Patents
Literature
65 results about "Middle phalanx" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glove virtual keyboard for baseless typing
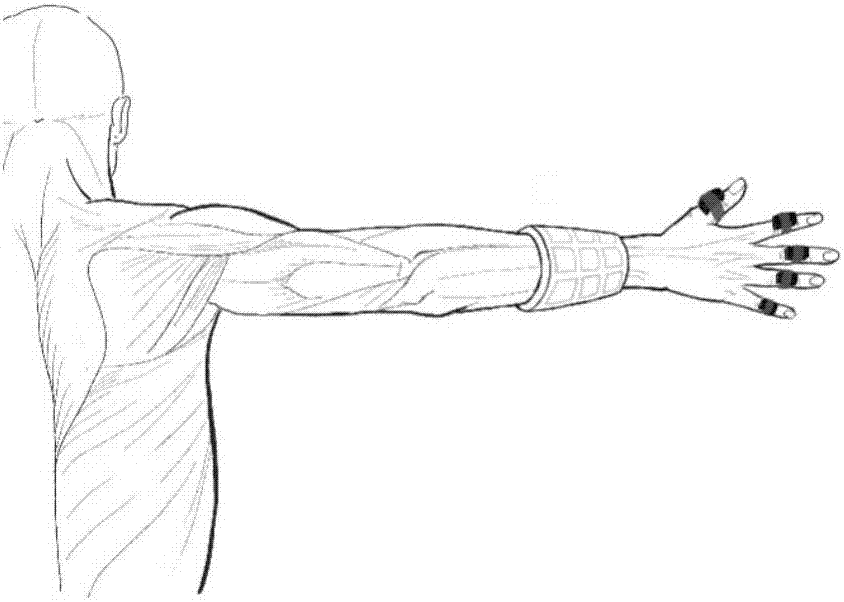
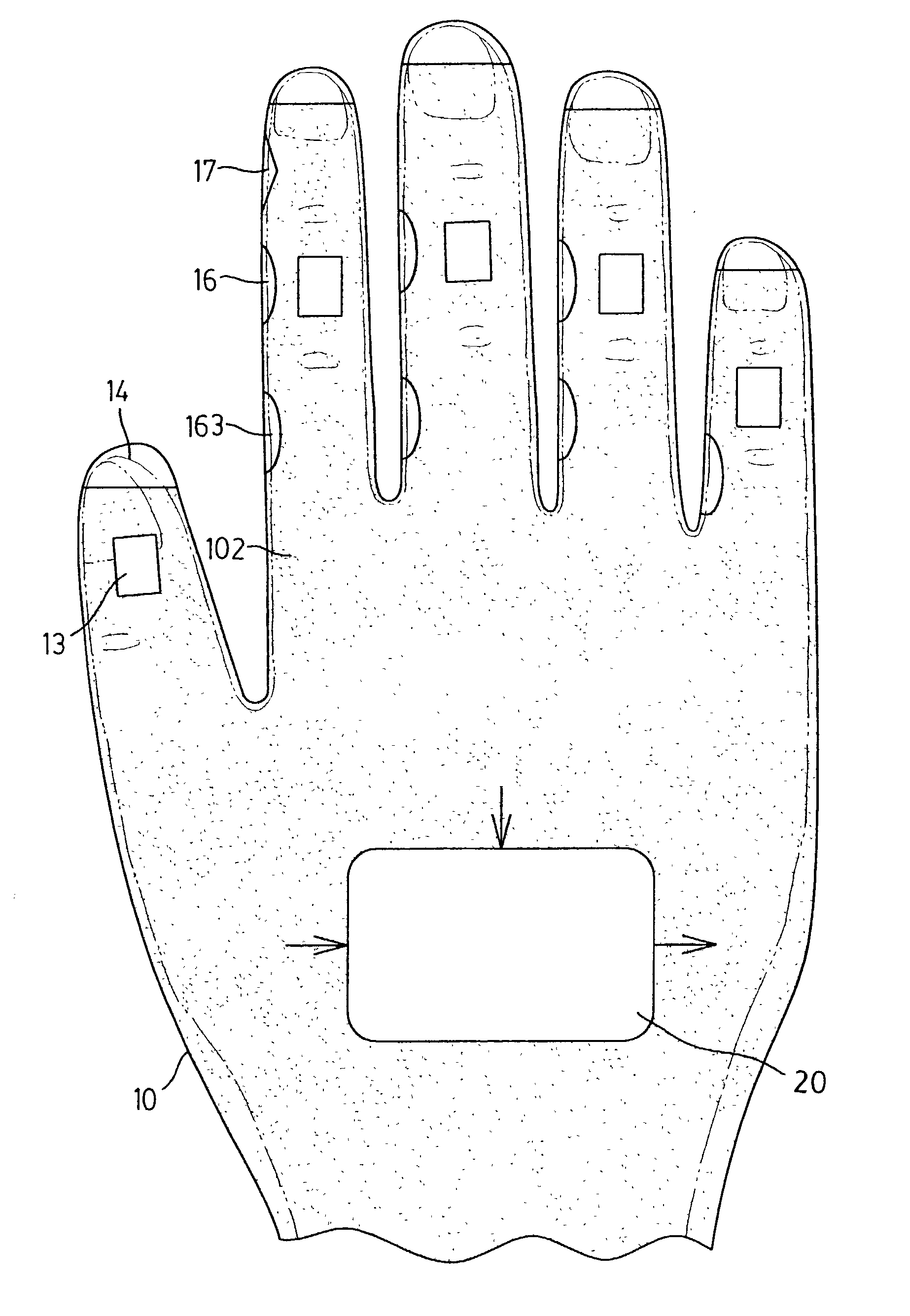
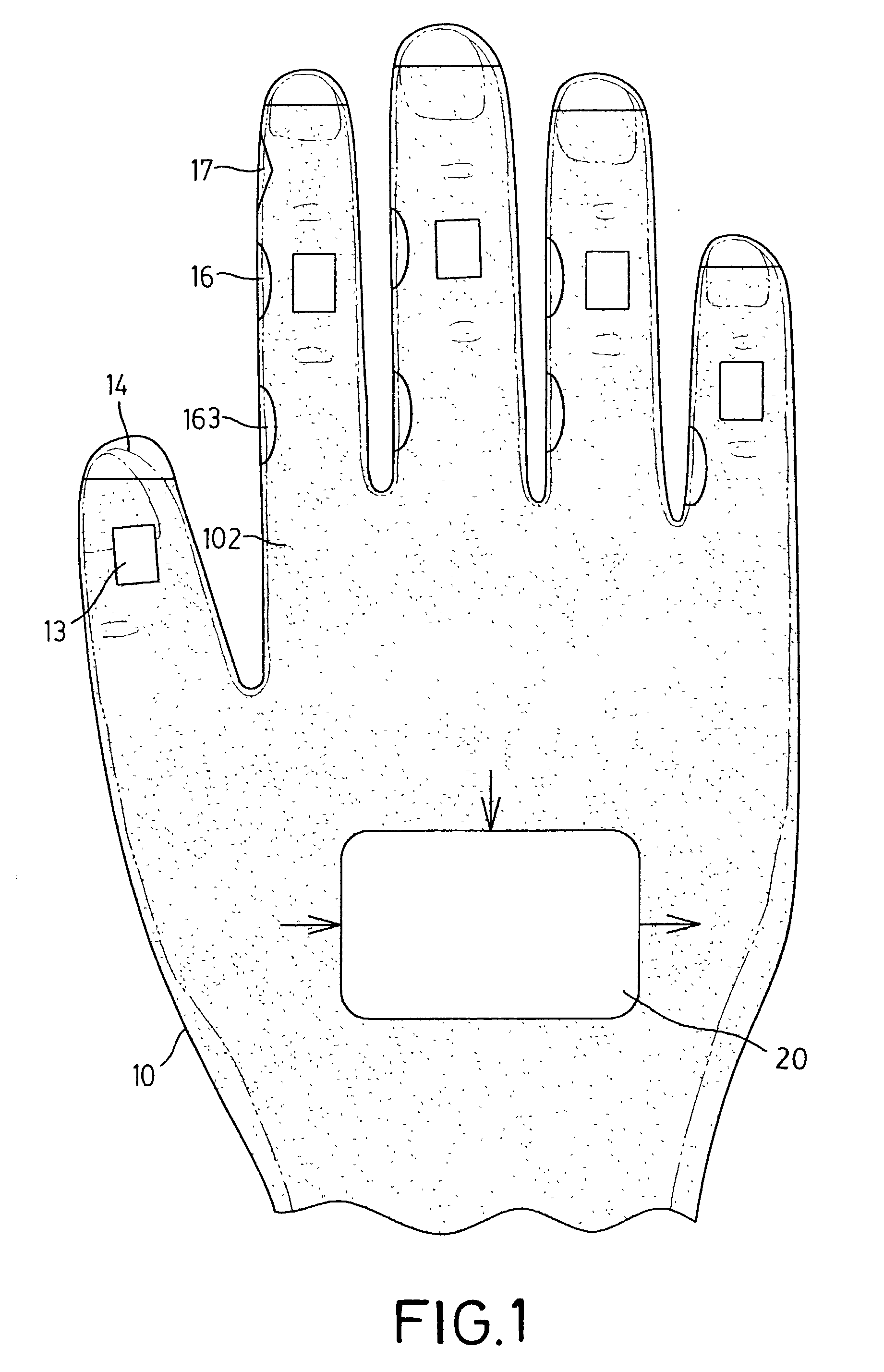
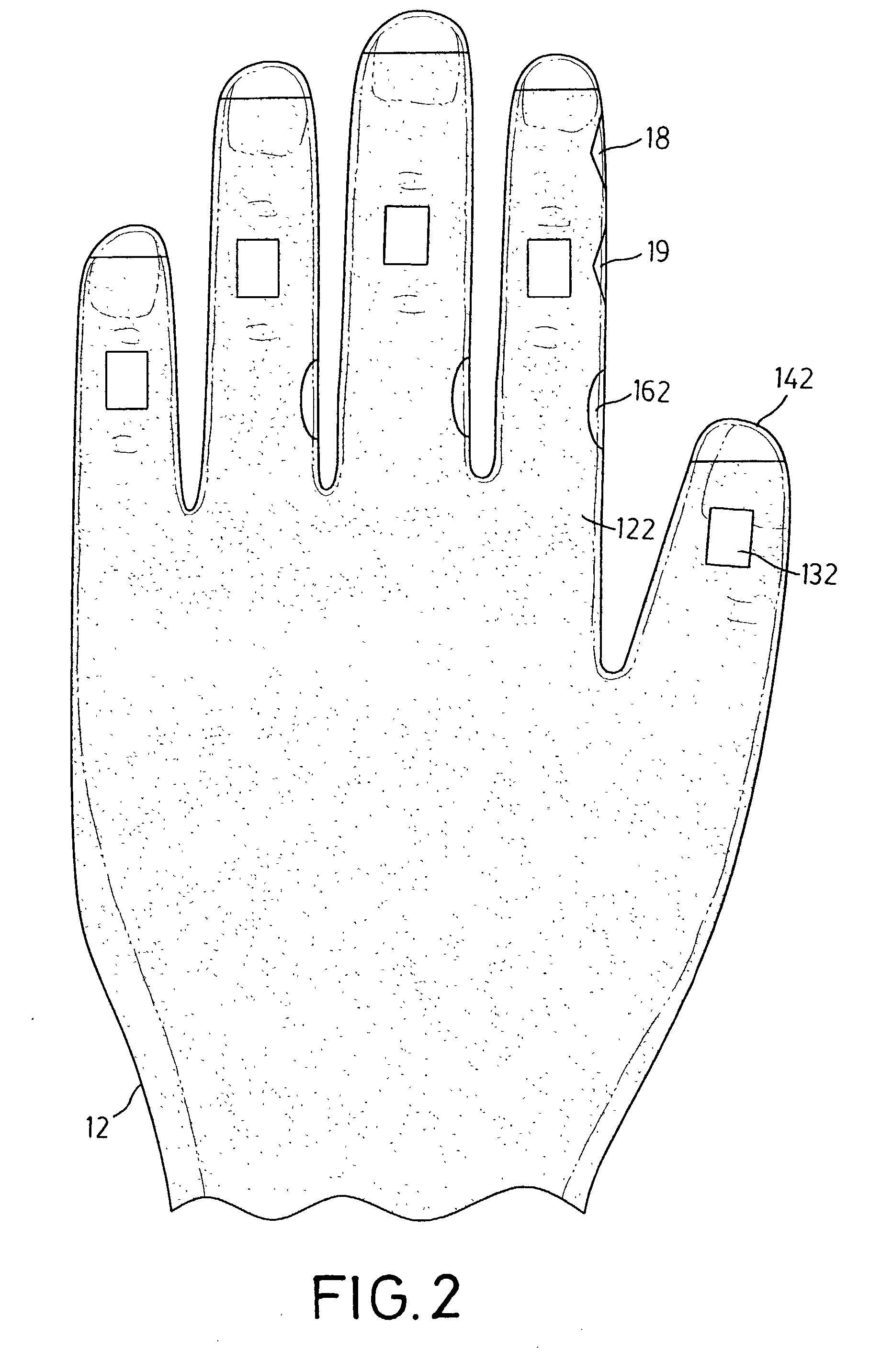
InactiveUS20040001097A1Efficiently and quickly input dataInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsContact padTyping
A data glove input device, serving as a virtual keyboard and enabling ten-finger-typing, has two palm bodies with glove fingers. A tilt sensor is mounted on the middle phalanx of each respective glove finger. It is used to detect the falling in one of multiple tilt angle ranges of the phalanx and to select a specific item from items in a particular column. The same tilt sensor for item selecting can also be used to validate a selection by detecting a tilt angle peak pulse. Multiple contact pads and multiple switch buttons are mounted on the lateral sides of glove fingers except the thumbs, and each of them, which is able to be touched by the thumb, is to switch the same signal selected by a tilt angle or a finger to represent another different item. Accordingly, the data glove can be finger tip uncovered and allows baseless virtual typing.
Owner:ZNGF FRANK +1
Interphalangeal Joint Implant Methods and Apparatus
ActiveUS20130325138A1Decreasing eliminating incidenceSimple procedureFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisSacroiliac jointMiddle phalanx
A method and apparatus for correcting malformed joints, in particular the “hammer toe” contraction of the proximal interphalangeal joint. The disclosure comprises a two-component implant: a proximal phalanx component and a middle phalanx component. An endosseous stem on each component is inserted axially into the end of a respective host bone and, after insertion, the components are attached. The attached components are held together in various ways, for example a detent arm / aperture mechanism. Each component can be cannulated to allow for the passage of a kirschner wire, if necessary, to stabilize adjacent joints such as the proximal interphalangeal joint. The bones of the treated joint can be set to form a desired angle by adjusting the angle formed by the corresponding endosseous stems.
Owner:GRAHAM MICHAEL
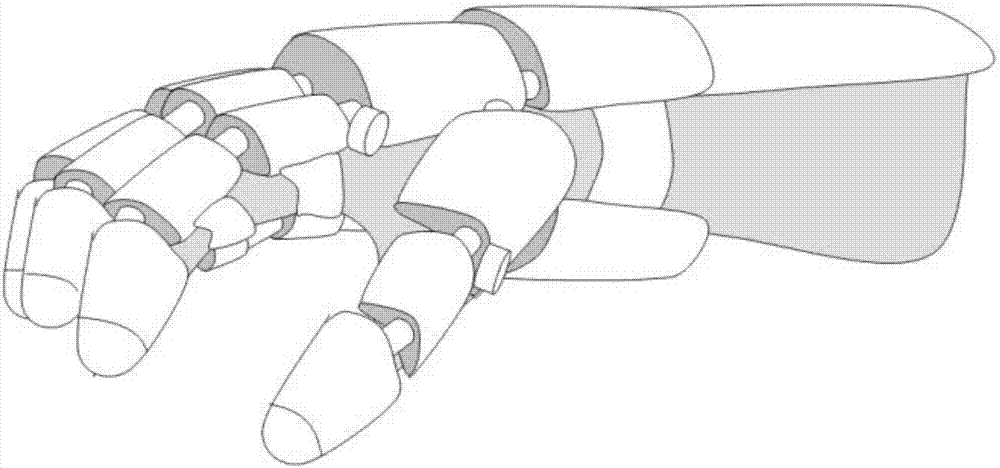
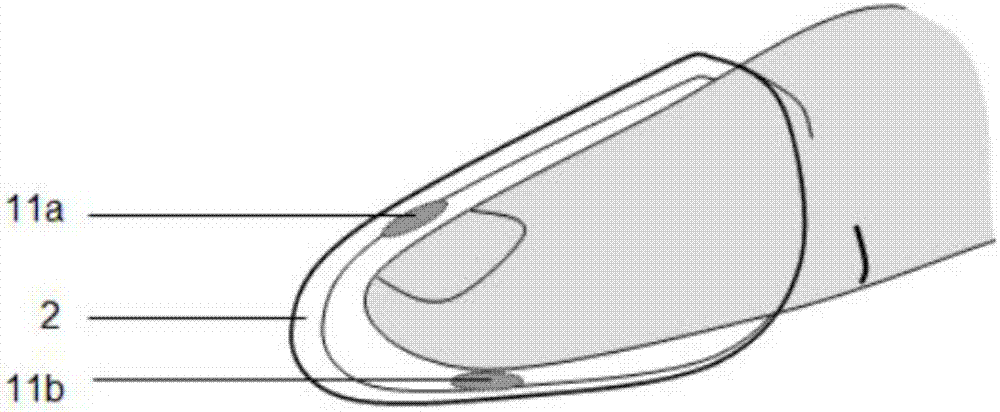
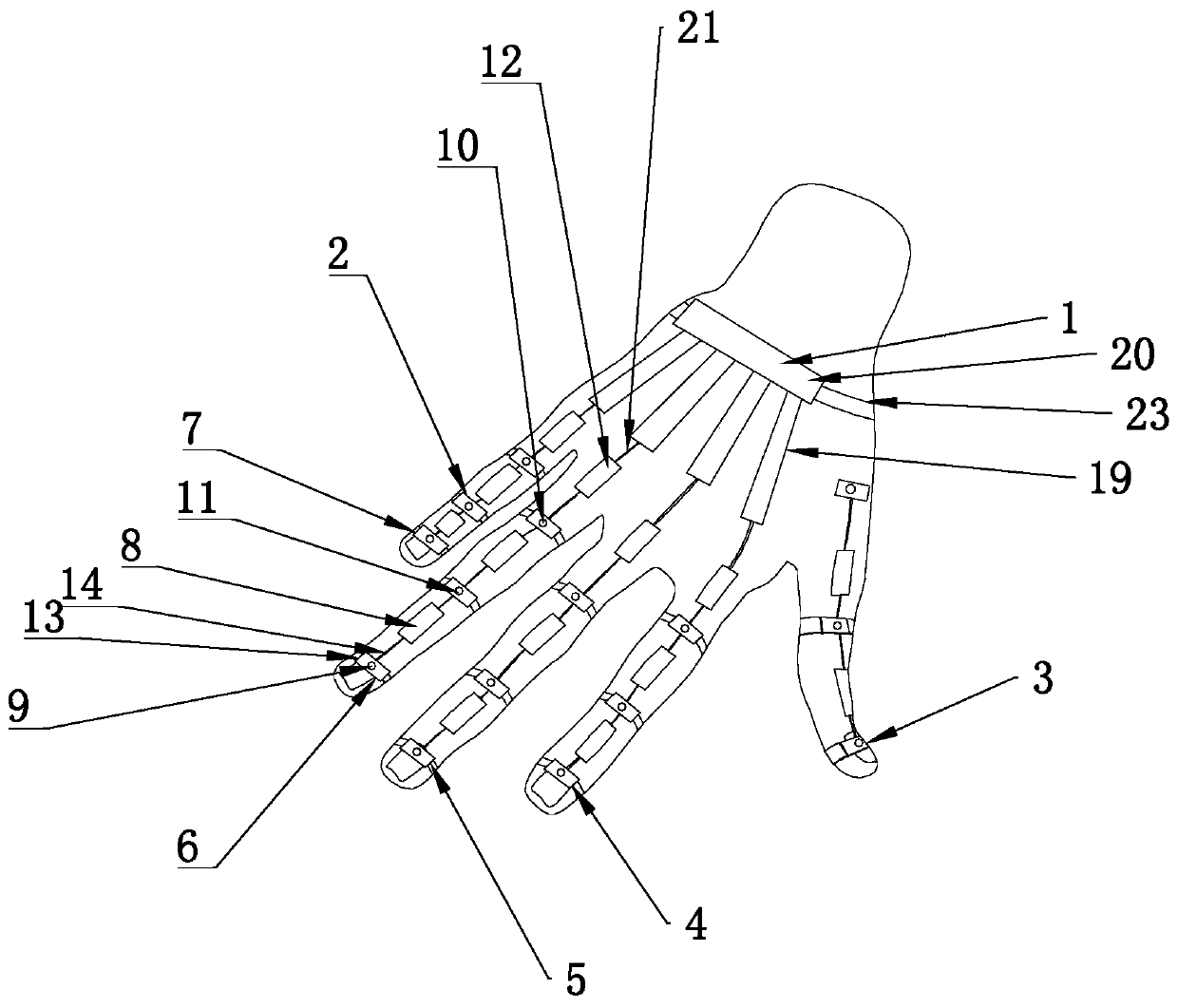
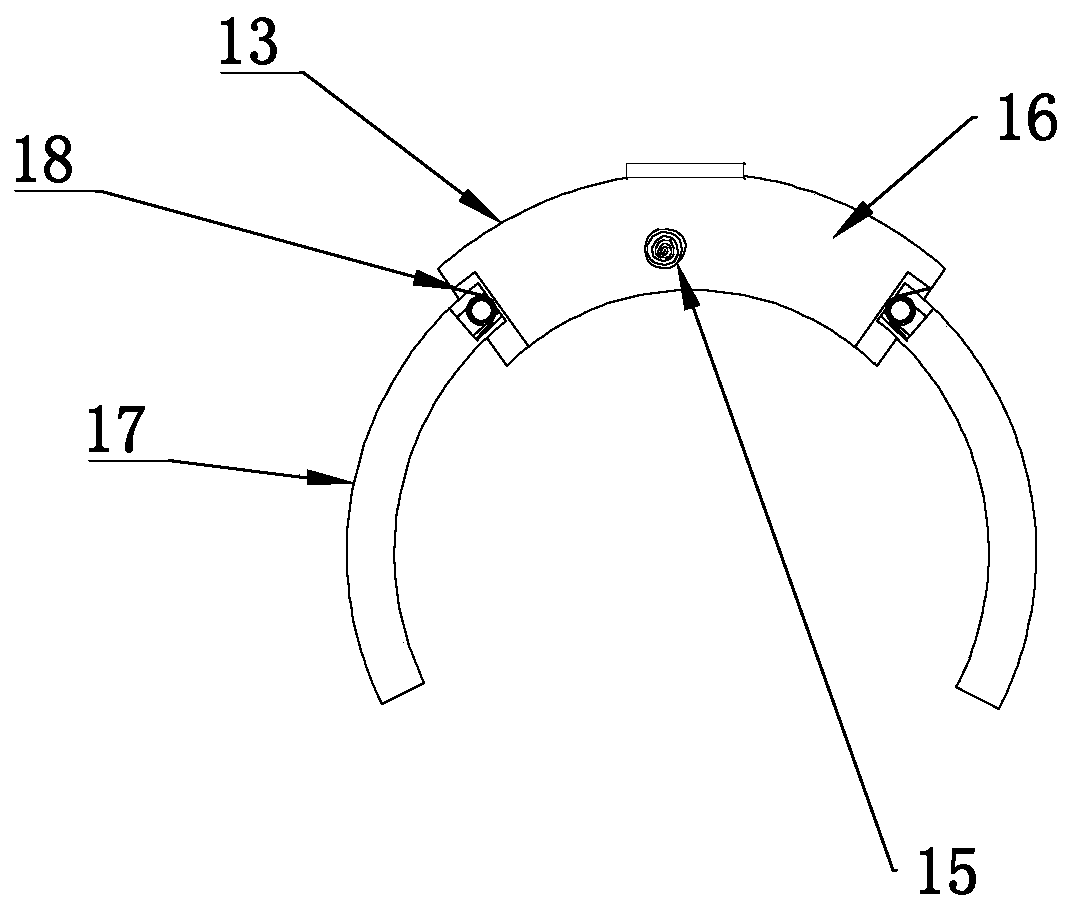
Hand-shaped manipulator
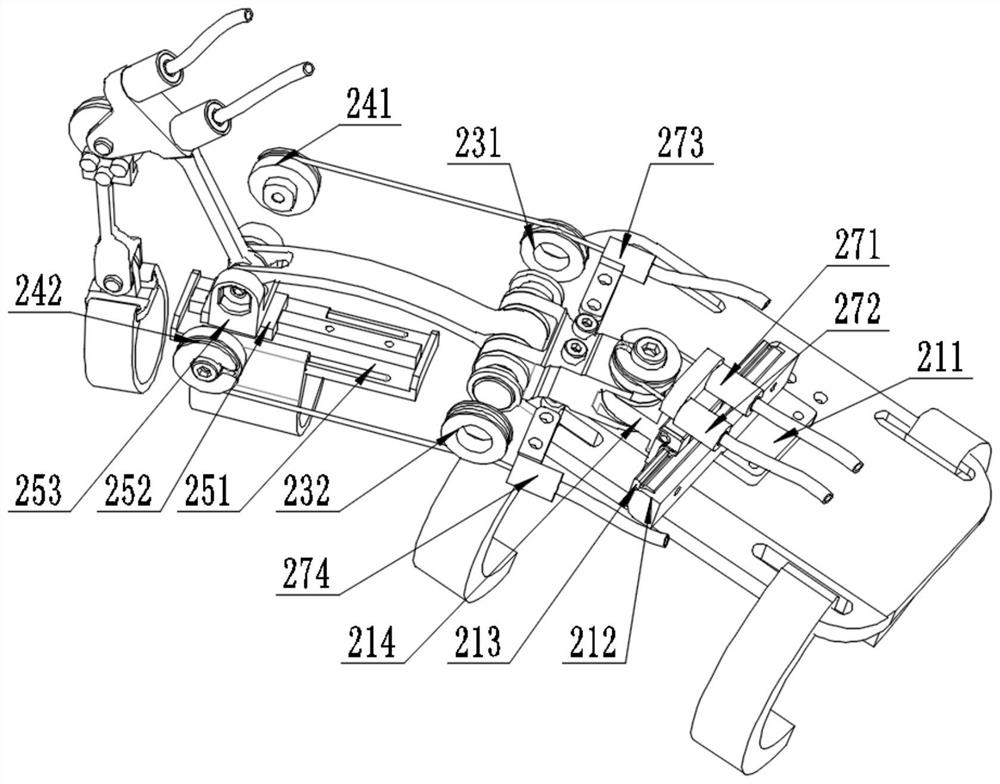
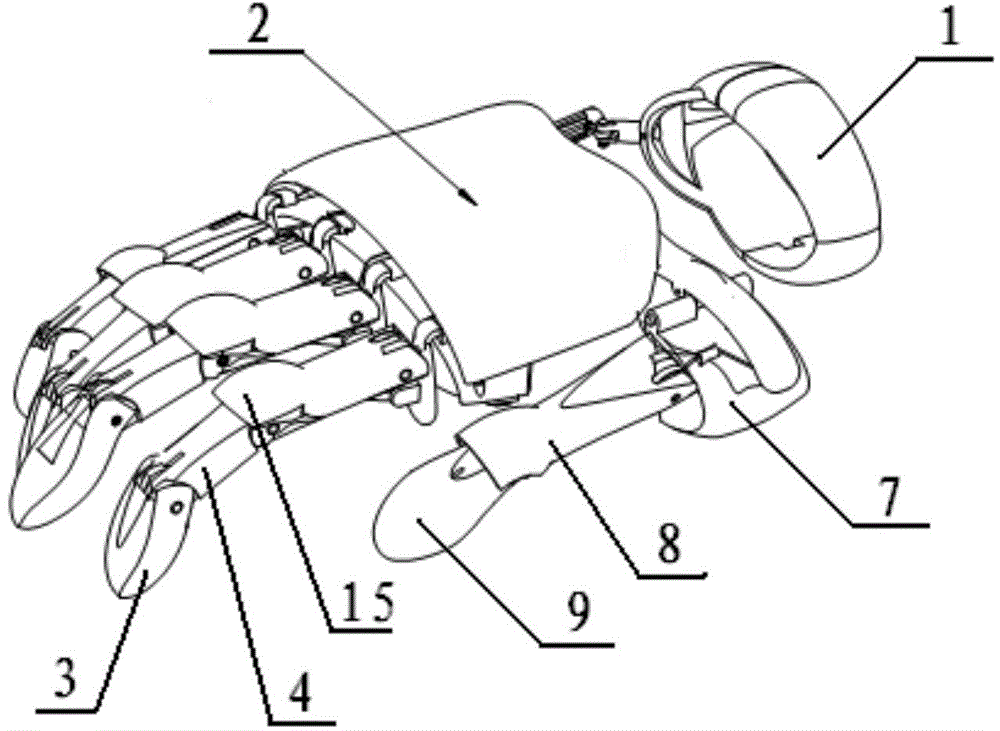
The invention discloses a hand-shaped manipulator which mainly comprises a hand, a wrist and a front arm, wherein the hand comprises a palm, A-type fingers, B-type fingers and a thumb. Grabbing is achieved through the A-type fingers and the thumb, and the B-type fingers are auxiliary fingers. Each A-type middle phalanx, each A-type proximal phalanx and each A-type base phalanx are controlled independently and respectively through four tendon ropes. Due to the fact that the B-type fingers have auxiliary functions, an underactuation control mode is adopted, and active control is performed on each middle phalanx through two tendon ropes. A thumb distal phalanx, a thumb middle phalanx and a thumb proximal phalanx are controlled independently through five tendon ropes. A wrist joint is matched with a spherical hinge through a cardan joint, and pitching and sideway moving can be achieved by means of telescopic movement of a pull rod. Parts of the manipulator can be manufactured easily, cost is low, and the manipulator has multiple functions achieved by a hand of a human, such as capturing, holding, grabbing, switch turning and the like. The hand-shaped manipulator is small in size, light in weight, flexible and accurate in operation, low in cost and wide in application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
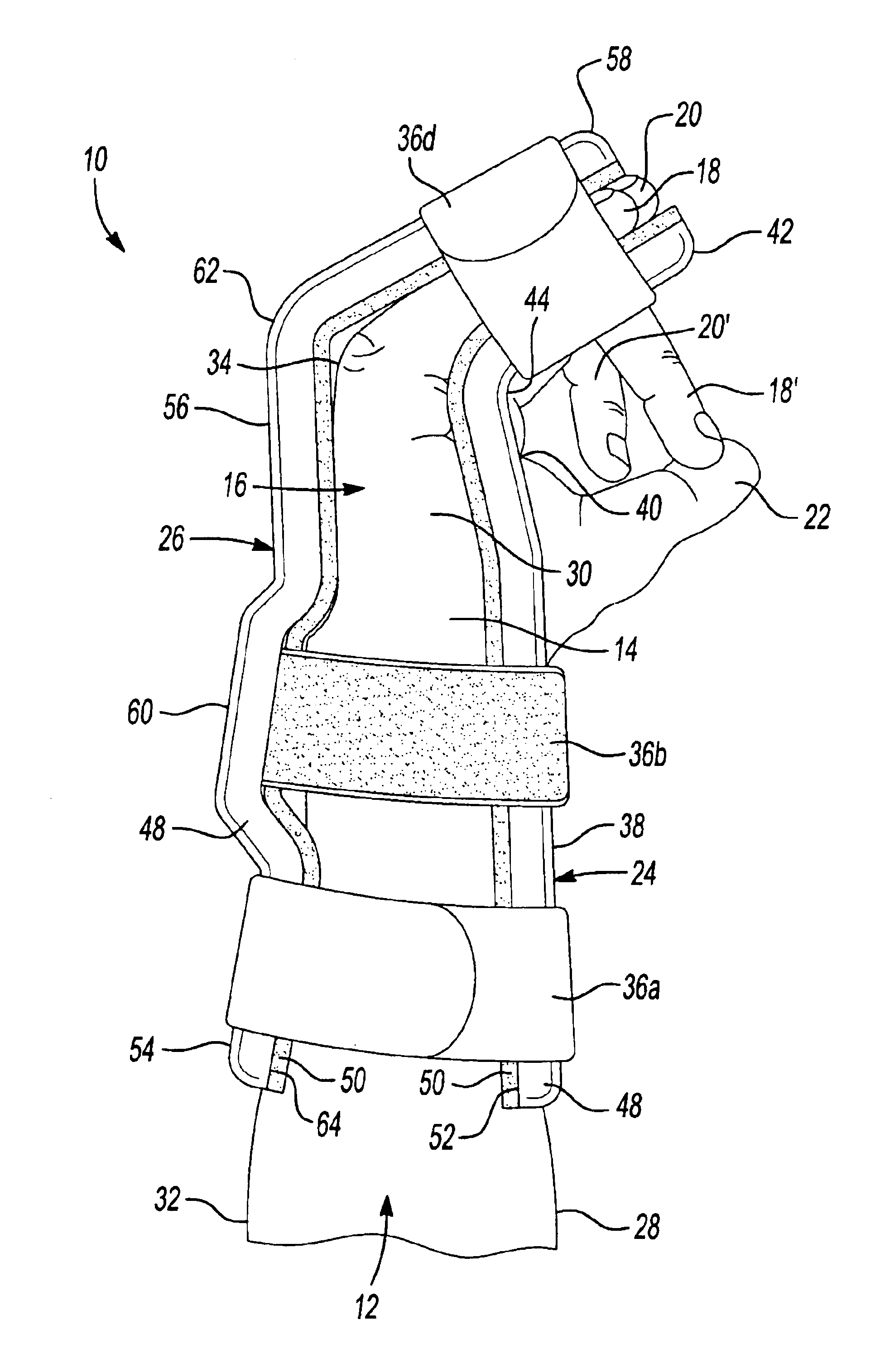
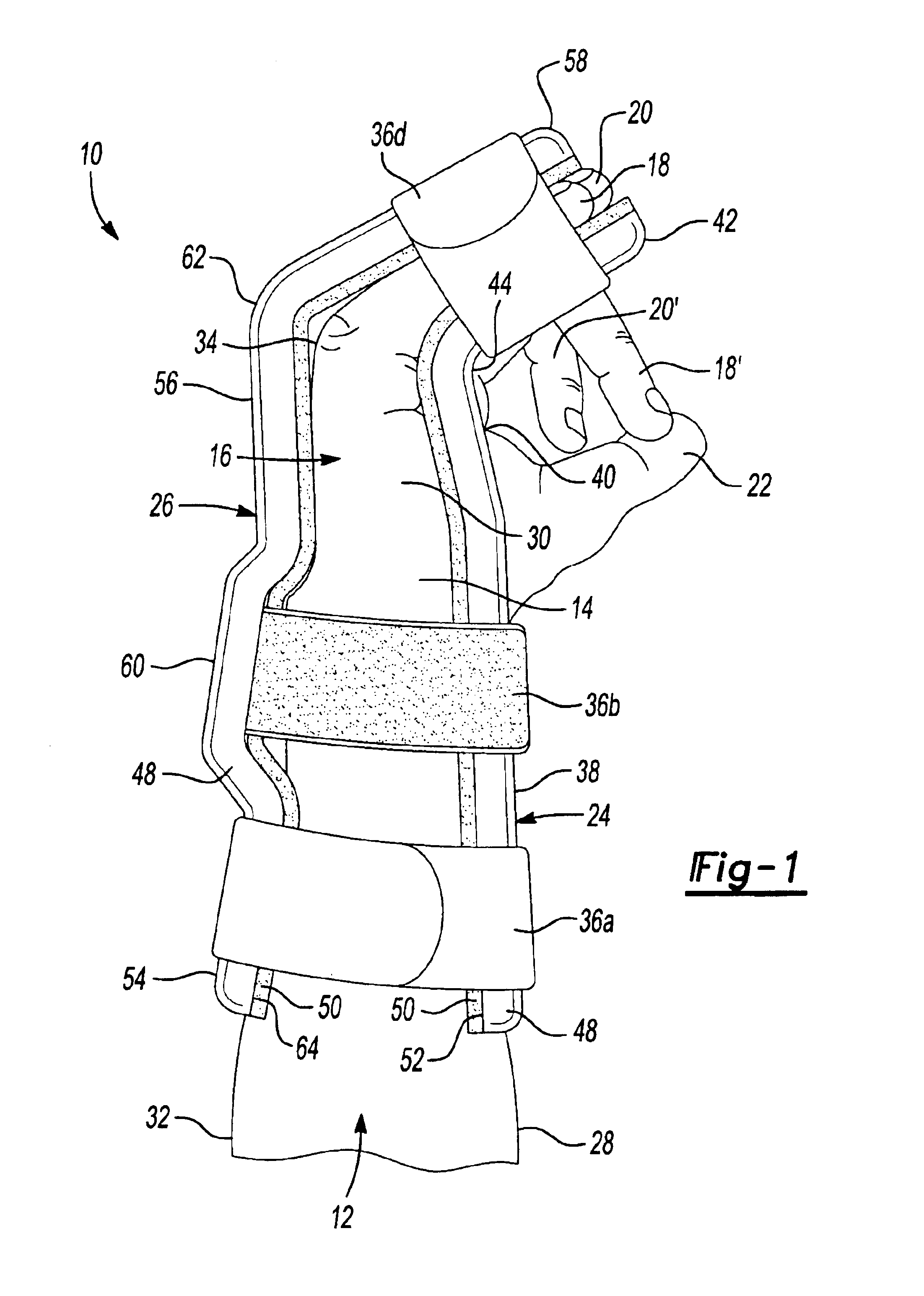
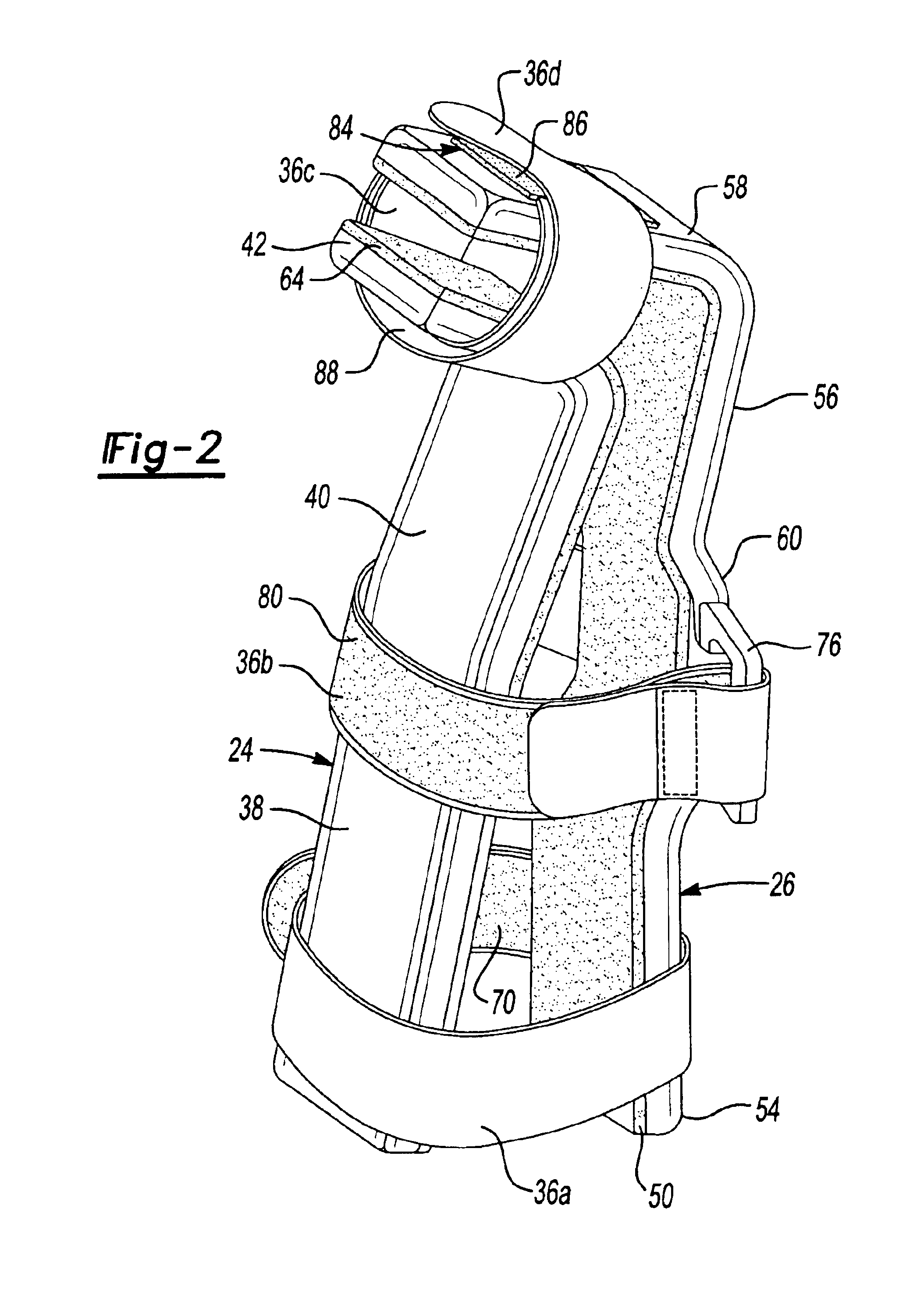
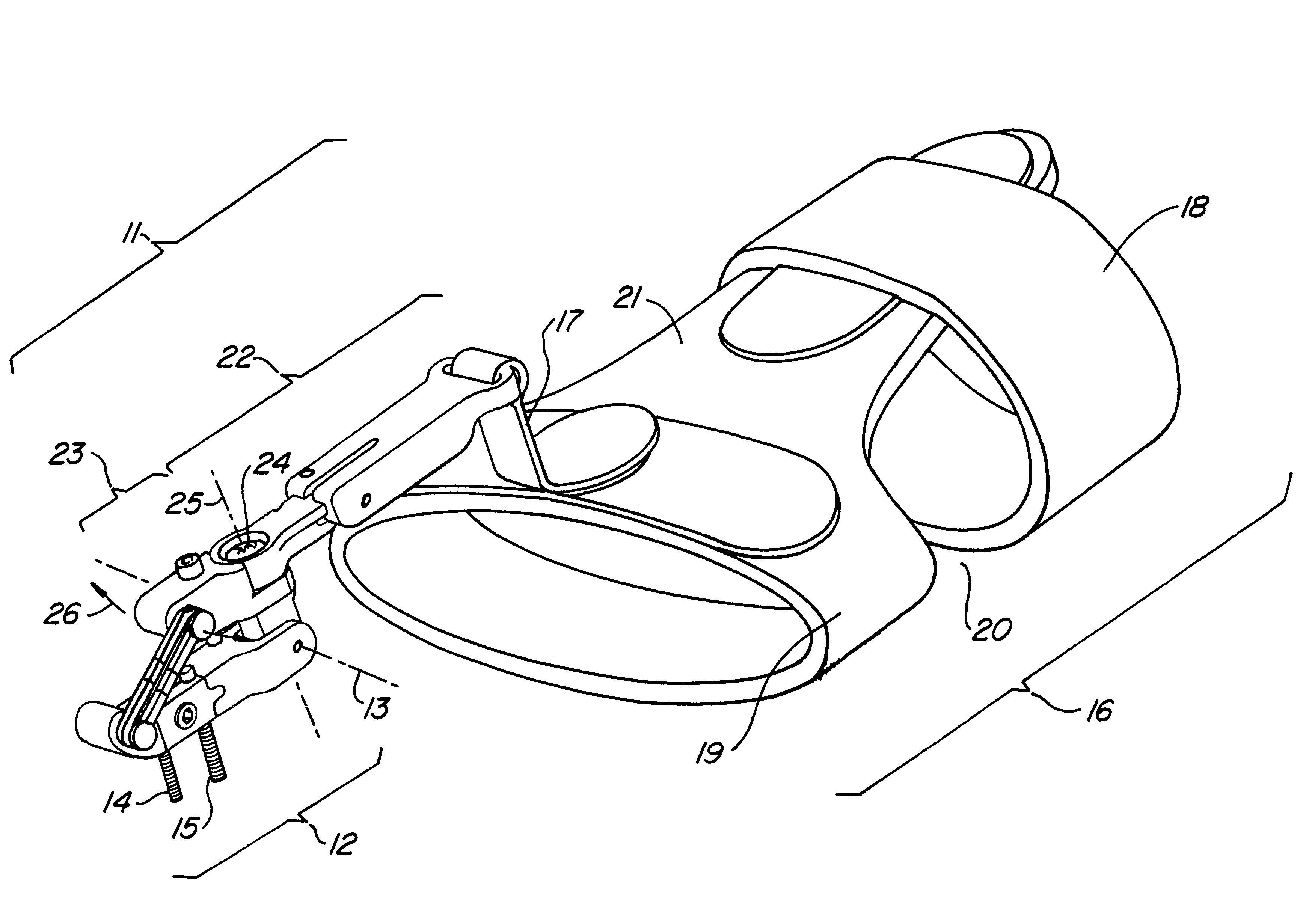
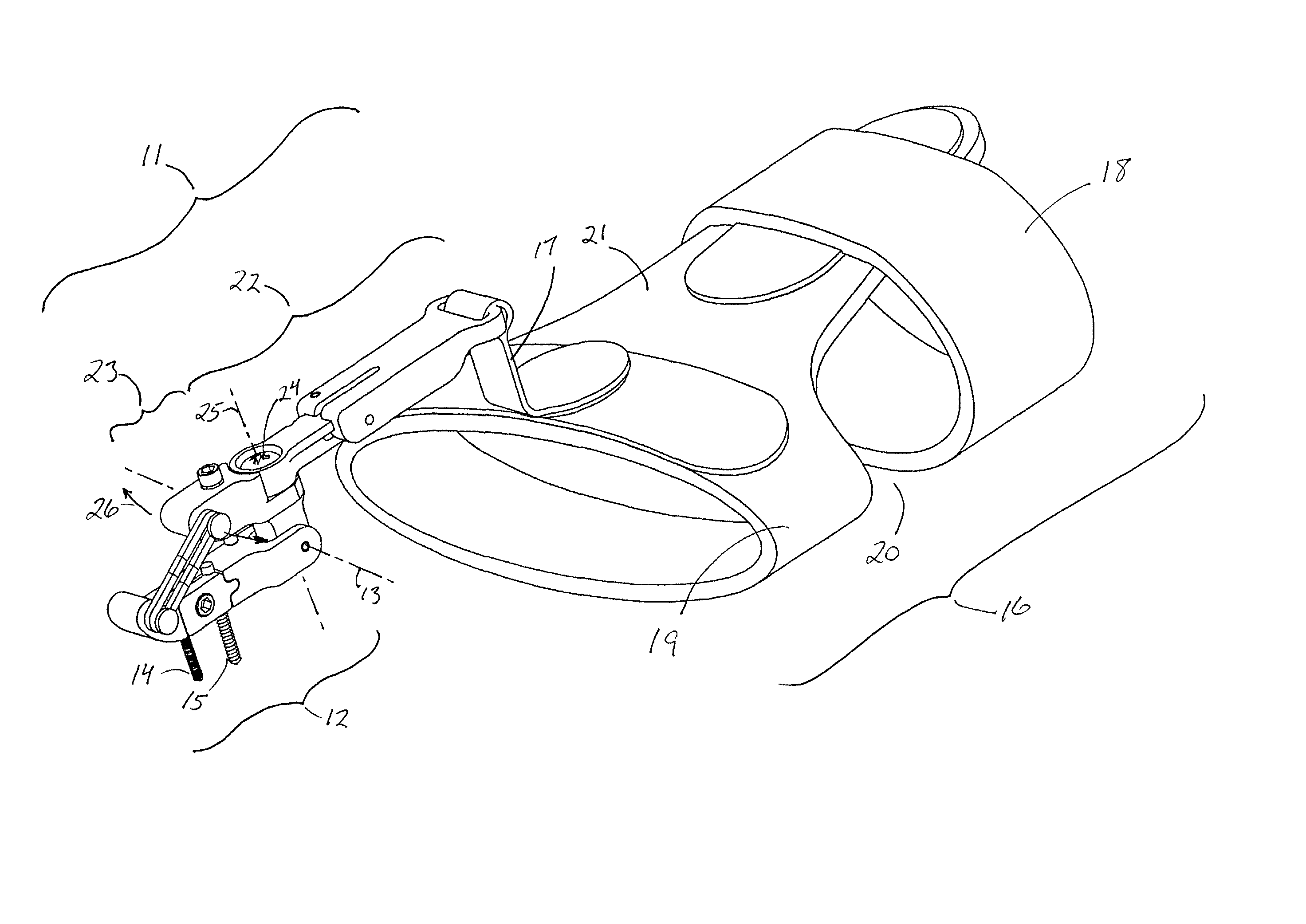
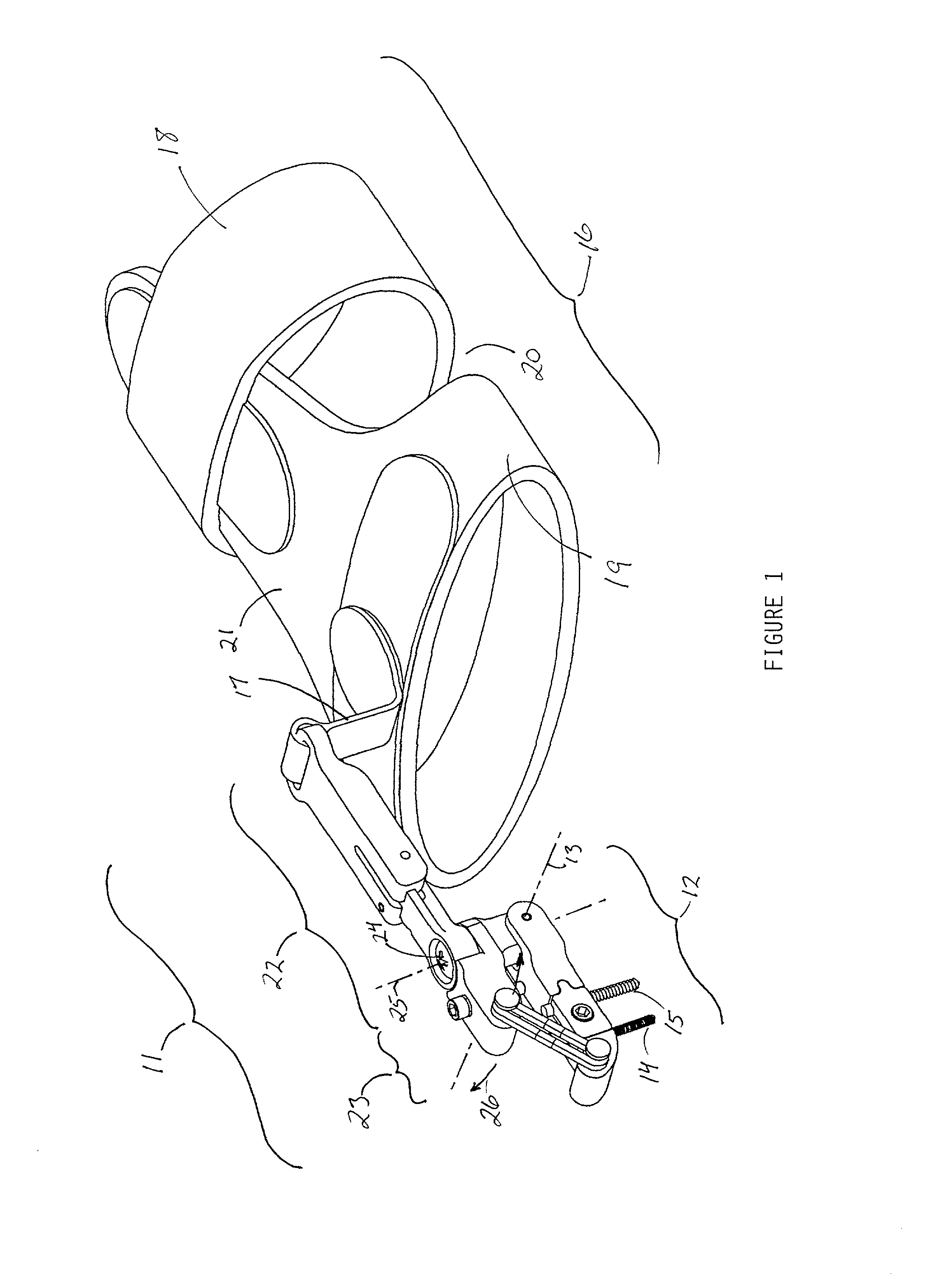
