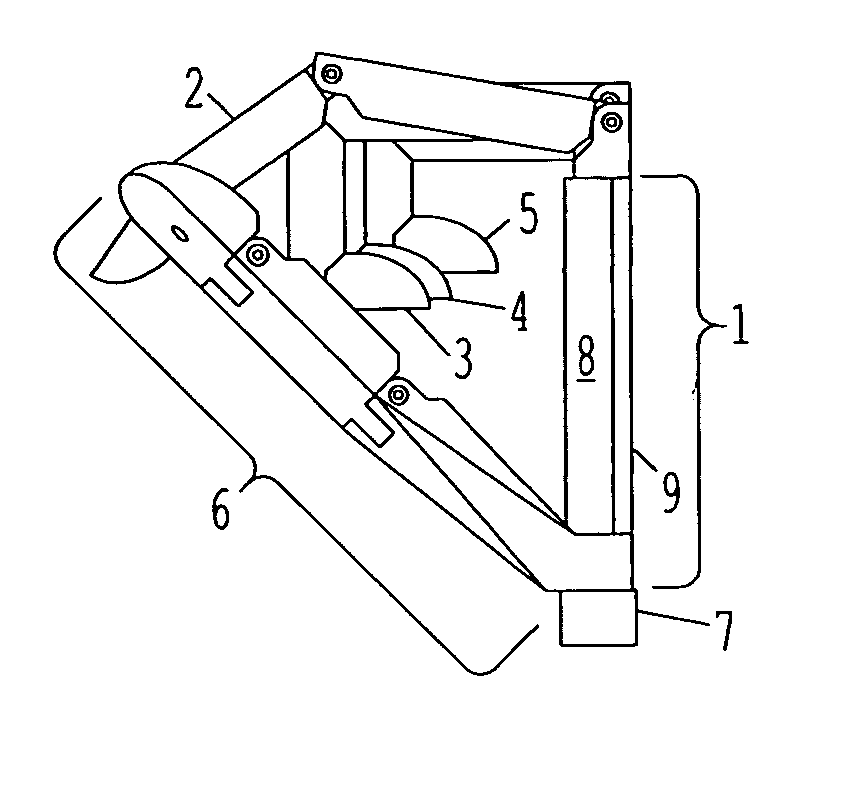
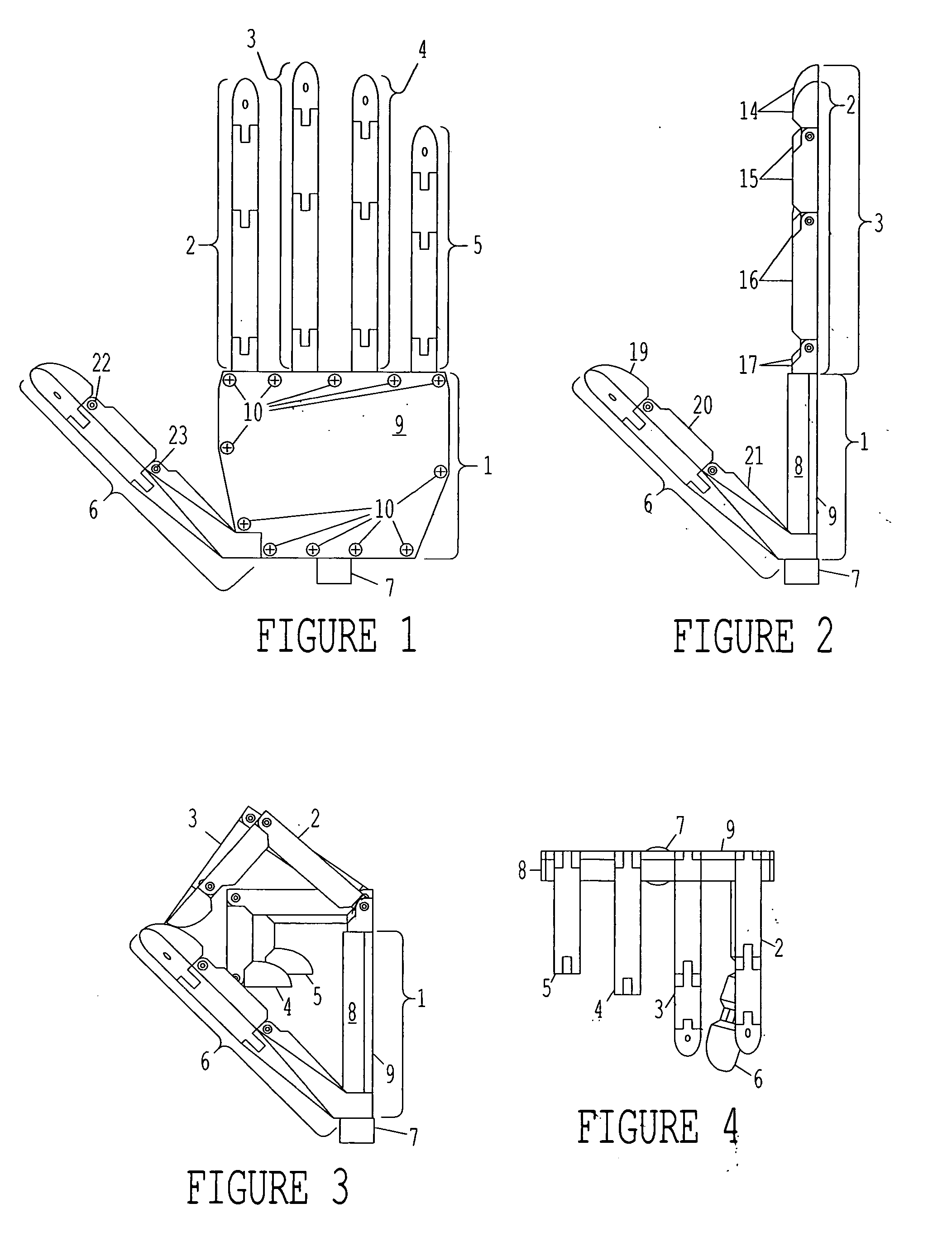
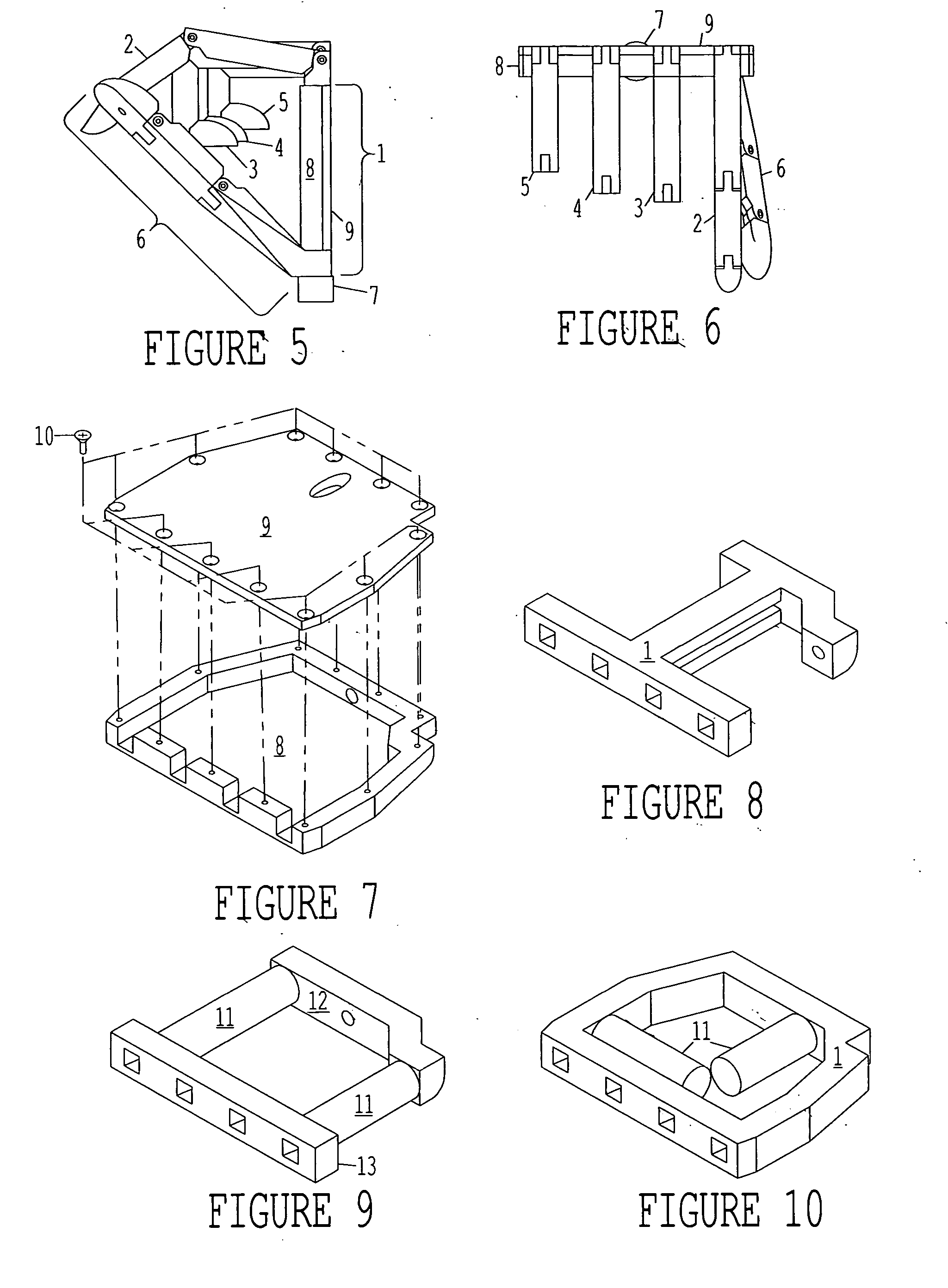
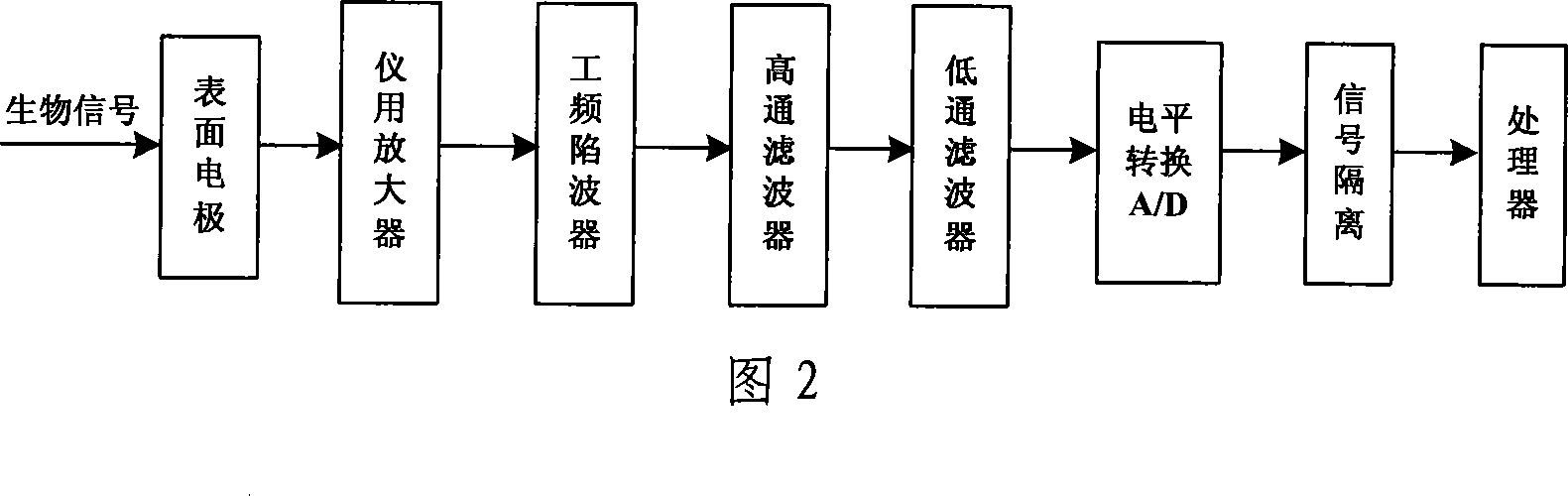
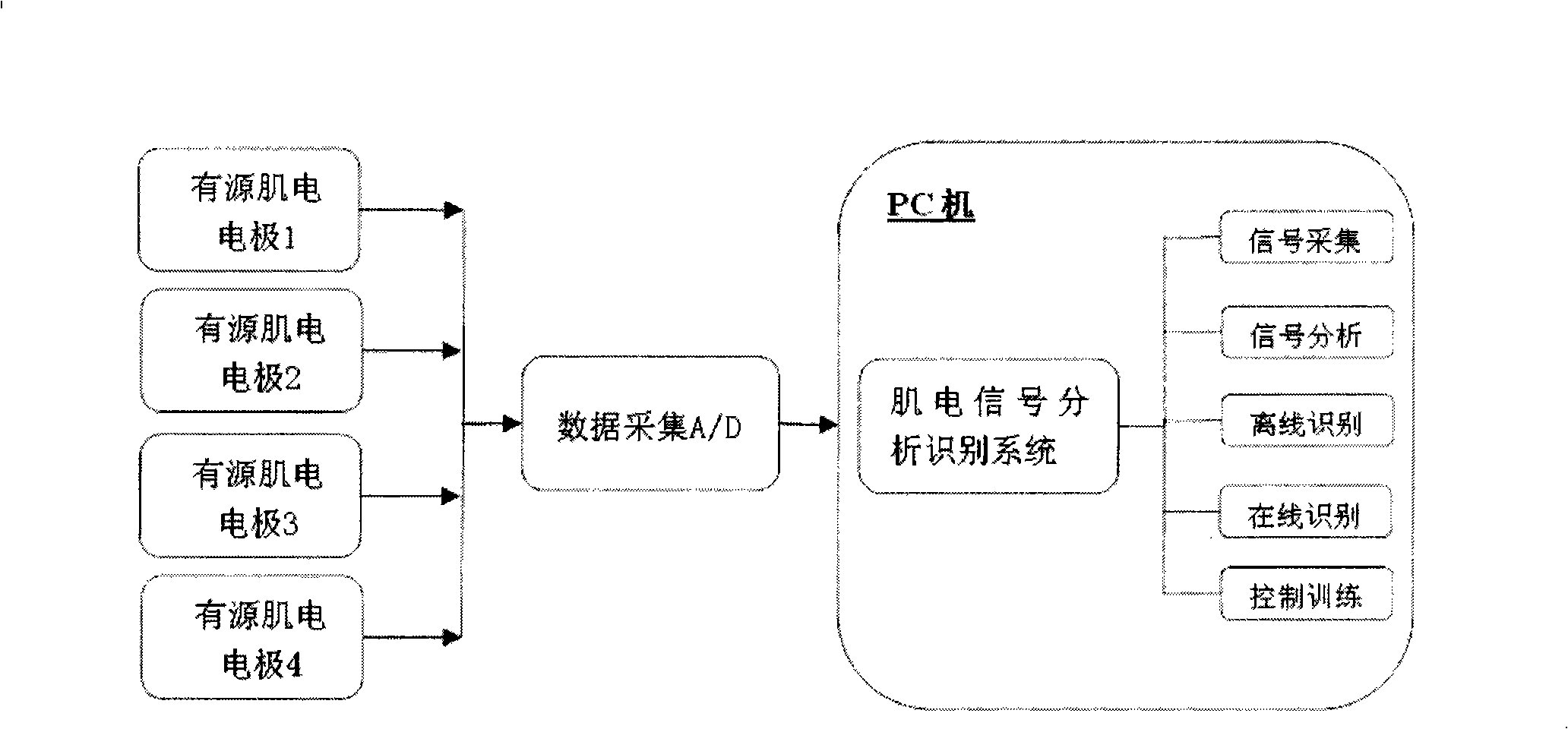
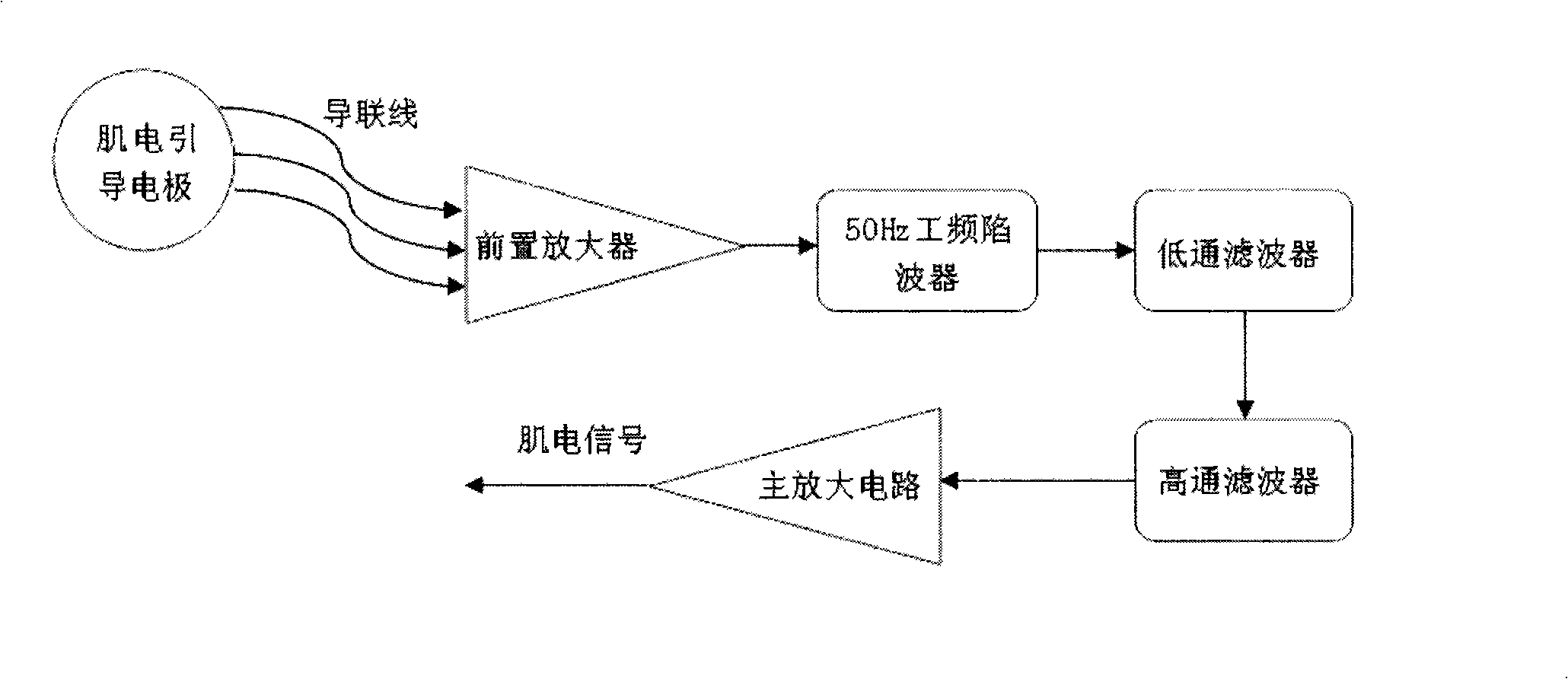
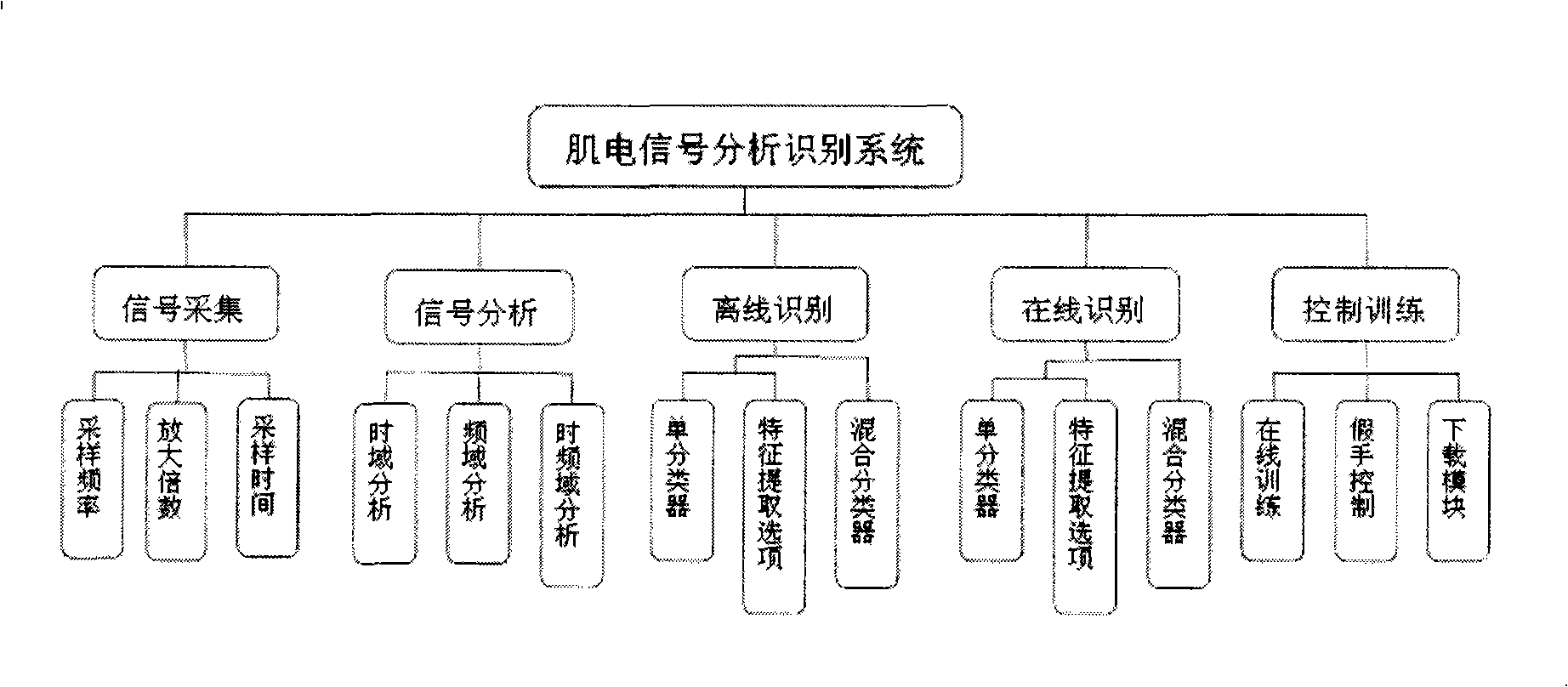
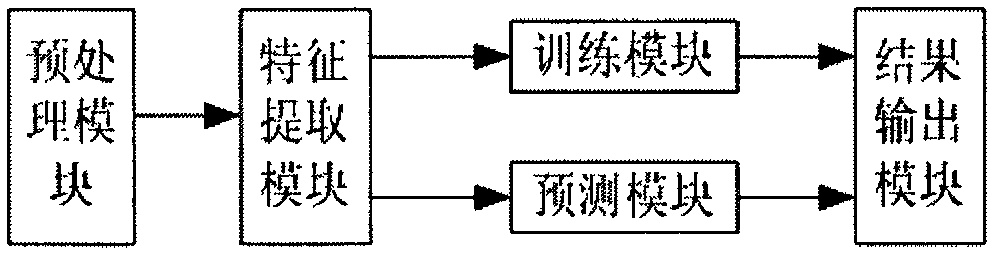
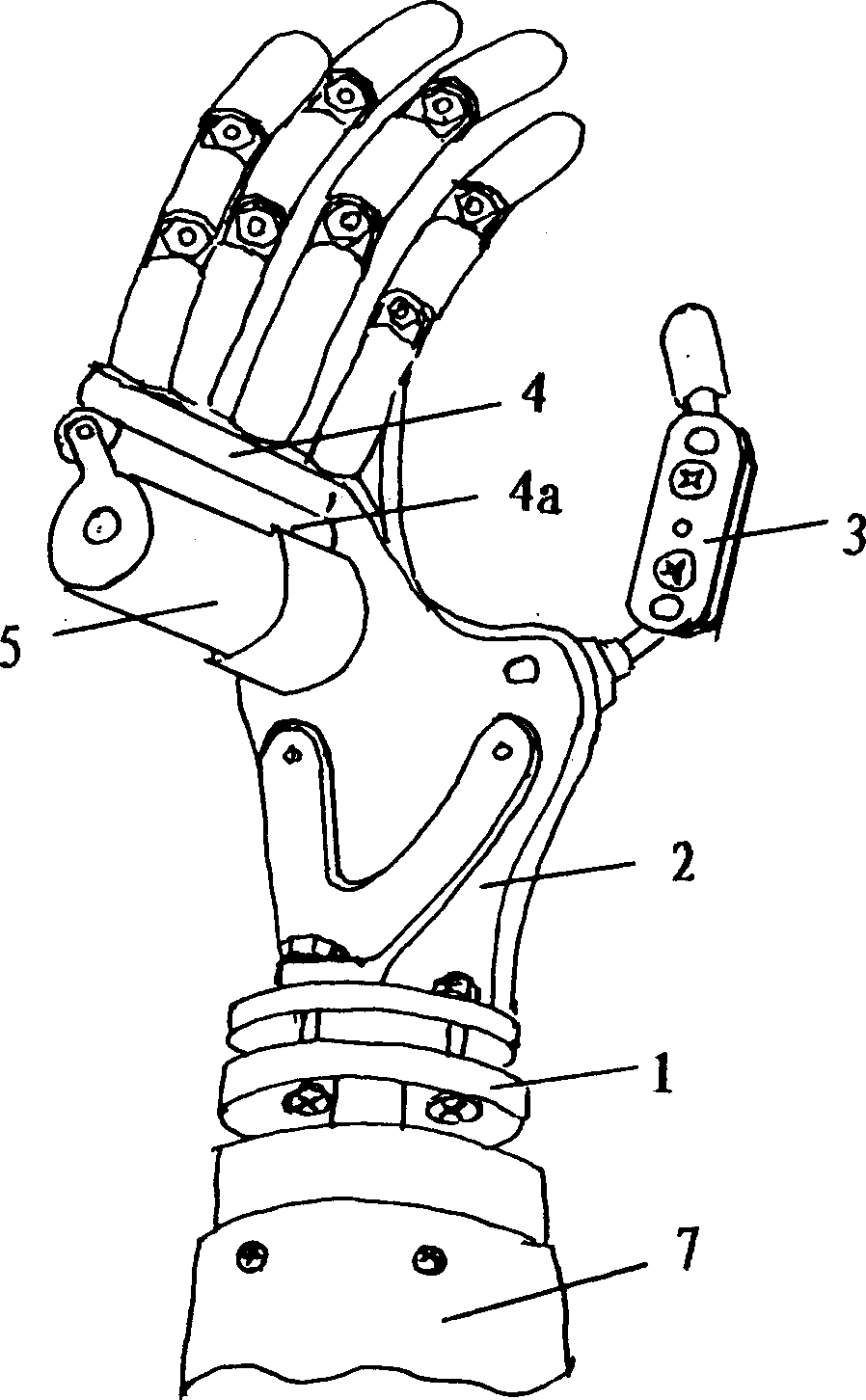
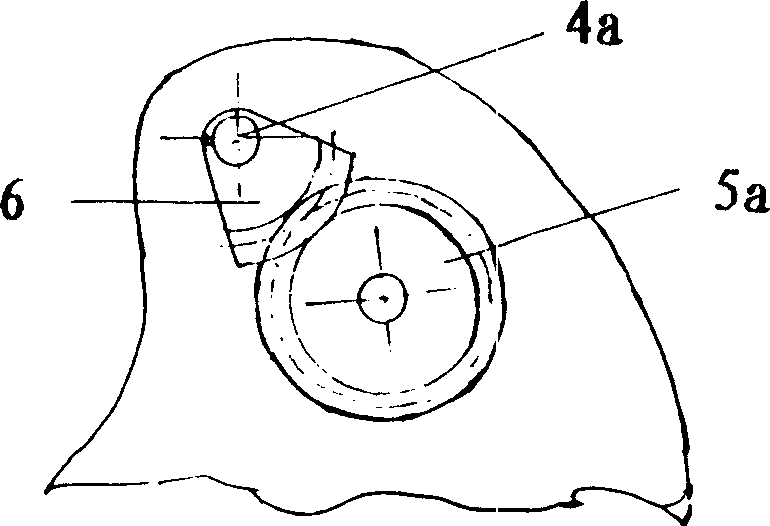
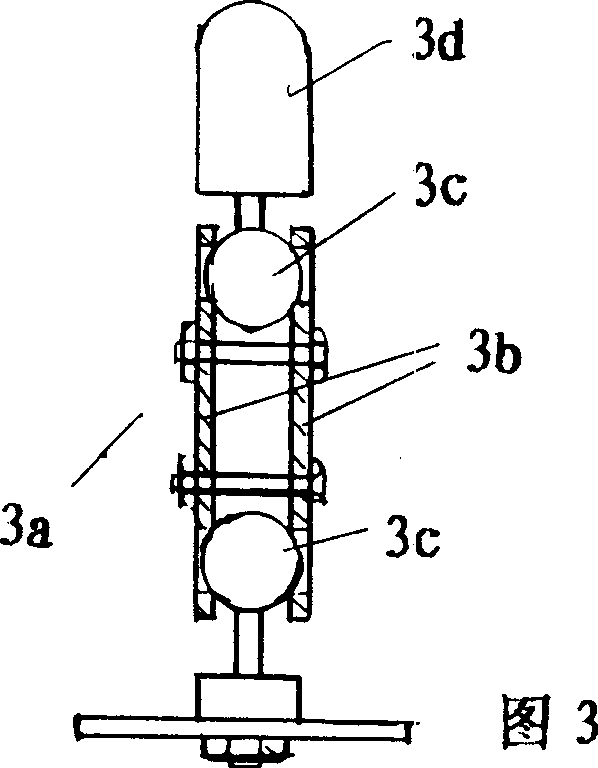
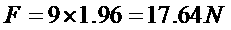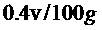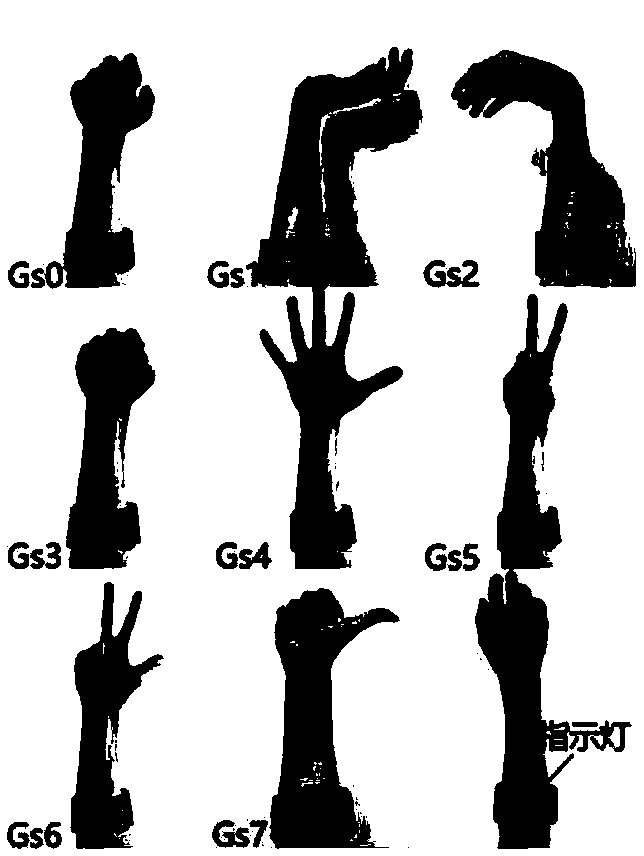Patents
Literature
229 results about "Artificial hand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
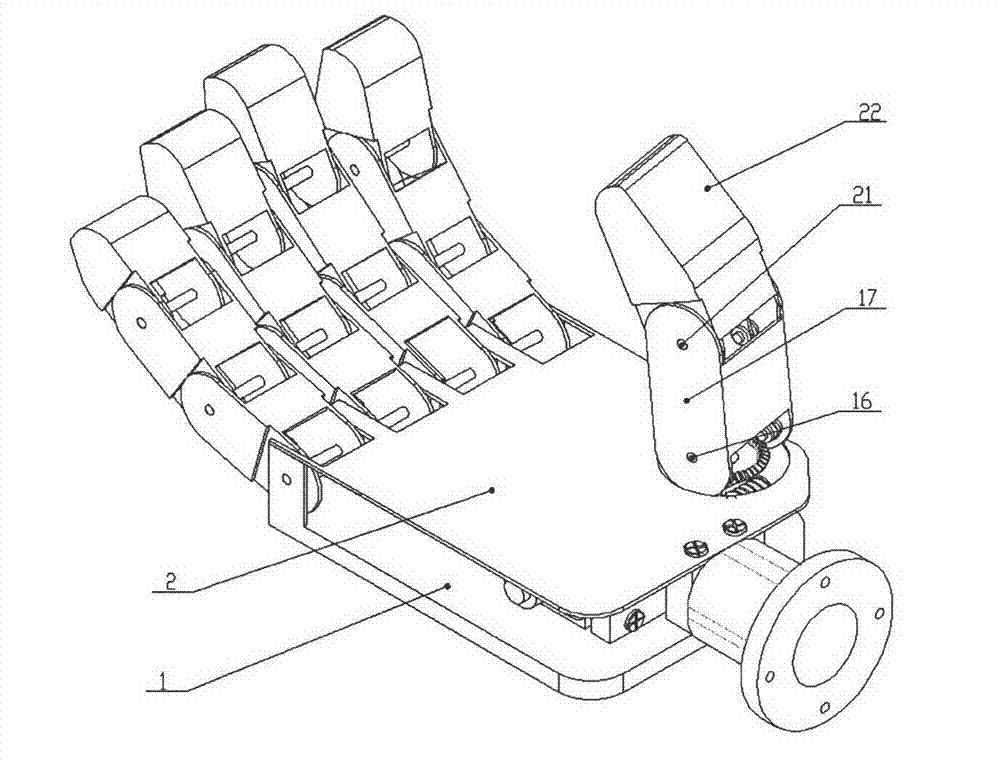
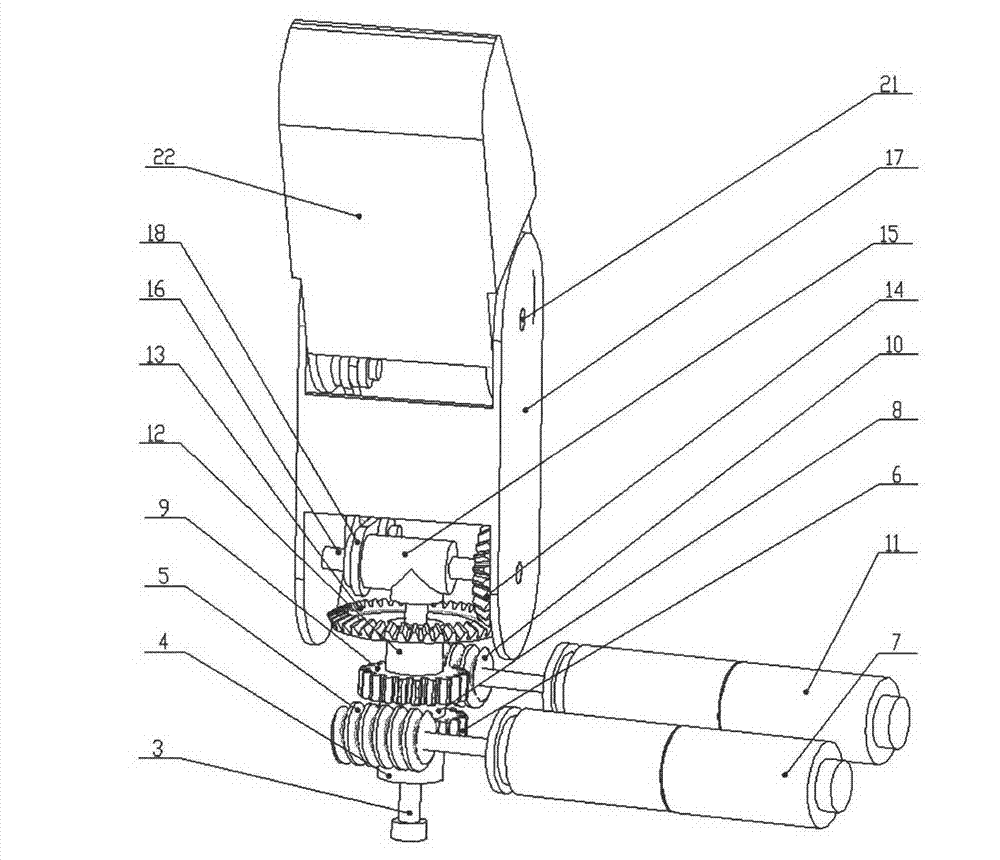
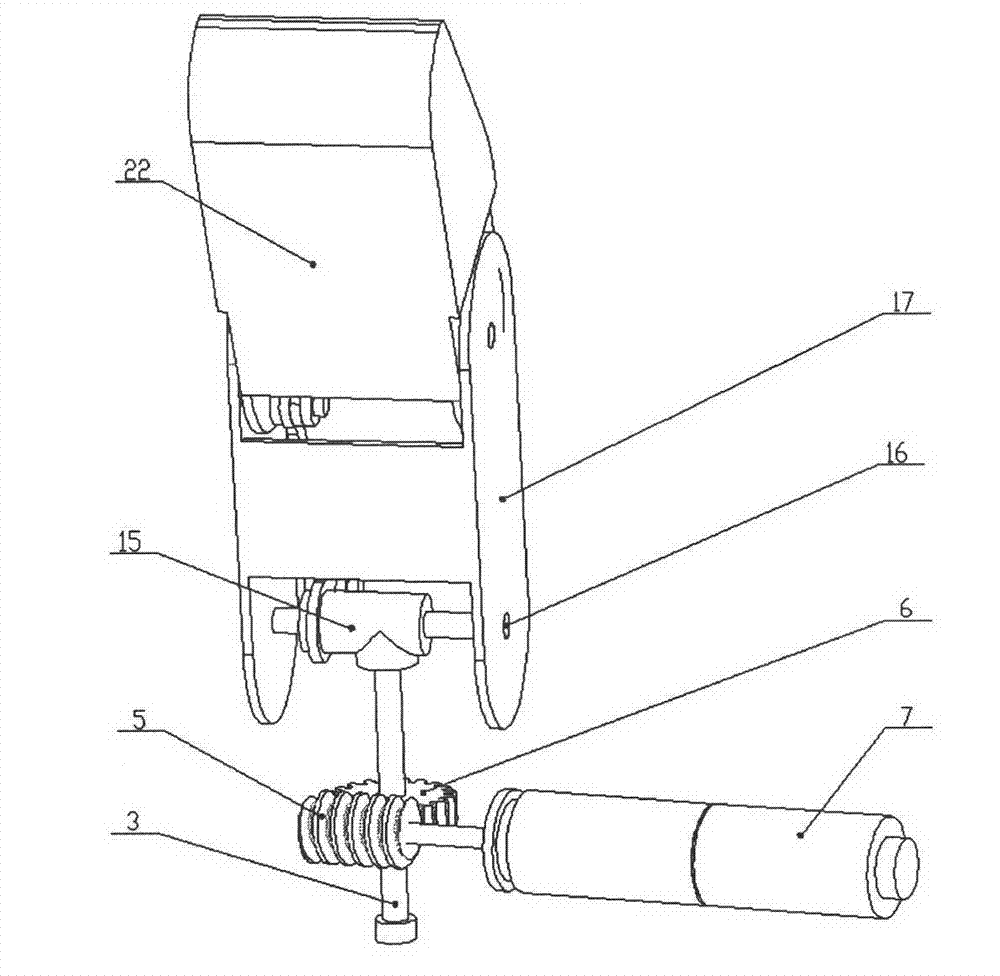
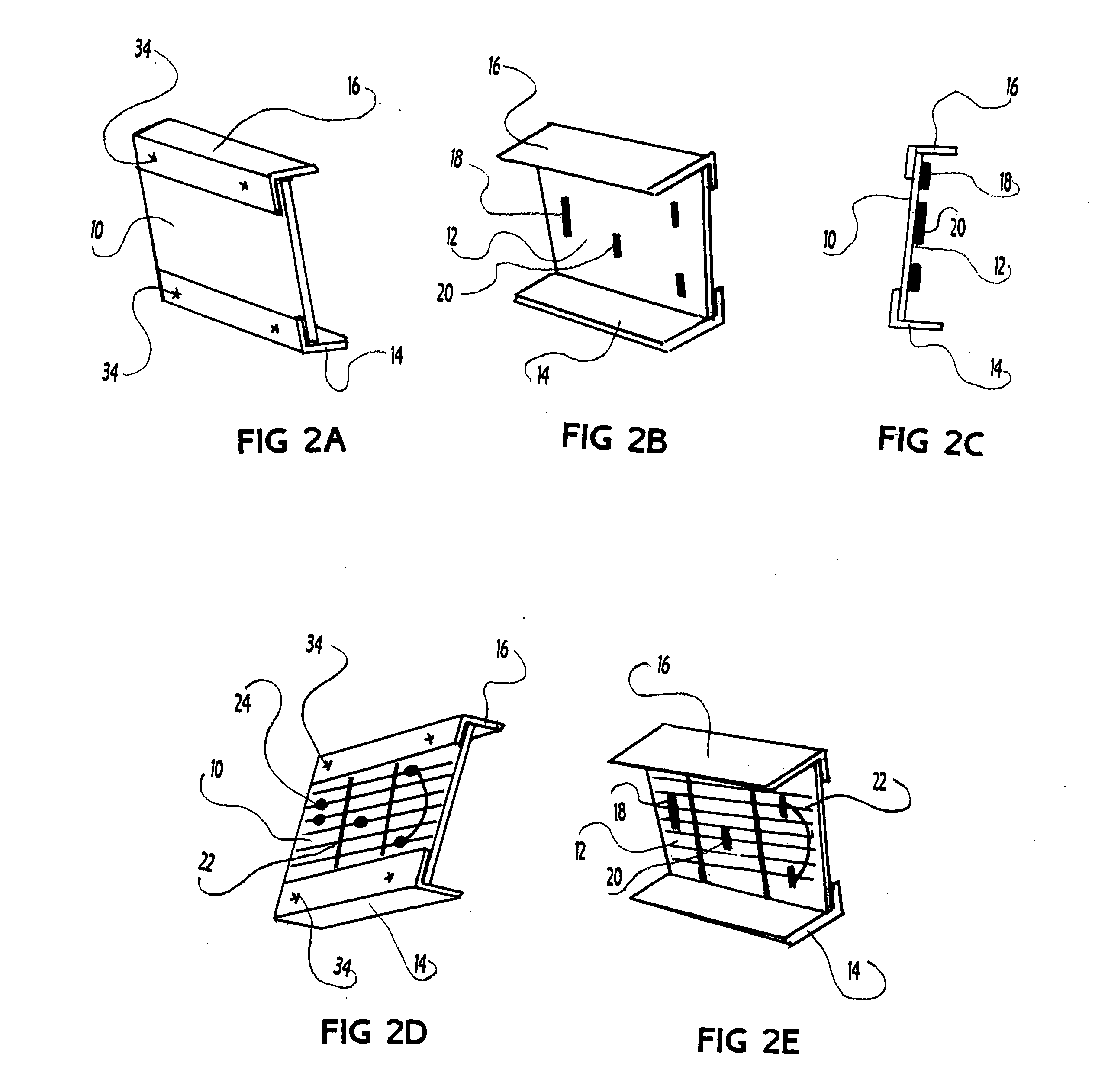
Prosthetic hand having a conformal, compliant grip and opposable, functional thumb
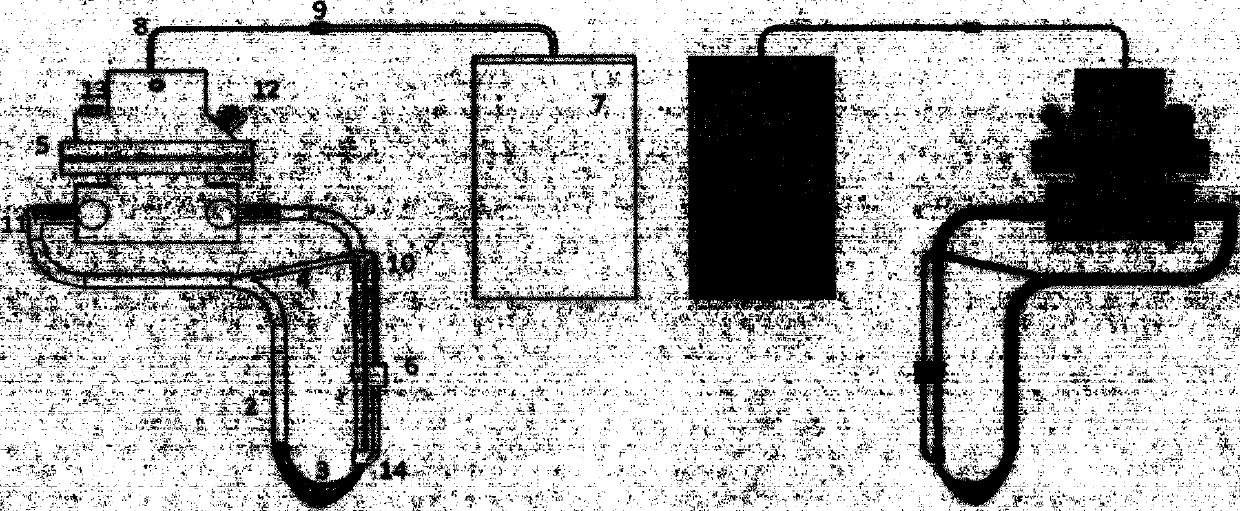
An anthropomorphic artificial hand having a mechanical system that allows for the digits to be compliant to pressure that tends to flex the digits, and provides for the digits to be self biasing to conform to the shape of the object being grasped. The hand comprises one to four fingers, with the fingers having up to three joints each. The hand may also comprise a thumb that can be rotated into and out of opposition of the fingers. The joints of the thumb are also self biasing to allow conformance to the object being grasped. The hand is of the voluntary closing operation, with all digits being self extending. This allows the hand to use two cables to operate if body powered (one for the fingers, one for the thumb). The hand may also be electronically powered using two channels for operating the fingers and thumb simultaneously.
Owner:WINFREY REX CLAYTON
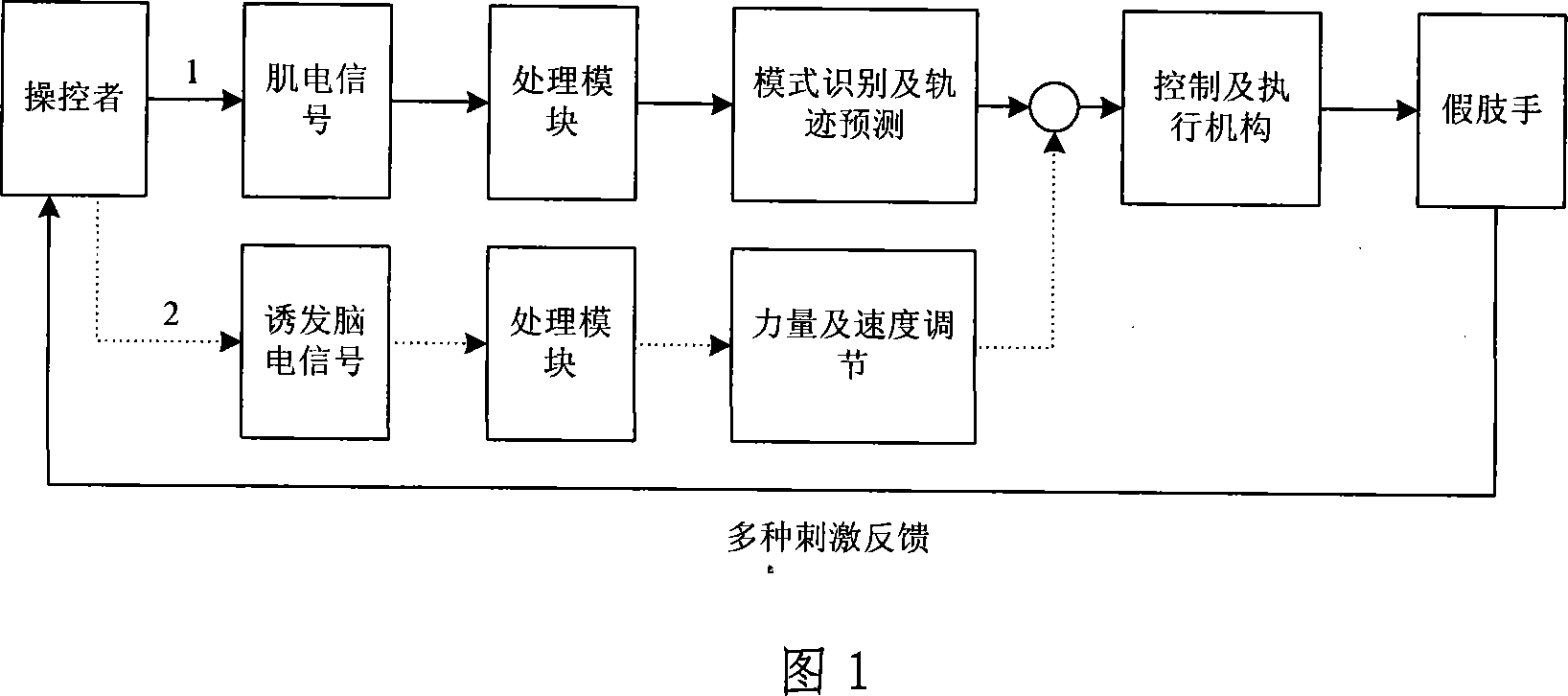
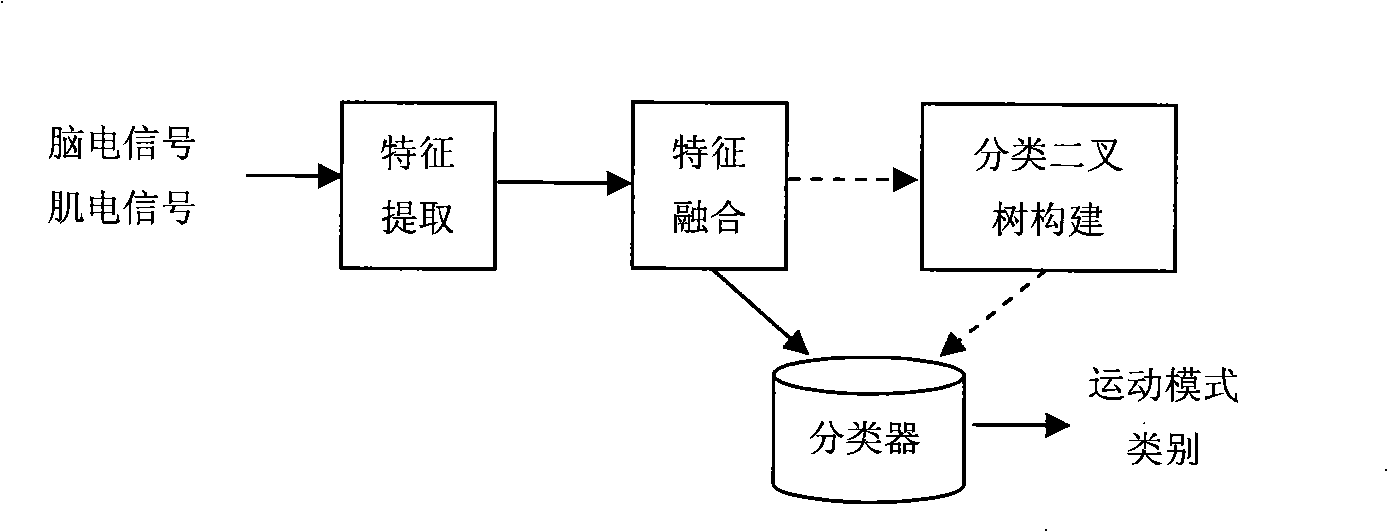
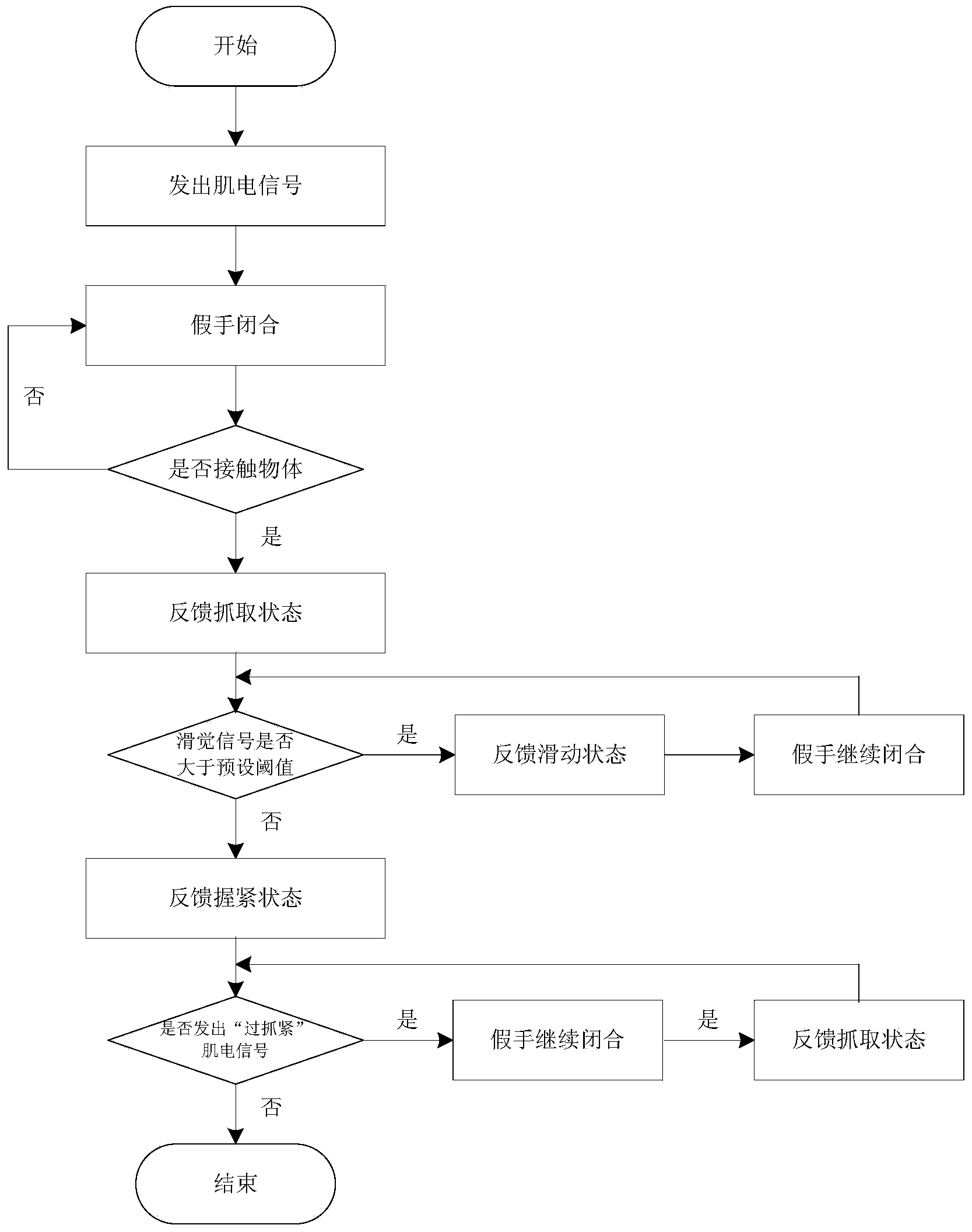
Artificial hand using muscle electrical and electroencephalogram cooperative control and controlling method thereof
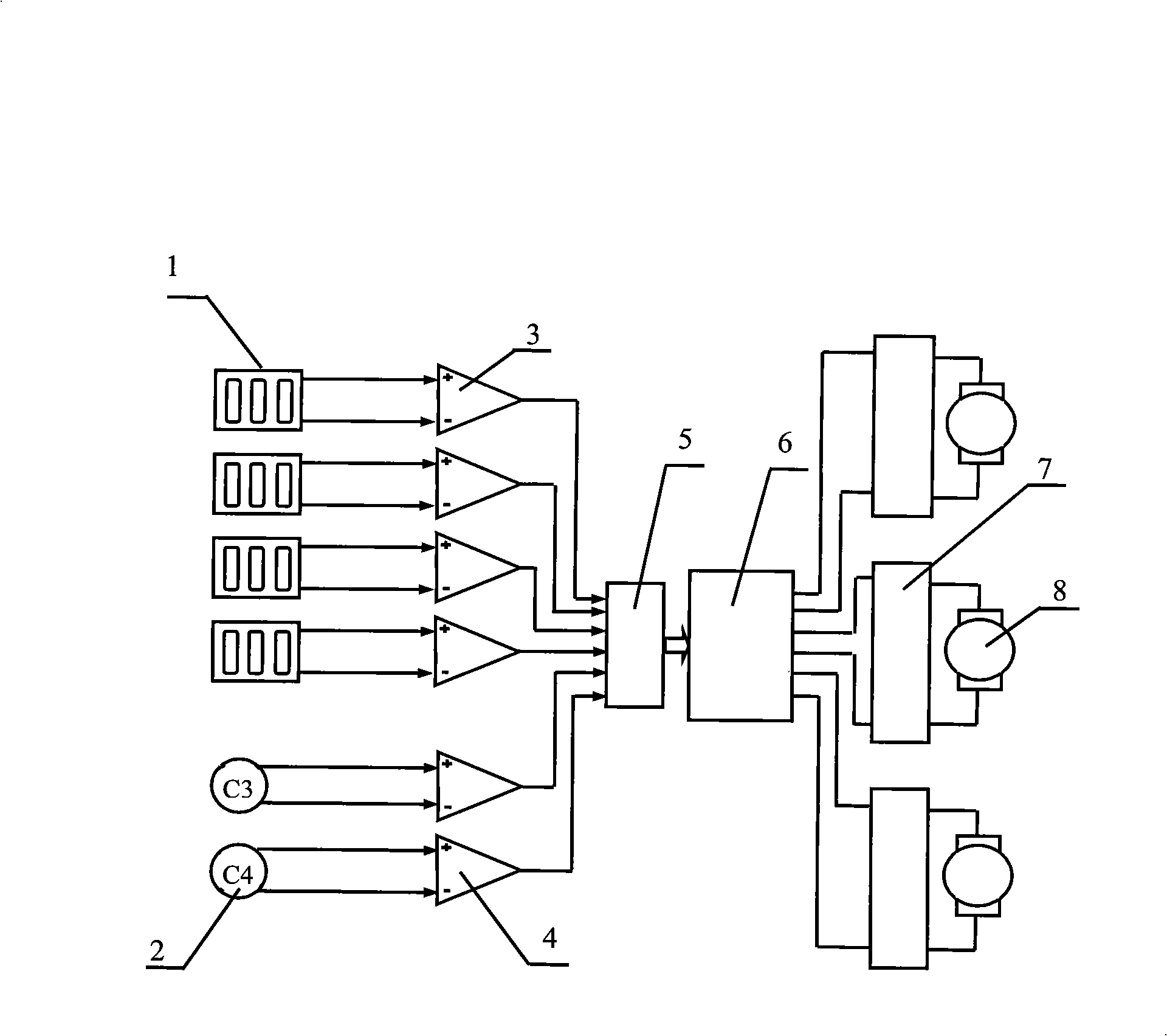
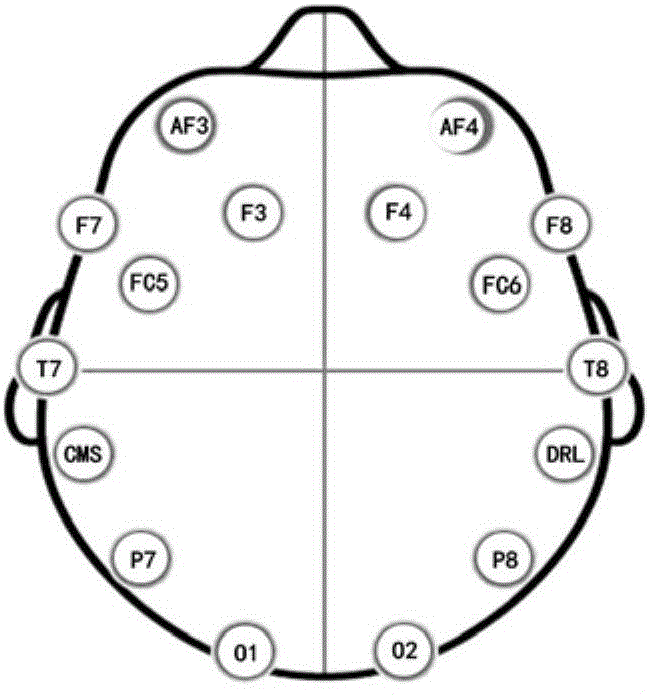
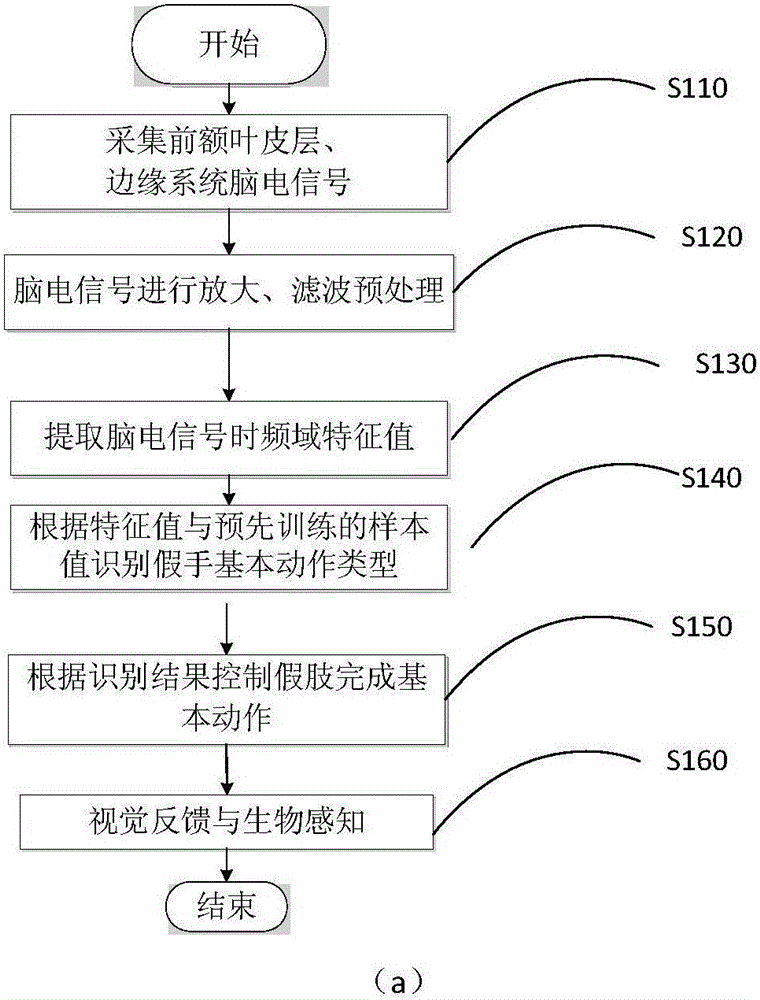
The invention relates to an artificial hand controlled by myoelectric and brain, comprising myoelectric and brain electrode, myoelectric and brain signal treatment module, A / D conversion data collection, myoelectric signal moving module identification and track prediction module, electrical artificial hand, touch and feel sensor, systematic feedback stimulation device, force and speed moderating module. The controlling method comprises following steps: collecting and enlarging myoelectric signal; collecting characteristic and identifying module; checking caught object condition, if the objection is not caught, a certain kind of physical stimulation signal will be sent to operator; checking brain information; outputting information to force and speed moderating module; output information controlling the electrical artificial hand. The invention overcomes limit of only taking myoelectric signal as signal source.