Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Less skill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
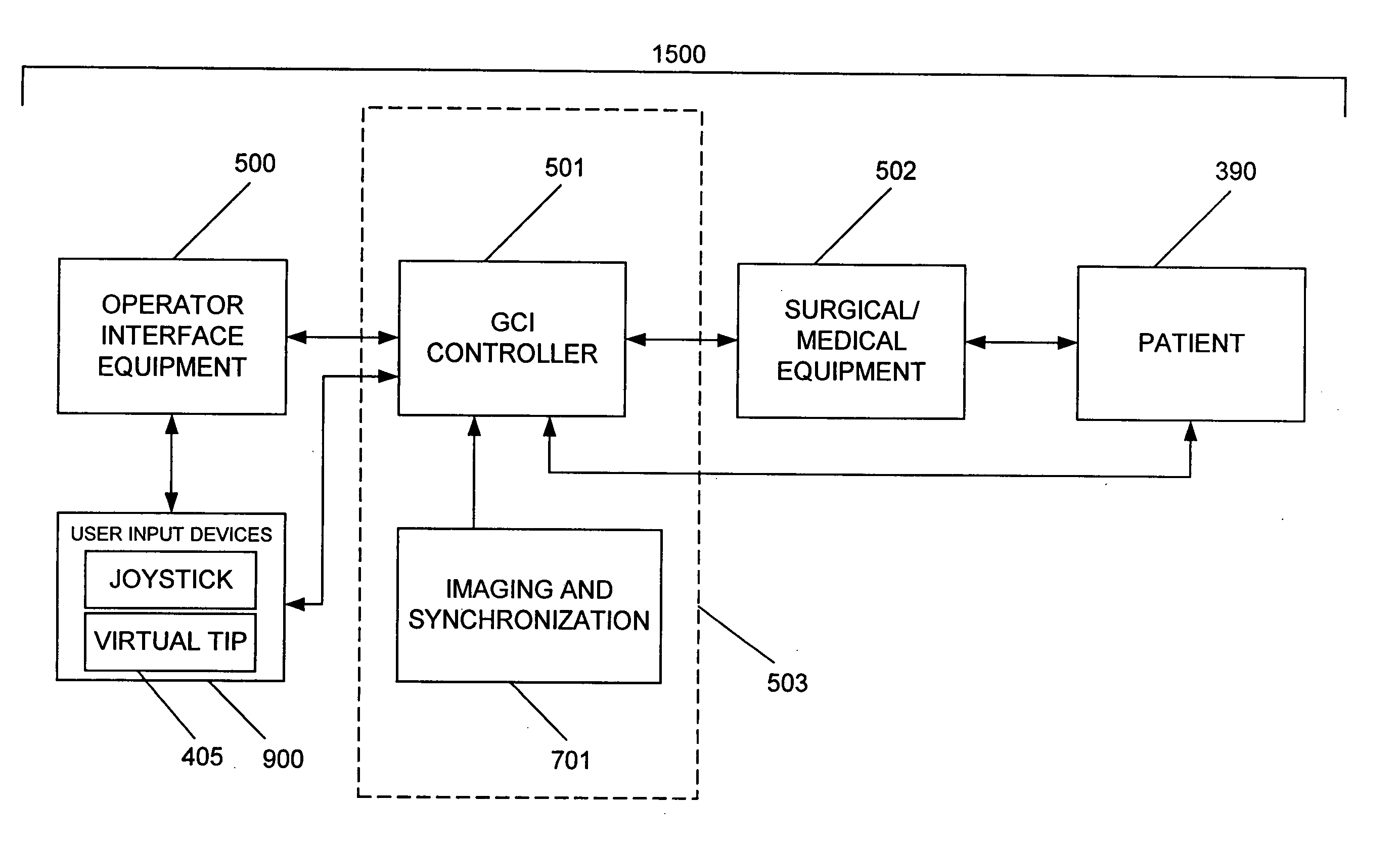
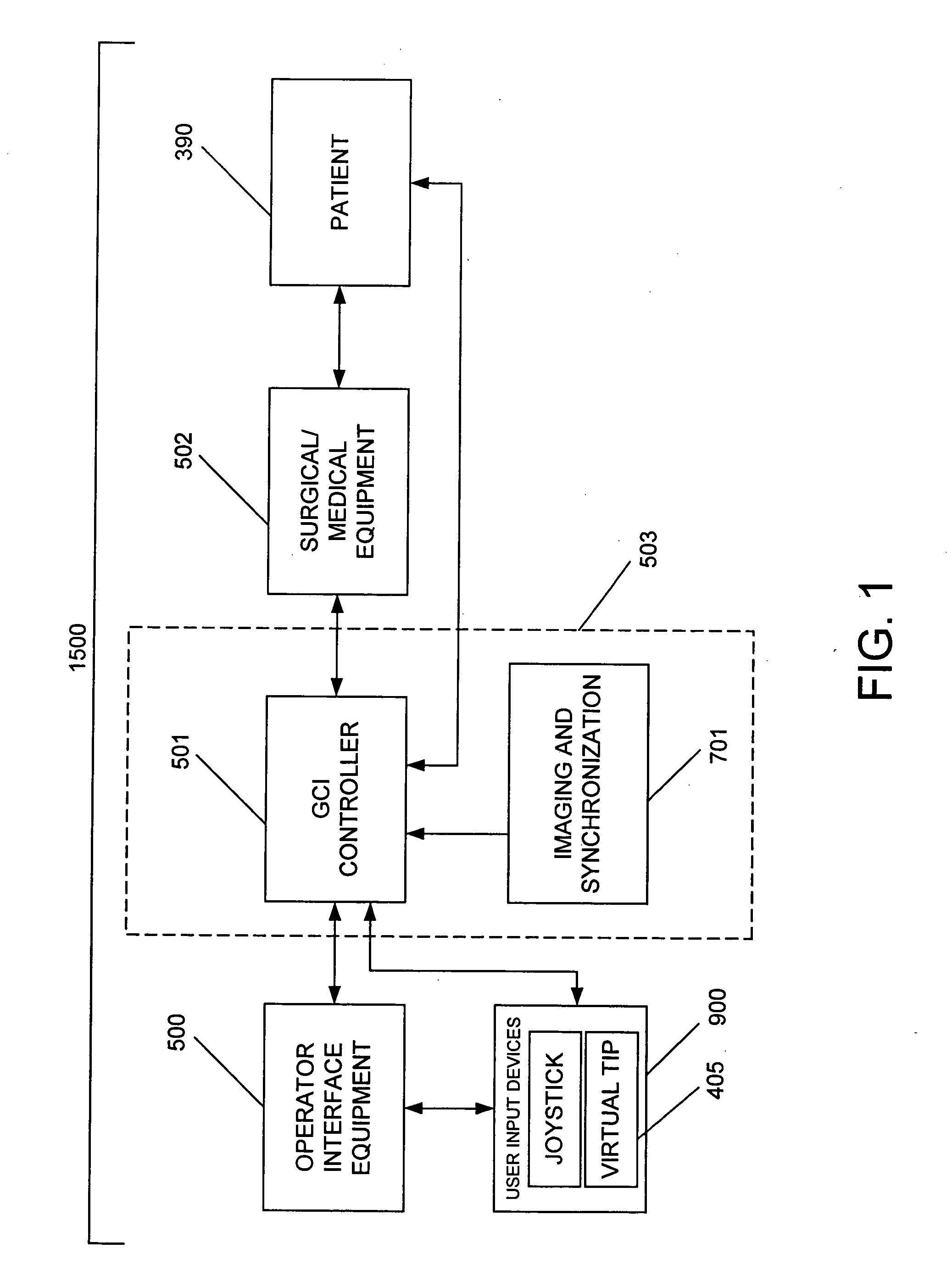
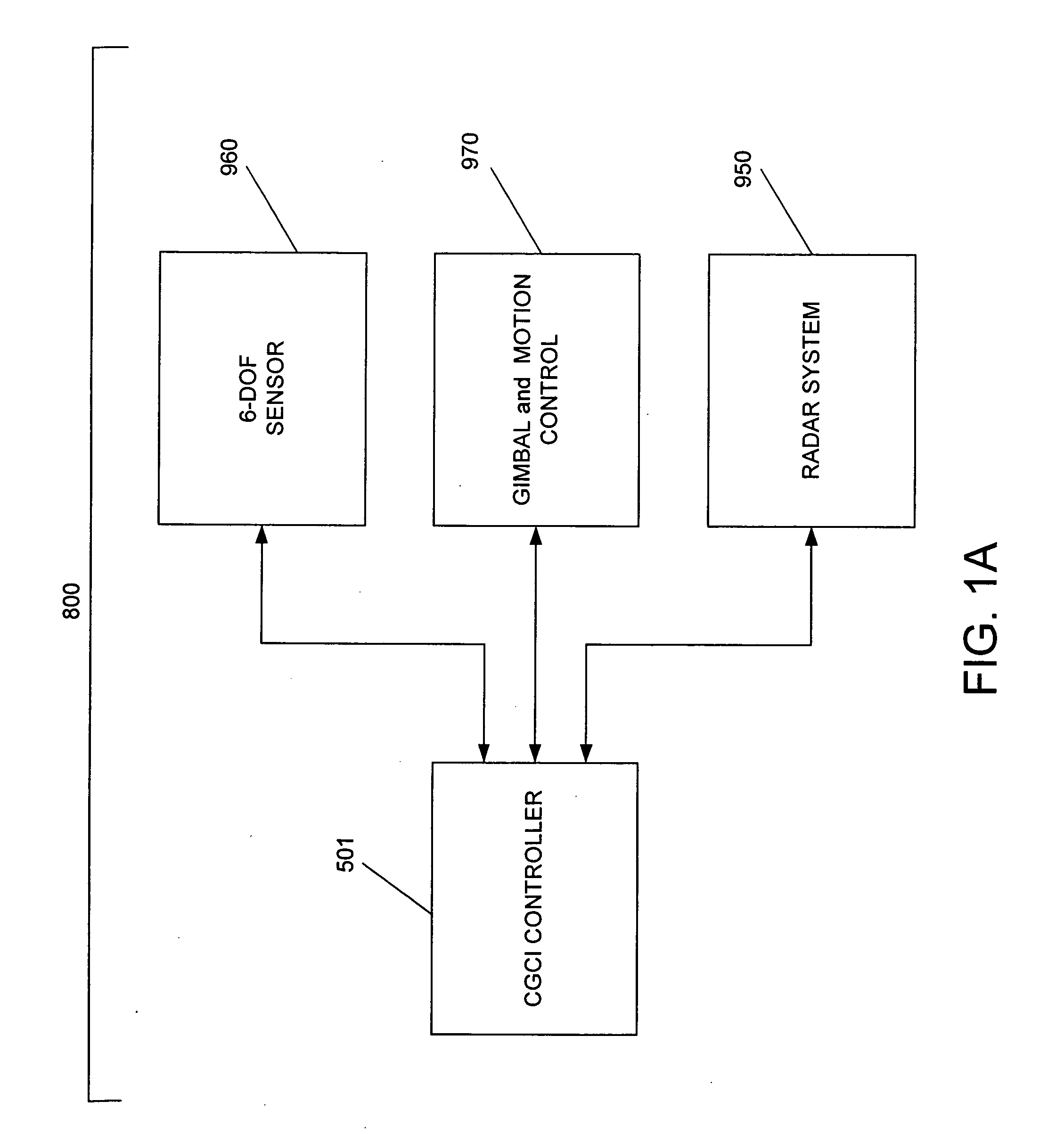
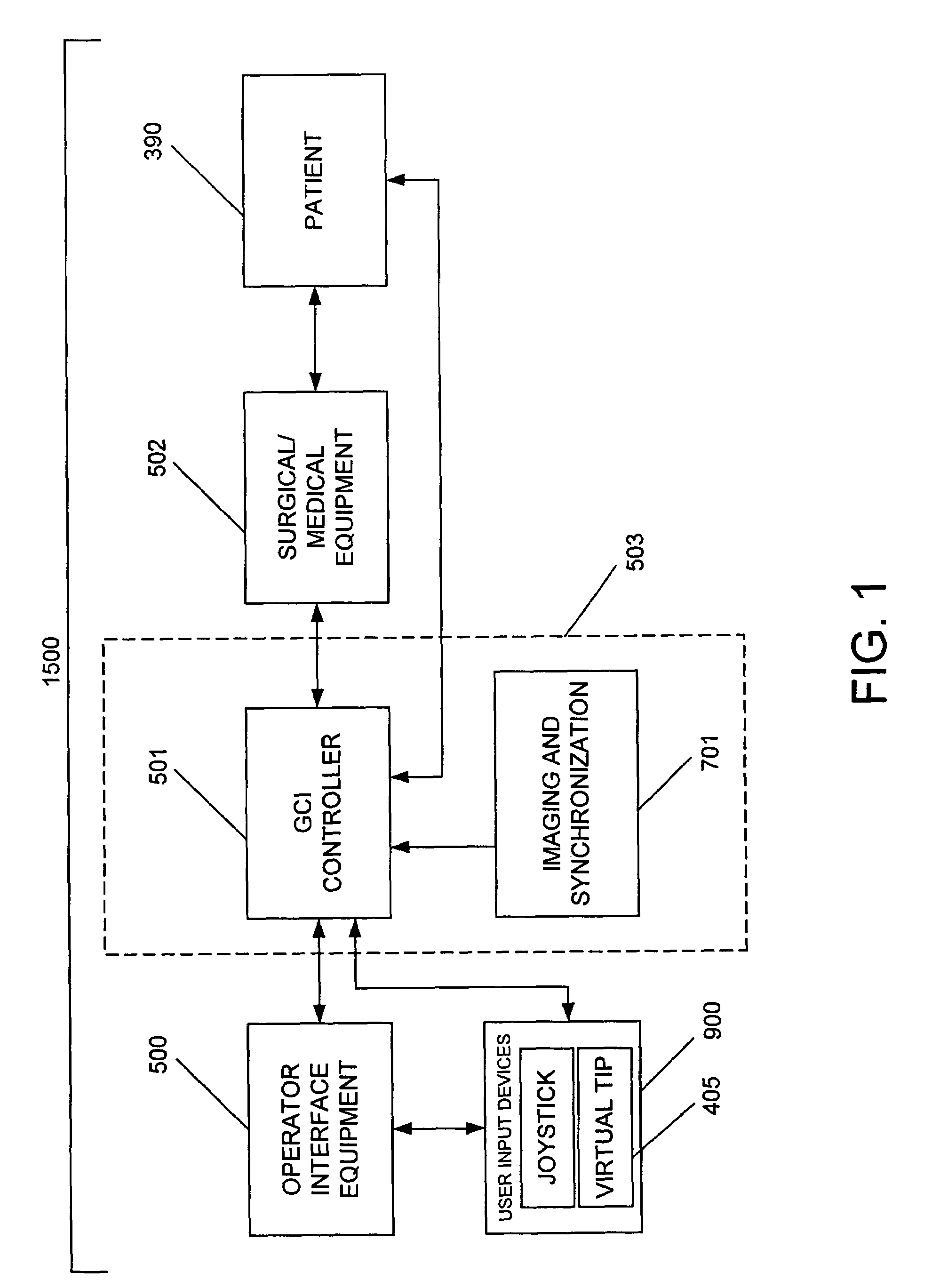
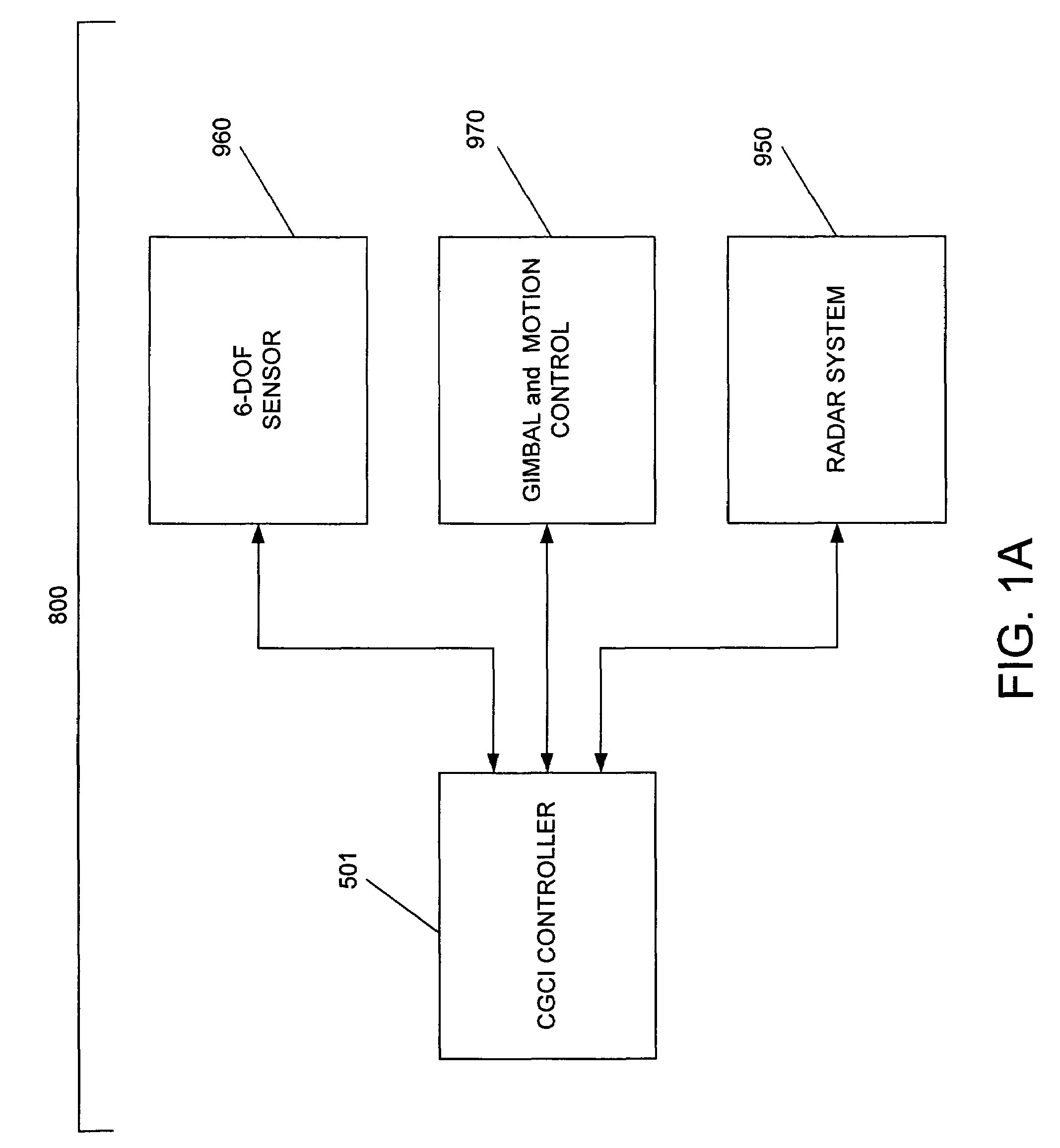
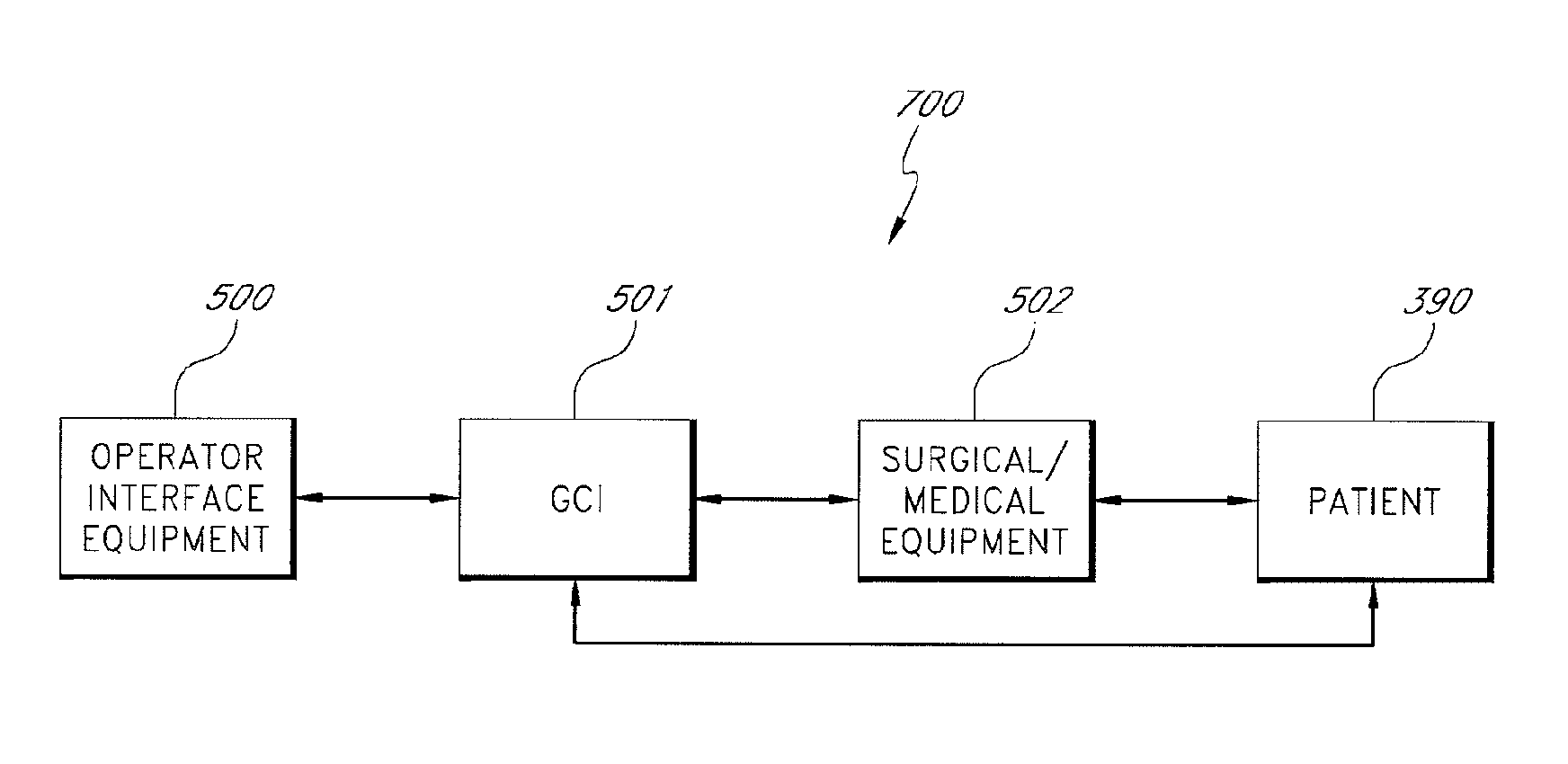
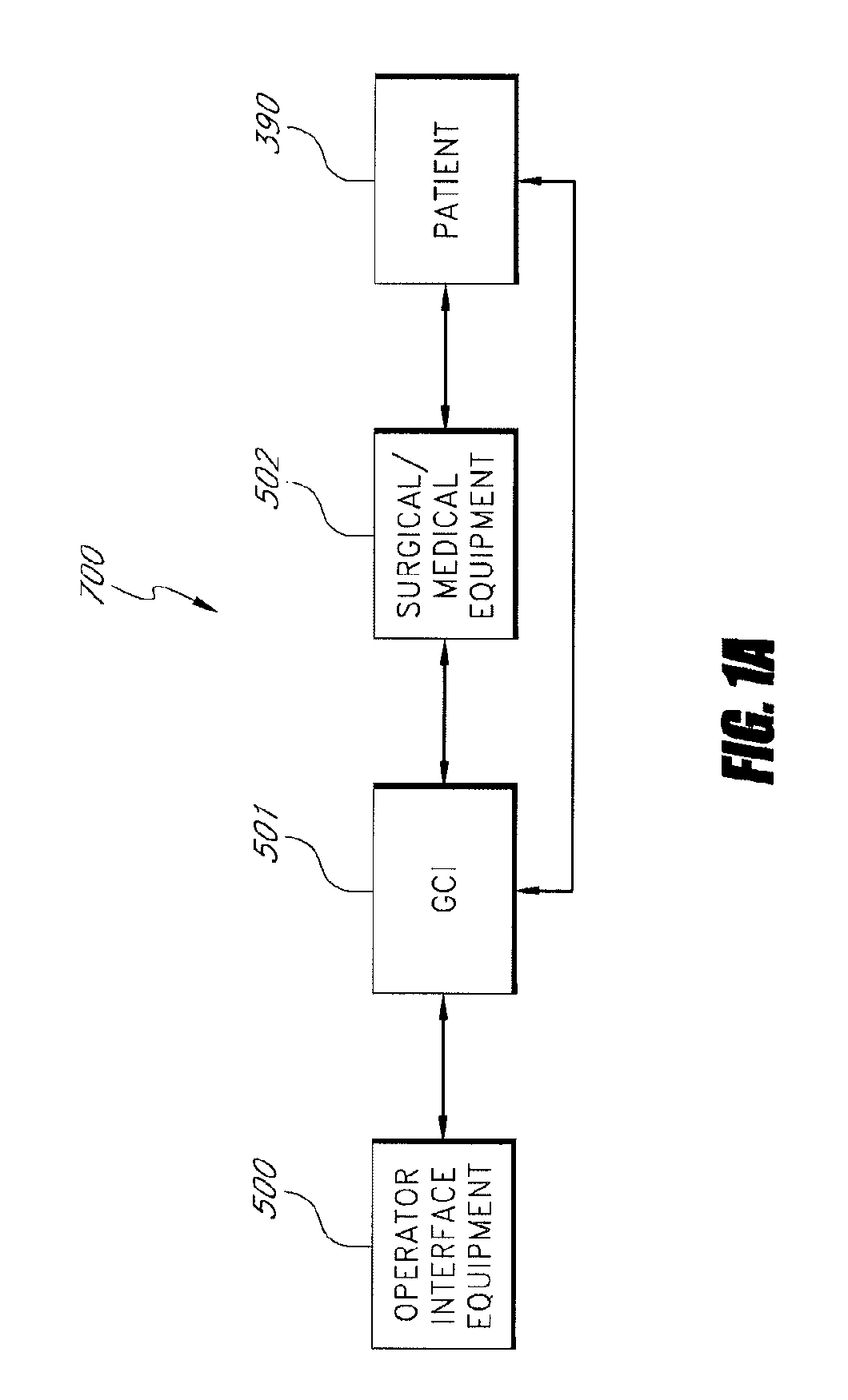
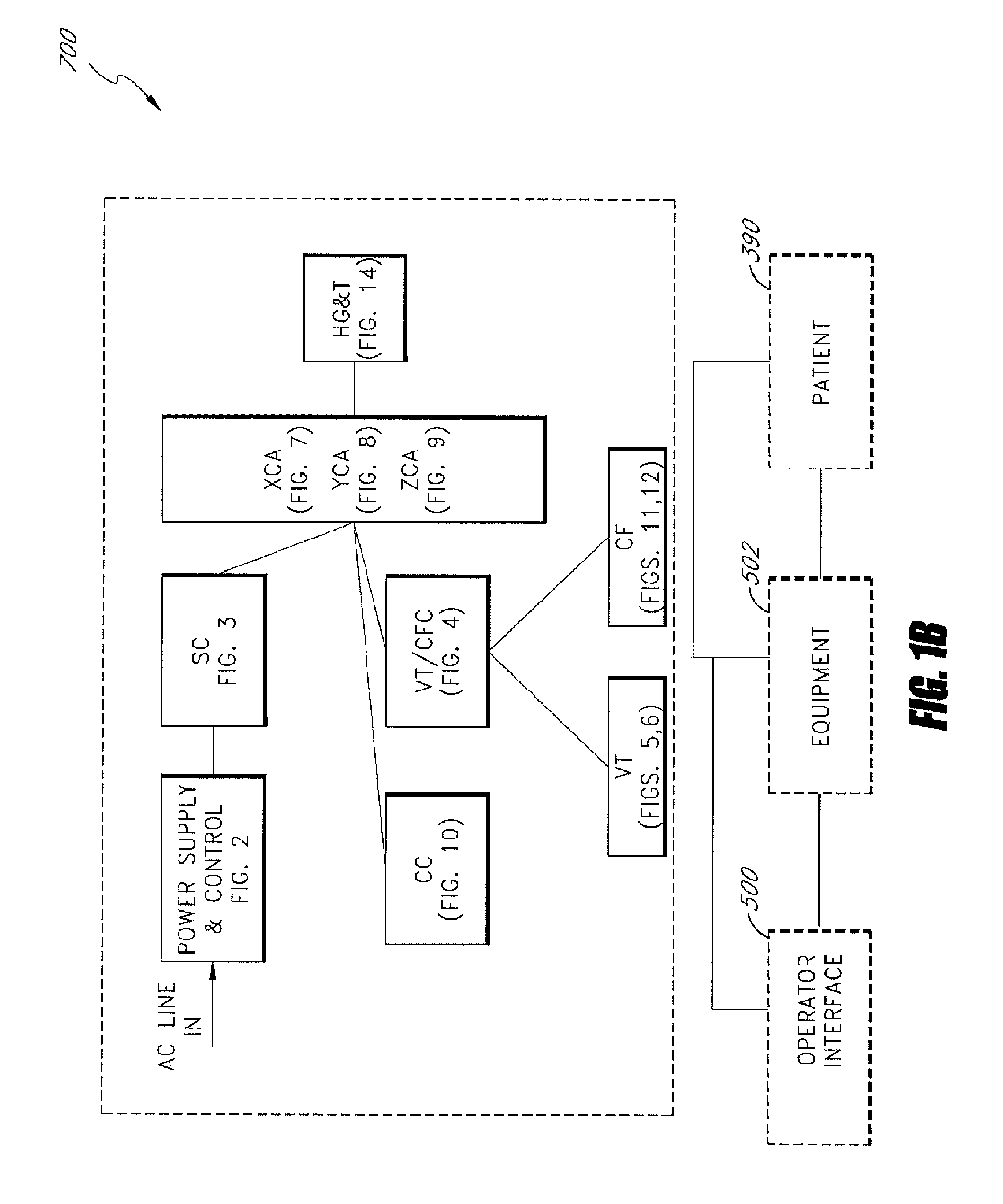
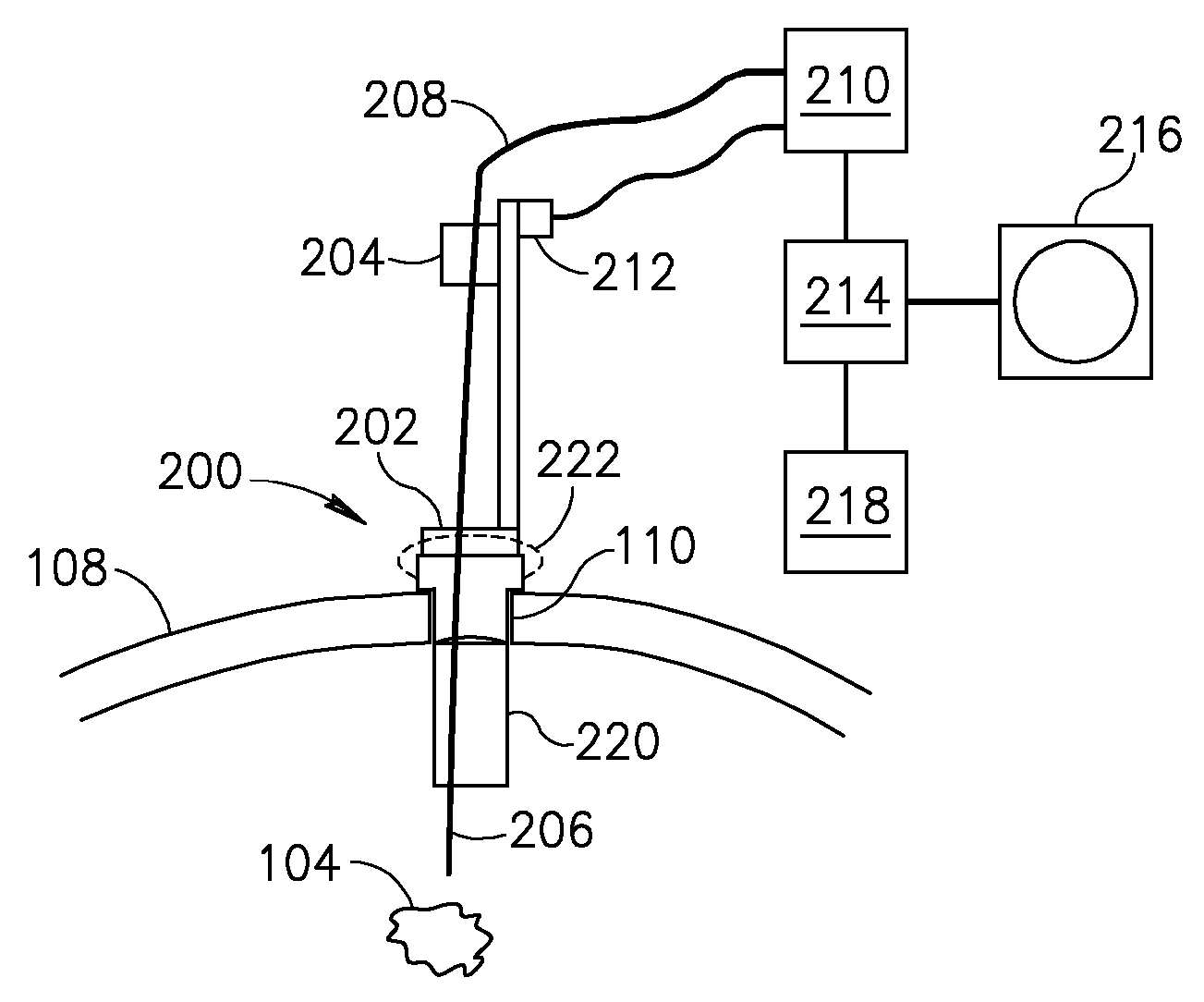
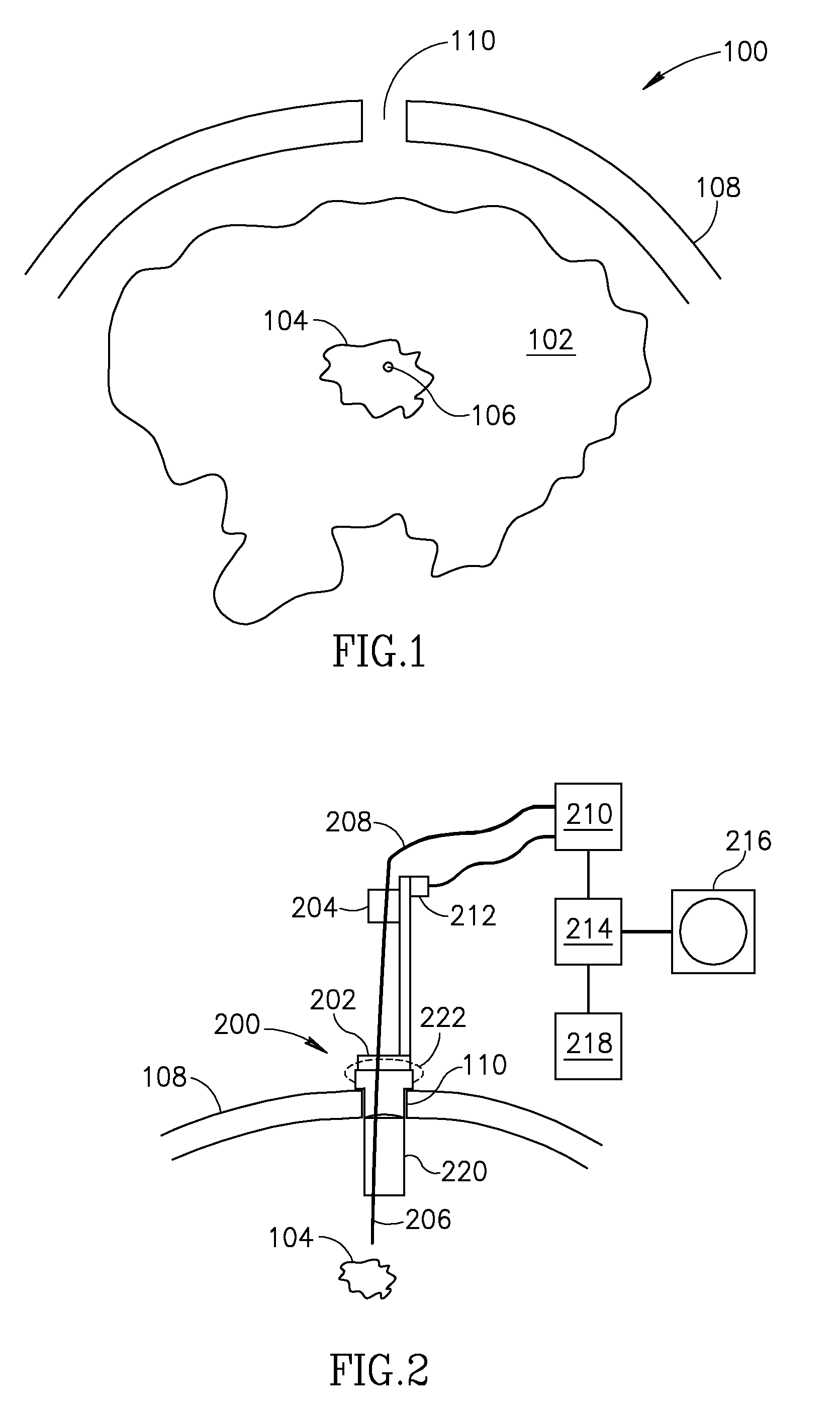
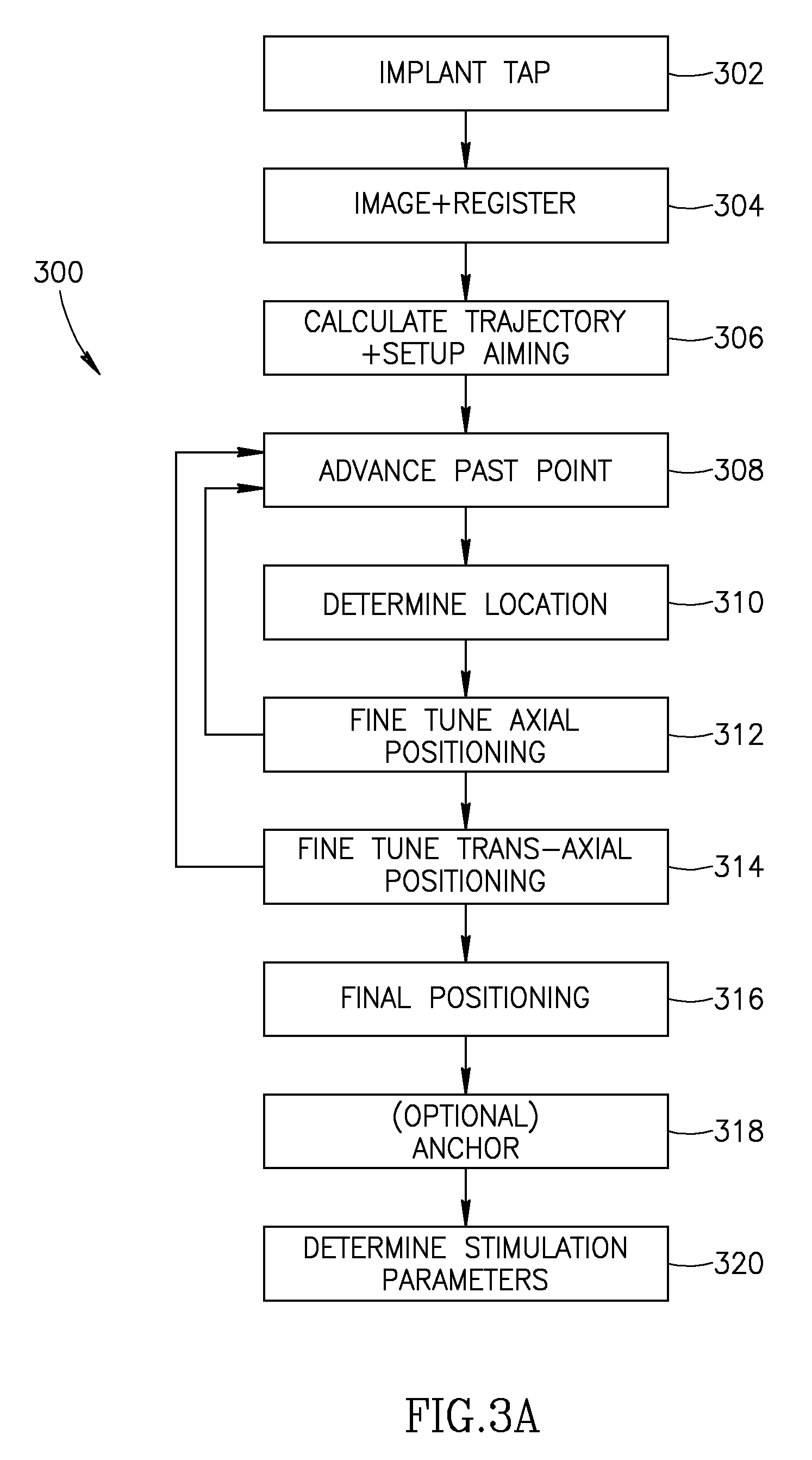
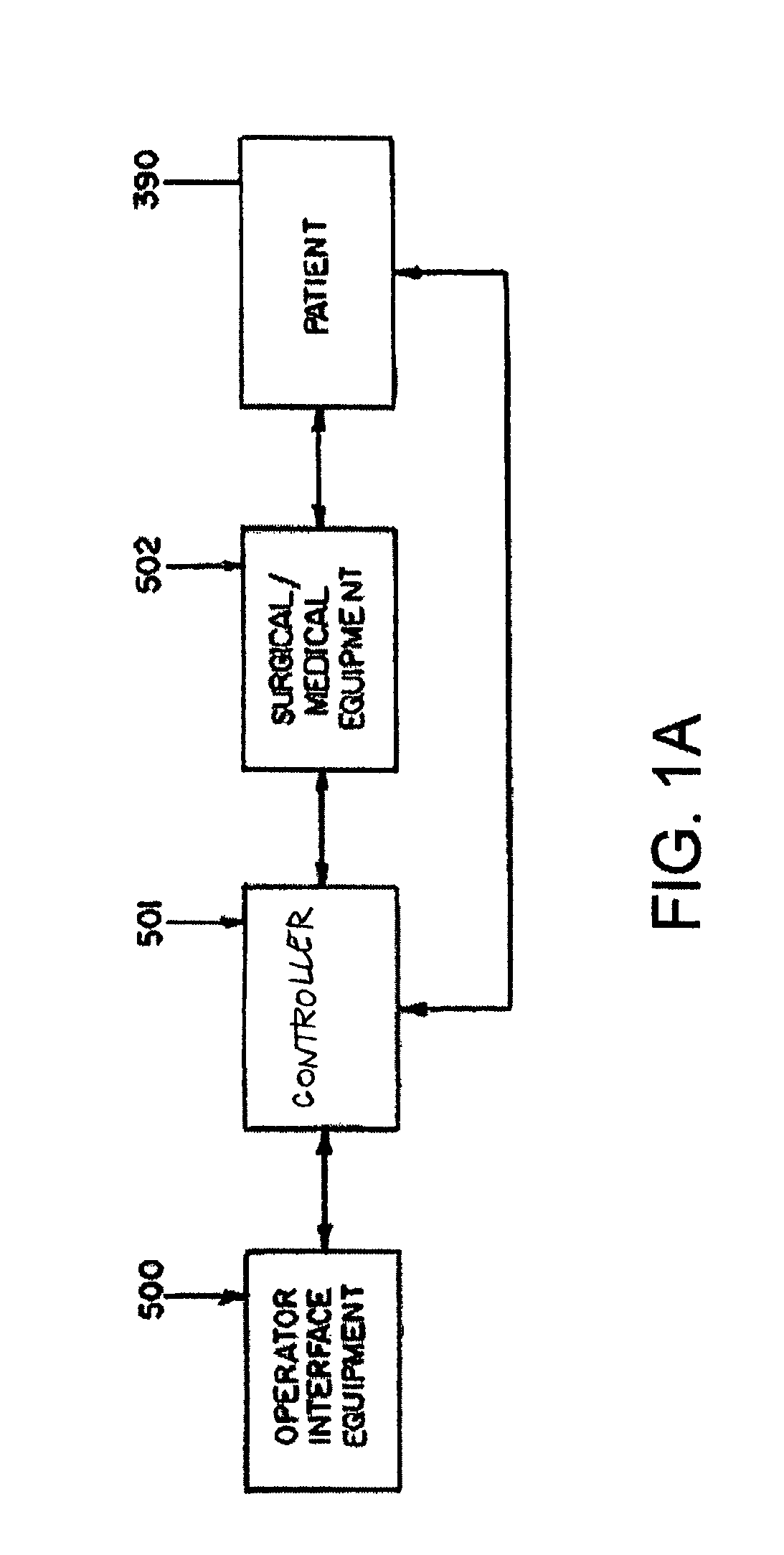
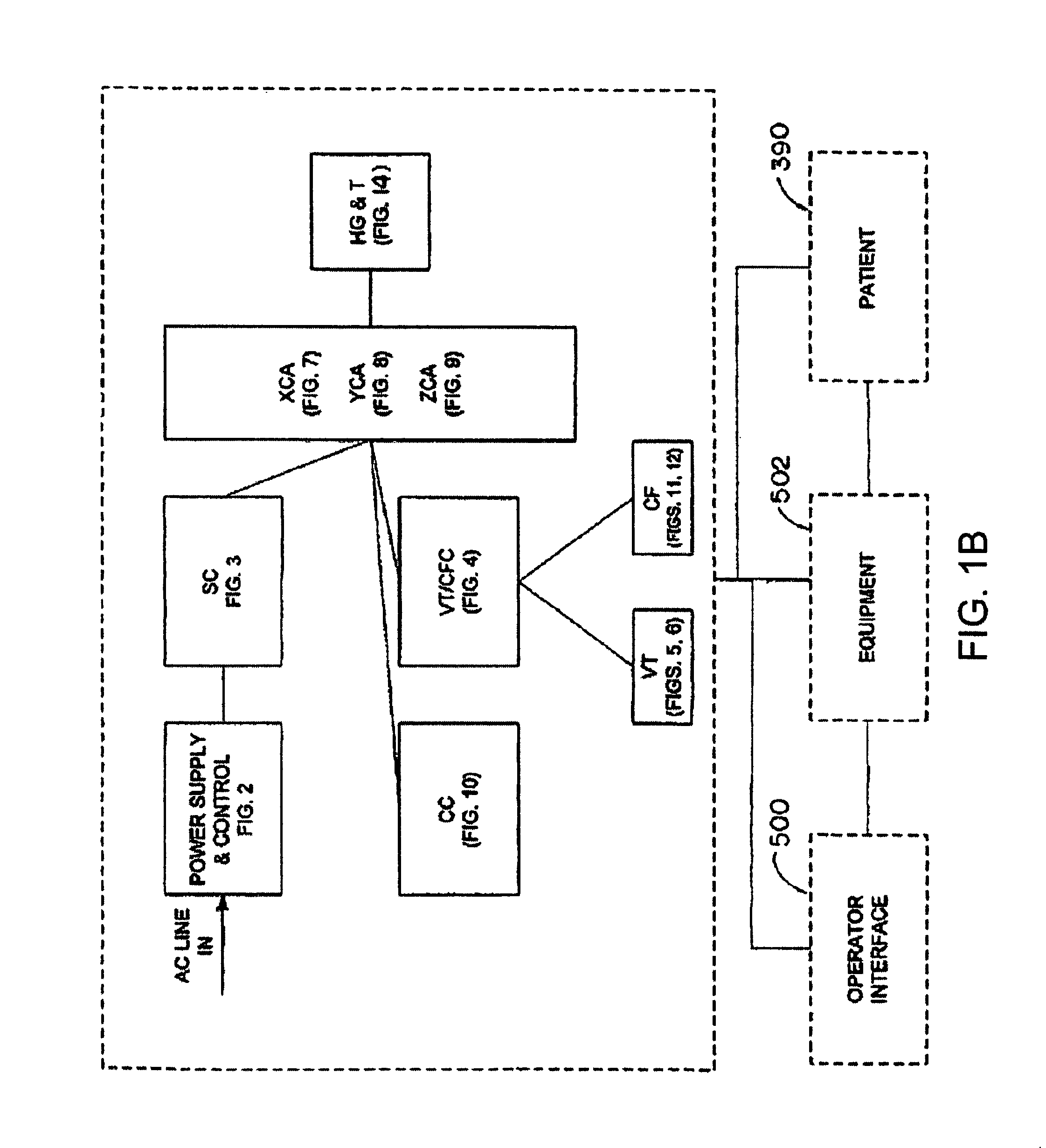
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS20050096589A1Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useEndoscopesMedical devicesRadar systemsGuidance control
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
System and method for radar-assisted catheter guidance and control
InactiveUS7280863B2Less trainingMinimizing and eliminating useMedical devicesEndoscopesRadar systemsTip position
A Catheter Guidance Control and Imaging (CGCI) system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons. The magnetic tip performs two functions. First, it allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined by using a radar system such as, for example, a radar range finder or radar imaging system. Incorporating the radar system allows the CGCI apparatus to detect accurately the position, orientation and rotation of the surgical tool embedded in a patient during surgery. In one embodiment, the image generated by the radar is displayed with the operating room imagery equipment such as, for example, X-ray, Fluoroscopy, Ultrasound, MRI, CAT-Scan, PET-Scan, etc. In one embodiment, the image is synchronized with the aid of fiduciary markers located by a 6-Degrees of Freedom (6-DOF) sensor. The CGCI apparatus combined with the radar and the 6-DOF sensor allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A virtual representation of the magnetic tip serves as an operator control. This control possesses a one-to-one positional relationship with the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, this control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hands in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of this control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Detection of nucleic acids and nucleic acid units
InactiveUS6127120AReduce riskReducing operator timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiology