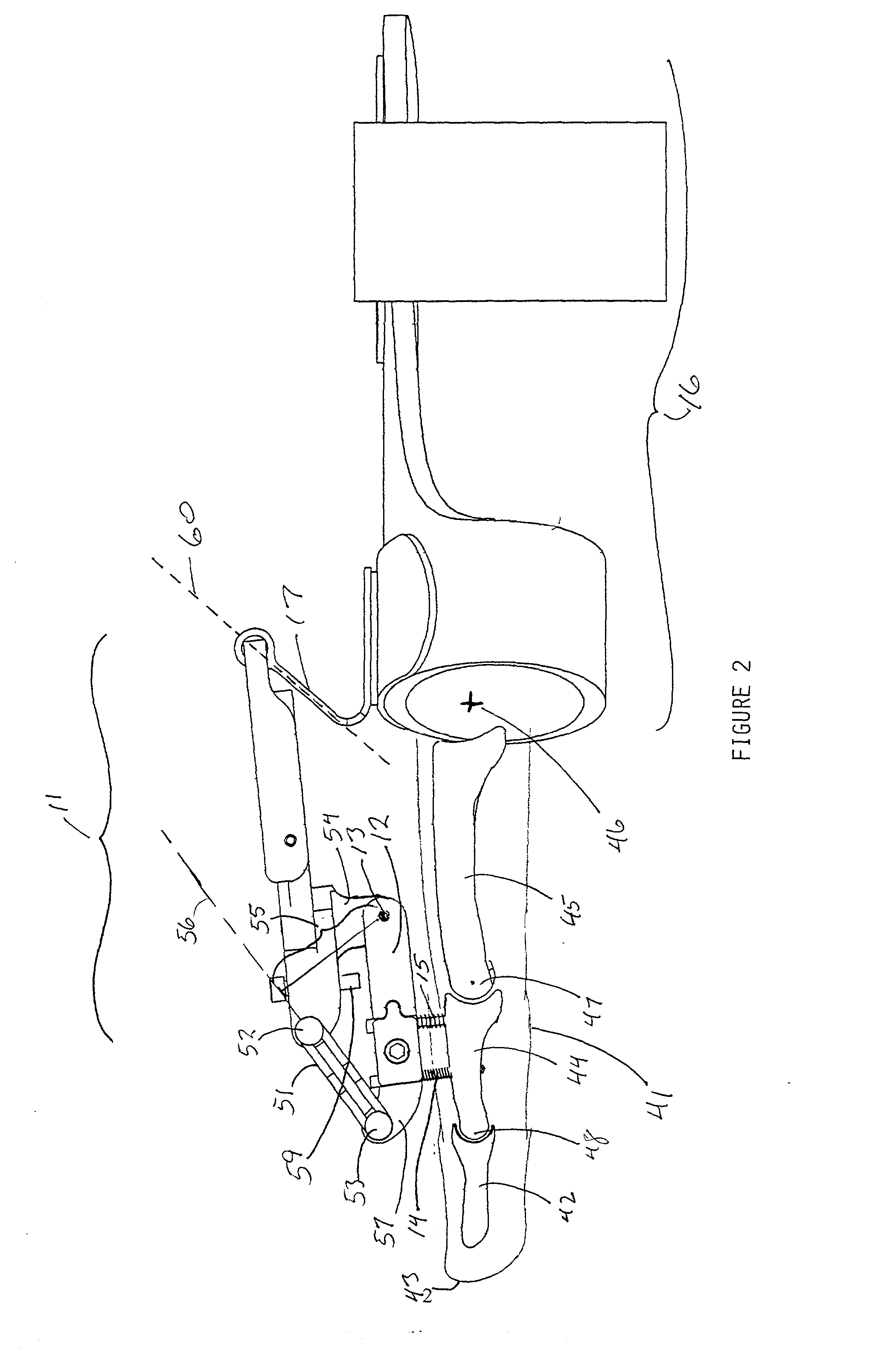
Universal hand splint
InactiveUS6913582B2Easy to removeEasily securedRestraining devicesFractureProximal phalanxDorsal hand
A gutter splint aids the healing of injuries to the metacarpals, proximal phalanges, and middle phalanges by substantially immobilizing the injured digits. The splint includes a volar member and a dorsal member. The volar member has a volar forearm support region for supporting a volar forearm, a volar palm support region for supporting a palm of the hand at a predetermined angle to the forearm, and a finger support region for supporting the fingers at a predetermined angle to the palm. The dorsal member has a dorsal forearm support region for supporting the dorsal forearm, a dorsal hand support region for supporting the hand at a predetermined angle to the dorsal forearm, and a finger support region for supporting the fingers at a predetermined angle to the dorsal hand. The volar member and dorsal member are flexibly secured to each other using a series of removable straps.
Owner:BREG
Chopsticks for learning
The invention relates to chopsticks for learning, which comprise a first chopstick body and a second chopstick body, wherein the first chopstick body is provided with a third finger locating slot and a thumb middle phalanx locating slot; the third finger locating slot is arranged on the outer side of the first chopstick body, and the thumb middle phalanx locating slot is arranged on the front side of the first chopstick body; the second chopstick body is provided with a thumb first phalanx locating slot, a forefinger locating slot and a middle finger locating slot; the thumb first phalanx locating slot is arranged on the front side of the second chopstick body; the forefinger locating slot is arranged on the outer side of the second chopstick body; and the middle finger locating slot is arranged on the rear side of the second chopstick body. Since the third finger locating slot, thumb middle phalanx locating slot, thumb first phalanx locating slot, forefinger locating slot and middle finger locating slot are arranged on the two chopstick bodies, the learner can quickly master the positions of the fingers on the chopstick bodies so as to locate the two chopstick bodies on the hand, and can also master the cooperative actions and use force of the fingers, so that the learner can quickly know how to use common chopsticks.
Owner:黄素瑛
Interphalangeal joint implant methods and apparatus
ActiveUS8764842B2Decreasing eliminating incidenceSimple procedureFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisProximal phalanxDetent
A method and apparatus for correcting malformed joints, in particular the “hammer toe” contraction of the proximal interphalangeal joint. The disclosure comprises a two-component implant: a proximal phalanx component and a middle phalanx component. An endosseous stem on each component is inserted axially into the end of a respective host bone and, after insertion, the components are attached. The attached components are held together in various ways, for example a detent arm / aperture mechanism. Each component can be cannulated to allow for the passage of a kirschner wire, if necessary, to stabilize adjacent joints such as the proximal interphalangeal joint. The bones of the treated joint can be set to form a desired angle by adjusting the angle formed by the corresponding endosseous stems.
Owner:GRAHAM MICHAEL
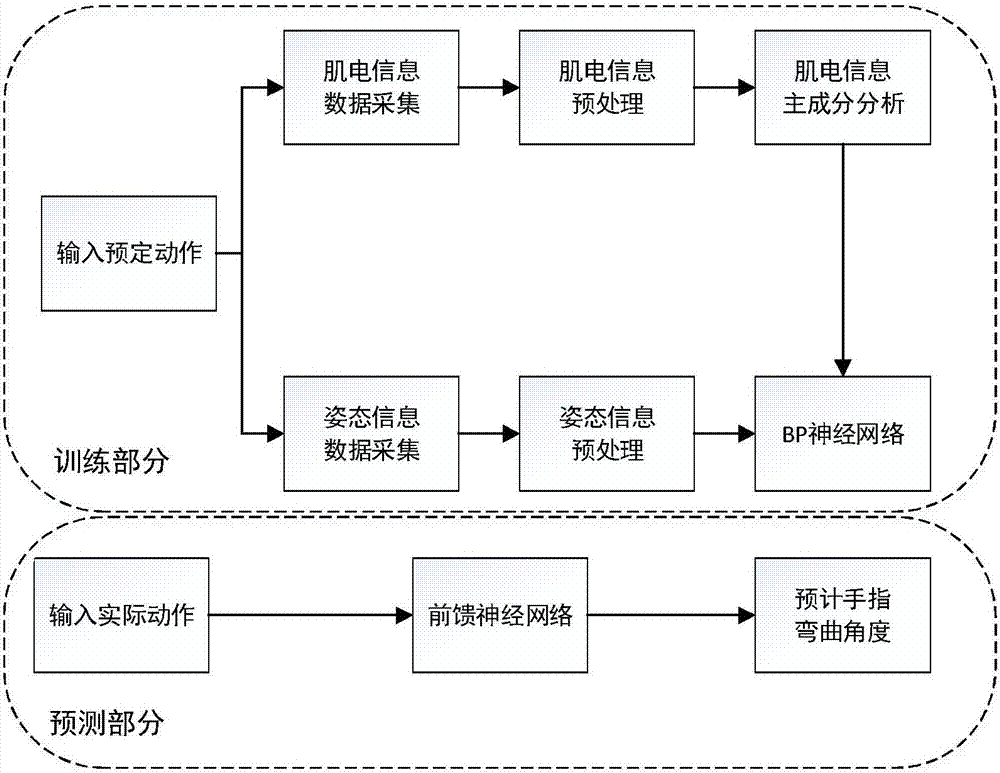
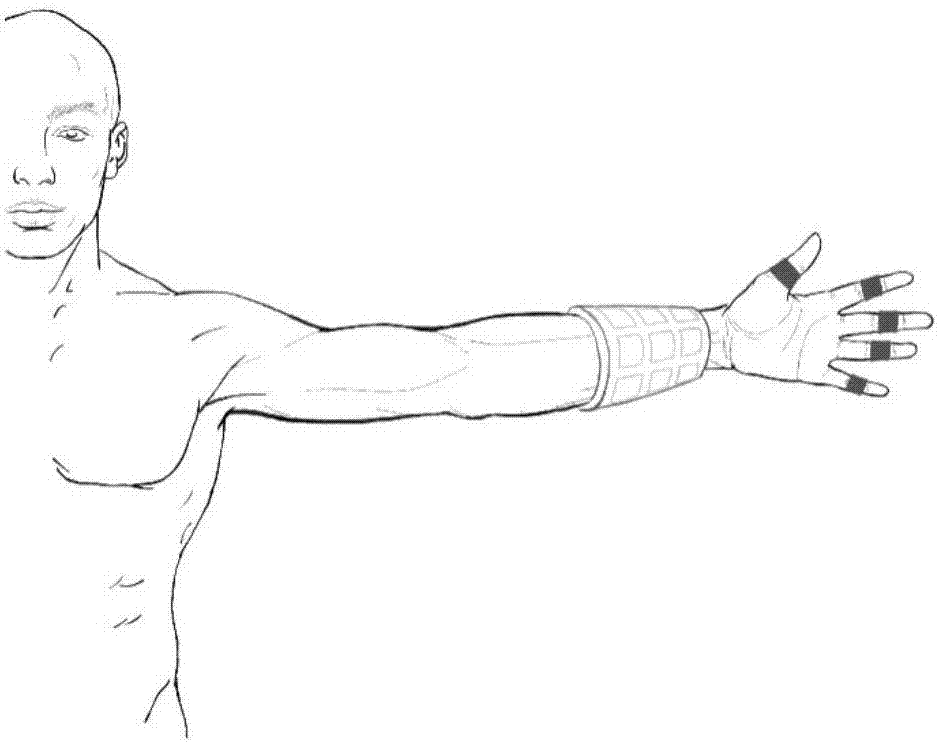
Multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on principal component analysis
ActiveCN107378944AReduce training timeShorten operation timePhysical therapies and activitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionPrincipal component analysisFinger joint
