Patents
Literature
53results about How to "Force can be applied" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
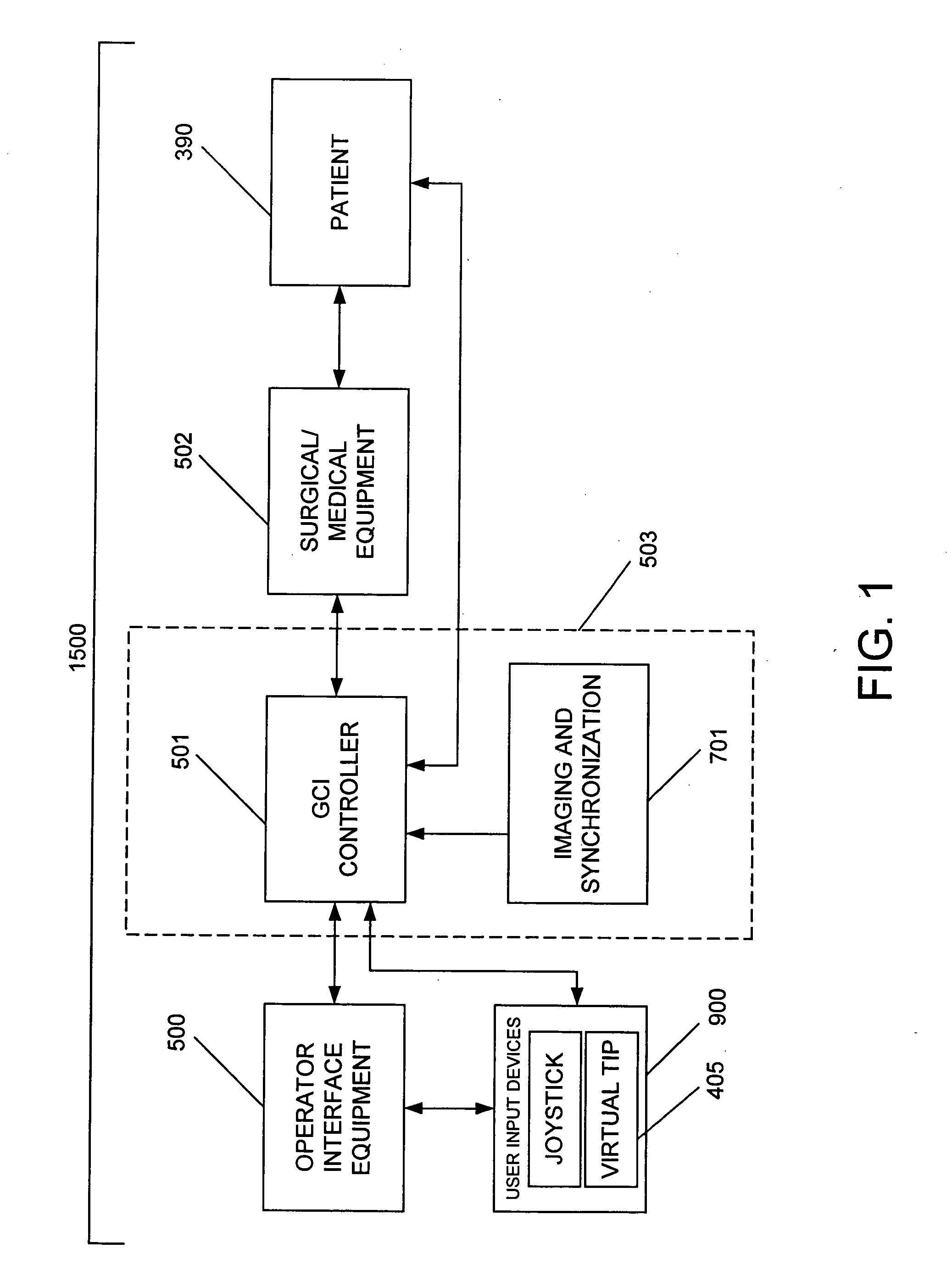
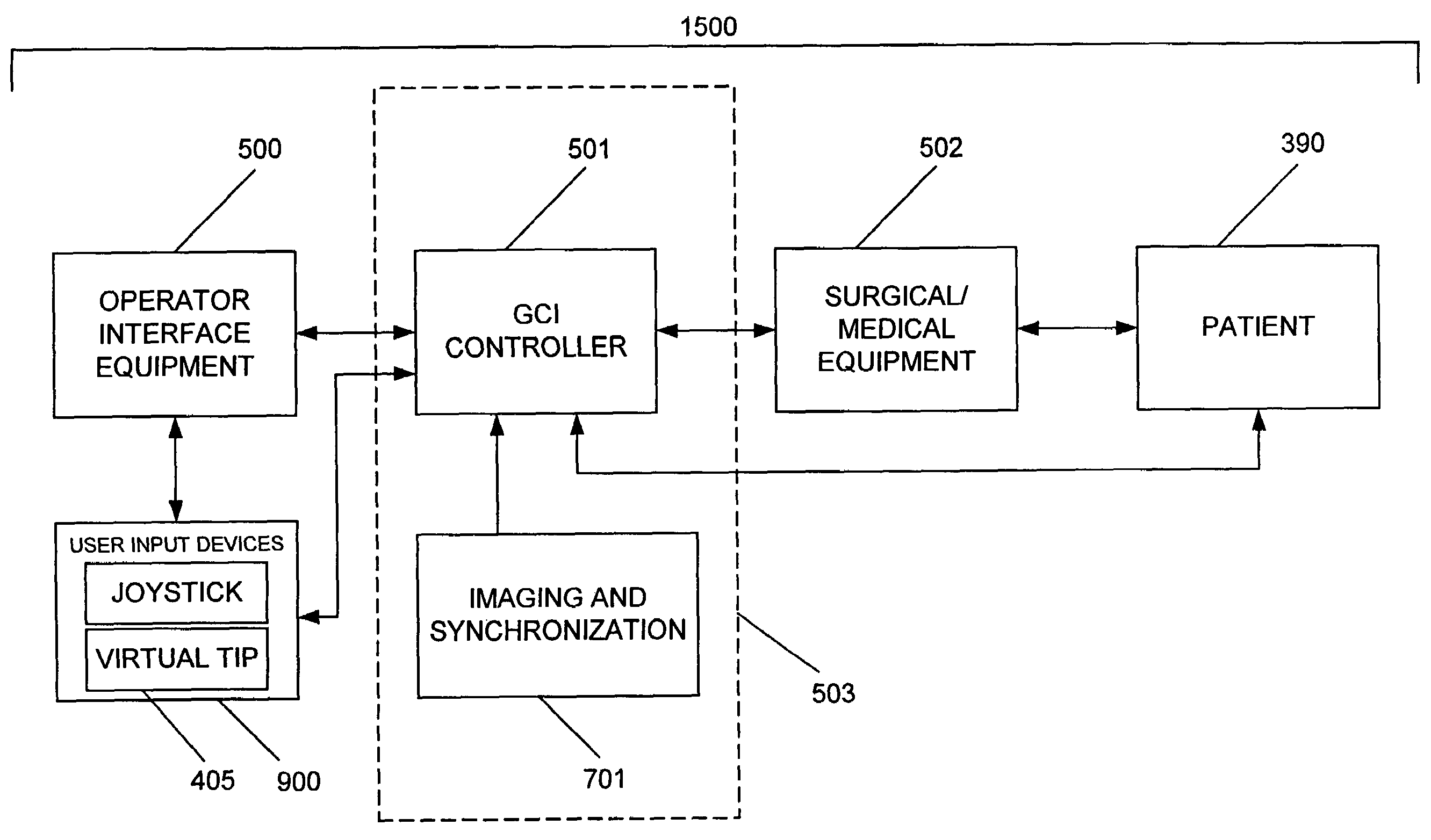
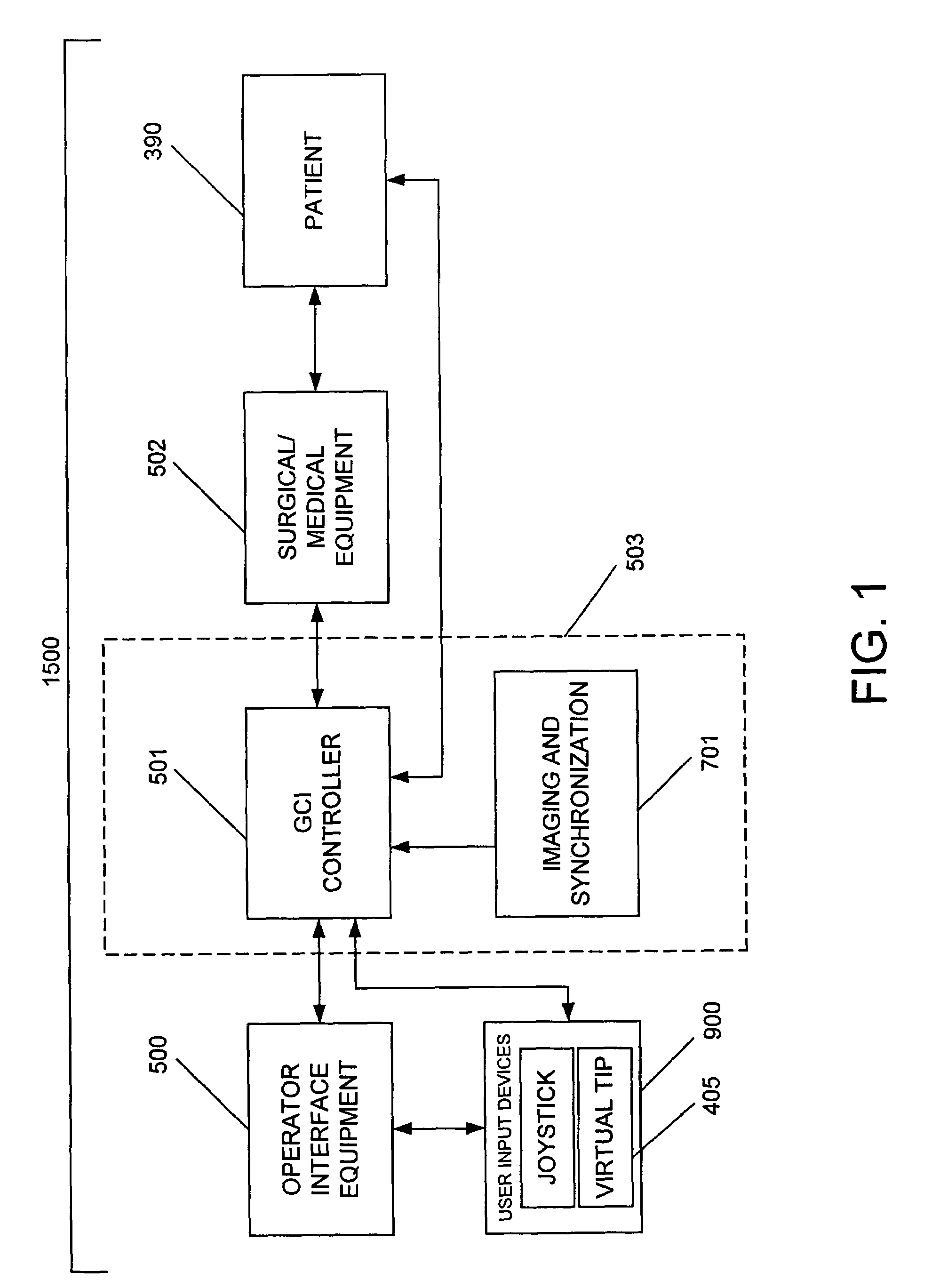
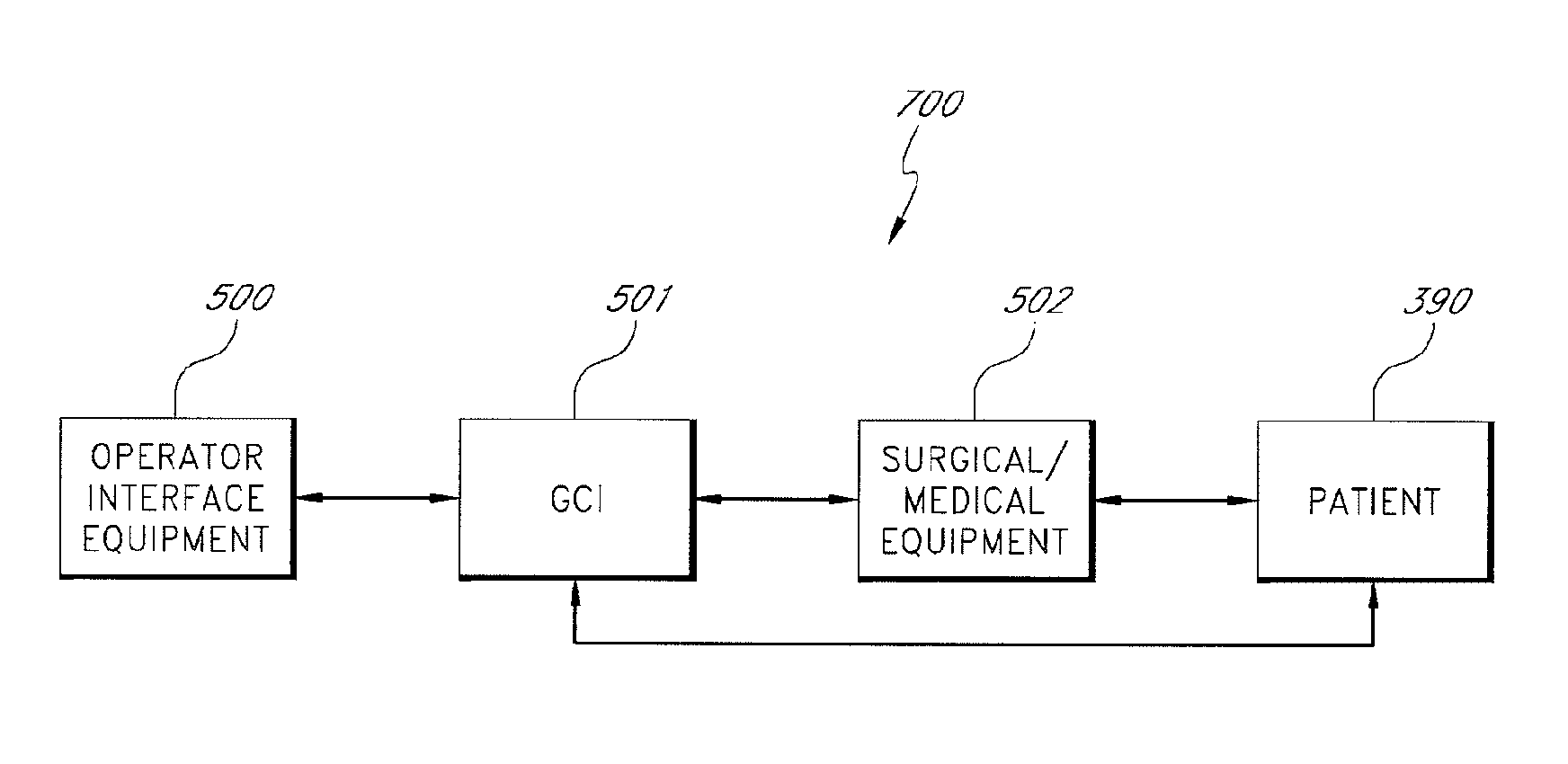
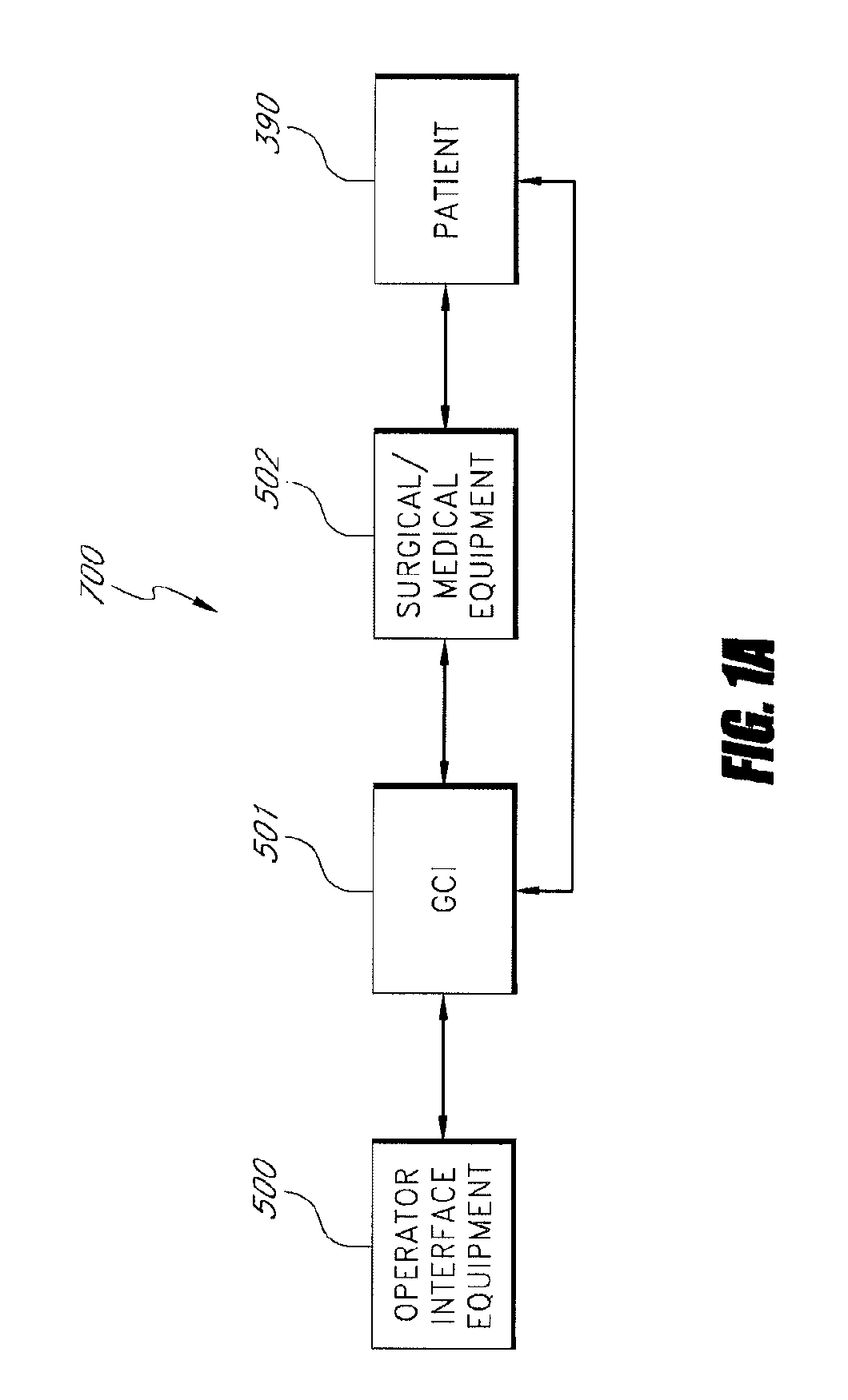
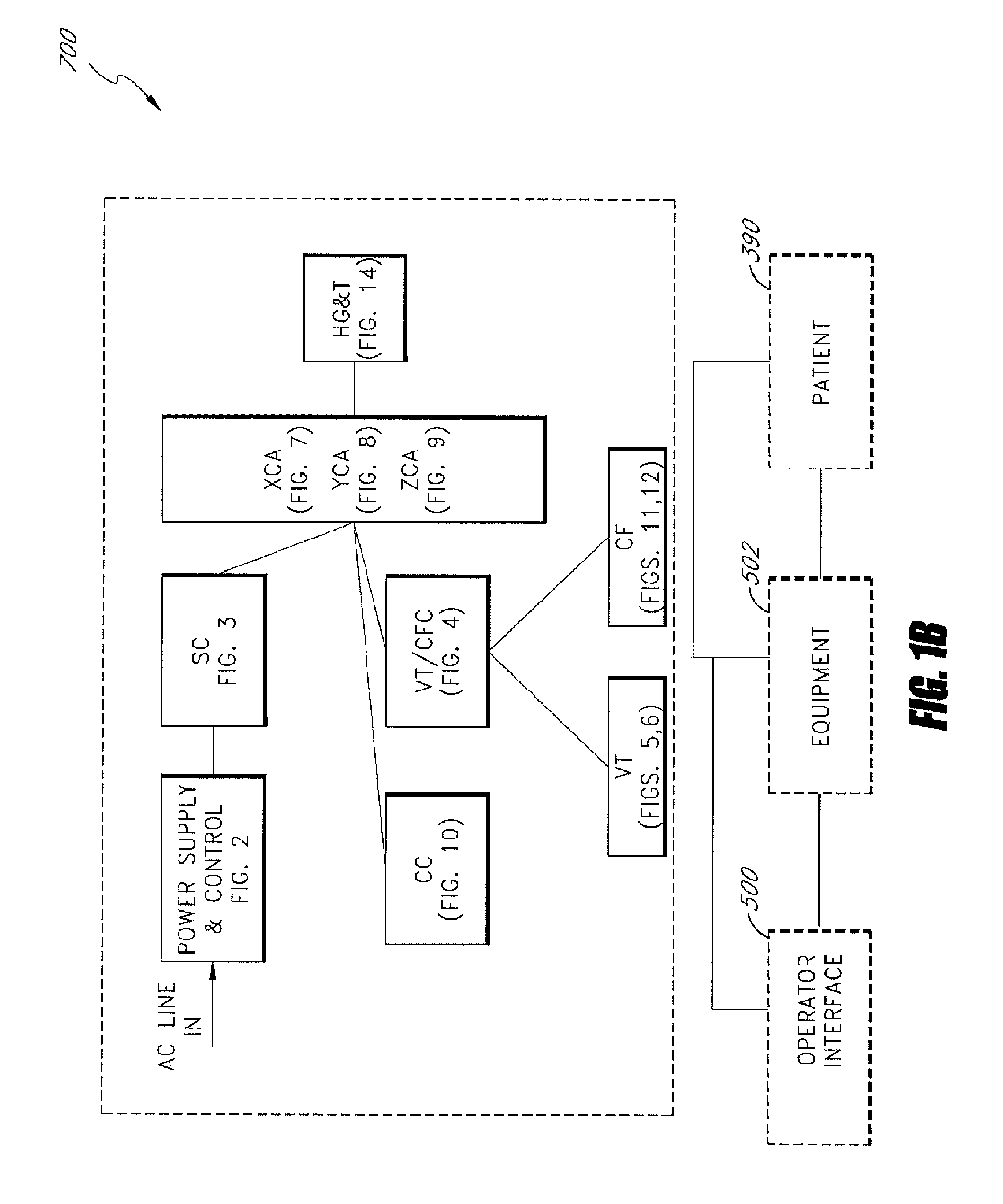
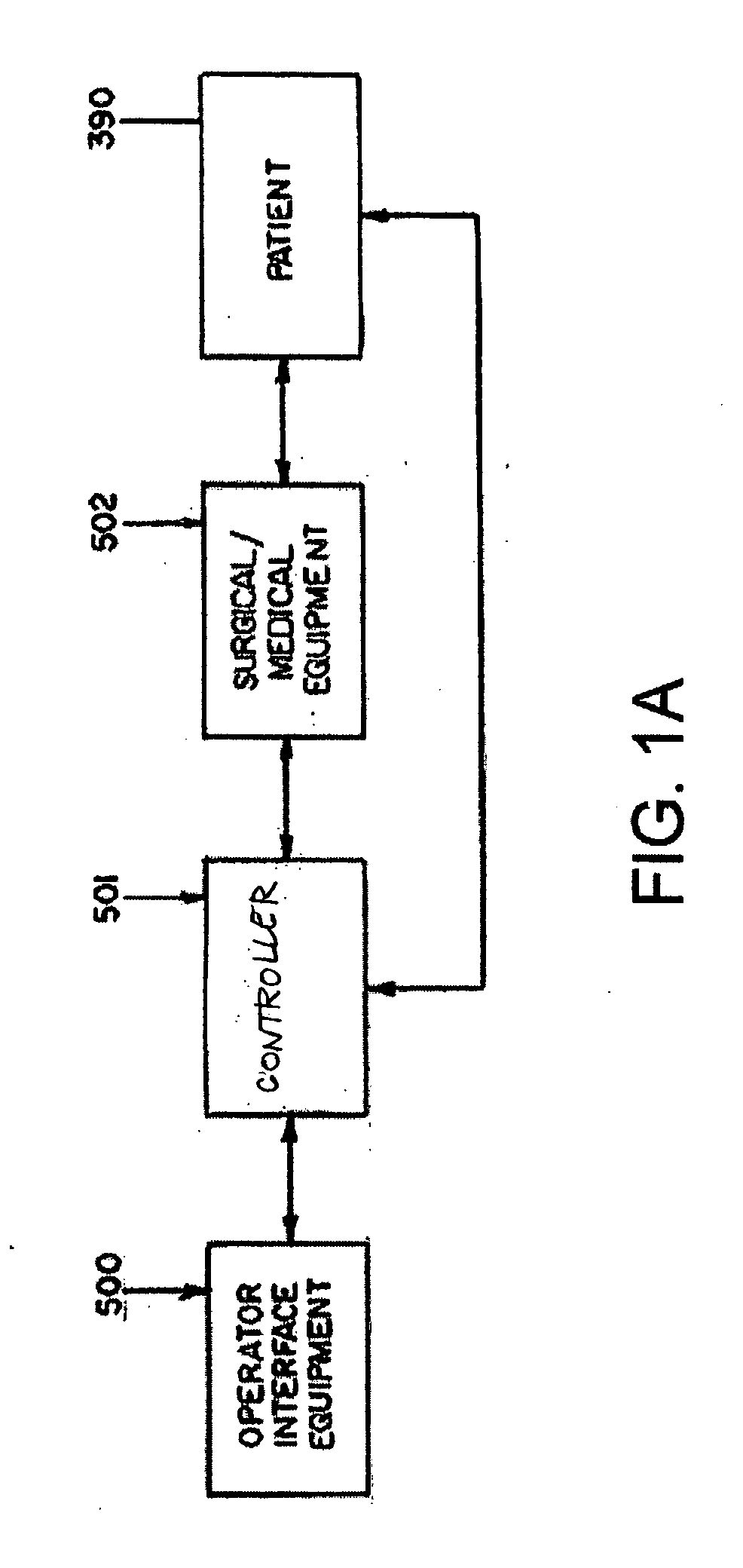
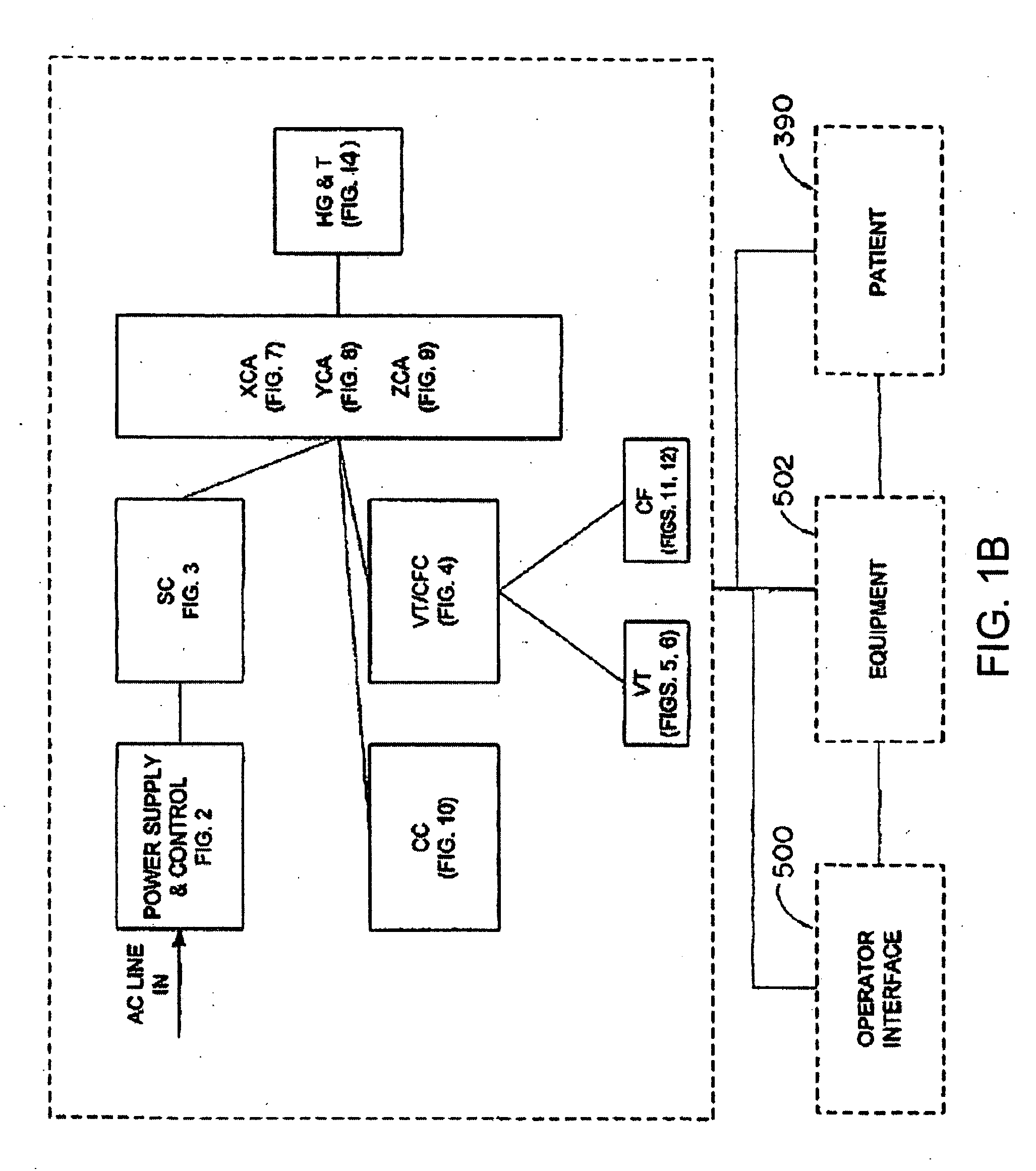
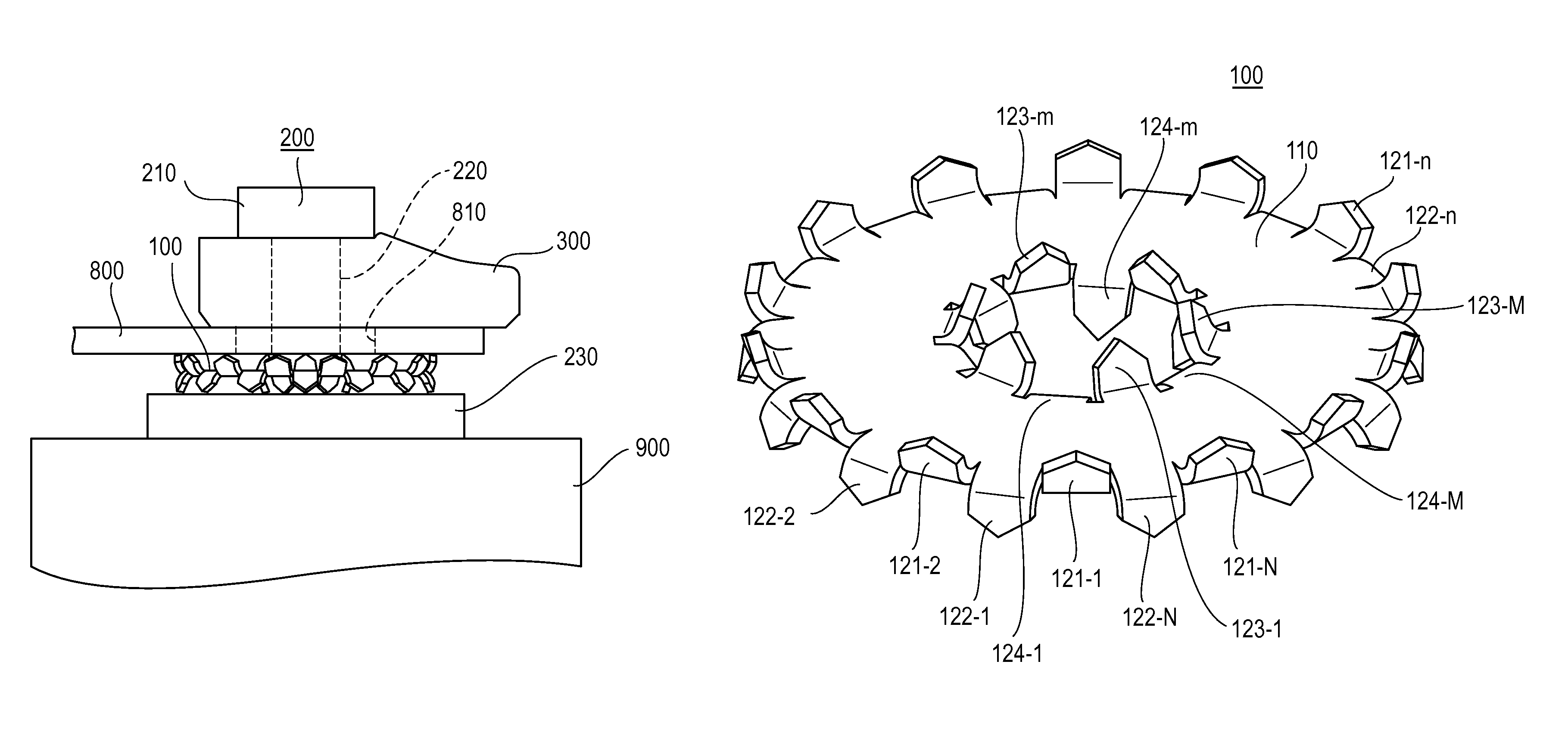
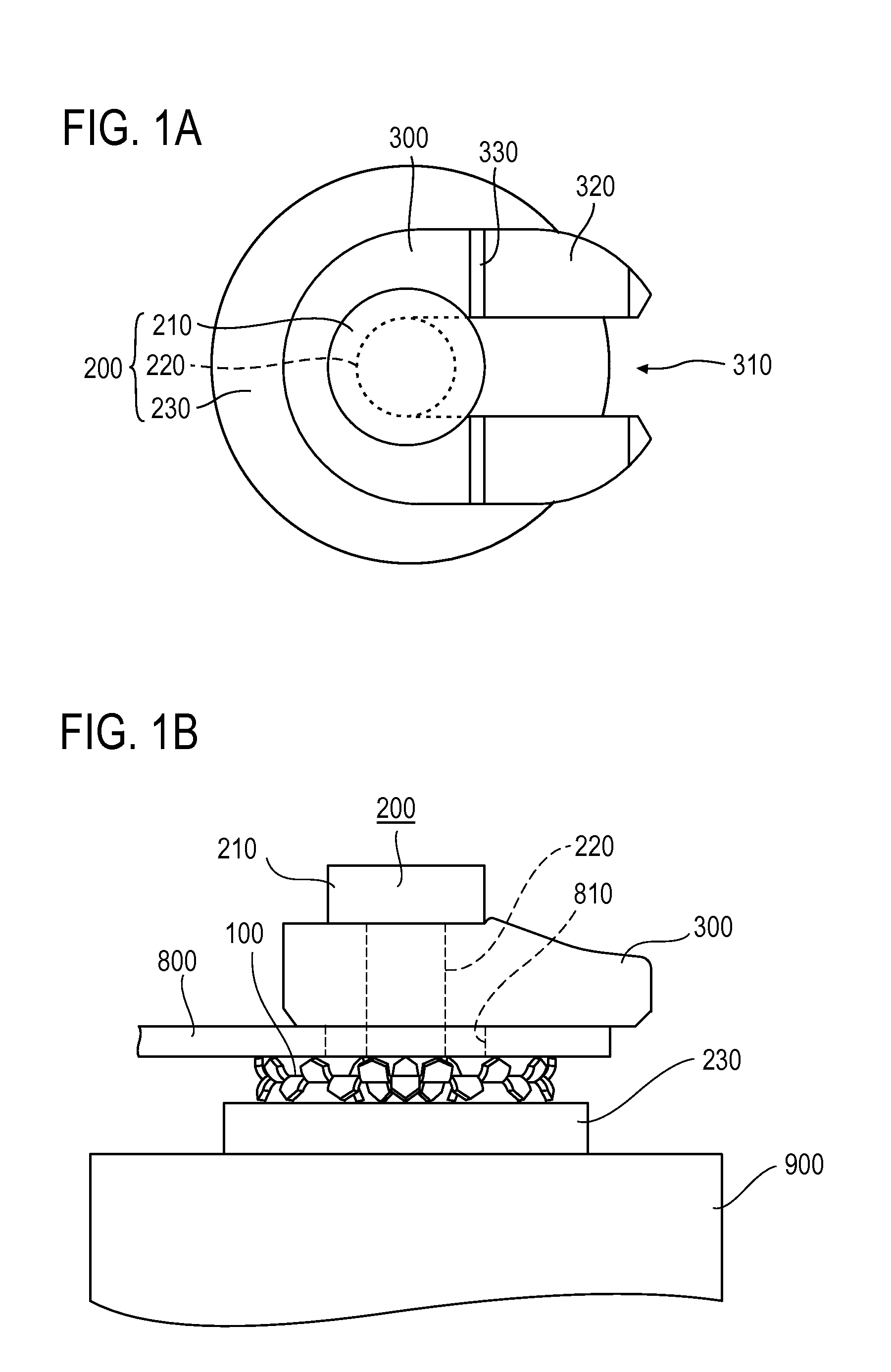
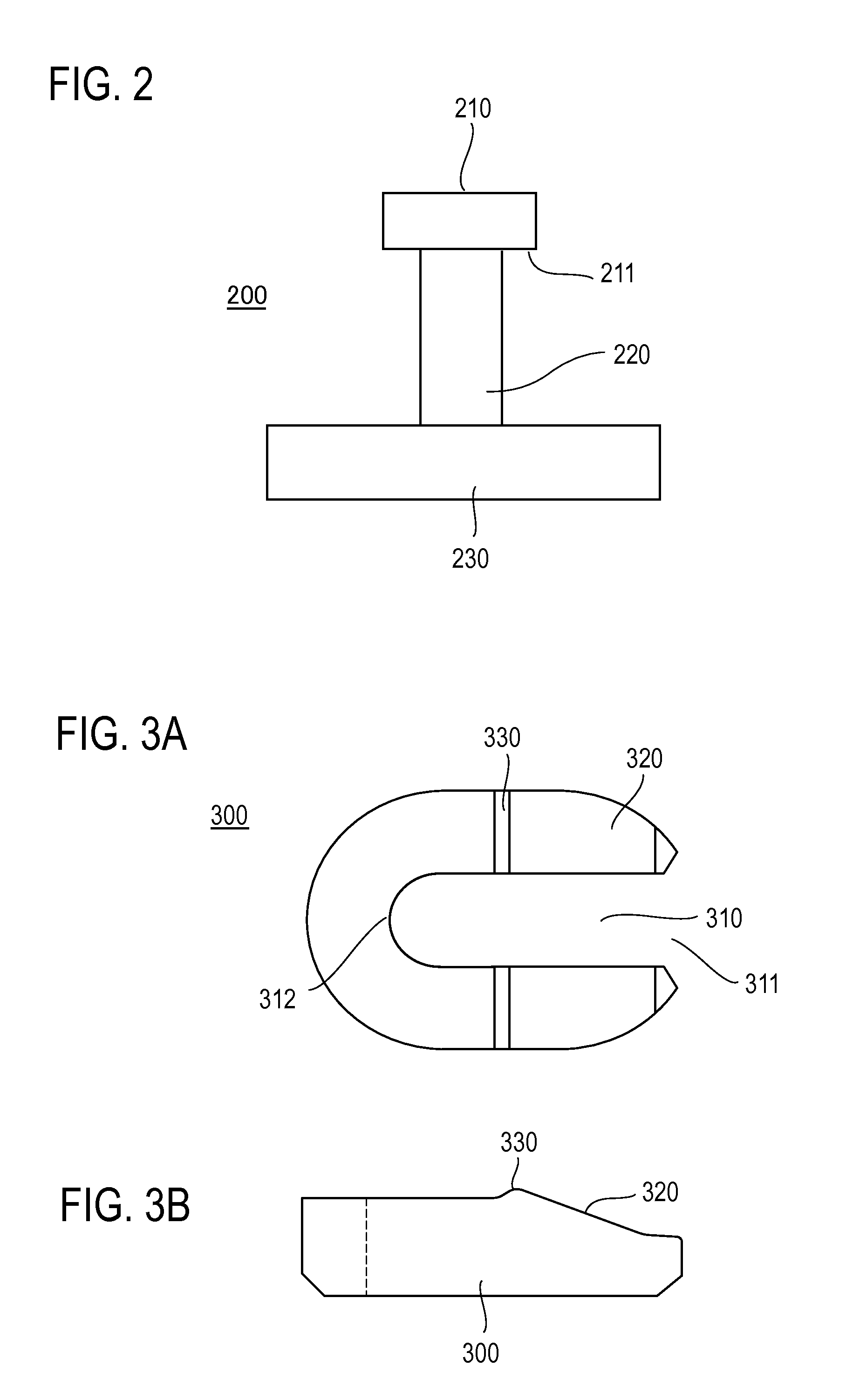
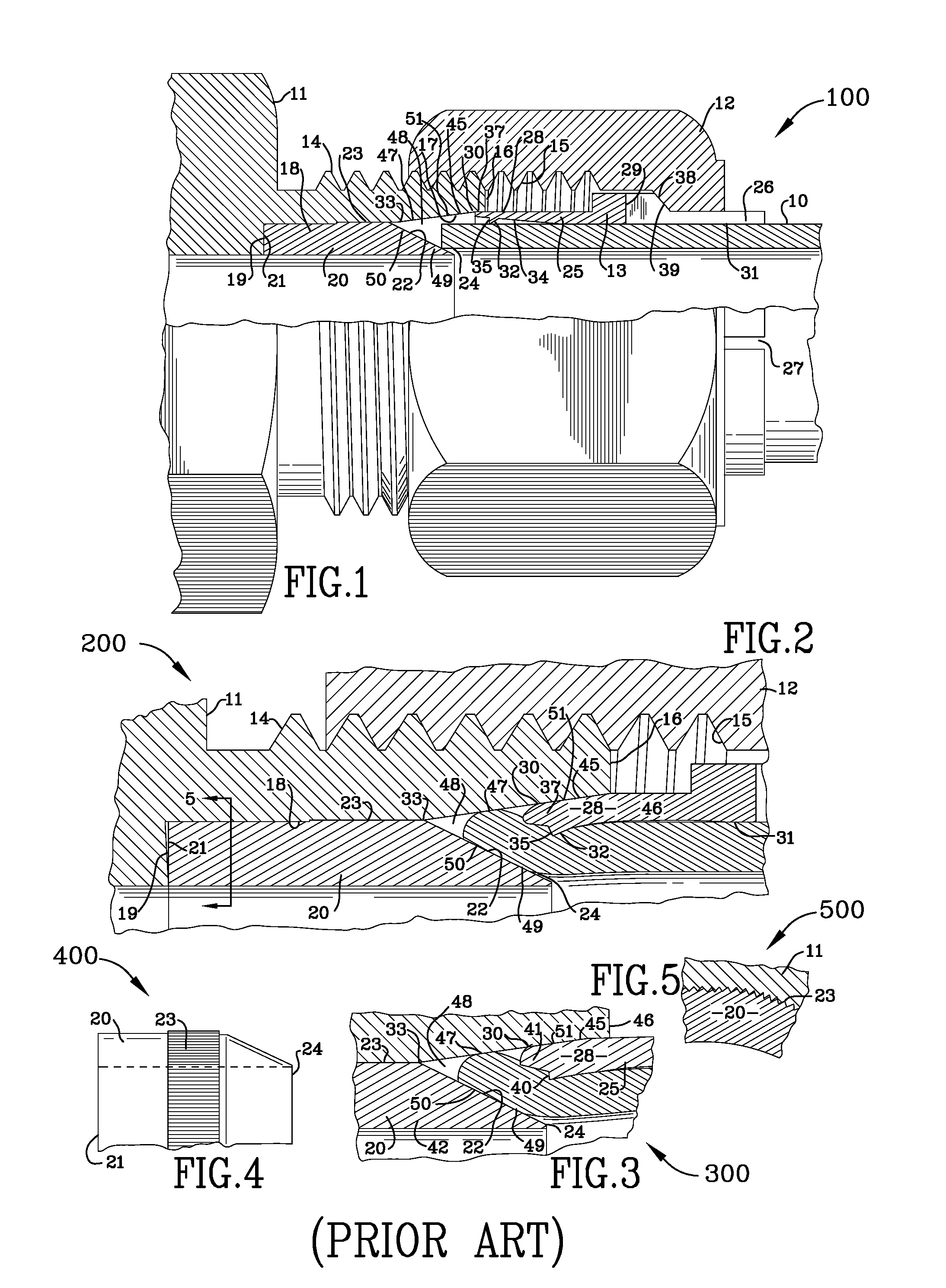
System and method for controlling movement of a surgical tool
InactiveUS20060116634A1Less trainingMinimizing x-ray and contrast material exposureSurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesEndoscopeBiopsy needles
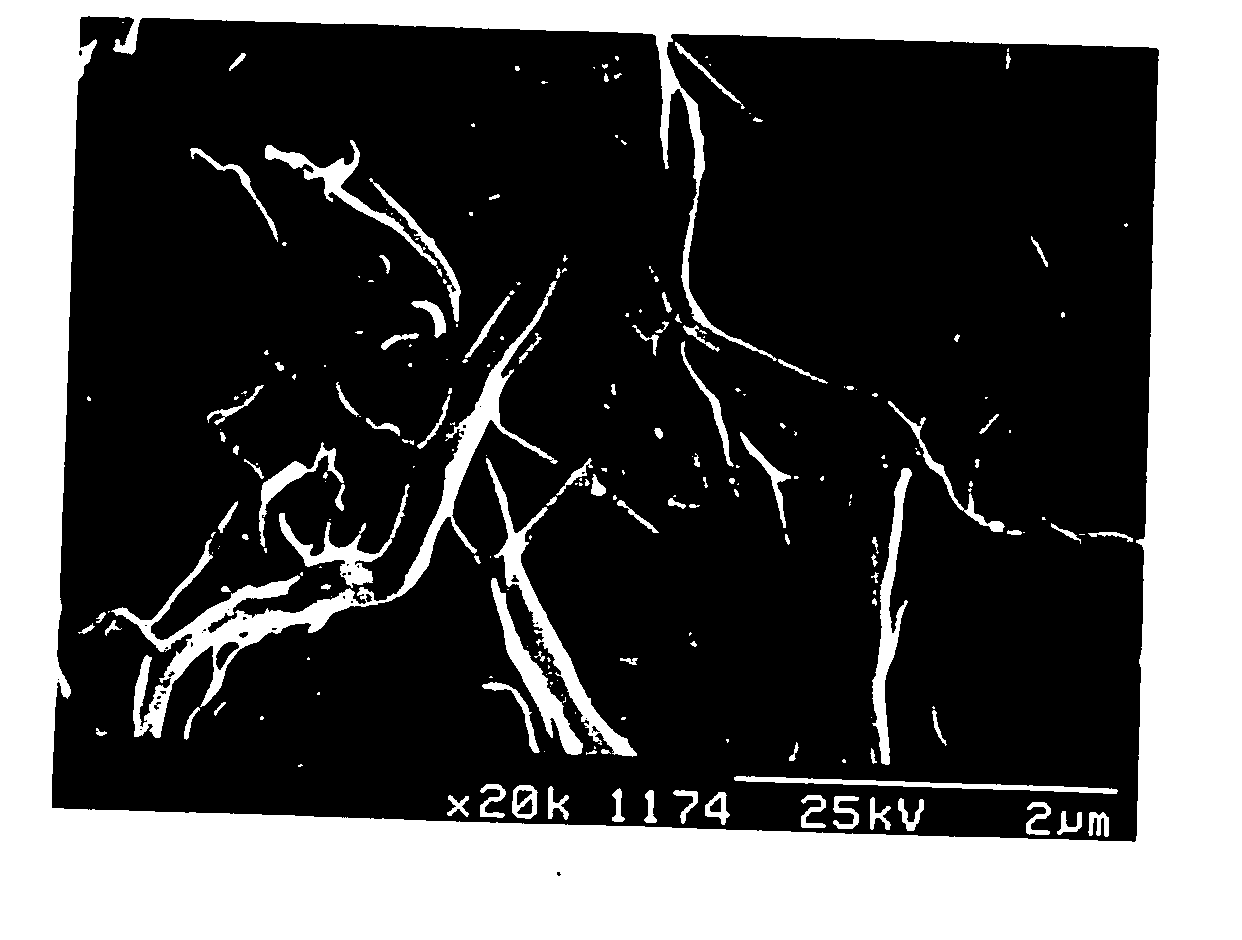
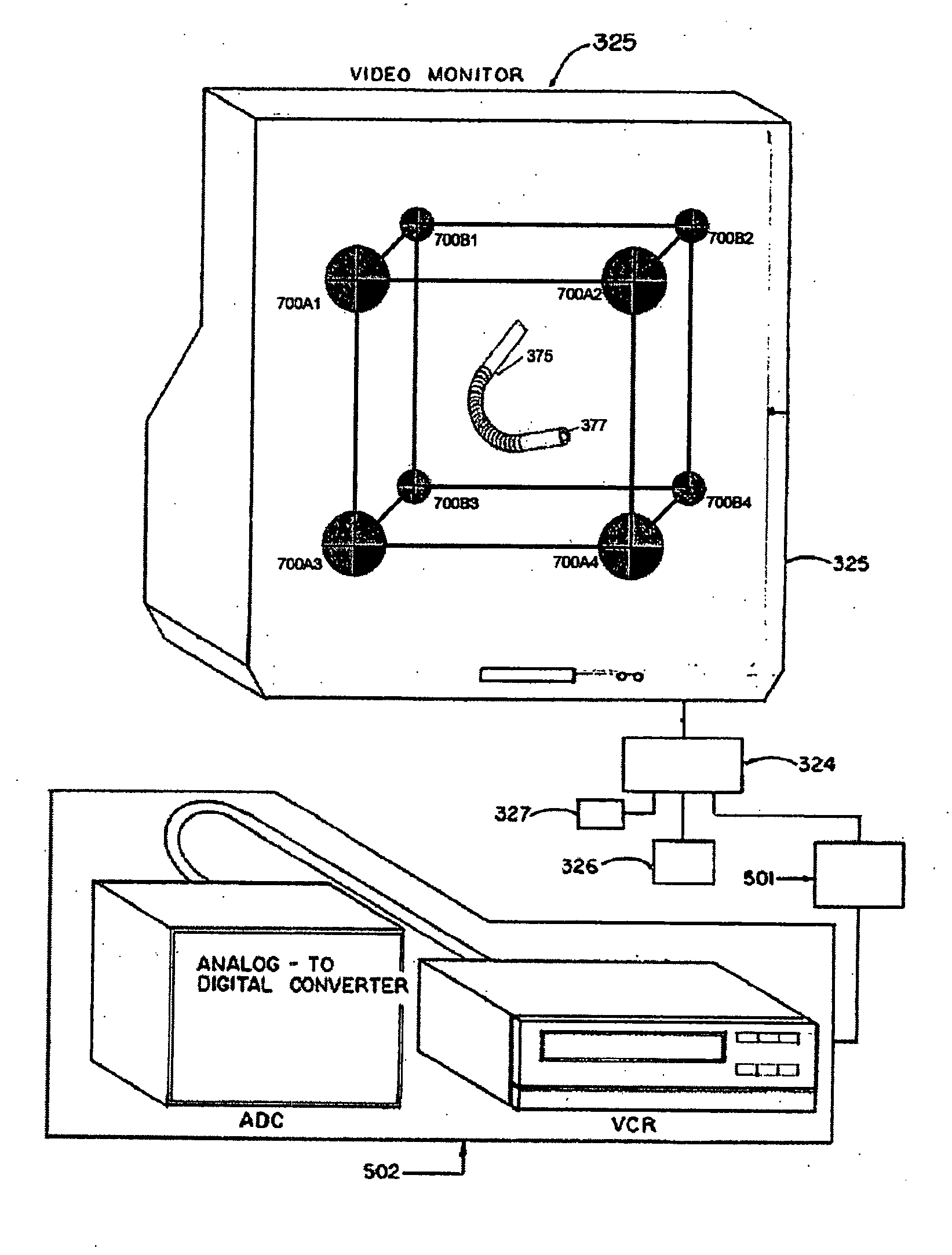
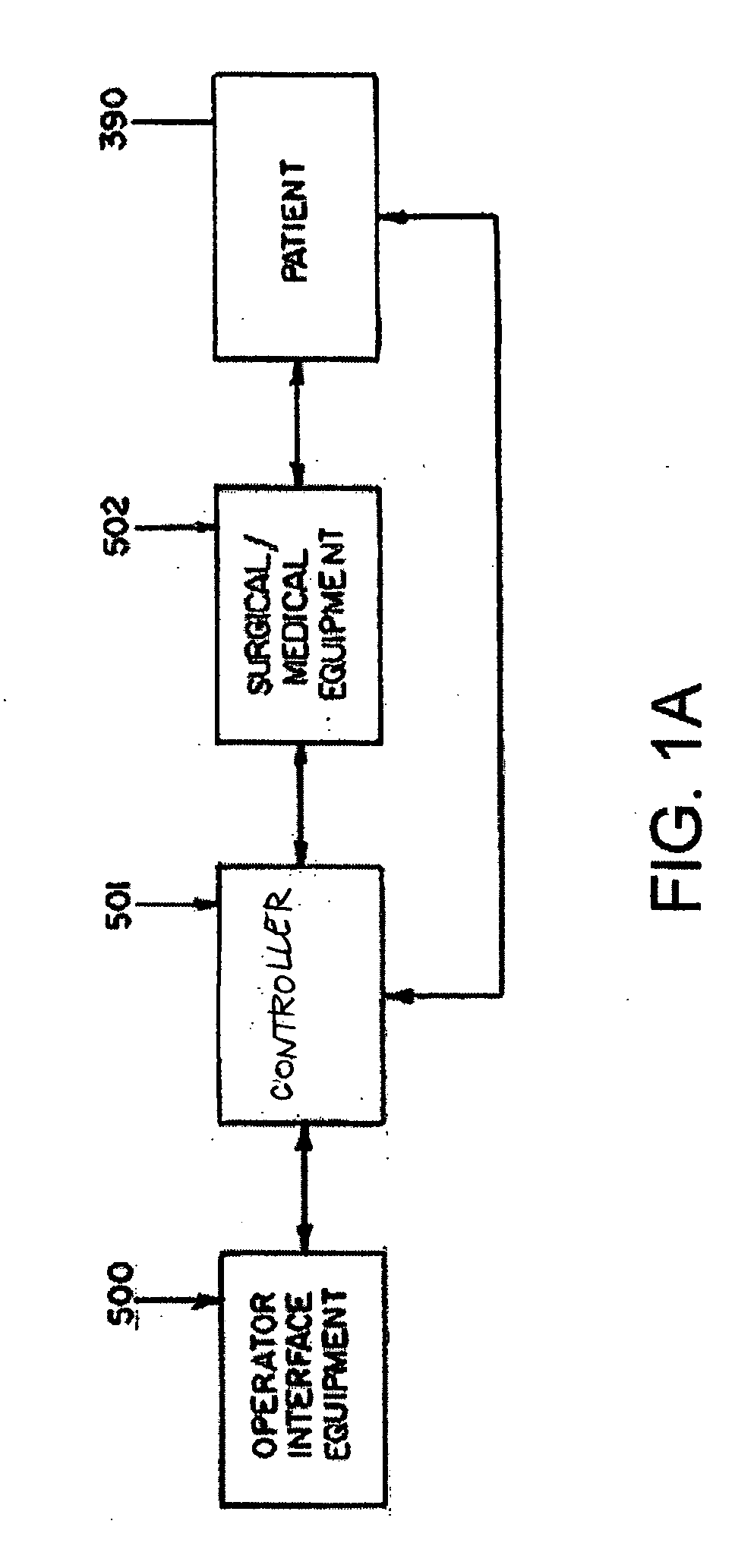
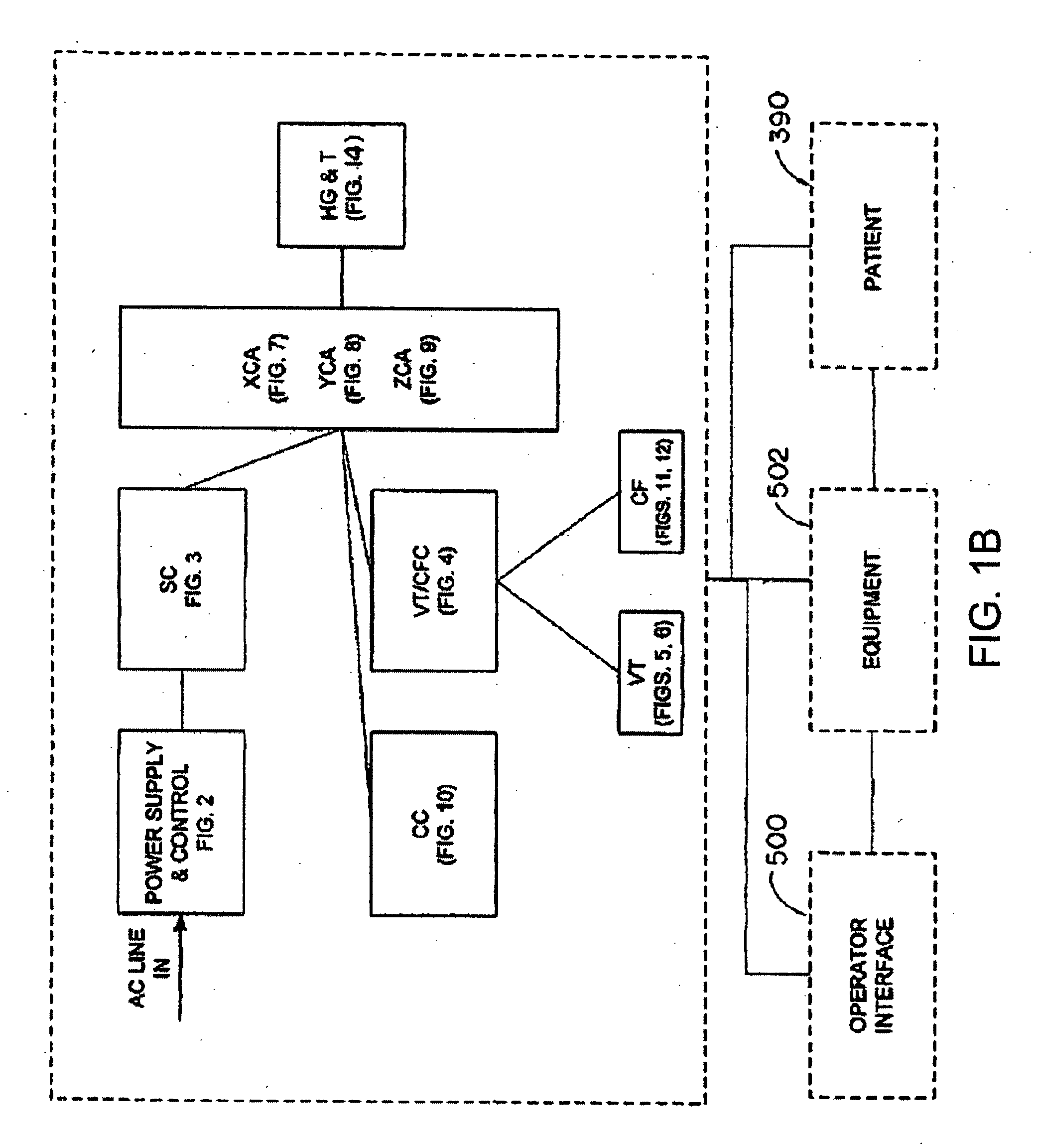
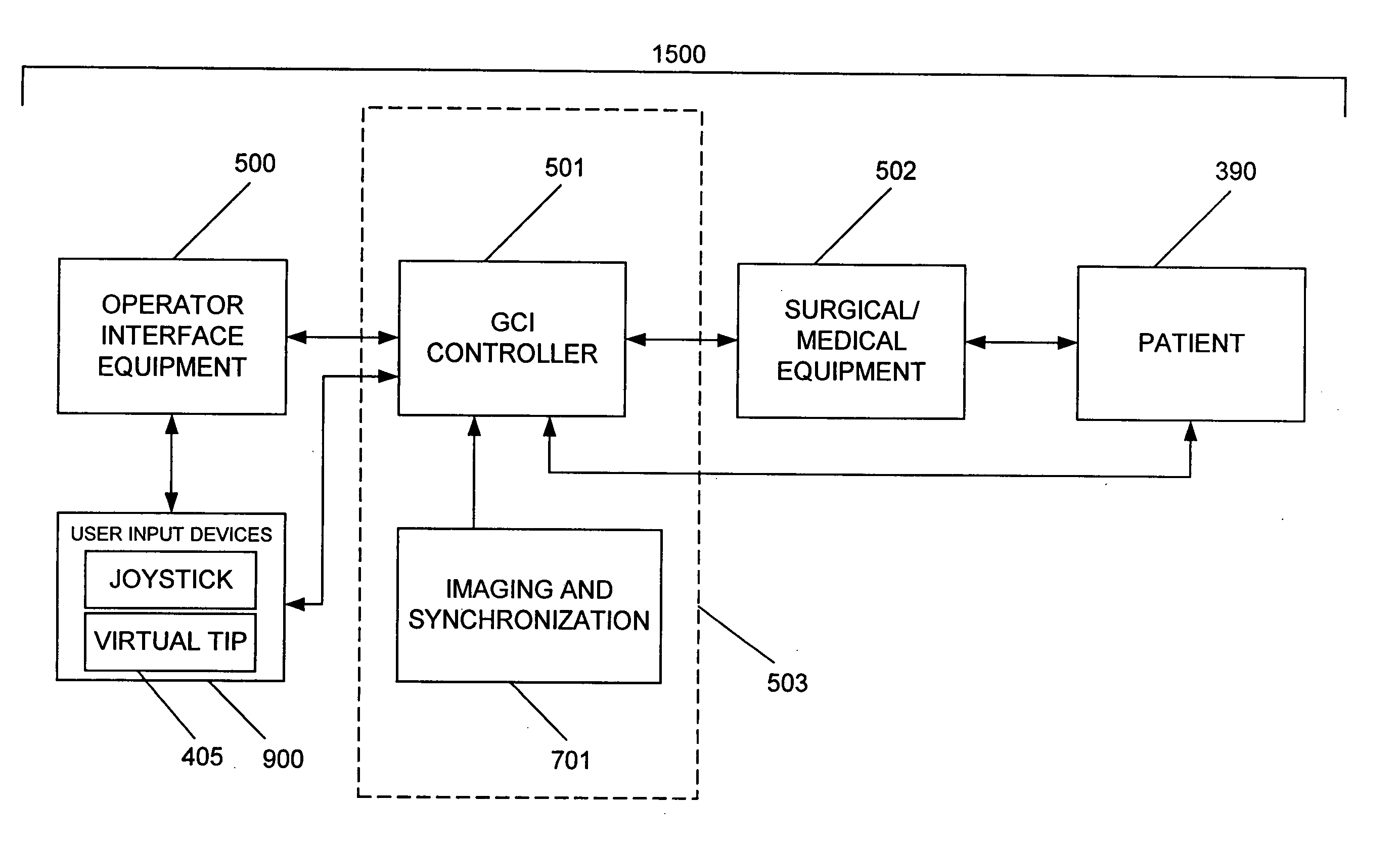
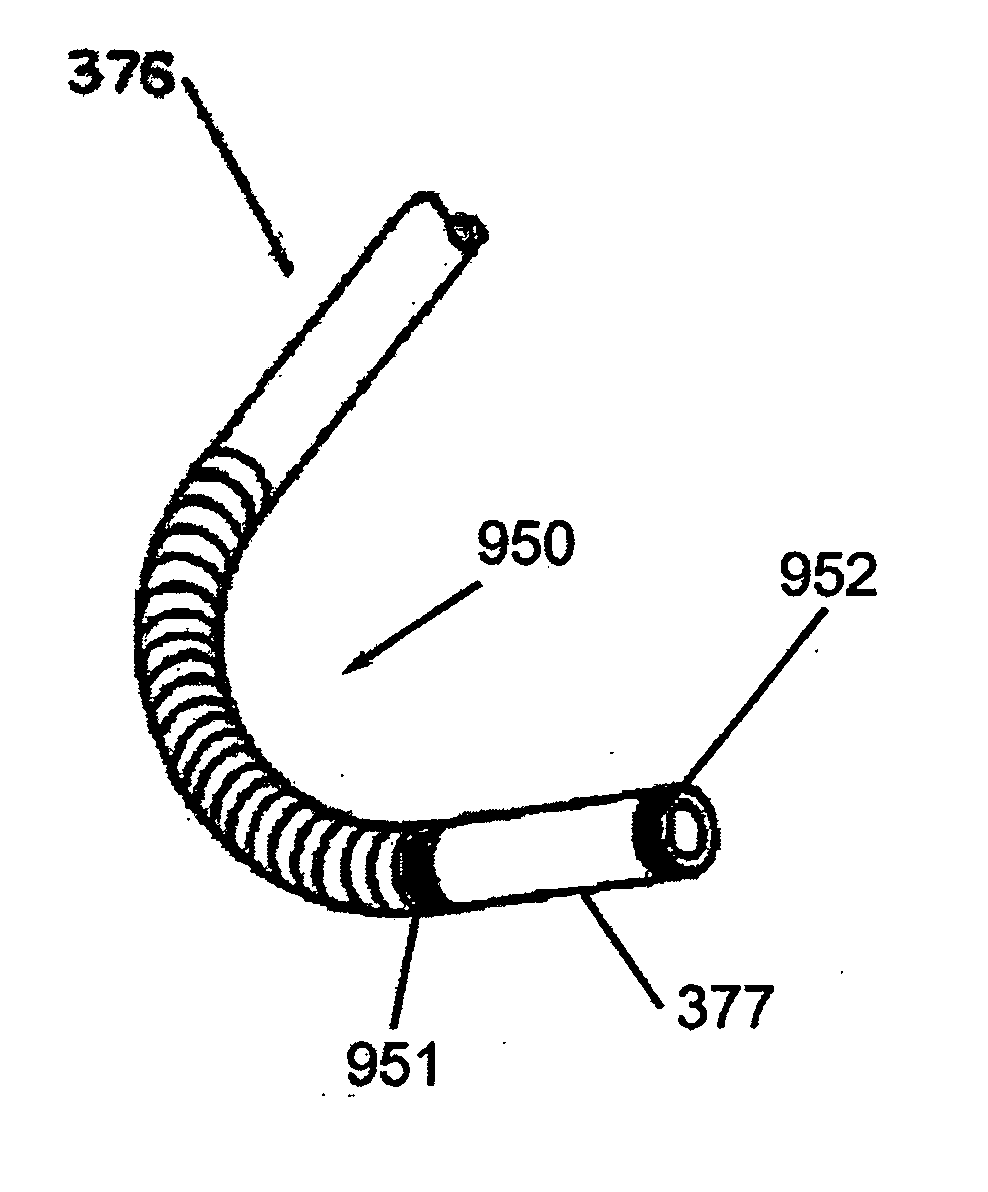
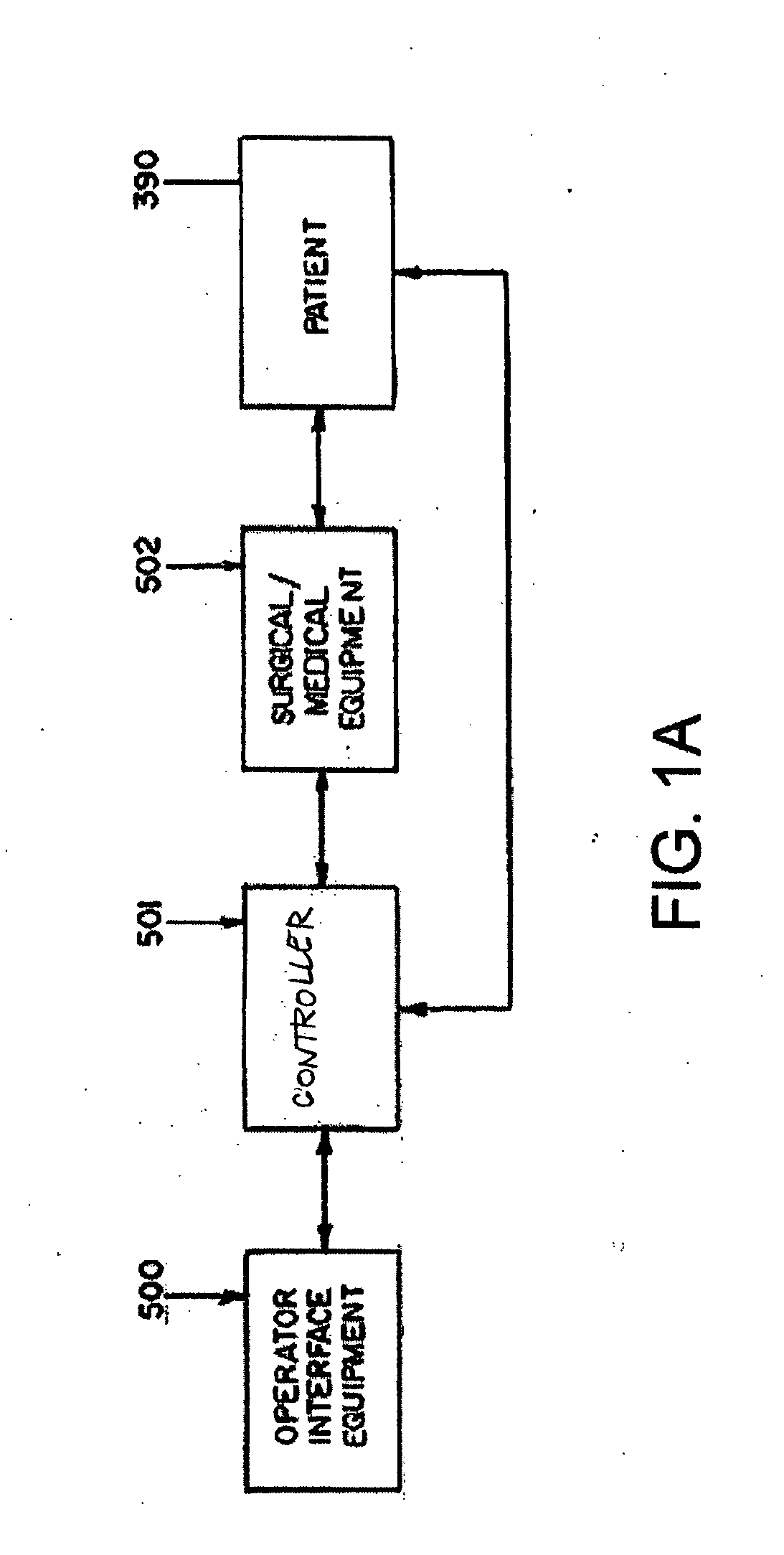
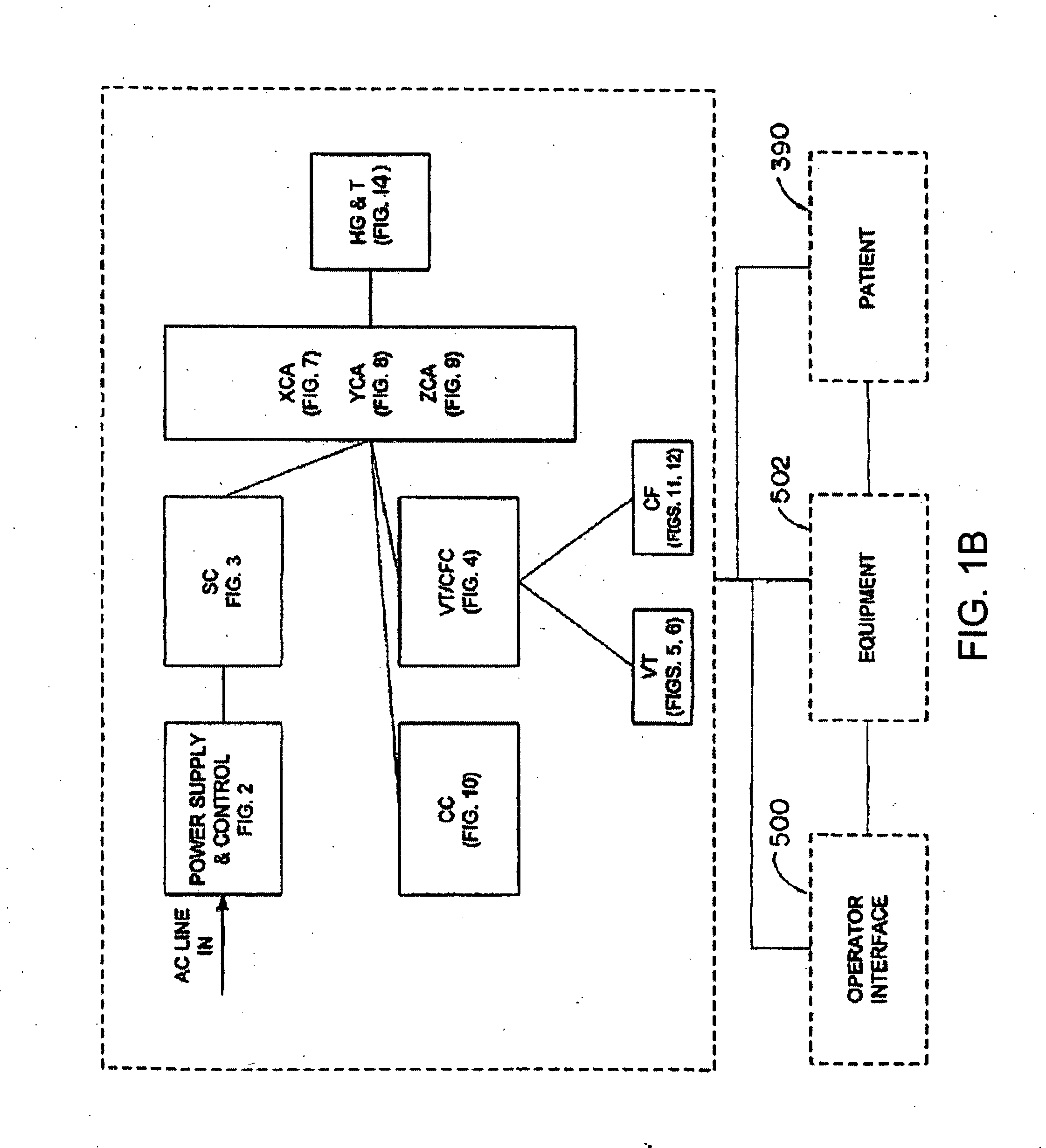
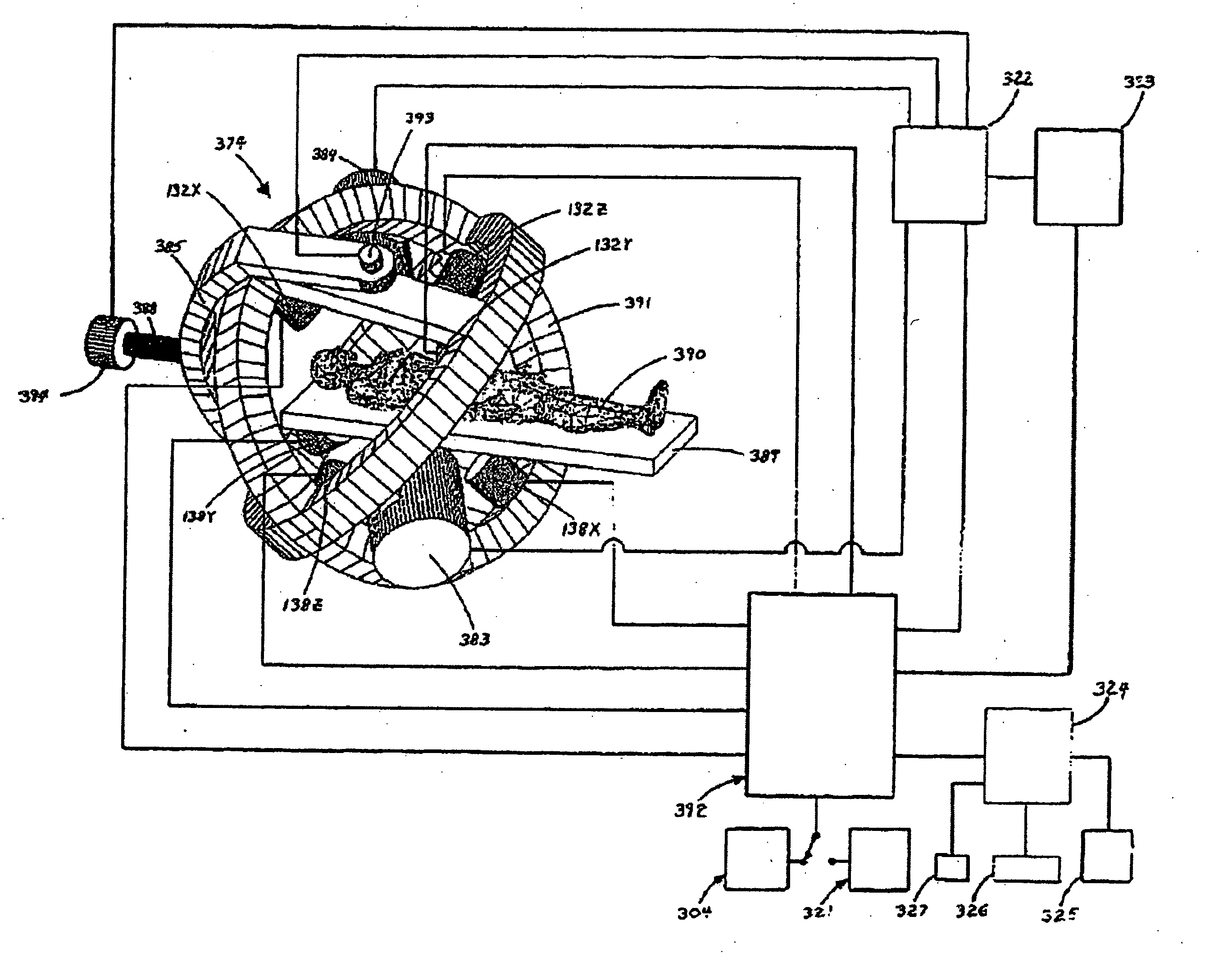
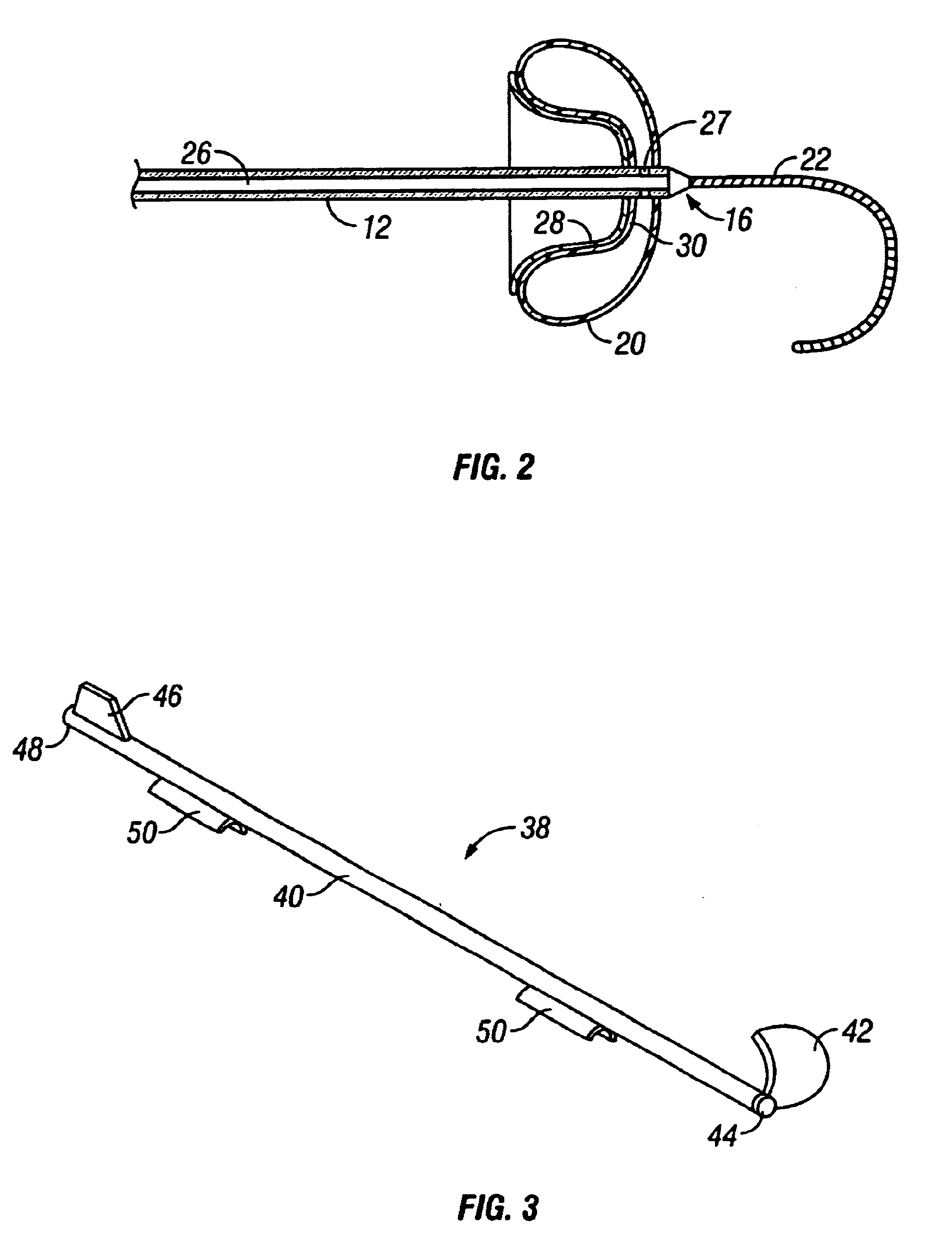
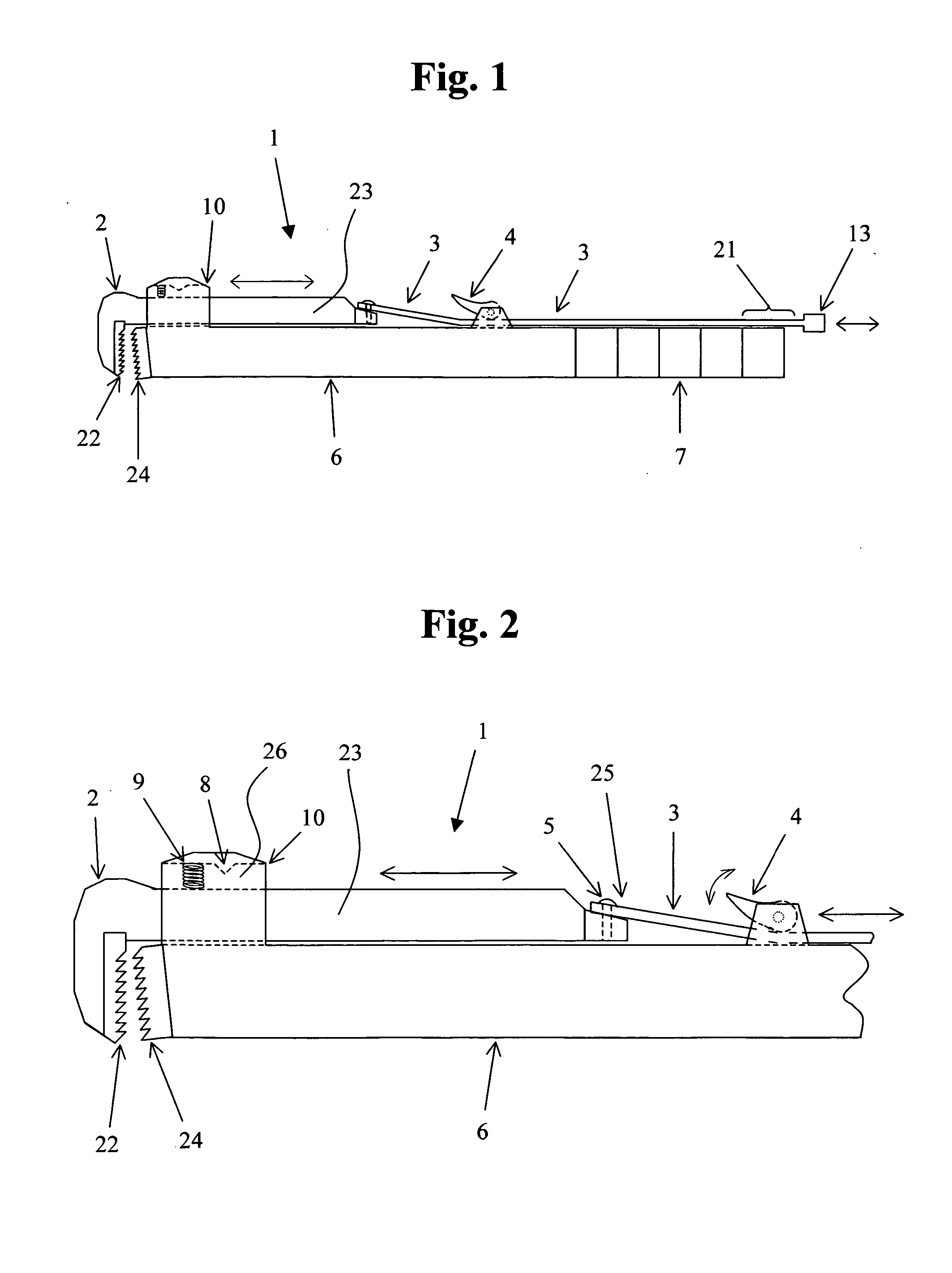
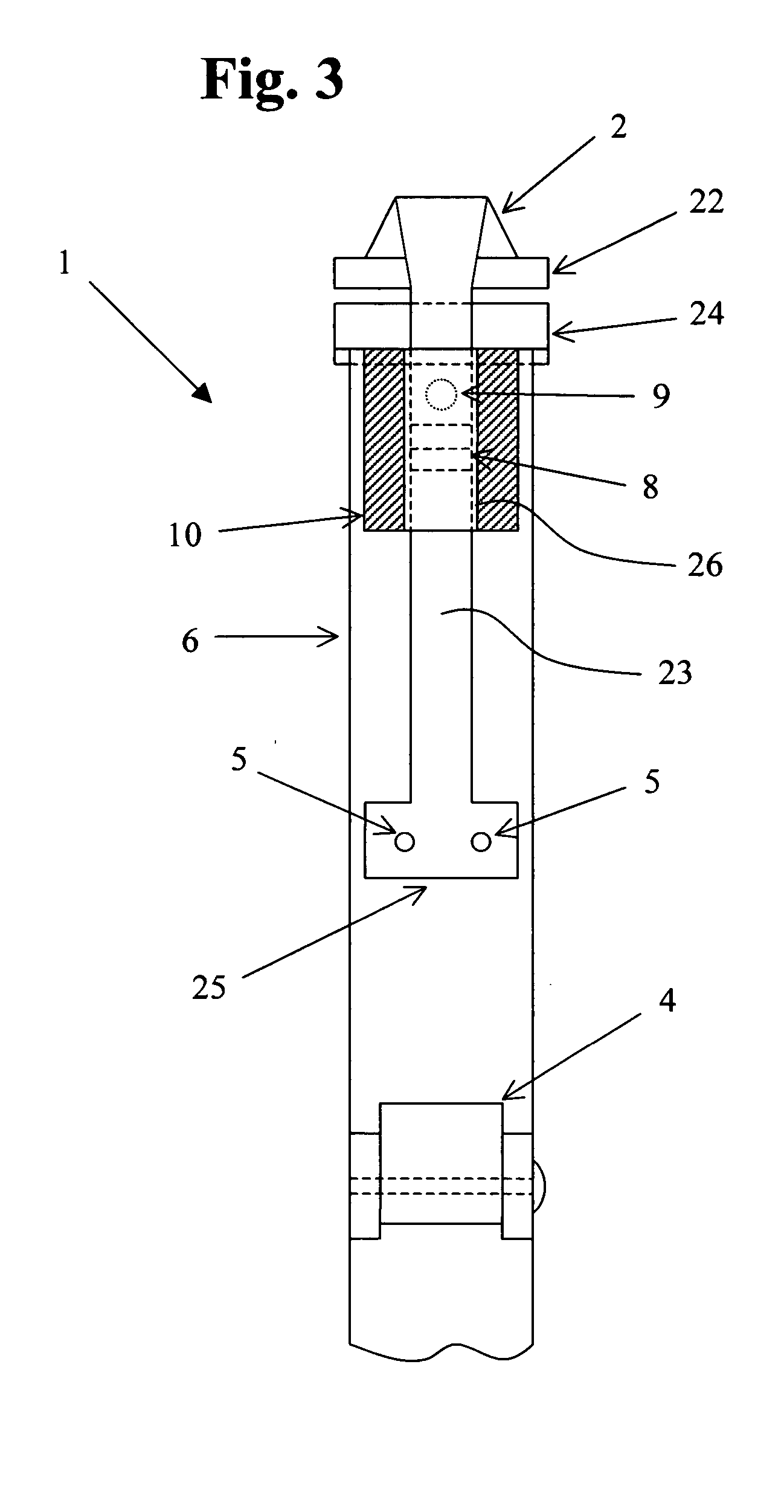
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
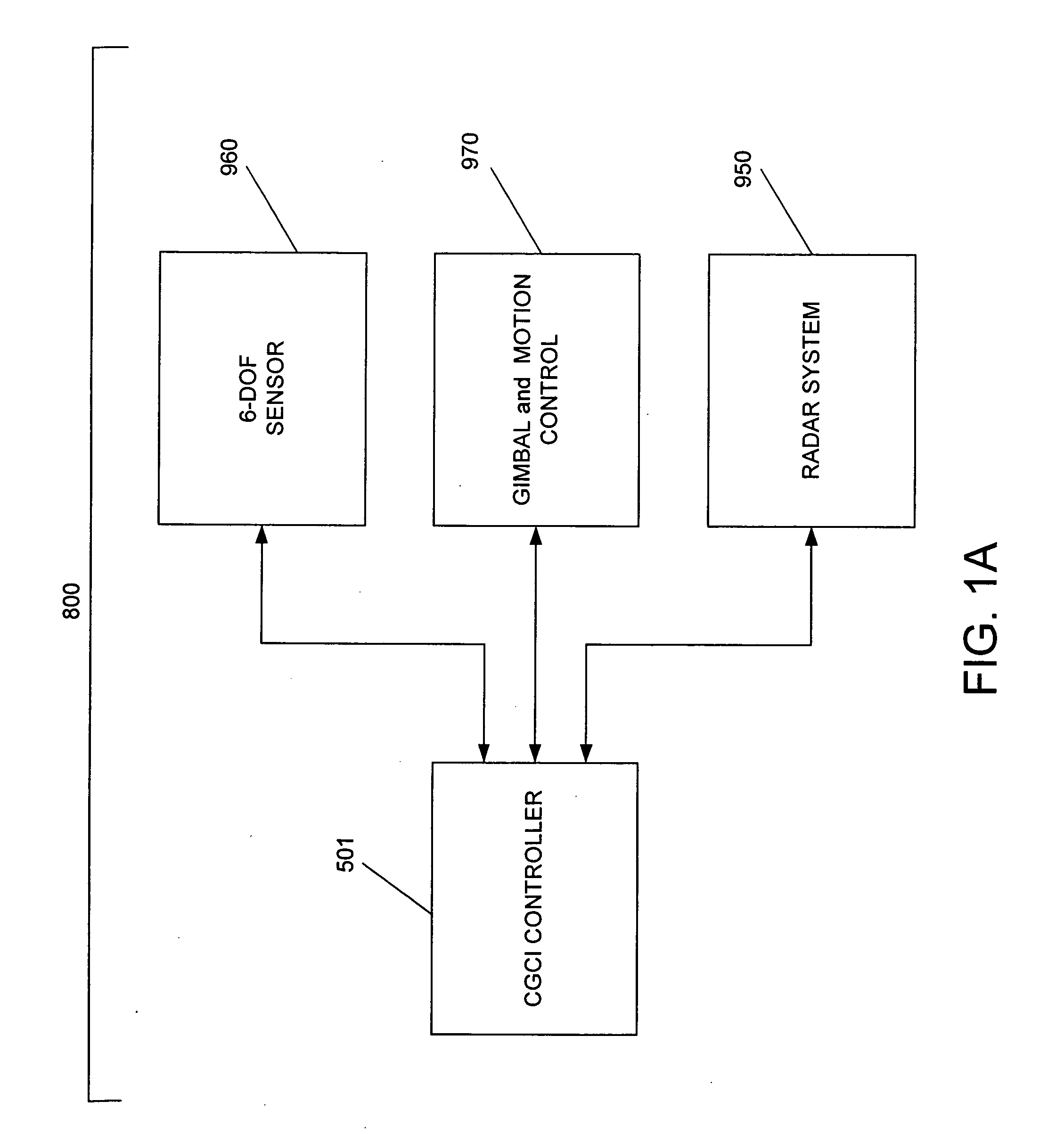