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 01830 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 21, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 21, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 05280 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 13, 1997The invention relates to the detection of target nucleic acids or nucleic acid units in a sample, by obtaining a SER(R)S spectrum for a SER(R)S-active complex containing, or derived directly from, the target. The complex includes at least a SER(R)S-active label, and optionally a target binding species containing a nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit. In this detection method, the concentration of the target present in the SER(R)S-active complex, or of the nucleic acid or unit contained in the target binding species in the SER(R)S-active complex, is no higher than 10-10 moles per liter. Additionally or alternatively, one or more of the following features may be used with the method: i) the introduction of a polyamine; ii) modification of the target, and / or of the nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit contained in the target binding species, in a manner that promotes or facilitates its chemi-sorption onto a SER(R)S-active surface; iii) inclusion of a chemi-sorptive functional group in the SER(R)S-active label. The invention also provides SER(R)S-active complexes for use in such a method, a kit for use in carrying out the method or preparing the complexes and a method for sequencing a nucleic acid which comprises the use of the detection method to detect at least one target nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides within the acid.
Owner:RENISHAW DIAGNOSTICS
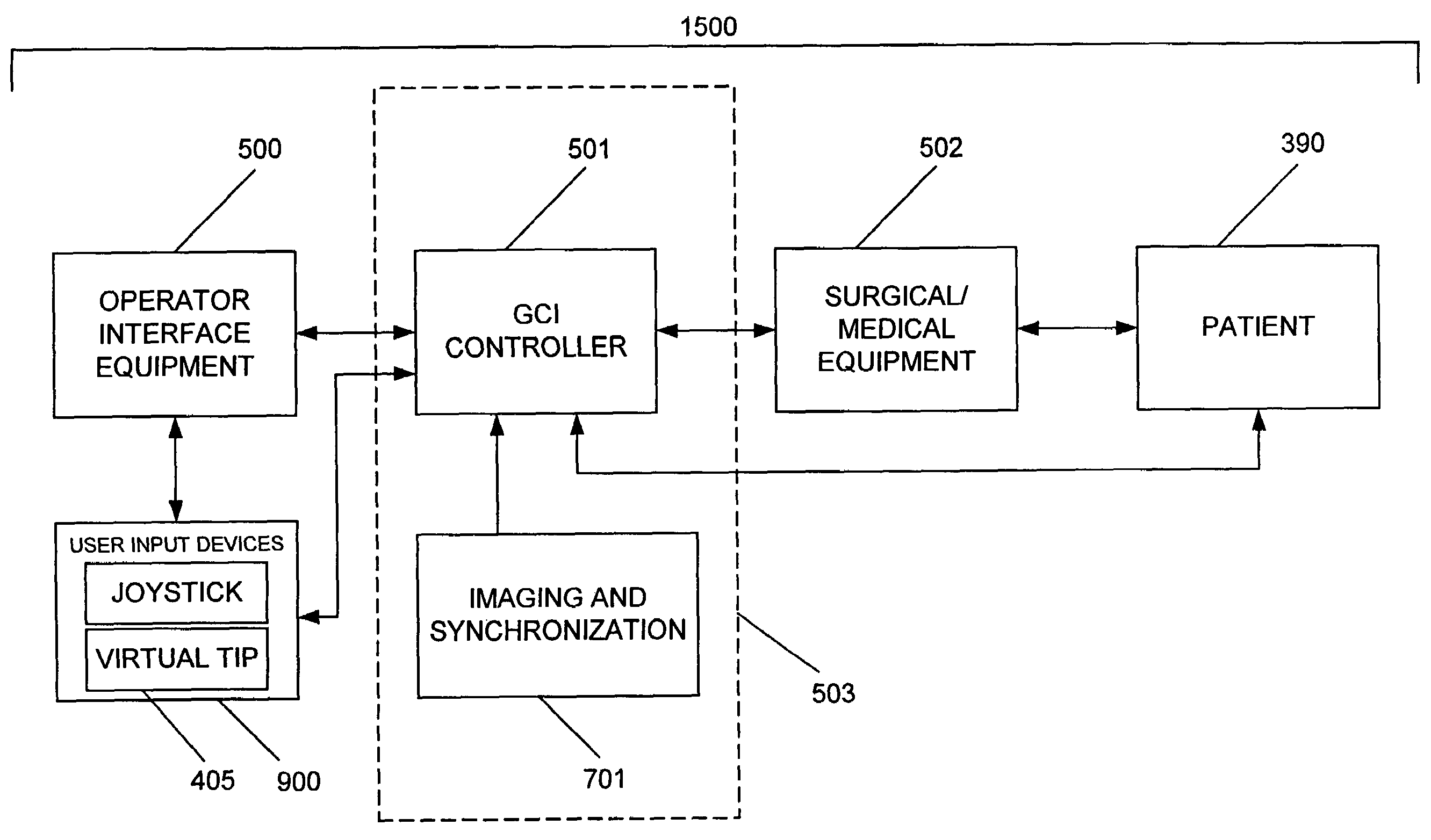
Apparatus and method for catheter guidance control and imaging
InactiveUS7769427B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionGuidance control
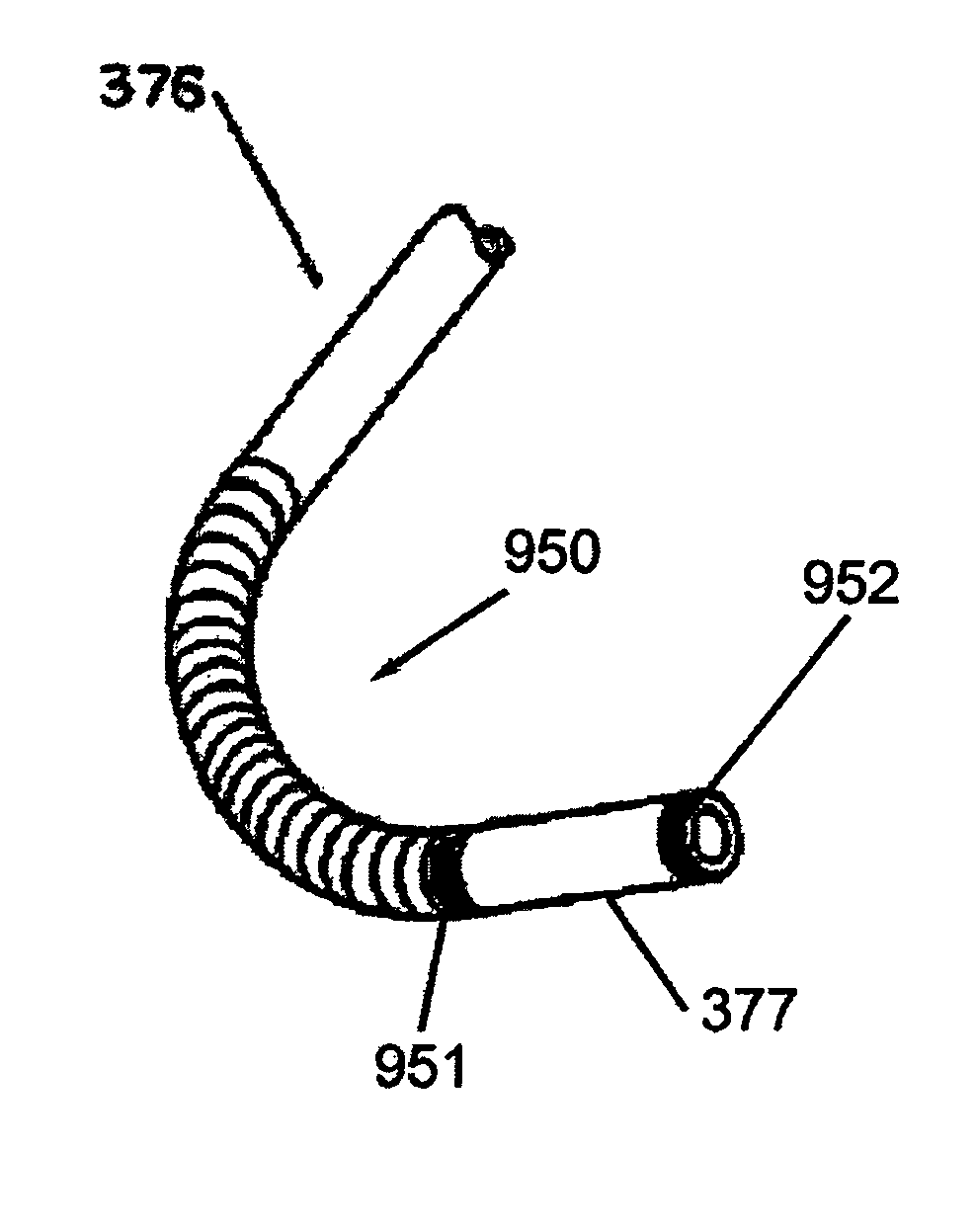
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and positioned. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Electrode System For Neural Applications
InactiveUS20070129770A1Prevents inference of drive mechanismFast and accurate determinationHead electrodesExternal electrodesSkullEnvironmental geology
Methods and apparatus for positioning electrodes in a skull. In some embodiments of the invention multiple measurements are made and a desired location is determined or estimated from the results of the measurements.
