Patents
Literature
105 results about "Metatarsophalangeal joints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
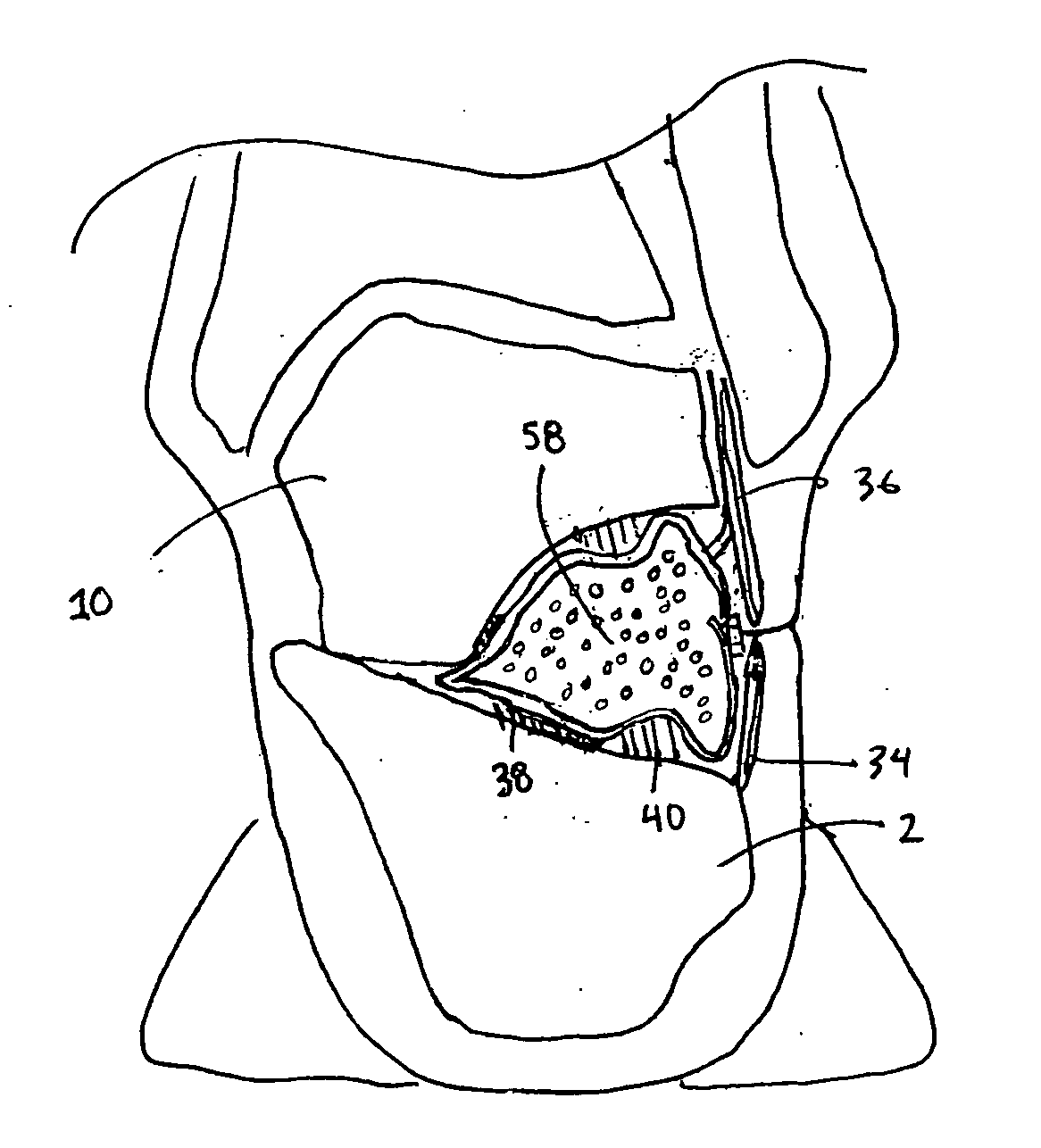
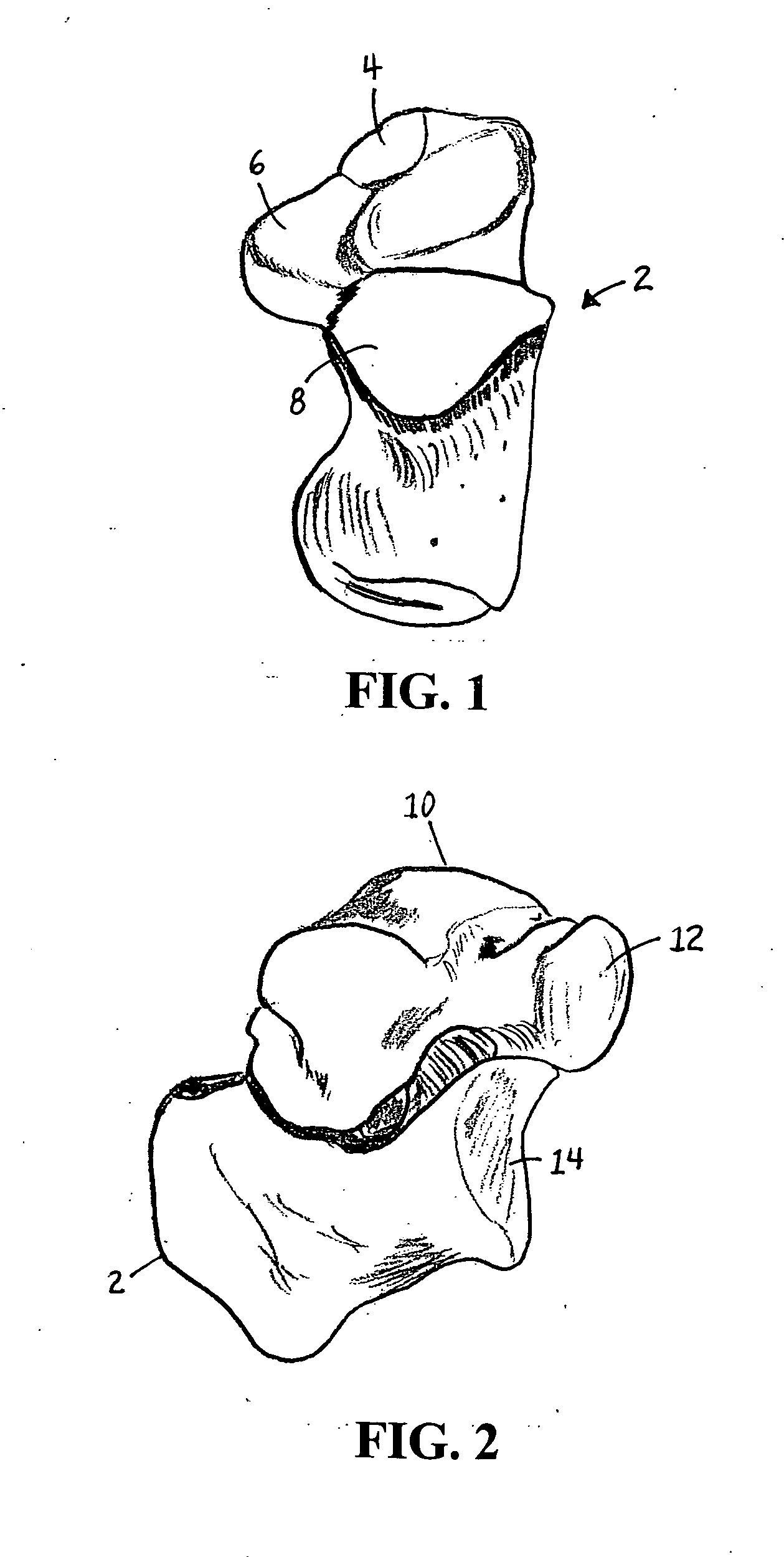
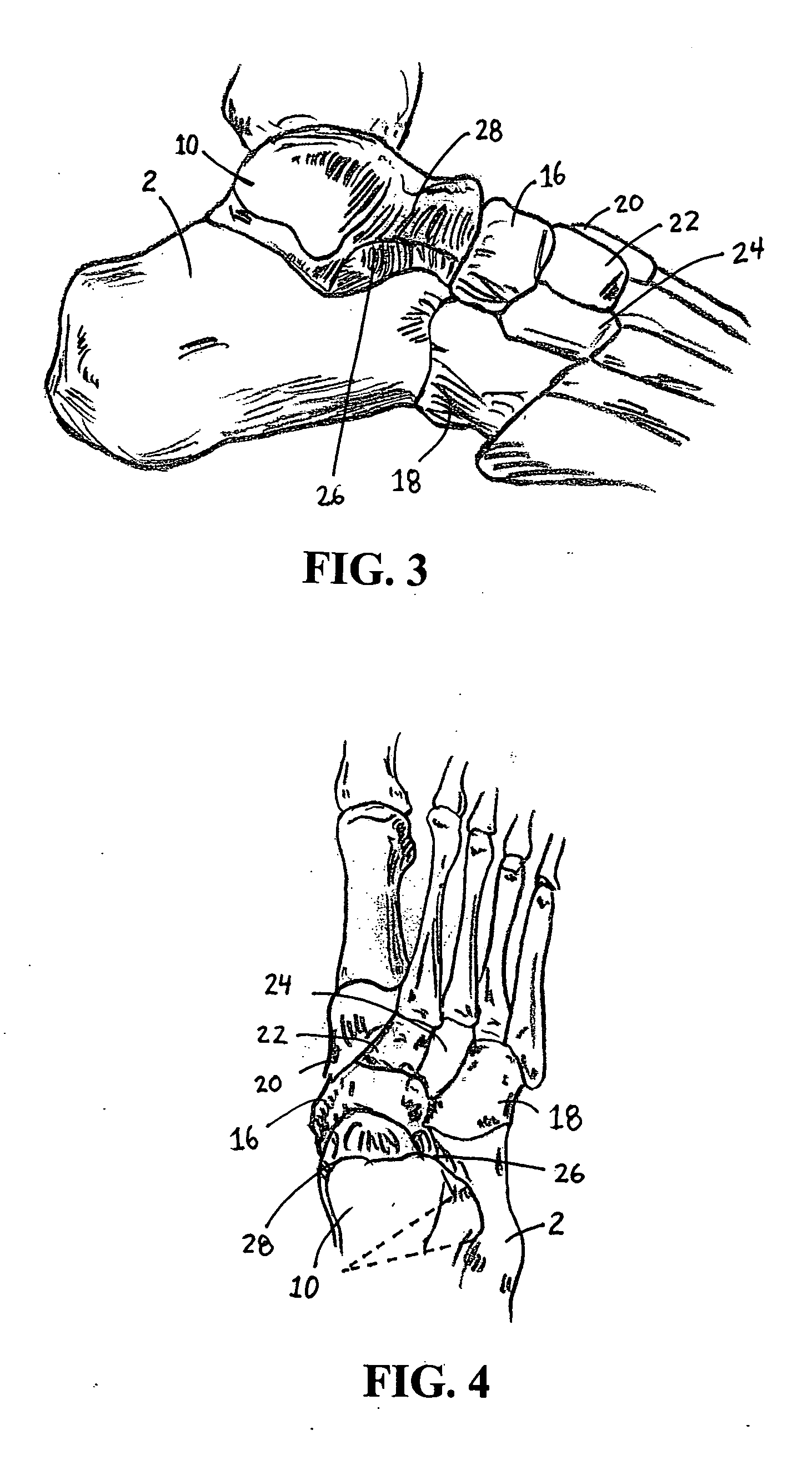
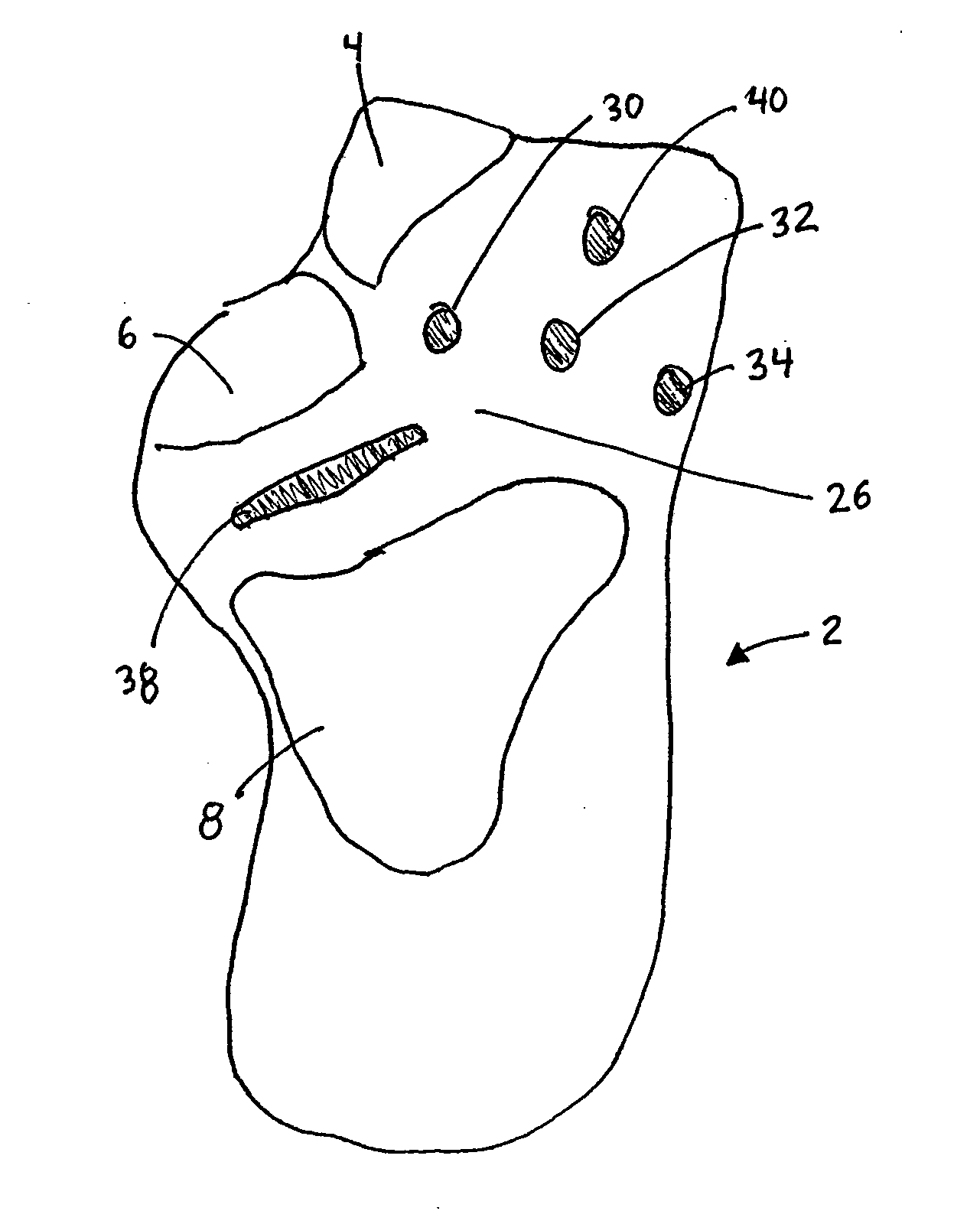
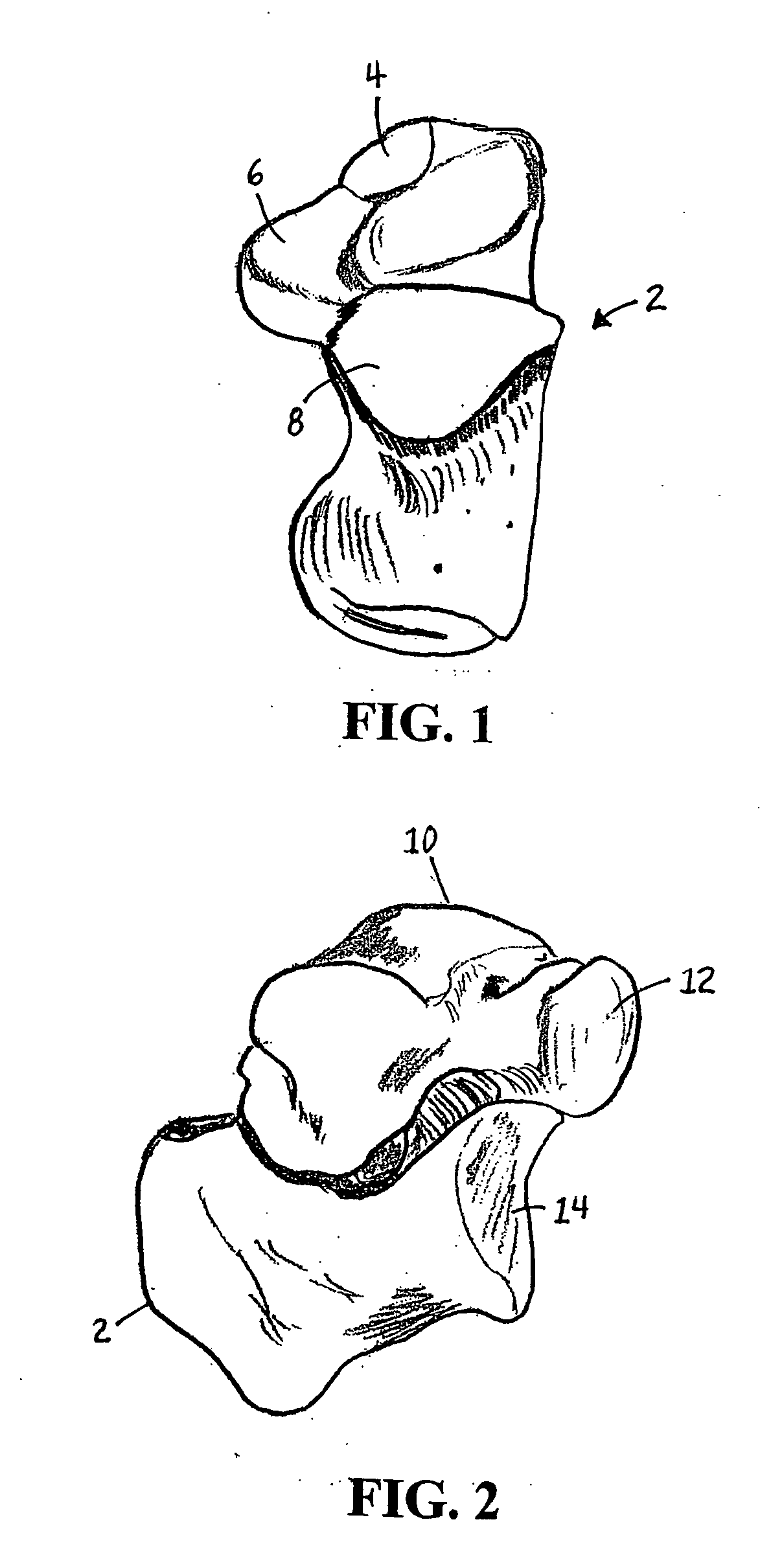
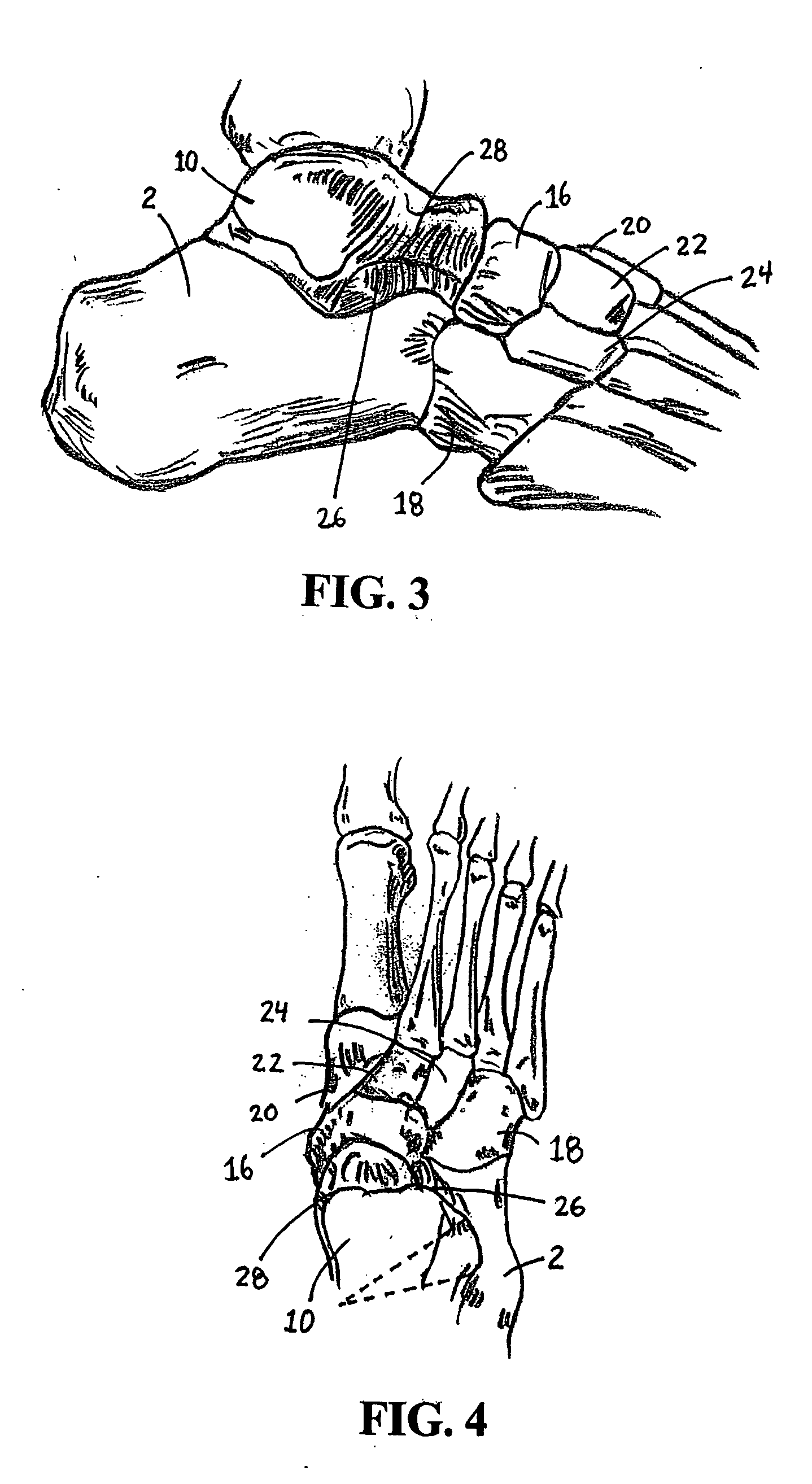
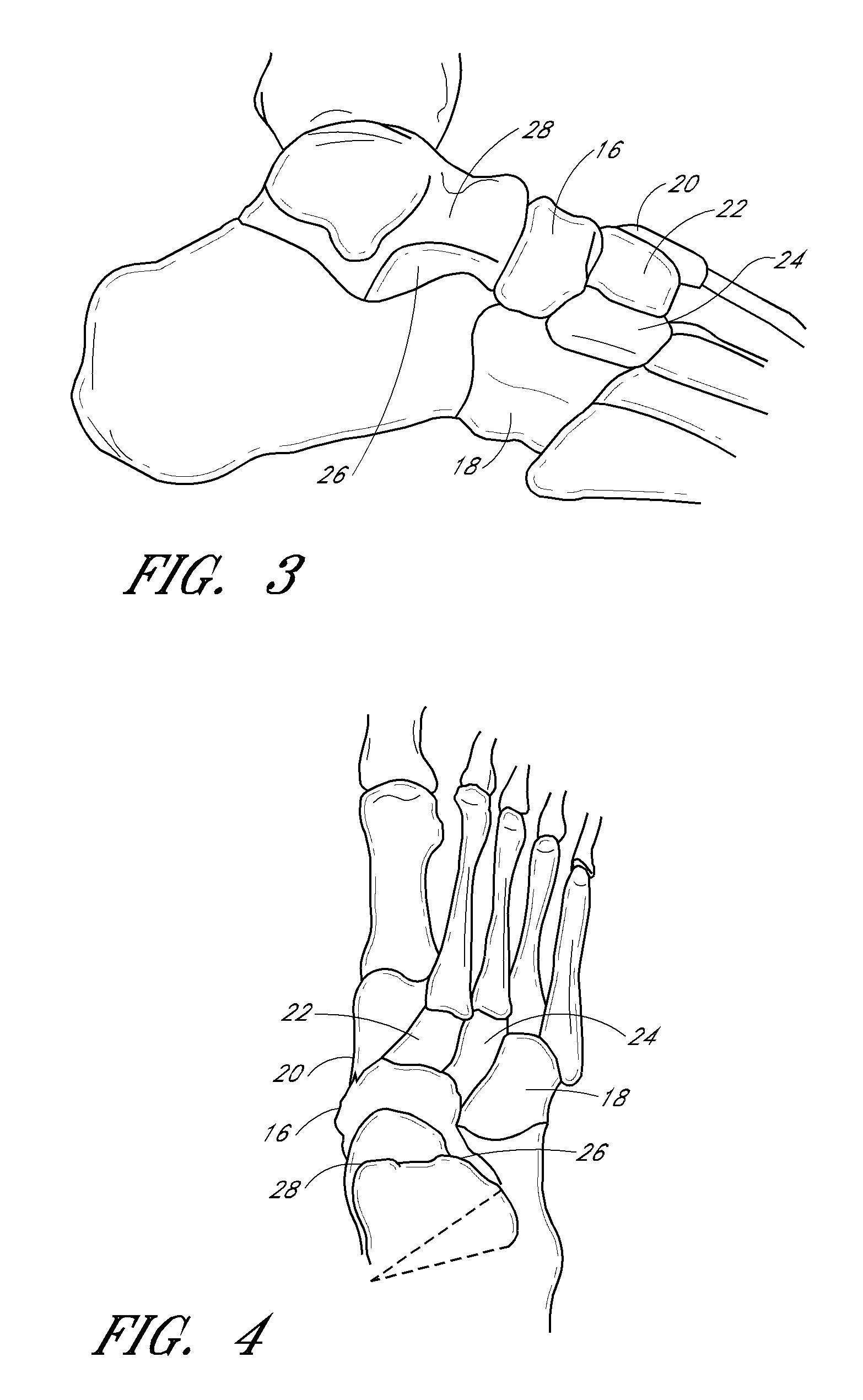
