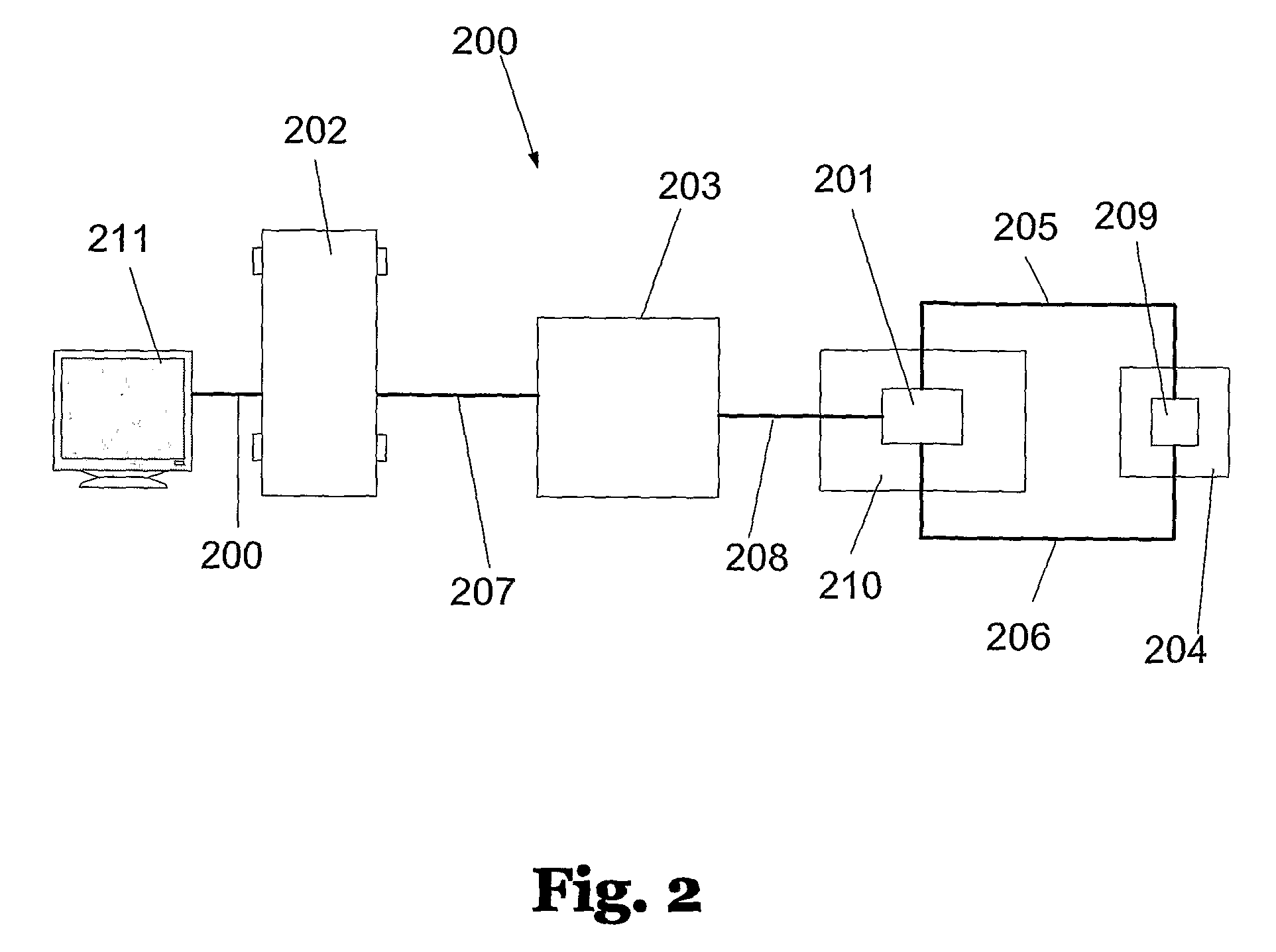
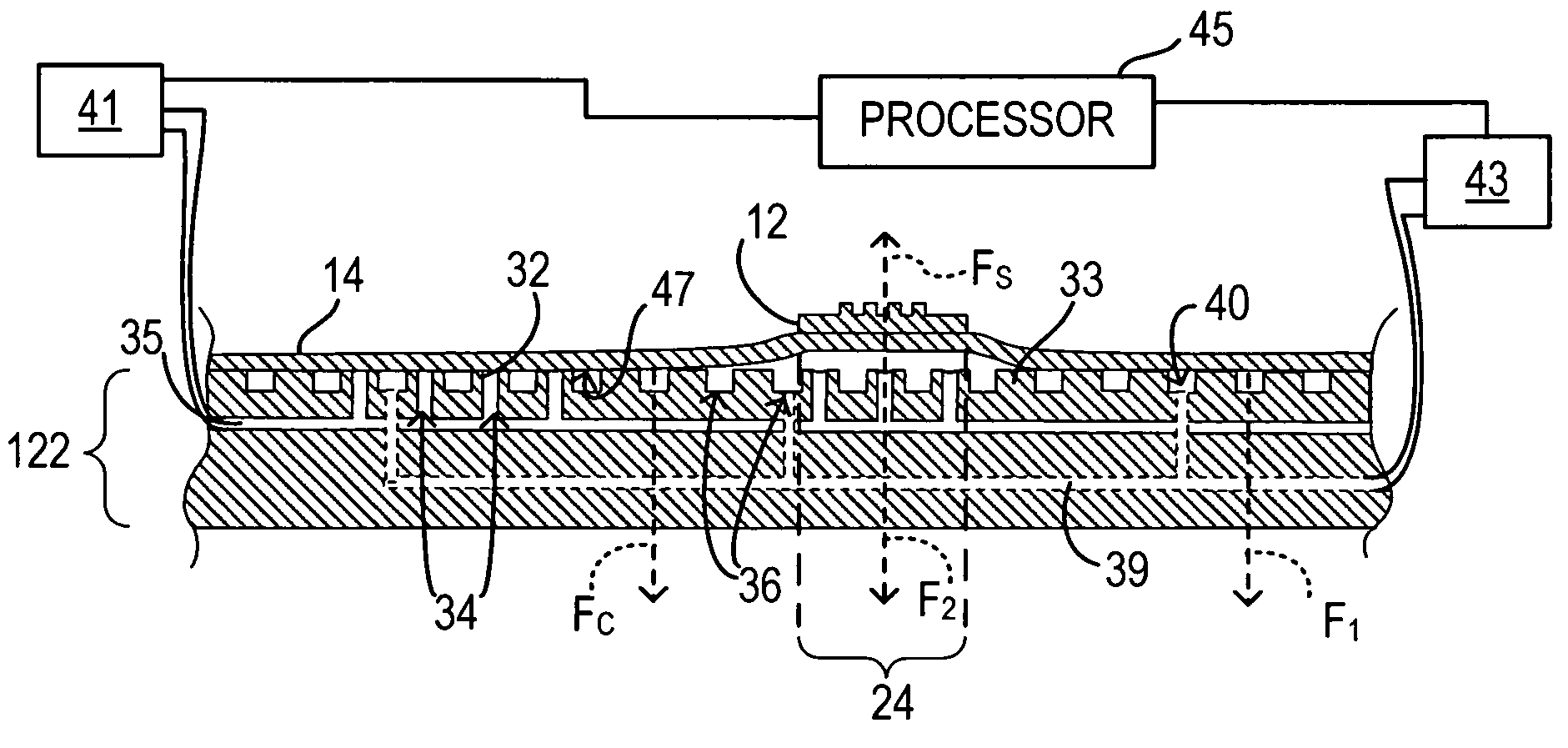
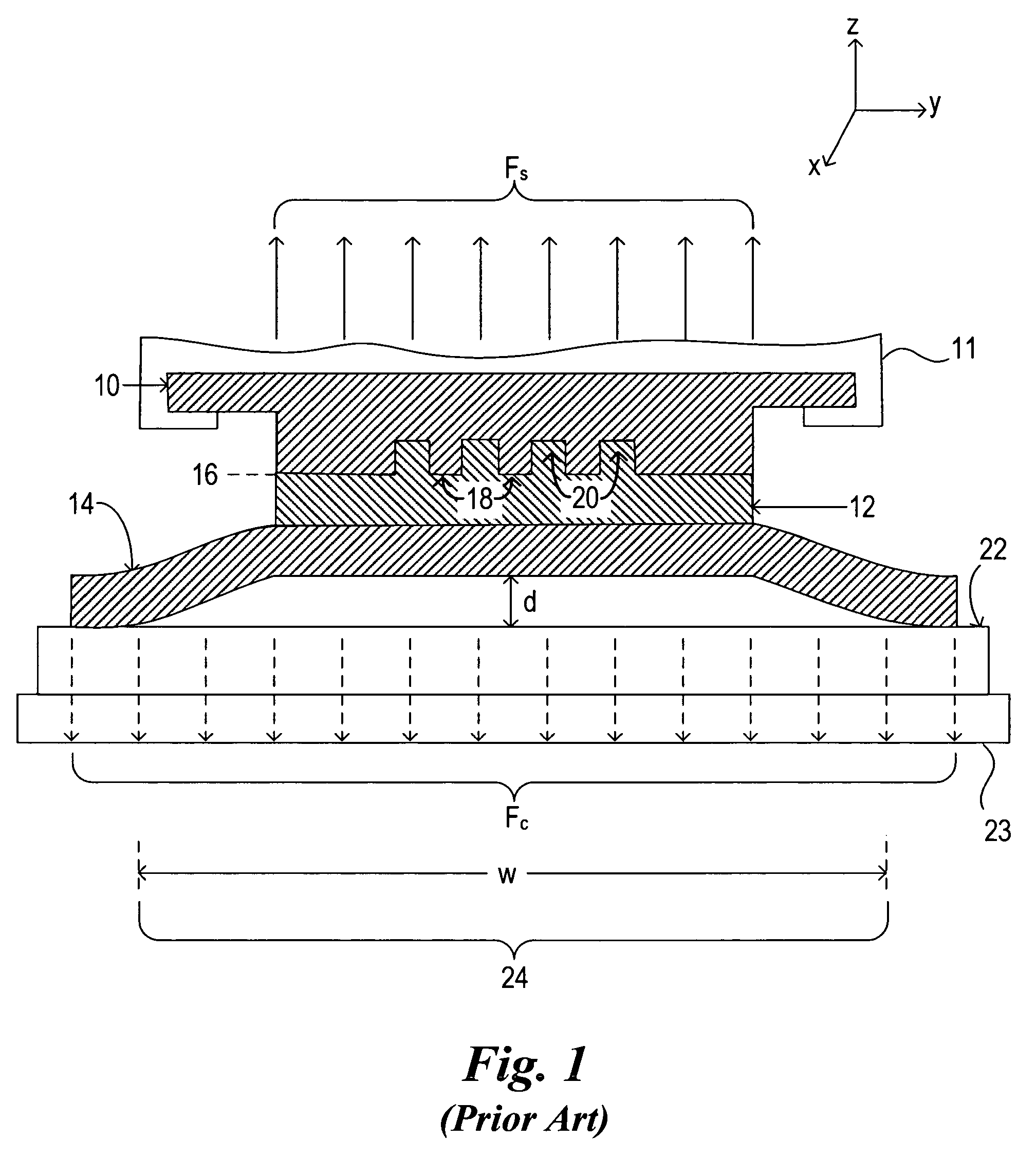
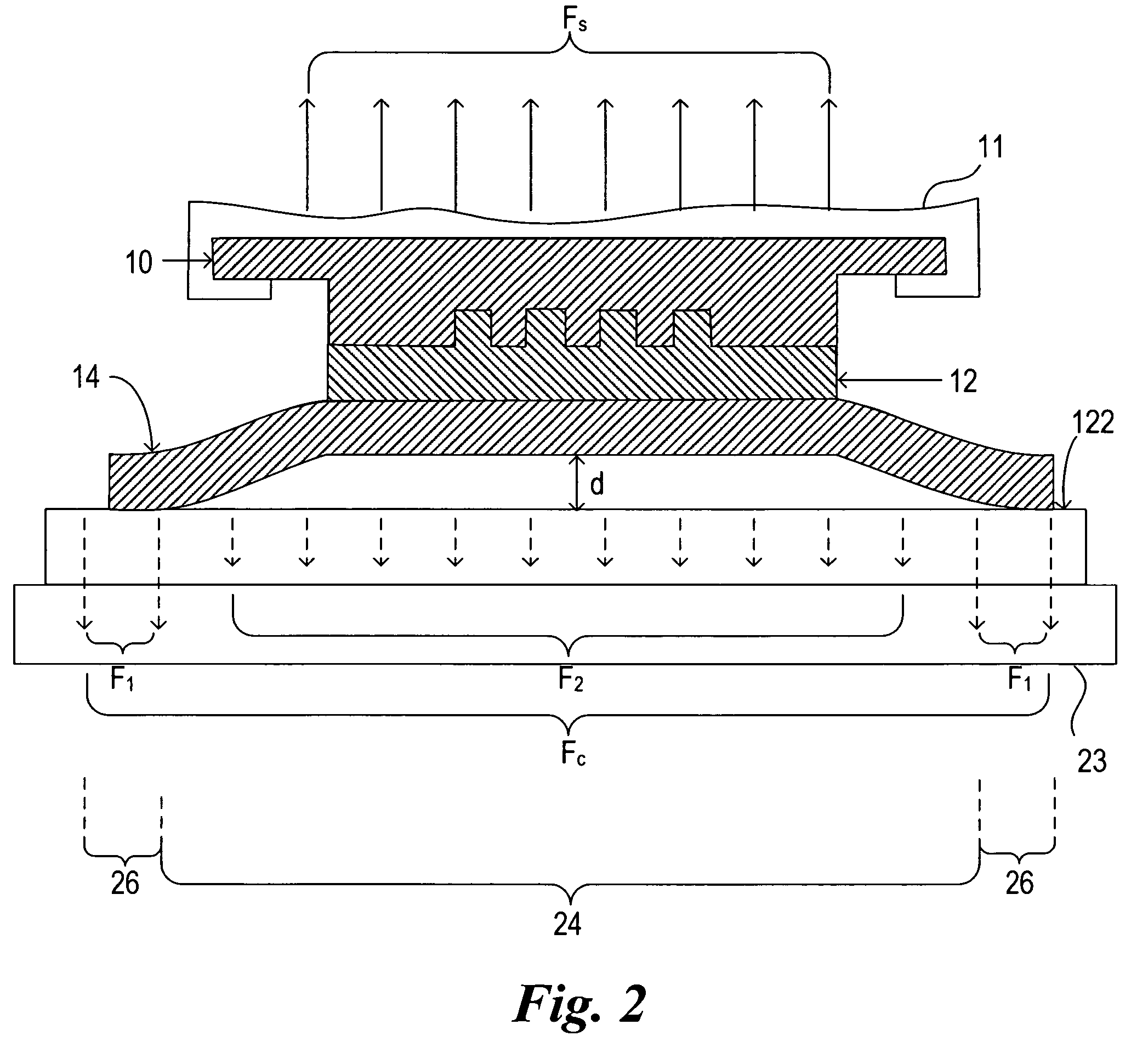
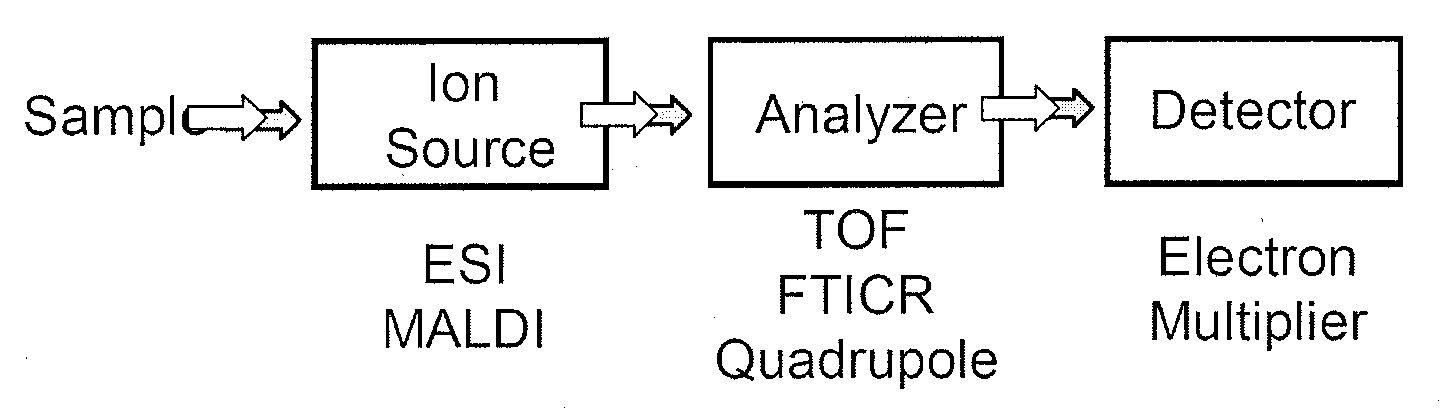
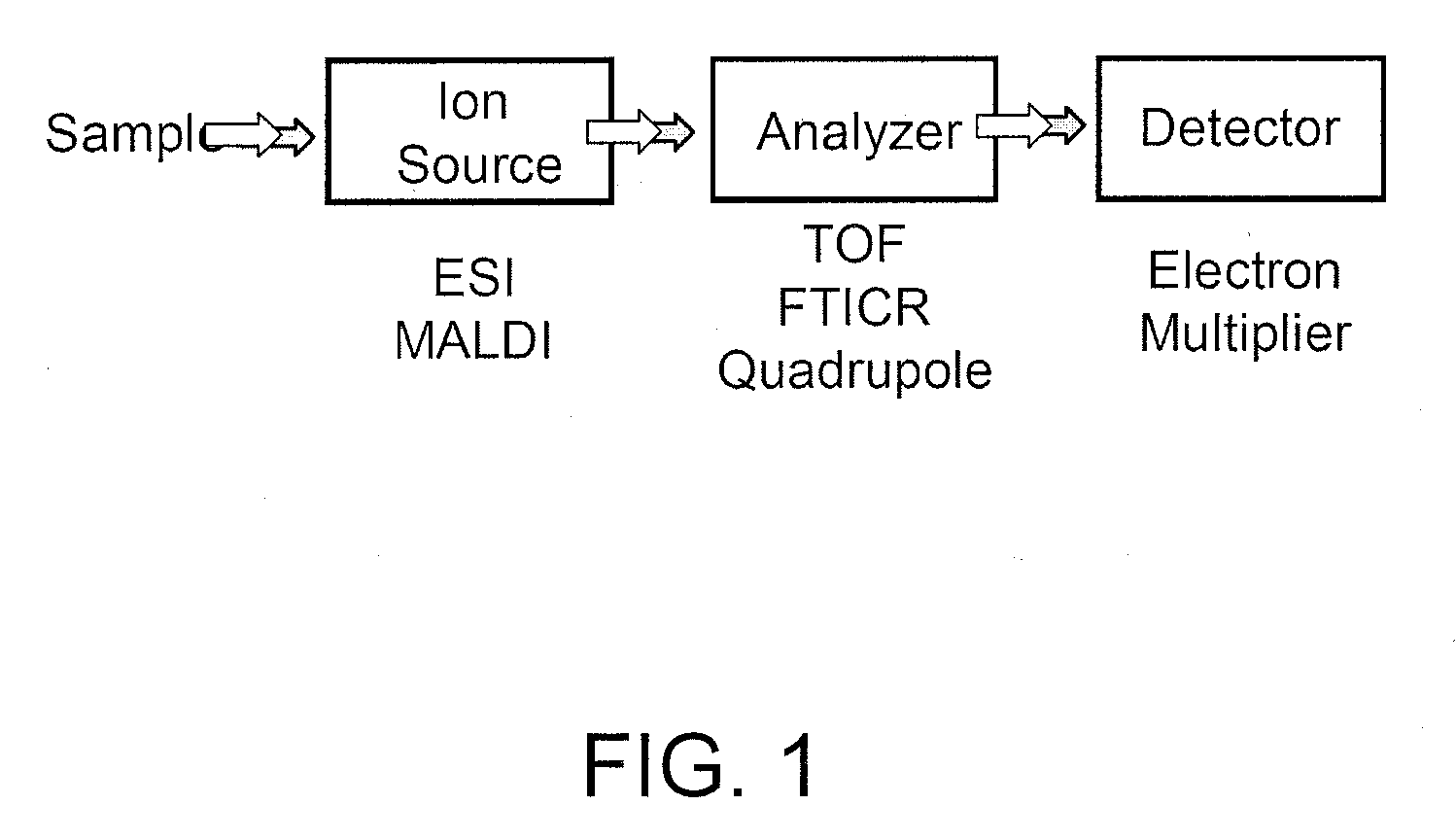
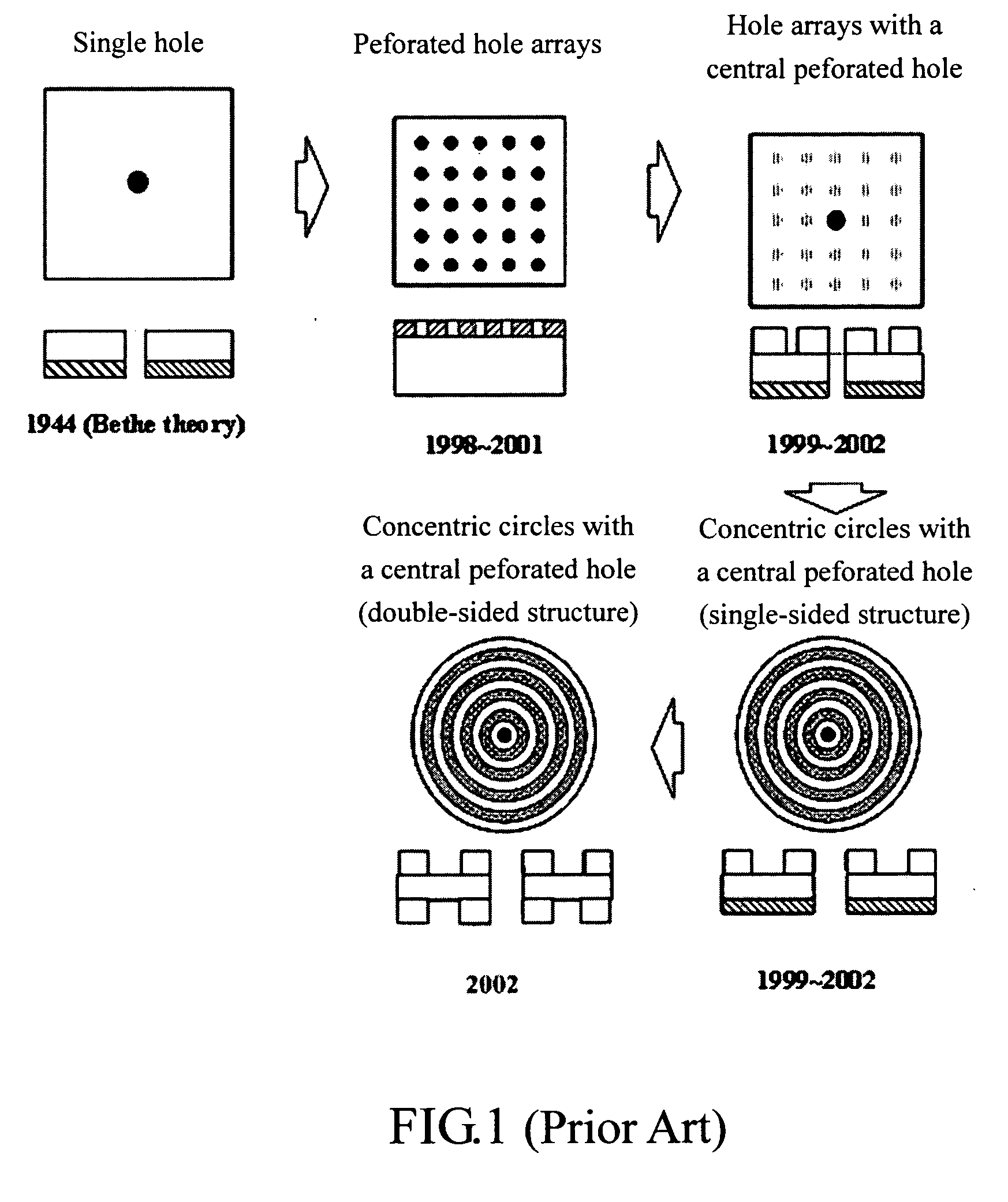
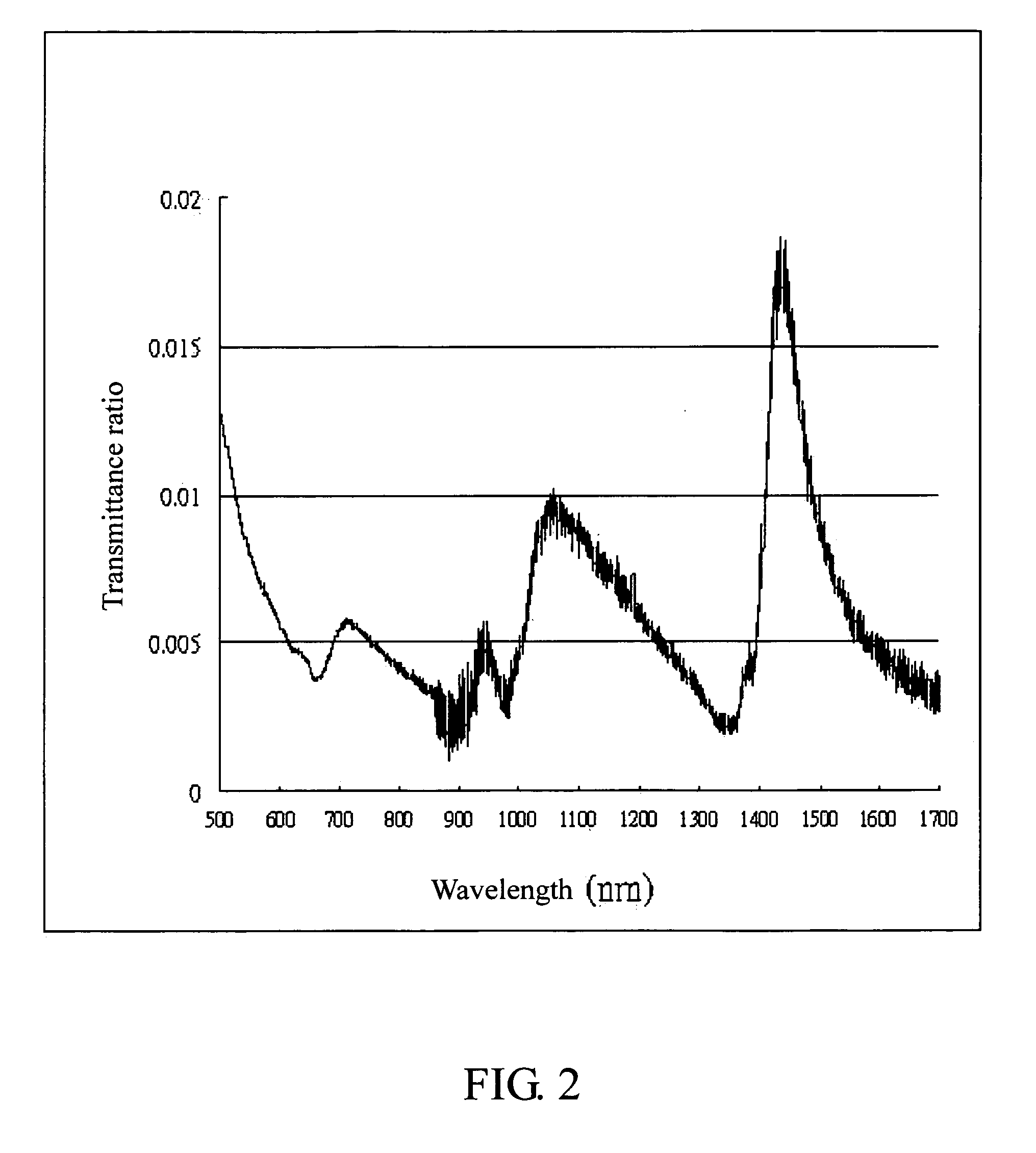
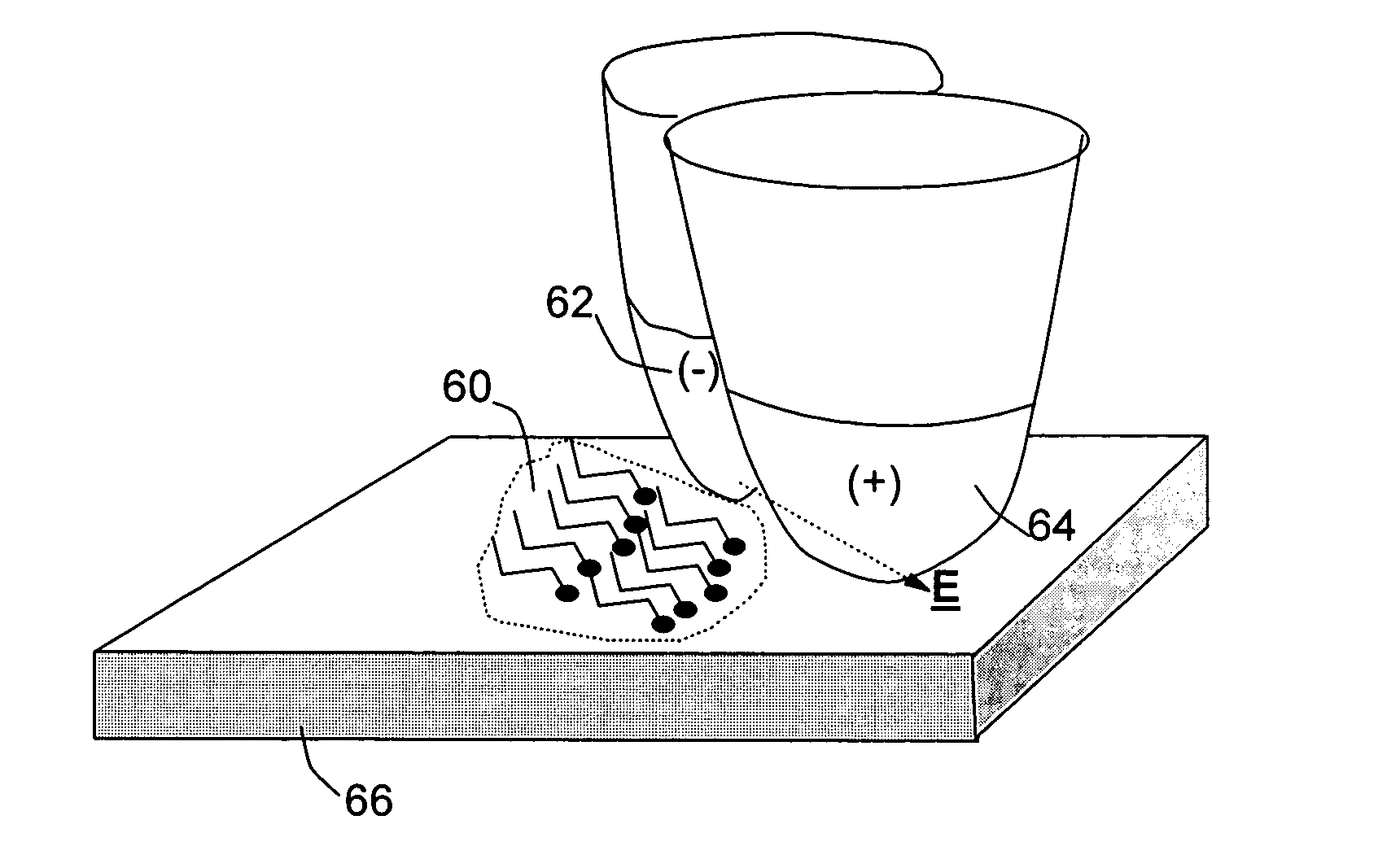
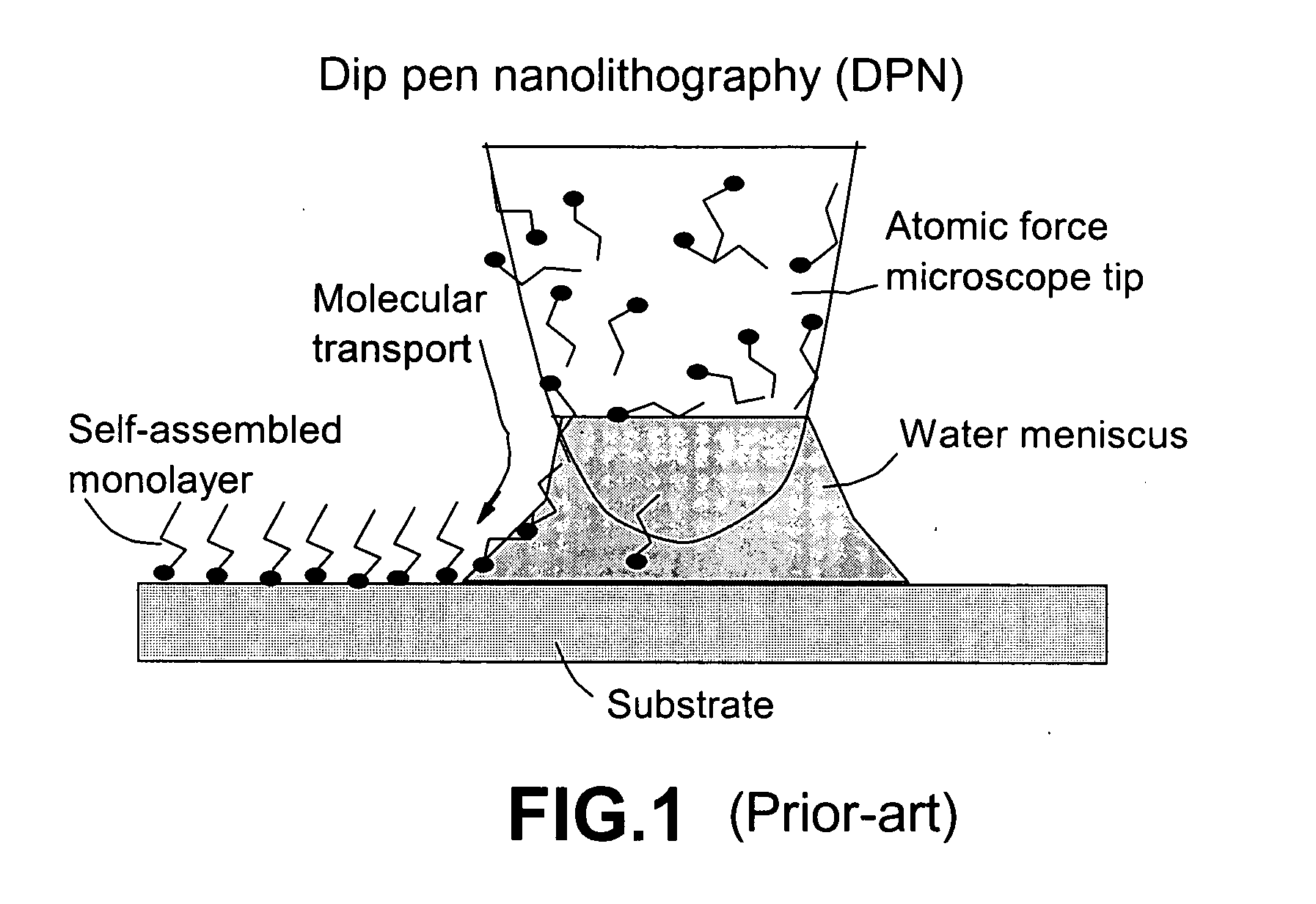
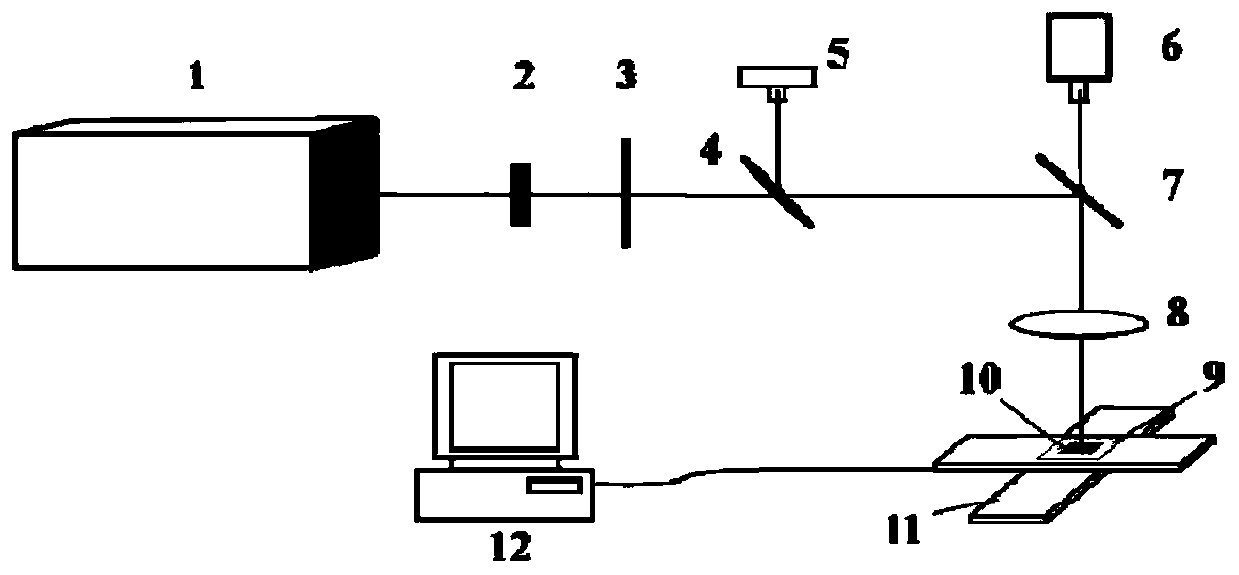
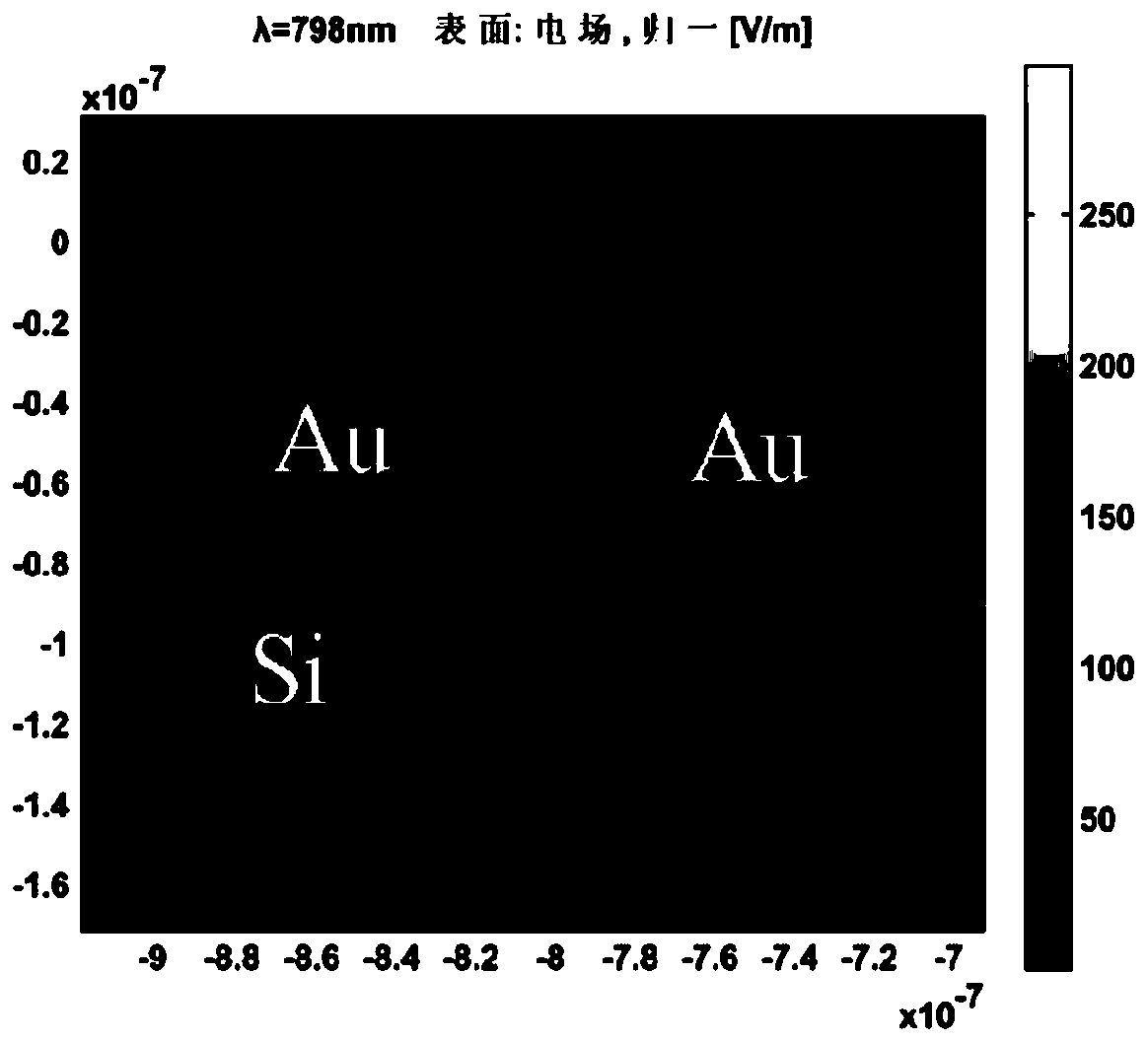
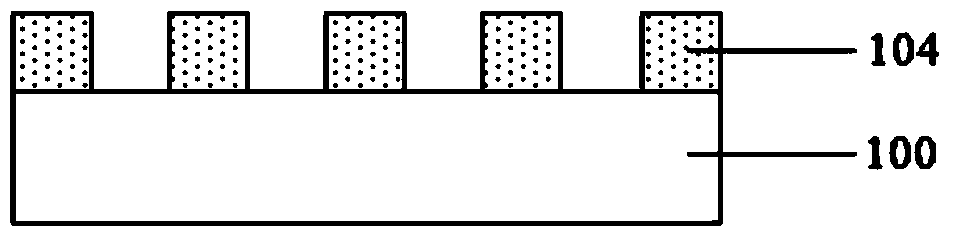
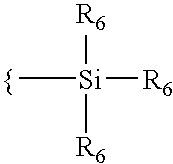Patents
Literature
197 results about "Nano manufacturing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nano manufacturing is both the production of nanoscaled materials, which can be powders or fluids, and the manufacturing of parts "bottom up" from nanoscaled materials or "top down" in smallest steps for high precision, used in several technologies such as laser ablation, etching and others. Nanomanufacturing differs from molecular manufacturing, which is the manufacture of complex, nanoscale structures by means of nonbiological mechanosynthesis (and subsequent assembly).
