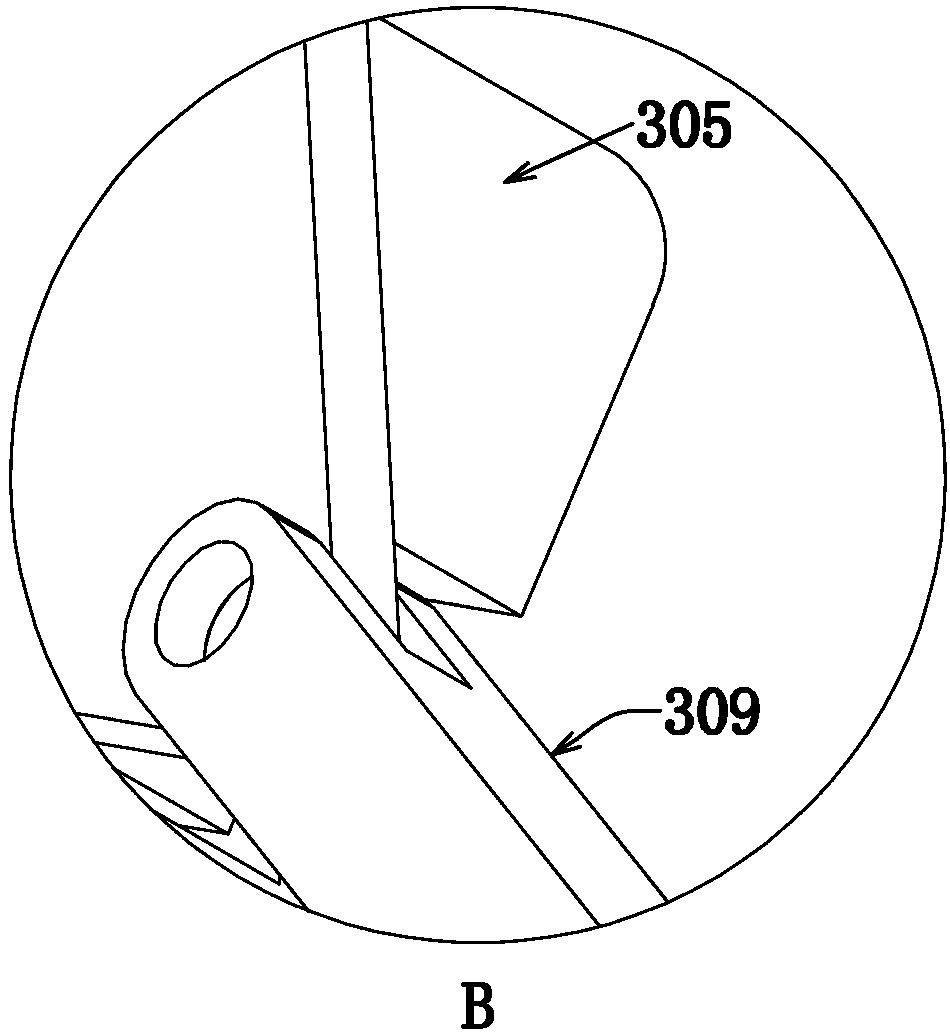
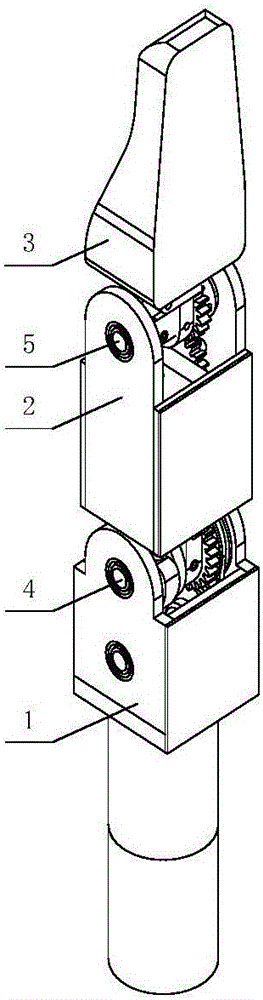
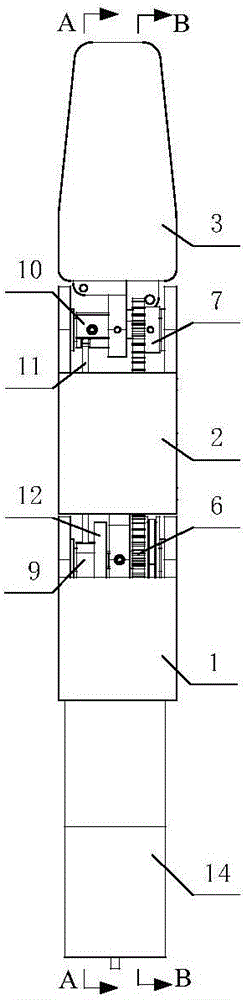
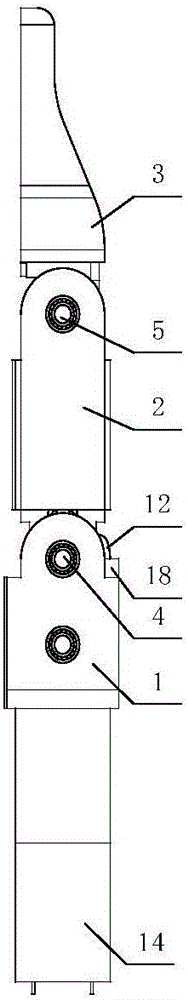
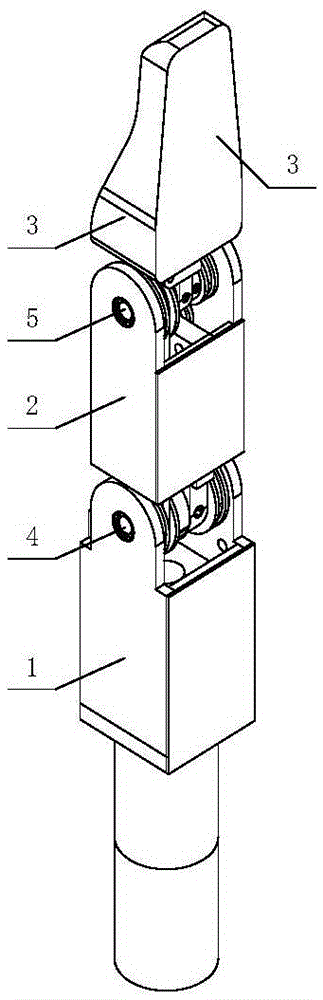
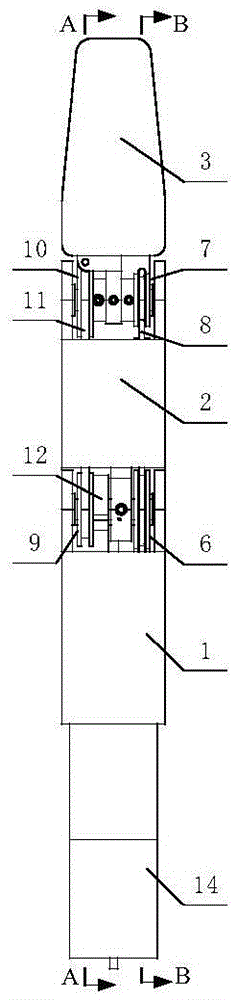
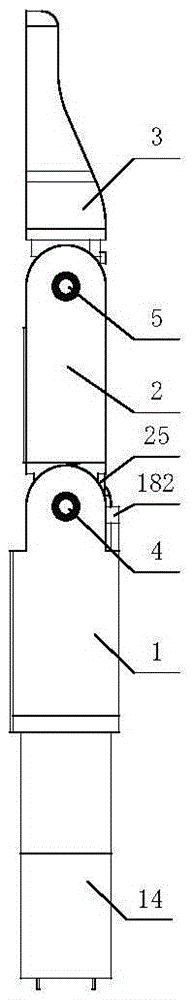
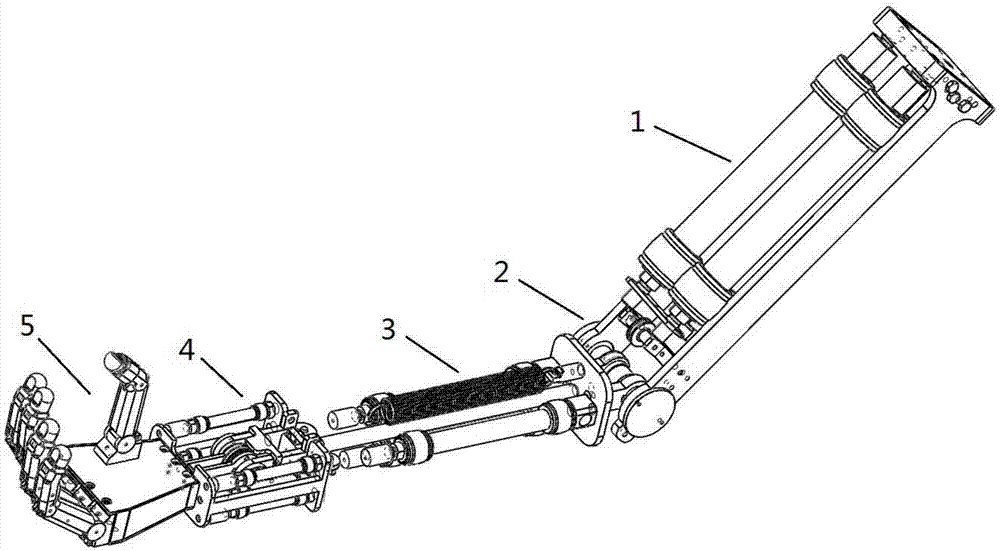
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Underactuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Underactuation is a technical term used in robotics and control theory to describe mechanical systems that cannot be commanded to follow arbitrary trajectories in configuration space. This condition can occur for a number of reasons, the simplest of which is when the system has a lower number of actuators than degrees of freedom. In this case, the system is said to be trivially underactuated.
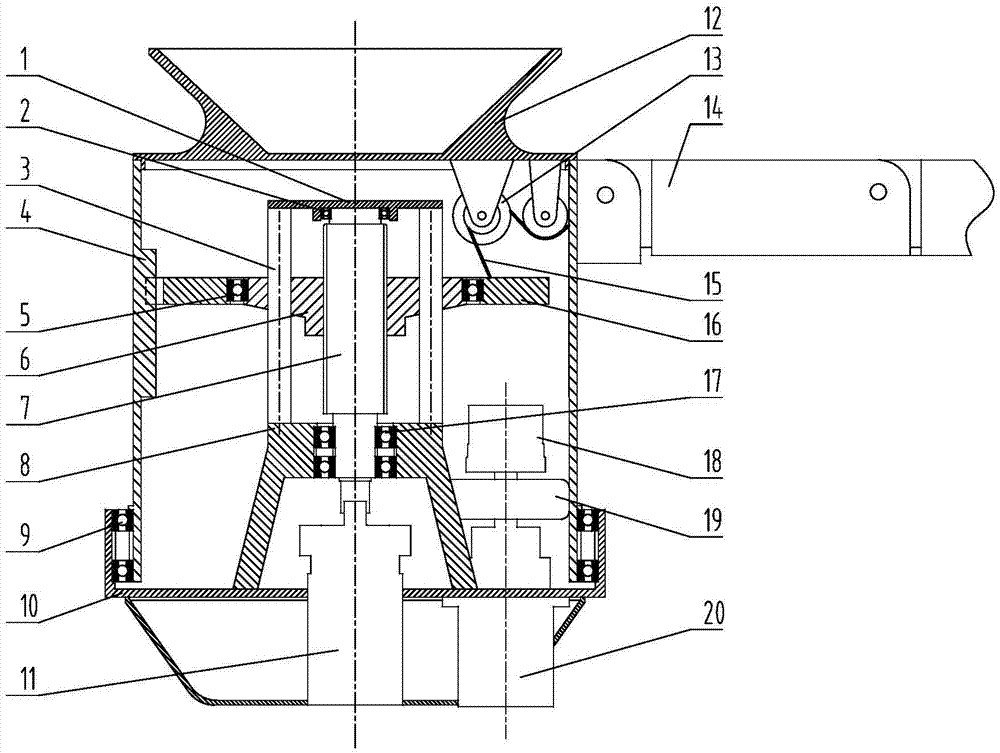
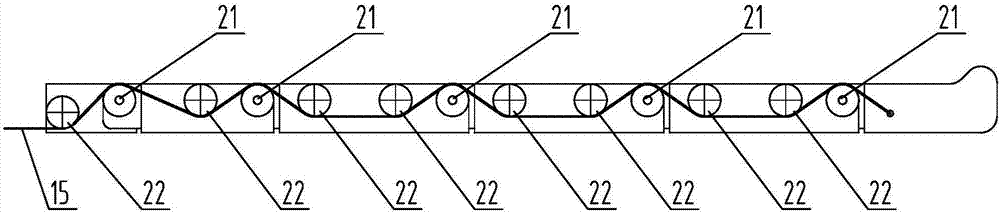
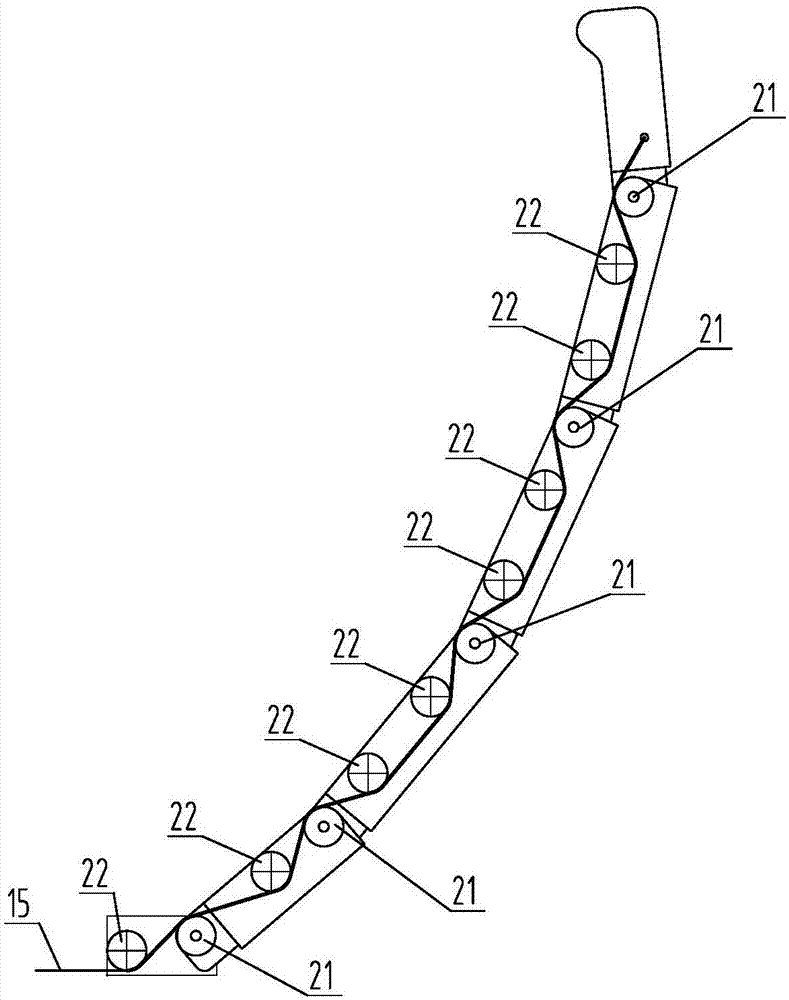
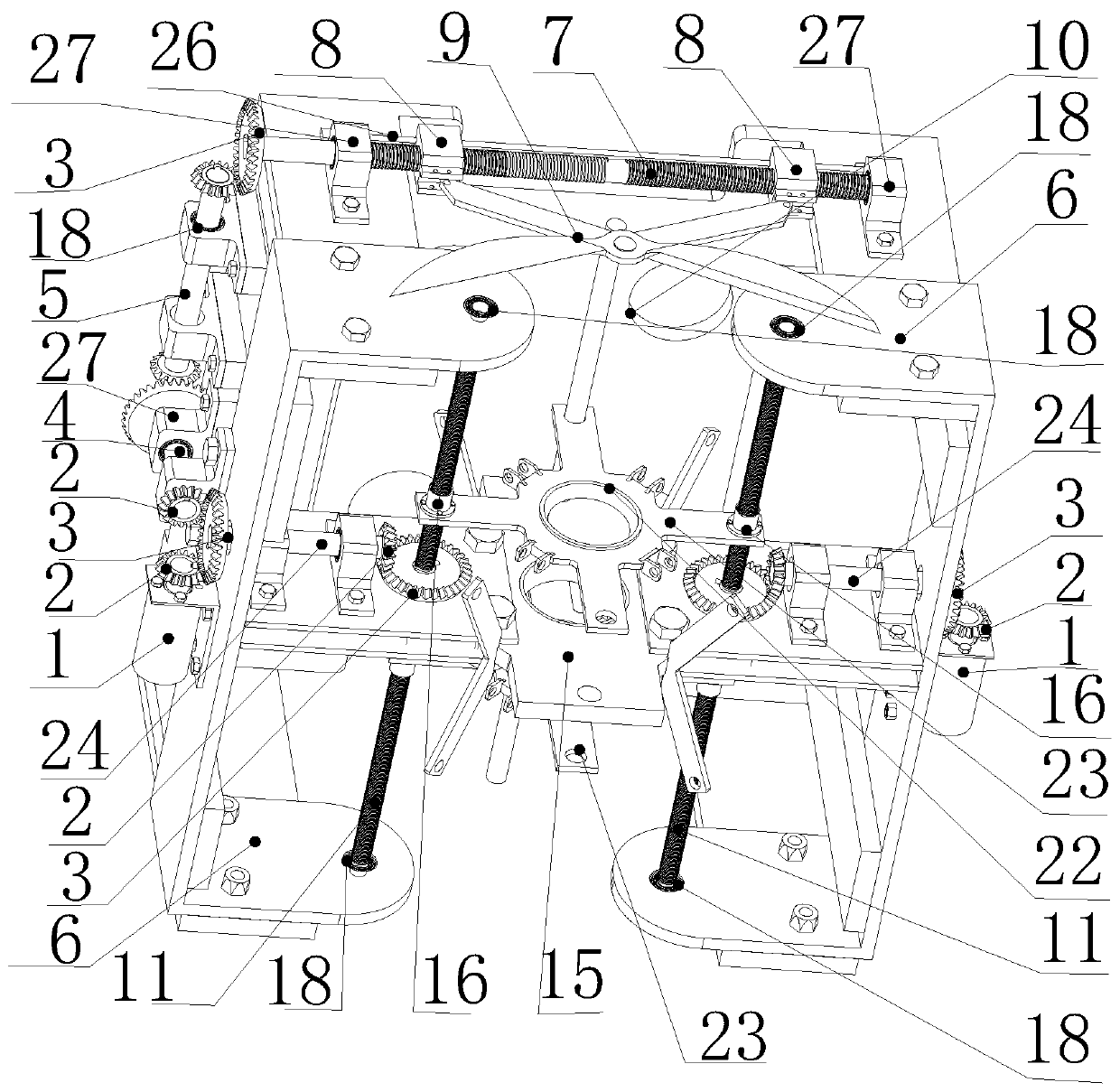
Capture spin elimination mechanism suitable for spin space fragments
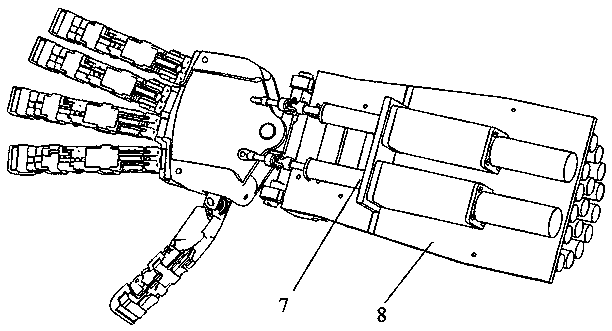
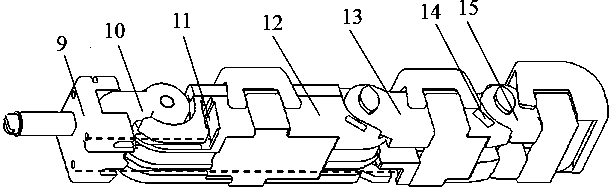
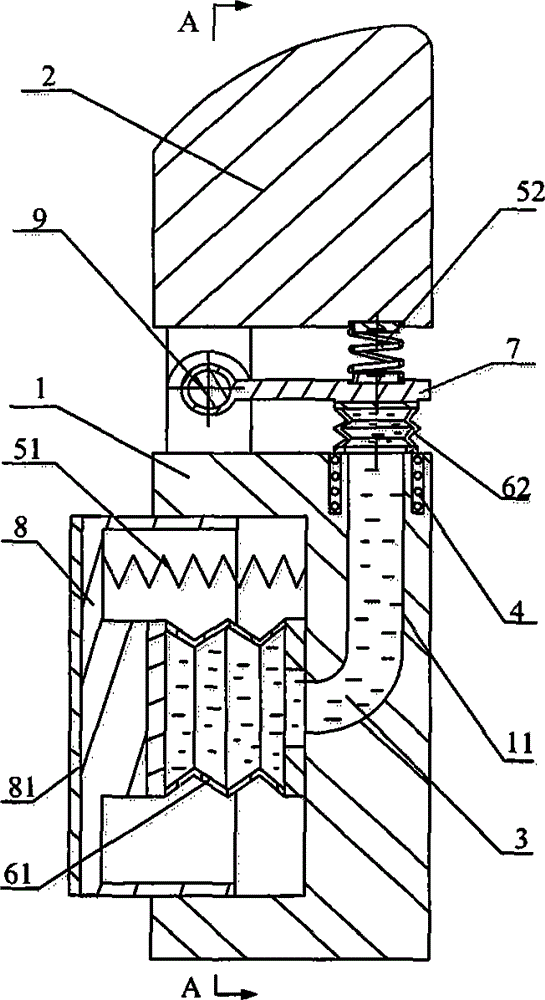
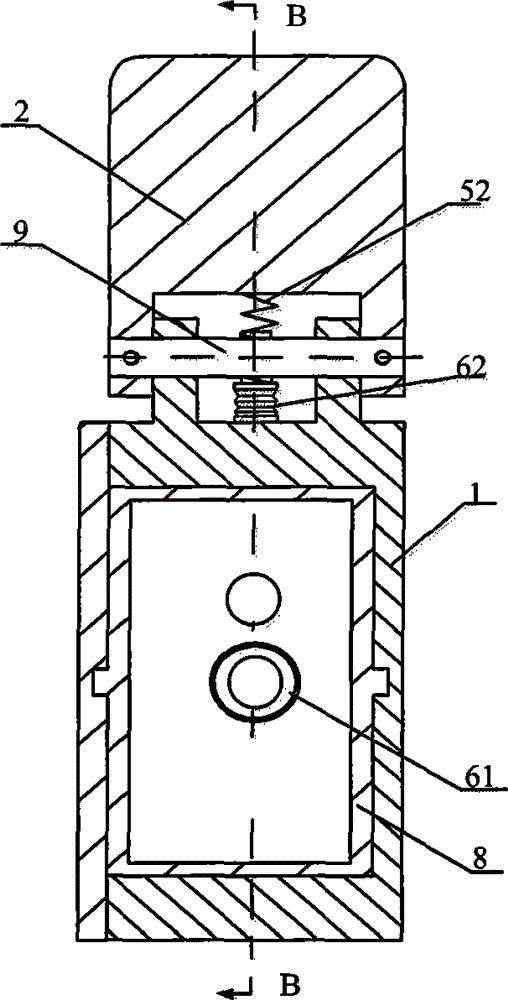
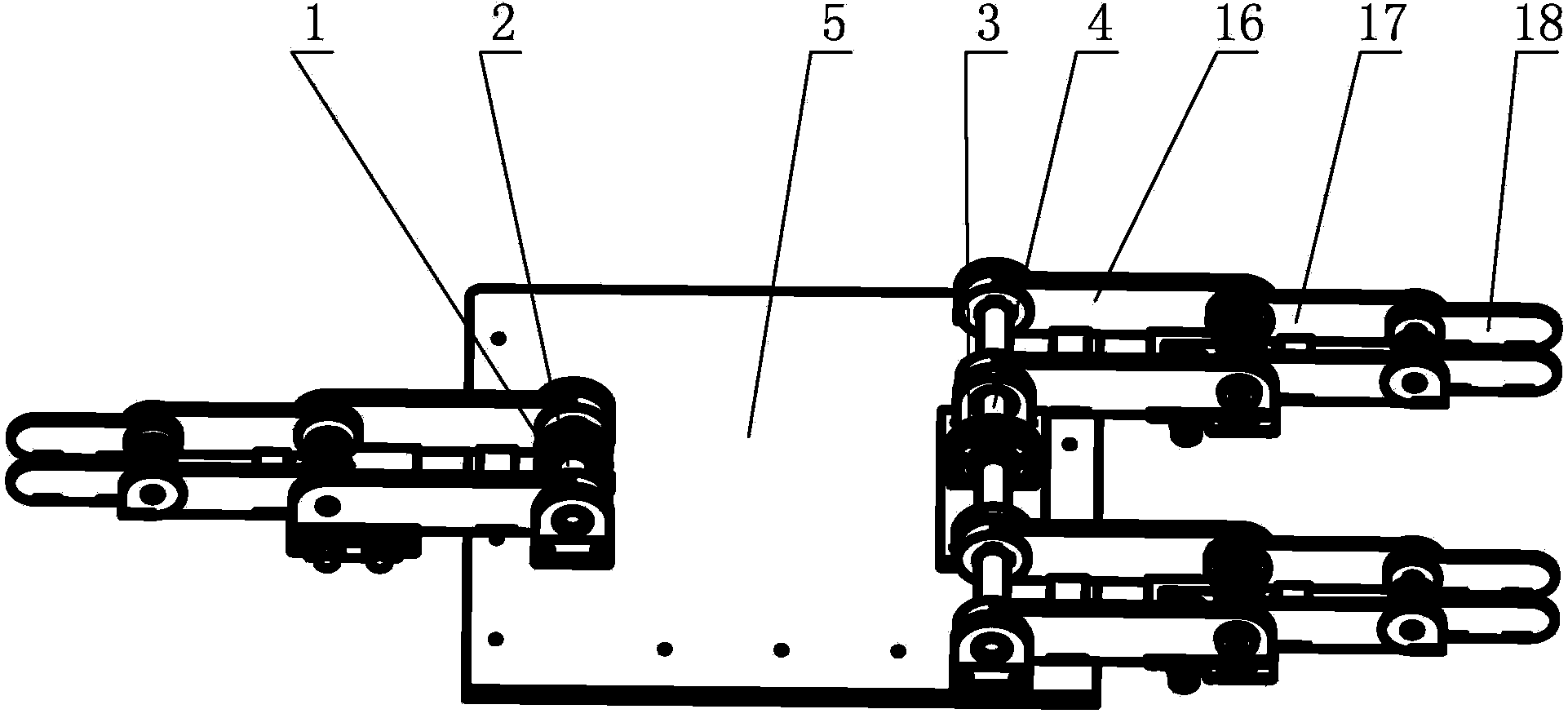
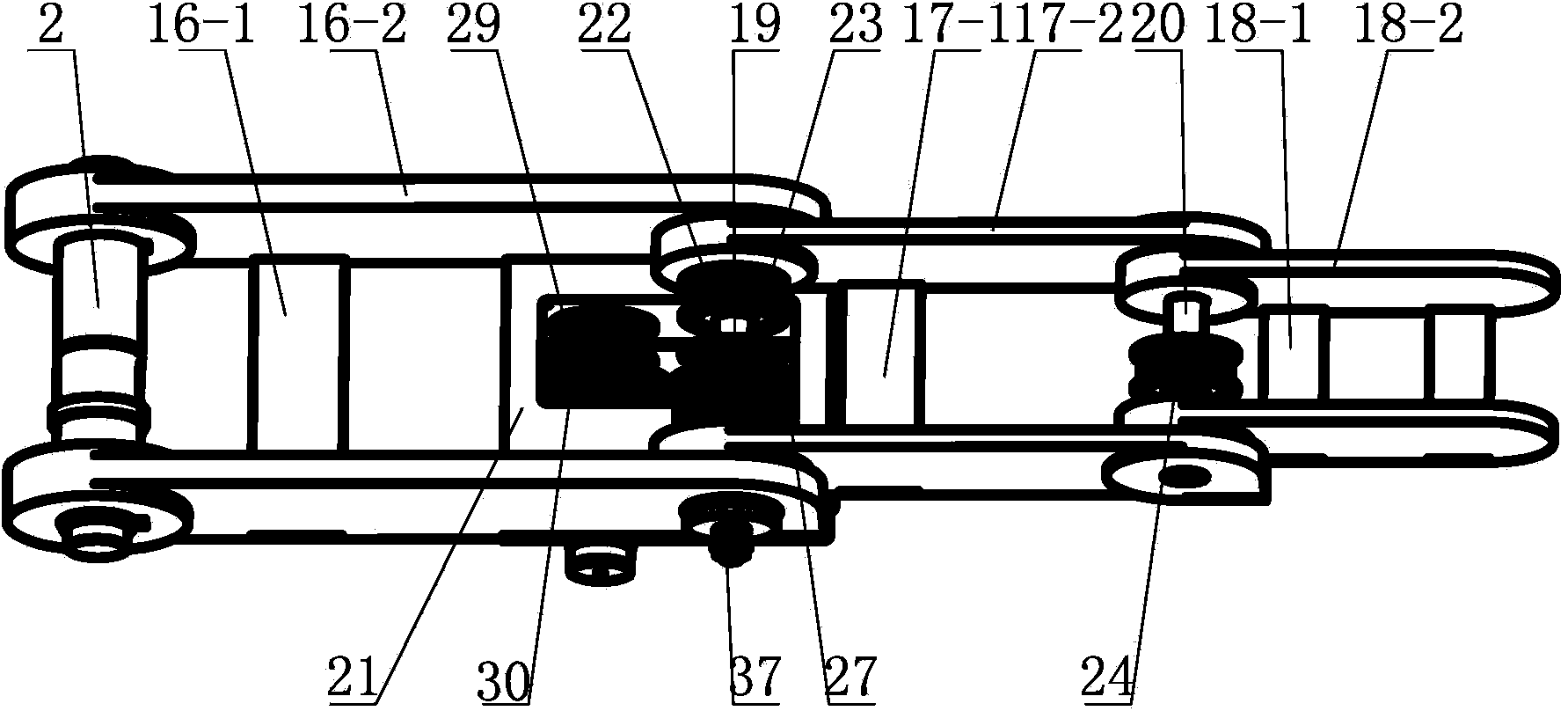
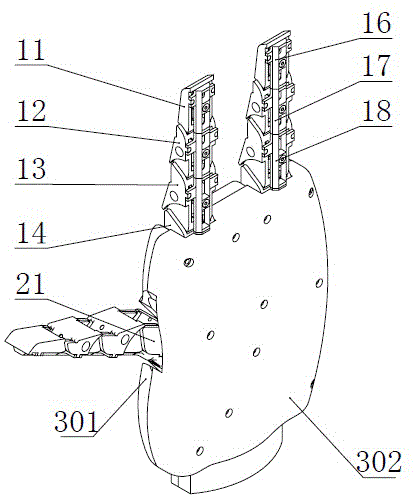
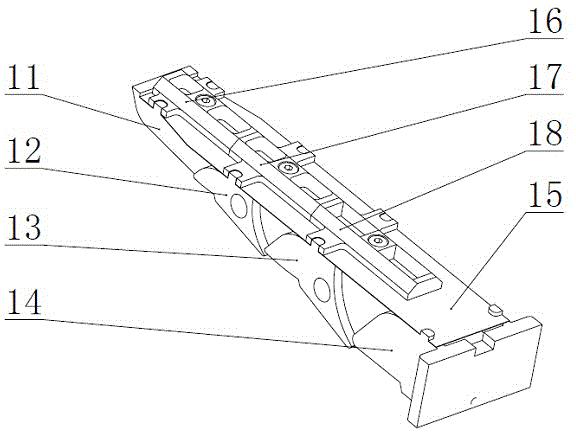
The invention provides a capture spin elimination mechanism suitable for spin space fragments. The capture spin elimination mechanism comprises a rotating part and a fixed part. Multiple finger mechanisms with underactuation mechanism forms are arranged on a shell at the front end of the rotating part, each finger mechanism is provided with multiple rotating joints, each joint is provided with a torsion spring, each finger is dragged by one rope to form an underactuation mechanism, bending actions can be completed, and adaptive capacity is achieved for contact shapes. The torsion spring of each joint resists traction force of the corresponding rope, and unbending power is provided for the fingers. All the fingers are arranged pairwise in an intersecting mode, and objects of different sizes can be held when the fingers close up. The ropes of all the fingers are fixed to a sliding block, and linkage can be achieved. The sliding block is located in the rotating part, can do translational motion relative to the rotating part along the rotating axis, but cannot rotate relative to the rotating part. The sliding block is driven by a lead screw-nut mechanism, and the sliding block is connected with a nut through a rotating pair.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
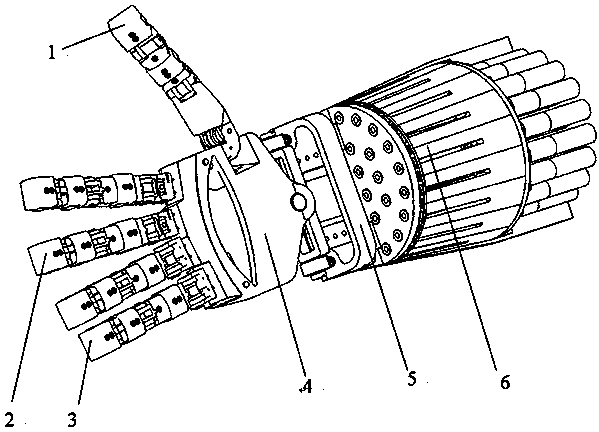
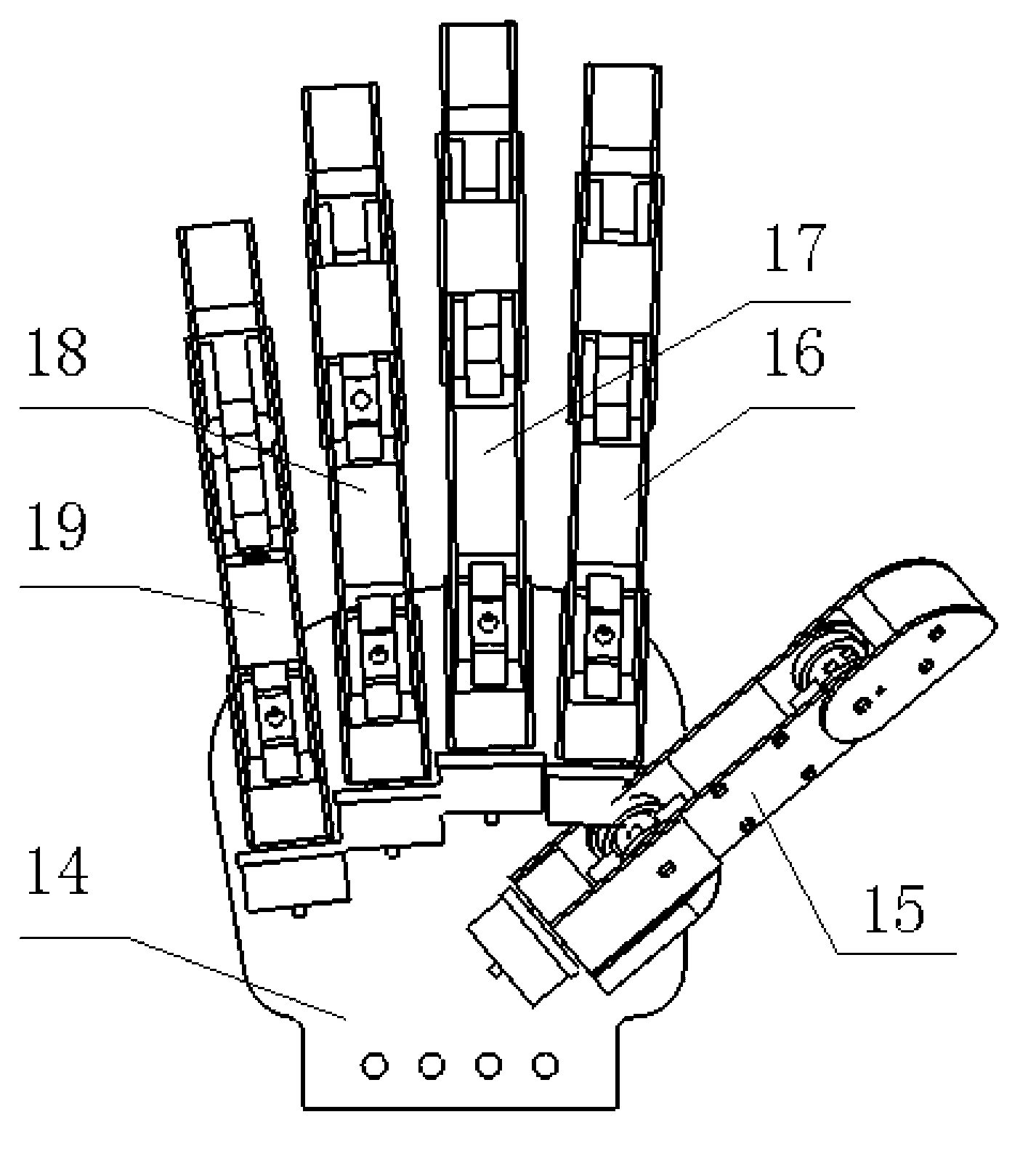
Hand-shaped manipulator
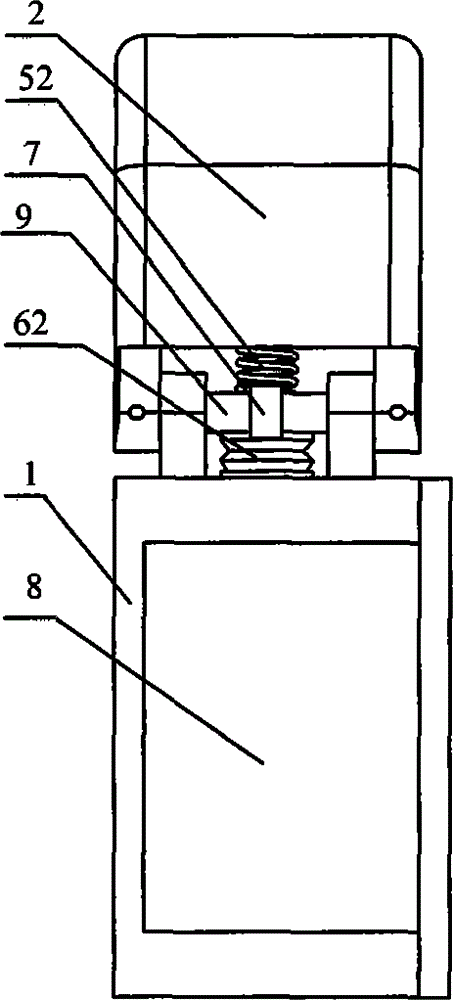
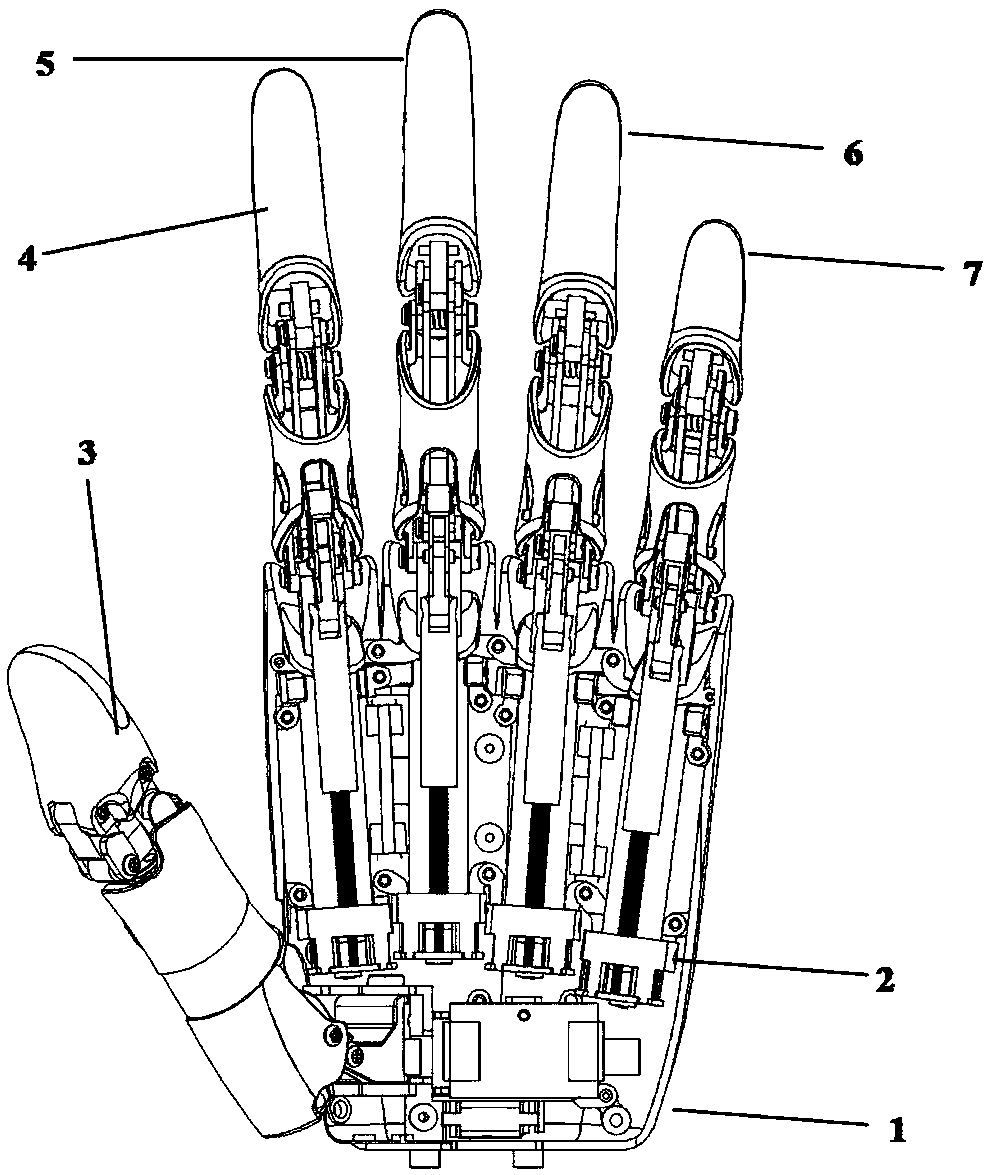
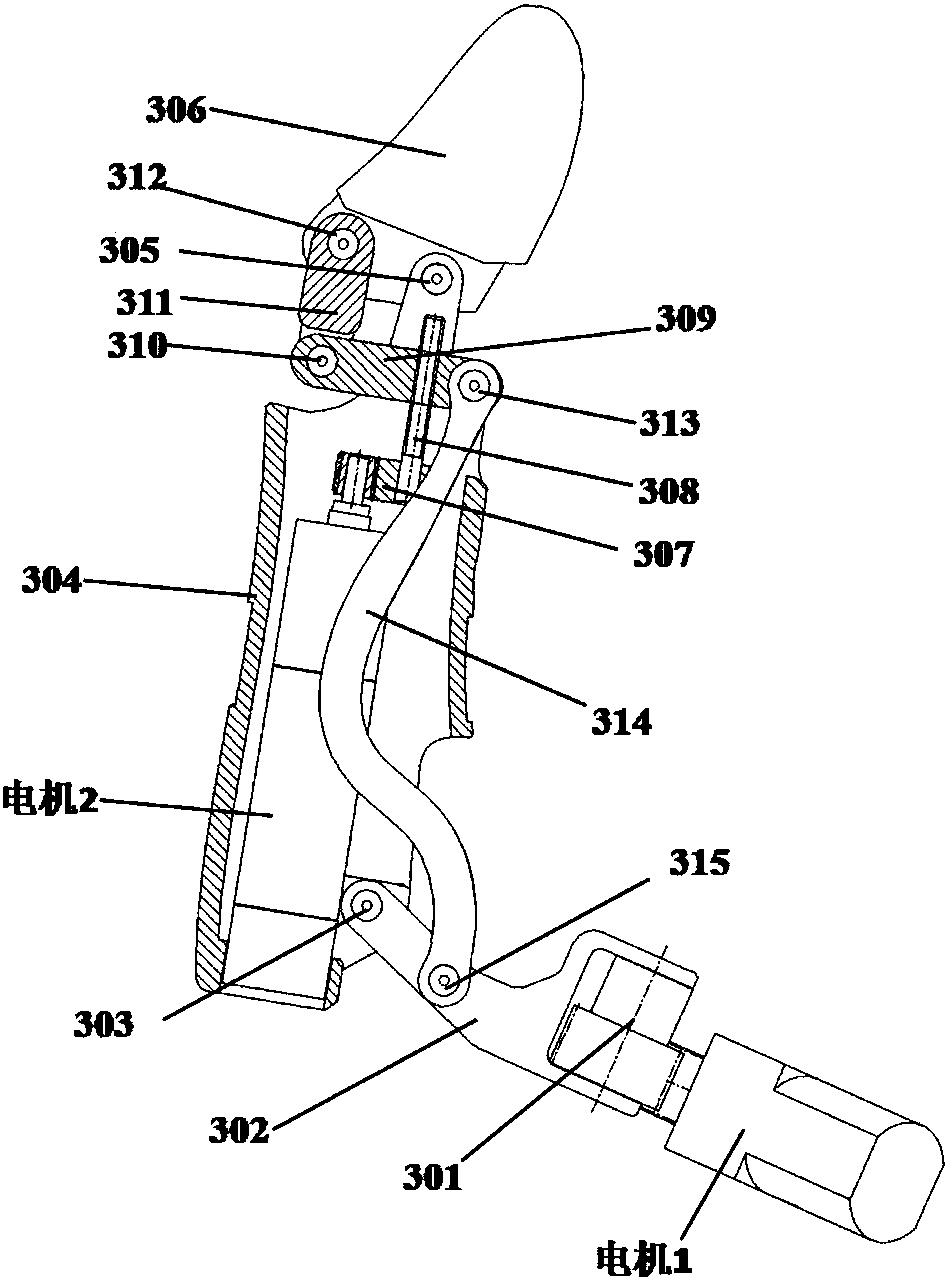
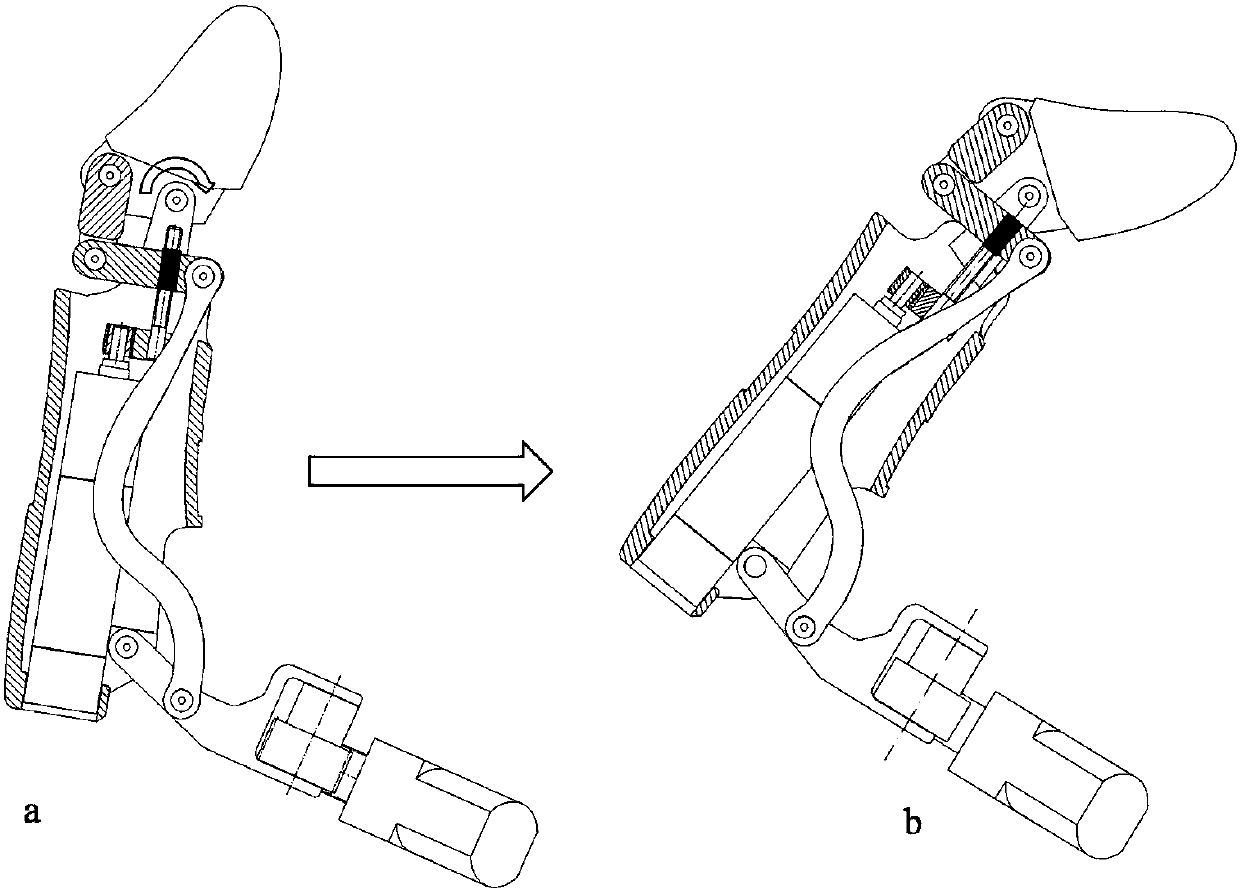
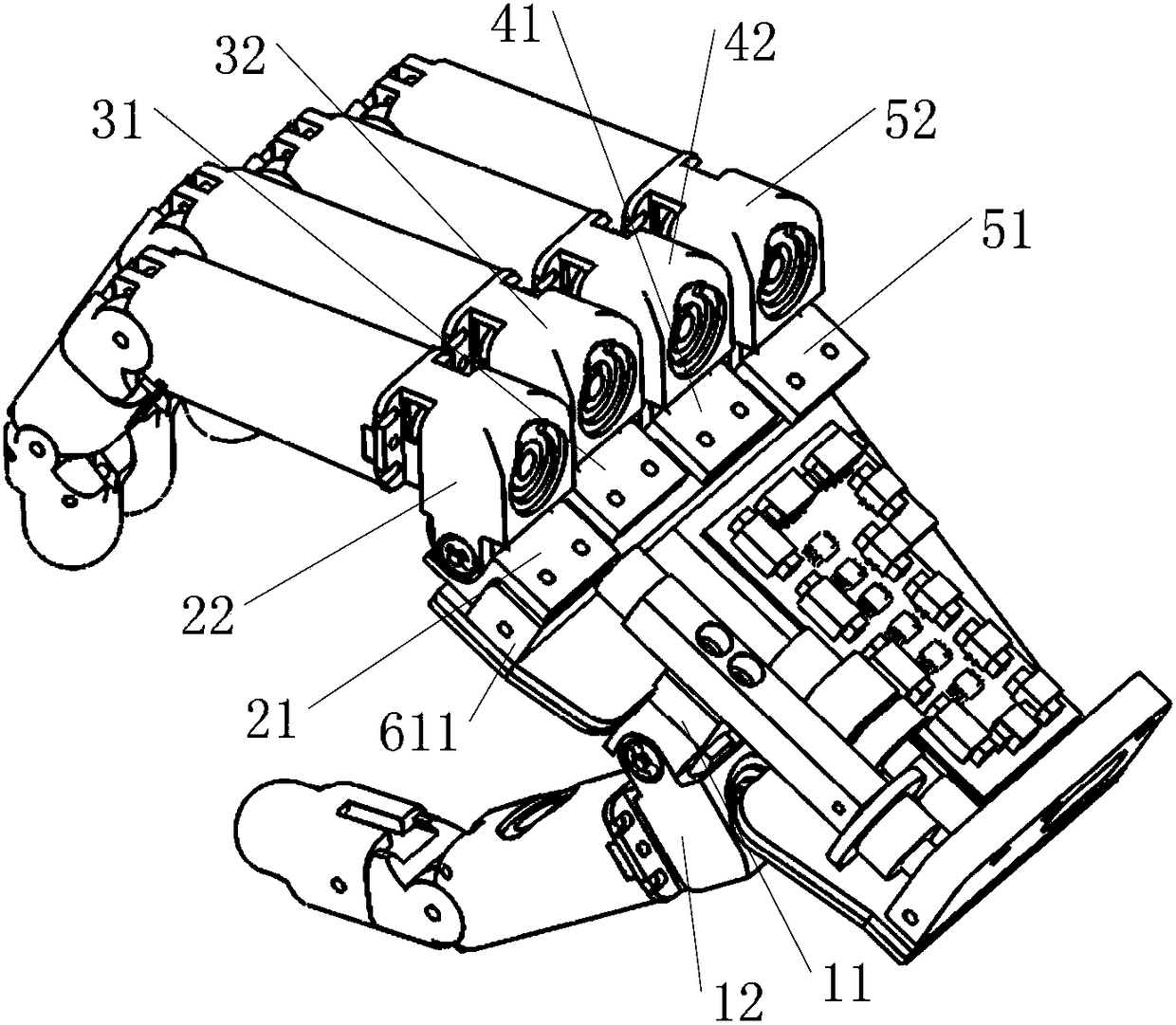
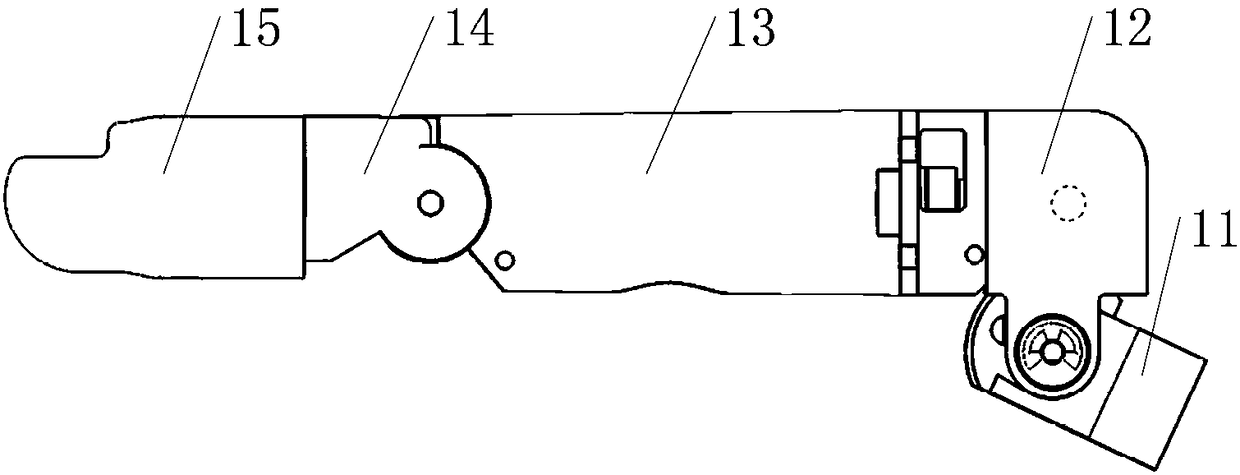
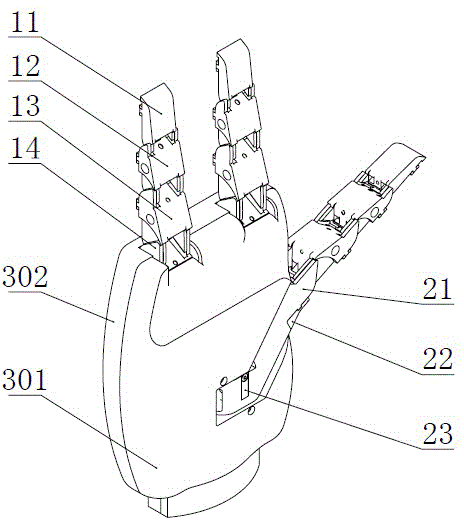
The invention discloses a hand-shaped manipulator which mainly comprises a hand, a wrist and a front arm, wherein the hand comprises a palm, A-type fingers, B-type fingers and a thumb. Grabbing is achieved through the A-type fingers and the thumb, and the B-type fingers are auxiliary fingers. Each A-type middle phalanx, each A-type proximal phalanx and each A-type base phalanx are controlled independently and respectively through four tendon ropes. Due to the fact that the B-type fingers have auxiliary functions, an underactuation control mode is adopted, and active control is performed on each middle phalanx through two tendon ropes. A thumb distal phalanx, a thumb middle phalanx and a thumb proximal phalanx are controlled independently through five tendon ropes. A wrist joint is matched with a spherical hinge through a cardan joint, and pitching and sideway moving can be achieved by means of telescopic movement of a pull rod. Parts of the manipulator can be manufactured easily, cost is low, and the manipulator has multiple functions achieved by a hand of a human, such as capturing, holding, grabbing, switch turning and the like. The hand-shaped manipulator is small in size, light in weight, flexible and accurate in operation, low in cost and wide in application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Magnetorheological fluid indirect-adaptive underactuation robot finger device
The invention relates to a magnetorheological fluid indirect-adaptive underactuation robot finger device, which belongs to the technical field of robot hands and comprises two finger sections, magnetorheological fluid, a coil, two spring parts, two flexible parts, a shifting block, a driving slider and a joint shaft. The device realizes the passive adaptive bending and grasping force locking keeping functions of the finger, and can grasp an object placed on a supporting surface. The device utilizes the reactive force of the object to drive the second finger section of the finger to turn around the joint shaft; moreover, by utilizing the solidification characteristic of the magnetorheological fluid in a magnetic field, after the reactive force of the object disappears, the device can still keep the object-holding curved structure of the finger; the device utilizes the spring parts to store and keep deformation elasticity which is generated when the object is squeezed in the beginning, consequently, grasping force which is continuously applied to the object by the second finger section is generated and kept, and a good object grasping effect is realized. The device is structurally simple, small and light, is easy to control, and is low in design, manufacturing, assembly and maintenance costs.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Underactuation human-simulation dexterous hand driven and controlled through micro-motor