Owner:YOUNIS IMAD
Anti-coring device for a surgical morcellator
InactiveUS20080039883A1Easy to disassembleLess skillVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsEngineeringMorcellator
An anti-coring device for a surgical morcellator, which morcellator has a rotatable cutting blade having a sharpened edge and an outer sleeve that is axially moveable on the cutting blade, includes a shield mounted on the distal end of the outer sleeve and axially moveable therewith to selectively cover and at least partially uncover the sharpened edge of the rotatable cutting blade. The shield includes a main body and a protrusion extending axially from the main body and partially about the circumference of the cutting blade. The shield is axially positionable on the cutting blade so that is selectively covers the entire circumference of the sharpened edge of the cutting blade with its main body or only covers a portion of the circumference of the sharpened edge of the cutting blade with its protrusion, leaving the remaining portion of the sharpened edge exposed.
Owner:ETHICON INC
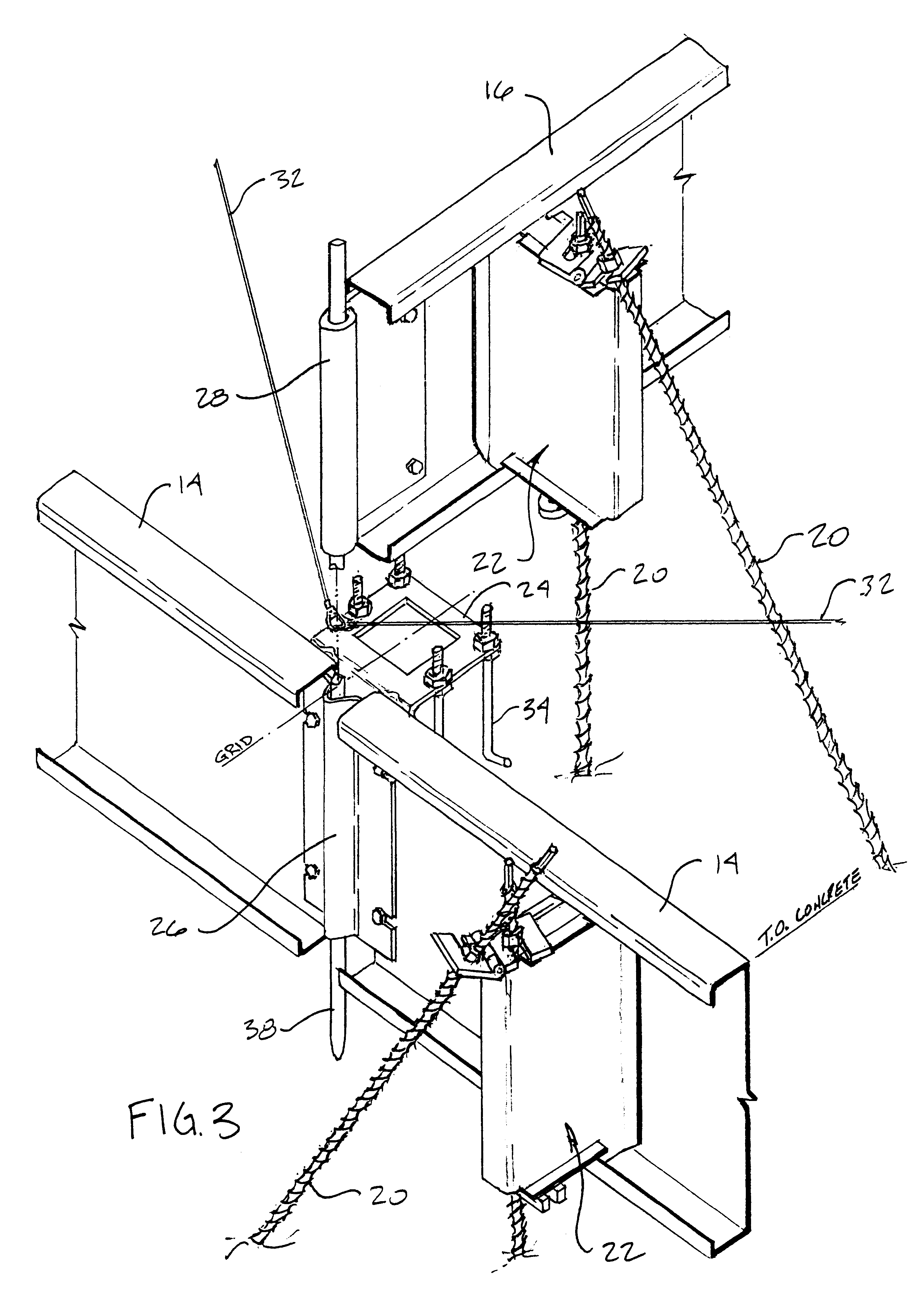
Slab foundation construction fixture, particularly as adapts standard girts for pre-use as foundation forms
InactiveUS6550213B1Easy to adjustLess laborFloorsBuilding repairsSteel moment frameCold-formed steel
A system for forming concrete slabs has been developed for commercial buildings having a steel moment-frame structure. This system utilizes the cold-formed-steel framing members, such as the wall girts shipped with a particular building package, to be first utilized as slab foundation forming elements before being framed into the building. The system defines foundation geometry upon simple assembly of the forming elements, and efficiently provides for placement of anchoring hardware which corresponds exactly to the connections of the structural frames.
Owner:BUTLER MICHAEL G
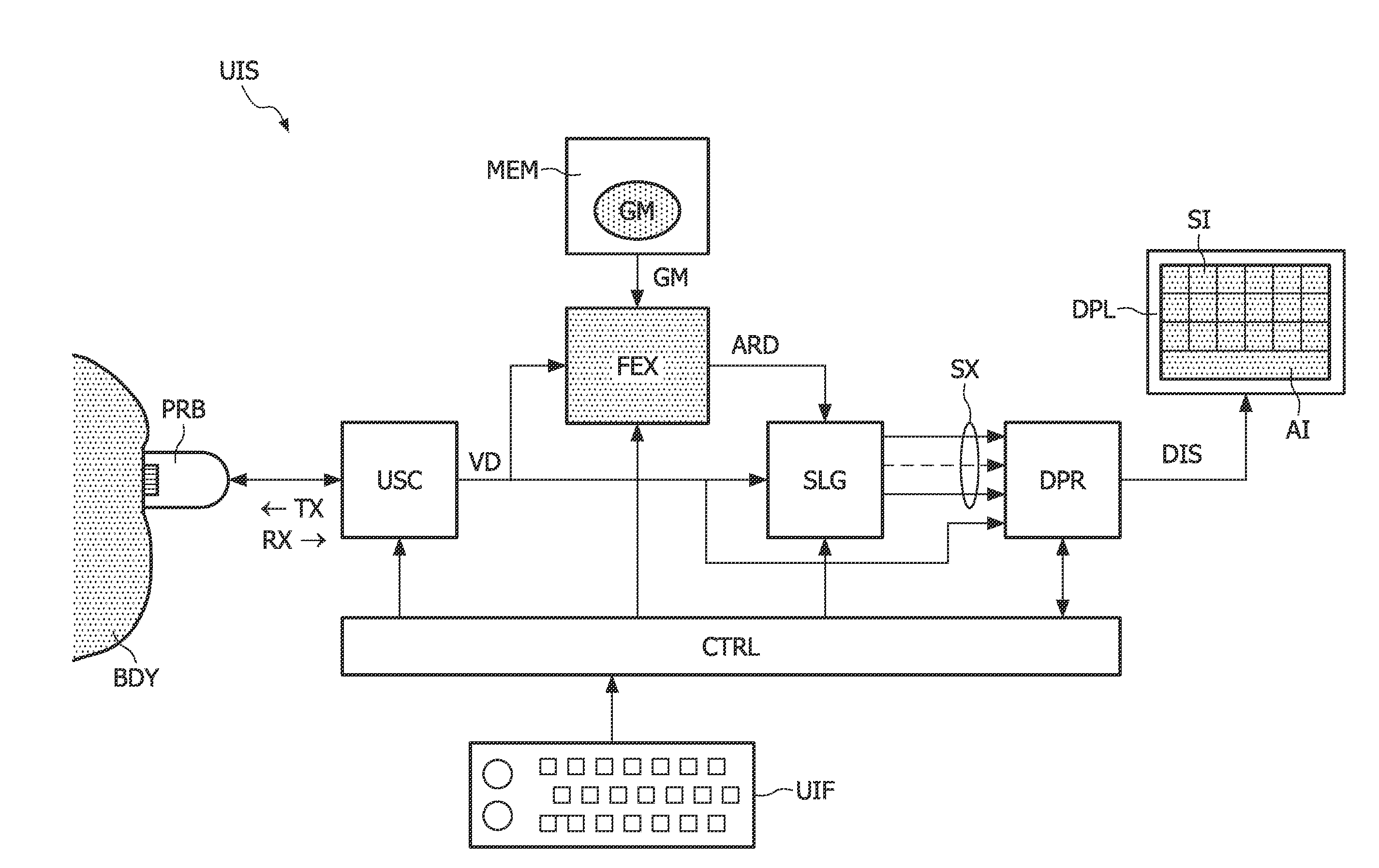
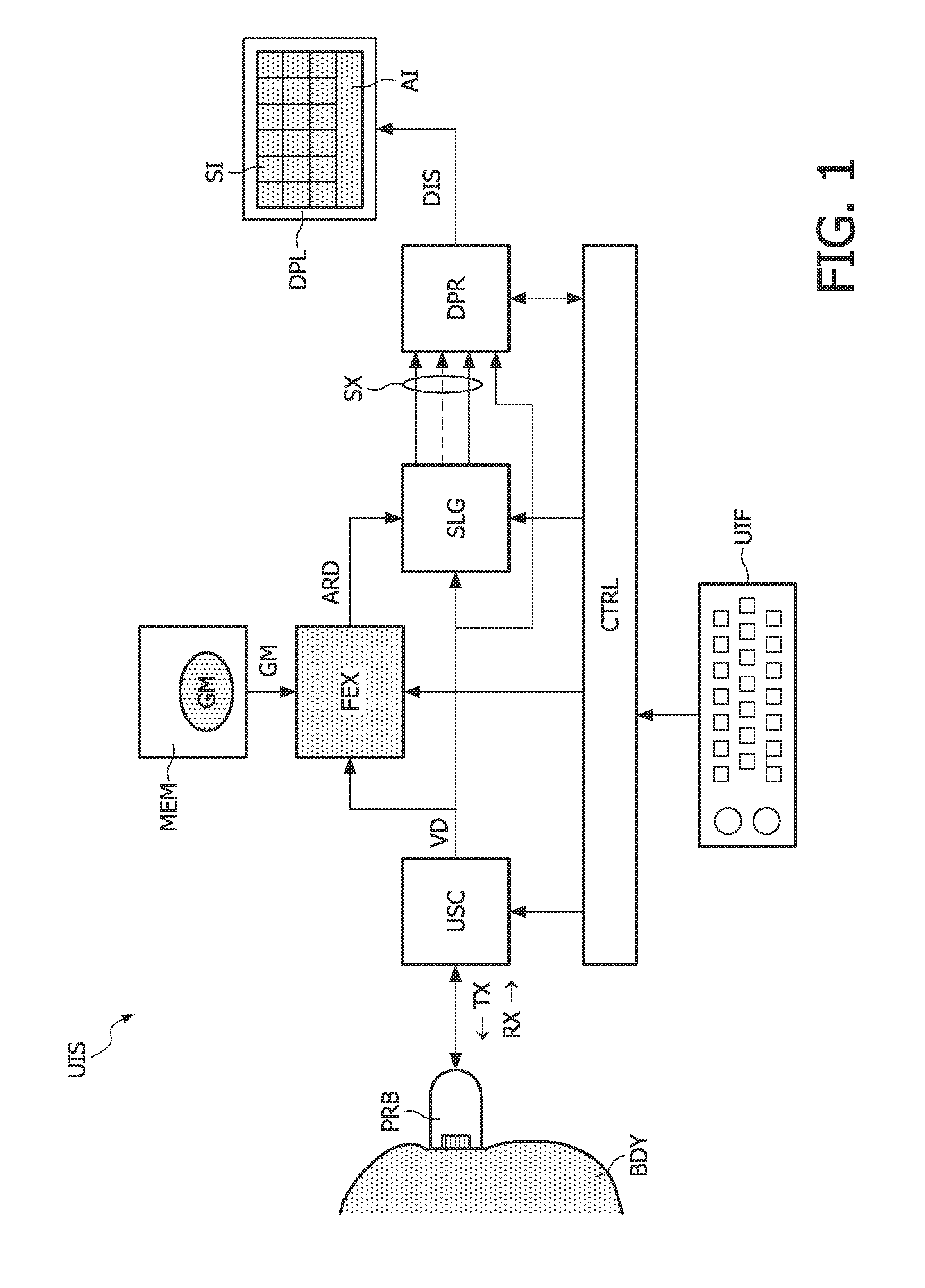
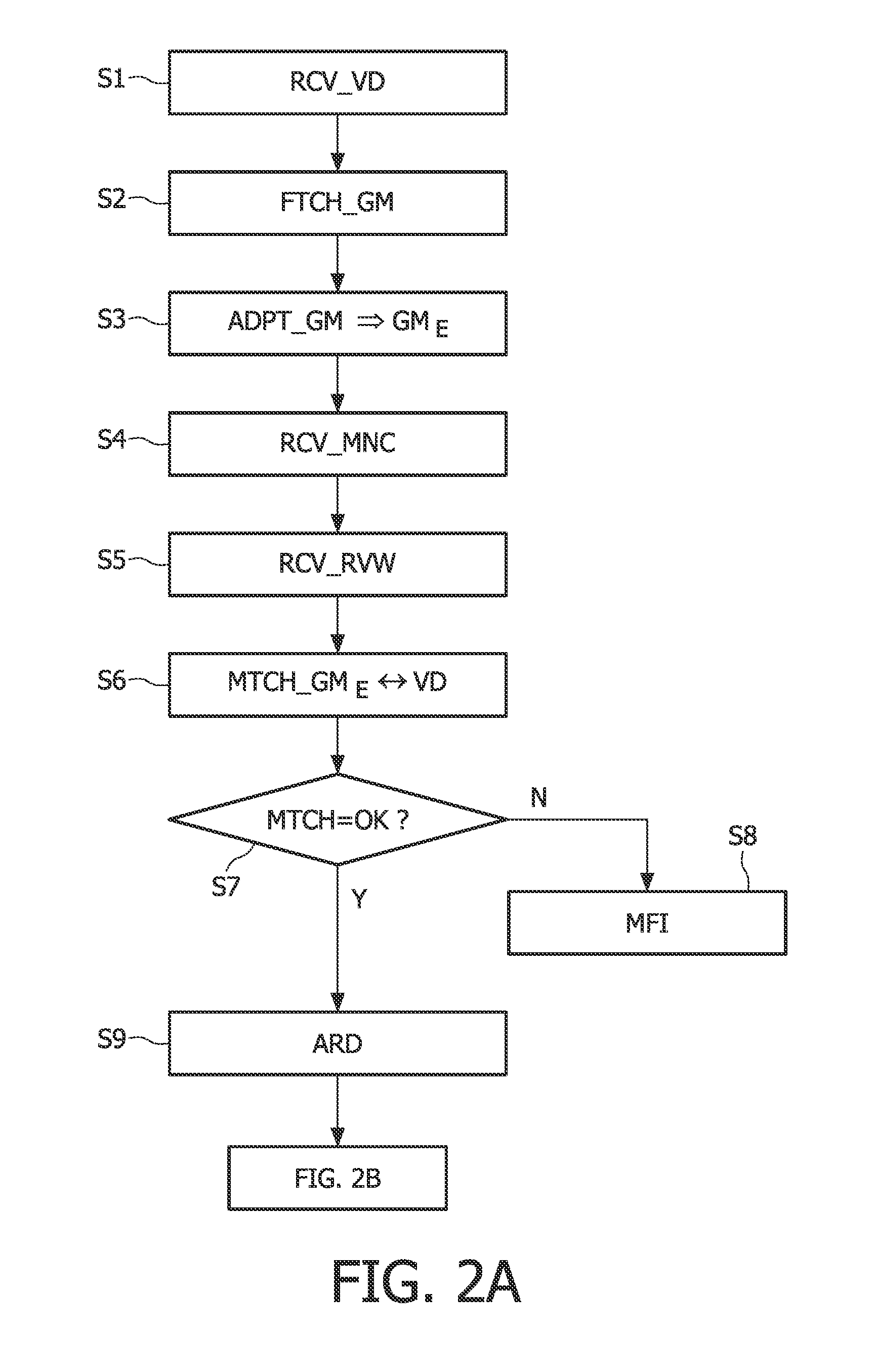
3-d ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20110201935A1Quicker and reliable analysisLess operator dependentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingFeature extraction
In an ultrasound imaging system (UIS), an ultrasound scanning assembly (USC) provides volume data (VD) resulting from a three-dimensional scan of a body (BDY). A feature extractor (FEX) searches for a best match between the volume data (VD) and a geometrical model (GM) of an anatomical entity. The geometrical model (GM) comprises respective segments representing respective anatomic features. Accordingly, the feature extractor (FEX) provides an anatomy-related description (ARD) of the volume data (VD), which identifies respective geometrical locations of respective anatomic features in the volume data (VD). In a preferred embodiment, a slice generator (SLG) generates slices (SX) from the volume data (VD) based on the anatomy-related description (ARD) of the volume data (VD).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS7873401B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