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS20020034757A1Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideAdhesive
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
Chucking system for nano-manufacturing
InactiveUS20060172031A1Weakening rangeReducing separation forceNanoinformaticsConfectioneryNano manufacturingBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed towards a chucking system, including, inter alia, a body having a surface with a pin extending therefrom having a throughway defined therein, and a land surrounding the protrusions defining a channel between the pin and the land. In a further embodiment, the body comprises a plurality of protrusions.
Owner:CANON KK
Nanocontact printing
InactiveUS20060141245A1Good reproducibilityConstant production of mastersMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesNano manufacturingSelf-assembly
A method of stamping of molecular patterns and / or devices based on the reversible self-assembly of molecules, particularly organic molecules is disclosed. This method is suitable for the stamping of almost any nanofabricated device and can be used to transferring a large amount of pattern information from one substrate to another at the same time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Artificial synapse chip interface for electronic prosthetic retina
InactiveUS7001608B2Efficient deliveryRecovery functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoElectron
The invention provides microfabricated devices and methods for directing the growth of a cell process to form an artificial synapse. The devices are called artificial synapse chips. The artificial synapse comprises a nanofabricated aperture (about 50–100 nm in size) that connects the cell process to a chemical or electrical means of neuronal excitation. Such an aperture width mimics the length scales of a natural synapse and thus emphasizes the localized spatial relationship between a neuron and a stimulation source. The invention further provides devices and methods for regenerating a nerve fiber into an electrode. The invention thus provides a regeneration electrode that uses a novel neural interface for stimulation and that uses novel surface methods for directing neuronal growth making possible in vivo connection of the devices to neural circuitry in a retina and other anatomical locations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