The invention discloses an underactuation human-simulation dexterous hand driven and controlled through a micro-motor. The underactuation human-simulation dexterous hand comprises a palm and five fingers, namely the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger, the ring finger and the little finger. The boundary dimension proportion of the underactuation human-simulation dexterous hand refers to a hand of a Chinese woman. The five fingers are independent of one another. The underactuation human-simulation dexterous hand has six driving freedom degrees, namely the freedom degree of rolling of a base joint of the thumb and the freedom degree of pitching of a middle joint of the thumb and the freedom degrees of pitching of base joints of other four fingers, in all. According to the relative angle, about 10-30 degrees, between a middle finger segment and a remote finger segment of a human hand when a frequently-used object is grabbed, the relative angle between a middle finger segment and aremote finger segment of the dexterous hand is fixed, and the design of a remote joint driven mechanism is simplified. The dexterous hand is small and exquisite in appearance and compact and simple instructure and has more than ten types of different grabbing gestures, and the effective and precise grabbing task can be finished.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHEQIAN APPL TECH CO LTD
Transformable three-finger dexterous hand
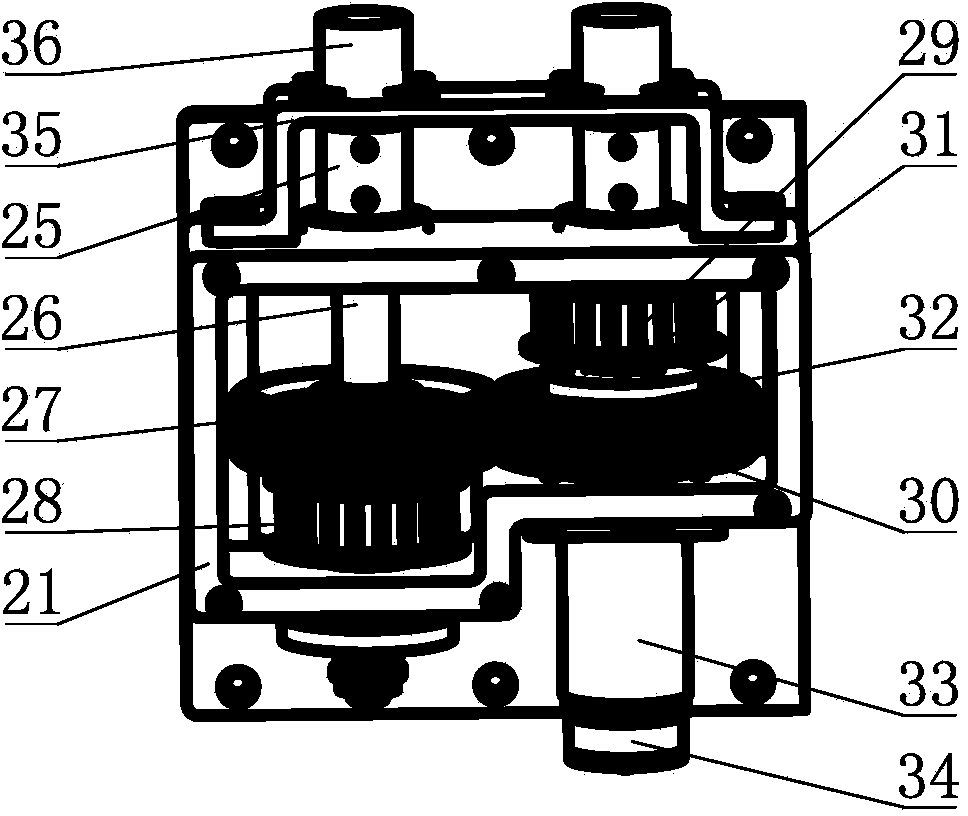
The invention discloses a transformable three-finger dexterous hand. The transformable three-finger dexterous hand comprises a deformation mechanism, underactuation fingers and a controller, the underactuation fingers are fixedly connected with the deformation mechanism, the controller is electrically connected with the deformation mechanism and the underactuation fingers, a plurality of gear setsare arranged in the deformation mechanism and drive the underactuation fingers to move, the underactuation fingers are provided with double parallelogram mechanisms for connecting finger tips with finger bases. The deformation mechanism composed of the multiple gear sets, the underactuation fingers connected through the double parallelogram mechanisms and the controller, the three-finger dexterous hand having multiple degrees of freedom, being simple to control and transformable, and being suitable for multiple grabbing pieces is formed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Underactuated lightweight human-simulated five-finger dexterous hand
ActiveCN108214520ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costGripping headsUnderactuationLittle finger
The invention belongs to the technical field of bionic robots, and particularly relates to an underactuated lightweight human-simulated five-finger dexterous hand. The underactuated lightweight human-simulated five-finger dexterous hand comprises a palm, five fingers, five finger bending and extension driving mechanisms, five rope transmission mechanisms and a thumb rotation driving mechanism, wherein the five fingers include a thumb, an index finger, a middle finger, a ring finger and a little finger which are installed on the palm in sequence by virtue of fixed seats; the five finger bendingand extension driving mechanisms are respectively installed on the five fixed seats and are respectively used for supplying power to the bending and extension of the five fingers; the five rope driving mechanisms are respectively installed in the five fingers and are connected with the corresponding finger bending and extension driving mechanisms, and the fingers are driven to bent and extend bythe finger bending and extension driving mechanisms through the rope driving mechanisms so as to form underactuation; and the thumb rotation driving mechanism is installed in the palm and is used fordriving the thumb to rotate. The underactuated lightweight human-simulated five-finger dexterous hand has the characteristics of the simple and compact structure, light weight, low cost, modular design, easiness in removal and replacement, high integration level, multiple degrees of freedom, small size, flexibility, good stability and the like, and the size of the underactuated lightweight human-simulated five-finger dexterous hand is similar to that of a hand.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-finger flexible hand performing device of robot
The invention discloses a three-finger flexible hand performing device of a robot. The three-finger anthropomorphic manipulator is of a tendon transmission structure on the basis of the underactuation principle, and is simple to control and small in cost; shape of an object can be adapted during grasping; the grasping control is achieved by the double-closed-loop principle; an outer loop is an angle loop, and while an inner loop is a pressure loop. The manipulator can be applied to the fields of home service, agricultural production and spatial detection, and can replace or assist human to finish the work; the anthropomorphic appearance design enables a certain of expression function, and some gestures can be performed to show some simple sign languages, so that the device can be applied to the field of assisting the disabled; humanized and multifunctional artificial hands can be provided to the disabled.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Flexible underactuation finger based on fin ray type structure
