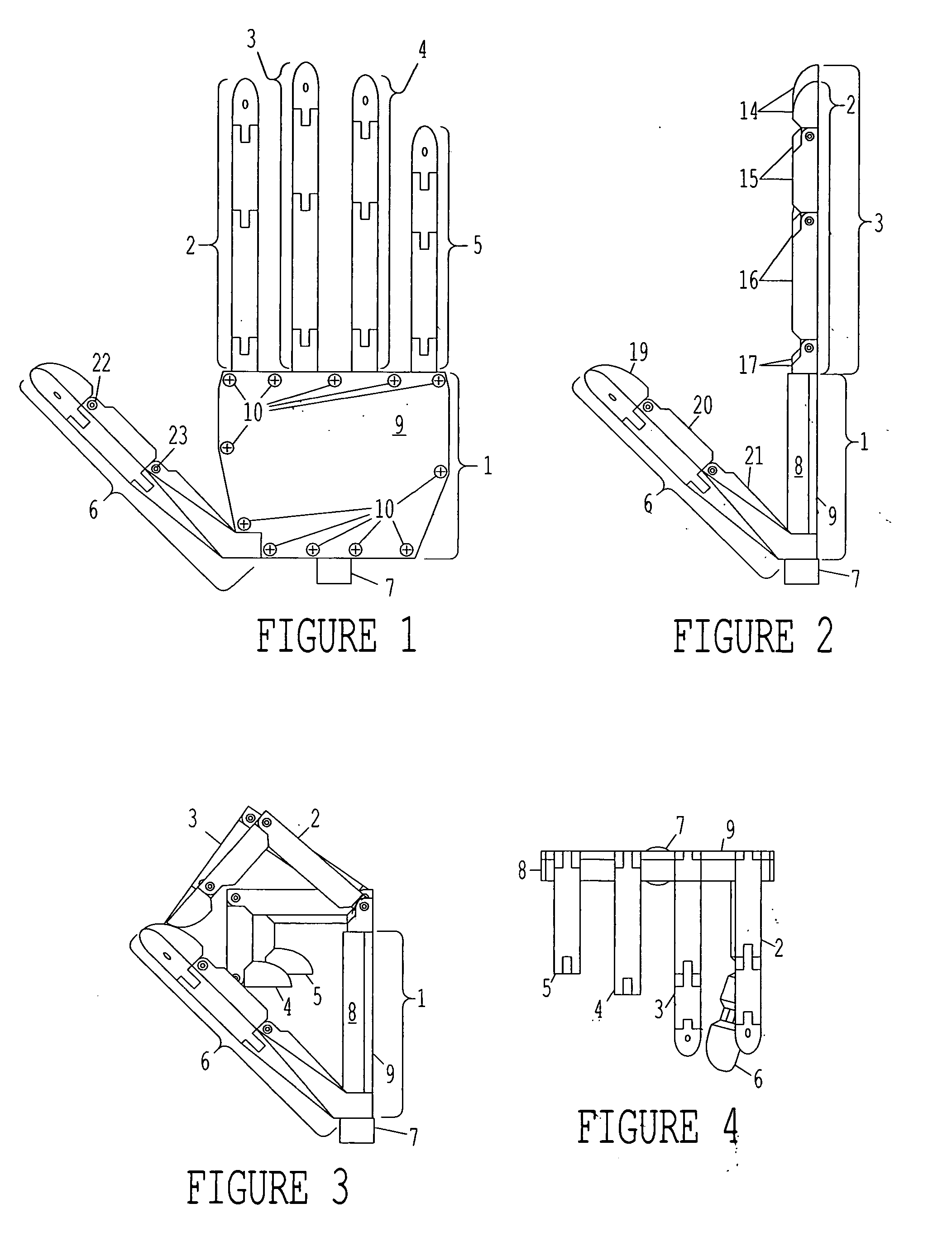
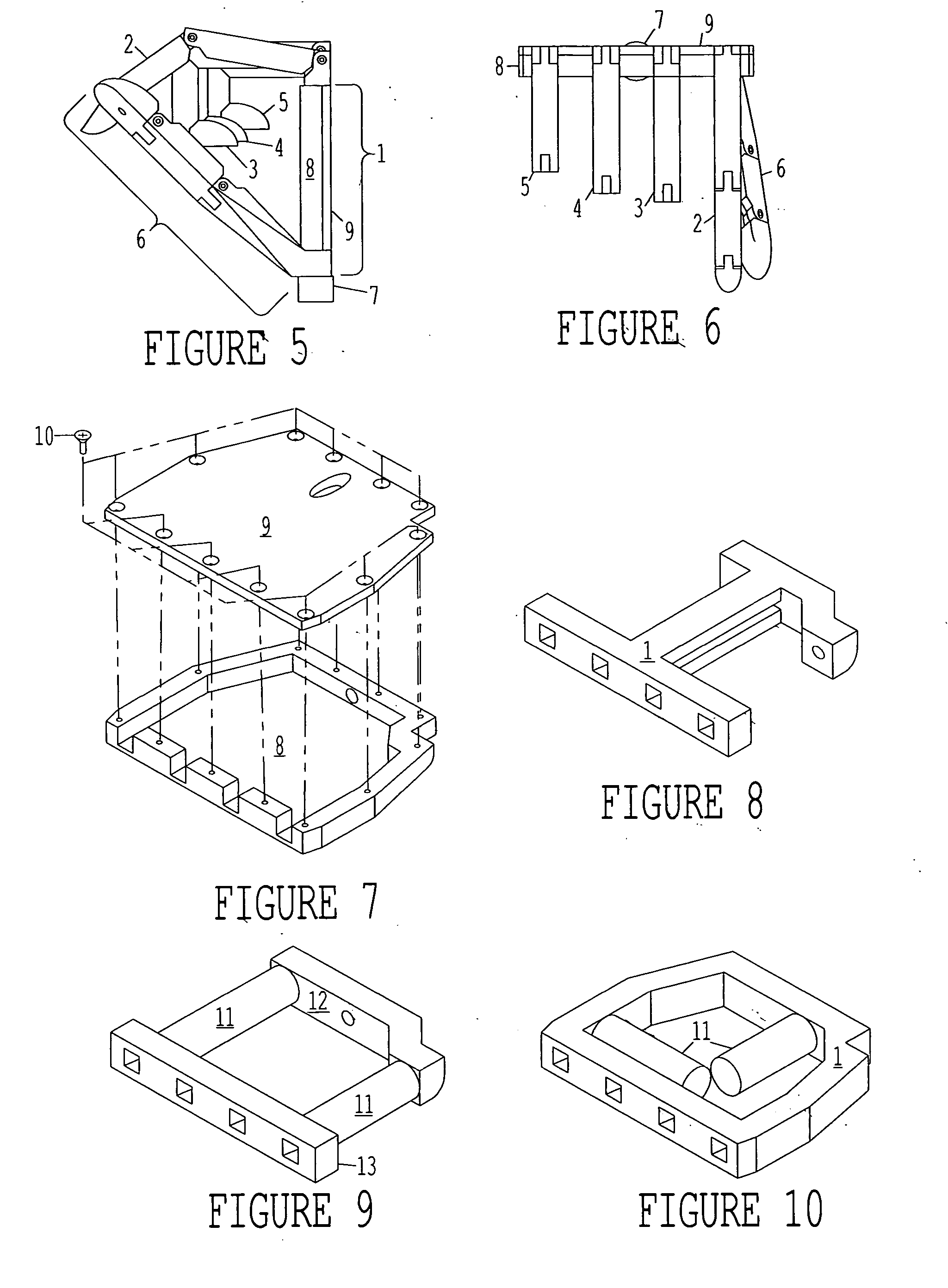
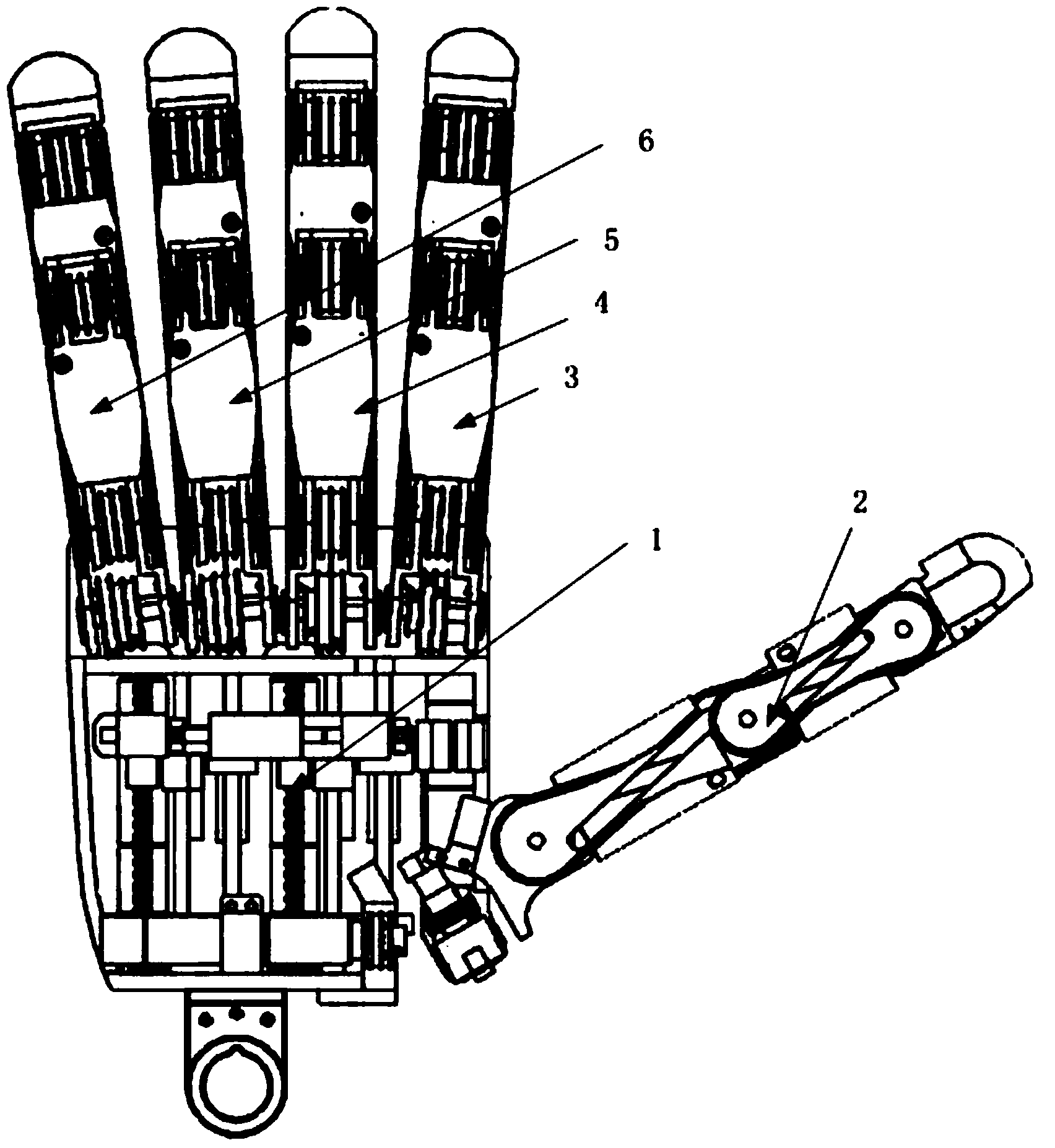
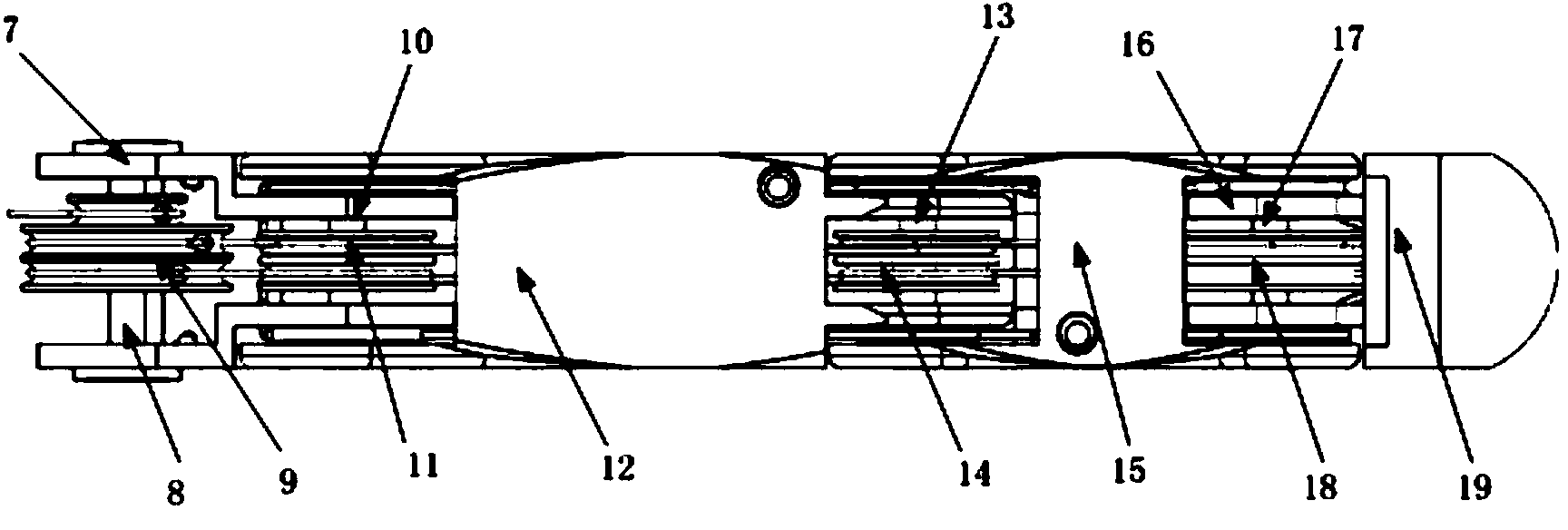
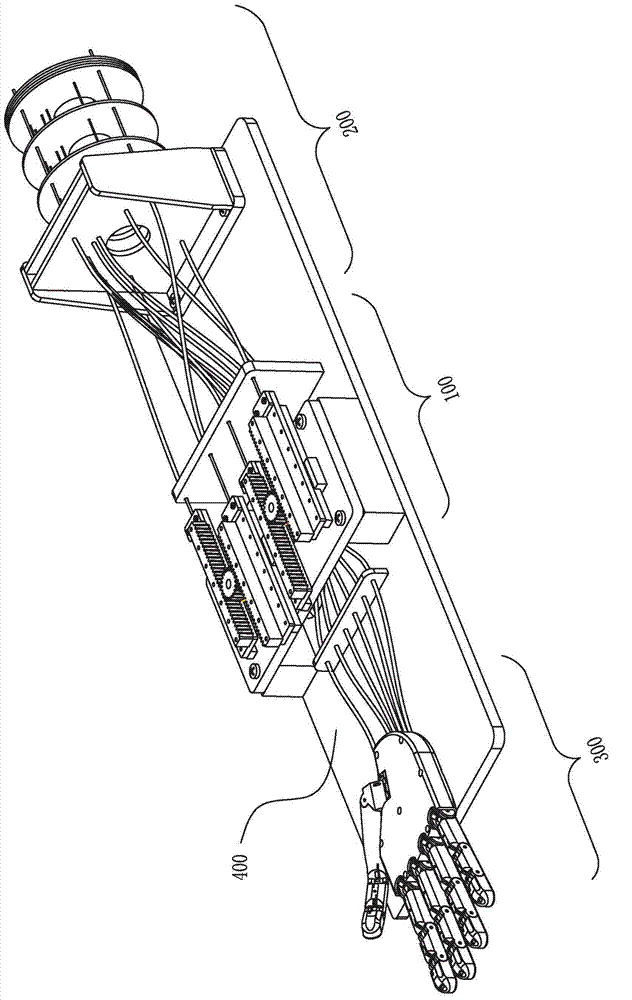
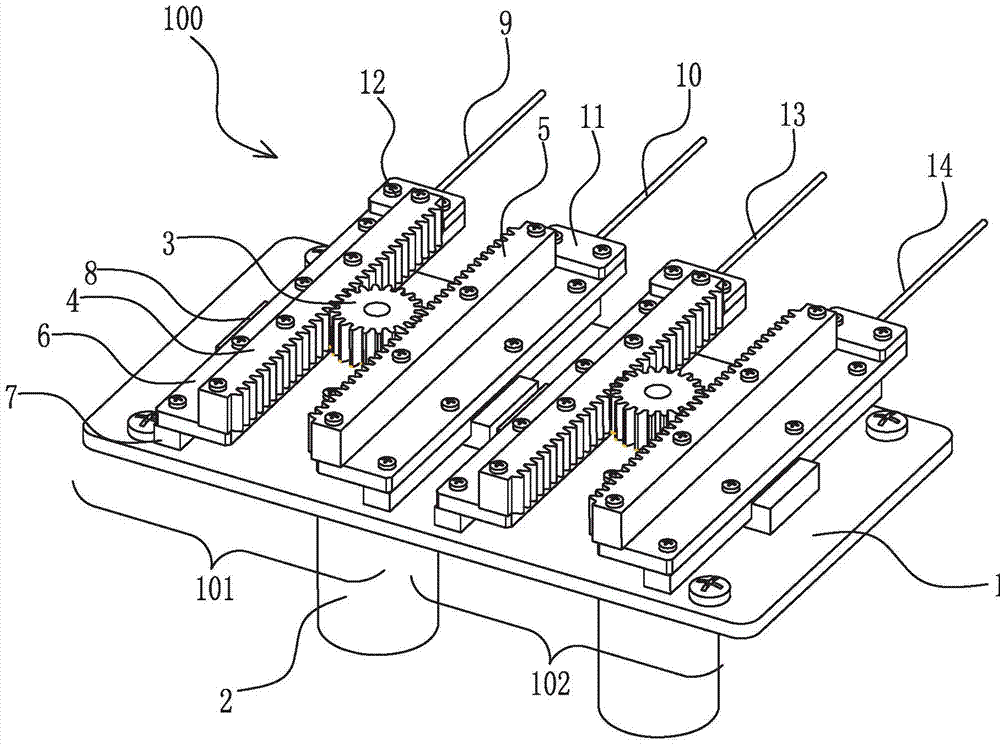
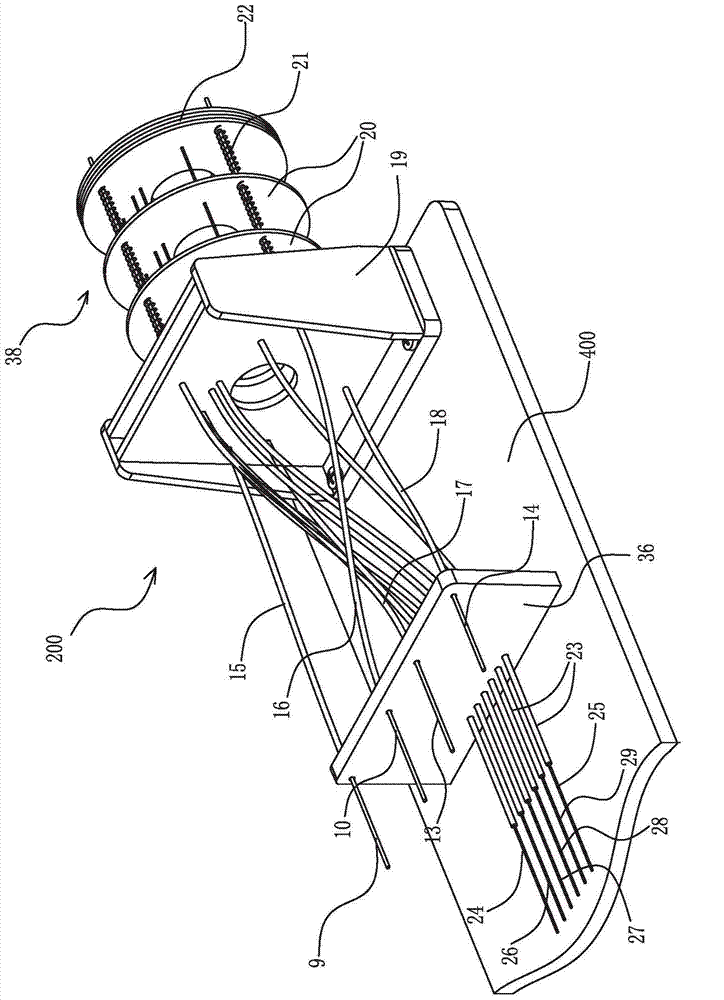
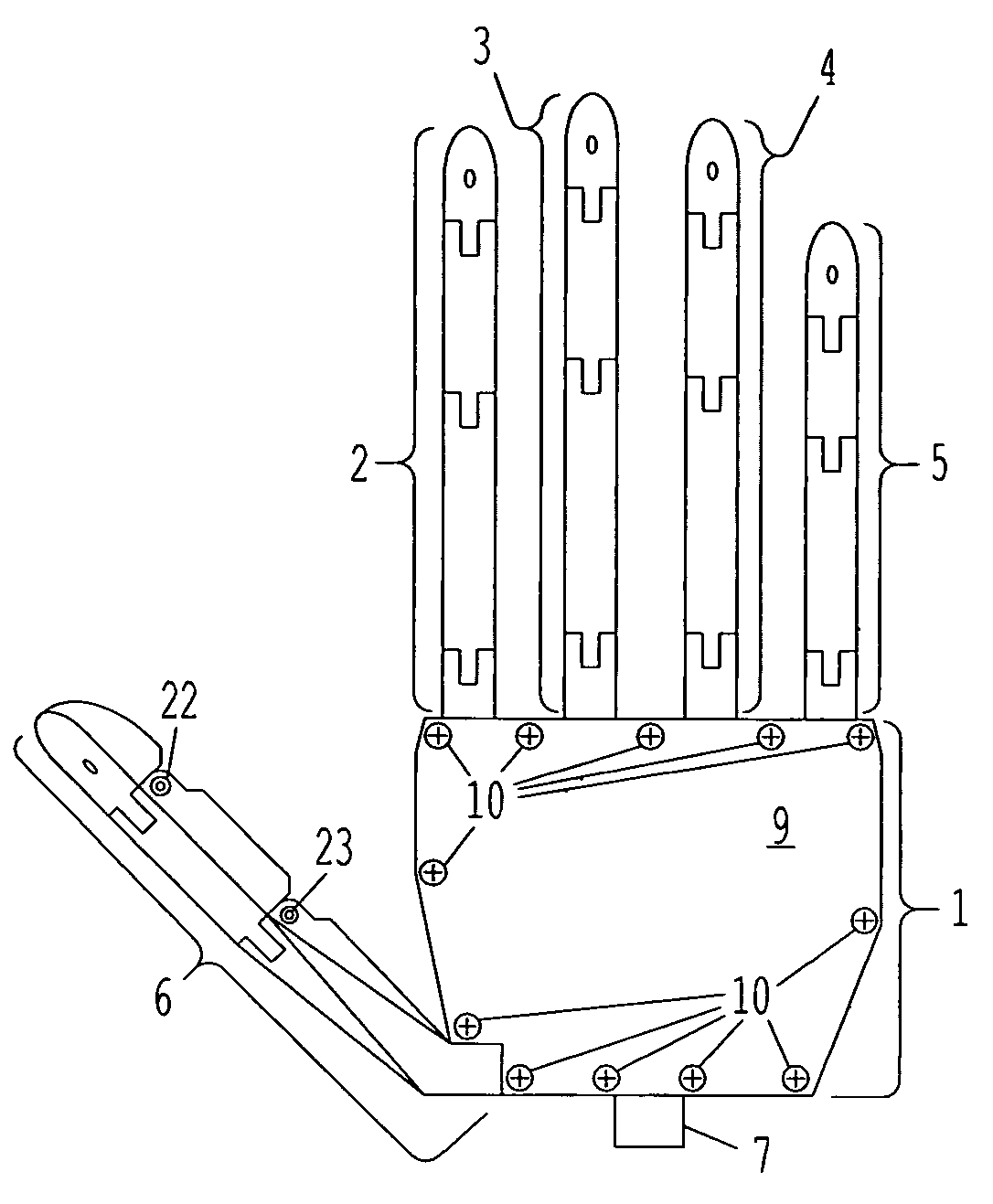
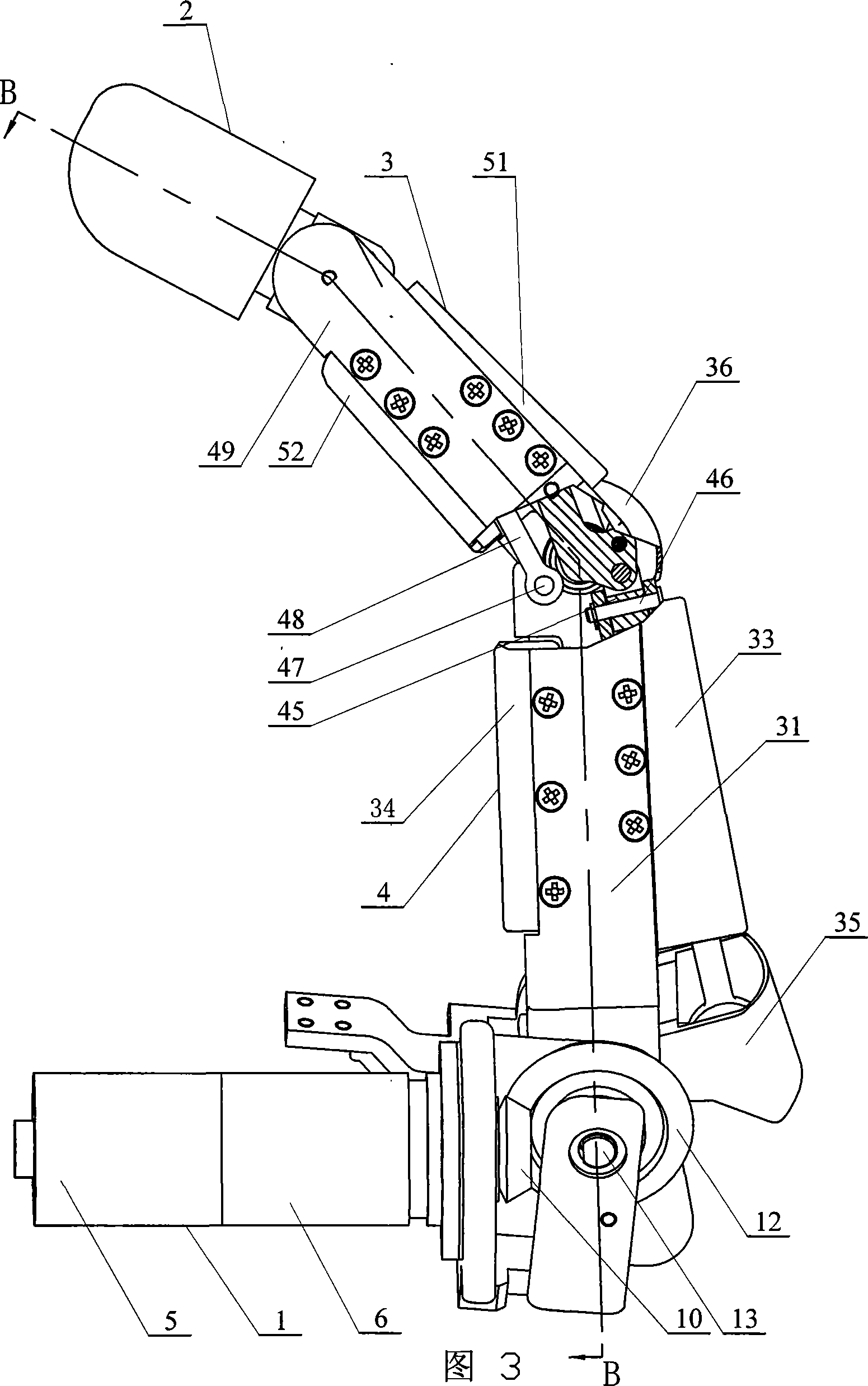
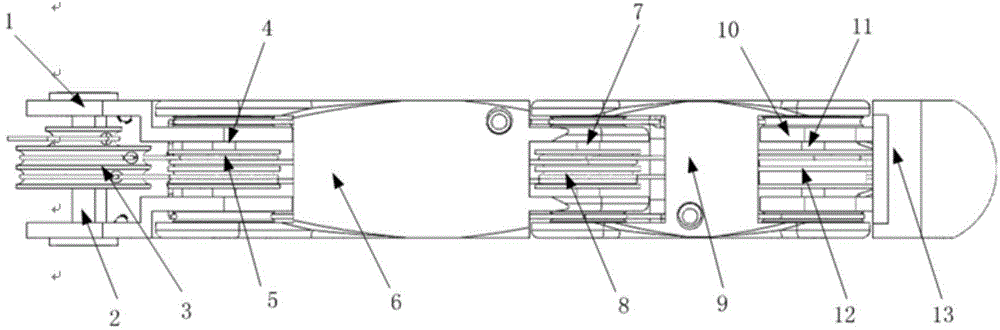
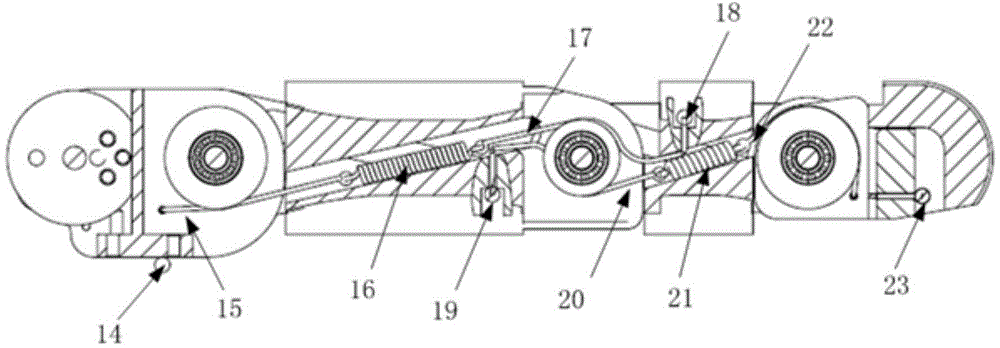
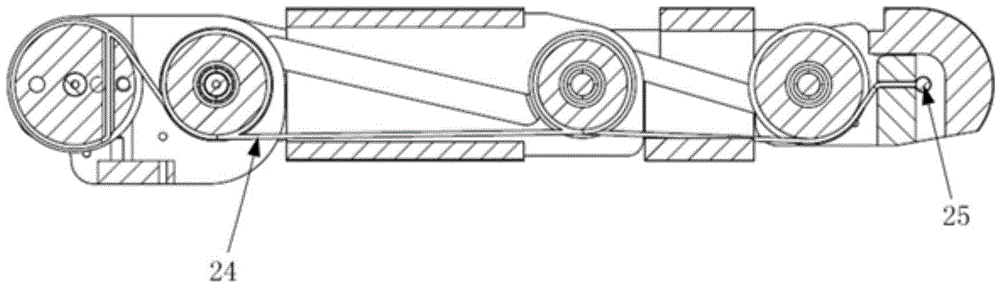
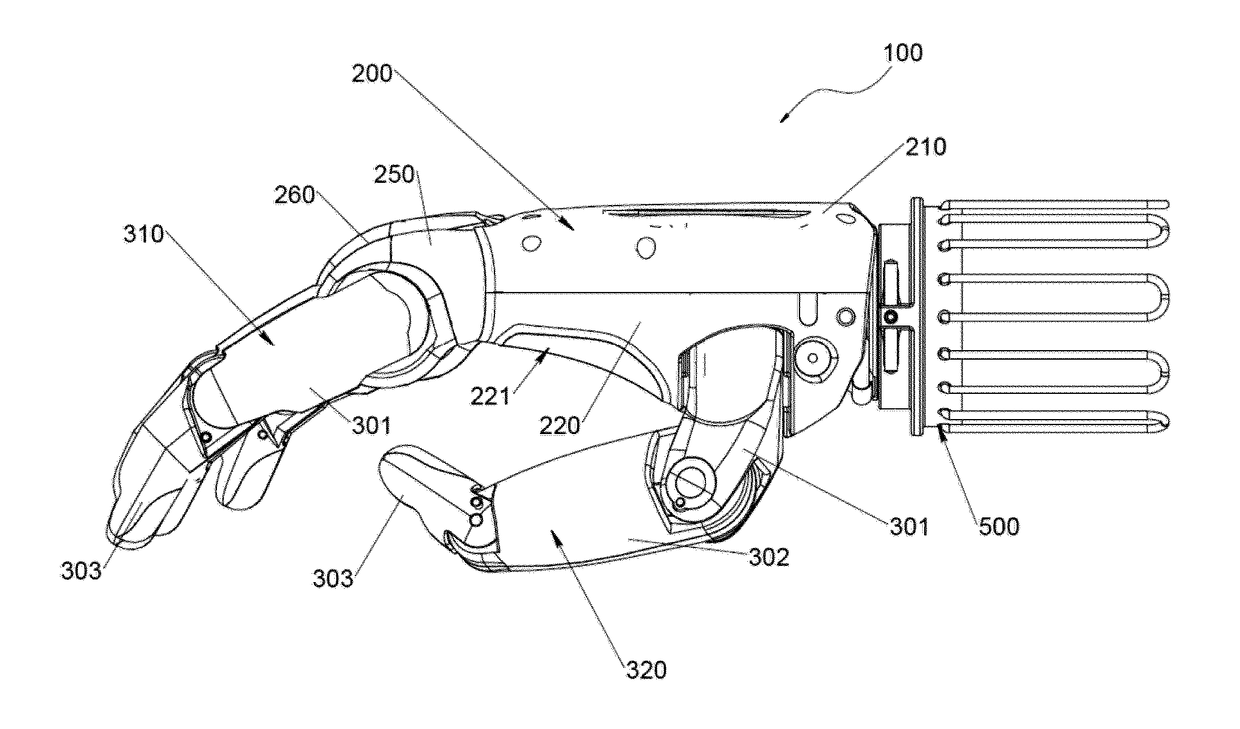
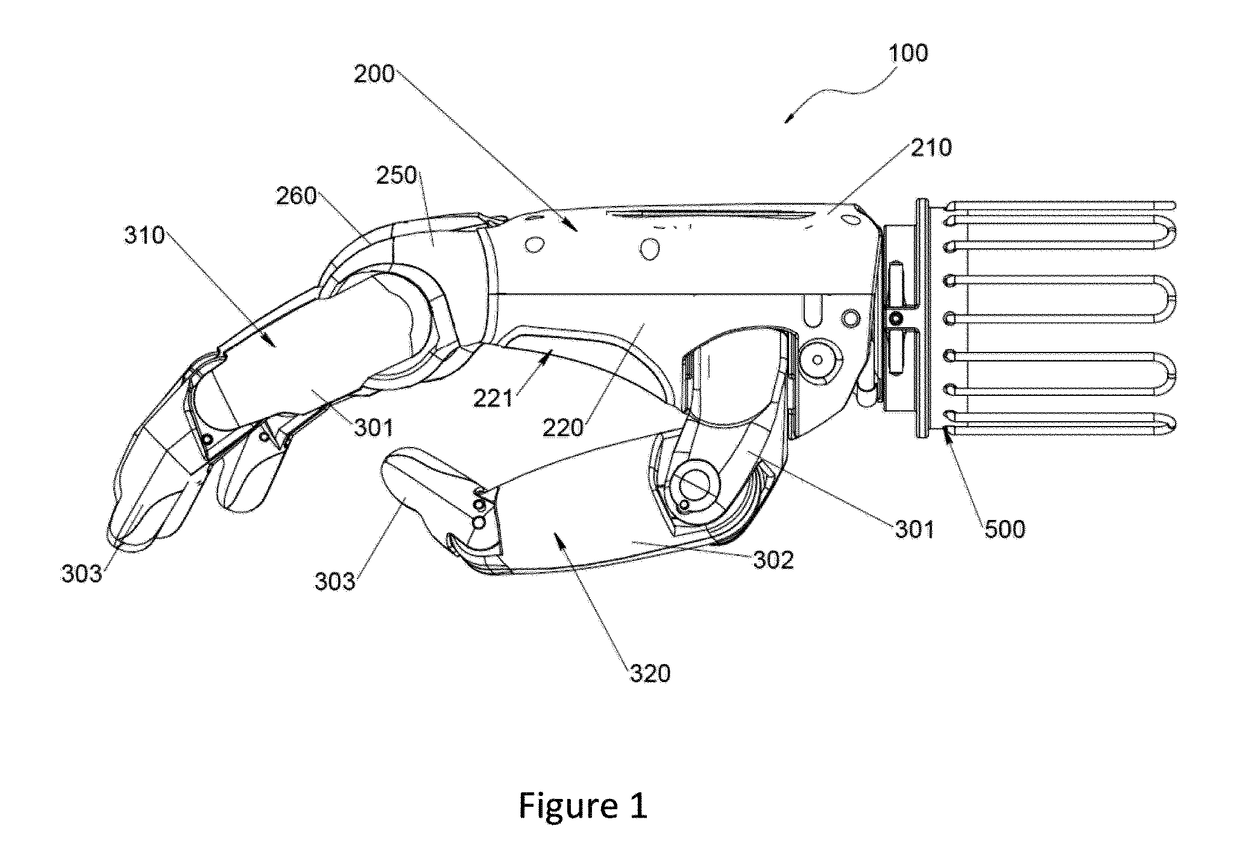
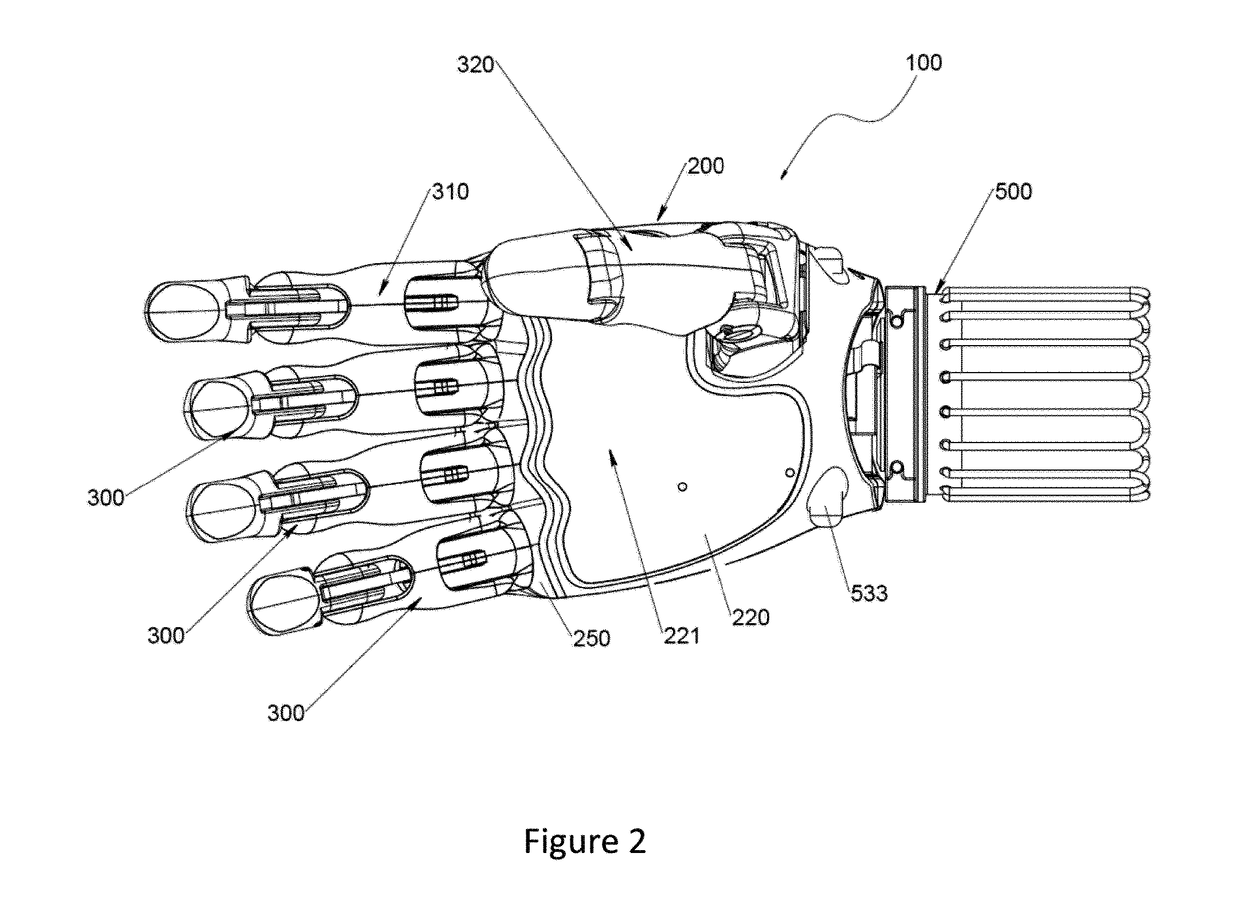
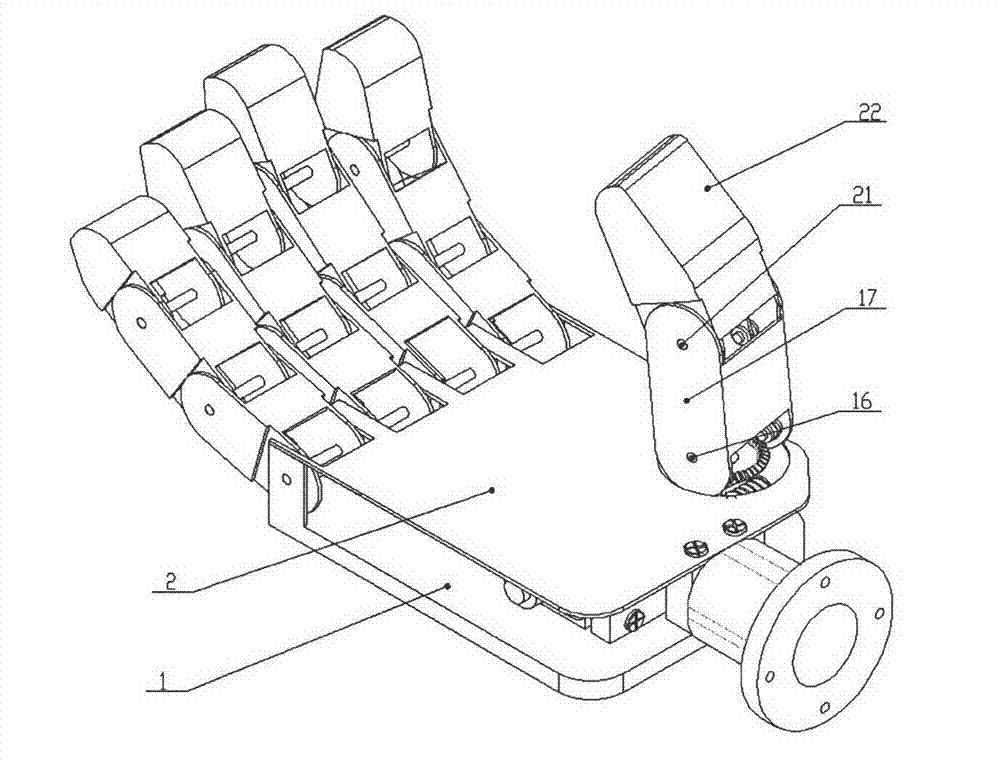
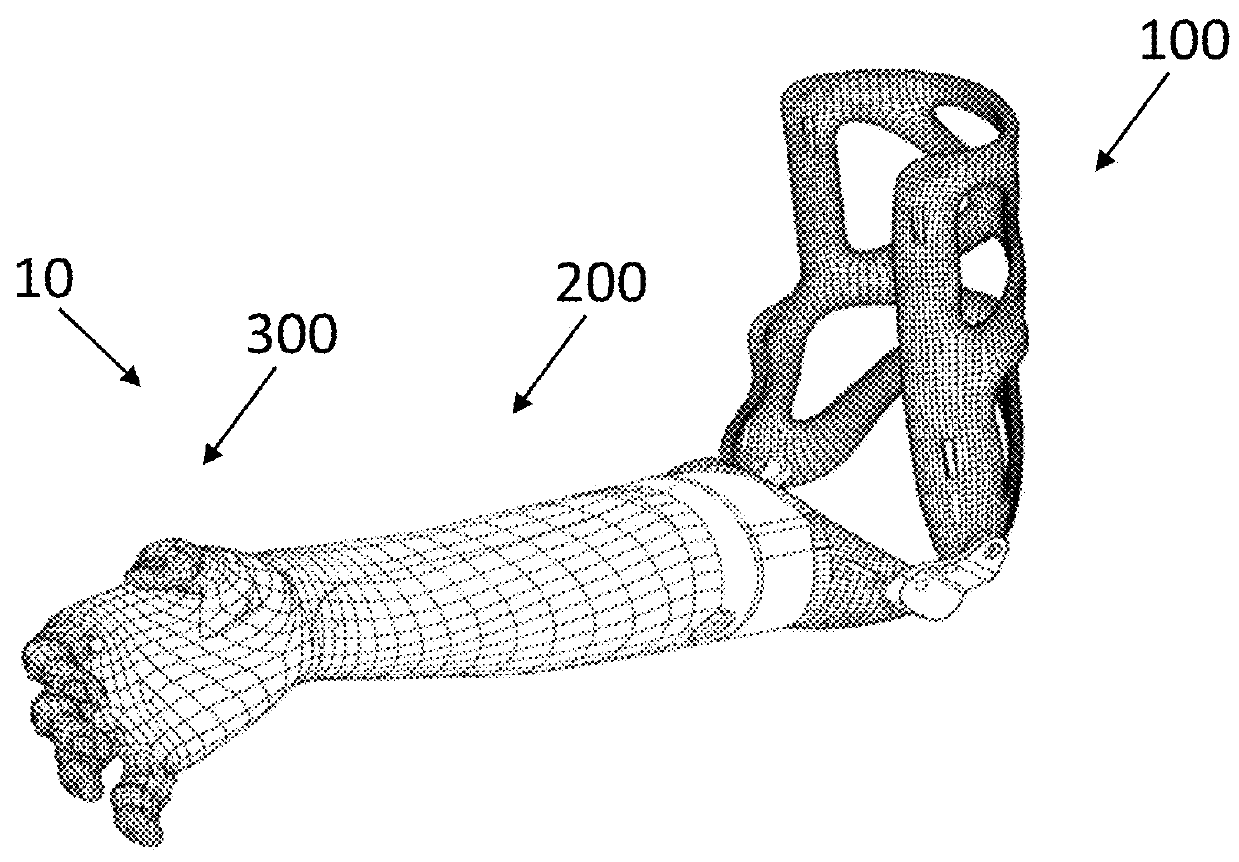
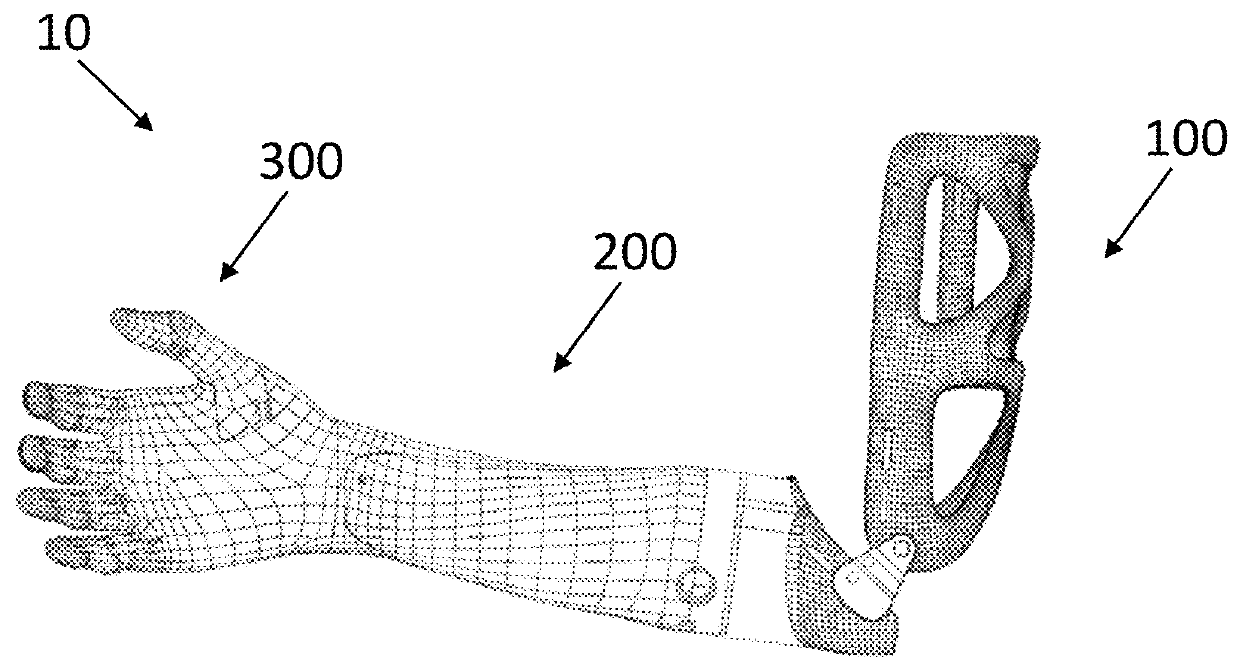
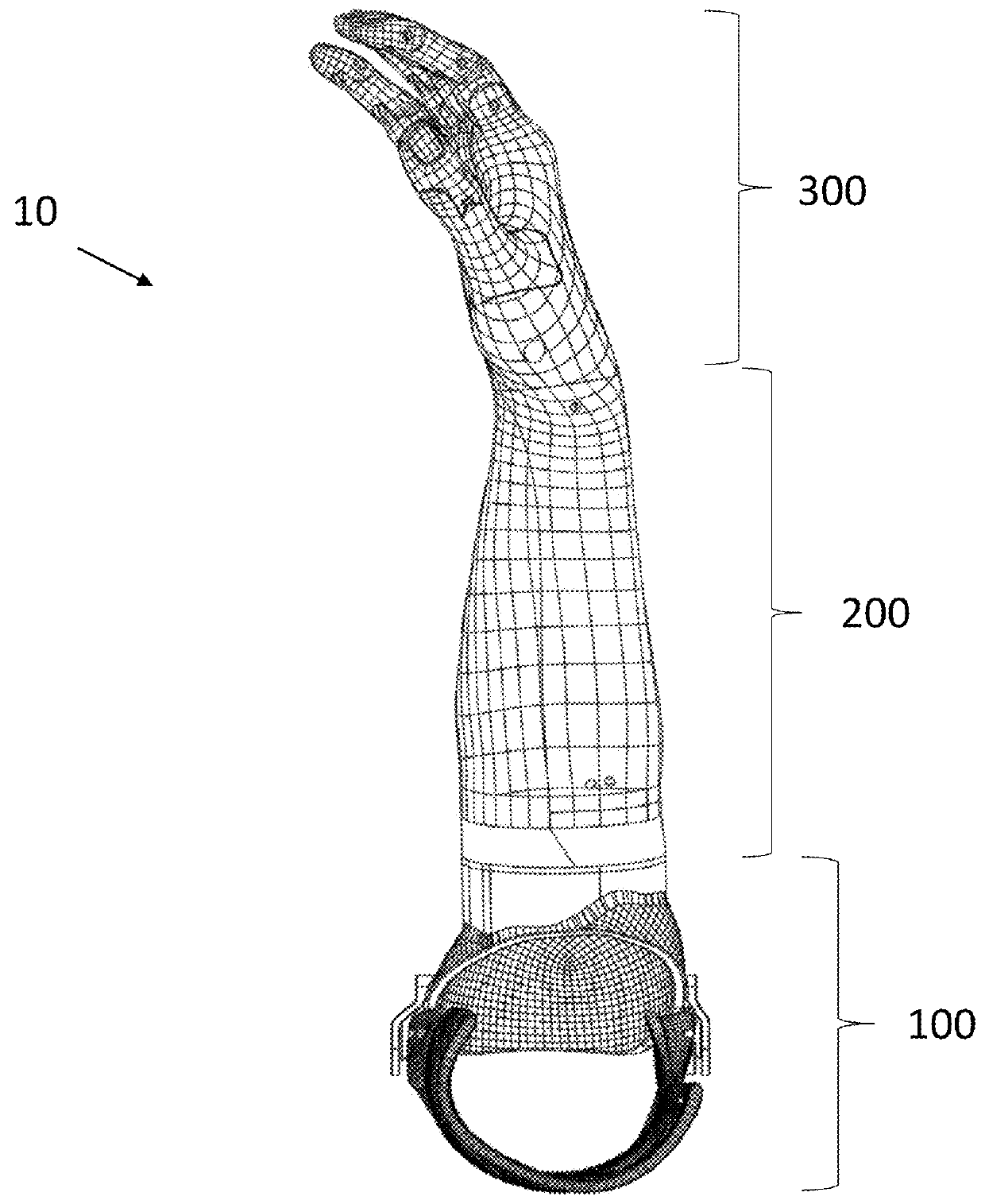
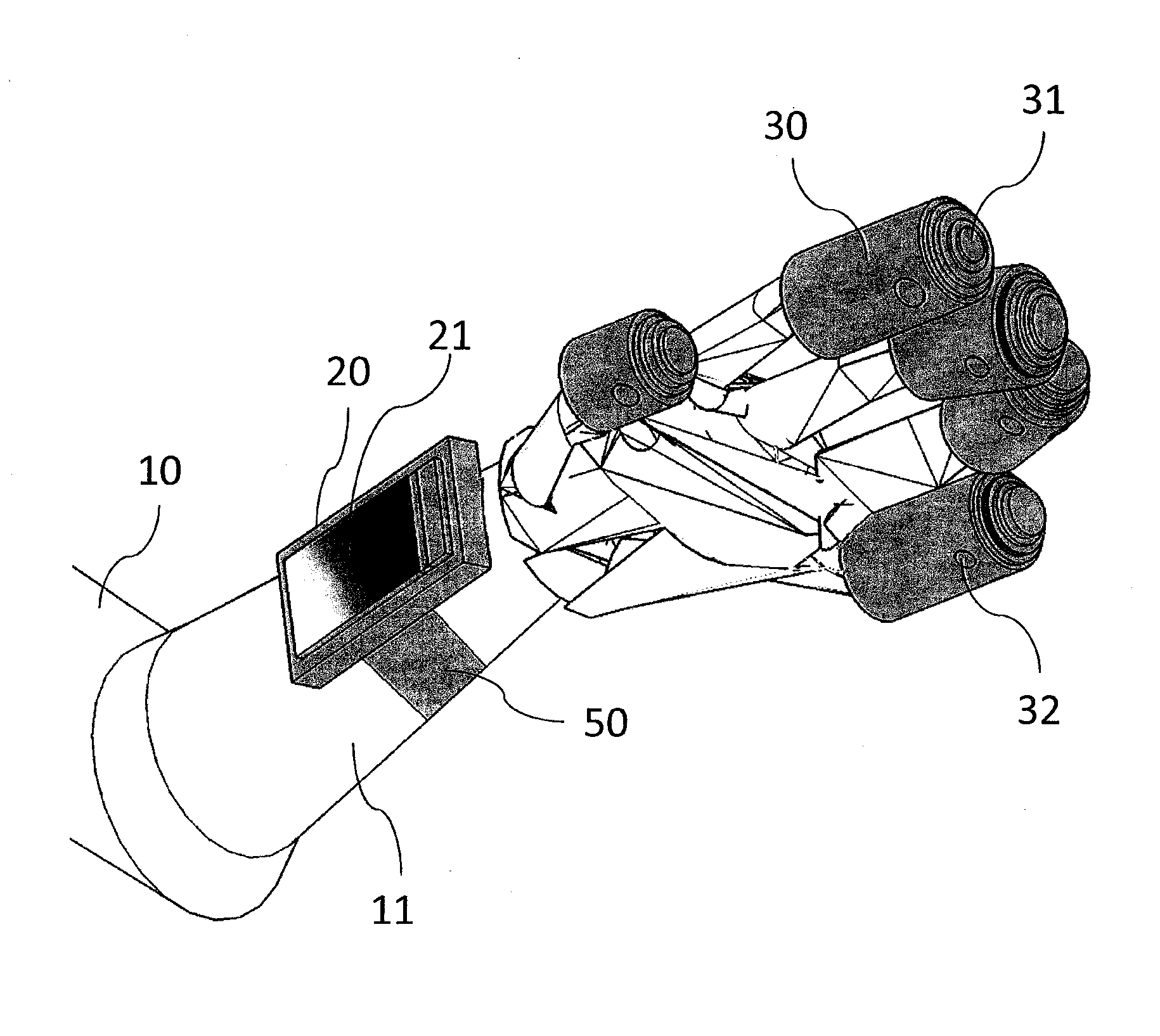
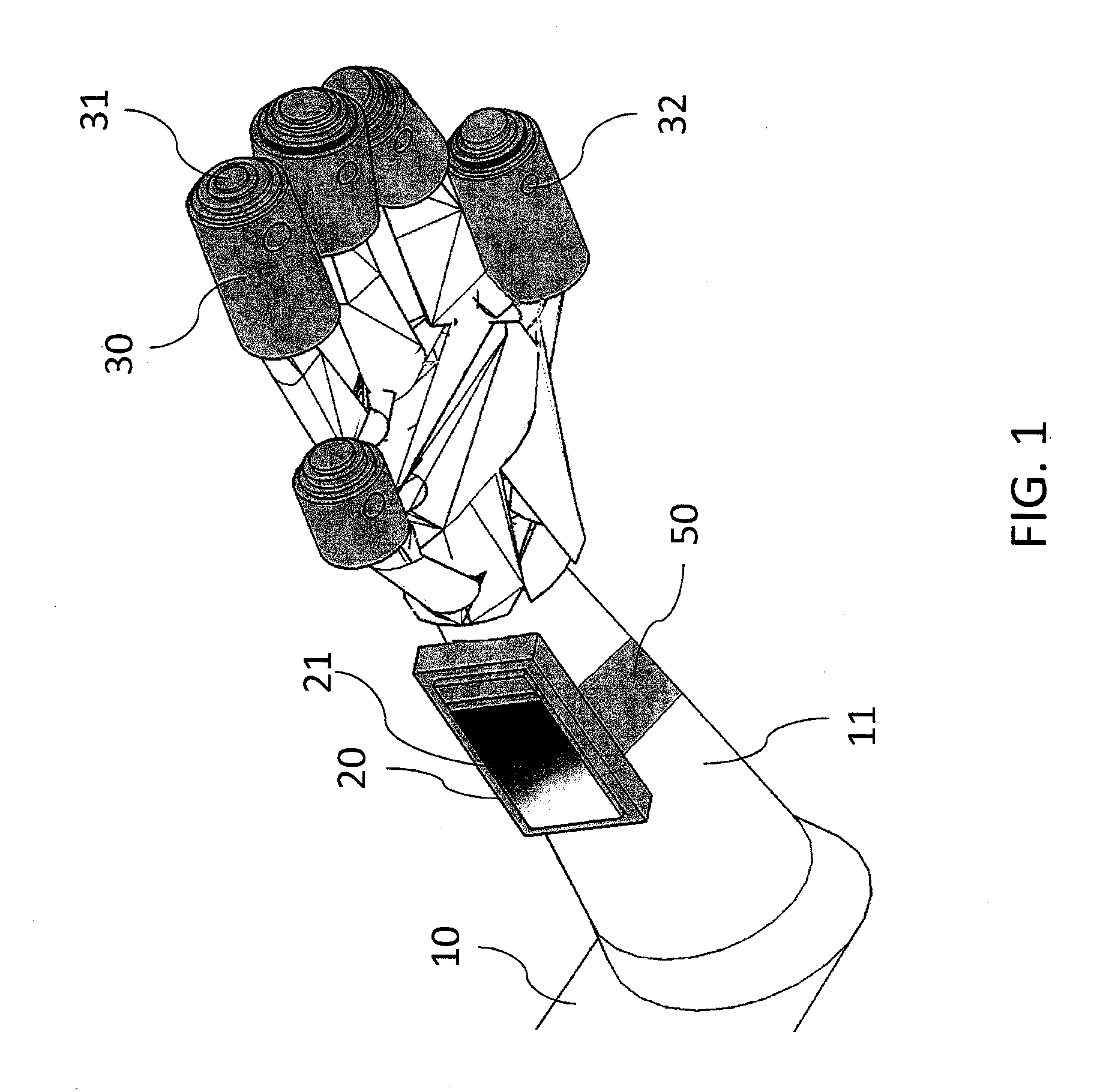
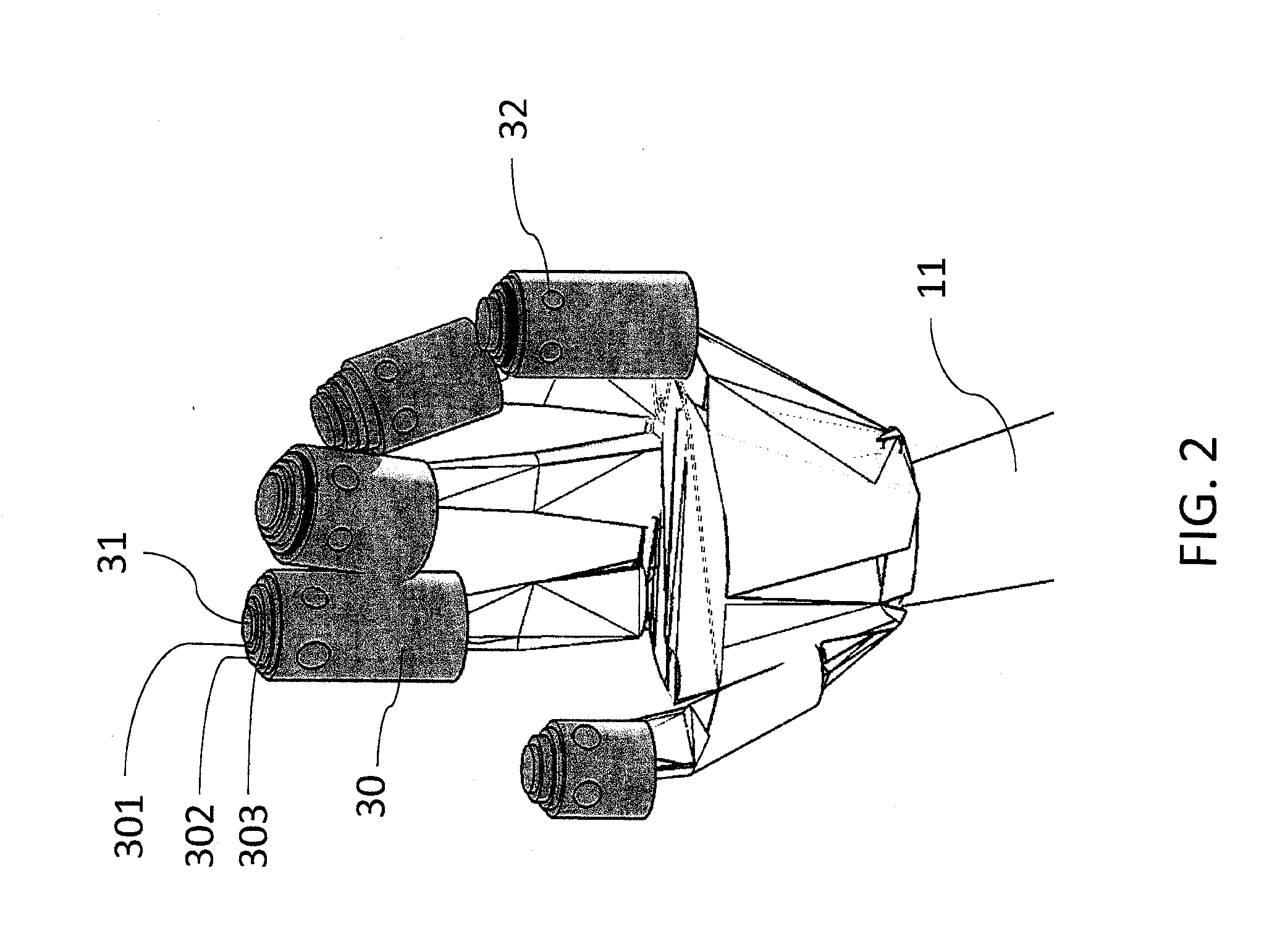
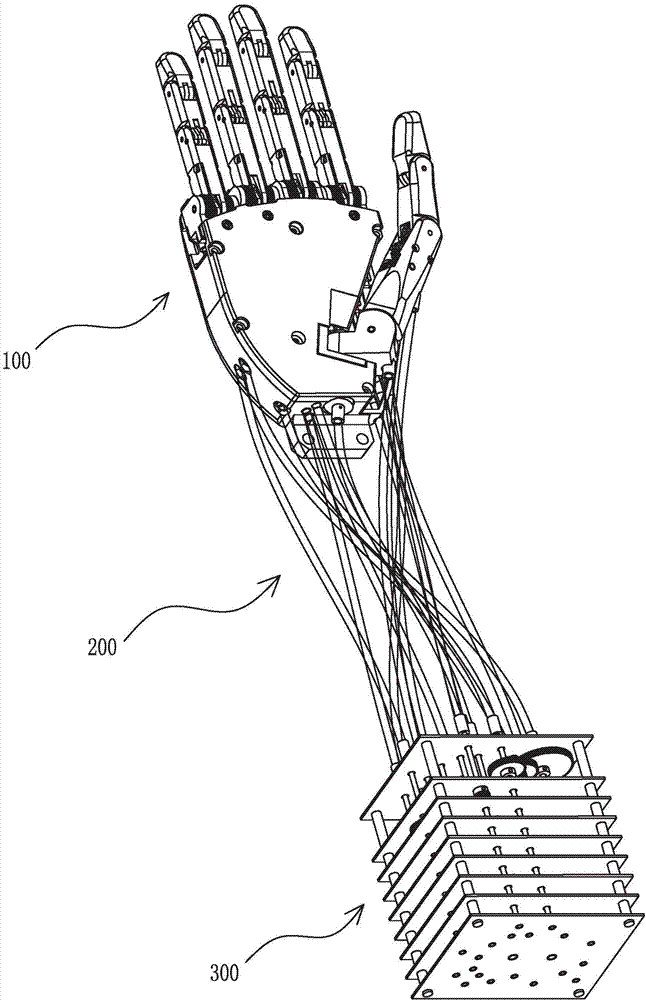
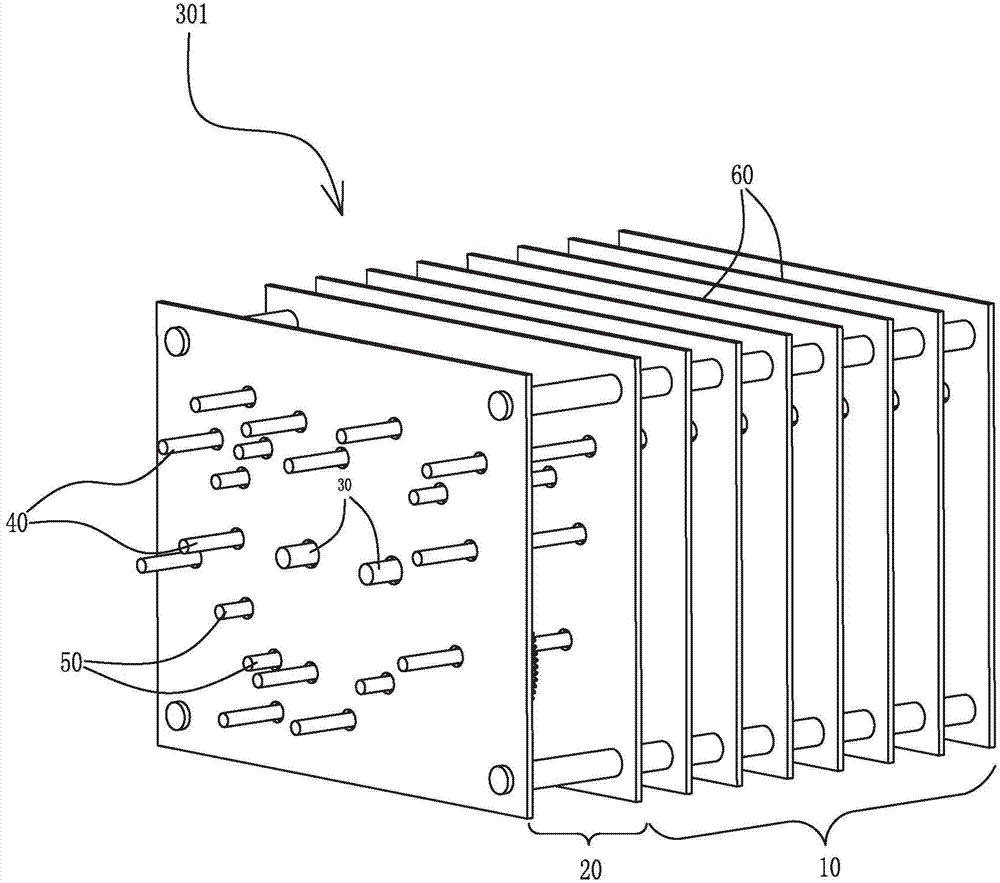
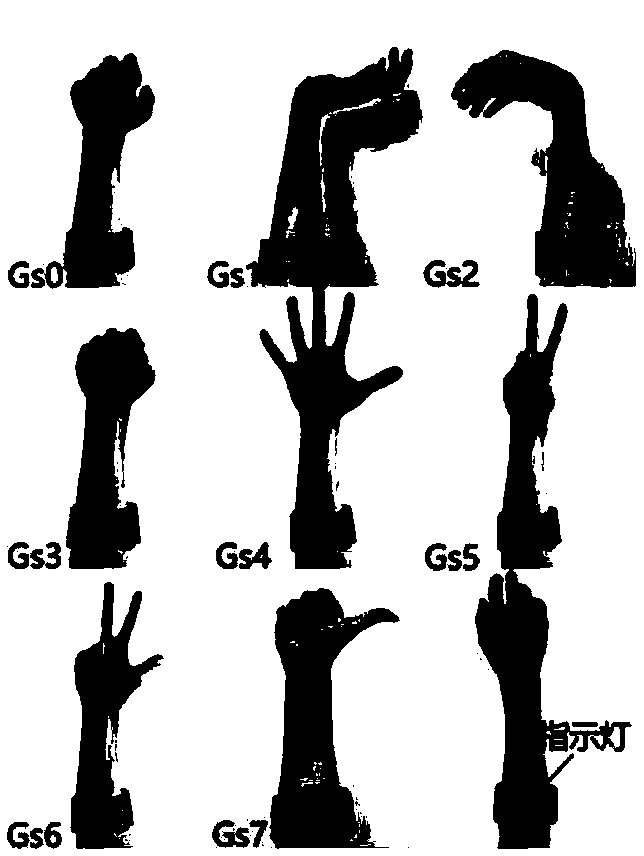Patents
Literature
230 results about "Prosthetic hand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
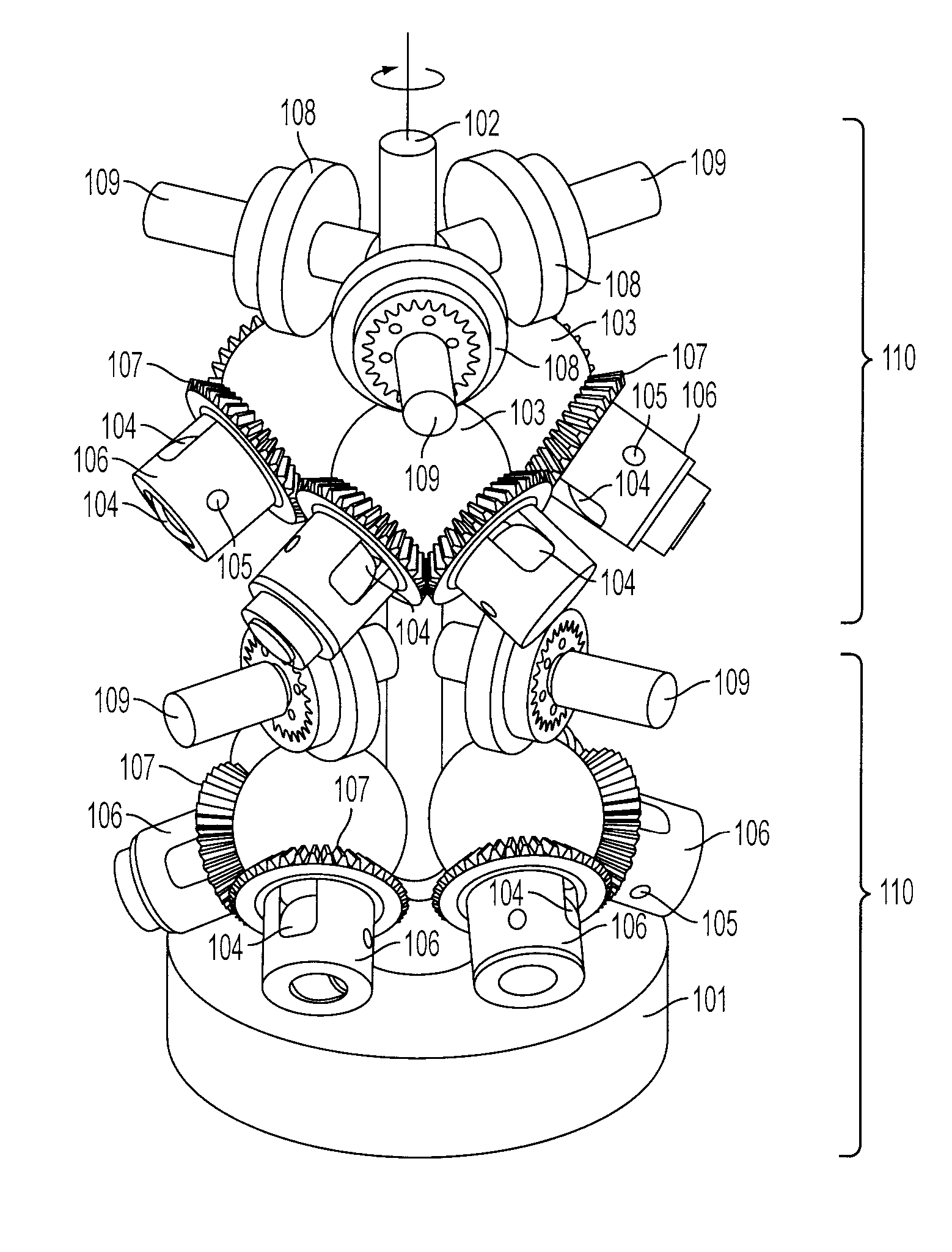
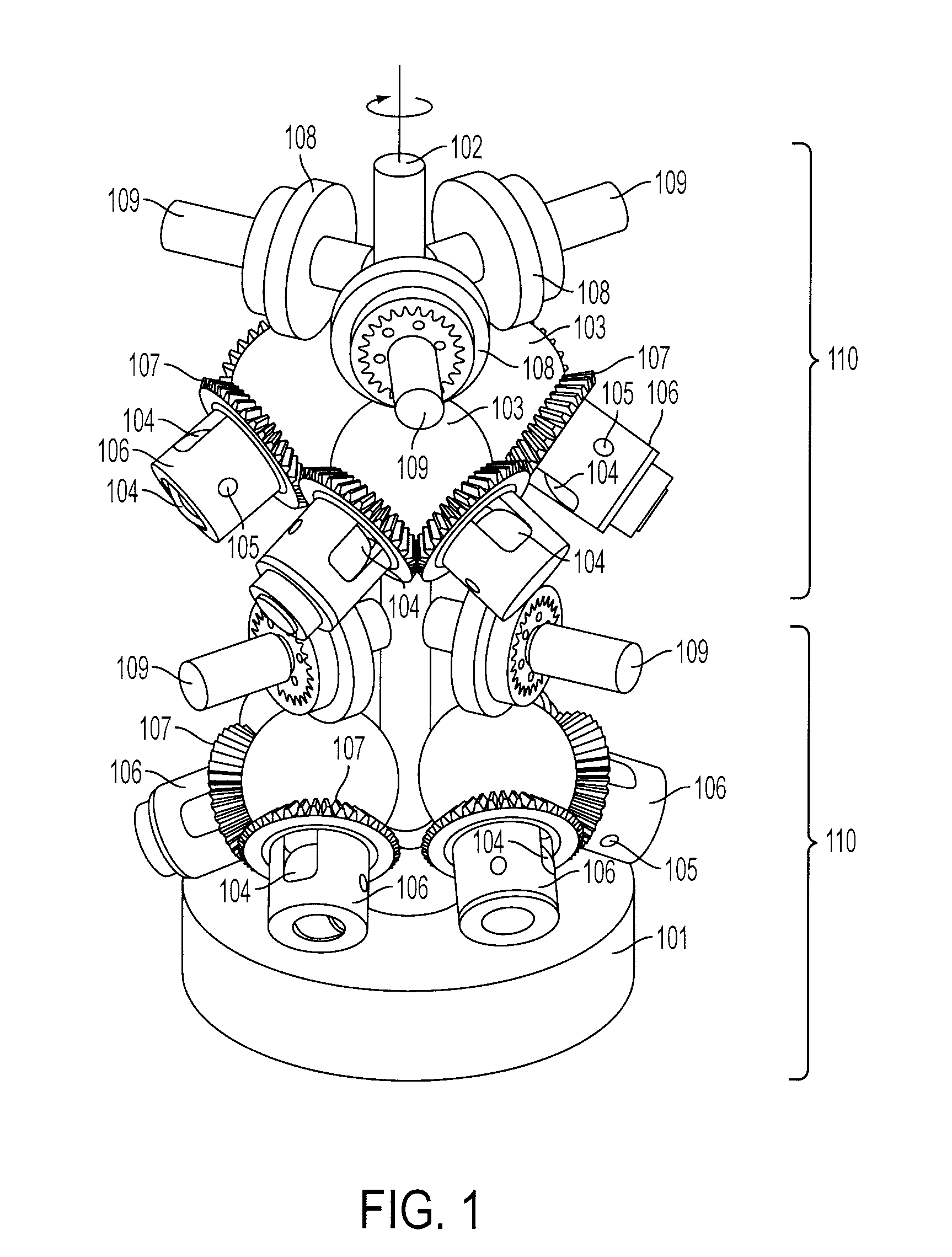
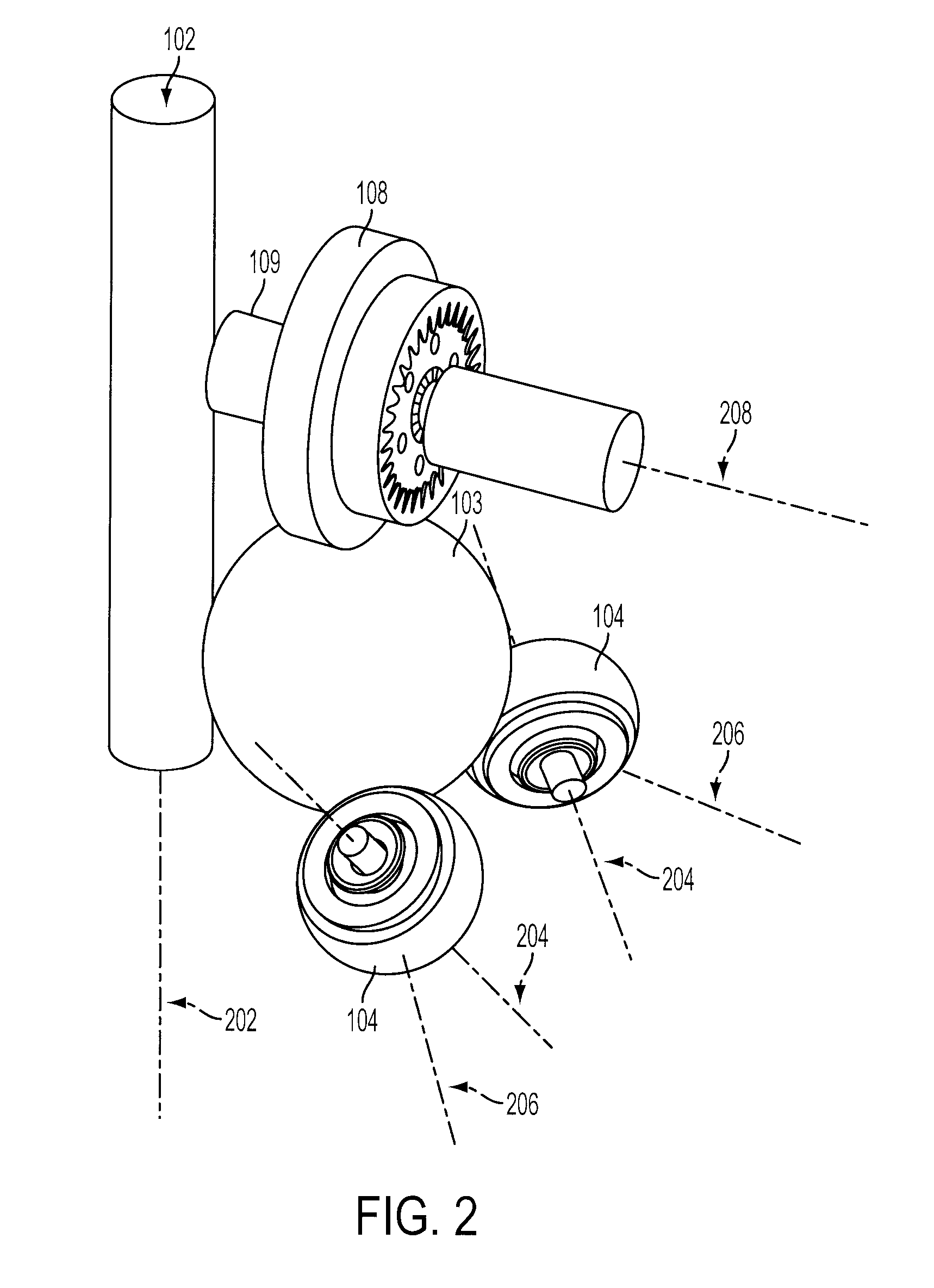
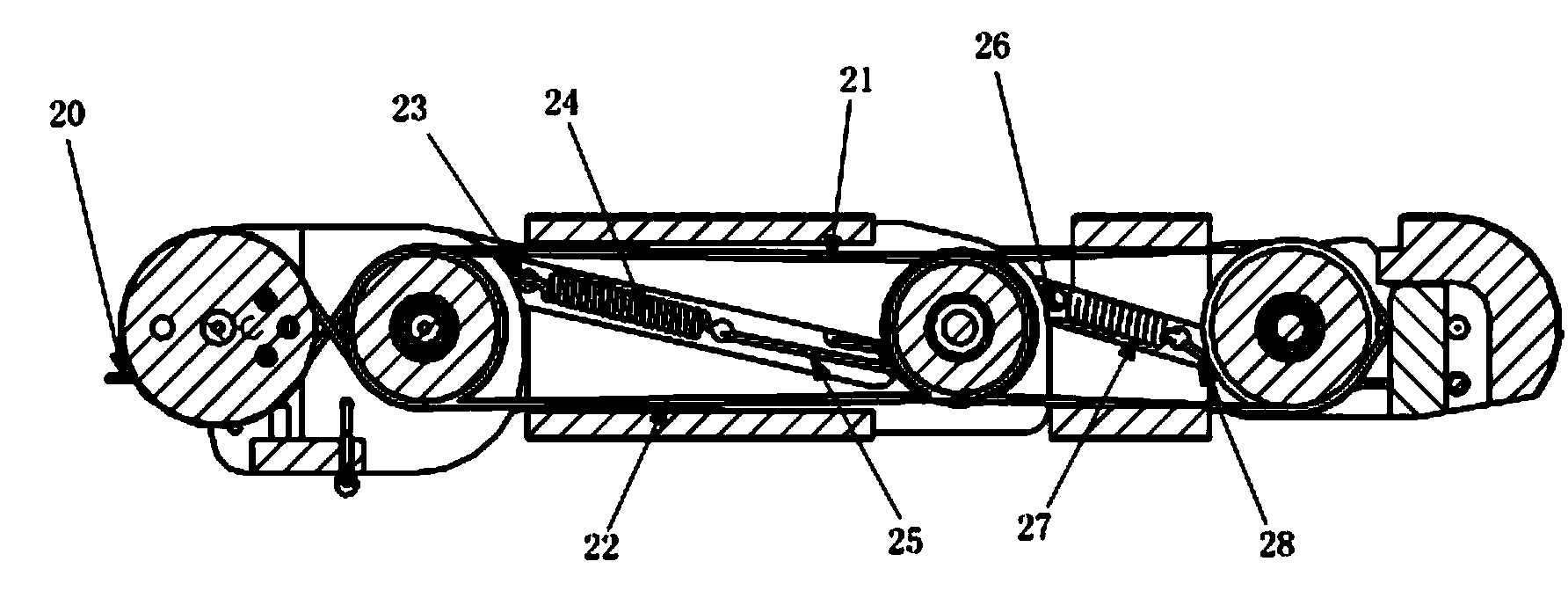
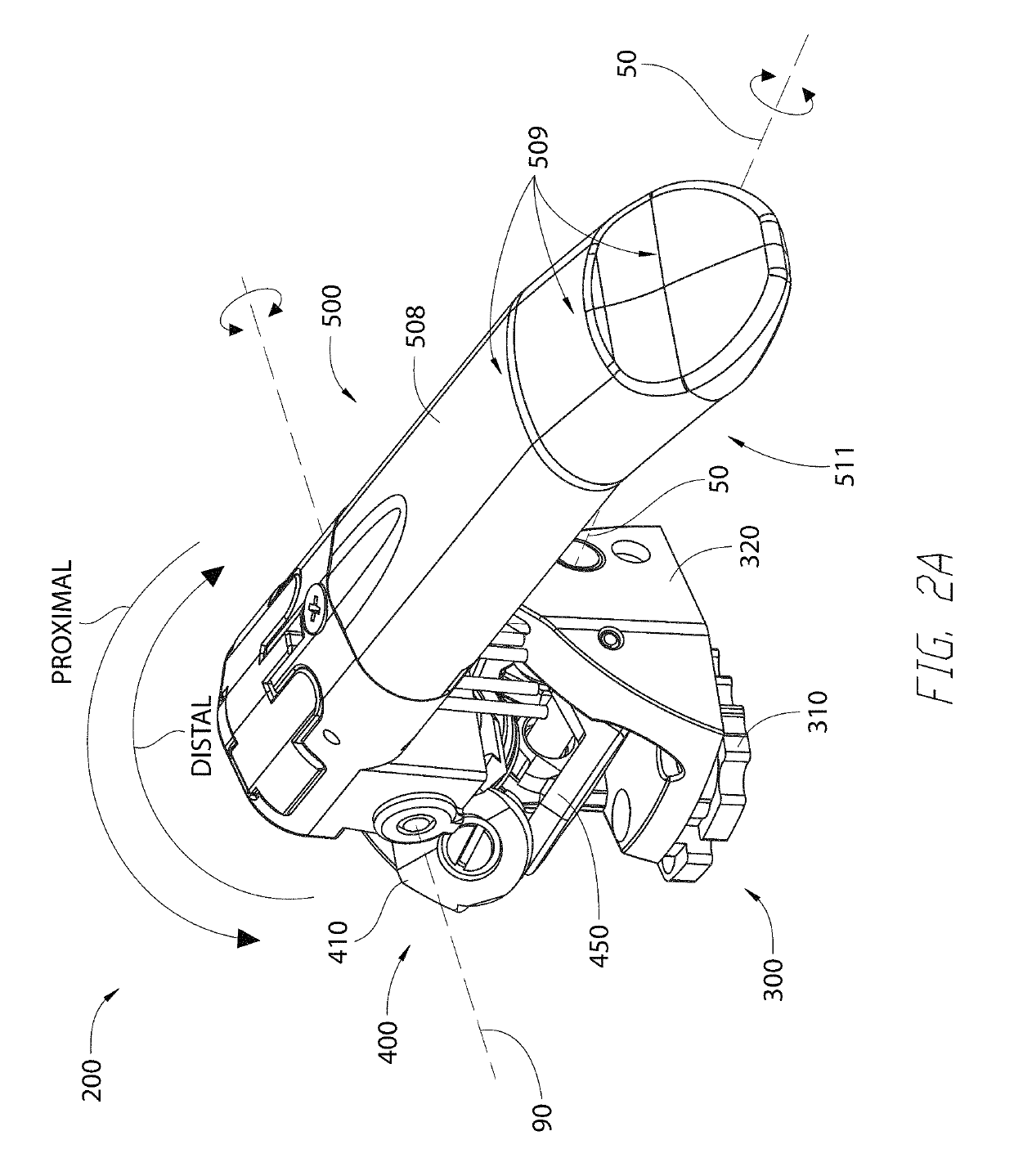
Continuously Variable Transmission with Mutliple Outputs