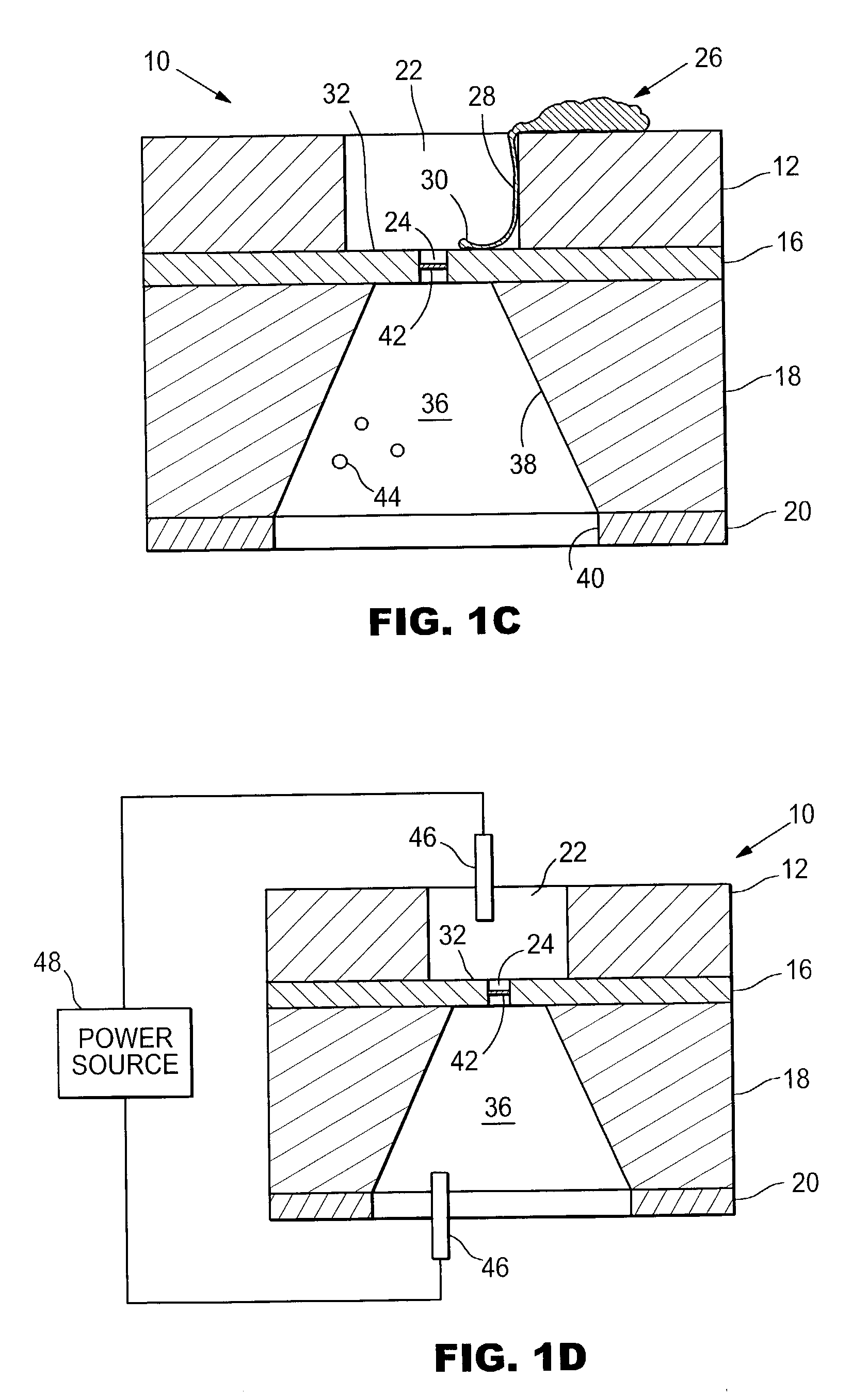
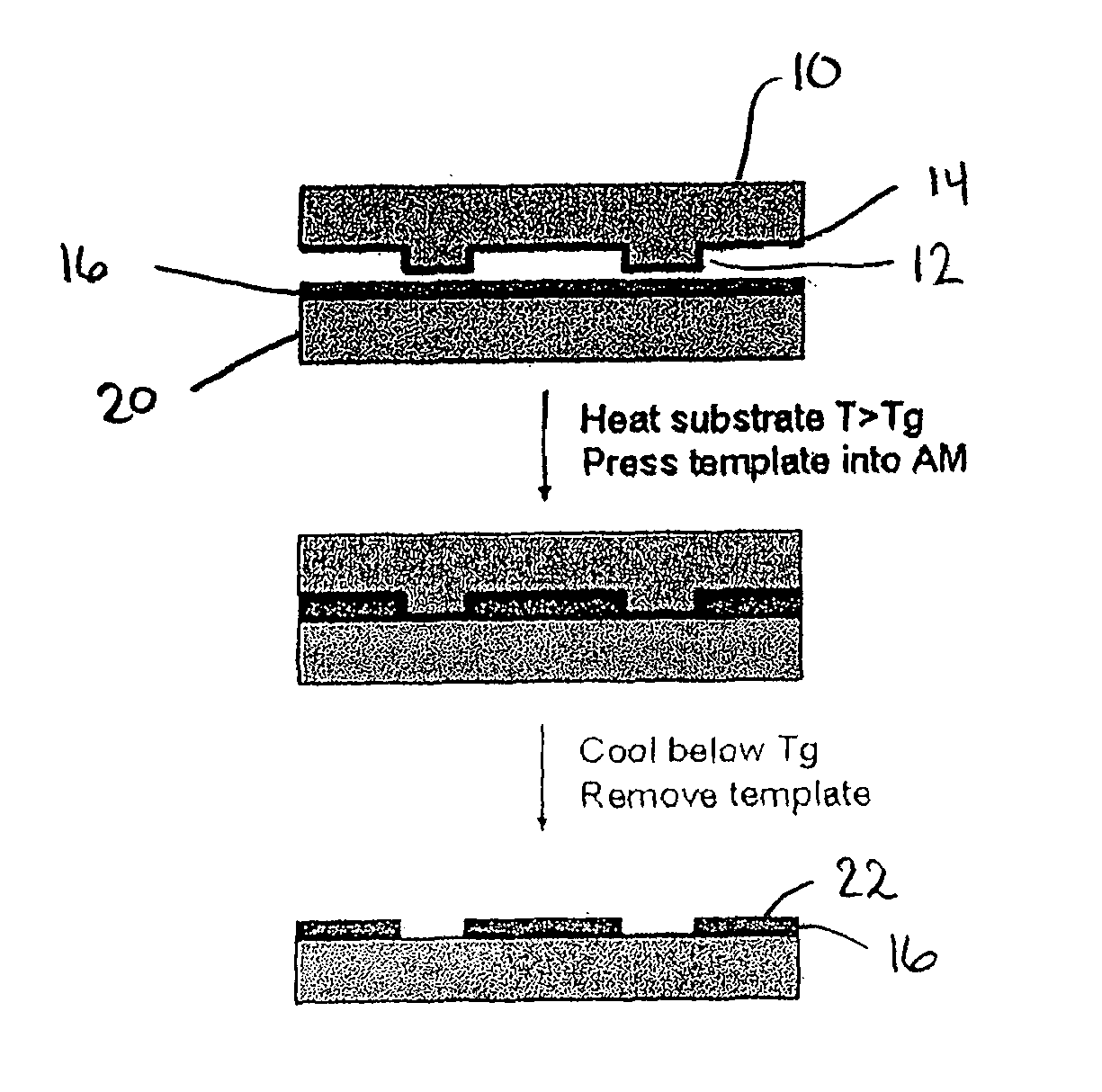
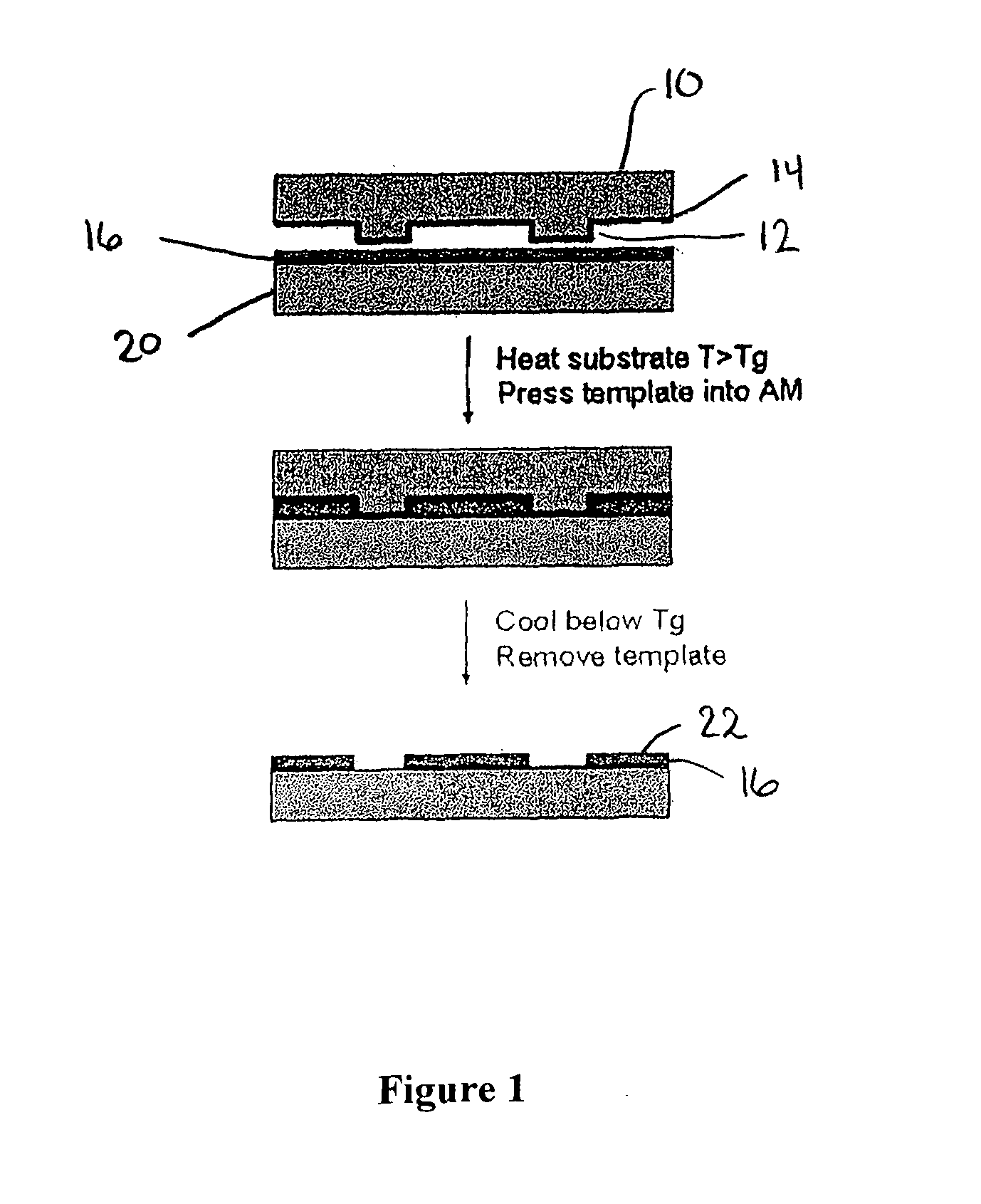
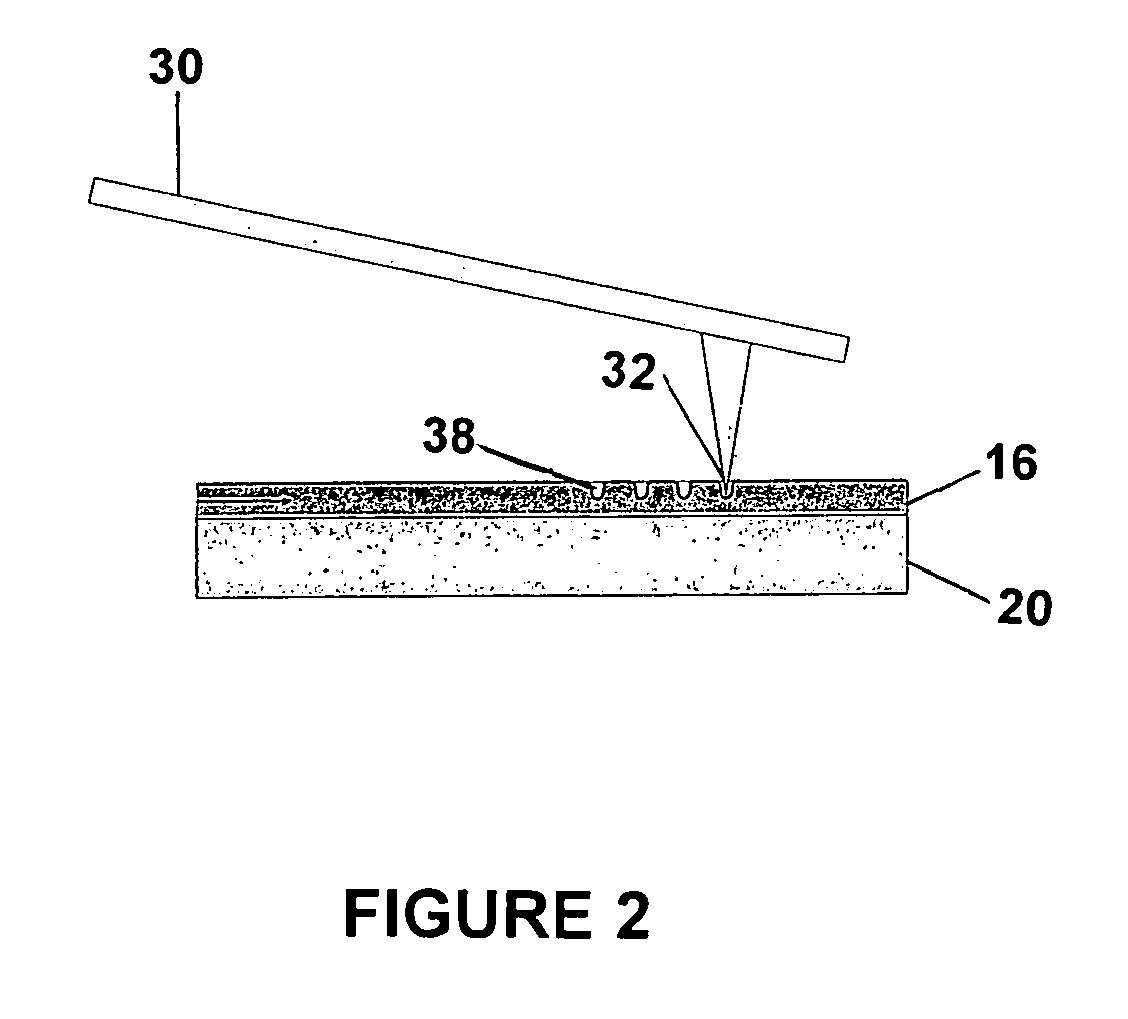
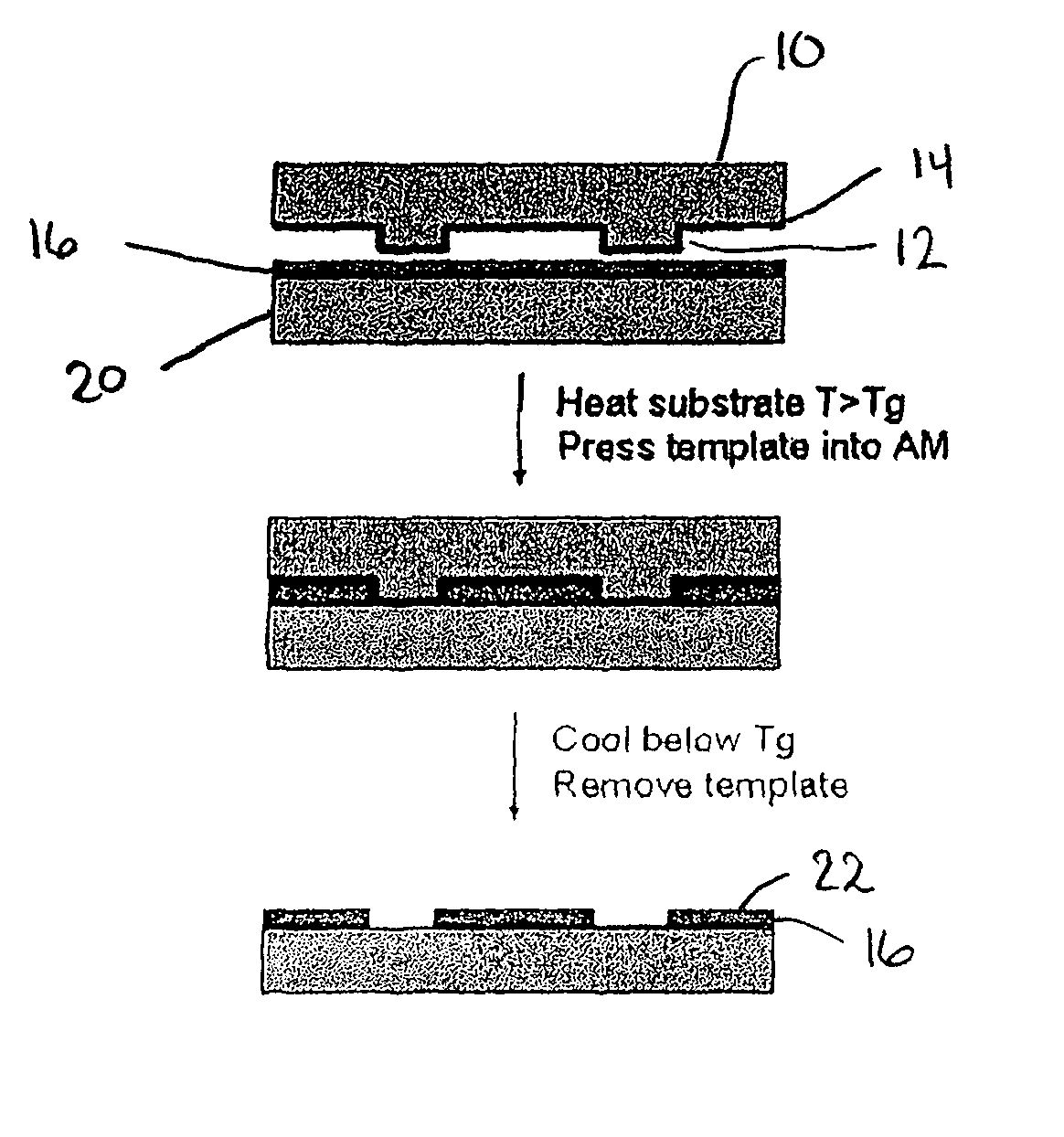
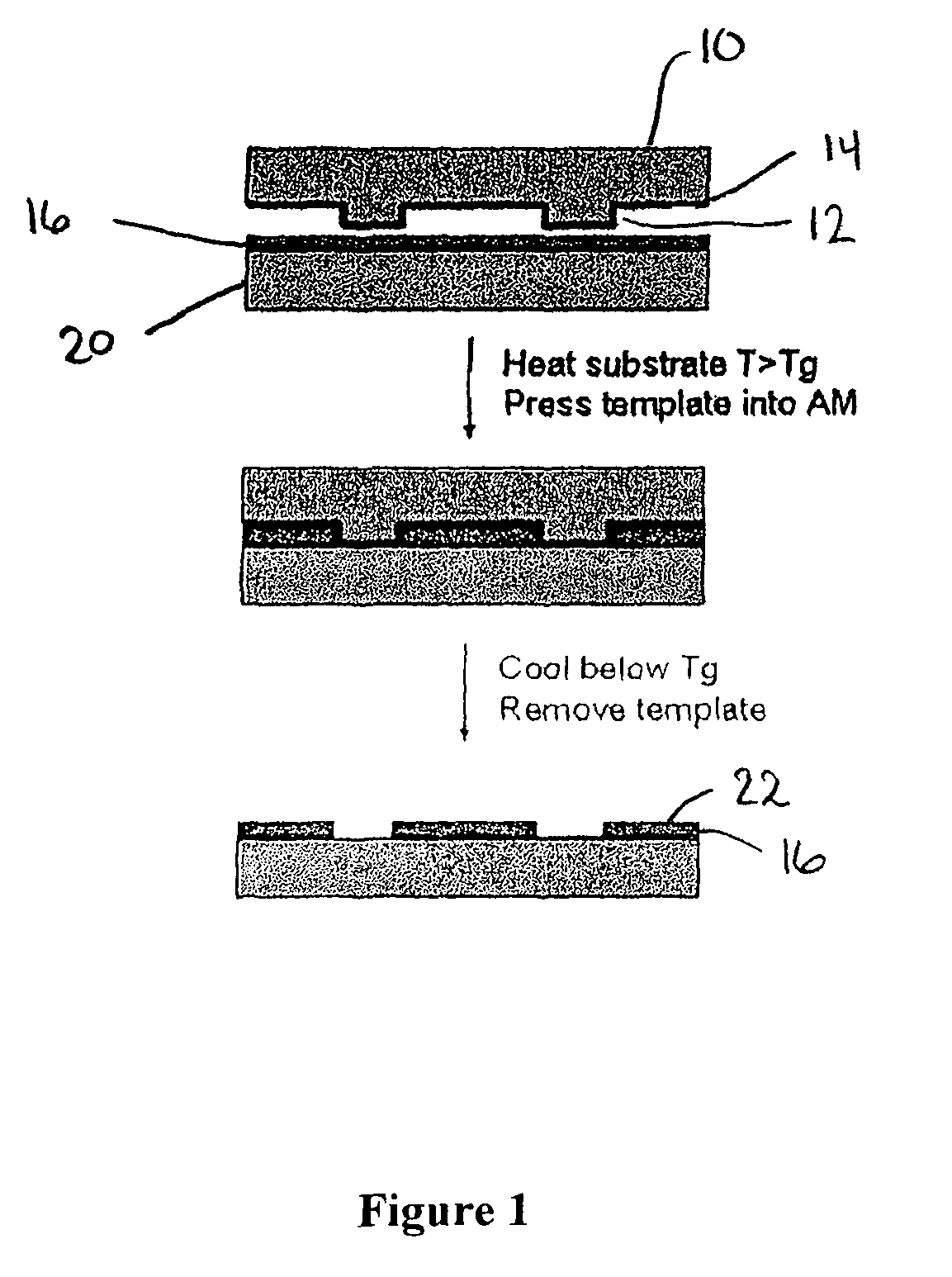
Method for Imprinting and Erasing Amorphous Metal Alloys
ActiveUS20100098967A1Surface roughnessLayered productsMechanical recordingMicron scaleNano manufacturing
The present invention relates to materials, methods and apparatuses for performing imprint lithography using amorphous metallic materials. The amorphous metallic materials can be employed as imprint media and thermoplastic forming processes are applied during the pattern transfer procedure to produce micron scale and nanoscale patterns in the amorphous metallic layer. The pattern transfer is in the form of direct mask embossing or through a serial nano-indentation process. A rewriting process is also disclosed, which involves an erasing mechanism that is accomplished by means of a second thermoplastic forming process. The amorphous metallic materials may also be used directly as an embossing mold in imprint lithography to allow high volume imprint nano-manufacturing. This invention also comprises of a method of smoothening surfaces under the action of the surface tension alone.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Near field super lens employing tunable negative index materials
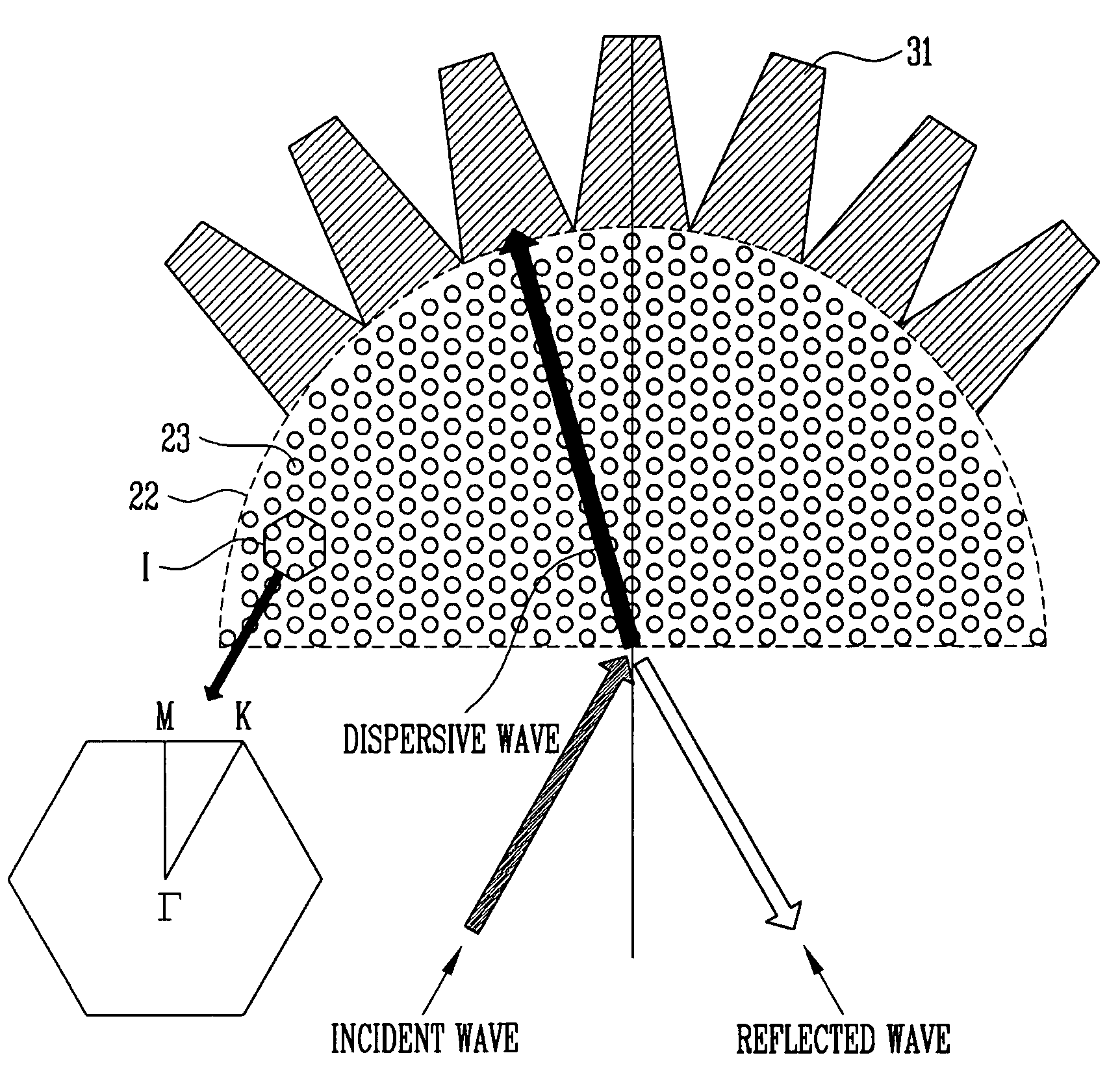
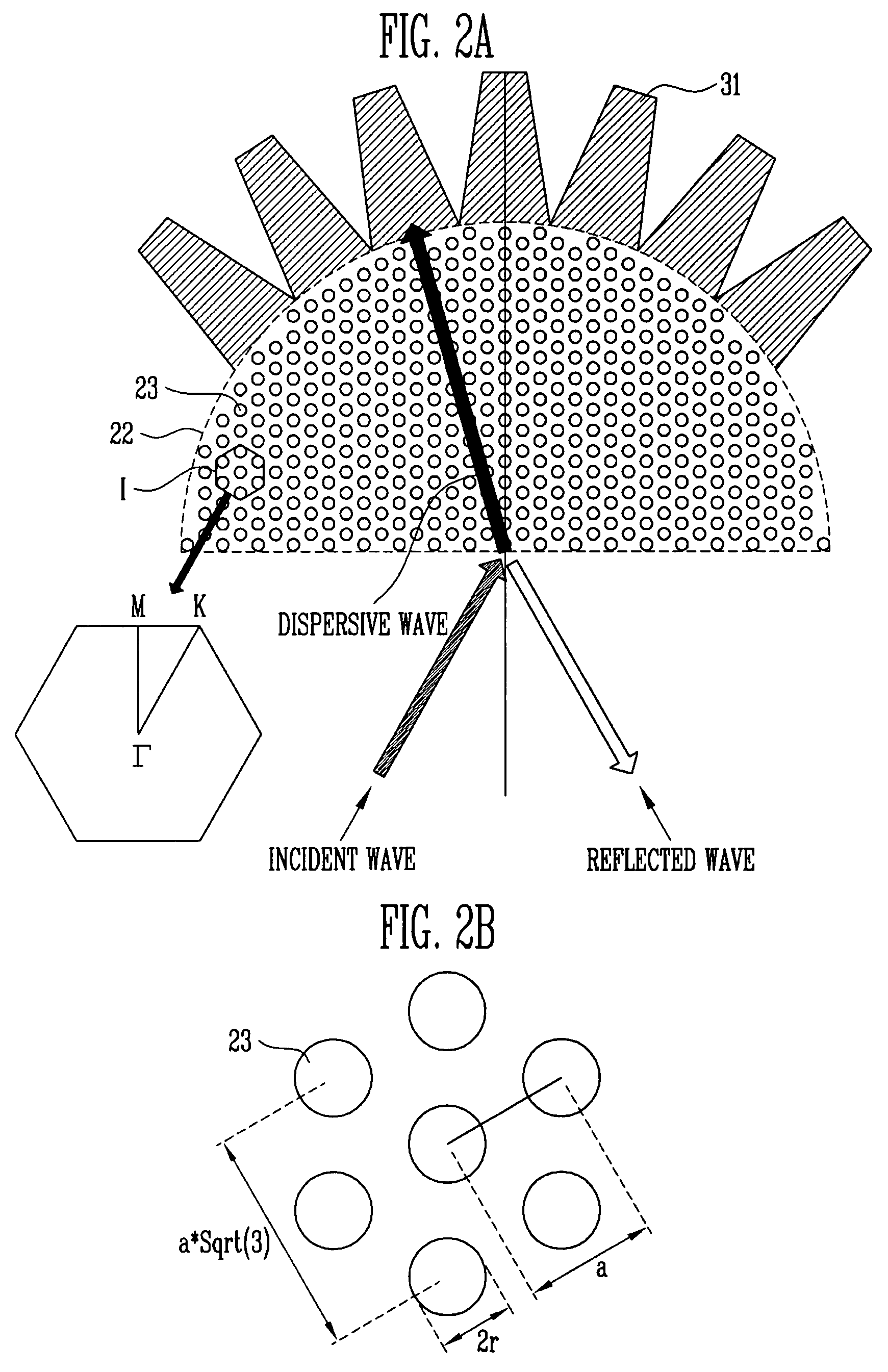
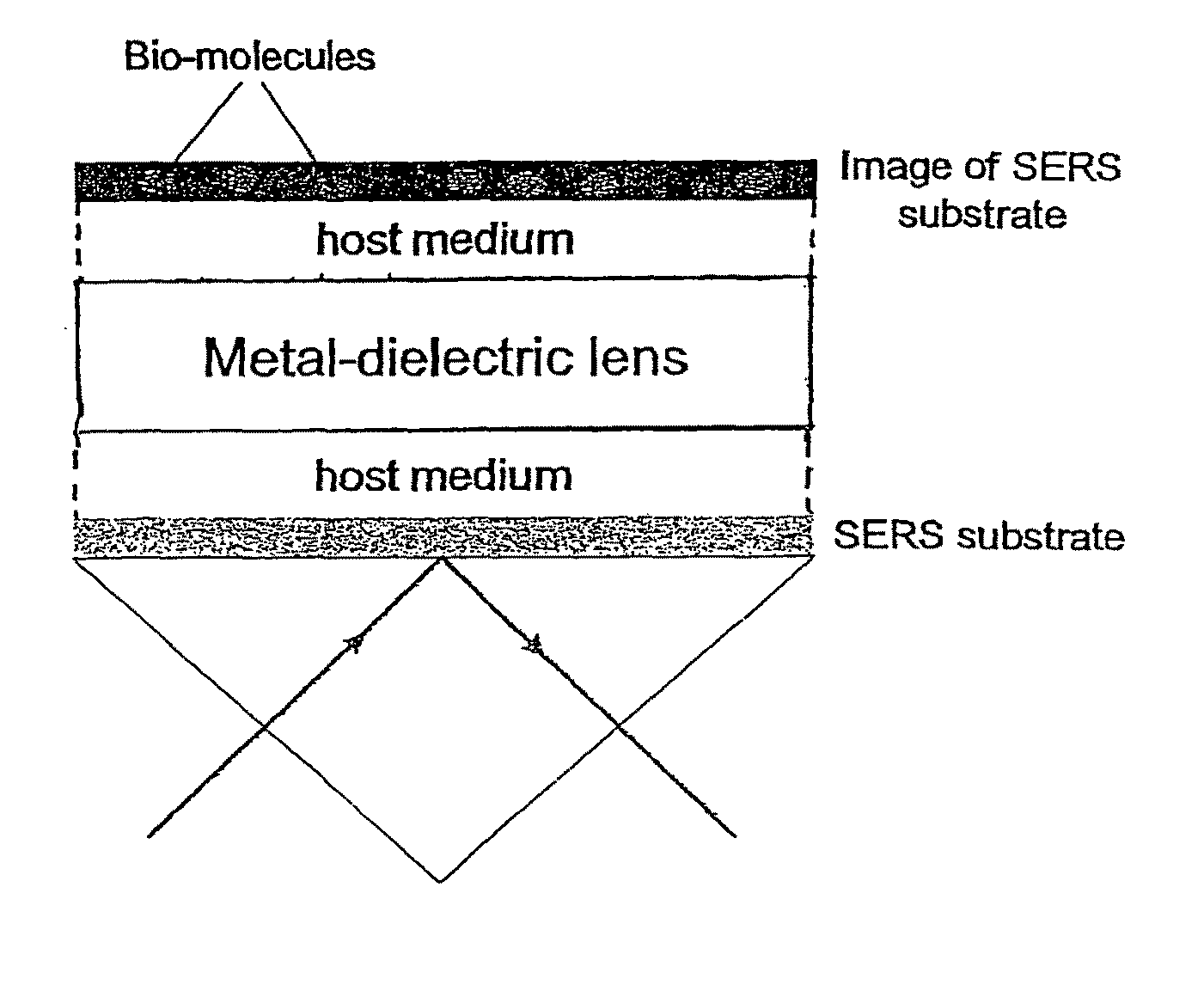
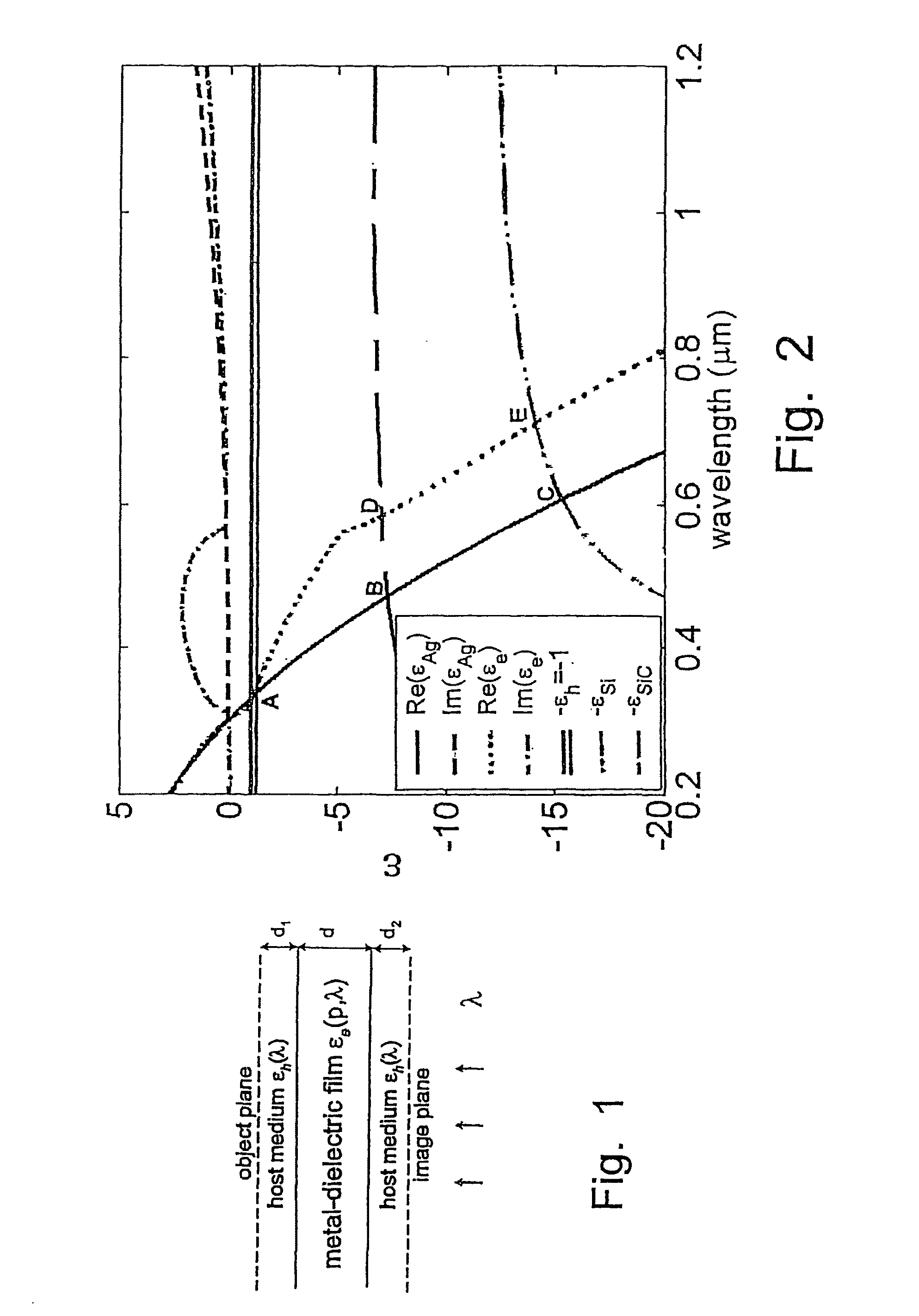
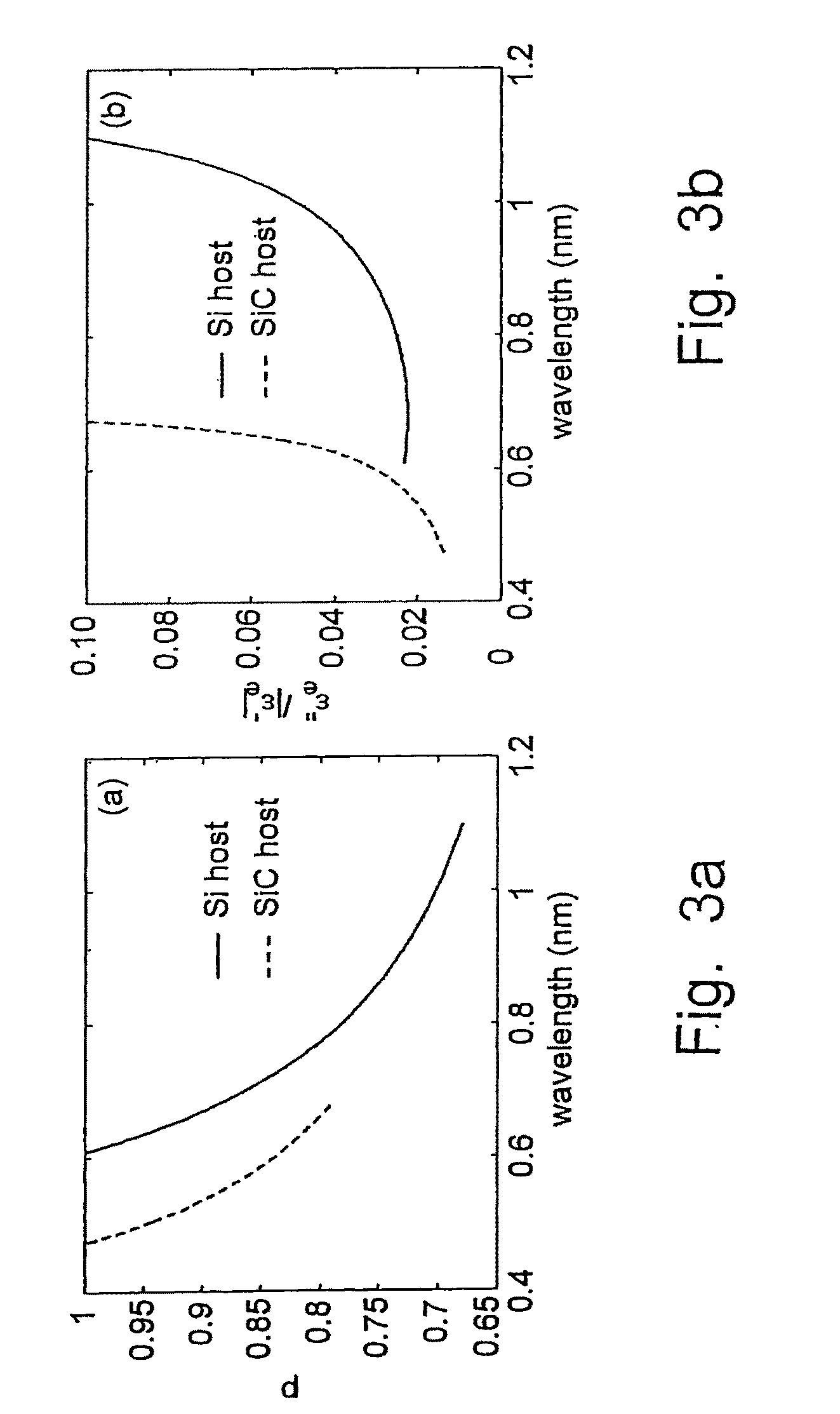
ActiveUS20100134898A1High resolutionFast and accurate calculationNanoopticsMicroscopesCamera lensBio molecules
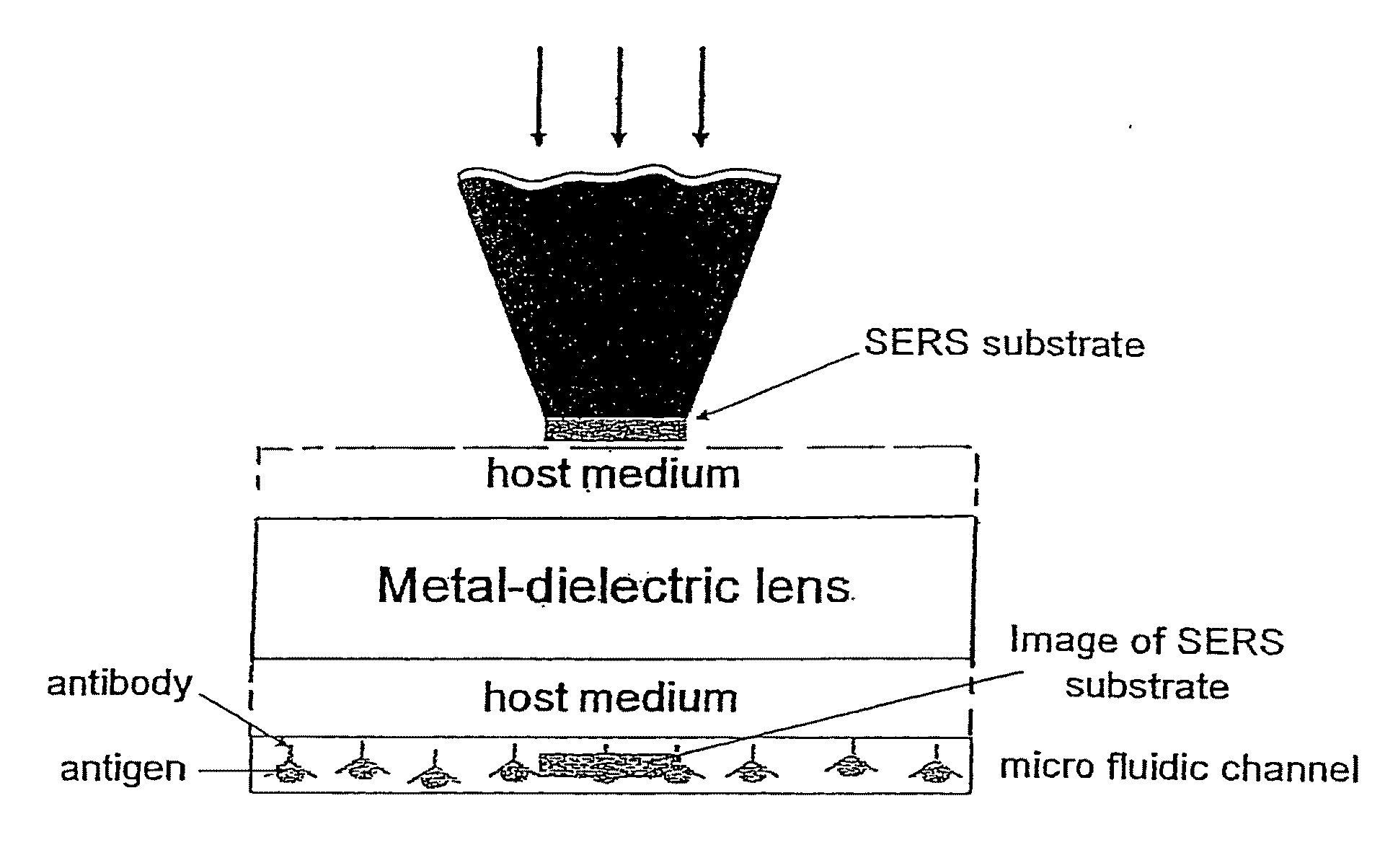
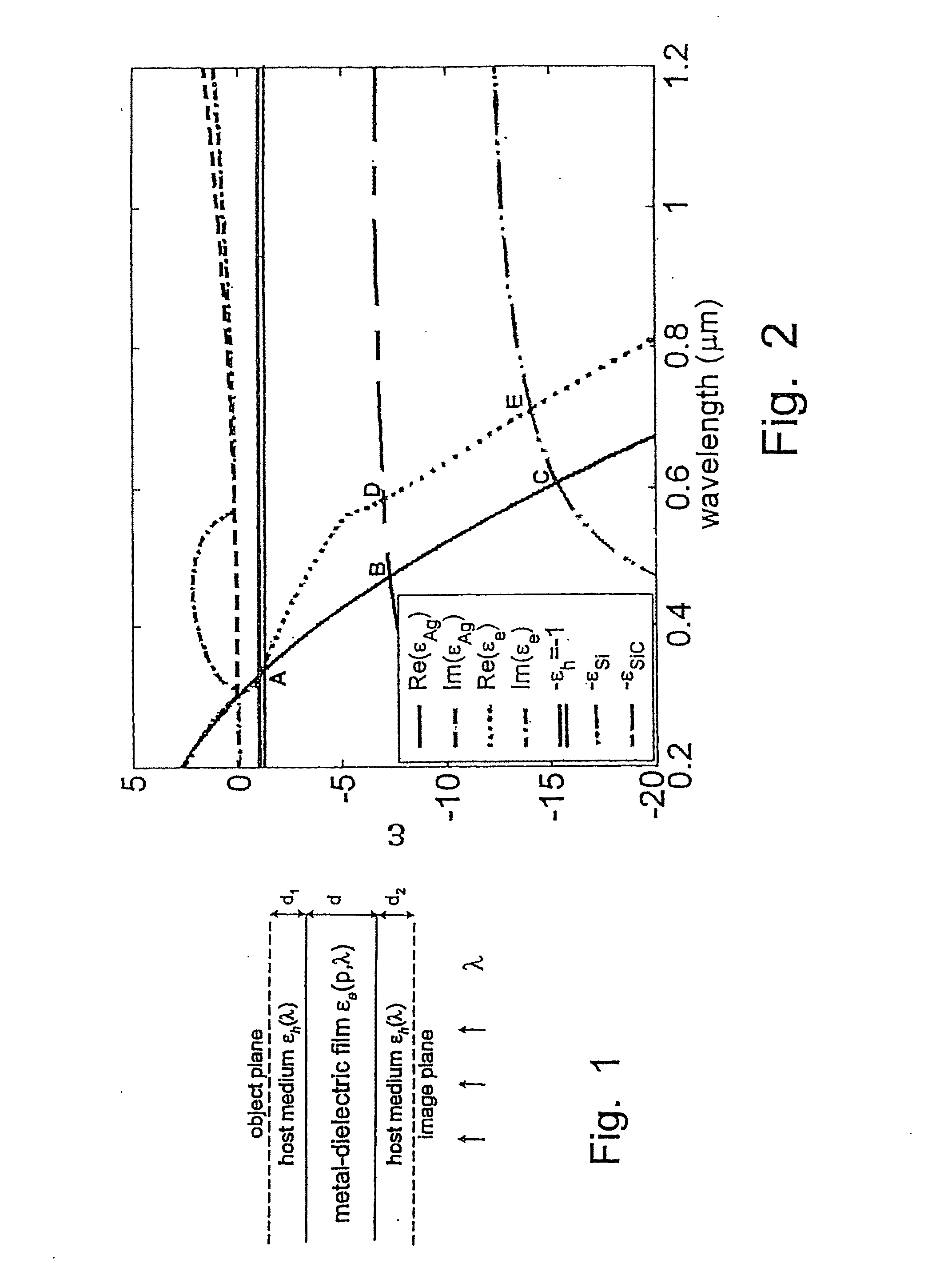
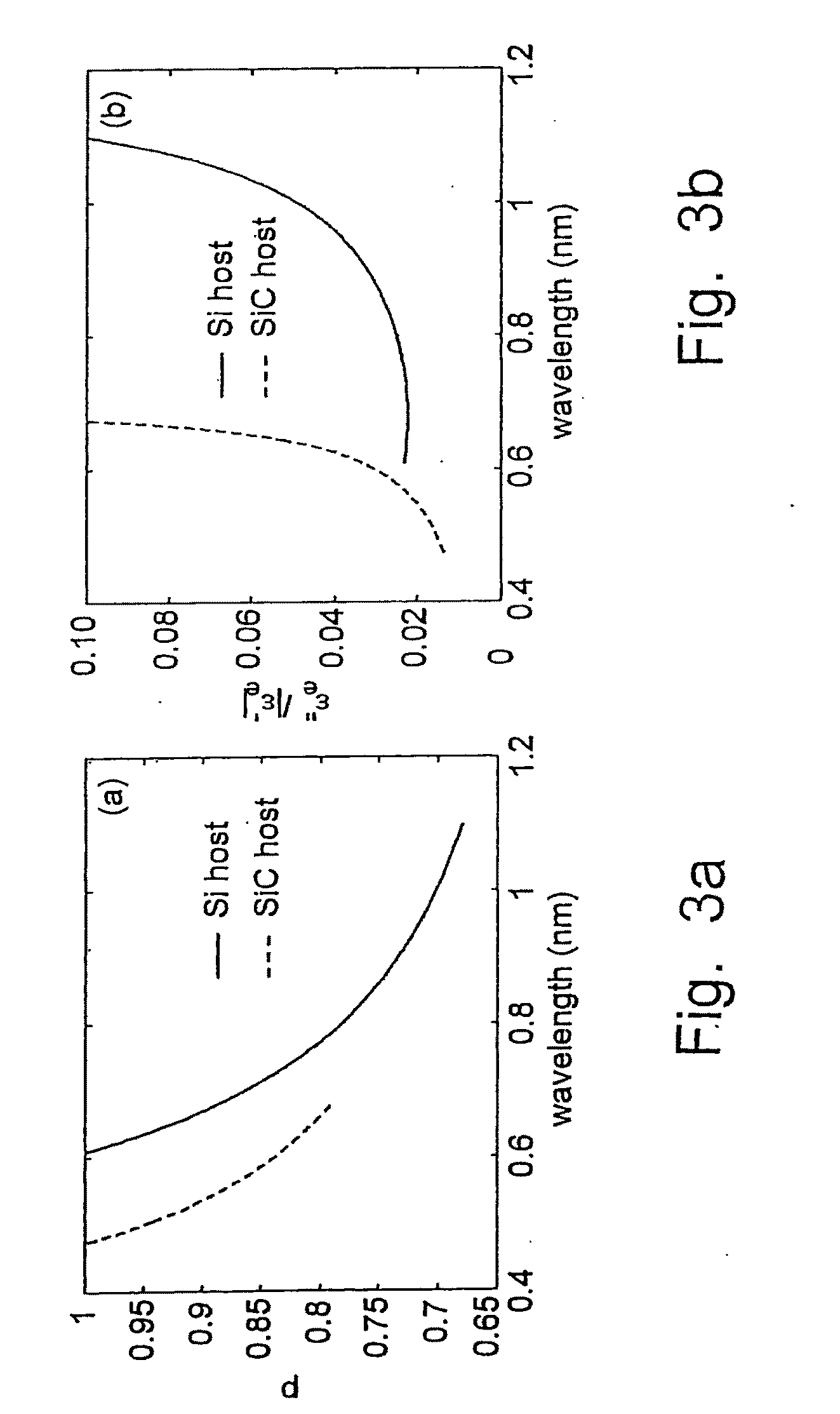
A tunable super-lens (TSL) for nanoscale optical sensing and imaging of bio-molecules and nano-manufacturing utilizes negative-index materials (NIMs) that operate in the visible or near infrared light. The NIMs can create a lens that will perform sub-wavelength imaging, enhanced resolution imaging, or flat lens imaging. This new TSL covers two different operation scales. For short distances between the object and its image, a near-field super-lens (NFSL) can create or enhance