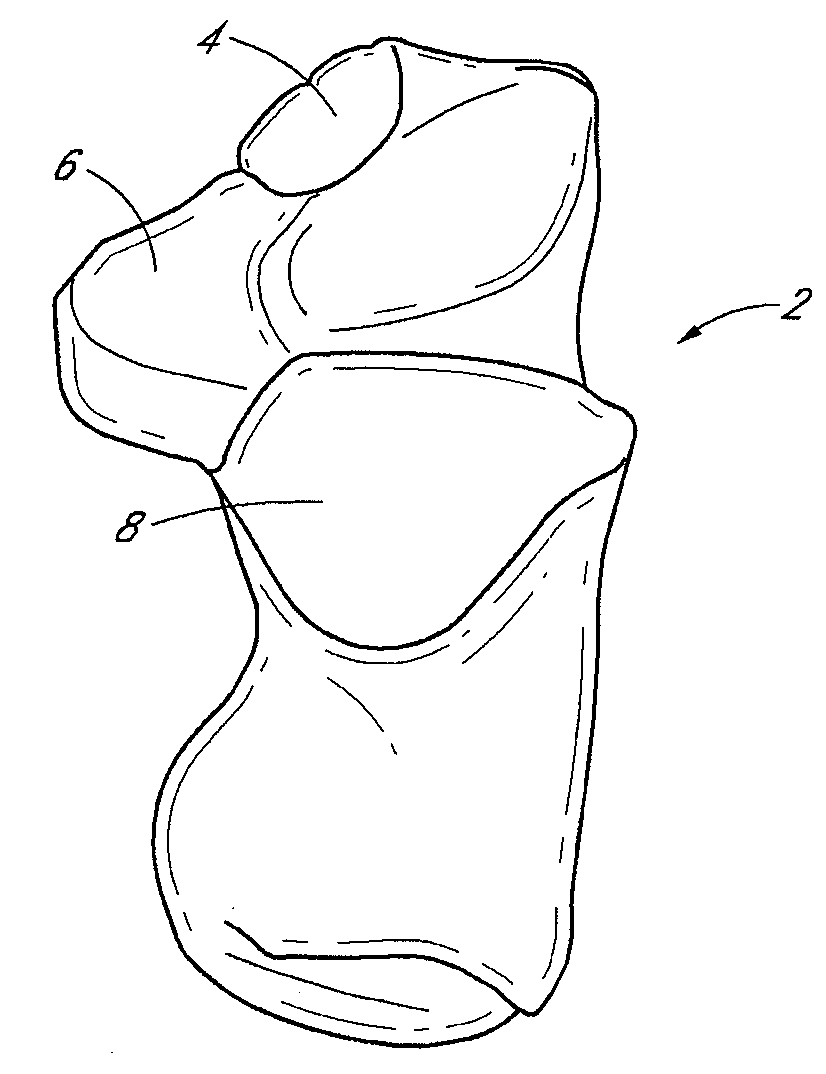
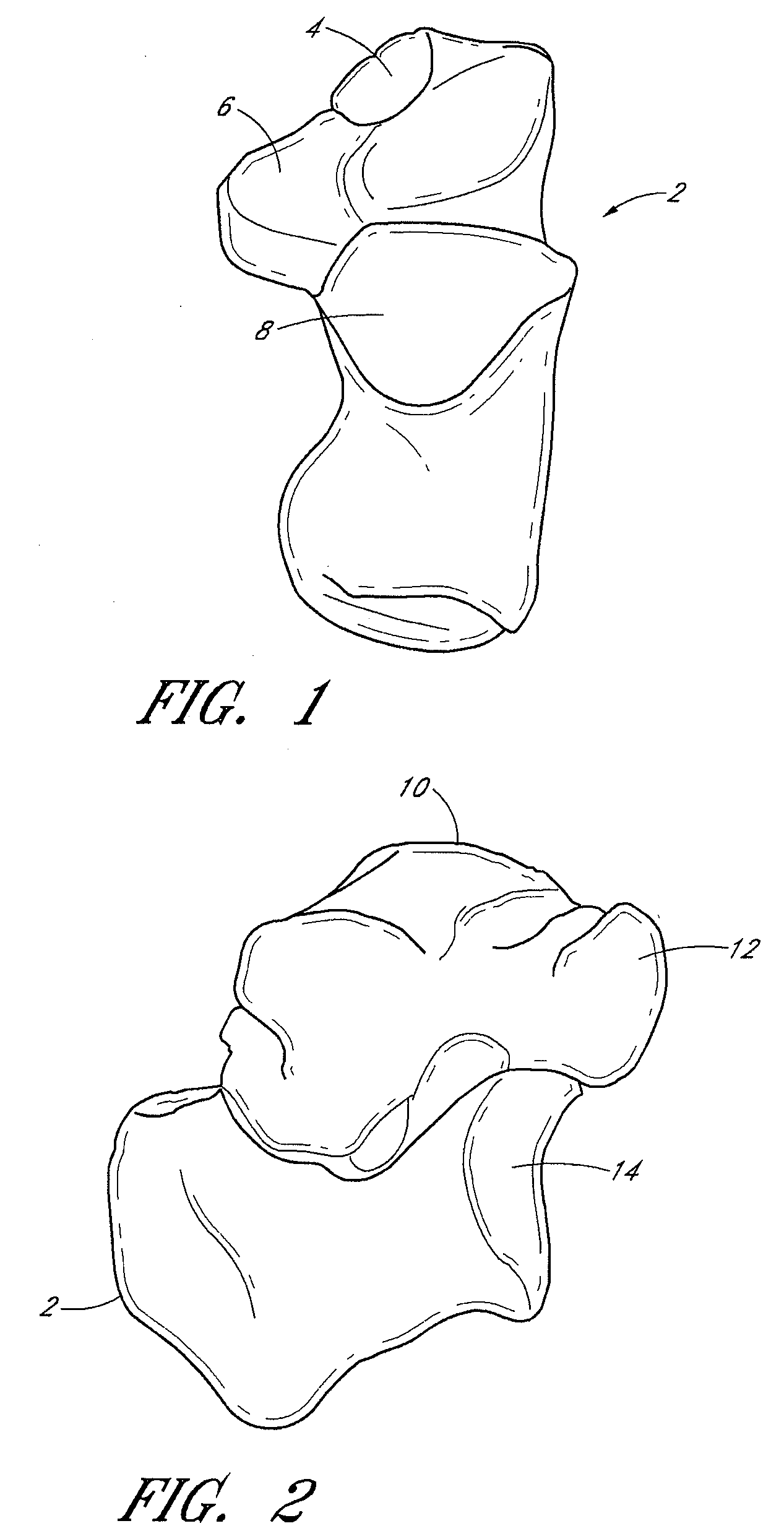
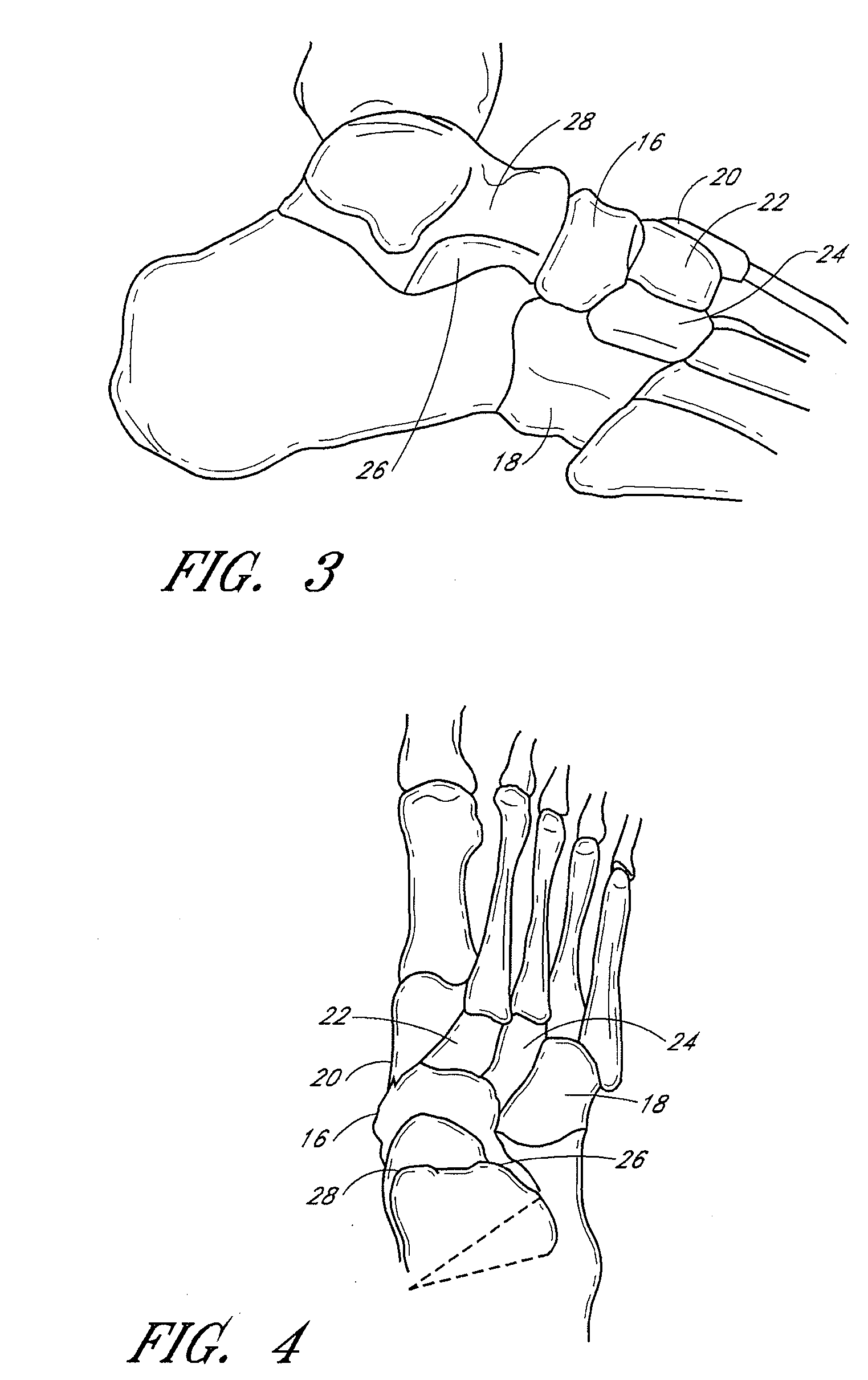
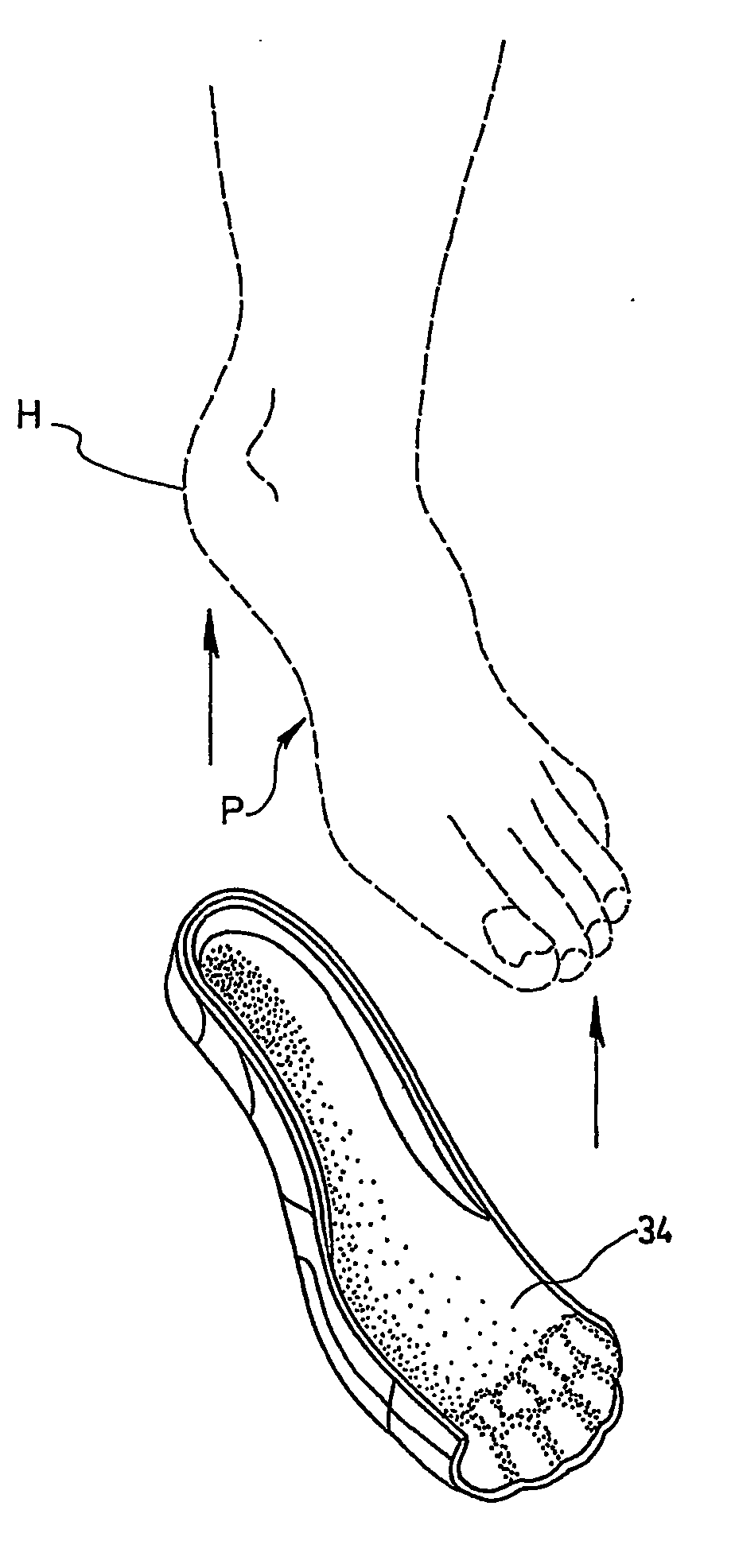
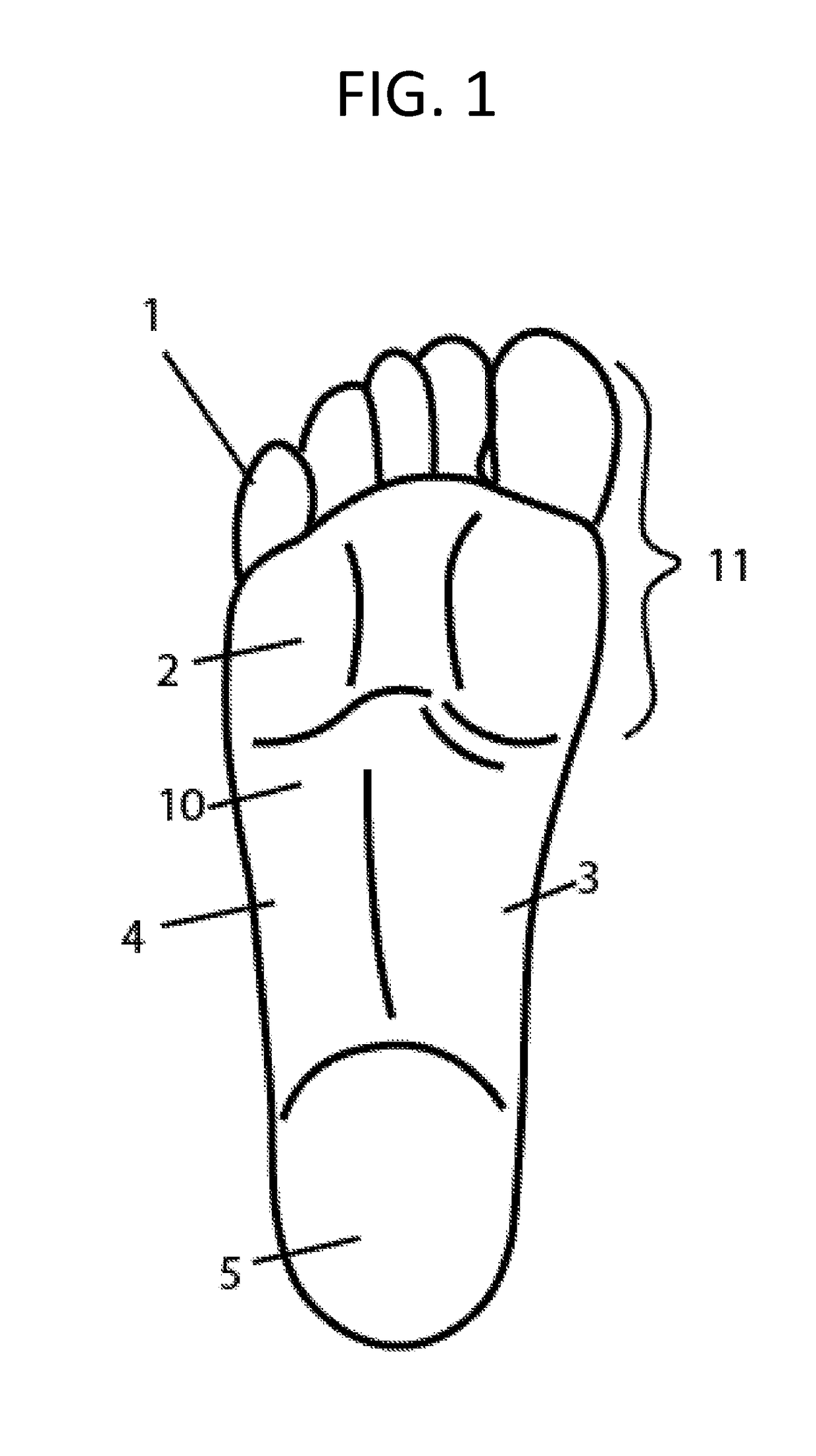
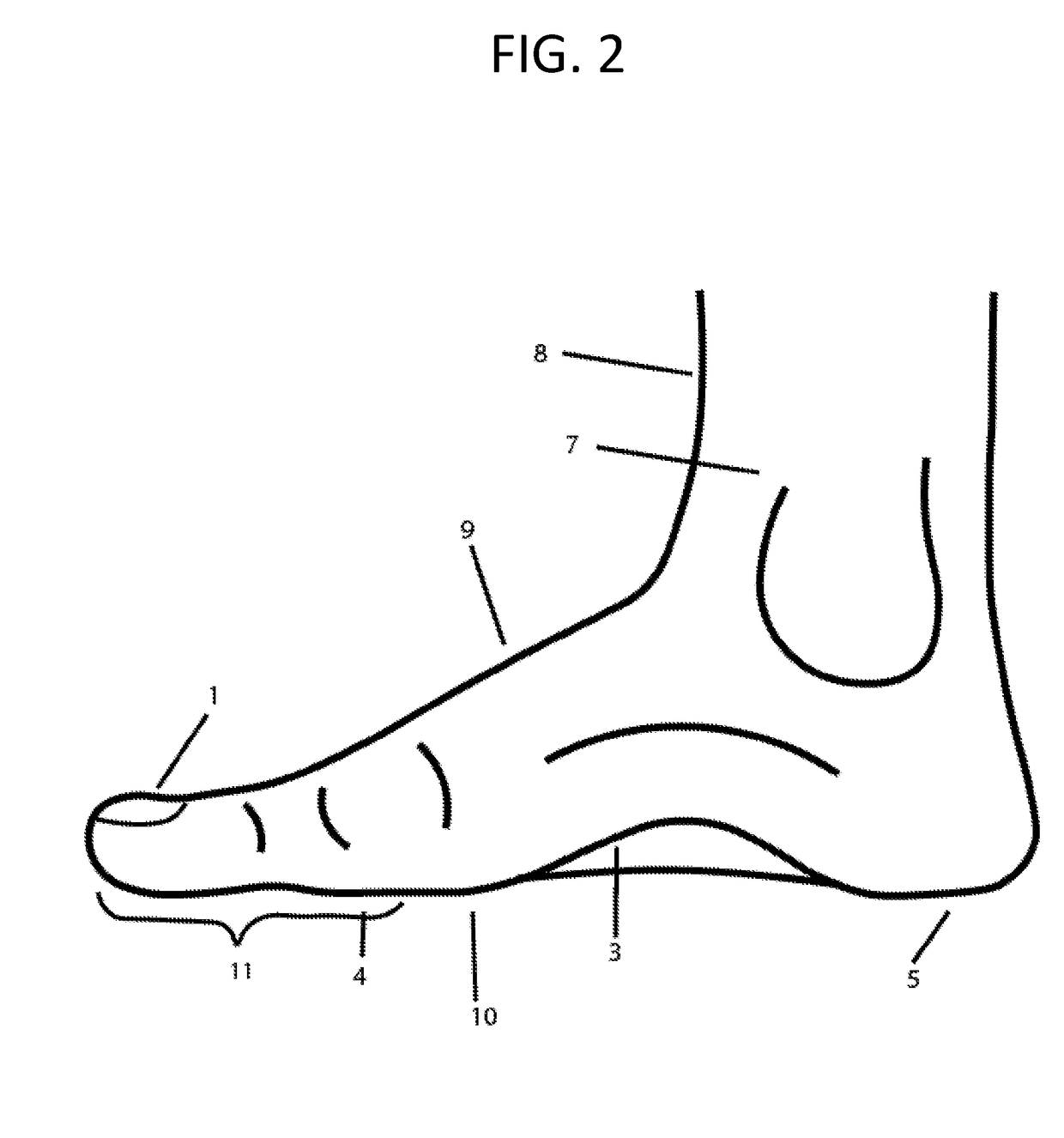
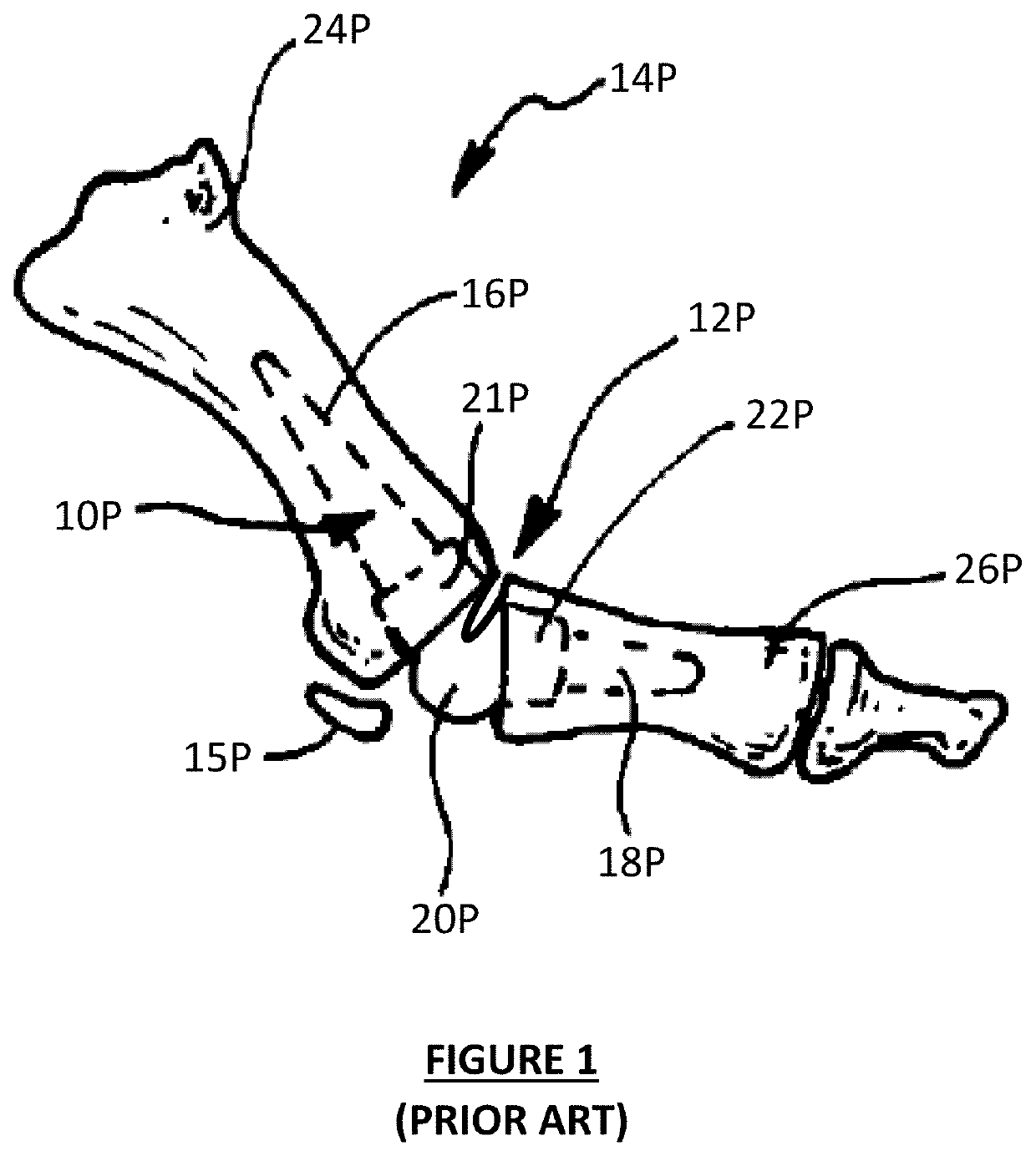
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints) are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges).