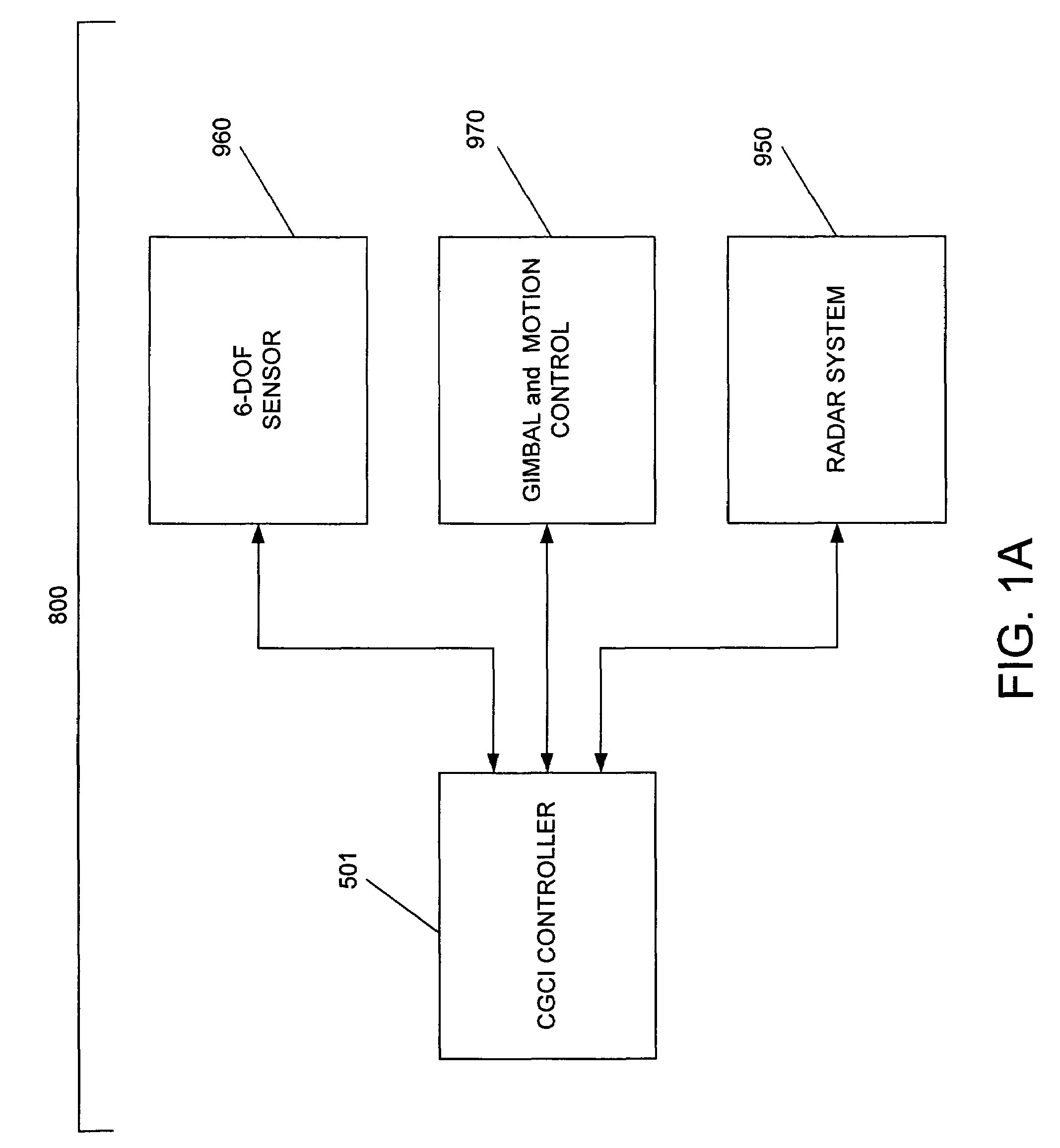
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS20050096589A1Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useEndoscopesMedical devicesRadar systemsGuidance control
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS7280863B2Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useMedical devicesEndoscopesRadar systemsTip position
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Apparatus and method for catheter guidance control and imaging
InactiveUS7769427B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionGuidance control
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and positioned. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS20060116633A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Apparatus and method for generating a magnetic field
InactiveUS20060114088A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMagnetsTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Methods and apparatus for forming anastomotic sites
InactiveUS6712831B1Reduce distractionsForce can be appliedSuture equipmentsWound clampsEnd to side anastomosisThree vessels
Apparatus and methods are provided for forming a working space on the interior wall of a blood vessel, such as the aorta. The working space is isolated from blood flow and permits creation of an anastomotic hole and subsequent suturing of the hole to form an end-to-side