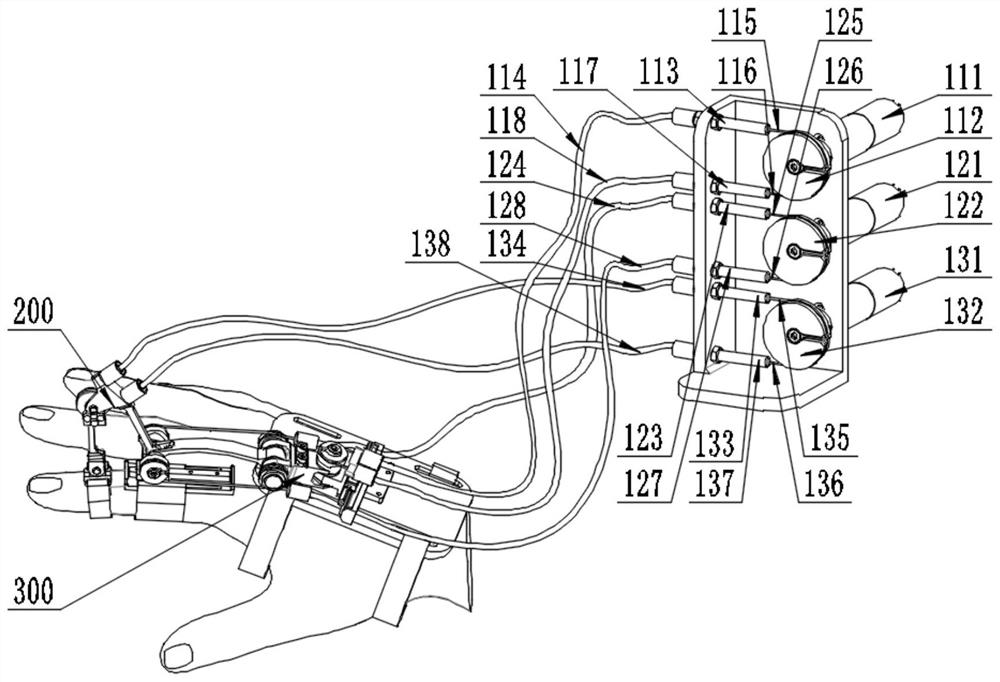
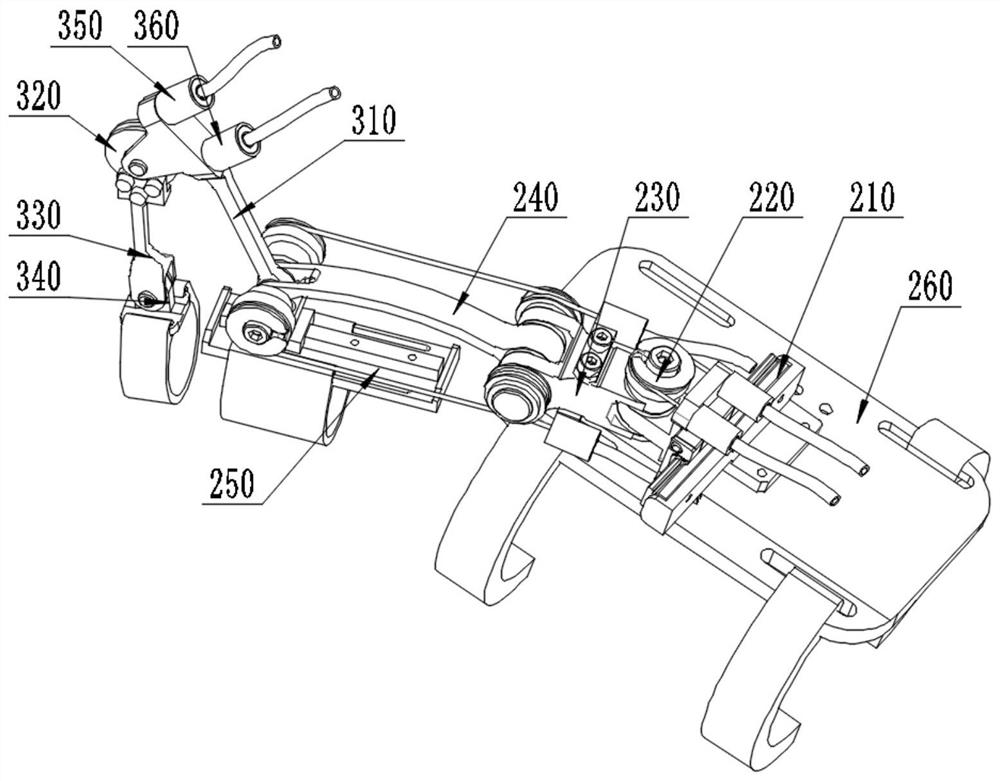
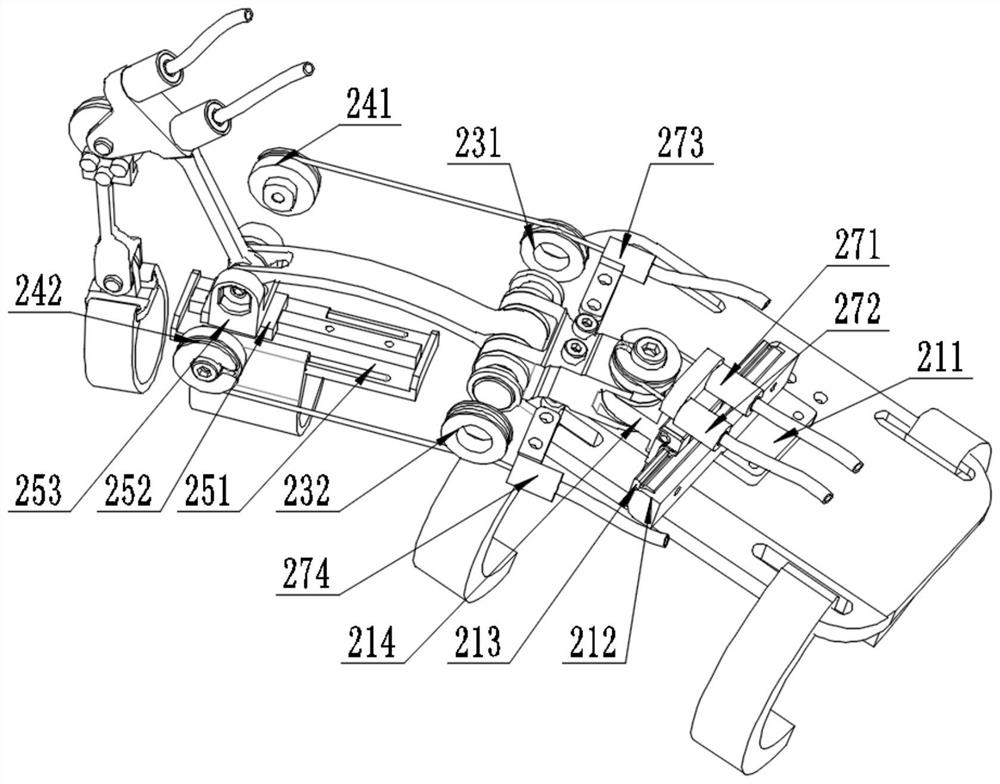
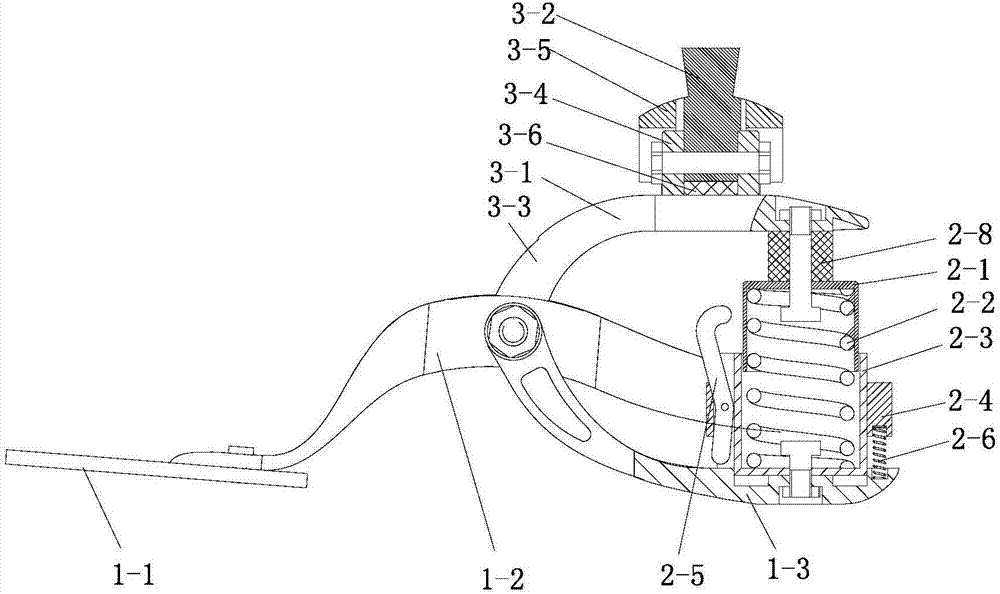
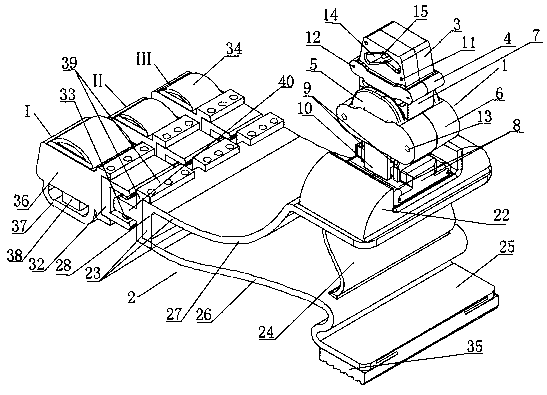
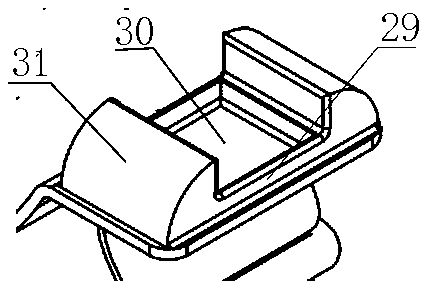
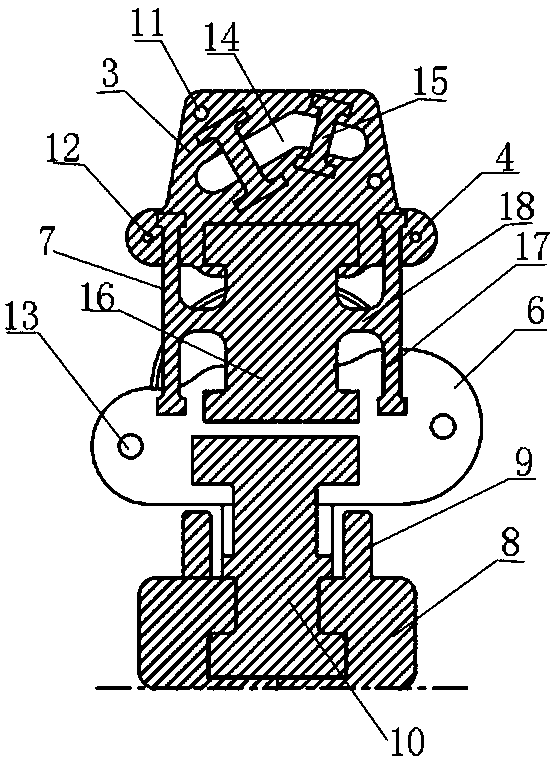
Patents
Literature
168 results about "Metatarsal joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
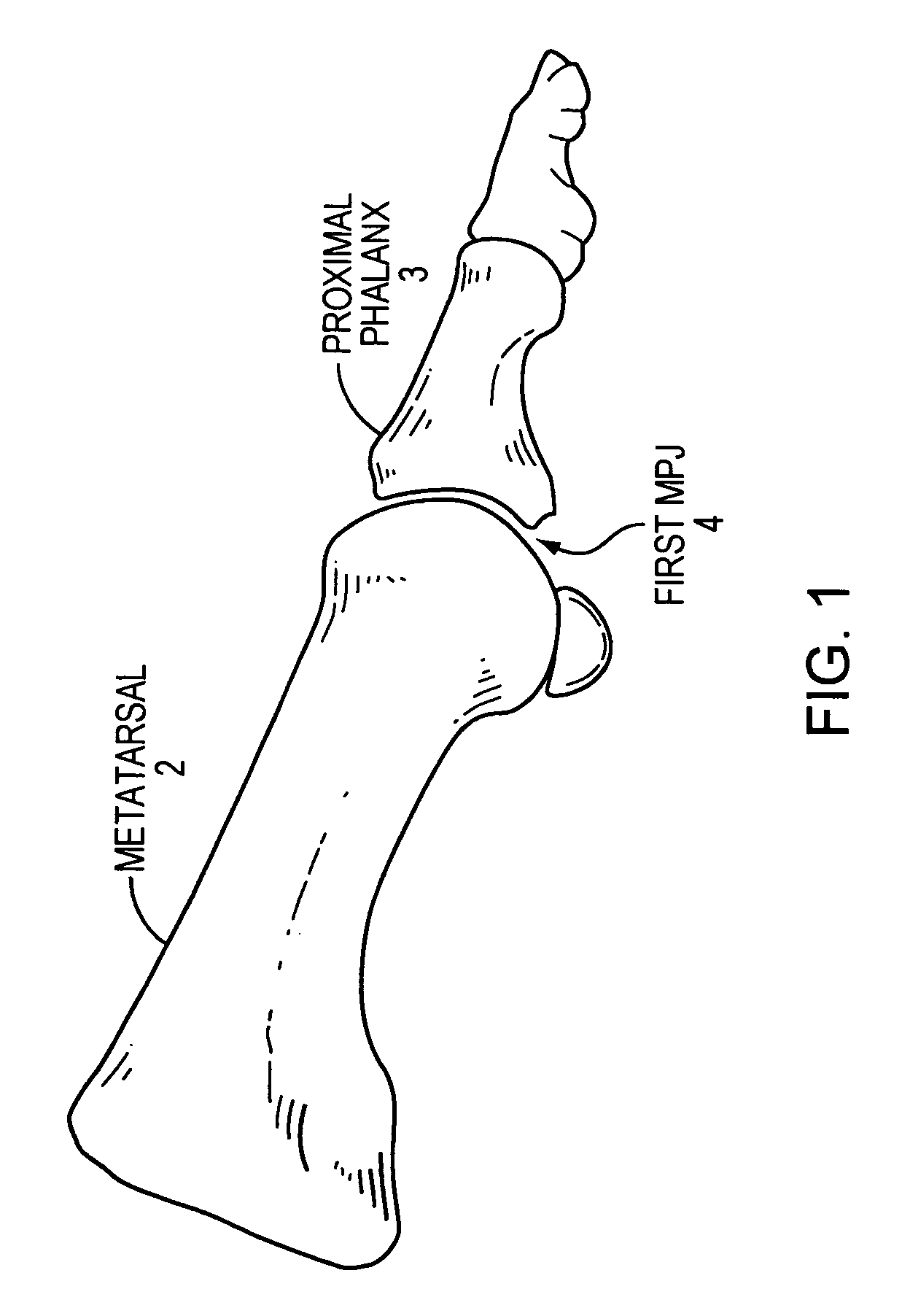
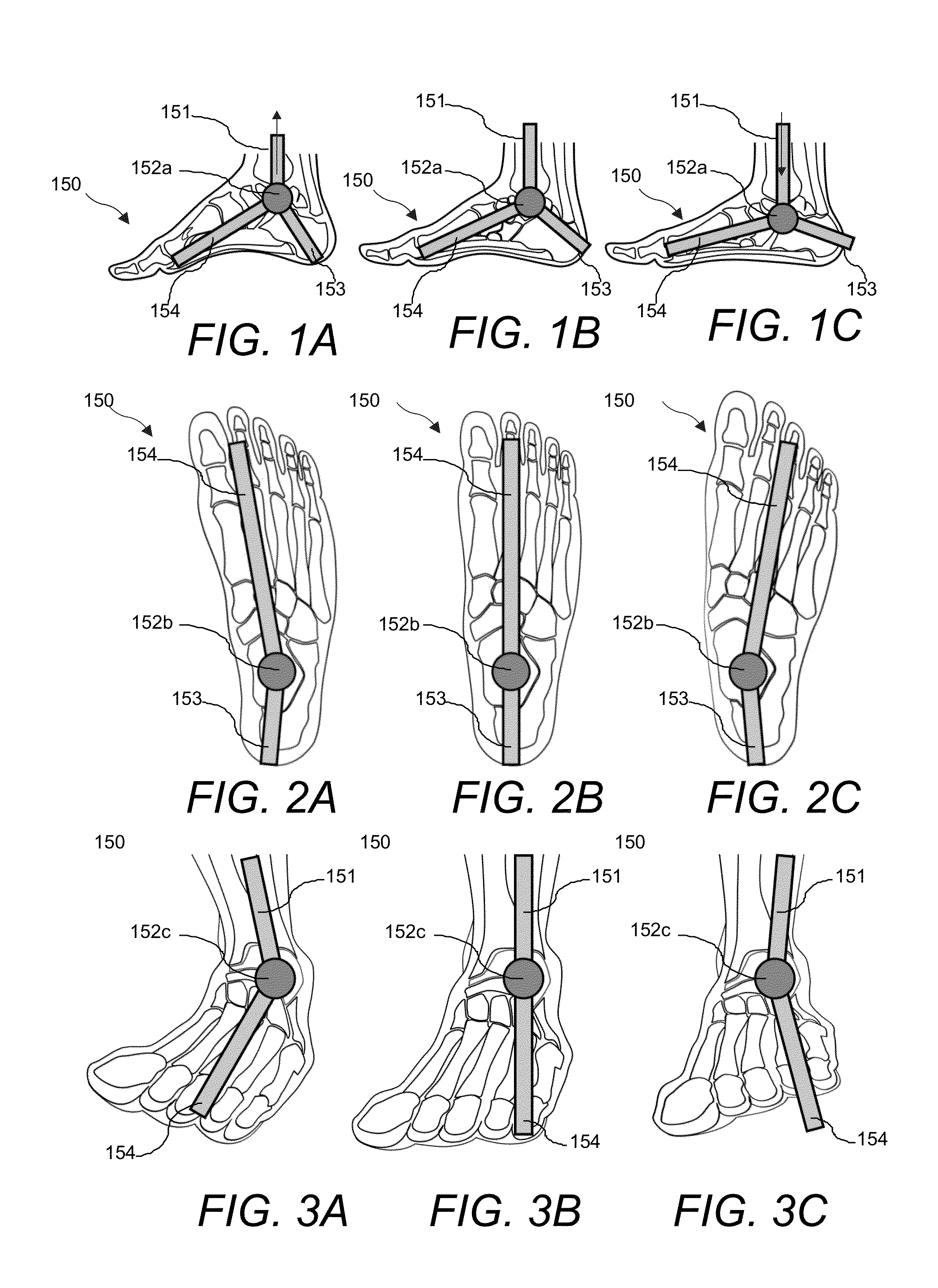
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints) are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges).