images of objects located at distances much less than the wavelength of light. For the far-zone, negative values are necessary for both the permittivity ε a permeability μ. While well-structured periodic meta-materials, which require delicate design and precise fabrication, can be used, metal-dielectric composites are also candidates for NIMs in the optical range. The negative-refraction in the composite films can be made by using frequency-selective photomodification.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
High-efficiency spectral purity filter for EUV lithography
InactiveUS7050237B2Simple and inexpensive wayImprove efficiencyMirrorsOptical filtersLithographic artistBlazed grating
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sensor for Detection of Single Molecules
InactiveUS20080149479A1High sensitivityReduce distortion problemsImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologySingle electronNano manufacturing
A single electron transistor device for sensing at least one particle, includes at least two electrodes positioned with a gap formed between the electrodes and an activation object positioned in the gap with an insulating layer between the activation object and each electrode. The activation object which is able to transfer electrons is arranged with at least one binding structure bonded to it for receiving the at least one particle. The electrodes are formed with an inter distance of less than 50 nm and the electrodes are connectable directly or indirectly to a signal acquisition system. The sensing device is arranged to allow a tunnelling current proportional to the presence of the at least one particle in the binding structure, to flow through the activation object. A method, and system using a single electron transistor device fabricated with micro / nano fabrication methods are also disclosed.
Owner:MIDORION
Chucking system for nano-manufacturing
InactiveUS7798801B2Weakening rangeMinimizing damageConfectioneryNanoinformaticsNano manufacturingBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed towards a chucking system, including, inter alia, a body having a surface with a pin extending therefrom having a throughway defined therein, and a land surrounding the protrusions defining a channel between the pin and the land. In a further embodiment, the body comprises a plurality of protrusions.