anastomosis, even while the heart is beating. The apparatus comprises tools including inflatable barriers, such as cup-shaped balloons, which engage the inner wall of the blood vessel with minimum trauma and maximum sealing. In a first embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a penetration at the site of the anastomotic attachment. In a second embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a second penetration axially spaced-apart from the site of the anastomotic attachment.
Owner:AARON V KAPLAN M D
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS7873401B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Conductor-connecting washer, connection mechanism using the same, and method of manufacturing conductor-connecting washer
InactiveUS8303357B2Reliably madeSmall loadMetal-working apparatusCoupling contact membersElectrical conductorMechanical engineering
A conductor-connecting washer arranged between two conductors to electrically connect the two conductors includes a metal plate portion including a washer hole in the middle and 24 or more contact protrusions integrally formed on each of both surfaces of the plate portion, 16 or more of which are bent alternately toward each of both surface sides along the outer circumference of the plate portion and 8 or more of which are bent alternately toward each of both surface sides along the inner circumference of the washer hole.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
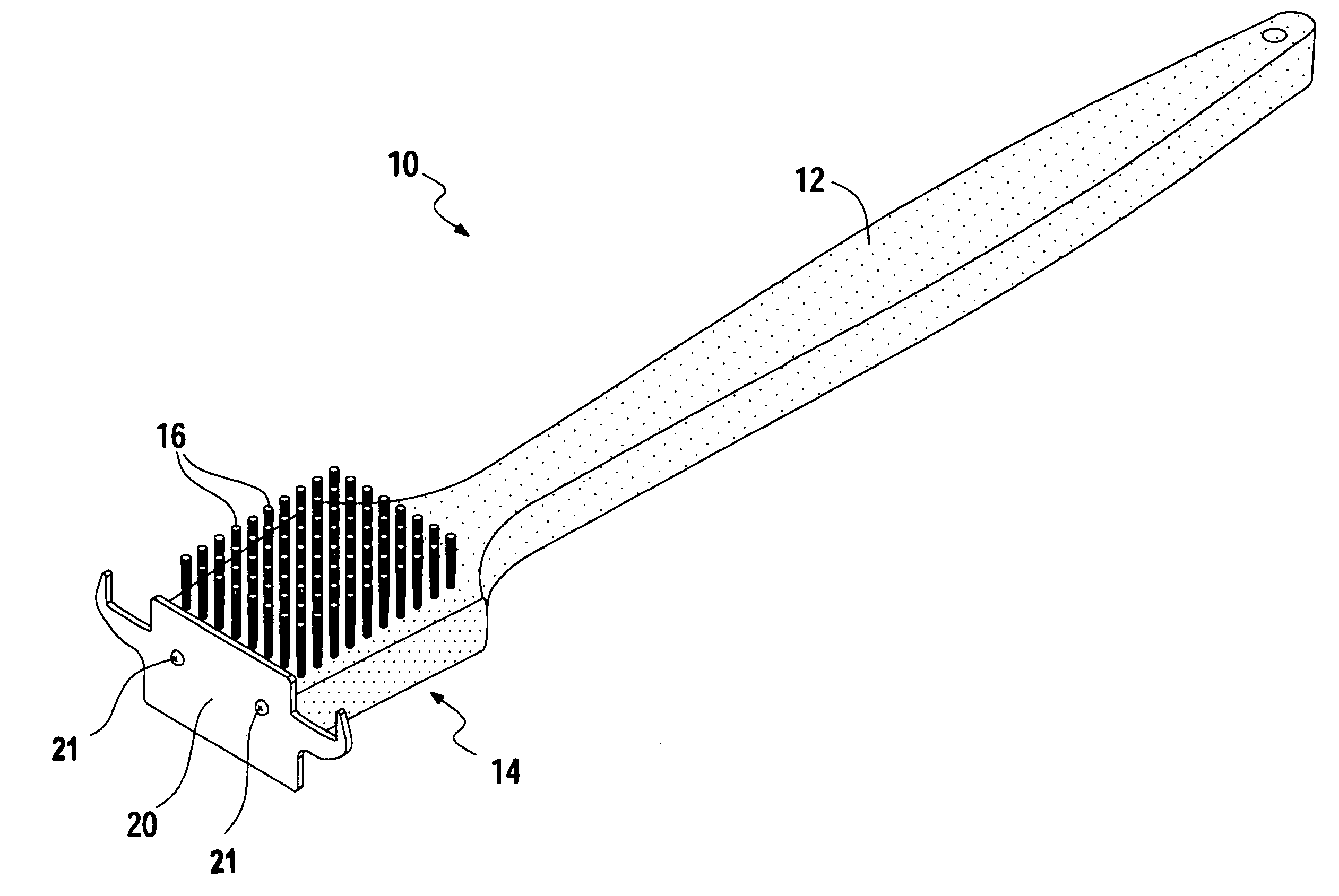
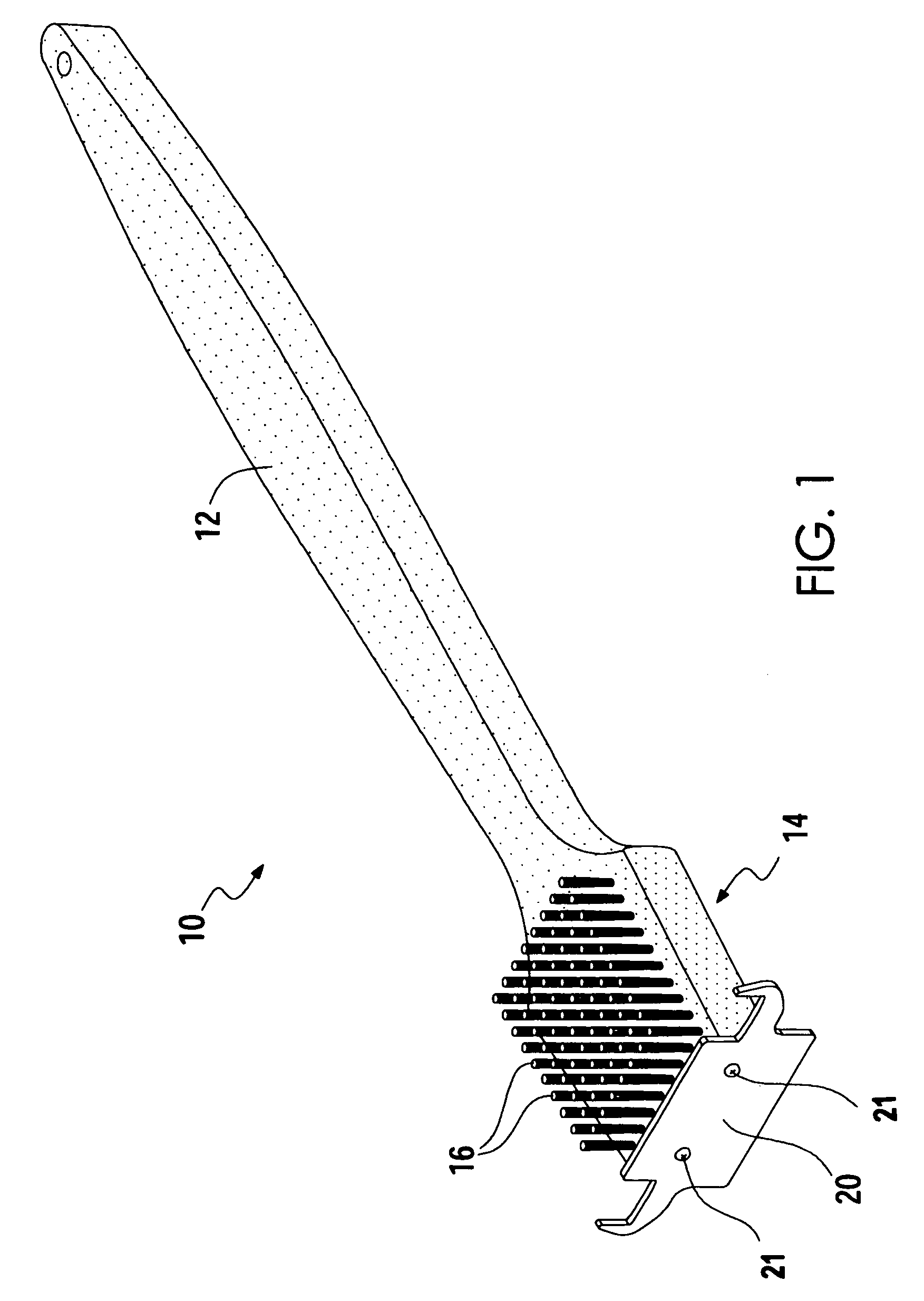
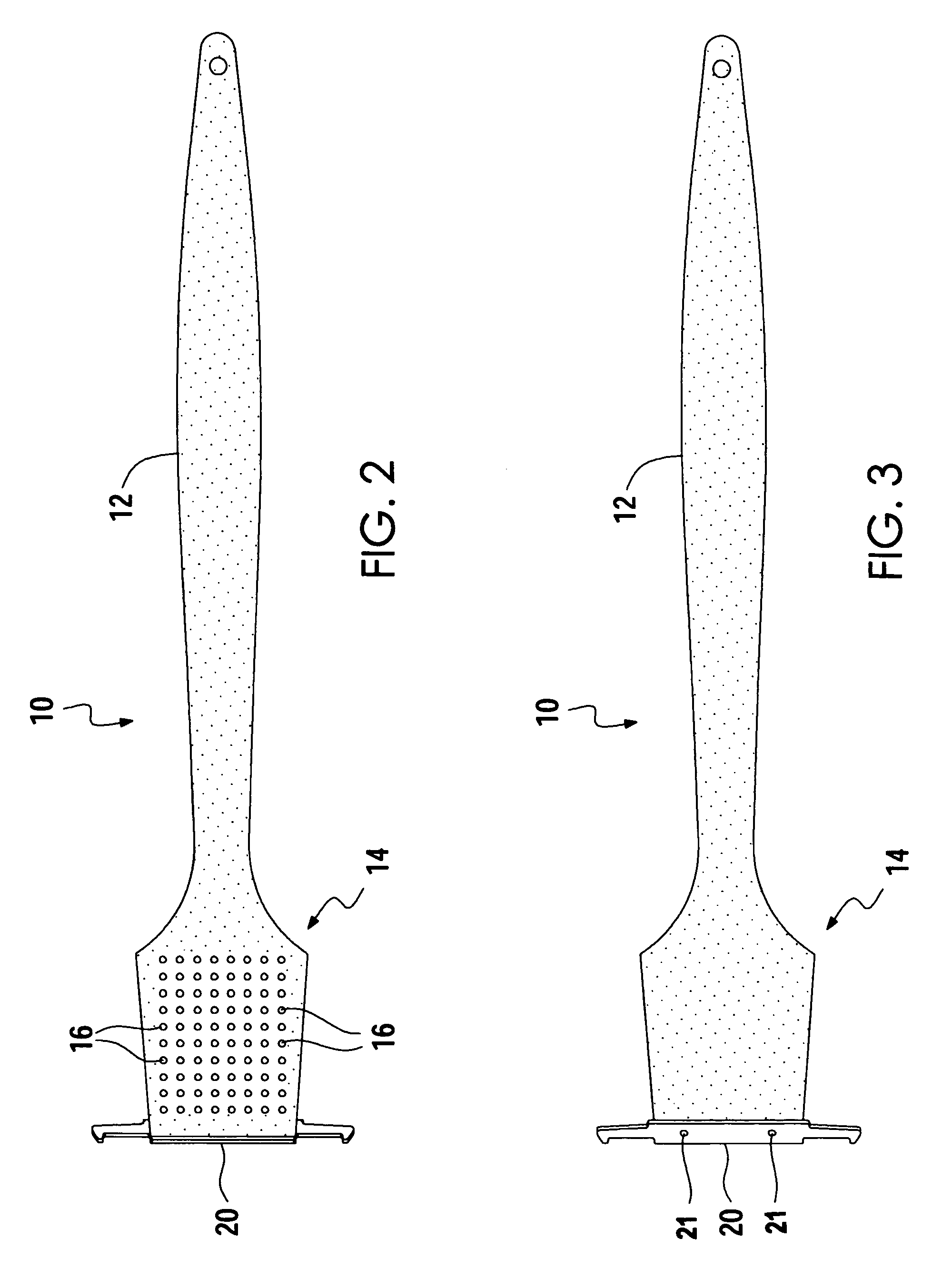
Grill brush
InactiveUS7039983B1Force can be appliedClean thoroughlyCarpet cleanersKitchenware cleanersBristleMechanical engineering
A grill brush assembly comprising an elongated handle portion, a head portion integral the head portion and extending from a forward end thereof constructed of rigid material such as but not limited to wood or molded polymeric material. The invention includes a plurality of bristles extending downward from the lower surface of the head portion, and a grill scraper fixedly attached to the forward edge of the head portion by suitable attachment means. The scraper of the present invention has an upper edge for scraping the uppermost surface of a series of grates, and an opposing pair of hook-like extension portions extending from opposite sides of the scraper. Each extension portion forms a pair of scraping faces for simultaneously engaging an uppermost surface of a single grill grate and the lowermost surface of an adjacent single grate. With a simple twist of the wrist an extension portion wraps around adjacent grill grates to easily and thoroughly clean all surfaces of the grates, top, bottom, and sides, with minimal strokes and without having to reposition the grill grate assembly.