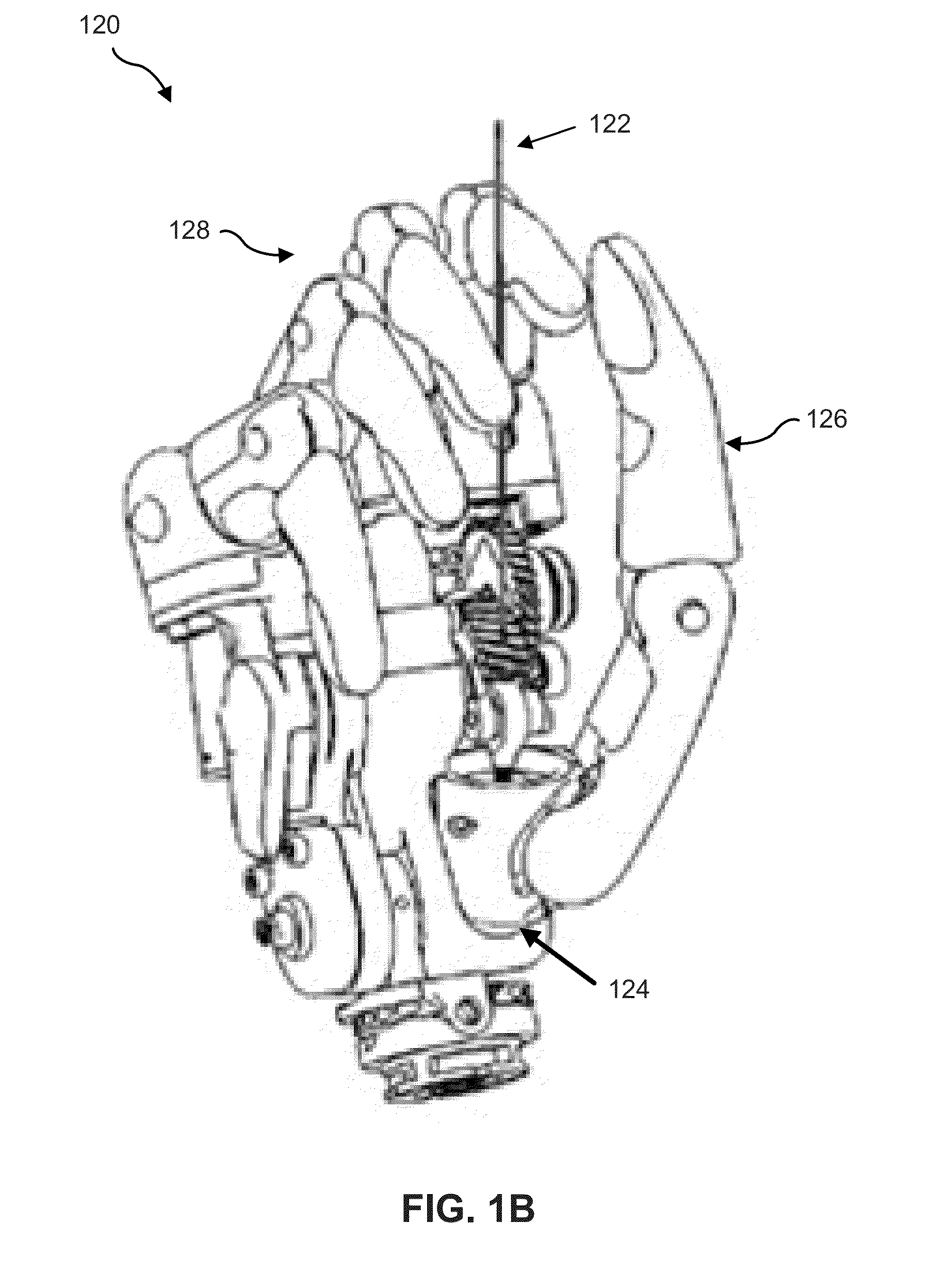
ActiveUS20080081728A1Efficient power utilizationSaving of weightFriction gearingsManual control with multiple controlling membersEngineeringProsthetic hand
A transmission or actuator offering multiple rotational outputs proportionate in speed to that of a common rotational input, each output according to its own ratio. The ratios are continuously variable between positive and negative values, including zero, and may be varied by electromechanical actuators under computer control. The transmission relates the output speeds one to another under computer control, and thus makes possible the establishment of virtual surfaces and other haptic effects in a multidimensional workspace to which the transmission outputs are kinematically linked. An example of such a workspace is that of a robotic or prosthetic hand.
Owner:HDT EXPEDITIONARY SYST
Prosthetic hand having a conformal, compliant grip and opposable, functional thumb
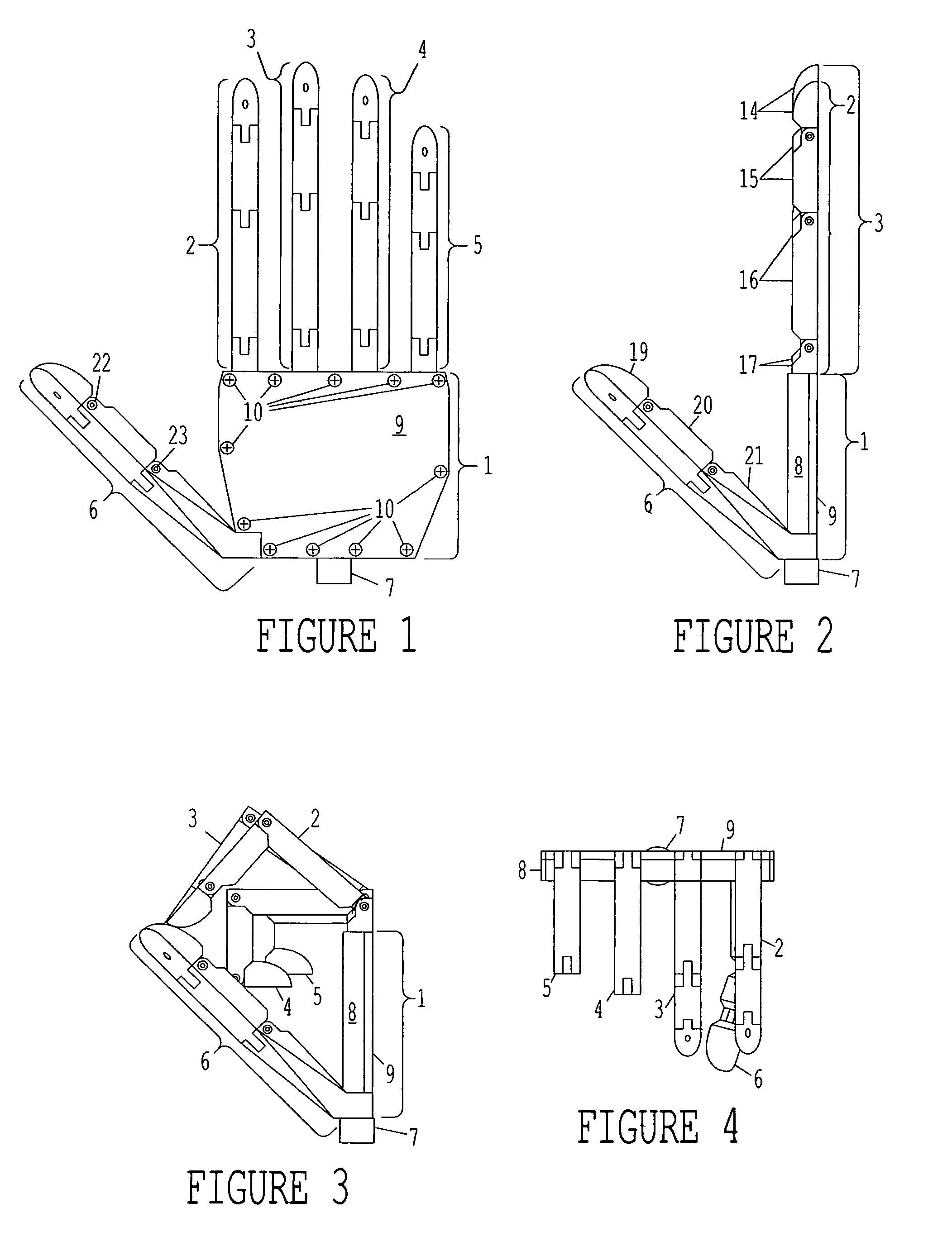
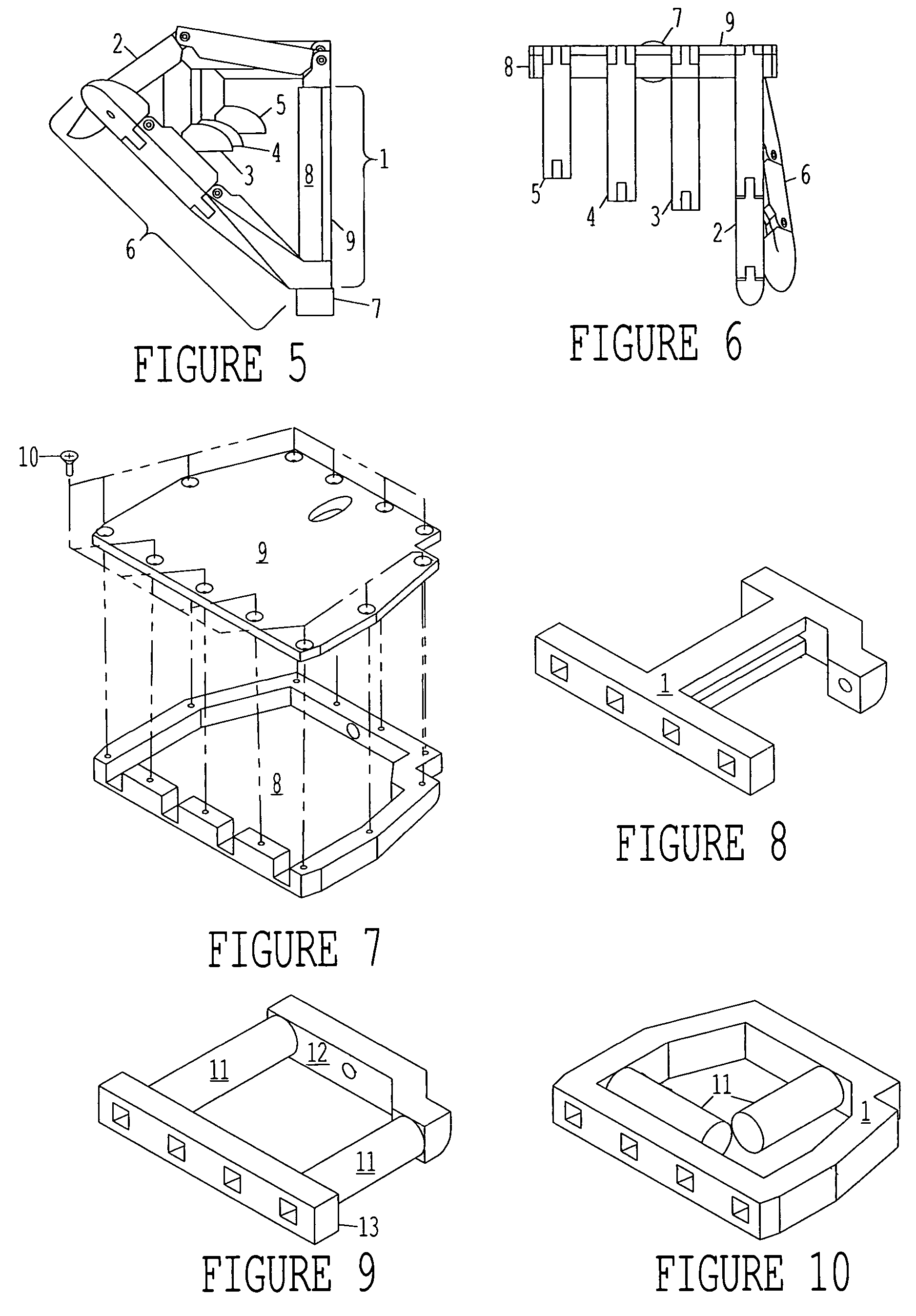
An anthropomorphic artificial hand having a mechanical system that allows for the digits to be compliant to pressure that tends to flex the digits, and provides for the digits to be self biasing to conform to the shape of the object being grasped. The hand comprises one to four fingers, with the fingers having up to three joints each. The