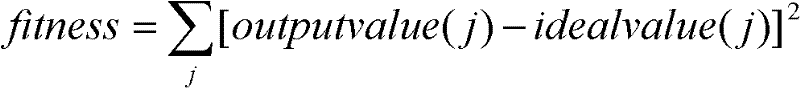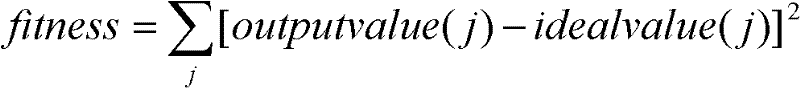Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Provide real-time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
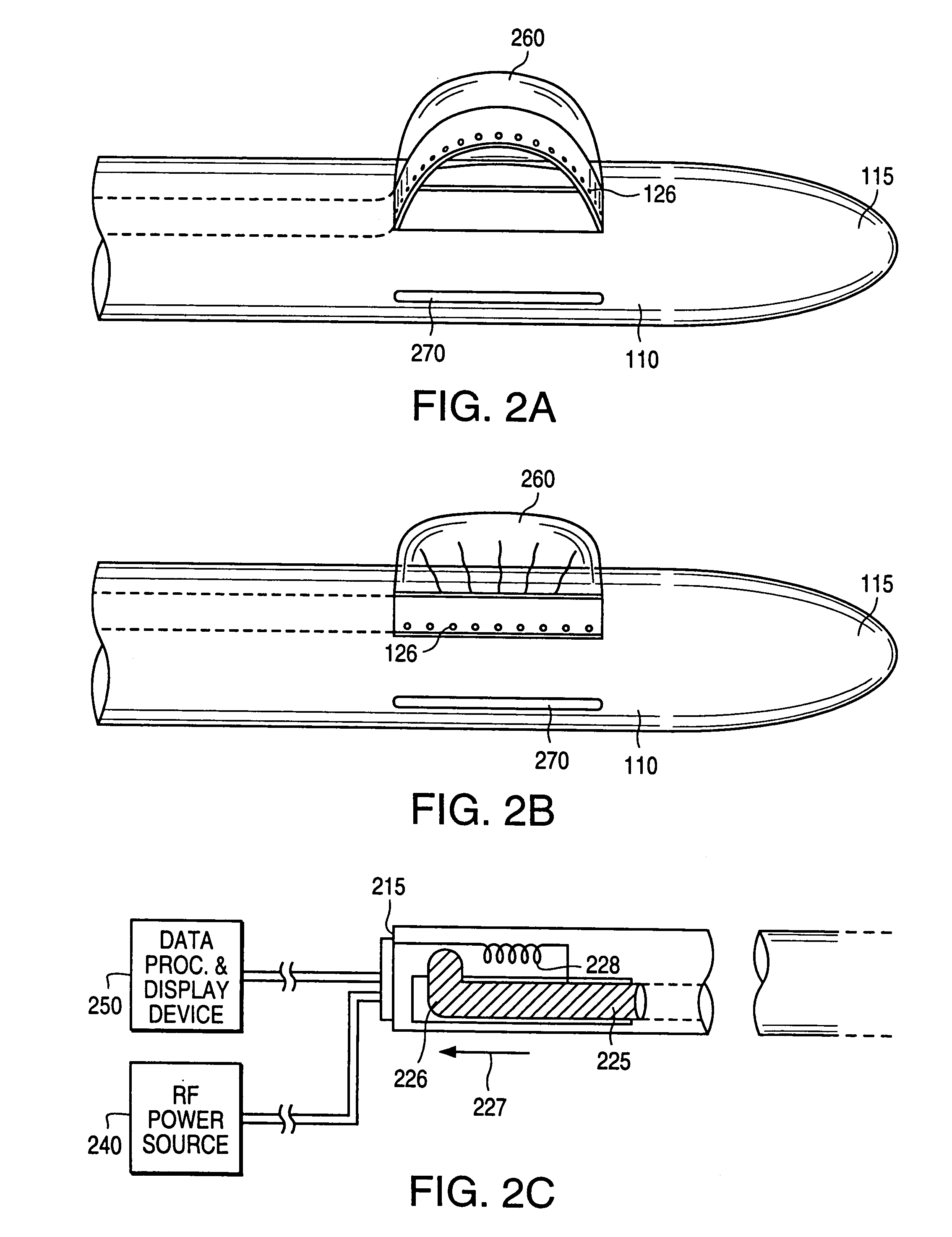
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
InactiveUS6863676B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimize complicationCannulasSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorTissue Collection
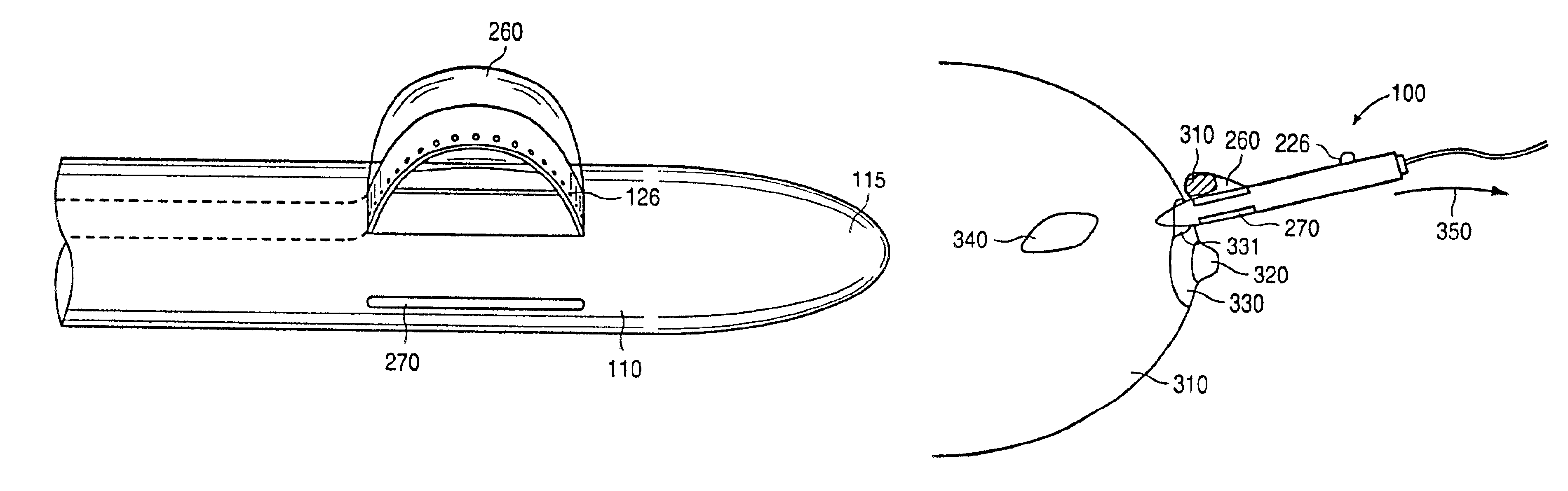
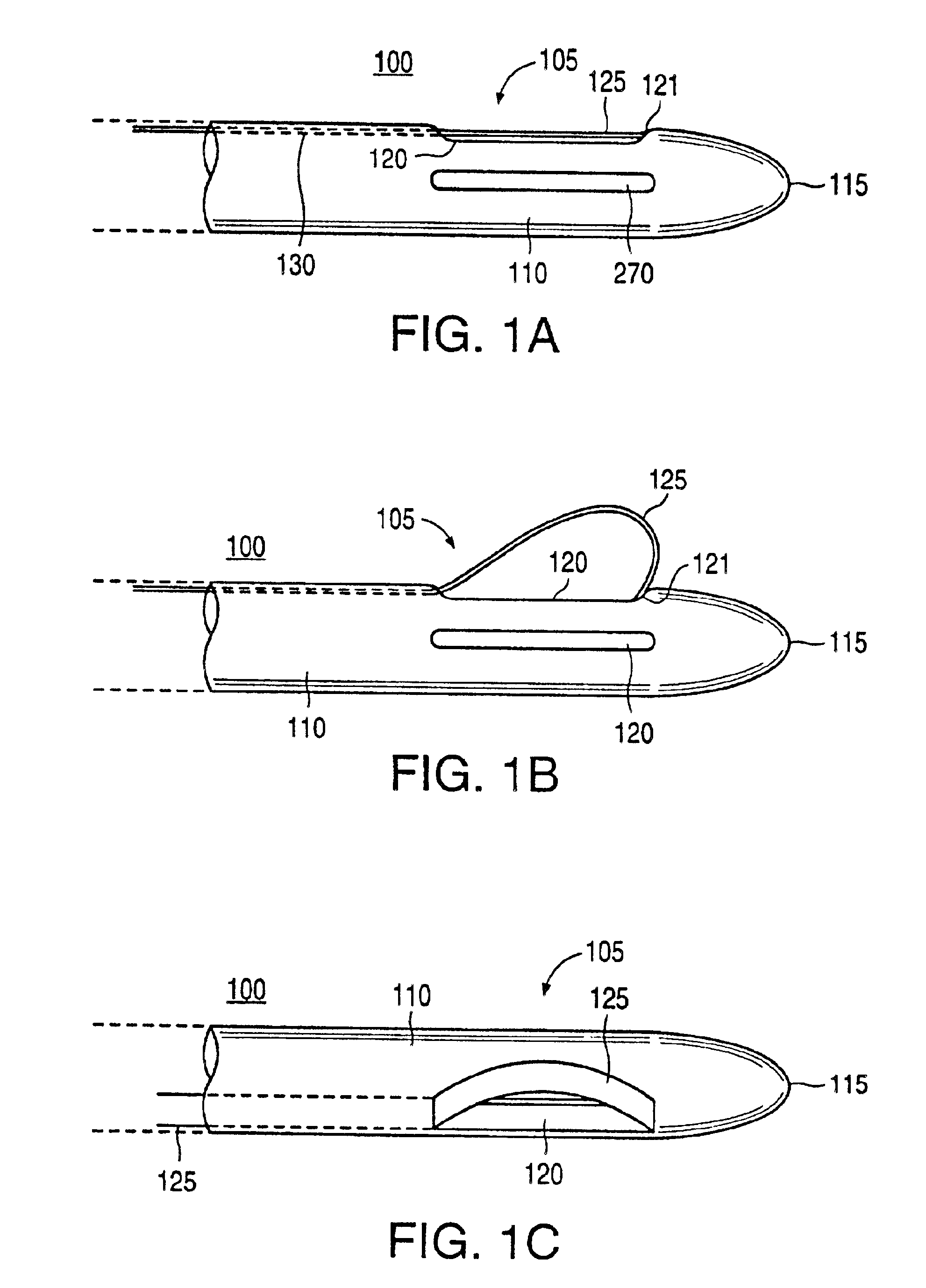
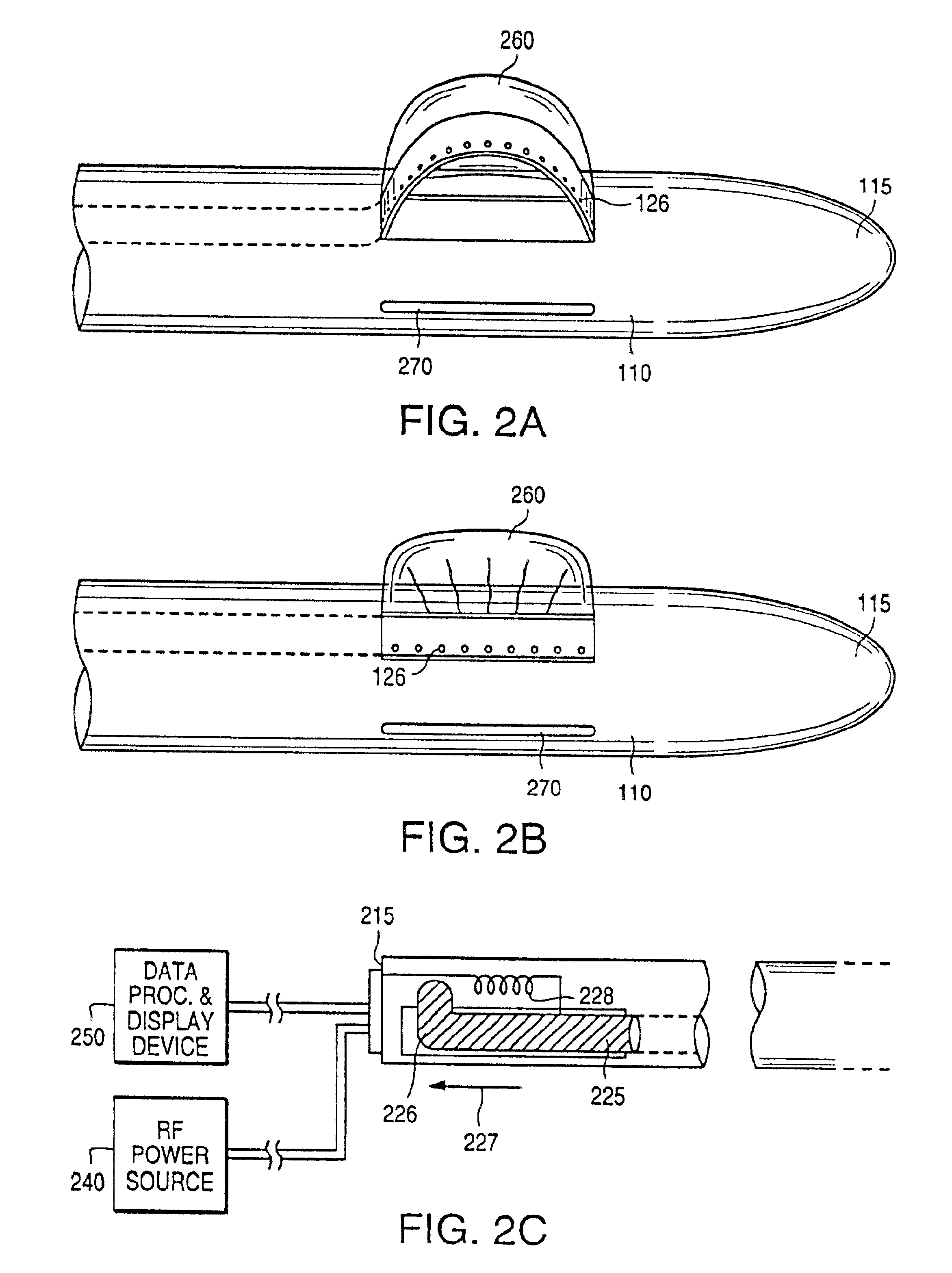
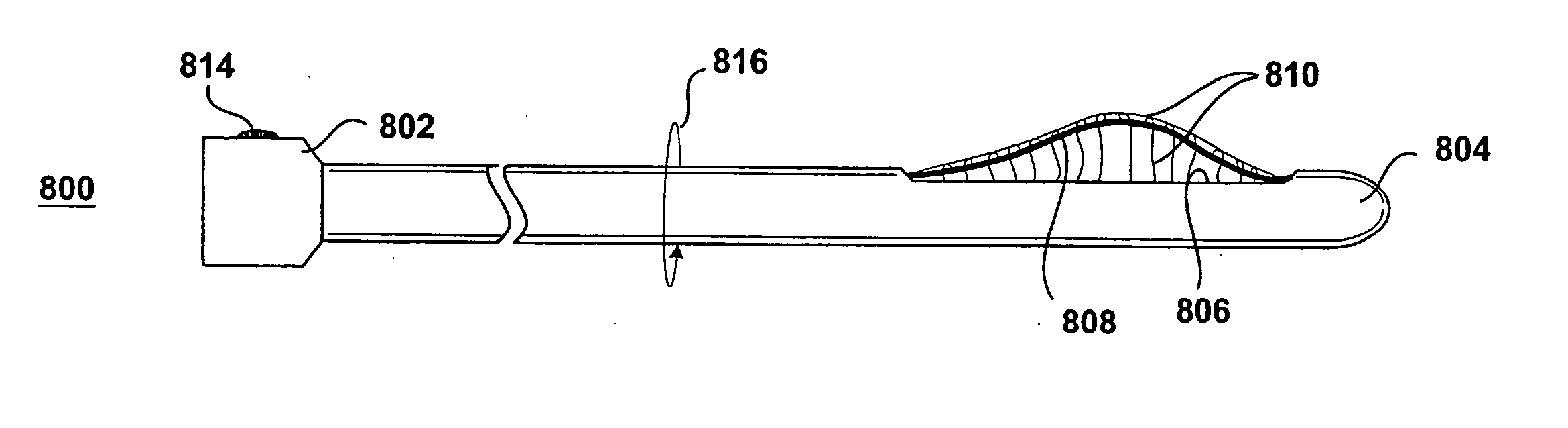
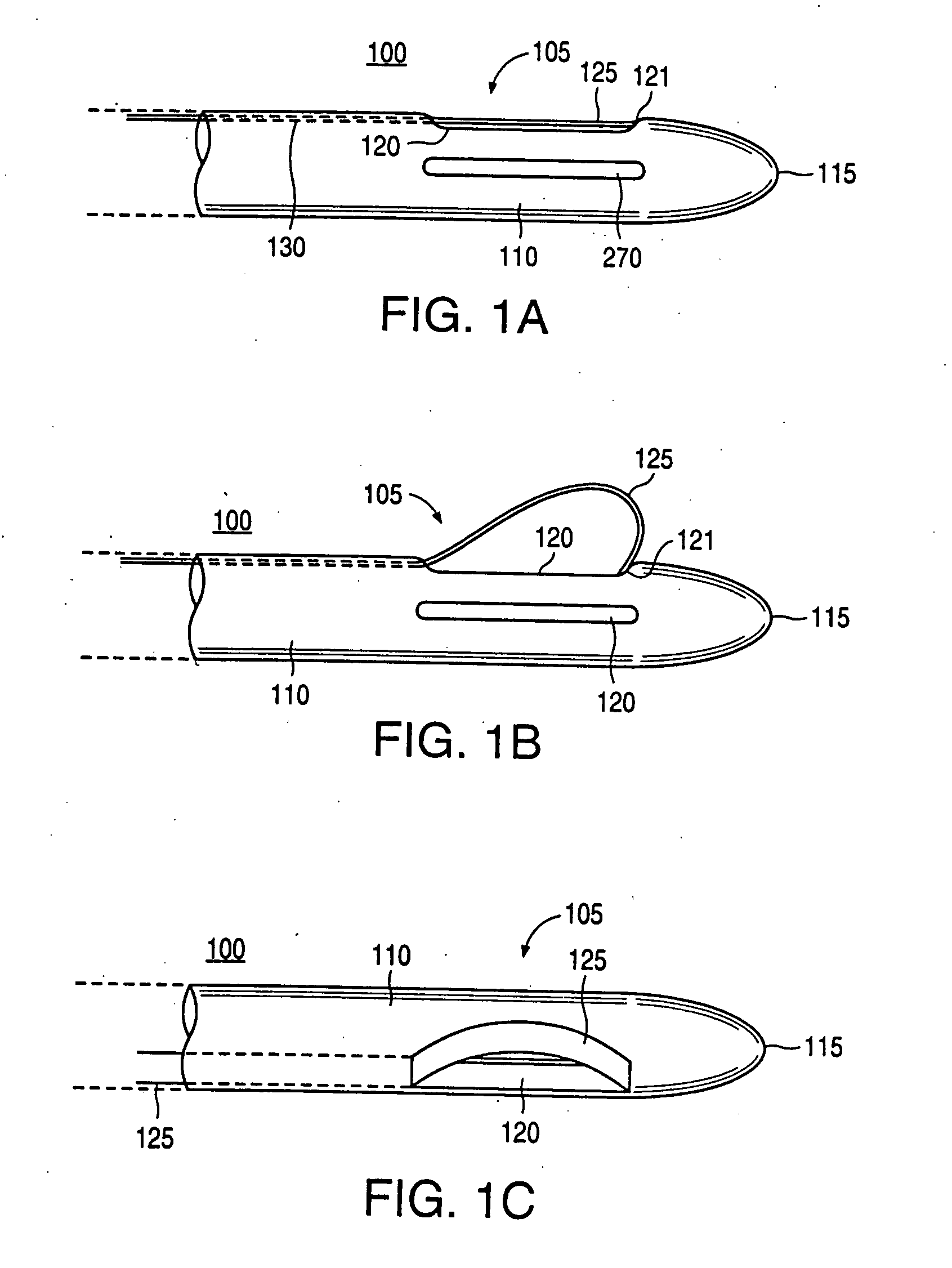
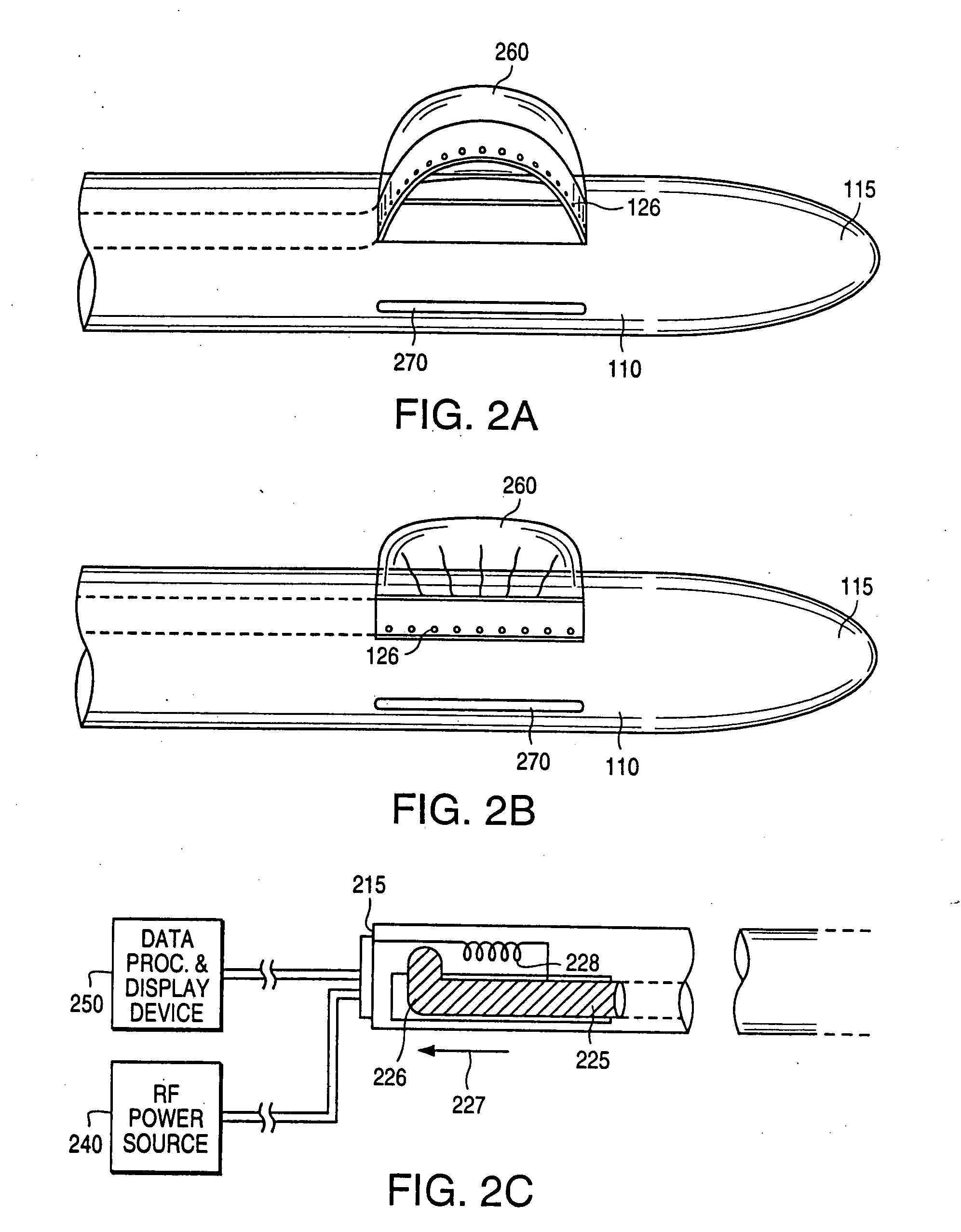
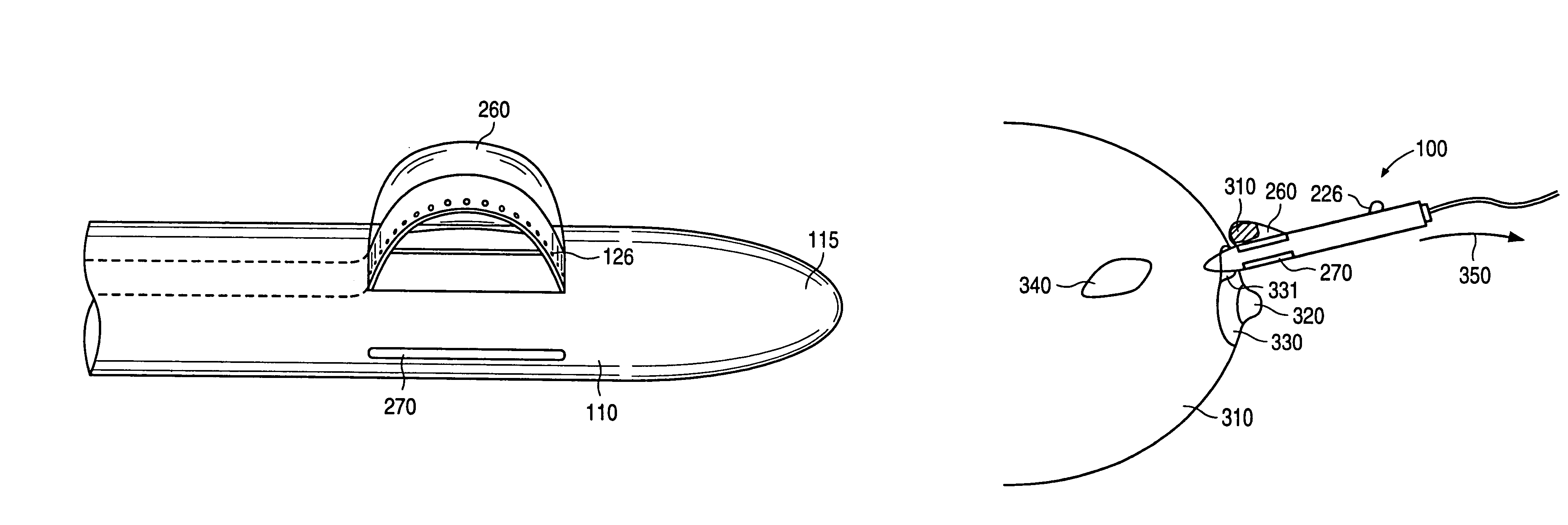
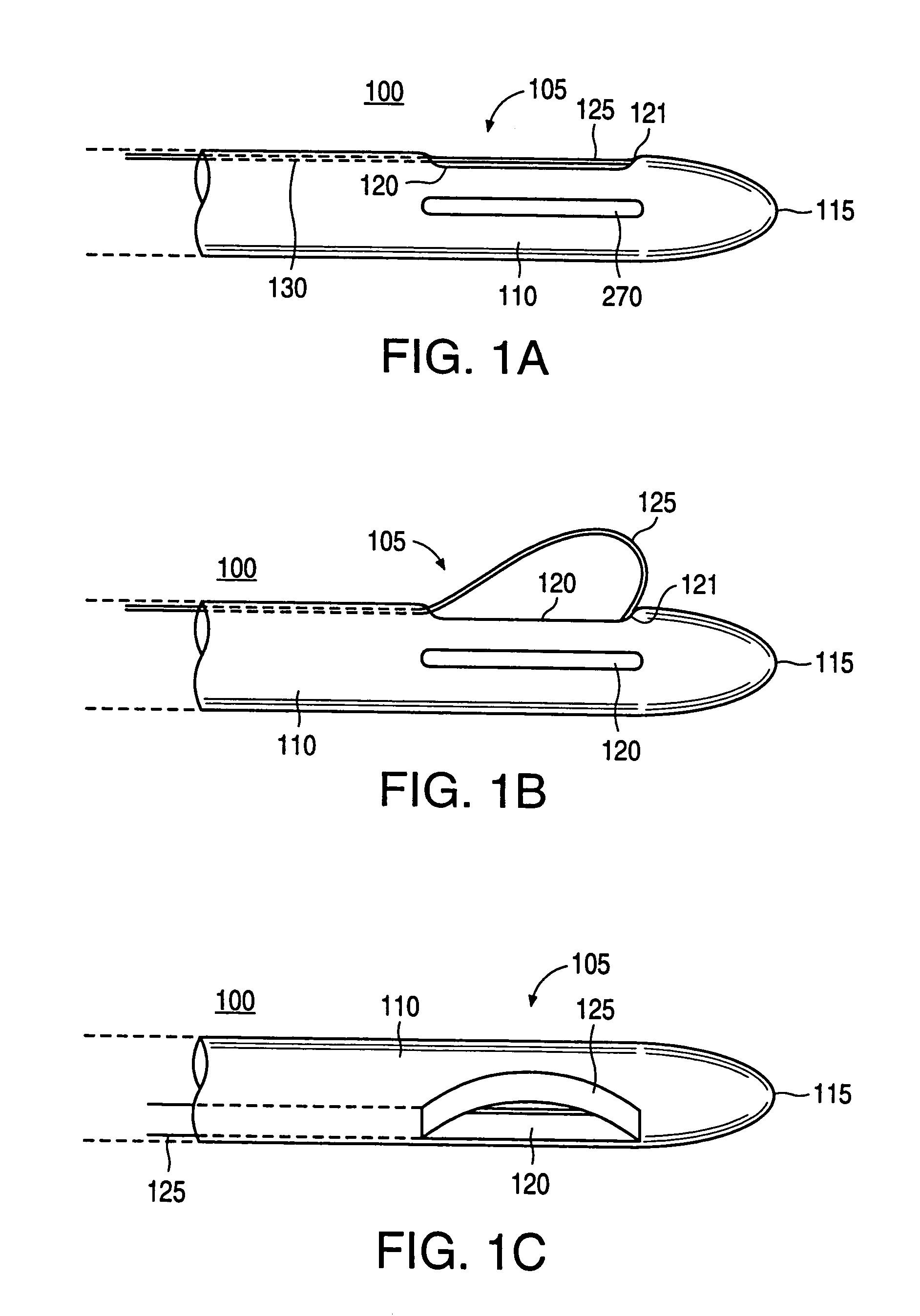
An excisional biopsy system includes a tubular member that has a proximal end and a distal end in which one or more windows are defined. A first removable probe has a proximal portion that includes a cutting tool extender and a distal portion that includes a cutting tool. The first removable probe may be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the cutting tool to selectively bow out of and to retract within one of the windows when the cutting tool extender is activated. A second removable probe has a proximal section that includes a tissue collection device extender and a distal section that includes a tissue collection device. The second removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the tissue collection device to extend out of and to retract within one of the windows when the tissue collection device extender is activated. A third removable probe may also be provided. The third removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member and may include an imaging device, such as an ultrasound transducer, mounted therein. By selectively activating the cutting tool and the tissue collection device while rotating the excisional device, a tissue specimen may be cut from the surrounding tissue and collected for later analysis.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
InactiveUS20050182339A1Efficiently and safely exciseMinimized in sizeSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorTissue Collection
An excisional biopsy system includes a tubular member that has a proximal end and a distal end in which one or more windows are defined. A first removable probe has a proximal portion that includes a cutting tool extender and a distal portion that includes a cutting tool. The first removable probe may be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the cutting tool to selectively bow out of and to retract within one of the windows when the cutting tool extender is activated. A second removable probe has a proximal section that includes a tissue collection device extender and a distal section that includes a tissue collection device. The second removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the tissue collection device to extend out of and to retract within one of the windows when the tissue collection device extender is activated. A third removable probe may also be provided. The third removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member and may include an imaging device, such as an ultrasound transducer, mounted therein. By selectively activating the cutting tool and the tissue collection device while rotating the excisional device, a tissue specimen may be cut from the surrounding tissue and collected for later analysis.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
