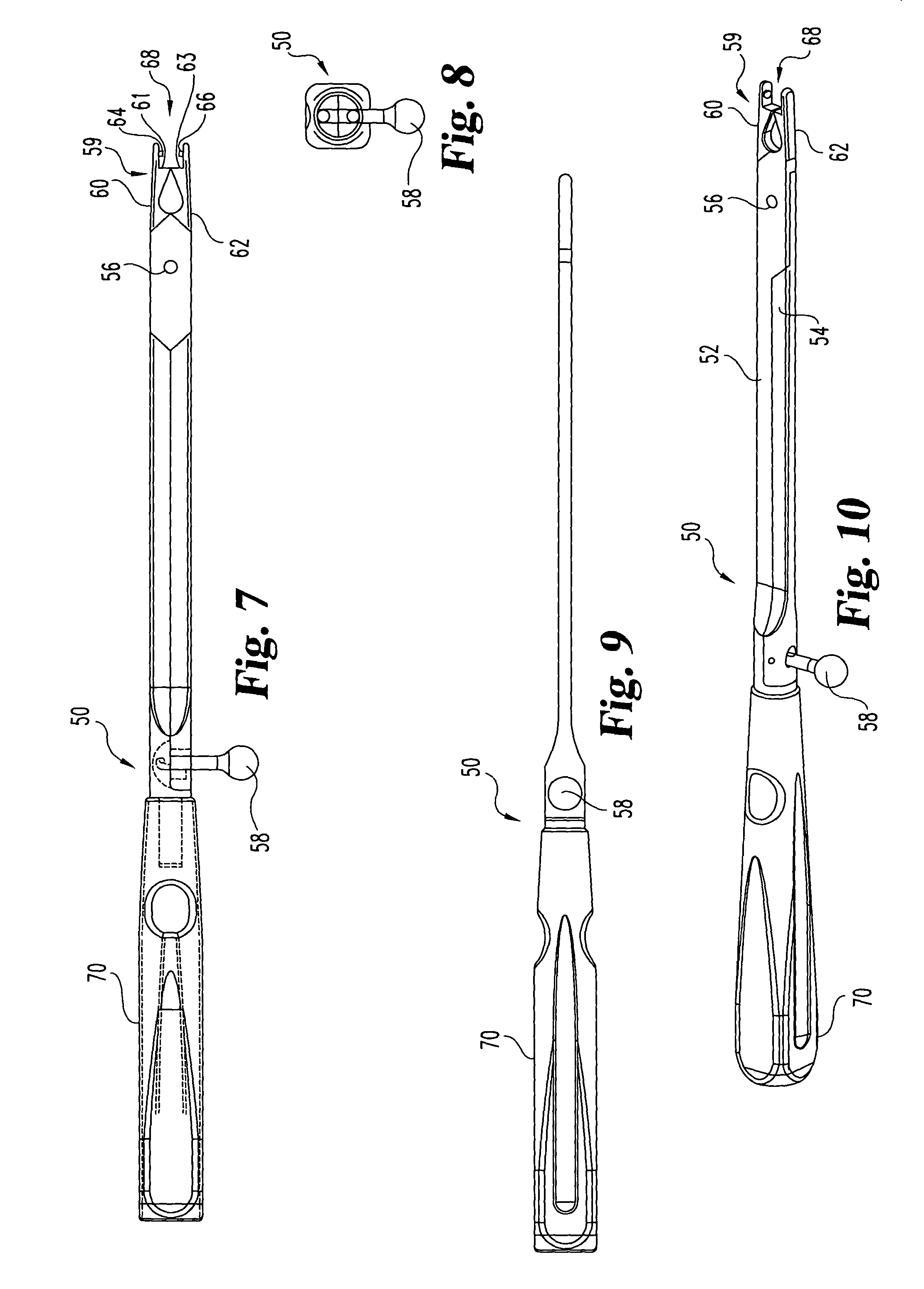
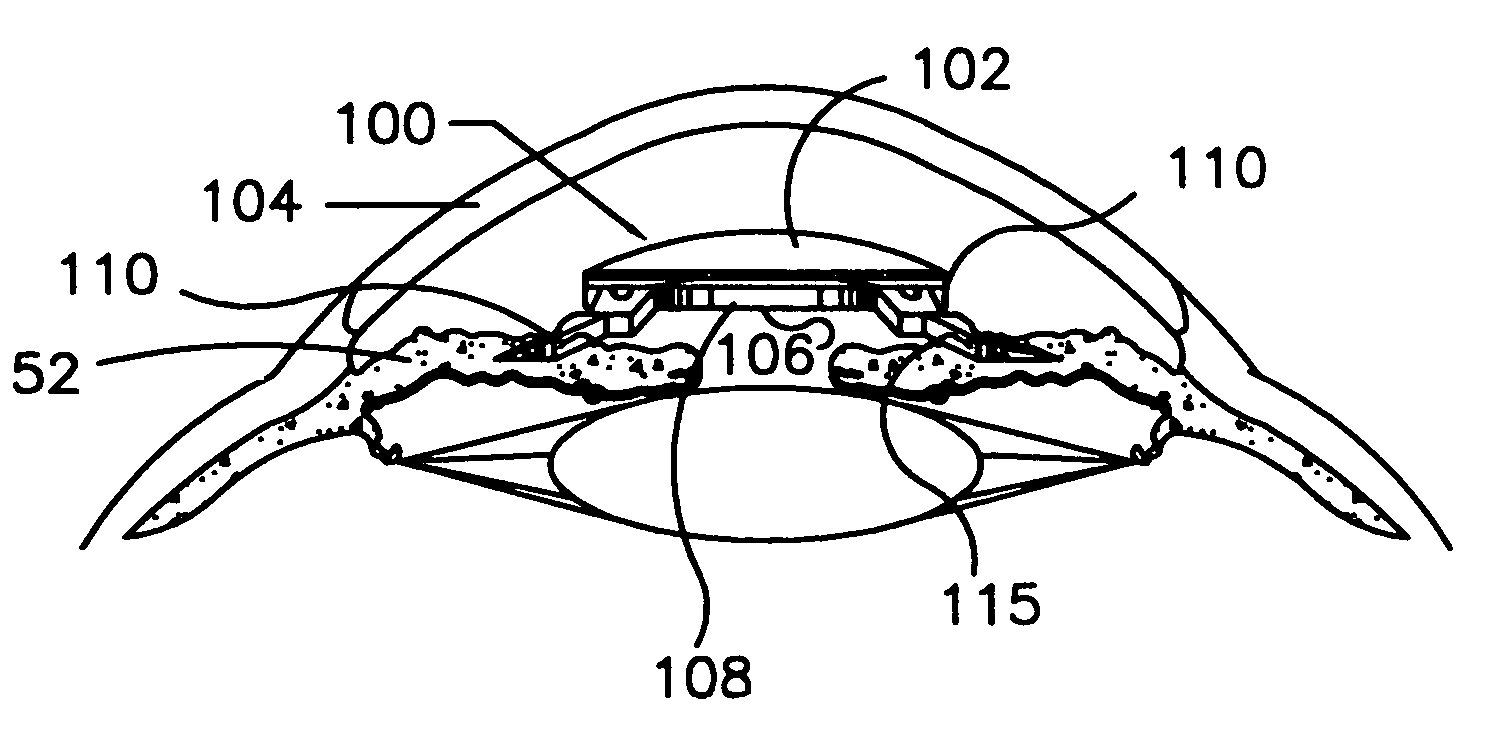
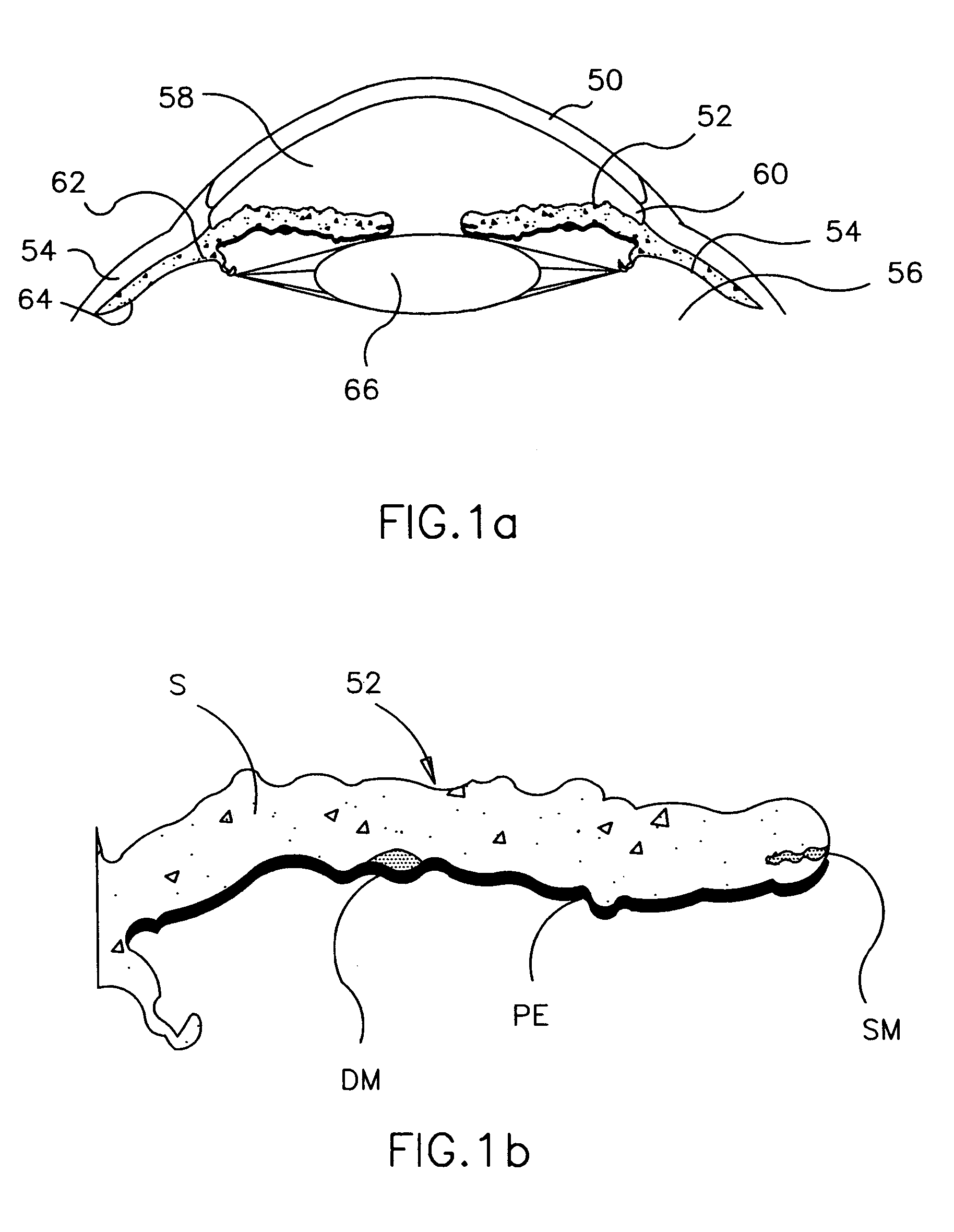
Refractive intraocular implant lens and method
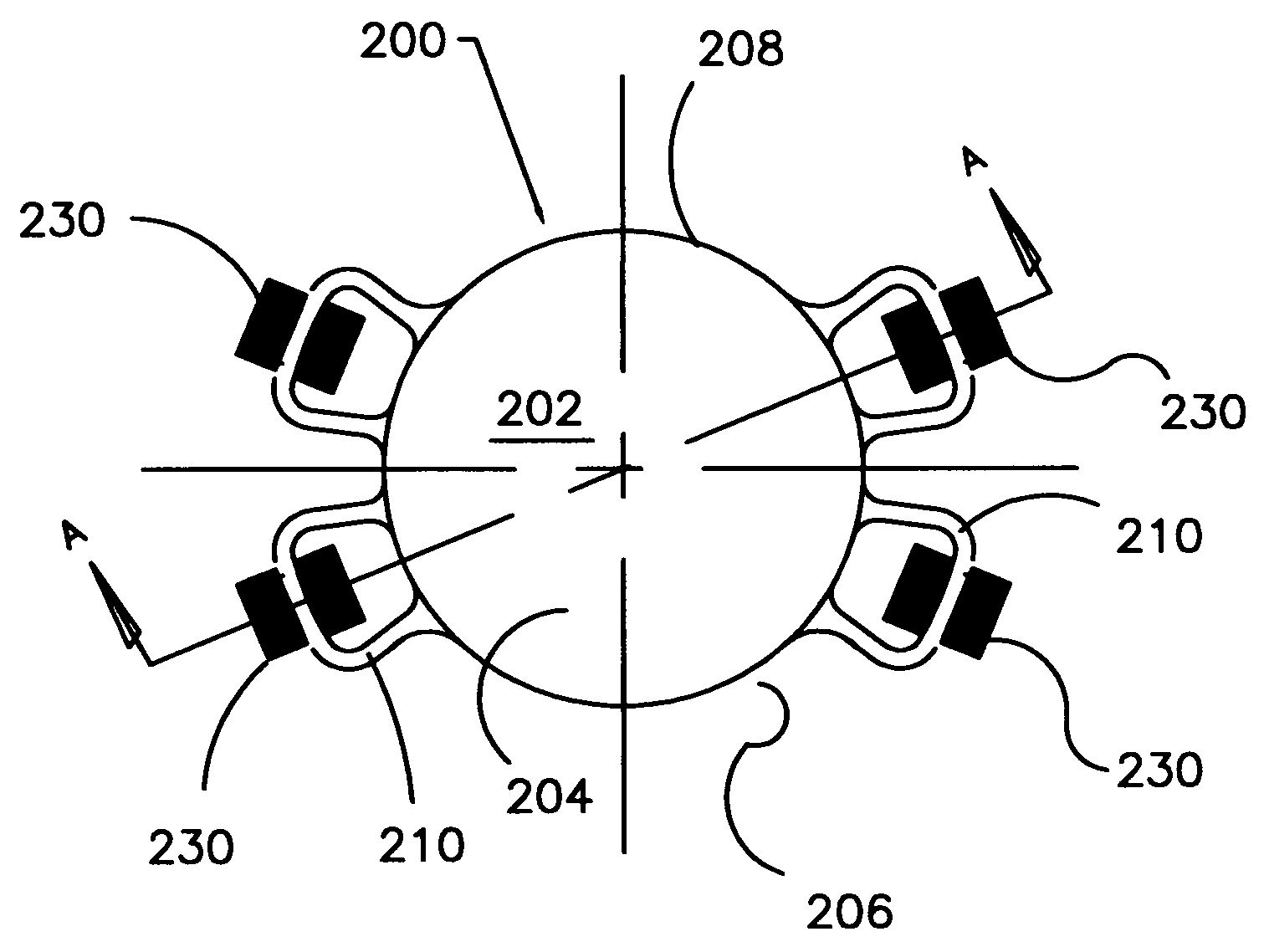
InactiveUS20050015143A1Easy to insertEasy to removeEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular implantLens implant
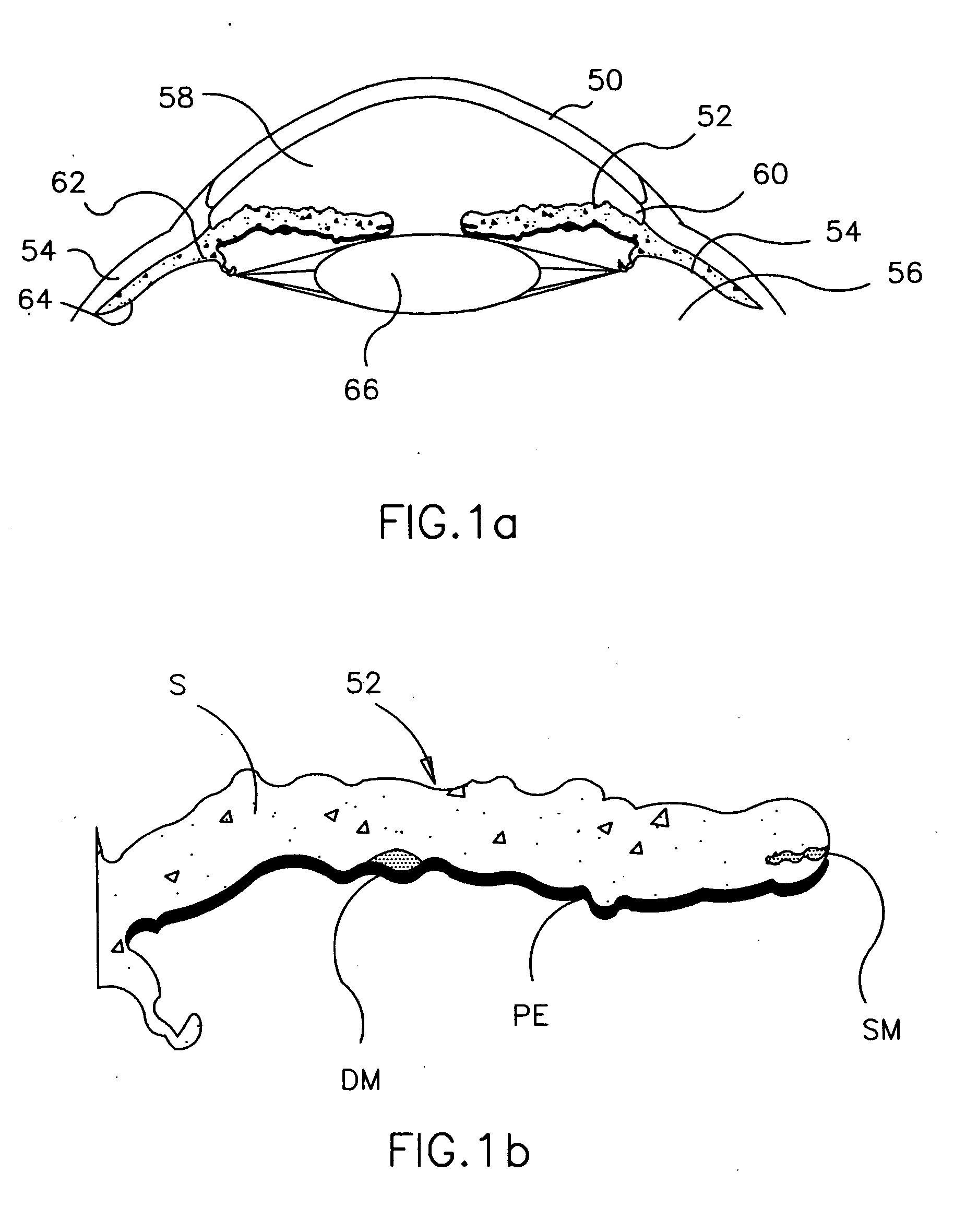
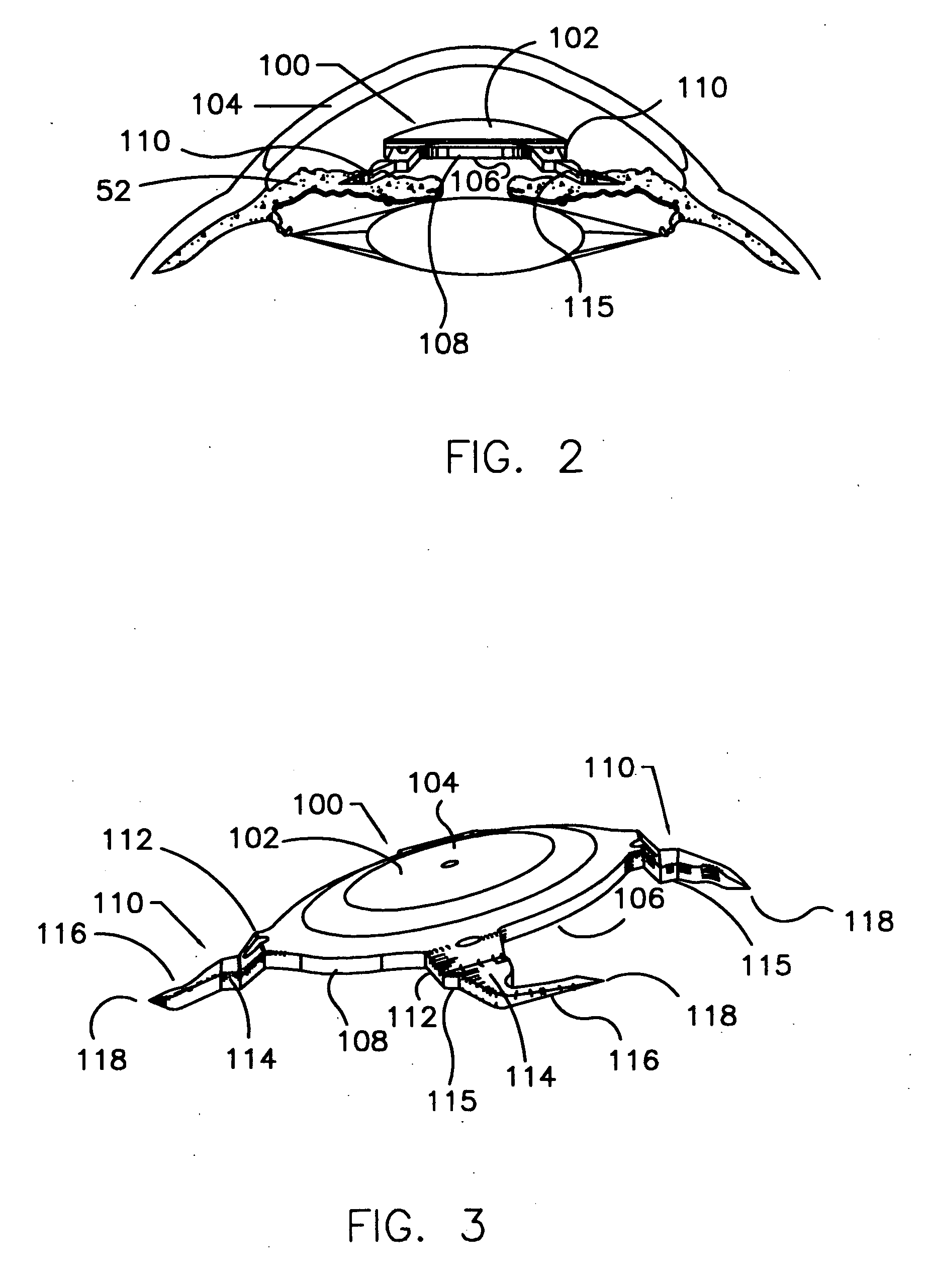
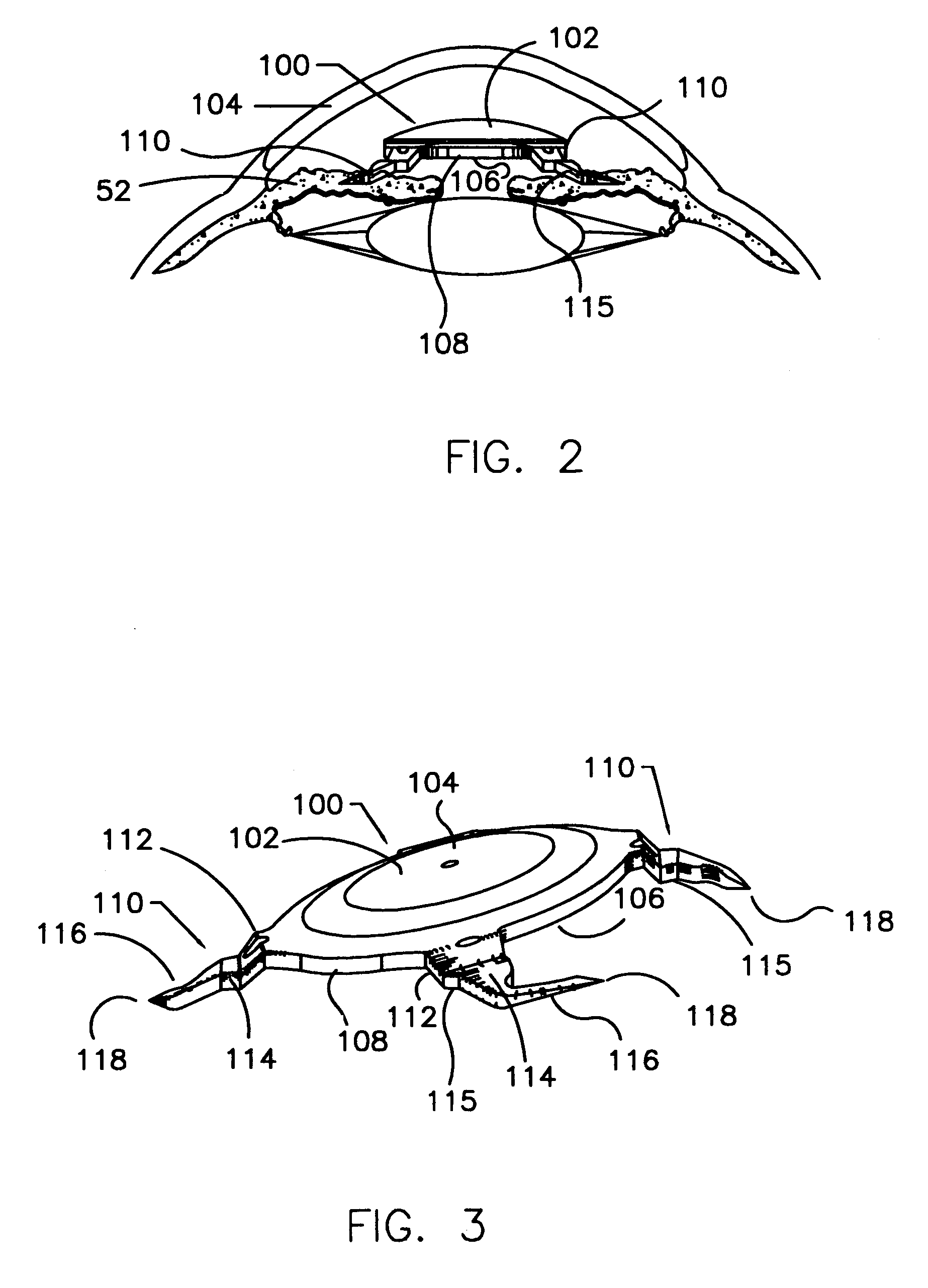
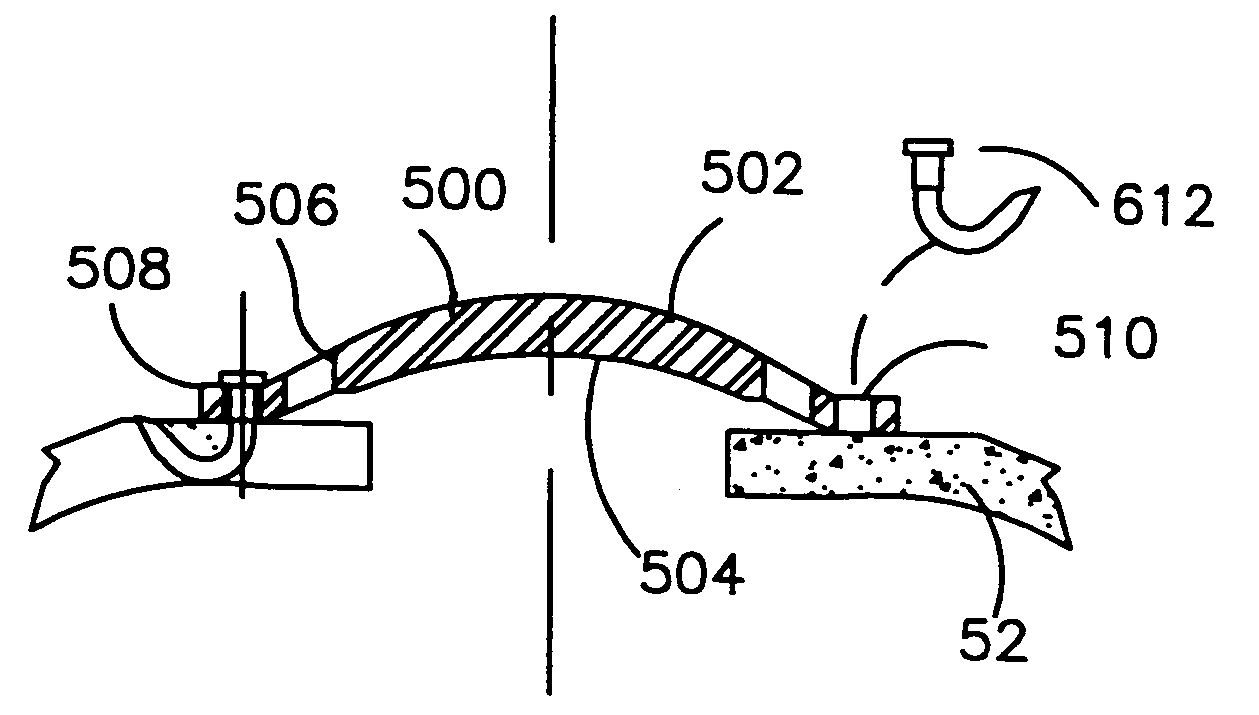
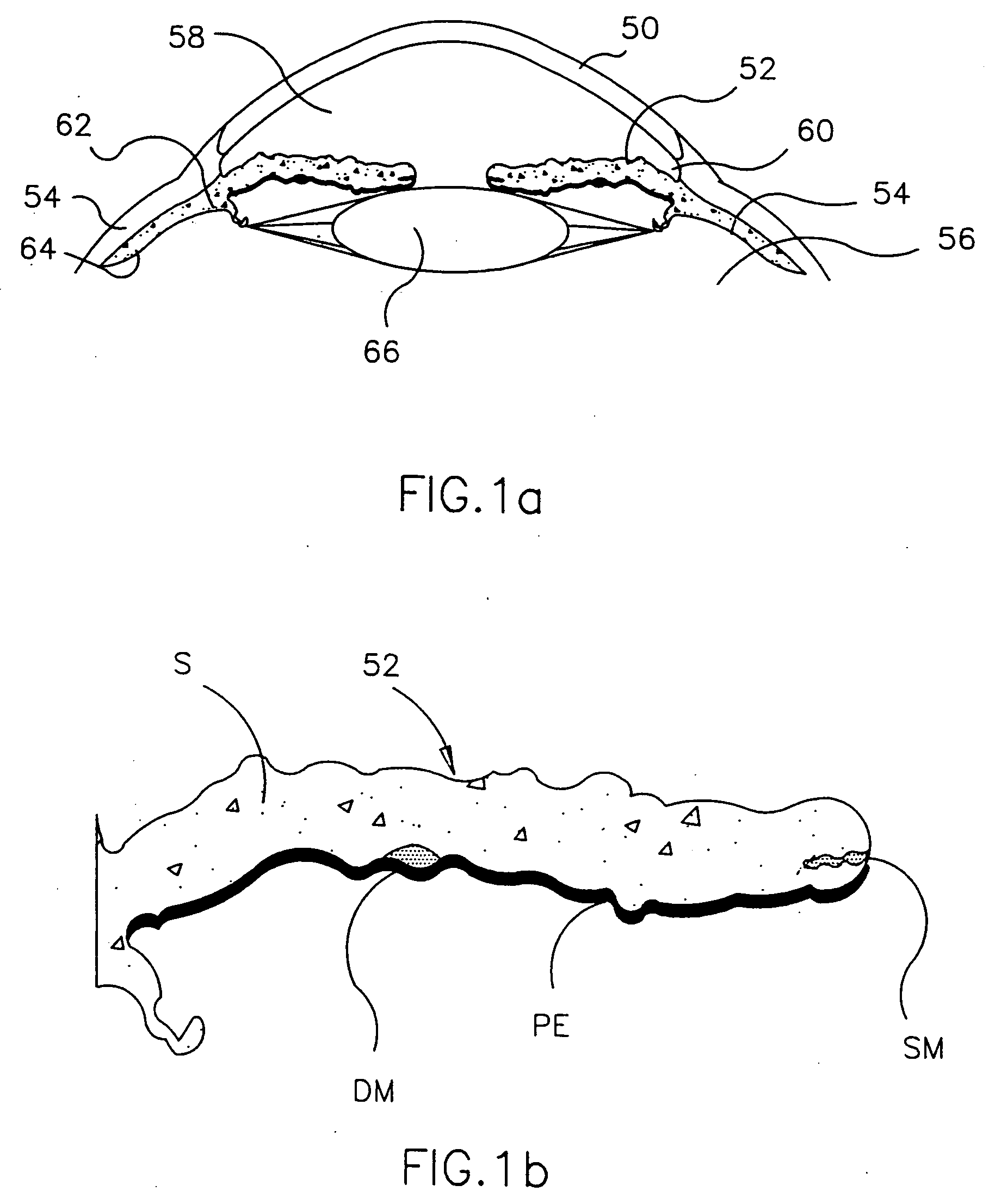