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Myoelectric control ability detecting and training method for hand-prosthesis with multiple fingers and multiple degrees of freedom
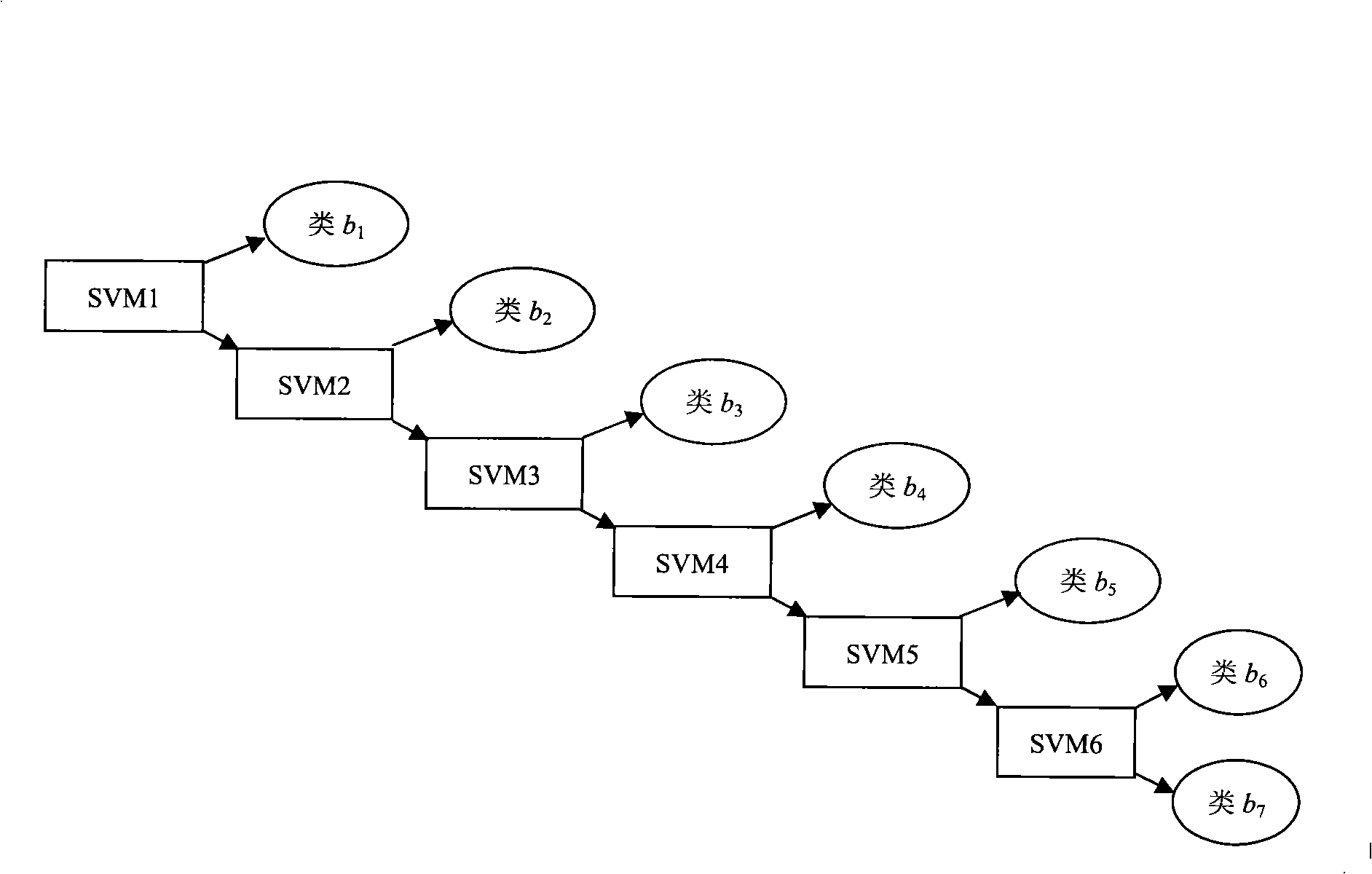
The invention relates to a detecting and training method of EMG controllability which is used for installing a pattern-recognition-based artificial hand with EMG control and hyperdactylia multiple degrees of freedom. The technical proposal of the method comprises procedures as follows: a signal acquisition module is used for collecting the myoelectric signal data of the surface of a stump; a signal analysis module is used for carrying out preliminary analysis for the collected data to determine that the collected myoelectric signal data of the surface of the stump has separability and the feature value of the optimal separability; an off-line recognition module is used for performing network training and recognizing the data to be recognized to the collected myoelectric signal data of the surface of the stump to determine an optimum classifier, the options of the optimal feature values and the selection of specific parameters; and a sufferer can do control training and on-line training by using an on-line recognition module and a control training module according to the determined combination of the optimal classifier and the options of feature values.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multimode under-actuated human finger simulation device with quick reflex grabbing function
The invention relates to a human finger simulation device on an artificial hand for the handicapped, in particular to a multimode under-actuated human finger simulation device with a quick reflex grabbing function. The device comprises a primary movement mechanism, a secondary movement mechanism, an elastic coupling link mechanism and a link surpassing mechanism and is capable of realizing human simulated grabbing movement. The primary movement mechanism is capable of realizing coupling under-actuated and adaptive under-actuated multimode grabbing actions by matching of a motor with the elastic coupling link mechanism, and the grabbing movement space of the artificial hand is greatly widened. The secondary movement mechanism is capable of realizing quick reflex grabbing of the human finger