InactiveUS7303531B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimized in sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasBiopsy methodsTissue Collection
An excisional biopsy device includes a tubular member having a window near a distal tip thereof; a cutting tool, a distal end of the cutting tool being attached near the distal tip of the tubular member, at least a distal portion of the cutting tool being configured to selectively bow out of the window and to retract within the window; and a tissue collection device externally attached at least to the tubular member, the tissue collection device collecting tissue excised by the cutting tool as the biopsy device is rotated and the cutting tool is bowed. An excision al biopsy method for soft tissue includes the steps of inserting a generally tubular member into the tissue, the tubular member including a cutting tool adapted to selectively bow away from the tubular member and an external tissue collection device near a distal tip of the tubular member; rotating the tubular member; selectively varying a degree of bowing of the cutting tool; collecting tissue severed by the cutting tool in the tissue collection device; and retracting the tubular member from the soft tissue. The tubular member may include an imaging transducer and the method may include the step of displaying information received from the transducer on a display device and the step of varying the degree of bowing of the cutting tool based upon the displayed information from the imaging transducer. Alternatively, the imaging transducer may be disposed within a removable transducer core adapted to fit within the tubular member.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
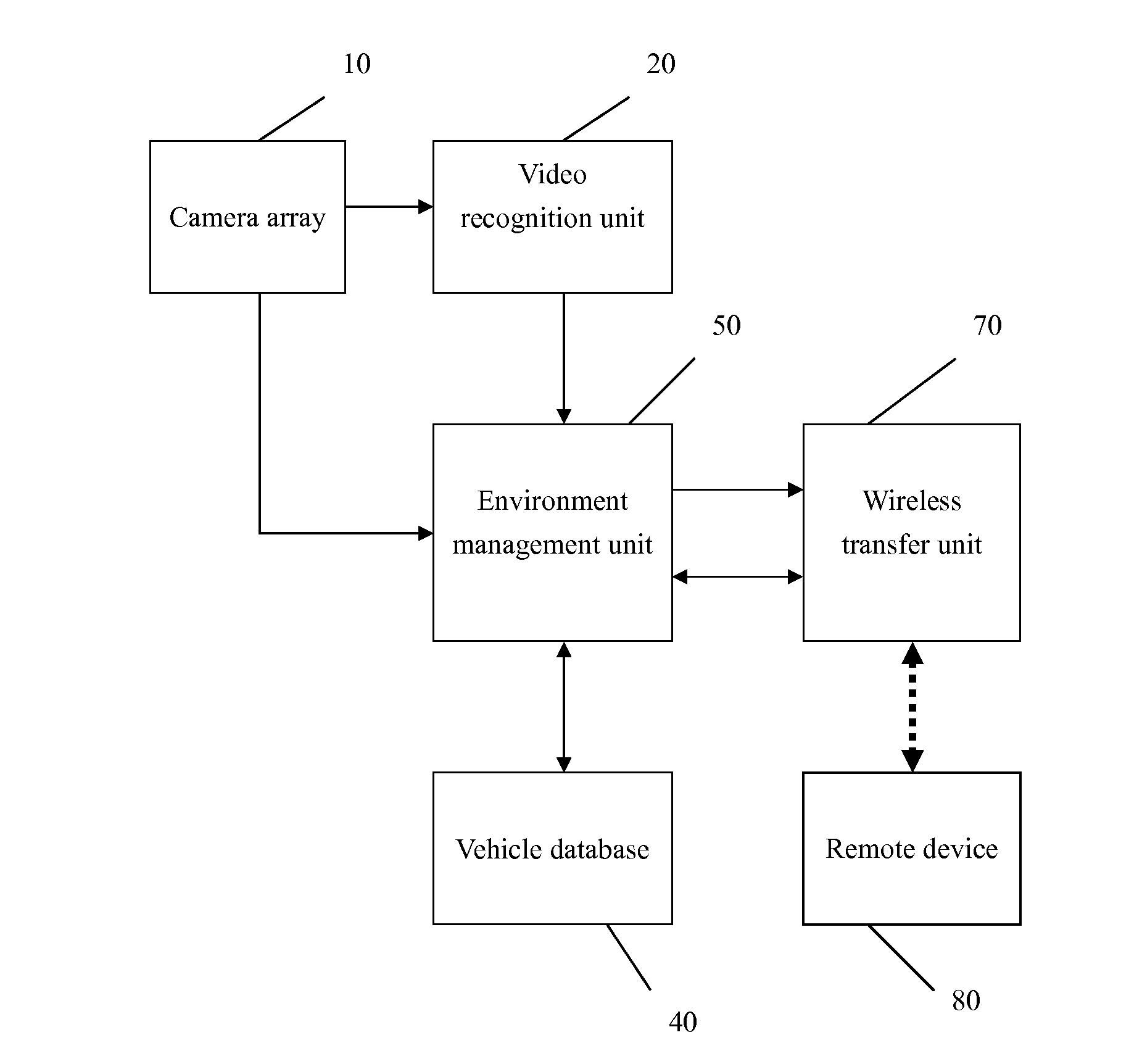
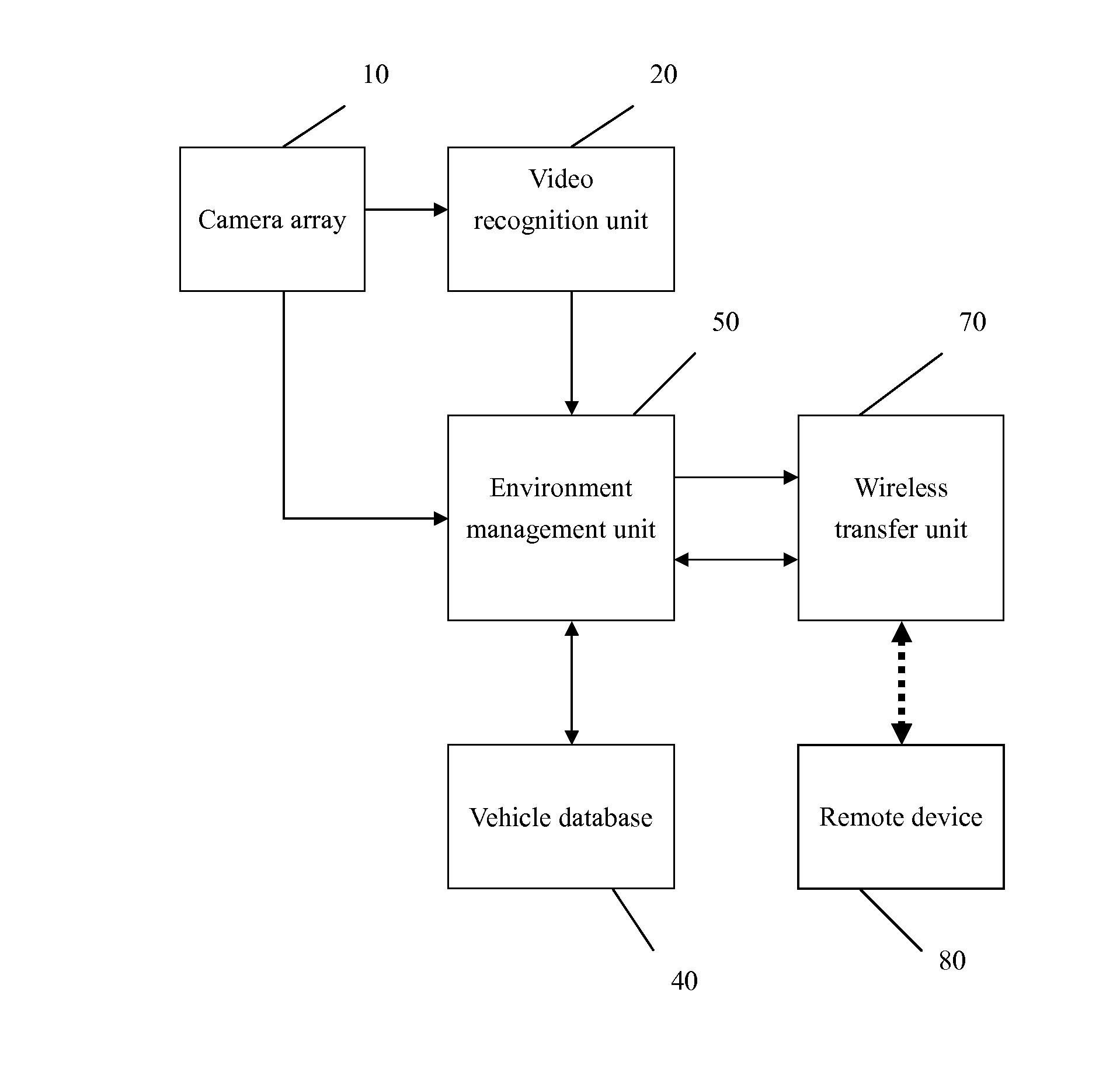
Remote vehicle management system by video radar
InactiveUS8340902B1Easy to captureEasy to understandVehicle testingTelevision system detailsObject basedData stream
A remote vehicle management system by video radar includes a camera array installed on the vehicle to capture and generate video data, video recognition units receiving the video data and converting into an object data stream, a vehicle database including static and dynamic data, an environment management unit generating a video radar data stream based on the object data stream and, a wireless transfer unit transmitting the radar data stream in a wireless medium, and a remote device reconstructing an illustrative screen based on the received video radar data stream by using specific icons or symbols, which is used to assist the operator of the vehicle to fully understand the actual situation so as to alleviate the human workload, reduce human mistakes and improve the efficiency of the vehicle management.
Owner:CHIANG YAN HONG