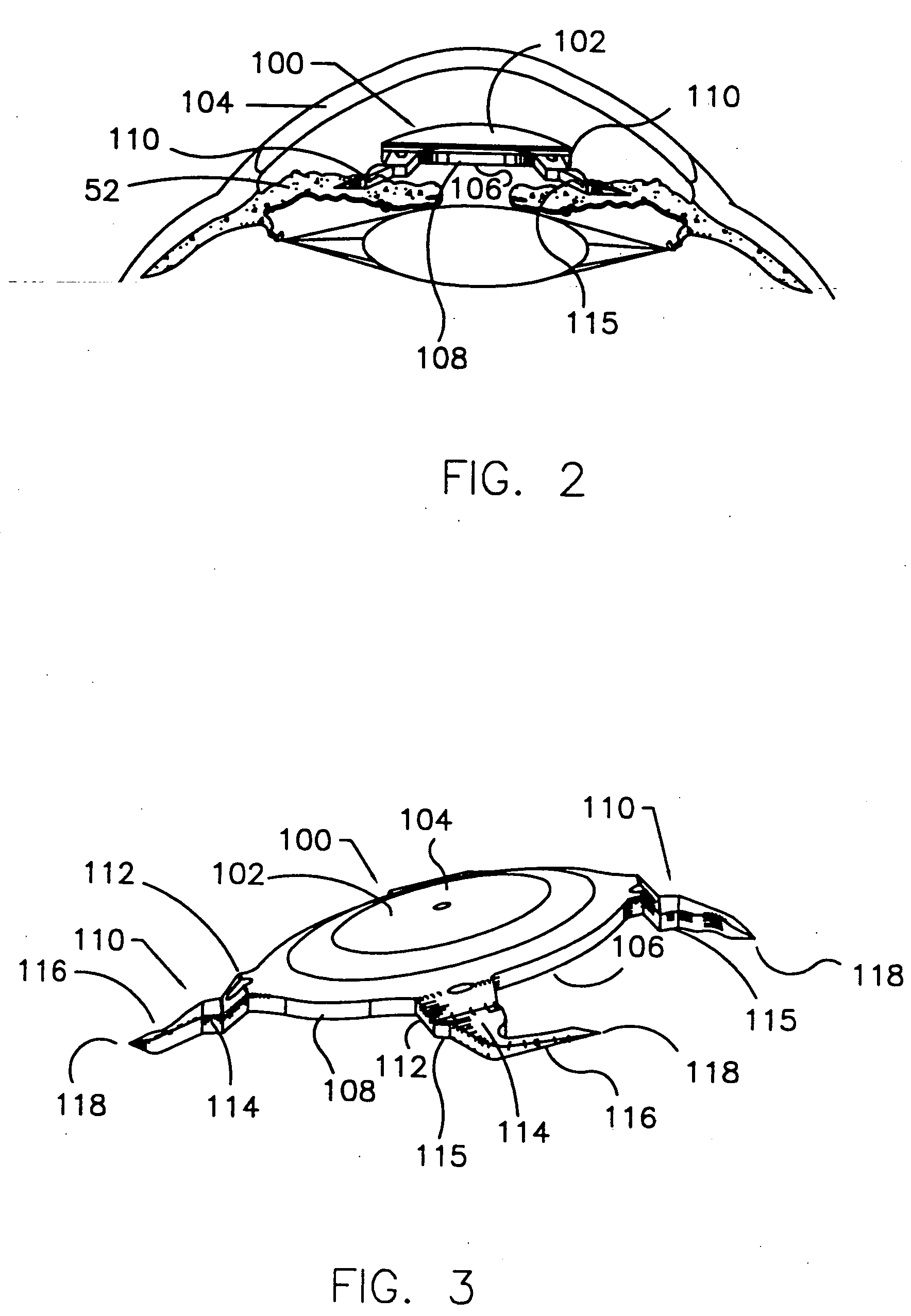
A refractive intraocular lens (104) and method of locating the lens within the eye and attaching the lens to the iris. The refractive intraocular lens (104) may be attached via a staple (230), a fastener (312), anchor (412) or by the tip of the haptic (118).
