Method for myoelectrically controlling artificial hand simulation system of virtual robot
A virtual robot and simulation system technology, applied in the field of myoelectric control virtual robot prosthetic hand simulation system, can solve the problems of inconvenient use, infrequent use, non-use, etc., and achieve intuitive visual feedback, high classification effect, and reliable simulation training environment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] In order to make the technical means, creative features, goals and effects achieved by the present invention easy to understand, the present invention will be further elaborated below in conjunction with illustrations and specific embodiments.
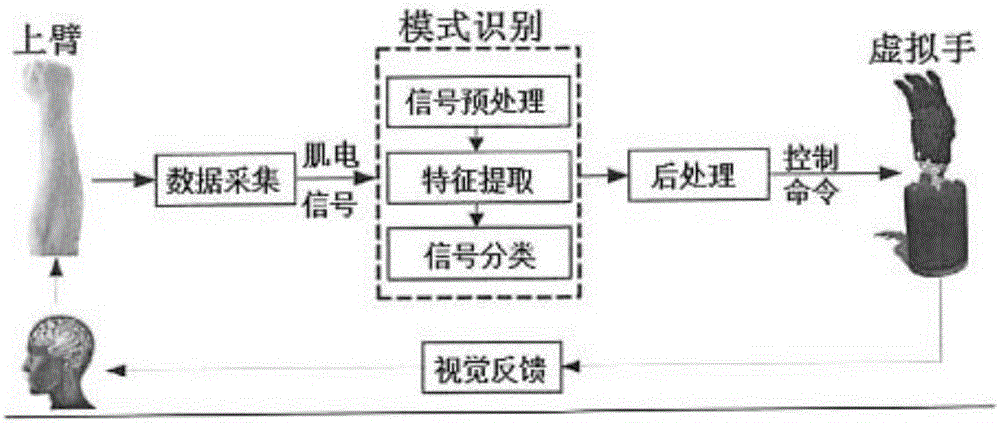
[0032] like figure 1 As shown, a kind of myoelectric control virtual robot prosthetic hand simulation system method proposed by the present invention comprises the following steps:
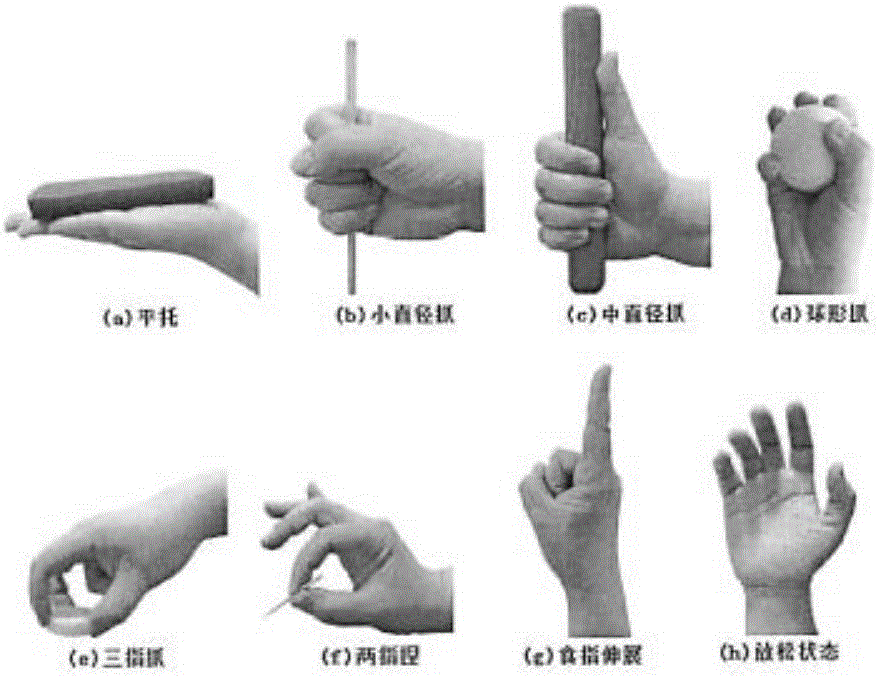
[0033] ①. Collect data on the right forearm of several healthy testers;
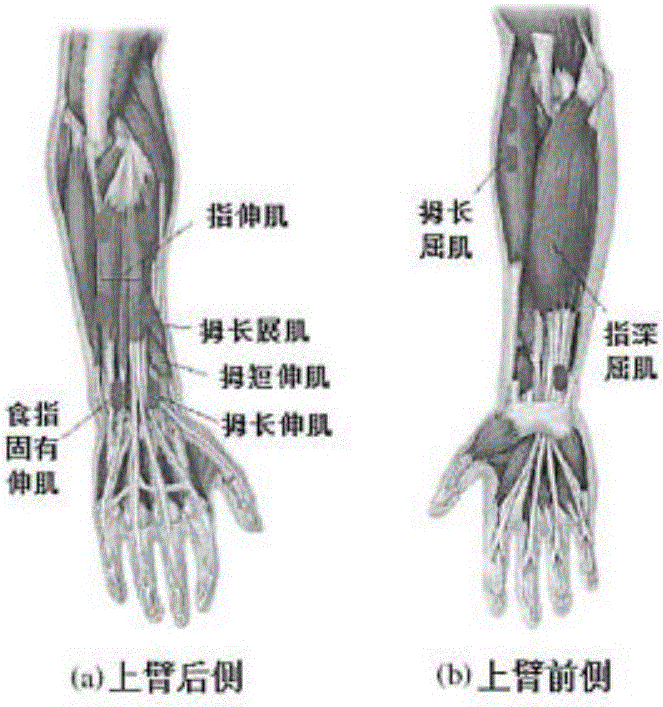
[0034] ②. Use electrodes attached to the skin layer above the relevant forearm muscles to collect surface electromyographic signals;
[0035] ③. 8-signal preprocessing of rectifying, amplifying and filtering surface electromyography signals;
[0036] ④. After signal preprocessing, feature extraction is performed on the EMG signal, and the steady-state feature quantity of the EMG signal is extracted;
[0037] ⑤. Divide the collected EMG steady-state feature into a training s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com