simulation device by the aid of a micro-actuator mechanism. When an article subjected to envelop grabbing is in external disturbance, a grabbing force pointing to the interior of the grabbed article is quickly outputted to compensate force and displacement output of the primary movement mechanism until the primary movement mechanism makes adjustment. Secondary movement has millisecond-scale response speed to realize human simulated quick reflex movement and anti-slip stable grabbing functions. The specific link surpassing mechanism guarantees the grabbing space of far dactyluses. The multimode under-actuated human finger simulation device is simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost and high in output force, has human simulation characteristics in terms of appearance and actions, and is particularly suitable for artificial hands for the handicapped.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
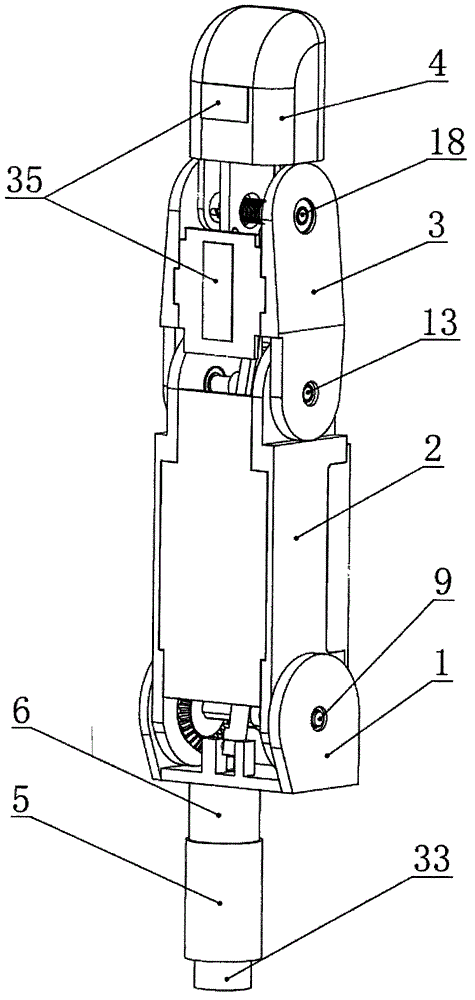
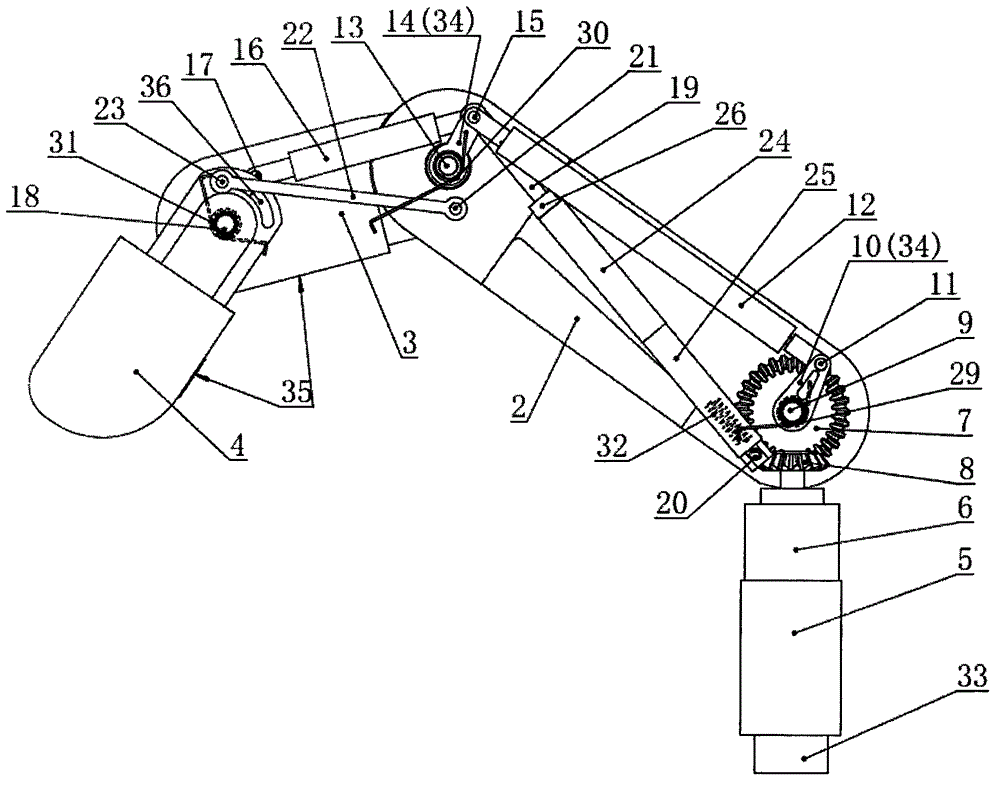
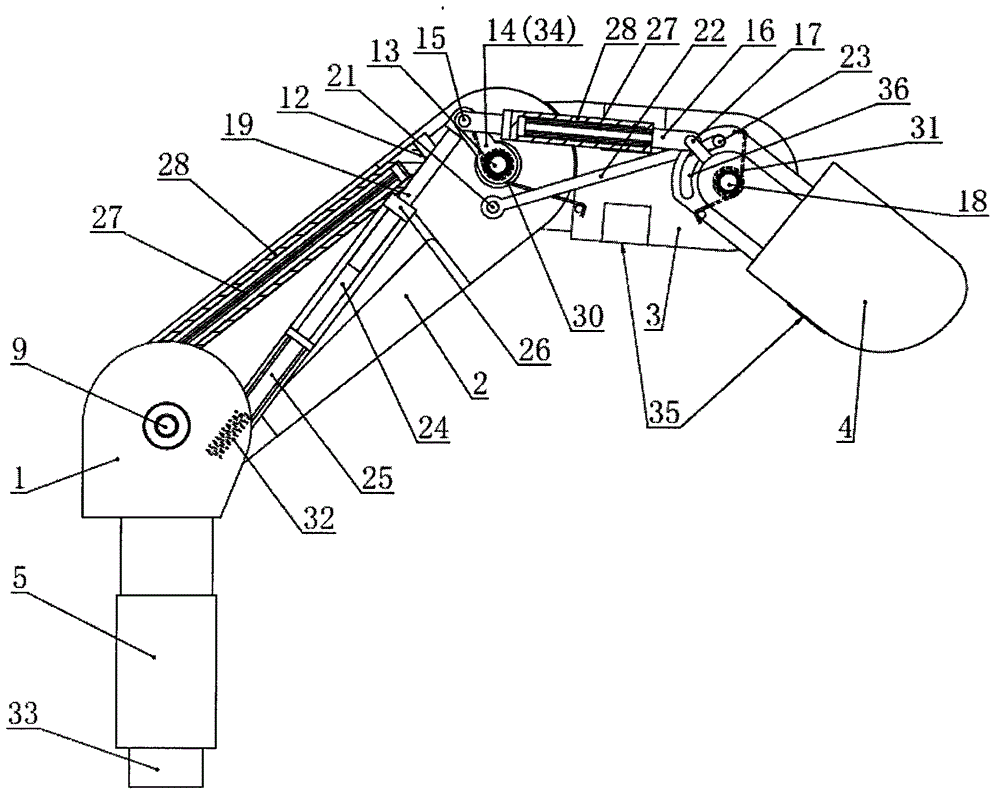
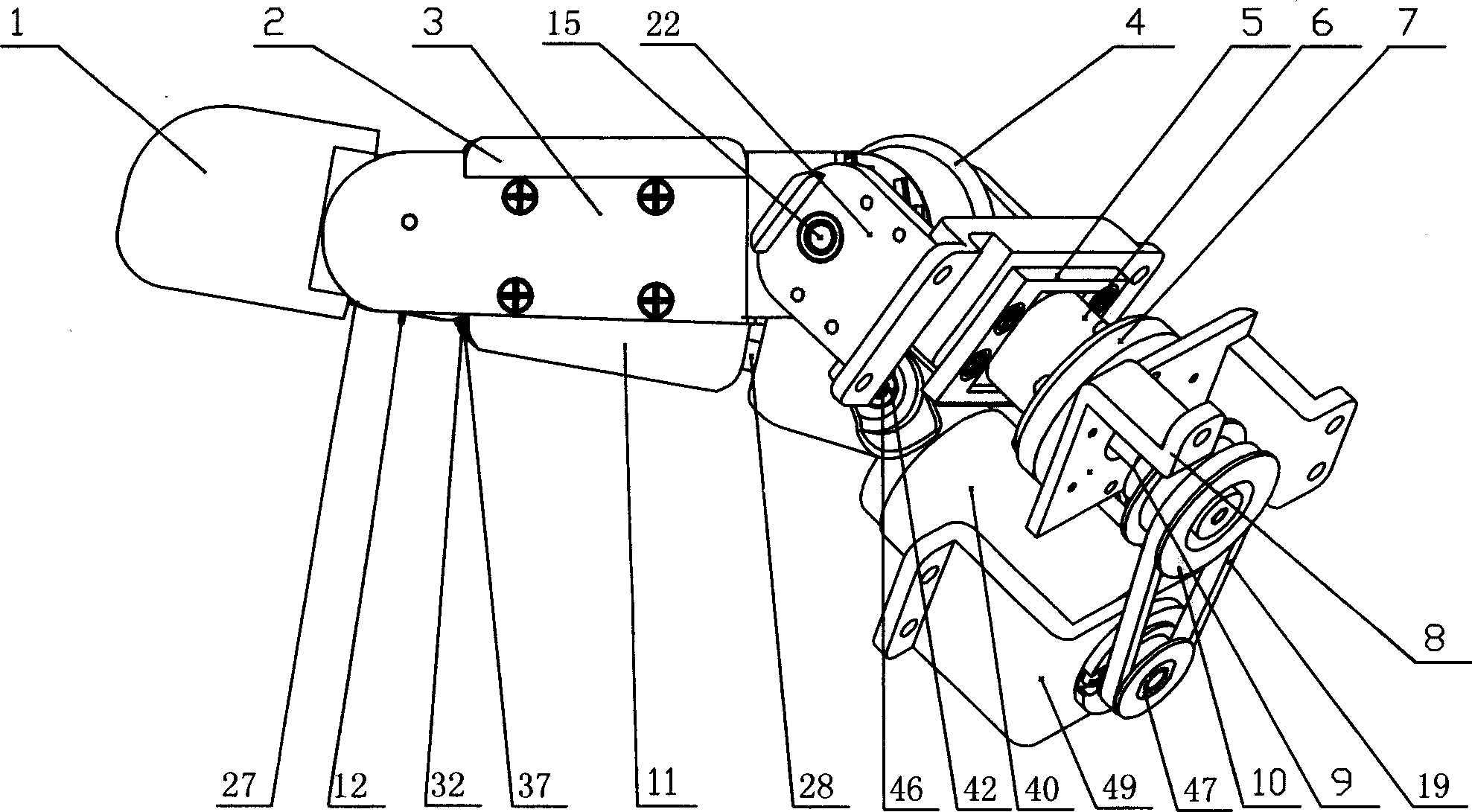
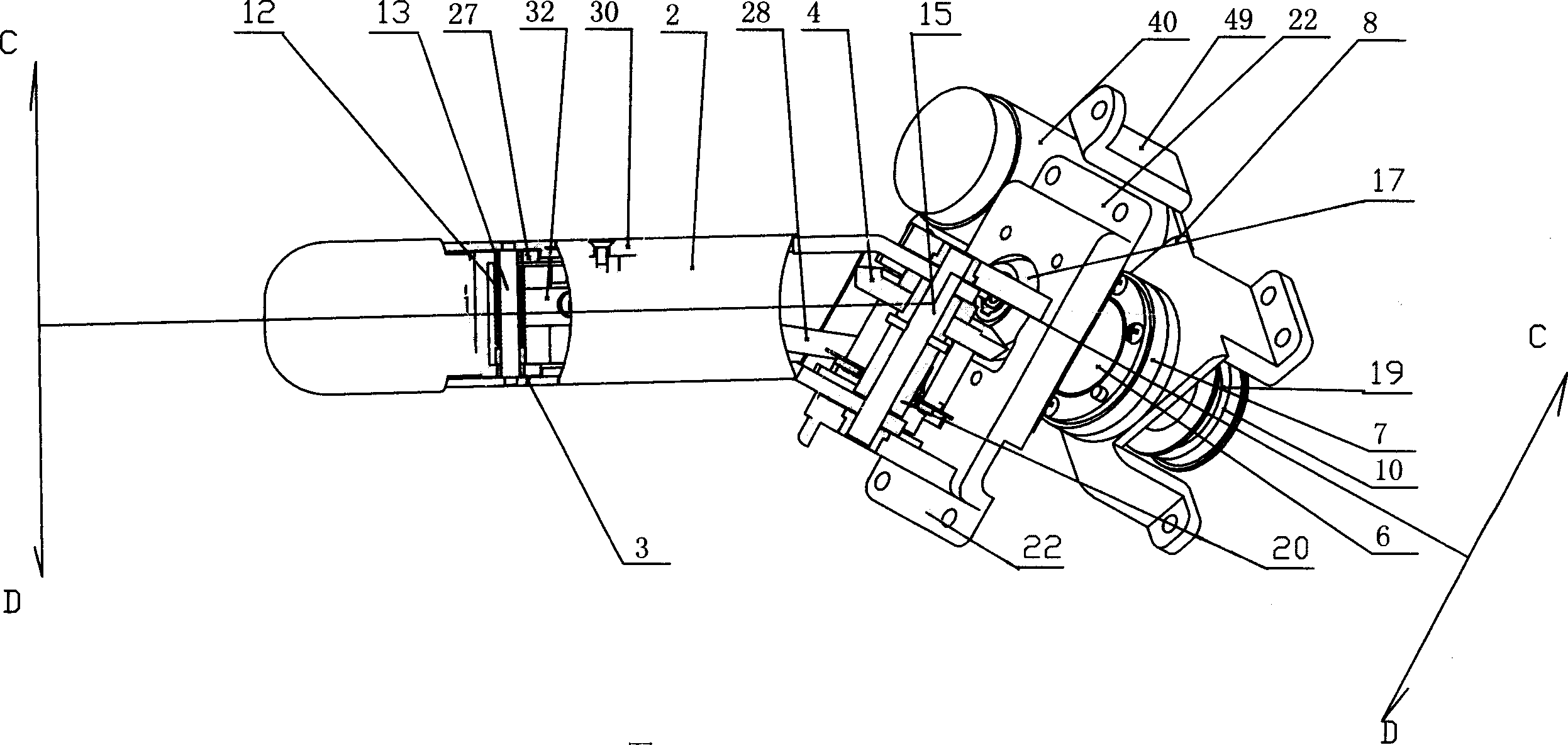
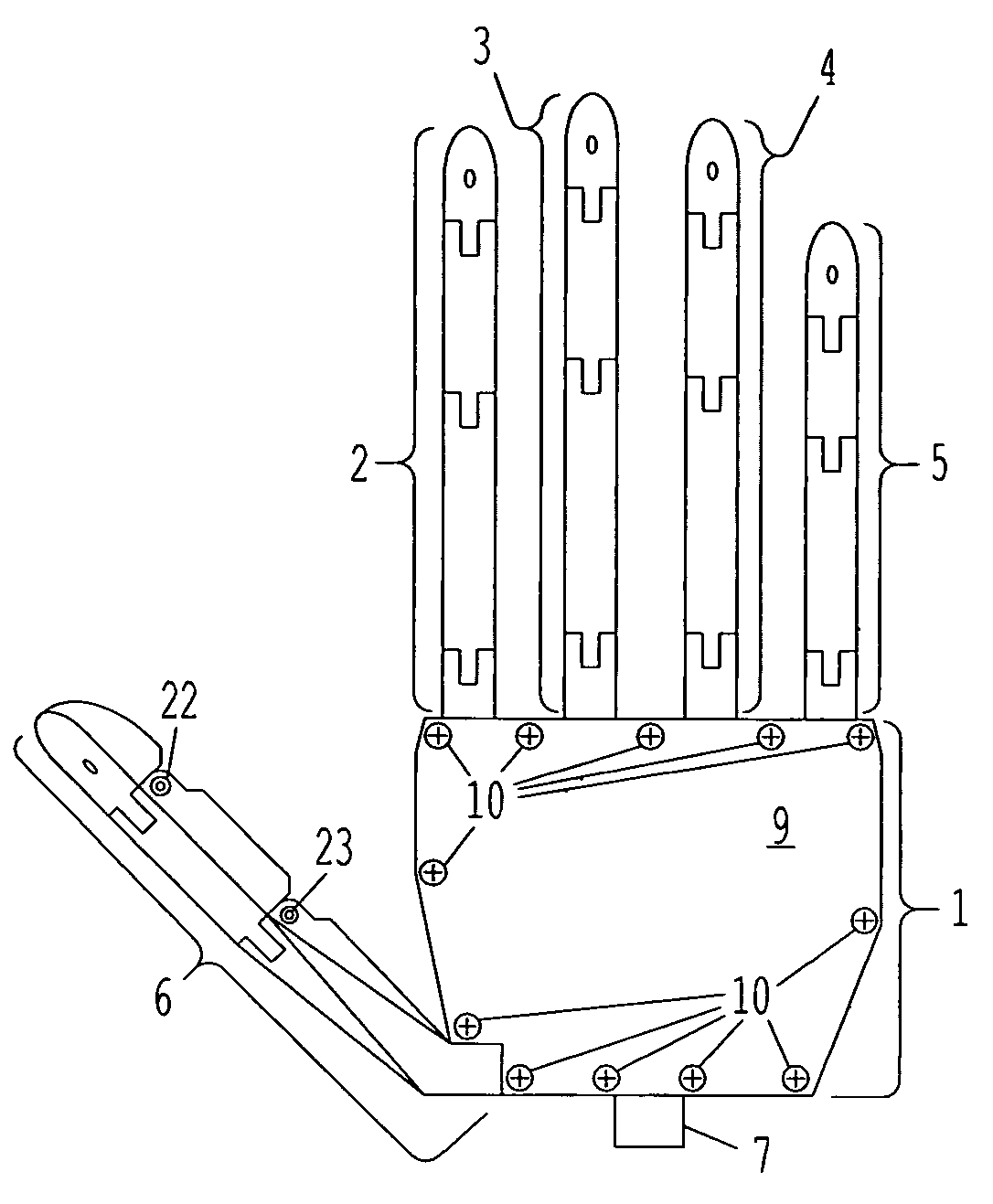
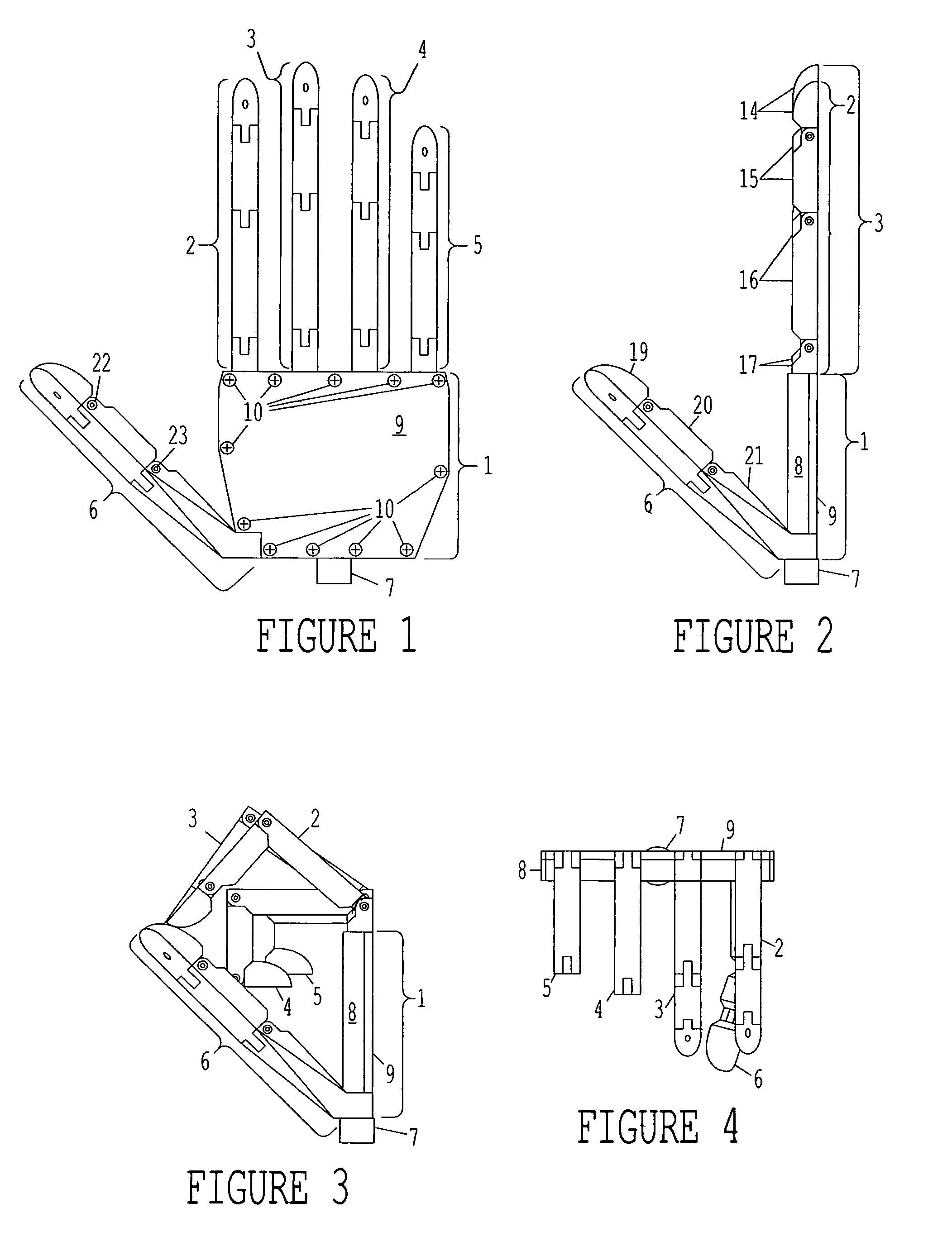
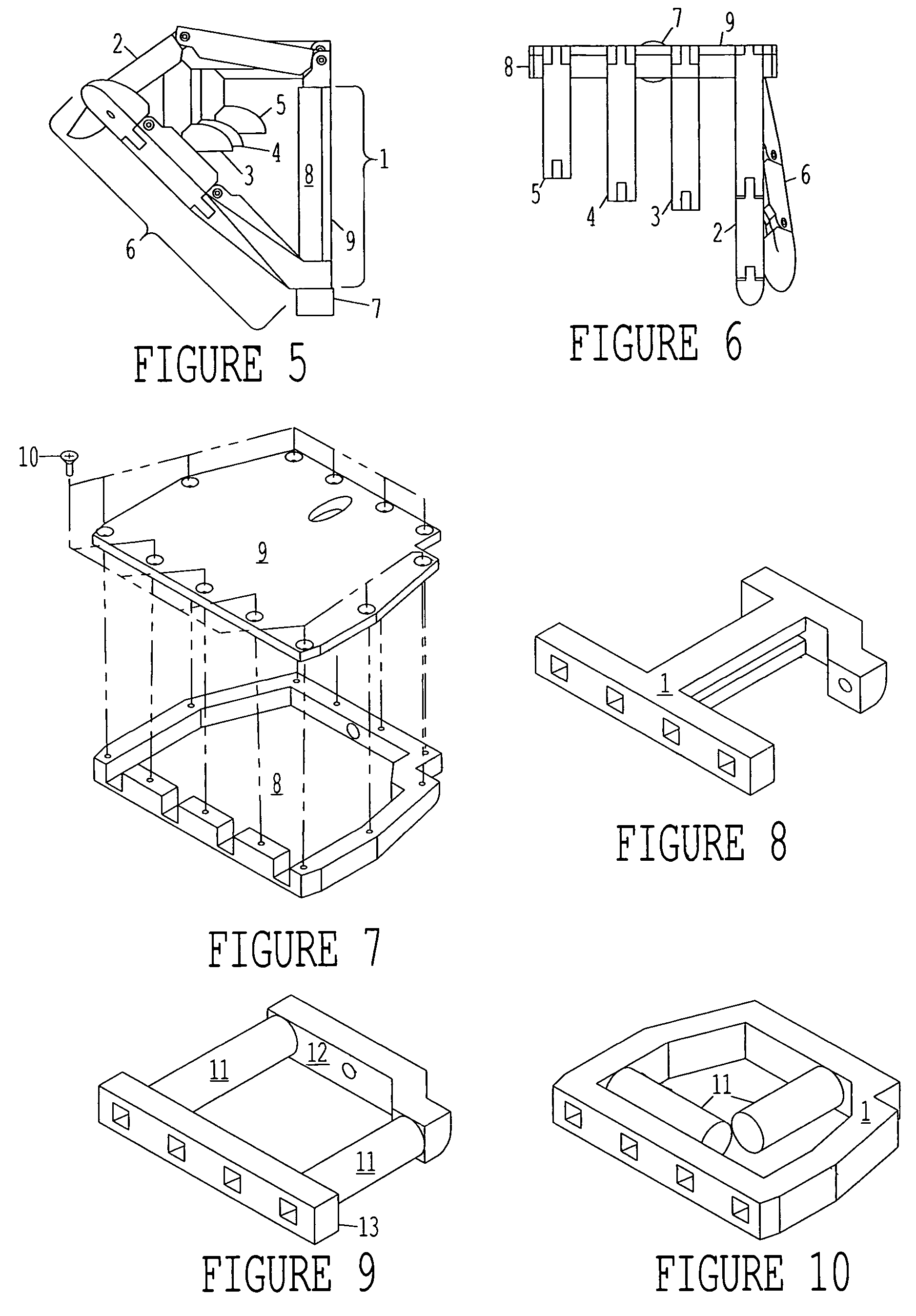
Thumb mechanism of underactuated self-adaptive hand prosthesis
The invention discloses a thumb device of little-driving self-adaptive artificial hand, which is characterized by the following: connecting one end of thumb finger-tip pin case (32) with the thumb finger-tip connecting rod pin shaft (37); fixing the thumb wheeled bearing (55) on the wave generator axle (54) under the thumb decelerator wheel (10); connecting the thumb decelerator wheel (10) with the wheeled pad (9) through the wheeled fixation pin (57); fixing the wave generator (52) of harmonic gear decelerator on the other end of the wave generator axle (54) of wheeled pad (9). The invention can display a 130 deg conical moving space in the moving course to realize the finger-pin little-driving movement, which is adaptive for the object shape to reach full-covering the object and stable grasping.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
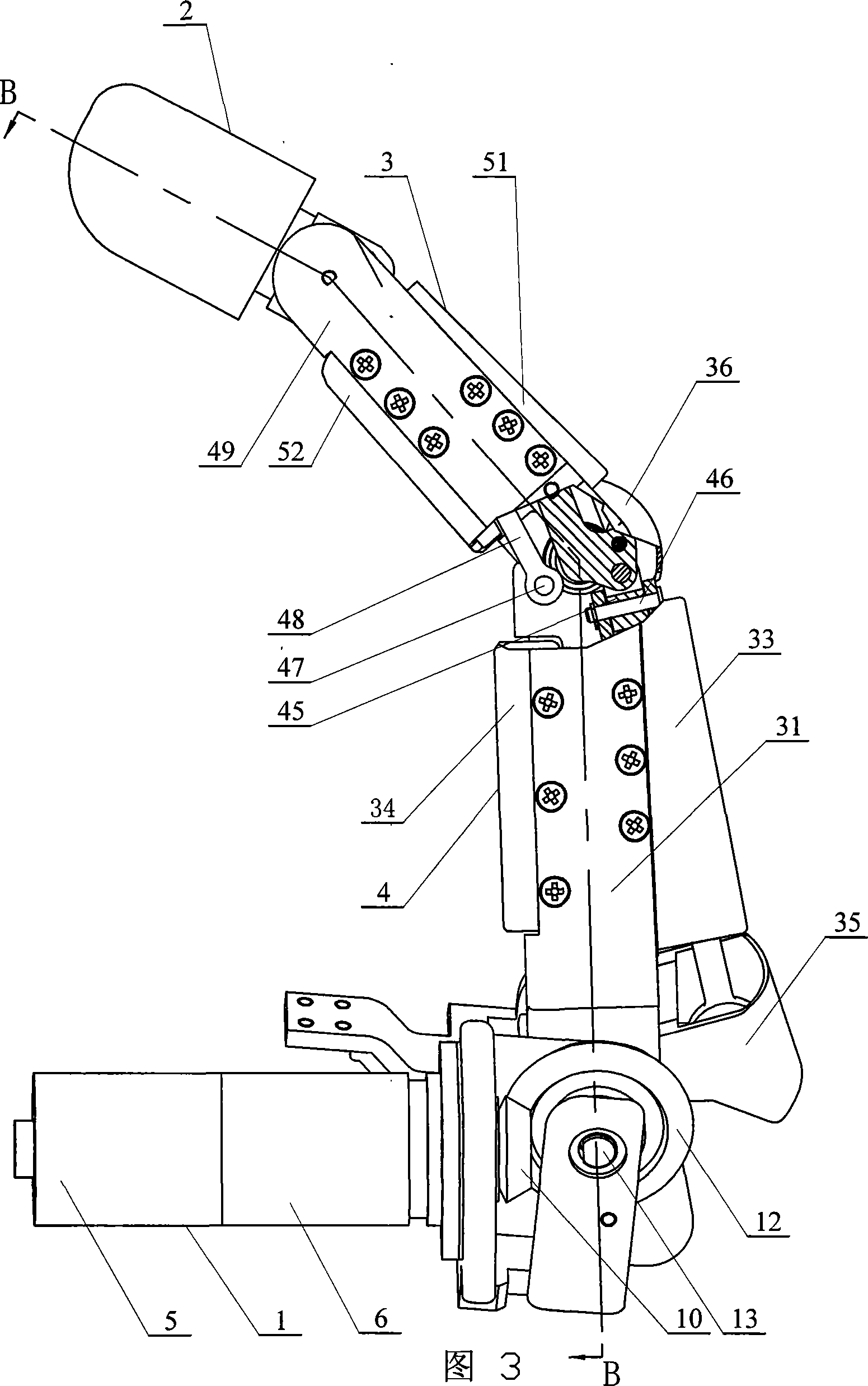
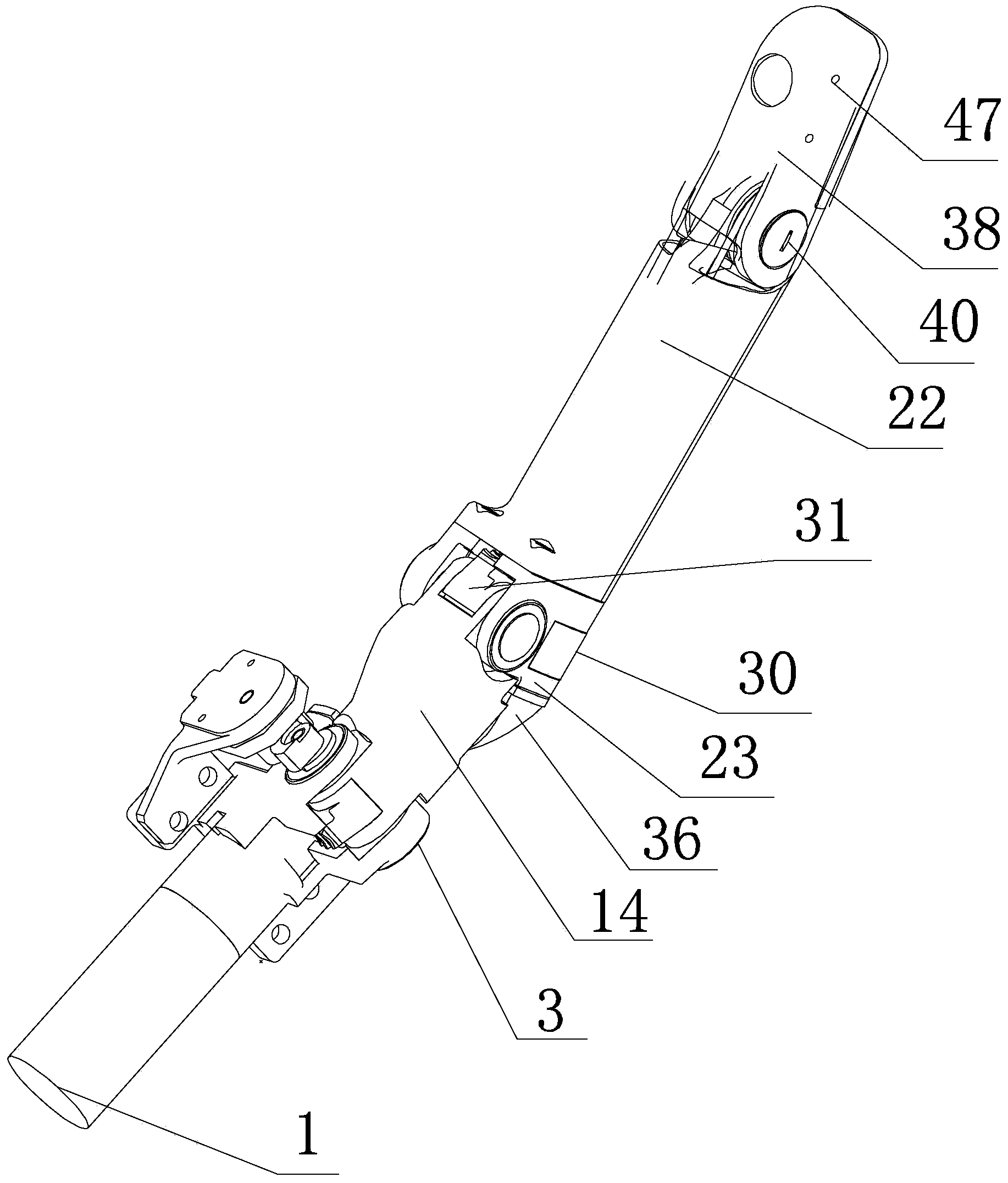
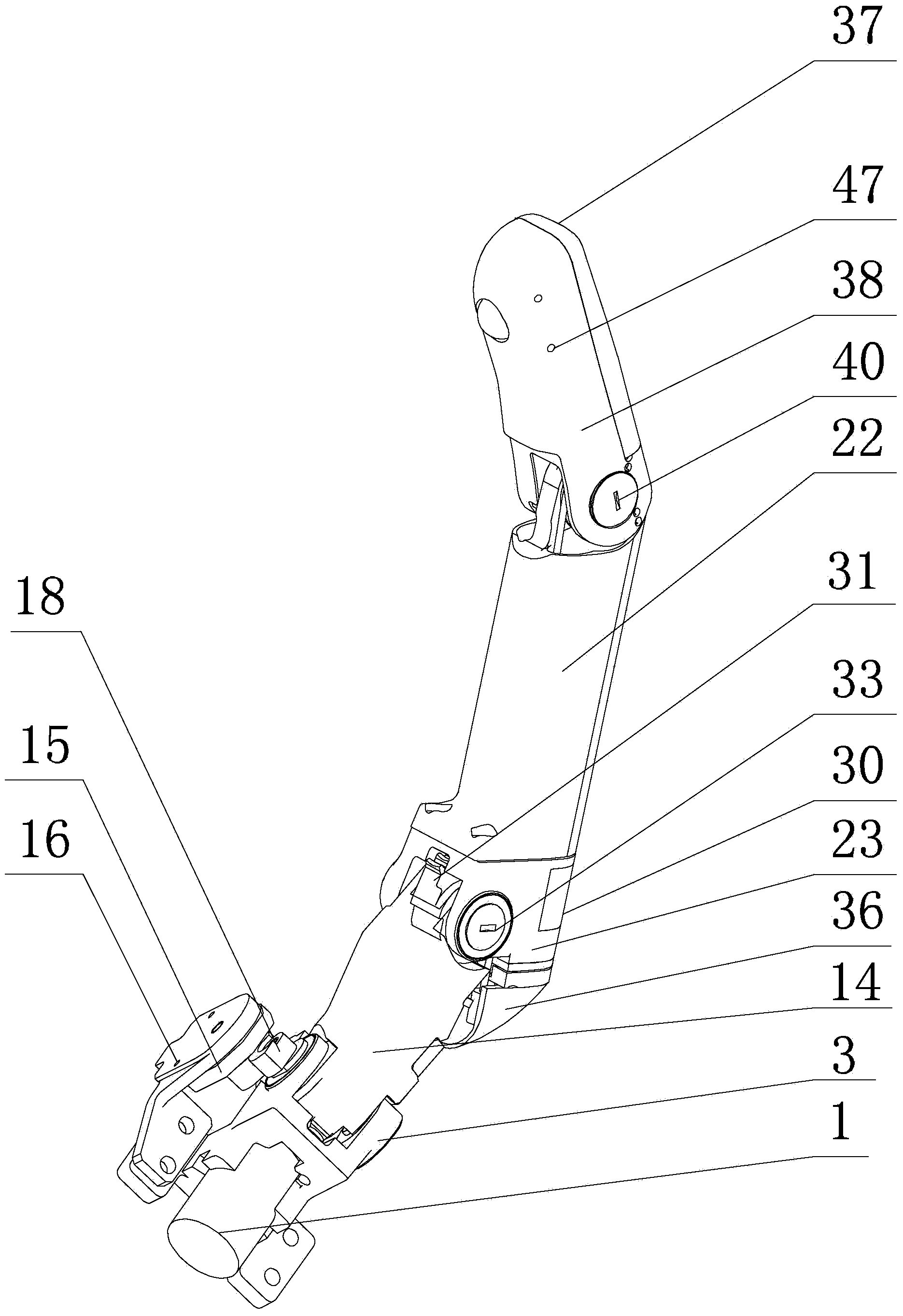
Five-degree-of-freedom artificial hand mechanism
InactiveCN101797749AIncrease freedomAchieve relative motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorArtificial handsReliable transmissionReduction drive