hand may also comprise a thumb that can be rotated into and out of opposition of the fingers. The joints of the thumb are also self biasing to allow conformance to the object being grasped. The hand is of the voluntary closing operation, with all digits being self extending. This allows the hand to use two cables to operate if body powered (one for the fingers, one for the thumb). The hand may also be electronically powered using two channels for operating the fingers and thumb simultaneously.
Owner:WINFREY REX CLAYTON
Under-actuated prosthetic hand capable of reproducing hand grasping function
The invention discloses an under-actuated prosthetic hand capable of reproducing a hand grasping function; the under-actuated prosthetic hand is provided with an interphalangeal drive mechanism and a thumb drive mechanism in a palm; finger bodies take pulleys as main parts, and transmission mechanisms arranged in fingers are sequentially and alternately wound on all the pulleys of the fingers by steel wire ropes; joints in the fingers are in flexible coupling by elastic components; the interphalangeal drive mechanism adopts two motors to drive four fingers and multiple degrees of freedom of the fingers in a synergetic way; a thumb body takes a pulley as a main part, the transmission mechanisms in the finger bodies take transmission ropes as transmission mediums, the interphalangeal drive mechanism adopts a gear component for transmission matching, and the four degrees of freedom of the thumb can be controlled by two motors. After the under-actuated prosthetic hand is adopted, self-adaptive grasping of various objects can be accurately completed, and the rich grasping operation function of a human hand can be reproduced; the under-actuated prosthetic hand has the characteristics of being compact in structure, smaller in size, lighter in weight, convenient to control, accurate in grasping action, and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Foot-operated controller
InactiveUS7186270B2Eliminate needProgramme controlComputer controlIndependent functionRadiotransmitter
A practical control device having up to eight independent channels of communication for simultaneously operating a plurality of electromechanical devices or for simultaneously performing a plurality of independent functions on an electromechanical device, such as a prosthetic hand, includes a foot-operated controller and a microprocessor. The foot-controller includes a plurality of pressure sensors mounted at selected locations on a substrate. The microprocessor converts sensor inputs from the foot-operated controller into commands for a controllable electromechanical device such as a prosthetic hand. Commands may be communicated via a radio transmitter or via hard-wiring.