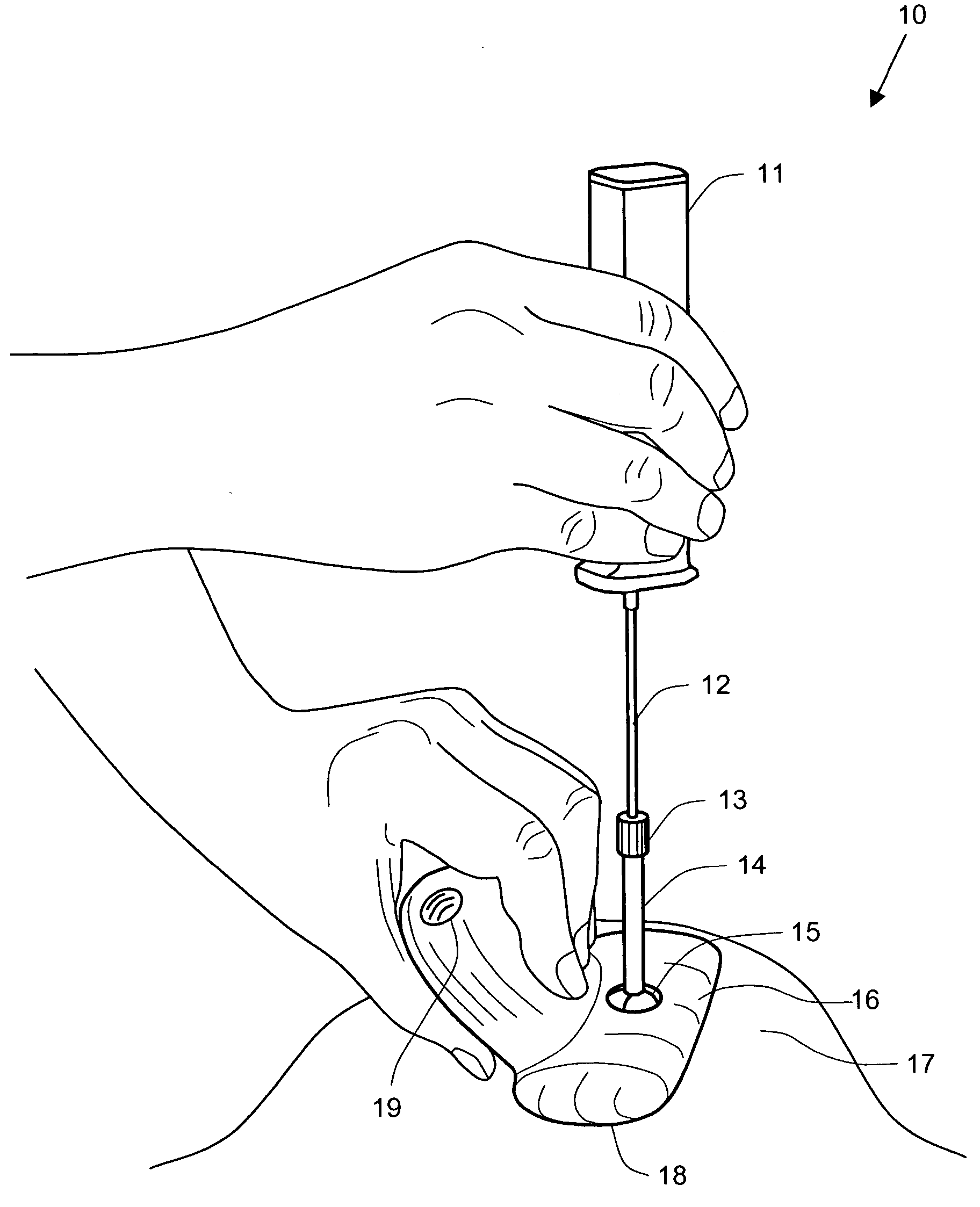
Device and method for biopsy guidance using a tactile breast imager
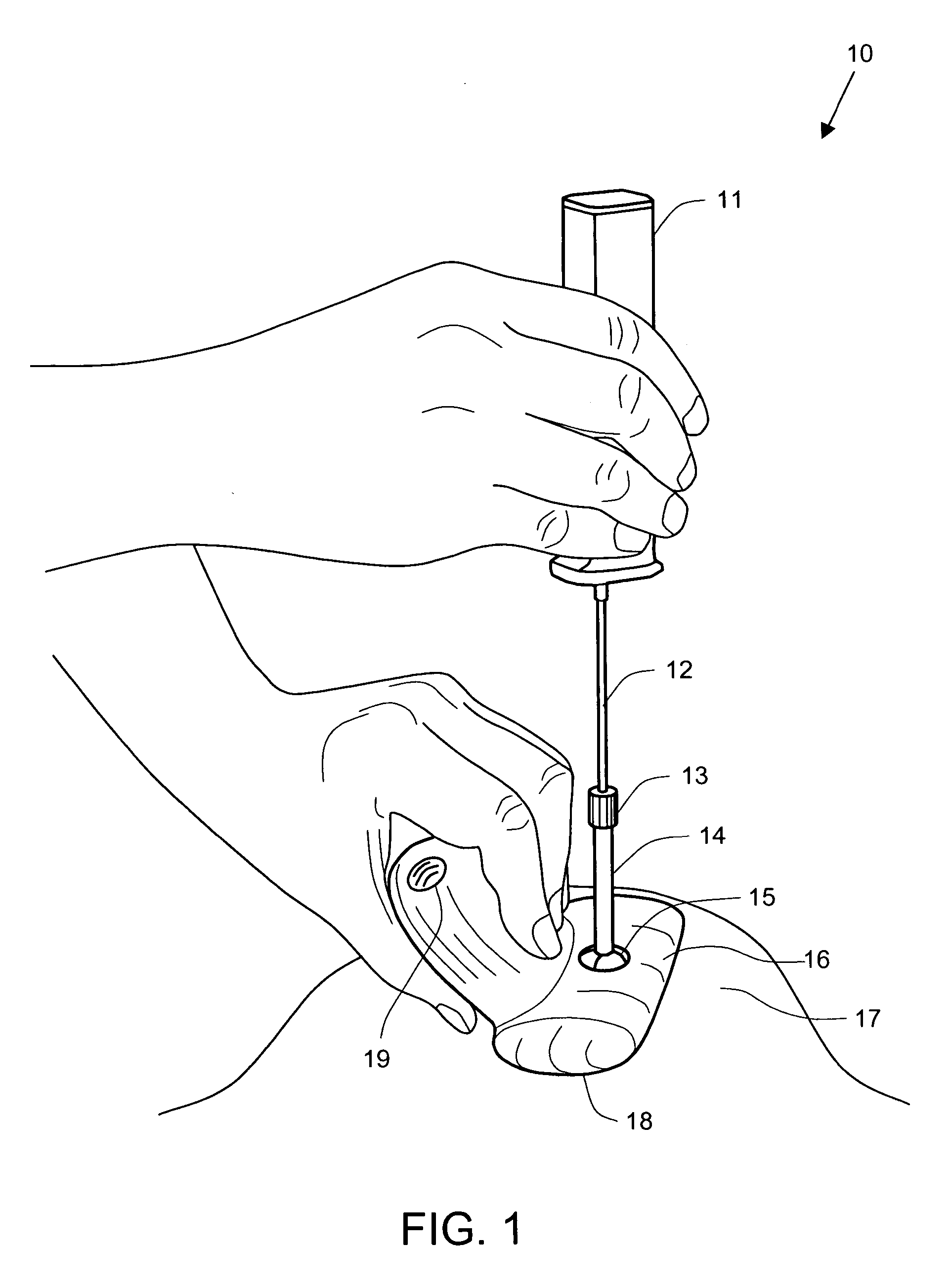
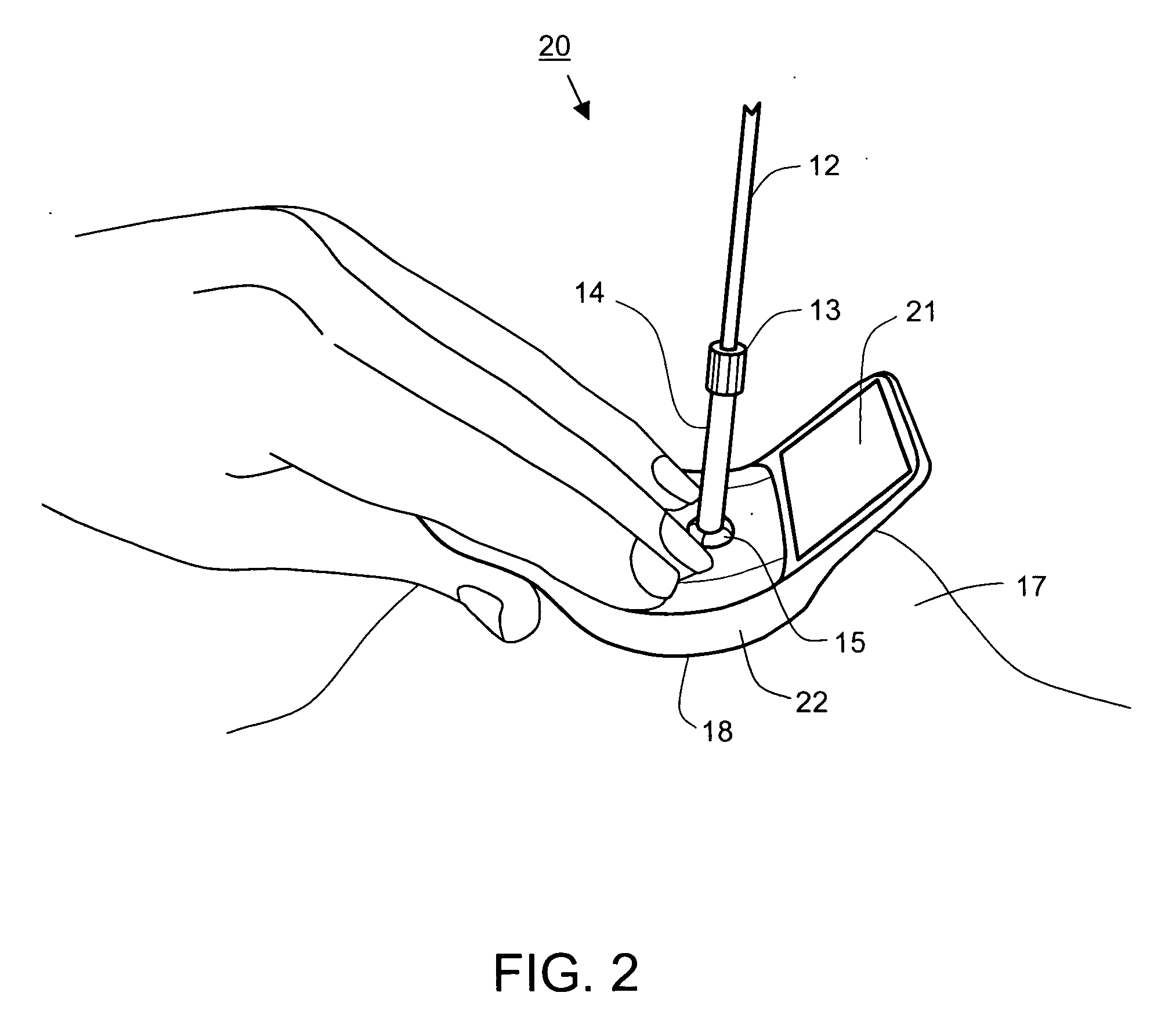
InactiveUS20040267121A1Provide real-timeIncreased sensitivity and repeatability and accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesBiopsy procedurePressure sense
A biopsy guidance device is enclosed based on a tactile imaging probe adapted to accept a biopsy gun. The tactile imaging probe includes a pressure sensing surface providing real-time 2-D images of the underlying tissue structures allowing to detect a lesion. A cannula is provided supported at a center point by a ball and socket joint. The joint is equipped with linear and angular sensors and supports the cannula with the ability to rotate thereof about the center point. The position, linear and angular displacement and direction of the needle tip of a biopsy needle placed inside the cannula is therefore known at all times and provided as a feedback signal to a physician. Also provided to a physician is a position of the target site at a lesion, as well as a linear and angular deviation of the needle tip away from the target site. Such audio, light, or visual feedback allows the physician to correct the insertion angle and depth to confidently reach the target site to perform a biopsy. Method is also disclosed to guide the biopsy procedure.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
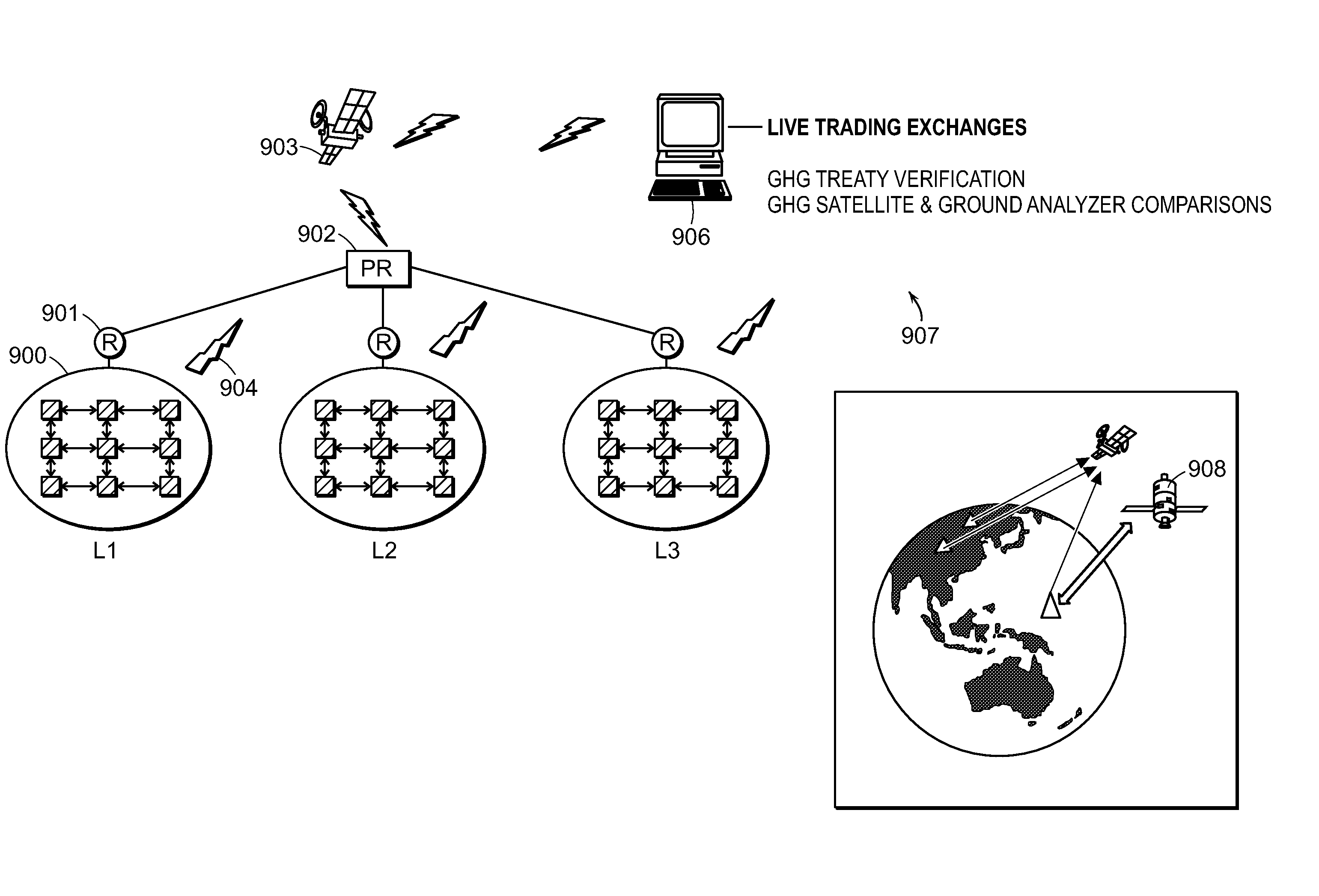
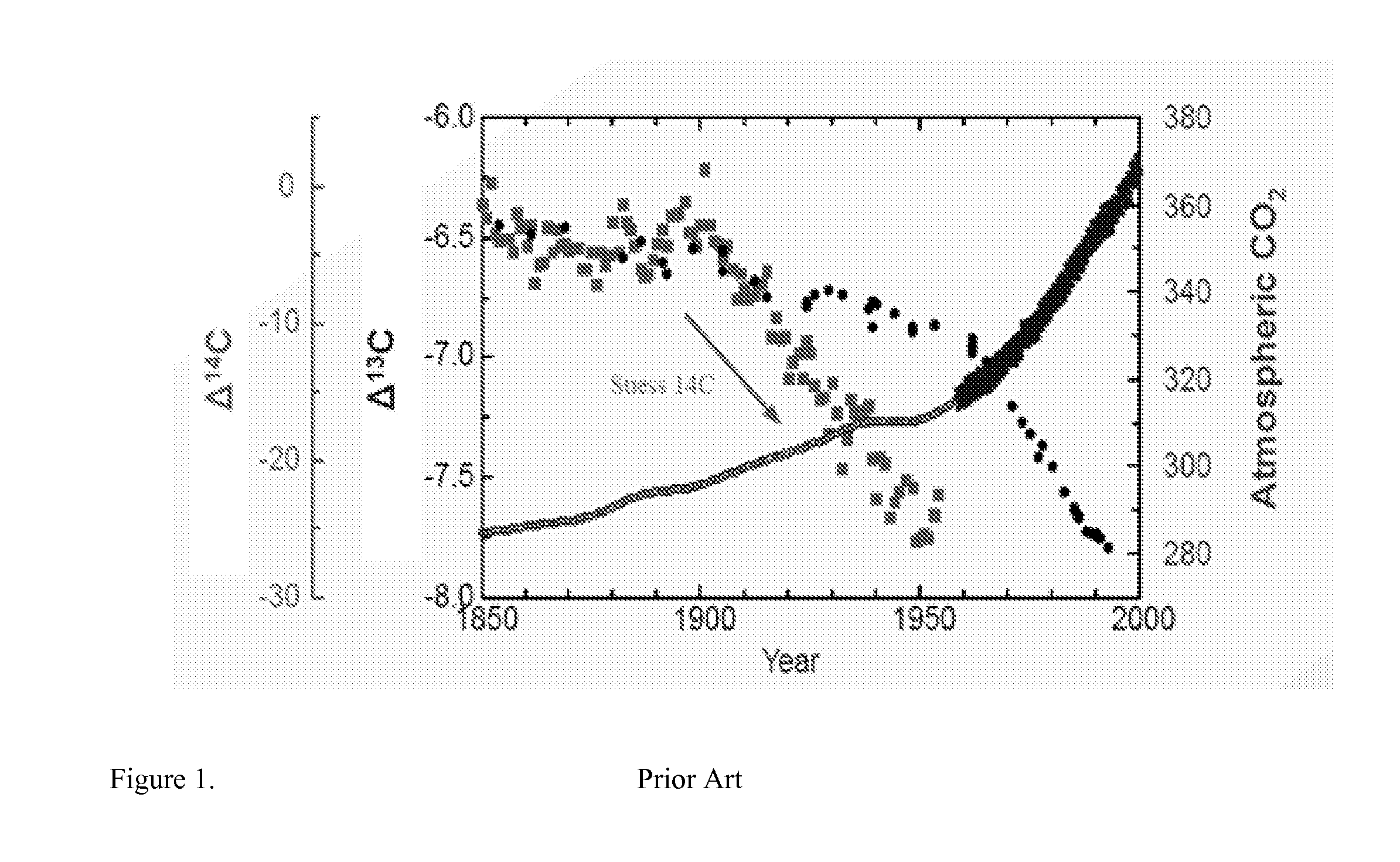
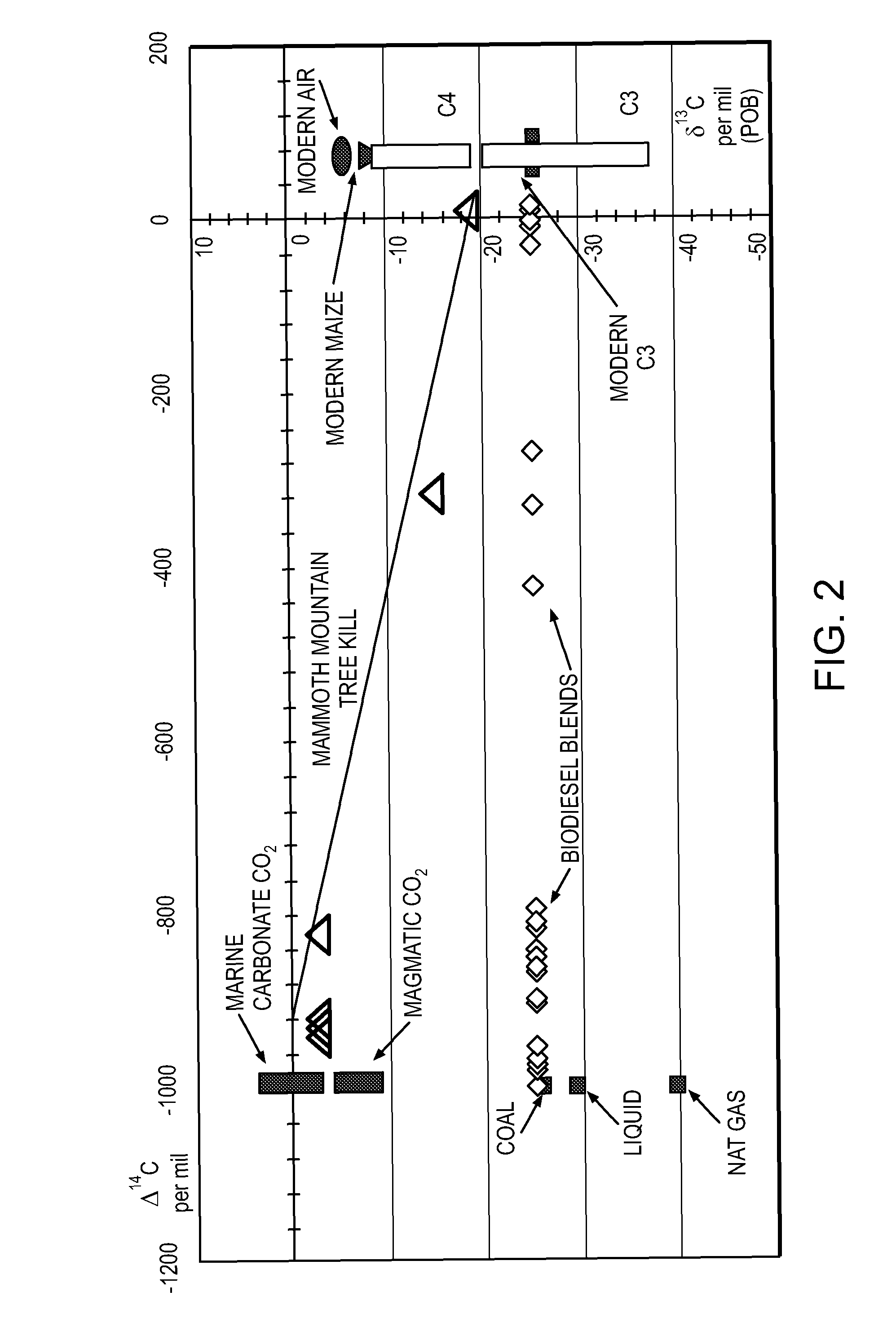
System of systems for monitoring greenhouse gas fluxes
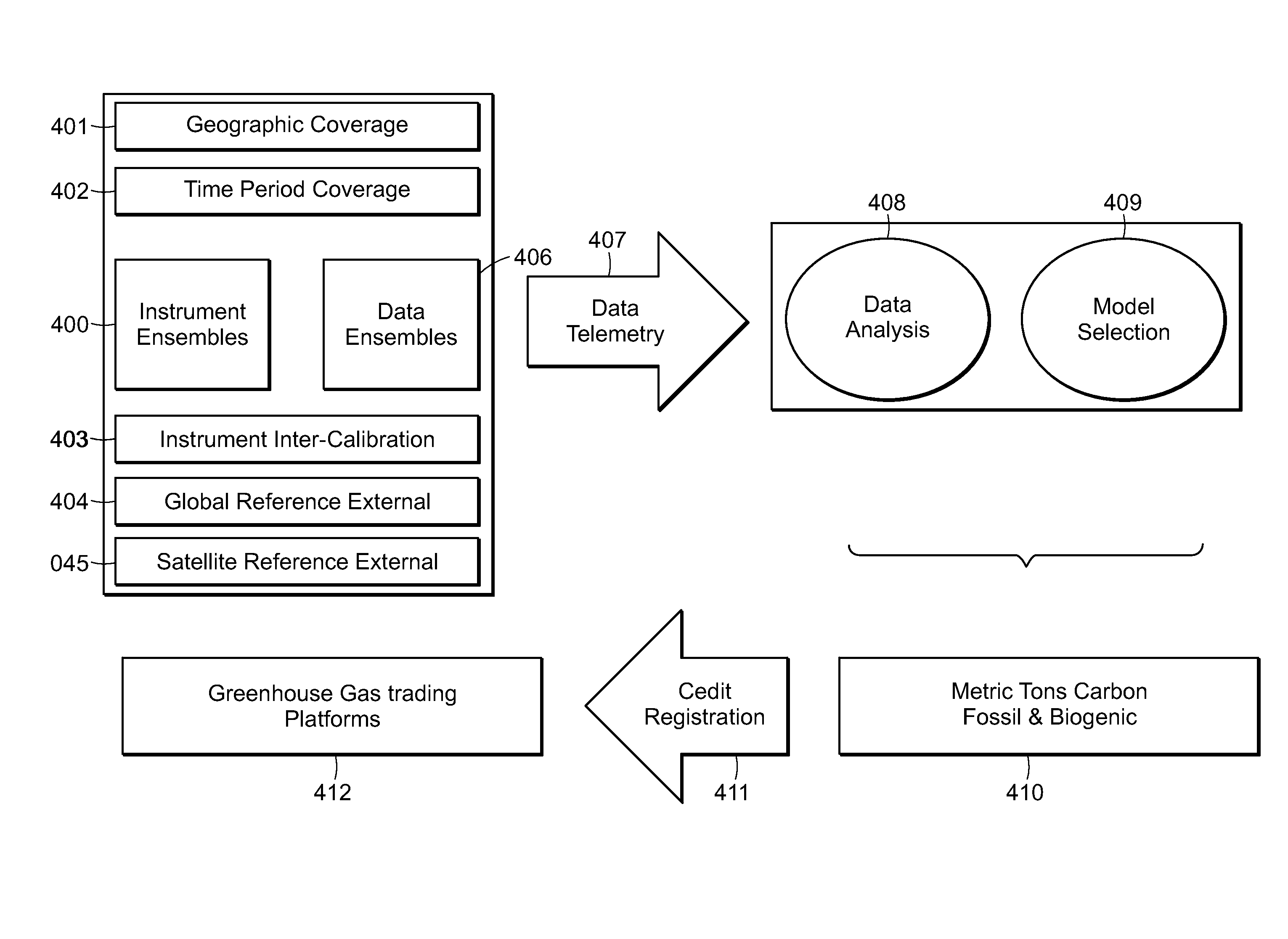
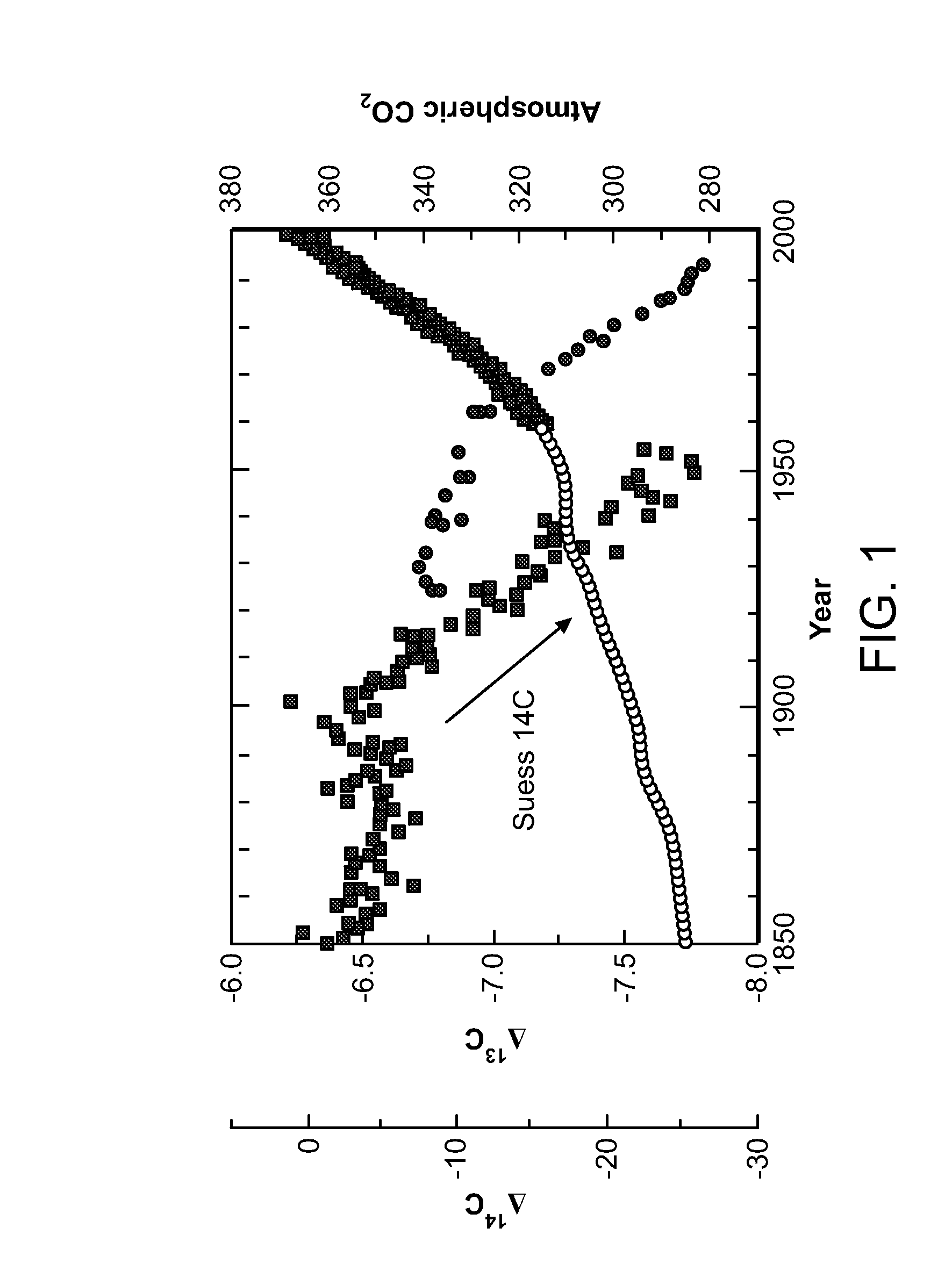
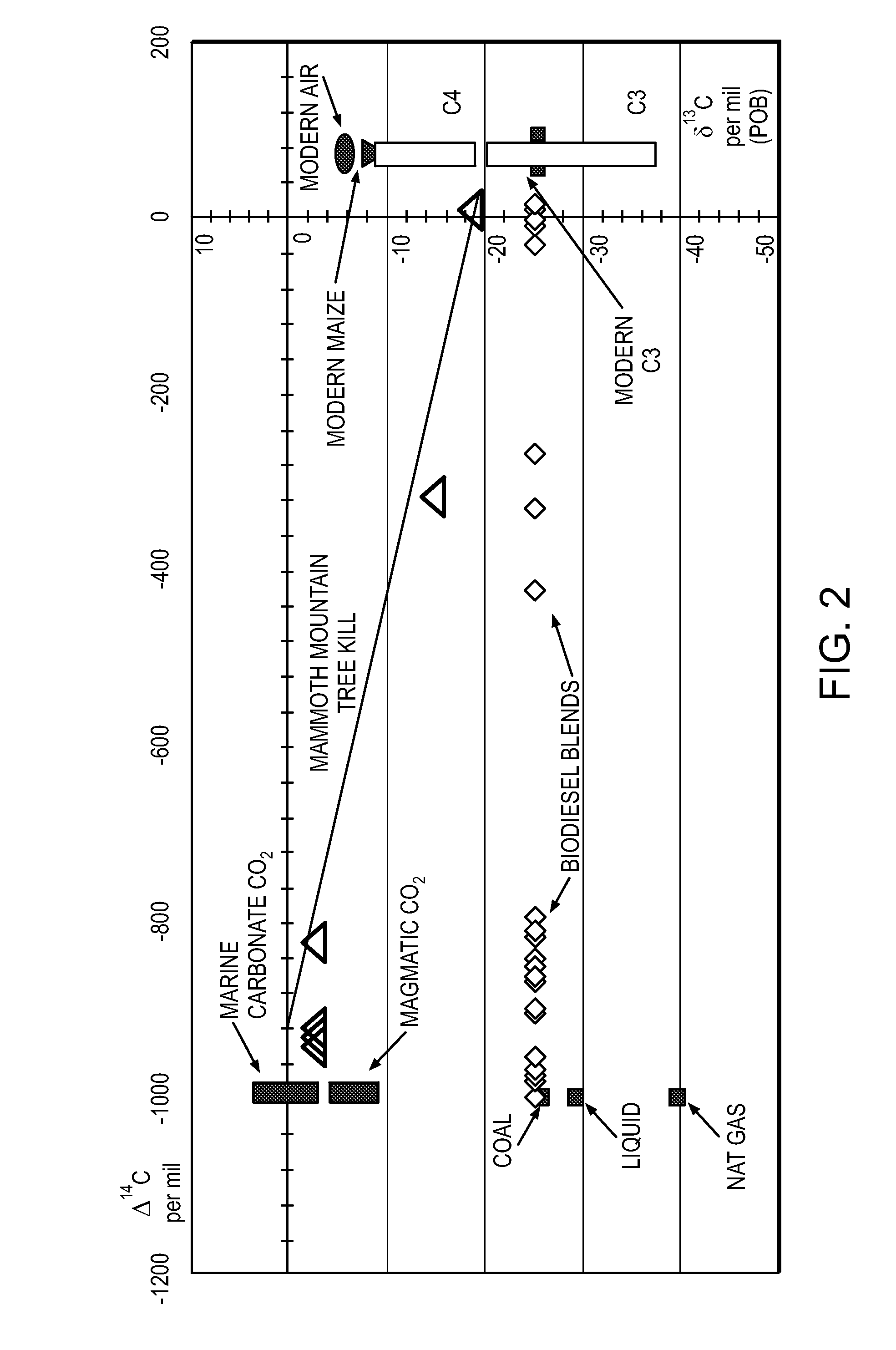
ActiveUS20100198736A1High precisionReduce uncertaintySustainable waste treatmentCarbon compoundsNatural sourceGreenhouse gas flux
A system of systems to monitor data for carbon flux, for example, at scales capable of managing regional net carbon flux and pricing carbon financial instruments is disclosed. The system of systems can monitor carbon flux in forests, soils, agricultural areas, body of waters, flue gases, and the like. The system includes a means to identify and quantify sources of carbon based on simultaneous measurement of isotopologues of carbon dioxide, for example, industrial, agricultural or natural sources, offering integration of same in time and space. Carbon standards are employed at multiple scales to ensure harmonization of data and carbon financial instruments.
Owner:PLANETARY EMISSIONS MANAGEMENT
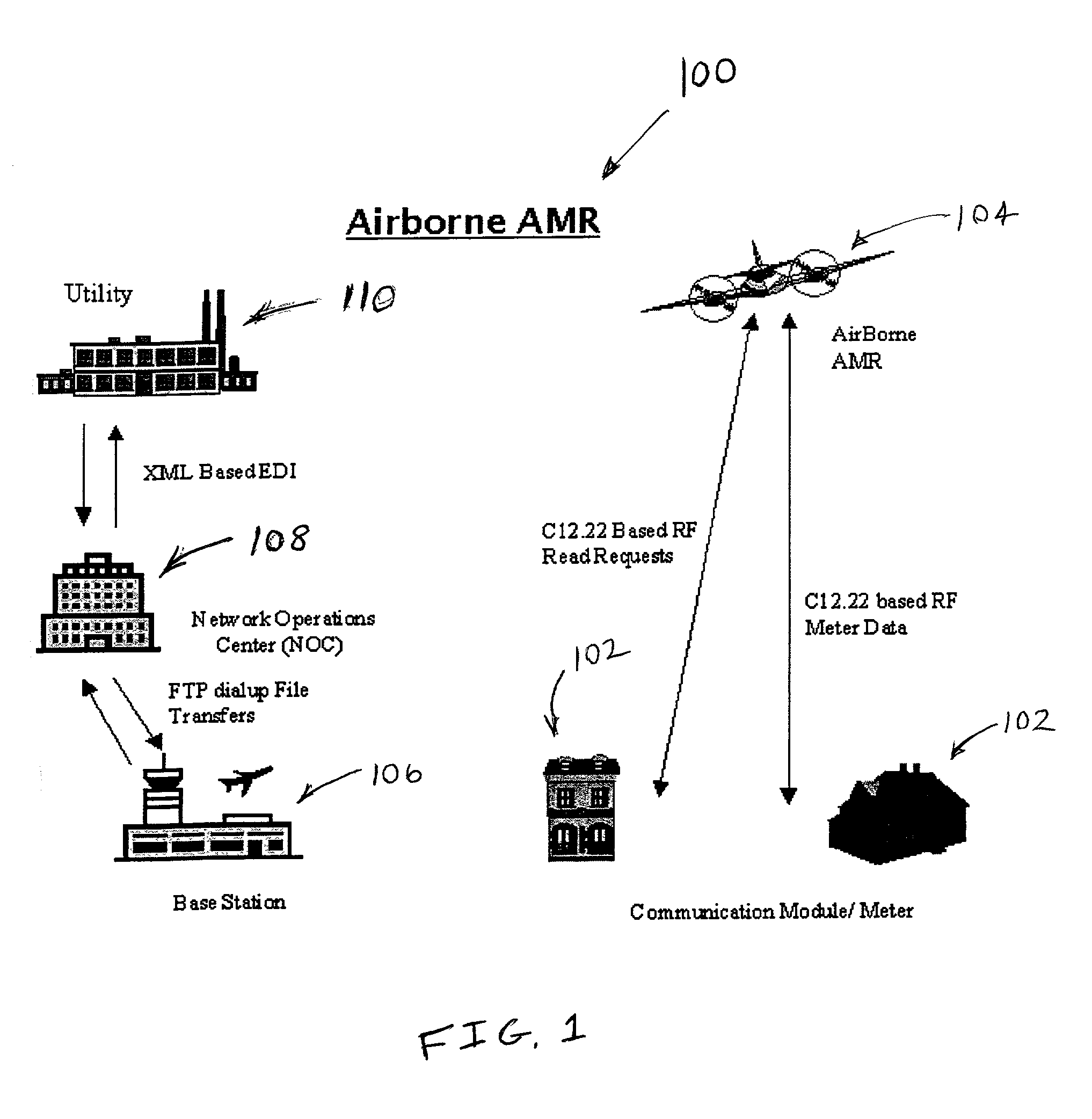
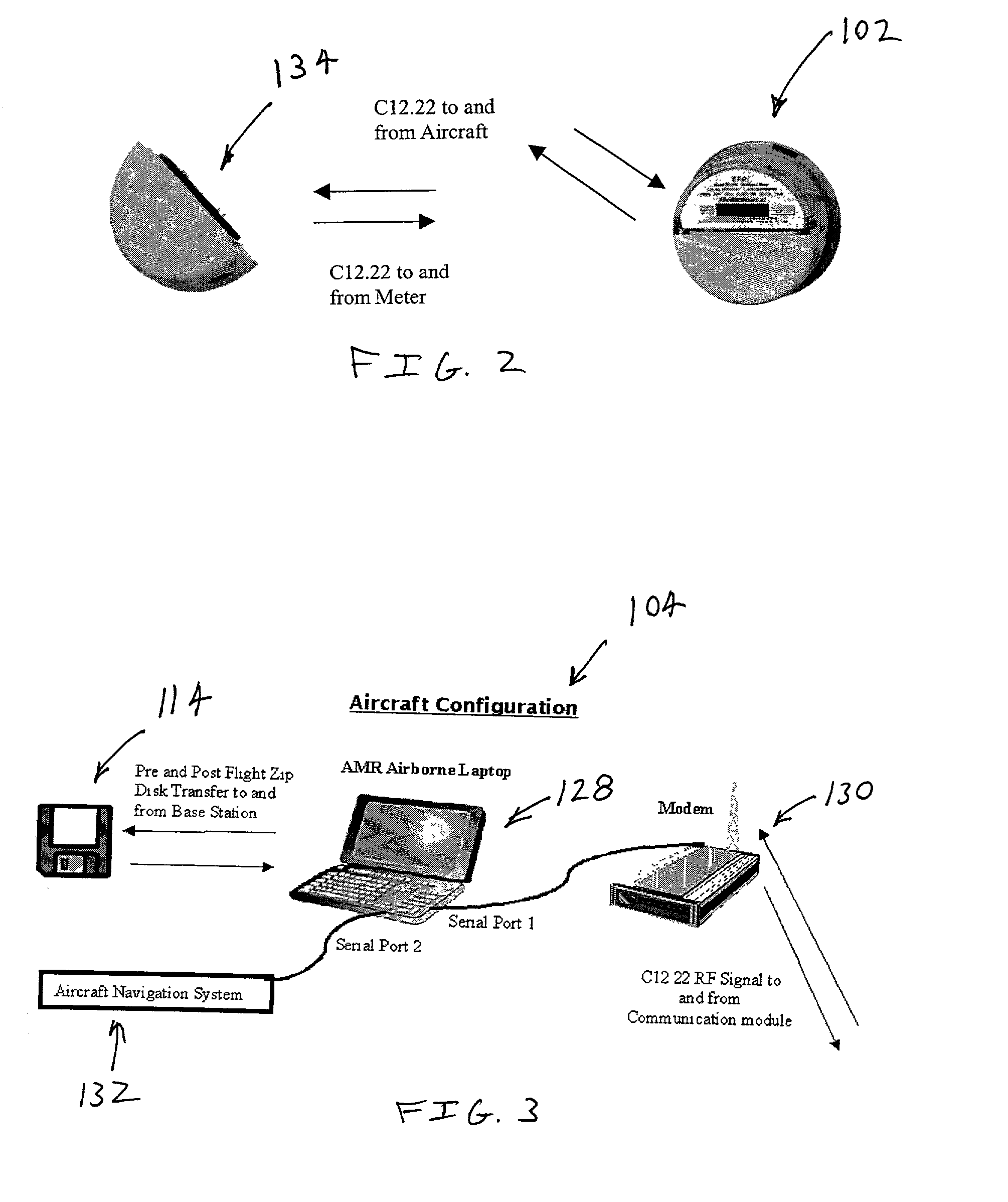
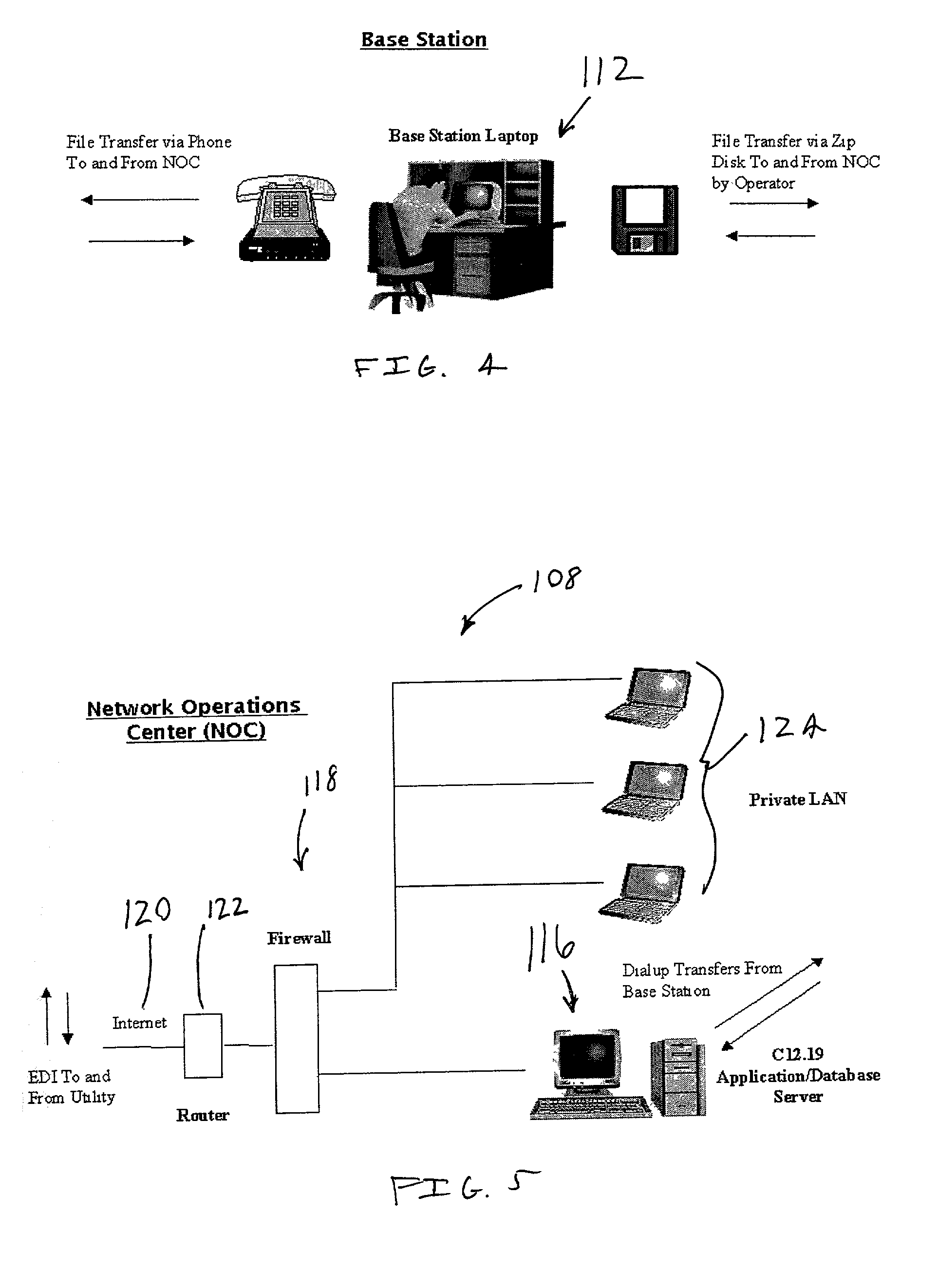
Method and system for airborne meter communication
InactiveUS20010038342A1Provide real-timeImprove accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsSpecial tariff metersCommunications systemNetwork operations center
An airborne meter communication system includes an airborne platform that communicates with ground based utility meters using radio frequencies. The airborne platform retransmits information received from the meters to a network operations center for further processing.