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on a principal component analysis. The control method comprises the follow steps that 1, an arm ring provided with a 24-channel array myoelectricity sensor is worn to a front arm of a testee, and five finger joint posture sensors are worn at the distal phalanx of a thumb of the subject and at the middle phalanxes of rest fingers of the testee respectively; 2, the testee conducts a five-finger independent bending and stretching training, and meanwhile, the myoelectricity sensing array data and the data of the finger joint posture sensors are collected; 3, the principal component analysis is used for decoupling the myoelectricity sensing data to form a finger movement training set; 4, the sensors worn on the fingers are removed after the training is finished; 5, data fitting is performed on the finger movement training set by adopting a neural network method, and a finger continuous motion prediction model is constructed; and 6, current bending angles of the fingers are predicted through the finger continuous motion model. According to the control method, the non-consistency of the discrete action modal classification can be overcome, and finally smooth control on an artificial hand is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multi-fingered robotic hand
A multi-fingered robotic hand comprises a base, a rotation member rotatably connected to an end of the base, a driving means, and a plurality of digits. The driving means is configured for driving the rotation member to rotate. Each digit comprises a proximal phalanx, a middle phalanx and a first transmission member. The proximal phalanx is connected to the rotation member. The middle phalanx is rotatably connected to the proximal phalanx. The first transmission member includes two ends respectively attached to the proximal phalanx and the middle phalanx, wherein the first transmission member is configured for transmitting rotation of the proximal phalanx to the middle phalanx.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Preparation method of conductive thermoplastic starch polymer and polymer-based humanoid soft finger with folding paper structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of a conductive thermoplastic starch polymer and a polymer-based humanoid soft finger with a folding paper structure, belongs to the technical field of humanoid fingers, and aims to solve the problems that in an existing humanoid soft finger with the variable rigidity realized by utilizing a thermal phase change material, the variable rigidity responsespeed is low due to long response time of conversion from a glass state to a high-elasticity state, and the joint motion flexibility and the rigidity of the humanoid soft finger cannot be realized atthe same time. The polymer-based humanoid soft finger comprises a finger root, a metacarpophalangeal joint, a proximal phalanx, an interphalangeal joint, a middle phalanx, a finger tip joint, a distal phalanx, a strain restraint layer, a variable rigidity layer, a cooling layer and a contact layer, wherein each joint is provided with a U-shaped groove, and the outer side of each joint is wrappedwith Yoshimura line type folding paper; and three self-made conductive thermoplastic starch polymer plates are arranged at the bottom of the finger. The humanoid soft finger not only can realize rapidand active control of the rigidity of the phalanxes, but also can realize synchronous and passive adjustment of joint flexible motion and joint rigidity, and has the advantages of fast variable rigidity, high adaptability and flexibility in motion.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Nailz Off Pro
InactiveUS20140007894A1Simple, user-friendlyEffectively deliver a solvent to the nailCurling devicesManicure/pedicureMedicineSolvent
The present invention relates generally to a system of delivering a solvent to the nail for the removal of polish, gel nails, gel polish, soak-off gel nails, soak-off gel polish or acrylic nails existing on the nail. The system may also be used for the delivery a multitude of substances such as oils, moisturizers, or medicines to the nail or fingertip of a user. The present invention employs the use of a synthetic cap to cover the fingertip to the middle phalanx, or the toe to ensure a substantially air-tight environment for effective delivery of solvents, oils, moisturizers, or medicines. The cap is hypoallergenic, multi-use and can be easily used by a single user (i.e., placing the caps on one hand and also the other).