Owner:CANON KK
Monolithic Multinozzle Emitters for Nanoelectrospray Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20100075428A1Promote formationPossibility for surface functionalizationBurnersParticle separator tubesNano manufacturingMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Novel and significantly simplified procedures for fabrication of fully integrated nanoelectrospray emitters have been described. For nanofabricated monolithic multinozzle emitters (NM2 emitters), a bottom up approach using silicon nanowires on a silicon sliver is used. For microfabricated monolithic multinozzle emitters (M3 emitters), a top down approach using MEMS techniques on silicon wafers is used. The emitters have performance comparable to that of commercially-available silica capillary emitters for nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hydrophobic surface, preparation method and application thereof in dropwise condensation heat transfer
InactiveCN103359684AAccelerated mergerAccelerated sheddingMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationMicro nanoLevel structure
The invention discloses a hydrophobic surface, a preparation method and application thereof in dropwise condensation heat transfer, and relates to the fields of micro-nano manufacturing, condensation heat transfer and the like. The hydrophobic surface has a micro-nano two-level structure, wherein the micro-nano two-level structure is anisotropic and the hydrophobic surface has anisotropic wettability. On one hand, the micro-nano two-level structure of the hydrophobic surface can promote realization of dropwise condensation, and can significantly improve the heat transfer efficiency compared with the common filmwise condensation,; on the other hand, the anisotropic wettability of the hydrophobic surface can affect condensation and fall of water drops to a certain extent and can accelerate discharge of liquid drops under the influence of gravity and other factors, thereby further improving the condensation heat transfer efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
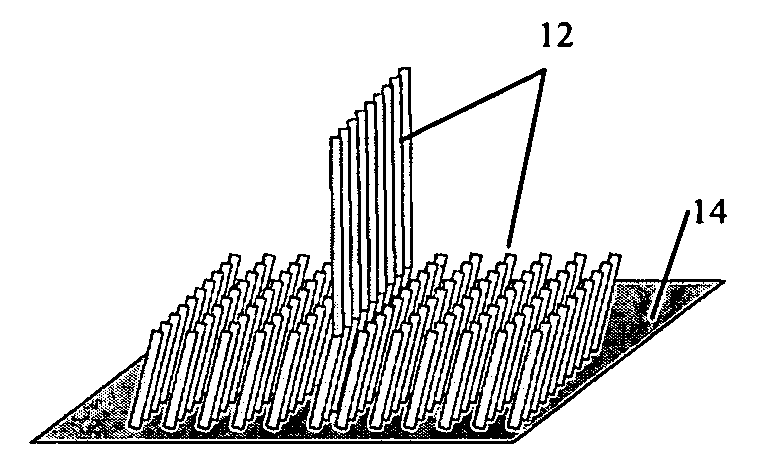
Gecko-like fasteners for disposable articles
Disposable absorbent article having nano-fabricated fastening means having adhesive bristles disposed on a substrate wherein said bristles effectively and adhesively engage a polymeric film or fibrous web on the opposite surface. In another embodiment, an absorbent article has a gecko closure comprising a substrate, a plurality of bonded bristles rising from the substrate, the bristles having a root segment, a middle segment and a tip segment, and having a height of about 0.5 μm to About 8 mm, with a diameter greater than about 0.05 μm.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Optical head capable of providing a subwavelength beams
The present invention provides an optical head with a single or multiple sub-wavelength light beams, which can be used in arenas such as photolithography, optical storage, optical microscopy, to name a few. The present invention includes a transparent substrate, a thin film, and a surface structure with sub-wavelength surface profile. The incident light transmits through the transparent substrate, forms a surface plasma wave along the sub-wavelength aperture located within the thin film, and finally re-emits through spatial coupling with the sub-wavelength profile of the surface structure. As the coupled re-emitting light beam or light beams can maintain the waist less than that of the diffraction limit for a few micrometers out of the surface with sub-wavelength profile in many cases, this invention can have applications ranging from micro or nano manufacturing, metrology, and manipulation by using light beams with waist smaller than the diffraction limit.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Field-assisted micro- and nano-fabrication method
InactiveUS20050112505A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanolithographyMolecular electronics
A direct-write micro- or nano-lithography method for depositing a functional material with a preferred orientation onto a target surface. The method includes the steps of (1) forming a precursor fluid to the functional material; (2) operating a sub-micrometer tip to discharge, on contact, the precursor fluid onto the target surface so as to produce a desired pattern of deposited functional material in sub-micrometer dimensions; and (3) during the pattern-producing step, subjecting the deposited material to a highly localized electric or magnetic field for attaining a preferred orientation in at least a portion of the functional material. The method is particularly useful for microfabrication, nanotechnology, and molecular electronics.
Owner:HUANG WEN C +1
Micro/nano-fabricated glucose sensors using single-walled carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7118881B2Strong specificityEasy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHydrogenGlucose sensors
A novel glucose sensor utilizing hydrogen-specific gas sensing capability of single walled carbon nanotubes assembled on microelectrodes. Highly specific glucose sensing was demonstrated using buffered sample solutions with clinically significant concentrations. The approach enables a simple but powerful bio-sensor reliably operating with a completely new principle, and opens up novel device applications where functional nano-components can be integrated into a bioMEMS device.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Large-stroke column coordinate two-photon polymerization processing method and device
InactiveCN104028890AHigh precisionGuaranteed accuracyLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a large-stroke column coordinate two-photon polymerization processing method and device and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano manufacturing. The method includes that a test piece is mounted on a C shaft turntable in a coaxial or abaxial manner, the C shaft turntable is in rotary motion around the z axis to enable femtosecond laser beams to be in circumferential motion relatively to the test piece, a C shaft is mounted on the x-axis sliding plate and is in linear feeding motion along the x-axis direction to enable the femtosecond laser beams to be in radial motion relatively to the test piece, the femtosecond laser beams are enabled to be in quick reciprocating motion along the radial direction of the C shaft turntable through swinging of a two-dimensional galvanometer around the x axis and the Y axis, feeding motion of a focusing center of the femtosecond laser beams along the z-axis direction is acquired through translational motion of a z-axis sliding plate along the z-axis direction, and when the test piece is mounted in the abaxial manner, rotating speed of the C shaft turntable can be changed in real time to enable the femtosecond laser beams to acquire a same speed at each expected scanning position. By the large-stroke column coordinate two-photon polymerization processing method and device, back-off of a moving shaft is avoided, disturbed paths can be tracked quickly and precisely, and quick processing of large-area three-dimensional micro-nano structures is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Impressing hard template in nanostructure
The invention relates to an impressing hard template in a nanostructure, which belongs to the field of nano manufacturing and is characterized in that a porous template with a hard material substrate is prepared by the porous AAO (anodic aluminum oxide) membrane technology and can be directly used as an impressing (from top to bottom) template after the hard substrate is added and the surface modification treatment is carried out. A porous AAO membrane can self-organize and grow into an ordered six-site symmetrical porous structure, and steep holes are uniformly distributed. When the porous AAO membrane is used as the template, various nanostructures and devices with optical, electrical and magnetic properties can be prepared by a processing method of directional assembling from bottom to top such as thermal evaporation, sputtering, deposition and electrochemical assembling. As the hard material substrate is added and the surface modification treatment is carried out, the AAO template technology is transplanted into the field of top-to-bottom surface micro-structure processing. Compared with the present technical method of the common electron beam direct writing, the manufacturing method for the impressing hard template with a nano-grade high-density structure not only has the obvious characteristics of low cost, short period and simple processing, but also can be widely used in the processing as well as researching of the nano-grade high-density surface nanostructure and particularly has broad prospects in the fields of semiconductor lighting and high-density storage. Meanwhile, as the hard substrate is increased, the shortcomings of the present brittle and fragile AAO template are overcome, thereby being more beneficial for duplication of the soft template.
Owner:SHANGHAI NANOTECH PROMOTION CENT +1
Plasma nano-structure assisted femtosecond laser nano-manufacturing method and system
InactiveCN109848565AEnhanced near-field damage effectWide range of machinable materialsLaser beam welding apparatusOptical diffractionNano structuring
The invention provides a plasma nano-structure assisted femtosecond laser nano-manufacturing method and system and belongs to the field of laser micronano-structure processing. Through the plasma nano-structure assisted femtosecond laser nano-manufacturing method and system, the problems that the optical diffraction limit is hard to break through during conventional laser precision machining, a hard and brittle material is hard to machine, the requirements for the machining environment are high, the cost is high and machining is hard to implement in the air environment are solved. According tothe method, through LSPR enhancement of a plasma nano-structure is motivated through femtosecond laser to generate a space height localized patterning optical near field beyond the optical diffraction limit on the surface of the material to be machined, and the material is subjected to area arrayed and patterned ultrahigh resolution nano-machining. Through the method, the limitation of the optical diffraction limit of a traditional machining method can broken through, and wide-range and high-precision parallel machining is realized. The method has the characteristics that the range of the machining material is wide, free special machining is realized, the cost is low, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Resolution testing standard board manufacturing method for super-resolution fluorescence microscope system
ActiveCN103712965AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldLuminous stabilityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusManufacturing technologyImage resolution
The invention discloses a resolution testing standard board manufacturing method for a super-resolution fluorescence microscope system. A nano-manufacturing technology and a nanoparticle self-assembling technology are used for manufacturing a fluorescent quantum dot line with a width of 20 to 100nm as a fluorescent super-resolution standard board. At present, a main means for detecting the resolution of a super-resolution fluorescence microscope is fluorescent nanospheres, but is very complex. The manufacturing method is simple and reliable, excellent fluorescent characteristics are ensured, and the manufactured super-resolution standard board can be directly used for testing the super-resolution fluorescence microscope system.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Hybrid buried/ridge planar waveguides
InactiveUS7006744B2Increase the use of spaceEasy to integrateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive index contrastSemiconductor structure
A hybrid waveguide structure having a combination of buried waveguide sections and ridge waveguide sections on the same substrate, share a common core layer. The buried waveguide sections provide the low index contrast desirable for couplers and other device components. The ridge waveguide sections provide the high index contrast needed for efficient low-loss tightly curved waveguides. The devices are fabricated starting from a low index contrast buried waveguide. Cladding material is then selectively removed by etching down from an upper surface either side of the waveguide core to a lower surface. This forms an enhanced index contrast ridge section of the waveguide. The other sections of the waveguide core remain buried and thus retain lower index contrast. Using this approach, a variety of optical devices, such as add / drop or add-after-drop multiplexers for WDM applications based on microrings or Mach-Zehnder interferometers, can be made with large feature sizes of several microns using silica-on-glass or silica-on-silicon technology, for example, and without having to use nanofabricated semiconductor structures.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Inorganic resist material and nano-fabrication method by utilizing the same
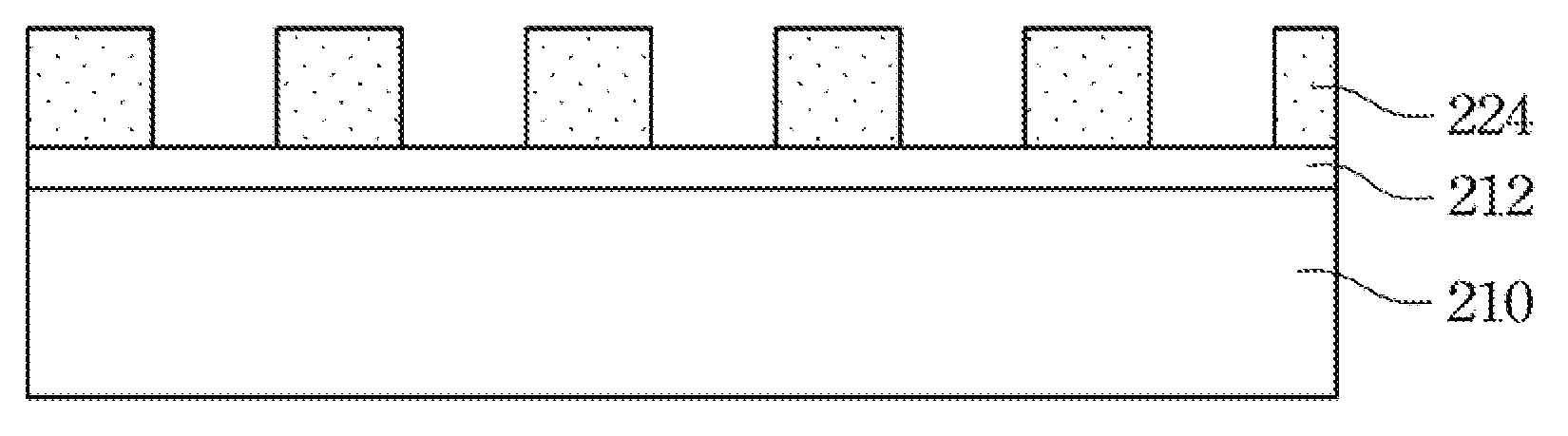
InactiveUS7465530B1Small sizePhotosensitive materialsNanoinformaticsLithography processNano manufacturing
An inorganic resist material is provided, which is an incomplete oxide of a phase-change material. The oxygen content in the inorganic resist material is lower than the stoichiometric oxygen content of a complete oxide of the phase-change material, and a general formula of the inorganic resist material is A1-xOx, in which A represents the phase-change material, and x is between 5 at. % and 65 at. %. The inorganic resist material can be used to form line patterns or recording pits with size smaller than the exposure light spot by using the laser of conventional lithography process as an exposure source.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
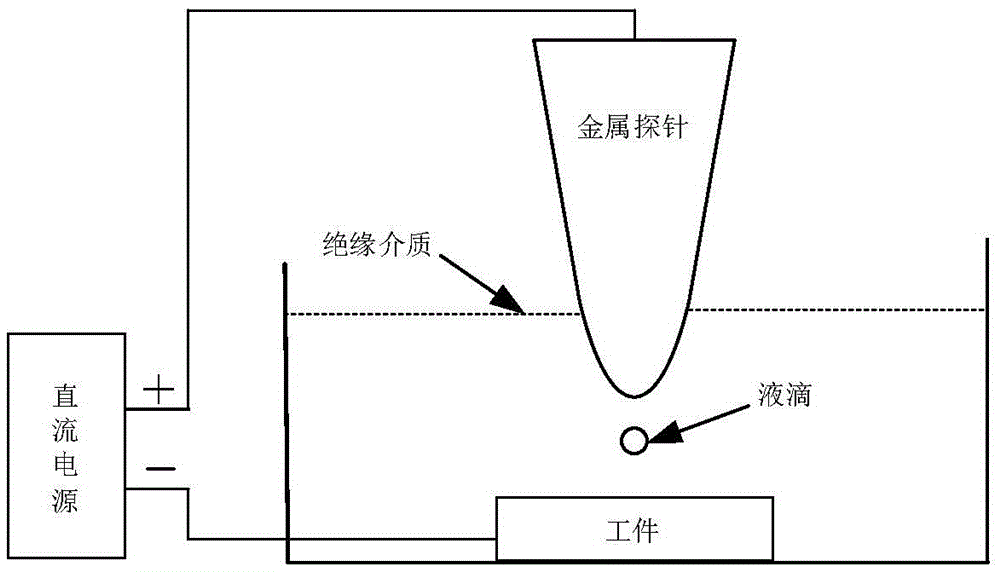
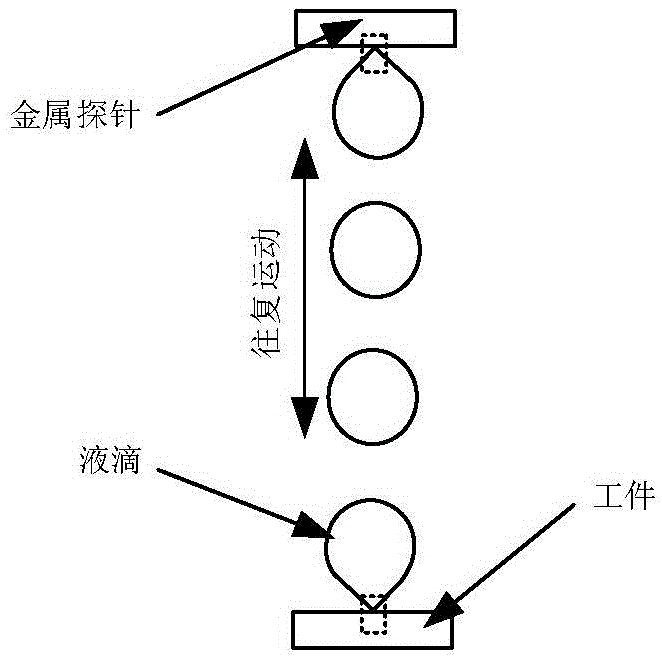
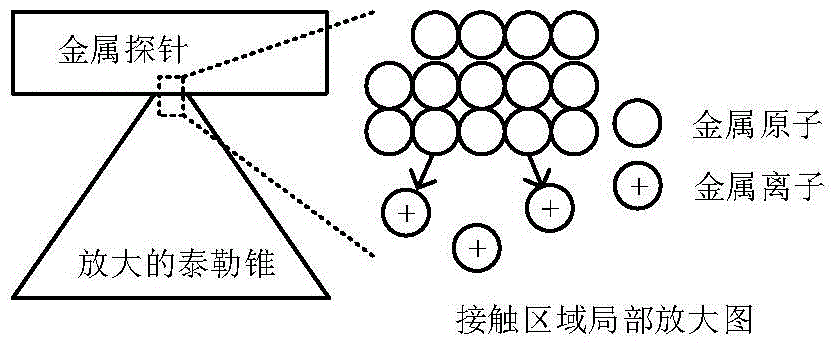
Micro-nano electrochemical deposition machining method based on liquid drop Taylor cone
ActiveCN105420763AAchieving Atomic-Level Deposition ProcessingEnables deposition processingElectroforming nanostructures3D structure electroformingMicro nanoManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a micro-nano electrochemical deposition machining method based on a liquid drop Taylor cone, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano manufacturing. The method comprises the steps that liquid drops containing deposited metal ions are firstly put between a metal probe and a workpiece, and the materials of the probe are deposited materials; the probe and the workpiece are both immersed in an insulating medium, and the insulating medium and water are not compatible; the probe and the workpiece are connected with the positive pole and the negative pole of a direct-current power source respectively; the liquid drops do reciprocating motion between the probe and the workpiece under the action of an electric field; and when the liquid drops are close to the probe and the workpiece, the Taylor cone is formed on the surfaces of the liquid drops under the action of the electric field, by means of the electrochemical action generated during contact of the liquid drop Taylor cone, the probe and the workpiece, metal atoms of the metal probe are changed into metal cations to enter the liquid drops, then the metal cations are carried by the liquid drops to the surface of the workpiece and conveyed to the surface of the workpiece through the liquid drop Taylor cone, the metal cations obtain electrons on the surface of the workpiece to be changed into atoms to be deposited, and therefore micro-nano electrochemical deposition machining is achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Nanoscale size structure measuring method and device
ActiveCN101799273AQuick extractionQuick measurementUsing optical meansMicro imagingManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a nanoscale size structure measuring method and a device, which can simultaneously measure parameters, such as nanoscale size structure width, depth, side corner and the like. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: vertically projecting a white light beam to the surface of a sample workpiece with a nanoscale size structure after filtering and polarizing; collecting the surface reflected signal of the sample workpiece; calculating to obtain a nanoscale size structure microscope imaging picture; matching a measured outoffocus scanning imaging allocation plan with a theory outoffocus scanning imaging allocation plan; and extracting to obtain the geometric parameter value of the nanoscale size structure is to be measured. The nanoscale size structure measuring device provided by the invention can provide a non-contact, non-destructive, low-cost and quick measuring means for various typical nanoscale size structures, such as isolated line array structure and intensive line array structure to which the lot sizing manufacturing technology relates, and the lot sizing manufacturing technology comprises the nanometer manufacturing technology, such as traditional photoetching, nano-imprint and the like based on imaging transfer.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for imprinting and erasing amorphous metal alloys
ActiveUS8641839B2Surface roughnessLayered productsMechanical recordingMicron scaleTransfer procedure
The present invention relates to materials, methods and apparatuses for performing imprint lithography using amorphous metallic materials. The amorphous metallic materials can be employed as imprint media and thermoplastic forming processes are applied during the pattern transfer procedure to produce micron scale and nanoscale patterns in the amorphous metallic layer. The pattern transfer is in the form of direct mask embossing or through a serial nano-indentation process. A rewriting process is also disclosed, which involves an erasing mechanism that is accomplished by means of a second thermoplastic forming process. The amorphous metallic materials may also be used directly as an embossing mold in imprint lithography to allow high volume imprint nano-manufacturing. This invention also comprises of a method of smoothening surfaces under the action of the surface tension alone.