Owner:WILLIS TIMOTHY R
Filamentary means for introducing agents into tissue of a living host
InactiveUS6884427B1Promote new bone formationMinimal traumaPowder deliverySkin implantsHair follicleSolid core
The present invention provides a filamentary structure for the introduction of agents into a living host, comprising a filament comprising a solid core and a porous sheath which coats at least a portion of the solid core. When the filamentary structure is to be permanently implanted into a living host, both the solid core and the porous sheath are bioabsorbable. When the filamentary structure is to be temporarily implanted into the skin of a living host to deliver agents, such as cells, therein, the porous sheath is preferably bioabsorbable but the core need only be biocompatable, not bioabsorabable. The devices and methods of the present invention enable one to regenerate hair follicles, to introduce genetically altered cells or encapsulated cells to a living host transdermally, to regenerate bones, and to deliver drugs transdermally.
Owner:ADERANS RES INST
Eccentric abrading head for high-speed rotational atherectomy devices
ActiveUS8597313B2Improve abilitiesMinimal traumaCannulasExcision instrumentsStenotic lesionRotational axis
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Tooth Implant
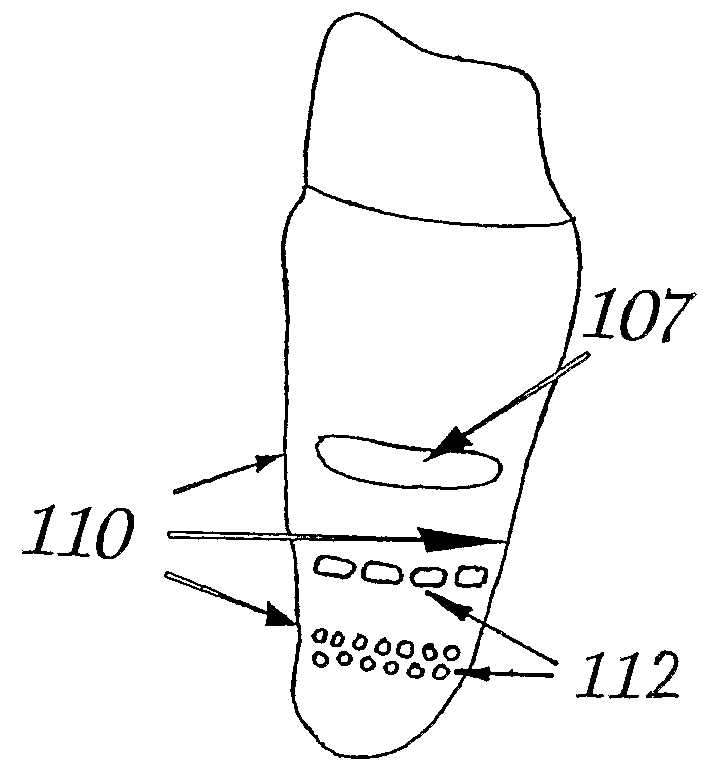
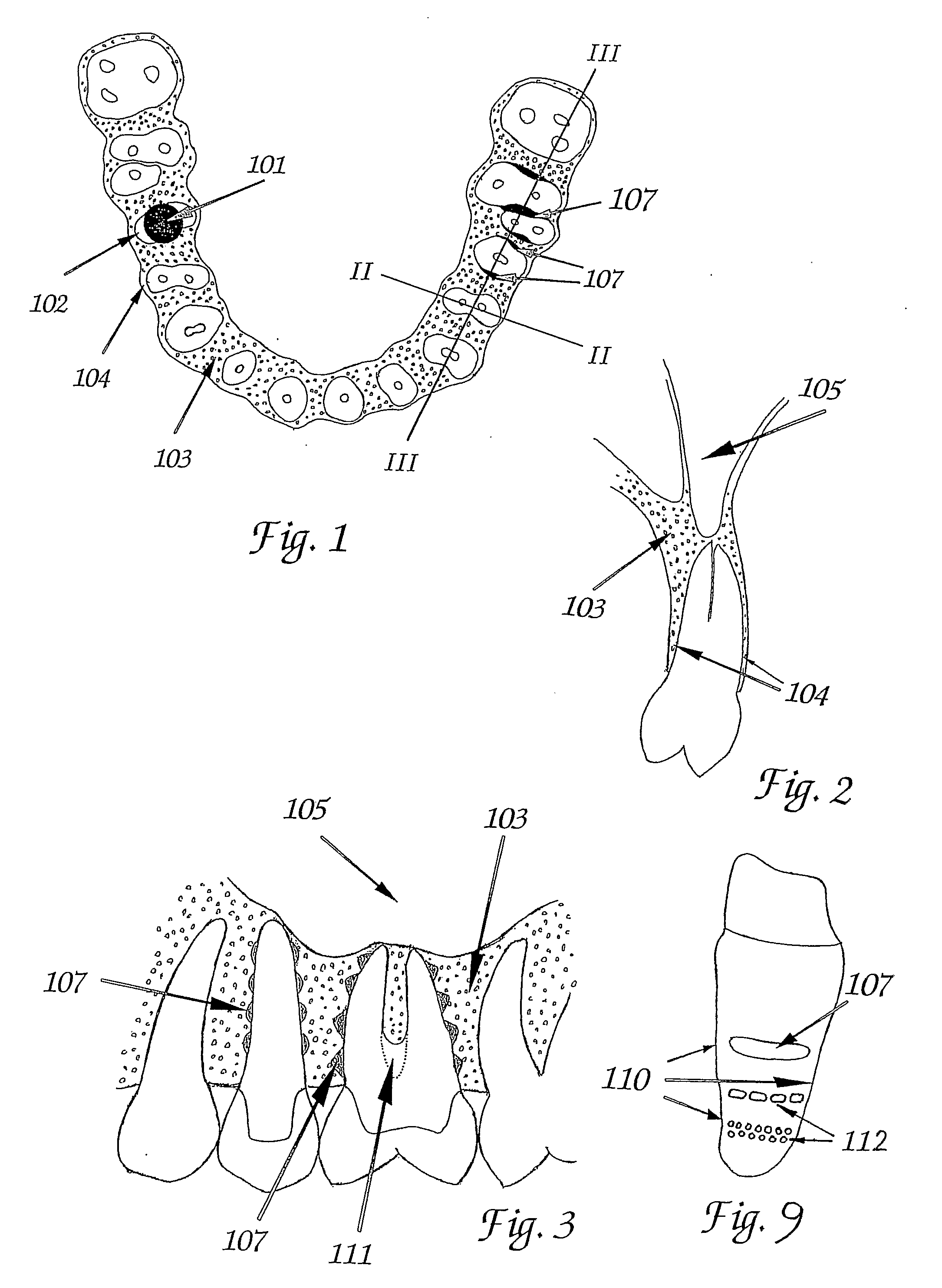
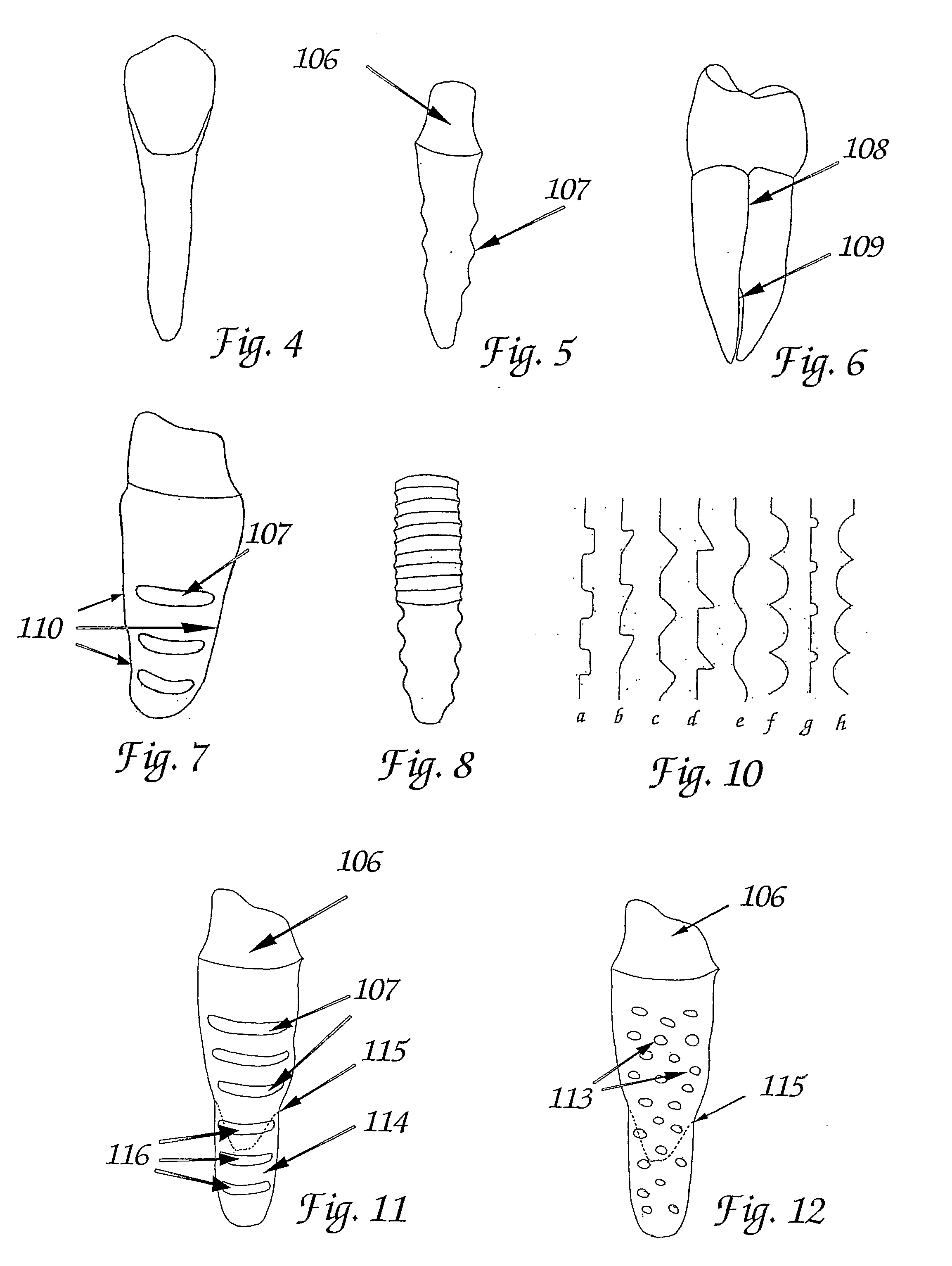
ActiveUS20090092944A1Short maintenance periodMinimal traumaDental implantsExtract toothThin cortical bone
The invention concerns a non rotation-symmetric but root-analogue or tooth socket-analogue dental implant of the same size and shape as the root of the extracted tooth with macro retentions protruding from the implant surface (107, 113, 116).Macro retentions (107, 113, 116) are strictly limited to surface areas of the implant in the interdental space next to spongy and thick bone and in case of the last molar, facing the bone at the end of the tooth row. The diameter of the dental implant in transverse direction next to the thin cortical bone buccal and lingual / palatinal is identical to the alveolar bone or preferably stands back to avoid any pressure induced resorption and fracture of the thin cortical bone layer, respectively, at any cost.