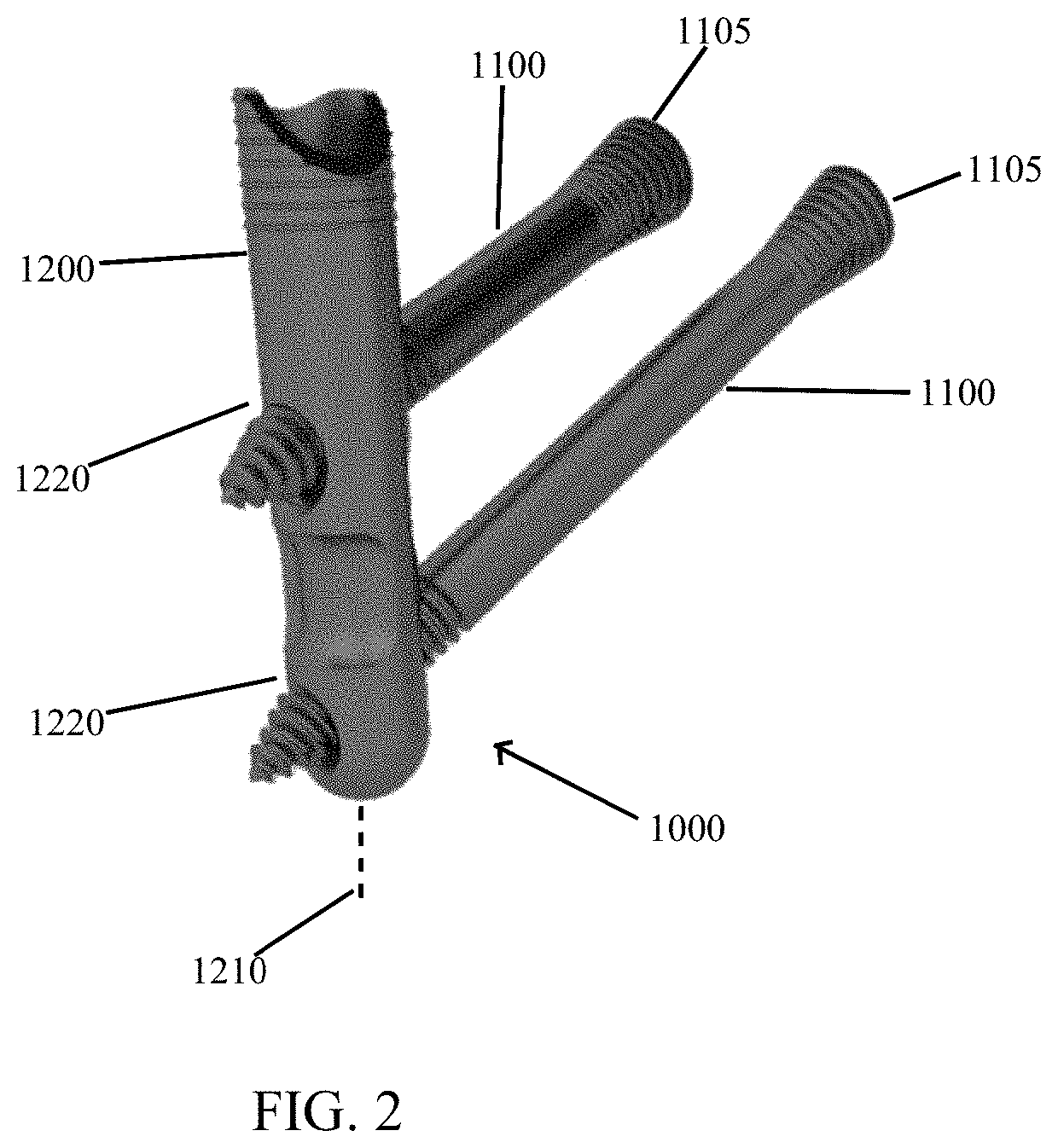
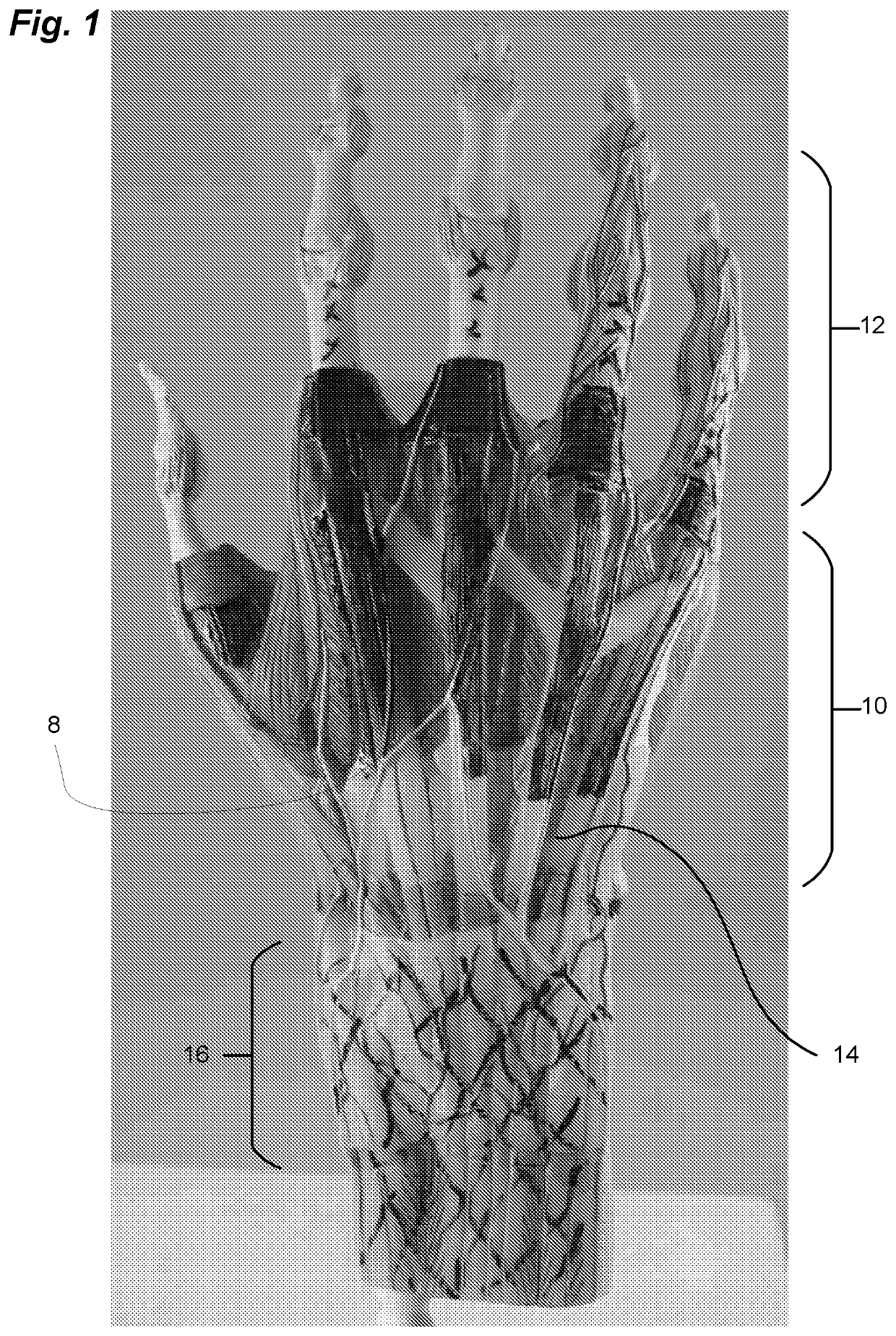
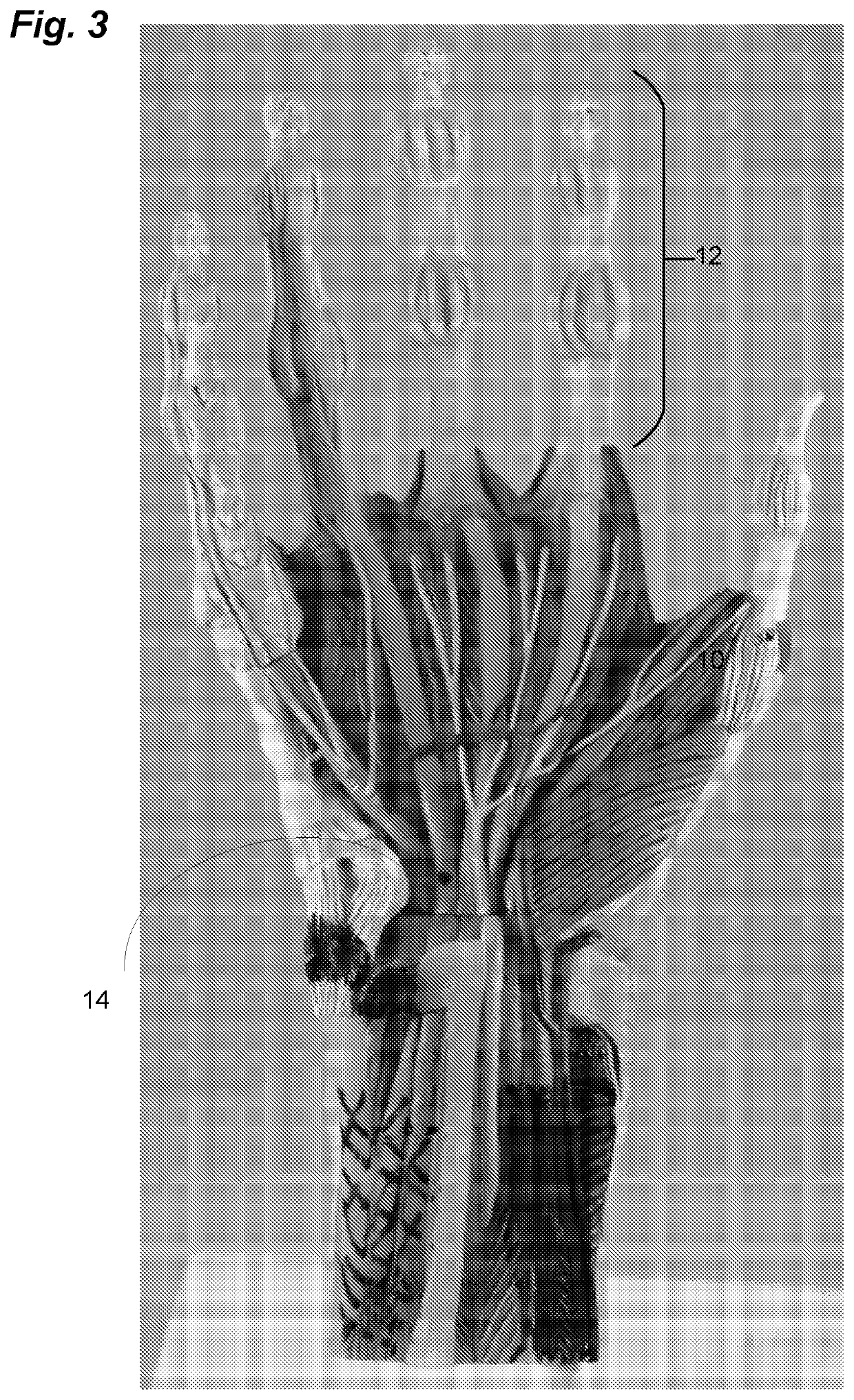
Surgical technique using a contoured allograft cartilage as a spacer of the carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb or tarso-metatarsal joint of the toe
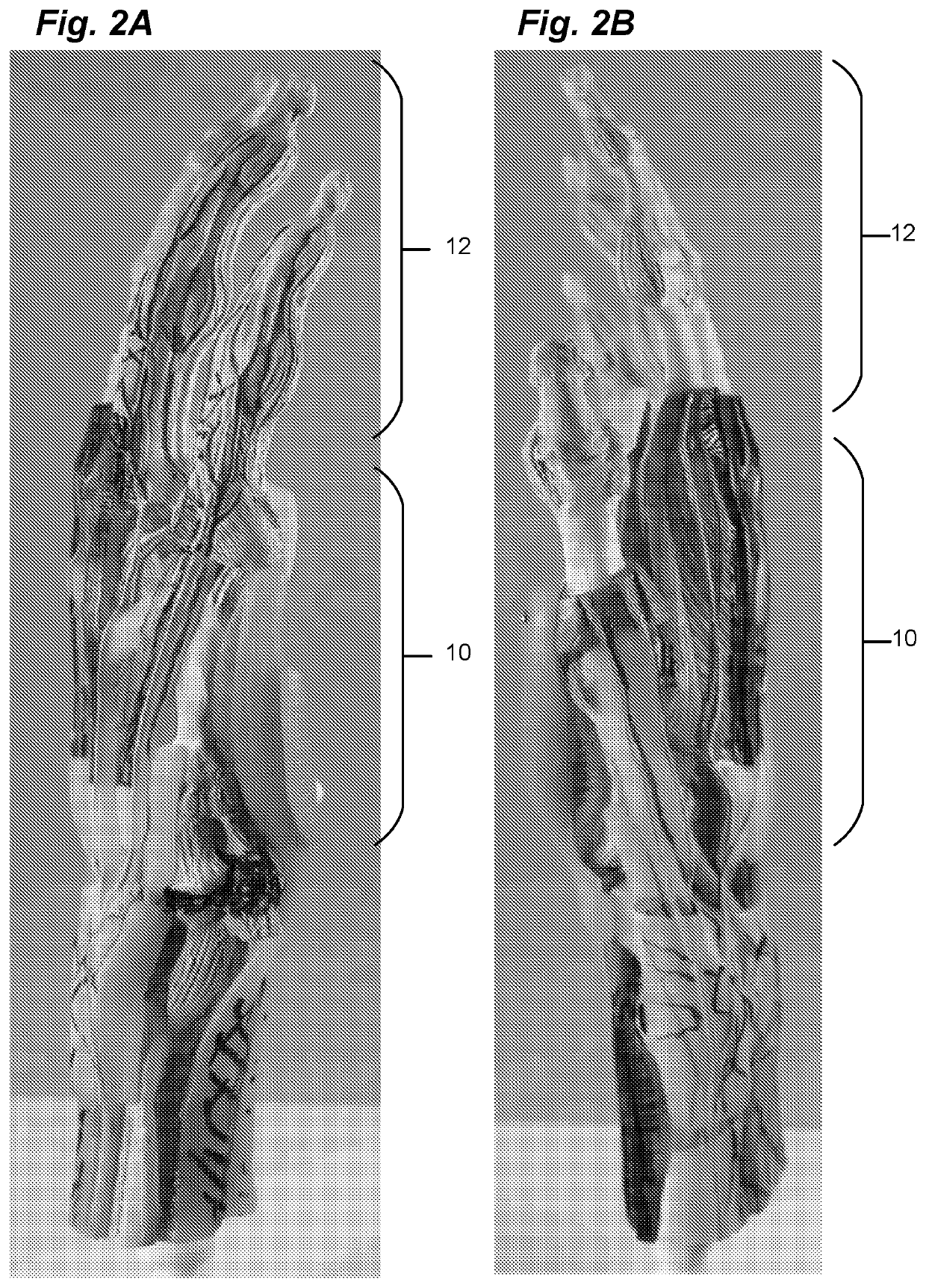
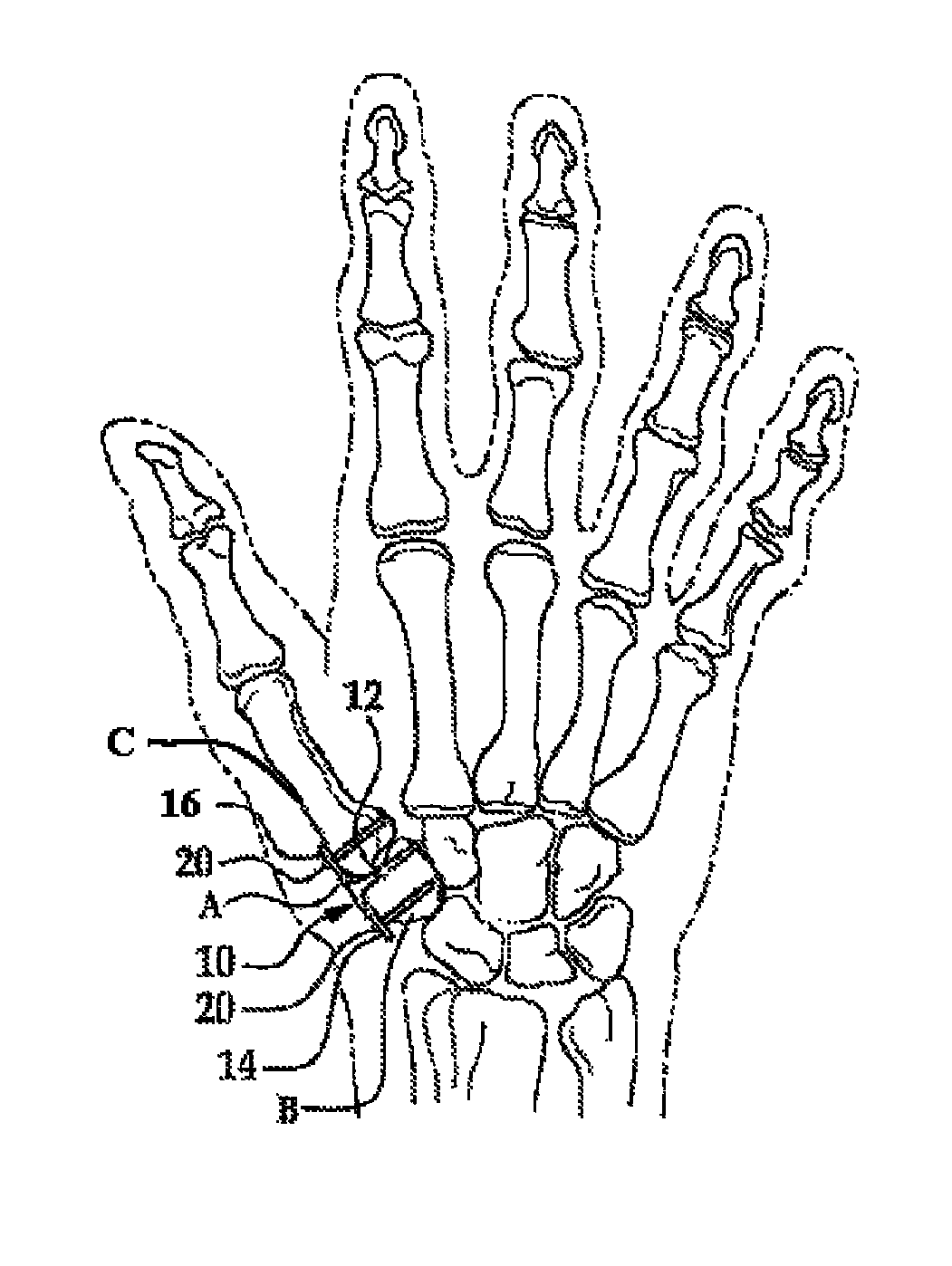
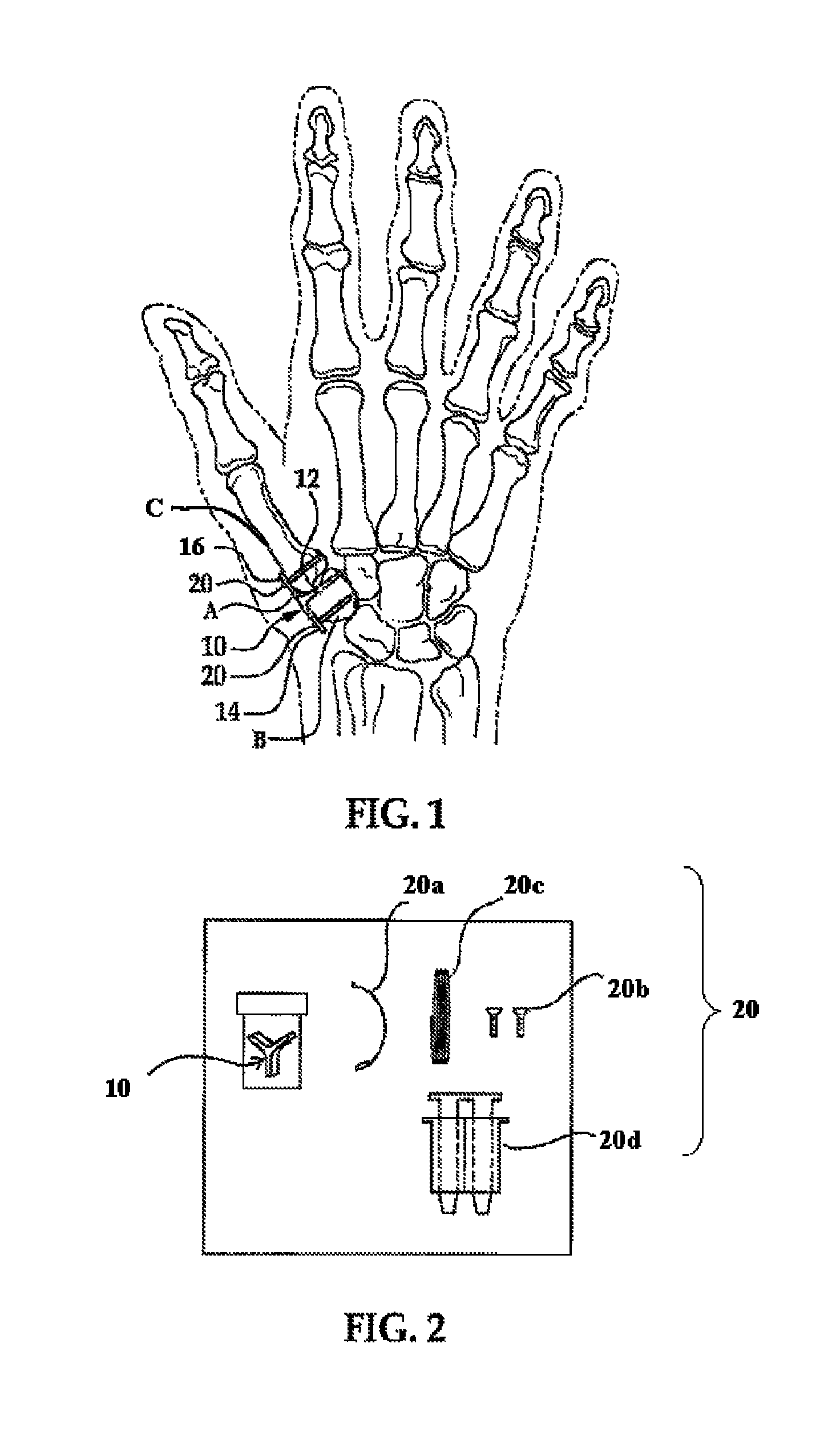
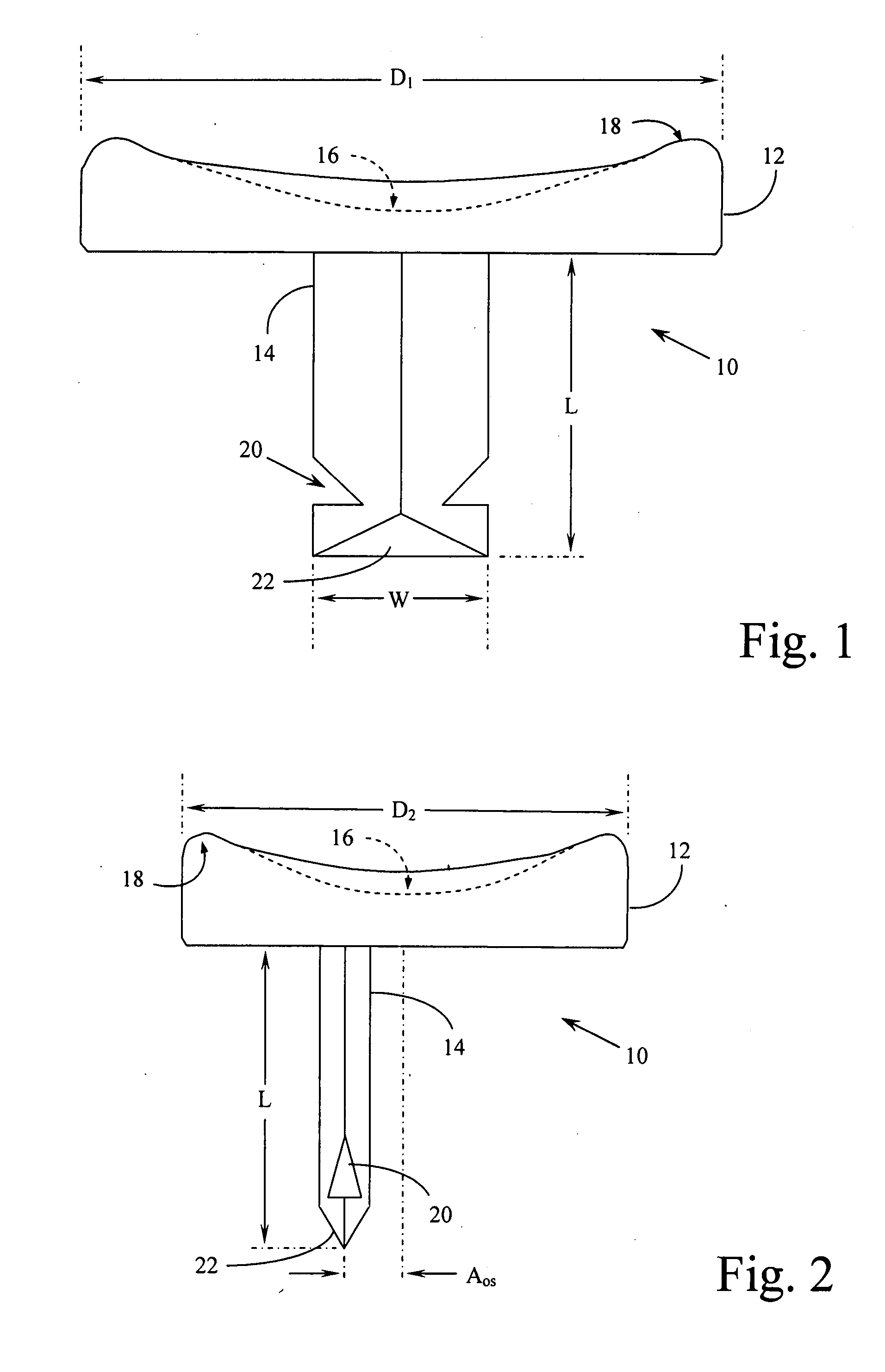
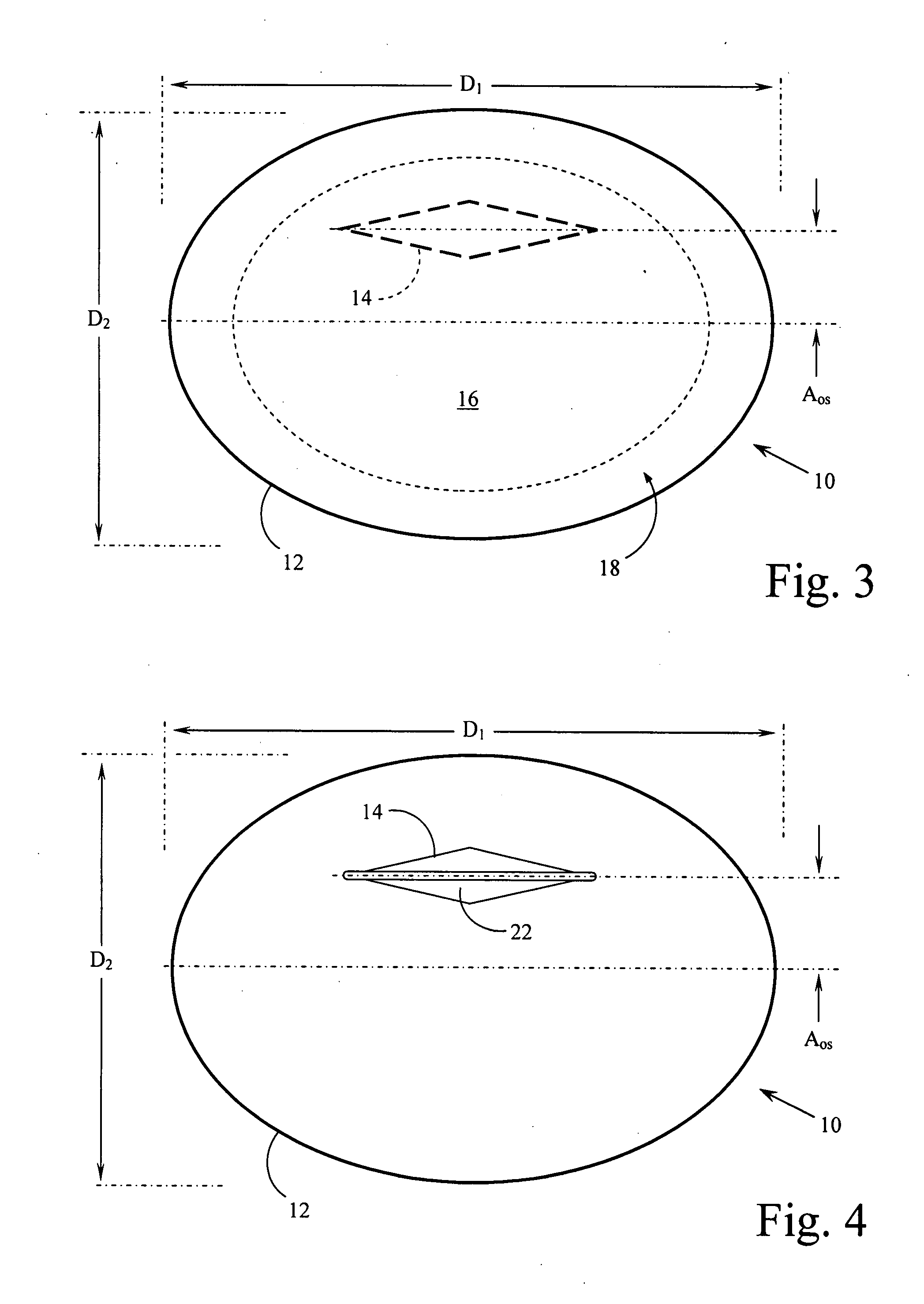
A spacer for implantation into a subject is provided that includes a sterilized piece of cartilaginous allograft tissue. The piece forms a Y-shape with a base adapted to insert within a first carpo-metacarpal joint or carpo-metatarsal joint of the subject, and has a first arm adapted to secure to a trapezium bone adjoining the joint, and a second arm adapted to secure to a proximal metacarpal or metatarsal bone adjoining the joint. A procedure for implanting the spacer includes exposing a target joint and abrading a bone surface interior to the joint to induce surface bleeding. The spacer base is then inserted into the joint. The spacer first arm is adhered to the first bone of the joint and the spacer second arm is adhered to the second bone of the joint. A kit is also provided for surgical implantation of the spacer.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL S
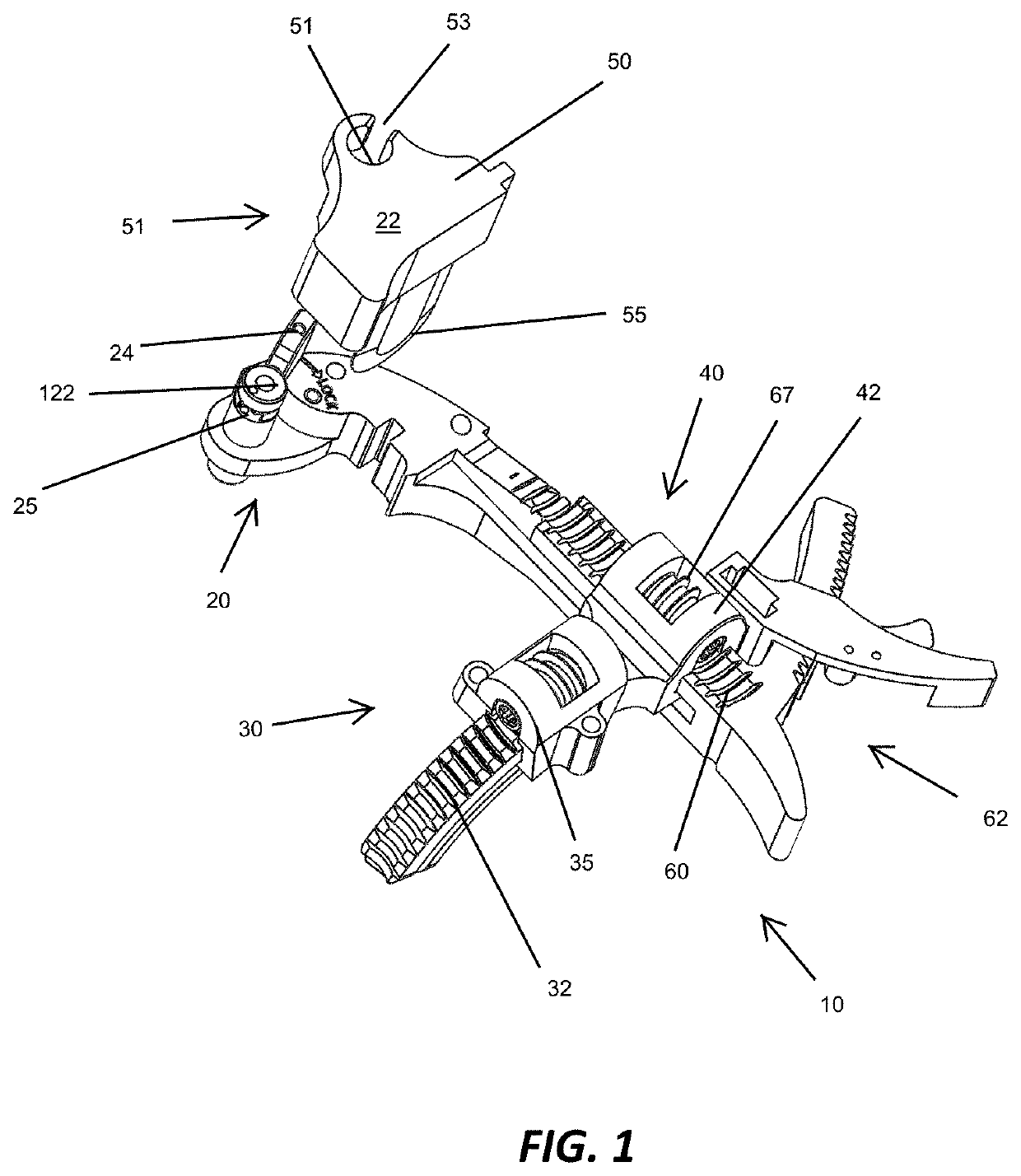
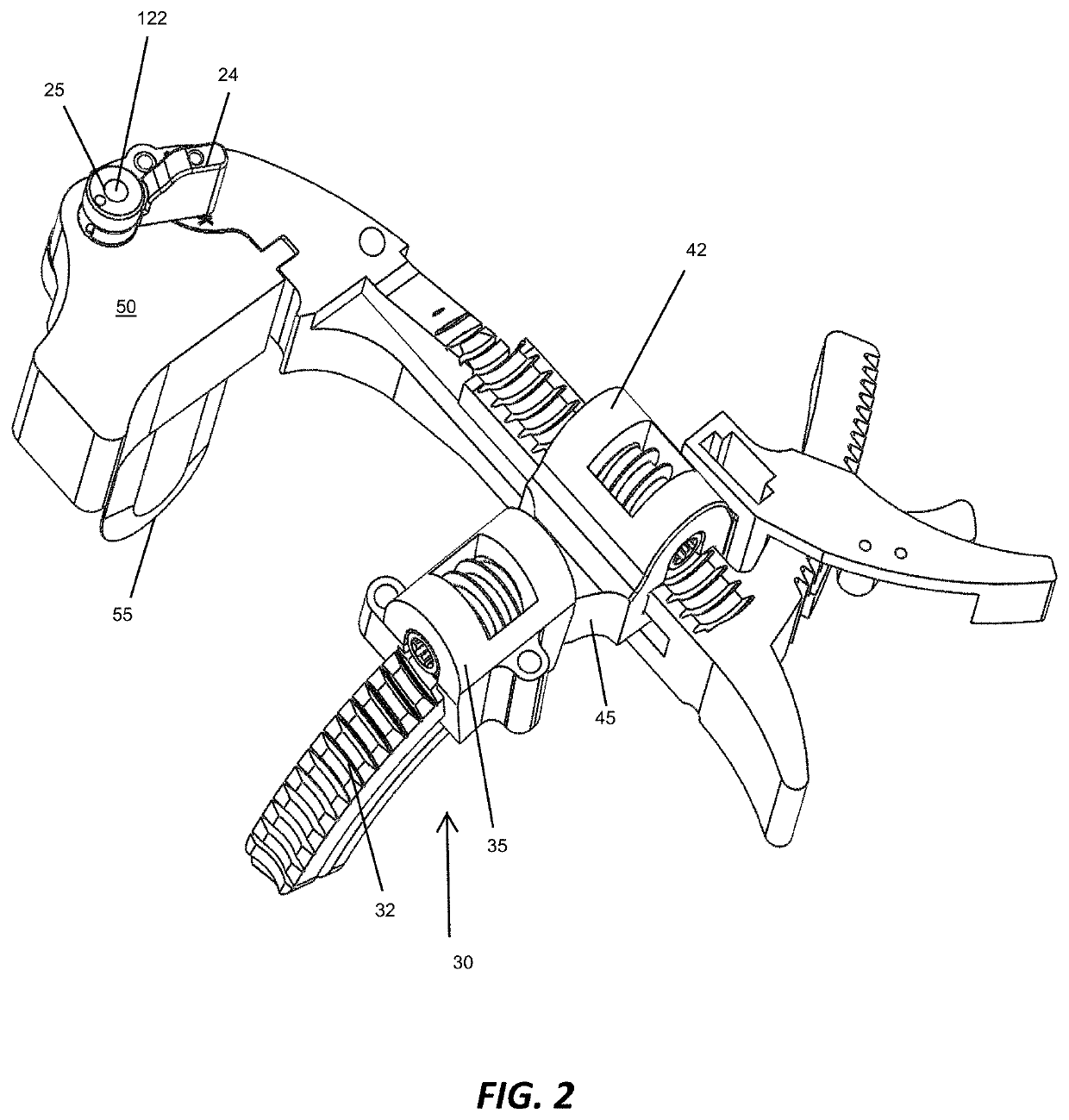
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
ActiveUS20060015109A1Facilitating intraoperativeFacilitating postoperative efficacyJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaSacroiliac joint
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
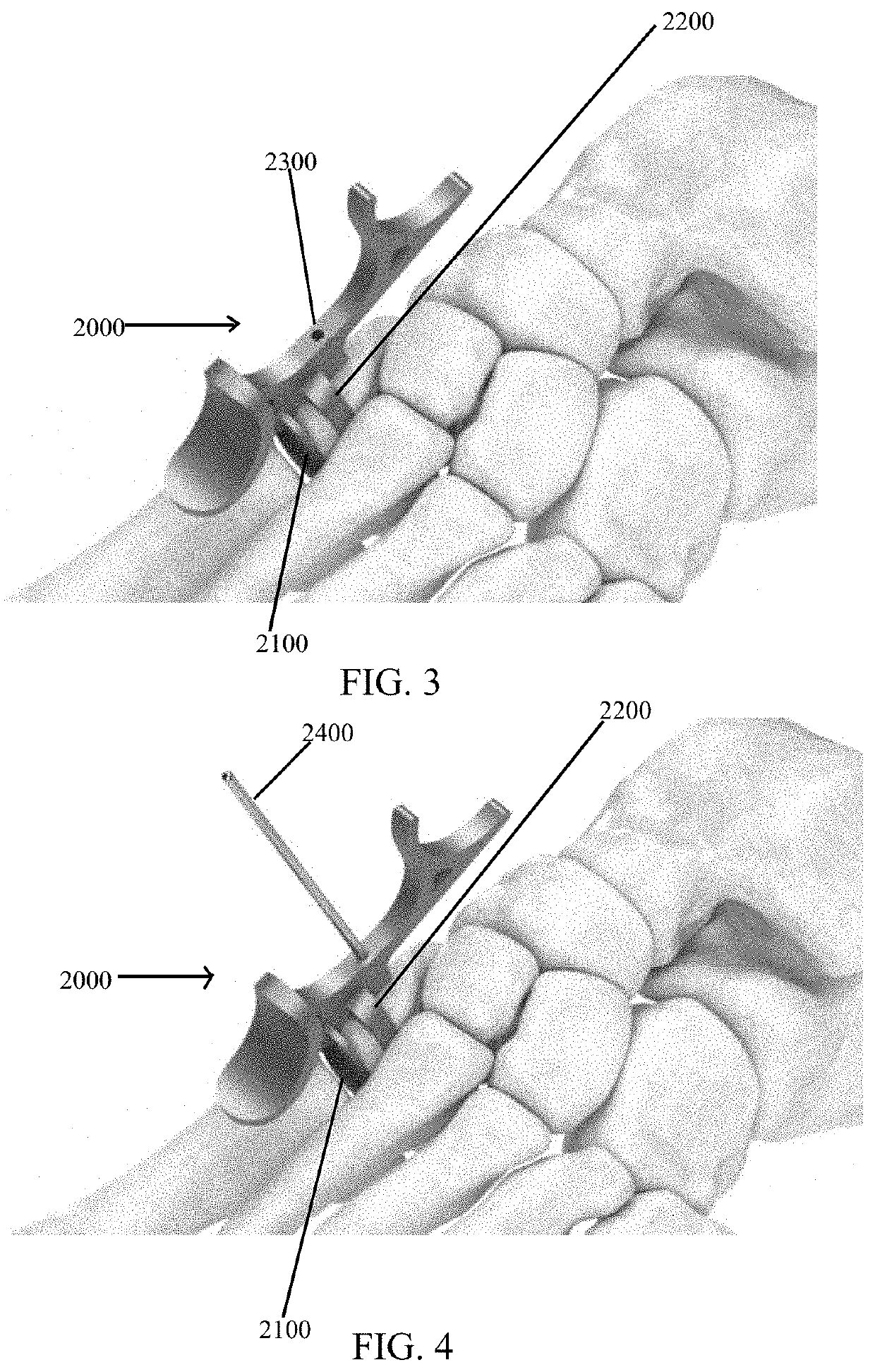
Hemi-implant for first metatarsophalangeal joint
InactiveUS20080221697A1Increase the lengthSimpler but effective retention structureAnkle jointsToe jointsJoint surfaceBiomedical engineering