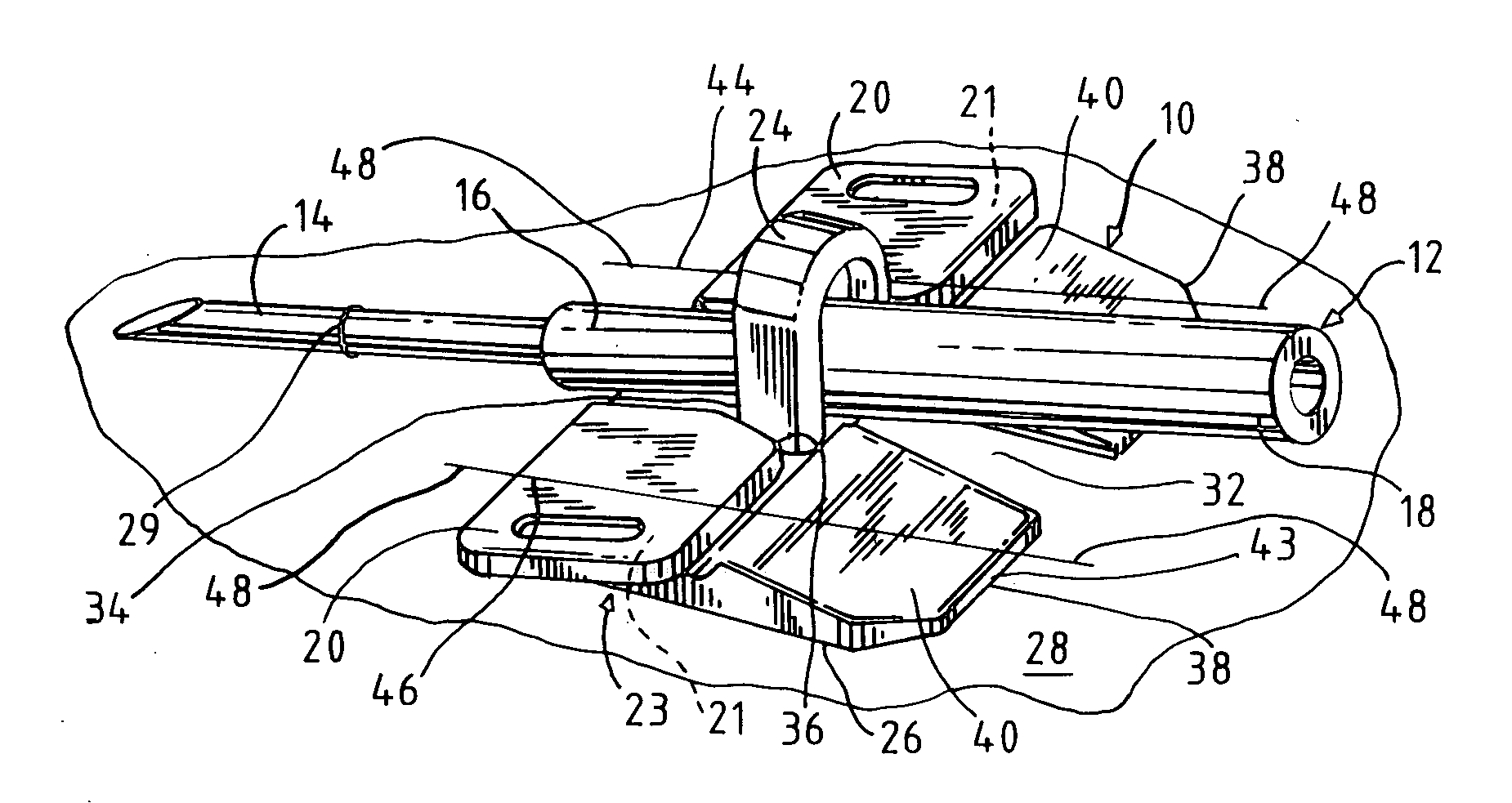
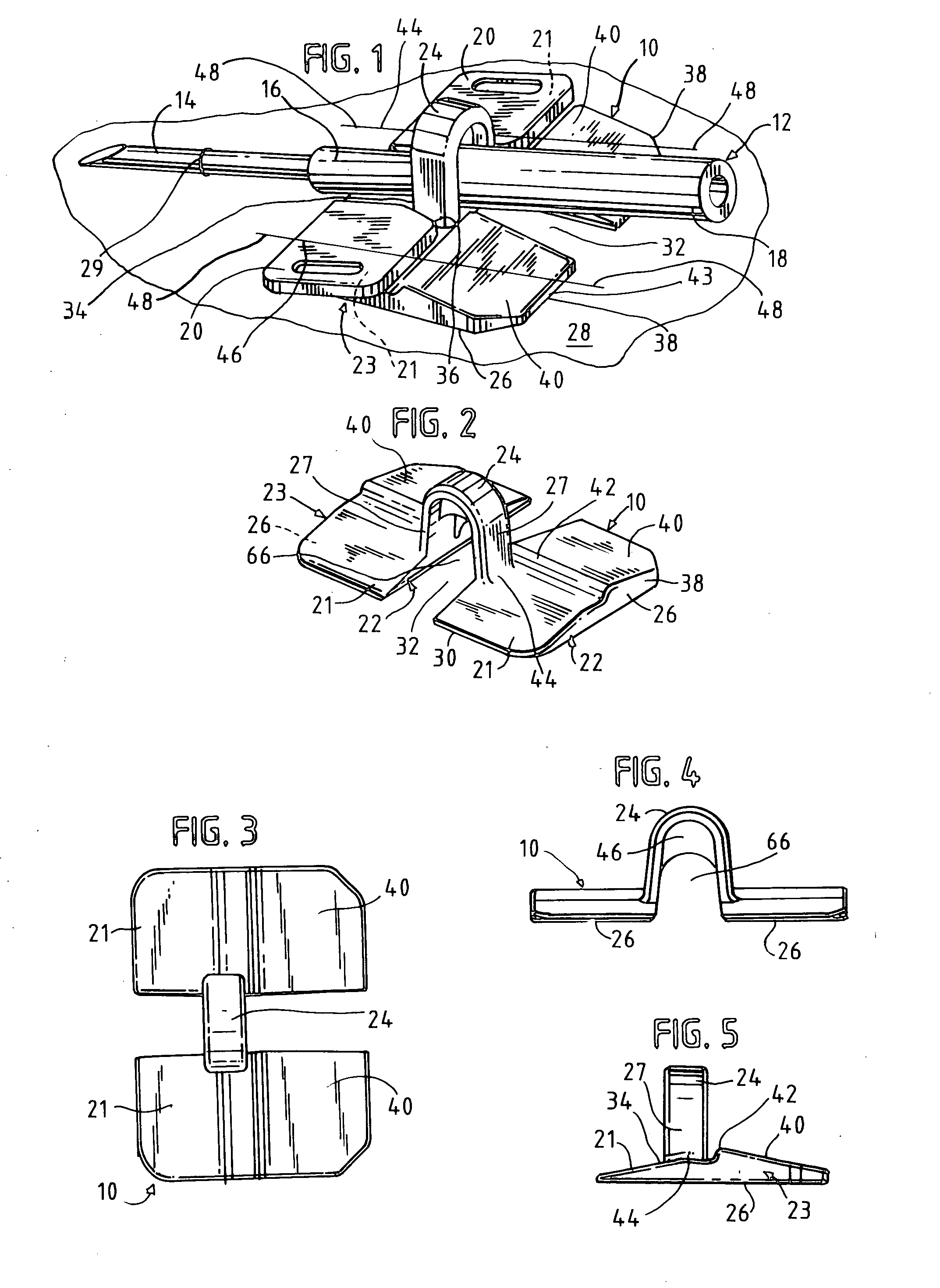
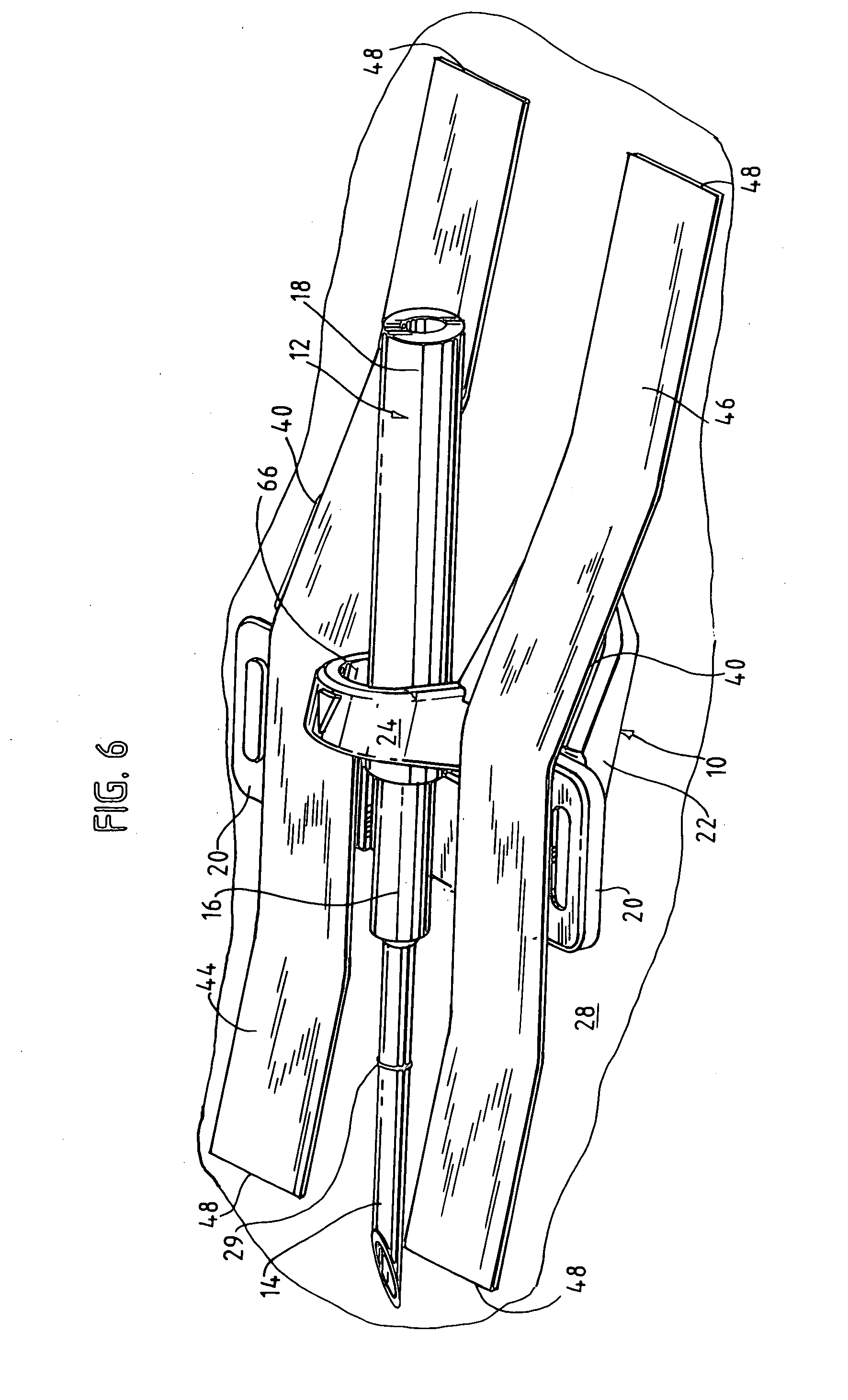
Needle alignment, needle securement and vessel stabilization device
InactiveUS20070265571A1Prevents clinician's lifting or bending of the tubingGreat easeCatheterInfusion needlesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A securement device for an intravenous, winged needle set, which comprises: an inverted U-shaped, self-supporting strap, the strap having vertical legs attached to a central portion of a base. The base has a bottom to rest on the skin of the patient. A portion of the base forward of the strap has an upper surface that slopes downwardly to a forward end at an angle to the skin and the bottom of the base. Improved retention and ease of application is provided with such a device.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
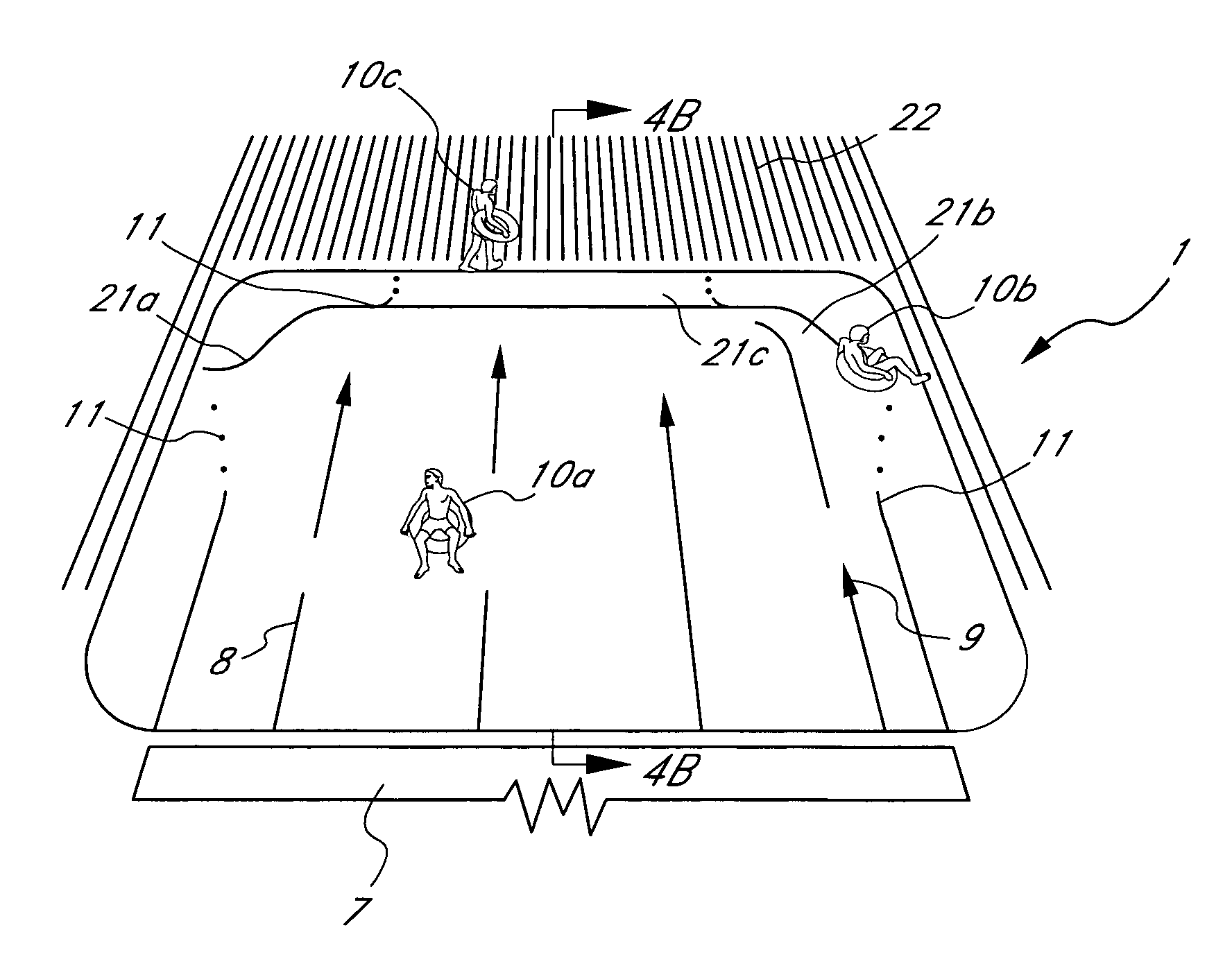
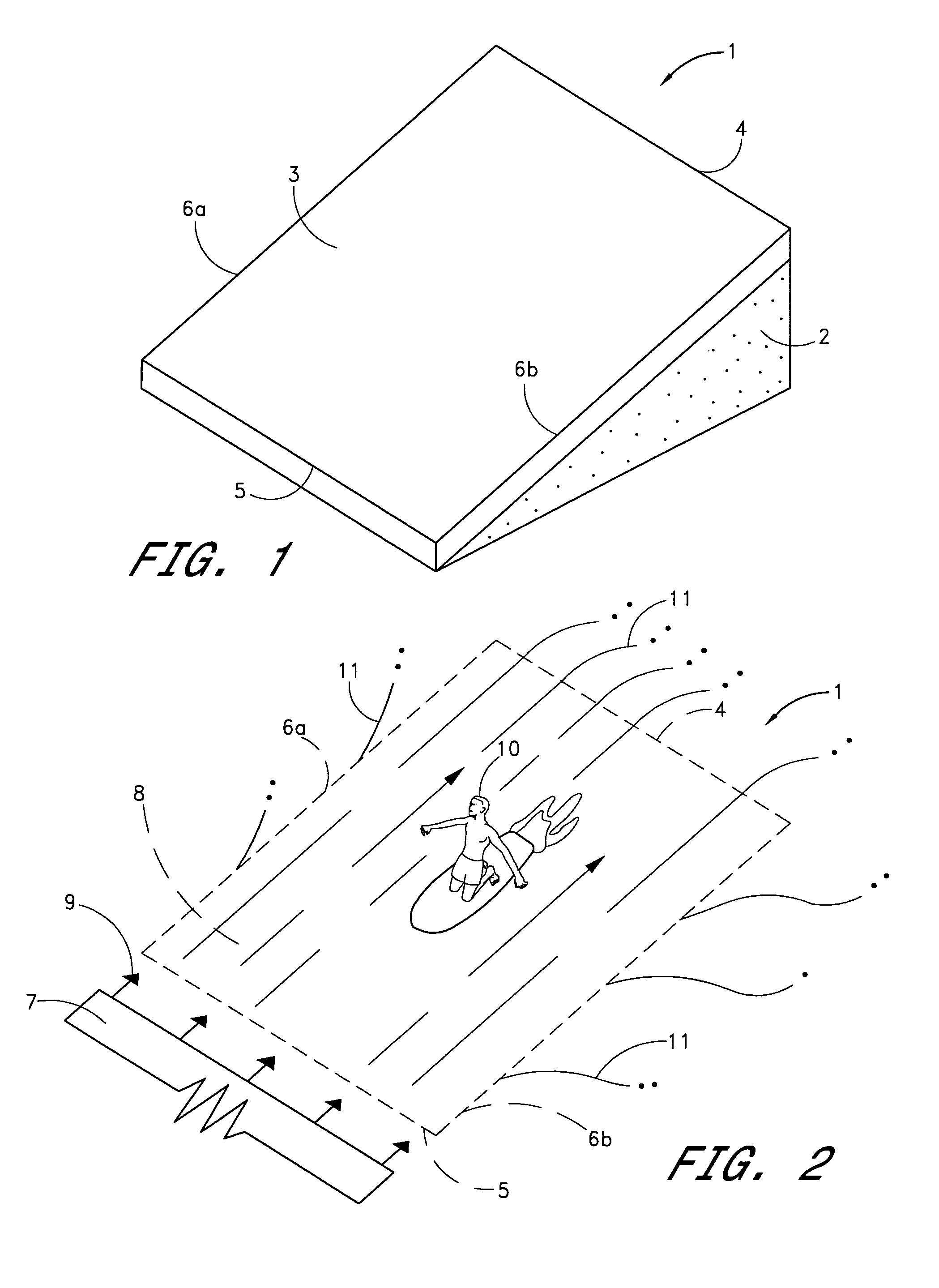
Water ride attraction
Owner:WHITEWATER WEST INDS
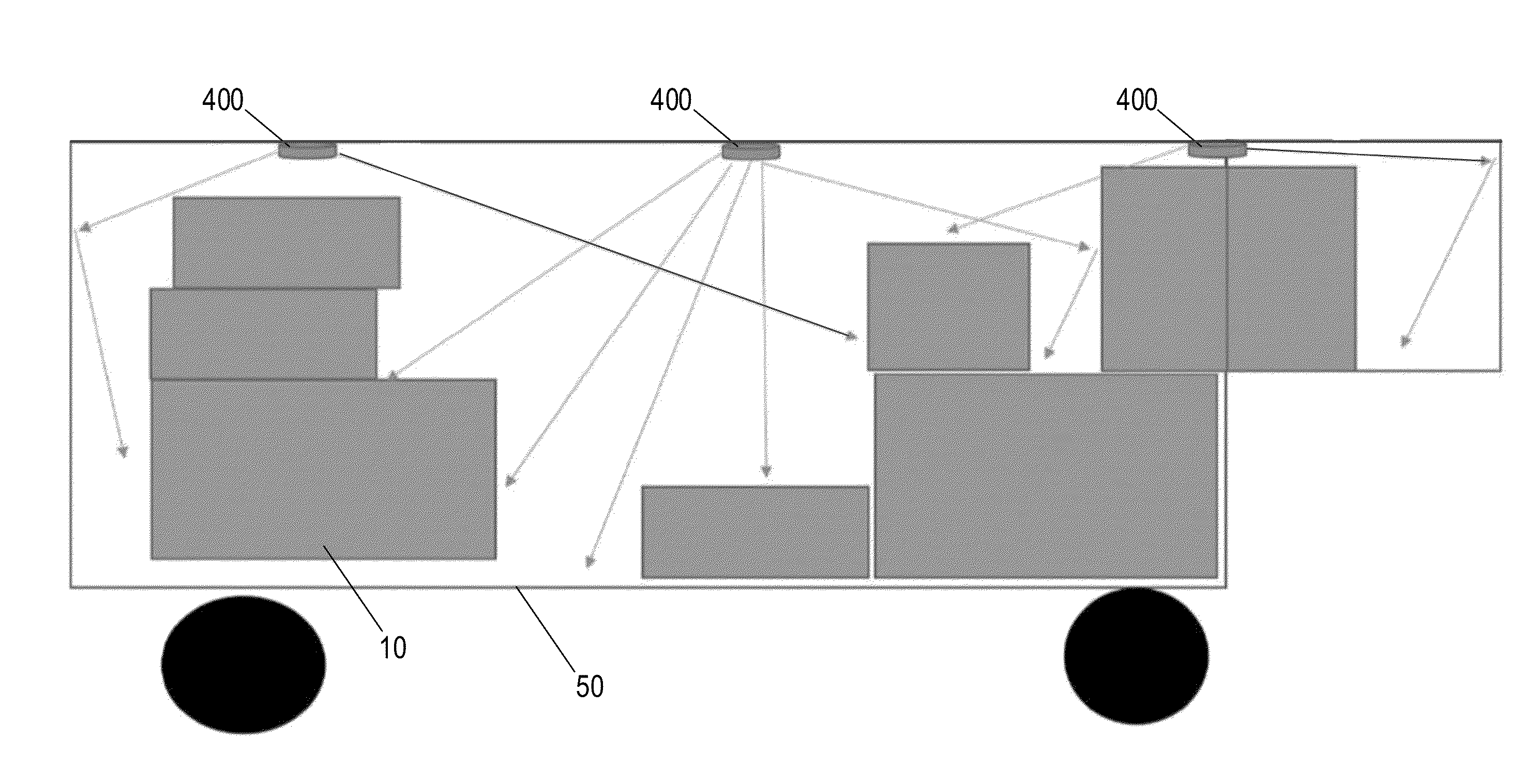
Concepts for Locating Assets Utilizing Light Detection and Ranging
ActiveUS20160180289A1Less skillFacilitate optimal space usageLogisticsElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringLight detection
Various embodiments are directed to systems and methods for utilizing Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) sensors to facilitate loading and unloading of assets into receptacles. The LIDAR sensors may be configured to detect the location of various surfaces (e.g., asset surfaces) within a receptacle such that mapping data indicative of the location of the detected surfaces may be generated. This mapping data may facilitate a determination of a total volume of unoccupied space within the receptacle and / or the identification of an unoccupied volume sufficient to accommodate an item having defined dimensions. The mapping data may additionally be indicative of the location of asset identifiers disposed on one or more detected surfaces to facilitate locating a particular asset associated with a provided asset identifier.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
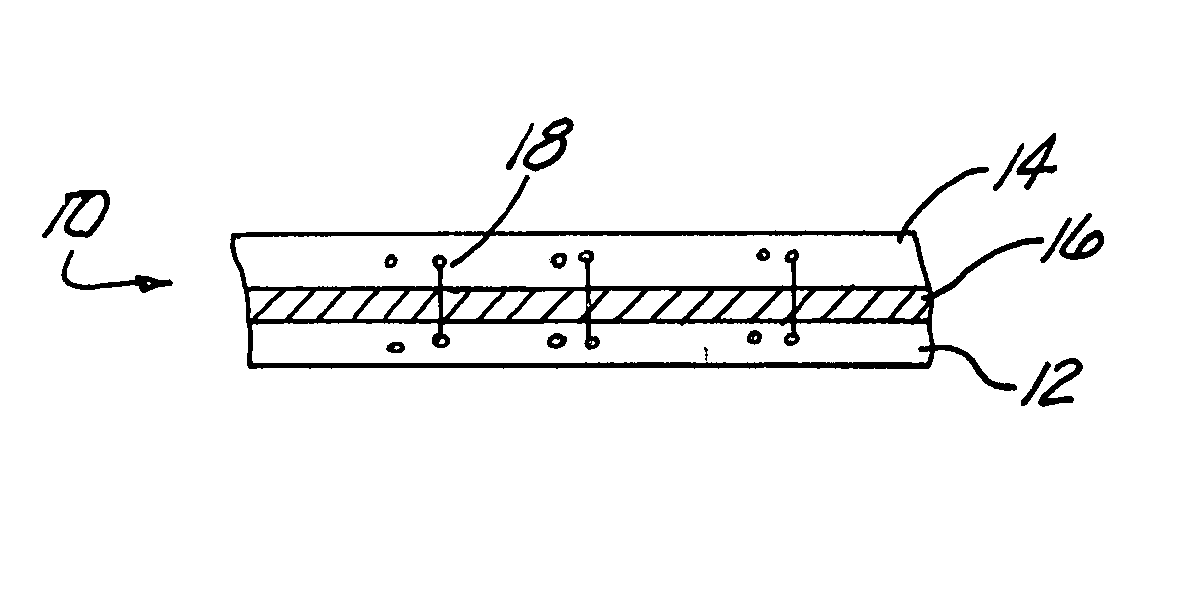
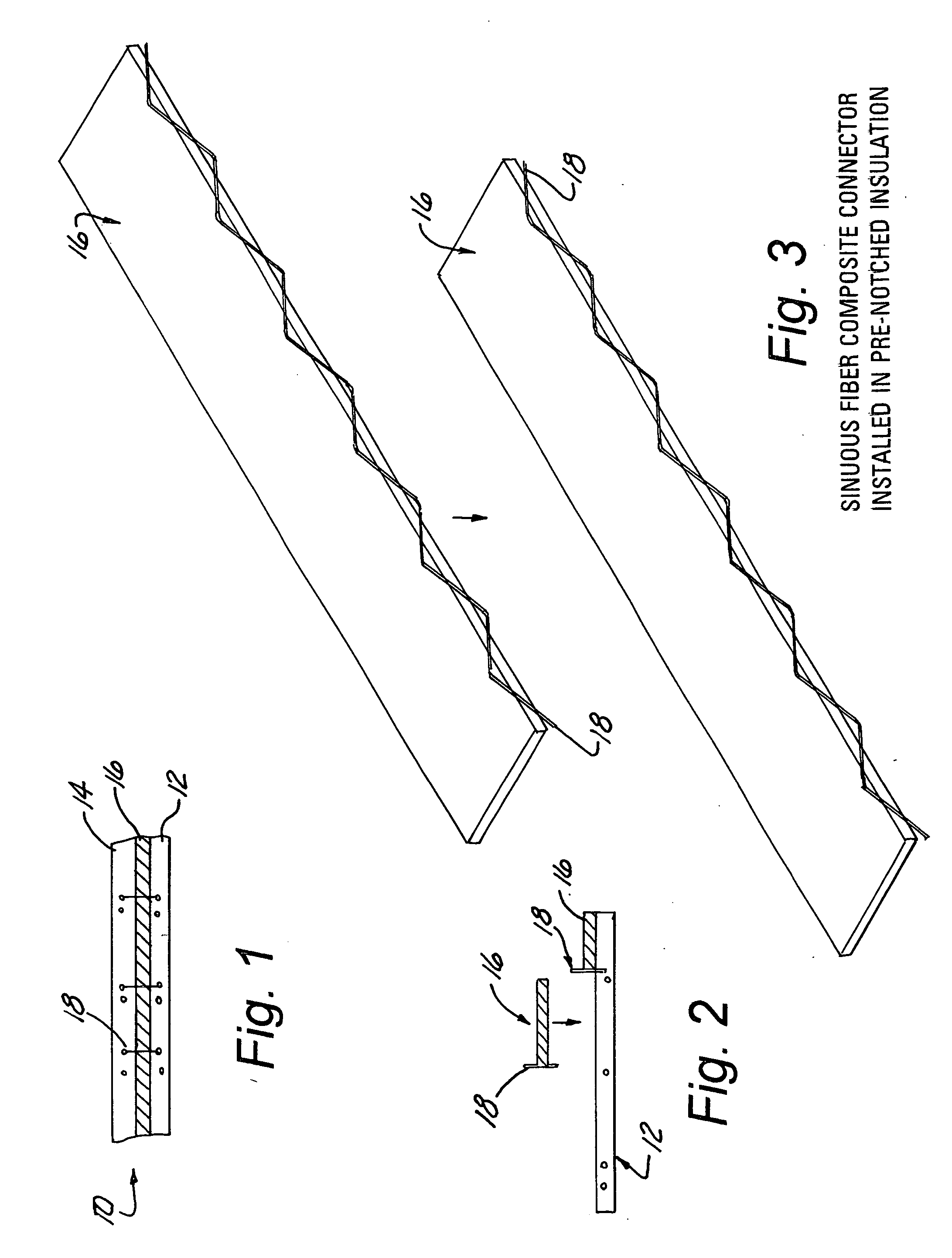
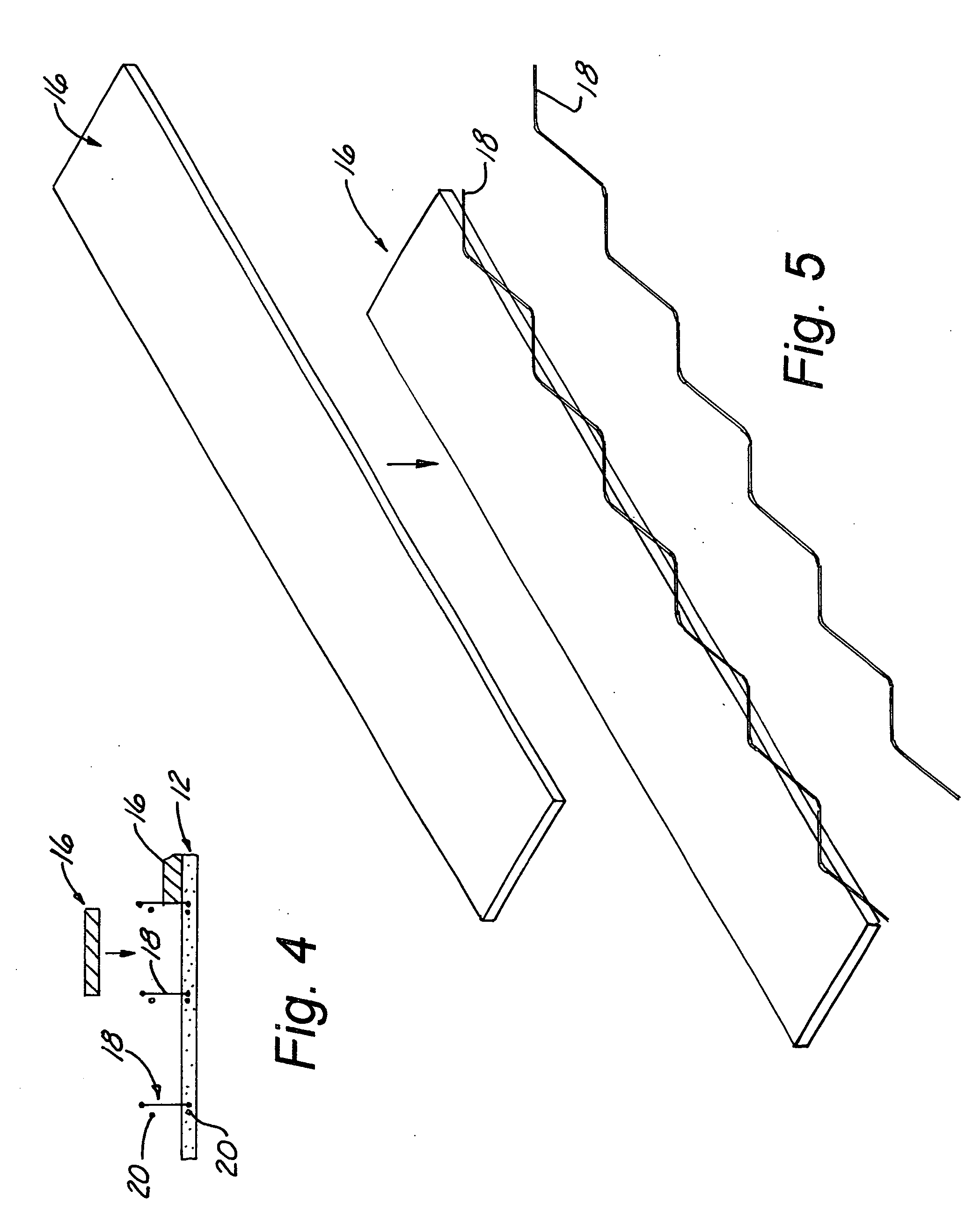
Sinuous composite connector system
InactiveUS20050102968A1Less skillLess-expensive to constructConstruction materialInsulation layerStructural engineering
The present invention is an insulated concrete wall panel consisting of two layers of concrete with and insulating layer in between the concrete layers. A sinusoidal-shaped, fiber-reinforced composite element connects the two concrete layers. The connector is imbedded in the two layers of concrete and passes through the insulation layer. The connector provides the requisite transmission of forces merely by being consolidated in the concrete layers.