Owner:PIRKER WOLFGANG
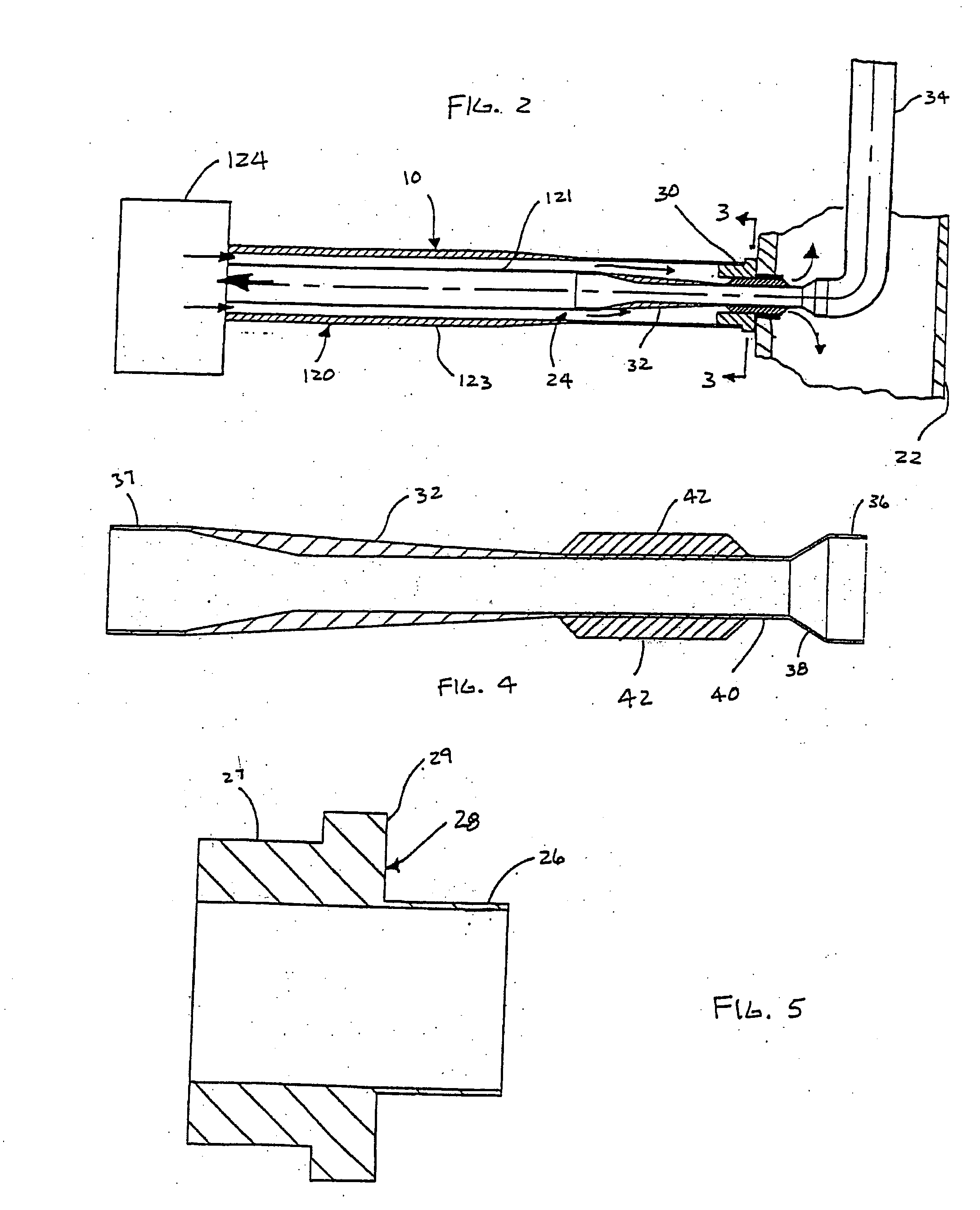
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS7625374B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionBone implantDiagnostic markersDonor boneIntervertebral space
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concave surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Refractive intraocular implant lens and method
InactiveUS7008449B2Easy to insertEasy to removeEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular implantLens implant
A refractive intraocular lens (104) and method of locating the lens within the eye and attaching the lens to the iris. The refractive intraocular lens (104) may be attached via a staple (230), a fastener (312), anchor (412) or by the tip of the haptic (118).
Owner:WILLIS TIMOTHY R
Methods and apparatus for forming anastomotic sites
InactiveUS20040215233A1Conveniently formedAvoid interferenceSuture equipmentsSurgical veterinaryEnd to side anastomosisThree vessels
Apparatus and methods are provided for forming a working space on the interior wall of a blood vessel, such as the aorta. The working space is isolated from blood flow and permits creation of an anastomotic hole and subsequent suturing of the hole to form an end-to-side anastomosis, even while the heart is beating. The apparatus comprises tools including inflatable barriers, such as cup-shaped balloons, which engage the inner wall of the blood vessel with minimum trauma and maximum sealing. In a first embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a penetration at the site of the anastomotic attachment. In a second embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a second penetration axially spaced-apart from the site of the anastomotic attachment.
Owner:MAGENTA MEDICAL CORP
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS20050261681A9Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantDonor boneIntervertebral space
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
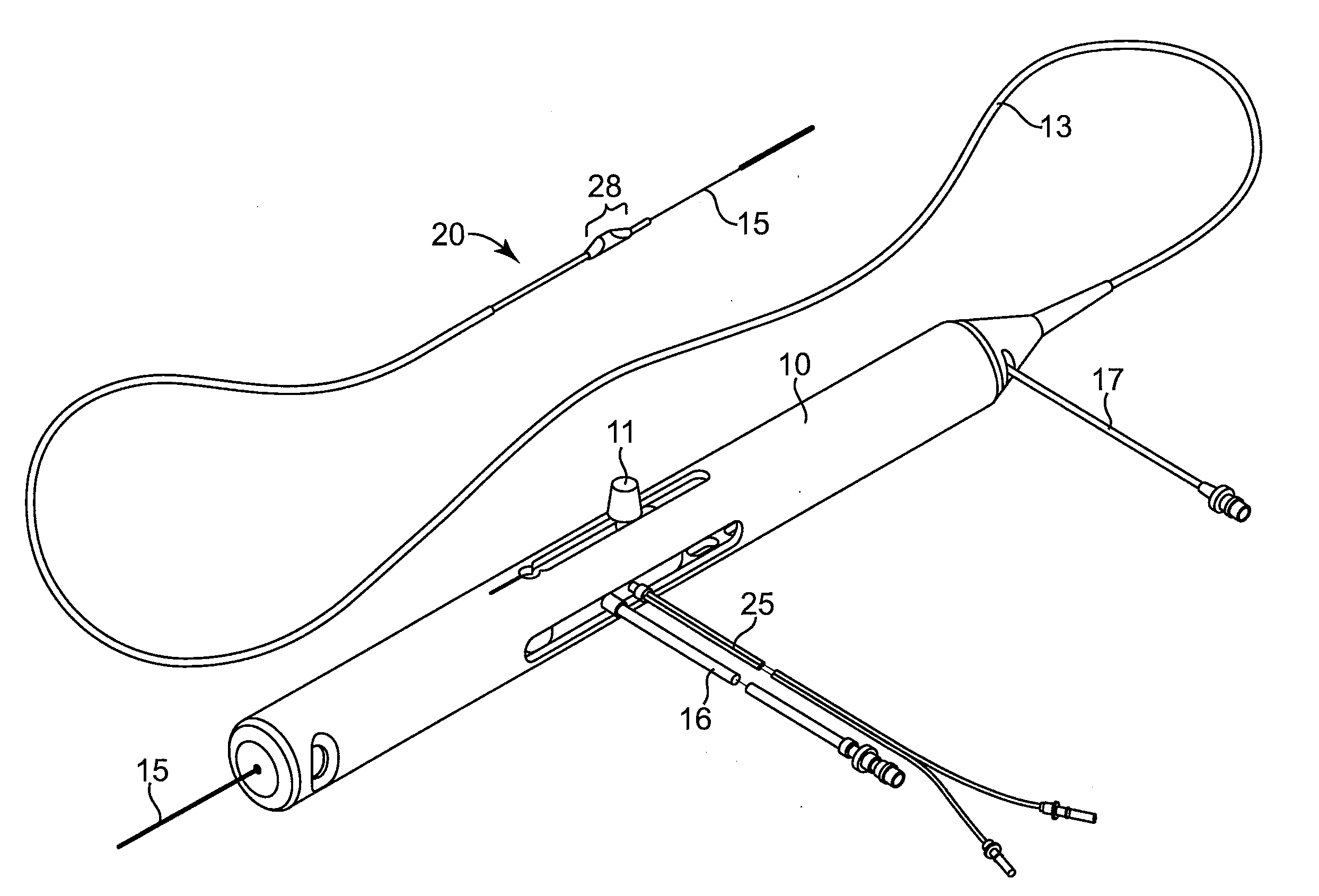
Method and system for implant delivery
InactiveUS20110275891A1Easy to storeImprove logisticBalloon catheterSurgeryBiomedical engineeringTarget site
The present invention relates to a system and method for the delivery of a treatment element, and in particular, to such a system and method in which an implantable treatment element is implanted at a target site.