Owner:GAGNON NOELLE MARIE
Rigid-soft coupling mechanical finger with variable-rigidity internal skeleton
The invention discloses a rigid-soft coupling mechanical finger with a variable-rigidity internal skeleton. The rigid-soft coupling mechanical finger comprises a soft finger body and the variable-rigidity internal skeleton arranged in the soft finger body, and the variable-rigidity internal skeleton comprises a proximal phalanx, a middle phalanx and a distal phalanx which are sequentially connected, wherein the middle phalanx is rotationally connected with the proximal phalanx and the distal phalanx, the proximal phalanx communicates with the distal phalanx, the proximal phalanx and the distalphalanx are internally provided with a first expansion membrane and a second expansion membrane correspondingly, and by injecting gas into the distal phalanx, the first expansion membrane and the second expansive membrane are expanded to deform so as to change rigidity. The rigid-soft coupling mechanical finger is attractive in structure, small in size and higher in adaptability, and the performance of the soft finger body is obviously improved; and safe and efficient interaction between the soft finger body and the environment is ensured, the grabbing ability and bearing capacity of the finger is also greatly improved, the size of a gripper device is decreased, and the space is saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fully-bionic brain-like intelligent electro-mechanical exoskeleton for hands and comprehensive control system thereof
ActiveCN107440887AEasy to operateBalance operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesBrain computer interfacingEngineering
The invention relates to a fully-bionic brain-like intelligent electro-mechanical exoskeleton for hands and a comprehensive control system thereof. The electro-mechanical exoskeleton is characterized by comprising finger tip bushes, middle phalanx exoskeletons, proximal phalanx exoskeletons, metacarpal bone exoskeletons, a finger stretching mechanical driving device, a finger bending mechanical driving device, finger stretching artificial tendons, finger bending artificial tendons, finger tip pressure and temperature sensors, force assistance sensors and joint angle sensors. The system comprises a multifunctional human brain computer interface helmet and a movement sensory system, and the multifunctional human brain computer interface helmet is connected with the fully-bionic brain-like intelligent electro-mechanical exoskeleton for the hands through the movement sensory system. With the control system, the electro-mechanical exoskeleton can be directly controlled to generate all kinds of action according to the intention of a human brain, and the electro-mechanical exoskeleton stably operates in balance by means of various methods, and can be widely applied to the fields of rehabilitation, life assistance and the like for people with limb movement and limb sensory function disturbance caused by neural system injury.
Owner:臧大维 +1
Data glove
PendingCN109710082APrecise wearingReduce biasInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingLittle fingerGyroscope
The invention discloses a data glove, wherein the palm base frame is used for being arranged on a palm part in a sleeving mode, and the finger detection mechanisms are arranged on finger parts in a sleeving mode. The finger detection mechanism comprises thumb, index finger and middle finger, a name finger detection mechanism and a little finger detection mechanism, each finger detection mechanismcomprises sensors worn on the hand backs of the three knuckles and two strain gauge sensors arranged among the three sensors. The strain gauge sensor is used for being attached to a finger joint, thesensors arranged on the three knuckles comprise a first gyroscope sensor provided with a distal phalanx; the second gyroscope sensor is arranged on the proximal phalanx; the third gyroscope sensor isarranged on the middle phalanx; bending degree sensing strips are arranged between the proximal phalanx ends of the index finger detection mechanism, the middle finger detection mechanism, the ring finger detection mechanism and the little finger detection mechanism and the palm base frame, and the bending degree sensing strips are used for being attached to finger joints and conveniently adjustedaccording to different hand types, so that collected finger joint action data are accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG IND & TRADE VACATIONAL COLLEGE
Intramedullary rod fixation system
ActiveUS9421049B2Minimize traumaIncreasing returnInternal osteosythesisFastenersIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
A method for fixation of a fracture of a bone having an intramedullary canal. An intramedullary rod is inserted into the intramedullary canal of the bone, wherein the intramedullary rod includes at least one proximal hole and at least one distal hole. Proximal and distal screws or pegs are inserted through the bone and through the proximal and distal holes in the rod, wherein the proximal and the distal screws or pegs are headless screws or pegs and are selected to have a size and are inserted through the proximal and distal holes in the rod such that the screws or pegs do not extend substantially beyond an exterior surface of the bone. Further described are apparatus and a kit for intramedullary fixation of fractures of bones of the hand. The methods, apparatus and kits of the invention are advantageously designed for percutaneous placement of intramedullary rods into the intramedullary canal of metacarpal or phalanx bones of the hand to stabilize fractures, and in particular in the proximal or middle phalanx bones of the hand. Rotational control is provided by locking screws or pegs through the rod, also placed percutaneously. Specific alignment jigs, drills, screw drivers and equipment may be used for placement of the rod and screws, wherein the rod and screws will stabilize the fracture.
Owner:ROGACHEFSKY RICHARD A
Finger structure and robot
ActiveCN111546366ACropping area reductionImprove integrityProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsProximal phalanxFinger structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and relates to a finger structure and a robot. In the finger structure, a proximal phalanx shell, a middle phalanx shell, a distal phalanx shelland a connecting rod form a four-rod mechanism, the proximal phalanx shell serves as a fixing frame, a driving assembly drives the middle phalanx shell to swing, the distal phalanx shell is in linkage with the connecting rod, the distal phalanx shell swings in the swinging direction of the middle phalanx shell, and the finger structure is integrally bent and straightened. The connecting rod is arranged to be a first bent section, and a notch of the first bent section faces the back face of the middle phalanx shell. When the finger structure is straightened, namely the distal phalanx shell isflush with the middle phalanx shell, the inner wall of the first near end at a distal phalanx opening extends into the bottom of the notch of the first bent section, so that the inner wall of the first near end can be closer to the center of the distal phalanx opening. The far finger opening of the finger structure can be manufactured to be small, and the integrity of the appearance of the distalphalanx shell is improved. Due to the existence of the first bent section of the connecting rod, when the distal phalanx shell is impacted, the connecting rod shows certain elasticity and absorbs theimpact.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
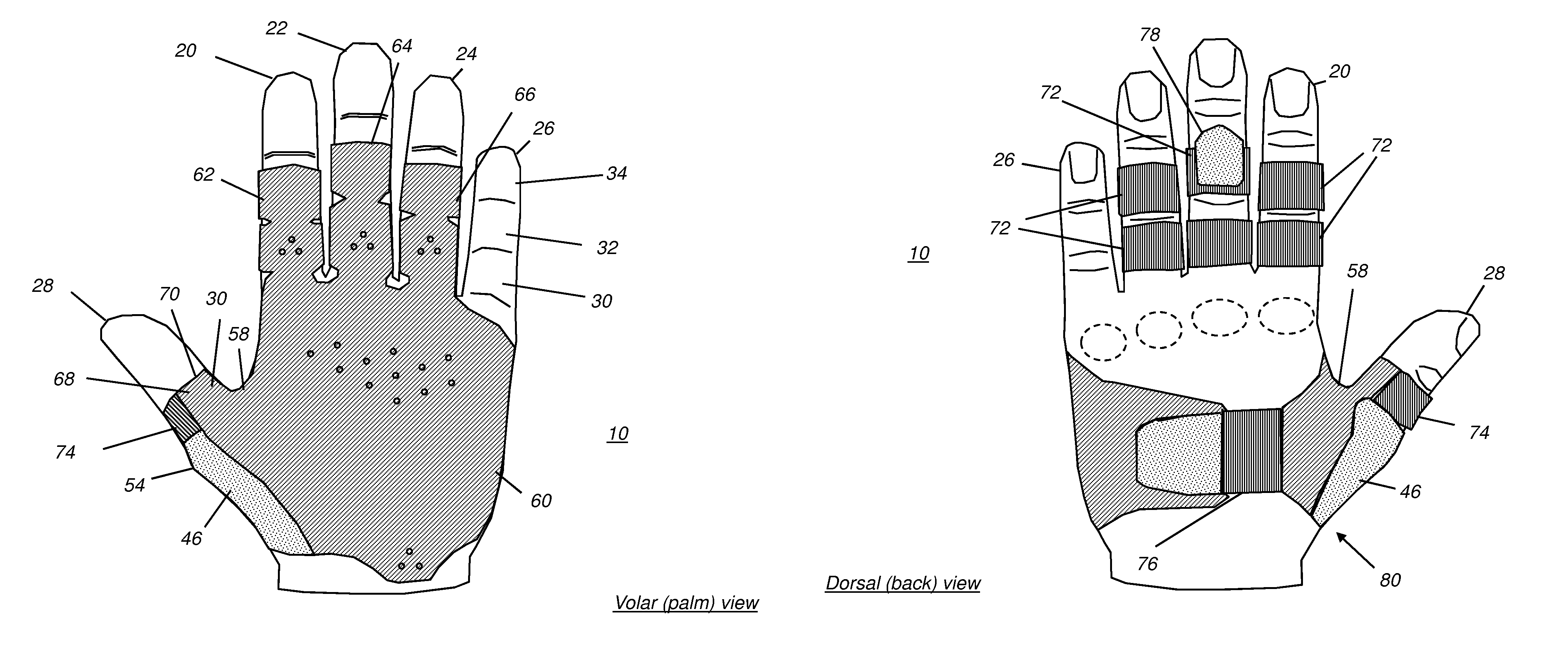
Protective hand covering
A protective hand covering has a membrane to cover the palm surface of the hand, leaving the small finger exposed and having first, second, and third extended finger portions over palm surfaces of proximal and middle phalanges of ring, middle, index fingers, and having an extended thumb portion extending onto the palm side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. A loop accepts the thumb and secures an edge of the extended thumb portion against the base of the thumb. Elastic bindings along edges of the finger portions of the membrane define holes for ring, middle, and index fingers. The elastic bindings urge the first, second, and third extended finger portions against palm side surfaces of proximal and middle phalanges of ring, middle, and index fingers. A cross strap extends across the dorsal side of the hand for releasable elastic tensioning.
Owner:THE CREW STOP INC
Finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot with adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching functions
ActiveCN112641598AImplement Adaptive AlignmentRelieve mechanical stressChiropractic devicesStretch exerciseExoskeleton robot
The invention belongs to the field of biomechanical engineering, aims to solve the problem that an existing finger rehabilitation robot assisting metacarpophalangeal joints in adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching movement cannot achieve self-adaptive alignment of man-machine joints, and particularly relates to a finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot with adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching functions. The finger rehabilitation exoskeleton robot comprises three driving assemblies, a metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly and a near-end joint transmission assembly, wherein inner and outer driving rope wheels in the metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly can control the adduction and abduction movement of the human hand under the driving of the first driving assembly; a first fixed rope wheel and a second fixed rope wheel in the metacarpophalangeal joint transmission assembly can control the flexion and stretching movement of the near-end phalanx under the driving of the second driving assembly; and the near-end joint transmission assembly can control the flexion and stretching movement of the middle phalanx under the driving of the third driving assembly. According to the invention, the self-adaptive alignment of the man-machine joints of the rehabilitation robot capable of doing the adduction, abduction, flexion and stretching movement can be realized, and meanwhile, the joint mechanical stress generated between a man and a machine can be effectively eliminated.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Underactuated robotic hand
Anthropomorphic robotic hand comprising a palm and a metacarpus configured to rotate with respect to said palm around an axis of rotation; four fingers substantially aligned and constrained to said palm and a finger opposable to them, each one of said aligned fingers comprising at least a proximal phalanx, a middle phalanx and a distal phalanx, and said opposable finger comprising a proximal phalanx and a distal phalanx, the proximal phalanges of each one of said aligned fingers being hinged to said palm in respective axes of rotation and the proximal phalanx of said opposable finger being hinged to said metacarpus in a respective axis of rotation; a motor; a plurality of bevel gear differential stages which transmit motion from said motor to said aligned fingers and to said opposable finger.
Owner:BIONIT LABS SRL
Adaptive robotic finger prosthesis for grasping arbitrary object shape
An adaptive robotic finger prosthesis according to the inventive concepts includes a proximal phalanx body configured to be worn on a proximal phalanx portion of a cut finger, a middle phalanx body connected to the proximal phalanx body and configured to function as a middle phalanx portion of the cut finger, a distal phalanx body connected to the middle phalanx body and configured to function as a distal phalanx portion of the cut finger, a first proximal phalanx link disposed under the proximal phalanx body, a second proximal phalanx link disposed on the proximal phalanx body and joint-connected to the first proximal phalanx link, and a proximal phalanx elastic member provided at a joint between the first proximal phalanx link and the second proximal phalanx link to provide elastic force.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
Medical device for correcting finger joint contractures
InactiveUS6592584B2Effective and controllable torqueImpose a torque on the PIP jointFractureInvalid friendly devicesProximal phalanxFinger joint
A finger suffering from contracture of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint is treated by application of a device that includes two pivotally joined sections, one of which is securable to the middle phalanx of the finger and the other to another portion of the patient's finger, hand or wrist, with an element that applies torque to the sections. The pivot axis of the two sections is dorsal to the finger, and the torque-producing element and the pivot axis define a moment arm whose length varies in inverse relation to the tension applied to the tensioning element. Torque is applied to the PIP joint without a functionally significant torque being applied to the metacarpal phalangeal (MP) joint, and the device requires attachment only to the dorsal aspect of the phalanx that is distal to the joint being treated rather than to both the distal phalanx and the proximal phalanx.
Owner:JOHN M AGEE & KAREN K AGEE TRUSTEES OF THE JOHN M AGEE TRUST
Multi-joint rigid-flexible coupling bionic soft finger
The invention relates to a multi-joint rigid-flexible coupling bionic soft finger comprising a near phalanx soft joint, a middle phalanx soft joint, a far phalanx soft joint, a rigid sealing end cover, a near phalanx rigid connecting piece, an interphalanx rigid connecting frame and a rigid fingertip. The near phalanx soft joint is independently controlled. A plurality of first gas cavities extending in the length direction of the near phalanx soft joint are formed in the near phalanx soft joint, inflation ports of all the first gas cavities are located at the first end of the near phalanx soft joint, the rigid sealing end cover is installed at the first end of the near phalanx soft joint, and the rigid sealing end cover is provided with gas inlets corresponding to the inflation ports of the first gas cavities correspondingly. The near phalanx rigid connecting piece is provided with an inflation opening, the middle phalanx soft joint is provided with a second gas cavity, the far phalanx soft joint is provided with a third gas cavity, and the inflation opening communicates with the second gas cavity and the third gas cavity. The middle phalanx soft joint and the far phalanx soft joint are each provided with a gridding cloth fiber strain limiting layer. When the soft finger horizontally grabs objects, effective grabbing force is provided.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Classification-combination light artificial hand
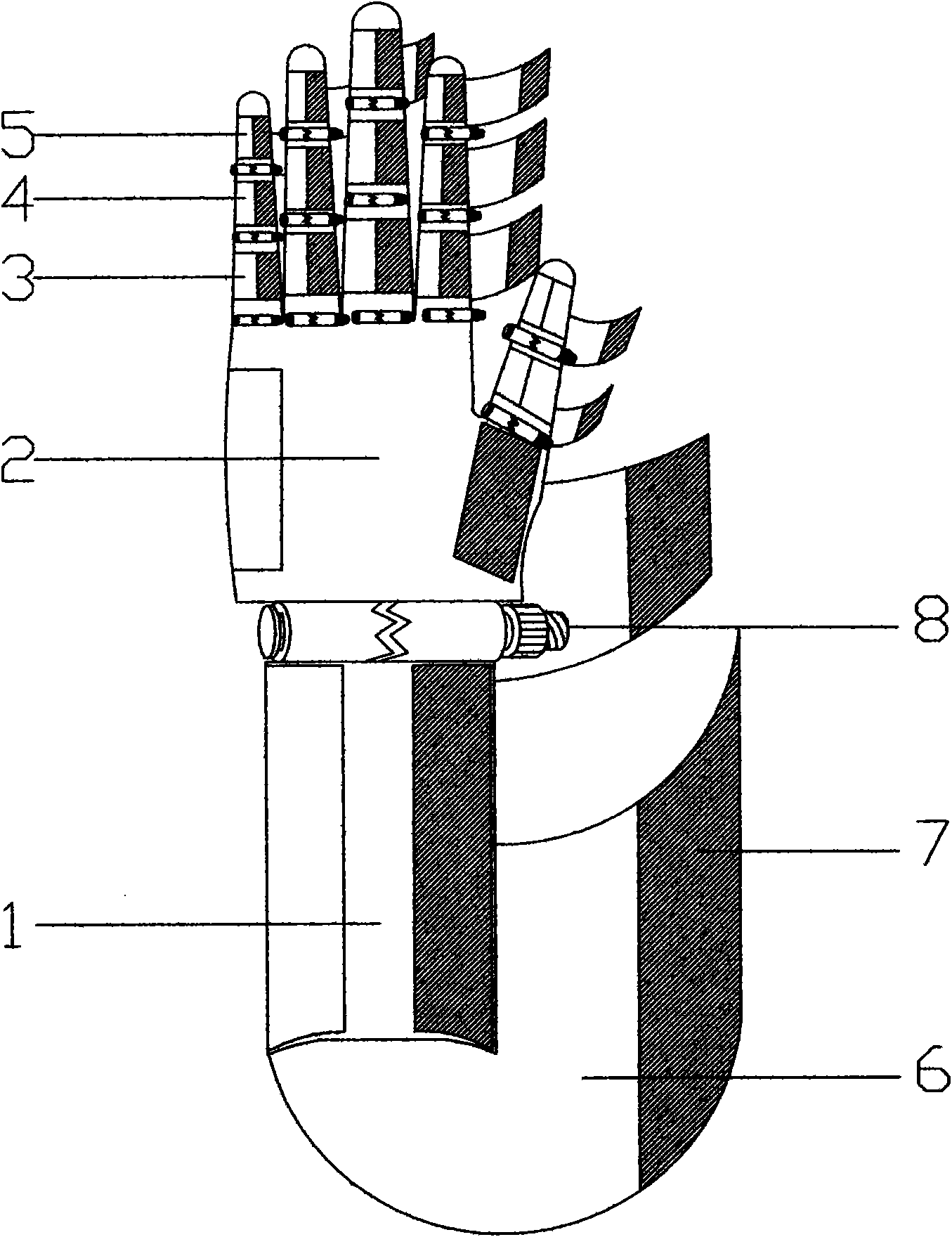
The invention discloses a classification-combination light artificial hand. The classification-combination light artificial hand can be applicable to persons of disabled fingers of different classes, and helps the persons to achieve daily actions to a certain extent such as holding, pinching and bending which can be completed by hands of normal persons. The classification-combination light artificial hand comprises a body module, a movement source module, a thumb module and finger modules. The thumb has the metacarpal bone disability class and the proximal phalanx disability class according to different disability conditions. The four fingers have the metacarpal bone disability class, the proximal phalanx disability class and the middle phalanx disability class. The artificial hand is in modular design, artificial limbs applicable to different conditions fall into different modules, and therefore disassembly, assembly, repair and replacement are facilitated; different control ways are selected for different finger disability conditions, so that little influence is caused by an artificial limb control mechanism on other activities of the hands, and the activities of the hands of the disabled are expanded to the greatest degree; the classification-combination light artificial hand is compact in structure, has the appearance approaching the shape of the hands, and can meet the psychological needs of the disabled.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Medical device for correcting finger joint contractures
InactiveUS20020169447A1Effective and controllable torqueImpose a torque on the PIP jointJoint implantsExternal osteosynthesisProximal phalanxFinger joint
A finger suffering from contracture of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint is treated by application of a device that includes two pivotally joined sections, one of which is securable to the middle phalanx of the finger and the other to another portion of the patient's finger, hand or wrist, with an element that applies torque to the sections. The pivot axis of the two sections is dorsal to the finger, and the torque-producing element and the pivot axis define a moment arm whose length varies in inverse relation to the tension applied to the tensioning element. Torque is applied to the PIP joint without a functionally significant torque being applied to the metacarpal phalangeal (MP) joint, and the device requires attachment only to the dorsal aspect of the phalanx that is distal to the joint being treated rather than to both the distal phalanx and the proximal phalanx.
