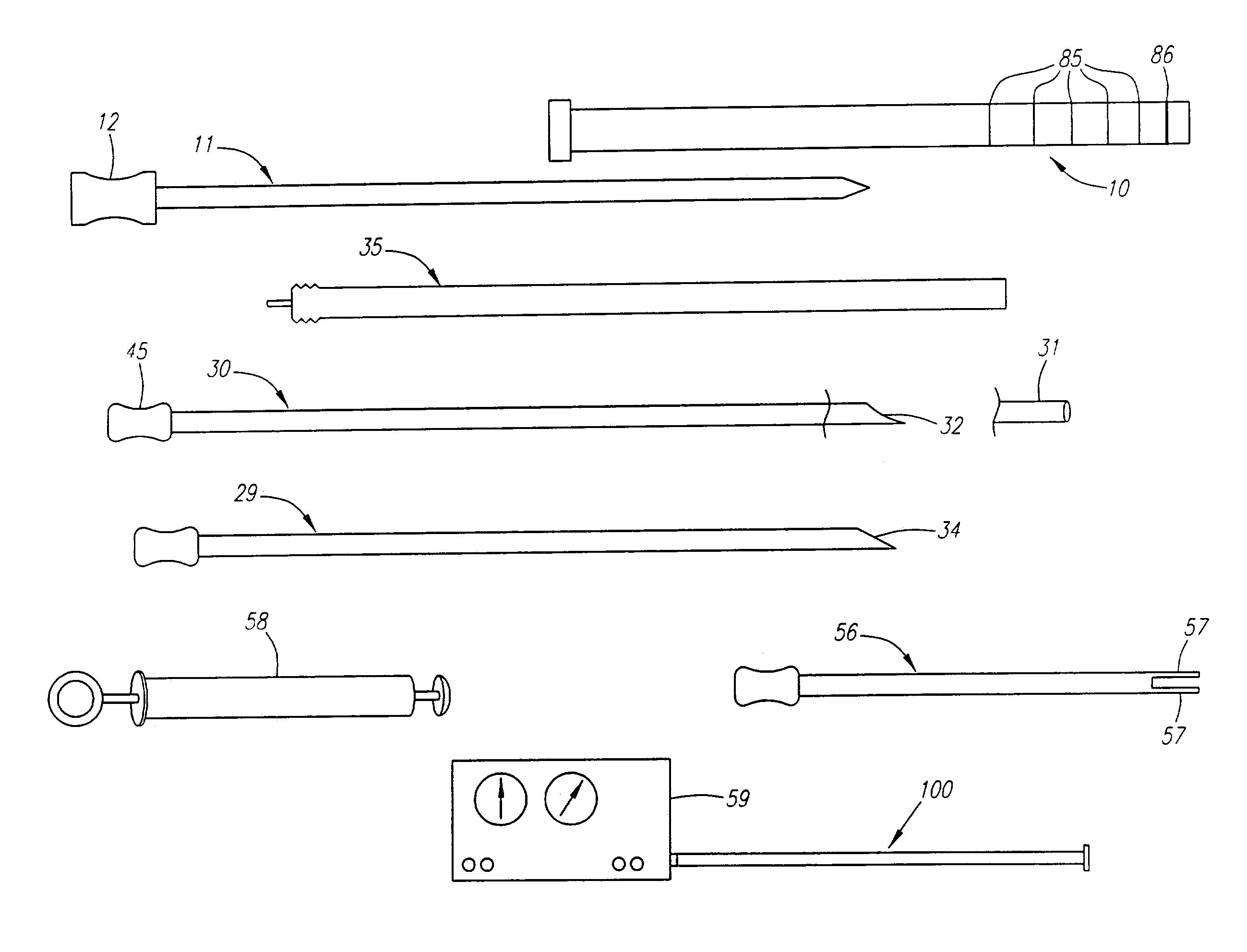
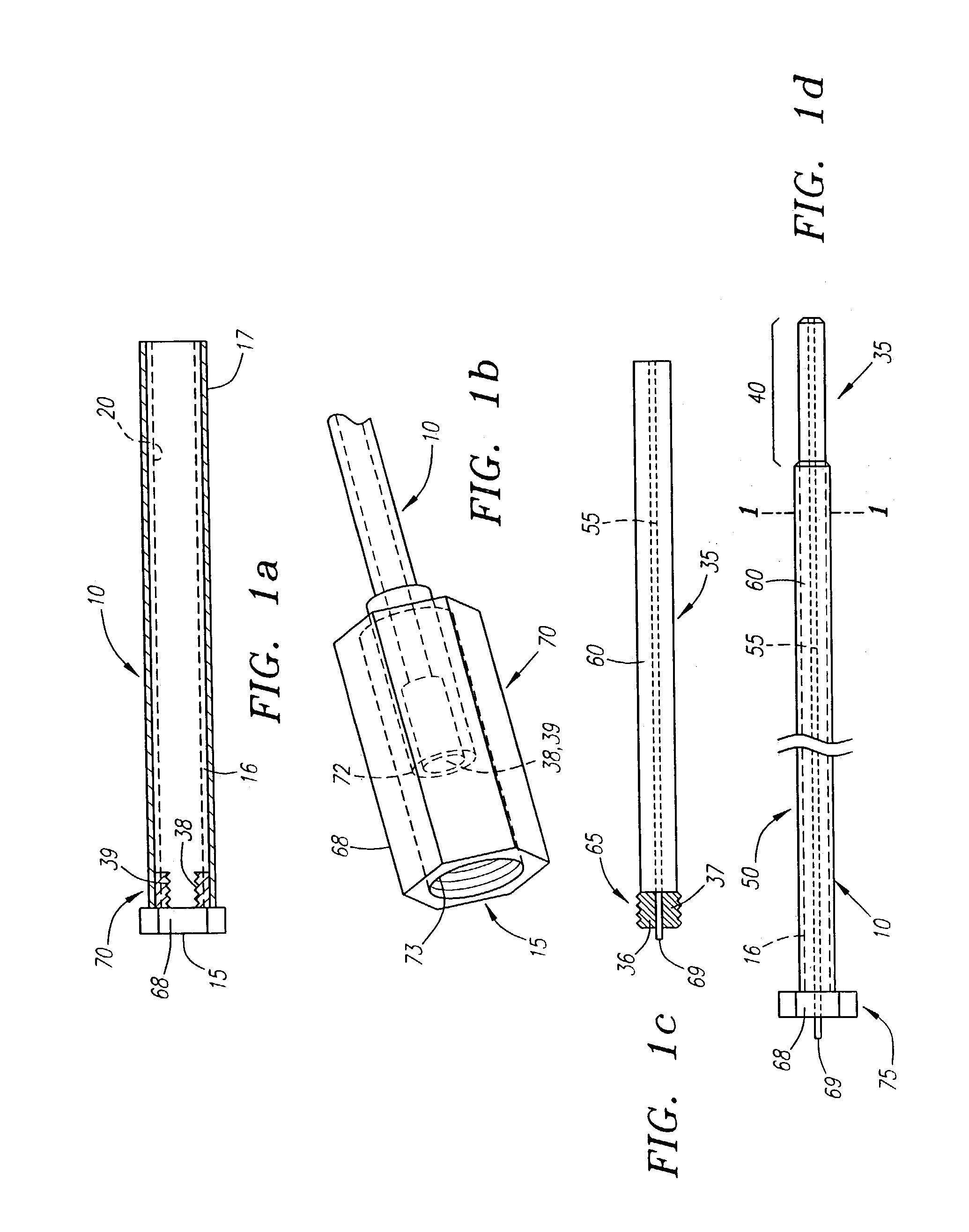
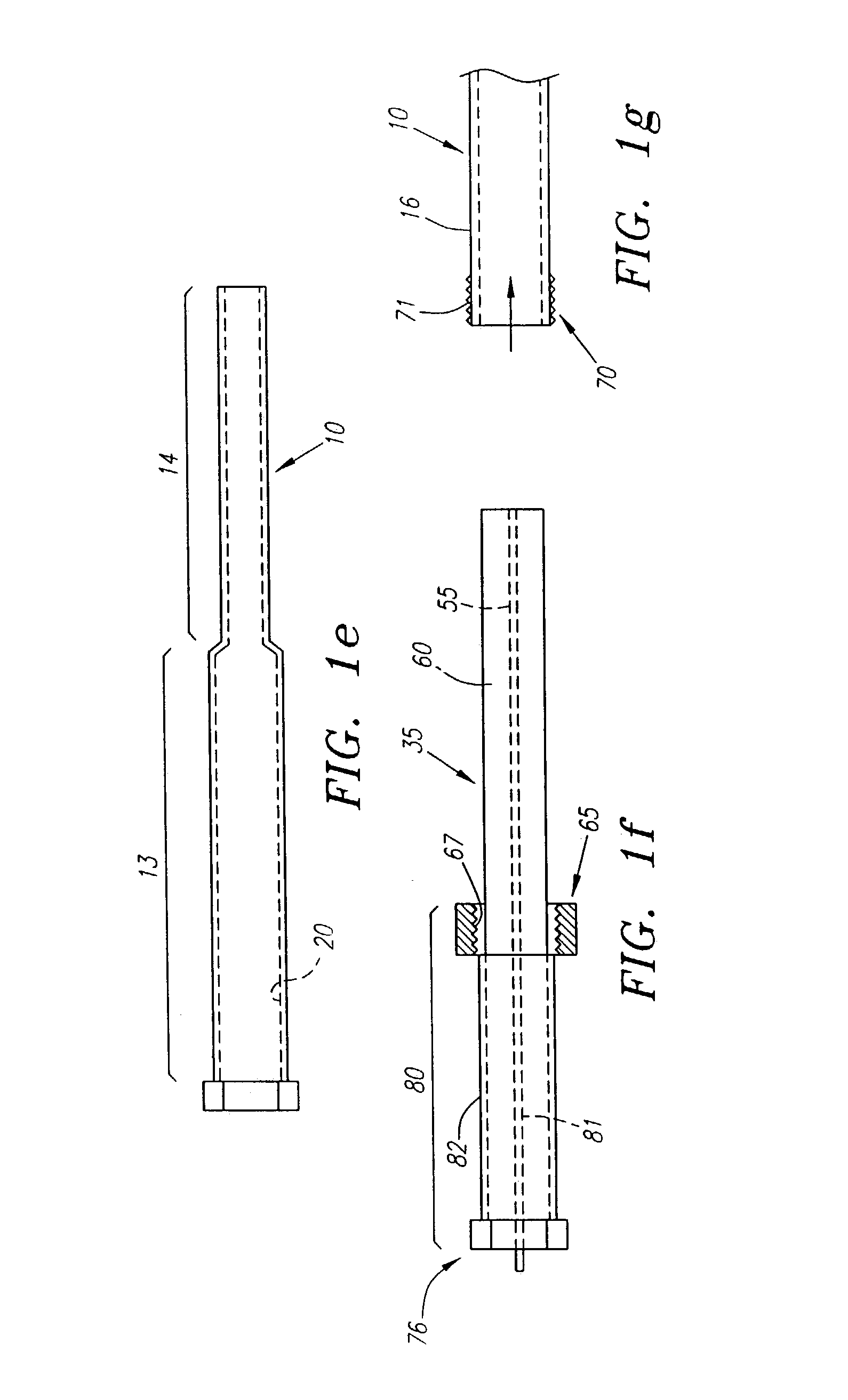
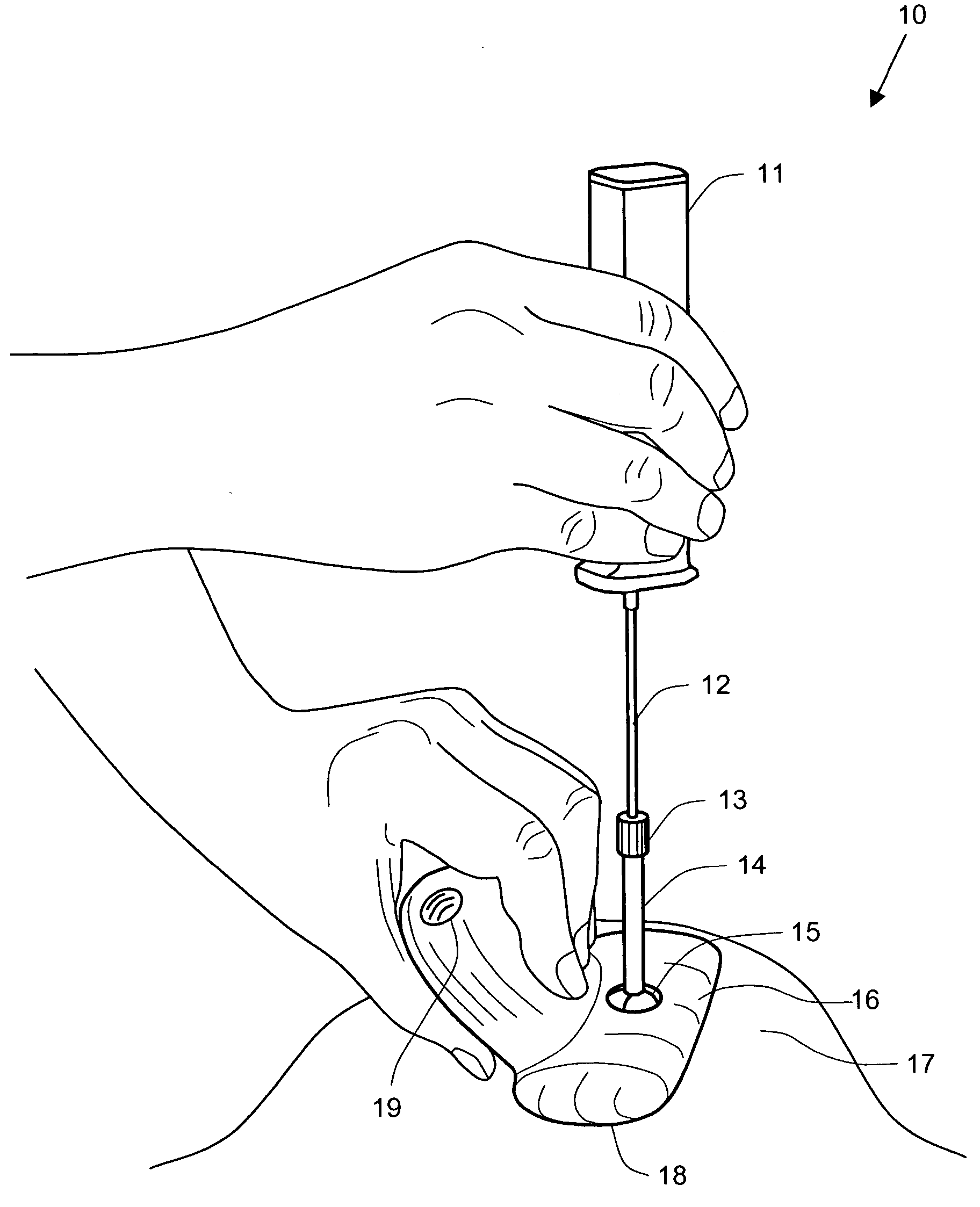
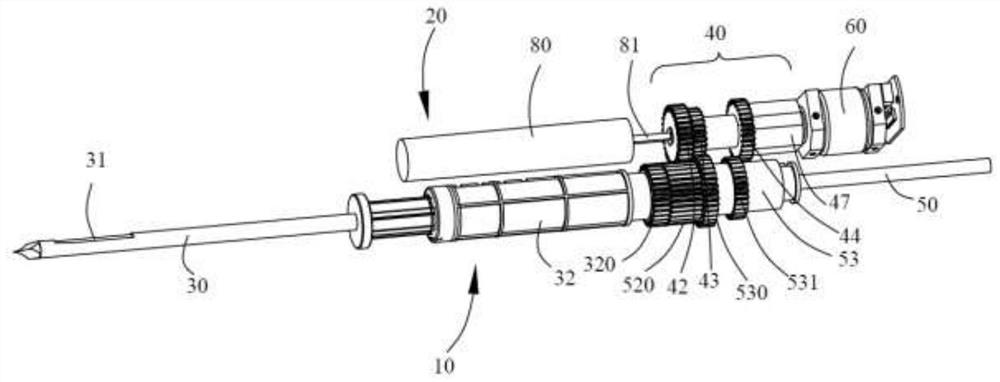
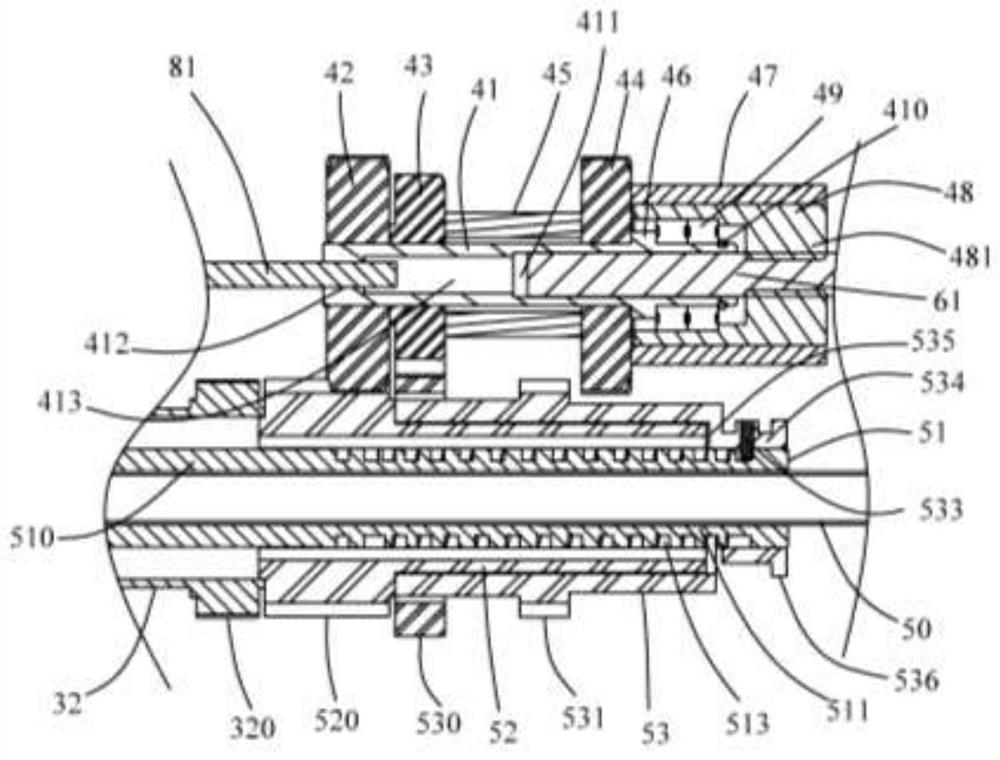
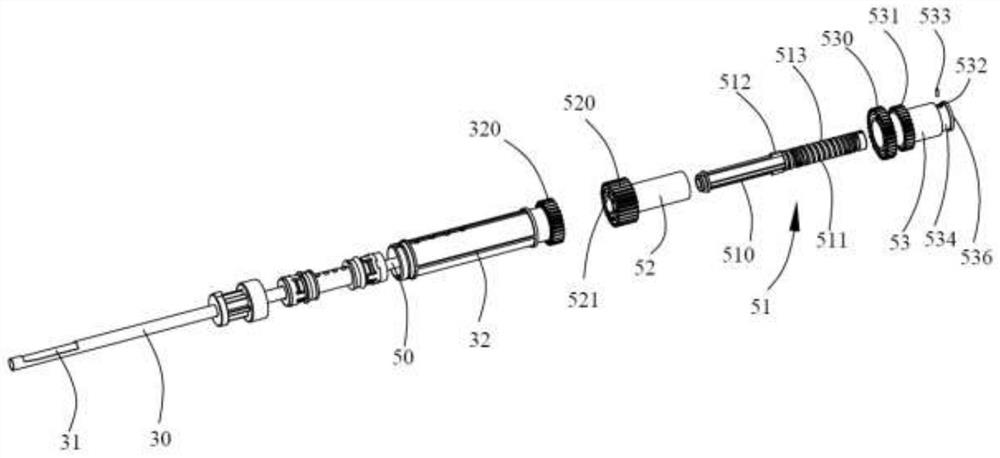
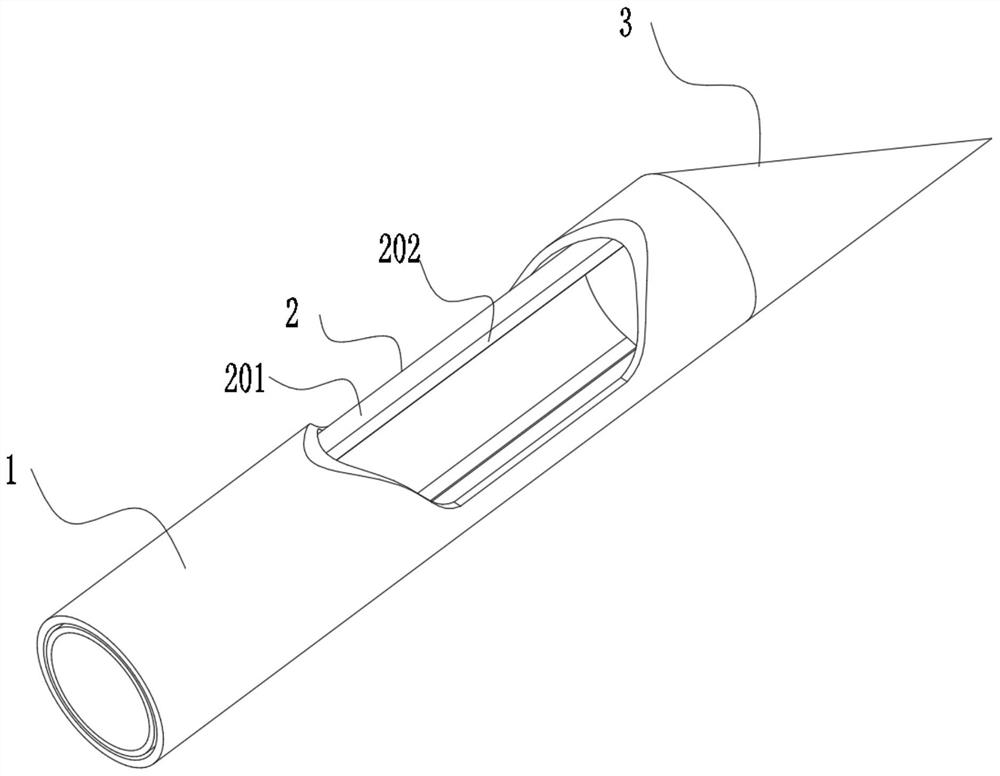
Patents
Literature
188 results about "Biopsy needles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Benefits. Needle biopsy is a reliable method of obtaining tissue samples that can help diagnose whether a nodule is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant. A needle biopsy is less invasive than open and closed surgical biopsies, both of which involve a larger incision in the skin and local or general anesthesia.
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS7160292B2Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFungating tumourMicrowave ablation
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device and method for biopsy guidance using a tactile breast imager
InactiveUS20040267121A1Provide real-timeIncreased sensitivity and repeatability and accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesBiopsy procedurePressure sense
A biopsy guidance device is enclosed based on a tactile imaging probe adapted to accept a biopsy gun. The tactile imaging probe includes a pressure sensing surface providing real-time 2-D images of the underlying tissue structures allowing to detect a lesion. A cannula is provided supported at a center point by a ball and socket joint. The joint is equipped with linear and angular sensors and supports the cannula with the ability to rotate thereof about the center point. The position, linear and angular displacement and direction of the needle tip of a biopsy needle placed inside the cannula is therefore known at all times and provided as a feedback signal to a physician. Also provided to a physician is a position of the target site at a lesion, as well as a linear and angular deviation of the needle tip away from the target site. Such audio, light, or visual feedback allows the physician to correct the insertion angle and depth to confidently reach the target site to perform a biopsy. Method is also disclosed to guide the biopsy procedure.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS20060116633A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Apparatus and method for generating a magnetic field