Owner:SILENSEED LTD
Endoscopic submucosal core biopsy device
InactiveUS20070123800A1Minimal traumaSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEndoscopeBody tissue
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Robotic guided endoscope
ActiveUS20130303883A1Reduce traumaLevel accuracyEndoscopesComputerised tomographsSurgical robotSurgery scheduling
Systems and methods for performing robotic endoscopic surgical procedures, according to a surgical plan prepared on a preoperative set of three dimensional images. The system comprises a surgical robot whose coordinate system is related to that of fluoroscope images generated intraoperatively, by using a three dimensional target having radio-opaque markers, attached in a predetermined manner to the robot or to another element to which the robot is attached, such as the spinal bridge or an attachment clamp. The robot is mounted directly or indirectly on a bone of the patient, thereby nullifying movement of the bone, or a bone tracking system may be utilized. The coordinate system of the intraoperative fluoroscope images may be related to the preoperative images, by comparing anatomical features between both image sets. This system and method enables the endoscope to be directed by the robot along the exact planned path, as determined by the surgeon.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
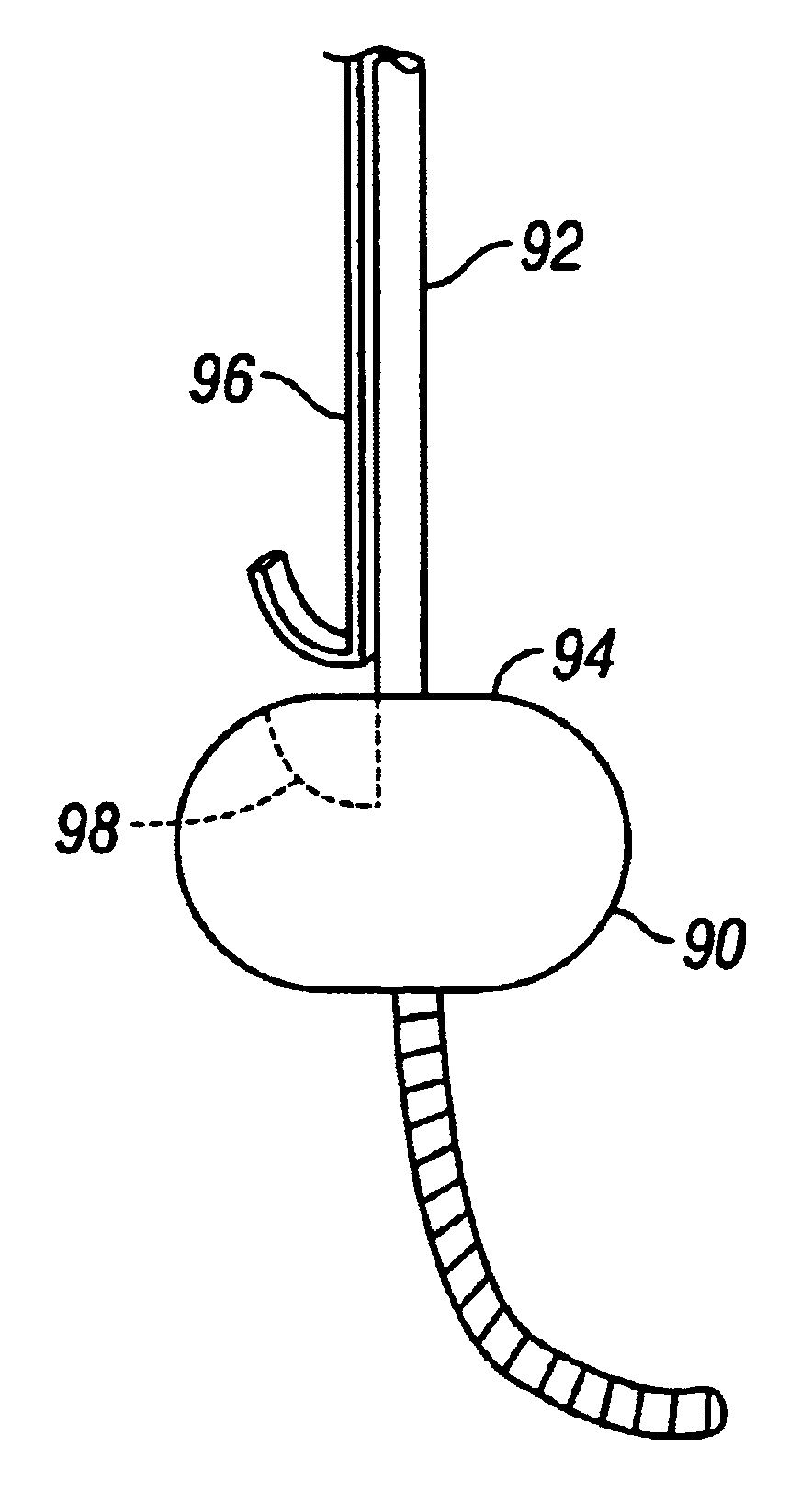
Endoscopic balloon tissue dissector and retractor
An instrument for endoscopic surgery comprises a retractor having independently spreadable retractor blades mounted at the distal end of a tube, through which a balloon dissector can be passed. The balloon is transparent, and the balloon dissector is provided with an image transmitter for visualization of tissue dissection.
Owner:KAMBIN PARVIZ +1
Distraction osteogenesis device and method
InactiveUS6293947B1Minimize traumaMinimize damageInternal osteosythesisInvalid friendly devicesSurgical operationOsteogenesis distraction
A device and method for performing distraction osteogenesis. The distraction osteogenesis device, in accordance with the present invention, is modular in construction, and has at least two bioabsorbable footplates having screw or rivet holes therein and an extendable member therebetween. The extendable member is used to change the distance between the footplates. When performing the distraction osteogenesis procedure, the footplates are affixed to the bone on either side of an osteotomy / fracture by means of bioabsorbable screws or rivet bone fasteners. The footplates are connected to one another by the extendable member which spans the osteotomy site and stabilizes the bone segments comprising the osteotomy / fracture. Following implantation of the distractor, the extendable member is periodically elongated to incrementally separate the segments of the bone affixed to the respective footplates. Osteogenesis within the osteotomy site is sustained as the juxtaposed ends of the bone segments incrementally separate. When the bone attains a desired length and / or curvature, further elongation of the distractor is discontinued and the newly formed bone is permitted to harden. The extendable member is disconnected from the footplates and surgically explanted. The bioabsorbable footplates and the bioabsorbable screws or rivets affixing the footplates to the bone are not disturbed during explantation of the extendable member and are absorbed by the body over time. The bioabsorbable footplates may be adapted for use with a variety of extendable members.
Owner:BUCHBINDER DANIEL
Methods and apparatus for automatic jet injection of bird eggs
An in ovo jet injection apparatus and related methods for treating live eggs. The jet injection apparatus includes one or more jet injection delivery devices configured to deliver one or more treatment substances to predetermined areas of eggs using a high pressure stream of the treatment substance(s). Multiple treatment substances can be delivered so that they are spatially and / or temporally separate. The devices and methods of the invention enable the effective use of a plurality of treatment substances, including those that are effective when used alone but can be noxious if mixed. The methods and apparatus for the jet injection of substances into embryonic chicks reduce the risk of mechanical injury to the developing birds that would be caused by injection needles. The methods and apparatus of the invention can also reduce the introduction of an infection into the chicks.