Catheter deliverable foot implant and method of delivering the same
InactiveUS20050197711A1Quality improvementAltering range of motionAnkle jointsToe jointsFirst metatarsalRange of motion
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating alignment of the foot to treat patients with flat feet, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and metatarsophalangeal joint dysfunction. An enlargeable implant is positioned in or about the sinus tarsi and / or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the foot. The implant is insertable by minimally invasive means and enlarged through a catheter or needle. Enlargement of the implant alters the range of motion in the subtalar or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint and changes the alignment of the foot or toe.
Owner:CACHIA VICTOR V
Catheter deliverable foot implant and method of delivering the same
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating alignment of the foot to treat patients with flat feet, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and metatarsophalangeal joint dysfunction. An inflatable implant is positioned in or about the sinus tarsi and / or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the foot. The implant is insertable by minimally invasive means and inflatable through a catheter or needle. Inflation of the implant alters the range of motion in the subtalar or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint and changes the alignment of the foot.
Owner:CACHIA VICTOR V
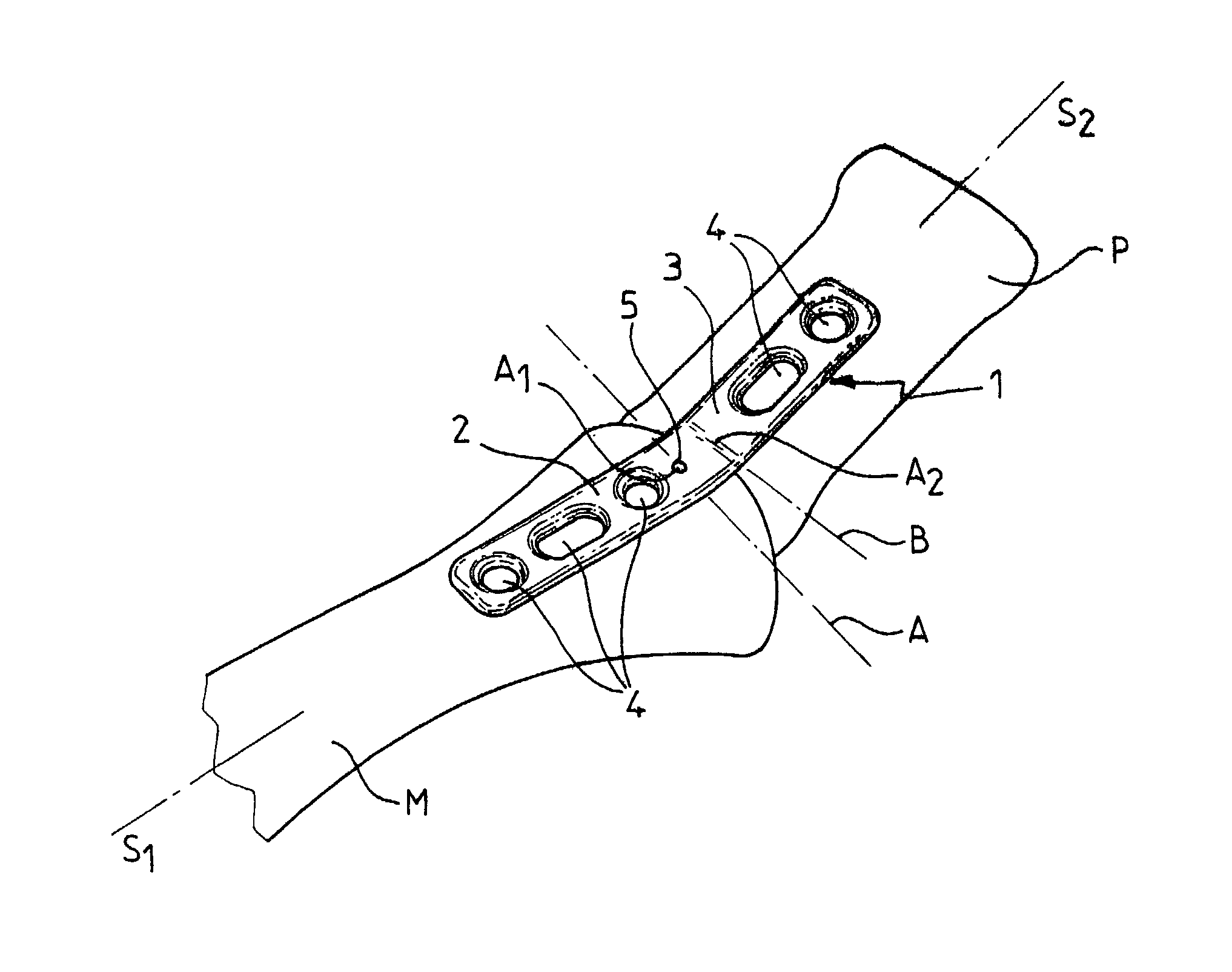
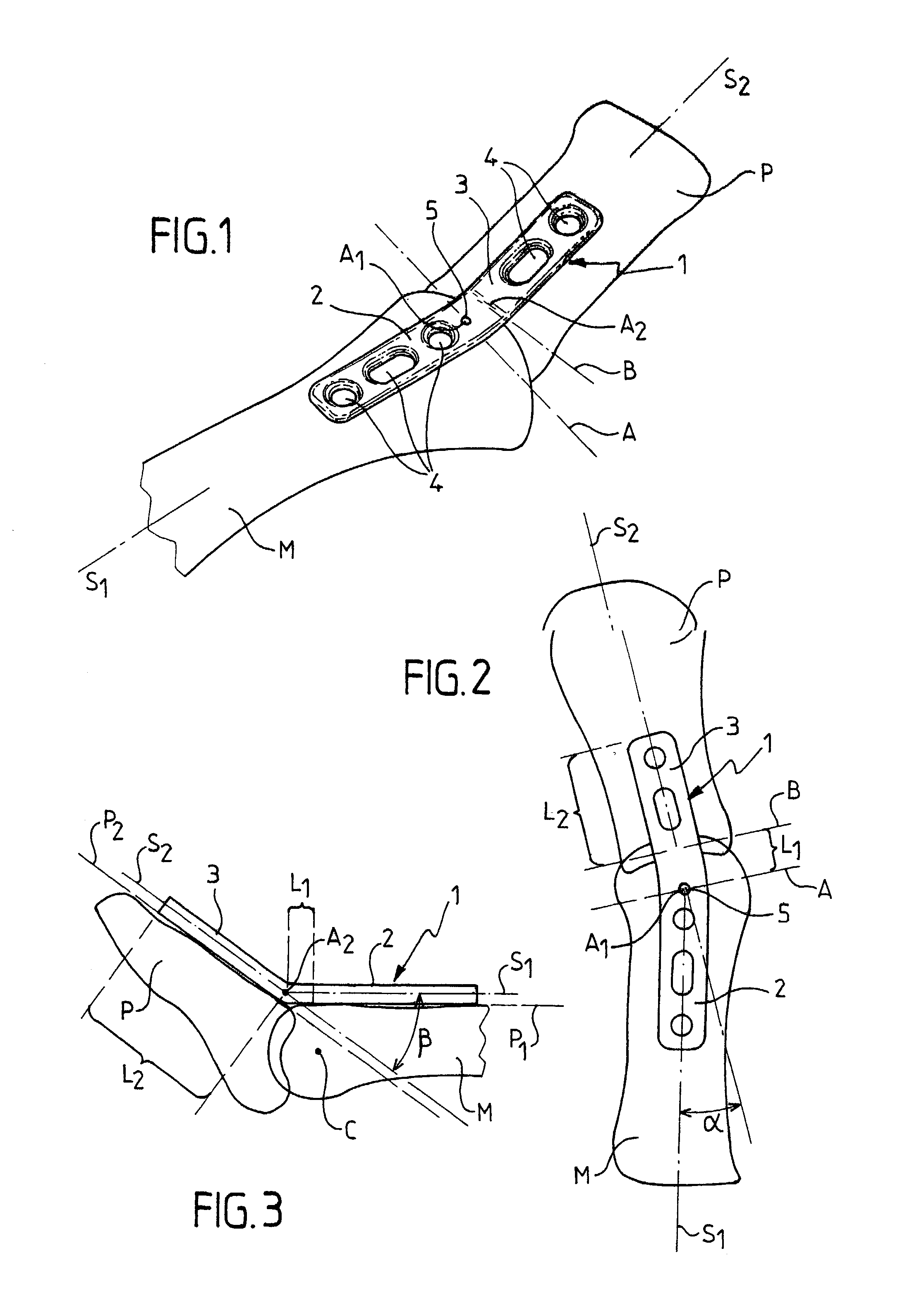
Plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular a metatarso-phalangeal joint
InactiveUS20030060827A1Improve accuracyEasy to placeJoint implantsBone platesJoint arthrodesisVertical plane
The invention relates to a plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular of a metatarso-phalanageal joint, for the purpose of performing arthrodesis, wherein: the plate comprises two sections, respectively a proximal section and a distal section, each section having a respective longitudinal axis of symmetry S1, S2 such that the projection onto a horizontal plane of tie axis of symmetry S2 of the distal section presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1 of the proximal portion, the projections intersecting at a point A; and the projection onto a vertical plane of the axis of symmetry S2 presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1, their intersection taking place at a point A2 which is distinct from the point A1
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
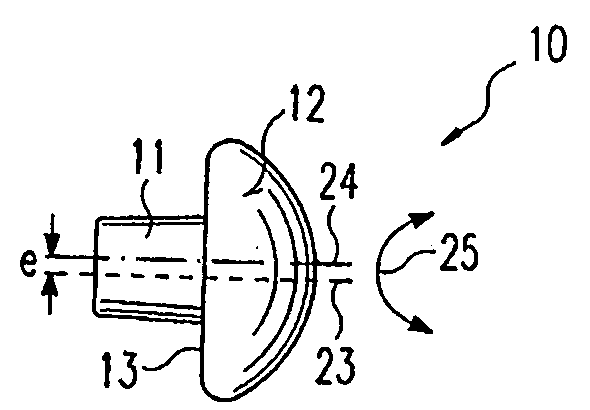
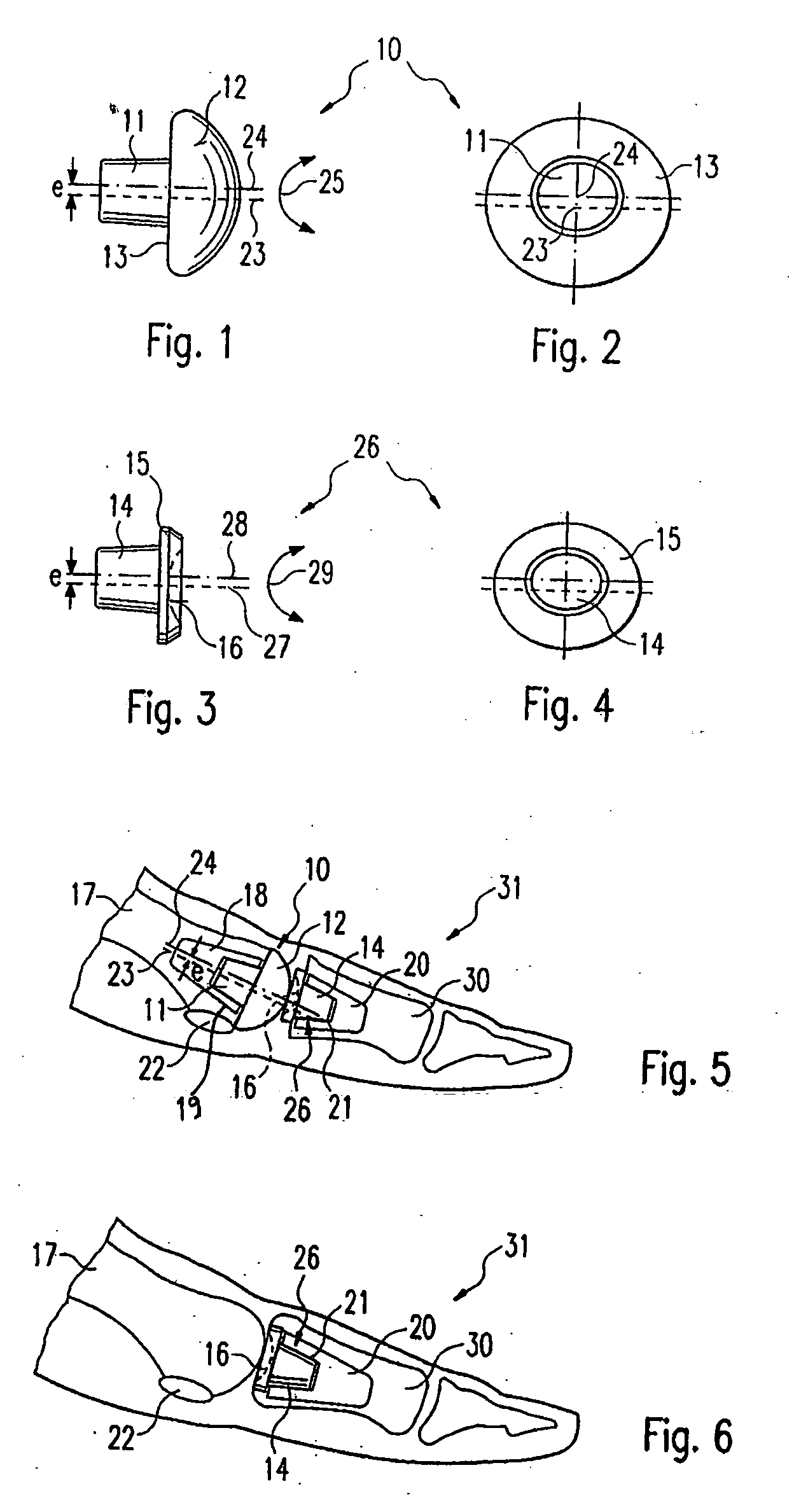
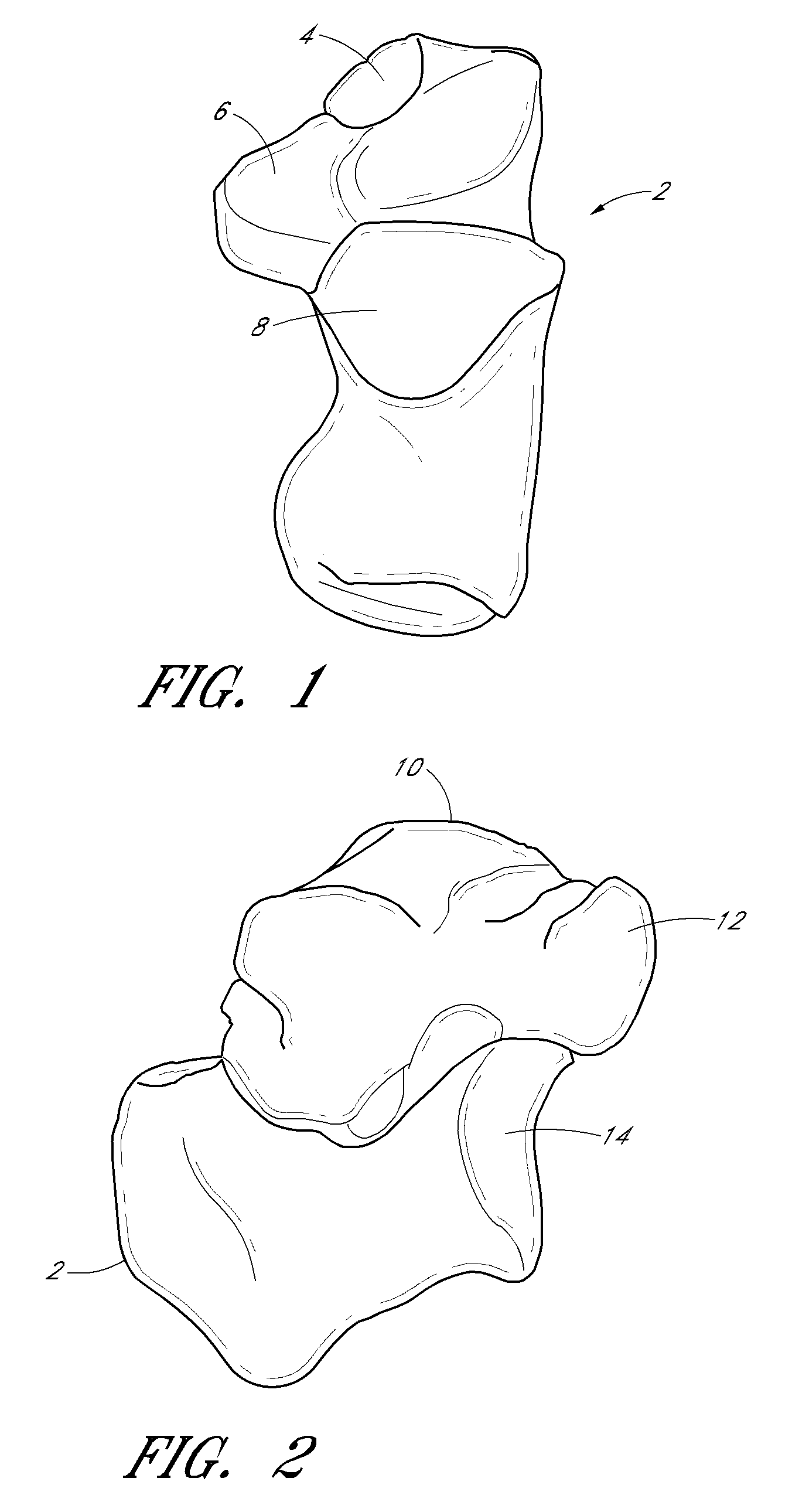
Endoprosthesis for a metatarsophalangeal joint
An endoprosthesis for a metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, especially a basal joint of a large toe, a toe joint or a finger joint, has a prosthesis-half defining a concave or convex prosthetic sliding surface, and means arranged eccentrically with respect to the prosthetic sliding surface of the prosthesis-half for anchoring the latter in the bone.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
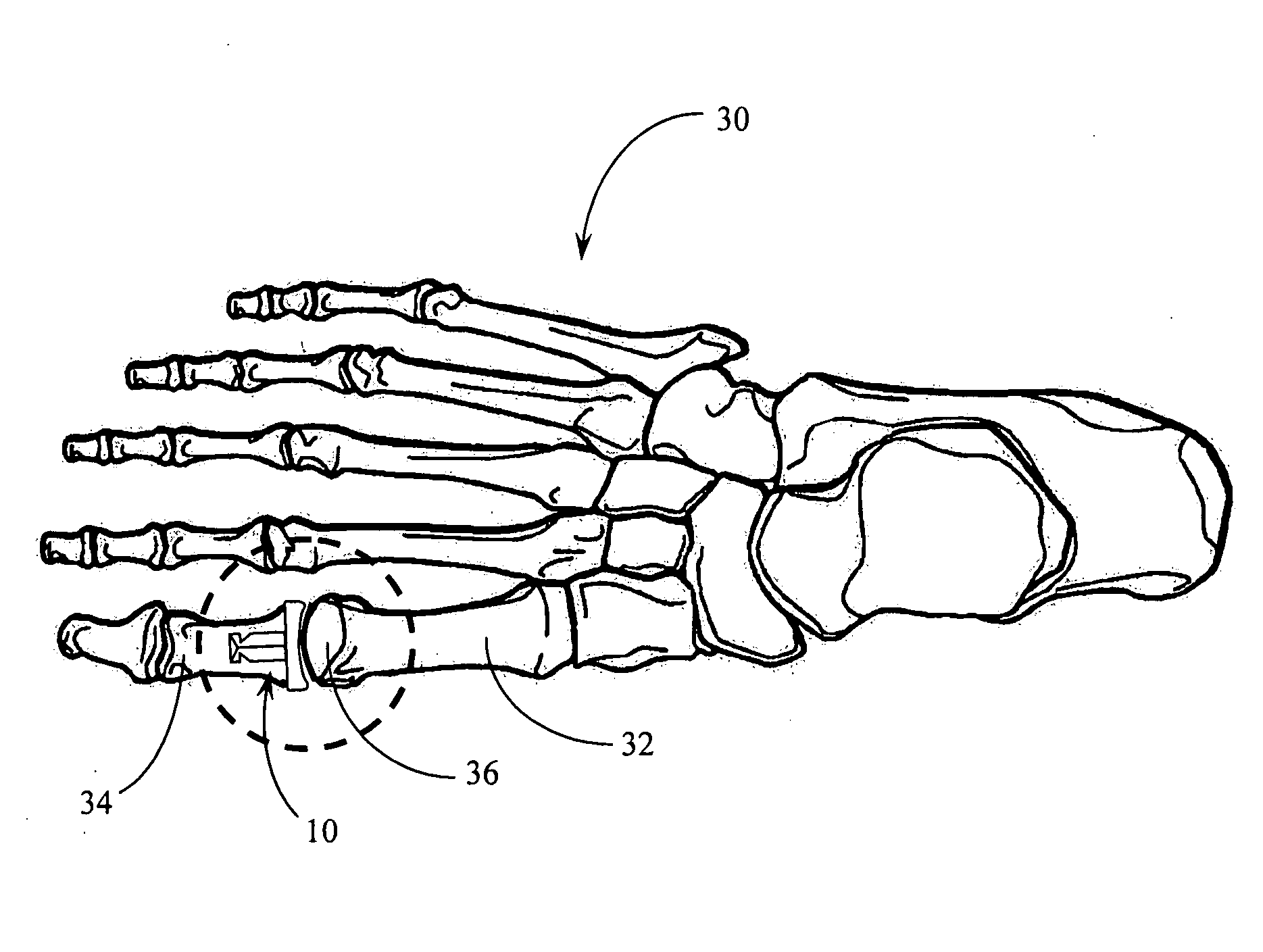
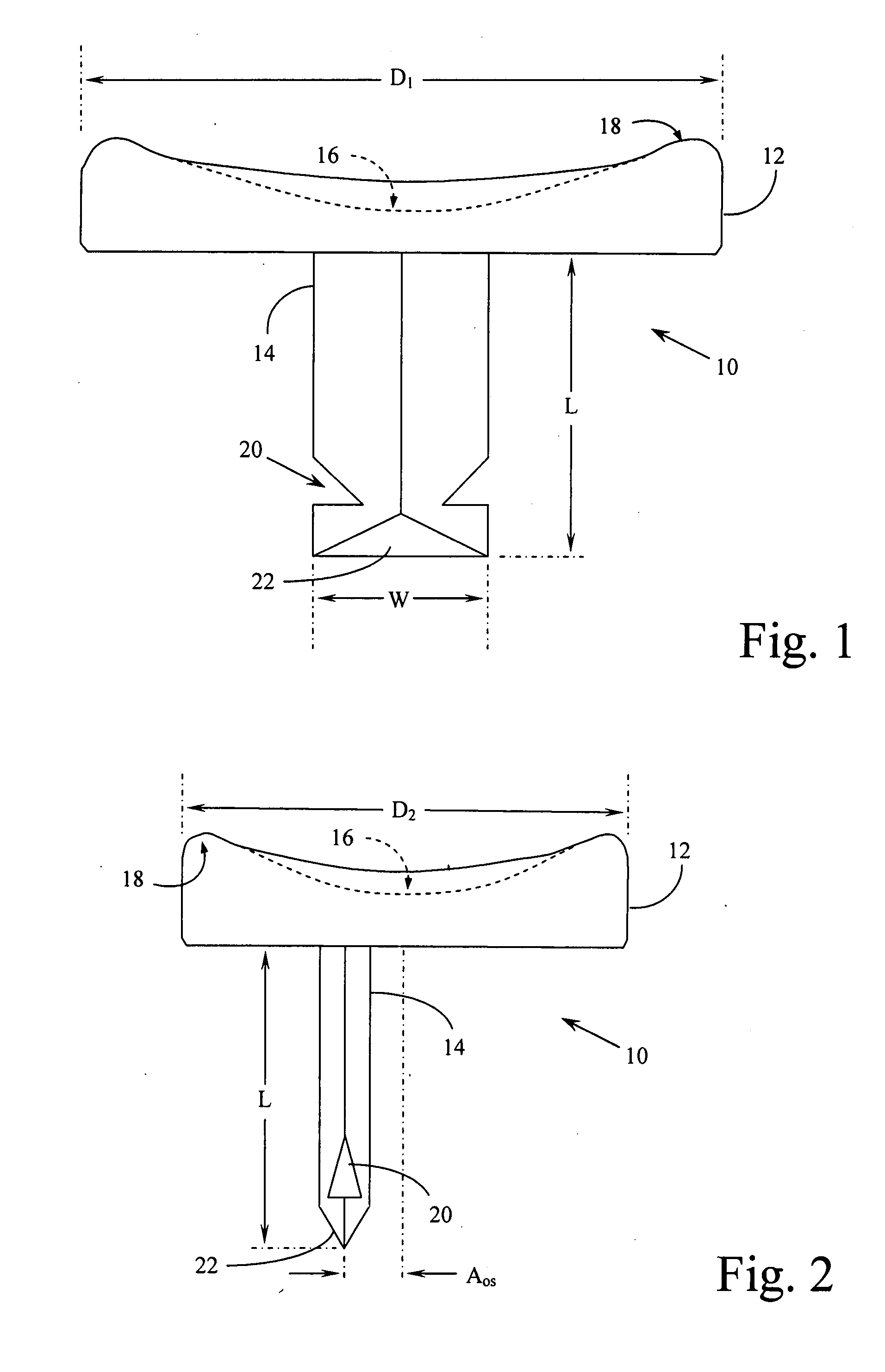
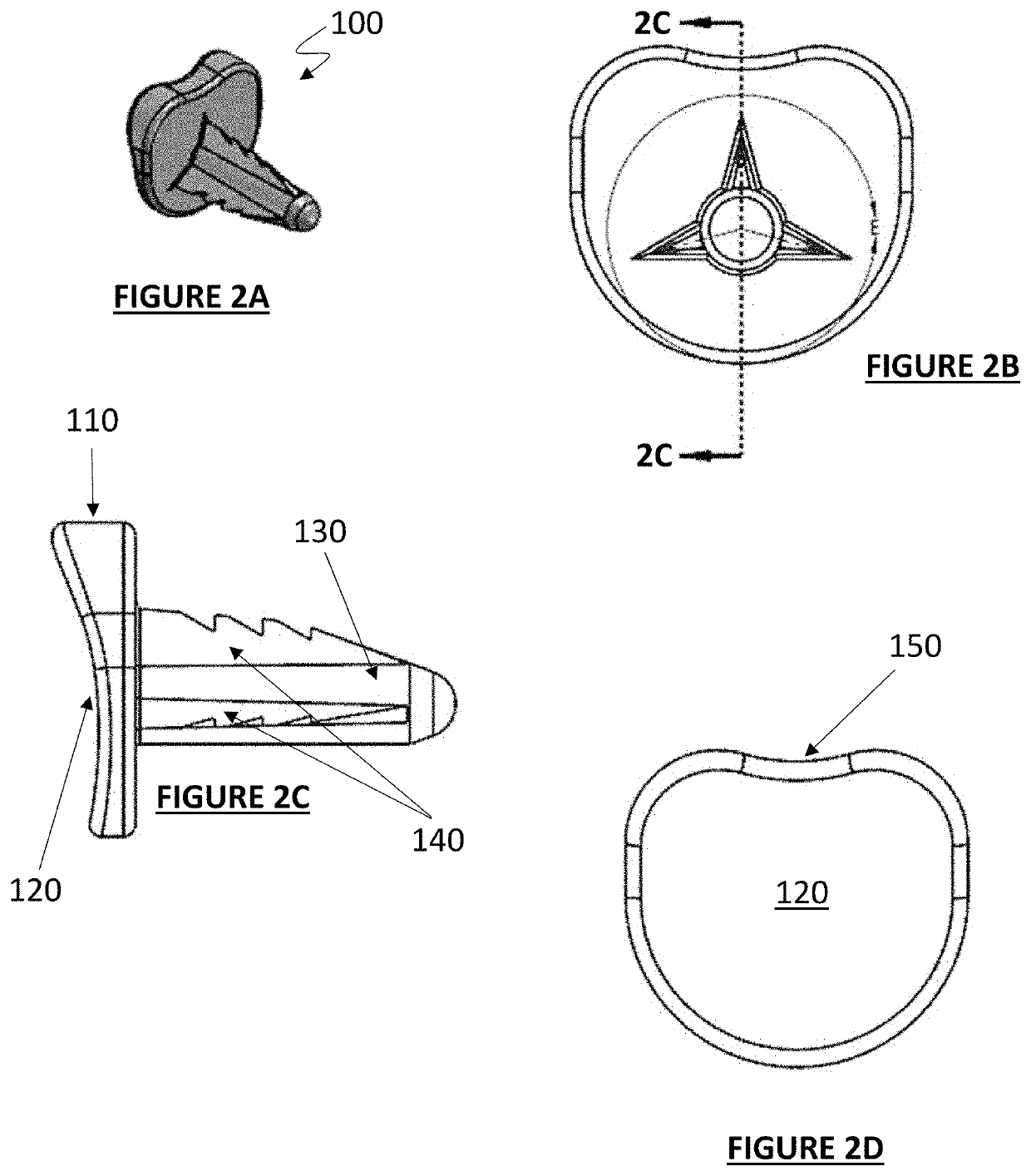