An improved implant for use primarily within the first metatarsophalangeal joint. The implant includes an elliptical, concave, joint surface positioned on a stem and is designed to be placed into a prepared proximal face of the phalanx. The implant is sized according to the patient and may be provided in a number of standard incremental sizes. The improvements relate primarily to the structure, size, and position of the stem that extends into the phalanx to support the implant. The stem is off-set from a center axis of the elliptical joint surface. This off-center placement allows for a longer stem. Single deep indentations on each side of the stem facilitate retention within the bone. A size selection tool is provided to facilitate the selection and placement of an appropriately sized implant. The tool further provides a template for positioning and placing the stem in the phalanx. A method for sizing and selecting the appropriate implant, and positioning and fixing the implant as a partial joint replacement, especially for the first metatarsophalangeal joint, is also described.
Owner:LOWE JOHN PATRICK TRUSTEE CHAPTER 7 CASE NO 09 51026 C IN THE UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIV
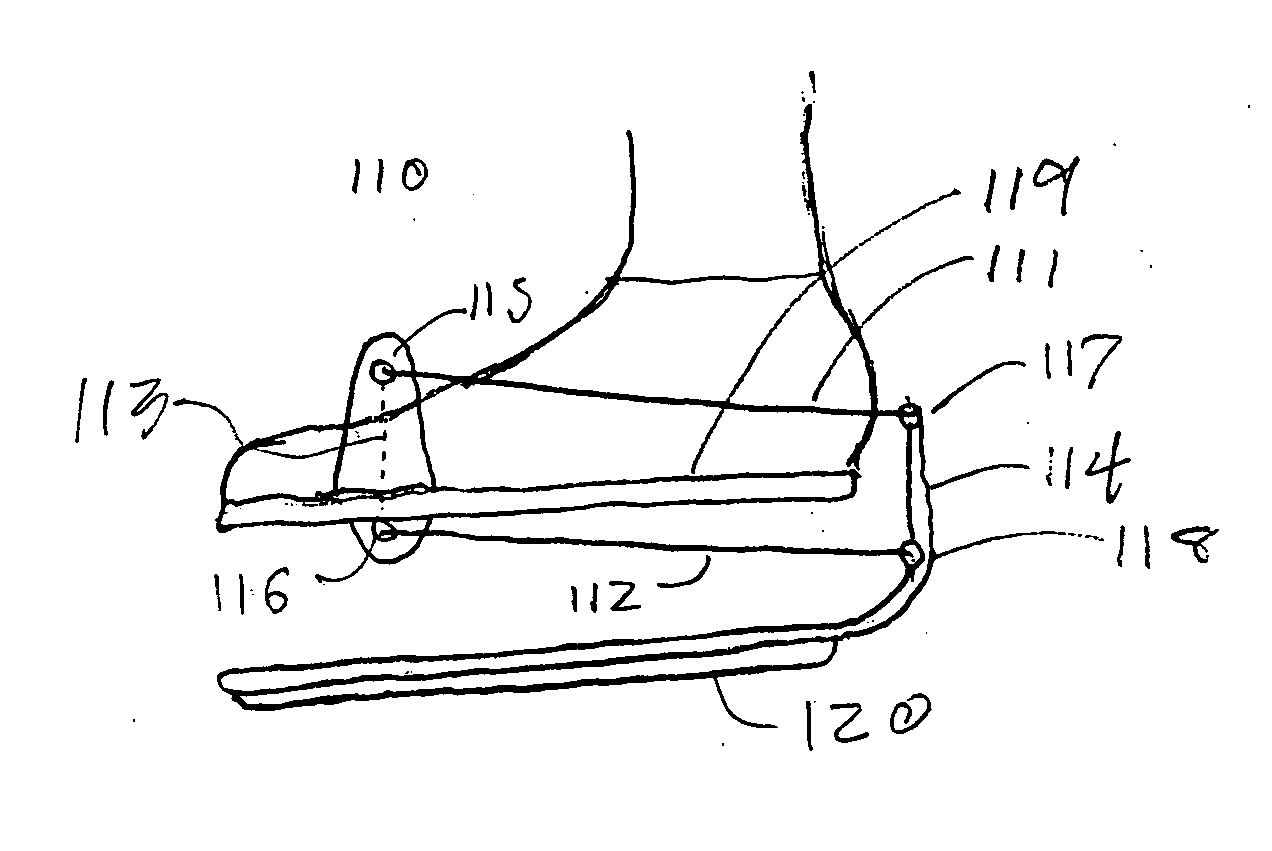
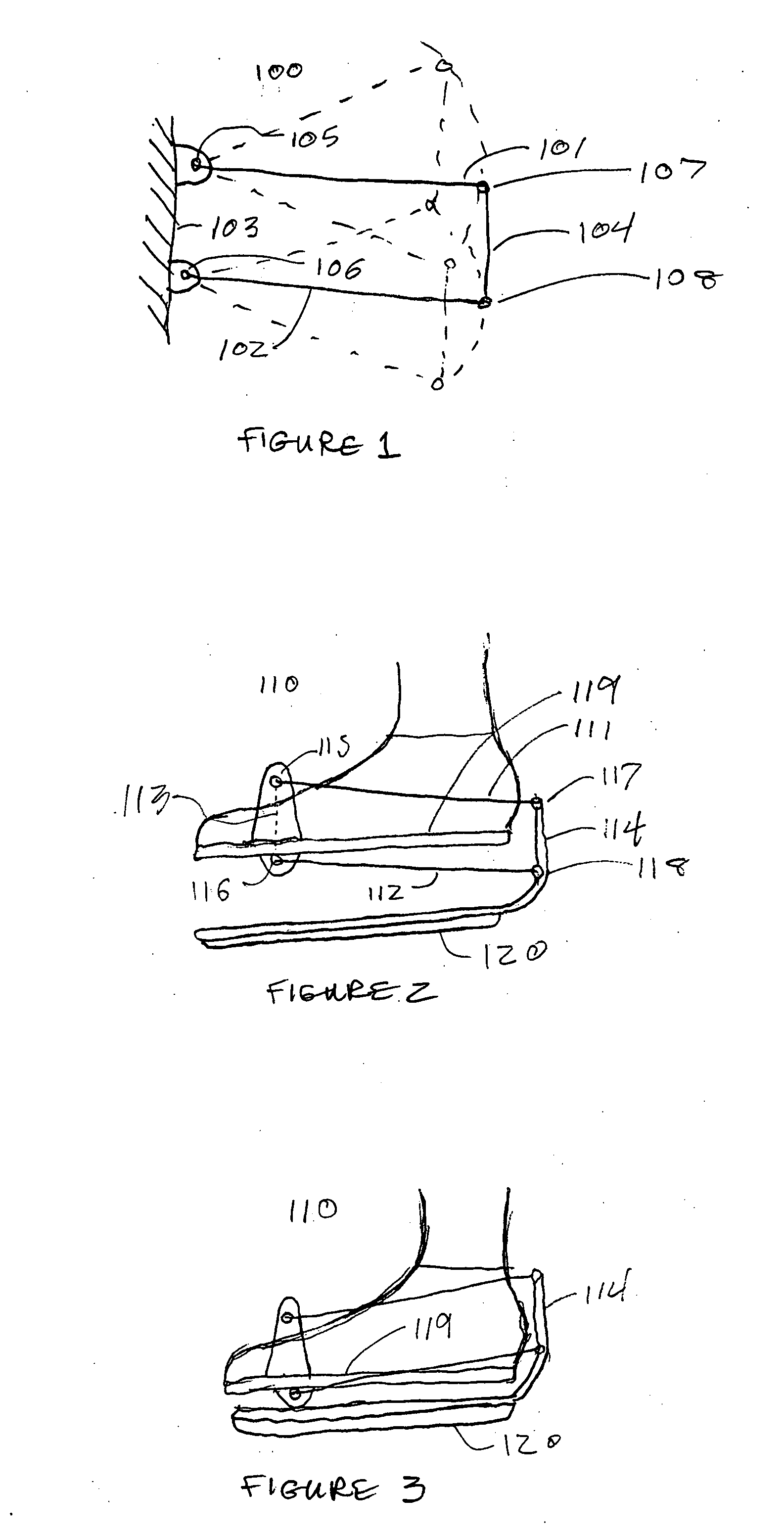
Orthopedic rehabilitation mechanism
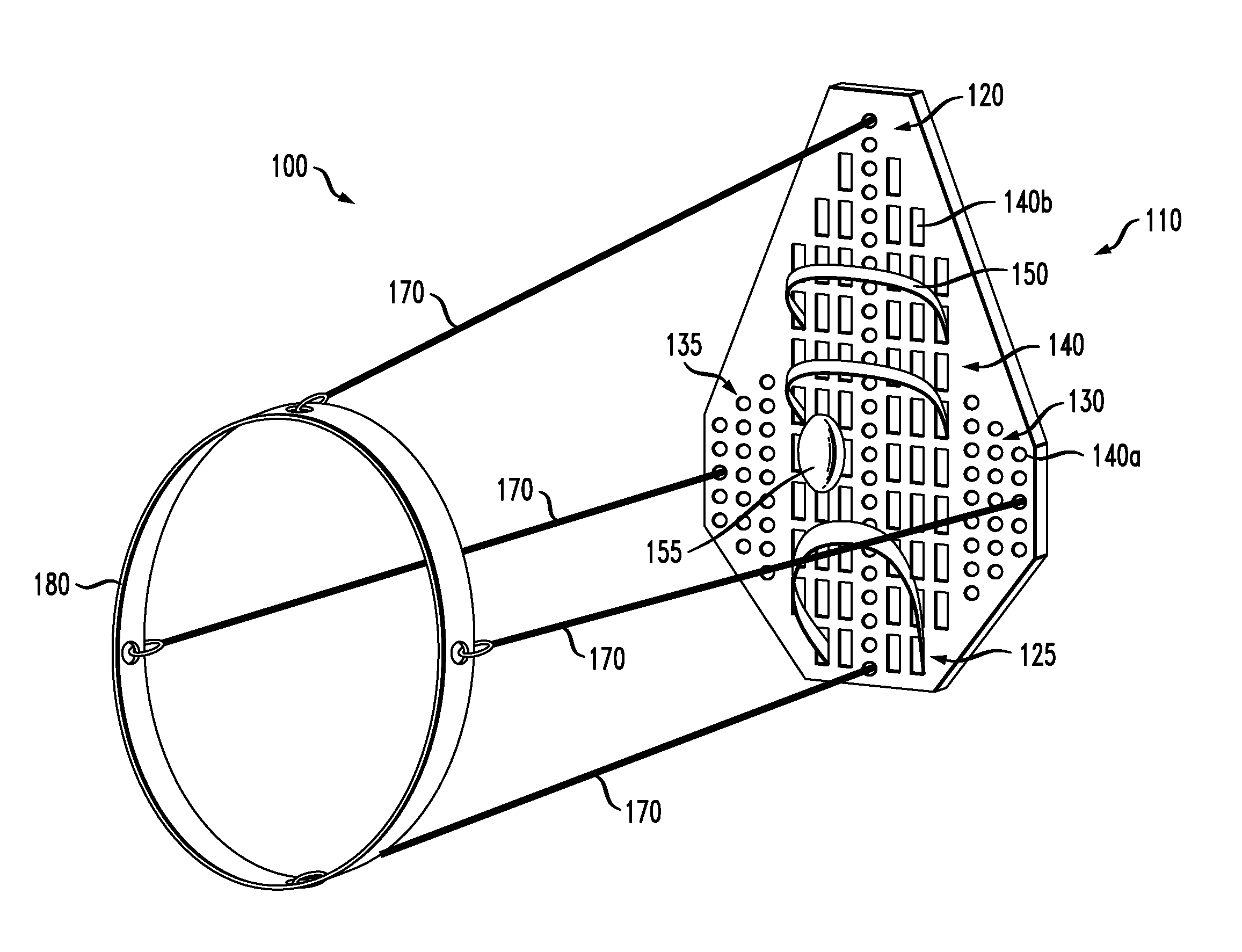
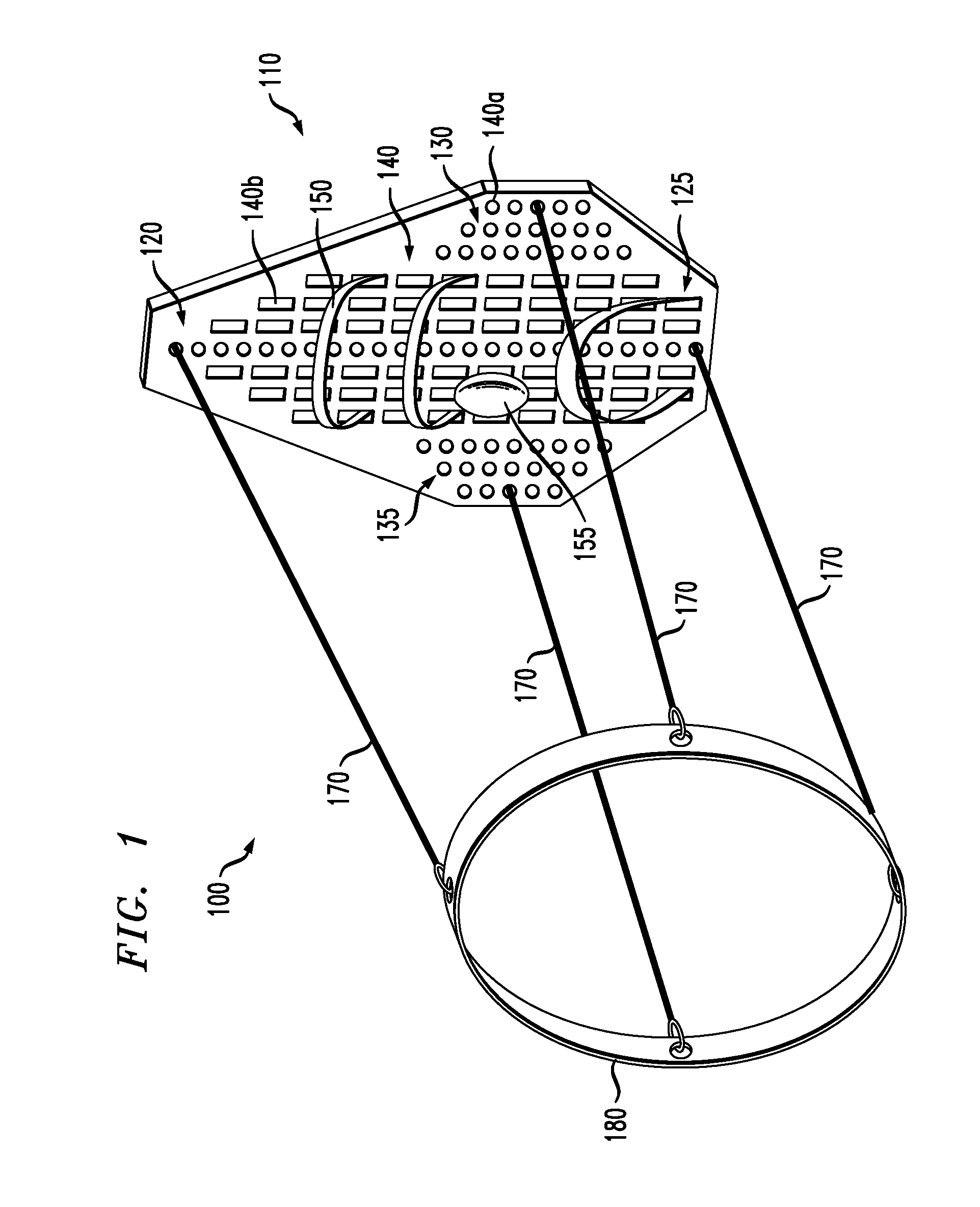
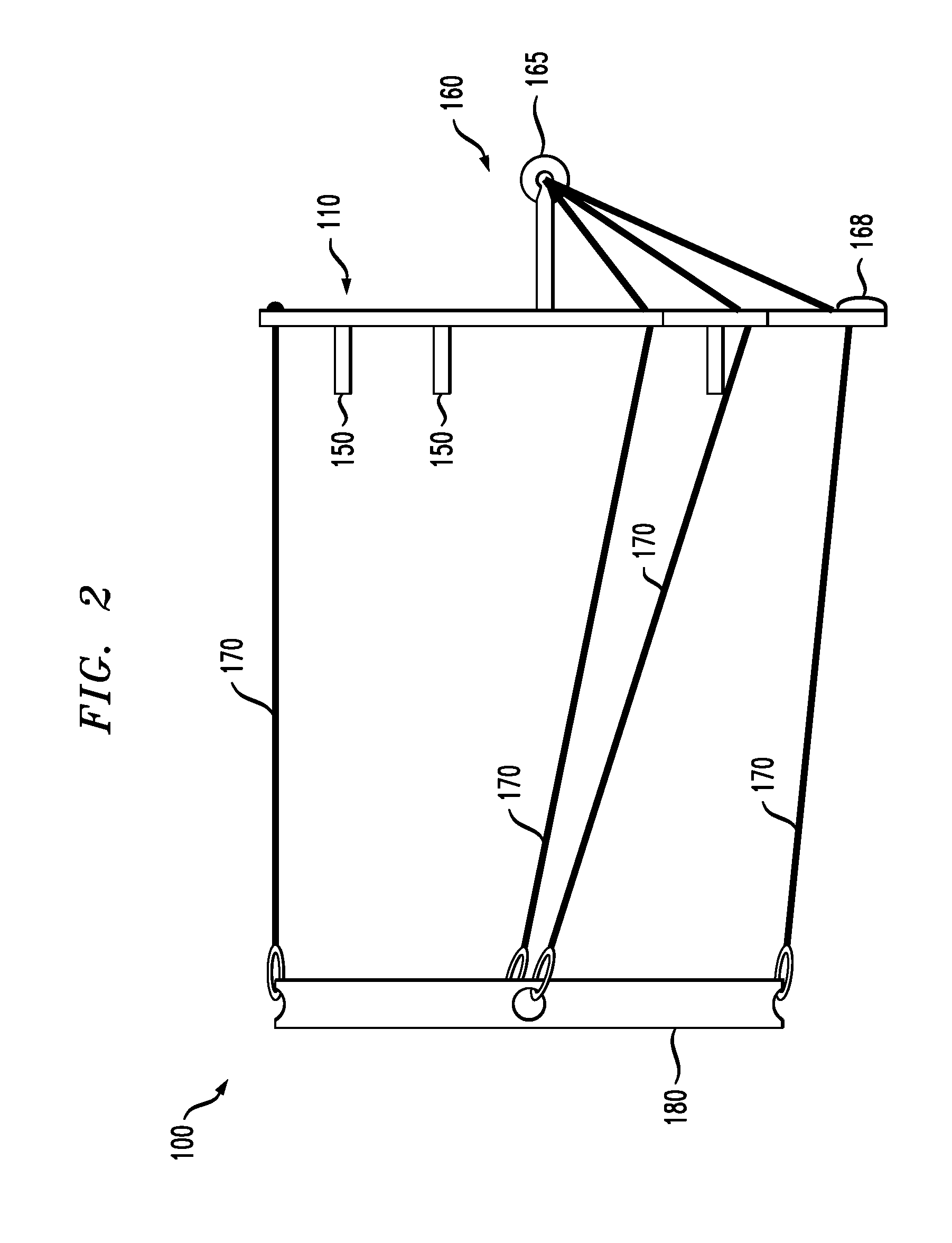
The present invention provides an orthopedic device for therapy and rehabilitation of joints to increase the range of motion of the joint, a method of manufacture therefor, and a method of operating the same. The orthopedic device, among other possible elements, may include a foot support element configured to substantially support a user's foot or ankle, at least two guide lines each having a first and a second end, wherein each of the first ends are coupleable to the foot support element. The orthopedic device, may further include a control member coupleable to each of the second ends, the control member configured to control the at least two guide lines to flex the user's foot or ankle in a plurality of directions.