Owner:OUTLAW DONALD S
Gingival retraction material
InactiveUS20050287494A1Drawback can be solvedHigh aspect ratioOrganic active ingredientsImpression capsFiberGingival tissue
A gingival retraction material is prepared using fibrillated fibers to improve viscosity and combining taste-modifying agent, color agent, and kaolin filler to form a paste-like structure having the viscosity ranging from 31.0×106 cP to 71.0×106 cP. The gingival material is injectable into the patient's gingival sulcus to provide a physical active force that widens the patient's gingival sulcus by means of the material viscosity and also to control gingival tissue fluid and hemostasis so as to keep the gingival sulcus dry for further mold impressions.
Owner:BIOTECH ONE
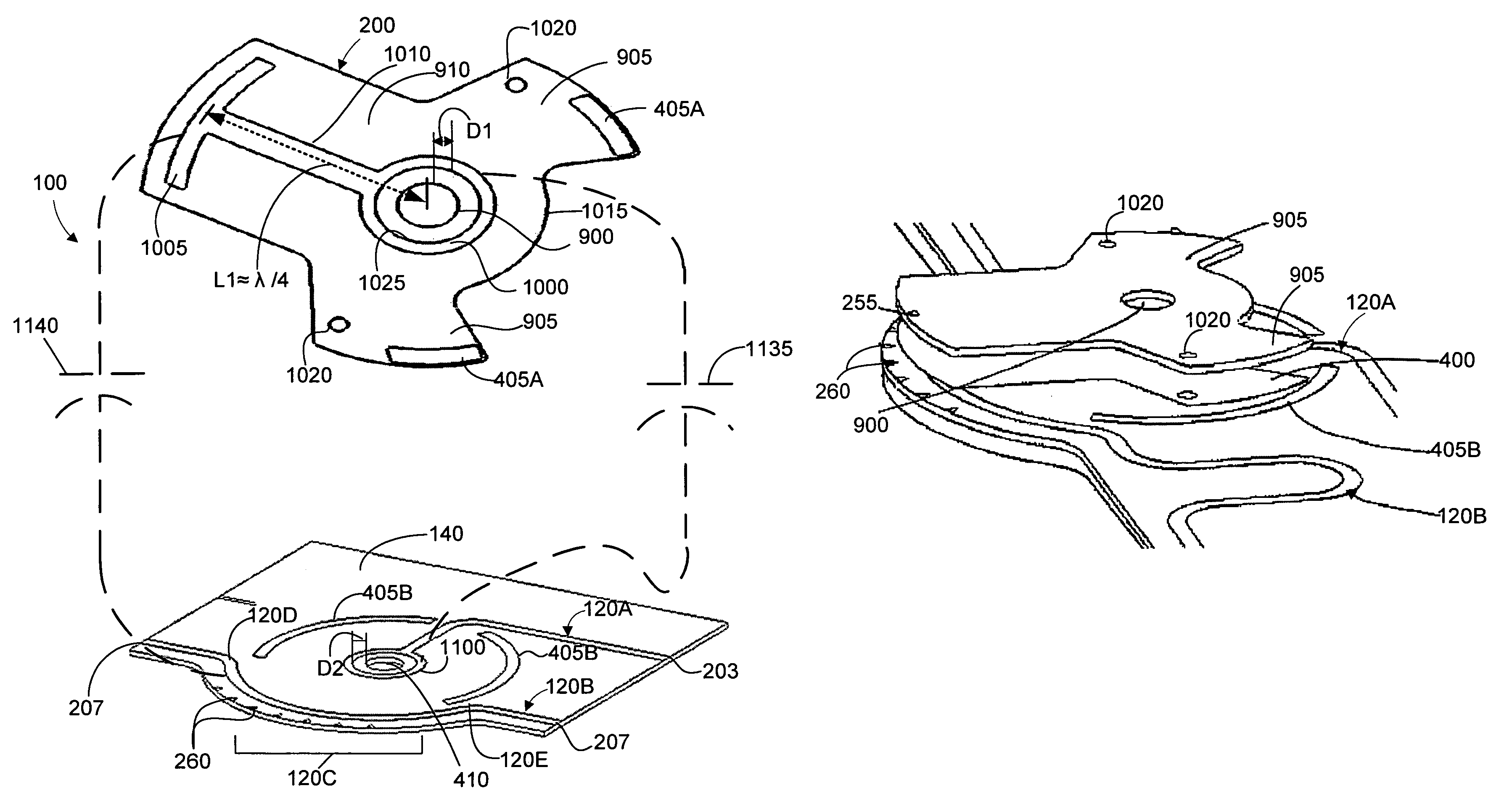
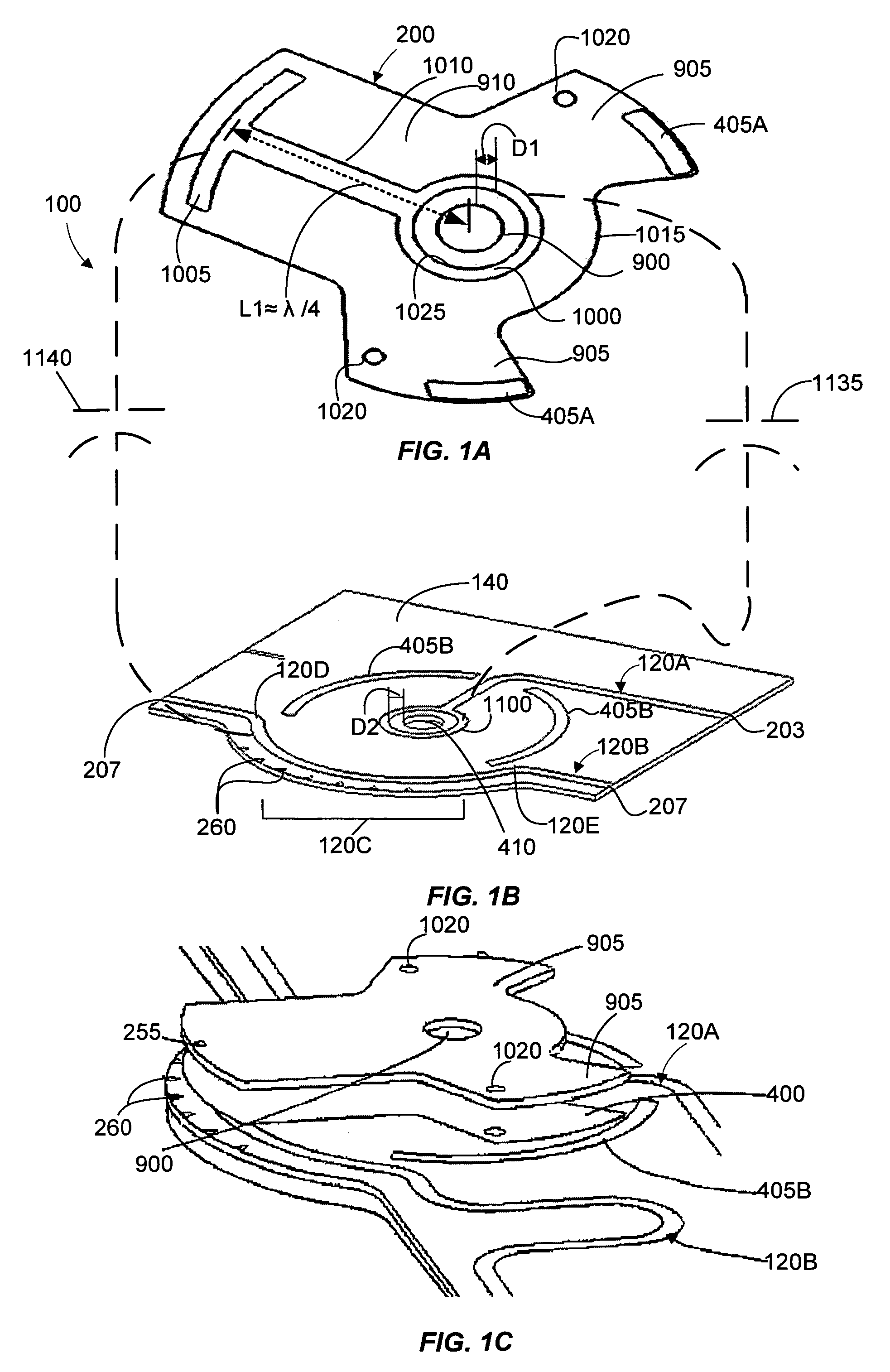
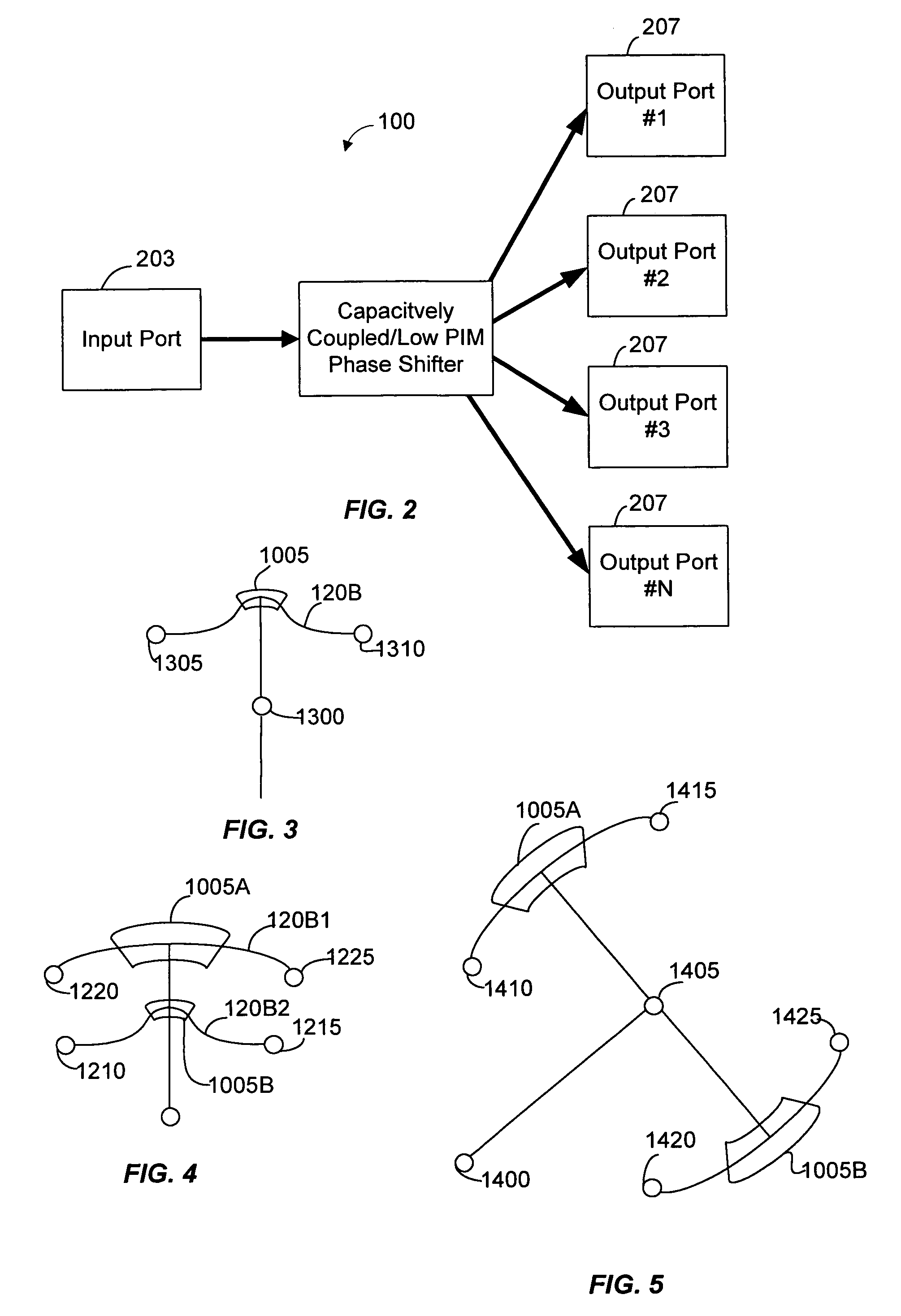
Microstrip phase shifter
InactiveUS7233217B2Easy constructionMinimize of assemblyAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitancePath length
A phase shifter adjusts the phase between two segments of an RF feed line that are fed with the phase shifter. Specifically, the phase shifter adjusts the phase between two signals in RF feed line segments by changing the electrical path lengths that RF energy travels down in each respective RF feed line. The phase shifter includes a coupling arm, a key, a spring, and a support architecture that fastens the phase shifter to a substantially planar surface. The support architecture is rotated manually or with a machine such as a motor. The coupling arm can include a coupling ring, a wiper element, a support trace, and a dielectric spacer. The phase shifting system is a relatively compact structure having a predetermined value of capacitance maintained between a coupling ring disposed on the coupling arm and a coupling ring disposed on a planar surface.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
String vibration suppressor for compound archery bows
InactiveUS8056548B1Reduce displacementForce can be appliedSpring gunsBows/crossbowsSuppressorEngineering
A vibration dampening device for use on compound archery bows. A device may be associated with one or more bow limb, with each device disposing a vibration damping bumper in position to shorten the vibrating length of the bow string at brace, compared to the vibrating length of a bow string of a comparable bow lacking the device(s). Certain embodiments couple bowstring vibration at brace with one or more cable. Preferred embodiments include a limb anchor adapted to distribute string-induced loading onto a bow limb at both sides of a string cam.
Owner:LARSON ARCHERY
Method and apparatus for therapeutic treatment of back pain
ActiveUS7201729B2Precision therapyEliminate side effectsOperating chairsOperating tablesDistractionMedicine
A therapeutic table construction which isolates a first portion of the patient's body to a fixed table portion and a second portion of the patient's body to a moveable table portion, and applies a distraction force to the moveable portion of the patient's body while positioning the portion of the patient's spine that is to be treated at an angle so as to isolate the portion of the patient's spine which receives the distraction force.
Owner:SPINEMED SALES INT
Devices and systems for compressing food articles
Devices and systems for compressing food articles are shown and described. Embodiments of the present invention can be used to squeeze, press, extrude, or otherwise process food articles. The disclosed embodiments can include a lever with a plurality of gear teeth, a base with a plurality of gear teeth, and a receptacle. The gear teeth can engage one another. The lever and base can be actuated to move a piston head into and out of the receptacle to compress food. A piston assembly of the compression tool can provide a mechanical advantage to provide relatively high compressive forces.