The invention discloses a flexible underactuation finger based on a fin ray type structure. The finger comprises a finger rack, a parallel transmission chain, a self-adaptation transmission chain, a drive component, a rigid knuckle and a flexible fin ray knuckle; the fin ray knuckle is a tail end knuckle of the finger, and the parallel transmission chain, the self-adaptation transmission chain andthe drive component are arranged on the finger rack, the rigid knuckle is in movable connection with the parallel transmission chain and the self-adaptation transmission chain at the same time, the efin ray knuckle is connected with the rigid knuckle through the self-adaptation transmission chain, the self-adaptation transmission chain is connected to the drive component, and is driven by the drive component to move so as to drive the parallel transmission chain to move and promote the rigid knuckle and the fin ray knuckle to generate adaptation motion, and meanwhile, the fin ray knuckle generates the adaptive deforming under the effect of the self-adaptation transmission chain.
Owner:广州青装技术合伙企业(有限合伙)
Self-adaption robot finger device of composite flexible drive flat clamp
InactiveCN105643647ALarge grabbing rangeIncrease in sizeJointsGripping headsUnderactuationDrive wheel
The invention discloses a self-adaption robot finger device of a composite flexible drive flat clamp, and belongs to the technical field of robot hands. The self-adaption robot finger device comprises a base, two finger segments, two joint shafts, a driver, two flexible drive parts, four drive wheels, a protruding block shifting disc, two spring parts, a limiting protruding block and the like. The device utilizes the driver, a closed-loop flexible part drive mechanism, an opened-loop flexible part drive mechanism, the two spring parts, the protruding block shifting disc, the limiting protruding block and the like to comprehensively achieve functions of parallel clamping and self-adaption grabbing; according to the difference of shapes and positions of target objects, the second finger segment can be moved horizontally to nip and hold the objects or can be expanded outwards for supporting, and the first finger segment and the second finger segment can be sequentially rotated to wrap the objects in different shapes and with different sizes; and the device is large in grabbing range; the underactuation manner is adopted, the driver is used for driving two joints, and a complex sensing and control system is not needed; and the device is compact in structure, small in size, low in manufacturing and maintaining cost and suitable for the robot hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
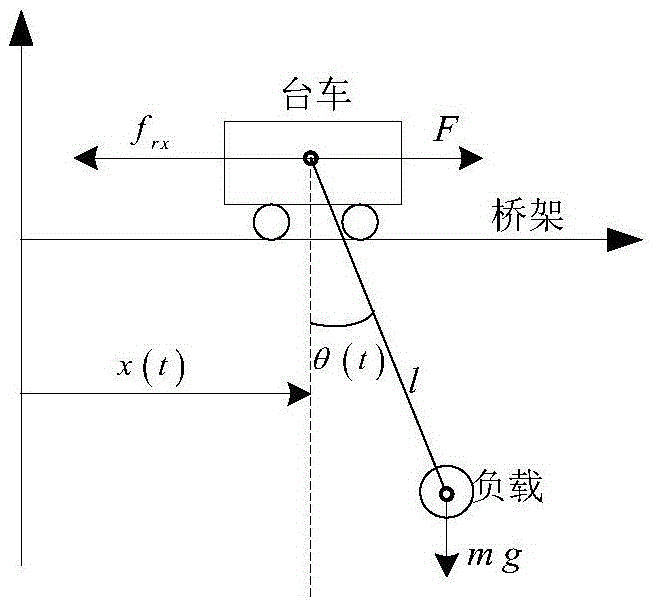
Bridge crane error tracker with initial load swing angle and trolley displacement and method
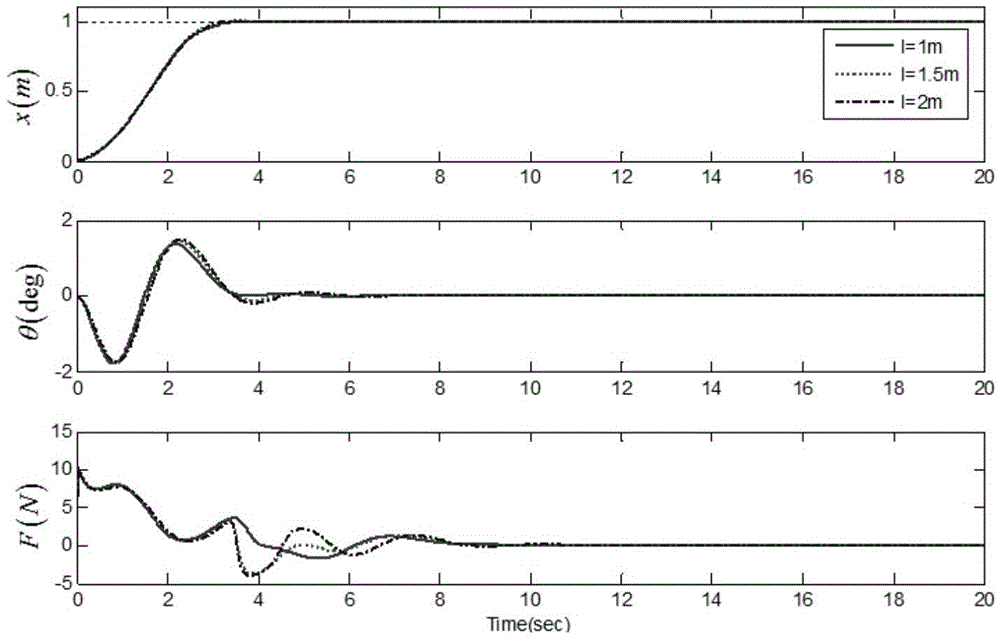
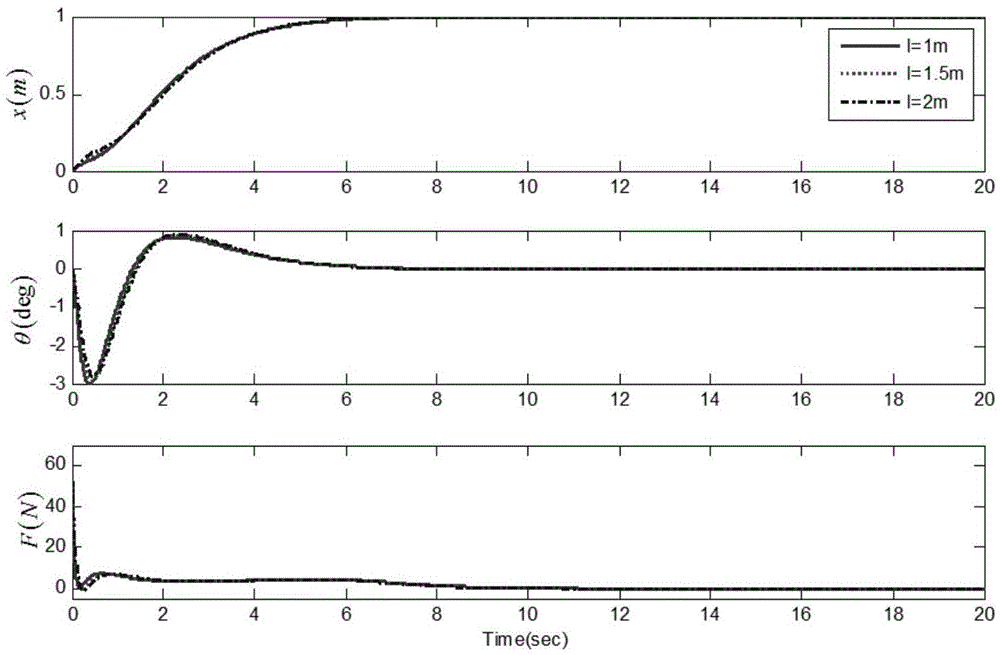
ActiveCN105600683AReliable controlShow validityLoad-engaging elementsUnderactuationLiapunov function
The invention discloses a bridge crane error tracker with an initial load swing angle and trolley displacement and a method. According to the method, an underactuation bridge crane system initial dynamical model is established; an expected trolley error trace and an expected swing angle error trace are given; error tracking signals for trolley positioning and load swinging are determined; an underactuation bridge crane system error tracking dynamical model is obtained; a target system model enabling a Lyapunov function to be stable is established, and the bridge crane error tracker with the initial load swing angle and trolley displacement is obtained according to the target system model and the underactuation bridge crane system error tracking dynamical model. The bridge crane error tracker has the advantages that under the condition that the initial load swing angle and initial trolley displacement which are zero in a conventional control method are expanded, the initial swing angle of a load and the initial displacement of a trolley are allowed to be of any values.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Underactuation self-adaptive capturing device capable of being folded and unfolded
ActiveCN103934829ASame structureImprove interchangeabilityGripping headsToolsUnderactuationGear wheel
The invention relates to a capturing device, in particular to an underactuation self-adaptive capturing device capable of being folded and unfolded. The underactuation self-adaptive capturing device capable of being folded and unfolded aims to solve the problems that an existing space robot is high in weight, complex in structure and poor in reliability and is provided with a great number of driving motors. According to the underactuation self-adaptive capturing device capable of being folded and unfolded, a single-finger root joint shaft is arranged on the upper surface of one end of a substrate, a two-finger root shared joint shaft is arranged on the upper surface of the other end of the substrate, a driving assembly is arranged on the lower surface of the substrate, a first transmission shaft is arranged on the lower surface of the substrate through a first bearing block, the single-finger root joint shaft is sleeved with a first synchronous belt wheel, the first transmission shaft is sleeved with a second synchronous belt wheel, the first synchronous belt wheel is connected with the second synchronous belt wheel through a synchronous belt, the middle of the two-finger root shared joint shaft is sleeved with a first gear, and the first gear is connected with the driving assembly. The underactuation self-adaptive capturing device capable of being folded and unfolded is used for the aerospace field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device