Owner:COMPOSITE TECH CO LLC
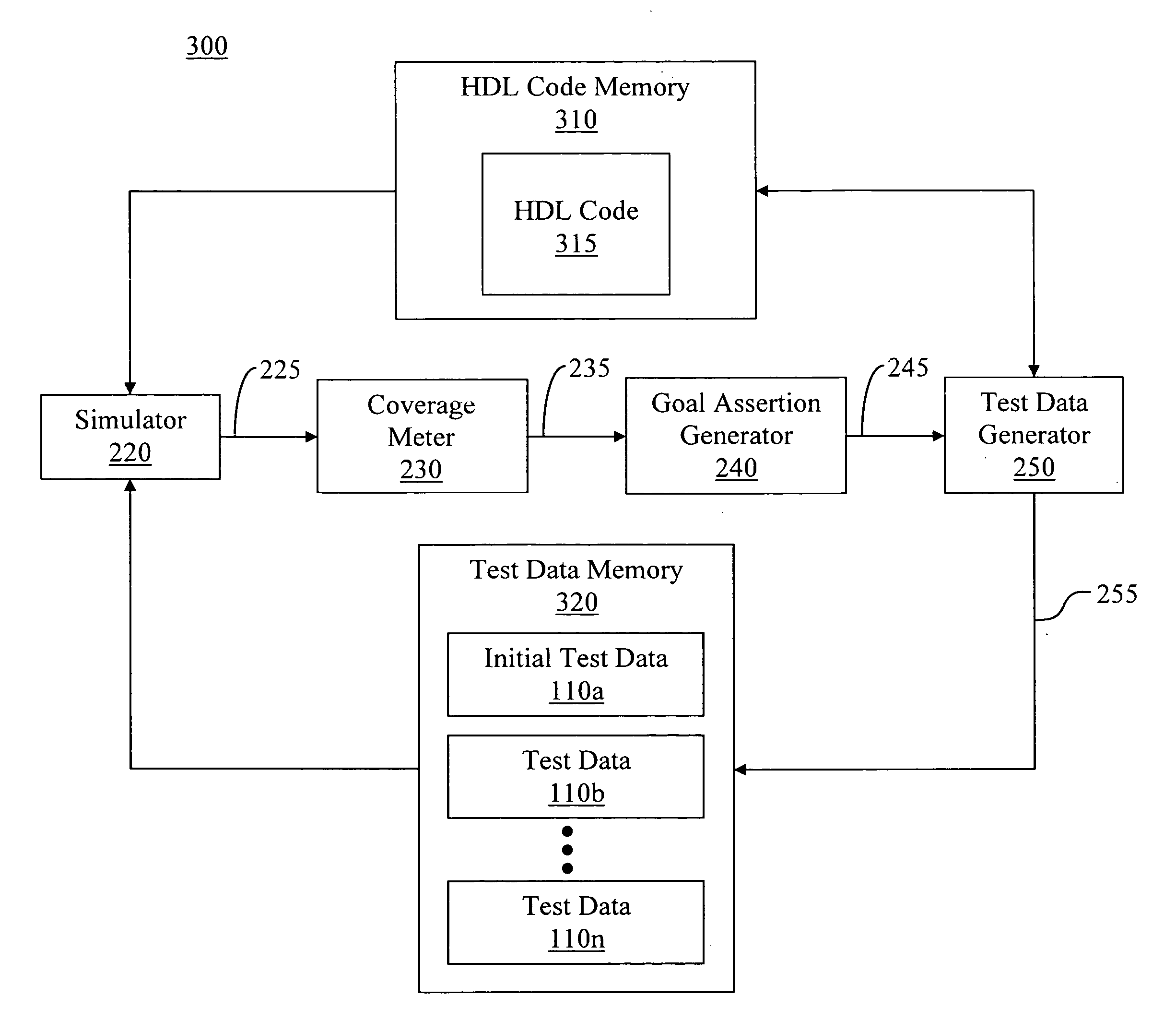
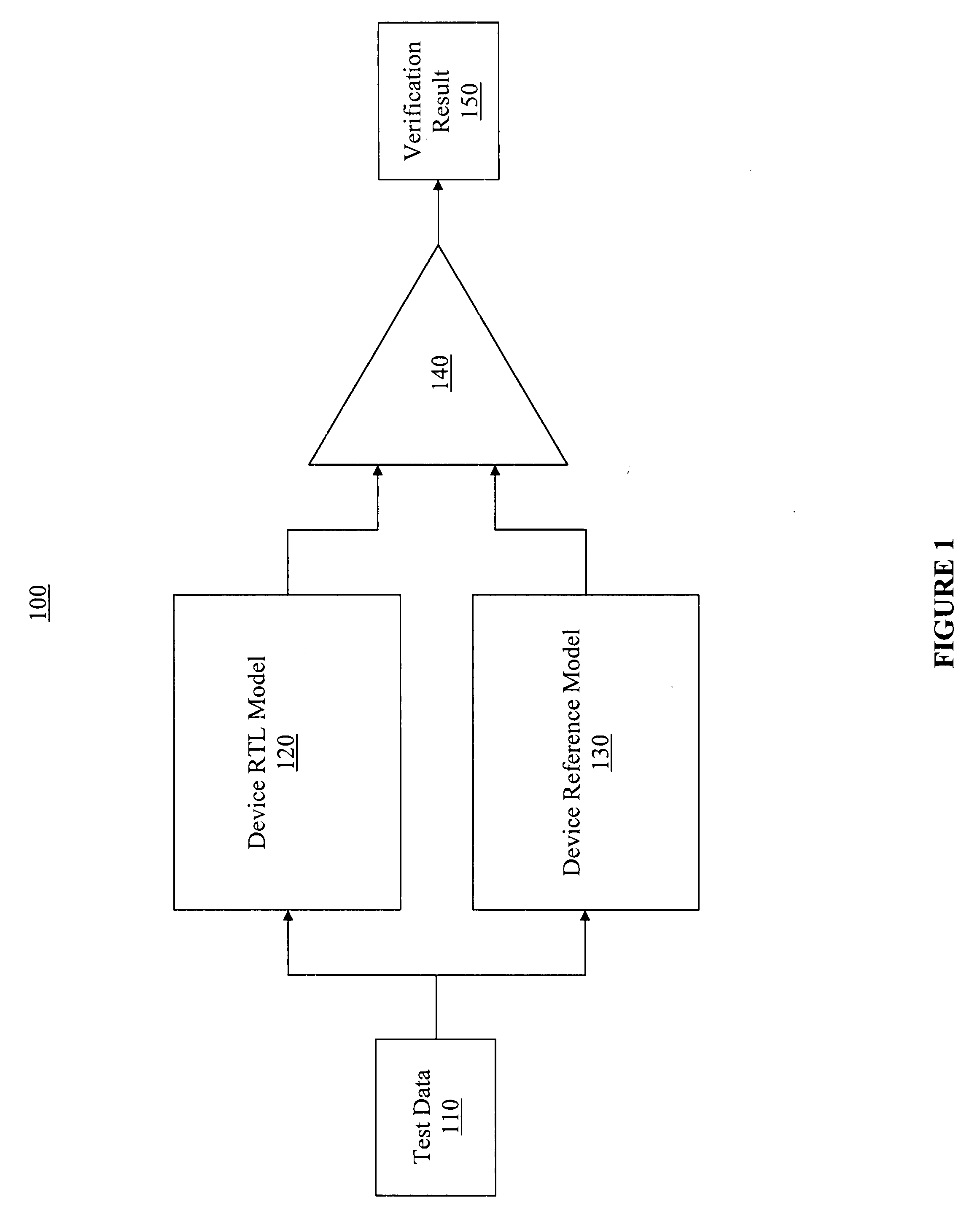
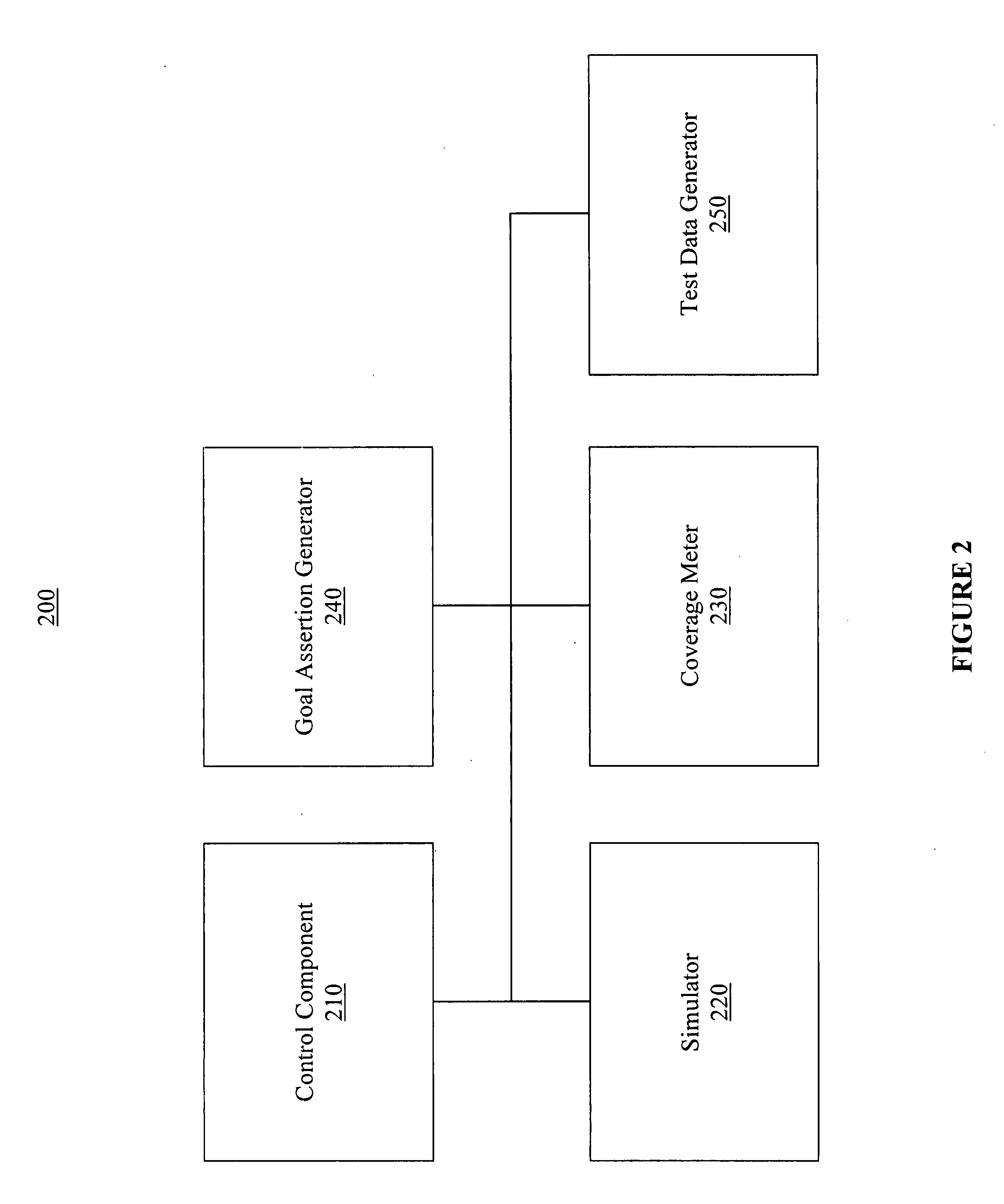
Automatic verification of device models
ActiveUS20090125290A1Less skillLow experience requirementError detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCode coverageModel Number
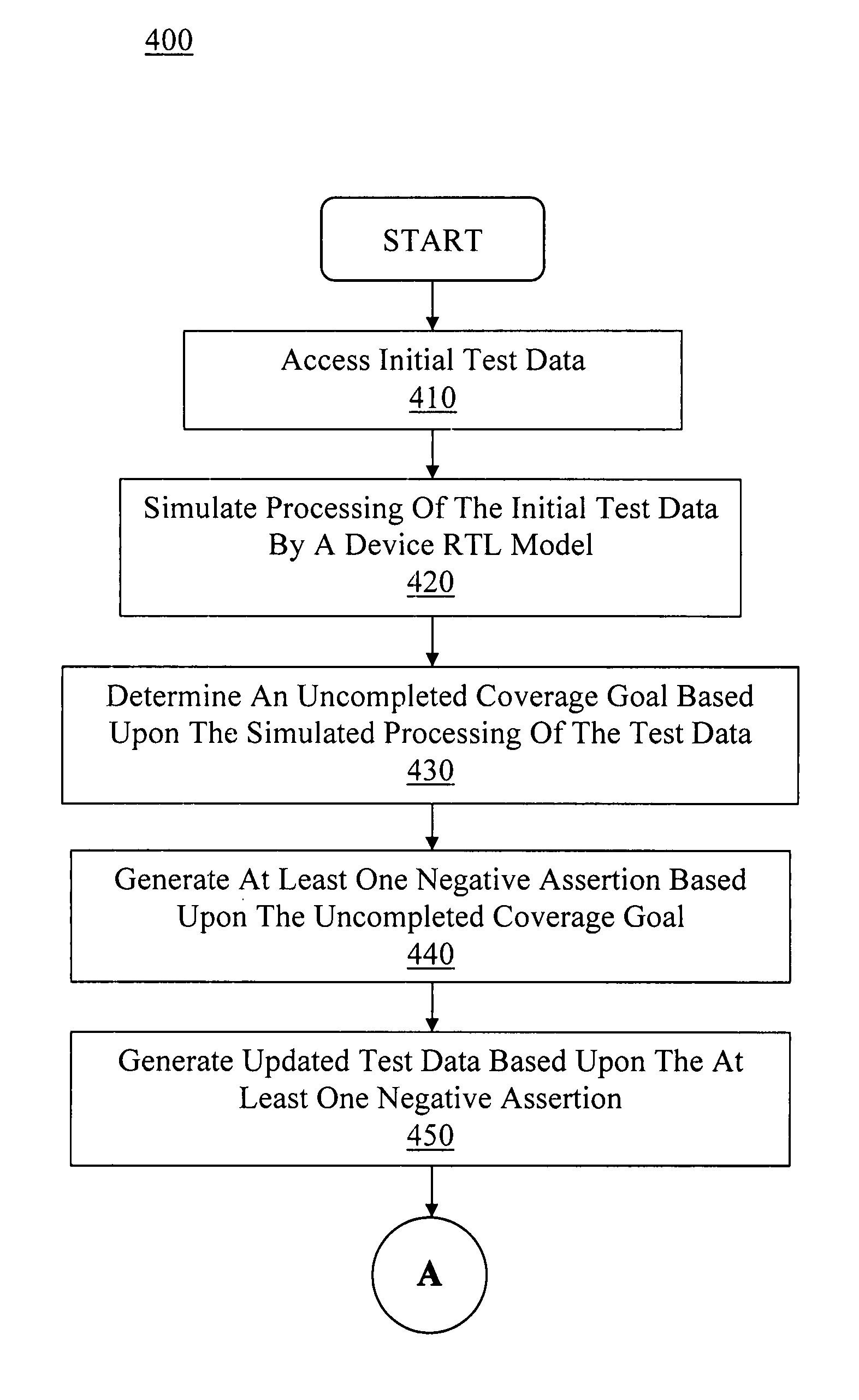
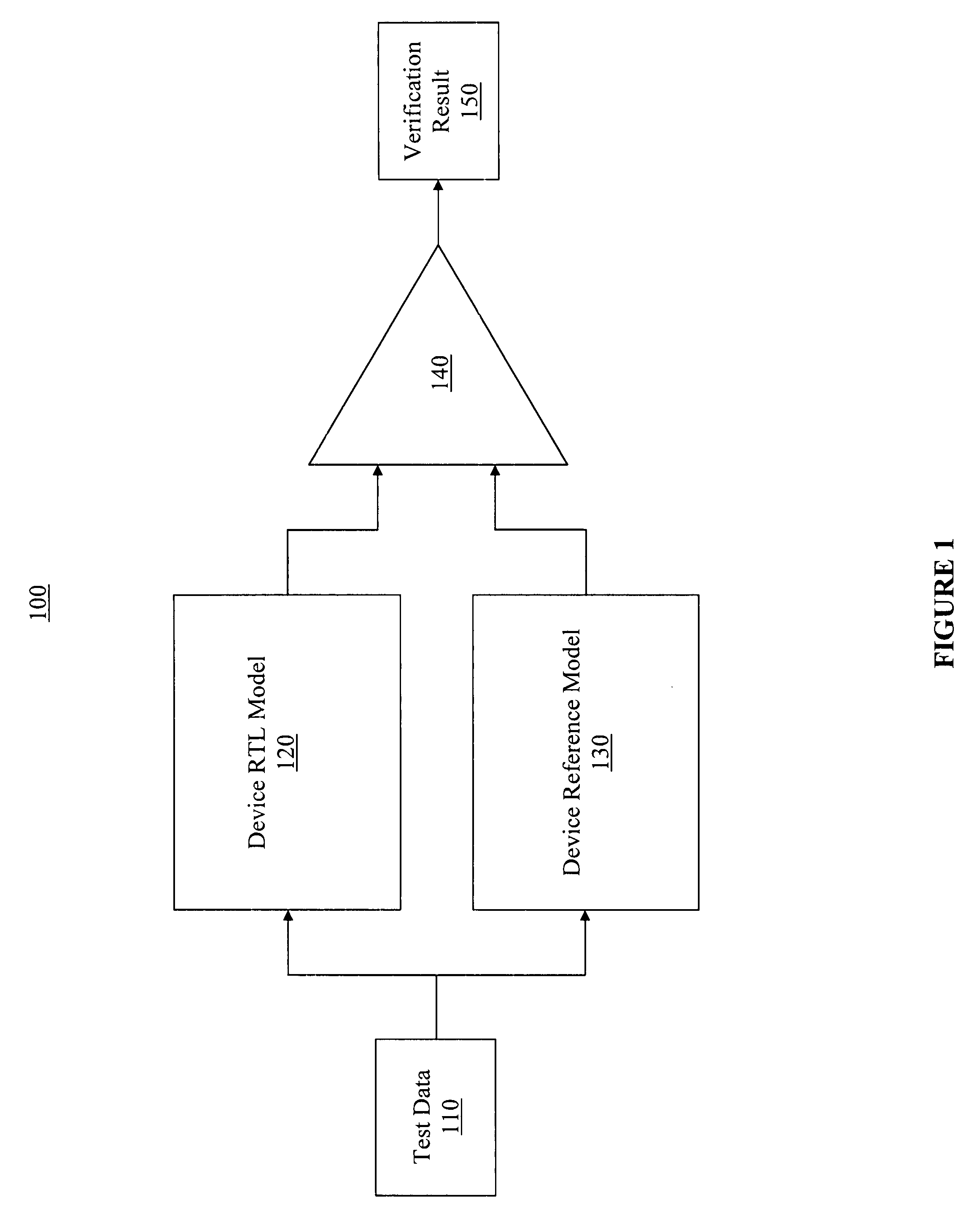
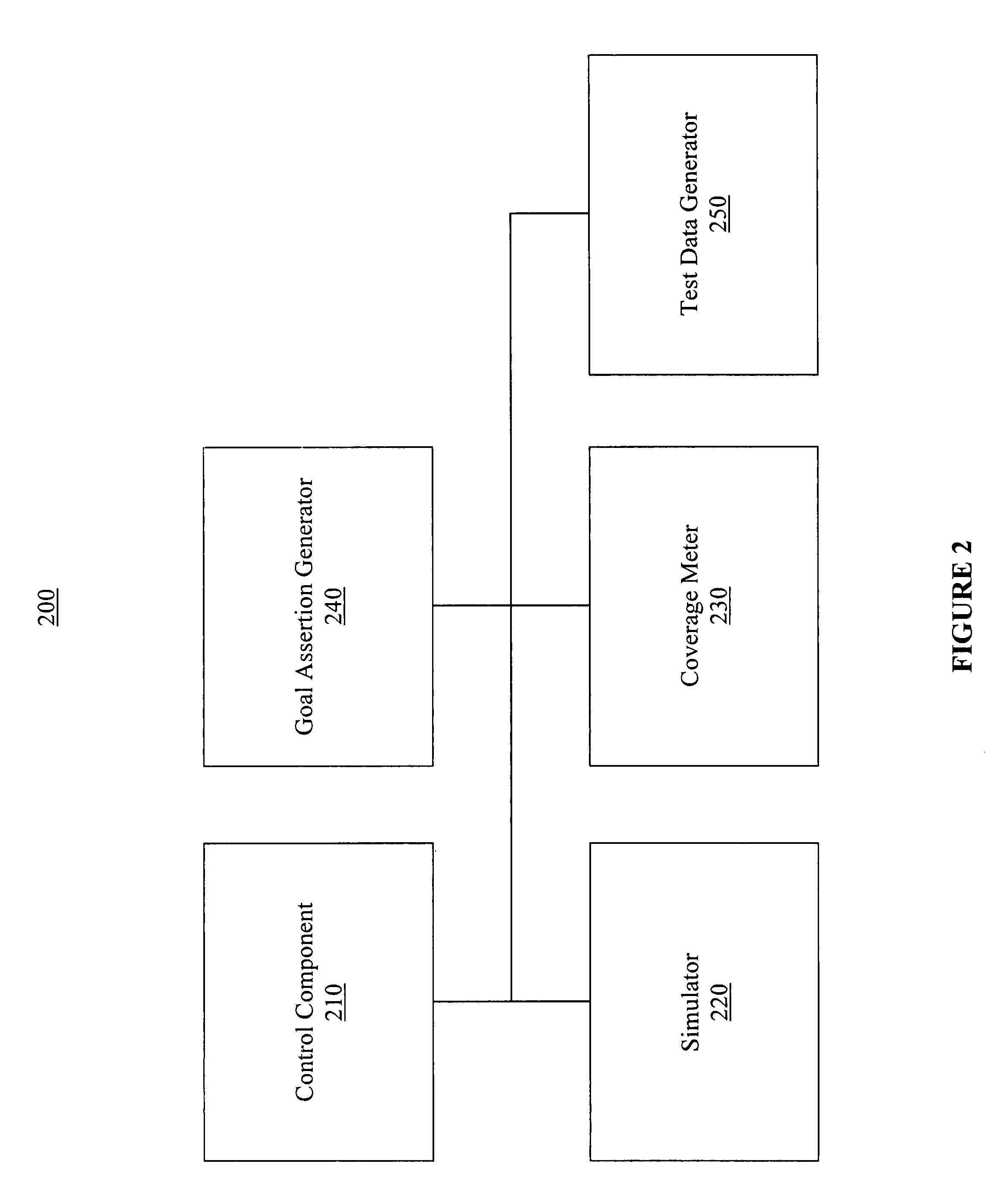
An efficient and cost effective mechanism for generating test files for automatic verification of a device model is disclosed. Uncompleted coverage goals determined based upon simulating processing of a test file by a design model may be expressed as negative assertions for input to a test data generator, where output from the test data generator may used to create a test file for completing all or some of the uncompleted coverage goals. The test data generator may indicate data which causes a property to fail, and therefore, may indicate test data which causes the uncompleted coverage goal to succeed. The initial test file may represent zero code coverage and / or zero functional coverage, thereby enabling the test data generator to automatically create one or more test files for accomplishing the more extensive code coverage goals and / or functional coverage goals. Functional coverage goals may be automatically generated by the test data generator.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
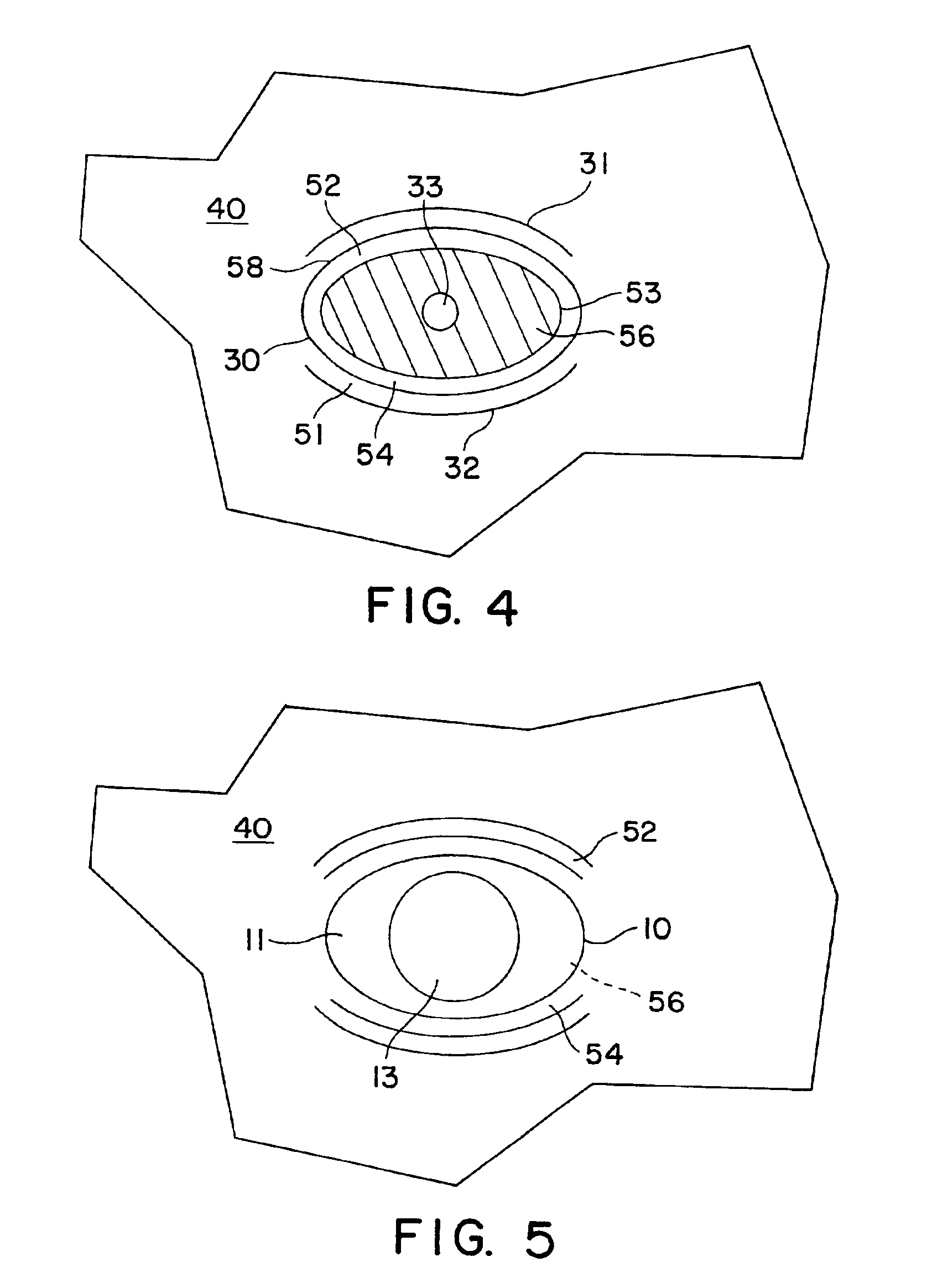
Manikin and eye device apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture
InactiveUS6923654B2Accurately and consistently and efficientlyLess skillOrganic chemistryEye implantsArtificial EyesOphthalmology
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture are disclosed for installing an artificial eye in a realistic, life-like sculpture, comprising an artificial eye of partially hemispherical shape, as well as a manikin with an eye-mounting area adapted to mate with such an artificial eye without risk of subsequent movement of the eye or of distortion of the features surrounding the eye-mounting area of the sculpture. Eye mounting pieces for retrofitting existing sculptures having conventional eye mounting areas to permit the accurate and life-like mounting of artificial eyes are also provided.