InactiveUS20060114088A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMagnetsTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Bioabsorbable marker having external anchoring means
ActiveUS6994712B1Release stressInhibit migrationInfusion syringesSurgeryPermanent markerBiopsy needles
A clip and a bioabsorbable marker are employed to mark a biopsy site. The former provides a permanent marker that is clamped onto tissue and that cannot migrate from the site over time. The latter is gradually bioabsorbed over time but the time may vary widely from weeks to months. In most embodiments, the clip and marker are integrally formed with one another at the time of manufacture. In one embodiment, the clip and marker are independently made but are joined to one another during the site-marking process. The markers are deployed by core biopsy needles of the type employing a vacuum, of the type that does not employ a vacuum, and by coaxial biopsy needles.
Owner:MEDICAL DEVICE TECH
Training aids and methods for needle biopsy
InactiveUS6568941B1Accurate tactile sensationFacilitate tactile learningEducational modelsHuman bodyPalpation
A training aid for teaching needle biopsy of the human breast. The inventive methods use breast models having lifelike properties providing accurate tactile sensation during palpation of the breast that enable a trainee to learn to locate modeled internal lesions and similar tissues in the breast. These same properties allow learning of tactile sensations indicating relative position and motion of biopsy needles during biopsy needling procedures. To facilitate tactile learning, the breast model includes an opaque skin that blocks the trainee view of a breast cavity containing modeled lesions, ensuring that needling procedures are performed based solely on "feel". The present invention also includes alternative training methods using a second breast model that is sufficiently transparent to allow viewing of modeled lesions from any relative position. The present invention includes training systems incorporating breast models and viewing stands and methods of training using these aids.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN MARK K
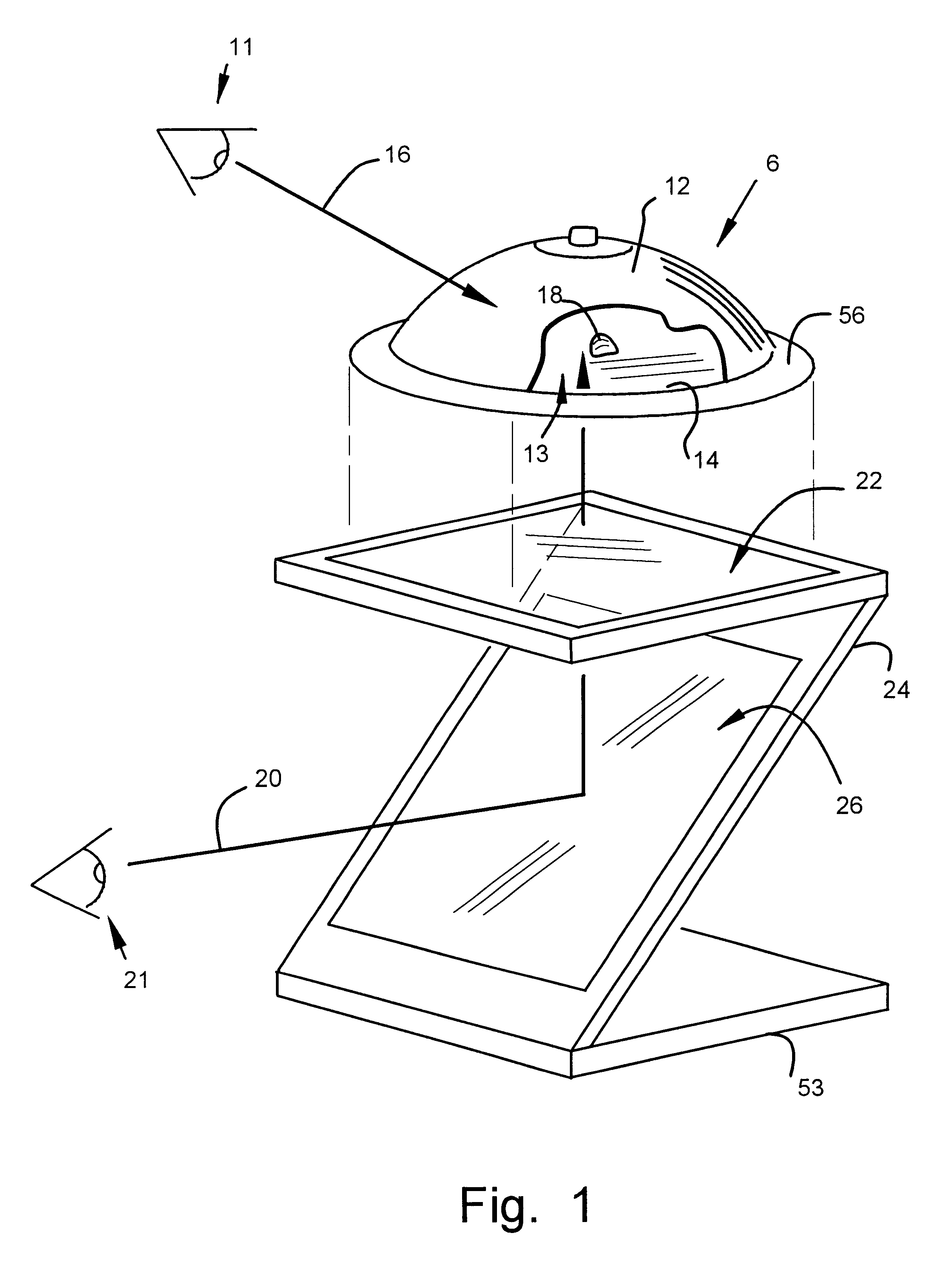
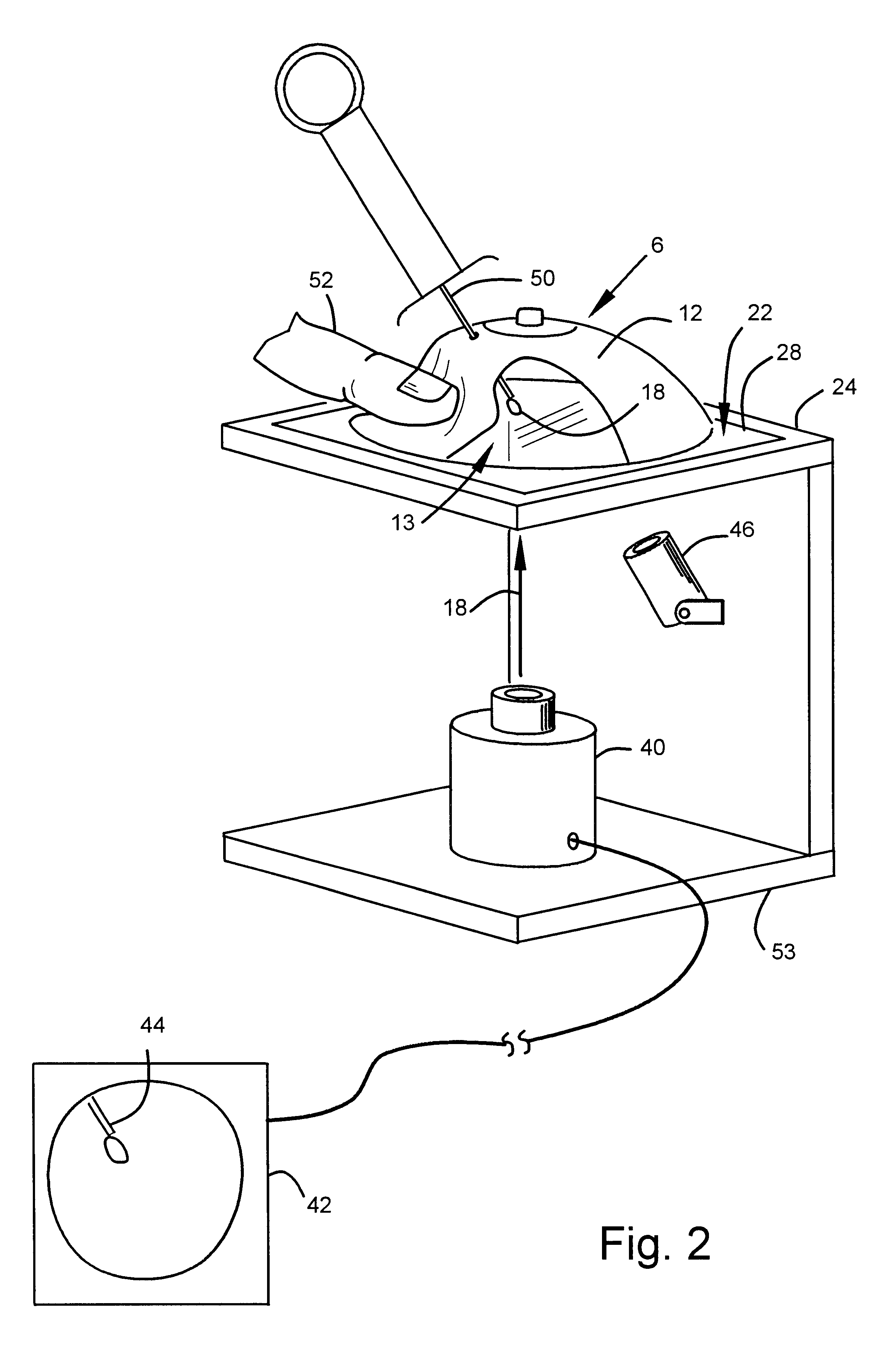
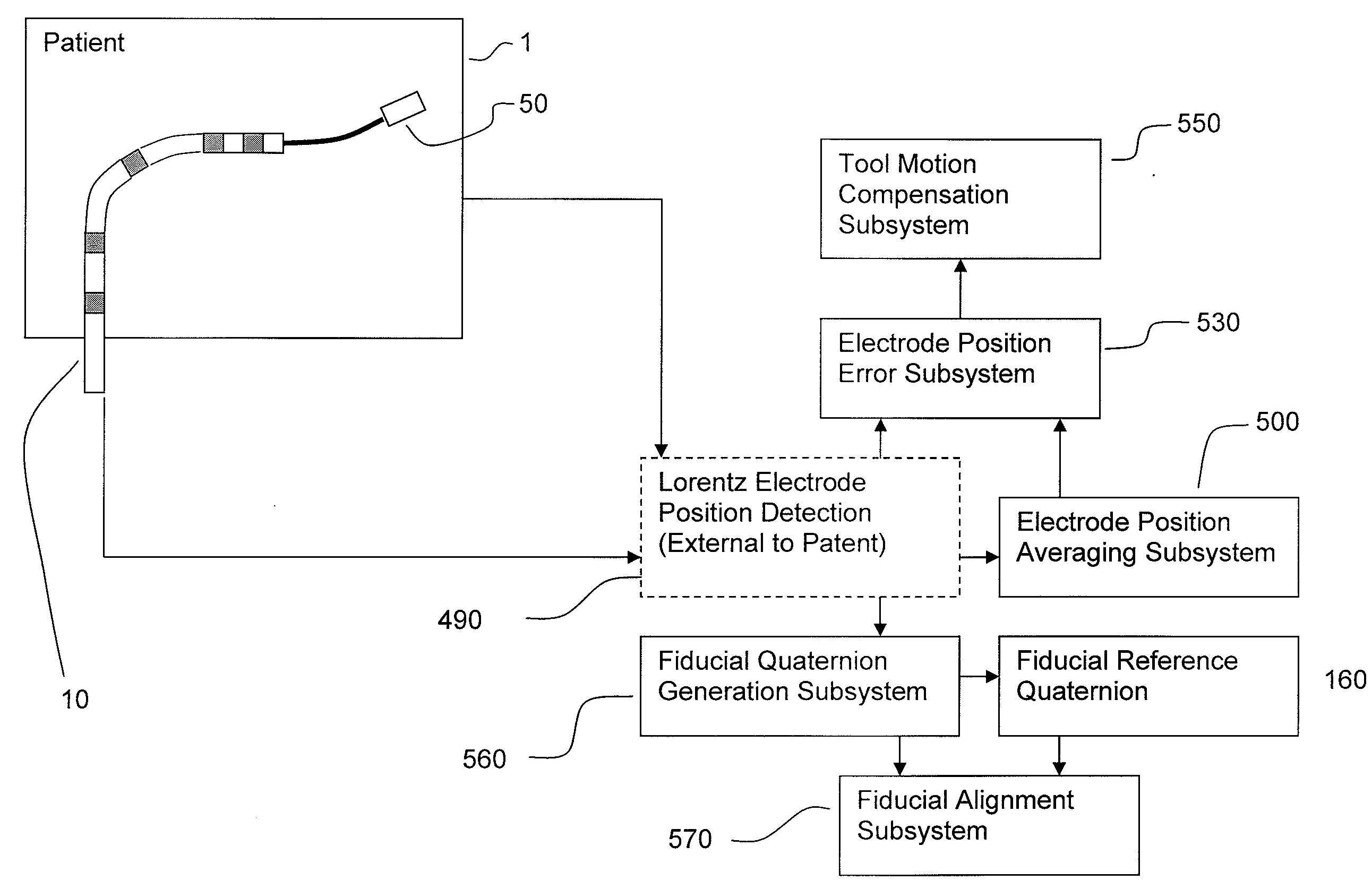
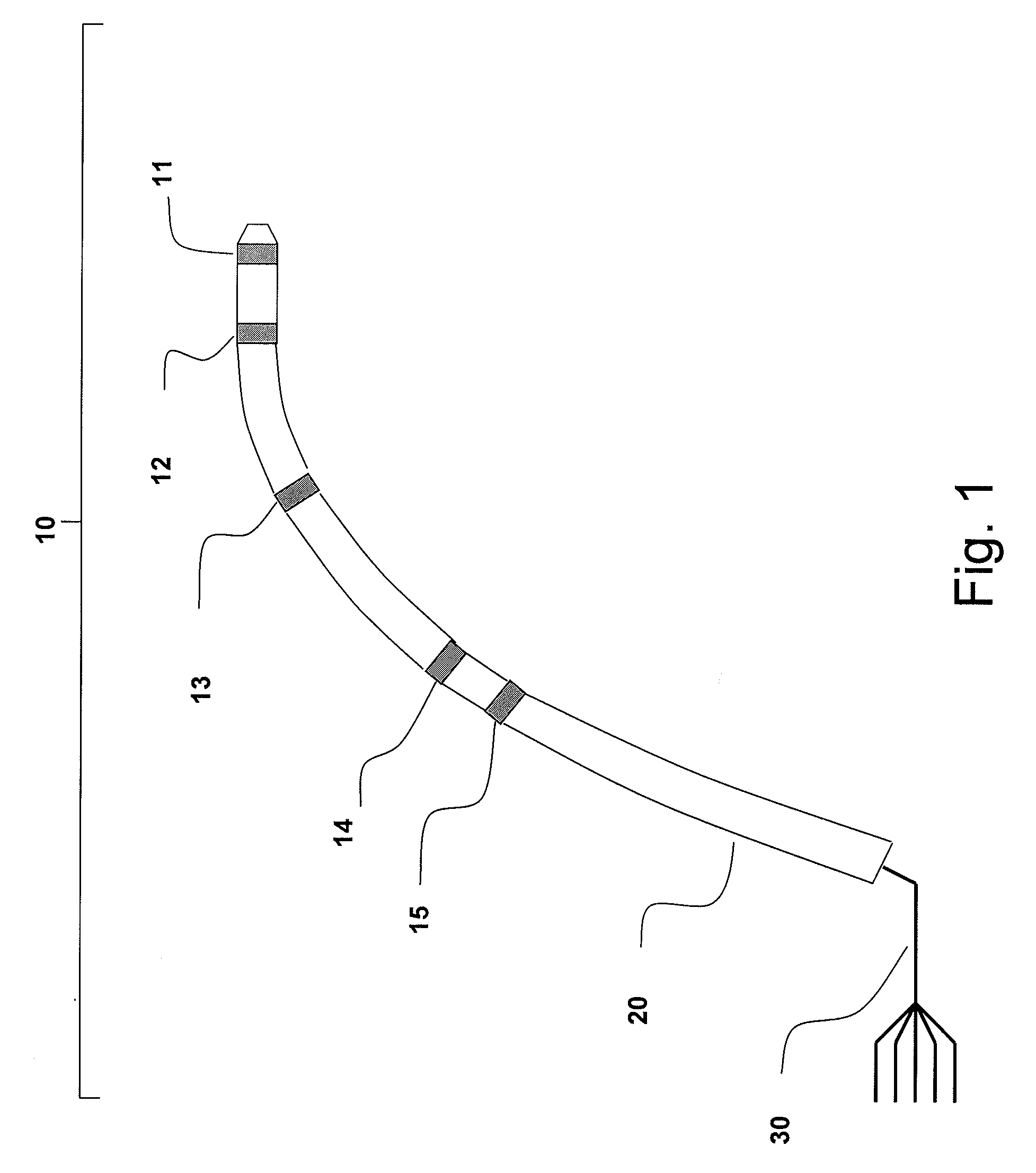
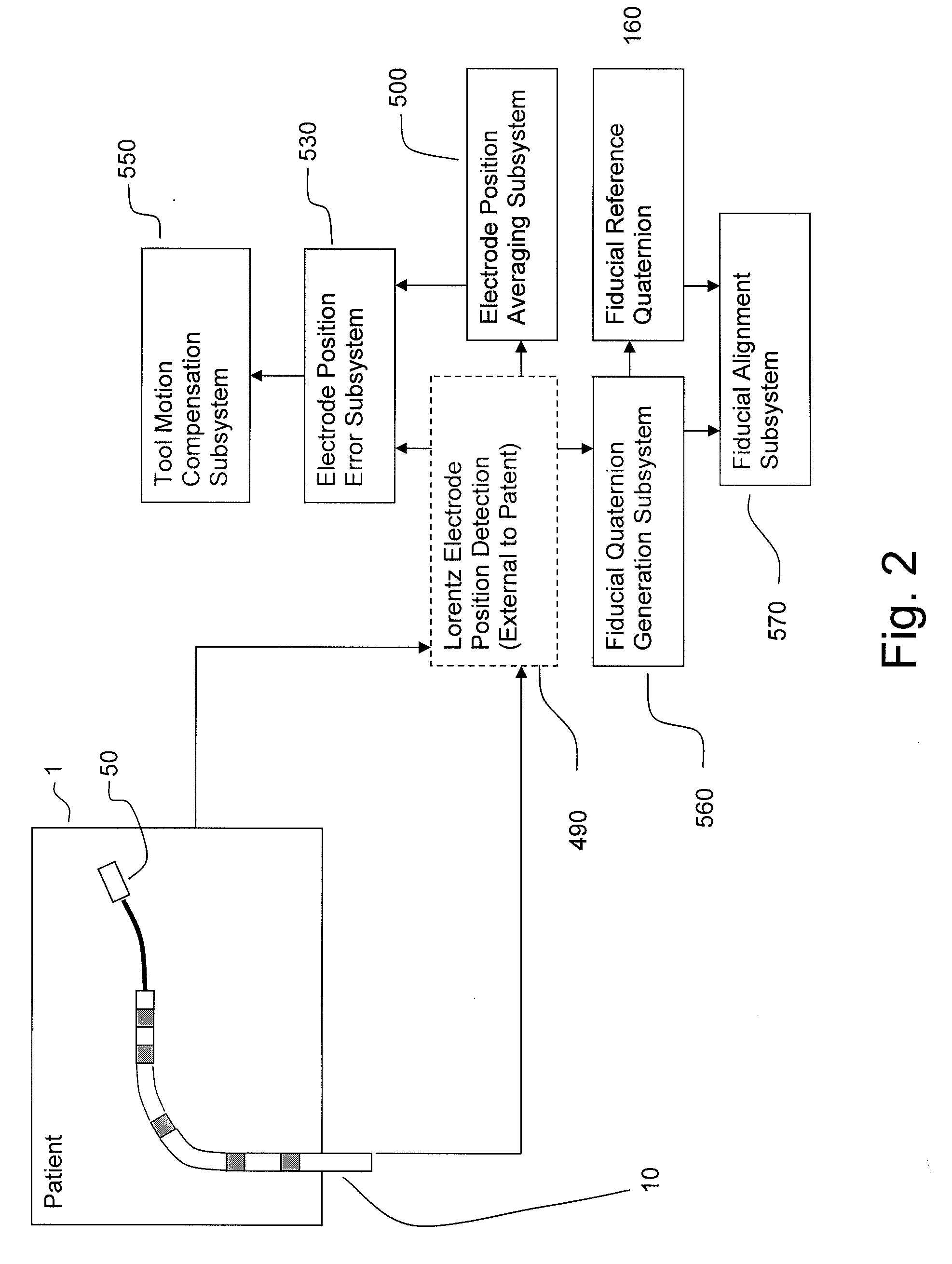
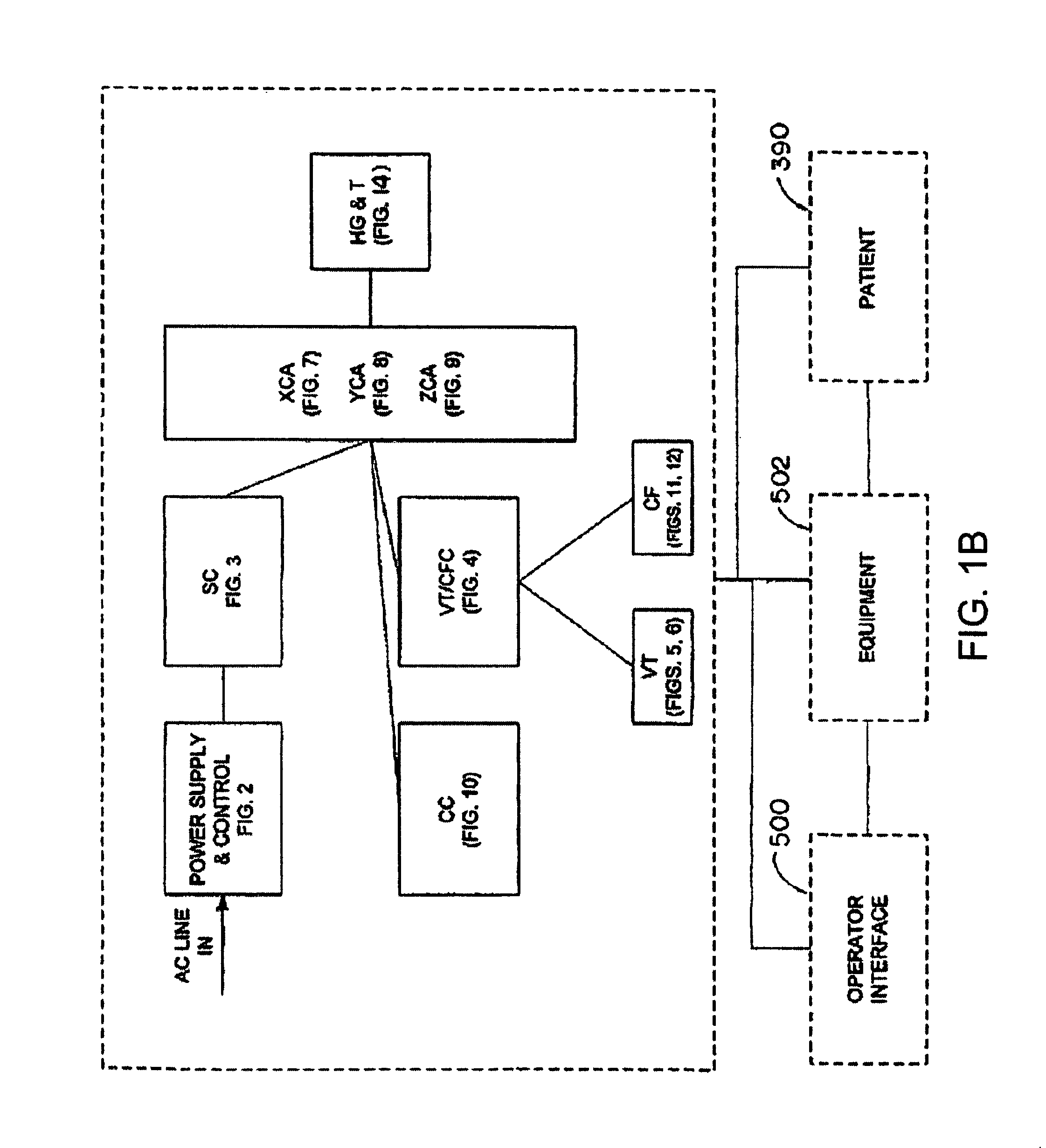
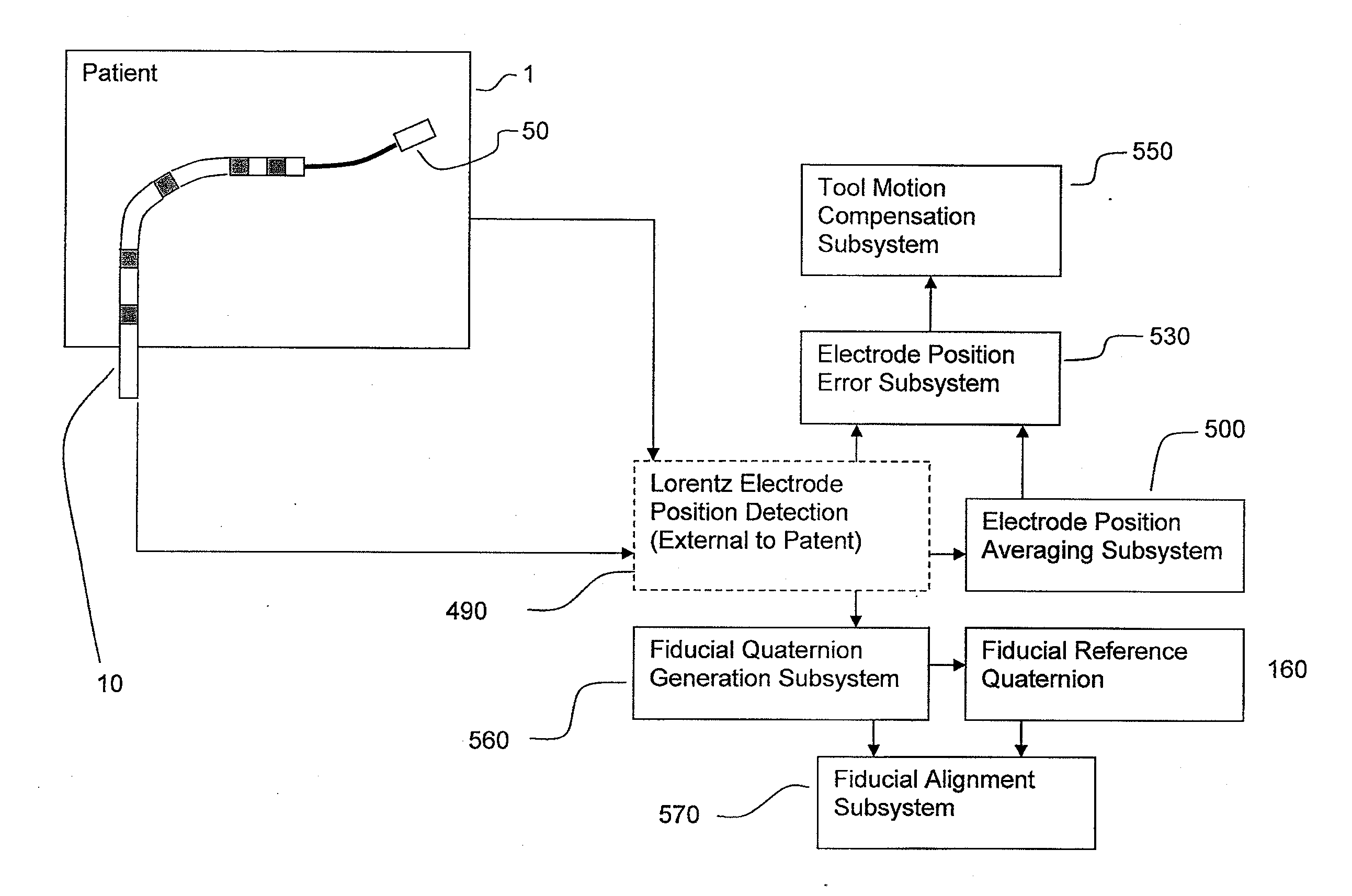
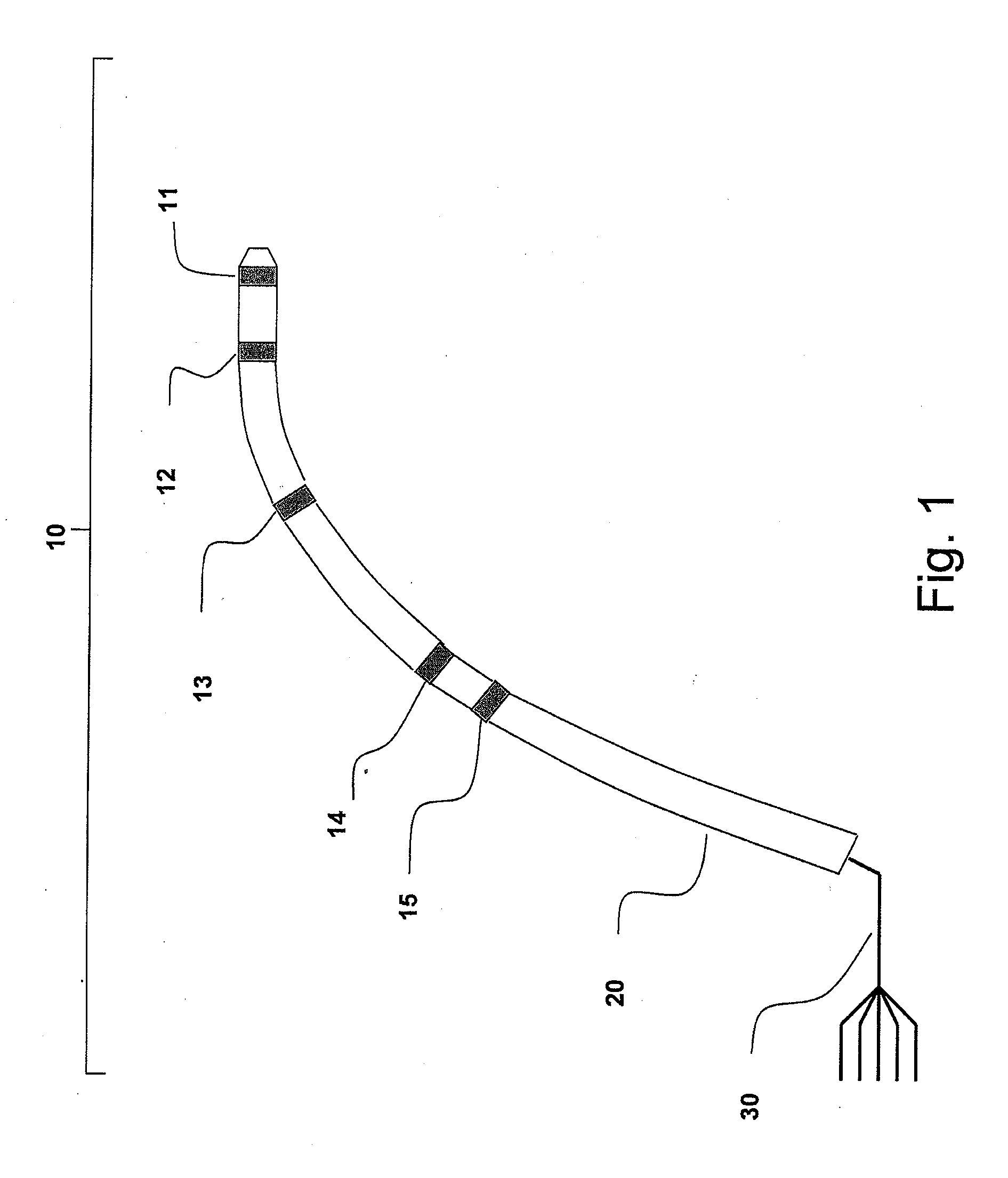