Owner:RODGERS DARELL E
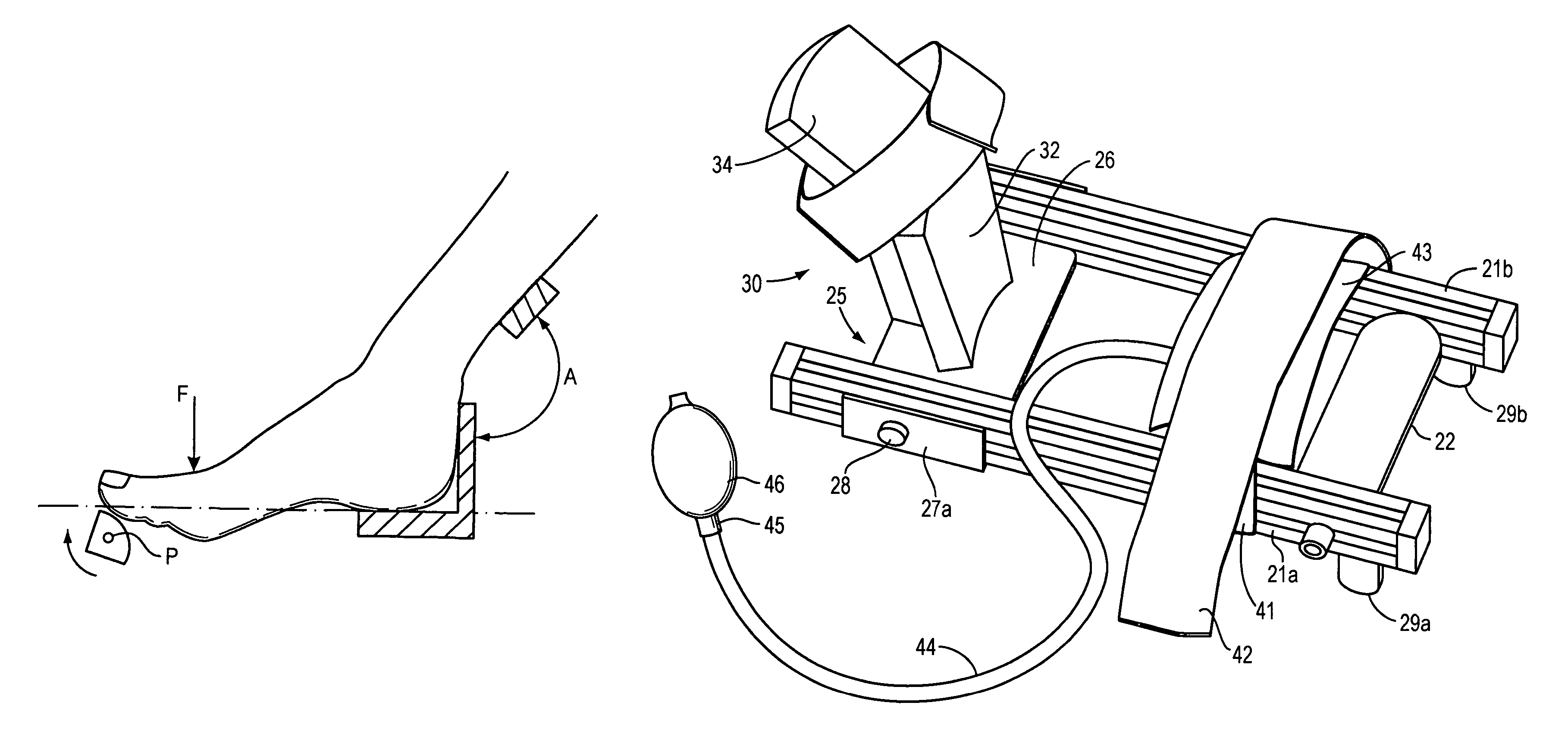
Method and apparatus for manipulating a toe joint
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to the manipulation of a joint to provide therapy. More specifically, some embodiments of the present invention use inflatable members and a three point bending concept to cause flexion in a toe joint for the purpose of increasing the range of motion of the toe joint. In one embodiment, a user's foot is placed in a frame with at least one toe atop a toe bar. An inflatable member is positioned atop the user's foot and held in position with a strap attached relative to the frame. As the inflatable member is inflated, the strap increases in tension urging the toe toward the toe bar and causing actuation of the joint at the base of the toe.
Owner:ERMI
Full suspension footwear
ActiveUS20060021262A1Maximize operating efficiencyMinimal torqueSolesUpperGround contactAnkle foot joint
A method and apparatus for enhancing the ability of a human to run and jump with comfort comparable to running barefoot on a trampoline and with control comparable to that of the unaided human form, yet with freedom from ankle-turning roll moments associated with substantial ground contact member (GCM) extension downwardly away from the sole of the foot including, a resiliently urged GCM constrained to two degrees of freedom: translation away from the sole of the user's foot and rotation about a longitudinal axis at ground level. The apparatus relates flexure of a GCM toe pressure member to comparable flexure of user's toes at the metatarsal joints. The apparatus also incorporates lower leg to ankle pivot bracing, and extends the GCM in downward direction parallel to the lower leg while mimicking user ankle articulation with parallelism-maintaining rotation about a downwardly resiliently urged transverse pivot axis similar to the user's own ankle joint for extended travel.