Owner:MERIAL INC
System and Method for Intracranial Implantation of Therapeutic or Diagnostic Agents
ActiveUS20090192487A1Precise positioningSimple and intuitive operationMedical devicesIntravenous devicesDiagnostic agentBrain tumor
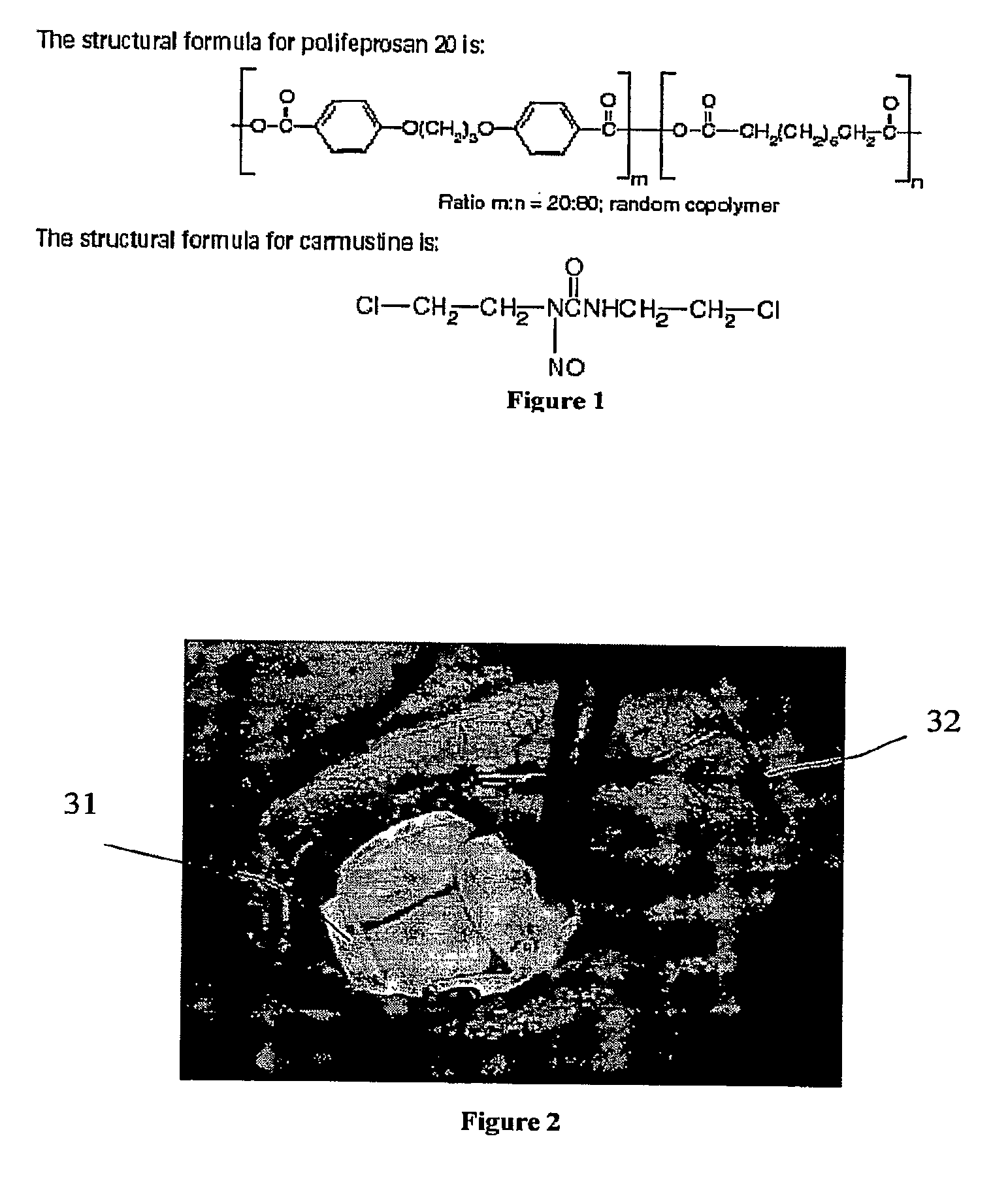
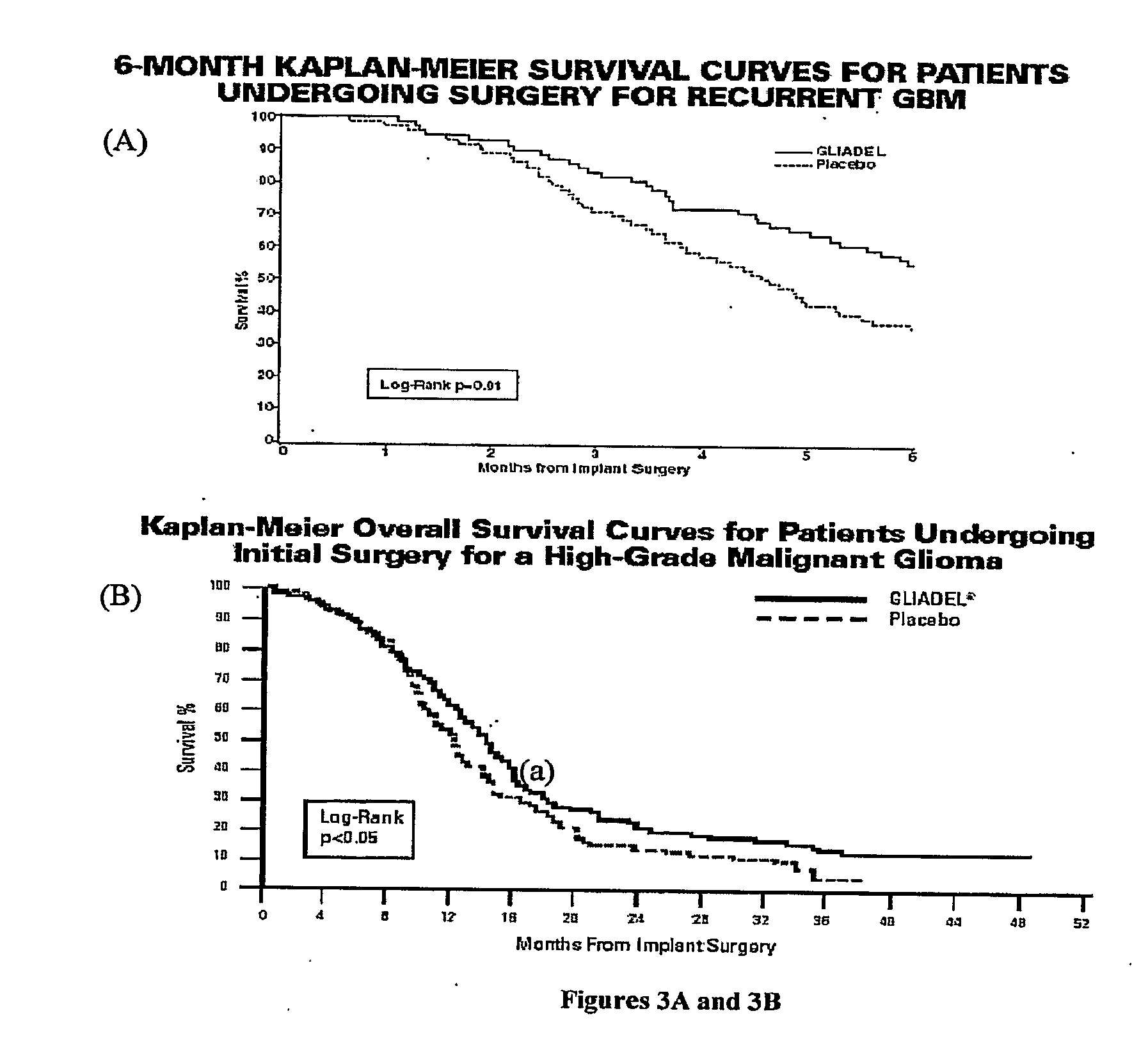
A system and related method for delivering the anti-tumoral agent carmustine or other types of diagnostic or therapeutic agents into the brain of a patient with a brain tumor includes an insertion device, a skull mount, and a reformulated geometry of the carmustine compound (or other material) optimized for use in the insertion device and for maximized biodegradation time. The insertion device may be front loaded with the carmustine material (or other material) and inserted through the mount on a skull, to the location of the brain tumor, where the carmustine (or other material) is then released. It should be appreciated that the diagnostic and / or therapeutic system and related method thereof are not necessarily limited to the brain of a subject. It may also be used in the organ structures or tubular structures, as well as portions and locations thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
Refractive intraocular implant lens and method
A refractive intraocular lens (104) and method of locating the lens within the eye and attaching the lens to the iris. The refractive intraocular lens (104) may be attached via a staple (230), a fastener (312), anchor (412) or by the tip of the haptic (118). The intraocular lens (104) works in combination with the human crystalline lens to treat conditions selected from the group consisting of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism.
Owner:WILLIS TIMOTHY R
Implantable Medical Devices, Methods of Use, and Apparatus for Extraction Thereof
InactiveUS20150080709A1Facilitated releaseMinimal traumaTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsNanoparticleMedical device
One aspect of the present disclosure relates to an implantable medical device. The implantable medical device can include a main body portion having at least one photosensitive nanoparticle associated therewith. Delivery of energy to the main body portion promotes extraction of said implantable medical device from a subject.
Owner:CHATURVEDI NEHA
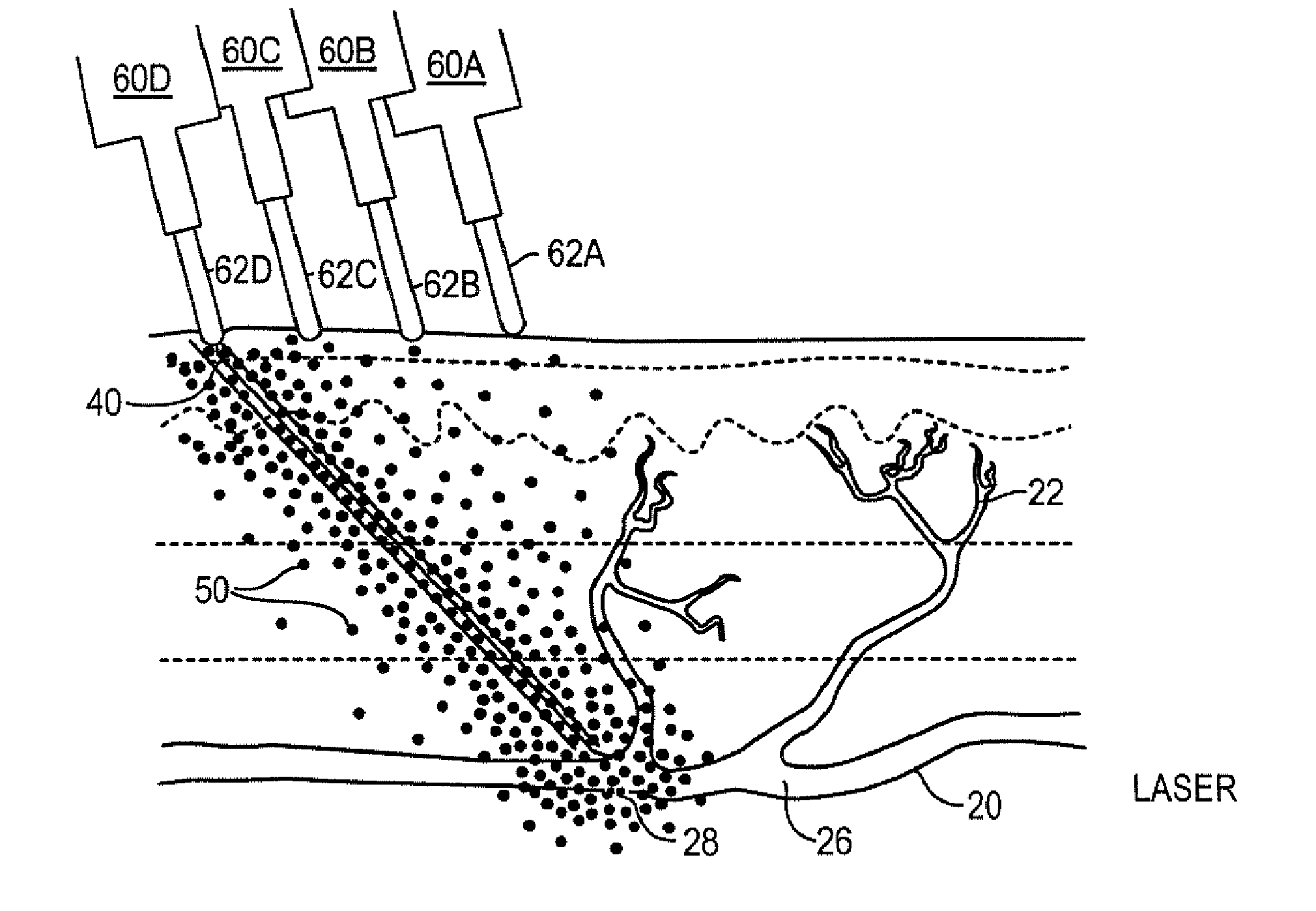
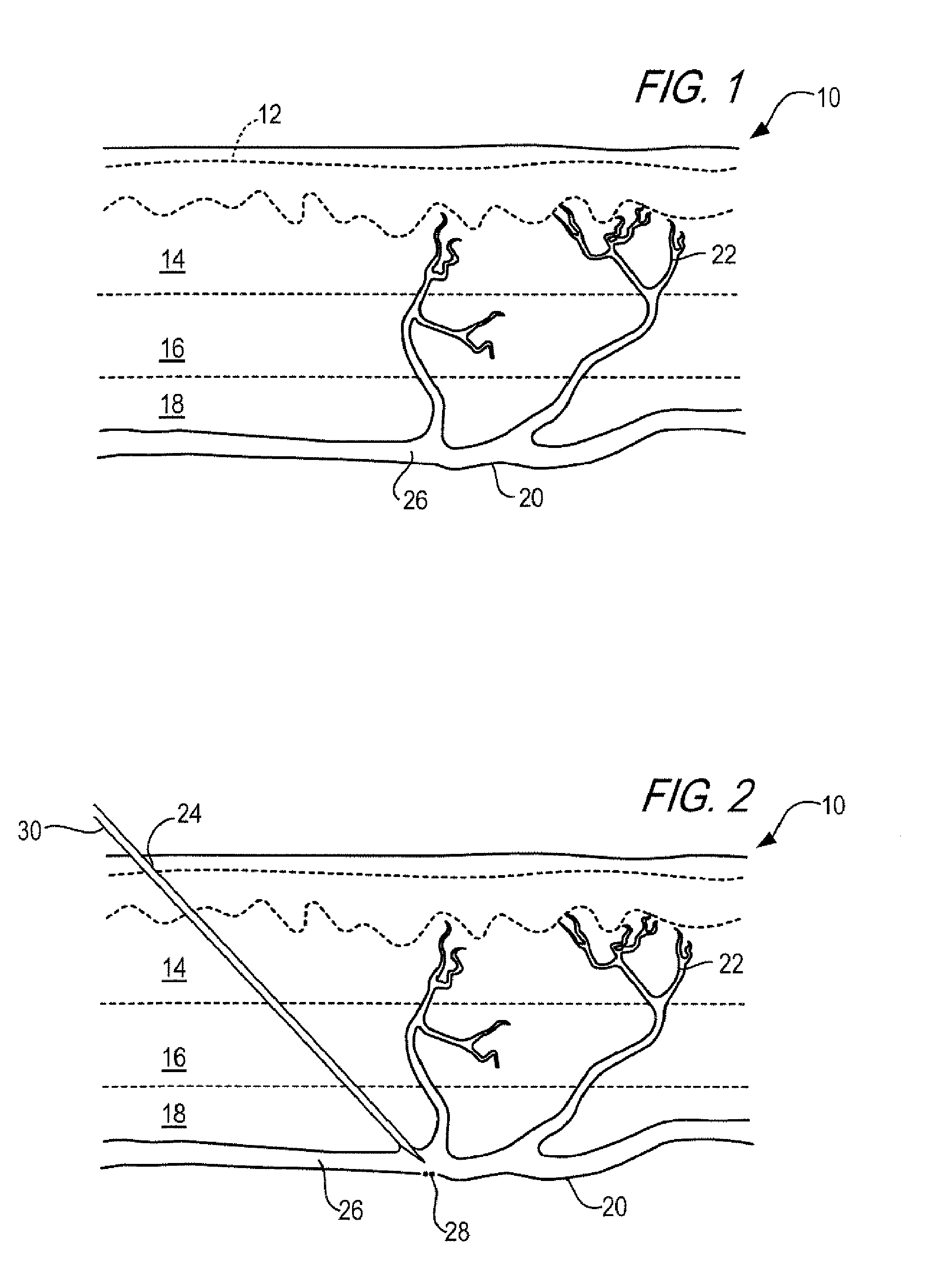
Method and kit for treatment of varicose veins and other superficial venous pathology
InactiveUS20070260229A1Reduce effectMinimal traumaSurgical instrument detailsLaser lightBiomedical engineering
A method is disclosed for treating superficial venous pathology in a patient. The method comprises the steps of: (a) percutaneously piercing a vein to be treated; and (b) directing intense pulse or laser light at the patient's skin predominantly within the area of skin manifesting physical, chemical and / or color changes caused by step (a). In a preferred method sclerotherapy is performed on the vein to be treated and then laser light is directed at the patient's skin substantially entirely within the area of skin manifesting the changes.