InactiveCN106335074ASimple grasping and pinching movementsSimple structureGripping headsUnderactuationClosed loop feedback
The invention discloses a robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device. The robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device comprises a palm unit and five fingers; each finger comprises four knuckles which are connected through a spring piece, finger cover plates, screws and nuts; and a palm comprises a bottom plate and a cover plate and is used for fixing a motor and the fingers. According to the robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device, simple grabbing and nipping actions can be achieved through a closed loop feedback system composed of a force sensor and an angle sensor. The robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device has the characteristics that every single finger is controlled in a tendon transmission mode through one motor based on the underactuation principle, so that the fingers can wrap an object in a self-adaptive mode when grabbing different objects. The robot five-finger dexterous hand executive device has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in grabbing control difficulty and high in reliability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
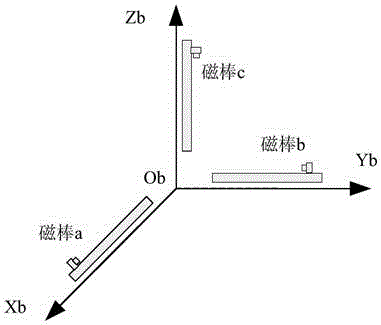
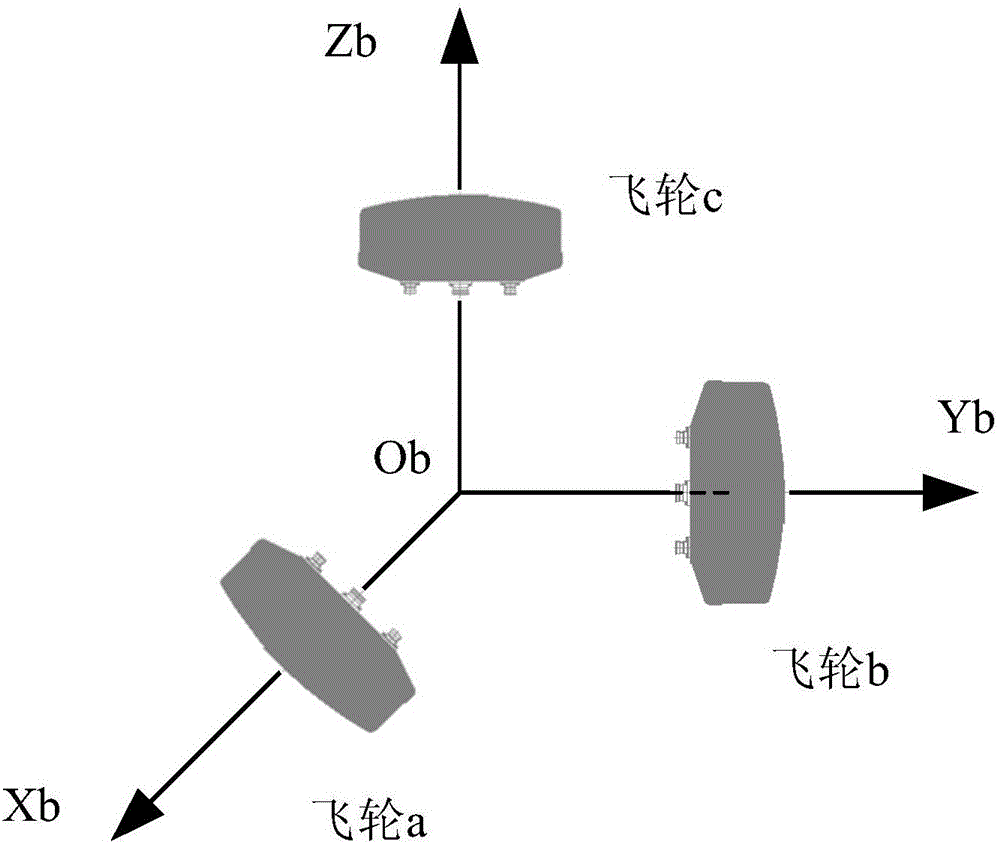
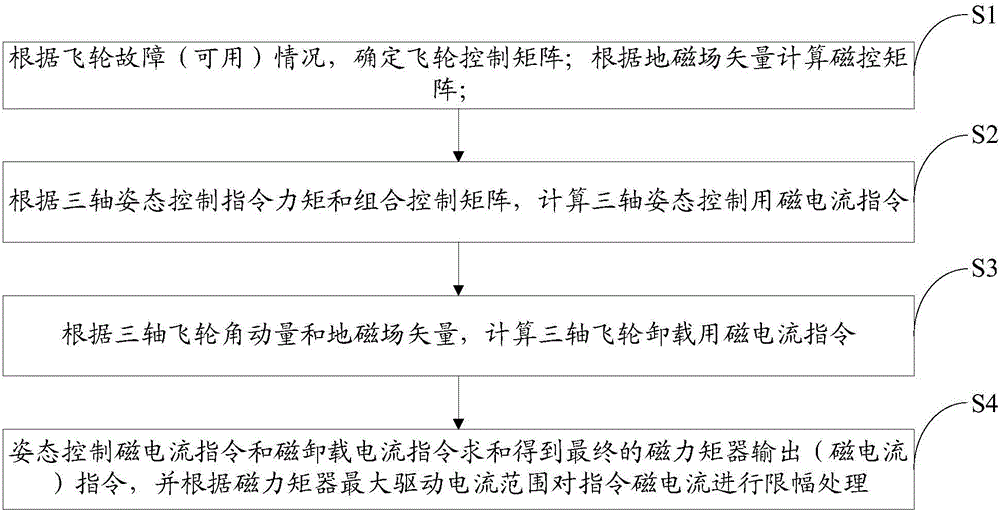
Method for realizing satellite three-axis attitude control by combining available flywheels with magnetic torquer in case of flywheel underactuation
ActiveCN106542120ADoes not affect attitude controlImprove reliabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsUnderactuationMagnetic tension force
A Method for realizing satellite three-axis attitude control by combining available flywheels with a magnetic torquer in case of flywheel underactuation comprises the following steps: (1) determining a magnetic control matrix Gamma(b) according to a geomagnetic field intensity vector B measured by a magnetometer, and determining a flywheel control matrix Kw according to the actual availability conditions of flywheels; (2) calculating a magnetic electric current command Izk=Kic*Mzk for three-axis attitude control; (3) calculating a magnetic electric current command Ixz=Kic*Mxz for three-axis magnetic unloading; and (4) calculating a magnetic torquer command Ick=Izk+Ixz, wherein when the magnetic torquer performs attitude control according to the magnetic torquer command, the available counteractive flywheels continue to perform attitude control based on a command torque Tc. According to the method, when only any two or even one flywheel is available in a system, the two or one available flywheel is combined with the three-axis magnetic torquer to realize high-precision satellite three-axis attitude control. The method is suitable for long-term earth pointing control or long-term sun pointing control and is also suitable for wide-angle maneuvering control of any attitude of a satellite.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator
InactiveCN104802180ASimple grasping and pinching movementsSimple structureJointsGripping headsUnderactuationClosed loop feedback
The invention discloses an underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator. The underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator comprises a palm, two fingers and a thumb; each finger comprises four joints which are connected through a spring plate, a finger cover plate and screws; the palm comprises a bottom plate and a cover plate and is used for fixing a motor and the fingers. According to the underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator, a closed-loop feedback system composed of a force sensor and an angle sensor is used to achieve simple grasping and nipping action. The underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator is characterized in that single finger is controlled through one motor by a tendon transmission manner on the basis of the underactuation principle, so that the finger can adapt to hold an object while grasping different objects; the underactuation type anthropopathic three-finger manipulator has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in difficulty at grasping control, and high in reliability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
High-bearing universal joint, mechanical arm joint and flexible mechanical arm
ActiveCN108177159AGuaranteed contact areaSolve the problem of underdriveProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsUnderactuationUniversal joint