Owner:FOOTE CHARLES A
Motion training apparatus and method
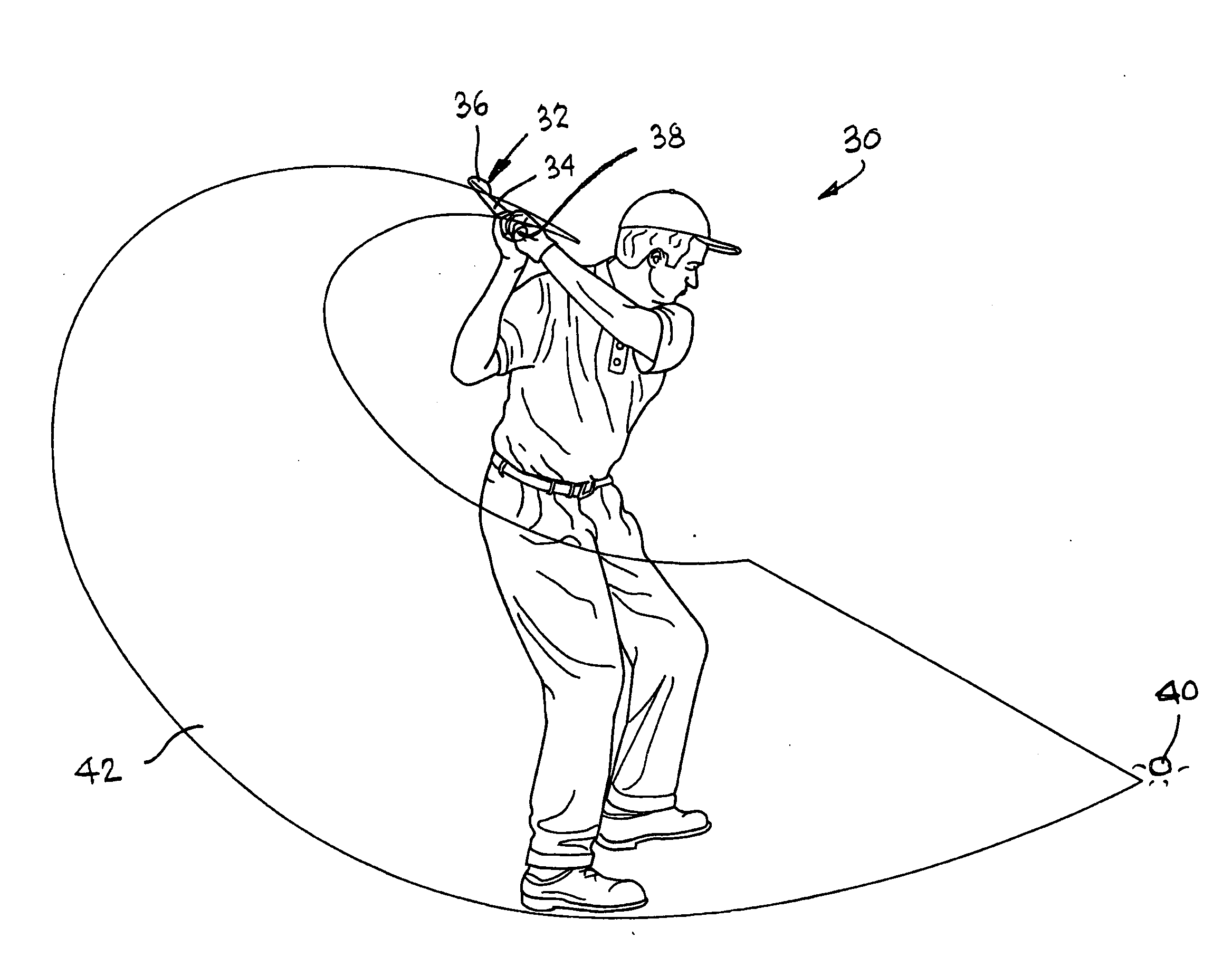
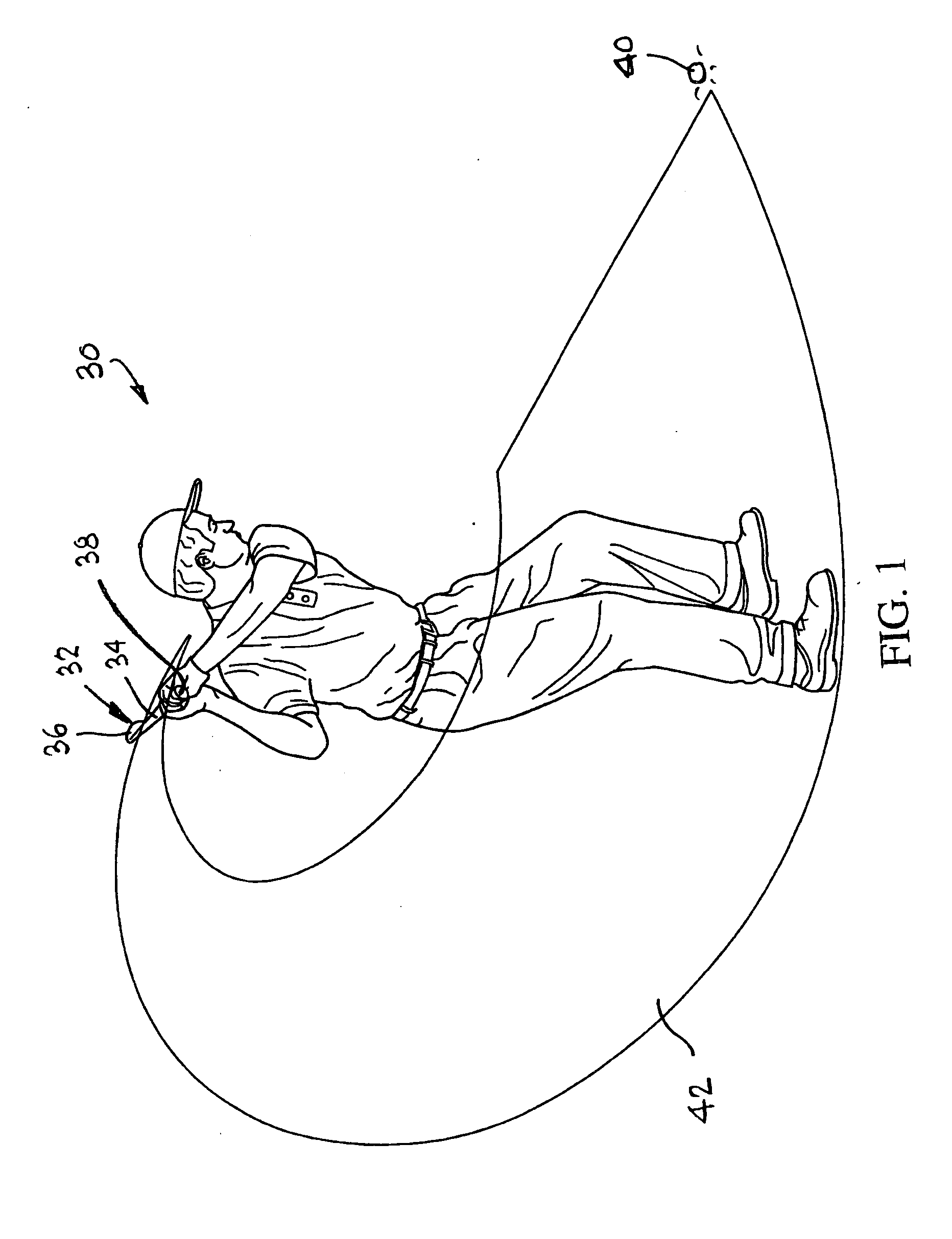
InactiveUS20070238538A1Easy to watchImprove viewing effectGymnastic exercisingVideo gamesEngineeringSport training
The invention is directed to a motion trainer for improving a person's movement of an implement by allowing the person to visualize the path of the implement during the movement. The motion trainer comprises an implement having a plurality of motion characteristic sensors located thereon for determining, among other things, the direction of the movement and the orientation of the implement during the movement. Biofeedback devices provide the person information regarding the positioning of the implement during the movement.
Owner:PRIESTER WILLIAM B
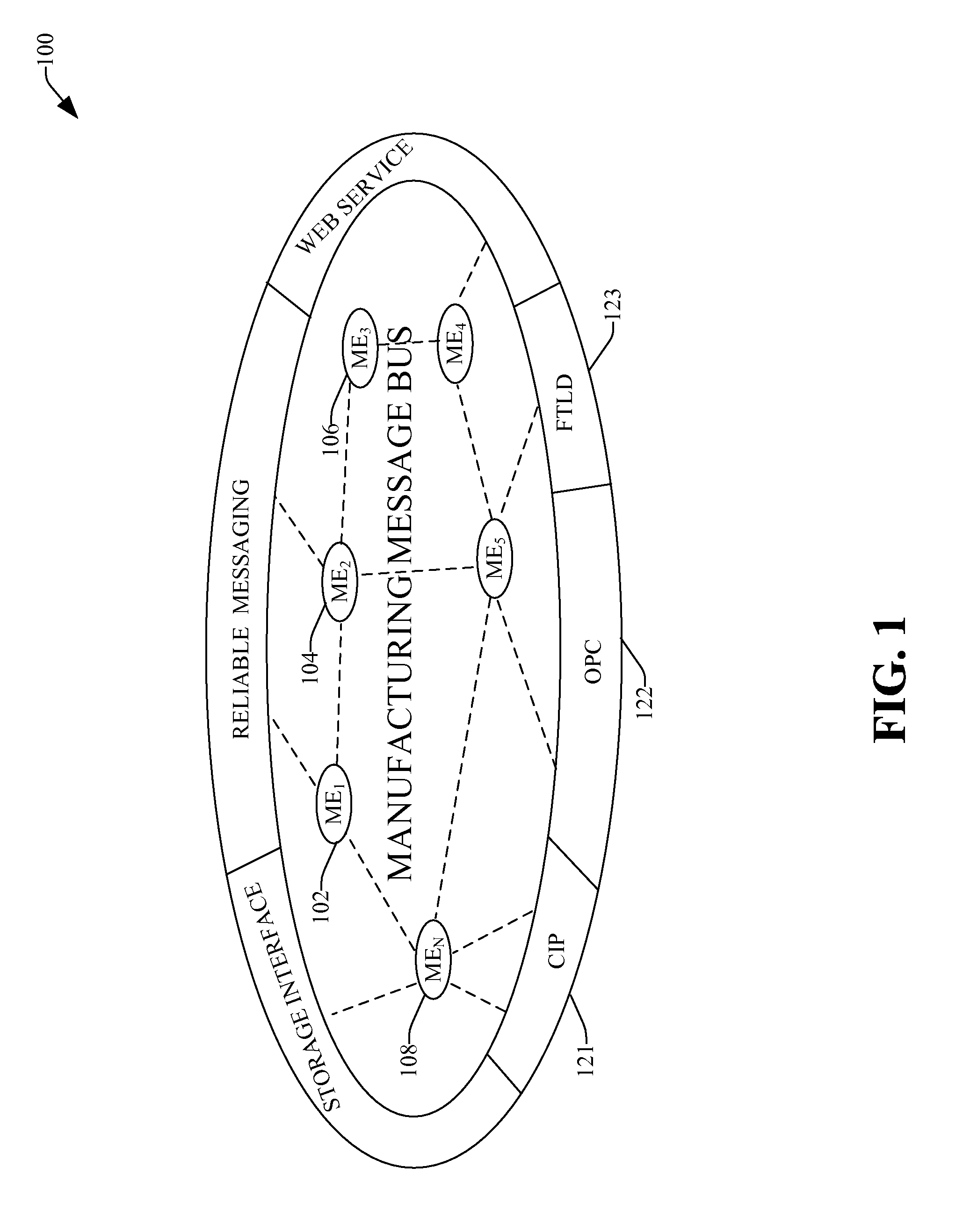
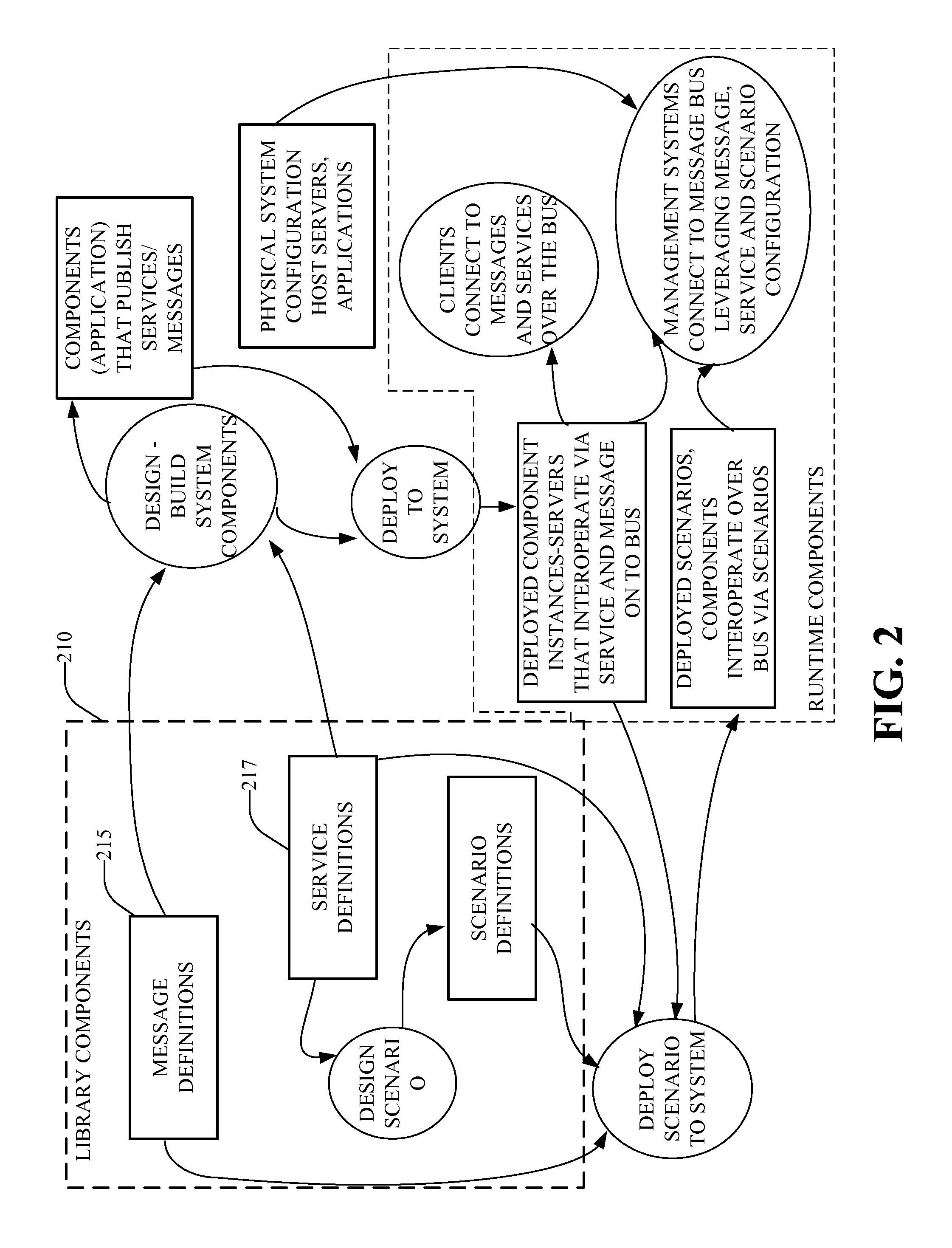
Distributed message engines and systems
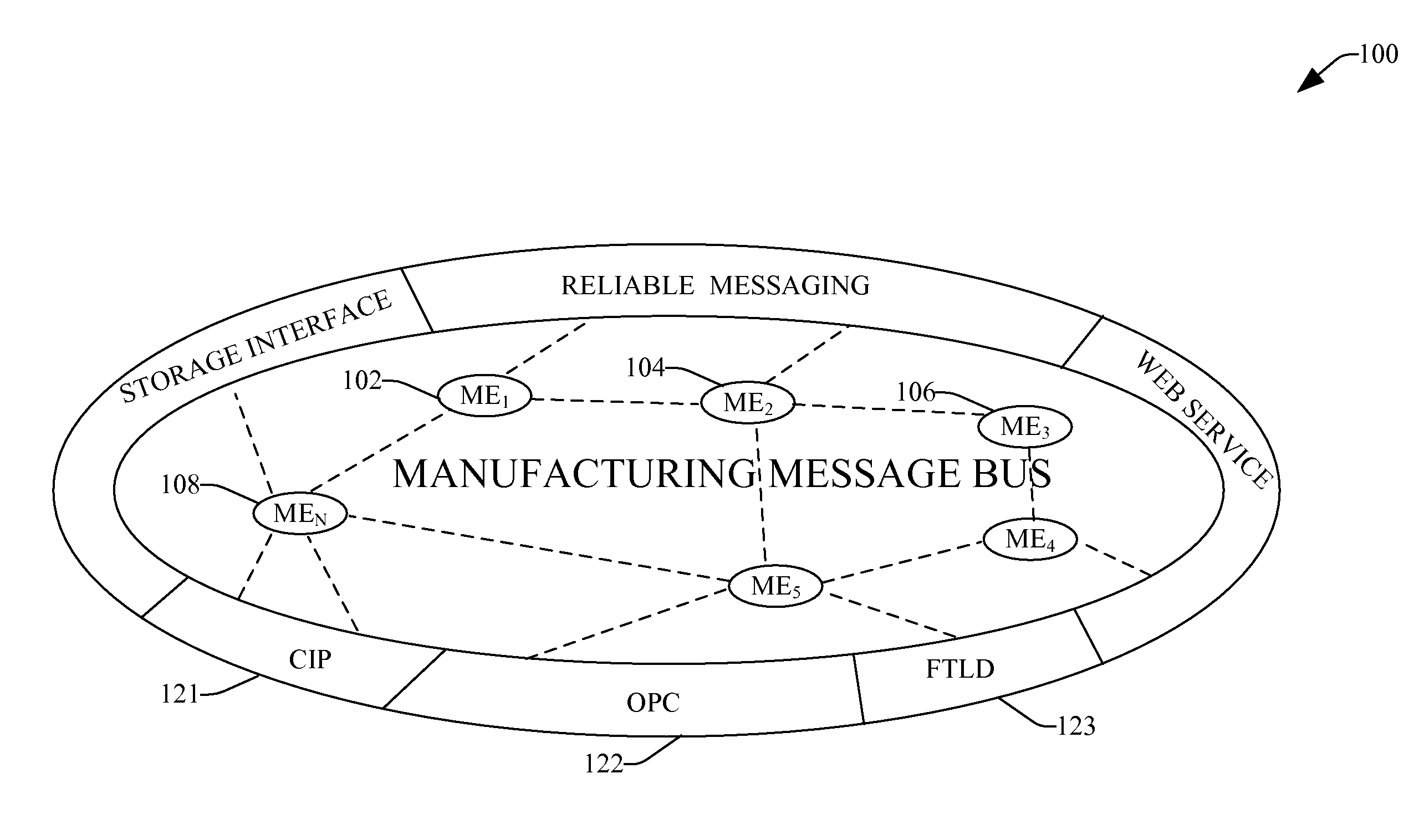
ActiveUS8127035B1Facilitate communicationMinimize complexityComputer controlMultiple digital computer combinationsMessage passingWhole systems
Systems and methods that facilitate messaging capabilities within a unified plant model (UPM) via employing a plurality of message engines that collaborate in such system. Linkage can be provided among the plurality of message engines, to provide real time interaction among the message engines / services, wherein each message engine normalizes messaging of various messaging protocols and formats. Also various systems of the UPM can map thereto—and provide a consistent interface where events are sent / received consistently across the system.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System for monitoring quality of water system
InactiveUS20070257806A1Detect presenceProvide real-timeWater/sewage treatmentTesting waterComputer scienceControl logic
A monitoring, detection and alarm for water systems includes a plurality of sensing components for detecting the presence of target contaminants in water and for measuring the overall quality of the water. The apparatus contains water sensing components, a database for storing sensor data and processors for data analysis using artificial intelligence. The apparatus provides control logic to take responsive action based on the results of the detection of the target contaminants. Responsive action includes, but is not limited to, generation of reports and alarm signals that are delivered in near real-time to users of the system.