Owner:YALE UNIV
High-efficiency spectral purity filter for EUV lithography
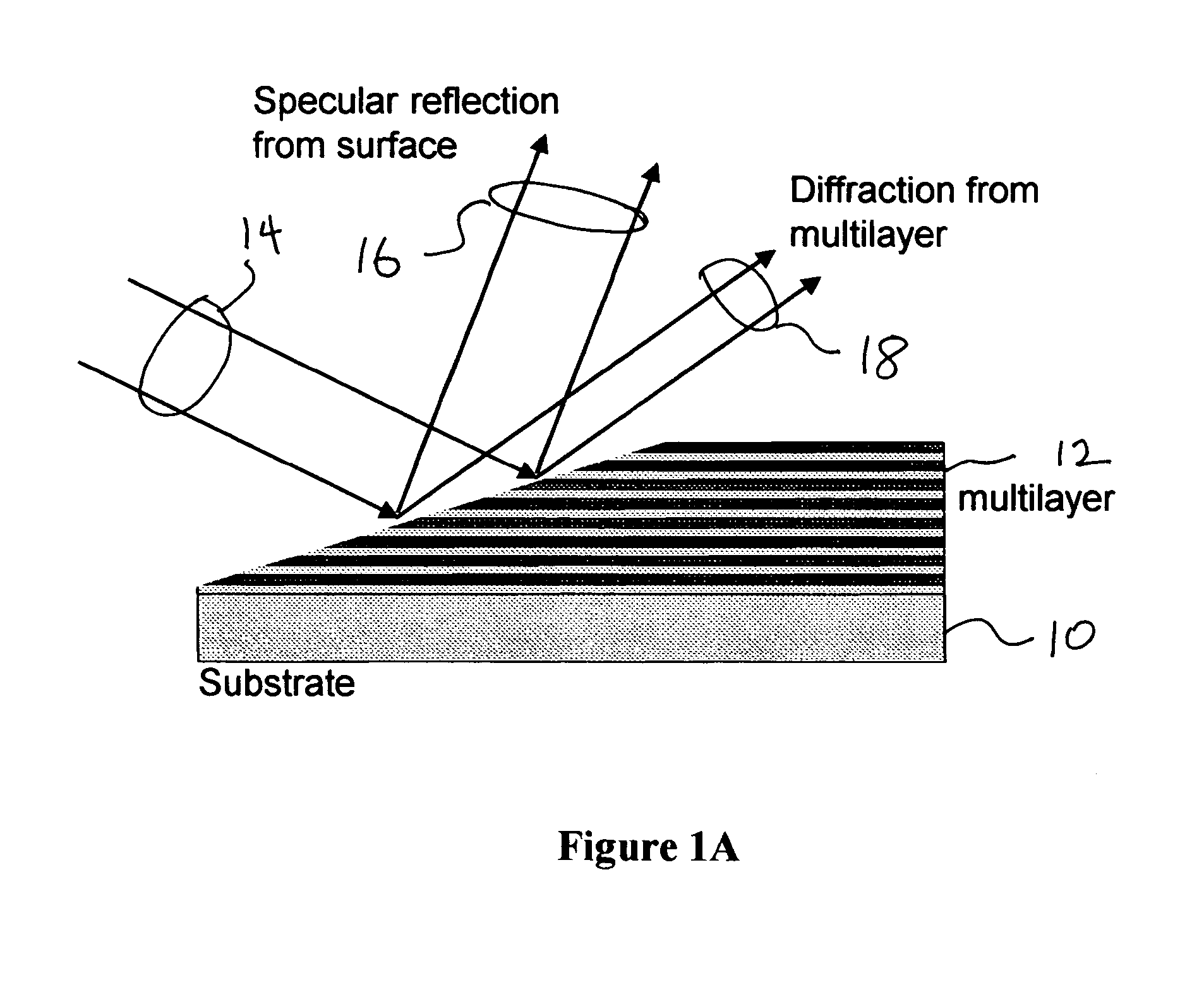
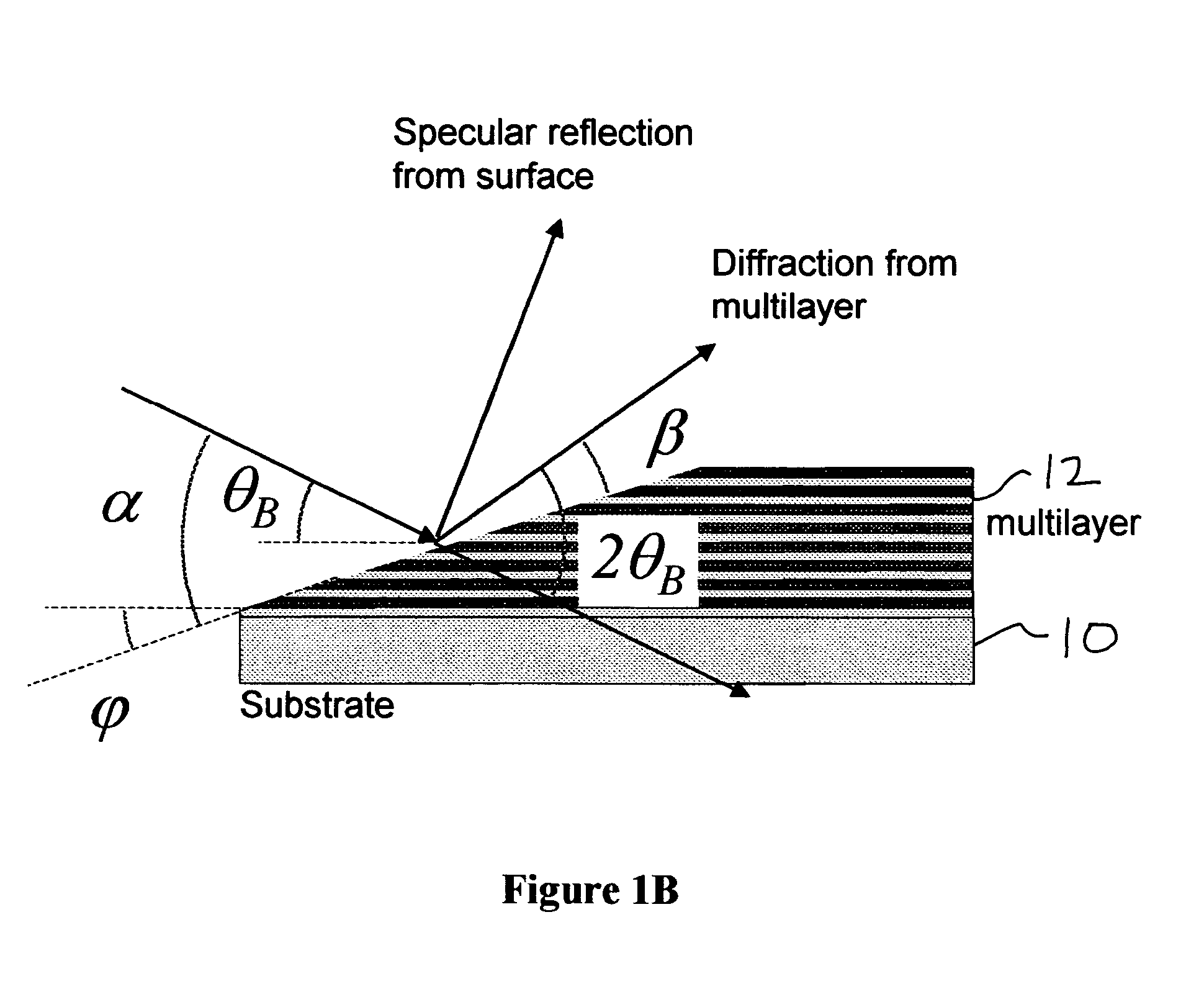
InactiveUS20060087738A1Simple and inexpensiveImprove efficiencyMirrorsNanoinformaticsLithographic artistBlazed grating
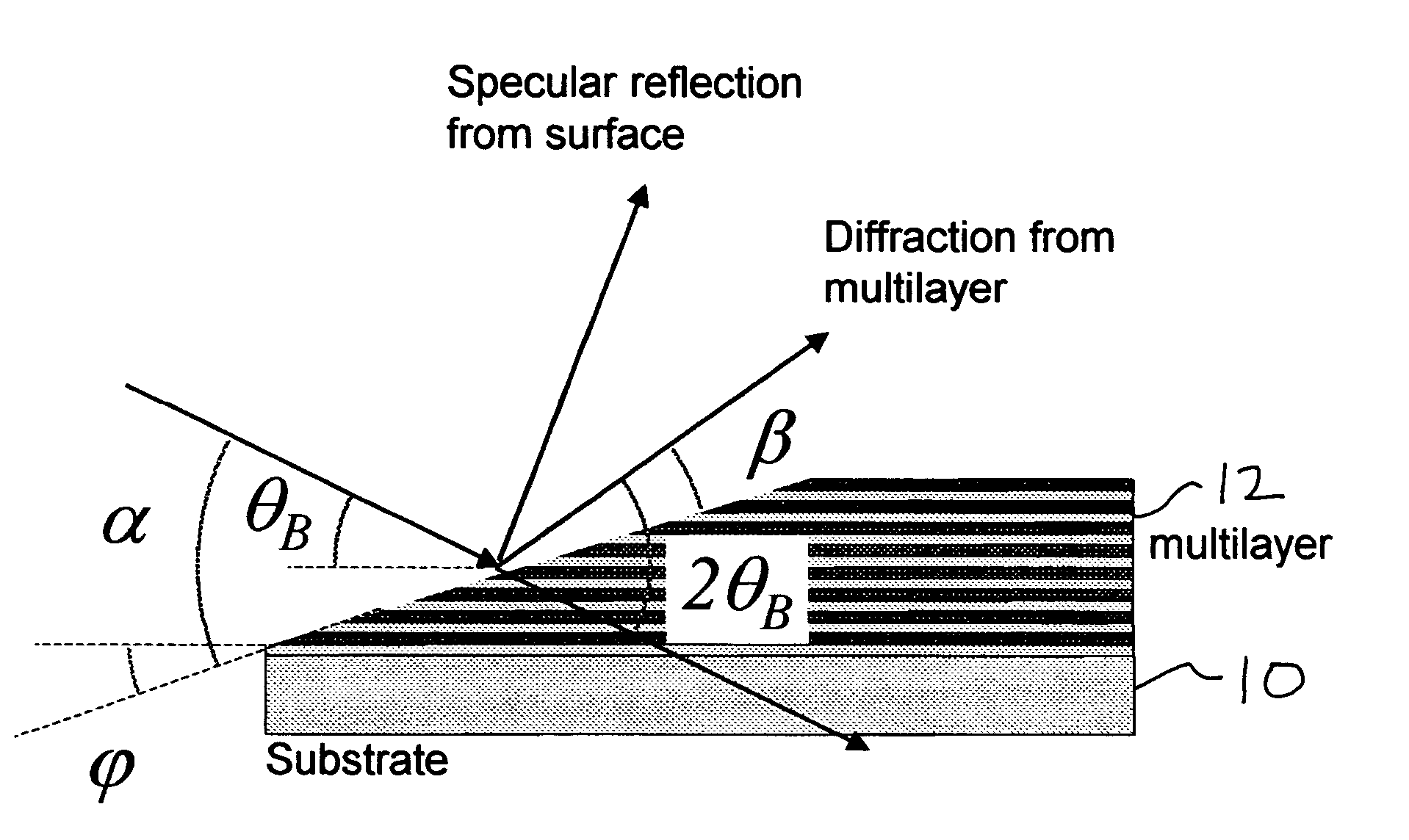
An asymmetric-cut multilayer diffracts EUV light. A multilayer cut at an angle has the same properties as a blazed grating, and has been demonstrated to have near-perfect performance. Instead of having to nano-fabricate a grating structure with imperfections no greater than several tens of nanometers, a thick multilayer is grown on a substrate and then cut at an inclined angle using coarse and inexpensive methods. Effective grating periods can be produced this way that are 10 to 100 times smaller than those produced today, and the diffraction efficiency of these asymmetric multilayers is higher than conventional gratings. Besides their ease of manufacture, the use of an asymmetric multilayer as a spectral purity filter does not require that the design of an EUV optical system be modified in any way, unlike the proposed use of blazed gratings for such systems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Two-dimensional Planar photonic crystal superprism device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080112669A1Shorten the timeSimple processPrismsNanoopticsManufacturing technologyEngineering
Provided are a two-dimensional planar photonic crystal superprism device and a method of manufacturing the same, in which a manufacturing process is simplified using a nanoimprint lithography technique, and thus price-reduction and mass production are facilitated. The two-dimensional planar photonic crystal superprism device includes: a single-mode input waveguide comprising a straight waveguide having a taper structure and a bending waveguide; a superprism formed on an output end side of the single-mode input waveguide and comprising a slab and a photonic crystal superprism; and a single-mode output waveguide comprising a straight waveguide having a taper structure and a bending waveguide, and formed adjacent to the photonic crystal superprism. Using the two-dimensional planar photonic crystal superprism device, it is possible to facilitate manufacturing of nano-photonic integrated circuits, photonic crystal integrated circuits and nano-photonic systems. In addition, a wavelength-selectable photonic crystal superprism device using high dispersion of photonic crystal, which is several hundred times the dispersion of conventional glass prism, can be manufactured using thermal / hot and ultraviolet nanoimprint lithography techniques corresponding to nano-manufacturing technology.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Near field raman imaging
ActiveUS8599489B2High resolutionFast and accurate calculationNanoopticsMicroscopesRaman imagingBio molecules
A tunable super-lens (TSL) for nanoscale optical sensing and imaging of bio-molecules and nano-manufacturing utilizes negative-index materials (NIMs) that operate in the visible or near infrared light. The NIMs can create a lens that will perform sub-wavelength imaging, enhanced resolution imaging, or flat lens imaging. This new TSL covers two different operation scales. For short distances between the object and its image, a near-field super-lens (NFSL) can create or enhance images of objects located at distances much less than the wavelength of light. For the far-zone, negative values are necessary for both the permittivity ∈ a permeability μ. While well-structured periodic meta-materials, which require delicate design and precise fabrication, can be used, metal-dielectric composites are also candidates for NIMs in the optical range. The negative-refraction in the composite films can be made by using frequency-selective photomodification.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Nano-fabrication method
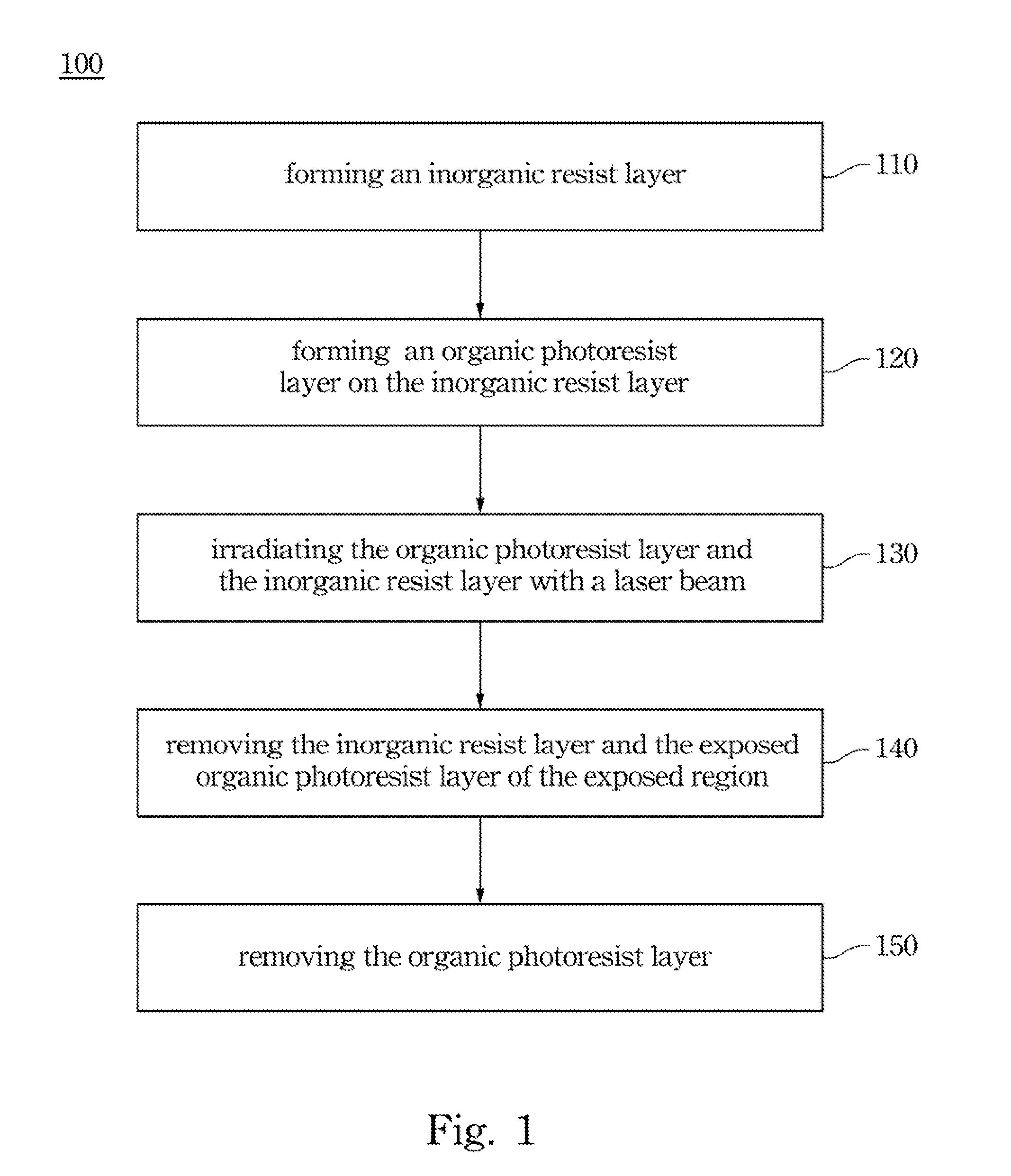
Disclosed herein is a nano-fabrication method, which includes the step of: (a) forming an inorganic resist layer on a substrate; (b) forming an organic photoresist layer on the inorganic resist layer; (c) irradiating both the organic photoresist layer and the inorganic resist layer with a laser beam to form a first exposed region of the inorganic resist layer and a second exposed region of the organic photoresist layer; (d) removing the inorganic resist layer of the first exposed region and the organic photoresist layer of the second exposed region to form a patterned inorganic resist layer and a patterned organic photoresist layer; and (e) removing the patterned organic photoresist layer from the patterned inorganic resist layer.