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, and provides a high-bearing universal joint, a mechanical arm joint and a flexible mechanical arm. A second slide ball comprises a first cavitywith the inner surface as a spherical surface; a first slide ball is rotationally arranged in the first cavity, and can slide along the inner surface of the first cavity; a ball base comprises a second cavity with the inner surface as a spherical surface; and a second slide ball is rotationally arranged in the second cavity, and can slide along the inner surface of the second cavity, so that the contact area between the first slide ball and the second slide ball and the contact area between the second slide ball and the ball base are guaranteed, and the load capacity is improved. A first limiting structure and a second limiting structure are provided for limiting rotation of the first slide ball along the latitude line and rotation of the second slide ball along the latitude line, so thatthe problem of underactuation of a general ball hinge structure is solved under the precondition of realizing universal rotation through combination of a motion between the first slide ball and the second slide ball and a motion between the second slide ball and the ball base.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Underactuation crane operating whole process active-disturbance-rejection control method of single parameter adjustment
ActiveCN109911773AImprove work efficiencyAccurately control working timeLoad-engaging elementsUnderactuationControl system
The invention discloses an underactuation crane operating whole process active-disturbance-rejection control method of single parameter adjustment. The underactuation crane operation whole process active-disturbance-rejection control method is characterized in that according to starting and target locations of a trolley, safety constraint conditions such as the speed, acceleration, and operating environment of the trolley are considered, an ideal operating track, with efficiency priority, of the trolley is generated, and after compared with the actual location of the trolley, an error feedbackcontrol law of trolley movement is constructed; an expanding state observer is designed according to a crane load oscillation state equation, an error feedback control law suppressing load oscillation is constructed, and then the trolley operating track and a load oscillation active-disturbance-rejection controller which are independent of system model parameters and can effectively suppress disturbance are formed; and Hurwitz stable matrix eigenvalues are used for generating relation with control system gains, thus fussy control system parameters are adjusted and converted to single parameter adjustment easy to implement, a crane can be operated according to the set ideal track in the whole process under the uncertainty model parameters and external disturbance, and swing angles are madeas small as possible.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Underactuation tail end tool of apple picking robot
The invention discloses an underactuation tail end tool of an apple picking robot. The underactuation tail end tool of the apple picking robot comprises a fruit posture self-adaption mechanism and a fruit separating and cutting mechanism, wherein the fruit separating and cutting mechanism is placed on the fruit posture self-adaption mechanism and the fruit posture self-adaption mechanism can be installed on a positioning mechanism of the apple picking robot. The fruit posture self-adaption mechanism of the tail end tool can adjust the fruit separating and cutting mechanism relative to the growing postures of fruit. The entirety of the fruit separating and cutting mechanism of the tail end tool is in an underactuation form, and the same set of action parts is adopted to achieve the order actions of fruit separating and fruit cutting in sequence. The underactuation tail end tool of the apple picking robot can be applied to the robot picking field, so that mechanical picking operation of spherical fruit like apples can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Connecting-rod underactuation bionics finger capable of self-adaptively grabbing
The invention provides a connecting-rod underactuation bionics finger capable of self-adaptively grabbing. The connecting-rod underactuation bionics finger comprises a first finger section, a second finger section, a small connecting rod and a crank connecting rod and further comprises a triggering actuating component, the triggering actuating component comprises a first plane, a first actuating portion and a second actuating portion, the first plane makes contact with an object to be grabbed, the first actuating portion is connected with the second finger section through an elastic mechanism,so that the triggering actuating component is made to be capable of performing reciprocating movements relative to the second finger section, and the second actuating portion is operably connected with the crank connecting rod, so that a crank connecting-rod mechanism is made to be driven by the triggering actuating component to perform pivot rotating movements relative to the second finger section. The connecting-rod underactuation bionics finger capable of self-adaptively grabbing is simple in a transmission scheme, smooth and steady in grabbing and high in precision, the structural volumeof the mechanism is small, and the connecting-rod underactuation bionics finger capable of self-adaptively grabbing is suitable for the design of the bionics finger of a humanoid robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Encircling swallowing type navel orange picking actuator
ActiveCN110495301ASolve technical problemsRenewable energy machinesPicking devicesUnderactuationEngineering