The invention provides a five-degree-of-freedom artificial hand mechanism, relates to an artificial hand mechanism and aims to solve the problems that the conventional artificial hand has single degree of freedom and cannot realize independent movement of each finger. Five drivers, five reducers and a palm circuit board are all integrated in a cavity of a palm; a thumb driver and a thumb reducer are arranged along a width direction of the palm, the four drivers except the thumb driver and the four reducers except the thumb reducer are arranged along a length direction of the palm, and a wrist and the palm are rotatably connected relatively; each driver is in transmission connection with the corresponding reducer, and the reducer is in transmission connection with a corresponding transmission mechanism; and a rotating part of each potentiometer is connected with the corresponding transmission mechanism, and the transmission mechanism is supported on a corresponding substrate. The five-degree-of-freedom artificial hand mechanism has five degree-of-freedom, and improves the flexibility of the artificial hand; and due to the simple and reliable transmission, relative motion of each finger is realized, and adaptive grasping of objects of different shapes and sizes is also realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for controlling electrically powered artificial hands by utilizing electro-coulogram and electroencephalogram information
InactiveCN101711709AReliable controlImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsProsthesisHand movementsControl signal
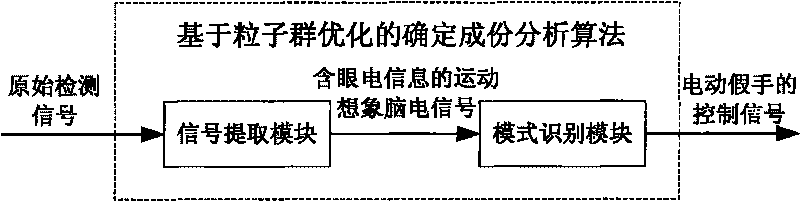
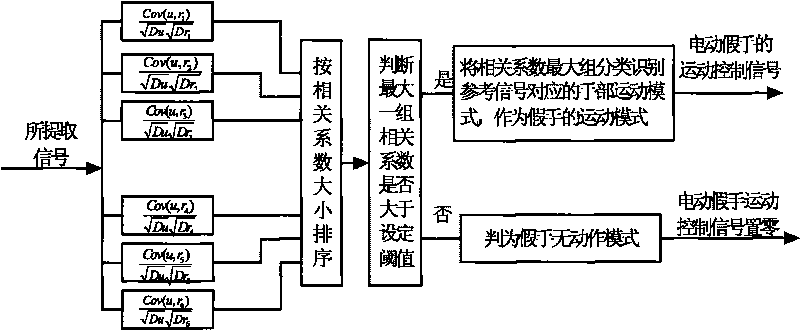
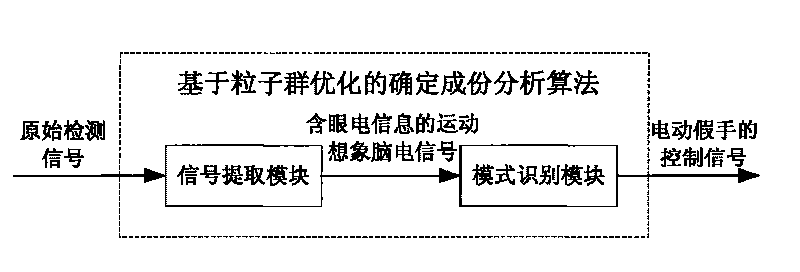
The invention relates to a method for controlling electrically powered artificial hands by utilizing electro-coulogram and electroencephalogram information. The traditional electrically powered hand control methods are not suitable for nerve paralysis people and paralytic people with seriously degenerated muscles. In the method, a scalp pick-up electrode in an electroencephalogram pick-up sensor is placed at the Fp1 or the Fp2 position of the forehead cerebelli anterior, determined by the international electroencephalogram association standard 10-20 lead system, and a reference electrode is placed at the pinna position; an original signal enters a micro processor after being processed; a determined component analysis method based on partical swarm optimization is applied to build the reference signal, extract an electroencephalogram signal containing electro-coulogram information and identify a hand movement pattern, and the micro processor outputs a corresponding control signal according to the identified result to control the electrically powered artificial hands to move. The method adopts an eye and brain coordination mode to express the hand movement consciousness and utilizes the useful information contained in an electro-coulogram signal to enhance the features of the electroencephalogram signal generated by the same movement consciousness; the identification correct rate of the hand movement pattern is high, and the electrically powered hand control is reliable.