Owner:JEFFREY ELKINS 2002 TRUST
Thumb mechanism of underactuated self-adaptive hand prosthesis
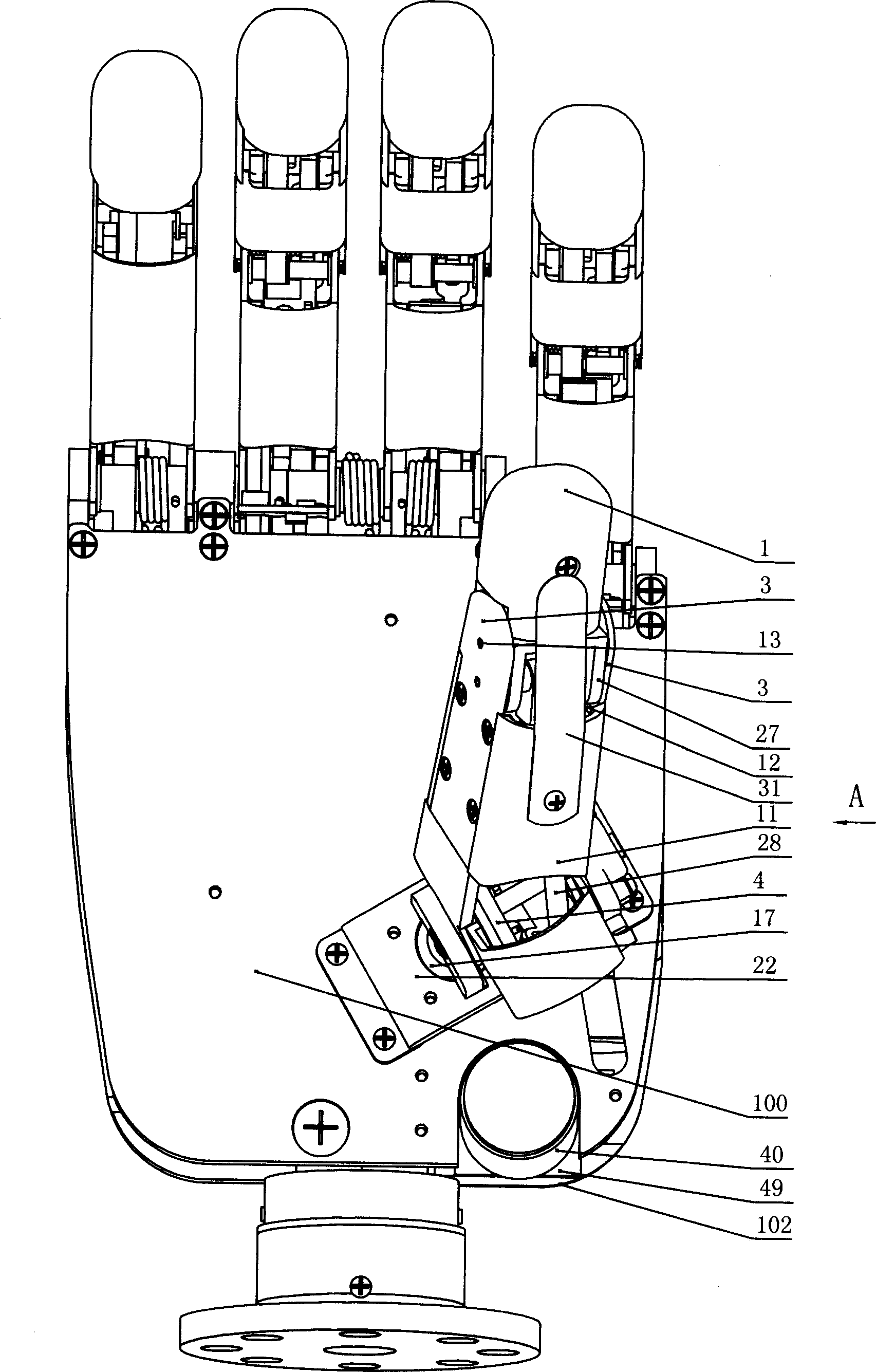
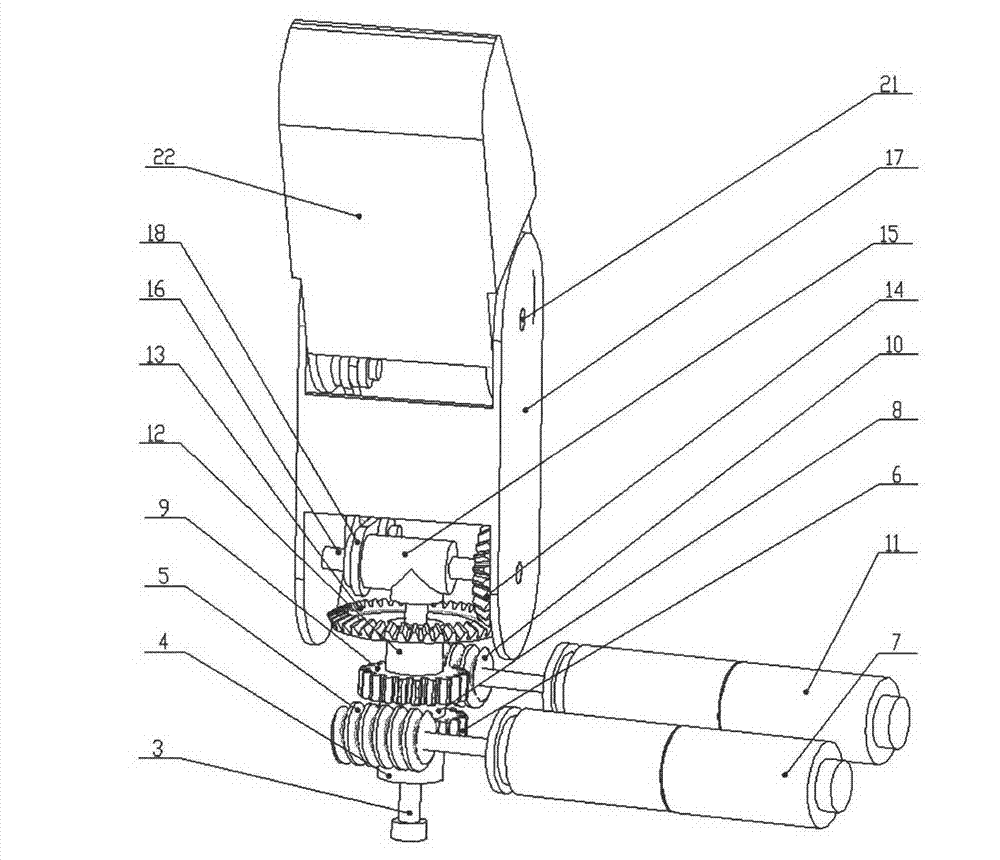
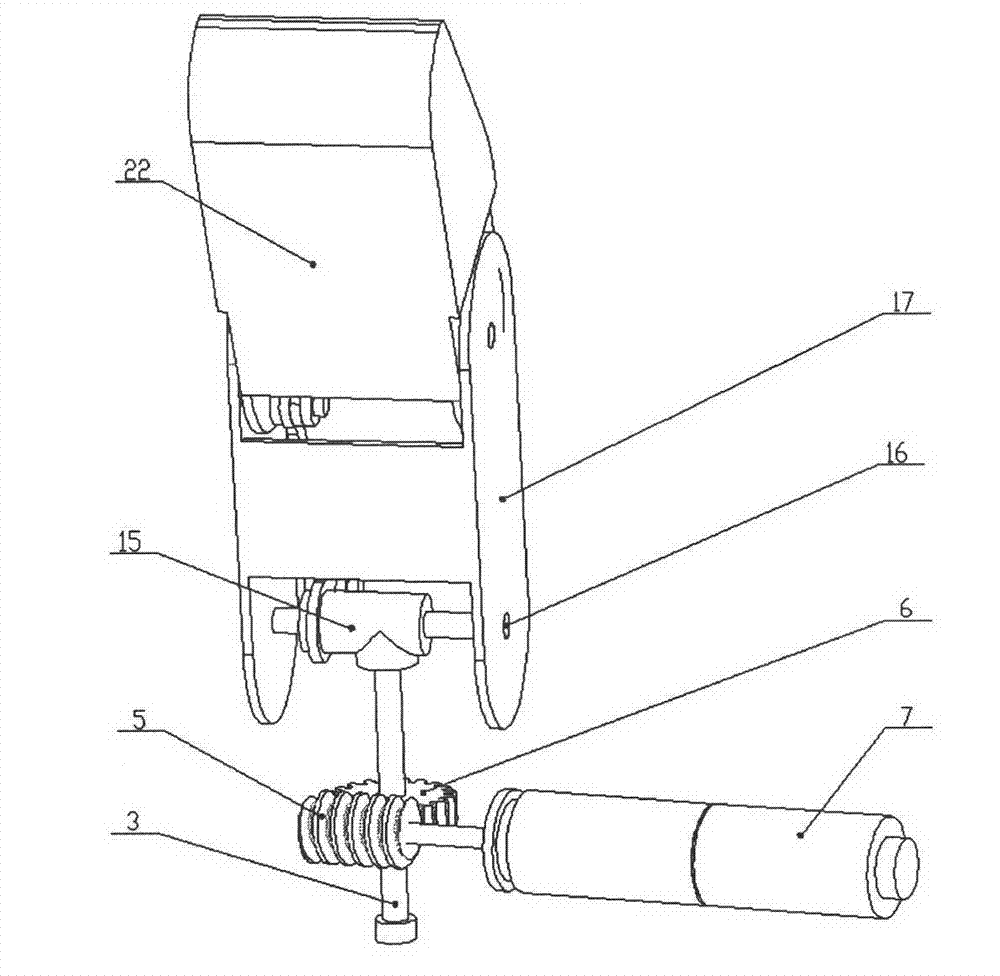
The invention discloses a thumb device of little-driving self-adaptive artificial hand, which is characterized by the following: connecting one end of thumb finger-tip pin case (32) with the thumb finger-tip connecting rod pin shaft (37); fixing the thumb wheeled bearing (55) on the wave generator axle (54) under the thumb decelerator wheel (10); connecting the thumb decelerator wheel (10) with the wheeled pad (9) through the wheeled fixation pin (57); fixing the wave generator (52) of harmonic gear decelerator on the other end of the wave generator axle (54) of wheeled pad (9). The invention can display a 130 deg conical moving space in the moving course to realize the finger-pin little-driving movement, which is adaptive for the object shape to reach full-covering the object and stable grasping.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-Grasp Prosthetic Hand
The present invention provides a prosthetic hand capable of multiple grasp types. The prosthetic finger units are underactuated both within and between the finger units using a differential mechanism arrangement. The locking movement of the prosthetic thumb unit is coupled to the differential mechanism. As the user repositions the prosthetic thumb unit, the differential mechanism is effected as to alter both the initial positions and force distribution of the prosthetic finger units. The present invention further provides an additive manufacturing molding method for making the same.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Enhanced-functionality prosthetic limb
InactiveUS20050234564A1Many functionsLong lastingArtificial handsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationThree degrees of freedom
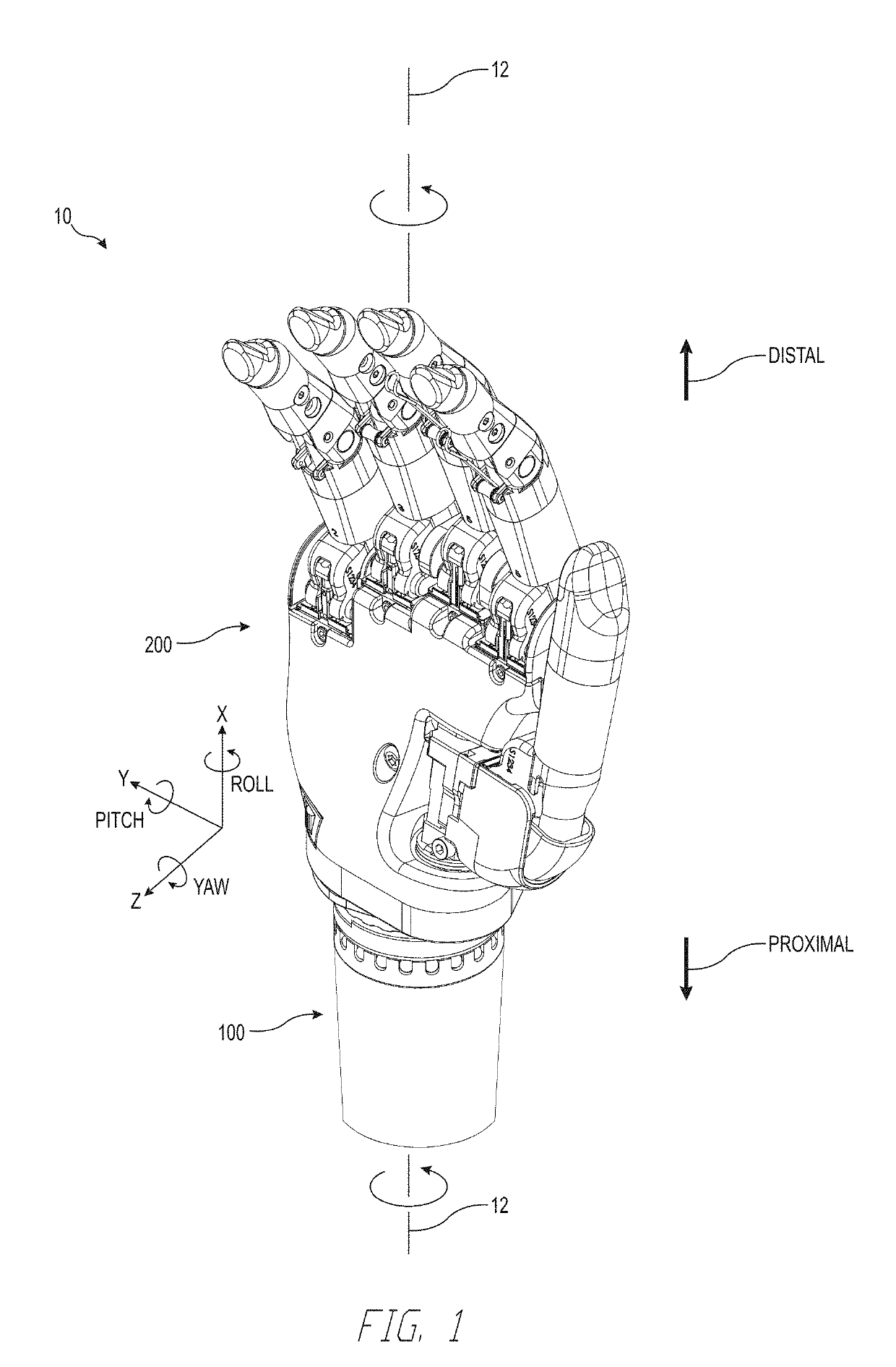
An enhanced-functionality prosthetic limb is disclosed, comprising a prosthetic hand or gripping device, and forearm, which may be body-powered or motor-powered, targeted primarily for pediatric use, attachable to the arm stump of a below-elbow, or above-elbow, with the inclusion of a prosthetic elbow, amputee individual, with incorporation of one or more of the following features: expandability in length or size to accommodate child growth or other expandability needs, grasp locking capability, individual finger locking capability, three degree of freedom wrist joint, dynamic tensional rotation control of wrist, dynamic grasp control to allow grasping of irregular objects, extended grasp for gripping larger objects, excessive force breakaway, and algorithms to support by user of care-provider adjustment of the prosthesis.
Owner:FINK RAINER +5
Wrist device for use with a prosthetic limb
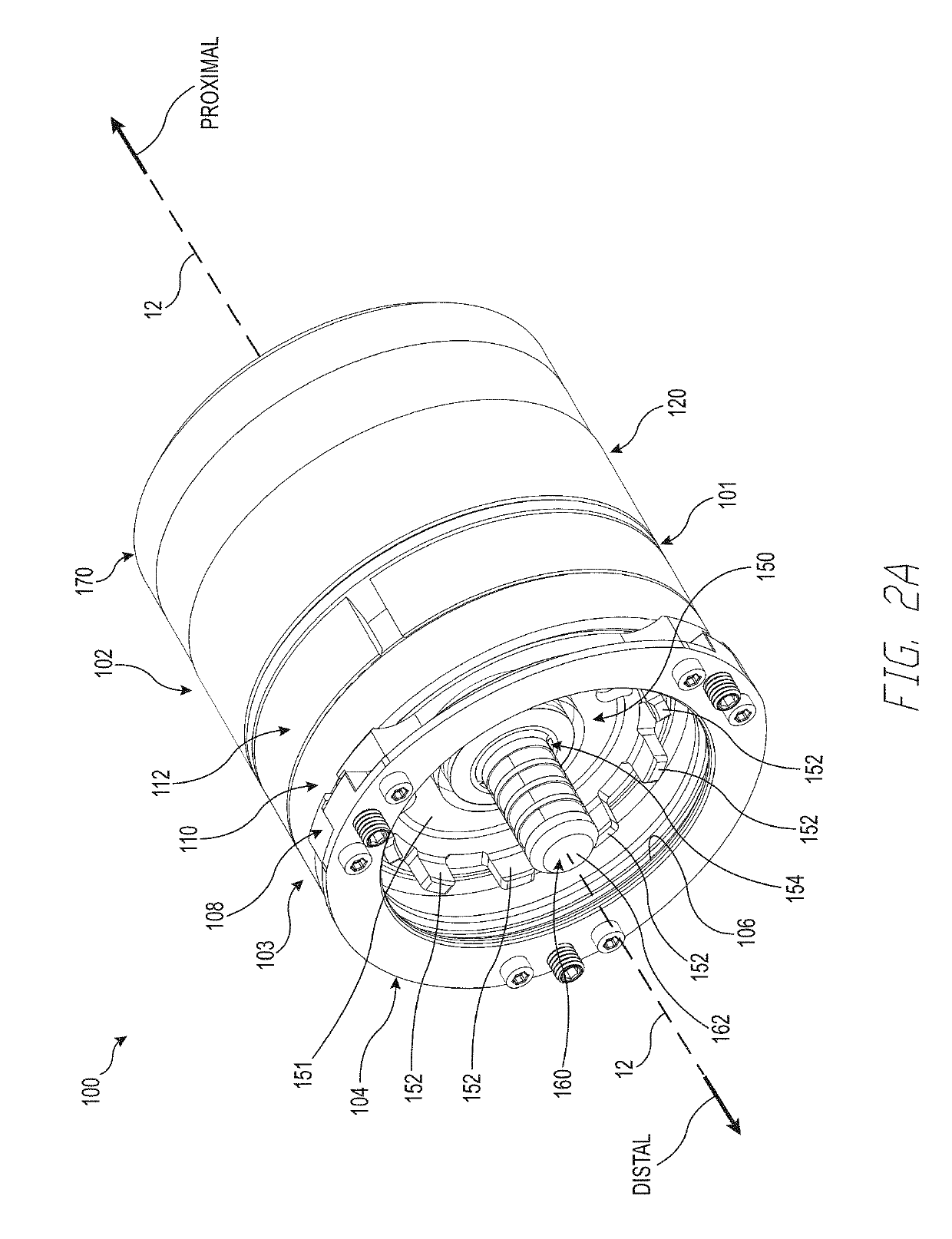
A wrist device is provided for use with a prosthetic limb. The wrist device includes a base plate that is configured for attachment to a prosthetic limb and a sliding lock plate that is slidably engaged with the base plate. Both the base plate and the sliding lock plate have openings. Also included in the invention is a semi-cylindrical rotator that is configured for attachment to a prosthetic hand. The semi-cylindrical rotator has slots configured to receive the sliding lock plate and is coupled to the base plate in a manner that allows the sliding lock plate to lock into the slots.
Owner:MOTION CONTROL
Continuum transmission mechanism-based under-actuated prosthetic hand
The invention discloses a continuum transmission mechanism-based under-actuated prosthetic hand, which comprises a motor driving unit, a continuum transmission mechanism and a mechanical hand, wherein the continuum transmission mechanism comprises a fixing plate, a plurality of fixing pipes, a plurality of guide pipes, a base, a plurality of driven wires, spacing discs and a locking disc; the motor driving unit comprises motors, output mechanisms and a plurality of driving wires; the mechanical hand comprises a palm and five fingers; each finger is provided with a plurality of knuckles; the rotation of the motors can be converted into the linear movement of the driving wires through the output mechanisms, and the continuum transmission mechanism can be driven to be deformed by the linear movement of the driving wires to move the driven wires of which one end of each is fixed with the locking disc, so that each finger of the mechanical hand is driven to finish corresponding actions. According to the continuum transmission mechanism-based under-actuated prosthetic hand, the use of a conventional rigid kinematic pair such as a hinge and a connecting rod is avoided, so that the system hysteresis is effectively eliminated, and the weight of the prosthetic hand is reduced; a great number of elastic alloy wires are used, so that the prosthetic hand is high in adaptability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Prosthetic hand having a conformal, compliant grip and opposable, functional thumb
An anthropomorphic artificial hand having a mechanical system that allows for the digits to be compliant to pressure that tends to flex the digits, and provides for the digits to be self biasing to conform to the shape of the object being grasped. The hand comprises one to four fingers, with the fingers having up to three joints each. The hand may also comprise a thumb that can be rotated into and out of opposition of the fingers. The joints of the thumb are also self biasing to allow conformance to the object being grasped. The hand is of the voluntary closing operation, with all digits being self extending. This allows the hand to use two cables to operate if body powered (one for the fingers, one for the thumb). The hand may also be electronically powered using two channels for operating the fingers and thumb simultaneously.
Owner:WINFREY REX CLAYTON
Systems and methods for prosthetic wrist rotation
Features for a prosthetic wrist and associated methods of rotation are described. The prosthetic wrist attaches to a prosthetic hand. Rotation of the prosthetic wrist is performed in combination with grip formation of the prosthetic hand. An IMU provides data associated with the orientation of the prosthetic hand. A desired grip for the prosthetic hand is selected, for example by gesture control. A rotation for the prosthetic wrist is determined based on the orientation of the prosthetic hand from the IMU data and on the selected desired grip. The prosthetic wrist techniques can also be used in combination with prosthetic arms, elbows and / or shoulders. Example structural configurations for the prosthetic wrist and hand are also provided.
Owner:TOUCH BIONICS
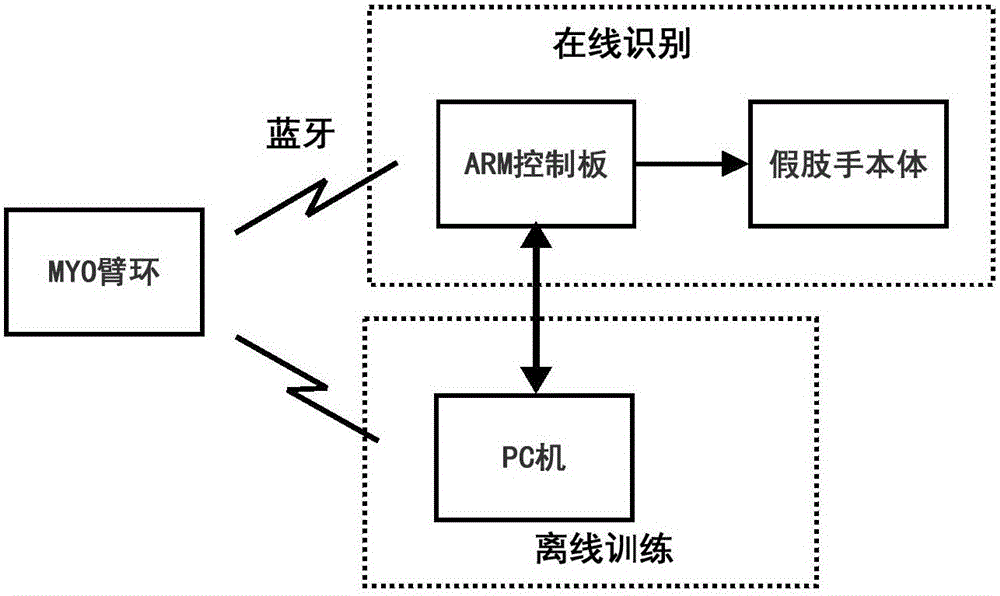
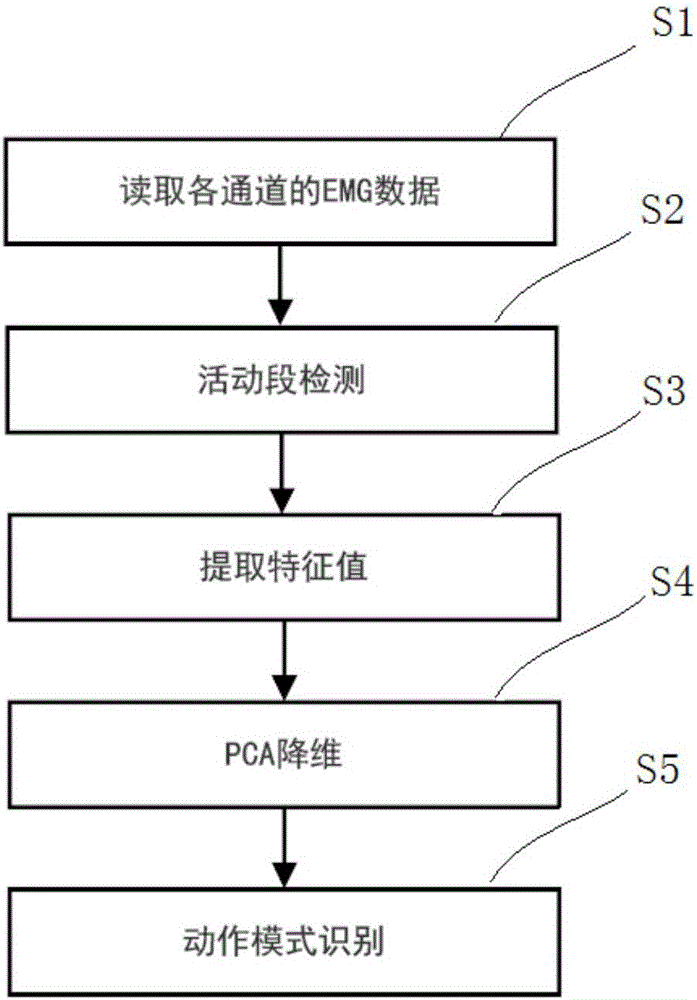
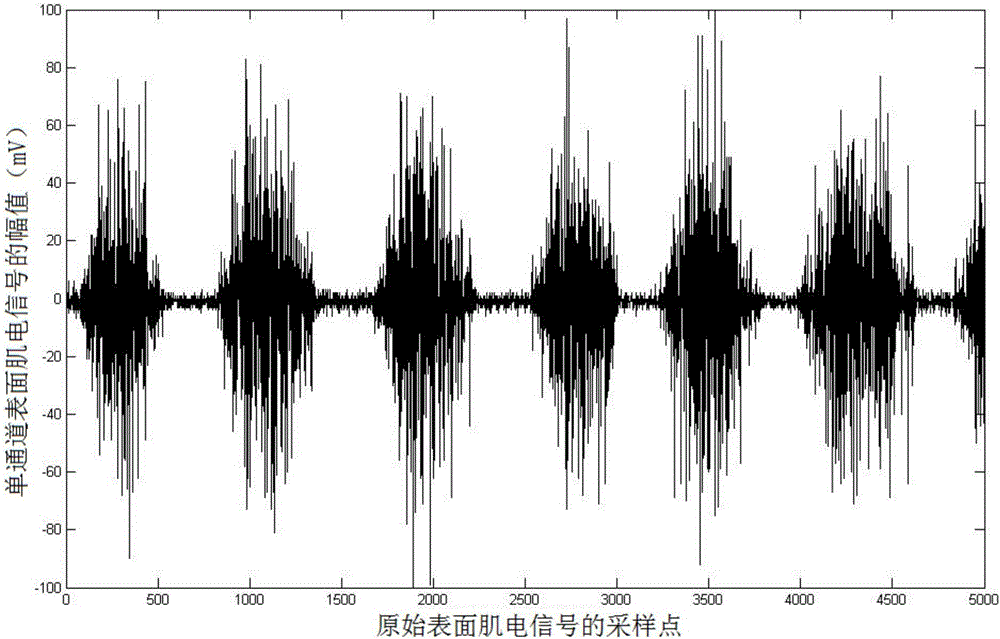
Prosthetic hand control method based on MYO armlet
The invention relates to a prosthetic hand control method based on an MYO armlet. An electromyographic signal of arm muscles is acquired in real time through the MYO armlet and read, the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal is extracted, hand motion mode is recognized online by means of the characteristic value and a well trained neural network model, and the motion mode is converted into a corresponding motor movement instruction which drives a prosthetic hand to make a corresponding motion; a method for training the neural network model comprises the steps of executing the hand motion, acquiring the electromyographic signal of arm muscles through the MYO armlet, reading the electromyographic signal, extracting the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal, and training the hand motion neural network model according to a sample of the characteristic value. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being convenient to use, low in cost, high in cost performance, wide in application range and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Myoelectric estimation method for motion moment of wrist joint
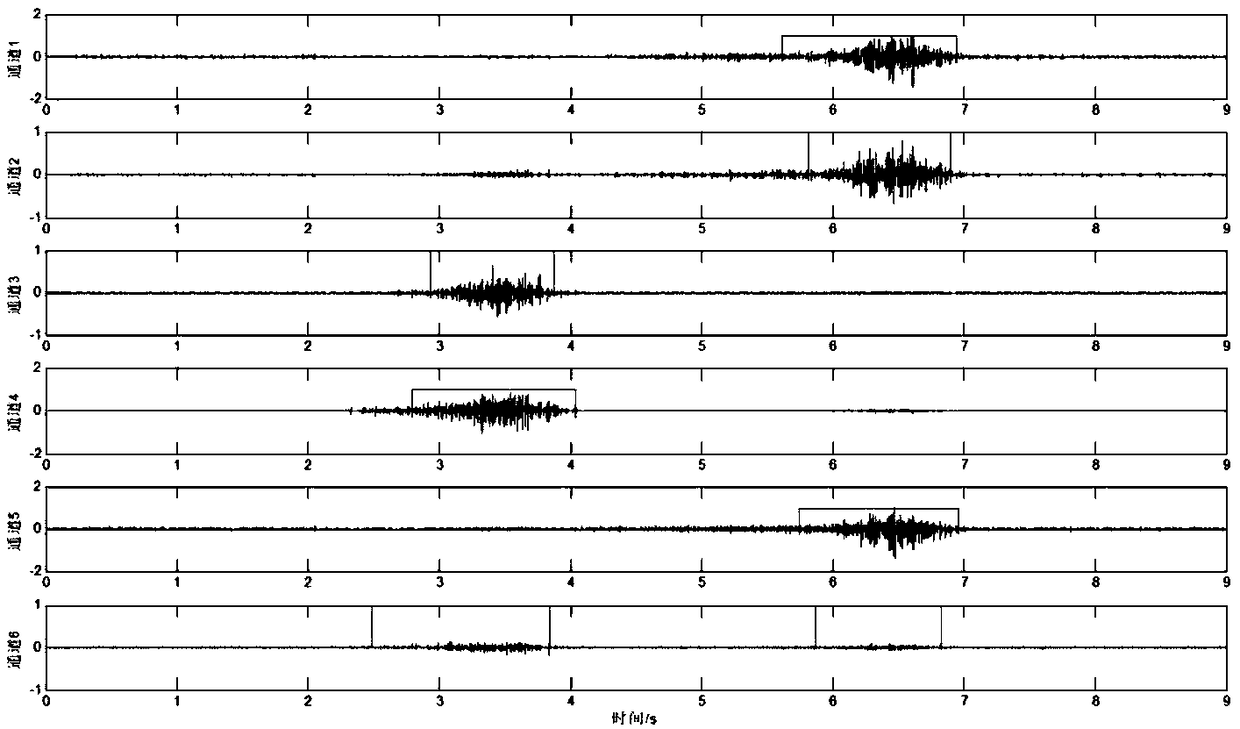
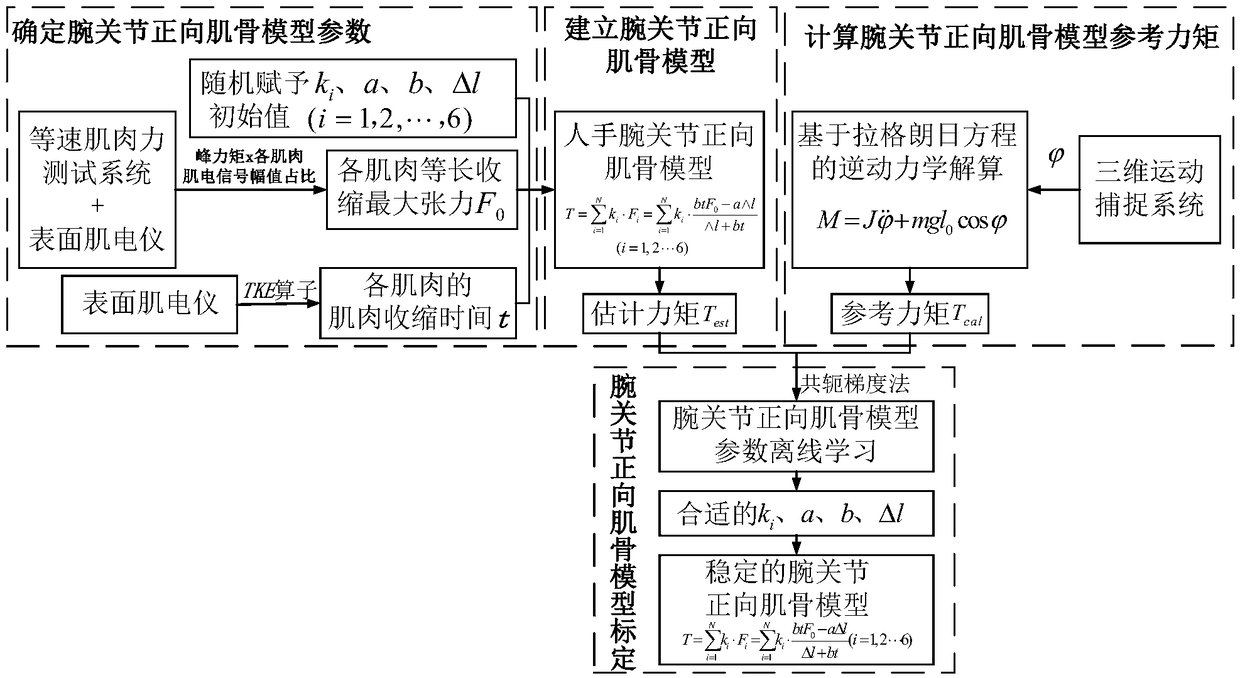
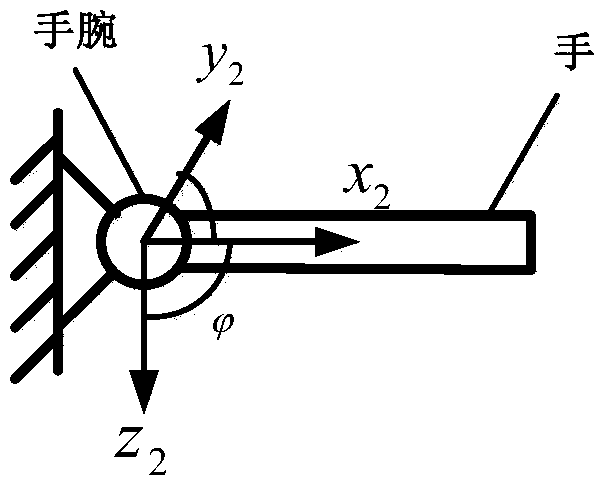
ActiveCN109259739AHigh tension precisionHigh resolutionDiagnostic signal processingSensorsThree dimensional motionWrist joints
The invention discloses a myoelectric estimation method for the motion moment of a wrist joint. The surface electromyography signals of six forearm muscles were collected in the process of wrist flexion and extension, and the muscle contraction time was calculated by TKE operator. The maximum isometric contraction tension of each muscle was measured synchronously by isokinetic muscle strength testing system and electromyograph. The forward muscle-bone model of wrist joint was established. The maximum tension of muscle contraction time and muscle contraction time was input, and the estimated torque at the limit position of wrist joint bending and extension was output. The kinematics data of the wrist joint during bending and stretching were obtained by using the three-dimensional motion capture system, and the reference moment at the limit position was calculated. Taking the square of the error between the estimated torque and the reference torque as the objective function, the conjugate gradient method is used to calibrate the forward muscle-bone model of the wrist joint, and the surface electromyography signal is used to estimate the torque of the wrist joint. The invention can beapplied to the fields of myoelectric artificial hand, rehabilitation medical treatment, bio-electric integration and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device
The invention relates to an underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device, which is provided with five independently controlled modular fingers and has 16 freedom degrees. The whole hand is driven by 11 motors; the dimension and the shape are similar to those of the hand of an adult. Except for a thumb, the other four fingers have the completely identical structures; the thumb has one freedom degree of doing longitudinal rotation around the palm base; through the arrangement of a rotating shaft, when the whole hand grasps objects, the grasping force of the forefinger, the ring finger and the small finger on the objects can be in symmetrical distribution at the two sides of the middle finger; the grasping stability is improved. Modular fingers are used; the two motors are respectively used for driving a finger base part joint, a middle joint and a tail end joint; the middle joint and the tail end joint are coupled by a structure-variable connecting mechanism; through a connecting rod mechanism, the relative positions of the two coupled finger joints after the contact with the objects can be actively regulated, so that the fingers can wrap the objects according to the shape of the grasped objects; the self adaptability to the appearance of the objects is high; the grasping action better conforms to the human hand. The structure of the whole hand is simple; the grasping force is great; the grasping rigidity is high; the control is simple; the grasping self adaptability is high; the underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device is applicable to the fields of disabled people artificial hands, explosive handling, nuclear equipment detection and humanoid robots.