Owner:JOHN M AGEE & KAREN K AGEE TRUSTEES OF THE JOHN M AGEE TRUST
Fixing orthosis after restoration of extensor tendon rupture
InactiveCN101773423AReduced flexion angleAvoid the disadvantages of fixation in strong flexionMedical sciencePhysical medicine and rehabilitationProximal phalanx
The invention relates to a fixing orthosis after the restoration of extensor tendon rupture, which is characterized in that: the fixing orthosis after the restoration of extensor tendon rupture is made of thermoplastic mounded plastic, and is divided into five parts: a front arm part, a hand back part, a proximal phalanx part, a middle phalanx part, and a distal phalanx part. Each part is provided with a fixing band and a woolen hasp, and an angle-adjusting hinge axis is arranged between two parts. During use, after the angles among the parts are adjusted by adjusting the hinge axes, the fixing orthosis can be fixed on the affected limb through the fixing band and the woolen hasp which are arranged on each part. The fixing orthosis has the following advantages that: the fixing orthosis can selectively fix corresponding joints, only fixes the joints of injured fingers and avoids the stiffness of normal finger joints; and after the operation, flexion angles of the fingers are gradually reduced by adjusting the hinge axes, and the defect that the fixing orthosis is always fixed at a strong flexion position after the operation is overcome.
Owner:乔永平
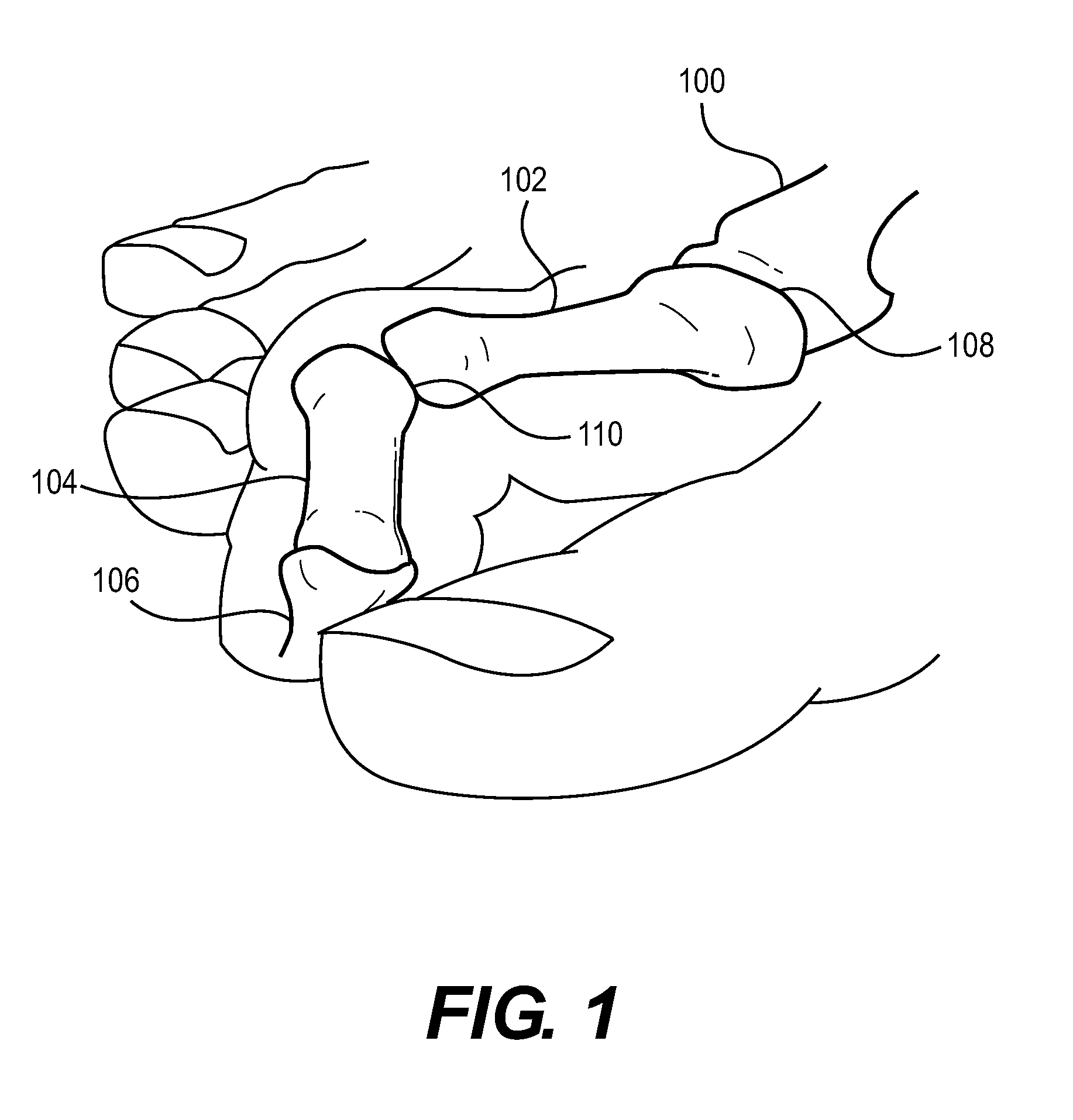
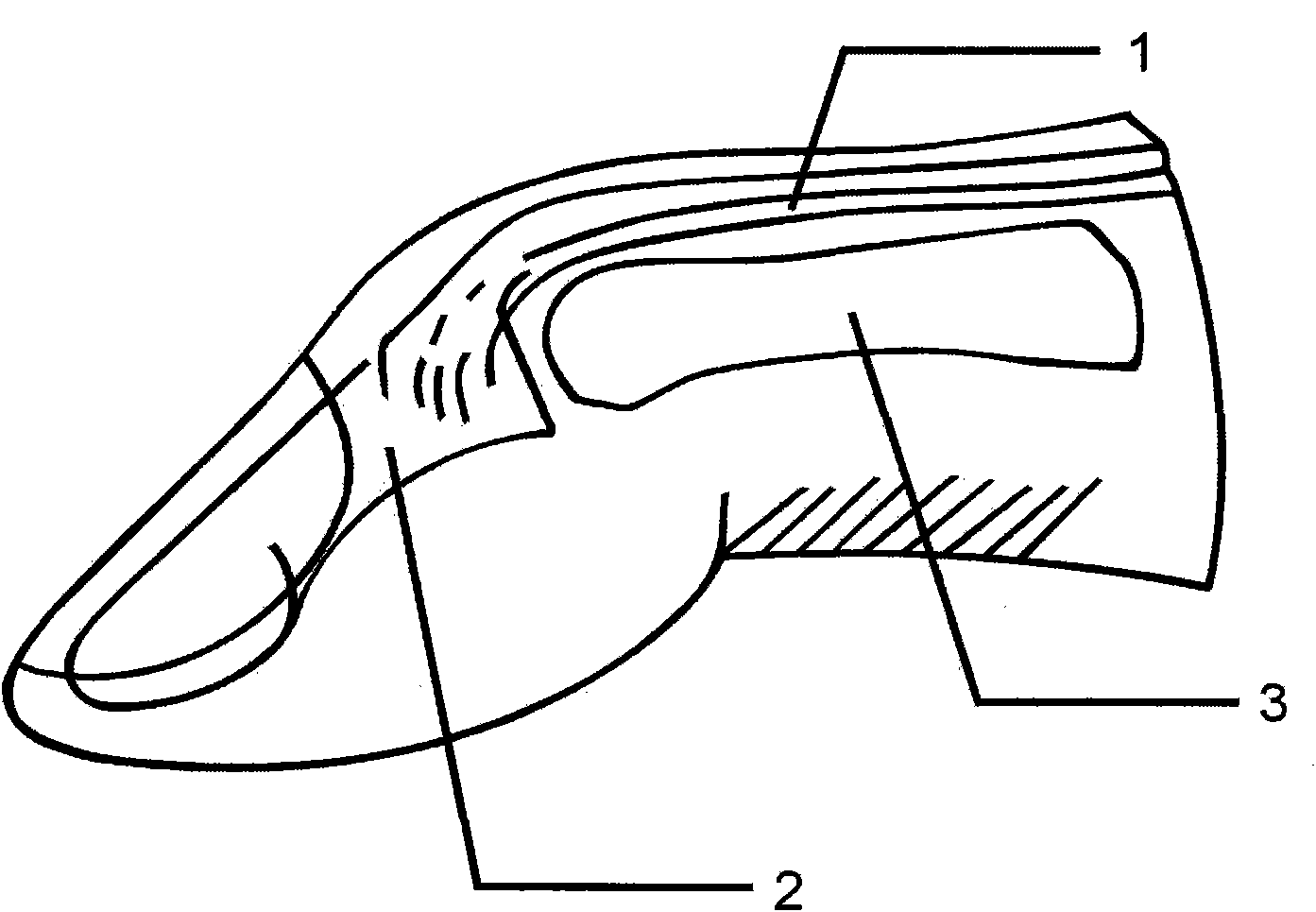
Implant for treating old mallet finger deformity
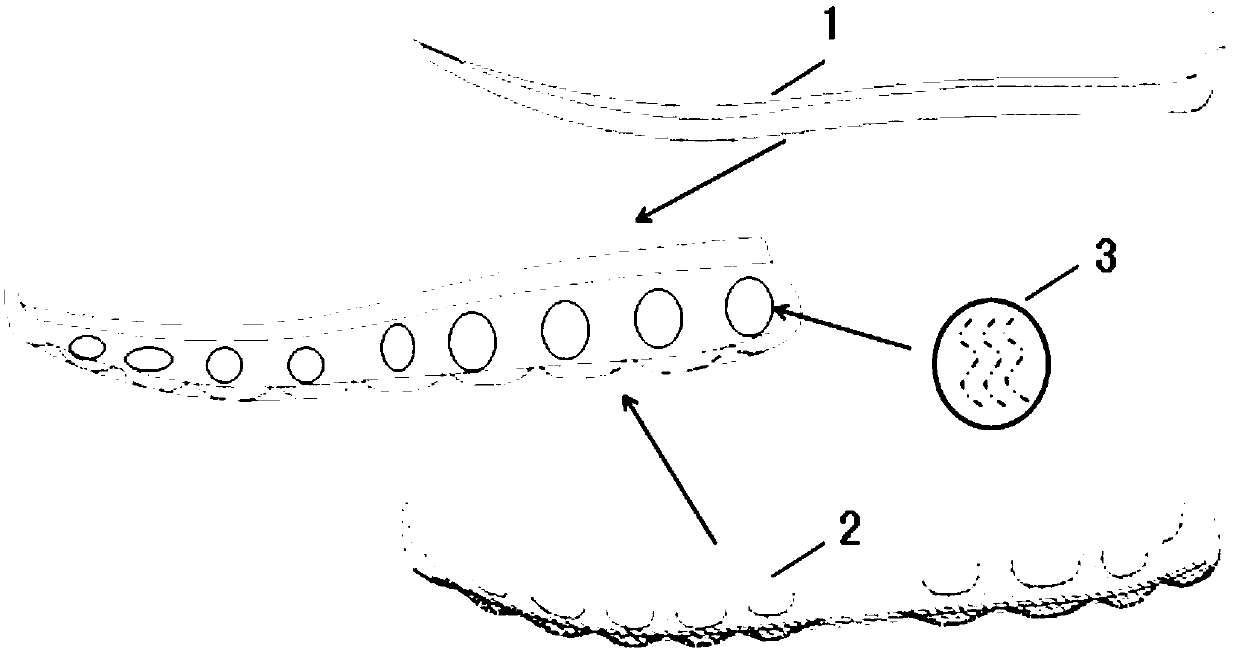
The invention discloses an implant for treating old mallet finger deformity, which aims to overcome problem of the old mallet finger deformity. The implant (4) is a flat solid unit which is surrounded by a bottom surface and an upper surface; the implant (4) is designed as an oblate solid unit, a flat rectangular solid unit, a flat square solid unit, or a flat elliptical solid unit; the bottom surface of the implant (4) is set as a plane or a curved surface which is the same as the reverse side of a middle phalanx (3); the upper surface of the implant (4) is set as a spherical surface, a cylindrical surface, or other curved surfaces; the implant (4) is adhered to the far end of the middle phalanx (3) by using bone glue; the bottom surface of the implant (4) is in contact with the reverse side of the middle phalanx (3); the upper surface of the implant (4) is in contact with an extensor tendon (1); a non-through hole with an internal screw thread is machined on the axis of symmetry of the implant (4), and the implant (4) is fixed at the far end of the middle phalanx (3) by using a screw (5); and the implant (4) is made from silica gel, titanium alloy, ceramics, artificial bone, andthe like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Biological information measurement device and pulse oximeter
InactiveUS20170086722A1Less easily fall off the fingerAvoid flowSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateMeasurement deviceProximal phalanx
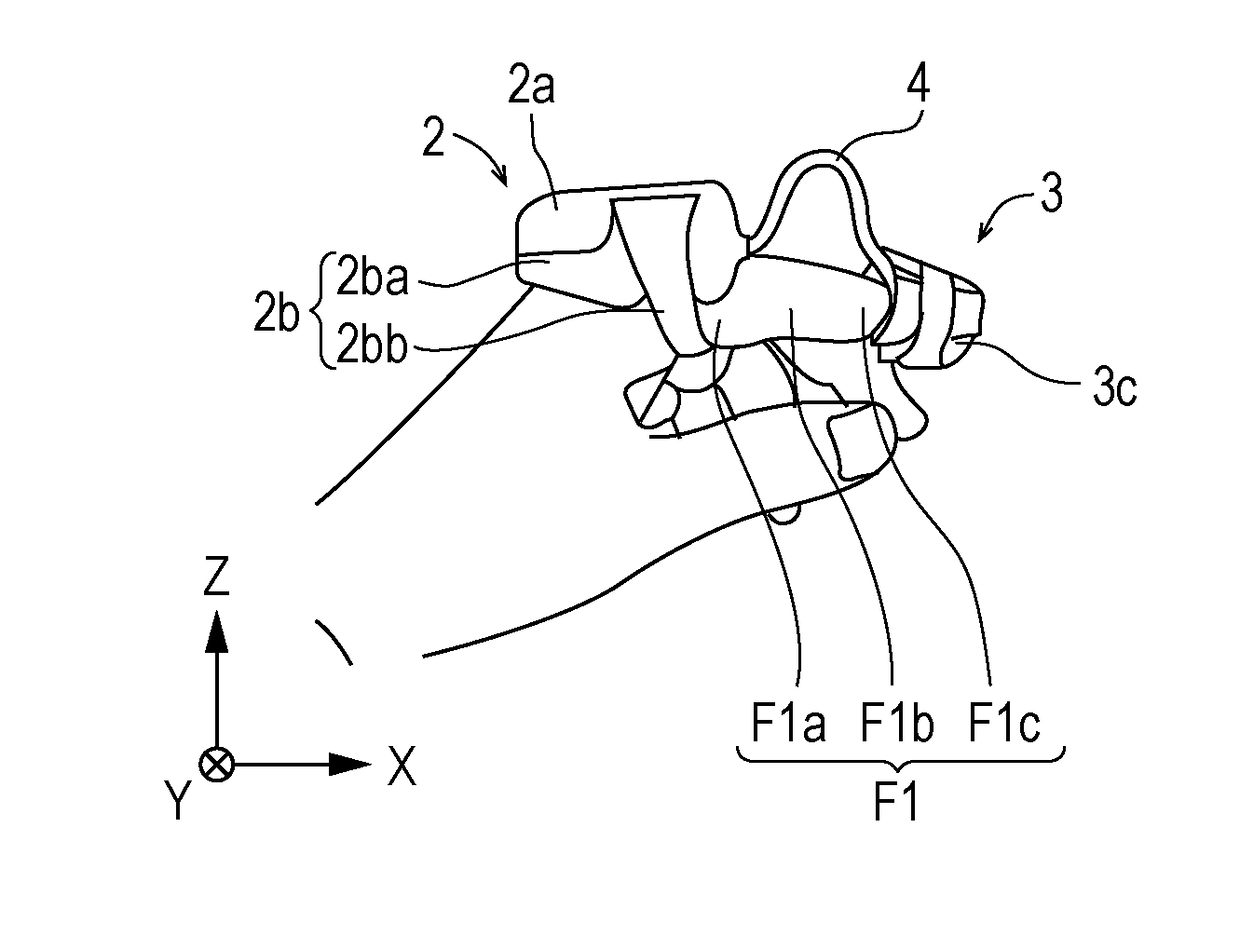
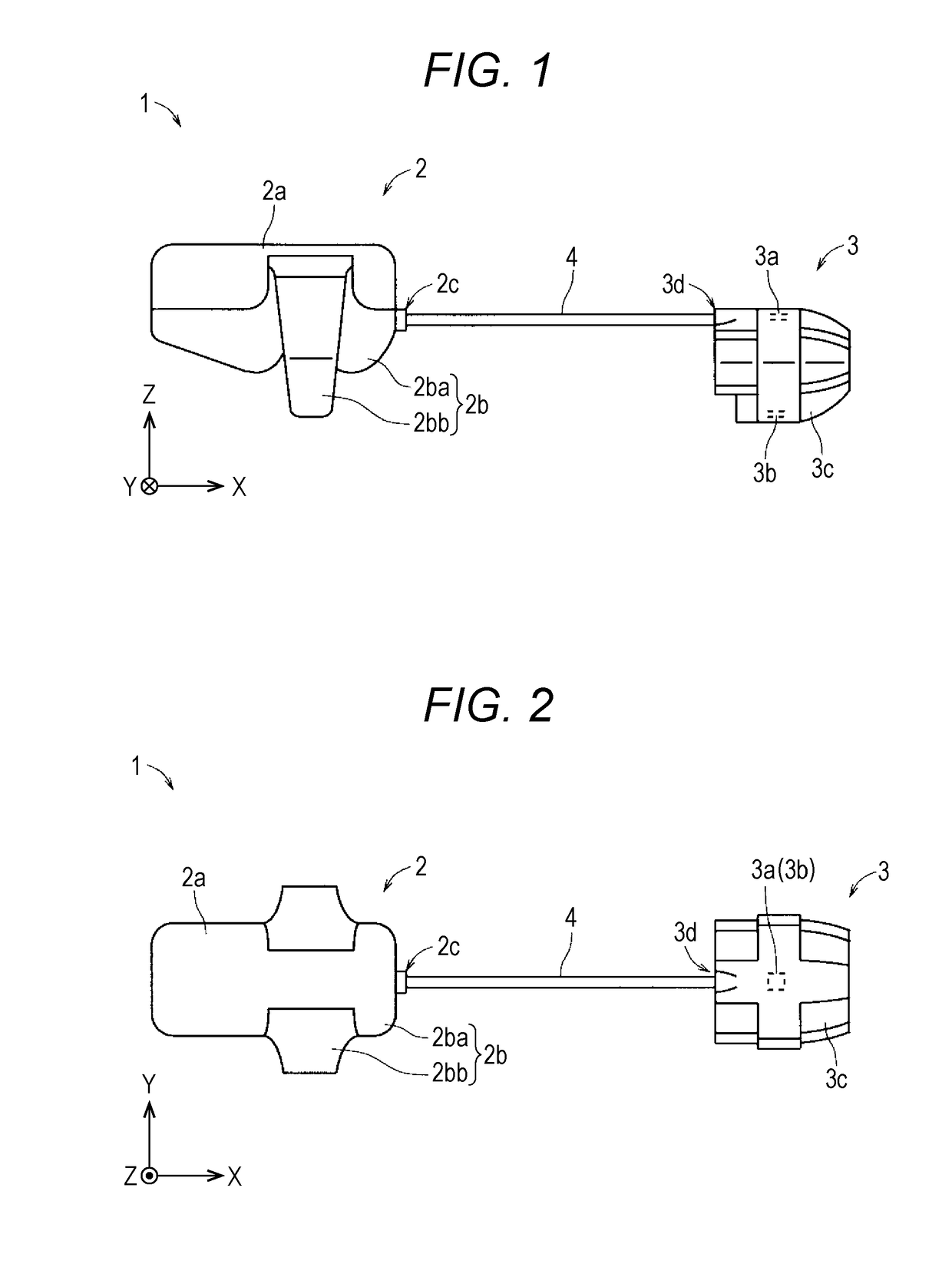