Owner:TOHICKON JOHNSON DEV
Disposable world-to-chip interface for digital microfluidics
ActiveUS20150148549A1Easy to useLess skillOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringDelivery system
The present disclosure sets forth incorporating microfluidic chips Interfaces for use with digital microfluidic processes. Methods and devices according to the present disclosure utilize compact, integrated platforms that interface with a chip upstream and downstream of the reaction, as well as between intermediate reaction steps if needed. In some embodiments these interfaces are automated, including automation of a multiple reagent process. Various reagent delivery systems and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
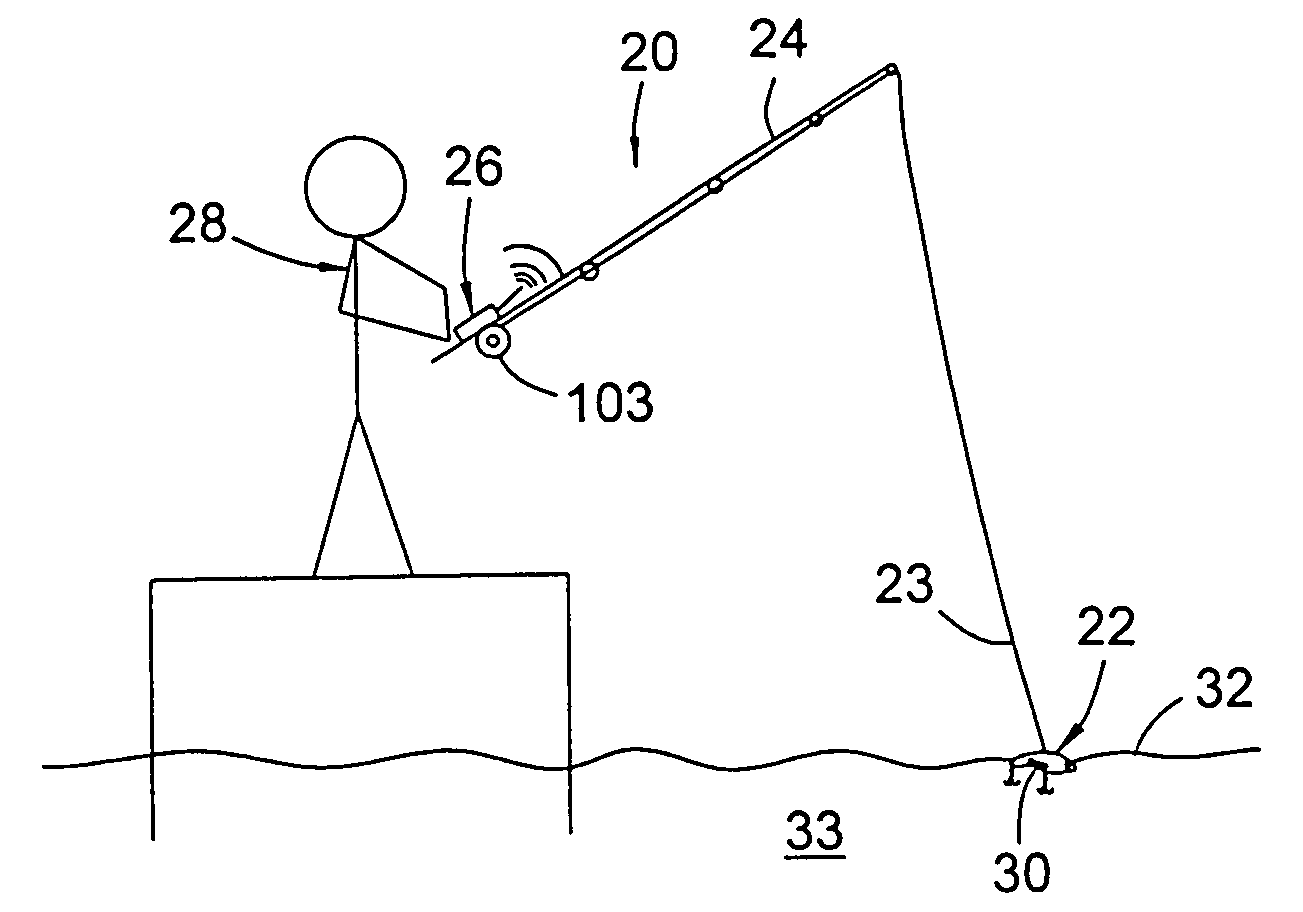
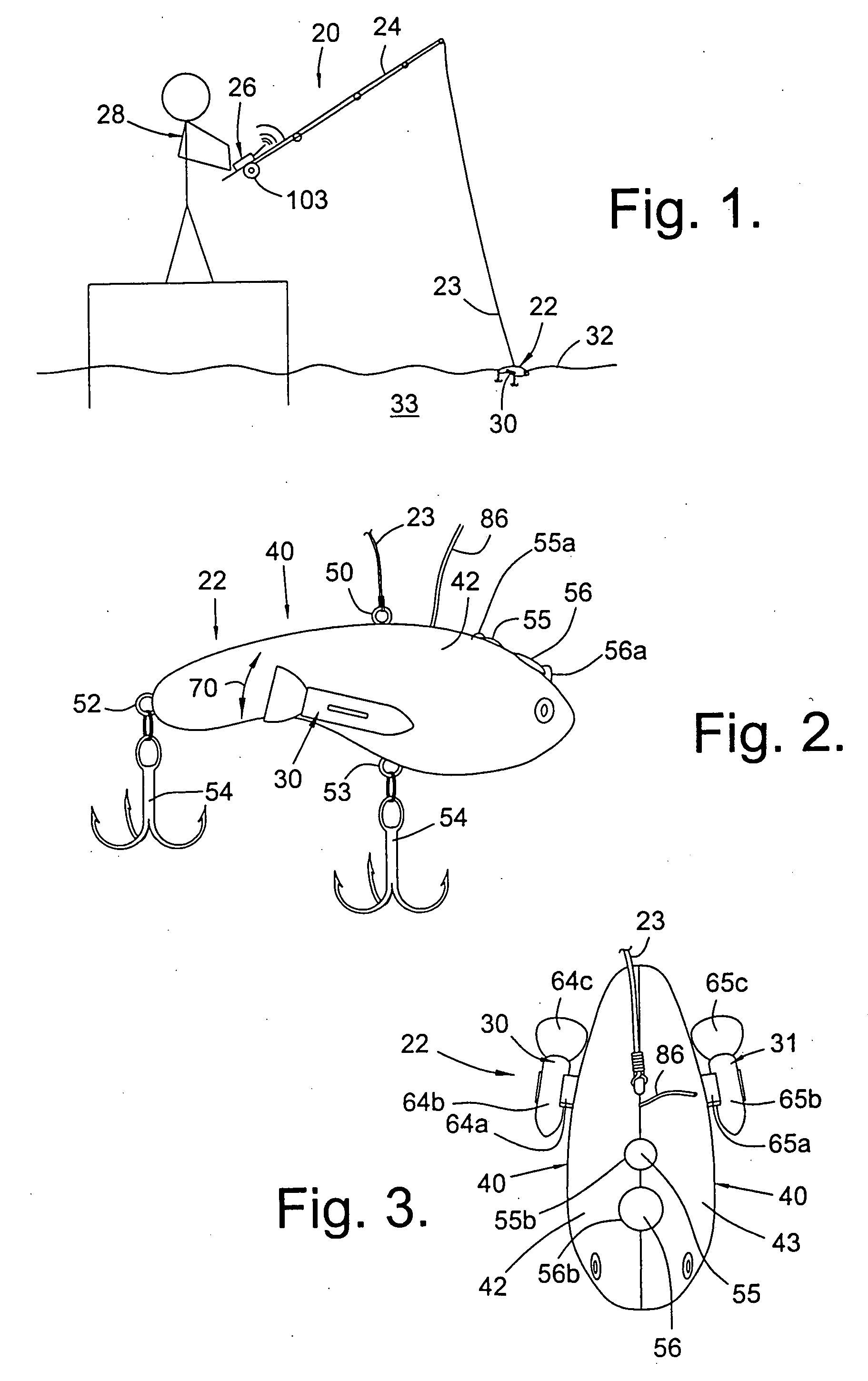
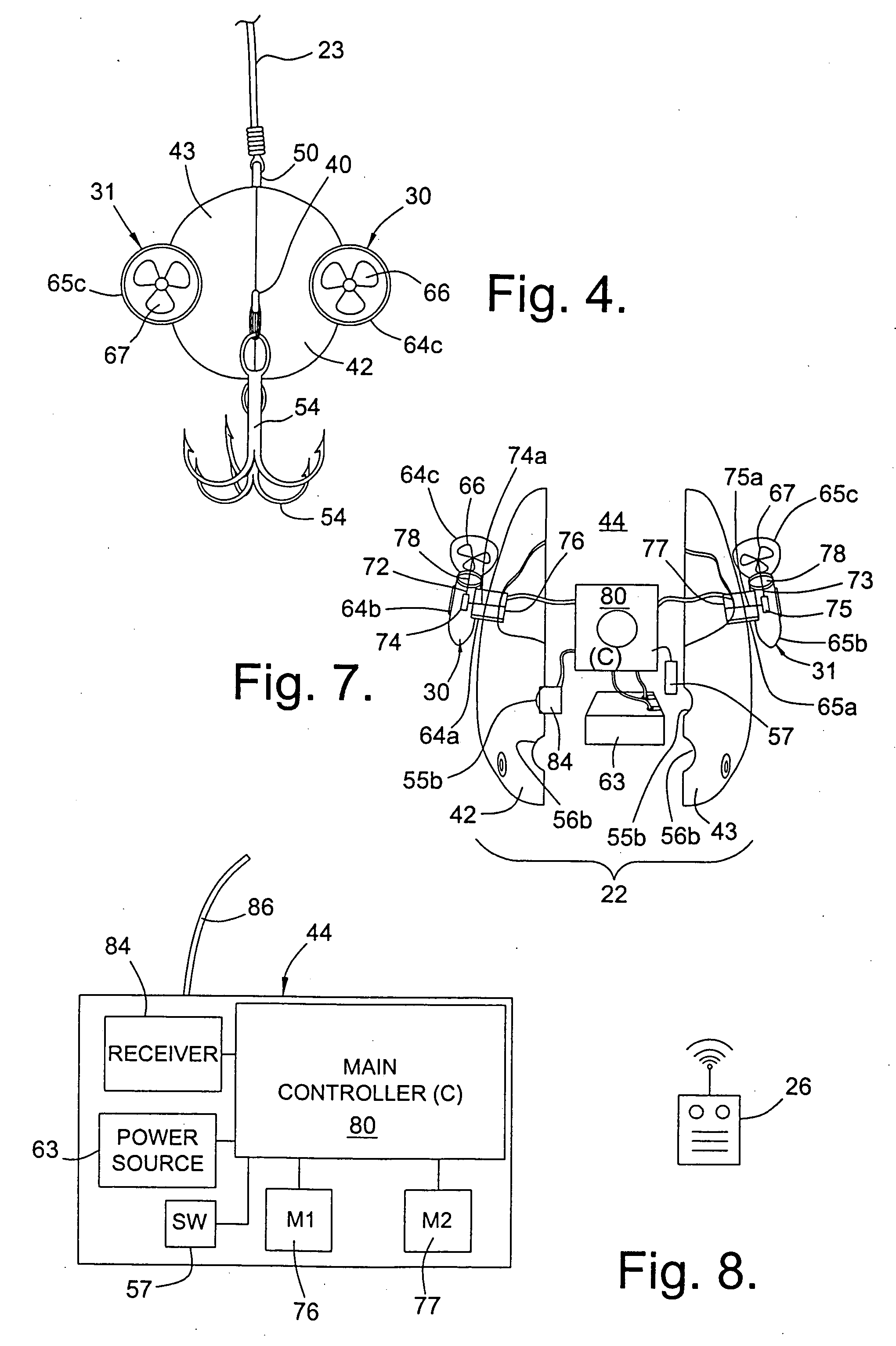
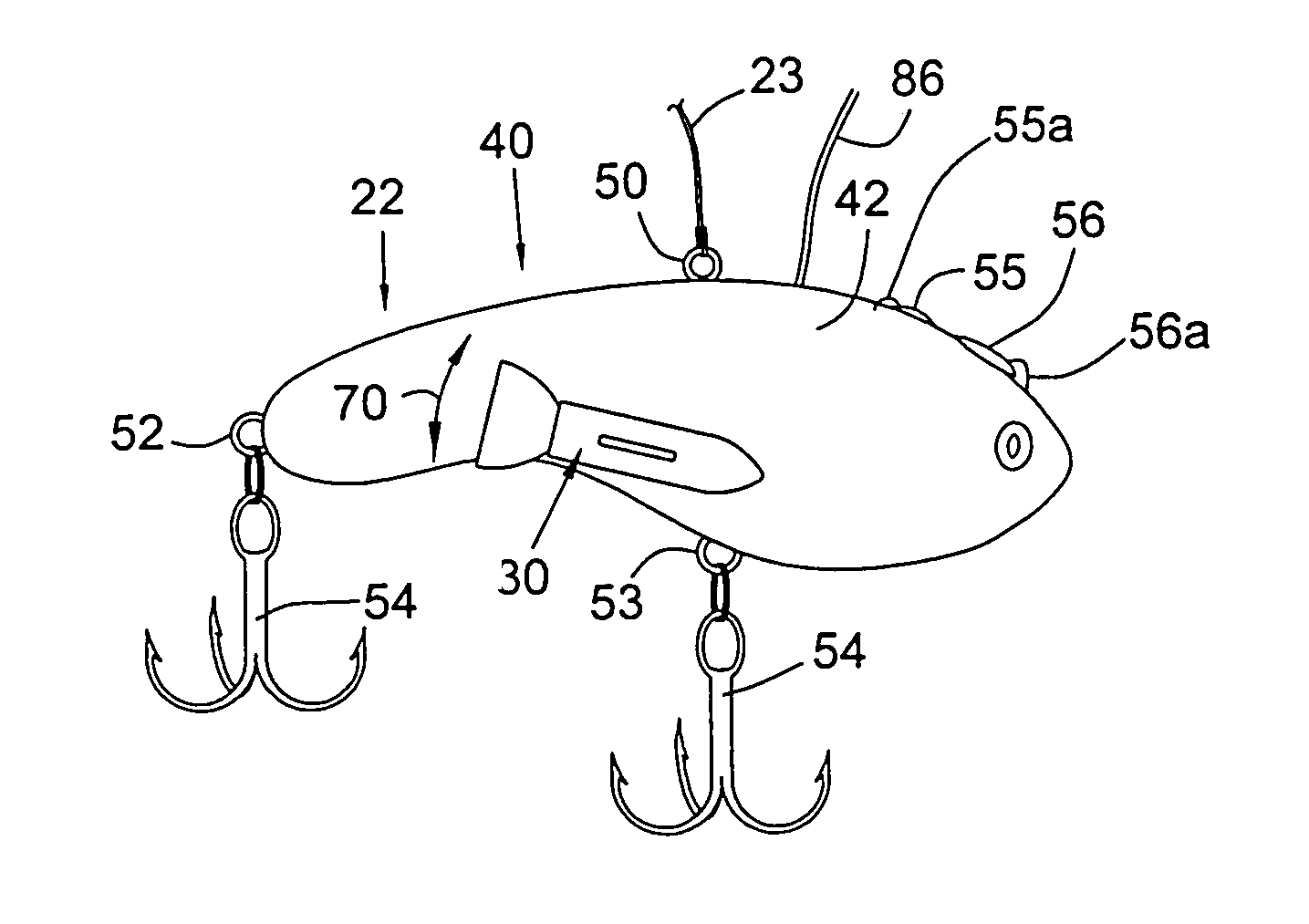
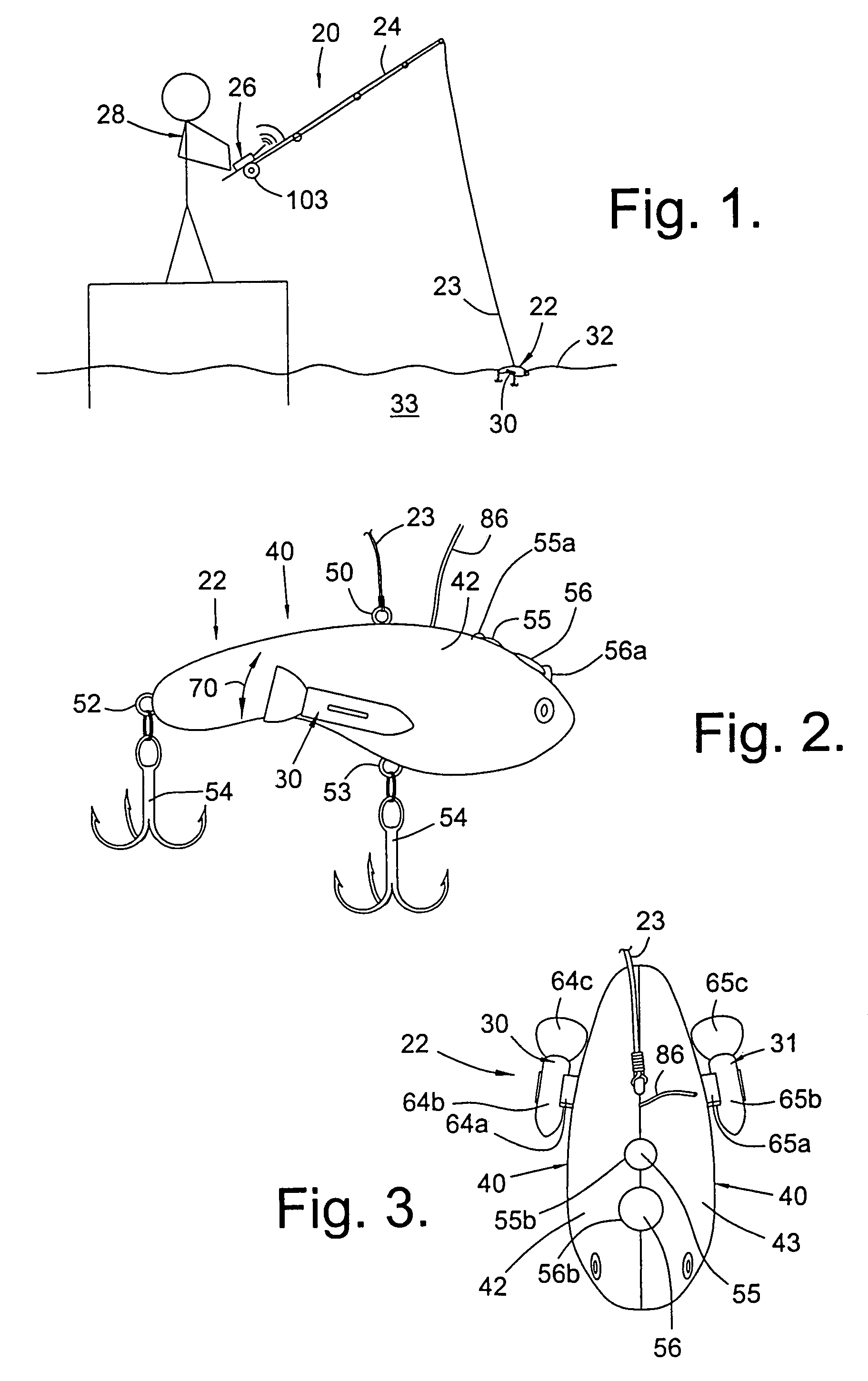
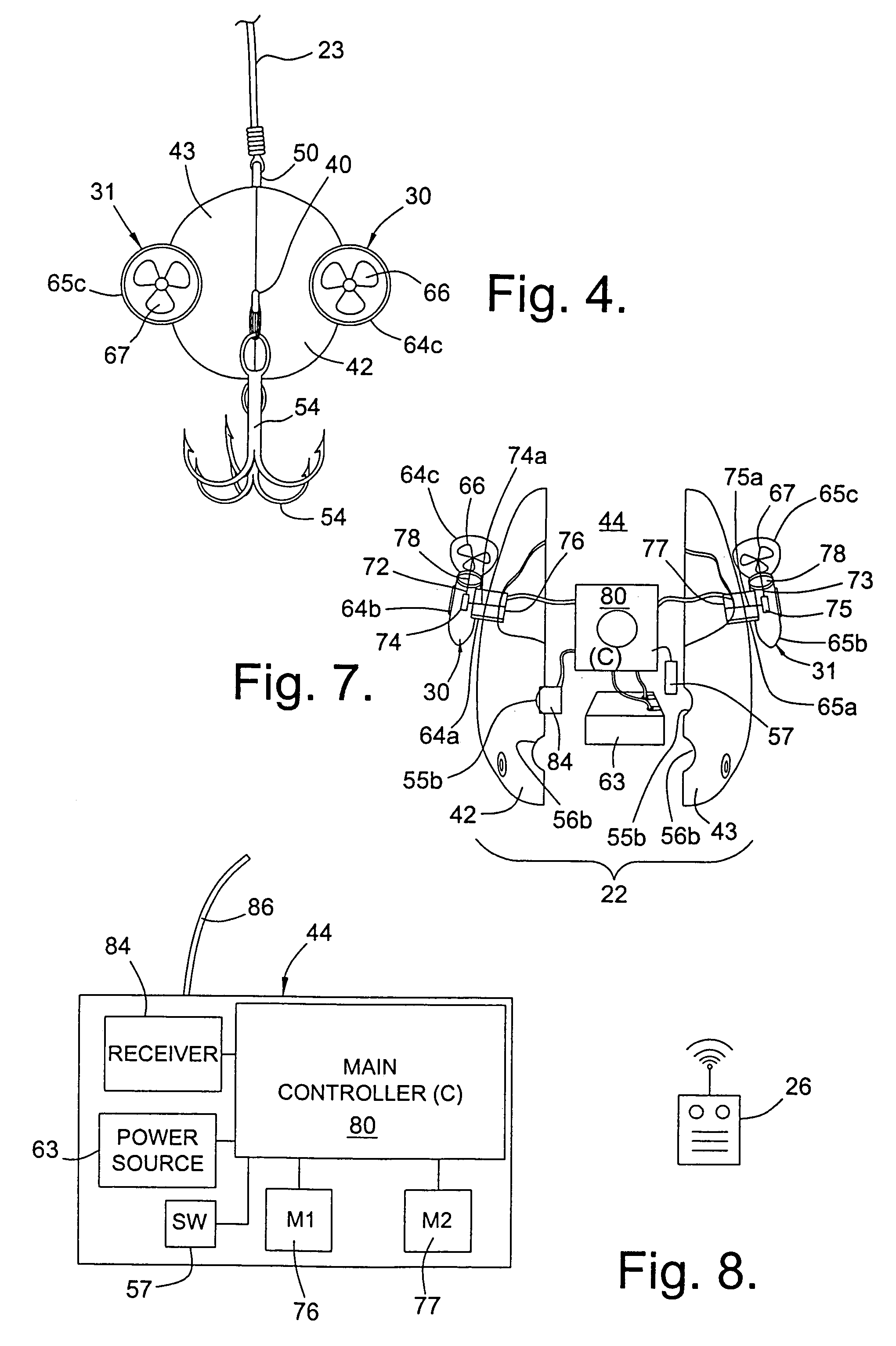
Controllable fishing lure
The present invention relates to a controllable fishing lure. The lure is remotely controlled by the angler by a radio control transmitter on the fishing rod or proximate thereto. The lure can be steered by depressing buttons on the radio control transmitter. The depressions cause radio signals to be emitted from the transmitter, these signals corresponding to the movements desired by depressing the buttons. The radio signals from the transmitter are then received by a receiver, through an antenna, in the lure. The received signals are then processed by a controller that activates propellers, disposed on the lateral sides of the lure, whereby the lure is steered to the desired location in the water.
Owner:MERLINE PAUL K
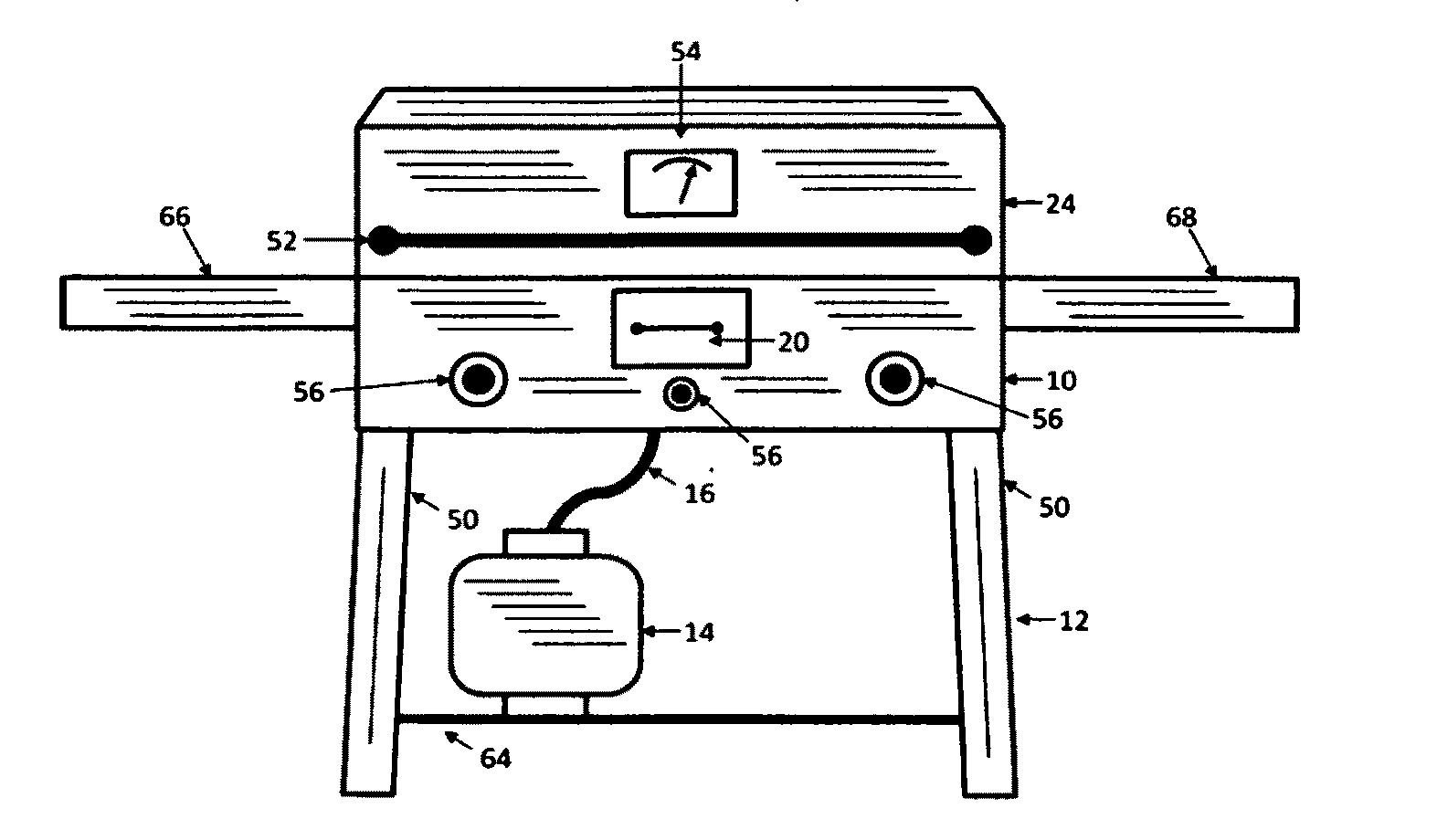
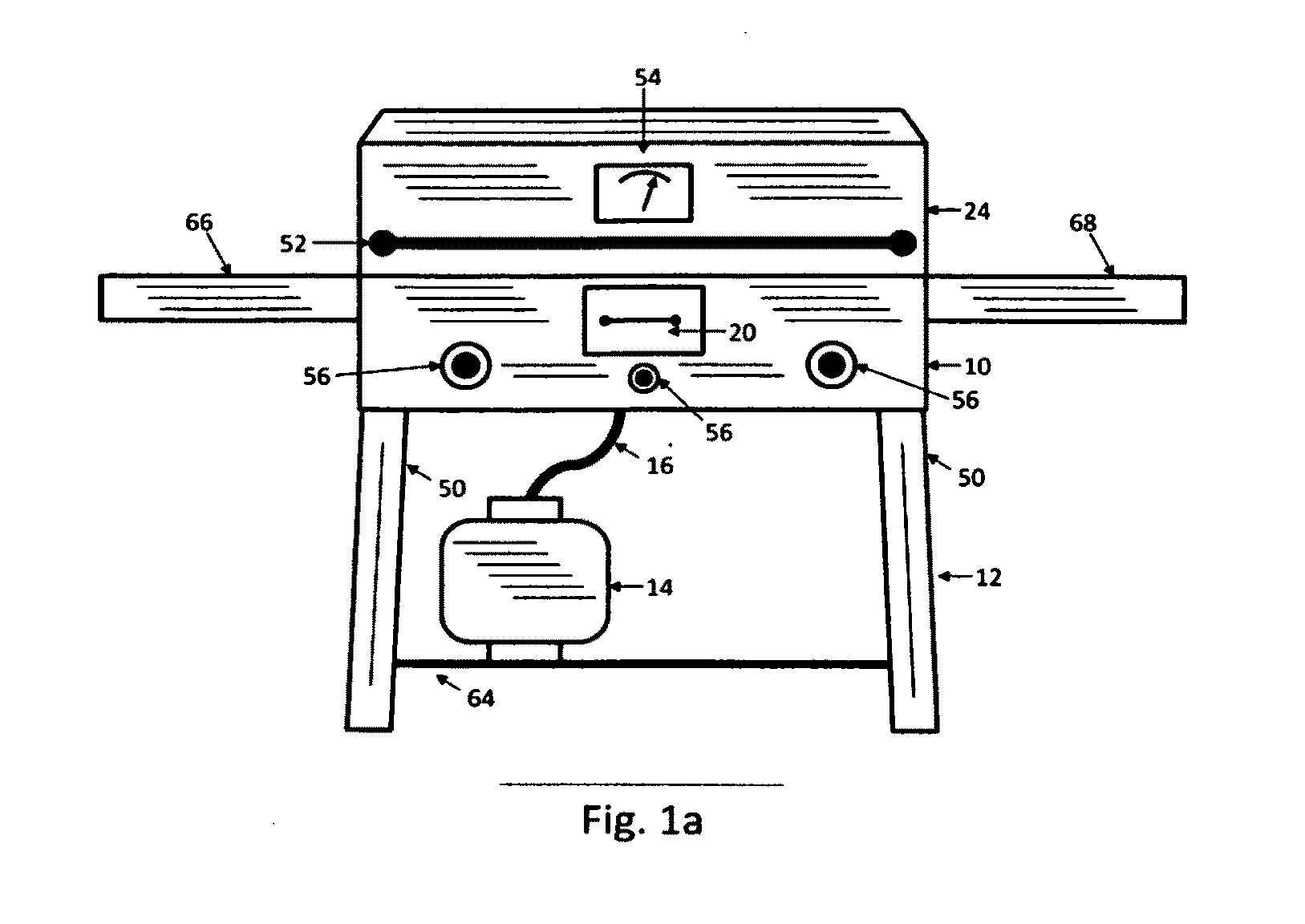
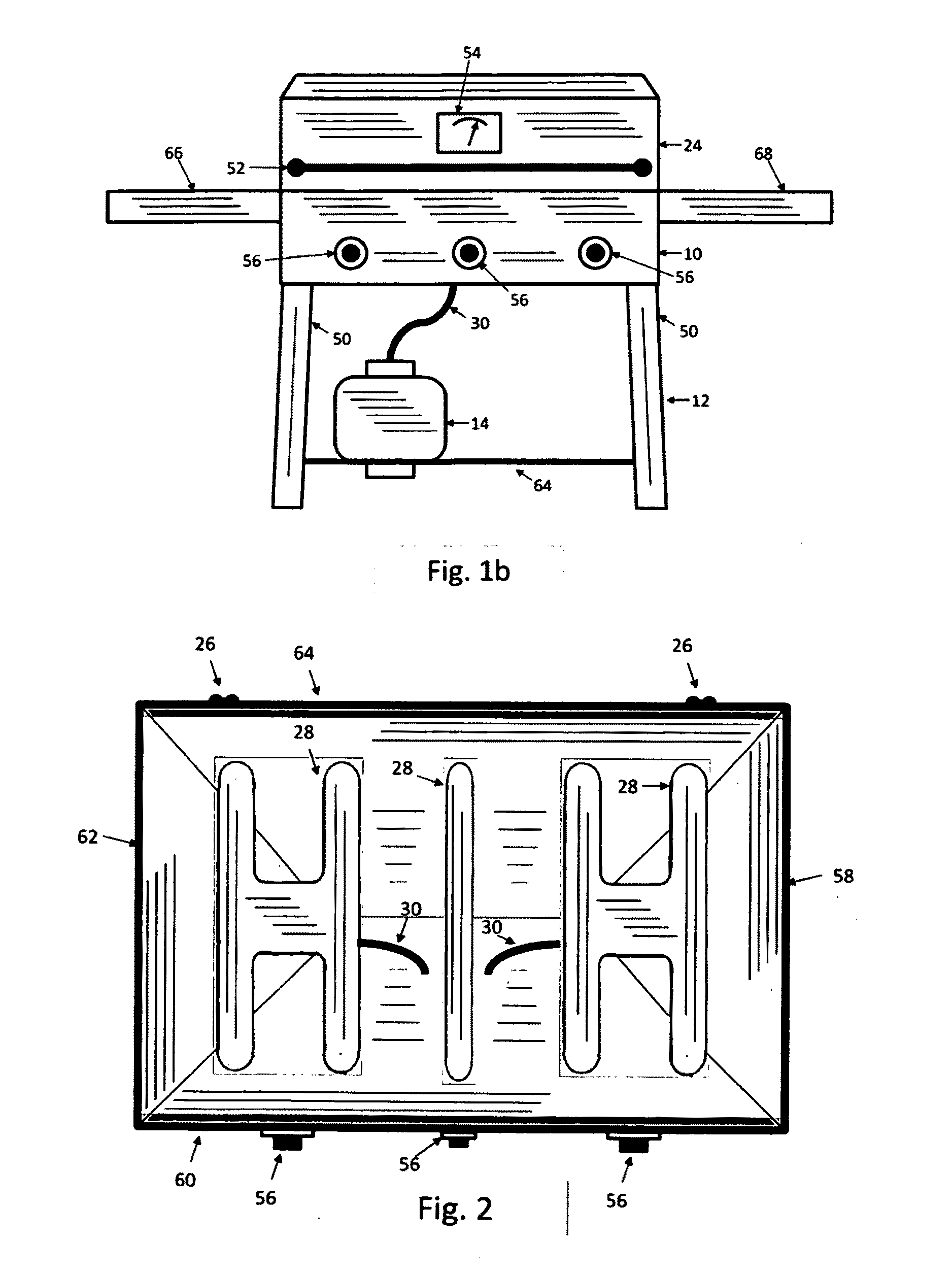
Barbecue Grill and Smoker
InactiveUS20110120442A1Minimal amountLess skillDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringSmoke
A barbecue grill, have an enclosed cooking container resting upon a support structure, the cooking enclosure having walls that enclose the cooking area and a clamshell lid for access, heating elements in the lower portion of the enclosure, connected to a fuel source, and containing within the cooking enclosure heating elements in the lower portion, grills for holding food and exposing it to the circulating air in the superior portion, and a drawer or drawers for wood, water, or other substances, which can be exposed to heat for the creation of smoke, steam or other result, consequently enabling the standard grilling process, but also providing a low skill, low effort means of enabling the slow smoking process as well as the simulated cooking of food over a wood fire.