Owner:CHEFN
Radiant heating arrangement with distortion compensation
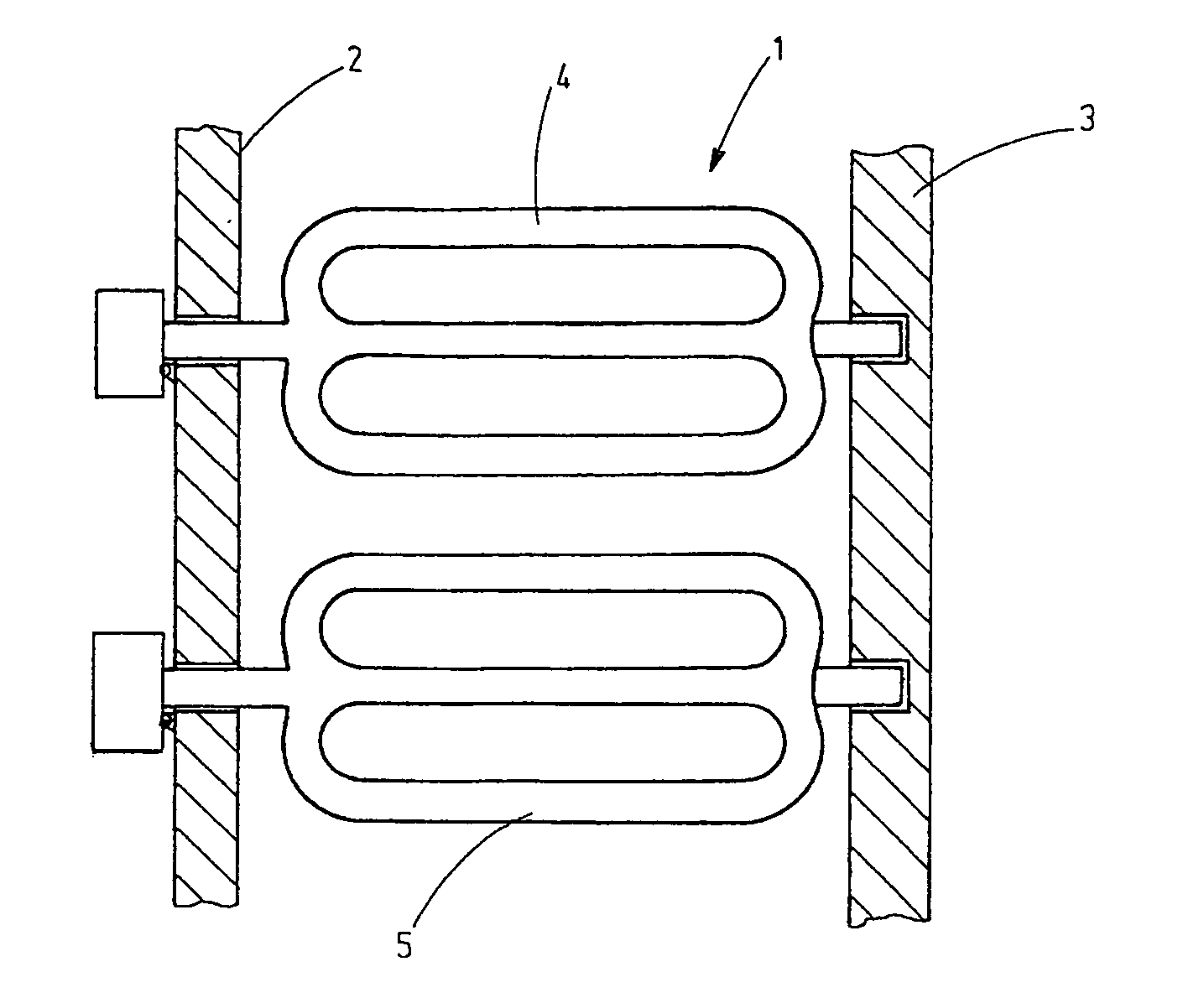
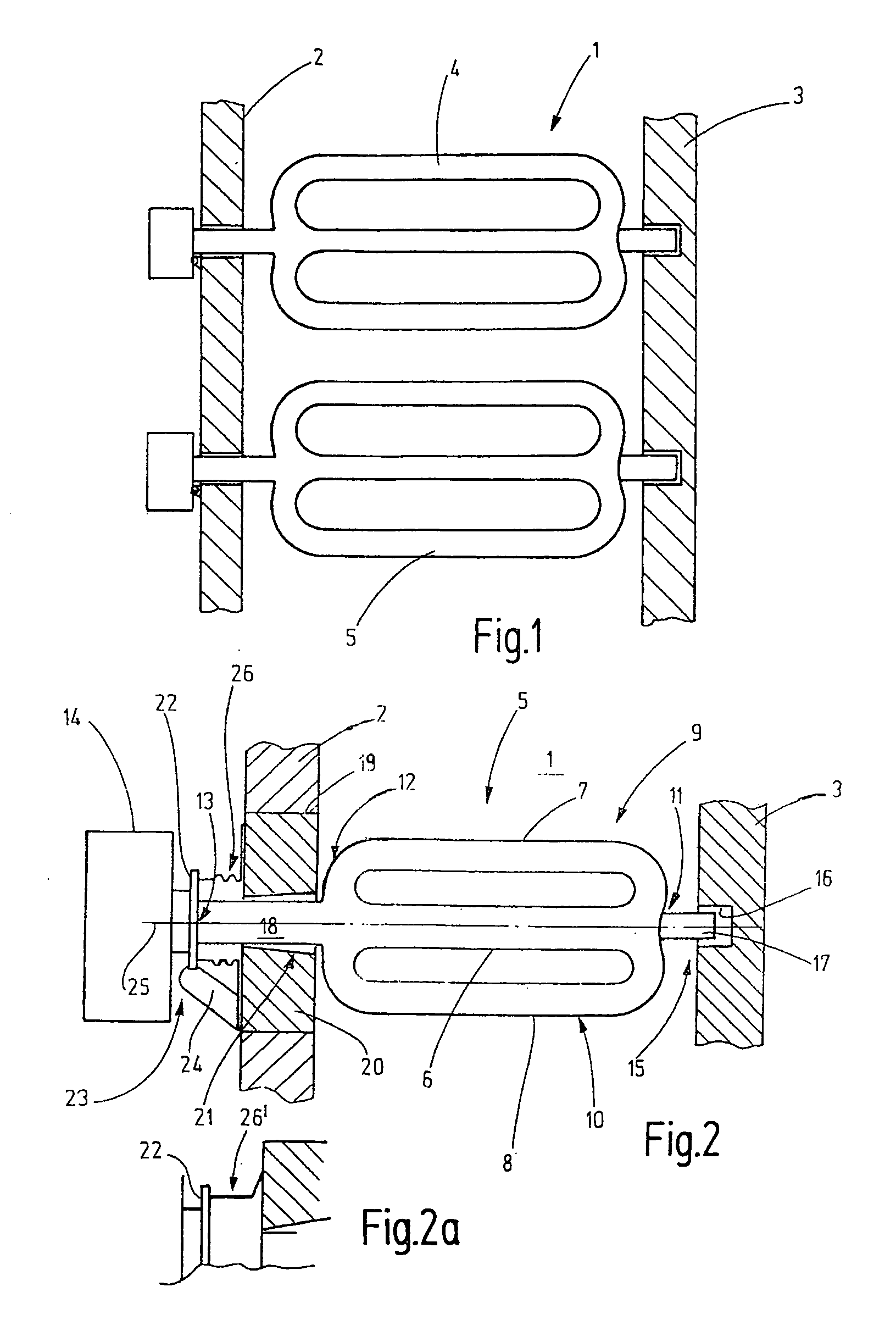
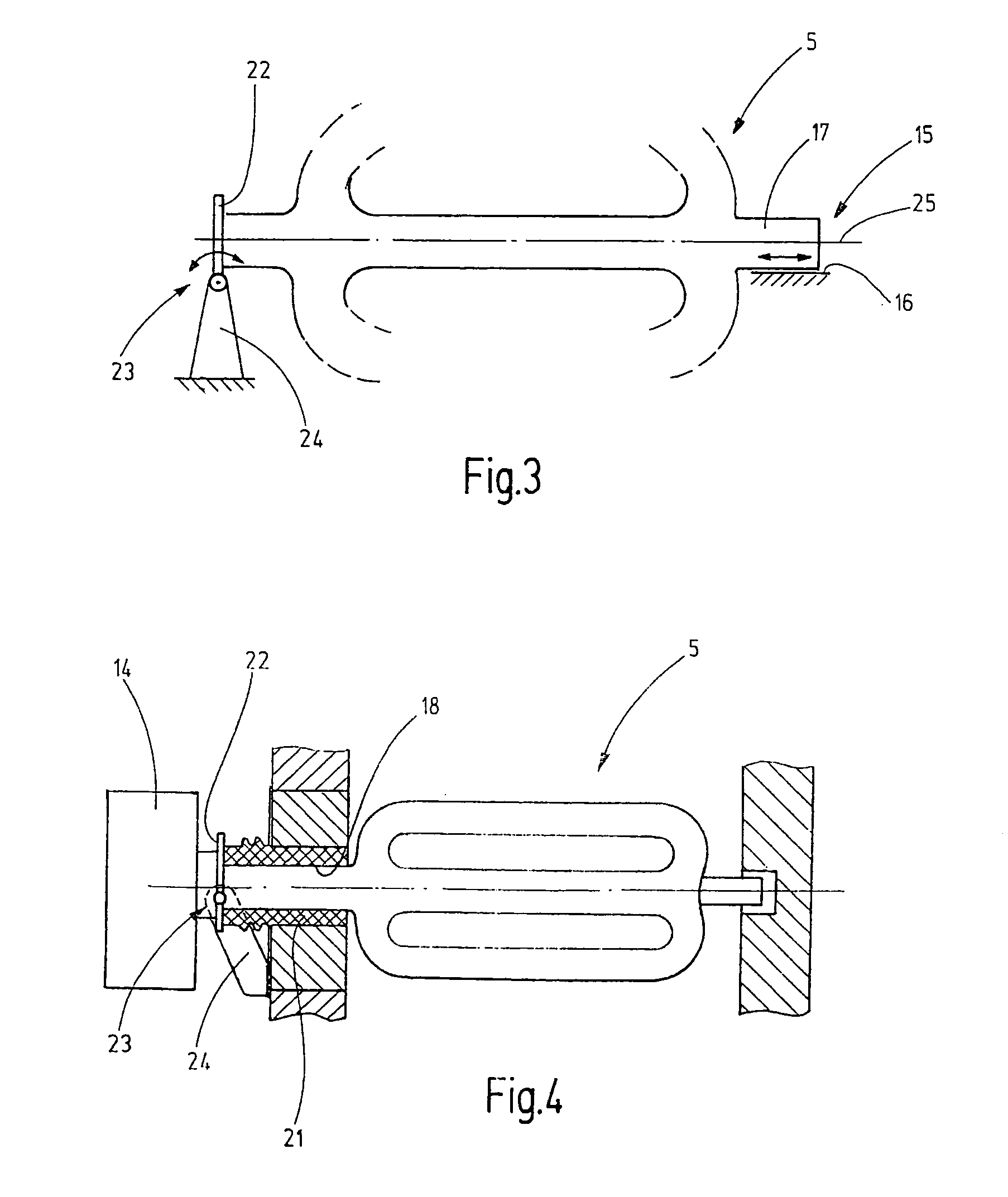
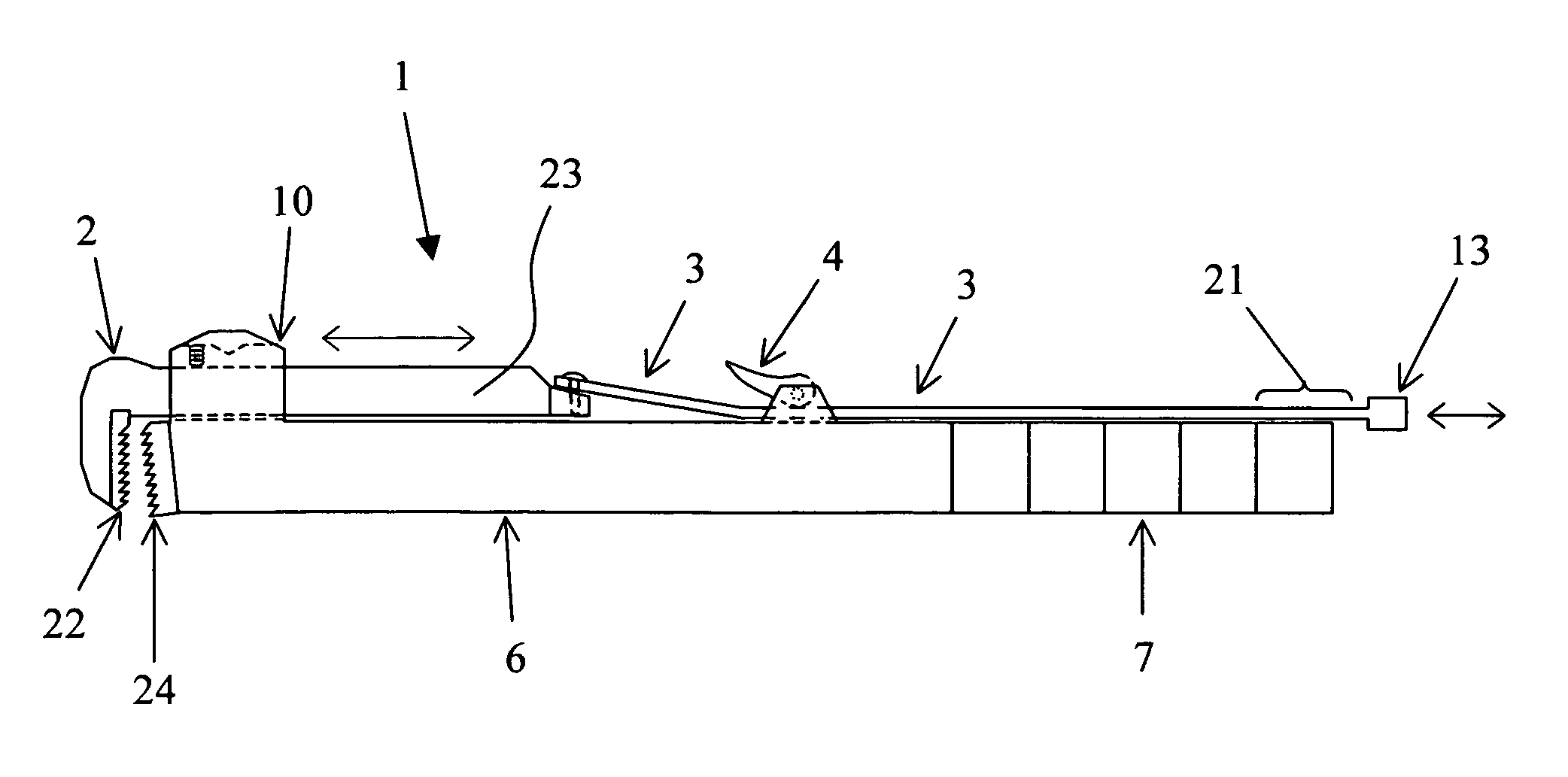
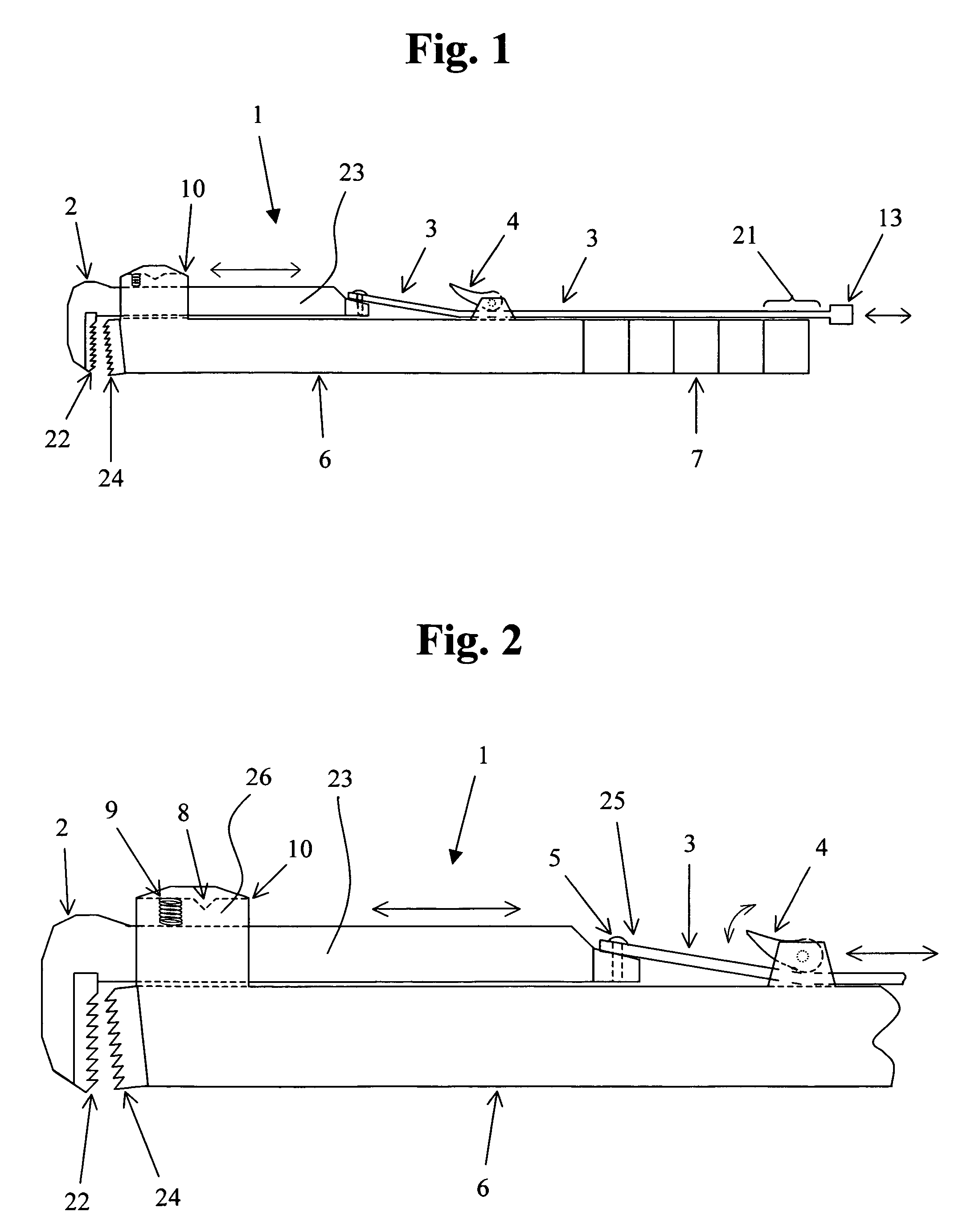
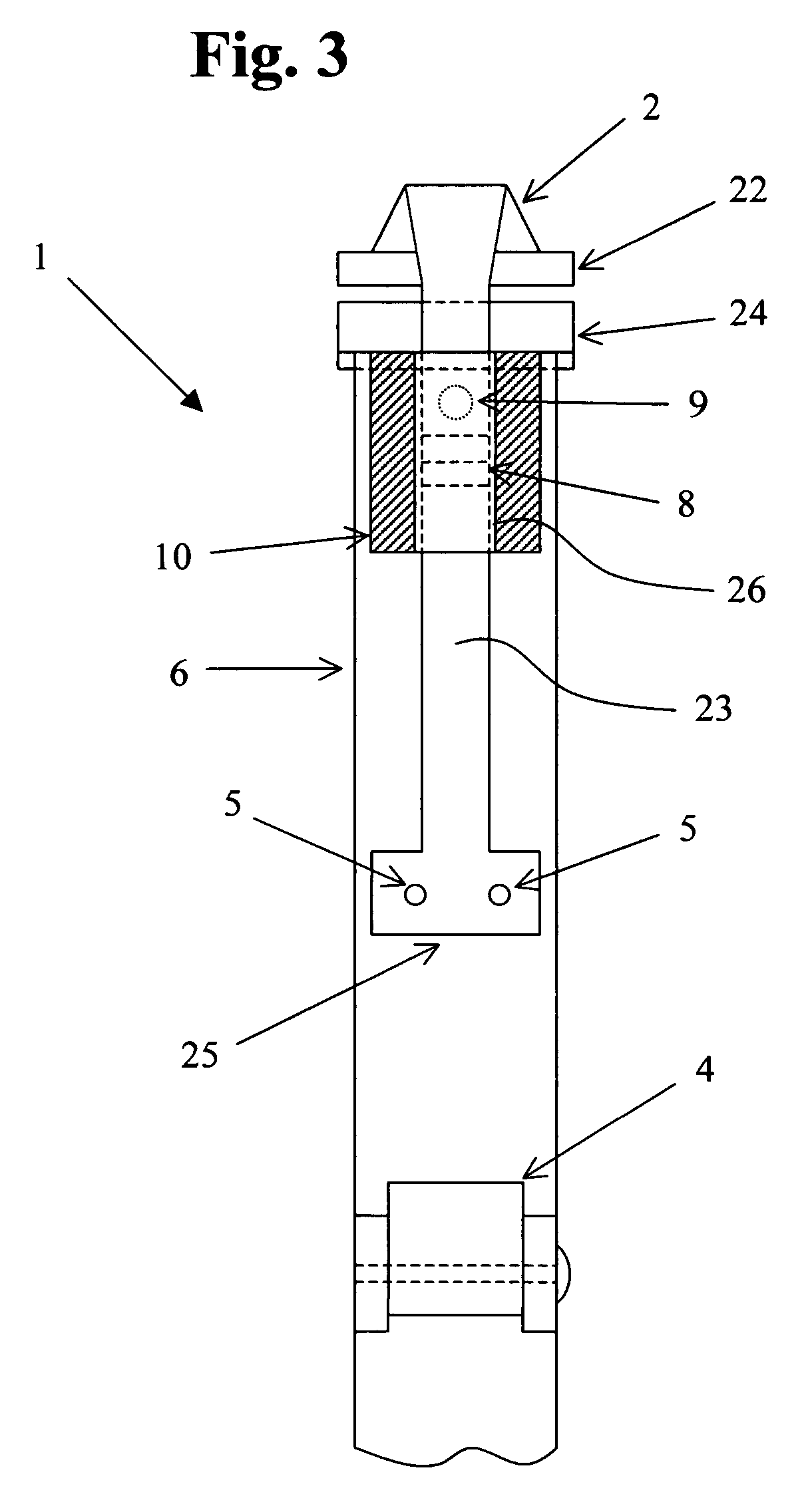
ActiveUS20110120453A1Force can be appliedFurnace componentsDomestic stoves or rangesDistortionEngineering
A radiant heat tube (5) comprises a tube body having a center section (6) and at least one recirculating section (7, 8) arranged next to the center section, said recirculating section forming a loop (9, 10) with said center section. A pivot joint bearing (23) is arranged on one end (12) of the radiant heat tube, while a sliding bearing (15) is arranged on the other end (11) of the radiant heat tube, said sliding bearing (15) being arranged opposite said pivot joint bearing (23). A burner (14) is disposed to heat the radiant heat tube (5).
Owner:WS WARMEPROZESSTECHN
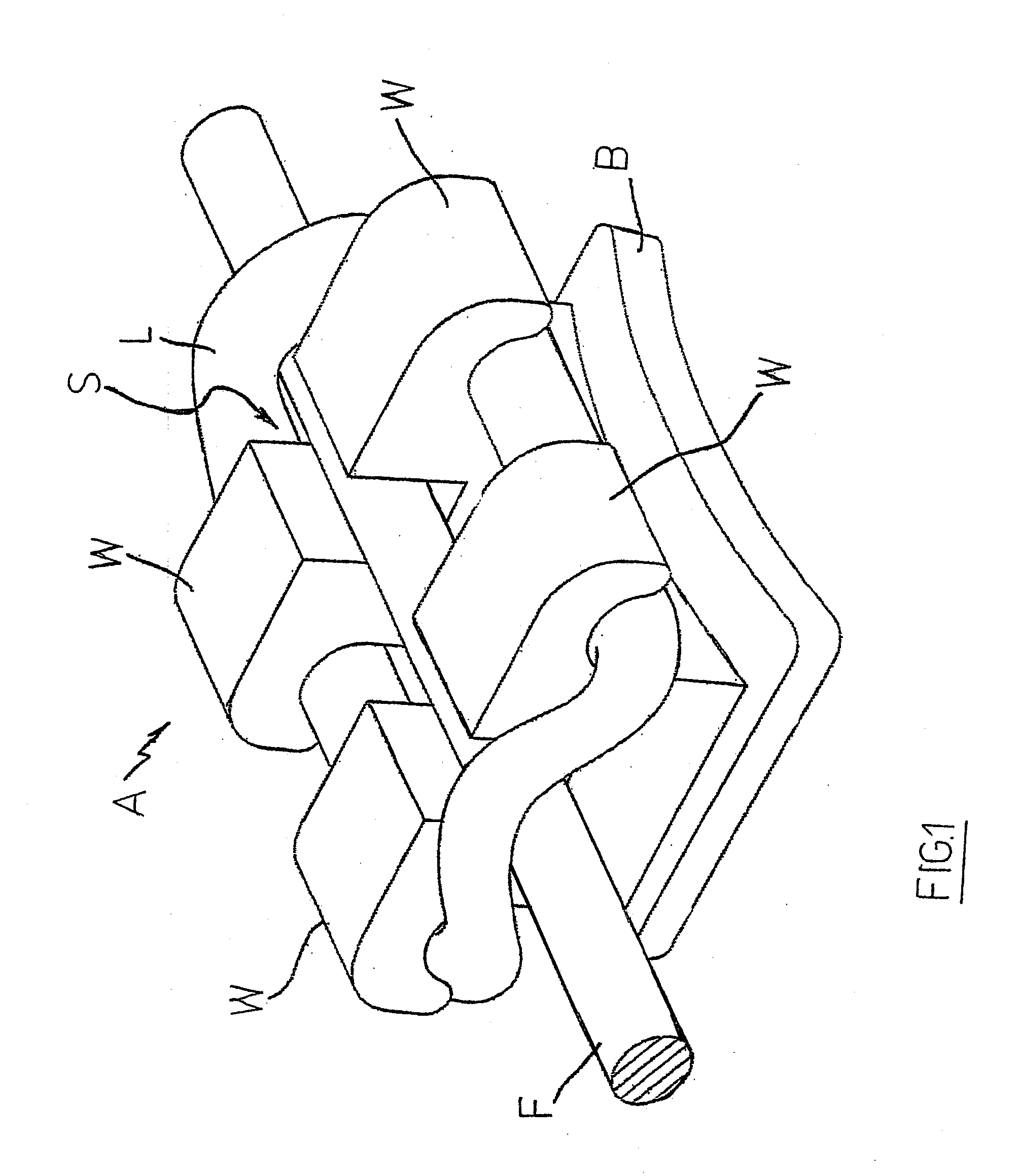
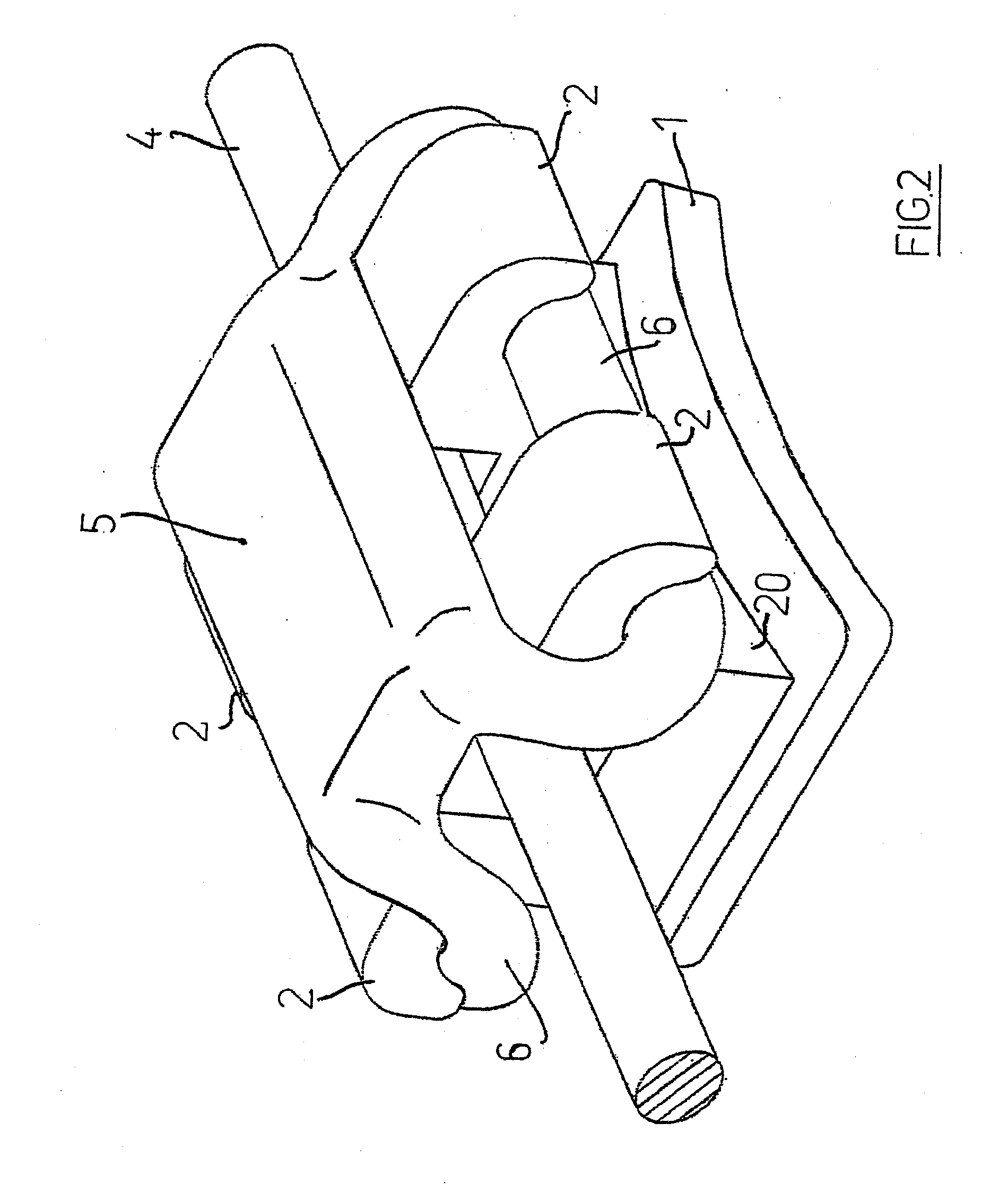
Ligature device
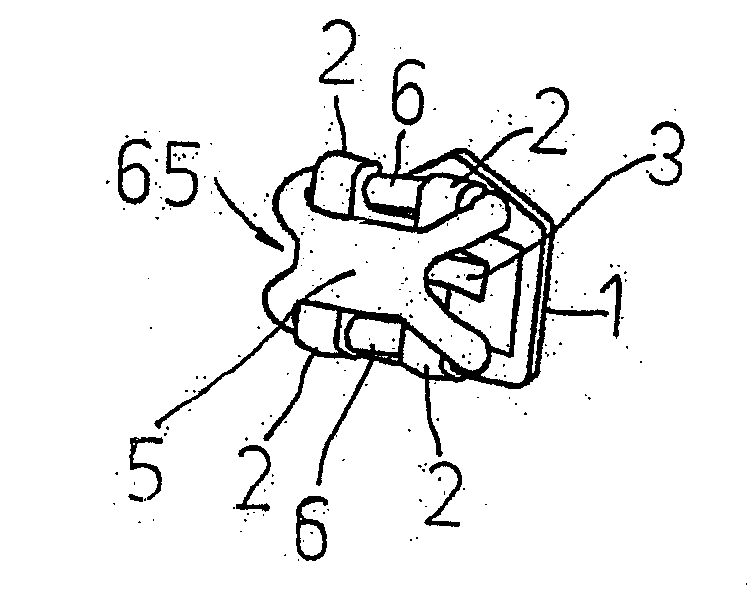
InactiveUS20080032249A1Reduce inconvenienceEliminating orArch wiresBracketsEngineeringOrthodontic ligature
Ligature device for orthodontic brackets, consisting of an elastic body with a central portion (5) and two lateral rings (6) positioned on two mesodistal sides of the central portion (5), on opposite sides with respect to the latter, the rings being intended to be stretched to be coupled with the wings (2) of an orthodontic bracket so that the central portion (5) results above the same bracket wings (2), characterized in that the lateral rings (6) form at least a curve (65) corresponding to a mesodistal side of the orthodontic bracket at the height of the wings (2), the vertex of the at least one curve (65) being turned toward the orthodontic bracket, that is to say toward the central portion (5) of the ligature device, the length (a) of each of the rings (6) exceeding the length (c) of the central portion (5) both when the rings (6) are stretched and un-stretched, so that the value of the ratio (a) / (c) is less than one in both the stretched and un-stretched configurations.
Owner:LEONE SPA
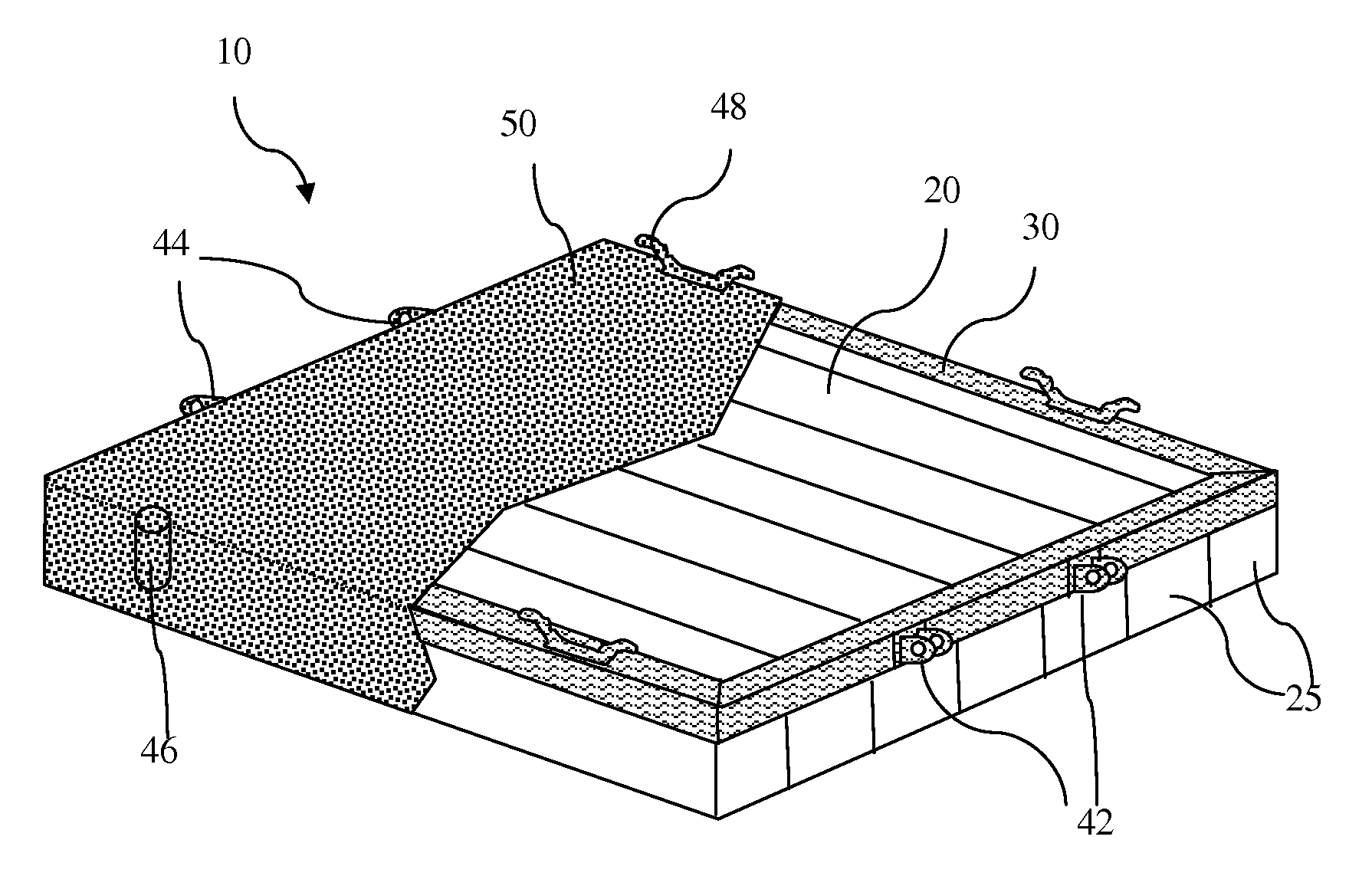
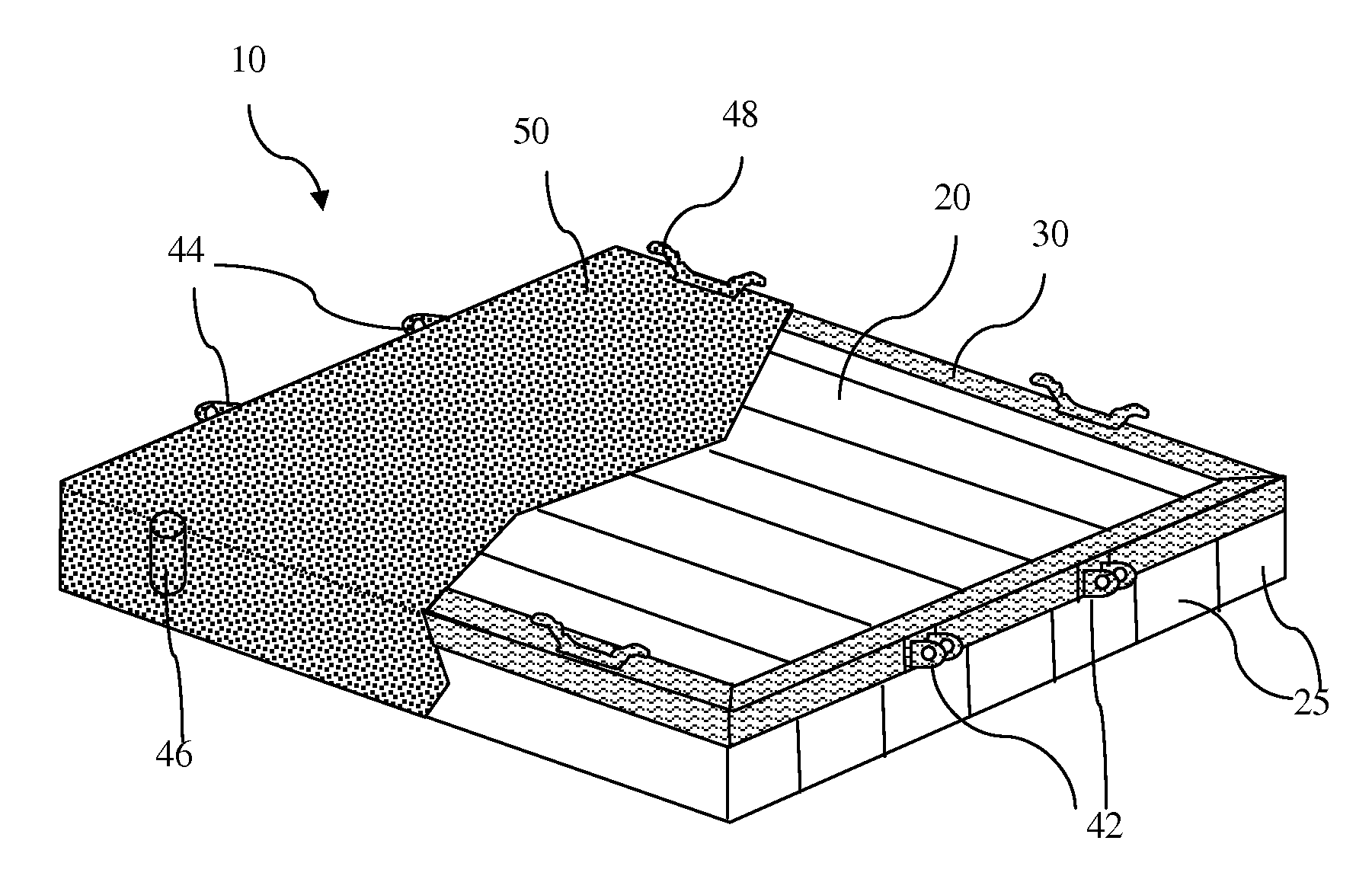
Floating dock system
InactiveUS20130019791A1Force can be appliedNon-magnetic metal hullsFloating buildingsEngineeringPolymer
A floating dock system contains a polymeric foam core, a structural collar, attachment means connected to the structural collar and a protective coating adhering to and completely covering the polymer foam core and structural collar and is free of decking or plates that are independent of the structural collar between the top surface of the polymeric foam core and the protective coating.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Lightweight wrench
A lightweight, adjustable wrench comprising of a moveable jaw with a reach that is shortened or lengthened with a strap or a cable. The loose end of the strap or cable is secured to the wrench's shank by a cam lock, or similar locking device. Since the strap or cable is the means for the wrench's jaws adjustment, a quicker and easier fit to the pipe or object to be gripped can be obtained. The wrench is more convenient to adjust, since the means for adjustment are located near the handle of the wrench as opposed to the shank end of present designs. The strap or cable adjustment also allows the wrench's shank and handle to be designed hollow and a larger diameter to reduce weight. The wrench can be made in any proportion for any sized application.