Owner:南通恒力重工机械有限公司
Bionic artificial hand
The invention provides a bionic artificial hand. The bionic artificial hand comprises a palm part, a finger part, and a thumb-index web part, the finger part includes a forefinger assembly, a middle finger assembly, a ring finger assembly, a little finger assembly, and a thumb assembly, wherein the forefinger assembly, the middle finger assembly, the ring finger assembly, and the little finger assembly are respectively connected to the upper end of the palm part in a detachable manner, the thumb-index web part is vertically and rotatably connected to the inside of the palm part, and the thumb assembly is detachably connected to the thumb-index web part. According to the bionic artificial hand, the thumb assembly can internally or externally rotate, and the forefinger assembly, the middle finger assembly, the ring finger assembly, the little finger assembly and the thumb assembly can be stretched or bent. The bionic artificial hand is light in weight and convenient for long time wearing and use for patients.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heart artery induction pulse taking training device and method allowing remote reproduction
The invention relates to a heart artery induction pulse taking training device and method allowing remote reproduction. The device is composed of a signal receiving control system, a diaphragm pump, a driving circuit of the diaphragm pump, a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS) pulse wave regulating system, a temperature control system, a feedback system and a bionic artificial hand model. A standard electrocardio signal triggers a heart pump to drive a bionic vessel to form pulse wave, the pulse wave is regulated by means of the auxiliary MEMS pulse wave regulating system, and pulse wave far end bionic reproduction of 28 pulses and simultaneous pulses of the 28 pulses based on attributes of pulse position, pulse quantity, pulse shape and pulse force is achieved. Meanwhile, simulation of other relevant information of temperature and the like is matched, pulse taking comprehensive information of a tested person at the far end is obtained, comprehensive reproduction is conducted, and the device and method can be used by traditional Chinese medical doctors to conduct remote diagnosis and treatment. By means of visualization, comprehensive reproduction of information of pulse taking and the like can be achieved further through the technology of the internet of things and the like, and cloud collection of information of four diagnostic methods is achieved.