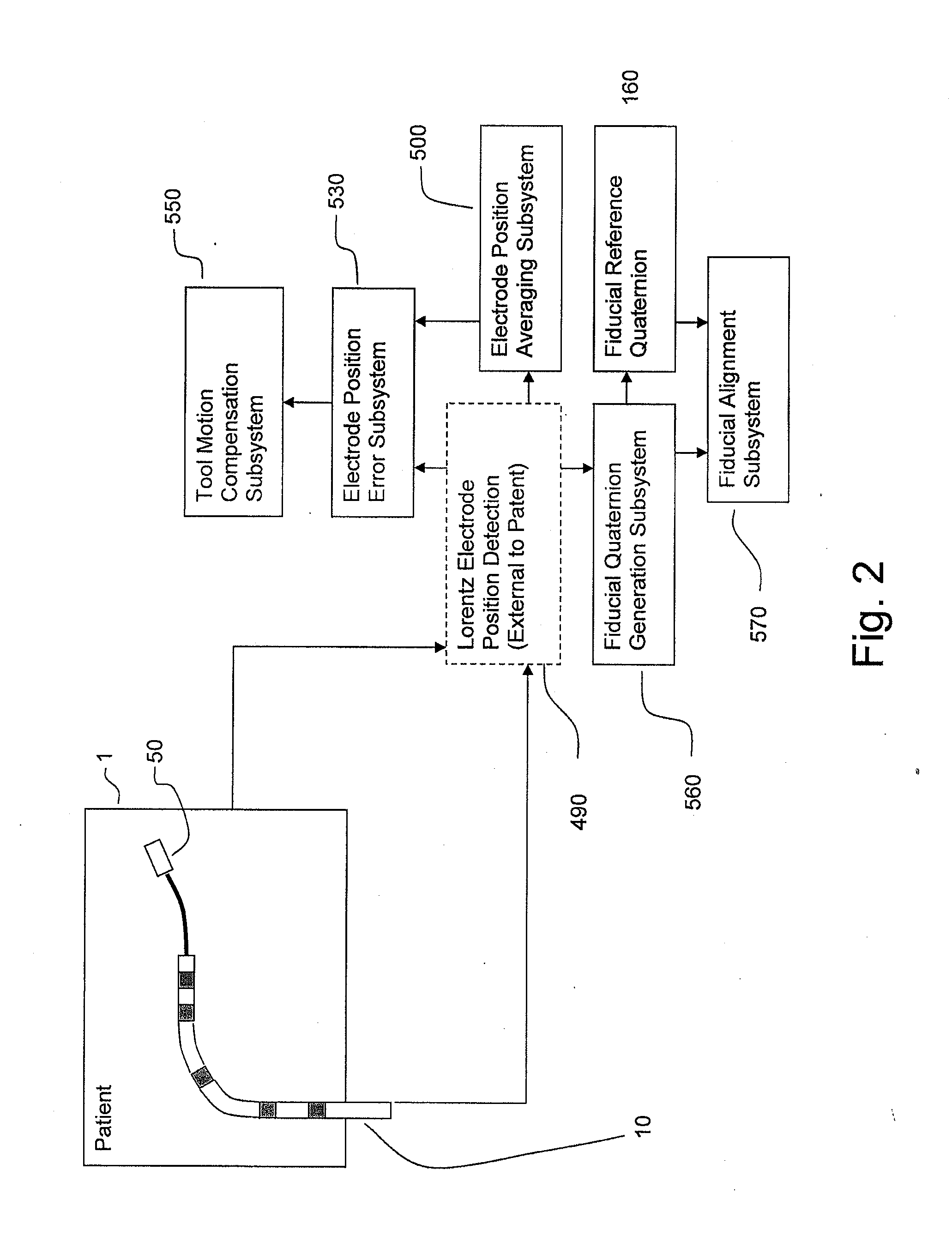
Apparatus and method for lorentz-active sheath display and control of surgical tools
InactiveUS20090253985A1Accurate assessmentEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringVeinBiopsy needles
The Lorentz-Active Sheath (LAS) serves as a conduit for other medical devices such as catheters, balloons, biopsy needles, etc. The sheath is inserted through a vein or other body orifice and is guided into the area of the patient where the operation is to be performed. The position and orientation of the LAS is tracked via an industry standard position detection system which senses electrical signals that are emitted from several electrodes coupled to the LAS. The signals received from the LAS are used to calculate an accurate and reliable assessment of the actual position of the LAS within the patient. The electrode signals also serve to create a reference frame which is then used to act as a motion compensation filter and fiducial alignment system for the movement of the LAS-hosted medical tool.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Multi-Excitation Diagnostic System and Methods for Classification of Tissue
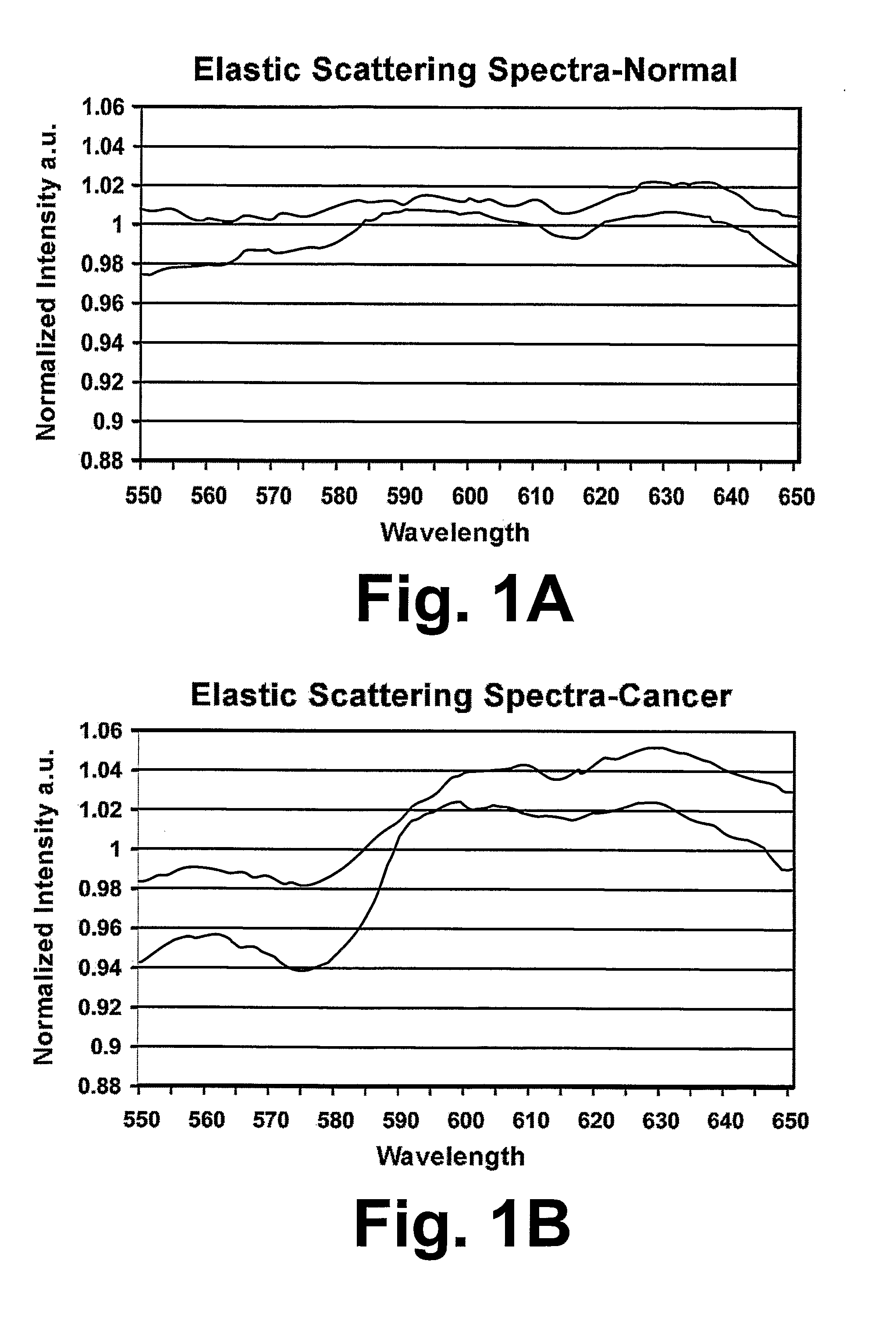
ActiveUS20080194969A1Medical data miningDiagnostics using lightFluorescenceExcitation emission matrix
Methods and systems for in vivo classification of tissue are disclosed. The tissue is irradiated with light from multiple light sources and light scattered and fluoresced from the tissue is received. Distinct emissions of the sample are identified from the received light. An excitation emission matrix is generated (1002). On-diagonal and off diagonal components of the excitation emission matrix are identified (1004, 1006, 1008). Spectroscopic measures are derived from the excitation emission matrix (1014), and are compared to a database of known spectra (1016) permitting the tissue to be classified as benign or malignant (1018). An optical biopsy needle or an optical probe may be used to contemporaneously classify and sample tissue for pathological confirmation of diagnosis.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Marker device for X-ray, ultrasound and MR imaging
InactiveUS20060293581A1Sharp contrastEasily introduced into tissueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMicrosphere
An imaging marker comprised of glass and iron-containing aluminum microspheres in a gel matrix which shows uniformly good contrast with MR, US and X-Ray imaging. The marker is small and can be easily introduced into tissue through a 12-gauge biopsy needle. The concentration of glass microspheres and the size dictate the contrast for US imaging. The contrast seen in MRI resulting from susceptibility losses is dictated by the number of iron-containing aluminum microspheres; while the artifact of the marker also depends on its shape, orientation and echo time. By optimizing the size, iron concentration and gel binding, an implantable tissue marker is created which is clearly visible with all three imaging modalities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
Biopsy needle and method
ActiveUS7491177B2SurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsConductive materialsUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS7873401B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Apparatus and method for lorentz-active sheath display and control of surgical tools
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Needle breast biopsy system and method of use
ActiveCN102481146AEasy to catchCapture suitable forSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTomosynthesisBiopsy procedure
A tilted needle biopsy assembly is provided for mounting on an x-ray system. Because the biopsy needle is angied relative to at least one of the detector and the x-ray source, x-ray imaging may be performed during the biopsy procedure without interference by the biopsy device. The angled biopsy needle additionally allows improved access to the axilla and chest wall of the patient. The stereotactic biopsy device of the present invention may be coupled to any x-ray system, whether upright or prone, including but not limited to mammography systems, tomosynthesis systems, and combination mammography / tomosynthesis systems. The system flexibly supports the use of any mode of image capture (i.e., scout, two dimensional mammogram, three-dimensional reconstructed volume) for either or both target visualization and target localization. With such an arrangement, a needle biopsy assembly having improved patient coverage is provided for use with a variety of different x-ray imaging platforms.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
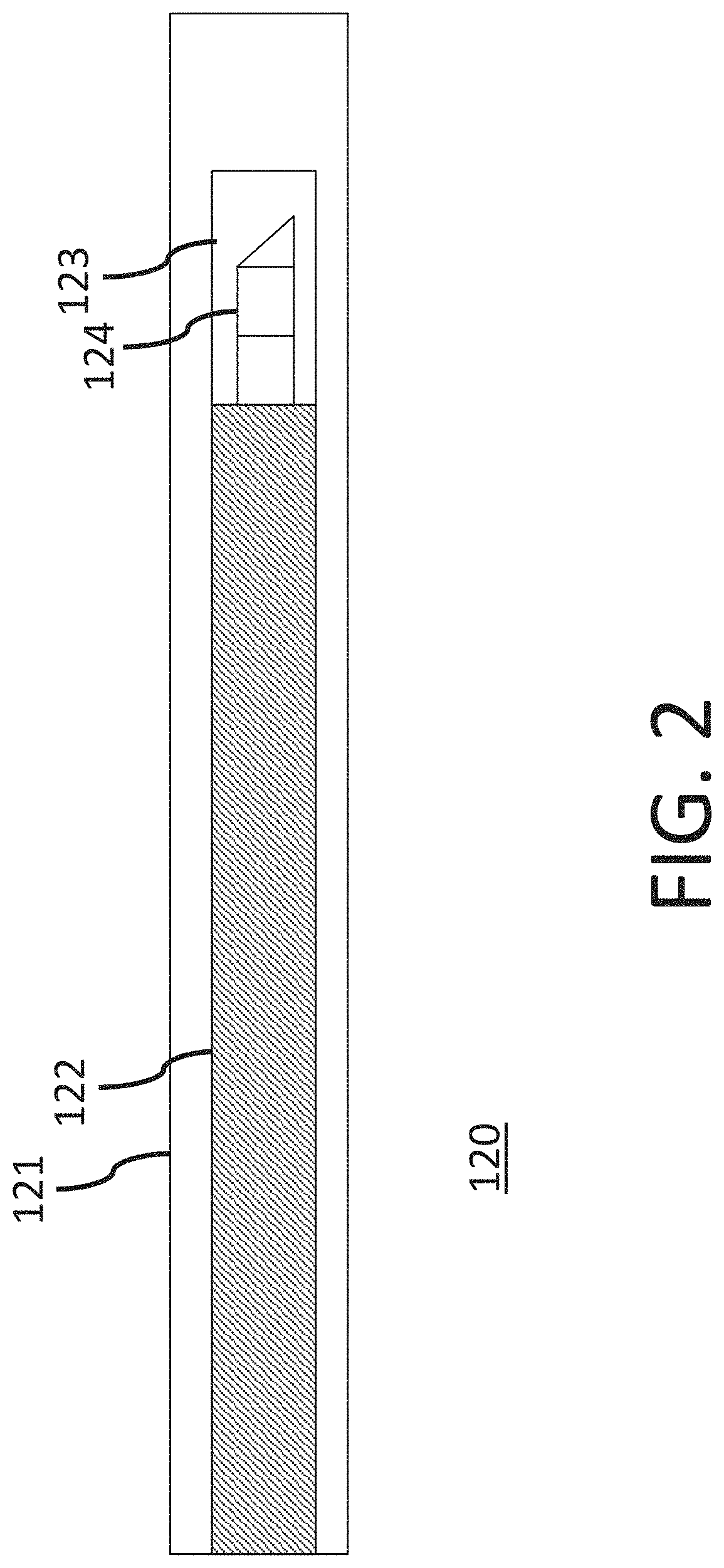
Apparatuses, methods, and storage mediums for lumen and artifacts detection in one or more images, such as in optical coherence tomography images