Owner:SOURCE SENTINEL
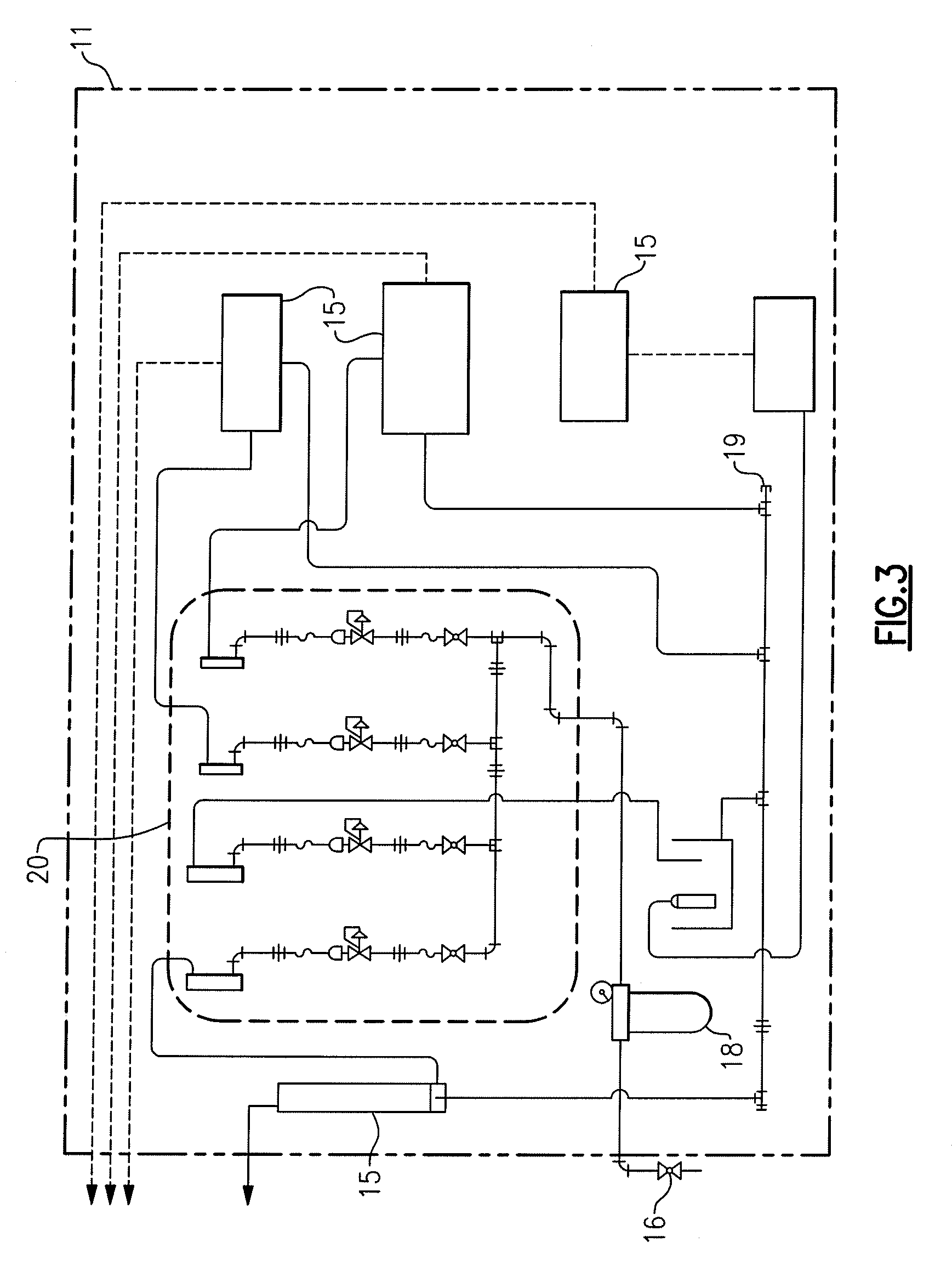
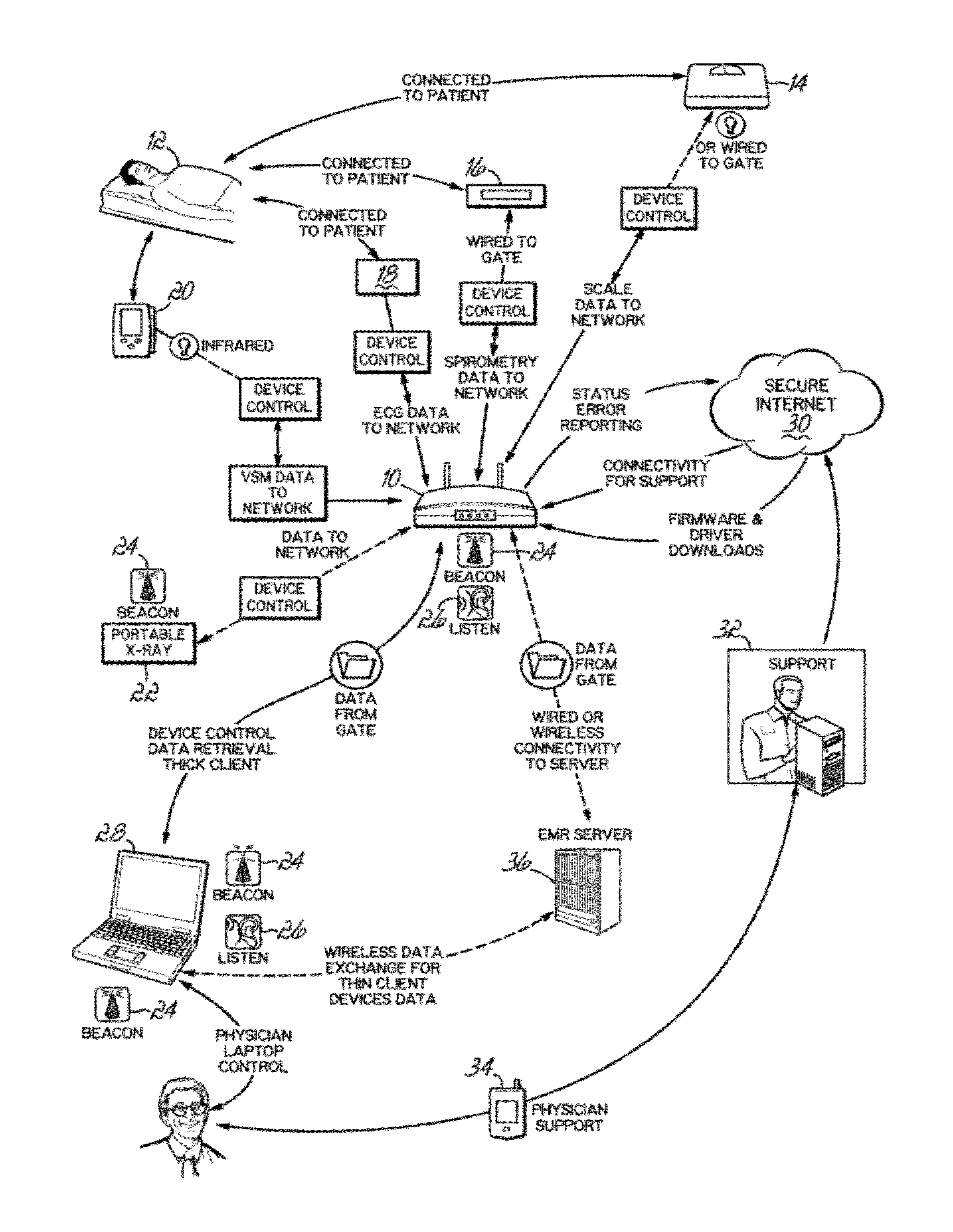
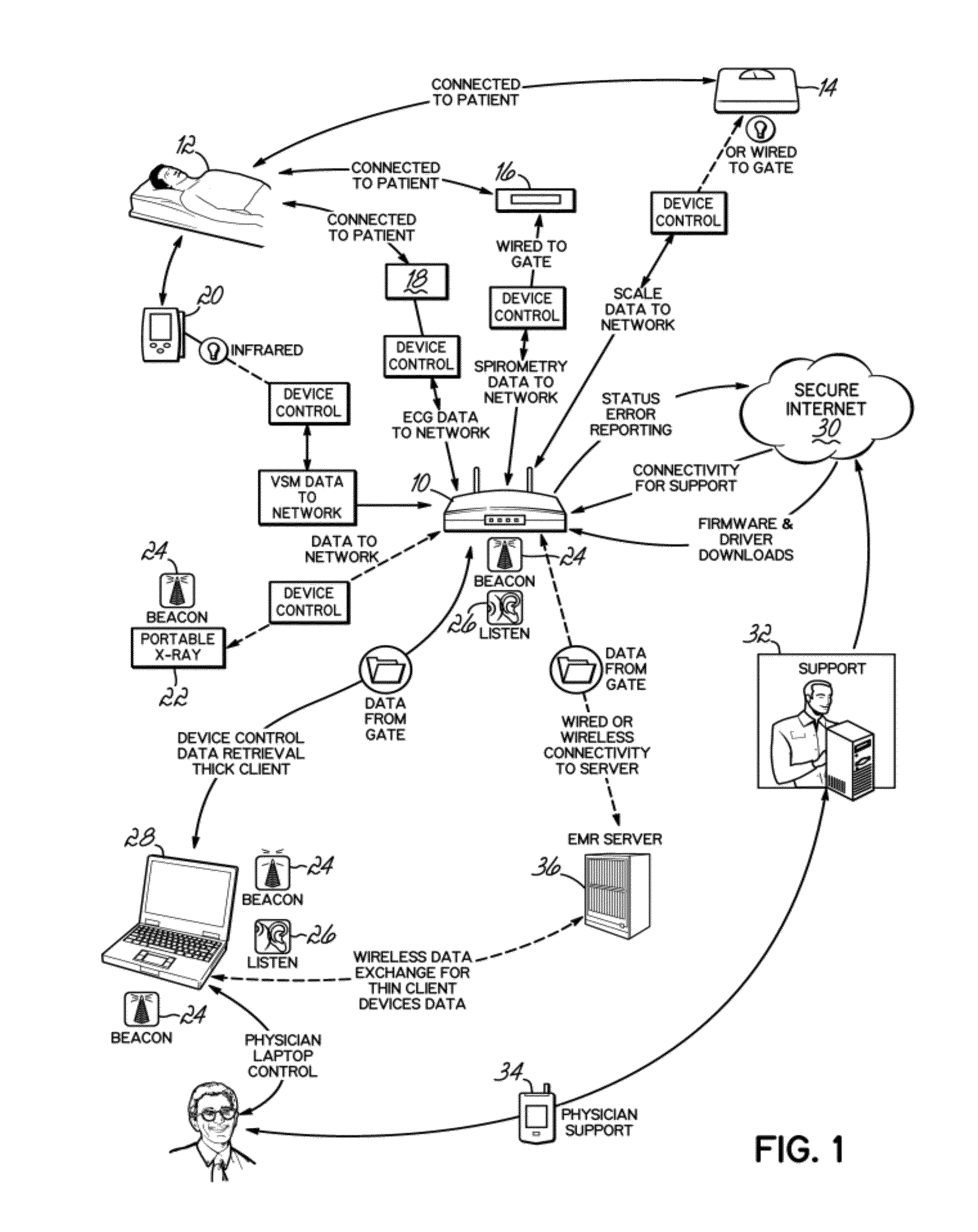
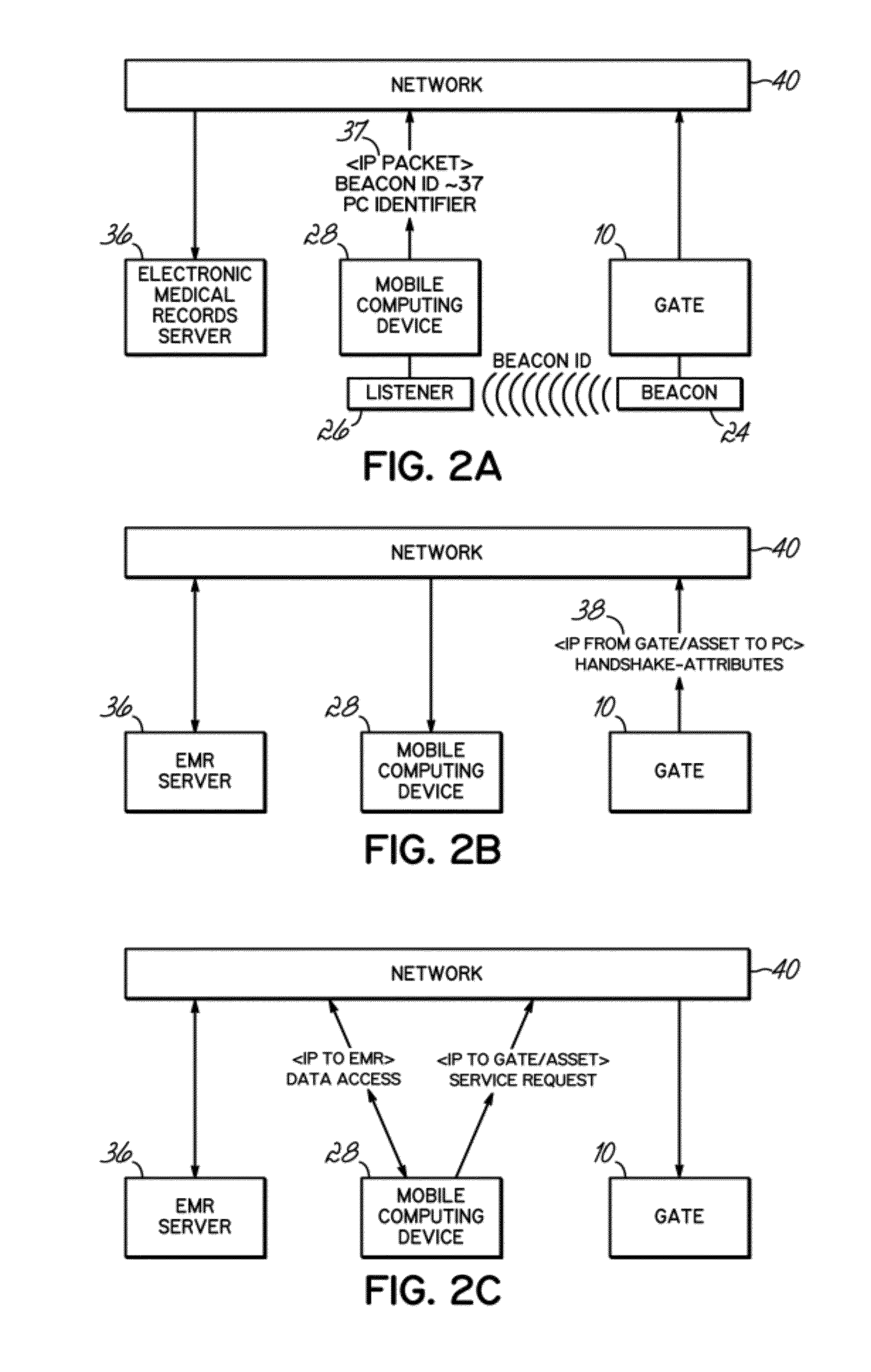
Networked interface appliance for improved medical device integration and physician workflow
ActiveUS8360975B1Improve reliabilityProvide real-timeData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsMedical recordArea network
A networked interface appliance for use in the medical arena that simplifies the connectivity of medical diagnostic devices to the portable computers in electronic medical record systems (EMR's). The appliance utilizes location support hardware and software to locate and map various tagged assets within the existing environment. The appliance automatically determines the proximity of nearby portable assets and computing devices, and creates network connection to each. Data obtained from a diagnostic device connected to the appliance is buffered and transmitted to portable computing devices connected to the appliance. Using specific IP addressing, support teams can connect to the appliance to diagnose and correct problems remotely using a local area network, wide area network or the Internet. A video port for remotely controlled video display and for local data acquisition is included. Location data from the appliance can be utilized in improving billing algorithms and workflow analysis. Asset management and location mapping of resources are also supported.
Owner:MIDMARK
Electrically operated viscous fluid dispensing apparatus and method
InactiveUS6318599B2Improved and more consistent dispensingNarrow downTemperatue controlPretreated surfacesEngineeringElectromagnetic field
An electrically operated fluid dispenser for dispensing a pattern of viscous fluid onto a substrate during a run mode. The dispenser is turned off and does not dispense the viscous fluid during a standby mode of operation. The dispenser includes a dispenser body having an outlet and an armature disposed in the dispenser body for movement between an opened position allowing a fluid flow from the outlet and a closed position preventing the fluid flow from the outlet. A coil is mounted adjacent the armature and selectively generates an electromagnetic field for moving the armature between the opened and closed positions. A controller includes different apparatus and methods for using the coil as a heater as well as providing other heat transfer devices on the dispensing valve to maintain a constant temperature either, during only the run mode or, during both, the run and the standby modes. The above dispensing valve heating control facilitates a design of an electrically operated fluid dispenser having a body with a fluid passage intersecting first and second sides of the body and a dispensing outlet in fluid communication with the fluid passage. The dispenser includes a heater and has feed member mounted to the first side of the body with one end of the fluid passage in the feed plate fluidly connecting with one end of the fluid passage in the dispenser body. The dispenser also has an cap mounted to the second side of the dispenser body to terminate the fluid passage on the second side of the dispenser body.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
Software enabled wizards
InactiveUS20020129004A1Provide real-timeDigital data processing detailsMarketingChemical industryTroubleshooting
The present invention relates to software enabled wizards that receive input from a user and use the input to generate a customized response. Embodiments of the present invention include design wizards, selection wizards and troubleshooting wizards advantageous for use in commerce, particularly within the chemical industry.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Planar multi-electrode array sensor for localized electrochemical corrosion detection
ActiveUS20070193887A1Easy to useReliable measurementCellsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEngineeringElectrode array
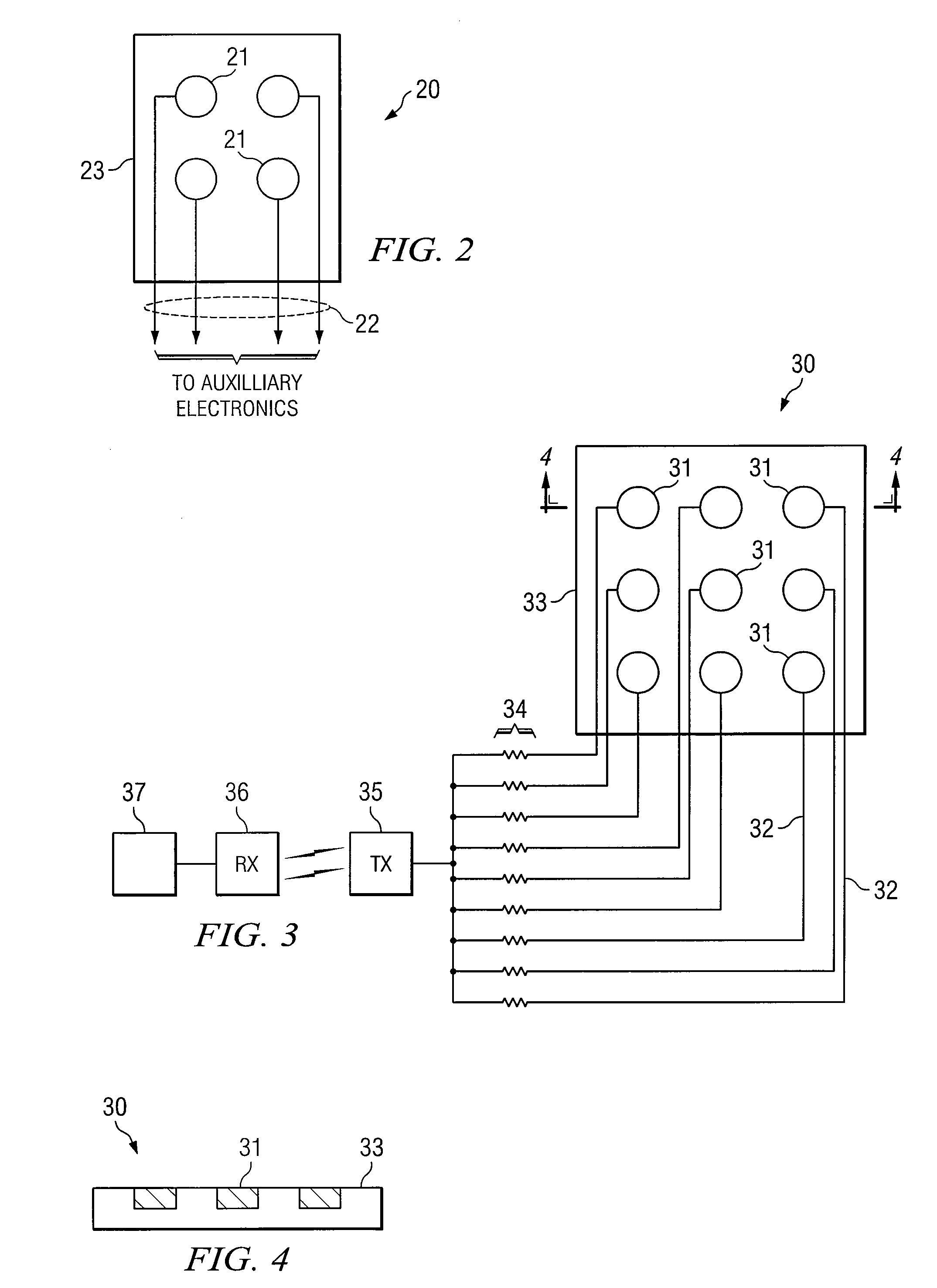
A planarized type of coupled multi-electrode corrosion sensing device. Electrode pads are fabricated on a thin backing, such as a thin film. Each pad has an associated electrical lead for connection to auxiliary electronic circuitry, which may include a resistor associated with each electrical pad. The design permits the device to be easily placed in small crevices or under coatings such as paint.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
System for monitoring quality of water system
InactiveUS7391333B2Detect presenceProvide real-timeWater/sewage treatmentTesting waterComputer scienceControl logic
A monitoring, detection and alarm for water systems includes a plurality of sensing components for detecting the presence of target contaminants in water and for measuring the overall quality of the water. The apparatus contains water sensing components, a database for storing sensor data and processors for data analysis using artificial intelligence. The apparatus provides control logic to take responsive action based on the results of the detection of the target contaminants. Responsive action includes, but is not limited to, generation of reports and alarm signals that are delivered in near real-time to users of the system.
Owner:SOURCE SENTINEL
System of systems for monitoring greenhouse gas fluxes
ActiveUS8595020B2Provide real-timeEasy to understandPigmenting treatmentSustainable waste treatmentNatural sourceGreenhouse gas flux
A system of systems to monitor data for carbon flux, for example, at scales capable of managing regional net carbon flux and pricing carbon financial instruments is disclosed. The system of systems can monitor carbon flux in forests, soils, agricultural areas, body of waters, flue gases, and the like. The system includes a means to identify and quantify sources of carbon based on simultaneous measurement of isotopologues of carbon dioxide, for example, industrial, agricultural or natural sources, offering integration of same in time and space. Carbon standards are employed at multiple scales to ensure harmonization of data and carbon financial instruments.
Owner:PLANETARY EMISSIONS MANAGEMENT
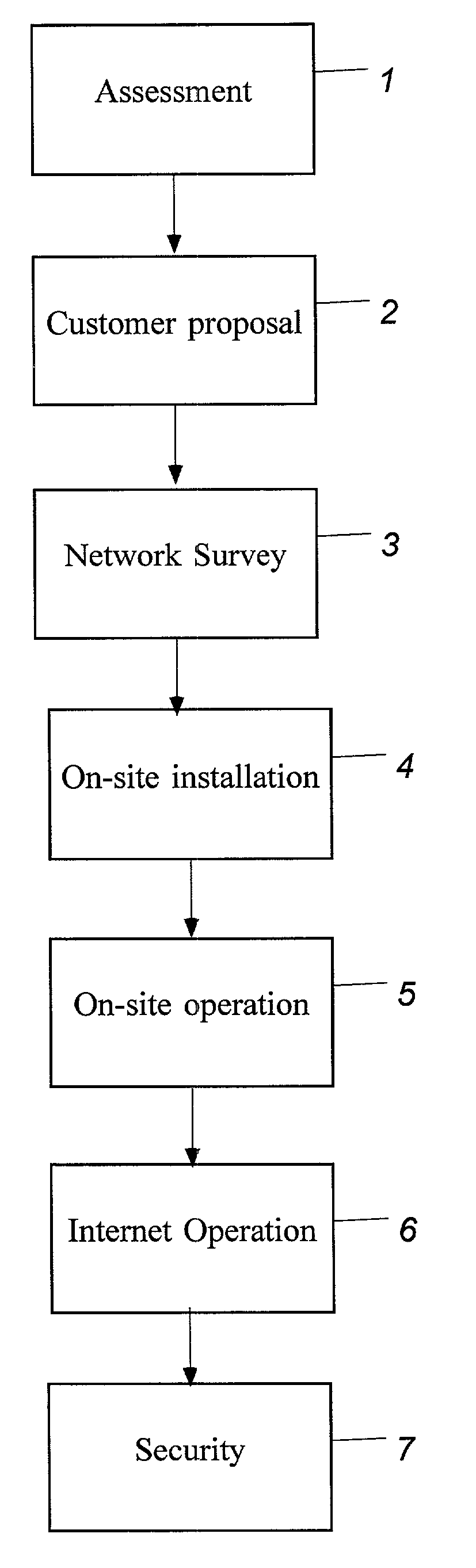
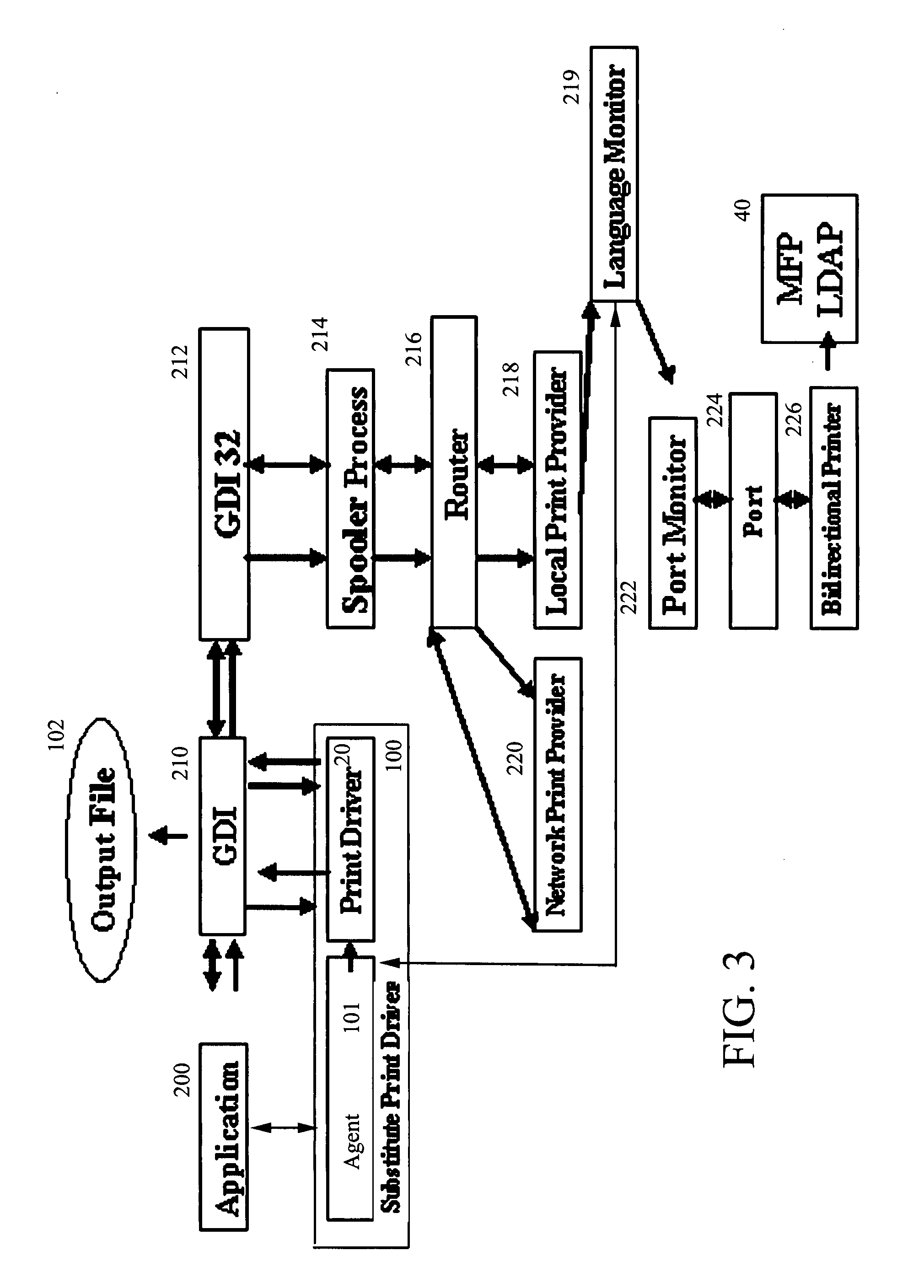
Network printing tracking system
ActiveUS7190478B2Avoid modificationAvoid changeDigital computer detailsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsWeb siteNetwork connection
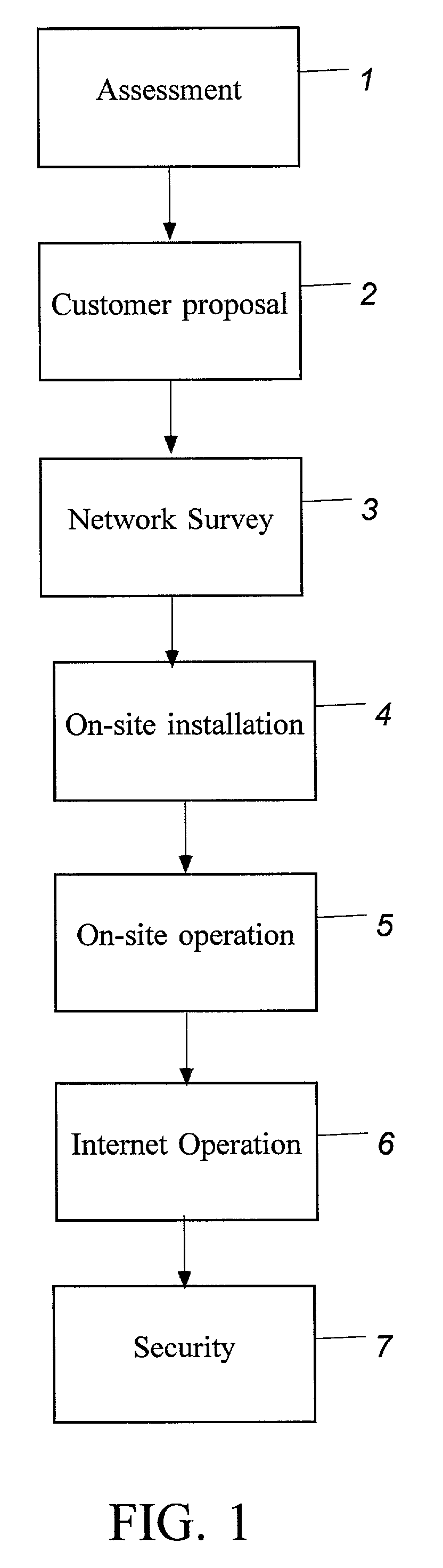
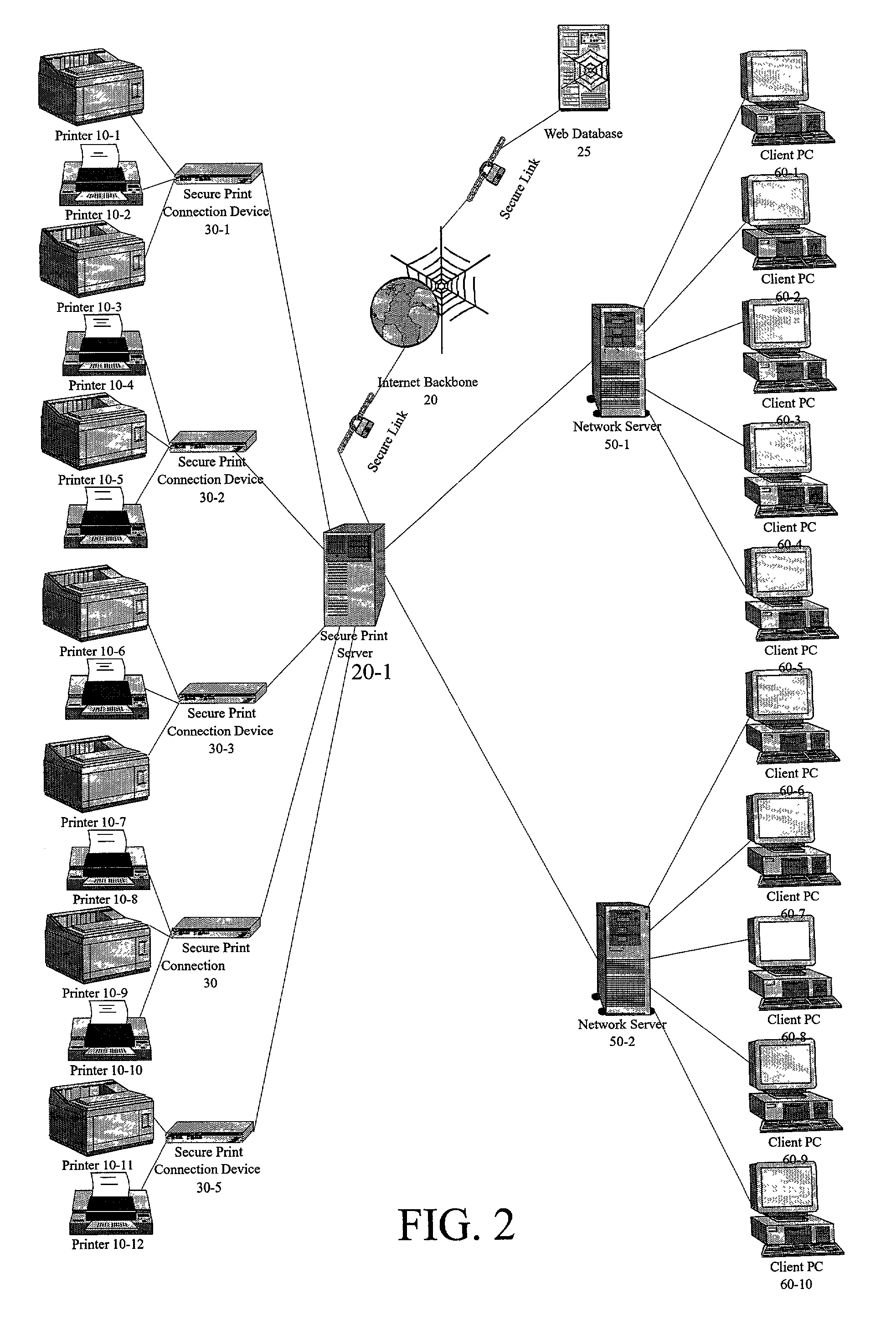
A system of hardware, software and a business method that enables printer and copier vendors to outsource network printing. The method is implemented on a local area network including a server PC, a plurality of connected client PCs, and a plurality of printers each networked through a secure network connection device that communicates only with Secure Print Servers. The business method comprises the steps of running Assessment Software over a test interval to determine a customer's printer cost per page, making an outsourcing proposal to the customer based on the customer's printer cost per page and a predetermined rationalization of printer layout, conducting a network survey to determine the customer's network characteristics, and installing print job tracking software on secure print servers attached to the customer's network. The print job tracking software captures all print traffic and automatically sends print job data to a secure web-site database for review by Dealers and Customers.