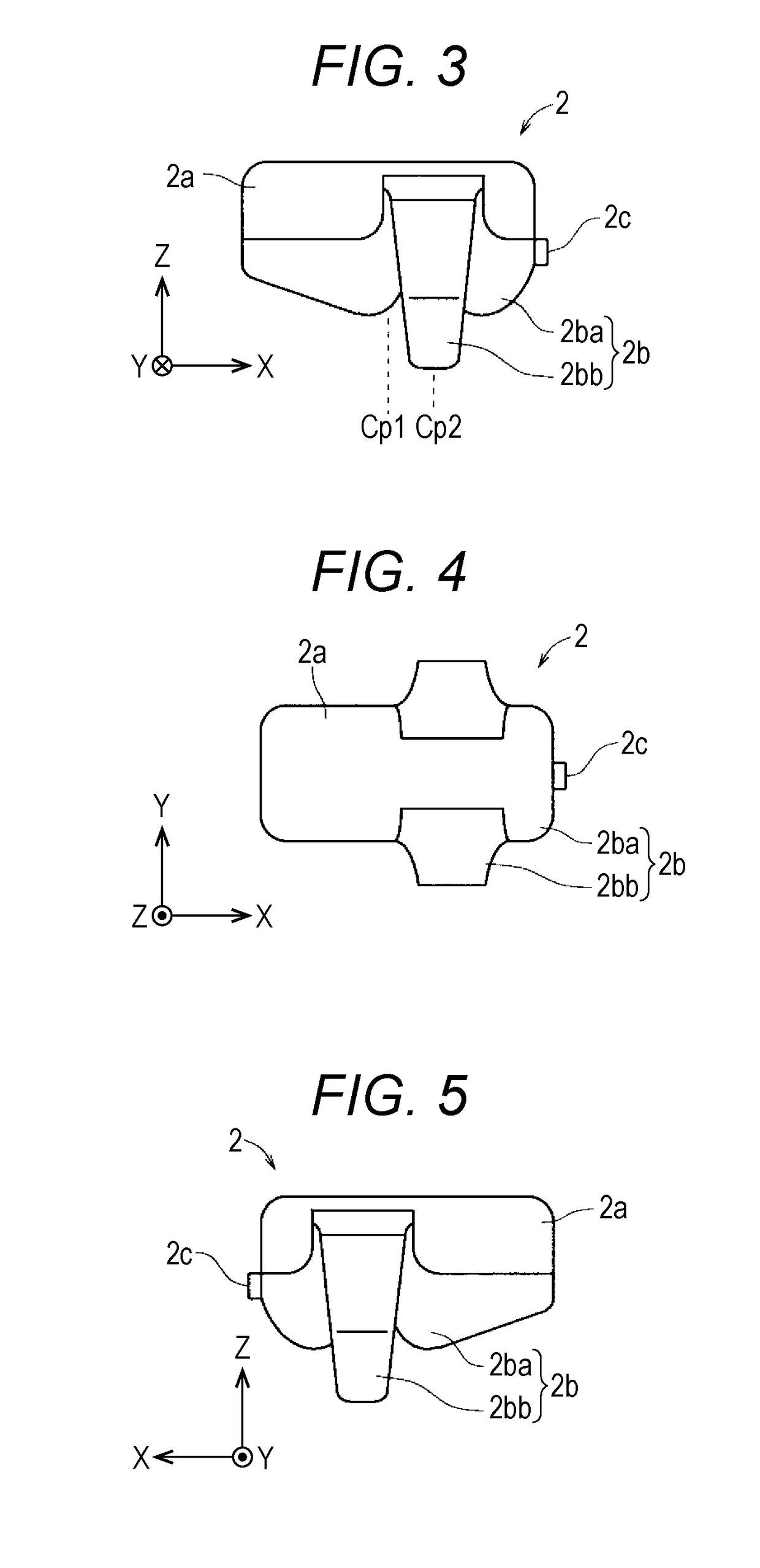
A biological information measurement device may include a body; a probe unit; and a connection portion which electrically connects the body and the probe unit. The body may include a casing in which a battery and an electrical circuit are incorporated; and a first fitting portion which is attached to the casing and worn on a first fitted portion including a portion of at least one of a proximal phalanx and a middle phalanx of one or more fingers of the subject body. The probe unit may include a light source unit and a light receiving unit; and a second fitting portion which is worn on a second fitted portion including a distal phalanx of one or more fingers of the subject body.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Dual Finger Elastomeric Wrap
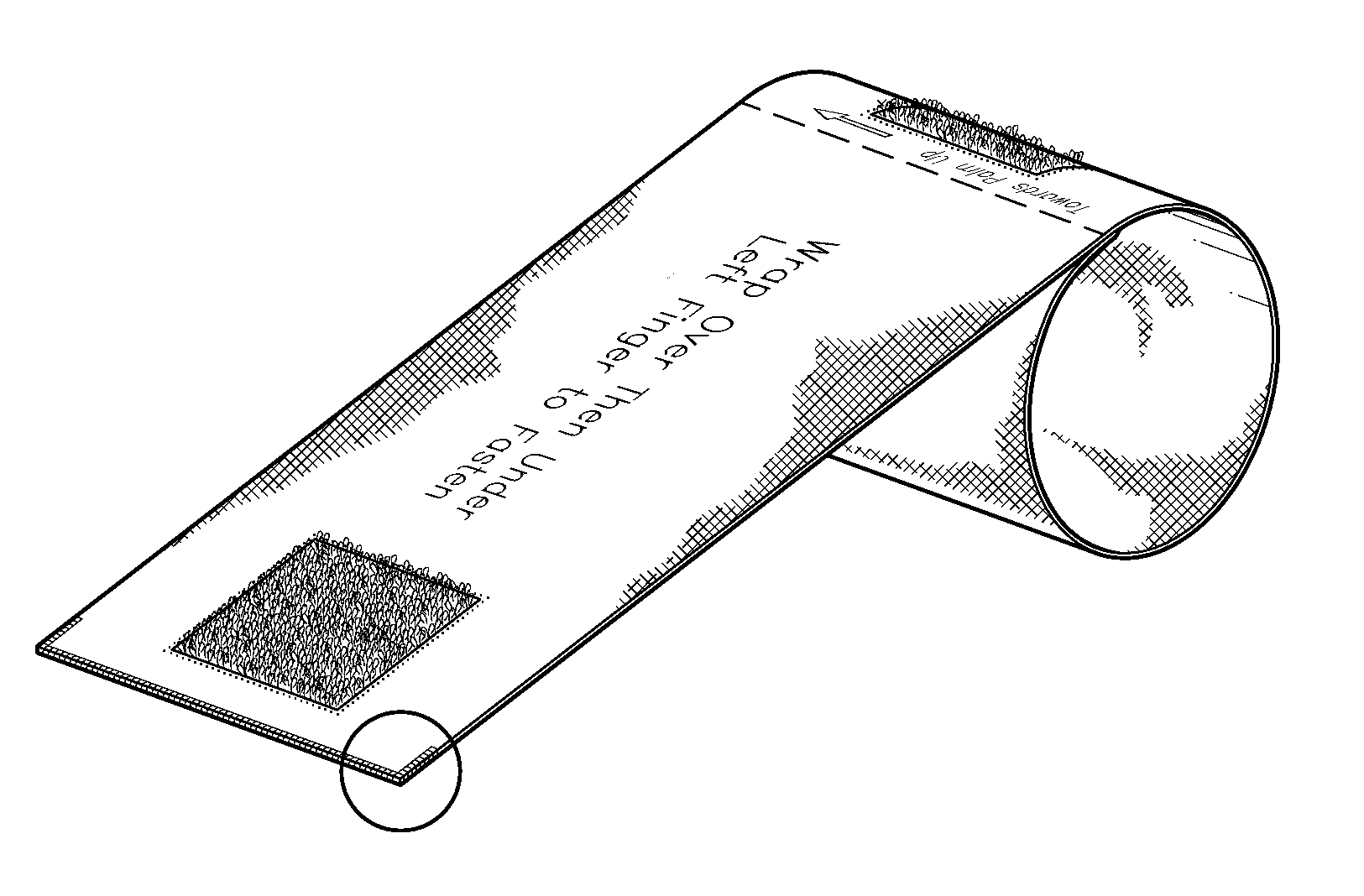
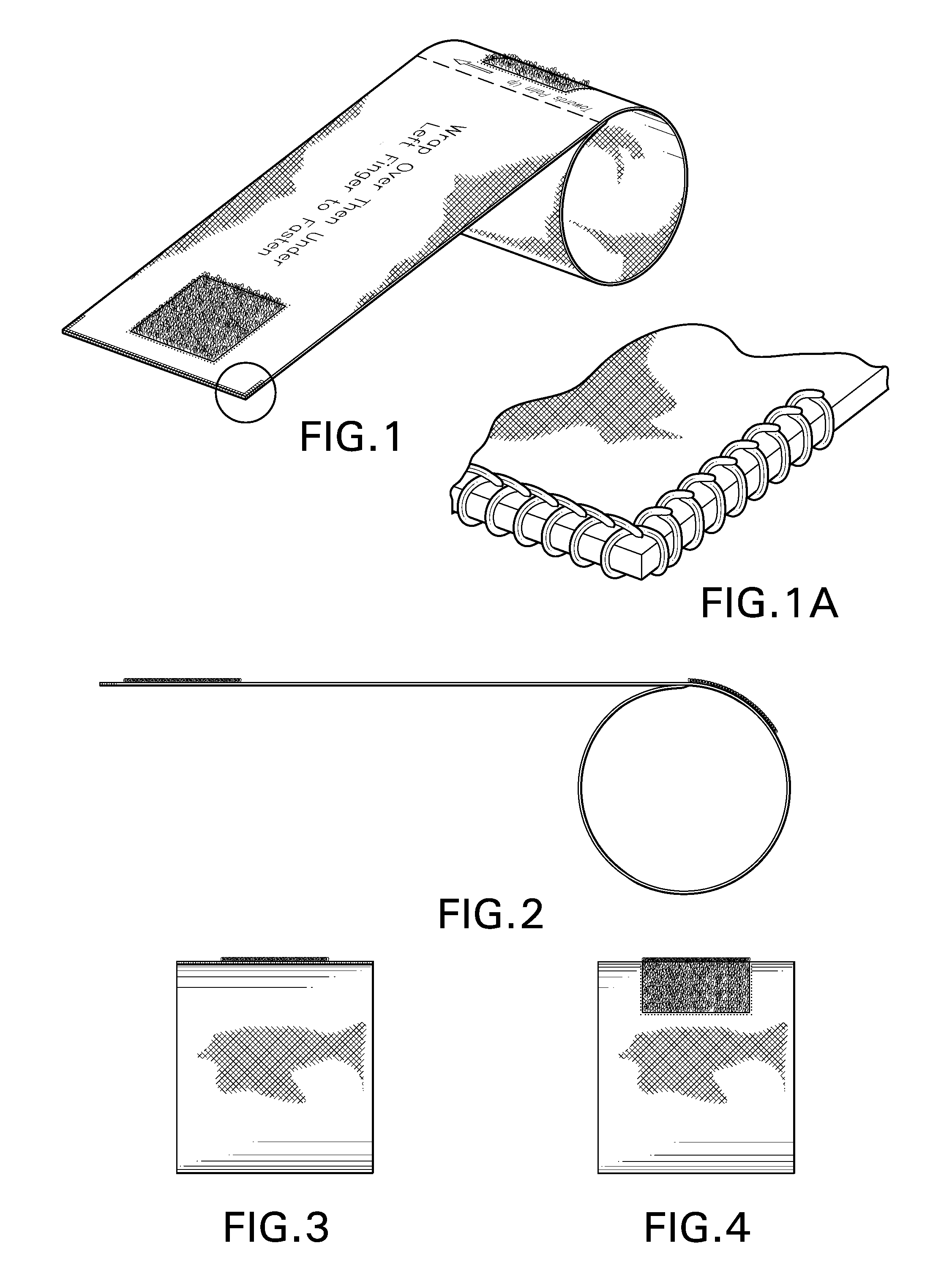
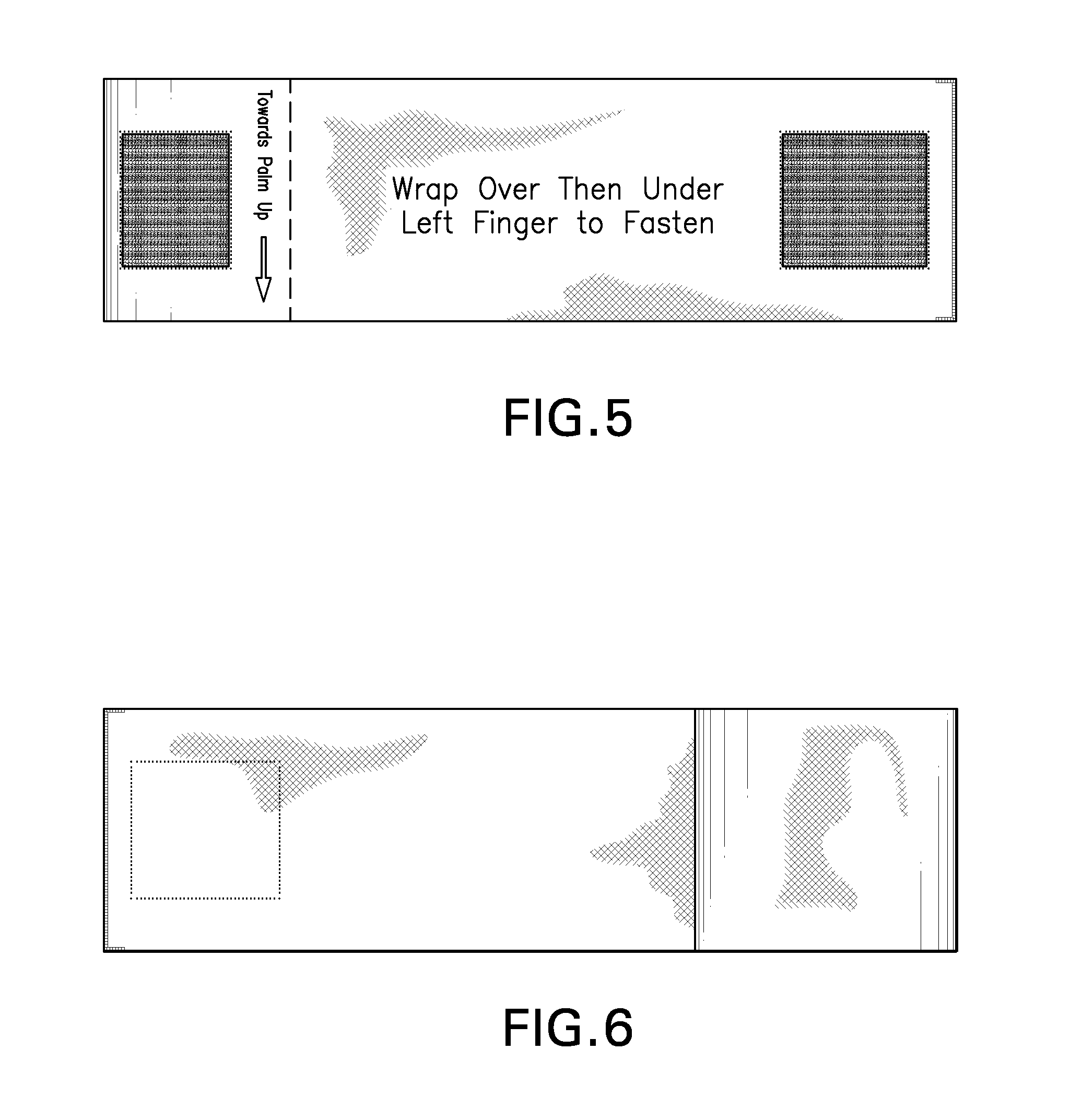
An elastomeric wrap for restricting two fingers during flexion and extension. The wrap covers the proximal phalanx and interphalangeal (PIP) knuckle and part of the middle phalanx of both fingers. Instructional text and directional graphics is silk screened onto the wrap. Fastening is constructed of two opposing strips of hook-and-loop fabric. Buttonhole and straight stitching techniques is used to secure and finish fabric. To form the wrap: First, face the palm upward, second, insert the ring or middle (plus index for right hand) finger into the anchor loop section, third, wrap the elongated section over then under the adjacent left finger, fourth, join one of the two affixed opposing hook-and-loop fabric strips on the elongated section with the other hook-and-loop fabric strip on the anchor loop section to fasten. The wrap is constructed of a strip of elastomeric fabric.
Owner:JONES ALTON JAMES
Sole for sports shoes and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN109645620AAchieve elasticityTo achieve the effect of cushioningSolesCushioningFirst metatarsal
The invention provides a sole for sports shoes and a preparation method and application thereof. A midsole of the sole herein includes: an upper sole component and a lower sole component; the upper sole component is a foam component having the upper surface covering the whole foot sole and a foam component and positioned in the position the closest to the foot sole; the lower sole component is a foam component having the lower surface the closest to the ground; both the upper sole component and the lower sole component are resin EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate) injection molding components; the upper sole component and the lower sole component are integrally formed into a midsole; the midsole has a plurality of closed cells, each cell receives gas having the pressure greater than or equal to one standard atmospheric pressure; the closed cells are positioned in the area of the first distal phalanxes to first metatarsal bones and second middle phalanxes, the area of the forefoot metatarsal bones and the heel calcaneal area. The sole provided herein can provide effective cushioning and elasticity, has low cost and light weight and has better user experience.