Owner:杜宇
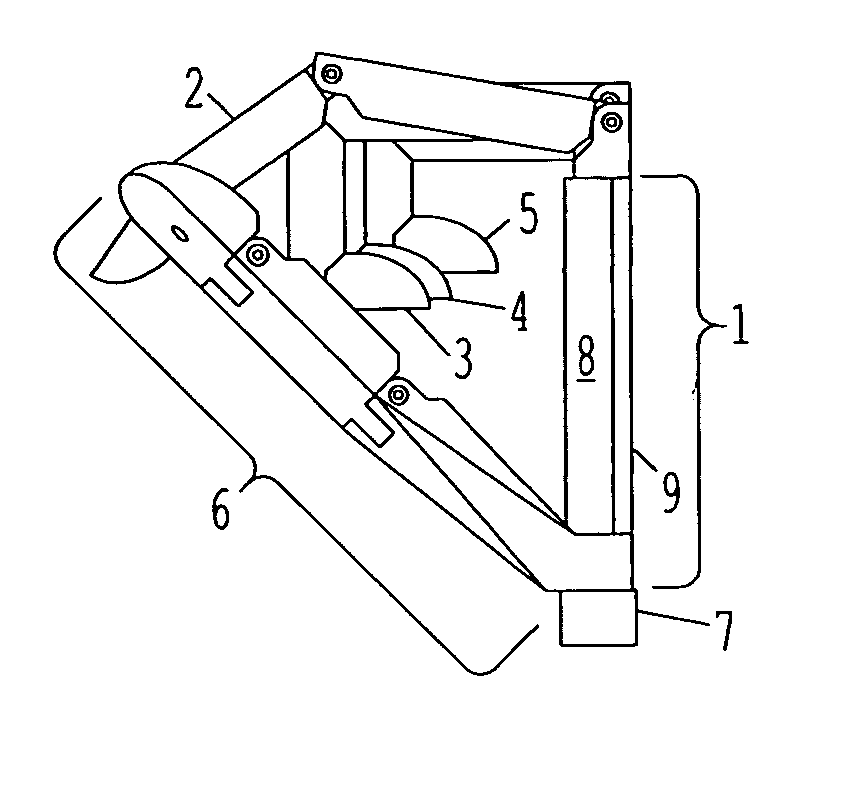
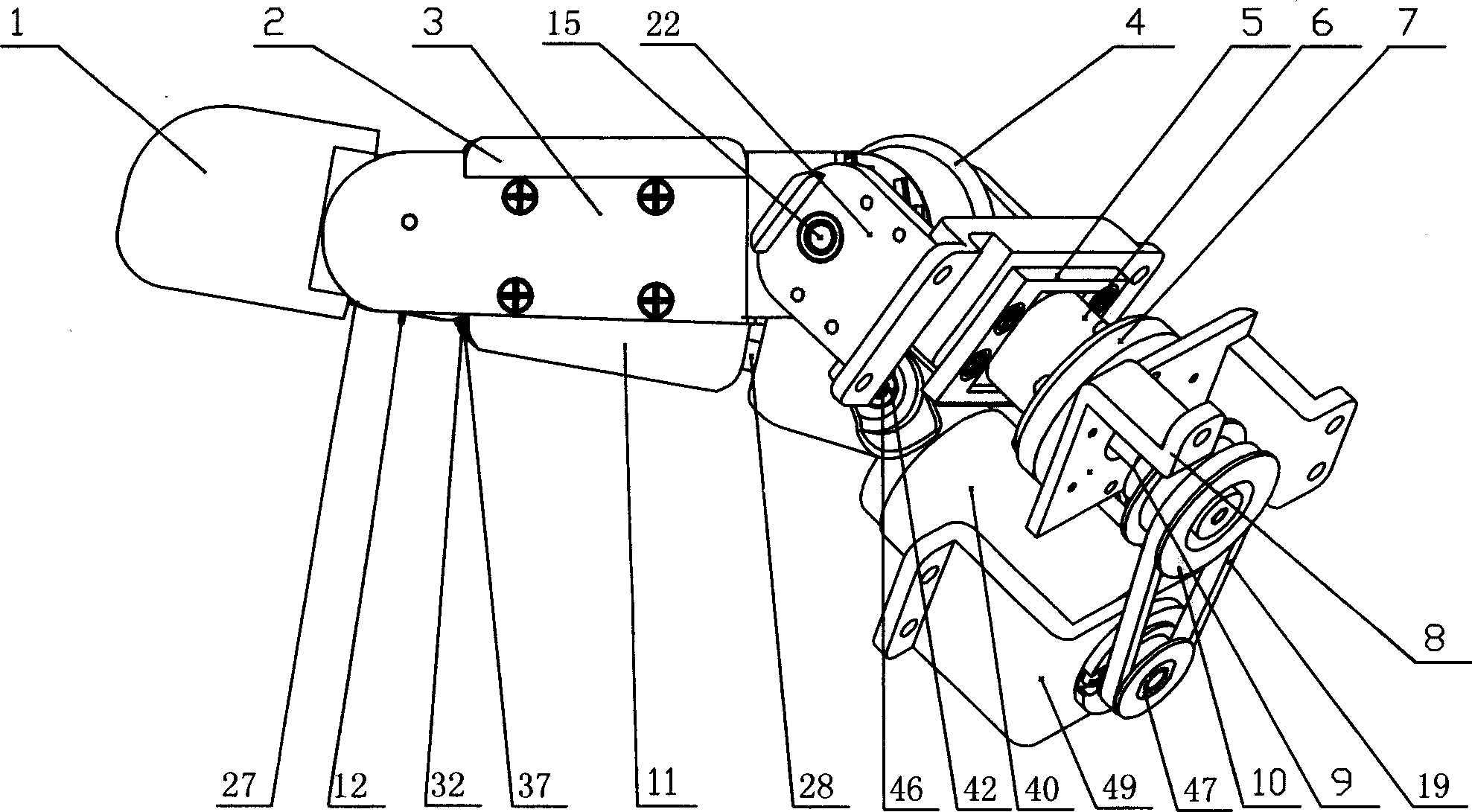
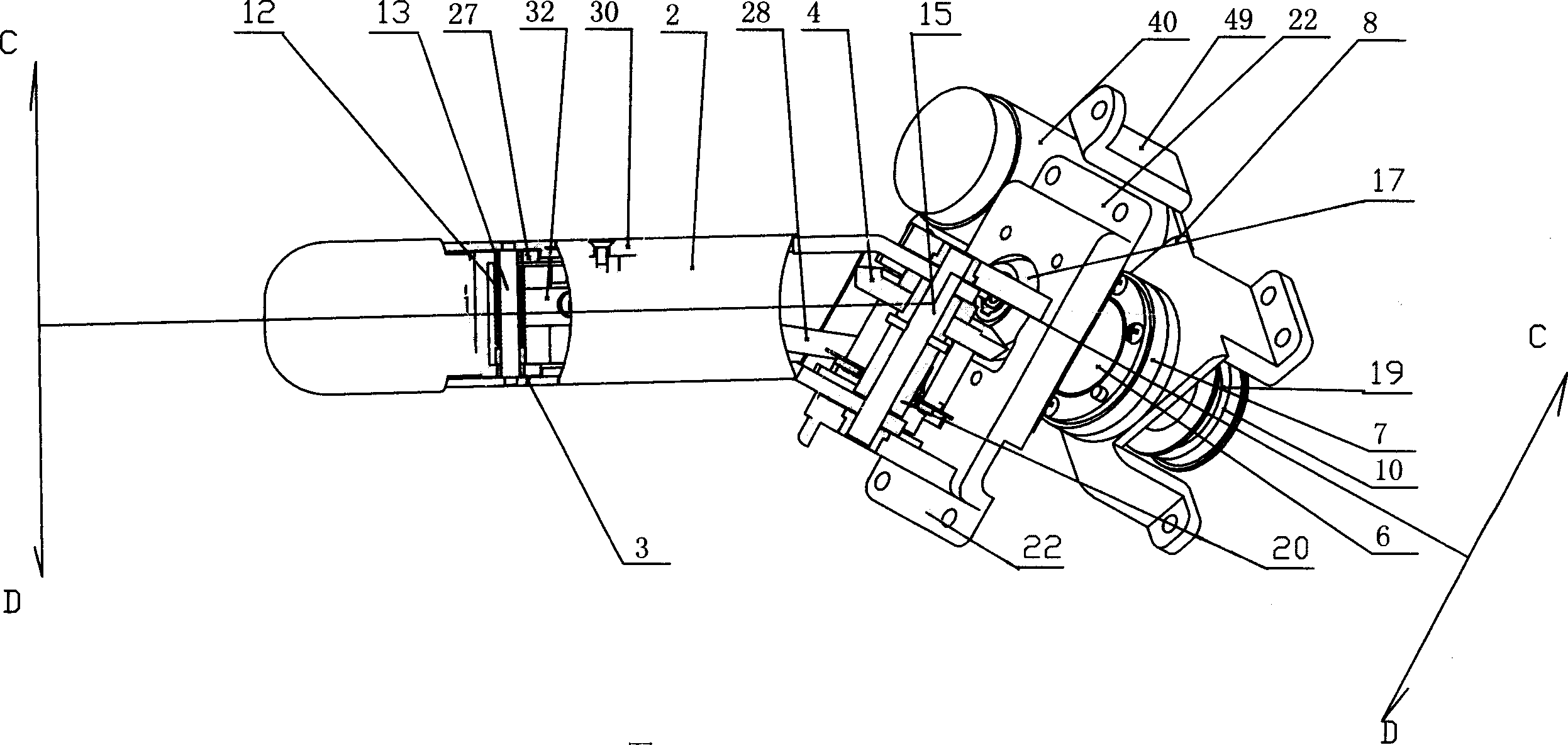
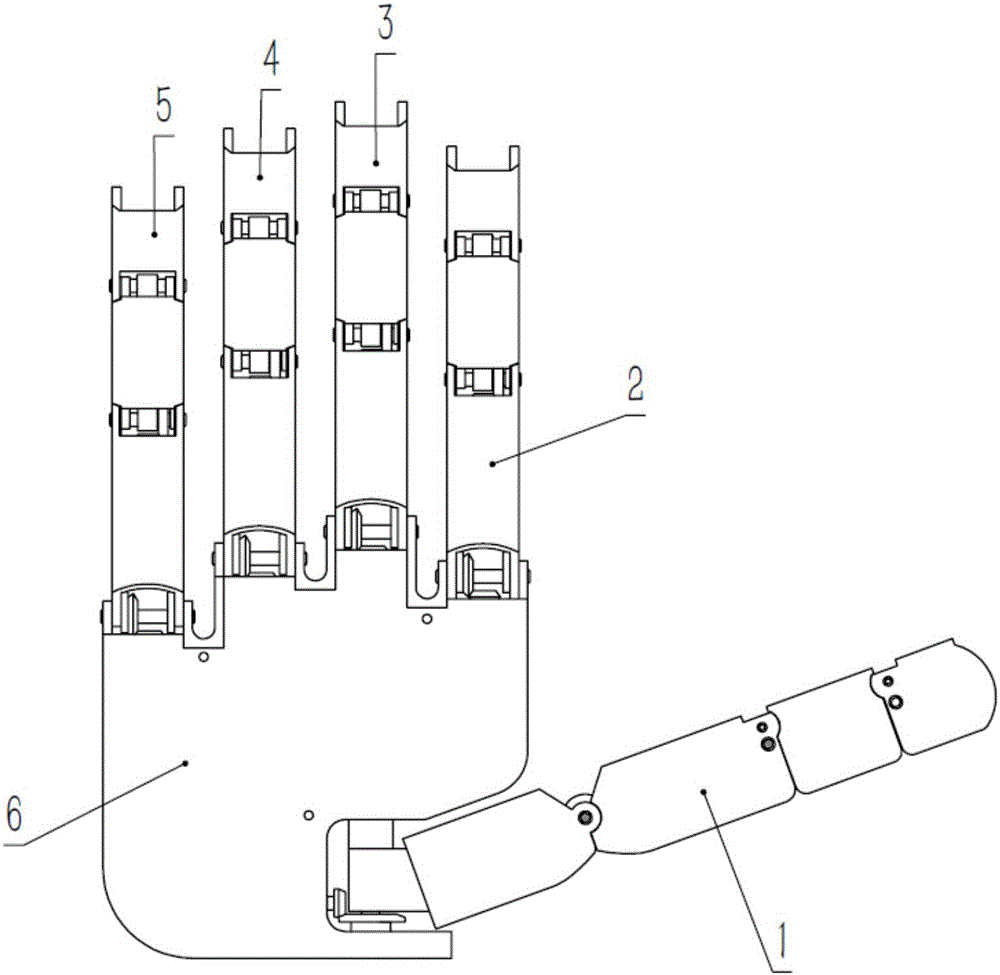
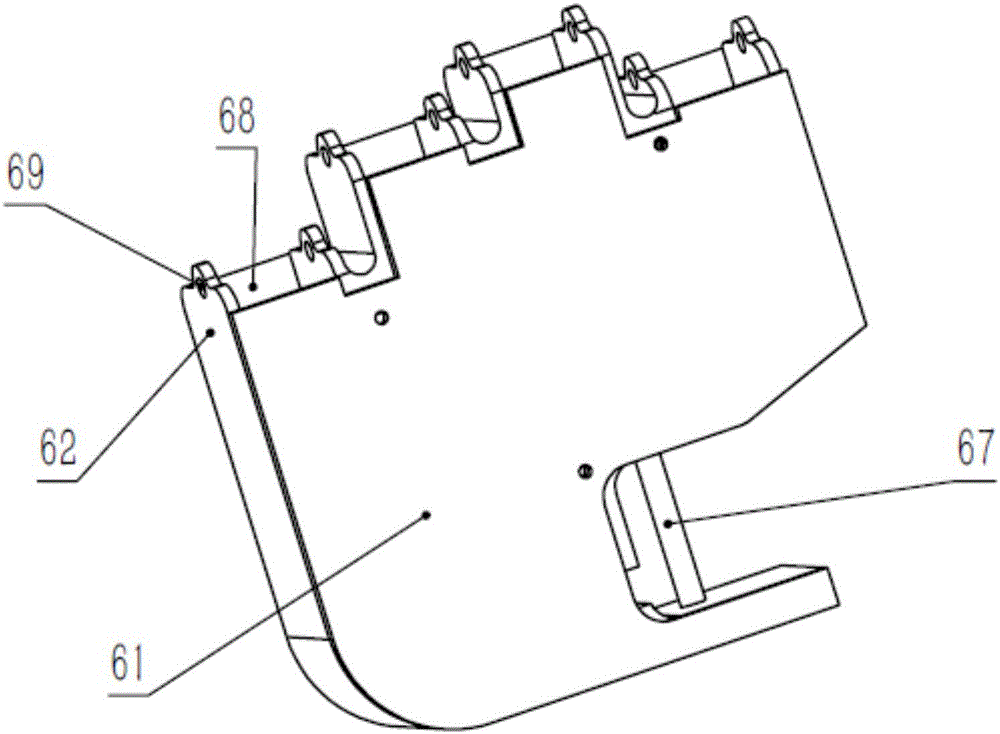
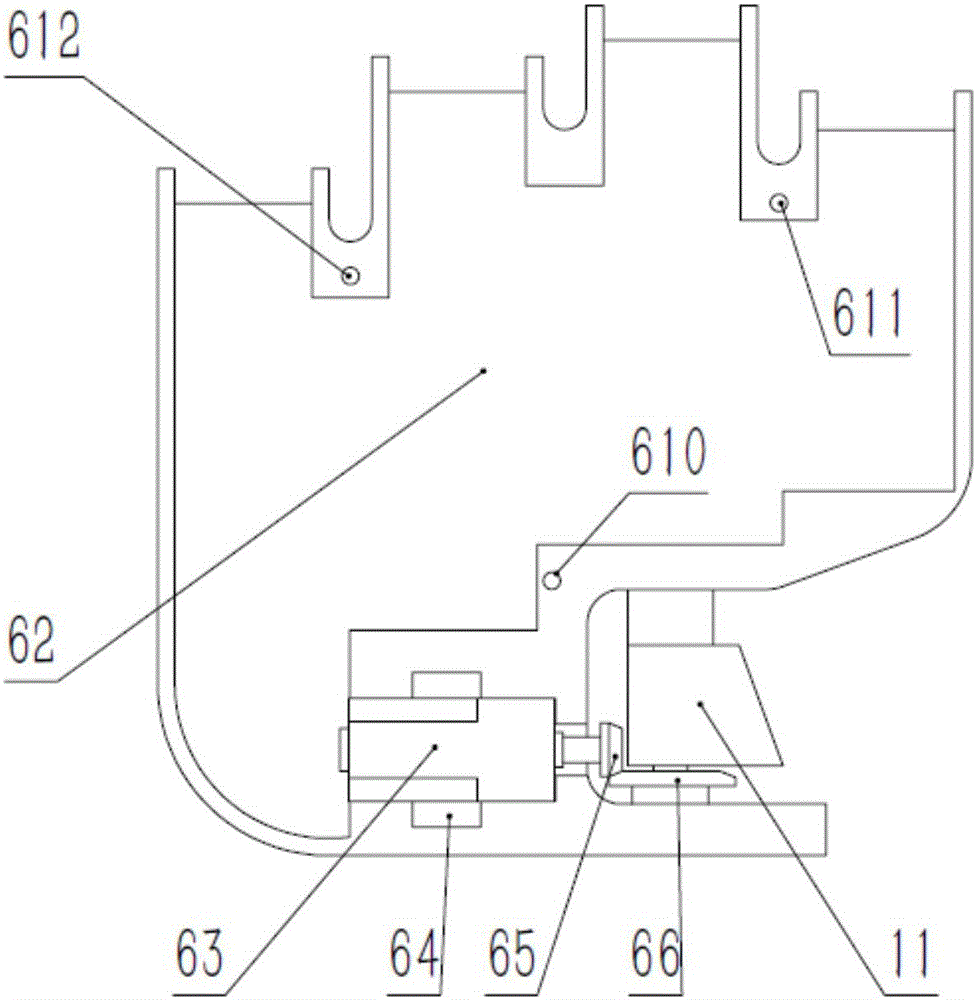
Thumb mechanism for under-driven adaptive prosthetic hand
InactiveCN101057791AImprove motor flexibilityHigh movement reliabilityArtificial handsEngineeringBiological activation
The invention discloses a thumb device for artificial hand. The driving device (1) is in rotary connection with the back part of near knuckle (4), the front part of near knuckle is in rotary connection with back part of middle knuckle (3), and the front end of middle knuckle is in rotary connection with the back part of far knuckle (2). The middle knuckle and near knuckle imitate deficient activation motion of real hand driven by middle knuckle shaft disk, the middle knuckle and far knuckle imitate coupling motion of real hand driven by coupling rod; and the knuckle number of thumb is imitative to that of real hand. The invention is characterized by simple structure, real-like appearance and flexible motion of each knuckle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Under-actuated finger capable of being flexibly coupled between joints
ActiveCN104400792AEffectively reproduce dynamic coordination lawsAchieve underactuationJointsGripping headsEngineeringProsthetic hand
The invention discloses an under-actuated finger capable of being flexibly coupled between joints. The finger takes pulleys as main components; transmission mechanisms in the finger are sequentially wound on various pulleys of the finger by virtue of a tensioning rope and anti-loose rope, and comprise two coupling springs and stay cords between finger knuckles, thus multi-freedom movement of the fingers is finished by one input. Through the under-actuated finger, a finger body cooperates with the transmission mechanisms in the finger to form the under-actuated finger; the adaptive ability during grabbing can be accurately achieved; meanwhile, the finger is suitable for prosthetic hand instruments in various complicated application environments due to embedded flexibility of the finger.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Automated hand
ActiveUS20180036145A1Prevent lateral movementProvide complianceGripping headsArtificial handsLocking mechanismEngineering
The invention relates to an automated hand, such as a prosthetic hand. In one form, the automated hand may be fluid compatible. In one form, the automated hand may comprise features to reduce the risk of harm to motors and / or other sensitive components of the hand when subject to an impact. In one form, the hand may comprise a wrist joint configured to allow the hand to curl and flex and / or to rotate. In one form, one or more digits of the hand may be individually controlled. In one form the hand may include a thumb rotation locking mechanism. In one form the hand may be provided with removable grip plates. In one form, the hand may be configured for use as a training hand.