Owner:DOCUMENT DYNAMICS LLC
Method and apparatus for limiting access to video communications
InactiveUS20060271949A1Determination be lowAccurate assessmentTelevision system detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlSatellite transmitterCable television
Owner:BROADCAST INTERACTIVE MEDIA
Motion training apparatus and method
InactiveUS8597133B2Effectively realistically visualizeProvide real-timeGymnastic exercisingVideo gamesEngineeringBiofeedback
The invention is directed to a motion trainer for improving a person's movement of an implement by allowing the person to visualize the path of the implement during the movement. The motion trainer comprises an implement having a plurality of motion characteristic sensors located thereon for determining, among other things, the direction of the movement and the orientation of the implement during the movement. Biofeedback devices provide the person information regarding the positioning of the implement during the movement.
Owner:PRIESTER WILLIAM B
NOx monitor using differential mobility spectrometry
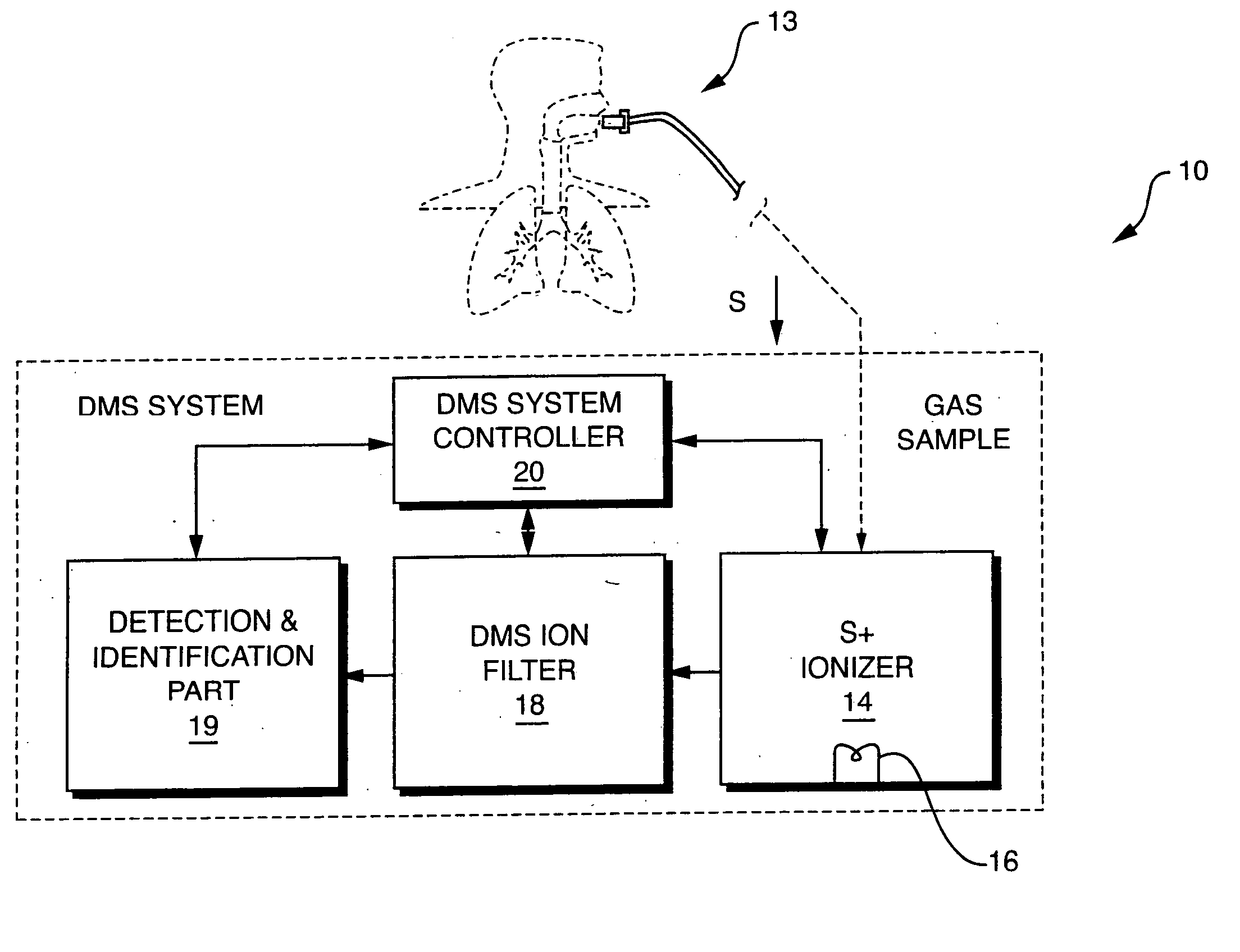
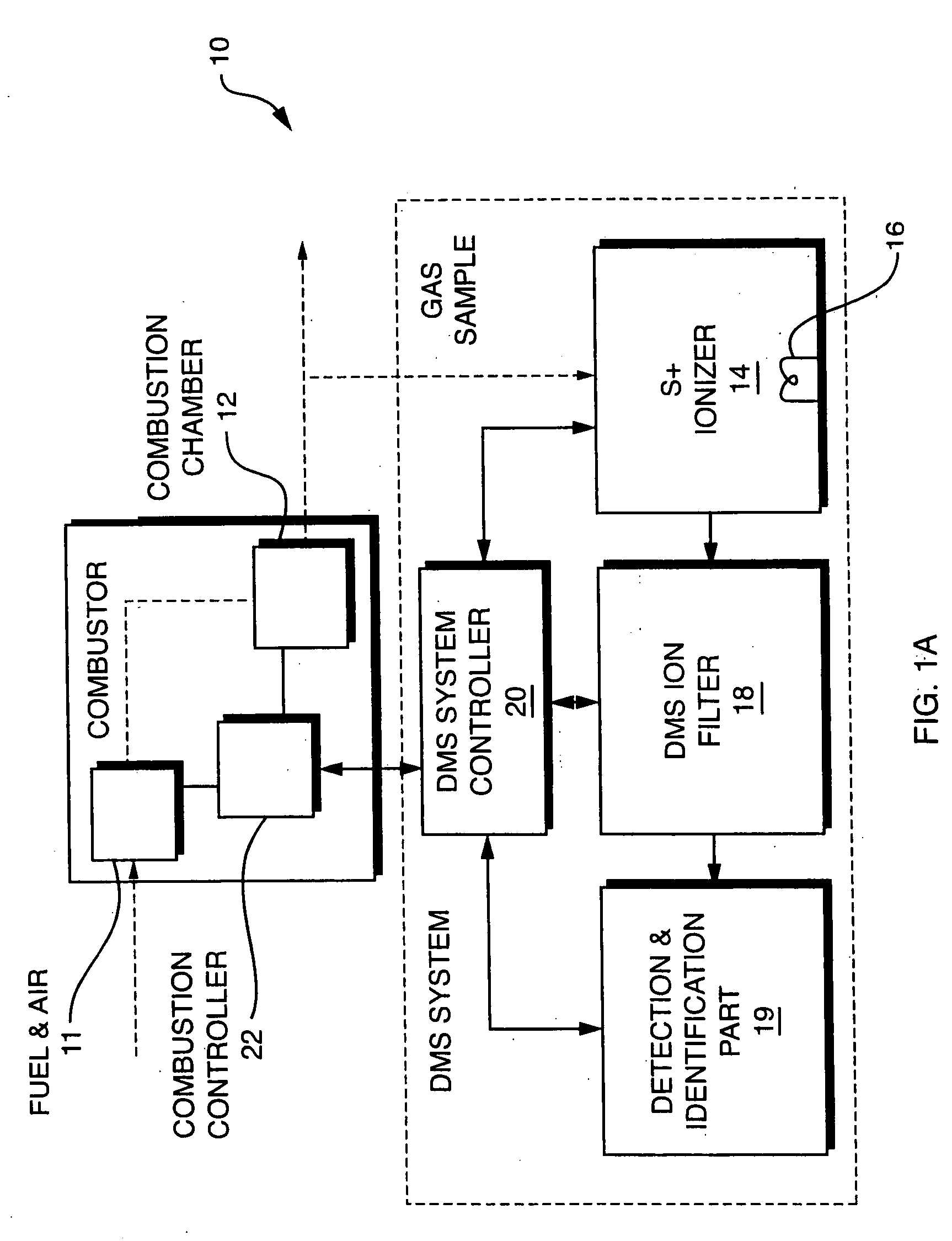
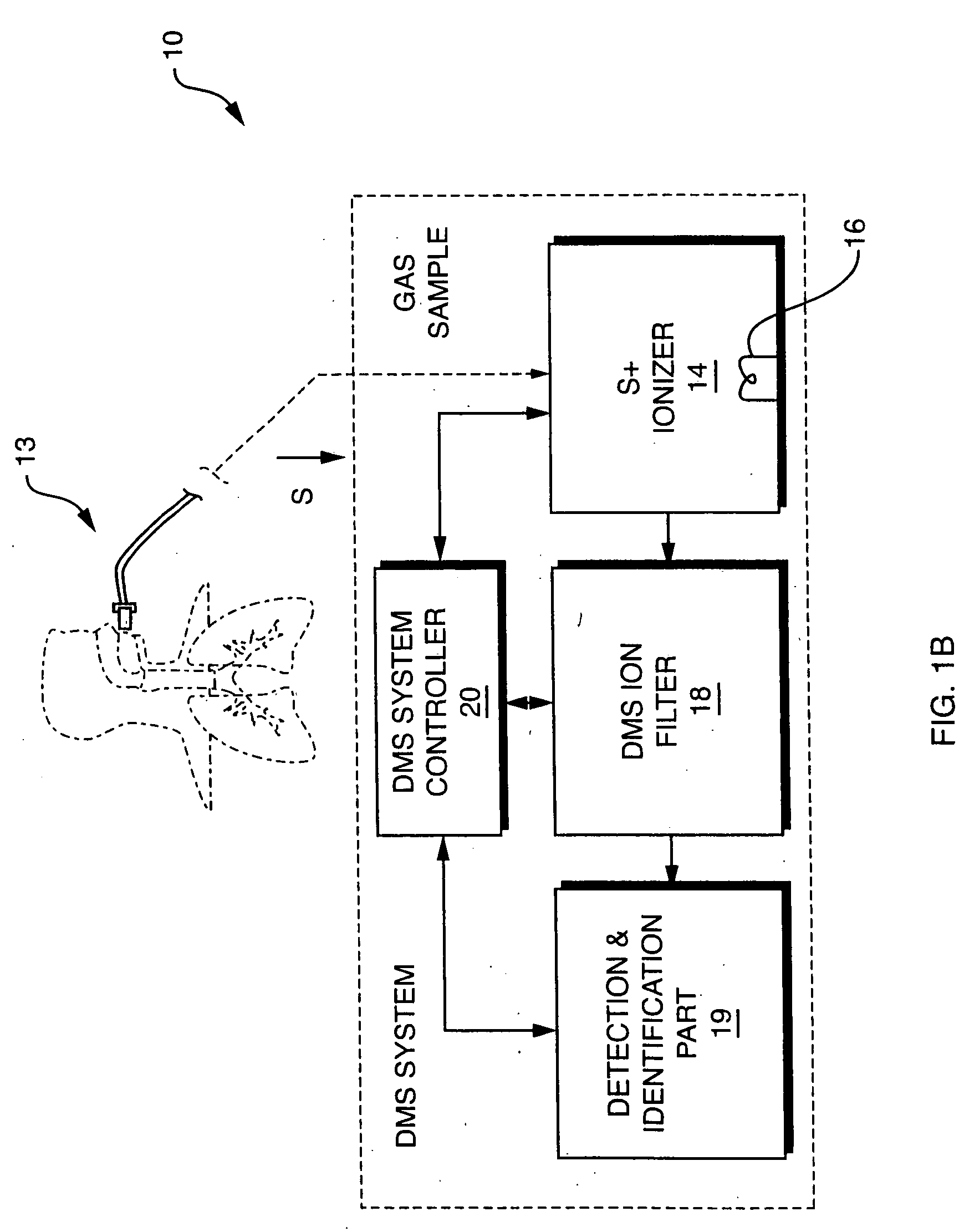
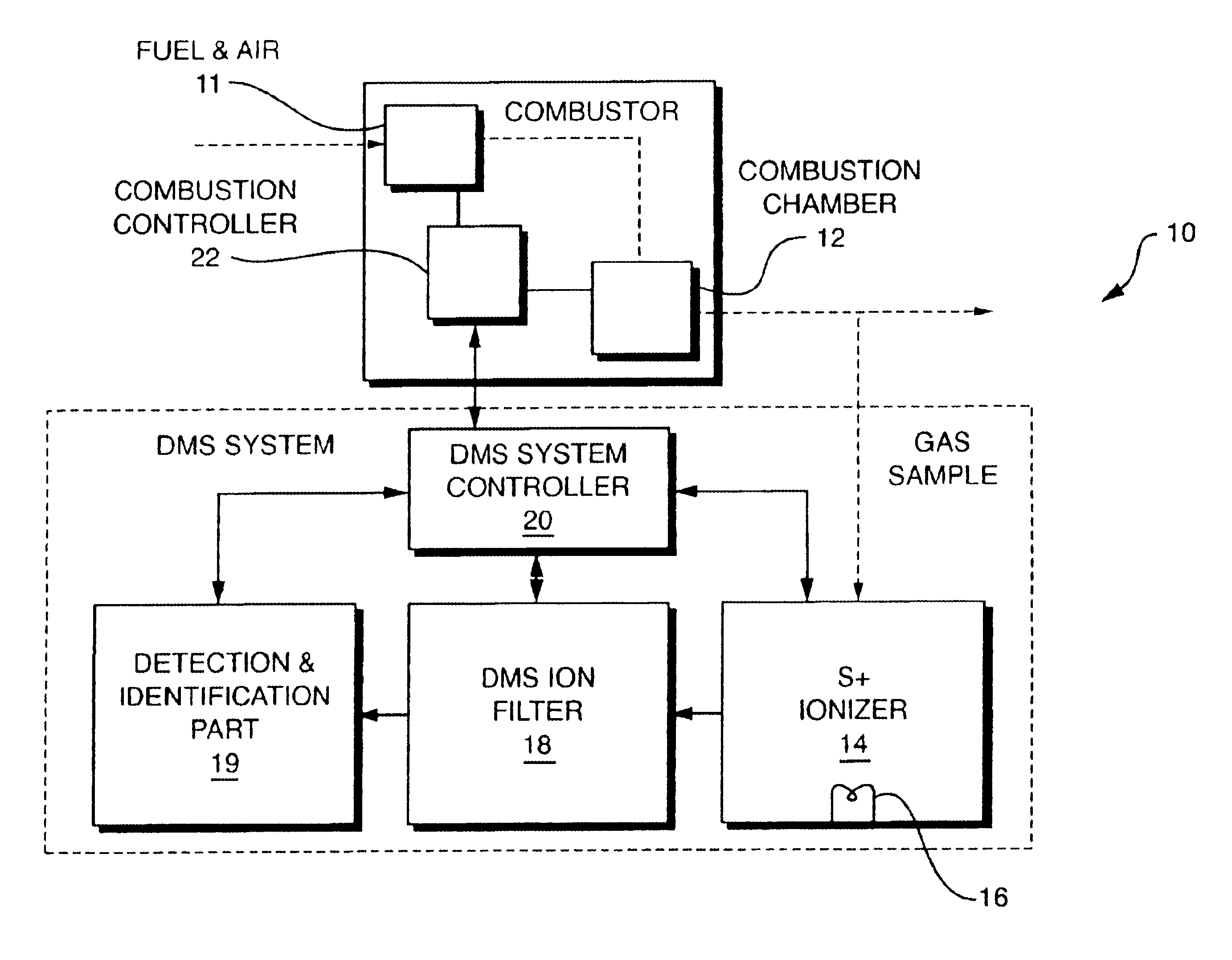
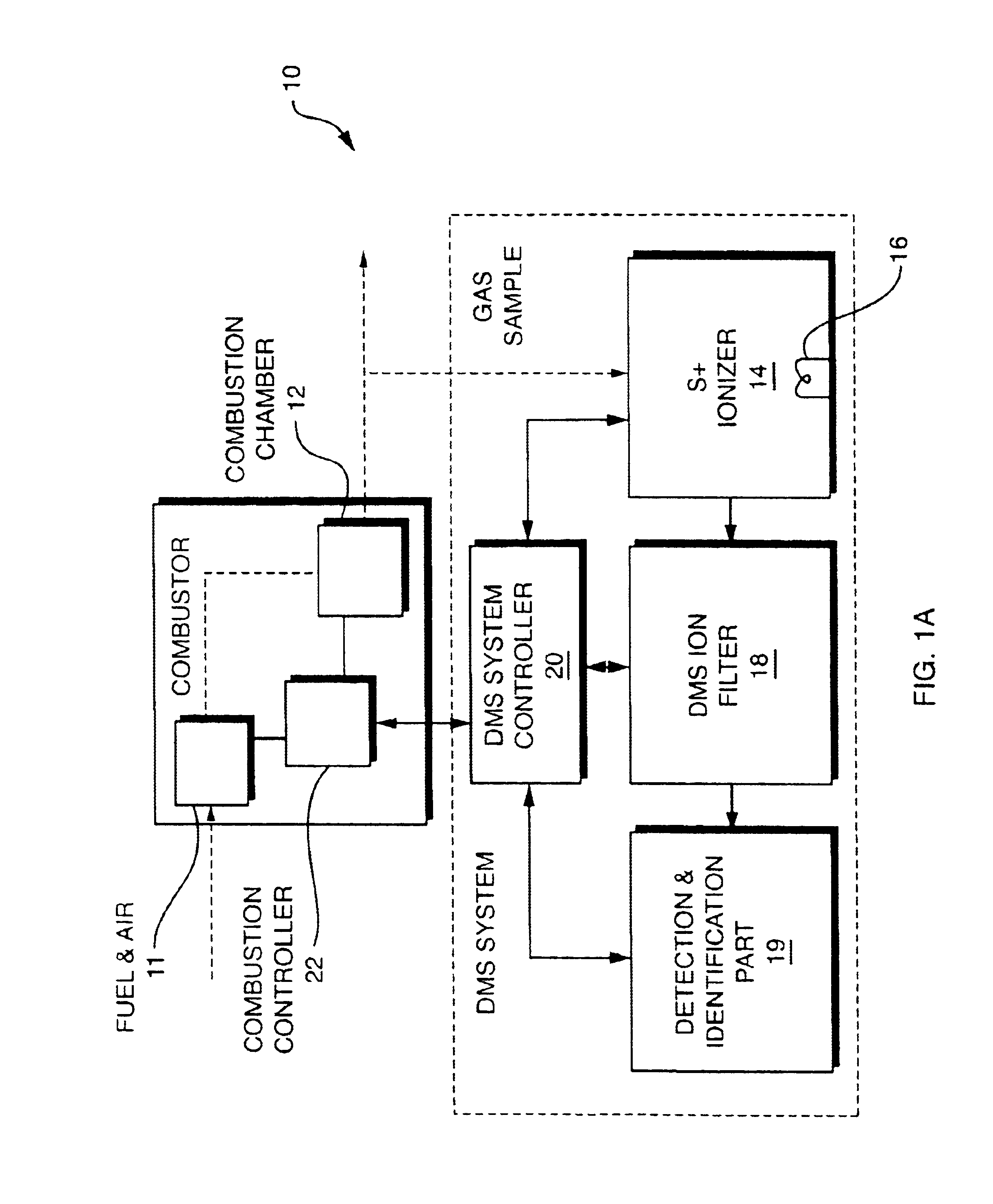
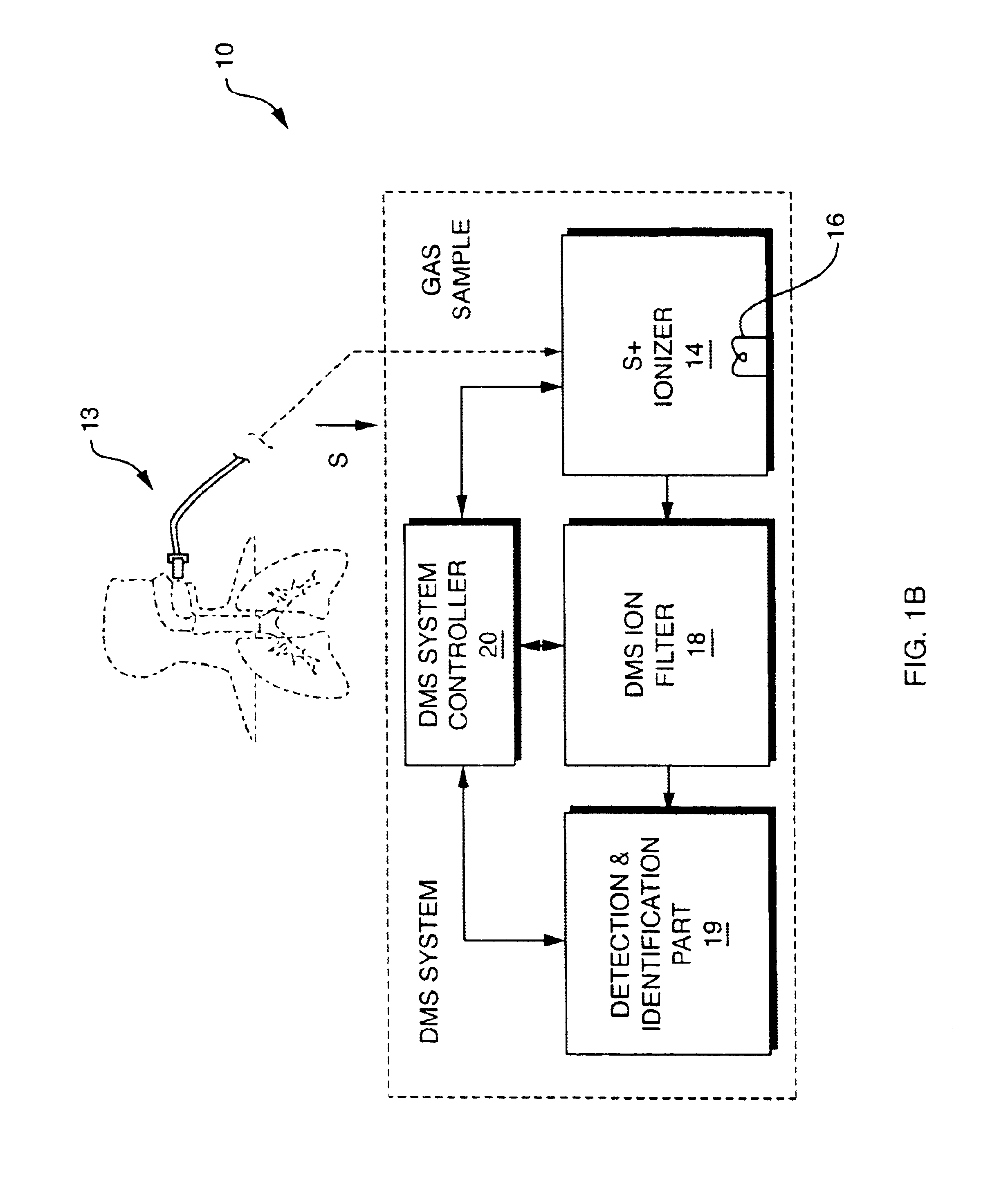
InactiveUS20050092914A1Fast response timeHigh sensitivityParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSystem usageIon source
System for detection and analysis of gas samples in fieldable real-time Differential Mobility Spectrometry (DMS) chemical sensor system which uses non-radioactive ion source for monitoring and detecting NOx emissions; provides reliable methods for detecting and monitoring of anthropogenic sources of NOx; also detection of NO in exhaled breath for patient health diagnosis.