The invention relates to an encircling swallowing type navel orange picking actuator, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural picking robots. The whole design concept is based on the bionics principle, motors are adopted for driving, picking and collecting are integrated through the force transmission between a plurality of pairs of bevel gears, and the underactuation of peduncle cutting, fixing and collecting driving is realized; the whole structure is symmetrically arranged, an encircling mode is adopted for fixing and limiting navel oranges to be picked, a swallowing mode is adopted for colleting picked navel oranges, a collecting net formed by the reasonable combination of elastic ropes and non-elastic ropes is used for ensuring that the whole actuator has only one continuous collecting channel in the picking process, and it is ensured that navel oranges can be continuously picked and collected. The actuator is novel in collecting mode, high in picking efficiency, simplein structure, convenient to control and high in expansibility and universality and causes less damage to navel oranges; multiple identical collecting units of the actuator can be connected together in series without increasing drives, and the requirement for a larger picking capacity is met.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
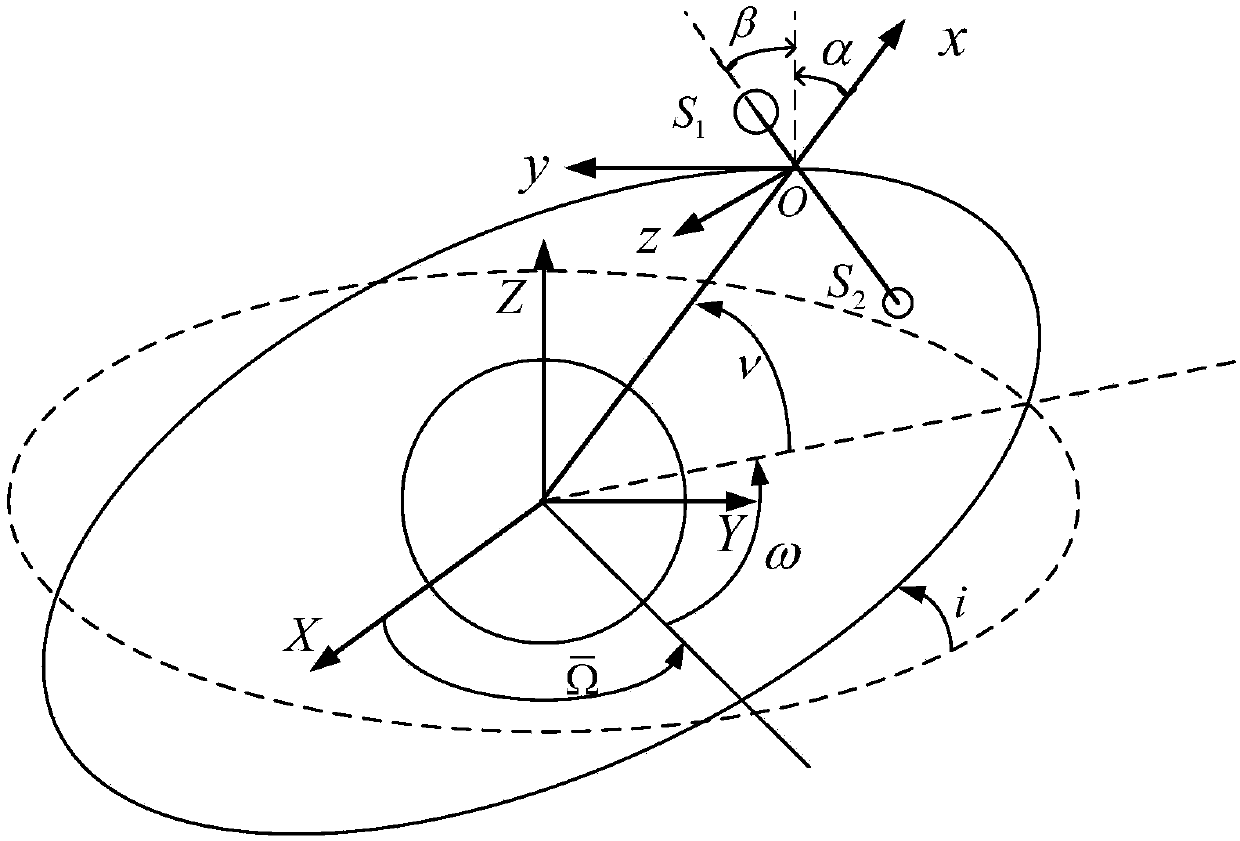
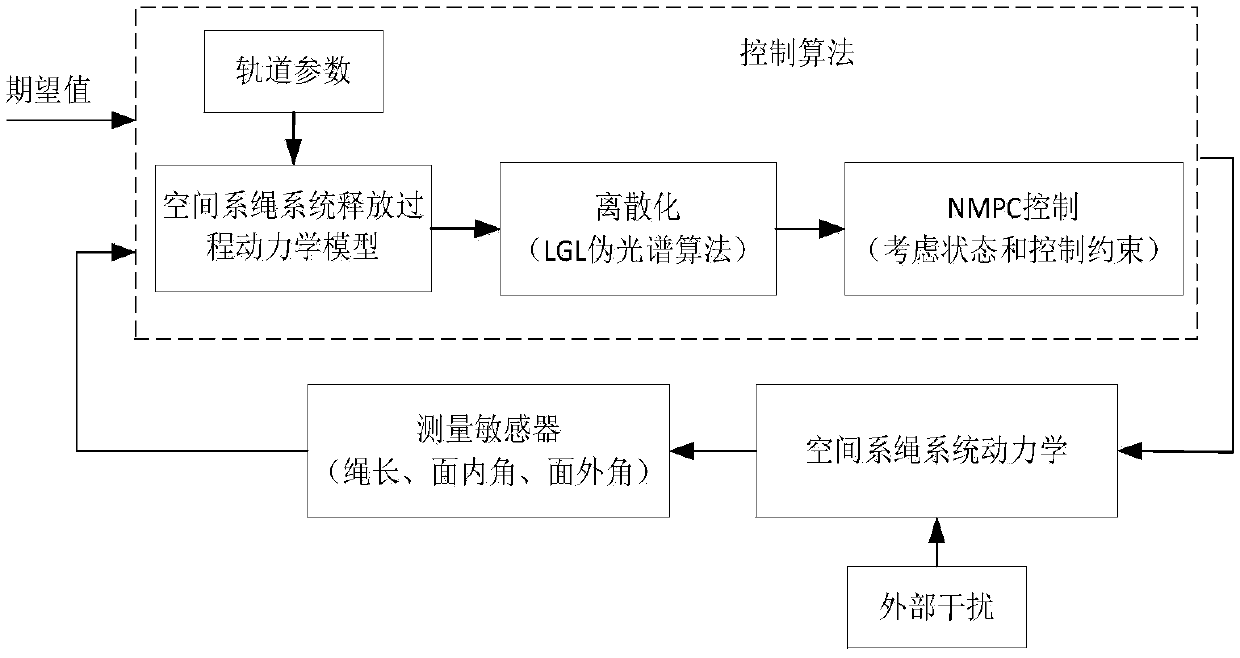
Space tether system unfolding control method based on nonlinear model predictive control
The invention provides a stability control method for unfolding of a three-dimensional space tether system operating in a low earth elliptical orbit in an initial stage. A tether is released to a desired length and the swing of the tether is restrained only by adjusting the limited tether tension without relying on other thrusters. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a two-body spacetether system dynamic model considering tether mass is established; S2, under the conditions such as disturbance, uncertainty, underactuation, restricted tether swing angle and tether tension, basedon a nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) algorithm, a pseudo-spectral algorithm is used for discretizing an original nonlinear model, and an open loop optimal problem in predictive control is transformed into a nonlinear programming problem for solving; and S3, according to the solution of the nonlinear programming problem, the control quantity of the next control period is determined to form the closed-loop control. Finally, the three-dimensional space tether system operating in the low earth elliptical orbit is stably released and unfolded in the initial stage.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Humanoid hand in underactuation exquisite transmission structure
ActiveCN103009398ACompact structureHigh transfer accuracyJointsGripping headsUnderactuationGear wheel
The invention discloses a humanoid hand in an underactuation exquisite transmission structure. The hand consists of five fingers, the thumb is composed of two joints, and other fingers respectively consist of three joints. The fingers except the thumb mainly consist of crown gears, cylindrical gears, crown gears connecting shaft and other relevant parts, all the joints are tightly connected into a whole, and the rotation of each finger can be realized through one motor: firstly, the first cylindrical gear is driven by a motor, the left crown gear and the right crown gear engaged with the first cylindrical gear rotate in the opposite direction, the finger joint rotation is realized, and meanwhile, the other cylindrical gear engaged with the finger joints is driven to rotate, so the transmission is transmitted to the next finger joint; and the transmission mode of the next two joints is similar to the former transmission mode. The humanoid hand in the exquisite transmission structure has the advantages that the structure is simple and compact, the transmission precision is high, the installation is convenient, the weight is light, the size is small, the required motors are few, and the humanoid hand is suitable for being used as the humanoid hand or being used on a mechanical arm.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Underactuation finger mechanism androdlike fruit and vegetable holding type picking mechanical arm end effector
The invention relates to the field of fruit and vegetable picking, in particular to a picking effector end mechanism used for rodlike fruits and vegetables. The problem that in the picking executing process of rodlike fruits and vegetables, the holding for fruits and vegetables can damage or unstably hold fruits and vegetables is solved. Underactuation fingers have certain motions when making contact with the rodlike fruits and vegetables, the holding intensity and angle can be adjusted according to the shapes of fruits and vegetables, and fruits and vegetables can be held better.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Gear-connecting bar driving parallel-clamping self-adaptive robot finger device
The invention discloses a gear-connecting bar driving parallel-clamping self-adaptive robot finger device and belongs to the technical field of robot hands. The gear-connecting bar driving parallel-clamping self-adaptive robot finger device comprises a base, two finger sections, two joint shafts, a driver, a plurality of gears, a plurality of connecting bars, a protruding block driving plate, a spring part, a limiting protruding block and the like. The device adopts the driver, a gear driving mechanism, a connecting bar driving mechanism, the spring part, the protruding block driving plate, the limiting protruding block and the like, the functions of parallel clamping and self-adaptive grabbing are achieved comprehensively; according to different target object shapes and positions, translational motion of the second finger section can be performed to nip objects or outward expansion of the second finger section is performed to support the objects; the first finger section and the second finger section can also be rotated in sequence to wrap the objects with different shapes and sizes; the device is wide in grabbing range; an underactuation mode is adopted, the driver is used for driving two joints, and a complicated sensing and control system is not needed; and the device is compact in structure, small in size, low in manufacturing and maintaining cost and applicable to the robot hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Parallel flexible component parallel clamping type adaptive robot finger device