Owner:WILLIAMS STEVEN ANDREW
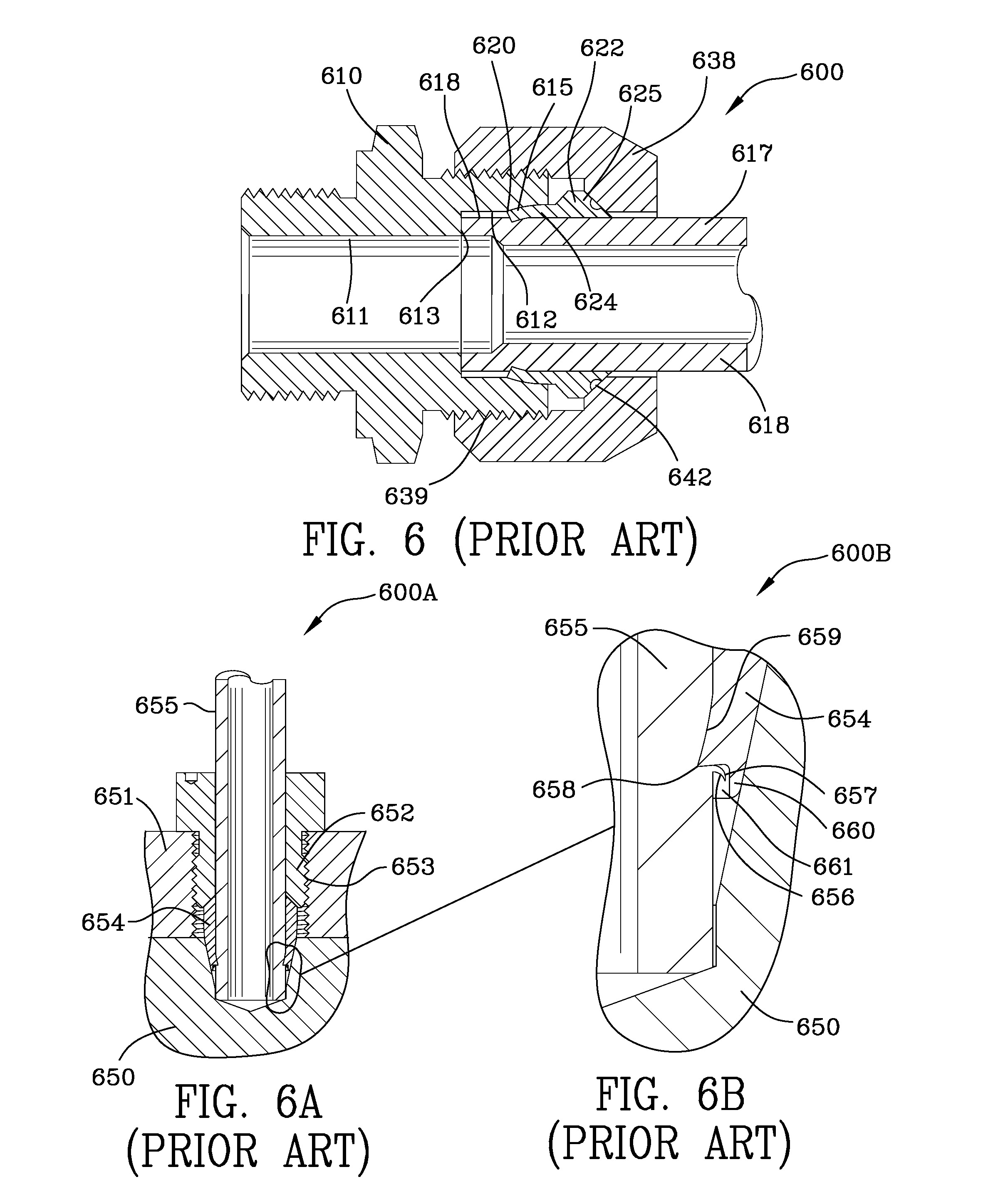
Tube compression fitting and flared fitting used with connection body and method of making same
InactiveUS20130025341A1Improve the immunityHigh strengthJoints with sealing surfacesCombined useEngineering
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN CORP
Method for improving a bowler's control over the release of a bowling ball from the bowling ball finger grip hole
InactiveUS7264553B1Force can be appliedPrevent movementBowling gamesIndoor gamesEngineeringDepth limit
A method of using a bowler's aid on the fingers inserted into the finger grip holes of the bowling ball and used to hold the ball. The bowler's aid is mounted on the finger or hand of the bowler by means of a fastening means. When the bowler's aid is in place, a finger pad finger pad shield is placed opposite the finger pad which may be connected to a load bearing means by a support means. The finger pad finger pad shield assists the bowler in using his or her natural force in the finger against the ball, for example when lifting the ball in its delivery, or in meeting the force of the ball against the finger. The bowler's aid may include a depth limiting means to control the depth of the bowler's finger in the hole of the bowling ball.
Owner:ADDINGTON RANDALL A +2
Devices and systems for compressing food articles
ActiveUS20100229736A1Easy to compressEasy to moveJuice extractionEggs preservationMechanical advantageGear tooth
Devices and systems for compressing food articles are shown and described. Embodiments of the present invention can be used to squeeze, press, extrude, or otherwise process food articles. The disclosed embodiments can include a lever with a plurality of gear teeth, a base with a plurality of gear teeth, and a receptacle. The gear teeth can engage one another. The lever and base can be actuated to move a piston head into and out of the receptacle to compress food. A piston assembly of the compression tool can provide a mechanical advantage to provide relatively high compressive forces.
Owner:CHEFN
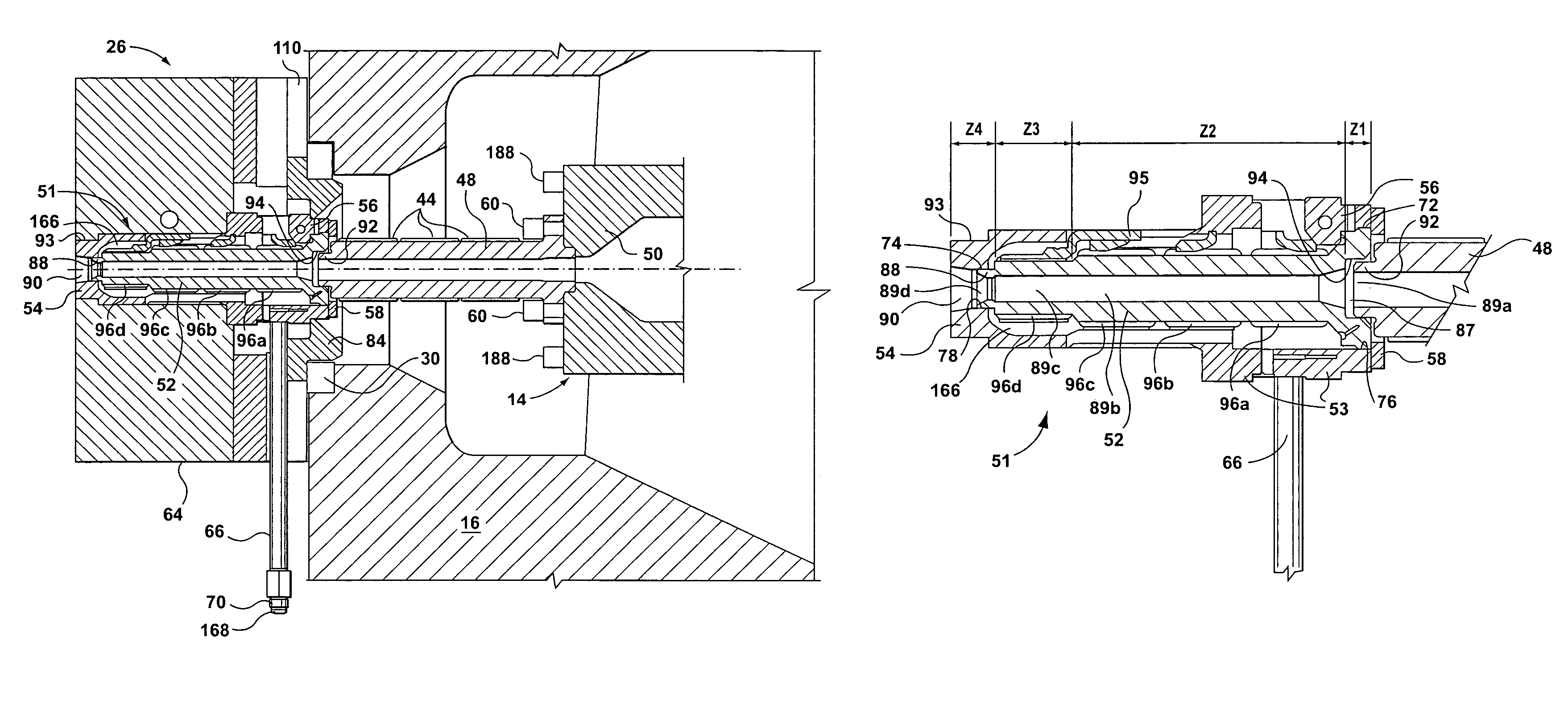
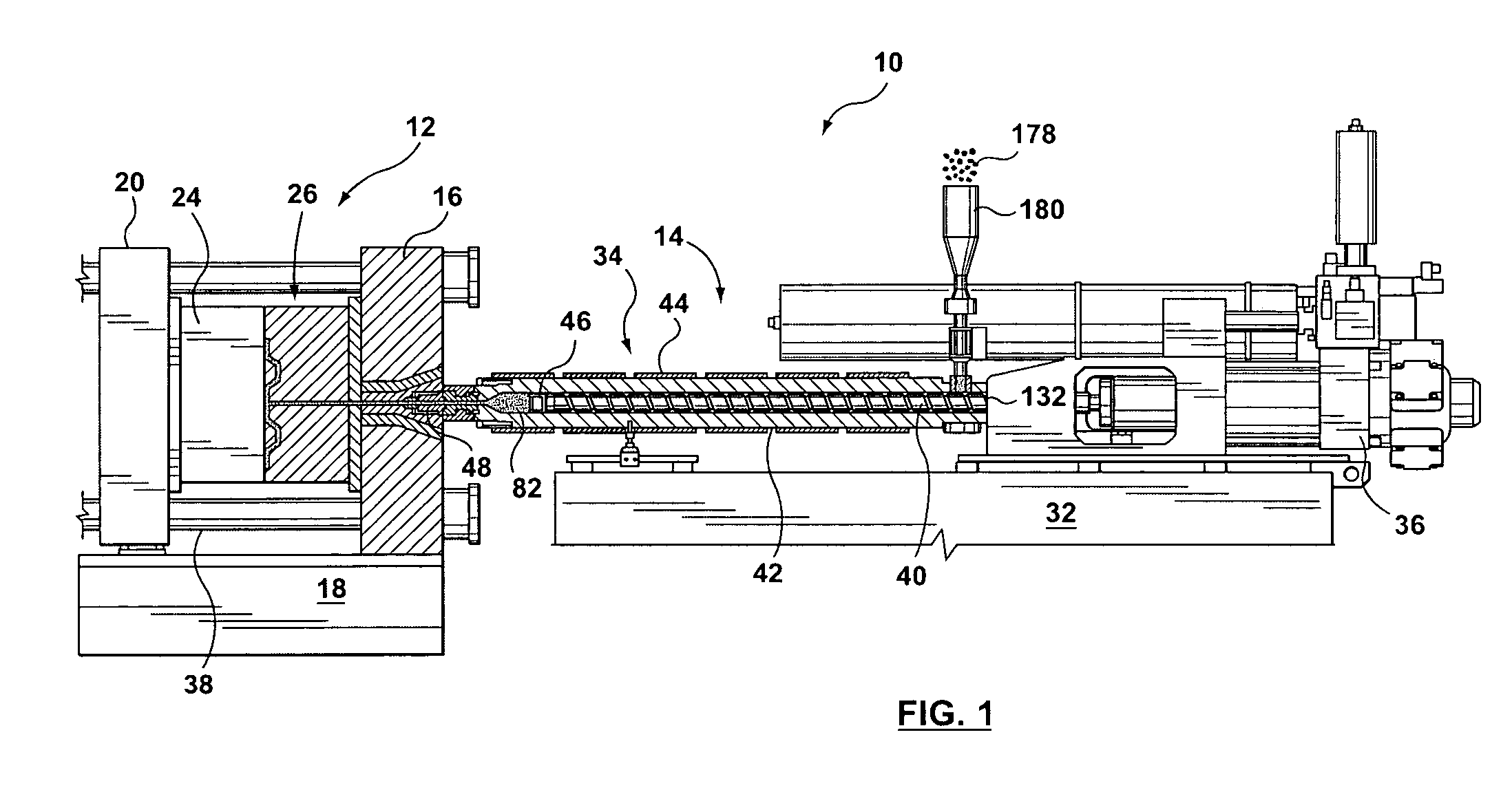
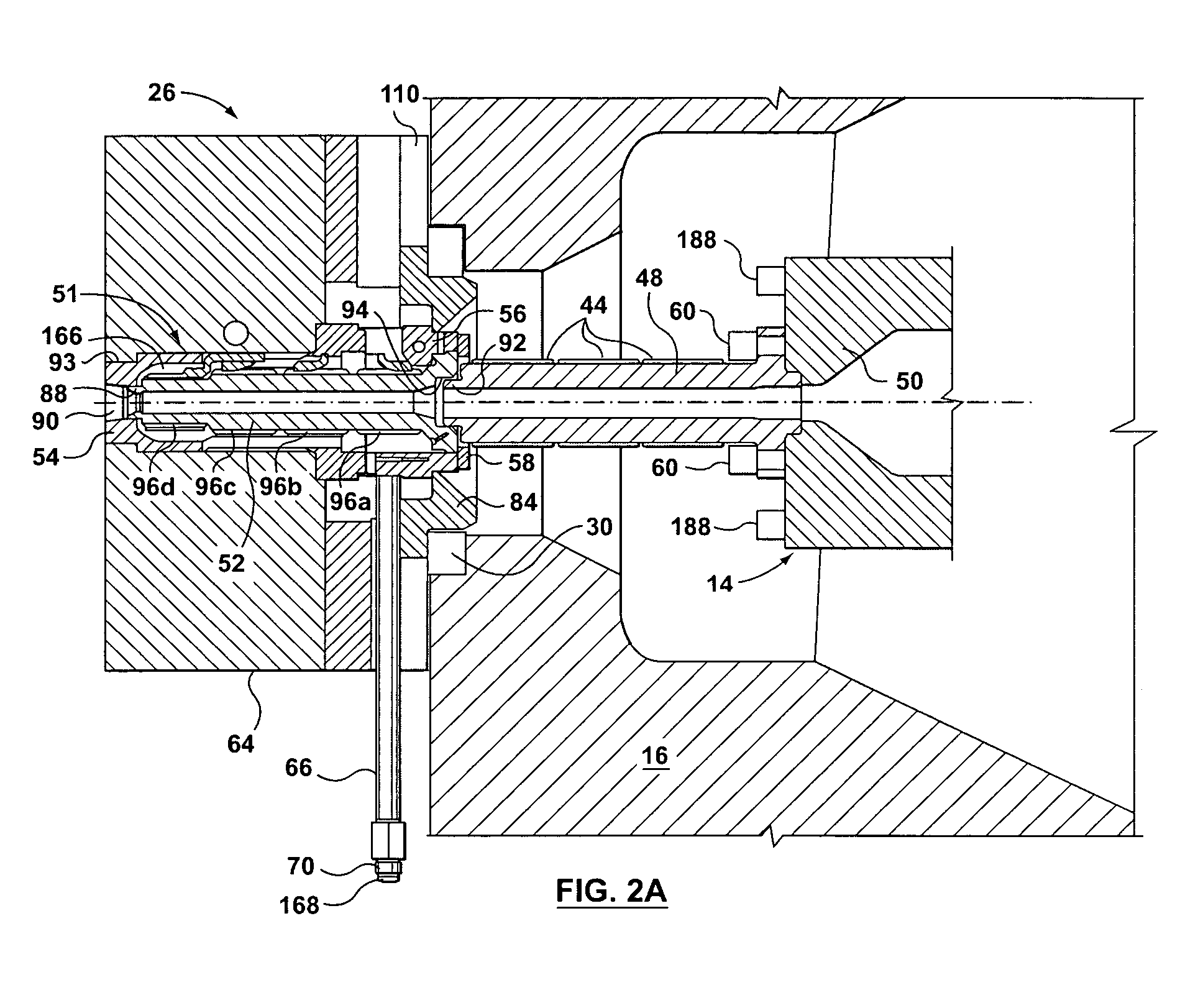
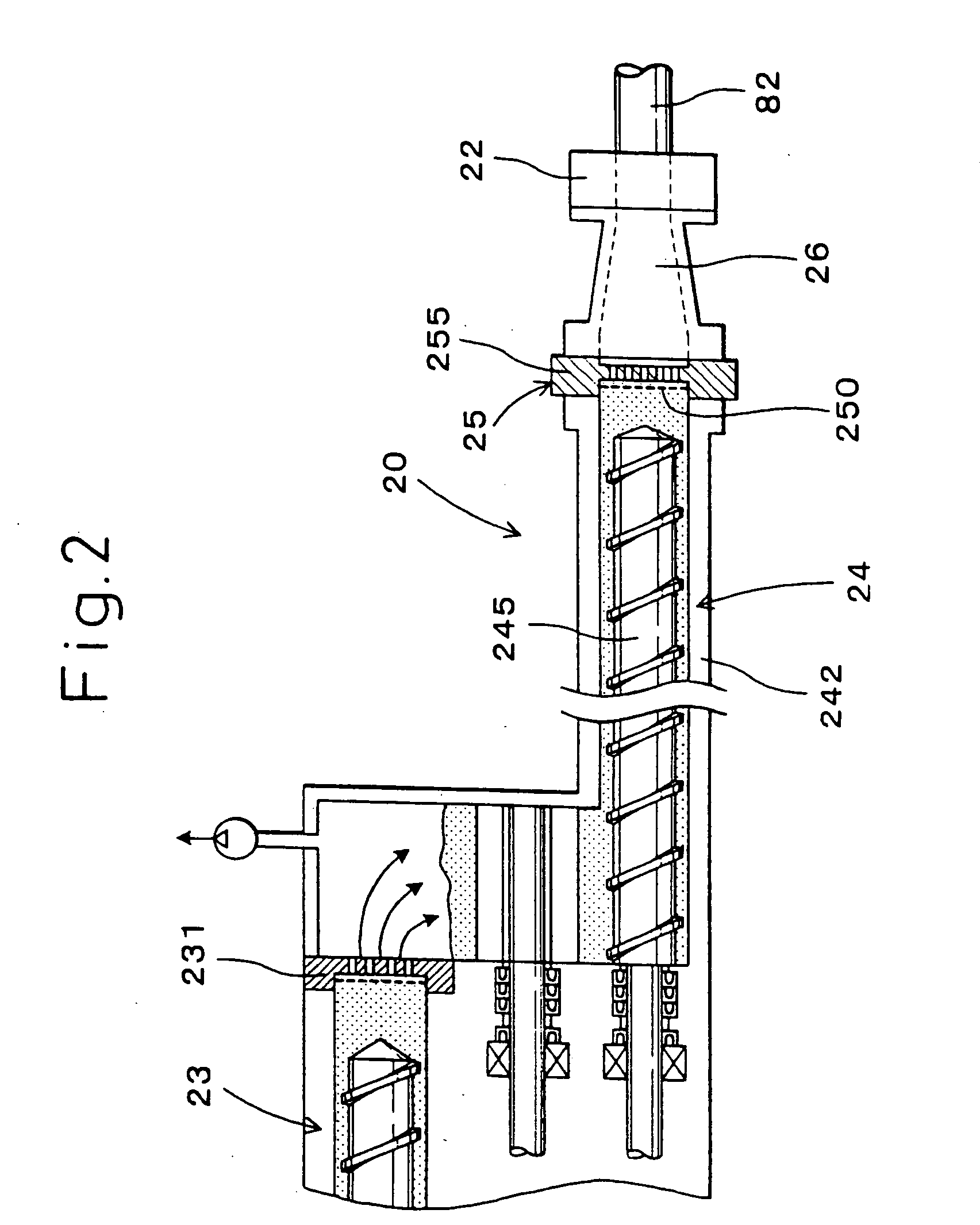
Sprue apparatus
InactiveUS7401639B2Reliable sealed connectionReliable configurationFood shapingTemperature controlShell molding
A sprue apparatus for use in a molding apparatus for connecting the melt duct of a molding machine nozzle with a runner system of a molding apparatus. The sprue apparatus includes a plurality of thermal regulators that regulate a plurality of thermal zones that segment the length of the sprue apparatus for the purpose of localized temperature control in support of a molding process. The plurality of zones may be thermally regulated such as to enable a substantially leak-free junction between the machine nozzle and the molding apparatus. The sprue apparatus may include an isolating coupler that substantially isolates a heated sprue bushing from carriage force. The invention has been found particularly useful when injecting metal alloys such as magnesium based alloys when in the thixotropic state.