Owner:KILLION DAVID L +1
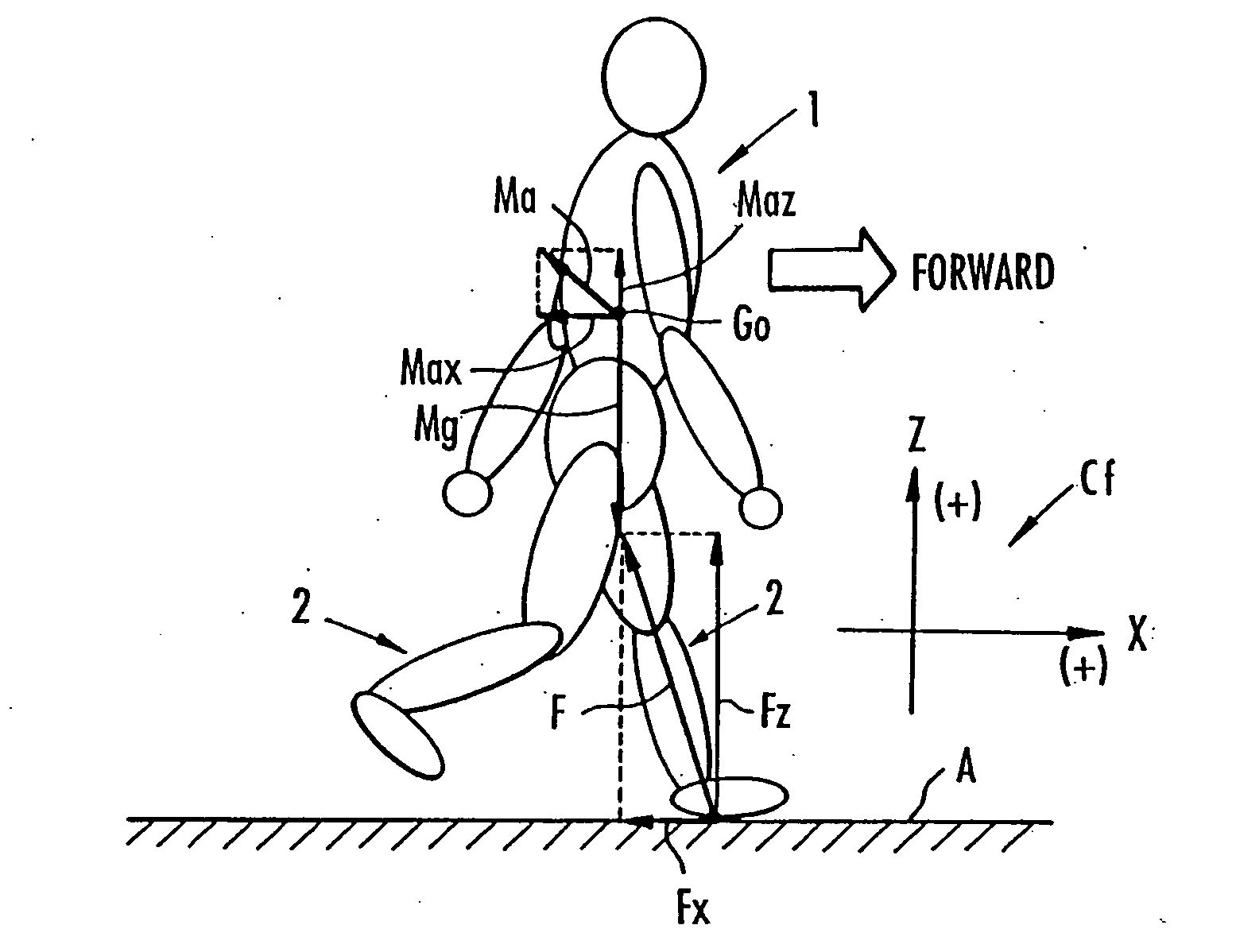
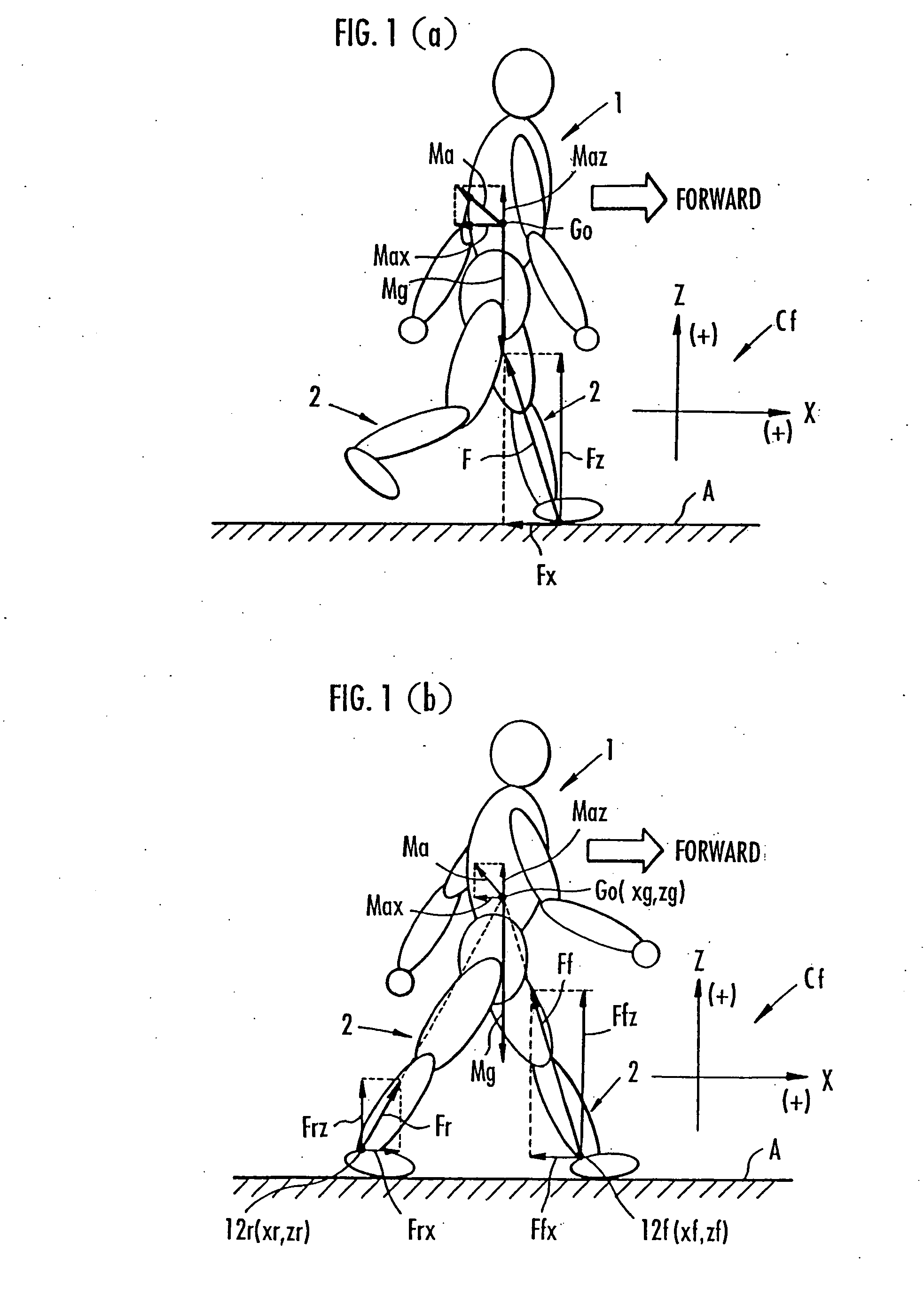
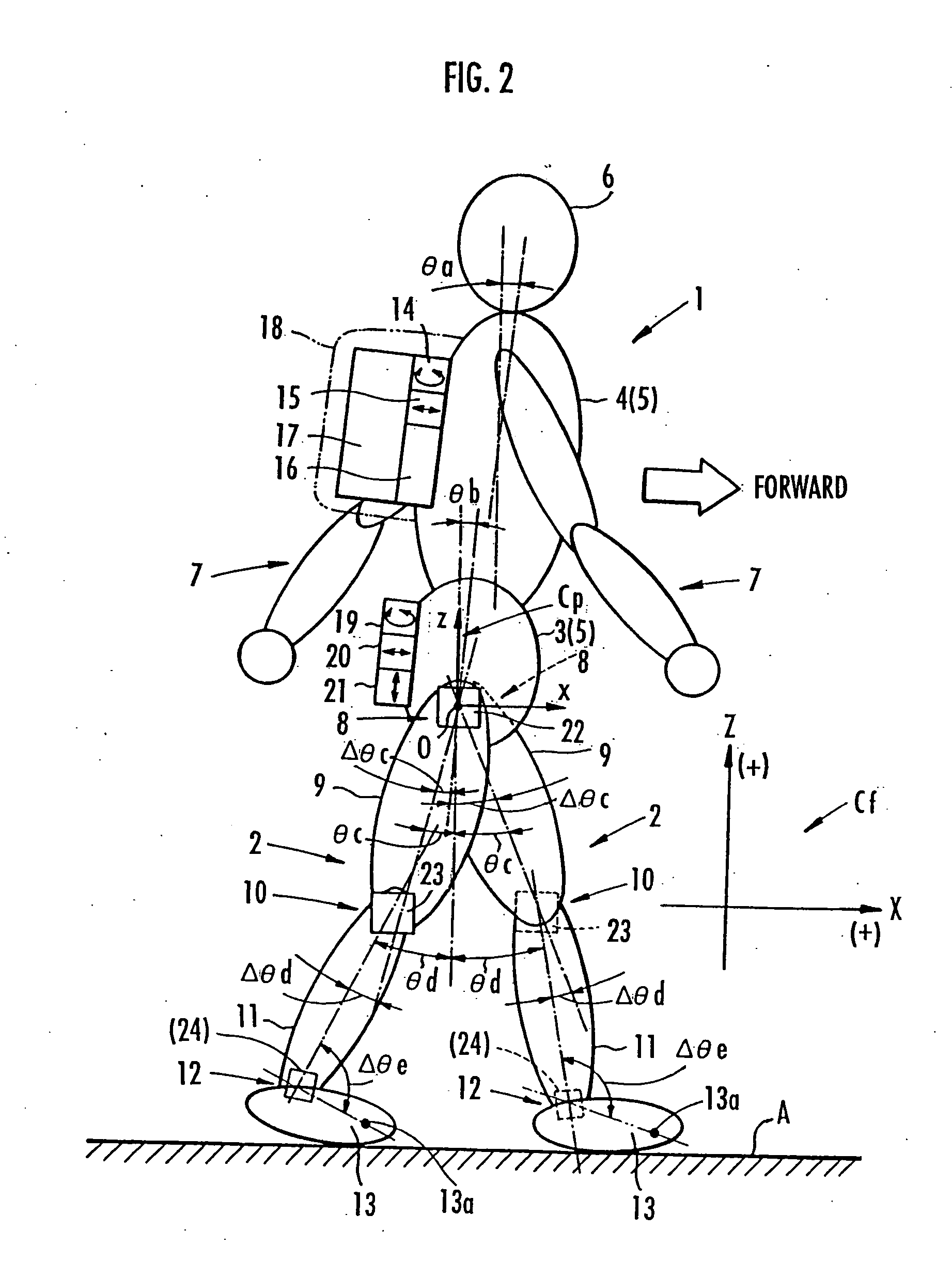
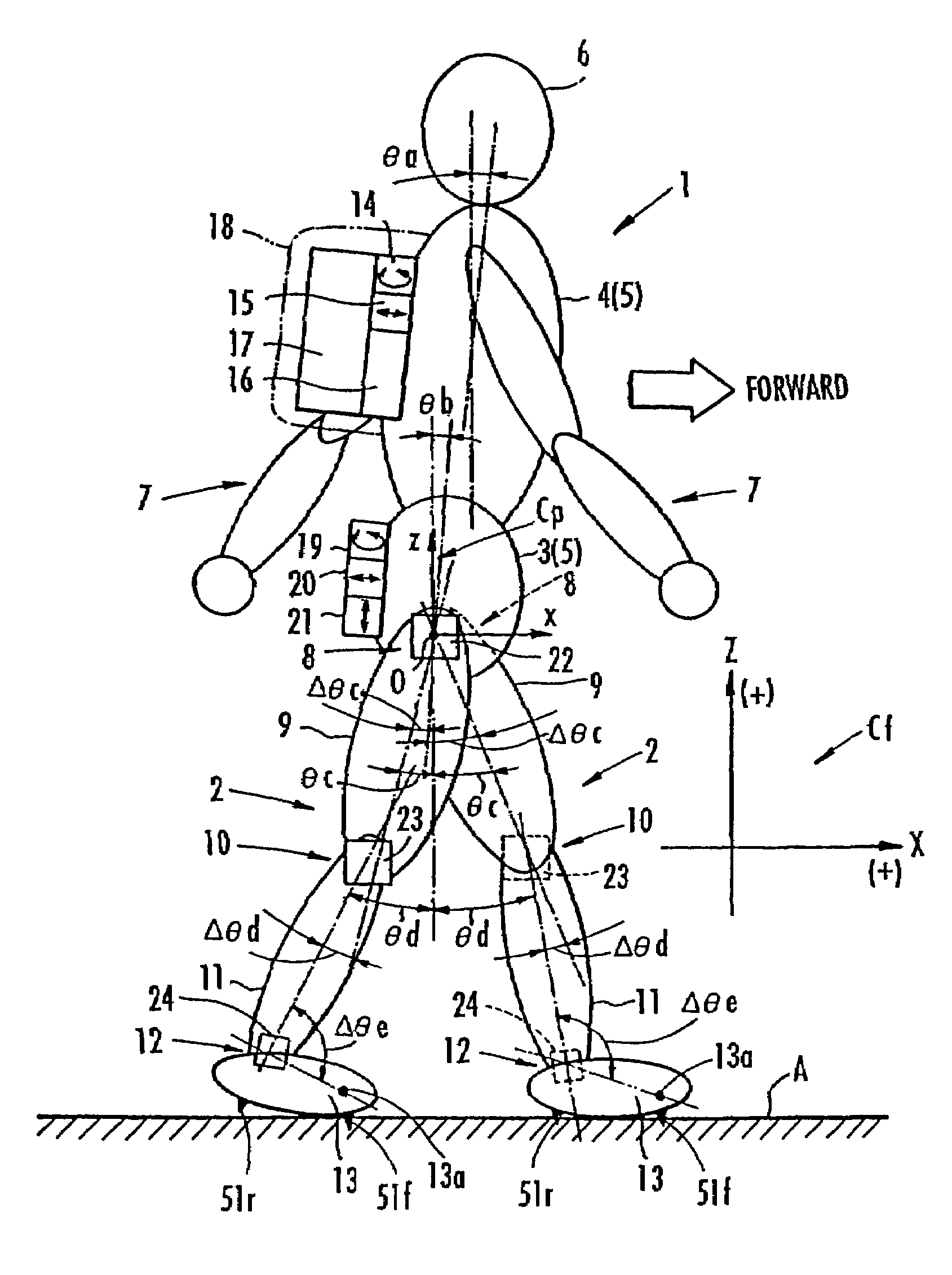
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS7119510B2Good estimateHigh accuracy of estimated valueProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
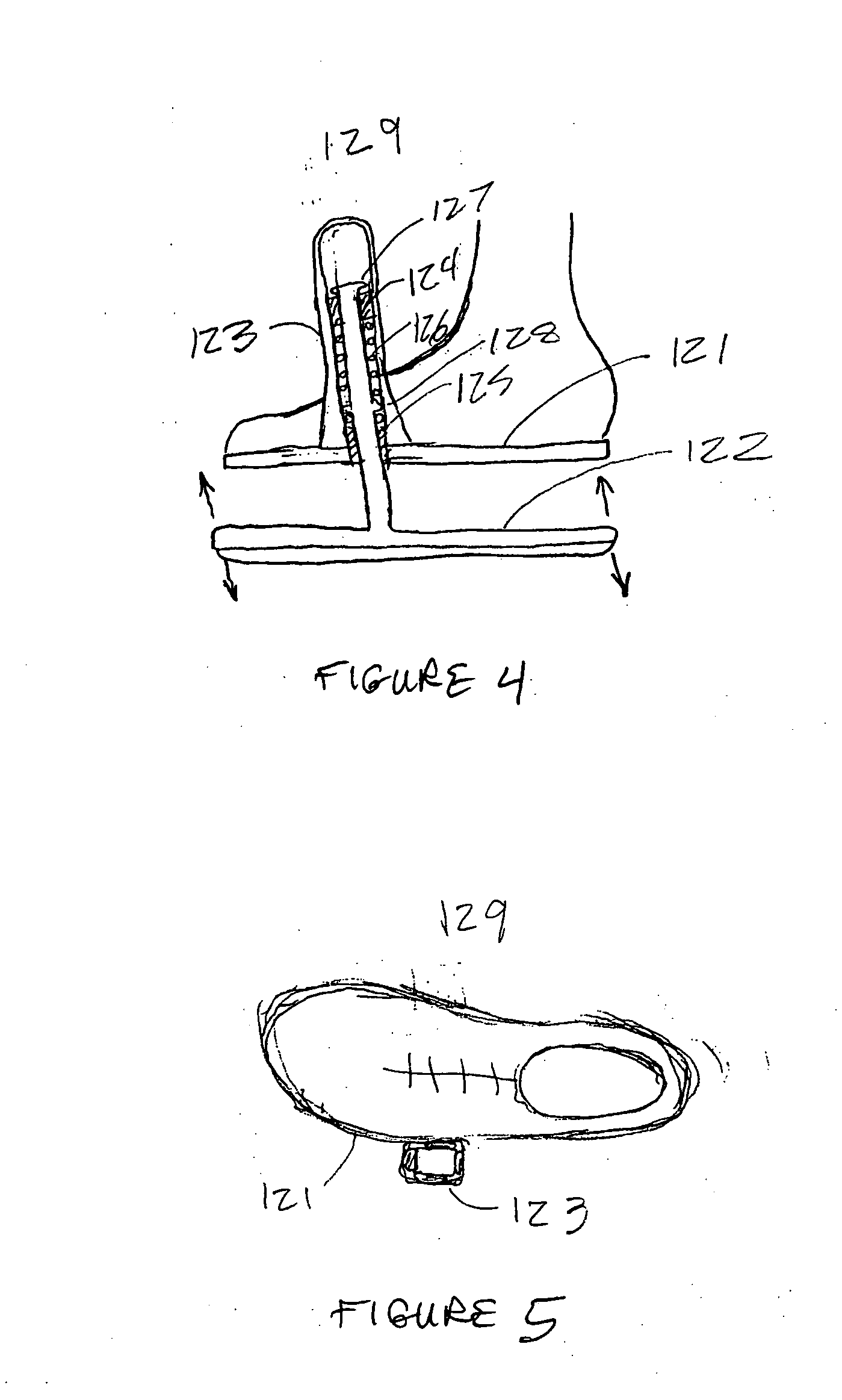
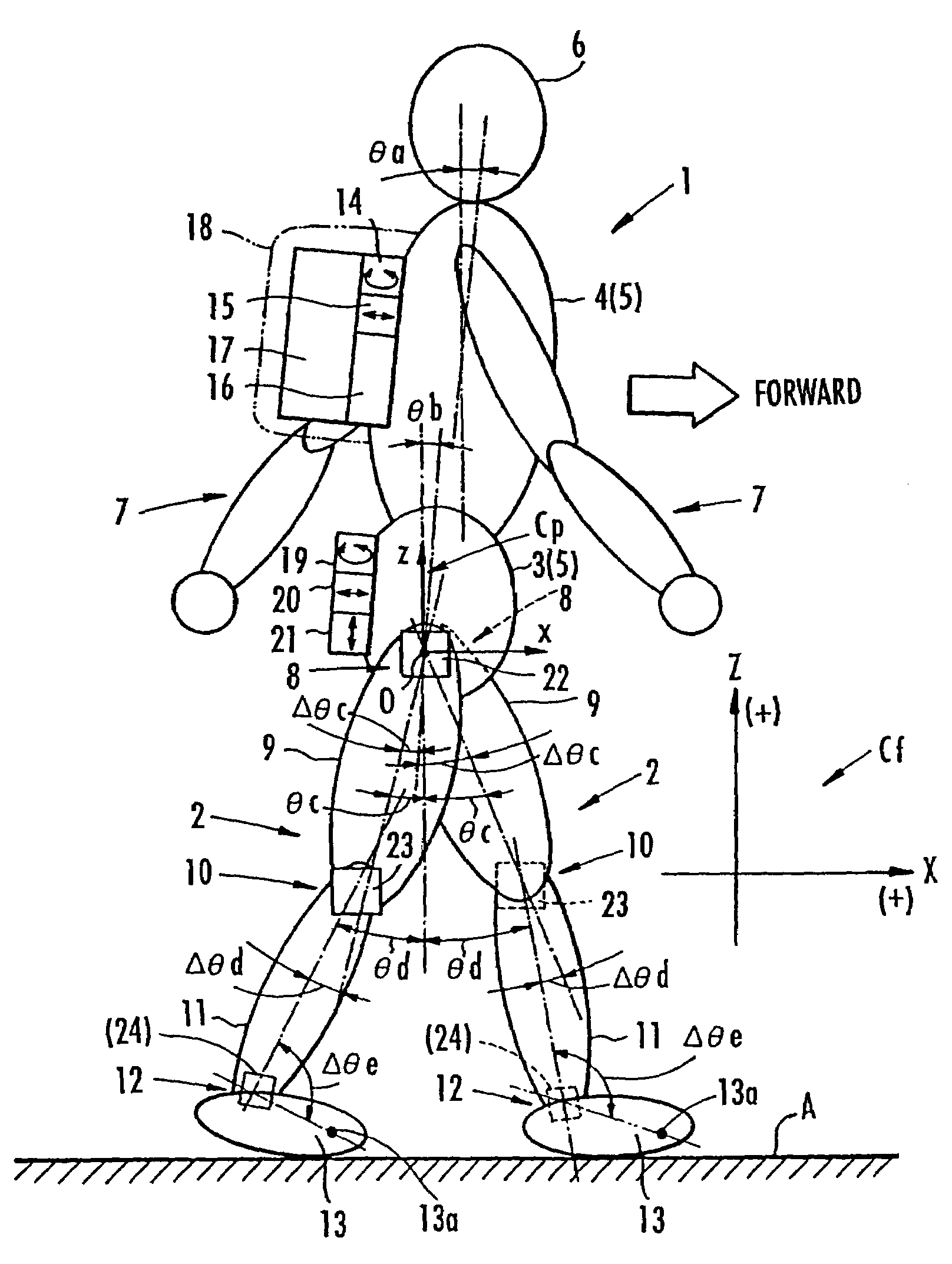
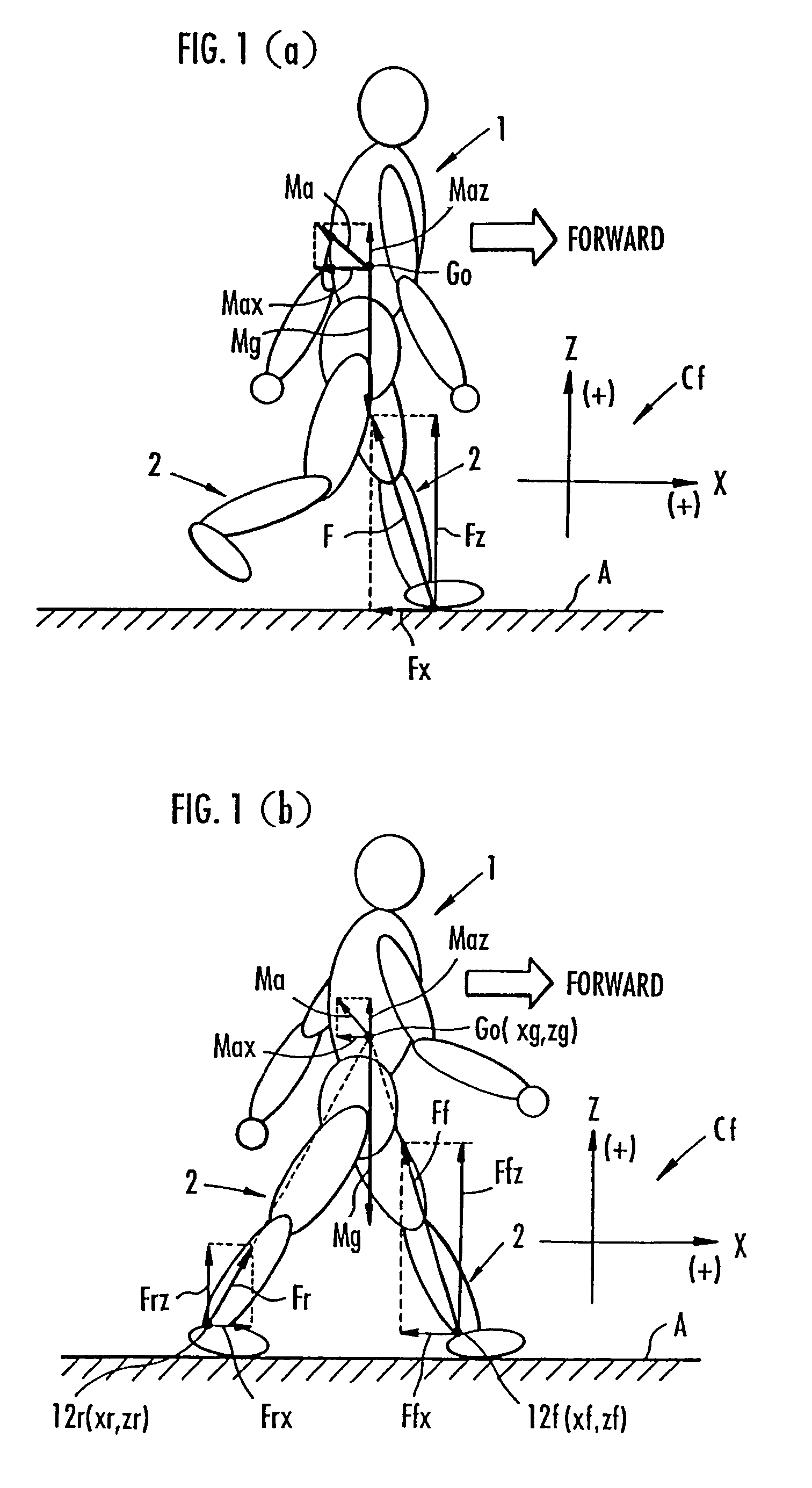
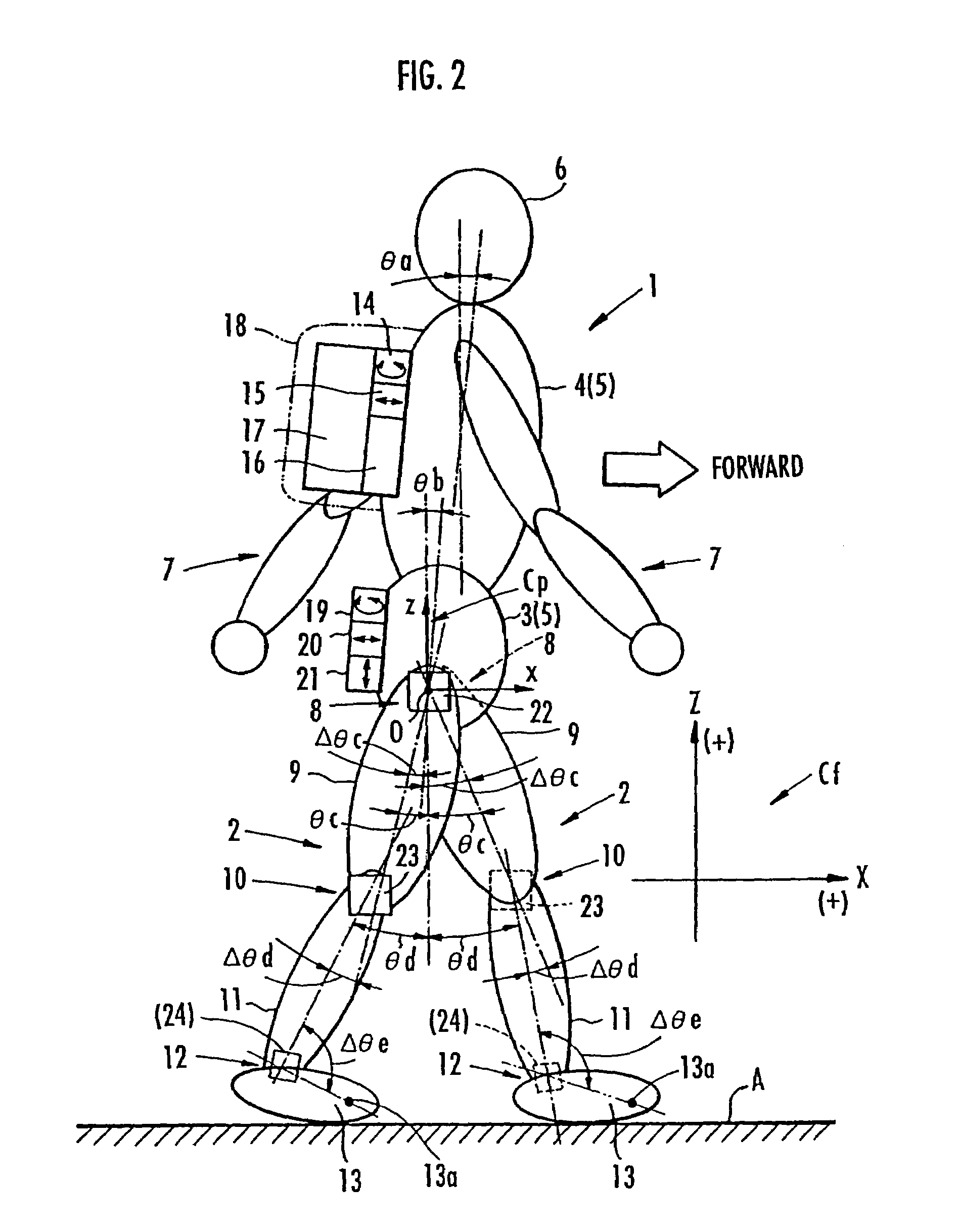
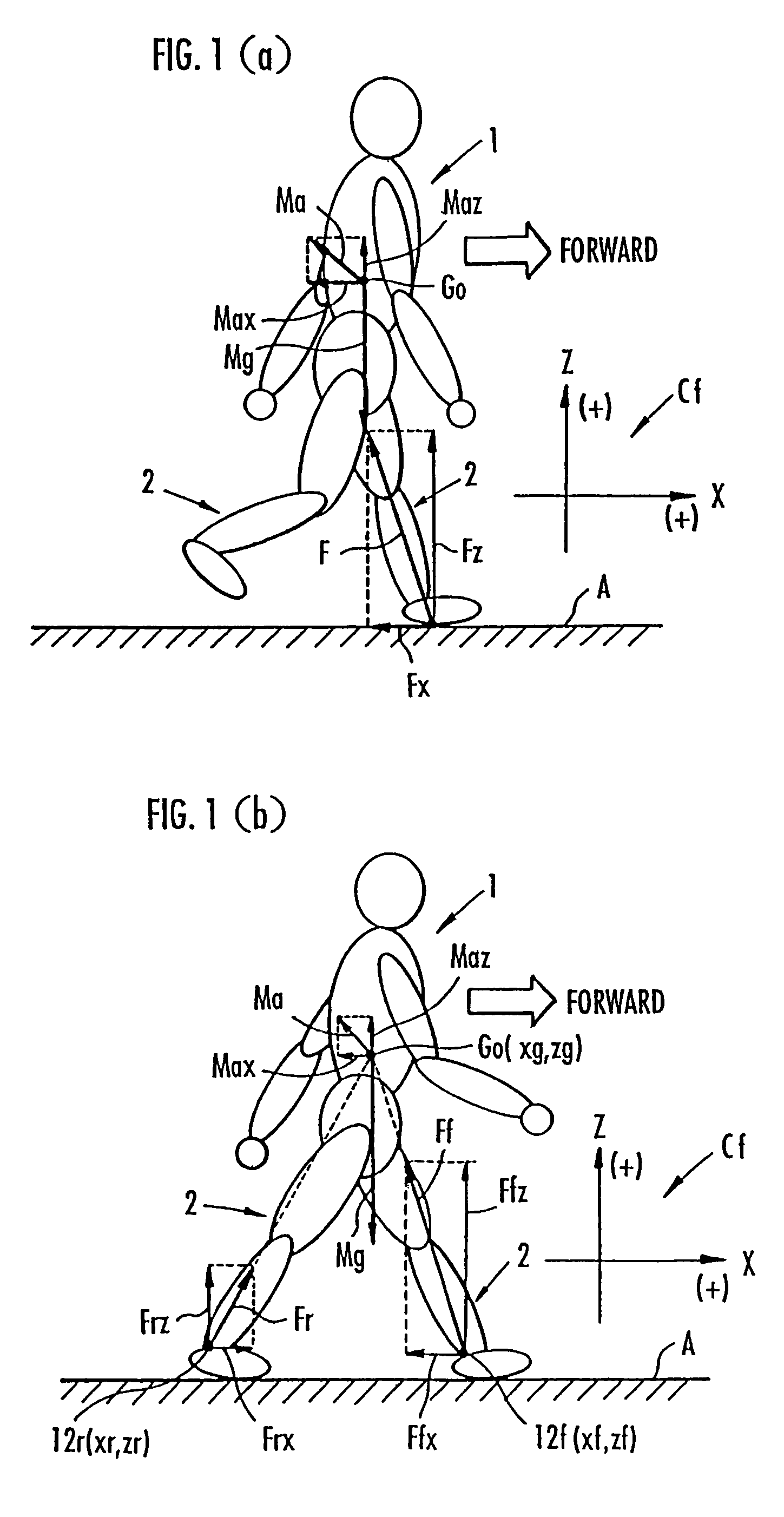
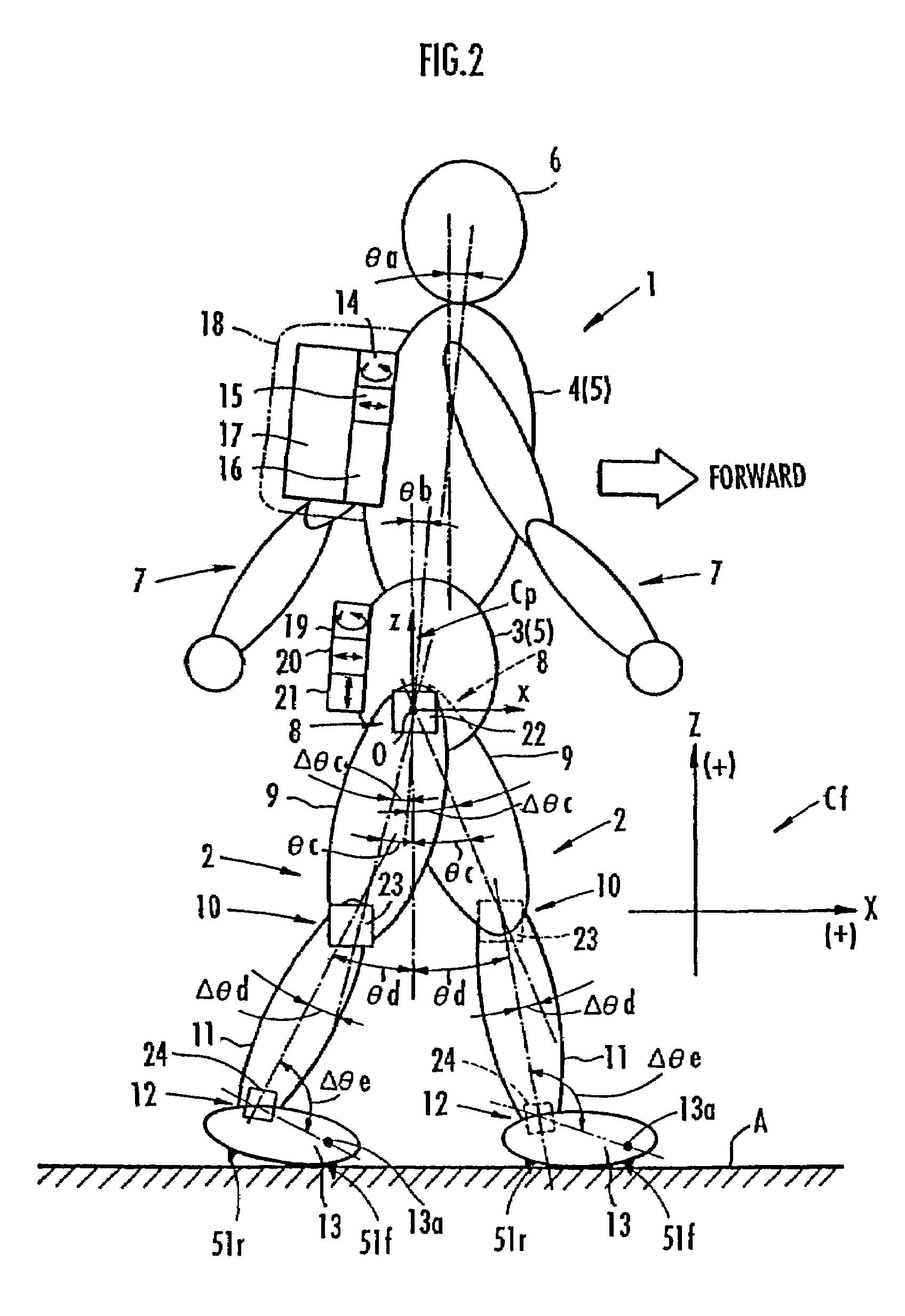
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Biomechanical custom made foot orthosis and method for making the same
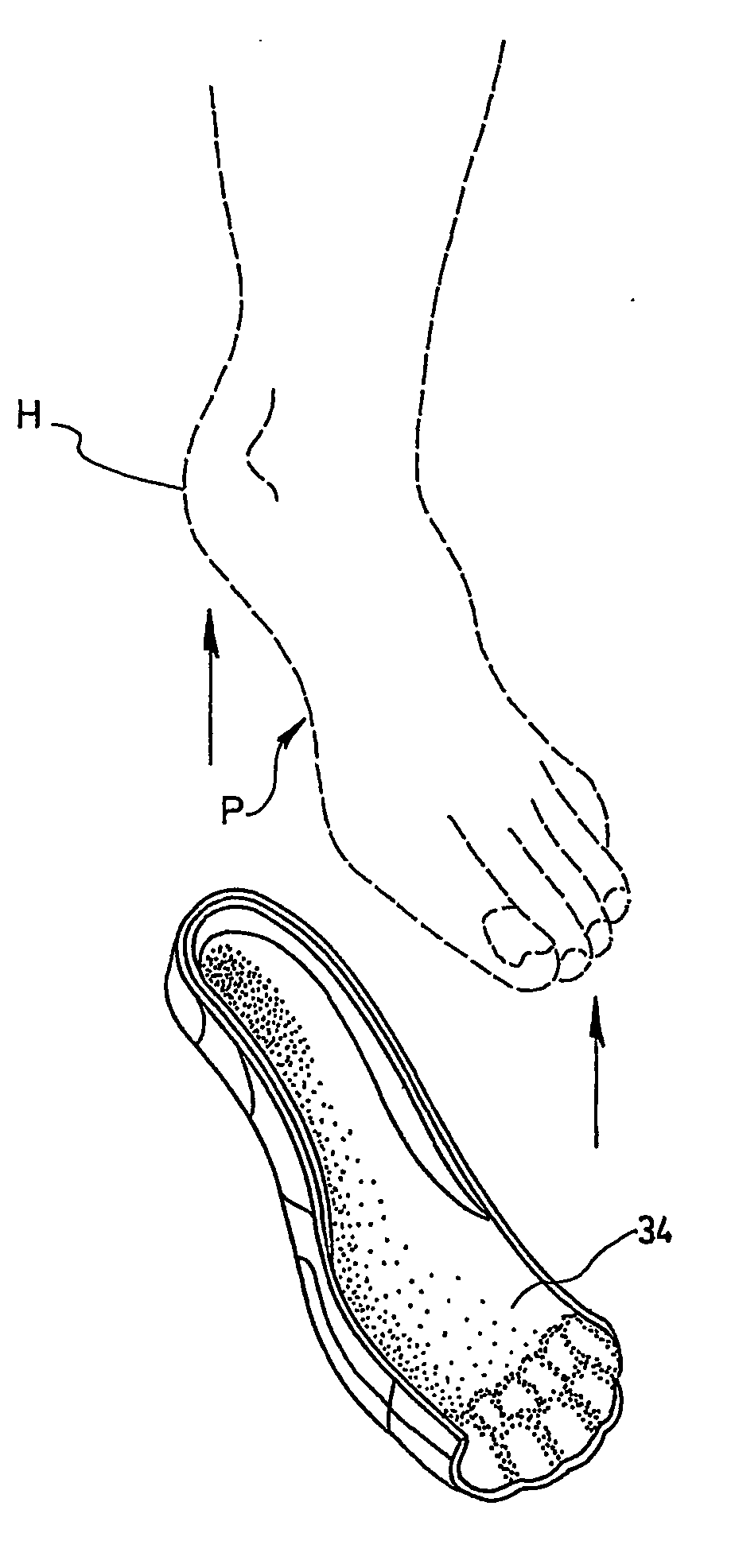
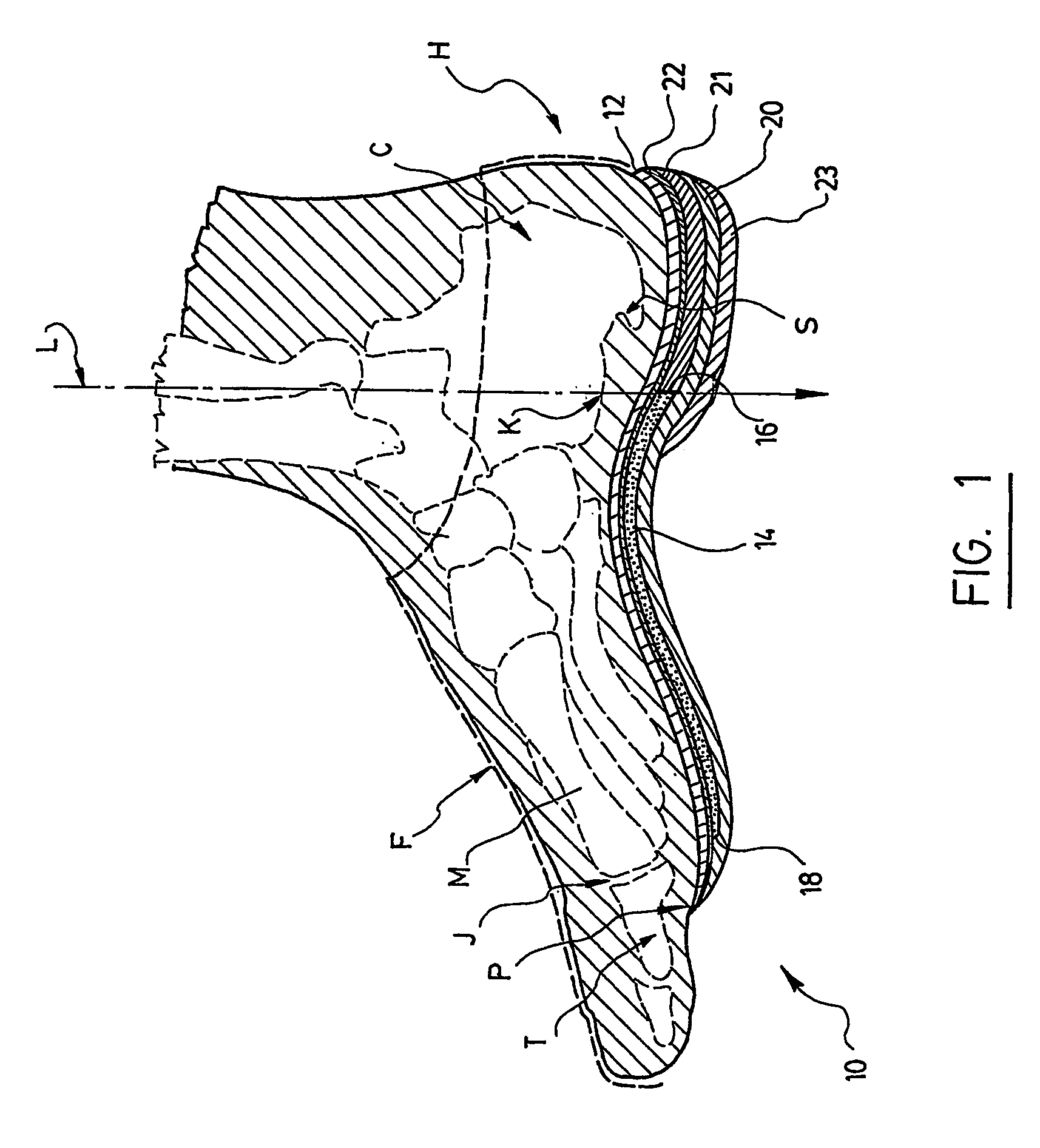
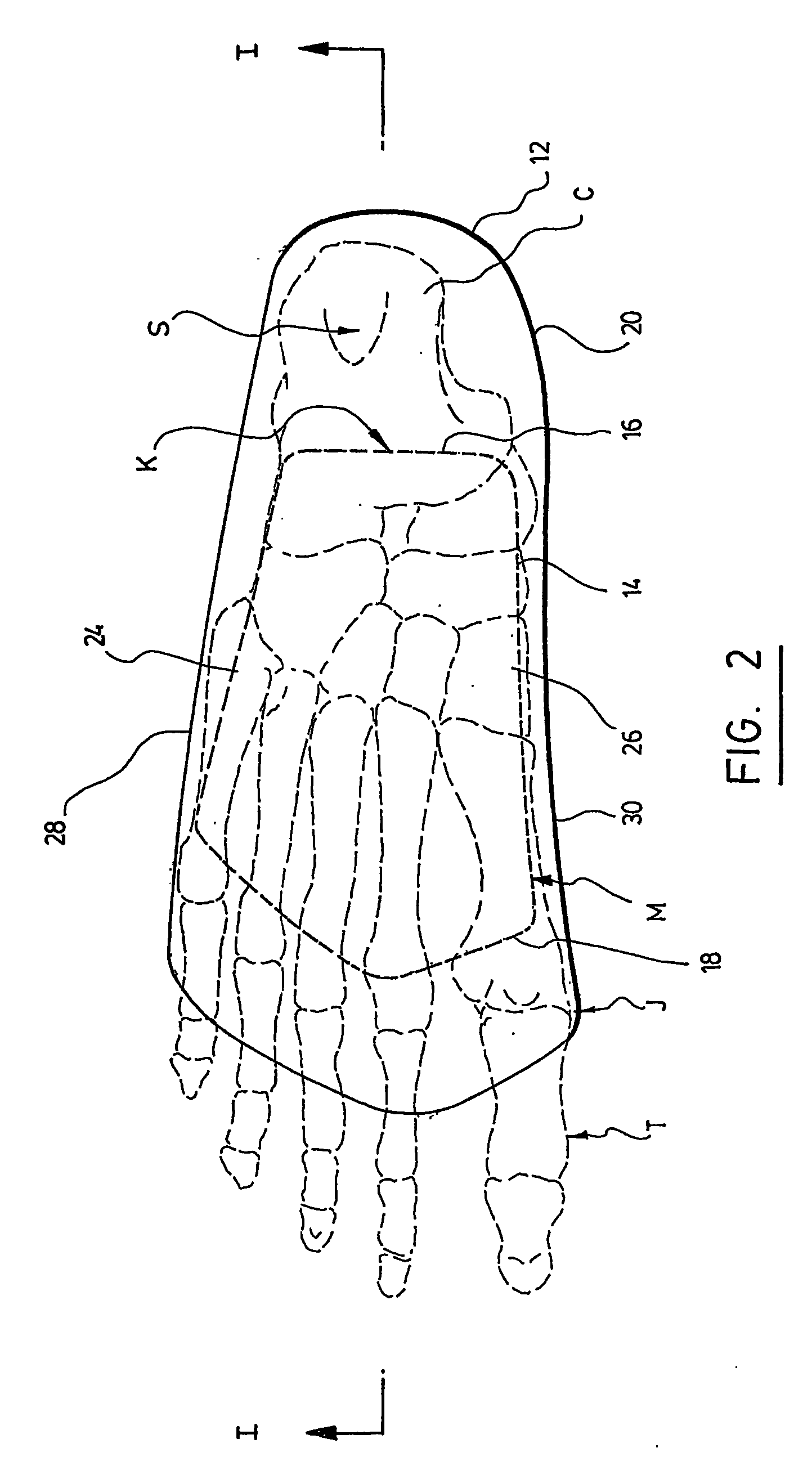
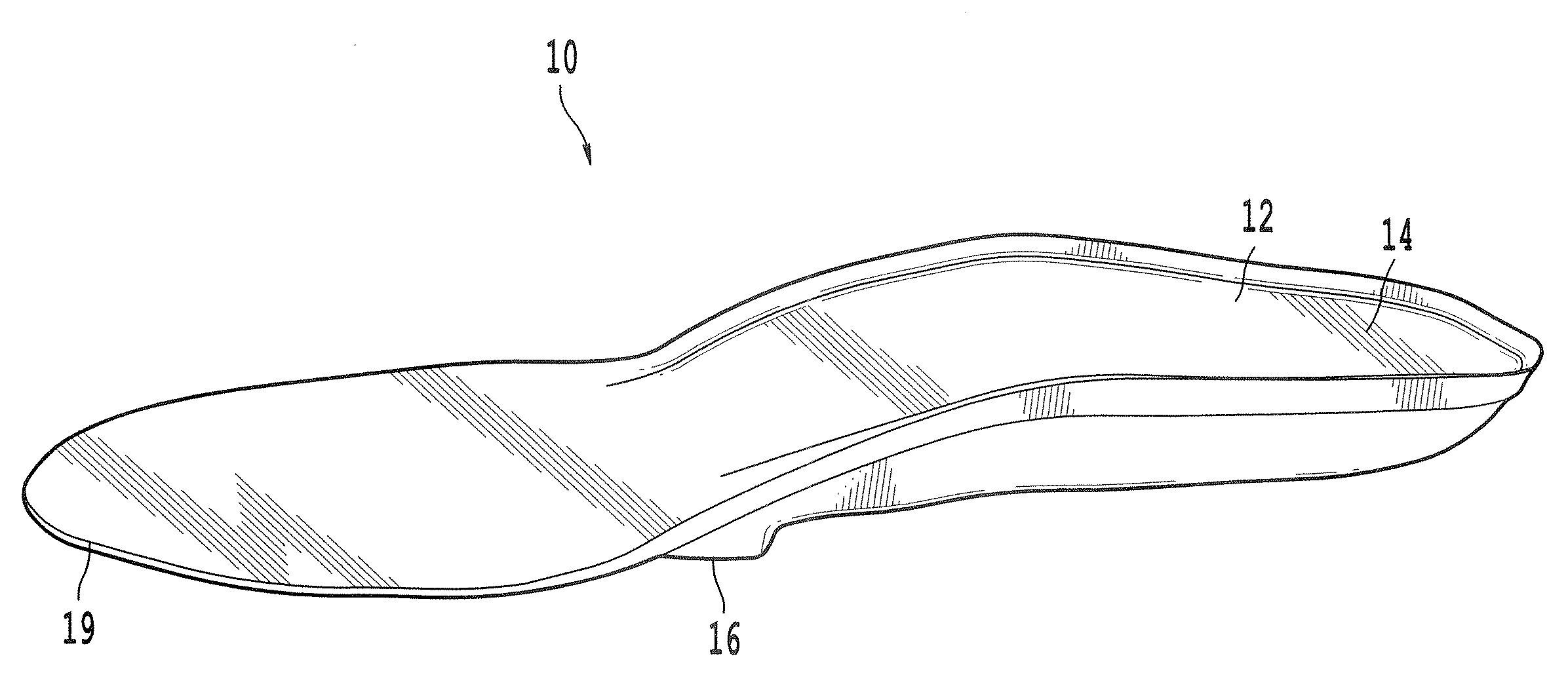
InactiveUS20060015050A1Relieve painRelieve pressureFoot measurement devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBiomechanicsOrthotic device
A biomechanical custom made foot orthosis (10) and a method for making the same. The orthosis (10) has a thermoformed flexible top layer (12) made of a first moldable synthetic rubber material, and a thermoformed flexible reinforcement core layer (14) made of a. moldable core material that is molded onto the top layer, (12). The core layer (14) has a posterior end (16) aligned with a mid anterior plantar prominence (K) of a calcaneus bone (C), and an anterior end (18) aligned near metatarsal-phalangeal joints (J) of the foot. The orthosis (10) also has a thermoformed flexible bottom layer (20) made of a second moldable synthetic rubber material that is molded onto the top layer (12) and the core layer (14). The core layer (14) is more rigid than the top and bottom layers (12, 20). The orthosis (10) corrects anatomic biomechanical deficiencies of the foot and ensuing body deficiencies.