Owner:DUNCAN DARIN JASON
Controllable fishing lure
The present invention relates to a controllable fishing lure. The lure is remotely controlled by the angler by a radio control transmitter on the fishing rod or proximate thereto. The lure can be steered by depressing buttons on the radio control transmitter. The depressions cause radio signals to be emitted from the transmitter, these signals corresponding to the movements desired by depressing the buttons. The radio signals from the transmitter are then received by a receiver, through an antenna, in the lure. The received signals are then processed by a controller that activates propellers, disposed on the lateral sides of the lure, whereby the lure is steered to the desired location in the water.
Owner:MERLINE PAUL K
Precision gun smith platform
A jig for finishing a workpiece with a handheld router or other handheld motor-driven rotational tool assembly is provided. The jig includes a baseplate that is precisely aligned and attached to a router. Guides, including a main guide and a support guide, are provided. The main guide is configured to precisely align with and fasten to the base plate in several different jig configurations. Right-angle adaptors attach to the guides and precisely align with and attach to the guides and the base plate to form several different jig configurations. Side plates secure the workpiece therebetween and provide a surface along which the main guide may slide to facilitate finishing operations on the workpiece.
Owner:STAGE 5 ENTERPRISES LLC
Disposable world-to-chip interface for digital microfluidics
ActiveUS9649632B2Easy to useLess skillLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisEngineeringReaction step
The present disclosure sets forth incorporating microfluidic chips interfaces for use with digital microfluidic processes. Methods and devices according to the present disclosure utilize compact, integrated platforms that interface with a chip upstream and downstream of the reaction, as well as between intermediate reaction steps if needed. In some embodiments these interfaces are automated, including automation of a multiple reagent process. Various reagent delivery systems and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
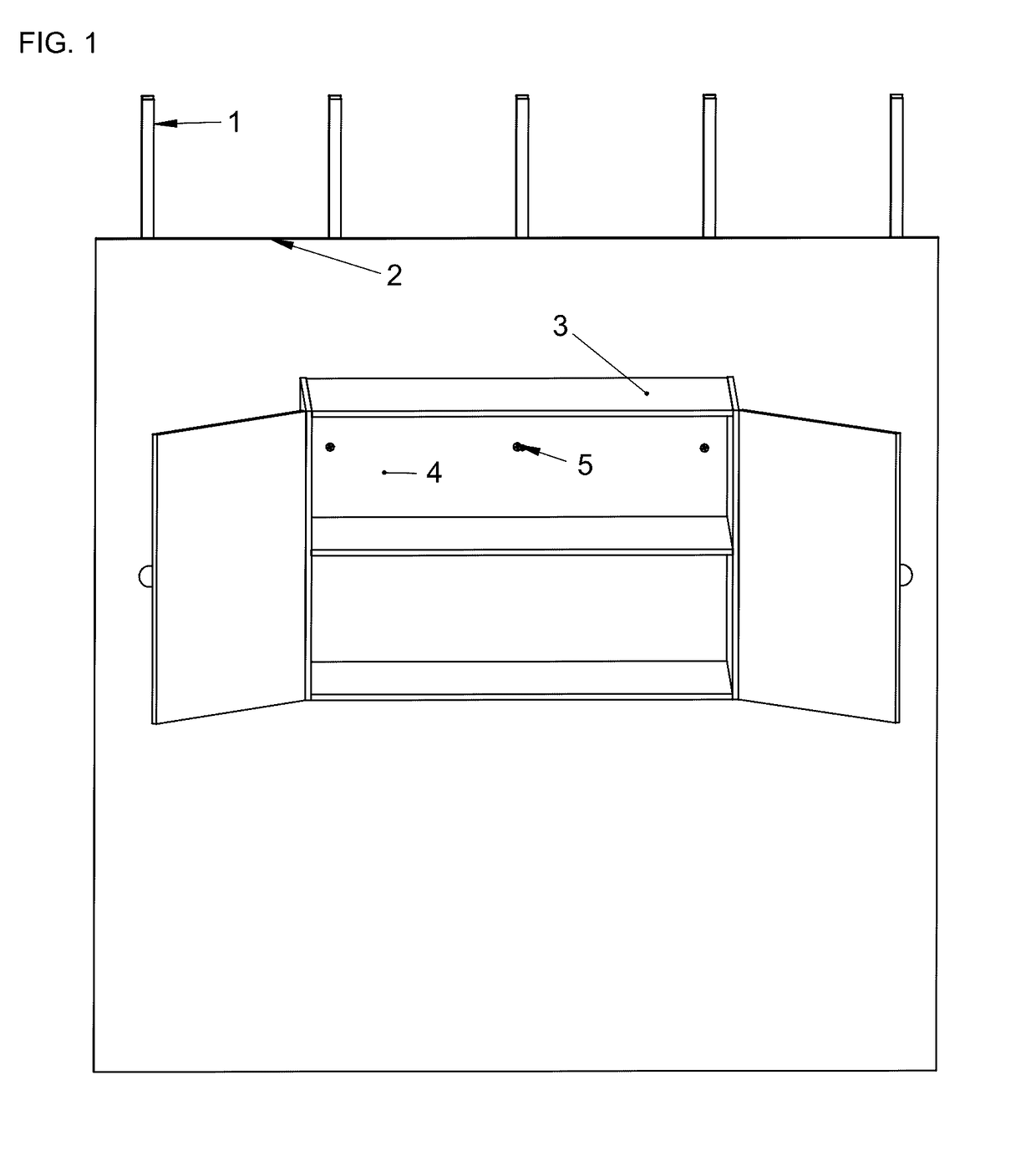
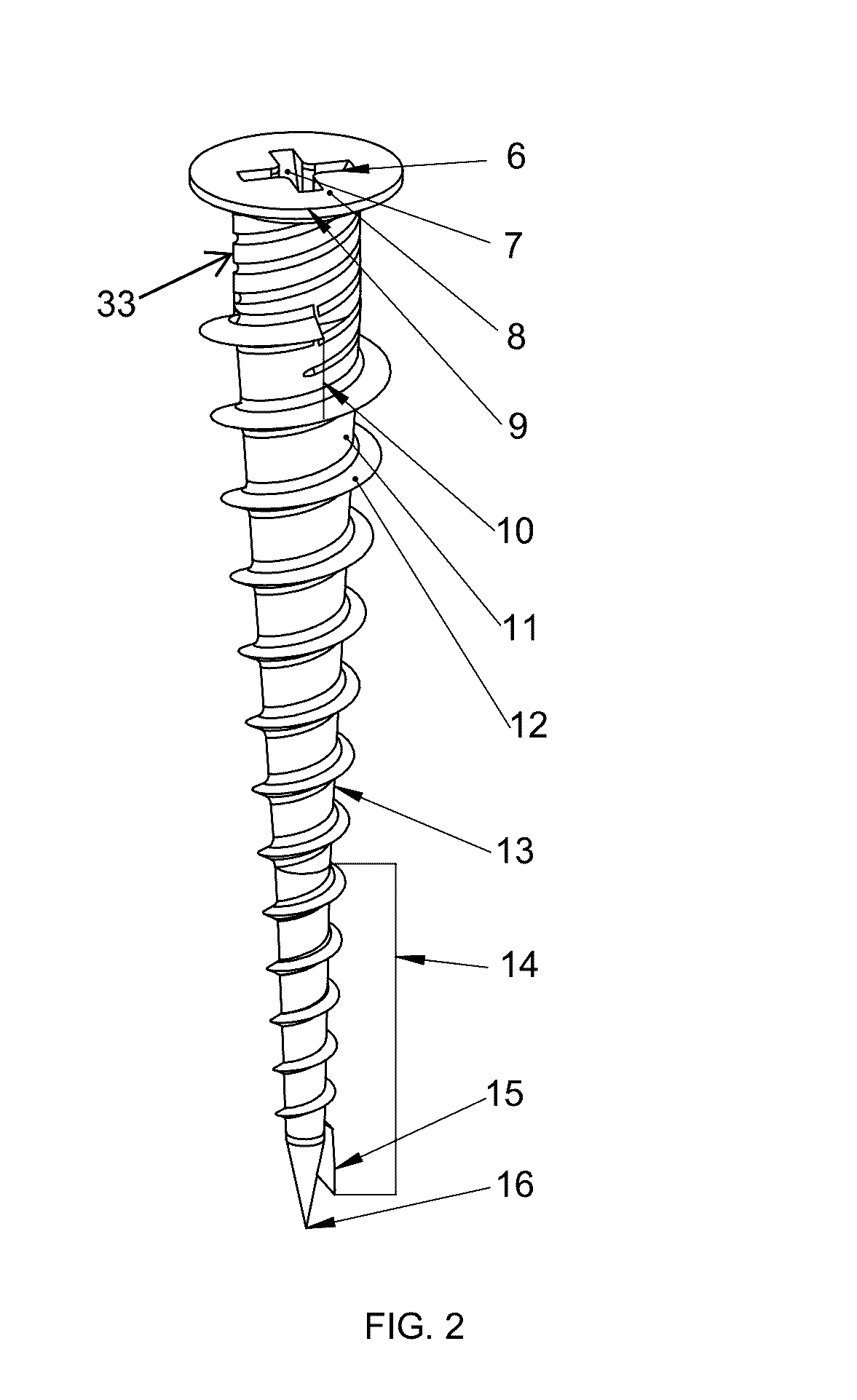
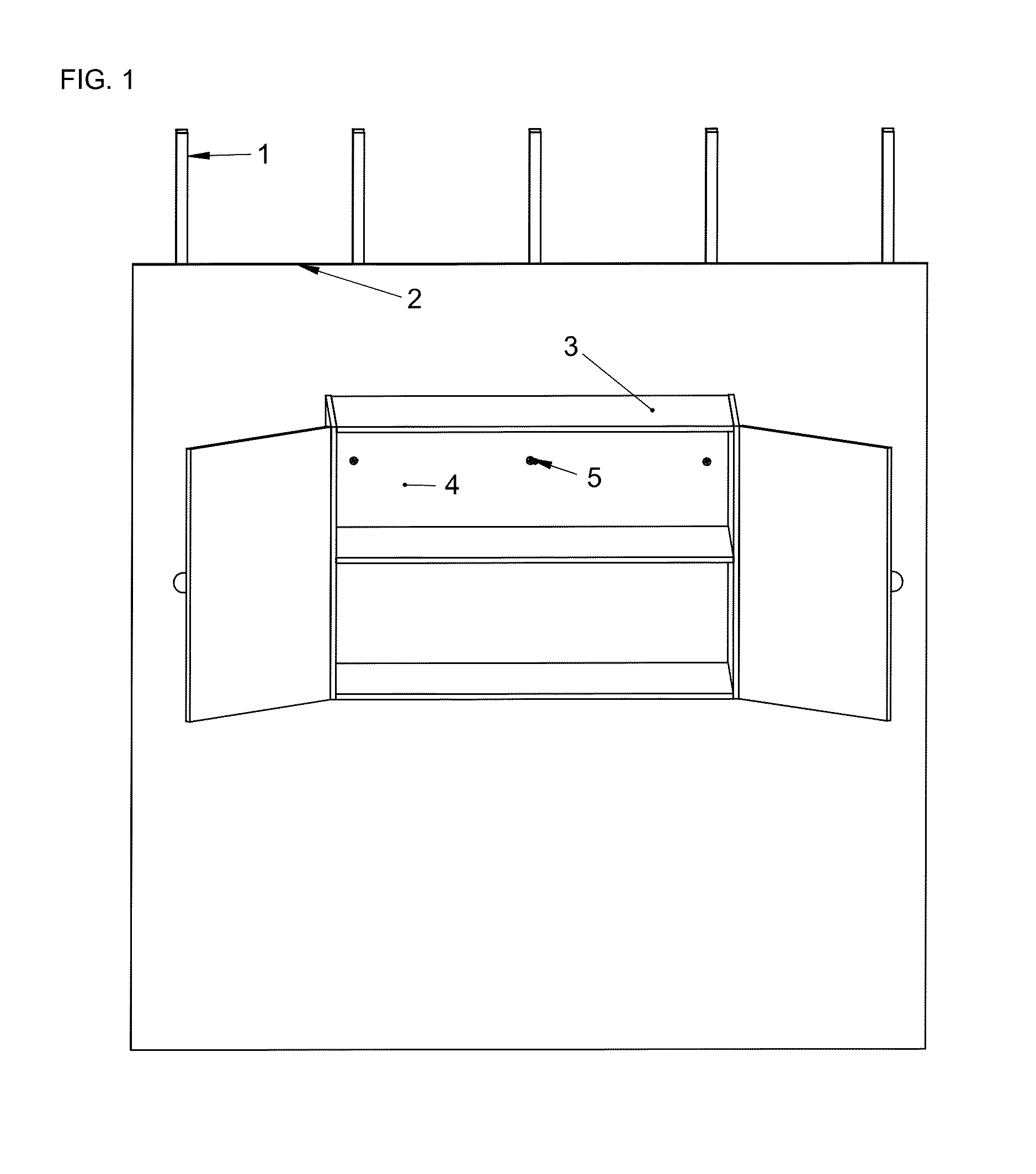
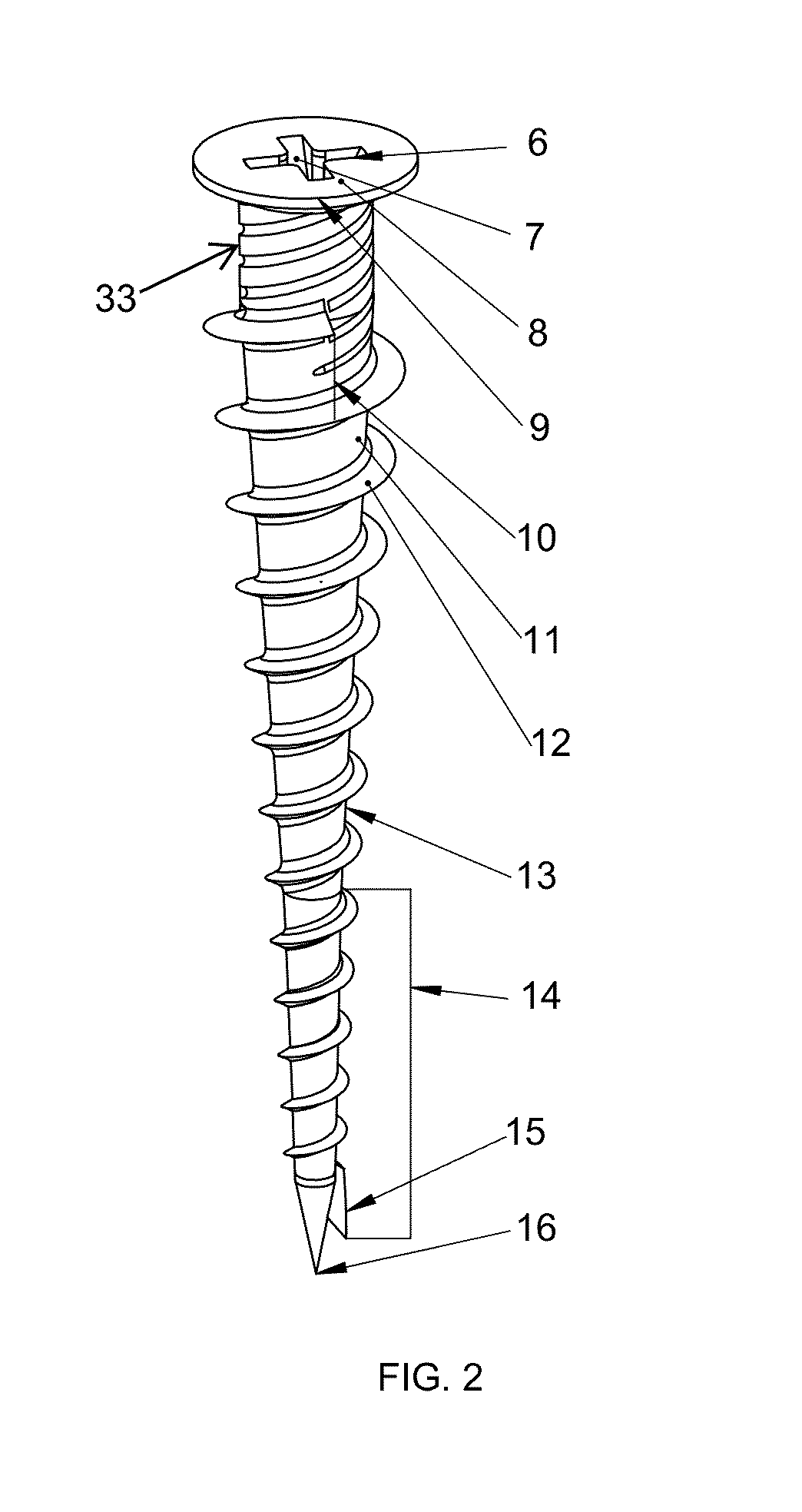
Steel stud anchor
A metal anchoring fastener fastens millwork onto walls constructed with wall cladding fastened to steel studs. The load typical of a loaded cabinet is borne by the steel stud anchors owing to the mate between the profile of the steel stud anchor and the layers of millwork and wall cladding and steel stud that said anchor penetrates. The pitch of the thread adorning the profile of the steel stud anchor progresses non-linearly along the length of said shaft, the shaft is generally non-linear in profile, and the thread profile is non-uniform along the length of said shaft. The anchor can also support a secondary screw concentrically penetrating the void at the center of the anchor, in order to hang loads from a wall, with or without millwork. Predrilling of the holes can enable installation of these zinc anchors.