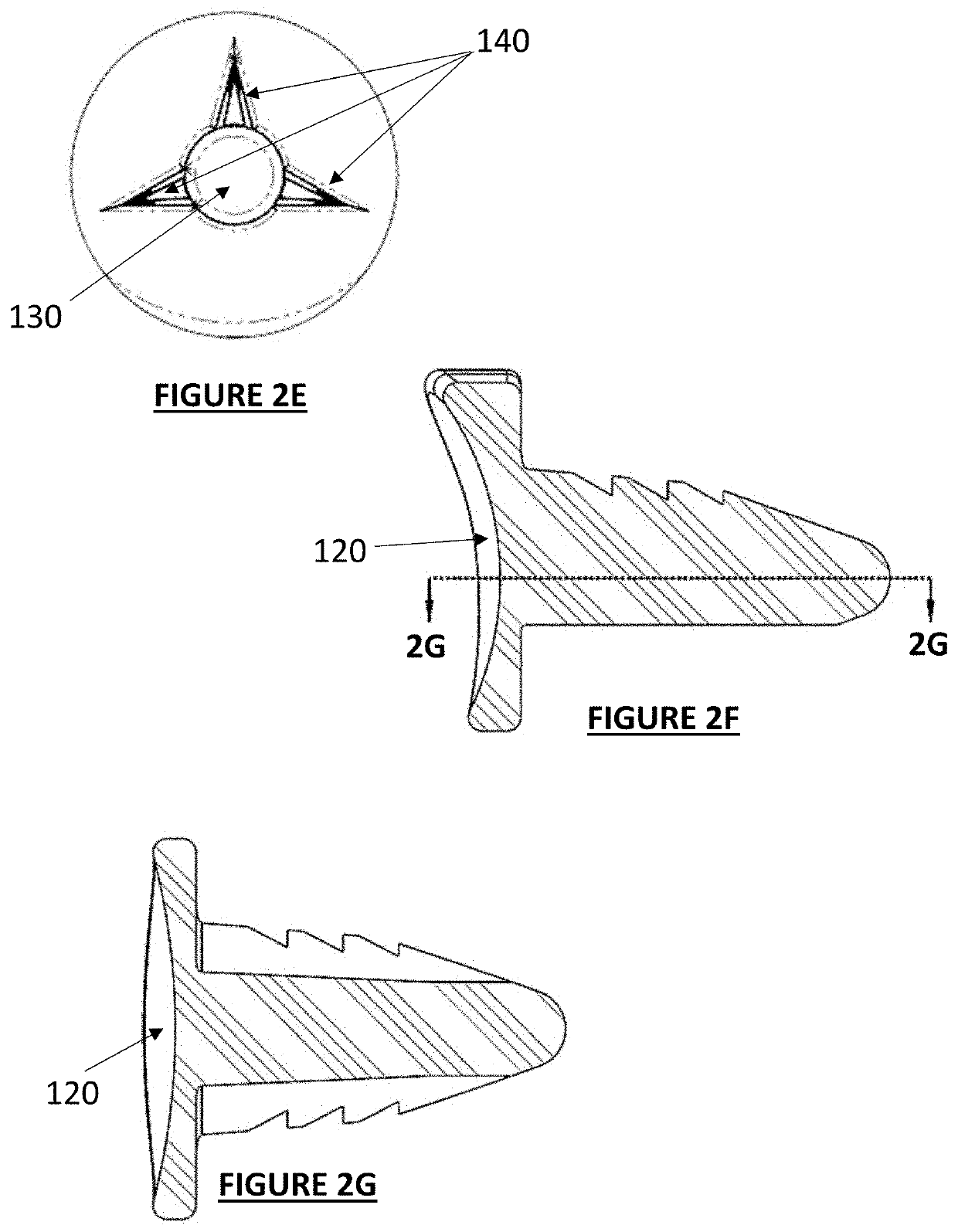
Hemi-implant for first metatarsophalangeal joint
InactiveUS20080221697A1Increase the lengthSimpler but effective retention structureAnkle jointsToe jointsJoint surfaceBiomedical engineering
An improved implant for use primarily within the first metatarsophalangeal joint. The implant includes an elliptical, concave, joint surface positioned on a stem and is designed to be placed into a prepared proximal face of the phalanx. The implant is sized according to the patient and may be provided in a number of standard incremental sizes. The improvements relate primarily to the structure, size, and position of the stem that extends into the phalanx to support the implant. The stem is off-set from a center axis of the elliptical joint surface. This off-center placement allows for a longer stem. Single deep indentations on each side of the stem facilitate retention within the bone. A size selection tool is provided to facilitate the selection and placement of an appropriately sized implant. The tool further provides a template for positioning and placing the stem in the phalanx. A method for sizing and selecting the appropriate implant, and positioning and fixing the implant as a partial joint replacement, especially for the first metatarsophalangeal joint, is also described.
Owner:LOWE JOHN PATRICK TRUSTEE CHAPTER 7 CASE NO 09 51026 C IN THE UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIV
Human-like biped robot foot structure
InactiveCN103738428AImproves upright walking stabilitySmooth landingVehiclesEngineeringDegrees of freedom
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
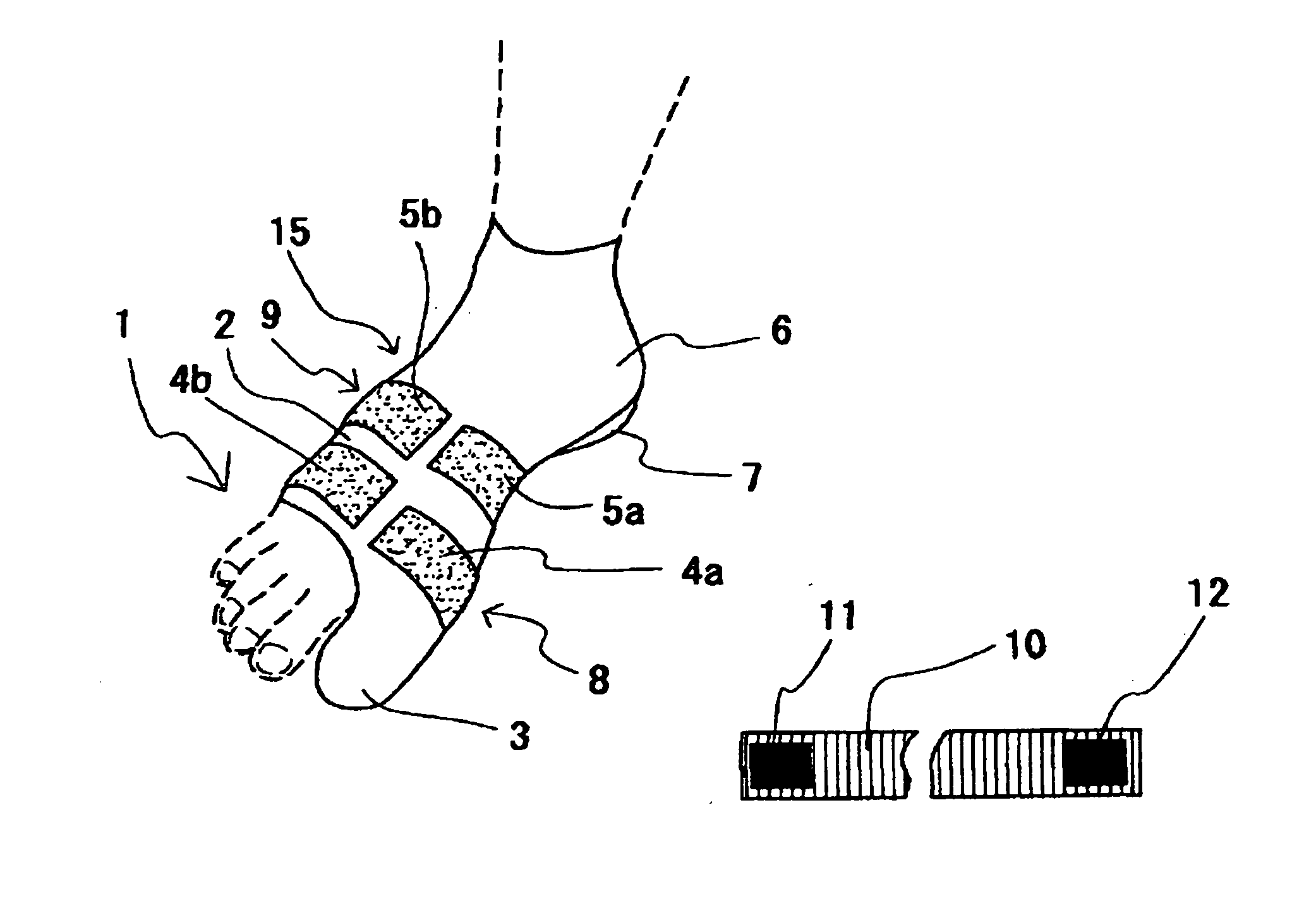
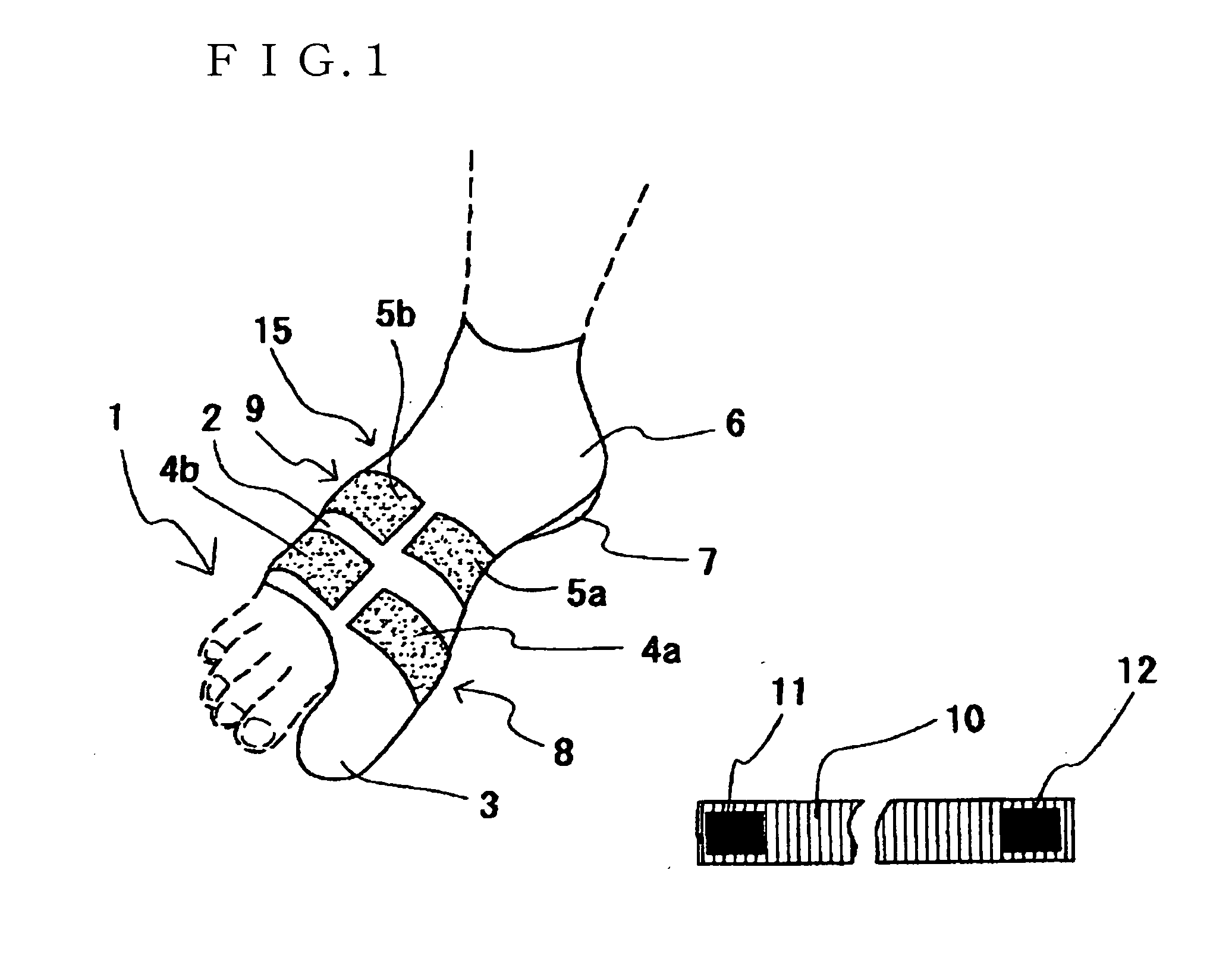
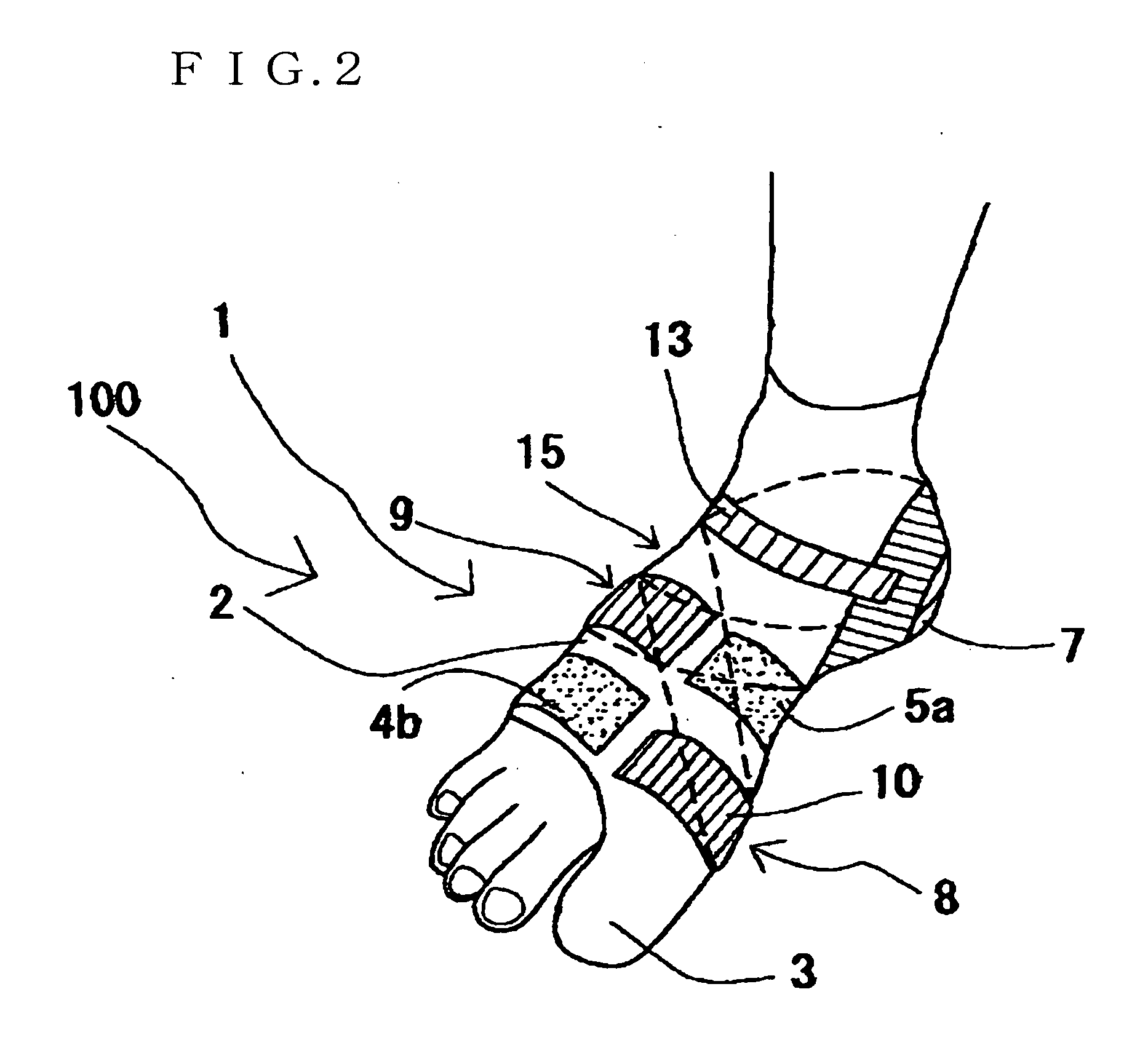
Corrective socks featuring elastic bands and reinforcing bands to correct hallux valgus and digitus quintus varus
In a corrective sock for correcting hallux valgus and digitus quintus varus of a foot, the sock has a foot portion, and an elastic band formed in the foot portion so as to cover both a metatarsophalangeal joint portion and a Lisfranc joint portion of the foot between which first, second, third, fourth and fifth metatarsals extend. A first reinforcing band is formed on the elastic band to cover a distal caput of the first metatarsal and a distal caput of the fifth metatarsal, and a second reinforcing band is formed on the elastic band to cover a proximal caput of the first metatarsal and a pioximal caput of the fifth metatarsal.
Owner:KASAHARA IWAO
Catheter deliverable foot implant and method of delivering the same
InactiveUS20080200989A1Altering range of motionAlters alignmentAnkle jointsToe jointsRange of motionFirst metatarsal
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating alignment of the foot to treat patients with flat feet, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and metatarsophalangeal joint dysfunction. An enlargeable implant is positioned in or about the sinus tarsi and / or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the foot. The implant is insertable by minimally invasive means and enlarged through a catheter or needle. Enlargement of the implant alters the range of motion in the subtalar or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint and changes the alignment of the foot or toe.