ActiveUS20190374109A1Improve objectImprove targetingImage enhancementMedical imagingOptical instrumentSystems approaches
One or more devices, systems, methods and storage mediums for performing optical coherence tomography (OCT) while detecting one or more lumen edges and / or one or more artifacts are provided. Examples of applications include imaging, evaluating and diagnosing biological objects, such as, but not limited to, for Gastro-intestinal, cardio and / or ophthalmic applications, and being obtained via one or more optical instruments, such as, but not limited to, optical probes, catheters, capsules and needles (e.g., a biopsy needle). Preferably, the OCT devices, systems methods and storage mediums include or involve a method, such as, but not limited to, for removing the detected one or more artifacts from the image(s).
Owner:CANON USA
Instrument For Concurrent Injection Of Anesthesia And Removal Of Specimens From A Body
InactiveUS20130046200A1Relieve painUse of procedureSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy procedureBiopsy instruments
The instant invention describes a biopsy instrument which is useful in removal of tissue or fluid samples from a body, such as bone and soft tissue biopsy procedures. The biopsy instrument is an improvement over other biopsy needles currently in use in that the biopsy instrument according to the instant invention can be used to reduce the pain associated with specimen removal procedures. The biopsy instrument generally comprises an outer cannula and an inner medical probe member. The inner medical probe member is constructed and arranged to contain one or more fluid dispensing members for dispensing a fluid which are in fluid communication with a fluid dispensing device. In this arrangement, the user has the ability to continually inject fluids, such as anesthetizing agents, directly at or near the spot of specimen removal, without the need to remove the surgical instrument or use a separate fluid injecting needle.
Owner:INVENTIT
Coherence range imaging using common path interference
ActiveUS20180045501A1Controlled and efficient reference signal and referenceControlled and efficient and reflectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOPHTHALMOLOGICALSLight propagation
One or more devices, systems, methods and storage mediums for performing common path optical coherence tomography (OCT) with a controlled reference signal and efficient geometric coupling are provided. Examples of such applications include imaging, evaluating and diagnosing biological objects, such as, but not limited to, for Gastro-intestinal, cardio and / or ophthalmic applications, and being obtained via one or more optical instruments, such as, but not limited to, optical probes (e.g., common path probes), common path catheters, common path capsules and common path needles (e.g., a biopsy needle). Preferably, the OCT devices, systems methods and storage mediums include or involve a reference reflection or a reference plane that is at least one of: (i) disposed in the collimation field or path; and (ii) is perpendicular (or normal) or substantially perpendicular (or substantially normal) to light propagation. One or more embodiments may include beam shaping optics to properly image luminal or other hollow structures or objects.
Owner:CANON USA
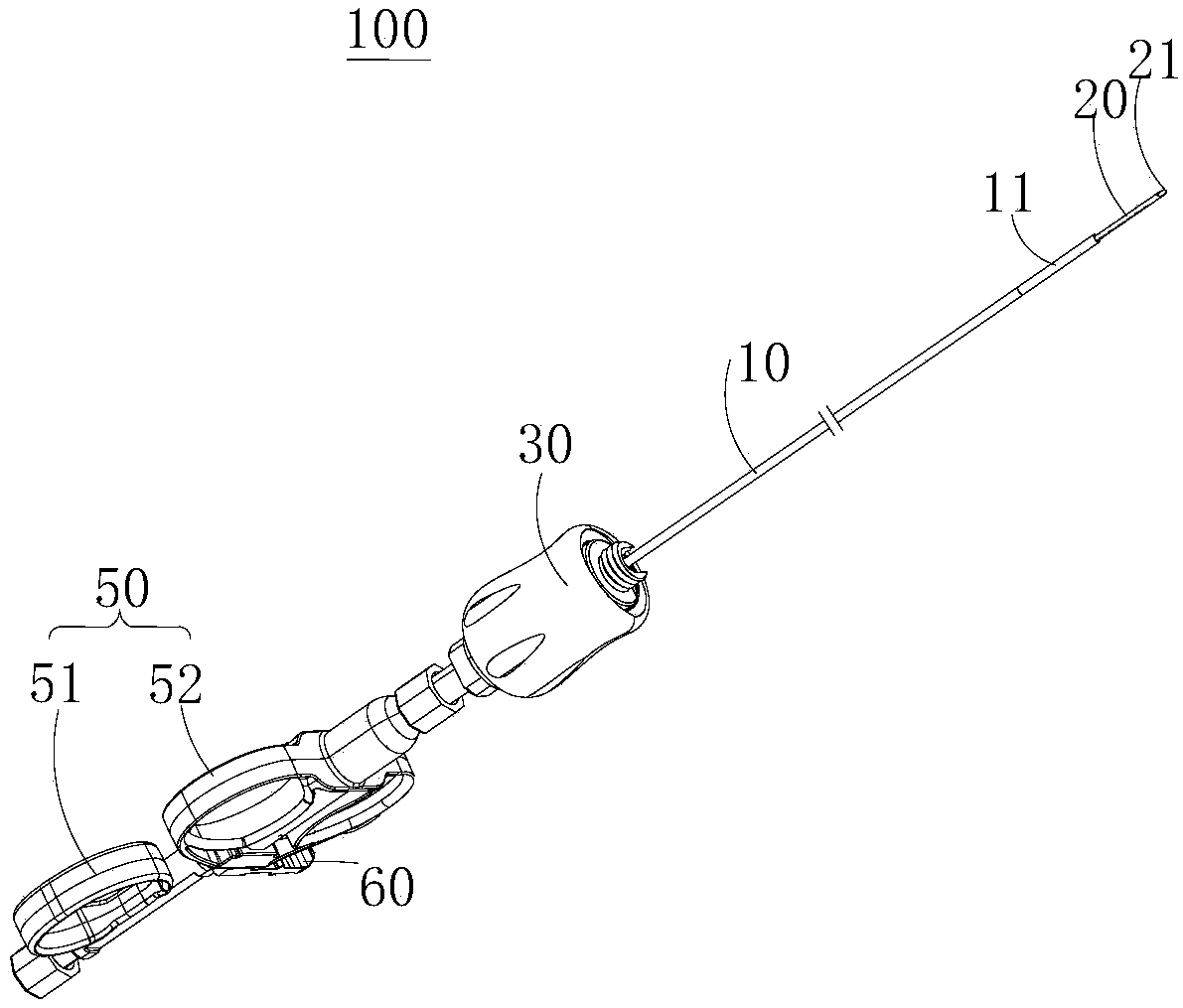
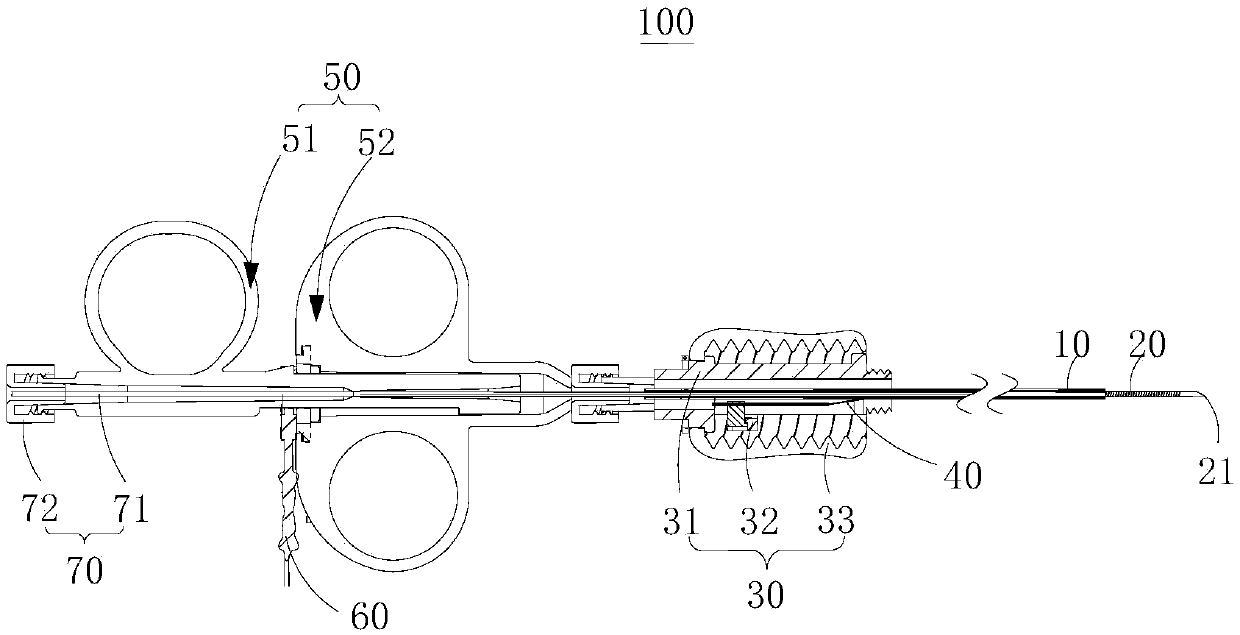
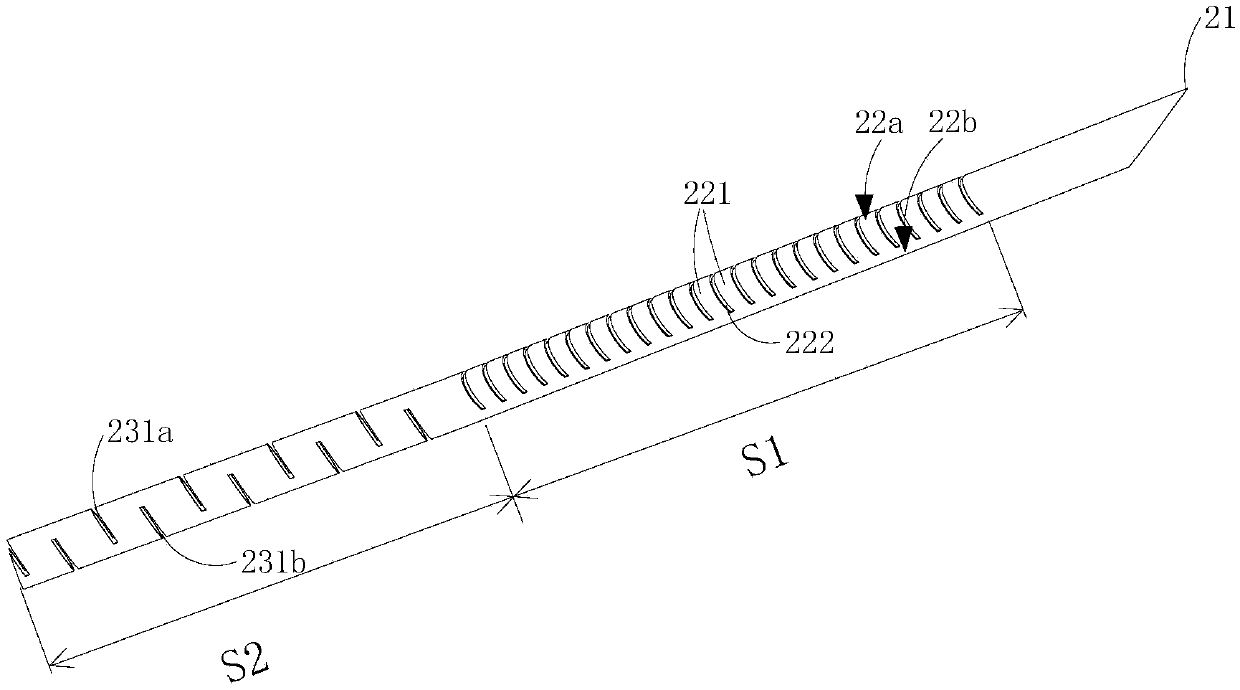
Bendable biopsy needle and biopsy system
PendingCN111248947ASmooth entrySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringBiopsy needles
The invention provides a bendable biopsy and a biopsy system. The bendable biopsy needle comprises a sheath, a needle body and a traction part, wherein a bendable section is arranged at a far end of the sheath, a far end of the traction part is connected with the bendable section, the traction part moves in the axial direction of the sheath to drive the bendable section to bend, the needle body ismovably mounted in the sheath in a penetrating manner, a far end of the needle body is a hollow structure, the far end of the sheath can be bended at different degrees by adjusting the bendable section at the far end of the sheath, so that the far end of the sheath can smoothly enter tiny and bent human cavities, and the far end of the needle body can enter these tiny and bent human cavities along the far end of the sheath to obtain biopsy tissue. Besides, the bending following section at the far end of the needle body is provided with a bending orientation structure, so that the bending following section can bend in the same direction along with the bendable section, the side where the needle point is located and the side, bending under the drive of the traction part, of the bendable section are located on the same side relative to the axis of the needle body, and the needle point can be prevented from piercing the inner wall of the sheath.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT)