Owner:牛欣 +2
Electric artificial hand combined controlled by brain electricity and muscle electricity and control method
The invention relates to a power-driven artificial hand controlled by the combination of brain electricity and myoelectricity and a control method thereof. The pattern treatment of a current 3-DOF myoeletricity artificial hand has poor accuracy. The power-driven artificial hand comprises a plurality of myoelectricity picking-up sensors and brain electricity picking-up sensors. The output end of a secondary processing circuit in the myoelectricity picking-up sensors and the brain electricity picking-up sensors is connected with the input end of an A / D switching circuit. Three electrical motors are connected with a driving circuit respectively. A micro processor is connected with the output end of the A / D switching circuit and the input end signal of the driving circuit respectively. The myoelectricity picking-up sensors and the brain electricity picking-up sensors collect surface myoelectric signals from the points of a disabled arm and brain electricity signals from the top of a head and an ear. After being amplified, filtered and processed by A / D switching, the surface myoelectric signals and the brain electricity signals are input into the micro processor for further processing so as to control a 3-DOF power-driven artificial hand. The power-driven artificial hand performs control by the combination of the myoelectric signals and the brain electricity signals and module recognition, so that the accuracy is high and the control of action is reliable.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Prosthetic hand having a conformal, compliant grip and opposable, functional thumb
An anthropomorphic artificial hand having a mechanical system that allows for the digits to be compliant to pressure that tends to flex the digits, and provides for the digits to be self biasing to conform to the shape of the object being grasped. The hand comprises one to four fingers, with the fingers having up to three joints each. The hand may also comprise a thumb that can be rotated into and out of opposition of the fingers. The joints of the thumb are also self biasing to allow conformance to the object being grasped. The hand is of the voluntary closing operation, with all digits being self extending. This allows the hand to use two cables to operate if body powered (one for the fingers, one for the thumb). The hand may also be electronically powered using two channels for operating the fingers and thumb simultaneously.