Owner:CACHIA VICTOR V
Ankle foot rehabilitation training device and balance training system
ActiveCN103961240ASimple structureEasy maintenanceChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesGravity centerEngineering
The invention provides an ankle foot rehabilitation training device and a balance training system. The lower end of a front supporting plate of the ankle foot rehabilitation training device is fixed to a base plate, a front foot sole pedal is hinged to the upper end of the front supporting plate, the front foot sole pedal is hinged to a rear foot sole pedal through a second pin shaft, first-second pin holes are formed in the bottom of the rear foot sole pedal, first-second pins are arranged in the first-second pin holes respectively, a first spherical hinge is respectively connected with a first pin and a third pin, a second spherical hinge is respectively connected with a second pin and a fourth pin, the third pin is connected with a first servo electric cylinder unit, the fourth pin is connected with a second servo electric cylinder unit, the first servo electric cylinder unit is connected with the base plate through a third spherical hinge, and the second servo electric cylinder unit is connected with the base plate through a fourth spherical hinge. The ankle foot rehabilitation training device can perform rehabilitation training on ankle joints and foot metatarsophalangeal joints of a patient respectively, the balance training system can change the position of the gravity center of the patient through the ankle foot rehabilitation training device, and therefore balance training is performed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
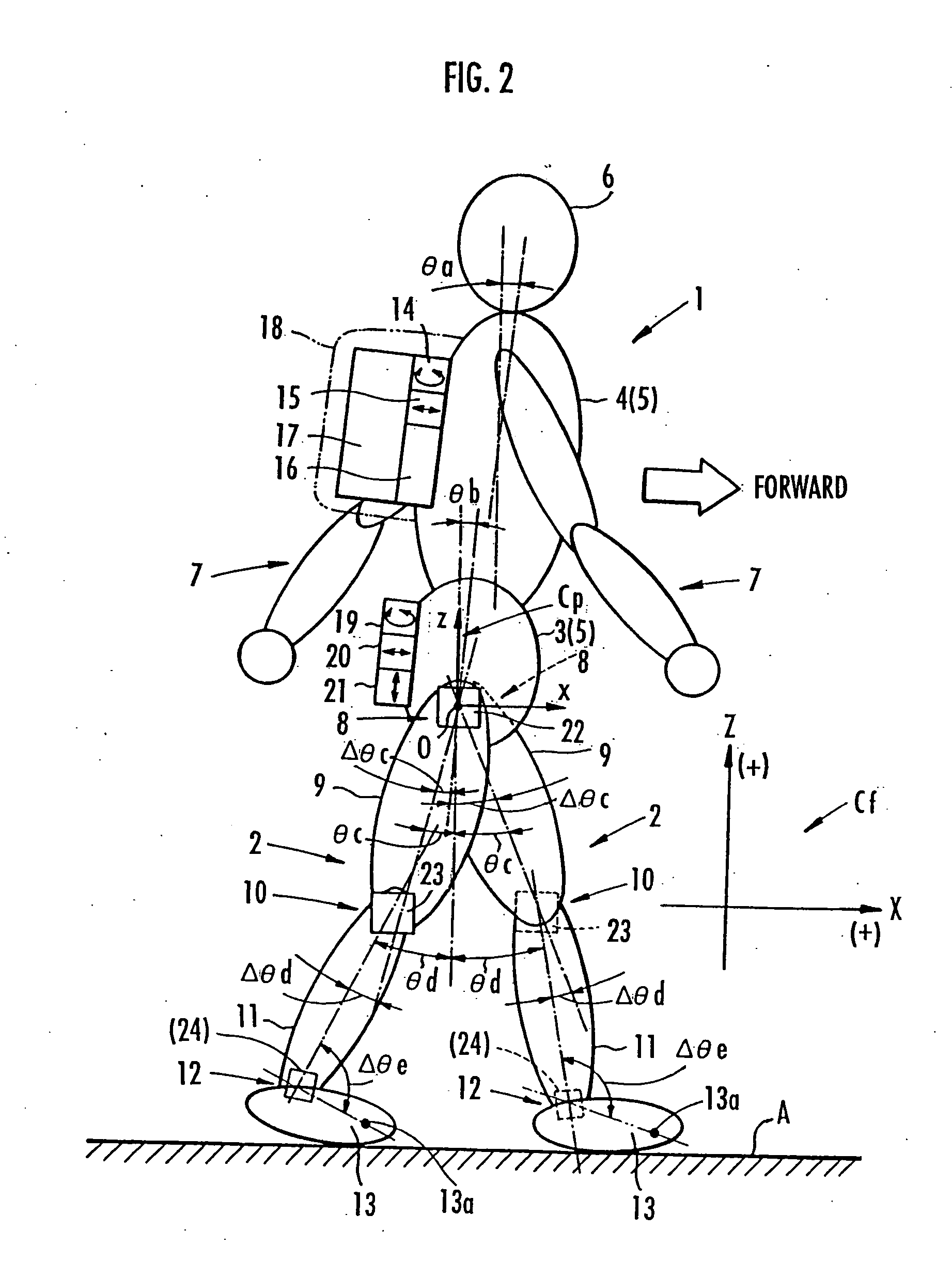
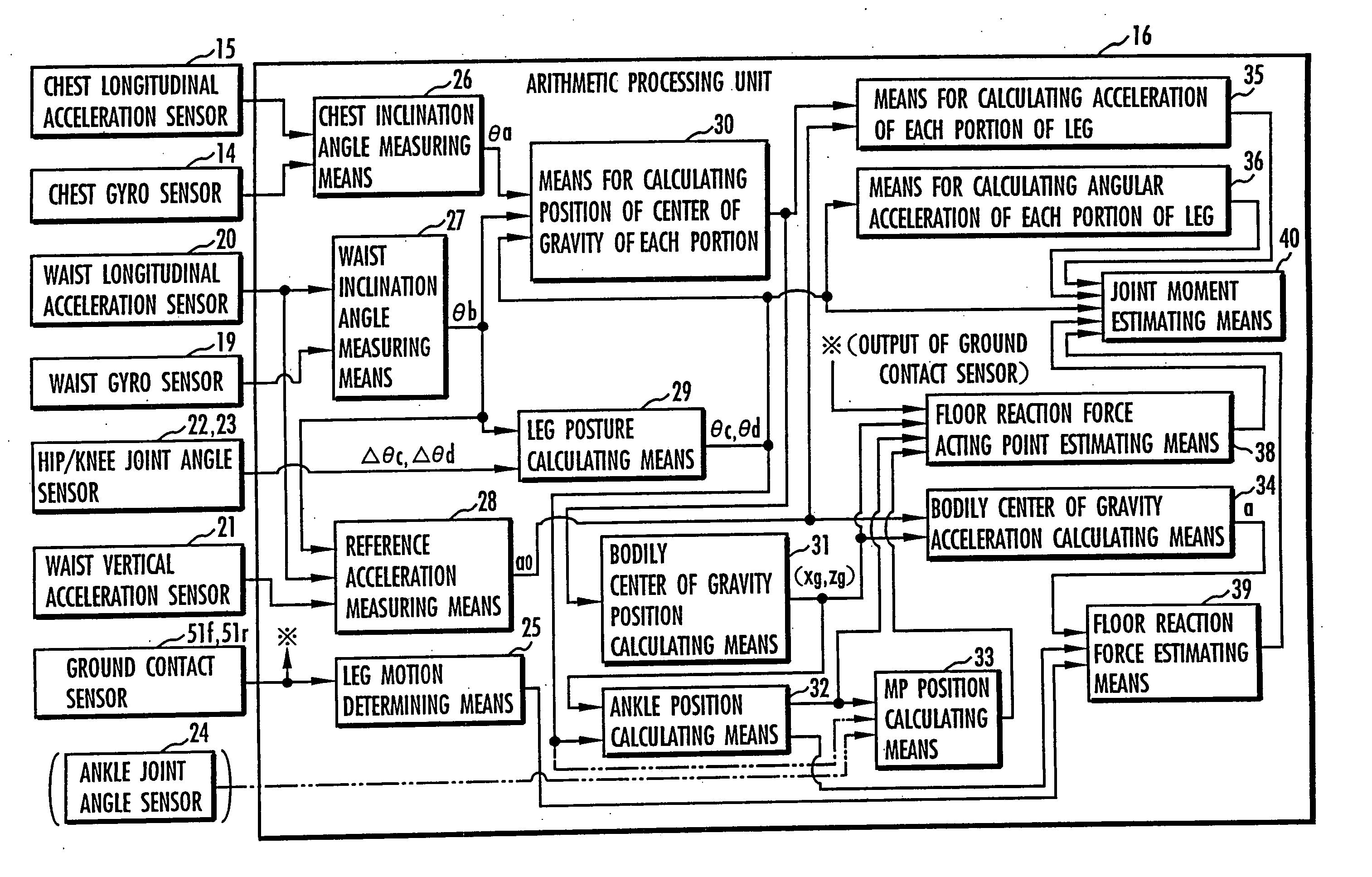
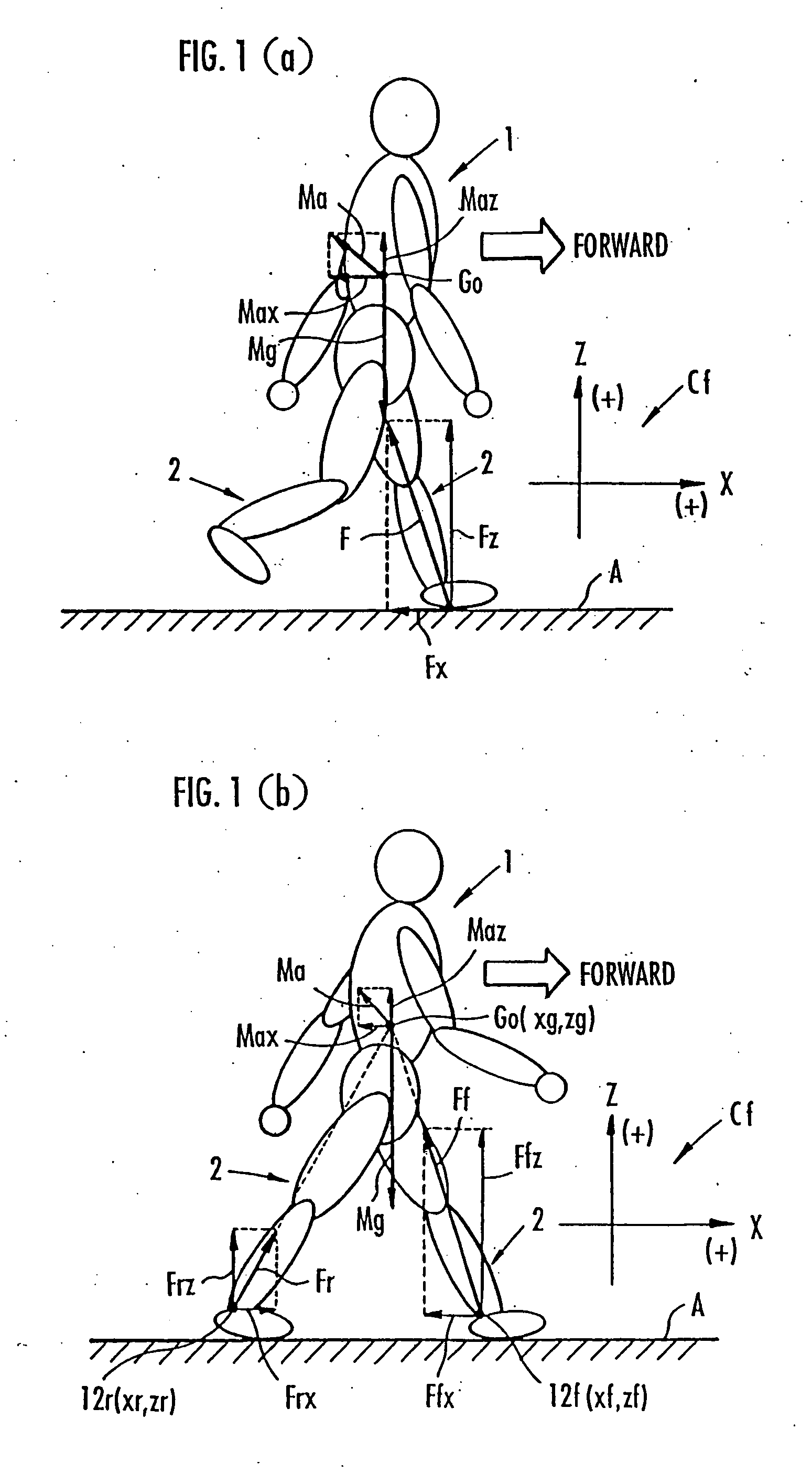
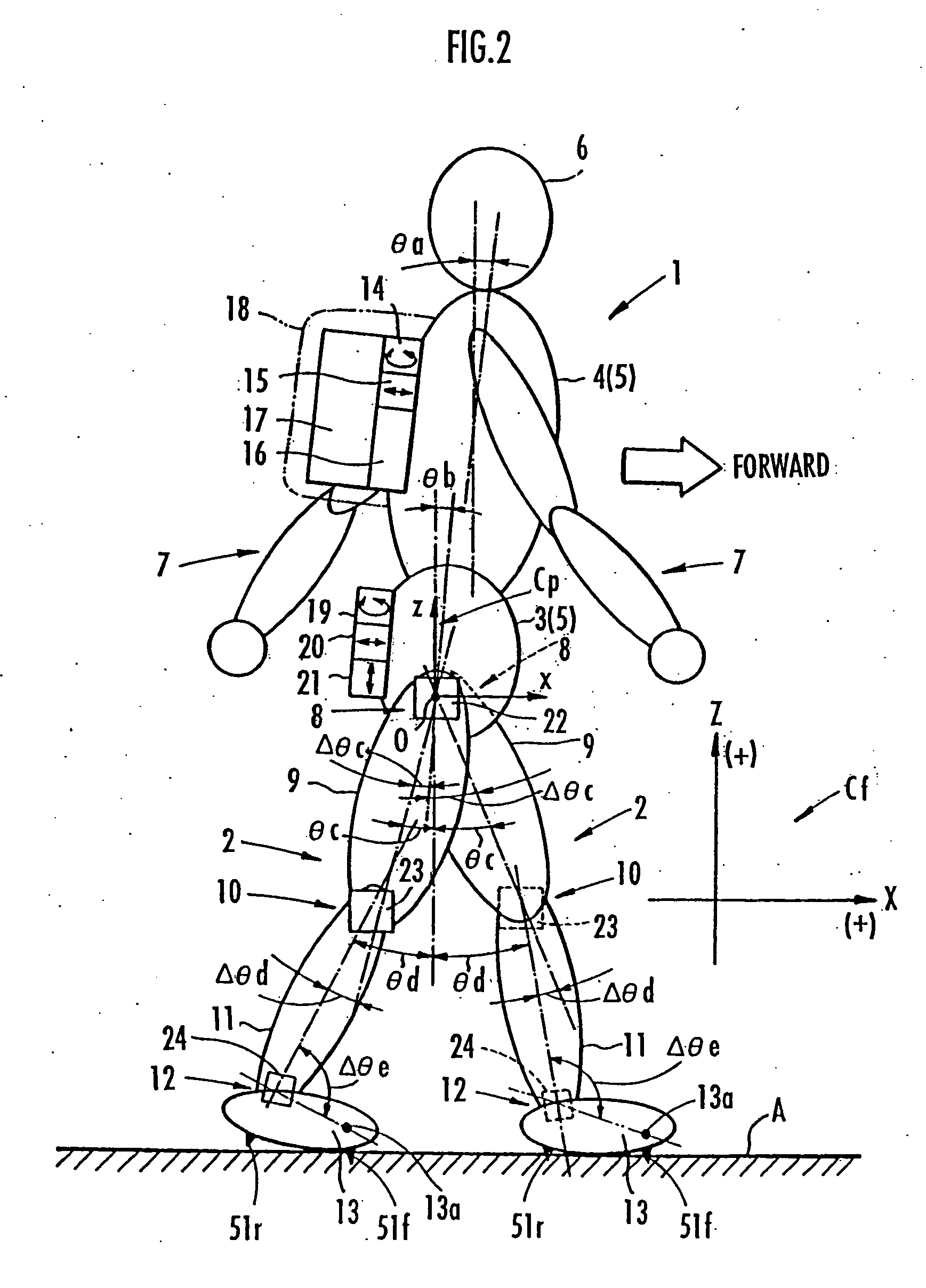
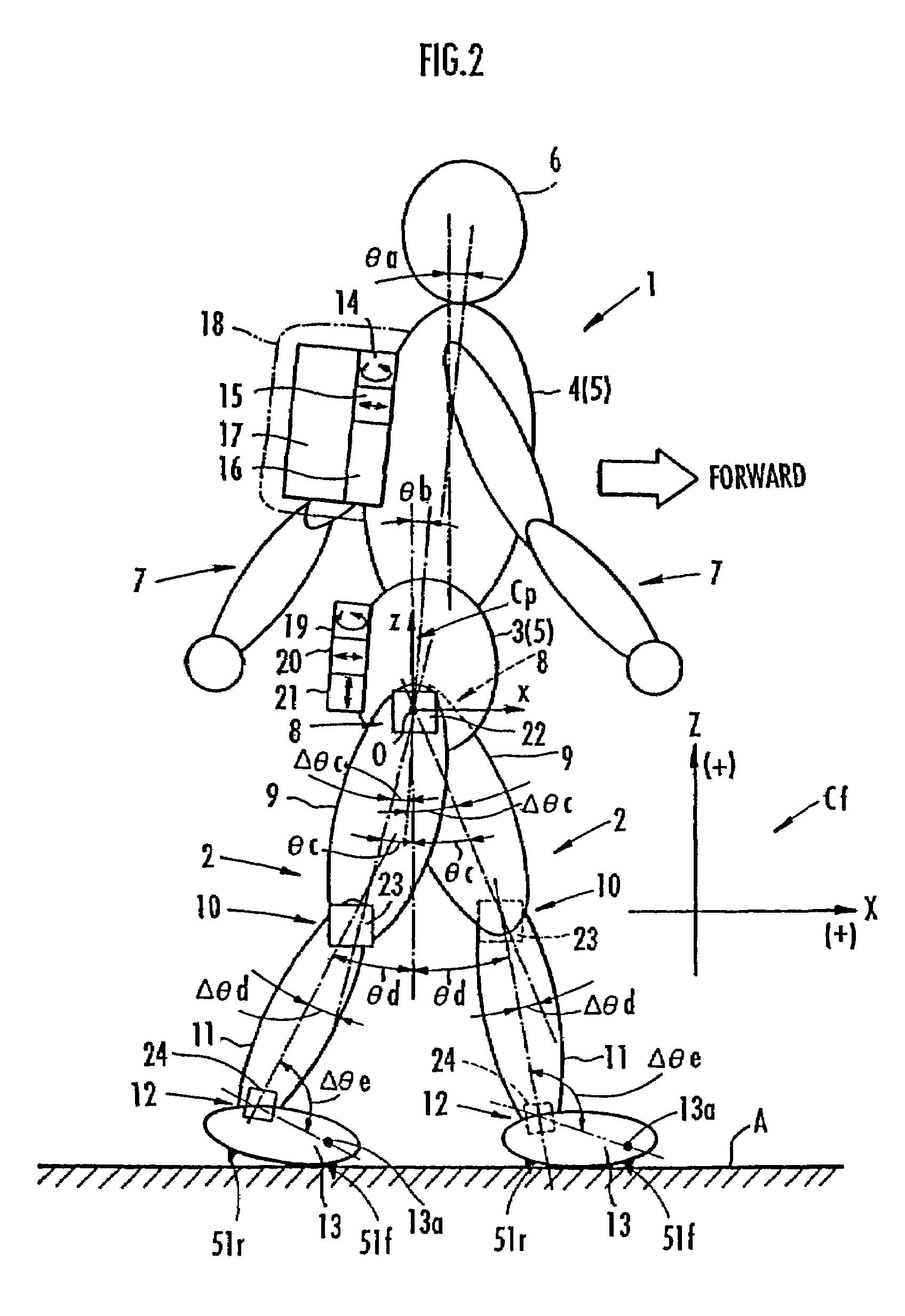
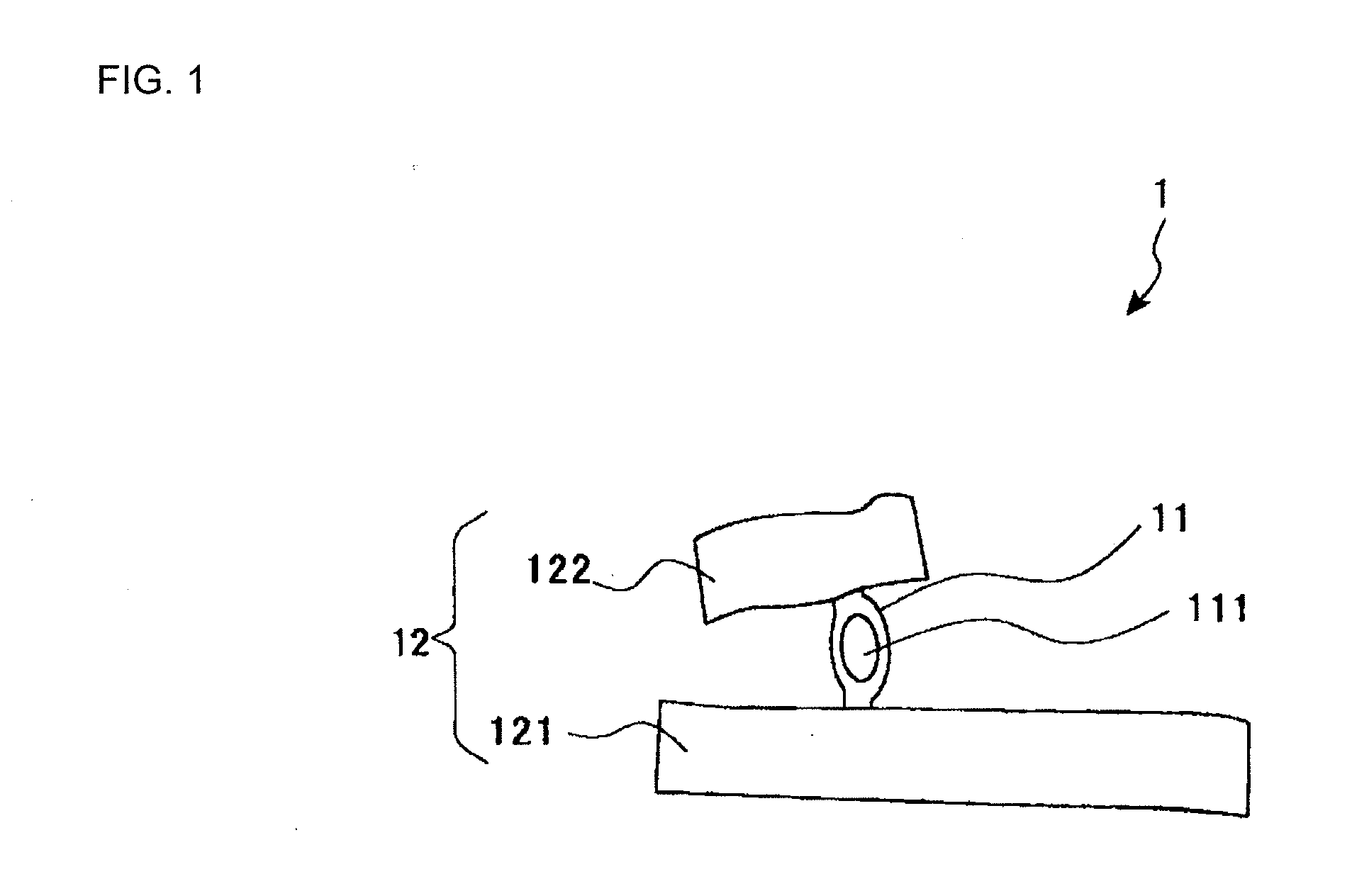
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS7119510B2Good estimateHigh accuracy of estimated valueProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
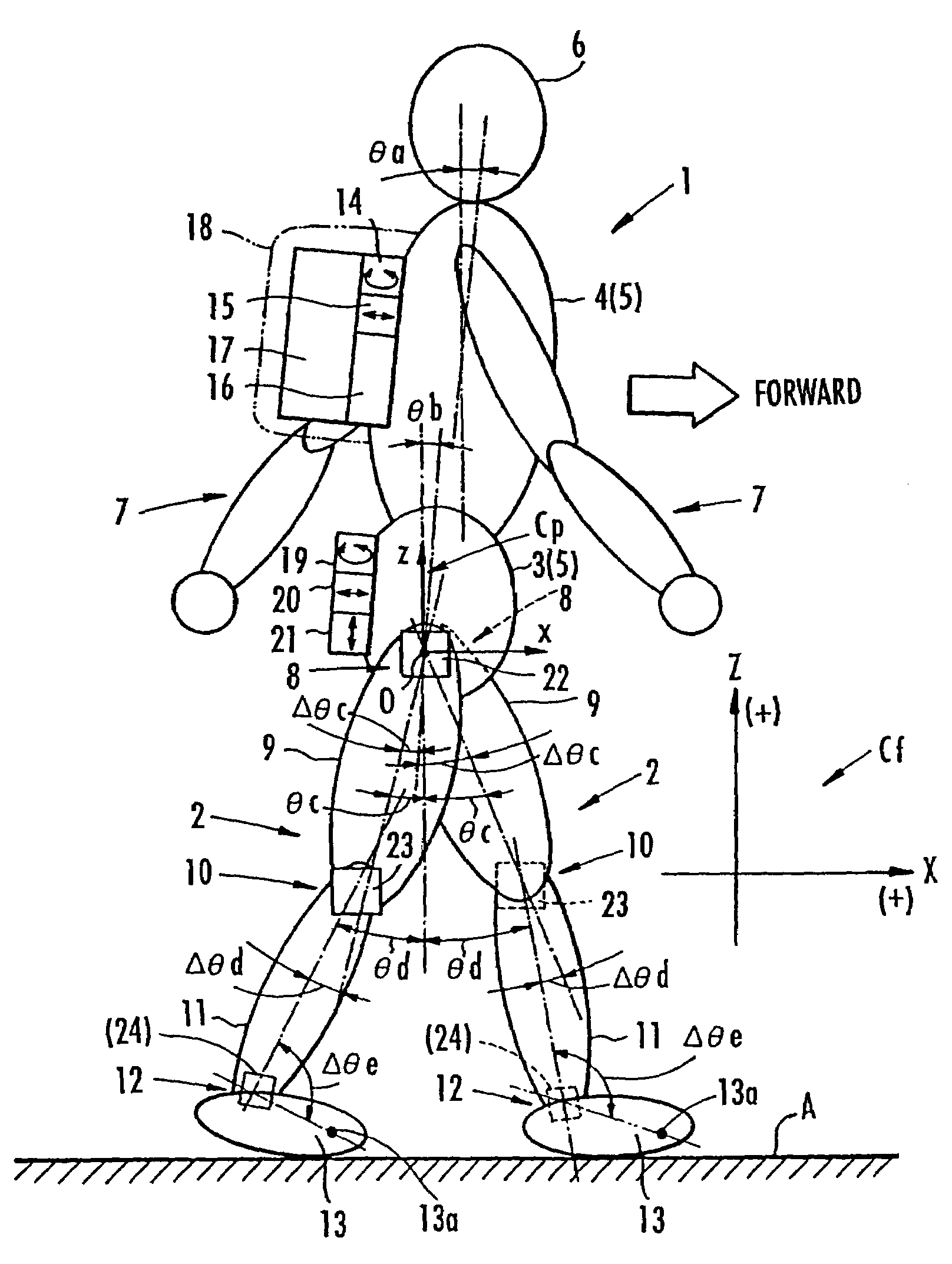
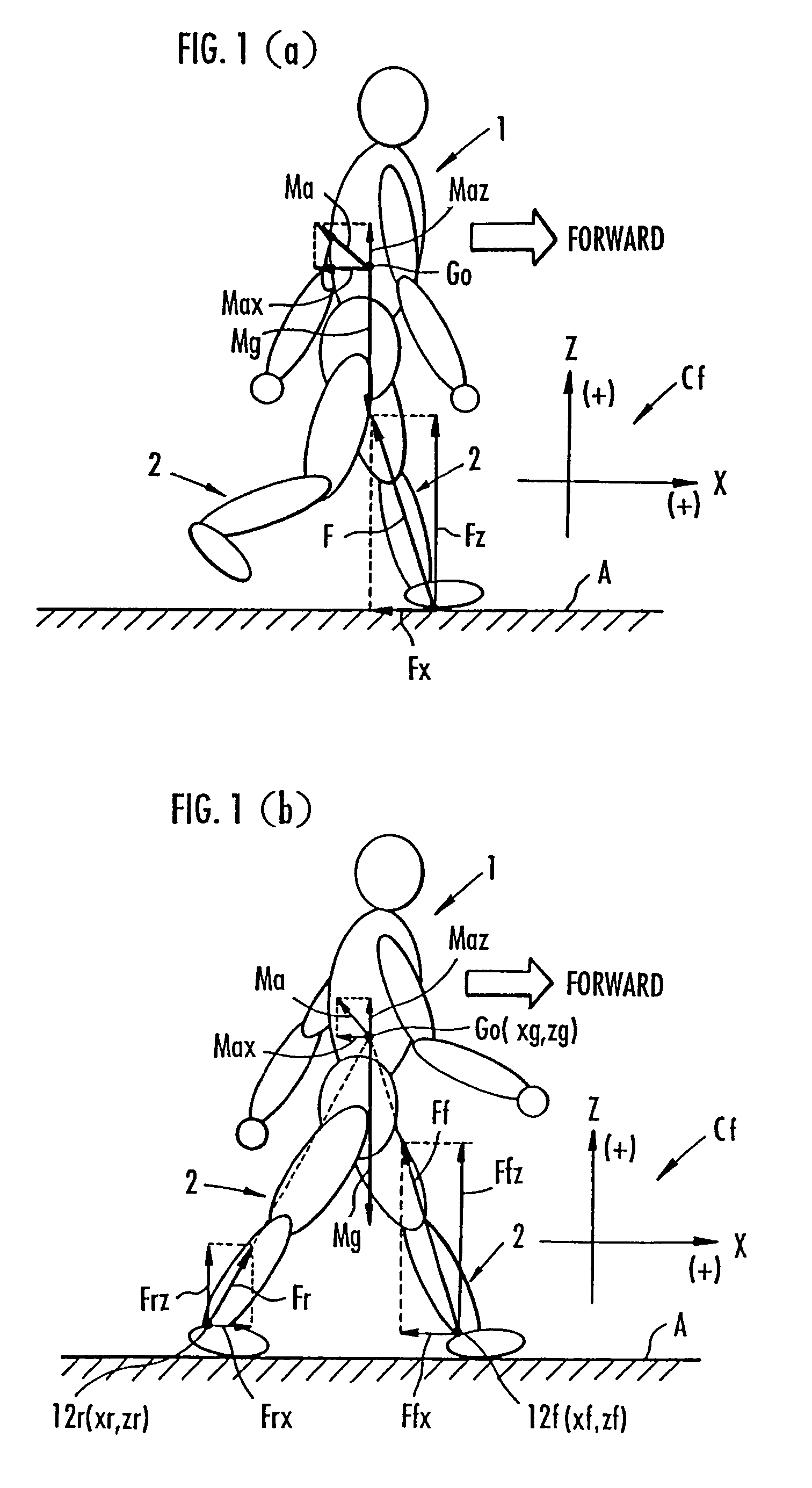
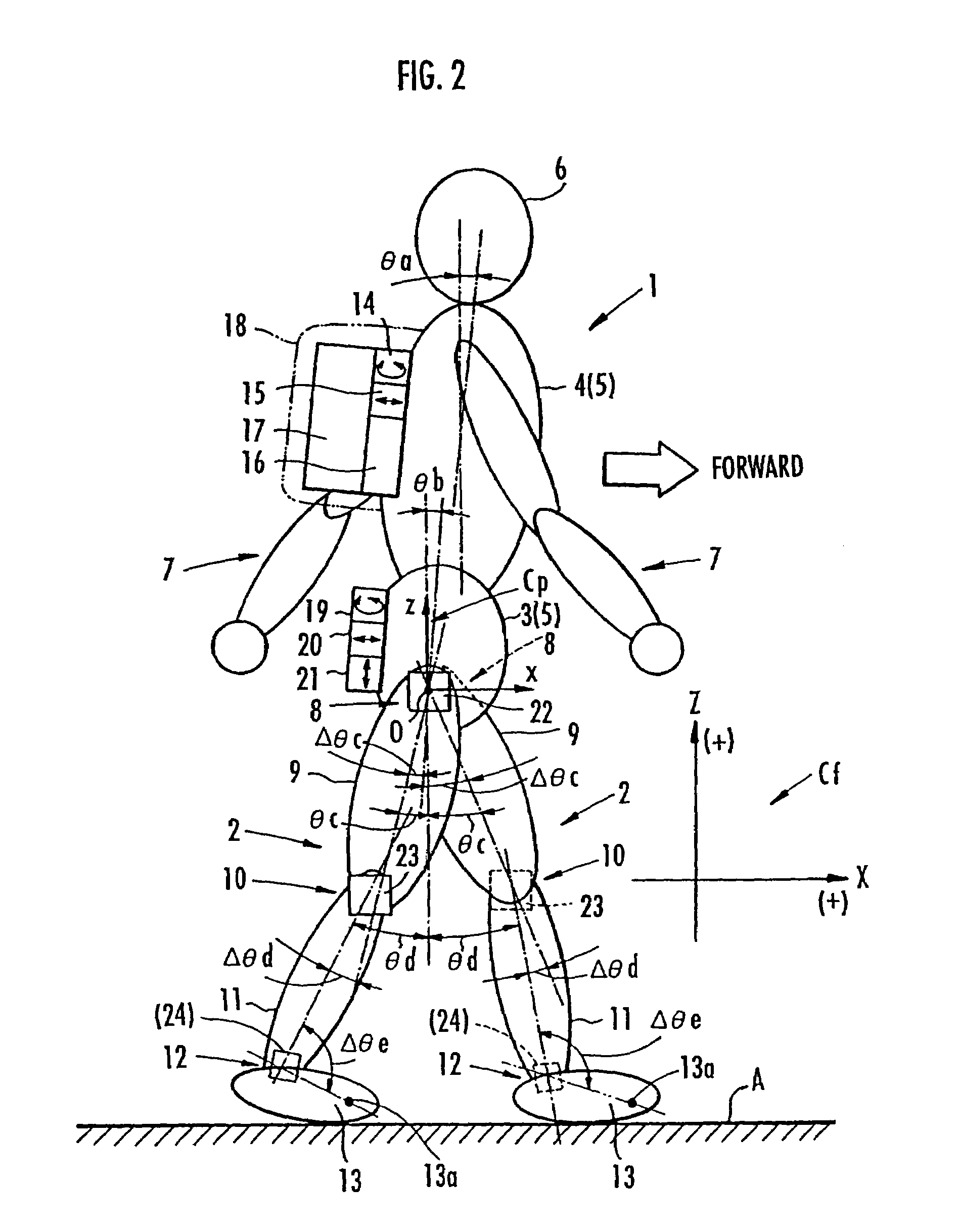
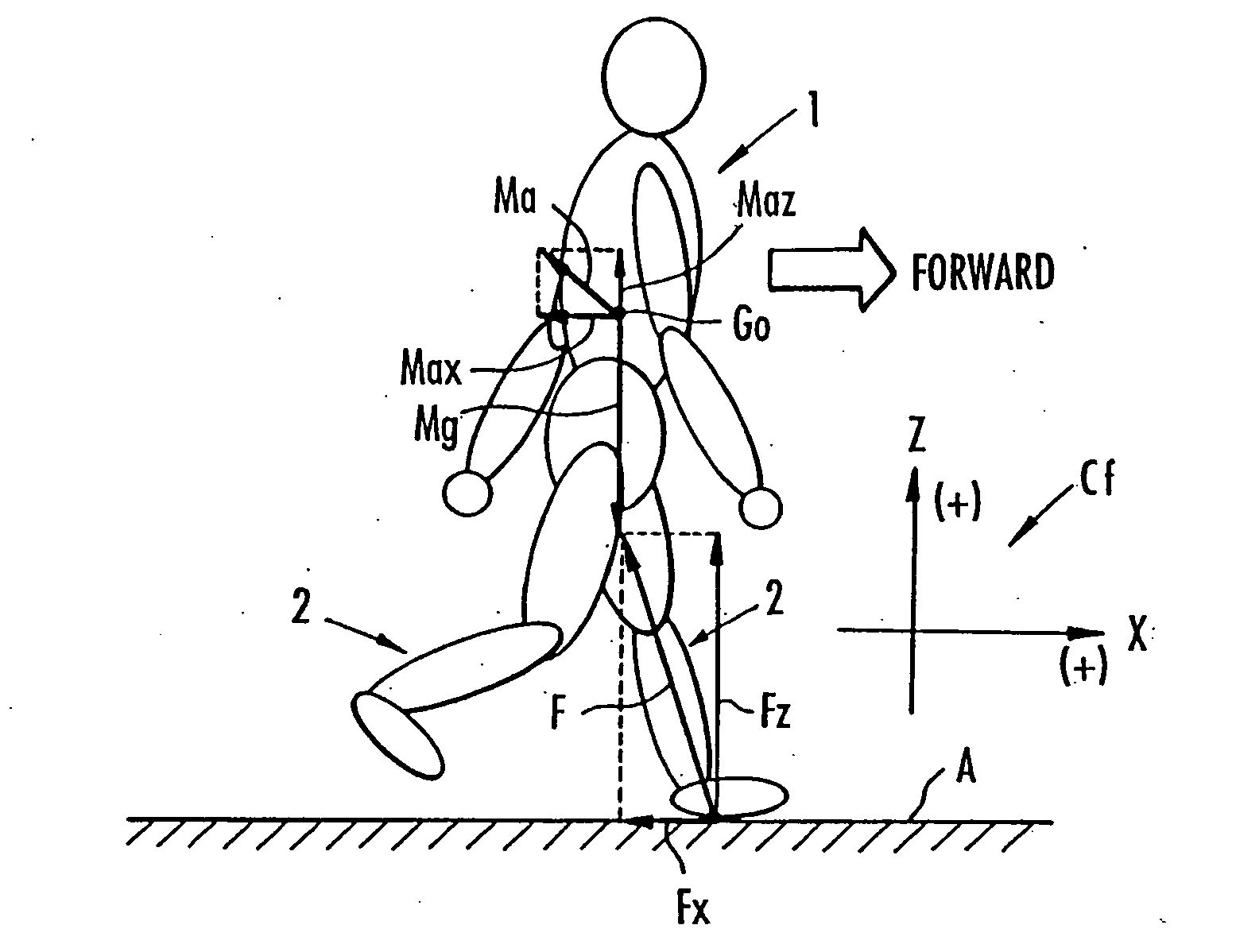
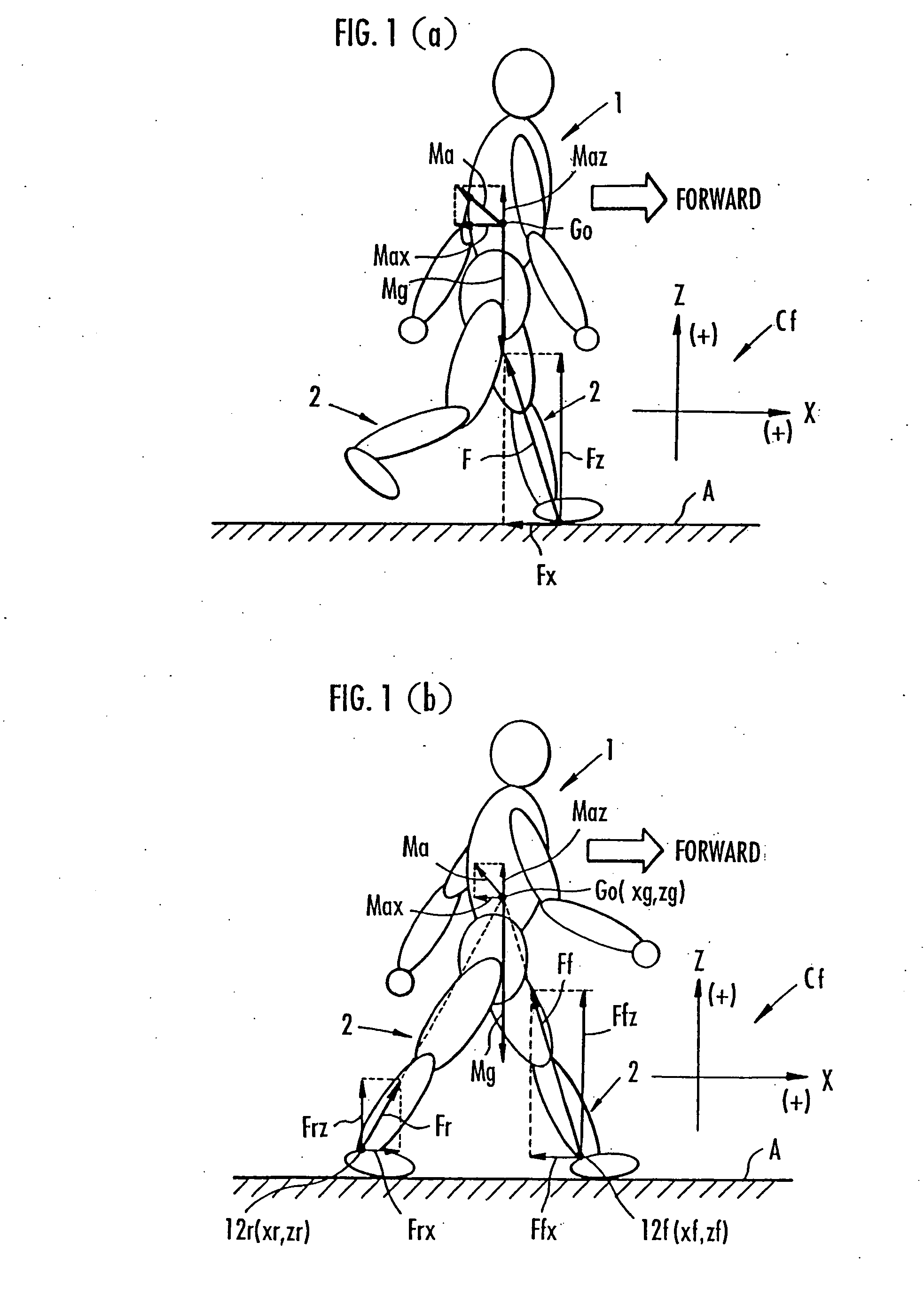
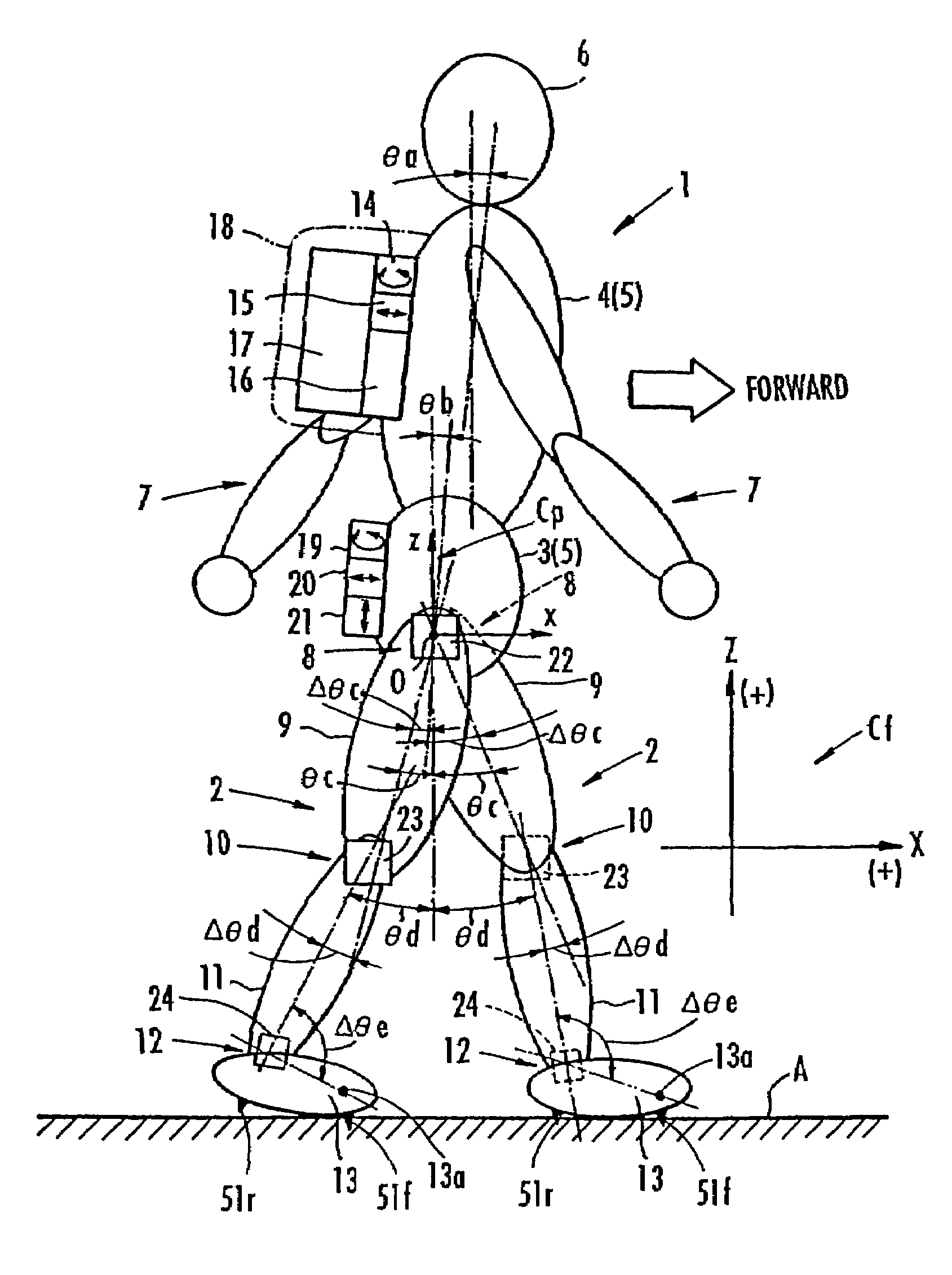
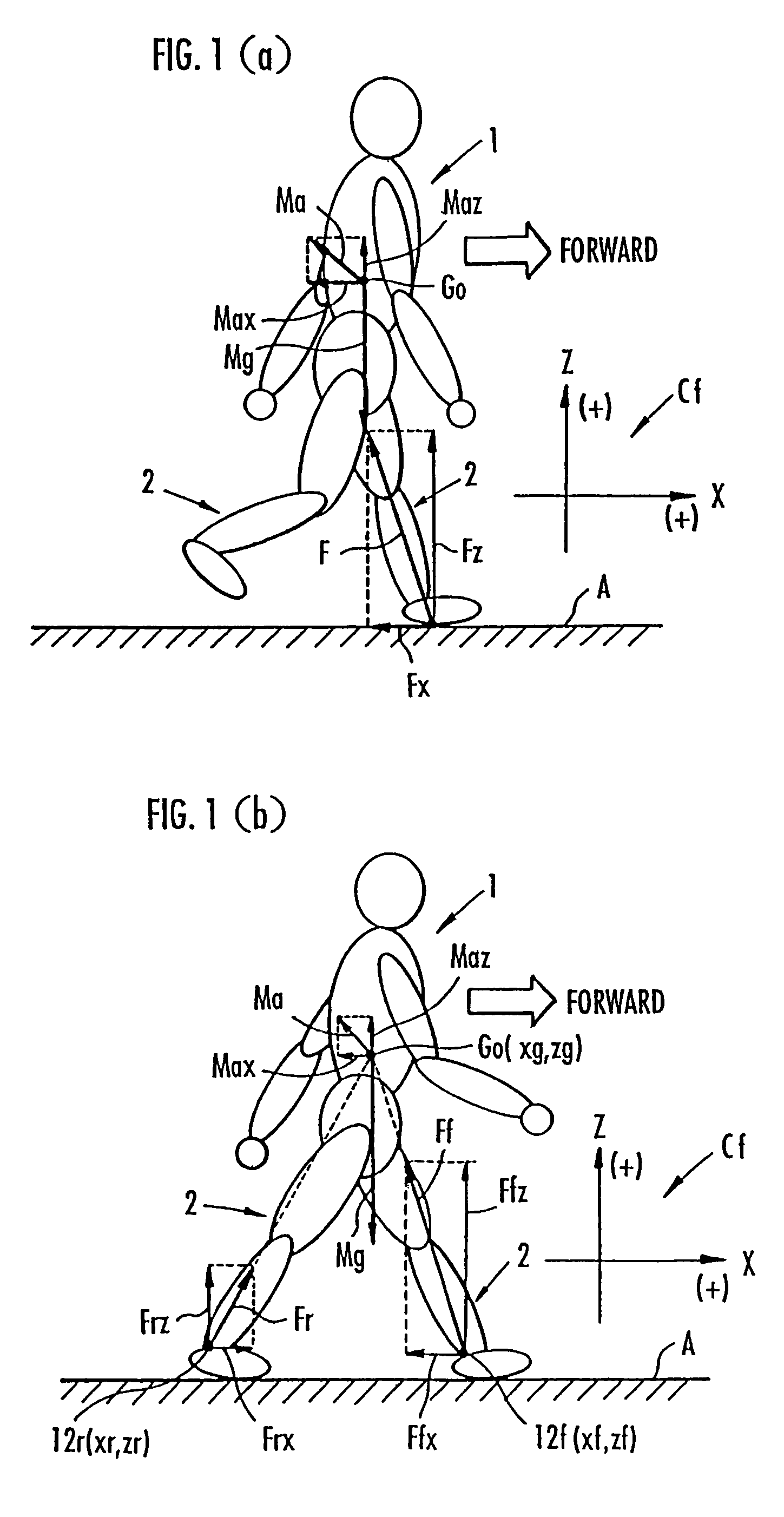
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Catheter deliverable foot implant and method of delivering the same
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating alignment of the foot to treat patients with flat feet, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and metatarsophalangeal joint dysfunction. An inflatable implant is positioned in or about the sinus tarsi and / or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the foot. The implant is insertable by minimally invasive means and inflatable through a catheter or needle. Inflation of the implant alters the range of motion in the subtalar or first metatarsal-phalangeal joint and changes the alignment of the foot.