Owner:BLEAU DANIEL
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS20060197485A1Simple arithmetic processingGood estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Foot support
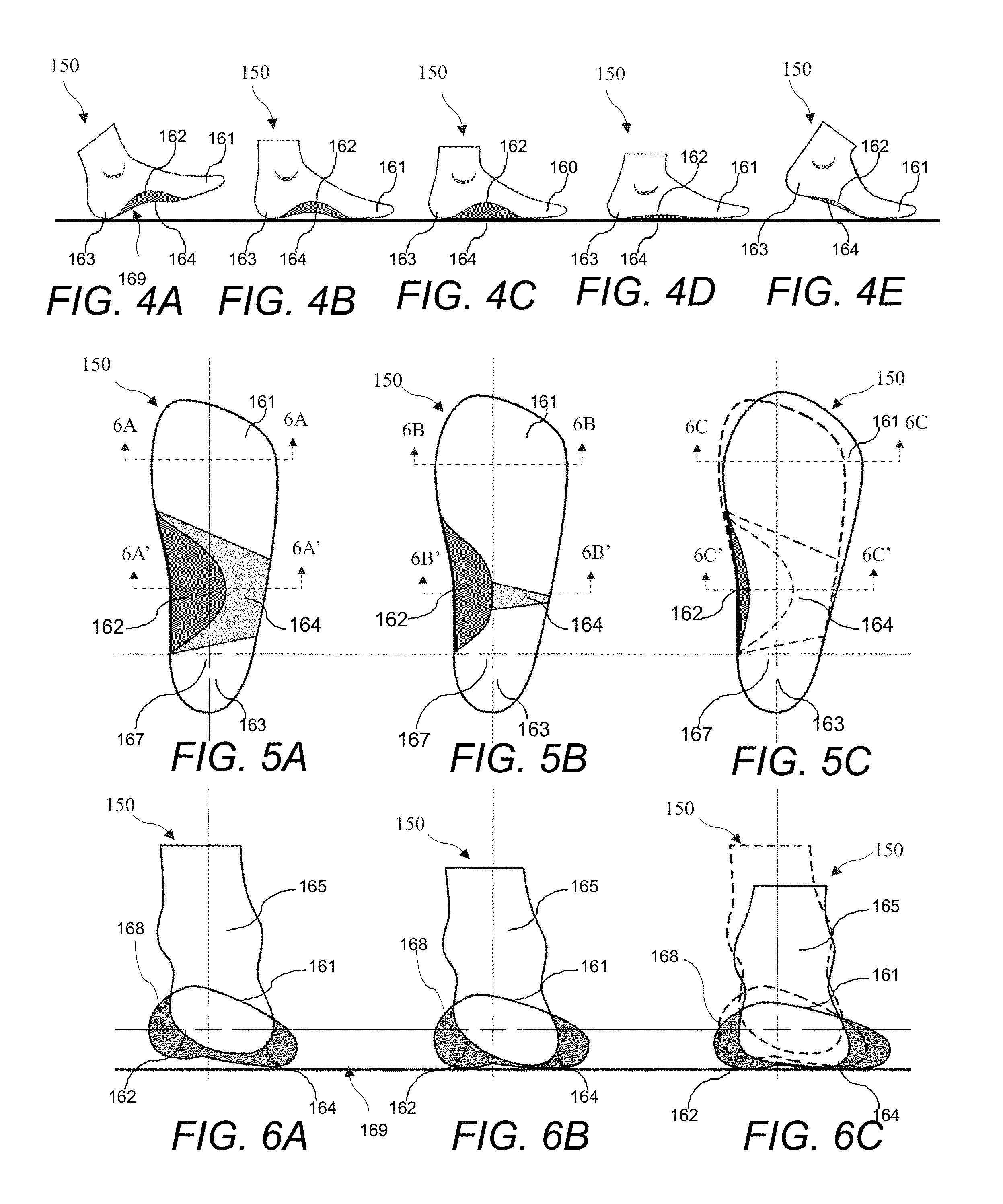
A foot support includes a base material having an area approximately a size of a foot, a deepened heel cup in an upper portion of a heel portion of the base material, a heel skive in a lower portion of the base material in a heel portion of the base material, and a top cover configured to cover substantially all of an upper surface of the base material. The heel skive is configured to add additional stability to the mid-tarsal and sub-talor joints by inverting them.
Owner:WEISS ALLAN G
Article of footwear with embedded orthotic devices
InactiveUS8640363B2Enhance comfort and fit and utilityMovement of footSolesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCalcaneusFoot region
Footwear including an integrated orthotics system provides support with progressive resistance in pronation and supenation motions of the foot during a gait cycle. The orthotics system includes an orthotic device between the mid-sole and the outsole and extend from the rear foot's calcaneus region to the forefoot region where the phalanges and metatarsal joints meets. The orthotic device includes contours mimicking a foot sole shape in an unloaded state. The orthotic system may also include a secondary external orthotic device embedded underneath the outsole to provide control in the mid foot region to achieve progressive compression resistance in the mid foot arch zones. The secondary device may be customizable to achieve a wide range of resistance level needed in mid foot compression by the wearer. The orthotics combined with the midsole and outsole provide progressive mid foot compression resistance and directional flex associated with pronatory motions of the foot.
Owner:HSU HENRY
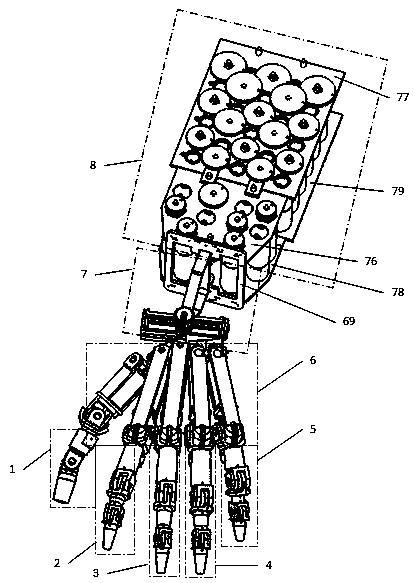
32-degree-of-freedom bionic compliant internal skeleton dexterous hand
ActiveCN110842962AIncrease production capacityEasy maintenanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsLittle fingerTendon sheath
The invention discloses a 32-degree-of-freedom bionic compliant internal skeleton dexterous hand. The dexterous hand uses an anatomy structure of a human hand for reference, a hand portion is of an inner skeleton type, and the outer surface is suitable for being covered with a flexible bionic skin layer with a certain thickness; a joint adopts double-driver antagonistic type drive, so that the compliance operation and the robustness are both taken into account; a tendon coupling piece and a tendon sheath fixing piece are adopted, so that the hand portion and a wrist portion can be easily disassembled and assembled; metacarpophalangeal joints of five fingers all have convolution degrees of freedom so that the fingers can automatically and compliantly adapt to a complex curved surface; a carpometacarpal joint of a thumb has two degrees of freedom of bending-stretching and annular rotation, a metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb has the degree of freedom of side sway, carpometacarpal joints of a ring finger and a small finger have degrees of freedom of bending-stretching and inward retracting-outward stretching, an opposing action can be performed so that complex pinching operationcan be executed; the axes of all the degrees of freedom of the multi-degree-of-freedom joint are orthogonal, so that control and motion planning calculation is facilitated; and the dexterous hand is very suitable for compliantly operating objects of complex shapes, so that production, disassembly, assembly and maintenance are facilitated.
Owner:NEUROCEAN TECH INC
Article of Footwear with Embedded Orthotic Devices
Footwear including an integrated orthotics system provides support with progressive resistance in pronation and supenation motions of the foot during a gait cycle. The orthotics system includes an orthotic device between the mid-sole and the outsole and extend from the rear foot's calcaneus region to the forefoot region where the phalanges and metatarsal joints meets. The orthotic device includes contours mimicking a foot sole shape in an unloaded state. The orthotic system may also include a secondary external orthotic device embedded underneath the outsole to provide control in the mid foot region to achieve progressive compression resistance in the mid foot arch zones. The secondary device may be customizable to achieve a wide range of resistance level needed in mid foot compression by the wearer. The orthotics combined with the midsole and outsole provide progressive mid foot compression resistance and directional flex associated with pronatory motions of the foot.
Owner:HSU HENRY
Bionic low-vibration walking wheel
InactiveCN105882782AFluctuation range of small wheel centerReduce the overall heightWheelsVehiclesVibration attenuationEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a bionic low-vibration walking wheel. The bionic low-vibration walking wheel comprises a first wheel leg mechanism and a second wheel leg mechanism, the first wheel leg mechanism is fixedly arranged on the second wheel leg mechanism through a plurality of connection bolts, and the first wheel leg mechanism and the second wheel leg mechanism are structurally identical. The bionic low-vibration walking wheel is designed on the basis of bionic engineering principles, the synergic foot movement of an ostrich and the energy absorption and vibration attenuation characteristics of the metatarsophalangeal joint tendons of the ostrich. When the walking wheel travels on the sandy ground and hard ground, wheel center fluctuation and vibration are evidently weakened while a traction performance of a normal walking wheel is achieved. The bionic low-vibration walking wheel is simple in structure, stable in operation, excellent in sinking resistance, low in soil disturbance according to the wheelmark and superior to a traditional walking wheel in traction performance. In addition, the bionic low-vibration walking wheel is low in wheel center fluctuation, the vibration attenuation effect is more evident along with the increasing of the rotation speed, and accordingly the comfortableness of a driver is improved, vehicular mechanical parts are less prone to fatigue failure, and the bionic low-vibration walking wheel is suitable for extensive popularization and application.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
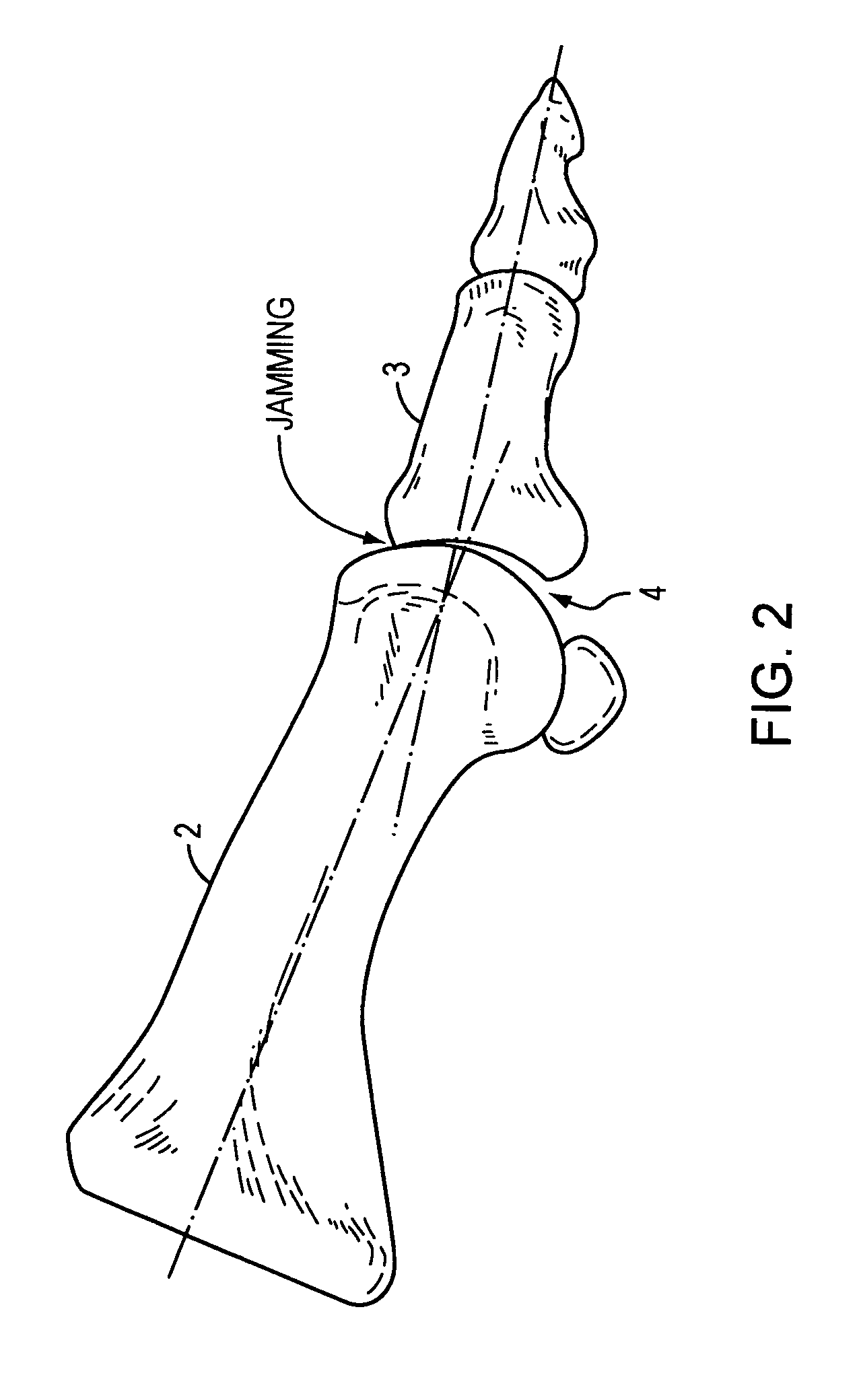
Methods of treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot
Disclosed is a method for treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot of a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of neuromuscular toxin to the mammal. Preferred embodiments include administering toxins capable of interfering with the connection between muscle and nerve, e.g. botulinum toxin, to the patient to treat such abnormalities as hallux abductovalgus, hallux varus, hallux limitus, and hallux rigidus.
Owner:RADOVIC PHILIP
Methods of treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot
Disclosed is a method for treating abnormalities of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot of a mammal comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of neuromuscular toxin to the mammal. Preferred embodiments include administering toxins capable of interfering with the connection between muscle and nerve, e.g. botulinum toxin, to the patient to treat such abnormalities as hallux abductovalgus, hallux varus, hallux limitus, and hallux rigidus.
Owner:RADOVIC PHILIP
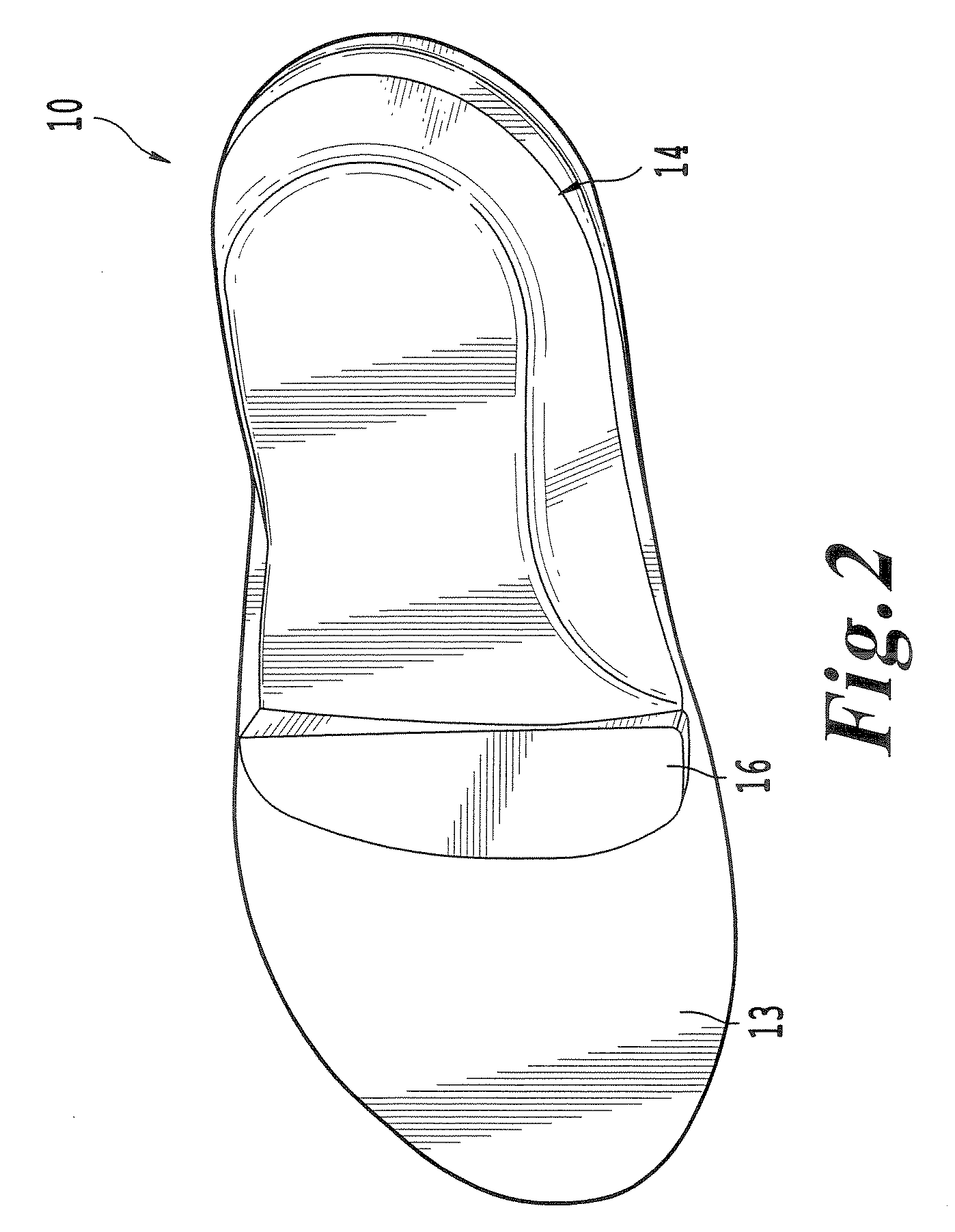
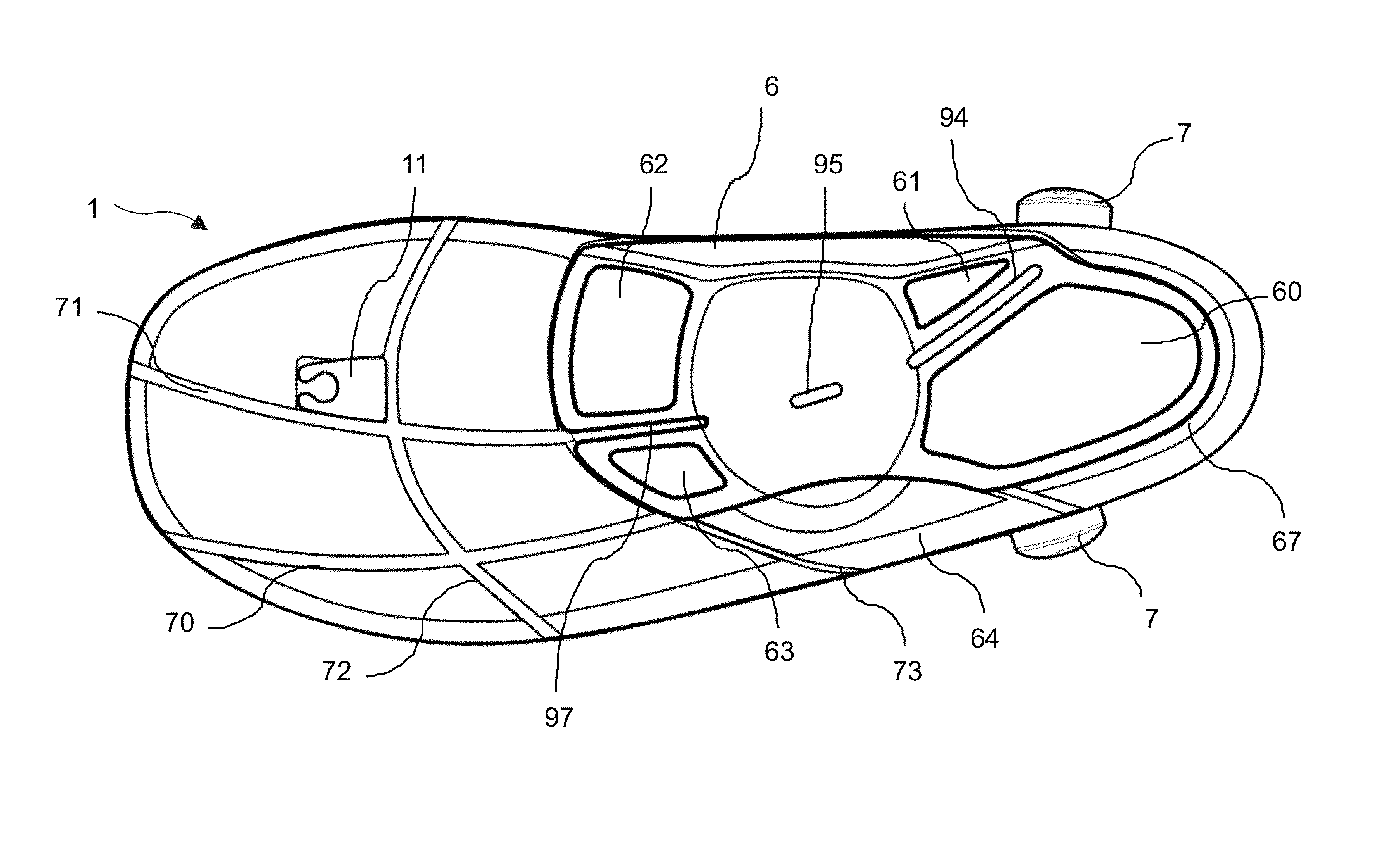
Shoe with a high heel to low heel conversion
A shoe that is convertible between a high heel mode and a low heel mode. There is a rigid shank that is adjustable along the longitudinal axis of the shoe between the various layers of the sole. The proximal end of the adjustable shank may be slid further under the metatarsophalangeal joints to accommodate the sweeping higher arch of a high-heeled shoe or the distal end of the adjustable shank may be slid closer to the back of the calcaneus bone to reduce the arch of the shoe. The different height heels are lockably affixed to the sole.