Owner:HUSKY INJECTION MOLDING SYST LTD
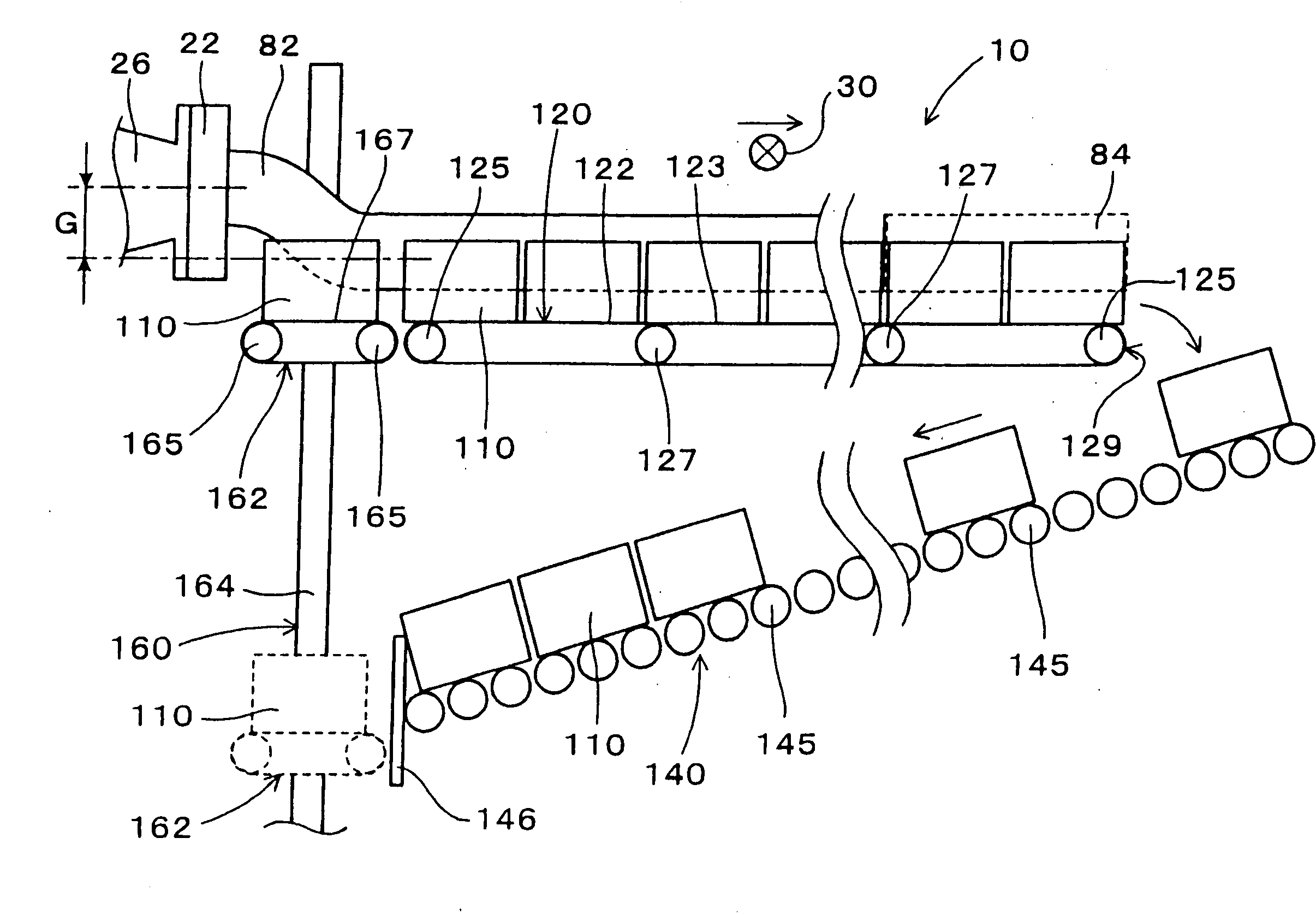
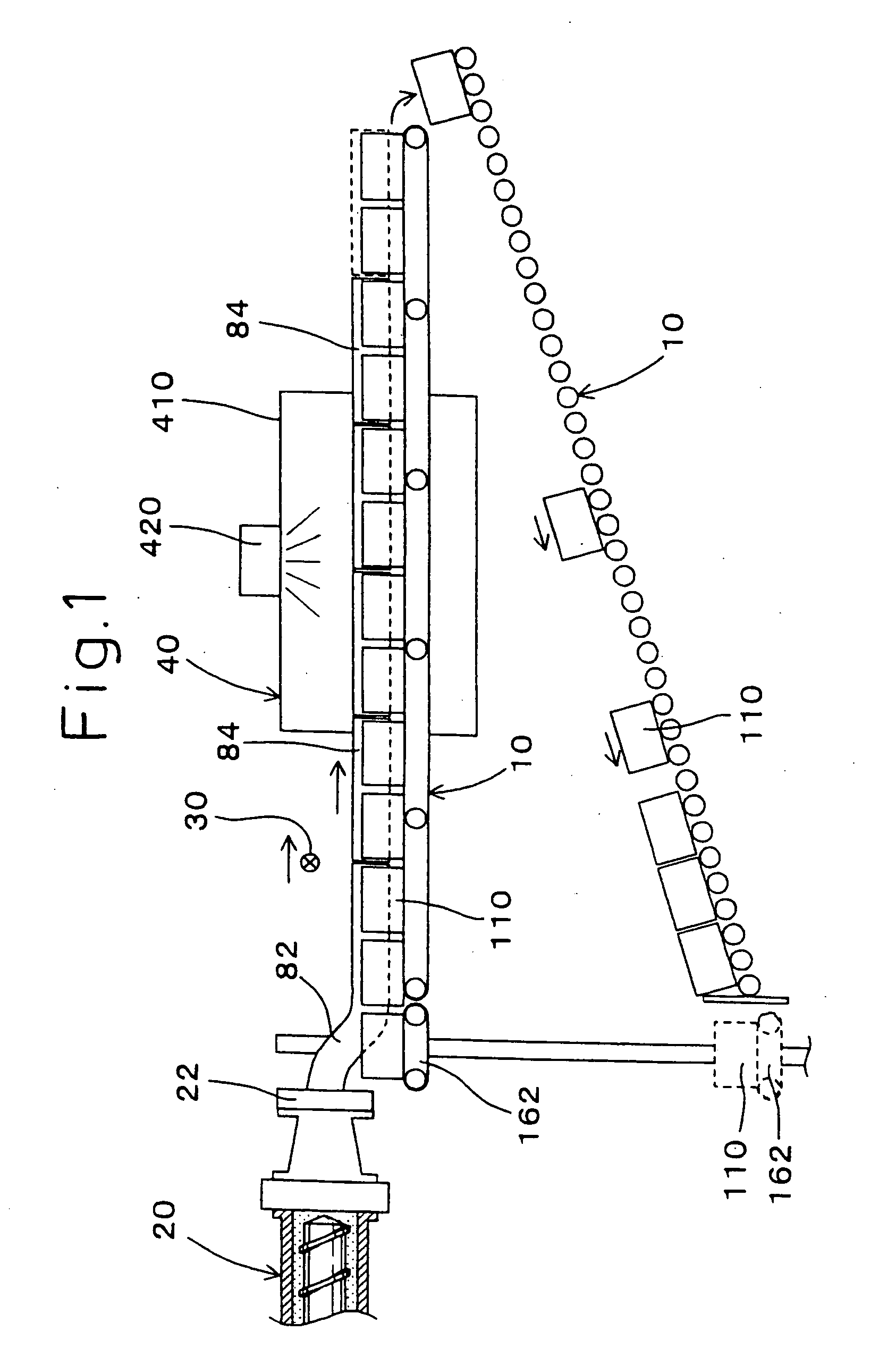
Method of conveying ceramic moldings
InactiveUS20070194480A1Shorten extruded lengthReduce weightDischarging arrangementMechanical conveyorsCeramic moldingMaterials science
The present invention relates to a conveying apparatus for guiding a rod-like ceramic molding, continuously extruded from a mold and extending from the mold while not yet cut, to a cutter for cutting the rod-like ceramic molding into ceramic blocks, each having a predetermined length. The conveying apparatus has pads, each having a placement surface for placing the rod-like ceramic molding while being in contact with the outer circumference of the rod-like ceramic molding, and the placement surface of the pad has an axial length shorter than a half of an axial length of the ceramic block to be cut by the cutter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
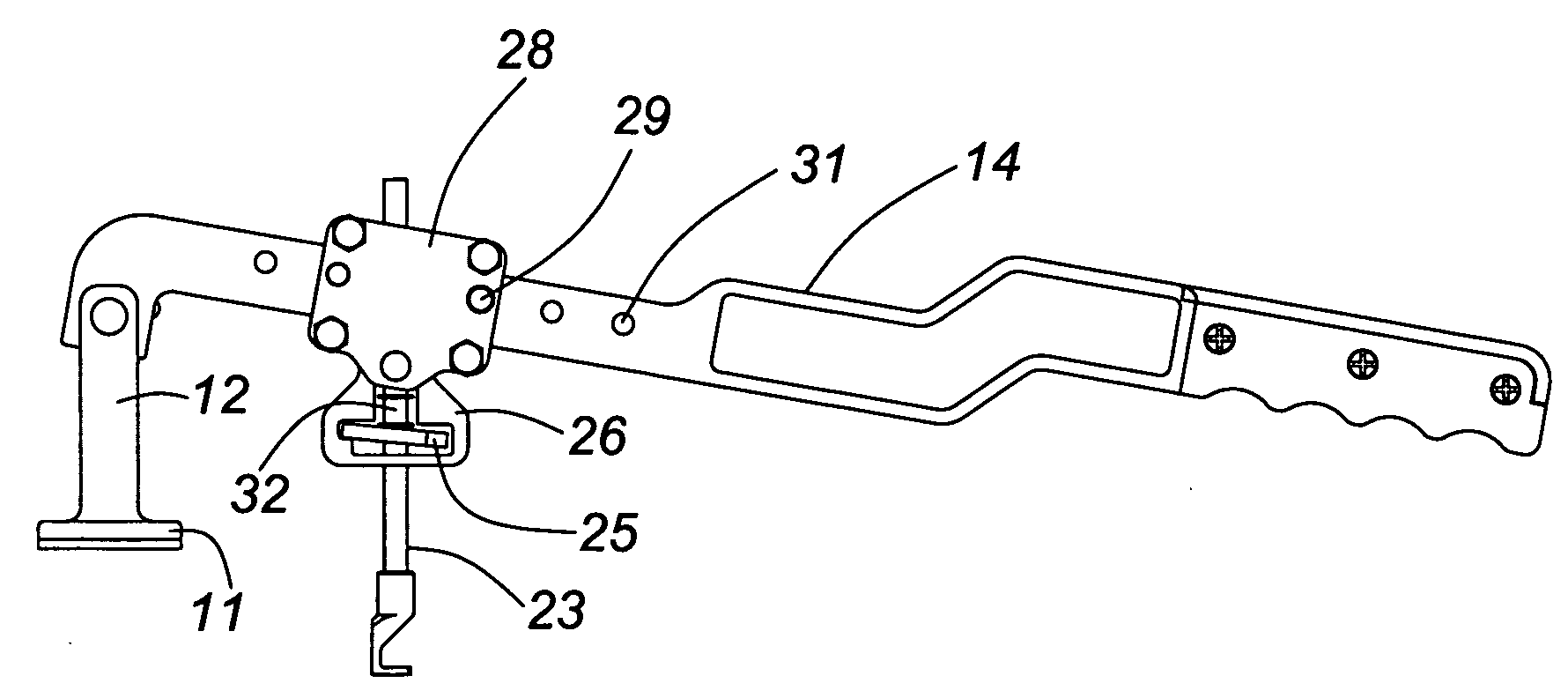
Tool for removing dents from sheet metal
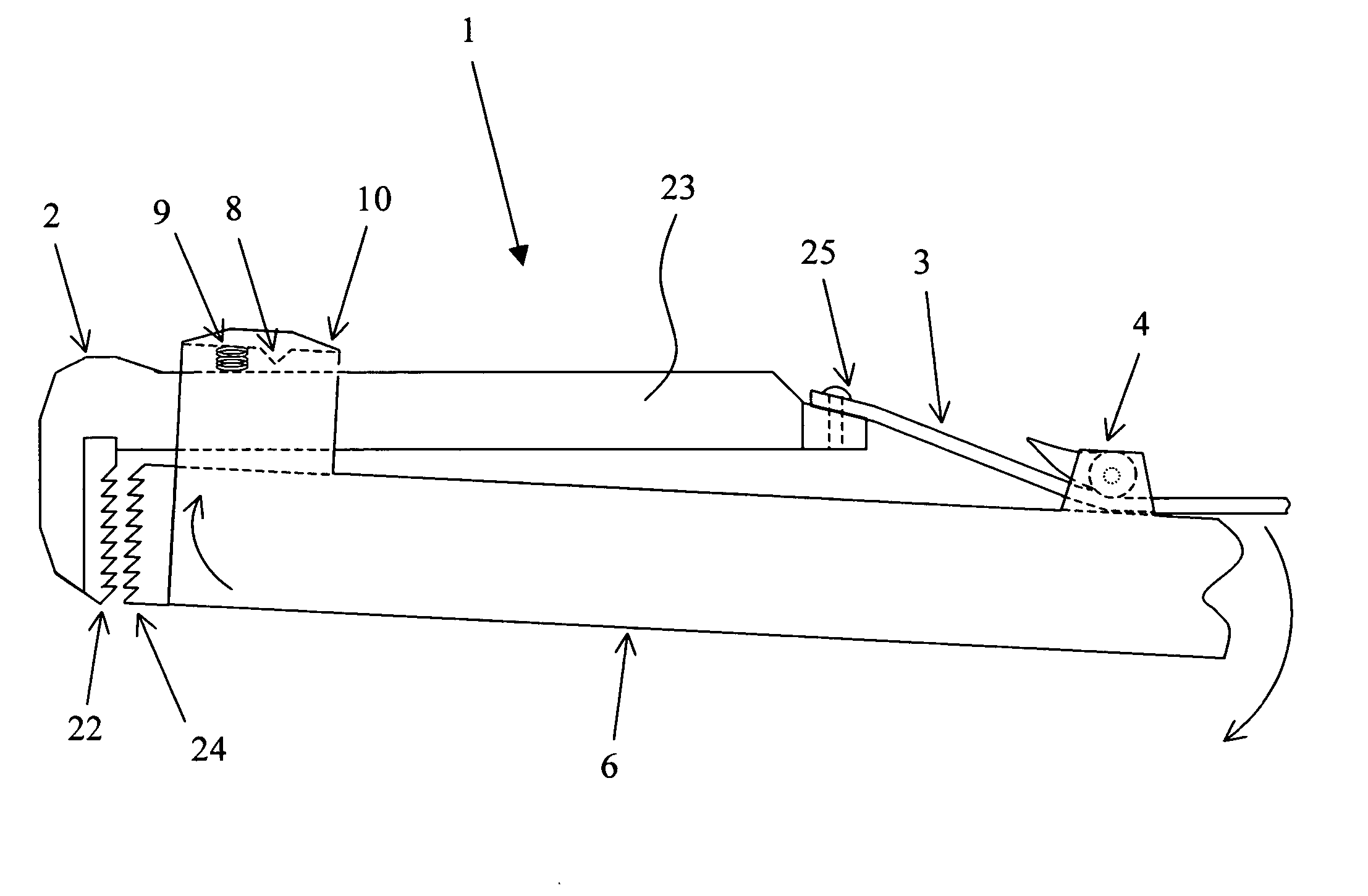
A tool for pulling a dent out of a sheet metal surface has a support post with a foot shaped to rest against a portion of the sheet metal surface adjacent the dent. The tool includes a hinged lever arm which is pivotally connected to this support post at a lever arm pivot point which is elevated above the foot and adjacent sheet metal region. The tool also includes a pulling rod for coupling, through a fastener or connecting means, to the dented portion of the surface which is to be drawn-out, the pulling rod being connected to the hinged lever arm through a pivoting joint. The pivoting joint of the pulling rod and the lever arm pivoting point are positionable through actuation of the lever arm able to lie in a common plane which is substantially parallel to the sheet metal surface into which the dent is to be drawn into alignment. The pulling rod is adjustable in its engagement with the lever arm to permit the lever arm to swing through a limited angular range. Coupling between the pulling rod and lever arm is either discrete or continuous. Fasting means connecting the tool to the sheet metal include a self-tapping, self-drilling screw or a bolt provided with a magnetic washer or magnetic head.
Owner:KNOWLES STEVEN MICHAEL
Tube compression fitting and flared fitting used with connection body and method of making same
InactiveUS20100059996A1Prevent crashSufficient lubricitySleeve/socket jointsFluid pressure sealed jointsCombined useHigh pressure
A high pressure tube compression fitting / flared fitting for use in combination with a thick-walled tube and a connection body wherein a sleeve is in engagement with a thick-walled tube. The sleeve is generally cylindrically shaped with the exterior thereof coated and then etched. The sleeve includes a sharp annular biting portion engaging the thick walled tube. The sleeve further includes an inner annular symmetric concavity which engages the thick-walled tube upon deformation thereof. The thick-walled tube includes a flared end portion. A gland about the thick-walled tube engages the sleeve forcing it into engagement with the frusto-conical portion of the connection body coupling the tube, tube fitting and connection body together. The flared end of the thick-walled tube interengages and seals the frusto-conical portion of the connection body. A process for making the device includes the step of placing the thick-walled tube into engagement with the frusto-conical portion of a die to flare the end portion of the thick-walled tube.
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN CORP
Flow control valve
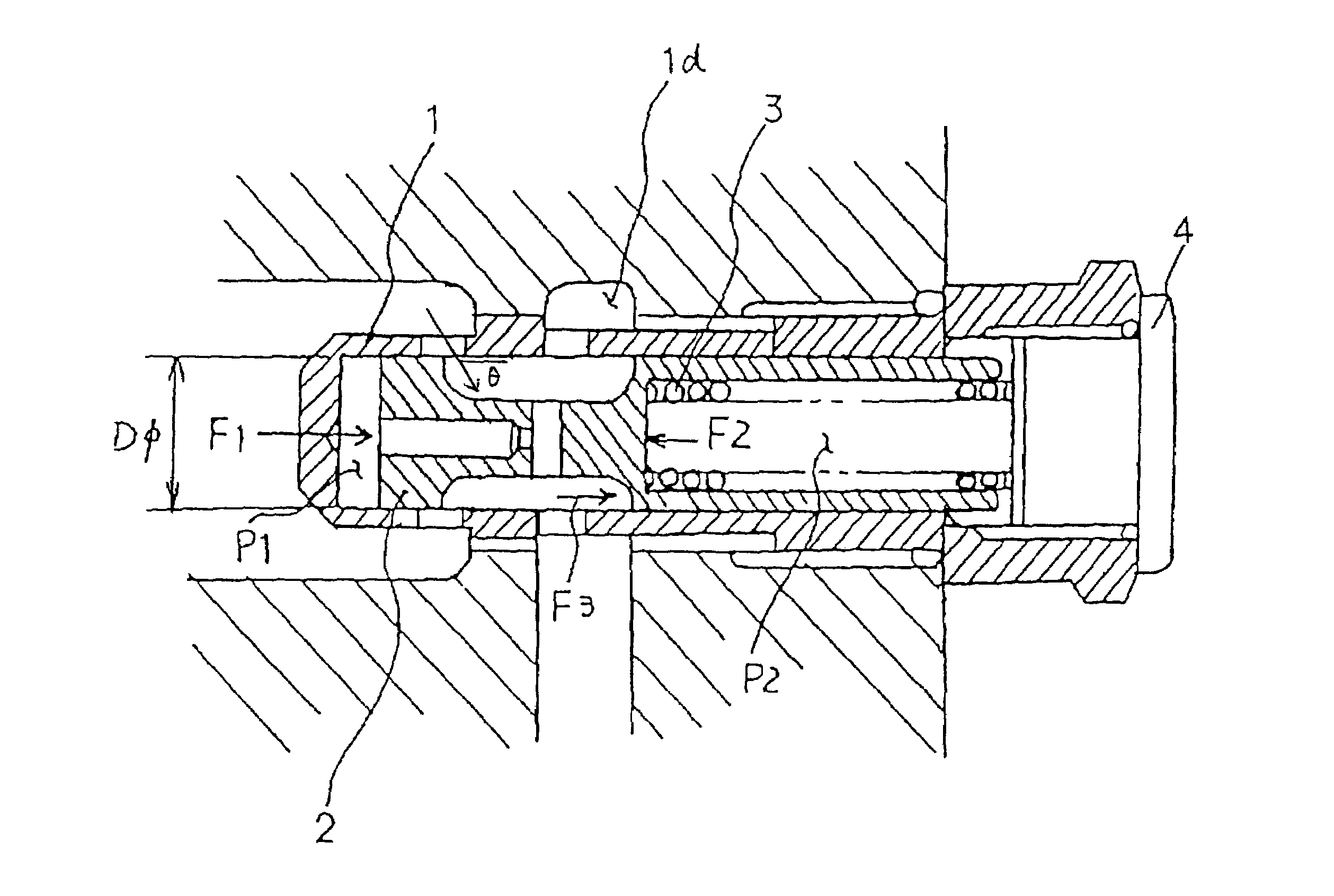
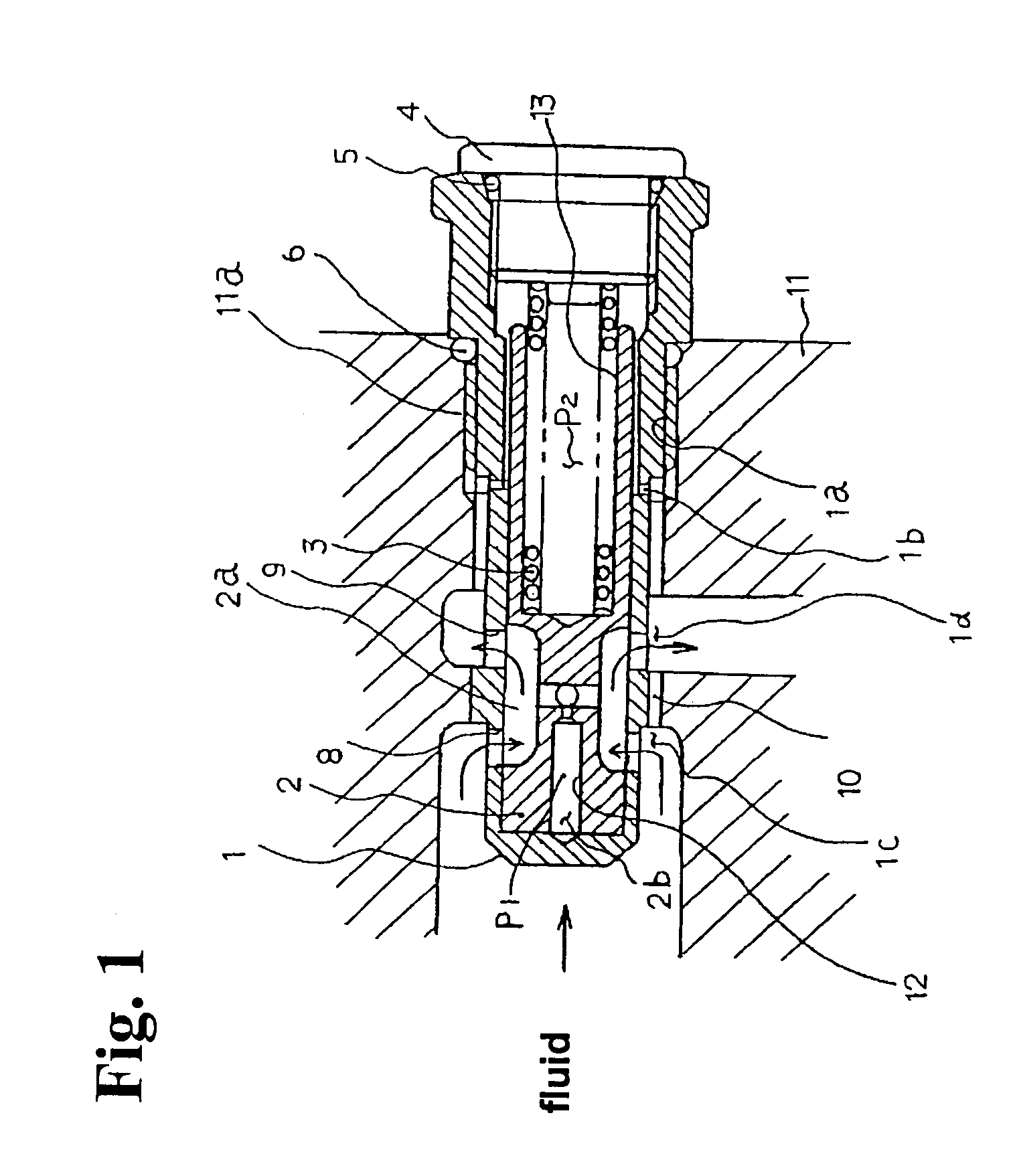
ActiveUS7013913B2Constant flowForce can be appliedOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesEngineeringControl valves
In a flow control valve, a spool is fitted into a cylindrical body including an input port and an output port. A spring is disposed between the spool and a flow rate setting plug at an end of the cylindrical body. A flow bypass communicating with the input port and the output port is provided on an outer peripheral portion of the cylindrical body. When a quantity of a fluid flowing through the flow control valve is reduced, the fluid flowing through the flow bypass compensates the reduction thereof. Accordingly, it is possible to maintain a constant flow rate.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Lightwieght wrench
A lightweight, adjustable wrench comprising of a moveable jaw with a reach that is shortened or lengthened with a strap or a cable. The loose end of the strap or cable is secured to the wrench's shank by a cam lock, or similar locking device. Since the strap or cable is the means for the wrench's jaws adjustment, a quicker and easier fit to the pipe or object to be gripped can be obtained. The wrench is more convenient to adjust, since the means for adjustment are located near the handle of the wrench as opposed to the shank end of present designs. The strap or cable adjustment also allows the wrench's shank and handle to be designed hollow and a larger diameter to reduce weight. The wrench can be made in any proportion for any sized application.
Owner:WILLIAMS STEVEN ANDREW
Sound insulation cover
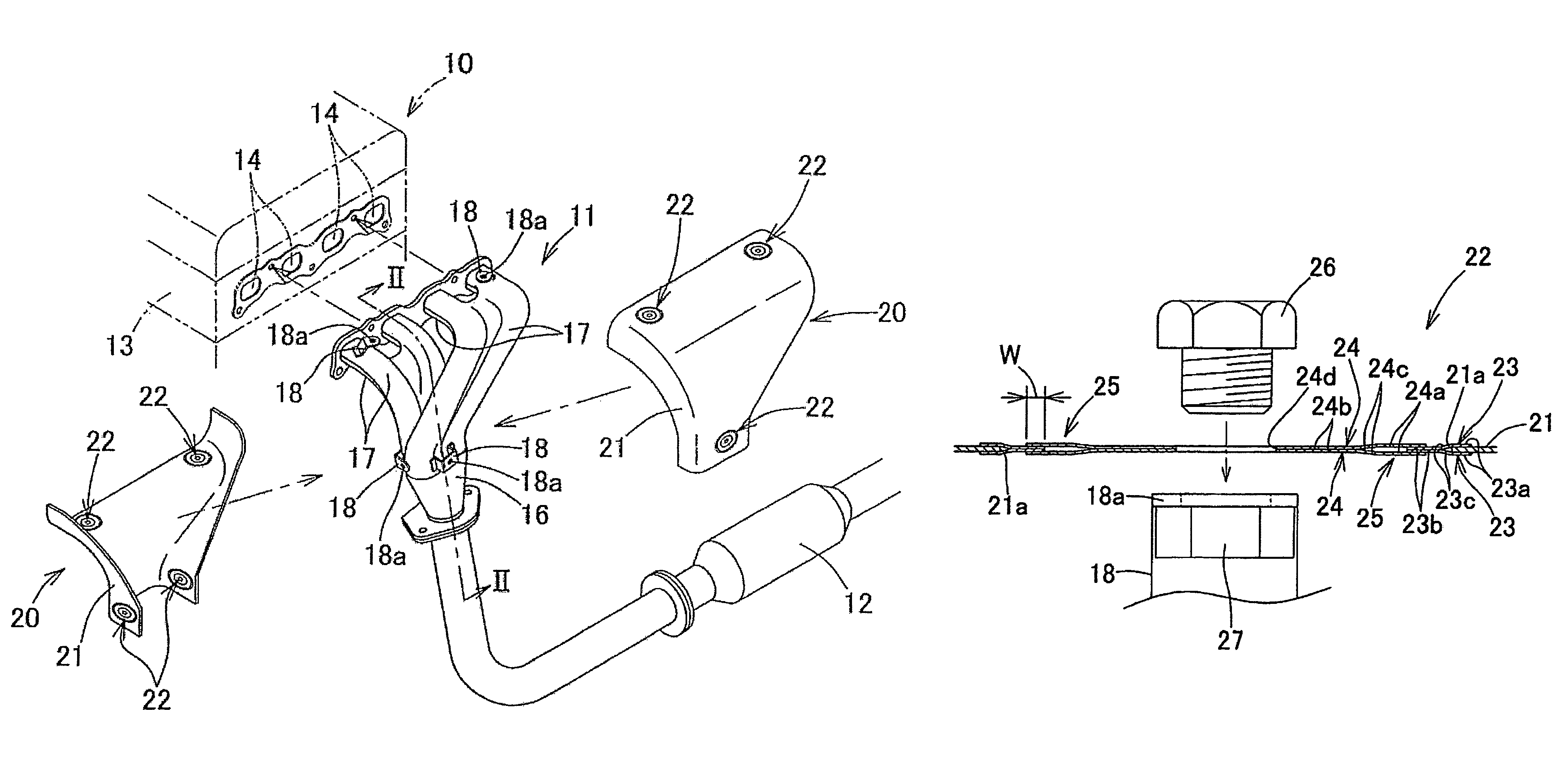
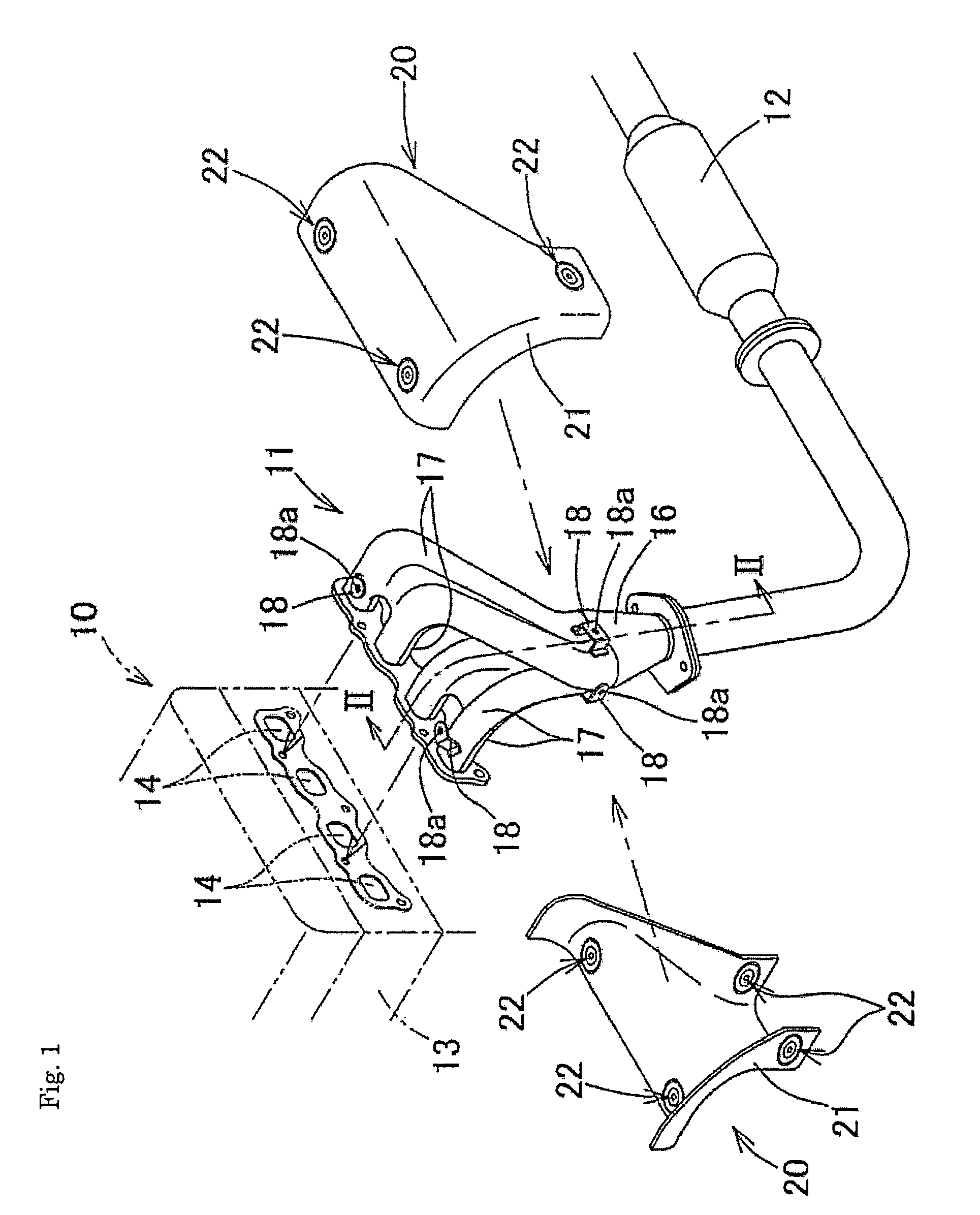
ActiveUS8291698B2Effective absorptionAvoid crackingExhaust apparatusVehicle fittings for lifting and manoeuvringEngineeringExhaust manifold
Owner:KOKUSAN BUHIN INDS CO LTD
Control Mechanisms and Methods of Tool-Holding Arm for Exoskeletons
ActiveUS20190291285A1Effective gravity compensationEasy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorMachine supportsEngineeringExoskeleton
A tool-holding arm includes a plurality of links and a tool coupling that removably secures a tool to the tool-holding arm. A first fluid spring provides a gravity-counteracting force to the tool-holding arm. A locking mechanism selectively locks the first fluid spring. An adjustment mechanism selectively adjusts an amount of the gravity-counteracting force provided by the first fluid spring.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com