Owner:CACHIA VICTOR V
Biomechanical custom made foot orthosis and method for making the same
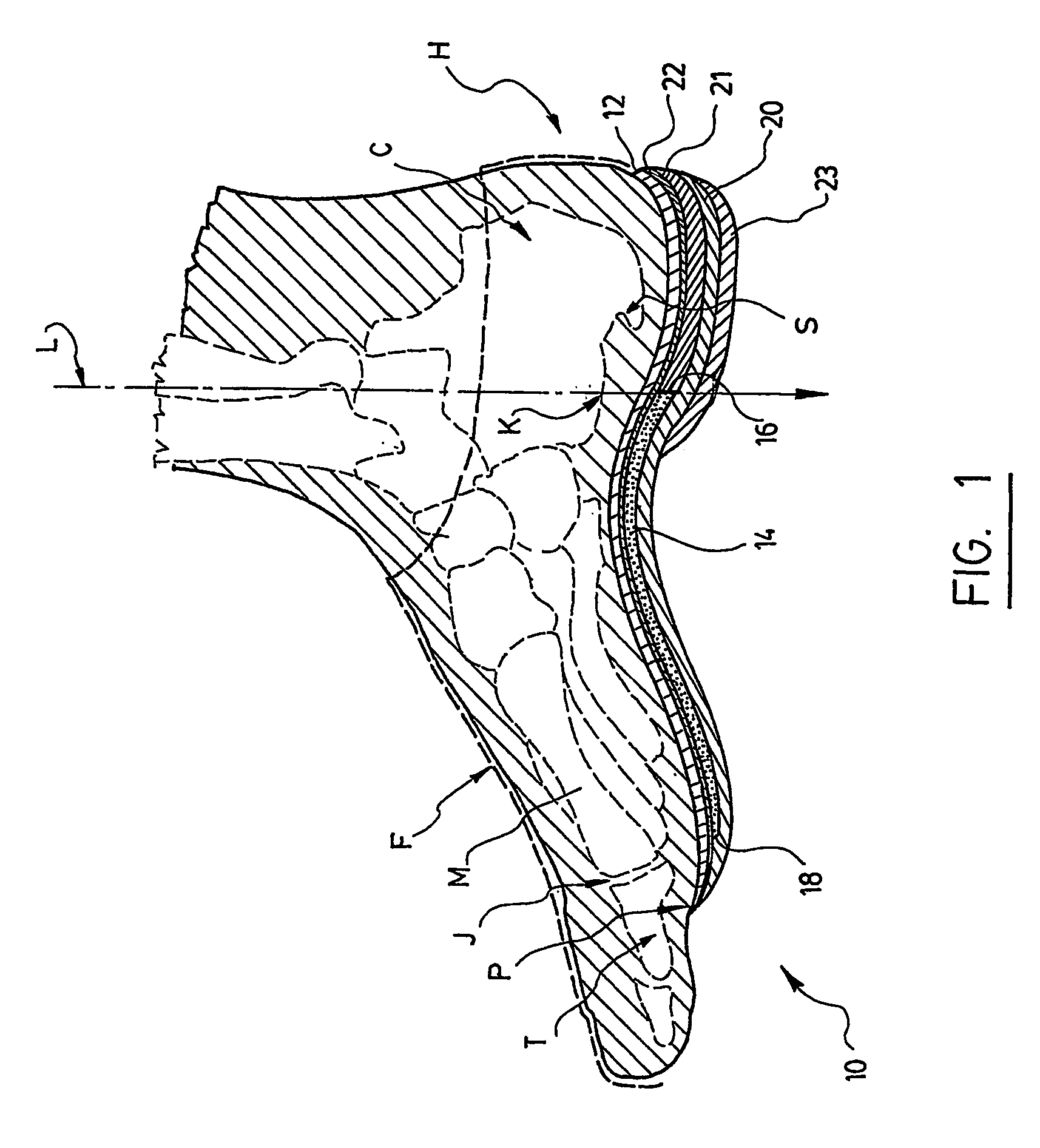
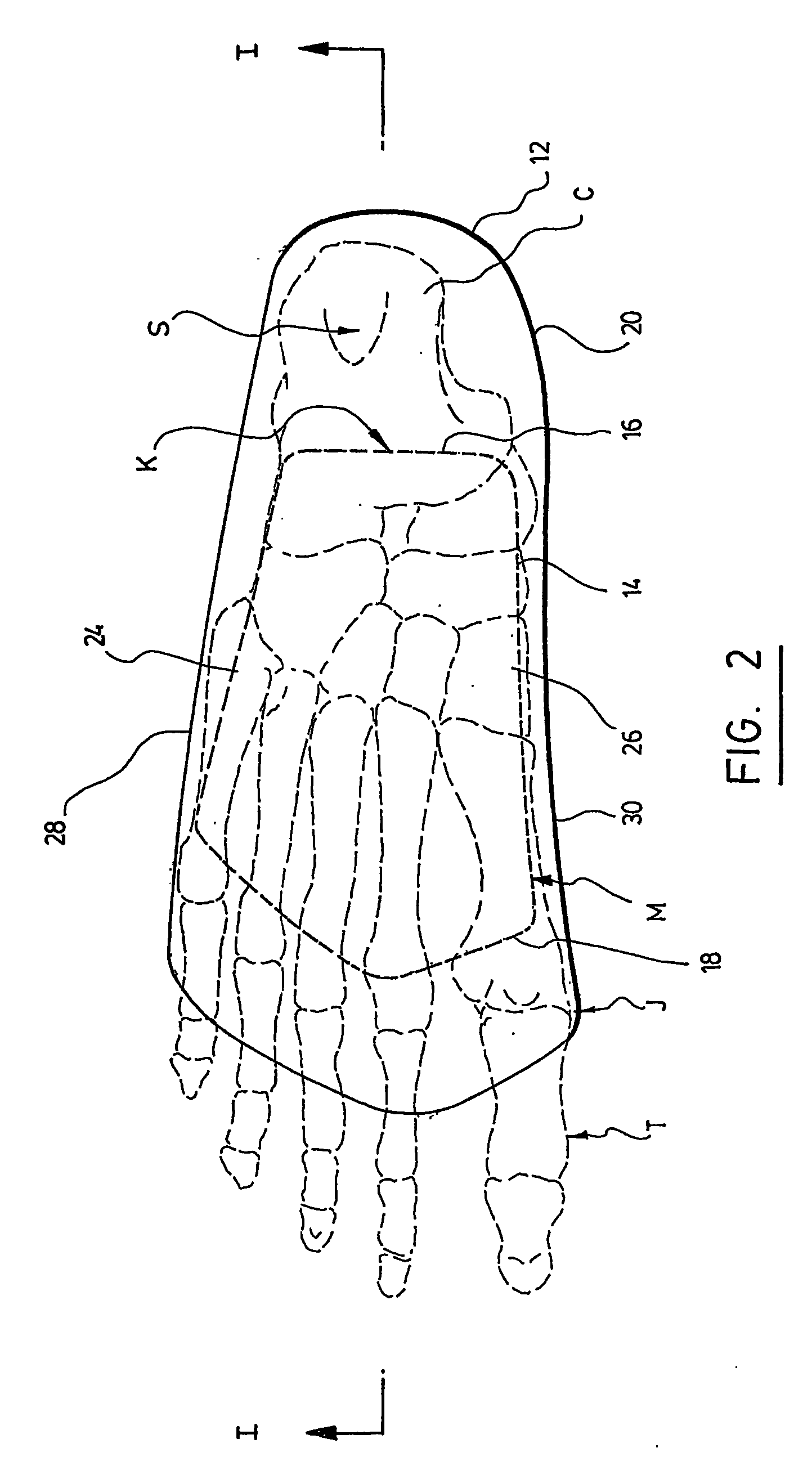
InactiveUS20060015050A1Relieve painRelieve pressureFoot measurement devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBiomechanicsOrthotic device
A biomechanical custom made foot orthosis (10) and a method for making the same. The orthosis (10) has a thermoformed flexible top layer (12) made of a first moldable synthetic rubber material, and a thermoformed flexible reinforcement core layer (14) made of a. moldable core material that is molded onto the top layer, (12). The core layer (14) has a posterior end (16) aligned with a mid anterior plantar prominence (K) of a calcaneus bone (C), and an anterior end (18) aligned near metatarsal-phalangeal joints (J) of the foot. The orthosis (10) also has a thermoformed flexible bottom layer (20) made of a second moldable synthetic rubber material that is molded onto the top layer (12) and the core layer (14). The core layer (14) is more rigid than the top and bottom layers (12, 20). The orthosis (10) corrects anatomic biomechanical deficiencies of the foot and ensuing body deficiencies.
Owner:BLEAU DANIEL
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS20060197485A1Simple arithmetic processingGood estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
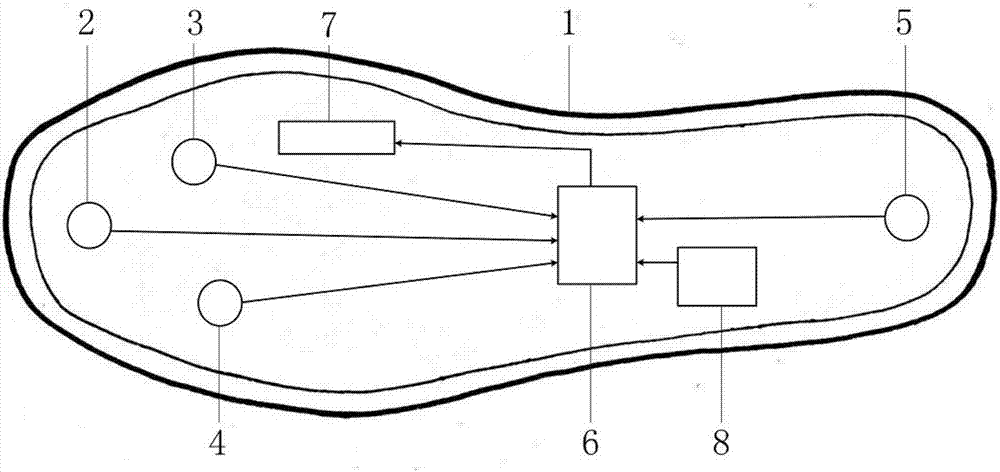
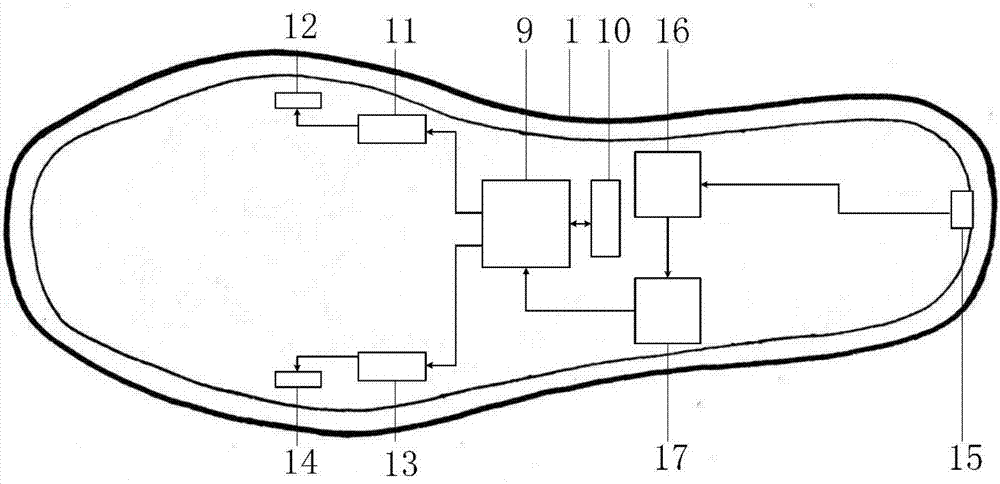
Wearable intelligent insole with health consultation function
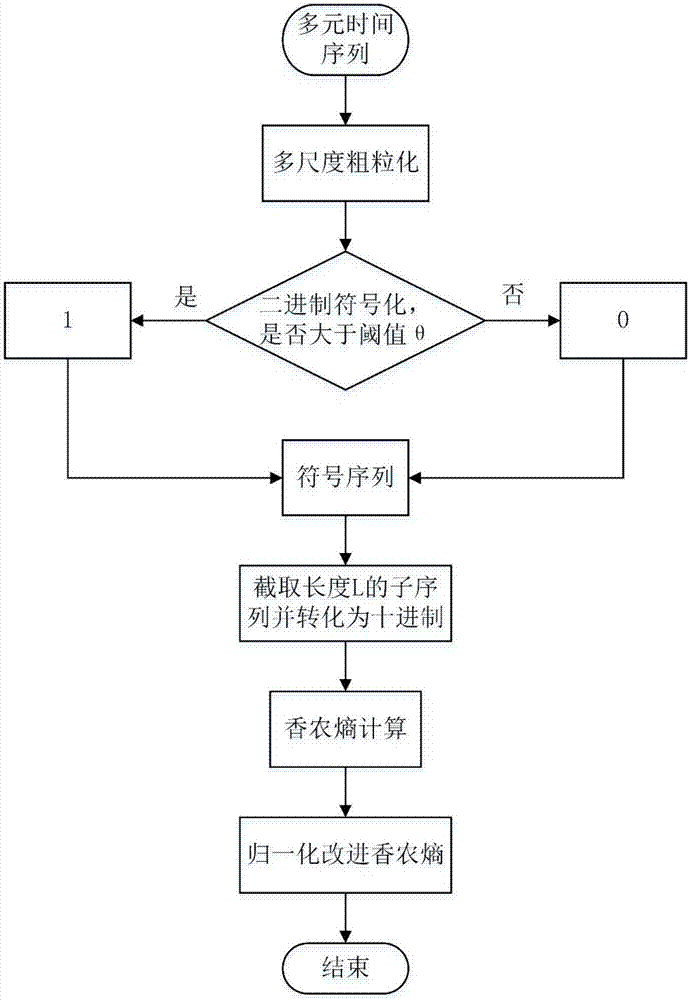
The invention discloses a wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function. The wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function comprises an insole base layer, flexible pressure sensors, a control circuit, a signal transmission circuit and a power supply device, wherein the flexible pressure sensors, the control circuit, the signal transmission circuit and the power supply device are arranged in the insole base layer. The flexible pressure sensors are put on corresponding positions of a tiptoe, a first metatarsophalangeal joint, a fourth metatarsophalangeal joint and a heel respectively, the signal output ends of the flexible pressure sensors are connected with the input end of the control circuit, the output end of the control circuit is connected with the input end of the signal transmission circuit, and the power supply device is connected with the control circuit for supplying power to the flexible pressure sensors. A main chip of the control circuit is integrated with the multi-ary-and-multi-scale-symbolic-entropy data analysis method, and the movement condition, the gait characteristics and the healthy condition of the human body are analyzed according to multiple pressure signals of the foot sole. According to the wearable intelligent insole with the health consultation function, signals of the abnormal gait and the healthy normal gait can be analyzed, processed and identified, and limitation of small data points is met; meanwhile, the coupling relationship between pressure signals of different parts of the foot sole is achieved, the accuracy and the efficiency of gait identification are improved, and the human health is conveniently and remotely monitored.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
ActiveUS20060200272A1Simple arithmetic processingImprove estimation accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, such as level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped. The horizontal position of any one of the center of gravity (G0), the ankle joint (12), and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is estimated as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point on the basis of the combination of the contact or no contact with the ground at a spot directly below the metatarsophalangeal joint 13a of the foot 13 and a spot directly below the ankle joint 12, which is detected by ground contact sensors 51f and 51r, respectively, provided on the sole of the foot 13. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Methods of treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot
Disclosed is a method for treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot of a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of neuromuscular toxin to the mammal. Preferred embodiments include administering toxins capable of interfering with the connection between muscle and nerve, e.g. botulinum toxin, to the patient to treat such abnormalities as hallux abductovalgus, hallux varus, hallux limitus, and hallux rigidus.
Owner:RADOVIC PHILIP
Methods of treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot
Disclosed is a method for treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot of a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of neuromuscular toxin to the mammal. Preferred embodiments include administering toxins capable of interfering with the connection between muscle and nerve, e.g. botulinum toxin, to the patient to treat such abnormalities as hallux abductovalgus, hallux varus, hallux limitus, and hallux rigidus.
Owner:RADOVIC PHILIP
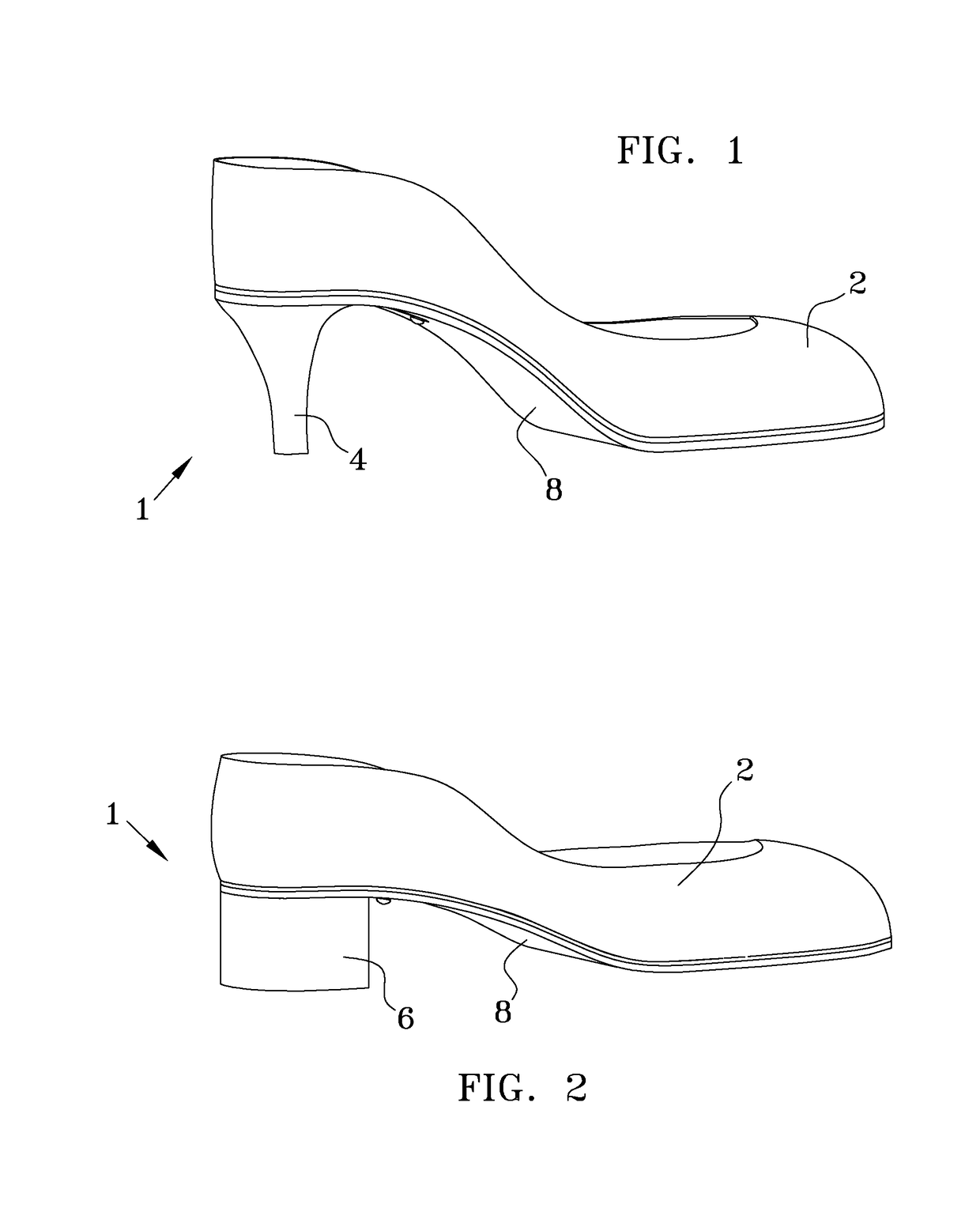
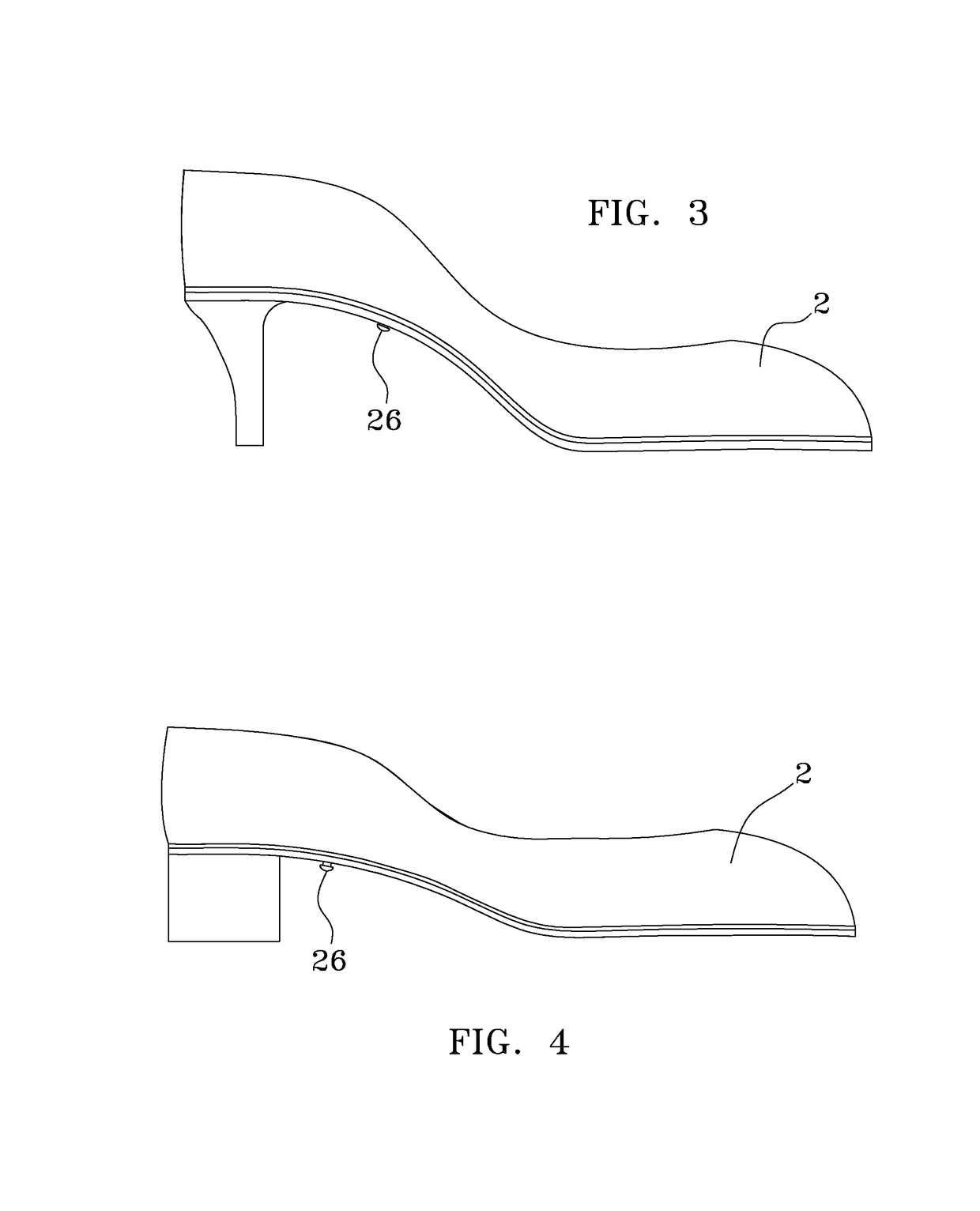
Shoe with a high heel to low heel conversion
A shoe that is convertible between a high heel mode and a low heel mode. There is a rigid shank that is adjustable along the longitudinal axis of the shoe between the various layers of the sole. The proximal end of the adjustable shank may be slid further under the metatarsophalangeal joints to accommodate the sweeping higher arch of a high-heeled shoe or the distal end of the adjustable shank may be slid closer to the back of the calcaneus bone to reduce the arch of the shoe. The different height heels are lockably affixed to the sole.