Owner:SIONEX
Supplemental side impact protection system for automotive vehicle
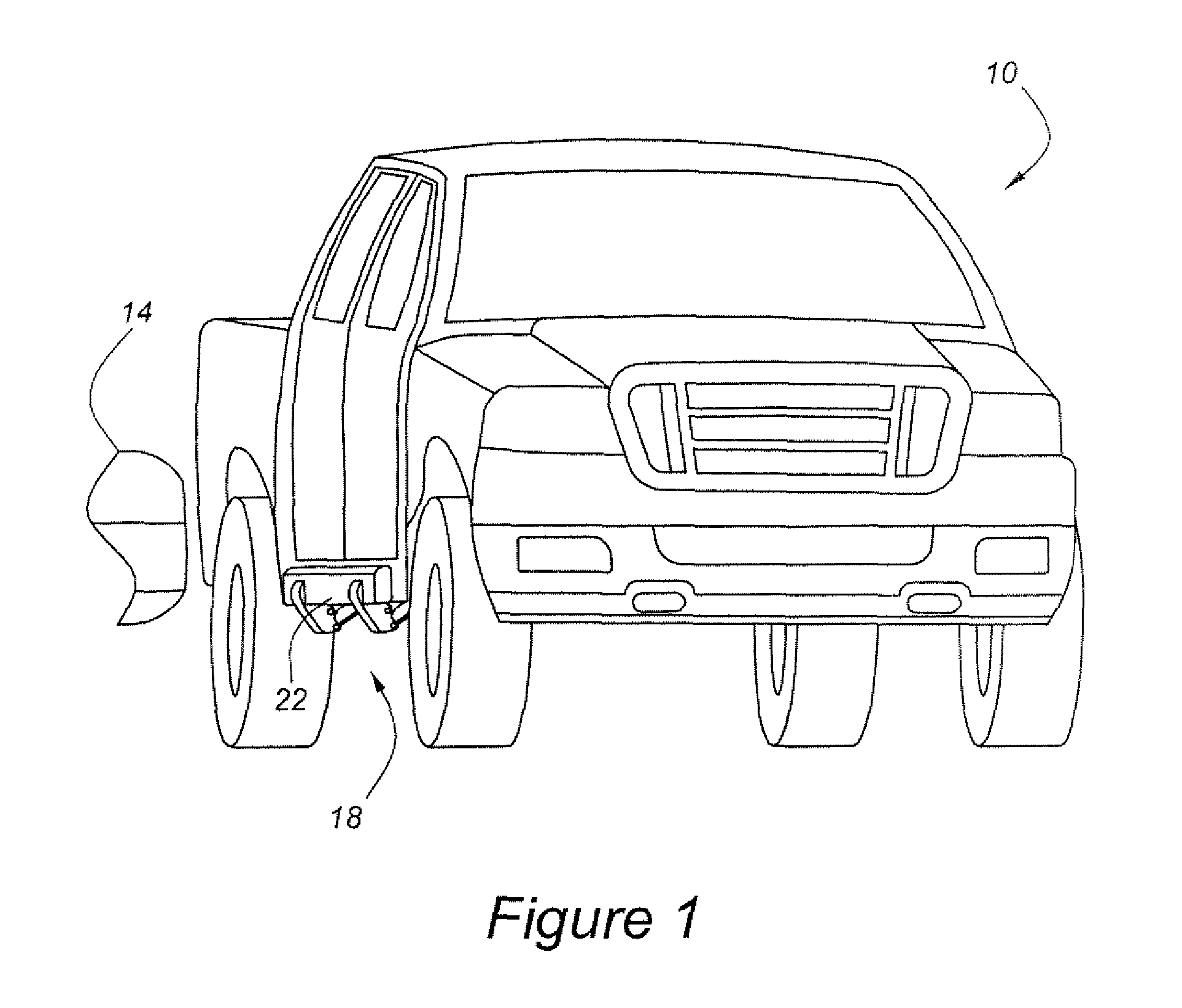
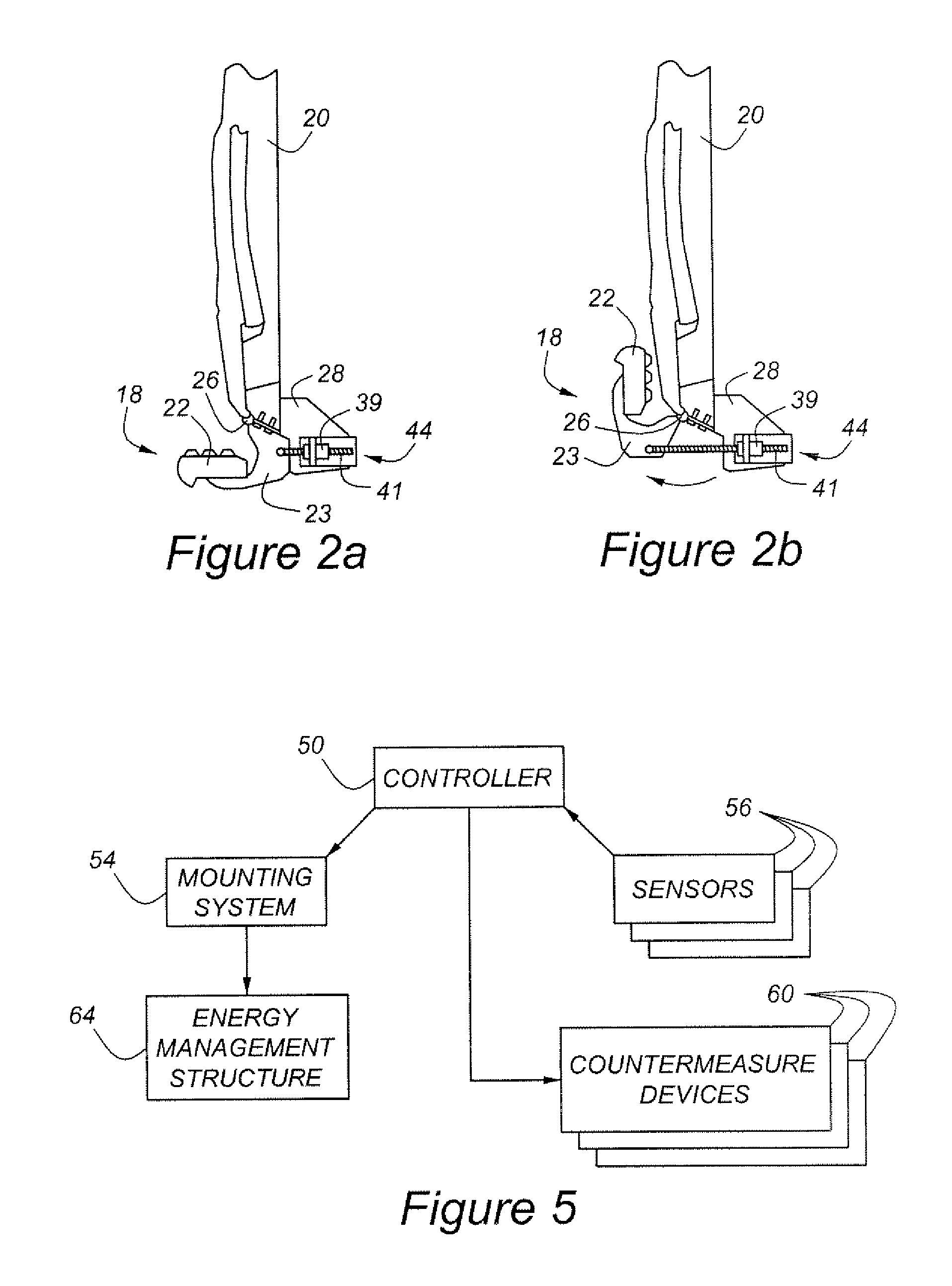
A supplemental impact protection system for an automotive vehicle includes an external energy management structure having a first position for normal vehicle operation and a second position for deployment during an impact event. A mounting system allows selective positioning of the energy management structure in either the first or second position, as determined by a controller which assesses an impact potential of the vehicle and operates the mounting system to move the energy management structure to the second, or deployed, position in the event that the assessed impact potential satisfies a predetermined threshold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for monitoring and reporting equipment operating conditions and diagnostic information
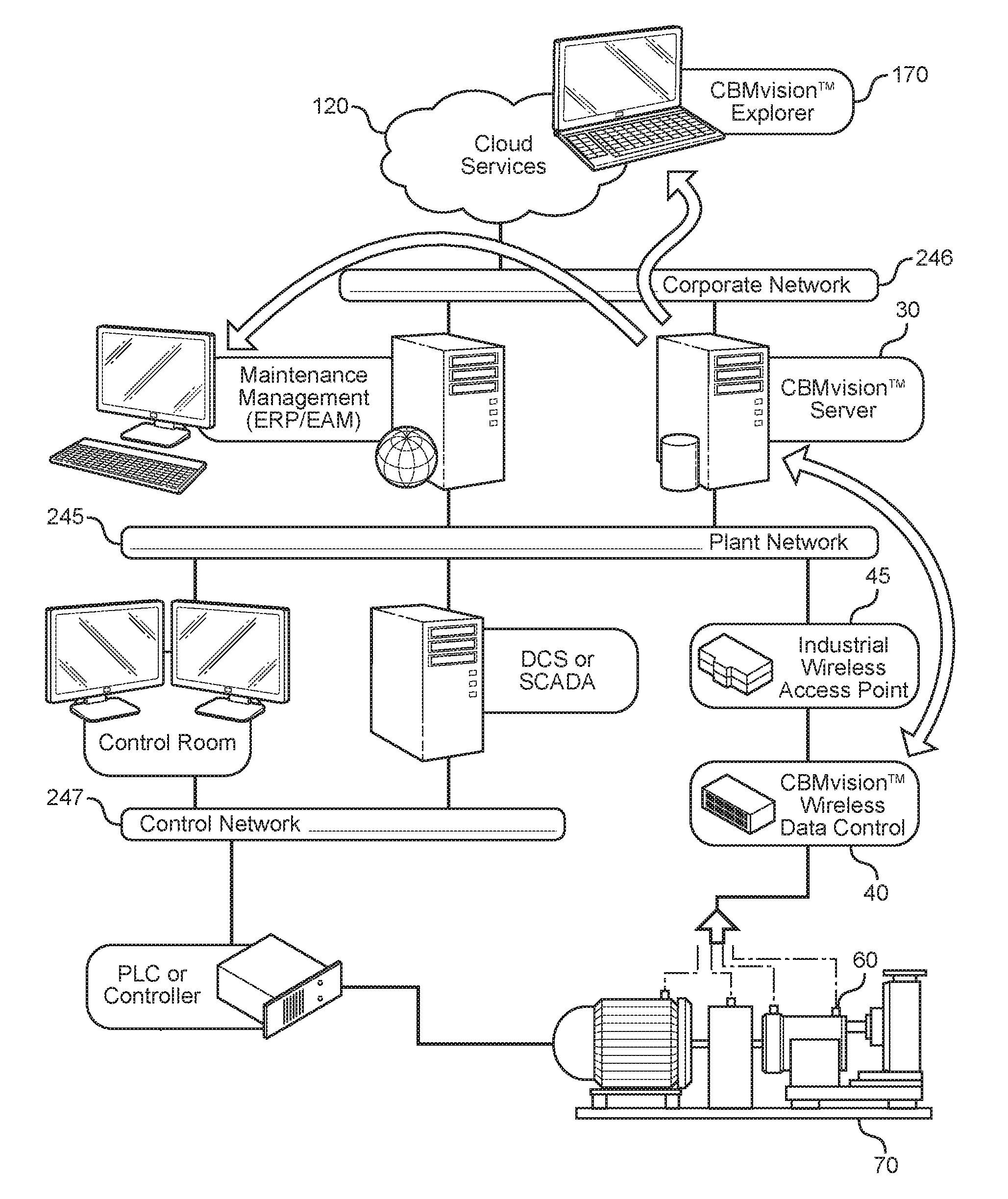
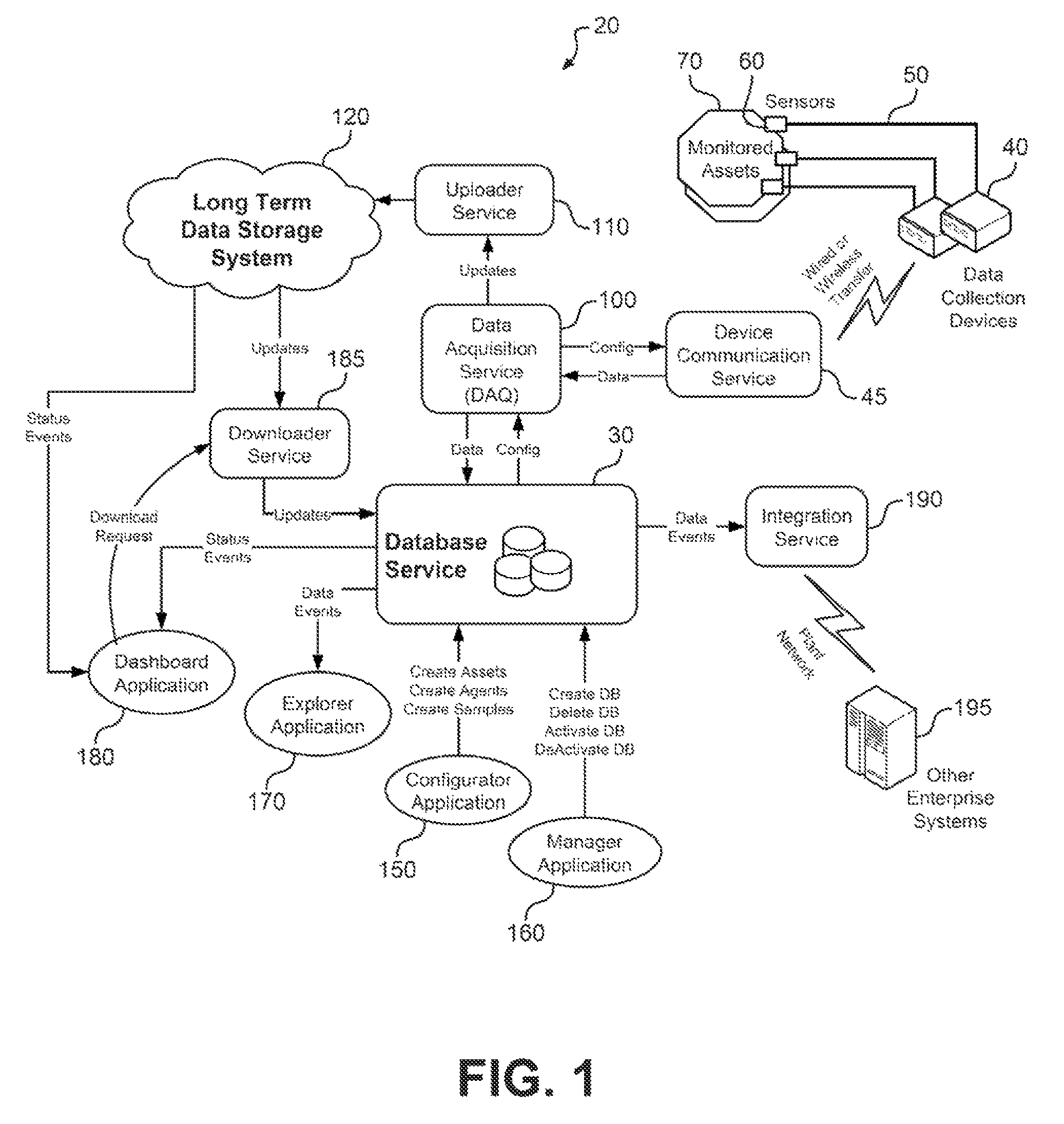
InactiveUS9400867B2Provide real-timeRegistering/indicating quality control systemsElectric testing/monitoringElectricityAnalysis data
A method and system (20) is provided for condition based monitoring reliability maintenance capabilities for an asset (70), such as one or more machines, by establishing a network including of a sensor (60) or a plurality of sensors installed, temporarily or in generally fixed locations, on asset (70), wherein sensor (60) provides time sequenced operational information in the form of data based on vibrations, temperature, electrical signals, or other operating conditions. Sensors (60) are connected to a local controller (40) which transmits the data via a local or wide area network (45), either through wired or wireless communication paths, in data packets, each containing divided portions of the operational information. The data packets are mapped and stored into multiple, dedicated databases for ease of retrieving and analyzing the data. Preferably, a cloud-based storage arrangement (120) is employed to storing the mapped data.
Owner:CBM ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS
System and method for distance assistance and coaching
InactiveUS20050135458A1Provide real-timeDigital computer detailsTransmissionTransceiverReal-time computing
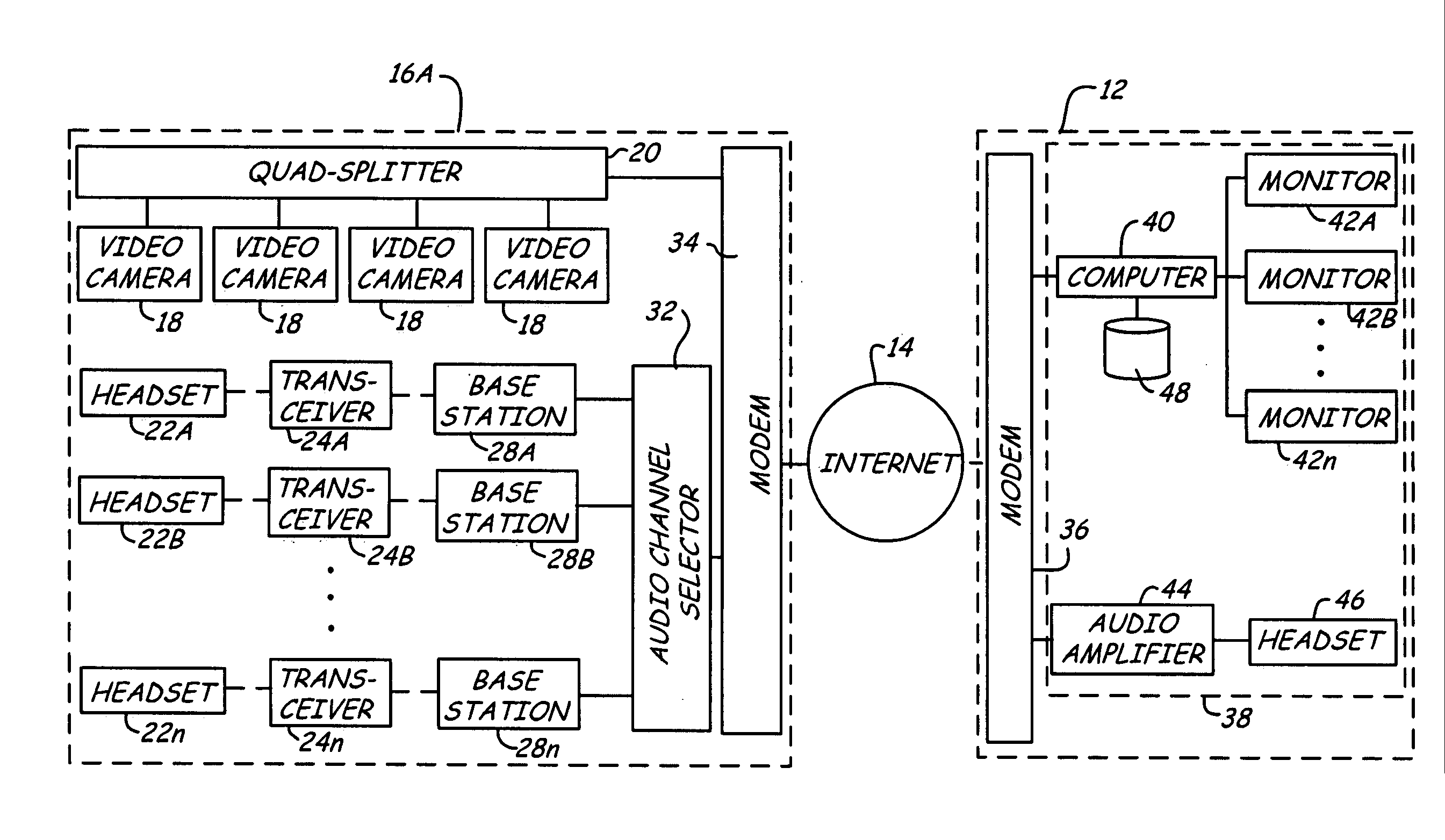
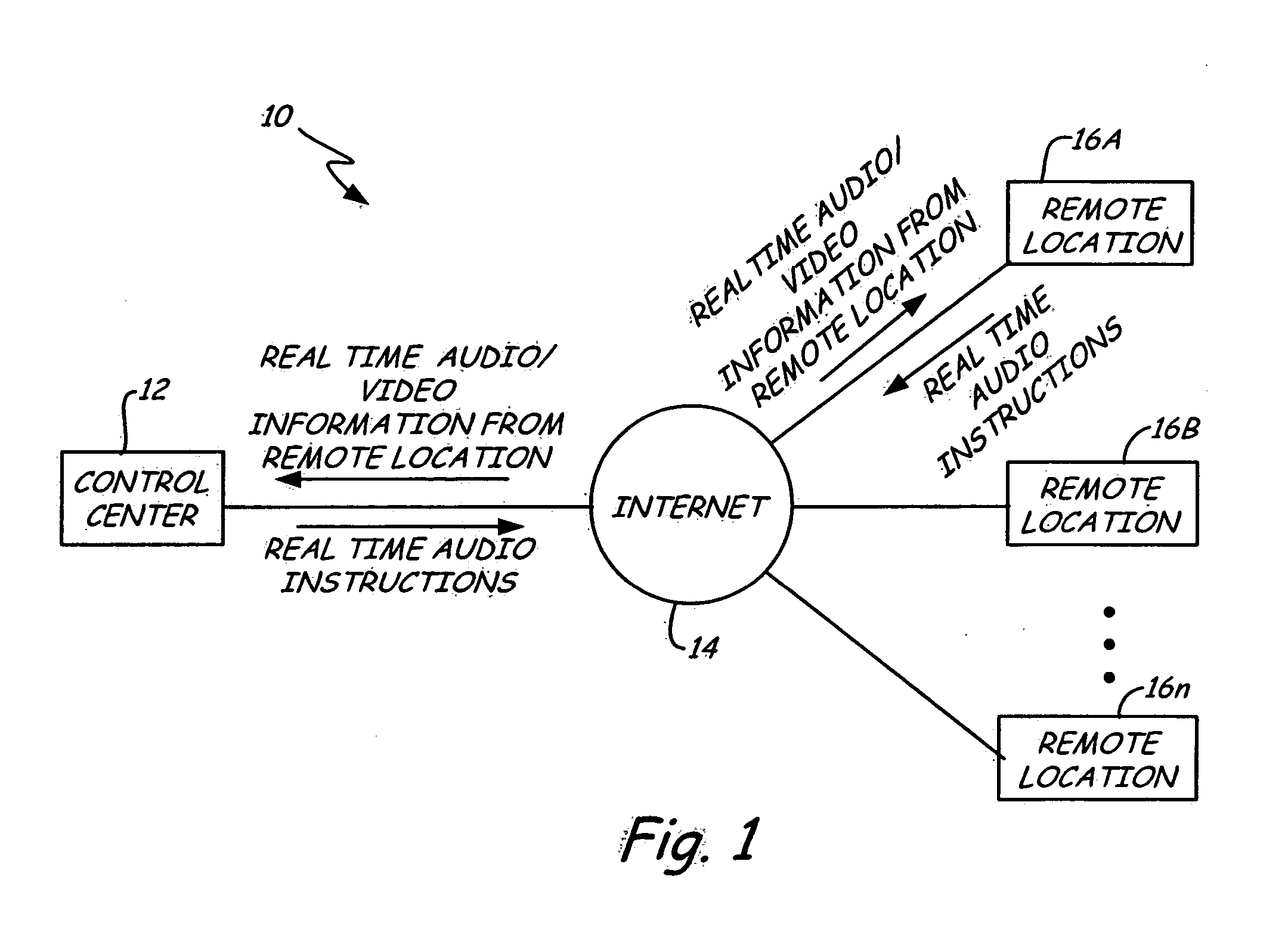
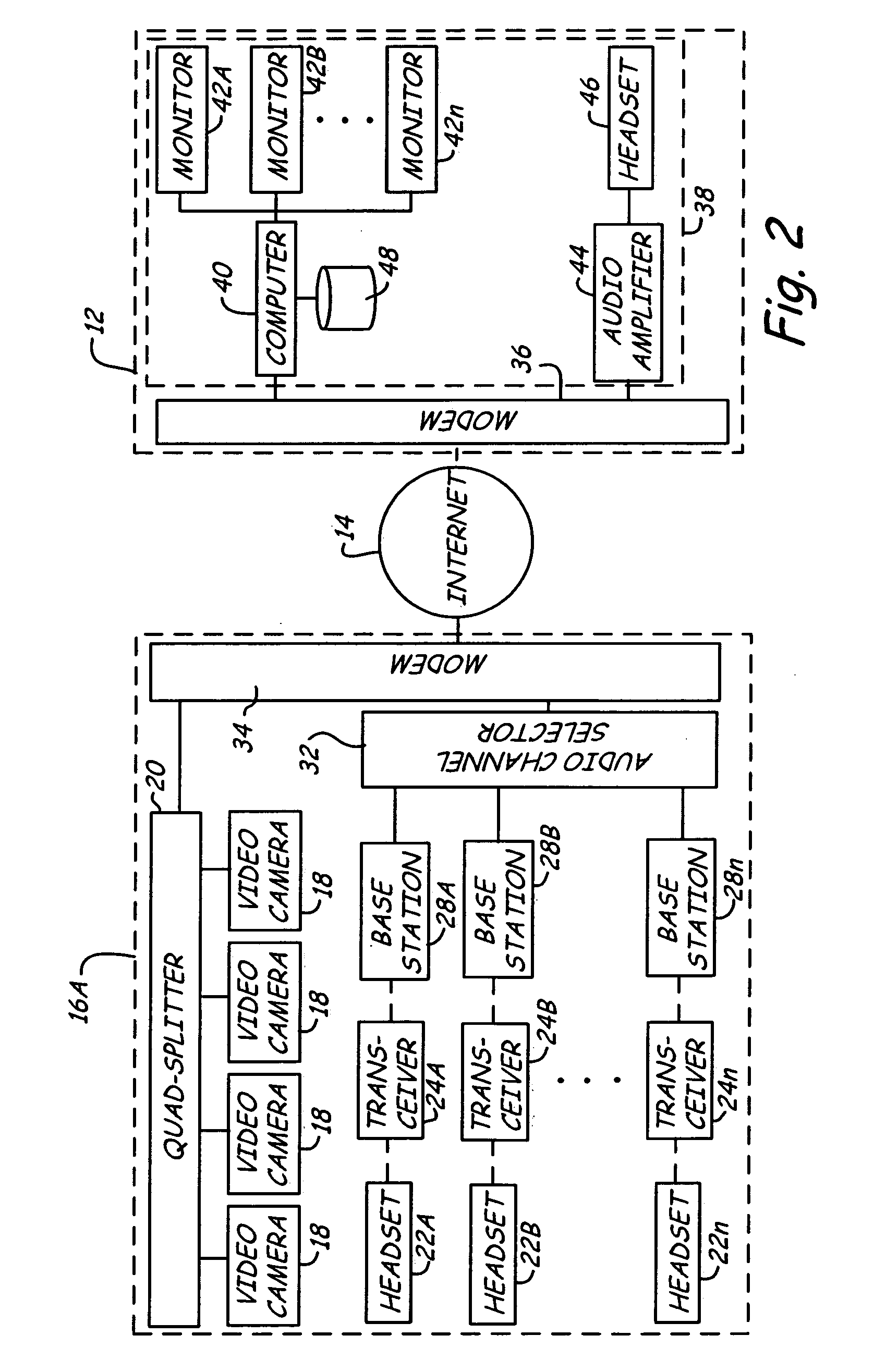
A distance assistance system including a plurality of remote locations connected to a central location through a network, wherein an operator at the central location selects a particular remote location to monitor. Each remote location includes a number of video cameras, the video signals generated by the video cameras is transported through the network to the central location and allows the operator to visually monitor in real time the remote location. Each remote location also includes a number of audio transceivers, allowing the operator at the central location to monitor real time audio information from the remote site, as well as communicate verbally in real time with representatives located at the remote site.