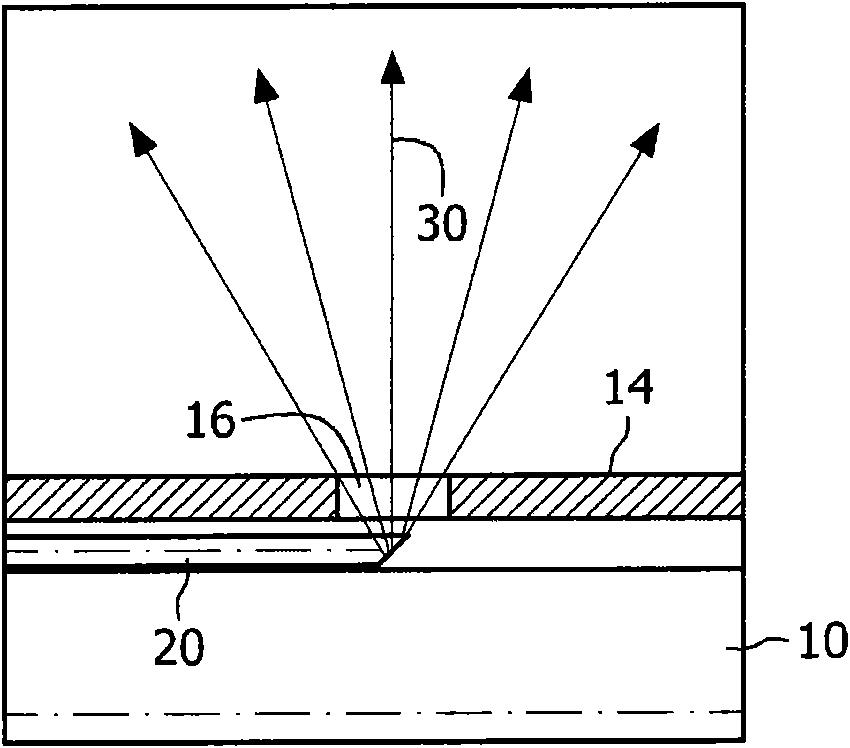
Biopsy device
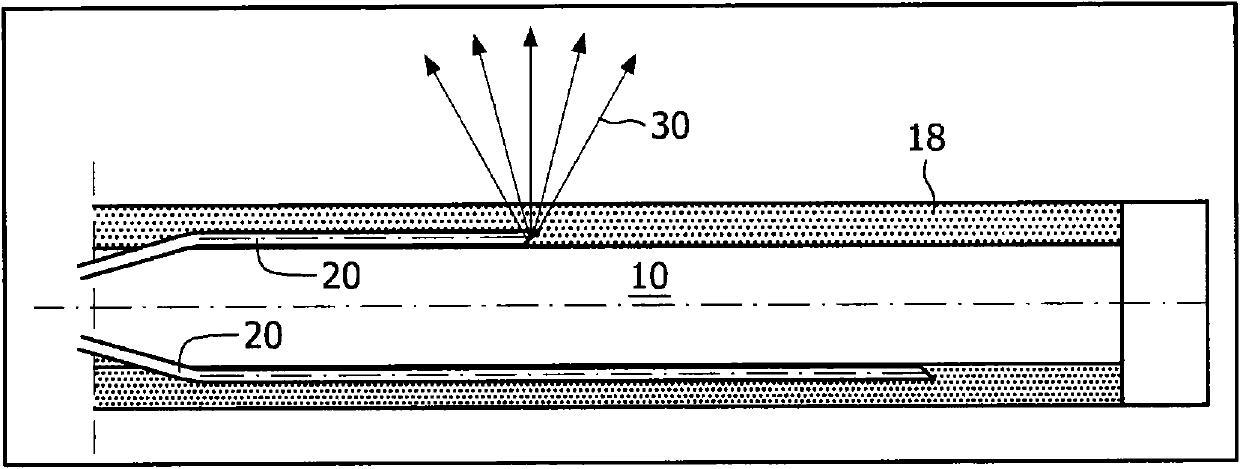
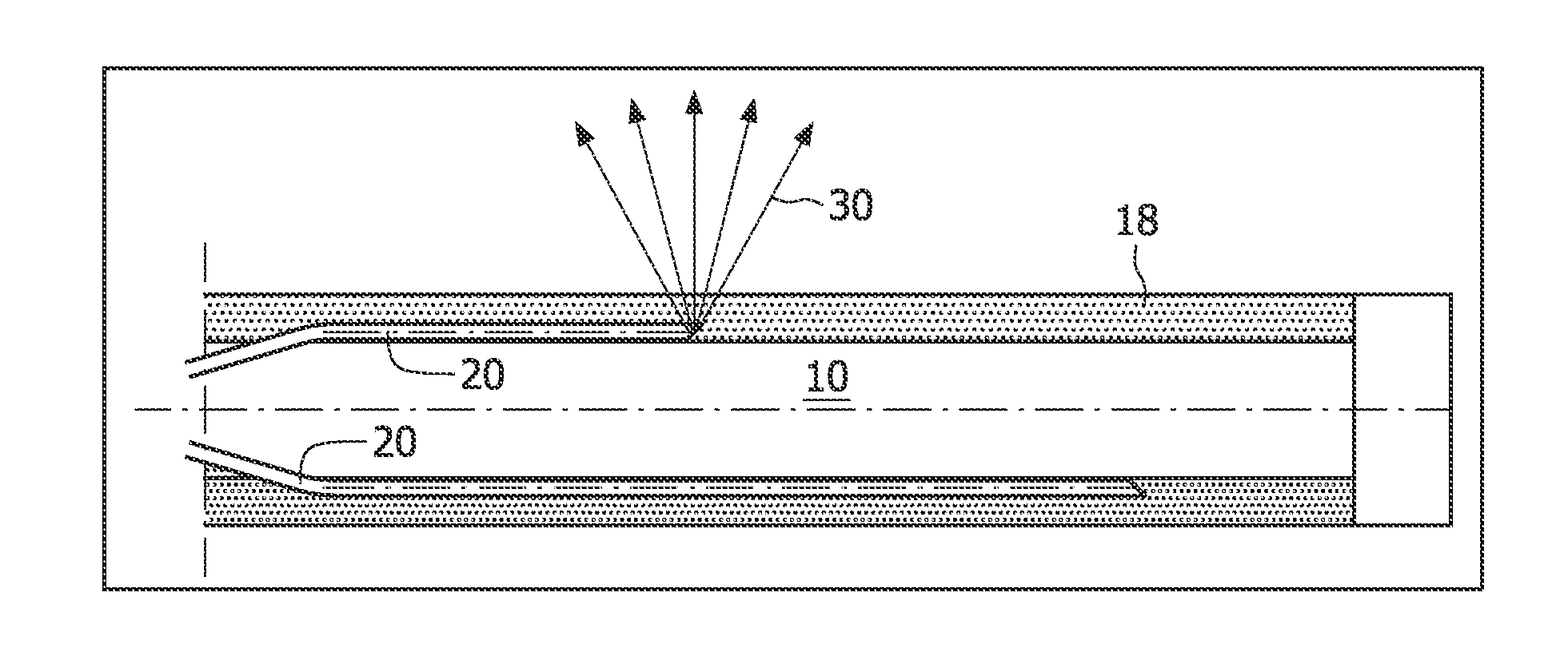
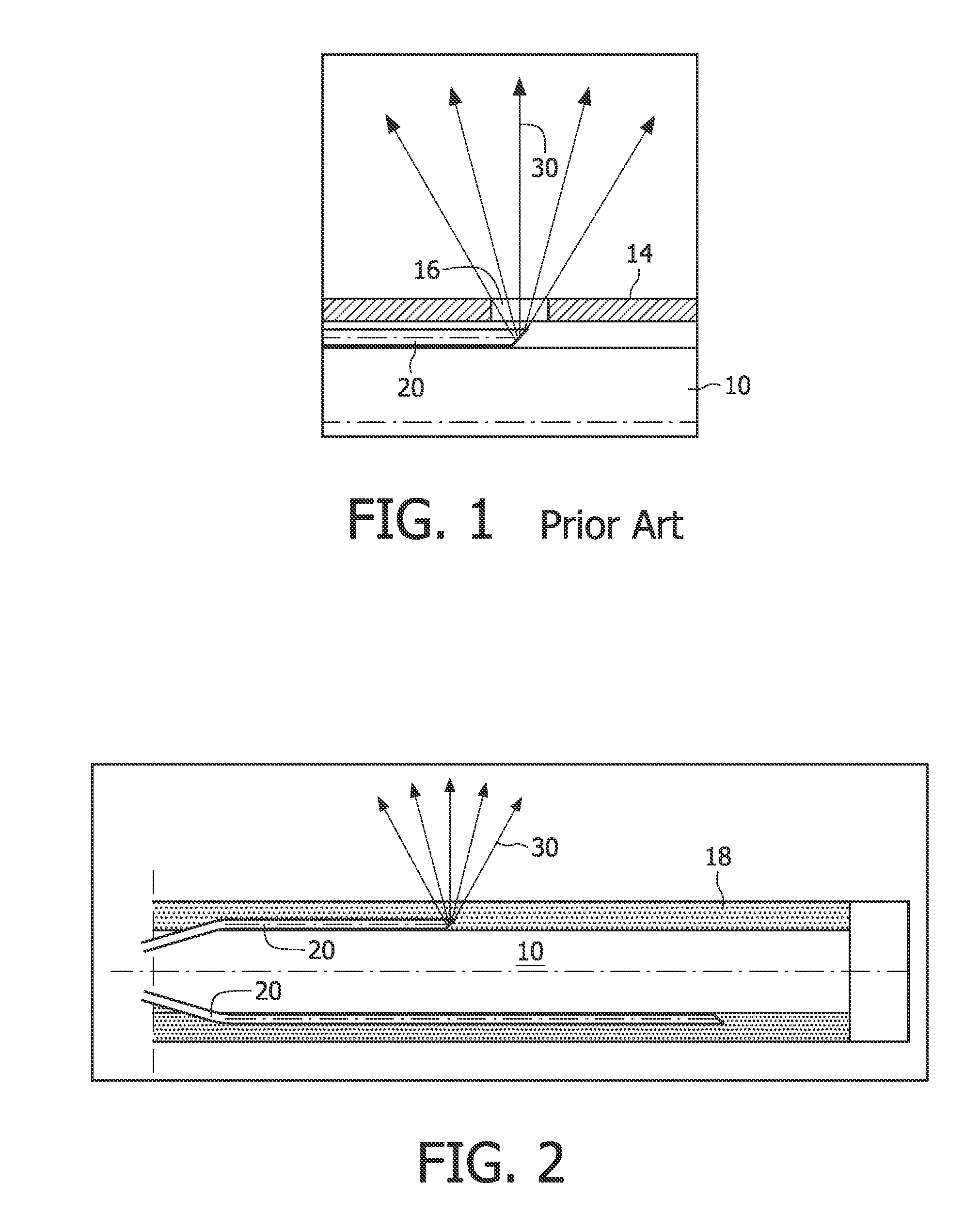
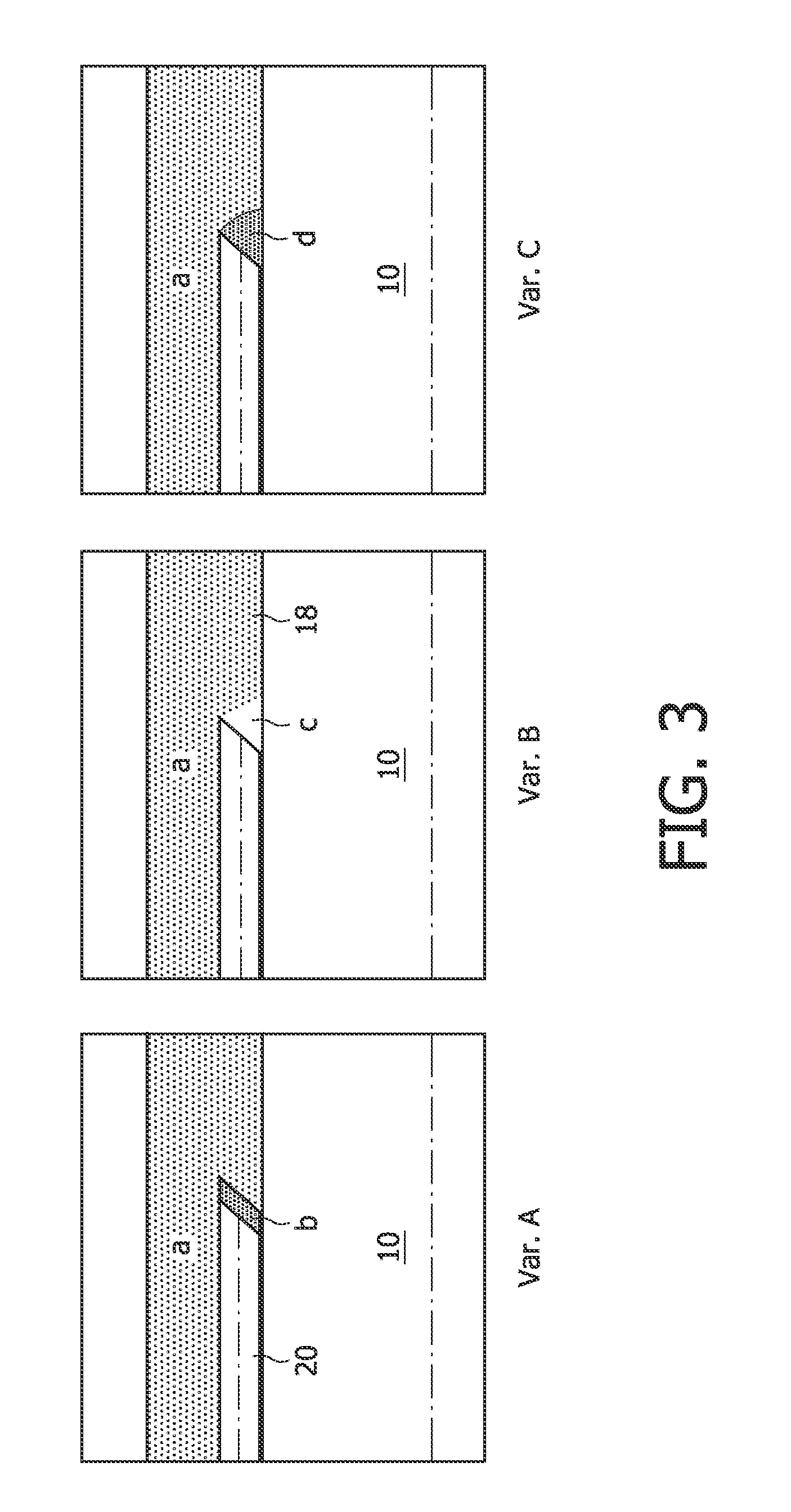
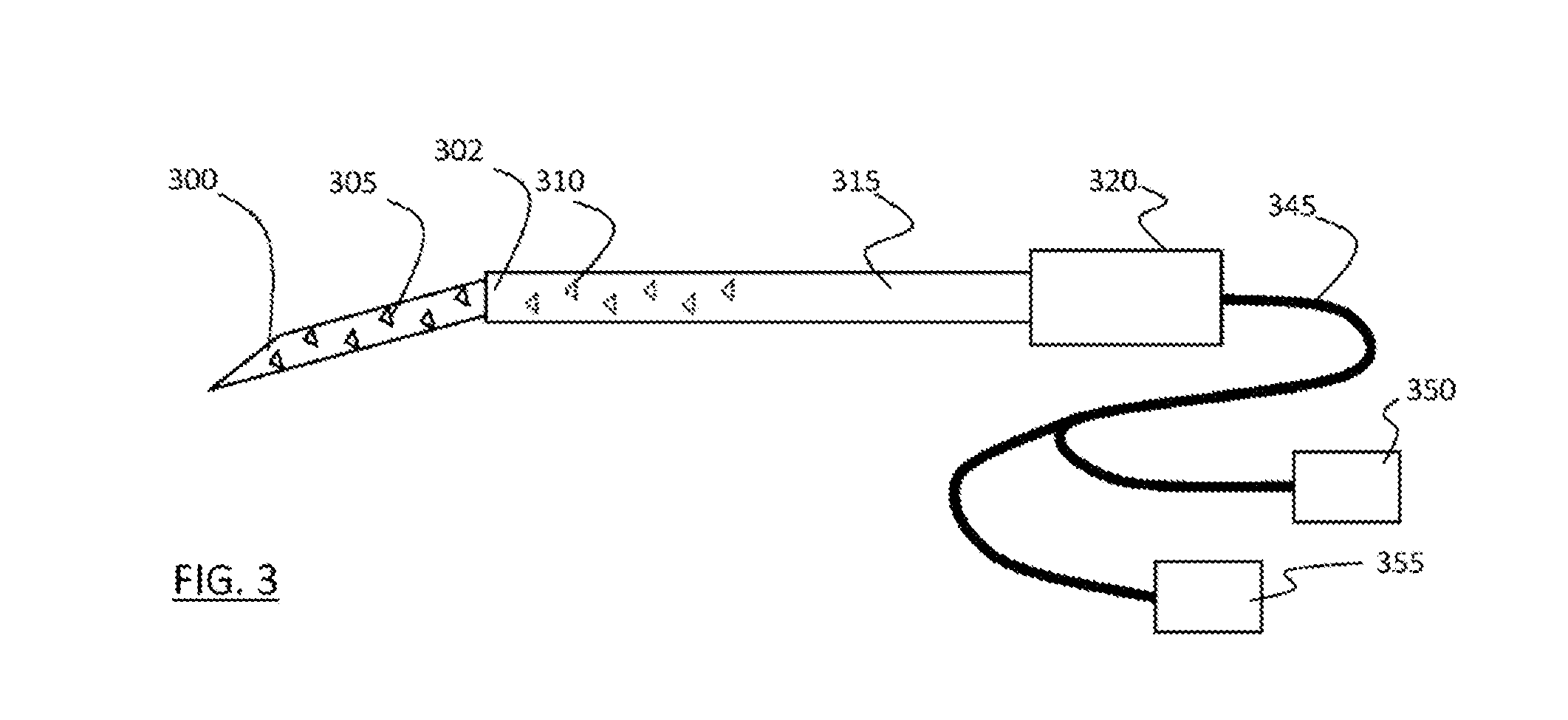
Biopsy needles equipped with fibres (20) allow tissue inspection to diagnoses. In order to allow detailed inspection side looking fibres should also be integrated around the needle. These fibres might be embedded in a transparent medium (18) to avoid direct contact of the sharp edges of the fibre to the tissue. A biopsy needle having such embedded fibres as well as a method for manufacturing said biopsy needle, based on curable transparent liquid, is provided by the invention.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Biopsy device
InactiveUS20110009772A1Easy to manufactureReduce manufacturing costSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFiberEngineering
Biopsy needles equipped with fibres (20) allow tissue inspection to diagnoses. In order to allow detailed inspection side looking fibres should also be integrated around the needle. These fibres might be embedded in a transparent medium (18) to avoid direct contact of the sharp edges of the fibre to the tissue. A biopsy needle having such embedded fibres as well as a method for manufacturing said biopsy needle, based on curable transparent liquid, is provided by the invention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
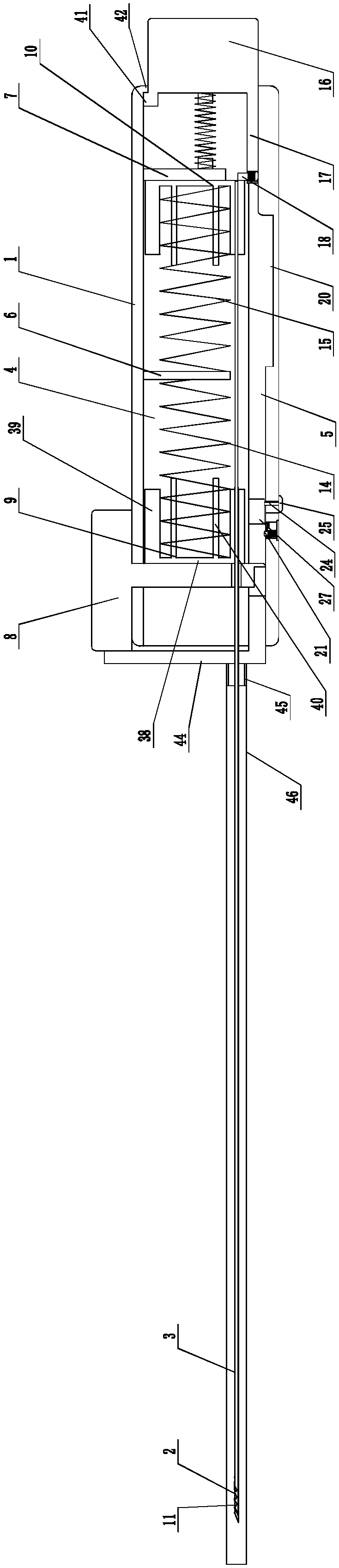
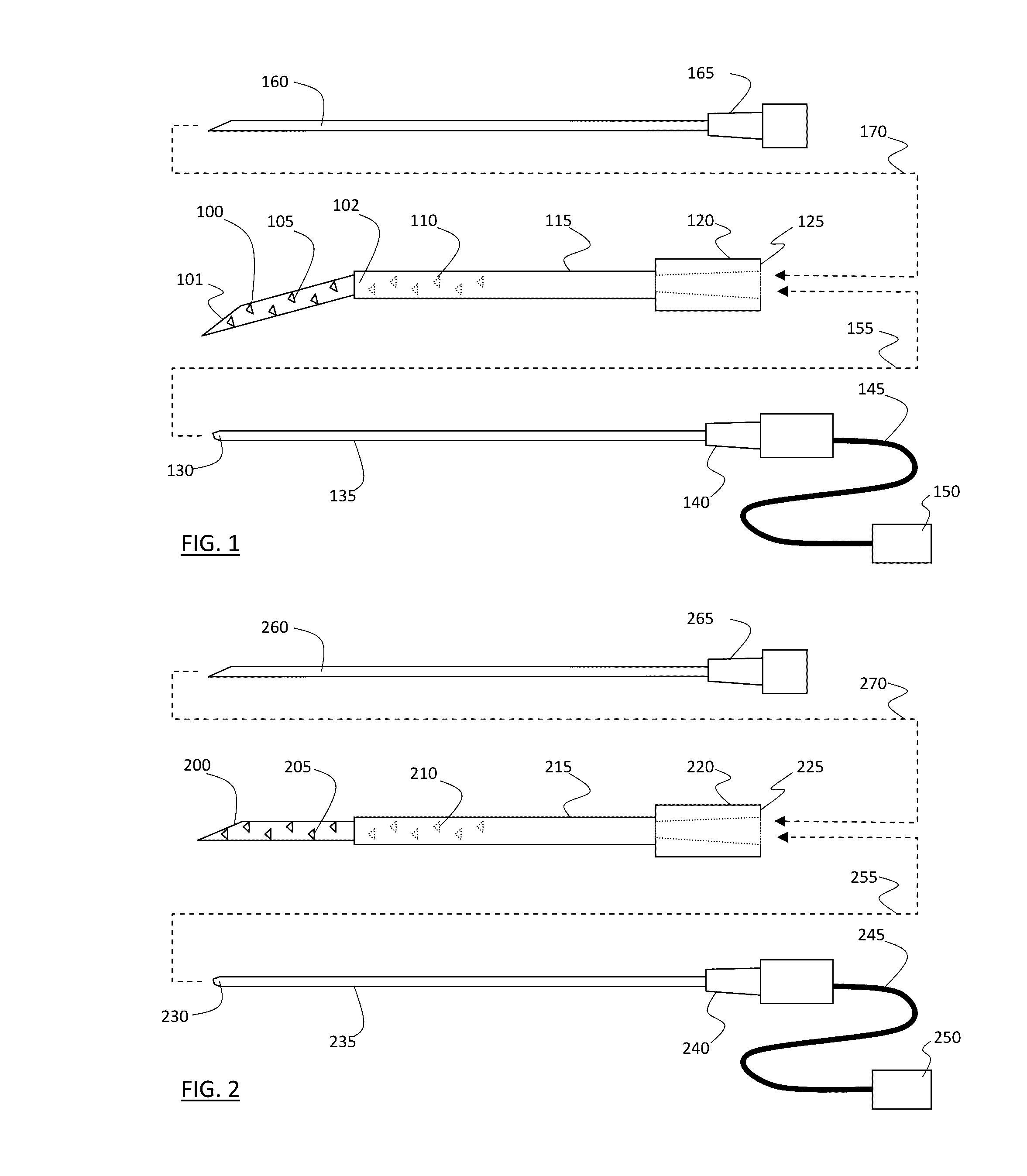
Biopsy needle for biopsy sampling, biopsy device, and methods of manufacturing a biopsy needle or a biopsy device
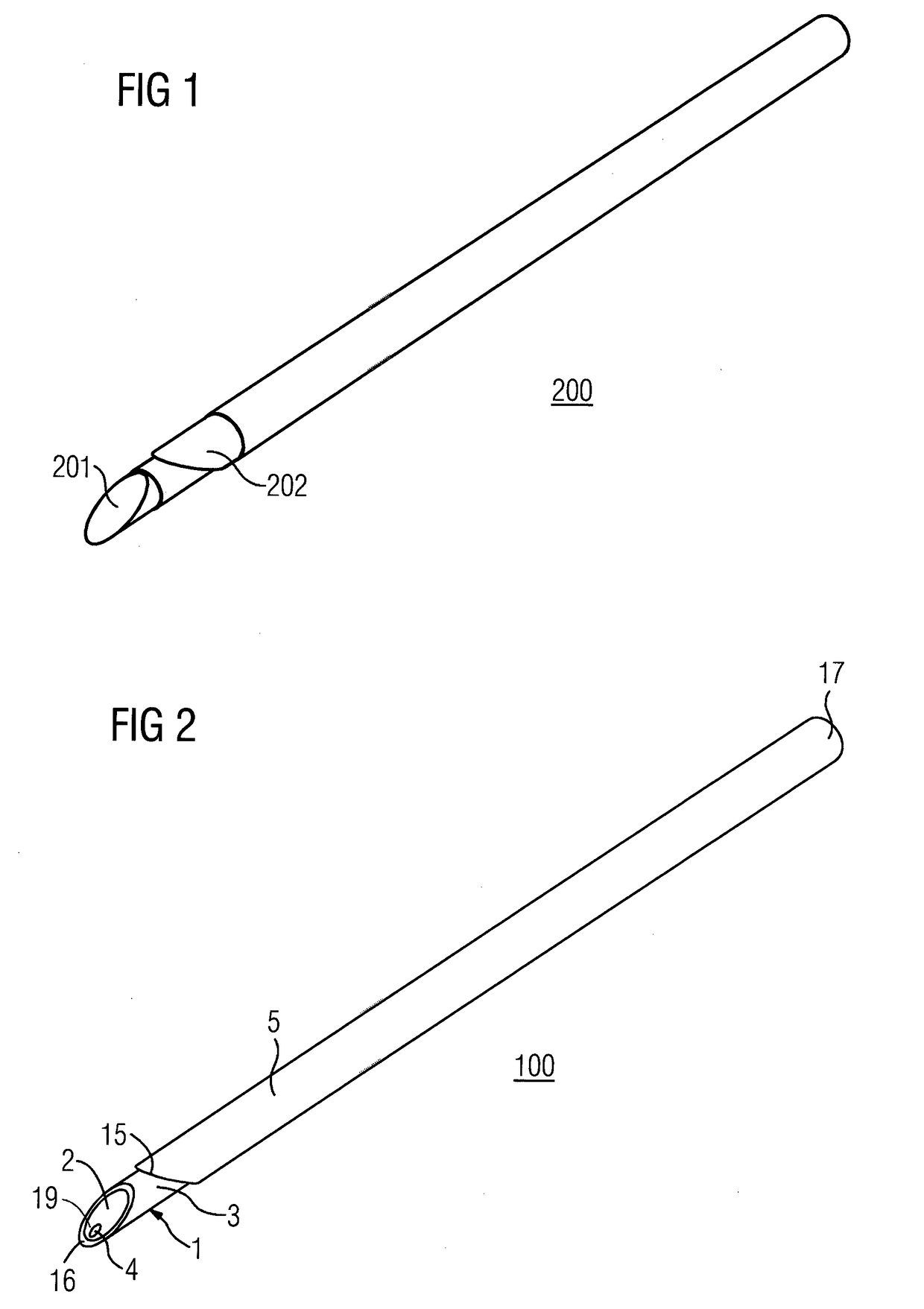
A biopsy needle (100) comprises a cannula (5) with a distal end (15), an inner needle (1) that has a sharpened distal end (16) and at least one biopsy cavity (7) that is located at a distance (L3) from the sharpened distal end (16). The cannula (5) and the inner needle (1) are configured so that the inner needle (1) is accommodated inside the cannula (5) and the inner needle (1) and the cannula (5) are movable with regard to each other. The inner needle (1) further comprises at least two measuring electrodes (1, 4; 3, 4) for measuring a bioimpedance spectrum, the measuring electrodes (1, 4; 3, 4) defining a measuring volume that is localized to the distal end (16) of the inner needle (1).