Owner:HIGH LOW HEEL LLC
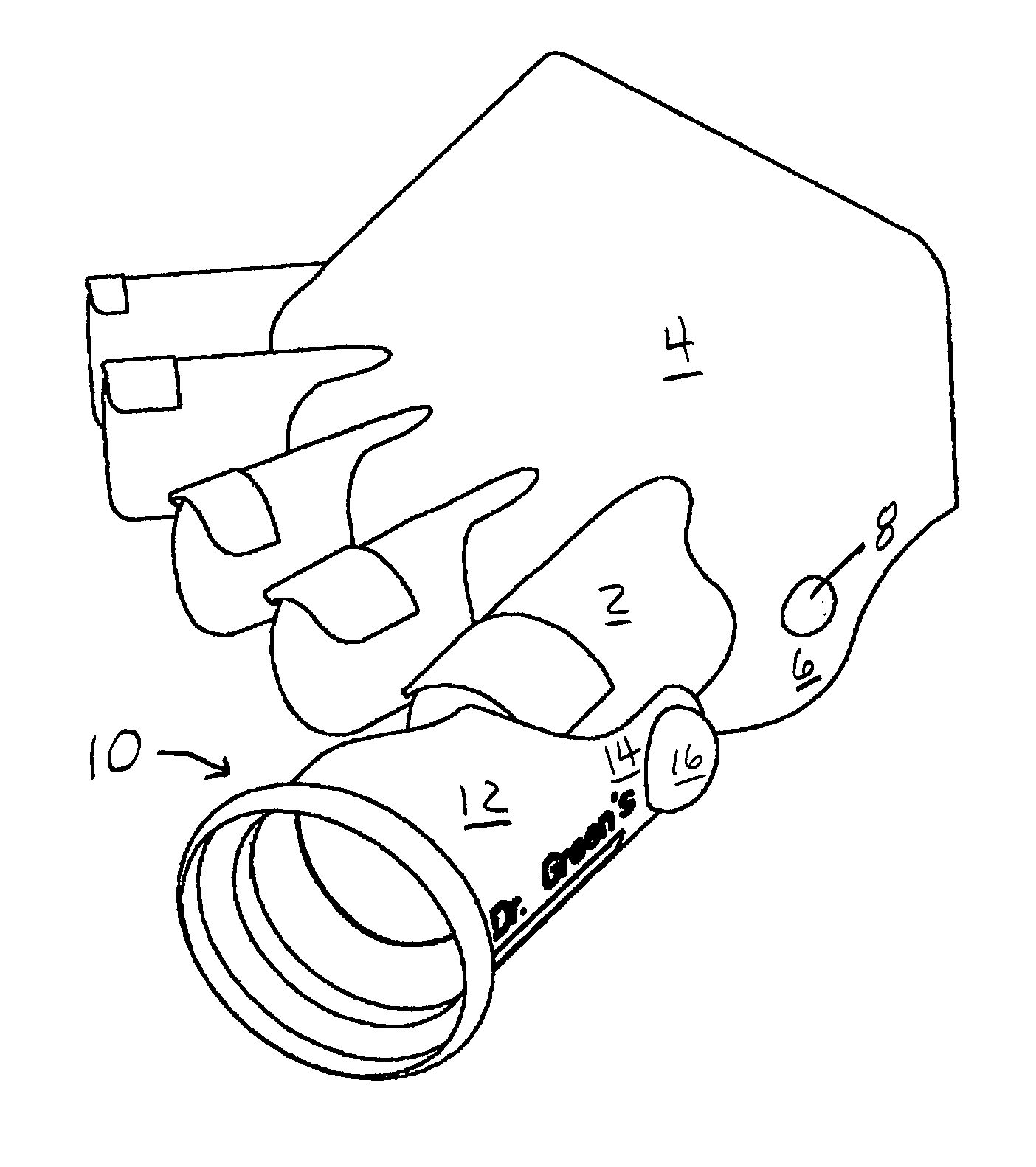
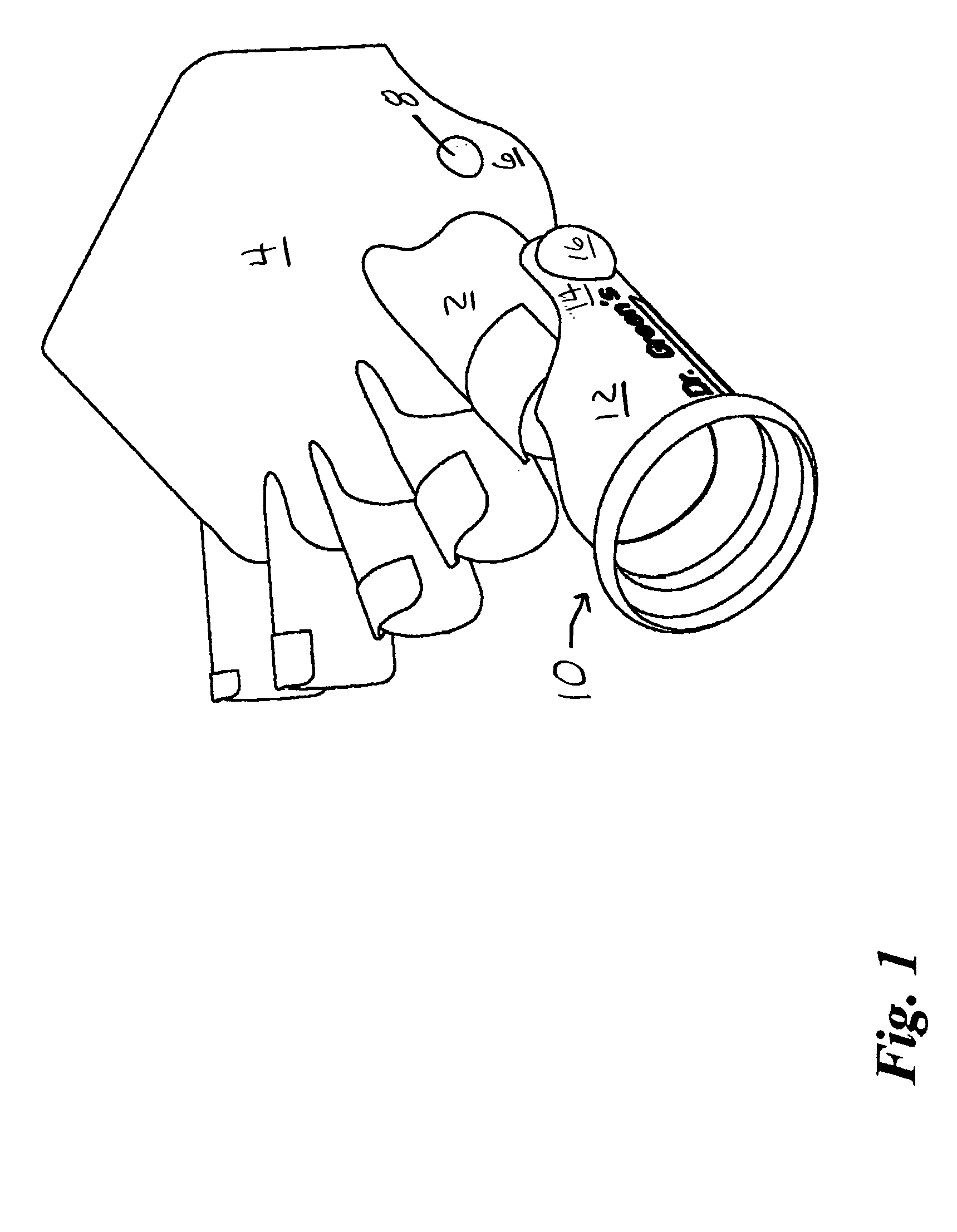
Diabetic toe protectors
A toe protector for protecting the toe and sores or bunions on the foot of a patient from irritation, abrasion, and impact, so as to promote healing is disclosed. The toe protector comprises a generally tubular body sized to substantially cover a toe of the user. The device is preferably fabricated from a soft, FDA approved silicon material, in a double-walled tubular configuration wherein inner and outer layers form an interstitial space. The interstitial space is filled with substance, such as a liquid or gel. A flap extends along the inside portion of the foot and includes a recessed portion sized and positioned for covering relation with bunions on the metatarsophalangeal joint or other sores. According to another aspect, the present invention provides a foot protector to be worn on the foot of a patient. The foot protector preferably incorporates one or more water-filled toe protectors as generally described above. Each of the embodiments may define a plurality of ventilation holes formed by welding of inner and outer portions.
Owner:GREEN ALLAN L +1
Reinforced stocking or sock for the prevention and/or treatment of hallux valgus
A stocking or sock with a foot portion includes a pocket for containing the big toe that is separate from the pocket(s) for the other toes. At least one medial reinforcement, integrally attached to the foot portion, entirely or partially surrounds the big toe pocket, while the medial part of the foot portion, and the posterior part or heel of the foot portion are anchored to the posterolateral or lateral part of foot portion, coming to bear on the anterior part of said pocket, counteracting any lateral deflections, and on the medial part, corresponding to the metatarsophalangeal joint and the first metatarsal of the foot, counteracting any medial deflections.
Owner:ARTHROVEN GMBH
Support for foot injuries
InactiveUS20120136293A1Easy to handleEffectively rectifying foot disordersFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringSacroiliac joint
A support for overpronation is provided with a fitted support, which can be fitted on a foot, and a fastening belt. One end of the fastening belt is detachably fixed to a position in the fitted support that corresponds to the first metatarsophalangeal joint, the middle section of the belt is wound around the heel and the other end is detachably fixed to a position in the fitted support that corresponds to the Lisfranc joint and / or Chopart's joint. With the heel section as an anchor, external force is provided in opposing directions, between the first metatarsophalangeal joint and the Lisfranc joint, or the first metatarsophalangeal joint and Chopart's joint. The support for oversupination is fitted in the opposite way, providing external force in opposing directions.
Owner:OOSAWA MITUNORI
Modified Shoe Permitting Forefoot Extension For Natural Supination and Pronation
A modified shoe that allows the forefoot to extend, creating an everted forefoot in relation to an inverted heel. This action of the foot creates a higher and contracted medial arch. The force of the first metatarsophalangeal joint and first phalange pushing against the ground tilts the rest of the foot at a slight angle to the lateral side, creating supination. The modified shoe also incorporates a unique process of pre-stretching forefoot flex grooves that will allow for a more efficient hinge at the metatarsophalangeal joints. This allows for the several biomechanical changes to a person's gait pattern. This shoe will allow for people to walk with a more natural gait pattern, and not the gait pattern that many people have adopted due to restrictive footwear. This shoe will be ideal for people with forefoot varus, and will have benefits for people with a neutral foot as well.
Owner:BROOKS KEVIN
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
ActiveUS7643903B2Improve estimation accuracyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactGravity center
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, such as level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped. The horizontal position of any one of the center of gravity (G0), the ankle joint (12), and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is estimated as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point on the basis of the combination of the contact or no contact with the ground at a spot directly below the metatarsophalangeal joint 13a of the foot 13 and a spot directly below the ankle joint 12, which is detected by ground contact sensors 51f and 51r, respectively, provided on the sole of the foot 13. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Perceptive blind guiding shoe
ActiveCN105769518ASimple structureMaterials are cheap and readily availableWalking aidsFootwearNervous systemFourth toe
The invention relates to a pair of perceptive blind guiding shoes. Each perceptive blind guiding shoe comprises a shoe pad, an upper and a sole, wherein the upper and the sole are fixed together, the shoe pad is arranged on the sole, the upper is fixedly connected with a shoe lining, the shoe lining is provided with nipple-like convex pins at positions corresponding to a big toe tip, a big toe convex point, a second toe tip, a third toe tip, a fourth toe tip, a small toe convex point, a first metatarsophalangeal joint convex point, a fifth metatarsophalangeal joint convex point and a back arc convex point of the shoe lining, and a forefoot sole of the shoe pad is provided with nipple-like convex pins at positions corresponding to a first and second toe cross point, a third and fourth toe cross point, a fourth and fifth toe cross point, a middle waist of the shoe pad, an upward bending point of a foot scaphoid, an outer side of a heel and an inner side of the heel. When the shoe touches an obstacle in a certain direction, the nipple-like convex pin in this direction stimulates a nervous system of the foot to allow the blind to make a response in time to prevent situations such as fallings and injuries from occurring, and the perceptive blind guiding shoes have the characteristics of convenience in use, avoidance of influences of external noisy environments and remarkable effect.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Formula for treating and preventing arthritis, synovitis and other orthopaedic diseases and complicating diseases
The invention relates to a formula for treating and preventing arthritis, synovitis and other orthopaedic diseases and complicating diseases and discloses a main compound extracted from mangosteen:Garcinia mangostana. In the main compound, alpha-mangostin serving as a main ingredient is used in combination with various common filters in pharmaceuticals industry to prepare various proper formulations including tablets, capsules, powders, suppositories and the like for oral or external use for treating and preventing arthritis diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, chronic infectious arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis and purulent arthritis as well as complicating diseases of the arthritis diseases such as inflammations of finger joints, metacarpophalangeal joints, wrist joints, elbow joints, shoulder joints, knee joints, spondyl joints, ankle joints, metatarsophalangeal joints and other joints. The alpha-mangostin content of the product of the invention is between 0.1 and 99.9 percent. The product manufactured by the formula can relieve the various inflammations and has certain analgesic effect. The product can be used alone or in combination with other substances.
Owner:陈霞
Footwear With Rocker Sole
InactiveUS20110314699A1Improved energy returnEncourages rolling gaitSolesHeelsEngineeringTarsal Joint
An article of footwear with a rocker sole has an outsole with a rocker sole element that has a rear apex located 20 to 45 millimeters, preferably, 35 to 40 millimeters rearwardly of the metatarsophalangeal joint area of the footwear and a generally curved surface extending forwardly and upwardly from the apex to a toe area of the footwear.
Owner:C & J CLARK INT
Carbon fiber energy-storing pseudarthrosis artificial limb simulating functions of intertarsal joint
The invention relates to a carbon fiber energy-storing pseudarthrosis artificial limb simulating functions of an intertarsal joint. The artificial limb comprises an S-shaped upper plate, a lower plate and a connecting structure and is characterized by also comprising a heel shrapnel and a trapezoidal groove structure, wherein the upper end of the trapezoidal groove structure is horizontal and is fixedly connected with the connecting structure; the lower end of the trapezoidal groove structure is inclined for 30 degrees and is fixedly connected with the heel shrapnel; the small groove opening of the trapezoidal groove structure is backward; the big groove opening of the trapezoidal groove structure is forward; and the S-shaped upper plate passes through the groove openings and is connected with the connecting structure. An upper bent part of the S-shaped upper plate is combined with the trapezoidal groove structure, so the transmission force and the jogging function of the intertarsal joint are tactfully simulated; and a lower bent part of the S-shaped upper plate and a toe part of a lower plate are combined into a unique structure, so the dorsiflexion of a metatarsophalangeal joint can be simulated. An opening of the heel shrapnel is downward and the lower part of the heel shrapnel is connected with the lower plate. The artificial limb has the characteristics of high strength, light weight, high elasticity, stability in standing, graceful travelling tread and the like.
Owner:DALIAN XINGKE CARBON FIBER
Motion toe systems and methods
ActiveUS20210059829A1Limit motionGood sittingWrist jointsAnkle jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
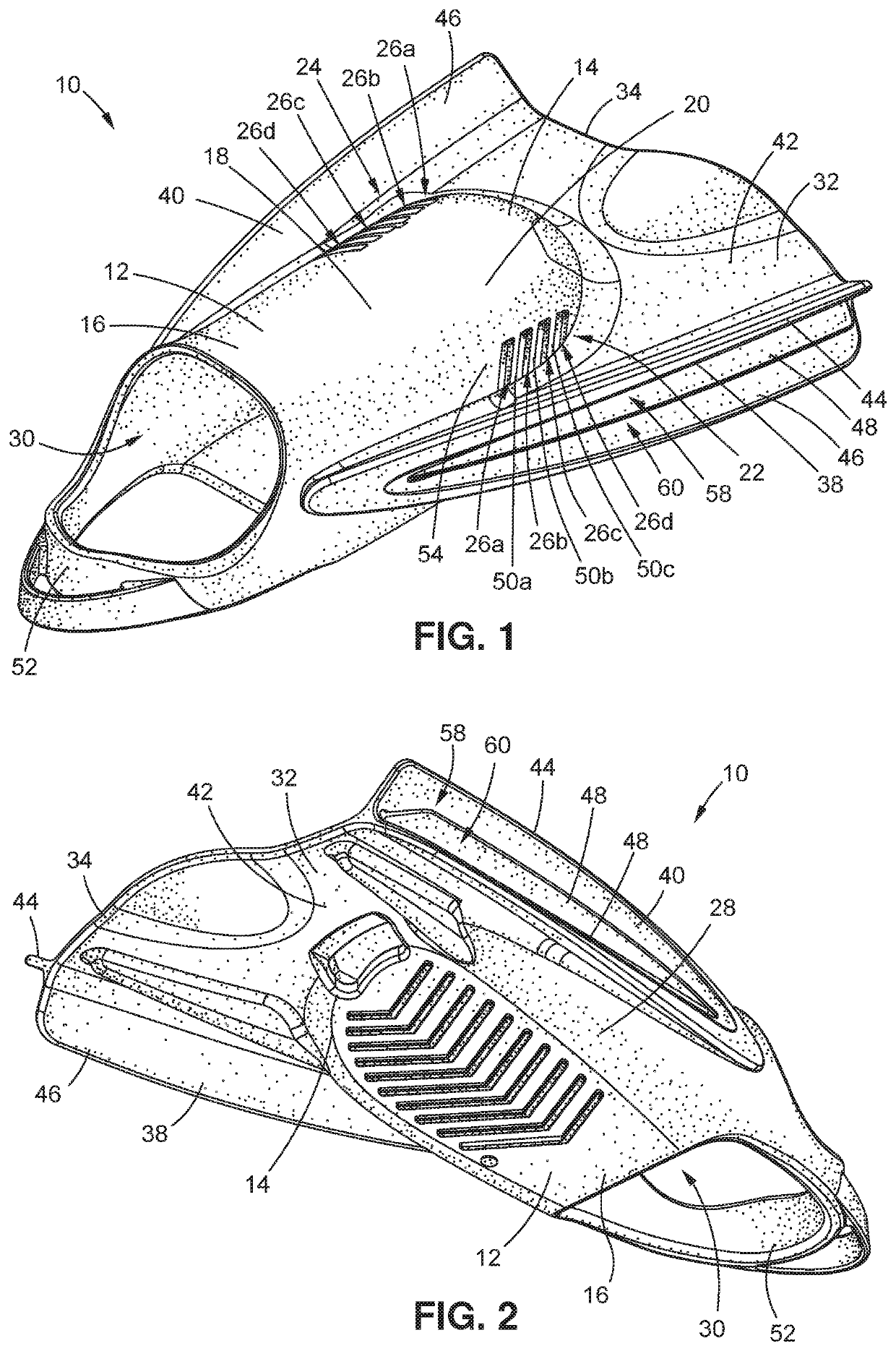
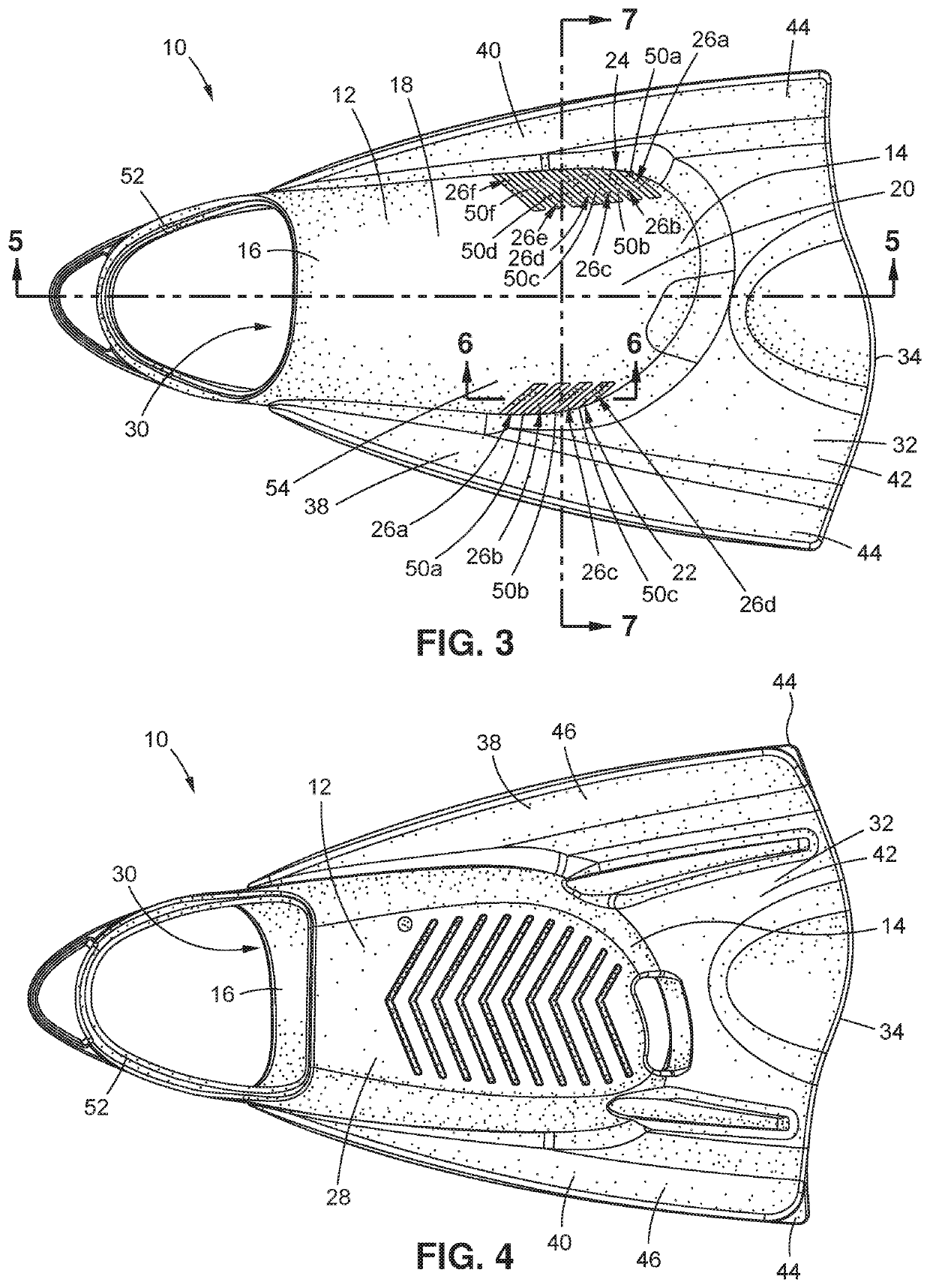
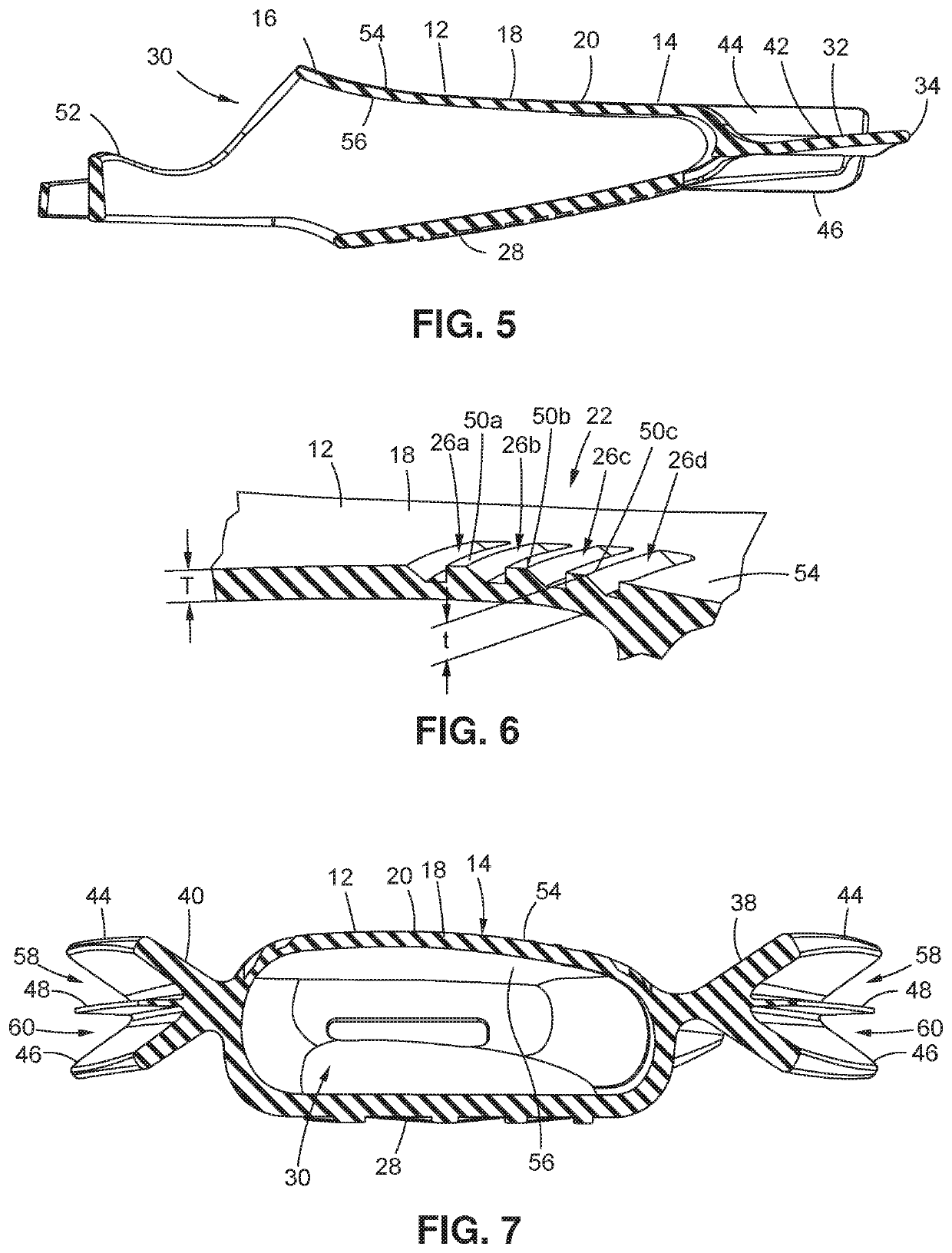
Disclosed are devices and related surgical methods for replacing some or all of a metatarsophalangeal joint of a patient.
Owner:MONTROSS WILLIAM +1
Device for correcting hallux valgus and method for producing device for correcting hallux valgus
InactiveUS20130110024A1Large correcting forceGood adhesionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesShape-memory alloySacroiliac joint
Provided is a device for correcting hallux valgus using a shape memory alloy, which can be easily worn and exert a large and adequate correcting force to thereby correct hallux valgus or hallux varus. The device for correcting hallux valgus comprises a correcting plate formed of a shape memory alloy and attachment members for attaching the same, said attachment members each being formed of an elastic fabric bag, wherein said correcting plate is attached, from the inward direction of the hallux, to the foot body and to the hallux body respectively by the first attachment member and the second attachment member, and an opening is formed in the part of the correcting plate being in contact with the first metatarsophangeal joint so that the hallux is corrected by positioning outward using the periphery of the opening as a supporting point.
Owner:FURUKAWA TECHNO MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com