Owner:SOVUS MEDIA
NOx monitor using differential mobility spectrometry
InactiveUS7019291B2Fast response timeHigh sensitivityParticle separator tubesSpectrum investigationNitrogen oxideIon source
System for detection and analysis of gas samples in fieldable real-time Differential Mobility Spectrometry (DMS) chemical sensor system which uses non-radioactive ion source for monitoring and detecting NOx emissions; provides reliable methods for detecting and monitoring of anthropogenic sources of NOx; also detection of NO in exhaled breath for patient health diagnosis.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
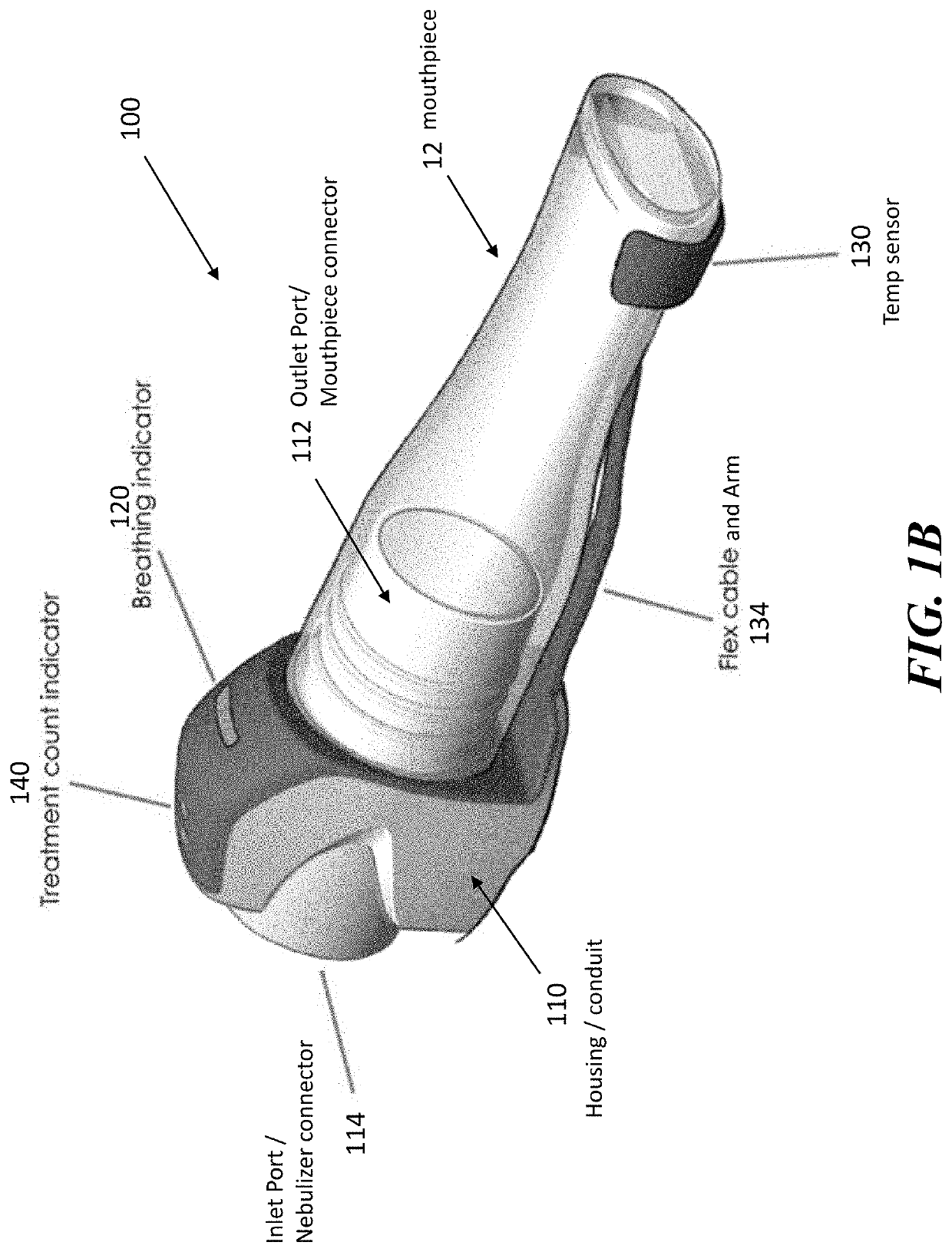
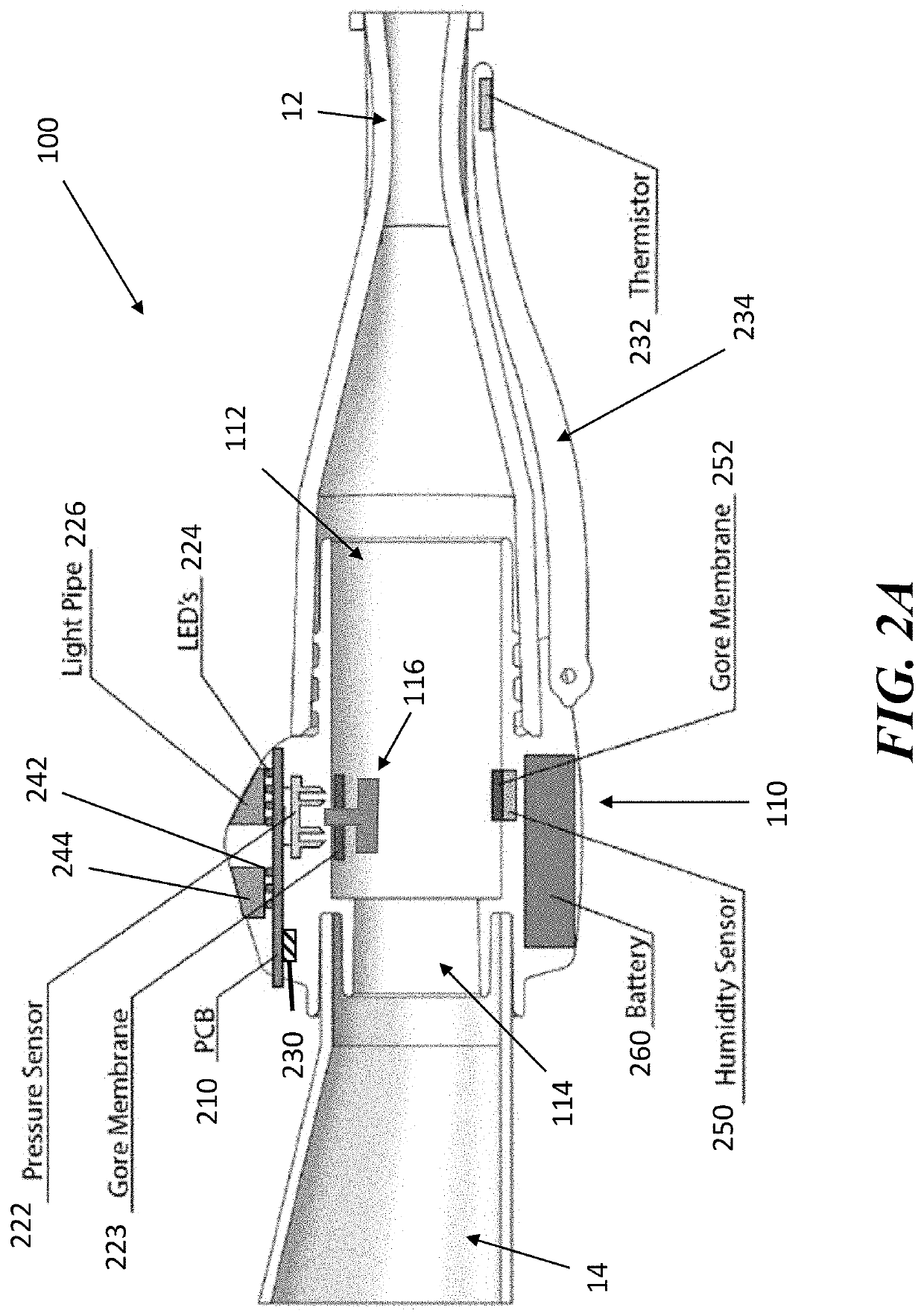
Nebulizer monitoring device, system and method
ActiveUS20200330719A1Facilitate complianceReal useRespiratorsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBiomedical engineeringIntensive care medicine
Described herein are devices, systems and methods for monitoring the use of a nebulized medication, such as can be administered using a nebulizer. These can be used for monitoring a patient undergoing treatment for COPD and improve compliance to the recommended therapy. Monitored parameters include flow, humidity and acceleration and provide data as to the quantity and quality of nebulizer use.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
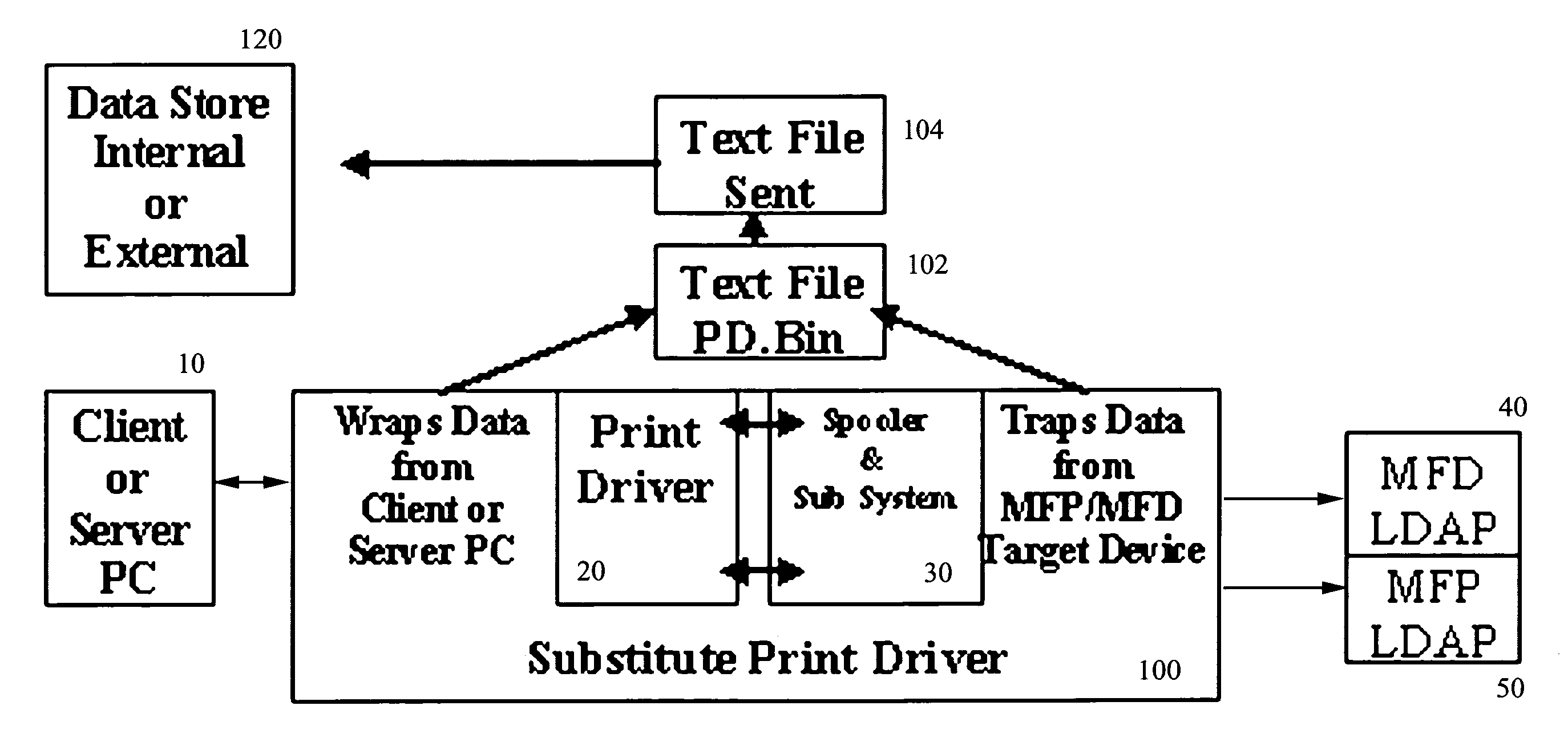
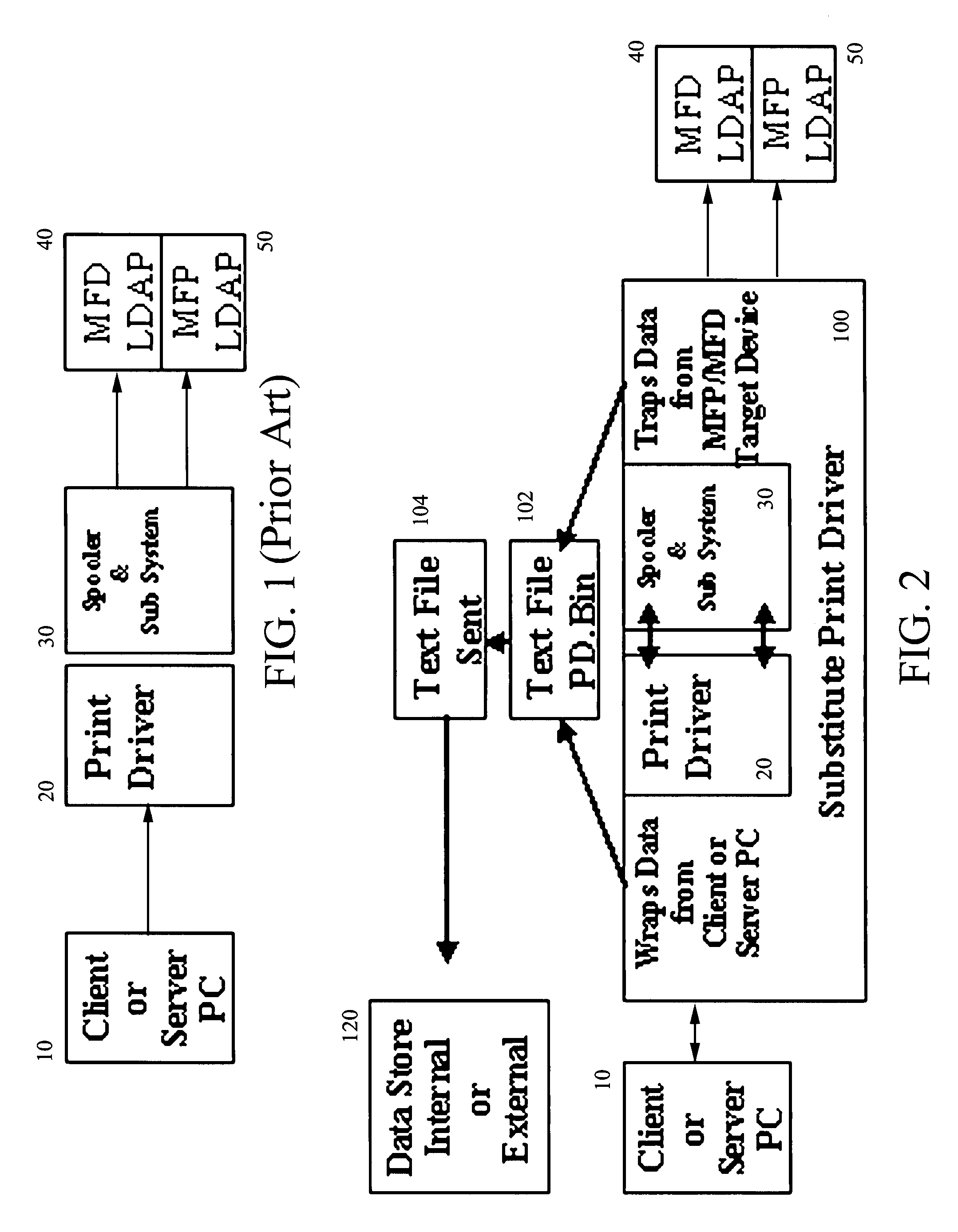
Network printing tracking system
ActiveUS7872772B2Provide real-timeEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusDigital computer detailsDocumentation procedureSoftware system
A software system and method for monitoring and tracking print transaction event history for a pipeline users, devices, applications and documents in a network environment. The system employs a substitute print driver that comprises the original OEM Print Driver installed at each client or server PC, and at each target output device, wrapped with installed “agent” software. This agent software combined with the original OEM print driver performs the following functions: 1) monitors document origination, generation, acquisition and destination metrics to and from the network pipeline of User(s) and Device(s) connected to the print server; 2) sends data to a data store which the customer and / or dealer controls, and 3) provides content management functionality of document delivery.
Owner:DOCUMENT DYNAMICS LLC
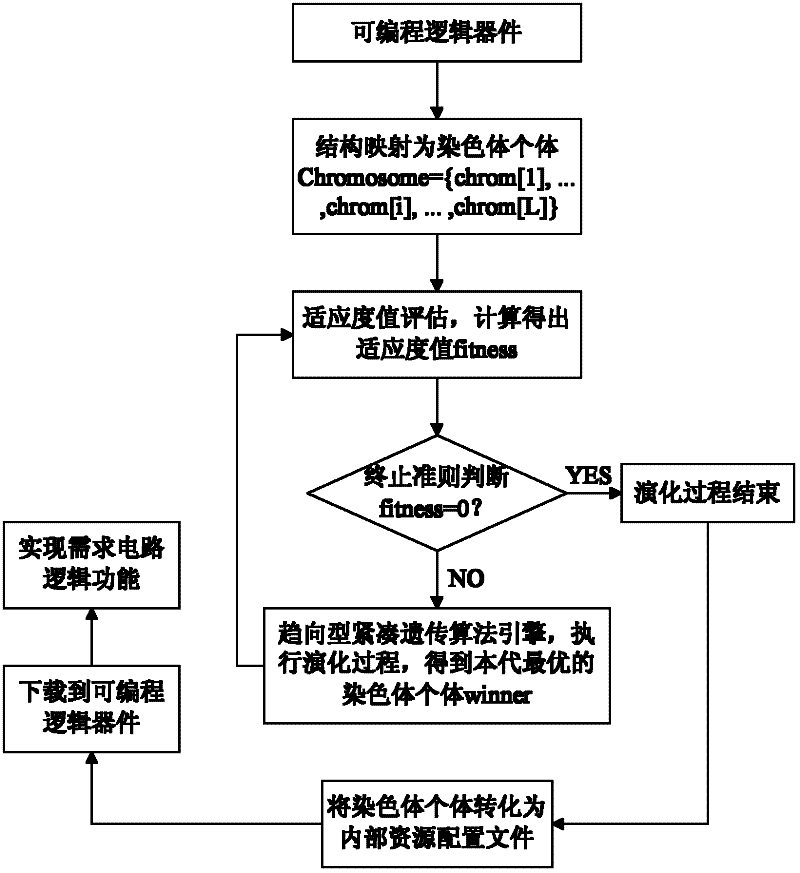
Evolvable hardware implementation method based on trend-type compact genetic algorithm
ActiveCN102254225AProvide real-timeEase of hardware implementationPhysical realisationEvolvable hardwareProgrammable logic device
The invention relates to an evolvable hardware implementation method based on a trend-type compact genetic algorithm, and the method comprises the following steps of: 1) obtaining configuration parameters of an actual programmable logic device; 2) mapping the configuration parameters of the actual programmable logic device and forming into chromosome individuals; 3) calculating the fitness of thecurrent chromosome individuals; and 4) identifying whether to terminate the evolvement according to the situation of the fitness. The evolvable hardware implementation method based on the trend-type compact genetic algorithm can be used for enhancing the search capability of a hardware configuration bit string, increasing the diversity of a candidacy solution space, obtaining high-quality and optimal hardware configuration structure bit string more fast, greatly increasing the convergence speed, reducing the time required by obtaining an optimal hardware circuit structure and enhancing the real-time performance of the actual evolvable hardware.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Work Collaboration System with Hierarchical Views, Media Sharing, and Messaging
InactiveUS20170206501A1Easy to viewEasy to updateOffice automationTransmissionUser deviceElectronic network
The present invention is a system that enable individuals, whether working pro se or part of organizations, to collaborate on work items across electronic networks. The major innovations are specific to the domain of work collaboration: 1) Organization of work topics in a hierarchical and tabular fashion with user interface tailored to traversing any hierarchy with ease; 2) Automatic adjustment of user interface based on the display size of user devices; 3) Use of templates to automate work item creations; 4) Roles that enable collaboration by active participants and viewing by passive stakeholders ; 5) Sharing of digital media within the context of applicable work hierarchies; 6) Notifications, typically sent to smart phones, to alert users regarding work topics that need attention; 7) Exchanges of text messages within the context of applicable work hierarchies.
Owner:WANG TSO JEN
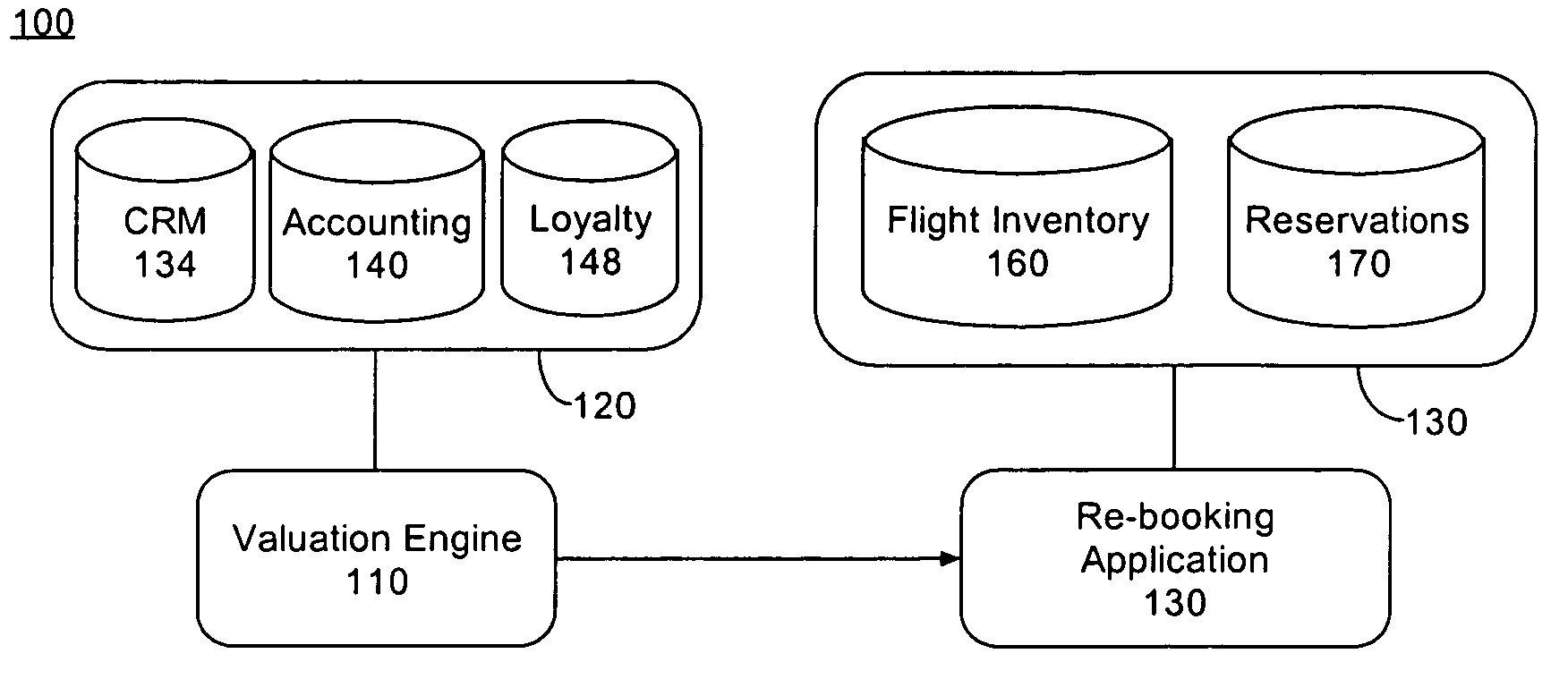
System and method for re-accommodating passengers
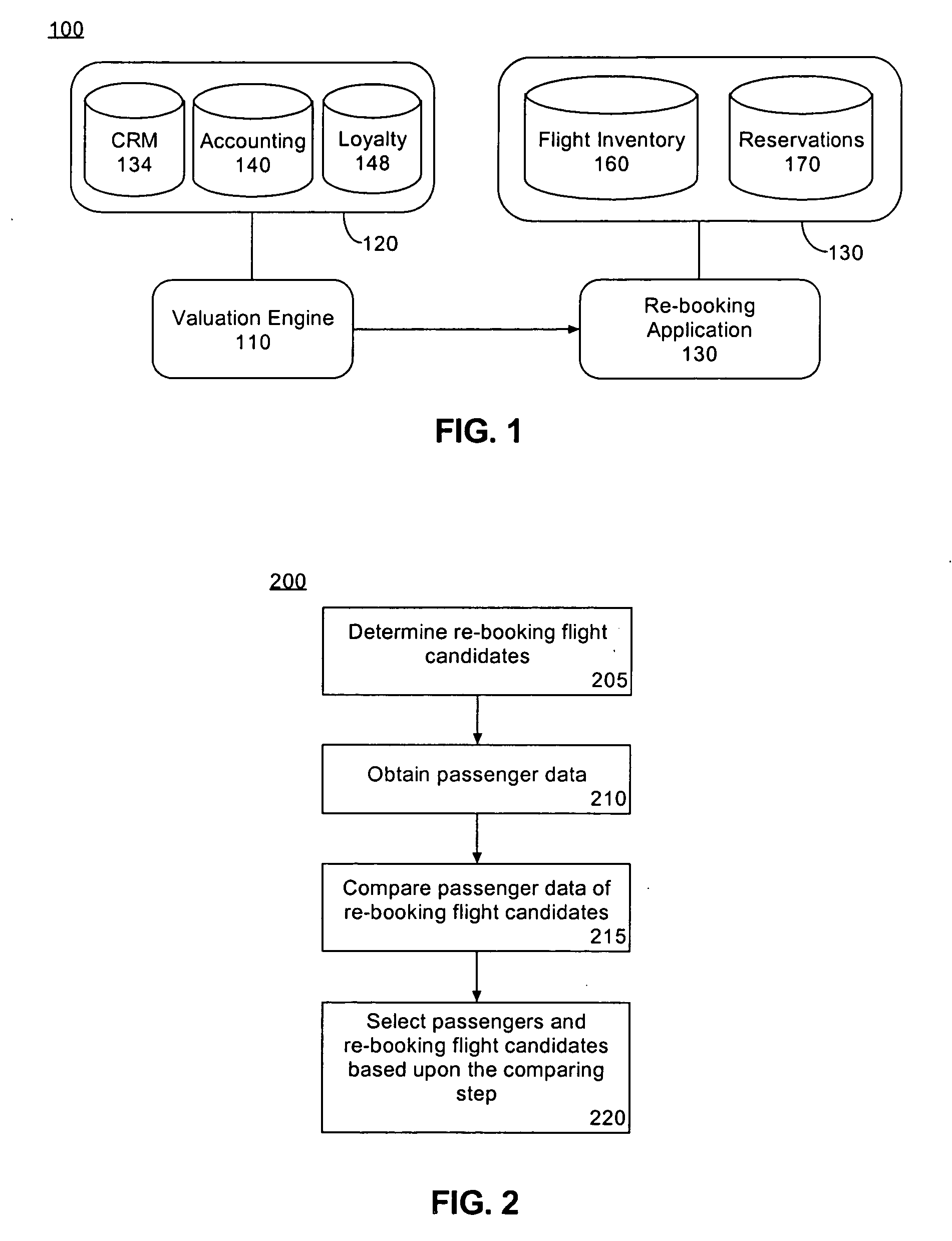
InactiveUS20050125263A1Provide real-timeReservationsSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationTransport engineering
A method for re-booking passengers who are unable to travel on scheduled flights can include the step of obtaining passenger data for the passengers. The passenger data is compared with at least one rule. Re-booking flights are offered to the passengers based upon the comparing step. A system for re-booking passengers who are unable to travel on scheduled flights is also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com