Owner:HALL FRANKLIN +1
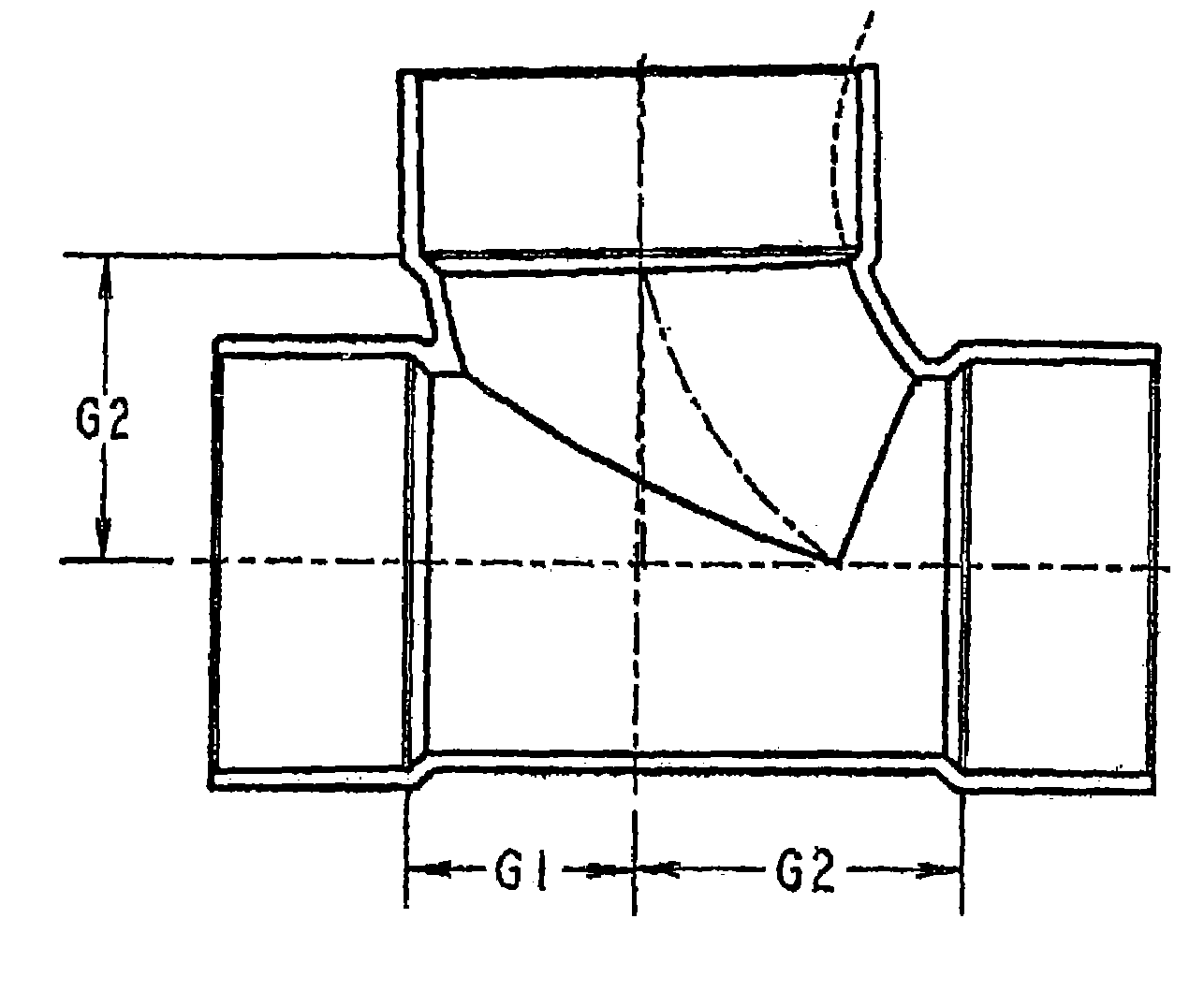
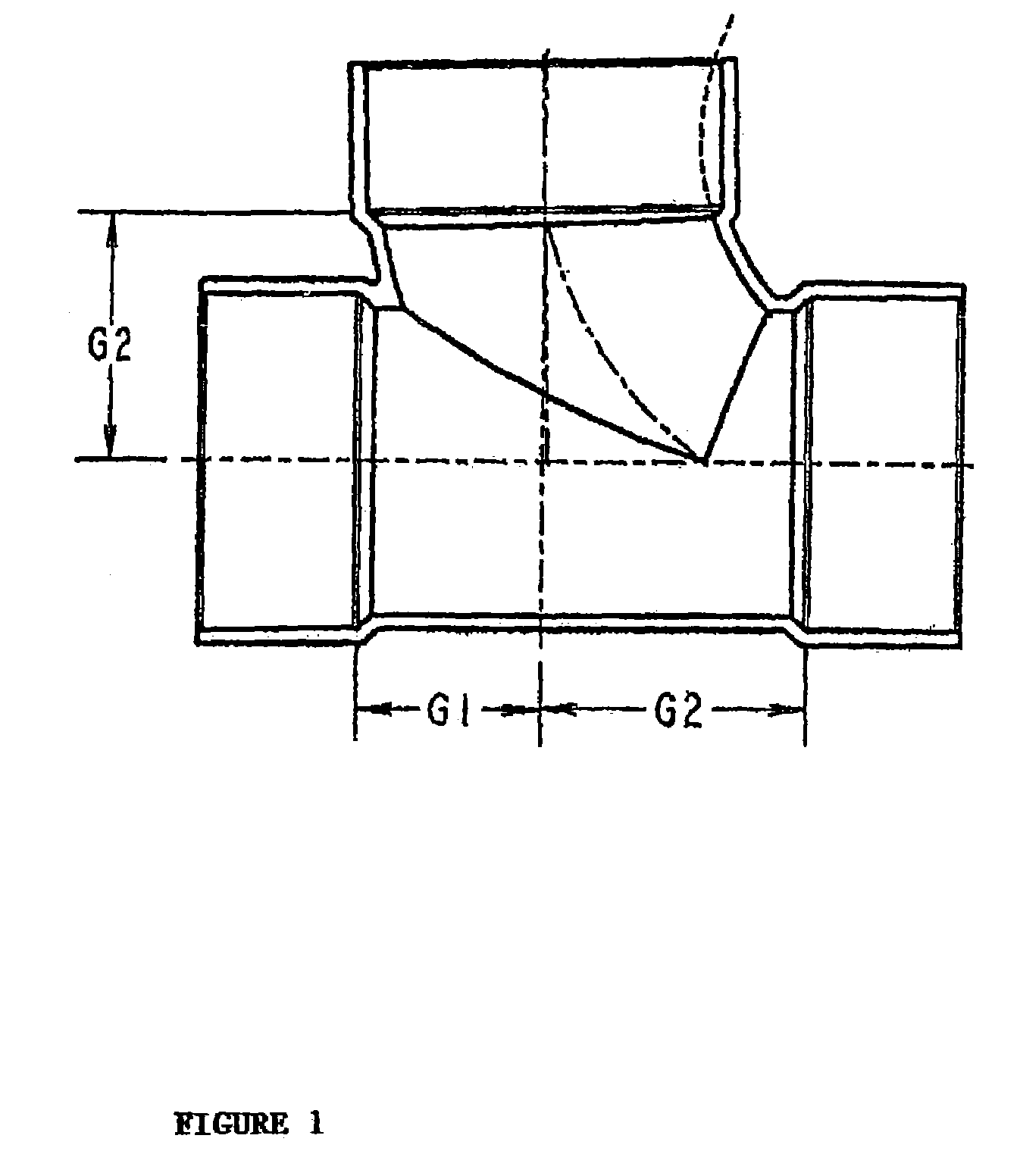
CPVC drain waste and vent fittings
InactiveUS7178557B2Easy to installCorrosive wastePipeline expansion-compensationLayered productsChlorinated polyvinyl chlorideEngineering
Owner:SPEARS MFG
Automatic verification of device models
ActiveUS8271252B2Less skillLow experience requirementError detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSource Data VerificationCode coverage
An efficient and cost effective mechanism for generating test files for automatic verification of a device model is disclosed. Uncompleted coverage goals determined based upon simulating processing of a test file by a design model may be expressed as negative assertions for input to a test data generator, where output from the test data generator may used to create a test file for completing all or some of the uncompleted coverage goals. The test data generator may indicate data which causes a property to fail, and therefore, may indicate test data which causes the uncompleted coverage goal to succeed. The initial test file may represent zero code coverage and / or zero functional coverage, thereby enabling the test data generator to automatically create one or more test files for accomplishing the more extensive code coverage goals and / or functional coverage goals. Functional coverage goals may be automatically generated by the test data generator.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
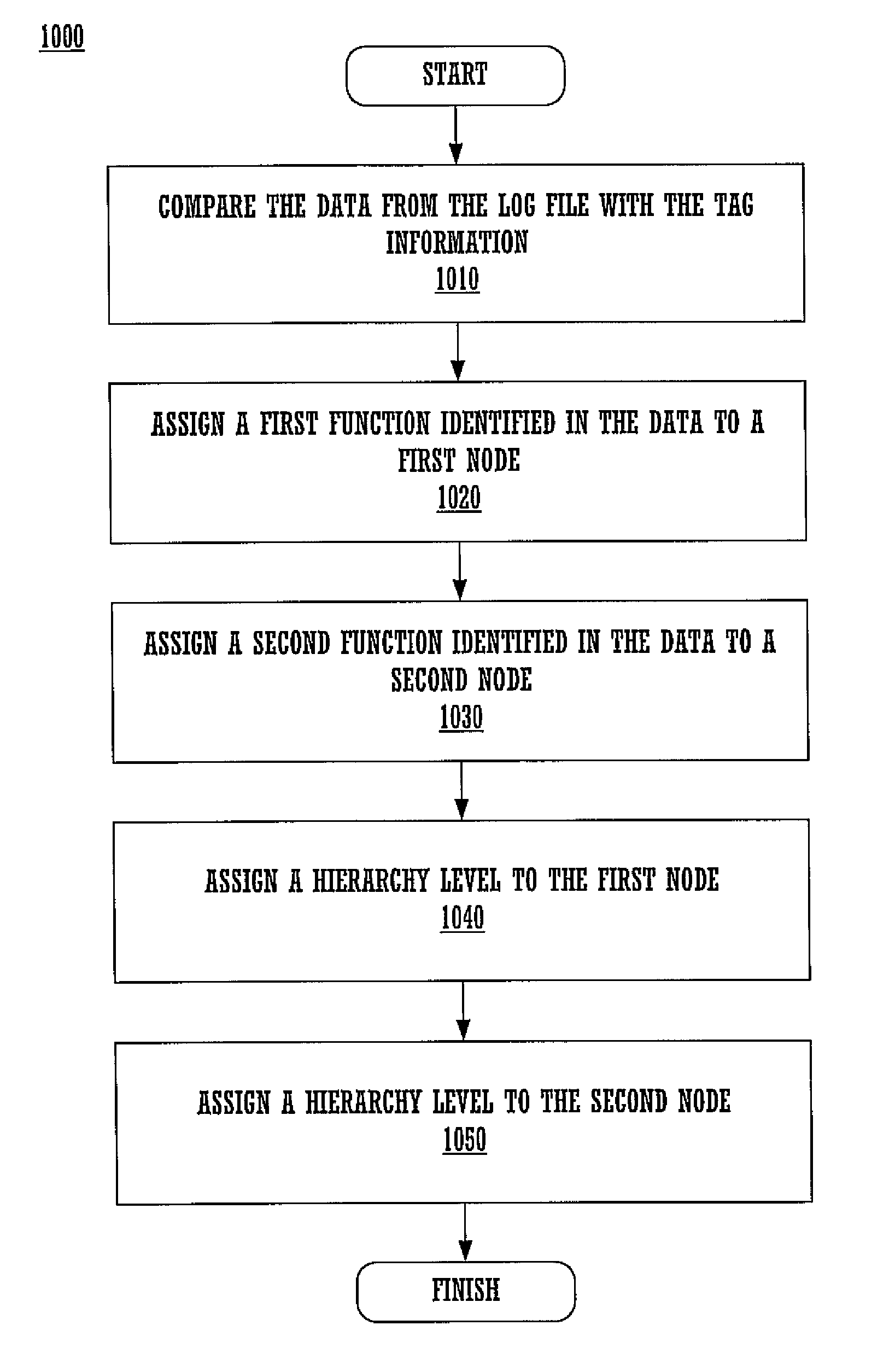
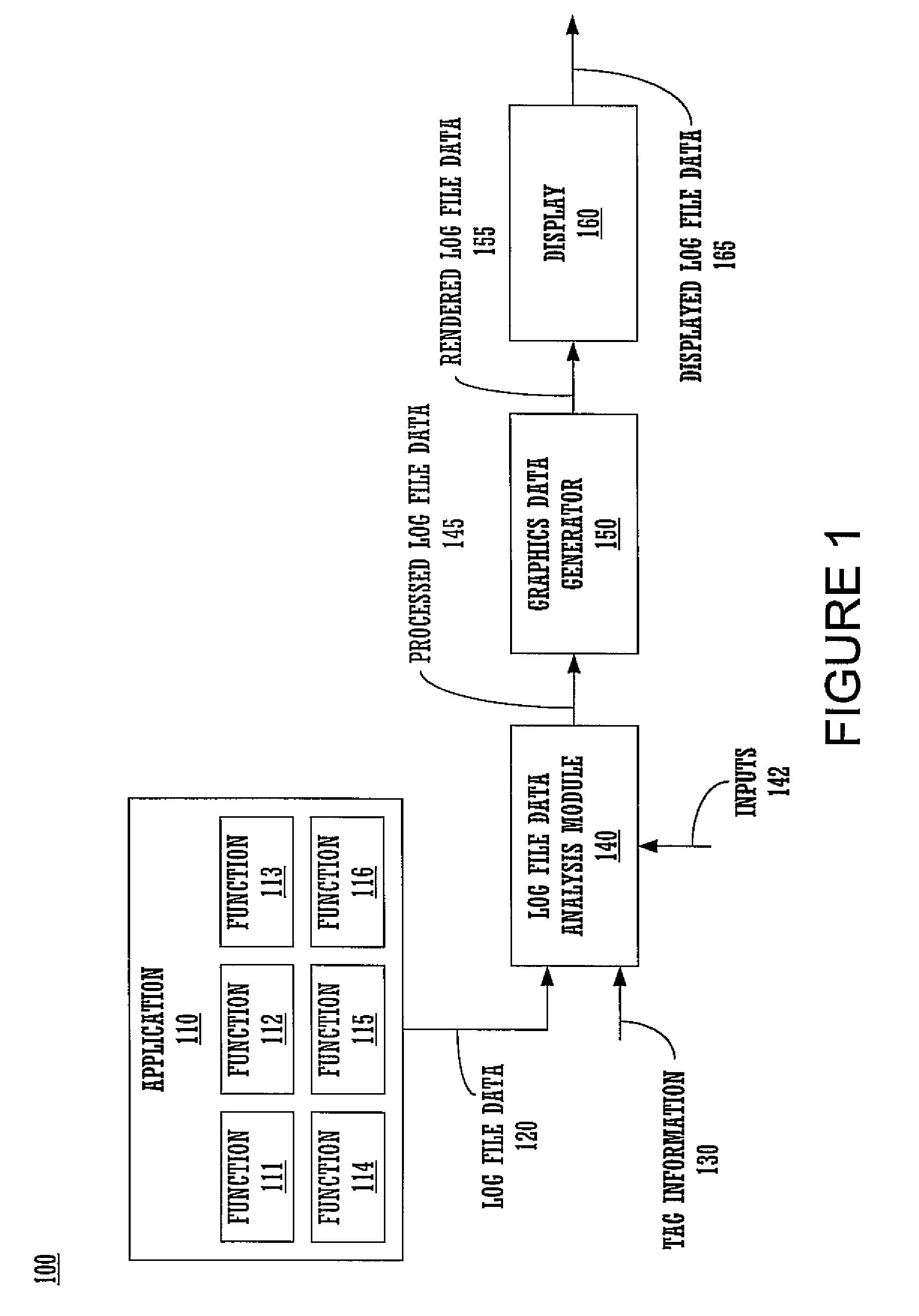
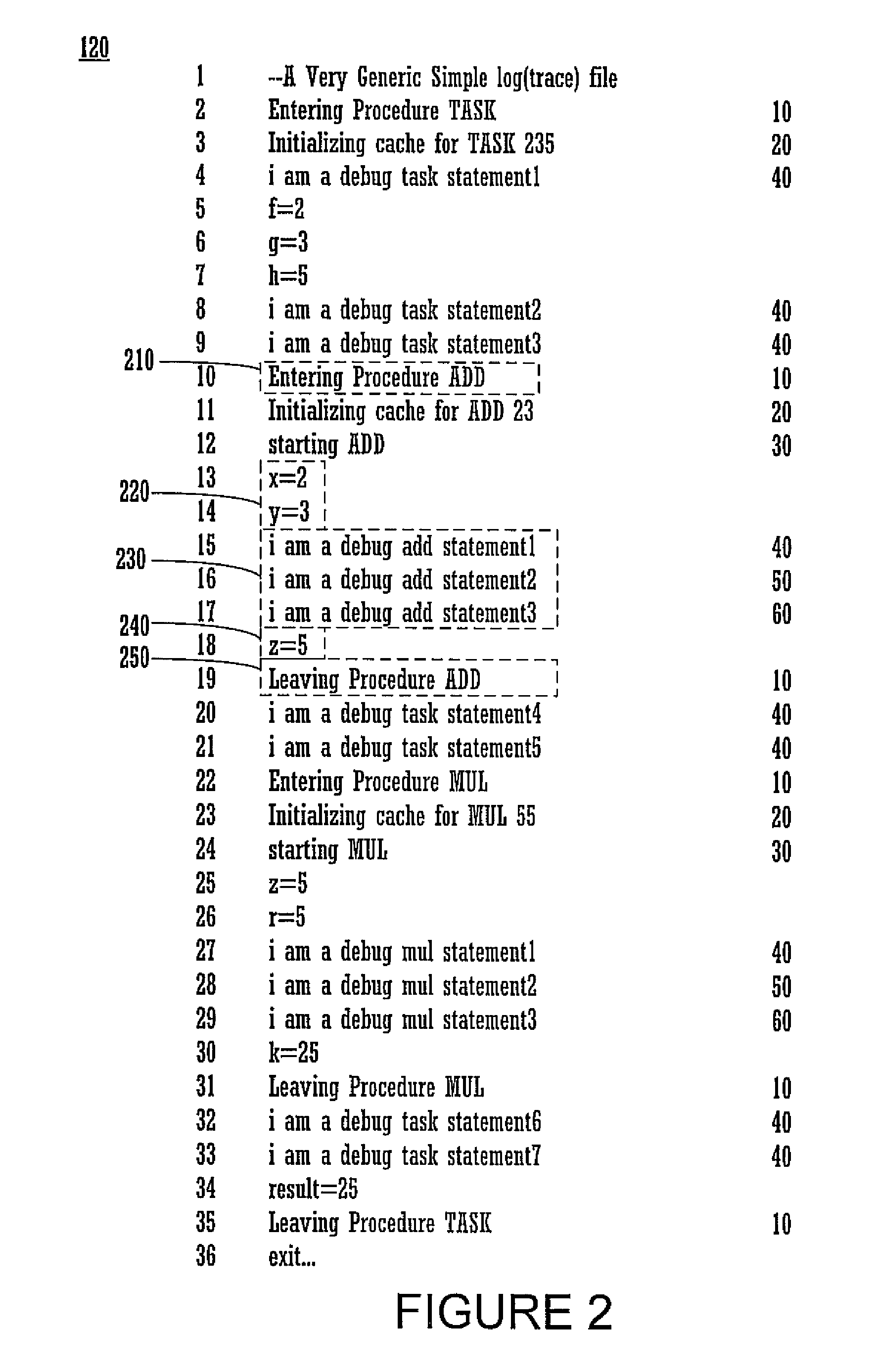
Method and system for log file processing and generating a graphical user interface based thereon
ActiveUS9098626B2Shorten the timeReduce difficultyHardware monitoringNatural language data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method and computer system for processing log file data, as well as to a graphical user interface for presenting the processed log file data is disclosed. Embodiments provide convenient mechanisms for processing log file data to generate a hierarchical representation of the log file data which more clearly indicates relationships between functions and information about one or more functions, where the log file data is processed in accordance with tag information associated with the application. The processed log file data may then be used to render a graphical user interface which displays the structured log file data. Nodes associated with nested functions may be indented with respect to parent nodes to indicate the nested relationship between functions. Additionally, the nodes may be expanded or collapsed to more clearly display the relationship between functions, to vary the amount of information displayed, etc.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Steel stud anchor
A metal anchoring fastener fastens millwork onto walls constructed with wall cladding fastened to steel studs. The load typical of a loaded cabinet is borne by the steel stud anchors owing to the mate between the profile of the steel stud anchor and the layers of millwork and wall cladding and steel stud that said anchor penetrates. The pitch of the thread adorning the profile of the steel stud anchor progresses non-linearly along the length of said shaft, the shaft is generally non-linear in profile, and the thread profile is non-uniform along the length of said shaft. The anchor can also support a secondary screw concentrically penetrating the void at the center of the anchor, in order to hang loads from a wall, with or without millwork. Predrilling of the holes can enable installation of these zinc anchors.
Owner:HALL FRANKLIN +1
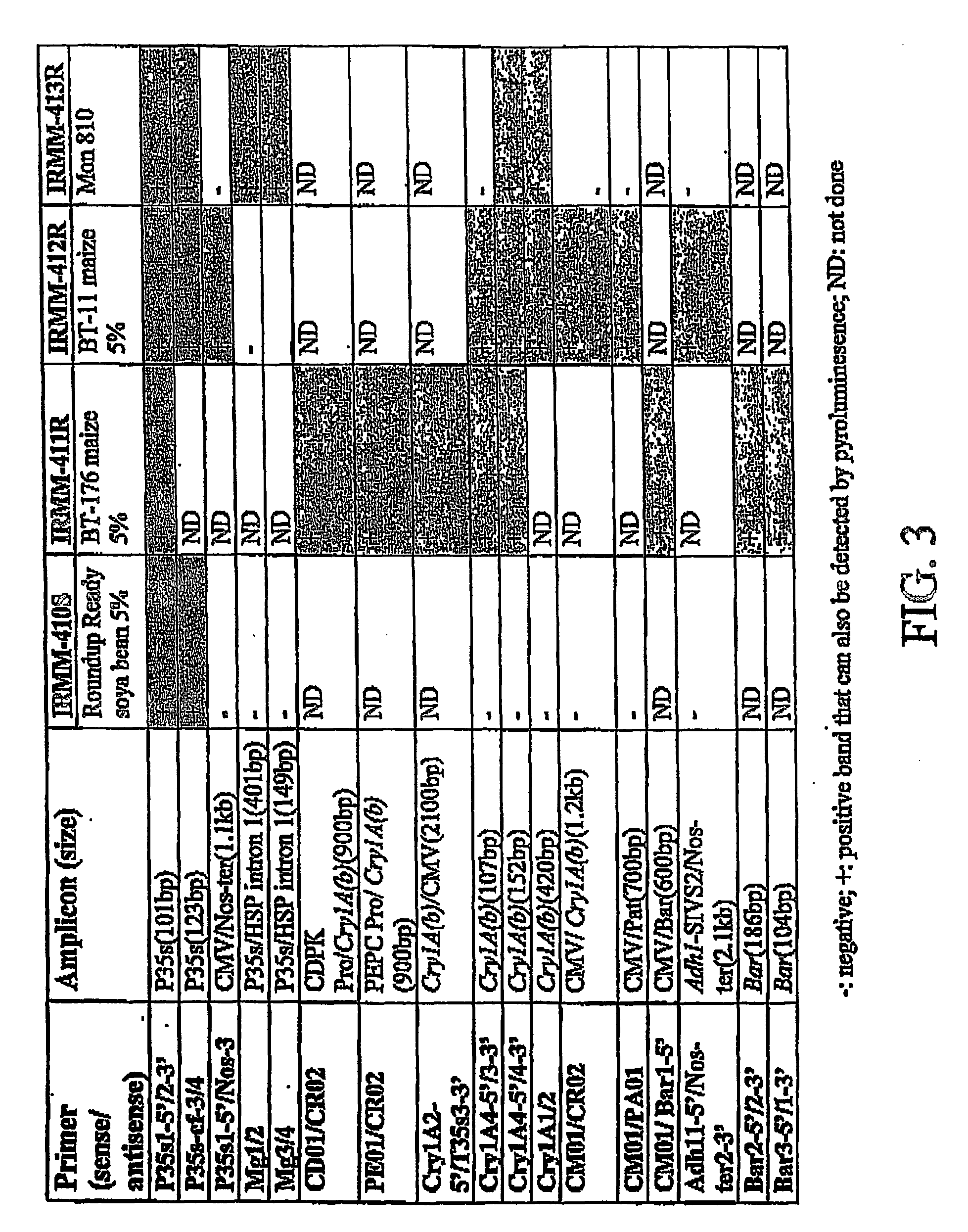
Detection of transgenes of genetically modified organisms using pyro luminescence
InactiveUS20070077561A1Facilitates polymerase-directed replicationHigh sensitivityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingTransgene
The present application provides a method for identifying the presence of a transgene of a genetically modified organism in a sample wherein the nucleic acid sequence of the transgene is replicated and detected as the release of PPi from the deoxynucleotide triphosphate precursors consumed in the replication reaction. This pyro luminescent detection system can be applied qualitatively or quantitatively to detect the presence of a specific transgene in a target DNA sample such as sample containing DNA from a genetically modified organism.
Owner:HONG YAN
Composite box building and the method of construction
The invention forms a composite building by using beams made from plastic foam coated with fiber reinforced concrete.
Owner:SAEBI NASSER
Manikin and eye device apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture
InactiveUS7371069B2Accurately and consistently and efficientlyLess skillDollsOrganic chemistryArtificial EyesOphthalmology
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture are disclosed for installing an artificial eye in a realistic, life-like sculpture, comprising an artificial eye of partially hemispherical shape, as well as a manikin with an eye-mounting area adapted to mate with such an artificial eye without risk of subsequent movement of the eye or of distortion of the features surrounding the eye-mounting area of the sculpture. Eye mounting pieces for retrofitting existing sculptures having conventional eye mounting areas to permit the accurate and life-like mounting of artificial eyes are also provided.
Owner:TOHICKON JOHNSON DEV
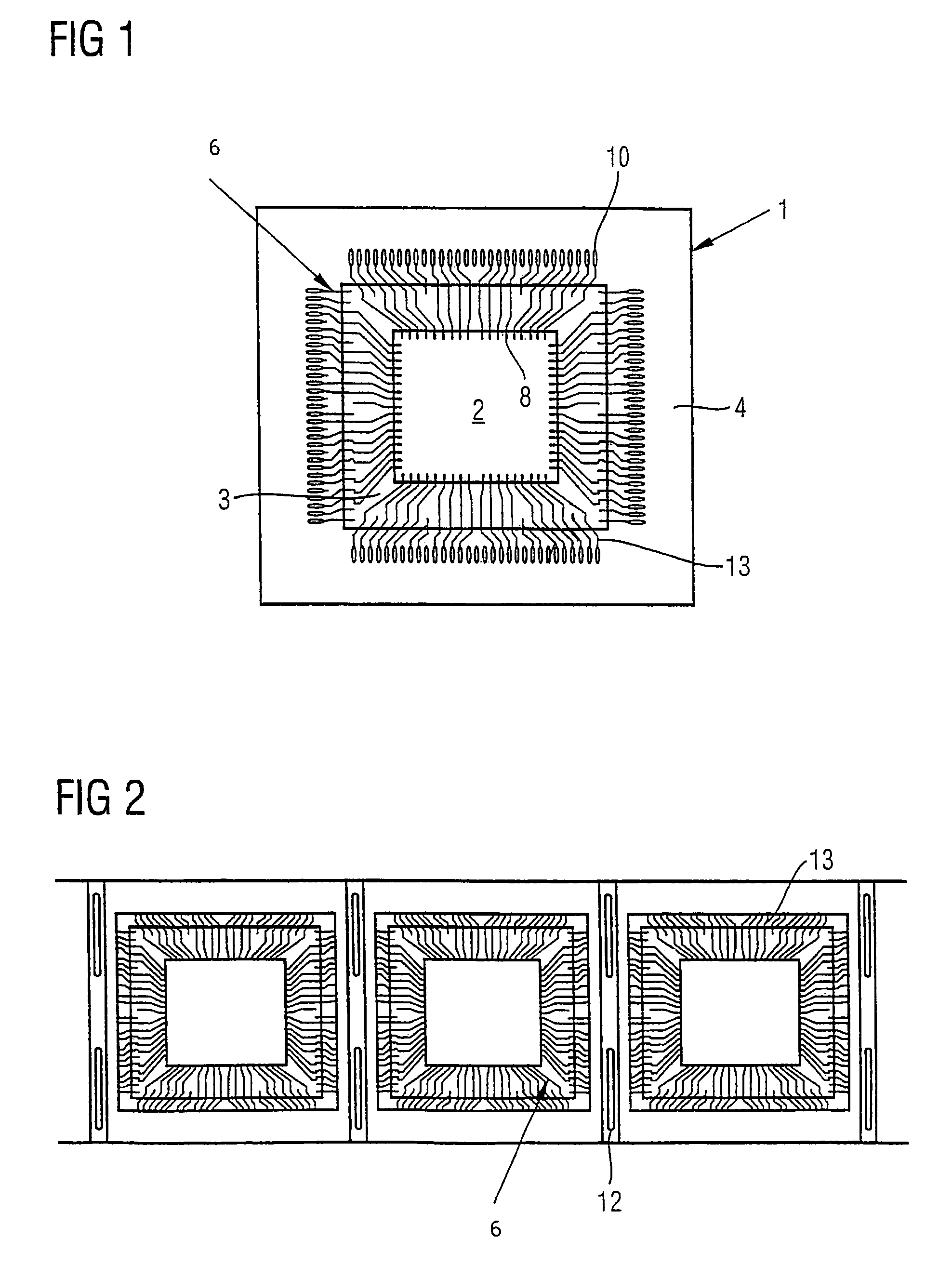
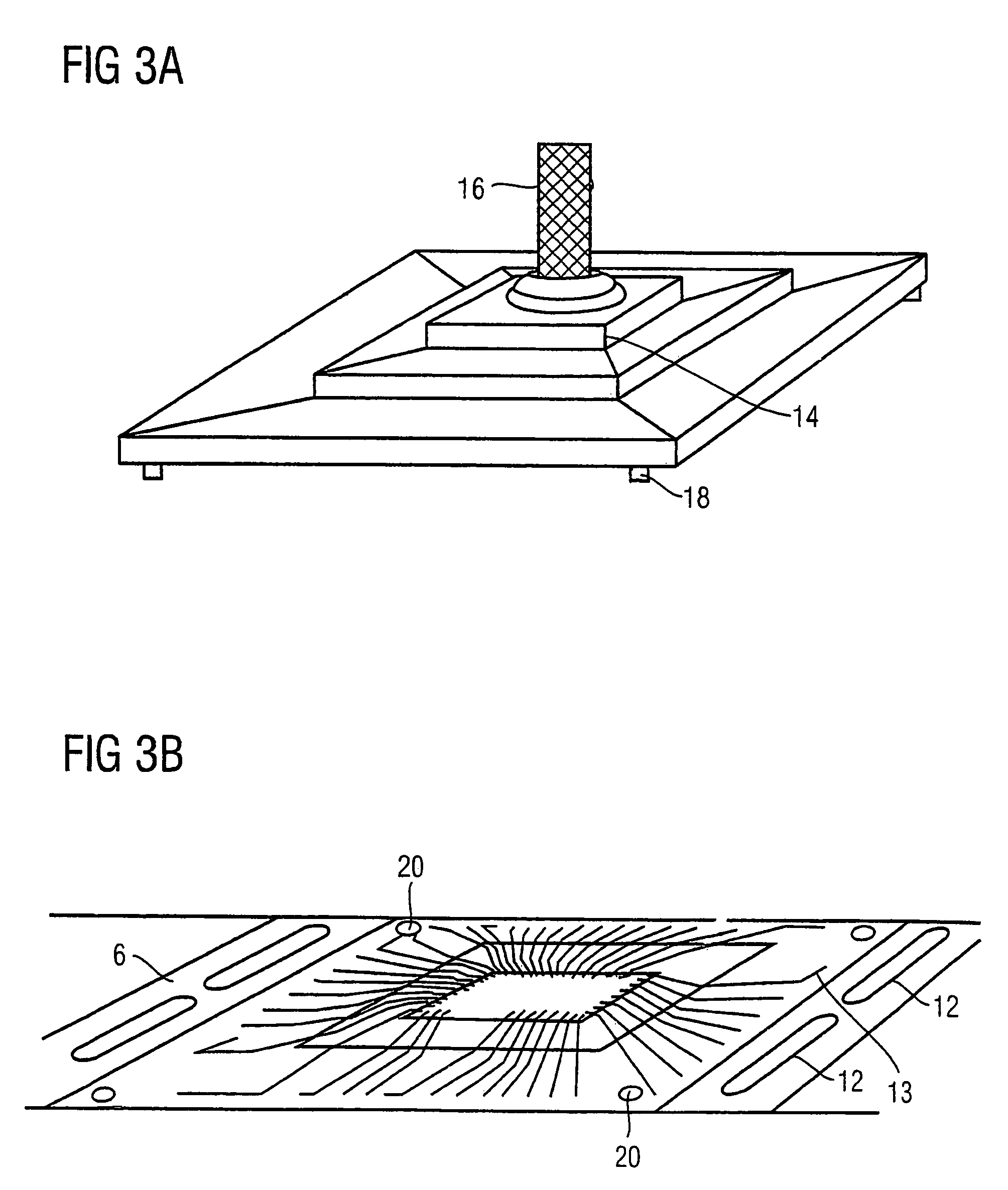
Method for connecting a die assembly to a substrate in an integrated circuit and a semiconductor device comprising a die assembly
InactiveUS7880277B2Improve efficiencyImprove bindingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringPhotonic integrated circuit
A semiconductor device includes a substrate, a die assembly attachable to the substrate and a flexible strip extending over the substrate and the die assembly. The flexible strip has one or more routing circuits carried thereon. The die assembly and the substrate are arranged to be electrically connected through the one or more routing circuits carried on the flexible strip.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com