Owner:5TH ELEMENT
Thumb mechanism of artificial hand
InactiveCN102896639AUnderactuated realizationWith self-locking functionJointsGripping headsGear wheelEngineering
The invention relates to a thumb mechanism of an artificial hand, in particular to a thumb mechanism of a humanoid hand and aims to solve the problem that a thumb of each of most existing artificial hand moves for grasp in one direction only. Rotation of a thumb of the thumb mechanism is achieved by worm-gear transmission. A function of bending for grasp is achieved for the thumb by worm-gear transmission and bevel gear transmission. A first knuckle and a second knuckle of the thumb are under-actuated by a plane four-bar mechanism. The thumb mechanism has the advantages that the thumb can rotate, bend for grasp and spatially move in a complex way during grasp motion of the thumb, the function of omnidirectional grasp can be achieved for the thumb, and various motion functions of a thumb of a human hand are achieved for the thumb of the thumb mechanism; a transmission mechanism of the thumb is in worm-gear transmission and has the self-locking function, and grasp torque of the thumb can be maintained after power failure of a motor; and the thumb mechanism is simple in structure, flexible to move, convenient to control, light in weight, small in size and large in thumb grasp strength.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Systems and methods for prosthetic wrist rotation
Features for a prosthetic wrist and associated methods of rotation are described. The prosthetic wrist attaches to a prosthetic hand. Rotation of the prosthetic wrist is performed in combination with grip formation of the prosthetic hand. An IMU provides data associated with the orientation of the prosthetic hand. A desired grip for the prosthetic hand is selected, for example by gesture control. A rotation for the prosthetic wrist is determined based on the orientation of the prosthetic hand from the IMU data and on the selected desired grip. The prosthetic wrist techniques can also be used in combination with prosthetic arms, elbows and / or shoulders. Example structural configurations for the prosthetic wrist and hand are also provided.
Owner:TOUCH BIONICS
Bionic prosthetic hand and device based on 3D printing
InactiveCN106974749AEasy to manufactureLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusArtificial handsMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
The invention provides a bionic prosthetic hand and device based on 3D printing. The hand comprises an electromyography sensor, a single chip microcomputer, a servo motor, a transmission structure and an actuator. The electromyography sensor is connected with the single chip microcomputer, which is used for collecting original electromyography signals and sending impulse signals to the single chip microcomputer. The single chip microcomputer is connected with the servo motor, which is used for sending driving signals to the servo motor correspondingly according to the original electromyography signals or the impulse signals. The servo motor is connected with the transmission structure, which is used for affecting the transmission mechanism connected with the actuator according to the driving signal, thereby achieving the control over movement attitudes of a flexible or elastic hand body in the actuator through the transmission mechanism. According to the bionic prosthetic hand and device based on the 3D printing, bending movements and attitude hold of fingers can be achieved through simple structures, and a variety of hand gesture movements can be completed. The bionic prosthetic hand and device based on the 3D printing have the advantages of being easy and convenient to manufacture, low in cost and high in degree of freedom.
Owner:北京展翼计划科技发展有限公司
Hand prosthesis
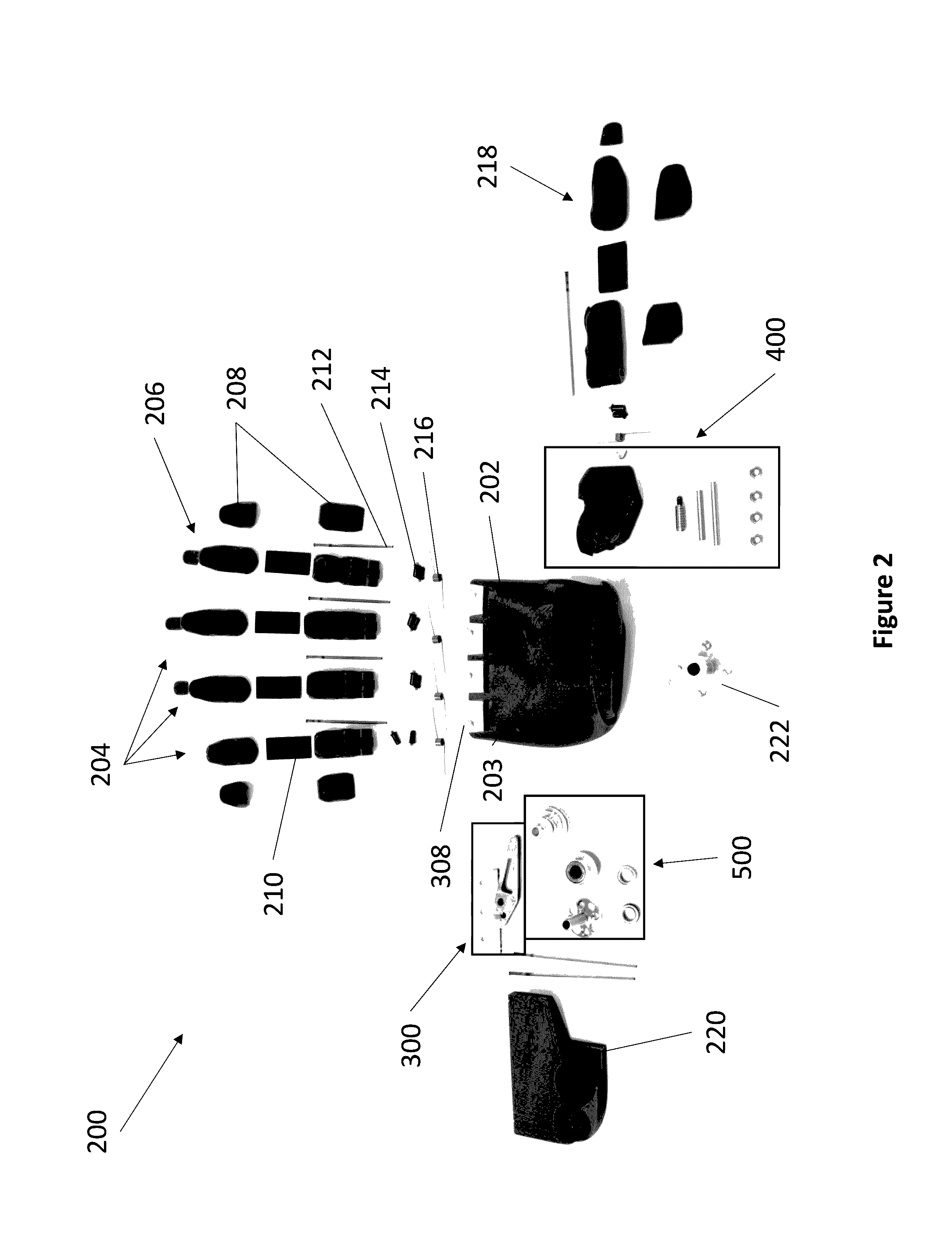
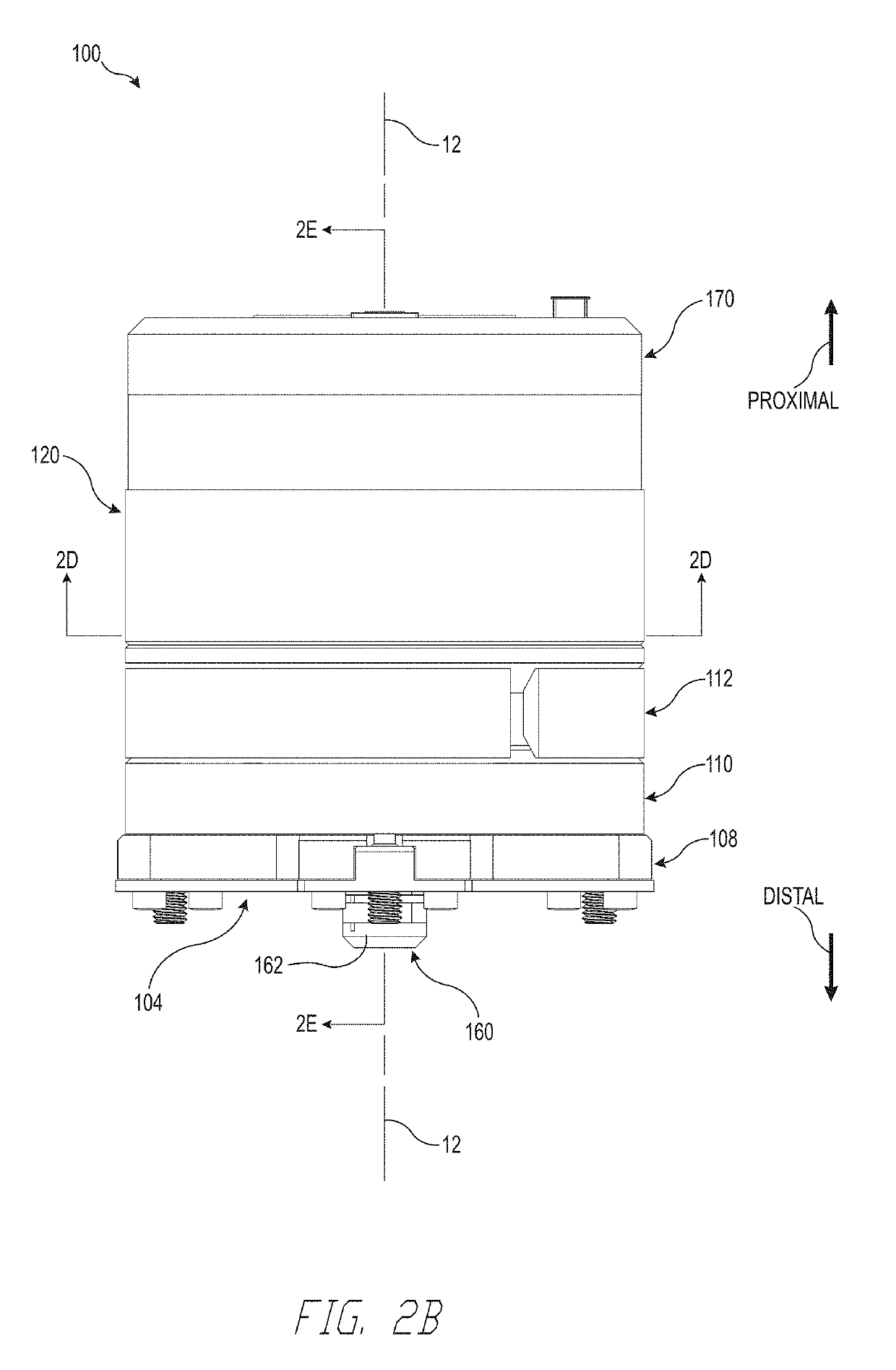
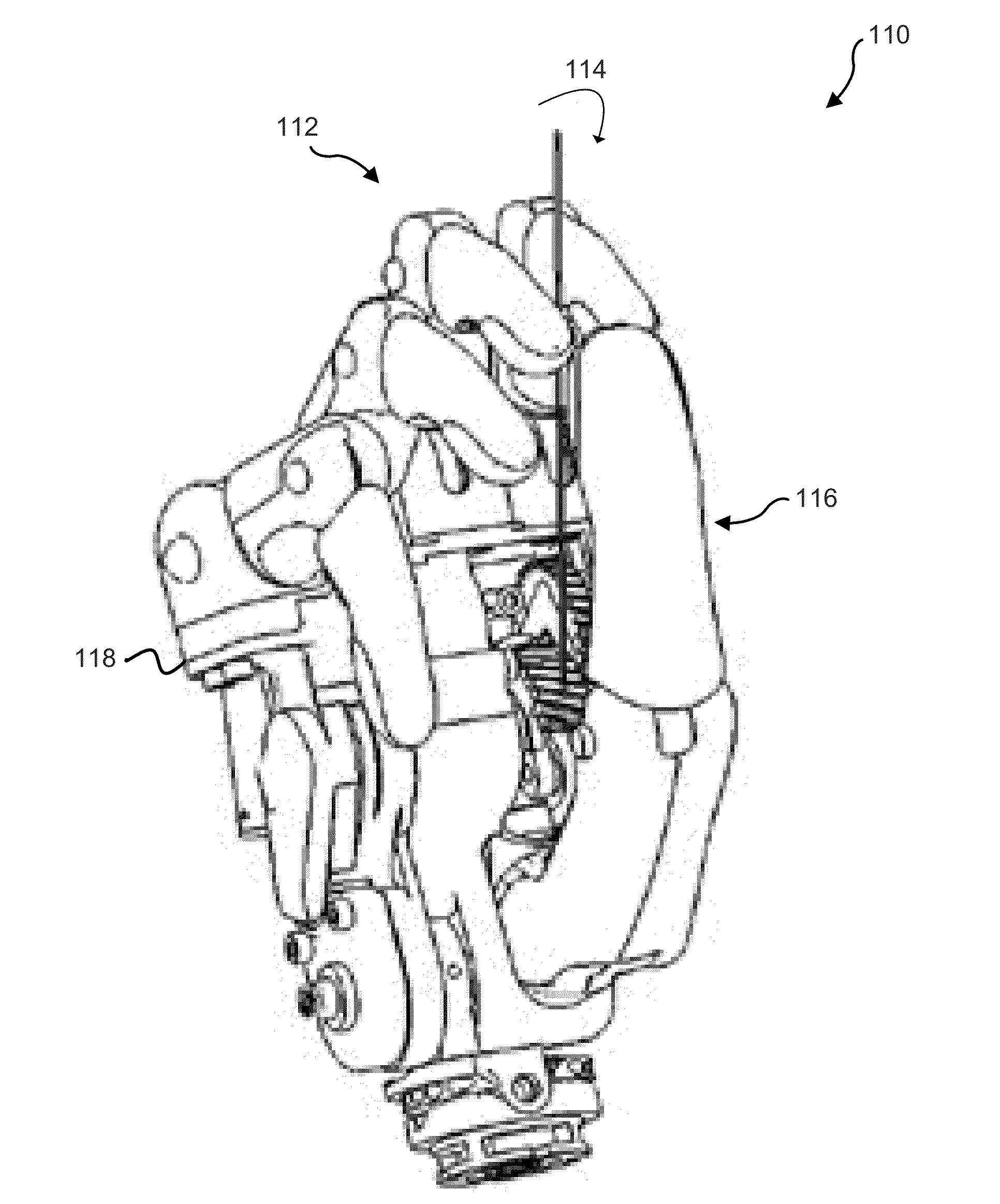
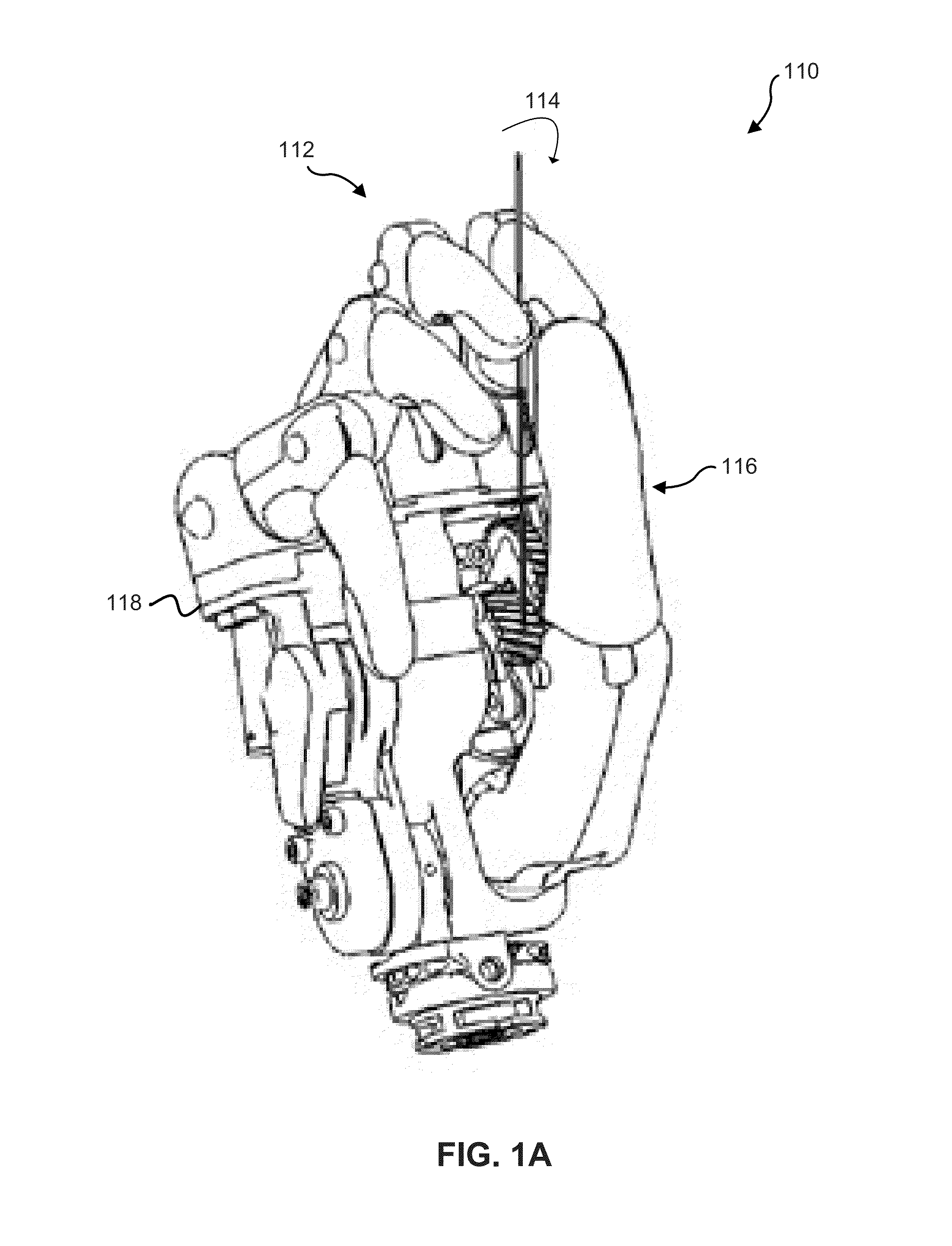
ActiveUS20140114439A1Gripping headsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationGear wheel
A prosthetic hand system may include a plurality of prosthetic fingers and a prosthetic thumb. The prosthetic hand system may include a thumb drive mechanism that may be used to actuate the prosthetic thumb. In some examples, the thumb drive mechanism may be configured to enable the prosthetic thumb to perform a pinching or grasping motion and a release motion. The prosthetic hand system may also include a backlock that enables the prosthetic thumb to maintain pinching or gripping pressure after a motor has been disengaged. The prosthetic hand system may also include a gear lock that may be configured to lock a finger joint. The prosthetic hand system may also include an adaptive gripping joint that may be located on each prosthetic finger. In some examples, the adaptive gripping joint may be configured to passively adapt the plurality of prosthetic fingers to one or more differently shaped objects.
Owner:MOTION CONTROL
Modular multi-degree-of-freedom underactuated bionic prosthetic hand
PendingCN108272537AShorten the lengthReduced flexibility requirementsArtificial handsReduction driveEngineering
The invention provides a modular multi-degree-of-freedom underactuated bionic prosthetic hand. The hand comprises a palm, a thumb and four fingers. The thumb and the fingers are independent modules which can be independently assembled and dismantled, each module is driven by a micro motor, each module is provided with two moving joints, and the movement of the two joints is coupled and is in an underactuated manner; a mechanical transmission chain of the fingers comprises a micro motor, a micro reducer, a spur gear pair, a sliding screw pair, pull ropes and a torsion spring, the mechanical transmission chain has two-layered arrangement and a returned-type layout is adopted. The invention further provides a wedge concave-convex type fixing device assembly. The motor of the fingers is transversely arranged along the palm, and it is ensured by a conical gear pair that the transmission chain can still be operated reliably when the attitudes of the fingers are changed. According to the bionic prosthetic hand, the motors are fixed on the palm, the bionic prosthetic hand has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in size, light in weight and reliable to operate.
Owner:唐山云时代科技服务有限公司
Prosthetic Arm With Adaptive Grip
An upper extremity prosthesis may include a prosthetic hand including a prosthetic thumb having a base and a tip, and a prosthetic index finger having a base and a tip. Actuators may be coupled to the upper extremity prosthesis. Prosthetic flexion tendons may have first ends operably coupled to the actuators and second ends coupled to the tips of the thumb and the index finger. Biasing systems may be operably coupled to the prosthetic thumb and the index finger. Upon actuation of the actuators in a first direction, the prosthetic flexion tendons cause the thumb and index finger to flex. Upon actuation of the linear actuators in a second direction opposite the first direction, the biasing systems cause the thumb and index finger to extend.
Owner:UNLTD TOMORROW INC
System and method for providing a prosthetic device with non-tactile sensory feedback
PendingUS20140277588A1Improve convenienceEase of useArtificial legsArtificial handsSensory FeedbacksChange color
A system and method for substituting vision based cues for lost sense of touch may employ a small electronic display or other non-tactile feedback mechanism that attaches to a prosthetic arm or other limb. Devices according to certain embodiments of the present invention include an array of pressure or other sensors that may be deployed against a prosthetic hand by structures such as finger cots or gloves containing the sensors. In one embodiment, an electronic display may be used to display a colored bar that moves from left to right, and changes colors along a gradient, as detected pressure on the sensors deposed against the hand increases. Movement across space and change in color are both easily discernable visual cues for these purposes.