Owner:ANTA CHINA
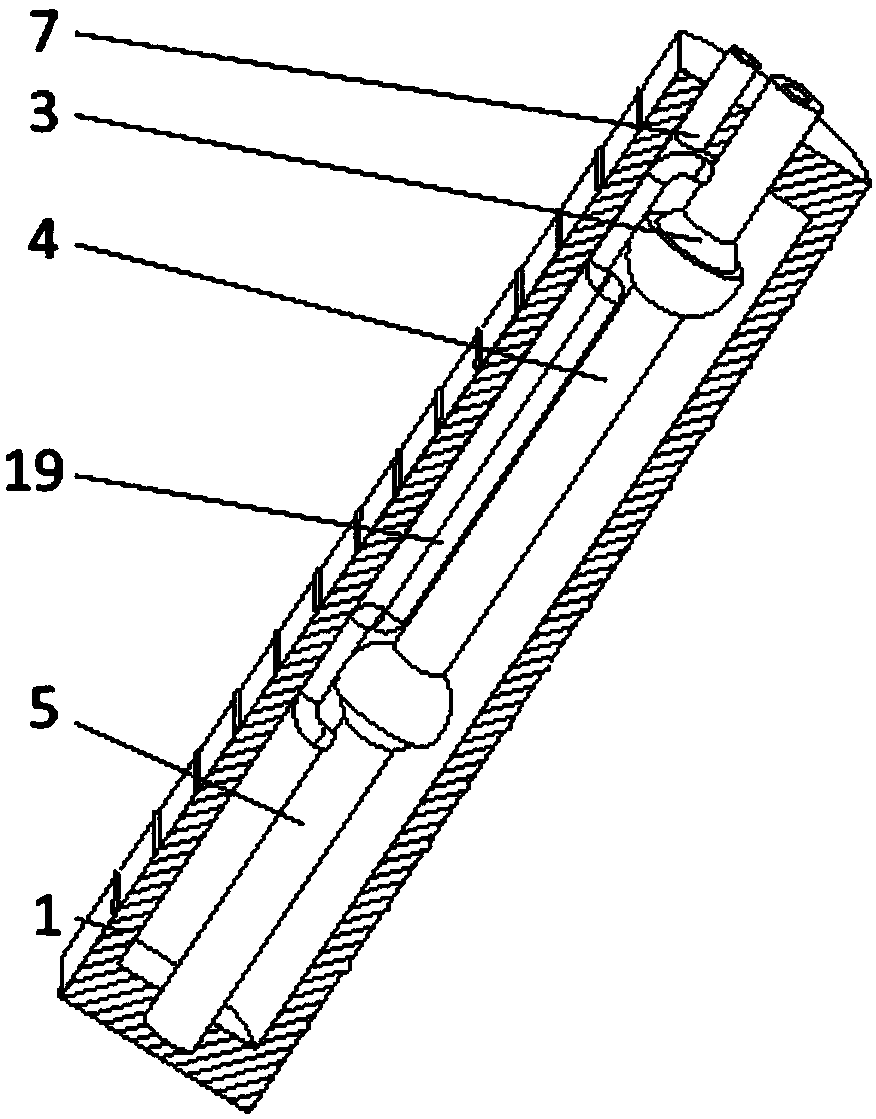
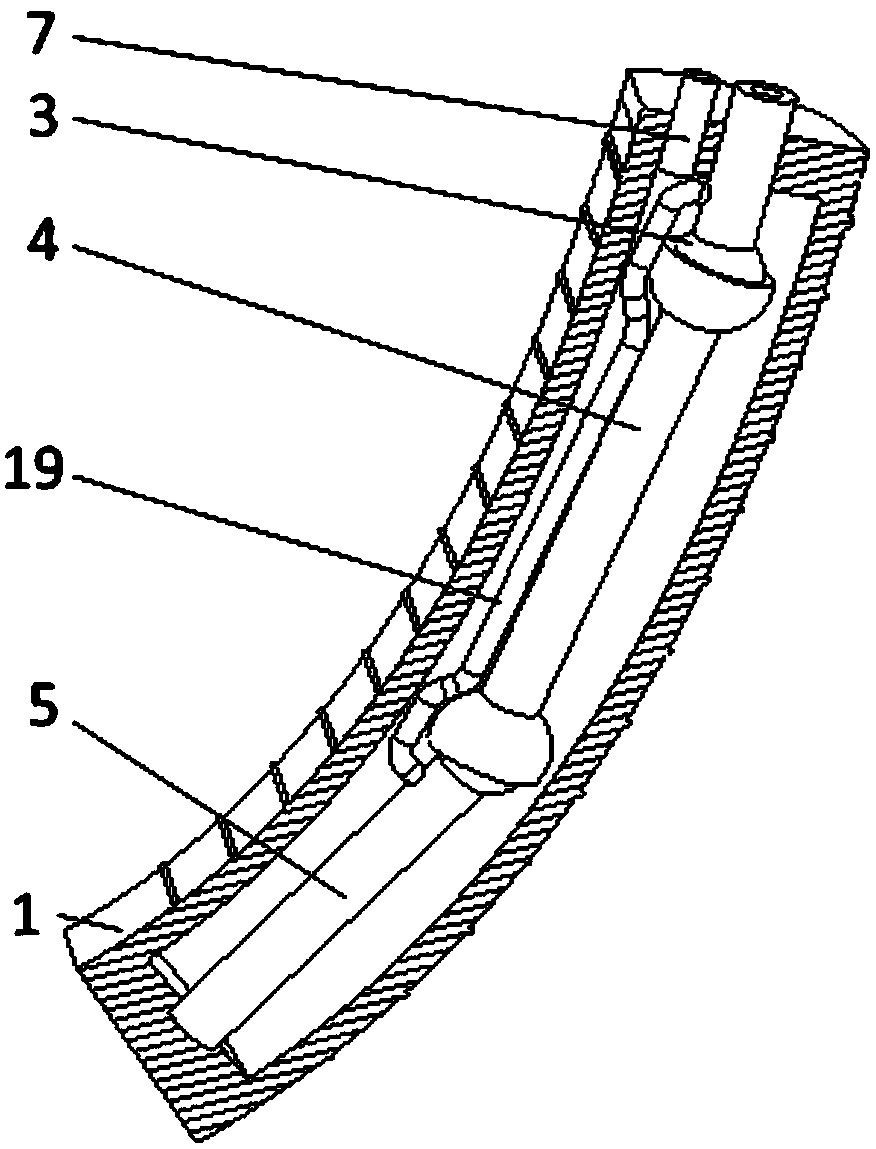
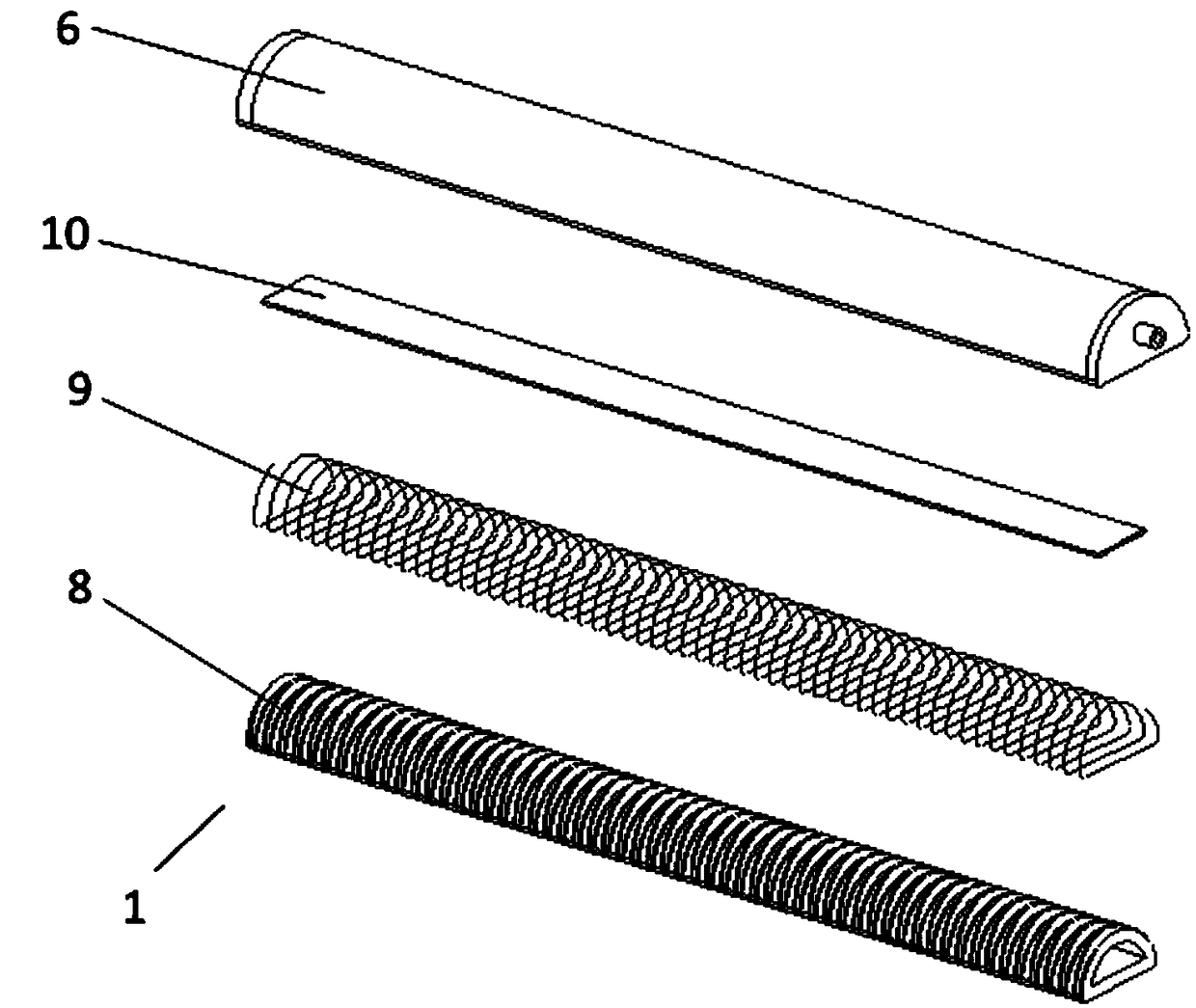
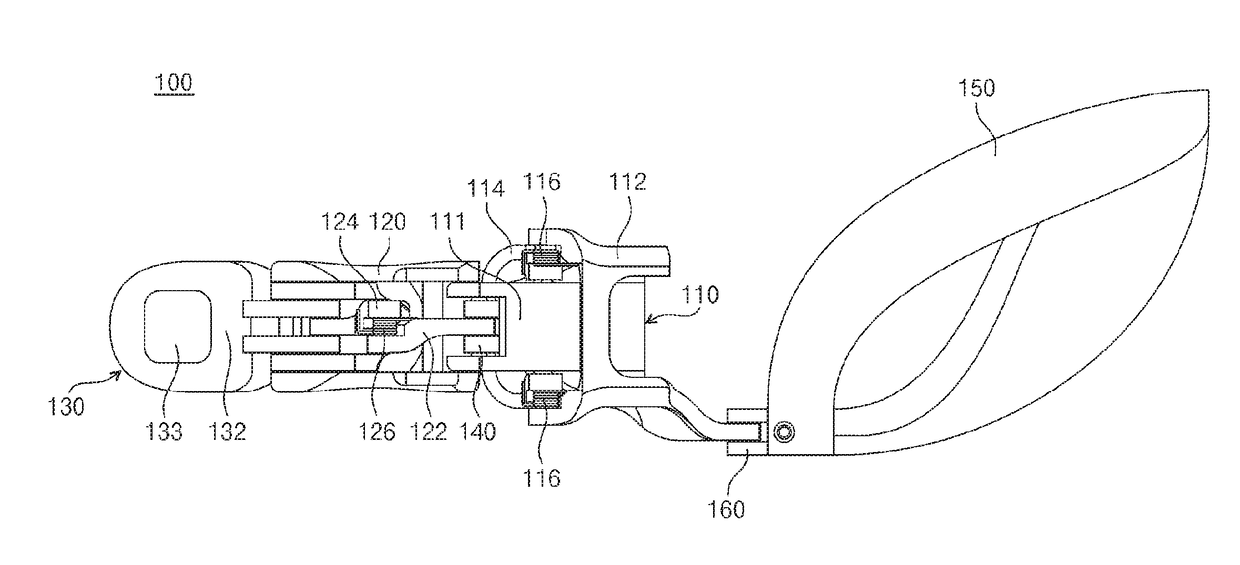
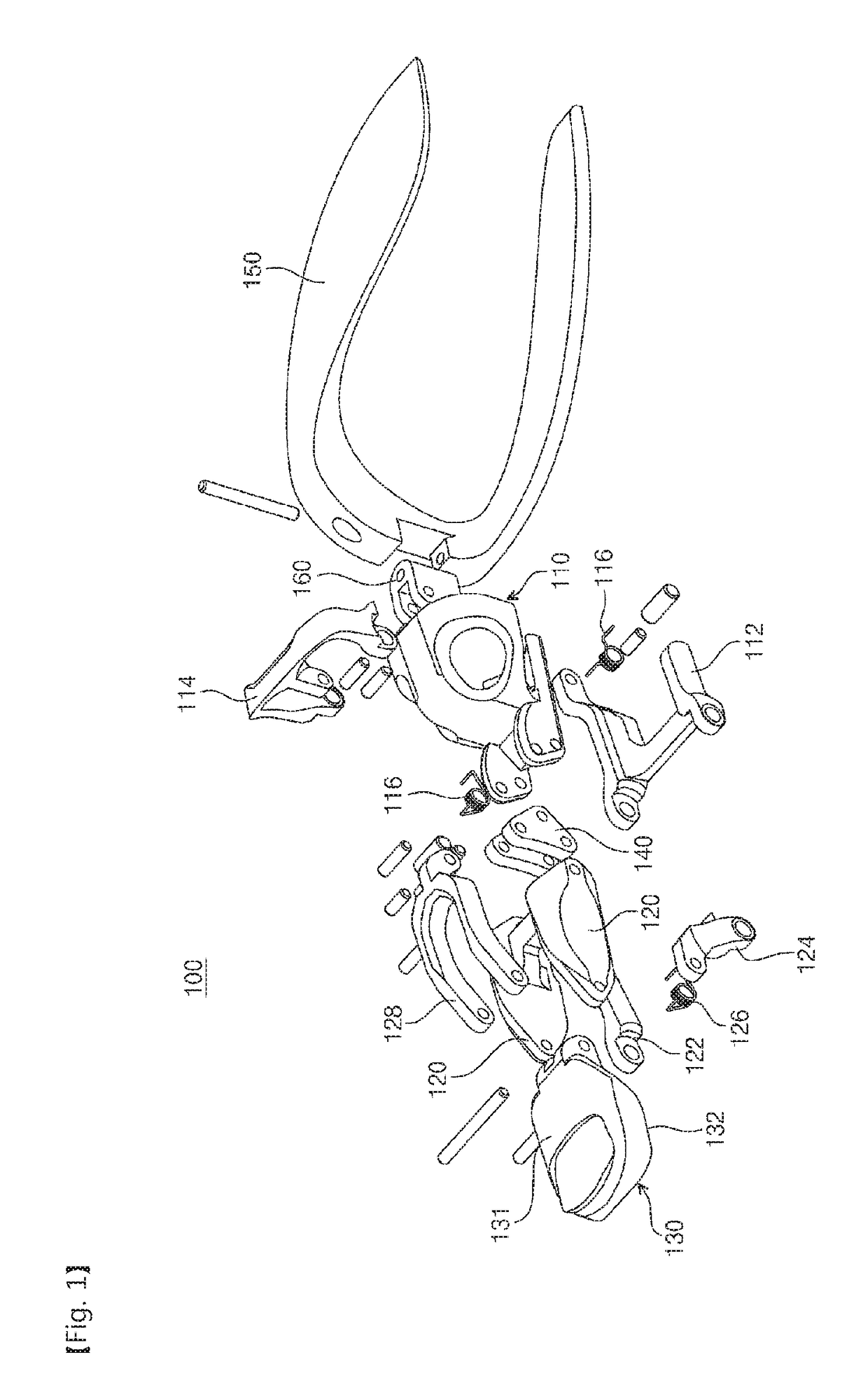
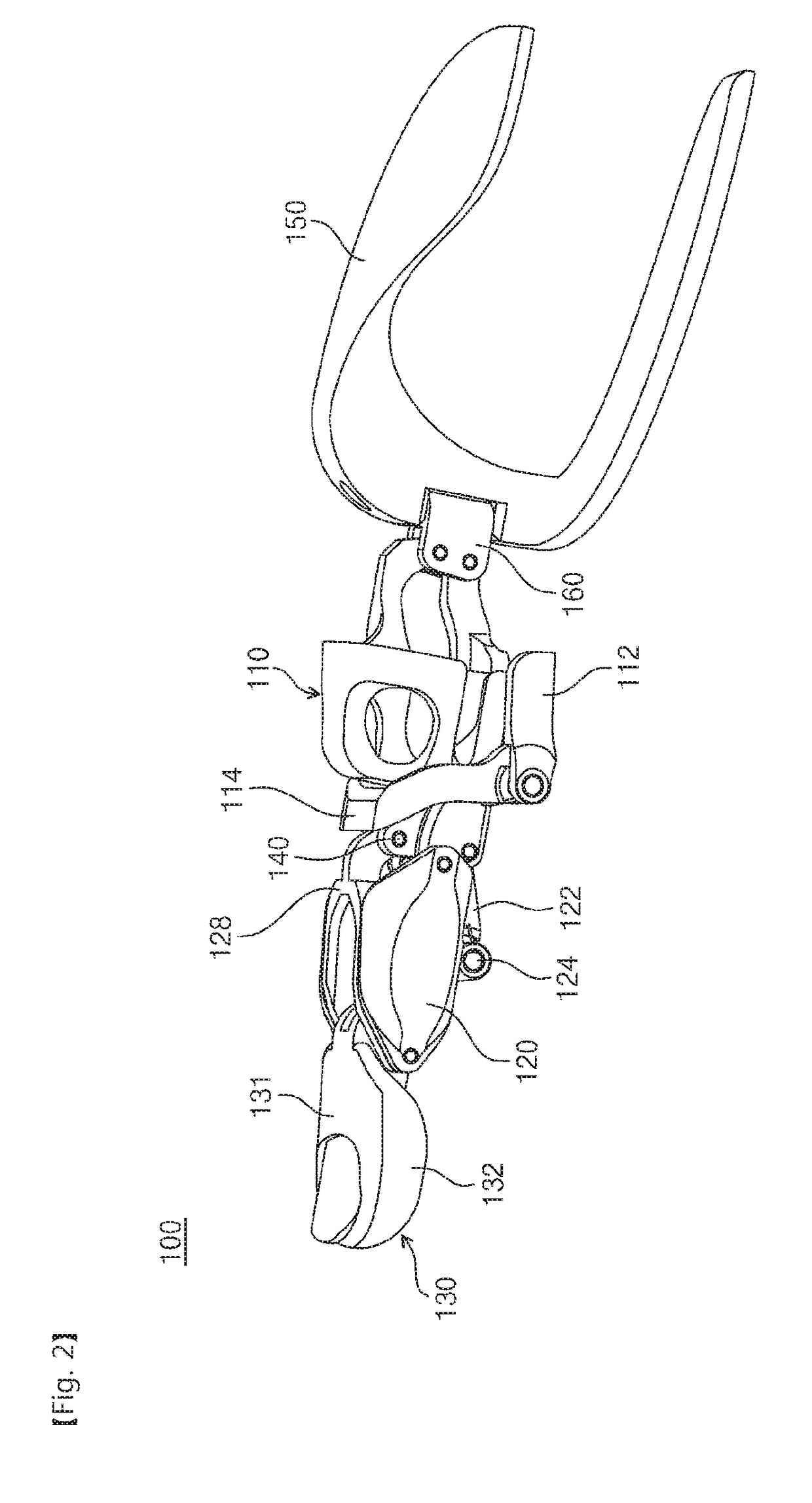
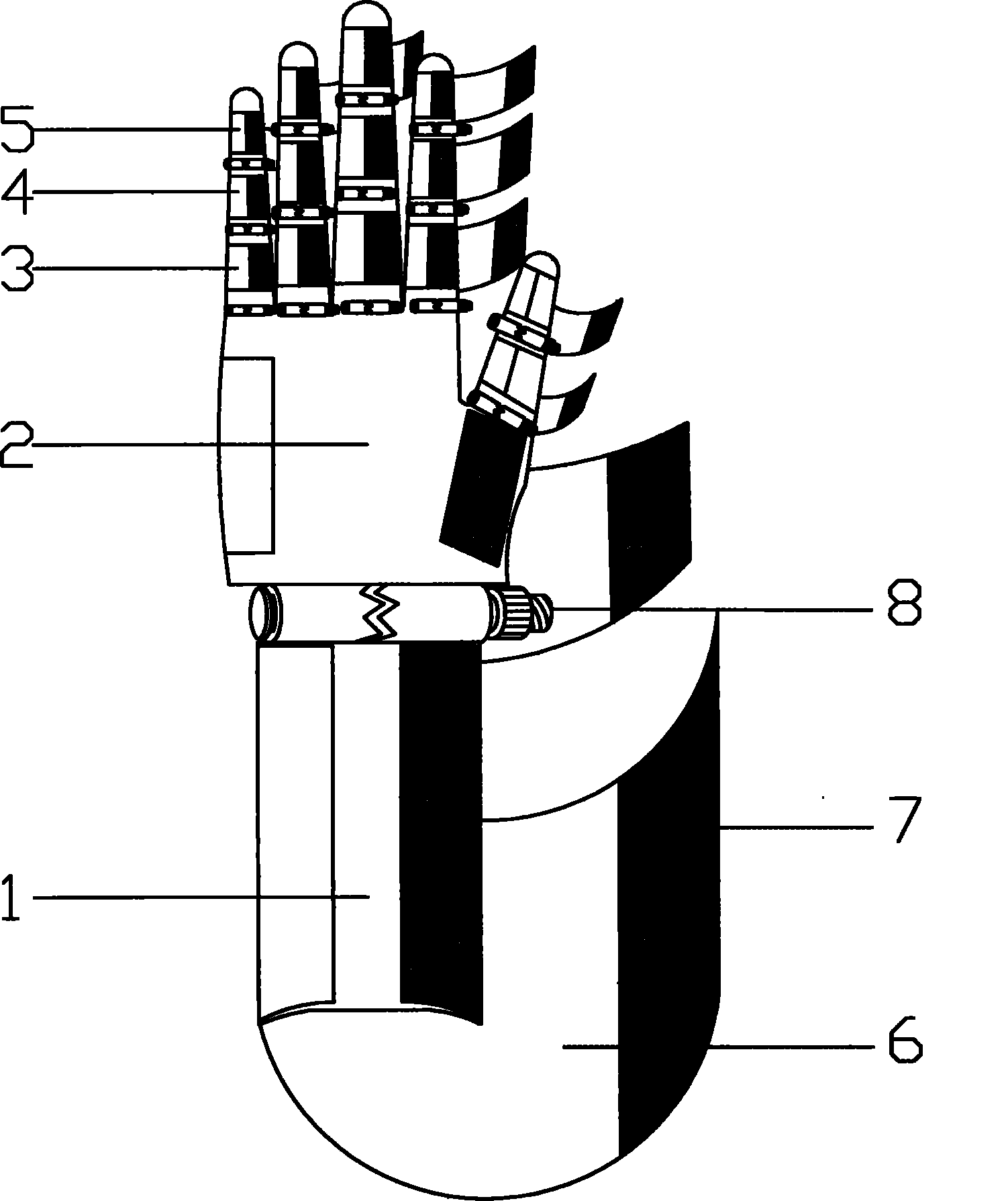
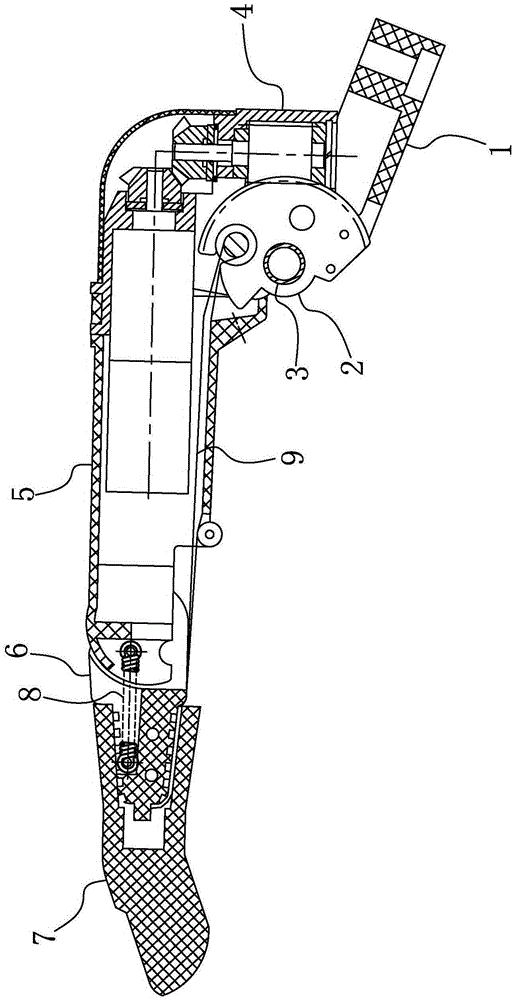
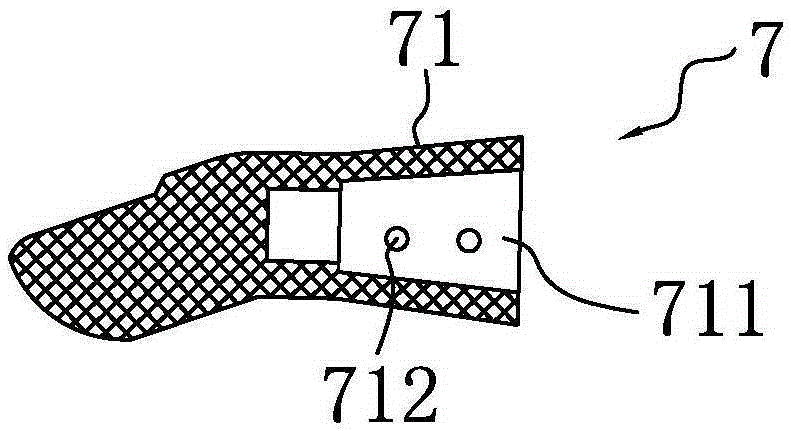
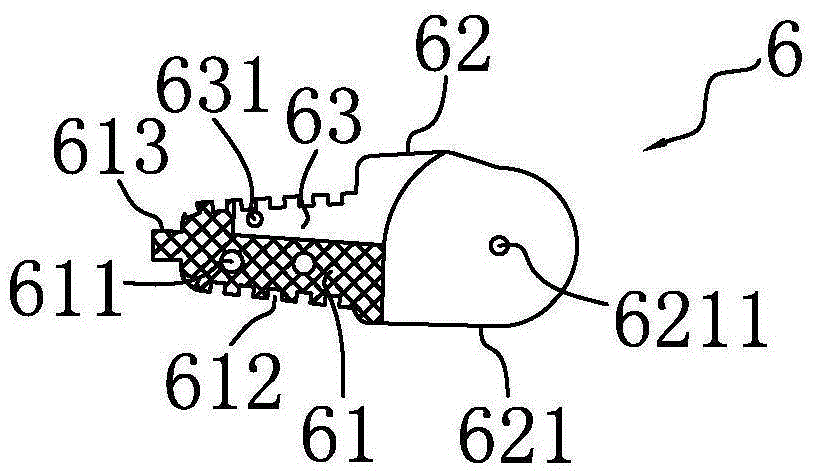
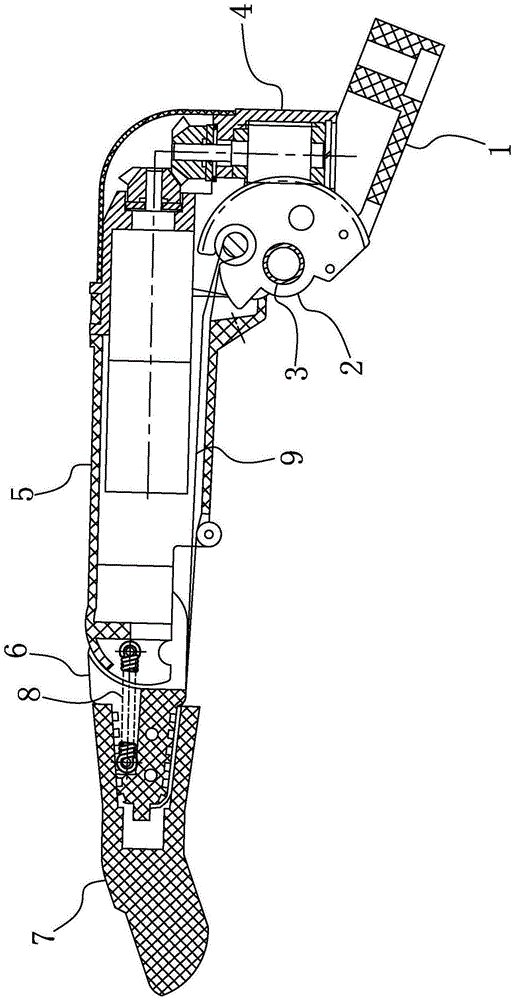
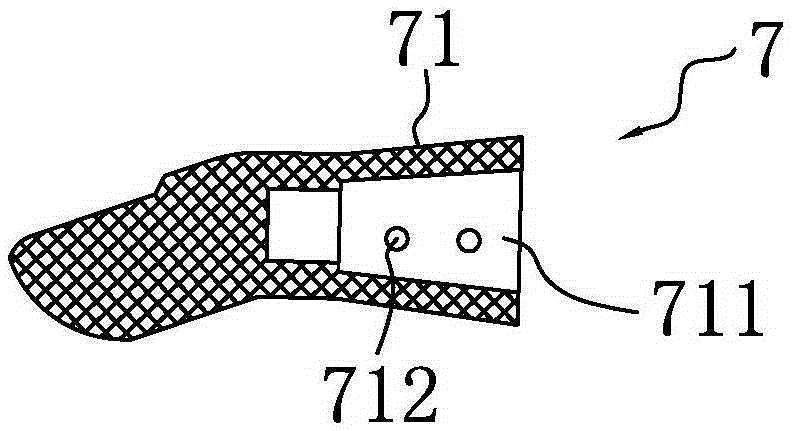
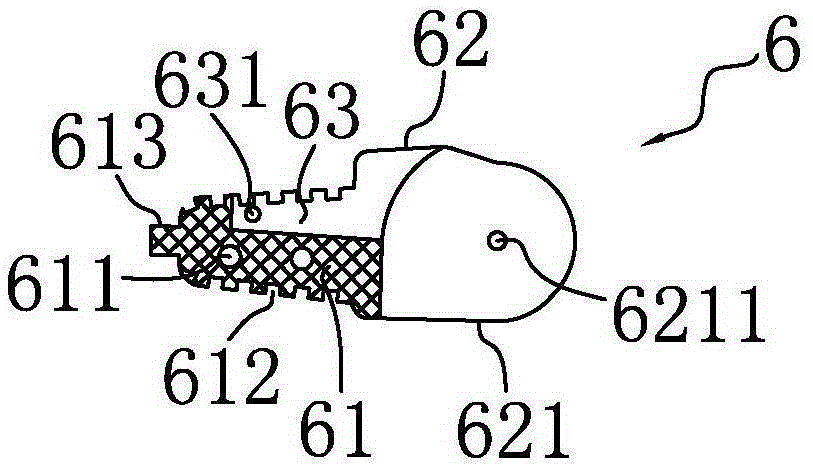
Connecting structure of finger distal phalanx and finger middle phalanx of prosthetic finger
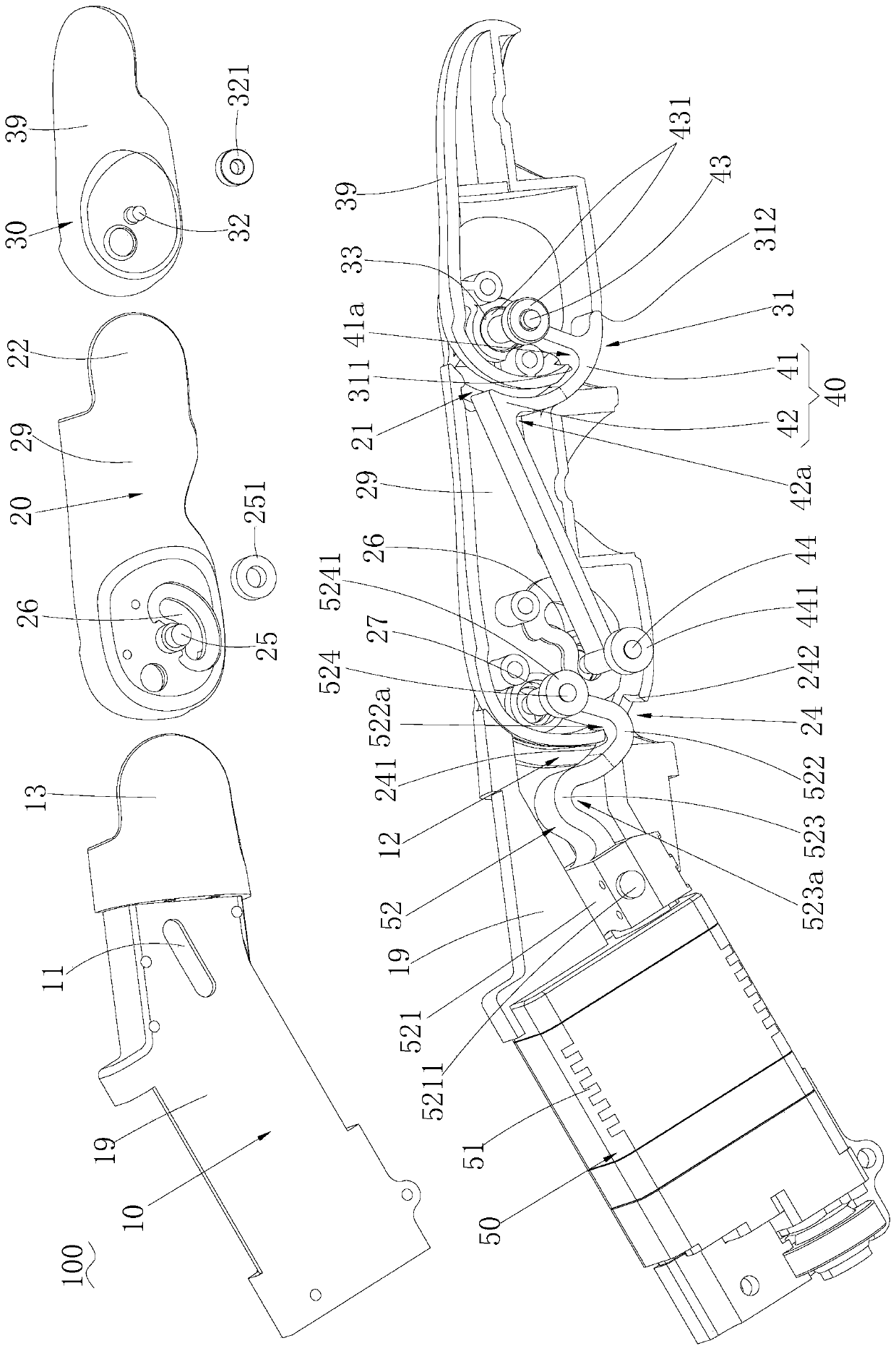
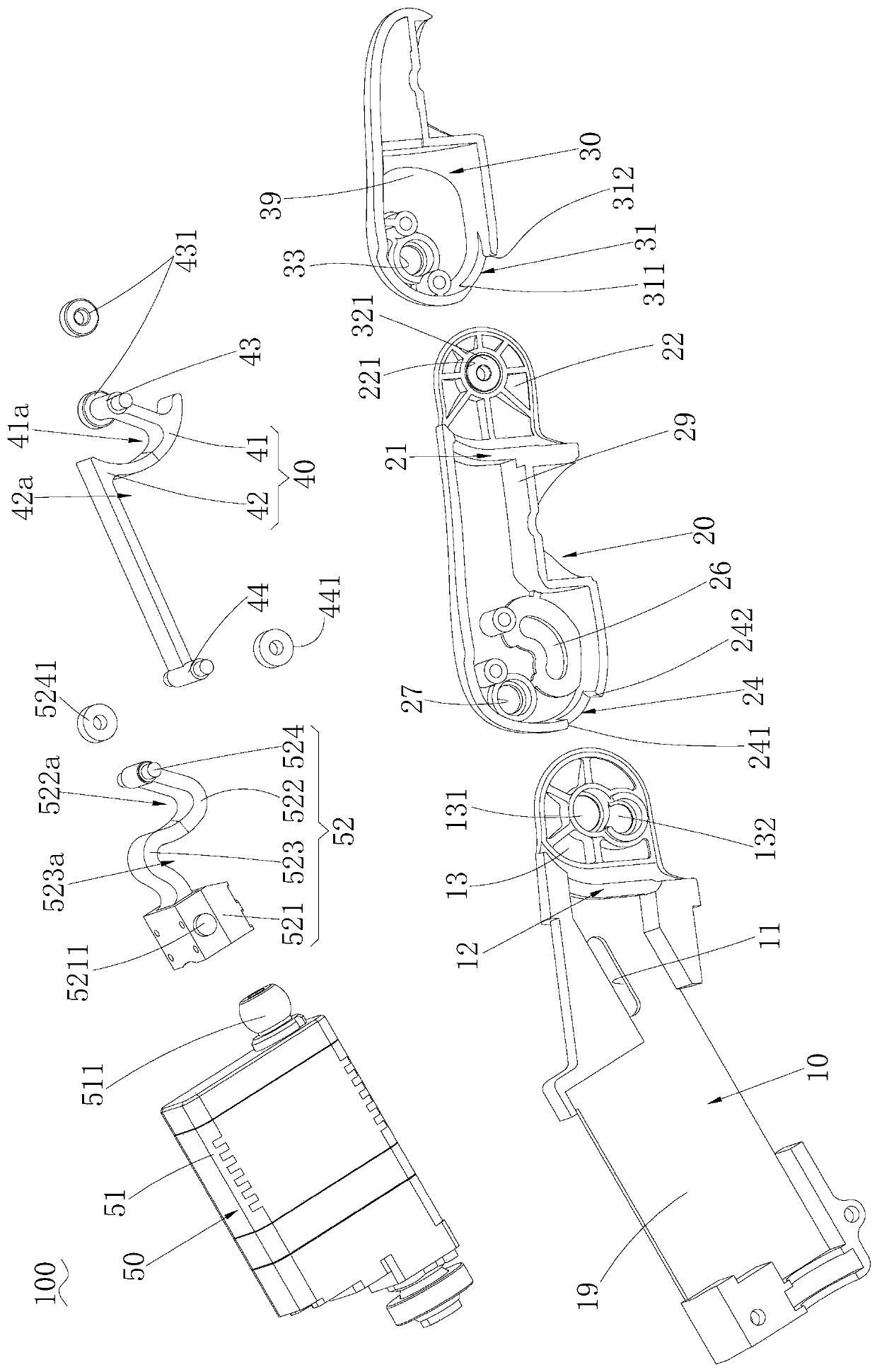
The invention provides a connection structure between a far knuckle and a near knuckle of a prosthetic finger. It includes a finger proximal knuckle (6) and a finger distal knuckle (7), and the finger proximal knuckle (6) includes a protruding head (61) and a proximal knuckle body thicker than the protruding head (61) (62), a set part (71) is provided on the far knuckle (7) of the finger, and a set cavity (711) matching the convex part (61) is provided in the set part (71) , the protruding portion (61) is located in the sleeve cavity (711), the sleeve portion (71) is sleeved on the protruding portion (61) and abuts against the proximal knuckle body (62). The present invention can leave assembly space for other parts, and is convenient for the pre-assembly of the finger near knuckle and other parts; it can make more contact points and contact surfaces between the finger near knuckle and the finger far knuckle, which is convenient for finger The assembly between the near knuckle and the far knuckle of the finger improves the reliability of the connection.