A parallel flexible component parallel clamping type adaptive robot finger device belongs to the technical field of robot hands. The parallel flexible component parallel clamping type adaptive robot finger device comprises a chassis, two finger sections, two joint shafts, a driver, two flexible components, four driving wheels with reasonably arranged radii, a lug dial, two spring components and two limit lugs. The device comprehensively realizes parallel clamping and universal grabbing functions. According to different target object shapes and positions, the second finger sections can move in parallel so as to pinch objects, and the first finger sections and the second finger sections can also be sequentially rotated so as to envelop objects in different shapes and sizes. The grabbing range of the device is large. Due to the adoption of an underactuation mode, two joints are driven by utilizing one driver, and complicated sensing and control systems are not required. The device is compact in structure, small in size, low in manufacture and maintenance costs and suitable for robot hands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pneumatic artificial muscle driven bionic arm
ActiveCN107972014AImprove flexibilitySimple structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorFinger flexionUnderactuation
The invention belongs to the technical field of bionic robots, and particularly relates to a pneumatic artificial muscle driven bionic arm. The arm comprises a large arm, an elbow joint, a small arm,a wrist joint, a hand, an elbow joint flexion and extension drive mechanism, a wrist joint flexion and extension drive mechanism, a wrist joint self-rotation drive mechanism and a finger flexion and extension drive mechanism; the elbow joint flexion and extension drive mechanism is arranged in the large arm, and is used for providing power for flexion and extension of the elbow joint, the wrist joint flexion and extension drive mechanism is arranged in the small arm, and is used for providing power for flexion and extension of the wrist joint, and underactuation is formed; the wrist joint self-rotation drive mechanism is arranged in the small arm, and is used for providing power for self rotation of the wrist joint; the finger flexion and extension drive mechanism is arranged in the wristjoint and is used for providing power for flexion and extension of the five fingers. The bionic arm is simple and compact in structure, flexible transmission is adopted, the mass is small, the cost islow, modular design is achieved, detaching and replacing are easy, and the beneficial effects of being high in integration, multiple in freedom degree, small and exquisite, flexible, similar to the arm of the adult, good in stability and the like are achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Four-rod four-wheel linear parallel clamping and self-adaption robot finger device
The invention discloses a four-rod four-wheel linear parallel clamping and self-adaption robot finger device, and belongs to the technical field of robot hands. The device comprises a base, two finger segments, a joint shaft, a motor, a plurality of connecting rods, a plurality of transmission wheels, two transmission parts, a driving moving wheel, a driven moving wheel, a limiting block, two spring parts and the like; through the device, functions of robot finger linear parallel clamping and self-adaptation grabbing can be achieved, the single motor is used for driving the two finger segments, and the underactuation effect is met; according to differences of object shapes and positions, automatic switching between the linear parallel clamping and self-adaptation modes can be achieved; according to the device, the second finger segment can be linearly moved in a parallel manner to clamp objects, good clamping of sheet parts on a worktable can be achieved, after the first finger segment makes contact with the object, the second finger segment can be automatically rotated to make contact with the object, and the holding effect with the large force can be obtained; the device can be automatically suitable for grabbing of the objects in the different shapes and with different sizes, the grabbing range is large, and stability and reliability are achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
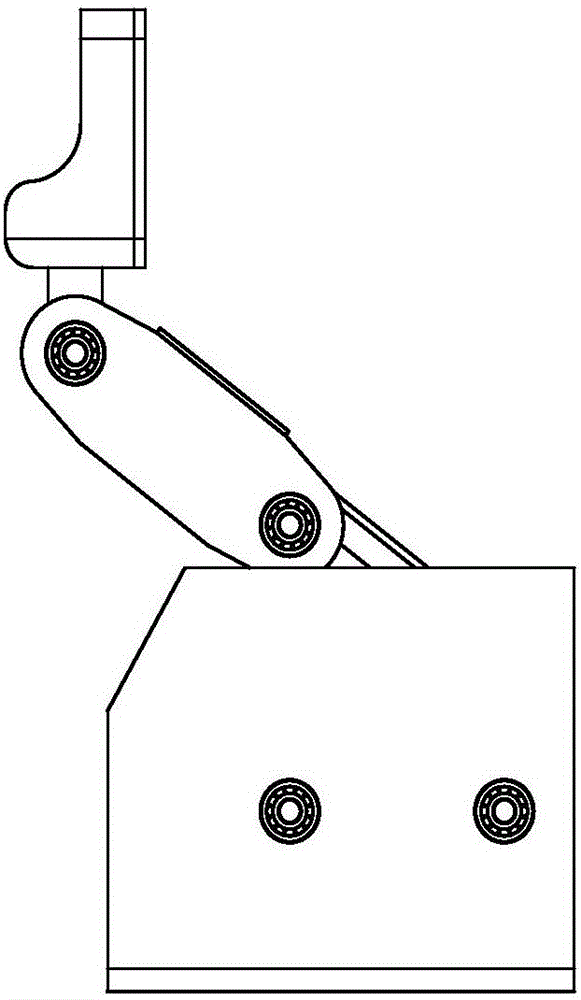
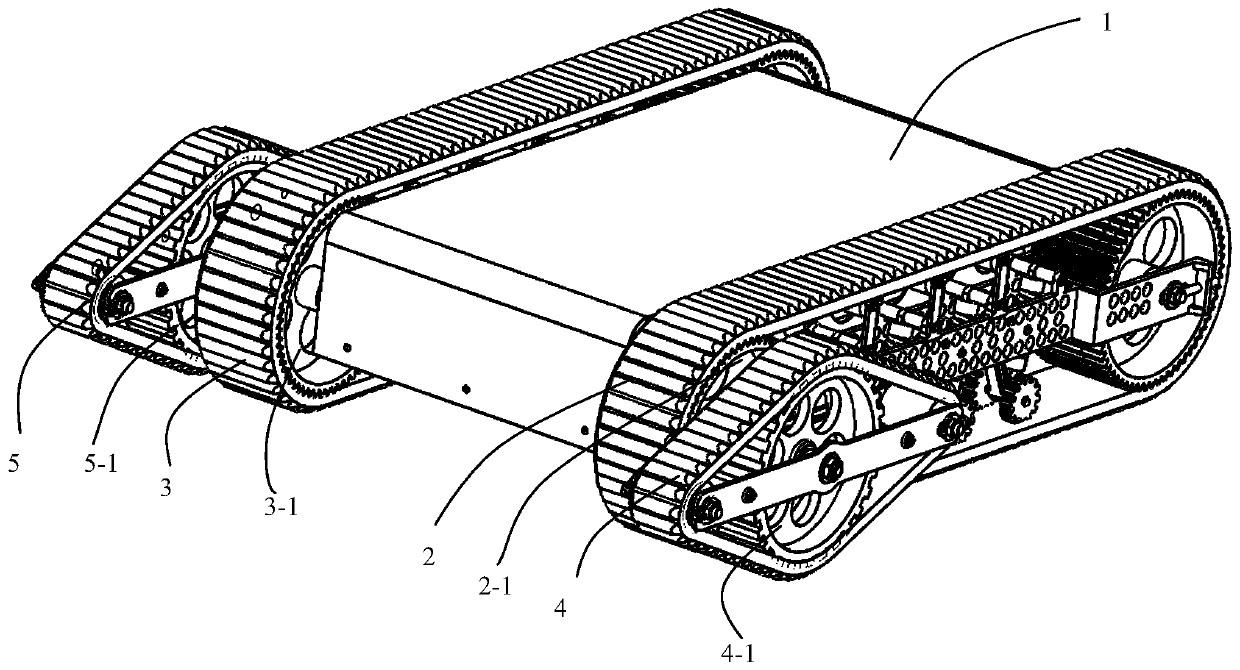
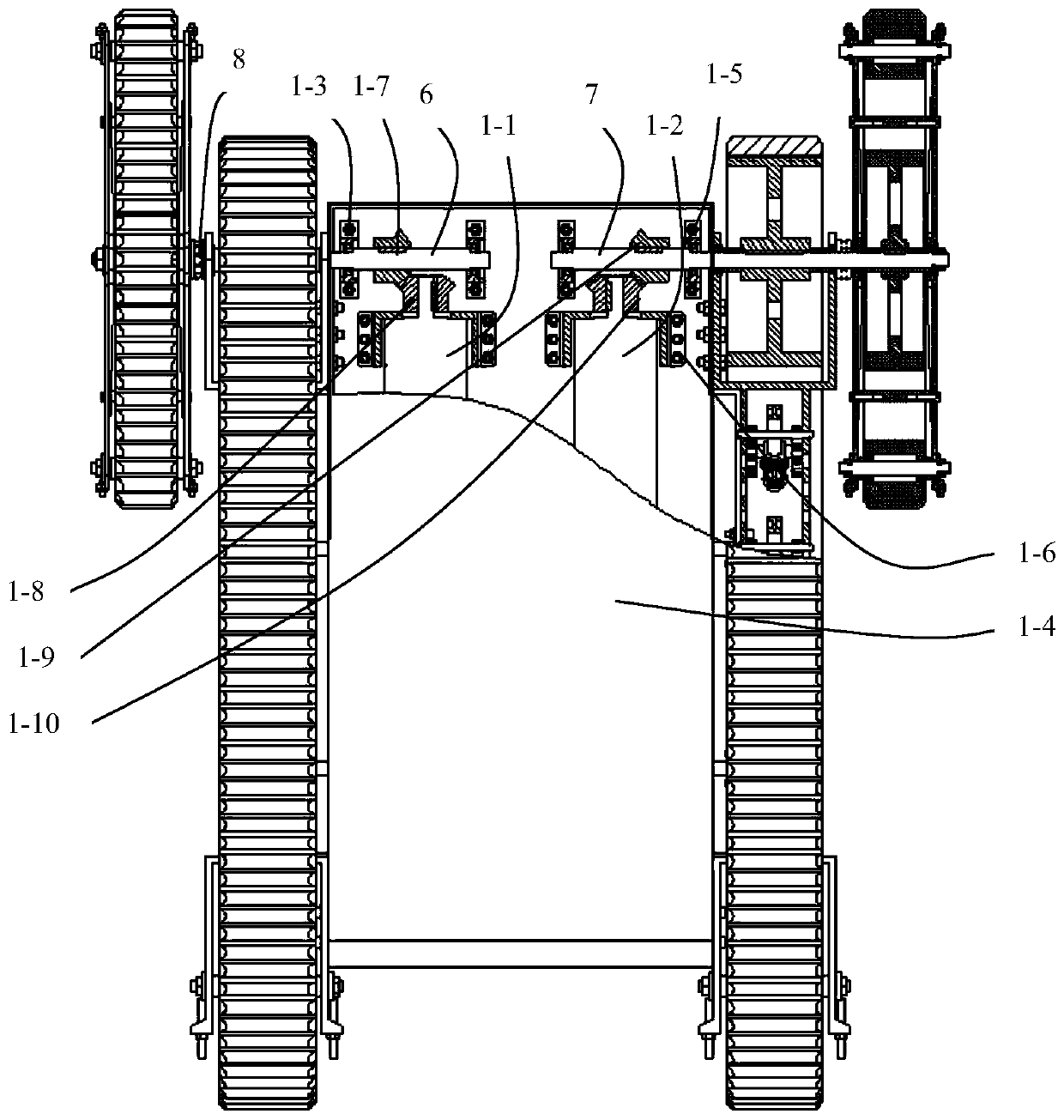
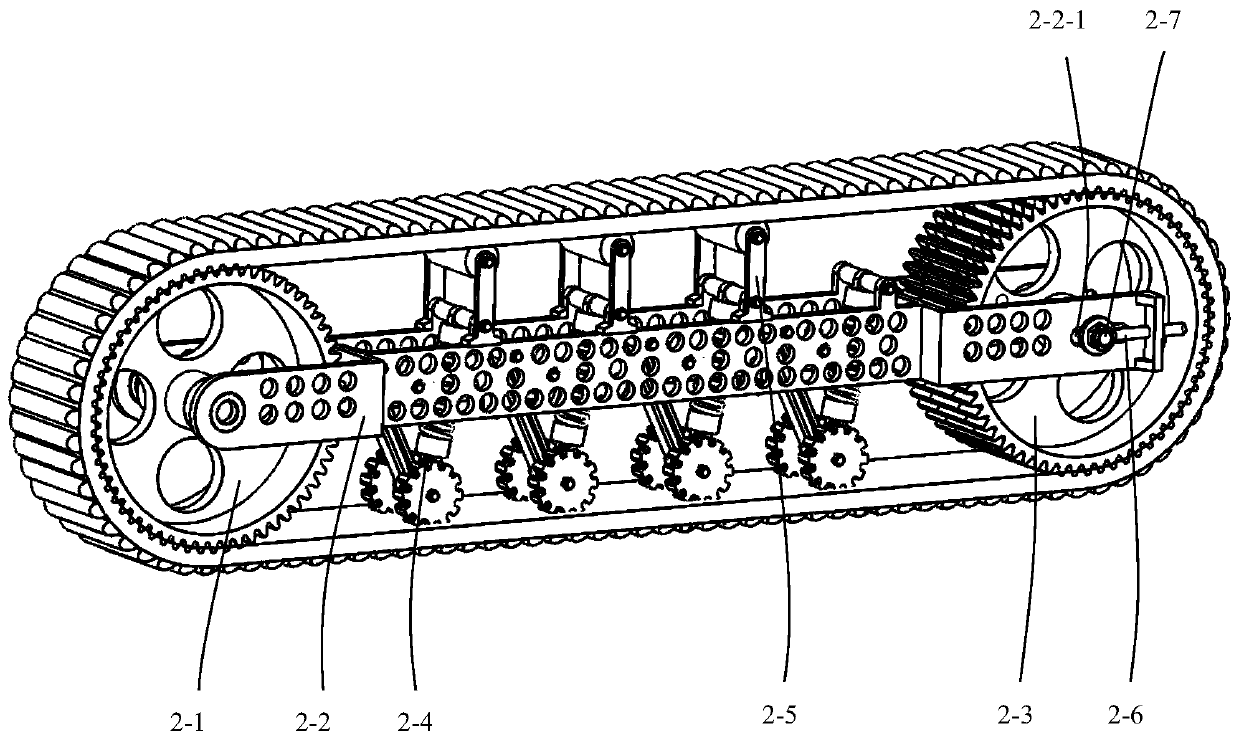
Adaptive underactuation track robot
PendingCN110450869AReduce weightReduce energy consumptionEndless track vehiclesUnderactuationDrive shaft