Owner:INJEQ
Puncture biopsy needle and method for applying same
ActiveCN108078596AEasy to operateGuaranteed accuracySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPuncture BiopsyBiopsy needles
The invention discloses a puncture biopsy needle and a method for applying the same. The puncture biopsy needle and the method have the advantages that the shortcomings of inconvenience in carrying out hemostasis on biopsy puncture positions and deterioration of the biopsy accuracy due to the fact that that existing biopsy needles are inconvenient to operate during puncture and acquired tissue slices can be easily mixed with tissues of other positions can be overcome by the aid of the puncture biopsy needle and the method; a medicine bag which is in the shape of an annular sheet is arranged onthe inner wall of an outer needle tube and is close to the front end of the outer needle tube, a stay is connected onto the medicine bag, the medicine bag can be torn by the aid of the stay, the stayis connected onto an inner needle and is far away from the front end of the inner needle, and the medicine bag is filled with hemostatic liquid; the puncture biopsy needle is convenient to operate inintegral use procedures, acquired tissue slices can be prevented from being mixed with tissues of other positions, and accordingly the biopsy accuracy can be guaranteed; slice sampling can be carriedout by three slice hook grooves, three portions of slice tissues can be detected, and accordingly the detection accuracy further can be improved; hemostasis can be directly carried out on biopsy puncture positions, and accordingly good hemostasis effects can be realized.
Owner:TONGLU QIANYAN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Rotating needle driver and apparatuses and methods related thereto
ActiveUS9610131B2Closed endLower insertion forceEar treatmentSurgical needlesBiopsy needlesBiomedical engineering
Featured is a medical instrument driver, a robotic apparatus embodying such a medical instrument driver and methods related thereto for inserting a medical instrument into tissue of a mammal (e.g., human). Such medical instruments include medical needles, biopsy needles, trocars, cutters and introducers. Such a medical instrument driver according to the present invention is configured and arranged so that medical instrument is rotated as it is being moved longitudinally for insertion into the tissue such that the medical instrument is spiraling as it pierces and traverses the tissue to the target area.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Echogenic probe
InactiveUS20170049993A1Direction easyImprove visualizationDiagnosticsSurgical needlesMedicineSpinal needles
Echogenic markers can be applied to probes such as medical needles, including radiofrequency cannulae, injection needles, biopsy needles, microwave antennae, and spinal needles, among others. For example, in certain embodiments, the probes may have a distal end, a proximal end, a shaft, and an echogenic feature in the form of one or more indentations on the shaft. In certain embodiments, the probes may have a first echogenic feature in the form of an indentation in a surface of the probe and a second echogenic feature in the form of a roughening of the surface of the probe.
Owner:COSMAN MEDICAL INC
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus and a method for imaging a specular object and a target anatomy in a tissue using ultrasond
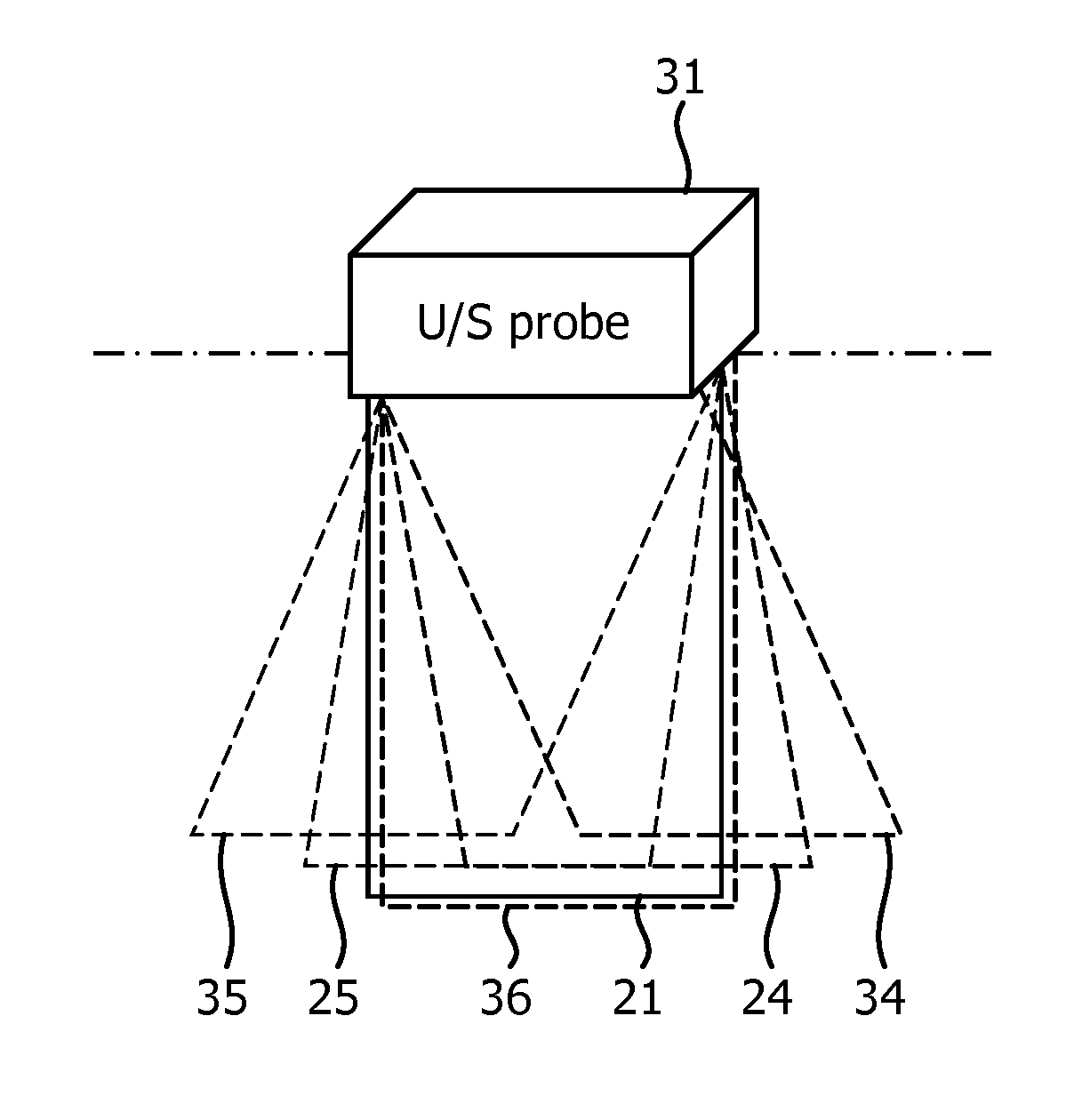
ActiveUS20150119701A1Increase frame rateMaintaining displayImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound imagingSonification
The invention relates to a method and an ultrasonic imaging apparatus (20) for imaging a specular object (such as a biopsy needle) and a target anatomy in a tissue, whereby the specular object remains visible even when its location deviates from a target plane (21) including the target anatomy.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Biopsy needle excitation device and full-automatic biopsy device
PendingCN112656457ASimple and fast operationAvoid failure to exciteSurgical needlesApparatus instrumentsBiopsy device
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to a biopsy needle excitation device and a full-automatic biopsy device. The biopsy needle excitation device comprises a shell, the needle outlet end of the shell is the front end, the end, away from the needle outlet end, of the shell is the rear end, and an excitation button and an excitation device are sequentially arranged in the shell in the direction from the rear end to the front end; the excitation button is used for triggering the excitation device; and the excitation device is used for executing needle withdrawing operation when being triggered, the excitation device is provided with a first upper chord button and a second upper chord button, and the first upper chord button and the second upper chord button are arranged in parallel left and right in the direction from the rear end to the front end. According to the technical scheme, the excitation structure is reasonably arranged, so that the biopsy needle is simpler to operate, the conditions that the biopsy needle cannot be excited, is mistakenly excited and the like due to a complicated structure can be avoided, and the biopsy needle excitation device is more flexible, safer and more reliable.
Owner:LEAPMED MEDICAL TECH
Biopsy guide with an ultrasound transducer and method of using same
ActiveUS9198688B2Increase flexibilityEasy and fast monitoringOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorComputer vision
A multi-position biopsy guide system and a method of using such biopsy guide system is proposed. The biopsy guide system comprises a 2D matrix ultrasound transducer (3) and comprises at least one biopsy needle guide (5) adapted for guiding a biopsy needle along a biopsy path (7). Therein, the multi-position biopsy guide system is adapted to controllably guide the biopsy needle along biopsy paths at variable locations with respect to the 2D matrix ultrasound transducer. Preferably, a location of the biopsy needle guide (5) with respect to the matrix ultrasound transducer may be determined and an ultrasound image in an image plane aligned with a biopsy path corresponding to the determined location of the biopsy needle guide may be acquired. Thereby, a biopsy process may be monitored for various locations and orientations of a guided biopsy needle.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Surgical robot system
The invention relates to a surgical robot system. Devices, systems, and methods for determining biopsy needle trajectories using a surgical robot. The surgical robot may be configured to plan a trajectory and move to a position along the planned trajectory. The surgical robot may be configured to receive a biopsy needle for aspirating a tissue sample from a patient and maintain its position alongthe trajectory.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Devices for supporting a medical instrument and methods of use
ActiveUS11109933B2Lower resistanceSurgical furnitureStands/trestlesSurgical ManipulationAnesthesia needle
Various implementations include a device for holding and supporting a medical instrument in a position. For example, the medical instrument may include a percutaneous procedure apparatus, such as a needle (e.g., biopsy needle, anesthesia needle) or needle holder. In some implementations, the device holds and supports the percutaneous procedure apparatus and liberates the procedure operator's hands from direct beam exposure, which lowers the risk of complications and radiation exposure to patients and procedure operators. The device also increases the effectiveness of the procedure by holding and supporting the apparatus in the intended position.
Owner:SEELY MORGAN MELISSA
Biopsy needle and biopsy device with same
PendingCN113017709AWon't clogEasy to operateSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringBiopsy device
The invention discloses a biopsy needle and a biopsy device comprising the biopsy needle and a driving device. The biopsy needle is used for being connected with a driving device and can be driven by the driving device to be switched to a differential rotating state or a constant-speed rotating state. The biopsy needle comprises an outer knife tube and an inner knife tube arranged in the outer knife tube in a sliding mode. In a differential rotation state, the inner knife tube rotates and translates relative to the outer knife tube. In the constant-speed rotating state, the inner knife tube only rotates relative to the outer knife tube. The driving device of the biopsy device can move to different positions to output power to the biopsy needle, and gear shifting operation is achieved, so that the biopsy needle is switched to different working states according to needs. In a differential rotation state, living tissues can be cut; In the constant-speed rotating state, the inner knife tube only rotates relative to the outer knife tube, a medicine can be injected through the inner knife tube and evenly diffused to the whole incision of living tissue, pain of a patient is relieved in time, hematoma can be circumferentially sucked and removed through the inner knife tube, and the inner knife tube cannot be blocked.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHENGCHUAN MEDICAL CO LTD
Tissue biopsy needle
PendingCN112155610AEasy to detectAvoid harmSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsTissue biopsyCore needle
The invention relates to the technical field of clinical medical treatment, and discloses a tissue biopsy needle. The tissue biopsy needle comprises a power mechanism, an outer sleeve needle and an inner core needle, wherein the inner core needle is embedded in the outer sleeve needle, a groove is formed in the side wall of the tail end of the outer sleeve needle, a semi-ring cutter correspondingto the groove is arranged on the inner core needle, and the power mechanism drives the semi-ring cutter to transversely rotate in the outer sleeve needle through a needle rod. The tissue biopsy needlehas the beneficial effects that in the process that a cutter opening of the inner core needle and a side cutter act together to cut tissue, the power mechanism drives the semi-ring cutter to rotate rapidly through the needle rod, rapid rotary cutting of the tissue to be detected is achieved to form a complete cylindrical sample, and the tissue is convenient to detect. In the cutting process, dueto the fact that rotary cutting is adopted, the outer sleeve needle and a needle tip are static, shaking cannot occur, damage to surrounding important organs is avoided, safety is greatly improved, and biopsy can be conveniently carried out on tissue such as large vascular gaps, dangerous organ sides, small nodules and lymph nodes.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL CANCER HOSPITAL +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com