Owner:ZORPIA ROBOT CO LTD
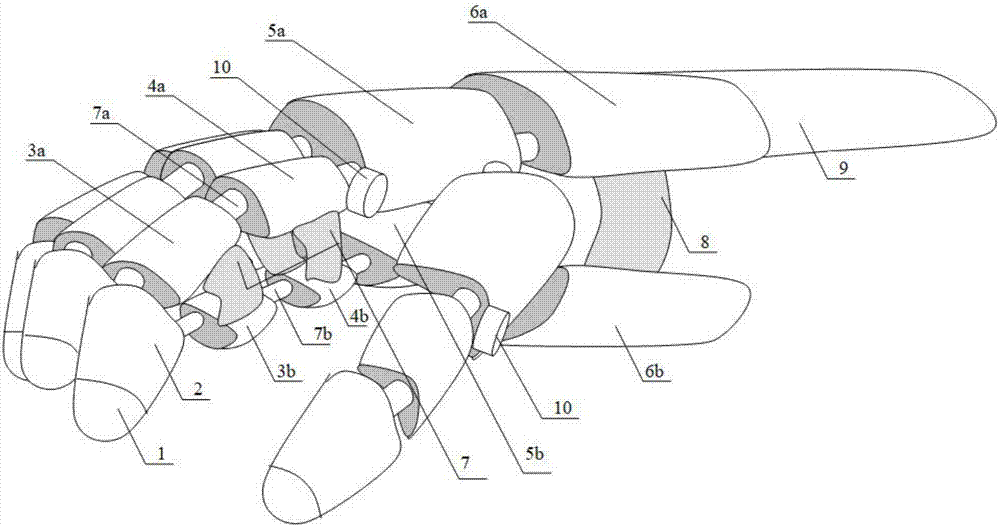
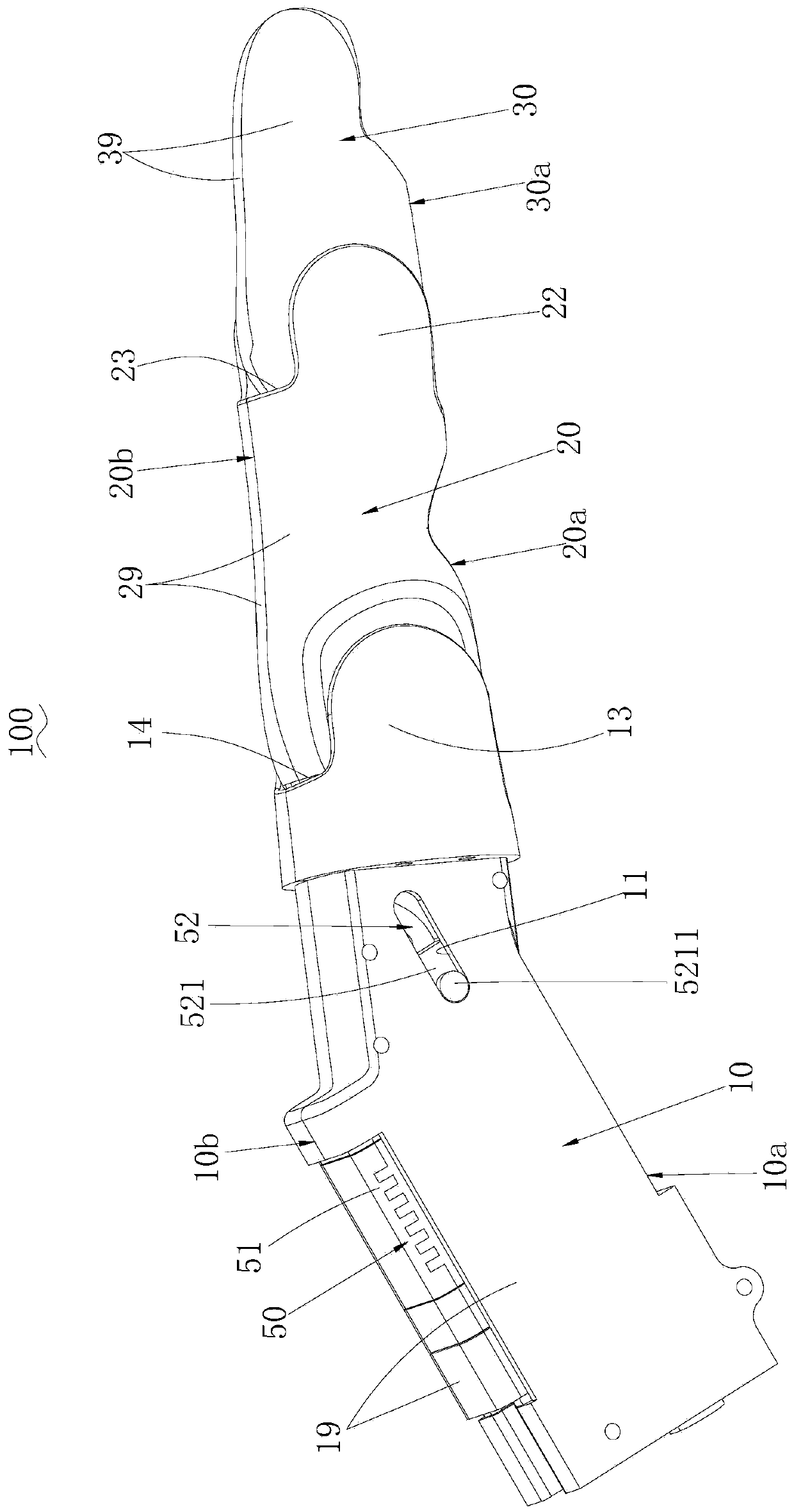
Connecting structure for middle phalanx and proximal phalanx of prosthetic thumb
The invention provides a connecting structure for a middle phalanx and a proximal phalanx of a prosthetic thumb. The connecting structure comprises the thumb proximal phalanx (5') and the thumb middle phalanx (6'), wherein the thumb middle phalanx comprises two thumb middle phalanx connecting wings (621'); the thumb proximal phalanx comprises a thumb proximal phalanx main body (51'), a thumb wing middle connecting part (52') and two thumb proximal phalanx connecting wings (521'); the thumb wing middle connecting part (52') is connected to thumb middle phalanx connecting wing concentric holes in the thumb middle phalanx connecting wing by virtue of a hinge cylinder which is provided with bumps on the side faces; and thumb middle phalanx locking pins (56') are inserted and fixedly arranged on the thumb proximal phalanx connecting wings (521') and the thumb middle phalanx connecting wings (621'). According to the connecting structure disclosed by the invention, by virtue of the thumb middle phalanx locking pins (56') which are inserted and fixedly arranged on the thumb proximal phalanx connecting wings (521') and the thumb middle phalanx connecting wings (621'), the middle phalanx of the thumb is locked, so that the structural diversity of a prosthetic hand is reduced.
Owner:ZORPIA ROBOT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com