Owner:PATT ELI ROBERT +2
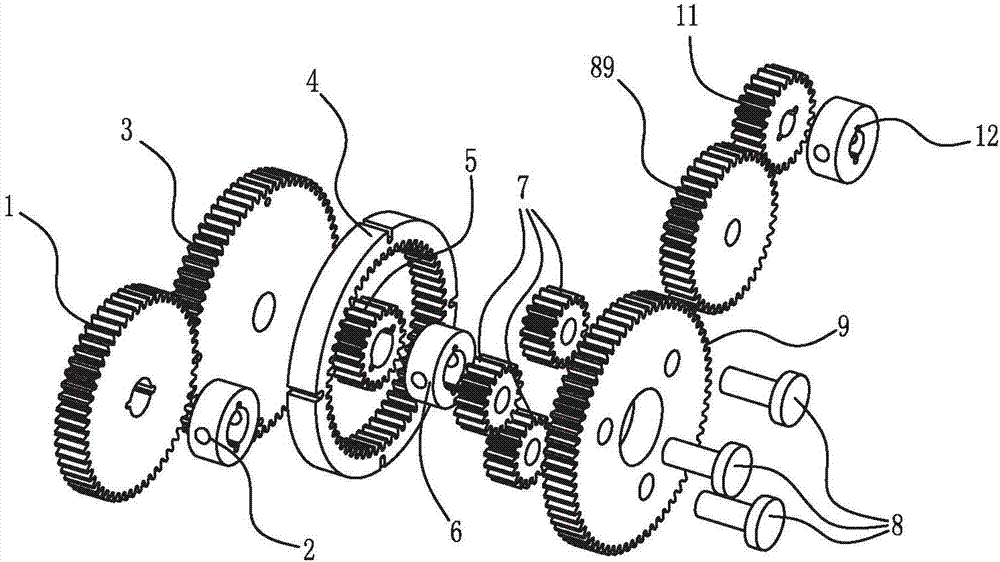
Under-actuated prosthetic hand system based on planetary gear trains
The invention discloses an under-actuated prosthetic hand system based on planetary gear trains. The under-actuated prosthetic hand system is used for realizing continuous hand motions. The under-actuated prosthetic hand system comprises three parts, namely a driving system, a transmission system and a mechanical hand, wherein the driving system comprises stepping motors and the planetary gear trains, the transmission system comprises transmission mechanisms such as flexible shafts, worm gears and worm rods, the mechanical hand comprises a palm and five fingers, and each finger is provided with multiple rotational joints. The input of two stepping motors can be converted into the rotation of thirteen output flexible shafts by the planetary gear trains in the driving system through a cooperative action mode, thus the motion of each joint on the mechanical hand can be cooperatively controlled, and some grabbing motions in daily life and the motion of rotating a rehabilitation training ball can be realized by the mechanical hand. According to the under-actuated prosthetic hand system disclosed by the invention, complicated grabbing motions are realized just through a two-input mode, the motion of the mechanical hand can be controlled by a disabled person who is in lack of a hand through less but accurate muscle signals, and the under-actuated prosthetic hand system has the advantages that the flexibility is high, and the use is convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
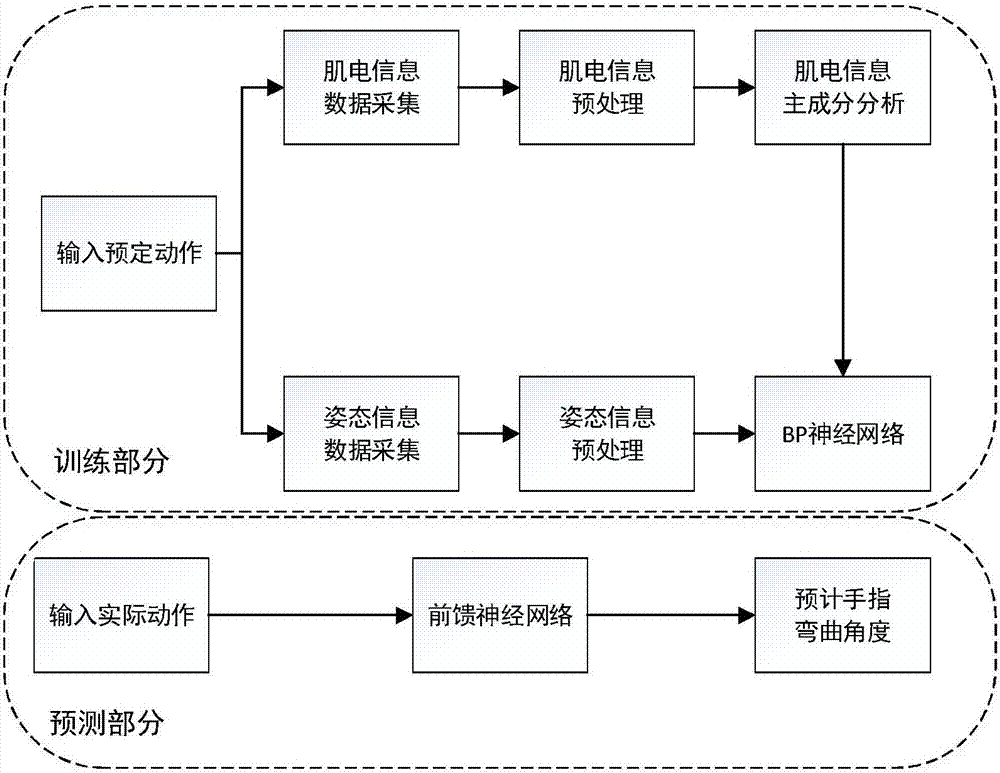
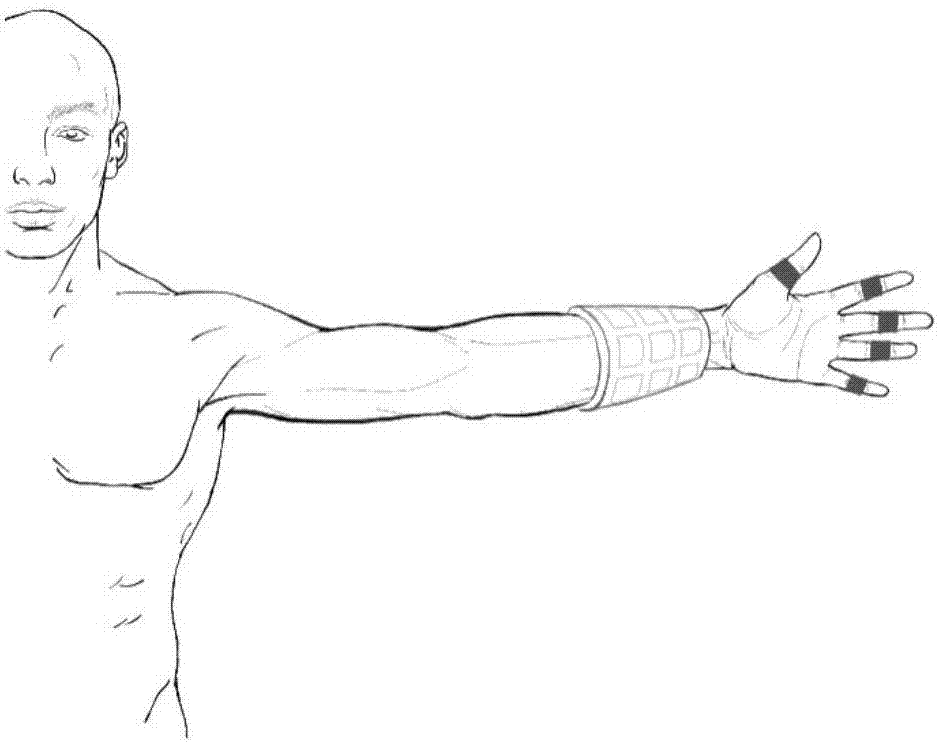
Multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on principal component analysis
ActiveCN107378944AReduce training timeShorten operation timePhysical therapies and activitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionPrincipal component analysisFinger joint
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on a principal component analysis. The control method comprises the follow steps that 1, an arm ring provided with a 24-channel array myoelectricity sensor is worn to a front arm of a testee, and five finger joint posture sensors are worn at the distal phalanx of a thumb of the subject and at the middle phalanxes of rest fingers of the testee respectively; 2, the testee conducts a five-finger independent bending and stretching training, and meanwhile, the myoelectricity sensing array data and the data of the finger joint posture sensors are collected; 3, the principal component analysis is used for decoupling the myoelectricity sensing data to form a finger movement training set; 4, the sensors worn on the fingers are removed after the training is finished; 5, data fitting is performed on the finger movement training set by adopting a neural network method, and a finger continuous motion prediction model is constructed; and 6, current bending angles of the fingers are predicted through the finger continuous motion model. According to the control method, the non-consistency of the discrete action modal classification can be overcome, and finally smooth control on an artificial hand is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
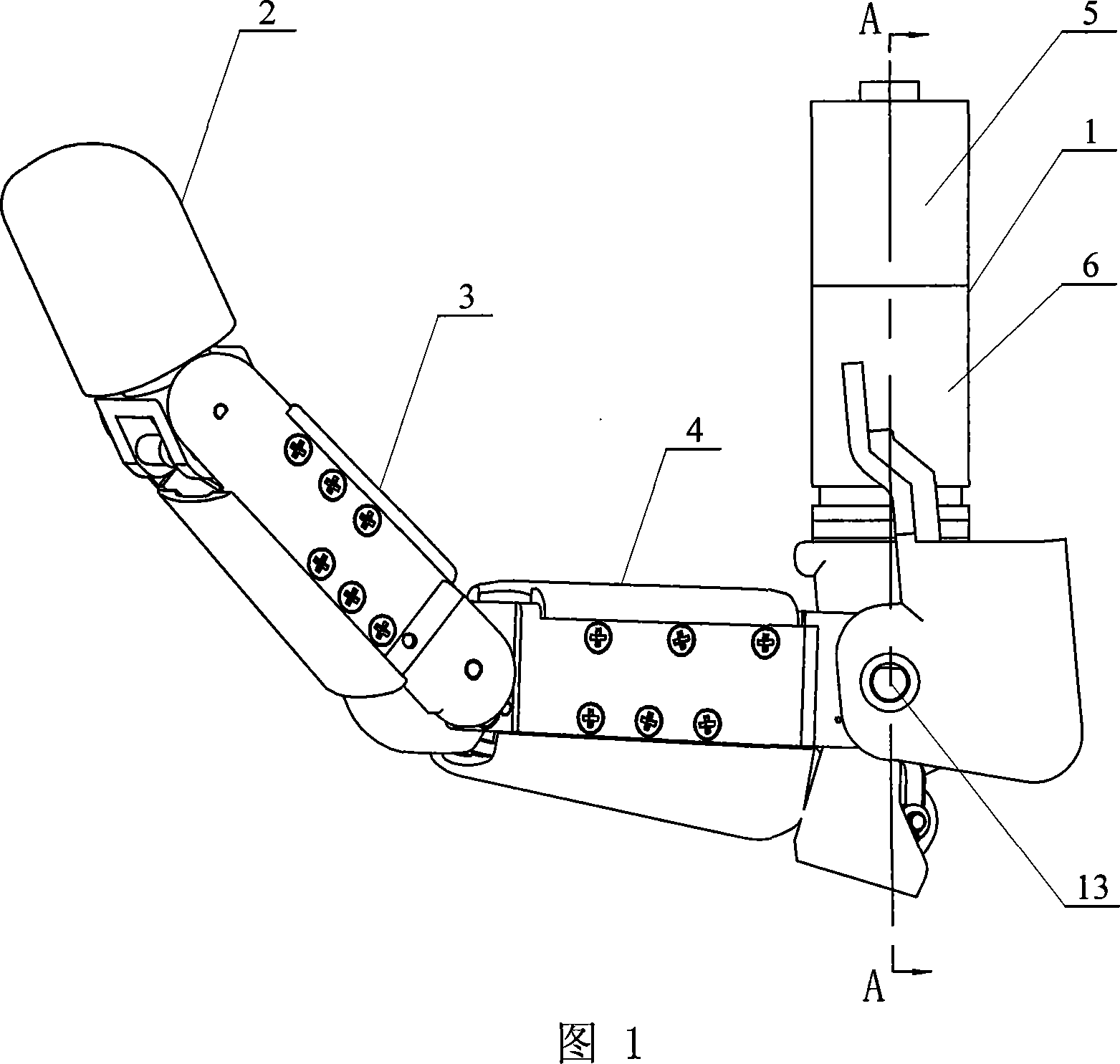
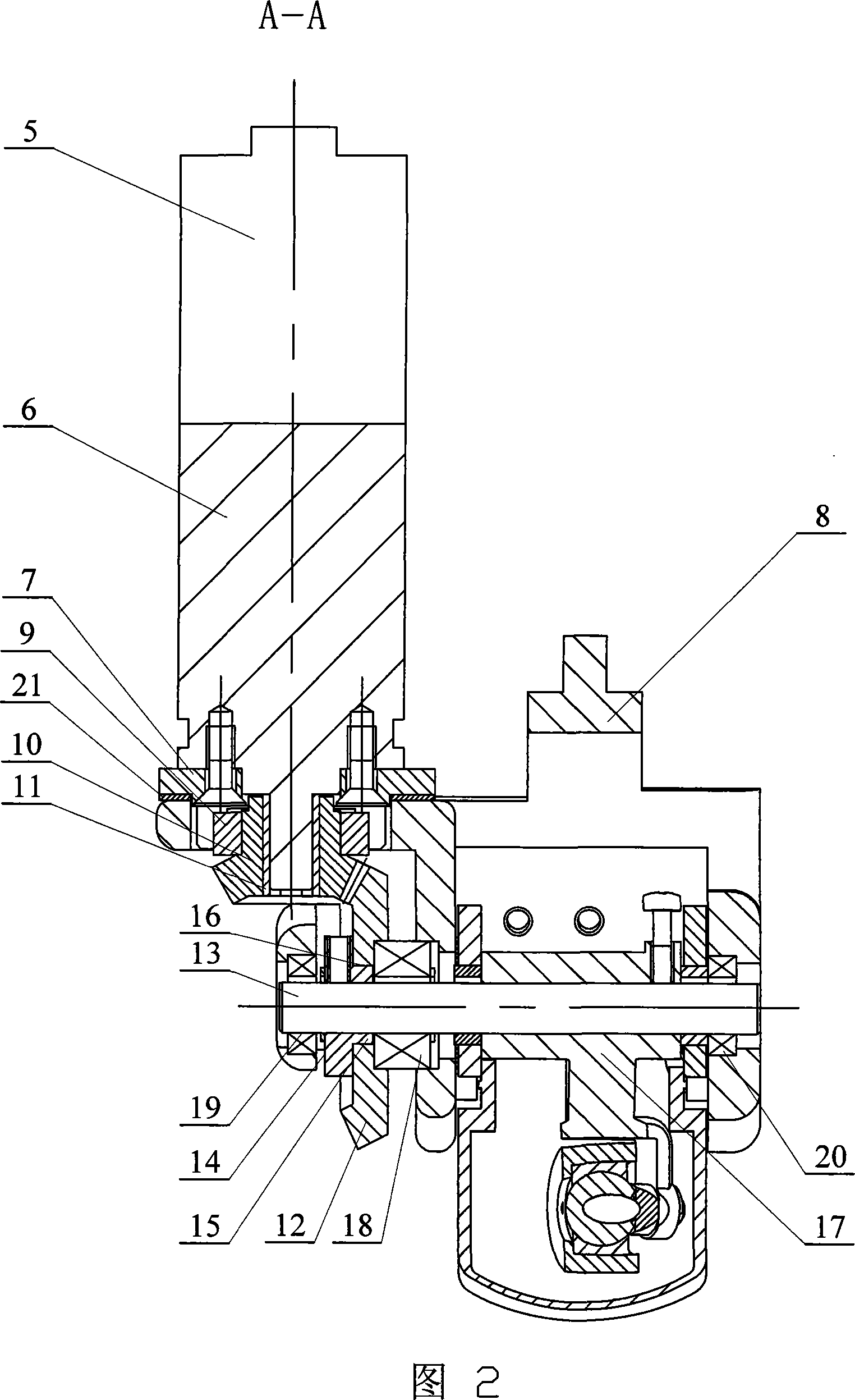
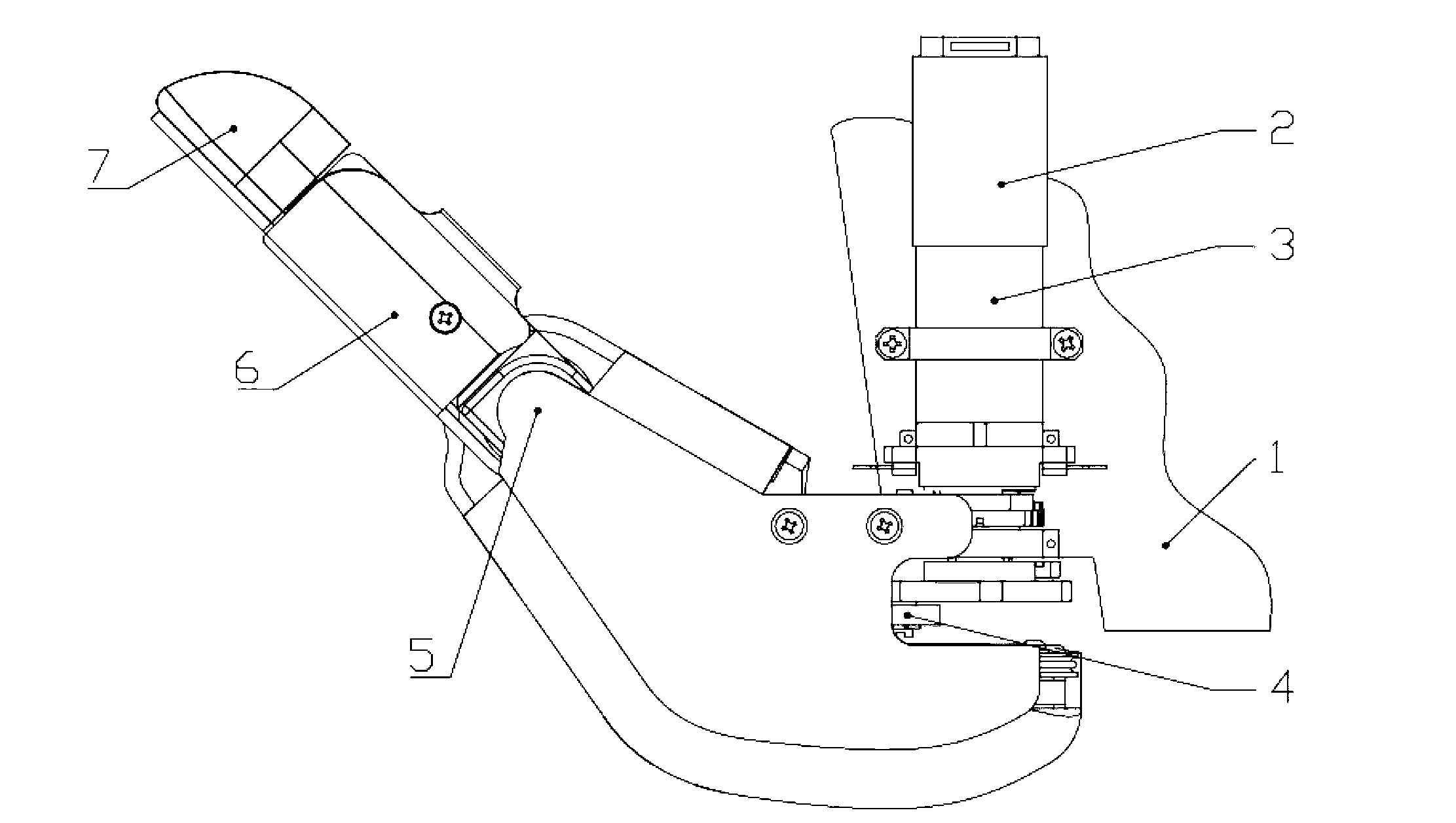
Thumb structure of prosthetic hand
ActiveCN103284821ARealize the envelopeAchieving a Power GripProsthesisReduction driveThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a thumb structure of a prosthetic hand and belongs to the field of medical apparatuses. The thumb structure of the prosthetic hand solves the problems that an existing thumb structure of the prosthetic hand is excessive in drives, heavy and insufficient in flexibility. The thumb structure of the prosthetic hand comprises a palm bottom plate, a servo motor, a speed reducer, transmission mechanism a near knuckle, a middle knuckle and a far knuckle, the servo motor and the speed reducer which are mutually connected are fixed on the palm bottom plate, the speed reducer is connected with the transmission mechanism which is connected with the near knuckle, and the near knuckle, the middle knuckle and the far knuckle are rotationally connected sequentially. The thumb structure of the prosthetic hand adopts the servo motor to drive a thumb to bend and laterally swing, has three degrees of freedom, is extremely similar to a human thumb in shape and moving mode, and is attractive in appearance, human simulated and practical. Experimental results show that the thumb structure of the prosthetic hand has great self-adaptive capability when matches with other fingers during gripping and can realize enveloping, precise gripping, powerful gripping and side nipping of complex objects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Powered prosthetic thumb
Features for a powered prosthetic thumb are described. The thumb provides for rotation of a digit that mimics the natural movement possible with a sound thumb. The thumb may attach to a full or partial prosthetic hand or socket on a residual limb. The thumb may include an upper assembly, including a prosthetic thumb digit, rotatably attached to a mount about a pinch axis and a lateral axis. The digit may rotate about only the pinch axis, only the lateral axis, or both the pinch and lateral axes simultaneously. A first actuator may actuate to cause rotation of the digit about the pinch axis. A second actuator may actuate to cause rotation of the digit about the lateral axis. The first and second actuators may be actuated together at appropriate speeds to cause rotation about both the pinch and lateral axes simultaneously. A swaying chassis may be rotatably connected with the upper assembly and a lower assembly about various offset axes to provide for rotation about the lateral axis.
Owner:TOUCH BIONICS
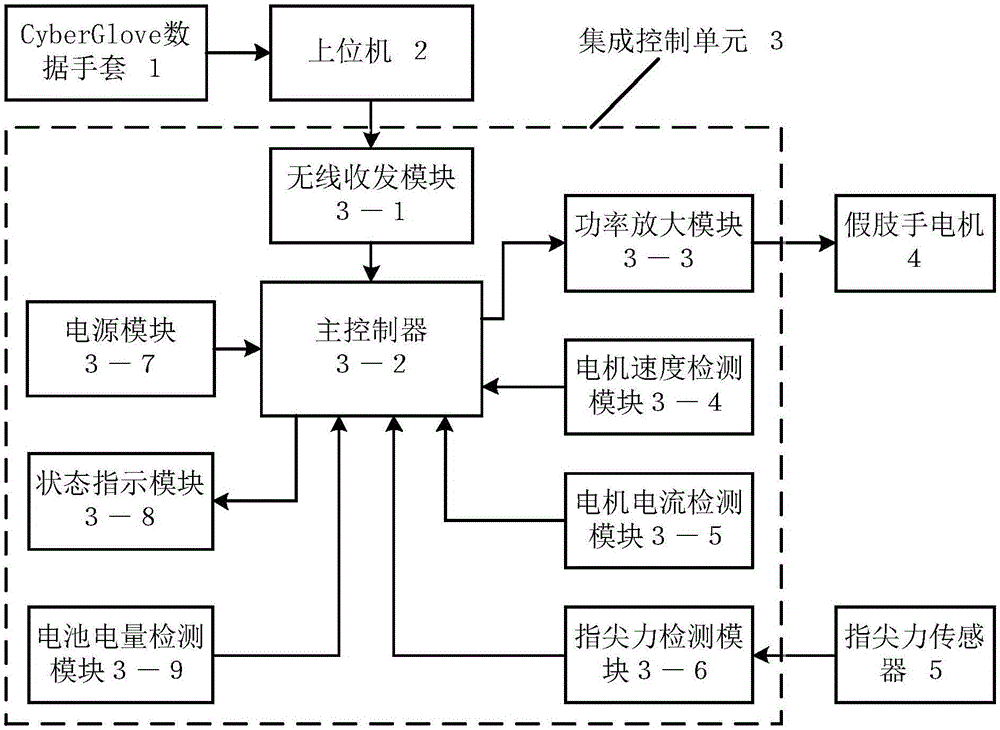
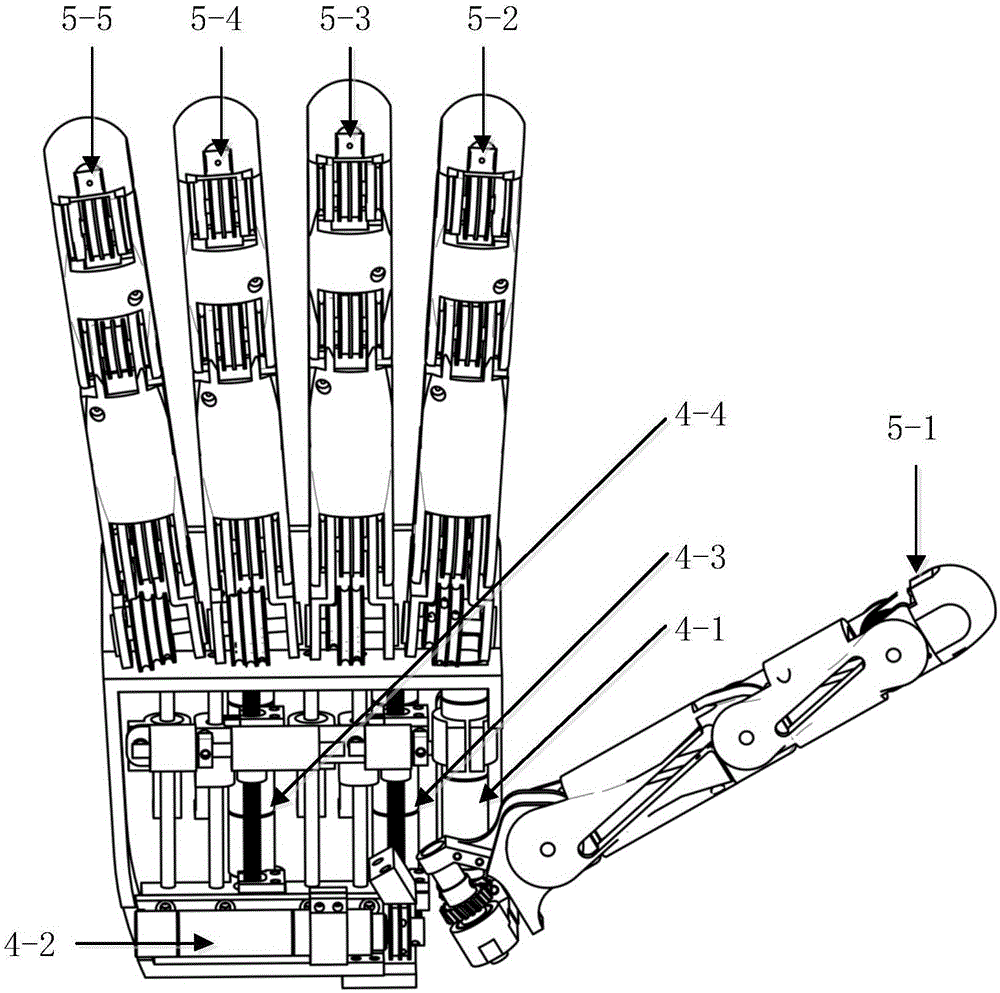
Embedded under-actuated prosthetic hand control system based on CyberGlove
ActiveCN105127973ACompact structureFlexible and convenient operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorProsthesisMotor speedEngineering
The invention discloses an embedded under-actuated prosthetic hand control system based on CyberGlove. The embedded under-actuated prosthetic hand control system comprises the CyberGlove, an upper computer, a motor assembly and an integrated control unit, wherein the CyberGlove is used for providing original movement data of a human hand, the upper computer is used for wirelessly transmitting the original movement data and command control, the motor assembly is used for driving a prosthetic hand to conduct various movements, and the integrated control unit is embedded into the prosthetic hand in the form of a integrated circuit plate and comprises a wireless receiving and transmitting module, a motor speed detection module, a motor current detection module, a fingertip force detection module, a master controller and a power amplification module. Through the embedded under-actuated prosthetic hand control system, movement control over the prosthetic hand can be conveniently achieved with the compact structure, the detects that an existing prosthetic hand control system is limited to a small number of preset control modes and hardware circuits are excessively huge can be overcome, and meanwhile movement accuracy and applicability in kinds of practical application can be significantly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A human-like dexterous EMG prosthetic hand control method based on gesture recognition
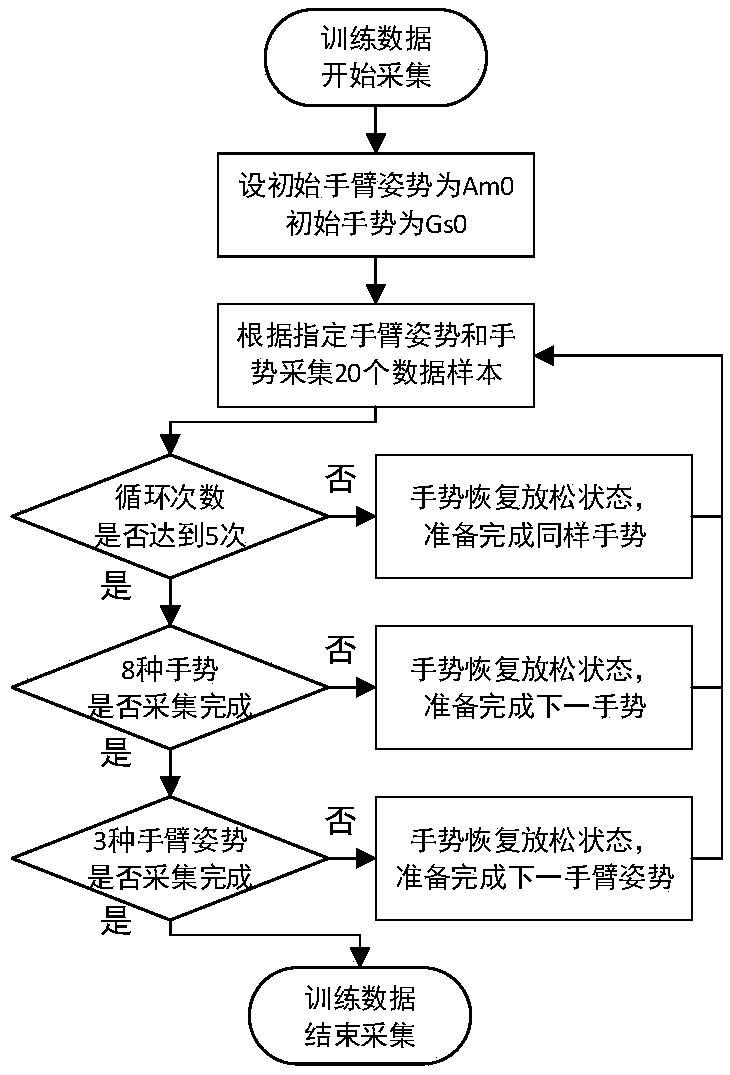
ActiveCN108983973AImprove wearing experienceImprove stabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTraining phaseProsthetic hand
The invention discloses a human-like dexterous EMG artificial hand control method based on gesture recognition, which recognizes eight kinds of gestures of a user in real time and operates the dexterous artificial hand to carry out synchronous action. The gesture recognition strategy of this control method is based on neural network algorithm, participants first completed eight preset gestures (relaxation, wrist valgus, wrist varus, fist-clenching, palm-extension, gesture 2, gesture 3 and thumb-upright) during the training phase, and then the system is able to recognize any one of the eight gestures randomly completed by the user in real time. The method uses a Tensorflow machine learning framework to learn weights and perform visual analysis. The method collects, trains and predicts the surface electromyography signal of a user, the comprehensive prediction accuracy of the 8 gestures reaches 97%, and the training is not needed when the gesture is worn again. When the subjects actuallycontrolled the artificial hand, the voting algorithm was used to optimize the real-time gesture prediction, and the synchronization rate of the artificial hand reached 99%.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com