Owner:WINFREY REX CLAYTON
Electric motor built-in false finger
The invention relates to an electric motor built-in false finger, which solves the problem that the effective utilization space of the existing artificial hand is insufficient. In the electric motor false finger, a microdisk type brushless electric machine is arranged in a base knuckle; a planetary reduction gear is arranged in the base knuckle, and an output shaft of the planetary reduction gear which is connected with a cone pinion which is externally meshed with a big bevel gear; a pre-tightening rope pulley is arranged on a first shaft of the middle between a substrate and a left side plate of the base knuckle; the big bevel gear is fixedly arranged on a circular end face of a first small straight gear; a first big straight gear is externally meshed with the first small straight gear; a second small straight gear is externally meshed with a second big straight gear which is fixedly connected with the left side plate of the base buckle; a transmission rope is arranged on a third shaft; the pre-tightening rope pulley is connected with the transmission rope by two wire cables; a connecting rod is connected with a far knuckle by a sixth shaft. The invention integrates the electric motor and an actuating mechanism in the interior of the finger, occupies small volume of a palm, has sufficient effective utilization space and liberates the space of the palm.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
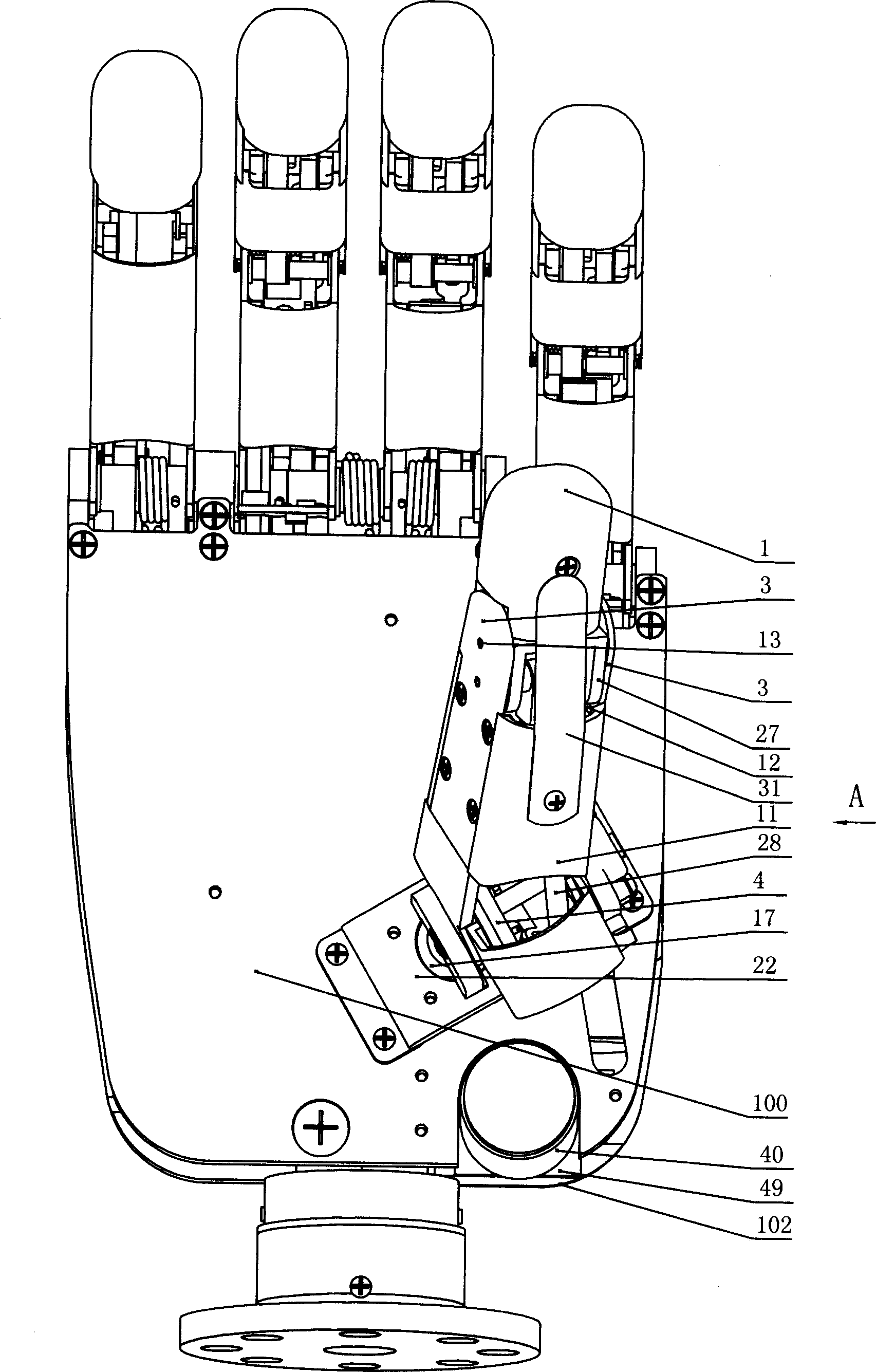
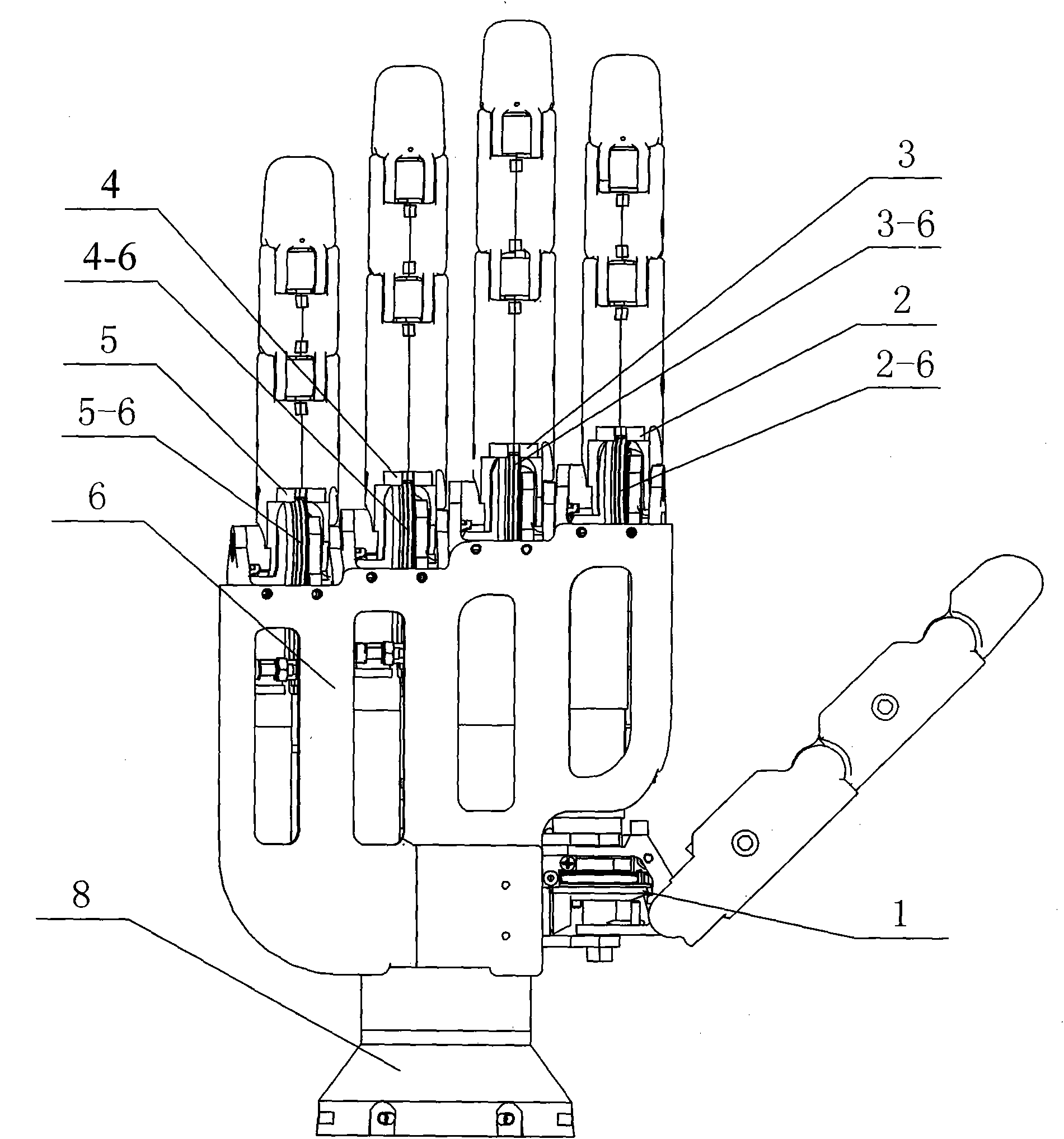
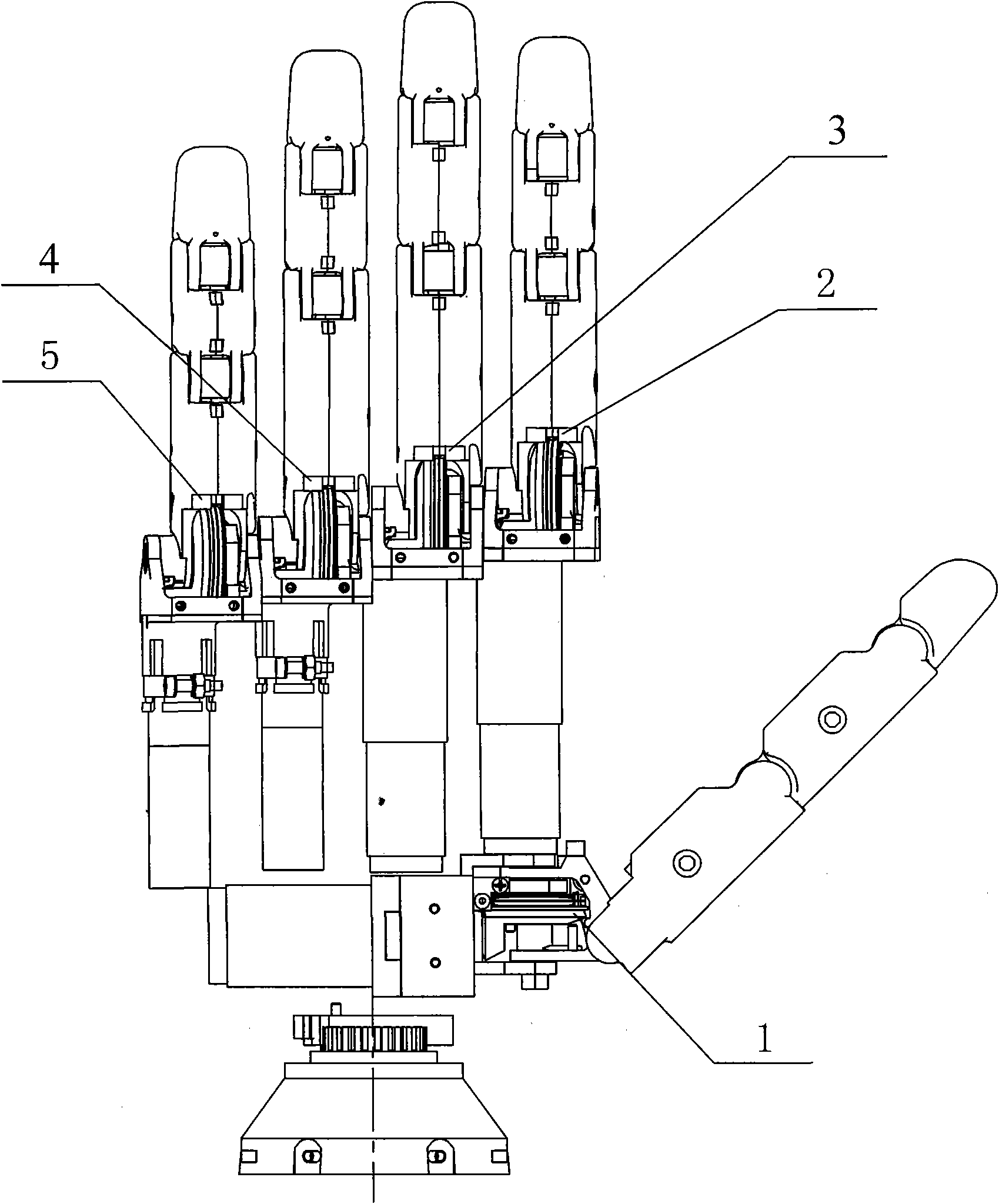
Underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device
The invention relates to an underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device, which is provided with five independently controlled modular fingers and has 16 freedom degrees. The whole hand is driven by 11 motors; the dimension and the shape are similar to those of the hand of an adult. Except for a thumb, the other four fingers have the completely identical structures; the thumb has one freedom degree of doing longitudinal rotation around the palm base; through the arrangement of a rotating shaft, when the whole hand grasps objects, the grasping force of the forefinger, the ring finger and the small finger on the objects can be in symmetrical distribution at the two sides of the middle finger; the grasping stability is improved. Modular fingers are used; the two motors are respectively used for driving a finger base part joint, a middle joint and a tail end joint; the middle joint and the tail end joint are coupled by a structure-variable connecting mechanism; through a connecting rod mechanism, the relative positions of the two coupled finger joints after the contact with the objects can be actively regulated, so that the fingers can wrap the objects according to the shape of the grasped objects; the self adaptability to the appearance of the objects is high; the grasping action better conforms to the human hand. The structure of the whole hand is simple; the grasping force is great; the grasping rigidity is high; the control is simple; the grasping self adaptability is high; the underactuated humanoid dexterous robotic hand device is applicable to the fields of disabled people artificial hands, explosive handling, nuclear equipment detection and humanoid robots.
Owner:杜宇
Thumb mechanism for under-driven adaptive prosthetic hand
InactiveCN101057791AImprove motor flexibilityHigh movement reliabilityArtificial handsEngineeringBiological activation
The invention discloses a thumb device for artificial hand. The driving device (1) is in rotary connection with the back part of near knuckle (4), the front part of near knuckle is in rotary connection with back part of middle knuckle (3), and the front end of middle knuckle is in rotary connection with the back part of far knuckle (2). The middle knuckle and near knuckle imitate deficient activation motion of real hand driven by middle knuckle shaft disk, the middle knuckle and far knuckle imitate coupling motion of real hand driven by coupling rod; and the knuckle number of thumb is imitative to that of real hand. The invention is characterized by simple structure, real-like appearance and flexible motion of each knuckle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
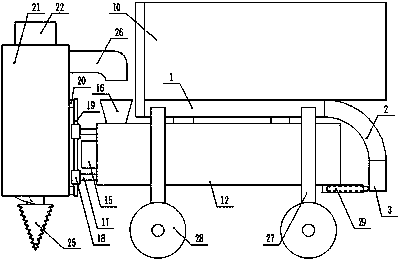
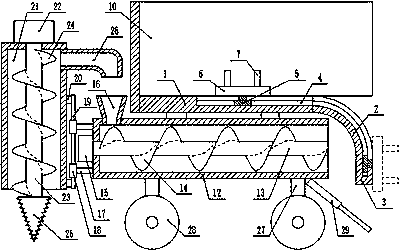
Hole-digging tree-planting robot for gardens
InactiveCN107667613AReasonable designEasy to makePlantingFurrow making/coveringSpiral bladeAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a garden digging tree planting robot, which comprises a horizontal plate, an arc-shaped plate at the side end of the horizontal plate, a vertical plate at the lower end of the arc-shaped plate, and a T-shaped groove in the horizontal plate, the arc-shaped plate, and the vertical plate. There is a T-shaped slider in the T-shaped slot, a slide plate on the T-shaped slide block, a fixing belt on the sliding plate, a through hole on the fixing belt, the fixing belt is fixed by bolts, a compartment on the top of the horizontal plate, and a partition in the compartment. There is a horizontal twisted cage at the lower end of the horizontal plate. There is a rotating shaft A inside the horizontal twisted cage. There is a spiral blade A on the rotating shaft A. The rotating shaft A is driven by a motor A. There is a horizontal twisted cage feeding port on the horizontal twisted cage. There is a sleeve on the fixed rod, and a vertical rod is inserted into the sleeve. During the whole process, it is only necessary to fix the saplings on the skateboard. There is no need to manually support and bury the saplings, which saves time and effort, and ensures stability. Even better, one person can dig holes and plant trees, which saves manpower. At the same time, there is no need to manually use a shovel to backfill the soil, which is highly efficient and very convenient.
Owner:北海南坡腕网络技术有限公司
Thumb mechanism of artificial hand
InactiveCN102896639AUnderactuated realizationWith self-locking functionJointsGripping headsGear wheelEngineering
The invention relates to a thumb mechanism of an artificial hand, in particular to a thumb mechanism of a humanoid hand and aims to solve the problem that a thumb of each of most existing artificial hand moves for grasp in one direction only. Rotation of a thumb of the thumb mechanism is achieved by worm-gear transmission. A function of bending for grasp is achieved for the thumb by worm-gear transmission and bevel gear transmission. A first knuckle and a second knuckle of the thumb are under-actuated by a plane four-bar mechanism. The thumb mechanism has the advantages that the thumb can rotate, bend for grasp and spatially move in a complex way during grasp motion of the thumb, the function of omnidirectional grasp can be achieved for the thumb, and various motion functions of a thumb of a human hand are achieved for the thumb of the thumb mechanism; a transmission mechanism of the thumb is in worm-gear transmission and has the self-locking function, and grasp torque of the thumb can be maintained after power failure of a motor; and the thumb mechanism is simple in structure, flexible to move, convenient to control, light in weight, small in size and large in thumb grasp strength.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Three-finger flexible hand performing device of robot
The invention discloses a three-finger flexible hand performing device of a robot. The three-finger anthropomorphic manipulator is of a tendon transmission structure on the basis of the underactuation principle, and is simple to control and small in cost; shape of an object can be adapted during grasping; the grasping control is achieved by the double-closed-loop principle; an outer loop is an angle loop, and while an inner loop is a pressure loop. The manipulator can be applied to the fields of home service, agricultural production and spatial detection, and can replace or assist human to finish the work; the anthropomorphic appearance design enables a certain of expression function, and some gestures can be performed to show some simple sign languages, so that the device can be applied to the field of assisting the disabled; humanized and multifunctional artificial hands can be provided to the disabled.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Real time control device and control method by two-degrees-of freedom myoelectricity artificial hand
InactiveCN101036601AAvoid Controlling SituationsReliable motion controlArtificial handsMicrocontrollerControl signal
The invention relates to a technology using the electromyography information to control the artificial hand. The existing hand with multiple degrees of freedom adopts the sequential control mode or the on-off switching mode to realize the control, which is lack of real-time performance and has bad bionic performance. The invention includes three electromyography electricity picking up sensors, connected with a last stage filtering and amplifying circuit, an A / D converting circuit, a SCM and two motors with two degree freedom electromyography artificial hand in order. The specific control method is: three electromyography electricity picking up sensors respectively collect the corresponding surface muscle electrical signal from the extensor carpi ulnaris, the flexor carpi ulnaris and the extensor digitorum of the human body, wherein the signals are inputted into the SCM after amplifying, filtering, A / D converting process; the SCM judges the intensity of the surface muscle electrical signal, and outputs the four-channel control signal, finally completes four actions of the artificial hand by the driving circuit to drive the motor of the artificial hand. The hand multiple movement mode identifying accurate rate of the invention can reach 100%, and realizes the real time control for the four actions of artificial hand having two degrees of freedom under the highly reliable recognition rate.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Two-degree-of-freedom modularized artificial hand thumb with moment of force, position and touch perception function
The invention discloses a two-degree-of-freedom modularized artificial hand thumb with a moment of force, position and touch perception function and relates to an artificial hand thumb. The two-degree-of-freedom modularized artificial hand thumb is used for solving the problems that matching between a prior artificial hand thumb and other fingers is poor, the grabbing function of the prior artificial hand thumb is limited, the prior artificial hand thumb is lack of the touch perception function, a transmission structure is complex and the modularization degree is low. The two ends of a metacarpal bone joint shaft are supported by fixed frames. A first worm gear and one end of a metacarpal bone base are arranged on the metacarpal bone joint shaft in a penetrating mode, wherein the first worm gear is located in one end of the metacarpal bone base. A first worm gear cover plate is arranged at one end of the metacarpal bone joint shaft, the metacarpal bone joint shaft is tightened through a metacarpal bone joint screw, and the other end of the metacarpal bone joint shaft is fixedly sleeved with a second plastic transmission gear. A position sensor is fixed to a sensor fixing frame, and a first plastic gear is installed on a transmission shaft of the position sensor, fixedly and axially connected with an inner hole of the position sensor and meshed with the second plastic transmission gear. The two-degree-of-freedom modularized artificial hand thumb is used on the palm of a robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
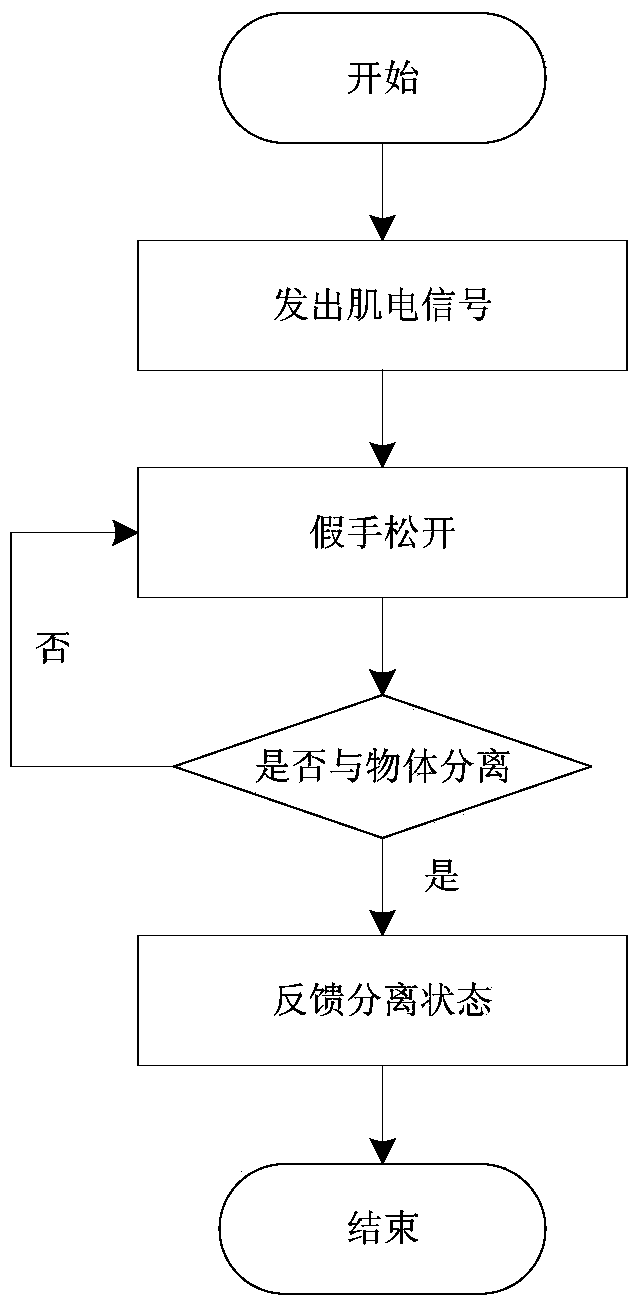
Intelligent artificial hand system
The invention relates to an intelligent artificial hand system which comprises an artificial hand body, a drive motor, a piezoelectric electret, a control terminal and a signal interaction module. The artificial hand body comprises a plurality of finger knuckles controlled by the drive motor. The control terminal controls the artificial hand body to grasp according to a first myoelectric signal. The piezoelectric electret collects a tactile signal and a slip sense signal, the control terminal controls whether the artificial hand body continues grasping or not according to the signals, and the signal interaction module feeds back stimulation to a stump. The signal interaction module also obtains a third myoelectric signal, and the control terminal controls the artificial hand body to grasp further according to the third myoelectric signal. The control terminal also controls the artificial hand body to open according to a second myoelectric signal. The intelligent artificial hand system overcomes the defect that a traditional artificial hand can not feel motion states or motion trends of an object relative to the artificial hand and can not control and adjust grasping strength, and is high in reliability and safety, low in cost and easy to popularize.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
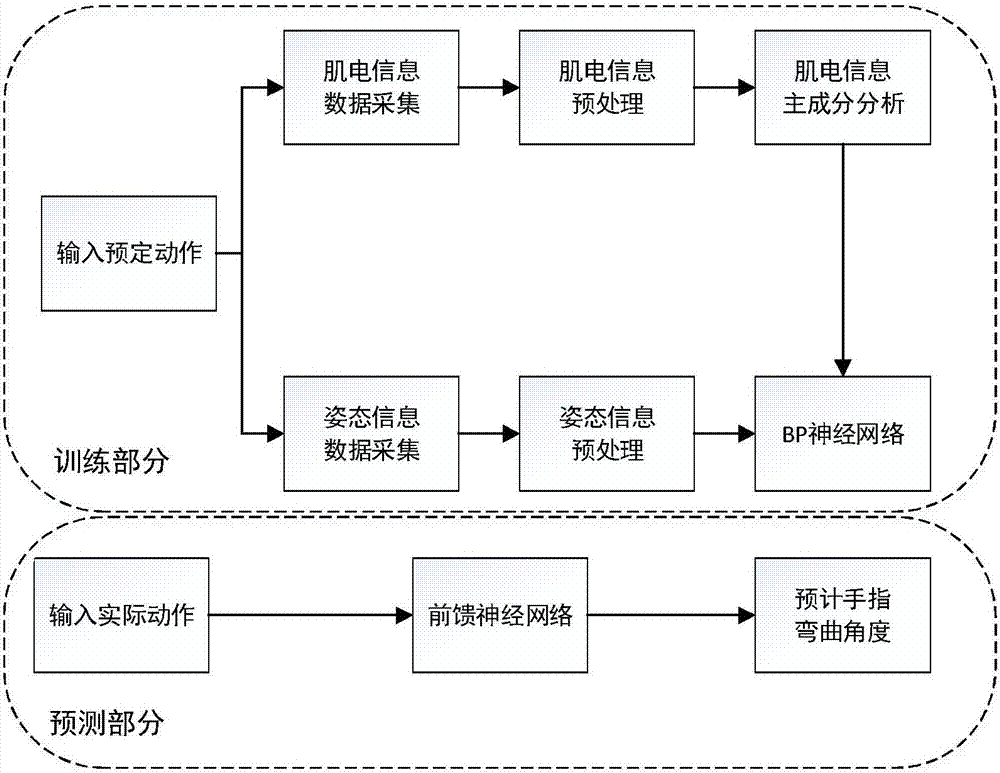
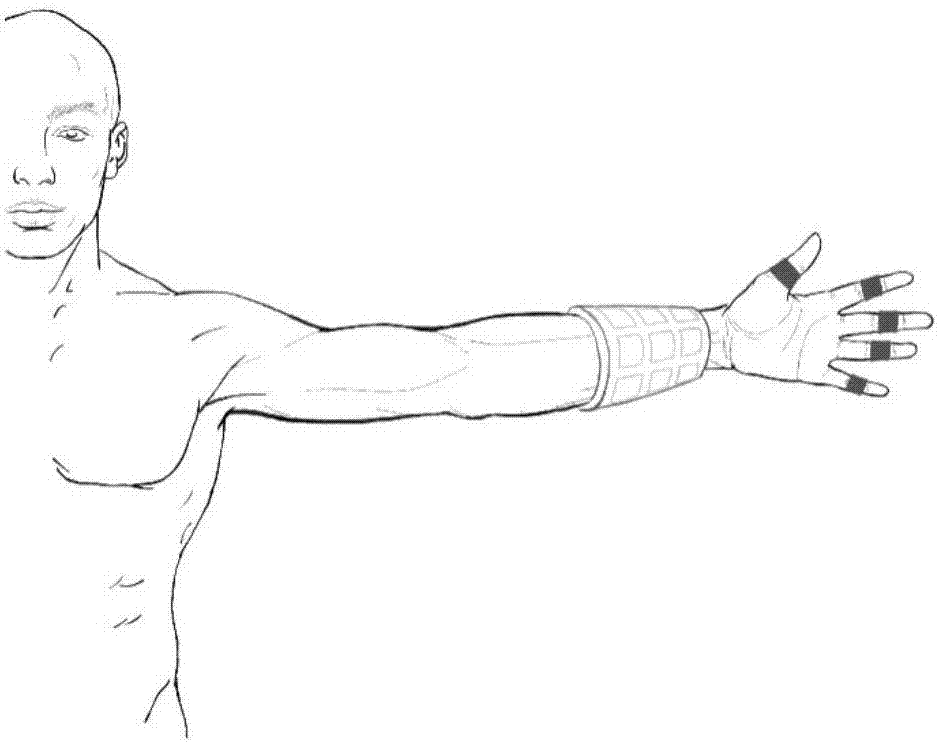
Multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on principal component analysis
ActiveCN107378944AReduce training timeShorten operation timePhysical therapies and activitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionPrincipal component analysisFinger joint
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional surface myoelectricity signal artificial hand control method based on a principal component analysis. The control method comprises the follow steps that 1, an arm ring provided with a 24-channel array myoelectricity sensor is worn to a front arm of a testee, and five finger joint posture sensors are worn at the distal phalanx of a thumb of the subject and at the middle phalanxes of rest fingers of the testee respectively; 2, the testee conducts a five-finger independent bending and stretching training, and meanwhile, the myoelectricity sensing array data and the data of the finger joint posture sensors are collected; 3, the principal component analysis is used for decoupling the myoelectricity sensing data to form a finger movement training set; 4, the sensors worn on the fingers are removed after the training is finished; 5, data fitting is performed on the finger movement training set by adopting a neural network method, and a finger continuous motion prediction model is constructed; and 6, current bending angles of the fingers are predicted through the finger continuous motion model. According to the control method, the non-consistency of the discrete action modal classification can be overcome, and finally smooth control on an artificial hand is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Artificial simulation arm
InactiveCN100998527AMeet the requirements of mechanical transmissionFunctional Movement FlexibilityArtificial handsHuman bodyTendon sheath
An artificial hand with multiple functions, no error operation and no complication is composed of such artificial units as finger bones, metacarpal bones, ulna, radius, muscle tendons, tendon sheaths, slide mechanism, muscles and skin. It can be connected to the crippled end of human radius by screw and its artificial muscle tendons can be linked with relative ones of human body by stitch.