Owner:NAVARRO LUIS +2
Low radial force filter
ActiveUS20160038271A1Not easy to wearMinimal traumaSurgeryDilatorsBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Reinforced PTFE medical barriers
ActiveUS8556990B2Uniform strengthPreventing dehiscence and splitting openSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone defectMembrane configuration
Systems, methods and devices usable in the repair of a bone defect are described. A portion of a bone defect is covered with a multilayered membrane that includes a reinforcing layer. A member of the reinforcing member is fastened to an area of bone and soft tissue is secured about the membrane. The membrane facilitates healing of the defect. One membrane comprises a plurality of layers that includes a binding layer and a PTFE layer which has a textured surface and a substantially smooth surface. The textured surface provides a top surface of the membrane and the substantially smooth surface contacts bone.
Owner:OSTEOGENICS BIOMEDICAL
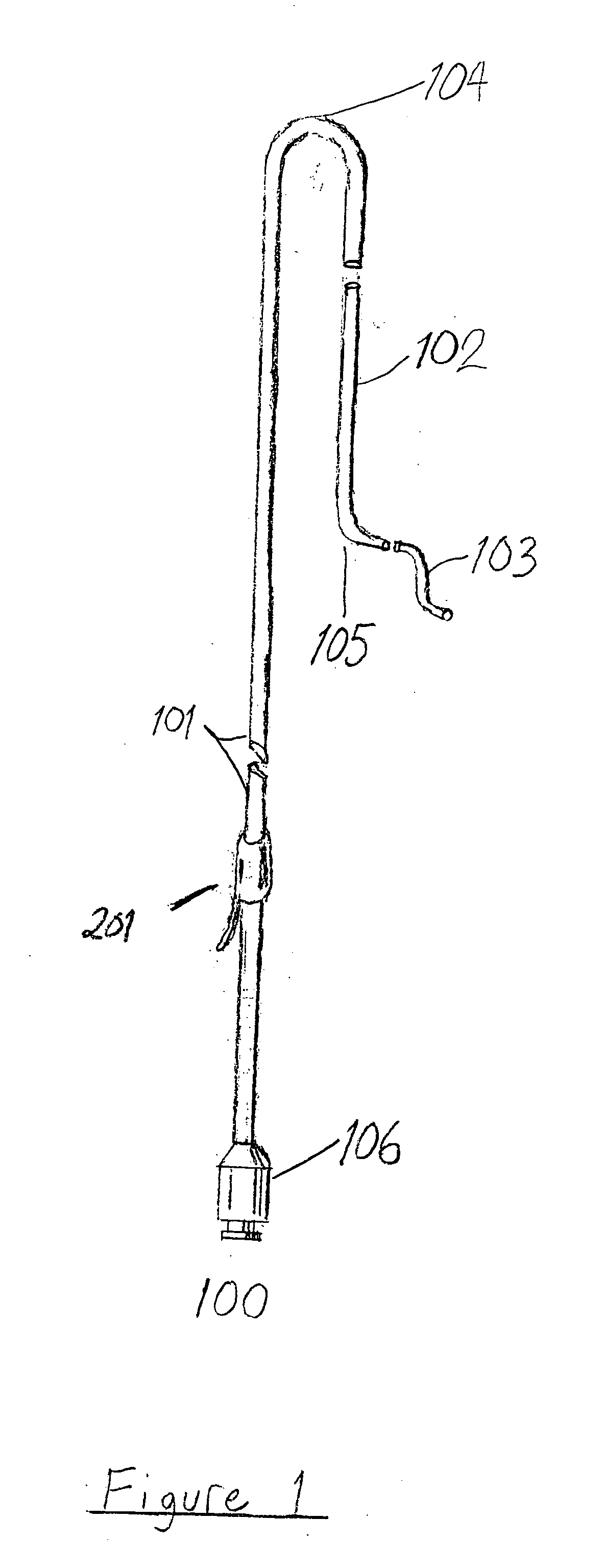
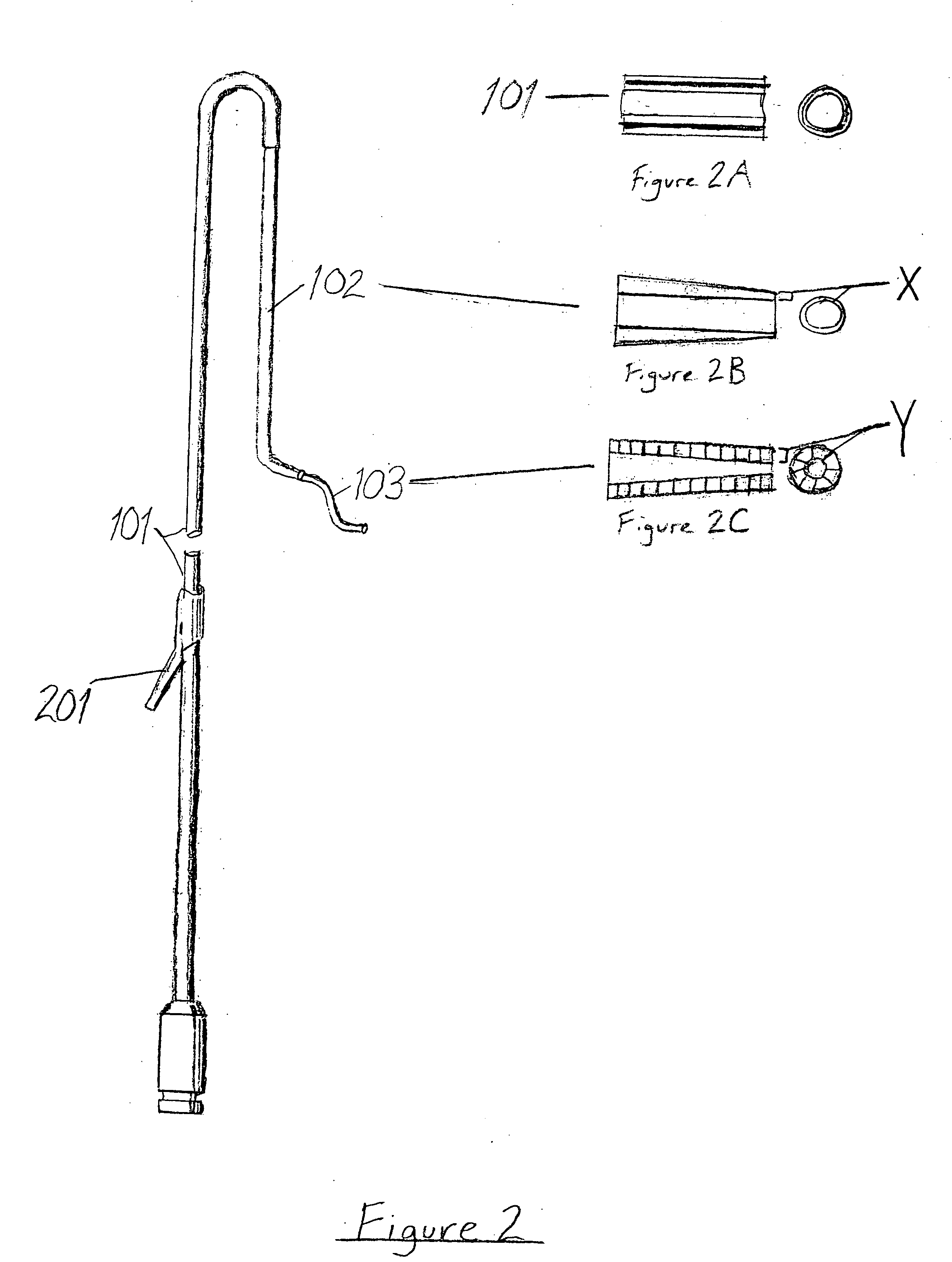
Pelvic arterial catheter
ActiveUS20050113801A1Minimal traumaHigh trafficCatheterRadiation diagnosticsArterial catheterTherapeutic intent
An improved angiographic catheter that allows selective catheterization of the bilateral pelvic arteries via a unilateral single common femoral arterial entry site for the purpose of introducing radioopaque iodinated contrast solutions for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The catheter has an optimal length, specific tapered and curved regions, and a progressively tapering diameter along its length. The catheter is made from a hybrid of soft, flexible hydrophilic and reinforced materials to allow for conformational changes in order to accommodate to the variety of vascular anatomy encountered in clinical angiographic practice.
Owner:VASCULAR SOLUTIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com