The invention discloses an adaptive underactuation track robot, which comprises a robot vehicle body, a first main track, a second main track, a first planet track, a second planet track, a first driving shaft and a second driving shaft. The first main track and the second main track as well as the first planet track and the second planet track are symmetrically mounted on the two sides of the robot vehicle body correspondingly, and the first planet track and the second planet track are mounted at the front end of the robot. The first driving shaft transmits power output by a first motor to the first main track and the first planet track, the second driving shaft transmits power output by a second motor to the second main track and the second planet track, and thus the robot is driven to move; when the first planet track and the second planet track travel on the flat ground, the front ends of the first planet track and the second planet track are tightly attached to the ground to be used as tracks, and when encountering obstacles such as steps, the first planet track and the second planet track can turn over around the first driving shaft and the second driving shaft to achieve passive adaptive obstacle crossing; and the robot can achieve the functions such as travelling, steering and obstacle crossing by being driven by only the two motors, thus the self-weight is decreased, the obstacle crossing time is shortened, the control cost is lowered, and the endurance time is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
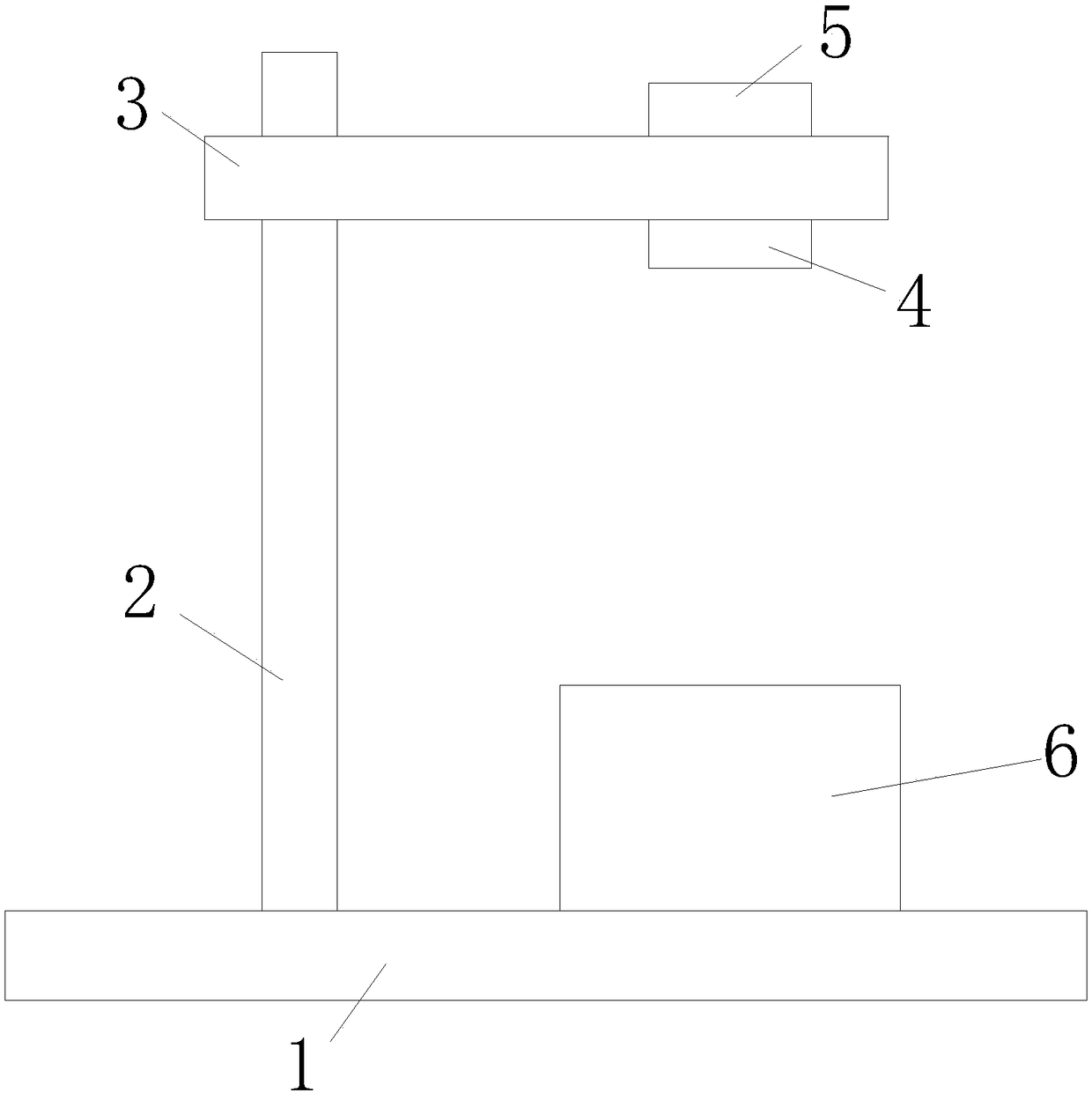
Three-dimensional image acquisition device
ActiveCN108600569AEasy to shootIncrease resistanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRubber ringUnderactuation
The invention discloses a three-dimensional image acquisition device, comprising a base, wherein an upright post is arranged on the base along a vertical direction, a bracket is arranged on the upright post, a microscope eyepiece is arranged at one end of the bracket far away from the upright post, a camera is arranged above the microscope eyepiece, the camera is in signal connection with a computer, a bearing table capable of driving a detection object to perform equidistant and intermittent rotation is arranged below the microscope eyepiece, and the bearing table is arranged on the base. According to the scheme of the invention, the detection object is photographed at an intermittent moment when the bearing table rotates, the operation of photographing steady and clear images can be facilitated, the practical range of the device can be increased through the arrangement of incomplete driving wheels, so that the device can be applied to image acquisition detection of the detection objects with different sizes; and through the arrangement of a rubber ring, the resistance of the rotation of a transmission shaft can be increased, the rotation inertia of the transmission shaft can be reduced, so that the transmission shaft can only rotate when the incomplete driving wheels are meshed with a transmission column gear, the transmission accuracy can be ensured, and the accuracy of image acquisition can be further guaranteed.
Owner:芜湖市奥尔特光电科技有限公司
Underactuation vacuum chuck paw having multiple grabbing modes
ActiveCN108453778AImproved ability to grab loadsWide range of sizesGripping headsUnderactuationFinger structure
The invention discloses an underactuation vacuum chuck paw having multiple grabbing modes. The underactuation vacuum chuck paw having the multiple grabbing modes comprises at least two fingers, a base, a motor and an air pump, each finger comprises an elastic plate which is provided with at least five hard phalanxes, the hard phalanxes are each covered with a silica membrane, a chuck connecting piece penetrates through the elastic plates, the hard phalanxes and the silica membranes to be connected with a chuck, the chuck is connected with the air pump through a guide pipe, and the fingers areconnected with the base and the motor through steel wires; and the base is provided with a finger support, a steel wire routing sliding wheel, the motor and a roller, the steel wires are carried on the steel wire routing sliding wheel to be connected with the roller, and the two fingers are the same in structure and are symmetrically installed on the finger support. By combining advantages of softand hard paws and through the manner that a soft material and a hard material are adopted at the same time on the structure, the paw grabbing loading capacity is improved to a certain degree, and thepaw can be applied to object grabbing and the like under multiple environments. The underactuation vacuum chuck paw can be applied to the fields including but not limited to domestic services, logistics and rubbish sorting.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
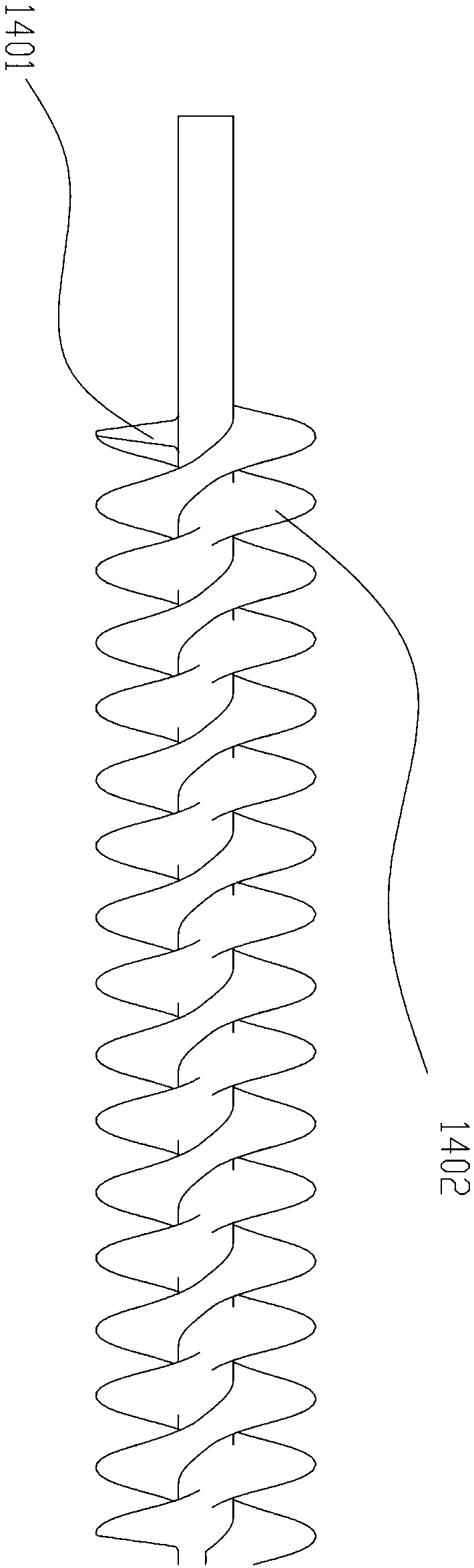
Dual spiral heating wire drawing machine added with underactuation stirring structure
The invention discloses a dual spiral heating wire drawing machine added with an underactuation stirring structure. The machine comprises a base, a motor, a coupler, an end cover, a radial bearing, afeeding opening, a hopper, the underactuation stirring structure, a machine cylinder, a support, a dual spiral heating screw rod, a screw rod screw groove, a wire drawing machine head, and a discharging opening. Multiple material inlet openings are formed, a raw material, a modifying agent and a coloring agent are directly and evenly mixed in the hopper, and production efficiency is improved; a dual spiral blade heating module is adopted, heating efficiency is improved, the temperature control precision is improved, and the problem that in the wire drawing process, a wire is prone to breakageis solved; the wire drawing machine sufficiently uses heat energy, and energy waste is reduced.
Owner:合肥矩阵三维技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com