Owner:RYTEC CORP
Deposition-free sealing for Micro- and Nano-fabrication
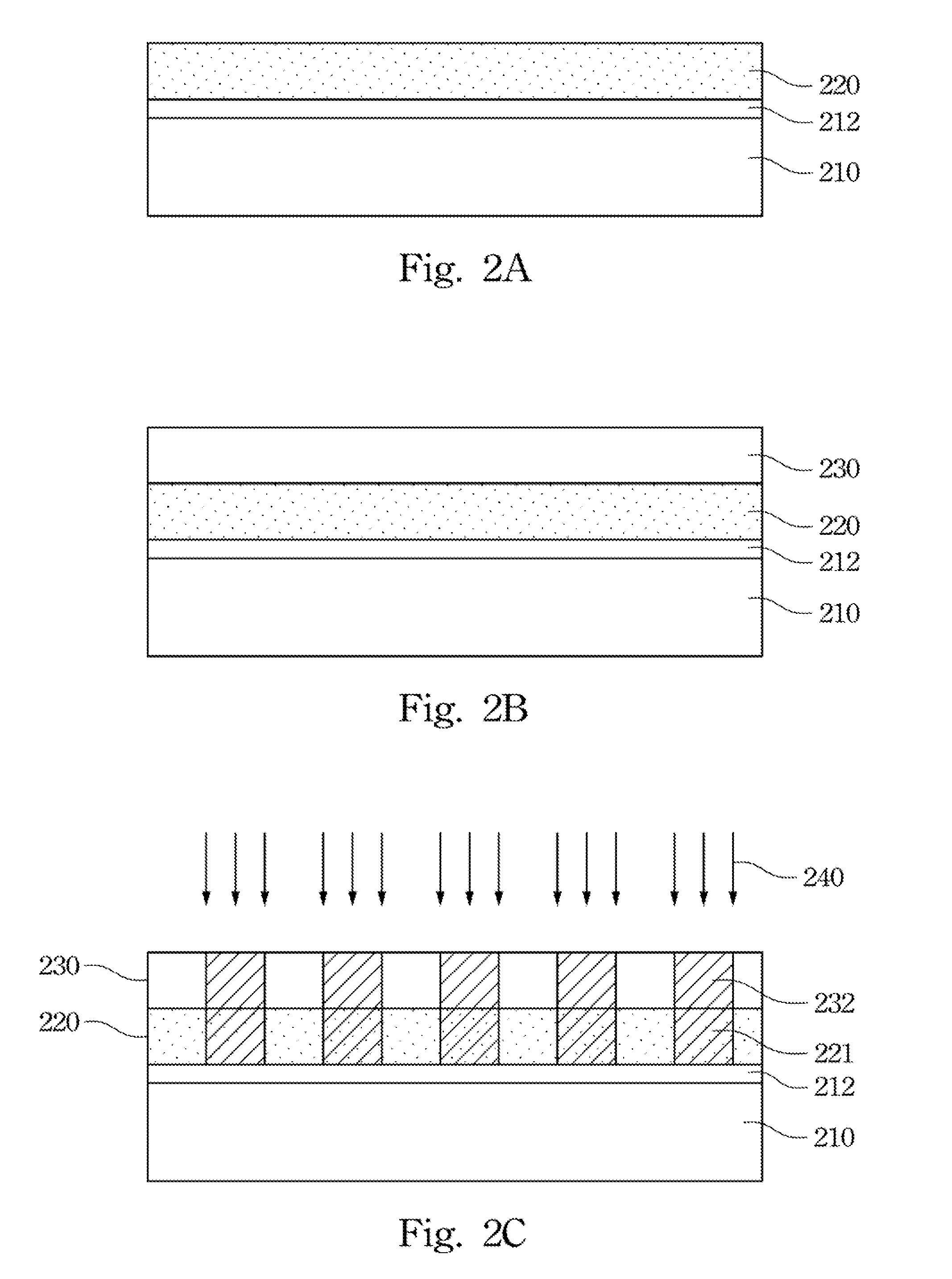
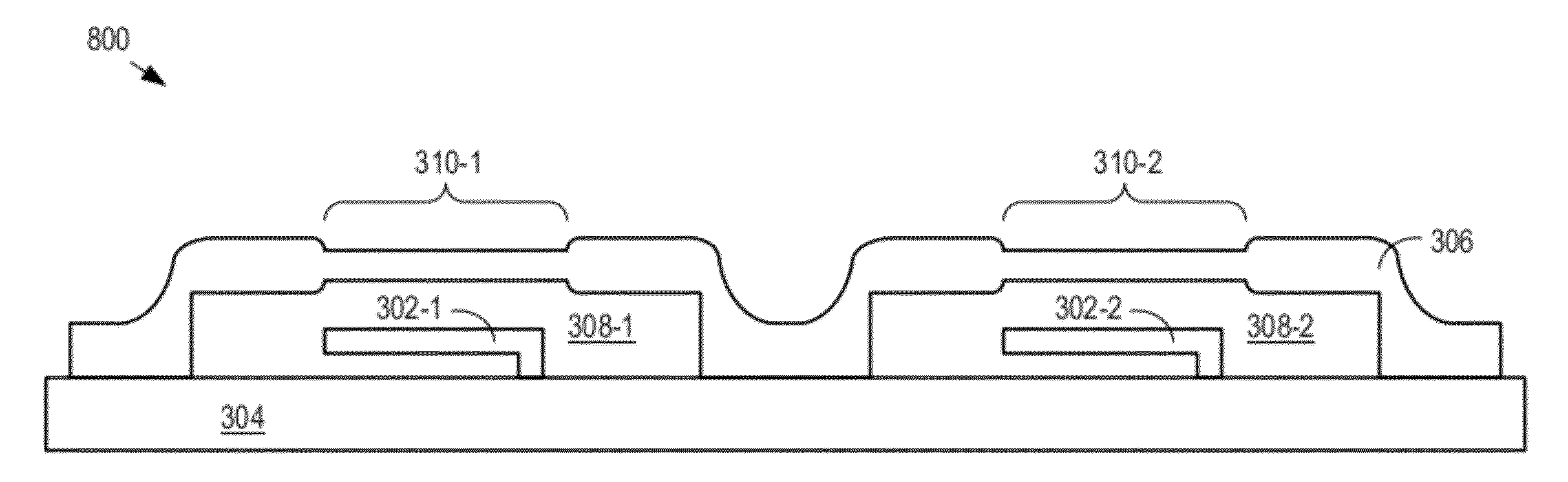
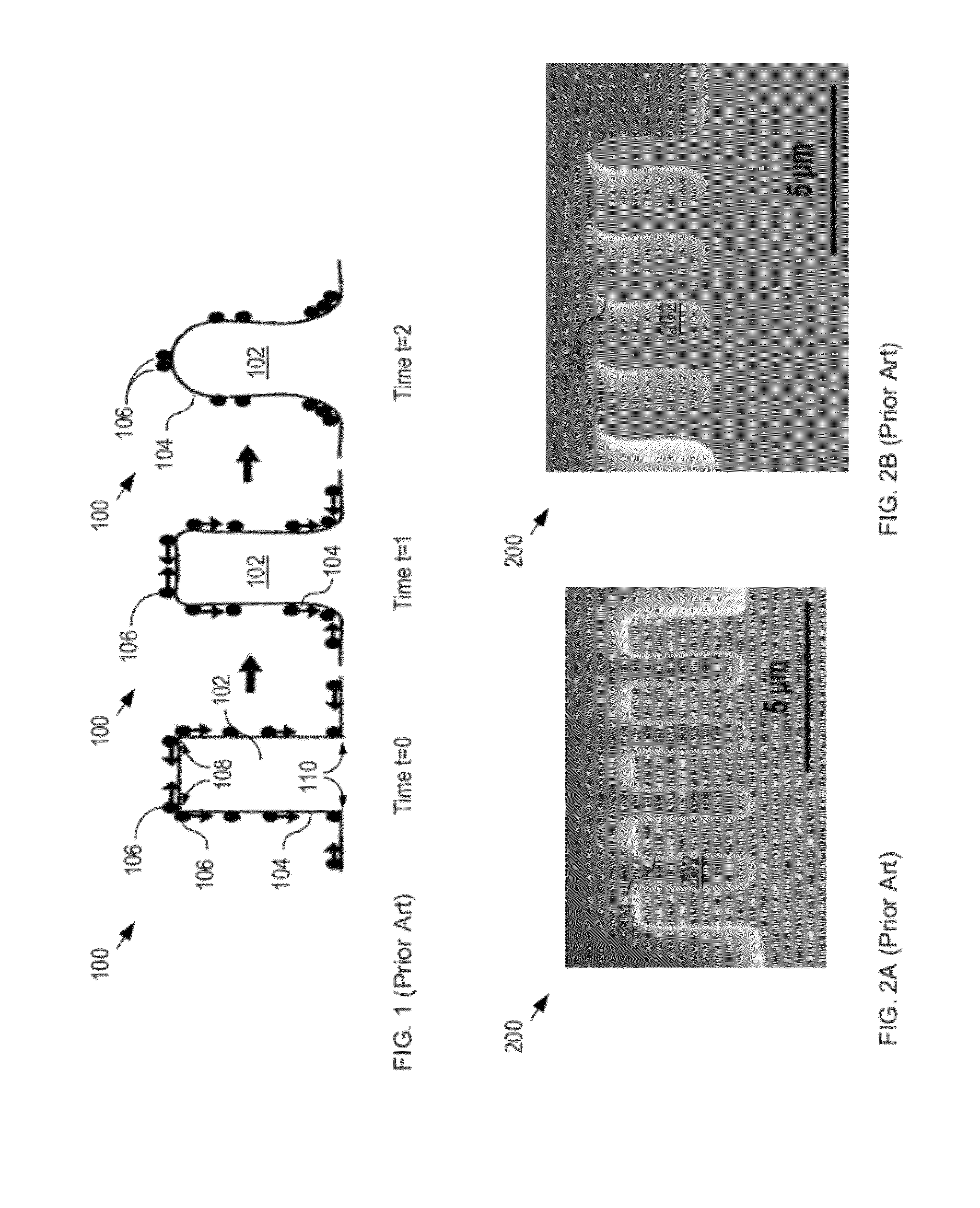
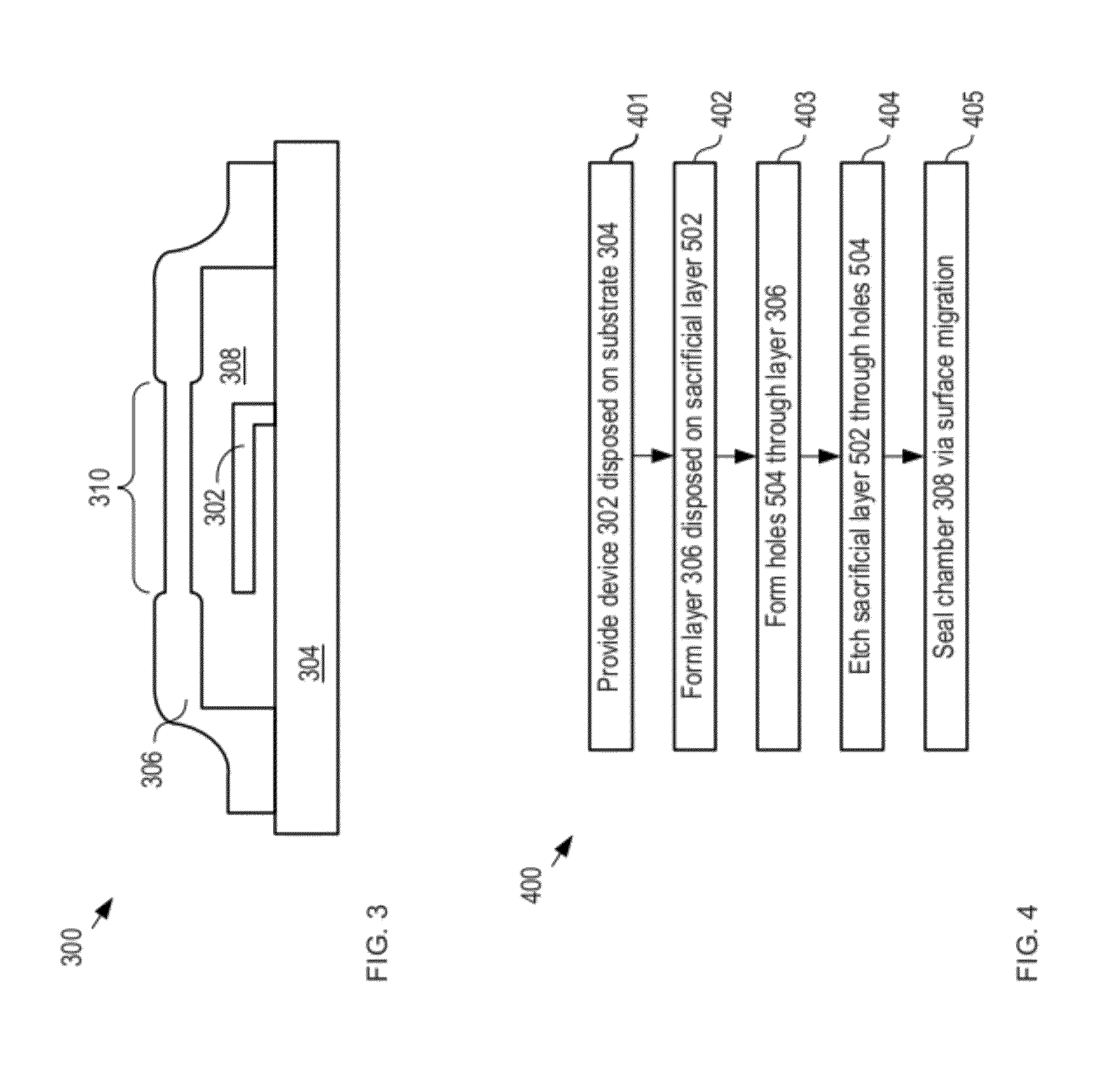
InactiveUS20120104589A1Lower average energyIncrease surface potentialSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNano manufacturingSealant
A method for sealing through-holes in a material via material diffusion, without the deposition of a sealant material, is disclosed. The method is well suited to the fabrication and packaging of microsystems technology-based devices and systems. In some embodiments, the method comprises forming sacrificial material release through-holes through a structural layer, removing the sacrificial material via an etch that etches the sacrificial material through the release through-holes, and sealing of the release through-holes via material diffusion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
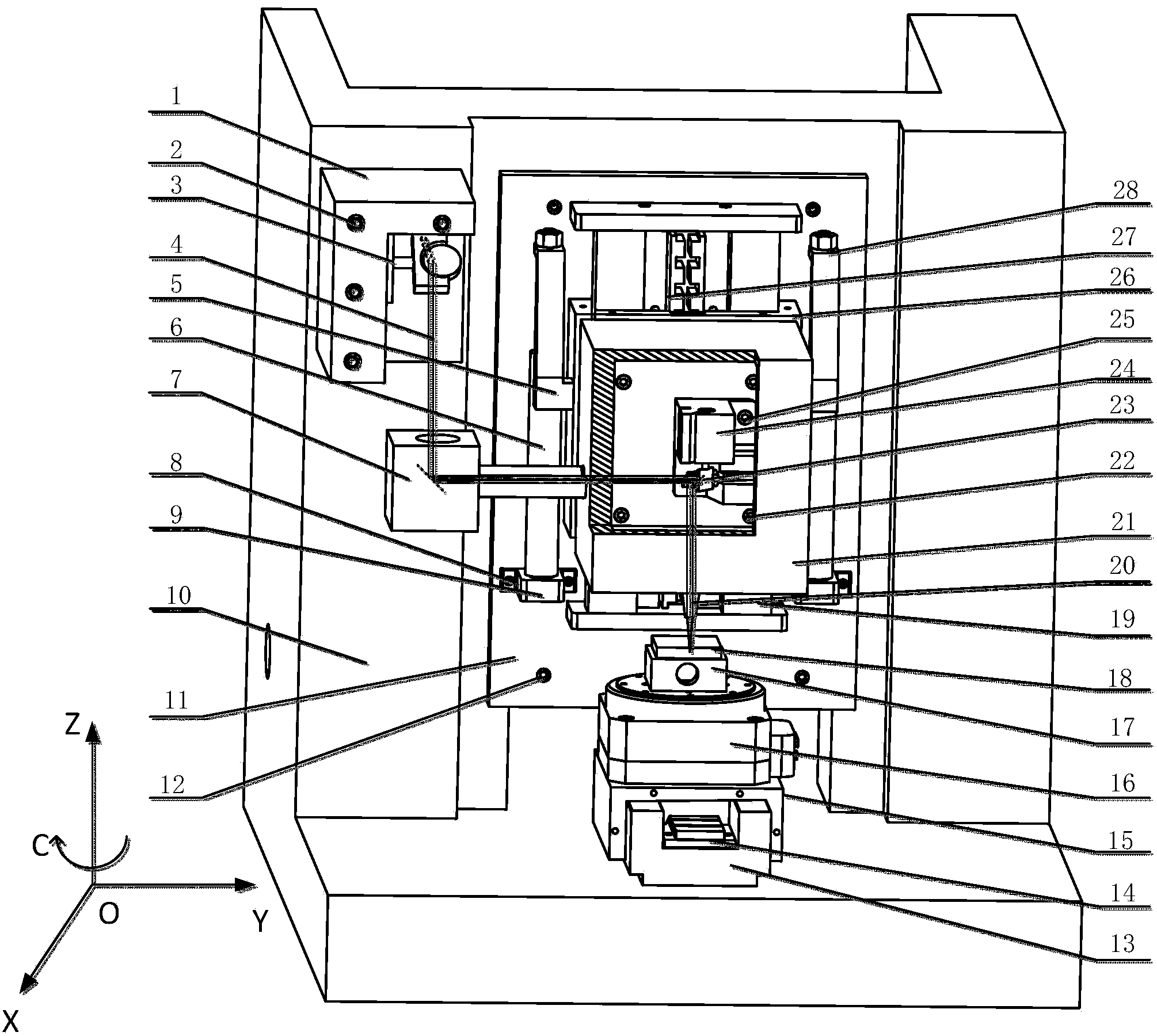
Preparation method of nano-imprint template in vector type AFM (atomic force microscopy) nano processing system
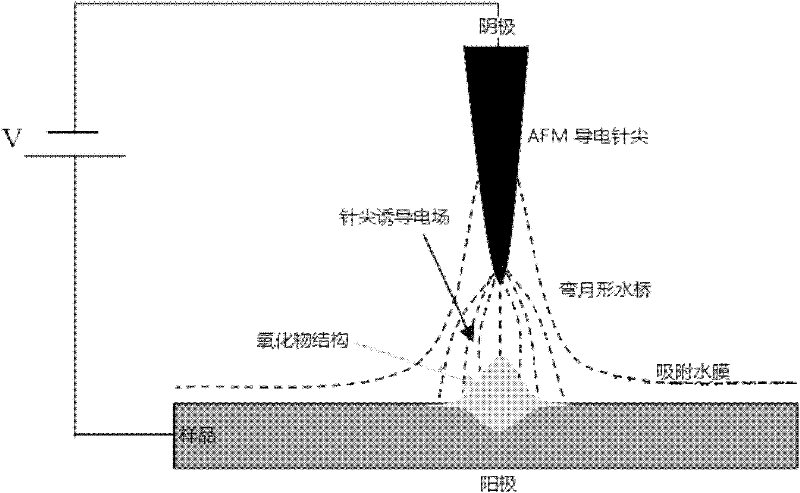
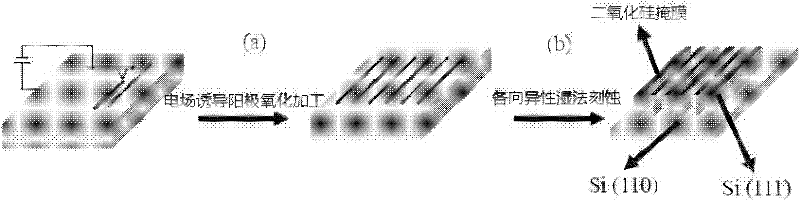
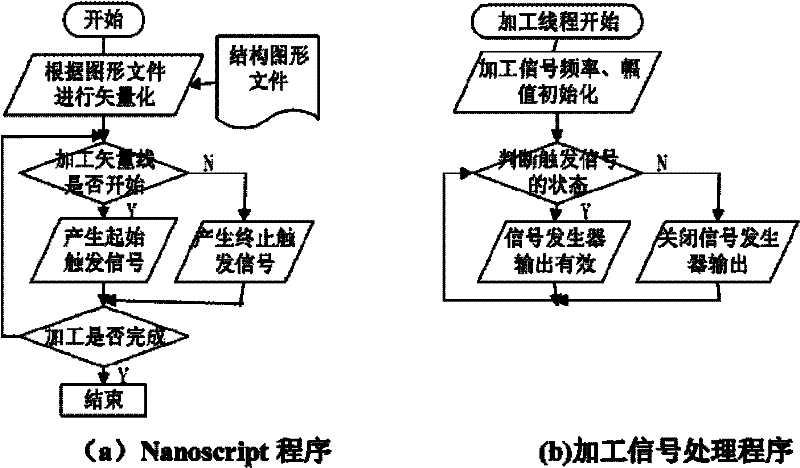
InactiveCN102303840AImprove machining accuracySmall processing scaleDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingAtomic force microscopyNano manufacturing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano-imprint template in a vector type AFM (atomic force microscopy) nano processing system, and belongs to the technical field of nano manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps that: the vectorization programming is performed on a required nano structure to obtain a macro document to be processed to control the movement of a pinpoint; the AFM enters an imaging mode scanning state, then begins scanning a sample surface, enters a script program mode after the scanning procedure is stable and a stable scanning image with good repeatability is obtained, invokes and imports the macro document (to be processed) obtained in the third step to a processing system to process; and the AFM enters a real-time imaging mode after the processing is finished, scans again to obtain a surface topography structure image of a processed structure, and finally uses a prepared nano pattern structure as a mask to transfer the nano structure image prepared by the anodic oxidation induced by an AFM electric field by combining with a high-selectivity anisotropism wet etching technology so as to manufacture the nano structure template.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com