Owner:HIGH LOW HEEL LLC
Full suspension footwear
A method and apparatus for enhancing the ability of a human to run and jump with comfort comparable to running barefoot on a trampoline and with control comparable to that of the unaided human form, yet with freedom from ankle-turning roll moments associated with substantial ground contact member (GCM) extension downwardly away from the sole of the foot, including a resiliently urged GCM constrained to two degrees of freedom: translation away from the sole of the user's foot and rotation about a longitudinal axis at ground level. The apparatus relates flexure of a GCM toe pressure member to comparable flexure of user's toes at the metatarsal joints. The apparatus also incorporates lower leg to ankle pivot bracing, and extends the GCM in downward direction parallel to the lower leg while mimicking user ankle articulation with parallelism-maintaining rotation about a downwardly resiliently urged transverse pivot axis similar to the user's own ankle joint for extended travel.
Owner:KILLION DAVID L +1
Implantable toe joint prosthesis
PendingCN112754737APromote ingrowthIncrease the binding rateAnkle jointsToe jointsArticular headToe joint prosthesis
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
Bunion correction system and method
ActiveUS20200015865A1Streamlined procedurePromote recoverySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringOsteotomy
A minimally invasive method of correcting a bunion includes performing an osteotomy to divide the metatarsal into first and second portions, implanting a nail in the first portion, securing a suture to the joint capsule, tensioning the suture to align the great toe with the metatarsal, attaching the suture to the nail, and fastening the nail to the second portion. A first guide block includes a plurality of coplanar passages to guide an instrument to create one or more holes in the metatarsal in advance of the osteotomy, and a second guide block includes a guide slot for another instrument to complete the osteotomy. The method can be performed through an incision of 0.5 inches or less. The nail includes an anchor portion for anchoring in the first portion, a head for attachment to a second portion, and can include a passage for attachment of the suture.
Owner:CROSSROADS EXTREMITY SYST
Arthritis Plate
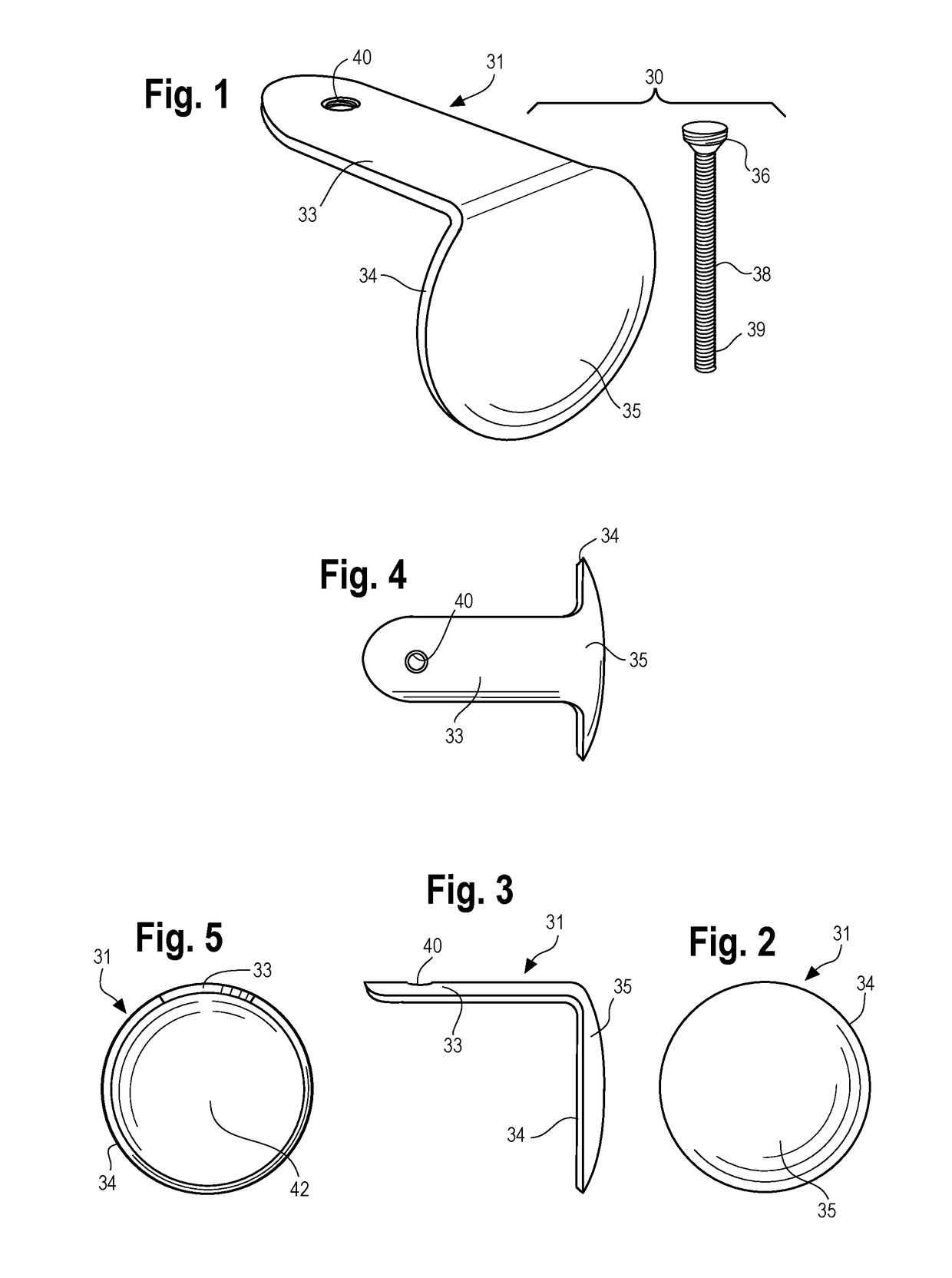
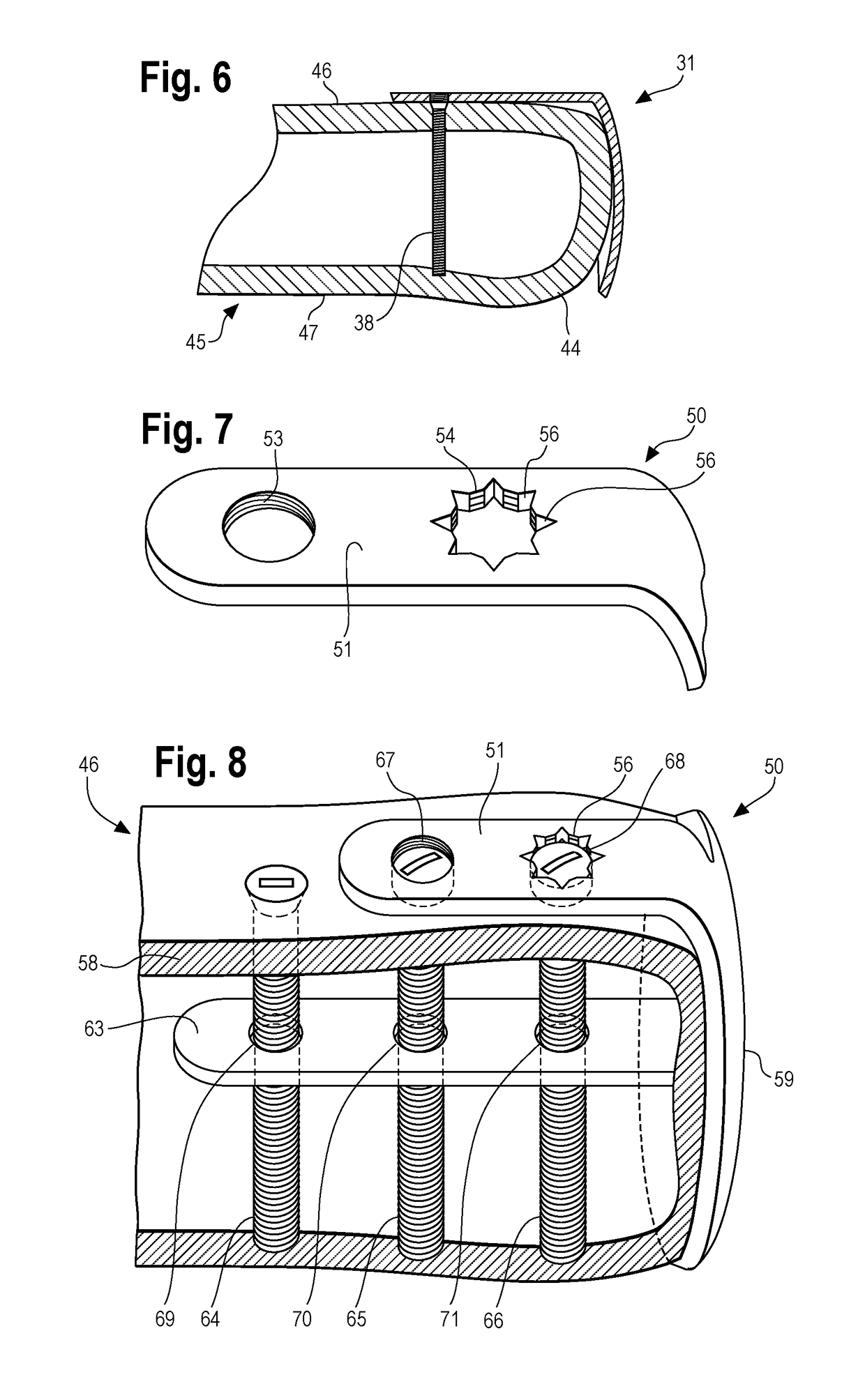
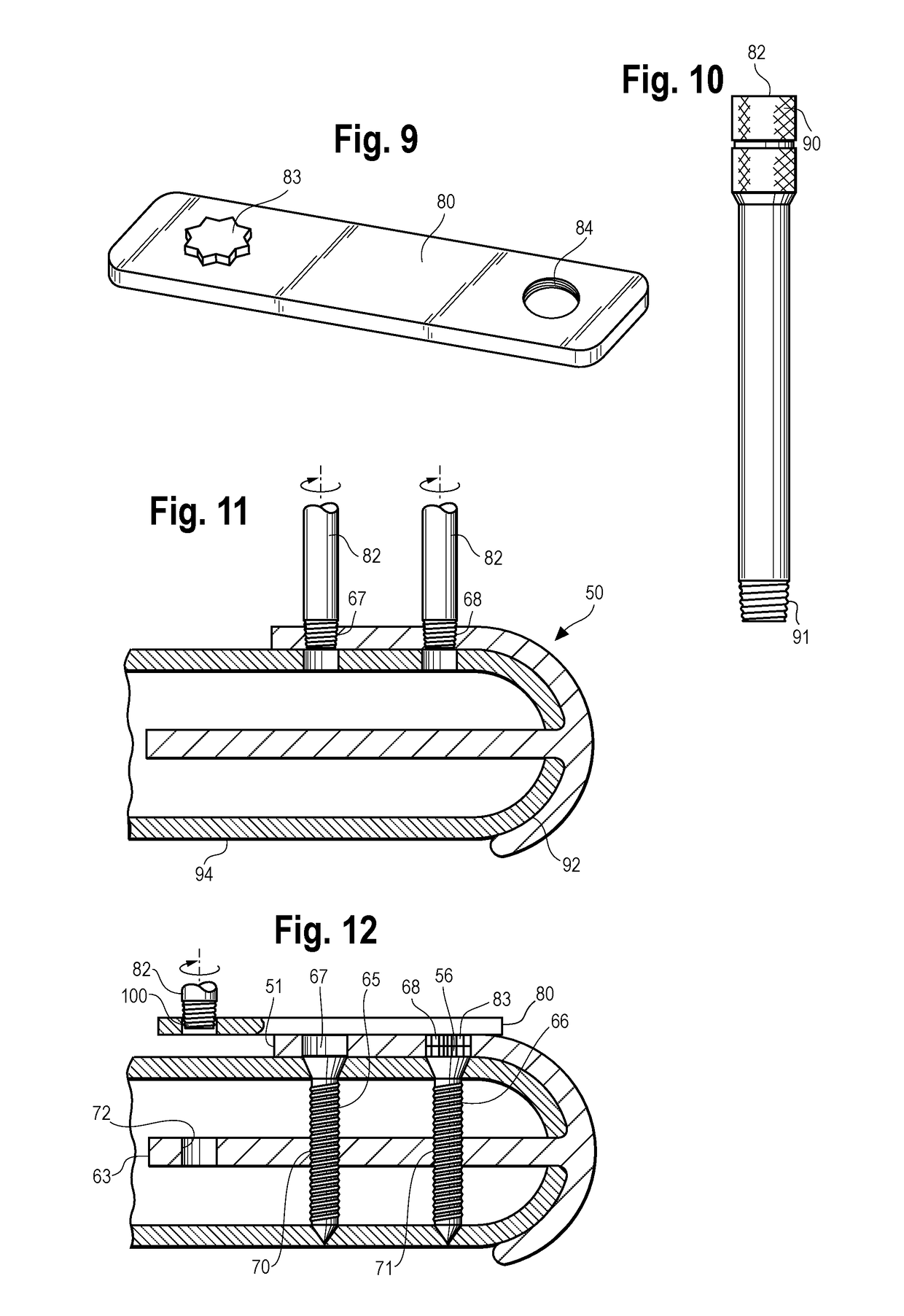
Disclosed are orthopedic implant kits. One disclosed kit comprises an implant having a joint head portion, the joint head portion having a generally convex distal surface and generally concave proximal surface, the implant comprising a post portion protruding proximally from the proximal surface, the post portion having a dorsal surface and a ventral surface (which is a plantar surface in the case of a metatarsal bone) and including a first threaded aperture extending therebetween, and a bone screw. The bone screw has a threaded shaft complementary to the threaded surface of the post portion and preferably is configured to provide bicortical fixation of the implant.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
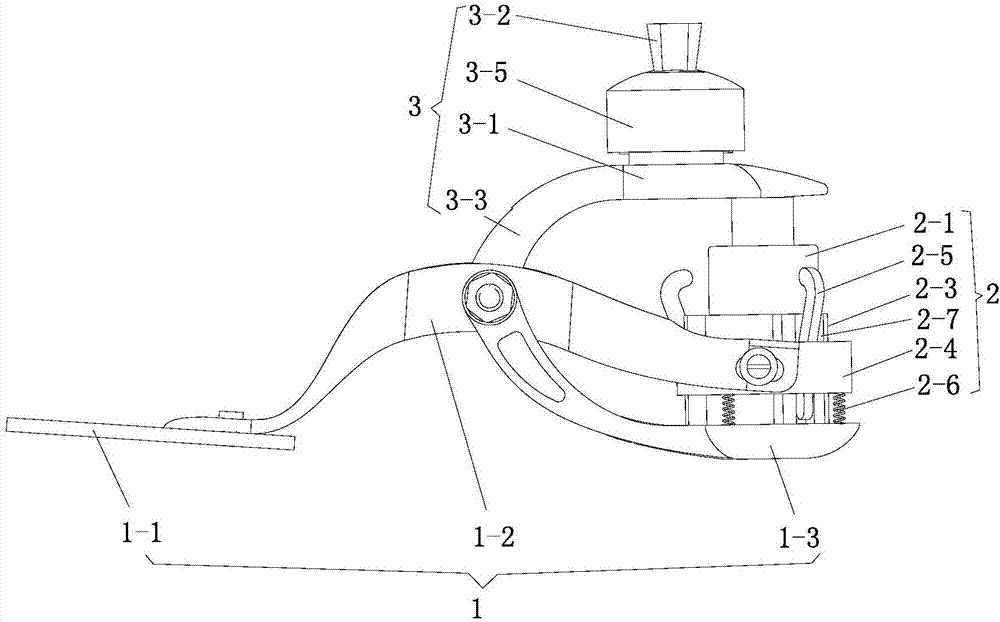
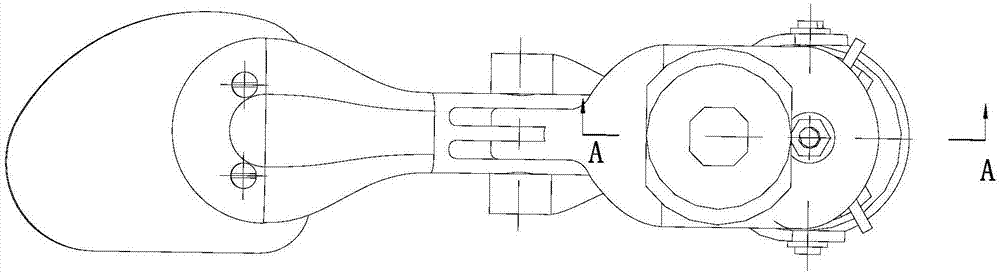
Finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot with adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching functions
ActiveCN112641598AImplement Adaptive AlignmentRelieve mechanical stressChiropractic devicesStretch exerciseExoskeleton robot
The invention belongs to the field of biomechanical engineering, aims to solve the problem that an existing finger rehabilitation robot assisting metacarpophalangeal joints in adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching movement cannot achieve self-adaptive alignment of man-machine joints, and particularly relates to a finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot with adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching functions. The finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot comprises three driving assemblies, a metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly and a near-end joint transmission assembly, wherein inner and outer driving rope wheels in the metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly can control the adduction and abduction movement of the human hand under the driving of the first driving assembly; a first fixed rope wheel and a second fixed rope wheel in the metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly can control the flexion and stretching movement of the near-end phalanx under the driving of the second driving assembly; and the near-end joint transmission assembly can control the flexion and stretching movement of the middle phalanx under the driving of the third driving assembly. According to the invention, the self-adaptive alignment of the man-machine joints of the rehabilitation robot capable of doing the adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching movement can be realized, and meanwhile, the joint mechanical stress generated between a man and a machine can be effectively eliminated.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Bone defect repair apparatus and method
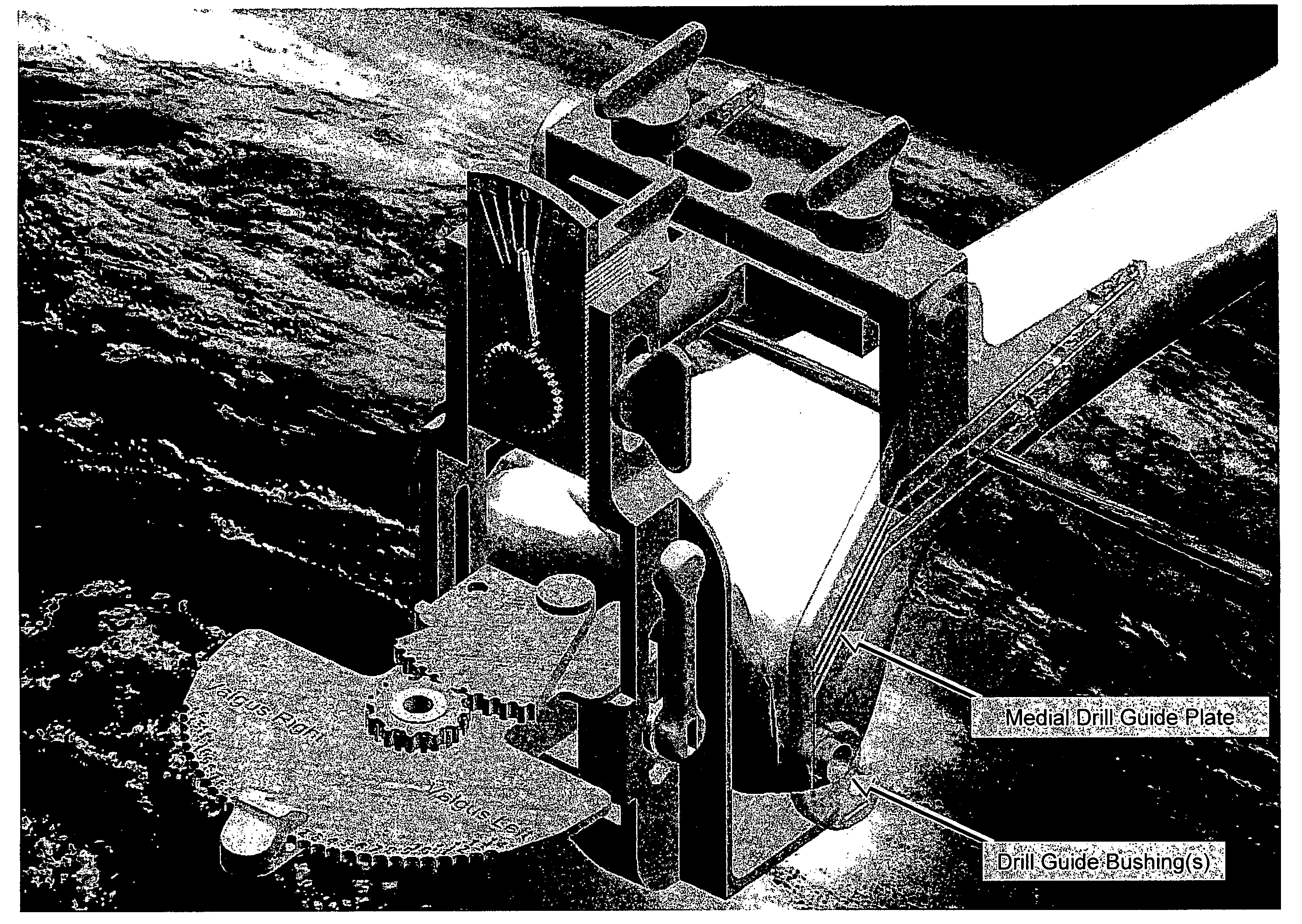
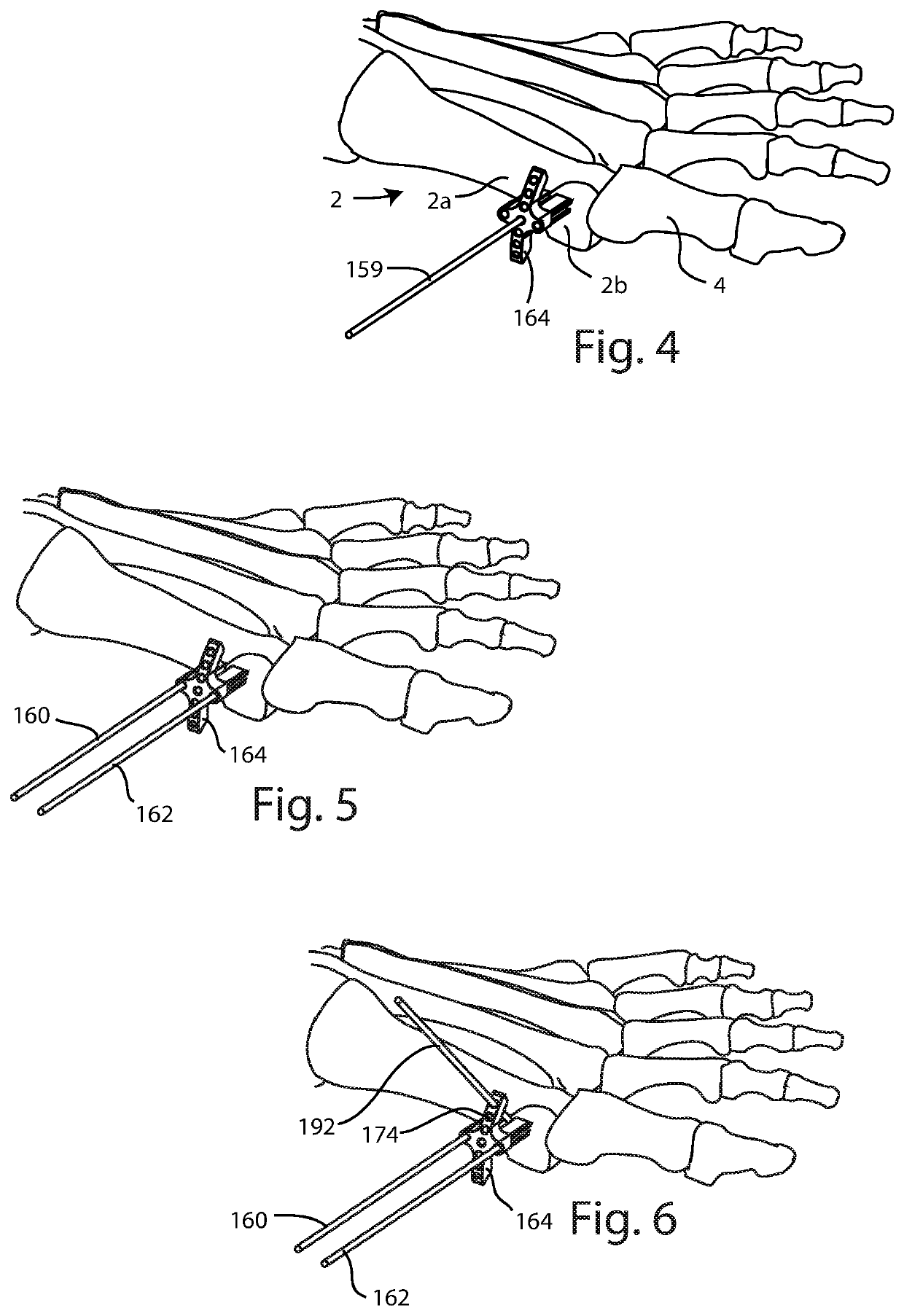
An orthopedic instrument assembly for placing an implant into a medial cuneiform of a foot, the assembly includes a targeting guide having a body with an elongated linear base. A threaded rack is disposed along the elongated linear base. A compression-distraction frame pre-compresses the joint prior to placement of a joint fixation element. The compression-distraction frame is translatably connected to the rack of the guide body base. The compression-distraction frame is releasably, statically connectable to a first metatarsal bone and a post. The post has a generally cylindrical shape and a longitudinal axis, and has a plurality of threaded cylindrical bores disposed therethrough at predefined angles relative to the longitudinal axis. The post is releasably, statically connectable to the targeting guide.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Bone align and joint preparation device and method
A bone displacement system includes an anchoring portion, a tool engaging portion, a compression distraction mechanism, a lateral body and a distal body. The anchoring portion has an aperture for receiving a wire to connect the anchoring portion to a proximal bone. The tool engaging portion is connected to the anchoring portion and is configured to connect a tool thereto. The compression-distraction mechanism is connected to the anchoring portion. The lateral body is connected to the compression-distraction mechanism by a ratchet. The lateral body has a downwardly depending portion for contacting a lateral bone. The distal body is connected to the compression-distraction mechanism. The distal body has an aperture for receiving a wire to connect the distal body to a distal bone. The compression-distraction mechanism is configured to move the anchoring portion relative to the distal body.