Owner:张为众
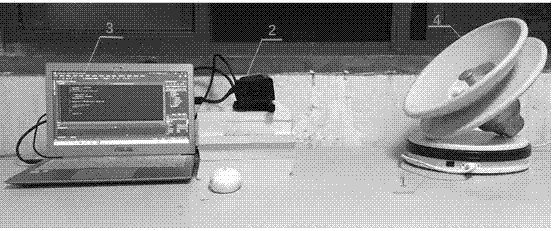
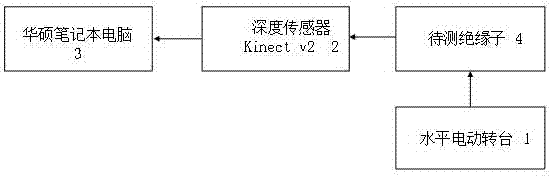
Three dimensional reconstruction-based insulator creepage distance measurement system and method
ActiveCN106910189AReduced measurement timeSimple and fast operationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsVoxelArtificial hand
The invention relates to a three dimensional reconstruction-based insulator creepage distance measurement system and method. The system comprises a horizontal electric rotary table, a Kinect v2 and a notebook computer. The method comprises the following operation steps: (1) depth images are collected, (2) a three dimensional model is reconstructed, (3) a cutting plane is searched, (4) grid voxel cutting operation is conducted and (5) creepage distance is calculated. According to the system and method disclosed in the invention, an object with an irregular shape is transformed into voxels for calculation via construction of the three dimensional model for an insulator. The method is simple in operation and accurate in calculation results; a problem that large measurement deviation can be caused when an artificial hand-operated rope is used for measuring the insulator creepage distance can be well solved; time can be saved for manufacture workers and measurement workers, repeated measurement due to inaccurate results can be prevented, and great convenience is provided for an insulator manufacture department and an insulator usage department.
Owner:HUIZHOU POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
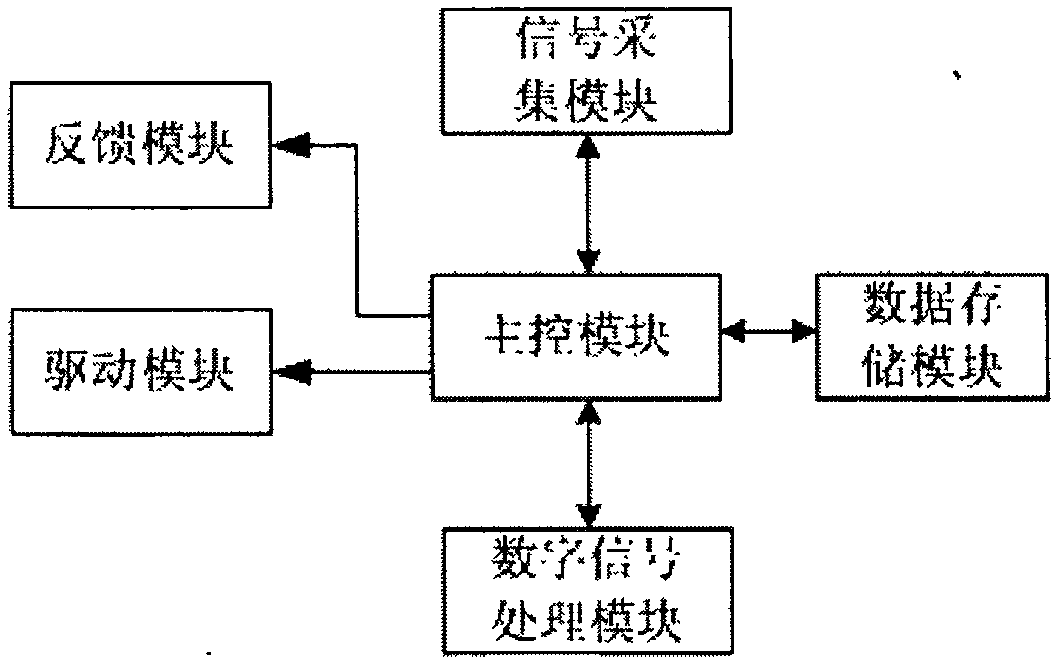
Artificial hand control system and method
The invention discloses an artificial hand control system and an artificial hand control method. The system comprises a signal acquisition module, a feedback module, a data storage module, a digital signal processing module and a driving module, wherein a master control module is connected with the signal acquisition module, the feedback module, the data storage module, the digital signal processing module and the driving module respectively; the master control module is used for cooperatively managing the signal acquisition module, the feedback module, the data storage module, the digital signal processing module and the driving module; and the signal acquisition module is connected with eight electrodes for recording electroencephalogram (EEG) and two electrodes for recording surface electromyography (SEMG). The system can integrate the EEG and SEMG information, and decodes the speed, accelerated speed and track of hand motion in real time; therefore, an artificial hand is flexibly controlled; moreover, the system is natural to use and convenient to maintain and does not need any implanted electrode.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Differential gear train coupled adaptive under-actuated finger device
A differential gear train coupled adaptive under-actuated finger device belongs to the technical field of artificial hands and comprises a base, three knuckles, three joint shafts, a transmission shaft, two transmission links, a motor, two differential gear train mechanism and a spring member. The differential gear train coupled adaptive under-actuated finger device has the special effect of integrating coupled grasping and under-actuated adaptive grasping. The differential gear train coupled adaptive under-actuated finger device is driven in coupled manner before contacting with an object, and can grasp the object in under-actuated adaptive manner after contacting with the object. The differential gear train coupled adaptive under-actuated finger device is adaptive to size and shape of the object to be grasped. The finger is basically the same as a human finger in terms of shape and grasping manner.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Simulated electronic artificial hand
InactiveCN1406560AMeet psychological needsRealize the function of free holiday handArtificial handsUniversal jointEngineering
A simulative artificial electronic hand is composed of wrist joint, palm seat linked to wrist joint, thumb, finger holder with 4 finger, miniature DC motor and 14 joints (two for thumb and three for each of fingers). Said wrist joint is a universal joint. The relative positions between joints and the angle of wrist joint can be regulated by another actual hand.
Owner:上海天竹康复科技发展有限公司
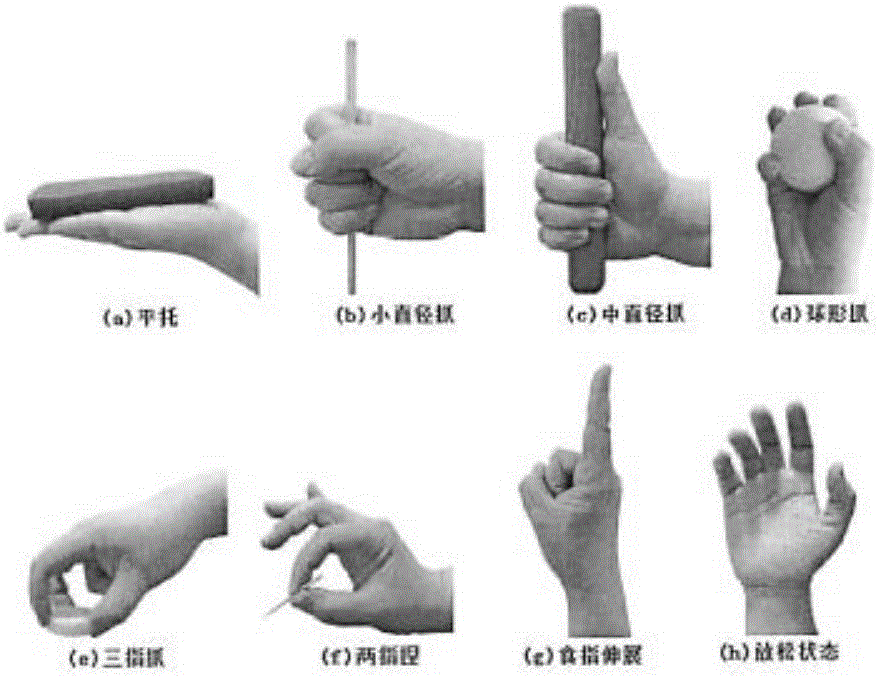
A human-like dexterous EMG prosthetic hand control method based on gesture recognition
ActiveCN108983973AImprove wearing experienceImprove stabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTraining phaseProsthetic hand
The invention discloses a human-like dexterous EMG artificial hand control method based on gesture recognition, which recognizes eight kinds of gestures of a user in real time and operates the dexterous artificial hand to carry out synchronous action. The gesture recognition strategy of this control method is based on neural network algorithm, participants first completed eight preset gestures (relaxation, wrist valgus, wrist varus, fist-clenching, palm-extension, gesture 2, gesture 3 and thumb-upright) during the training phase, and then the system is able to recognize any one of the eight gestures randomly completed by the user in real time. The method uses a Tensorflow machine learning framework to learn weights and perform visual analysis. The method collects, trains and predicts the surface electromyography signal of a user, the comprehensive prediction accuracy of the 8 gestures reaches 97%, and the training is not needed when the gesture is worn again. When the subjects actuallycontrolled the artificial hand, the voting algorithm was used to optimize the real-time gesture prediction, and the synchronization rate of the artificial hand reached 99%.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
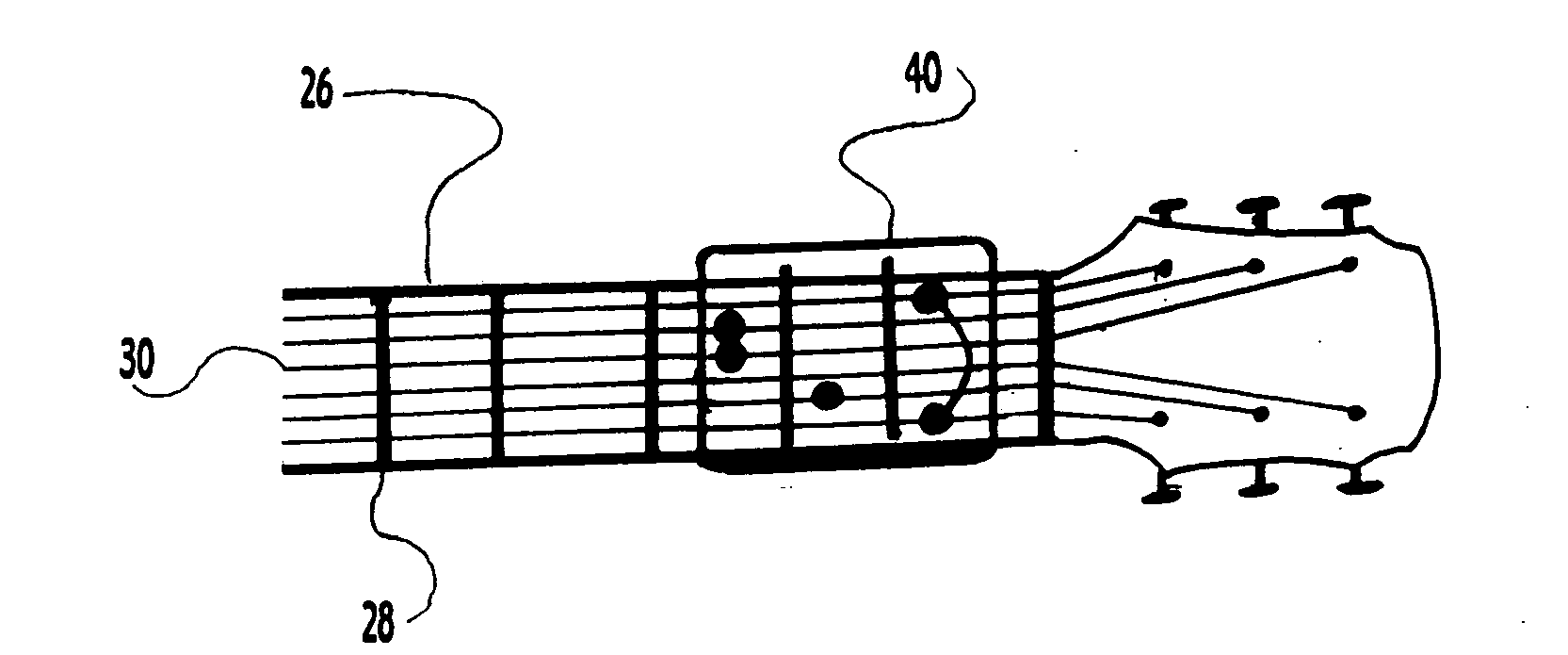
Handi-guitar (for the handicapped guitar player)
InactiveUS20050145089A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsStringed musical instrumentsEngineeringArtificial hand
A thin flat body of clear plastic with a key pad (20) on the inside back base (12), and a chord scale (22) on the outside front of the base (10). The chord scale is fitted with braille nodules (24) for guiding the proper placement of the fingers on the EZ chord. On the bottom or lower side of the base (10) (12) is a gripping angle (14) for the learning chord device. On the top or upper side, and bottom or lower side of the base (10) (12) are gripping angles (14) (16) for the universal chord device. One EZ chord is a device that when manipulated by a human hand, or an artificial hand, is pressed and positioned onto the guitar neck, fret and strings to form and sound guitar chords and / or notes. The EZ chord devices can be used by mentally, physically, or visually handicapped people as well as non-handicapped people, to play and / or learn to play the guitar.
Owner:DAVIS BARRY MARK
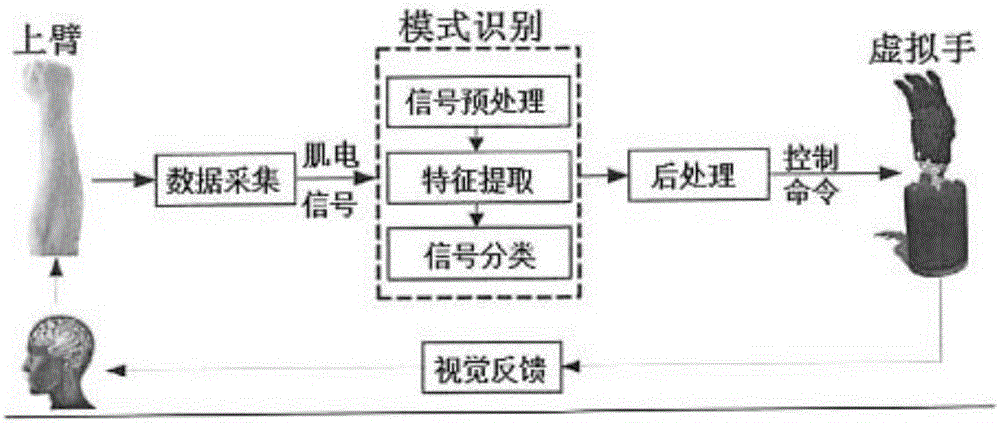
Method for myoelectrically controlling artificial hand simulation system of virtual robot
ActiveCN106420124AImprove classification performanceReliable simulation training environmentDiagnostic signal processingSensorsSignal classificationData acquisition
The invention provides a method for myoelectrically controlling an artificial hand simulation system of a virtual robot. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting data of a right front arm of a tester; (2) adopting an electrode clung to a skin layer above related forearm muscle for collecting a myoelectricity signal; (3) performing signal pretreatment of rectifying, amplifying and filtering on the myoelectricity signal; (4) performing feature extraction on the myoelectricity signal and extracting a stable feature vector of the myoelectricity signal; (5) cutting the collected stable feature vector into a training set and a test set, utilizing the training set to train the selected classifier and then classifying the signals of the test set; (6) transferring the signal data after the signal classifying process to the after-treatment link; (7) after the after-treatment for the signal, namely, controlling a command signal and sending the command signal to a virtual hand simulation system; (8) assuming a visual feedback function by the virtual hand in the artificial hand simulation system of the robot and feeding the real-time state of the virtual hand to the brain; (9) judging if the hand action is an assumed action by a user through visual feedback.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com