Owner:MEDARTIS AG
Foot orthosis with comprehensive method for correcting deformities of the transverse arch of the foot in cases of static transverse flatfoot compounded by hallux valgus, with possible preventive and post-operative applications.
InactiveUS20180243121A1Strengthen foot muscleGood effectChiropractic devicesCorrective surgeryOrthopedic department
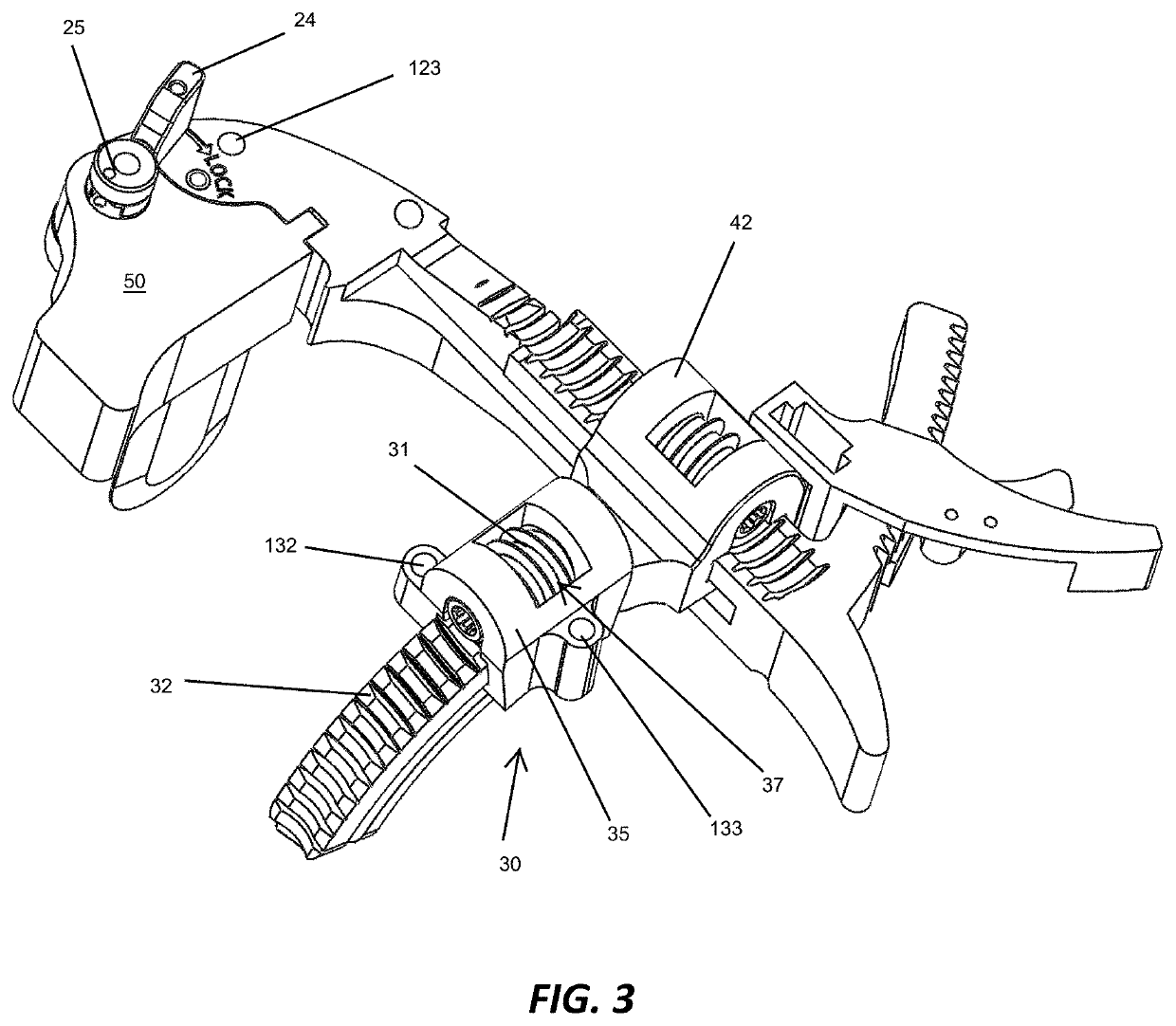
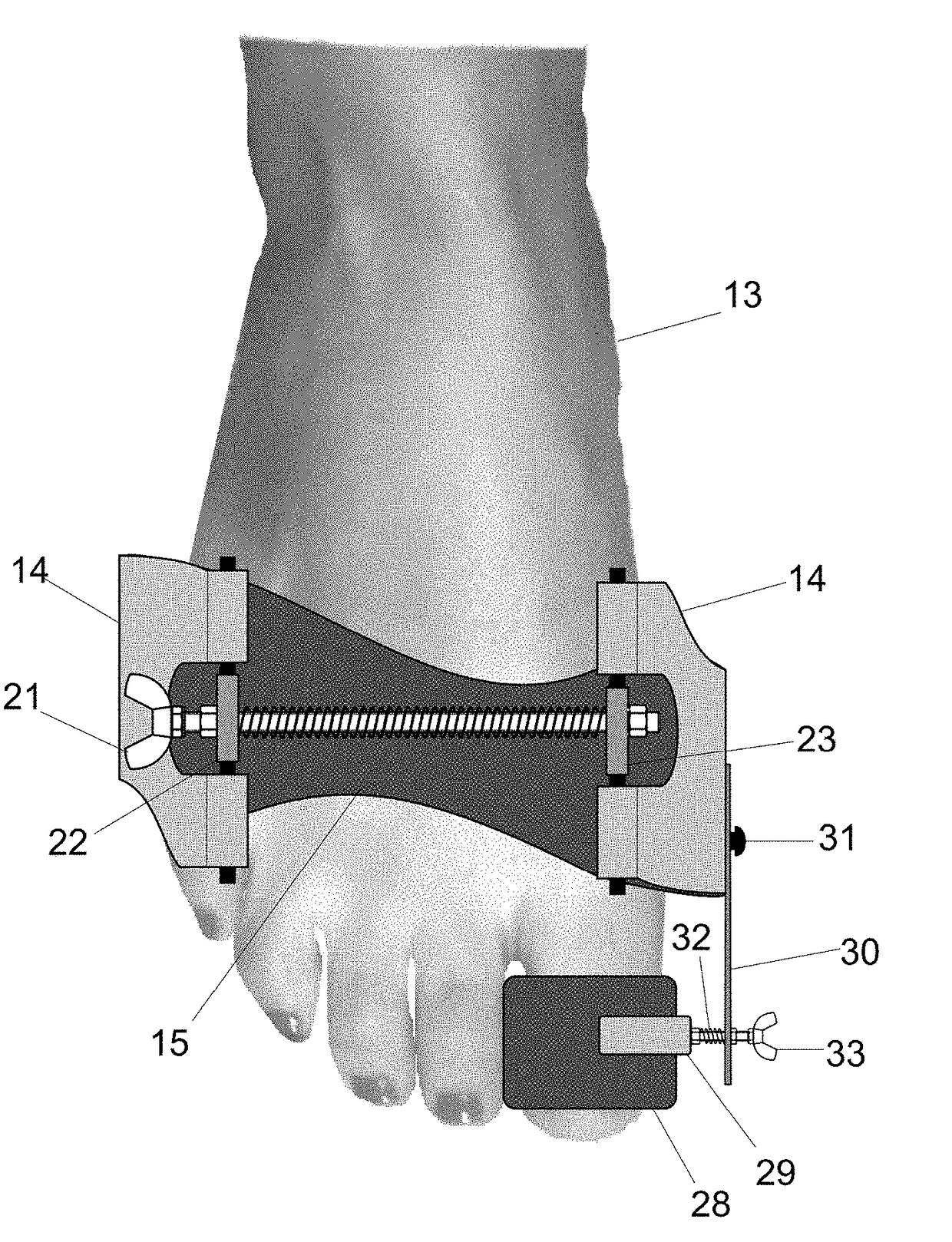
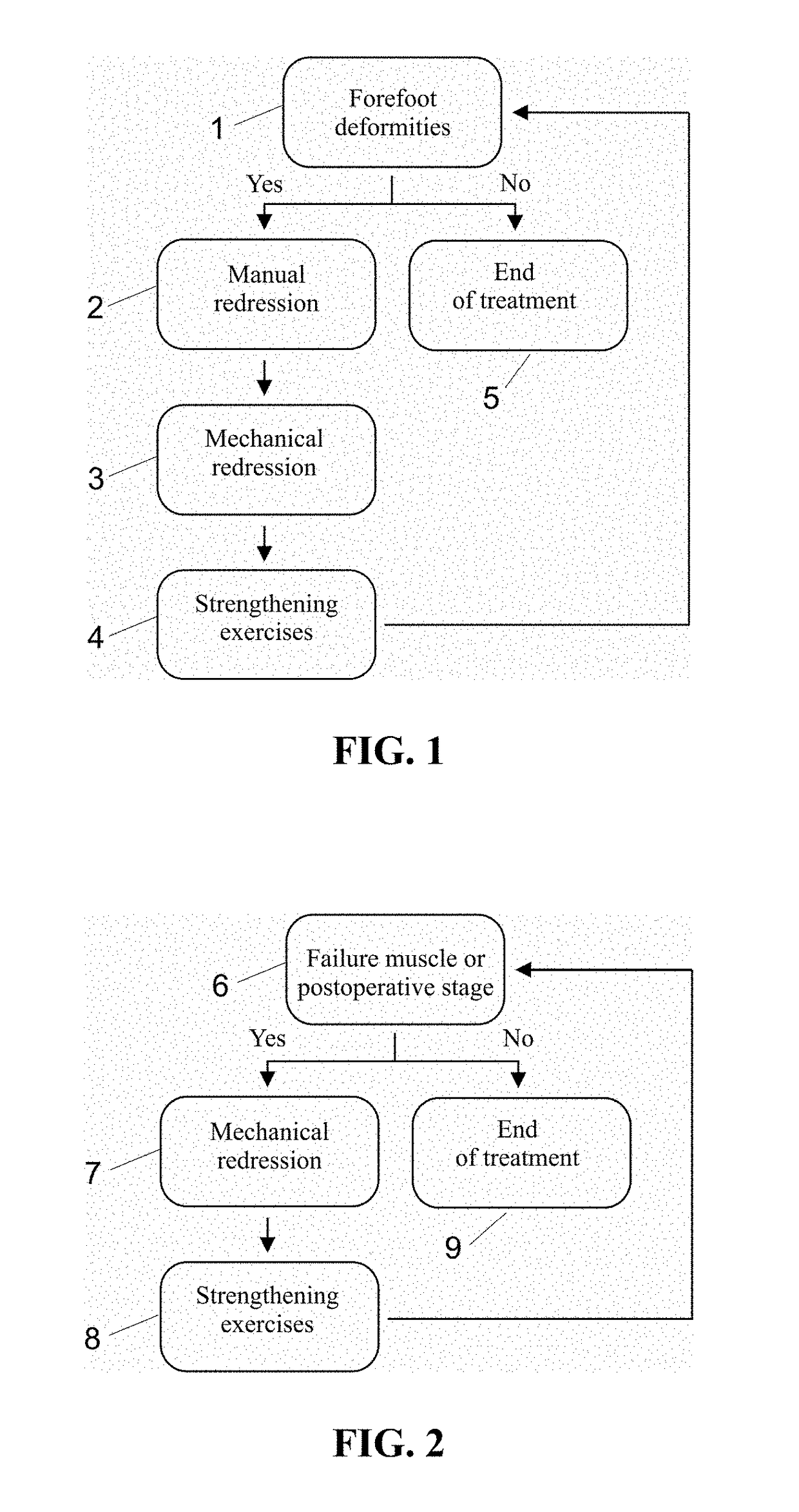
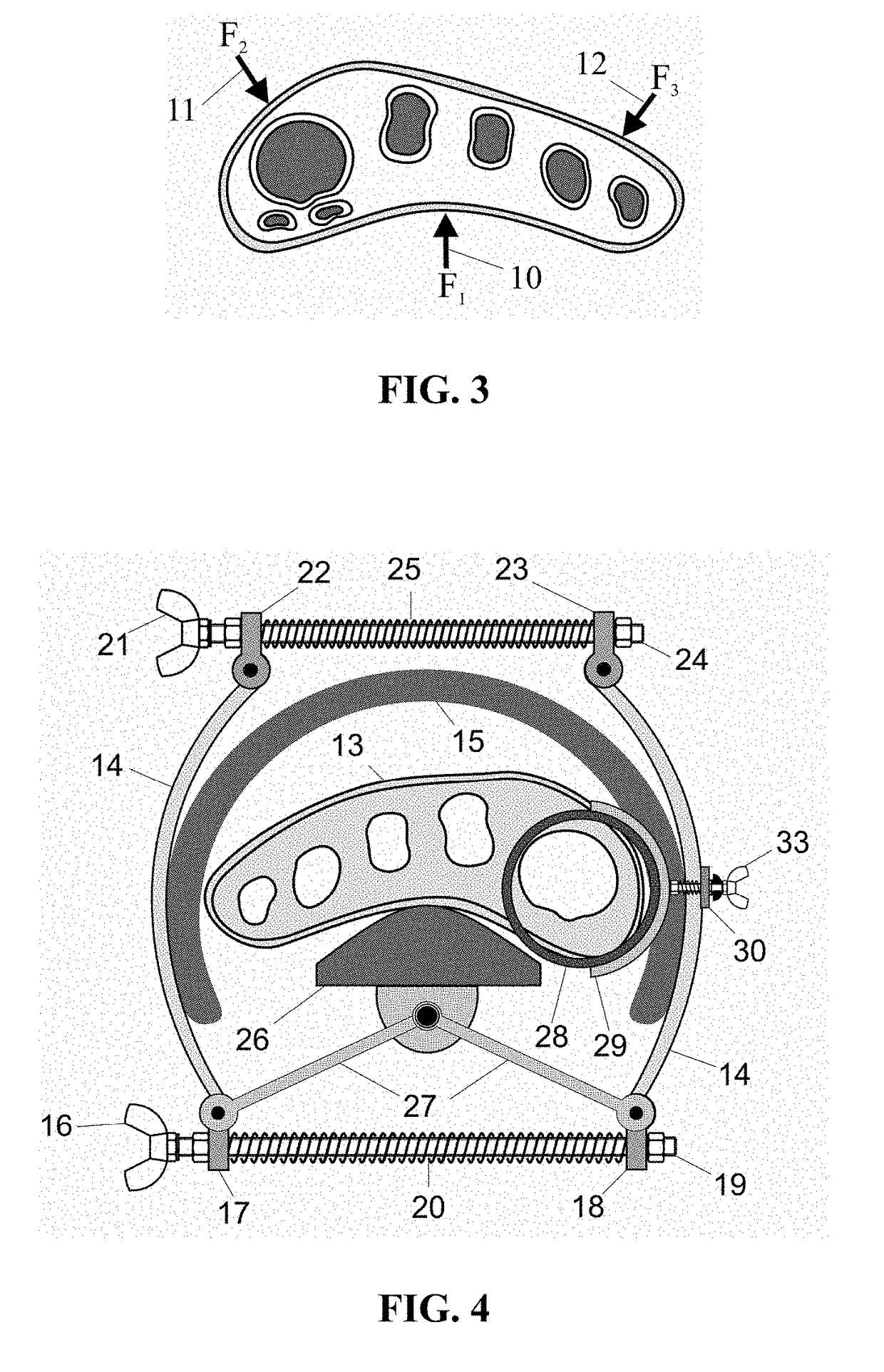
The proposed method is an innovative approach to correcting orthopedic deformities. It involves gradual manual mobilization of contracture soft tissues and diminutive foot joints by a physiotherapist, followed by mechanical reinforcement of the resulting effect by an orthosis which depresses and push the Ist, IVth and Vth metatarsal bones while elevating or actually blocking the fall the immobile IInd and IIIrd metatarsal bones according to the “three forces” rule. Correction transverse arch foot runs simultaneously with the correction of hallux valgus (if necessary). The propose method comprises sequentially applied passive redression (manual treatment), and a follow-up with the use of a specially designed orthosis (mechanical treatment). The method is suitable for patients undergoing preparation for corrective HV surgery and for post-operative HV. Method can be used preventively e.g. in women who frequently wear high-heel shoes and in for those who need to remain standing for prolonged periods of time.
Owner:DYGUT JACEK MAREK +1
High impact-resistive protective glove
A glove for hand protection during sports, conforming to hands, fingers, and thumb, extending from carpal bones to cover proximal phalanges up to the proximal interphaiangeal joint comprising impact-absorbing materials: an outer glove conforming to hand, fingers, and thumb extending from carpal bones to cover distal phalanges, comprising abrasion-resistant materials.
Owner:MCPP INC
Light intelligent energy-storage energy-releasing ankle prosthesis
PendingCN107536662AAvoid excessive wearEffortless walkingArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationIliac screw
The invention discloses a light intelligent energy-storage energy-releasing ankle prosthesis. The ankle prosthesis comprises a bionic foot, an ankle joint and a tibia connecting mechanism, and the bionic foot comprises a sole, an arcuate metatarsus and a heel, wherein one end of the metatarsus is fixed to the sole, the other end of the metatarsus is connected with the ankle joint through a bolt, and the extension of the front end of the heel is hinged to the middle of the metatarsus; the ankle joint comprises a spring cover, a central spring, a buffer inner ring, a buffer outer ring, multiplelocking hooks and multiple supporting springs, wherein the buffer inner ring is fixed to the heel, the central spring is arranged in the buffer inner ring in a sleeved mode, the spring cover is arranged at the top end of the central spring in a sleeving mode, a plurality of locking hook grooves are formed in the buffer inner ring, the buffer outer ring is arranged outside the buffer inner ring ina sleeved mode, one ends of the supporting springs are fixed to the heel, and the other ends of the supporting springs are fixed to the bottom end of the buffer outer ring; the tibia connecting mechanism comprises a talus bone and a tibia connecting screw, wherein the front end of the talus bone is hinged to the middle of the metatarsus, the other end is connected with the spring cover, two supporting lugs are arranged on the top surface of the talus bone, and one end of the tibia connecting screw is fixed between the two supporting lugs in a penetrating mode.
Owner:重庆德勒夫科技有限公司
Bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on rigid-flexible coupling
ActiveCN111150528AImprove experienceLow costArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention aims to provide a bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on rigid-flexible coupling. The bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle andfoot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling comprises a shank part, and a foot part; the shank part comprises an upper shell, an upper shell connecting plate piece, an auxiliary metatarsal dorsiflexion limit assembly, a middle shell, a passive support and upper-middle shell connecting piece, a lower shell, an introversion and extroversion limit assembly, and a passive support and middle-lower shell connecting piece; the upper shell, the upper shell connecting plate piece, the auxiliary metatarsal dorsiflexion limit assembly, the middle shell and the lower shell are all made of hard materials; and the passive support and upper-middle shell connecting piece and the passive support and middle-lower shell connecting piece are both made of soft materials. The bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling has the characteristics of being high in flexibility, self-stabilized, self-balanced, impact-resistant and the like;and thus, the bionic passive flexible low-energy-consumption ankle and foot prosthesis based on the rigid-flexible coupling is capable of perfecting natural-gait walking of an amputee, and improvingself-walking energy efficiency of the amputee.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
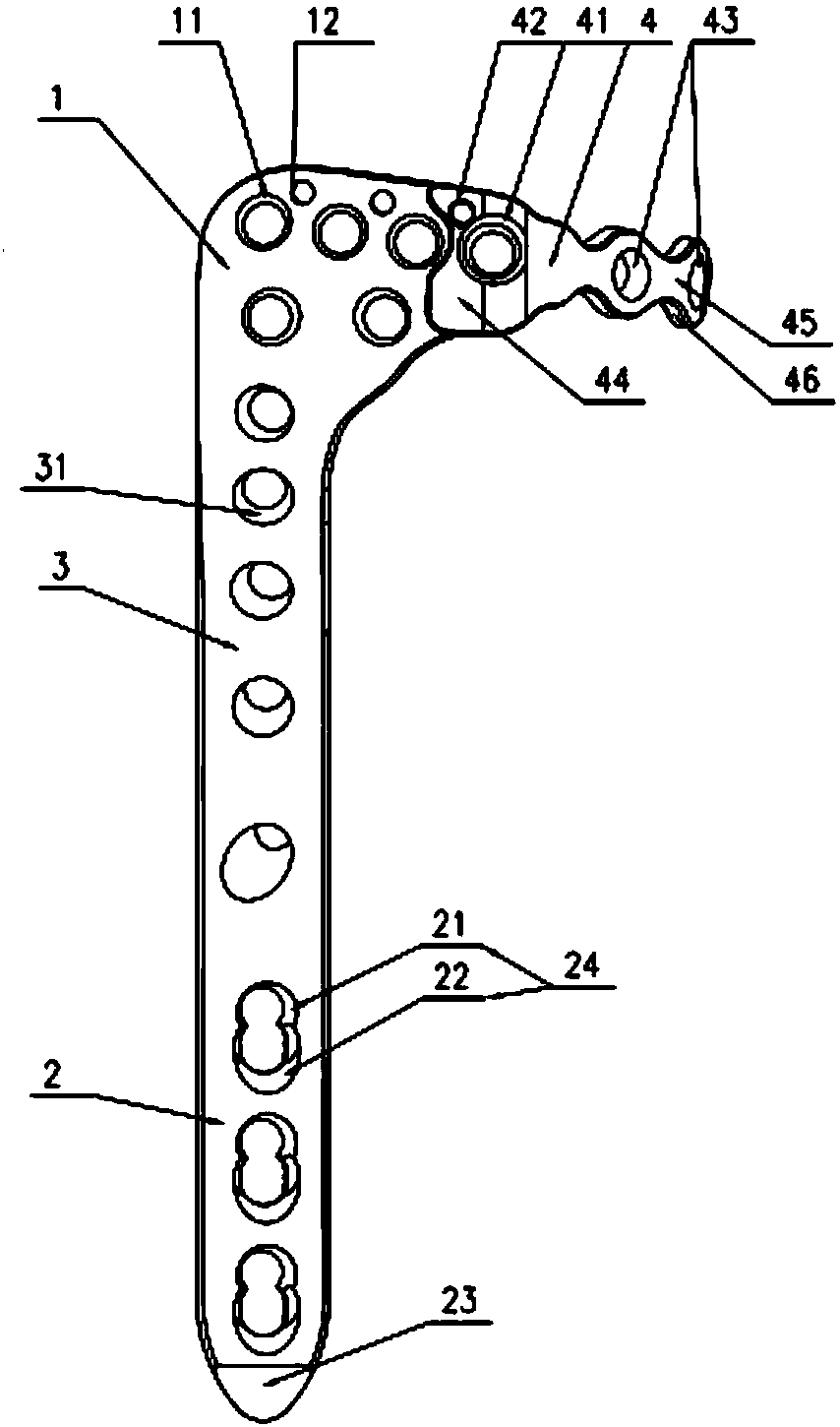
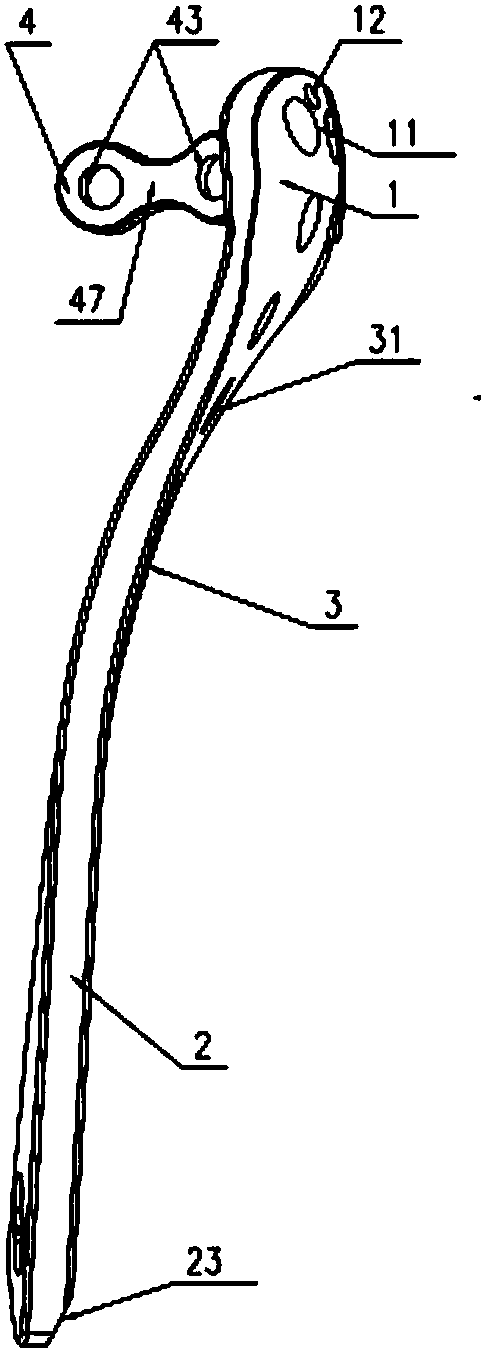
Proximal tibia outer side locking plate
The invention provides a proximal tibia outer side locking plate. The proximal tibia outer side locking plate comprises a main body component and a connecting plate component, wherein the main body component is used for fixing a proximal tibia outer side; the main body component comprises a head part, a rod part and a connecting part for connecting the head part with the rod part; the head part wraps and fixes an outer side column of a proximal tibia platform; the rod part is attached to the outer side surface of a tibial shaft and is fixed; the connecting part is adhered to a tibia surface and is bent; the connecting plate component is connected with the head part and is used for fixing a connecting plate component of a rear side column of the proximal tibia platform. By the main body component, the outer side of a tibia is fixed; by the design of the connecting plate component, fixation to the rear side column of the proximal tibia platform is enhanced, so that the proximal tibia outer side locking plate can be used in surgeries such as proximal tibia fracture, metaphysis fracture, intra-articular fracture and periprosthetic fracture. In addition, the head part of the main body component warps the outer side column of the proximal tibia platform. Compared with an existing curved-surface bone fracture plate, the proximal tibia outer side locking plate is fixed firmly and reliably.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINETIC MEDICAL
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
ActiveUS7643903B2Improve estimation accuracyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactGravity center
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, such as level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped. The horizontal position of any one of the center of gravity (G0), the ankle joint (12), and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is estimated as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point on the basis of the combination of the contact or no contact with the ground at a spot directly below the metatarsophalangeal joint 13a of the foot 13 and a spot directly below the ankle joint 12, which is detected by ground contact sensors 51f and 51r, respectively, provided on the sole of the foot 13. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com